Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
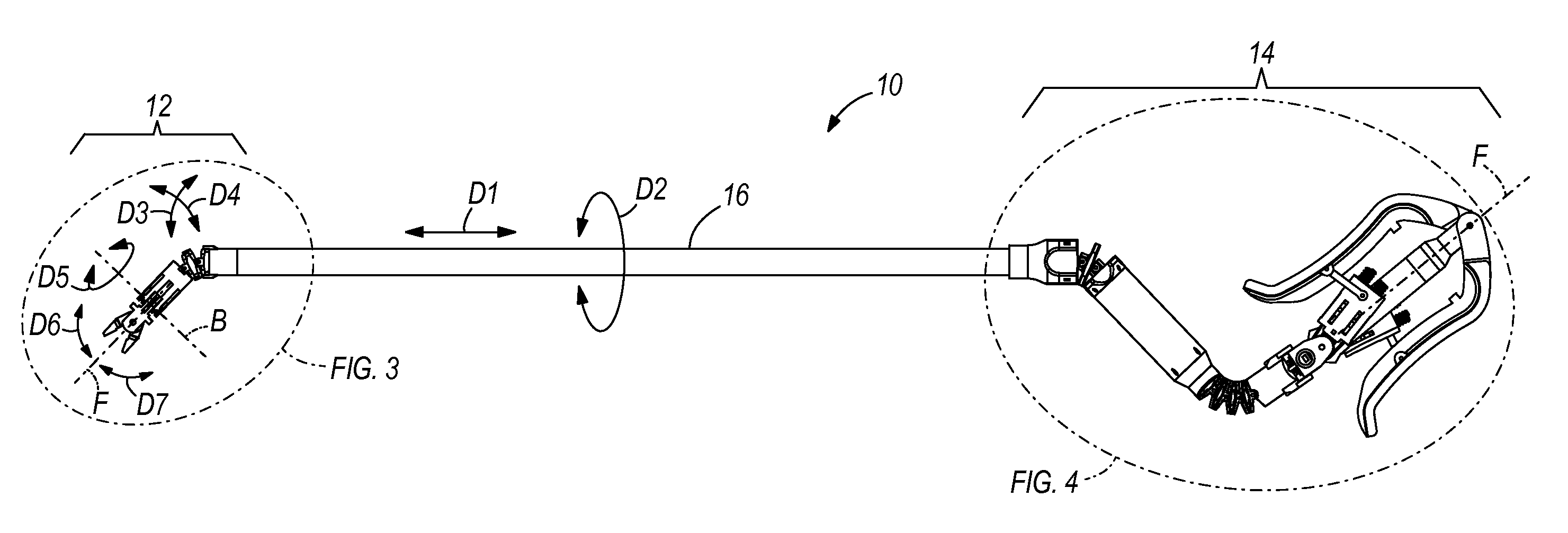
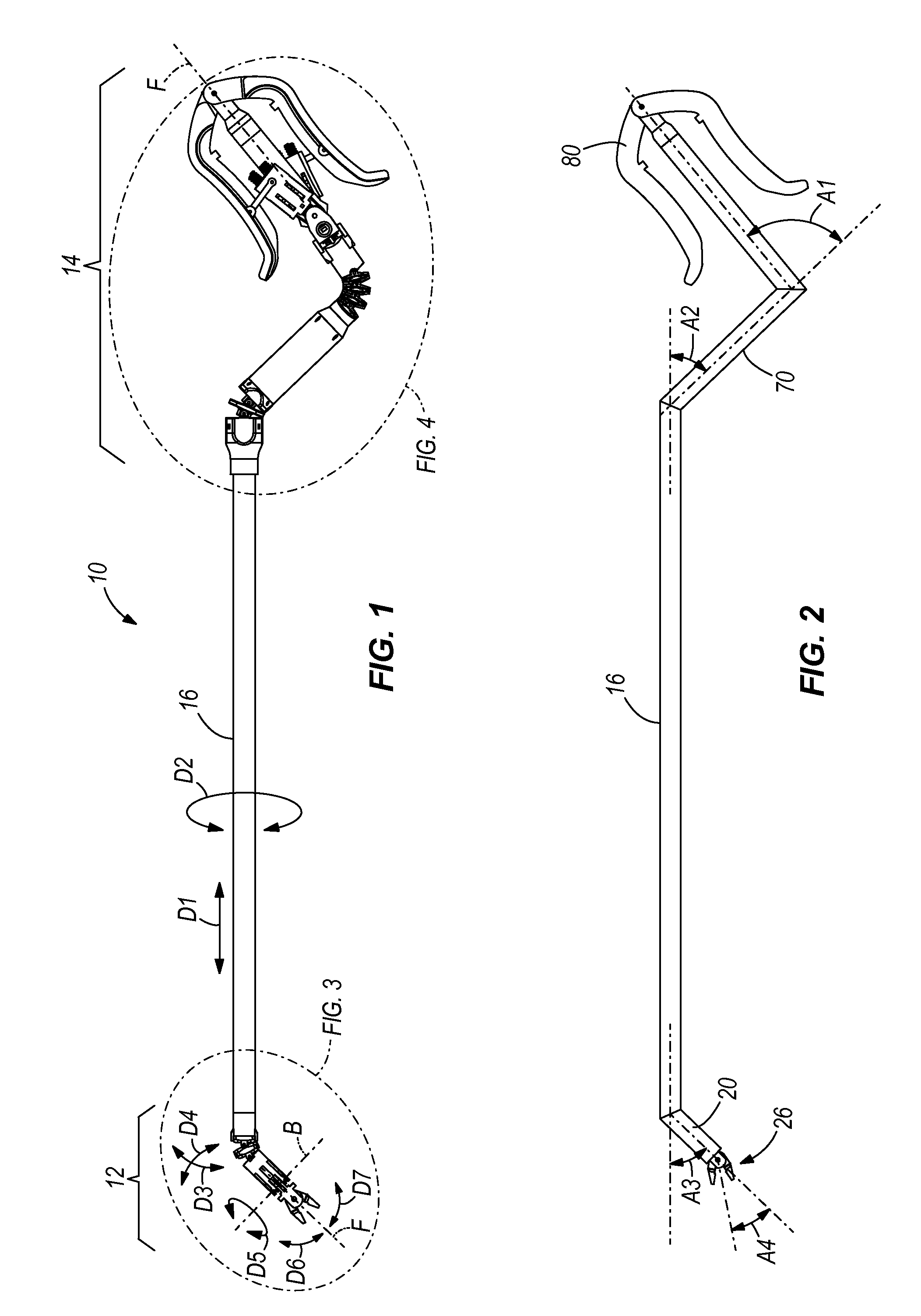
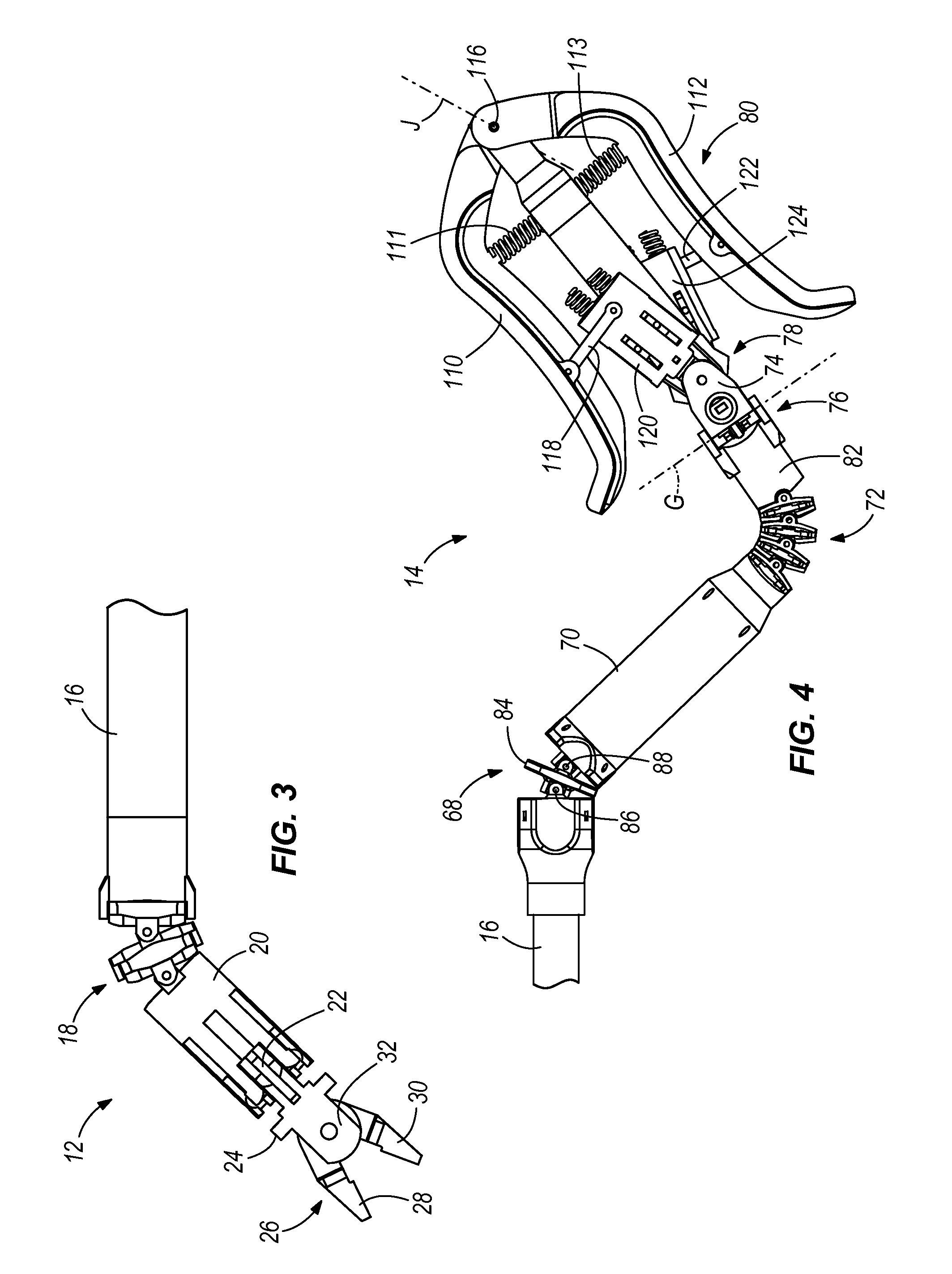
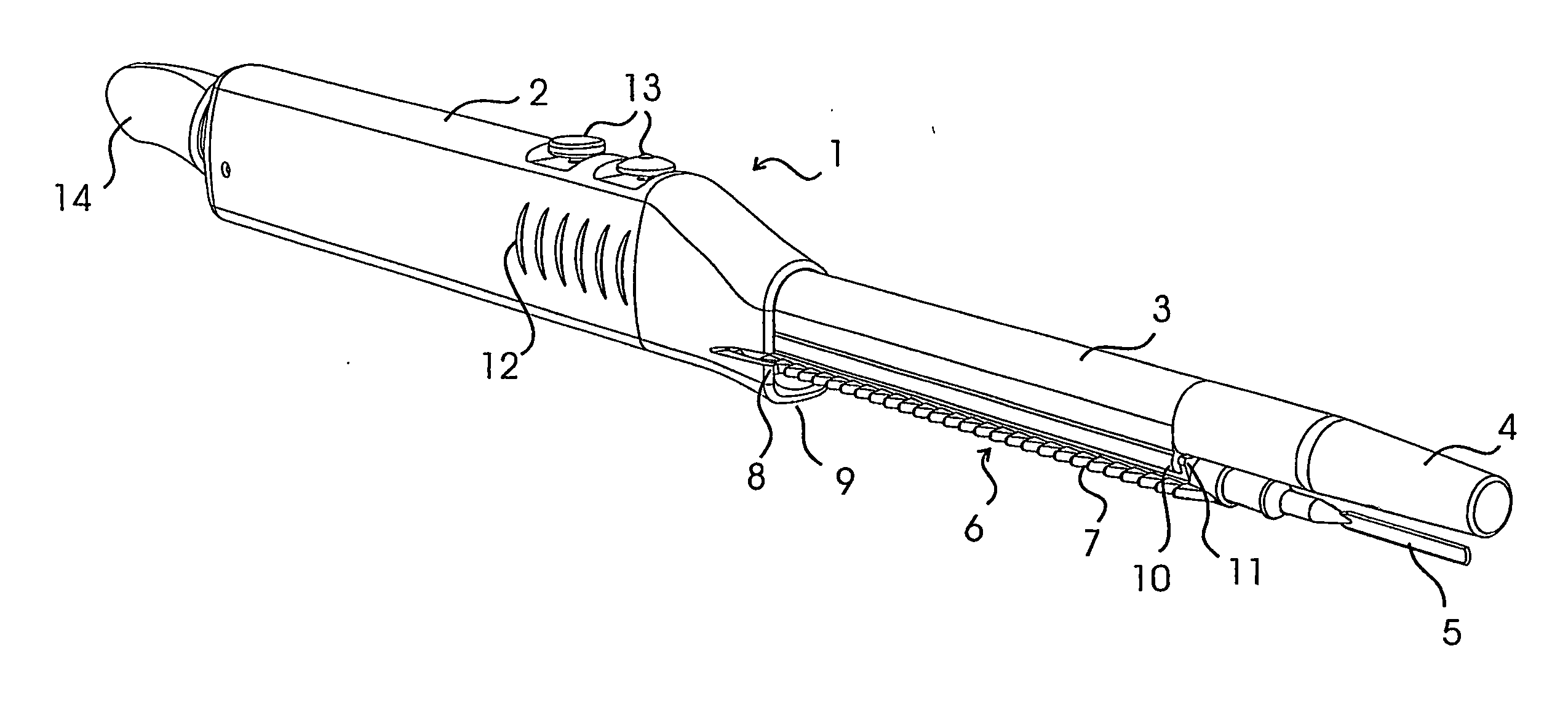
93 results about "Surgeon hand" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
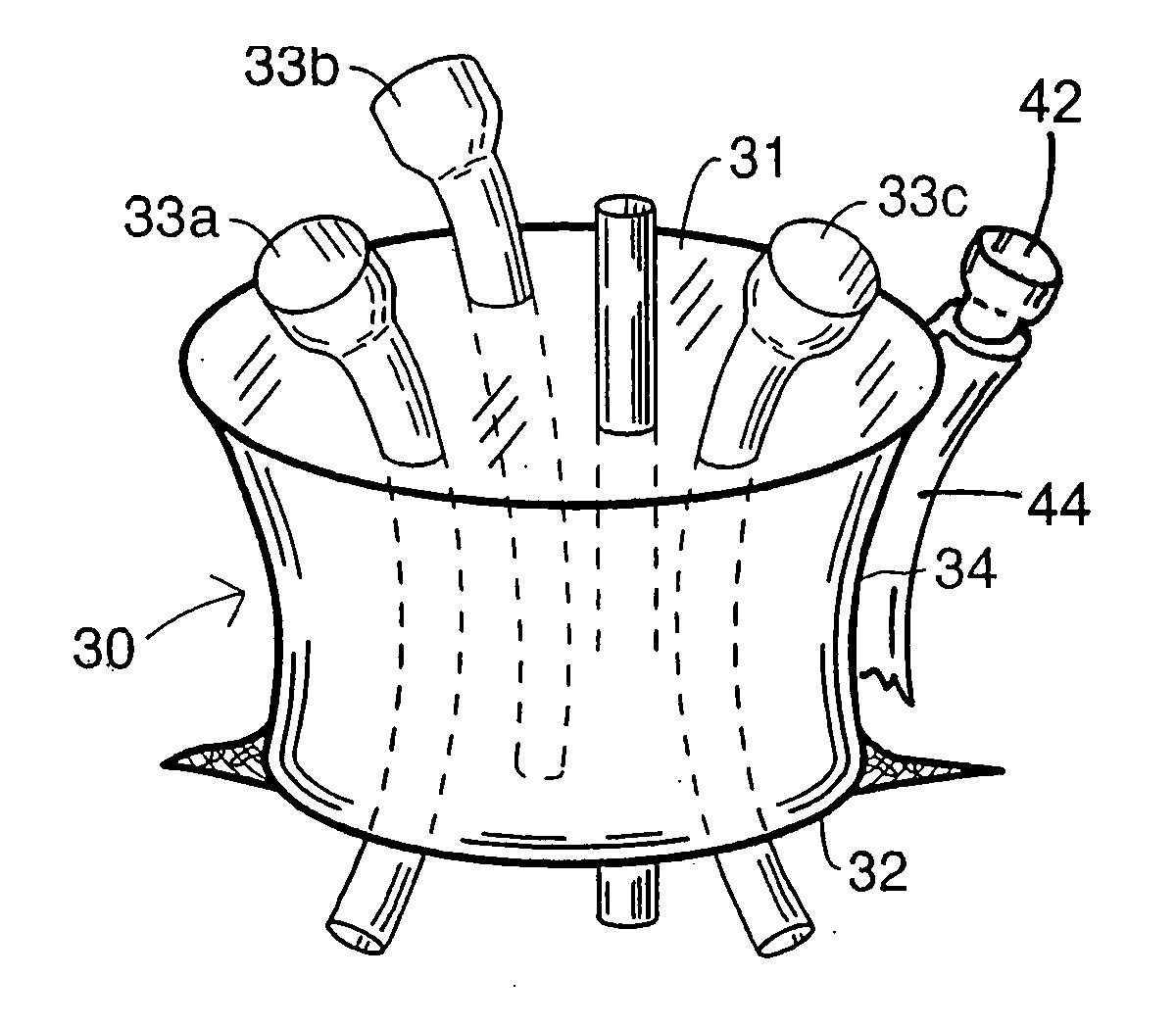
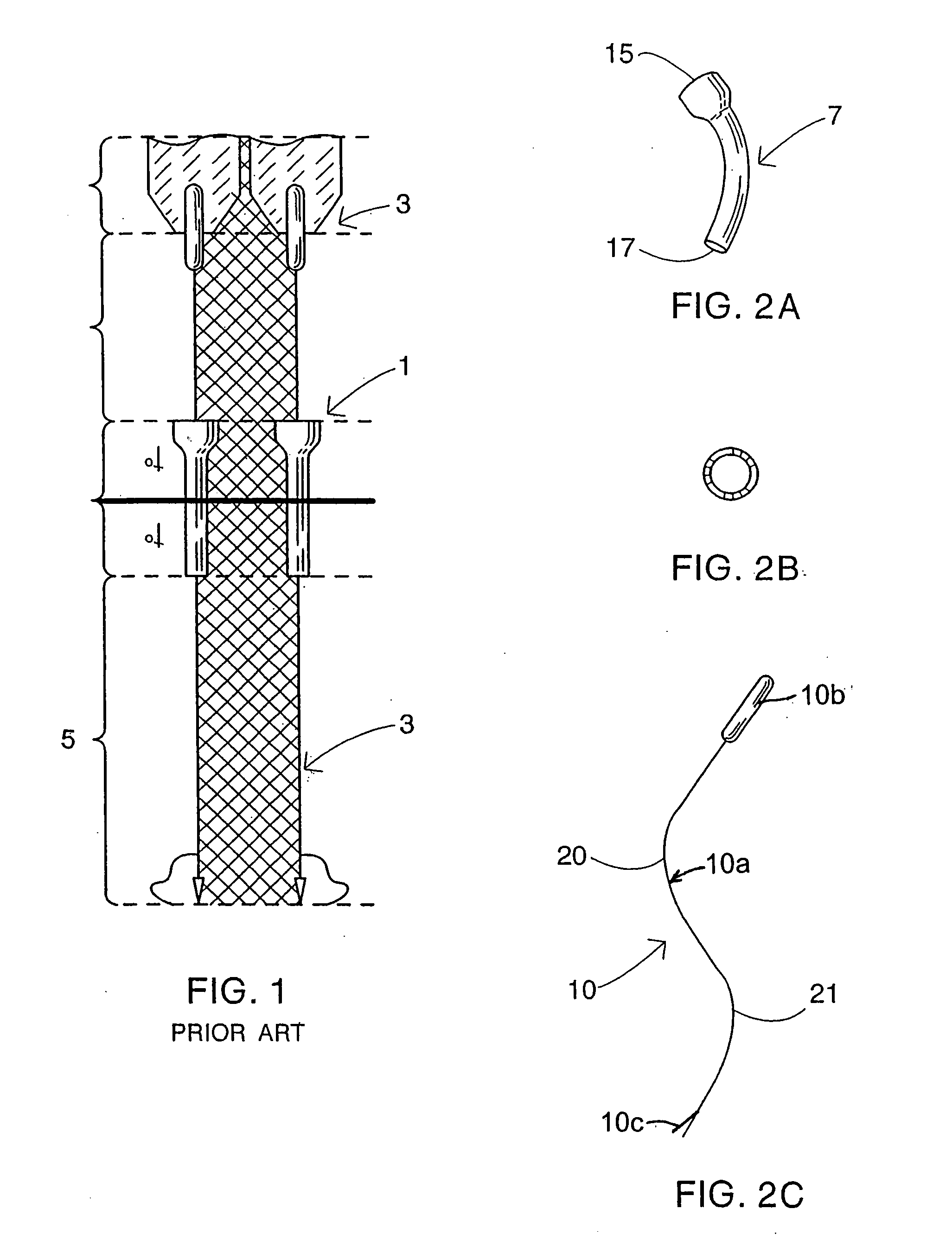
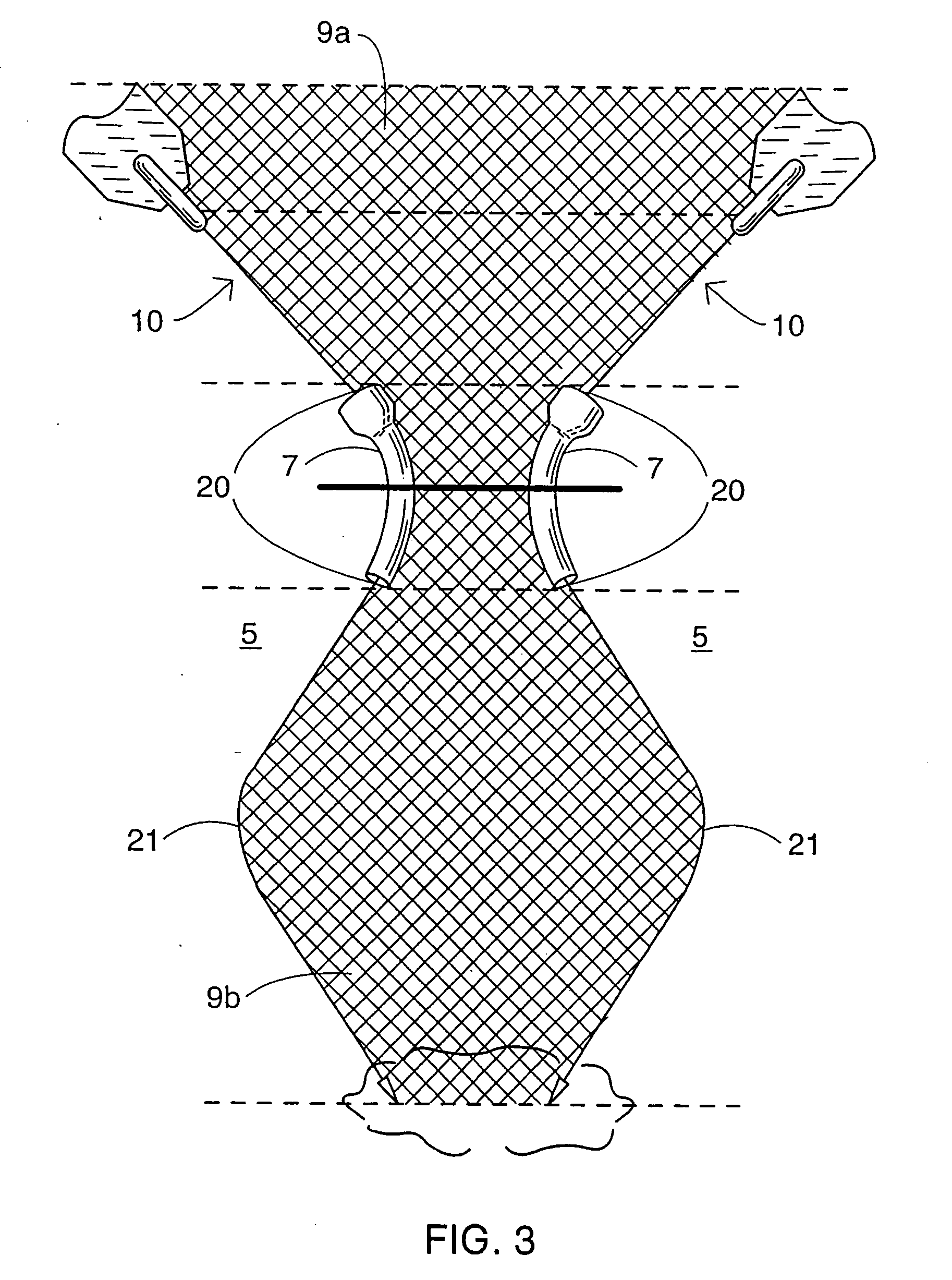
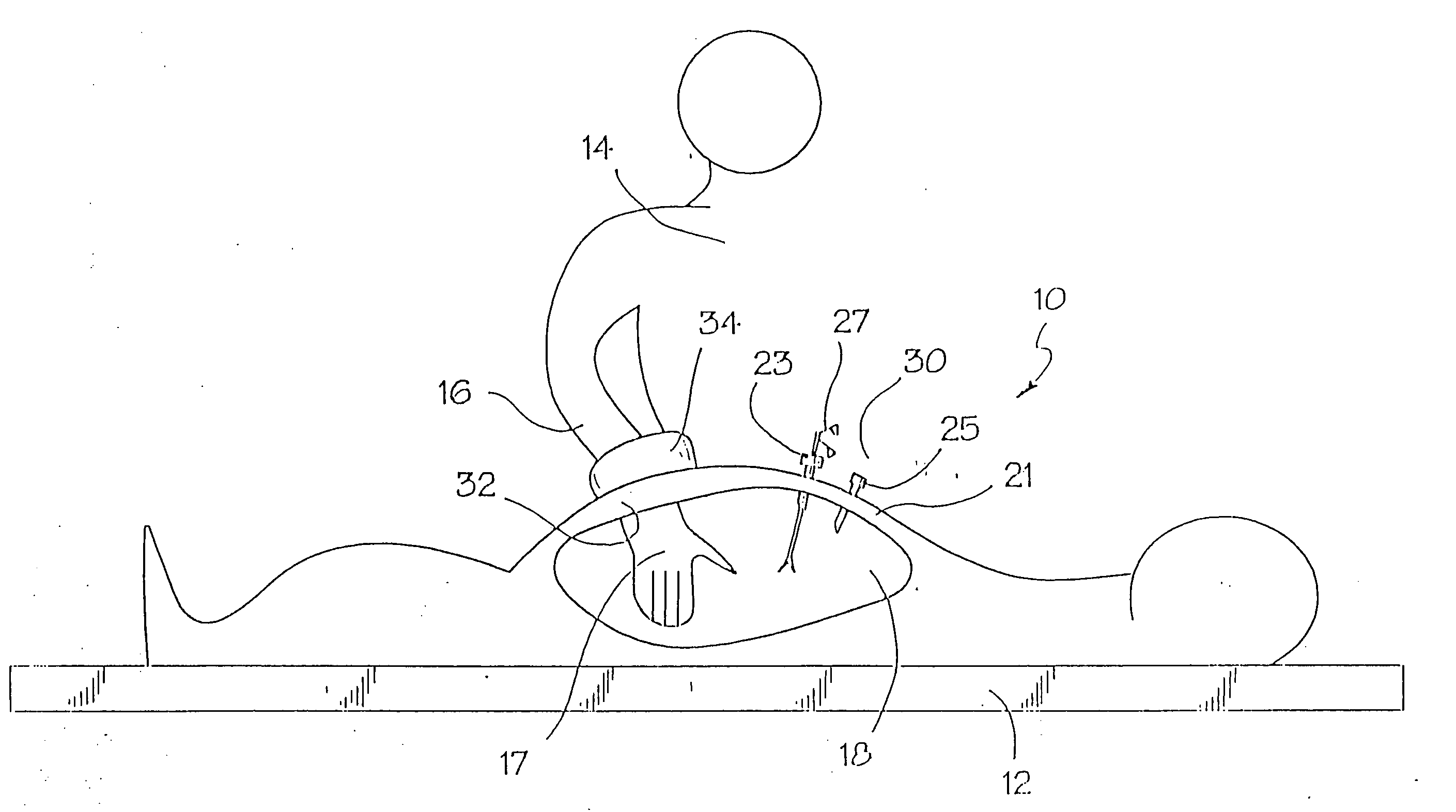
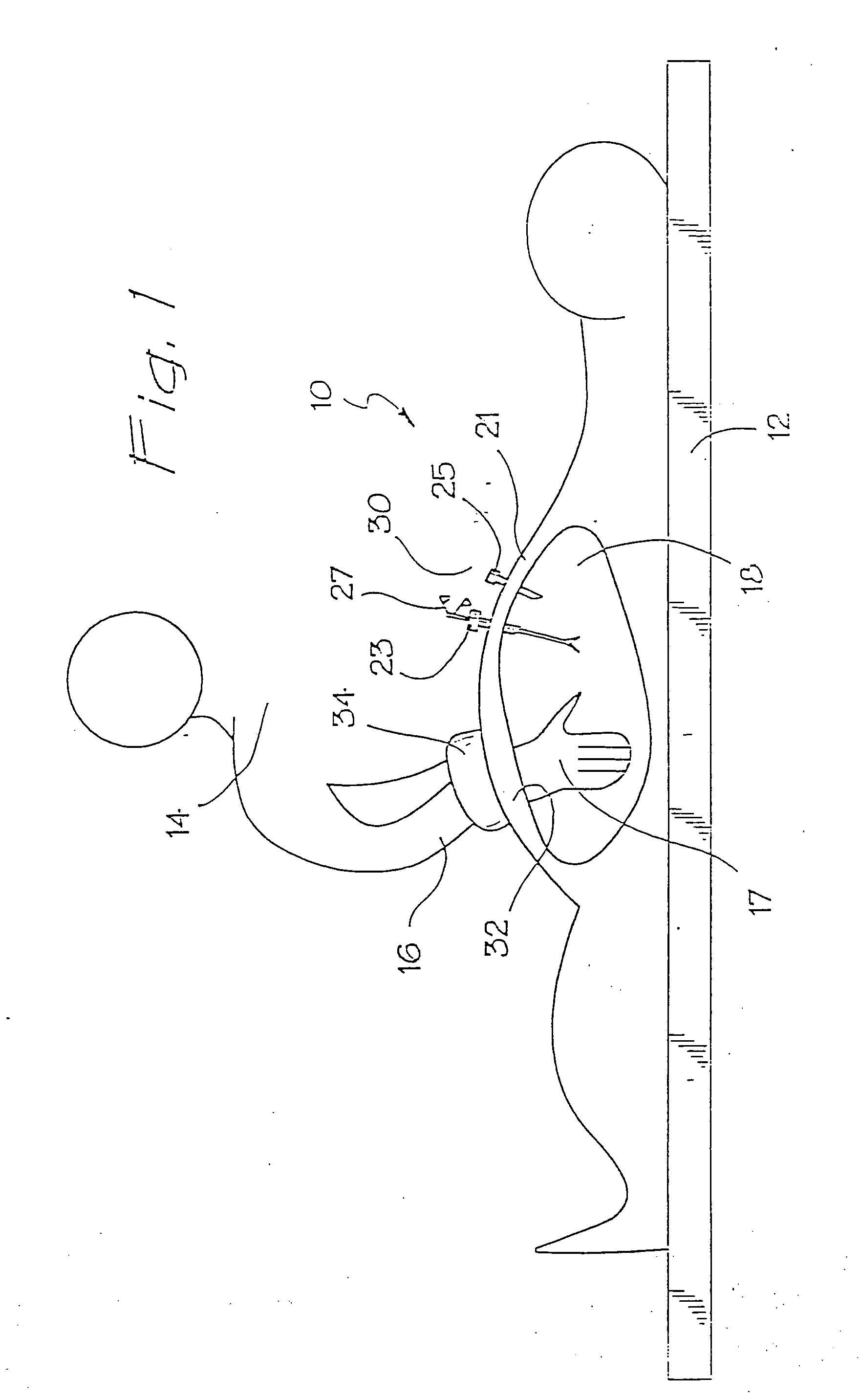
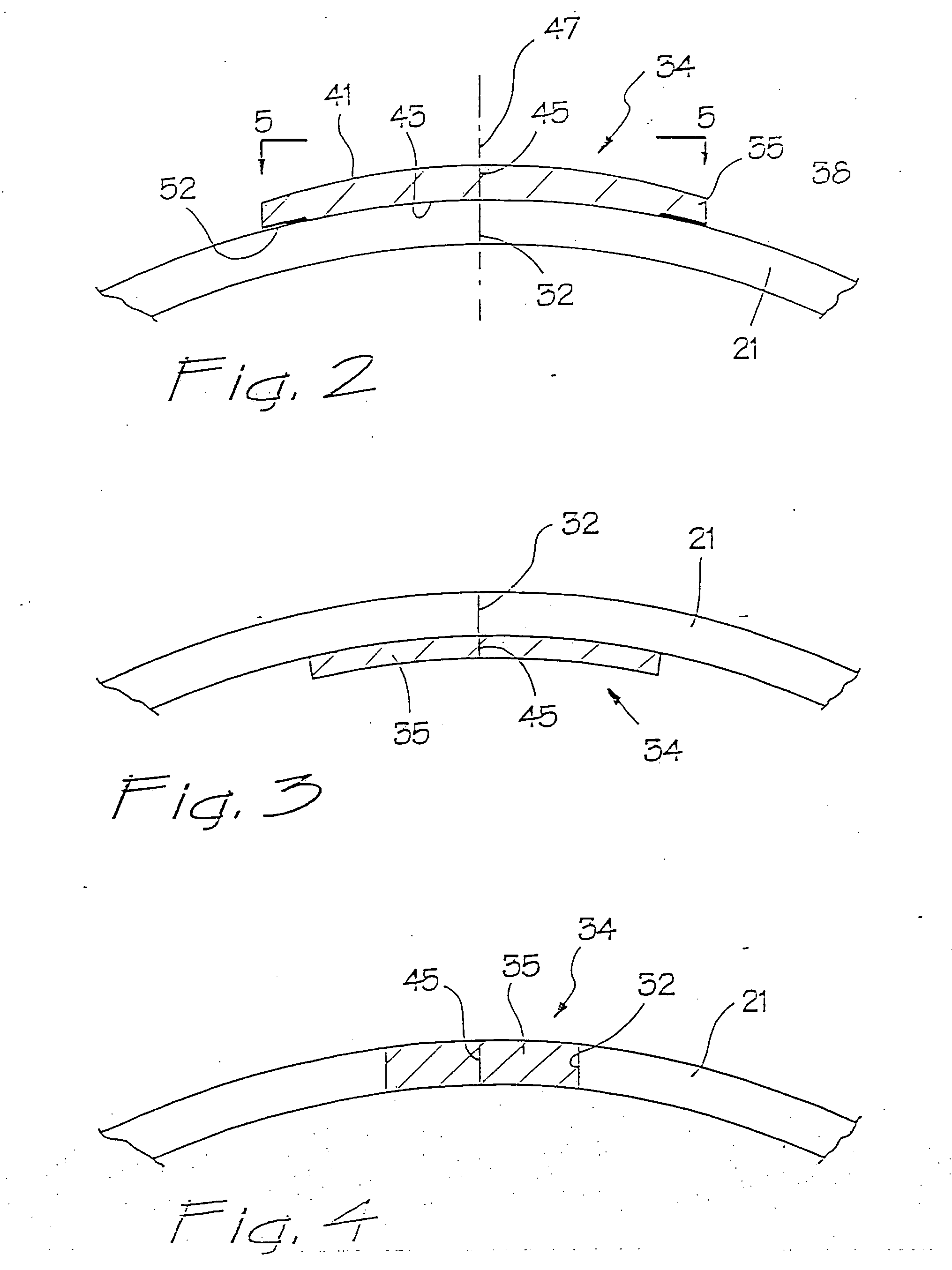
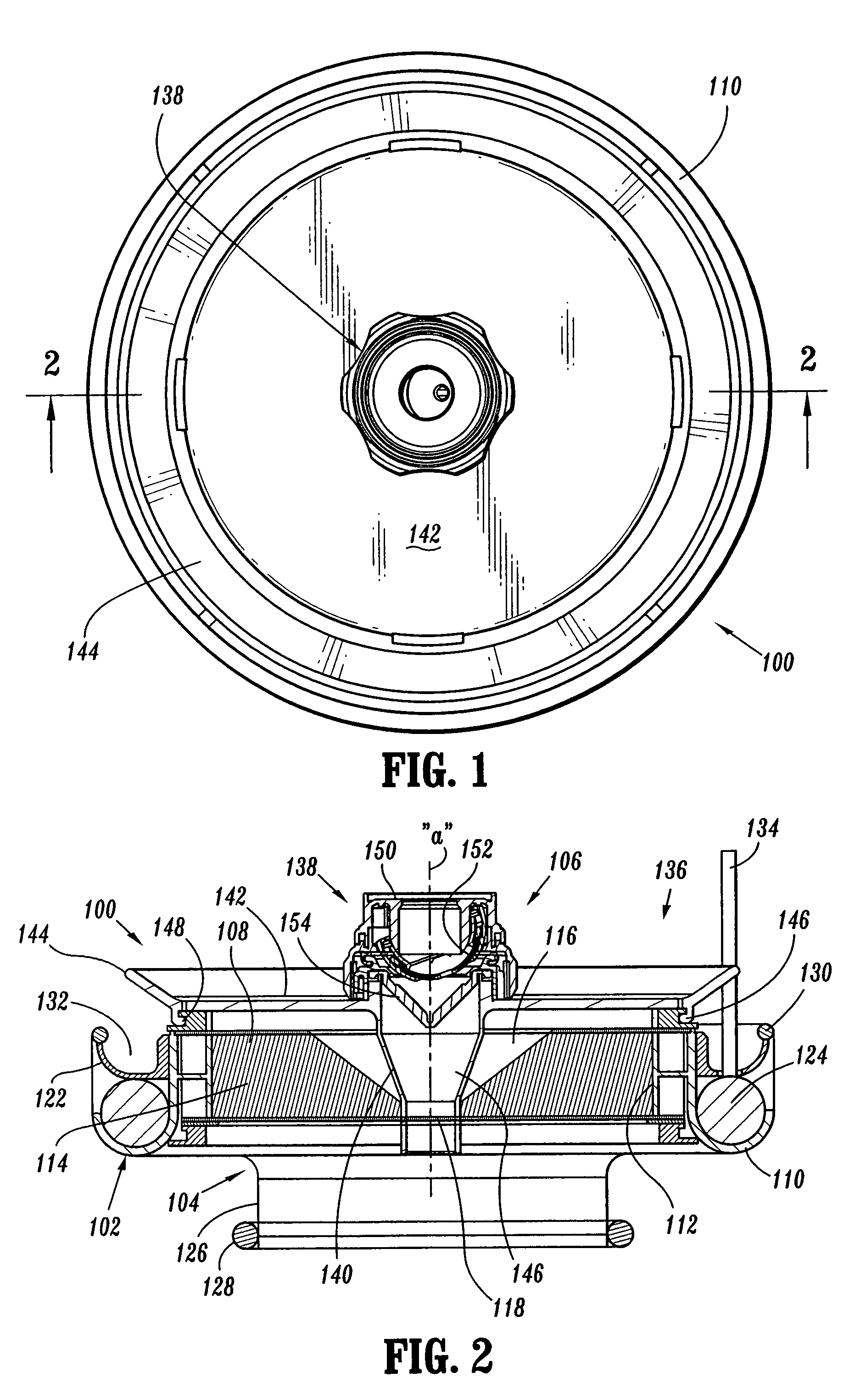
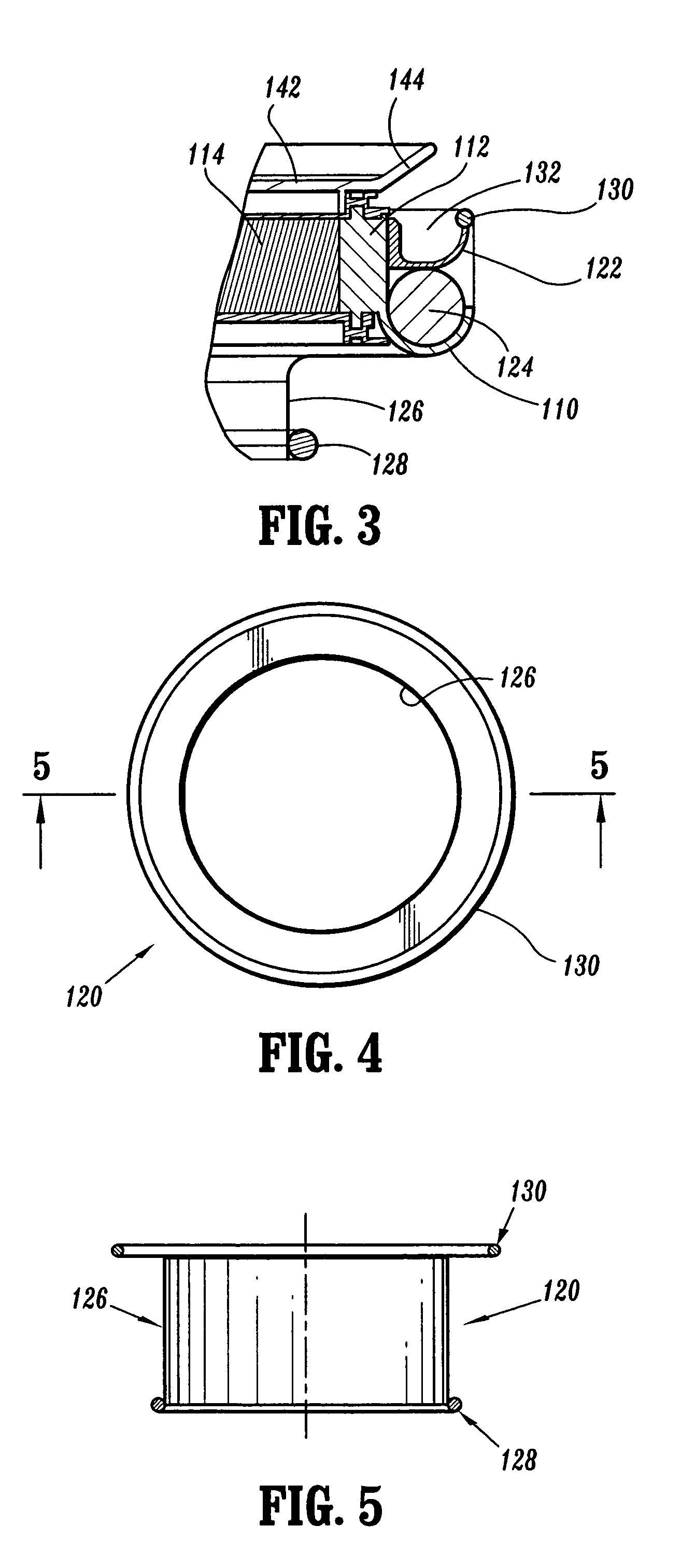
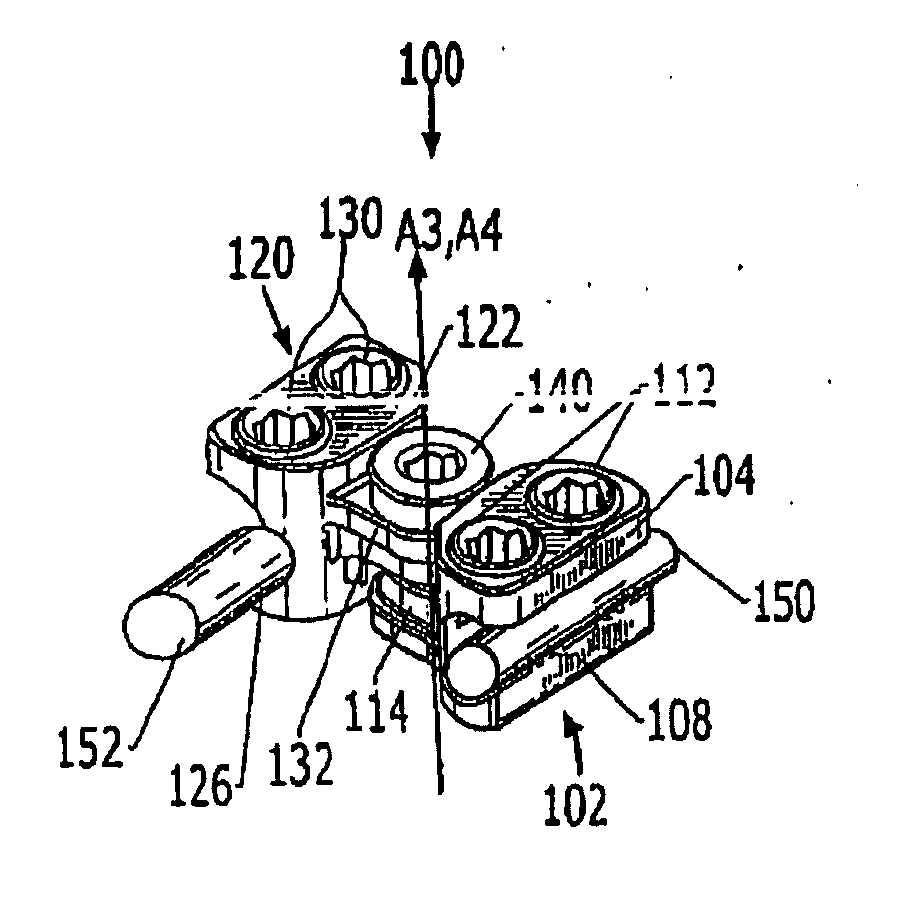
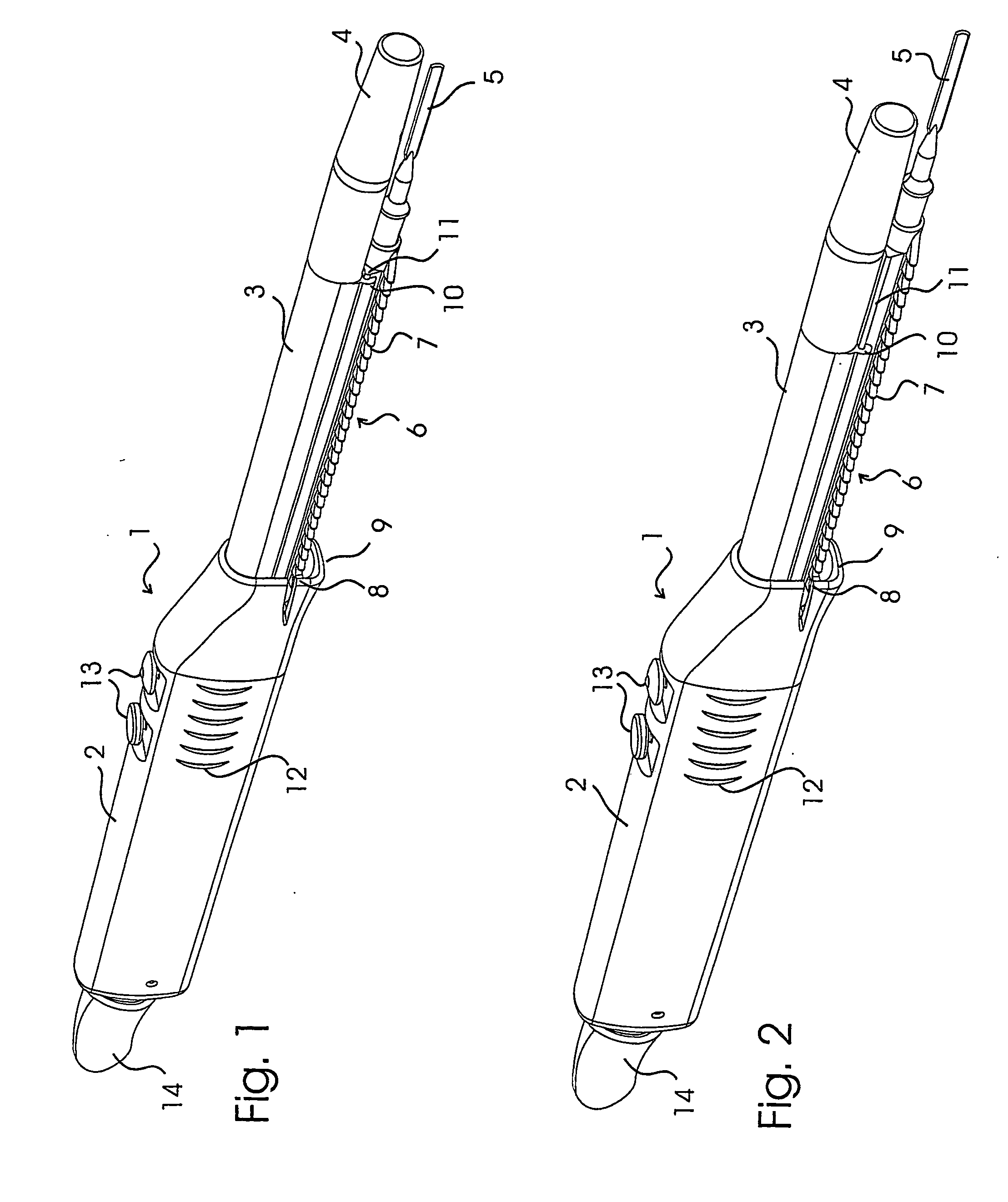
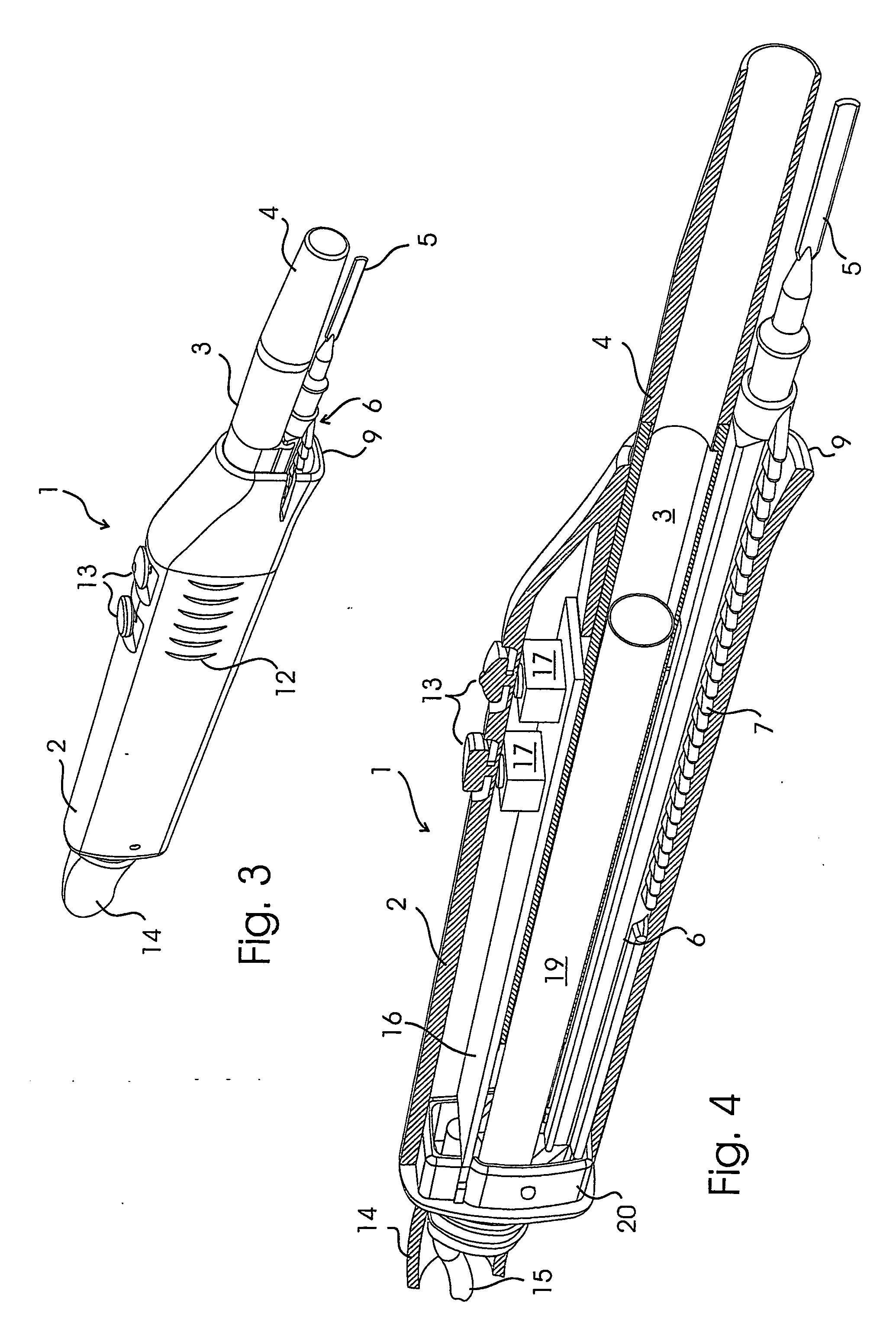
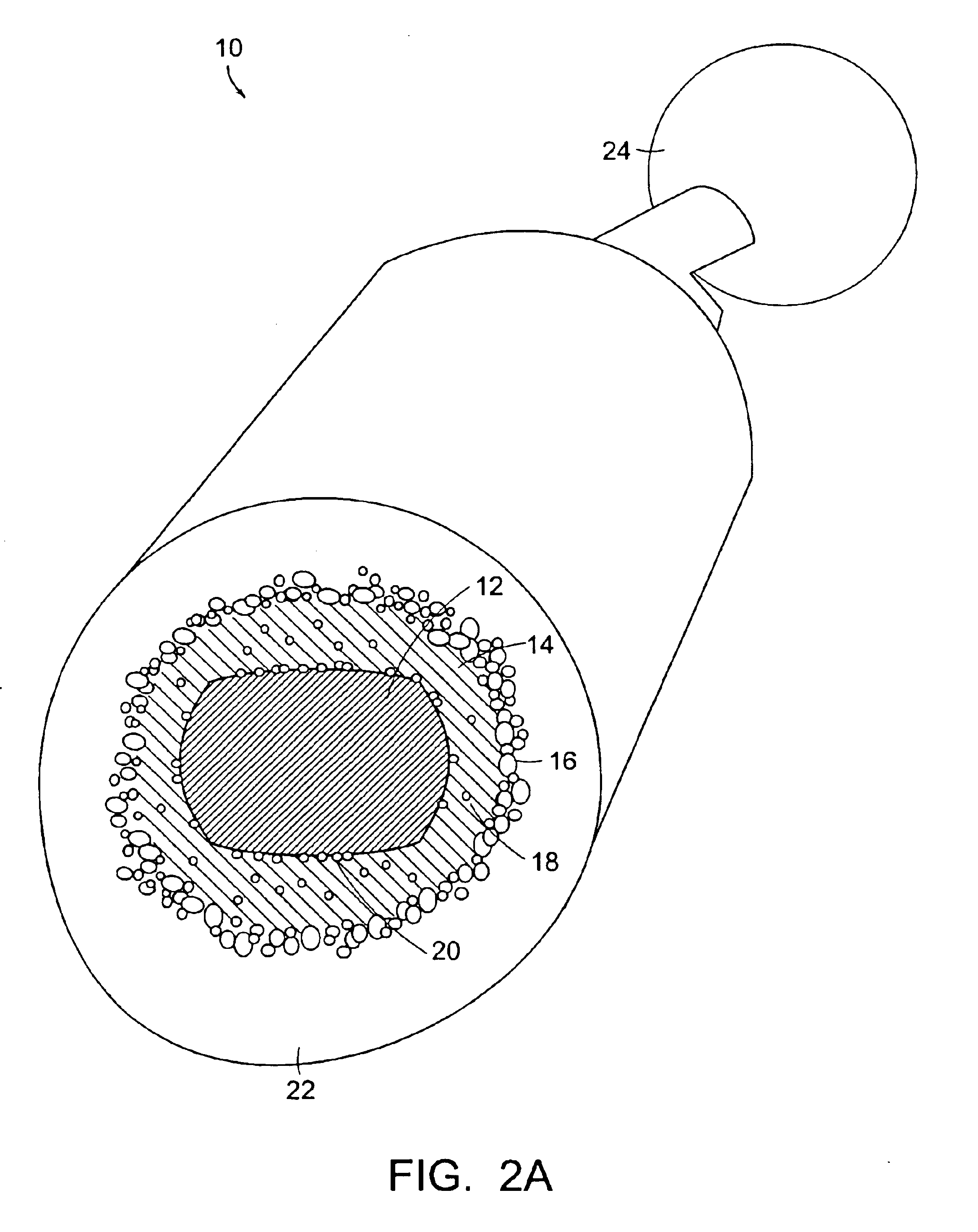
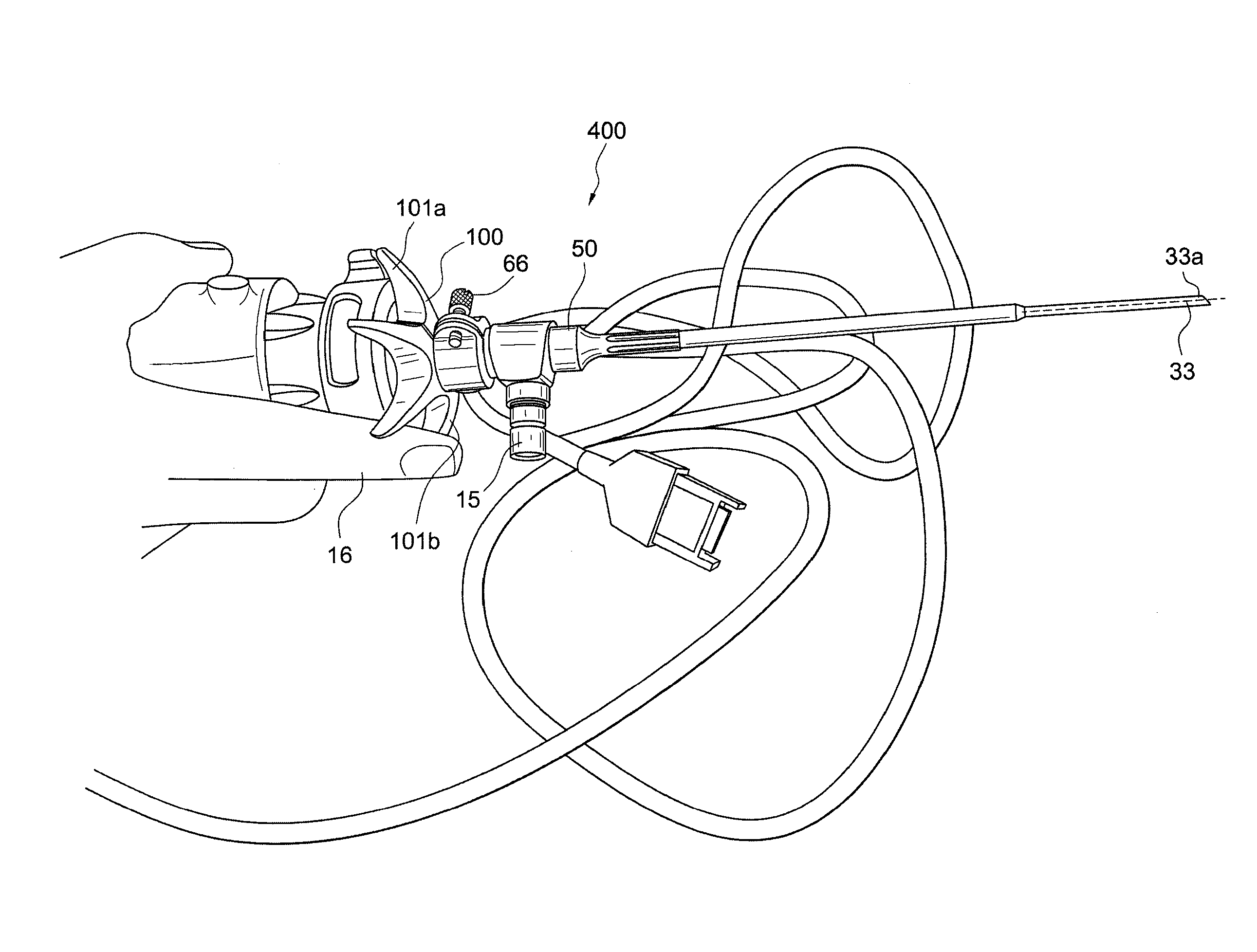
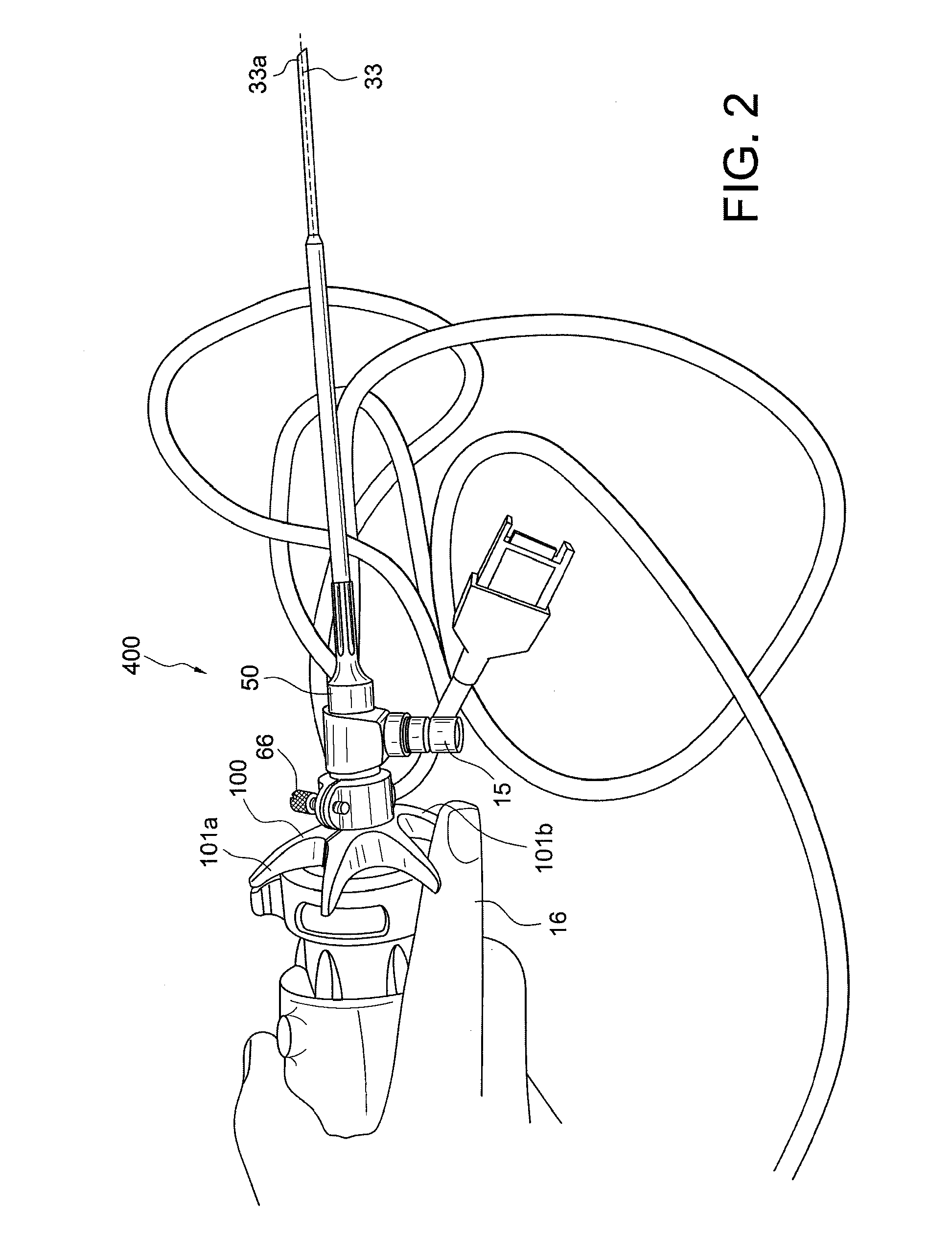
A surgical sealing device
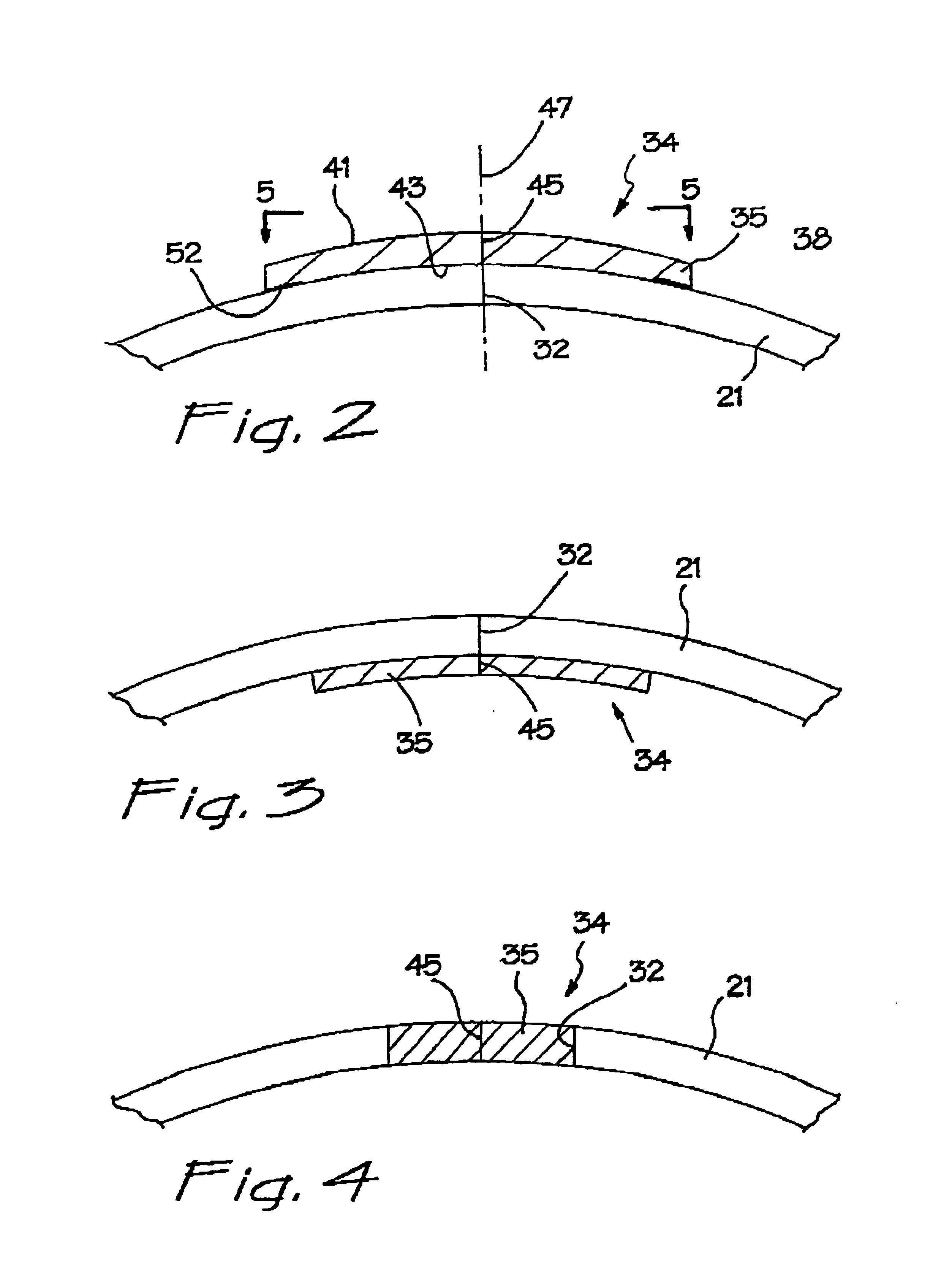
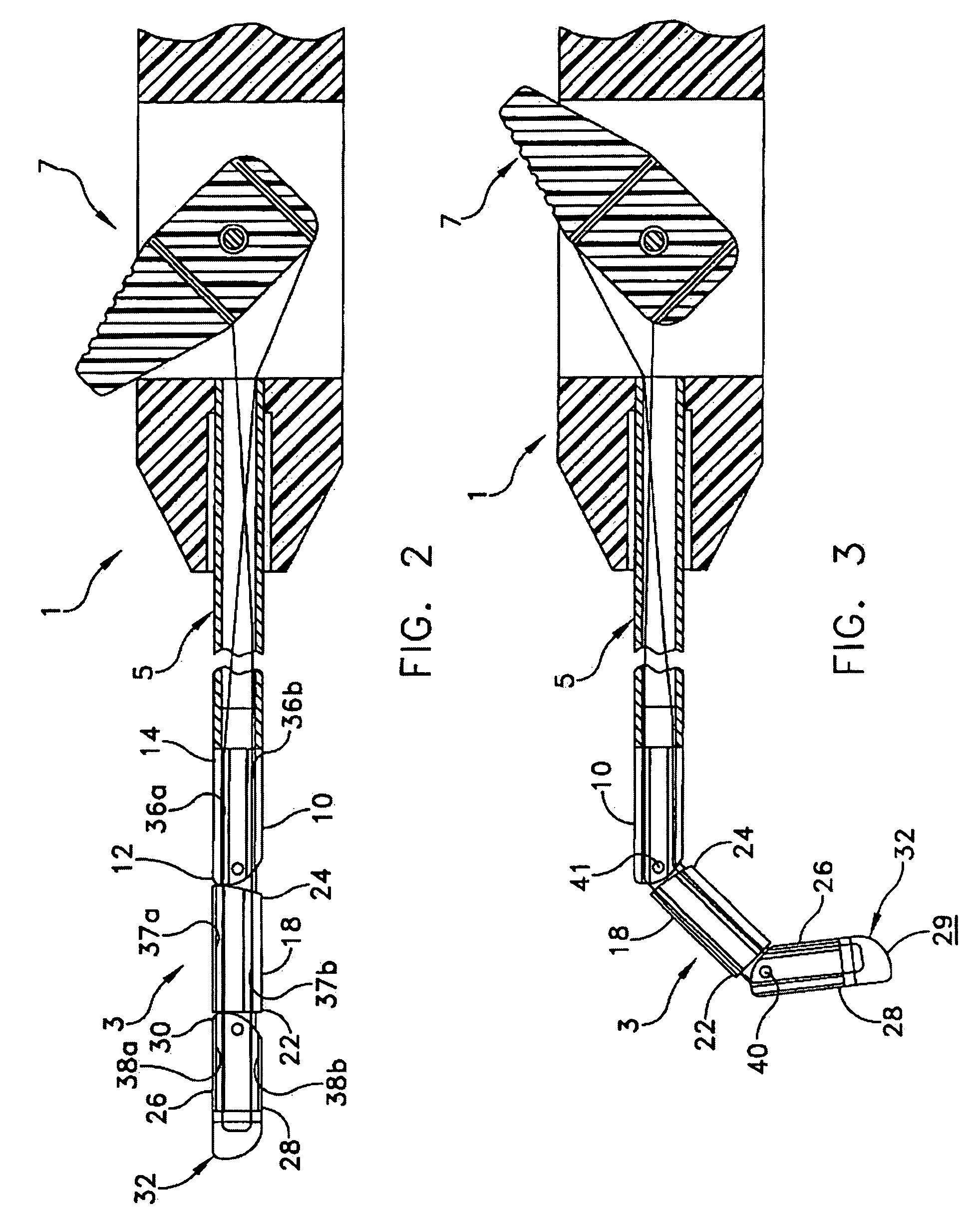
A surgical sealing device (405), suitable for use during a surgical procedure such as a laparoscopic procedure or a hand-assisted laparoscopic procedure, comprises a first sealing member (5) and a second sealing member (6). A thin slit is defined between the sealing members (5, 6). In a closed