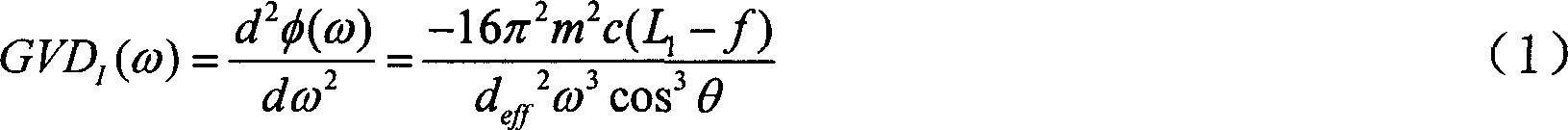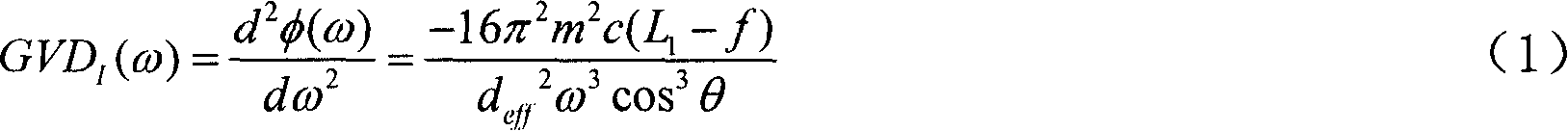Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
31 results about "Third order dispersion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Third Order Dispersion. Dispersion related to a third-order dependence of the phase change on the Frequency offset. Third-order Dispersion results from the frequency dependence of the Group Delay dispersion.
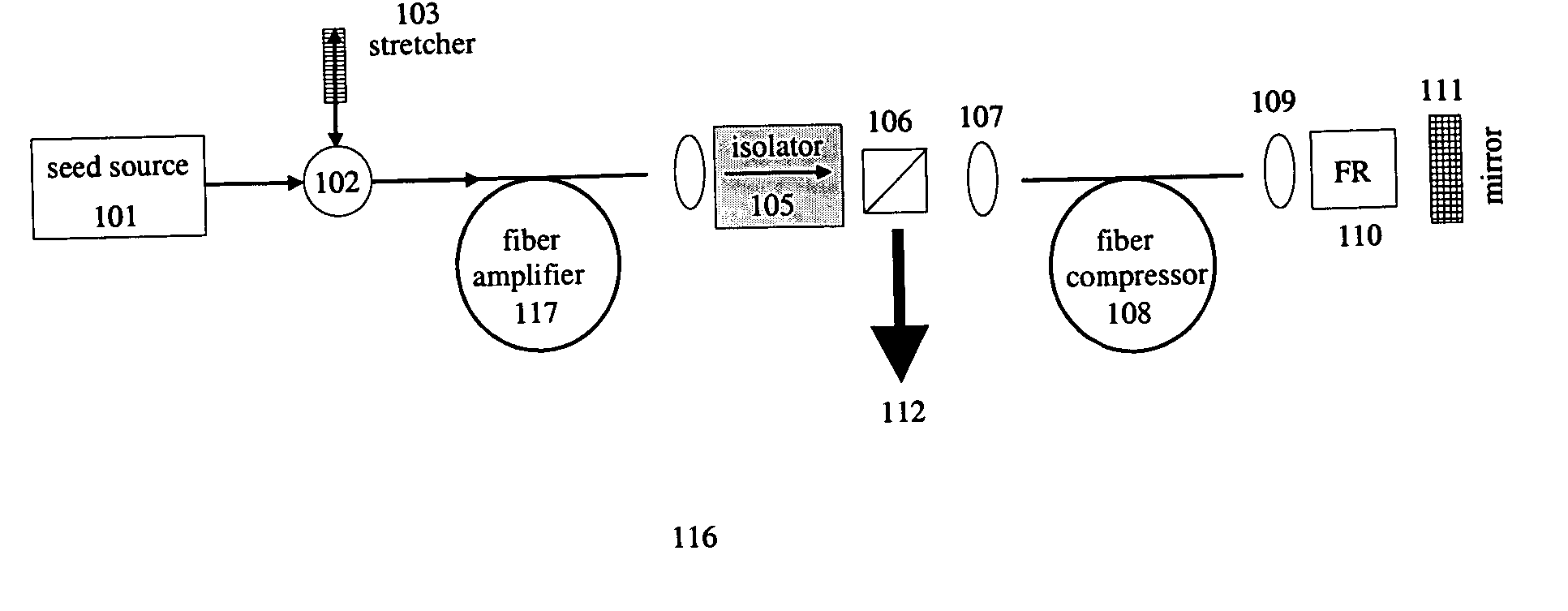
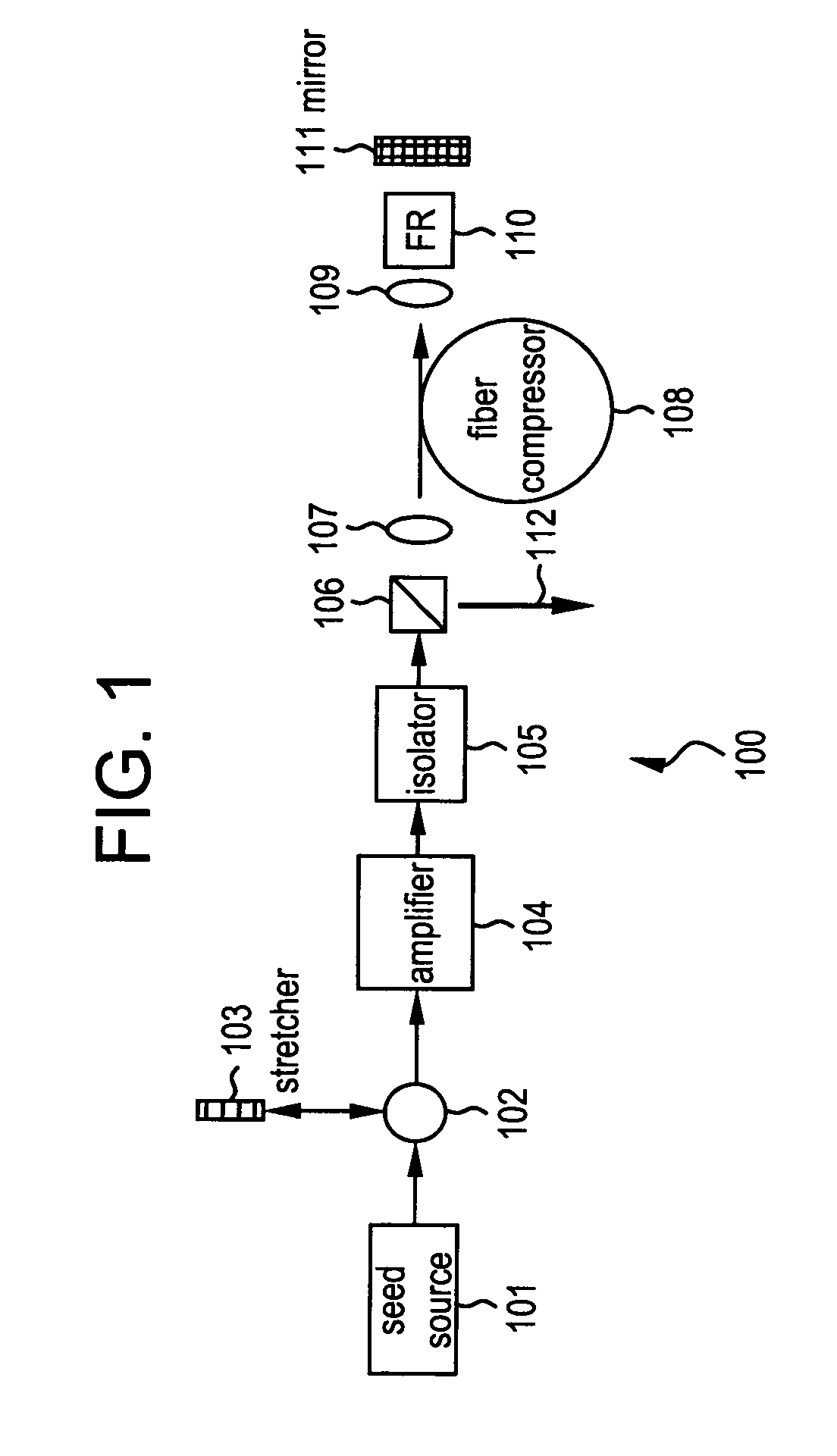
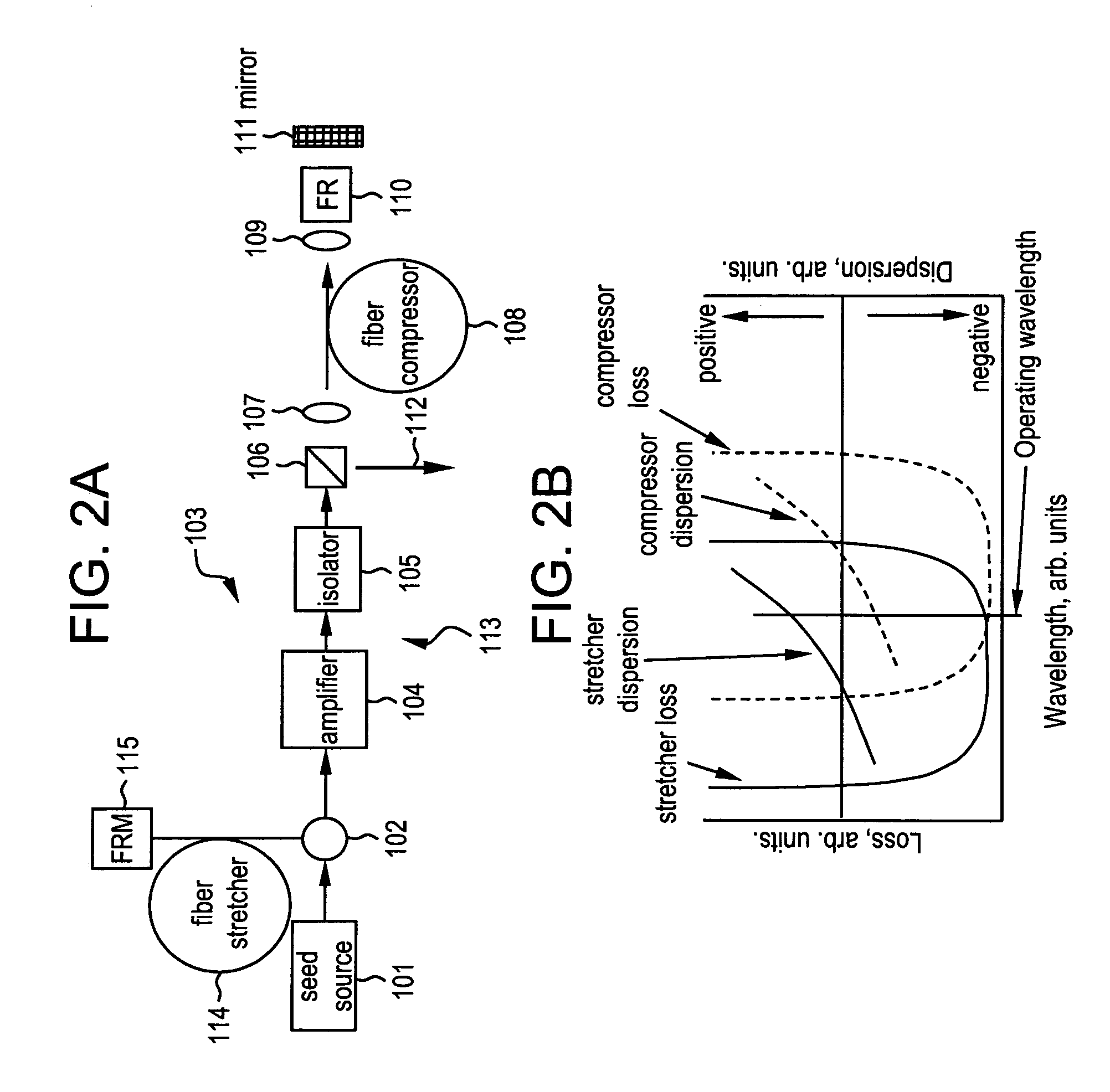
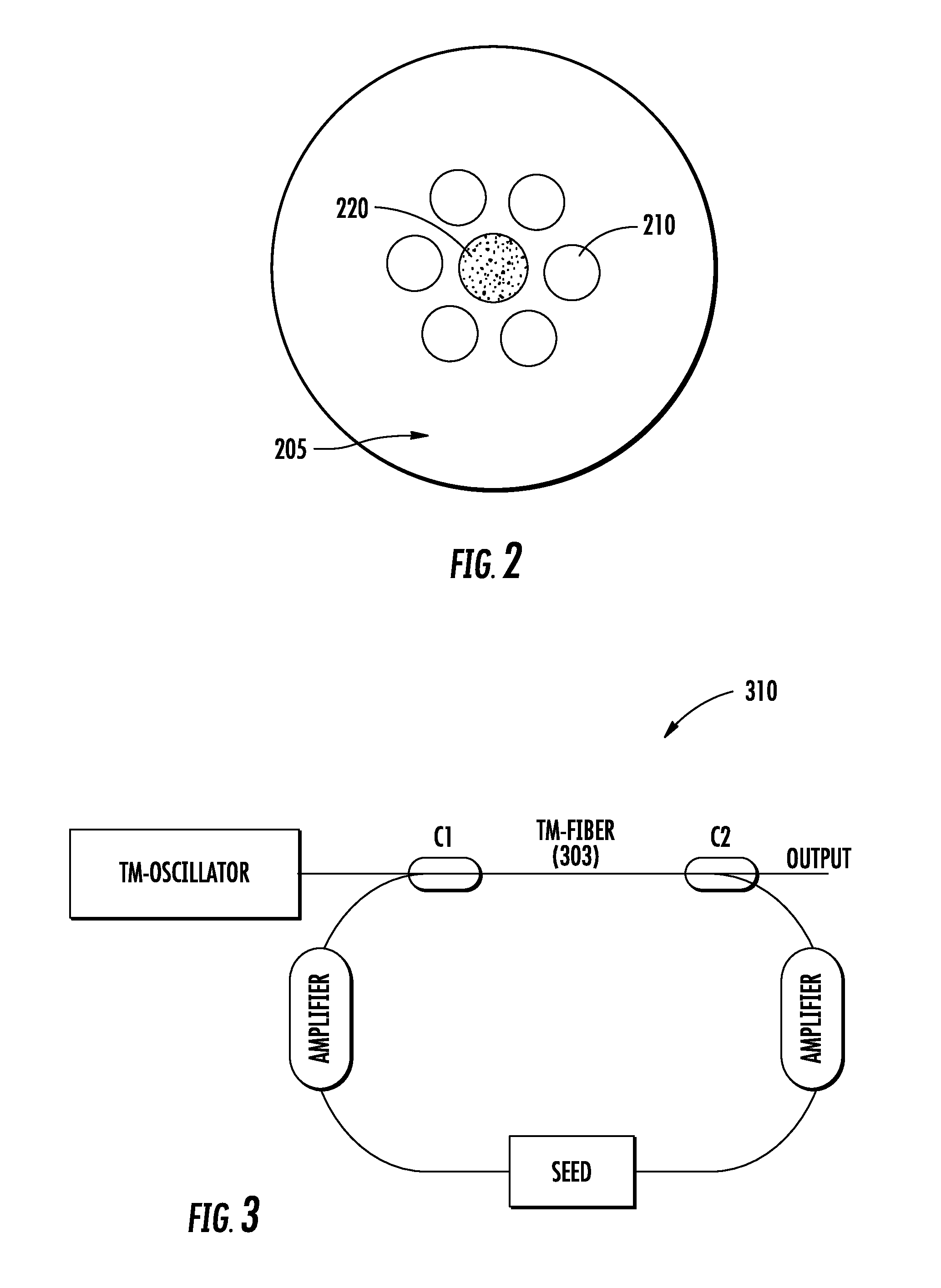
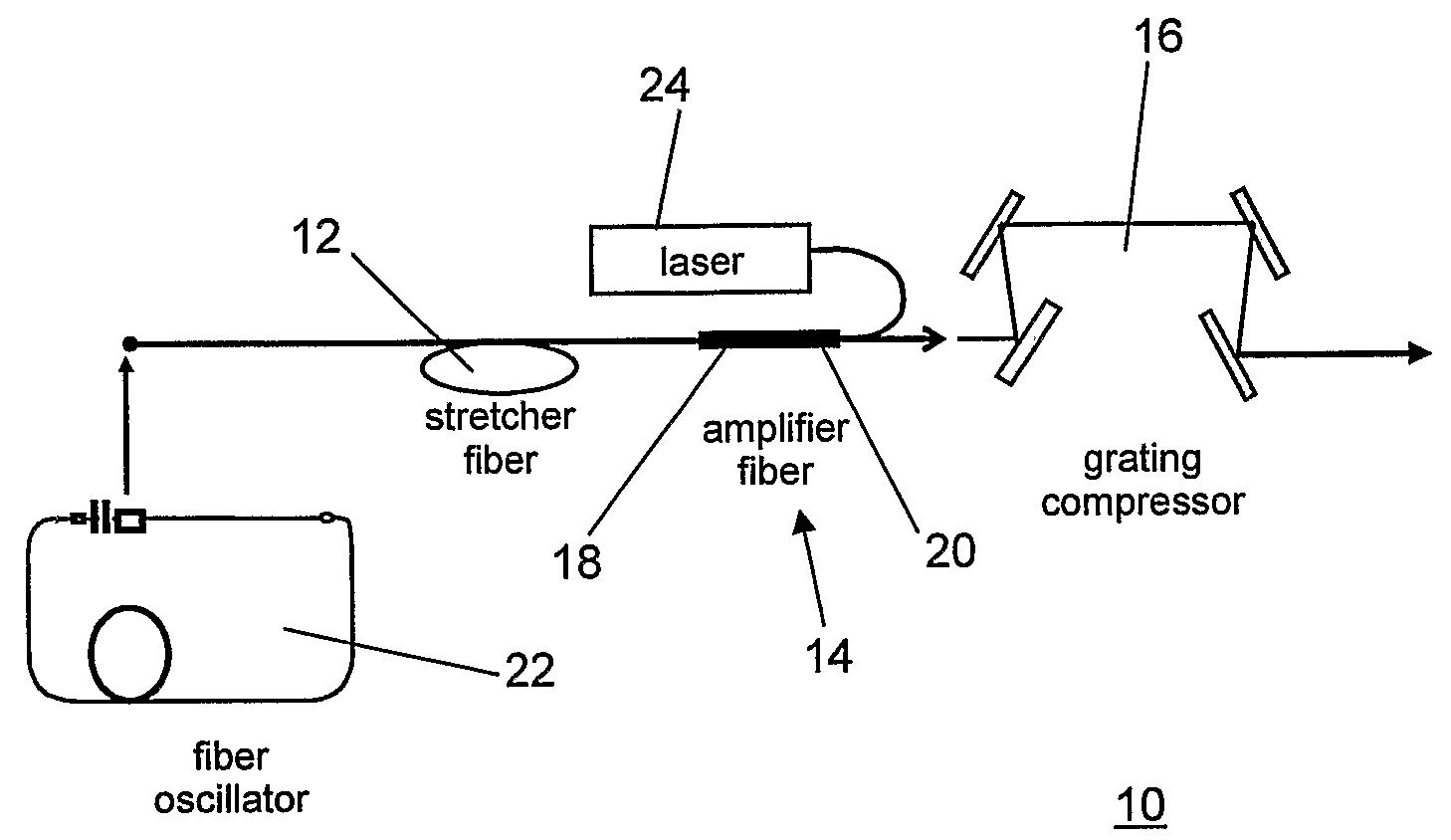
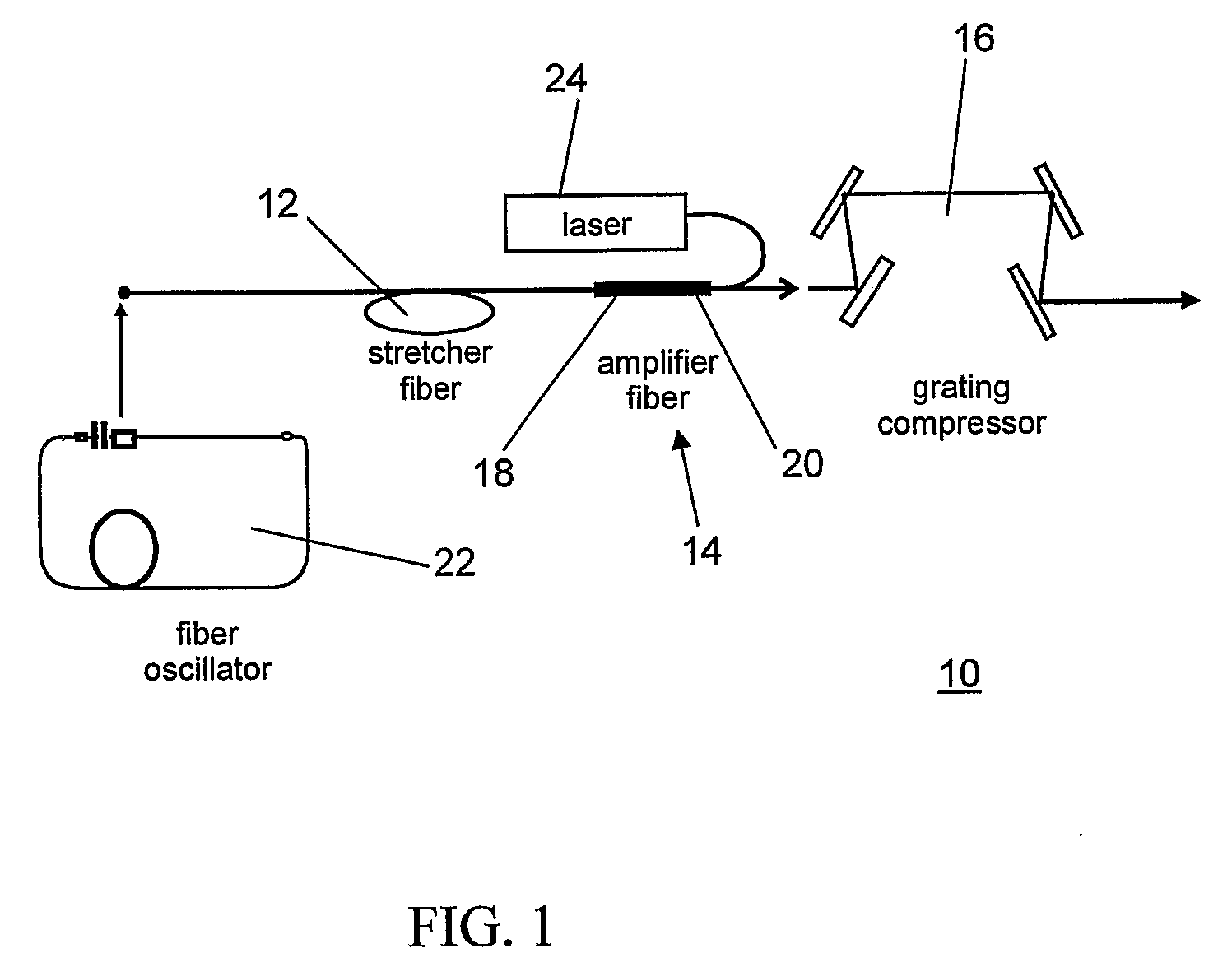
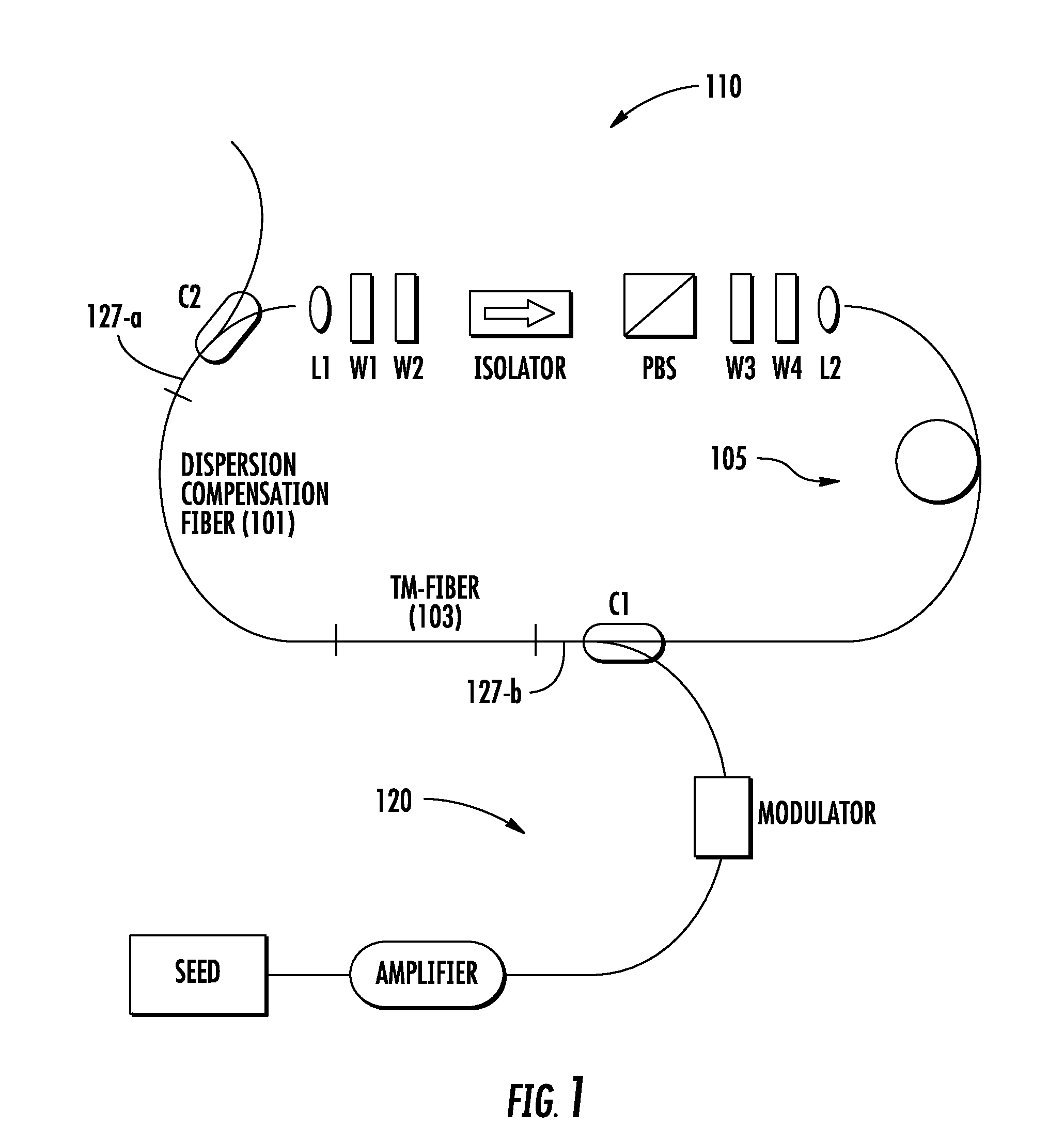
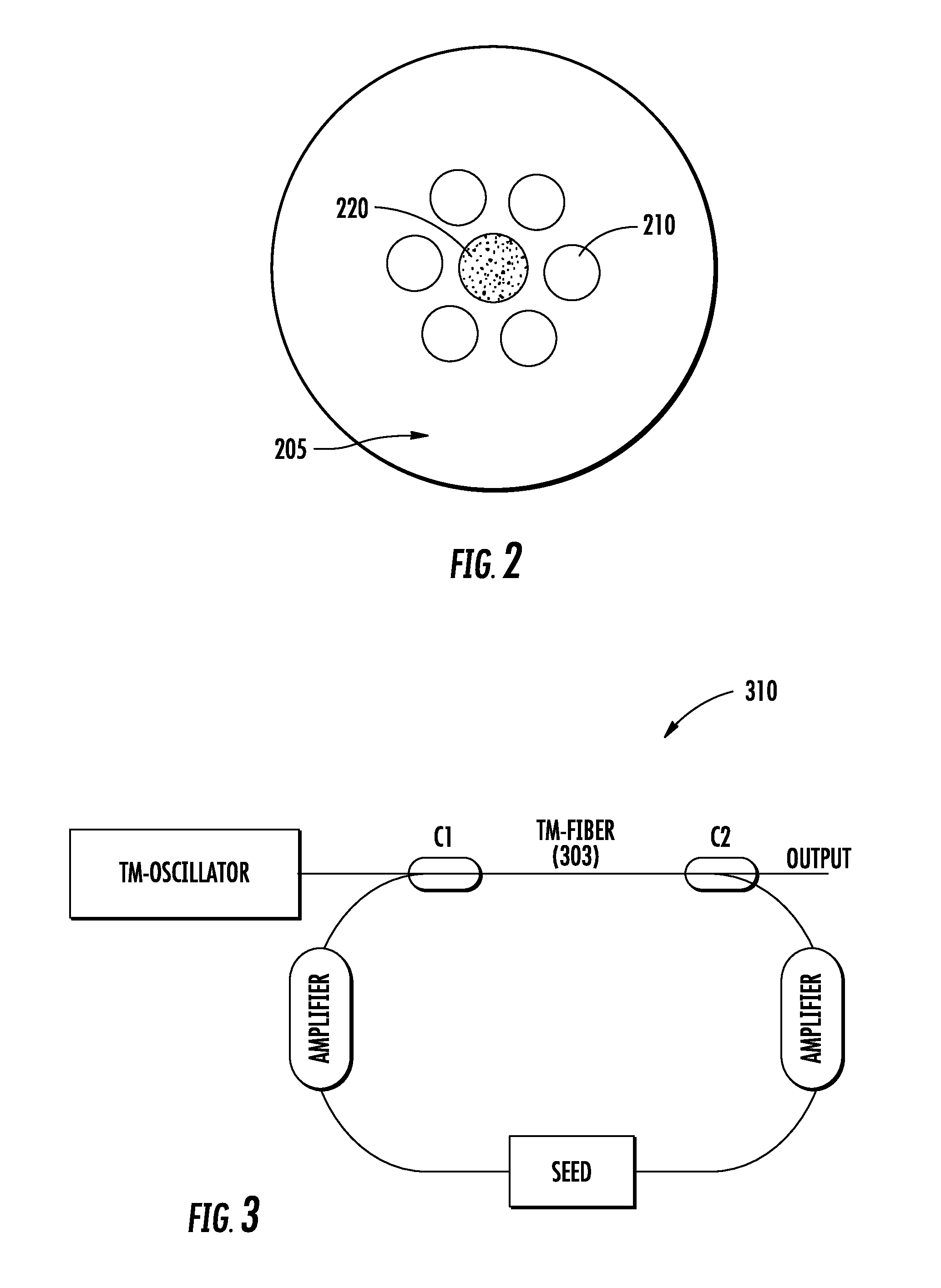
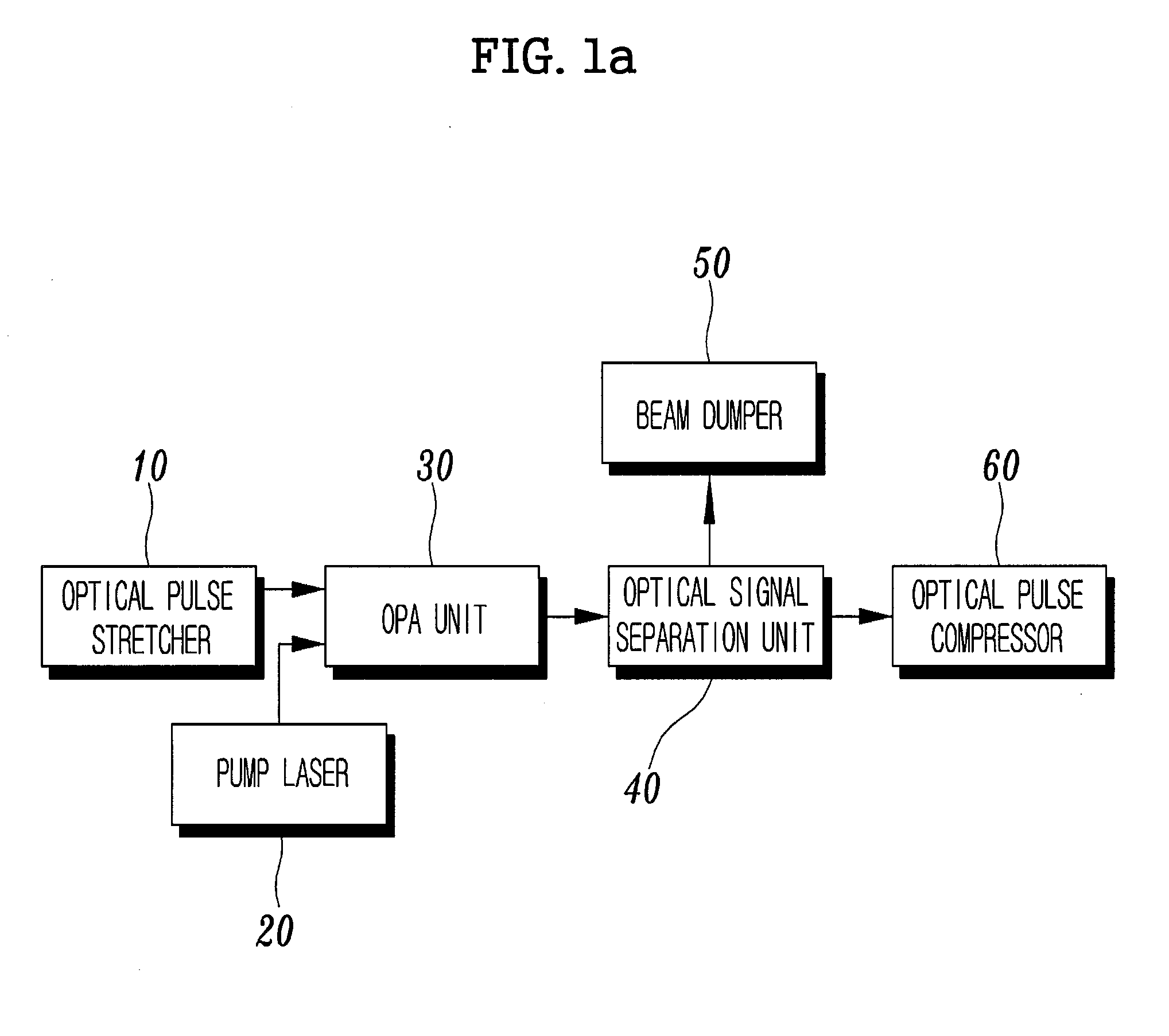
All-fiber chirped pulse amplification systems
InactiveUS20050105865A1Improve overall utilizationImprove performanceFibre transmissionCoupling light guidesLow noiseGrating
By compensating polarization mode-dispersion as well chromatic dispersion in photonic crystal fiber pulse compressors, high pulse energies can be obtained from all-fiber chirped pulse amplification systems. By inducing third-order dispersion in fiber amplifiers via self-phase modulation, the third-order chromatic dispersion from bulk grating pulse compressors can be compensated and the pulse quality of hybrid fiber / bulk chirped pulse amplification systems can be improved. Finally, by amplifying positively chirped pulses in negative dispersion fiber amplifiers, low noise wavelength tunable seed source via anti-Stokes frequency shifting can be obtained.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
All-fiber chirped pulse amplification systems
InactiveUS7414780B2Improve overall utilizationImprove performanceCoupling light guidesFibre transmissionLow noiseGrating
By compensating polarization mode-dispersion as well chromatic dispersion in photonic crystal fiber pulse compressors, high pulse energies can be obtained from all-fiber chirped pulse amplification systems. By inducing third-order dispersion in fiber amplifiers via self-phase modulation, the third-order chromatic dispersion from bulk grating pulse compressors can be compensated and the pulse quality of hybrid fiber / bulk chirped pulse amplification systems can be improved. Finally, by amplifying positively chirped pulses in negative dispersion fiber amplifiers, low noise wavelength tunable seed source via anti-Stokes frequency shifting can be obtained.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Compact, coherent, high brightness light sources for the mid and far ir
ActiveUS20120205352A1High energyReduce widthLaser using scattering effectsLaser beam welding apparatusFiber Bragg gratingOptoelectronics
Compact high brightness light sources for the mid and far IR spectral region, and exemplary applications are disclosed based on passively mode locked Tm fiber comb lasers. In at least one embodiment the coherence of the comb sources is increased in a system utilizing an amplified single-frequency laser to pump the Tm fiber comb laser. The optical bandwidth generated by the passively mode locked Tm fiber comb laser is further decreased by using simultaneous 2nd and 3rd order dispersion compensation using either appropriate chirped fiber Bragg gratings for dispersion compensation, or fibers with appropriately selected values of 2nd and 3rd order dispersion. Fibers with large anomalous values of third order dispersion, or fibers with large numerical apertures, for example fibers having air-holes formed in the fiber cladding may be utilized.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
Spectral coverage OCT imaging method based on optical scanning delay line and the system
InactiveCN101040778AAvoid mistakesEliminate phase shift errorsDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhase shiftedGrating
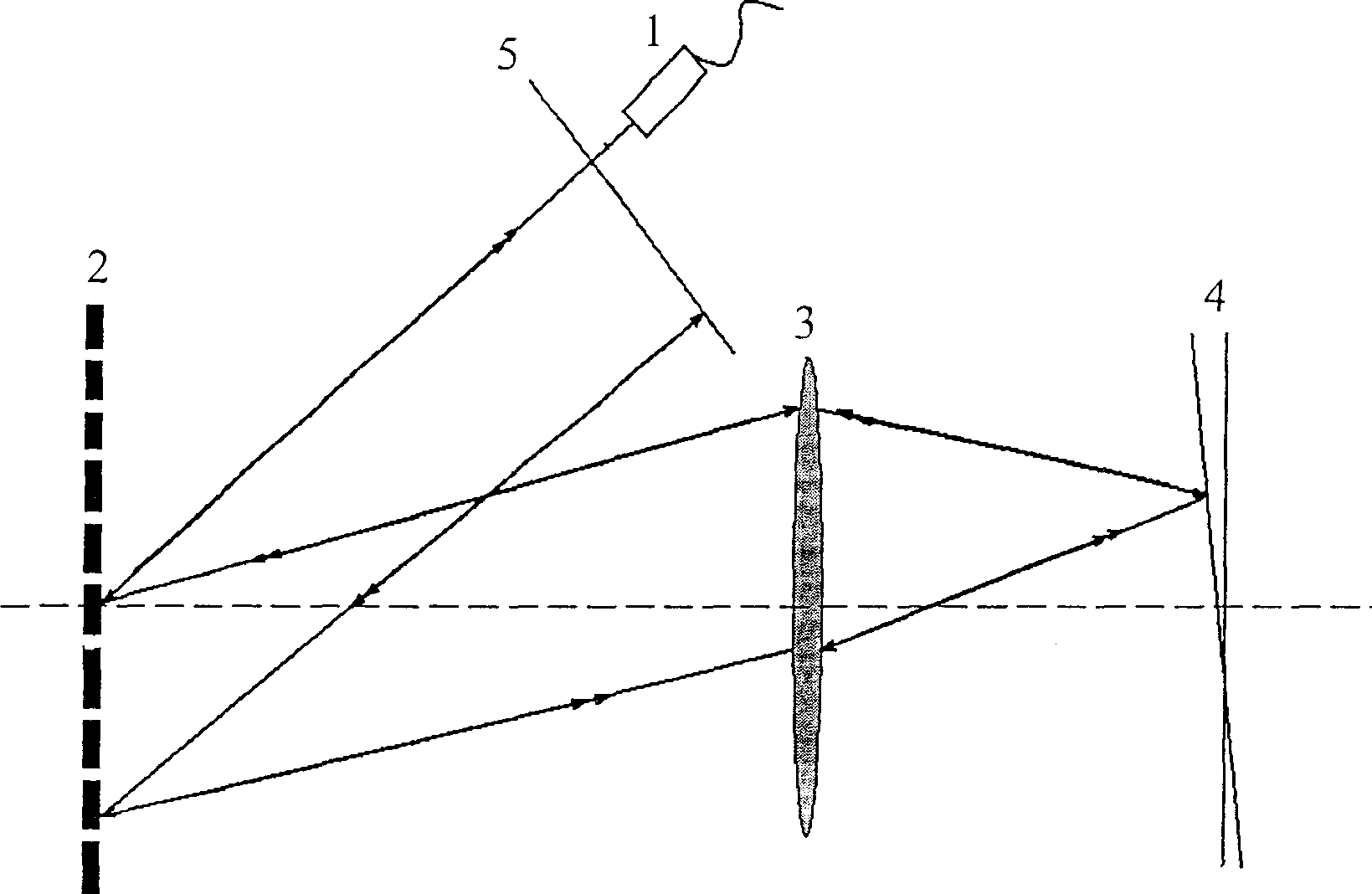
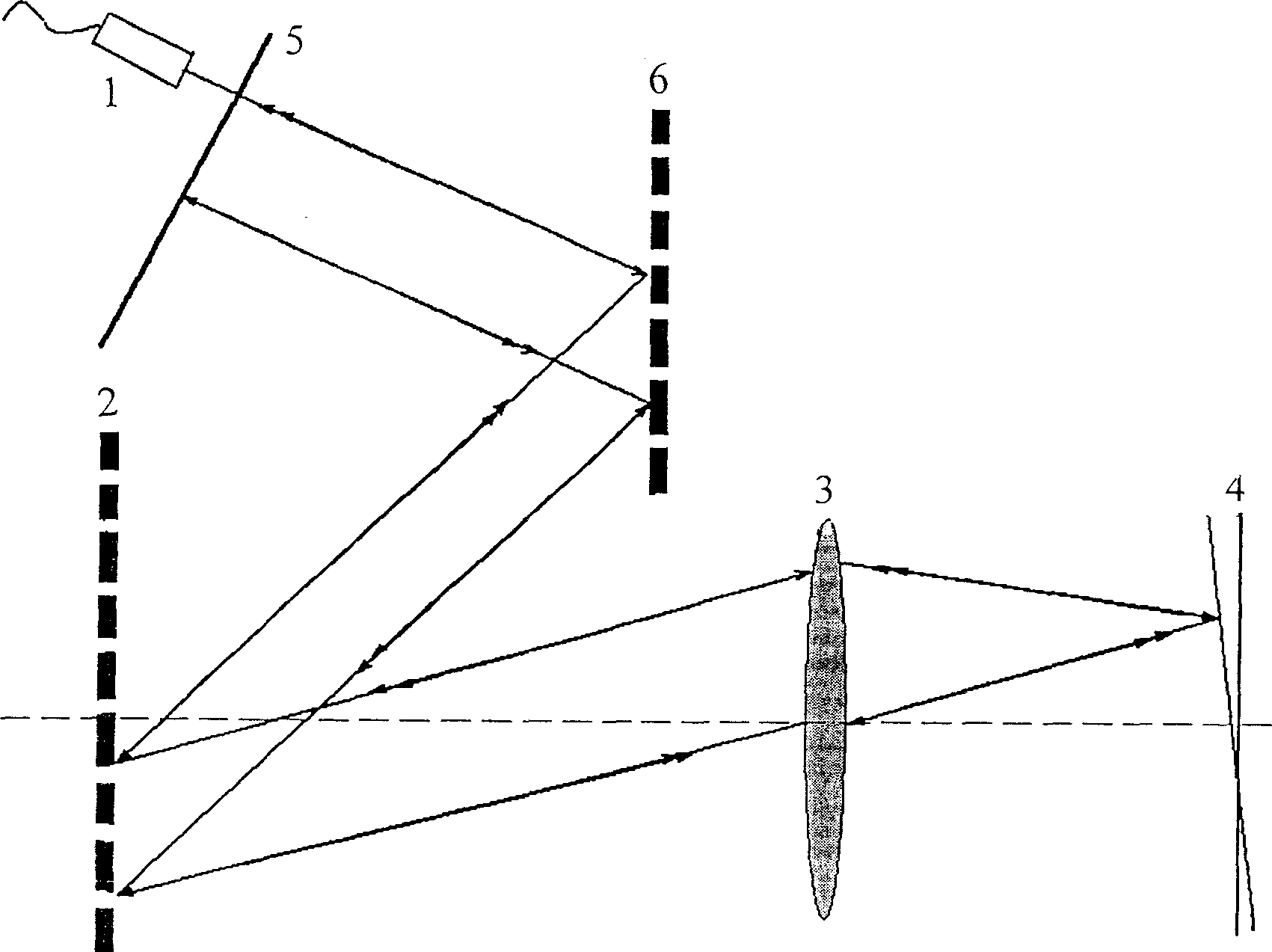
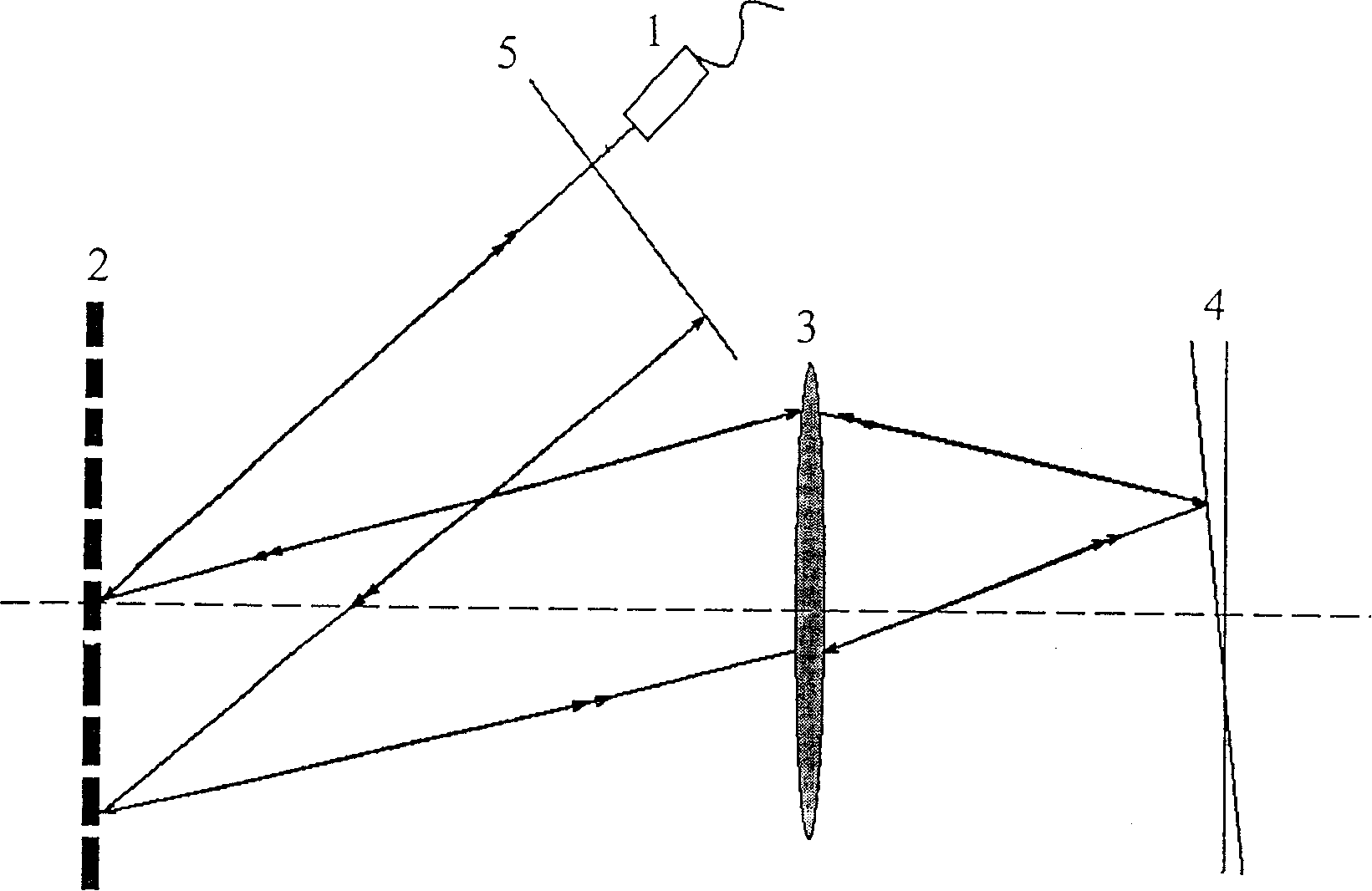
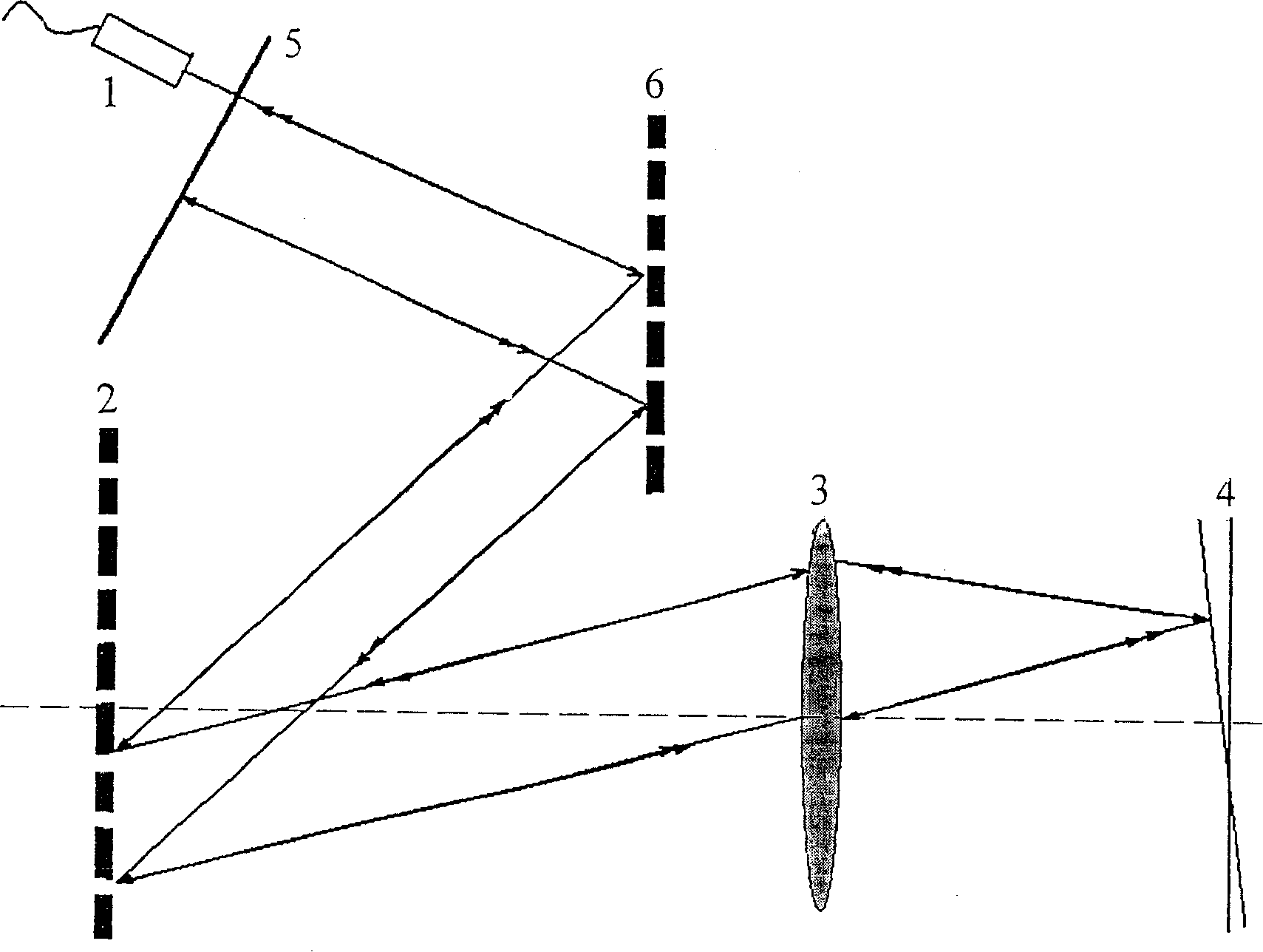
