Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
94 results about "Lateral approach" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
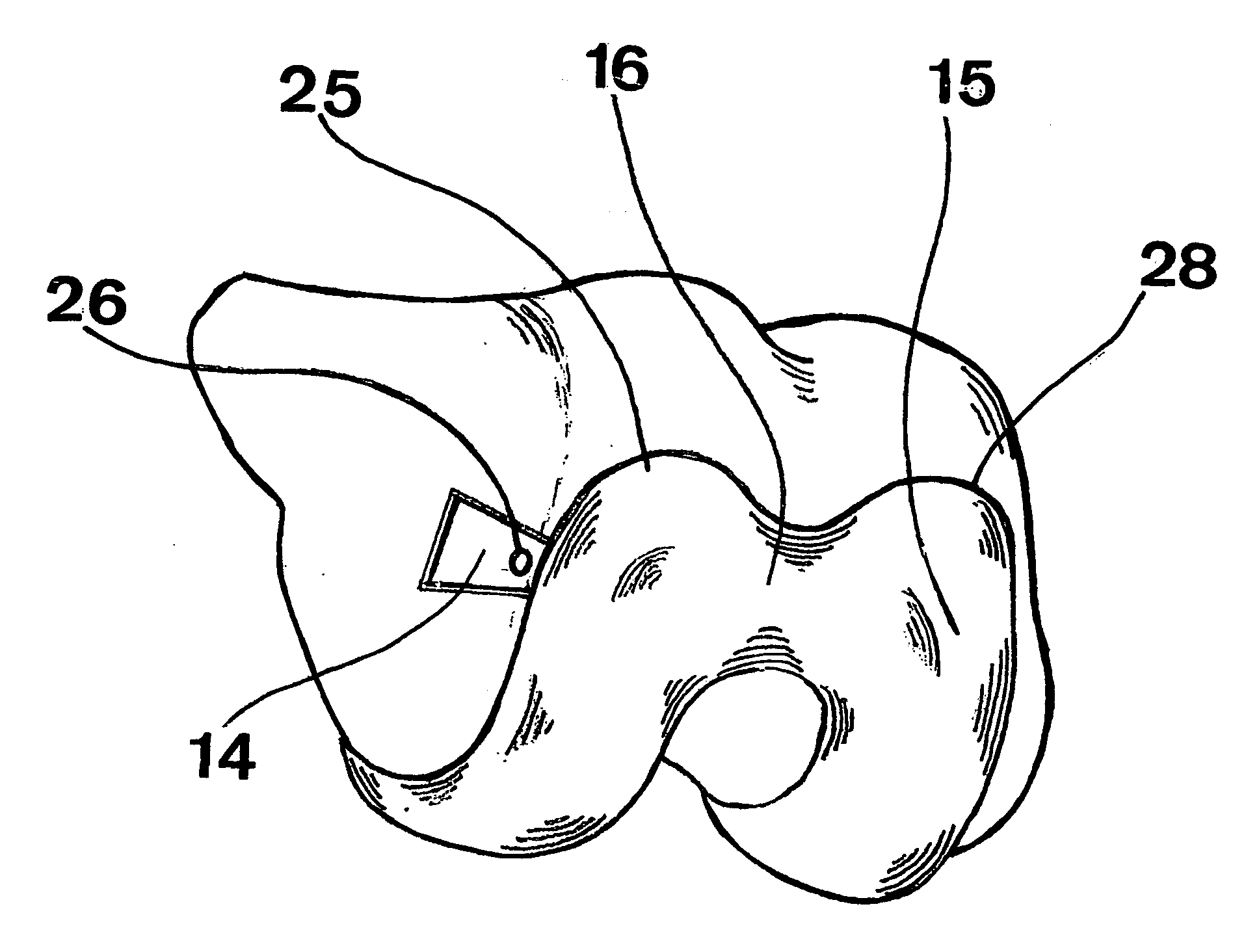
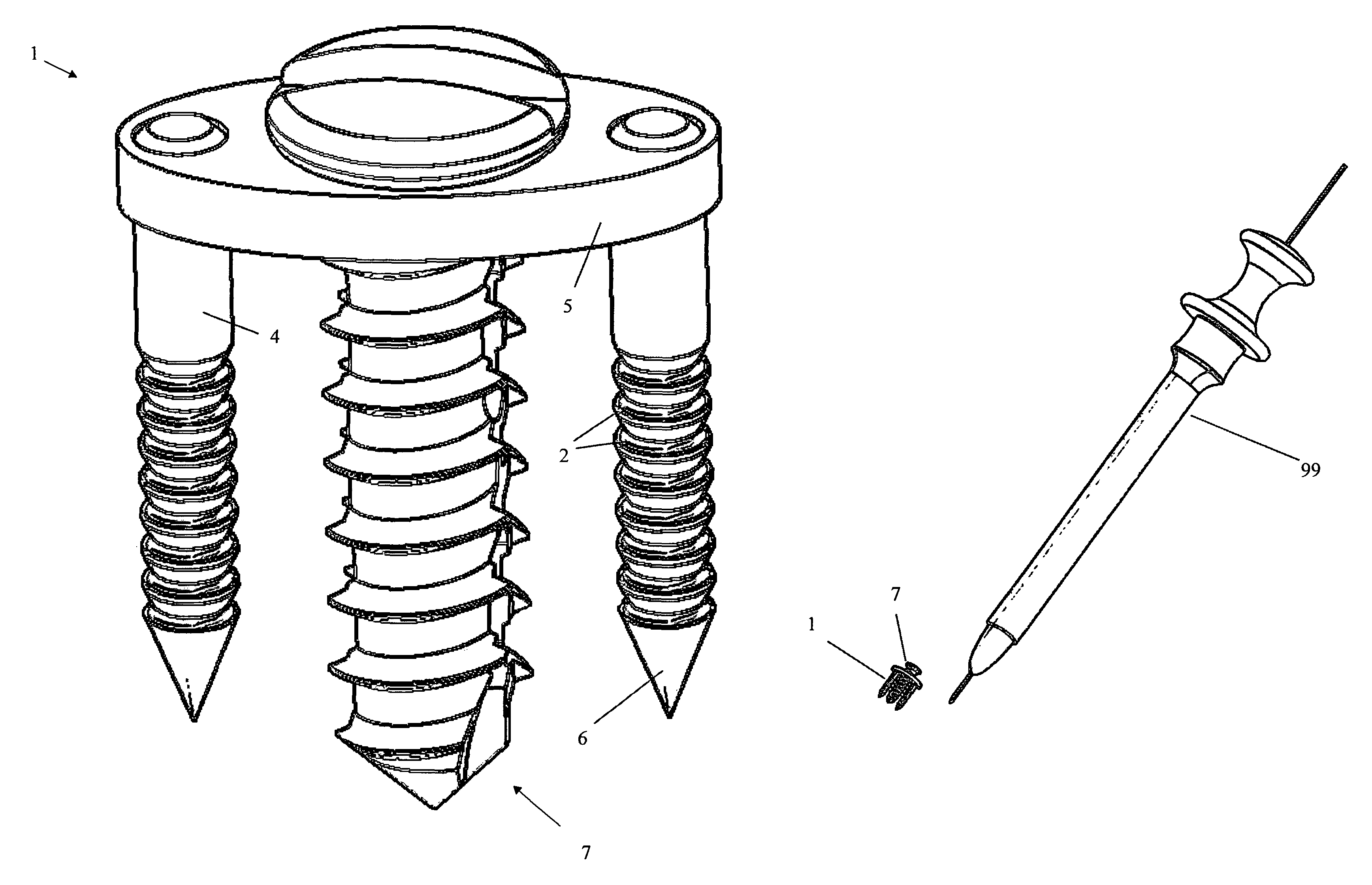
Lateral approach The lateral approach is used for insertion of a sliding hip screw or multiple screws after closed reduction of a proximal femoral fracture. The incision can be extended proximally to accommodate a trochanteric stabilizing plate.
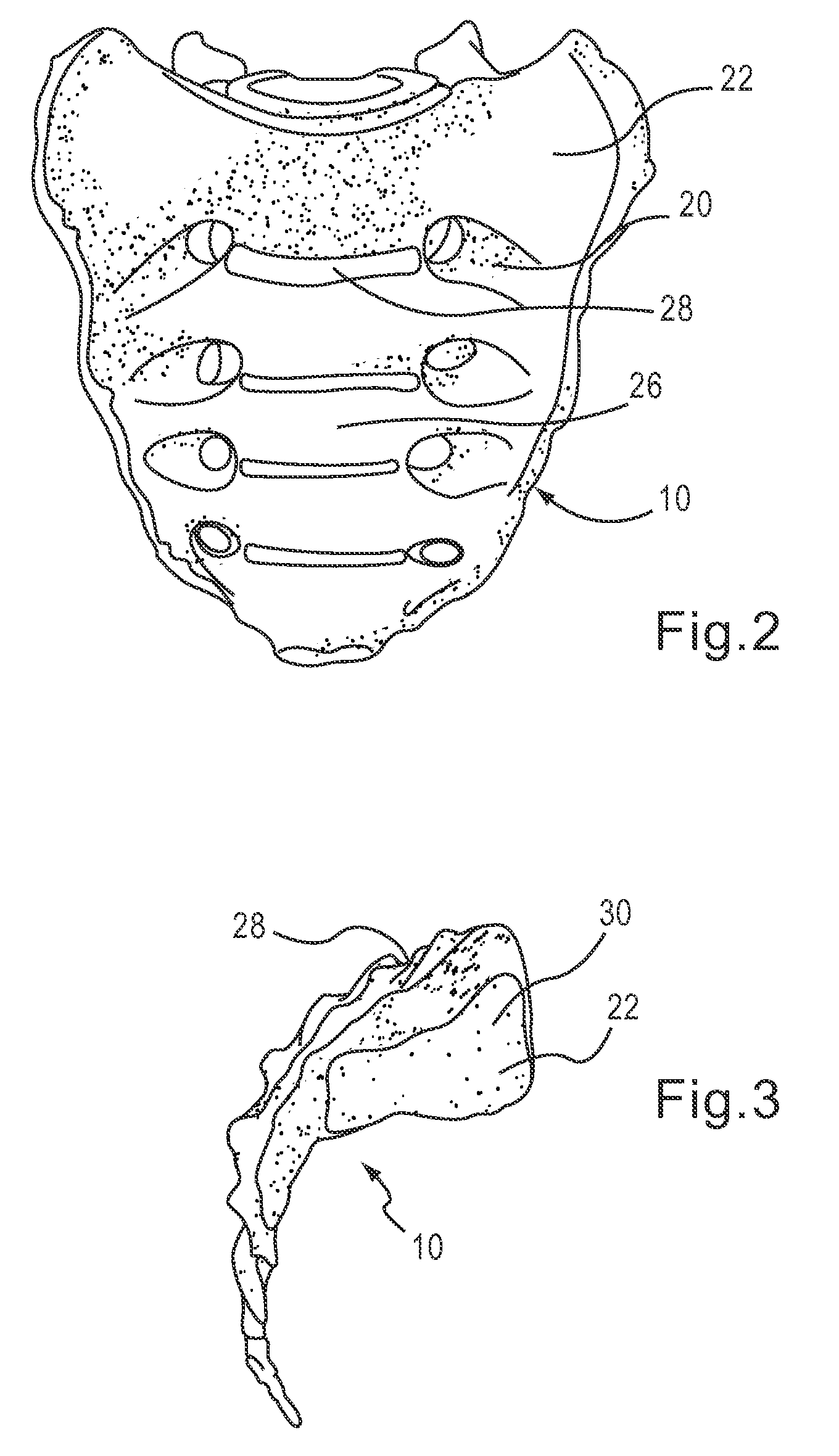
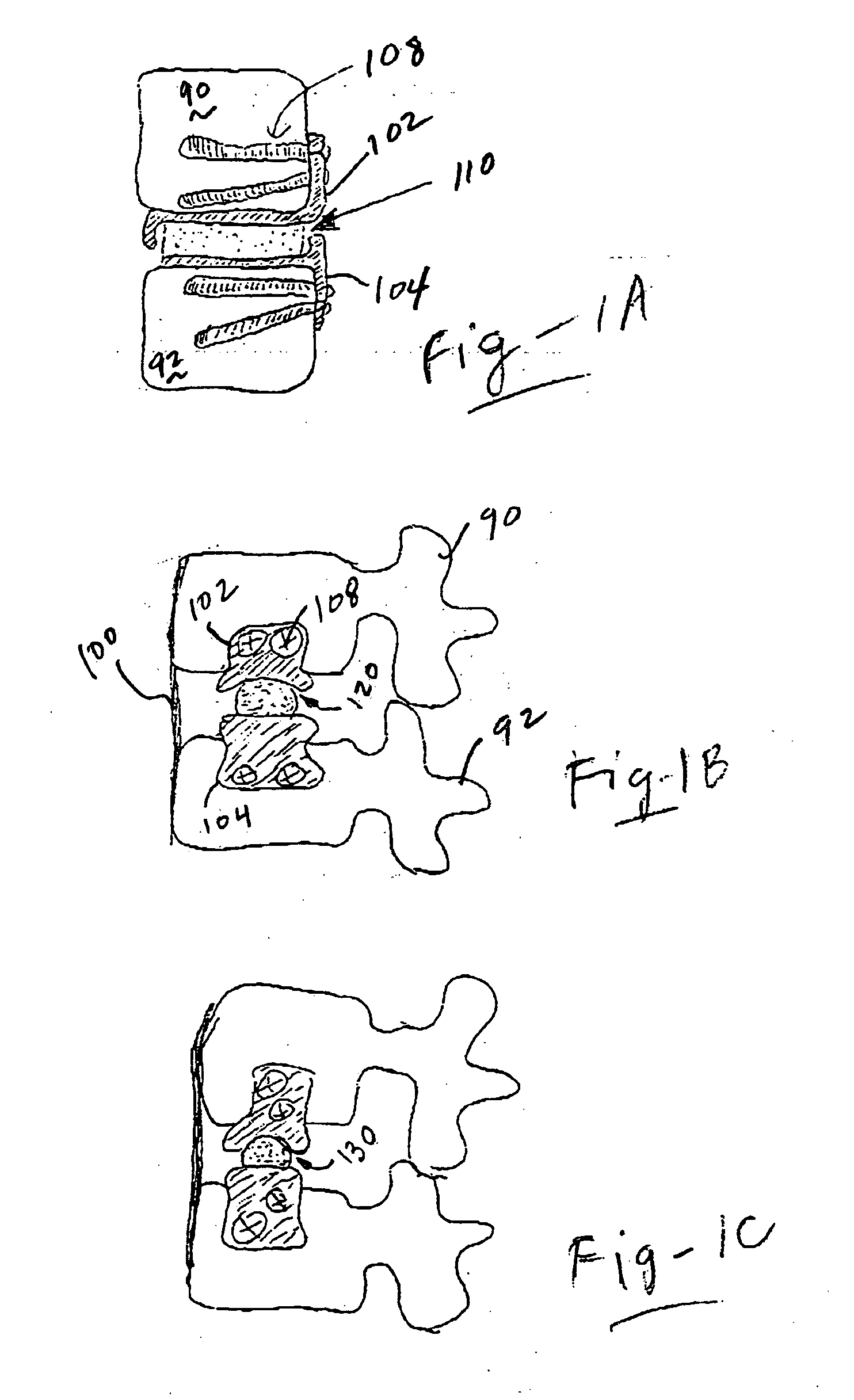
Devices and techniques for a posterior lateral disc space approach
This invention relates to devices and instruments for implant insertion through a posterior lateral opening to the disc space. The instruments include an implant inserter, and the devices include a spinal fusion implant engageable by the implant inserter. The implant provides bilateral support of the adjacent vertebrae when inserted into the disc space from a postero-lateral approach.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