configuration, the first sealing member (5) overlaps the distal end opening of a passageway (2) through the second sealing member (6) to prevent leakage of insufflation gases out of an abdomen (4). In an open configuration, the first sealing member (5) is retracted to reveal the distal end opening of the passageway (2) and thus facilitate passage of an object, such as a surgeon's hand or forearm (3), into the abdomen (4). The device (405) comprises a planar support element (406) fixedly attached to the proximal exterior surface (408) of the first sealing member (5). The first sealing member (5) is fixedly attached to the second sealing member (6) at an attached region (409), with a detached region (407) remaining detached from the second sealing member (6). The support element (406) acts as a stiffening element to increase the stiffness of the detached region (407) of the first sealing member (5) to minimise the deformation of the detached region (407) of the first sealing member (5) when the surgeon's hand / forearm (3) is pushed through the passageway (2). It is thus easier for the surgeon to retract the first sealing member (5) laterally to reveal the distal end opening of the passageway (2) by pushing the hand / forearm (3) through the passageway (2) and easier for the surgeon to pass the hand / forearm (3) through the device (405) and gain access to the abdomen (4).
Owner:ATROPOS LTD
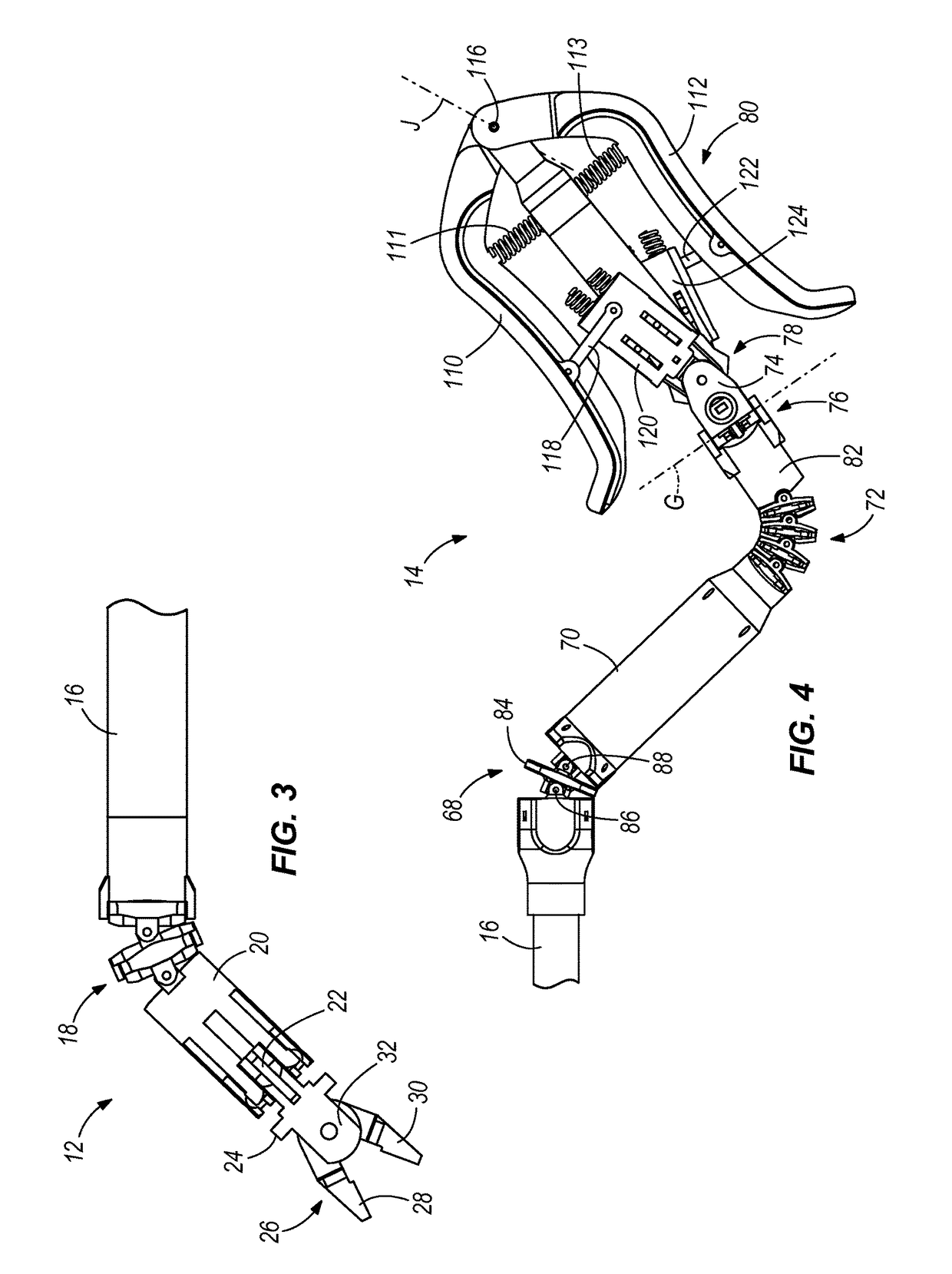
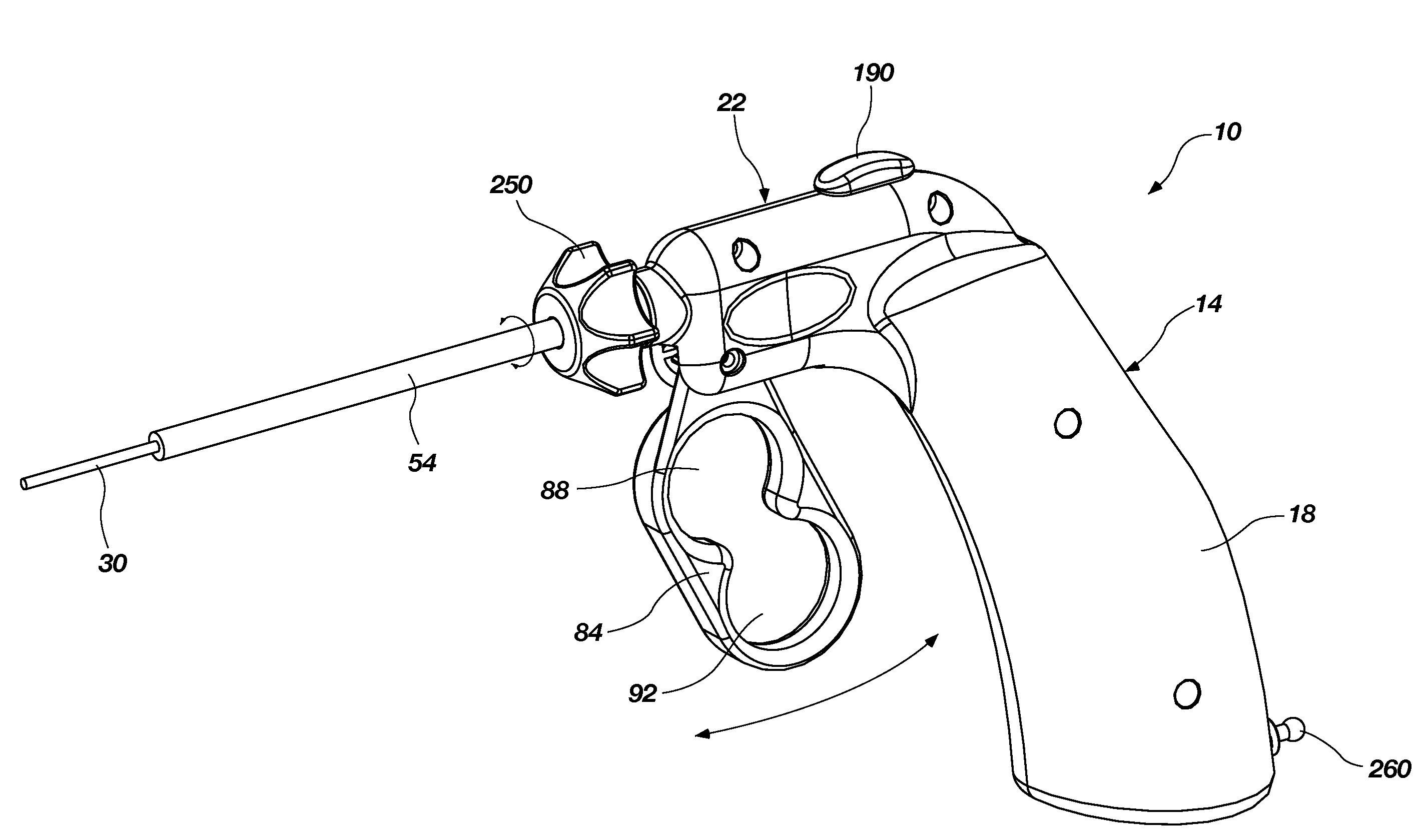
Laparoscopic surgical instrument
A laparoscopic surgical instrument configured to be ergonomic and anthropometrically correct, the laparoscopic surgical instrument comprising: (a) an ergonomic handle configured to orient a hand of a surgeon in a functional position, the handle comprising a handle grip; (b) an actuating mechanism actuatable by a finger and supported by the handle, the actuating mechanism comprising an actuator shaft and a gearing assembly operable to displace the actuator shaft with a mechanical advantage upon actuation of a trigger by the surgeon; (c) a locking mechanism configured to lock the actuating mechanism in one of a plurality of positions, the locking mechanism comprising a release located in an anthropometrically correct position; and (d) a working shaft having a proximal end coupled to and operable with the actuator shaft, the working shaft having an elongate configuration and a distal working end configured to couple a surgical tool to be manipulated by the surgeon via the handle and the actuating mechanism to perform a surgical function.
