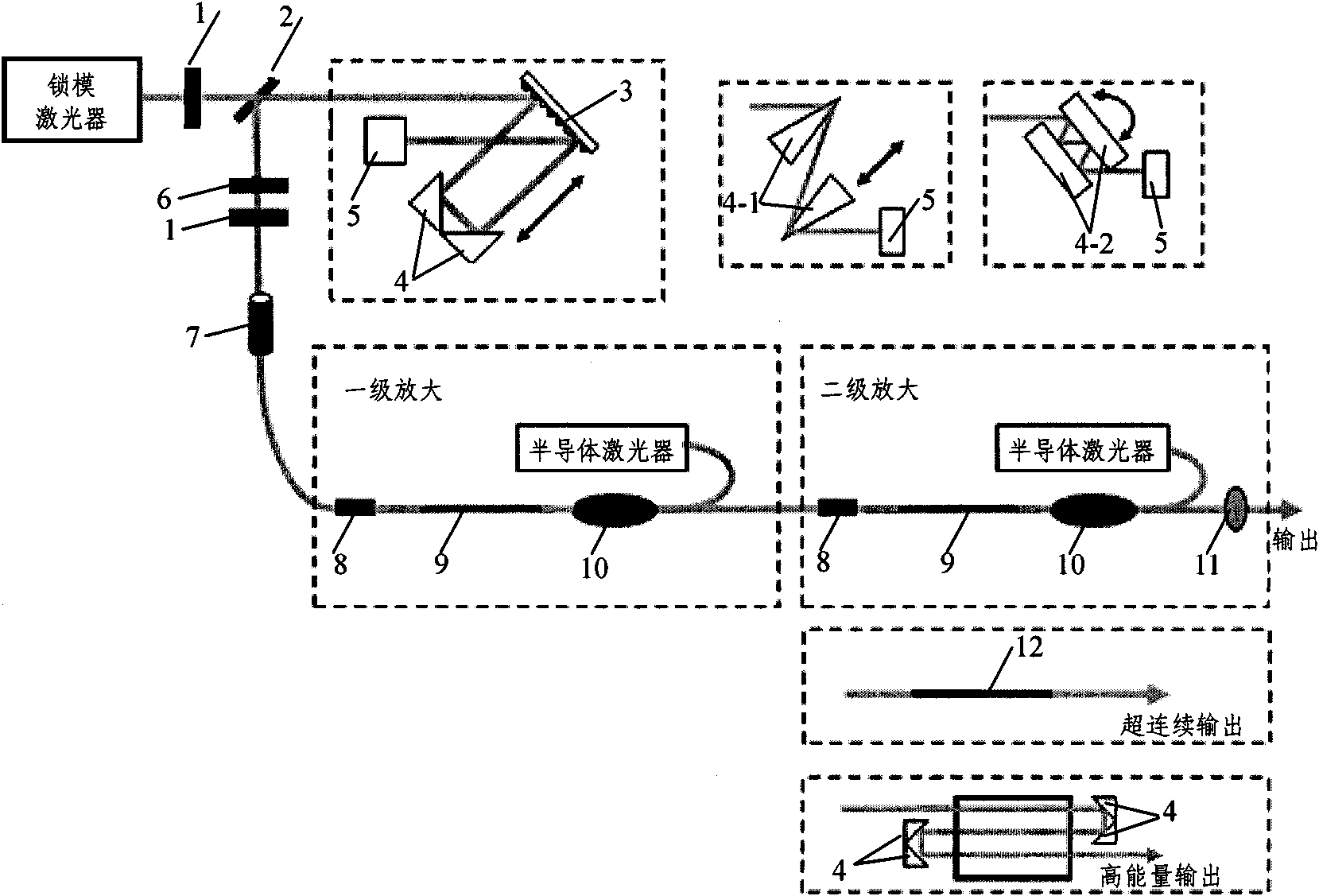
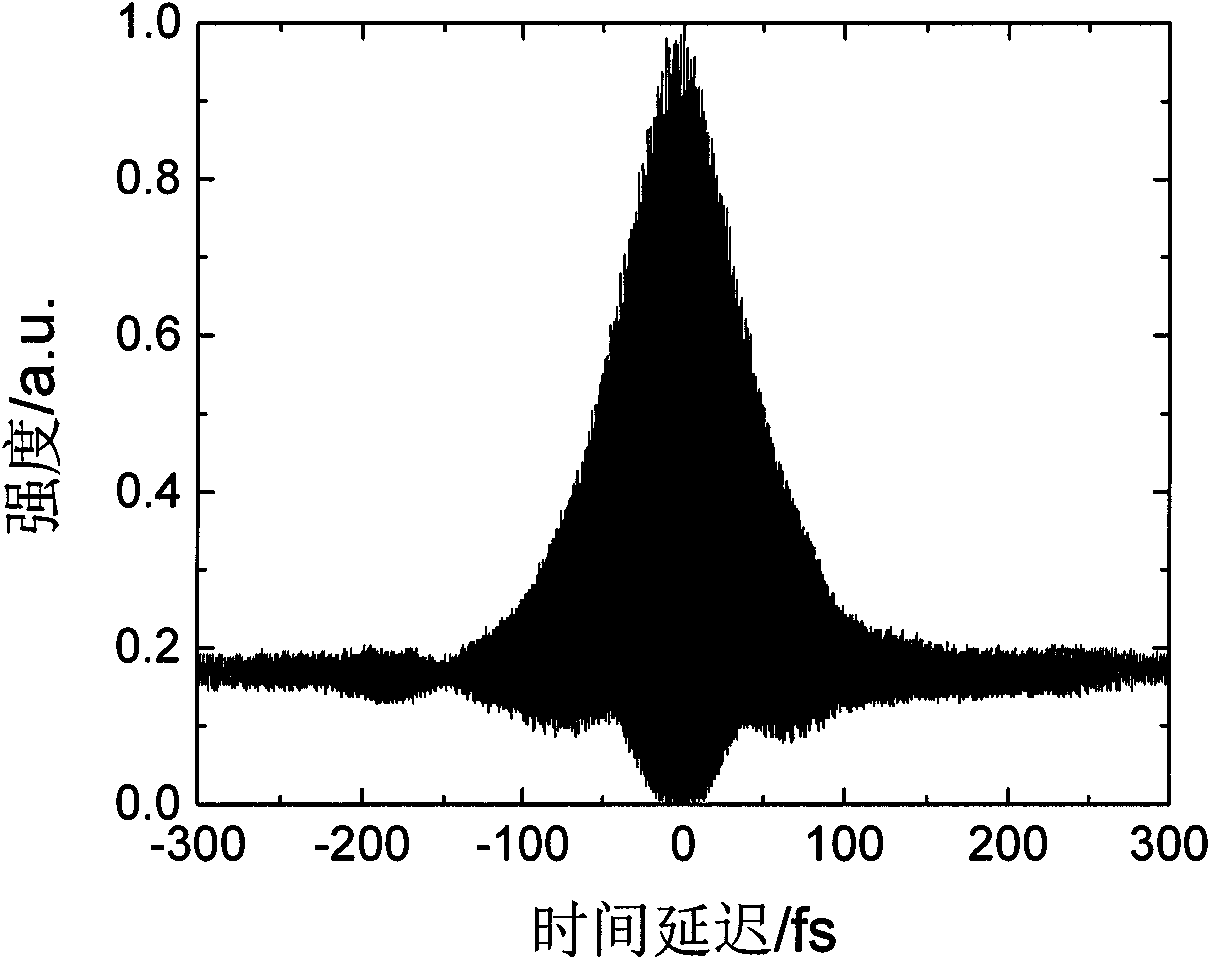
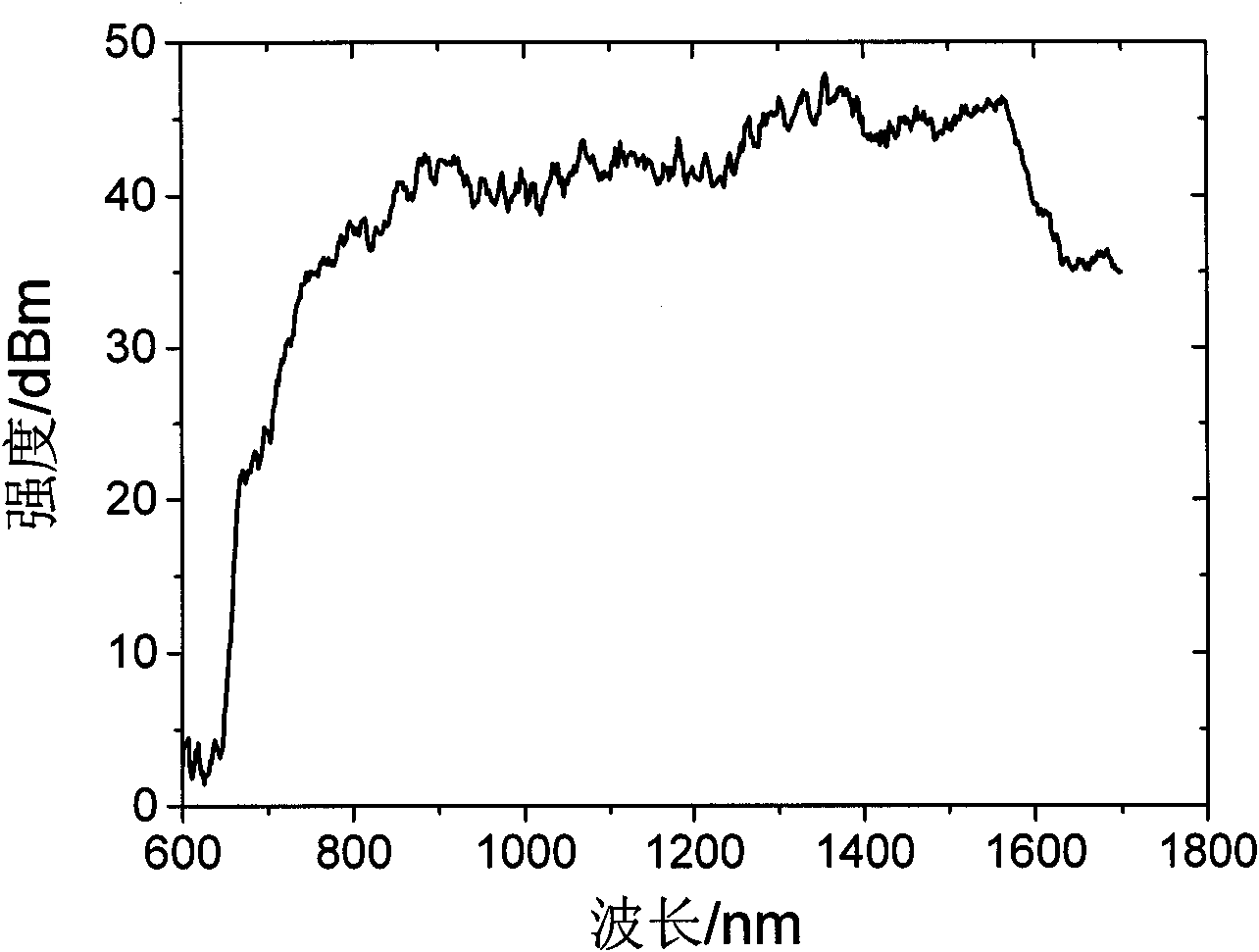
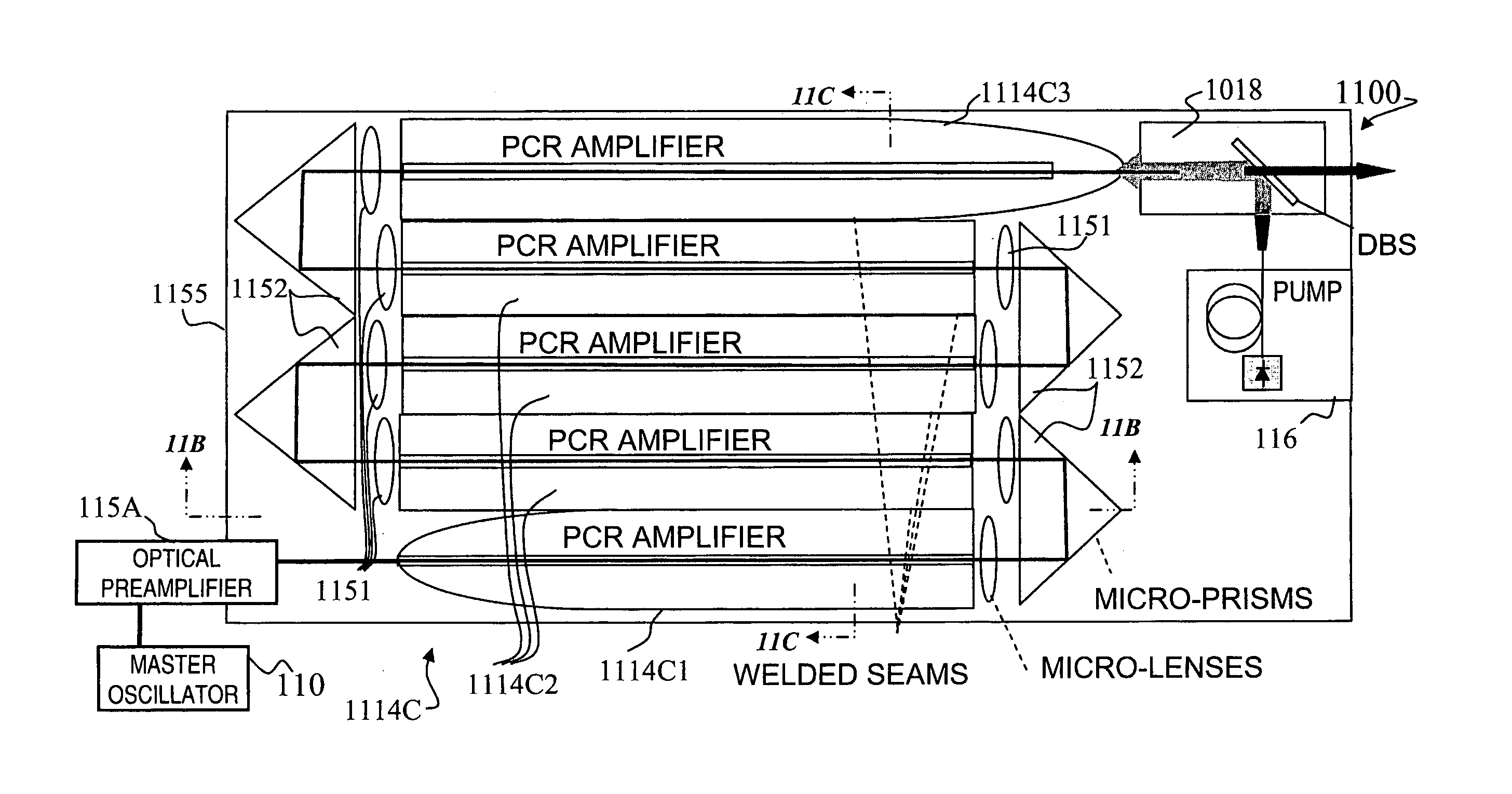
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
125results about How to "High pulse energy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
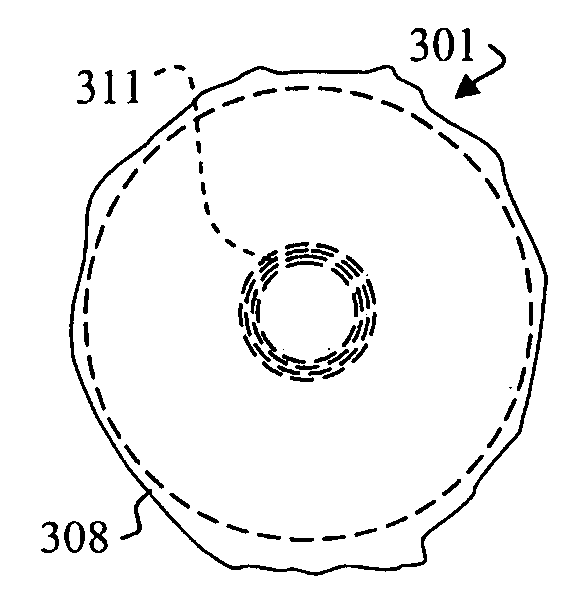
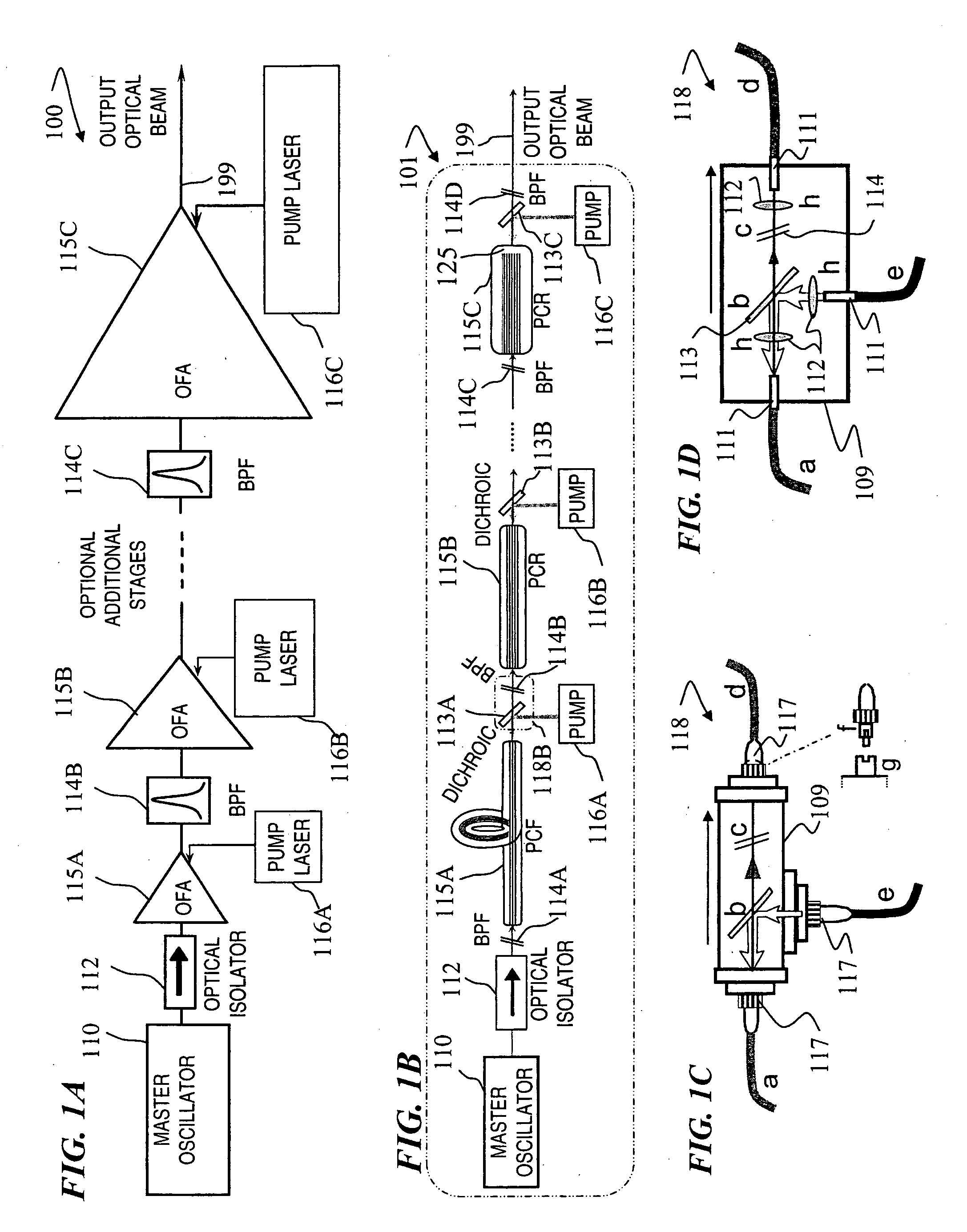
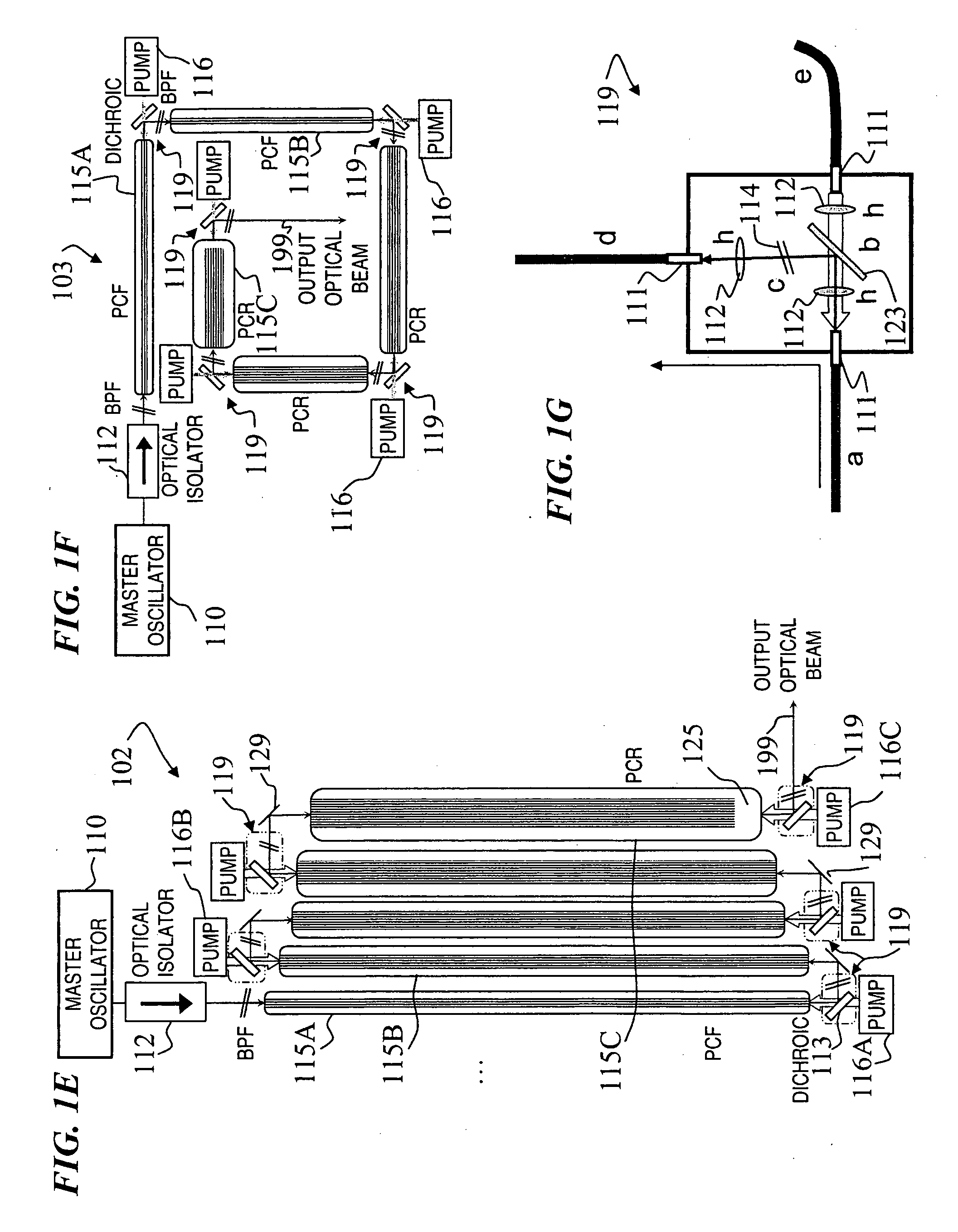
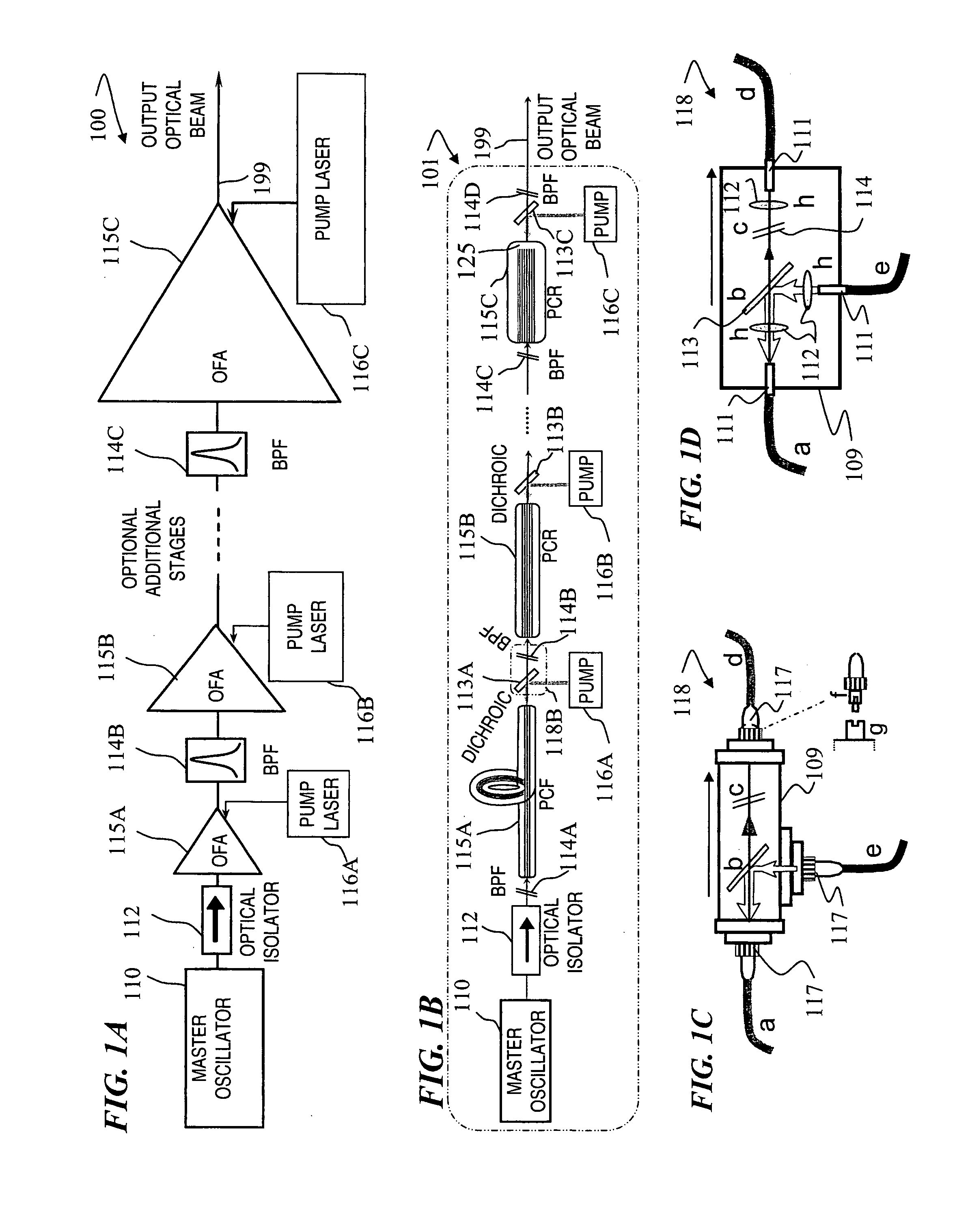
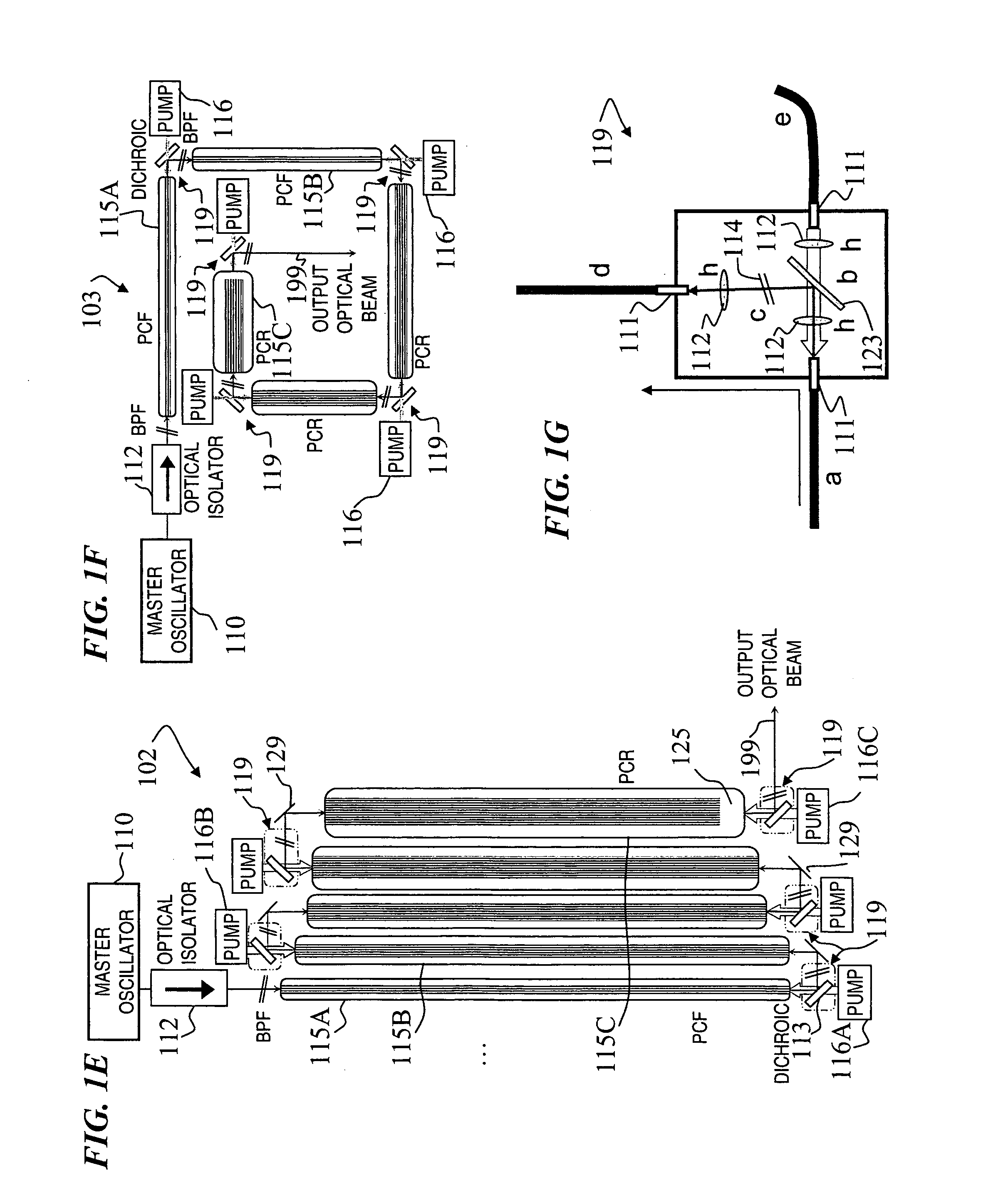
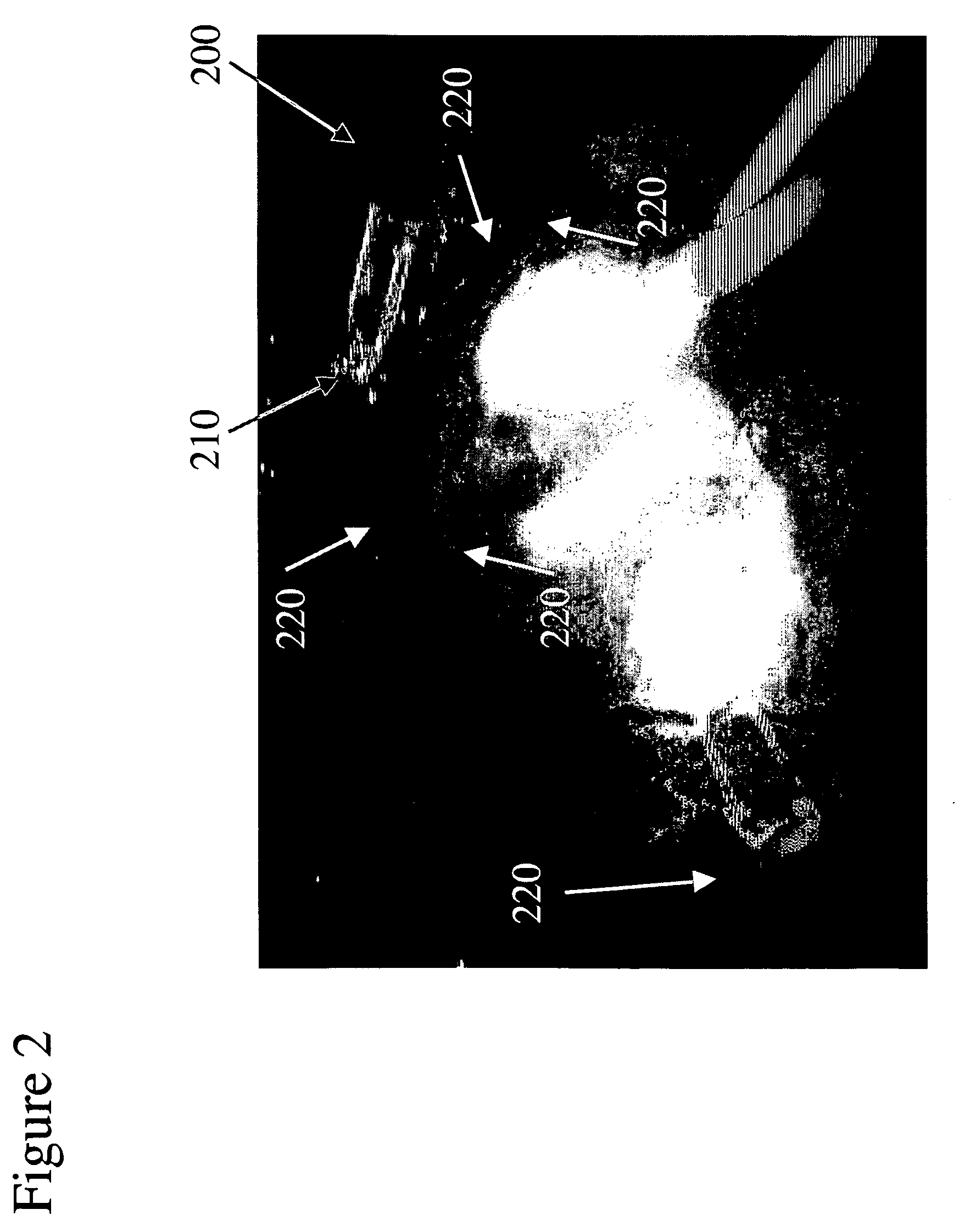
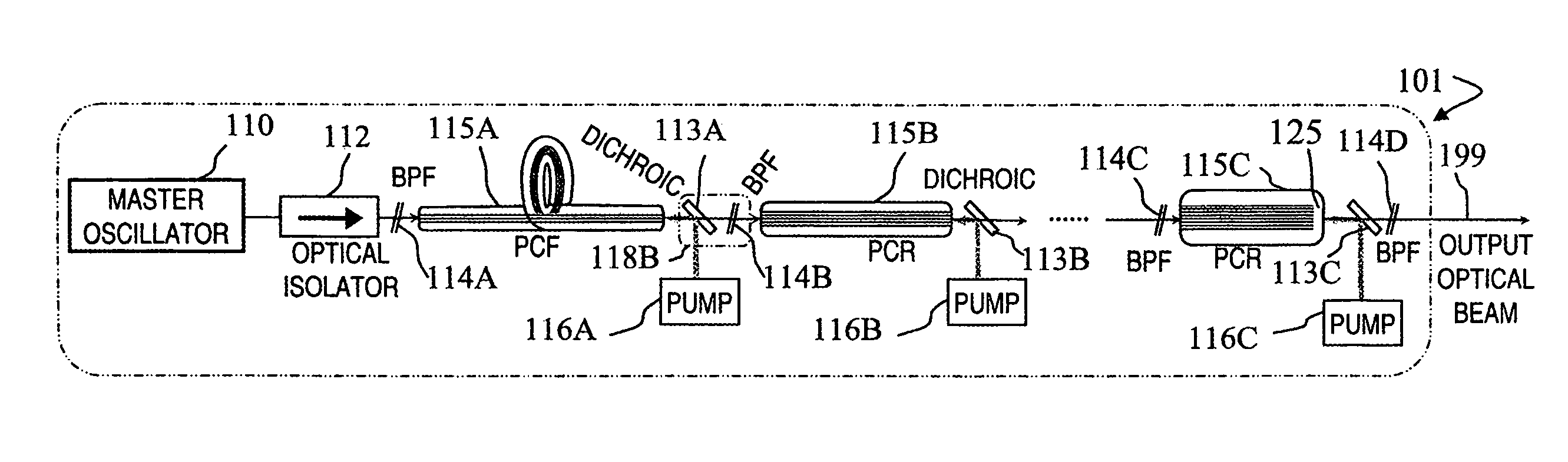
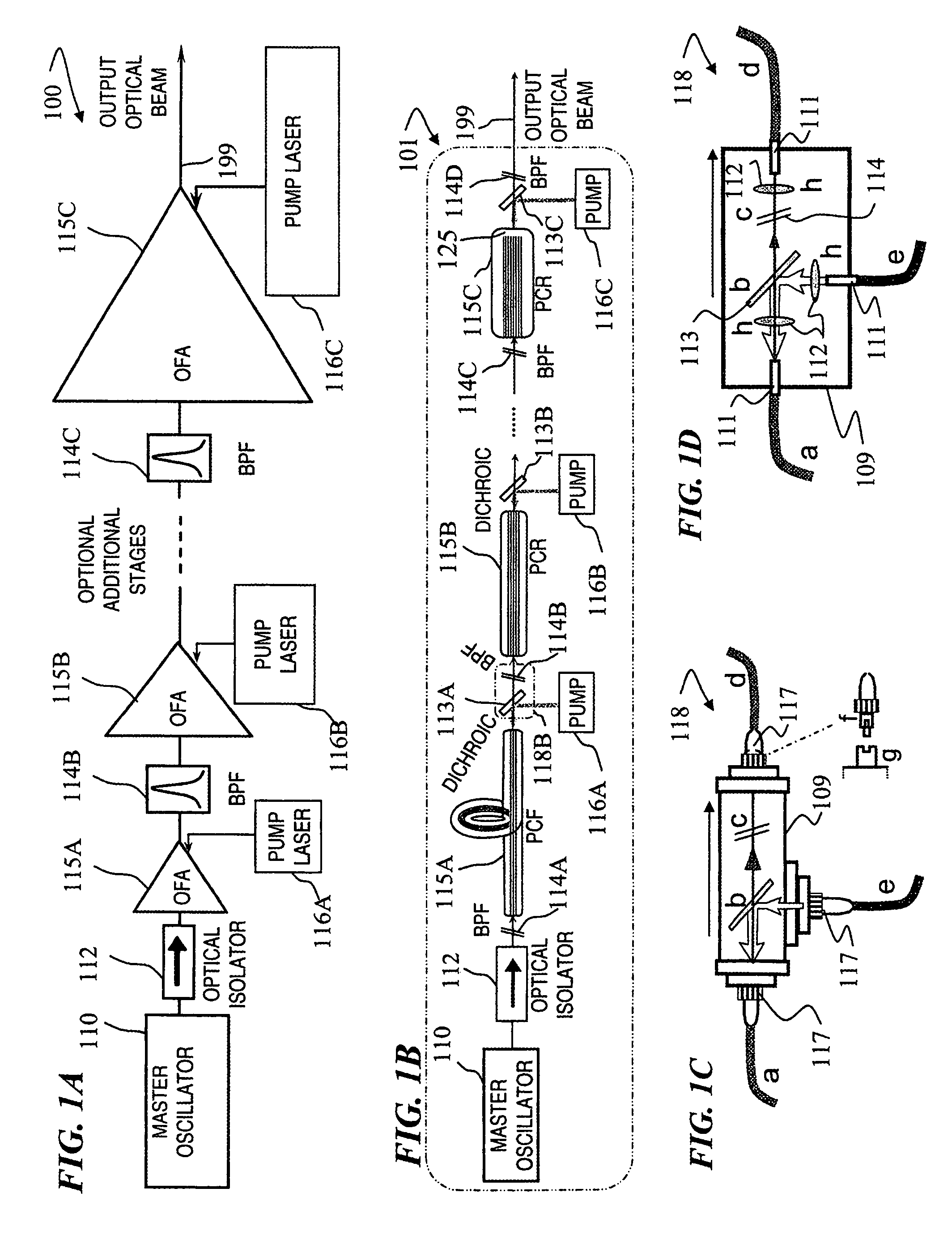
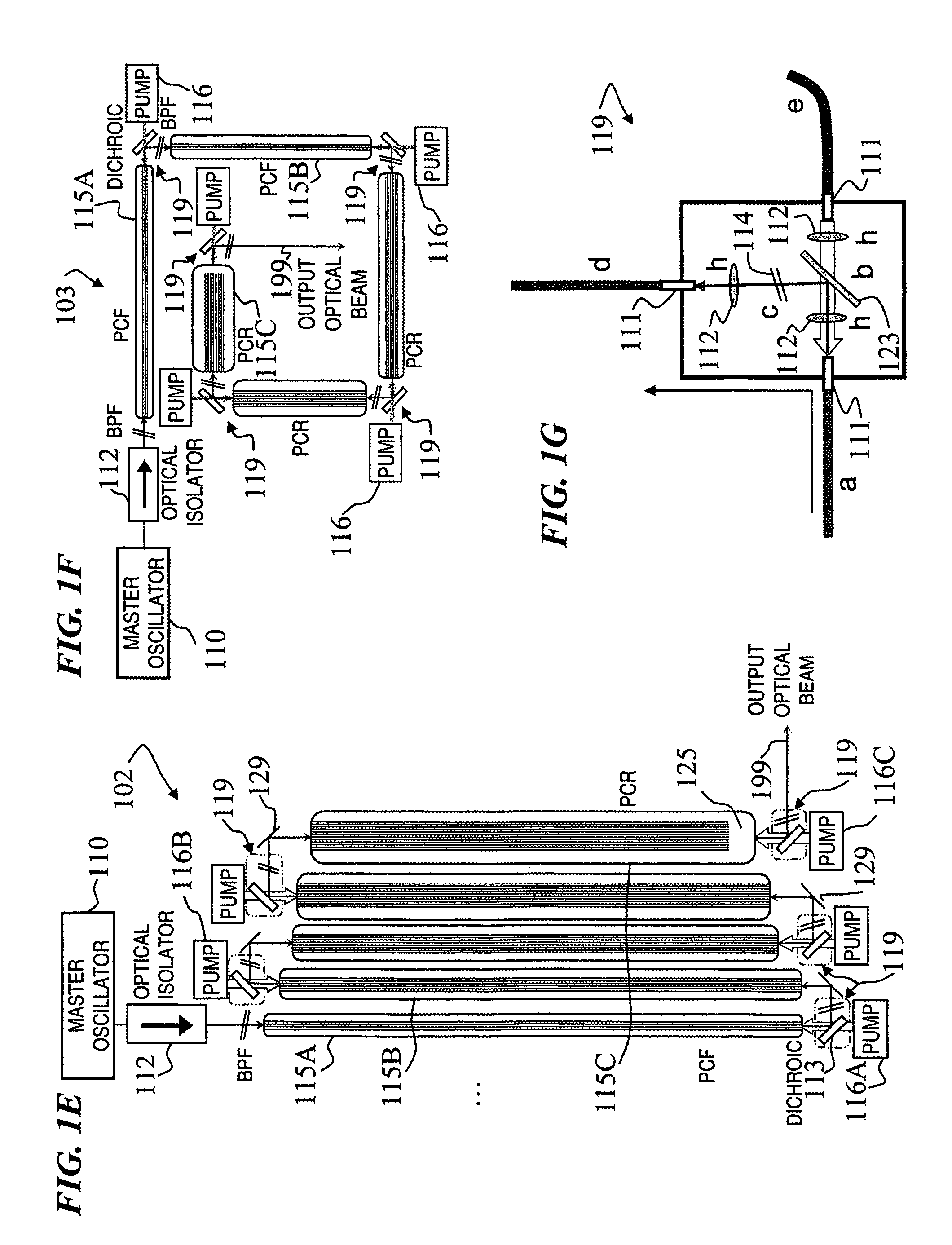
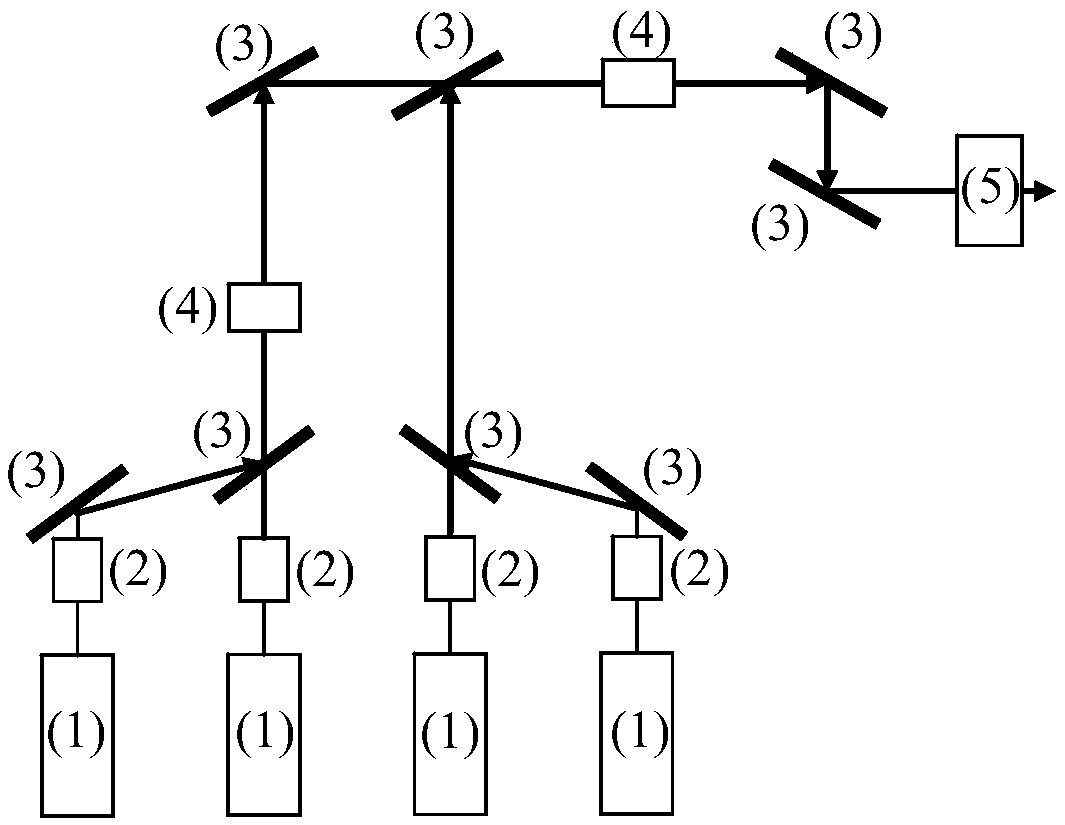
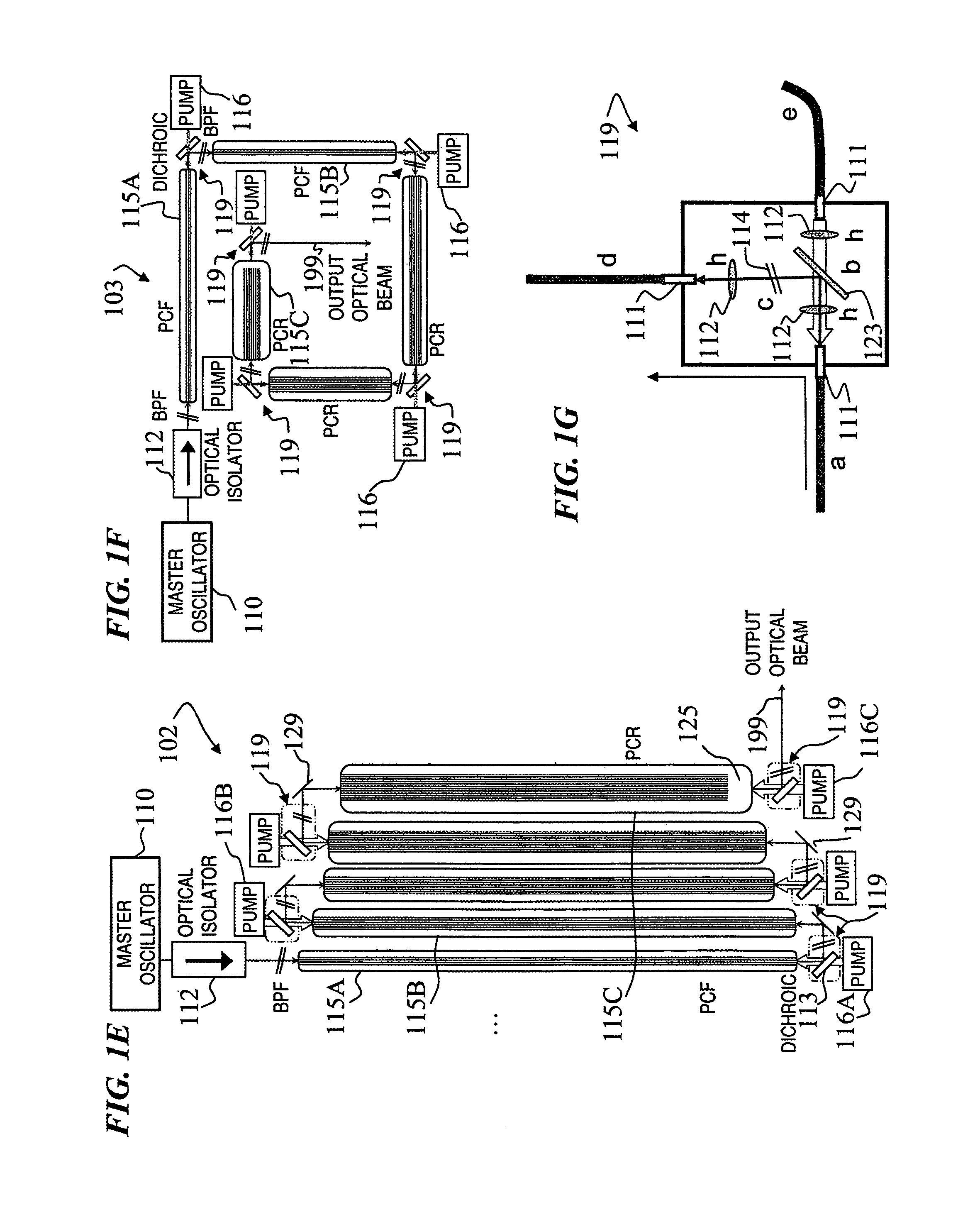
Fiber- or rod-based optical source featuring a large-core, rare-earth-doped photonic-crystal device for generation of high-power pulsed radiation and method
ActiveUS20070041083A1High peak powerHigh pulse energyGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingRare earthEngineering