The invention discloses a spectrum OCT (optical coherent tomography) image method and relative system based on optical scanning delay line, wherein it arranges an optical scanning delay line in a reference arm of a spectrum OCT system, to realize scatter-free phase shift of reference light and system scatter compensation. And when guides in optical scanning delay line based on double gratings, the invention can generate group speed scatter and third-order scatter formed by any marks in large change range, to accurately match the scatters of reference arm and sample arm in spectrum OCT system. The scatter-free phase shift and scatter compensation can assure the axial resolution ratio of spectrum OCT system, eliminate coherent noise, and expand the image depth for one time. The invention is significant for dual-spectrum OCT system with ultra-high resolution ratio.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
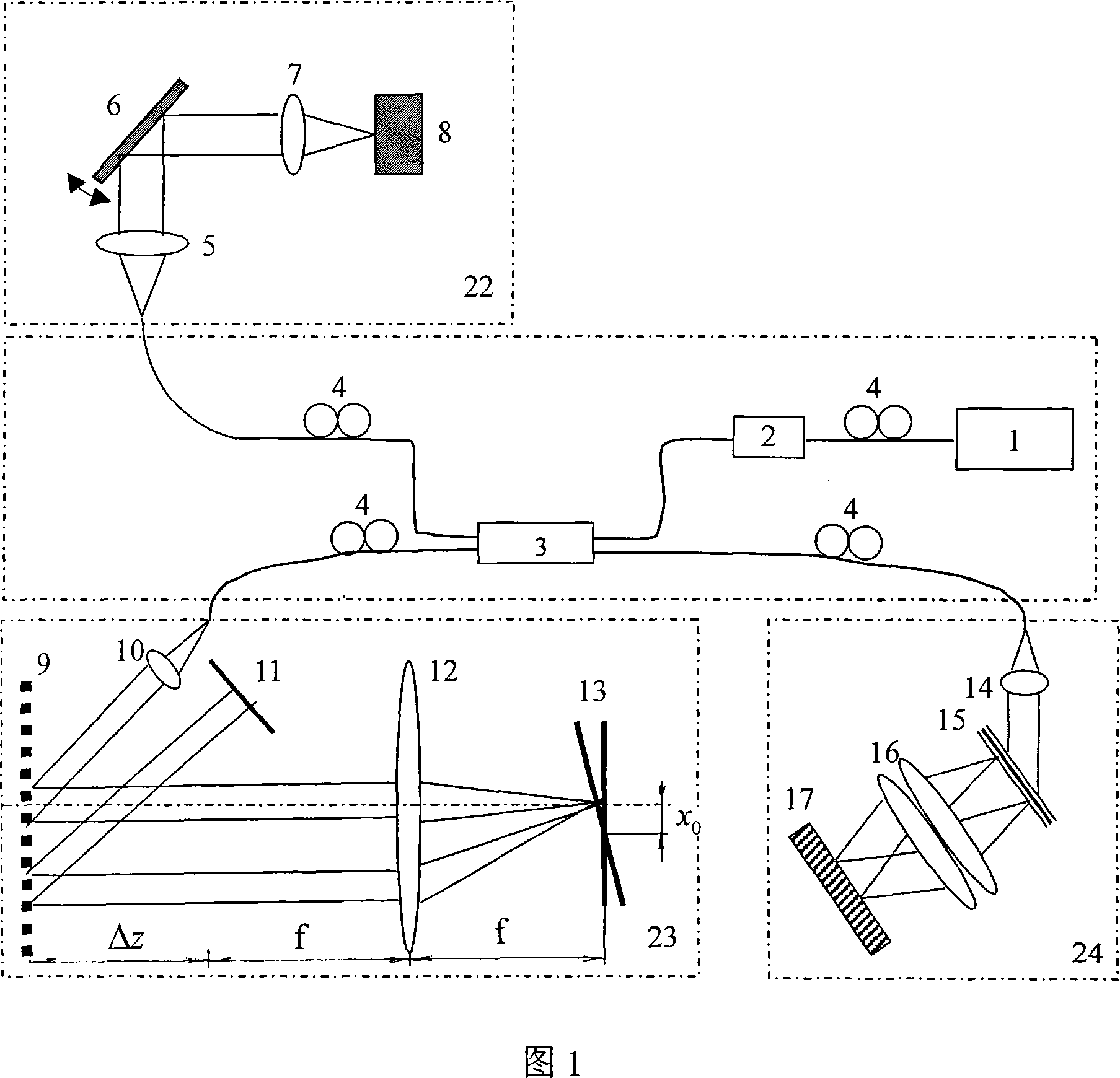
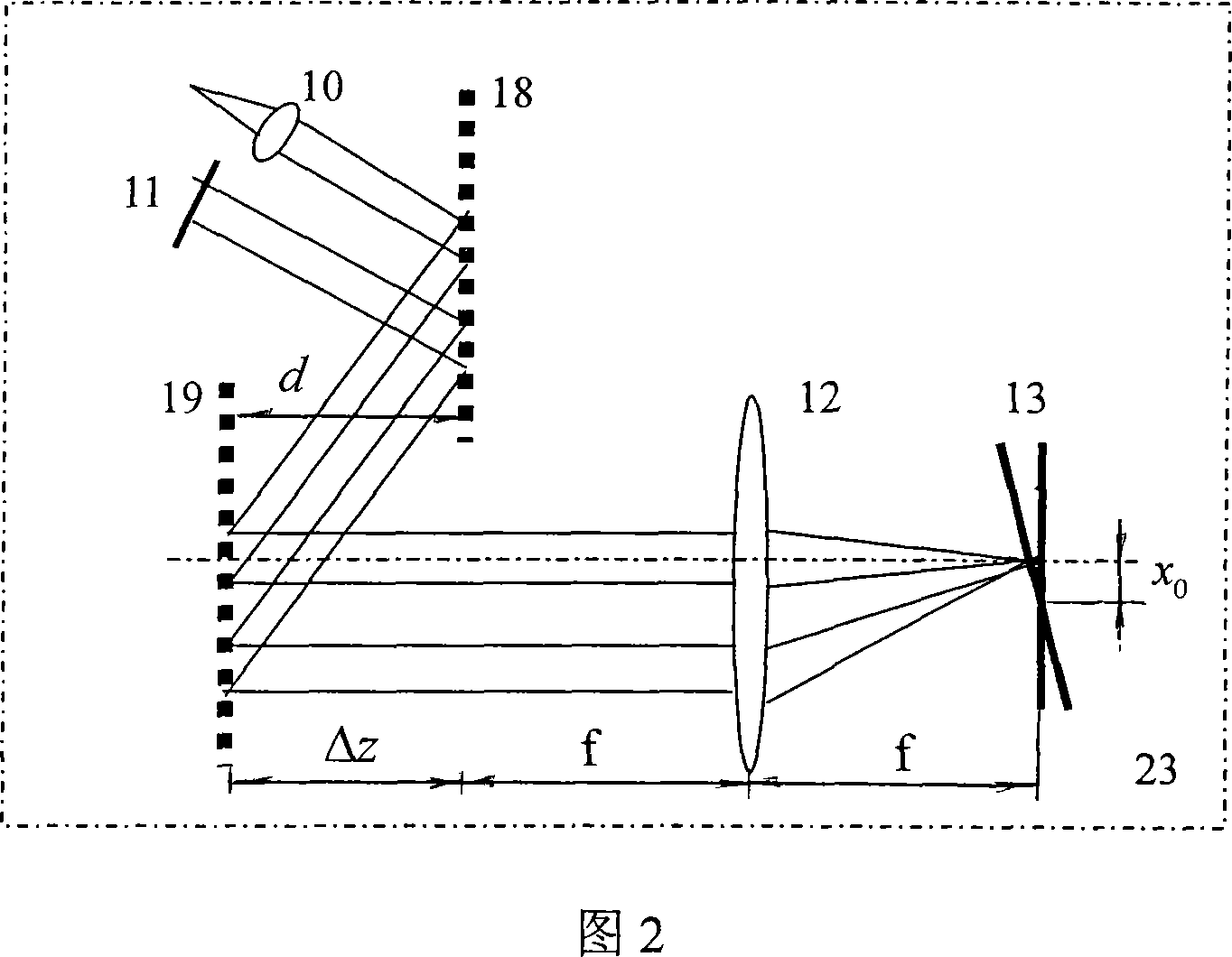
Compression design for high energy short pulse fiber laser
ActiveUS20070014317A1Quality improvementIncrease flexibilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingHigh energy
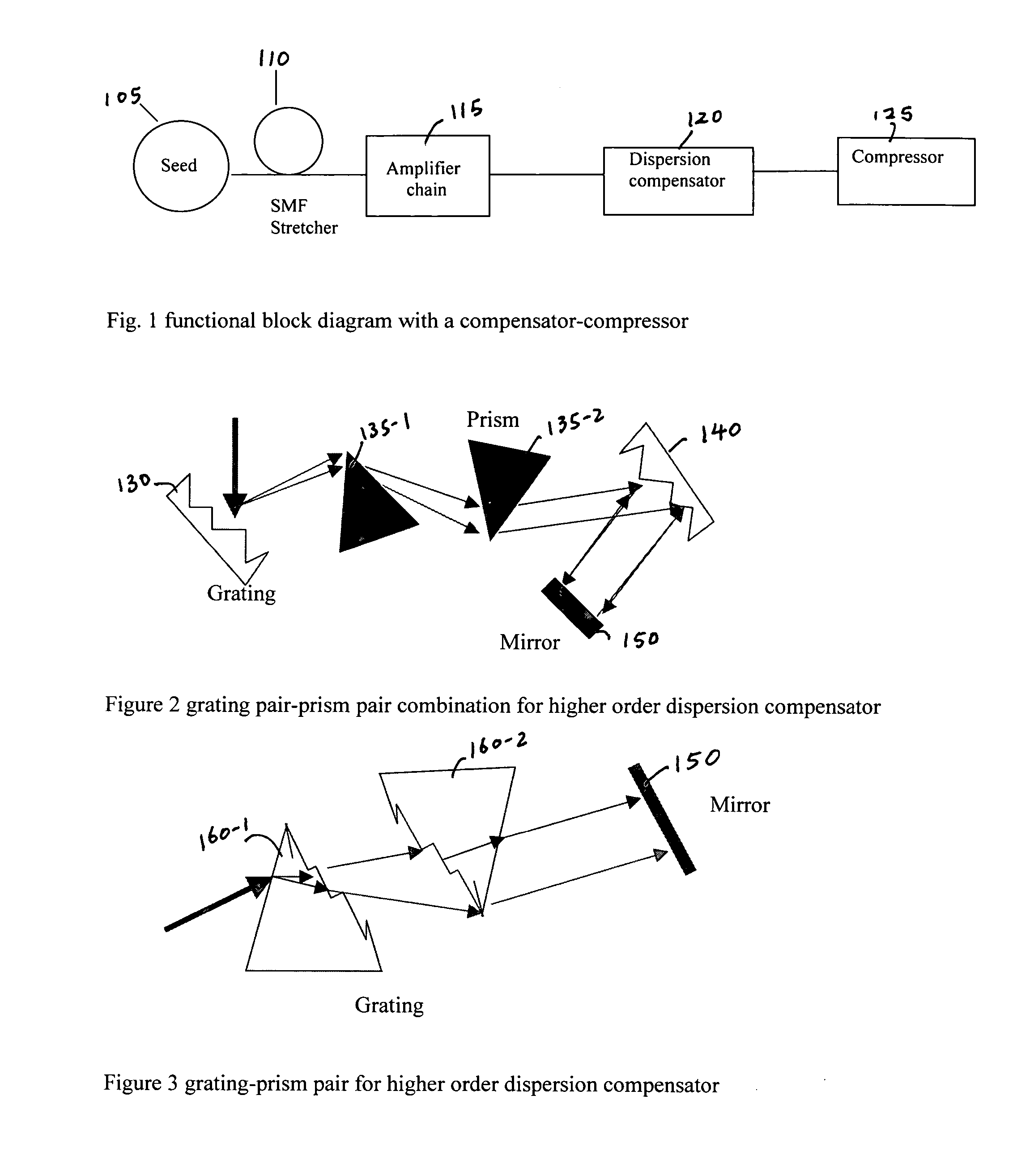
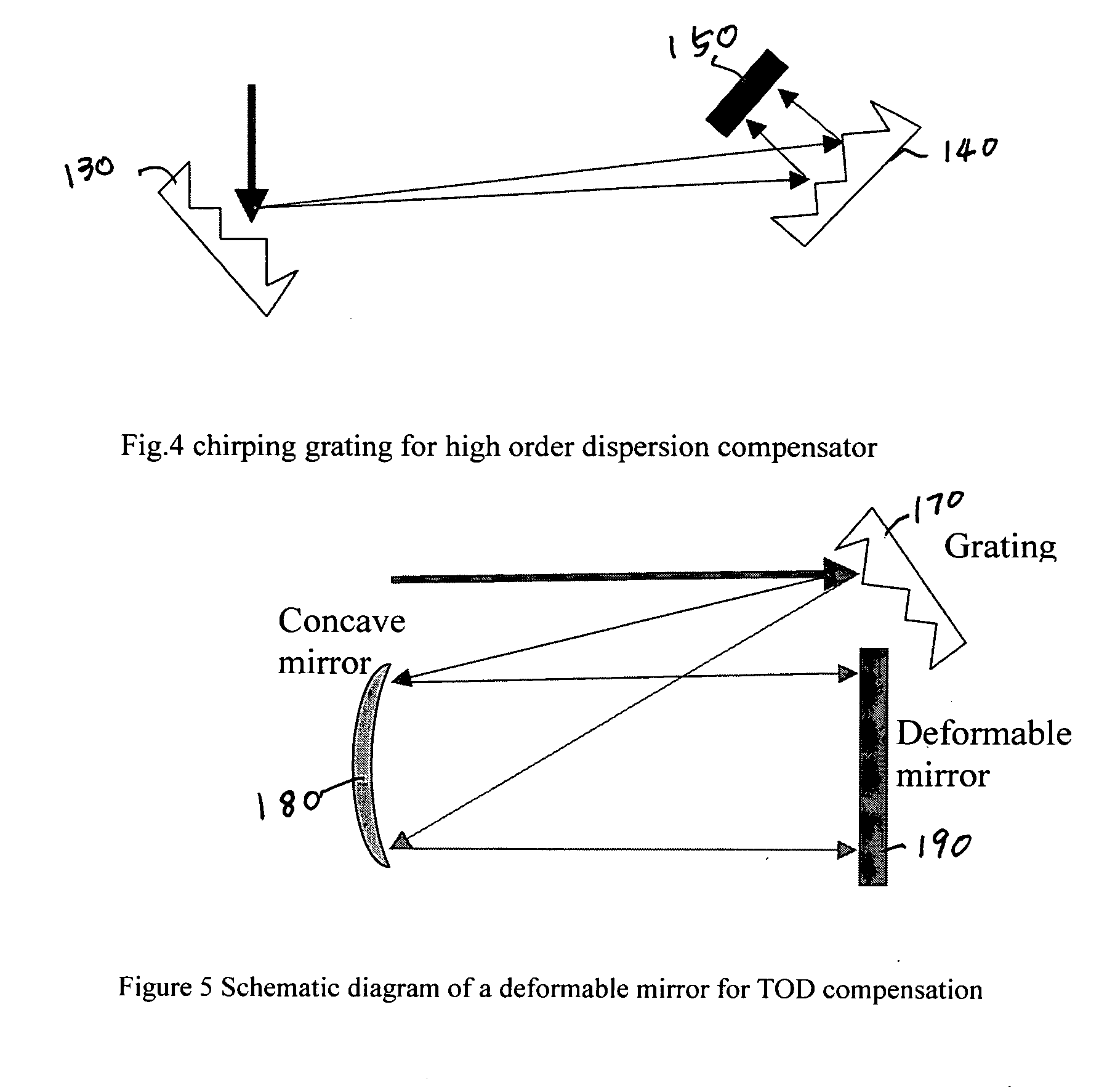
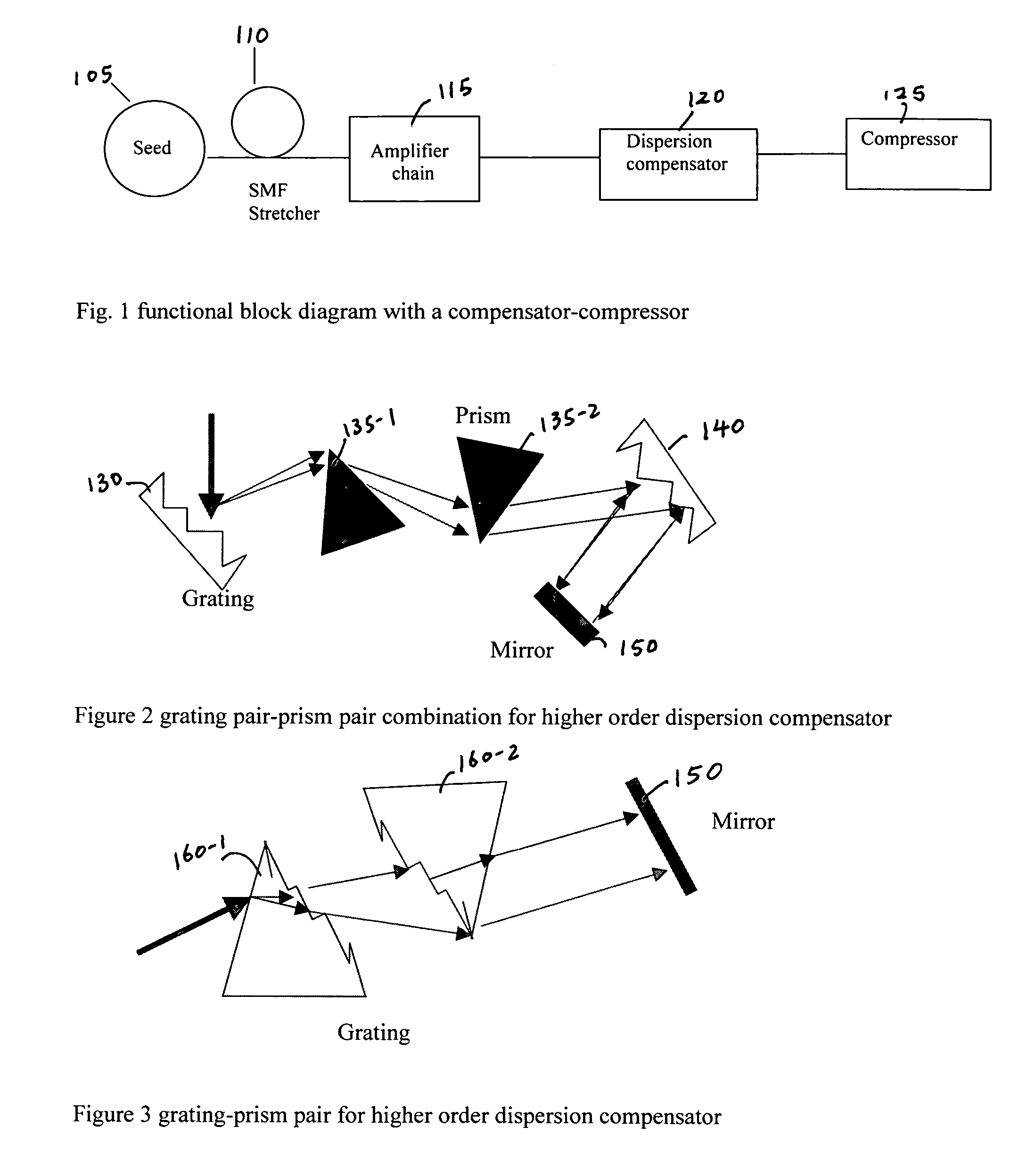
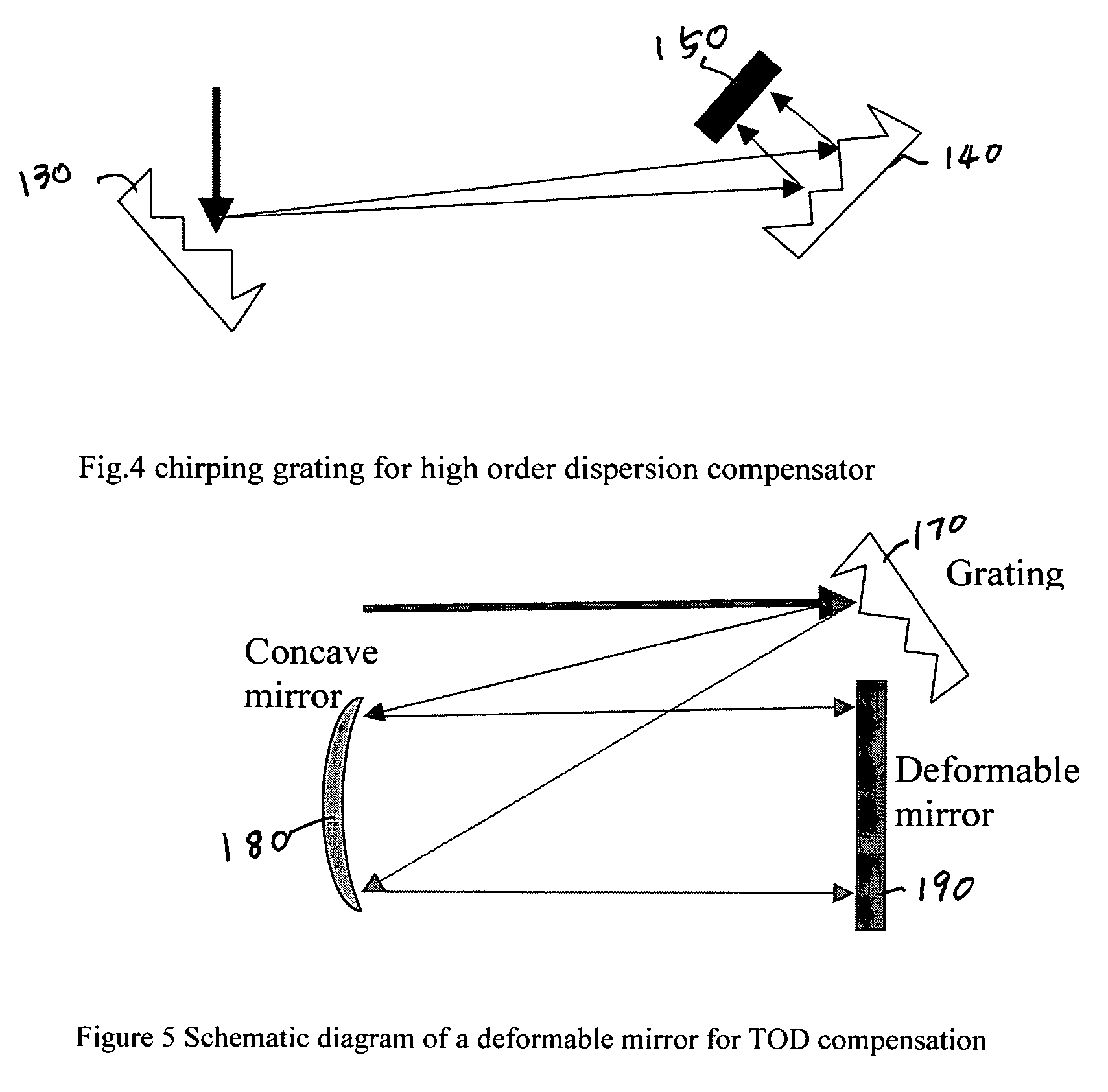
A fiber Chirped Pulse Amplification (CPA) laser system includes a fiber mode-locking oscillator for generating a laser for projecting to a fiber stretcher for stretching a pulse width of the laser. The fiber CPA laser system further includes a multistage amplifier for amplifying the laser and a high-order dispersion compensating compressor for compensating high order dispersions and compressing the pulse width of the laser. The high-order dispersion compensating compressor further includes a pair of gratings coupled with a pair of prisms, a grating pair engraved on the surfaces of a pair of prisms, a chirped grating pair and a phase modulator consists of a grating and a deformable mirror, for generating a negative group velocity dispersion (GVD) and a negative third order dispersion (TOD) for the laser.
Owner:POLARONYX
Optical component and dispersion compensation method
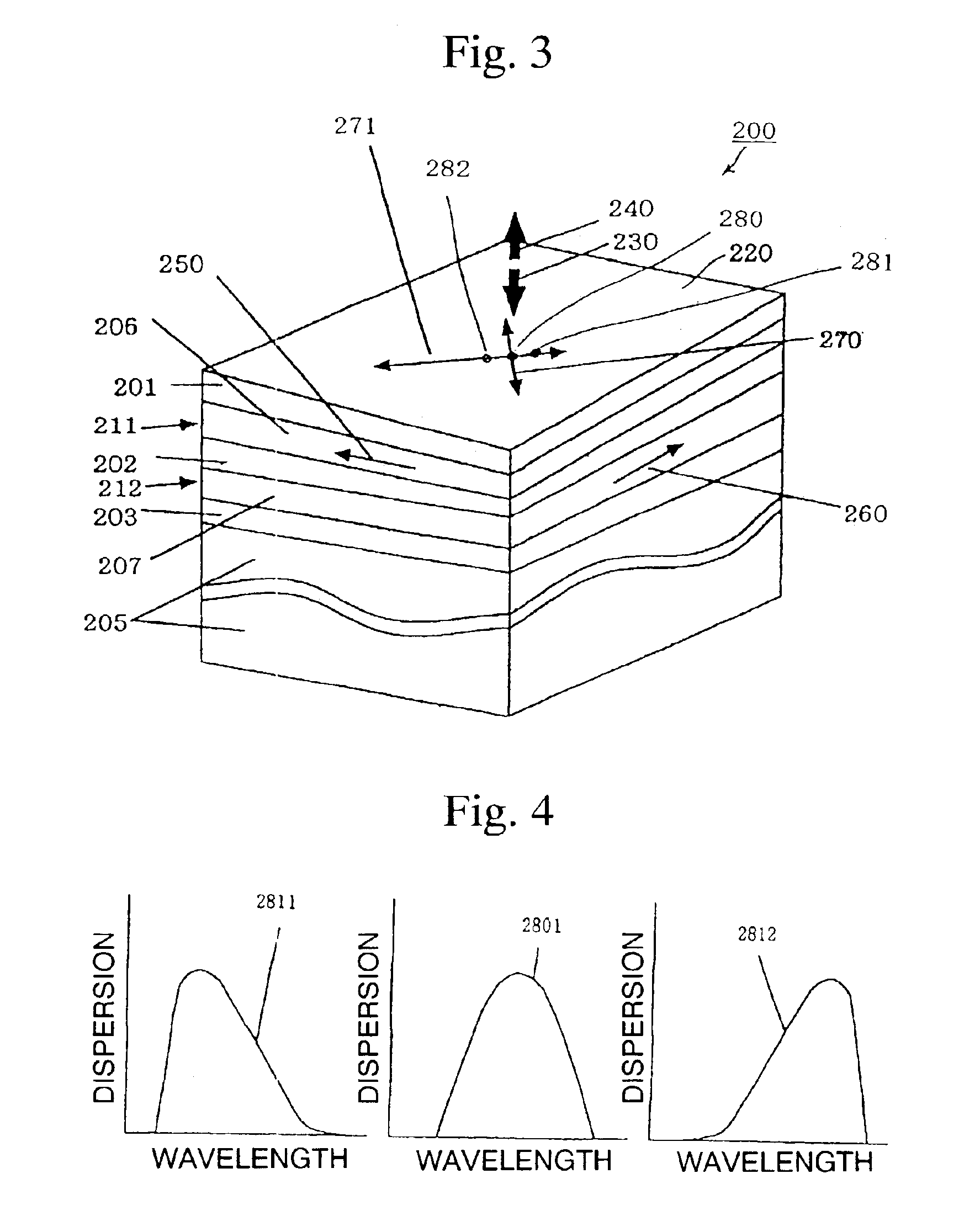
InactiveUS6943951B2Coupling light guidesDistortion/dispersion eliminationDispersion compensationThird order dispersion
An optical component of the present invention is compensated its optical dispersion, including third order dispersion, at low loss using optical dispersion compensating element comprising multi-layer film. In the optical component, an optical dispersion compensating element and a functional element are connected in series along an optical path.
Owner:OYOKODEN LAB +1
Dispersion compensating method and system for optically coherent chromatographic imaging
InactiveCN1887220ALarge dispersion adjustment rangeWide Compensation Spectral RangeSurgeryMaterial analysis by optical meansGratingPhase retardation
The present invention discloses dispersion compensating method and system for optically coherent tomographic imaging (OCT). The system has one increased blazed grating parallelly set with the original blazed grating in a single grating fast scanning optical delay line, and thus one independently regulated variable of interval between two blazed gratings and capacity of generating group velocity dispersion and third-order dispersion in great varying range and arbitrary sign combination, so that the OCT system may obtain precise matching between the dispersion of the reference arm and the dispersion of the sample arm and longitudinal resolution approaching the theoretical calculated value. The double grating system has wide dispersion regulating range, wide compensation spectrum range and small residual dispersion other than the capacity of independently controlling phase delay and group delay, and possesses three functions of depth scan, phase modulation and dispersion compensation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
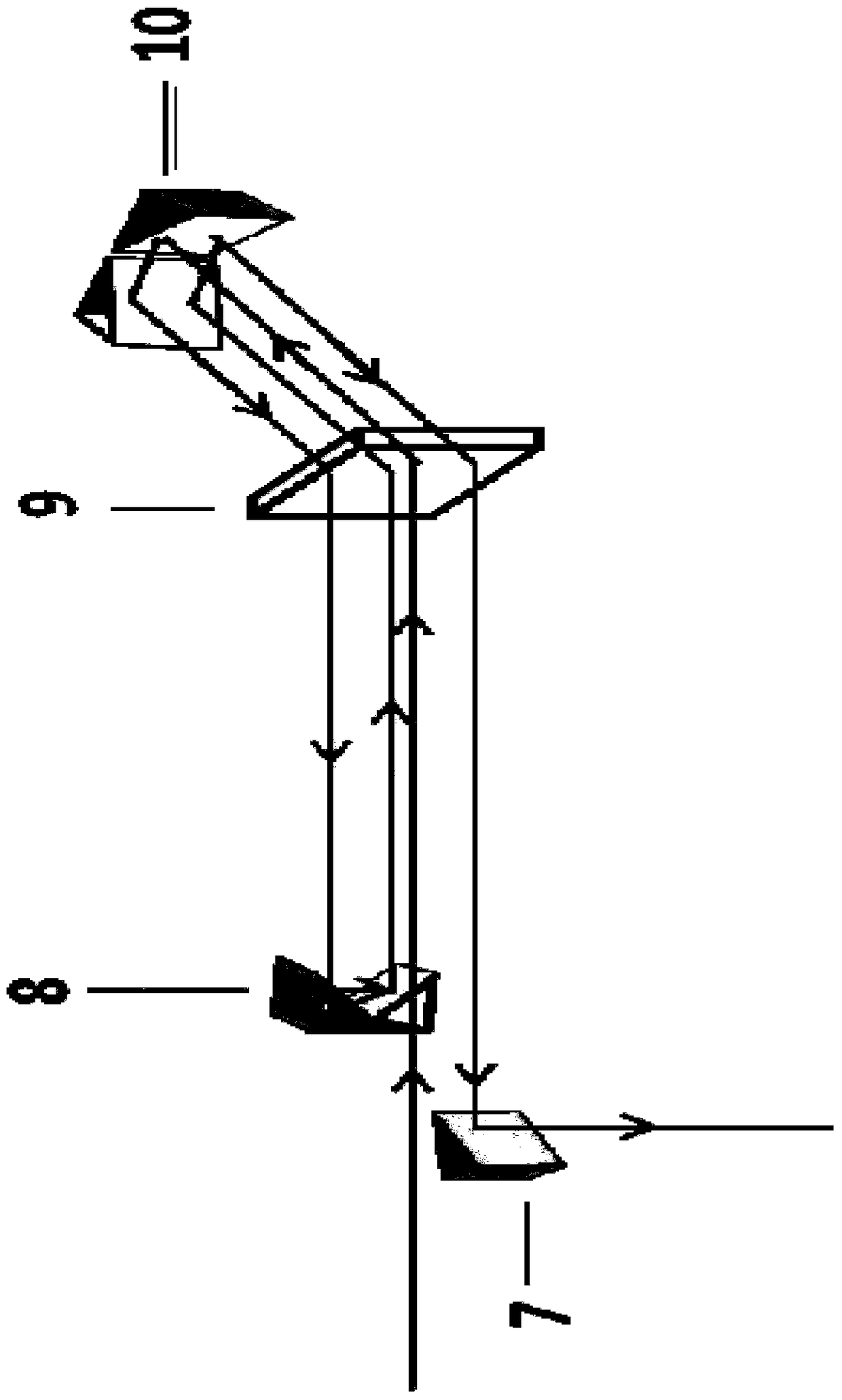
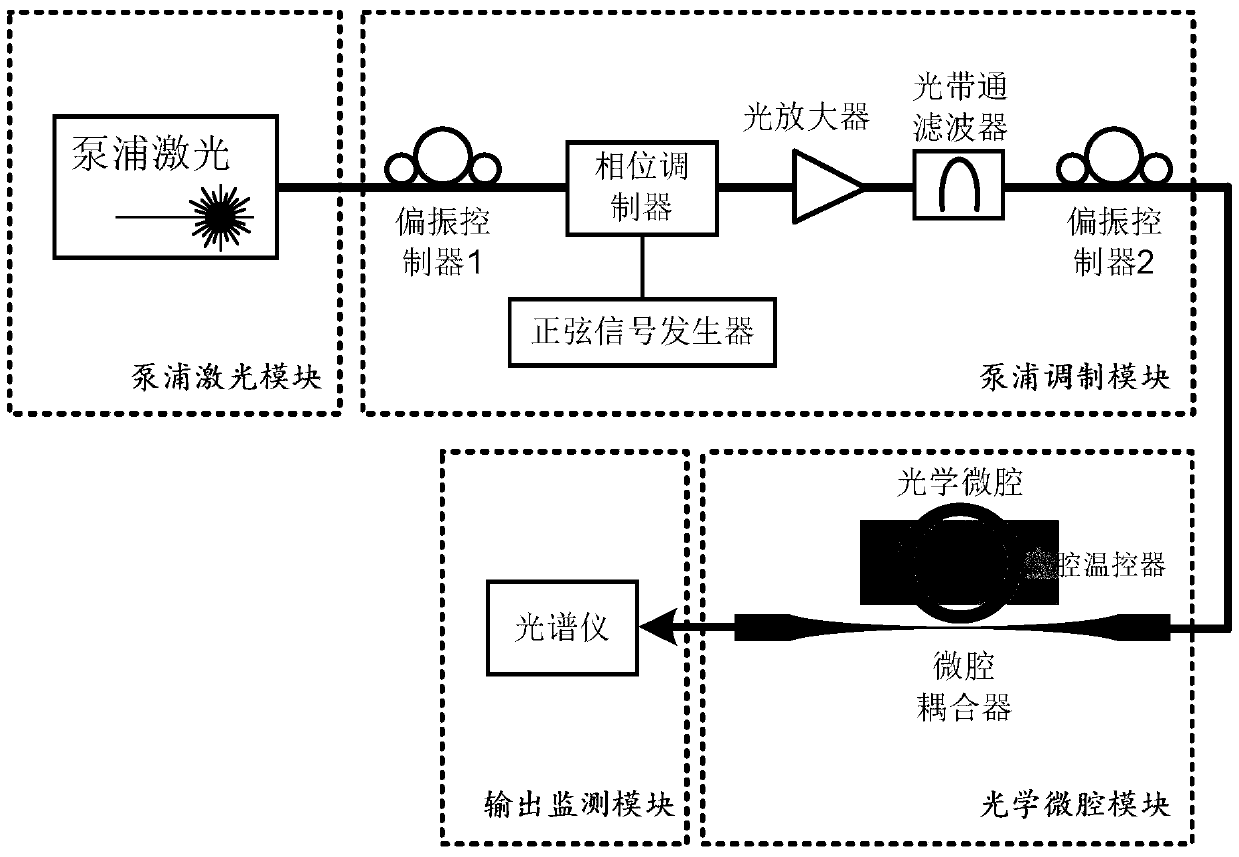
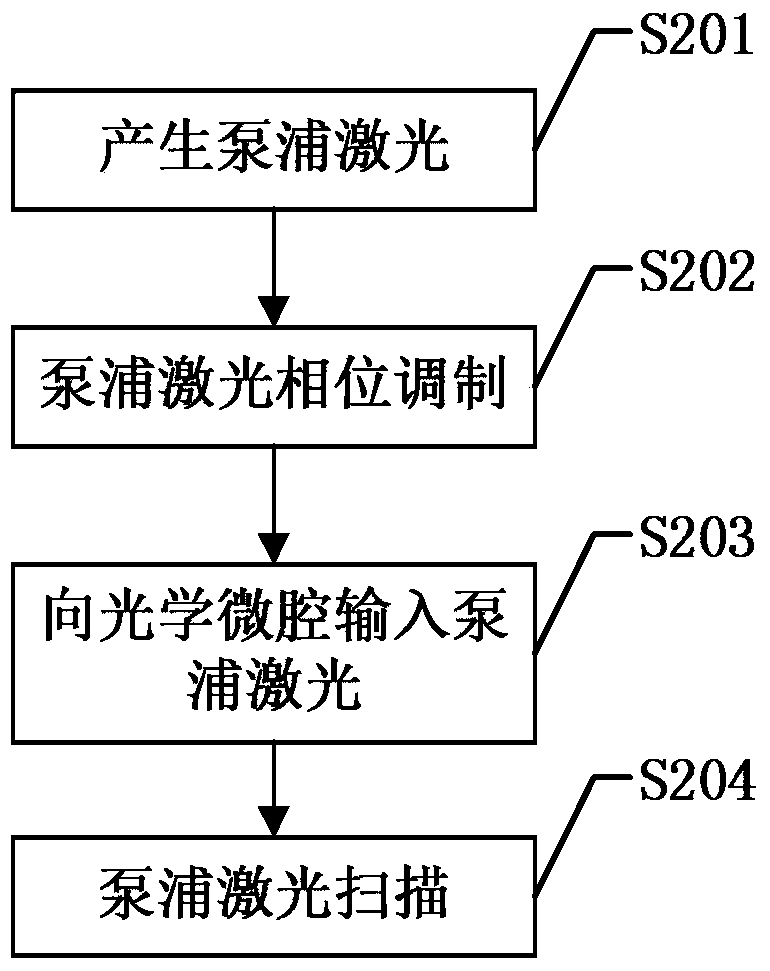
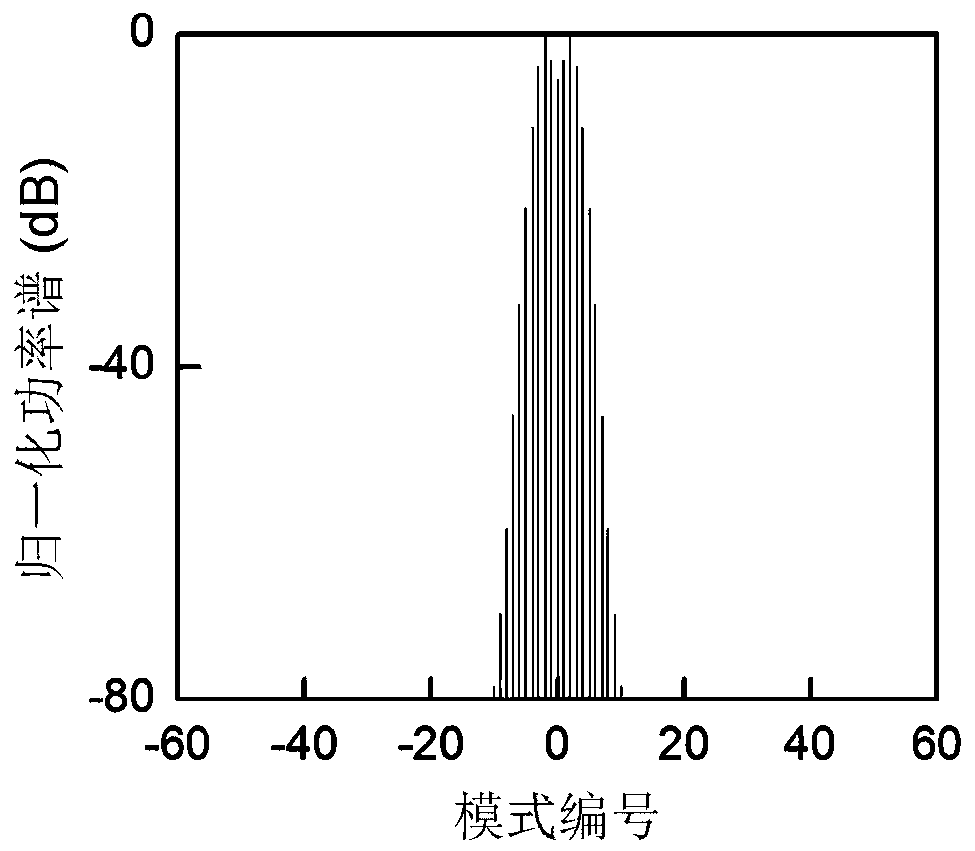
Certainty soliton mode locking method for Kerr optical frequency comb in optical microcavity
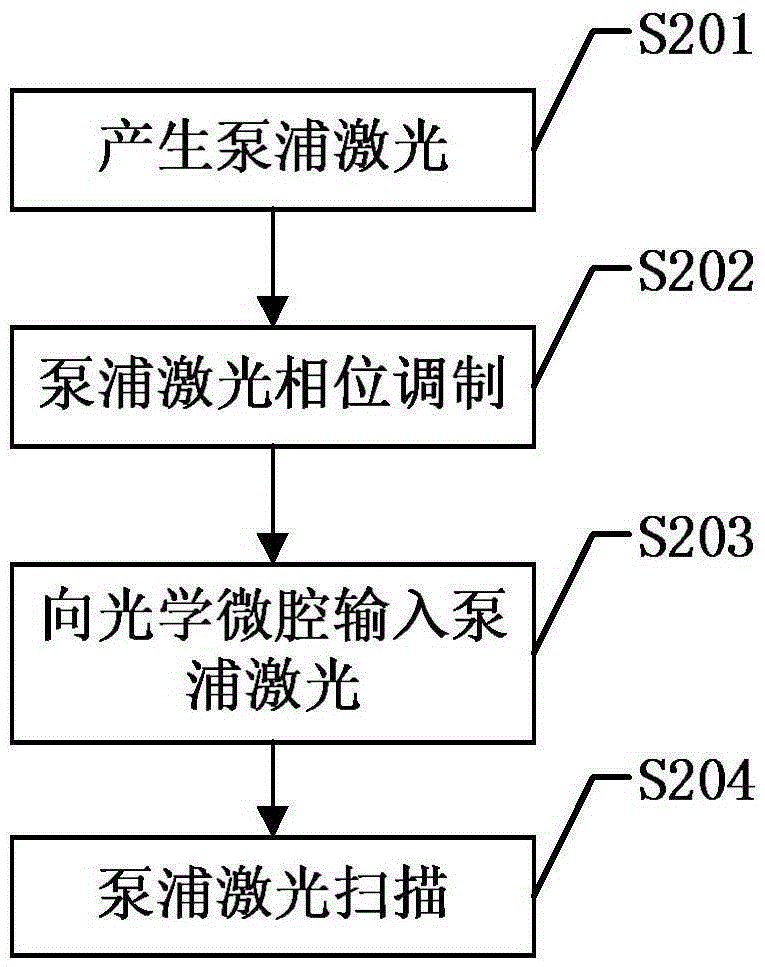
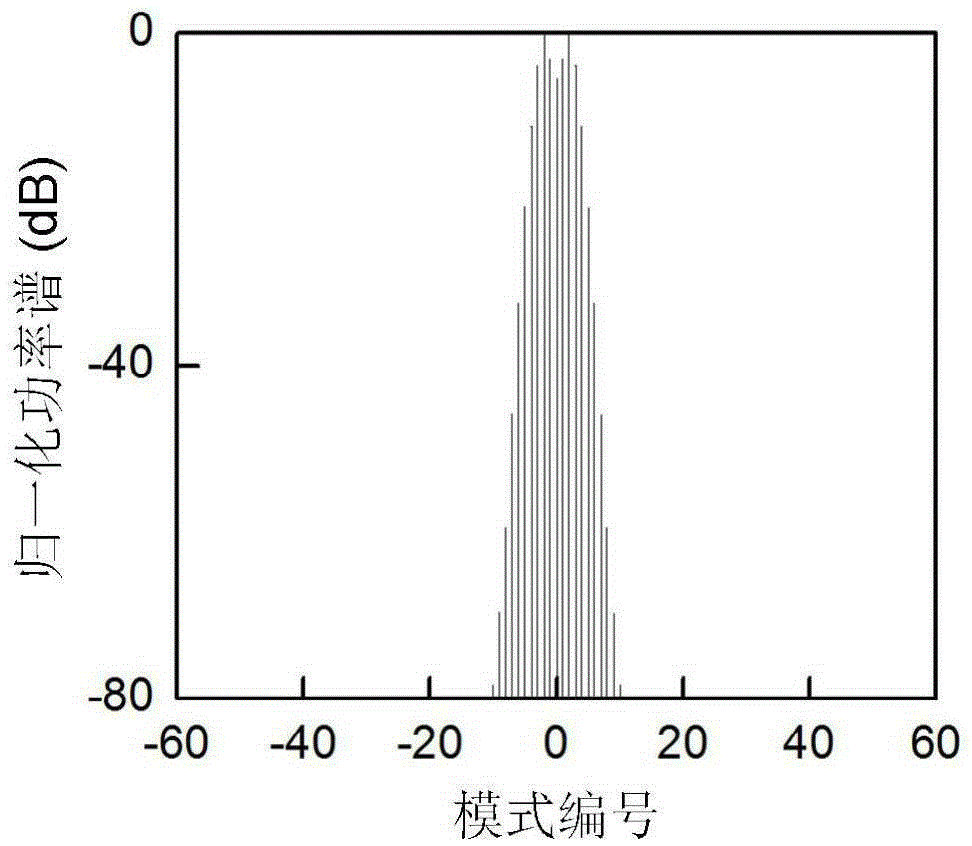