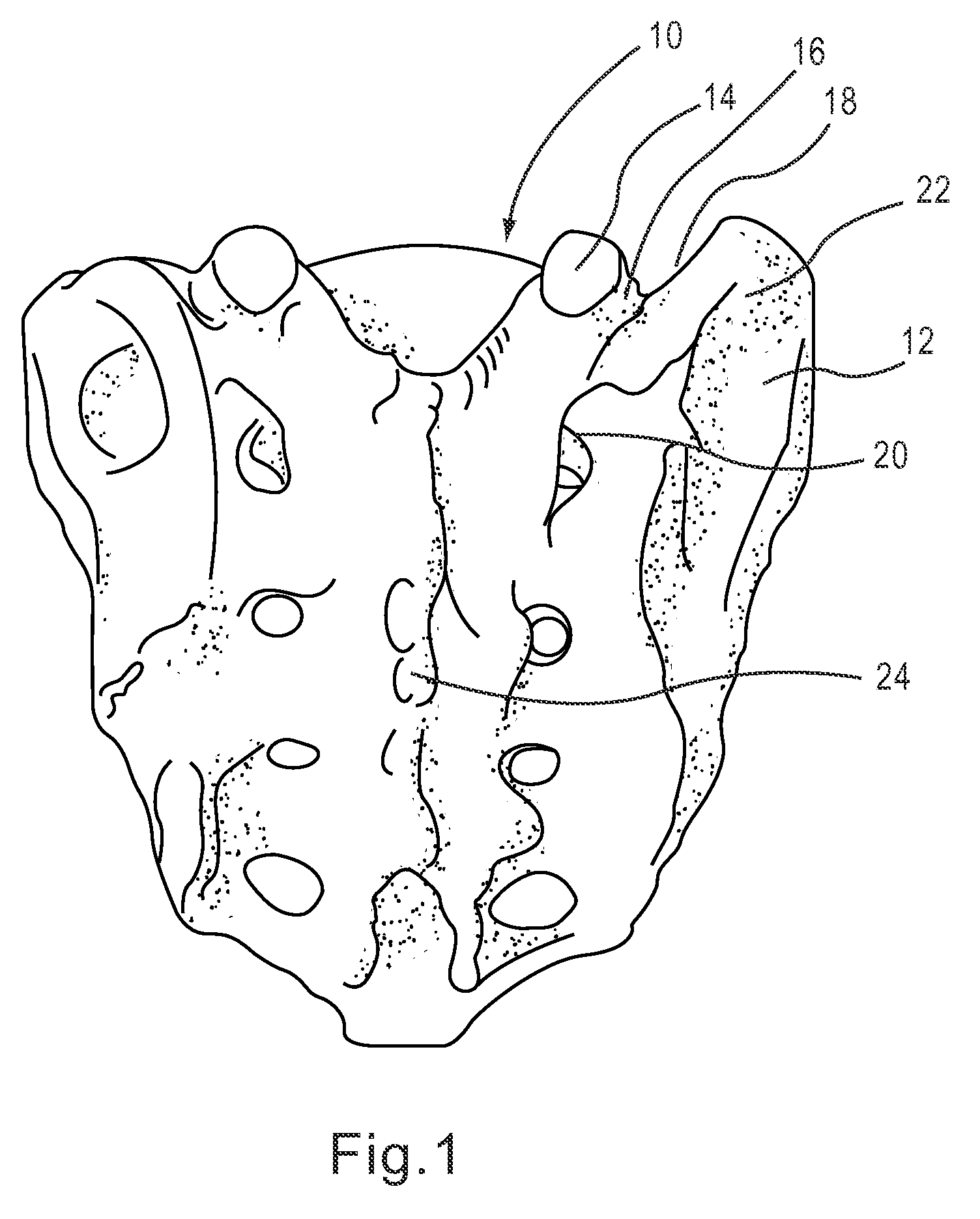
Kit and methods for medical procedures within a sacrum
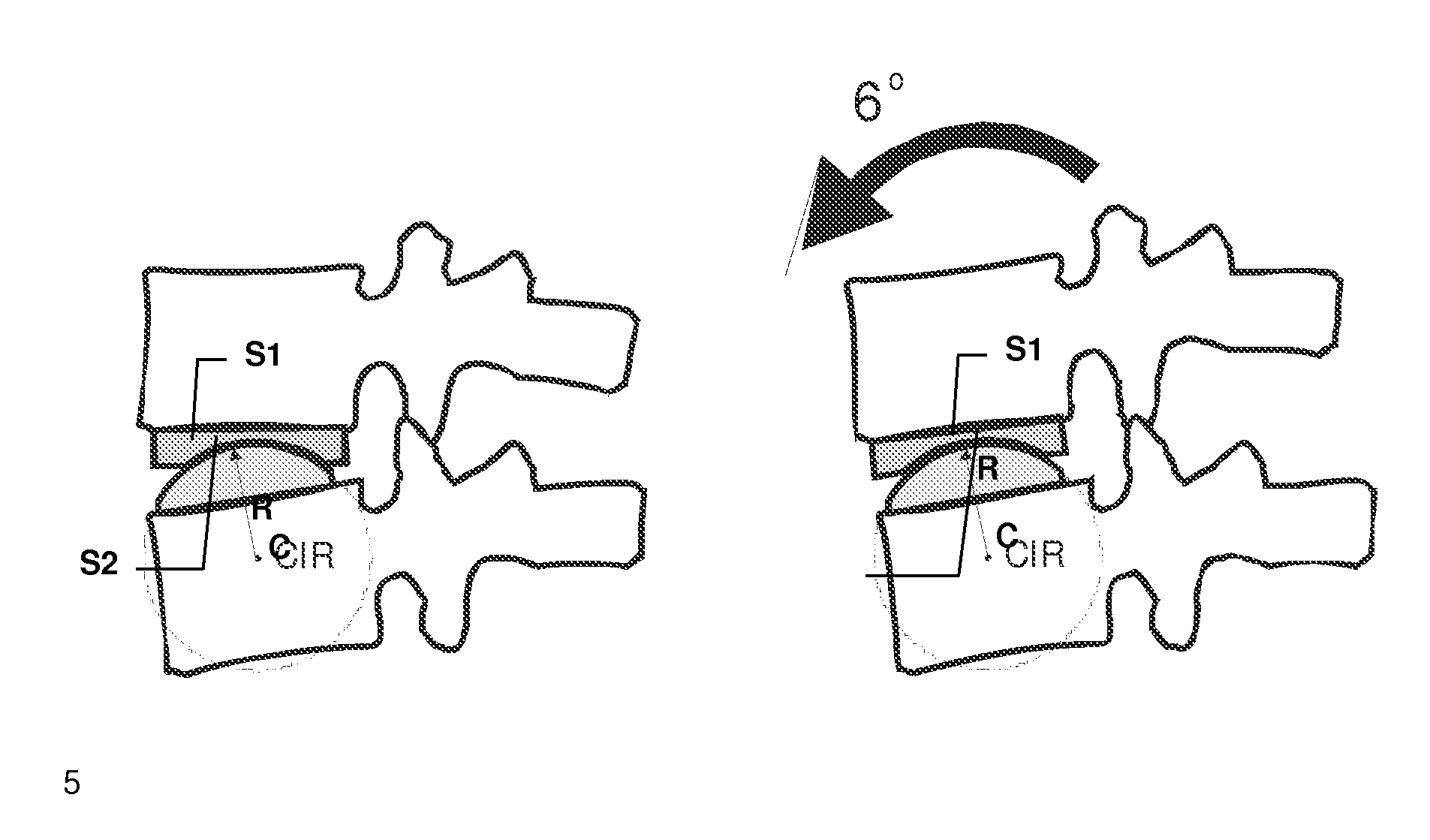
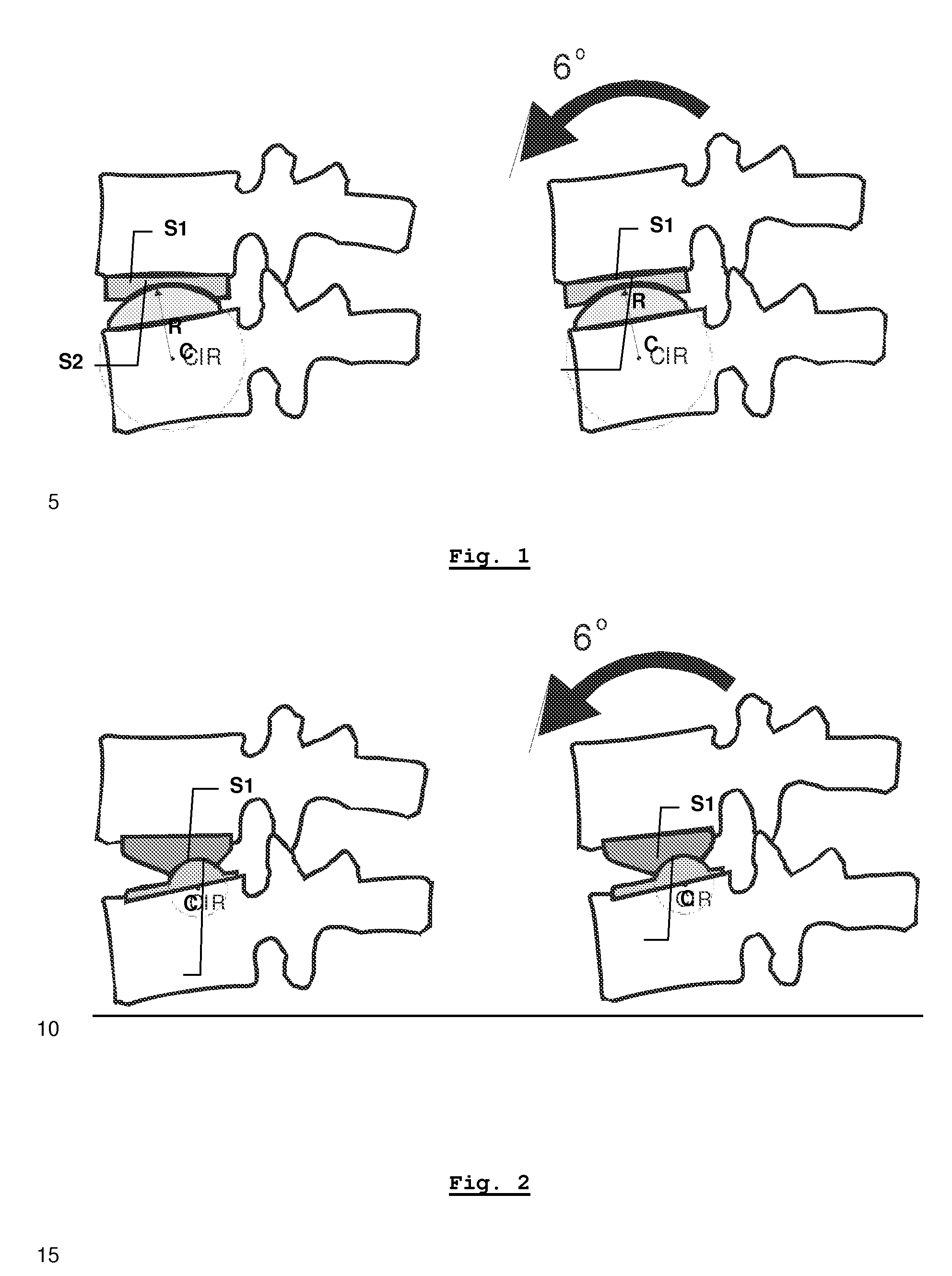
Devices and methods for performing a procedure within a sacrum are disclosed herein. In one variation, a method includes imaging a spine with a fluoroscopy device to provide a view of the sacrum. An anatomical landmark is identified based on the imaging, and a breach zone is defined based on the imaging. The anatomical landmark is used to identify an entry point and guide a medical device in a medial-to-lateral approach into a sacral ala region of the sacrum to perform a medical procedure within the sacral ala. In some embodiments, the anatomical landmark can be, for example, a pedicle, and in some embodiments, the anatomical landmark can be, for example, a V notch. In some embodiments, an entry point is identified using two anatomical landmarks. For example, the anatomical landmarks can be an S1 foramen of the side being accessed and a sacroiliac joint.