A method and apparatus use a photonic-crystal fiber having a very large core while maintaining a single transverse mode. In some fiber lasers and amplifiers having large cores problems exist related to energy being generated at multiple-modes (i.e., polygamy), and of mode hopping (i.e., promiscuity) due to limited control of energy levels and fluctuations. The problems of multiple-modes and mode hopping result from the use of large-diameter waveguides, and are addressed by the invention. This is especially true in lasers using large amounts of energy (i.e., lasers in the one-megawatt or more range). By using multiple small waveguides in parallel, large amounts of energy can be passed through a laser, but with better control such that the aforementioned problems can be reduced. An additional advantage is that the polarization of the light can be maintained better than by using a single fiber core.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
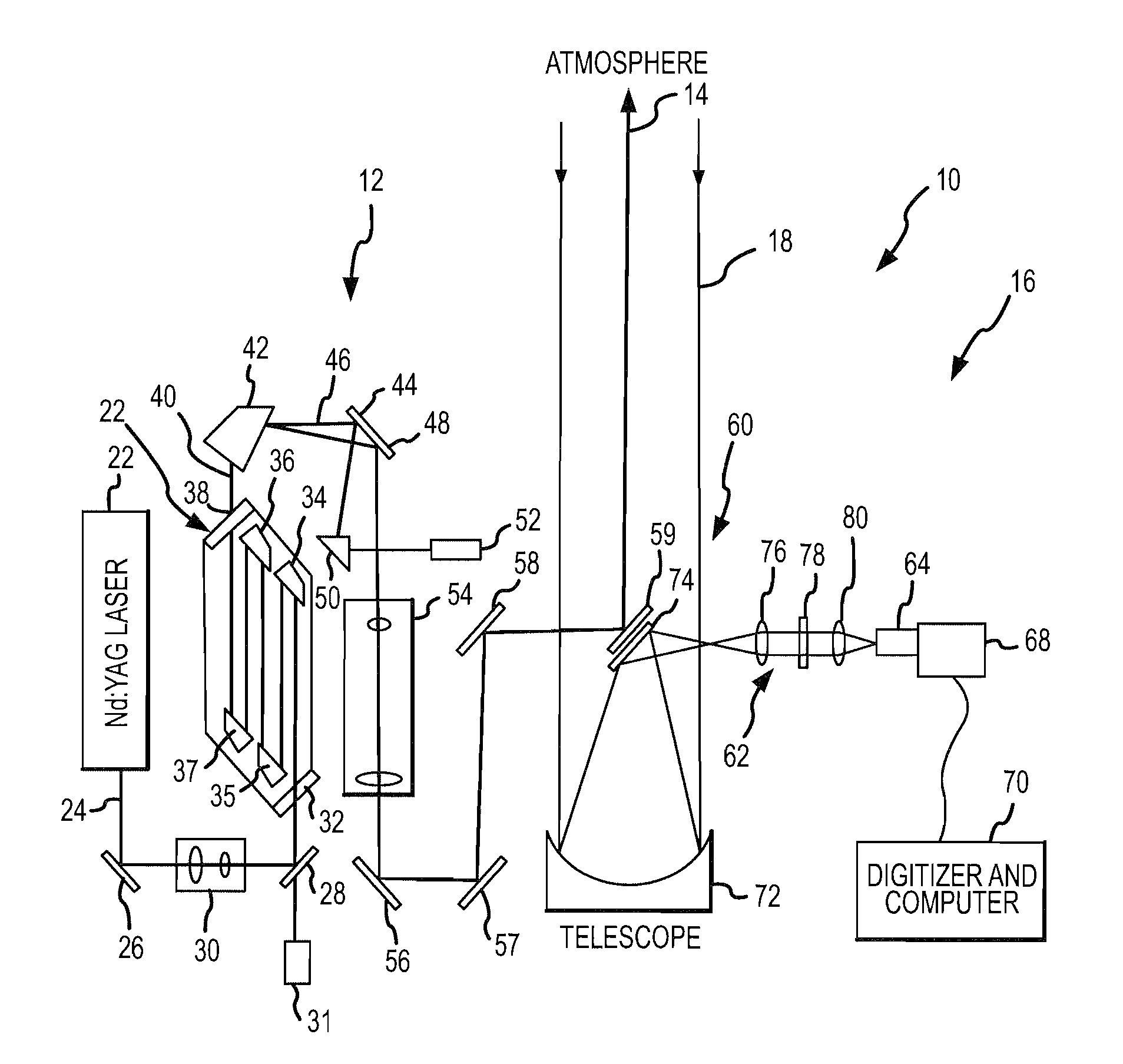
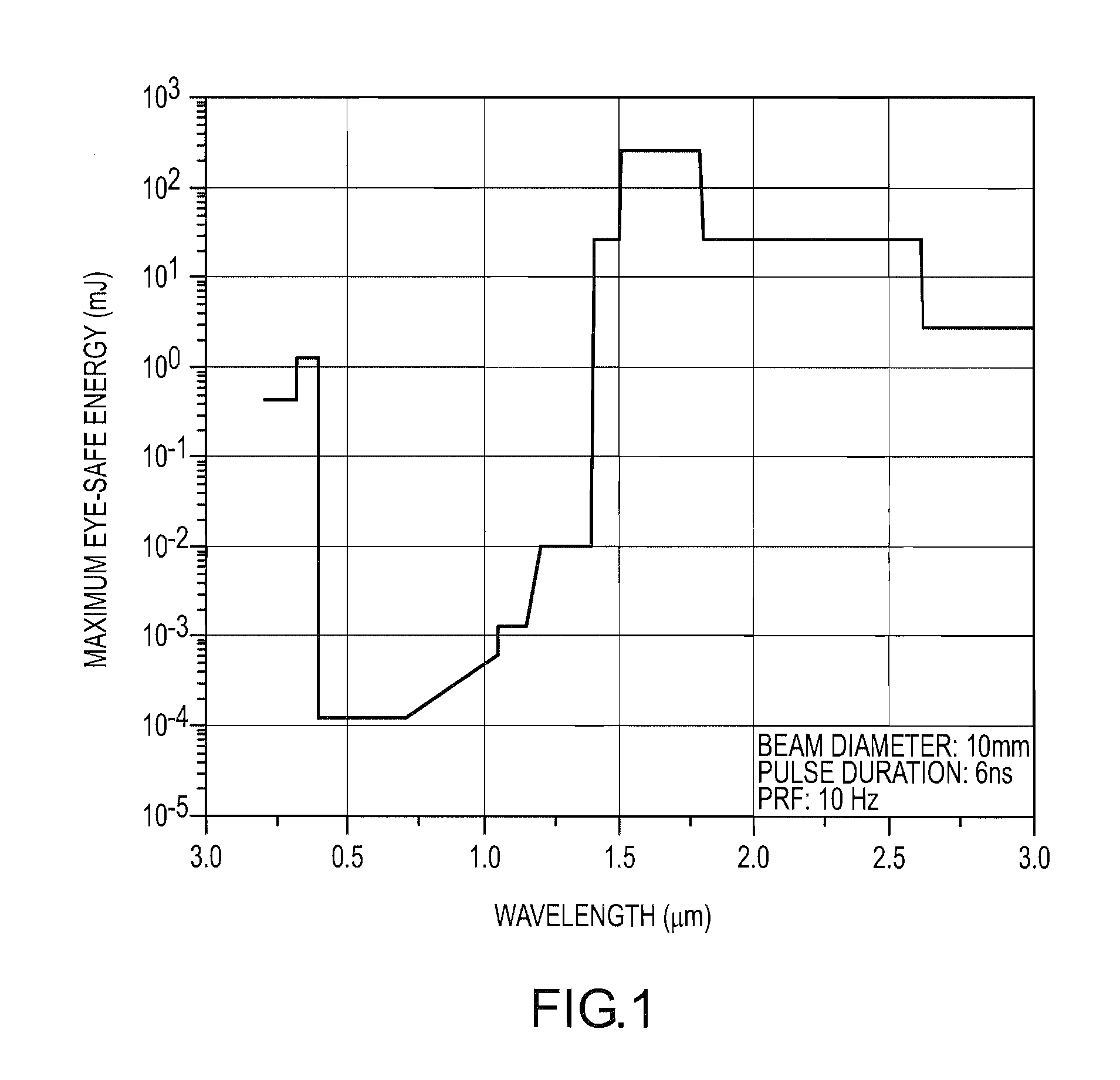
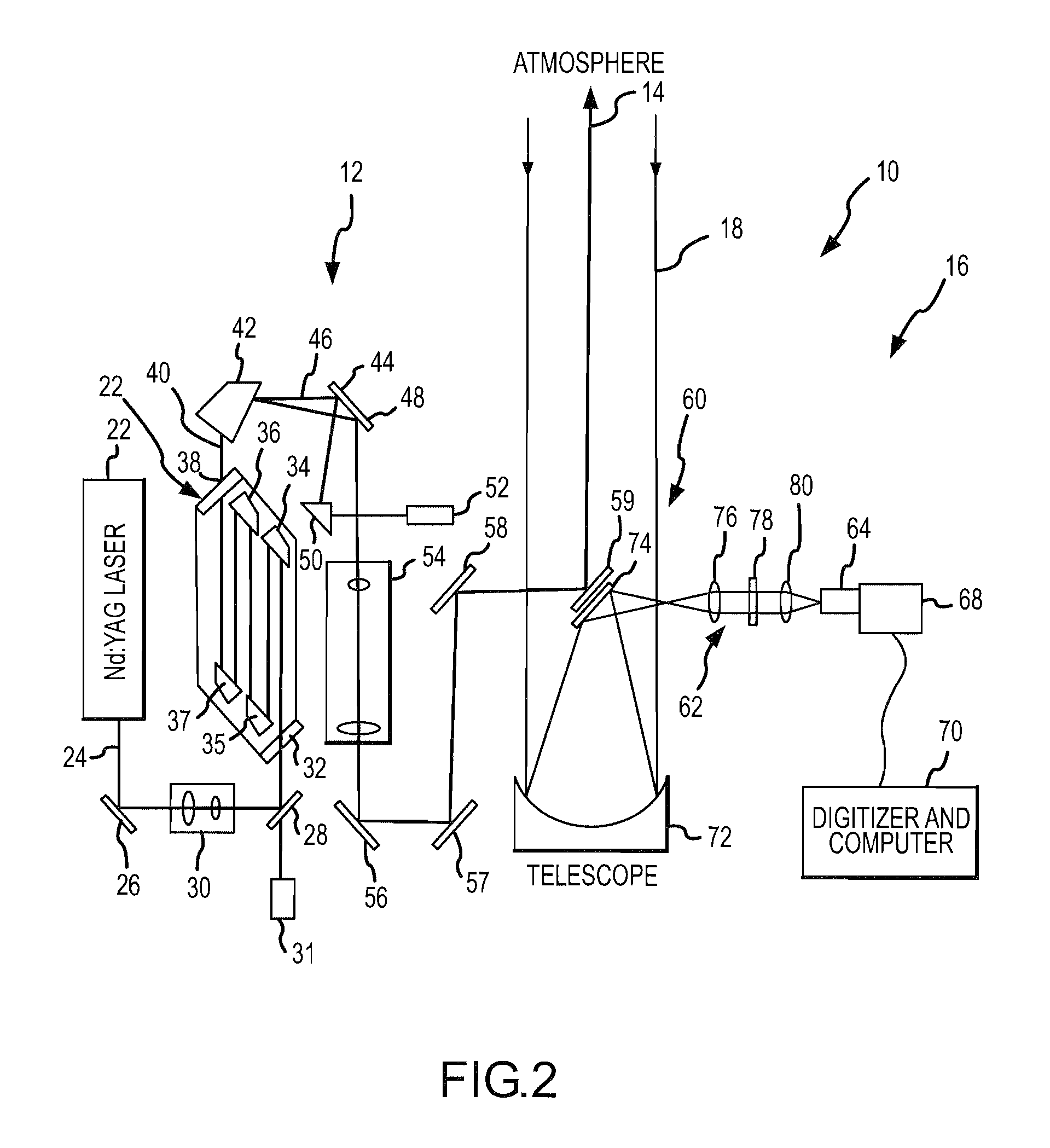
High pulse-energy, eye-safe lidar system
ActiveUS7583364B1High pulse energyMinimal divergenceOptical rangefindersMaterial analysis by optical meansImage resolutionPulse energy