The invention discloses a certainty soliton mode locking method for a Kerr optical frequency comb in an optical microcavity. A pump laser power is set to be less than optical microcavity parametric oscillation threshold valve power; the generated pump laser is modulated; the frequency of a modulating signal is accordant with free frequency spectrum width of the optical microcavity; the amplitude of the modulating signal is obtained by calculating three-order dispersion value of the optical microcavity; the pump laser, after being subjected to phase modulation, enters the optical microcavity through a microcavity coupler in a coupling manner; the coupling coefficient is controlled to enable the optical microcavity to work in a critical coupling state; the pump laser is scanned from a long wavelength direction to a short wavelength direction in the optical microcavity; the spectrum of the output pump laser is collected at the output end of the optical microcavity; and in case that the current pump laser spectrum comprises a smooth envelope, the soliton mode locking is finished, and the scanning is stopped. According to the certainty soliton mode locking method for the Kerr optical frequency comb in the optical microcavity, the problems of high randomness, low reliability, high probability of disturbance and the like of the existing Kerr optical frequency comb mode locking scheme are overcame, so that the rapid and accurate soliton mode locking is realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
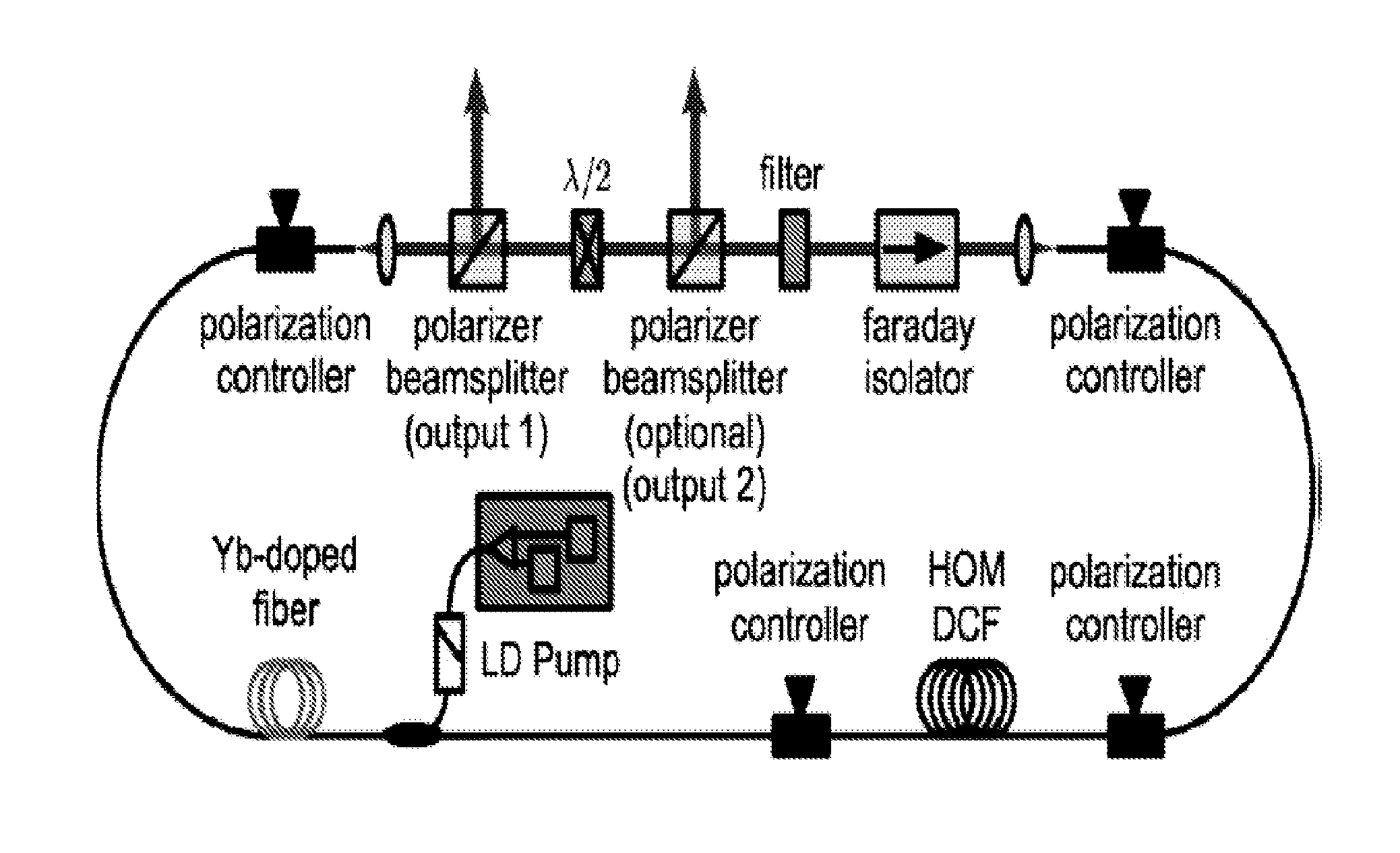
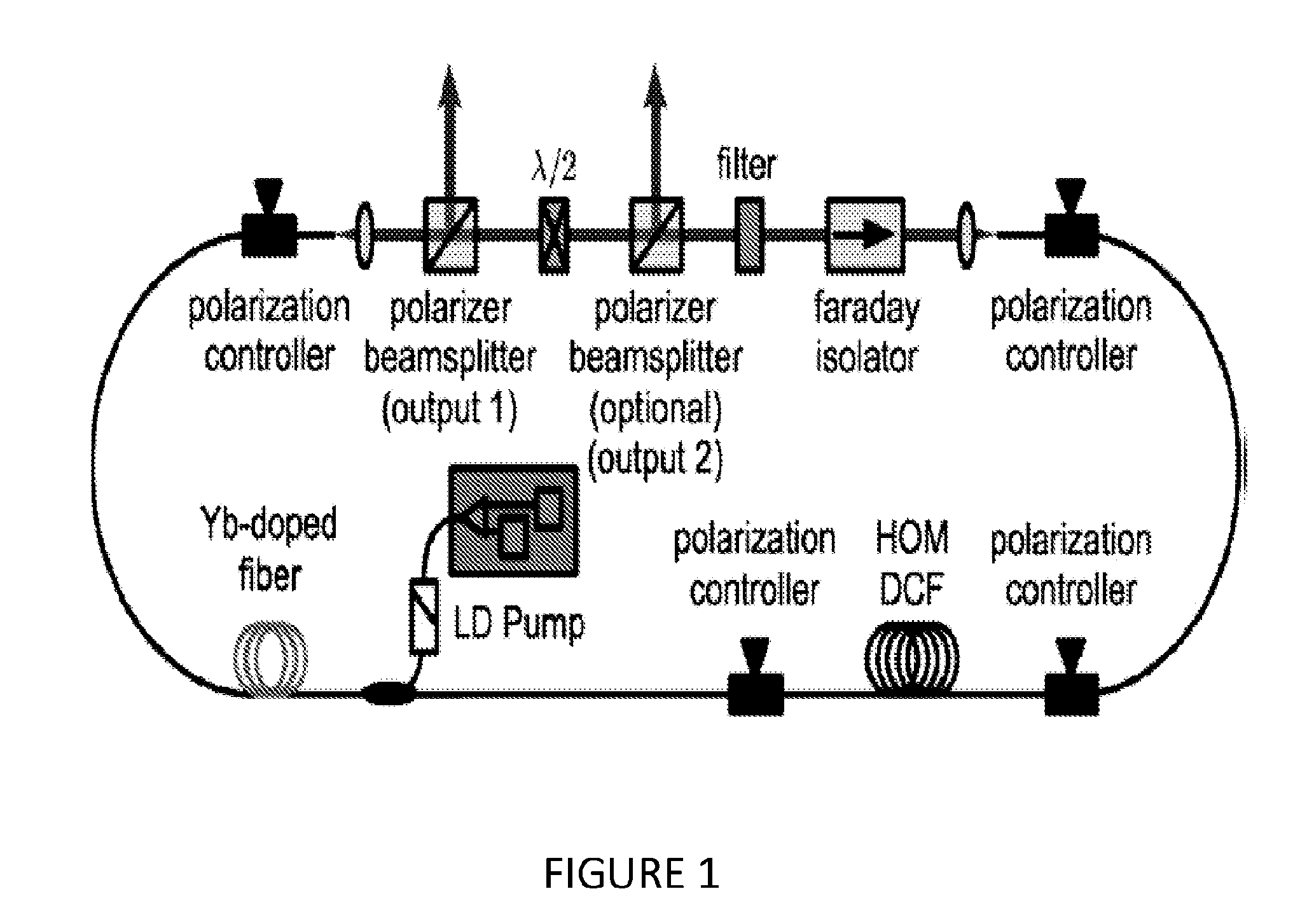
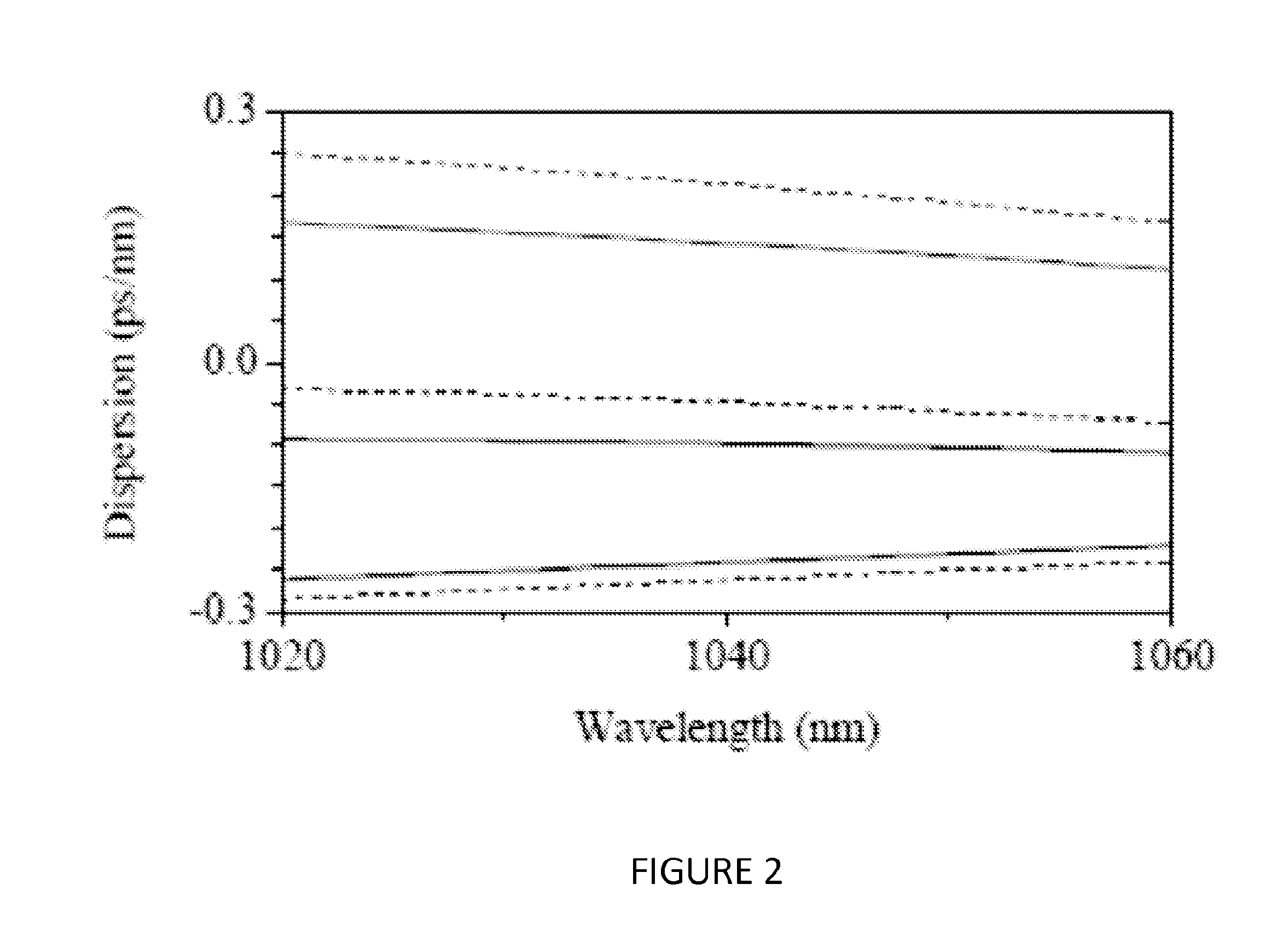
High-fidelity, high-energy ultrashort pulses from a net normal-dispersion yb-fiber laser with an anomalous dispersion higher-order-mode fiber
InactiveUS20140376576A1Good dispersionActive medium shape and constructionOptical light guidesFiber chromatic dispersionPulse parameter
Embodiments of the present invention generally relate to high energy, ultrashort pulses from a net normal dispersion ytterbium fiber laser with an anomalous dispersion higher-order mode fiber. More specifically, embodiments of the present invention relate to a fiber oscillator with all-fiber dispersion compensation delivering pulse parameters comparable to solid-state oscillators having good compensation of higher order dispersion and intracavity nonlinearities. In one embodiment of the present invention, an oscillator comprises a length of single mode fiber and a length of higher-order mode fiber, where the group delay dispersion (GDD) of the higher-order mode fiber is chosen to match 50% or more of the GDD of the single mode fiber; wherein a third-order dispersion of the oscillator matches a nonlinear phase buildup in a cavity of the oscillator, and the nonlinear phase buildup is dependent upon the pulse energy of the oscillator.
Owner:VIENNA UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +1
Optical delay element
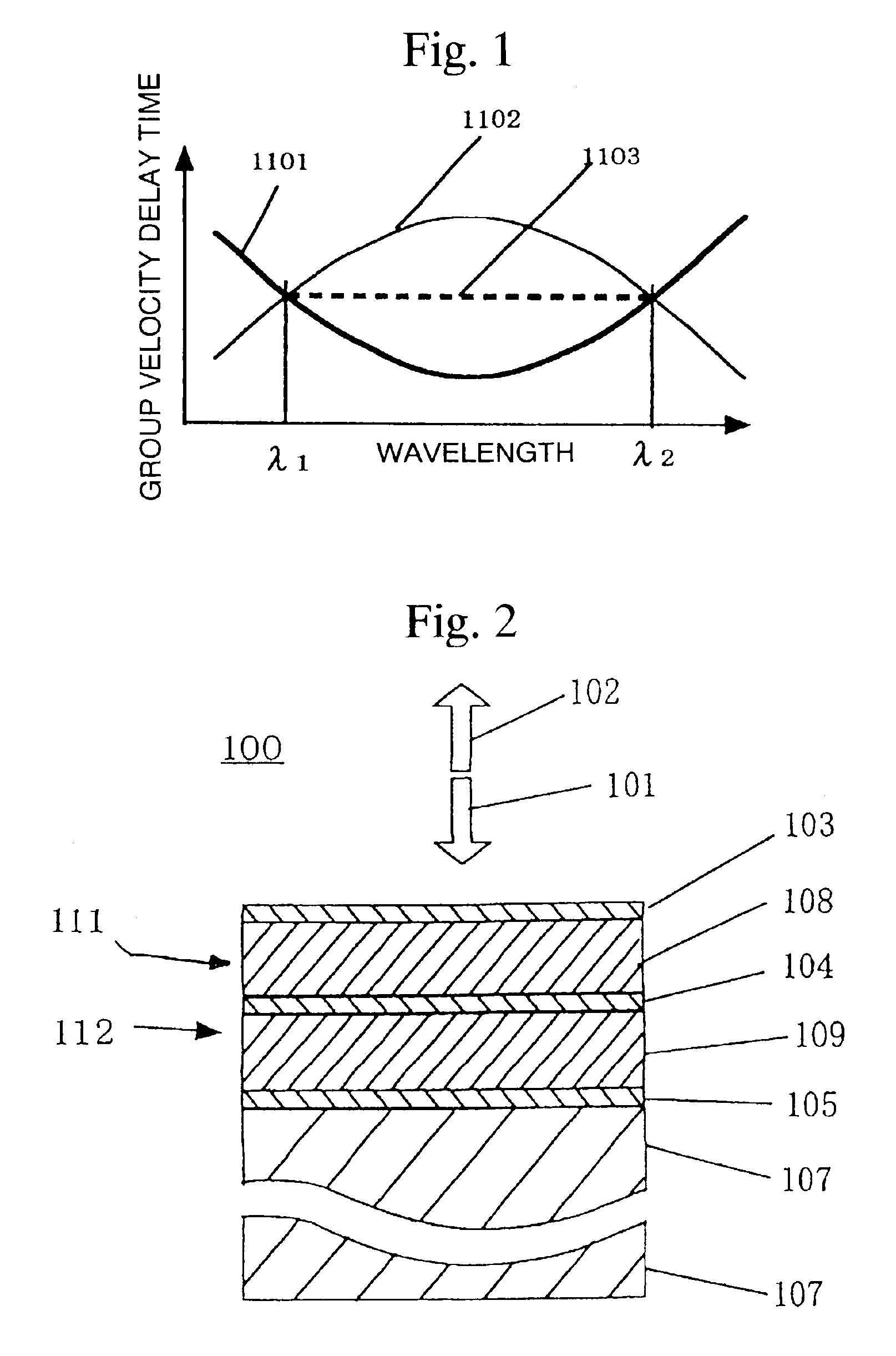
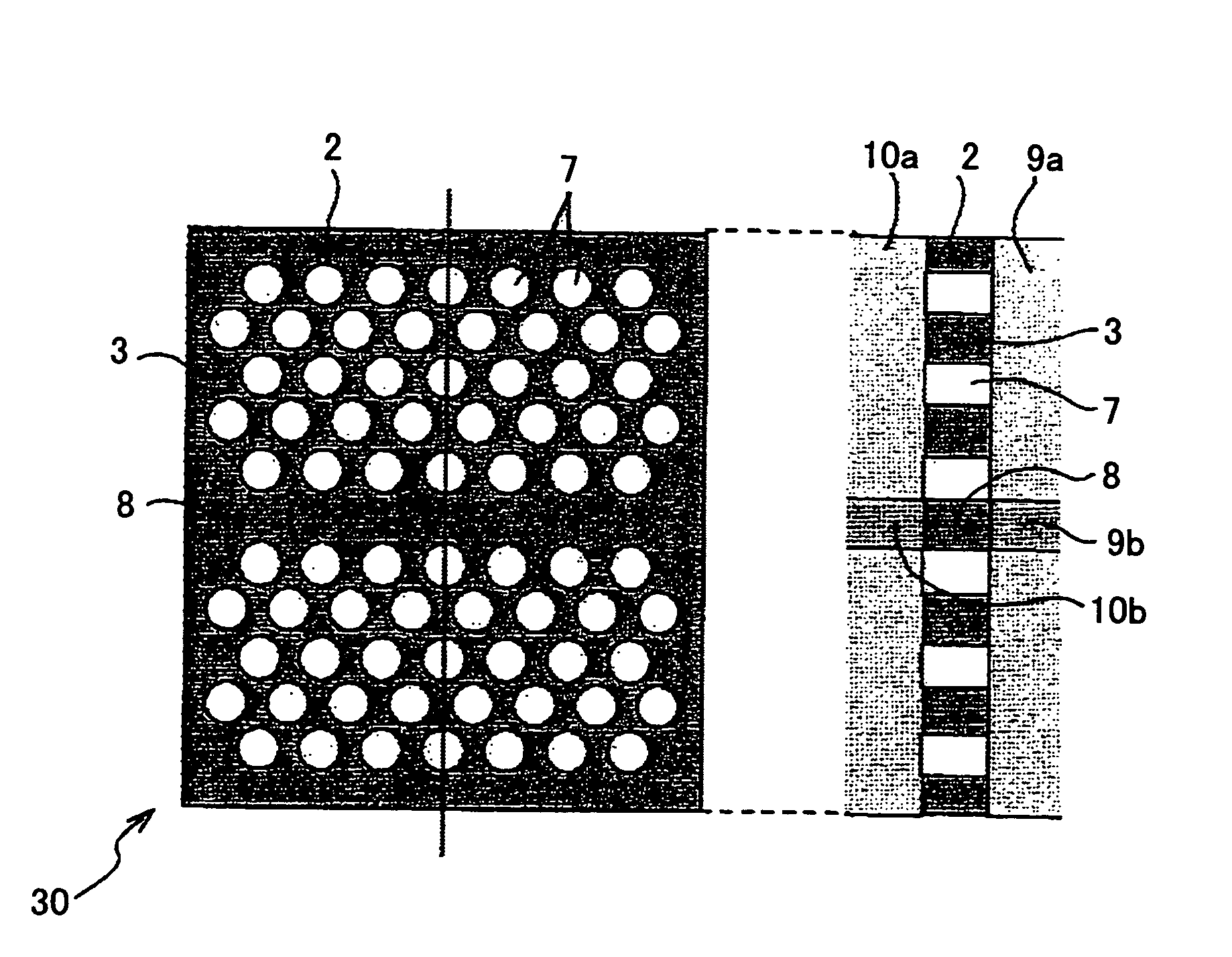
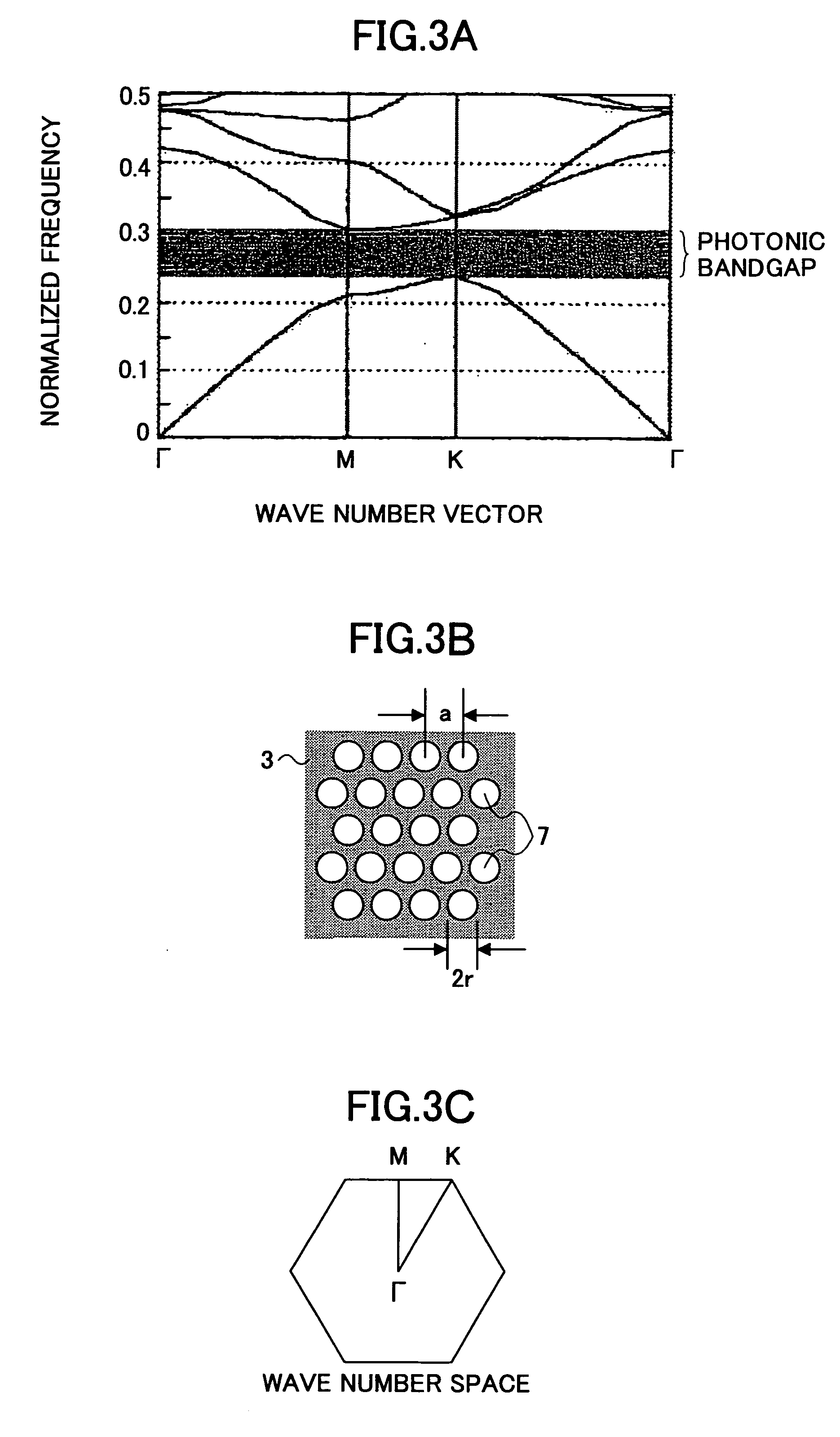
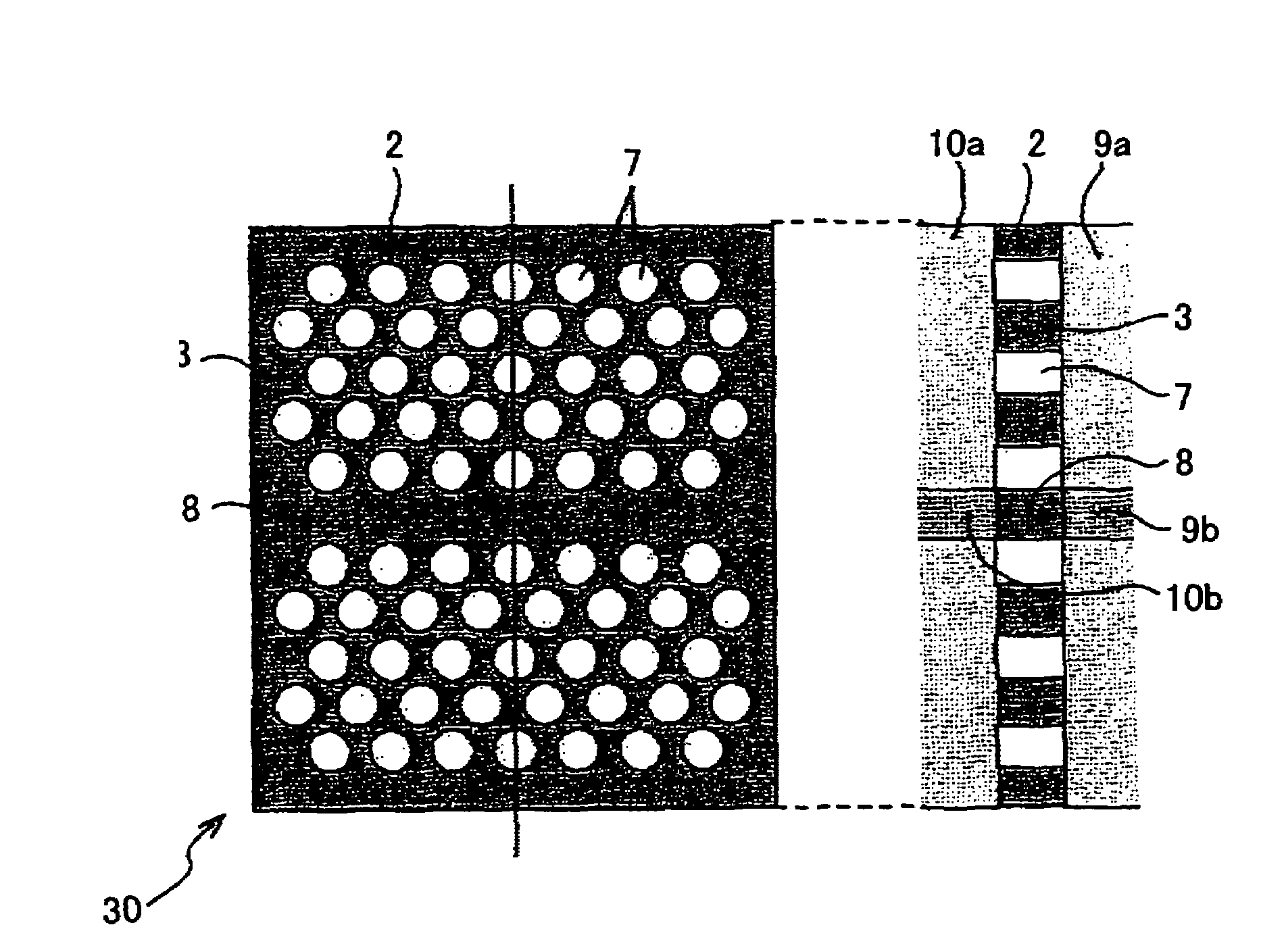
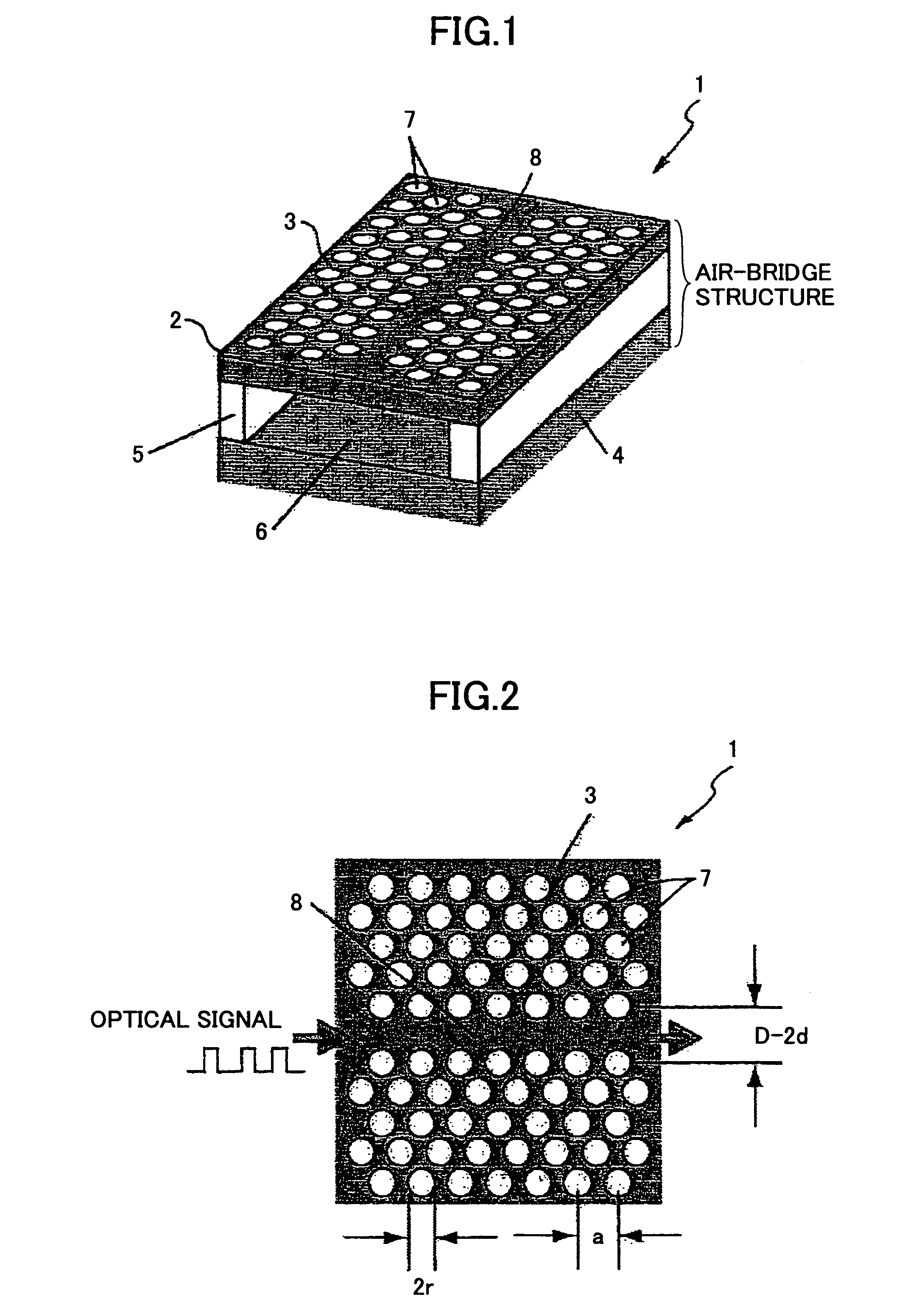
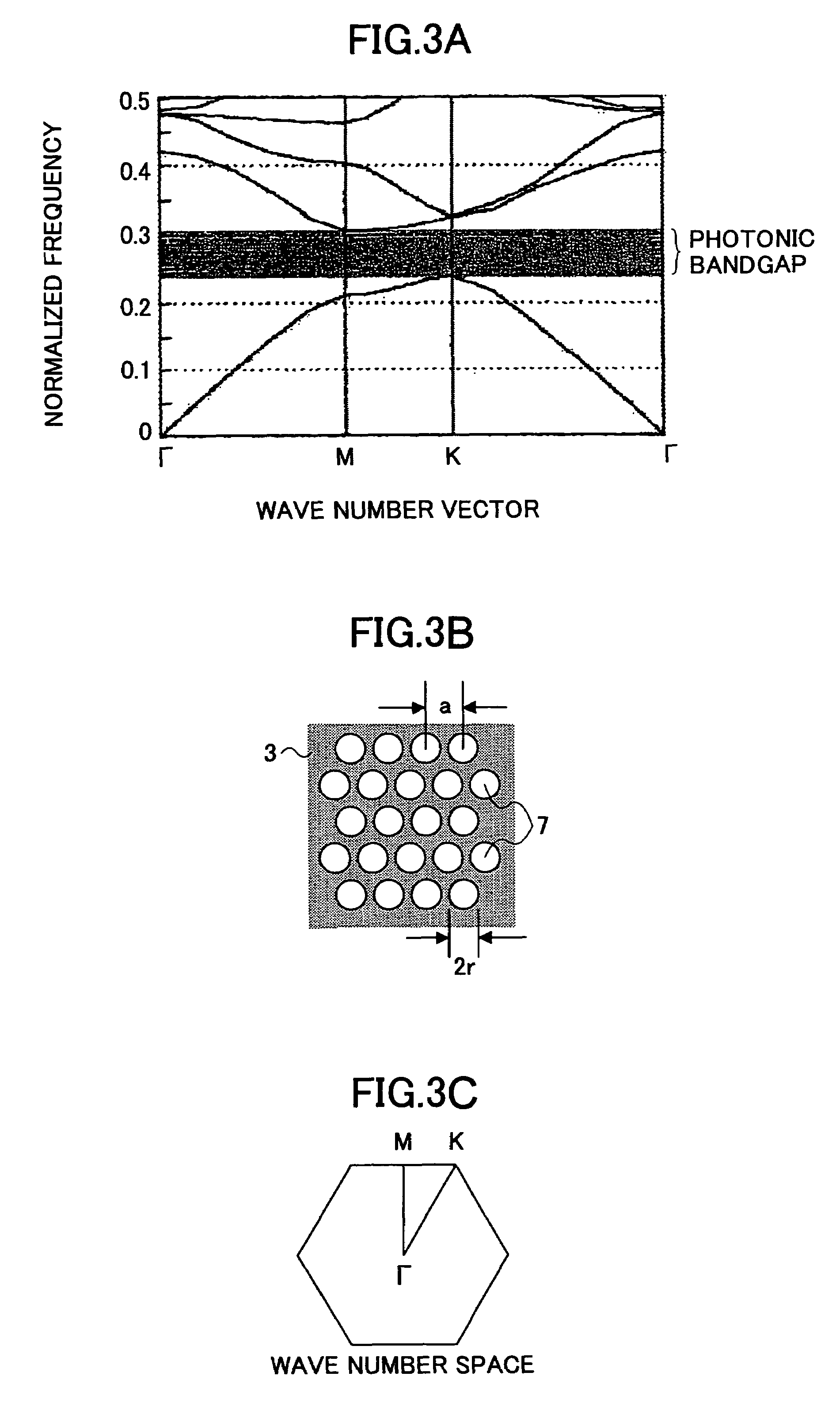
ActiveUS20060083472A1Extended wavelength rangeLower the volumeNanoopticsCoupling light guidesRefractive indexPhotonic crystal structure
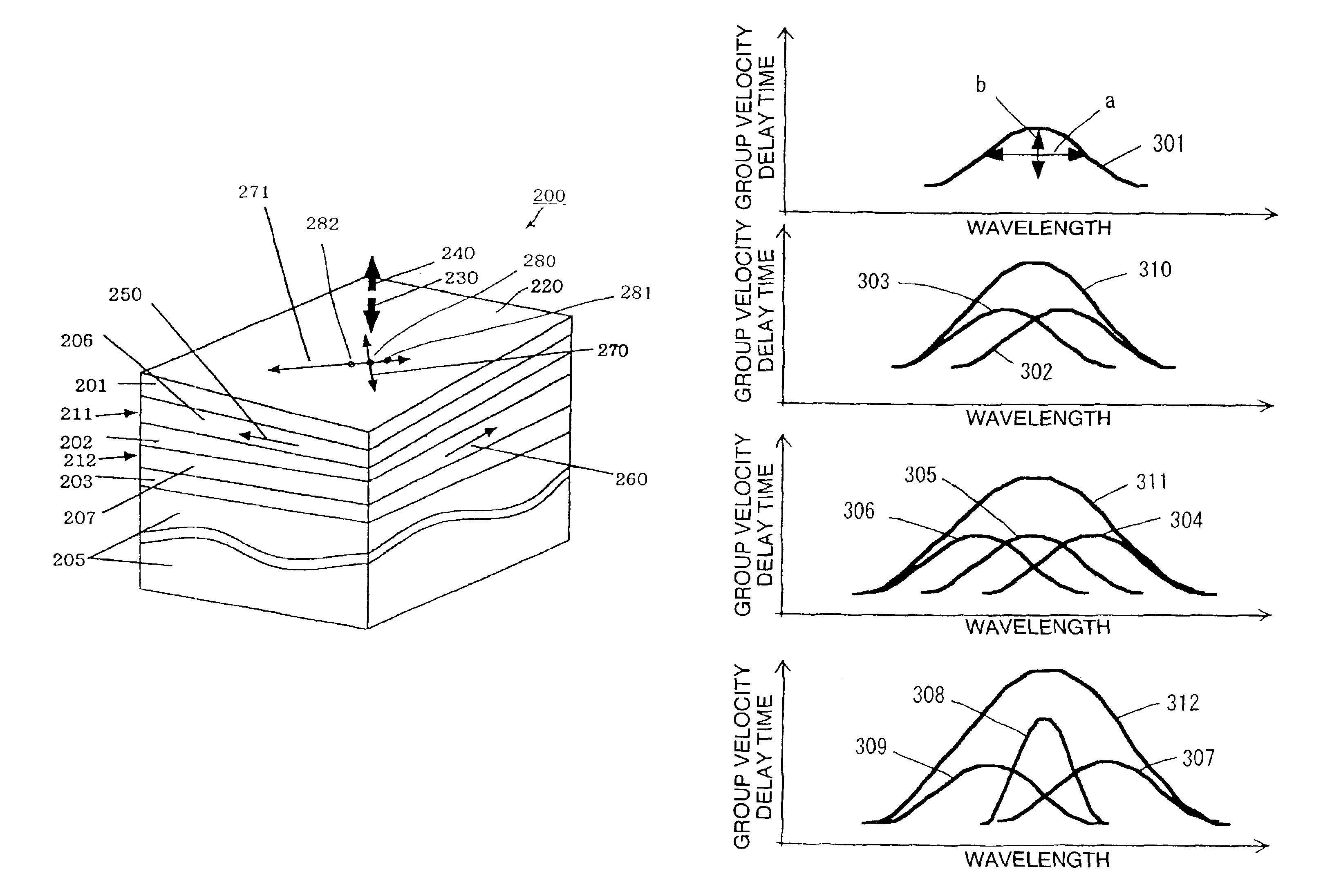
An optical delay element including a photonic crystal line defect optical waveguide is disclosed that has a large group refractive index and has small or nearly constant wavelength dispersion of the group refractive index in a wide wavelength region for practical use. The optical delay element includes a line defect optical waveguide formed in a photonic crystal structure, and the volume of the line defect optical waveguide is less than the volume of a single line defect optical waveguide. Thereby, the waveguide band of the line defect optical waveguide has two zero points in the third order dispersion curve of the line defect optical waveguide, and the sign of the third order dispersion curve is inverted near the zero points. Therefore, the waveguide band of the line defect optical waveguide is modified, and this enables expansion of the wavelength region having a large group refractive index, small wavelength dispersion of the group refractive index, and small wavelength dispersion of the speed of optical pulses.
Owner:RICOH KK +1
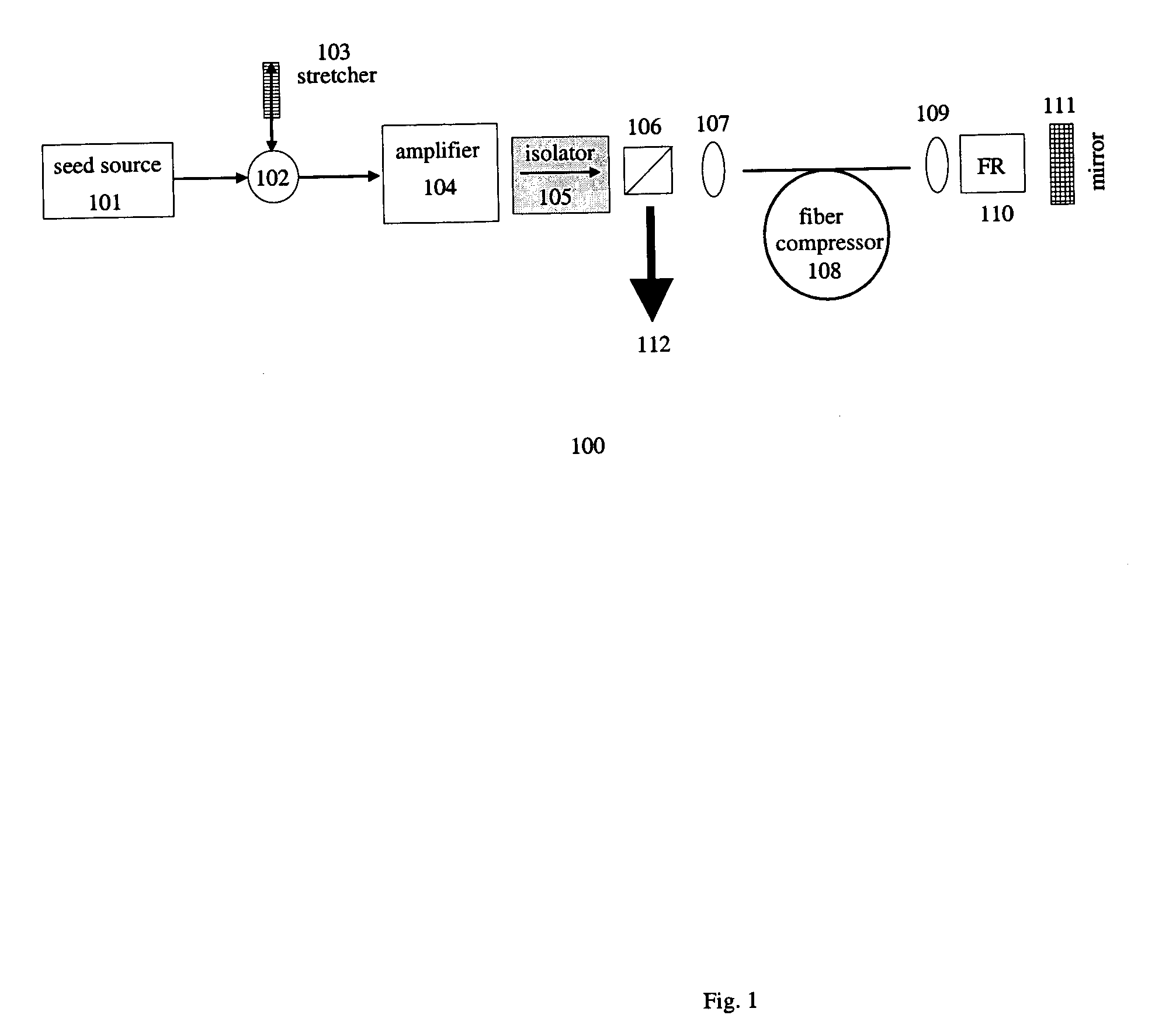
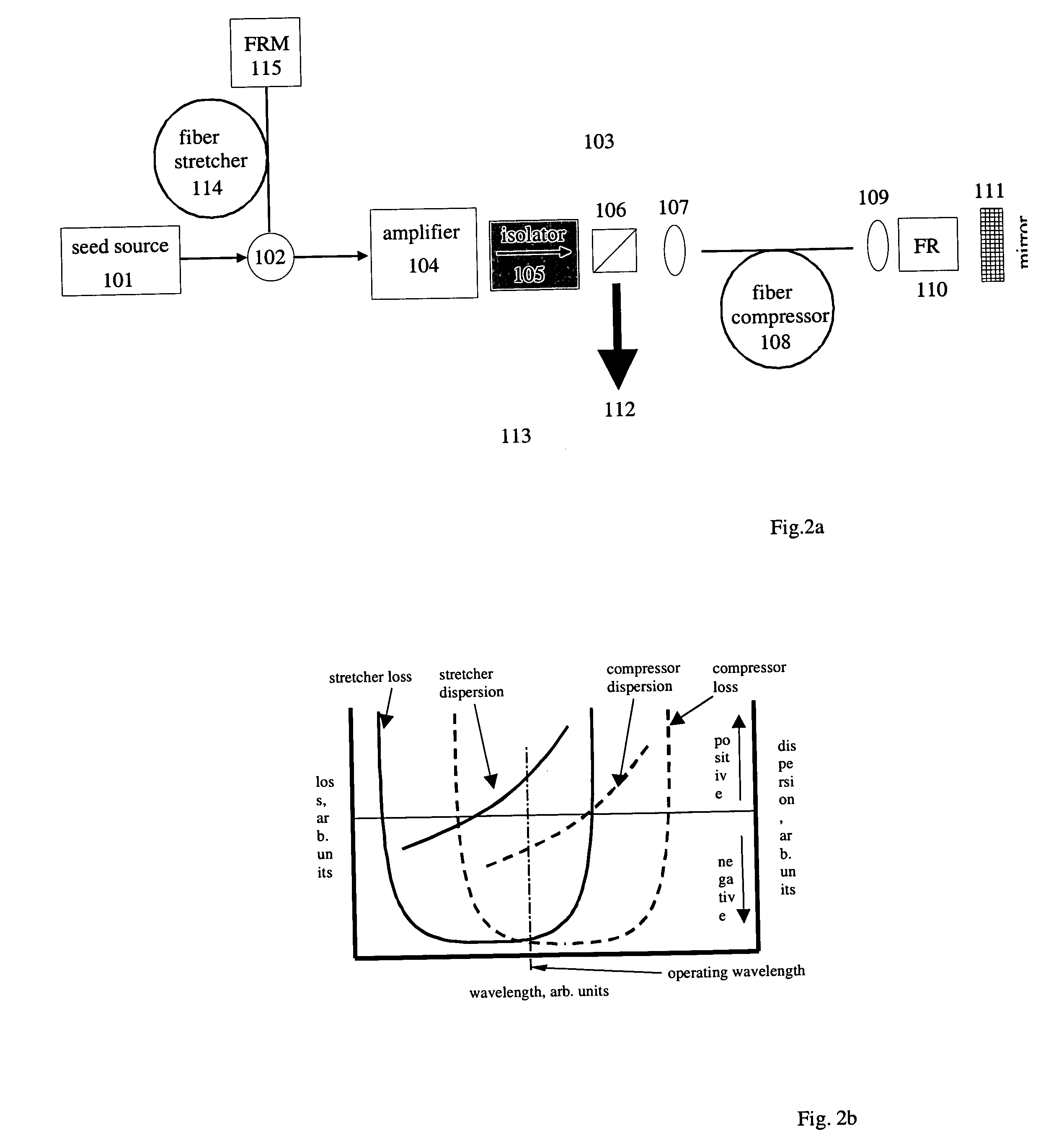
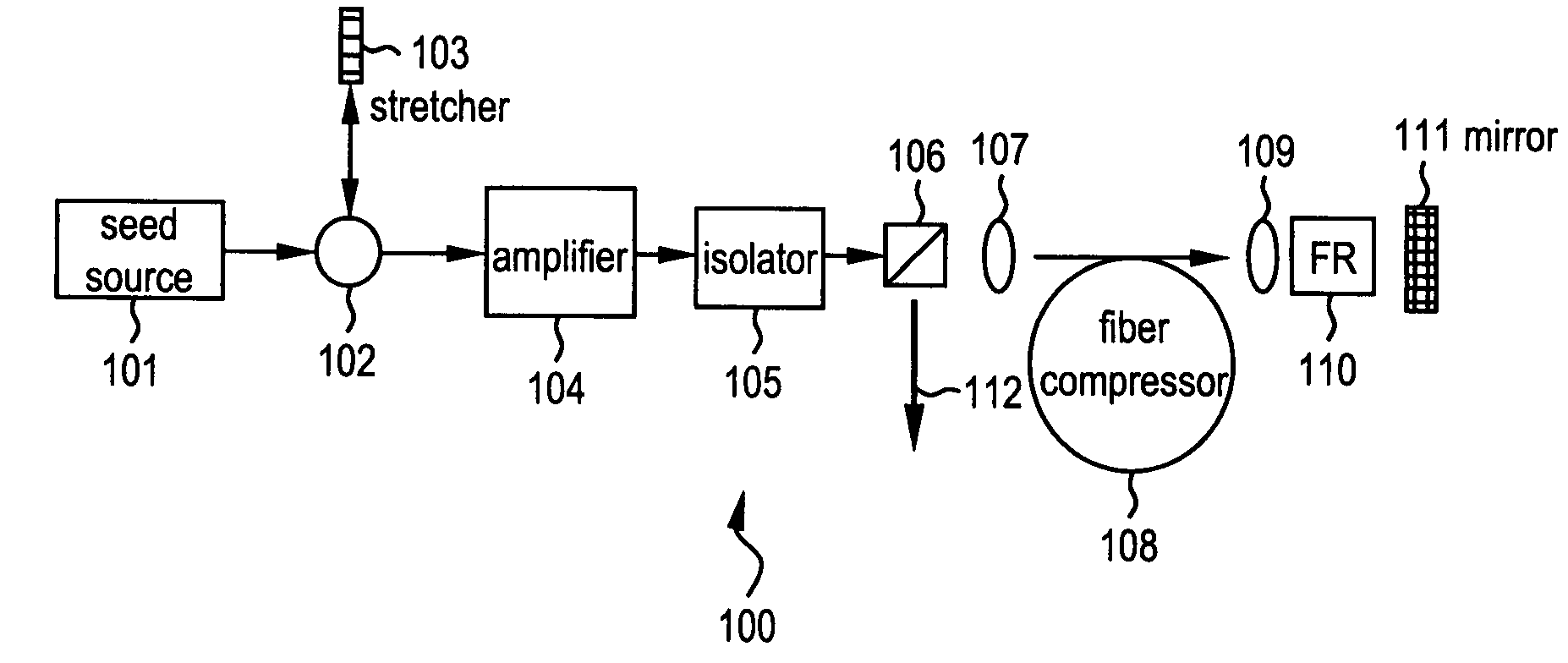
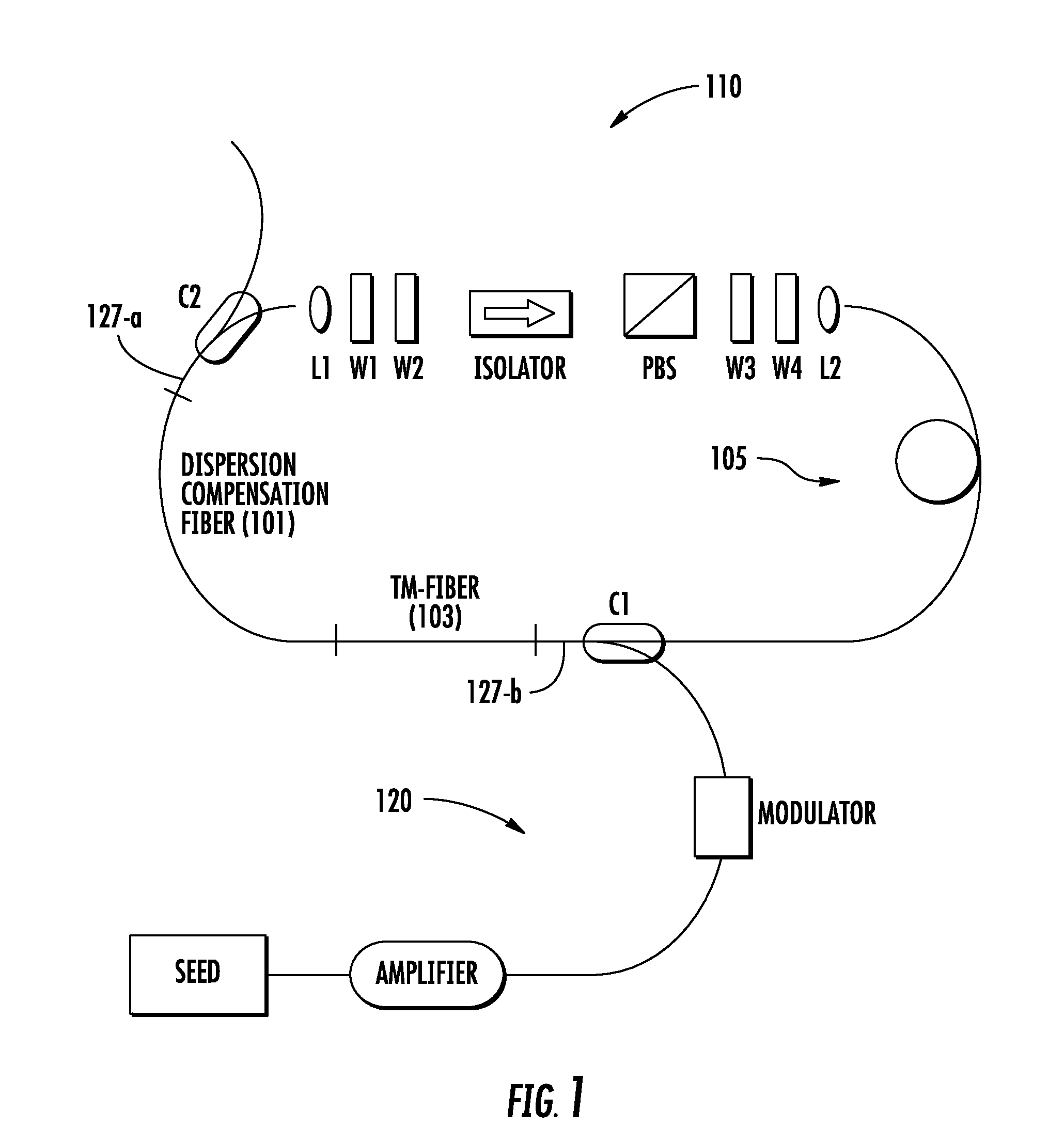
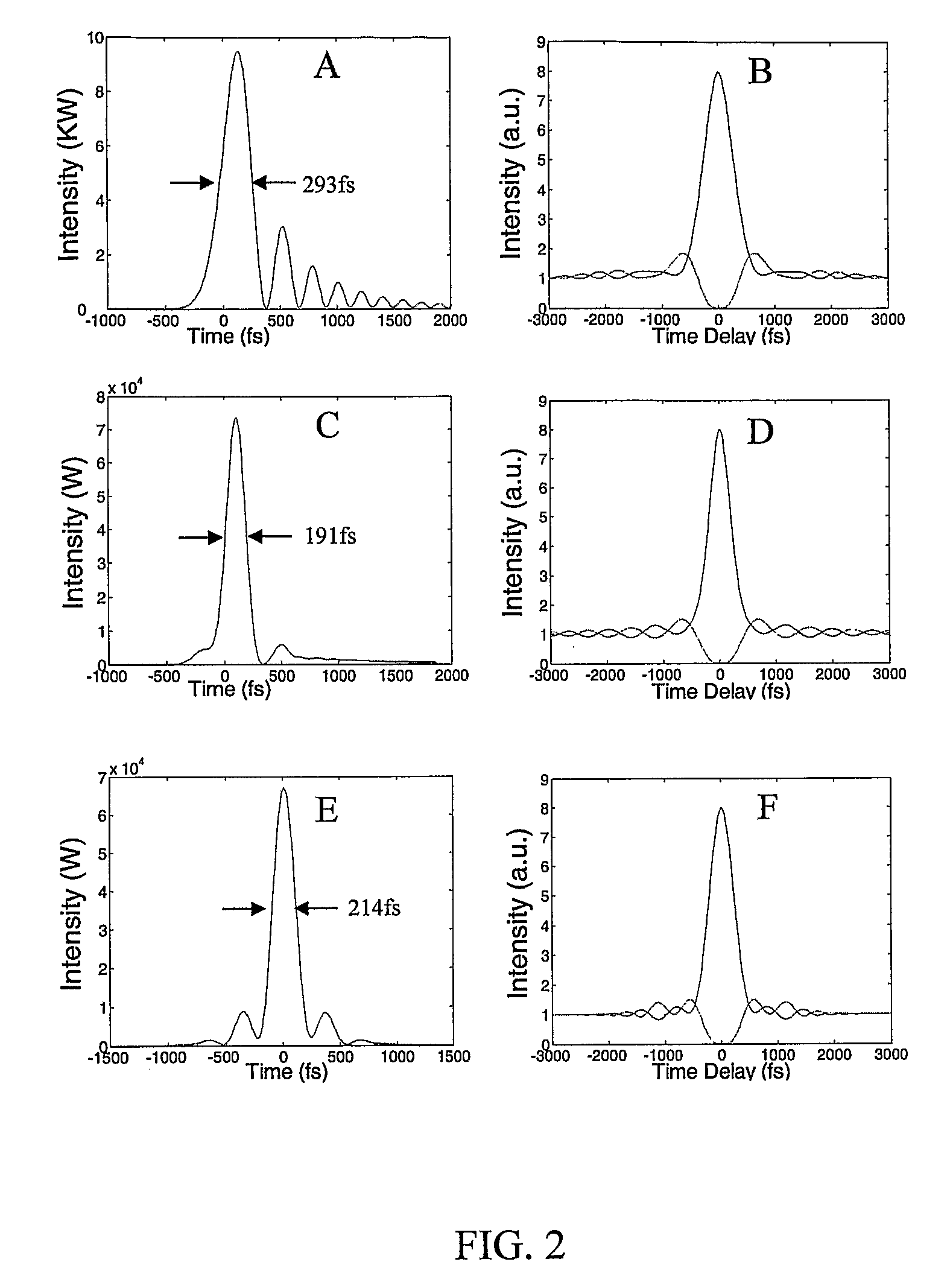
Chirped pulse fiber amplifier
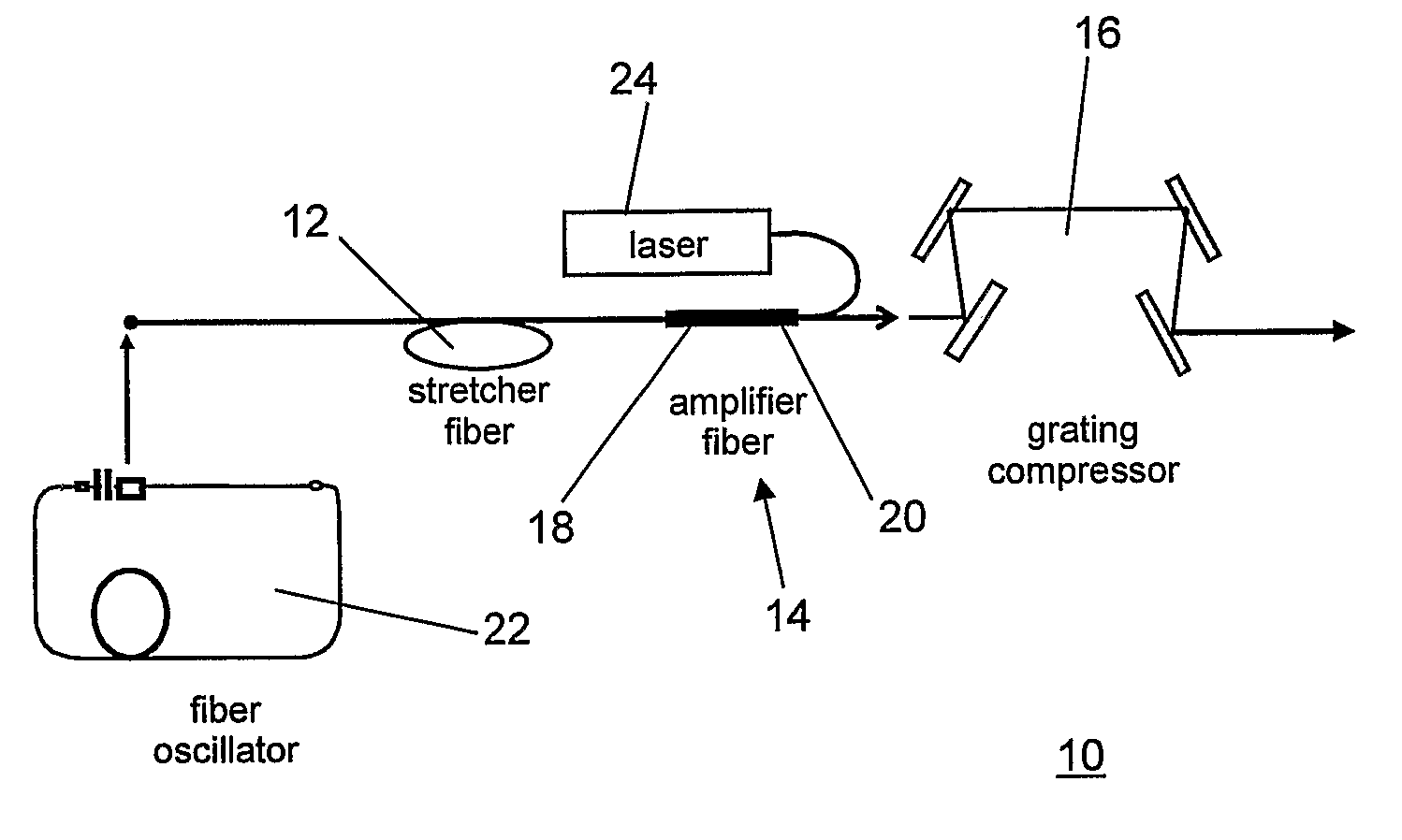
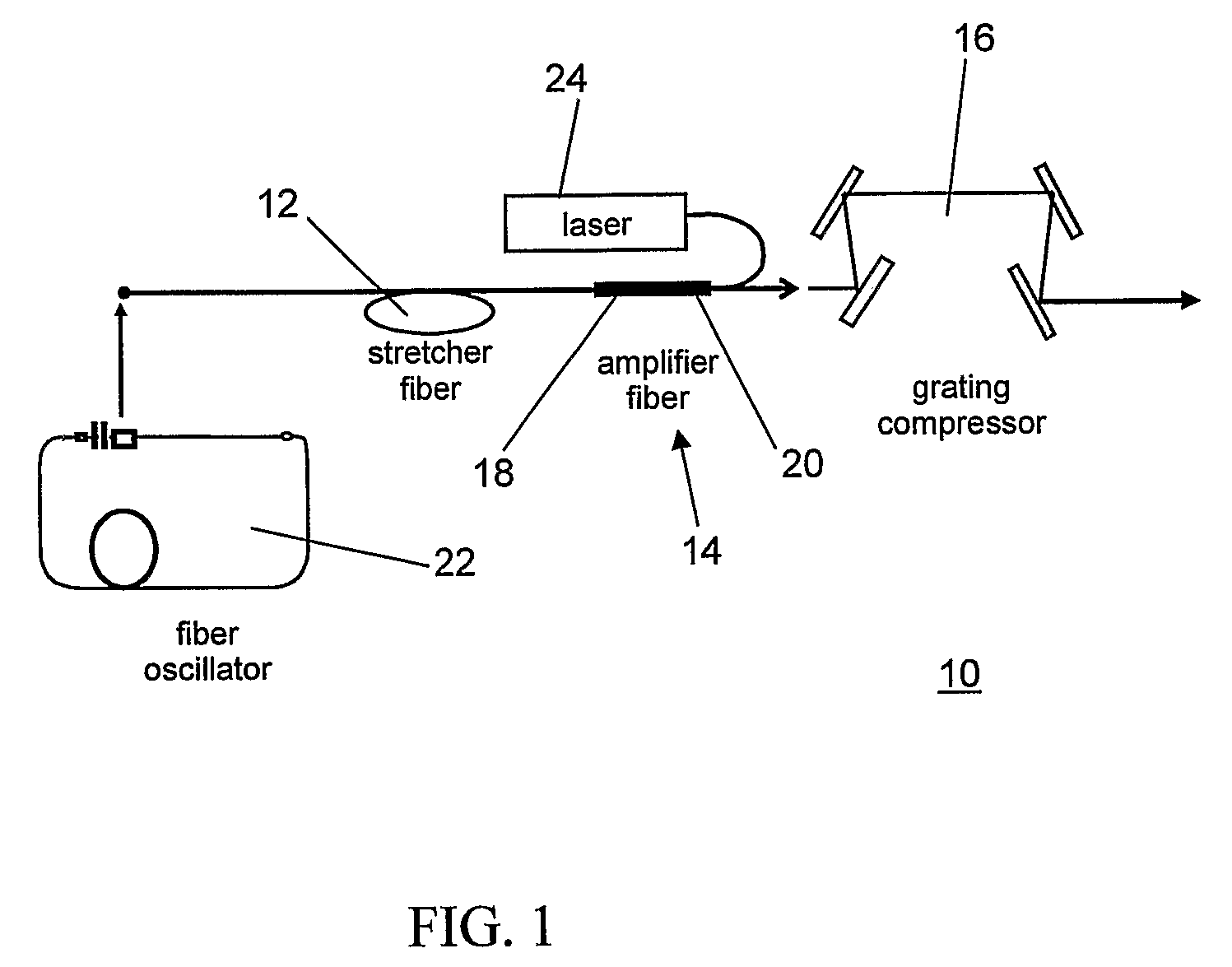
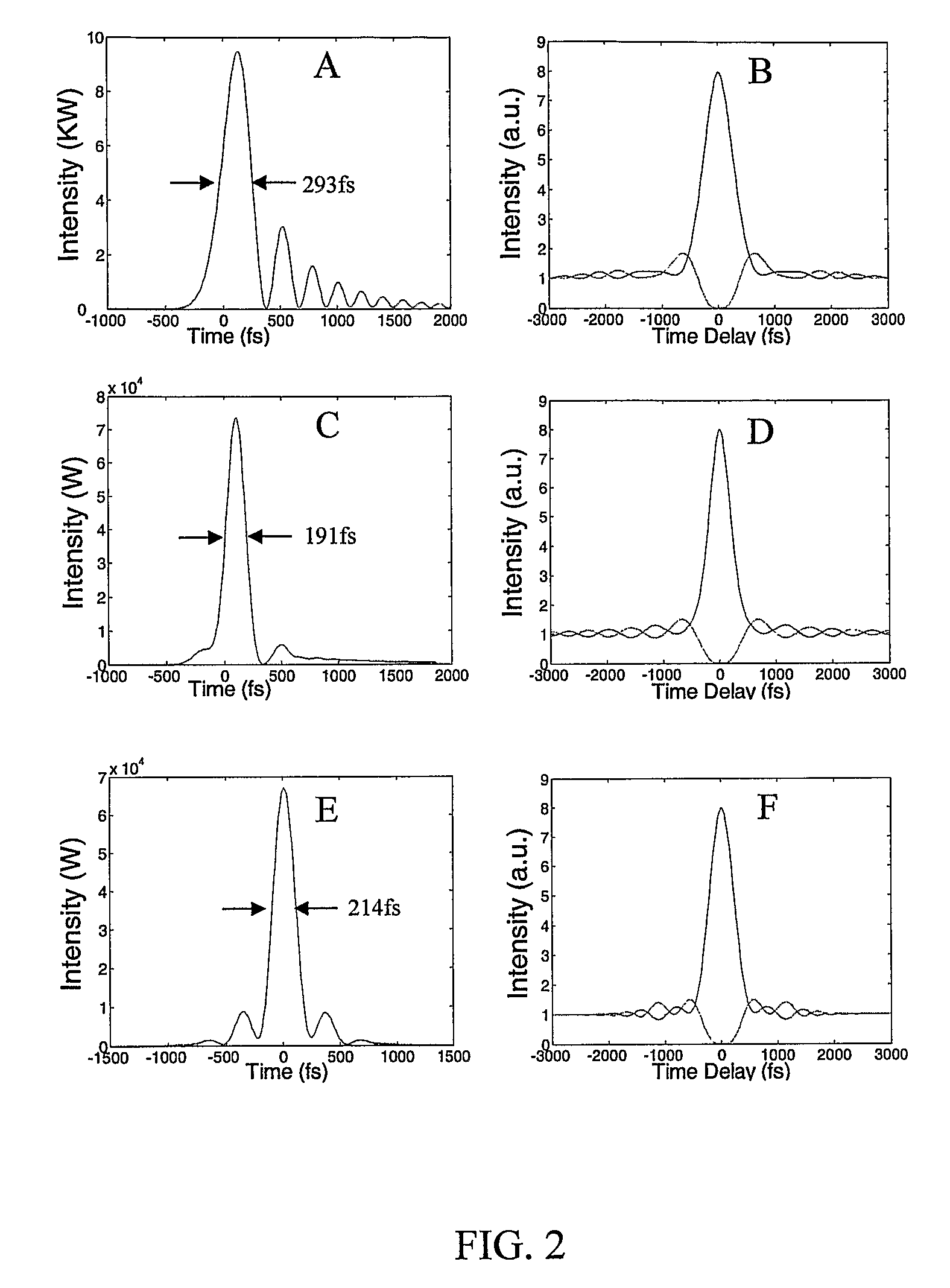
