Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
93 results about "Anterior approach" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
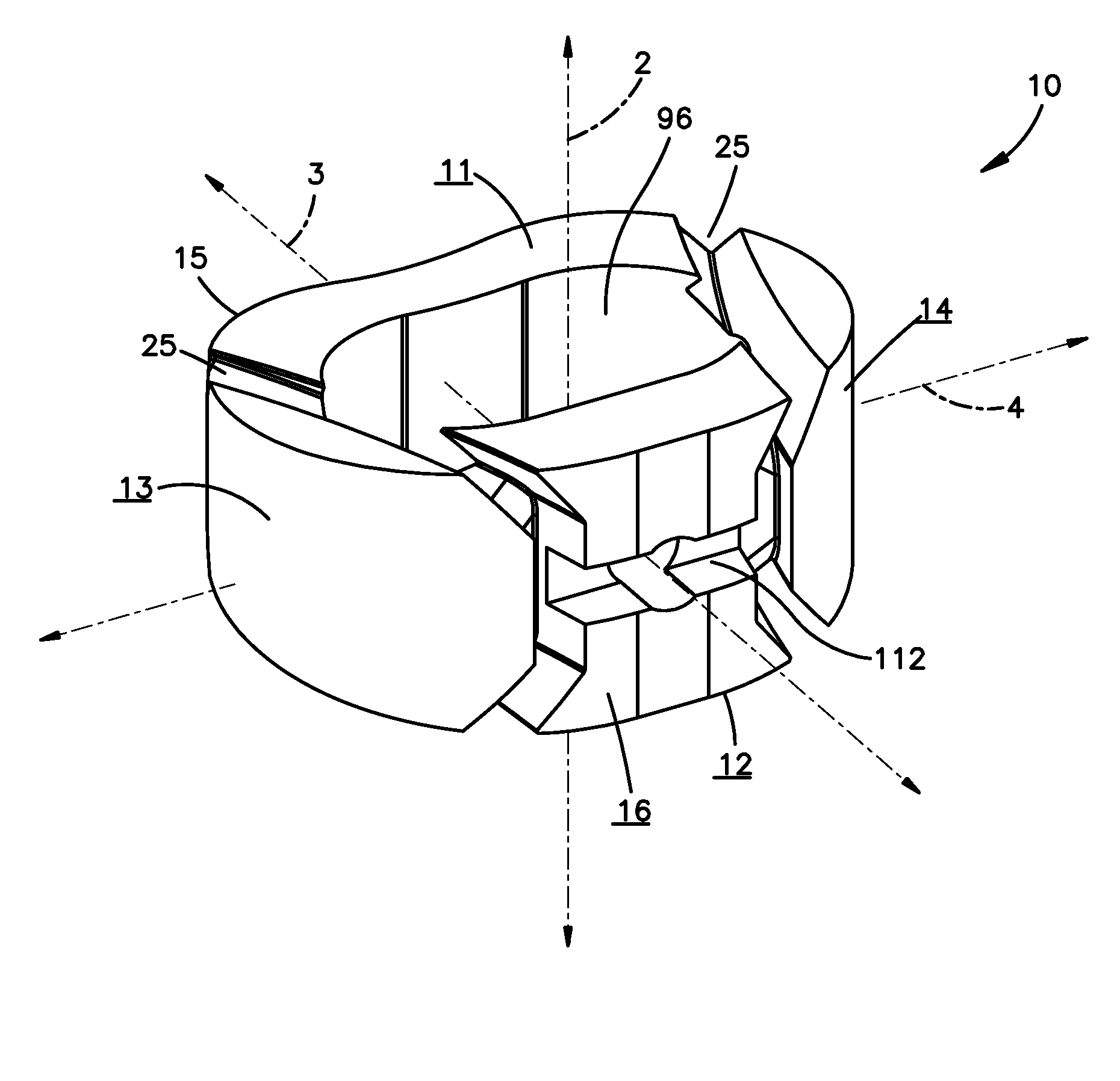
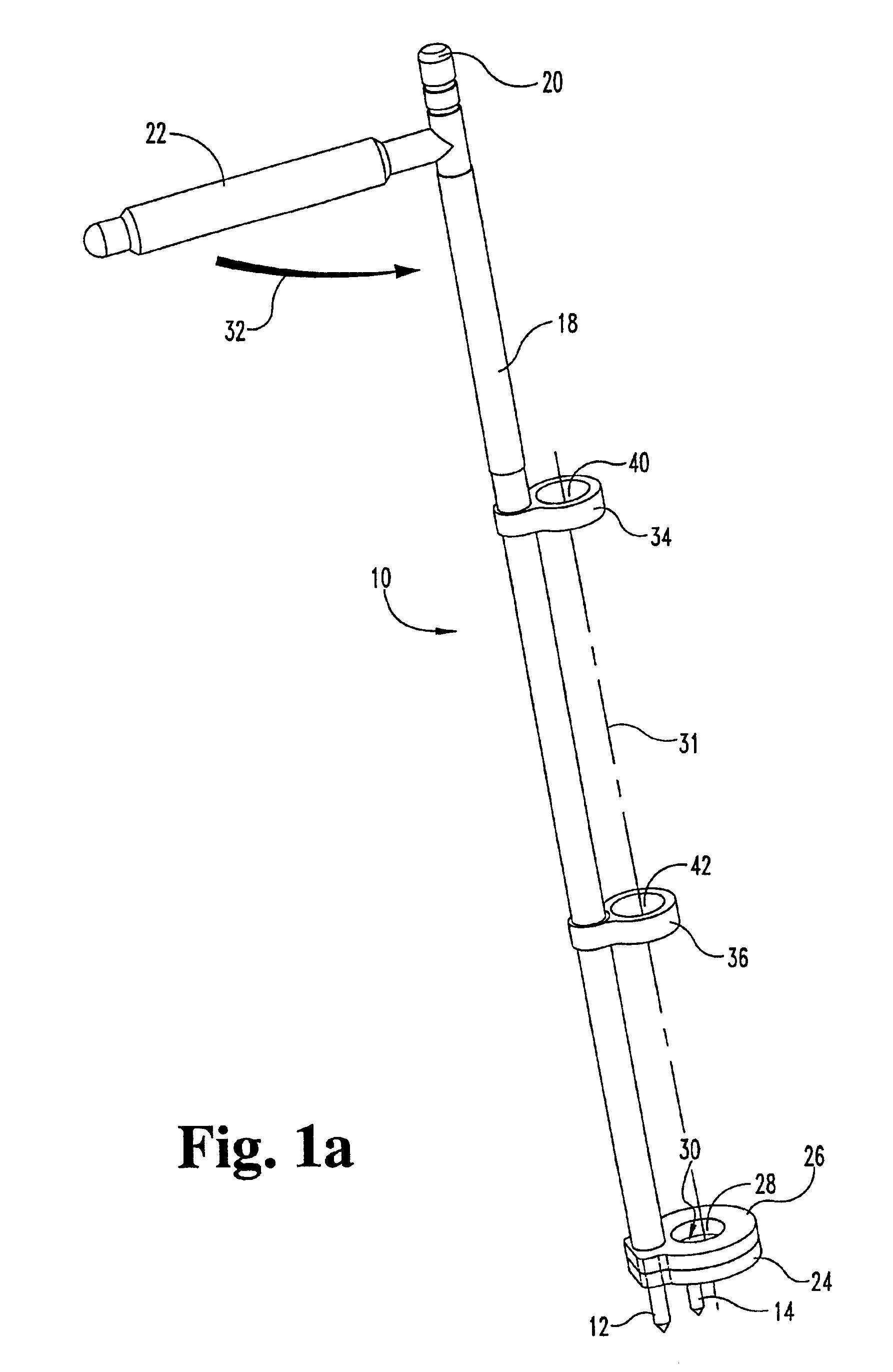
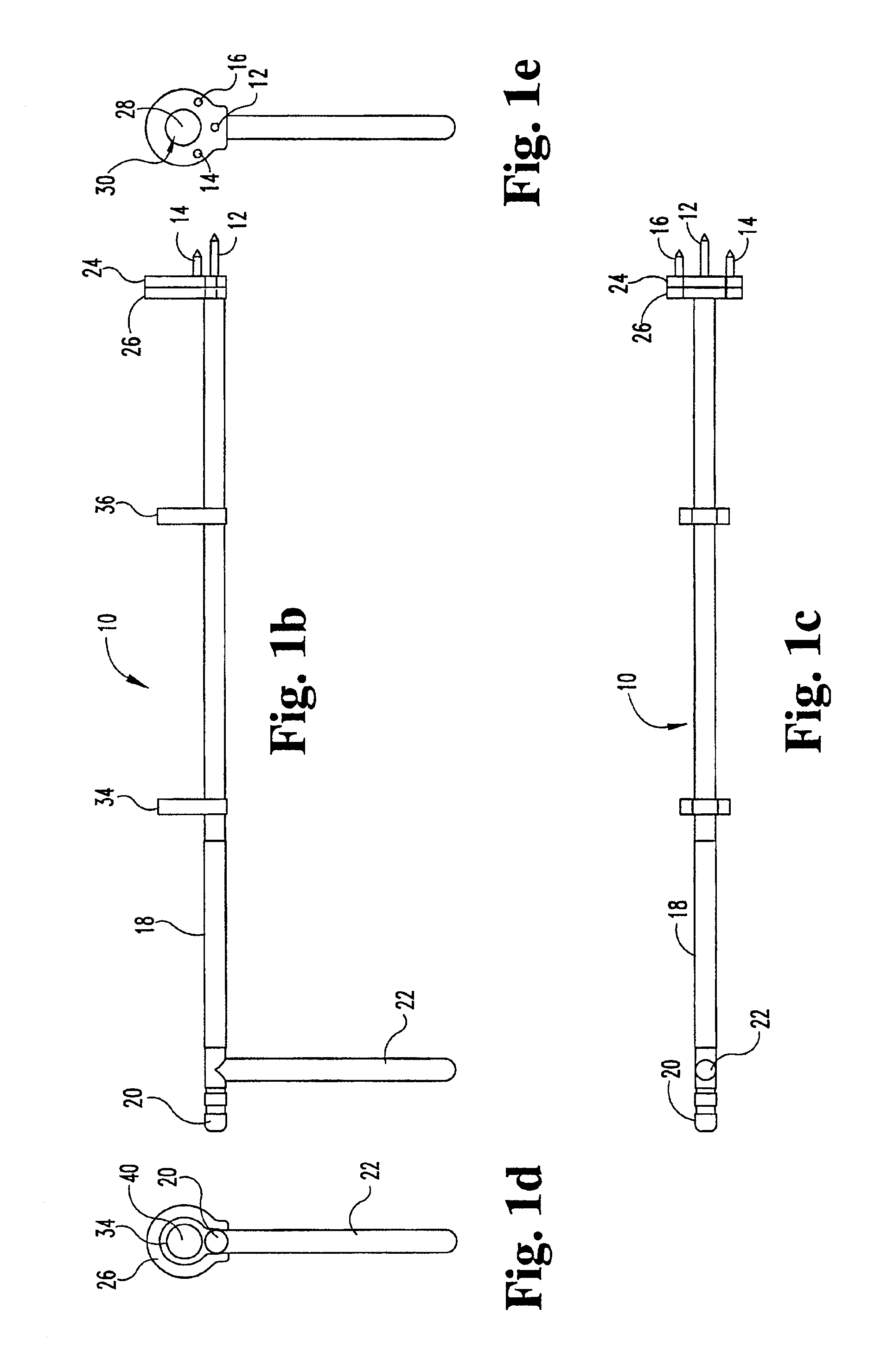
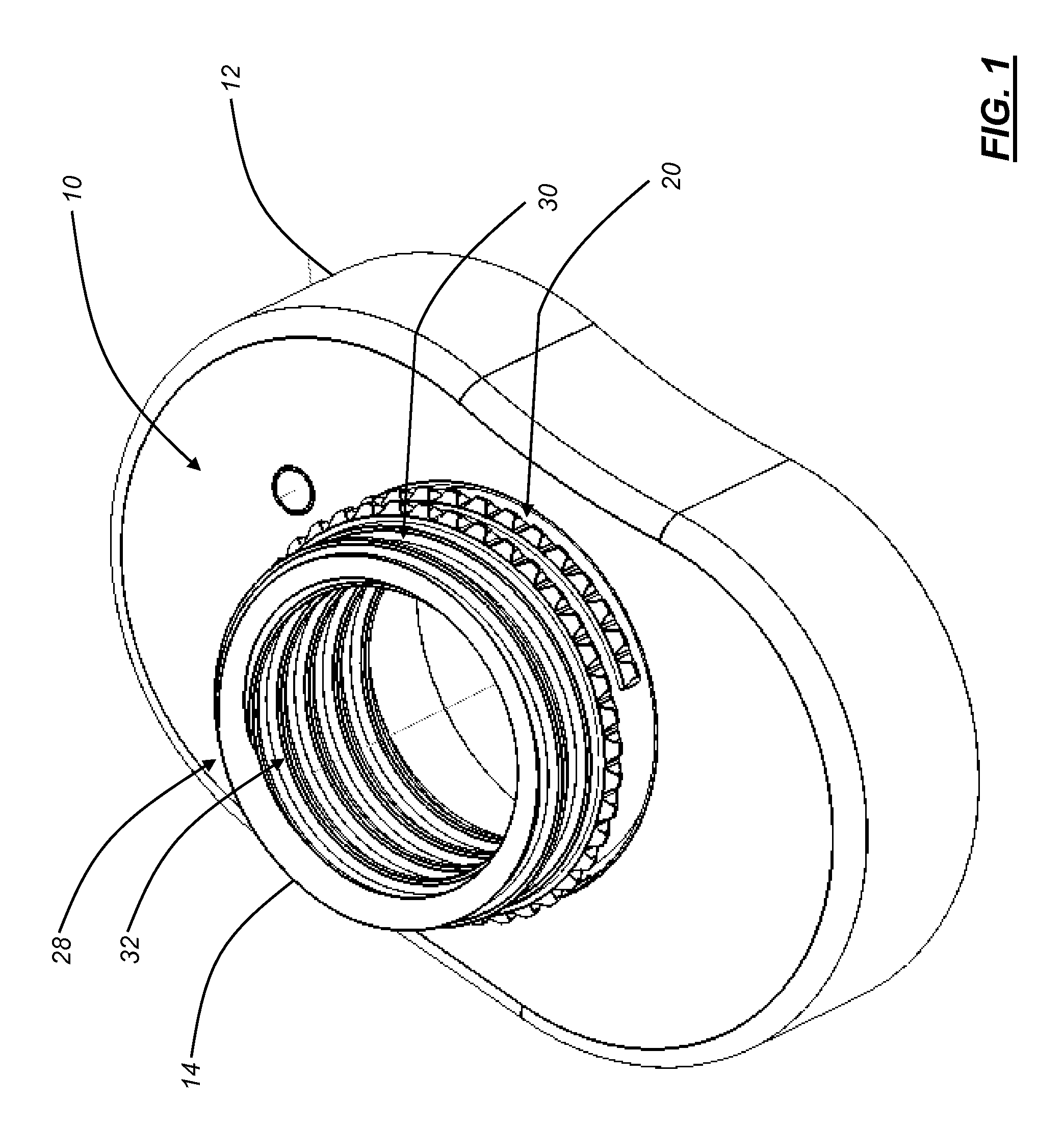
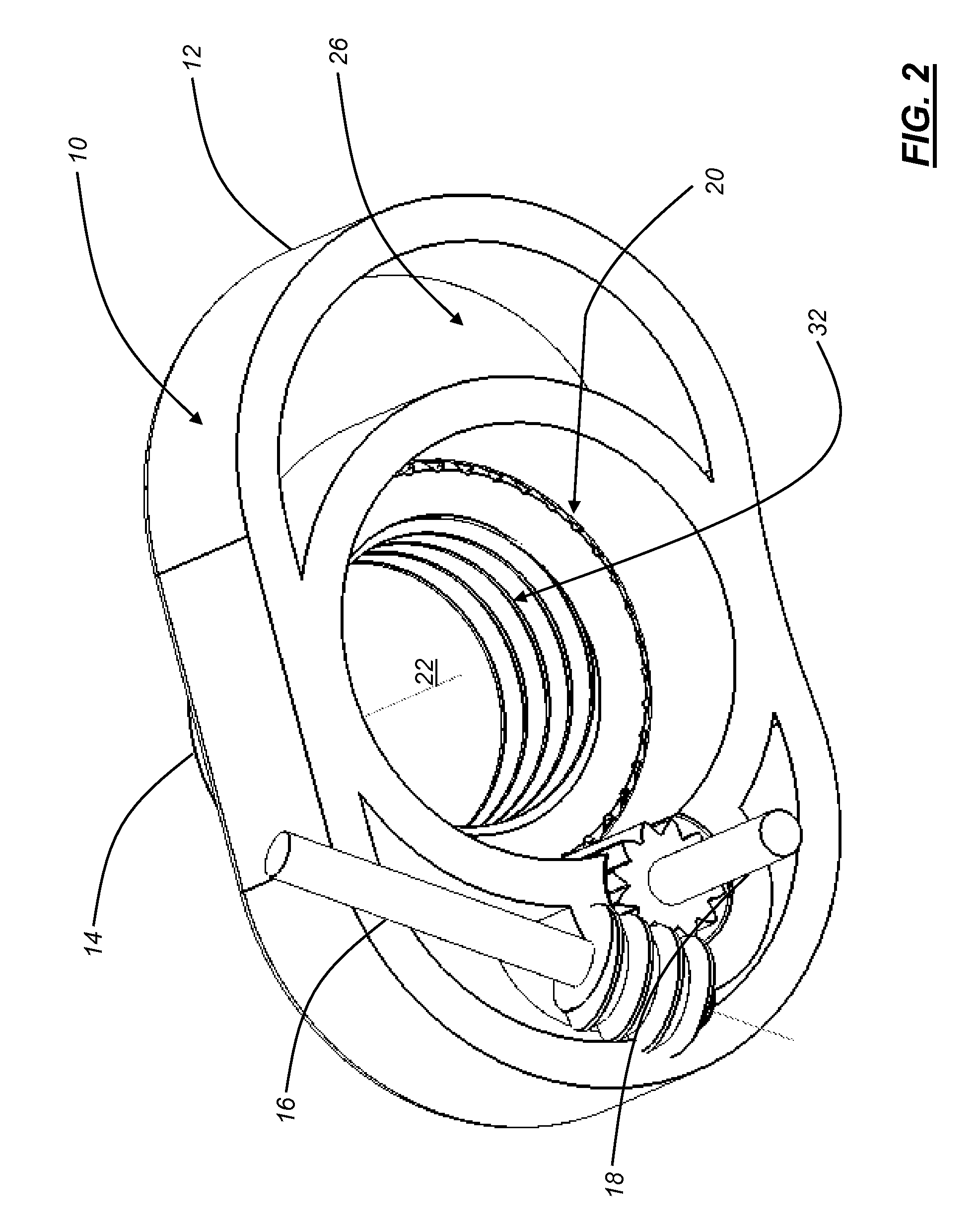
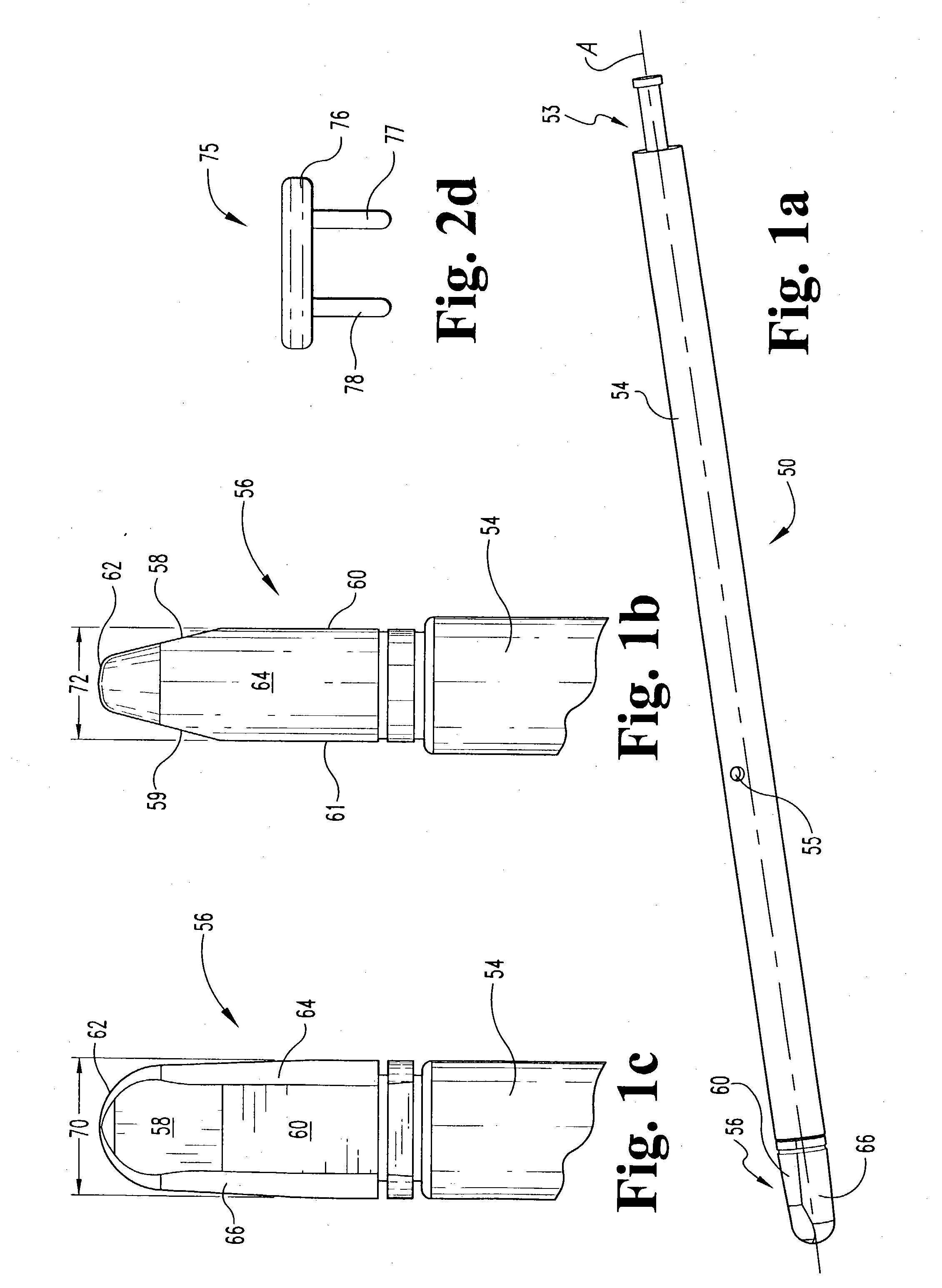
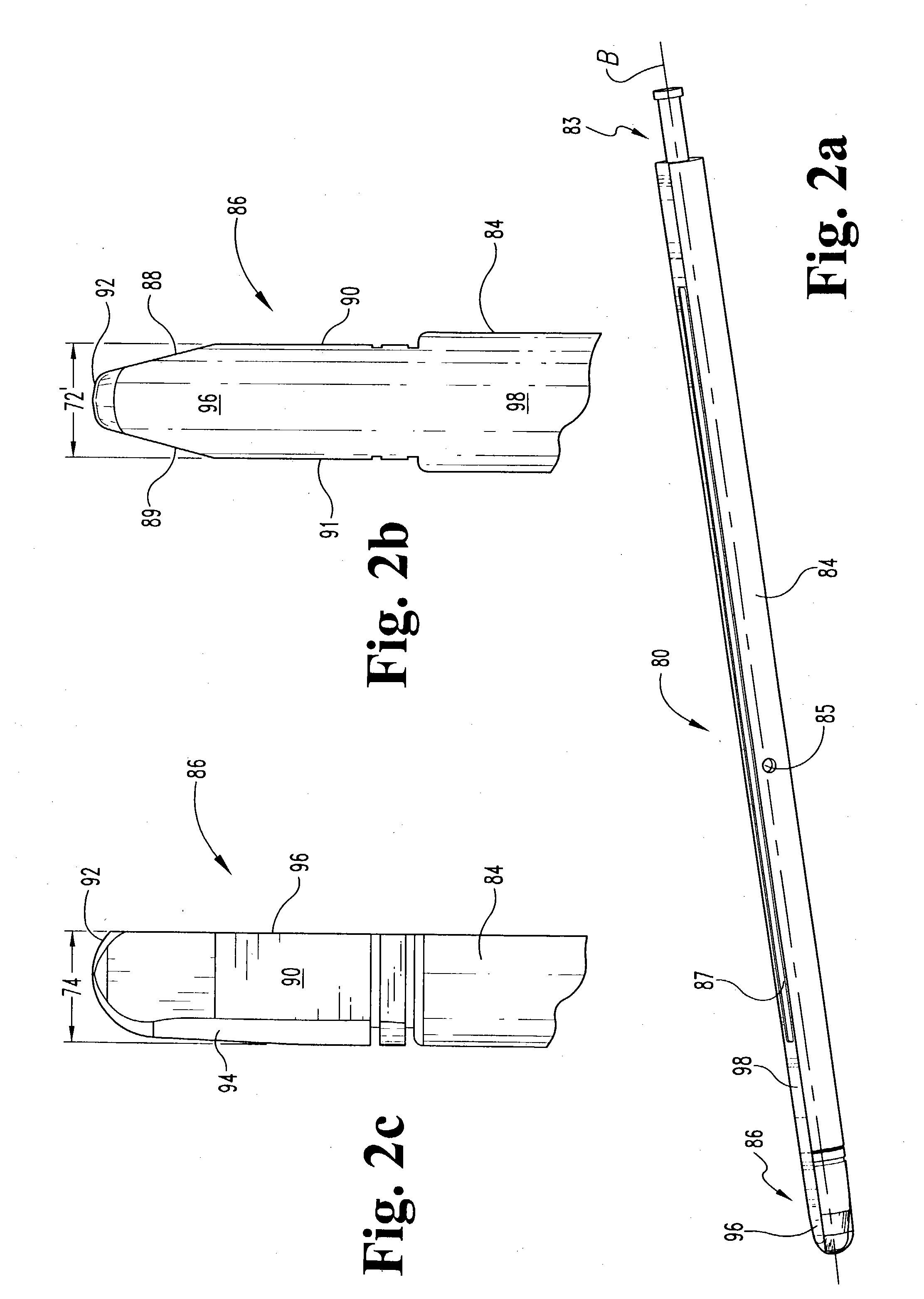
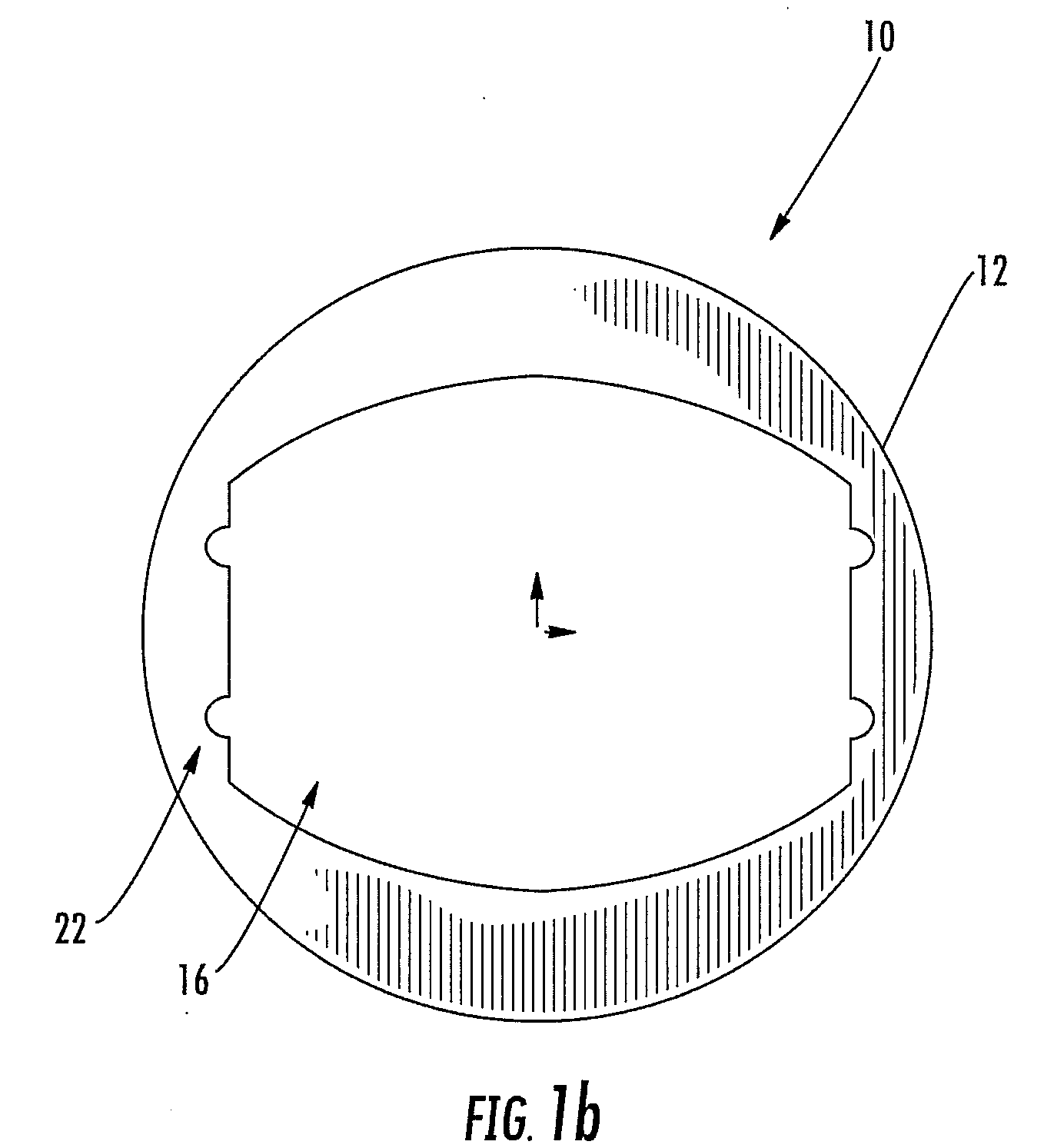
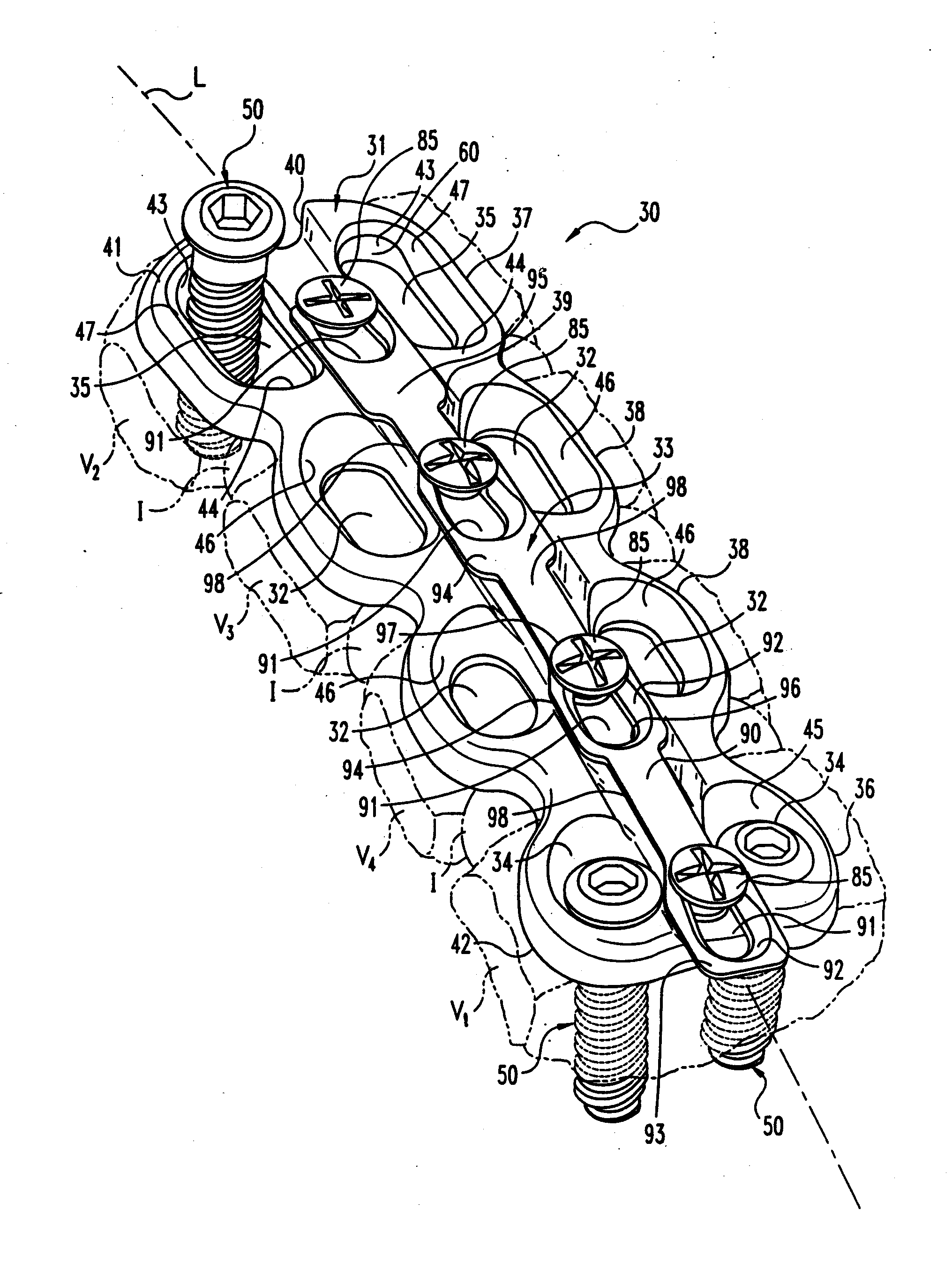
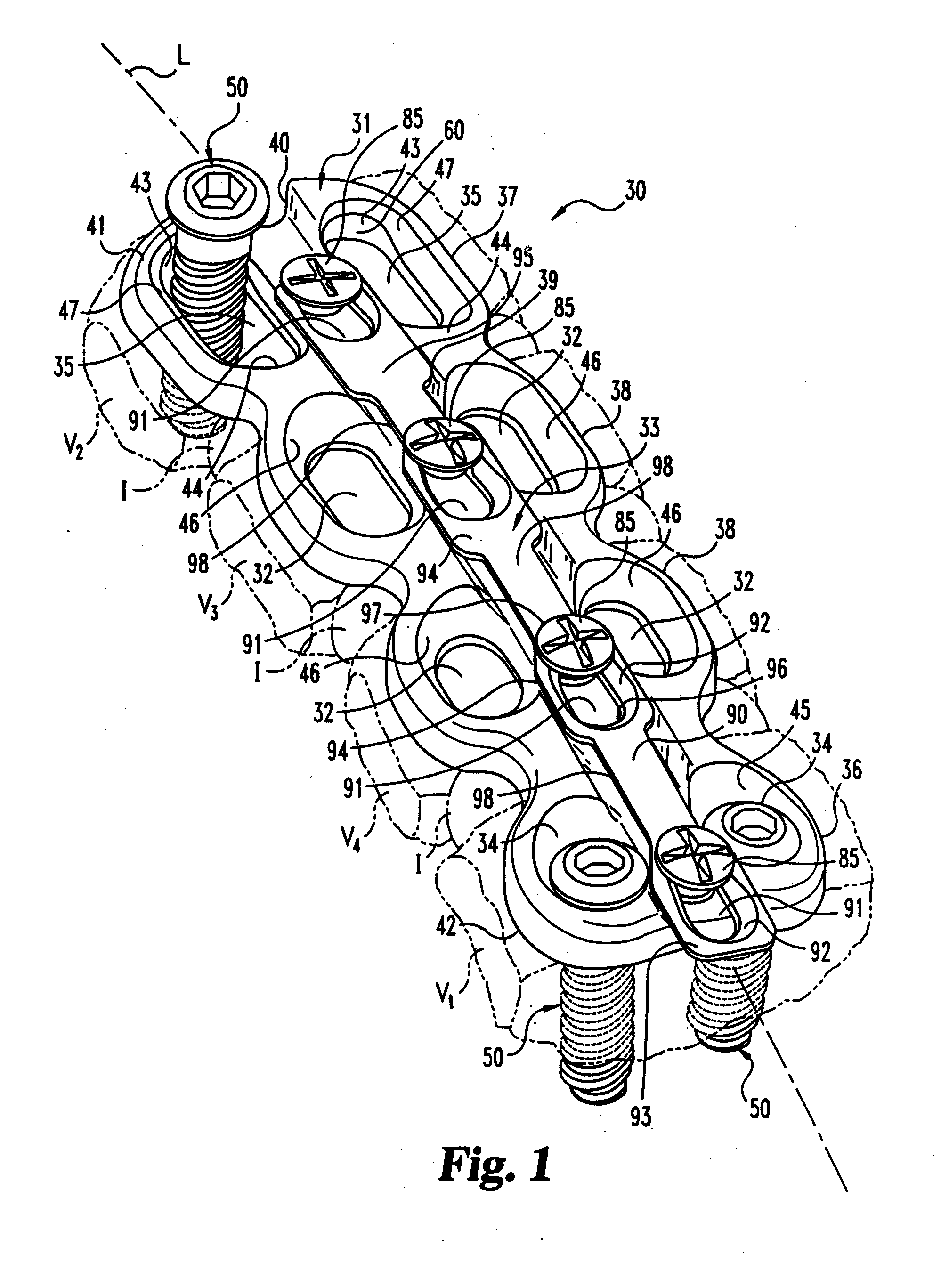
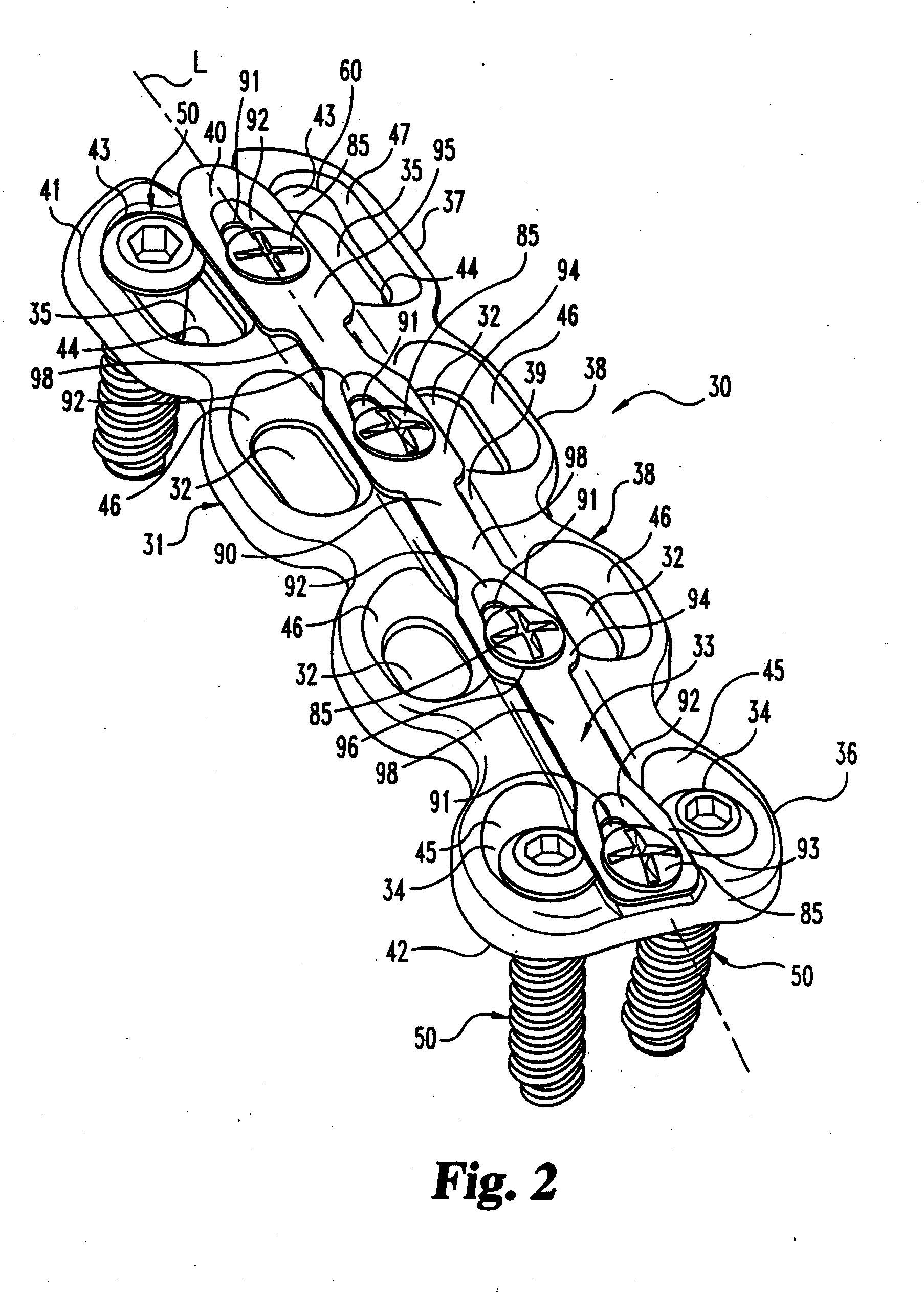
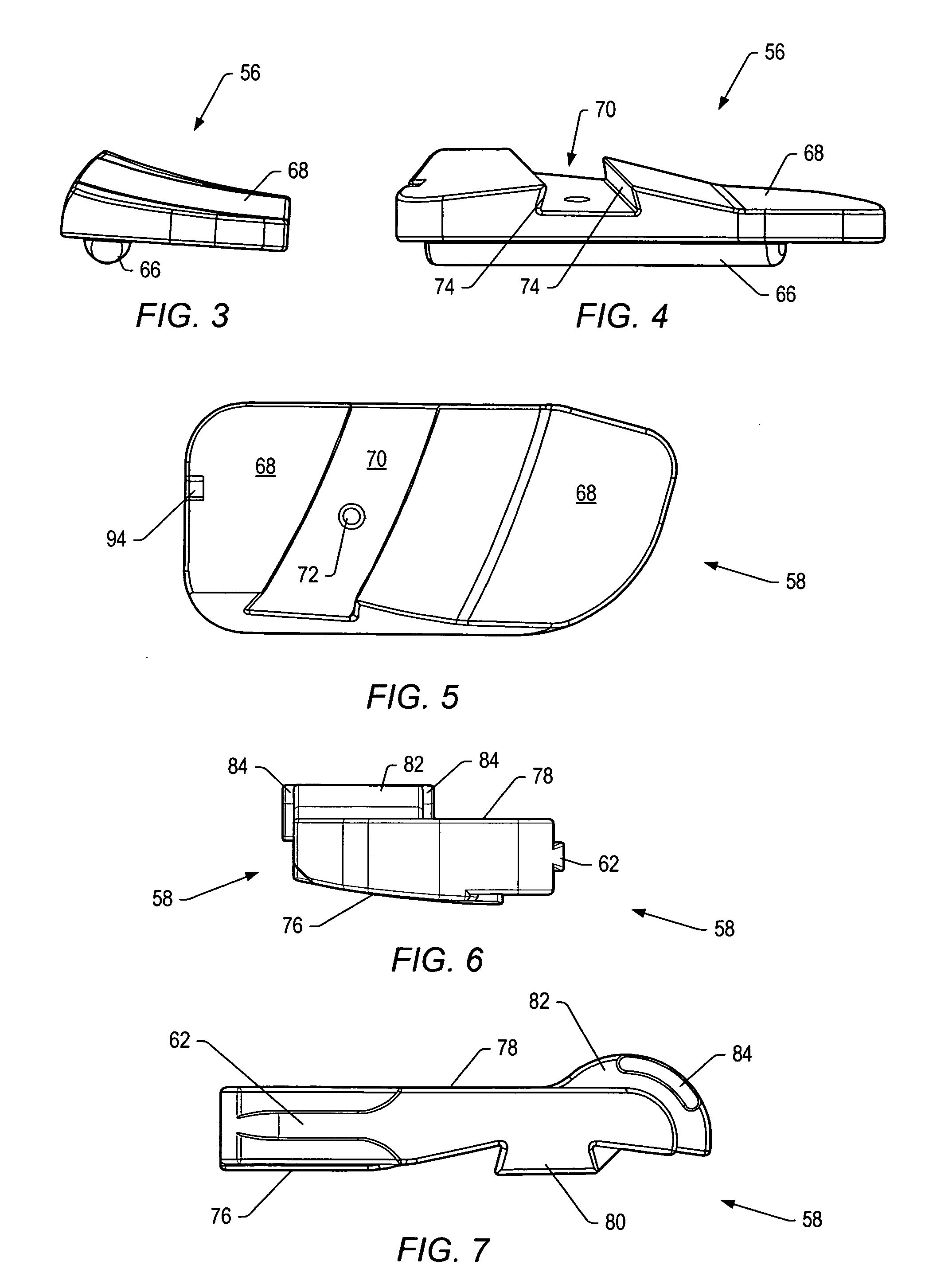
Intervertebral implant with blades for connecting to adjacent vertebral bodies
An intervertebral implant (300) for insertion into an intervertebral disc space between adjacent vertebral bodies or between two bone portions. The implant includes a spacer portion (310), a plate portion (330) operatively coupled to the spacer portion and one or more blades (350) for securing the implant to the adjacent vertebral bodies. The blades preferably include superior and inferior cylindrical pins (360) for engaging the adjacent vertebral bodies. The implant may be configured to be inserted via a direct lateral transposals approach. Alternatively, the implant may be configured for insertion via an anterior approach.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
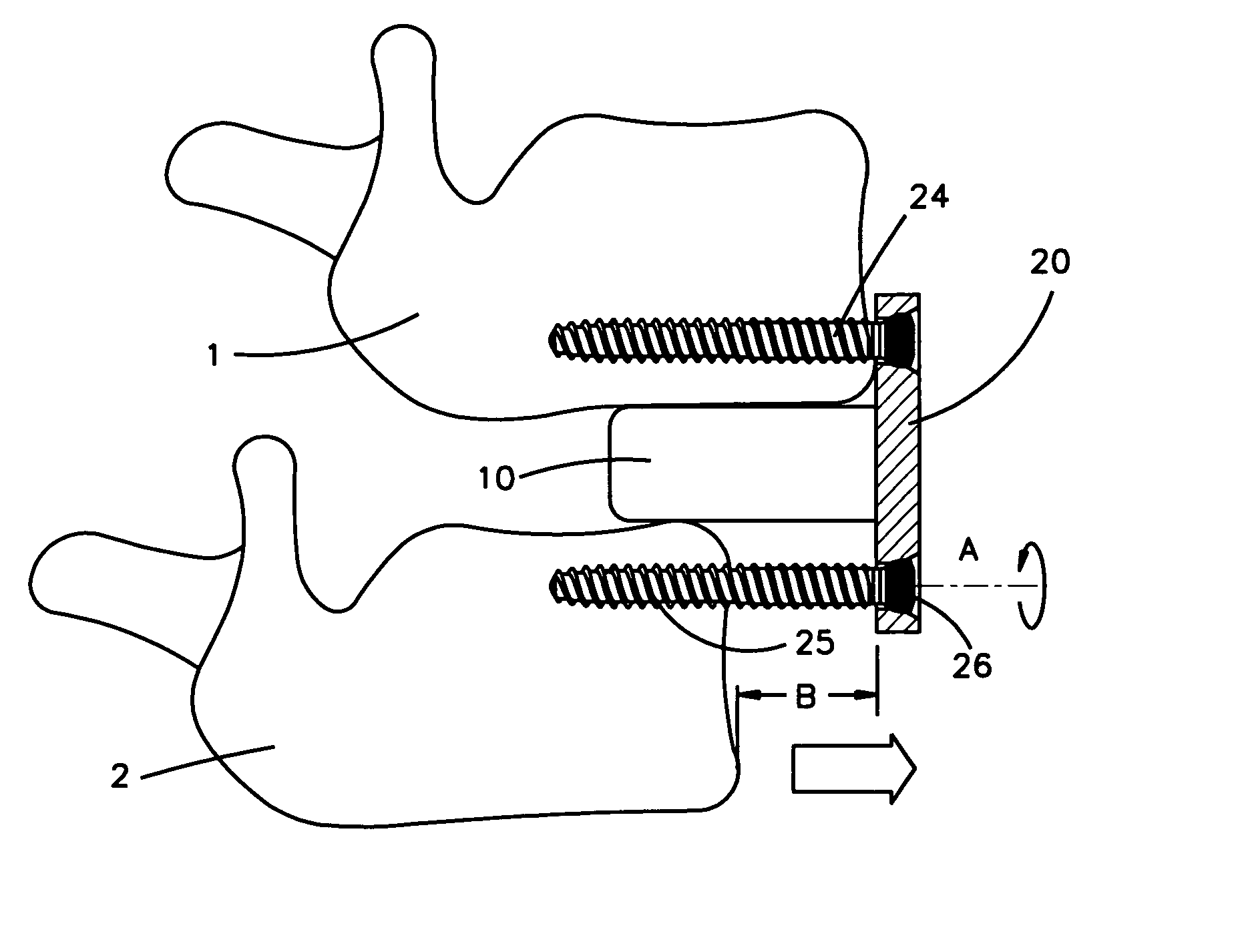
Method and instrumentation for vertebral interbody fusion
A method and instrumentation particularly adapted for disc space preparation from an anterior approach to the spine. In one aspect, an expandable template is provided having guides to guide a cutting device for bilateral formation of openings in the disc space. In another aspect, an improved guide member is provided for guiding a cutting tool. Still further, the invention provides an improved double barrel guide sleeve with a central distraction extension and lateral non-distracting extensions. Optionally, the guide sleeve includes windows and covers to selectively cover the windows. An improved reamer with an internal chamber and optional modular coupling is also provided. A depth stop is provided to selectively engage a tool shaft and a guide sleeve to control tool penetration into the disc space. A method of using the disclosed instruments is also provided.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Intradiscal devices including spacers facilitating posterior-lateral and other insertion approaches
Apparatus and methods are used to expand and / or connect disc replacement devices in situ, allowing such devices to be inserted through smaller openings including posterior as well as an anterior approaches to the spine. Other embodiments reside in nucleus replacements that do not expand within the disc space, providing improved longevity compared to existing NRs. Embodiments of the invention may be used in the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spine. The invention may also be used in other joints such as, the knee, prosthetic knees, prosthetic hips, or other joints in the body.