Owner:KYPHON
Devices and techniques for a posterior lateral disc space approach
This invention relates to devices and instruments for implant insertion through a posterior lateral opening to the disc space. The instruments include an implant inserter, and the devices include a spinal fusion implant engageable by the implant inserter. The implant provides bilateral support of the adjacent vertebrae when inserted into the disc space from a postero-lateral approach.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Vertebral Body Replacement
The present invention involves a system and methods for assembling and implanting a vertebral body implant. The vertebral body implant includes, but is not necessarily limited to, an expandable core body and endplates that can be attached at both ends. Endplates of various shapes, sizes and angles are attachable to the expandable core in a plurality of positions so that a suitable vertebral body implant can be implanted between vertebrae from an anterior, anterior-lateral, lateral, posterior or posterior-lateral approach.
Owner:NUVASIVE
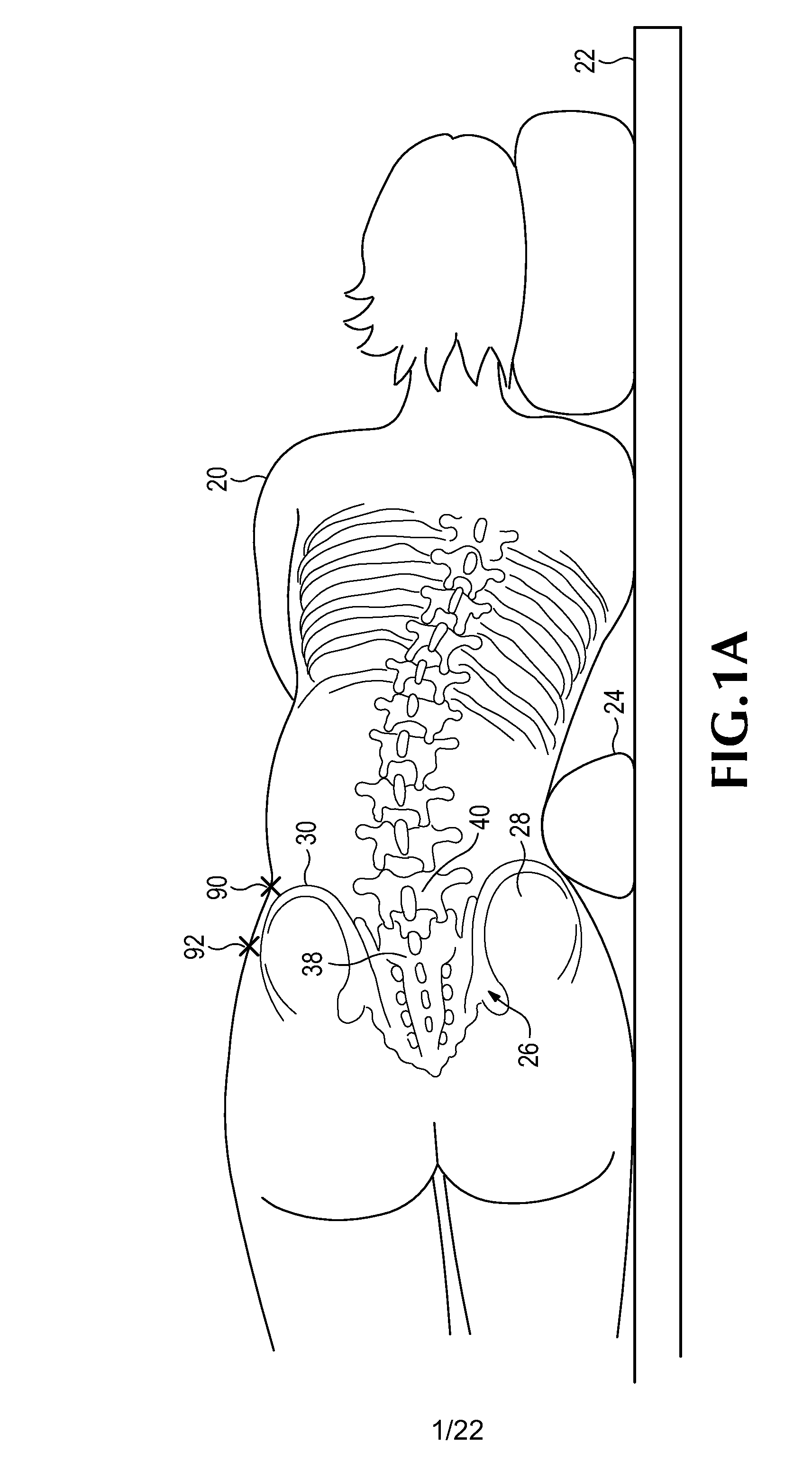
Minimally-invasive retroperitoneal lateral approach for spinal surgery
InactiveUS20120035730A1Realize distributionMinimize traumaSurgerySpinal implantsSpinal columnIntervertebral spaces
A method is disclosed for introducing a spinal disc implant into an intervertebral space of a subject. The subject is placed in a lateral position, and the anterior face of the spinal disc intervertebral space is accessed, between the L5 and S1 vertebrae, from an anterior and lateral retroperitoneal approach. An operative corridor to the anterior face of the spinal disc space is established by introducing a retractor instrument anterolaterally to the spinal disc space between the anterior superior iliac spine and the anterior inferior iliac spine. The damaged spinal disc contents are removed from the intervertebral space through the operative corridor, and the implant is advanced into the intervertebral space at an oblique angle and pivoted to position the implant substantially laterally within the intervertebral space. Elongated retractor and insertion instruments, as well as a modified disc implant, are also disclosed for carrying out the method.
Owner:PANTHEON SPINAL
Instruments and Methods for Non-Parallel Disc Space Preparation
ActiveUS20110319898A1Less endplate damageHigh preparation symmetryEar treatmentCannulasMedicineIntervertebral disk
Flexible shavers and curved access ports that reduce access and trajectory problems associated with conventional lateral approaches to the lower spine. These devices and methods allow for preparing a disc space in the lower spine at an angle that is parallel to the disc space. Consequently, these devices and methods allow for preparing with less endplate damage.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Lateral-approach artificial disc replacements
InactiveUS20050261773A1Facilitates bone ingrowthHigh strengthJoint implantsSpinal implantsMobile bearingSacroiliac joint
Artificial disc replacements (ADRS) are configured for implantation using a lateral, anterior-lateral, or posterior-lateral approach. A first component having a first segment resides in the disc space for articulation purposes, with a second segment adapted for fixation to the lateral outer surface of one of the vertebral bodies. A second component having a first segment resides in the disc space for articulation purposes, with a second segment adapted for fixation to the lateral outer surface of the other vertebral body. The first segments of the two components may articulate against one another without a spacer, or a spacer forming a mobile bearing may be disposed between the first segments of the two components. In the preferred embodiment, one or both of the two components are in the form of bent plates such that the second segment is positioned against a lateral wall for fixation. In the preferred embodiment, screws are used through the second segment and into a vertebral body. The screws are located in different vertical locations, and may diverge or converge vertically or horizontally to resist pull-out.
Owner:ANOVA
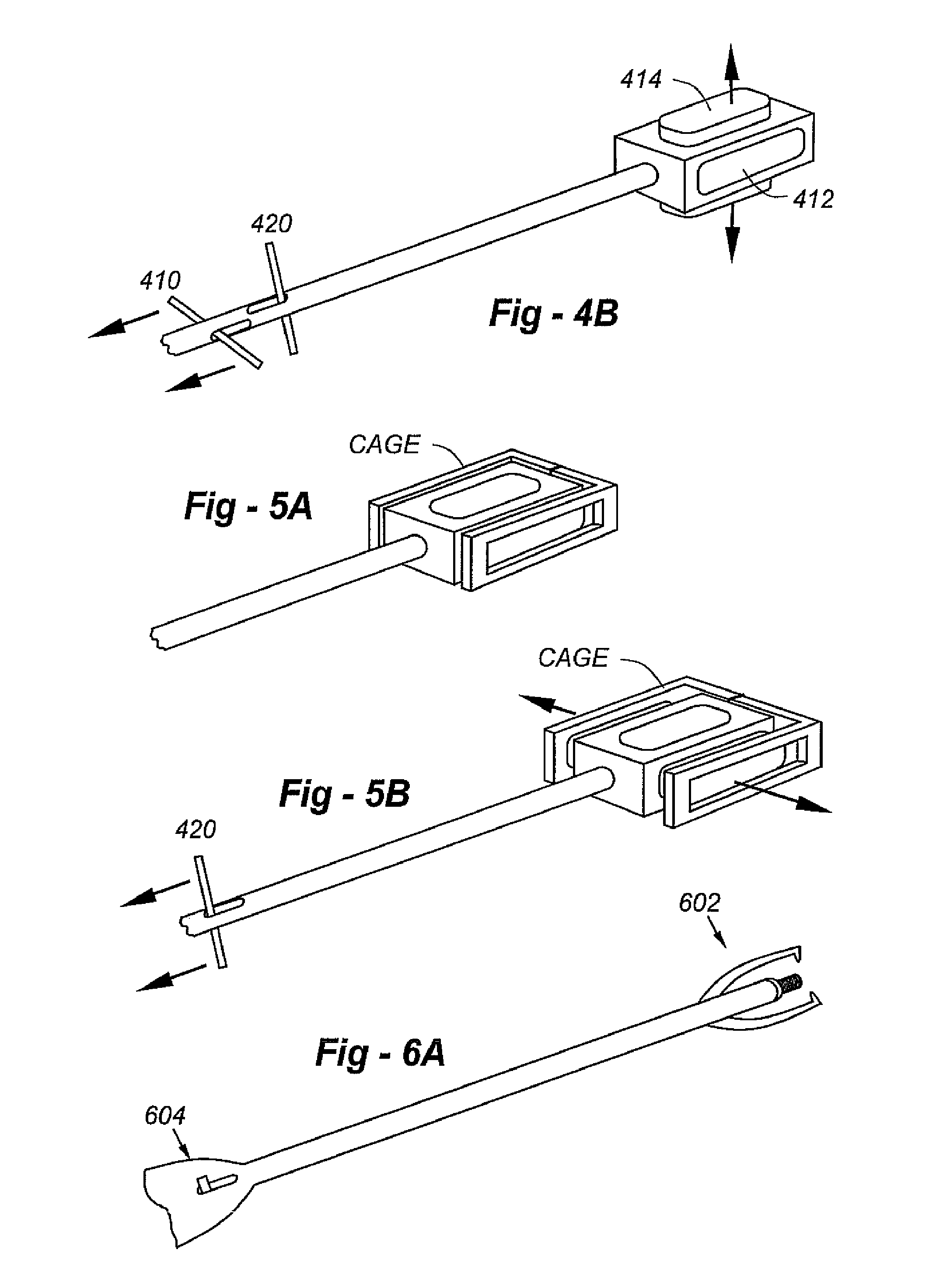
Percutaneous posterior lateral in-situ cage
Implants, tools and techniques facilitate a percutaneous posterior lateral approach to the placement of an in-situ cage, and an inventive cage design to meet this objective. In terms of apparatus, the invention includes a laterally expandable cage, including a locking gate, enabling the system to be introduced into an intradiscal space through a minimally invasive percutaneous posteo-lateral approach. In addition to the cage designs, adapted to hold bone graft and / or other biologic materials, the invention includes other novel instruments, including an introducer associated with cage placement, deployment and closure.
