Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1244 results about "Multi segment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Definition: Multi-Segment Marketing. Instead of focusing on a target market as is the usual trend of companies to better position their product, multi-segment marketing aims at the market as a whole and attempts to maximize the reach in order to generate as many sales as possible.
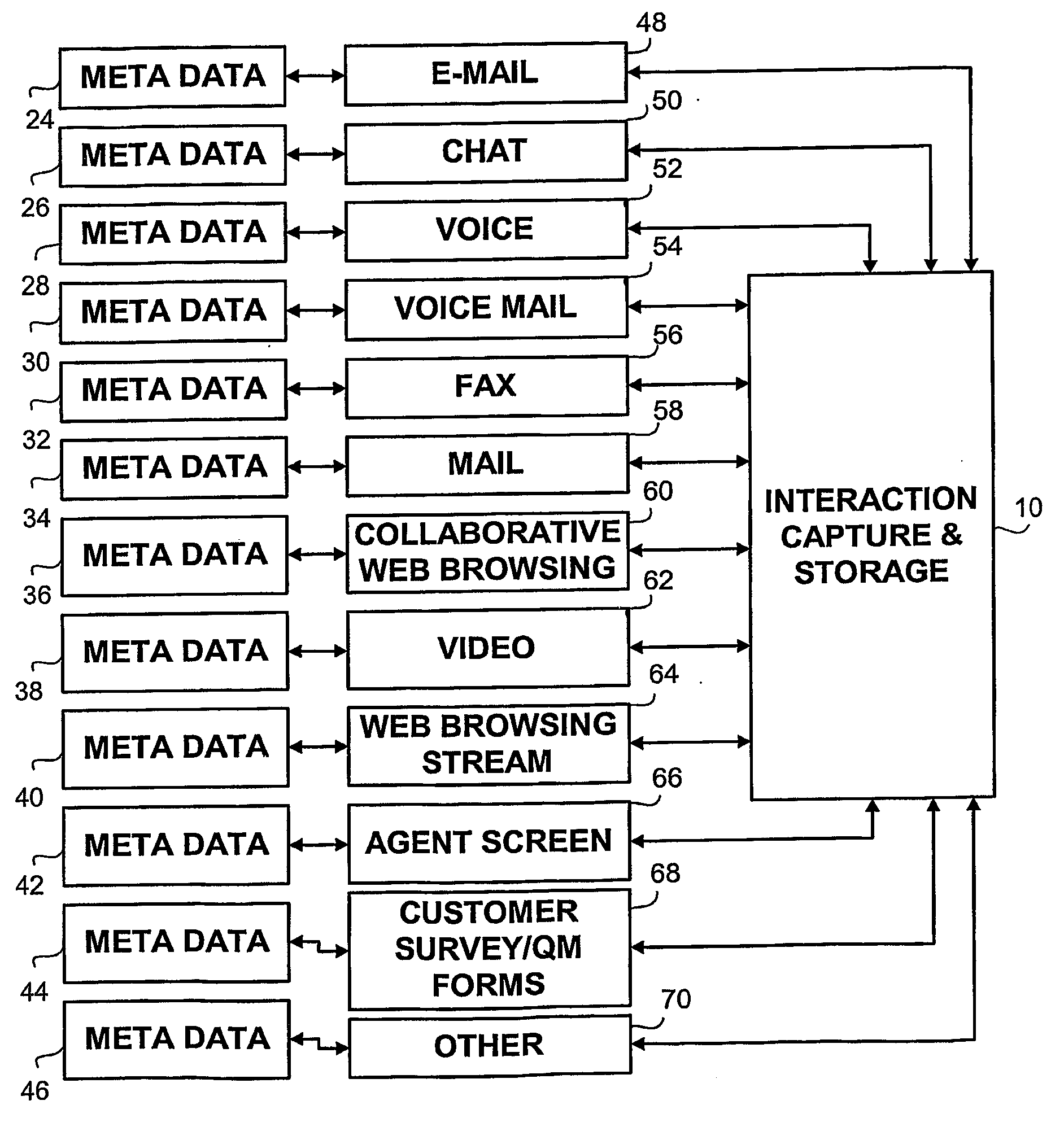
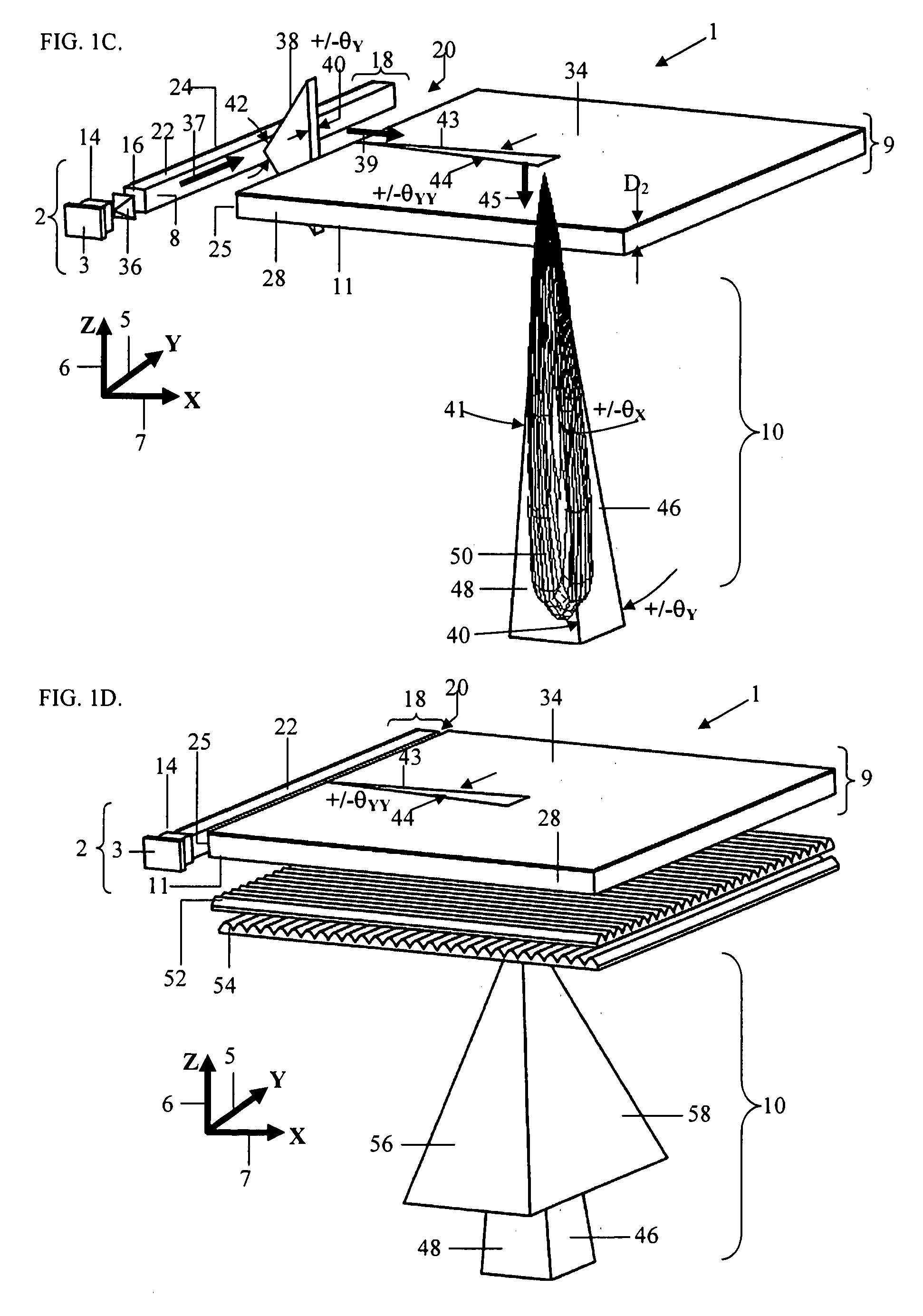
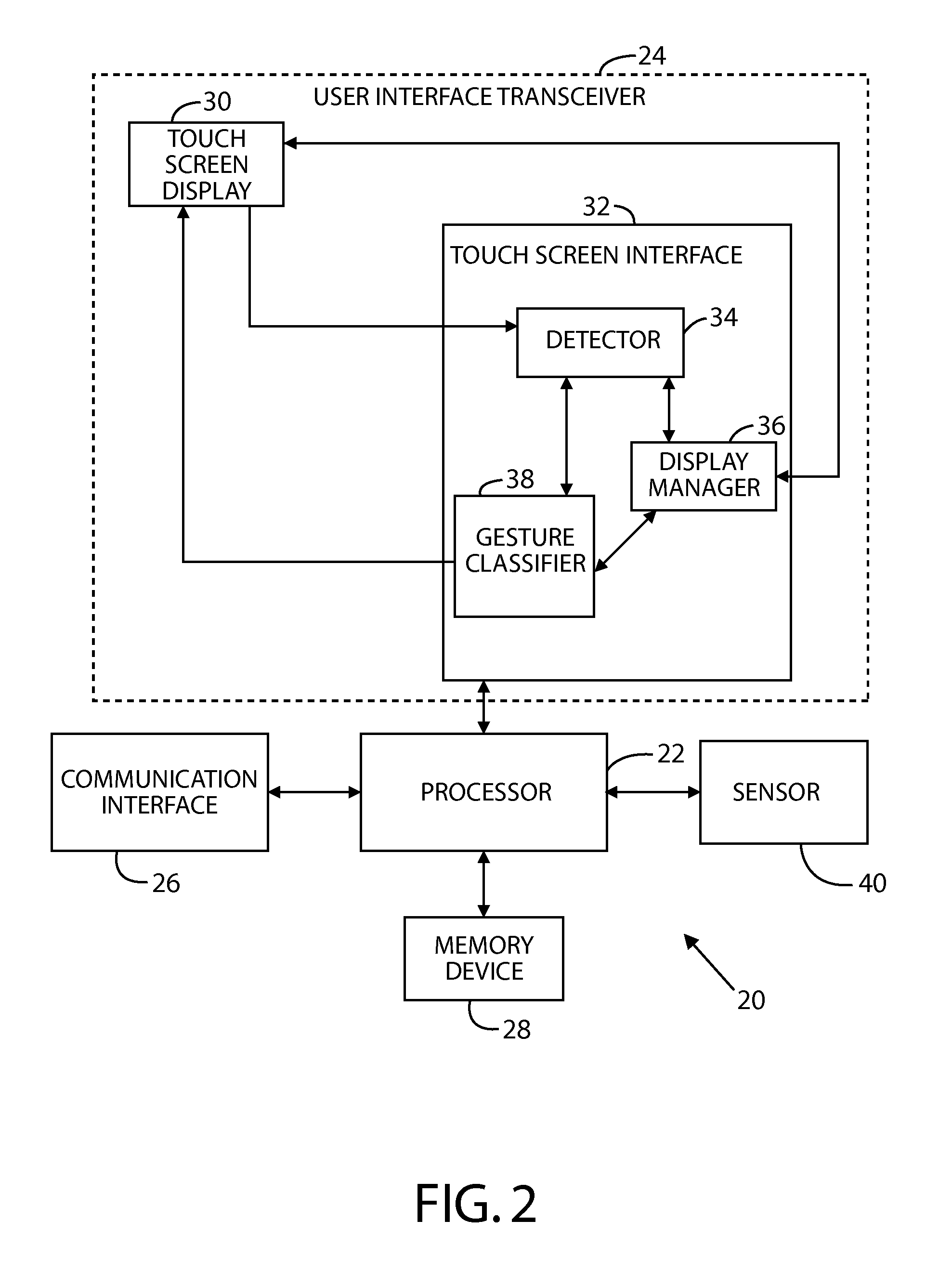
Method, apparatus and system for capturing and analyzing interaction based content
InactiveUS20110206198A1Digital data processing detailsSpecial service for subscribersData informationMulti segment
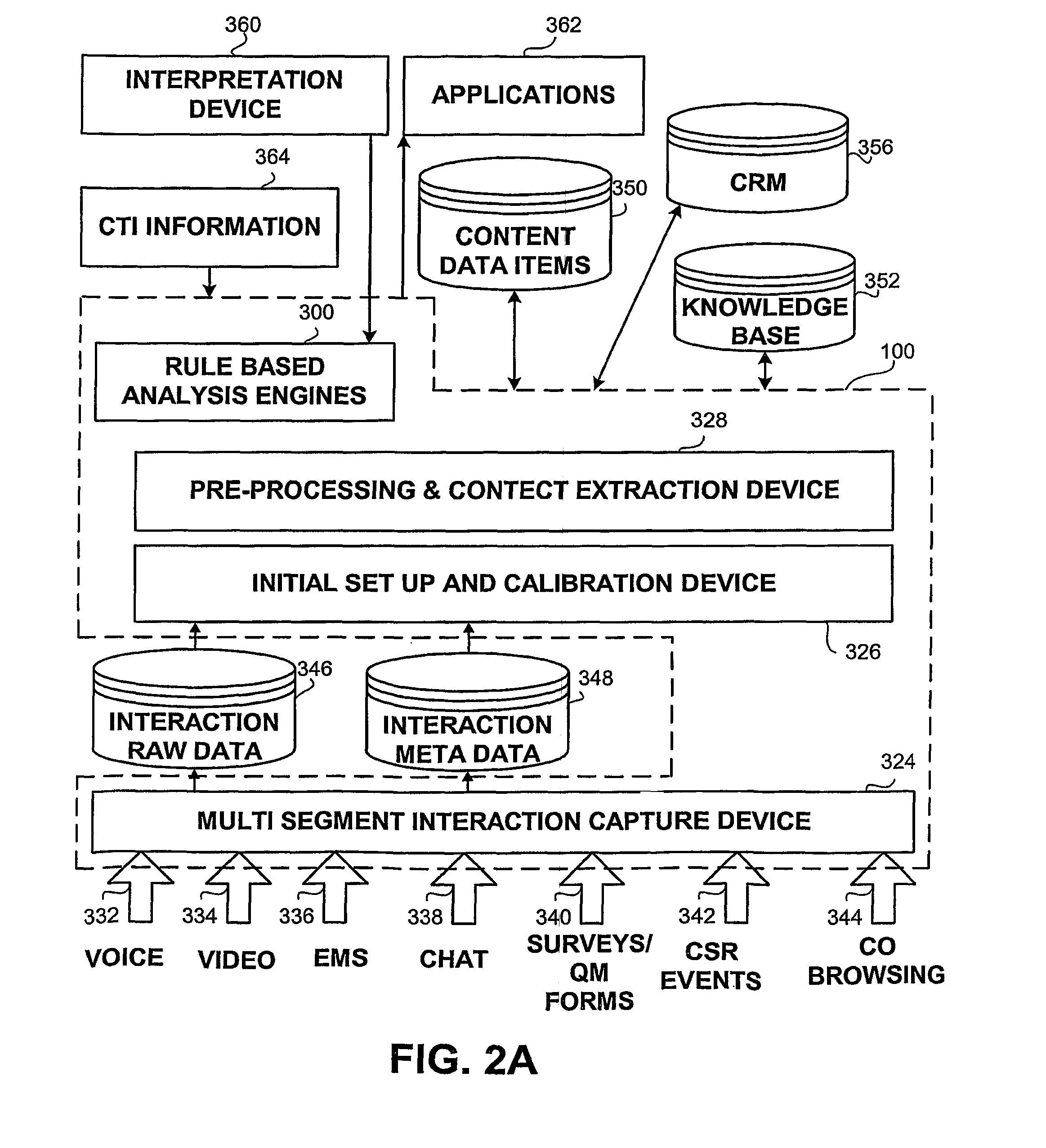
An apparatus and methods for capturing and analyzing customer interactions the apparatus comprising interaction information units, interaction meta-data information units associated with each of the interaction information units, a rule based analysis engine component for receiving the interaction information, an adaptive database, an interaction capture and storage component for capturing interaction information, a multi segment interaction capture device, an initial set up and calibration device and a pre processing and content extraction device.