Owner:FERREE BRET A +1
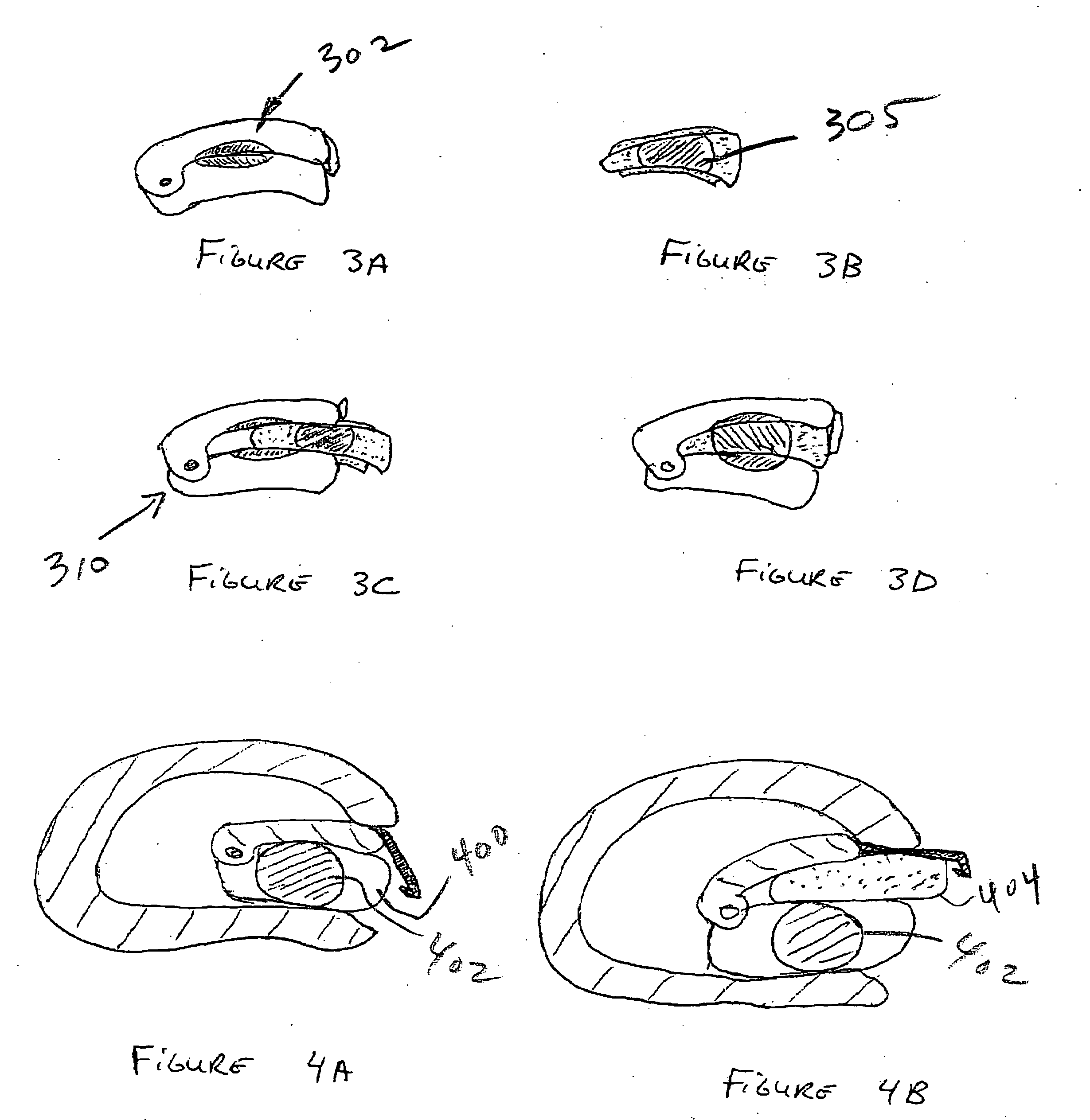
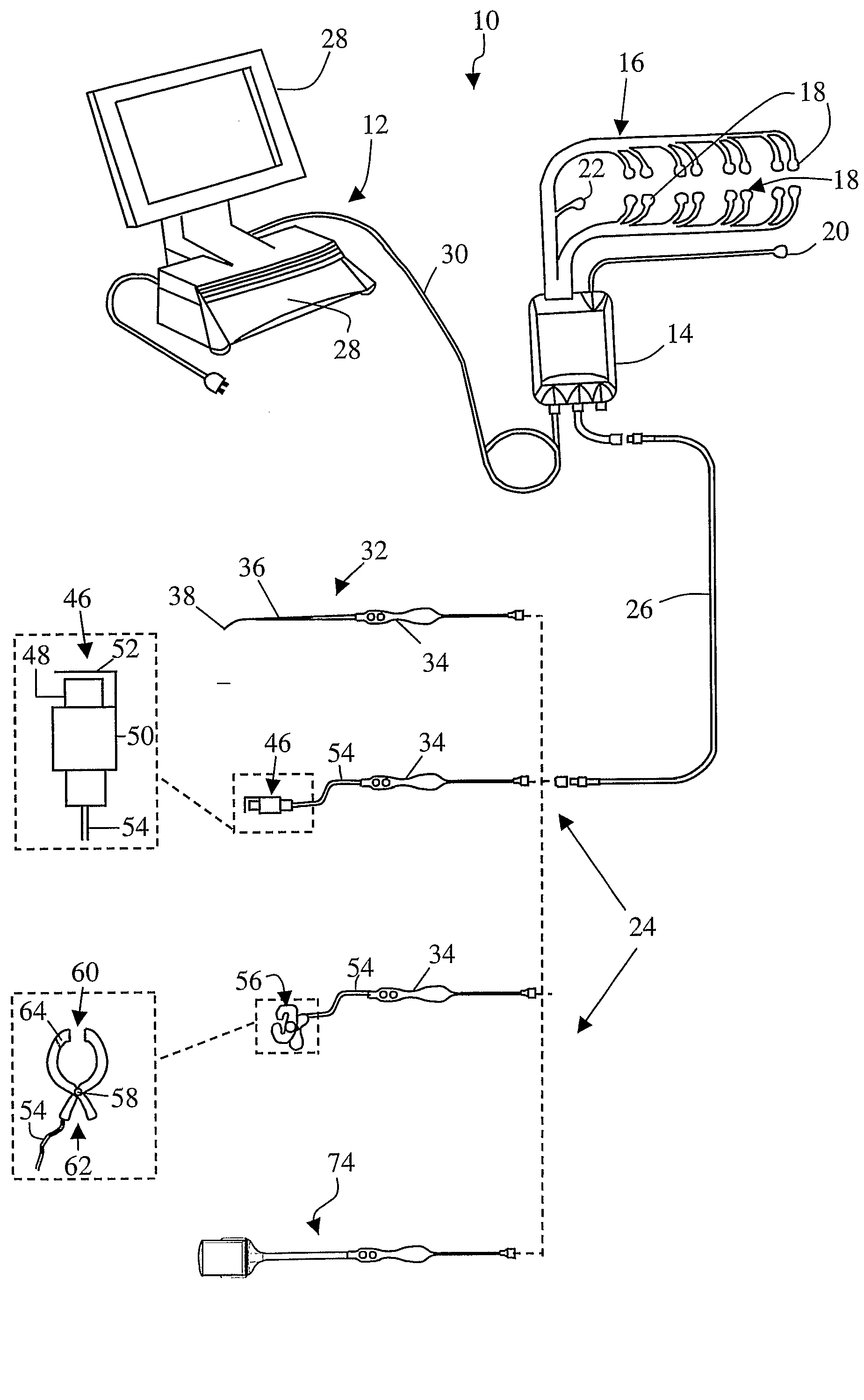
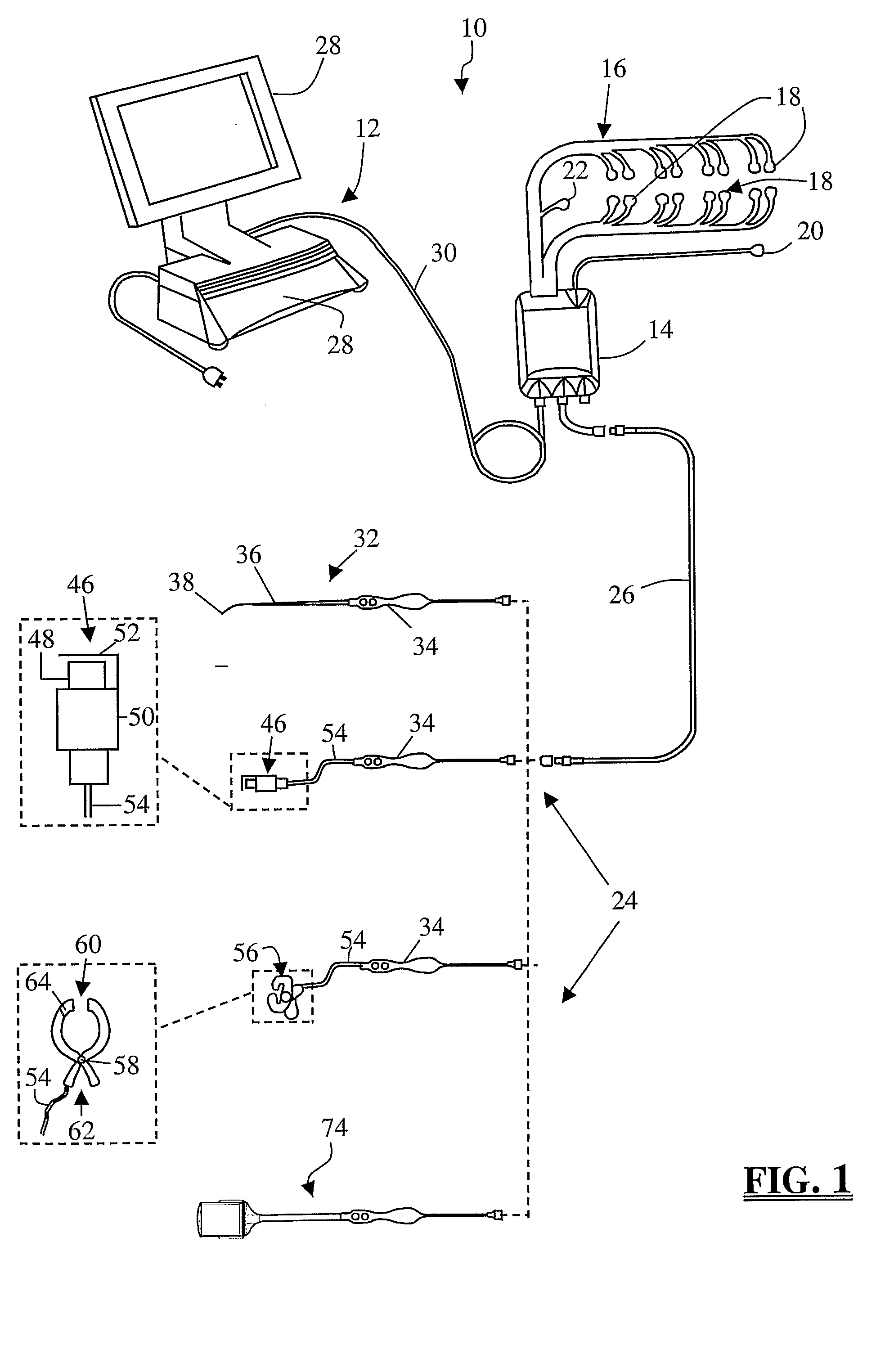
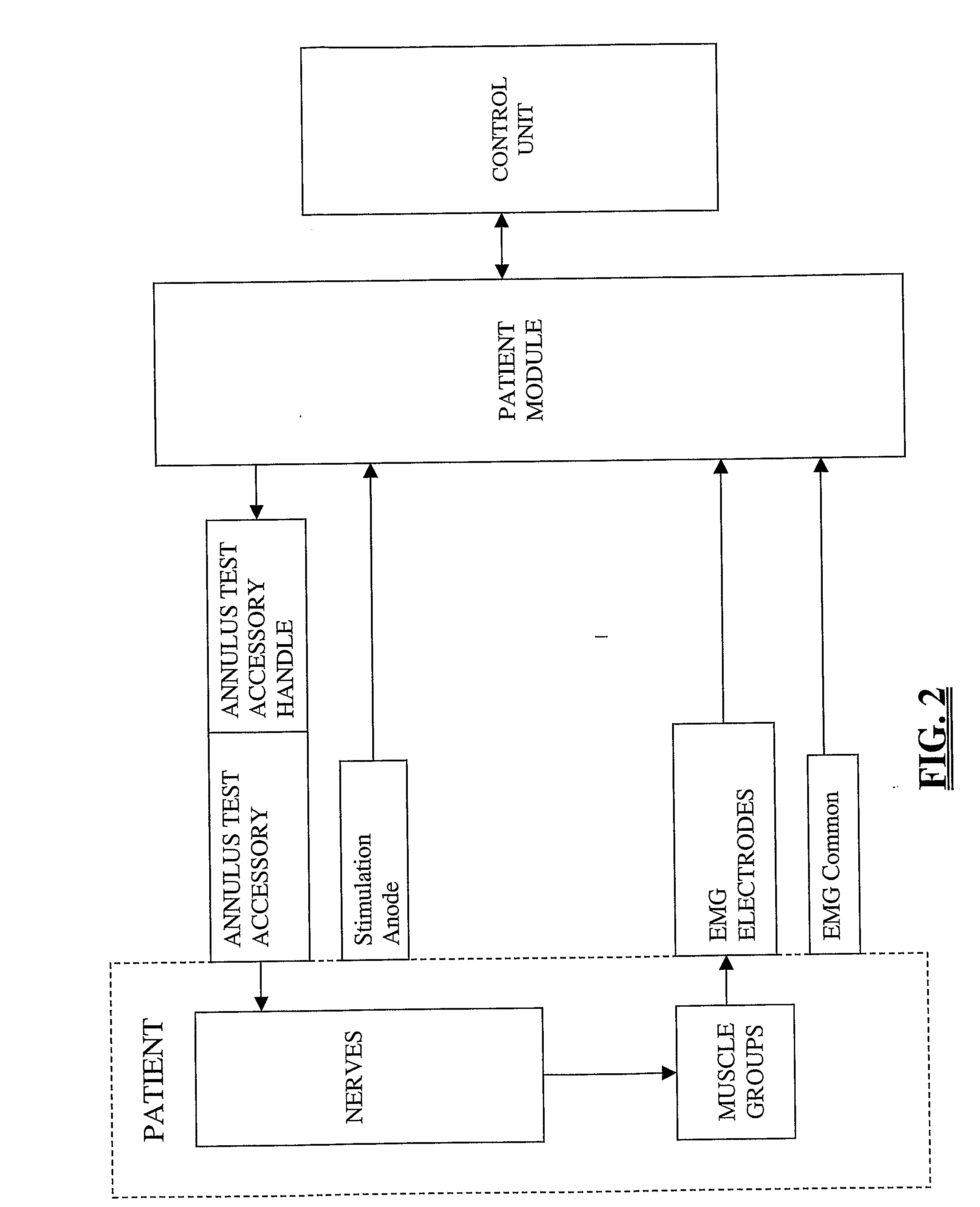
System and Methods for Monitoring During Anterior Surgery
The present invention involves a system and methods for nerve testing during anterior surgery, including but not limited to anterior total disc replacement surgery, nucleus replacement, and interbody fusion.
Owner:NUVASIVE
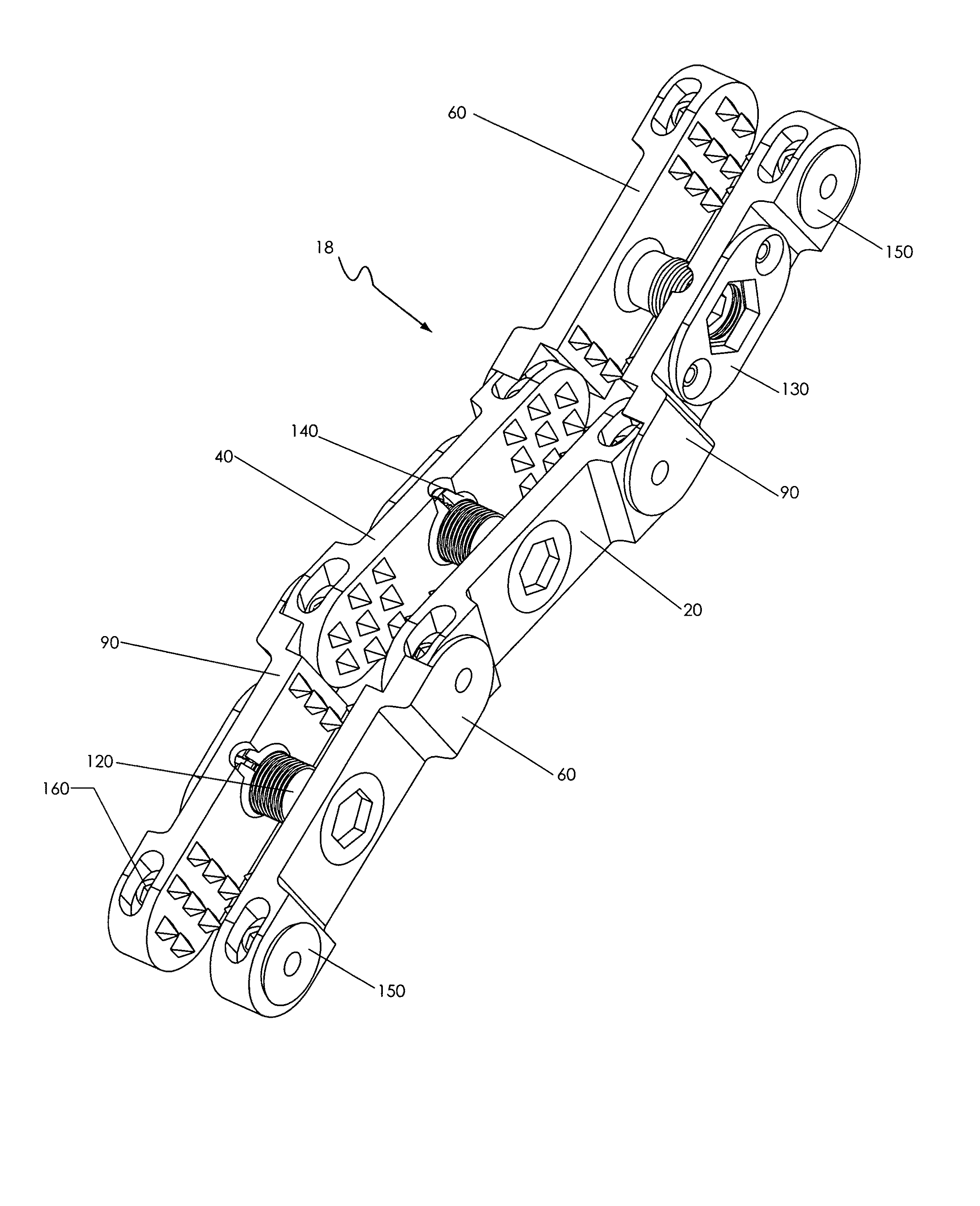
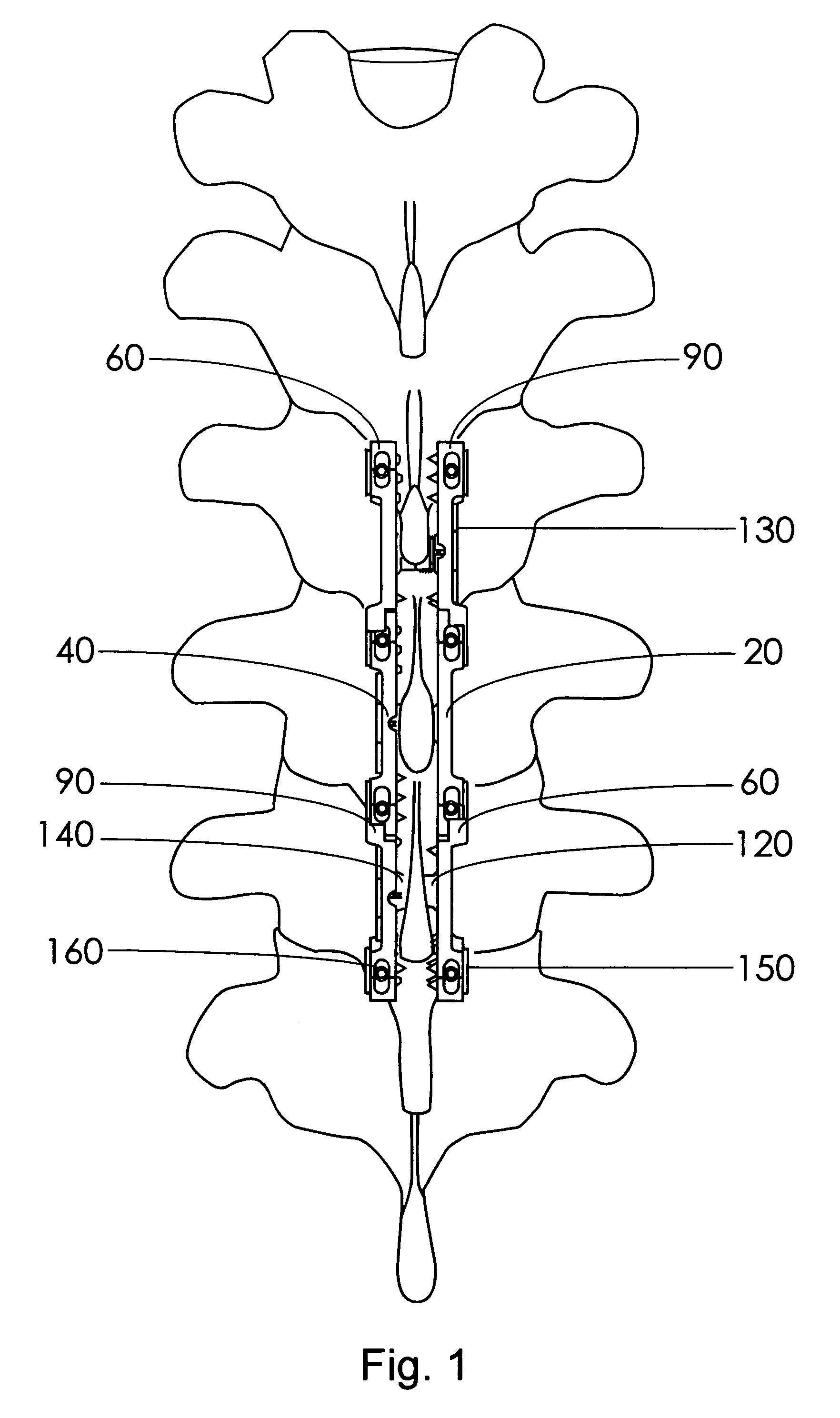
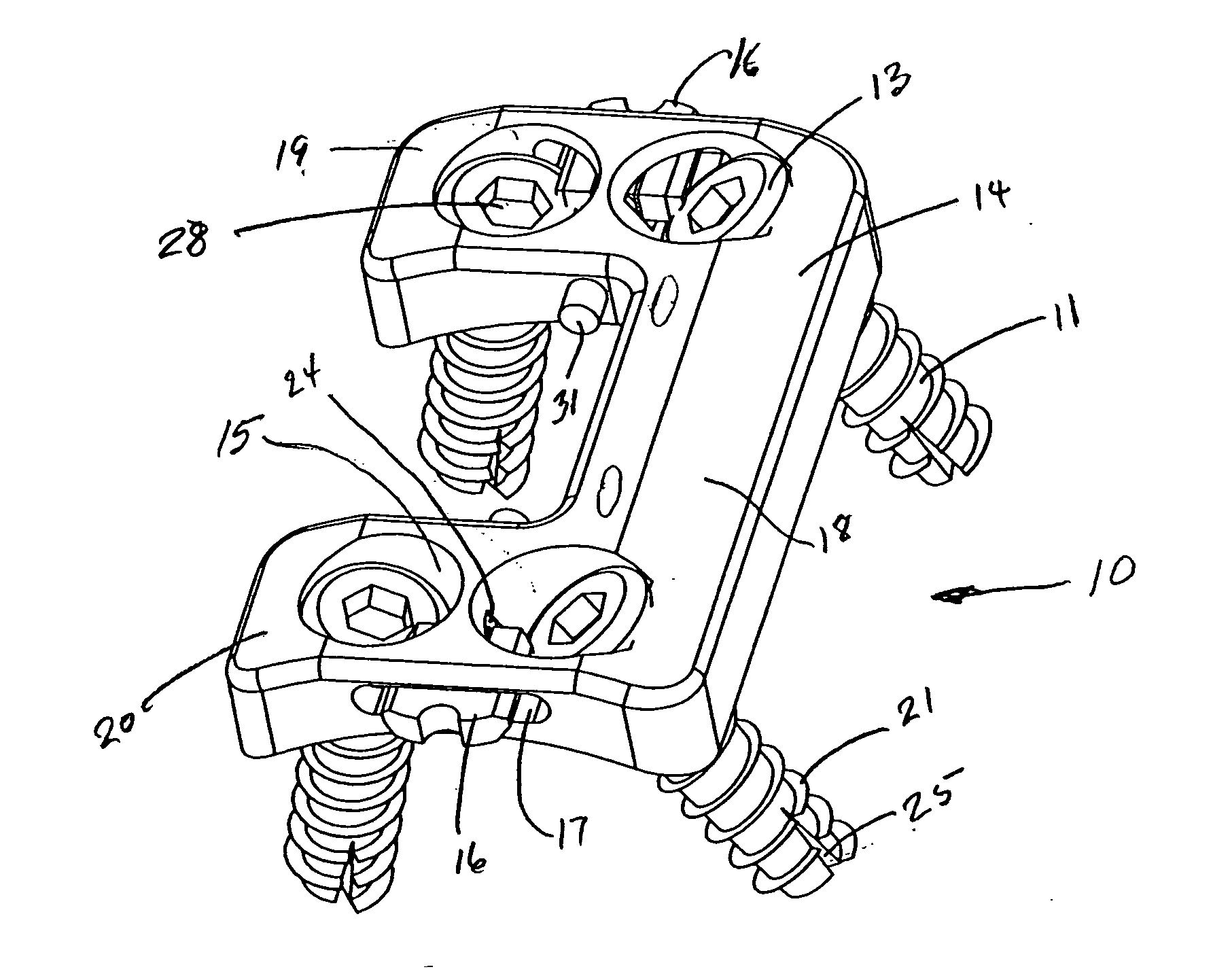
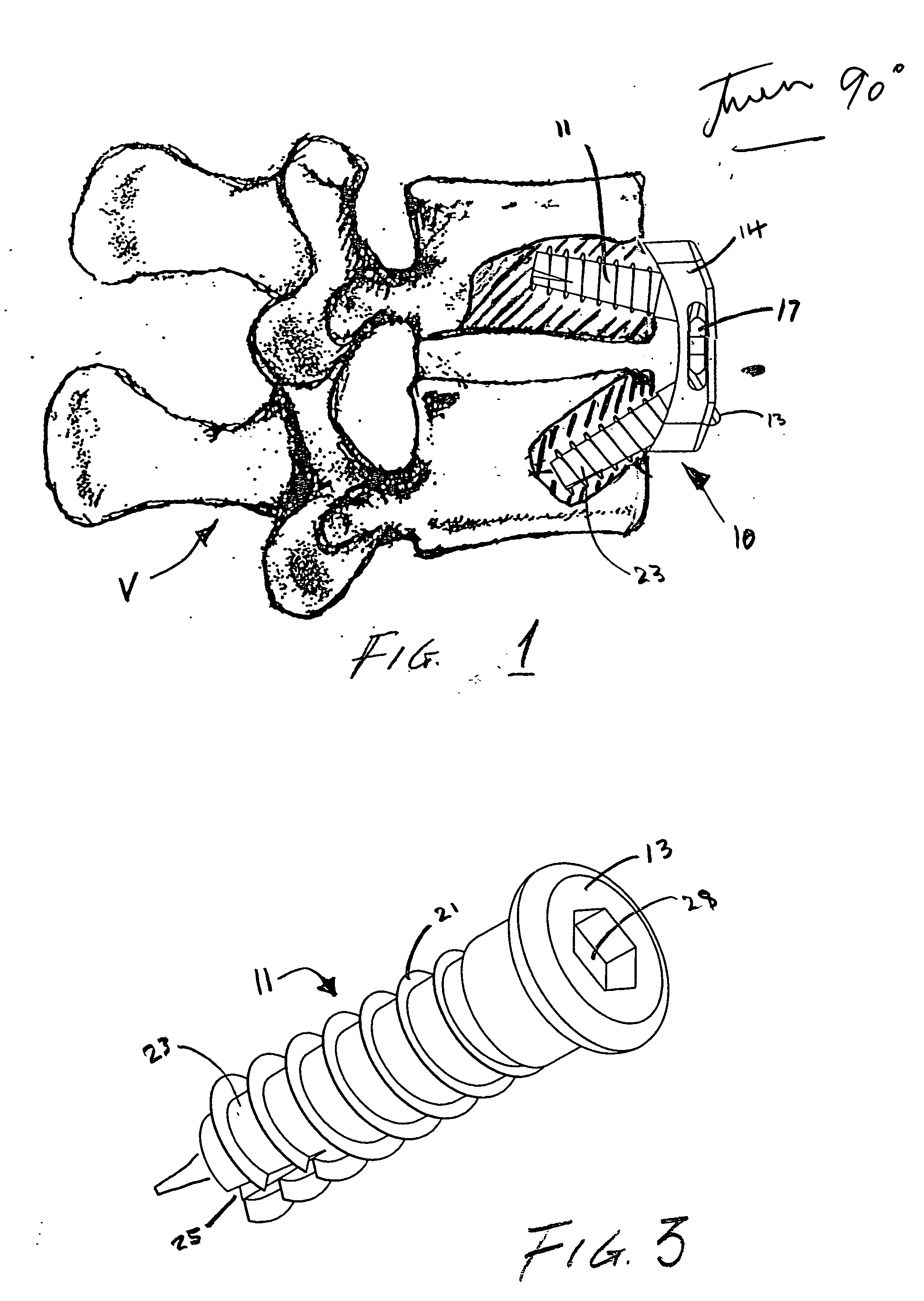
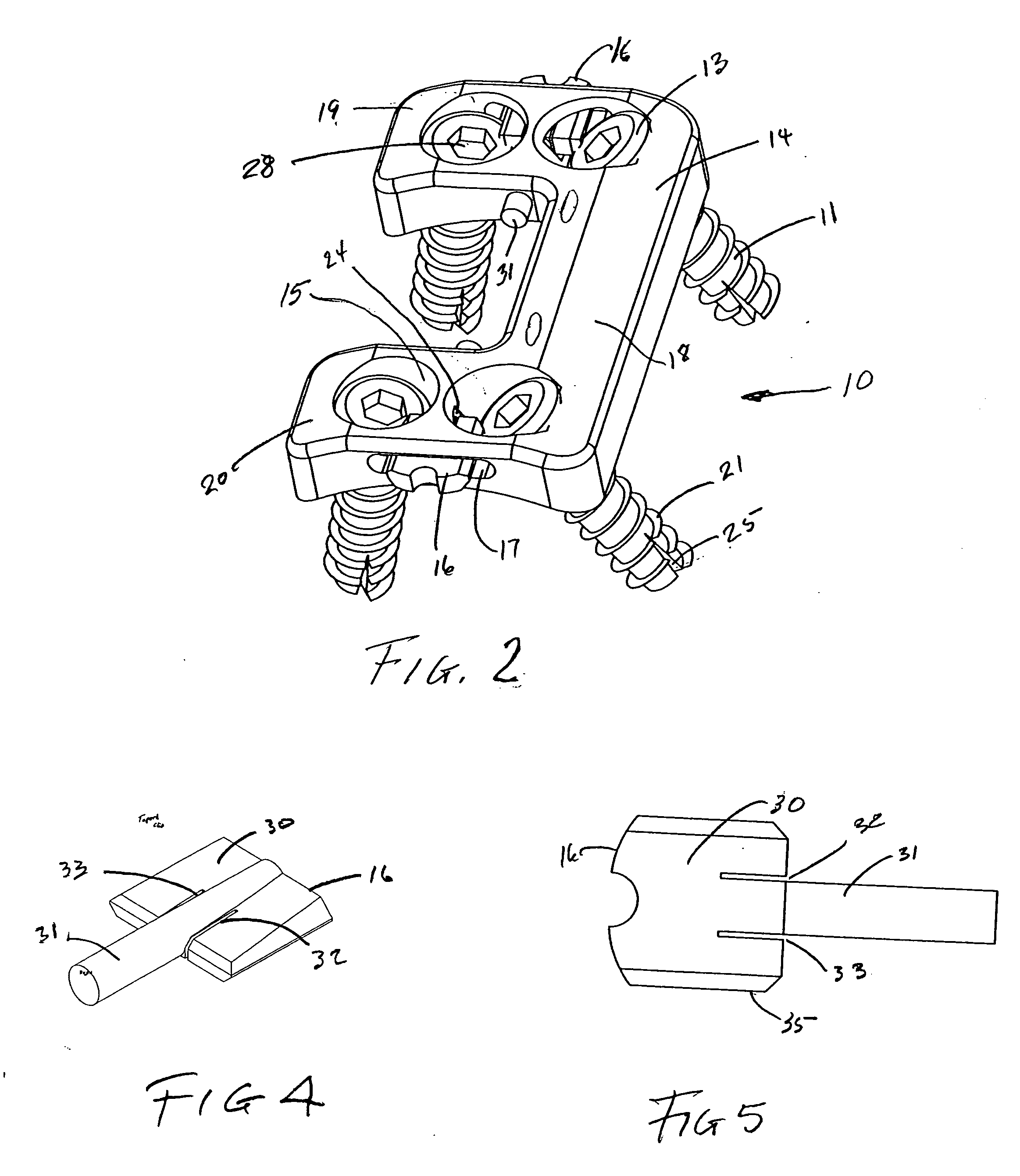
Spinous process stabilization device and method
InactiveUS20090264927A1Easy to integrateInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsCoronal planeEmbedded teeth
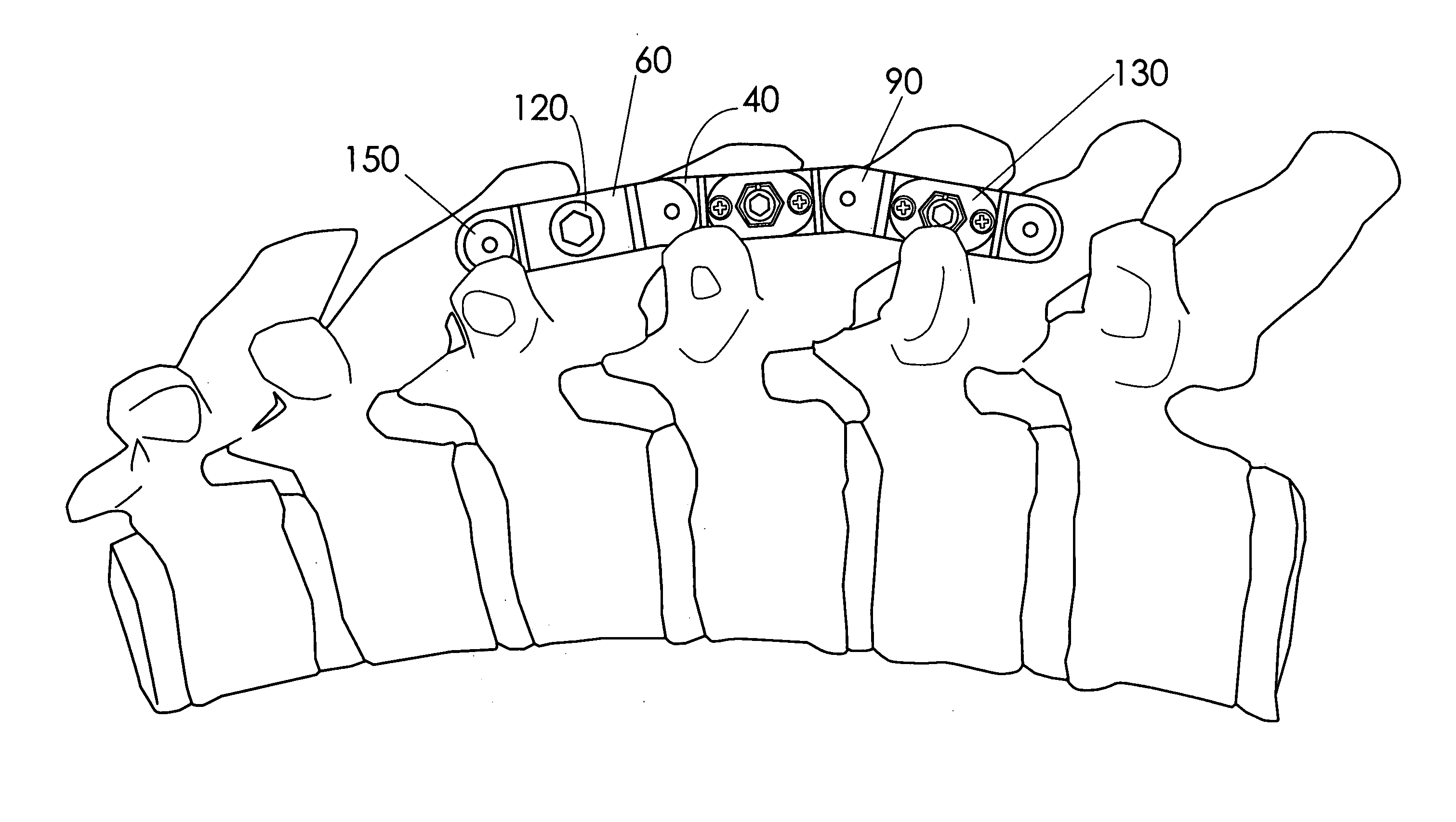
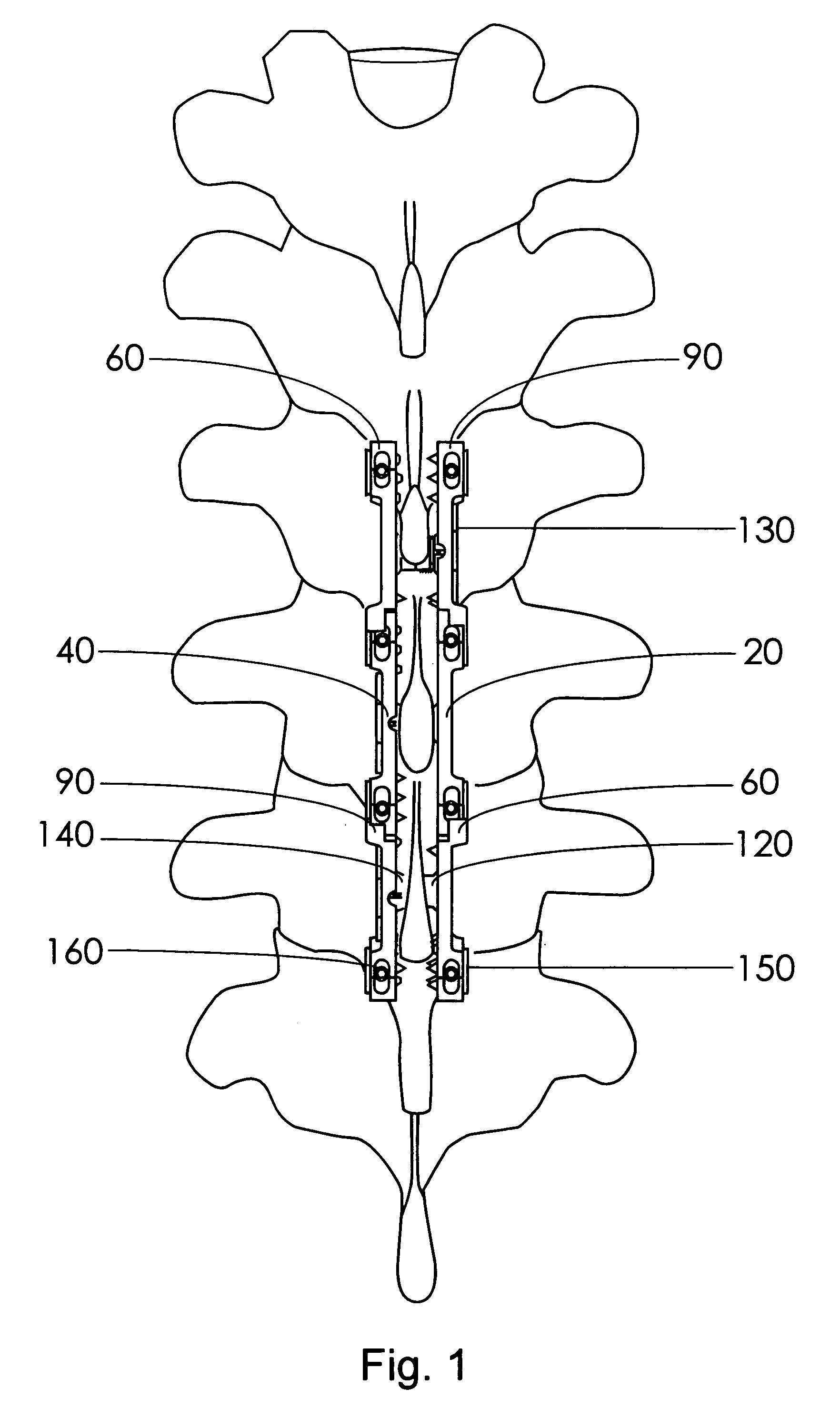
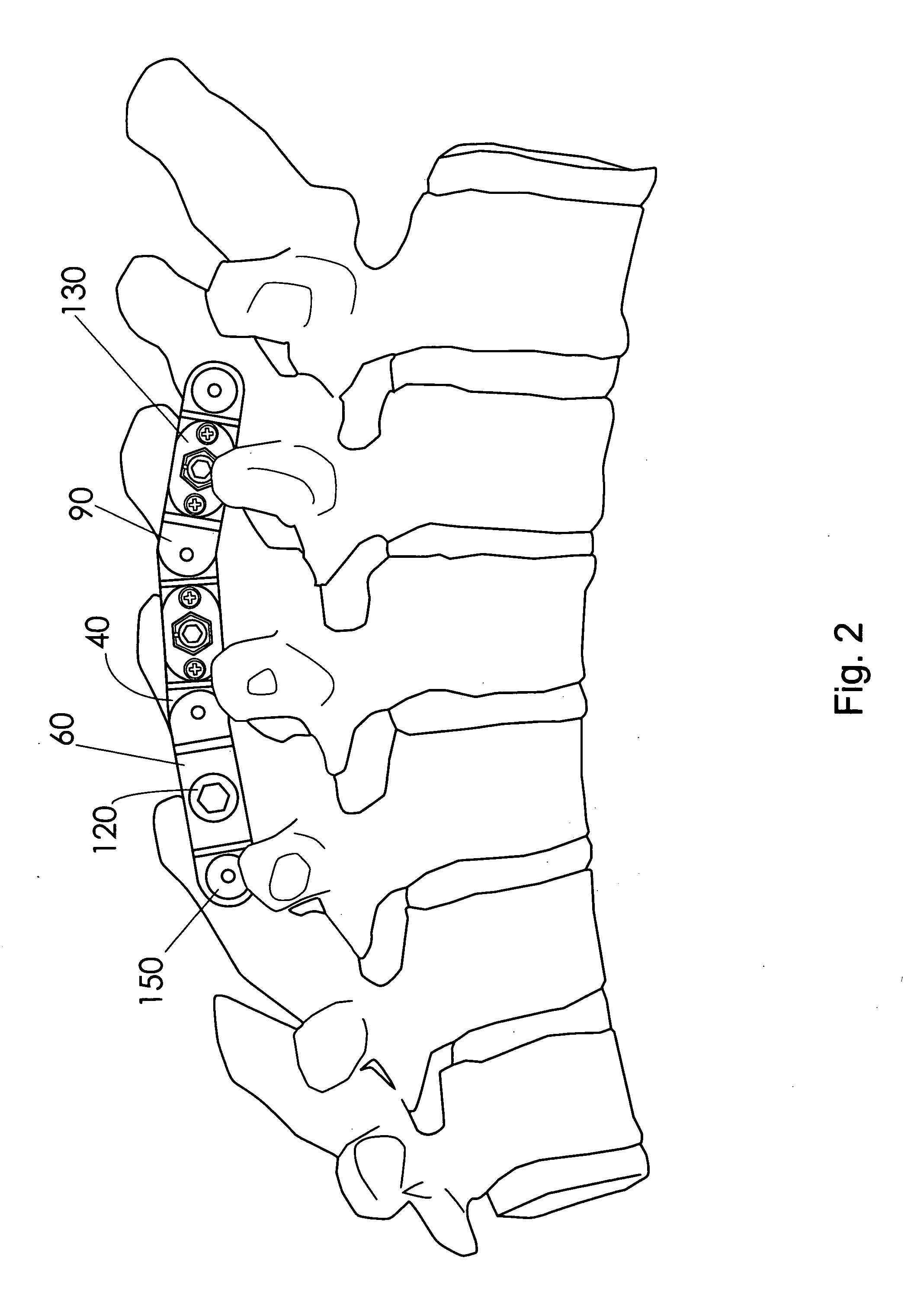
A fixation device to immobilize a spinal motion segment and promote posterior fusion, used as stand-alone instrumentation or as an adjunct to an anterior approach. The device functions as a multi-level fusion system including modular single-level implementations. At a single-level the implant includes a pair of plates spanning two adjacent vertebrae with embedding teeth on the medially oriented surfaces directed into the spinous processes or laminae. The complementary plates at a single-level are connected via a cross-post with a hemi-spherical base and cylindrical shaft passed through the interspinous process gap and ratcheted into an expandable collar. The expandable collar's spherical profile contained within the opposing plate allows for the ratcheting mechanism to be correctly engaged creating a uni-directional lock securing the implant to the spine when a medially directed force is applied to both complementary plates using a specially designed compression tool. The freedom of rotational motion of both the cross-post and collar enables the complementary plates to be connected at a range of angles in the axial and coronal planes accommodating varying morphologies of the posterior elements in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine. To achieve multi-level fusion the single-level implementation can be connected in series using an interlocking mechanism fixed by a set-screw.
Owner:GINSBERG HOWARD JOESEPH +2
Method and instruments to treat spondylolisthesis by an anterior minimally invasive approach of the spine
InactiveUS20070123989A1Reducing surgical morbidityReduce morbidityInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsSurgical treatmentLumbar vertebrae
A method for intra-operative surgical treatment of spondylolisthesis by an anterior minimally invasive approach of the lumbar spine includes inserting an interbody spacer between two vertebrae, attaching an anatomically designed reduction plate to at least one of the two vertebrae, and attaching the interbody spacer to the reduction plate by a fastening means through a central borehole of the reduction plate and the interbody spacer. The interbody spacer may be attached to the anteriorly positioned vertebra by at least bone screw. The upper and lower parts may be attached to the upper and lower vertebra by at least one bone screw to stabilize the displaced vertebral segment of the spine.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Prosthesis and method of implantation
InactiveUS20060015188A1Easy to implantAvoid crackingBone implantJoint implantsLess invasive surgeryBone prosthesis
A bone prosthesis for implantation at a joint is adapted to closely replicate the normal loading of the femur and is suitable for implantation using a single incision anterior approach, a form of minimally invasive surgery (MIS). The bone prosthesis comprises a stem adapted for orientation with a medial trabecular stream of the femur.
Owner:THE JAMES B GRIMES & TRACIE LYNN GRIMES 1998 TRUST
Surgical access system and related methods
A retractor-based access system for performing minimally invasive spine surgery via an anterior approach. The anterior access system and related methods of the present invention involve a plurality of retractor blades under the control of a single retractor handle apparatus.
Owner:NUVASIVE
Methods and instrument for vertebral interbody fusion