Owner:CTL MEDICAL CORP
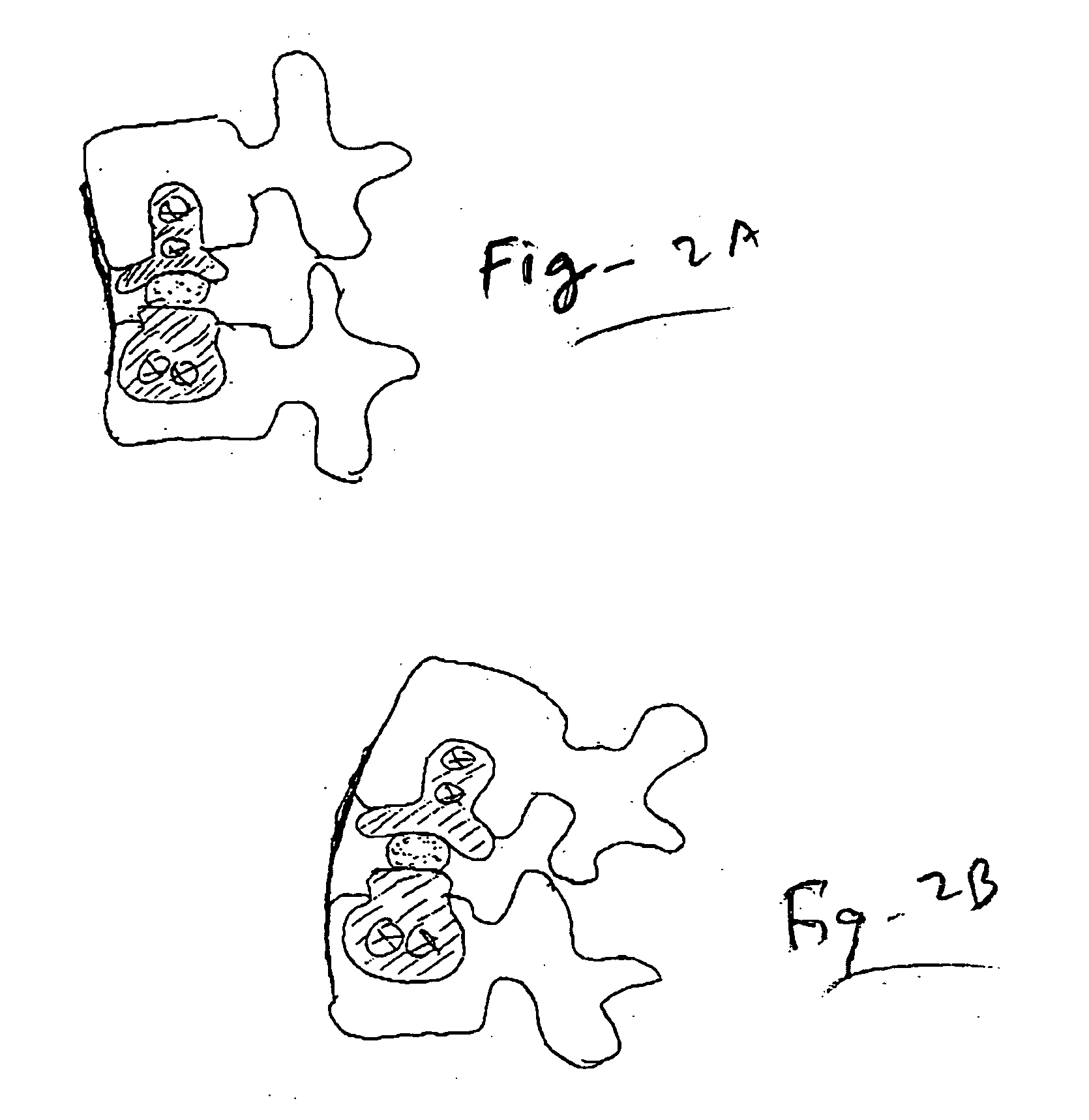
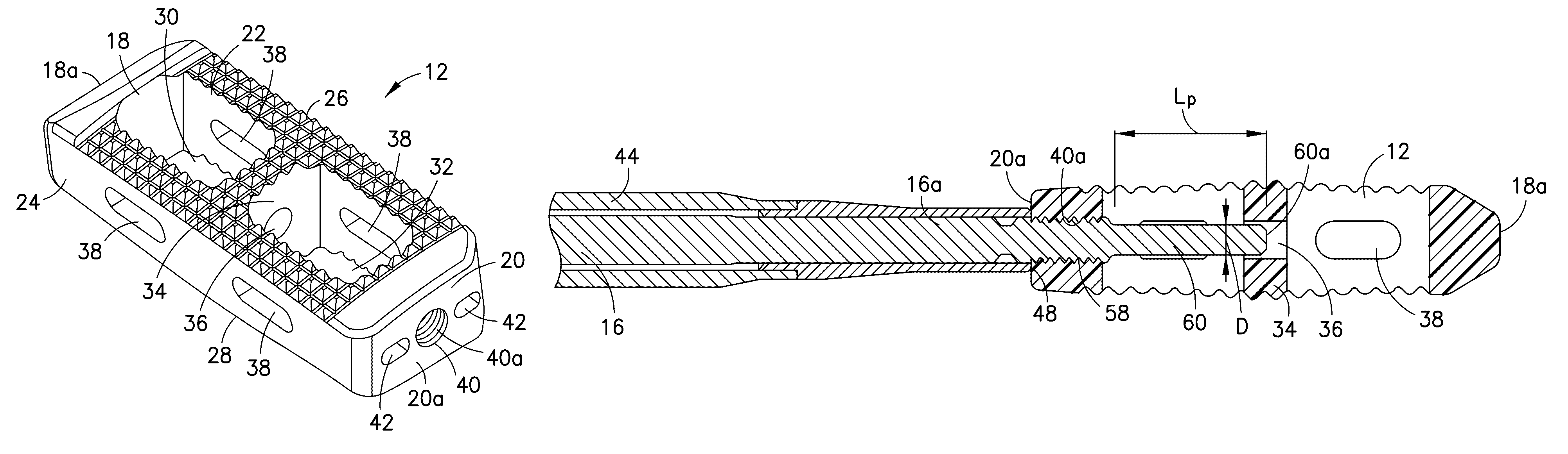
Interbody fusion device with separable retention component for lateral approach and associated methods
ActiveUS20130297029A1Preventing undesirable lossInhibit migrationBone implantSpinal implantsBiomedical engineeringFastener
The claimed invention is directed to a spinal fusion device comprising a load-bearing interbody component configured to fit between two adjacent vertebrae, wherein the interbody component comprises one or more openings to allow access to the vertebrae, a retention component that is configured to at least partially close the one or more openings of the interbody component and one or more fasteners that are coupled to the retention component to compress the two adjacent vertebrae to the interbody component, and methods of using a spinal fusion device.
Owner:SPINESMITH PARTNERS
Configurable Intervertebral Implant
ActiveUS20160007983A1Stabilize spineReduce the overall heightInternal osteosythesisSurgical needlesIntervertebral discIntervertebral space
The present disclosure relates to a surgical device, such as a surgical implant, which may be used in several types of procedures. More specifically, the present disclosure relates to implants for use in an anterior, posterior, posterior lateral or direct lateral approach to the disc space. The surgical device may be manipulated in various manners to accommodate delivery through a minimally invasive portal in one configuration and adjusted to a second configuration once placed in the intervertebral space. A delivery system for placing the surgical device in a body is also disclosed.
Owner:MIGHTY OAK MEDICAL INC
Intervertebral disc prosthesis for universal application
InactiveUS20090082867A1Improve wear resistanceStable frictionSpinal implantsInstabilityBiocompatibility Testing
An Invertebral Disc Model Prosthesis, of the type denominated of double articulation, to substitute the function and the movement of intervertebral discs, for universal application due to its principal characteristic of being able to be used as a constrained, semi-constrained or non-constrained prosthesis, specially indicated for treatment of pathological degenerative of the intervertebral discs, discal hernias, by anterior approach, transition syndromes of supra-adjacent disc, chronic lumbagos resistant to conserver treatment, chronic adjacent vertebral instability, made from materials of proved biocompatibility, endowed with a low profile that makes it optimum for its implant in the human being and which consists of three pieces, two plates, upper and lower, and am intermediate piece , which serves for the substitution of the discs of the lumbar and cervical column, capable of being placed by the anterior or lateral approach.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
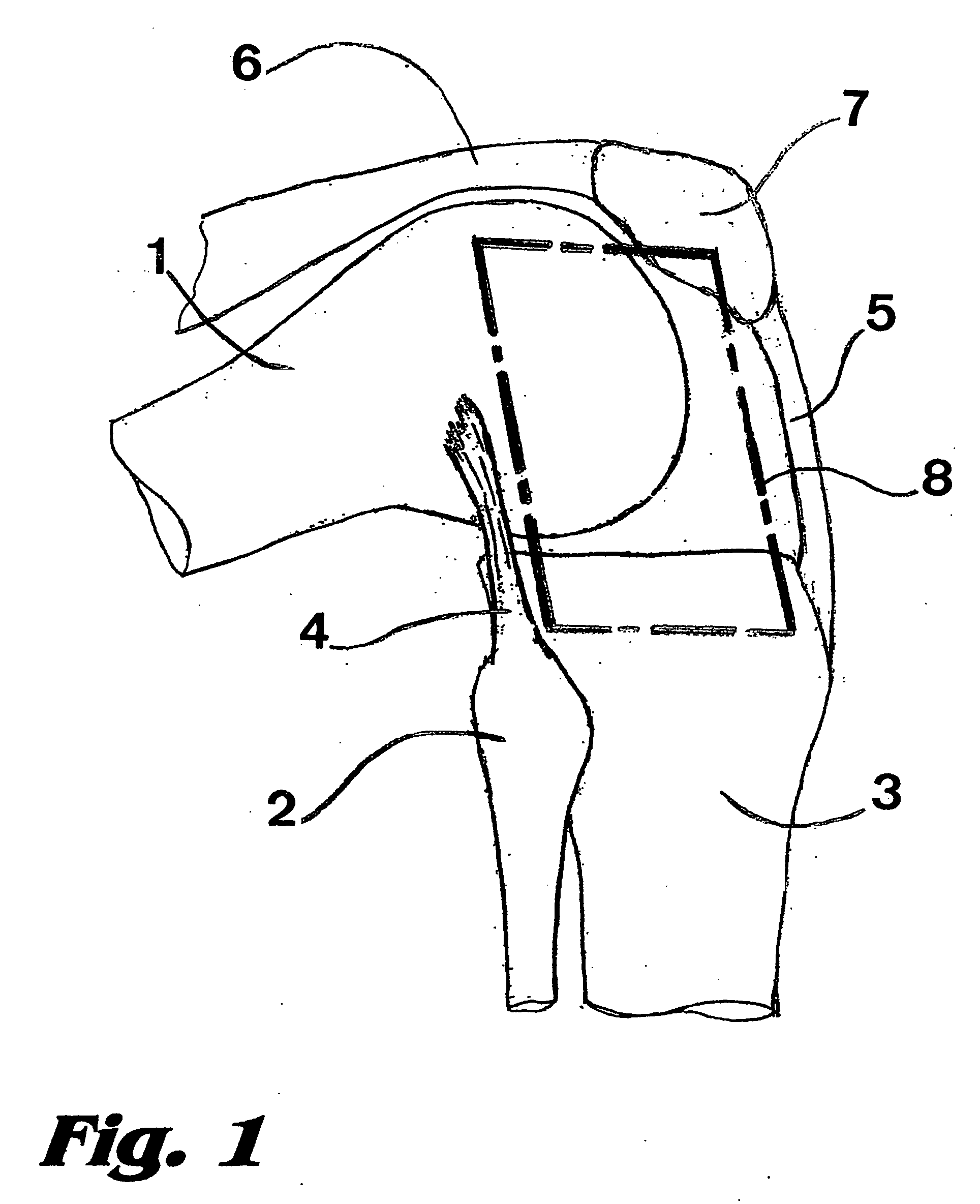
System for Approaching the Spine Laterally and Retracting Tissue in an Anterior to Posterior Direction
InactiveUS20180206834A1Less manipulationImprove efficiencySurgerySpinal implantsSpinal columnSurgical department
The invention now summarized here is directed toward a surgical device that enables utilization of the lateral approach to the spine with the ability to retract tissue in an anterior-to-posterior direction. The invention also incorporates a surgical method for utilization of the above-mentioned surgical device, embodiments of which incorporate steps for approaching the anterior portion of the disc space, retracting soft tissue in a generally posterior direction, removing disc material, placing a bone graft and removing the associated instrumentation.