Owner:NICE SYSTEMS
Chemical vapor deposition reactor
InactiveUS8778079B2Improve the deposition effectOptimize geometrySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid transferring devicesGas phaseProcess engineering
Owner:VALENCE PROCESS EQUIP
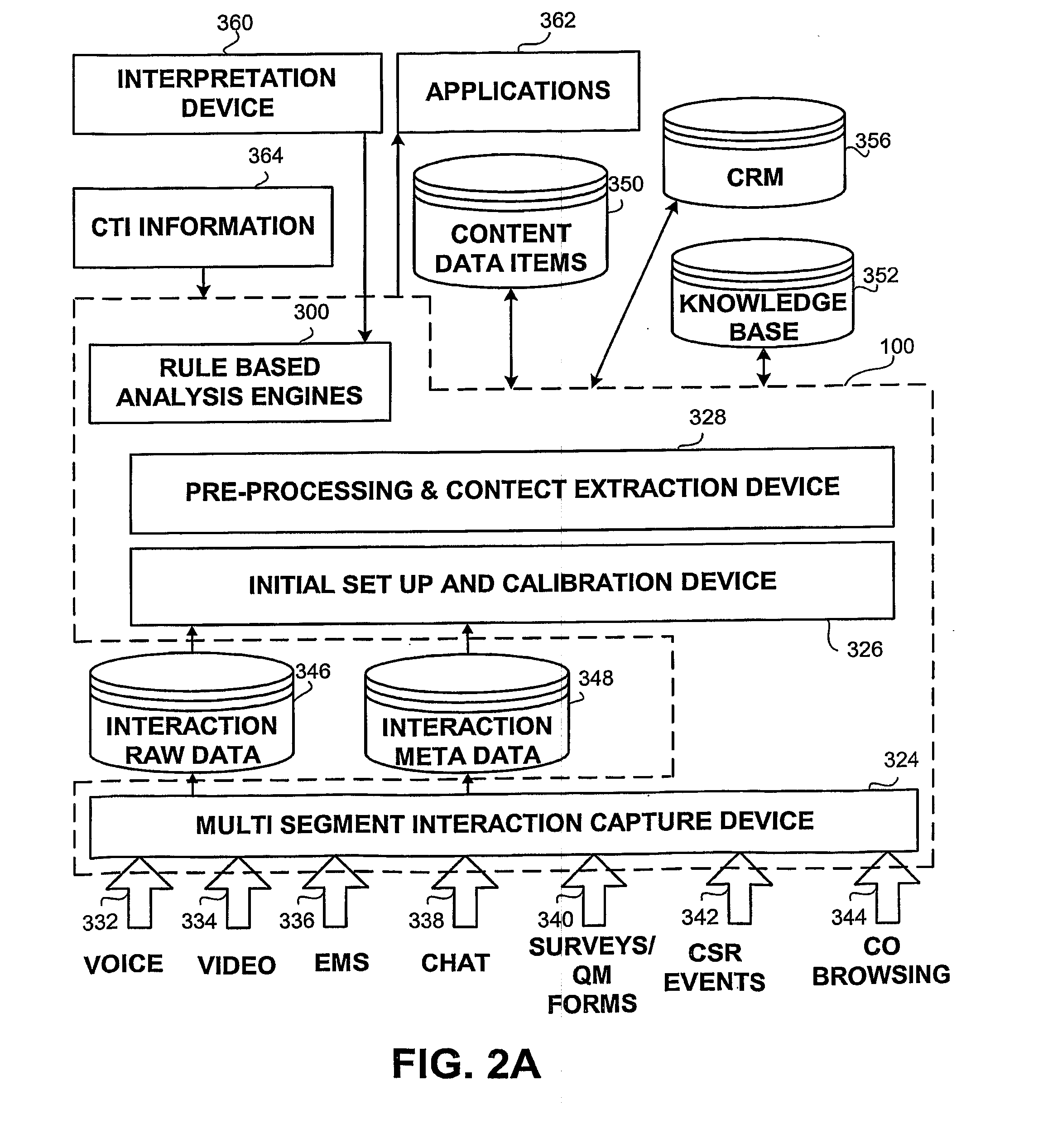
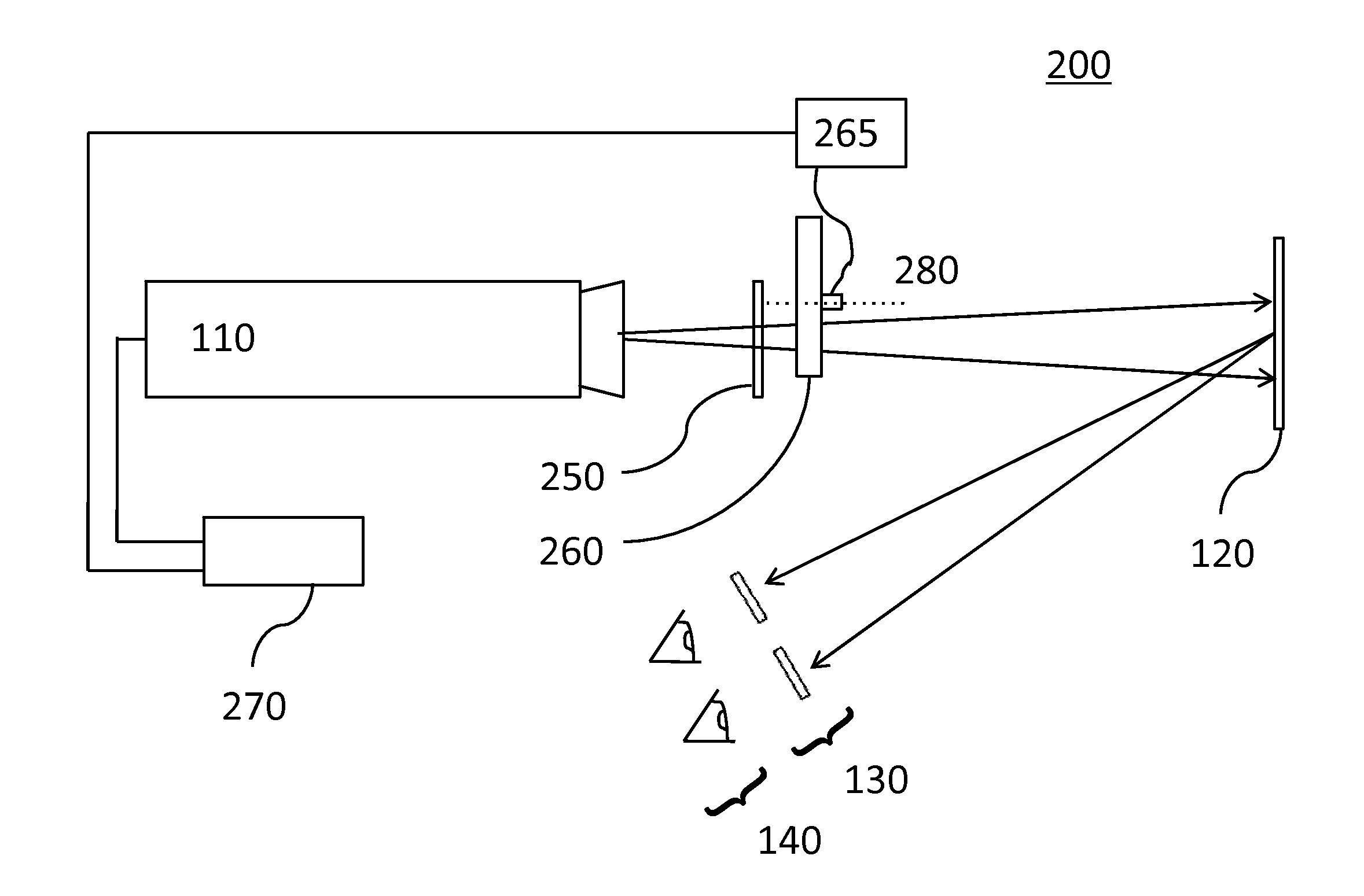
Method apparatus and system for capturing and analyzing interaction based content
The present invention provides a method and apparatus (100) for capturing and analyzing customer interactions, the apparatus comprising a multi-segment interaction capture device (324), an initial set up and calibration device (326), a pre-processing and context extraction device (328) and a rule-based analysis engine (300).
Owner:NICE LTD
Apparatus for microwave heating of a planar product including a multi-segment waveguide element
InactiveUS8173943B2Uniform heating patternReduce impactMultiple-port networksMicrowave heatingMicrowaveCharacteristic impedance
The invention relates to a microwave waveguide element for matching a standard waveguide input port to an enlarged waveguide output port. In the waveguide element, a plurality of intermediate waveguide segments is cascaded in the propagation direction of the microwave energy to first split the waveguide element into two symmetrical waveguide branches and then combine the branches at the output port. Thus, the width of the waveguide element is gradually enlarged and the input port is matched to the output port. The intermediate waveguide segments are preferably dimensioned such that respective characteristic impedances are approximately matched with each other for the fundamental mode.
Owner:RAUTE OY
Multi-segment, nesting, low profile cable management arm
A foldable cable management apparatus for holding cables in a rack mounted system. The apparatus includes a plurality of segments pivotally attached to one another. One or more of the plurality of segments include cable trays for holding the cables and include cable fasteners. One or more of the plurality of segments is adapted to nest with other segments so that the combined depth of the apparatus is less than the sum of the depths of the individual segments. In a three segment embodiment, a first segment of the plurality of segments is pivotally attached to a first attachment plate, the first attachment plate securing the first segment to a rack and also pivotally attached to a second segment of the plurality of segments, which in turn is pivotally attached to a third segment of the plurality of segments, the third segment being pivotally attached to a rack mounted component, wherein the cable tray of the third segment substantially fits within the depth of the second segment and adjacent to the channel formed in the second segment when the third segment is folded into the second segment.
Owner:DELL PROD LP
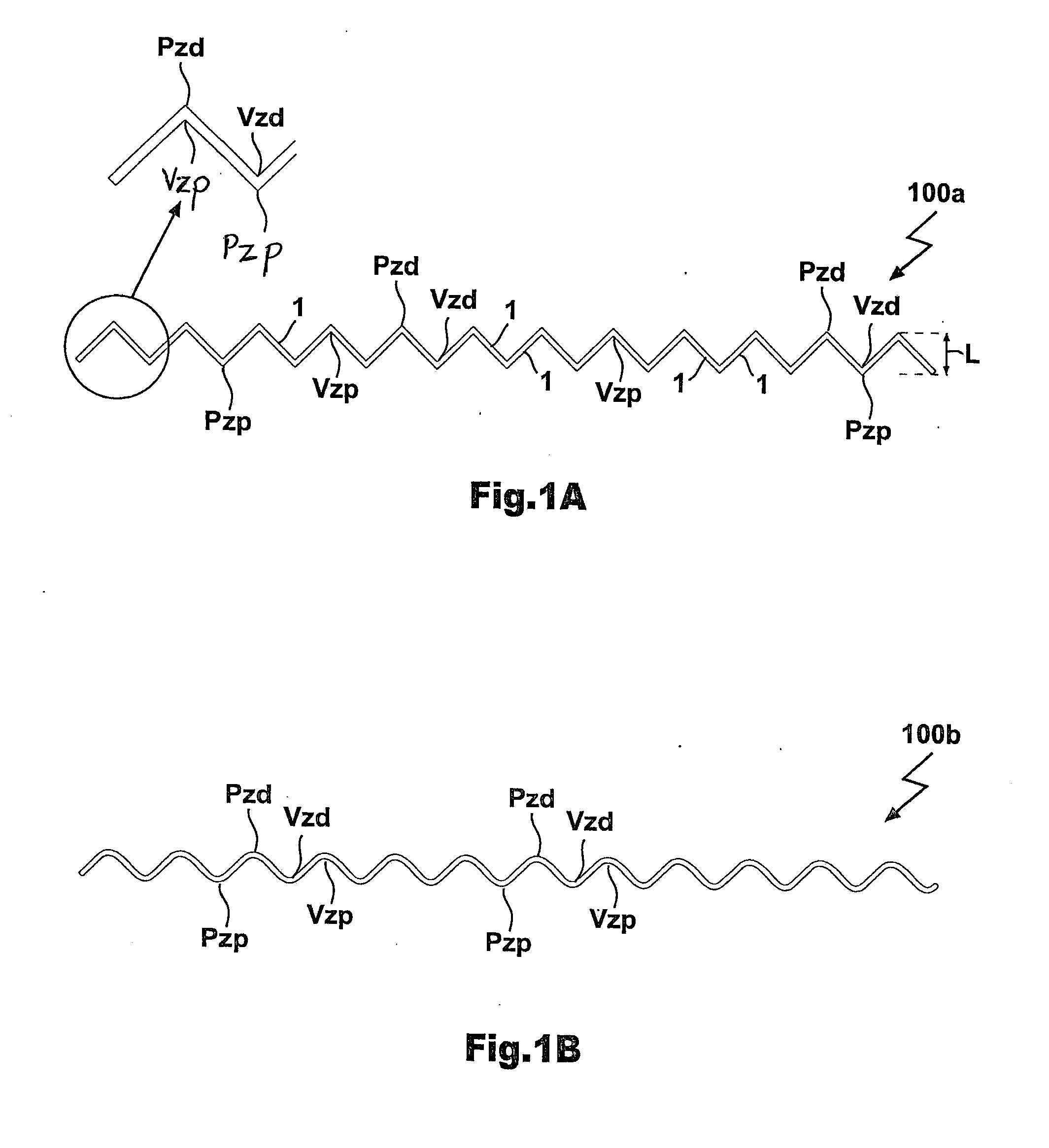
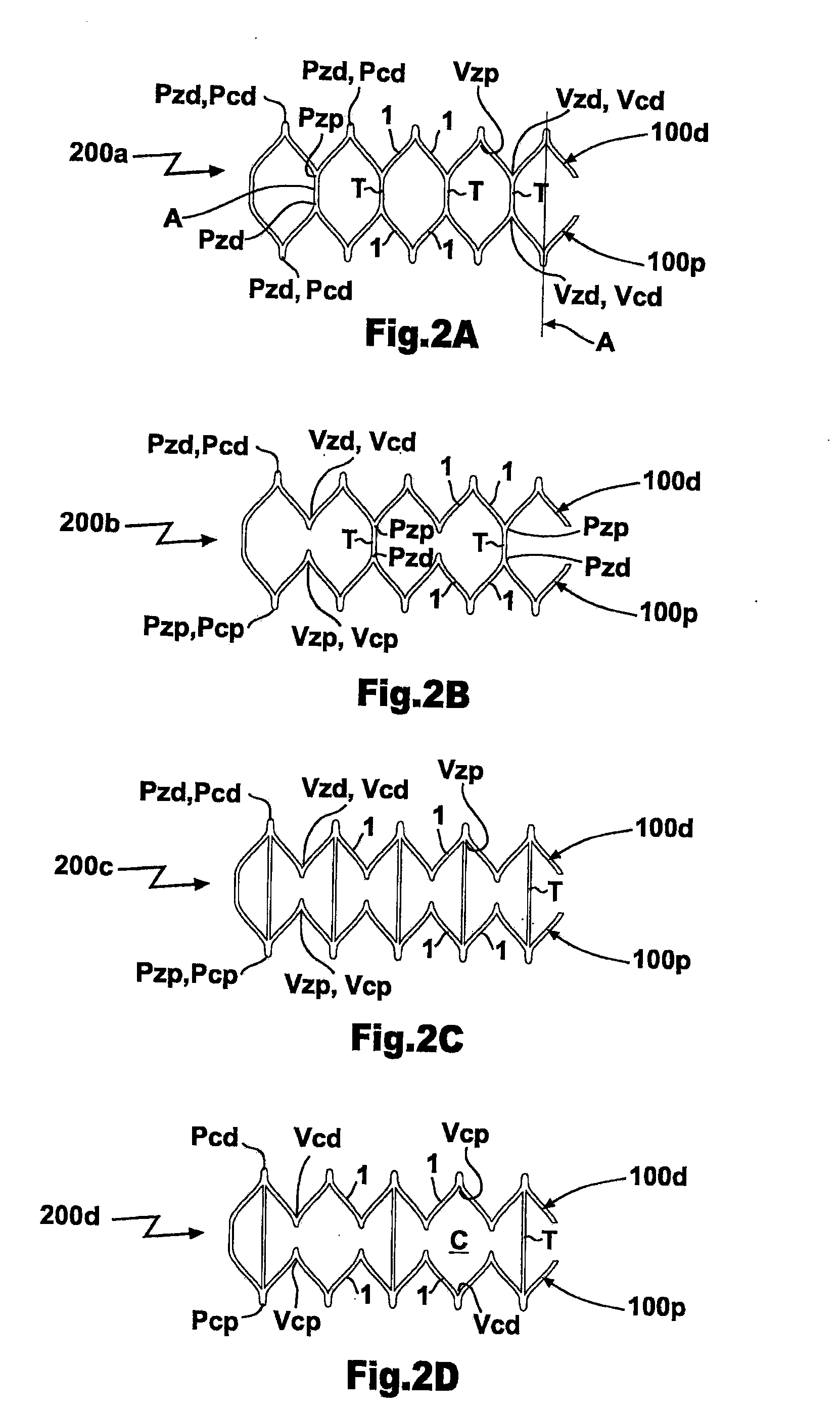
Multi-Segment Modular Stent And Methods For Manufacturing Stents
InactiveUS20100174358A1Increase flexibilityImprove the forceStentsBlood vesselsInterconnectorModularity
A modular stent comprises at least one stent module including an intermediate segment consisting of one of either a closed-cell segment or a Z-segment and a pair of end segments connected to respective longitudinal ends of said intermediate segment, each end segment consisting of the other of said closed-cell segment or Z-segment, each closed-cell segment consisting solely of at least one annular closed-cell ring and each Z-segment consisting solely of at least one annular Z-ring. A method of manufacturing a stent form a small diameter tube includes laser-cutting the small diameter tube to define a plurality of longitudinally adjacent Z-rings, providing interconnector portions of said tube integrally joining facing aligned or offset Z-rings, expanding the small diameter tube, and removing predetermined interconnector portions from the expanded tube to provide the predetermined desired arrangement of interconnected closed-cell rings and Z-rings.
Owner:RABKIN DMITRY J +2
Multi-segment single panel grip
ActiveUS6843732B1Same resistance to shockOvercome disadvantagesWallsSynthetic resin layered productsSingle plateEngineering
A grip for the handle of a golf club having multiple two layer panels that are wrapped about an underlisting sleeve. The edges of the panels are adhesively sealed together. The grip reduces impact and shock and provides a feeling of tackiness in the manner of a spirally wrapped polyurethane-felt grip while allowing the use of multiple color panels and easy instillation onto a golf club shaft.
Owner:WINN INC
Chemical vapor deposition reactor
InactiveUS20120111271A1Improve the deposition effectOptimize geometrySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLiquid transferring devicesGas phaseProcess engineering
A CVD reactor, such as a MOCVD reactor conducting metalorganic chemical vapor deposition of epitaxial layers, is provided. The CVD or MOCVD reactor generally comprises a flow flange assembly, adjustable proportional flow injector assembly, a chamber assembly, and a multi-segment center rotation shaft. The reactor provides a novel geometry to specific components that function to reduce the gas usage while also improving the performance of the deposition.
Owner:VALENCE PROCESS EQUIP
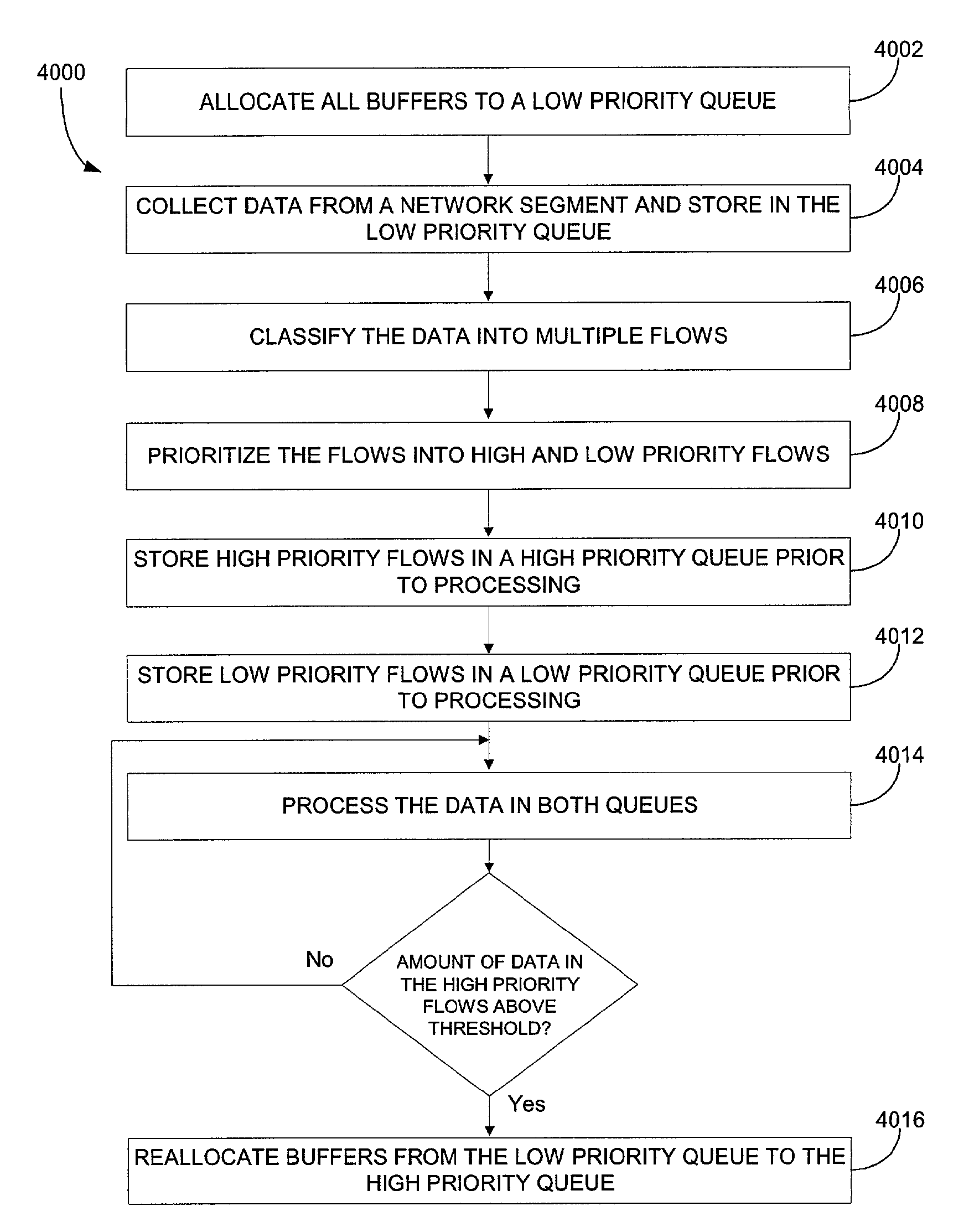
Multi-Segment Network Application Monitoring and Correlation Architecture
InactiveUS20100091676A1Improve performanceError preventionTransmission systemsApplication serverAnalysis data
A system, method and computer program product are provided for network and network application monitoring. Accordingly, one or more media modules are each coupled to an associated network segment. In the case of network application monitoring, each media module is coupled to a network segment on which a network application is running. Each media module monitors and collects data relating to traffic on the associated network segment corresponding to the network application, wherein each media module is tailored for network analysis. An application server module is coupled to the at least one media module and receives the data and analyzes the data for helping to improve the performance of the network and / or network application.