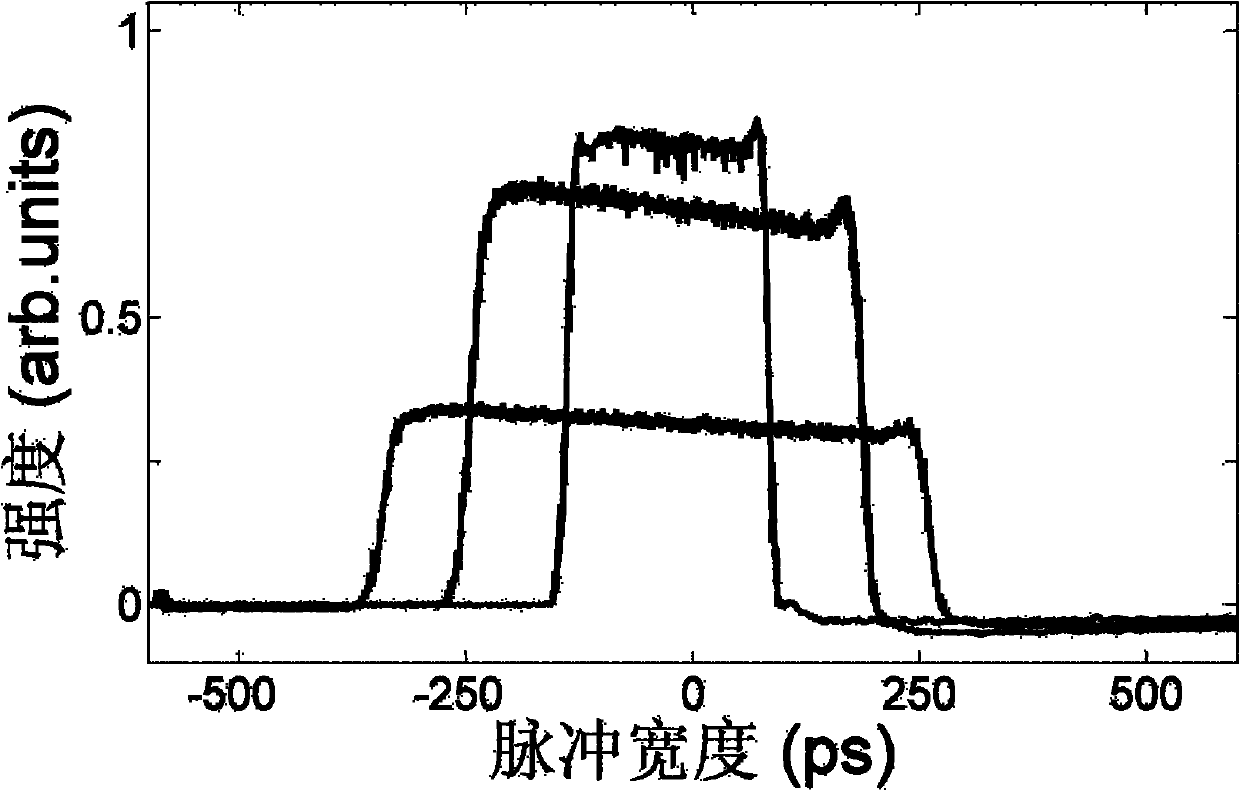
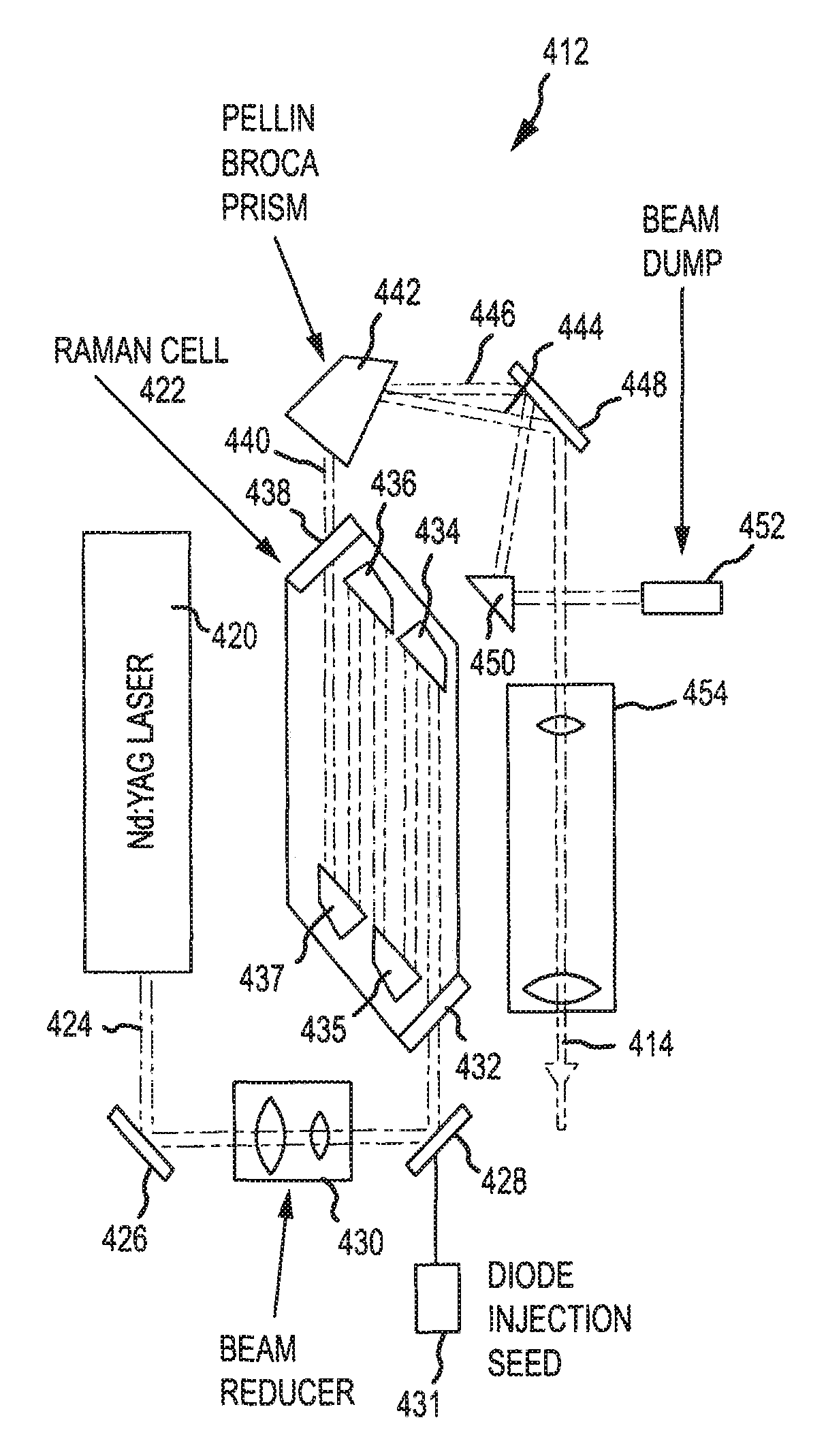
An eye-safe atmospheric aerosol lidar featuring high transmit pulse energy to generate strong backscatter from long ranges in a single pulse together with an optically efficient receiver is disclosed. The transmitter employs a gas cell and non-focused laser beam geometry to convert short wavelength laser light to substantially safer and longer wavelength light by stimulated Raman scattering. The longer wavelength light is substantially safer than the shorter wavelength light thereby allowing the safe transmission of high energy pulses. The transmitter also features a diode injection seed and a beam expander which are effective to reduce the divergence of the long wavelength light below the field-of-view of the receiver. The receiver employs a telescope, collimating lens, interference filter, focusing lens, avalanche photodiode detector, amplifier and analog to digital converter. The transmit beam and receiver field of view are coaxial. Initial results demonstrate the ability of such technology to elucidate the structure of the atmosphere with high temporal and spatial resolution.