Owner:MIS IP HLDG LLC
System and methods for spinal fusion
ActiveUS9186261B2Increase surface areaBoost rateBone implantJoint implantsSpinal columnBiomedical engineering
A spinal fusion system and related methods involve the use of a spinal fusion implant of non-bone construction. The spinal fusion implant is particularly suited for introduction into the disc space via a lateral approach to the spine.
Owner:NUVASIVE
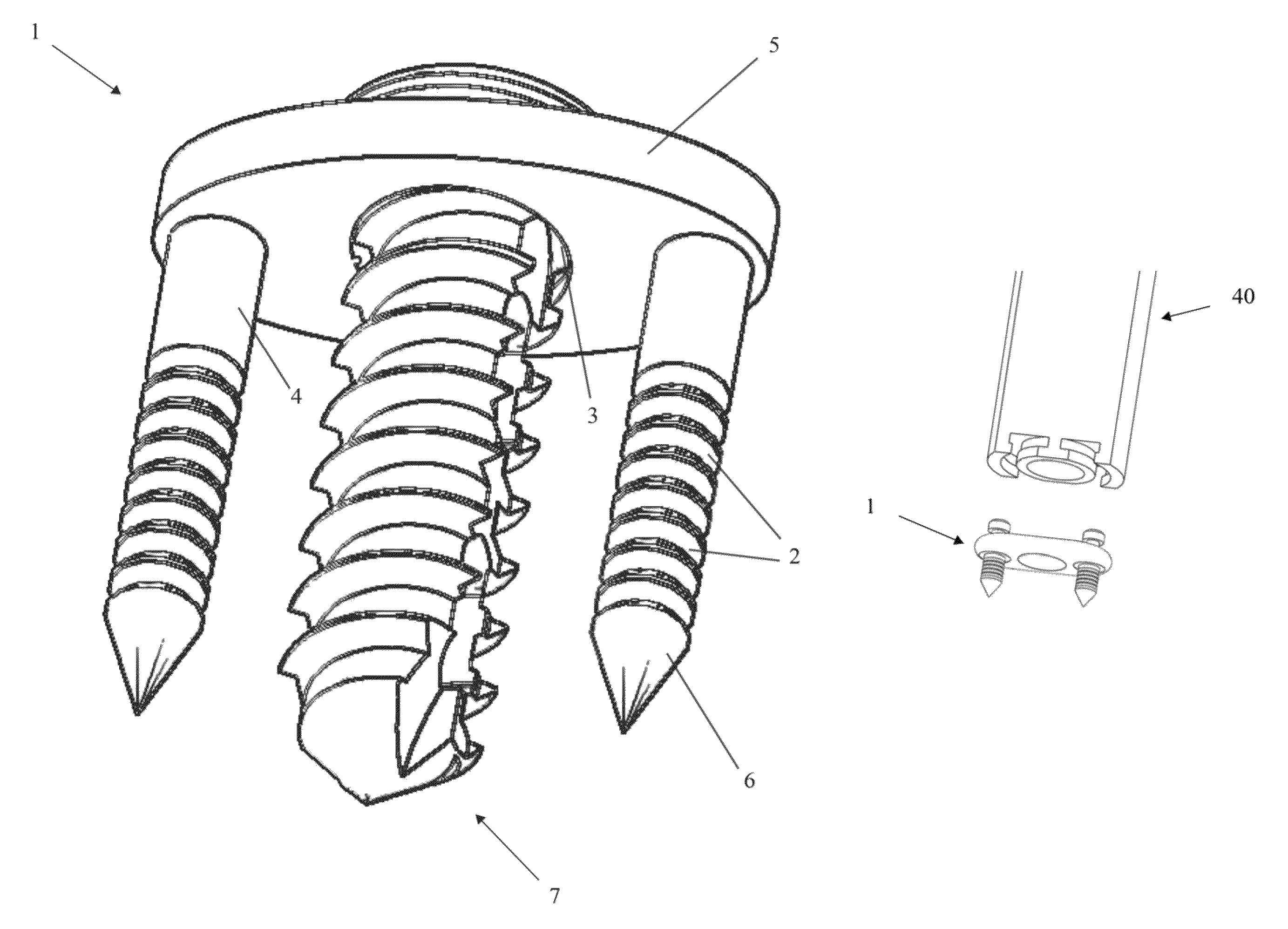
Method of lateral facet approach, decompression and fusion using screws and staples as well as arthroplasty
ActiveUS20100280555A1Good for long-term fixationImprove stabilitySuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisPosterior approachFixation method
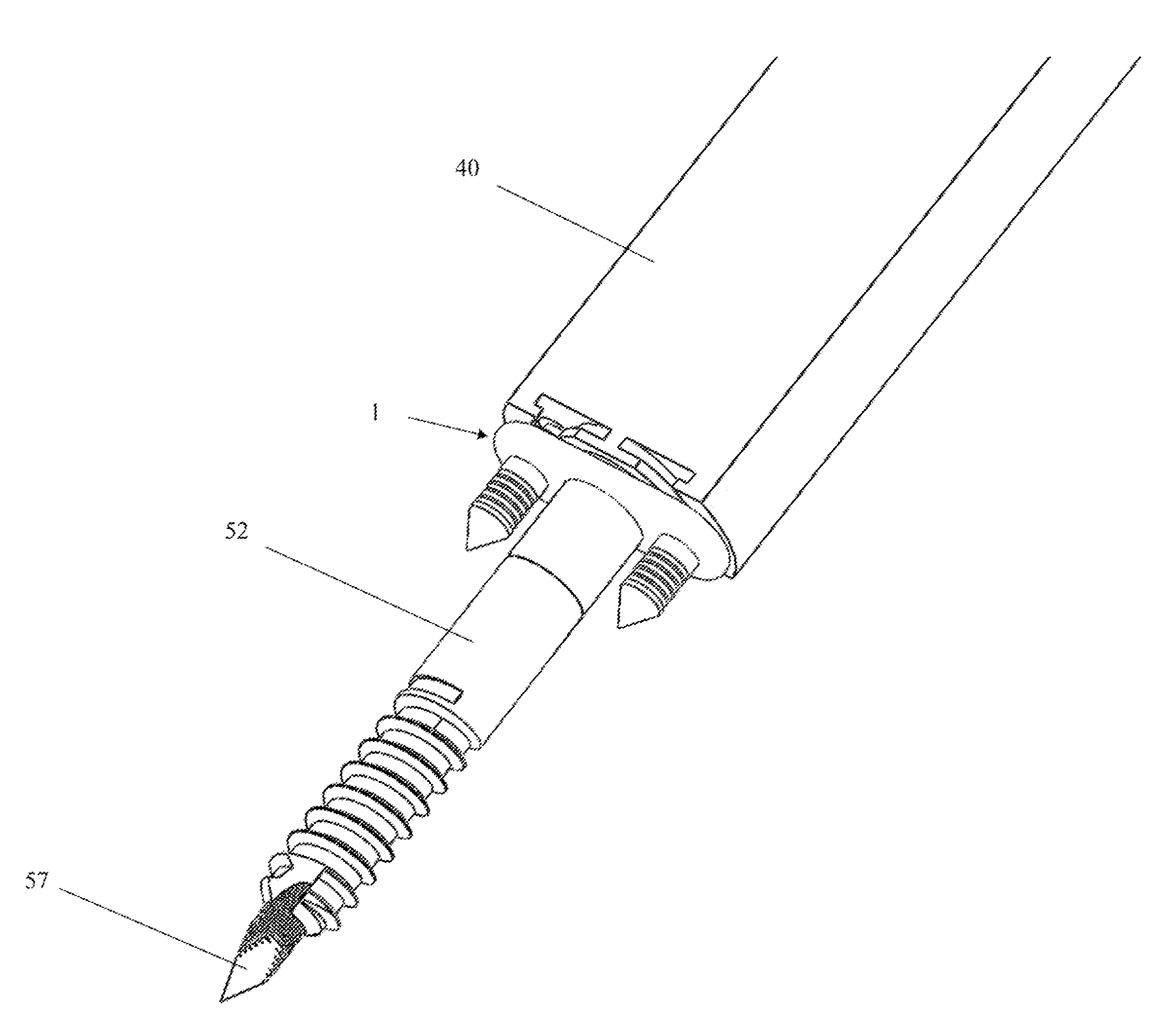
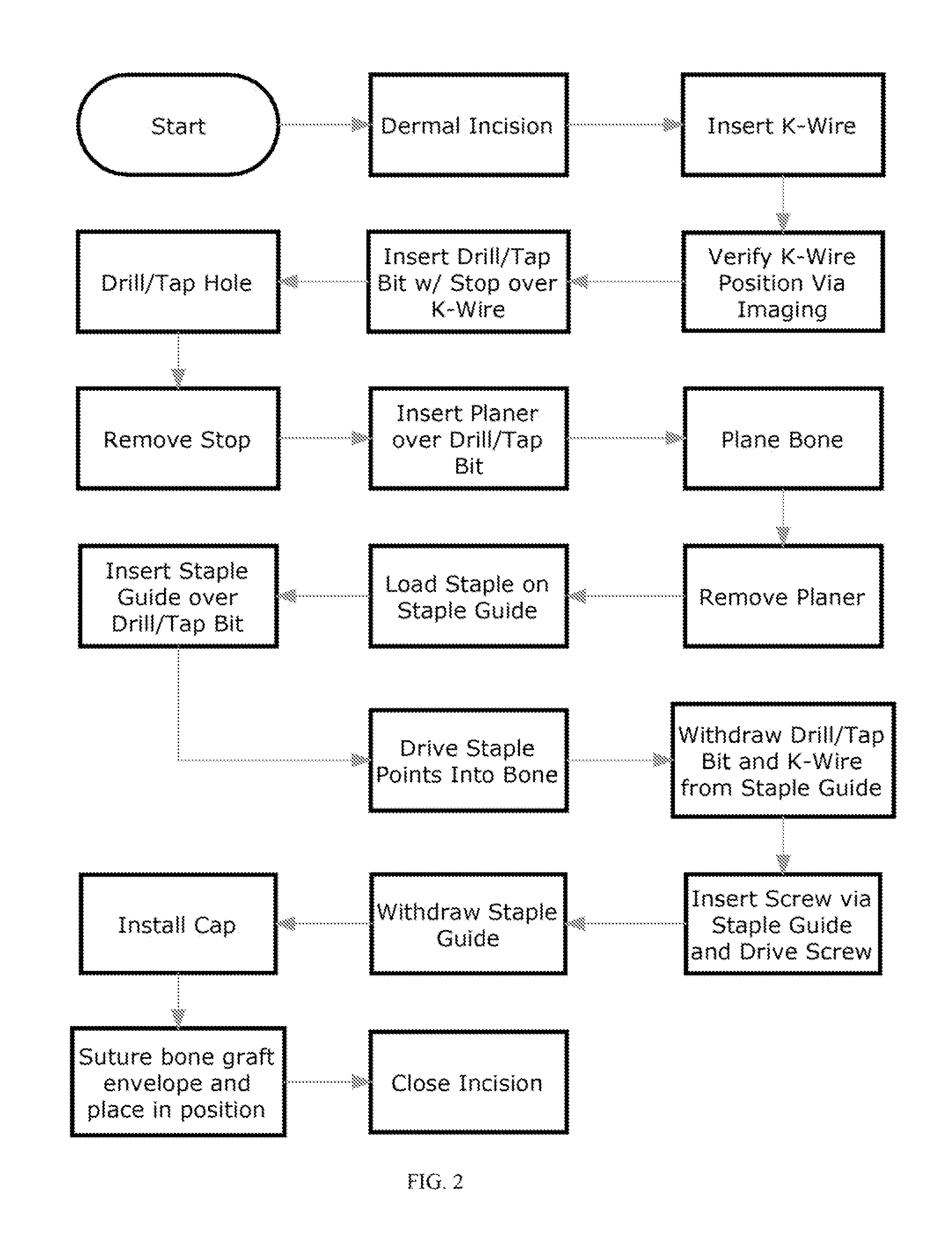
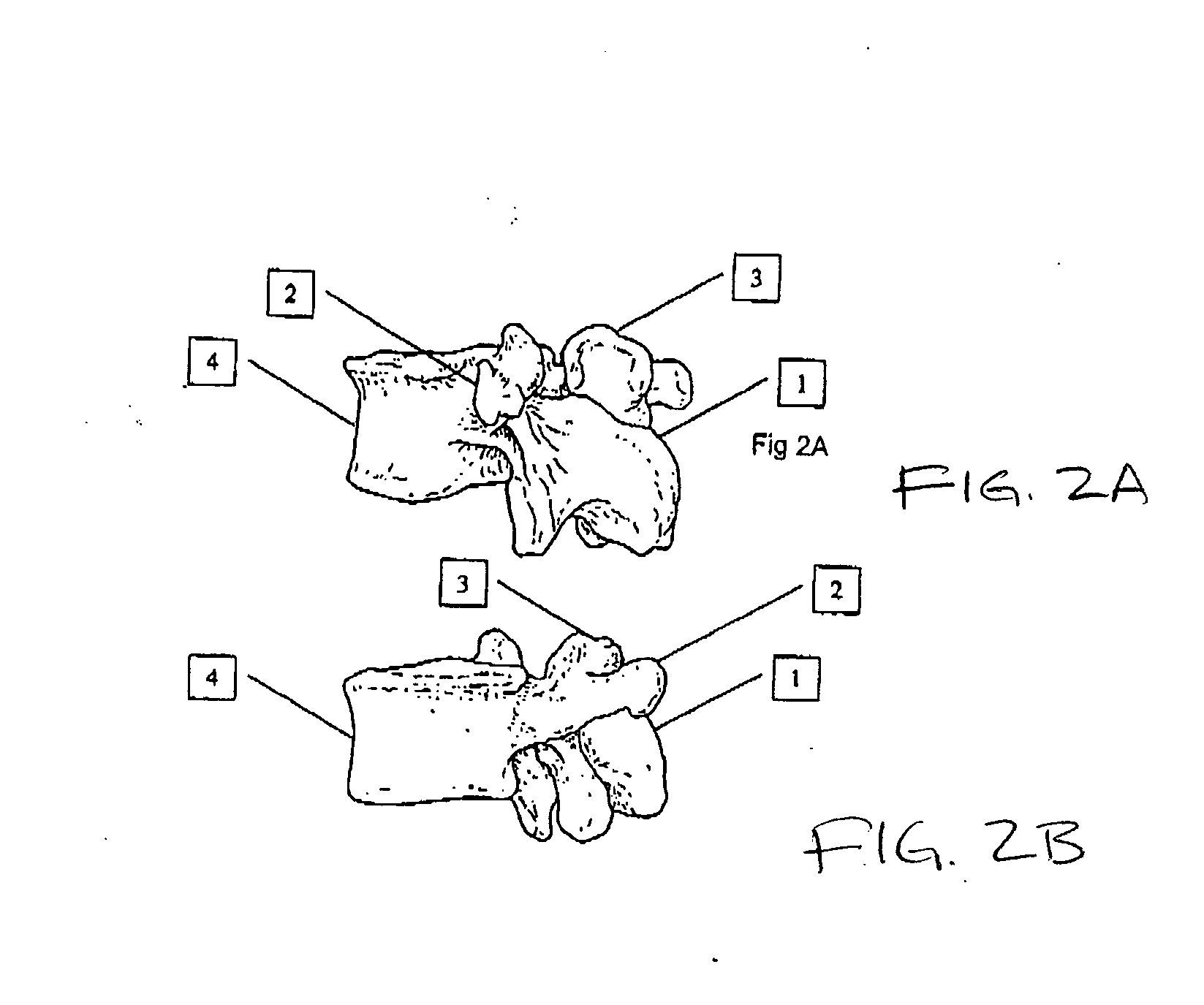
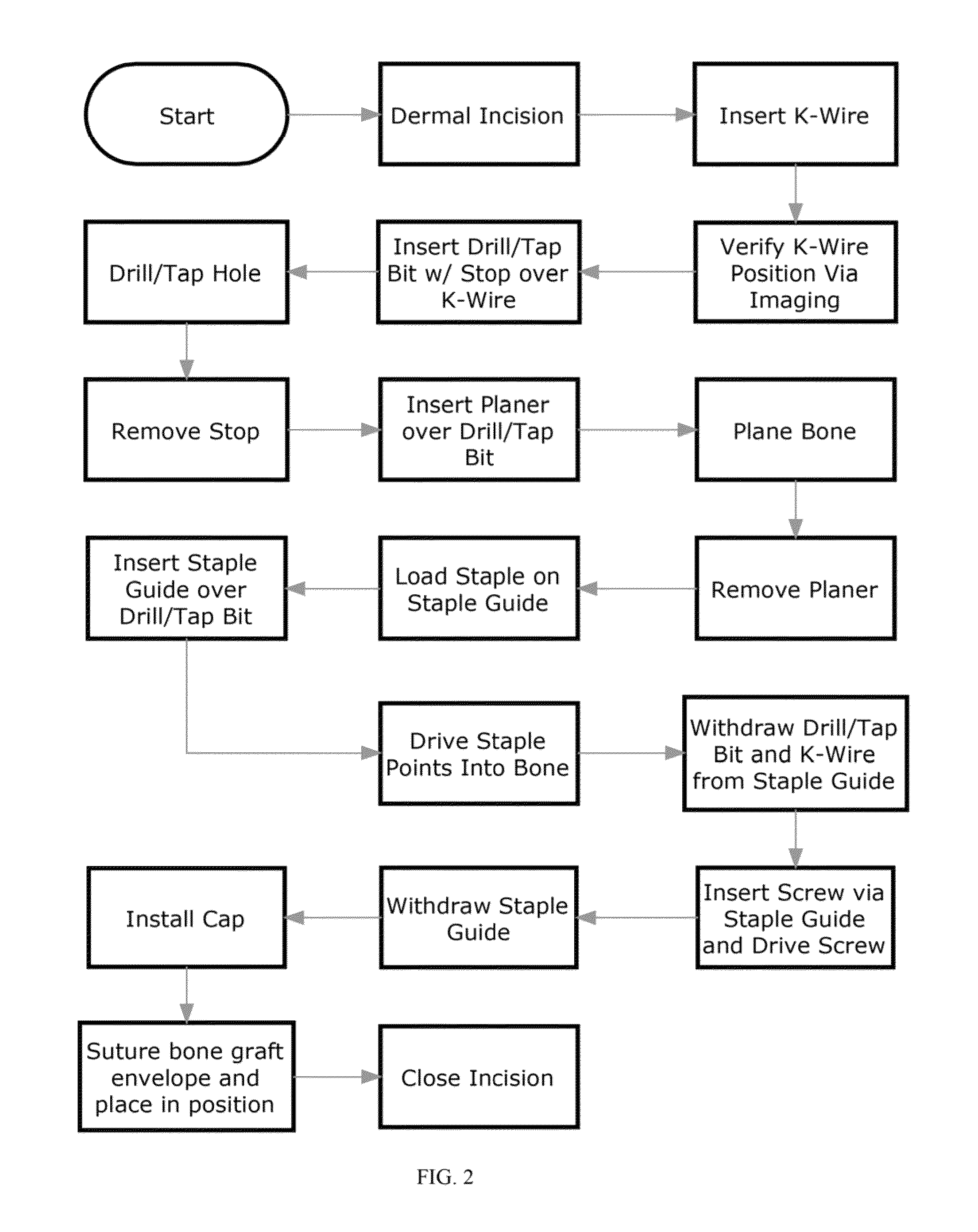
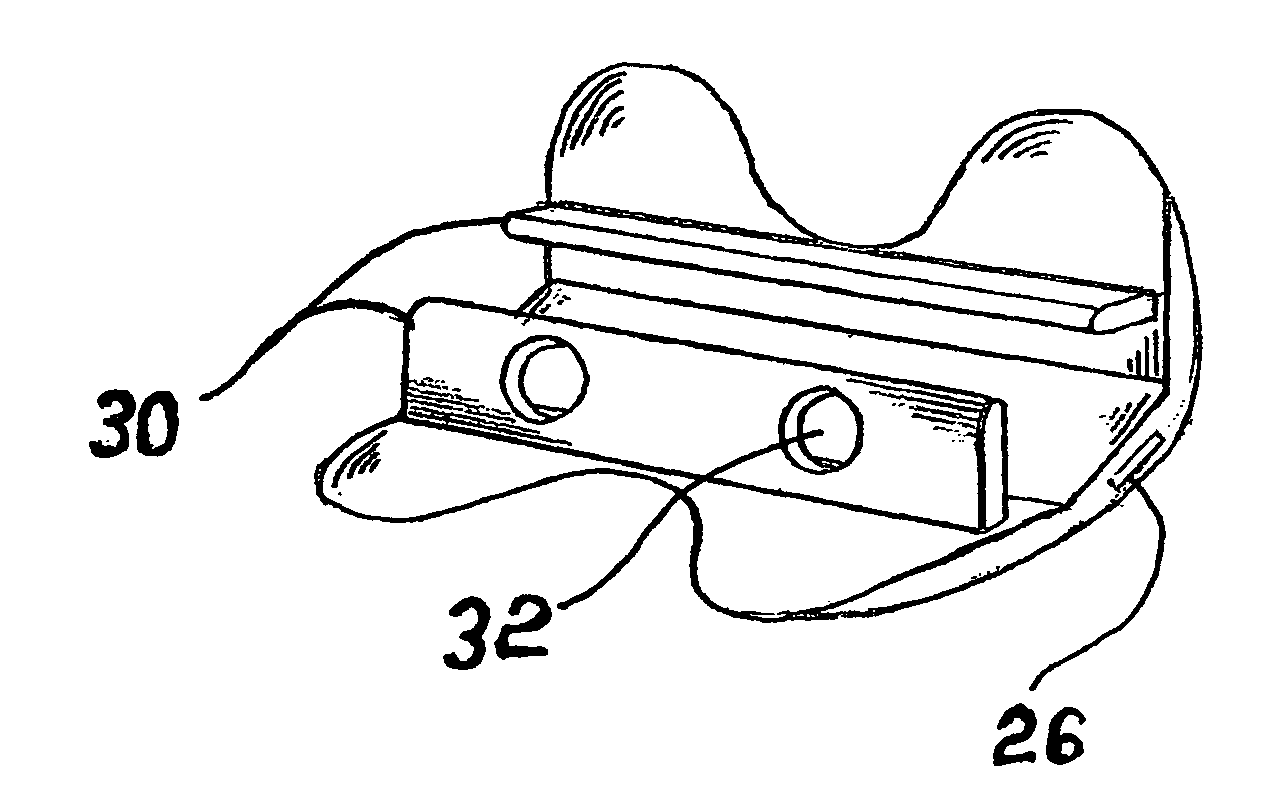
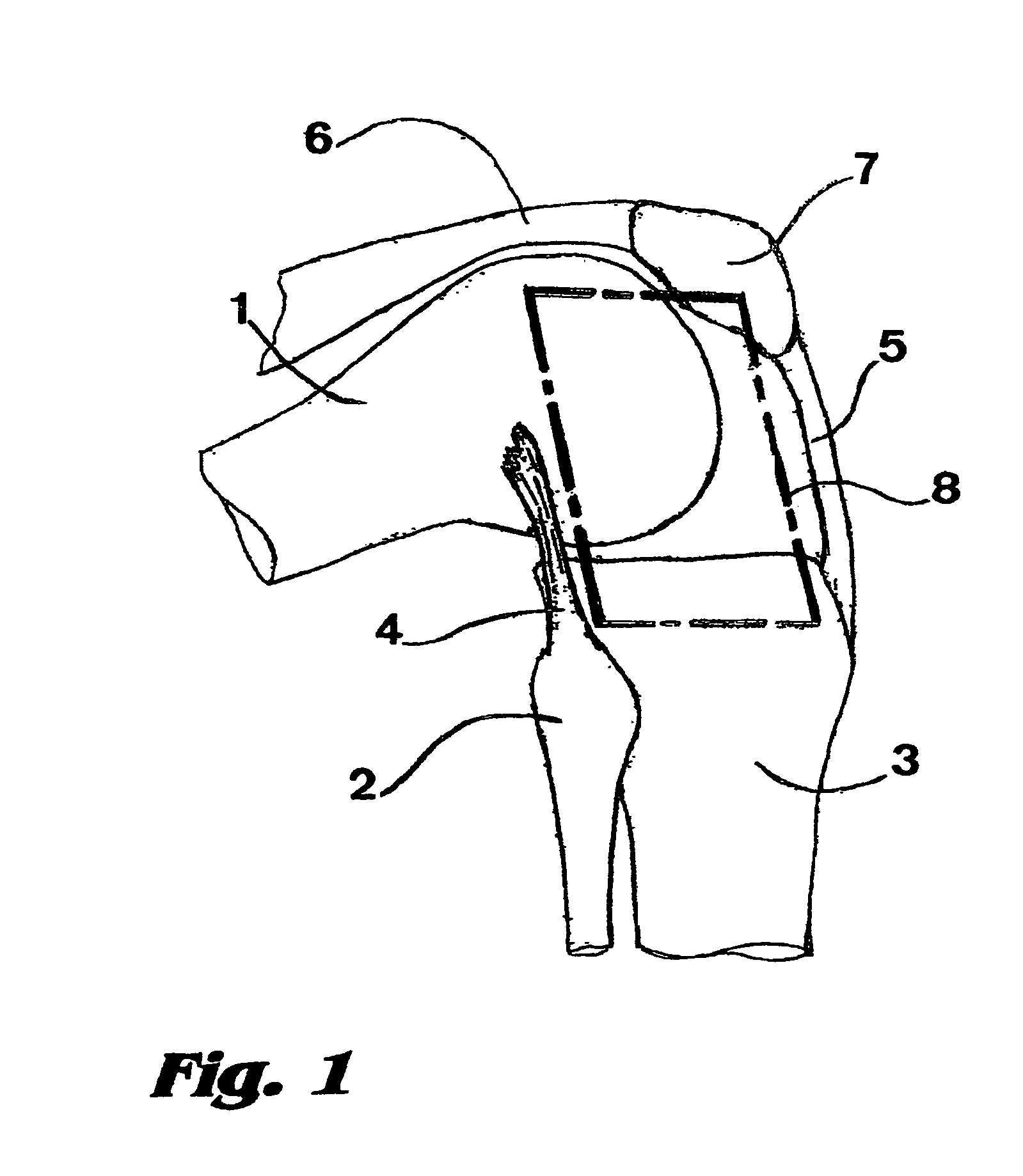
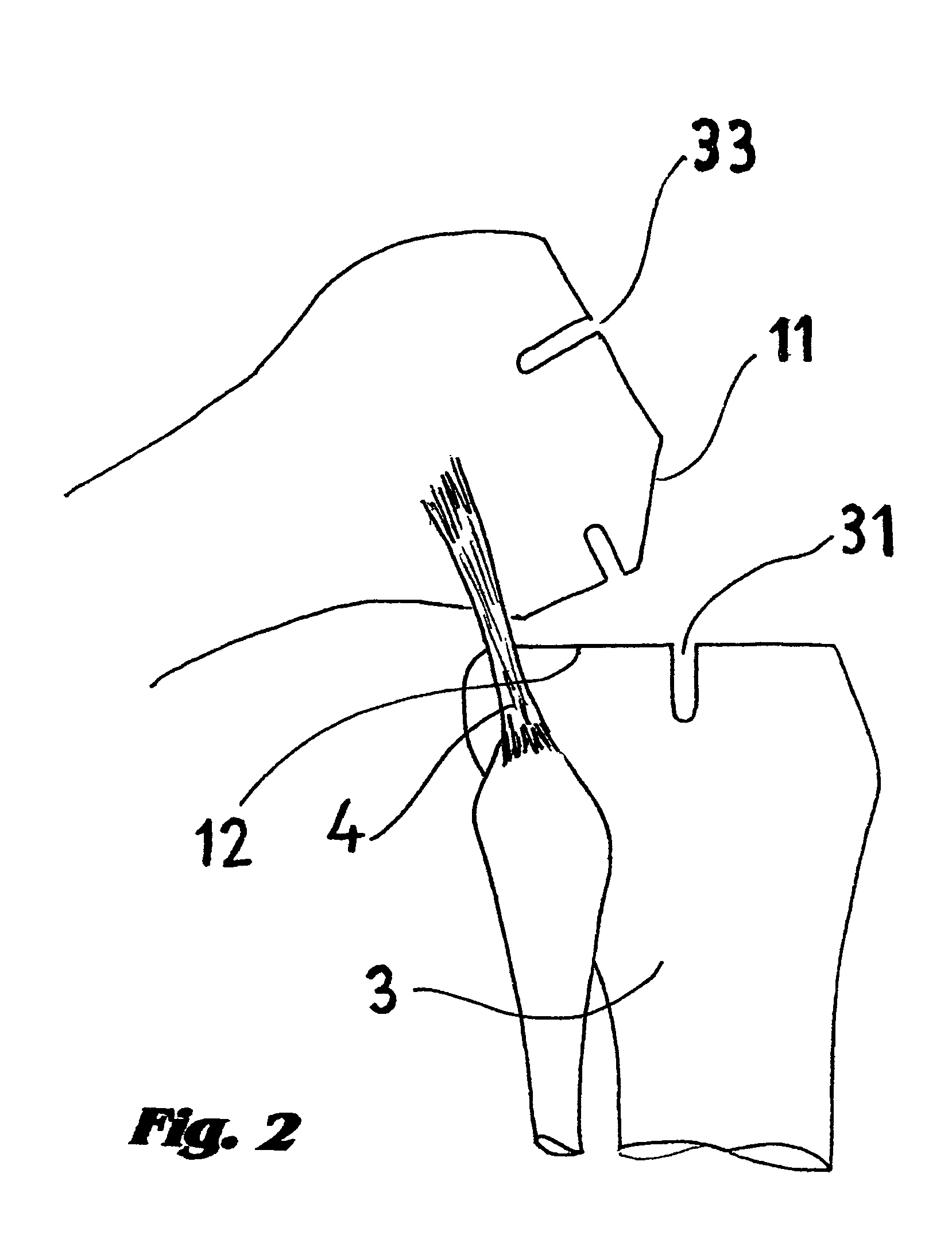
A method of performing vertebral facet fusion by lateral approach and related devices. The lateral approach to facet fusion involves identifying the lateral mass and introducing any of the fixation methods known or described herein laterally at one or more facets through the use of a Kirschner wire guide, a cannulated bone drill and cooperatively cannulated staple guide. A surgical bone staple have a perforated bridge is used across the lateral facet joint where fixation is required. Where fusion is desired, a bone screw have lateral perforations of the shank is inserted through the cannulated staple guide and bridge perforation at the joint to promote fusion. A staple cap and graft container for overlay grafting may be utilized for additional fusion. The method involves less surgical time, reduced blood loss and discomfort for the patient as compared to the posterior approach.
Owner:AFLATOON KAMRAN +1
Transosseous spine core approach method implant and instrumentation
InactiveUS20070118219A1Simple procedureShorten operation timeInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSurgical approachBiomedical engineering