Owner:NETWORK GENERAL TECH
Thin illumination system
ActiveUS20100315833A1Without compromise in sharpnessModerate brightnessPlanar light sourcesMechanical apparatusLight beamEffect light
The present invention introduces a new class of thin doubly collimating light distributing engines for use in a variety of general lighting applications, especially those benefiting from thinness. Output illumination from these slim-profile illumination systems whether square, rectangular or circular in physical aperture shape is directional, square, rectangular or circular in beam cross-section, and spatially uniform and sharply cutoff outside the system's adjustable far-field angular cone. Field coverage extends from + / −5- to + / −60-degrees and more in each meridian, including all asymmetric combinations in between, both by internal design, by addition of angle spreading film sheets, and angular tilts. Engine brightness is held to safe levels by expanding the size of the engine's output-aperture without sacrifice in the directionality of illumination. One form of the present invention has a single input light emitter, a square output aperture and the capacity to supply hundreds of lumens per engine. A second multi-segment form of the invention deploys one light emitter in each engine segment, so that total output lumens is determined by the number of segments. Both types of thin light distributing engines provide input light collimated in one meridian and a light distributing element that maintains input collimation while collimating output light in the un-collimated orthogonal meridian, in such a manner that the system's far-field output light is collimated in both its orthogonal output meridians. The present invention also includes especially structured optical films that process the engine's doubly collimated output illumination so as to increase its angular extent one or both output meridians without changing beam shape or uniformity.
Owner:SNAPTRACK +1
Multi-segment optical retarder for creating 3D images
A multi-segment optical retarder that can be used with or within a single projector for creating 3D images. The multi-segment optical retarder is coupled to an actuator used to effect some predetermined linear, rotary, or oscillating movement of the multi-segment optical retarder such that a fast axis orientation of each segment is substantially constant relative to itself over time and for a given area of incidence.
Owner:VIAVI SOLUTIONS INC
Control of electroluminescent displays
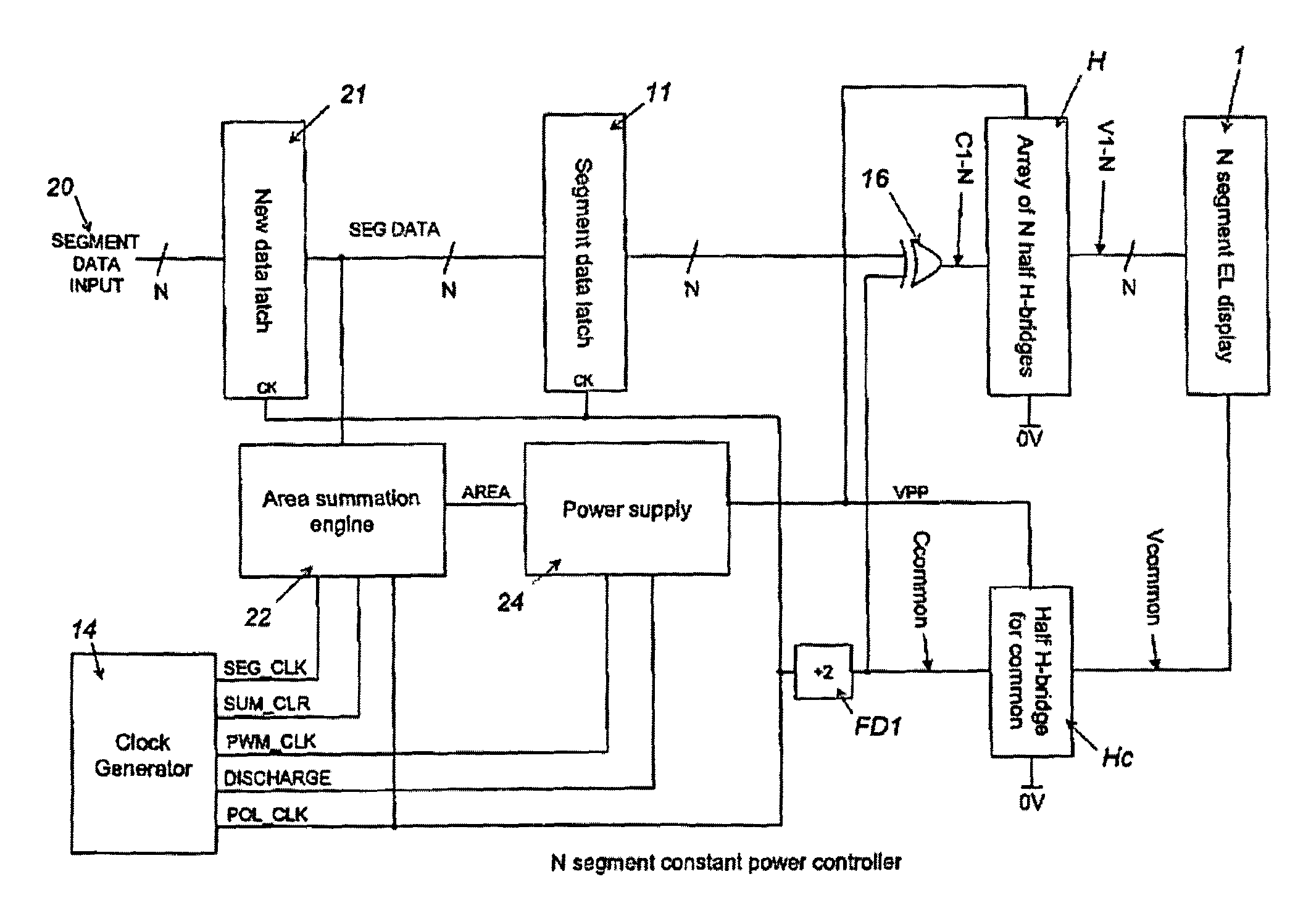
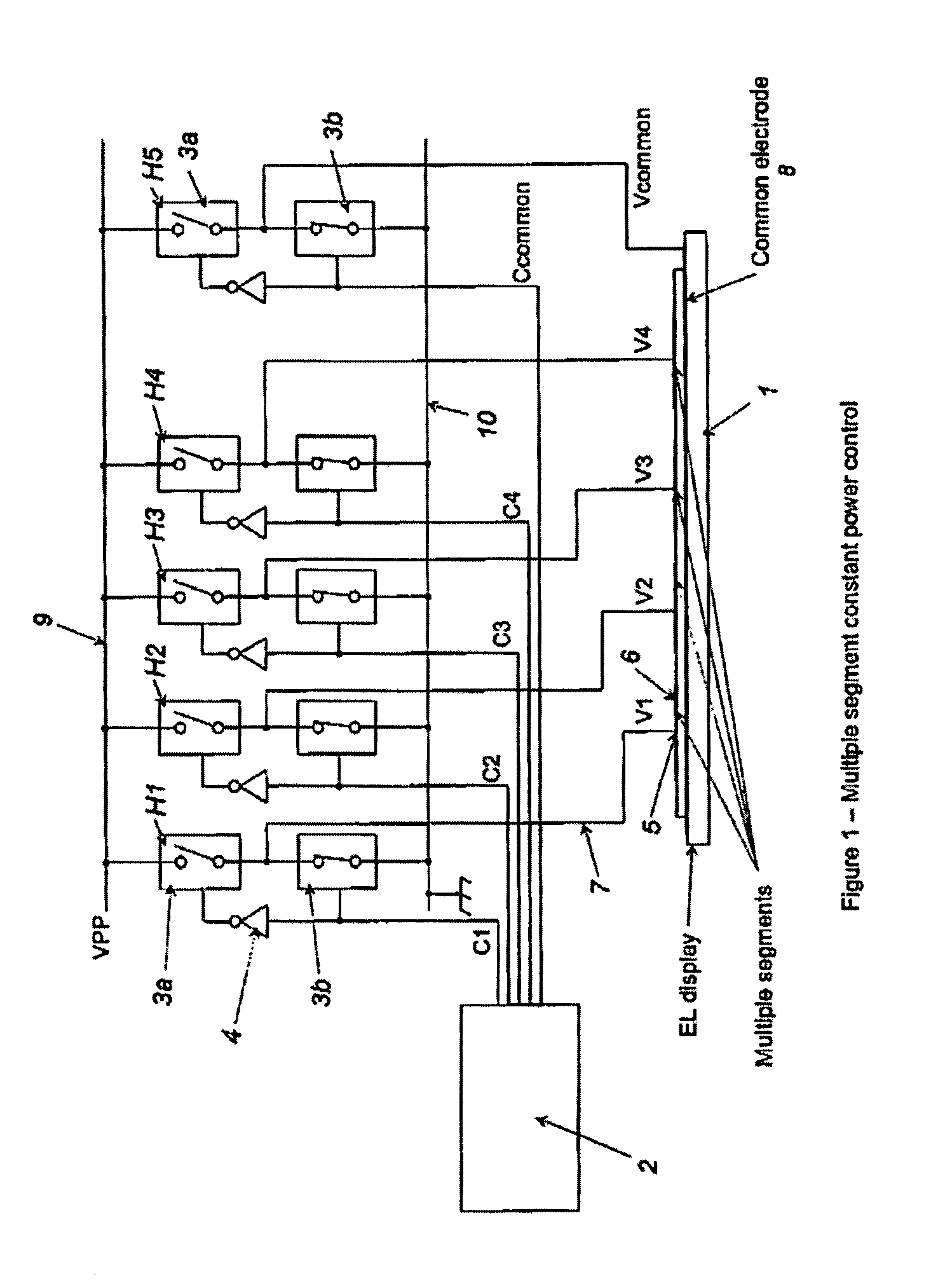
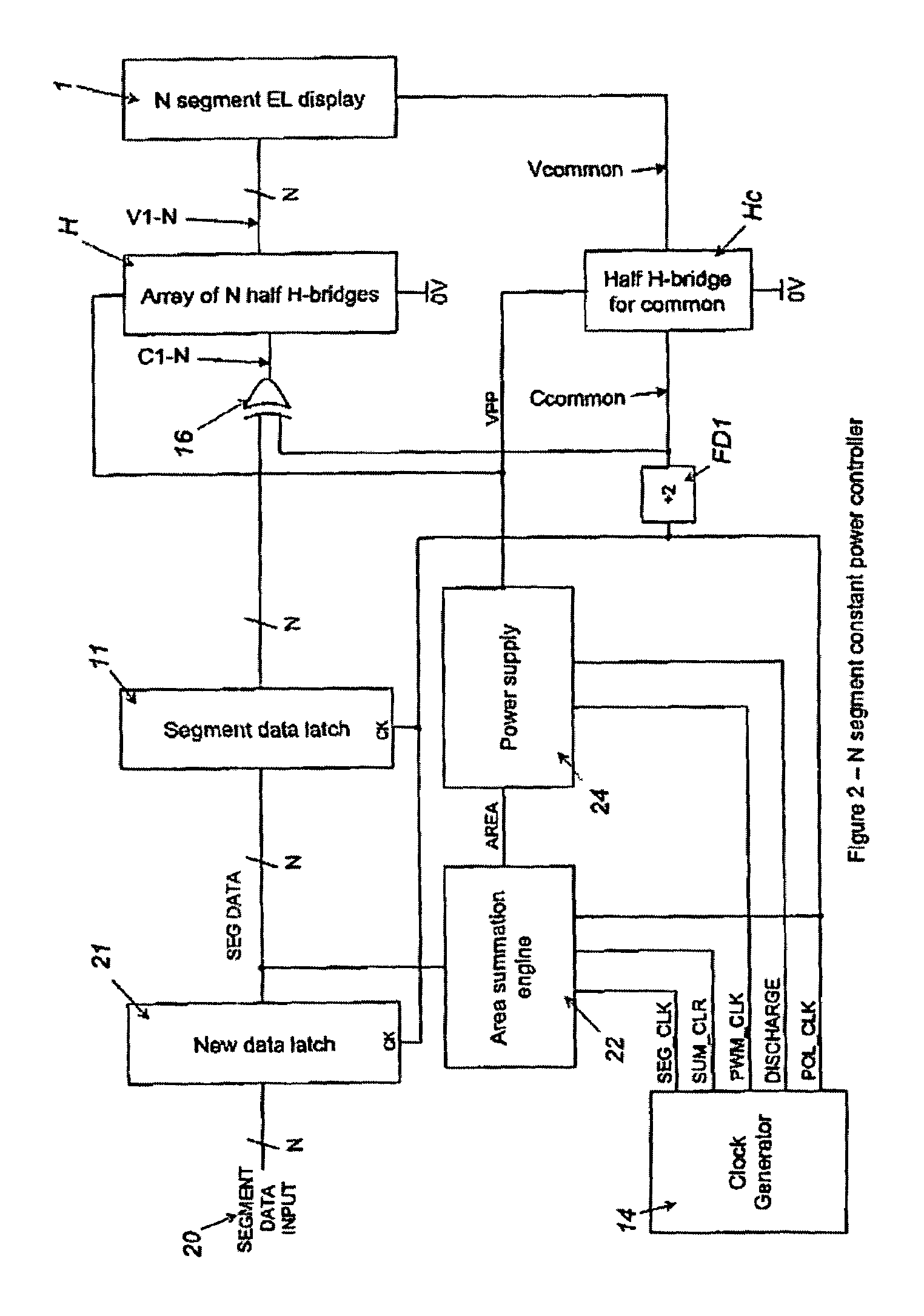
InactiveUS7119493B2Remove loadSmall voltage dropElectrical apparatusElectroluminescent light sourcesElectricityControl signal
A controller for use with a multi-segment electroluminescent display 1. Control signals C1–CN control a plurality of half H-bridges H and Hc, the terminals of the half H-bridges being connected respectively to ground and to a high voltage DC supply 9. One of said half H-bridges provides a common output Vcommon and the remaining H-bridges provide drive voltages V1–VN for the segments of the display. The H bridges are driven by an oscillator 14 so that an AC voltage is selectively applied to the segments of the display. A power supply 24 provides a predetermined amount of power per unit area of the display. This is controlled by an area summation engine 22 having a segment data input, a segment counter and a memory containing area data corresponding to the segment(s) of the display. Based on the input from the segment data input, the area(s) of the segment(s) that are to be lit are obtained from the memory and summed to provide the total area to be lit. This is fed to the power supply 24, which then feeds the correct amount of power to display 1 via the half H-bridges.