Methods and instrumentation particularly adapted for disc space preparation for insertion of implants from an anterior approach to the spine are provided. The instruments include a guide sleeve defining a channel having overlapping cylindrical working channel portions and lateral non-distracting extensions extending from reduced thickness wall portions. The guide sleeve has an overall reduced width configuration. A pair of distractors are provided. A first distractor includes a shaft and distal tip, each having convex walls. A second distractor includes a shaft and distal tip including a recessed area at least along the tip. The first distractor is at least partially received within the recessed area of the second distractor when the first and second distractors are in side-by-side relation and a reduced overall width of the distractors is obtained. Preferably, the first and second distractors are used with the guide sleeve. Methods using the disclosed instruments are also provided.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Anterior lumbar interbody fusion cage device and associated method
The present invention provides a cage device for performing spinal fusion, including: a housing defining one or more ports that is selectively disposed in an intervertebral space between adjacent vertebrae; one or more extensible retention structures that are selectively advanced out of the housing through the one or more ports and into one or more endplates of the adjacent vertebrae; and one or more actuation mechanisms for selectively advancing the one or more extensible retention structures out of the housing through the one or more ports and into the one or more endplates of the adjacent vertebrae. In one exemplary embodiment, the one or more actuation mechanisms consist of at least one worm gear / mandrel pair. The one or more extensible retention structures are selectively advanced out of the housing through the one or more ports and into the one or more endplates of the adjacent vertebrae with a rotational motion. Preferably, the one or more extensible retention structures are configured such that they may contain a bone graft. In one exemplary embodiment, the housing is selectively disposed in the intervertebral space between the adjacent vertebrae using an anterior approach.
Owner:CTL MEDICAL CORP
Spinous process stabilization device and method
A fixation device is provided to immobilize a spinal motion segment and promote posterior fusion, used as stand-alone instrumentation or as an adjunct to an anterior approach. The device functions as a multi-level fusion system including modular single-level implementations. At a single-level the implant includes a pair of plates spanning two adjacent vertebrae with embedding teeth on the medially oriented surfaces directed into the spinous processes or laminae. The complementary plates at a single-level are connected via a cross-post passed through the interspinous process gap The freedom of rotational motion of both the cross-post and collar enables the complementary plates to be connected at a range of angles in the axial and coronal planes accommodating varying morphologies of the posterior elements in the cervical, thoracic and lumbar spine. To achieve multi-level fusion the single-level implementation can be connected in series using an interlocking mechanism fixed by a set-screw.
Owner:GINSBERG HOWARD JOESEPH +2
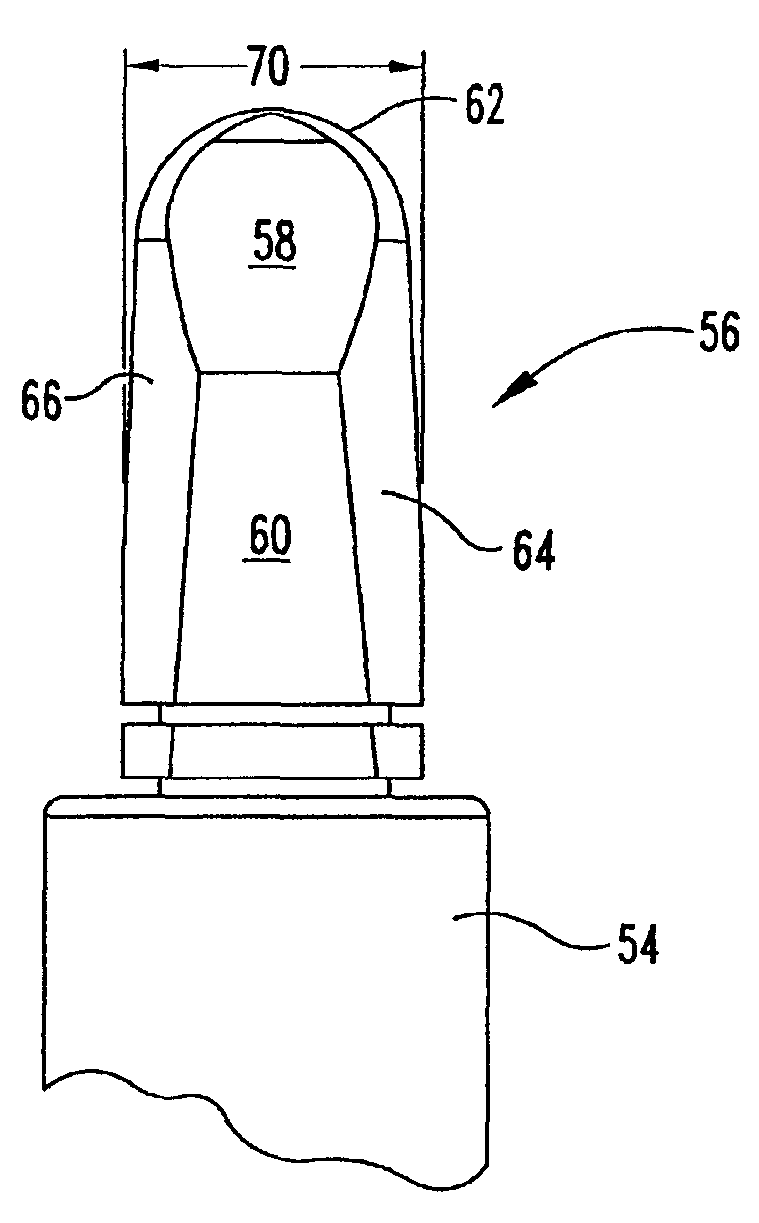
Percutaneous cervical disc reconstruction
Methods and devices for fixing a defect in a vertebral disc of a patient. One method includes inserting a guide wire into a disc using an anterior approach to create a path. At least a portion of the herniated nucleus pulposus is removed. A disc reconstruction device is then advanced into the disc and fastened to the disc or at least one of the surrounding vertebrae. Alternatively, a passage could be formed in the cranial or caudal vertebra using an angled anterior approach that terminates in a region of the disc containing the herniated nucleus pulposus. At least a portion of the herniated nucleus pulposus is removed. A disc reconstruction device that has a bone in-growth component and a soft tissue in-growth component is then implanted in the passage. Devices having bone and soft tissue in-growth components and having a flexible spine with a plurality of ribs are also described.
Owner:ANOVA
Check reins for artificial disc replacements
InactiveUS7156848B2Restore motion limiting functionPrevent excessive spinal motionInternal osteosythesisLigamentsAnterior longitudinal ligamentRange of motion
Check reins in the form of elongated members are used to limit the extreme range of motion which would otherwise be permitted by some ADR designs. The check reins serve two main purposes. First, they retain disc spacers, if present. Additionally, the wedge shape of ADRs and the removal of the Anterior Longitudinal Ligament (ALL) and a portion of the Annulus Fibrosus (AF) to insert the ADR from an anterior approach, favor anterior extrusion of disc spacers. In preferred embodiments the check reins are therefore limited to the anterior portion of the periphery of the ADR. Second, check reins serve to prevent excessive spinal motion. Again, although they may be helpful in other locations, anterior check reins help restore the motion limiting functions of the ALL and AF that were removed in anterior approaches to the spine.