The transosseous spinal core approach (TOSCA) represents a novel approach to the interior of the spine or disc space by removing a core from a first bone and performing a procedure, and / or making further enlargements and cuts in the first bone and performing a procedure, and / or making another cut into an adjacent disc space from the first bone hole and performing a procedure and / or continuing by cutting into another second bone and performing a procedure. The process can be further extended into additional spine levels by extending the cutting process. A core can be made at more than one level. The preferred surgical approach is a posterior lateral approach. An anterior surgical approach can be used as well. Any practical surgical approach or any combination of surgical approaches can be utilized to gain access to the first bone. Once the surgical soft tissue access to the first bone is completed TOSCA can be used to gain access to the interior of a vertebral body or disc space. After the procedure is completed in a vertebral body or disc space, usually at least a portion of the bone core is replaced to fill in the core hole.
Owner:HYDE JR EDWARD R
Safe cutting heads and systems for fast removal of a target tissue
ActiveUS20130144292A1Easy to disassembleFacilitate entryDiagnosticsExcision instrumentsTransforaminal approachPosterior approach
A safe and efficient cutting heads for removing a target tissue from a subject during a surgical procedure are provided, the cutting heads composing a part of systems that address several problems, including clogging of state-of-the-art systems during removal of such tissue, for example. The target tissue can include any tissue that is accessible through a small surgical opening, for example, a joint tissue such as a meniscus or an intervertebral tissue, such as a nucleus pulposus. The devices can be referred to as orthopedic tissue removal devices having cutting heads associated with vacuum systems, making the systems useful in several procedures, including X-LIF (lateral approach to an intervertebral fusions) procedures, T-LIF (transforaminal approach to intervertebral fusions) procedures, P-LIF (posterior approach to intervertebral fusions), and a percutaneous, transforaminal approach (Kambin triangle access).
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Method of correcting a lateral trajectory on approach as a function of the energy to be reabsorbed
ActiveUS20130238174A1Analogue computers for vehiclesSpecial data processing applicationsEngineeringFlight management system