Owner:UNIV FOR ATMOSPHERIC RES
Method and apparatus for dicing of thin and ultra thin semiconductor wafer using ultrafast pulse laser
InactiveUS7804043B2Minimize heating effectImprove machine qualityWelding/soldering/cutting articlesMetal working apparatusPicosecond laserBeam polarization
The present invention relates to the apparatus, system and method for dicing of semiconductor wafers using an ultrafast laser pulse of femtosecond and picosecond pulse widths directly from the ultrafast laser oscillator without an amplifier. Thin and ultrathin semiconductor wafers below 250 micrometer thickness, are diced using diode pumped, solid state mode locked ultrafast laser pulses from oscillator without amplification. The invention disclosed has means to avoid / reduce the cumulative heating effect and to avoid machine quality degrading in multi shot ablation. Also the disclosed invention provides means to change the polarization state of the laser beam to reduce the focused spot size, and improve the machining efficiency and quality. The disclosed invention provides a cost effective and stable system for high volume manufacturing applications. An ultrafast laser oscillator can be a called as femtosecond laser oscillator or a picosecond laser oscillator depending on the pulse width of the laser beam generated.
Owner:LASERFACTURING
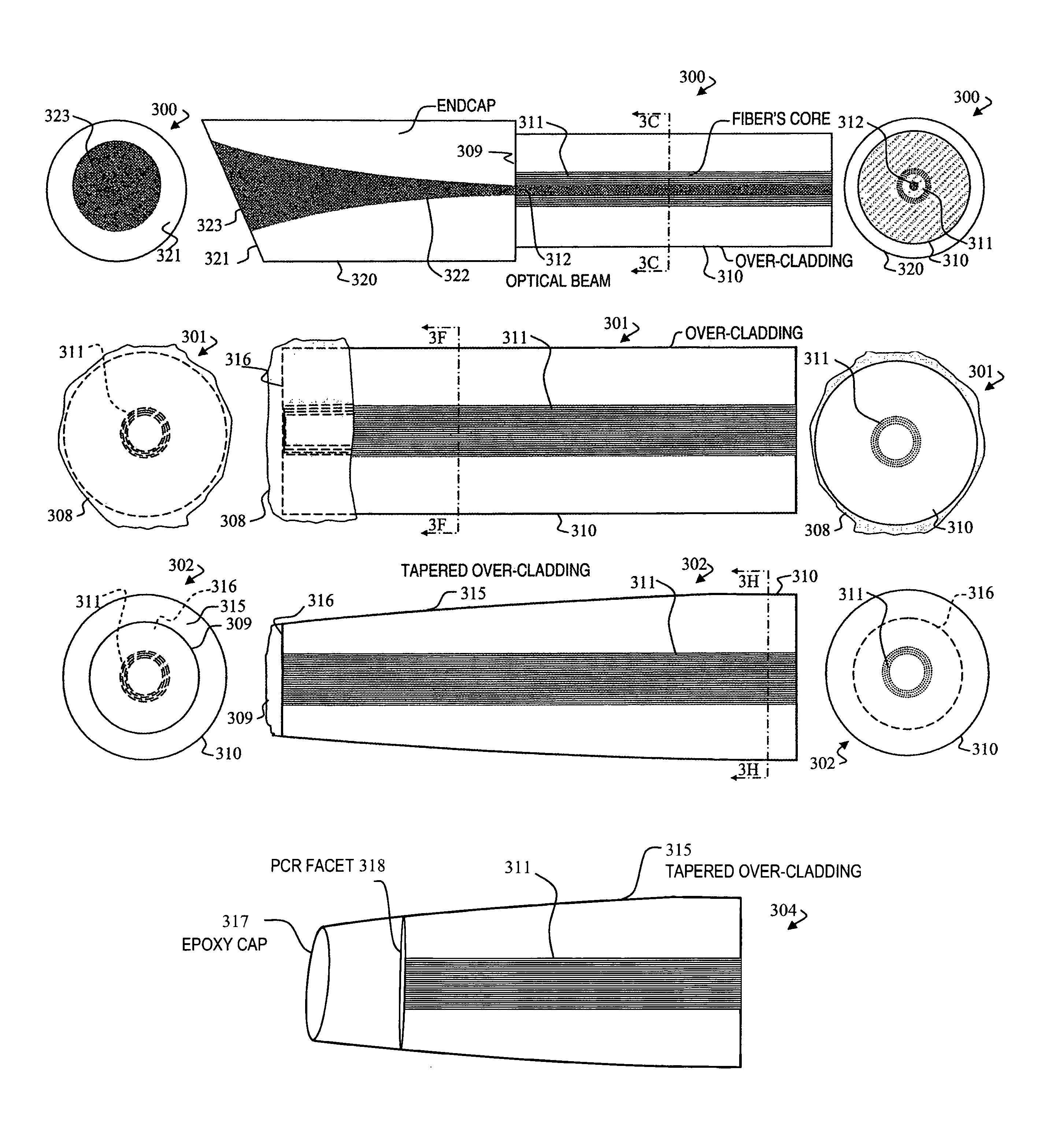
Multi-segment photonic-crystal-rod waveguides for amplification of high-power pulsed optical radiation and associated method
InactiveUS20070104431A1High peak powerHigh pulse energyLaser detailsCladded optical fibreOptical radiationPromiscuous behaviour
A method and apparatus use a photonic-crystal fiber having a very large core while maintaining a single transverse mode. In some fiber lasers and amplifiers having large cores problems exist related to energy being generated at multiple-modes (i.e., polygamy), and of mode hopping (i.e., promiscuity) due to limited control of energy levels and fluctuations. The problems of multiple-modes and mode hopping result from the use of large-diameter waveguides, and are addressed by the invention. This is especially true in lasers using large amounts of energy (i.e., lasers in the one-megawatt or more range). By using multiple small waveguides in parallel, large amounts of energy can be passed through a laser, but with better control such that the aforementioned problems can be reduced. An additional advantage is that the polarization of the light can be maintained better than by using a single fiber core.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
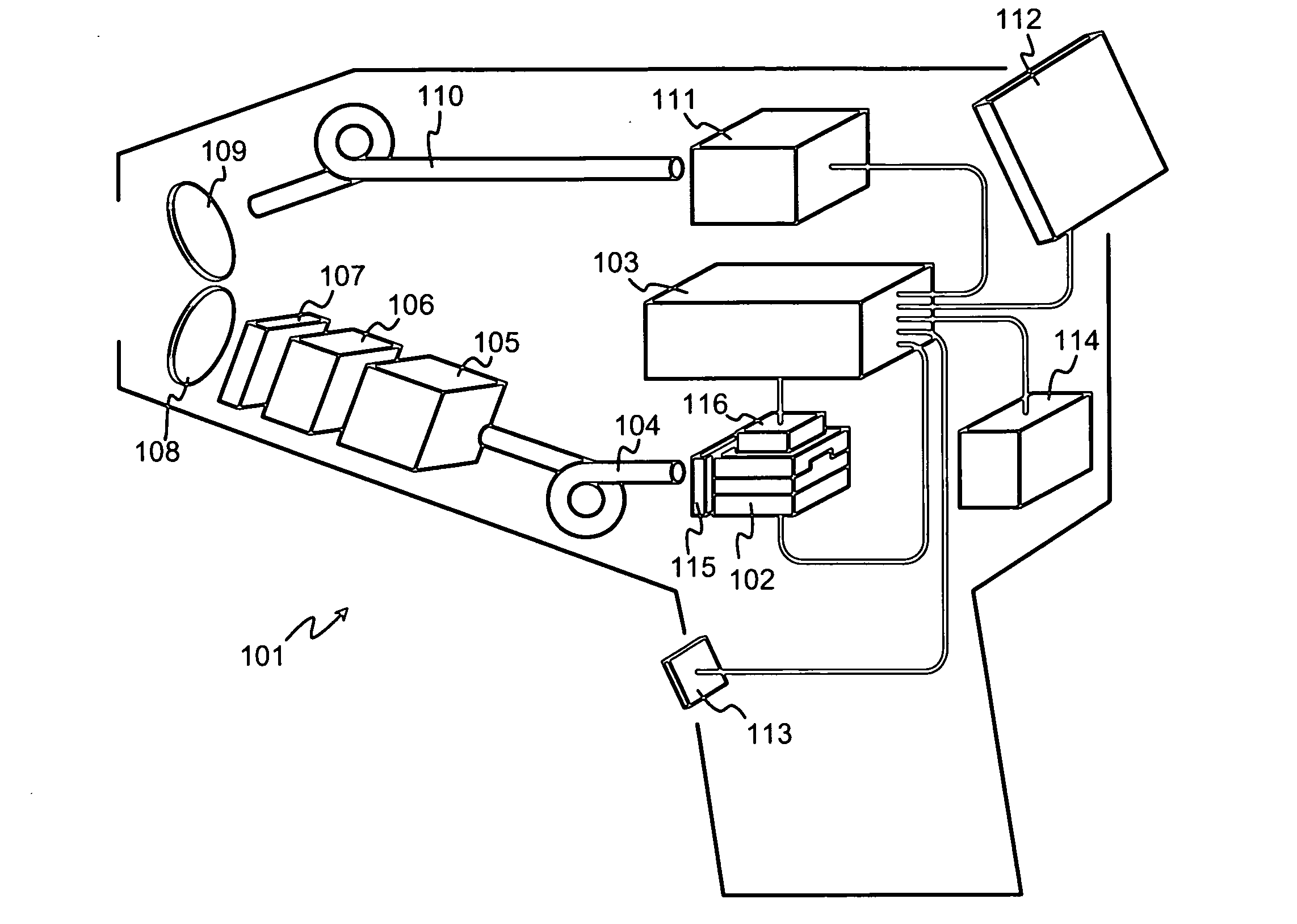
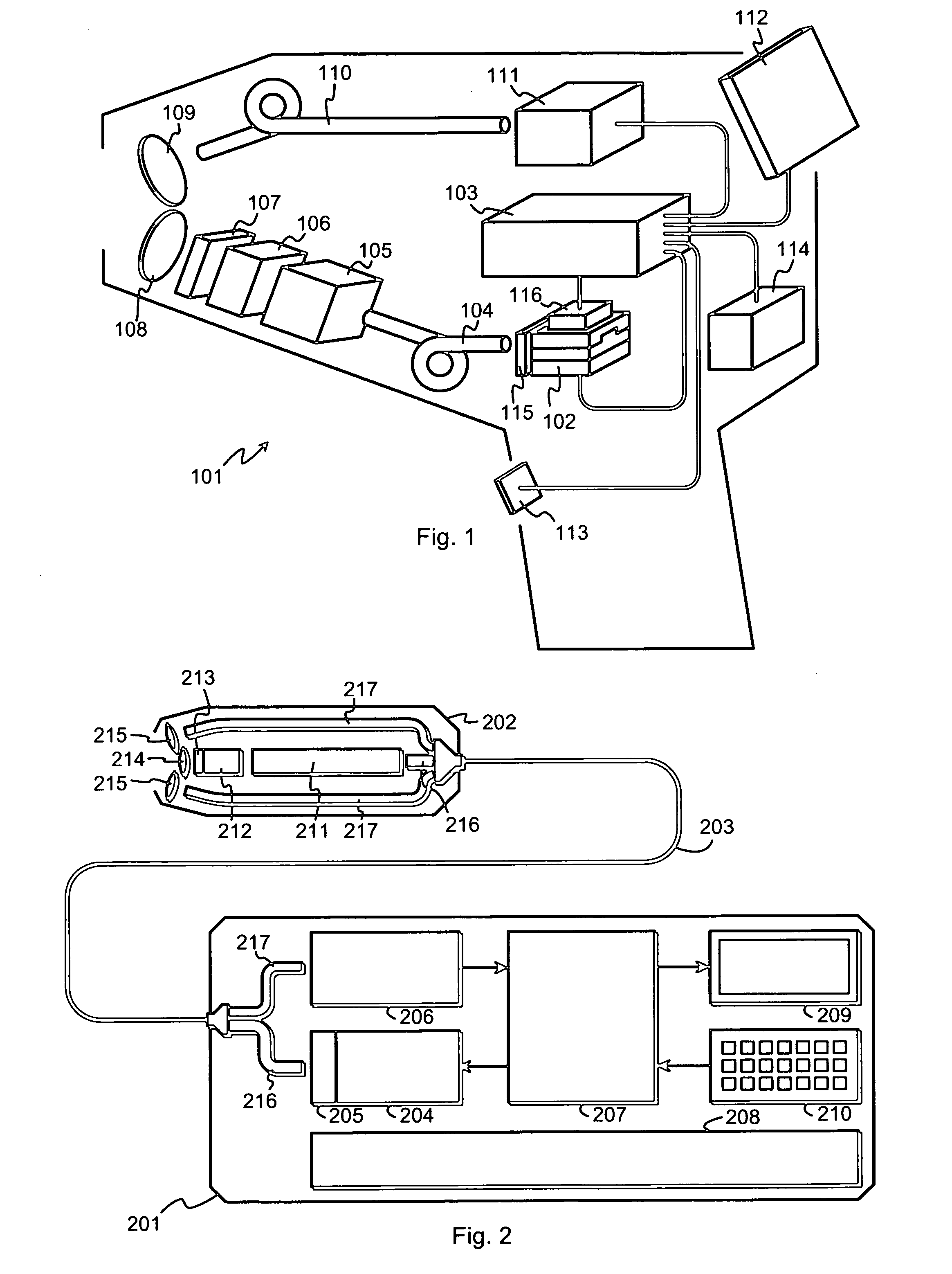
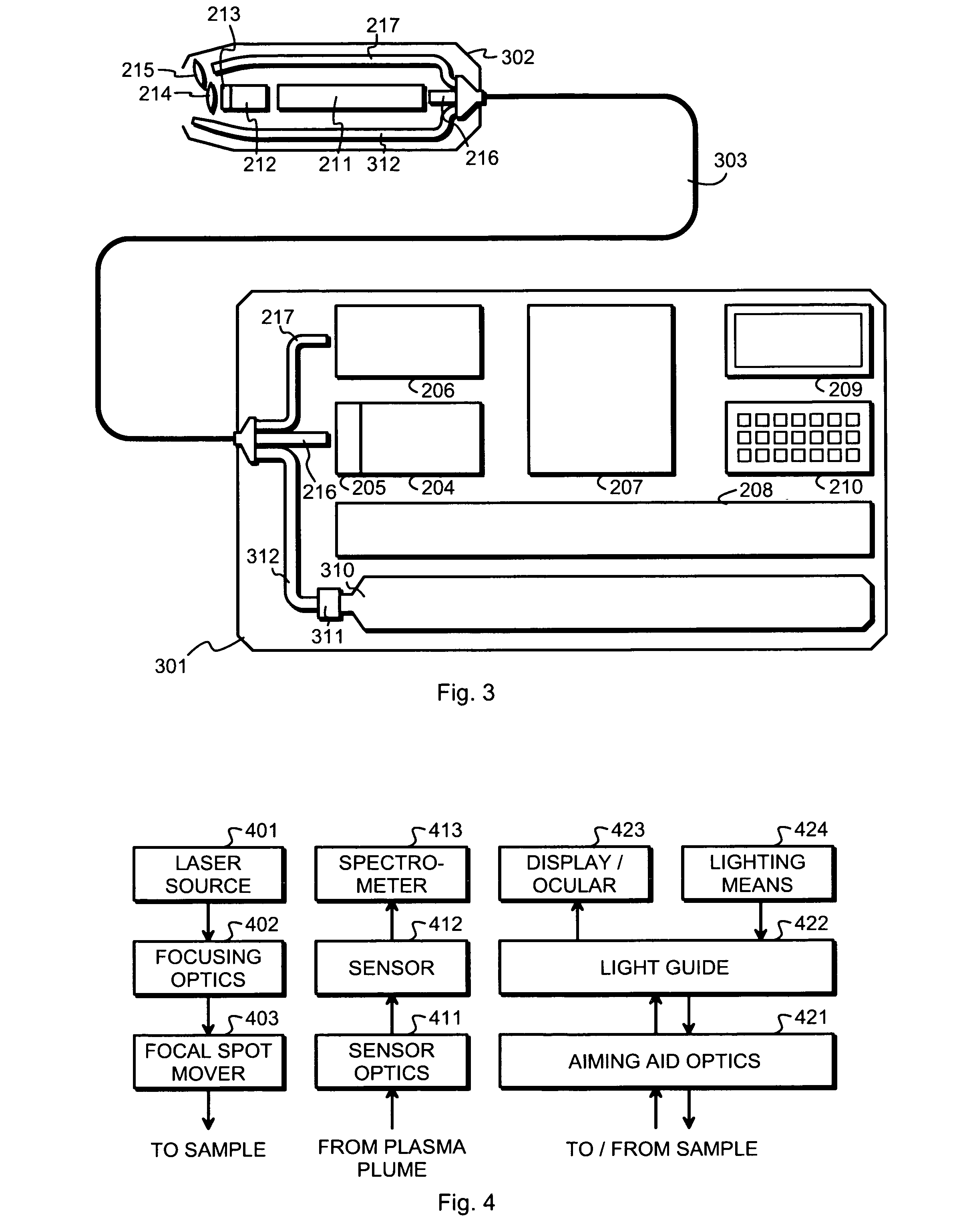
Practical laser induced breakdown spectroscopy unit
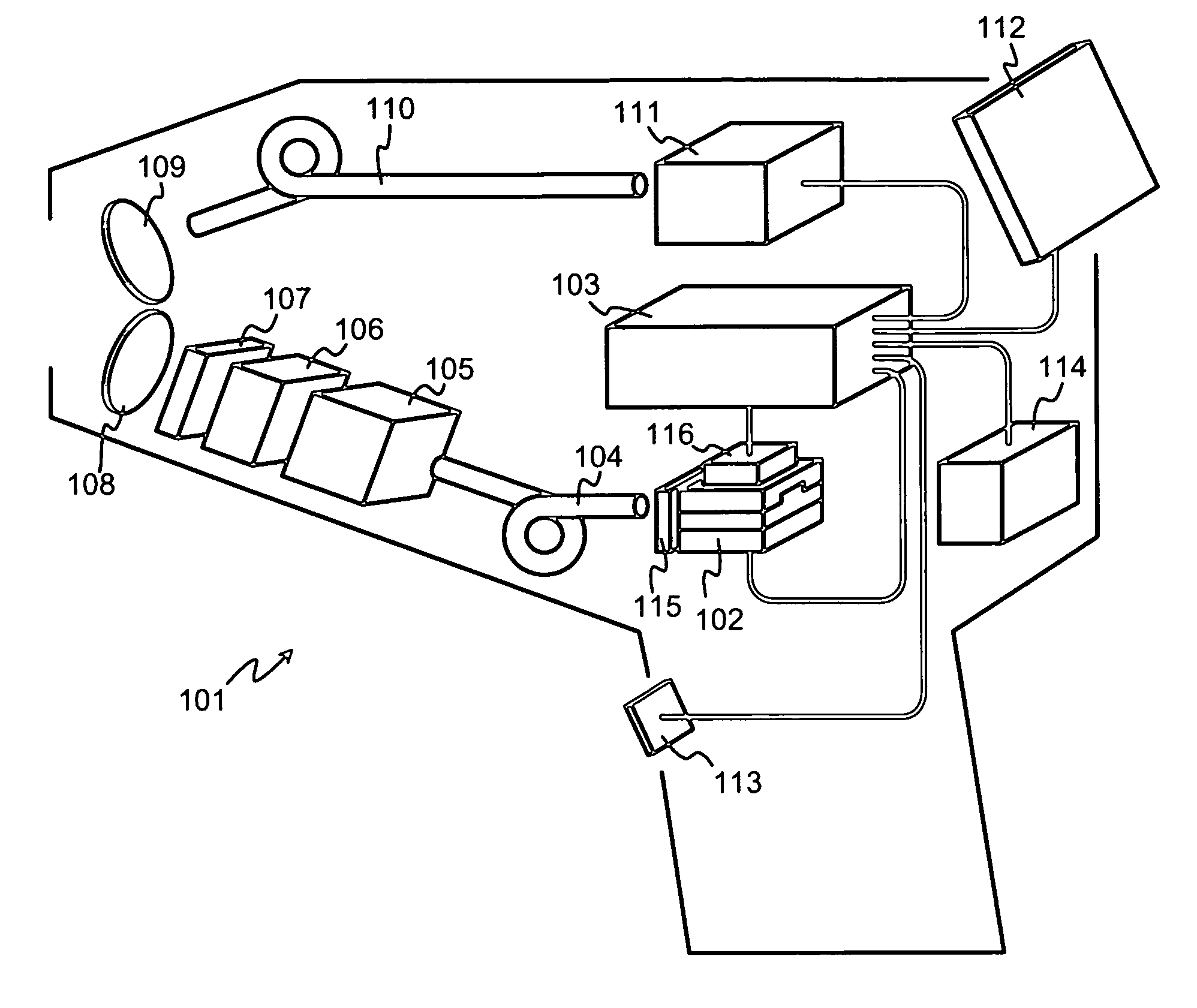
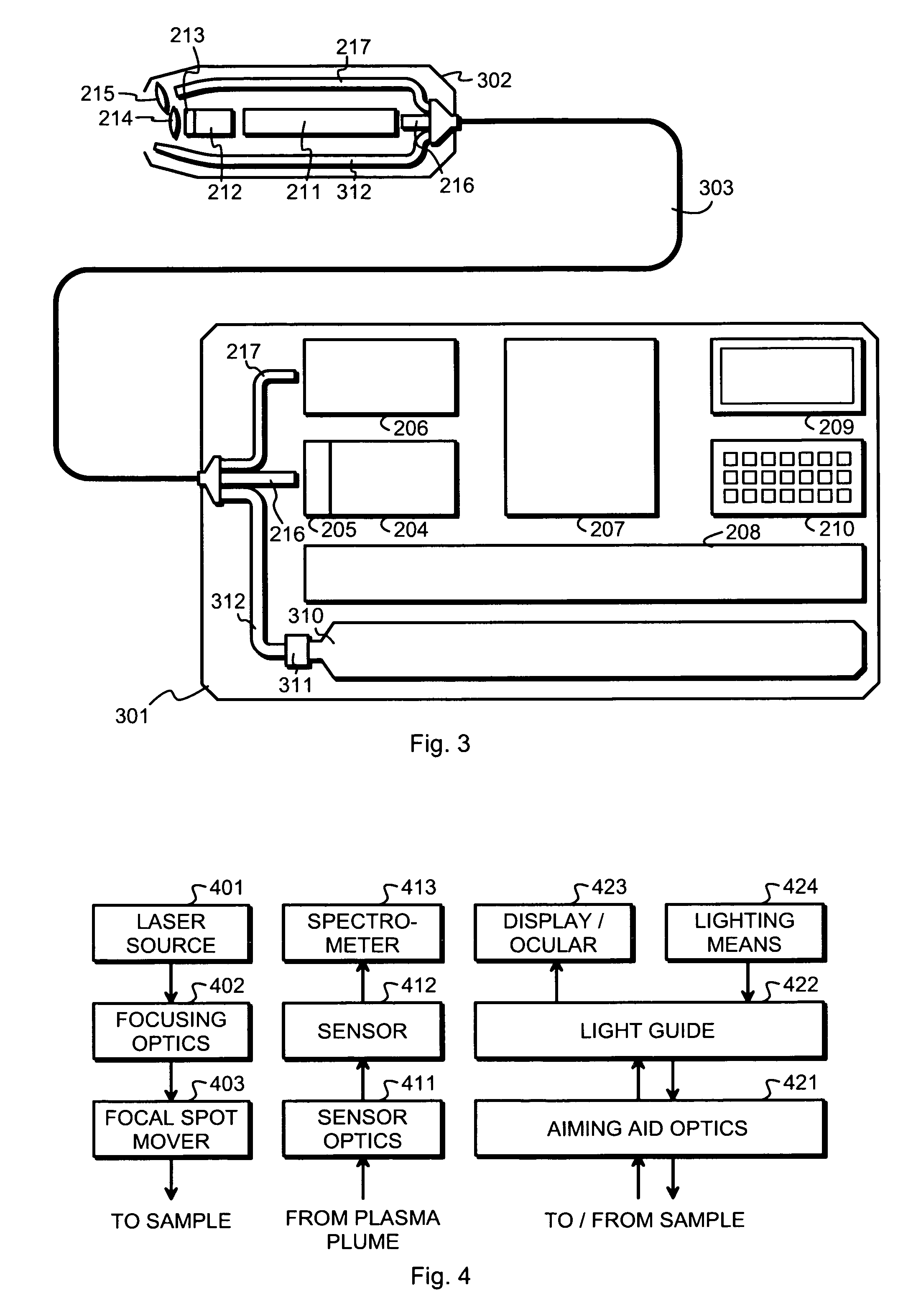
ActiveUS20080151241A1Easy to reachHigh energy consumptionRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationLaser-induced breakdown spectroscopyLaser beams