Owner:FERREE BRET A
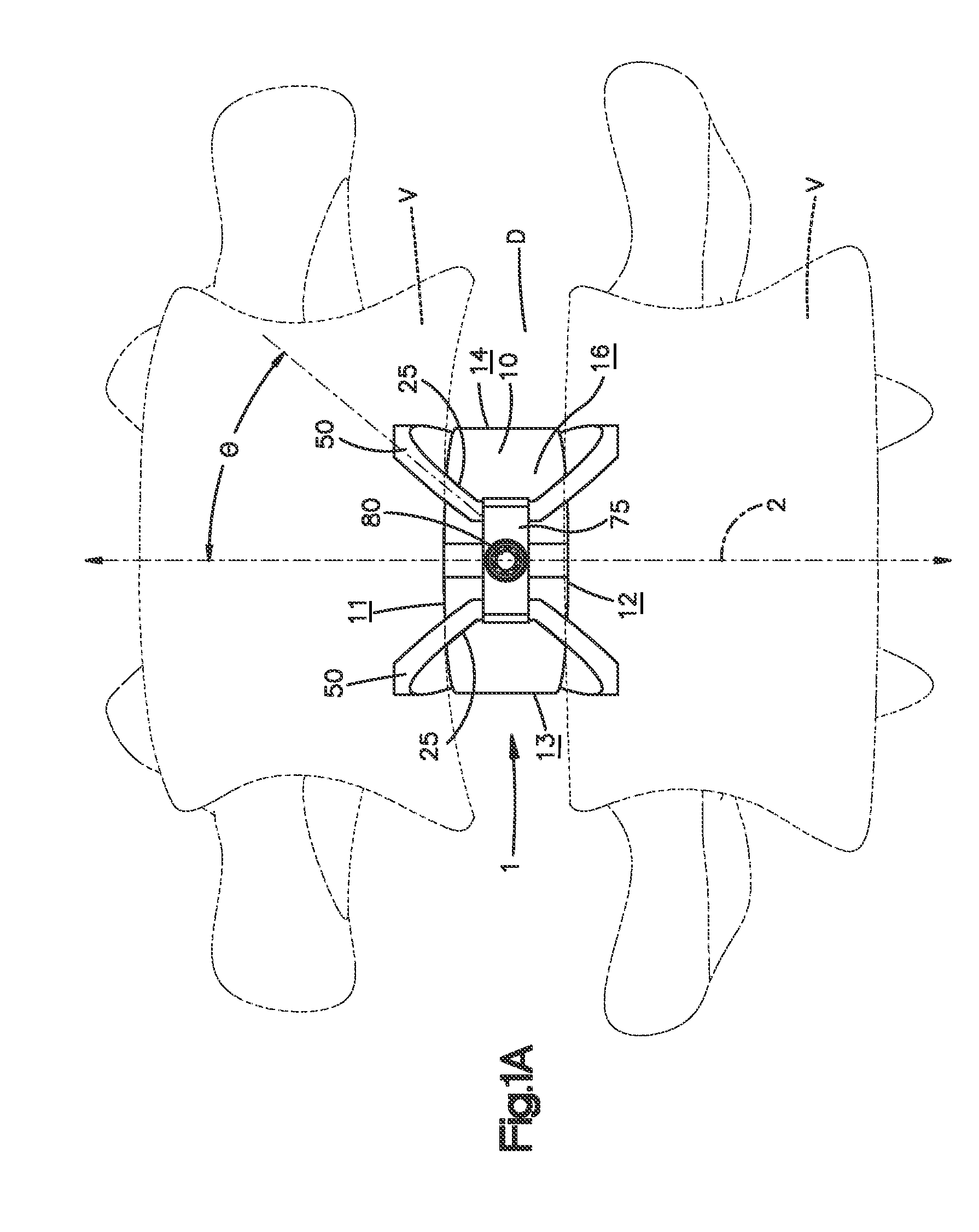
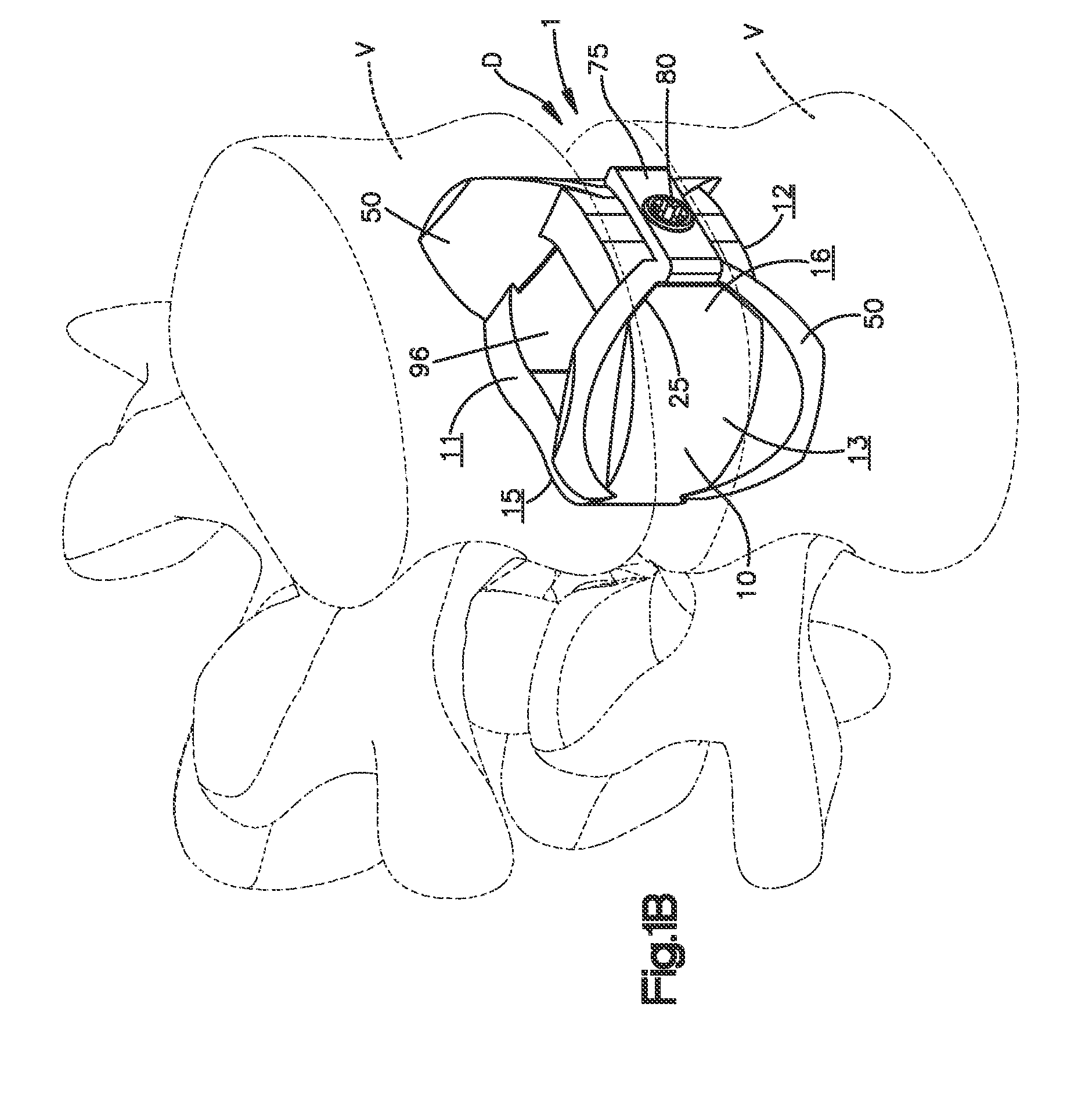
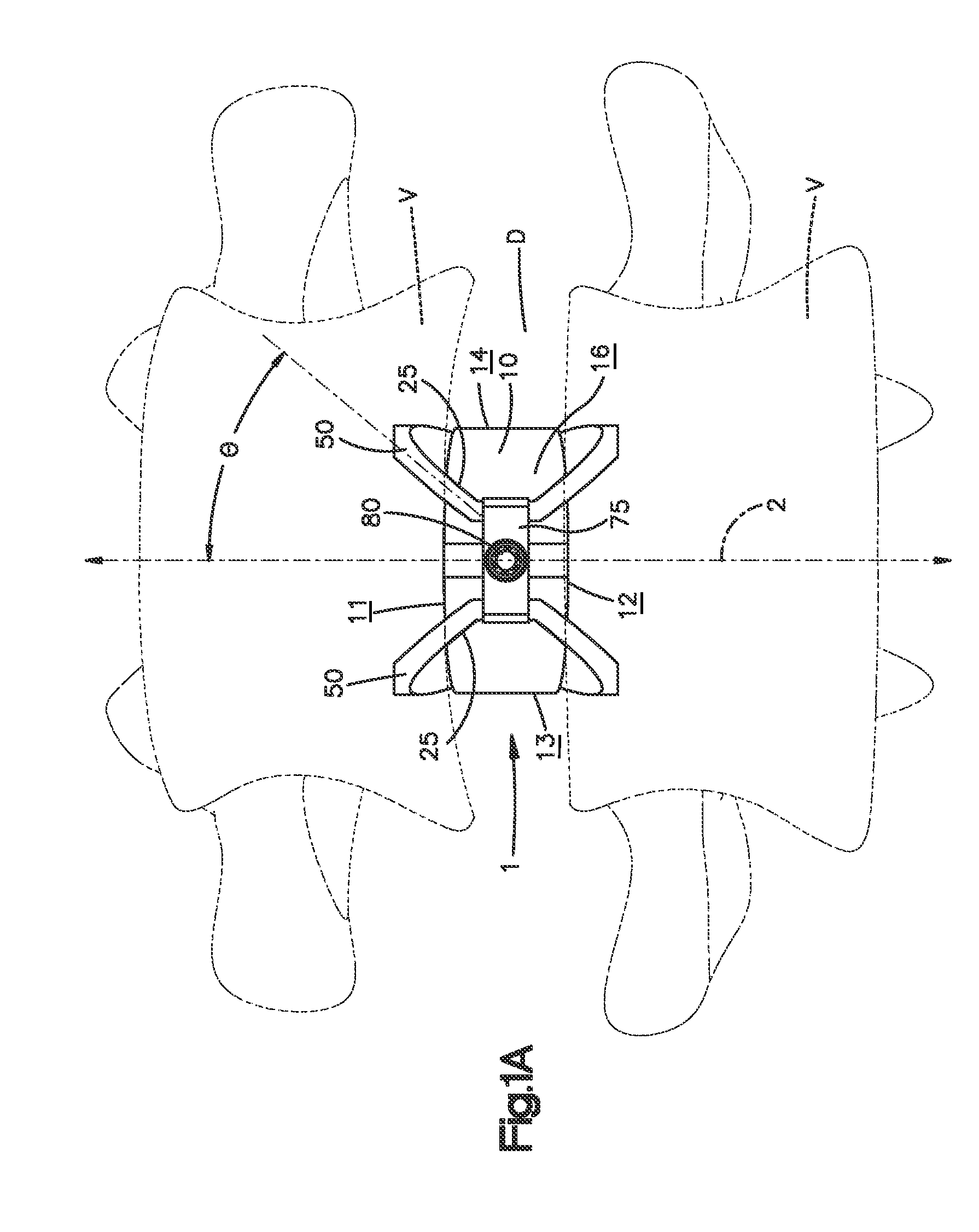
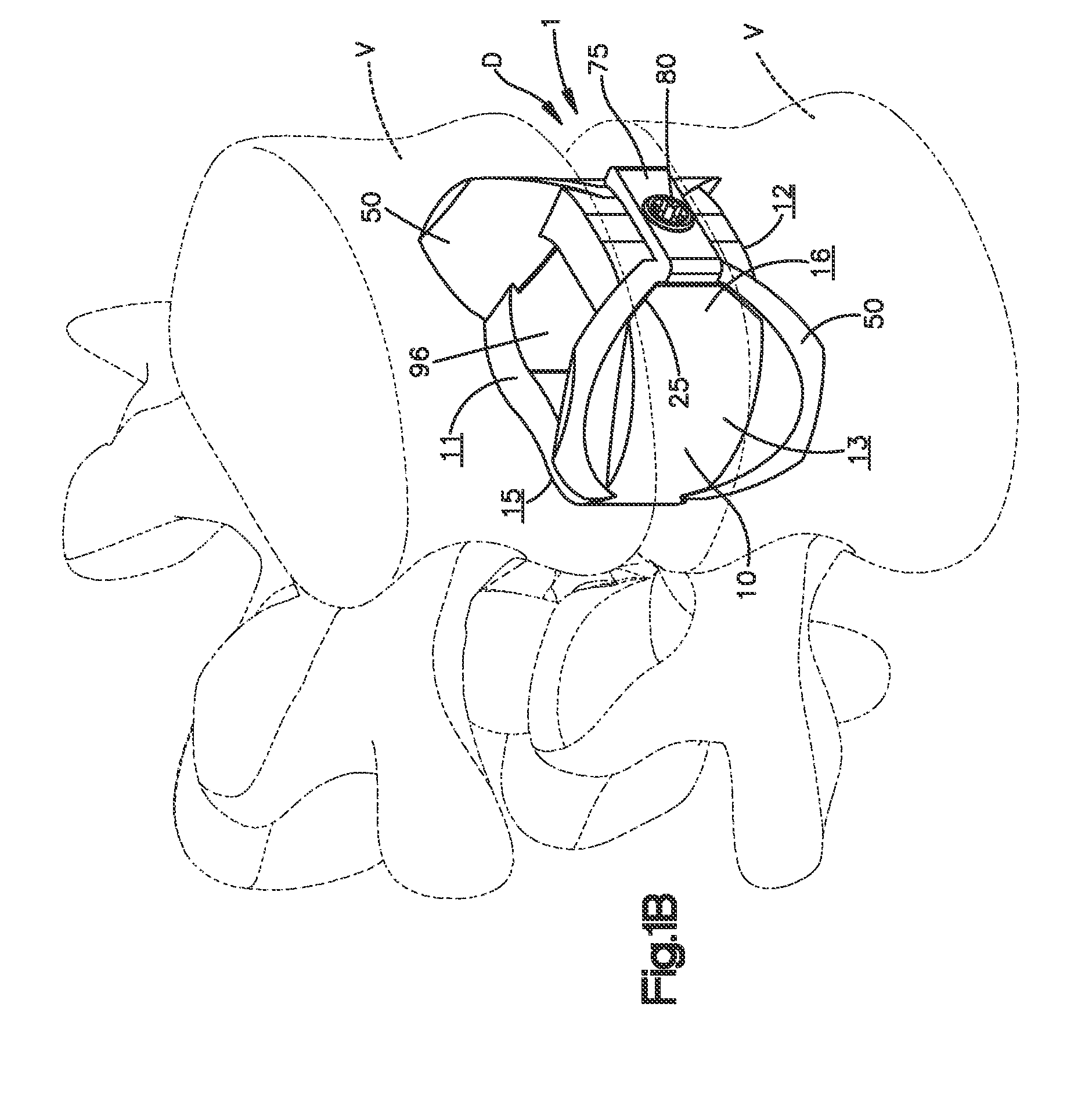
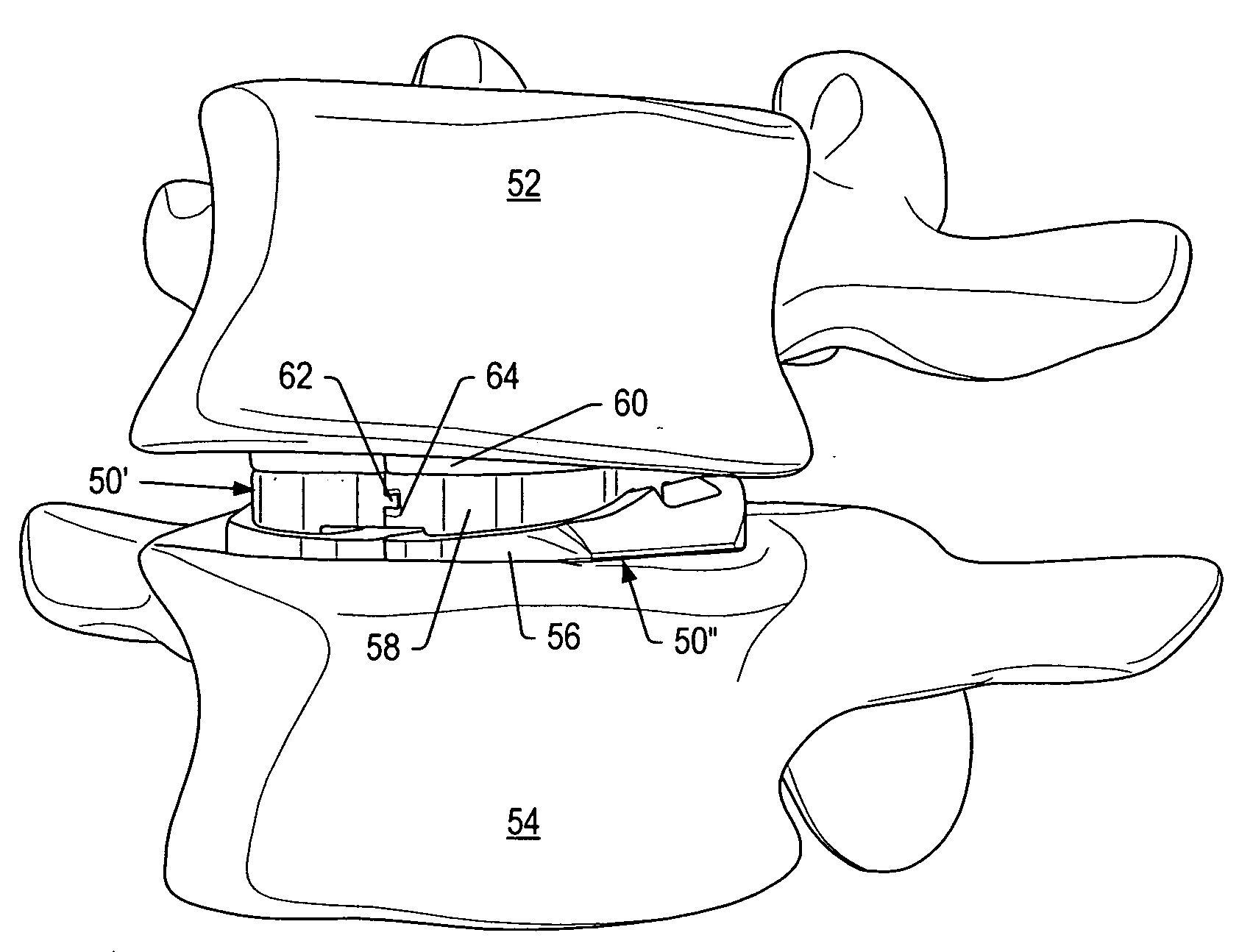
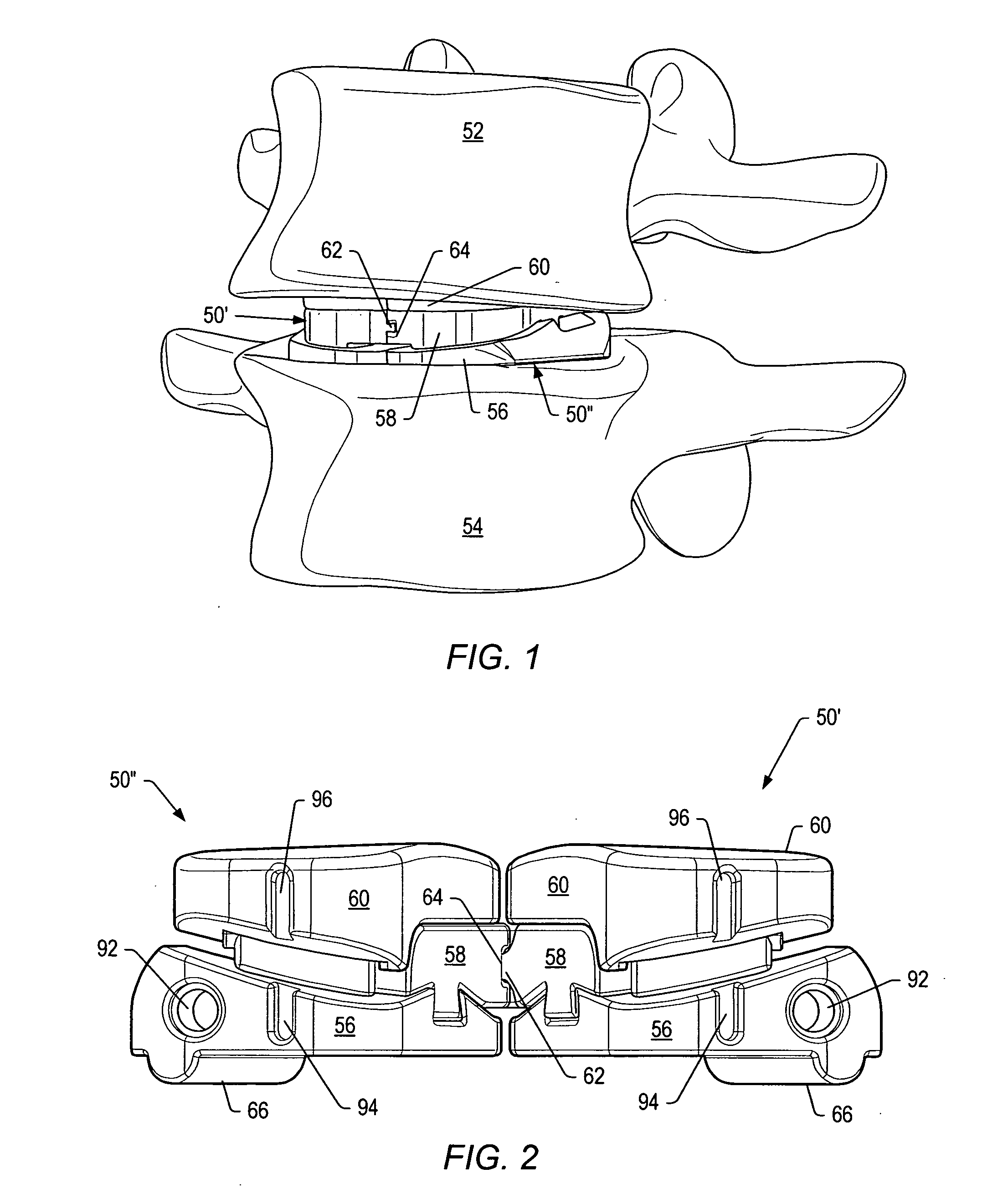
System and method for an intervertebral implant
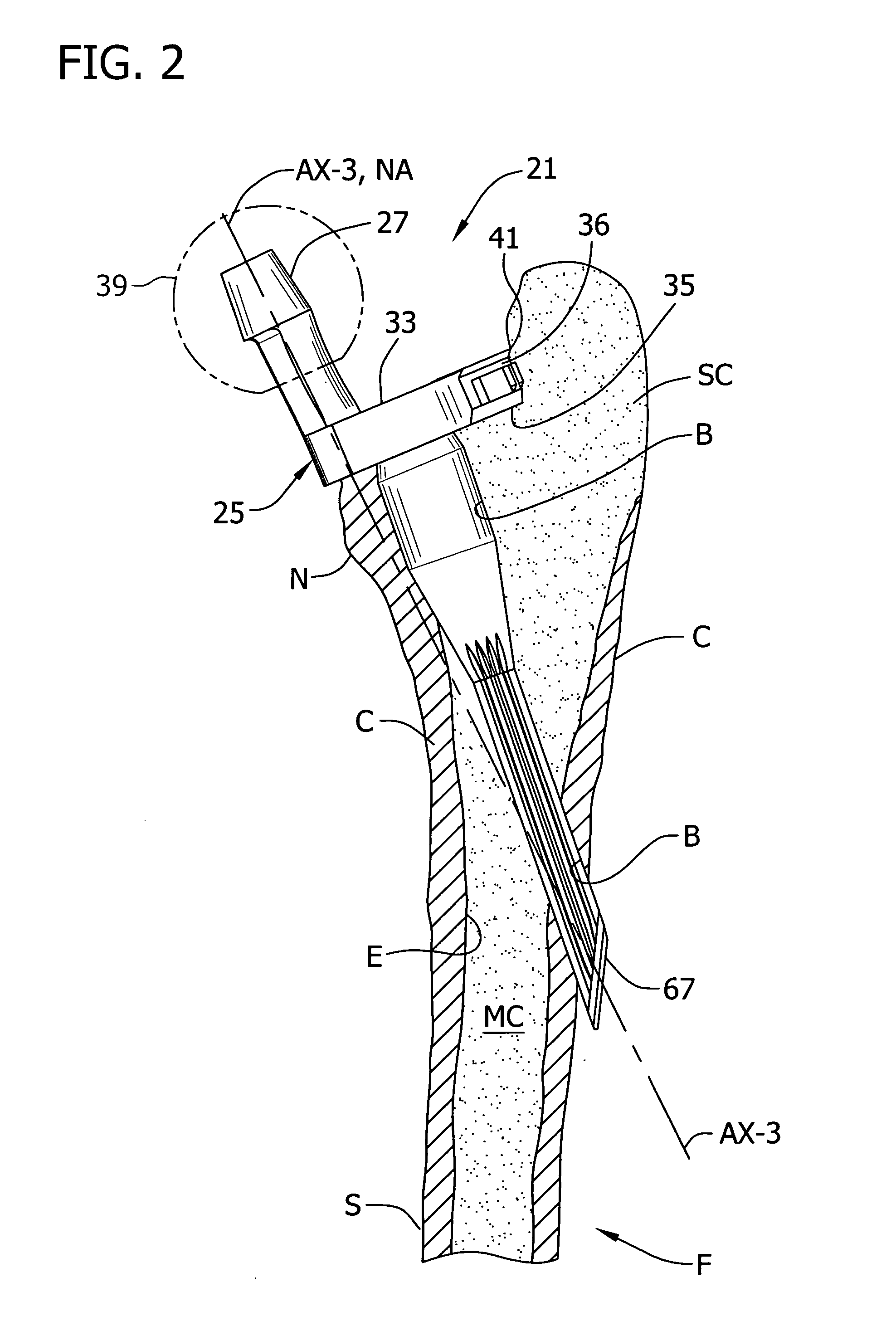
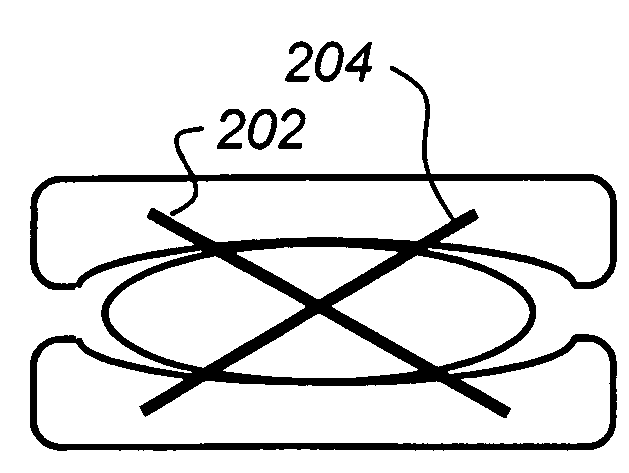
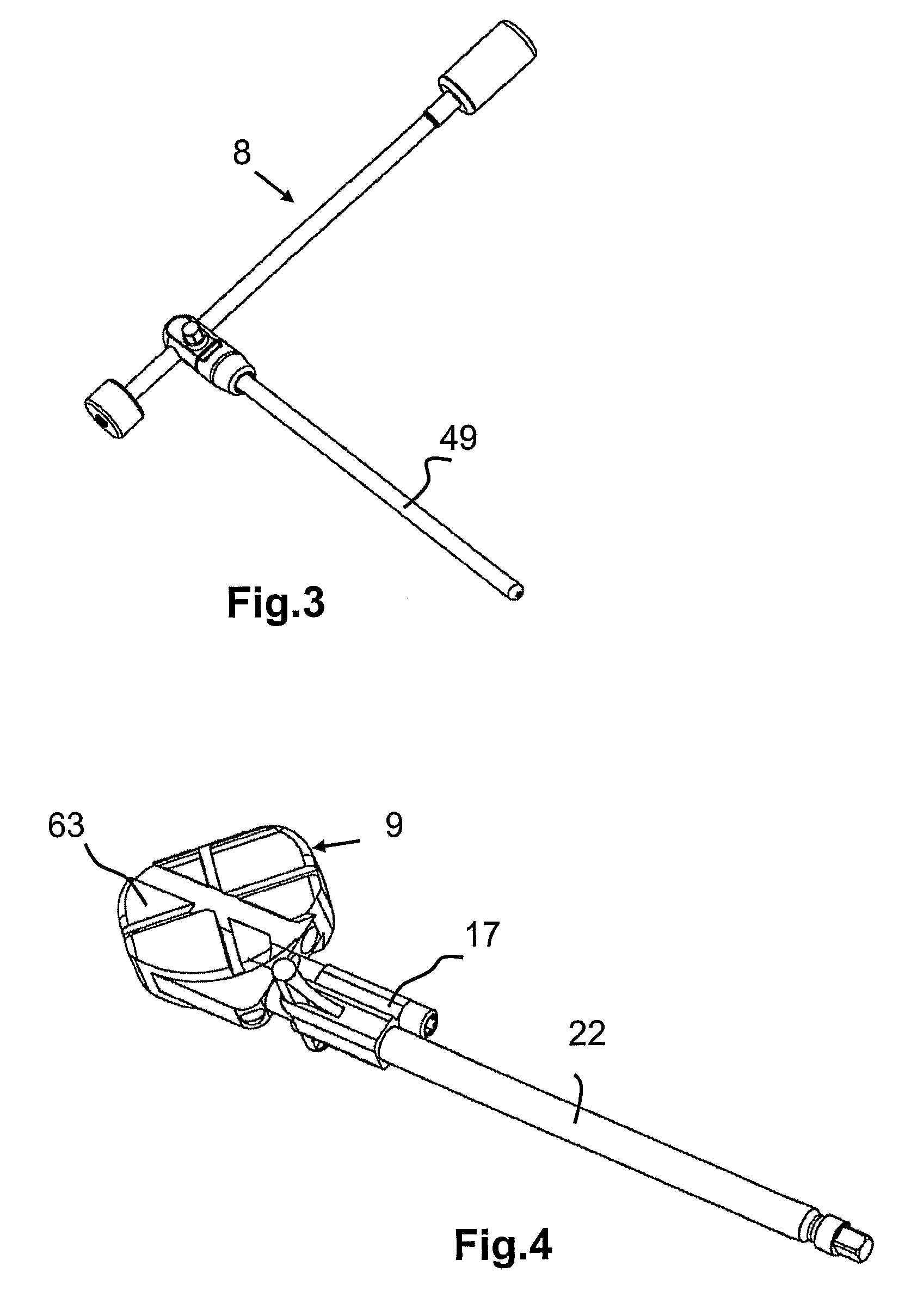
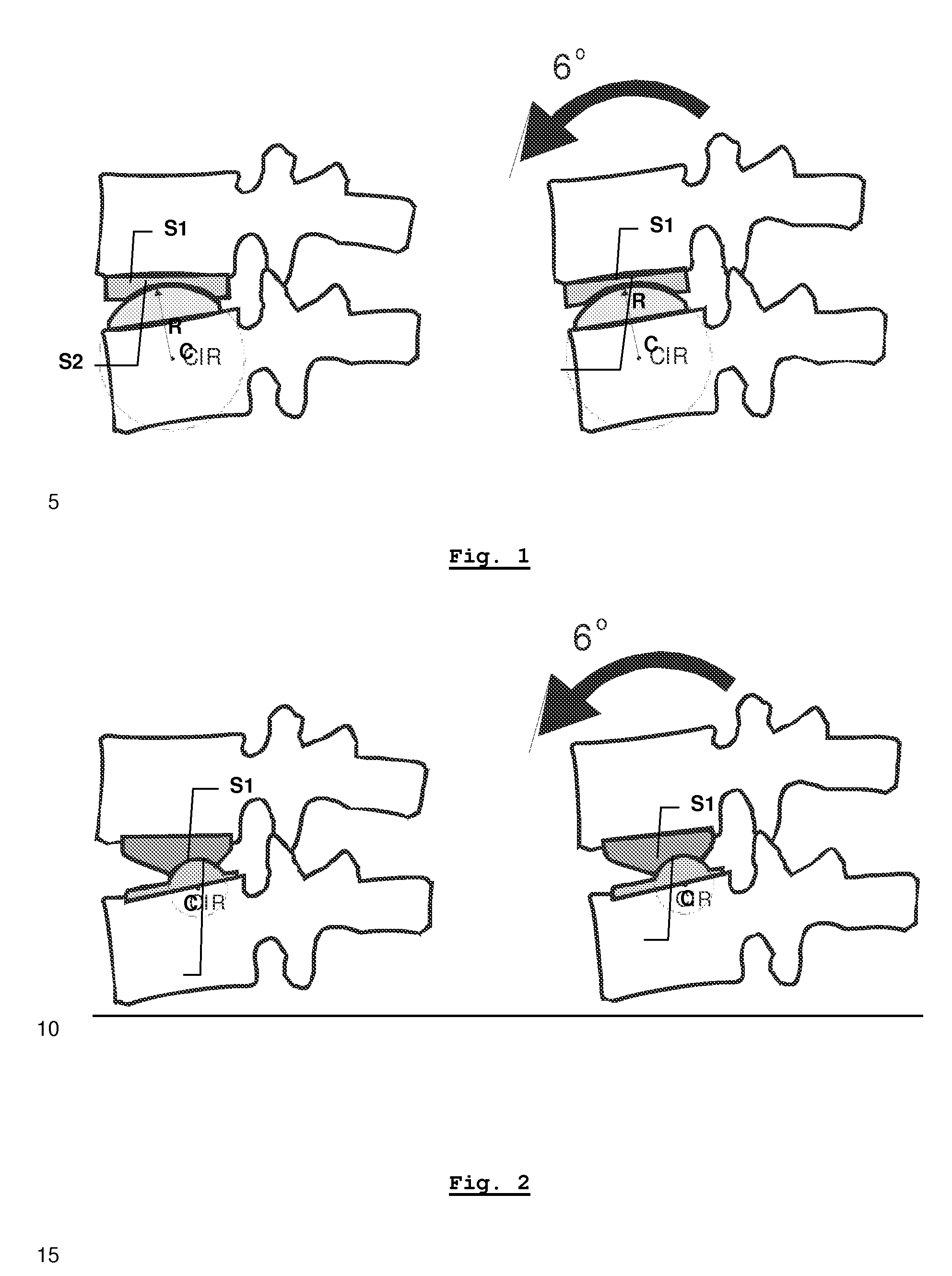
ActiveUS20090216330A1Easy accessEasy to produceDiagnosticsSpinal implantsIntervertebral spaceAnterior approach
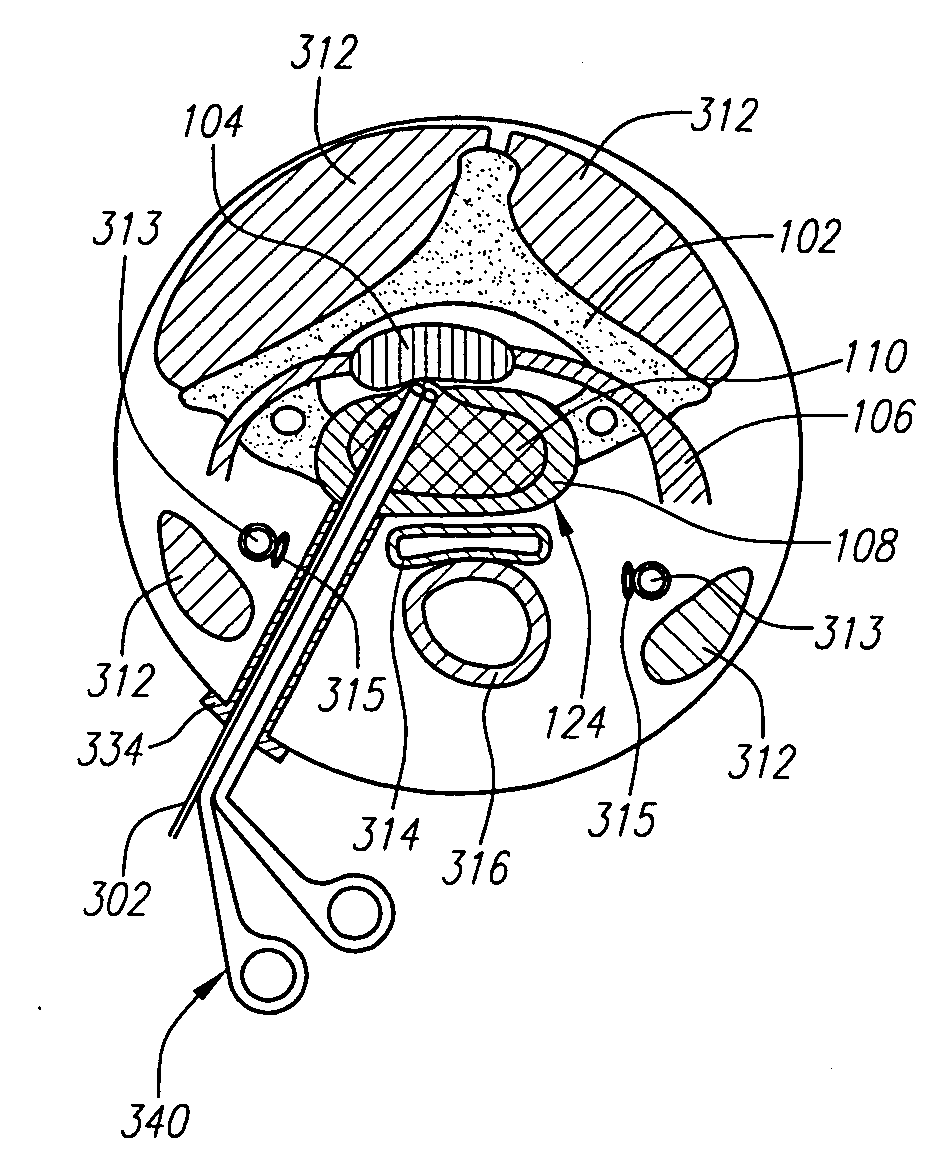
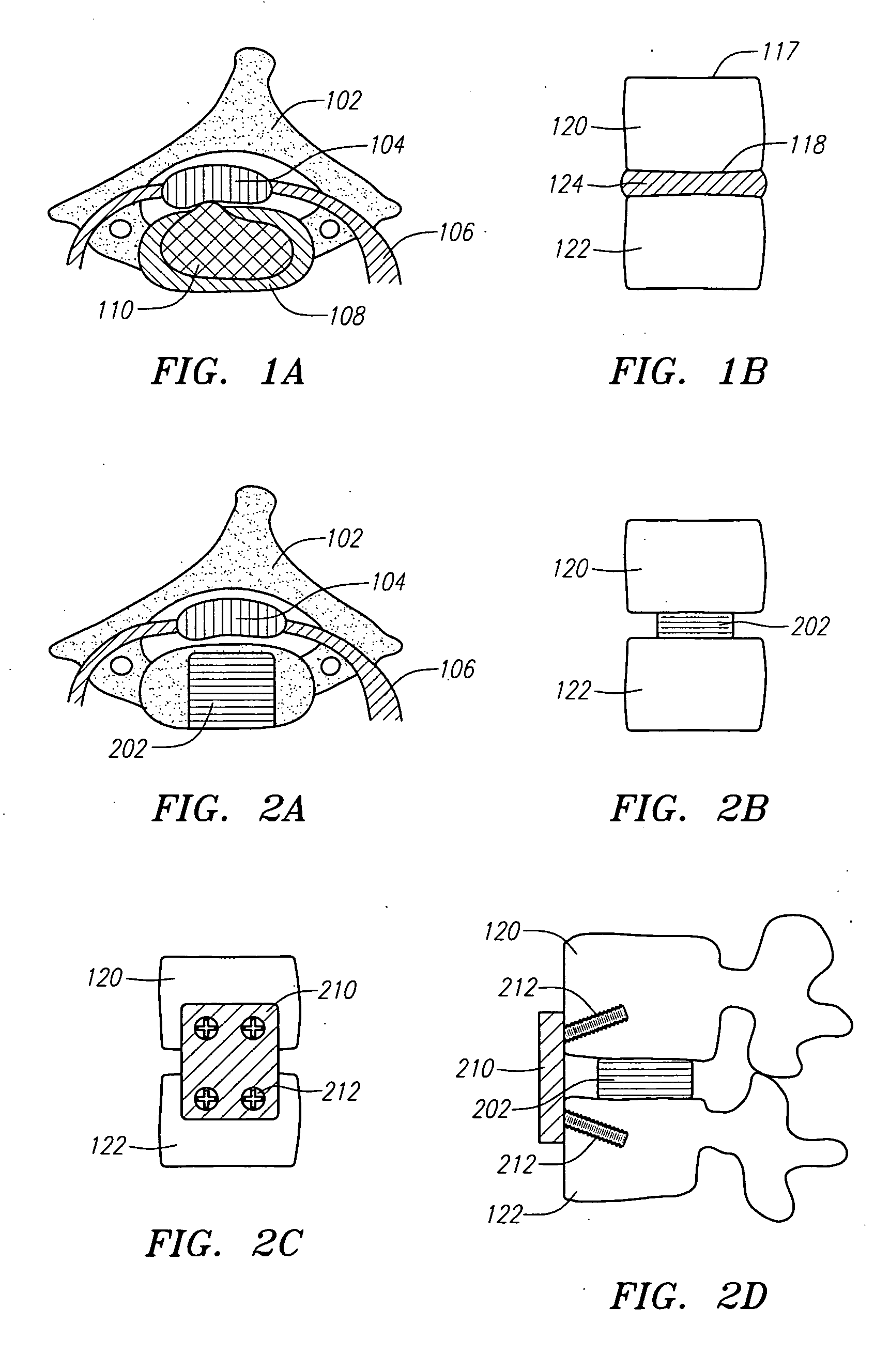
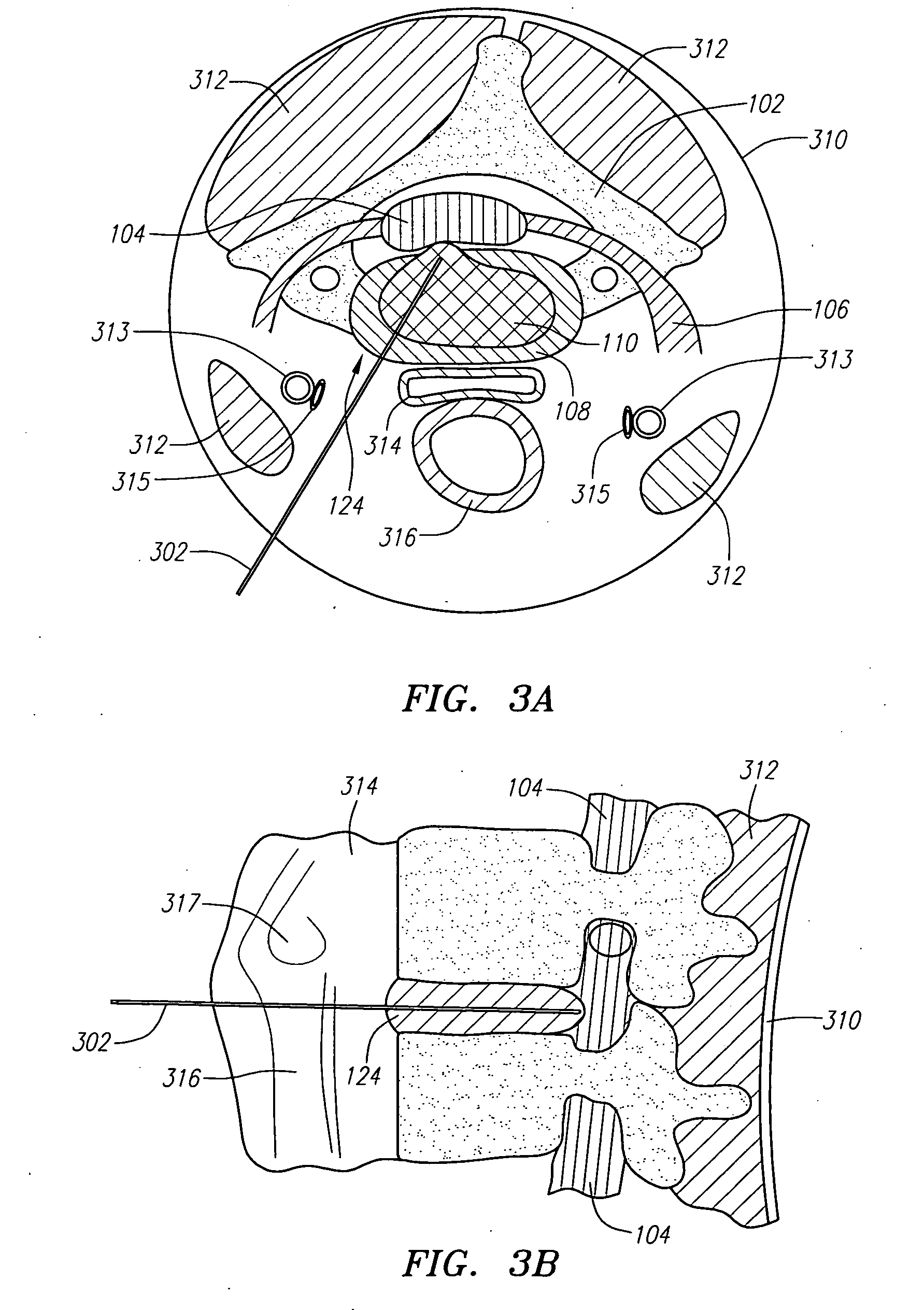
The invention relates to the preparation of an intervertebral space with a trial implant (9), the insertion of an implant (5, 6, 7), the inserters (13, 16), and the method for feeding and inserting the implant (5, 6, 7) by means of an oblique anterior approach. In the novel improved method, the associated instruments (13, 16) for inserting an implant (5, 6, 7) into an intervertebral space, in particular for the lumbar spine at an oblique anterior angle of 45° was developed, the left side of the body being preferred for insertion of the implant (5, 6, 7). Either the implant (5, 6, 7) can be inserted all in one, or first the upper part (5) and lower parts (7) and then the inlay (6) may be inserted. By insertion by means of the left oblique anterior approach at 45°, optimum utilization of the area of the intervertebral space is ensured (footprint), and better retention of the implant is guaranteed by the exact chiselling at an angle of 90° normal to the respective intervertebral surface.
Owner:CENTINEL SPINE LLC
Vertebrally-mounted tissue retractor and method for use in spinal surgery
InactiveUS20090088604A1Easy positioningEasy to insertInternal osteosythesisCannulasSurgical siteAnterior approach
A retractor system and associated method are provided to manage soft tissue around a spinal surgical field. The system includes a hollow retractor with proximal and a distal apertures and an internal circumferential surface connecting the apertures, the surface and the apertures defining an operating volume and the area of the distal aperture defining an operating field. The system may further include other elements such as a handling tool to facilitate placement and removal of the retractor, a bone cutting tool, a trajectory control sleeve to guide the bone cutting tool, and / or an implantable bone plate upon which to position the retractor. A method for spinal surgery, particular from an anterior approach, includes positioning the retractor at a surgical site, and performing a medical procedure through the operating volume provided by the retractor.
Owner:TRANS CORP
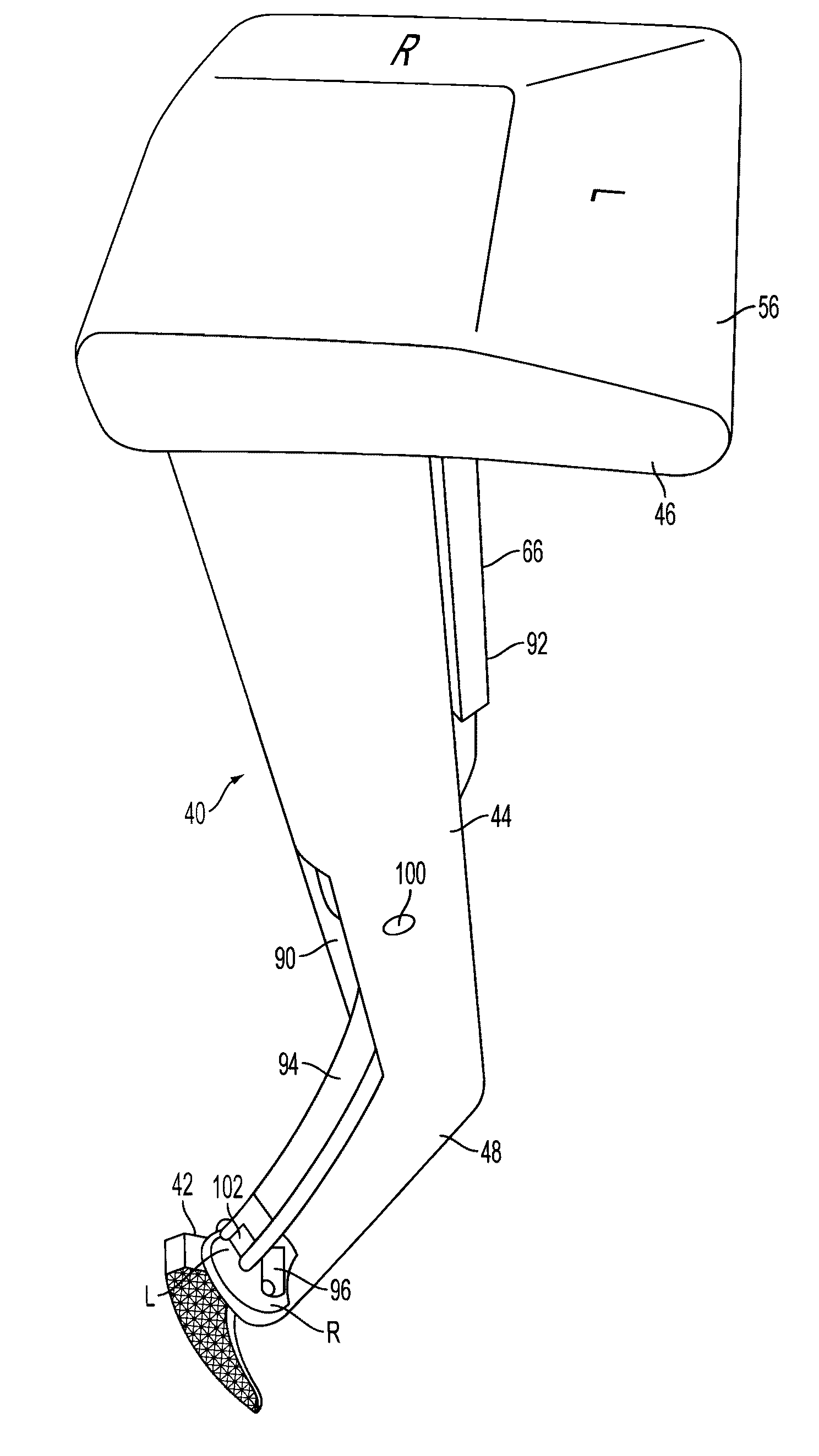
Universal double offset surgical instrument