Owner:SHORTI RAMI +1
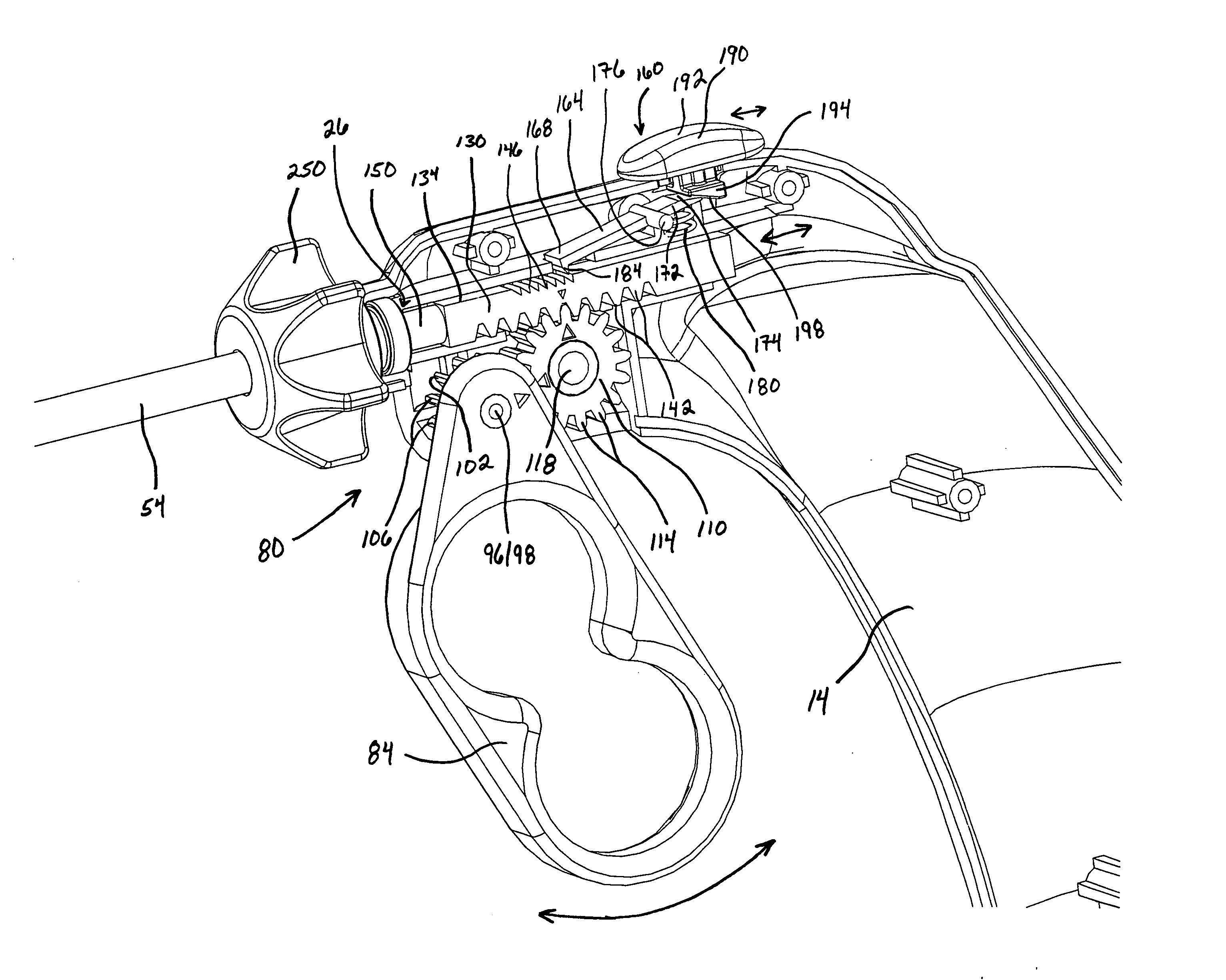
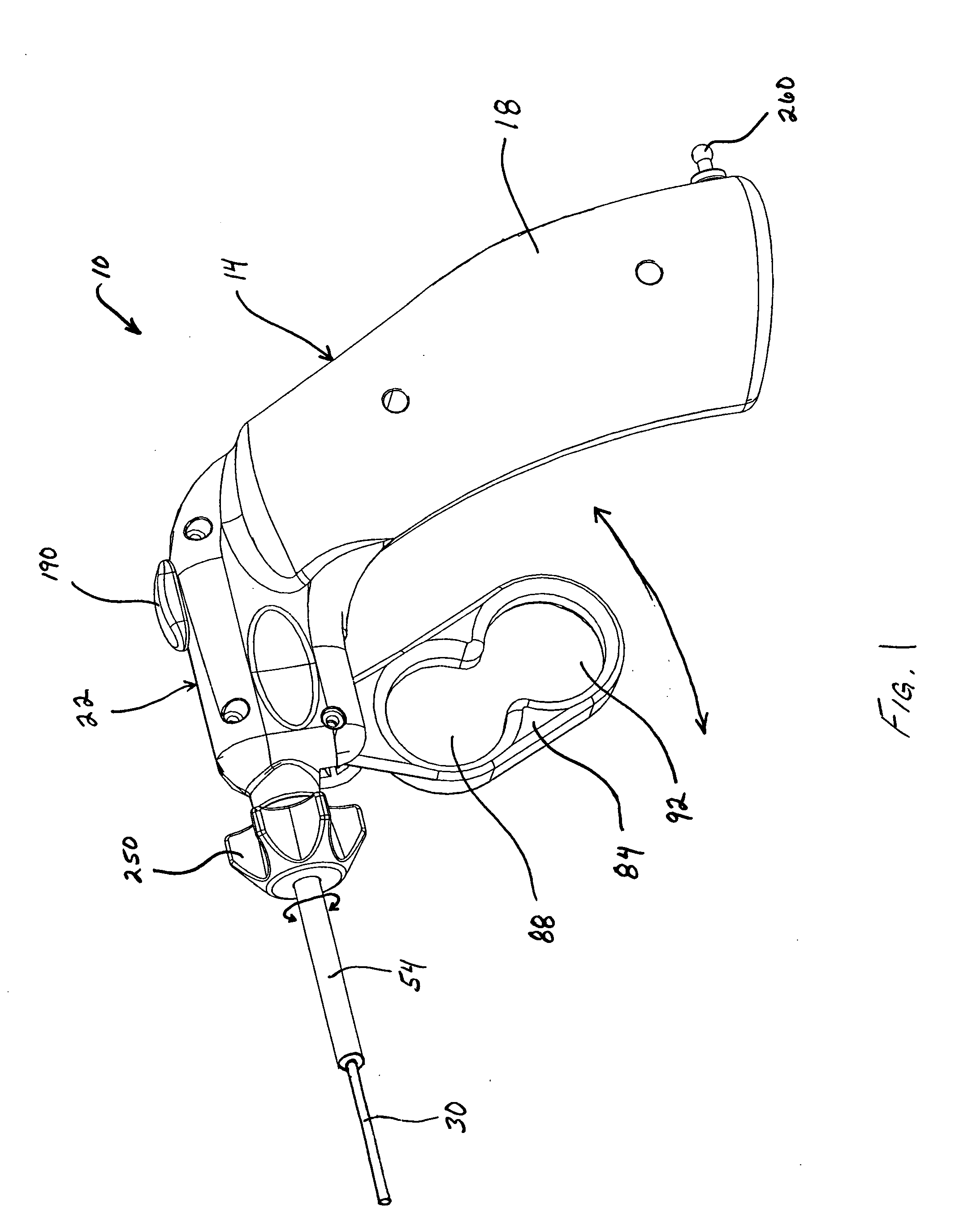
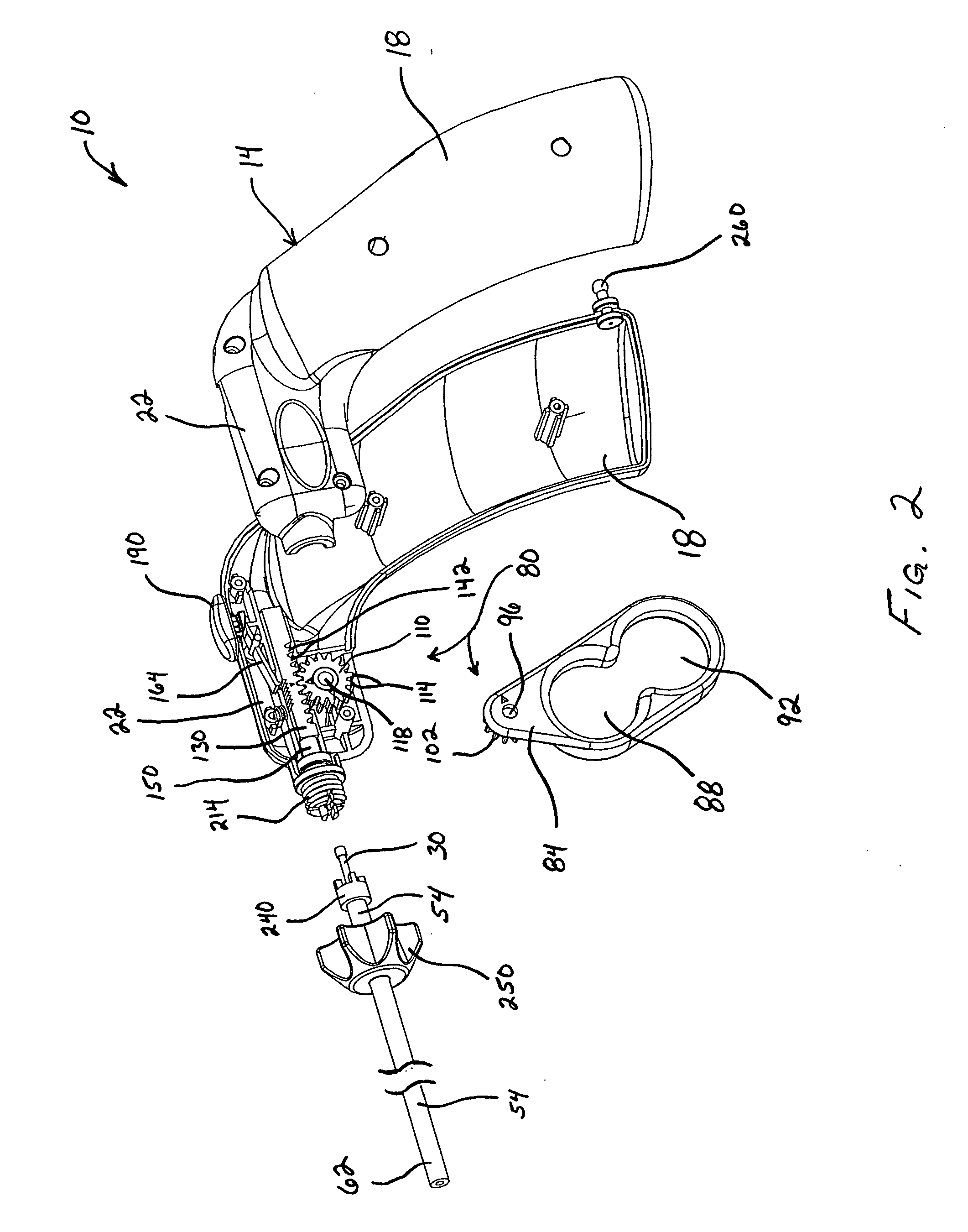
Dexterous surgical manipulator and method of use
ActiveUS9901412B2Simple interfaceEasy to learnDiagnosticsSurgical manipulatorsEngineeringSacroiliac joint
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Surgical access apparatus and method
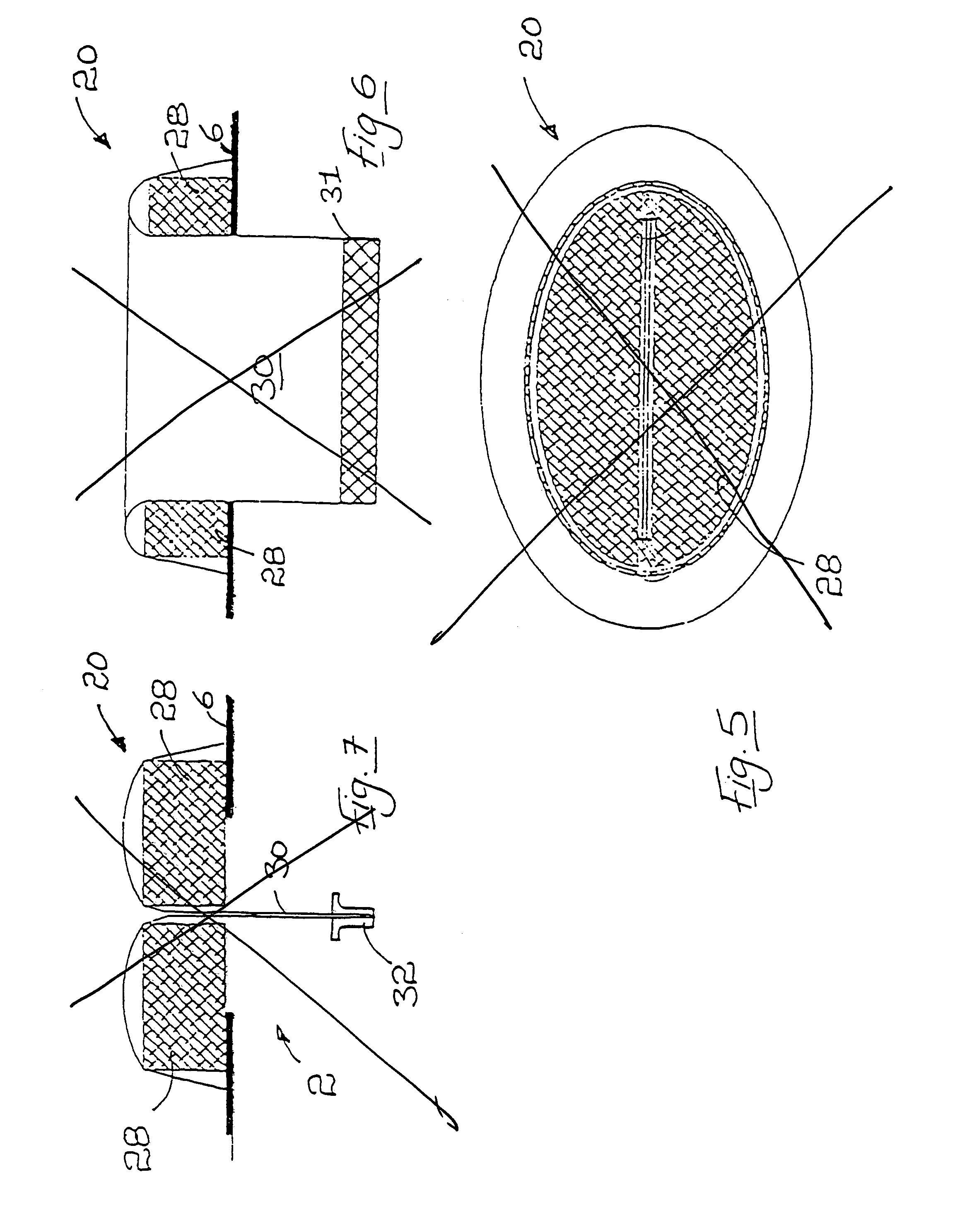
A surgical access device includes a single valve that forms a seal with the body wall and provides an access charnel into a body cavity. The valve has properties for creating a zero seal in the absence of an instrument as well as an instrument seal with instruments having a full range of instrument diameter. The valve can include a gel and preferably an ultragel comprised of an elastomer and an oil providing elongation greater than 1000 percent and durometer less than 5 Shore A. The shore valve can be used as a hand port where the instrument comprises the arm of a surgeon, thereby providing hand access into the cavity. A method for making the surgical access device includes the combining or a gelling agent with an oil, preferably in a molding process. A method for using the device includes steps for creating an opening with the instrument. In a particular process, an organ can be removed from the body cavity through the single valve to create an organ seal while the organ is addressed externally of the body cavity. The valve and method are particularly adapted for laparoscopic surgery wherein the abdominal cavity is insufflated with a gas thereby requiring the zero seal, the instrument seal, and the organ seal in various procedures.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Laparoscopic instruments and trocar systems and related surgical method
InactiveUS20080027476A1Increase workspaceEasy to take backSuture equipmentsCannulasAbdominal cavityPERITONEOSCOPE
Laparoscopic instruments and trocars are provided for performing laparoscopic procedures entirely through the umbilicus. A generally C-shaped trocar provides increased work space between the hands of the surgeon as well as S-shaped laparoscopic instruments placed through the trocar when laparoscopic instrument-trocar units are placed through the umbilicus. In order to facilitate retraction of intra-abdominal structures during a laparoscopic procedure, an angulated needle and thread with either one-or two sharp ends is provided. Alternatively, an inflatable unit having at least one generally C-shaped trocar incorporated within the unit's walls can be placed through the umbilicus following a single incision. Generally S-shaped laparoscopic instruments may be placed through the generally C-shaped trocars to facilitate access to intra-abdominal structures.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Laparoscopic Surgical Instrument
A laparoscopic surgical instrument configured to be ergonomic and anthropometrically correct, comprising: a) an ergonomic handle configured to orient a hand of a surgeon in a functional position, the handle comprising a wall structure defining an interior portion, and adapted to contain at least a portion of one or more working mechanisms; b) an actuating mechanism actuatable by the surgeon and supported within the interior portion of the handle; c) a working shaft having a proximal end coupled to and operable with the actuating mechanism, the working shaft having an elongate configuration and a distal working end configured to couple a surgical tool to be manipulated by the surgeon; and d) means for accessing the interior portion of the handle to expose an inner side of the wall structure and at least a portion of each of the working mechanisms for cleaning, sterilization and maintenance purposes.
Owner:SHORTI RAMI
Laparoscopic illumination apparatus and method
InactiveUS6939296B2Improve rendering capabilitiesImprove tear resistanceCannulasRestraining devicesPERITONEOSCOPESurgical site