In the field of the calculation of the approach trajectory of an aircraft, and relating to a method for determining a corrected lateral approach trajectory as a function of the energy to be reabsorbed before the landing, and also to a flight management system making it possible to determine the corrected lateral trajectory, a method comprises: determining an energy of the aircraft Eaero upon crossing the runway threshold on the basis of a predetermined approach trajectory and of a current state of the aircraft, said state comprising at least one current altitude, a current ground speed and a mass of the aircraft; comparing the energy Eaero with a predetermined maximum energy Emax, and when the energy Eaero is greater than the energy Emax, determining the corrected lateral approach trajectory as a function of the difference between the energy of the aircraft Eaero and the maximum energy Emax.
Owner:THALES SA
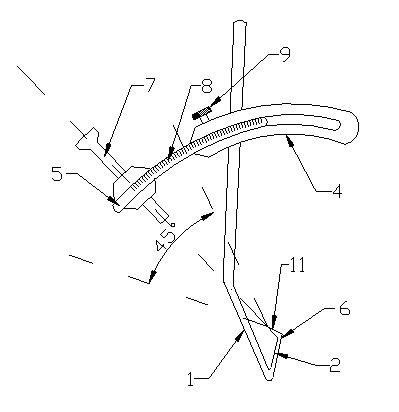
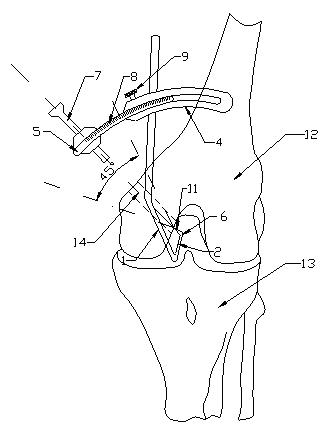
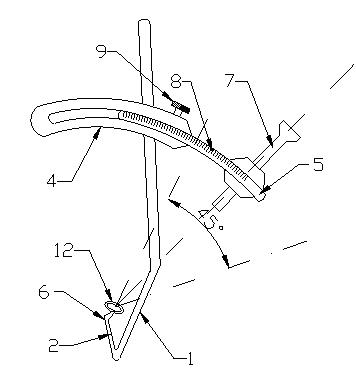
Knee joint anterior and posterior cruciate ligament femoral tunnel positioner
The invention relates to a knee joint anterior and posterior cruciate ligament femoral tunnel positioner. The positioner comprises a hook body, wherein the hook head of the hook body extends in the knee joint cavity and points to the anterior and posterior cruciate ligament femoral insertion; the long stem of the hook head is upward and above the front of the femur of knee joint and is connected with an arc chute which is arranged laterally; a curved lever which can slide relatively to the arc chute is embedded in the arc chute; and the movable end of the curved lever is provided with a drillstem guide sleeve which directly points to the tip of the ligament hook head. By adopting the positioner of the invention, the problem that the previous arthroscope can perform observation only through the lateral approach and the visual blind area is caused, can be solved; and the reconstruction of femoral tunnel can be better performed from the physical point of the ligament, thus the reconstruction of femoral tunnel in clinic has higher repeatability and operability, the accuracy degree of operations is greatly increased, the operating time is reduced, and the positioner has great use value and wide market space.