Owner:PELIKON
Multi-Segment Lateral Cage Adapted to Flex Substantially in the Coronal Plane
The present invention concerns several fusion devices and methods for laterally inserting a fusion device at an initial trajectory that is not parallel to the disc space. Each fusion device incorporates components that enable flexing, bending or pivoting of the device during its final approach to the prepared disc space.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
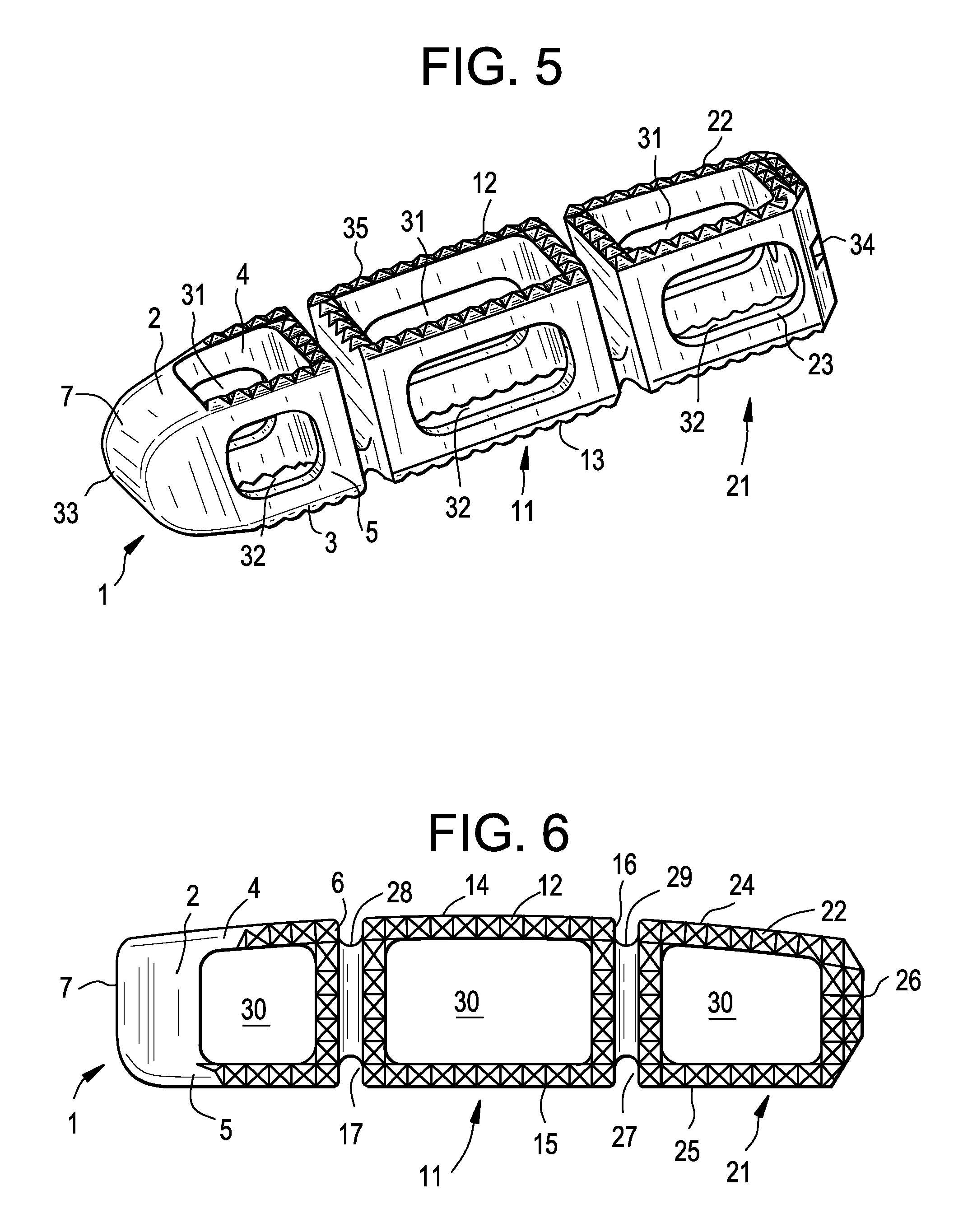
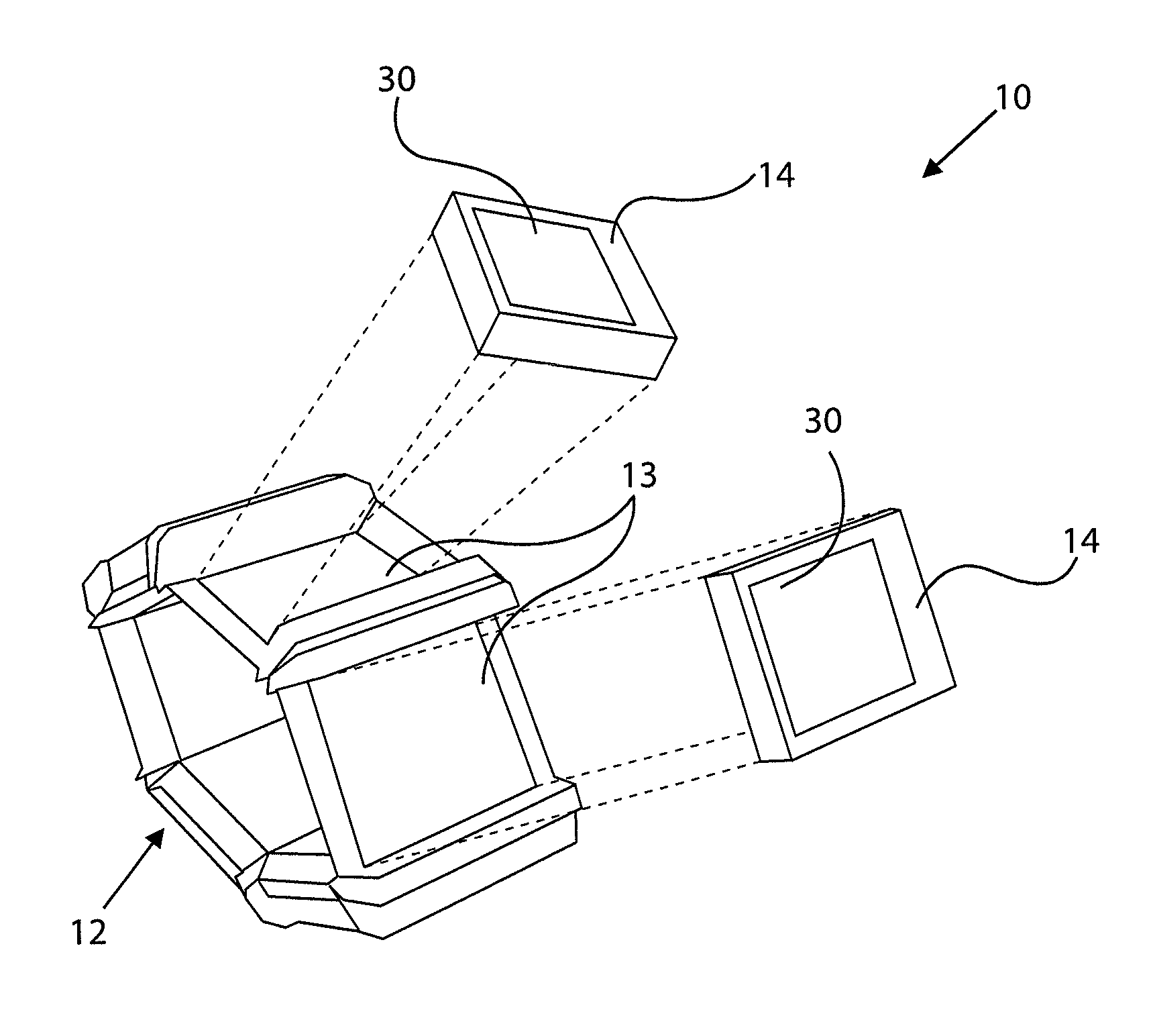
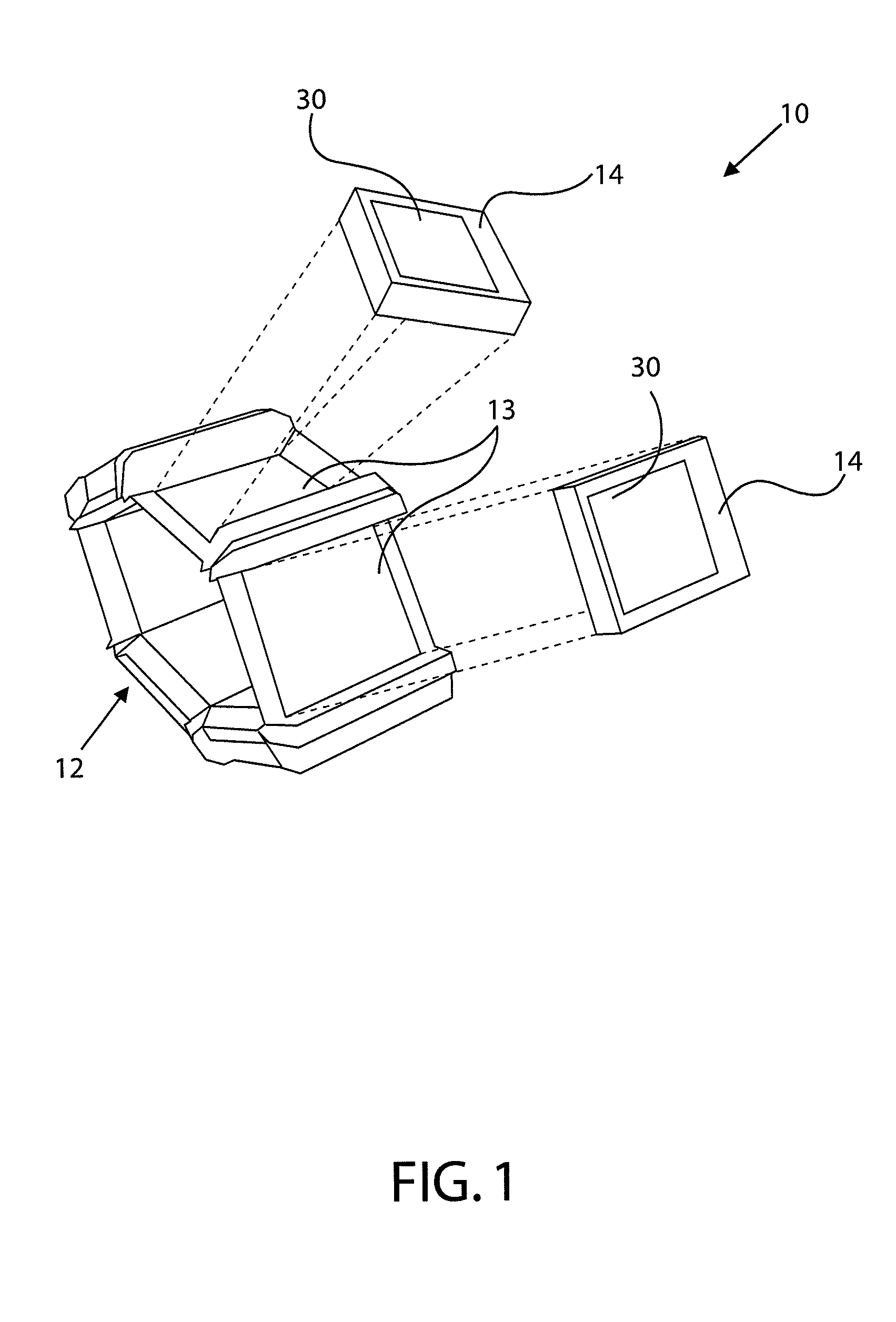
Multi-segment wearable accessory
ActiveUS8872729B2Reduce in quantityConducive to diversificationElectronic time-piece structural detailsDevices with multiple display unitsMulti segmentComputer science
A method, apparatus and computer program product are provided to facilitate the use of a multi-segment wearable accessory. In this regard, methods, apparatus and computer program products are provided for controlling and, in some instances, interacting with a multi-segment wearable accessory. In the context of a method, an orientation of each of a plurality of segments of a multi-segment wearable accessory is determined relative to an axis through the multi-segment wearable accessory, such as by determining an angle of each of the plurality of segments relative to the axis through the multi-segment wearable accessory. A relative ordering of the plurality of segments of the multi-segment wearable accessory may then be determined based upon the orientation of each of the plurality of segments relative to the axis.
Owner:NOKIA TECH OY
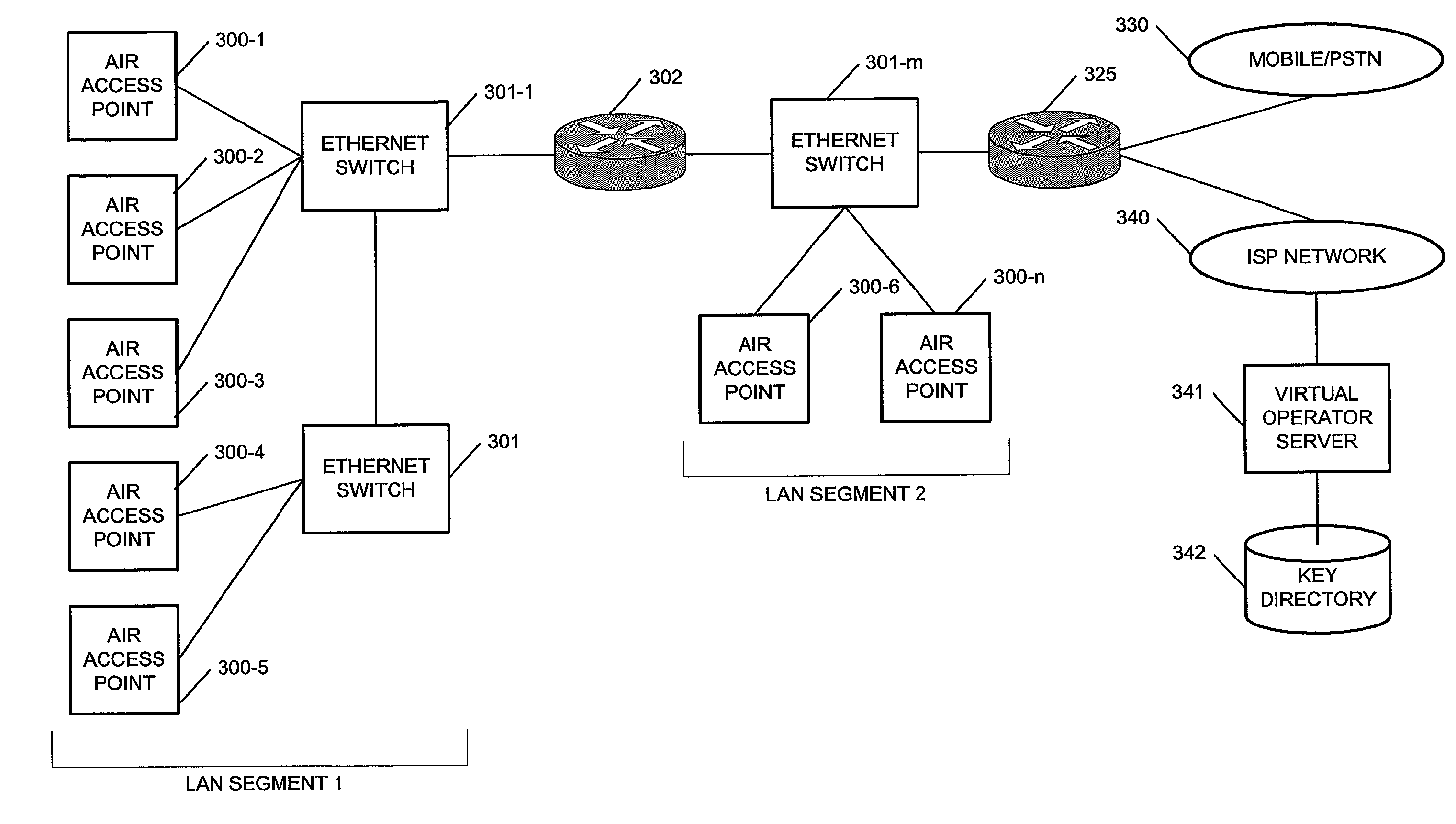
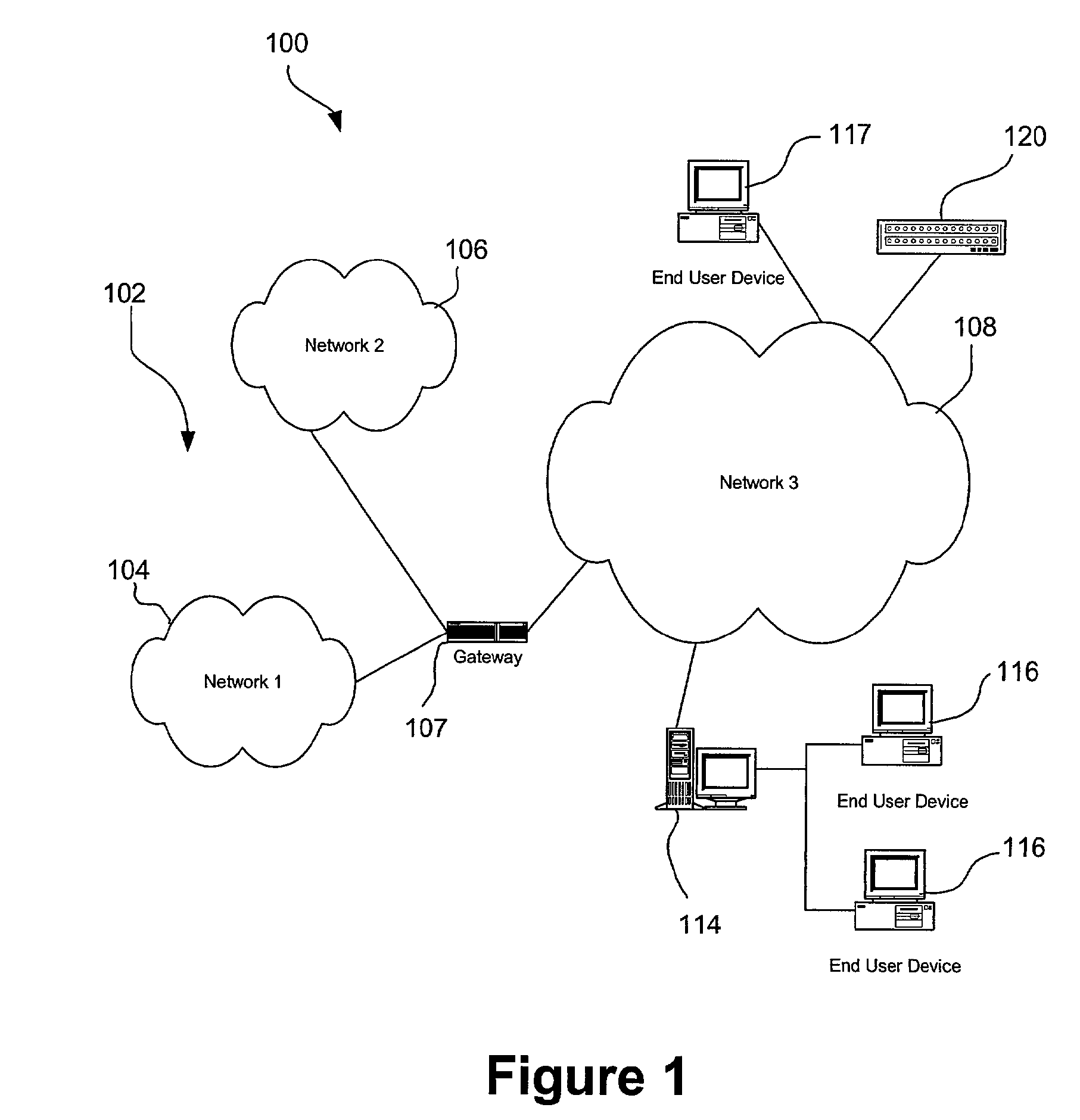
Apparatus for public access mobility LAN and method of operation thereof
ActiveUS7483411B2Key distribution for secure communicationAccounting/billing servicesAir interfaceThe Internet
Public wireless communications will increasingly extend into wireless LAN (WLAN) environments in order to meet the ubiquitous access, high data rate, and local services demands of future Internet appliances. By relying on IP-level services mechanisms, the Public Access Mobility LAN (PAMLAN) can simultaneously support different air interfaces, franchises for multiple services providers, and a multi-segment LAN environment including handoffs. The PAMLAN supports virtual operator LANs representing different network services providers, authorization and accounting mechanism, support of multiple air interfaces, and local IP mobility. A router associated with each base station realizes this highly distributed IP networking environment, and a QoS-enabled switched Ethernet core supports virtual networks and QoS services.
Owner:NEC CORP
Activity and workout updates
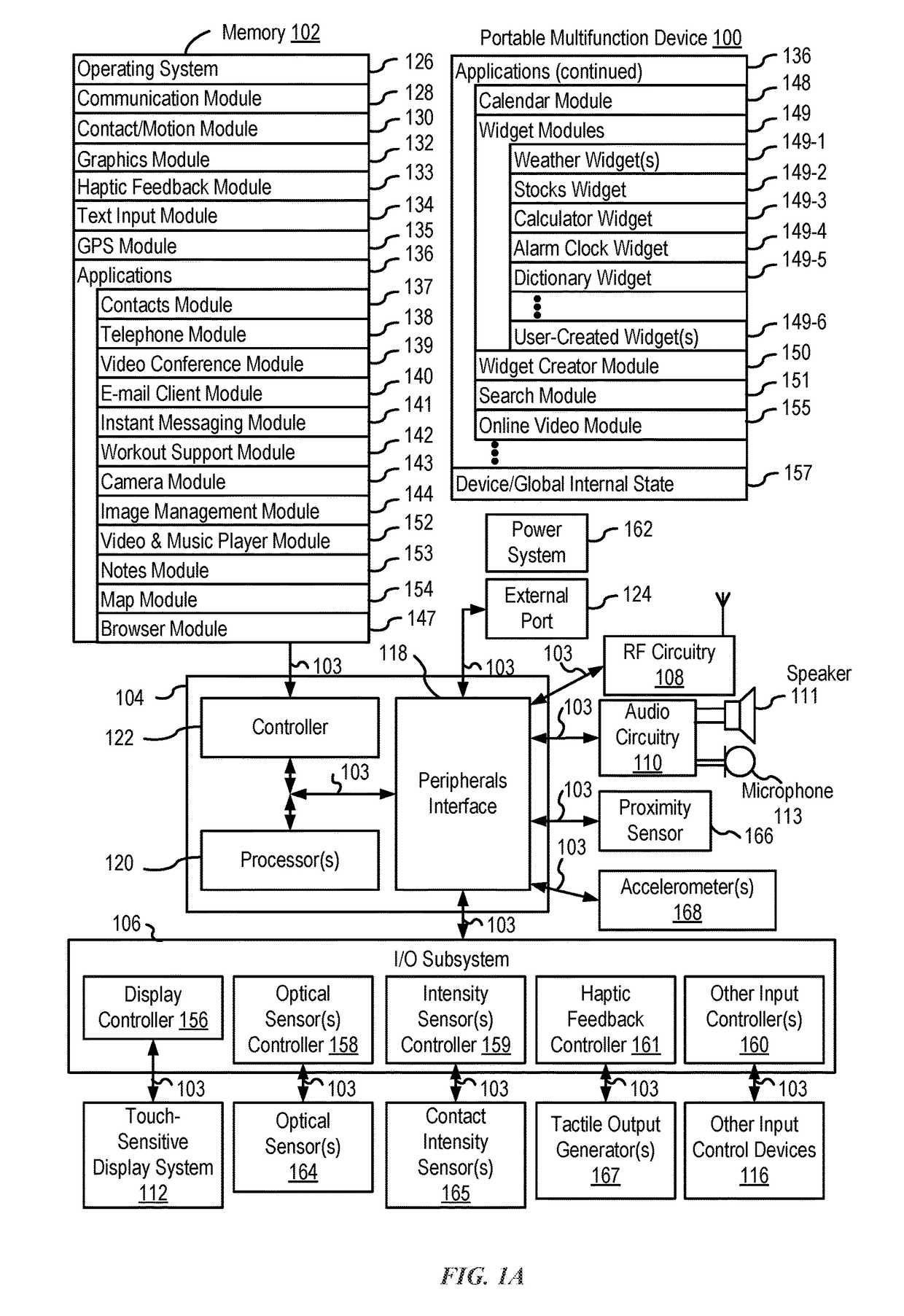
ActiveUS20170354845A1Faster and efficient methodFaster and efficient and interfacePhysical therapies and activitiesHealth-index calculationMulti segmentHuman–computer interaction
The present disclosure generally relates to navigating, viewing, and sharing activity and workout data and interacting with workout and / or activity applications. In some examples, scrolling of activity data is based on the content being displayed. In some examples, friends' activity data may be viewed. In some examples, a notification and workout data for a friend's completed workout is received and displayed. In some example, the activity data received from friends is viewed and managed. In some examples, workout data for a multi-segment workout is displayed in a three-dimensional stack on a map. In some examples, a workout application operates in a limited mode until a touch input is received with a characteristic intensity that is greater than a threshold intensity.