Instruments for use in anterior approach total hip arthroplasty. Instruments according to certain embodiments of the invention connect to a shaping member such as a broach, reamer or osteotome that is used to prepare the intramedullary canal of a desired femur or other bone for total hip arthroplasty. Such an instrument according to such embodiments can be configurable to allow operation on either the left or right leg, and in doing so to provide lateral offset and anterior offset of the instrument handle relative to the shaping member so that the patient's gut, musculature or other bodily portions may be avoided while still providing desired leverage and control over the shaping member to prepare the intramedullary canal.
Owner:SMITH & NEPHEW INC
Methods and instrumentation for vertebral interbody fusion
InactiveUS7244258B2Reduced width configurationDiagnosticsJoint implantsSpinal columnAnterior approach
Methods and instrumentation particularly adapted for disc space preparation for insertion of implants from an anterior approach to the spine are provided. The instruments include a guide sleeve defining a channel having overlapping cylindrical working channel portions and lateral non-distracting extensions extending from reduced thickness wall portions. The guide sleeve has an overall reduced width configuration. A pair of distractors are provided. A first distractor includes a shaft and distal tip, each having convex walls. A second distractor includes a shaft and distal tip including a recessed area at least along the tip. The first distractor is at least partially received within the recessed area of the second distractor when the first and second distractors are in side-by-side relation and a reduced overall width of the distractors is obtained. Preferably, the first and second distractors are used with the guide sleeve. Methods using the disclosed instruments are also provided.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Anterior cervical spine instrumentation and related surgical method
InactiveUS20080046084A1Avoid expulsionShorten the timeInternal osteosythesisSpinal implantsIntervertebral spaceGraft size
In various exemplary embodiments, the present invention provides a set of less invasive cervical spine instruments that are used to achieve cervical disc decompression, bone preparation, and the alignment of one or more matched sized bone grafts prior to cervical plate placement. This set of less invasive cervical spine instruments, and the related surgical method, result in reduced surgical time, the preparation of a precise machined bone surface while simultaneously maintaining the cervical disc decompression height of the intervertebral endplates, the selection of one or more prefabricated bone dowel grafts sized to match the machined bone surface and maximizing the surface contact required for cervical spine fusion, the placement of the one or more prefabricated bone dowel grafts (e.g. side by side) that can be of different diameters in order to fully exploit the intervertebral space available, and the alignment of the cervical plate using a cervical spine instrument that is matched to align with the one or more prefabricated bone dowel grafts beneath the cervical plate.