An apparatus for performing laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy comprises a handheld unit with a pump laser and a controller. A combination of a solid laser medium and a Q-switch receive a laser beam from said pump laser. Focusing optics focus laser pulses from said combination to a focal spot at a sample. Light collection optics collect light from plasma induced of sample material by focused laser pulses. A spectrometer receives collected light and produces information describing its spectral distribution. A power source delivers electric power to other parts of the apparatus. The pump laser, combination, focusing optics, light collection optics, spectrometer and power source are parts of said handheld unit.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH TECH ANALYTICAL SCI FINLAND OY
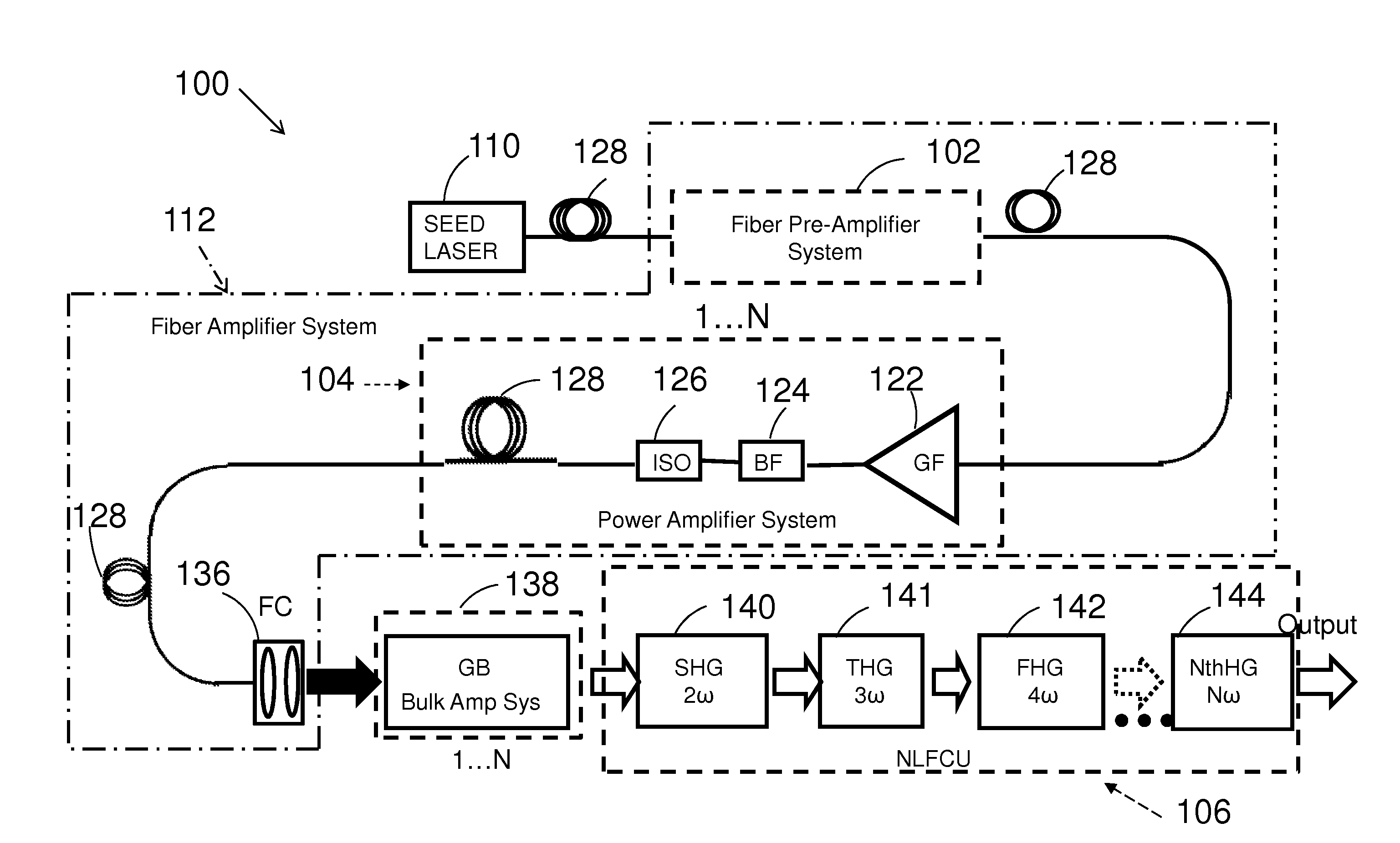
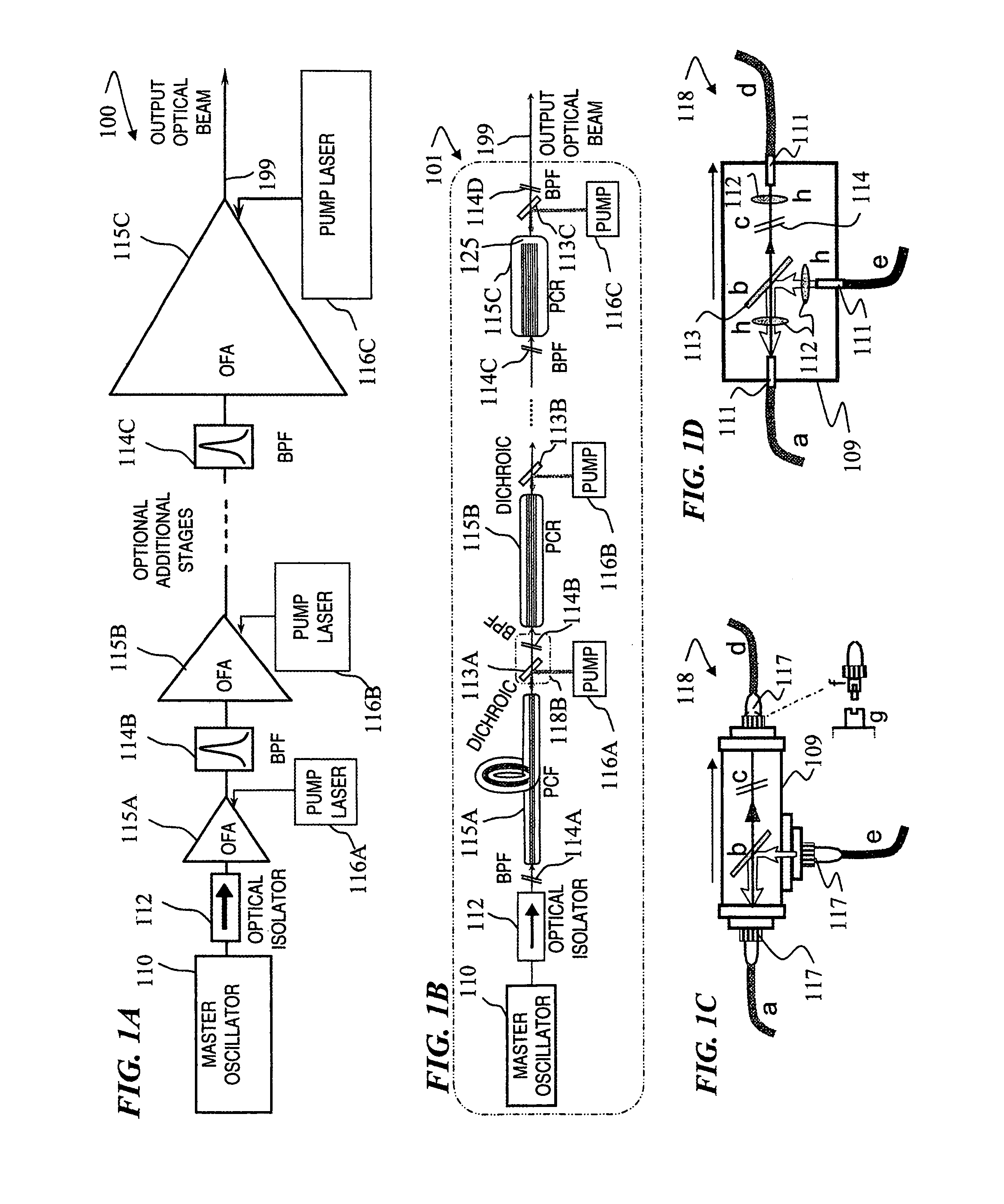
Ultraviolet fiber laser system
InactiveUS20130044768A1Quality improvementLower the volumeLaser using scattering effectsFrequency conversionUltraviolet
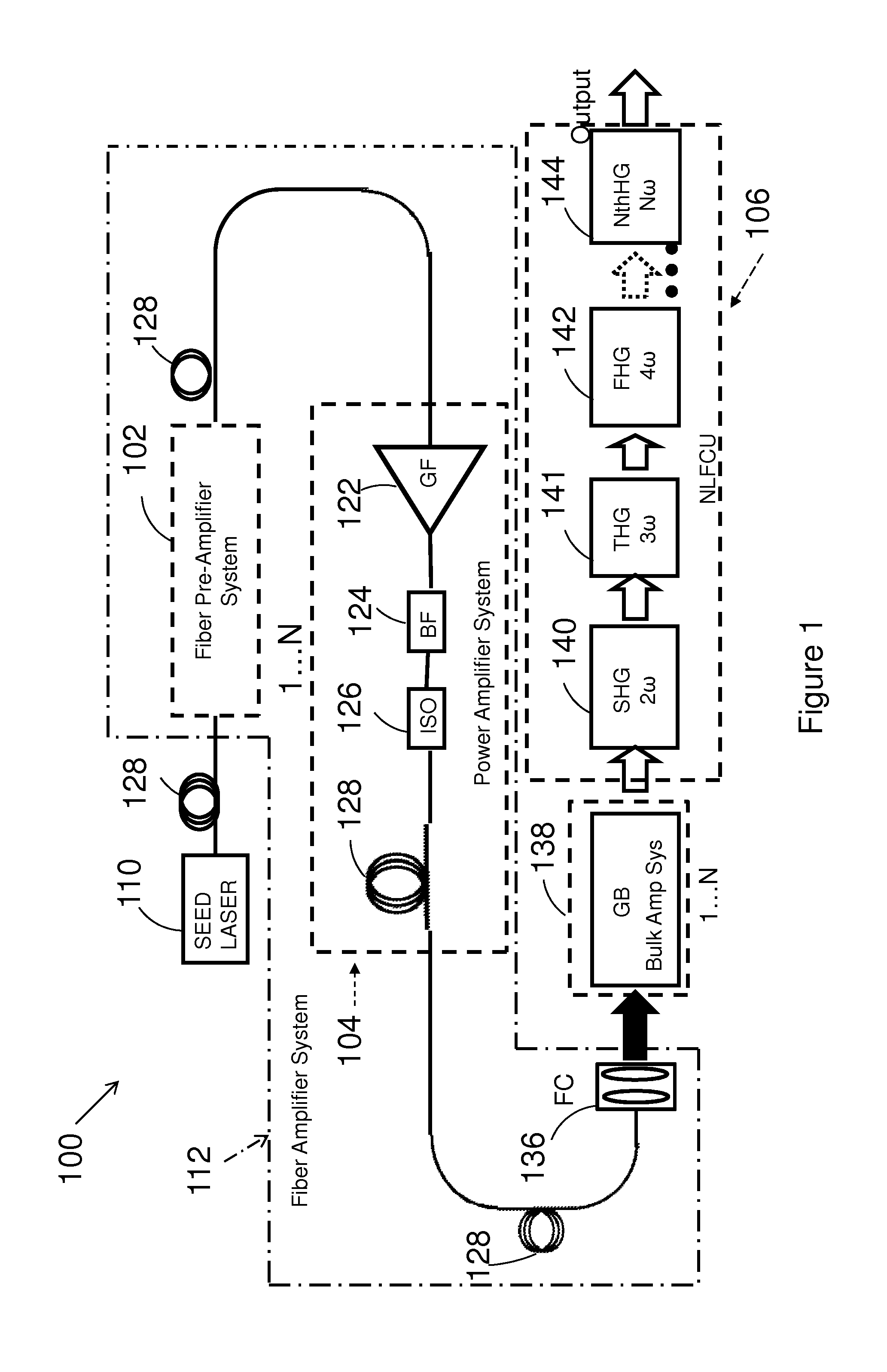
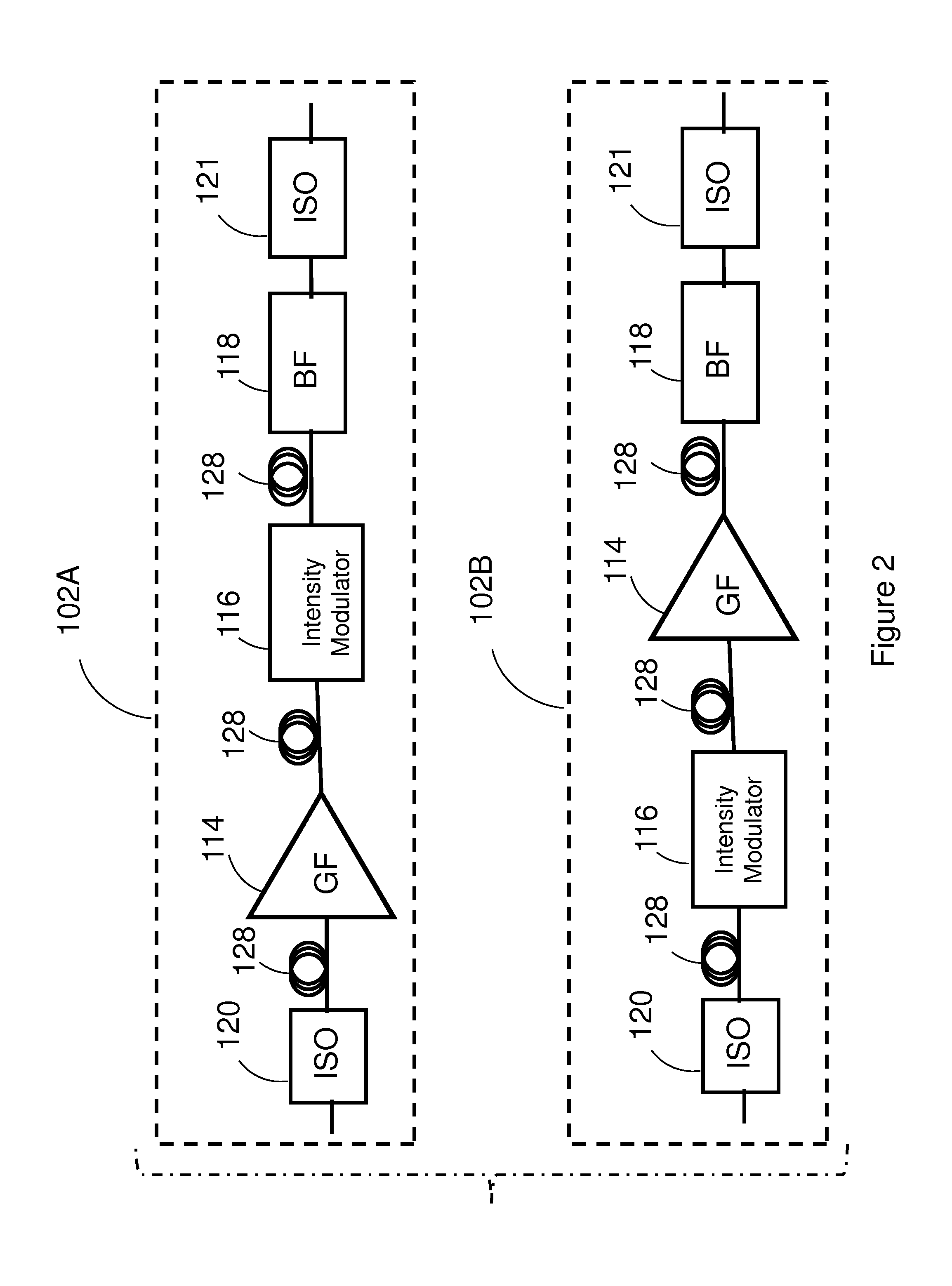
Laser master oscillator—power amplifier system for generating high pulse energy, high average power laser pulses in the ultraviolet 191.25-201.25 nm and 243-246.25 nm spectral ranges, and in the visible 450-537.5 nm spectral range with controllable pulse duration and pulse repetition rate employ a master oscillator seed laser operating in the infra-red spectral range, and a single series connected chain of hybrid fiber—bulk crystalline amplifiers coupled to a non-linear frequency conversion unit to convert the laser pulses to the ultraviolet and visible spectral ranges.
Owner:VERALAS
Ultraviolet fiber laser system
InactiveUS20140050234A1Quality improvementLower the volumeLaser using scattering effectsFrequency conversionUltraviolet
Laser master oscillator-power amplifier system for generating high pulse energy, high average power laser pulses in the ultraviolet 191.25-201.25 nm and 243-246.25 nm spectral ranges, and in the visible 450-537.5 nm spectral range with controllable pulse duration and pulse repetition rate employ a master oscillator seed laser operating in the infra-red spectral range, and a single series connected chain of hybrid fiber-bulk optical amplifiers coupled to a non-linear frequency conversion unit to convert the laser pulses to the ultraviolet and visible spectral ranges.
Owner:VERALAS
Practical laser induced breakdown spectroscopy unit
ActiveUS7394537B1High energy consumptionReduce energy consumptionEmission spectroscopyRadiation pyrometryLaser-induced breakdown spectroscopyLaser beams
An apparatus for performing laser-induced breakdown spectroscopy comprises a handheld unit with a pump laser and a controller. A combination of a solid laser medium and a Q-switch receive a laser beam from said pump laser. Focusing optics focus laser pulses from said combination to a focal spot at a sample. Light collection optics collect light from plasma induced of sample material by focused laser pulses. A spectrometer receives collected light and produces information describing its spectral distribution. A power source delivers electric power to other parts of the apparatus. The pump laser, combination, focusing optics, light collection optics, spectrometer and power source are parts of said handheld unit.
