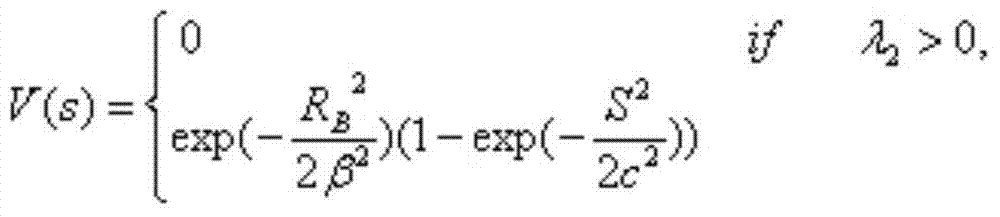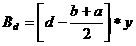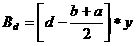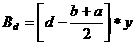Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
389 results about "Coronal plane" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A coronal plane (also known as the frontal plane) is any vertical plane that divides the body into ventral and dorsal (belly and back) sections.
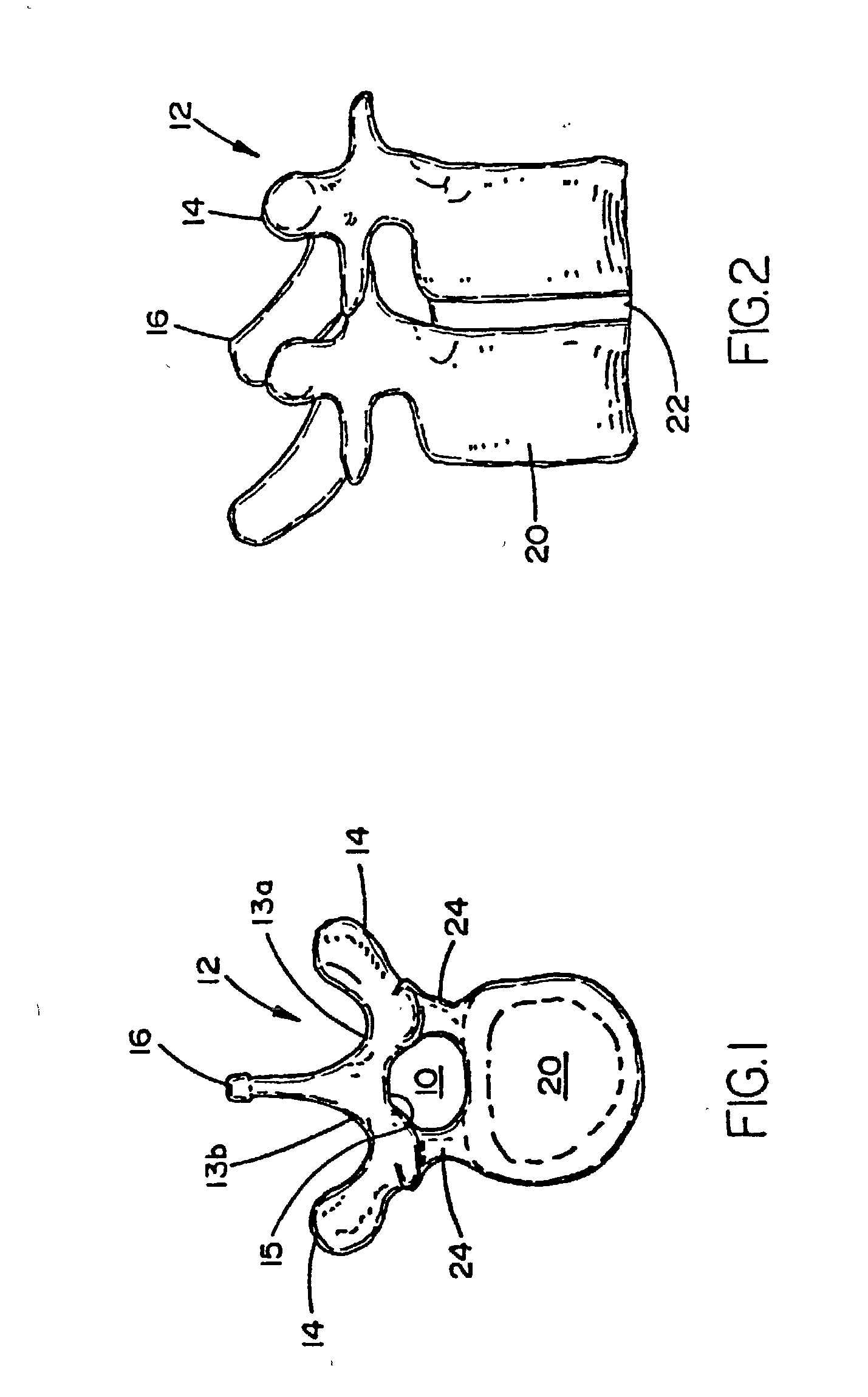
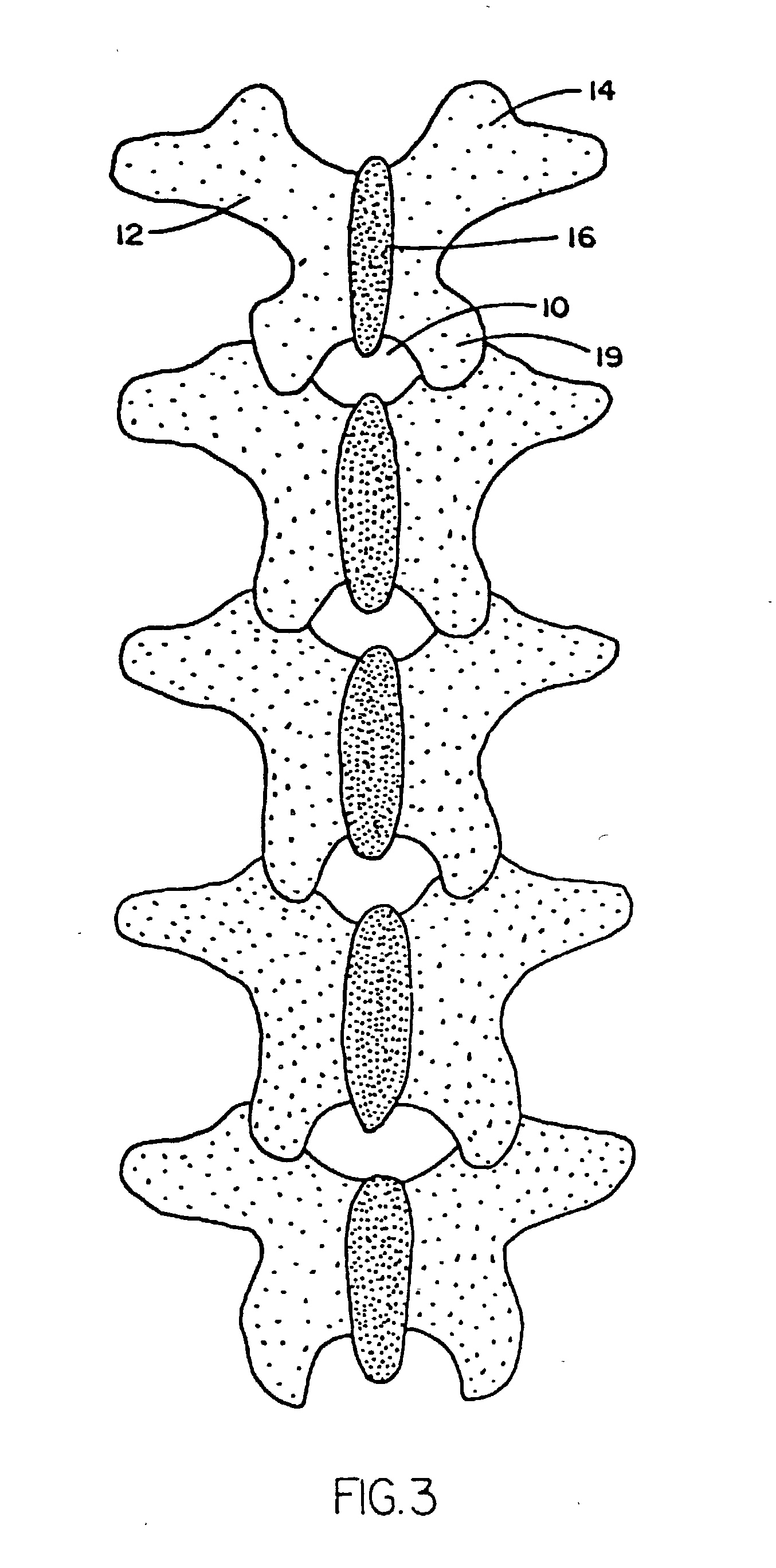
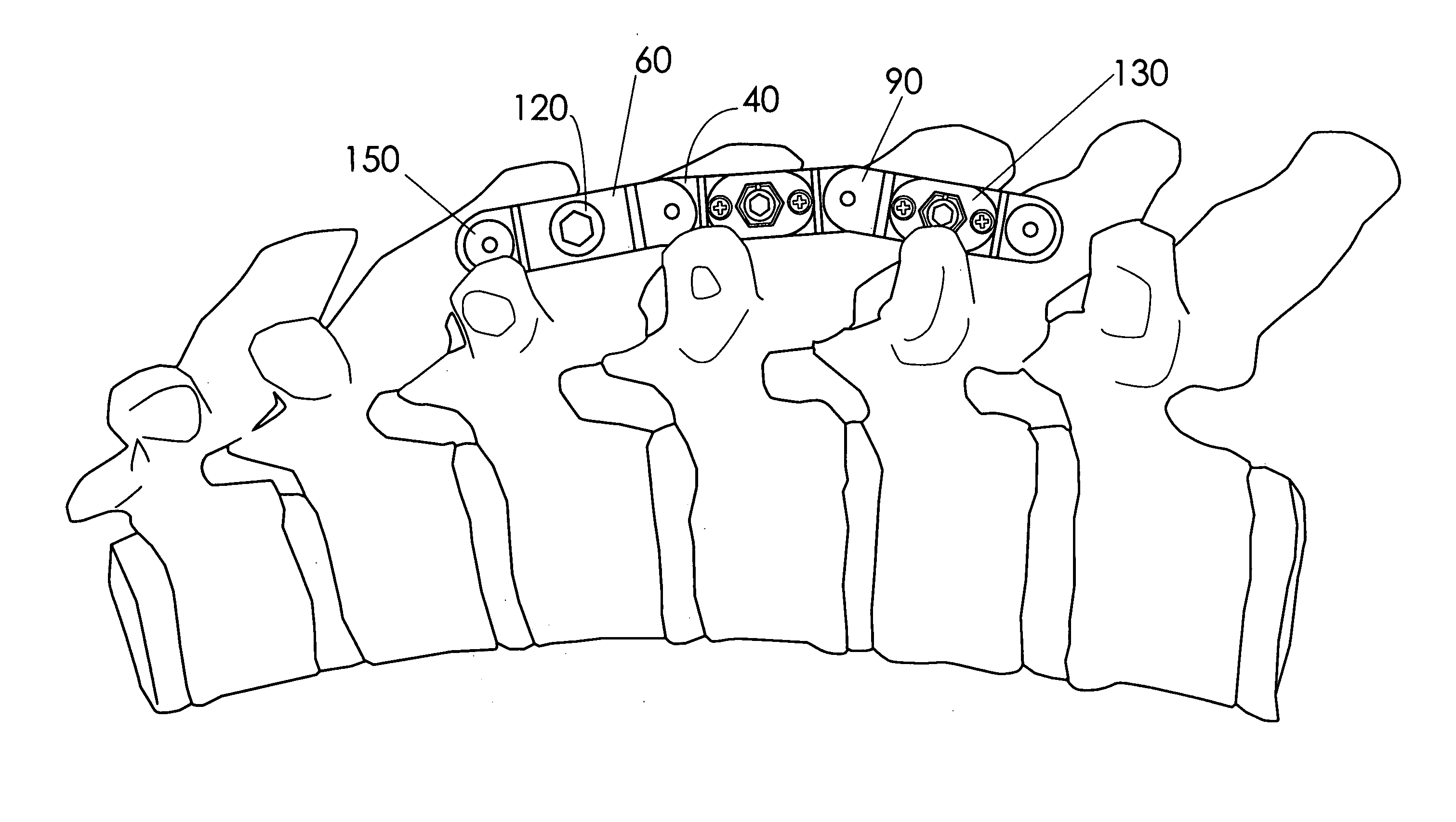
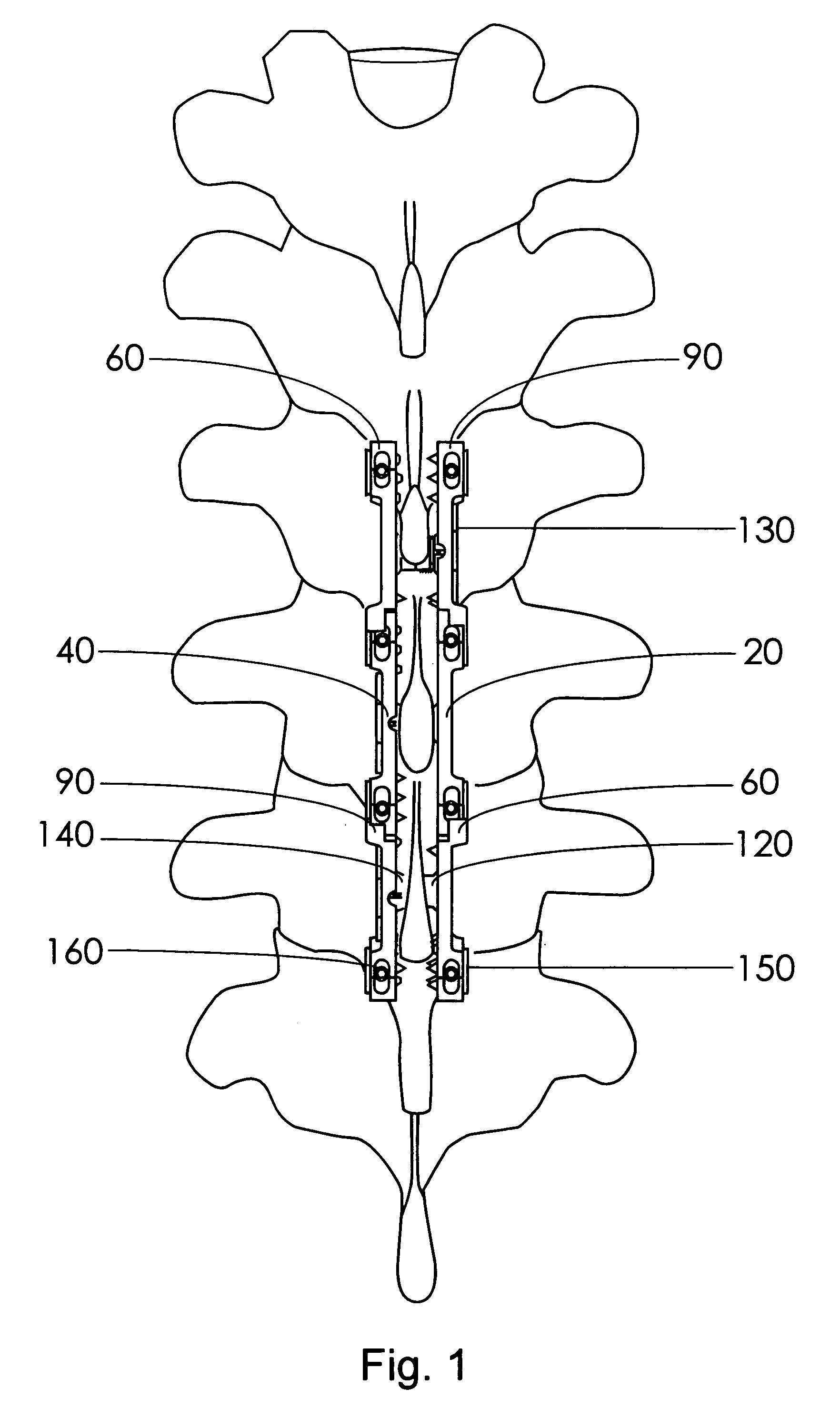
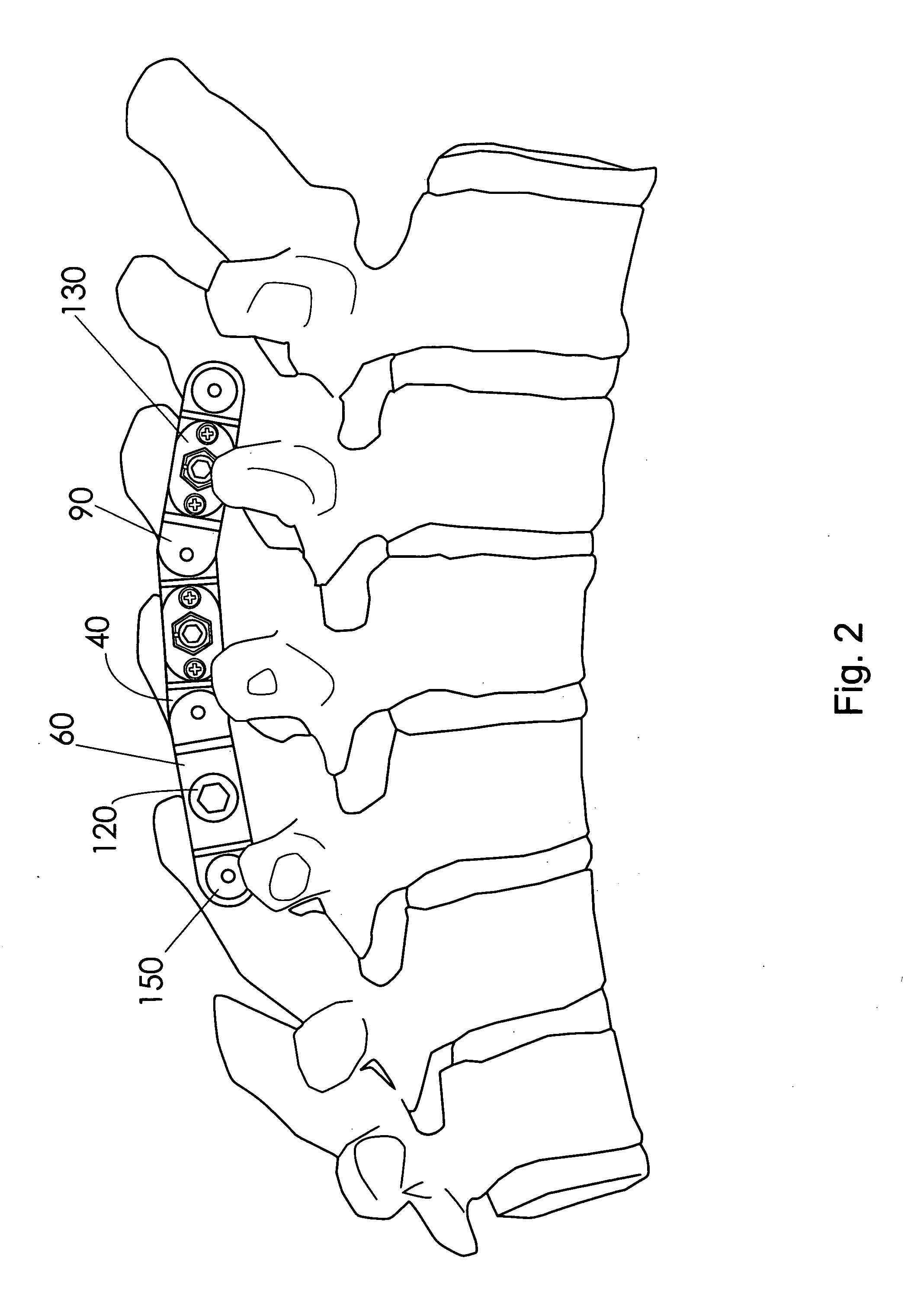
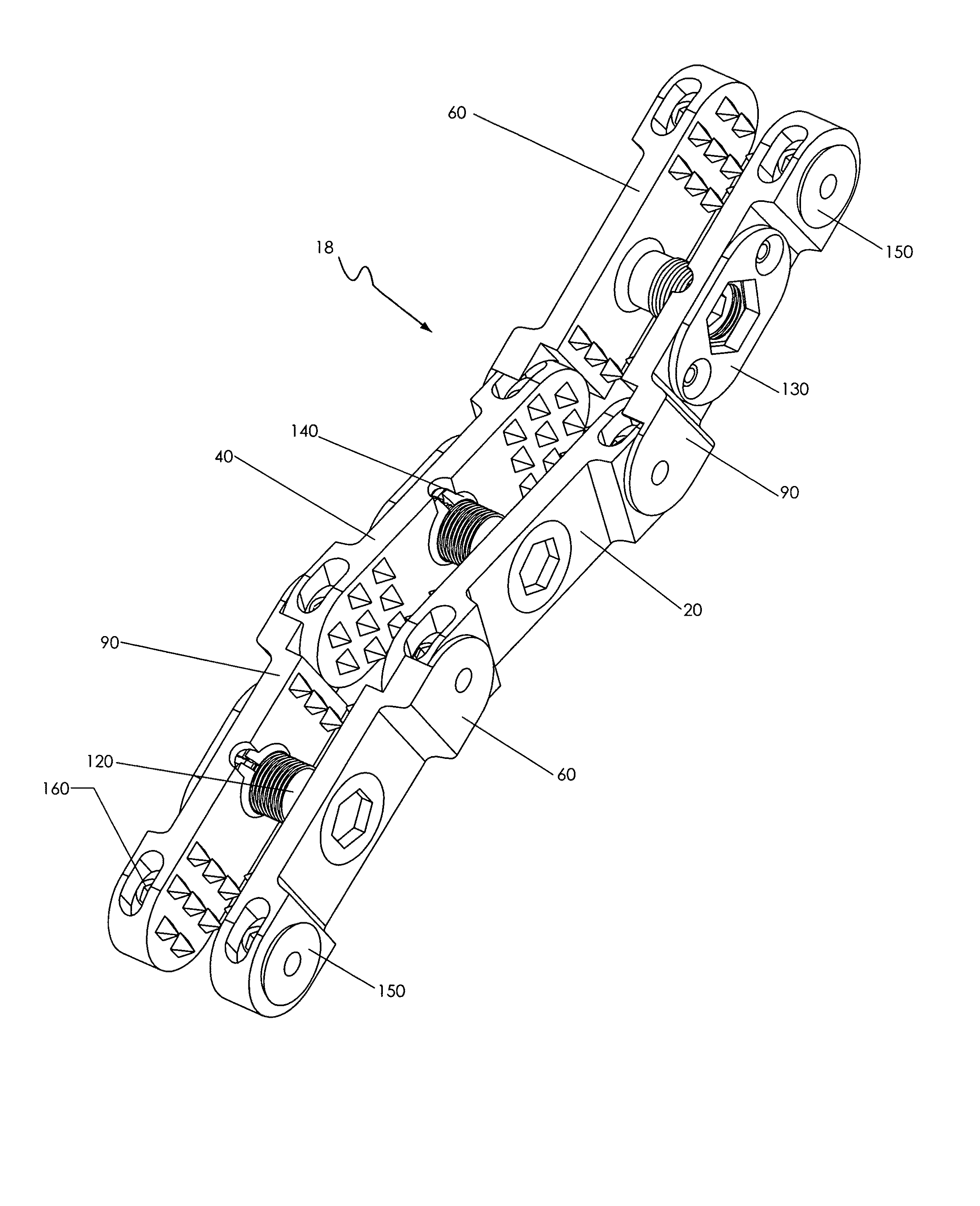
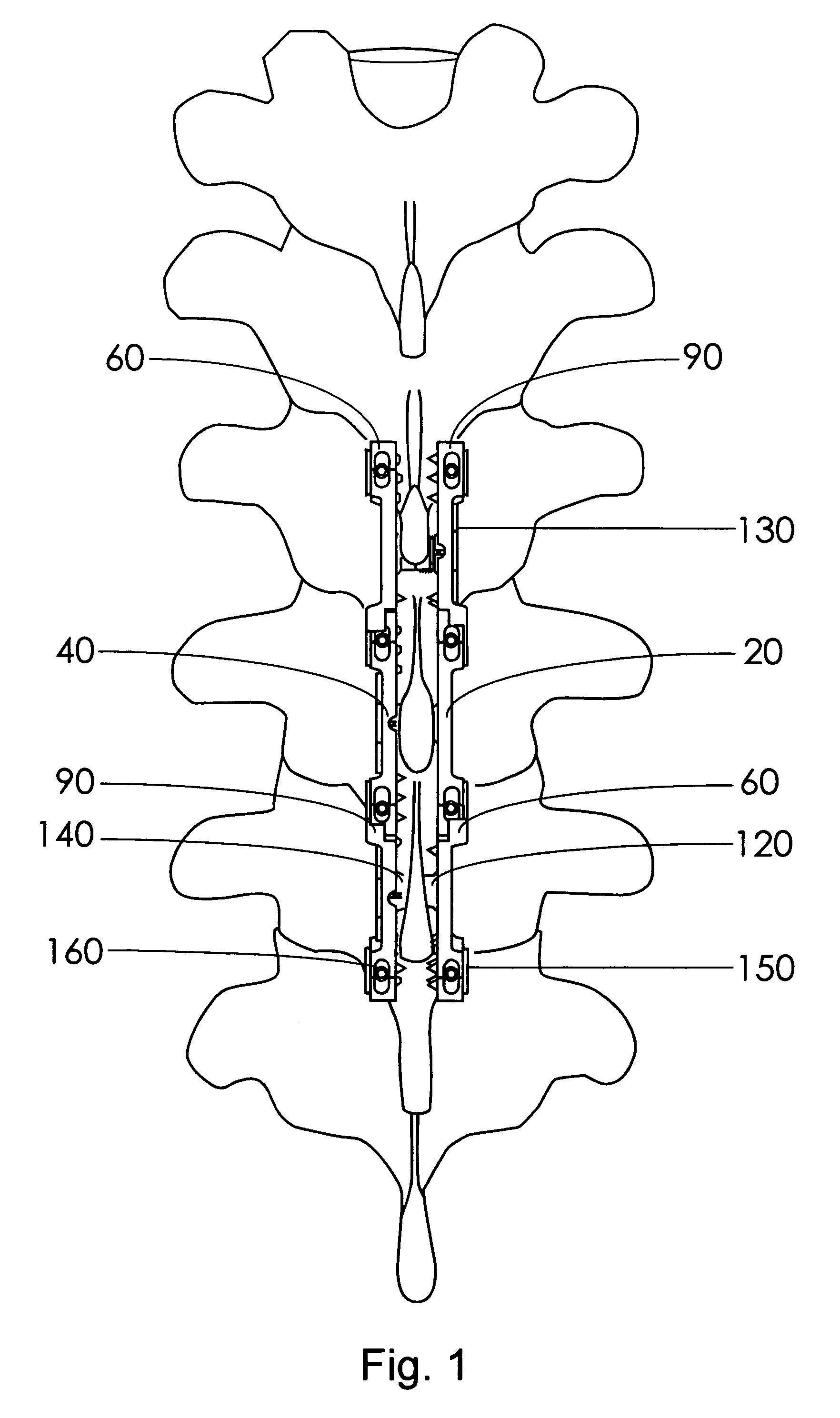
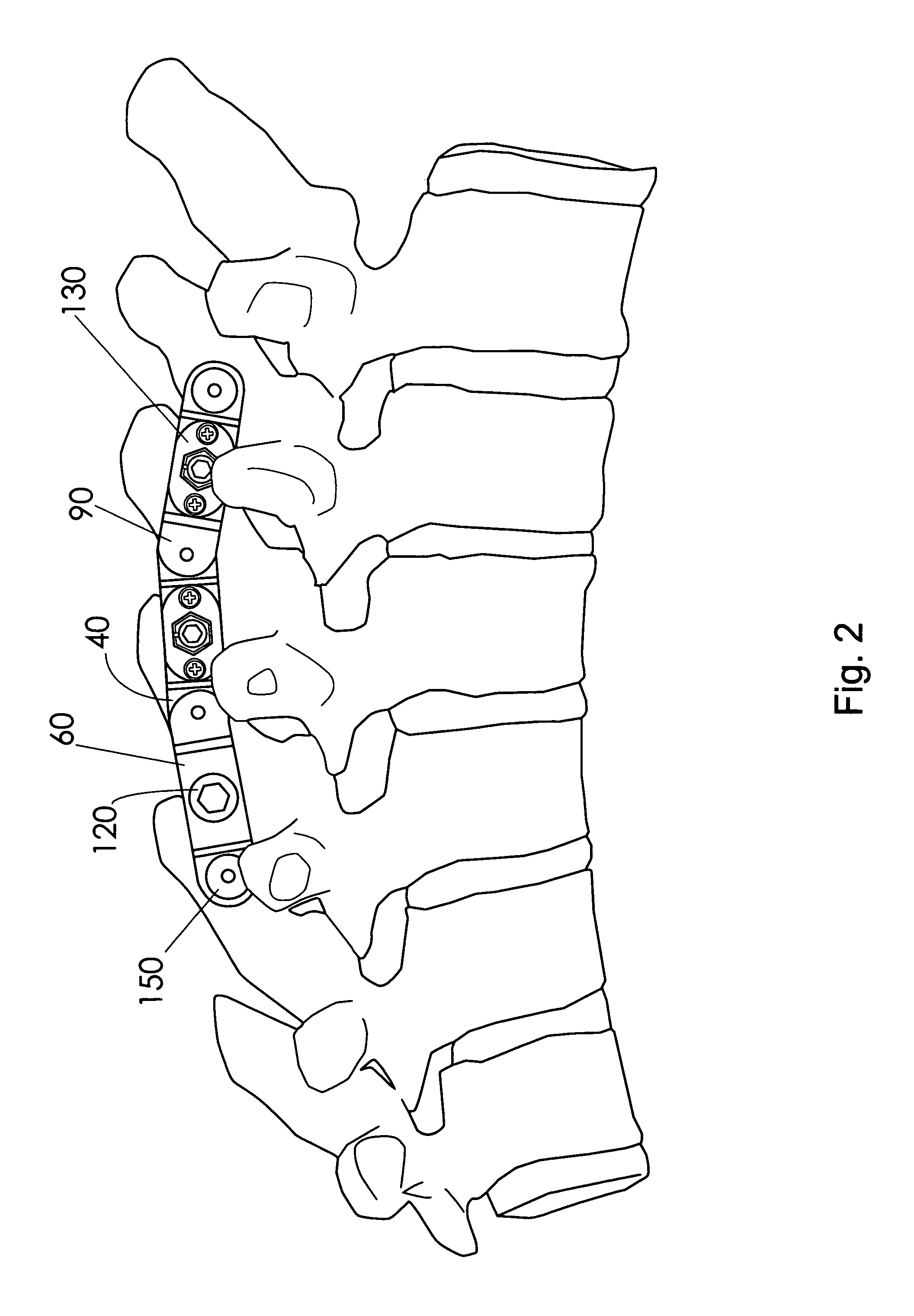
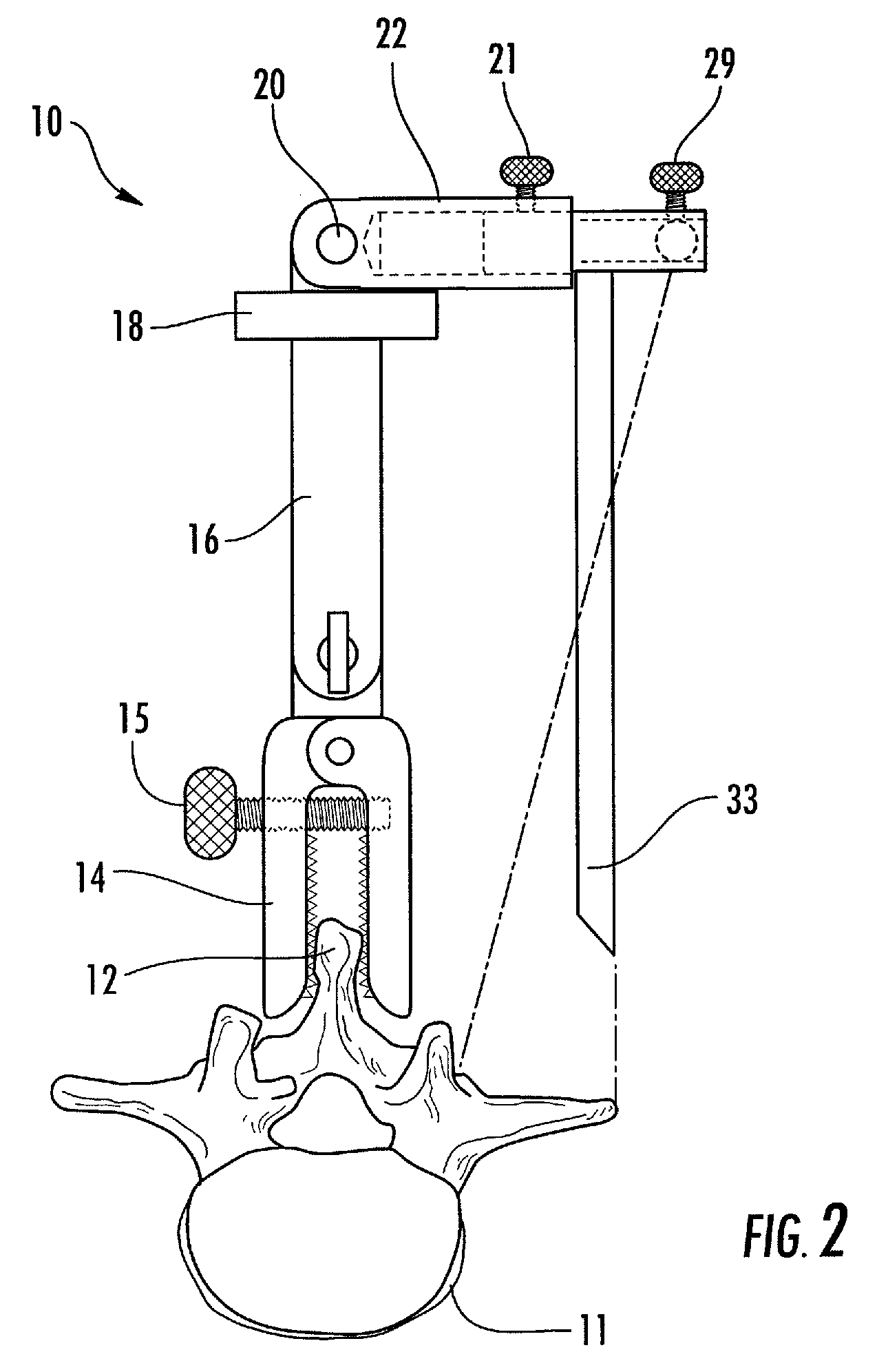
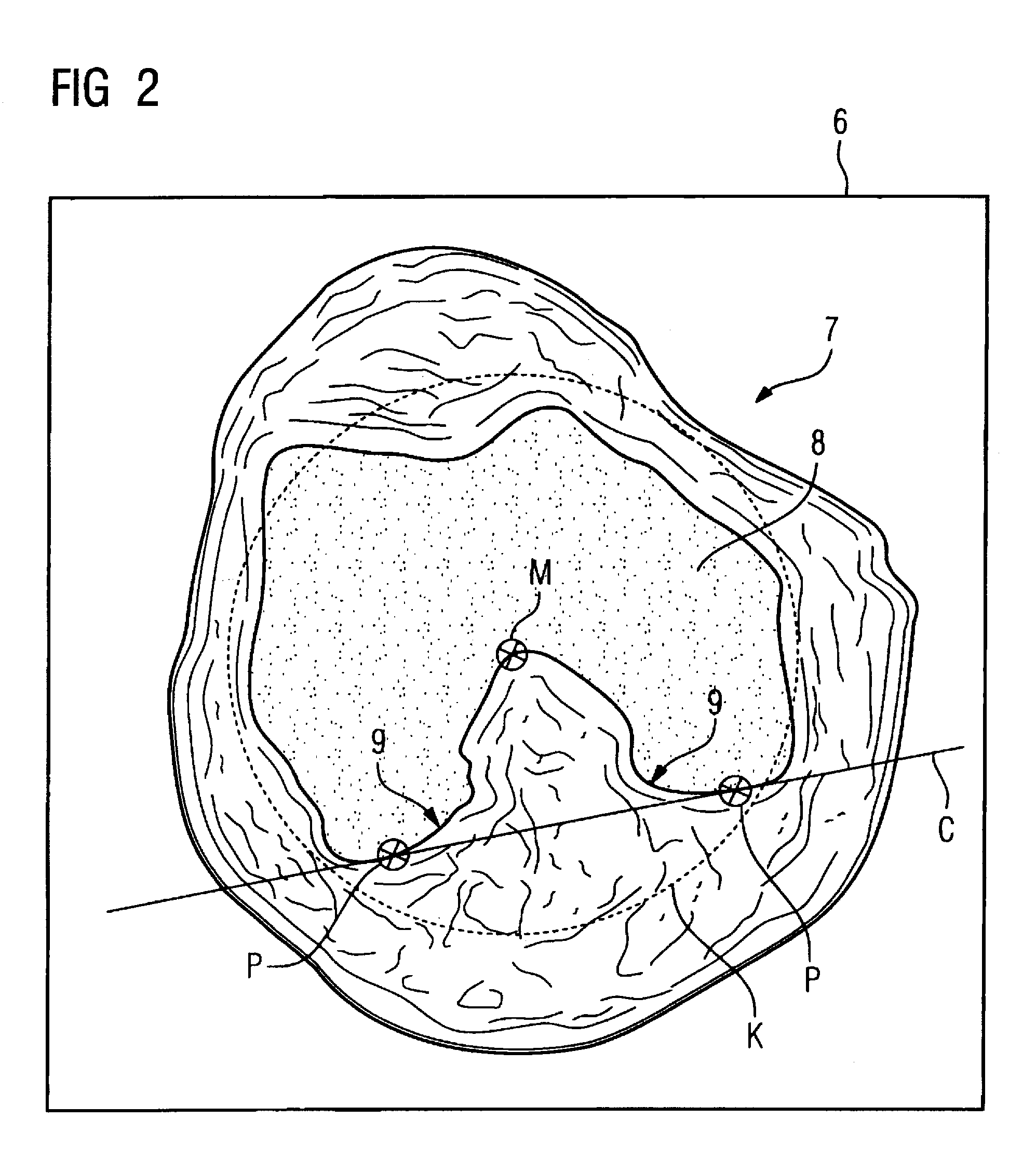
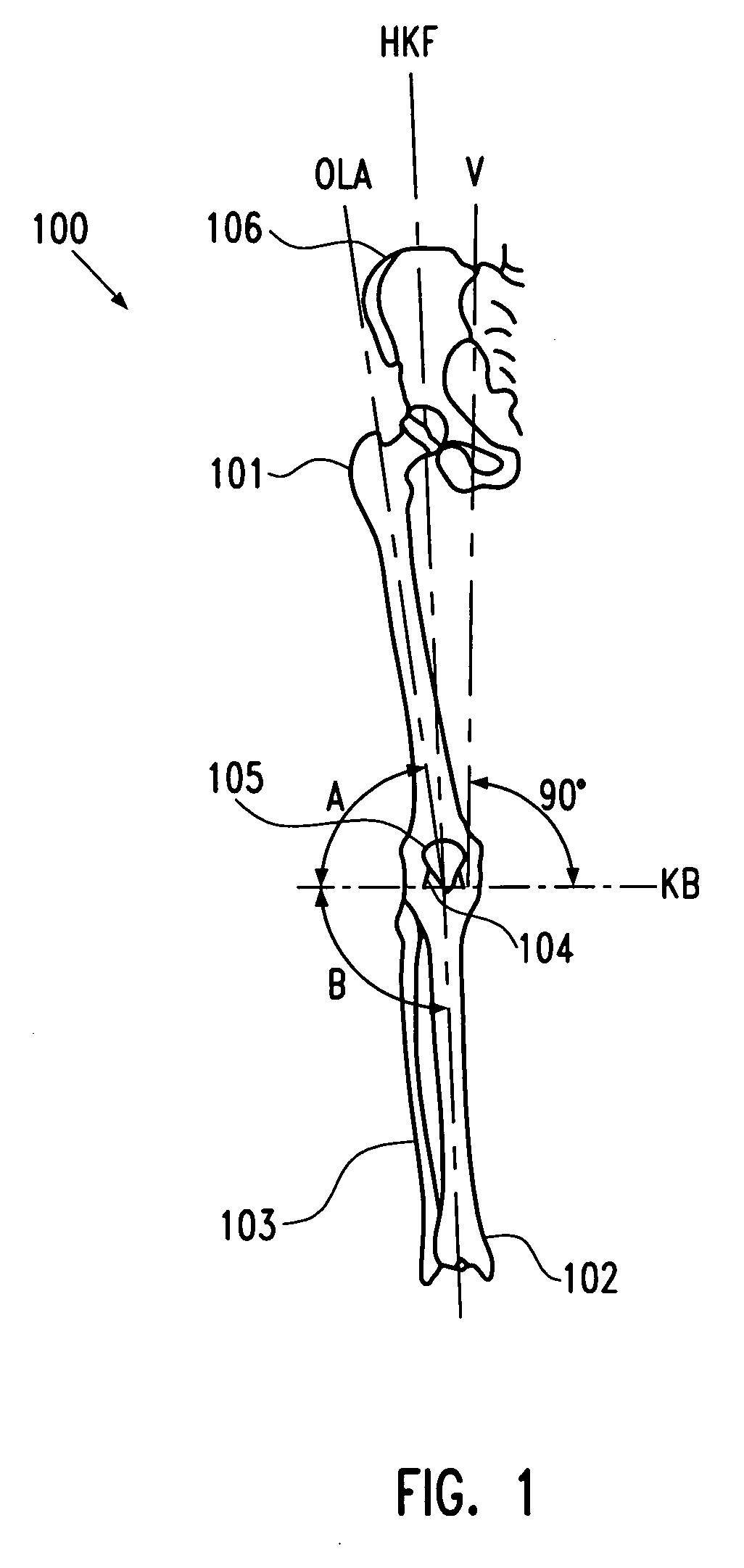
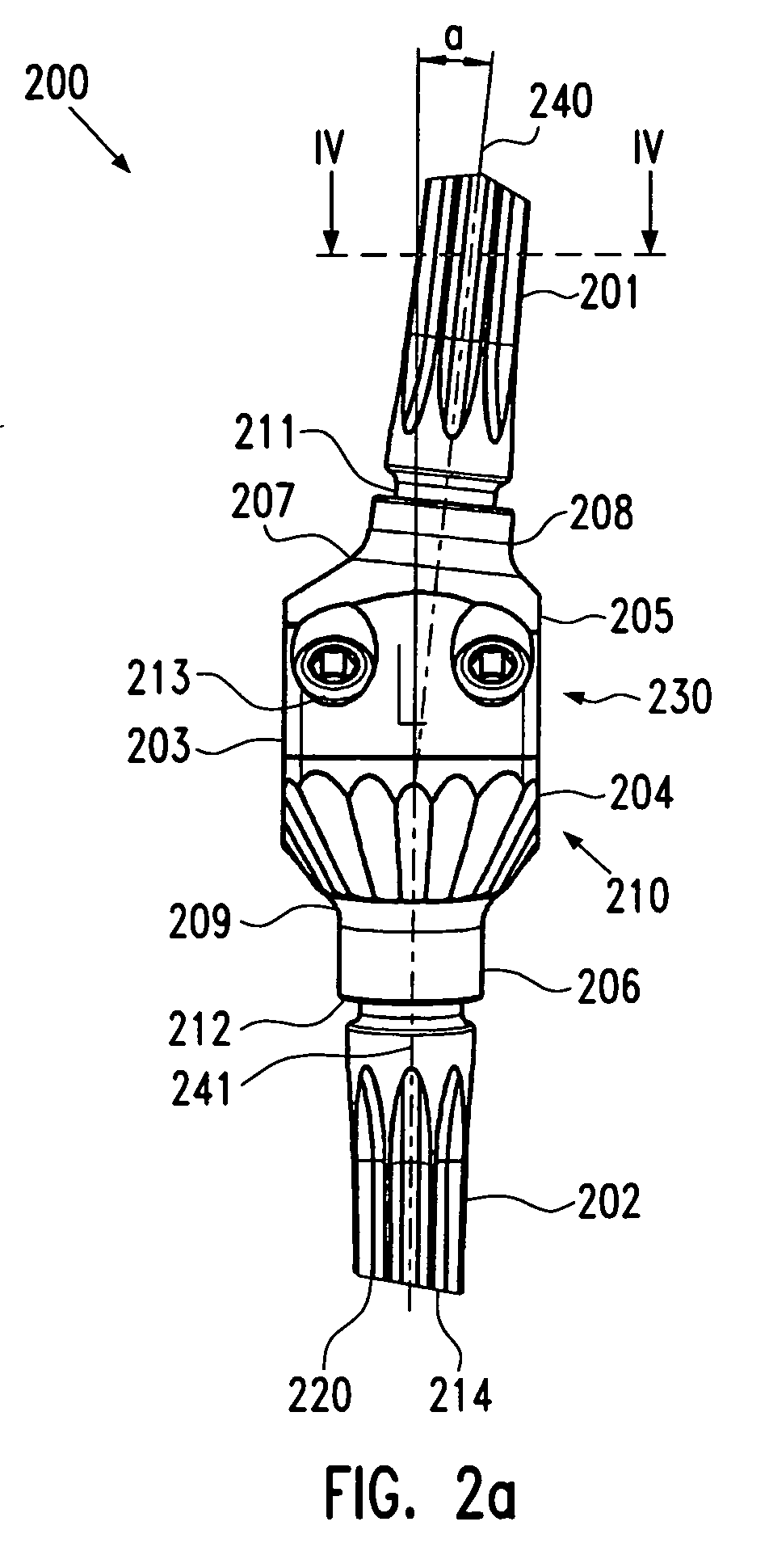
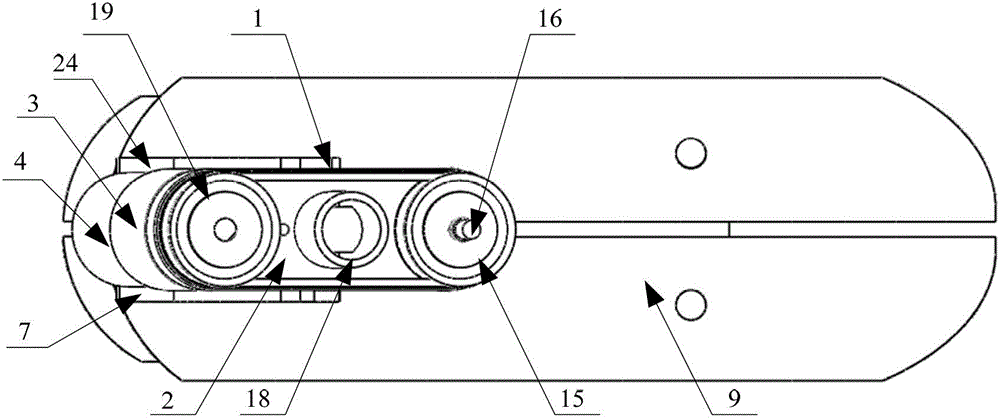
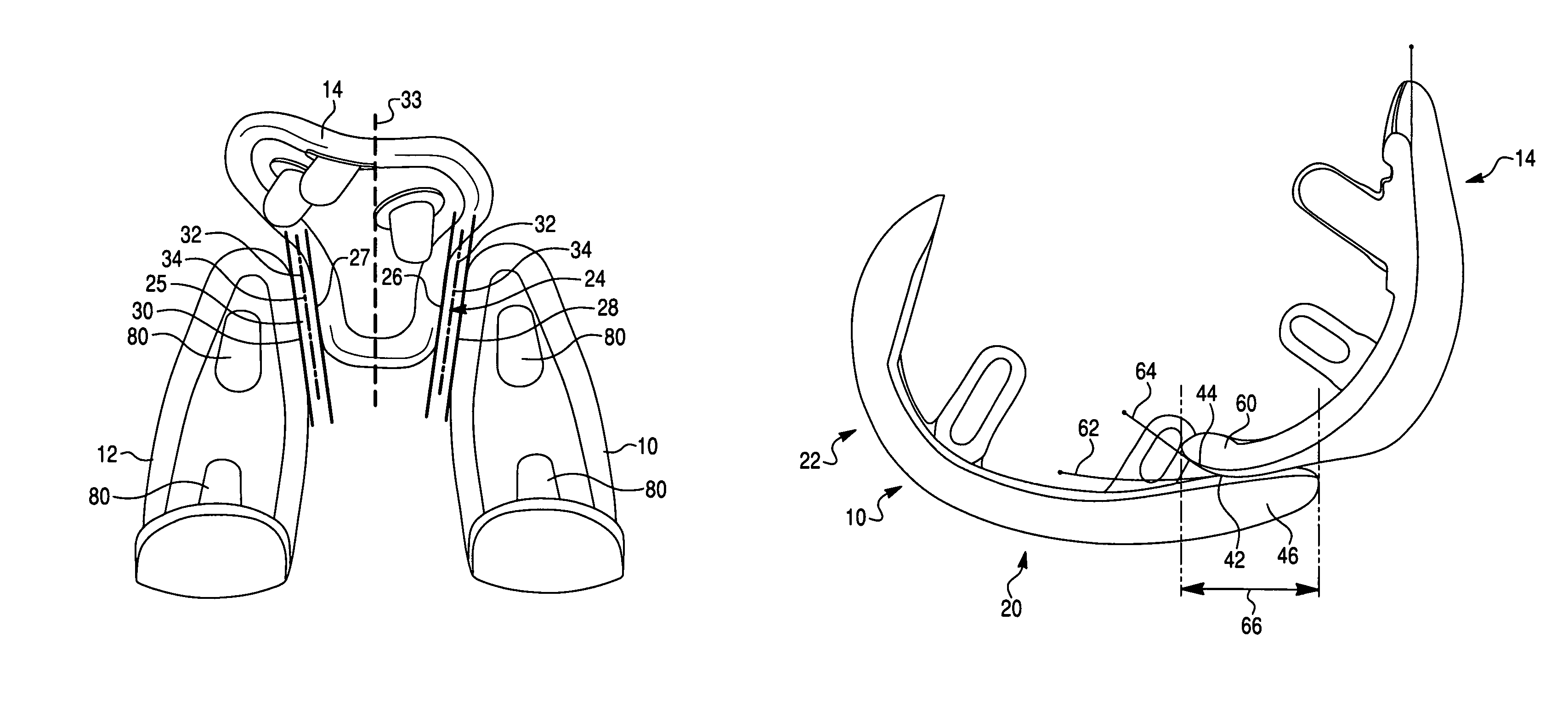
Instrument and method for the insertion and alignment of an intervertebral implant
ActiveUS20060084986A1The method is simple and reliablePrecise alignmentInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsDistractionCoronal plane
The present invention includes pin guides and methods for placing pins in adjacent vertebrae. The present invention also includes methods for placing pins in adjacent vertebrae using the pin guides described herein. The present invention also includes an intervertebral implant insertion and alignment instrument, a distraction instrument, an intervertebral implant insertion guide, and methods for inserting an implant into an intervertebral space. Despite existing tools and techniques, present positioning of implants in intervertebral spaces and pins in adjacent vertebrae often depend on a surgeon's skill, experience and technique. Practice of the present invention can aide in the placement of an implant into an intervertebral space and placement of pins in adjacent vertebrae, e.g., midline to the coronal plane spine and / or parallel to vertebral endplates that abut the intervertebral space.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
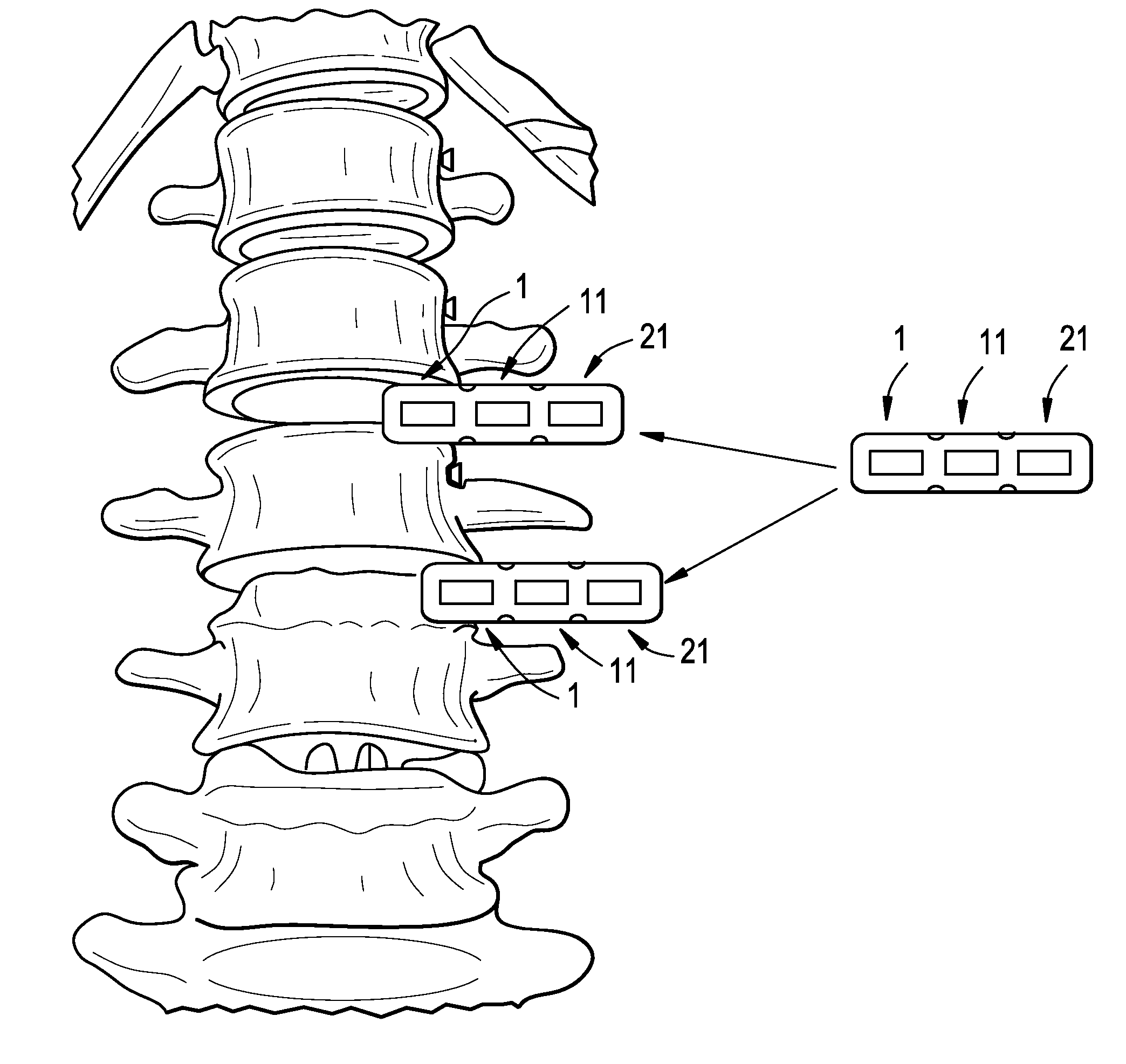
Adjustable tandem connectors for corrective devices for the spinal column and other bones and joints
InactiveUS20060079892A1Easy to tightenPrevent rotationSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnCoronal plane