A short-pulse fiber amplifier system (10) is designed so that nonlinear phase shifts and third-order dispersion are purposely introduced that compensate each other. In particular, the nonlinear phase shift accumulated in the amplifier is compensated by the third-order dispersion of the combination of a fiber stretcher (12) and a grating compressor (16). In the presence of third-order dispersion, an optimal nonlinear phase shift reduces the pulse duration, and enhances the peak power and pulse contrast compared to the pulse produced in linear propagation.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
Mid-infrared chirped pulse amplifying device
ActiveCN104391416AReduce usageEliminate third order dispersionNon-linear opticsPicosecond laserBeam splitter
The invention discloses a mid-infrared chirped pulse amplifying device. The mid-infrared chirped pulse amplifying device comprises a femtosecond laser, a synchronous narrowband picosecond laser, a beam splitter, a near-infrared pulse stretcher, a non-linear frequency converter, an optical parametric chirped pulse amplier and a mid-infrared pulse compressor. Due to the fact that grism pairs and grating pairs are matched with each other to serve as the pulse stretcher and the pulse compressor, usage of a mid-infrared pulse stretcher is avoided, residual third-order dispersion in compression pulses in the process that the grating pairs serve as the pulse stretcher and the pulse compressor is eliminated, and the mid-infrared chirped pulse amplifying device is particularly suitable for generation of mid-infrared ultra-short ultra-strong pulse lasers with the frequency lower than hundreds of femtoseconds.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
Compact, coherent, high brightness light sources for the mid and far IR
ActiveUS8787410B2High energyReduce widthLaser using scattering effectsLaser beam welding apparatusFiber Bragg gratingOptoelectronics
Compact high brightness light sources for the mid and far IR spectral region, and exemplary applications are disclosed based on passively mode locked Tm fiber comb lasers. In at least one embodiment the coherence of the comb sources is increased in a system utilizing an amplified single-frequency laser to pump the Tm fiber comb laser. The optical bandwidth generated by the passively mode locked Tm fiber comb laser is further decreased by using simultaneous 2nd and 3rd order dispersion compensation using either appropriate chirped fiber Bragg gratings for dispersion compensation, or fibers with appropriately selected values of 2nd and 3rd order dispersion. Fibers with large anomalous values of third order dispersion, or fibers with large numerical apertures, for example fibers having air-holes formed in the fiber cladding may be utilized.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
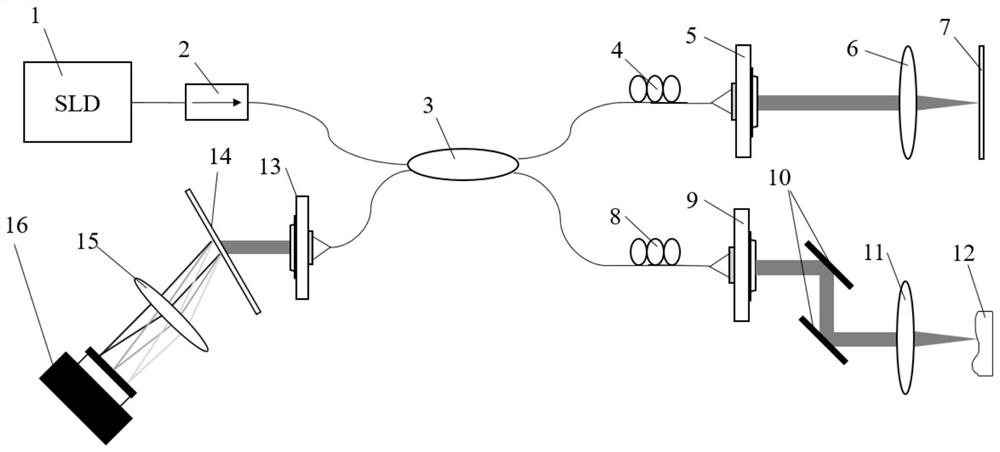
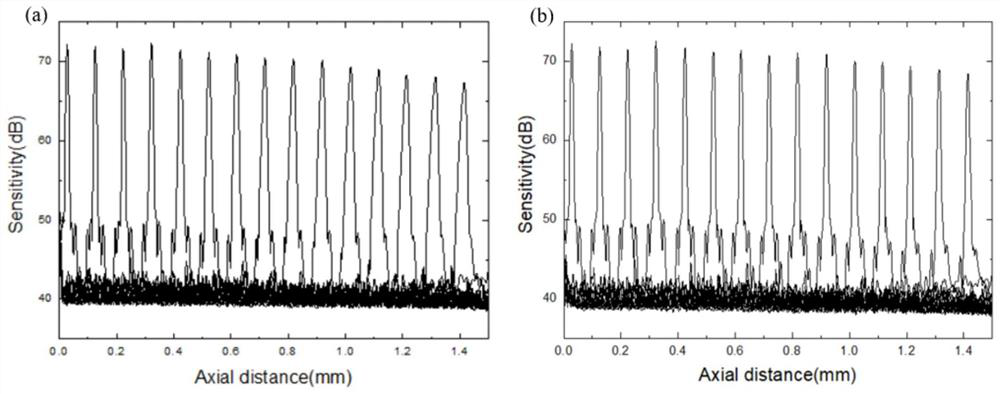
Dispersion compensation method based on Fourier domain optical coherence tomography technology
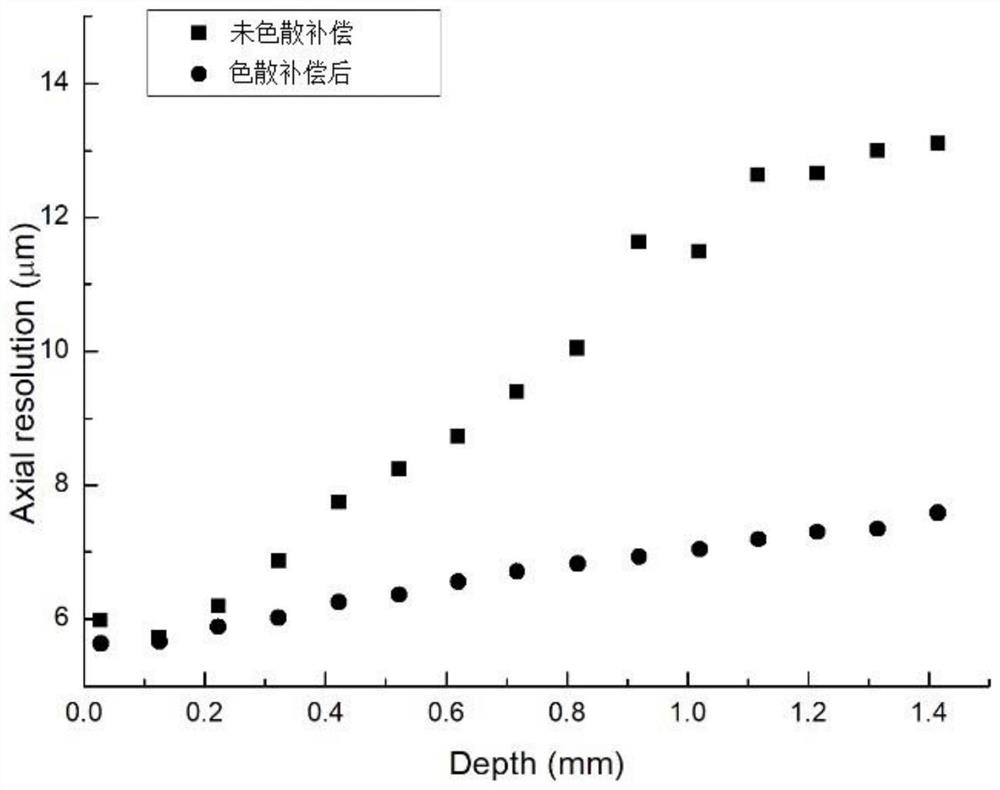
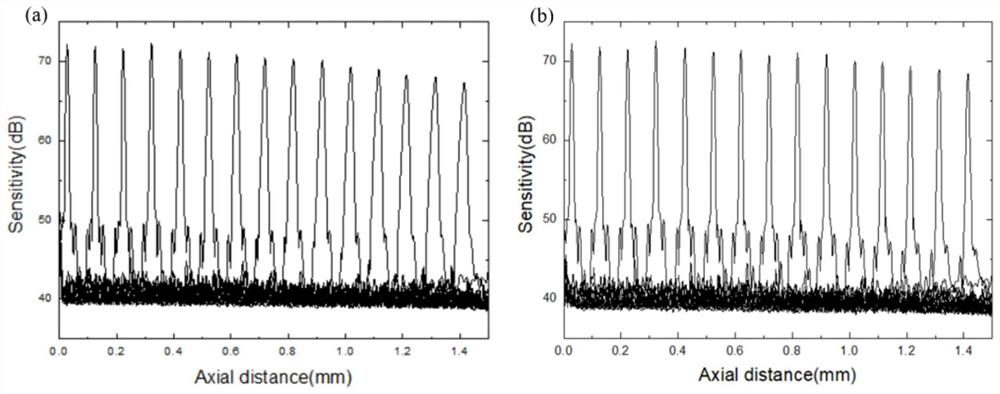
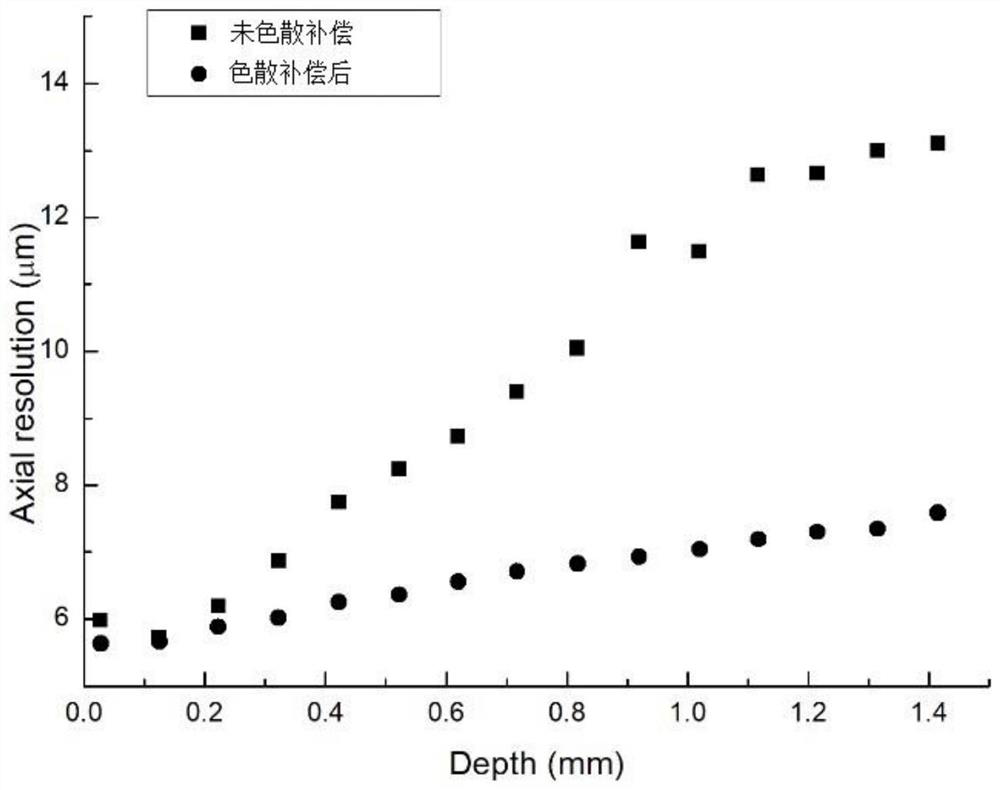
ActiveCN112597947AImproved Axial ResolutionEasy to operateCharacter and pattern recognitionImage resolutionAnalytic signal
The invention discloses a dispersion compensation method based on a Fourier domain optical coherence tomography technology, which belongs to the technical field of optical coherence tomography. An interference signal is obtained according to a light intensity signal of output light of a Fourier domain optical coherence tomography system, then the interference signal is converted to obtain a complex interference signal, namely an analytic signal, a relation between a phase and a wave number is extracted, and third-order polynomial fitting is carried out; and finally, phase compensation is conducted on the analytic signal by utilizing the calculated second-order dispersion factor and third-order dispersion factor to realize the effect of eliminating the influence of high-order dispersion inthe Fourier domain optical coherence tomography imaging system and achieve the purpose of improving the axial resolution of the Fourier domain optical coherence tomography imaging system. The method is simple in operation mode, and dispersion compensation in continuous real-time imaging can be realized only by one-time measurement and calibration in an experiment.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Apparatus for spectrum-doubled optical parametric chirped pulse amplification (OPCPA) using third-order dispersion chirping