Owner:HITACHI HIGH TECH ANALYTICAL SCI FINLAND OY
Compact, coherent, high brightness light sources for the mid and far ir
ActiveUS20120205352A1High energyReduce widthLaser using scattering effectsLaser beam welding apparatusFiber Bragg gratingOptoelectronics
Compact high brightness light sources for the mid and far IR spectral region, and exemplary applications are disclosed based on passively mode locked Tm fiber comb lasers. In at least one embodiment the coherence of the comb sources is increased in a system utilizing an amplified single-frequency laser to pump the Tm fiber comb laser. The optical bandwidth generated by the passively mode locked Tm fiber comb laser is further decreased by using simultaneous 2nd and 3rd order dispersion compensation using either appropriate chirped fiber Bragg gratings for dispersion compensation, or fibers with appropriately selected values of 2nd and 3rd order dispersion. Fibers with large anomalous values of third order dispersion, or fibers with large numerical apertures, for example fibers having air-holes formed in the fiber cladding may be utilized.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
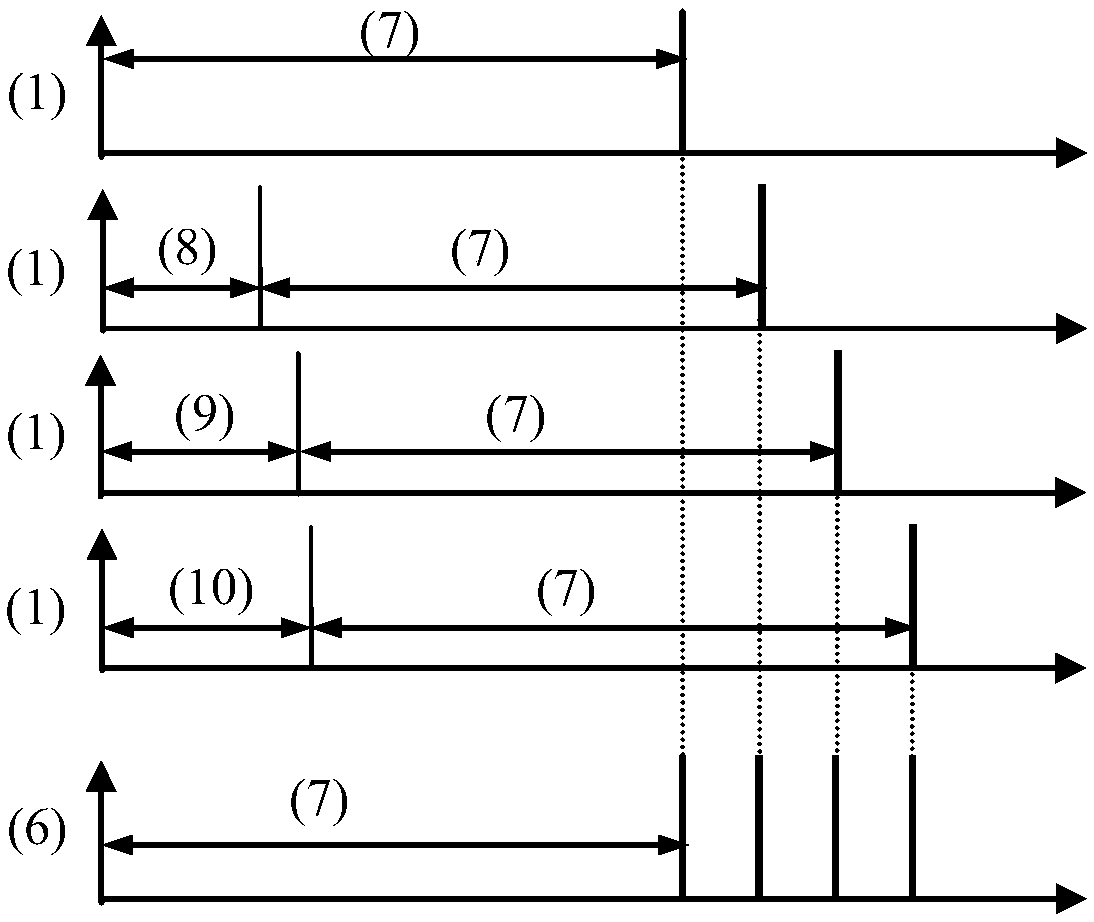
Inexpensive variable rep-rate source for high-energy, ultrafast lasers
InactiveUS20080130099A1High pulse energyReduce repetition rateLaser optical resonator constructionLaser using scattering effectsFiberCost effectiveness
System for converting relatively long pulses from rep-rate variable ultrafast optical sources to shorter, high-energy pulses suitable for sources in high-energy ultrafast lasers. Fibers with positive group velocity dispersion (GVD) and self phase modulation are advantageously employed with the optical sources. These systems take advantage of the need for higher pulse energies at lower repetition rates so that such sources can be cost effective.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Inexpensive variable rep-rate source for high-energy, ultrafast lasers
InactiveUS7330301B2High pulse energyReduce repetition rateCladded optical fibreLaser optical resonator constructionFiberCost effectiveness
System for converting relatively long pulses from rep-rate variable ultrafast optical sources to shorter, high-energy pulses suitable for sources in high-energy ultrafast lasers. Fibers with positive group velocity dispersion (GVD) and self phase modulation are advantageously employed with the optical sources. These systems take advantage of the need for higher pulse energies at lower repetition rates so that such sources can be cost effective.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Negative dispersion pulse widening optical fiber amplifying device
The invention discloses a negative dispersion pulse widening optical fiber amplifying device, which comprises a mode-locked laser, a negative dispersion unit, a primary amplifying unit, a secondary amplifying unit and an output unit, wherein the mode-locked laser generates seed light pulse; the negative dispersion unit is arranged at the emergent side of the seed light pulse of the mode-locked laser to widen the seed light pulse and enable the seed light pulse to have negative chirp; the primary amplifying unit receives the seed light pulse with the negative chirp, which is output by the negative dispersion unit, carries out primary amplification, and further carries out positive dispersion compensation on the negative chirp in the seed light pulse to shorten the seed light pulse; the secondary amplifying unit receives the seed light pulse output by the primary amplifying unit, carries out secondary amplification, and further carries out positive dispersion compensation on the negative chirp in the seed light pulse to shorten the seed light pulse; and the output unit is connected with the secondary amplifying unit and outputs the amplified seed light pulse. The invention makes the pulse of the output end of the optical fiber amplifier shortest via the negative dispersion widening, simplifies the system, reduces the loss, increases the pulse energy after the amplifier, and effectively reduces the cost.
Owner:PEKING UNIV +1
Multi-segment photonic-crystal-rod waveguides coupled across a free-space gap and associated method
ActiveUS7260299B1High peak powerHigh pulse energyLaser detailsCladded optical fibreEngineeringMulti segment
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Lasers and LiDAR
ActiveCN109950784BShorten cavity lengthReduce volumeLaser detailsElectromagnetic wave reradiationHigh peakOptical axis
A laser and a laser radar, the laser comprises: a pump unit, a gain unit, a Q-switching unit and a light splitting unit arranged in sequence along an optical axis; the pump unit generates pump light; the gain unit includes a gain medium; the The Q-switching unit includes a saturable absorber; the light splitting unit generates outgoing laser light and a plurality of tuned lights of different wavelengths; a resonant reflection surface and a scanning unit, the resonant reflection surface is located between the gain unit and the pump unit , the scanning unit is located on the optical path of the plurality of tuned lights, and the scanning unit selects one from the plurality of tuned lights and returns the selected tuned light according to the original optical path. The laser is a tunable laser that can realize Q-switching, can obtain higher peak power and greater pulse energy, and can effectively shorten the cavity length and volume of the resonator cavity, which is conducive to the realization of high integration and high peak power. Consideration of value power.
Owner:HESAI TECH CO LTD
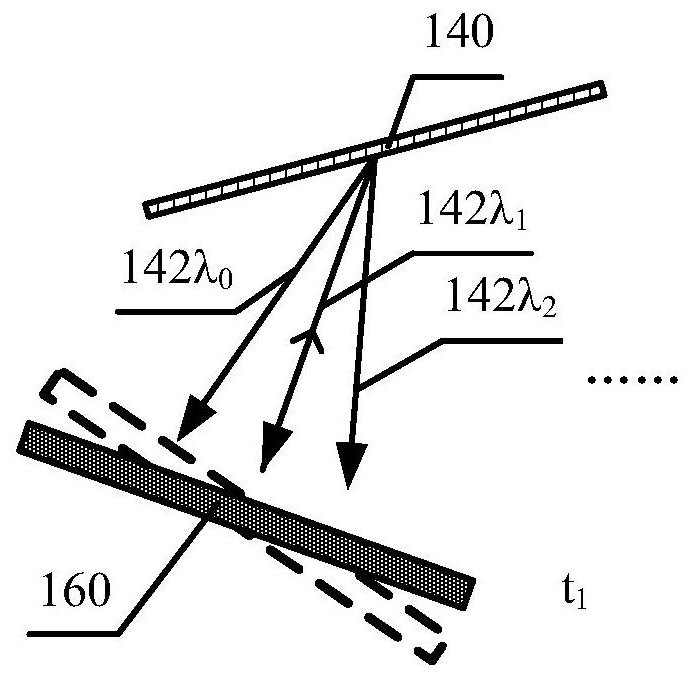
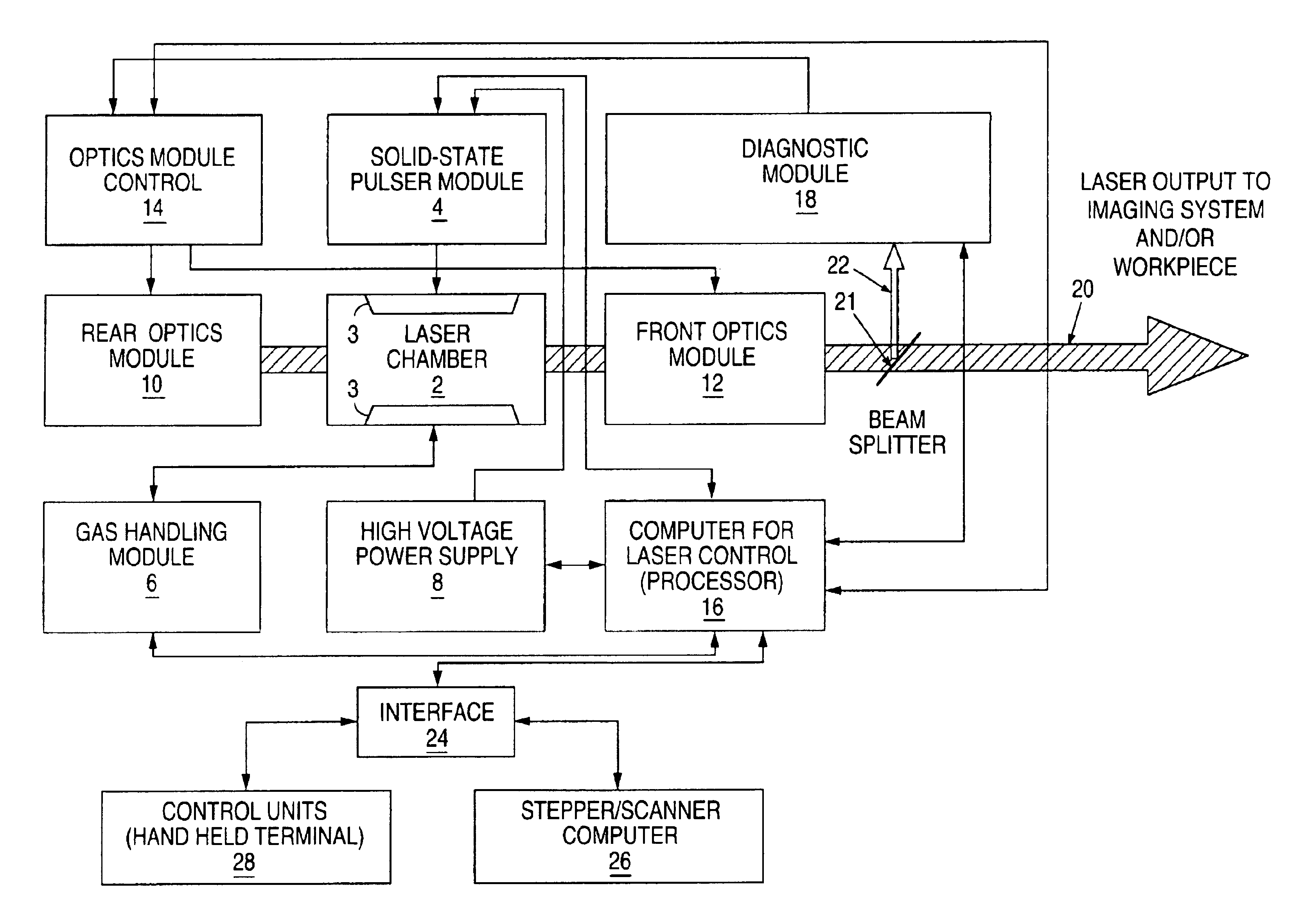
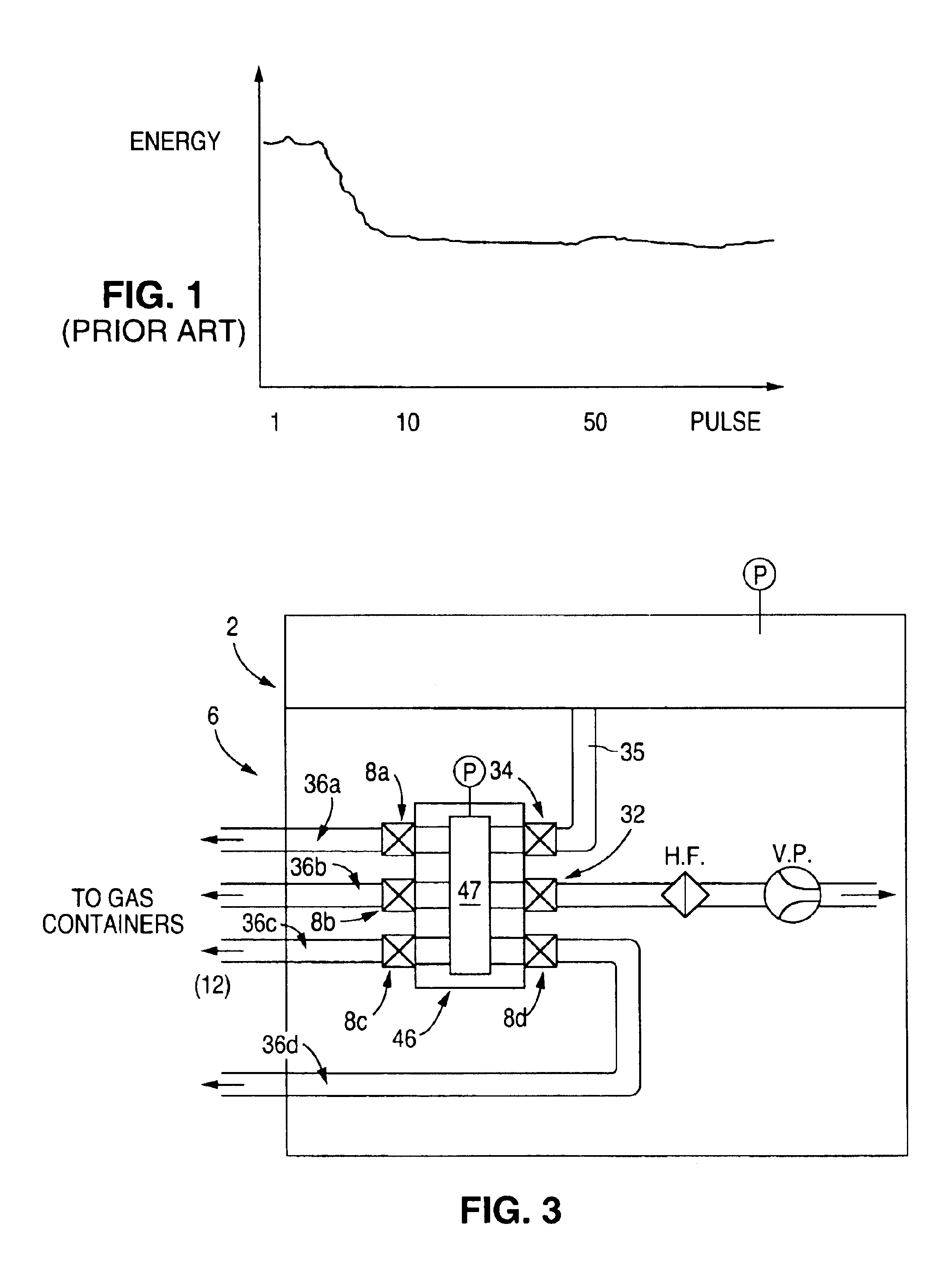
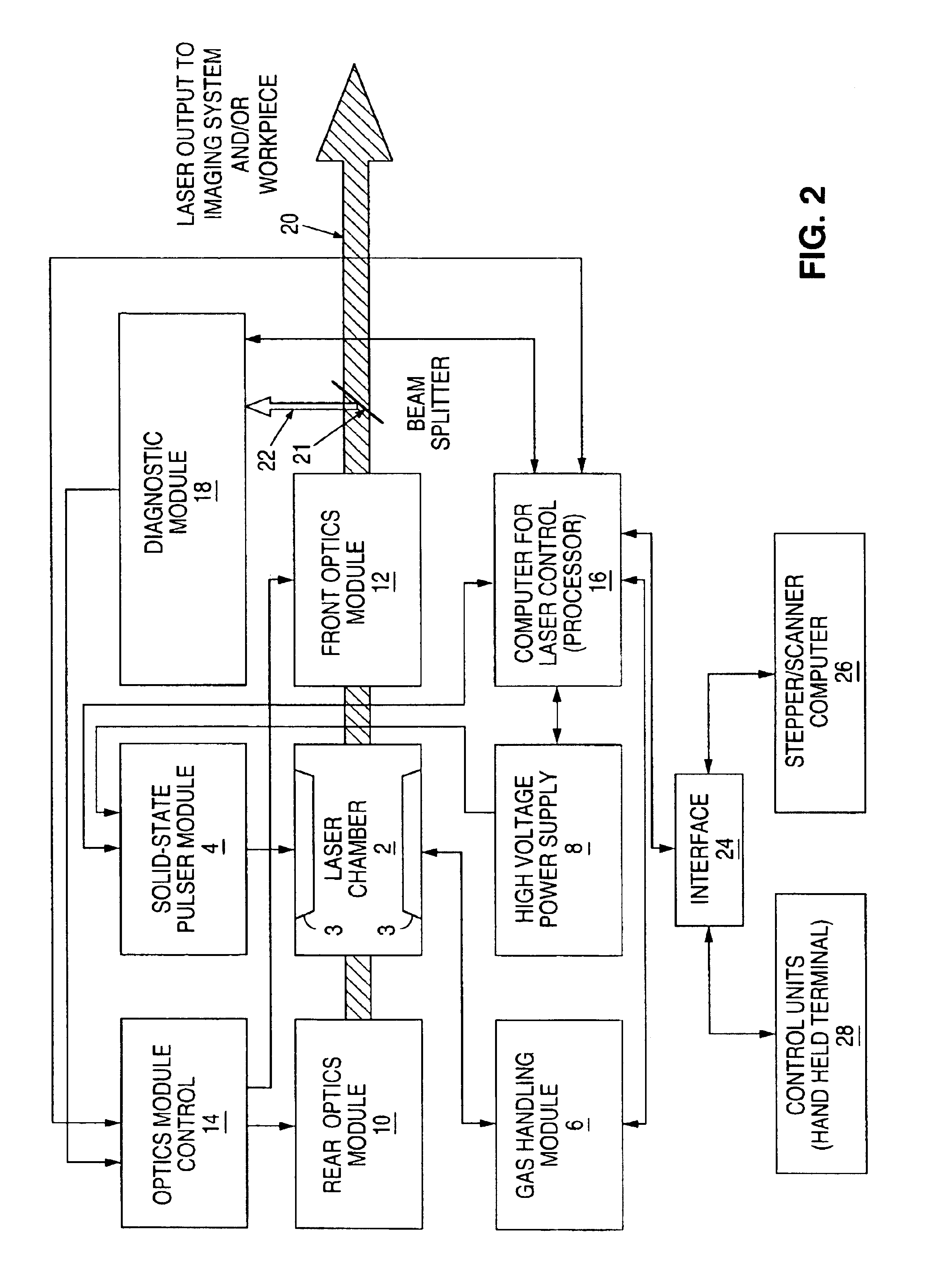
Energy control for an excimer or molecular fluorine laser
InactiveUS6727731B1High pulse energyImprove performanceMultiple input and output pulse circuitsActive medium materialEnergy controlPulse counting
A method and gas replenishment algorithm for excimer and molecular fluorine lasers is based on parameters upon which gas aging more closely depends than pulse count, such as input energy to the electrical discharge, and also preferably time. A burst control method and algorithm includes measuring the energies of initial pulses of a first burst occurring after a long burst break, calculating values of input voltages for the initial pulses that would bring output energies of the individual laser pulses or groups of pulses to substantially the same values, and applying the calculated voltages in a subsequent first burst after a long burst break to achieve substantially same predetermined output energy values for the pulses or groups of pulses. Similar operations may be performed for one or more subsequent bursts following the first burst. The values for the first burst may be maintained in a first table of input voltage values to be read by a processor which signals a power supply circuit to apply the voltages according to the voltage values in the table. The values for subsequent bursts may be maintained in a second table, and a third table, etc. A final table such as the third table may be used for all subsequent bursts until another long burst break again occurs, after which the first table is again used for the first burst following the long burst break.