Owner:APPLE INC
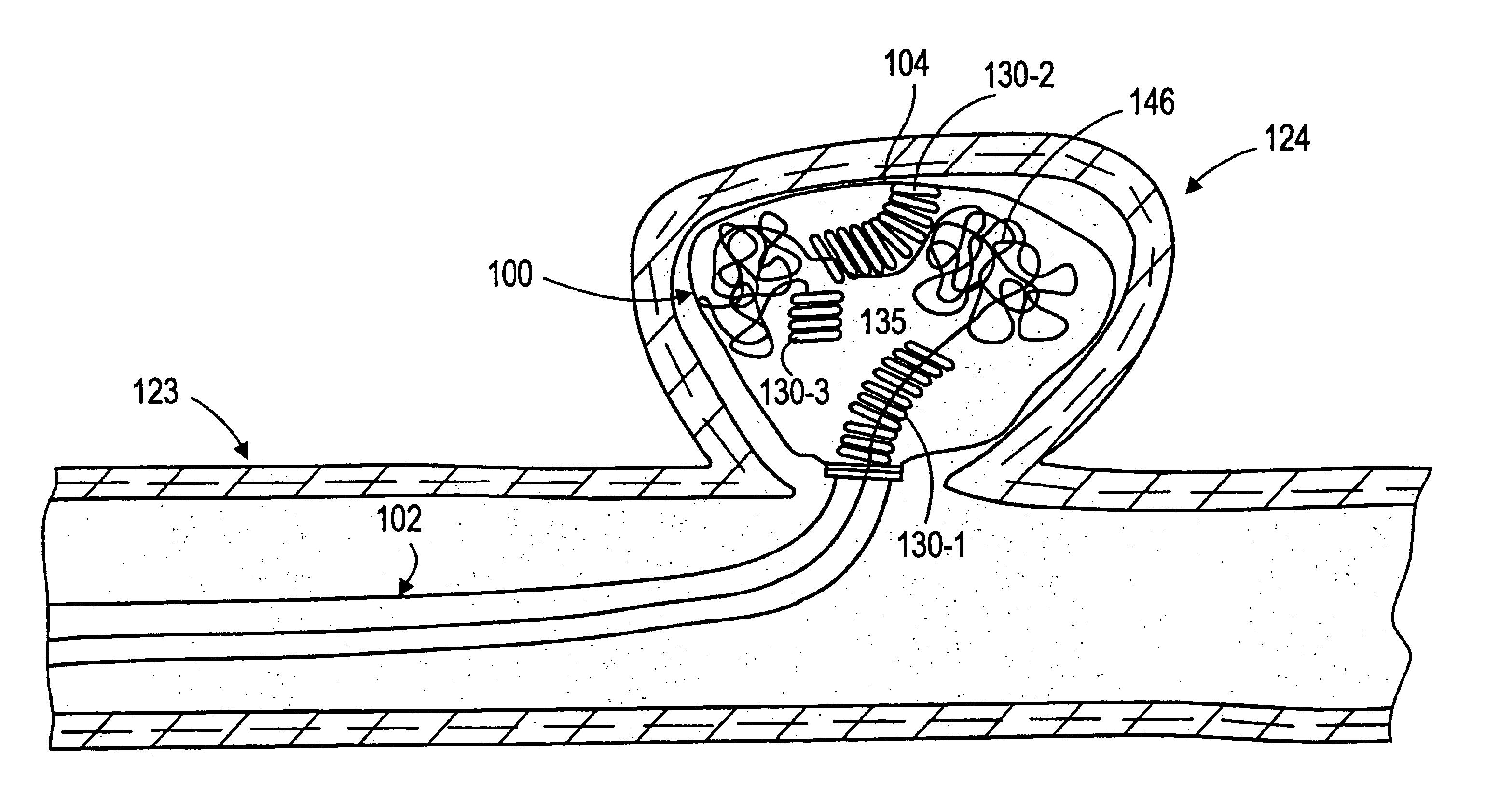
Aneurysm liner with multi-segment extender
A device for treating an aneurysm including an aneurysm liner expandable to form an inner cavity and a plurality of extender segments supported in the aneurysm liner. The device includes an axial constraint coupled to the plurality of extender segments in the liner to axially constrain extender segments in end to end alignment to bias the liner in a collapsed profile.
Owner:STRYKER EURO OPERATIONS HLDG LLC +1
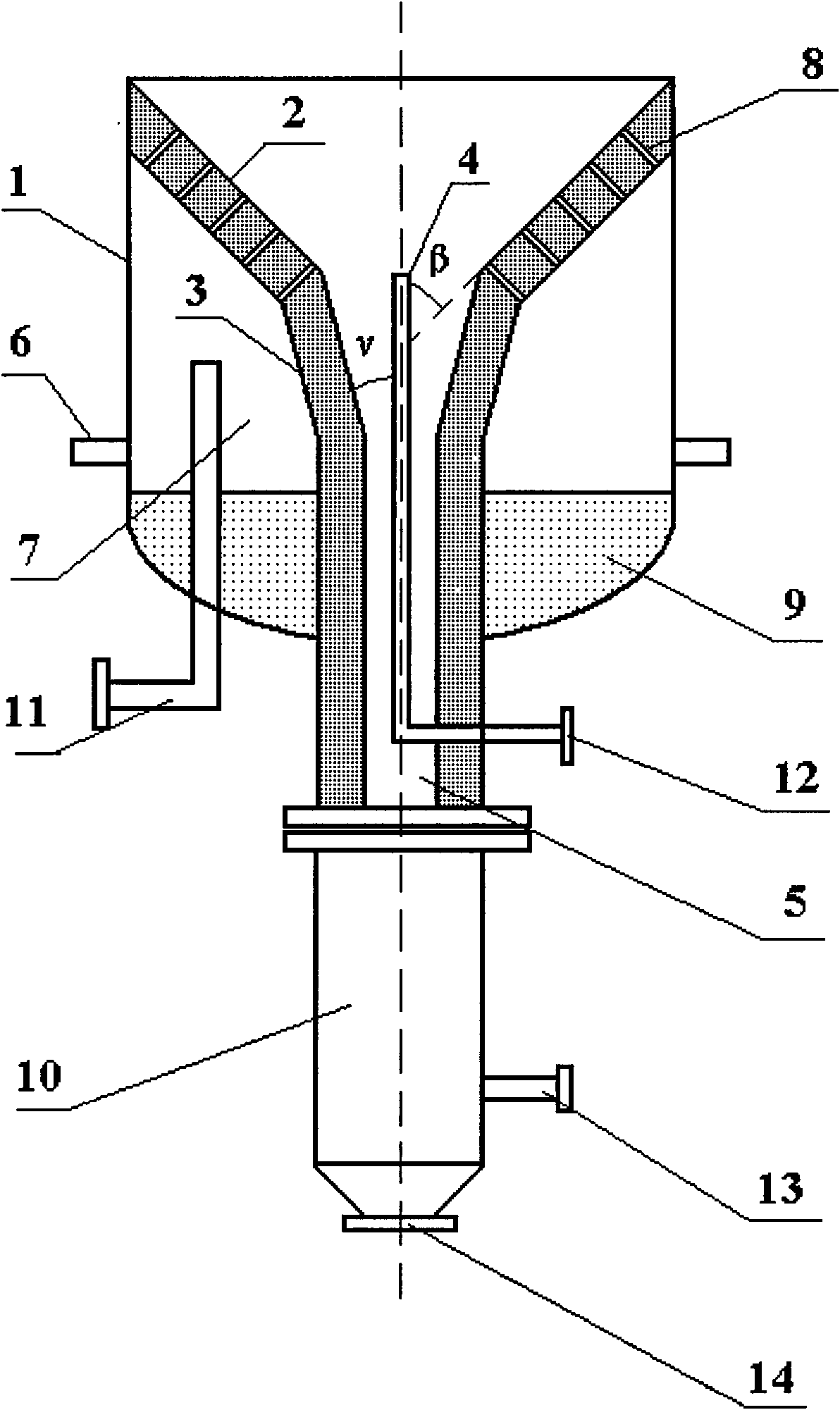
Method and device for gasifying multi-segment staged converted fluidized bed
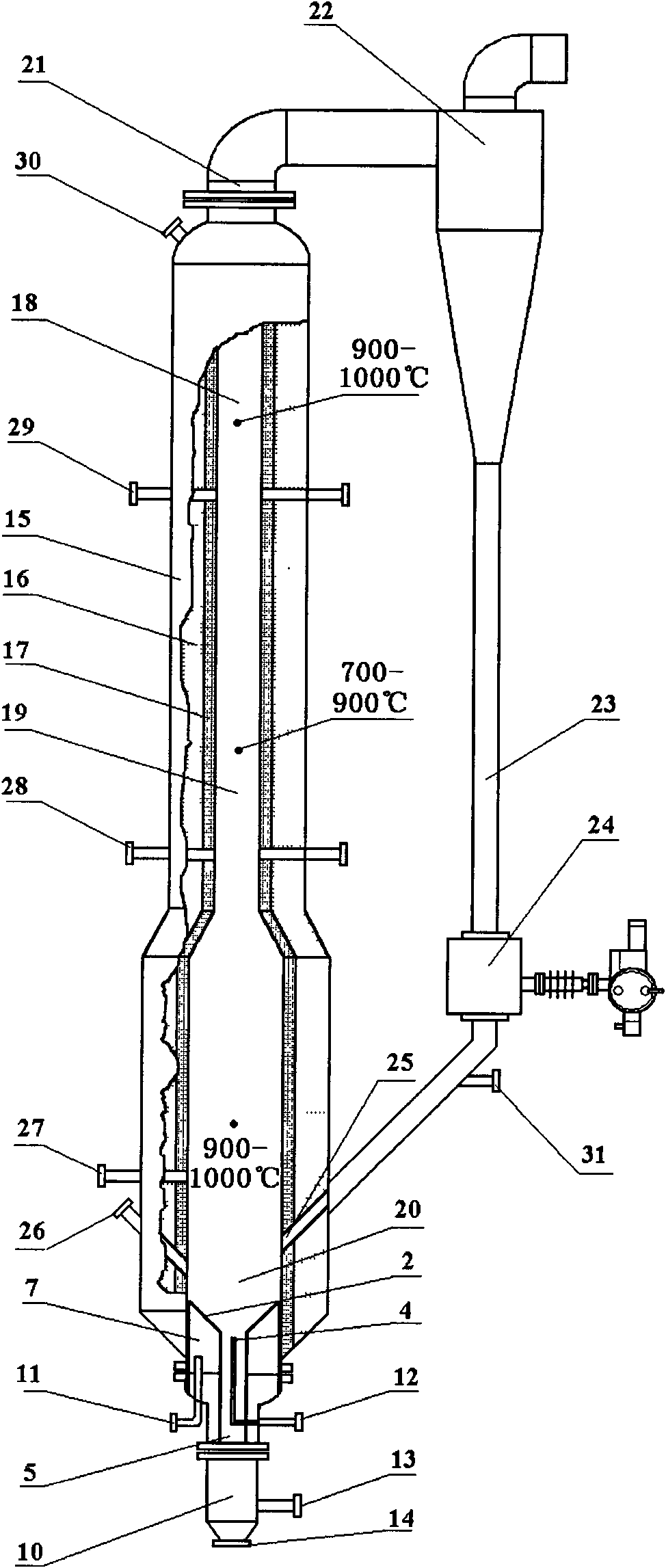
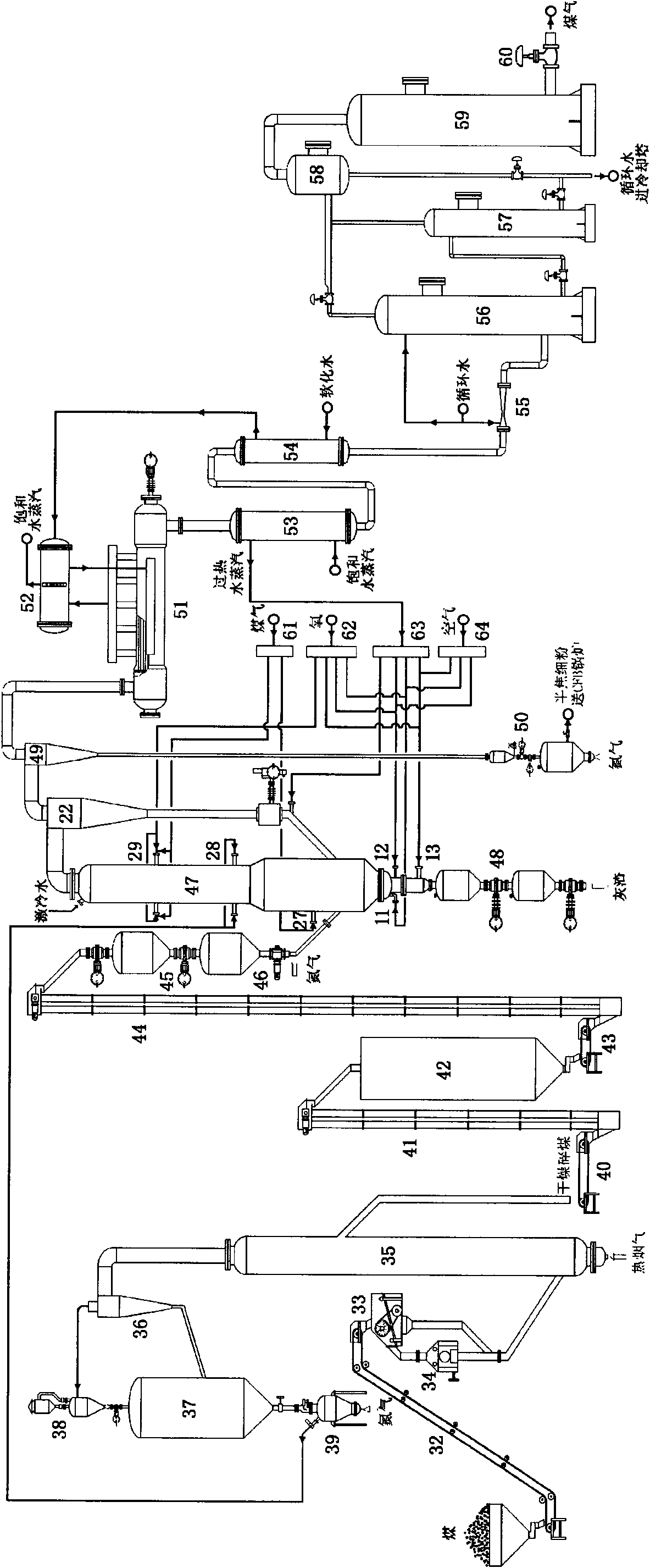
ActiveCN101942344ALow ash carbon contentExtended stayEnergy inputCombined combustion mitigationFluidized bedProcess engineering
The invention relates to method and device for gasifying a multi-segment staged converted fluidized bed. The method comprises the following steps of: supplying coal; supplying gas; gasifying; slagging; and conveying fine powder. The device for gasifying the multi-grade staged converted fluidized bed comprises an agglomerating ash separating unit, a pyrolyzing and gasifying reactor of the multi-segment staged fluidized bed and a semicoke fine powder cyclic feeding unit. The invention has the advantages of high volume utilization rate of a gasifying oven, great handling capacity and high utilization rate of total carbon, is suitable for a coal staging and converting system and can be singly used for producing gas for mass coal-based methane synthesis and coal chemical industry.
Owner:SHANXI INST OF COAL CHEM CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Multi-segment network application monitoring and correlation architecture
InactiveUS8185651B2Improve performanceMultiple digital computer combinationsData switching networksTraffic capacityAnalysis data
Owner:NETWORK GENERAL TECH
Thin illumination system
The present invention introduces a new class of thin doubly collimating light distributing engines for use in a variety of general lighting applications, especially those benefiting from thinness. Output illumination from these slim-profile illumination systems whether square, rectangular or circular in physical aperture shape is directional, square, rectangular or circular in beam cross-section, and spatially uniform and sharply cutoff outside the system's adjustable far-field angular cone. Field coverage extends from + / −5- to + / −60-degrees and more in each meridian, including all asymmetric combinations in between, both by internal design, by addition of angle spreading film sheets, and angular tilts. Engine brightness is held to safe levels by expanding the size of the engine's output-aperture without sacrifice in the directionality of illumination. One form of the present invention has a single input light emitter, a square output aperture and the capacity to supply hundreds of lumens per engine. A second multi-segment form of the invention deploys one light emitter in each engine segment, so that total output lumens is determined by the number of segments. Both types of thin light distributing engines provide input light collimated in one meridian and a light distributing element that maintains input collimation while collimating output light in the un-collimated orthogonal meridian, in such a manner that the system's far-field output light is collimated in both its orthogonal output meridians. The present invention also includes especially structured optical films that process the engine's doubly collimated output illumination so as to increase its angular extent one or both output meridians without changing beam shape or uniformity.