Owner:US SPINE INC
Static anterior cervical plate
ActiveUS20050177161A1Avoid displacementAvoid traumaInternal osteosythesisFastenersIntervertebral spaceAnterior approach
A bone plate for use in anterior cervical spinal fixation has interlocking components to prevent dislodgement of the plate due to anatomical forces. The plate is formed in the shape of a block letter C and the exposed surface is smooth to prevent trauma to internal body tissue. The plate spans the intervertebral space with each end attached to an adjacent vertebrae by bone screws threadably engaged with the bone. The distal ends of the bone screws The plate has a screw lock in each end for preventing the locking screws from backing out.
Owner:ATLAS SPINE
Anterior cervical plating system and method
InactiveUS20070203492A1Easy to fuseEasy to incorporateInternal osteosythesisBone platesSpinal columnAnterior approach
The present invention is directed to a system for anterior fixation of the spine that utilizes an elongated fixation plate. The plating system stabilizes the spine and promotes fusion and incorporation of a graft or implant in a portion of the spinal column. In one aspect of the invention, the fixation plate has a first end with a pair of holes. Bone screws extend through the holes to rigidly secure the plate to a first vertebra. The second end of the plate is provided with a pair of slots through which bone screws extend for engagement with a second vertebra. The screws extending through the slots are translatable in the slot to maintain compression of the spinal column portion. The plating system includes a retainer assembly that prevents screw back out. Methods and instruments relating to the plating system are also described.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Method and instrumentation for vertebral interbody fusion
InactiveUS7776046B2Reduce in quantityLimit amount of retractionDiagnosticsInvalid friendly devicesDistractionSpinal column
A method and instrumentation particularly adapted for disc space preparation from an anterior approach to the spine. In one aspect, an expandable template is provided having guides to guide a cutting device for bilateral formation of openings in the disc space. In another aspect, an improved guide member is provided for guiding a cutting tool. Still further, the invention provides an improved double barrel guide sleeve with a central distraction extension and lateral non-distracting extensions. Optionally, the guide sleeve includes windows and covers to selectively cover the windows. An improved reamer with an internal chamber and optional modular coupling is also provided. A depth stop is provided to selectively engage a tool shaft and a guide sleeve to control tool penetration into the disc space. A method of using the disclosed instruments is also provided.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Dynamic extension plate for anterior cervical fusion and method of installation
An osteosynthetic plate assembly and a method of installing the osteosynthetic plate assembly is disclosed. The osteosynthetic plate assembly comprises a dynamic extension plate having a first end portion for connection to a first vertebrae, a second end portion for connection to a second vertebrae, and a dynamic flexible portion extending between the first and second end portions. The dynamic extension plate is configured for coupling with a cervical fusion plate. A method of installing the dynamic extension plate to adjacent vertebrae comprises the steps of engaging a connector of the dynamic extension plate with a coupling of a cervical fusion plate, and mounting the dynamic extension plate to the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:AESCULAP INC
Intervertebral disc prosthesis for universal application
InactiveUS20090082867A1Improve wear resistanceStable frictionSpinal implantsInstabilityBiocompatibility Testing
An Invertebral Disc Model Prosthesis, of the type denominated of double articulation, to substitute the function and the movement of intervertebral discs, for universal application due to its principal characteristic of being able to be used as a constrained, semi-constrained or non-constrained prosthesis, specially indicated for treatment of pathological degenerative of the intervertebral discs, discal hernias, by anterior approach, transition syndromes of supra-adjacent disc, chronic lumbagos resistant to conserver treatment, chronic adjacent vertebral instability, made from materials of proved biocompatibility, endowed with a low profile that makes it optimum for its implant in the human being and which consists of three pieces, two plates, upper and lower, and am intermediate piece , which serves for the substitution of the discs of the lumbar and cervical column, capable of being placed by the anterior or lateral approach.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Anterior cervical plating system
The present invention relates to systems and methods for spinal fusion. More particularly, one embodiment of the present invention relates to an anterior cervical plating system.