Connectors for interconnecting rods, fixed to vertebrae and other bones of a subject include a body portion and two recesses or pockets for receiving the rods. These connectors are generally able to be secured to the rods by a tightening a fastener or retaining member from above the spine, which can facilitate the procedure for the surgeon. The connectors can include rotatable or stationary pockets, mating members that pivot and / or translate within the coronal plane of the subject to adjust to the positions of the rods, and extension shafts that pivot to adjust for rod angle.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
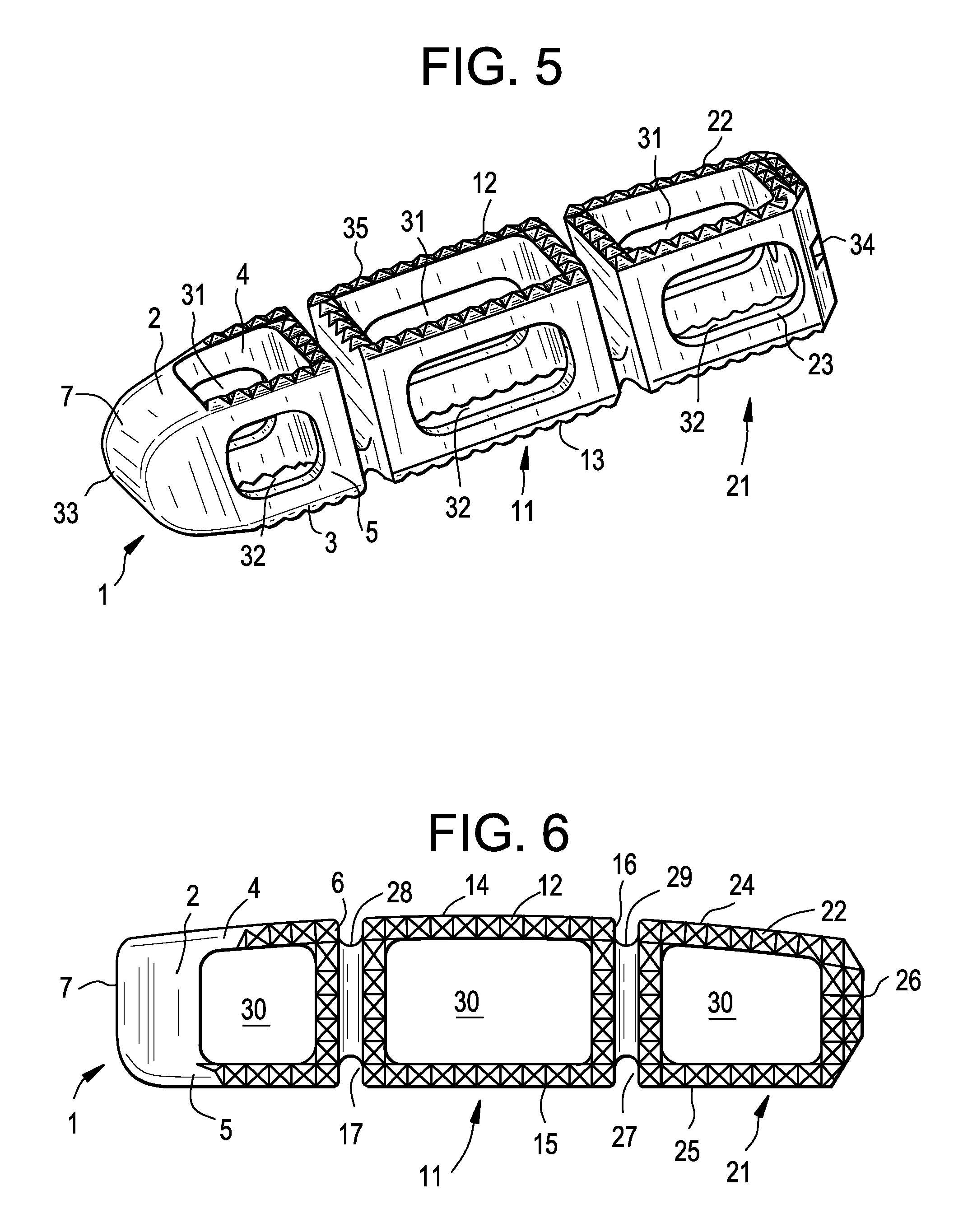
Multi-Segment Lateral Cage Adapted to Flex Substantially in the Coronal Plane
The present invention concerns several fusion devices and methods for laterally inserting a fusion device at an initial trajectory that is not parallel to the disc space. Each fusion device incorporates components that enable flexing, bending or pivoting of the device during its final approach to the prepared disc space.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Spinous process stabilization device and method
InactiveUS20090264927A1Easy to integrateInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsCoronal planeEmbedded teeth
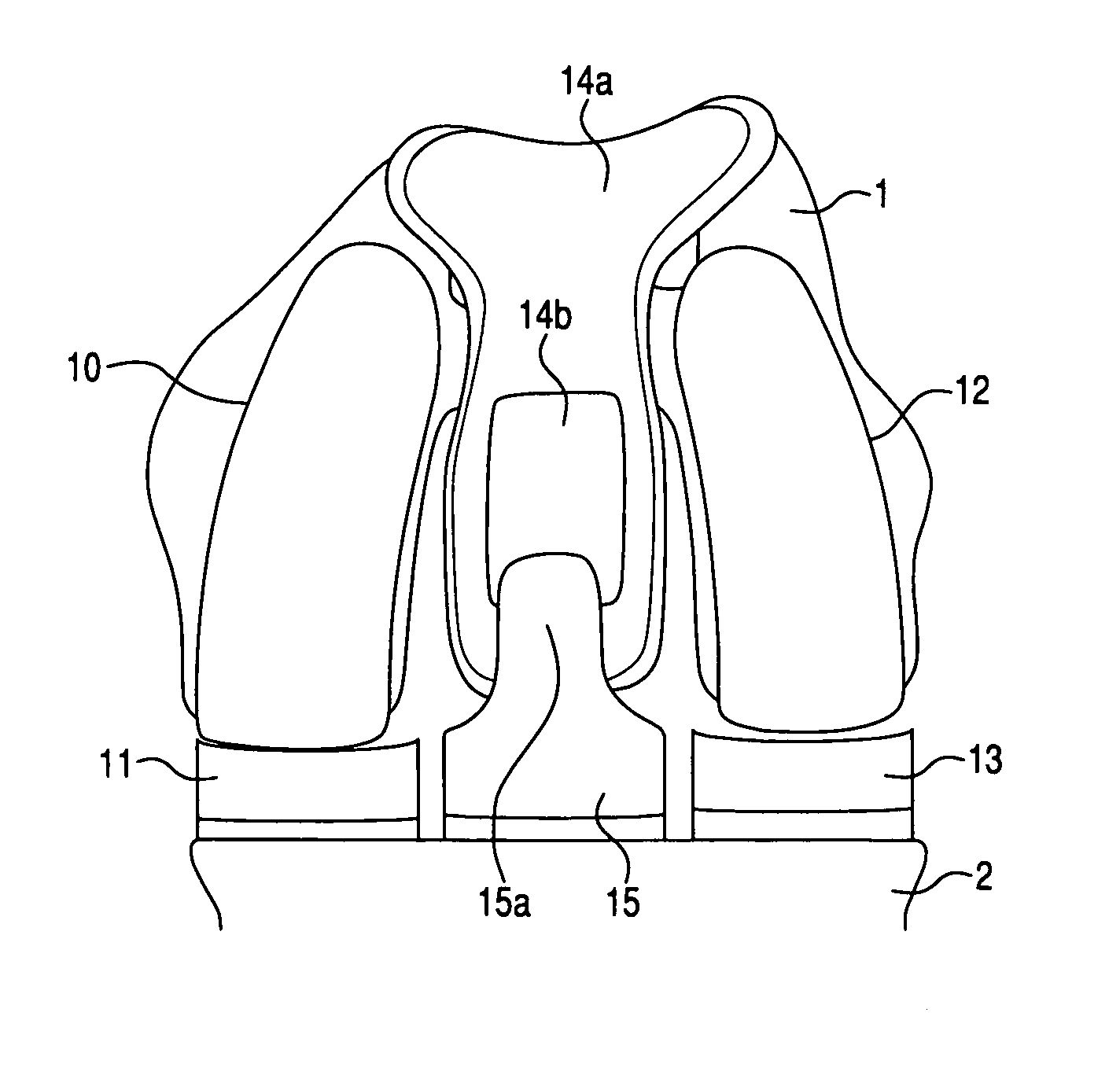
A fixation device to immobilize a spinal motion segment and promote posterior fusion, used as stand-alone instrumentation or as an adjunct to an anterior approach. The device functions as a multi-level fusion system including modular single-level implementations. At a single-level the implant includes a pair of plates spanning two adjacent vertebrae with embedding teeth on the medially oriented surfaces directed into the spinous processes or laminae. The complementary plates at a single-level are connected via a cross-post with a hemi-spherical base and cylindrical shaft passed through the interspinous process gap and ratcheted into an expandable collar. The expandable collar's spherical profile contained within the opposing plate allows for the ratcheting mechanism to be correctly engaged creating a uni-directional lock securing the implant to the spine when a medially directed force is applied to both complementary plates using a specially designed compression tool. The freedom of rotational motion of both the cross-post and collar enables the complementary plates to be connected at a range of angles in the axial and coronal planes accommodating varying morphologies of the posterior elements in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine. To achieve multi-level fusion the single-level implementation can be connected in series using an interlocking mechanism fixed by a set-screw.