An access device particularly adapted for use in laparoscopic surgery facilitates access with instruments, such as the hand of the surgeon, across a body wall and into a body cavity. The device can be formed of a gel material having properties for forming a zero seal, or an instrument seal with a wide range of instrument diameters. The gel material can be translucent facilitating illumination and visualization of the surgical site through the access device.
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Surgical access device
InactiveUS7214185B1Improve application flexibilityEasy to placeCannulasDiagnosticsSurgical operationLess invasive surgery
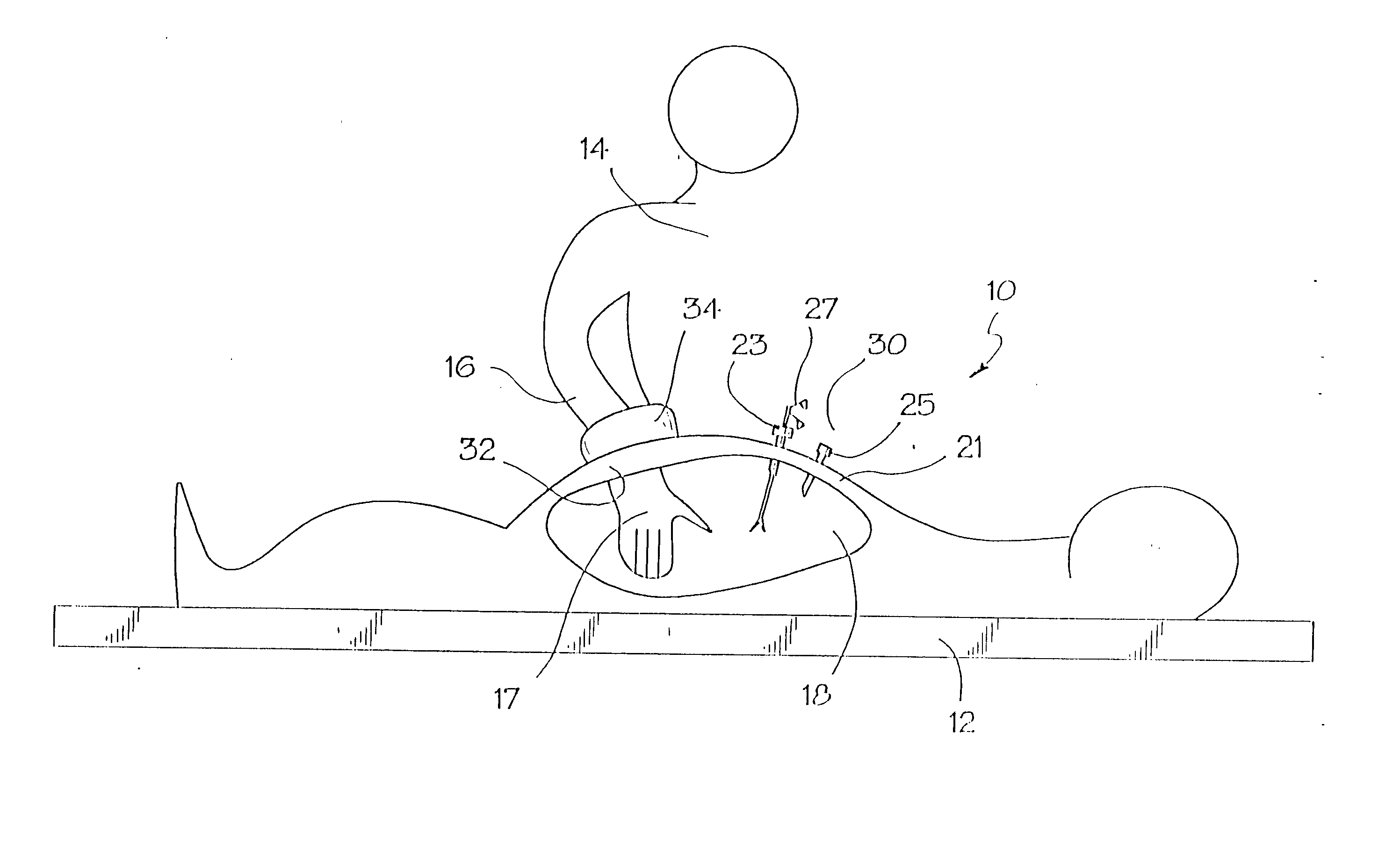
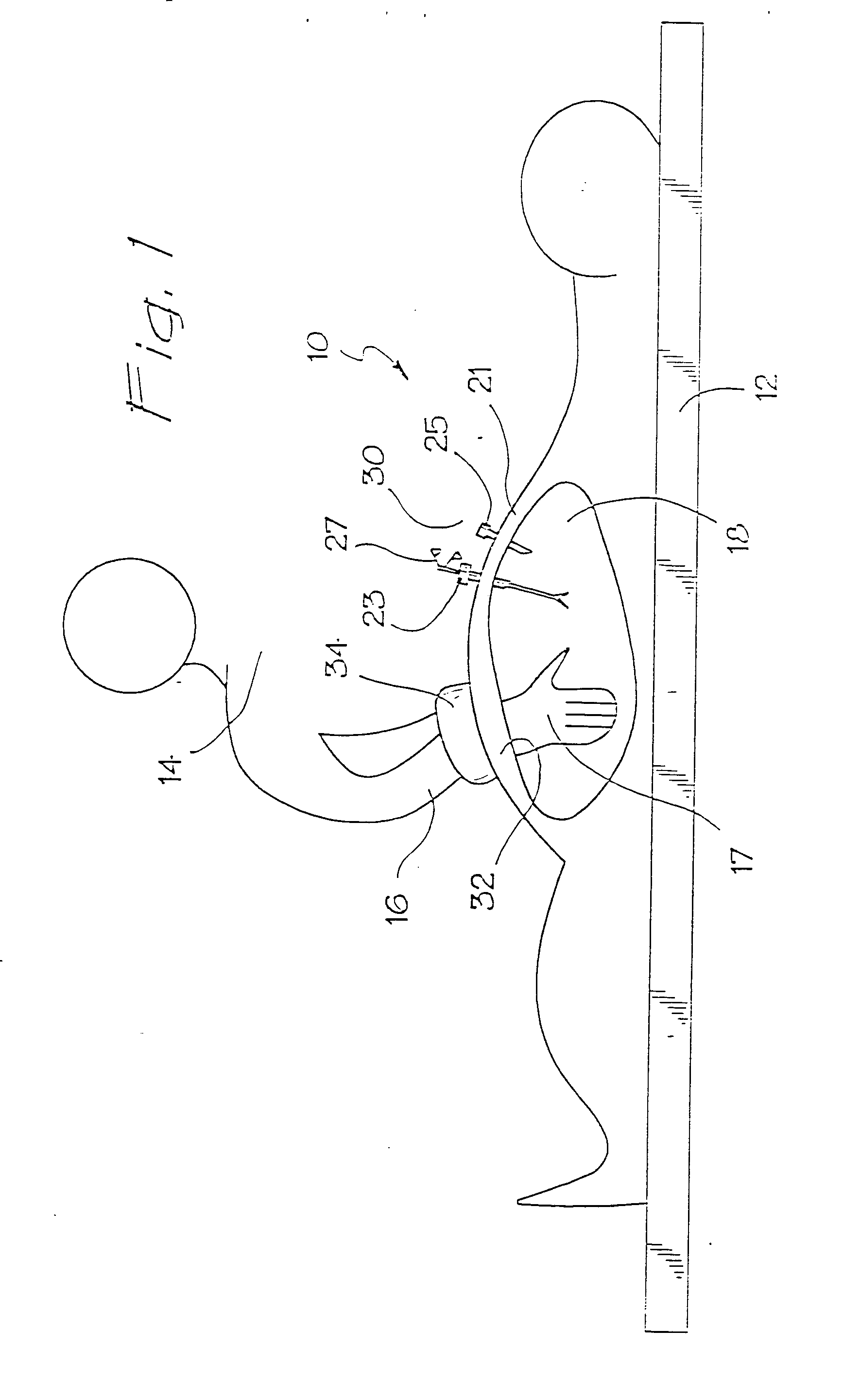
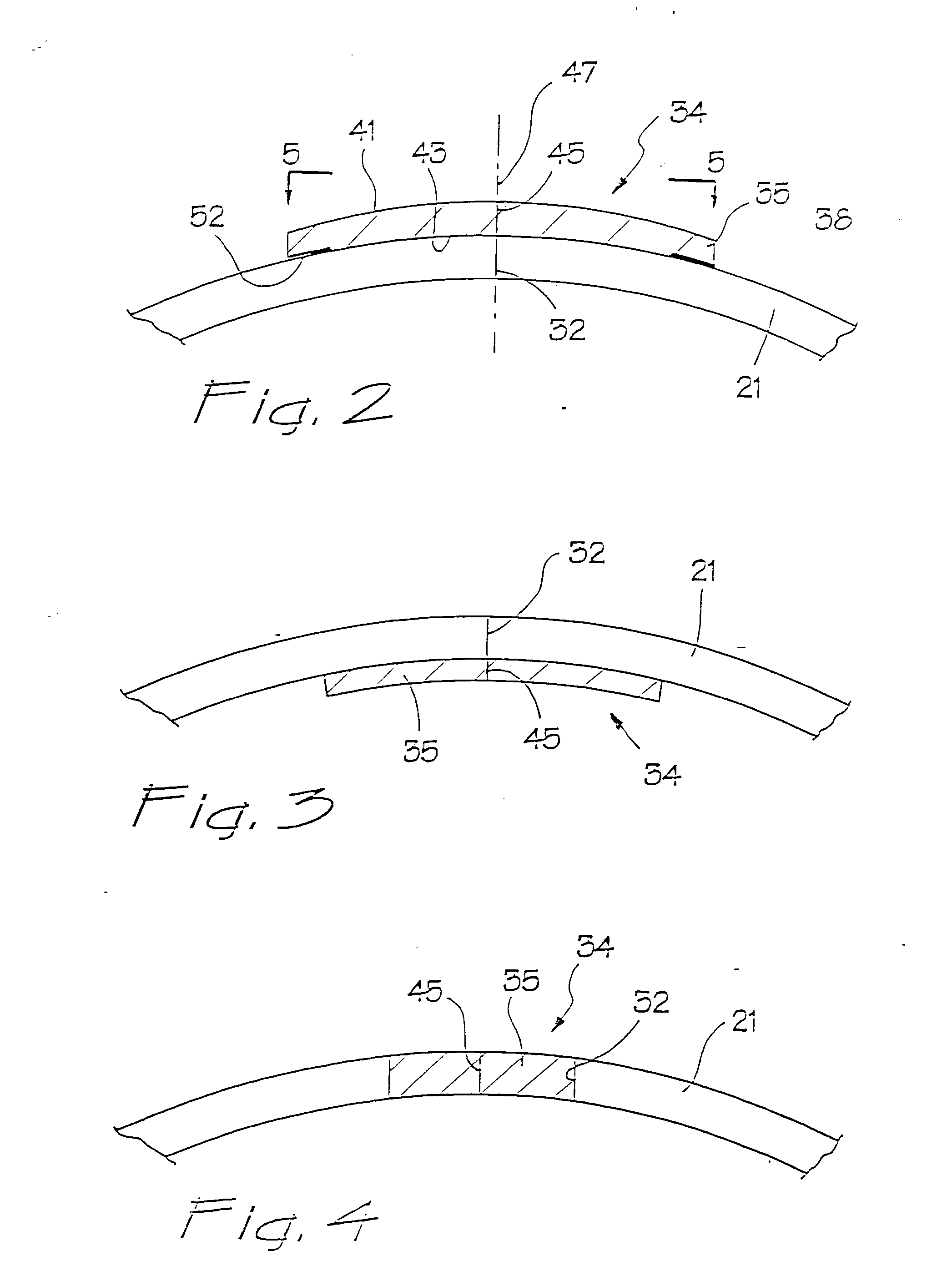
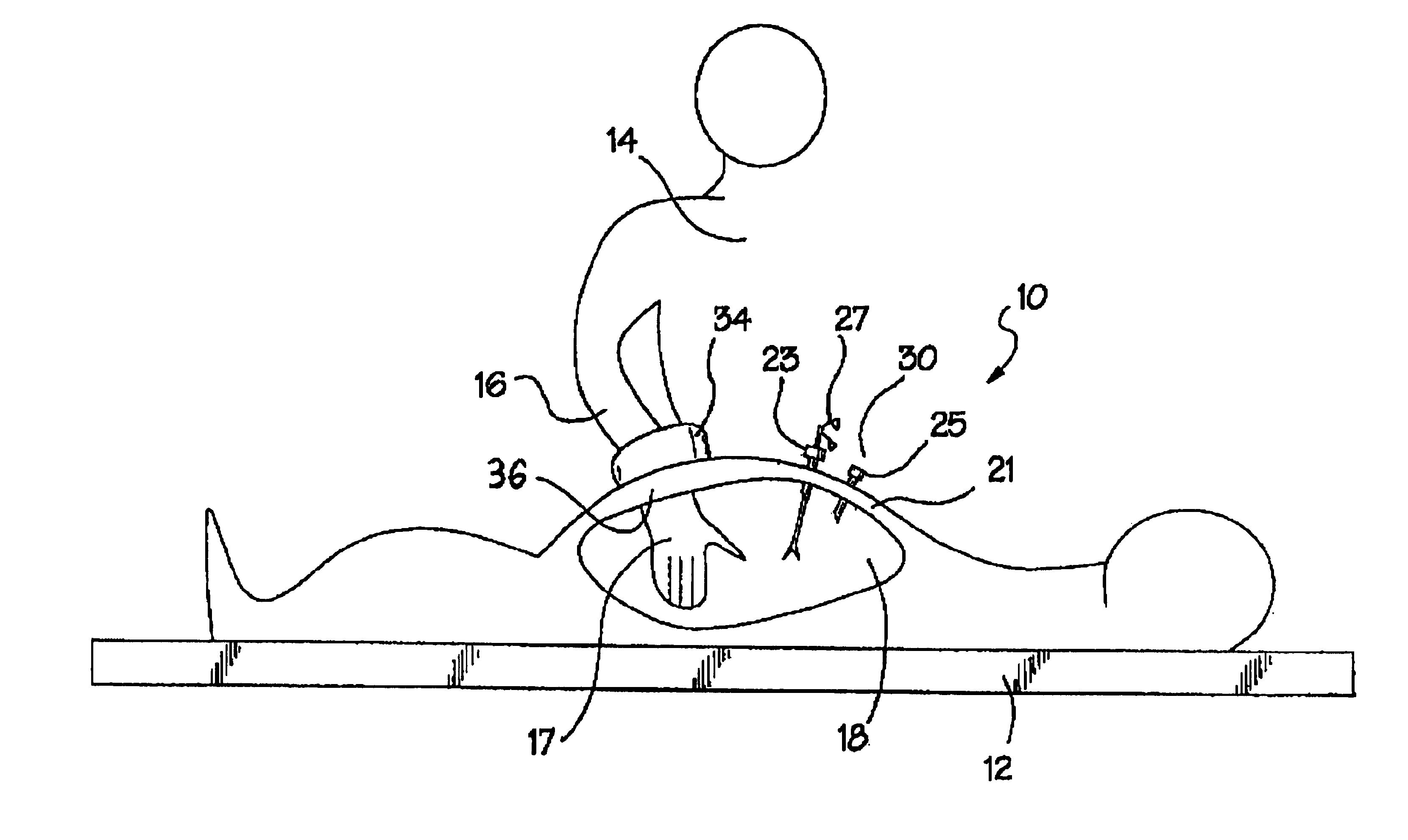
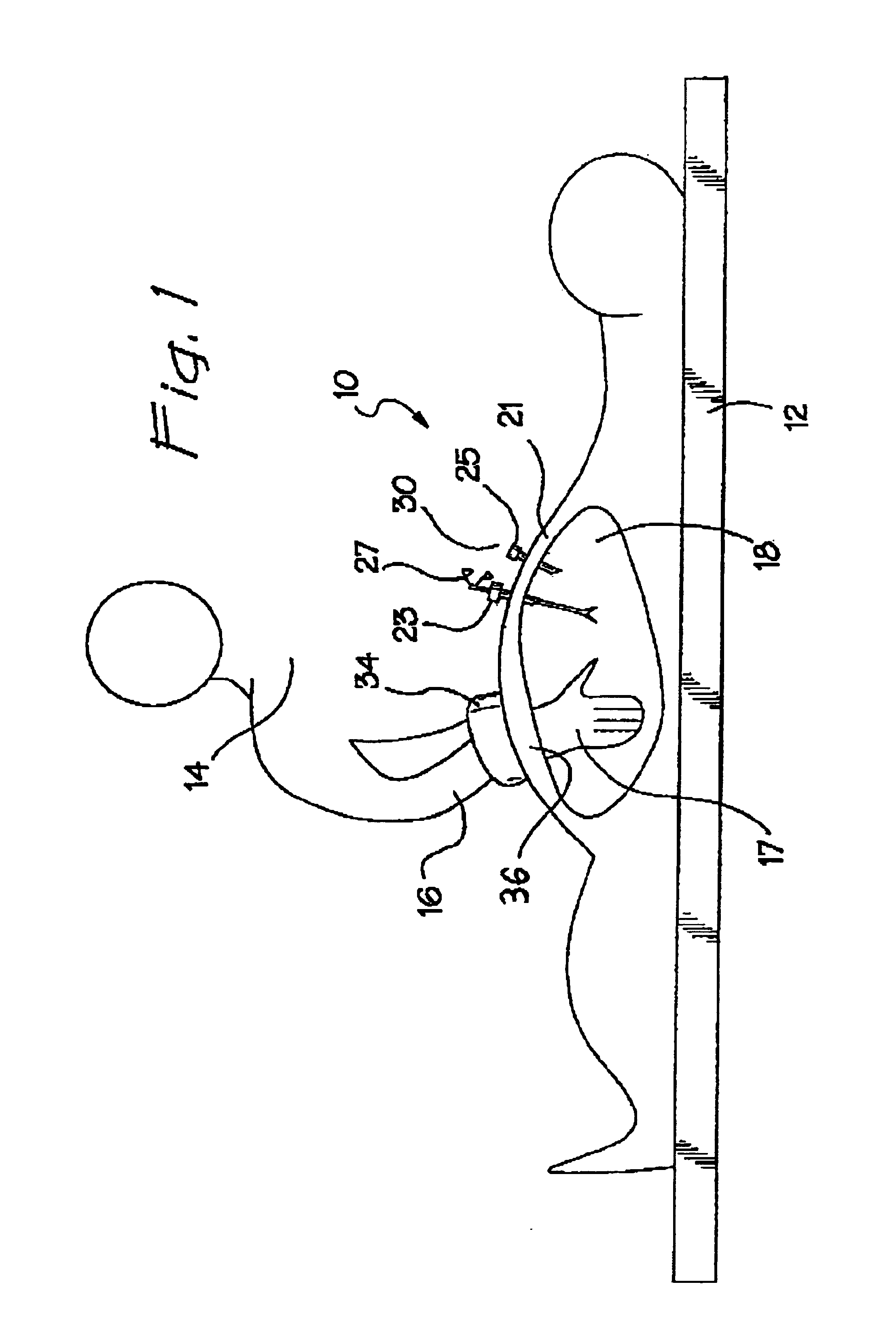
A surgical device for use in minimally invasive surgery in which body cavity is accessed by a surgeon though an access port defined by the device, the device including a body cavity engagement feature for insertion into the incision to locate the device in position, fixing feature with a ring that attaches the device to the patient's skin, and a toroid cell having a bladder filled with a liquid or a gel to prevent substantial leakage of gas from the body cavity and formed to mould about a substantial portion of a surgeon's hand or surgical instrument on insertion.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Method and apparatus for performing minimally invasive surgical procedures
InactiveUS6905460B2Reserved functionHigh precisionProgramme controlSuture equipmentsRobotic armSurgical site
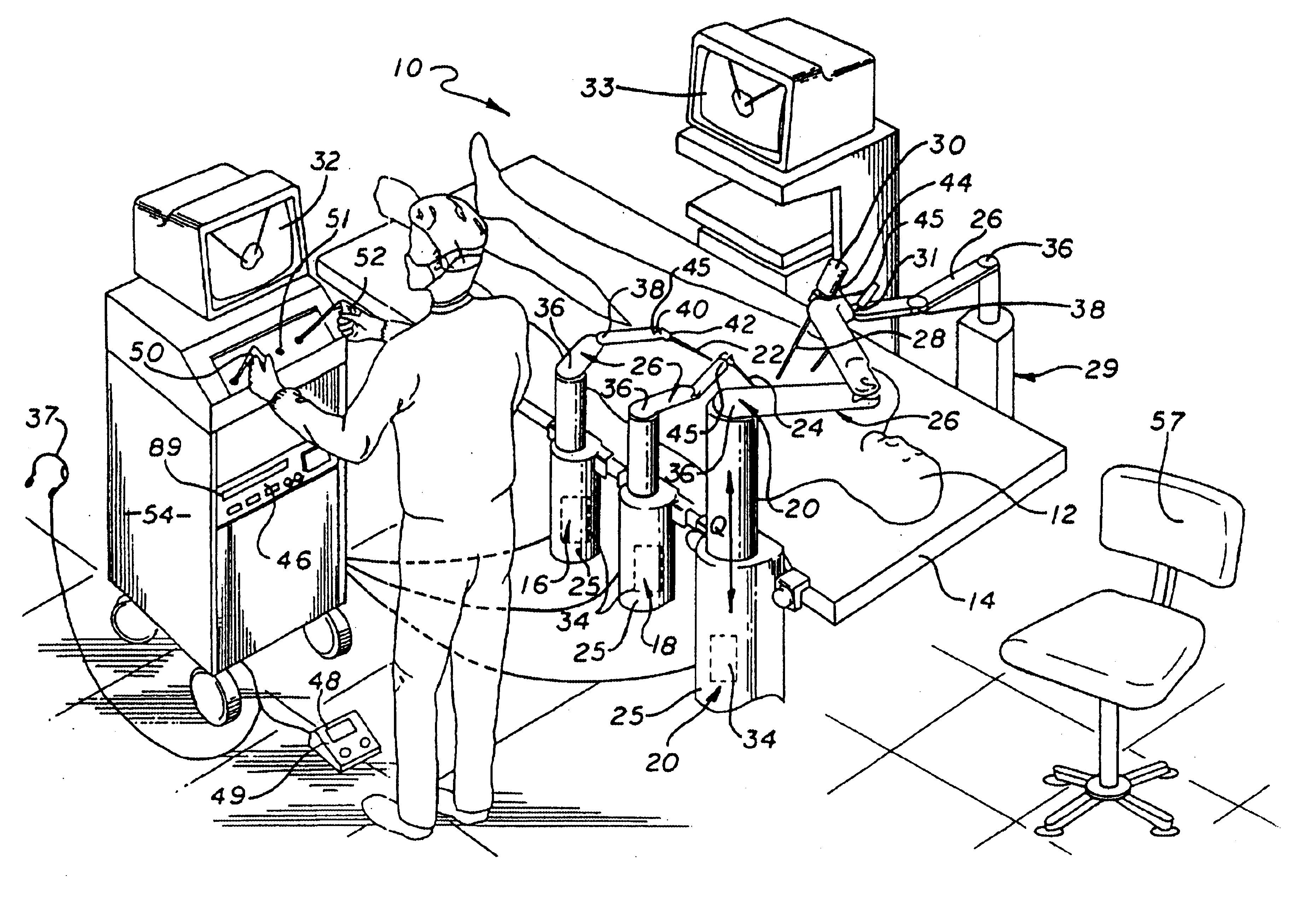
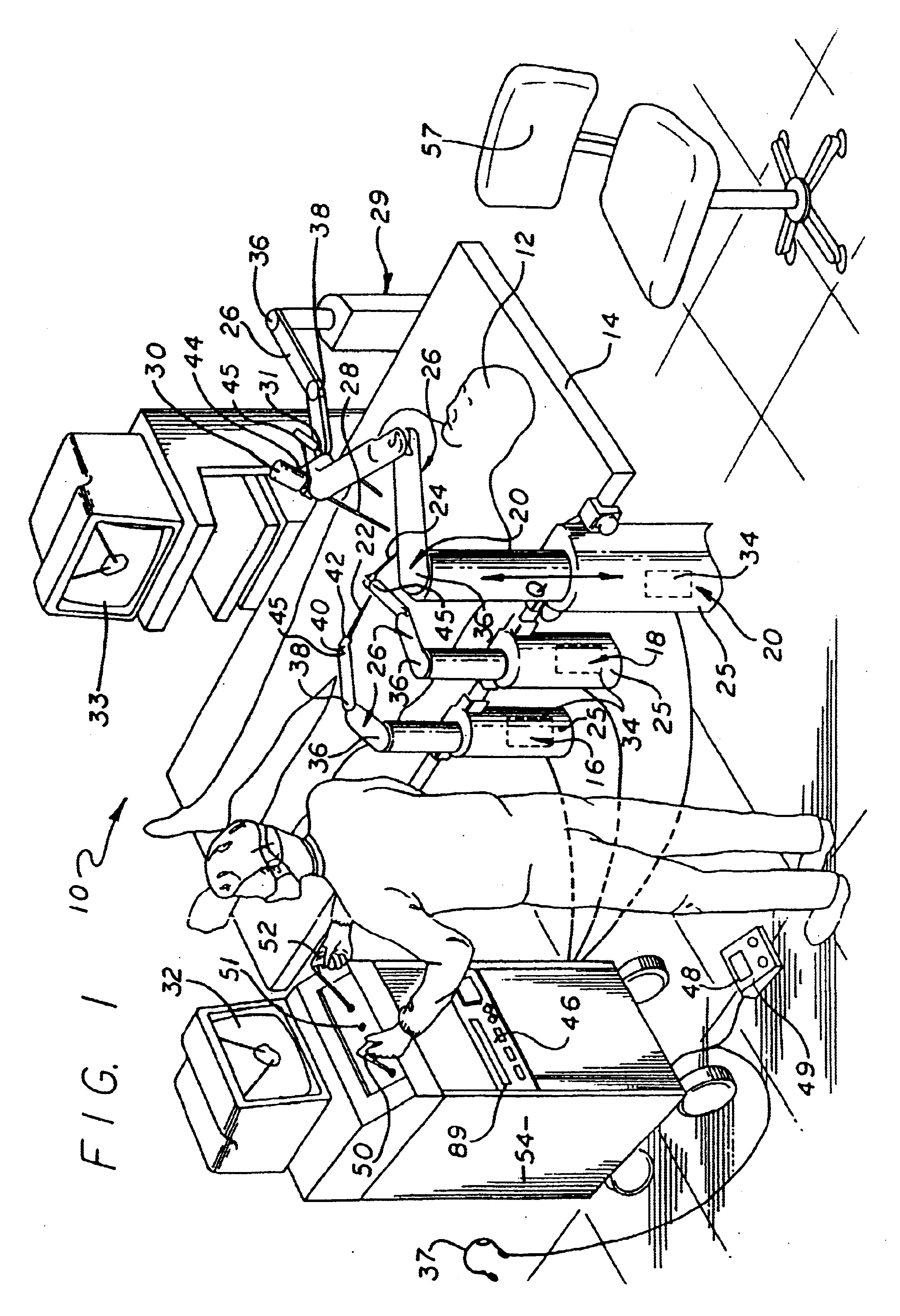
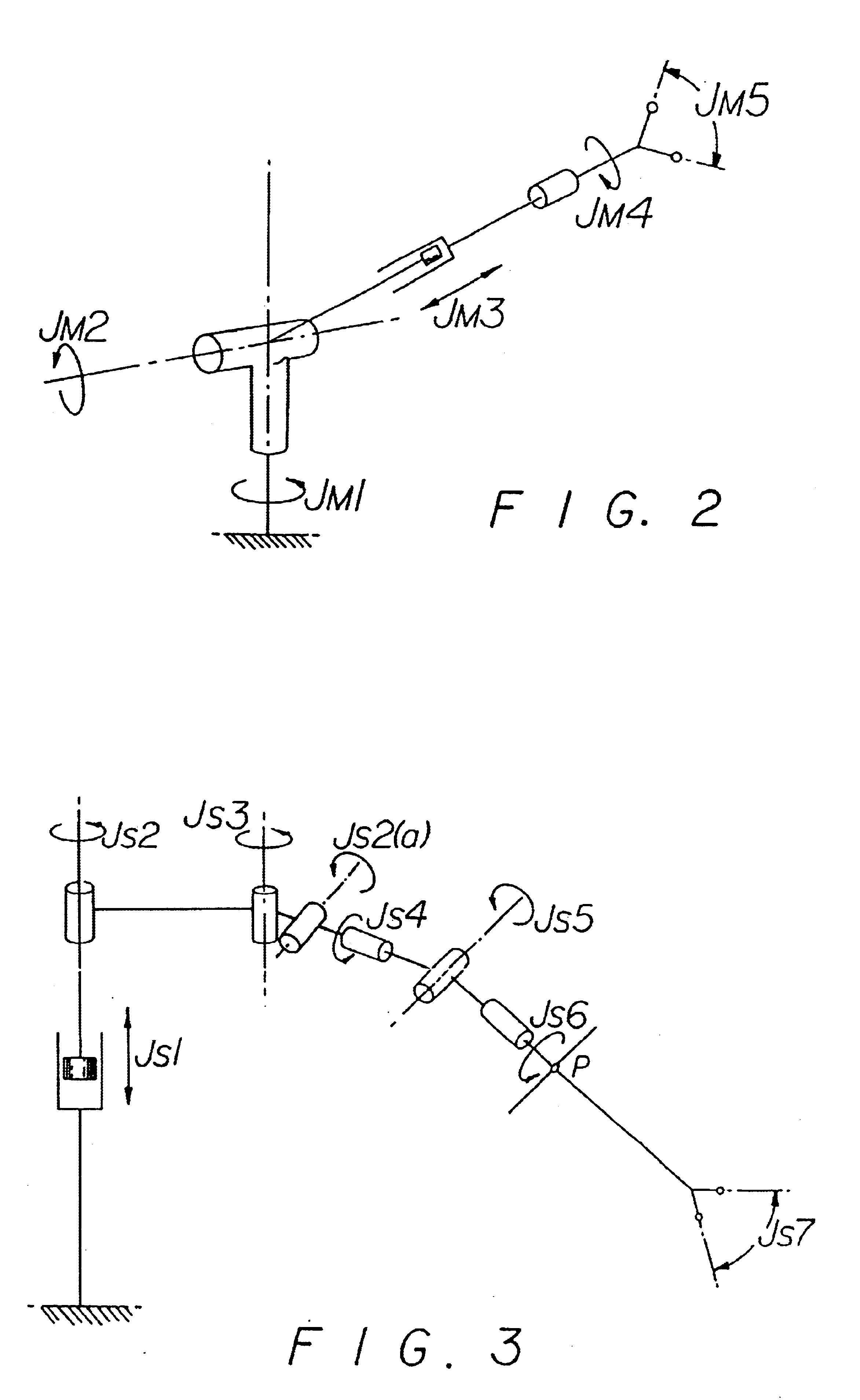
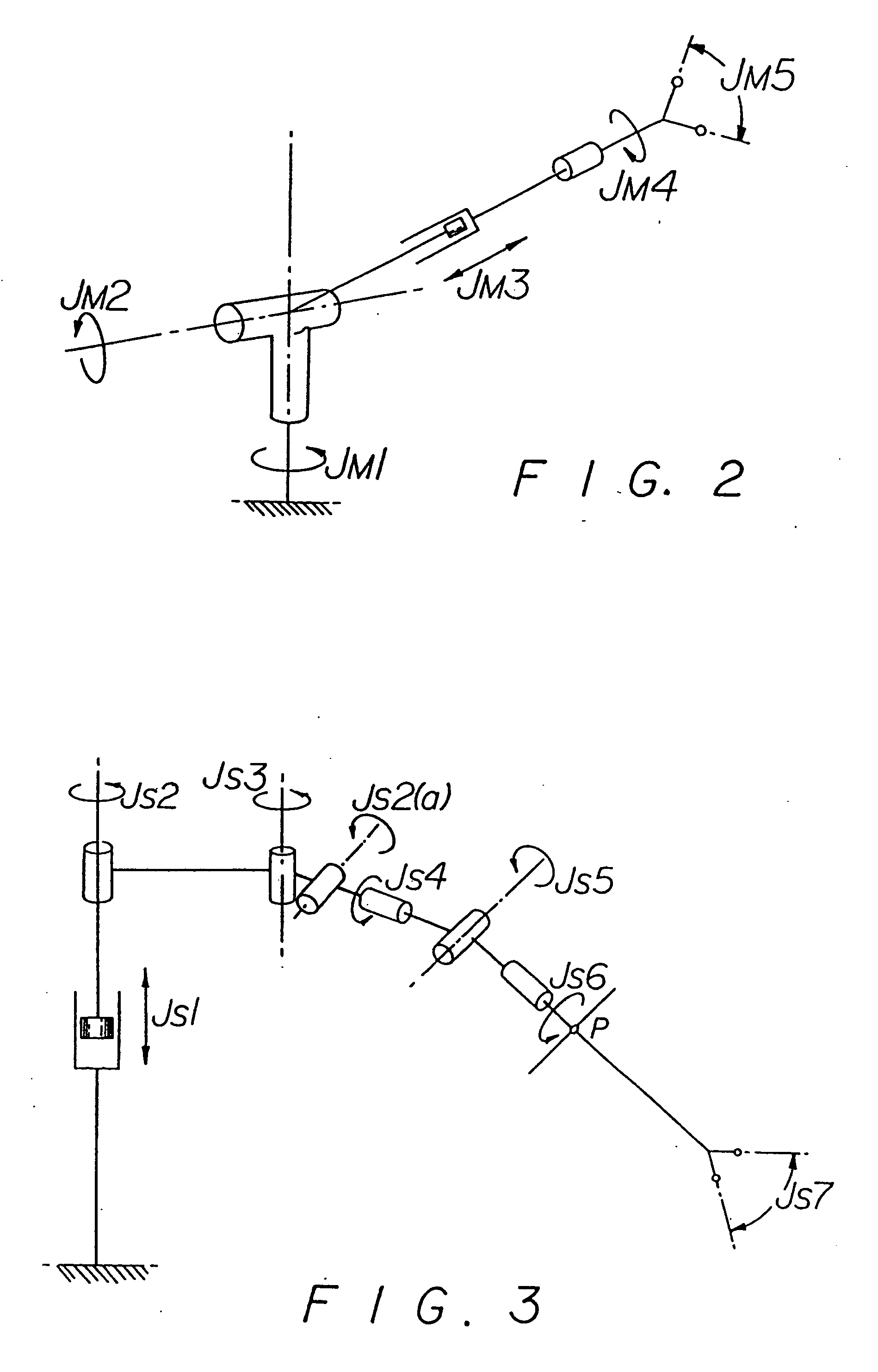
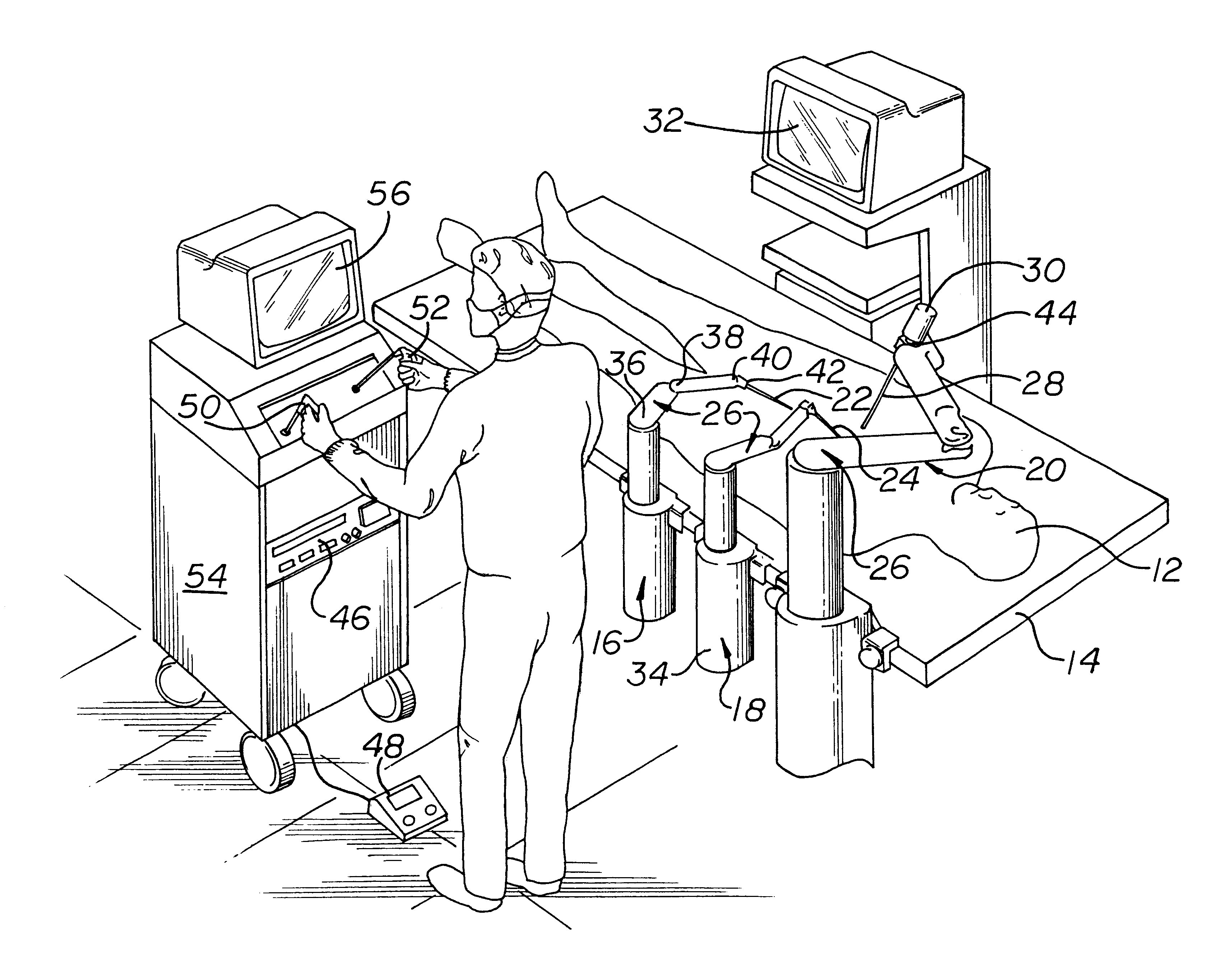
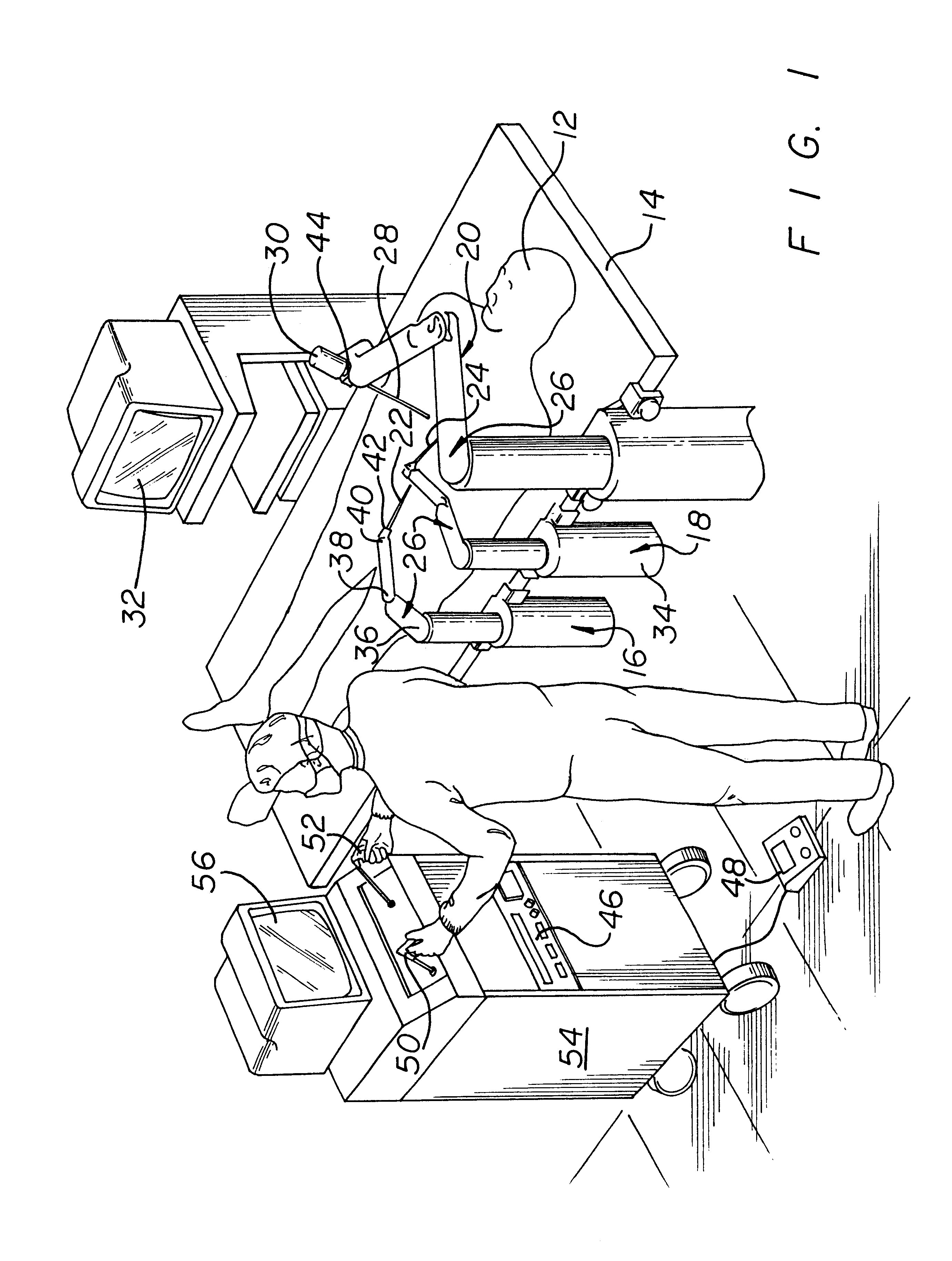
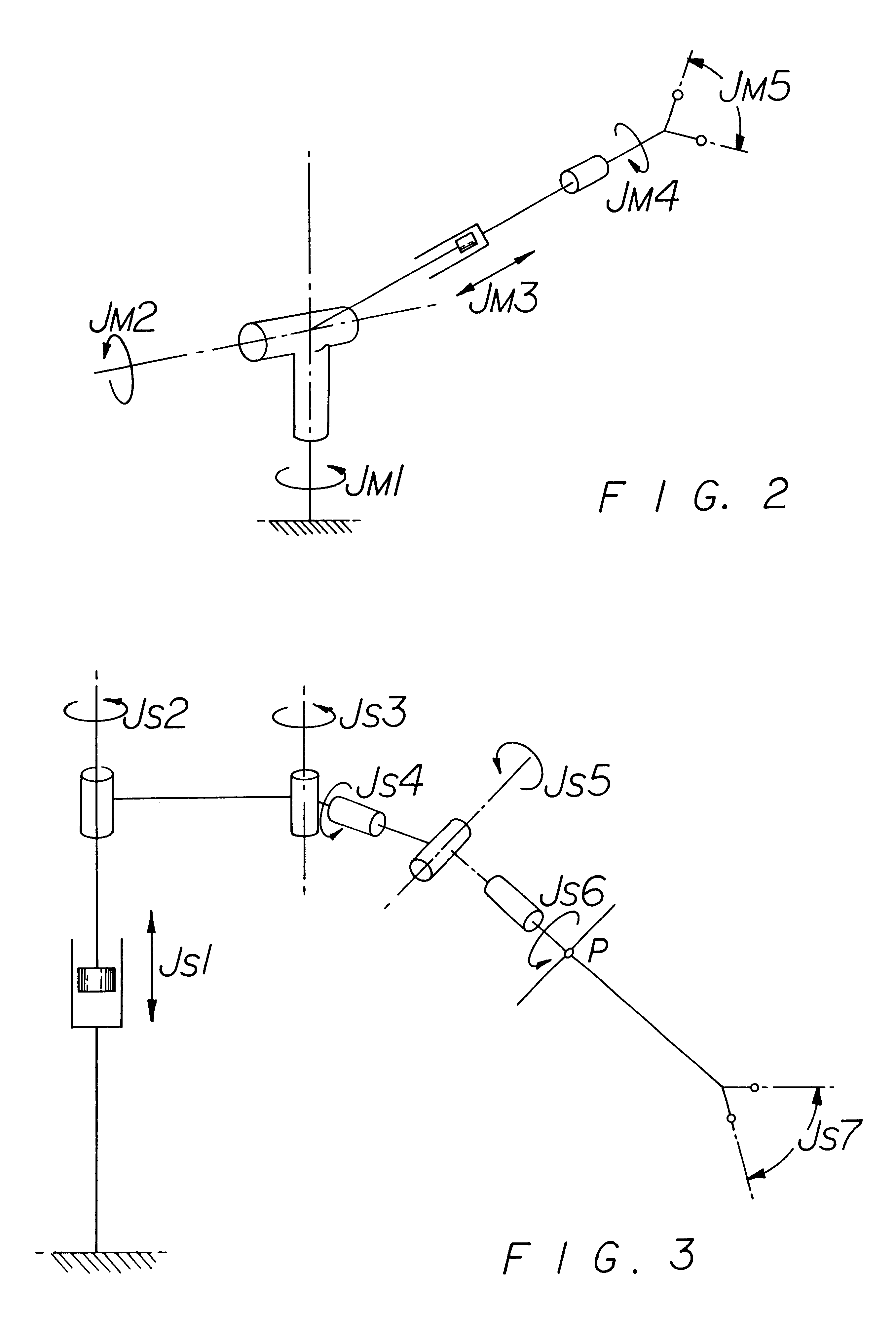
A system for performing minimally invasive cardiac procedures. The system includes a pair of surgical instruments that are coupled to a pair of robotic arms. The instruments have end effectors that can be manipulated to hold and suture tissue. The robotic arms are coupled to a pair of master handles by a controller. The handles can be moved by the surgeon to produce a corresponding movement of the end effectors. The movement of the handles is scaled so that the end effectors have a corresponding movement that is different, typically smaller, than the movement performed by the hands of the surgeon. The scale factor is adjustable so that the surgeon can control the resolution of the end effector movement. The movement of the end effector can be controlled by an input button, so that the end effector only moves when the button is depressed by the surgeon. The input button allows the surgeon to adjust the position of the handles without moving the end effector, so that the handles can be moved to a more comfortable position. The system may also have a robotically controlled endoscope which allows the surgeon to remotely view the surgical site. A cardiac procedure can be performed by making small incisions in the patient's skin and inserting the instruments and endoscope into the patient. The surgeon manipulates the handles and moves the end effectors to perform a cardiac procedure such as a coronary artery bypass graft.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Endoscopic pedicle probe
InactiveUS6855105B2Directly and accurately determinedAvoid parallaxSurgeryEndoscopesControl mannerSurgical department
An endoscopic pedicle probe for use during spinal surgery to form a hole in a pedicle for reception of a pedicle screw. The probe has an enlarged proximal end for cooperation with the hand of the surgeon so that the probe can be pushed through the pedicle in a controlled manner, and an elongate hollow shaft terminating in a distal tip end. A fiber optic cable or endoscope is placed in the hollow shaft and connected with a monitor to enable the surgeon to visually observe the structure adjacent the tip end of the probe during surgery, whereby the probe may be accurately placed in the pedicle for subsequent accurate placement of the pedicle screw in the hole formed with the probe.