Owner:LAMBDA PHYSIK
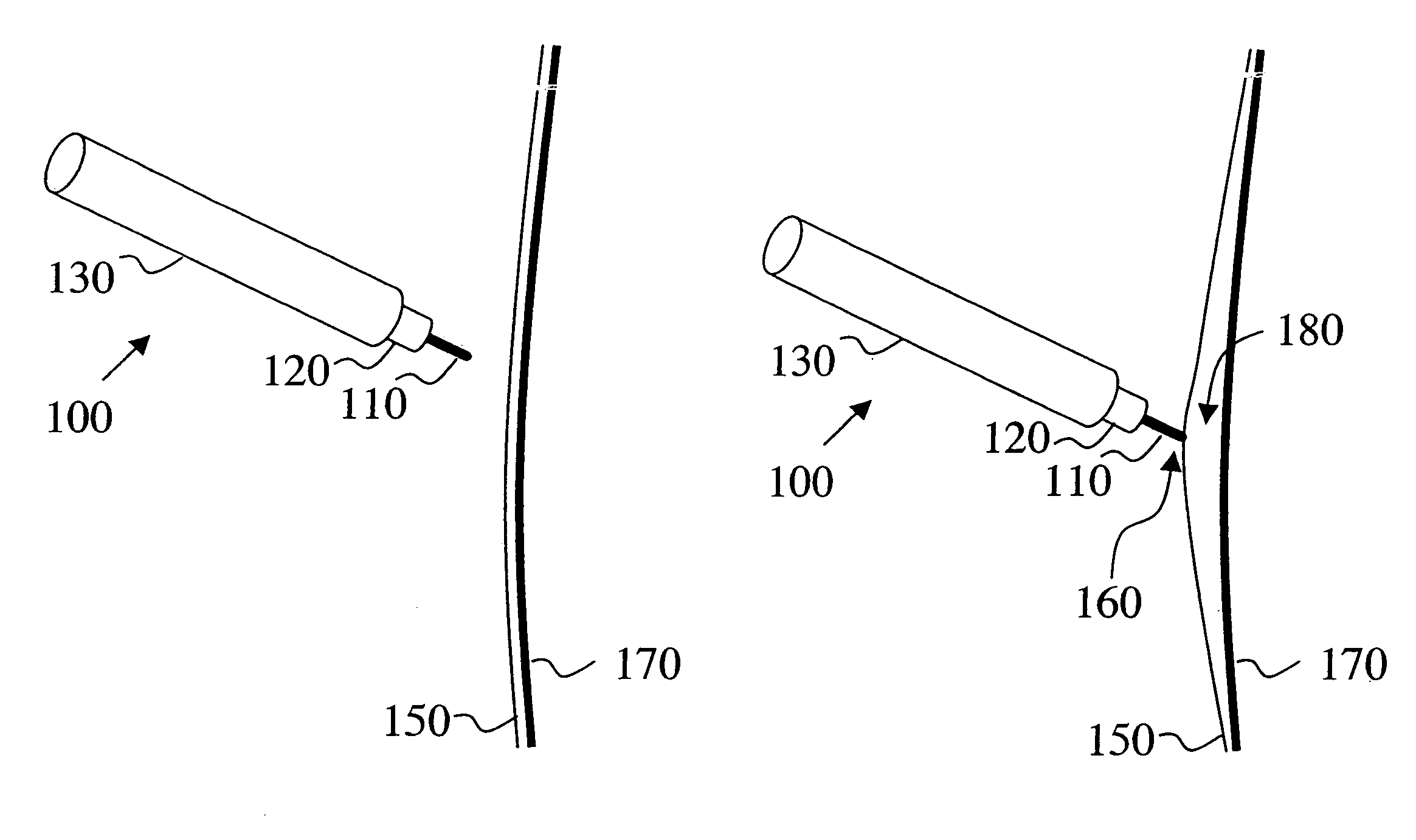
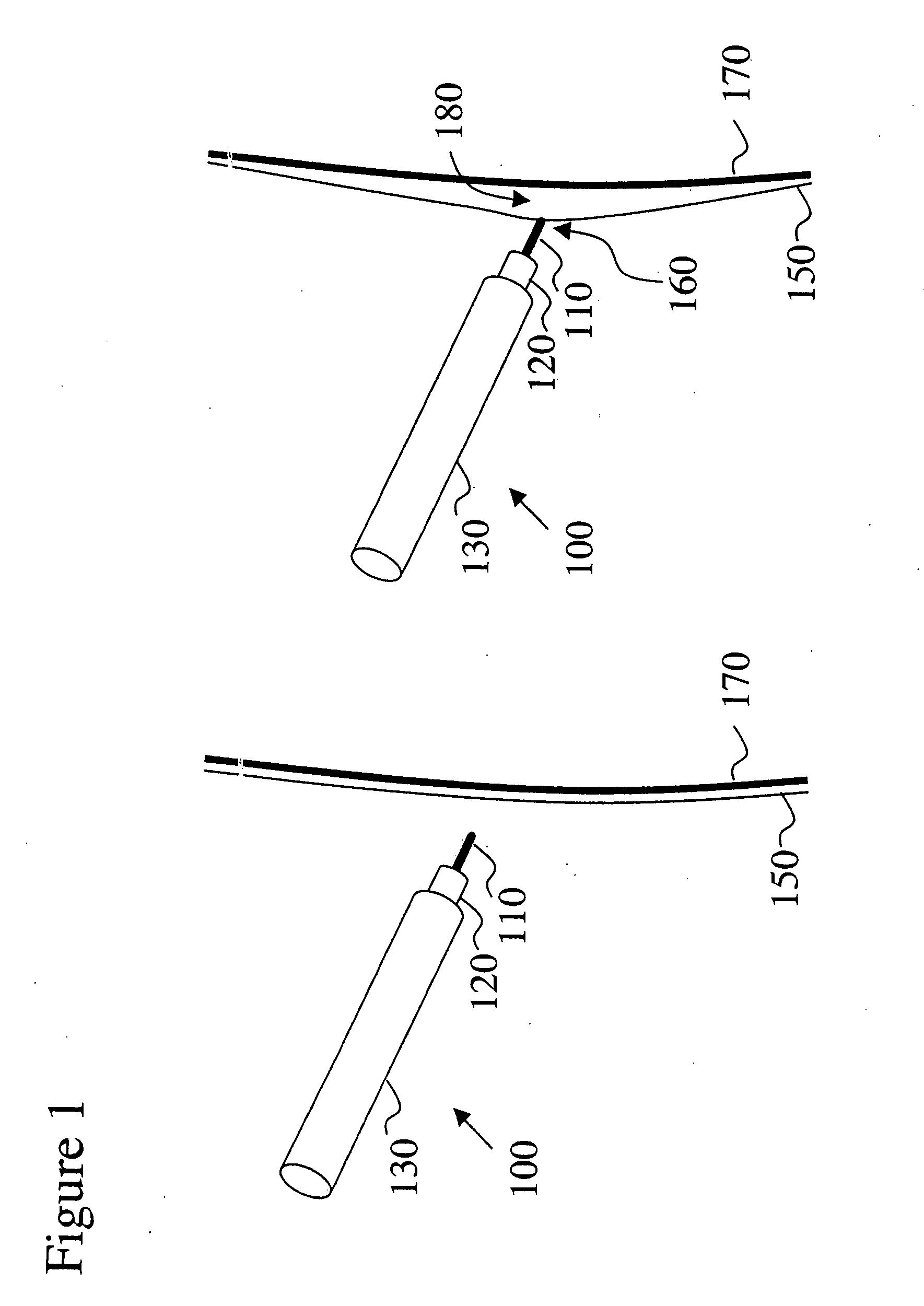
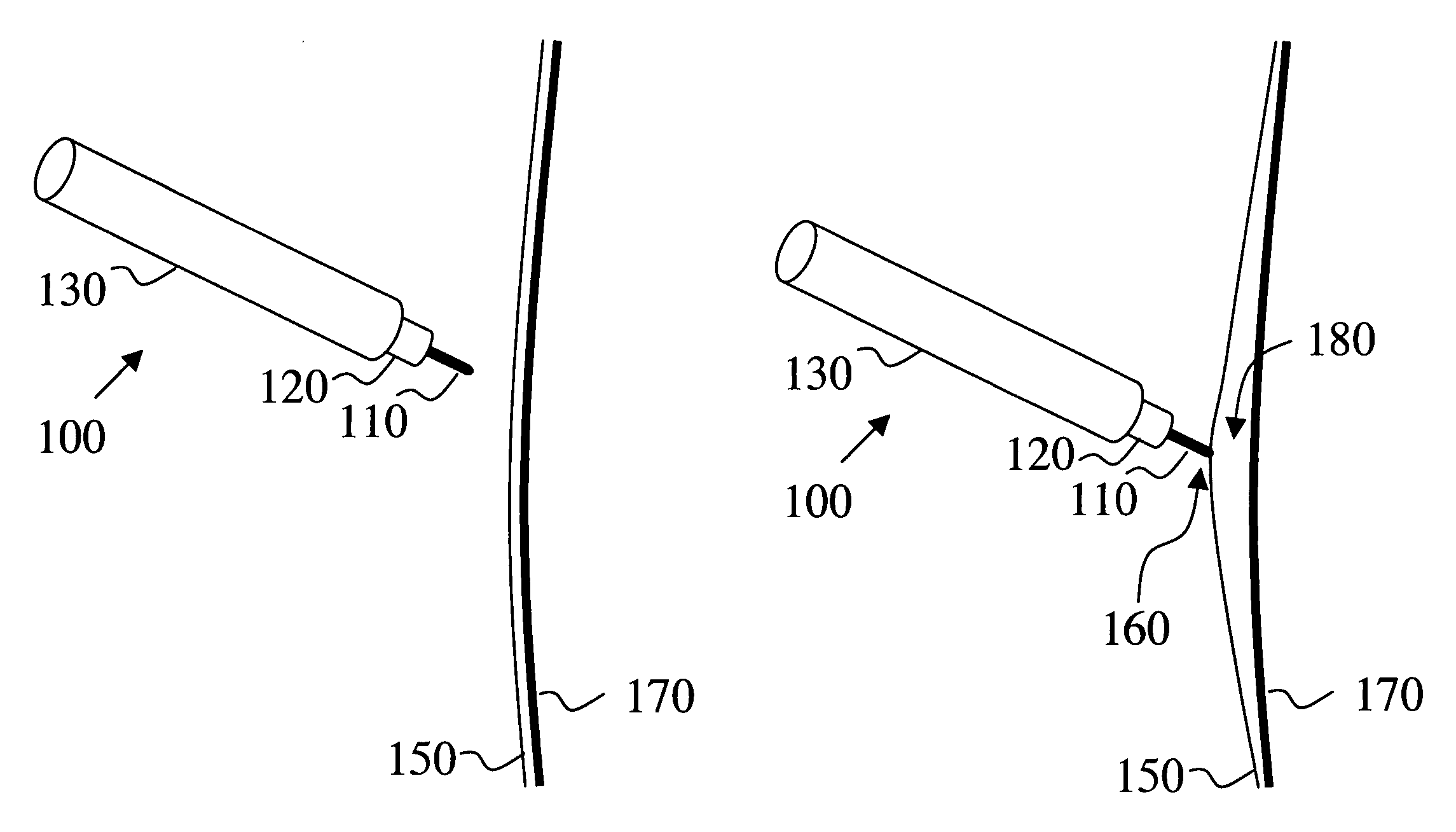
Electro-adhesive tissue manipulation method
InactiveUS20080119842A1High pulse energySufficient energyEye surgeryDiagnosticsElectricityPulse energy
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Electro-adhesive tissue manipulator
InactiveUS20050021028A1High pulse energySufficient energyEye surgeryDiagnosticsElectricityPulse energy
An electro-adhesive tissue manipulator capable of manipulating tissue with a single conducting element is provided. The manipulator includes a conducting element, an electrical means and a control means capable of generating a first and a second pulse on demand. The first pulse generates an adhesive state between the conducting element and the tissue layer strong enough to manipulate the tissue layer. The second pulse, which has higher pulse energy than the first pulse, generates a non-adhesive state to detach the adhered tissue layer from the conducting element. The electro-adhesive device could be combined with a medical instrument to enhance the capabilities of the medical instrument so that it can manipulate tissue. The advantage of the present invention, in contrast to mechanical tools, is that tissue can be manipulated with a single tip of a conducting element, without folding and piercing of the tissue, thus avoiding damage to the tissue.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method and apparatus for long-range lidar and active imaging with optical output from a photonic-crystal rod
InactiveUS7375877B1High peak powerHigh pulse energyGlass making apparatusLaser constructional detailsEngineeringMultiple modes
A method and apparatus use a photonic-crystal fiber having a very large core while maintaining a single transverse mode. In some fiber lasers and amplifiers having large cores problems exist related to energy being generated at multiple-modes (i.e., polygamy), and of mode hopping (i.e., promiscuity) due to limited control of energy levels and fluctuations. The problems of multiple-modes and mode hopping result from the use of large-diameter waveguides, and are addressed by the invention. This is especially true in lasers using large amounts of energy (i.e., lasers in the one-megawatt or more range). By using multiple small waveguides in parallel, large amounts of energy can be passed through a laser, but with better control such that the aforementioned problems can be reduced. An additional advantage is that the polarization of the light can be maintained better than by using a single fiber core.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN ACULIGHT CORP
Laser processing method for steel sieve tube slit
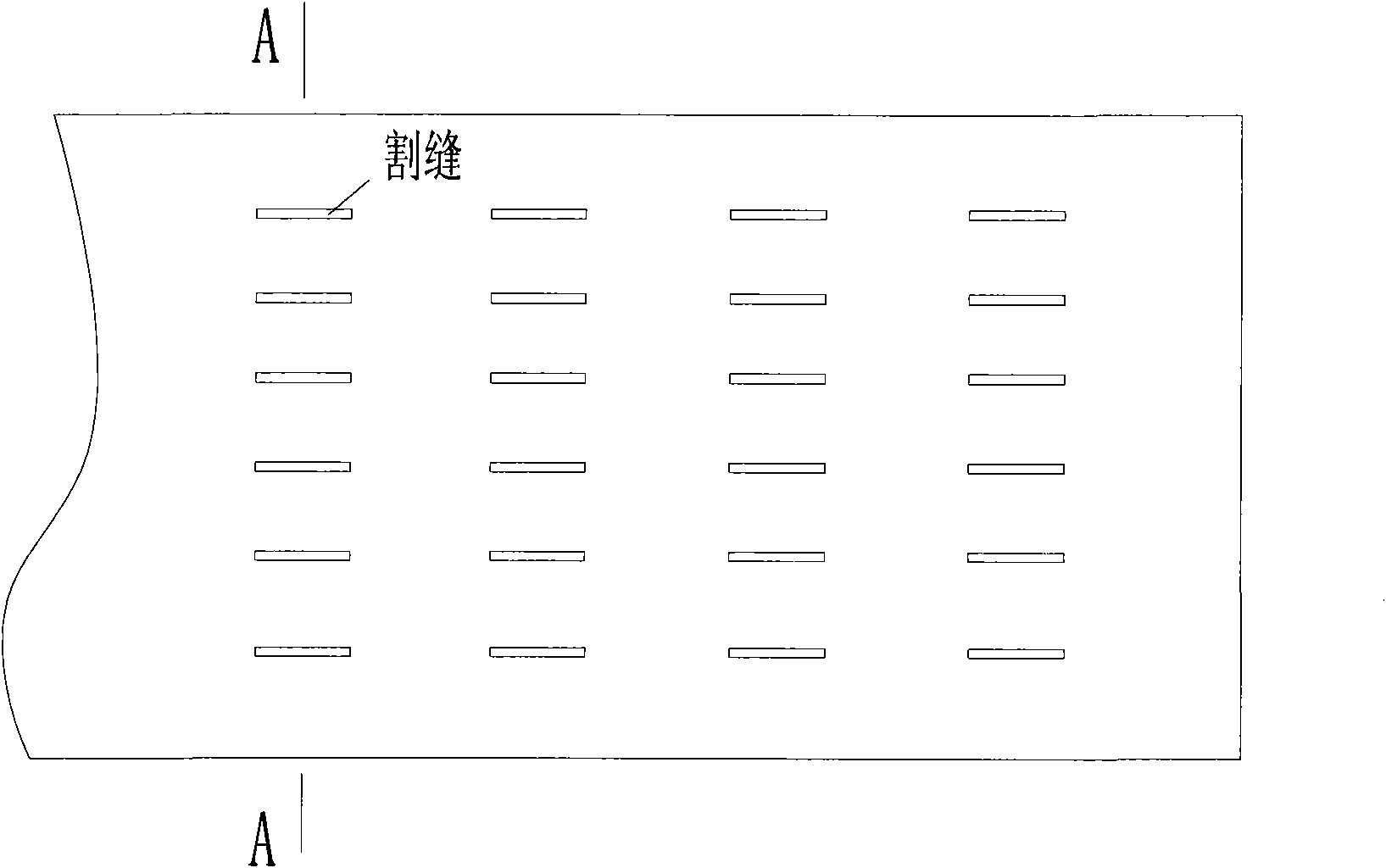
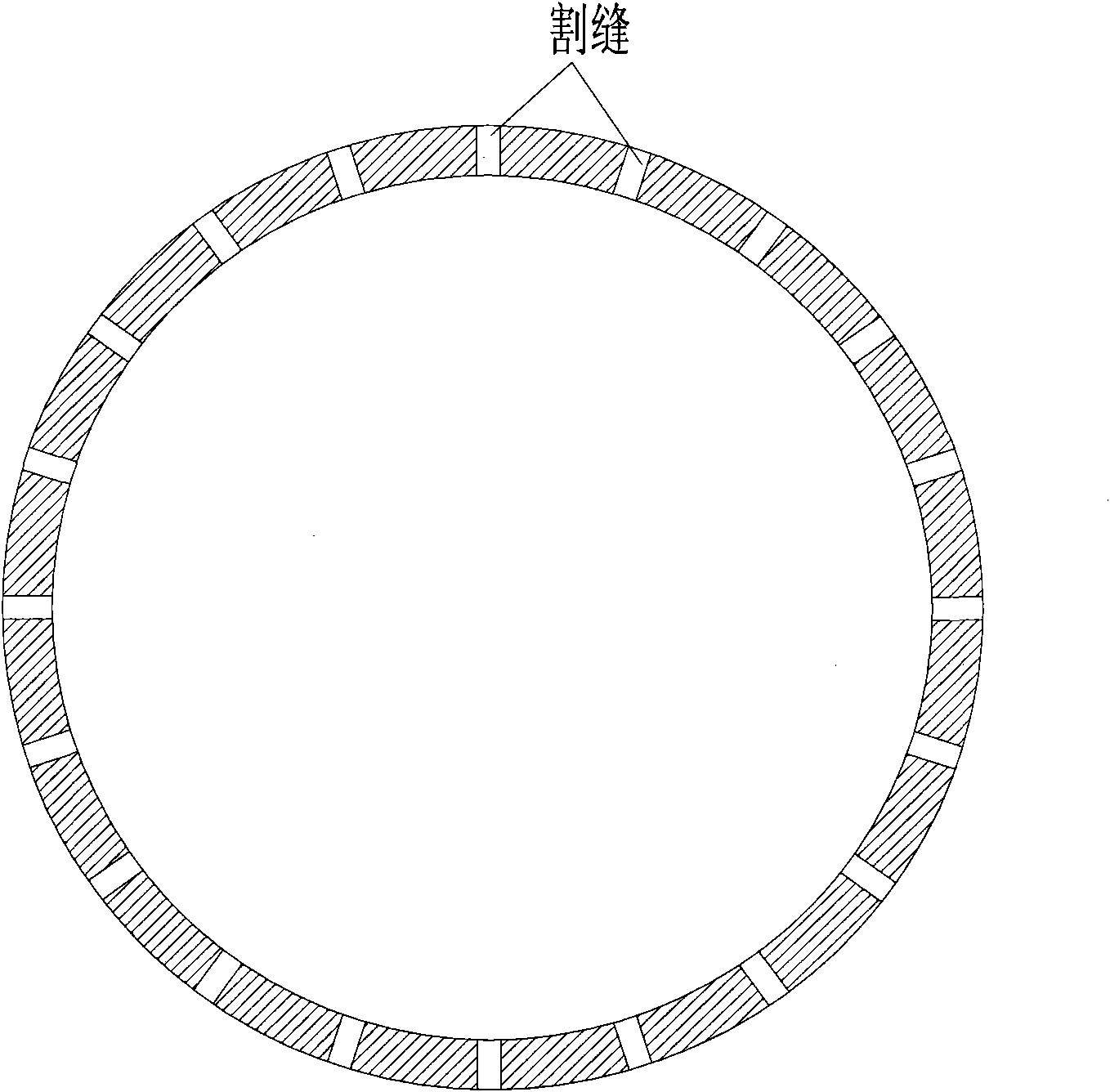
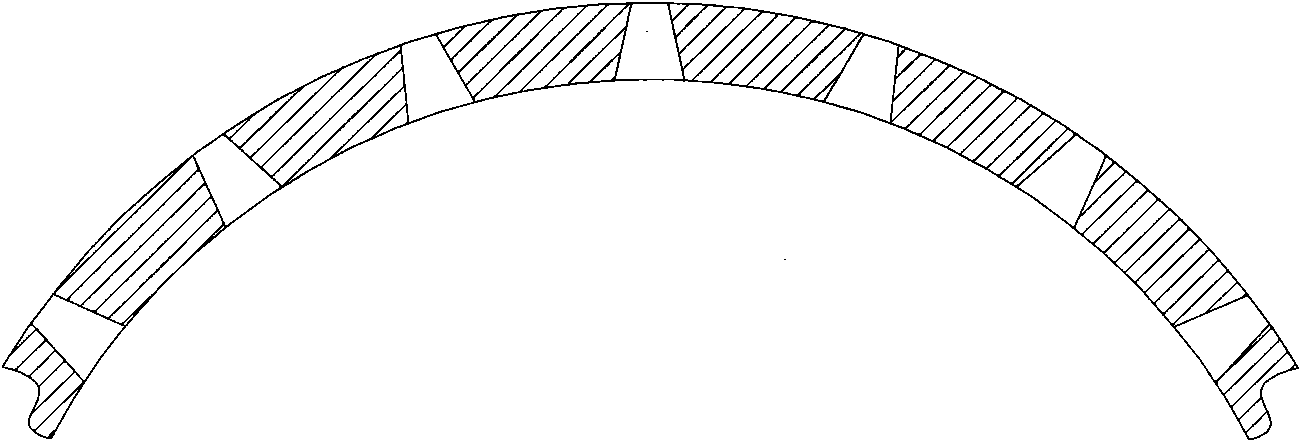
InactiveCN101890582AGuaranteed trafficGuaranteed flow rateLaser beam welding apparatusLaser processingChemical reaction
The invention discloses a laser processing method for a steel sieve tube slit. One end point of one long edge of the slit is used an initial point. The method comprises the following steps of: perforating a hole at the initial point of a cut by using pulse laser, and then finishing the cutting of the whole slit from the initial point by using continuous laser. During cutting, oxygen is used as an auxiliary gas, the metal at a cutting point is further heated by using reaction heat released by the reaction of the oxygen and the molten iron at the cutting point, meanwhile the molten iron is changed into ferroferric oxide with good liquidity by using chemical reaction, and the ferroferric oxide is blown away the cutting point by using airflow so as to ensure continuous cutting. The processing method solves the problems of irregular slit shape, slag adhesion at the cut and oblique blowing trace in the conventional laser cut sieve tube slit.
Owner:北京宏诚拓业科技发展有限公司 +1
Particle image speed measuring device, method and system
InactiveCN108896783AImproved speed measurement capabilityImprove time resolutionFluid speed measurementAcquisition timeImage resolution
The invention discloses a particle image speed measuring device, method and system. The device comprises a laser unit for emitting the laser to a to-be-measured region; an acquisition unit for acquiring the particle image of the to-be-measured region; a control unit electrically connected with the laser unit and the acquisition unit to control the movement and / or state of the laser unit and the acquisition unit, wherein the laser unit emits at least two beams of laser, and the light emitting time sequence between the laser beams satisfies the incremental or decreasing relation; the acquisitionunit at least comprises two acquisition channels, and the acquisition time of each acquisition channel meets the incremental or decreasing relation, and corresponds to the light emitting time sequence of each beam in the laser unit in sequence. The device and the method overcome the contradiction that the light emitting frequency and the pulse energy of a single laser are difficult to improve atthe same time, the problem of high-speed photography is solved, and the resolution of the measurement system is greatly improved.
Owner:PLA PEOPLES LIBERATION ARMY OF CHINA STRATEGIC SUPPORT FORCE AEROSPACE ENG UNIV
Photonic-crystal-rod amplifiers for high-power pulsed optical radiation and associated method
InactiveUS7379237B1High peak powerHigh pulse energyGlass making apparatusOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingOptical radiationEngineering
A method and apparatus use a photonic-crystal fiber having a very large core while maintaining a single transverse mode. In some fiber lasers and amplifiers having large cores problems exist related to energy being generated at multiple-modes (i.e., polygamy), and of mode hopping (i.e., promiscuity) due to limited control of energy levels and fluctuations. The problems of multiple-modes and mode hopping result from the use of large-diameter waveguides, and are addressed by the invention. This is especially true in lasers using large amounts of energy (i.e., lasers in the one-megawatt or more range). By using multiple small waveguides in parallel, large amounts of energy can be passed through a laser, but with better control such that the aforementioned problems can be reduced. An additional advantage is that the polarization of the light can be maintained better than by using a single fiber core.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Internal combustion engine
InactiveUS7499477B2High magnificationQuality improvementEngine ignitionMachines/enginesCombustion chamberEngineering
The invention relates to an internal combustion engine with a laser ignition device (1), Q-switched, pumped solid-state laser with a pulsed pumped light source (30), a solid laser crystal (2), enclosed in a resonator, a Q-switch (4), for increasing the power density, at least one output mirror (6) and a focussing device (7), by means of which the laser beam (26) may be focussed in a combustion chamber.