Owner:GINSBERG HOWARD JOESEPH +2
Spinous process stabilization device and method
A fixation device is provided to immobilize a spinal motion segment and promote posterior fusion, used as stand-alone instrumentation or as an adjunct to an anterior approach. The device functions as a multi-level fusion system including modular single-level implementations. At a single-level the implant includes a pair of plates spanning two adjacent vertebrae with embedding teeth on the medially oriented surfaces directed into the spinous processes or laminae. The complementary plates at a single-level are connected via a cross-post passed through the interspinous process gap The freedom of rotational motion of both the cross-post and collar enables the complementary plates to be connected at a range of angles in the axial and coronal planes accommodating varying morphologies of the posterior elements in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine. To achieve multi-level fusion the single-level implementation can be connected in series using an interlocking mechanism fixed by a set-screw.
Owner:GINSBERG HOWARD JOESEPH +2
Spinous process fixated bilateral drilling guide
InactiveUS20100023018A1Precise positioningAccurate and repeatable drilling and screw placementProsthesisOsteosynthesis devicesAnatomical landmarkCoronal plane
The application describes a bilateral drilling and screw placement guide adapted for fixation to the spinous process of a vertebral body. The positioning and surgical guiding instrument is adapted for use during a spinal surgical procedure in conjunction with a drilling tool, fastening device, e.g. a pedicle screw, K-wire or the like. The guide includes an engagement device for attachment to a region of the spinous process, to which an adjustably attached support member is affixed. This allows for immobilizing the guide upon the spinous process anatomical landmark, in a specific orientation with respect thereto. The guide includes a bilaterally adjustable drill guide assembly for precise anatomical positioning of the drill and screw placement guides bilaterally about the sagittal, axial and coronal planes so as to enable the defining of a plurality of drilling axes extending toward the vertebral body. The device further provides for adjustment to account for anatomical variations in width along the axial plane, and includes pointing and angular positioning functionality to insure repeatable and reliable pilot hole and screw placement along a plurality of angles.
Owner:ALPHA GUIDE HLDG LLC
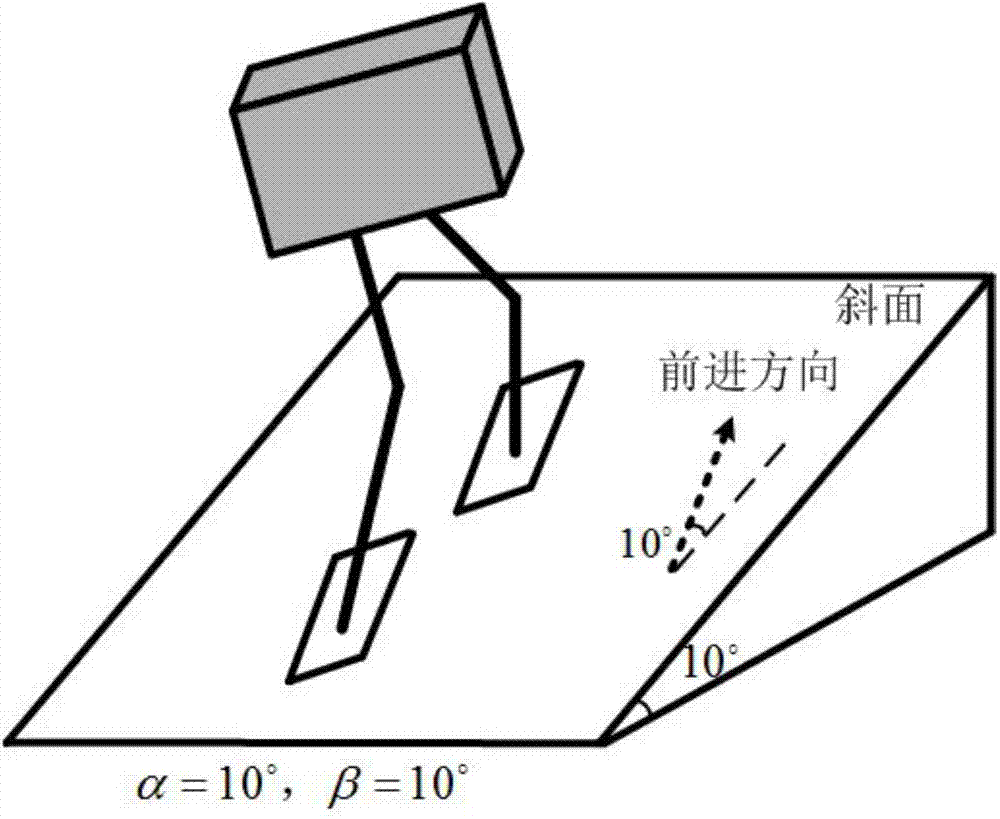
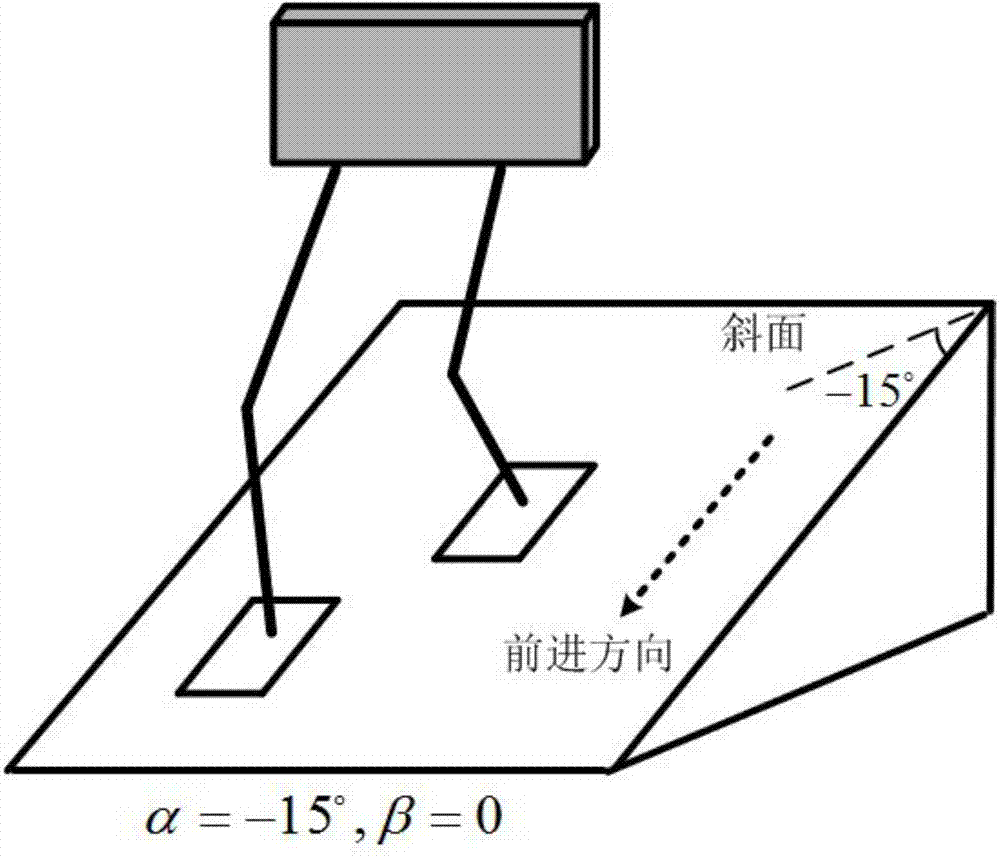
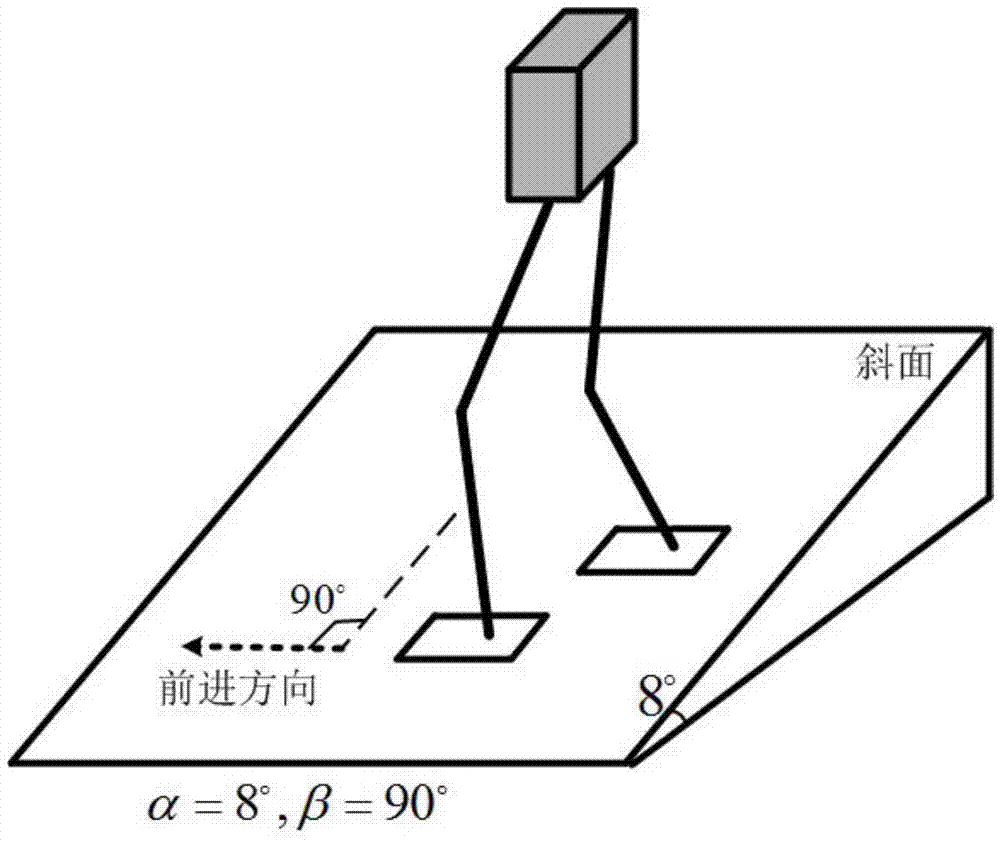
Gait planning method for walking of biped robot along slope
ActiveCN104331081AImprove environmental adaptabilityMovement coordination and natureAttitude controlCoronal planeDecomposition
The invention discloses a gait planning method for walking of a biped robot along a slope, and belongs to the technical field of robots. The method contains two core theories, namely, non-orthogonal decomposition and synthesis of a three-dimensional linear inverted pendulum and gait planning based on a biped long linear inverted pendulum. The method comprises the steps of gait parameter configuration, non-orthogonal decomposition of a three-dimensional linear inverted pendulum, foot trajectory planning based on three times of spline interpolation, centroid trajectory planning of a sagittal plane and a coronal plane based on a biped long linear inverted pendulum, non-orthogonal synthesis of the centroid trajectories of the sagittal plane and the coronal plane, and solving of joint trajectories of a robot based on inverse kinematics. By adopting the method of the invention, stable walking of a biped robot along all directions of a slope can be effectively achieved. The method is universal, simple in algorithm and high in practicality.
Owner:BEIJING INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGYGY
Multi-compartmental prosthetic device with patellar component transition
A prosthetic device for forming at least a portion of a joint may have a plurality of segmented components fixed relative to a femur of a body including: a patellofemoral component and a condyle component. Each segmented component may be configured such that a placement at which the segmented component will be fixed relative to the femur is not constrained by a connection to another of the segmented components that is fixed relative to the femur. In an installed configuration, the patellofemoral and condyle components may be fixed relative to the femur such that: a gap is provided between an edge of the patellofemoral component and an opposing edge of the condyle component, and a transition region is provided that extends from a first femoral coronal plane that intersects the patellofemoral component to a second femoral coronal plane that intersects the condyle component.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
Devices for performing fusion surgery using a split thickness technique to provide vascularized autograft
A technique for providing vascularized autograft to a fusion site in the posteriolateral aspect of a lumbar fusion mass by using a split-thickness laminoplasty technique, is disclosed in co-pending U.S. Provisional Application 60 / 379,371 filed on May 10, 2002 and U.S. patent application Ser. No. ______ filed concurrently with the present application. Devices used to accomplish osteotomies of the laminae, facet joints, and transverse processes are disclosed. The devices include a shaft that can guide the devices, a method of deploying a wire bone saw for dividing these structures through a coronal plane, leaving the periosteum, musculature, and hence blood supply intact. This novel and non-obvious technique will allow for the application of vascularized autograft to the fusion bed in posterior or posteriolateral fusion of the spine.
Owner:TRUSPINE USA
Mr method and apparatus for determining coronal and sagittal image planes from an image data set of a knee joint
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
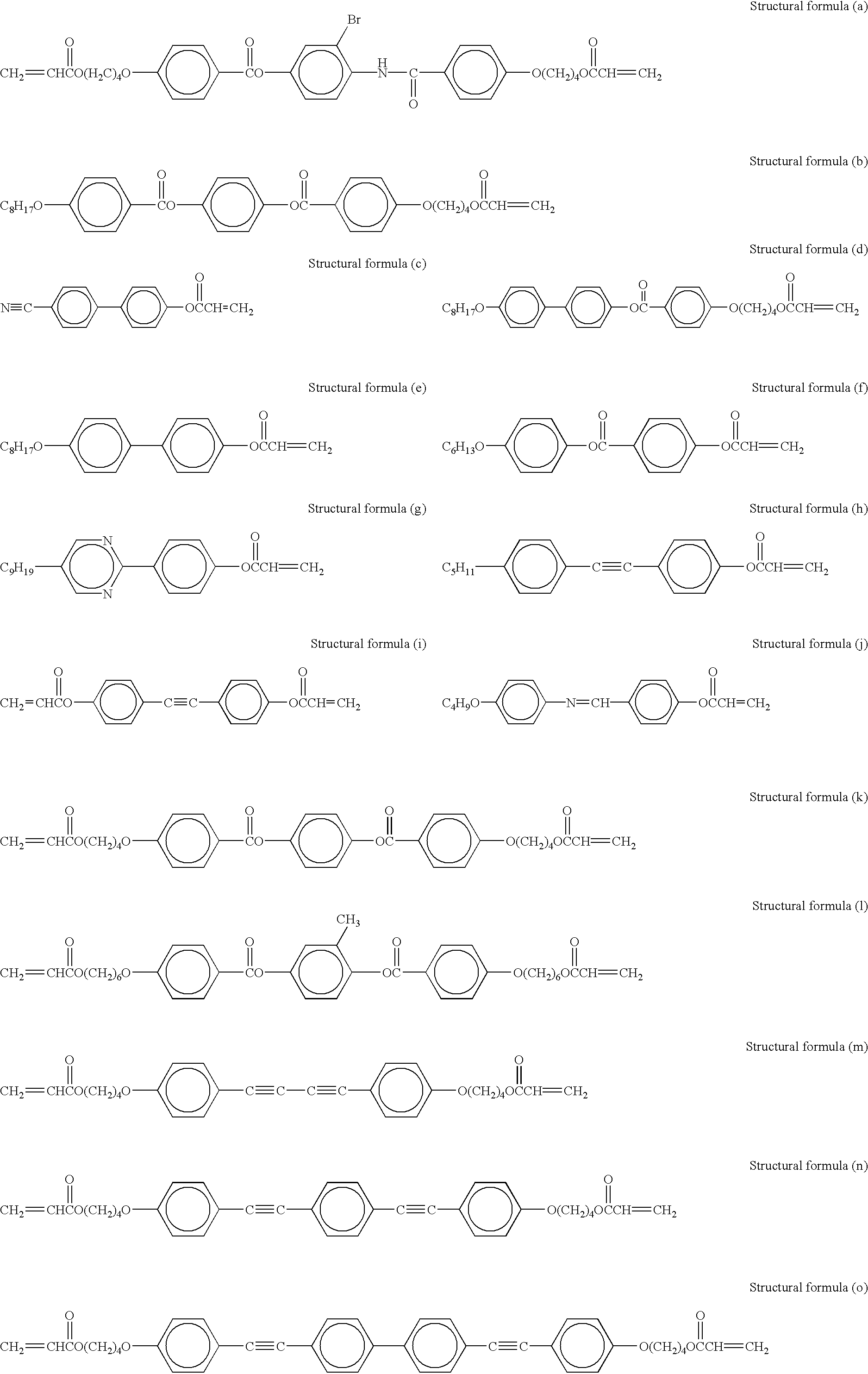
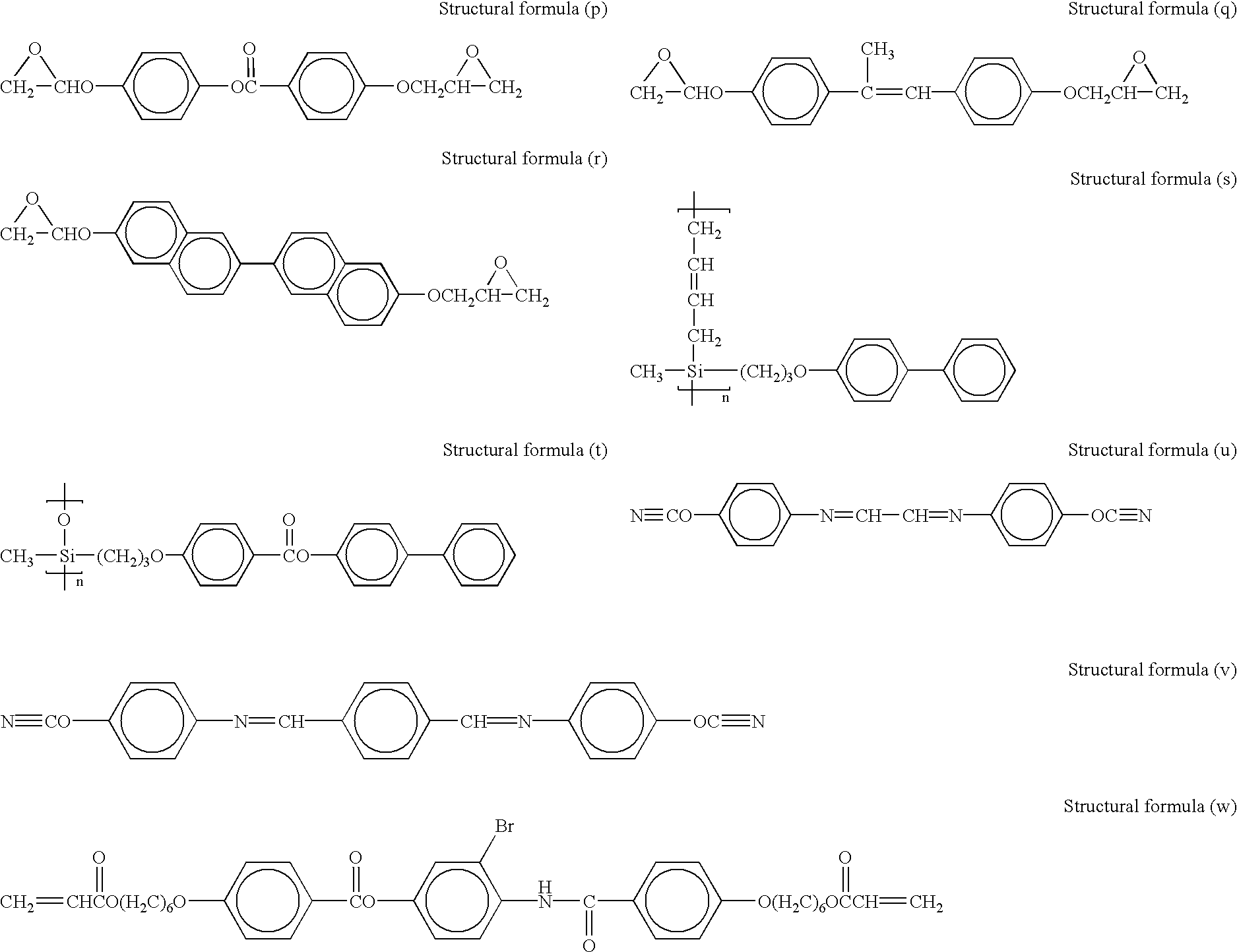
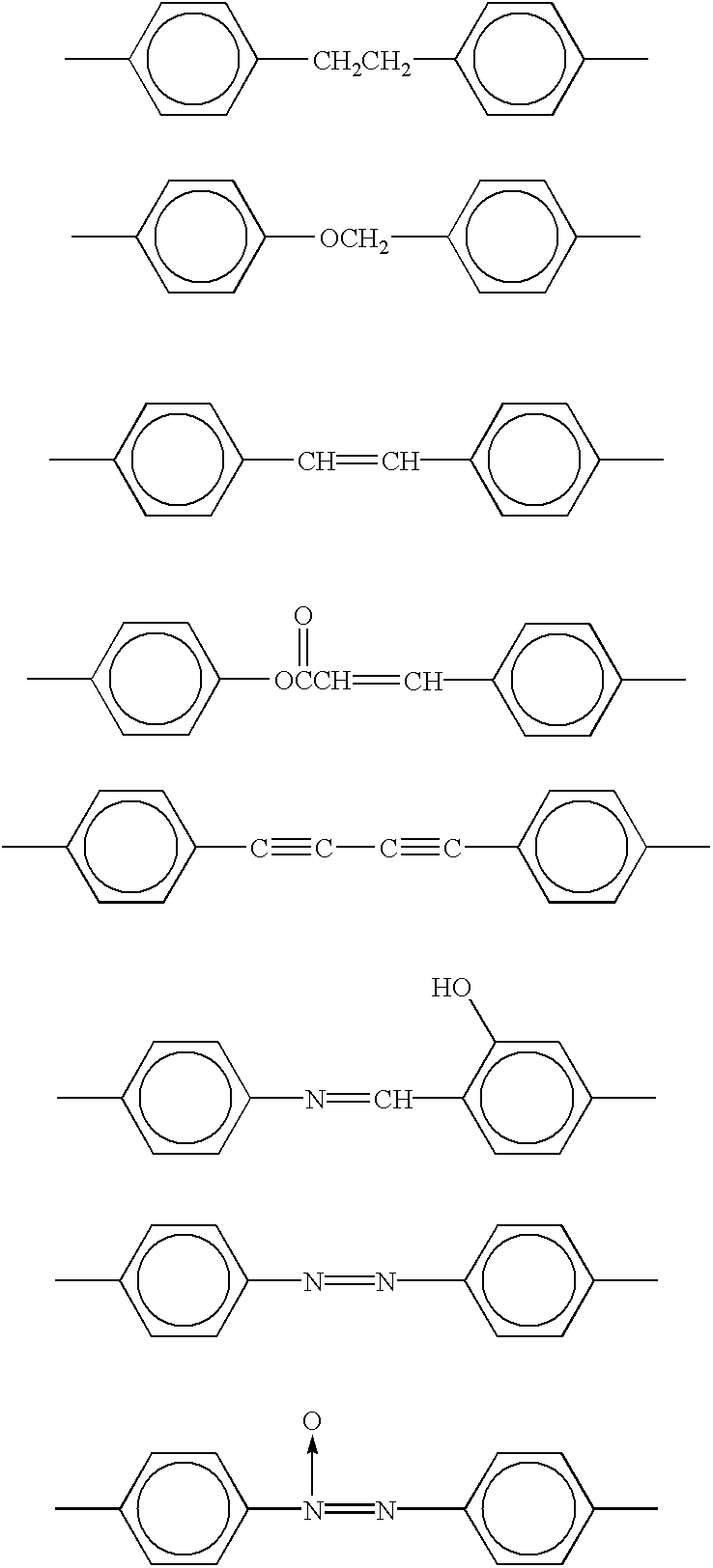
Wall-structured body and process for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20030143343A1Liquid crystal compositionsThin material handlingCoronal planeMaterials science
An object of the present invention is to provide a wall-structured body having a high aspect ratio which can be produced at low cost. A wall-structured body has molecules having orientation axes, wherein the molecules are formed by polymerizing a compound having a polymerizable functional group, and the orientation axes of the molecules are aligned in one direction. The wall-structured body has molecules having orientation axes, the molecules have an orientation parameter of 0.5 or more to the orientation axes. The wall-structured body has side-surfaces which face each other and cross a horizontal plane, wherein an angle between the horizontal plane and a tangent line at ½A long from the horizontal plane is 85° to 95° in a cross-section where the wall-structured body is cut vertically to the horizontal plane and at a plane crossing the side-surfaces, when "A" expresses a length of at least one of the side-surfaces.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP
Instrument and method for the insertion and alignment of an intervertebral implant
ActiveUS8298235B2The method is simple and reliablePrecise positioningInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsDistractionCoronal plane
The present invention includes pin guides and methods for placing pins in adjacent vertebrae. The present invention also includes methods for placing pins in adjacent vertebrae using the pin guides described herein. The present invention also includes an intervertebral implant insertion and alignment instrument, a distraction instrument, an intervertebral implant insertion guide, and methods for inserting an implant into an intervertebral space. Despite existing tools and techniques, present positioning of implants in intervertebral spaces and pins in adjacent vertebrae often depend on a surgeon's skill, experience and technique. Practice of the present invention can aide in the placement of an implant into an intervertebral space and placement of pins in adjacent vertebrae, e.g., midline to the coronal plane spine and / or parallel to vertebral endplates that abut the intervertebral space.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Arthrodesis module and method for providing a patient with an arthrodesis
An endoprothetical connection element for creating a knee arthrodesis comprises a coupling element that comprises a first fastener and a second fastener. The first fastener is adapted for connection with a first fastening element corresponding to the first fastener that is provided at a shaft insertable into a femur of a patient. The second fastener is adapted for connection with a second fastening element corresponding to the second fastener that is provided at a shaft insertable into a tibia of the patient. The coupling element is formed such that a first longitudinal axis of the femoral shaft connected to the first fastener and a second longitudinal axis of the tibial shaft connected to the second fastener include an angle different from 180 degrees which, when implanted into the body of the patient, is lying in a coronal plane of the patient.