Owner:OPTICAL SPINE LLC
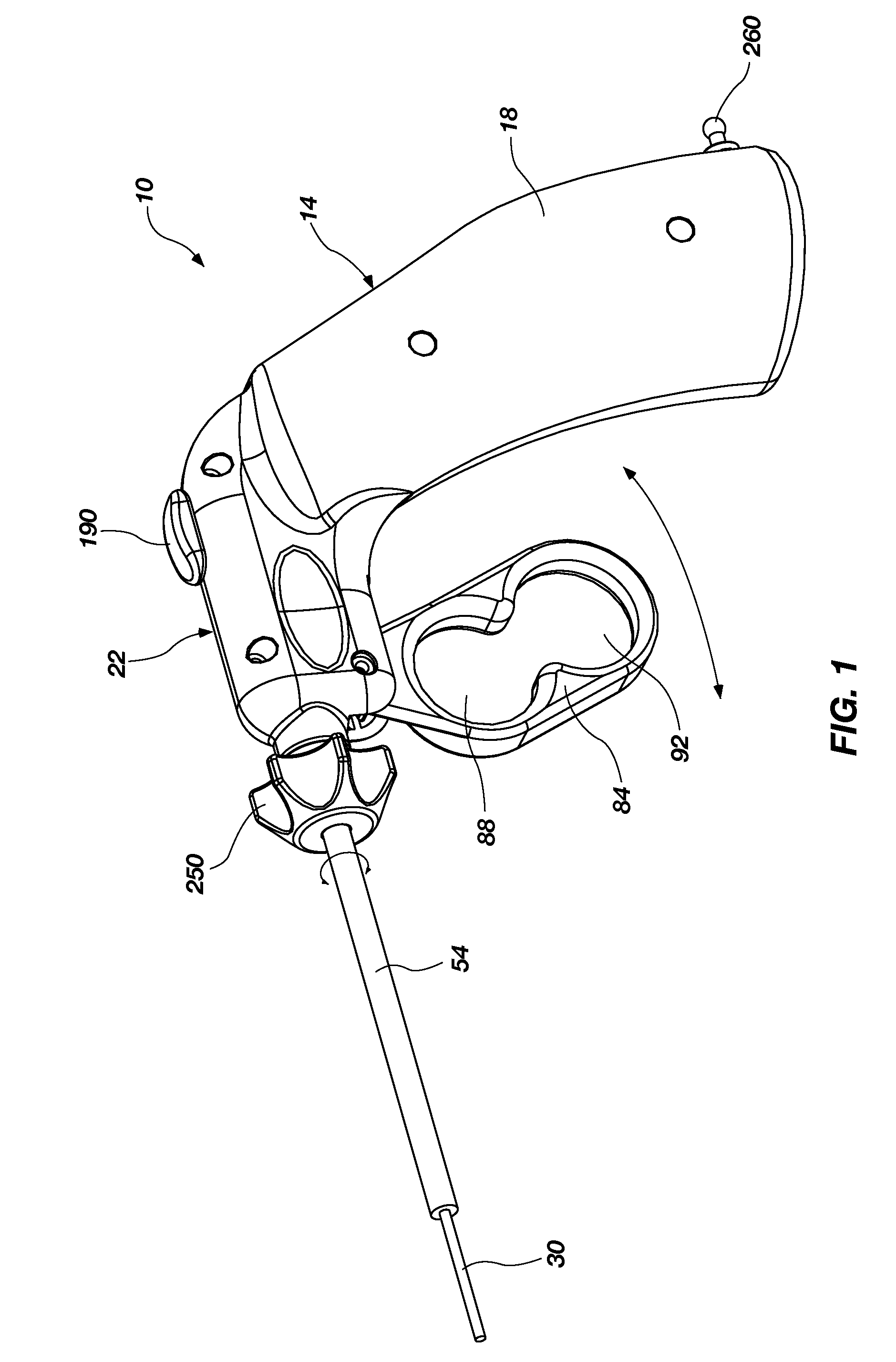
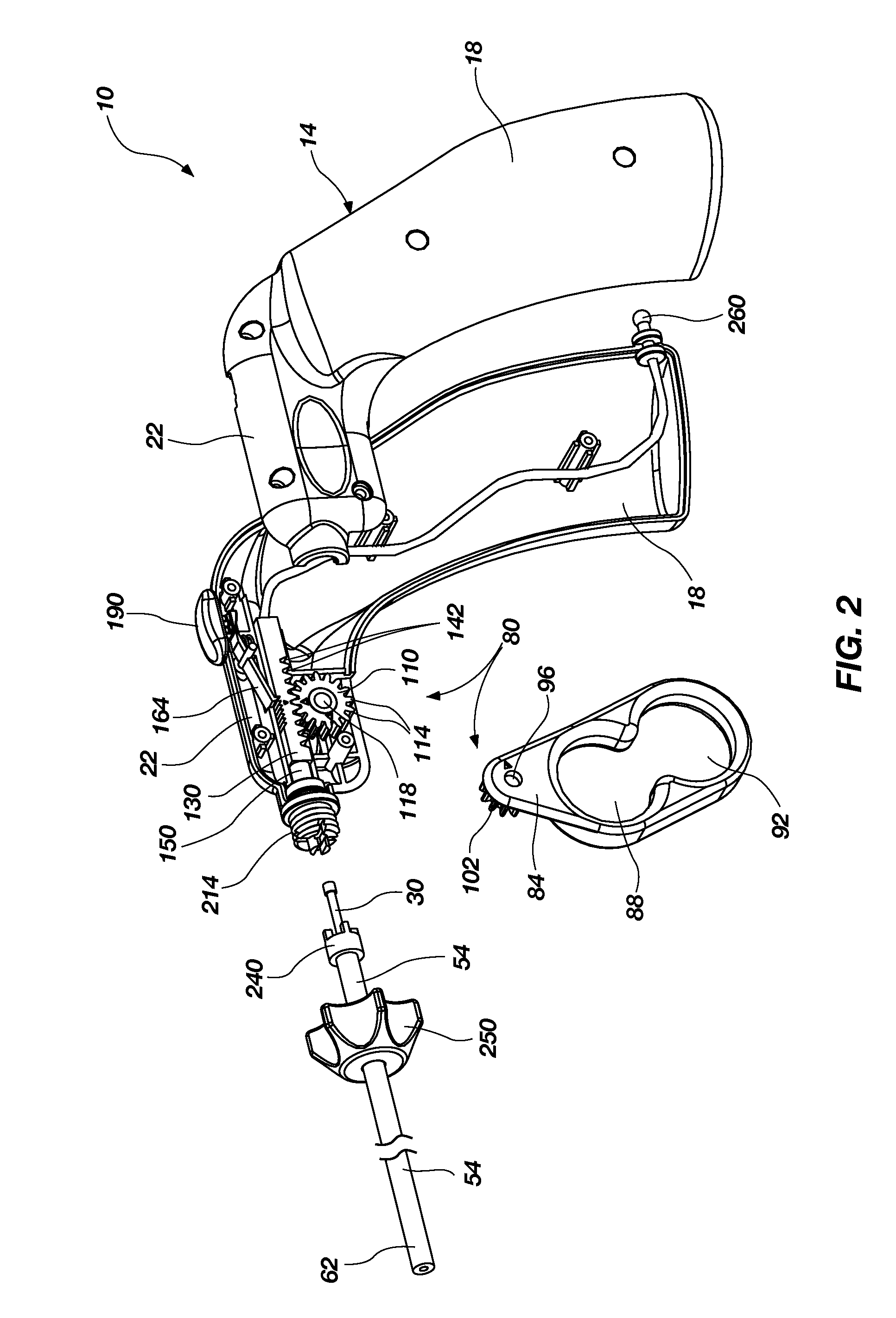
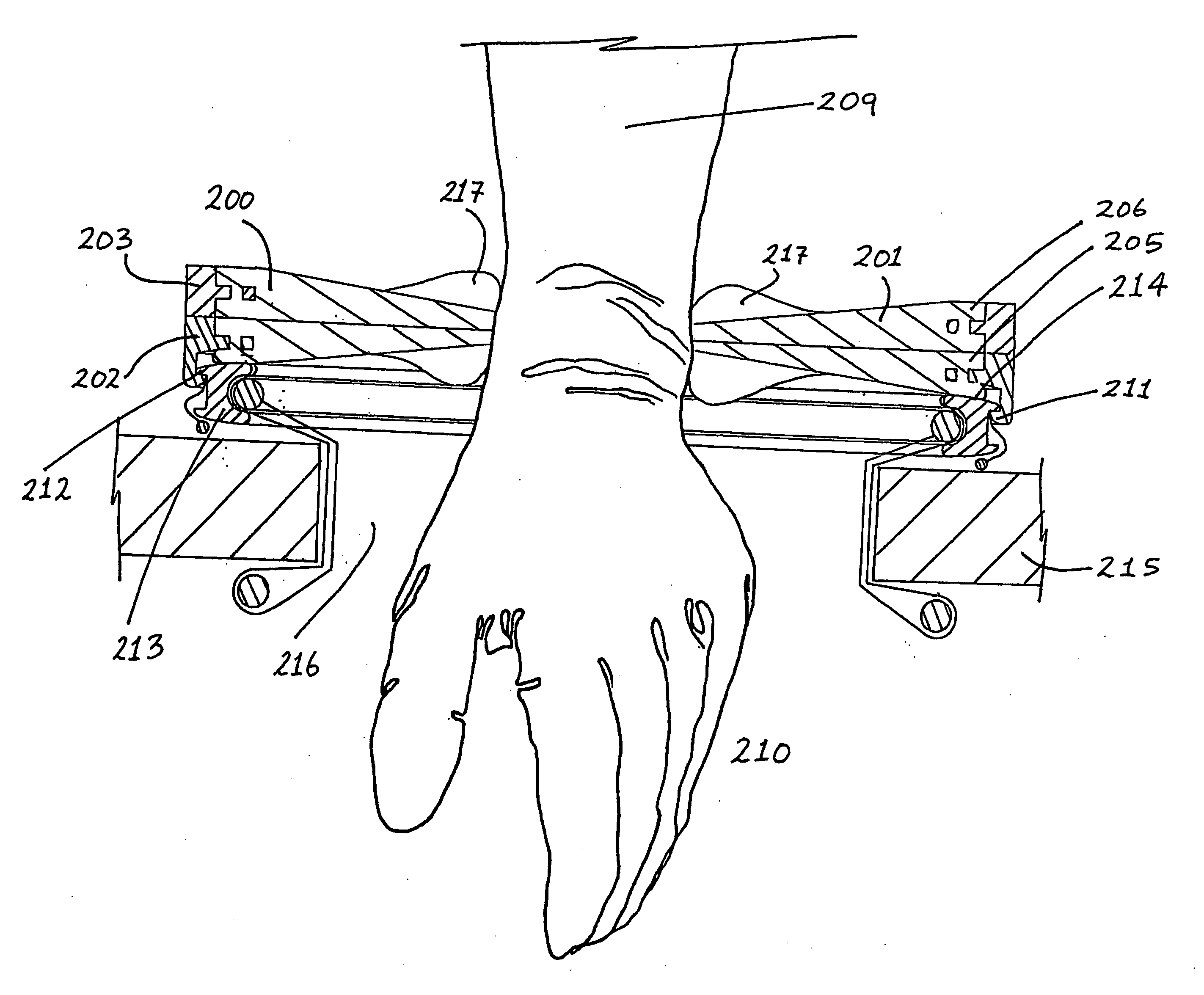
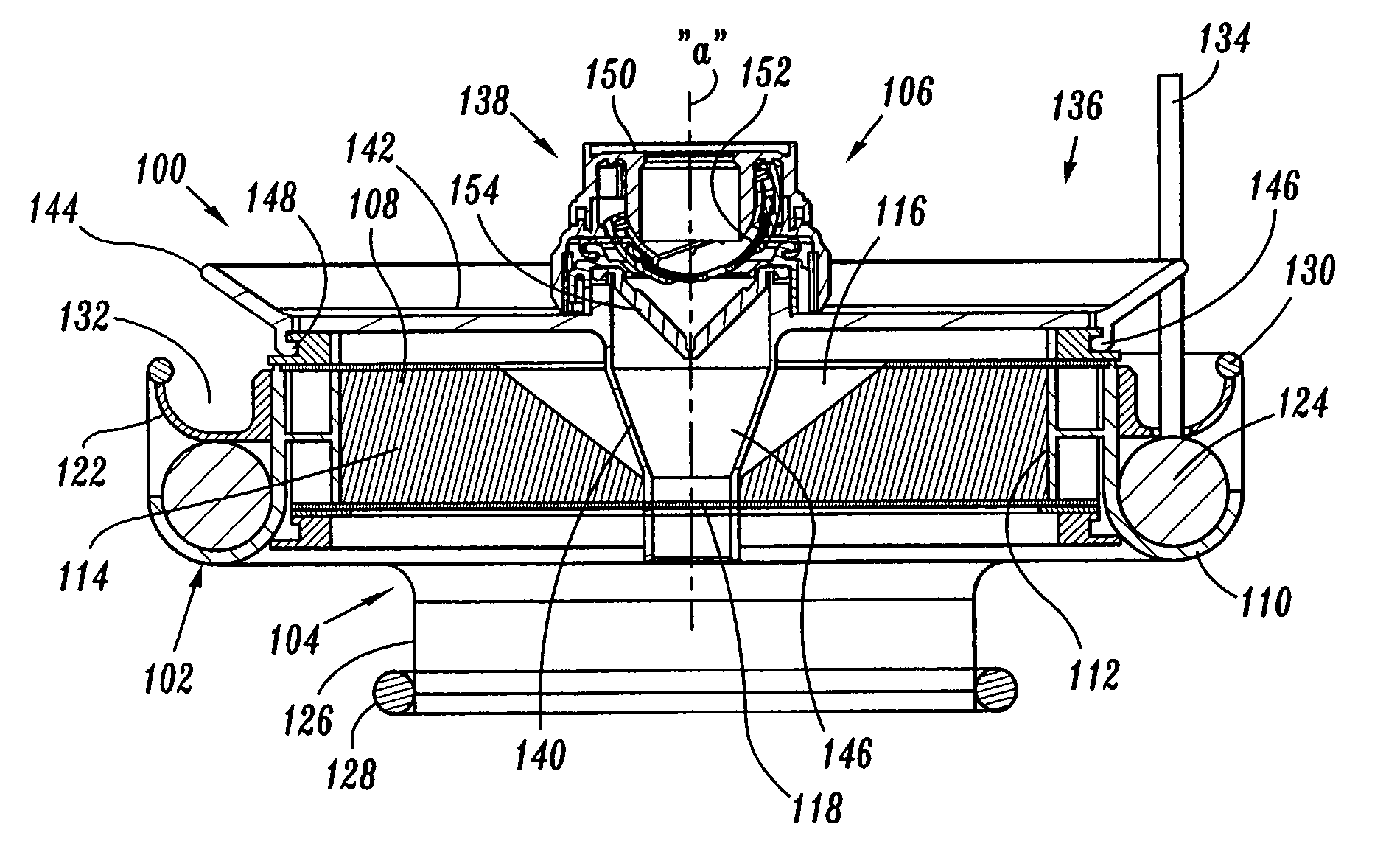
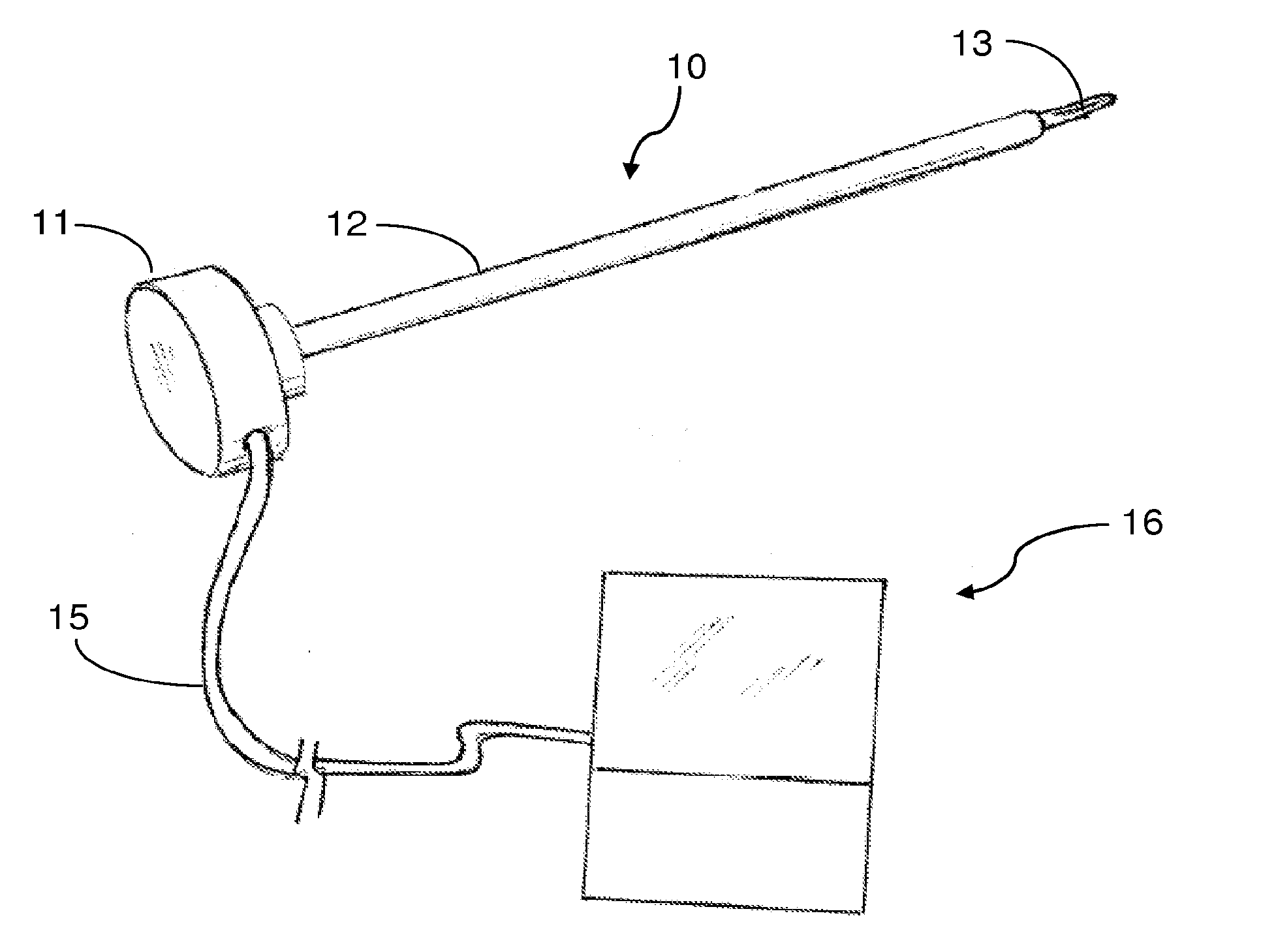
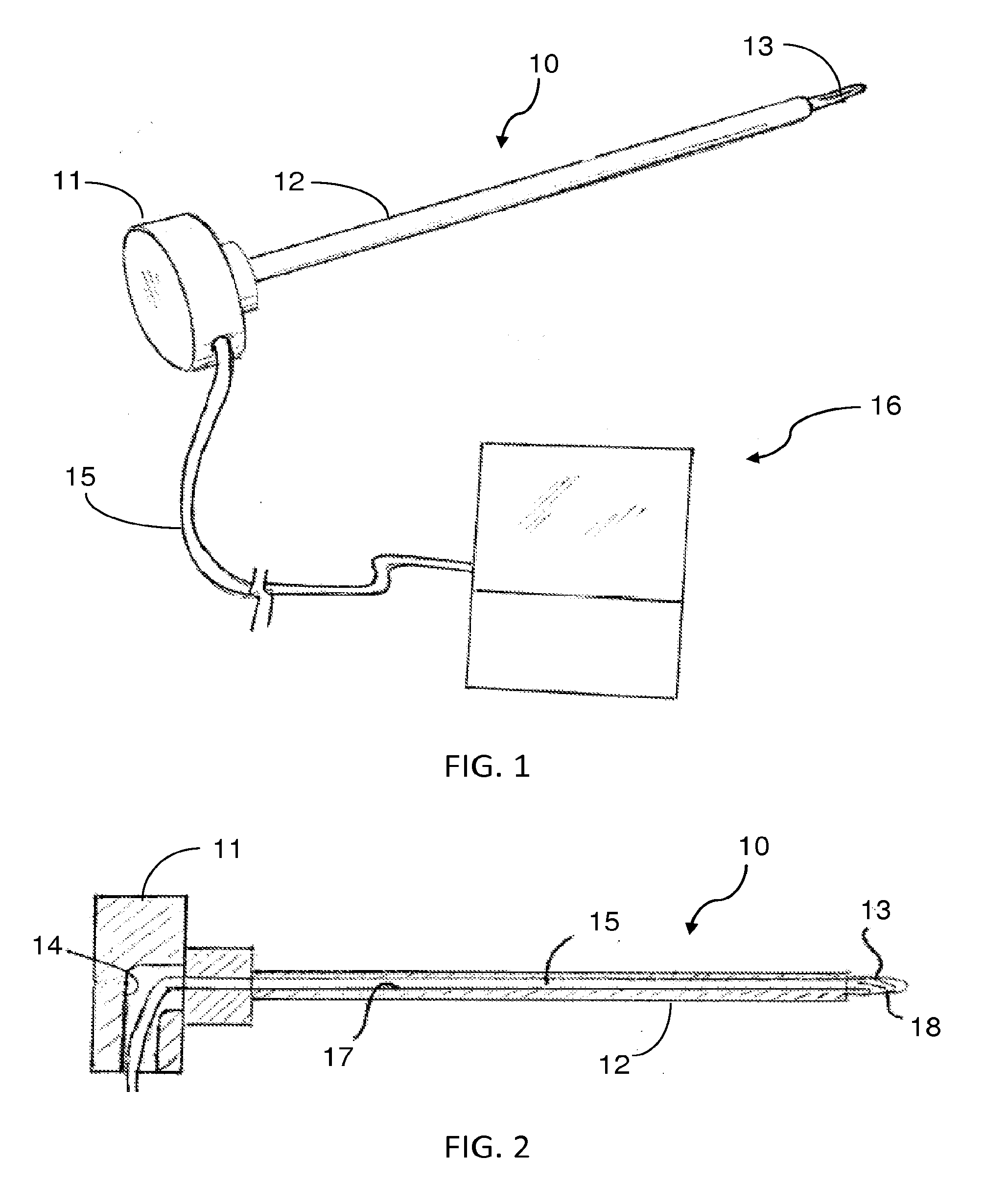
Surgical hand access apparatus
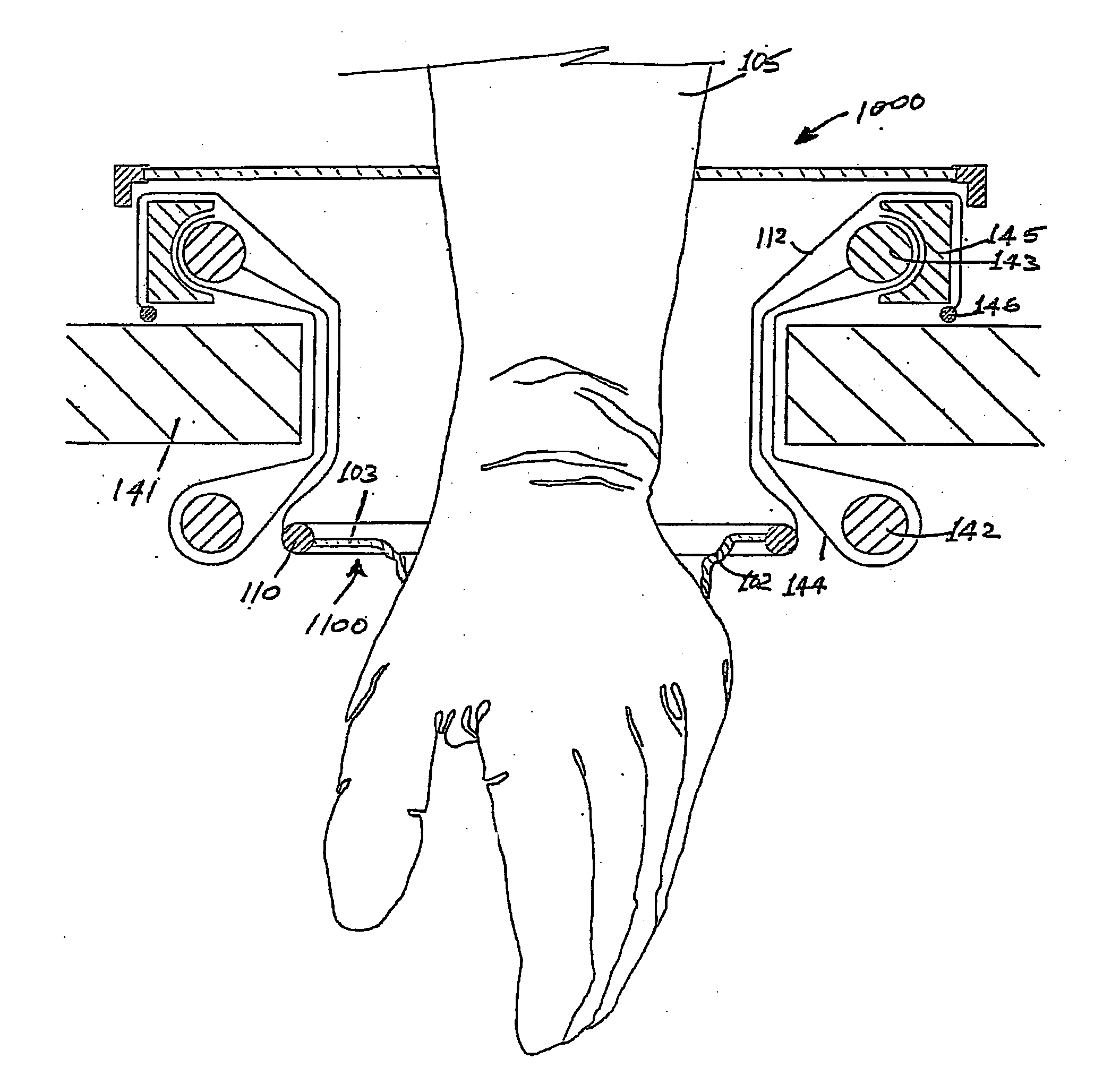
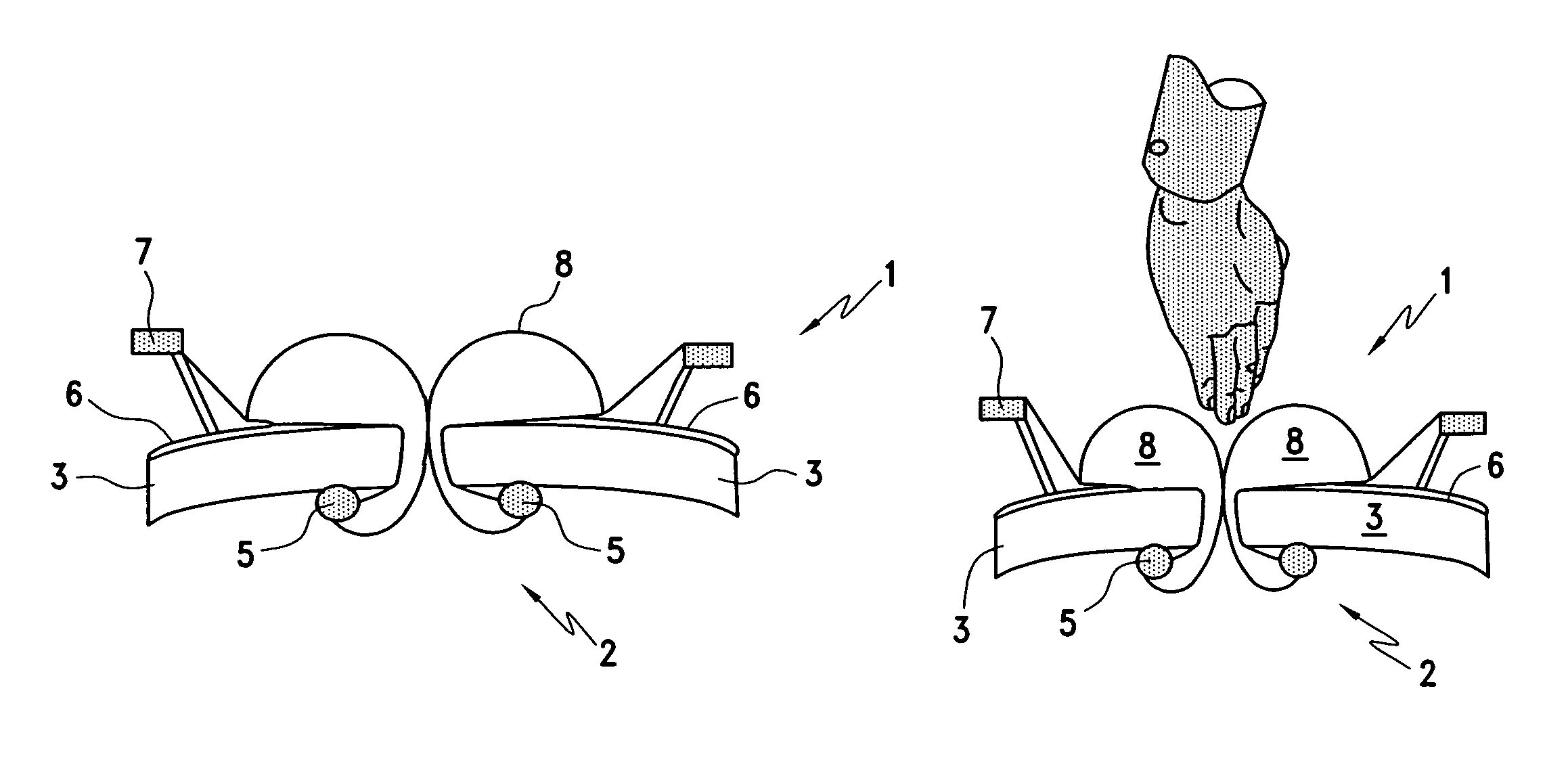
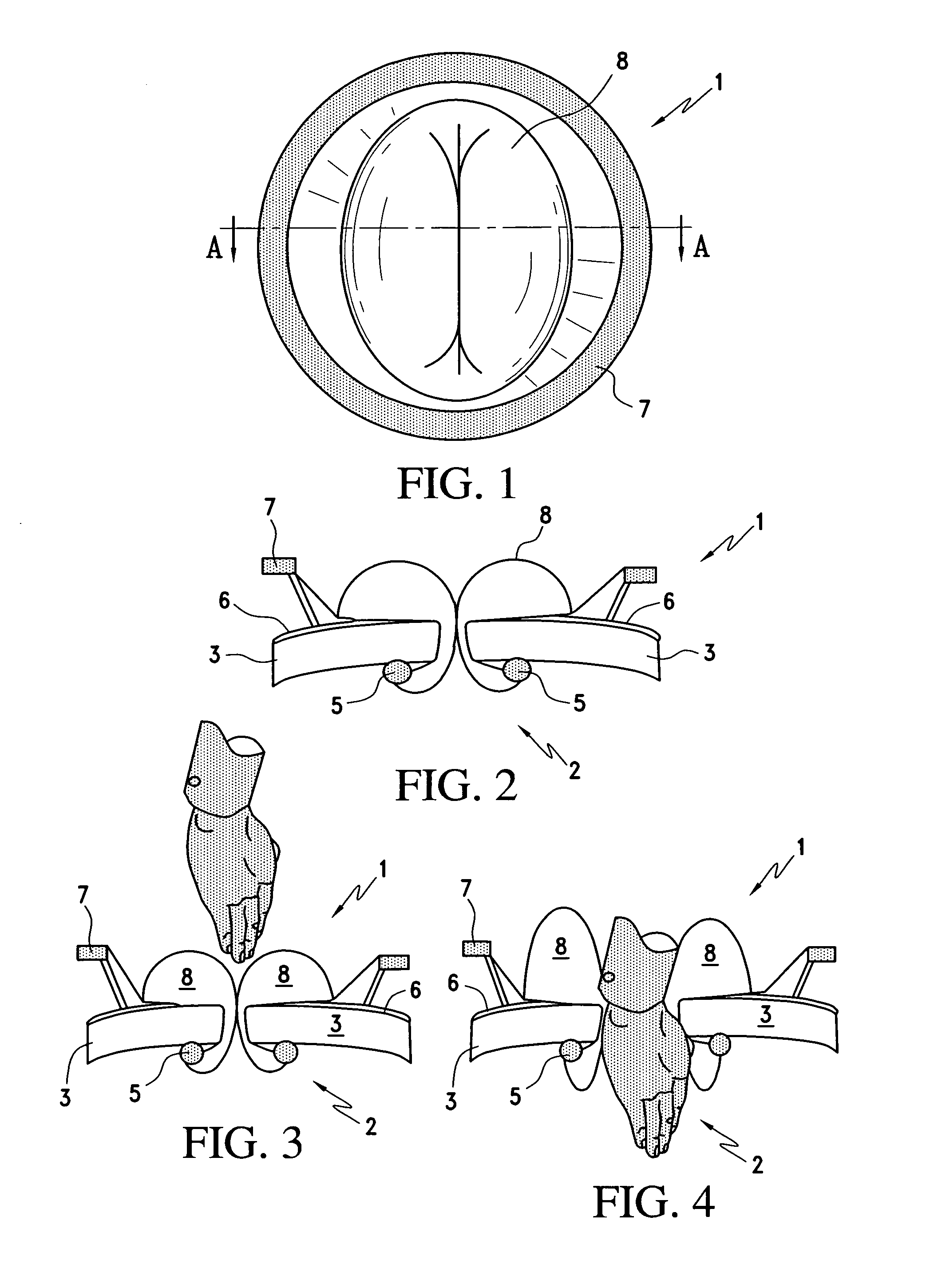
A surgical access apparatus adaptable to permit the sealed insertion of either the surgeon's hand and / or surgical instruments during laparoscopic and endoscopic surgical procedures includes an access housing defining a central longitudinal axis and having a longitudinal opening extending therethrough for passage of a surgeon's hand, a retractor base mounted to the access housing and having a flexible liner for positioning within the incision to engage tissue portions defining the incision, and a trocar adapter which is releasably mounted to the access housing. The trocar adapter includes a trocar sleeve positioned for reception within the longitudinal opening and a trocar valve adapted to receive a surgical instrument in fluid tight relation therewith. The access housing may include a seal adapted to form a seal about each of the surgeon's arm and the trocar sleeve. The seal is adapted to close in absence of the surgeon's arm or the trocar sleeve.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
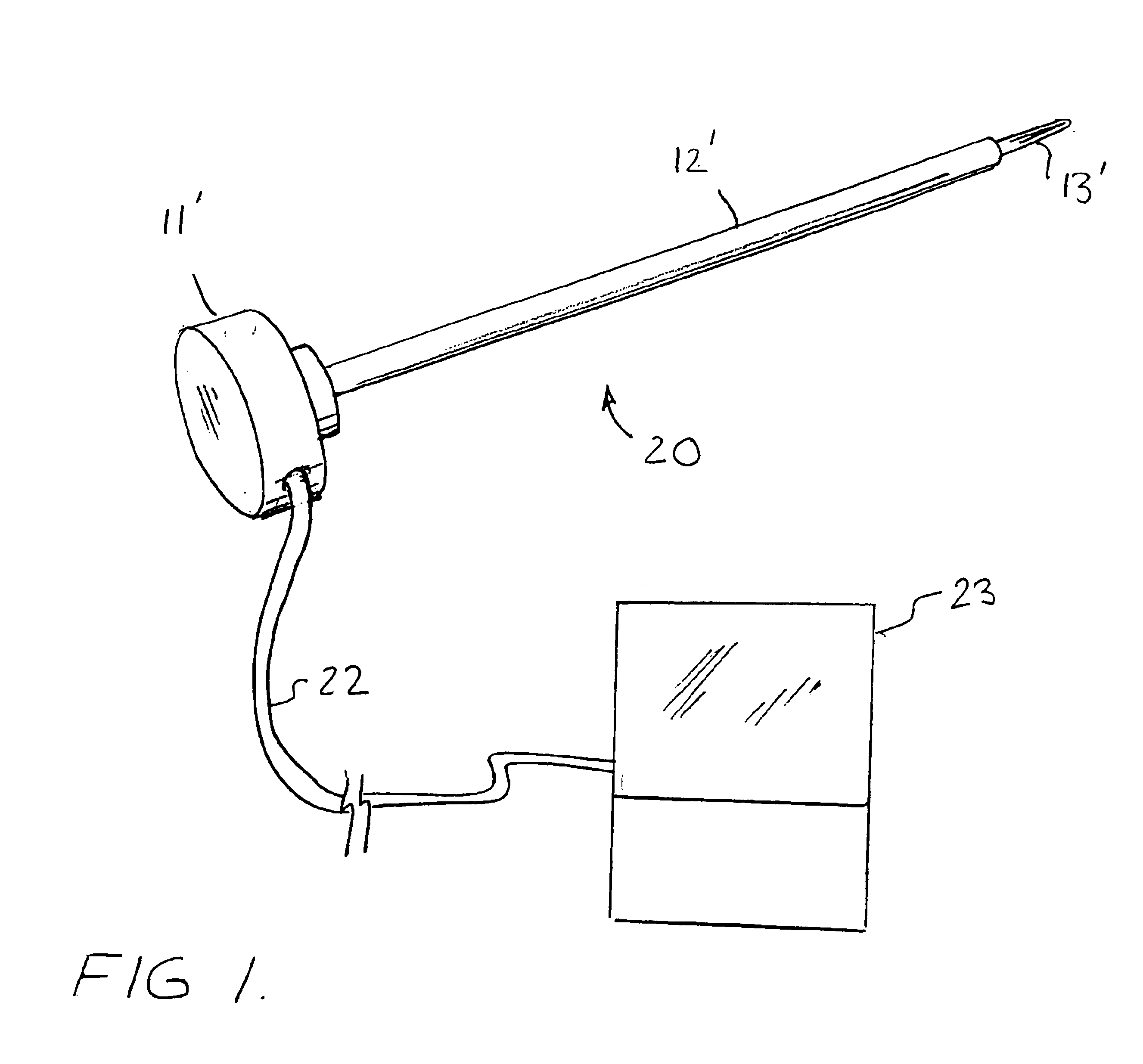
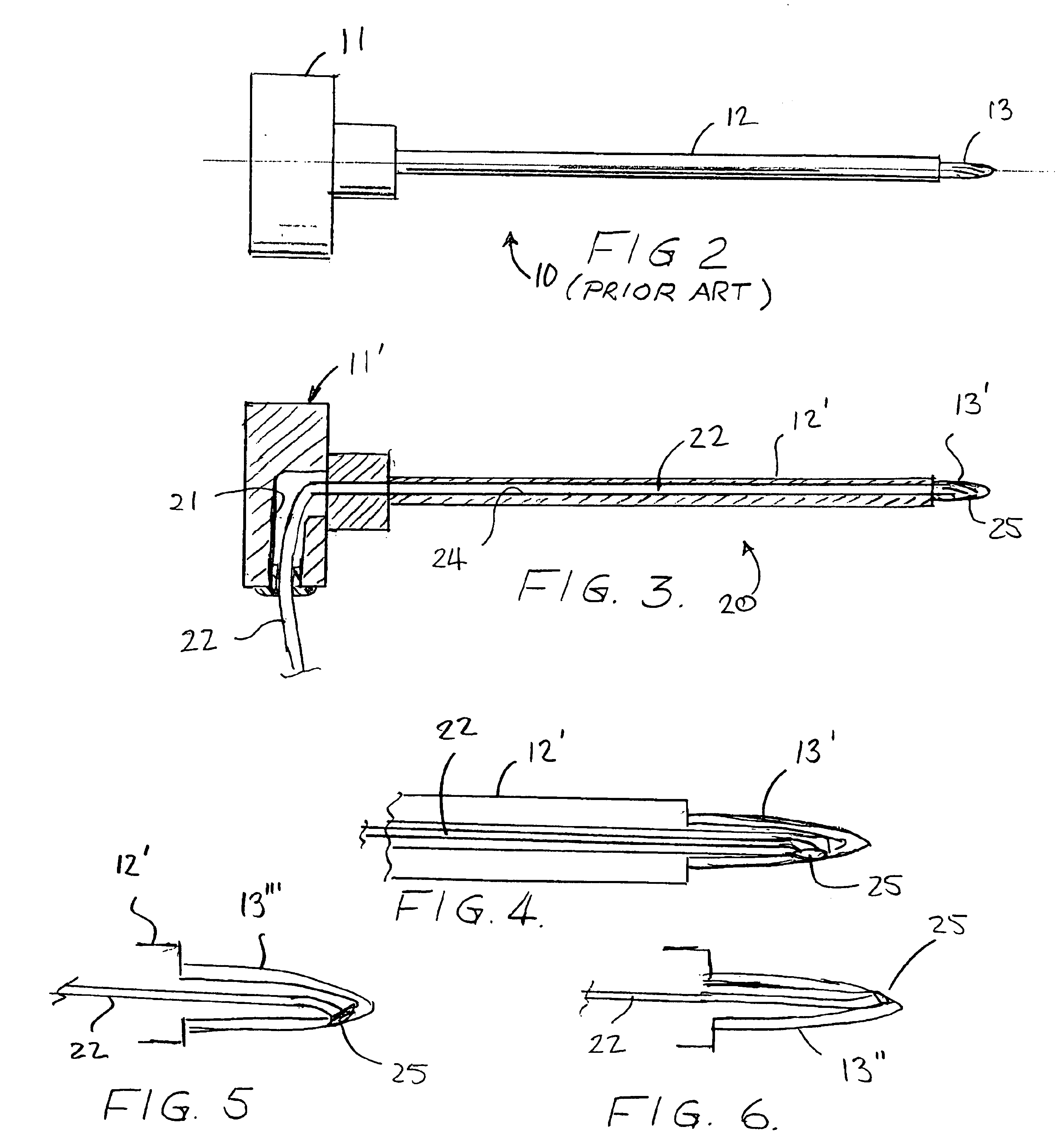
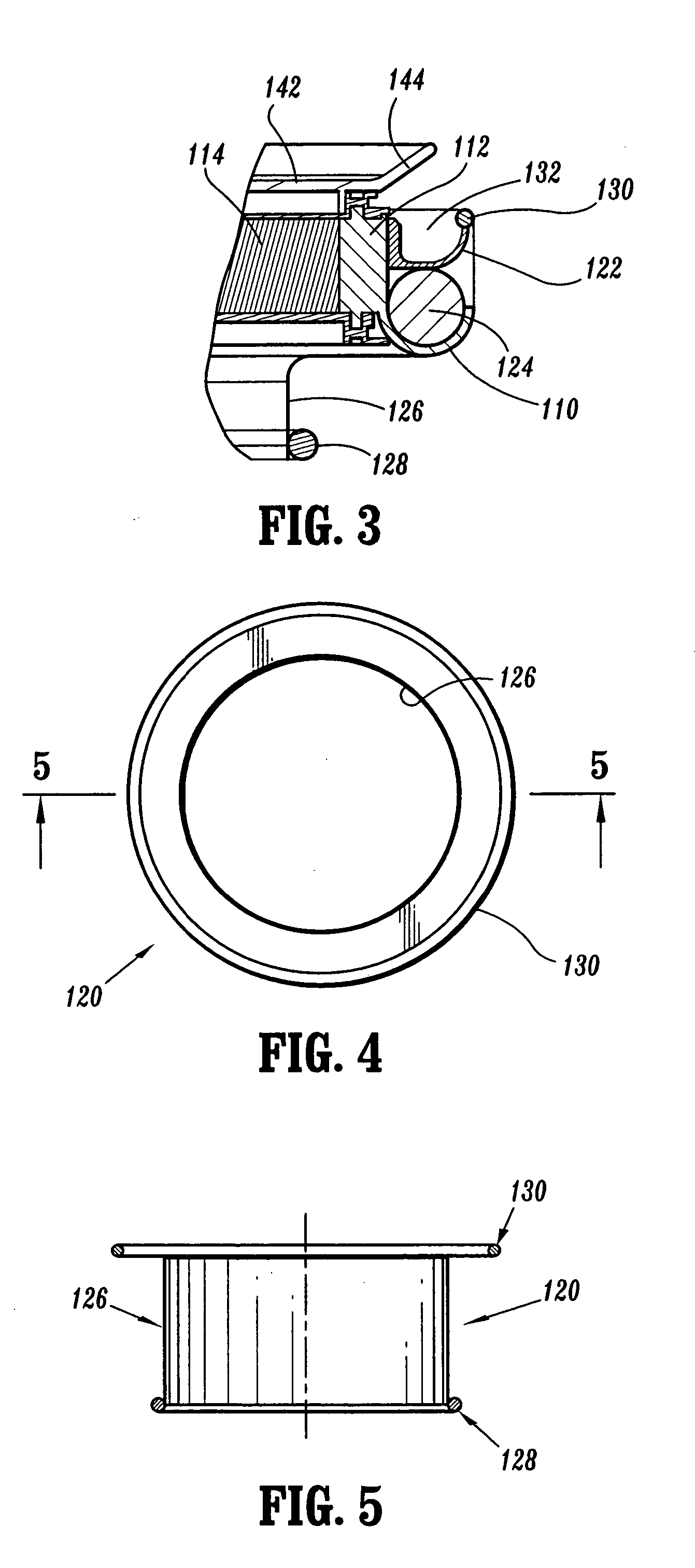
Surgical sealing device
A surgical sealing device comprises sealing device of a gelatinous elastomeric material, a distal ring element and a proximal ring element. The ring elements are twisted relative to one another to twist the valve body into a twisted configuration to seal across a wound opening. The ring elements are snap-fitted together to maintain the valve in the twisted configuration. By passing an object, such as surgeon's hand through the valve, the opposing sidewalls of a lumen through the valve may be forced radially apart to partially open the lumen, and thereby enable the surgeon's hand to access the interior of the abdomen. The valve remains twisted during insertion of the surgeon's hand through the valve to minimise the loss of insufflation gases from the abdomen.
Owner:ATROPOS LTD
Surgical access apparatus and method
Owner:APPL MEDICAL RESOURCES CORP
Surgical hand access apparatus