Owner:AVL LIST GMBH
780 nm high-power optical-fiber femtosecond laser device
InactiveCN104283097ANot affected by dispersionReduce nonlinear effectsActive medium shape and constructionNon-linear opticsSeeds sourceComputer module
The invention discloses a 780 nm high-power optical-fiber femtosecond laser device. The laser device comprises a laser device seed source, a laser spreading and amplifying module, a laser compression module and a laser frequency doubling module, the laser device seed source and the preceding modules are sequentially connected, the laser spreading and amplifying module is composed of a chirped pulse spreading sub module, a pulse separation sub module and an optical fiber amplifying sub module, and the laser device seed source and the modules all work at the waveband of 1560 nm. A mixed pulse spreading mode is adopted, pulses are spread from 100 fs to 1ns in a small work space, the amplified pulses are compressed to below 100 fs through non-linear compression of a single-mode fiber, and ultimately the pulses reach 780 nm after frequency doubling of non-linear crystals. The laser device has the advantages of being high in stability, simple in structure, small and ingenious in size, low in cost and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI LANGYAN OPTOELECTRONICS TECH
All solid-state angular momentum tunable laser device with stable pulse energy
ActiveCN102684061ACompact structureEasy to operateOptical resonator shape and constructionActive medium materialParticle physicsOptical communication
The invention relates to an all solid-state angular momentum tunable laser device with stable pulse energy. The all solid-state angular momentum tunable laser device comprises a pumping source, an optical coupling system, a resonant cavity, a solid laser medium and a saturable absorber; the pumping source is a semiconductor laser diode; the solid laser medium is a doped laser material Nd: YAG or Nd: YVO4; the saturable absorber is a Cr: YAG or GaAs crystal; and the resonant cavity consists of an input mirror and an output mirror or consists of a coating film on the incident surface of the solid laser medium and a coating film on an emergent surface of the saturable absorber. Laser output by the laser device provided by the invention is pulse laser with fixed energy and further has an optical angular momentum, and the continuous change of the angular momentum can be realized through altering the power of pump light. The laser device provided by the invention can be used for aspects such as optical communication, cold atom trapping, dynamic optical storage, and quantum computation. The tunable laser device is low in cost, small in size, stable in energy, high in peak power and tunable in the angular momentum and is flexible to adjust.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Device and method for measuring and imaging second harmonic and multi-photon generation scattered radiation
ActiveUS20150233820A1Increase signal strengthEfficient detectionPolarisation-affecting propertiesScattering properties measurementsLight beamPulse energy
Embodiments of the subject invention relate to a method and apparatus for performing measurements using multiphoton or second harmonic generation (SHG) scattered radiation from a sample including a turbid (scattering) medium includes providing a beam of laser pulses from a laser source having high pulse energies and a repetition rate; splitting the beam of laser pulses into two or more partial beams and focussing and overlaying the partial beams on a sample including the turbid medium; and detecting multiphoton and second harmonic radiation scattered from the sample.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
All-fiber structural laser system capable of generating high-energy wave-free split rectangular pulse
InactiveCN102005689ASimple structureLow costActive medium shape and constructionHigh energyErbium doping
The invention discloses an all-fiber structural laser system capable of generating high-energy wave-free split rectangular pulse, which aims to solve the technical problems that the current erbium-doped fiber laser has low pulse energy and poor stability and is difficult to realize rectangular pulse output. The all-fiber structural laser system comprises two wavelength division multiplexers, an erbium-doped fiber, a first polarization controller, a polarization dependent isolator, a second polarization controller and an output coupler connected in turn through an intra-cavity single mode fiber, wherein the input ends of the two wavelength division multiplexers are provided with pumping light sources. The length of the erbium-doped fiber is 10 to 20 meters, the total length of the single mode fiber is 5 to 10 meters, and the whole intra-cavity net dispersion is kept in a large positive value. The all-fiber structural laser system has the advantages of simple structure, low price, good stability and the like on application; and compared with a solid laser for generating high-energy rectangular pulse, the all-fiber structural laser system has the advantages of high pumping efficiency, adjustment convenience, good pulse quality and the like, and is easy for fiber coupling.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
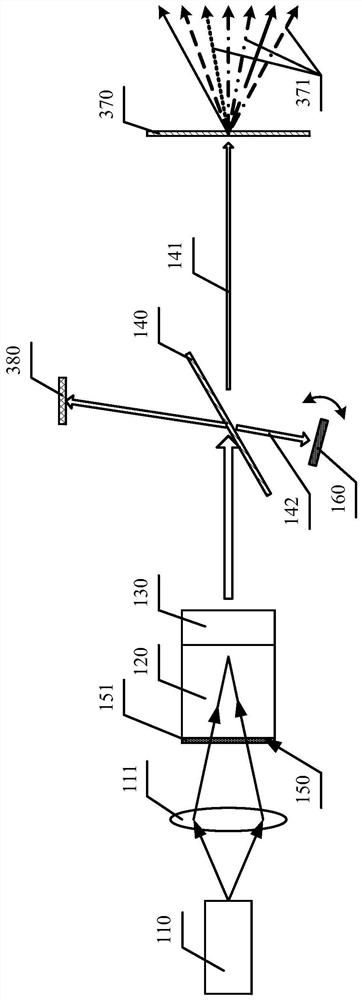
Micro-pulse laser radar light source with high pulse energy
InactiveCN105161961ACompensation lossIncreased pulse energy and beam qualityOptical resonator shape and constructionPolarizerOptical path
The invention relates to a micro-pulse laser radar light source with high pulse energy. The light source is formed by an oscillator stage and an amplifier stage; and the light path of the amplifier stage and the light path of the oscillator stage are in a coaxial mode. At the oscillator stage, a dual-path Q switch is used for compensating thermal depolarization loss of a laser; dual-path outputs are amplified respectively by the independent amplifier stage and then are combined, thereby realizing functions of thermal depolarization compensation and energy amplification. At the oscillator stage, a holophote, a laser crystal rod, two dielectric film polarizers, two Pockels boxes, and two output coupling mirrors are successively arranged on the light path; the two dielectric film polarizers are arranged at a brewster angle, incident surfaces of other elements are parallel to each other; and two end surfaces of the laser crystal rod are parallel to each other. According to the invention, losses of output energy by thermal depolarization can be compensated and the output energy can be amplified further; compared with the prior art, the conversion efficiency, the pulse energy, and the light beam quality of the light source are substantially improved; and the detection distance and detection precision of the micro-pulse laser radar are enhanced.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Raman cell for high power applications
ActiveUS7869469B1Improved medium circulationReduce and substantially avoid multiple illuminationLaser using scattering effectsLight demodulationCell culture mediaLight beam
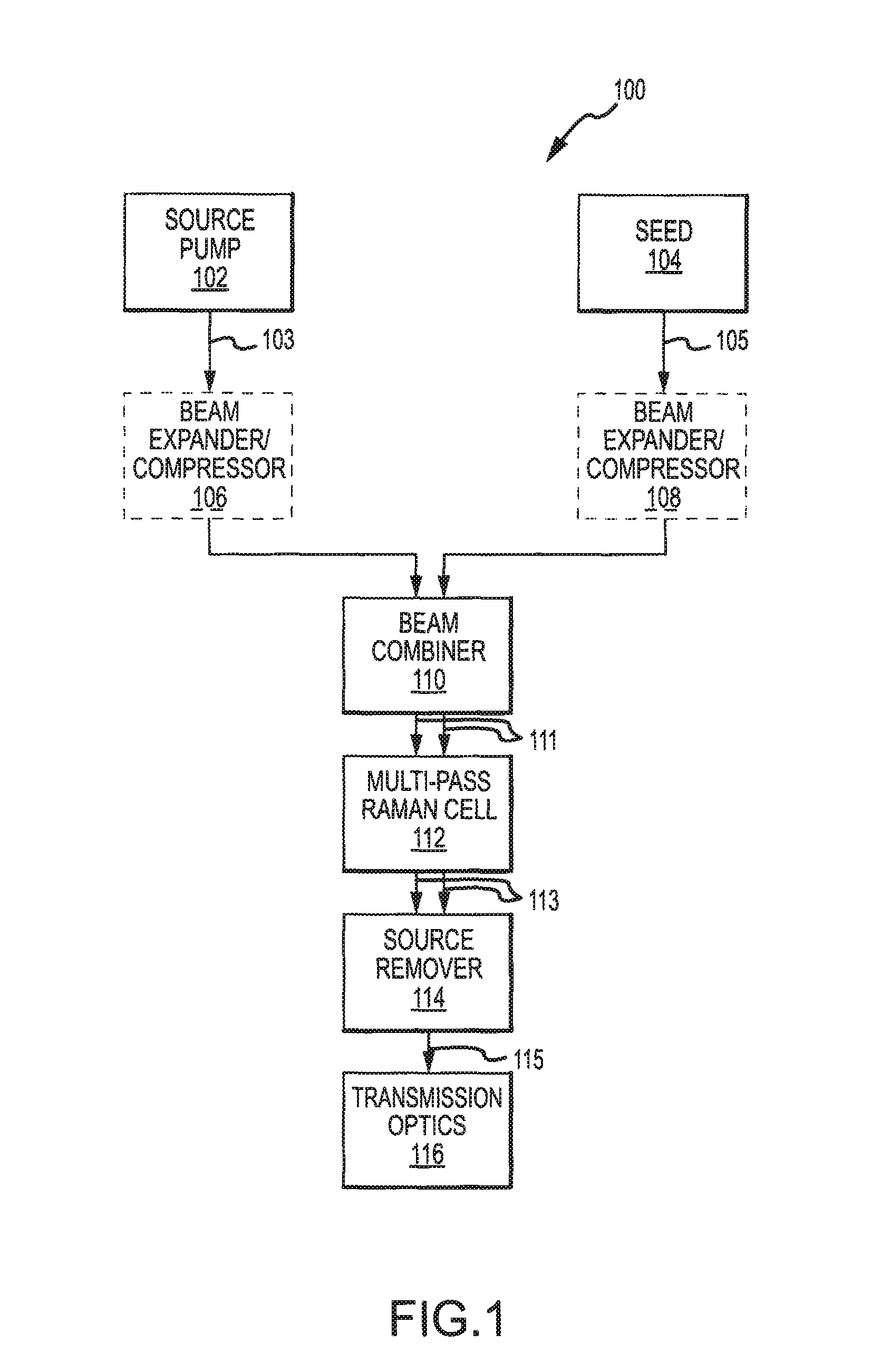
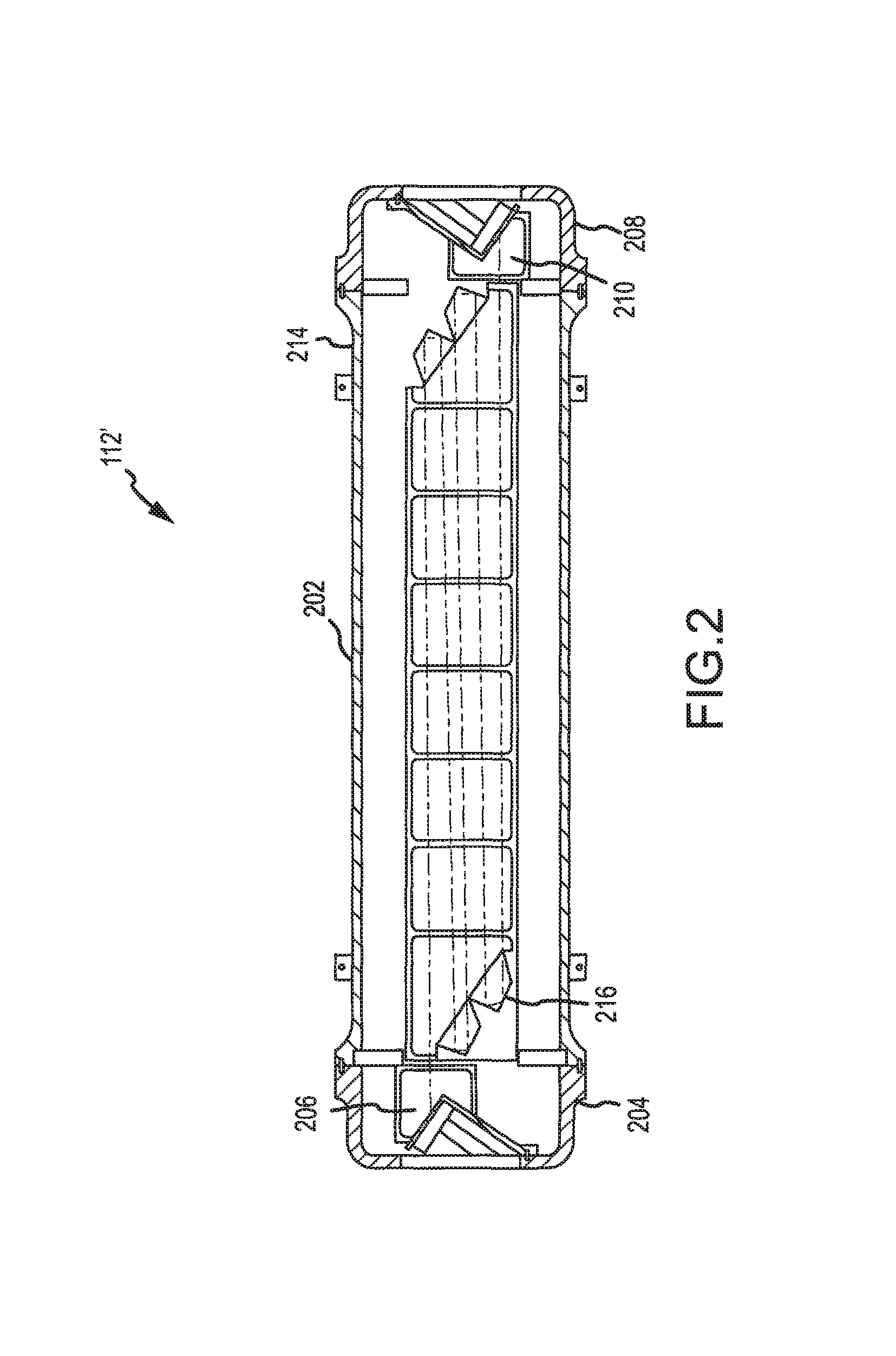
A Raman shifter is provided with improved optical efficiency and robustness, particularly for high power applications. In one embodiment, a source system (100) includes a source pump laser (102) and a seed laser (104). Beams from the pump laser (102) and seed laser (104) combine for transmission into a Raman cell (112). Folding optics define a multi-pass pathway through the Raman cell (112). Such folding optics may include an internal reflectance element. An entry window into the Raman cell, an exit window from the Raman cell, and the internal reflectance elements include surfaces disposed at a Brewster angle relative to the incident beam. The Raman cell medium is circulated in a direction transverse to the beam pathways through the cell. In this manner, improved optical efficiency and robustness is achieved as well as improved performance over a significant wavelength band.
Owner:UNIV FOR ATMOSPHERIC RES
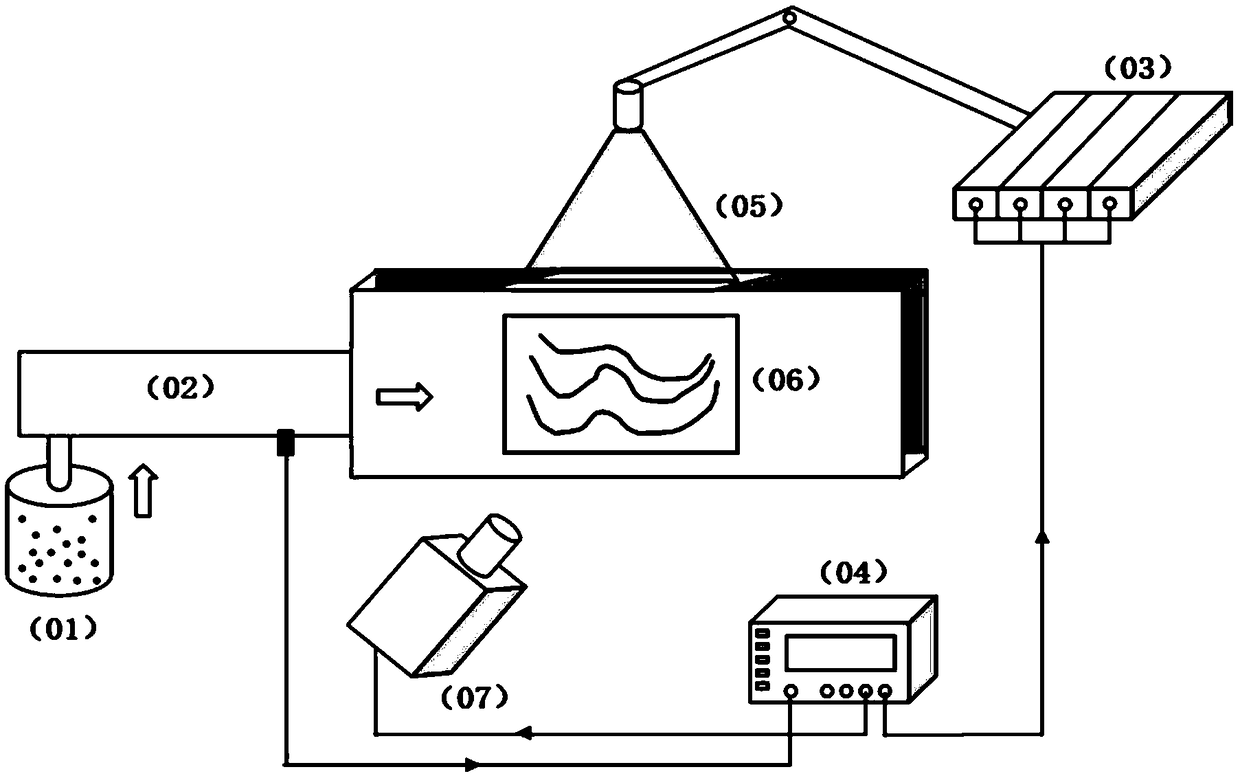
Laser roughening machine by laser focusing head array
InactiveCN1401456AReduced stabilityReduce volumeRollsLaser beam welding apparatusNumerical controlOptoelectronics
A laser roughening machine with laser-gathering head array for metal surface, especially the surface of roller, is disclosed. The laser beam from laser device is amplified and then splitted into multiple beams, which are transmitted via relative optical fibres to the laser-gathering heads arranged by the form of rectangular, parallelogram or linear array on a small moving platform fixed the rotation shaft of numerally controlled machine-tool. After the roller to be roughened is fixed to the machine-tool and then rotating, the laser beams from said array scan on the surface of roller to generate pit matrix. Its advantages are short period and high uniformity of pit matrix.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method of laser processing a wafer
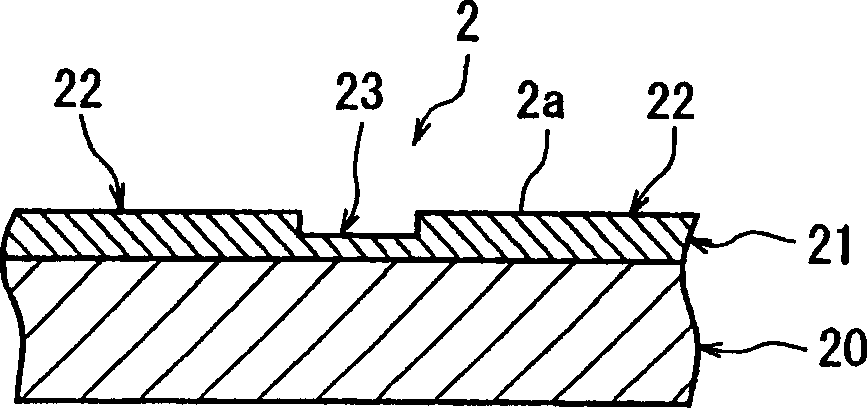
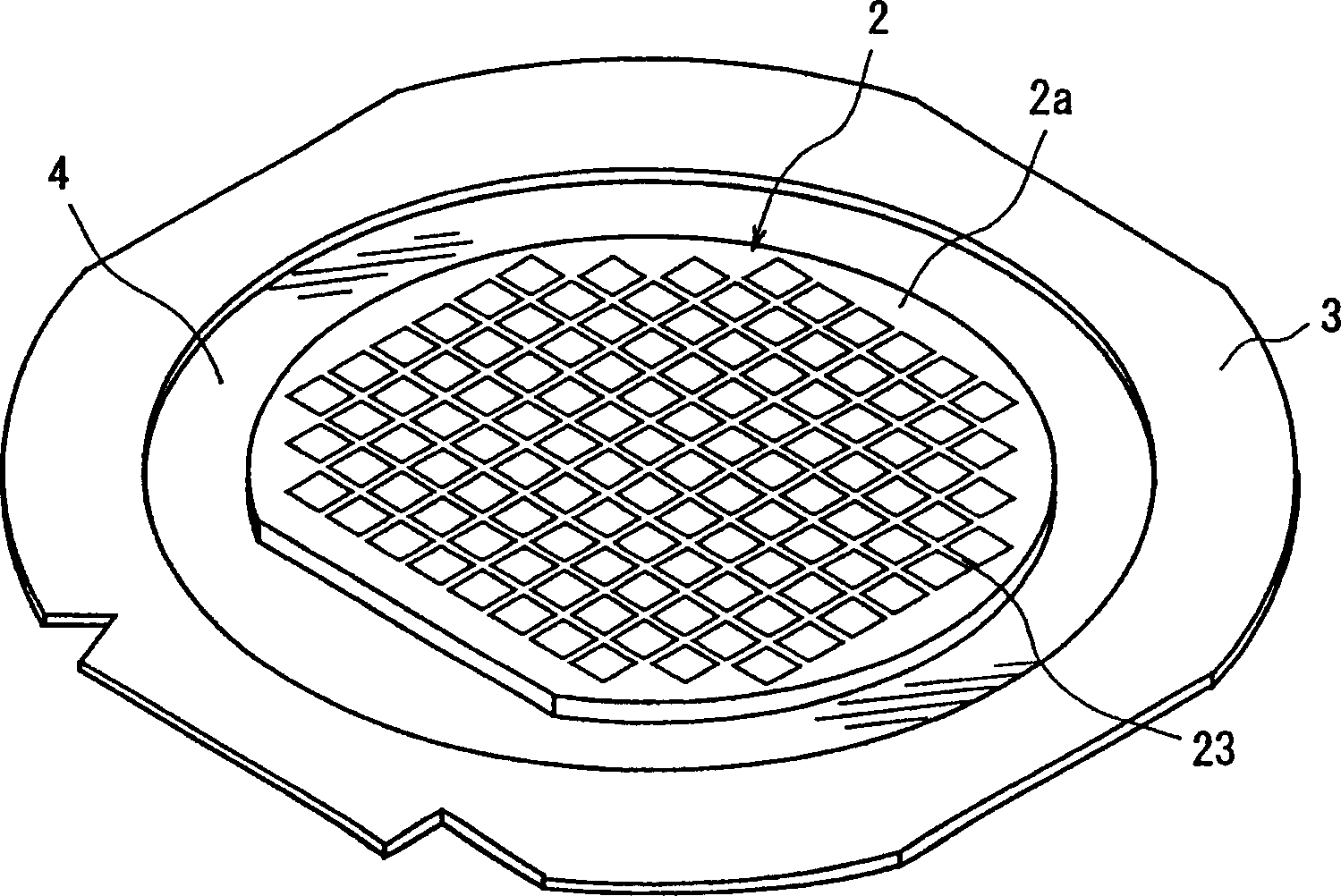
InactiveCN1803374AHigh pulse energyEasy to splitSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingWelding/soldering/cutting articlesLaser processingEngineering
A method of laser processing a wafer having a plurality of devices that are composed of a laminate layer laminated on the front surface of a substrate, along a plurality of streets for sectioning the devices, comprising a first groove forming step for applying a first laser beam having absorptivity for the wafer along the streets of the wafer at predetermined intervals to form two grooves for preventing the flaking of a layer, which divide the laminate layer; and a second groove forming step for applying a second laser beam having absorptivity for the wafer to the center between the two grooves for preventing the flaking of a layer, which have been formed along the streets of the wafer by the first groove forming step, along the streets of the wafer to form a dividing groove having a predetermined depth in the laminate layer and the substrate.
Owner:DISCO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com