InactiveUS20090251769A1Eliminate dispersionShort pulse widthExcitation process/apparatusDiffraction gratingsChirped pulse amplificationOptoelectronics
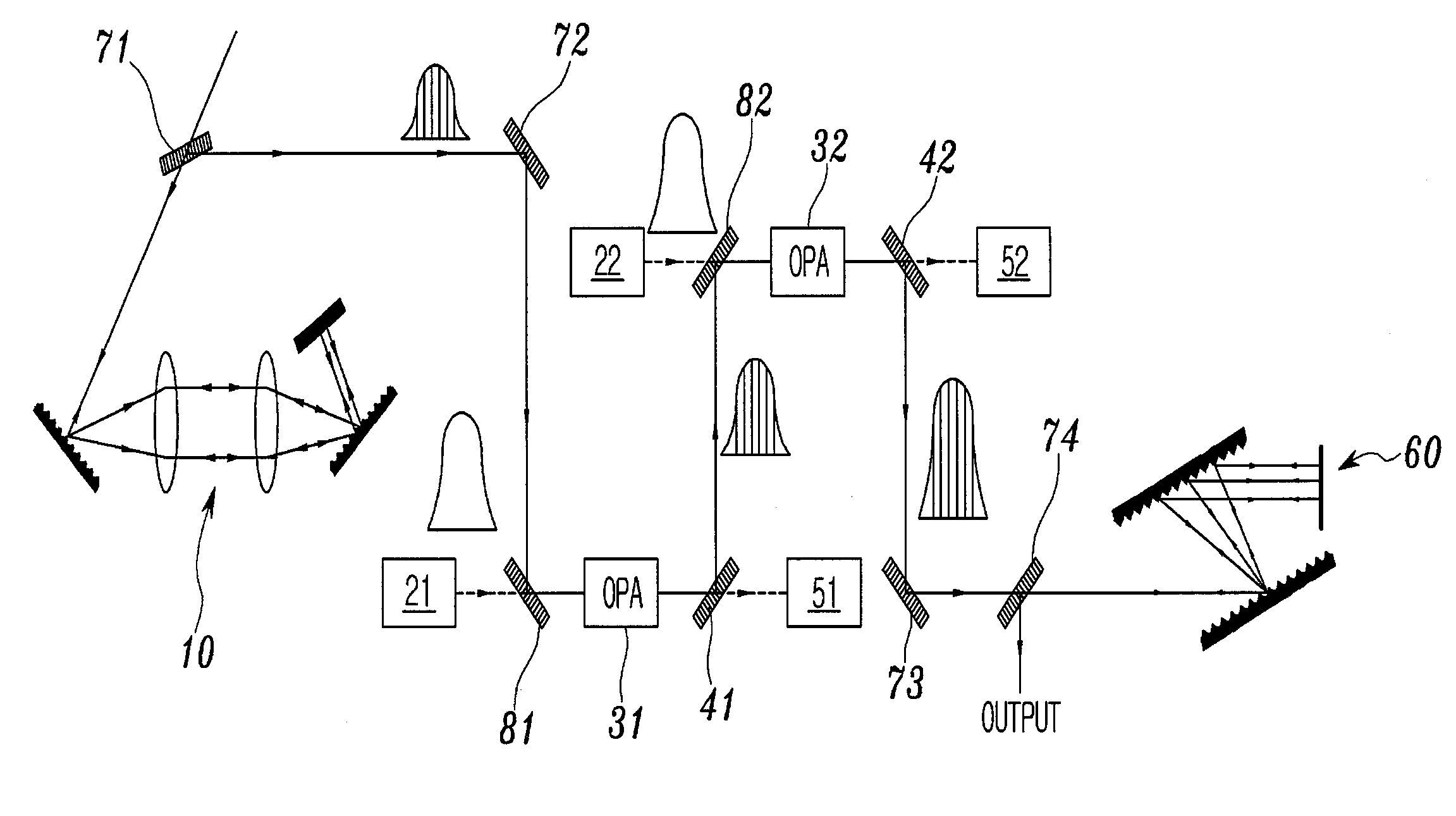
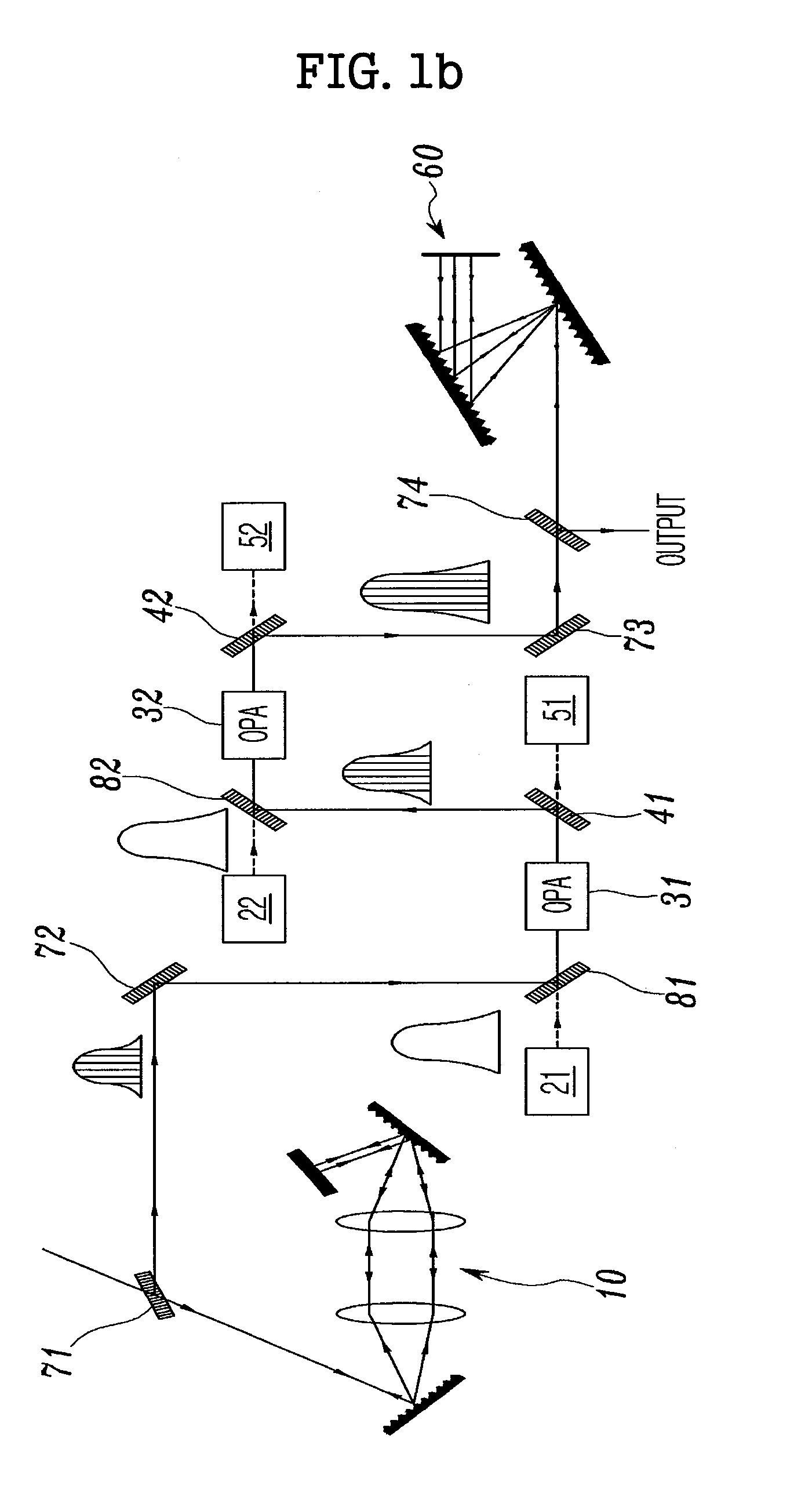
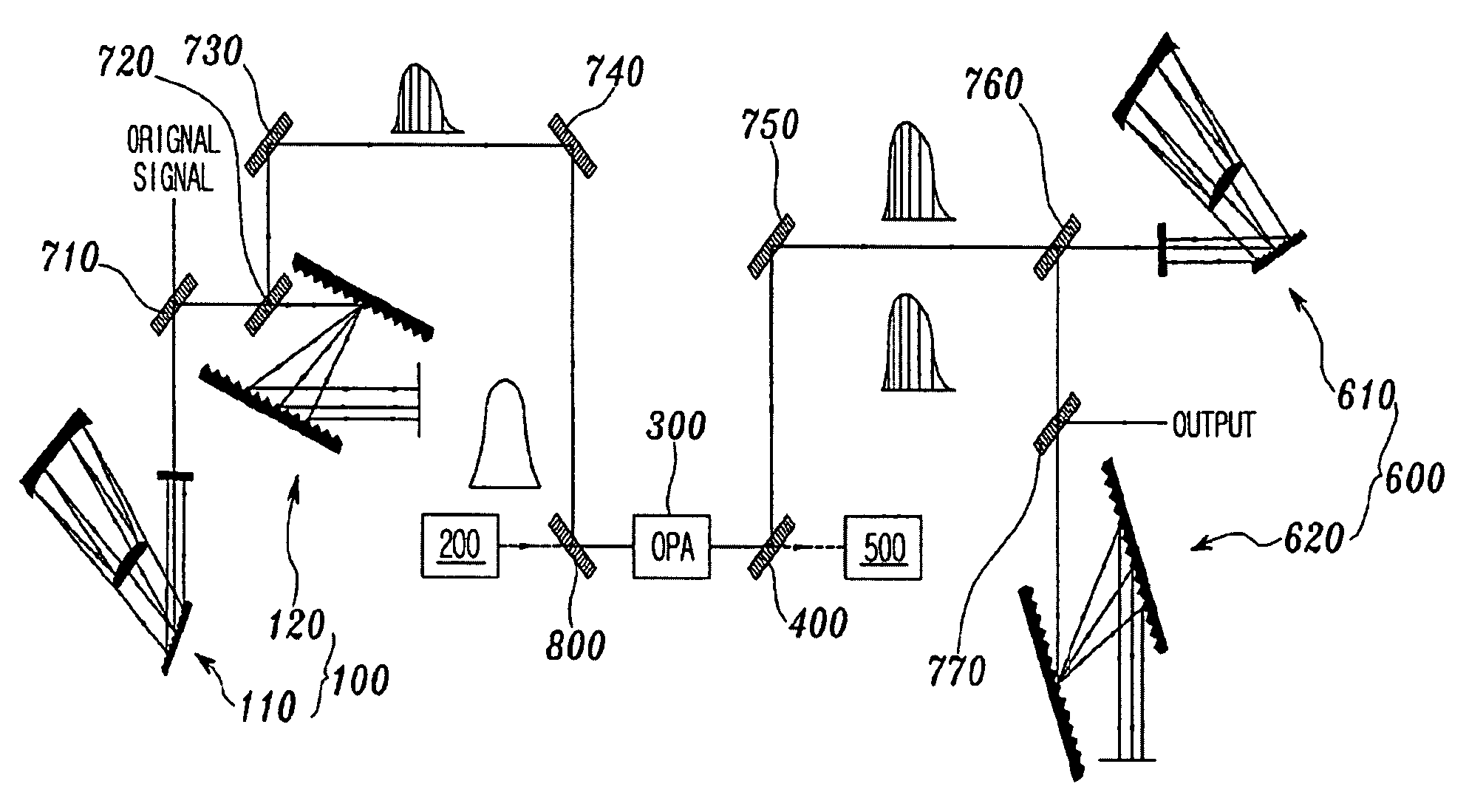
The present invention relates to an OPCPA apparatus. The OPCPA of the present invention includes an optical pulse stretcher (100) for outputting chirped laser light using odd-order dispersion (third-order dispersion is mainly used). A pump laser (200) outputs pump laser light. An OPA unit (300) receives the pump laser light and the chirped laser light (signal), amplifies the signal using the pump laser light, and generates an idler. An optical signal separation unit (400) separates output light of the OPA unit into the signal, the idler, and remaining light (pump). An optical pulse compressor (600) compensates for pulse chirping caused by odd-order dispersion that is imparted by the optical pulse stretcher, thus temporally compressing the signal and the idler, which overlap each other.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Apparatus for spectrum-doubled optical parametric chirped pulse amplification (OPCPA) using third-order dispersion chirping
InactiveUS8049956B2Short pulse widthGood compensationLaser detailsDiffraction gratingsChirped pulse amplificationLaser light
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Compression design for high energy short pulse fiber laser
ActiveUS7593434B2Quality improvementIncrease flexibilityLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionGratingHigh energy
A fiber Chirped Pulse Amplification (CPA) laser system includes a fiber mode-locking oscillator for generating a laser for projecting to a fiber stretcher for stretching a pulse width of the laser. The fiber CPA laser system further includes a multistage amplifier for amplifying the laser and a high-order dispersion compensating compressor for compensating high order dispersions and compressing the pulse width of the laser. The high-order dispersion compensating compressor further includes a pair of gratings coupled with a pair of prisms, a grating pair engraved on the surfaces of a pair of prisms, a chirped grating pair and a phase modulator consists of a grating and a deformable mirror, for generating a negative group velocity dispersion (GVD) and a negative third order dispersion (TOD) for the laser.
Owner:POLARONYX
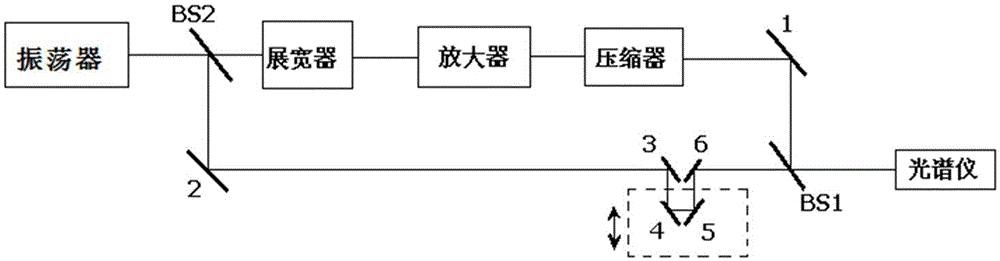
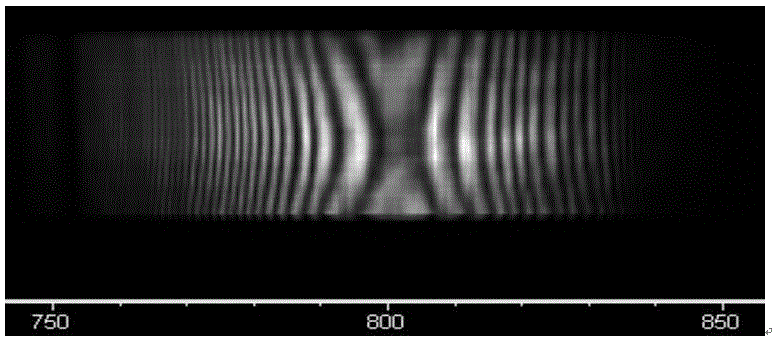
Method for debugging compressor of ultra-short pulse laser system
The invention provides a method for debugging a compressor of an ultra-short pulse laser system. The method comprises the following steps of: exporting a part of laser output by an oscillator as reference light by using a half mirror; guiding the reference light and main laser passing a whole system to the same spectrograph to generate an interference pattern, wherein bright fringes and dark fringes in the interference pattern are spectral domain and spatial domain comprehensive equiphase lines; determining rest second-order and third-order chromatic dispersion in a visualized manner by using the shapes of the equiphase lines; adjusting the grating distance and rotating angle of a parallel grating pair of the compressor in order to flatten and widen the equiphase lines and obtain ultra-short pulse laser output. The method may debug the compressor of the large ultra-short pulse laser system in a visualized and simple manner.
Owner:LASER FUSION RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF ENG PHYSICS
Novel femtosecond optical fiber amplifier
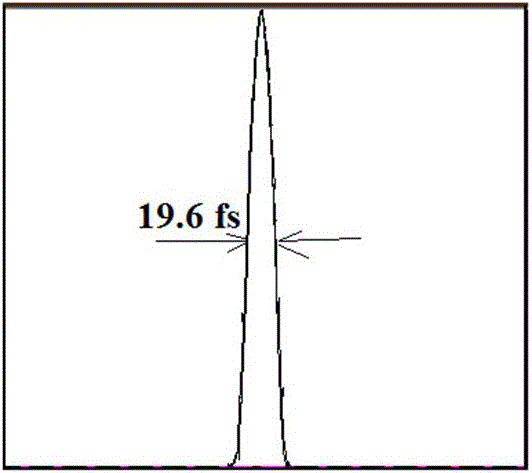
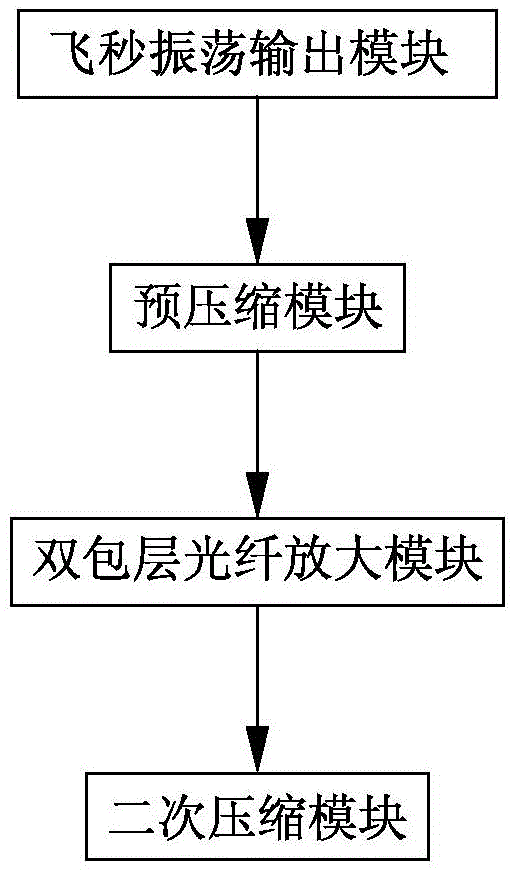
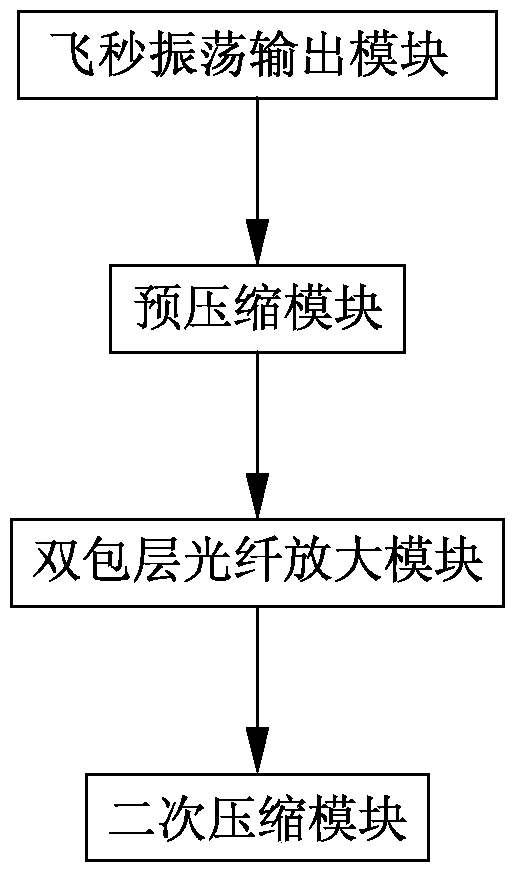
ActiveCN104901152ACompact structureGood output pulse shapeActive medium shape and constructionDouble-clad fiberThird order dispersion