Owner:BREHM PETER
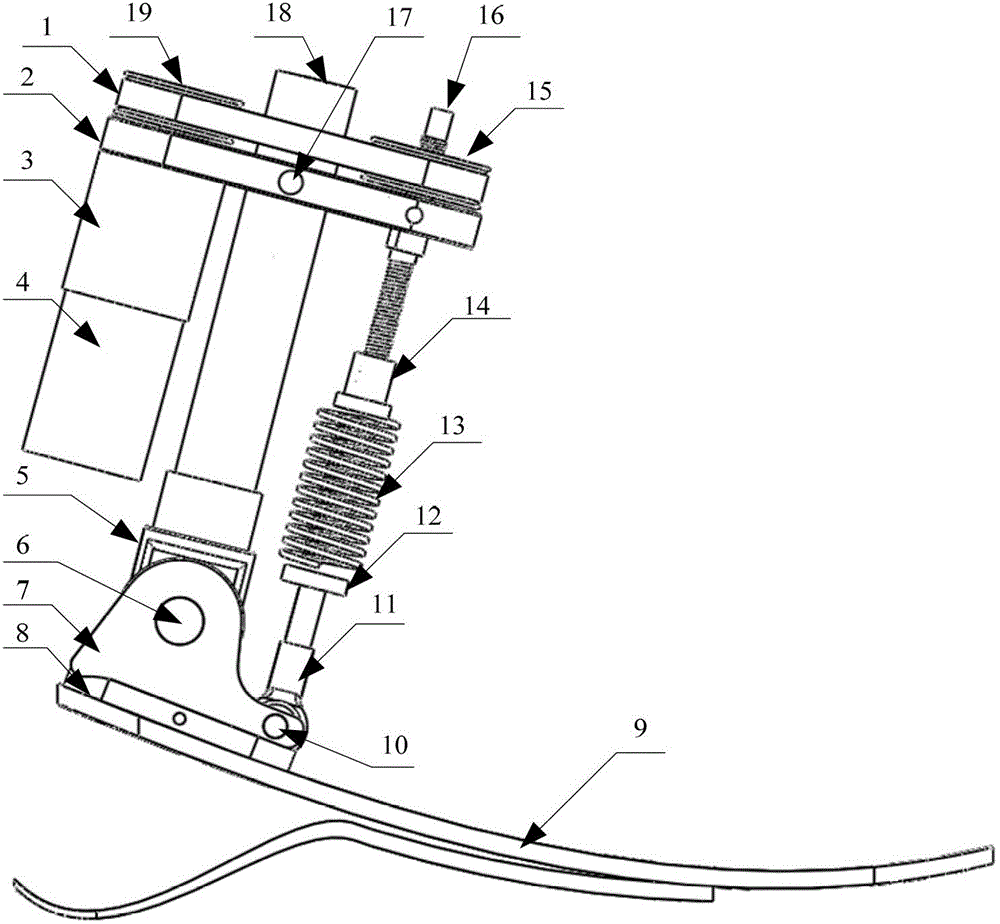
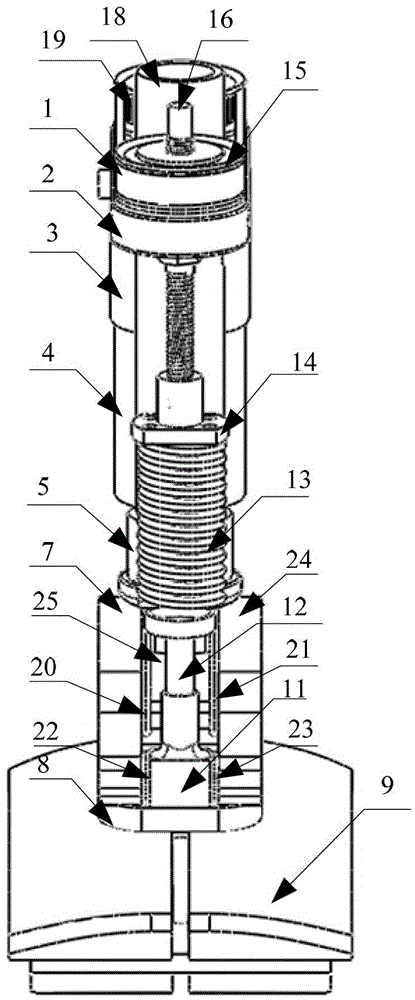
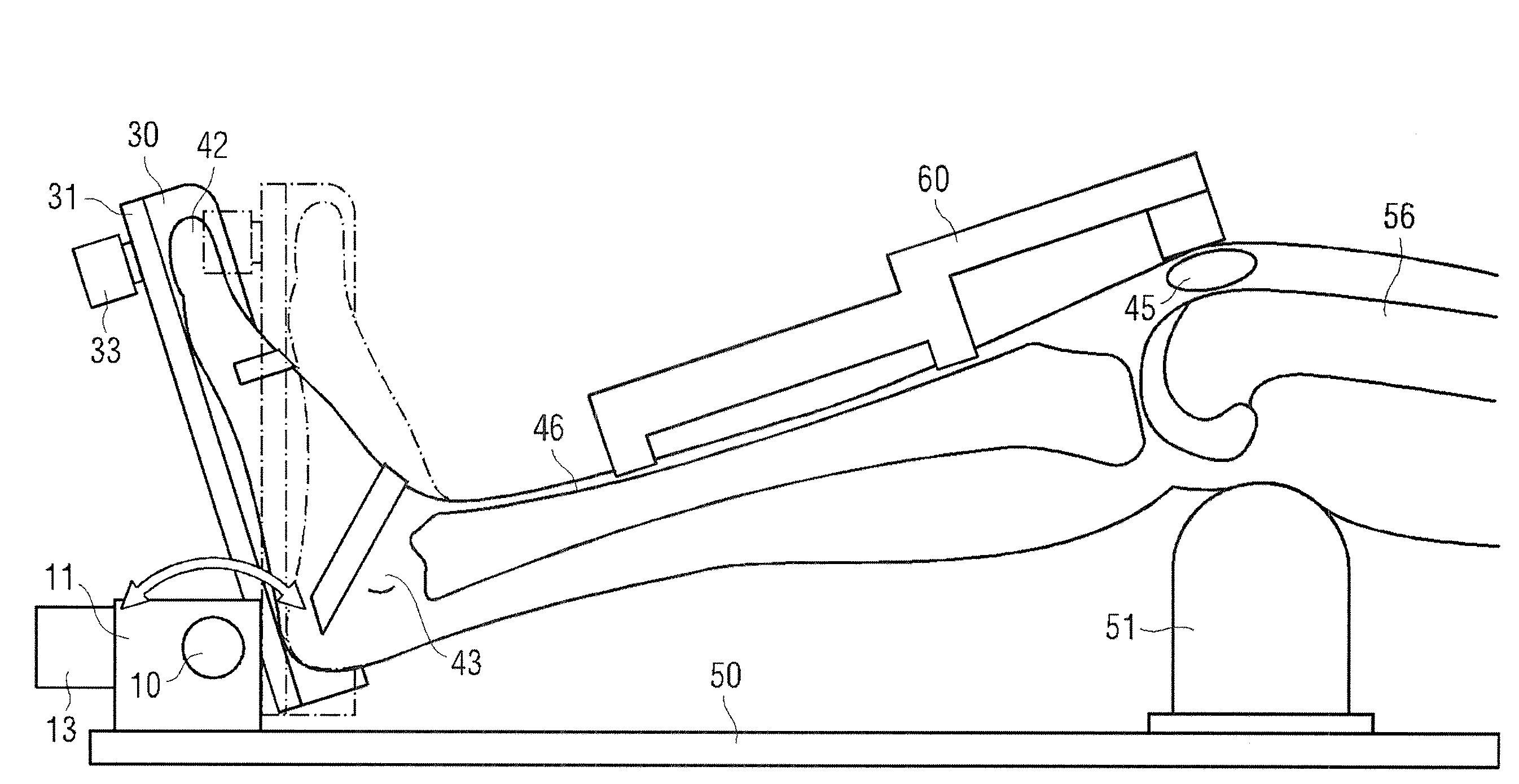
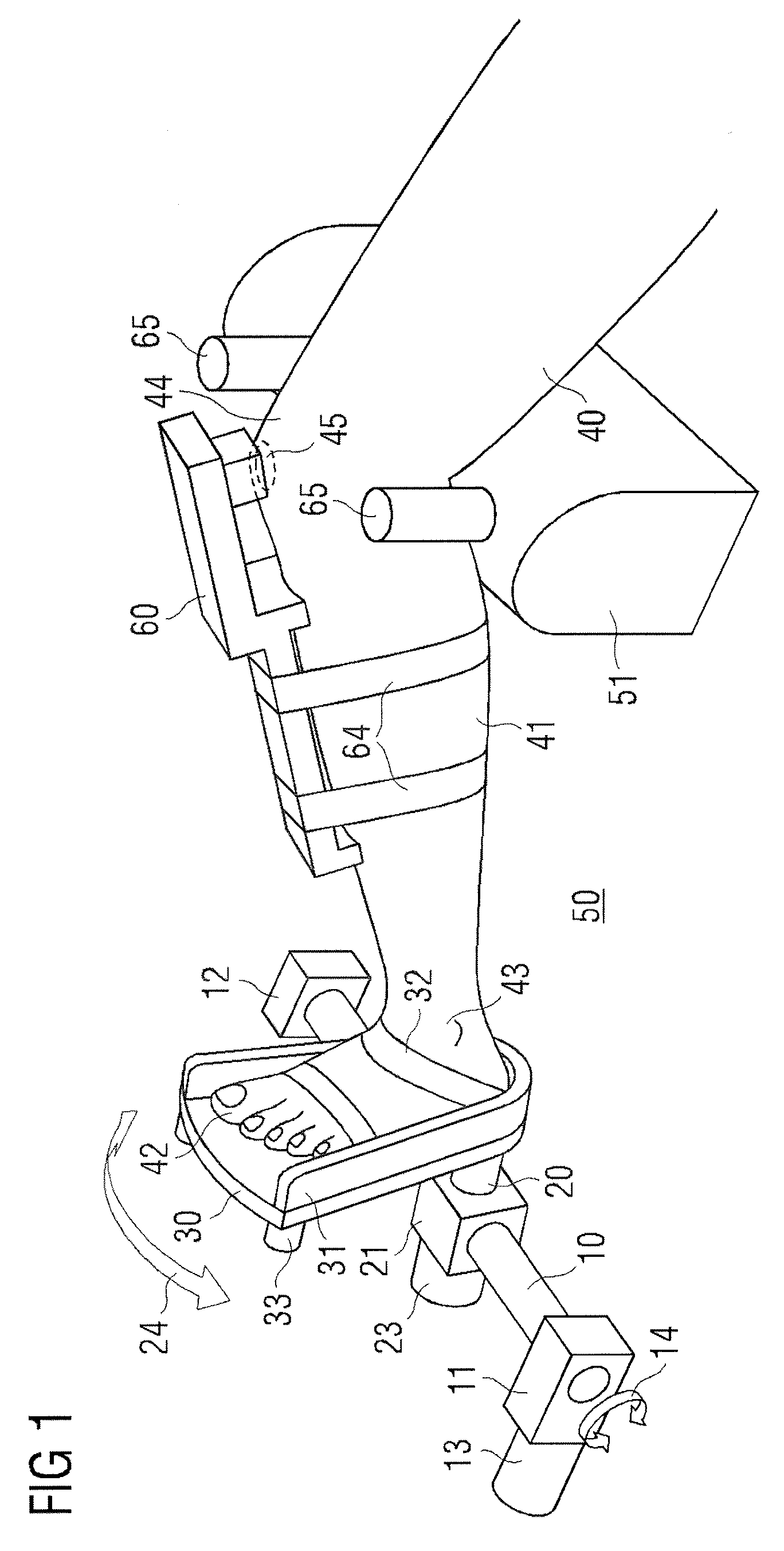
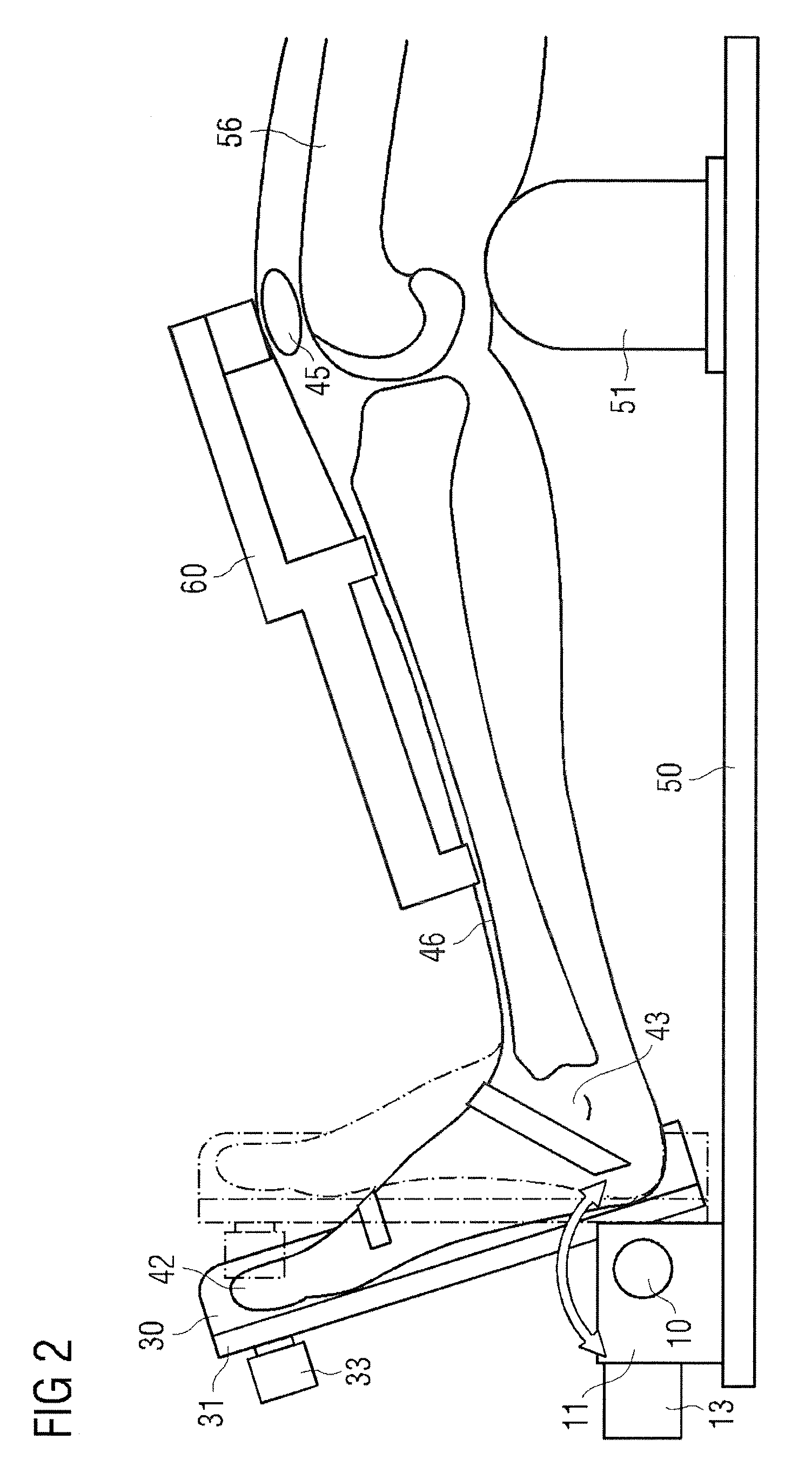
Active-passive type ankle joint prosthesis and movement mode thereof
The invention discloses an active-passive type two-degrees-of freedom ankle joint prosthesis, comprising a carbon fiber energy storage sole, a motor, a speed reducer, a motor fixing supporting seat, a belt pulley transmission device, a carbon fiber pipe, a ball screw, an energy storage springs, joint bearings, energy storage rubber rings and joint supporting seats, wherein the carbon fiber energy storage sole is connected with the carbon fiber pipe through the joint supporting seats; the motor fixing supporting seat is connected with the carbon fiber pipe through an active pin; the motor is fixedly arranged on one end of the motor fixing supporting seat; the ball screw is fixedly arranged on the other end of the motor fixing supporting seat; two ends of the motor fixing supporting seat are connected by the belt pulley transmission device; the energy storage springs areis connected with a ball screw nut; and the energy storage rubber rings are connected with the joint bearings and the joint supporting seats through a shaft. The ankle joint prosthesis provided by the invention not only can completely provide required energy for human gait, but also can adapt to various landforms; in addition, the ankle joint prosthesis can completely imitate movement angles of a human ankle joint on a sagittal plane or a coronal plane; and therefore, the normal walking requirement of an amputation patient can be satisfied better.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Laser cladding process for abrasion-resistant anticorrosion coating of water turbine unit runner
InactiveCN101994112AExcellent wear resistance and corrosion resistanceImprove wear resistanceMetallic material coating processesMelting tankCoronal plane
The invention discloses a laser cladding method for an abrasion-resistant anticorrosion coating of a water turbine unit runner. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps of: performing surface cleaning on greasy dirt and rust layers on the surface of the water turbine unit runner; then selecting iron-based alloy powder, making the alloy powder discharged from an automatic powder feeding head fall into a laser molten pool by adopting laser equipment and an adjustable automatic powder feeding device, adjusting the powder feeding amount, and forming uniform and dense laser claddings on the processing surfaces of the upper and lower coronal planes, wherein the thicknesses of the laser claddings reach 0.2 to 1.8 millimeters; and finally, checking the processing parts of the upper and lower coronal planes of the runner by using a dye penetrant inspection method, wherein the processing parts are required without defects of cracks, air holes and the like. The laser cladding coating is uniform and dense, forms firm metallurgical bonding together with a matrix, has good abrasion resistance and anticorrosion performance, and can remarkably improve the abrasion-resistant and anticorrosion performance of the water turbine unit runner and prolong the service life of the water turbine unit runner.
Owner:SHENYANG DALU LASER COMPLETE EQUIP
Method for acquiring three-view drawing of medical image
InactiveCN101692286AReduce the number of trianglesReduce drawing time2D-image generation3D-image renderingSagittal planeImaging processing
The invention provides a method for acquiring a three-view drawing of medical image, which belongs to the technical field of image processing. The method comprises: firstly, acquiring a CT medical image and performing the three-dimensional reconstruction of the medical image to obtain a three-dimensional image; reading the three-dimensional image and obtaining a three-dimensional reconstructed image by reducing the triangular plates in the three-dimensional image by using triangular plate simplification technology to reduce the image drawing time and the occupation of a memory; computing a three-view drawing normal vector and a three-view drawing position coordinate of a point according to the three-dimensional coordinate of the point in the three-dimensional reconstructed image and acquiring a cross section view, a coronal plane view and a sagittal plane view which pass through the point by conversion matrix processing, namely, acquiring the grey values of all points in the cross section view, the coronal plane view and the sagittal plane view by using a trilinear interpolation method to acquire the cross section view, the coronal plane view and the sagittal plane view. In the method, the triangles in the three-dimensional image are reduced to reduce the image drawing time and the occupation of the memory and improve interaction.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
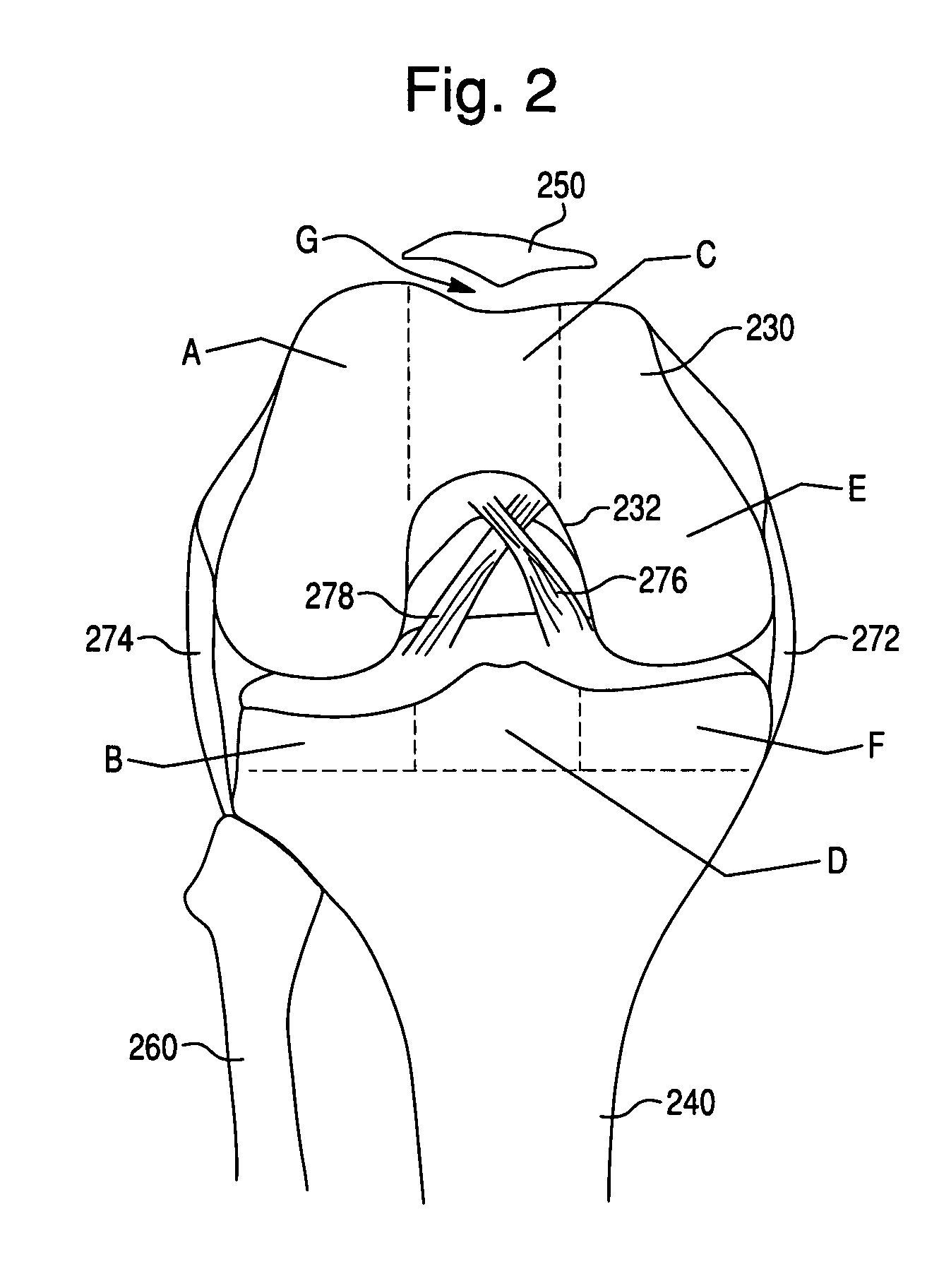
Device and method for knee ligament strain measurement
InactiveUS20090264797A1Good repeatabilityHigh precisionPerson identificationChiropractic devicesCoronal planePhysical medicine and rehabilitation
A device for measuring displacement of the tibia in relation to the femur in response to an applied force or torque on the tibia. A first shaft is tiltable about a first axis close to the ankle and approximately parallel to the coronal plane of the patient's body. A second shaft is connected to the first shaft and is rotatable about a second axis perpendicular to the first axis, and is close to the ankle and approximately parallel to the tibia. A foot support platform is mounted on the second shaft, the foot support platform being configured for attachment of the foot at a fixed position. A displacement test device is provided for applying forces to the tibia and measuring the shift or displacement of the proximal tibia relative to the distal femur.