A surgical access apparatus adaptable to permit the sealed insertion of either the surgeon's hand and / or surgical instruments during laparoscopic and endoscopic surgical procedures includes an access housing defining a central longitudinal axis and having a longitudinal opening extending therethrough for passage of a surgeon's hand, a retractor base mounted to the access housing and having a flexible liner for positioning within the incision to engage tissue portions defining the incision, and a trocar adapter which is releasably mounted to the access housing. The trocar adapter includes a trocar sleeve positioned for reception within the longitudinal opening and a trocar valve adapted to receive a surgical instrument in fluid tight relation therewith. The access housing may include a seal adapted to form a seal about each of the surgeon's arm and the trocar sleeve. The seal is adapted to close in absence of the surgeon's arm or the trocar sleeve.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
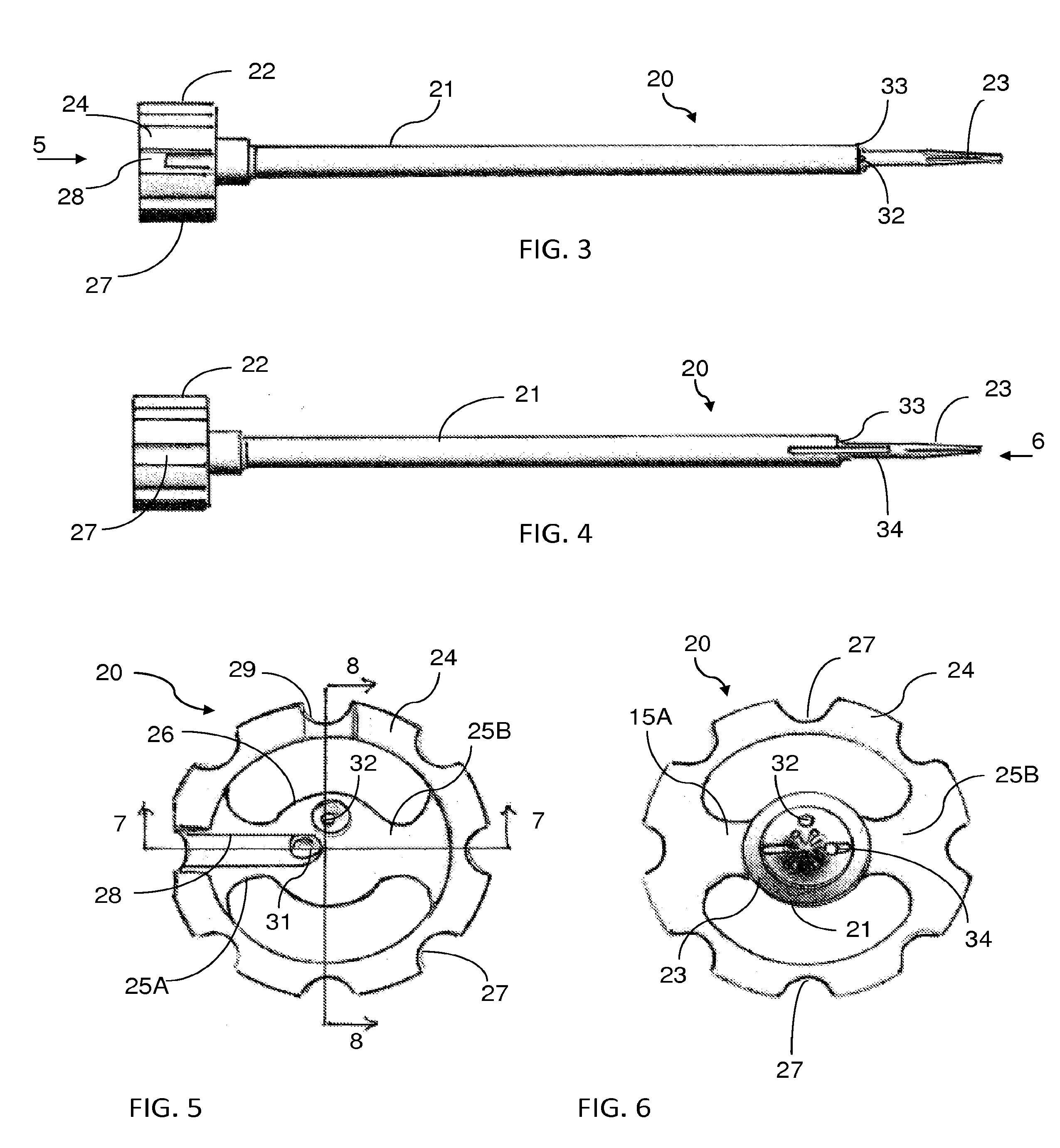
Adjustable tandem connectors for corrective devices for the spinal column and other bones and joints
InactiveUS20060079892A1Easy to tightenPrevent rotationSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisSpinal columnCoronal plane
Connectors for interconnecting rods, fixed to vertebrae and other bones of a subject include a body portion and two recesses or pockets for receiving the rods. These connectors are generally able to be secured to the rods by a tightening a fastener or retaining member from above the spine, which can facilitate the procedure for the surgeon. The connectors can include rotatable or stationary pockets, mating members that pivot and / or translate within the coronal plane of the subject to adjust to the positions of the rods, and extension shafts that pivot to adjust for rod angle.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC
Axially Reciprocating Microsurgical Instrument with Radially Compressed Actuator Handle
ActiveUS20120116361A1Smooth rotationEasily otherwise movedEye surgeryExcision instrumentsReciprocating motionEngineering
A microsurgical instrument has a pair of operative surgical surfaces that are moved relative to each other in shearing or grasping procedures performed by the instrument. The instrument has a handle containing an elongate center rod with a ring mounted for reciprocating movement on the rod. A tube is secured to the ring and a shaft extends through the tube and is secured to the rod. The handle also includes a plurality of resilient arms that extend along the length of the rod and engage against a sliding surface of the ring on the rod. The plurality of actuator arms are alternatively manually compressed radially inwardly by the surgeon's hand and released by the surgeon's hand to allow the arms to flex radially inwardly and outwardly. The inward and outward movement of the plurality of arms reciprocates the ring on the handle rod and causes the tube and shaft to move axially relative to each other.