The invention discloses a novel femtosecond optical fiber amplifier which is characterized by comprising the components of a femtosecond oscillation output module which is used for outputting polarized light with positive dispersion ray, a pre-compression module which is used for pre-compression and obtaining certain negative dispersion light, a double-clad optical fiber amplifying module which is used for energy amplification and restraining third-order dispersion through phase adjustment, and a secondary compression module which is used for outputting after secondary compression; wherein the femtosecond oscillation output module, the pre-compression module, the double-clad optical fiber amplifying module and the secondary compression module are successively arranged. The novel femtosecond optical fiber amplifier has a compact structure. Two compression modules are used and can perform cooperated adjustment for obtaining an optimal output pulse shape. Firstly, little negative dispersion is introduced into the femtosecond oscillation output module beforehand. Pre-amplification is performed through the pre-compression module. The pulse energy can be effectively amplified, and simultaneously a sidelobe energy caused by the third-order dispersion of an optical pulse after amplification is reduced, thereby obtaining the pulse with an approximate Fourier transform limited shape. The novel femtosecond optical fiber amplifier is particularly suitable for a micro-machining industry which is very sensitive to thermal effect.
Owner:广东华奕激光技术有限公司
Dispersion compensating method and system for optically coherent chromatographic imaging
InactiveCN100398057CLarge dispersion adjustment rangeWide Compensation Spectral RangeSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsGratingPhase retardation
The present invention discloses dispersion compensating method and system for optically coherent tomographic imaging (OCT). The system has one increased blazed grating parallelly set with the original blazed grating in a single grating fast scanning optical delay line, and thus one independently regulated variable of interval between two blazed gratings and capacity of generating group velocity dispersion and third-order dispersion in great varying range and arbitrary sign combination, so that the OCT system may obtain precise matching between the dispersion of the reference arm and the dispersion of the sample arm and longitudinal resolution approaching the theoretical calculated value. The double grating system has wide dispersion regulating range, wide compensation spectrum range and small residual dispersion other than the capacity of independently controlling phase delay and group delay, and possesses three functions of depth scan, phase modulation and dispersion compensation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Chirped pulse fiber amplifier
A short-pulse fiber amplifier system (10) is designed so that nonlinear phase shifts and third-order dispersion are purposely introduced that compensate each other. In particular, the nonlinear phase shift accumulated in the amplifier is compensated by the third-order dispersion of the combination of a fiber stretcher (12) and a grating compressor (16). In the presence of third-order dispersion, an optimal nonlinear phase shift reduces the pulse duration, and enhances the peak power and pulse contrast compared to the pulse produced in linear propagation.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
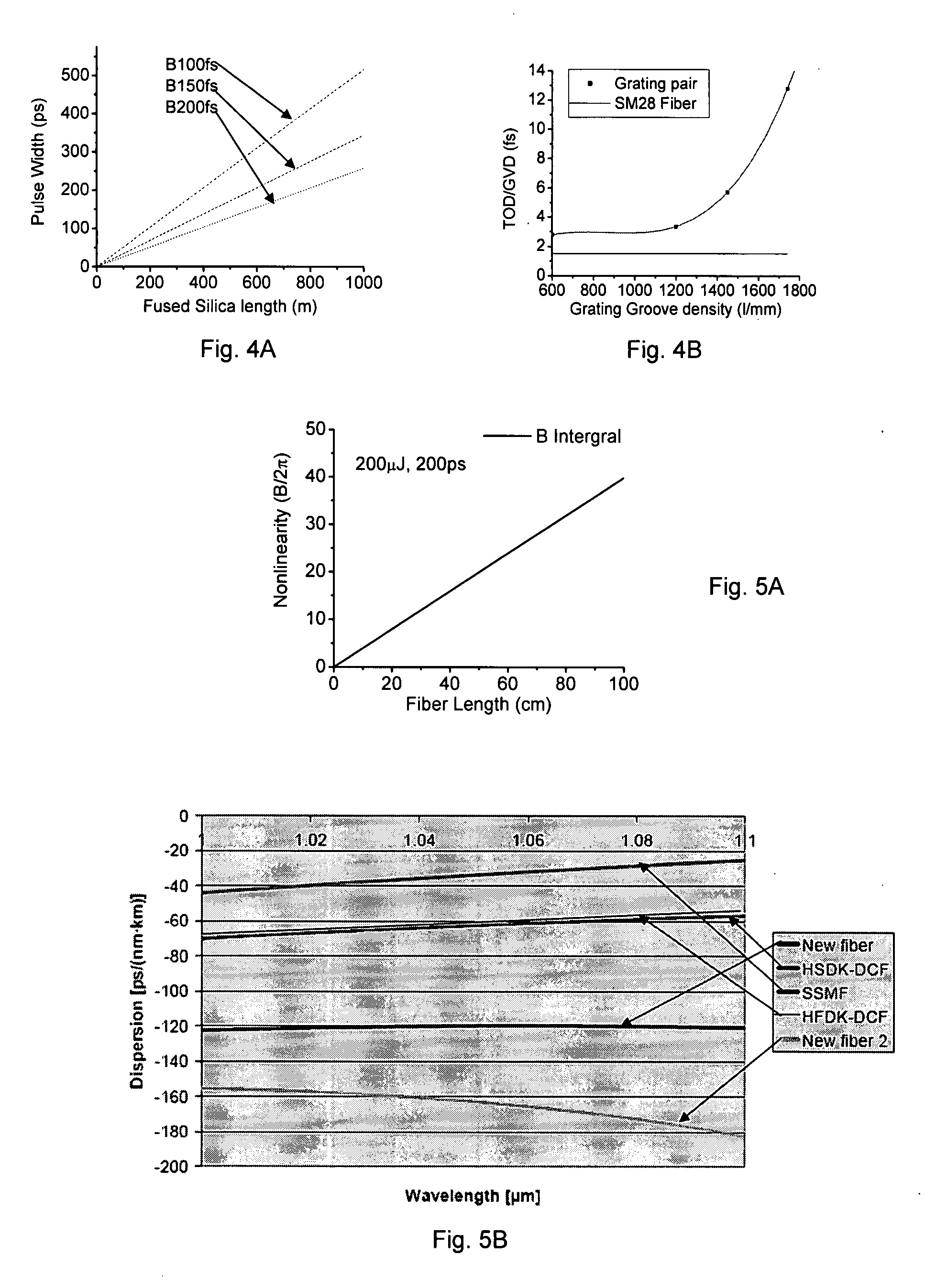
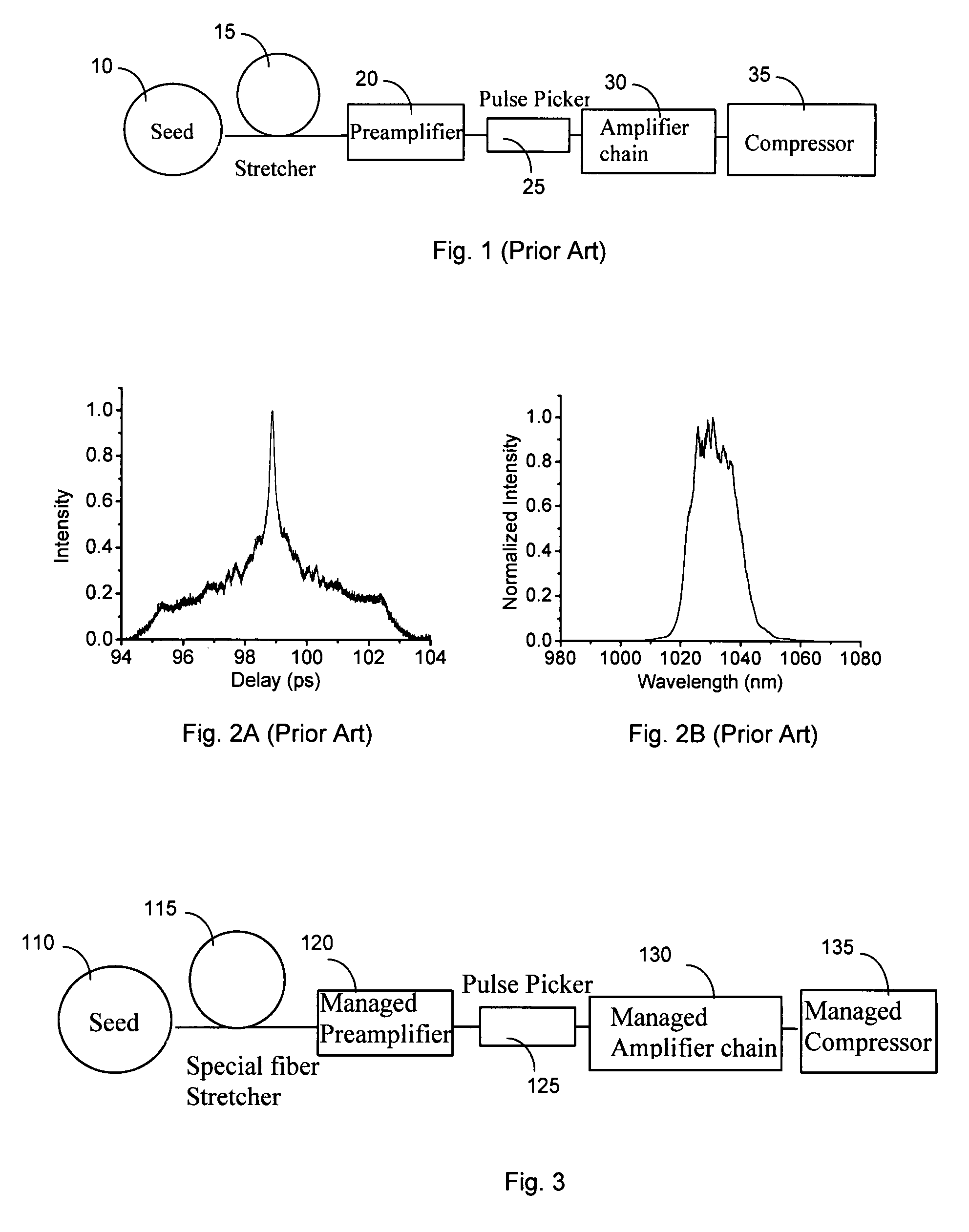
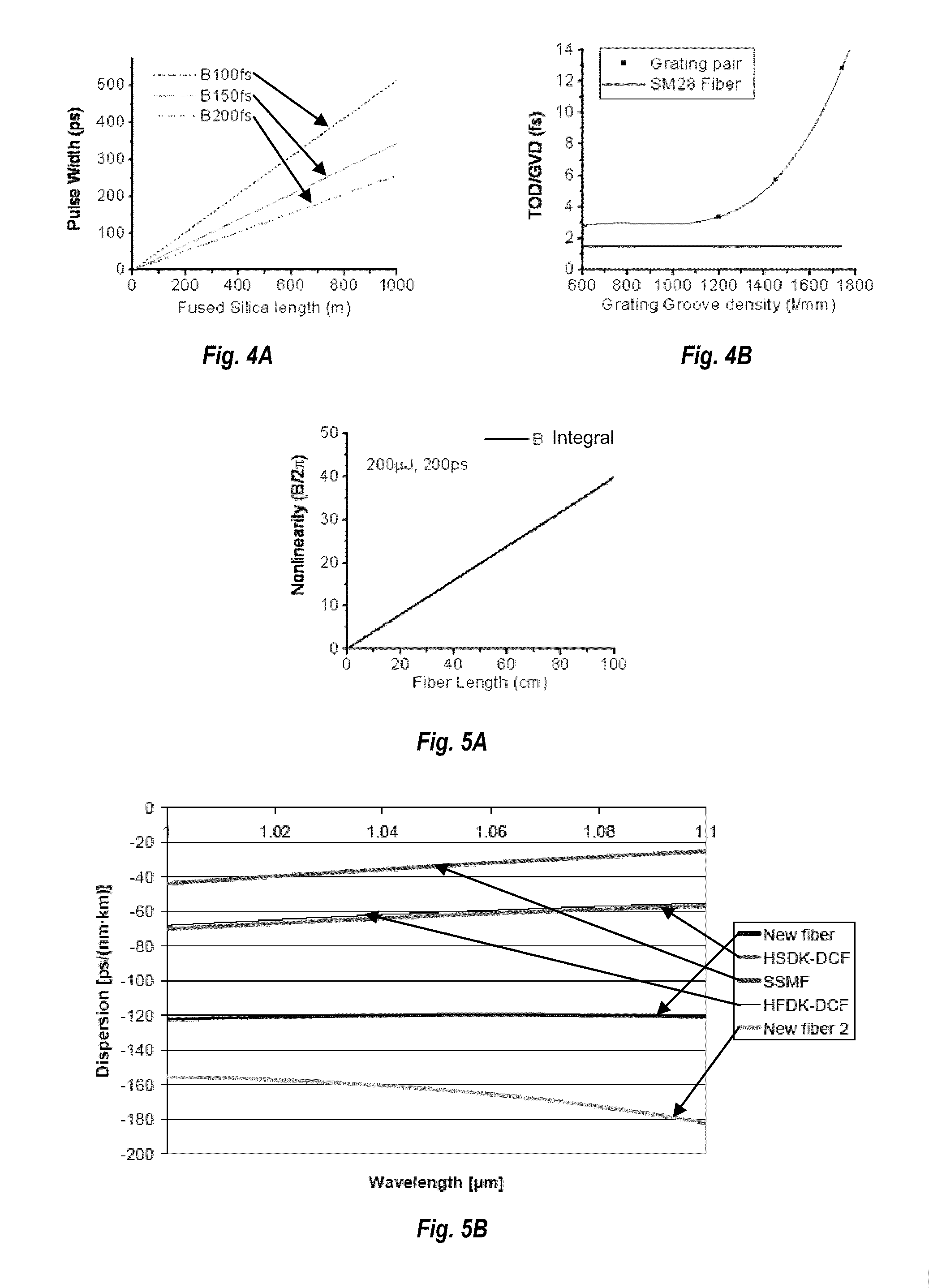
Nonlinearity and dispersion management for pulse reshpaing in high energy fiber amplifier
ActiveUS20080068702A1Good dispersionReduce dispersionLaser detailsAnalogue computers for electric apparatusGroup velocity dispersionHigh energy
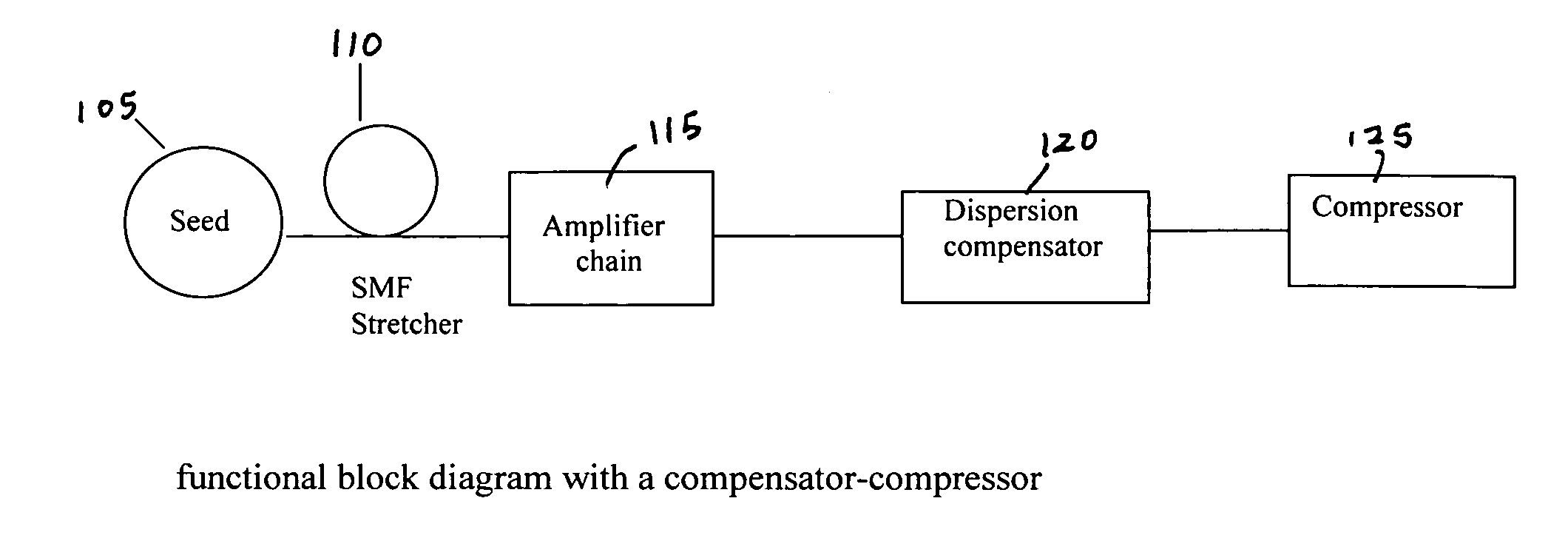
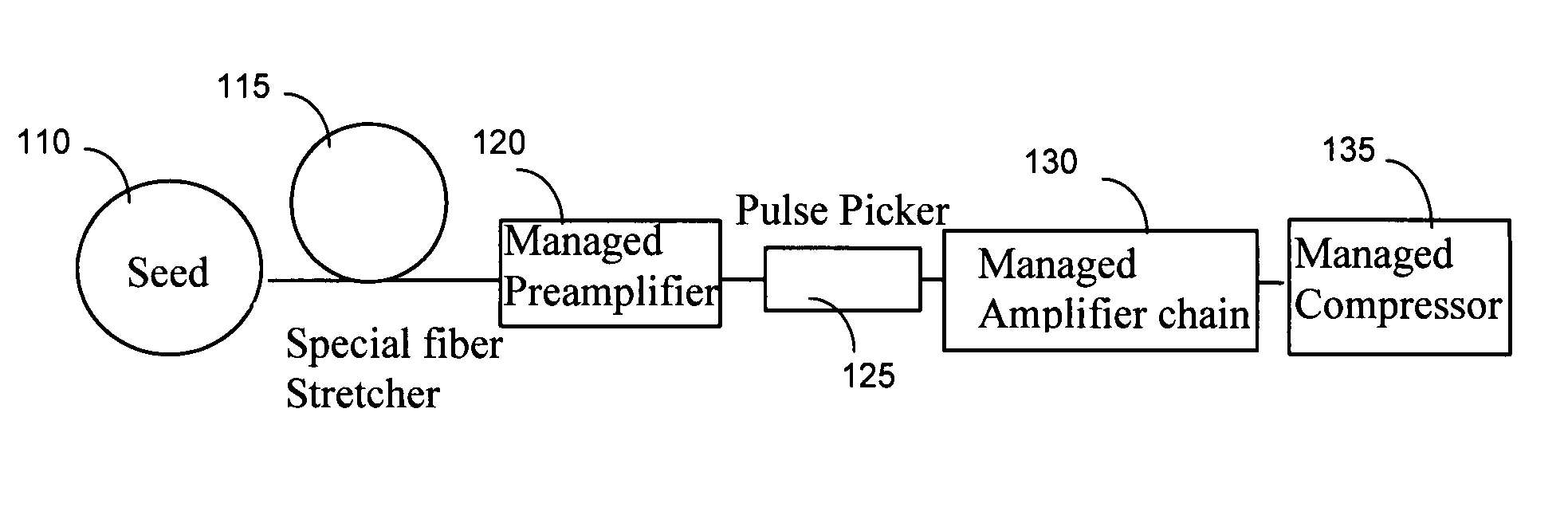
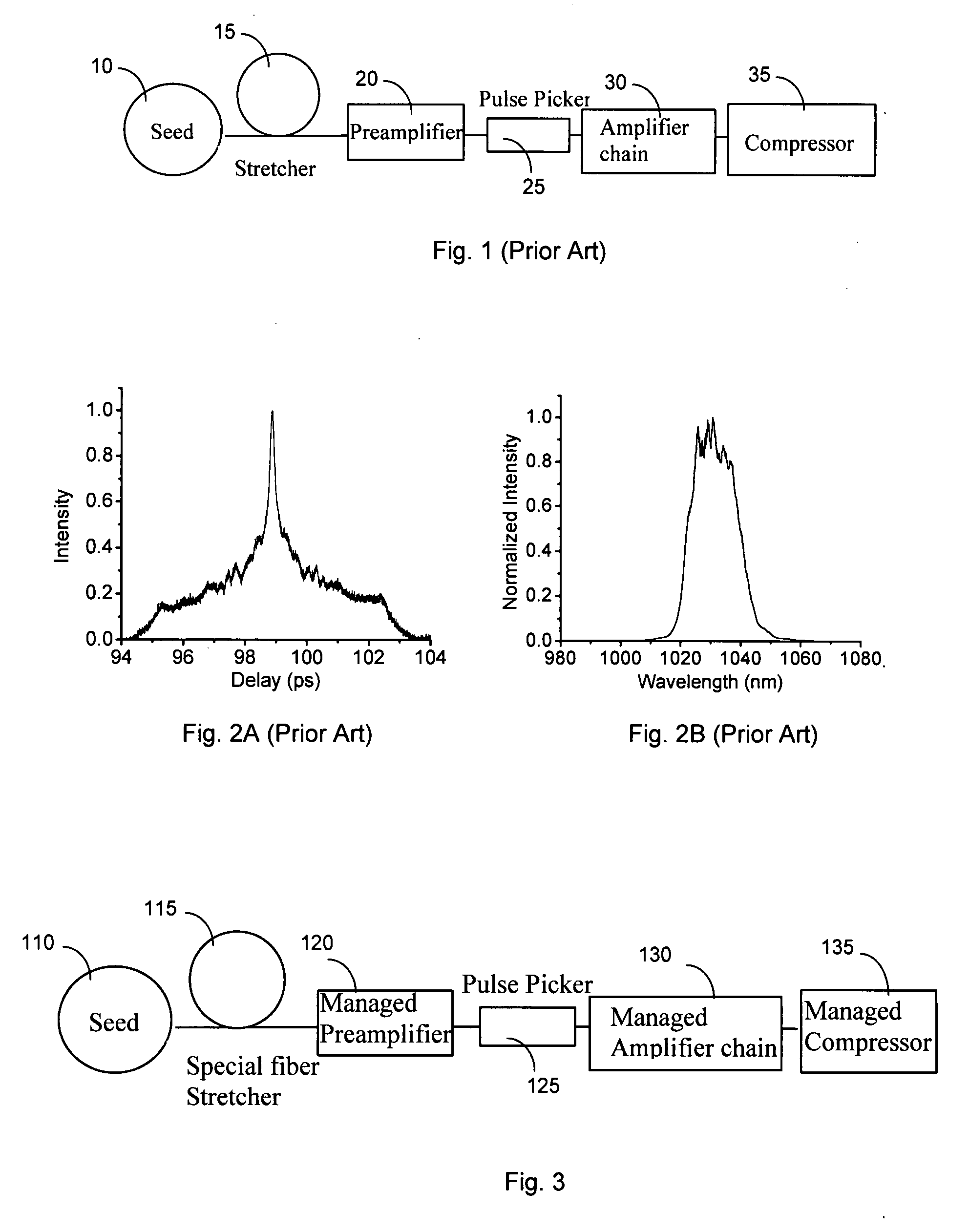
A short pulse fiber laser amplification system includes a special fiber stretcher, managed preamplifier, managed amplifier chain, and managed compressor to control an increase of a passive dispersion by managing a third order dispersion (TOD) to a group velocity dispersion (GVD) ratio for matching a nonlinearity chirp. In an exemplary embodiment, the TOD to GVD ratio is managed between approximately 1.5 to 15 fs to match a nonlinearity in range between 1π to 10π. In another exemplary embodiment, the TOD to GVD ratio is managed between approximately 15 to 705 fs to match a nonlinearity in range between 1π to 50π.
Owner:POLARONYX
Nonlinearity and dispersion management for pulse reshaping in high energy fiber amplifier
ActiveUS7813035B2Laser detailsAnalogue computers for electric apparatusHigh energyGroup velocity dispersion