Owner:MAYR HERMANN
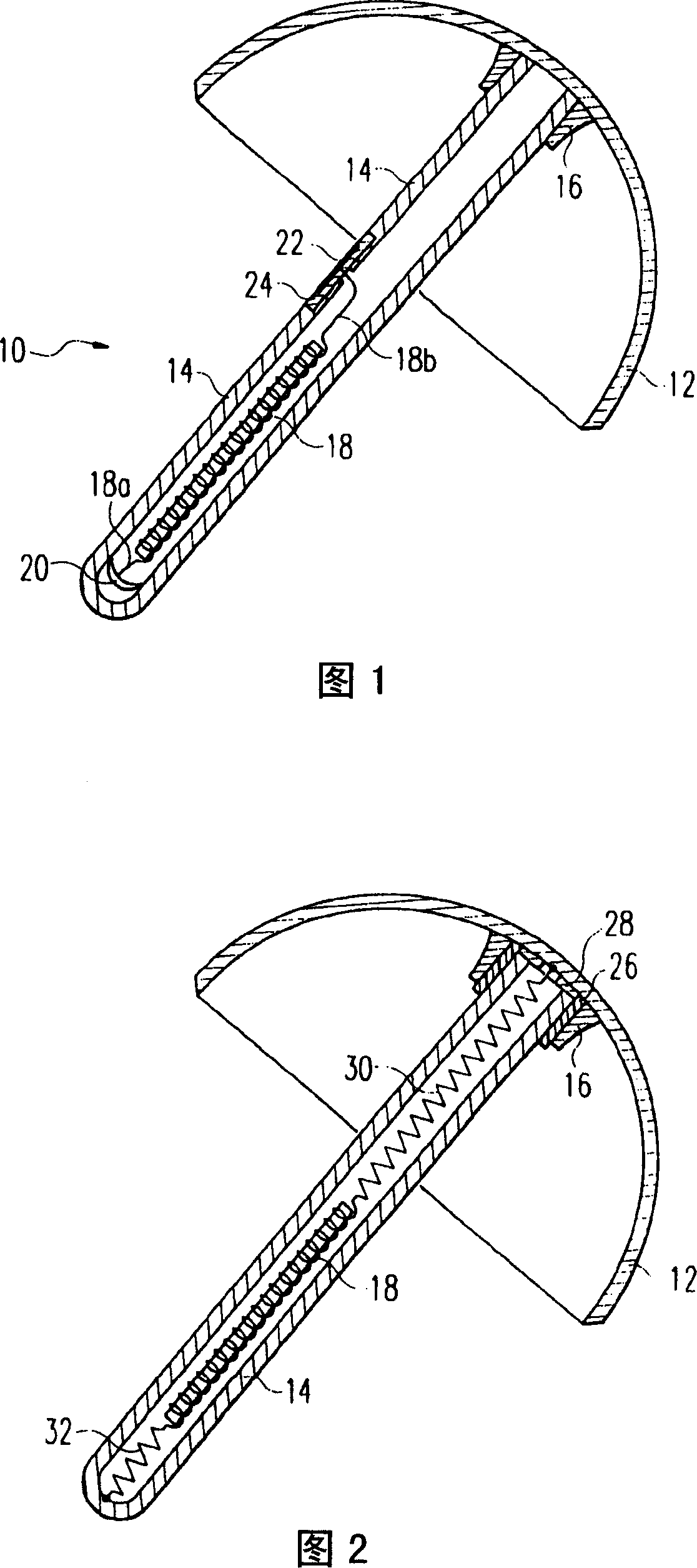
Coronal implanter in femoral head
The invention relates to a femur crown implant (10), which comprises crow element (12) and the pin (14) fixed on the concave inner surface, wherein the couple winding (18) is inside the pin, while each end (18a, 18b) is connected to the organism electrode; one organism electrode is formed by crown element (12) while another one is formed by electrode (22); the electrode (22) is insulated with the pin or at least one part of pin. The invention uses external winding to generate low-frequency alternative-current in the couple winding (18), while said current will pass two organism electrodes into the femur of implant, to accelerate the activation of skeleton (as Kraus-Lechner).
Owner:NEUE MAGNETODYN
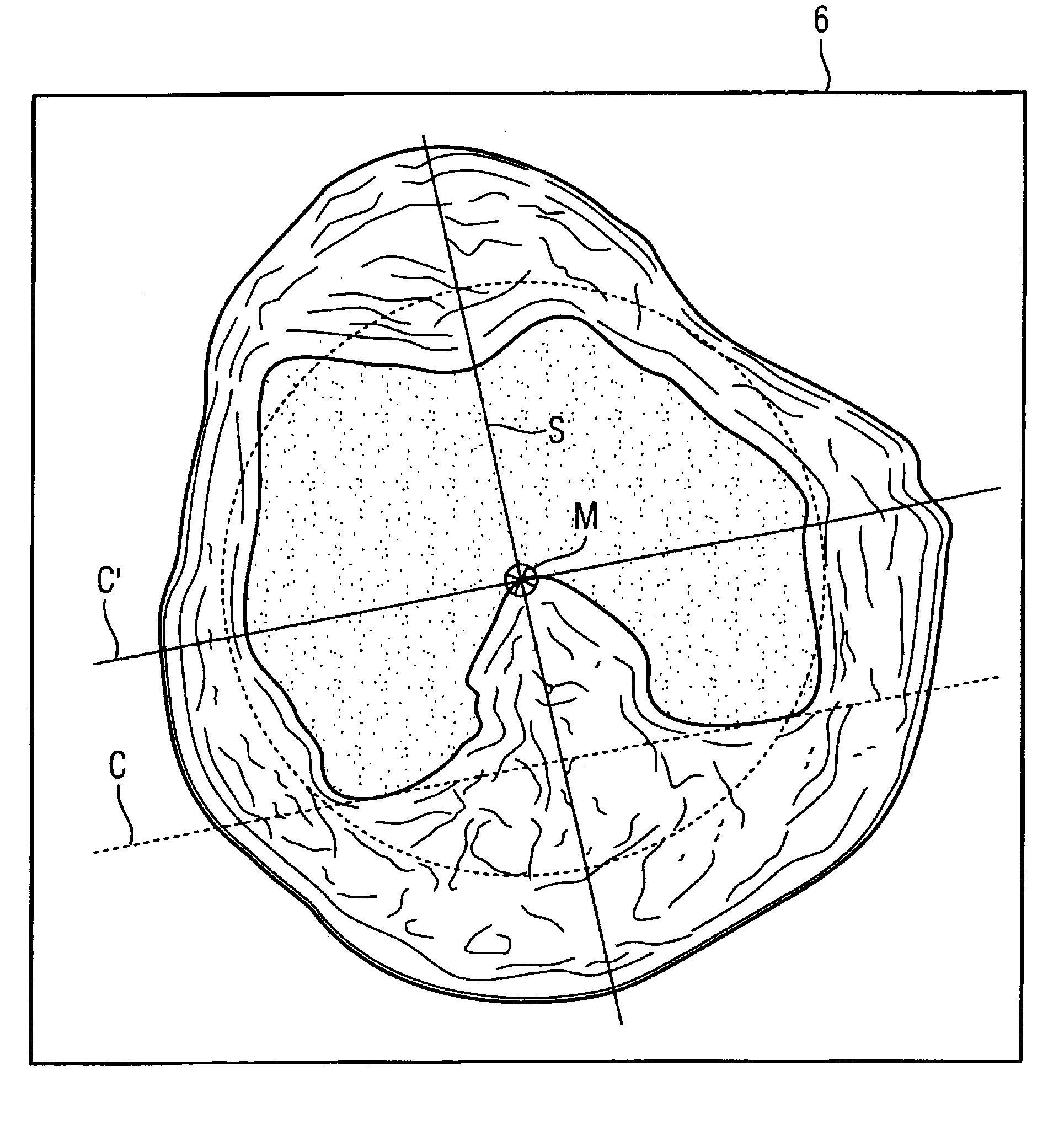
Method for determining and measuring frontal head posture and frontal view thereof
InactiveUS20070106182A1Improve balanceAddress bad outcomesPerson identificationCharacter and pattern recognitionCoronal planeNose
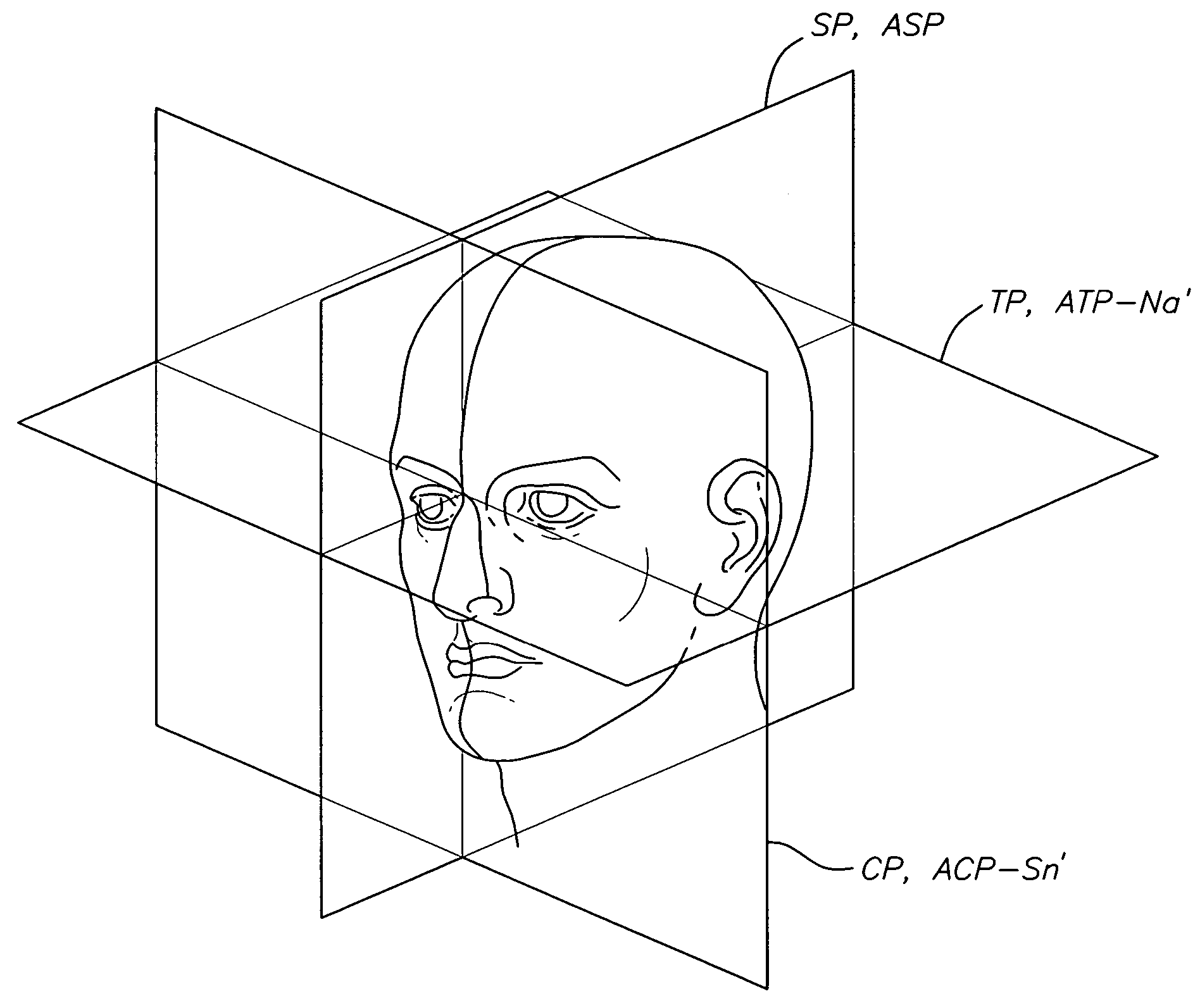
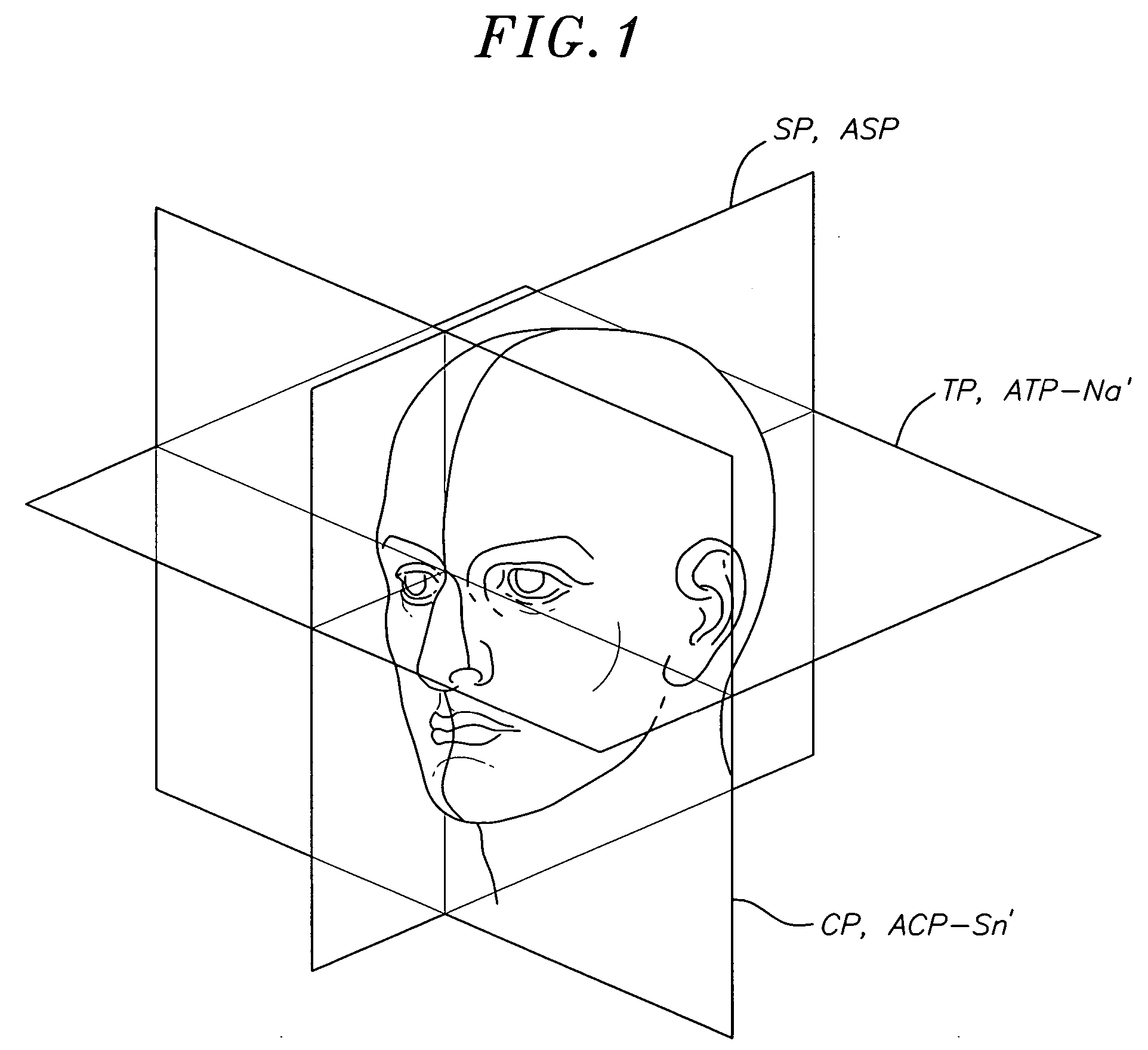
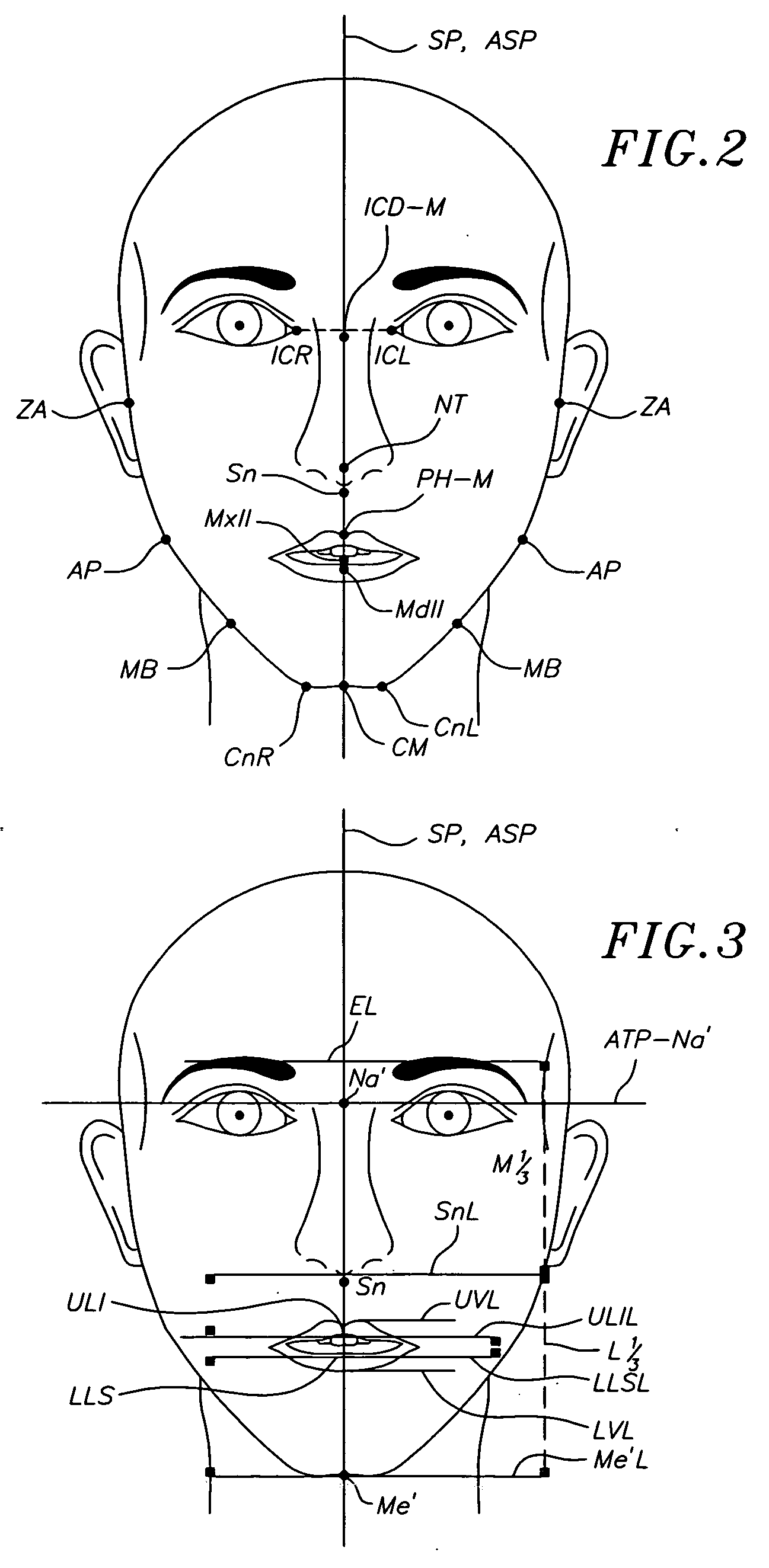
A method for determining and measuring profile and frontal head posture and front views thereof to establish a 3-D model of a patient's head and face. In the method, a patient places his or her head in a natural head position and establishes a postural sagittal plane. Additionally, the practitioner may move the patients head to a corrected sagittal plane. If still necessary, an anatomic sagittal plane that comprises an anatomical midline of the patient's face when viewed from a frontal view is constructed. An profile anatomical coronal plane is located and aligned with the frontal anatomical sagittal plane. Next, an anatomical transverse plane is established through the soft tissue nasion and aligning it perpendicularly to the anatomical sagittal and coronal planes. By developing the 3 planes a 3-D reference frame is established from which soft tissue and hard tissue landmarks are identified and measured.
Owner:G WILLIAM ARNETT & SALLY A WARNER ARNETT TRUSTEES OF THE WARNER ARNETT TRUST +1
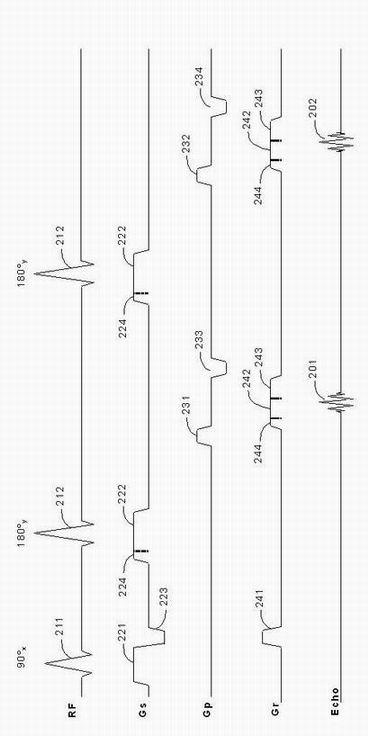
Gradient system time delay correction method for fast spin echo pulse sequence
InactiveCN102096054AReduce hardware costsReduce system complexityMagnetic measurementsFast spin echoCoronal plane
The invention provides a gradient system time delay correction method for a fast spin echo pulse sequence. In the method, a gradient system time delay is corrected by correcting a gradient pulse, and an amplitude synthetic matrix for correcting the gradient pulse is calculated by using the normalized gradient system time delay. By the method, the influence of the gradient system time delay on thefast spin echo pulse sequence is overcome, and the hardware cost and the system complexity of a magnetic resonance imaging system are not increased; and even if the gradient system time delays in x, y and z directions are unequal, the power of a gradient power amplifier is not enough to provide overshooting impulse with larger amplitude in a gradient waveform. By the method, the gradient system time delay can still be corrected so as to enhance the image quality of a sagittal plane, a coronal plane, a cross section and various diagonal planes in a fast spin echo image.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY +1
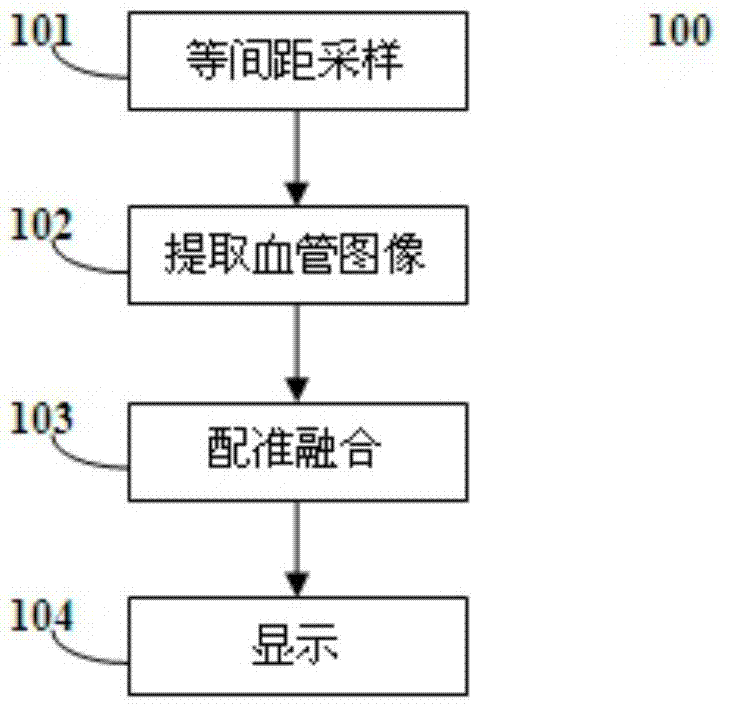
Multimodal multi-dimensional blood vessel fusion method and system
InactiveCN103942772AImprove stabilityImprove registration accuracyImage enhancementMedical equipmentVertical plane
The invention discloses a multimodal multi-dimensional blood vessel fusion method and a multimodal multi-dimensional blood vessel fusion system, and relates to medical equipment data image processing. The method comprises the steps of respectively extracting blood vessel images in a plurality of medical images, and extracting blood vessel center lines corresponding to the blood vessel images; registering and fusing the blood vessel center lines through an iterated near point algorithm, so as to obtain three-dimensional data; and synchronously displaying the three-dimensional data in the way of the cross-sectional image of cross sections, coronal planes and vertical planes. According to the method, other information outside the blood vessels can be rejected, so that no other covers can be generated when a doctor observes the blood vessels.
Owner:CREALIFE MEDICAL TECH BEIJING
Automatic optimal view determination for cardiac acquisitions
A method, system, and apparatus of determining optimal viewing planes for cardiac image acquisition, wherein the method includes acquiring a set of sagittal, axial, and coronal images of a heart, where the axial and coronal images intersect with the sagittal image orthogonally, and where the heart has a natural axis and a left ventricle (“LV”) with a bloodpool, a bloodpool border, and an apex. The method also includes making a map of the bloodpool border, and using the map to create a full coordinate frame oriented along the natural axis.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
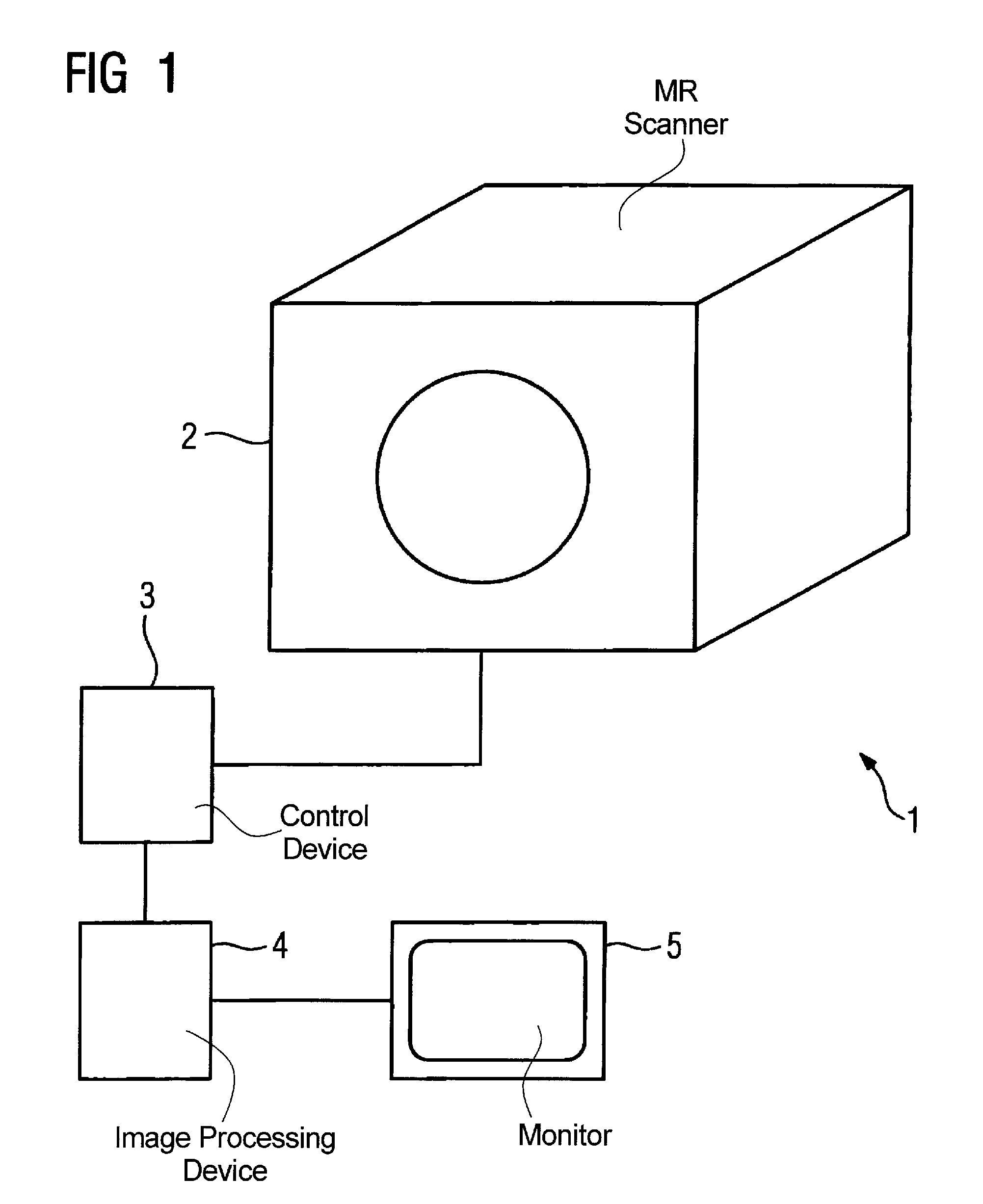
Magnetic resonance positioning scanning method and device
ActiveCN103142230AAdjustment Automatic PreciseImprove scanning efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSagittal planeVertical plane
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance positioning scanning method and device. The method comprises the following steps of moving an electric-control scanning bed so as to enable a scanning part to be aligned to the central area of a magnet after a target is in position; starting magnetic resonance positioning scanning, acquiring an echo signal, and rebuilding the echo signal to obtain a vertical plane positioning image and a coronal plane positioning image of the scanning part; extracting outline information of the scanning part of the vertical plane positioning image and the coronal plane positioning image through an image segmentation recognition algorithm, and judging whether a distance between the outline edge of the scanning part and a frame stays in a preset threshold value range or not; and automatically calculating an adjusting distance and an adjusting direction when the distance between the outline edge of the scanning part and the frame does not stay in the preset threshold value range, controlling the electric-control scanning bed to move according to the calculated adjusting distance and the adjusting direction, restarting the magnetic resonance positioning scanning, and displaying a vertical plane positioning image and a coronal plane positioning image, which are rebuilt after the magnetic resonance positioning scanning is restarted.