Owner:ORTHOFIX US LLC
Anterior Lumbar Fusion Method and Device
ActiveUS20140277502A1Area maximizationAdd supportJoint implantsSpinal implantsLumbar vertebraeAnterior approach
A method and devices for placing spinal implants including placing the implants completely within a spaced defined between adjacent vertebral bodies where the implants are supported by the cortical bone of the vertebral bodies. An insertion instrument places the implants in pairs with a variable-sized space placed in between. The implants are made of a biocompatible material and are particularly suited for anterior lumbar interbody fusion surgery. The spinal implants used to facilitate spinal fusion, correct deformities, stabilize and strengthen the spine.
Owner:NUTECH SPINE
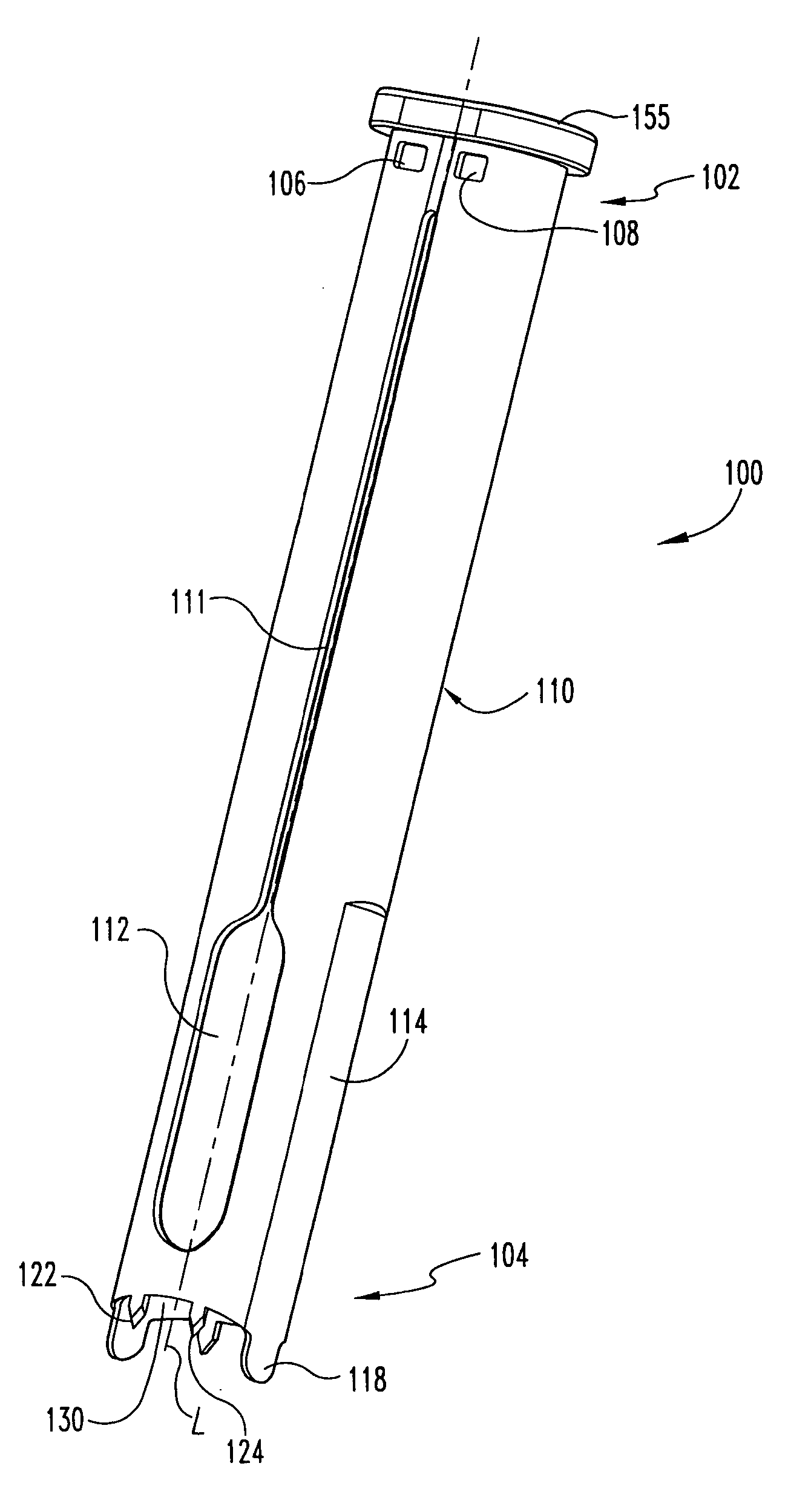
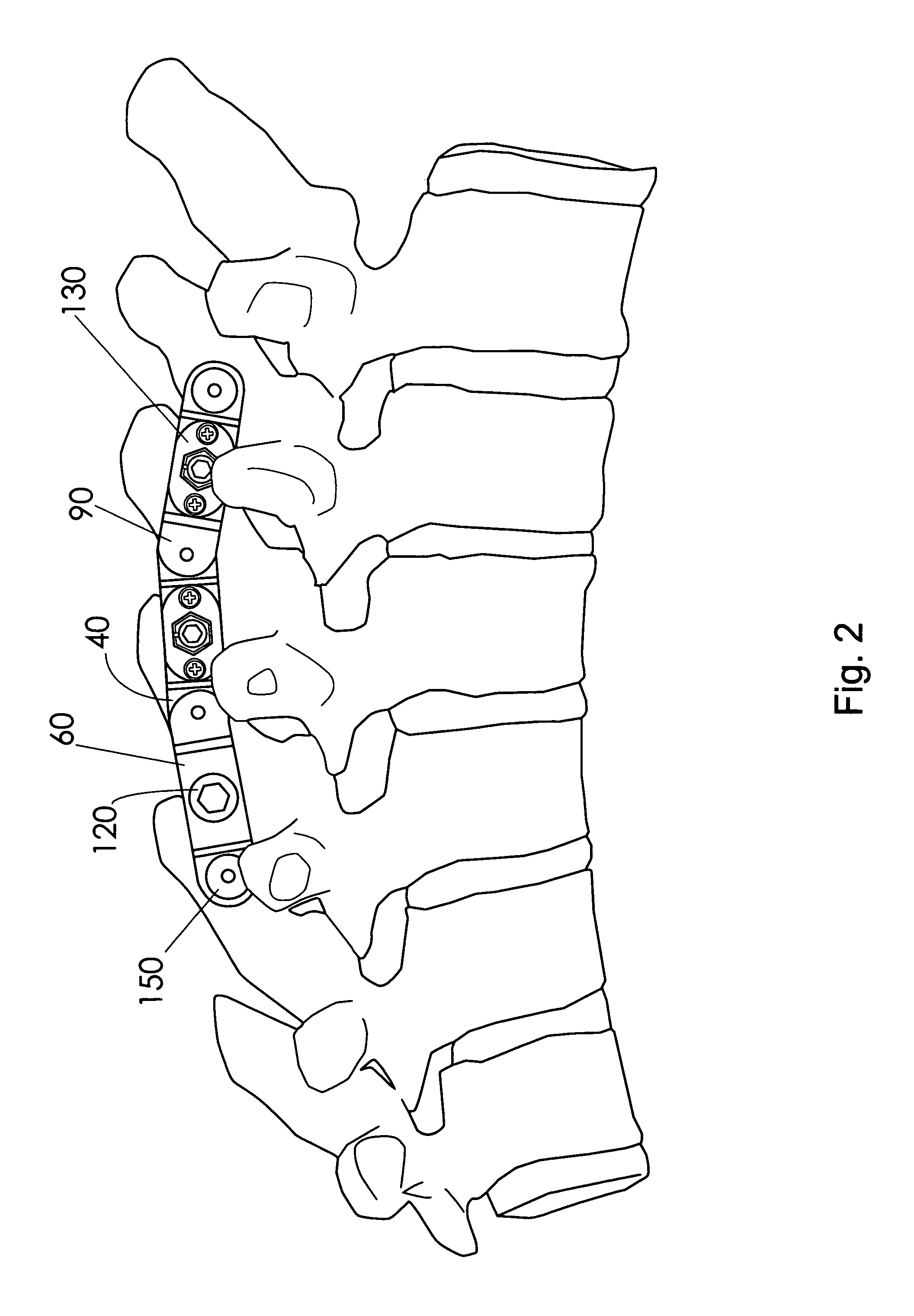
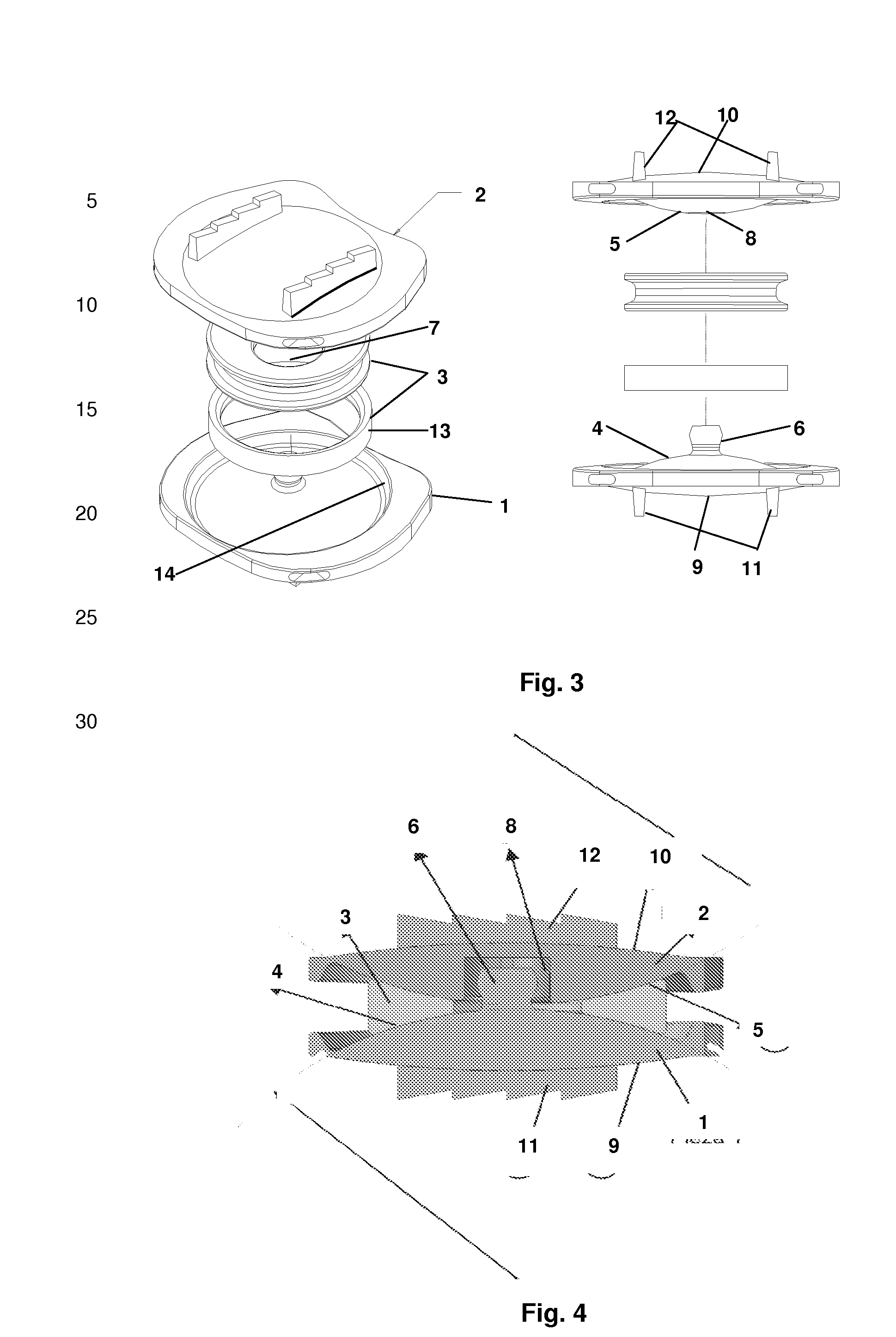
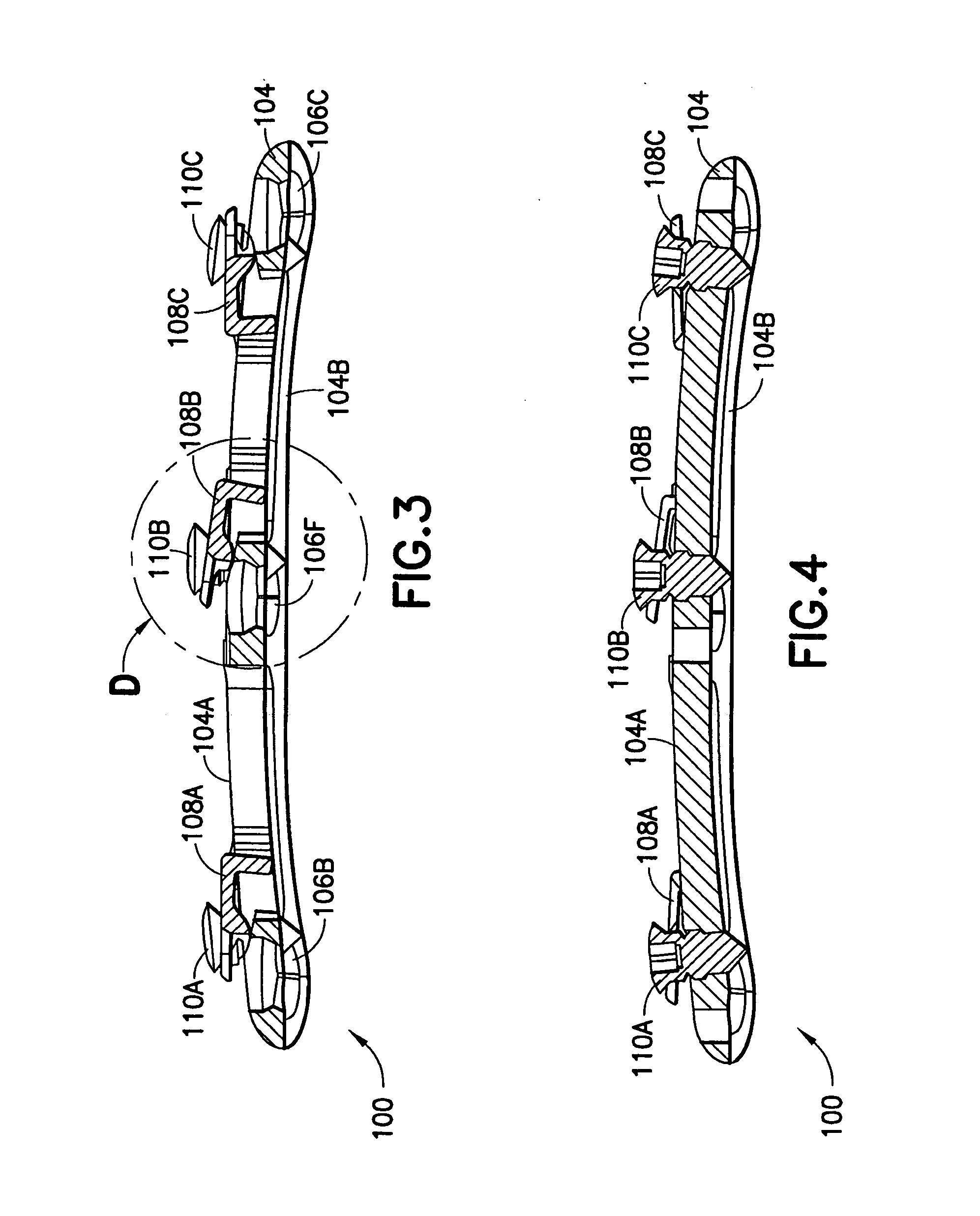
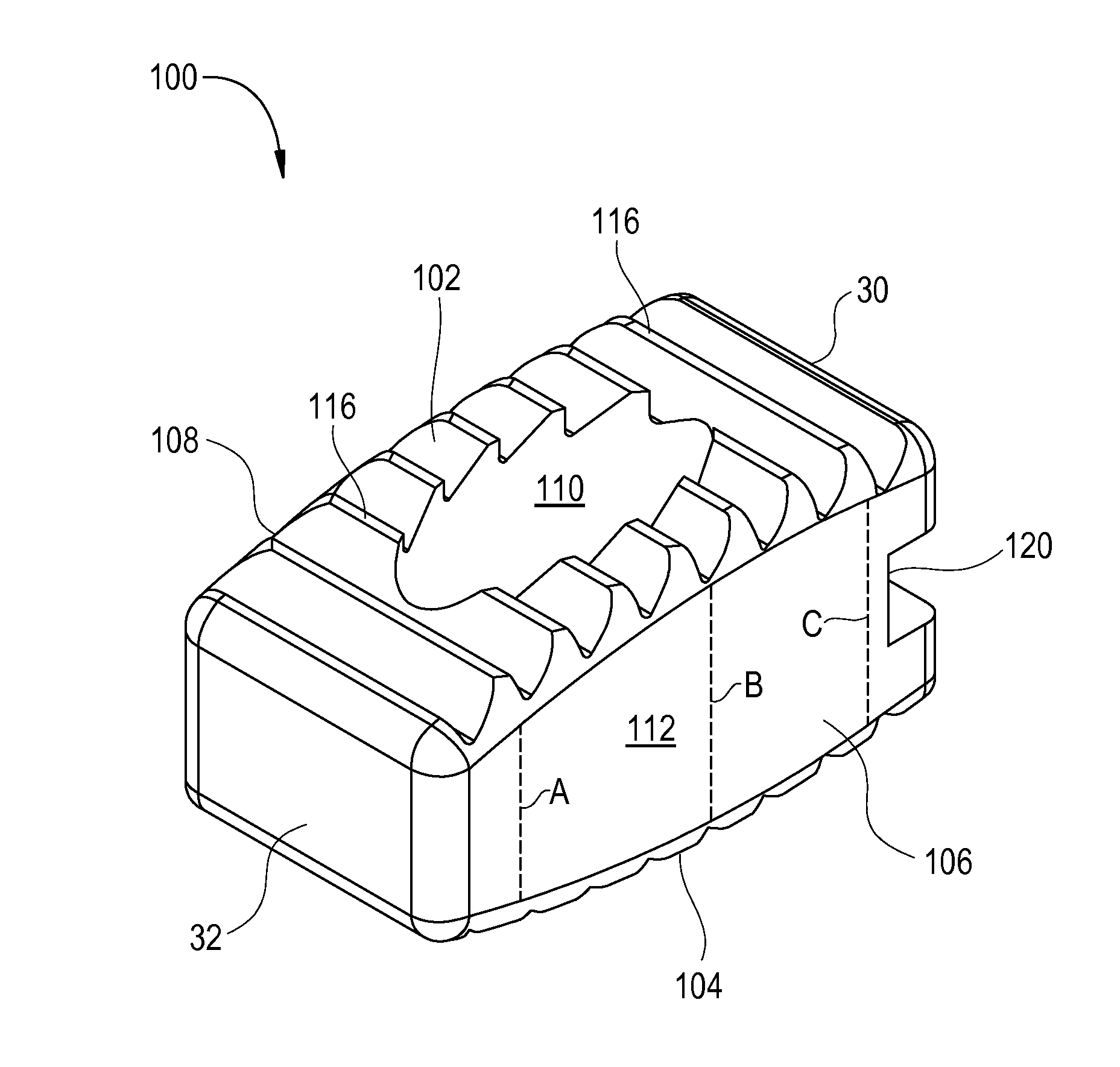
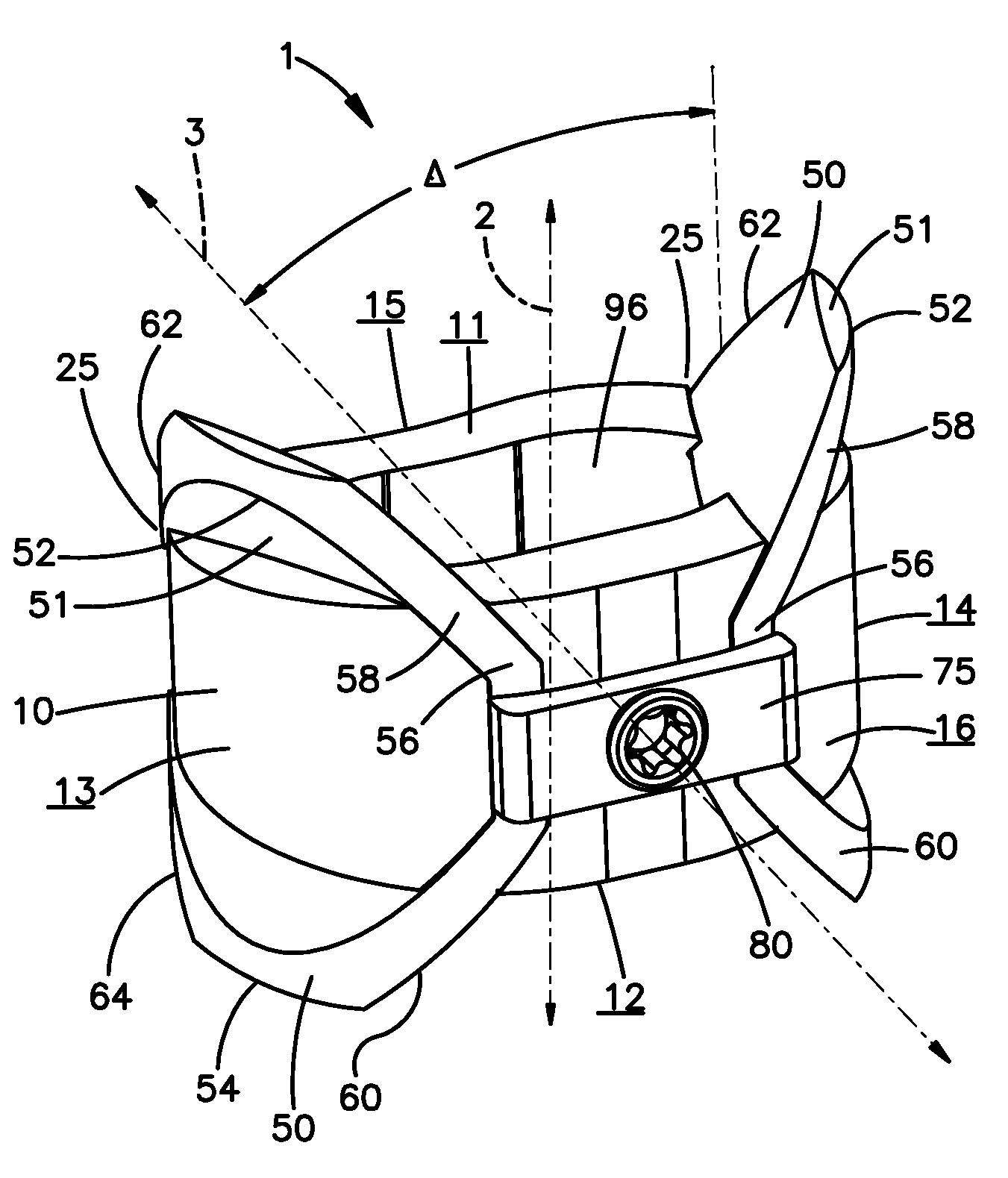
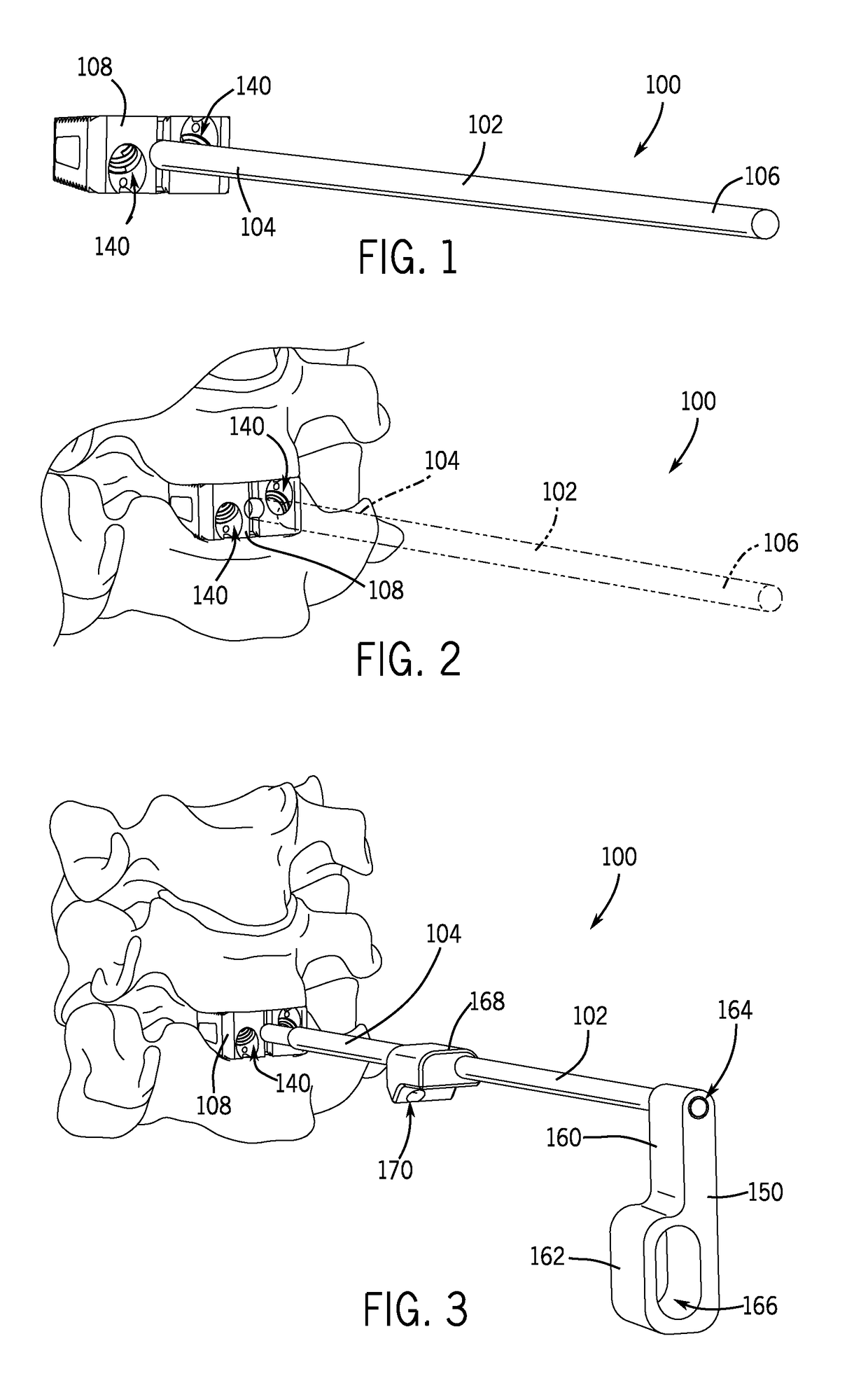
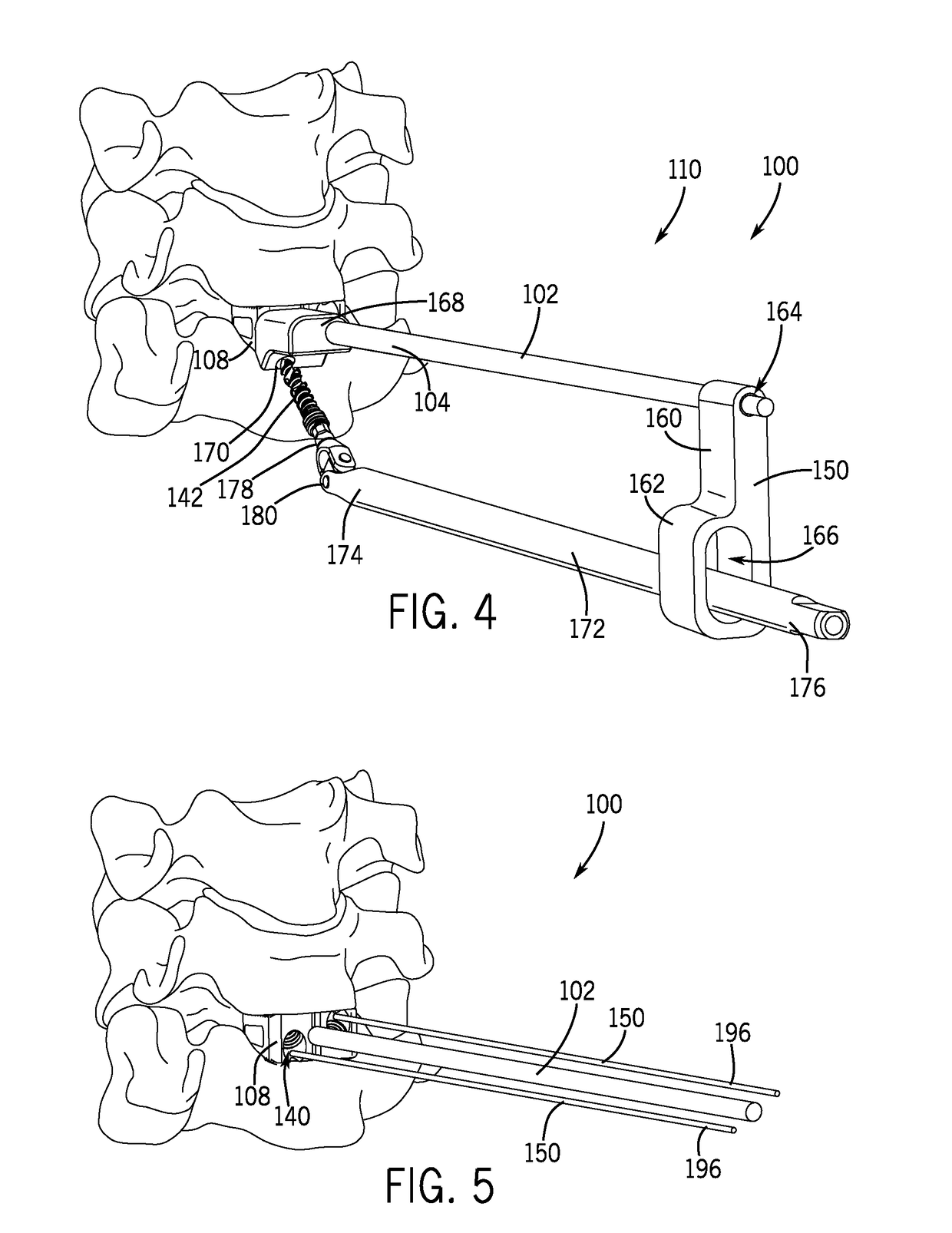
Intervertebral implant with blades for connecting to adjacent vertebral bodies
An intervertebral implant (300) for insertion into an intervertebral disc space between adjacent vertebral bodies or between two bone portions. The implant includes a spacer portion (310), a plate portion (330) operatively coupled to the spacer portion and one or more blades (350) for securing the implant to the adjacent vertebral bodies. The blades preferably include superior and inferior cylindrical pins (360) for engaging the adjacent vertebral bodies. The implant may be configured to be inserted via a direct lateral transposals approach. Alternatively, the implant may be configured for insertion via an anterior approach.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
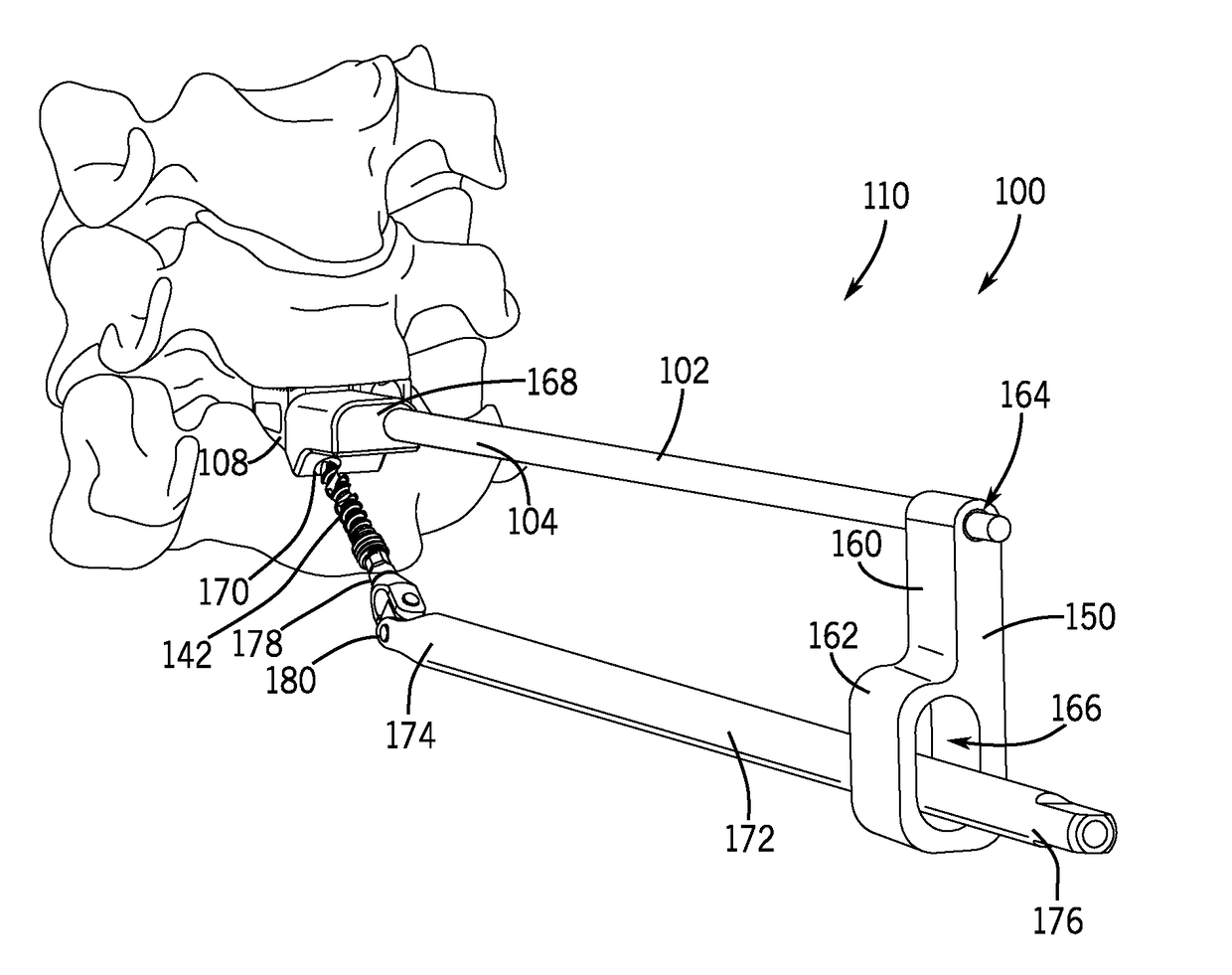
Spinal joint implant delivery device and system
ActiveUS20180303631A1Minimal tissue retractionPrevent rotationInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnIntervertebral joint
Provided herein are devices, systems, apparatus and methods for accessing the cervical spine via an anterior approach and implanting a spinal fixation member between two vertebrae of the cervical spine in the disc or intervertebral joint space, such as in an ACDF procedure. The delivery device includes a distal end that can be anchored to the spinal fixation member. Once anchored to the spinal fixation member, the delivery device is operable to both advance and attach the spinal fixation member within a cervical disc joint space.
Owner:PROVIDENCE MEDICAL TECH
Artificial functional spinal unit system and method for use
A method of stabilizing a human spine is provided. The spine may be stabilized by inserting one or more dynamic interbody devices in a disc space between a first vertebra and a second vertebra. A dynamic interbody device may be inserted using an anterior approach. One or more dynamic interbody devices may be inserted using a posterior approach. One or more of the dynamic interbody devices may allow for coupled axial rotation and lateral bending of the first vertebra relative to the second vertebra. The spine may also be stabilized by installing one or more posterior dynamic stabilization systems.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE INC
Vertebral Body Replacement and Insertion Methods
ActiveUS20170304066A1Small openingShorten recovery timeDiagnosticsSurgeryAnterior approachVertebral bone
A vertebral body replacement device, dimensioned for implantation between a first and second vertebral bone is described. The vertebral body replacement device includes a superior endcap, an inferior endcap and a central core between the superior and inferior endcaps. The vertebral body replacement device further includes a fusion aperture extending through the superior and inferior endcaps and central core. The vertebral body replacement device is made of radiolucent material and can be implanted from a lateral or anterior approach to the spine.
Owner:NUVASIVE
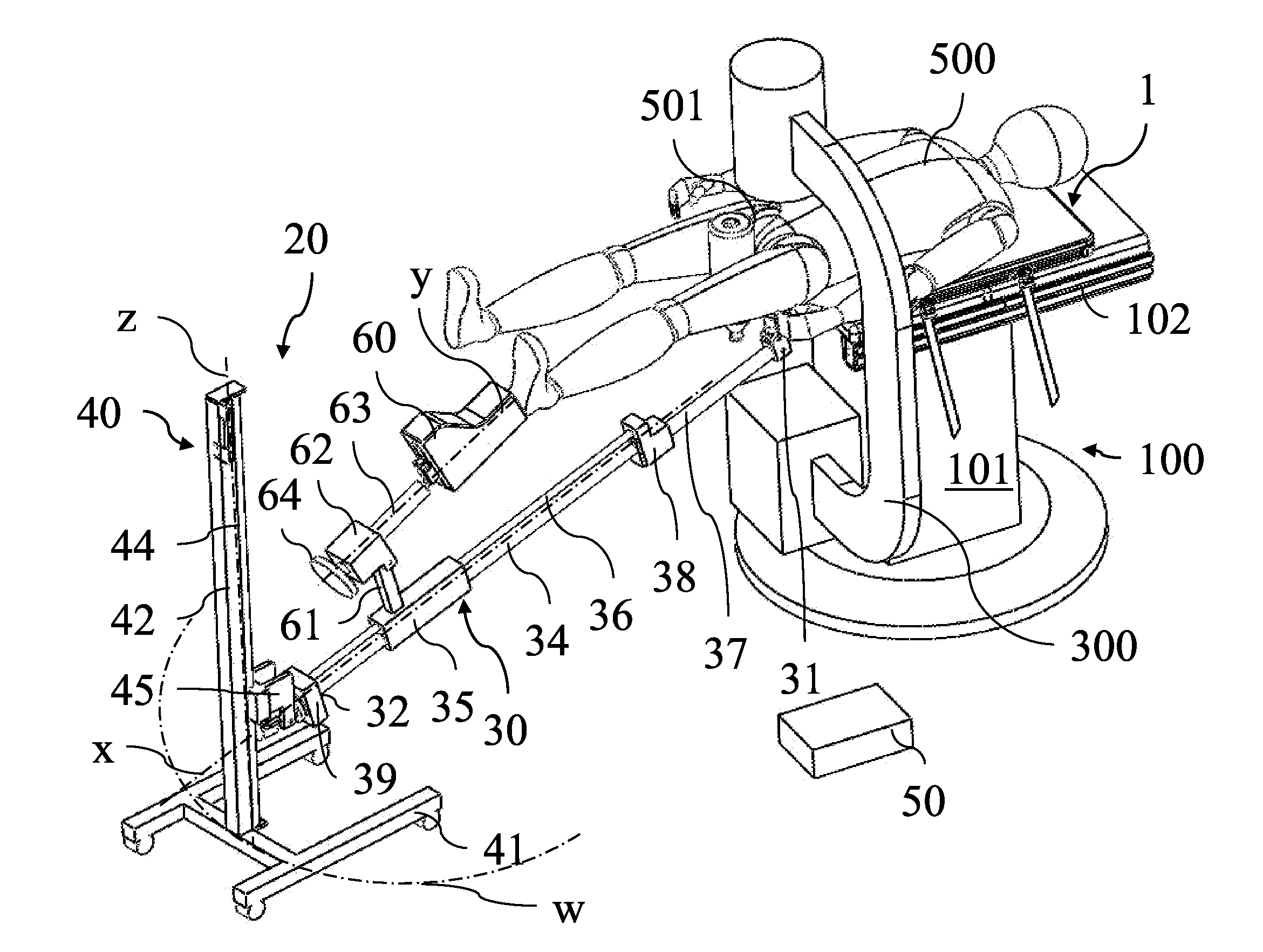
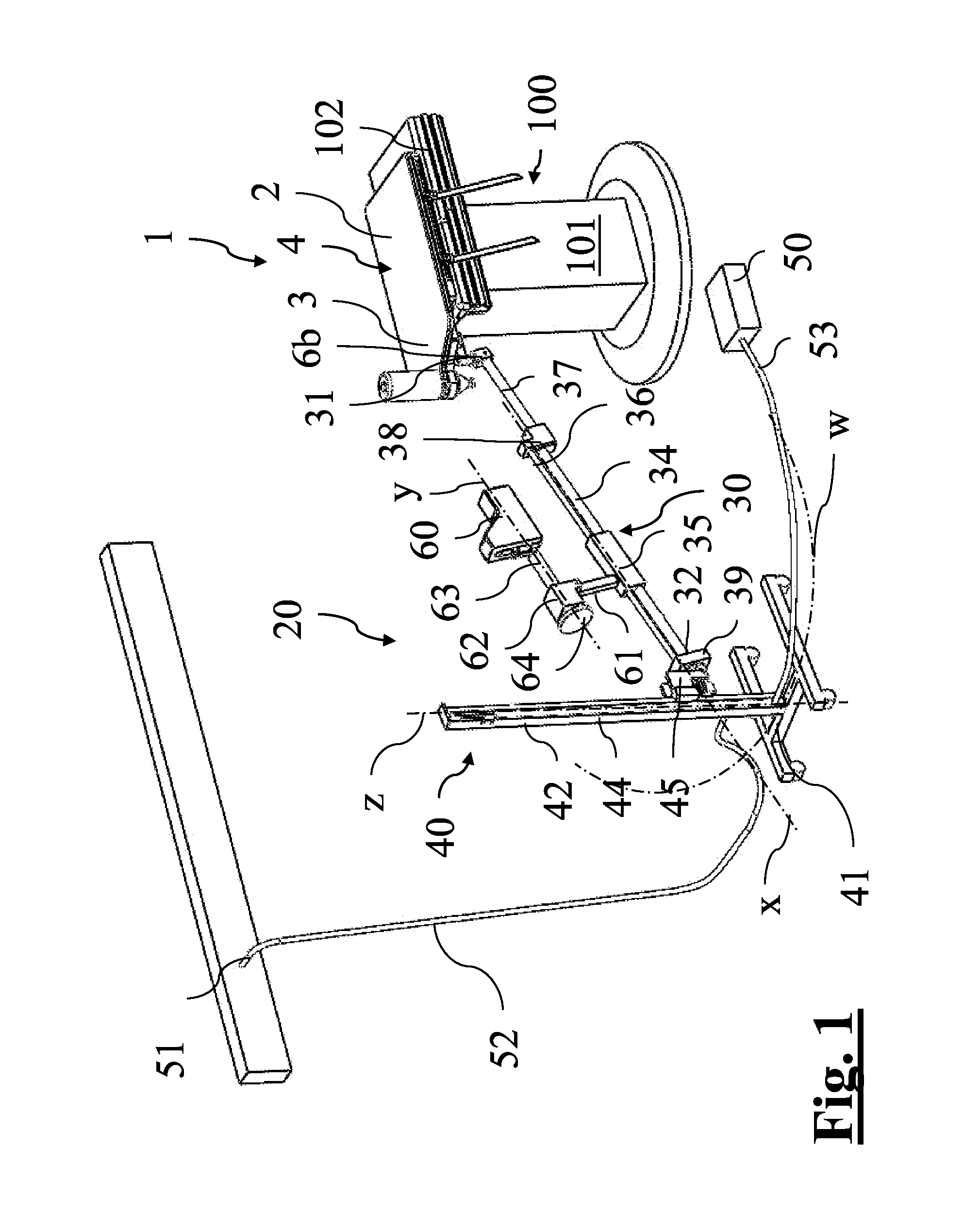
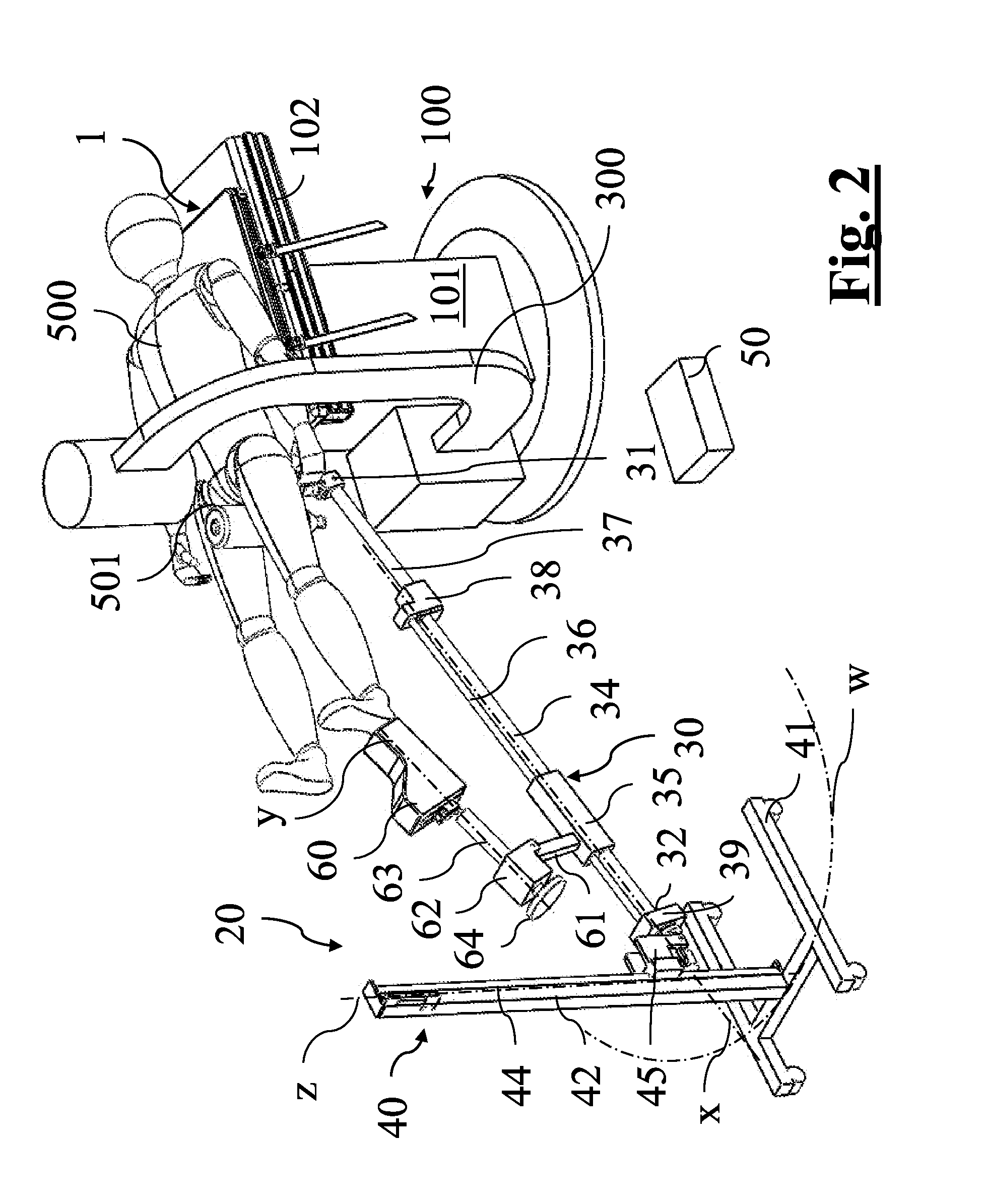
Adapter plane for surgical table, in particular for hip replacement surgery with anterior approach
ActiveUS20150245971A1Relieve pressurePrevent forward movementOperating tablesPatient positioning for diagnosticsHip joint replacement operationMuscles of the hip
Adapter plane (1′) for surgical table, comprising a main portion (2′) and a secondary portion (3′) which define—at the top part—a surface (4′) for supporting the patient, said secondary portion (3′) being arranged for supporting at least one pelvis portion of the patient, said adapter plane (1′) being rigidly couplable above said surgical table with the main portion (2′) overlapping the surgical table and the secondary portion (3′) projecting with respect to the surgical table, at least the secondary portion (3′) of said adapter plane (1′) being made of radiotransparent material.
Owner:MEDACTA INT SA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com