Owner:SNAPTRACK +1
Multi-segment wearable accessory
InactiveUS20130271350A1Reduce in quantityConducive to diversificationElectronic time-piece structural detailsDevices with multiple display unitsMulti segmentHuman–computer interaction
A method, apparatus and computer program product are provided to facilitate the use of a multi-segment wearable accessory. In this regard, methods, apparatus and computer program products are provided for controlling and, in some instances, interacting with a multi-segment wearable accessory. In particular, a method, apparatus, and computer program product are provided that determine an orientation of a plurality of segments of a multi-segment wearable accessory, identify one of the segments to be associated with a peripheral device at least partially based upon the orientations determined, and provide for an association of the segment identified with the peripheral device. In this way, a particular segment may be selected to present content relating to the peripheral device or vice versa, for example, based on the orientation of the segment with respect to the peripheral device and / or the other segments.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
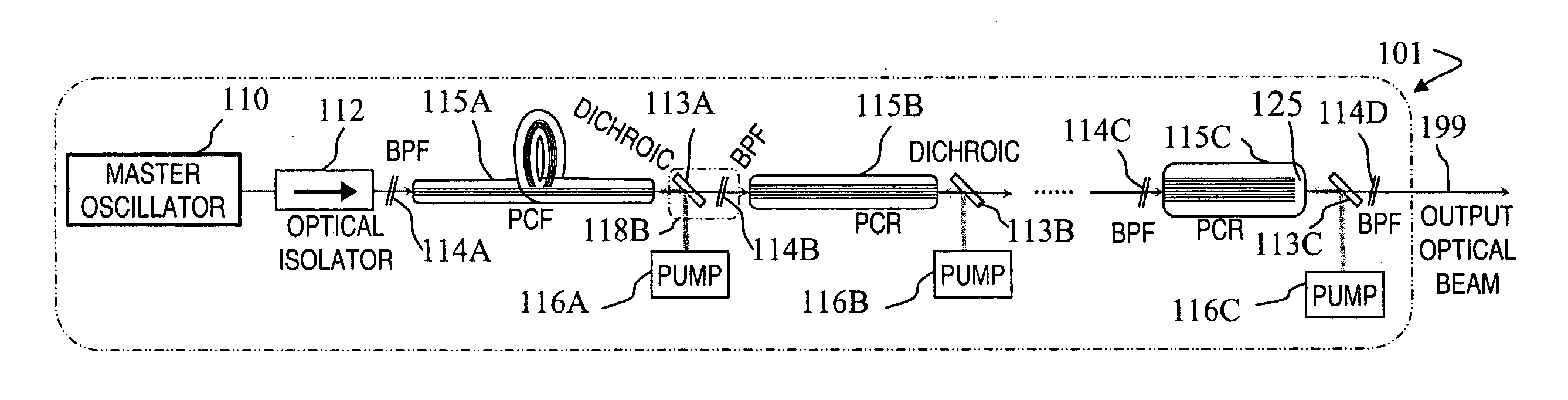
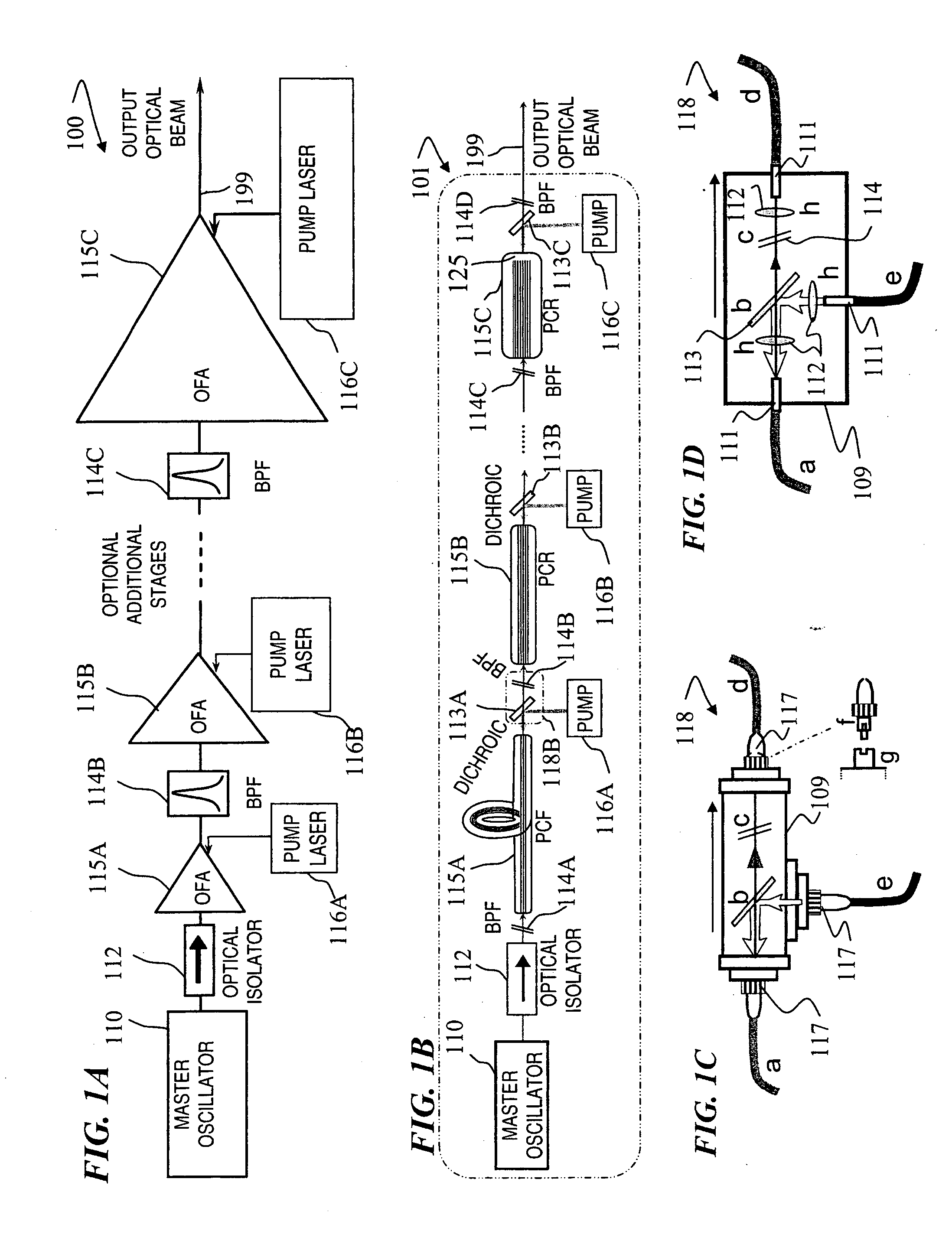
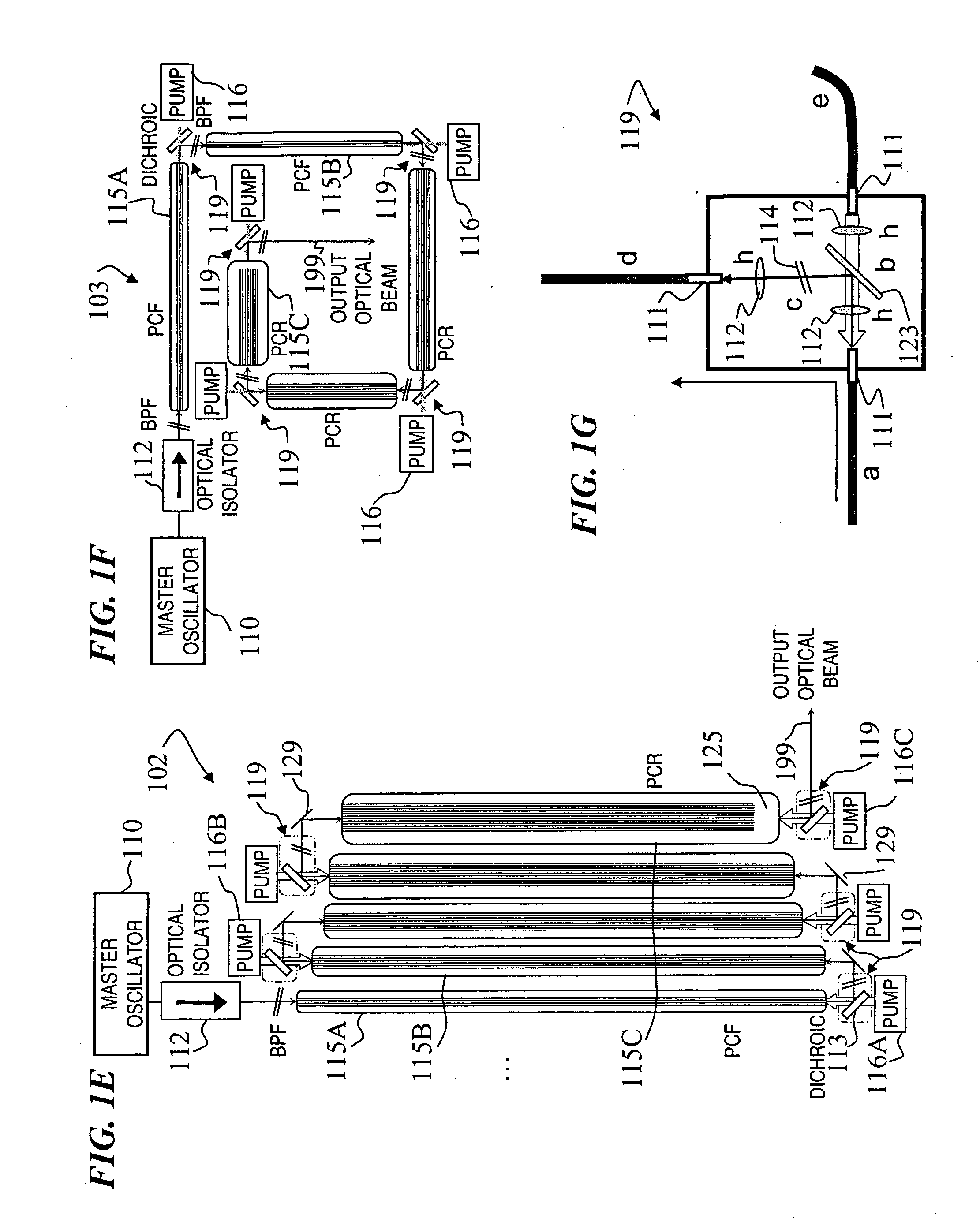
Multi-segment photonic-crystal-rod waveguides for amplification of high-power pulsed optical radiation and associated method
InactiveUS20070104431A1High peak powerHigh pulse energyLaser detailsCladded optical fibreOptical radiationPromiscuous behaviour
A method and apparatus use a photonic-crystal fiber having a very large core while maintaining a single transverse mode. In some fiber lasers and amplifiers having large cores problems exist related to energy being generated at multiple-modes (i.e., polygamy), and of mode hopping (i.e., promiscuity) due to limited control of energy levels and fluctuations. The problems of multiple-modes and mode hopping result from the use of large-diameter waveguides, and are addressed by the invention. This is especially true in lasers using large amounts of energy (i.e., lasers in the one-megawatt or more range). By using multiple small waveguides in parallel, large amounts of energy can be passed through a laser, but with better control such that the aforementioned problems can be reduced. An additional advantage is that the polarization of the light can be maintained better than by using a single fiber core.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
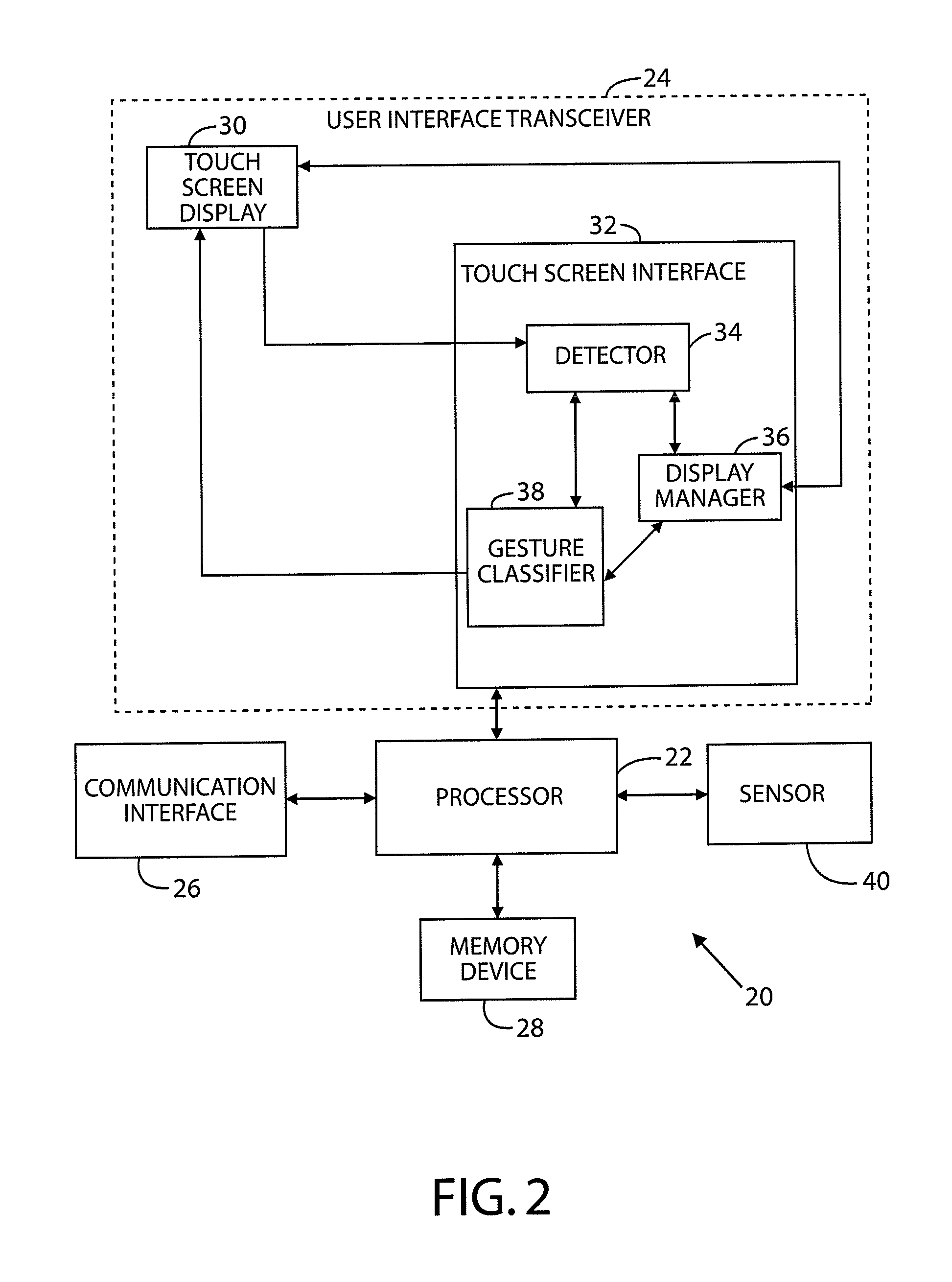
Method for detecting gestures using a multi-segment photodiode and one or fewer illumination sources
ActiveUS20120280904A1Input/output for user-computer interactionCathode-ray tube indicatorsAnalog signalMulti segment
A gesture sensing device includes a multiple segmented photo sensor and a control circuit for processing sensed voltages output from the sensor. The control circuit processes the sensed voltage signals to determine target motion relative to the segmented photo sensor. The control circuit includes an algorithm configured to calculate one of more differential analog signals using the sensed voltage signals output from the segmented photo sensors. A vector is determined according to the calculated differential analog signals, the vector is used to determine a direction and / or velocity of the target motion.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Cutting insert for high feed face milling
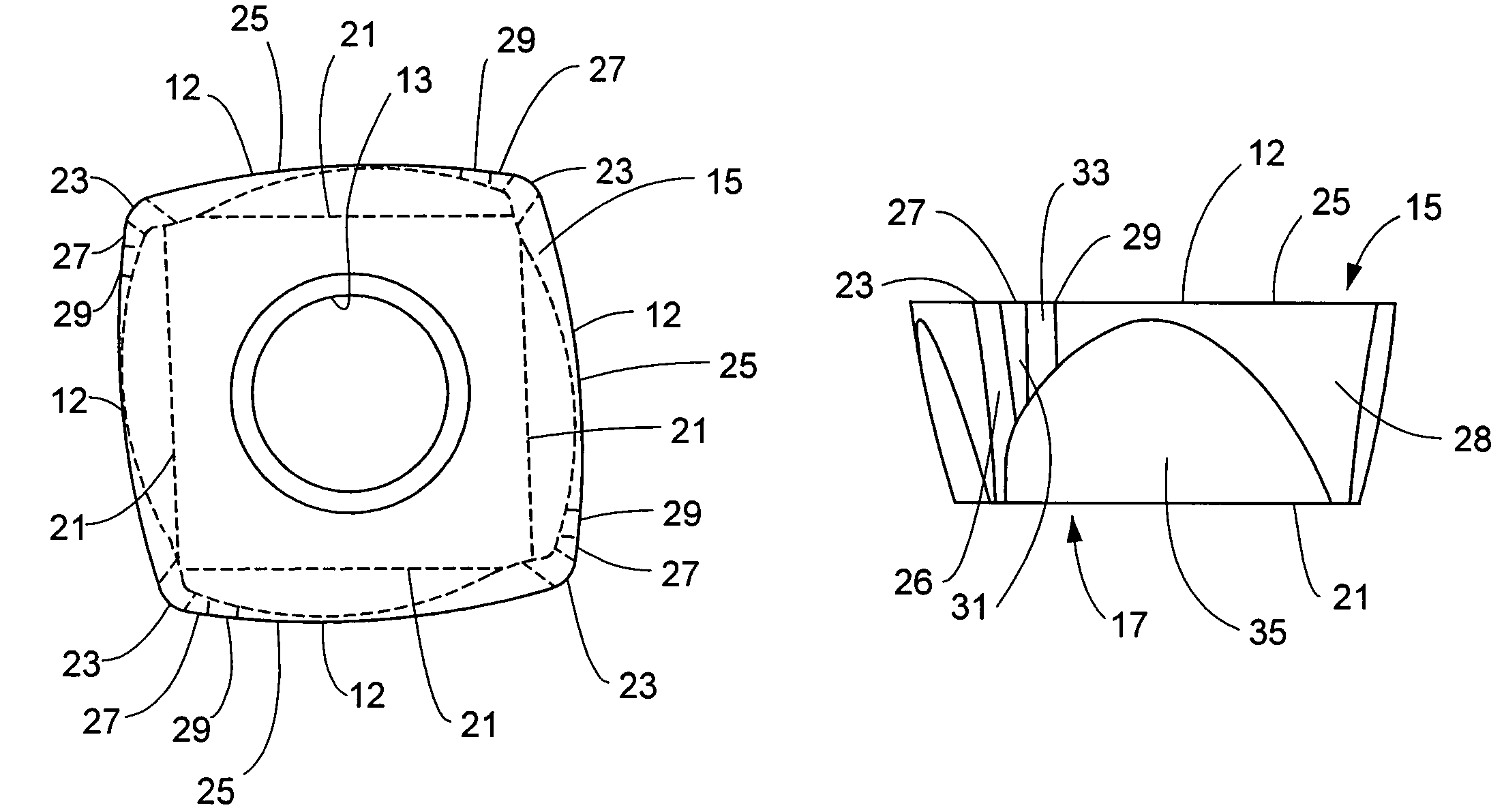
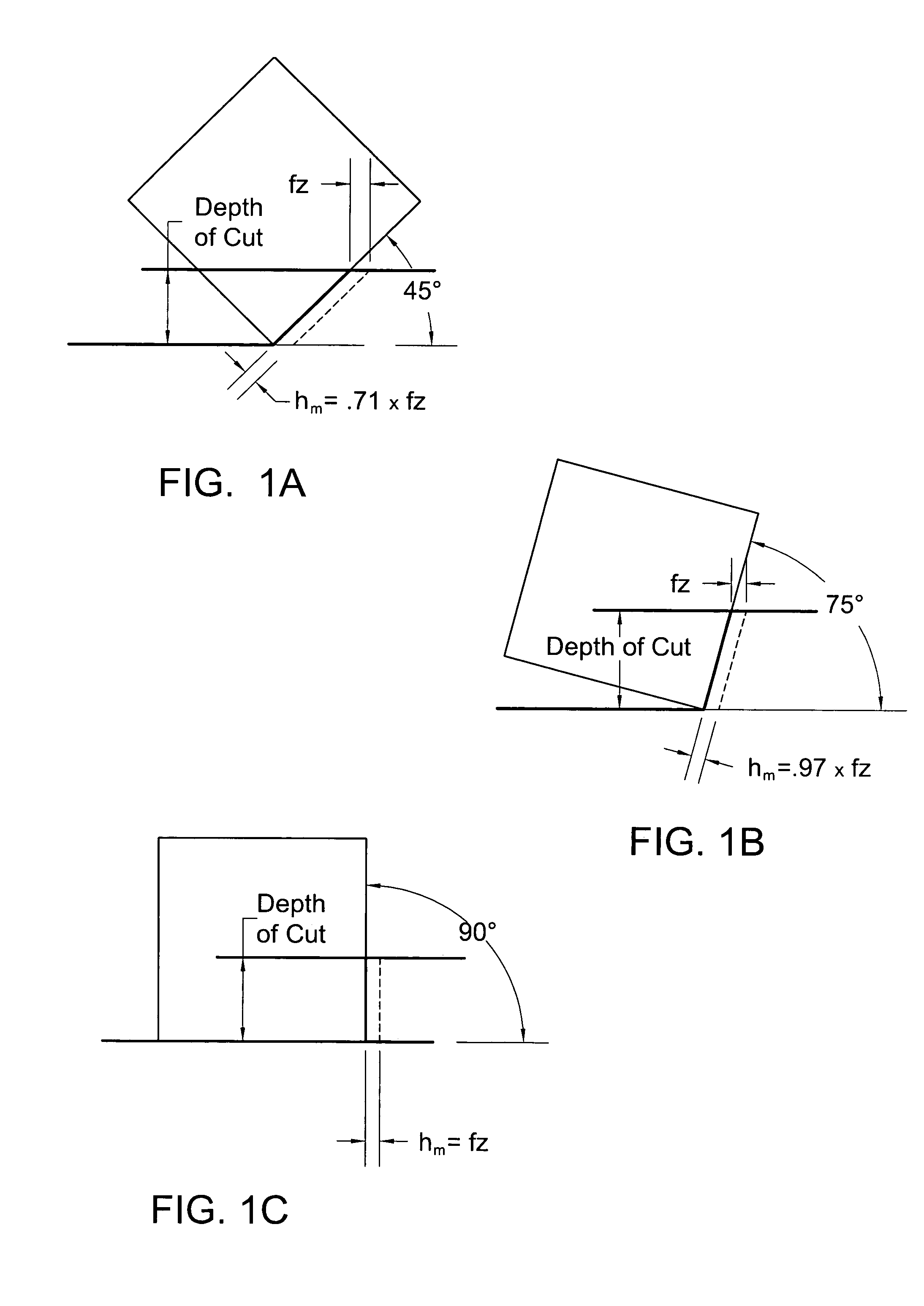
InactiveUS7220083B2Increase feed rateReduce forceTransportation and packagingMilling cuttersEllipseEdge strength
A cutting insert for milling operations, such as, face milling, slot milling, plunge milling, and ramping operations. The cutting insert exhibits a combination of favorable cutting edge strength, and unique cutting edge geometry, thus, allowing milling operations at relatively high feed rates. The cutting insert includes at least four cutting edges, wherein at least one of the cutting edges is a convex cutting edge. Certain embodiments of square cutting inserts will have four convex cutting edges which may be connected by nose corners. The convex cutting edge may comprise at least one of a circular arc, a portion of an ellipse, a portion of a parabola, a multi-segment spline curve, a straight line, or combinations of these. Wherein the convex cutting edge comprises a circular arc, the circular arc may have a radius greater than or equal to two times a radius of the largest circle that may be inscribed on the top surface.