A short pulse fiber laser amplification system includes a special fiber stretcher, managed preamplifier, managed amplifier chain, and managed compressor to control an increase of a passive dispersion by managing a third order dispersion (TOD) to a group velocity dispersion (GVD) ratio for matching a nonlinearity chirp. In an exemplary embodiment, the TOD to GVD ratio is managed between approximately 1.5 to 15 fs to match a nonlinearity in range between 1π to 10π. In another exemplary embodiment, the TOD to GVD ratio is managed between approximately 15 to 705 fs to match a nonlinearity in range between 1π to 50π.
Owner:POLARONYX
A mid-infrared chirped pulse amplification device
ActiveCN104391416BReduce usageEliminate third order dispersionNon-linear opticsPicosecond laserConverters
The invention discloses a mid-infrared chirped pulse amplifying device. The mid-infrared chirped pulse amplifying device comprises a femtosecond laser, a synchronous narrowband picosecond laser, a beam splitter, a near-infrared pulse stretcher, a non-linear frequency converter, an optical parametric chirped pulse amplier and a mid-infrared pulse compressor. Due to the fact that grism pairs and grating pairs are matched with each other to serve as the pulse stretcher and the pulse compressor, usage of a mid-infrared pulse stretcher is avoided, residual third-order dispersion in compression pulses in the process that the grating pairs serve as the pulse stretcher and the pulse compressor is eliminated, and the mid-infrared chirped pulse amplifying device is particularly suitable for generation of mid-infrared ultra-short ultra-strong pulse lasers with the frequency lower than hundreds of femtoseconds.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
A Dispersion Compensation Method Based on Fourier Domain Optical Coherence Tomography
ActiveCN112597947BImproved Axial ResolutionEasy to operate2D-image generationImage resolutionAnalytic signal
The invention discloses a dispersion compensation method based on Fourier domain optical coherence tomography technology, which belongs to the technical field of optical coherence tomography. The invention obtains the interference signal according to the light intensity signal of the output light of the Fourier domain optical coherence tomography system, and then transforms the interference signal to obtain a complex interference signal, that is, an analytical signal, and then extracts the relationship between the phase and the wave number and performs a third-order polynomial simulation. Finally, use the calculated second-order and third-order dispersion factors to perform phase compensation on the analytical signal to achieve the effect of eliminating the effect of high-order dispersion in the Fourier domain optical coherence tomography system, and to improve the Fourier domain optical coherence layer. The purpose of analyzing the axial resolution of the imaging system. The operation mode of the invention is simple, and the dispersion compensation in the continuous real-time imaging can be realized only by measuring and calibrating once in the experiment.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
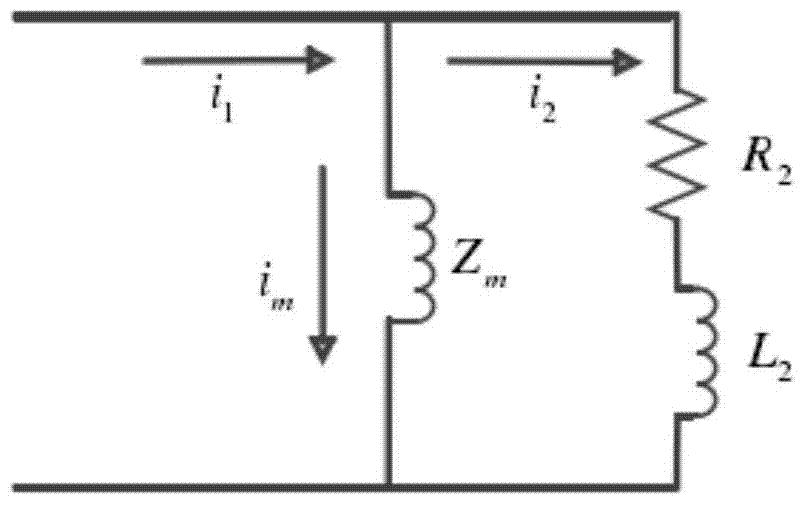
A Current Transformer Saturation Detection Method Based on Third-Order Central Moment
ActiveCN105067906BAvoid defects with a large degree of dispersionLow hardware and software requirementsElectrical testingForm factor measurementsPeak valueEngineering
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER SCHEDULING CONTROL CENT OF GUIZHOU POWER GRID CO LTD +2
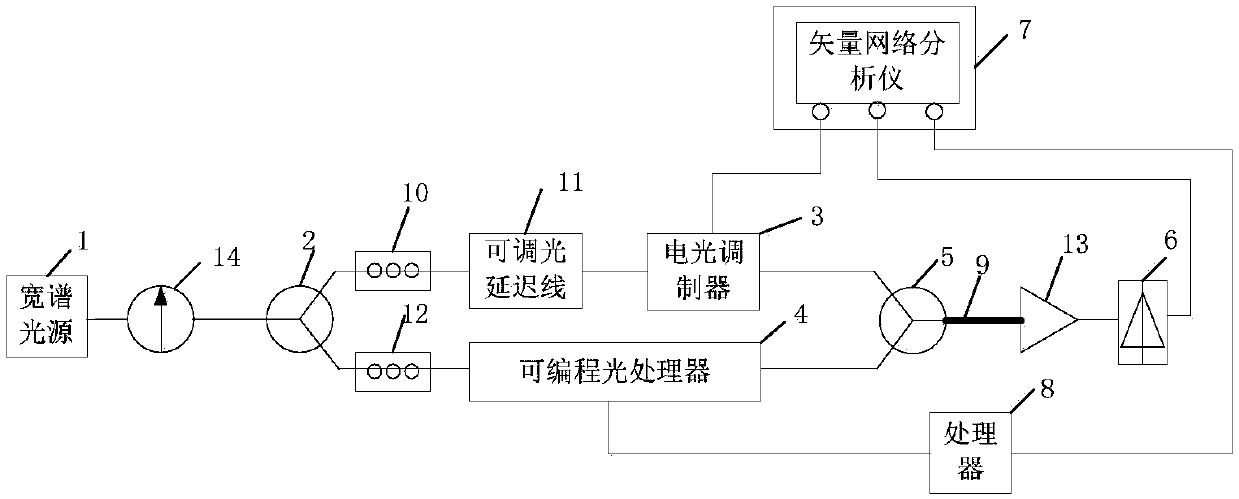
System and method for accurately measuring three-order dispersion of optical fiber
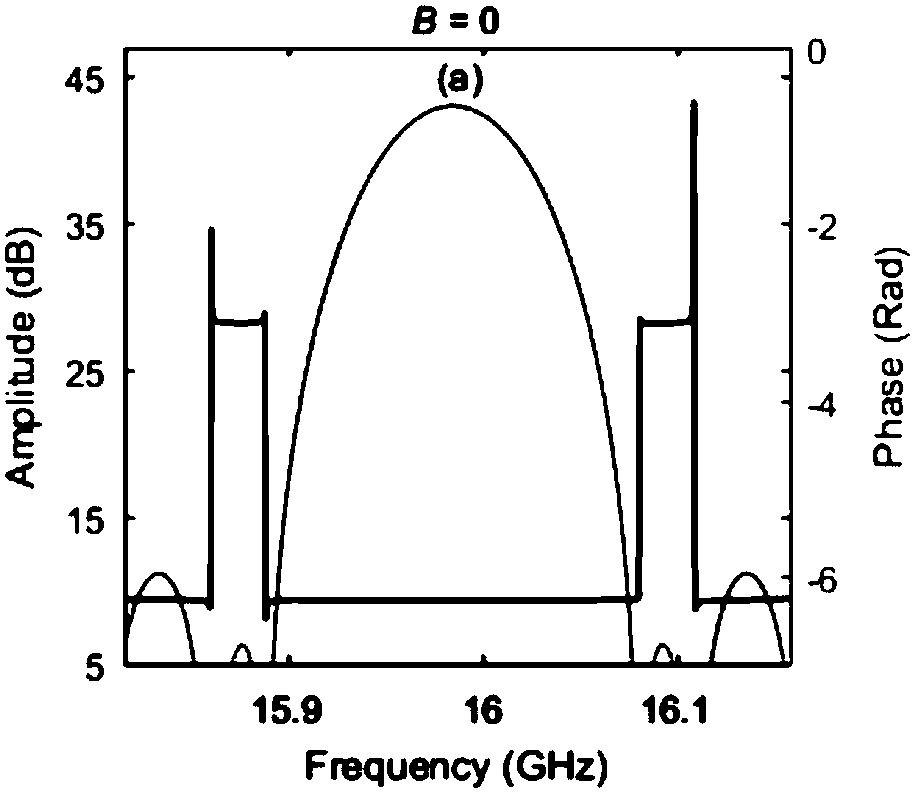
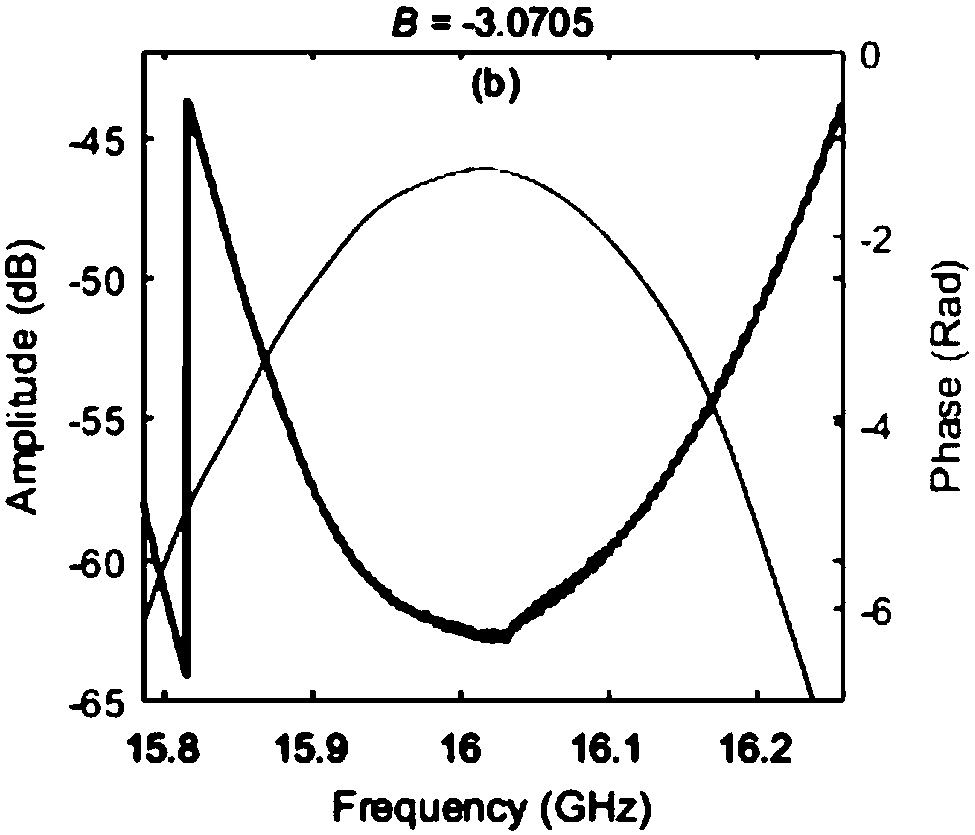
The invention discloses a system and method for accurately measuring three-order dispersion of an optical fiber. The system comprises a wide spectrum light source, a light splitting device, an electro-optic modulator, a programmable optical processor, a light merging device, a photoelectric detector, a vector network analyzer and a processor. A passband broadening factor B is calculated by the processor according to system response data of the vector network analyzer, whether the passband broadening factor B exceeds a preset threshold is judged, and if so, the processor iteratively calculatesa dispersion compensation coefficient and continuously controls the programmable optical processor to produce a new compensation baseband signal until the passband broadening factor B does not exceedthe preset threshold. When the calculated passband broadening factor B does not exceed the preset threshold, it indicates that the three-order dispersion value in the optical fiber is accurately compensated, and the three-order dispersion value in the to-be-measured optical fiber is accurately determined according to the final passband broadening factor B in accordance with the relationship between the compensation amount and the residual amount.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A Novel Femtosecond Fiber Amplifier