Owner:SHENZHEN ANKE HIGH TECH CO LTD
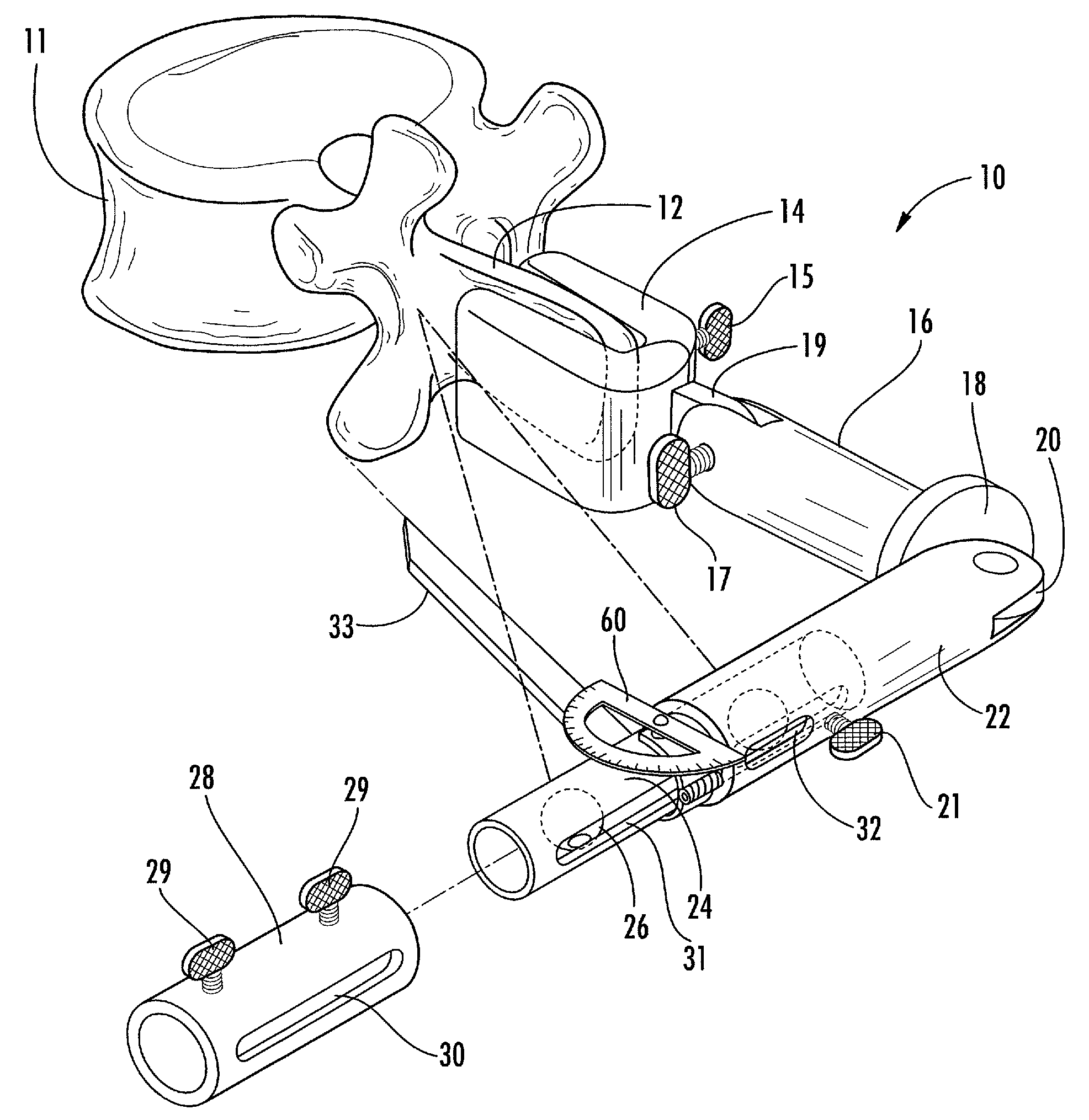
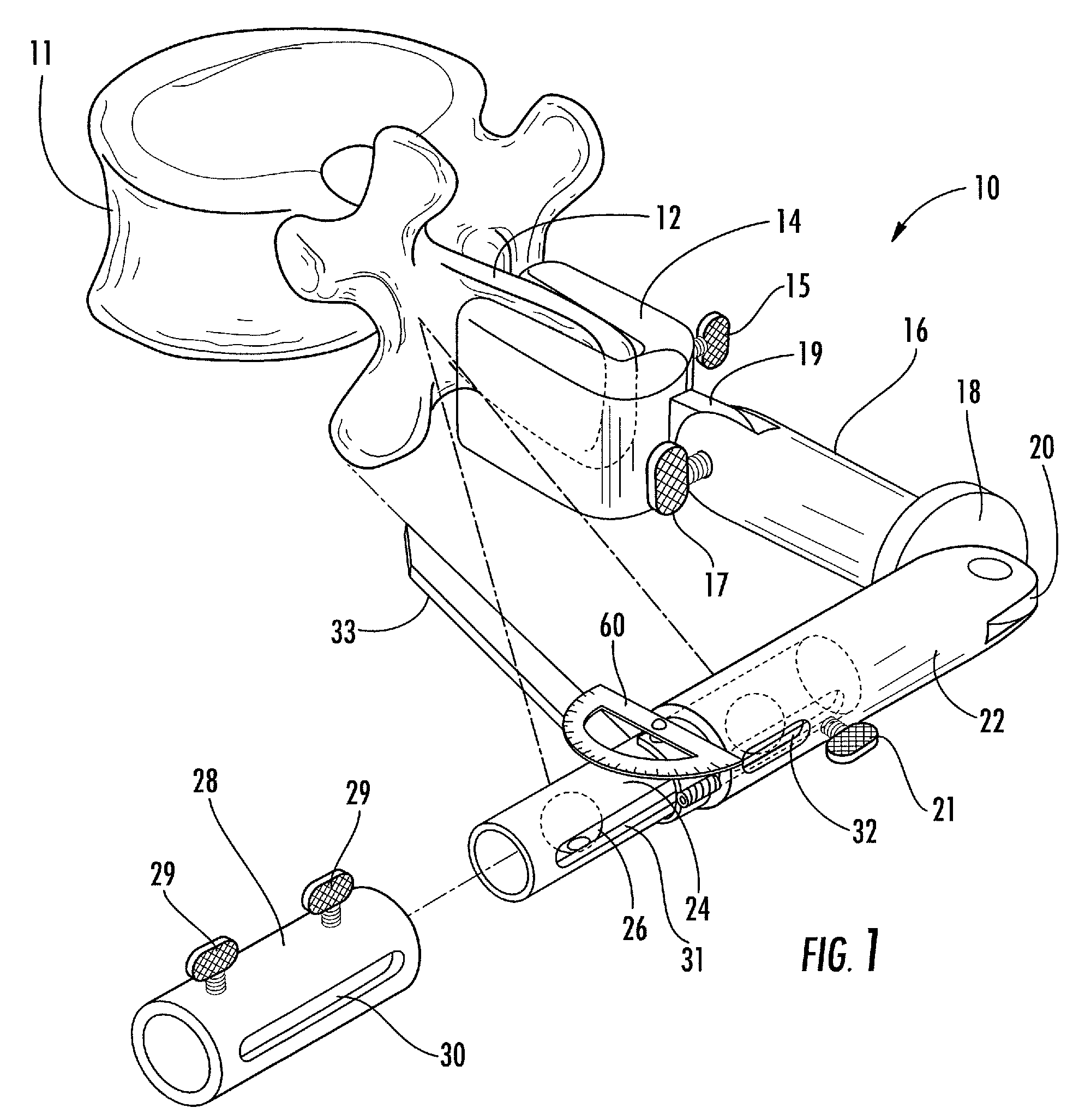
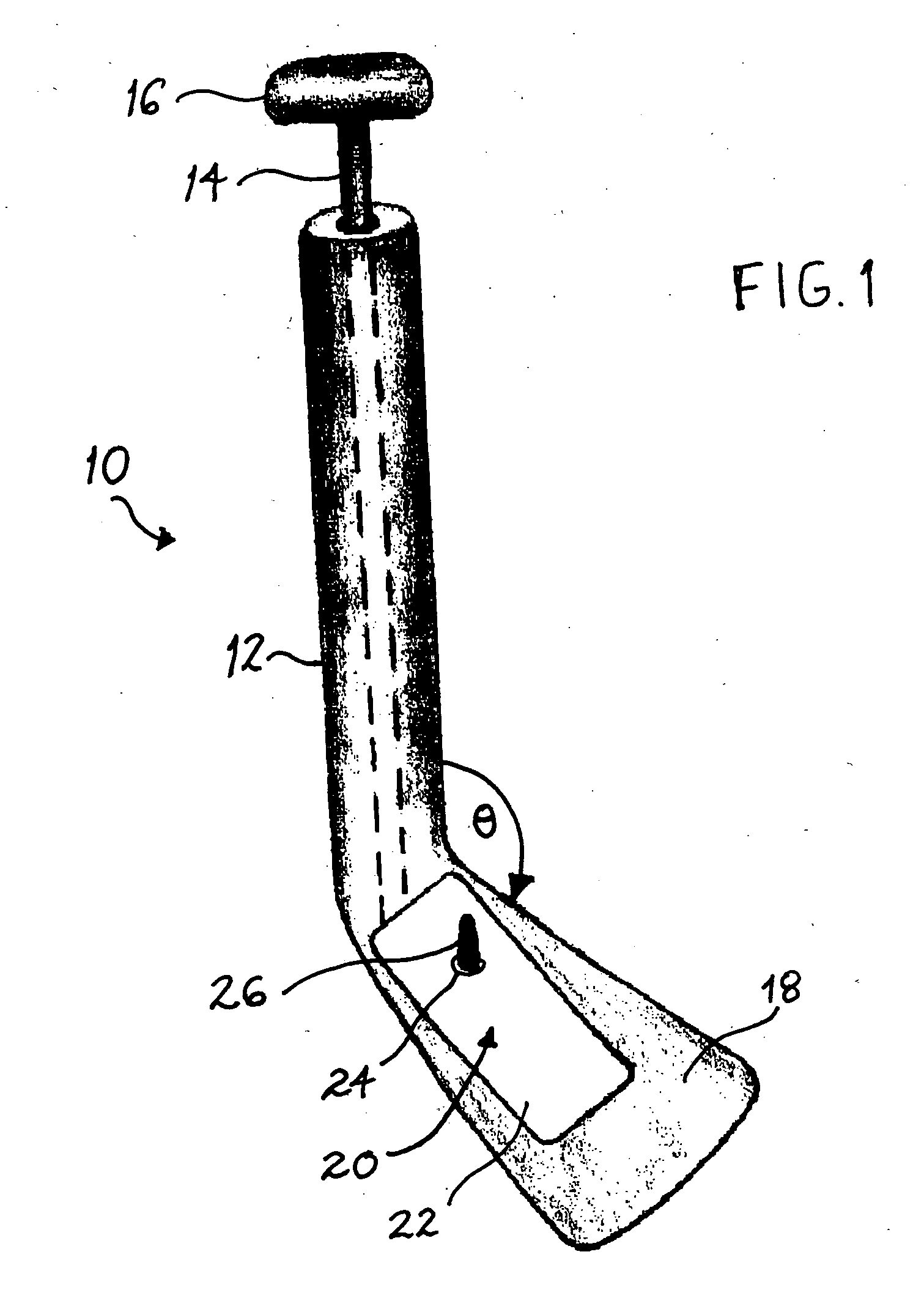
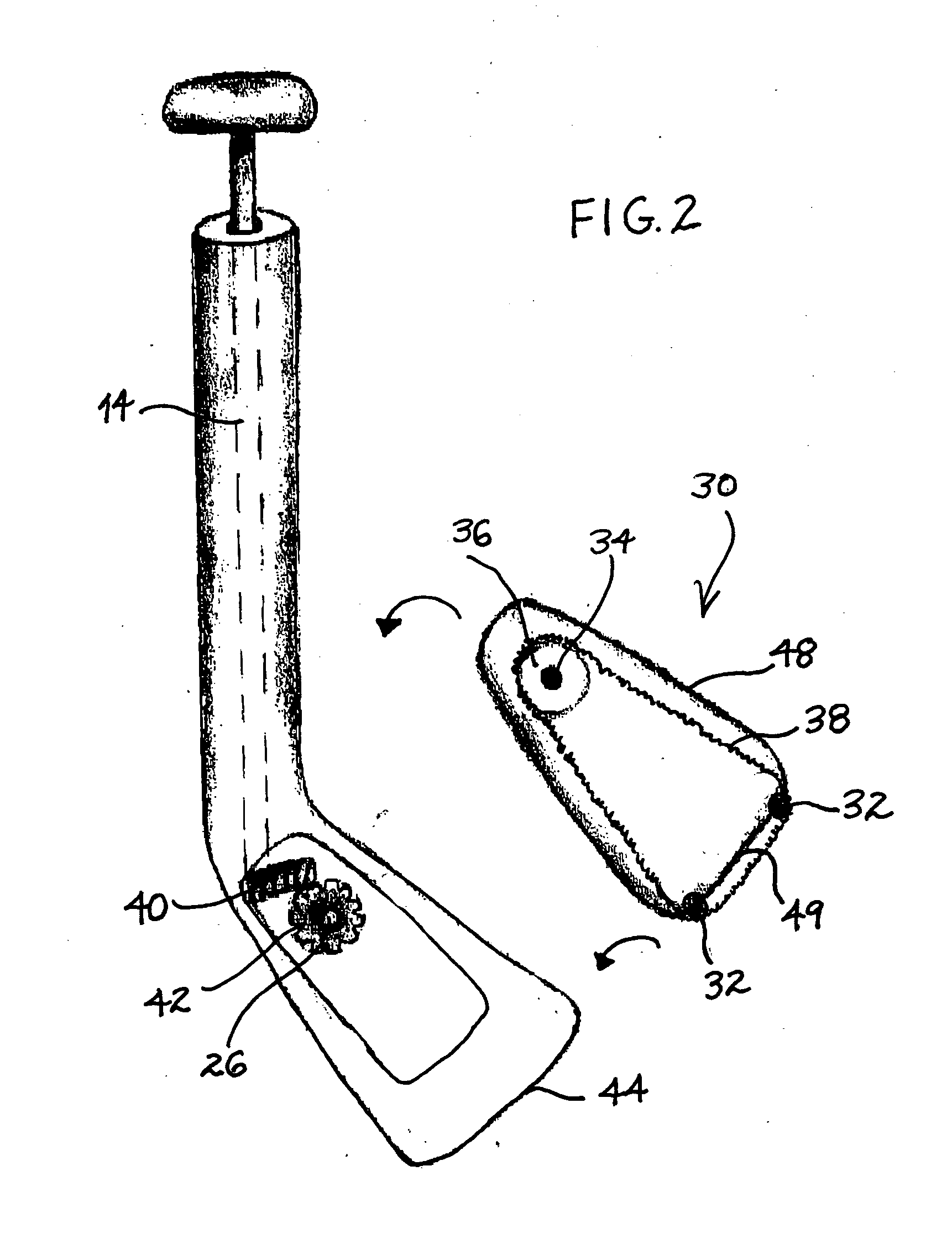
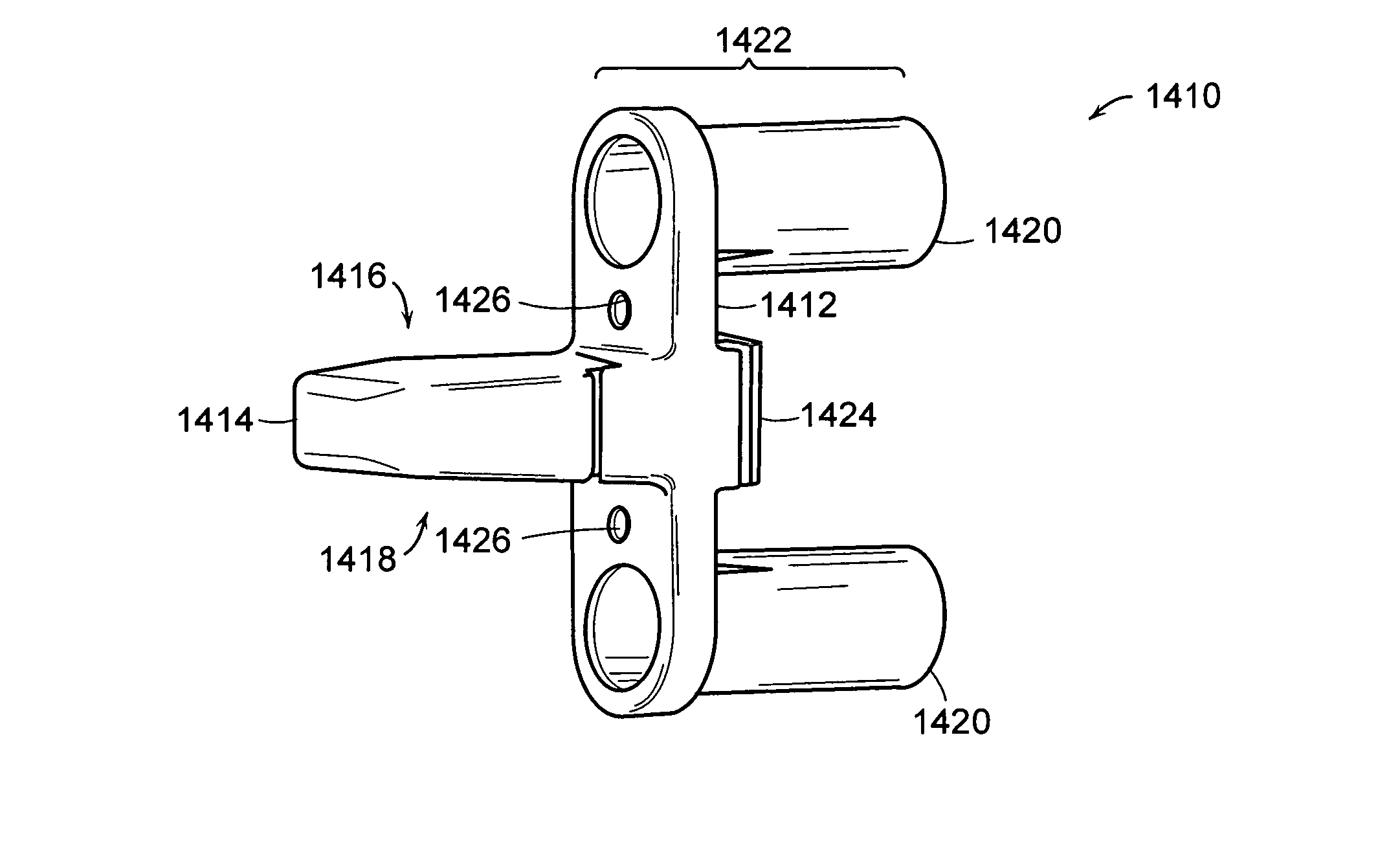
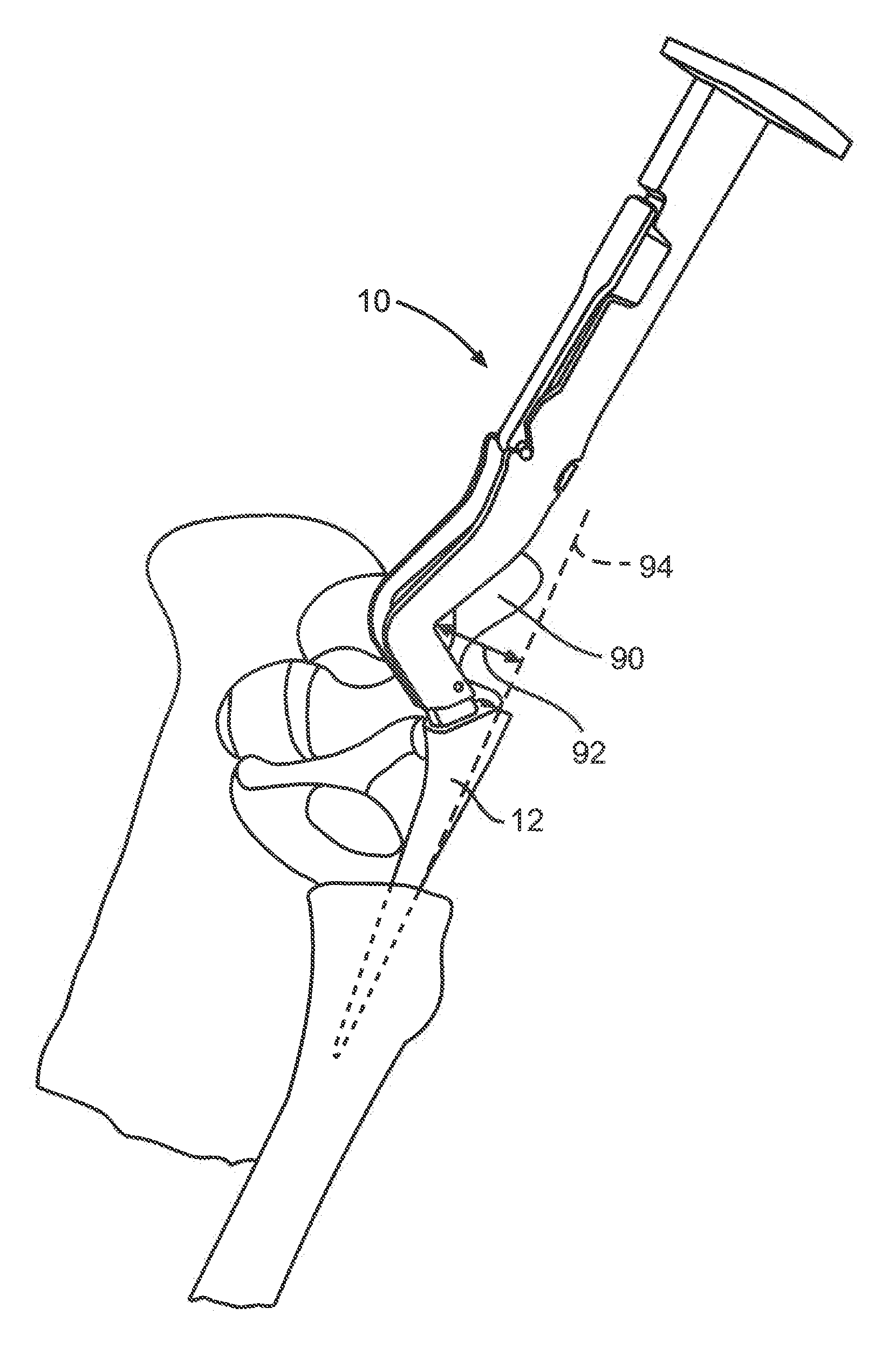
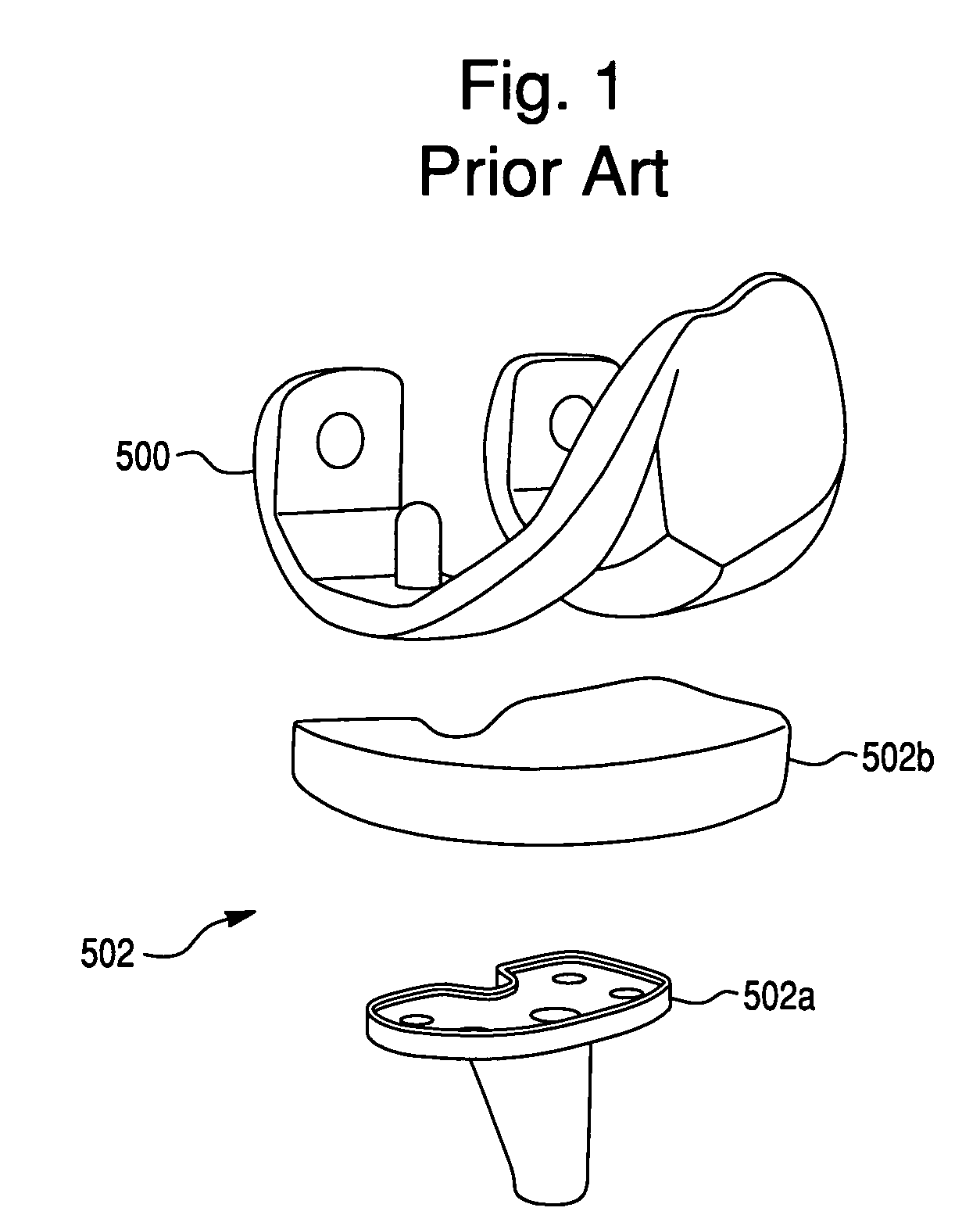
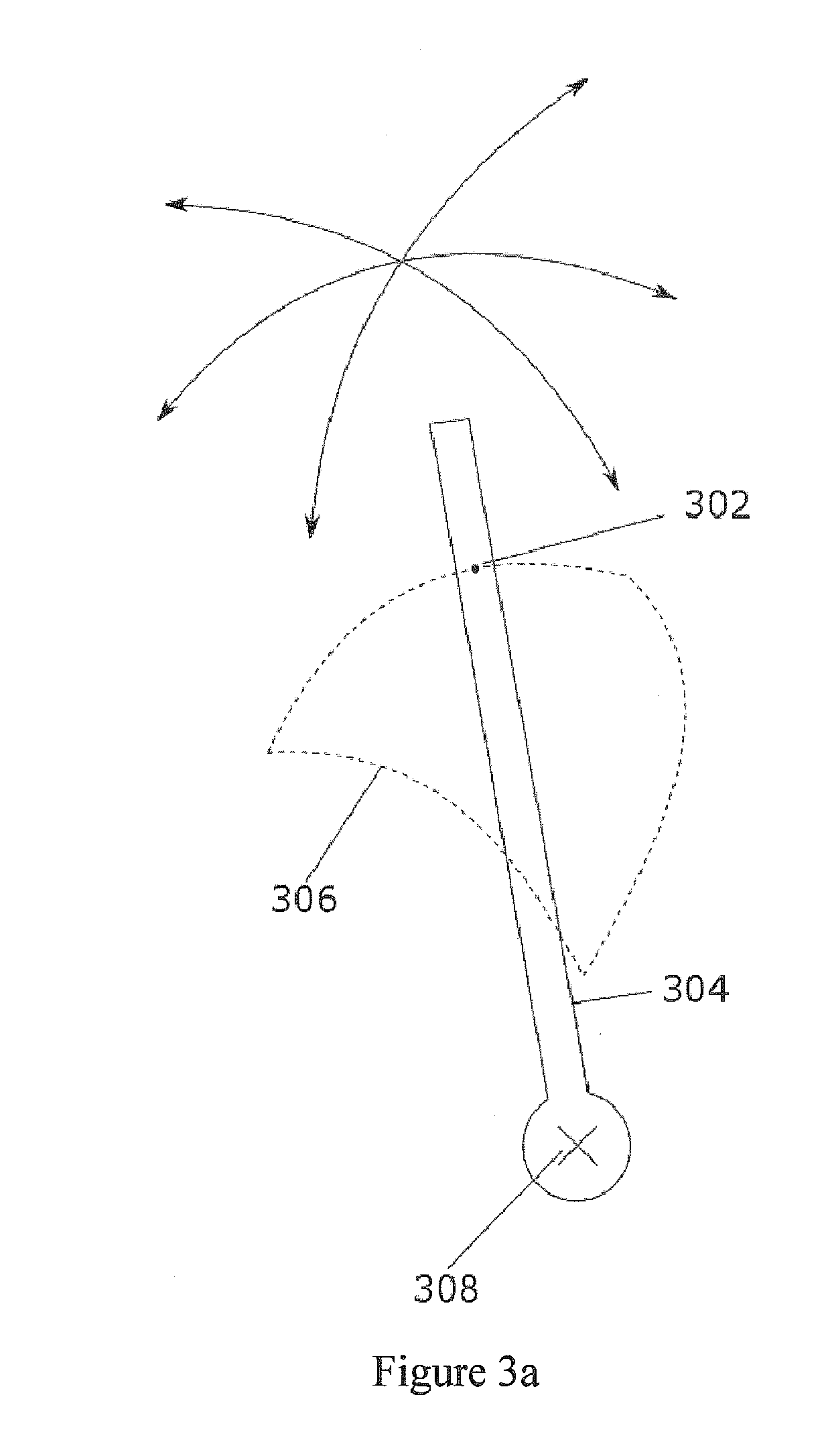
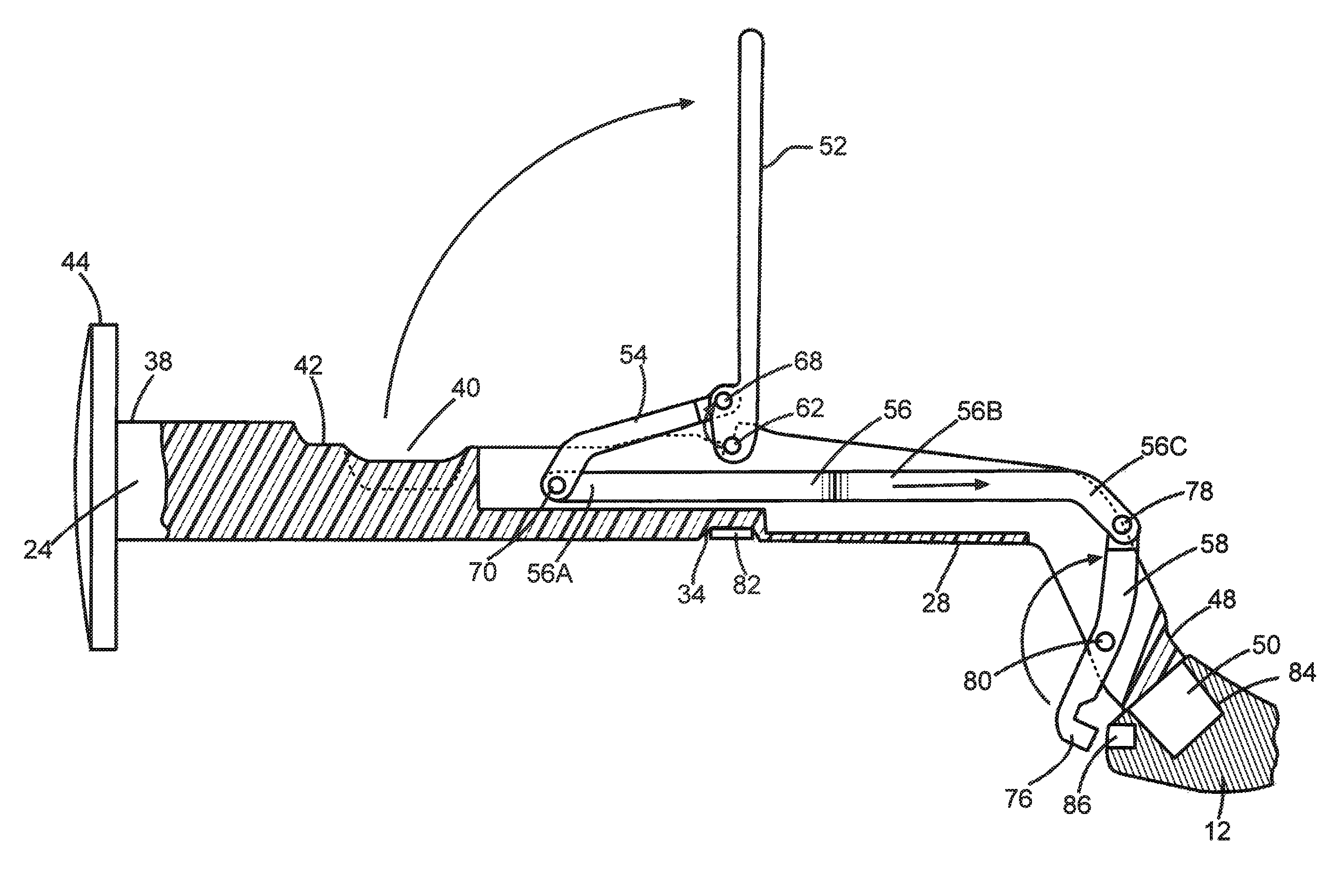
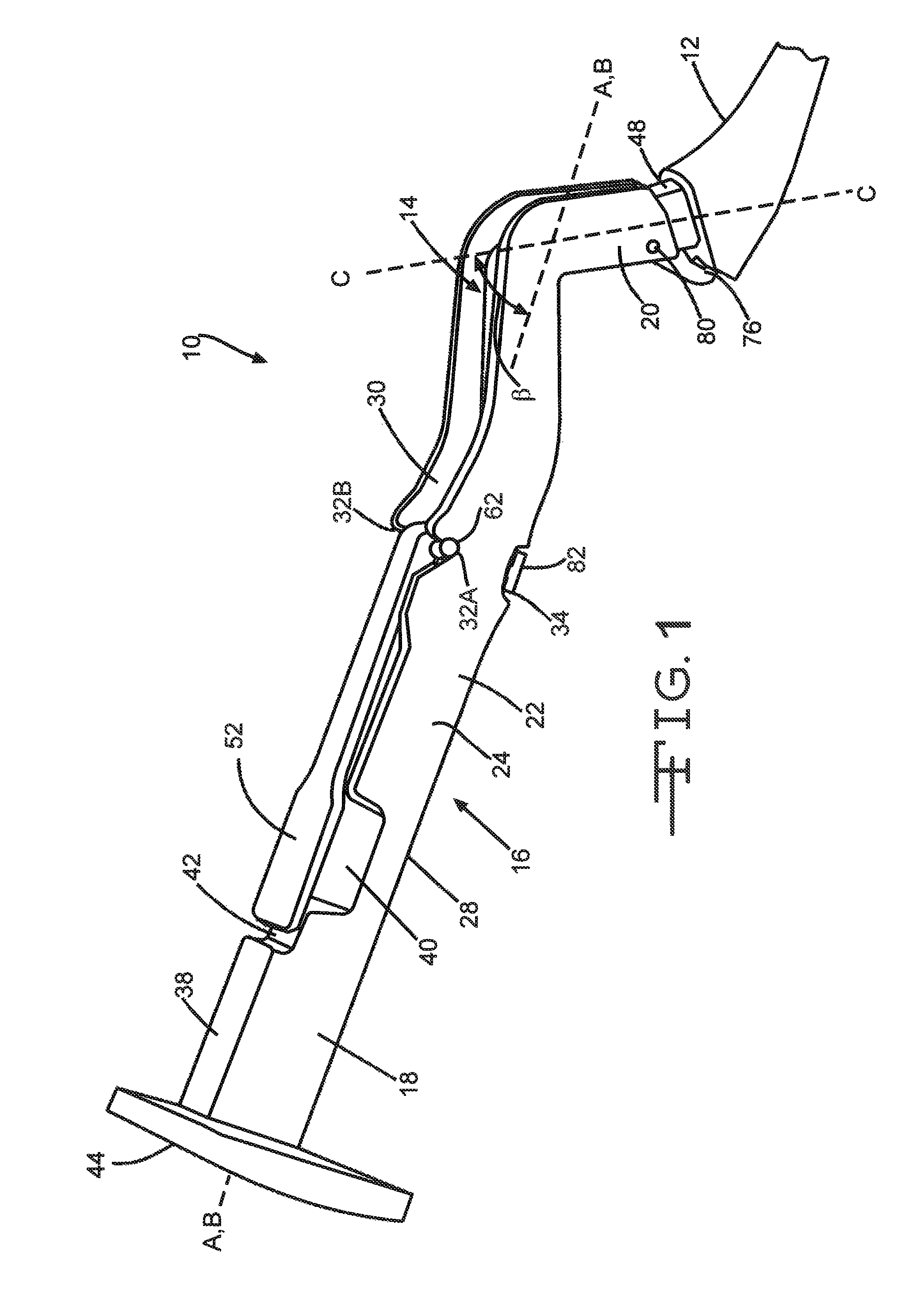
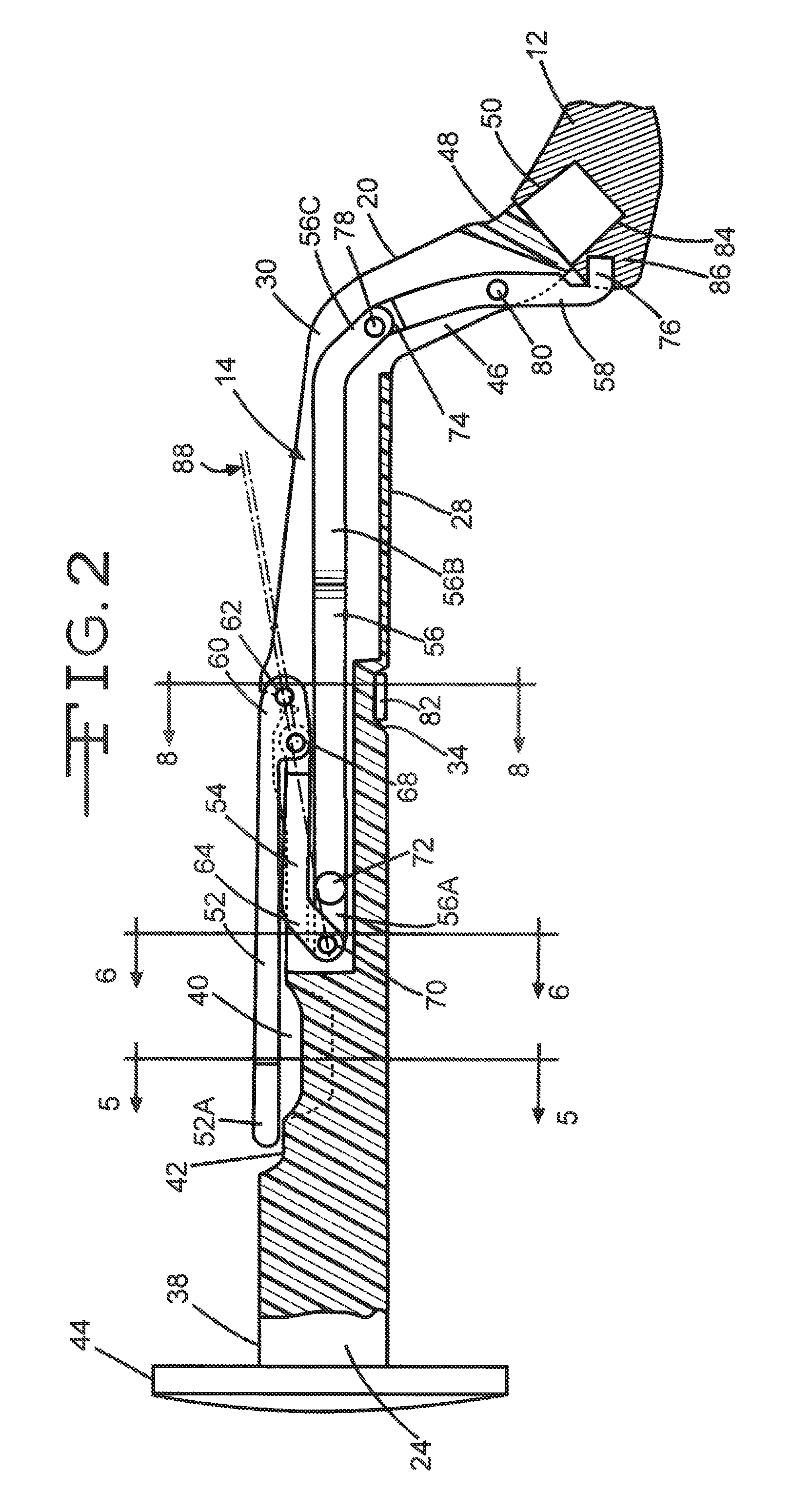
Double Offset Surgical Tool Handle Assembly To Provide Greater Offset From The Coronal Plane
Owner:VIANT AS&O HLDG LLC
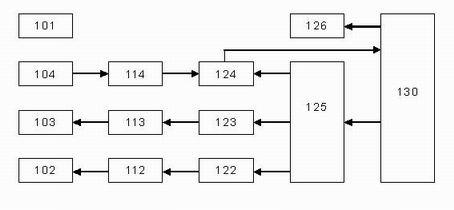
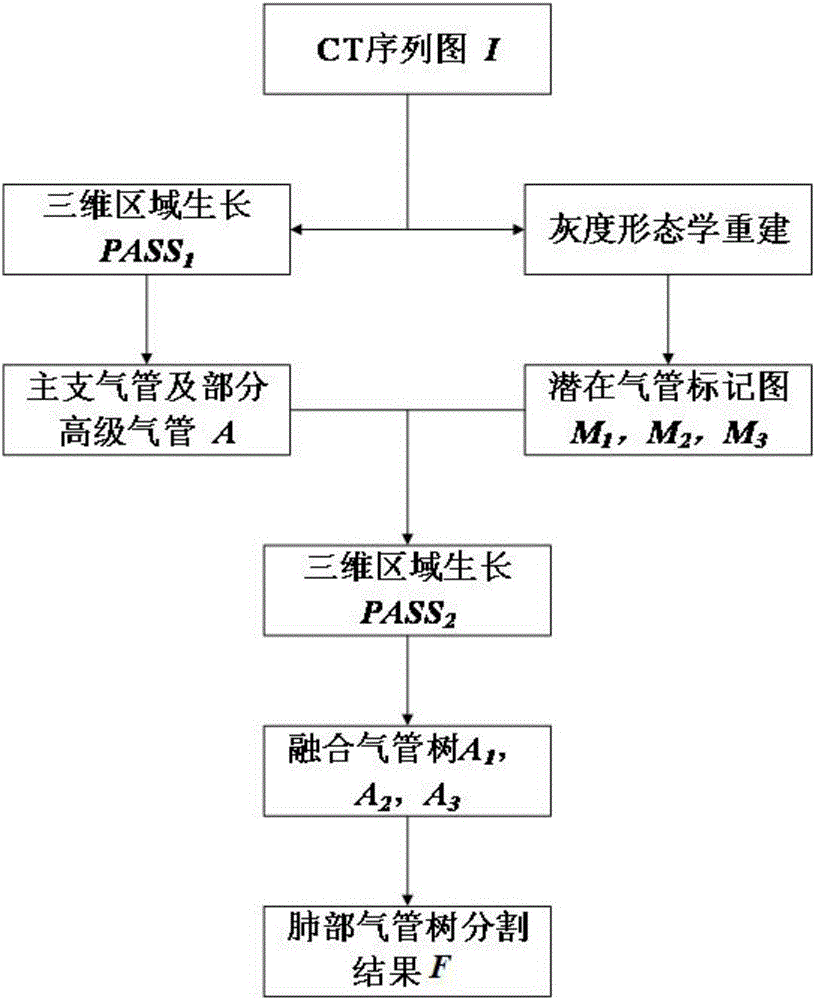
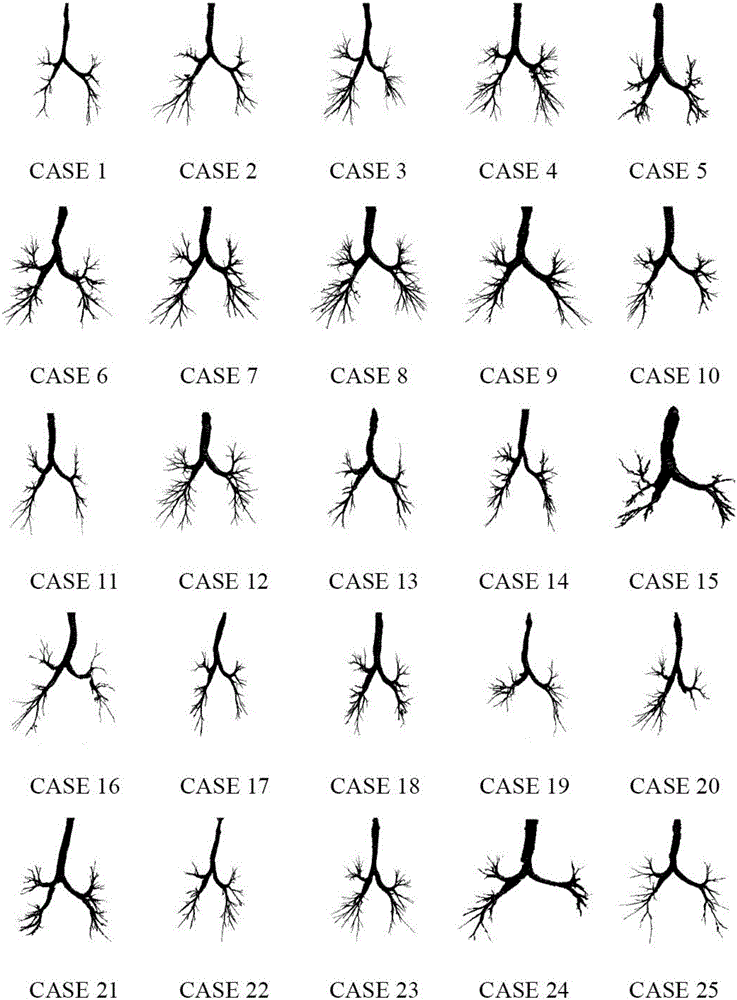
Two-pass region growing and morphological reconstruction combination-based lung airway tree segmentation method
ActiveCN106097305AIncrease the number of branchesReduce the ratioImage enhancementImage analysisMorphological operatorsCoronal plane
The invention aims to provide a two-pass three-dimensional region growing and morphology combination-based lung airway tree segmentation algorithm for solving the problem to realize effective segmentation of a lung airway tree. The two-pass region growing and morphological reconstruction combination-based lung airway tree segmentation method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of automatically obtaining a seed point P1 of three-dimensional region growing from a serial section image; performing first-pass region growing by taking P1 as the seed point to obtain a lung main airway tree; setting a multi-scale morphological operator, and obtaining corresponding airway marking graphs in three anatomic positions of a cross section, a coronal plane and a sagittal plane by utilizing gray-scale morphological reconstruction operation; performing second-pass region growing by taking the lung main airway tree as a basis and the airway marking graphs in the three anatomic positions as limitation conditions to obtain corresponding segmented airway trees; and fusing the segmented airway trees to obtain a final lung airway tree segmentation result F.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH +1
Multi-compartmental prosthetic device with patellar component transition