Owner:KENNAMETAL INC
Method, apparatus and system for capturing and analyzing interaction based content
InactiveUS8204884B2Digital data processing detailsSpecial service for subscribersData informationMulti segment
An apparatus and methods for capturing and analyzing customer interactions the apparatus comprising interaction information units, interaction meta-data information units associated with each of the interaction information units, a rule based analysis engine component for receiving the interaction information, an adaptive database, an interaction capture and storage component for capturing interaction information, a multi segment interaction capture device, an initial set up and calibration device and a pre processing and content extraction device.
Owner:NICE SYSTEMS
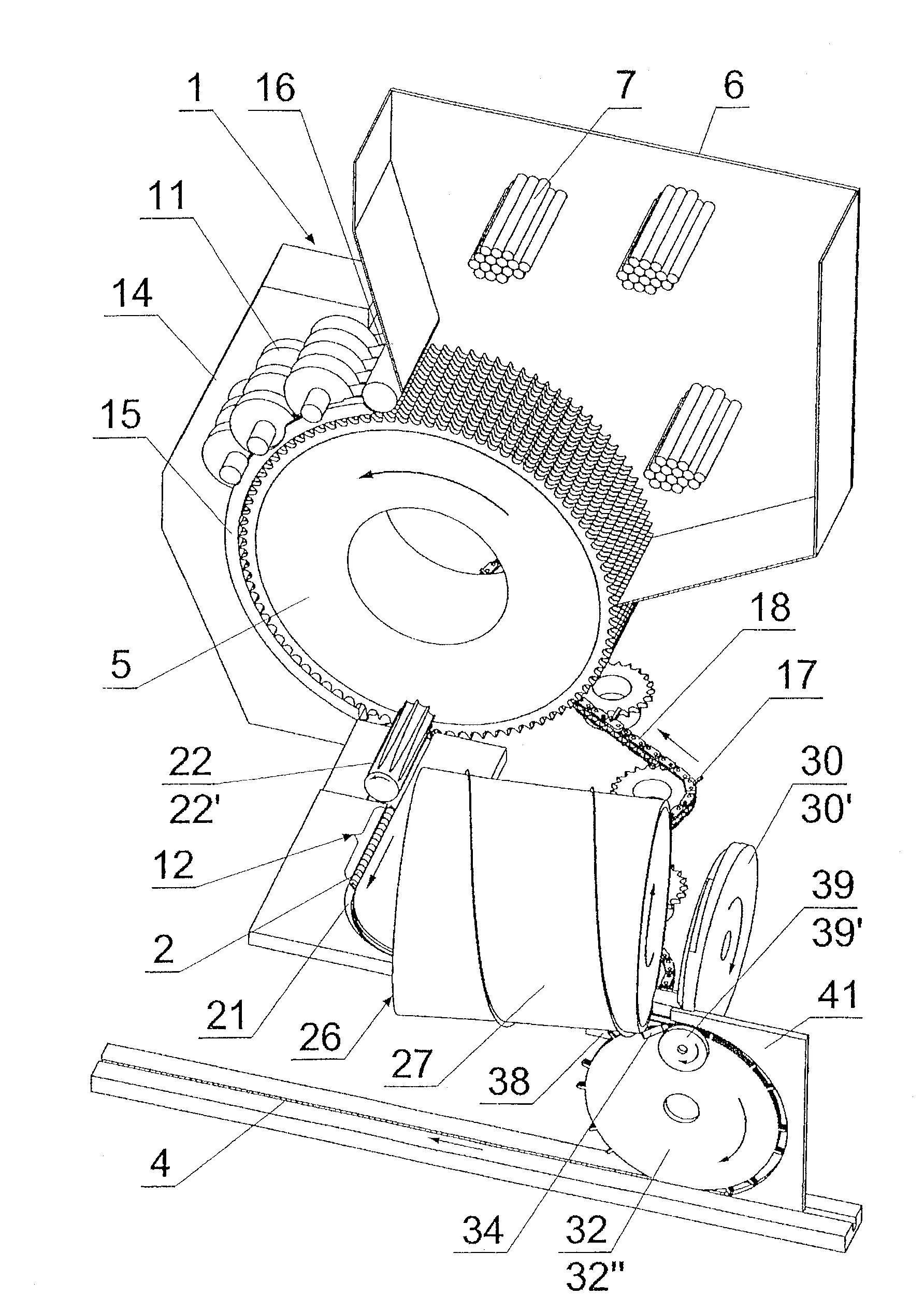
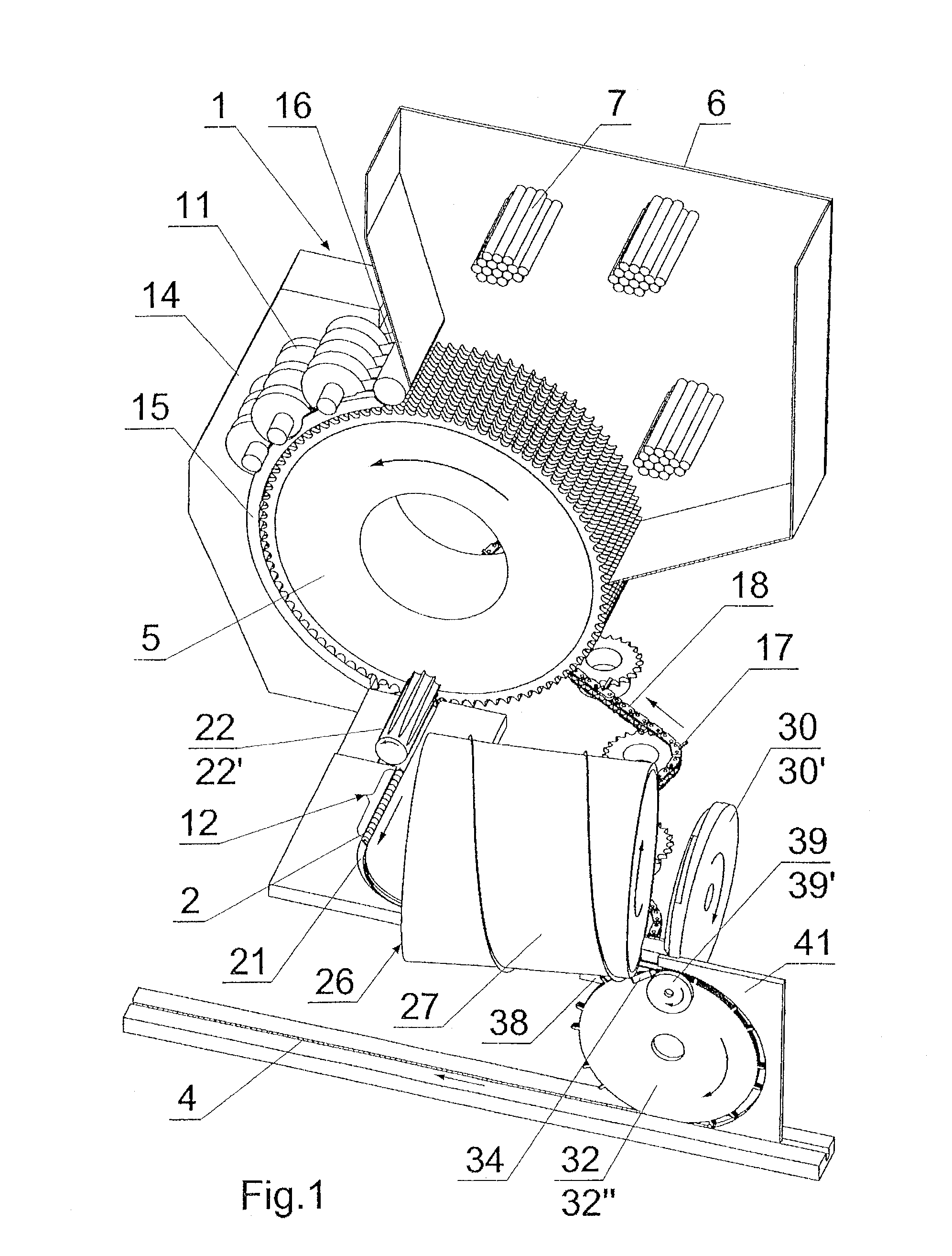
Method and apparatus for compiling groups of filter segments when producing multi-segment filter asemblies
ActiveUS20090145449A1Increase speedEnsure controlCigar manufacturePaper/cardboard wound articlesFluteComputer module
A method of making segmented filters including moving substantially identical segments of one type at uniform rate to a transferring element, which places each segment separately on an exit path. Setting of the filter segments in a repeating group on the exit path is accomplished by delay in collecting segments by a transferring element in each module of the apparatus. Uniform positioning is effected using the transferring element which includes uniformly spaced drivers, and non-uniform positioning is effected using the transferring element with non-uniformly spaced drivers. The apparatus includes a guiding element positioned adjacent to a cutting drum and has a wall closing a channel for a set of segments drawn out of a flute on the drum. The filter set is led through the channel with the aid of a dog of a chain and is advanced by a worm surface of a pushing together drum. A separator positioned at the end of the channel which separates single filter segments and may be a disc cam pushing out the segment onto the transferring element between two neighbouring drivers into a chamber created by a supporting element. A stream of compressed air from nozzle directed towards the area between a shoe guide and separator helps separate and stabilize the filter segment.
Owner:PHILIP MORRIS USA INC
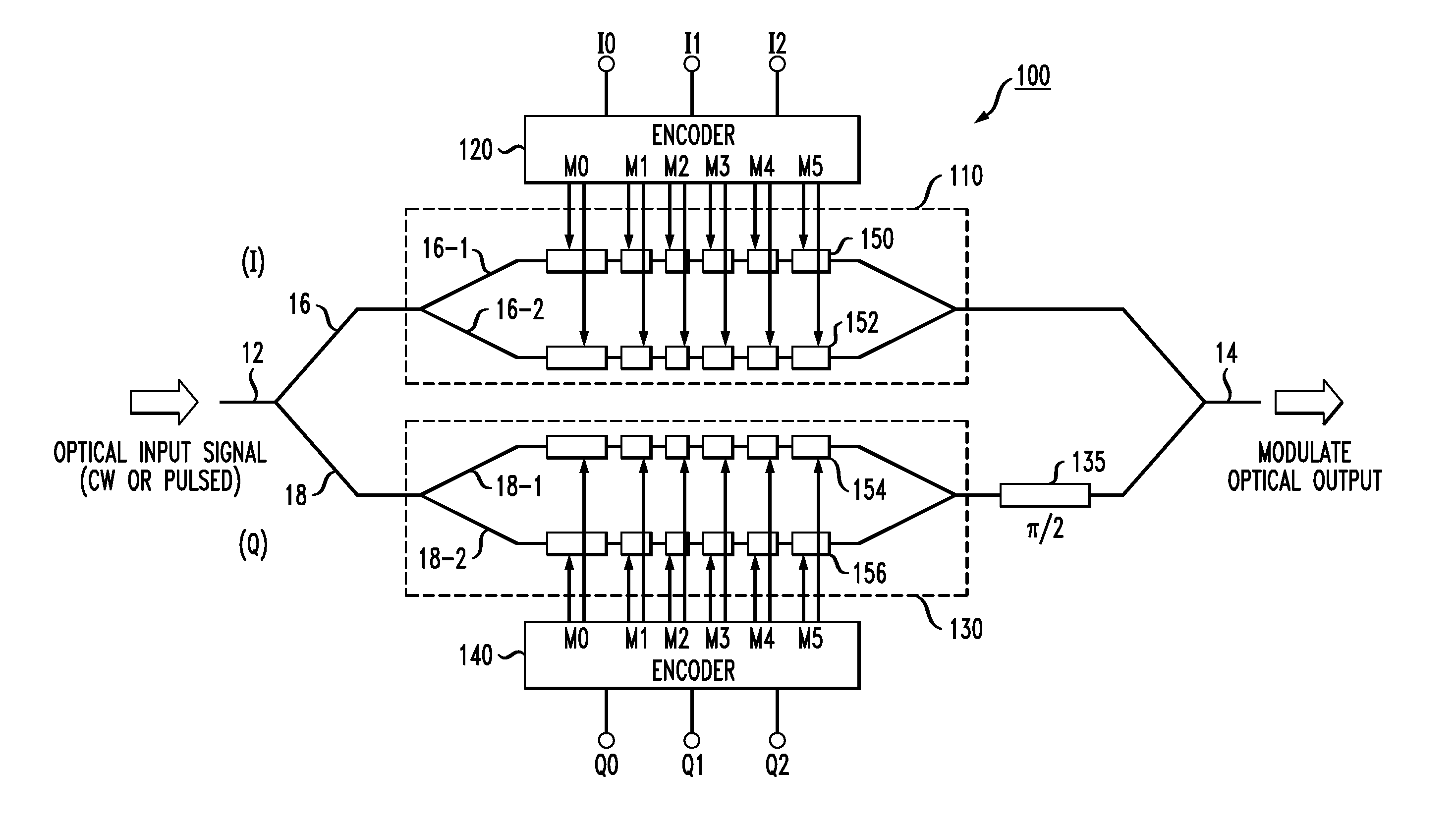
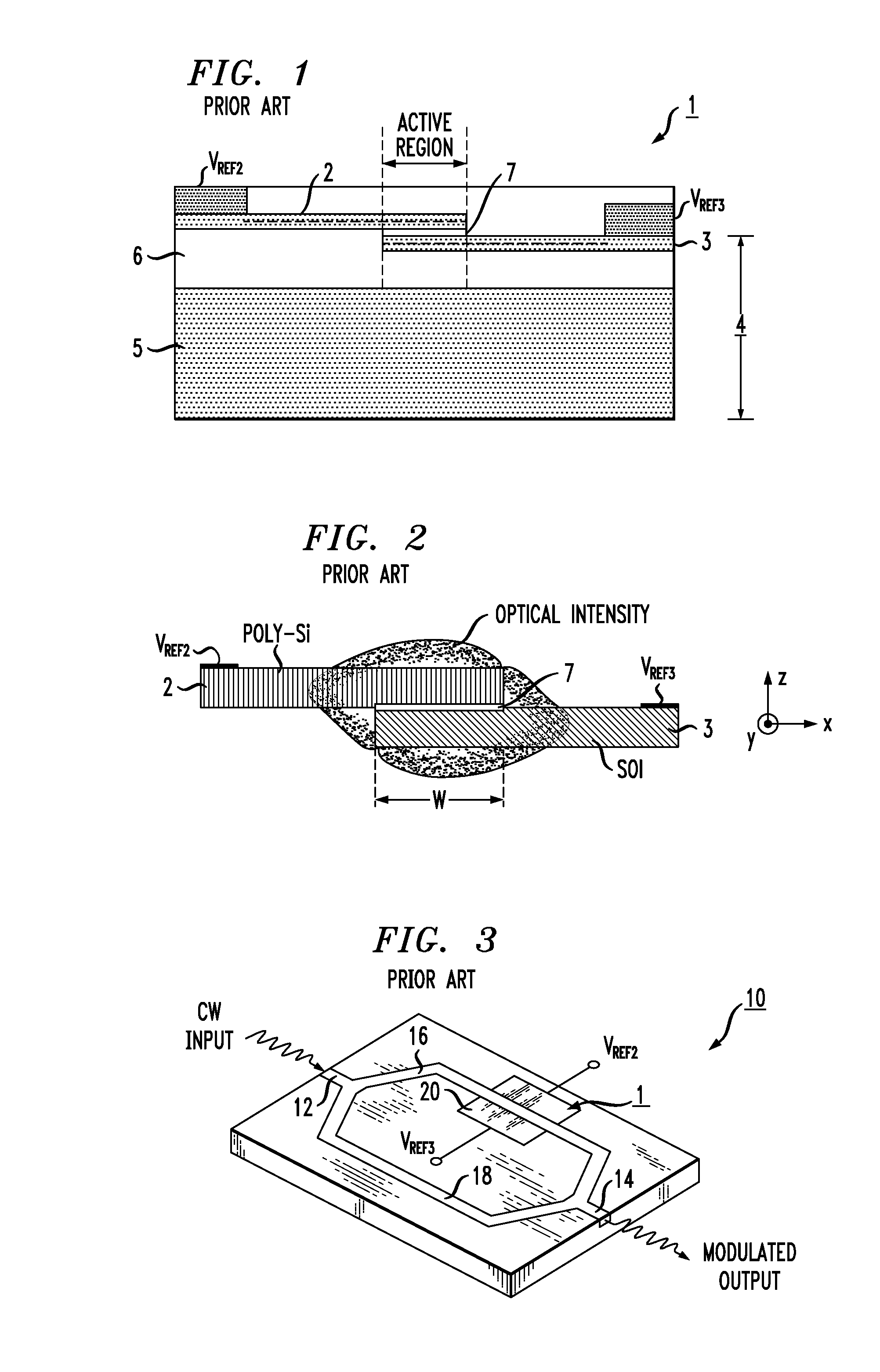
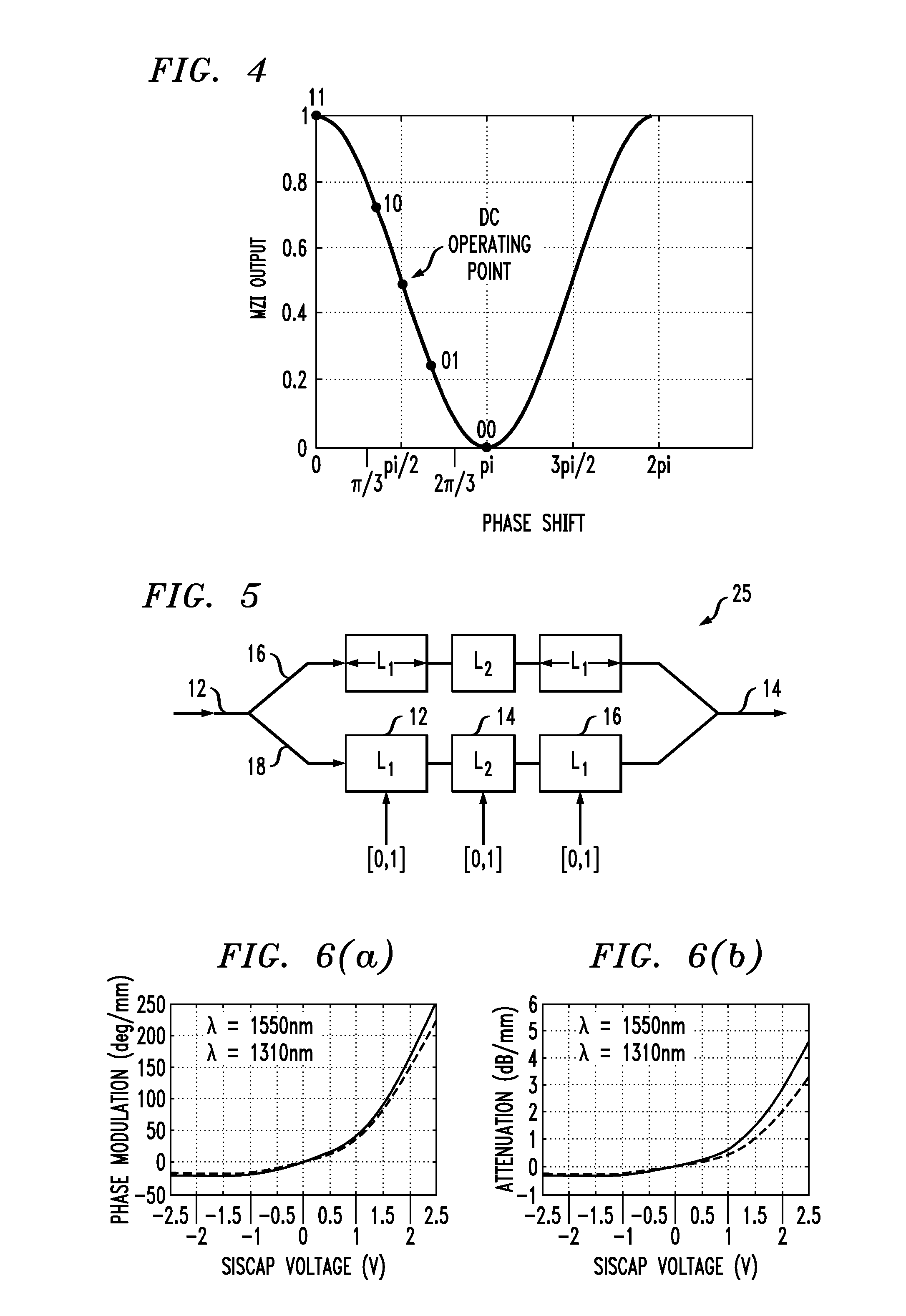
Advanced Modulation Formats for Silicon-Based Optical Modulators
ActiveUS20110044573A1Electromagnetic transmissionOptical waveguide light guideMulti segmentWaveguide
A silicon-based optical modulator is configured as a multi-segment device that utilizes a modified electrical data input signal format to address phase modulation nonlinearity and attenuation problems associated with free-carrier dispersion-based modulation. The modulator is formed to include M separate segments and a digital signal encoder is utilized to convert an N bit input data signal into a plurality of M drive signals for the M modulator segments, where M≧2N / 2. The lengths of the modulator segments may also be adjusted to address the nonlinearity and attenuation problems. Additional phase adjustments may be utilized at the output of the modulator (beyond the combining waveguide).