Owner:SYNERGETICS USA
Laparoscopic surgical instrument
A laparoscopic surgical instrument configured to be ergonomic and anthropometrically correct, the laparoscopic surgical instrument comprising: (a) an ergonomic handle configured to orient a hand of a surgeon in a functional position, the handle comprising a handle grip; (b) an actuating mechanism actuatable by a finger and supported by the handle, the actuating mechanism comprising an actuator shaft and a gearing assembly operable to displace the actuator shaft with a mechanical advantage upon actuation of a trigger by the surgeon; (c) a locking mechanism configured to lock the actuating mechanism in one of a plurality of positions, the locking mechanism comprising a release located in an anthropometrically correct position; and (d) a working shaft having a proximal end coupled to and operable with the actuator shaft, the working shaft having an elongate configuration and a distal working end configured to couple a surgical tool to be manipulated by the surgeon via the handle and the actuating mechanism to perform a surgical function.
Owner:SHORTI RAMI +1
Functional navigator
InactiveUS20070015987A1Improve securityPositive and precise detectionSurgical navigation systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringCamera imageSurgical department
The invention relates to a device which is used intra-operatively to localise carcinogenic tumours and ganglia precisely and in a three-dimensional manner and to correlate the surgical instruments with the images in real time. The structural elements of the functional navigator include: a surgical navigator, a camera which is used to obtain functional images, the position-finding elements of the camera and the surgical instruments and the specific software program which combines all of the information from the aforementioned elements. The surgical navigator is essentially characterised in that the position of the cameras which acquire the functional images is controlled by the navigator by means of emitters or reflectors which are disposed in said cameras. The information relating to the camera images and the position of same, which is determined by the navigator, is analysed by a specific software program and combined with the position of the surgeon's surgical instruments in order to obtain images.
Owner:CONSEJO SUPERIOR DE INVESTIGACIONES CIENTIFICAS (CSIC) +1
Method and apparatus for performing minimally invasive surgical procedures
InactiveUS20050228365A1Reserved functionHigh precisionProgramme controlSuture equipmentsRobotic armSurgical site
The system includes a pair of surgical instruments that are coupled to a pair of robotic arms. The instruments have end effectors that can be manipulated to hold and suture tissue. The robotic arms are coupled to a pair of master handles by a controller. The handles can be moved by the surgeon to produce a corresponding movement of the end effectors. The movement of the handles is scaled so that the end effectors have a corresponding movement that is different, typically smaller, than the movement performed by the hands of the surgeon. The scale factor is adjustable so that the surgeon can control the resolution of the end effector movement. The movement of the end effector can be controlled by an input button, so that the end effector only moves when the button is depressed by the surgeon. The input button allows the surgeon to adjust the position of the handles without moving the end effector, so that the handles can be moved to a more comfortable position. The system may also have a robotically controlled endoscope which allows the surgeon to remotely view the surgical site. A cardiac procedure can be performed by making small incisions in the patient's skin and inserting the instruments and endoscope into the patient. The surgeon manipulates the handles and moves the end effectors to perform a cardiac procedure such as a coronary artery bypass graft.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Apparatus for performing minimally invasive cardiac procedures with a robotic arm that has a passive joint and system which can decouple the robotic arm from the input device
InactiveUS6905491B1Minimally invasiveComfortable postureSuture equipmentsProgramme controlRobotic armEngineering
A system for performing minimally invasive cardiac procedures. The system includes a pair of surgical instruments that are coupled to a pair of robotic arms. The instruments have end effectors that can be manipulated to hold and suture tissue. The robotic arms are coupled to a pair of master handles by a controller. The handles can be moved by the surgeon to produce a corresponding movement of the end effectors. The movement of the handles is scaled so that the end effectors have a corresponding movement that is different, typically smaller, than the movement performed by the hands of the surgeon. The scale factor is adjustable so that the surgeon can control the resolution of the end effector movement. The movement of the end effector can be controlled by an input button, so that the end effector only moves when the button is depressed by the surgeon. The input button allows the surgeon to adjust the position of the handles without moving the end effector, so that the handles can be moved to a more comfortable position. The robotic arm may contain a passive joint that provides an additional degree of freedom. Additionally, the system may include a disconnect input device that decouples the arm from an input device such as the handles.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
Dexterous surgical manipulator and method of use
ActiveUS20120277762A1Easy to learnEasy to useDiagnosticsSurgical manipulatorsEngineeringSacroiliac joint
A surgical manipulator includes an internal working end having an internal joint, and an external control interface linked to the internal working end for controlling the internal working end. The external control interface includes at least one lever defining a grip volume for a surgeon's hand when gripping and operating the at least one lever, and an external joint linked to the internal joint for controlling the internal joint. The external joint is positioned substantially within the grip volume.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Length adjustable electro-surgical pencil with suction means
InactiveUS20060264928A1Easy to adjustSurgical instruments for heatingSurgical instruments using microwavesEffective lengthEngineering
An electro-surgical (ES) pencil of the kind that includes an elongated housing having a longitudinal axis, a surgical electrode having a tip and a longitudinal axis that is aligned parallel to the longitudinal axis of the housing, the electrode a suction tube having a top and a longitudinal axis that is aligned parallel to the longitudinal axis of the housing and being offset from the longitudinal axis of the electrode, a suction hose connecting the suction tube with a suction unit, an electrical wire for providing electrical power to the pencil and being placed inside the hose. With this arrangement, an ES pencil is provided that is easily adjustable and customizable. In addition, since both the tip of the suction tube and the tip of the electrode are displaceable with respect to the location of the surgeon's hand, the effective length of the ES pencil can be simply and easily changed.
Owner:LINA MEDICAL
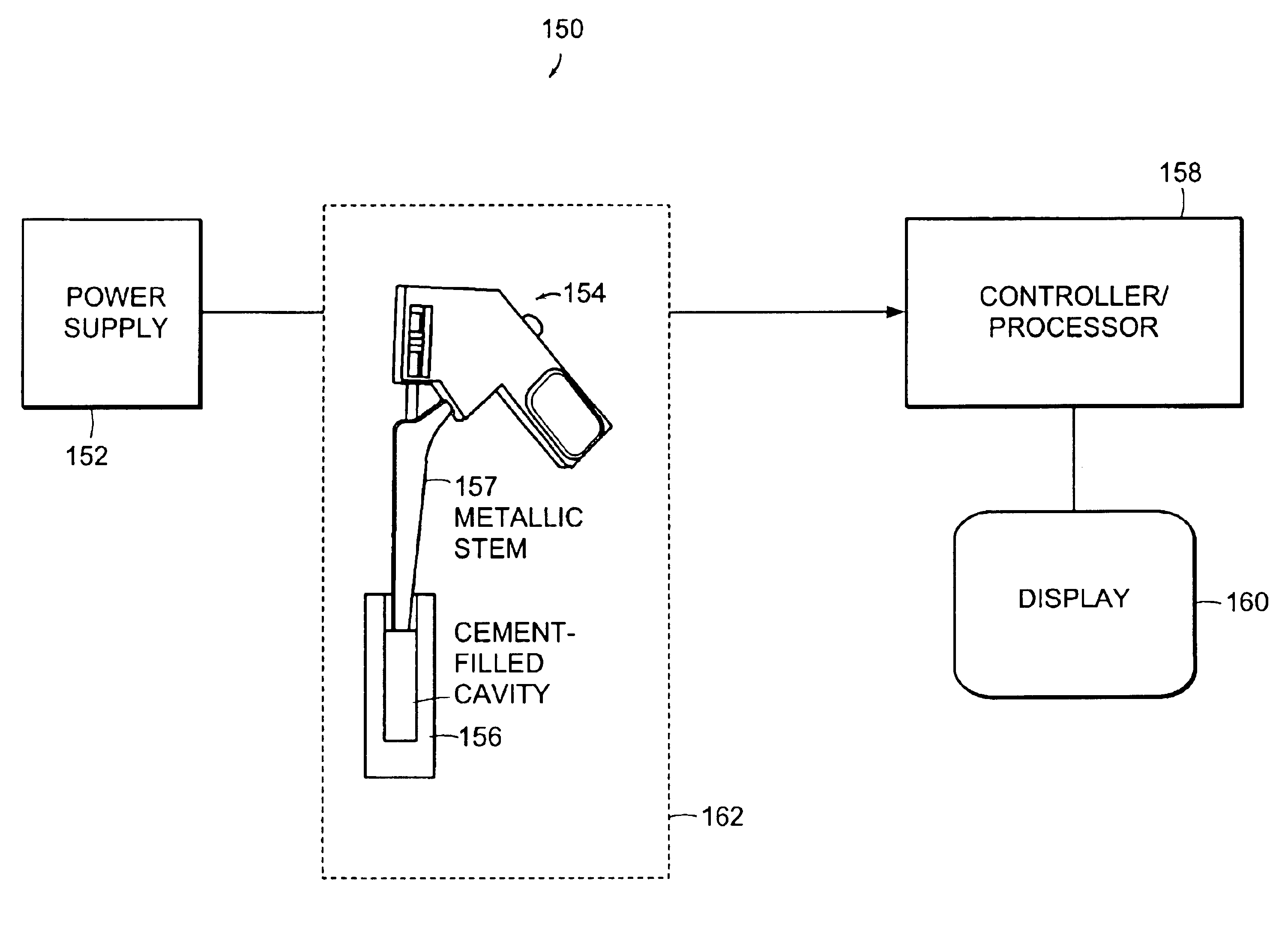
System and methods for reducing interfacial porosity in cements
InactiveUS6884264B2Reducing pores, or air pocketsReduce the possibilityUltrasound therapyBone implantPorosityHand held
The present invention provides a system and a method for reducing pores, or air pockets, that form at the interface between the material used to attach or adhere the surface of a component, such as a prosthesis, to a site.A preferred embodiment of the invention includes an actuator that controls a coupler which transmits energy to a prosthesis being inserted into a material to reduce porosity at an interface between the prosthesis and the material.The system of the present invention can include an oscillating hand-held device that vibrates the stem component of an orthopedic prosthesis at a particular frequency and amplitude. The device is typically held by the hand of the surgeon, who guides the vibrating prosthesis into the cement-filled medullary cavity.
Owner:CAMBRIDGE POLYMER GROUP
Illuminated endoscopic pedicle probe with dynamic real time monitoring for proximity to nerves
InactiveUS20150342621A1Prevent breachDirectly and accurately determinedSpinal electrodesElectromyographyVisual observationMonitoring system
An endoscopic pedicle probe for use during spinal surgery to form a hole in a pedicle for reception of a pedicle screw has an enlarged proximal end for cooperation with the hand of the surgeon and an elongate shaft terminating in a distal tip that may be pushed through the pedicle to form the hole. An integrated endoscope and light extend through the shaft to enable the surgeon to visually observe the target area, and a conduit extends through the shaft to convey a fluid to irrigate the target area. In a preferred form the probe is connected with an electromyographic or mechanomyographic monitoring system to alert the surgeon when a breach is about to occur. In a further embodiment, two endoscopes are associated with the probe. The complete probe may be disposable, or just the tip may be detachable for disposal or replacement.
Owner:OPTICAL SPINE LLC
Arthroscope rotation mechanisms and methods of endoscopic rotation
A rotation mechanism (rotating device) that can be easily accessed by the surgeon's finger to rotate an endoscope or similar instrument. The rotation mechanism is a device / component with a “starfish” configuration, which can be attached to the endoscope / arthroscope just distal to the eyepiece (or to an alternate attachment to a camera). The starfish component has a plurality of projections that extend radially from the endoscope axis, and beyond the diameter of the mechanism on the camera head that grasps the arthroscope eyecup. The projections can be easily accessed by the surgeon's finger to rotate the endoscope.
Owner:ARTHREX
Motion and orientation sensing module or device for positioning of implants
InactiveUS20140135744A1Surgical navigation systemsSurgical systems user interfaceHand movementsCombined use
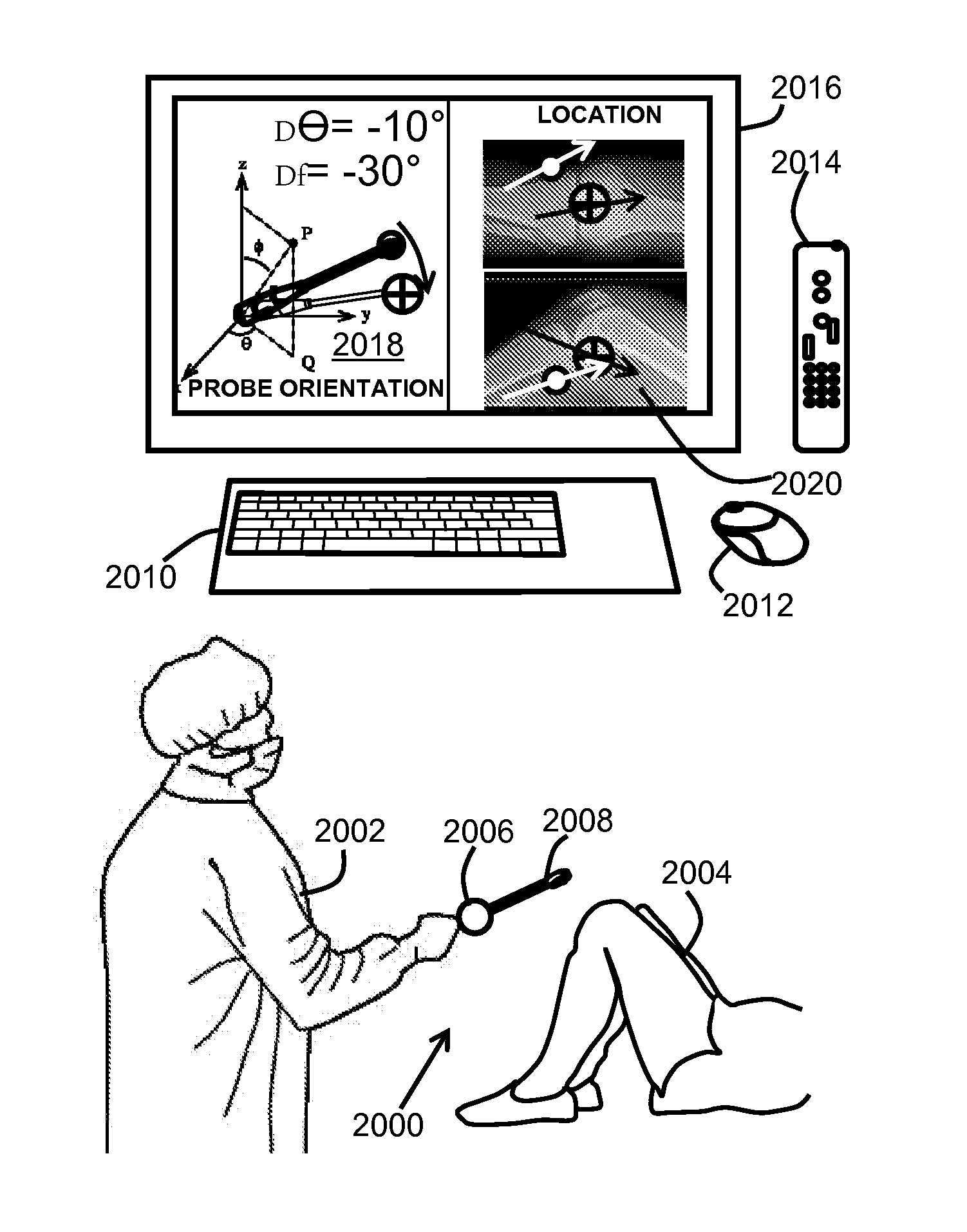
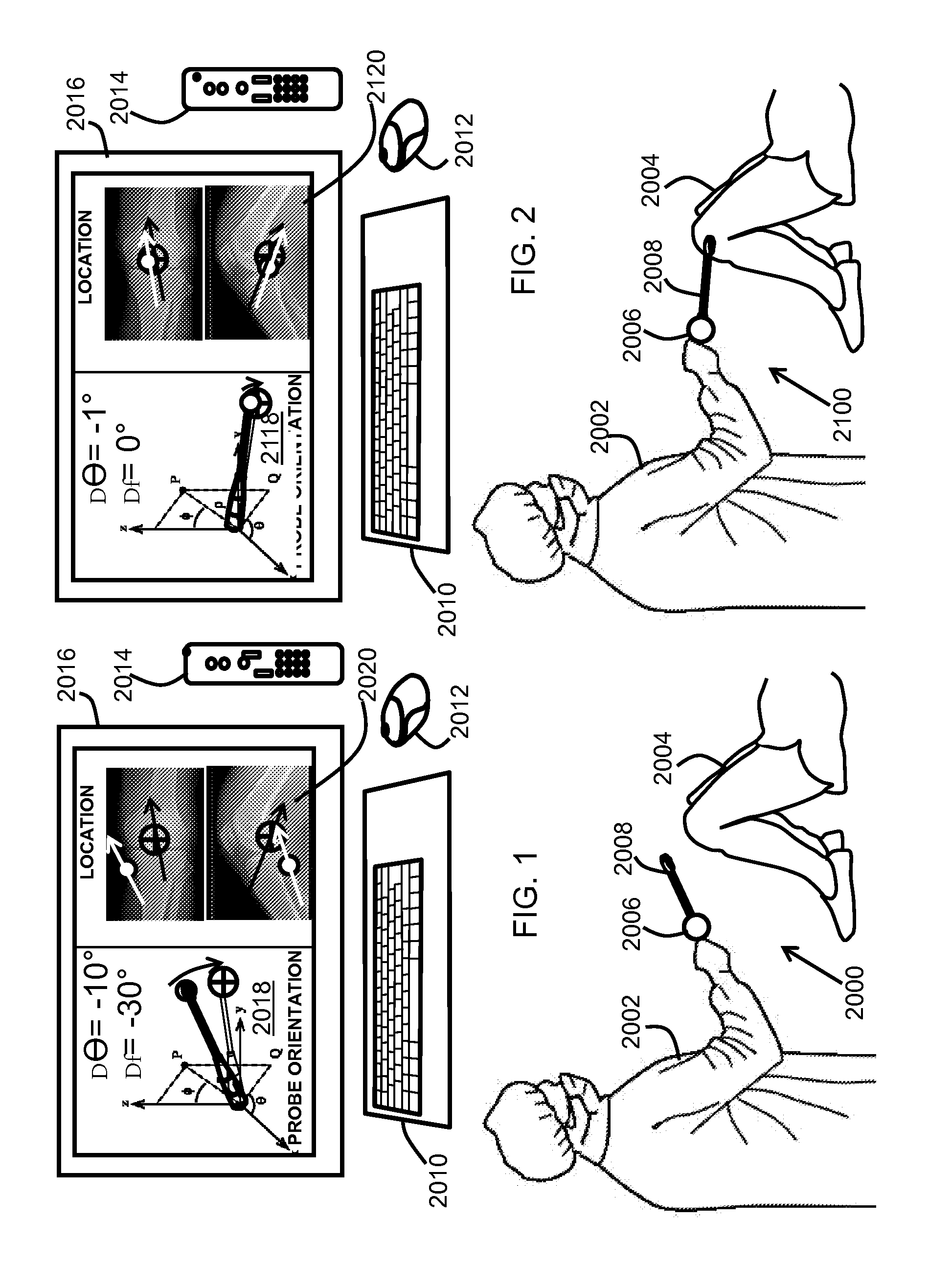
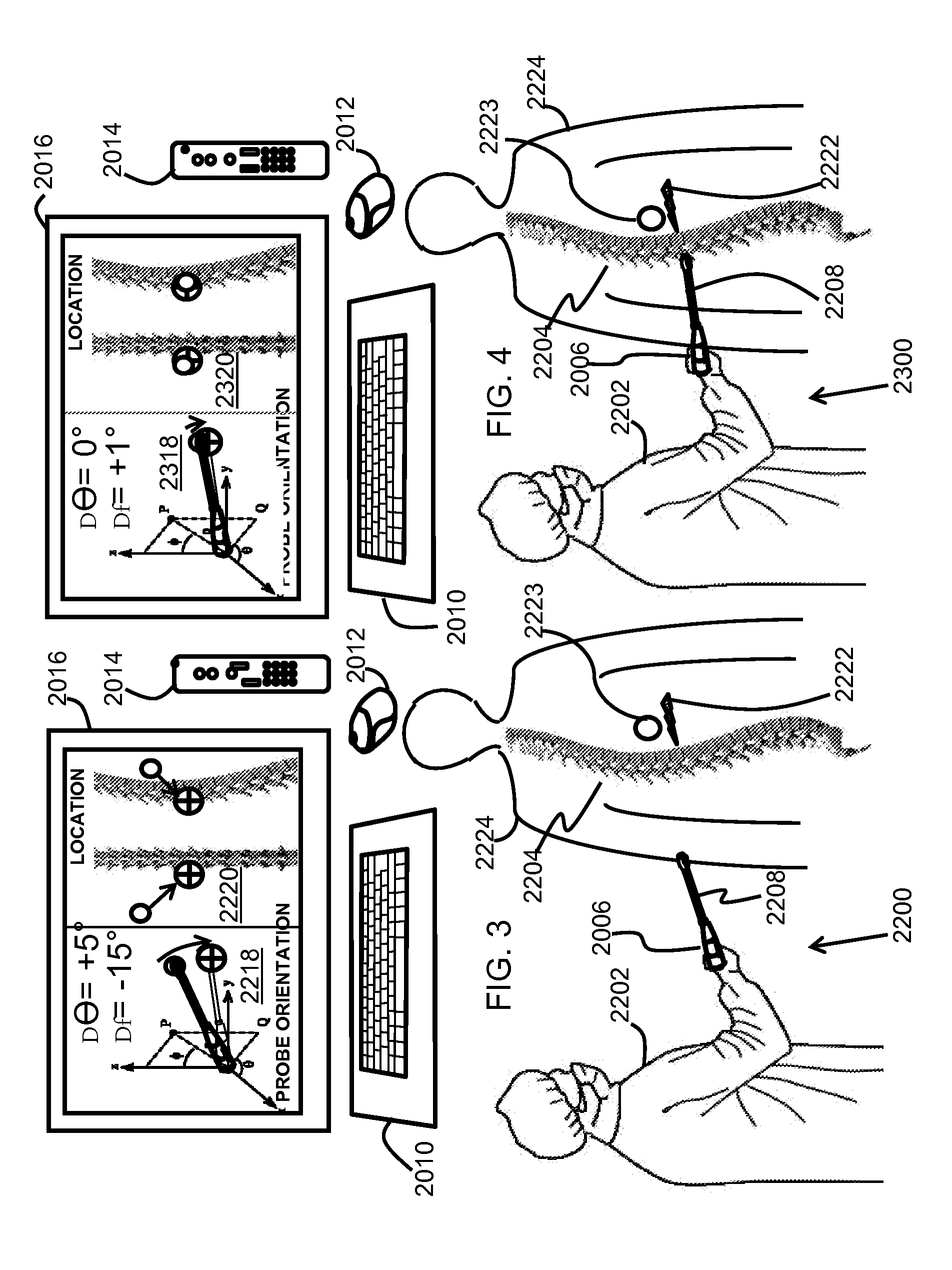
At least one embodiment is directed to a tracking system for the muscular-skeletal system. The tracking system can identify position and orientation. The tracking system can be attached to a device or integrated into a device. In one embodiment, the tracking system couples to a handheld tool. The handheld tool with the tracking system and one or more sensors can be used to generate tracking data of the tool location and trajectory while measuring parameters of the muscular-skeletal system at an identified location. The tracking system can be used in conjunction with a second tool to guide the second tool to the identified location of the first tool. The tracking system can guide the second tool along the same trajectory as the first tool. For example, the second tool can be used to install a prosthetic component at a predetermined location and a predetermined orientation. The tracking system can track hand movements of a surgeon holding the handheld tool within 1 millimeter over a path less than 5 meters.
Owner:ORTHOSENSOR
Articulated surgical probe and method for use
A surgical probe includes an articulated digit located at a distal end of a positioning shaft having a longitudinal axis. An actuator is located at a proximal end of the positioning shaft that is operatively connected to the articulated digit so as to move it between a continuous range of positions from an extended position to a substantially curved position while maintaining a kinesthetic relationship between a surgeon's finger engaging the actuator and the articulated digit. Preferably, the surgeons finger position and shape directly correspond to the position and shape of the articulated digit. A method is provided for probing, dissecting, and retracting anatomical structures.
Owner:DYNAMIC SURGICAL INVENTIONS
Muscular-skeletal tracking system and method
At least one embodiment is directed to a tracking system for the muscular-skeletal system. The tracking system can identify position and orientation. The tracking system can be attached to a device or integrated into a device. In one embodiment, the tracking system couples to a handheld tool. The handheld tool with the tracking system and one or more sensors can be used to generate tracking data of the tool location and trajectory while measuring parameters of the muscular-skeletal system at an identified location. The tracking system can be used in conjunction with a second tool to guide the second tool to the identified location of the first tool. The tracking system can guide the second tool along the same trajectory as the first tool. For example, the second tool can be used to install a prosthetic component at a predetermined location and a predetermined orientation. The tracking system can track hand movements of a surgeon holding the handheld tool within 1 millimeter over a path less than 5 meters.
Owner:ORTHOSENSOR
Arthroscope rotation mechanisms and methods of endoscopic rotation
A rotation mechanism (rotating device) that can be easily accessed by the surgeon's finger to rotate an endoscope or similar instrument. The rotation mechanism is a device / component with a “starfish” configuration, which can be attached to the endoscope / arthroscope just distal to the eyepiece (or to an alternate attachment to a camera). The starfish component has a plurality of projections that extend radially from the endoscope axis, and beyond the diameter of the mechanism on the camera head that grasps the arthroscope eyecup. The projections can be easily accessed by the surgeon's finger to rotate the endoscope.
Owner:ARTHREX
Surgical robot and robotic controller
ActiveUS20070265638A1Enhance the surgeon's humanly limited sensesAccurate harmonizationProgramme-controlled manipulatorPaper/cardboard articlesNerve networkEngineering
The present invention was developed by a neurosurgeon and seeks to mimic the results of primate neurological research which is indicative of a human's actual neurological control structures and logic. Specifically, the motor proprioceptive and tactile neurophysiology functioning of the surgeon's hands and internal hand control system from the muscular level through the intrafusal fiber system of the neural network is considered in creating the robot and method of operation of the present invention. Therefore, the surgery is not slowed down as in the art, because the surgeon is in conscious and subconscious natural agreement and harmonization with the robotically actuated surgical instruments based on neurological mimicking of the surgeon's behavior with the functioning of the robot. Therefore, the robot can enhance the surgeon's humanly limited senses while not introducing disruptive variables to the surgeon's naturally occurring operation of his neurophysiology. This is therefore also a new field, neurophysiological symbiotic robotics.
Owner:MACDONALD DETTWILER & ASSOC INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com