A prosthetic device for forming at least a portion of a joint may have a plurality of segmented components fixed relative to a femur of a body including: a patellofemoral component and a condyle component. Each segmented component may be configured such that a placement at which the segmented component will be fixed relative to the femur is not constrained by a connection to another of the segmented components that is fixed relative to the femur. In an installed configuration, the patellofemoral and condyle components may be fixed relative to the femur such that: a gap is provided between an edge of the patellofemoral component and an opposing edge of the condyle component, and a transition region is provided that extends from a first femoral coronal plane that intersects the patellofemoral component to a second femoral coronal plane that intersects the condyle component.
Owner:MAKO SURGICAL CORP
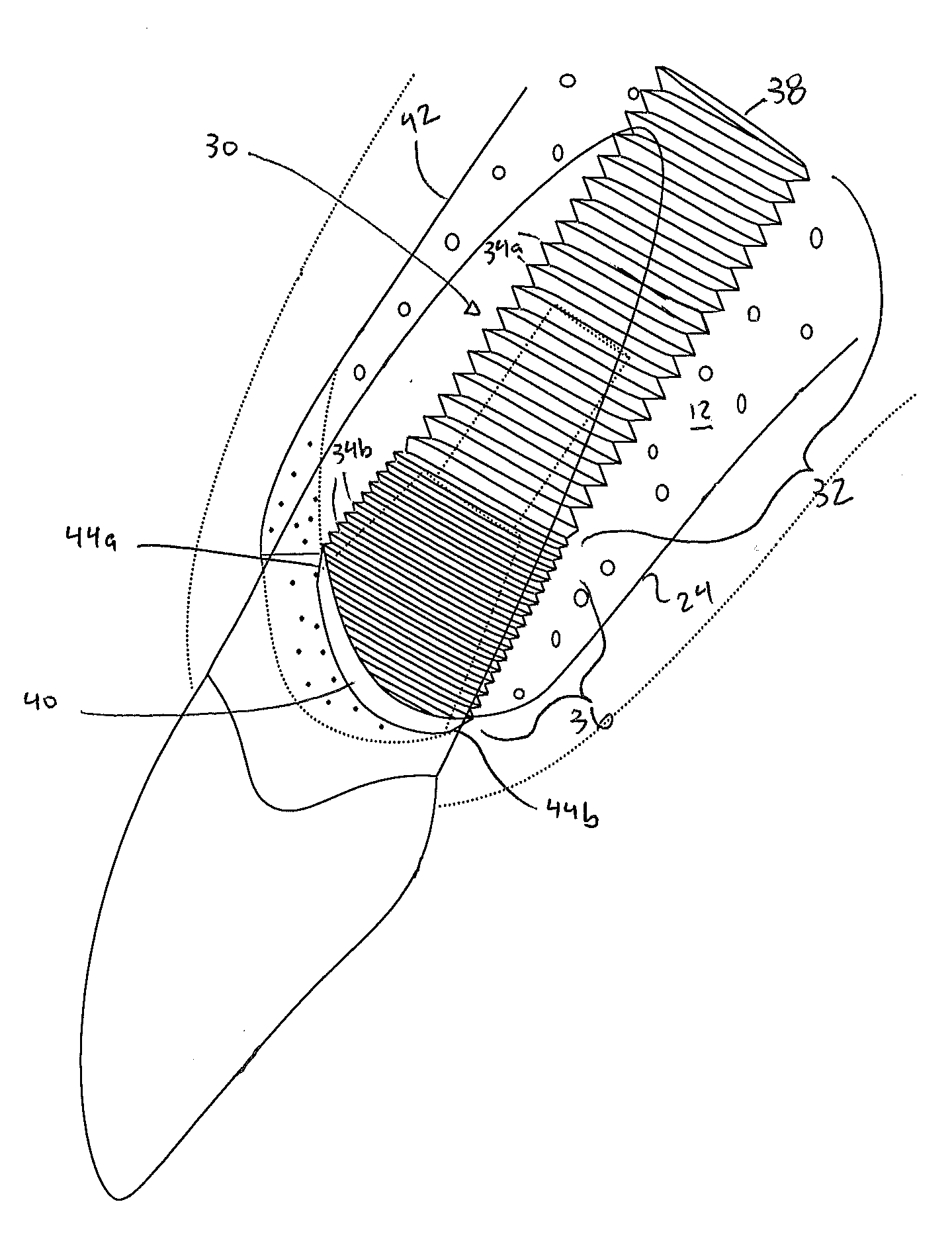
Modified asymmetrical dental implant
An asymmetrically placement designed to preserve bone by having the coronal aspect being compatible with the bony anatomy at the time of tooth extraction. The implant may be of either a single or two stage design. By modifying the top of the implant fixture to partially mimic the bony anatomy at the time of extraction more crestal bony anatomy can be preserved and bone growth encouraged.
Owner:DENTAL DESIGN CONSULTANTS
Systems, methods and devices for calculating hip center of rotation, adjusting parameters of joint replacement for pelvic tilt and calculating leg length and offset
ActiveUS20170119475A1Surgical navigation systemsJoint implantsHip joint replacement operationCoronal plane
Systems and methods are described herein to calculate implant orientation measurements of an acetabular cup implant in hip replacement surgery, such surgery performed with minimally invasive incisions. Surgeons may obtain real-time updated implant orientation measurements that compensate for pelvic tilt of a patient, such tilt measured pre-operatively. Implant orientation measurements may be measured from the patient's anterior pelvic plane, supine coronal plane, standing coronal plane or any other reference plane that the surgeon may find useful. Also disclosed are systems, methods and devices to measure hip center of rotation and provide leg length and offset measurements in hip replacement surgery.