Owner:CISCO TECH INC
Multi-segment wind turbine blade and method for assembling the same
ActiveUS20090162208A1Easy alignmentEngine manufactureFinal product manufactureScarf jointTurbine blade
A multi-segment wind turbine blade comprises at least two blade segments. A first spar cap segment is attached to a first blade segment and a second spar cap segment is attached to a second blade segment. The first and second spar cap segments are configured to form a scarf joint. First and second spar cap brackets are attached in locations of the first and second spar cap segments, respectively, selected to facilitate alignment of the first and second spar cap segments at the scarf joint. At a field site, the first and second spar cap segments are bonded after fastening the first and second spar cap brackets.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
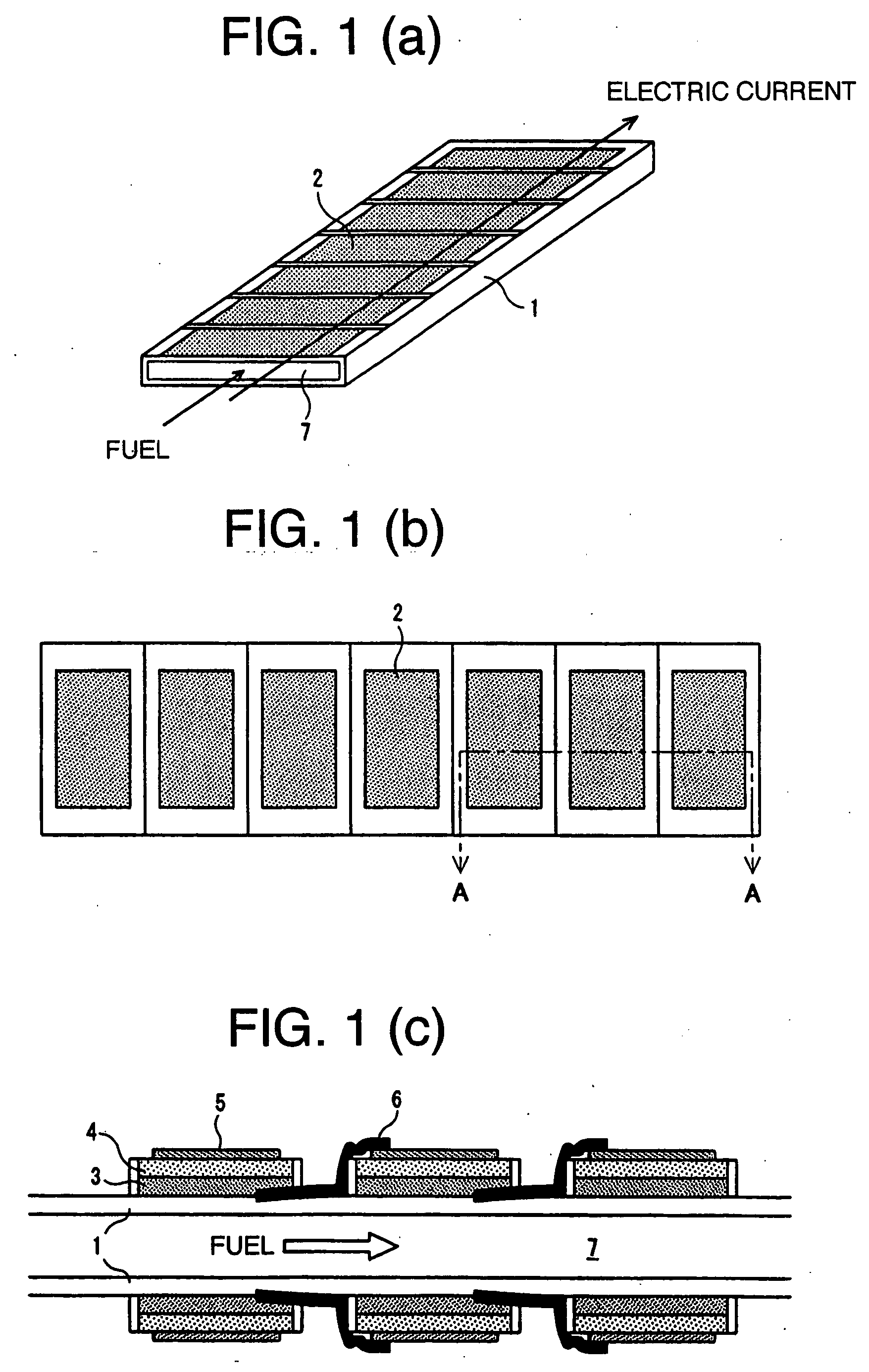
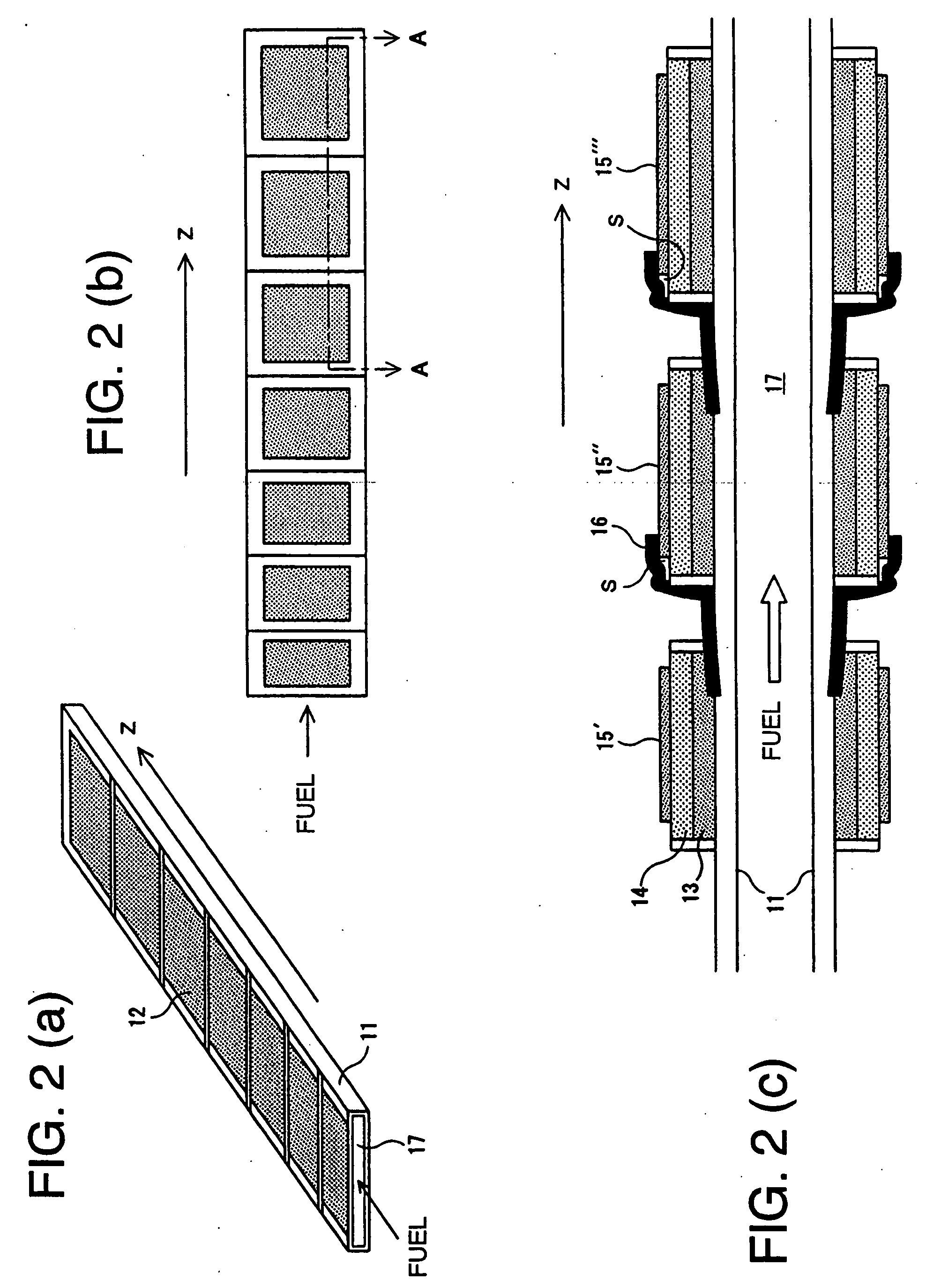
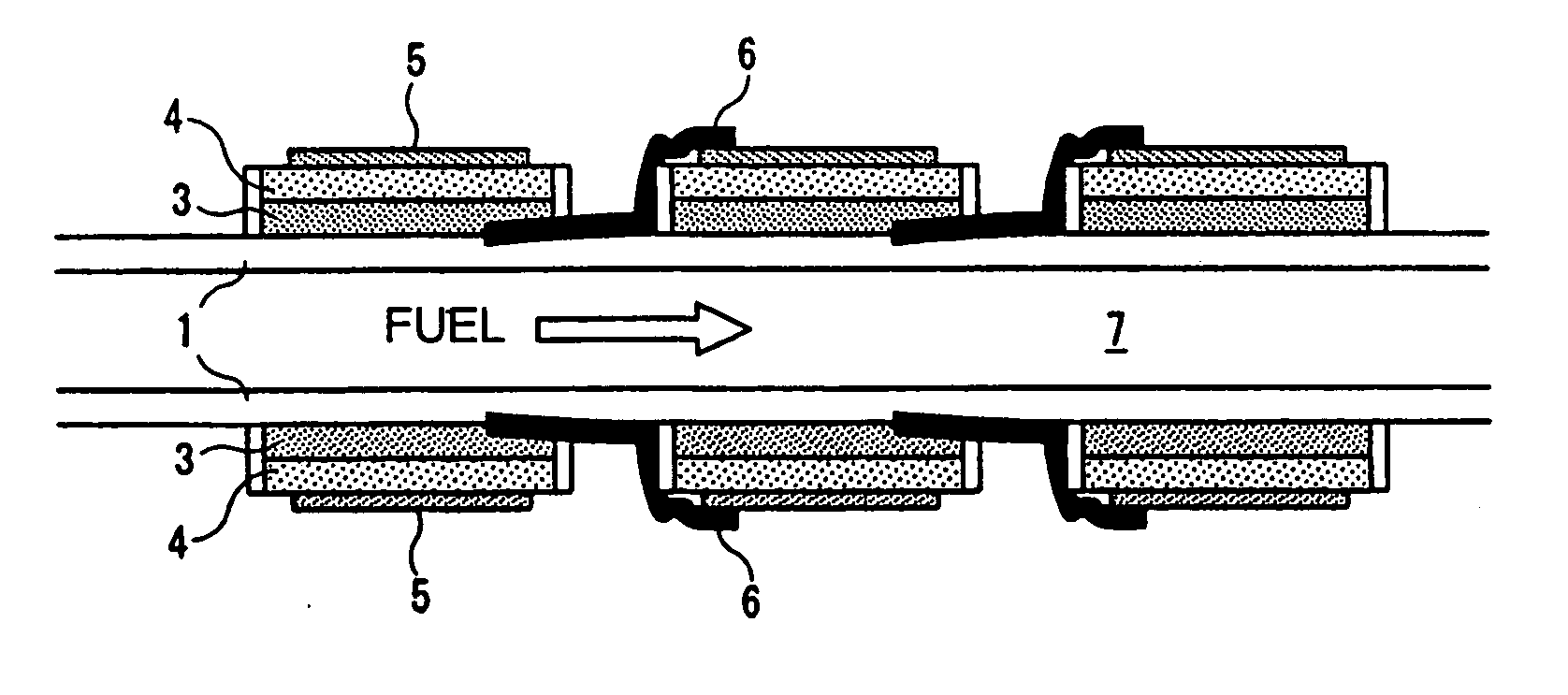
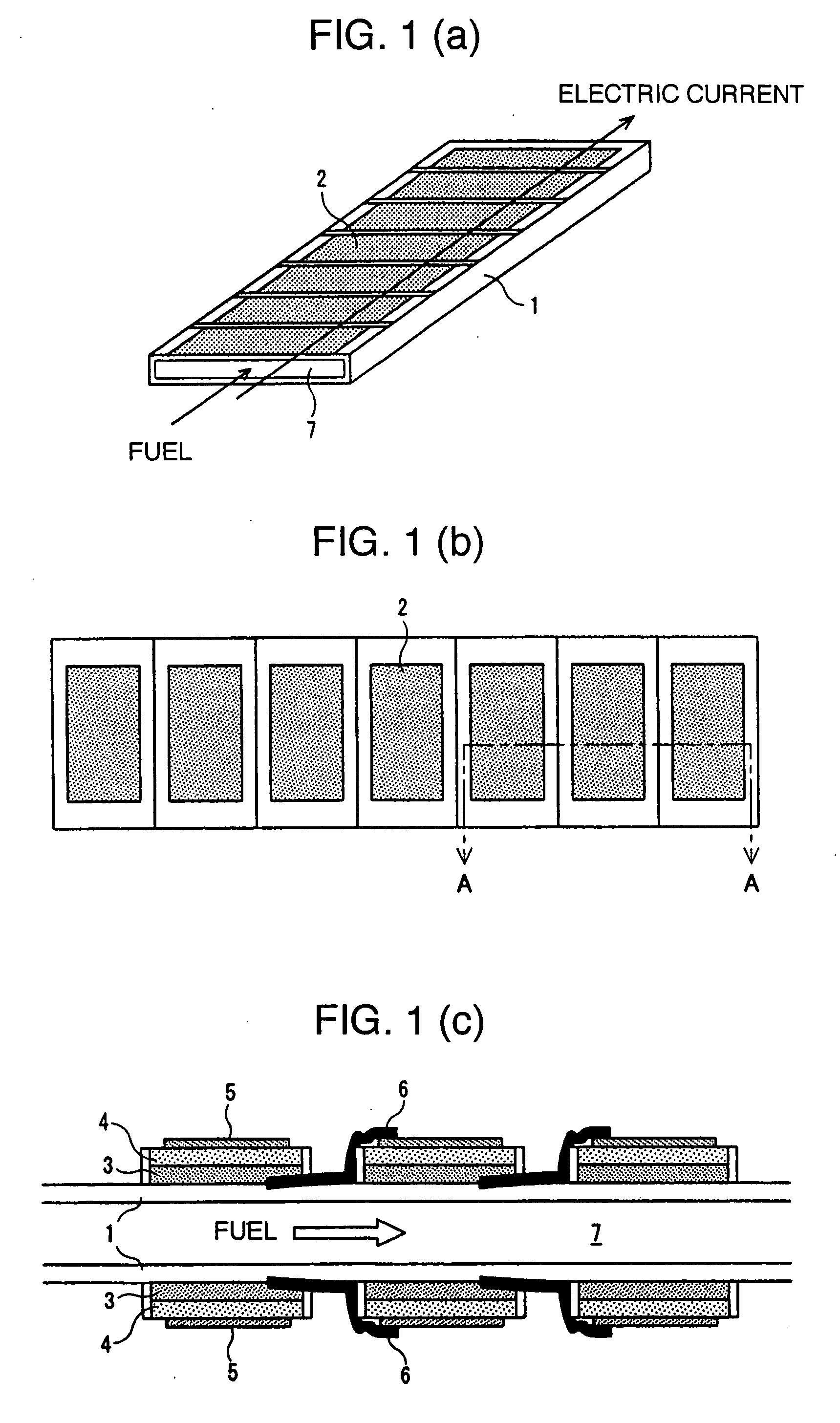
Solid-oxide shaped fuel cell module
ActiveUS20060147778A1Increase currentImprove efficiencyReactant parameters controlFuel cells groupingFuel cellsInterconnector
There is provided a solid oxide fuel cell module comprising a substrate with an internal fuel flow part provided therein, at least a face thereof, in contact with cells, and interconnectors, being an insulator, a plurality of the cells each comprised of an anode, an electrolyte, and a cathode, stacked in sequence, formed on a surface of the substrate, and the interconnectors each electrically connecting in series the cells adjacent to each other, wherein the respective cells are varied in area along the direction of fuel flow, and solid oxide fuel cell bundled modules using the same. With the solid oxide fuel cell module of a multi-segment type, according to the invention, it is possible to aim at higher voltage, and to attain improvement in power generation efficiency, and current collecting efficiency.
Owner:TOKYO GAS CO LTD
Method for fabricating solid oxide fuel cell module
ActiveUS20060153974A1High gas-sealing performanceImprove productivityFuel cells groupingFinal product manufactureProduction rateElectricity
There is provided a method of manufacturing a solid oxide fuel cell module comprising a plurality of cells each made up of a fuel electrode, an electrolyte, and an air electrode sequentially formed on a surface of a substrate with an internal fuel flow part provided therein, at least a face of the substrate, in contact with the cells, and interconnectors, being an insulator, and the cells adjacent to each other, being electrically connected in series through the intermediary of the respective interconnectors, said method of manufacturing the solid oxide fuel cell module comprising the steps of co-sintering the respective fuel electrodes, and the respective electrolytes, subsequently forming a dense interconnector out of a dense interconnector material, or an interconnector material turning dense by sintering in at least parts of the solid oxide fuel cell module, in contact with the respective fuel electrodes, and the respective electrolyte, and forming an air electrode on the respective electrolytes before electrically connecting the air electrode with the respective dense interconnectors. With the invention, it is possible to solve various problems of sinterability, encountered in the process of manufacturing the solid oxide fuel cell module of a multi-segment type, and to secure electrical contact of the parts of the respective dense interconnectors, in contact with the fuel electrodes while attaining high gas-sealing performance by the agency of the respective dense interconnectors, and electrolytes, thereby enhancing productivity.
Owner:TOKYO GAS CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com