ActiveCN104901152BCompact structureGood output pulse shapeActive medium shape and constructionDouble-clad fiberThermal effect
The invention discloses a novel femtosecond optical fiber amplifier, which is characterized by comprising a femtosecond oscillation output module arranged in sequence for outputting linearly polarized light with positive dispersion, and a precompression for precompressing and obtaining a certain negative dispersion light. module, a double-clad optical fiber amplification module for energy amplification and self-phase adjustment to suppress third-order dispersion, and a secondary compression module for output after secondary compression. The structure of this case is compact, and two compression modules are used, which can be adjusted in conjunction to obtain the best output pulse shape. First, a small amount of negative dispersion is pre-introduced in the femtosecond oscillation output module. At the same time, the side lobe energy caused by the third-order dispersion of the amplified optical pulse is weakened, and a pulse with an approximate shape of the Fourier transform limit is obtained, which is very suitable for the micromachining industry that is very sensitive to thermal effects.
Owner:广东华奕激光技术有限公司
Deterministic soliton mode-locking method for Kerr optical combs in optical microcavities
The invention discloses a deterministic soliton mode-locking method for a Kerr optical comb in an optical microcavity. The power of the pumping laser is set to be lower than the parametric oscillation threshold power of the optical microcavity, and the generated pumping laser is modulated. The frequency of the modulated signal is the same as The free spectrum width of the optical microcavity is consistent, and the modulated signal amplitude is calculated according to the third-order dispersion value of the optical microcavity. The phase-modulated pump laser is coupled into the optical microcavity through the microcavity coupler, and the coupling coefficient is controlled so that the optical microcavity The cavity works in the critical coupling state. In the optical microcavity, the pump laser is scanned from the long wavelength direction to the short wavelength direction, and the output spectrum of the pump laser is collected at the output of the optical microcavity. Once the current spectrum of the pump laser has a smooth package network, indicating that the soliton mode locking has been completed at this time, stop scanning. The present invention overcomes the problems of strong randomness, poor reliability and susceptibility to disturbance of the existing Kerr optical comb mode-locking scheme, thereby realizing soliton mode-locking rapidly and deterministically.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
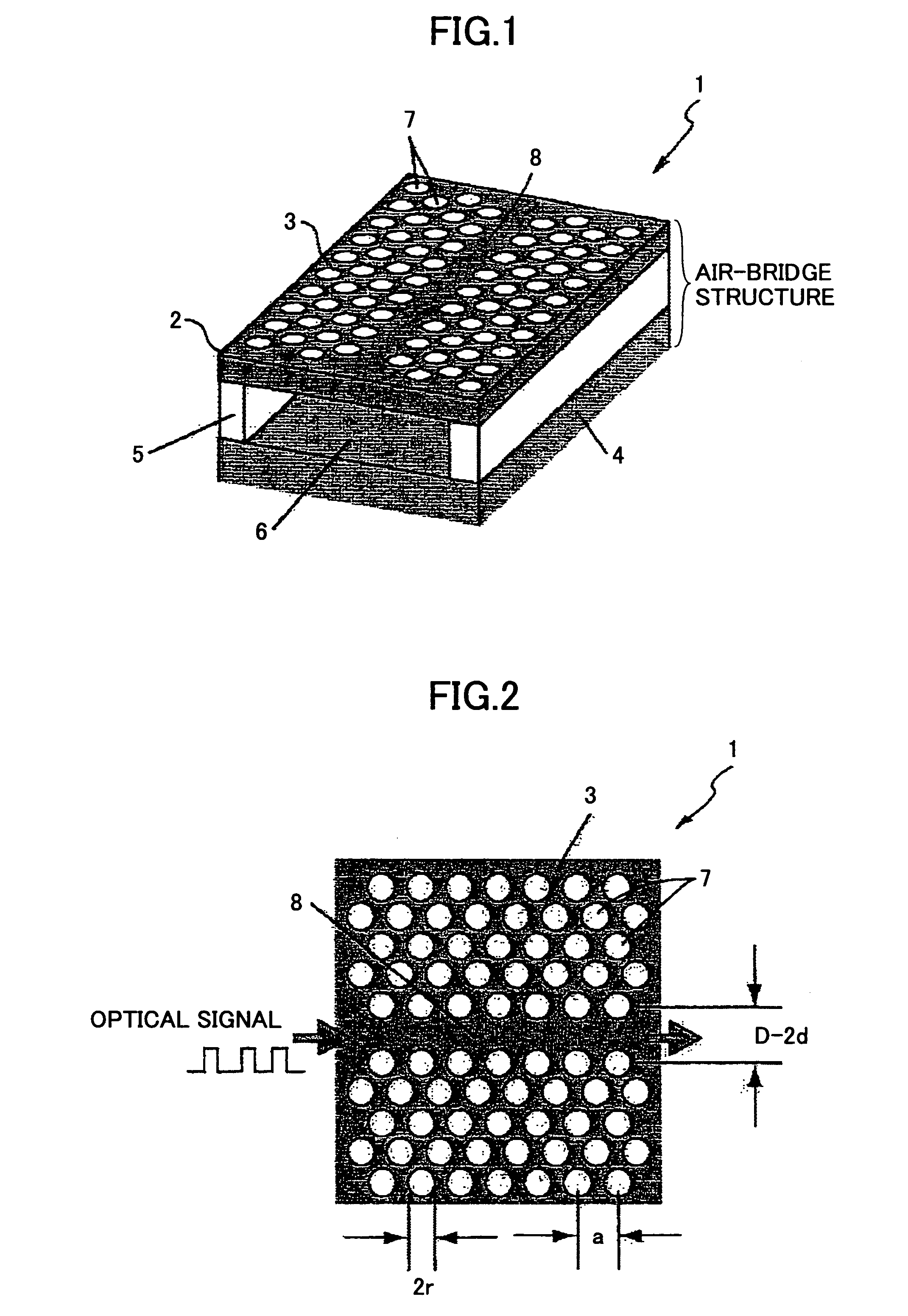
Optical delay element
ActiveUS7242839B2Lower the volumeExtended wavelength rangeNanoopticsCoupling light guidesRefractive indexPhotonic crystal structure
An optical delay element including a photonic crystal line defect optical waveguide is disclosed that has a large group refractive index and has small or nearly constant wavelength dispersion of the group refractive index in a wide wavelength region for practical use. The optical delay element includes a line defect optical waveguide formed in a photonic crystal structure, and the volume of the line defect optical waveguide is less than the volume of a single line defect optical waveguide. Thereby, the waveguide band of the line defect optical waveguide has two zero points in the third order dispersion curve of the line defect optical waveguide, and the sign of the third order dispersion curve is inverted near the zero points. Therefore, the waveguide band of the line defect optical waveguide is modified, and this enables expansion of the wavelength region having a large group refractive index, small wavelength dispersion of the group refractive index, and small wavelength dispersion of the speed of optical pulses.
Owner:RICOH KK +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com