Owner:INTELLIJOINT SURGICAL
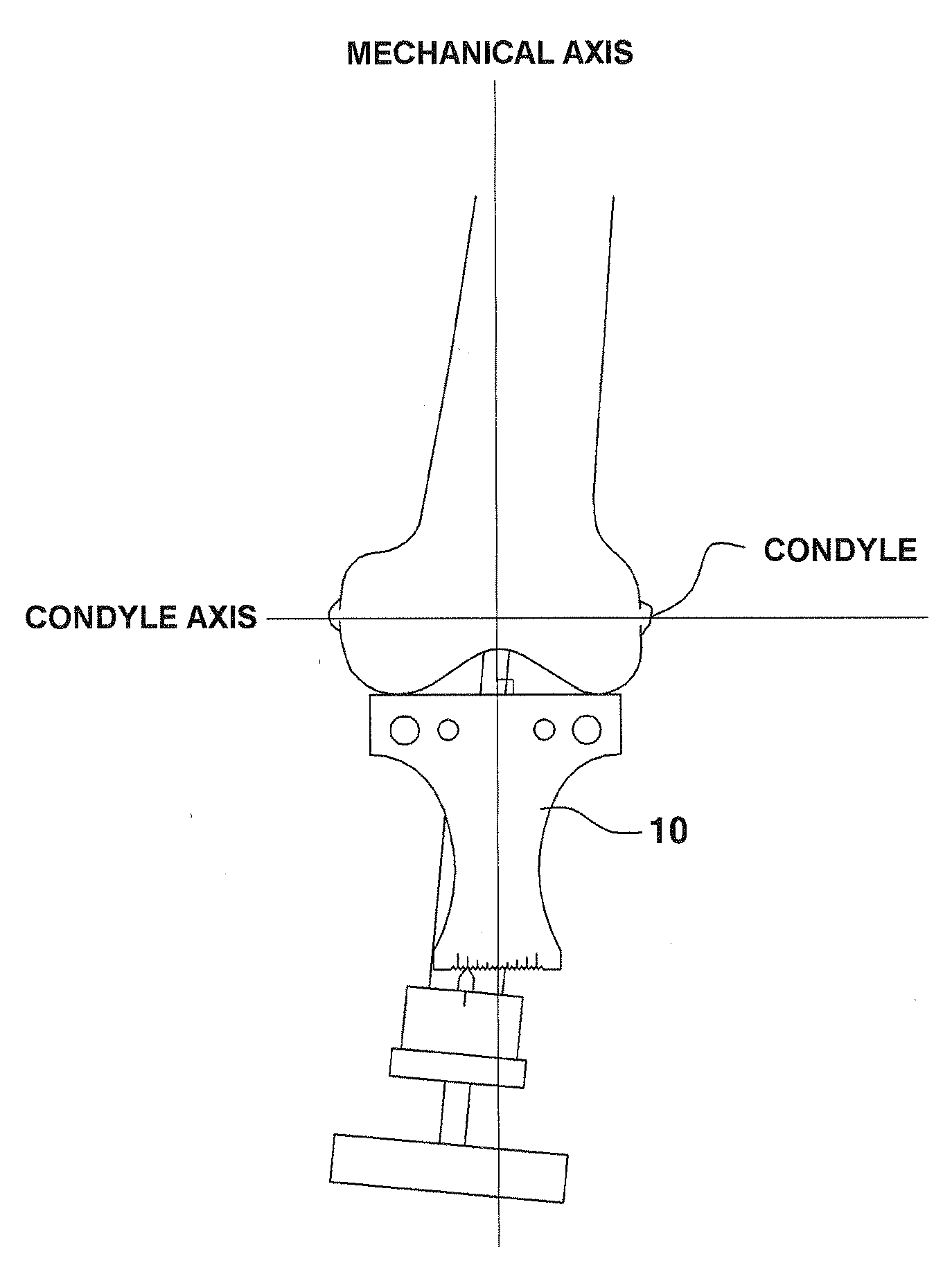
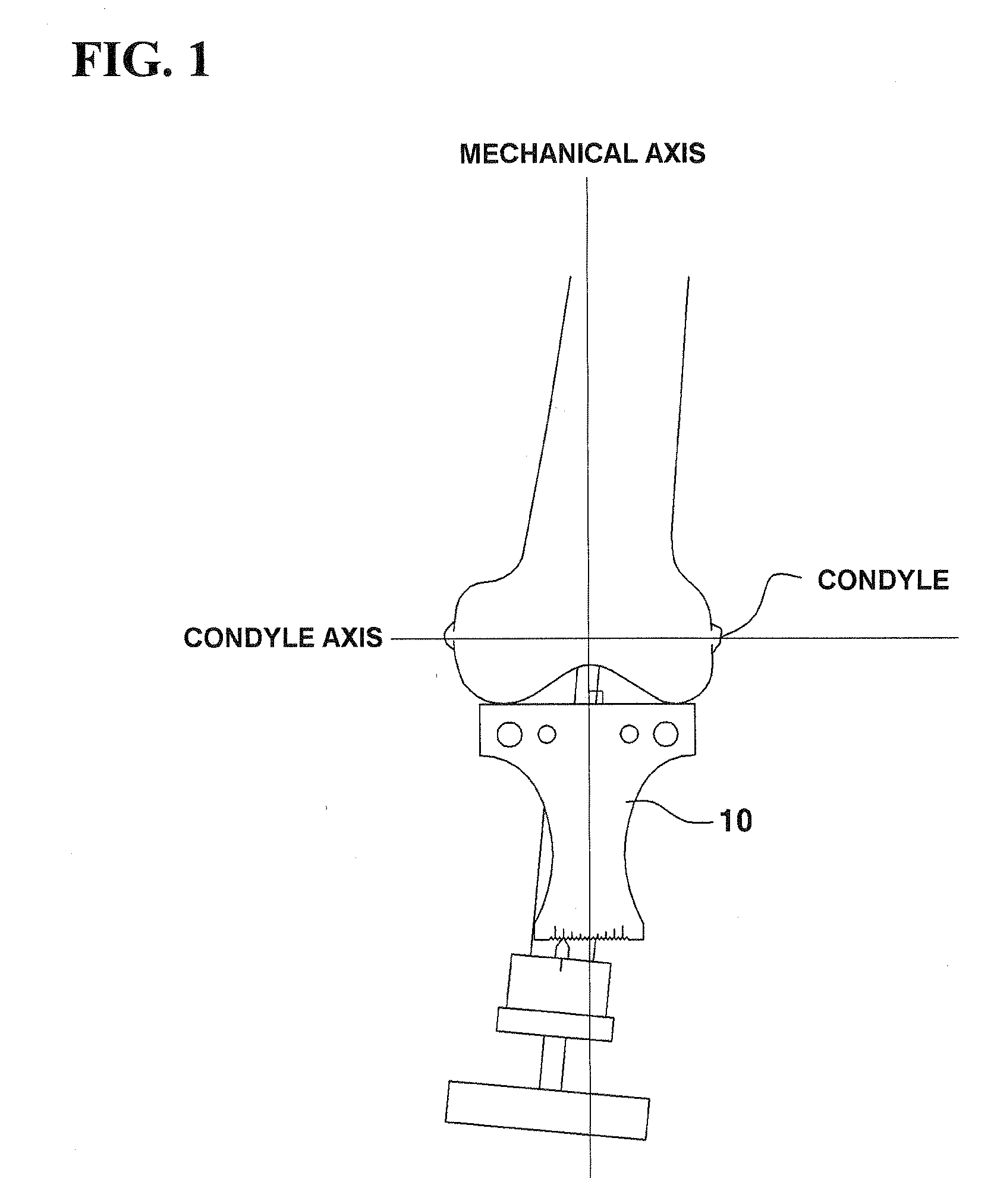
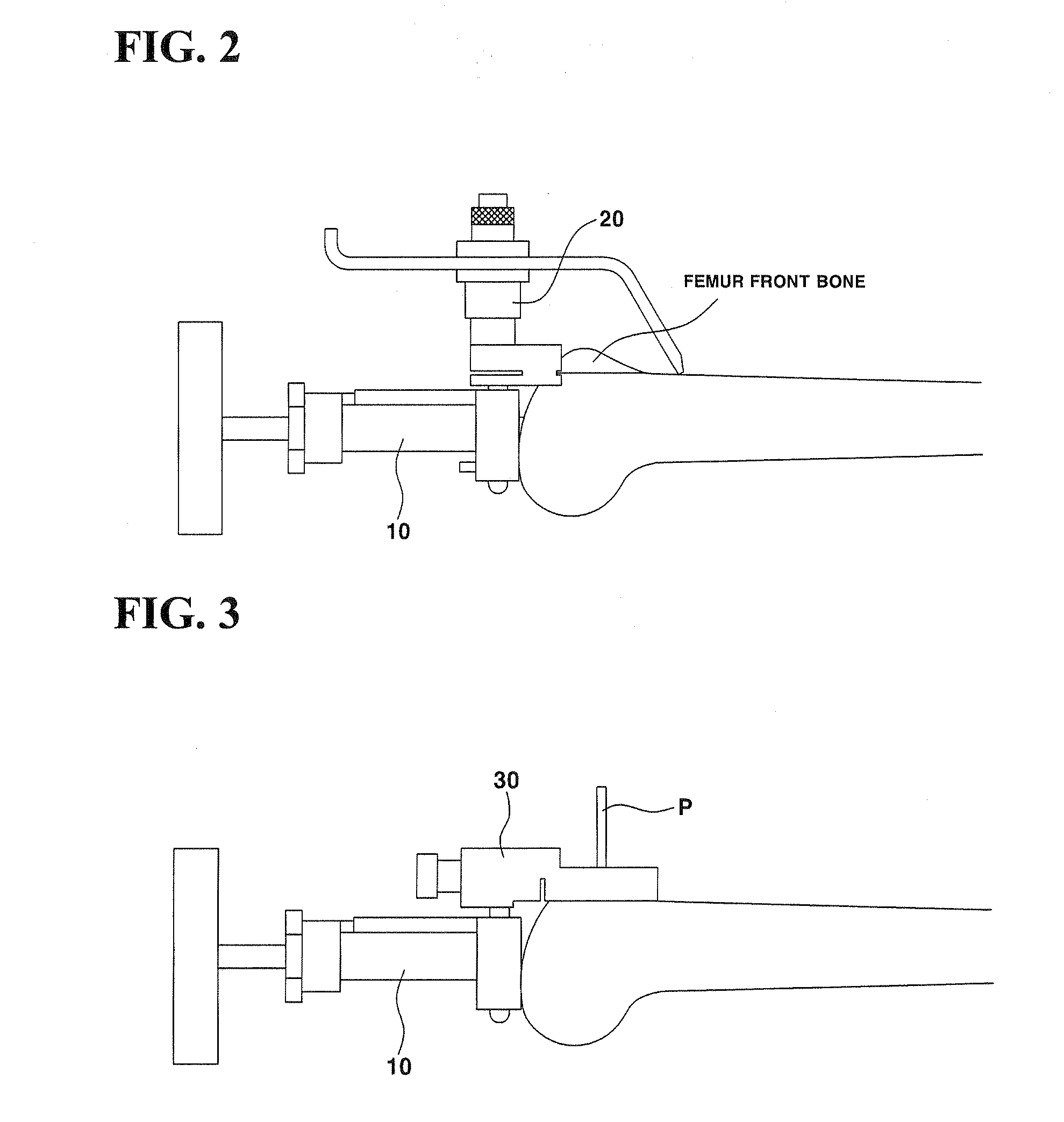
Device for Aligning and Guiding Femoral Resection Guide and Femoral Implant Impactor
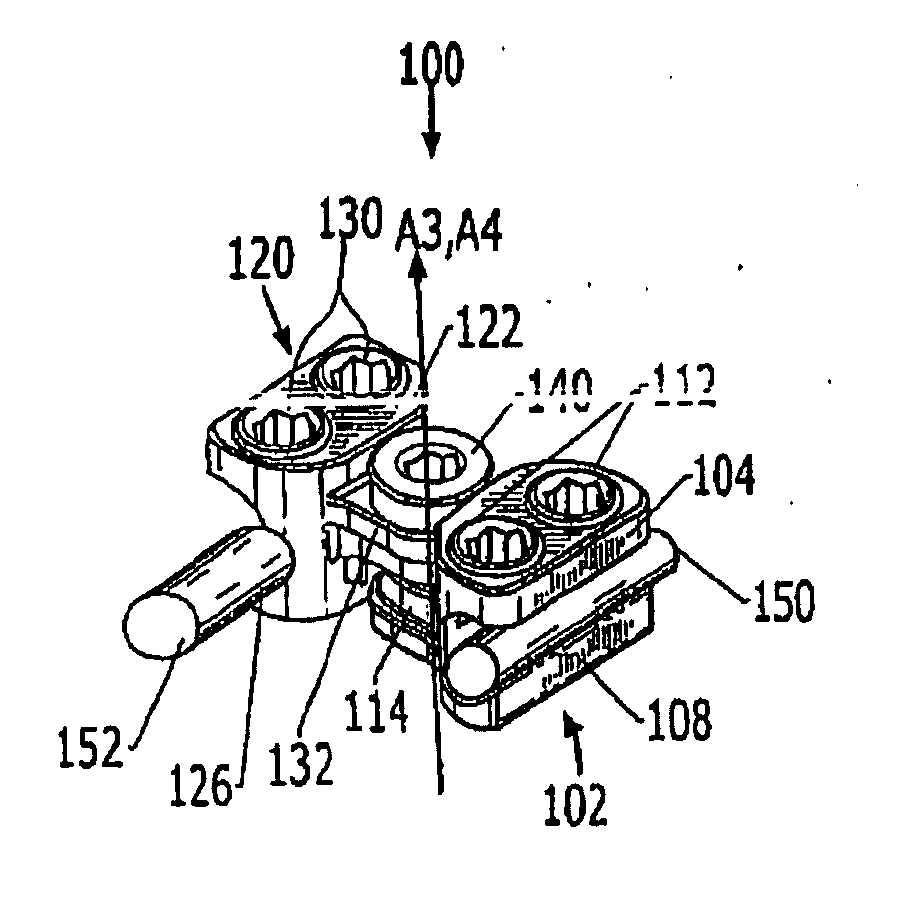
The present invention discloses a device for aligning and guiding a femoral resection guide and a femoral implant impactor, whereby the femoral resection guide and the femoral implant impactor are aligned perpendicular to the mechanical axes of the coronal plane and sagittal plane of the femur at the bottom end of the femur, and are guided so as to be rotation-aligned and mounted in parallel with a condyle axis connecting the inner condyle and outer condyle. The device comprises a main frame 110, joint bars 120 which are arranged extended downward from one end portion of the main frame 110 so as to be inserted and joined into the femoral resection guide 200 or femoral implant impactor 300, a support bar 130 which is arranged extended downward from the other end portion of the main frame 110, a first long bar 140 which is joined to the top surface of the one end portion of the main frame 110 to be arranged in parallel with the mechanical axis of the coronal plane of the femur, and a second long bar 150 which is joined to the support bar 130 to be arranged in parallel with the mechanical axis of the sagittal plane of the femur.
Owner:IND ACADEMIC COOPERATION FOUND UNIV OF INCHEON
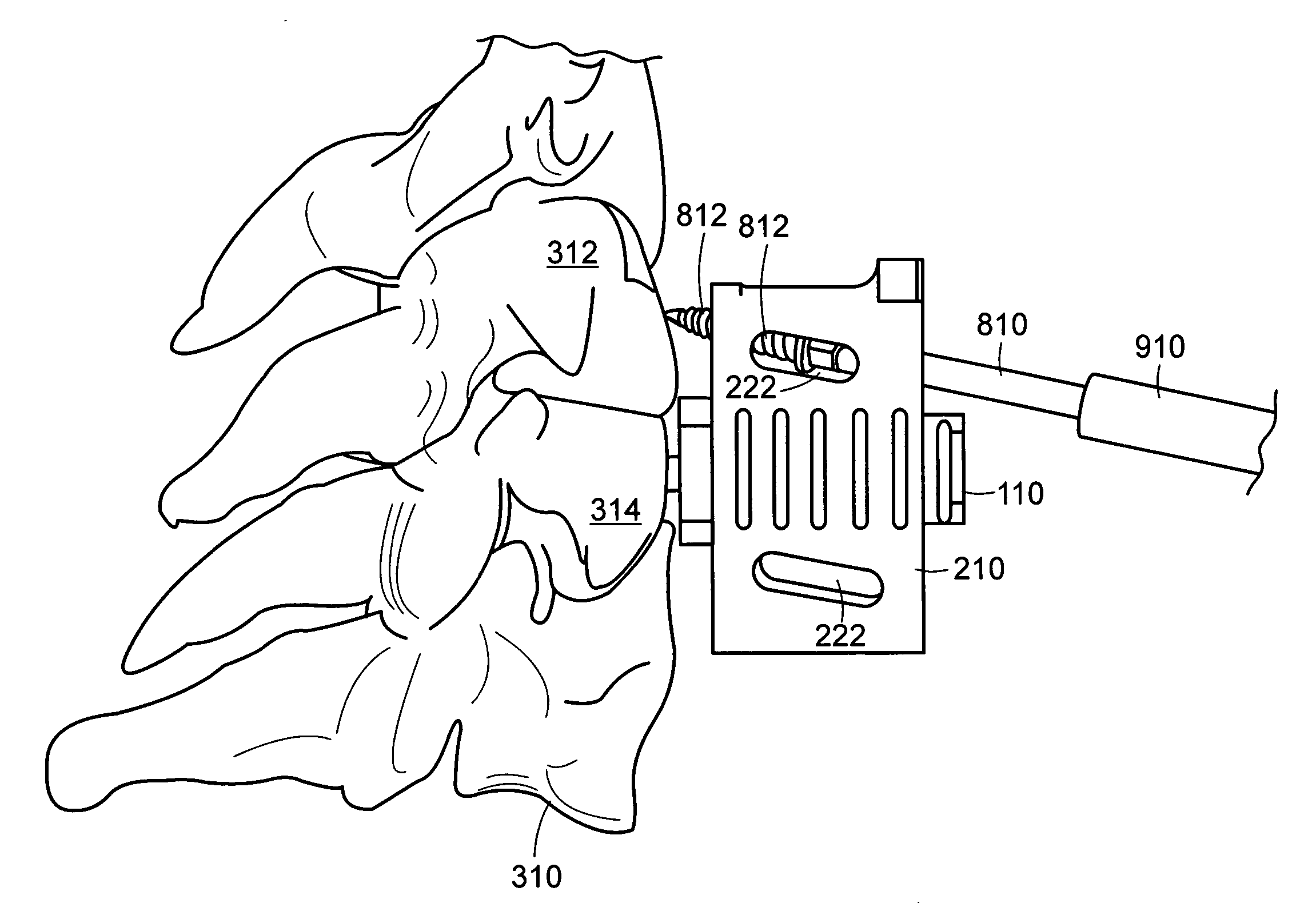
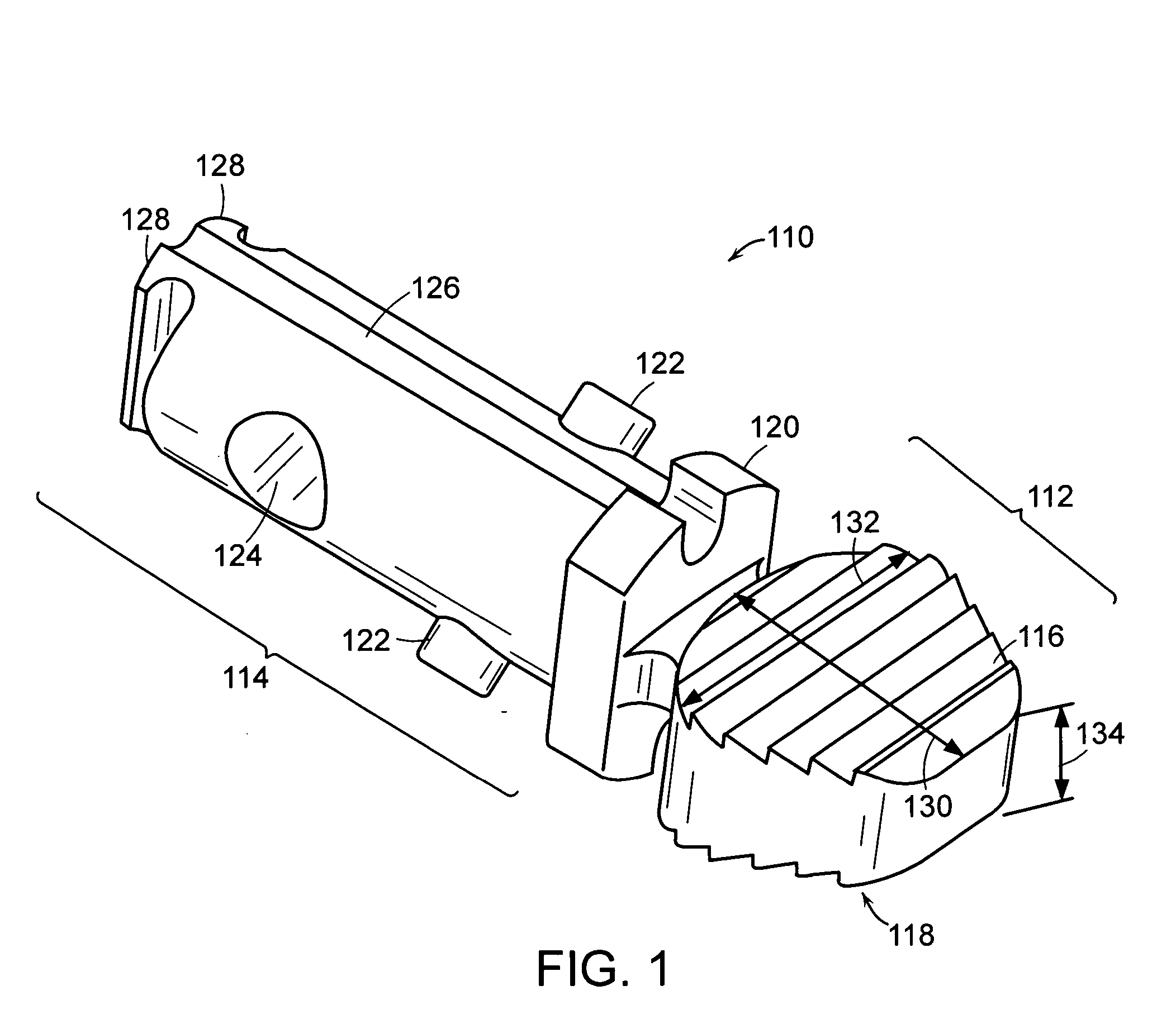
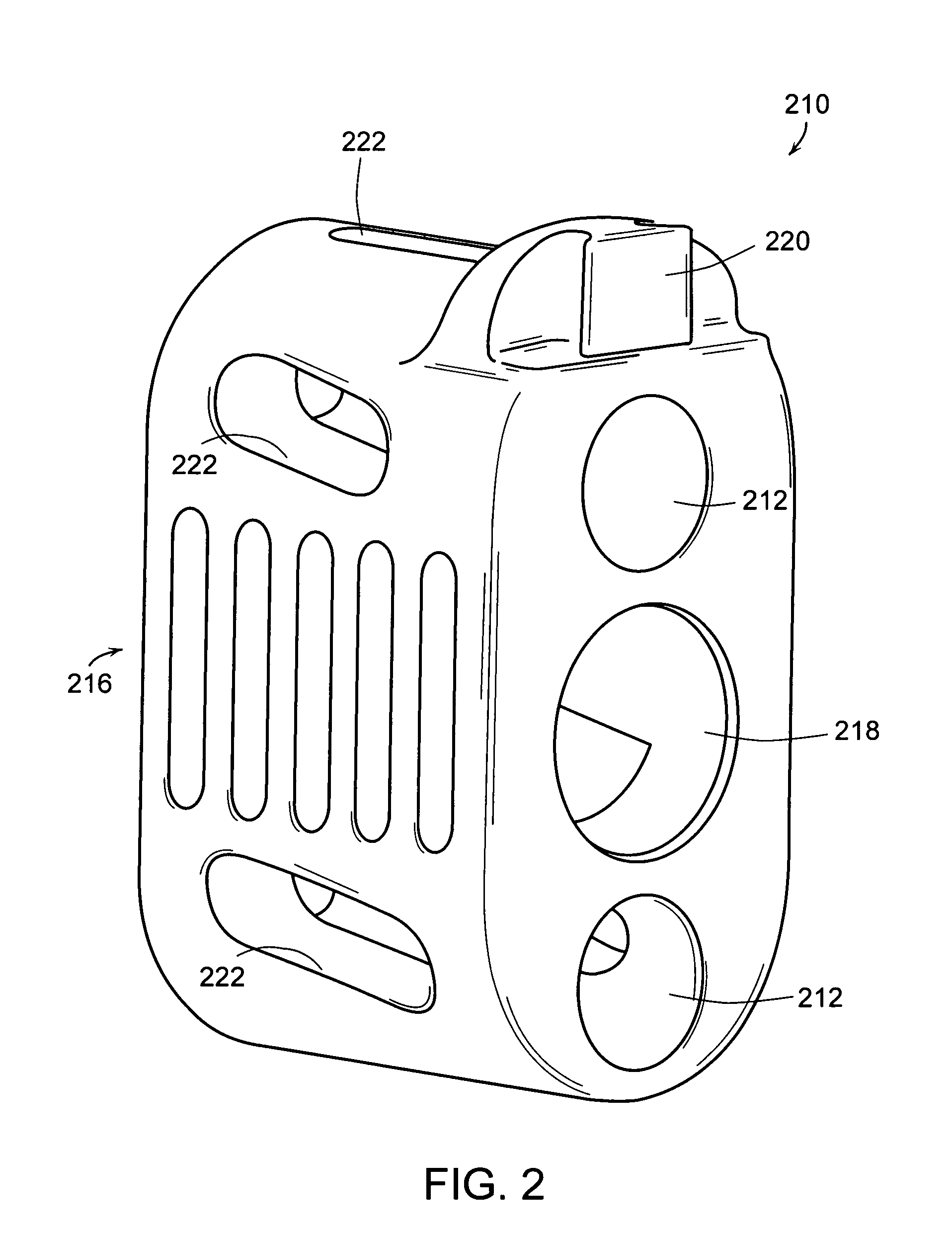
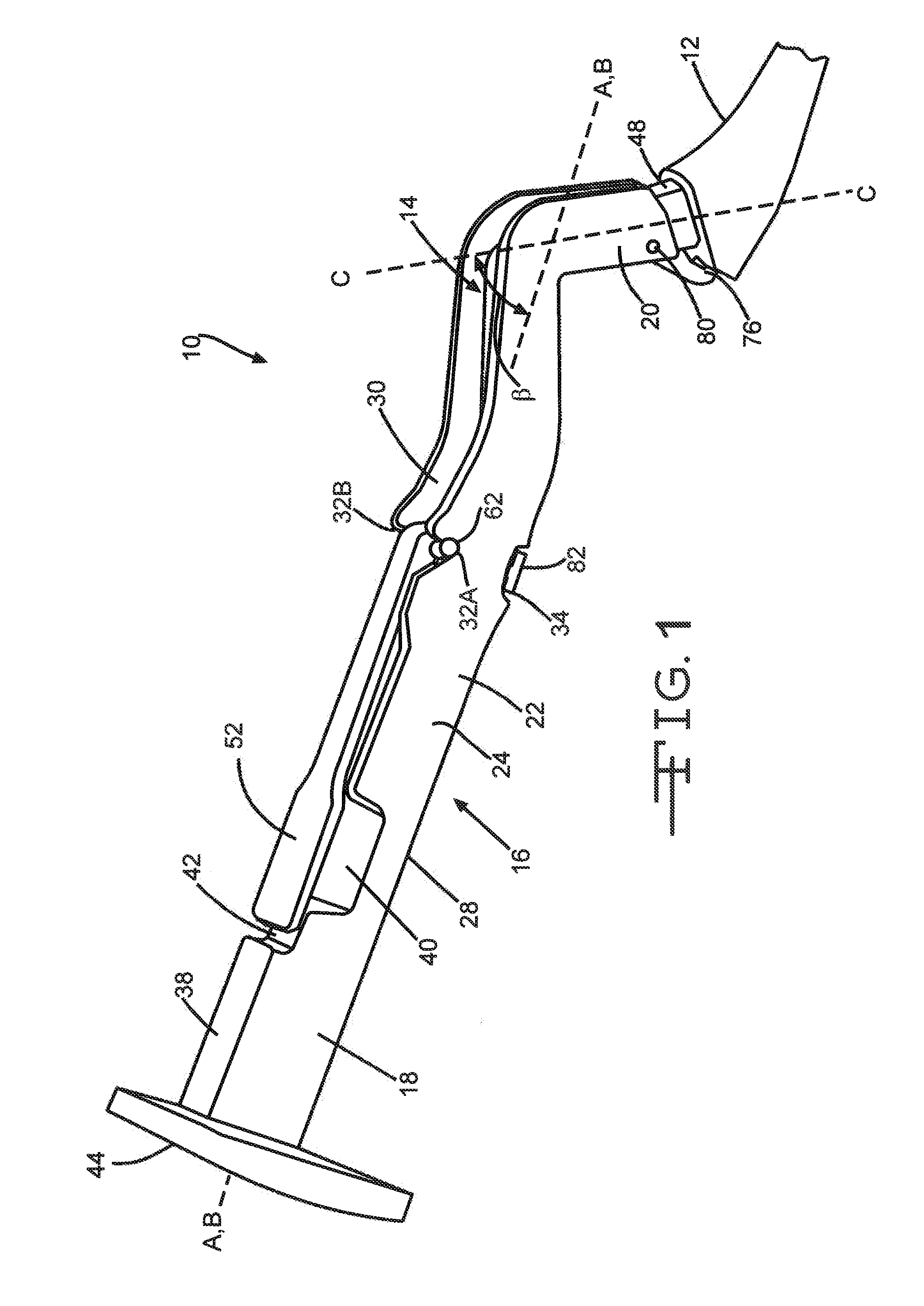
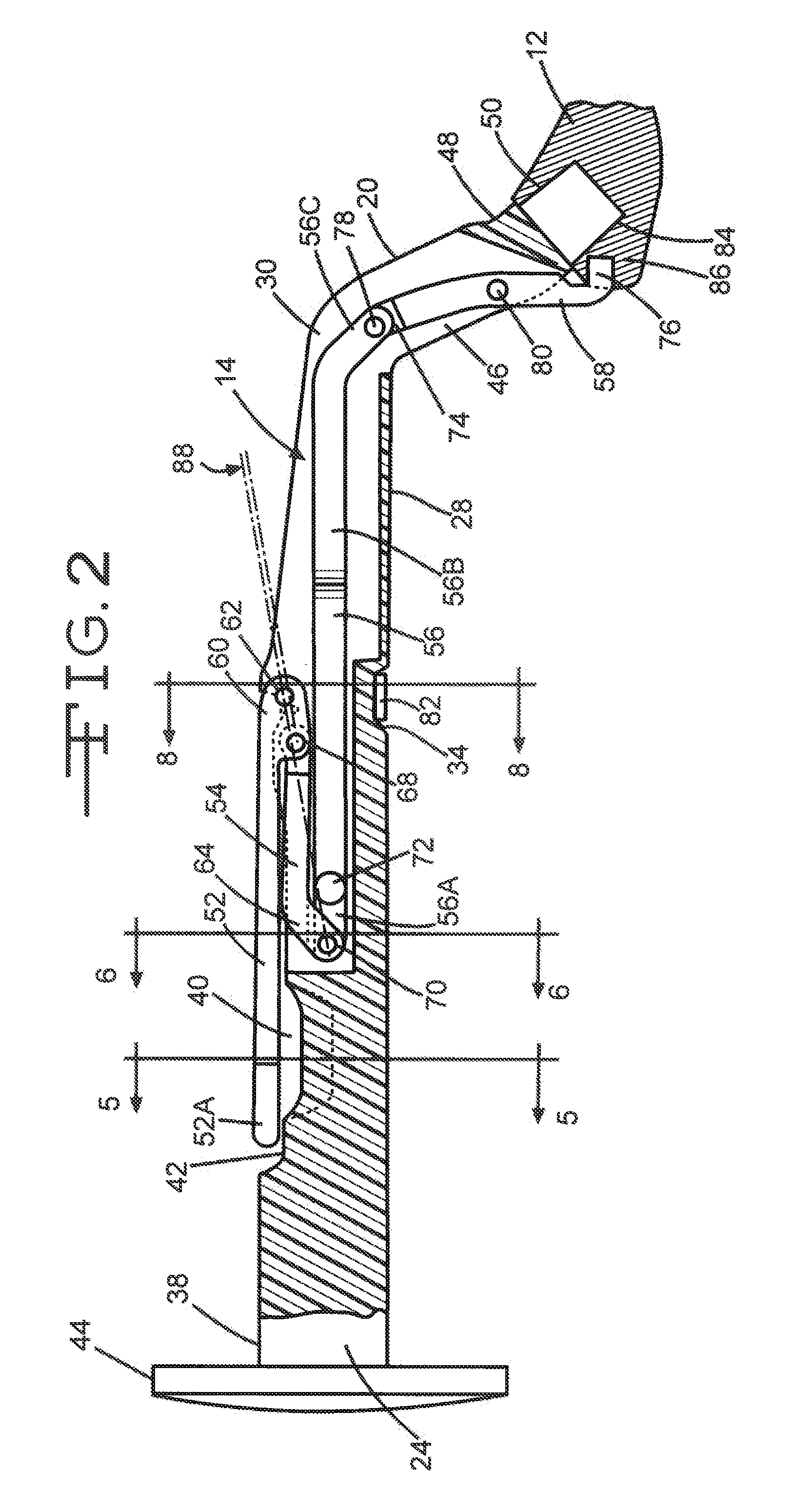
Double offset surgical tool handle assembly to provide greater offset from the coronal plane
ActiveUS8657833B2Avoid separationEasy to sterilizeFemoral headsOsteosynthesis devicesCoronal planeMechanical engineering
A surgical tool handle for releasable connection to a surgical tool is described. The tool handle comprises a housing providing a linkage chamber extending from a proximal housing grip end to a distal housing tool end for receiving a tool. A tool linkage is partially housed within the linkage chamber. That way, manipulation of the tool linkage causes a locking pawl to pivot with respect to the housing from an open configuration ready to receive a tool for attachment to the housing to a closed configuration engageable with the tool supported at the distal housing tool end.
Owner:VIANT AS&O HLDG LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com