Owner:FUZHOU GENERAL HOSPITAL OF NANJING MILITARY COMMAND P L A
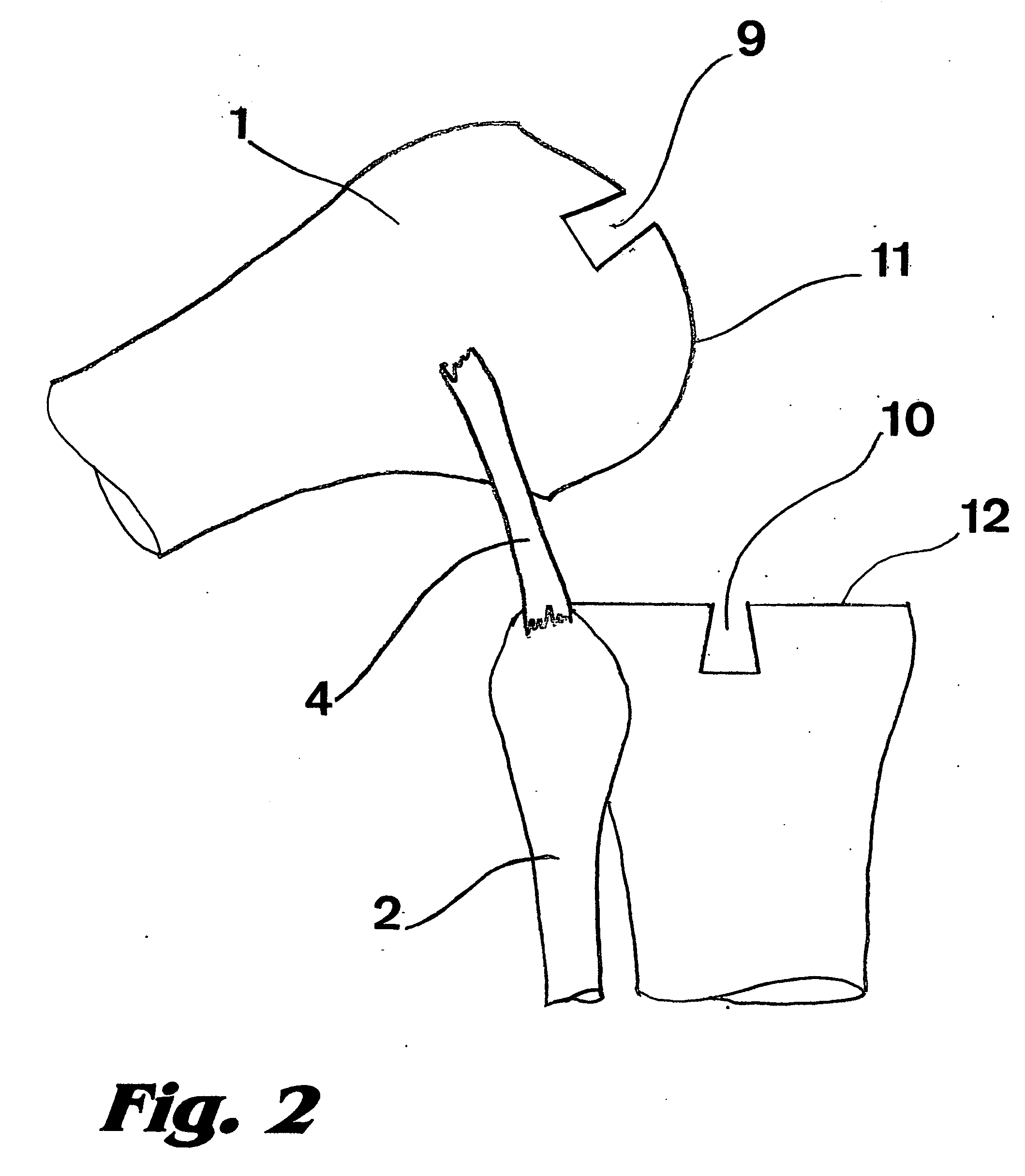
Method and device for placing materials in the spine
A device and method for removing tissue, and if required, other undesired materials from an intervertebral disc or vertebral body. An elongated arcuate, and preferably S-shaped tool is used to progressively remove material from the interior of the mammalian intervertebral disc or vertebral body. A sheath introduces the elongated tool by a posterior, postero-lateral or lateral approach. The shape of the elongated tool is formed within a guide or lumen of the sheath for transportation through the sheath. The elongated tool assumes its predetermined arcuate shape when no pressure or force is applied to the tool by the sheath as the elongated tool exits the sheath. The device and method allow positioning of new material in the intervertebral disc and / or vertebral body. The new material may be tissue, therapeutic agents, mechanical devices such as spacers, or agents that will fuse vertebral bodies.
Owner:FORREST LEONARD EDWARD
Bicondylar knee resurfacing prosthesis
A bicondylar knee resurfacing prosthesis for limited knee resurfacing procedure inserted through a direct mini lateral approach, which avoid disruption of the extensor mechanism or damage to the quadriceps tendon. The inventive device includes a reduced femoral component, a metallic tibial tray and a polyethylene tibial insert.A metallic reduced femoral component having a thin polished convex articular surface in a form of two condyles, medial and lateral, connected with an intercondylar bridge. The concave surface having a metallic dovetail transverse ridge across the entire width of the femoral component precisely positioned at the level of maximum weight bearing contact in full extension. The concave surface provides fine asperities and voids to allow bone ingrowth or can be cemented using conventional methyl methacrylate bone cement.The tibial tray provides a dovetail recess along the superior surface and transversely across its entire width, which will slidingly receive the polyethylene tibial insert. The bottom surface of the metallic tibial tray in contact with the tibial plateau has a dovetail ridge, which extends transversely along the entire width of the tibial component securing the tibial component to the resected tibial plateau.The tibial insert is made of polyethylene and has the same shape and size of the tibial metallic tray. It provides a dovetail that matches the one on the tibial tray so it can be easily driven in and locked in place. The surface of the tray provides two shallow condylar grooves that conformably match the condylar convex surfaces of the metallic femoral component.
Owner:TERMANINI ZAFER
Method of lateral facet approach, decompression and fusion using screws and staples as well as arthroplasty
ActiveUS8986305B2Improve stabilityFixationSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisPosterior approachFixation method
A method of performing vertebral facet fusion by lateral approach and related devices. The lateral approach to facet fusion involves identifying the lateral mass and introducing any of the fixation methods known or described herein laterally at one or more facets through the use of a Kirschner wire guide, a cannulated bone drill and cooperatively cannulated staple guide. A surgical bone staple have a perforated bridge is used across the lateral facet joint where fixation is required. Where fusion is desired, a bone screw have lateral perforations of the shank is inserted through the cannulated staple guide and bridge perforation at the joint to promote fusion. A staple cap and graft container for overlay grafting may be utilized for additional fusion. The method involves less surgical time, reduced blood loss and discomfort for the patient as compared to the posterior approach.
Owner:AFLATOON KAMRAN +1
Percutaneous posterior lateral in-situ cage
Implants, tools and techniques facilitate a percutaneous posterior lateral approach to the placement of an in-situ cage, and an inventive cage design to meet this objective. In terms of apparatus, the invention includes a laterally expandable cage, including a locking gate, enabling the system to be introduced into an intradiscal space through a minimally invasive percutaneous posteo-lateral approach. In addition to the cage designs, adapted to hold bone graft and / or other biologic materials, the invention includes other novel instruments, including an introducer associated with cage placement, deployment and closure.
Owner:CTL MEDICAL CORP
Minimally invasive spine internal fixation system
InactiveUS20090112261A1Strong interfaceIncrease percentageSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisInternal fixationLumbar vertebral column
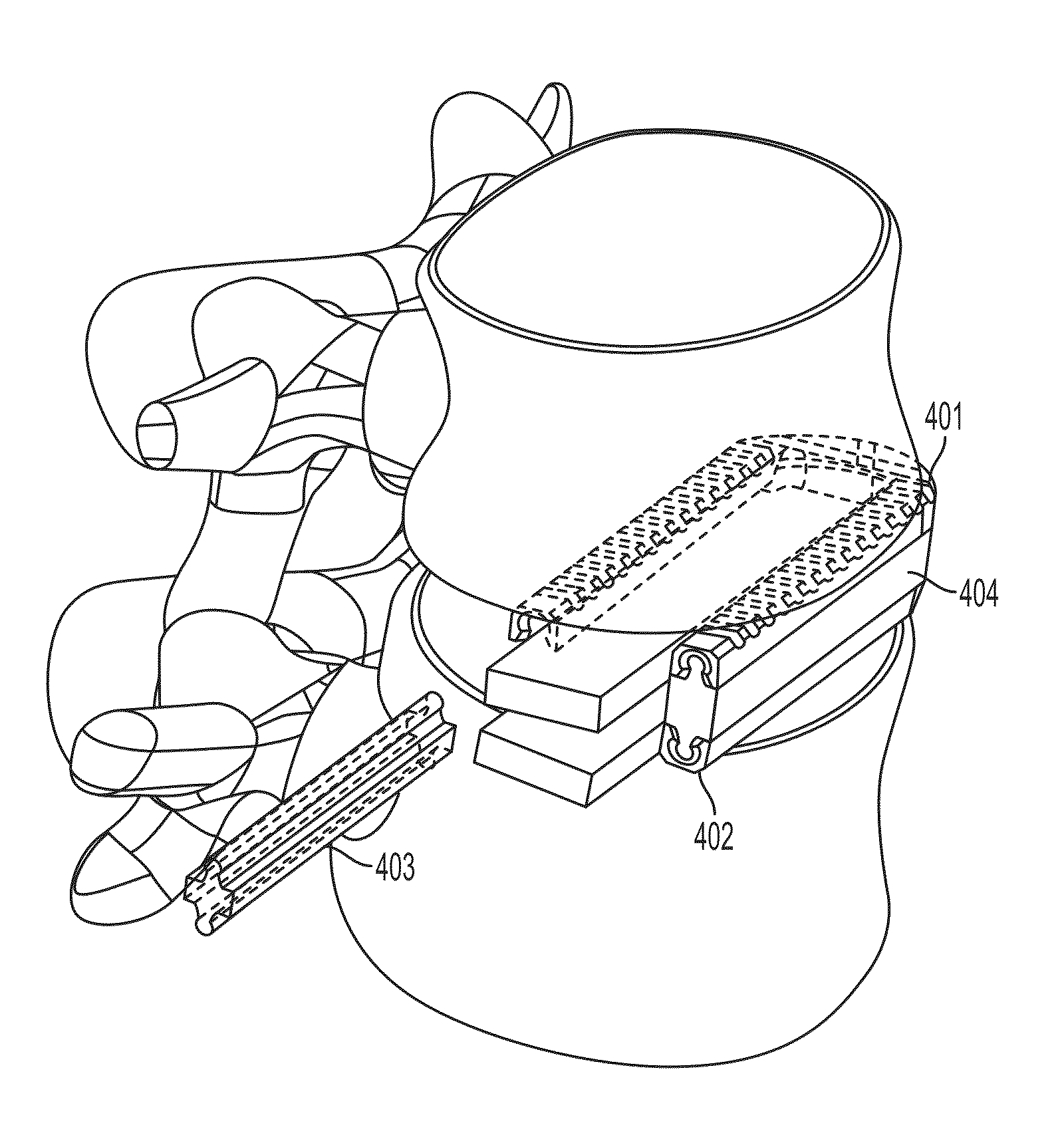
A minimally invasive modular system is disclosed for stabilizing the anterior column of the spine through an anterior or lateral approach. Bone anchors are implanted into the vertebral bodies of adjacent vertebrae and serve as a foundation for a fixation system. The anchors comprise an interface surface that allows an interconnecting link to be secured to the anchors in a low-profile manner with minimum protrusion beyond the vertebral members. The link may be secured to the bone anchors to affect a compressive interlocking force between the bone anchors and vertebrae.
Owner:BARRY RICHARD J
Discectomy kits with an obturator, guard cannula
ActiveUS20130144320A1Easy to disassembleFacilitate entryDiagnosticsExcision instrumentsSurgical operationForamen intervertebrale
Discectomy kits with obturator, guard cannulas are provided. The kits have a safe and efficient cutting heads for removing a target tissue from a subject during a surgical procedure are provided, the cutting heads composing a part of systems that address several problems, including clogging of state-of-the-art systems during removal of such tissue, for example. The target tissue can include any tissue that is accessible through a small surgical opening, for example, a joint tissue such as a meniscus or an intervertebral tissue, such as a nucleus pulposus. The devices can be referred to as orthopedic tissue removal devices having cutting heads associated with vacuum systems, making the systems useful in several procedures, including X-LIF (lateral approach to an intervertebral fusions) procedures, T-LIF (transforaminal approach to intervertebral fusions) procedures, P-LIF (posterior approach to intervertebral fusions), and a percutaneous, transforaminal approach (Kambin triangle access).
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Bicondylar resurfacing prosthesis and method for insertion through direct lateral approach
A bicondylar implantable prosthesis resurfaces only the weight bearing portion of the patient's femur. The prosthesis includes a thin shell convexly curved outer articular surface including a medial condyle, a lateral condyle, and an intercondylar bridge, and a concave inner surface of the prosthesis that has at least one transverse ridge extending across the width of the prosthesis. When the prosthesis is implanted on the weight bearing portion of the femur, the entire outer surface of the curved articular surface is sized to resurface substantially only the weight bearing portion and no portion of the patello-femoral joint of the knee. The prosthesis is configured to be implantable by a lateral insertion through a direct lateral approach to a retropatellar region of the patient's knee joint, during which insertion the at least one transverse ridge guides the prosthesis along a laterally resected surface of the femur.
Owner:TERMANINI ZAFER
Method of lateral facet approach, decompression and fusion using screws and staples as well as arthroplasty
ActiveUS8894651B2Improve stabilityCheap manufacturingSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisPosterior approachLateral mass
A method of performing vertebral facet fusion by lateral approach and related devices. The lateral approach to facet fusion involves identifying the lateral mass and then introducing any of the fixation methods known or described herein laterally at one or more facets through the use of a hollow cannula. A surgical bone staple have a perforated bridge is used across the lateral facet joint where fixation is required. Where fusion is desired, a bone screw have lateral perforations of the shank is inserted through the bridge perforation at the joint to promote fusion. The staple and screw may be used in conjunction with one another or individually. The facet joint may be distracted prior to fixation to increase the foraminal space and decompress the neural structures to relieve pain. The method involves less surgical time, reduced blood loss and discomfort for the patient as compared to the posterior approach.
Owner:AFLATOON KAMRAN
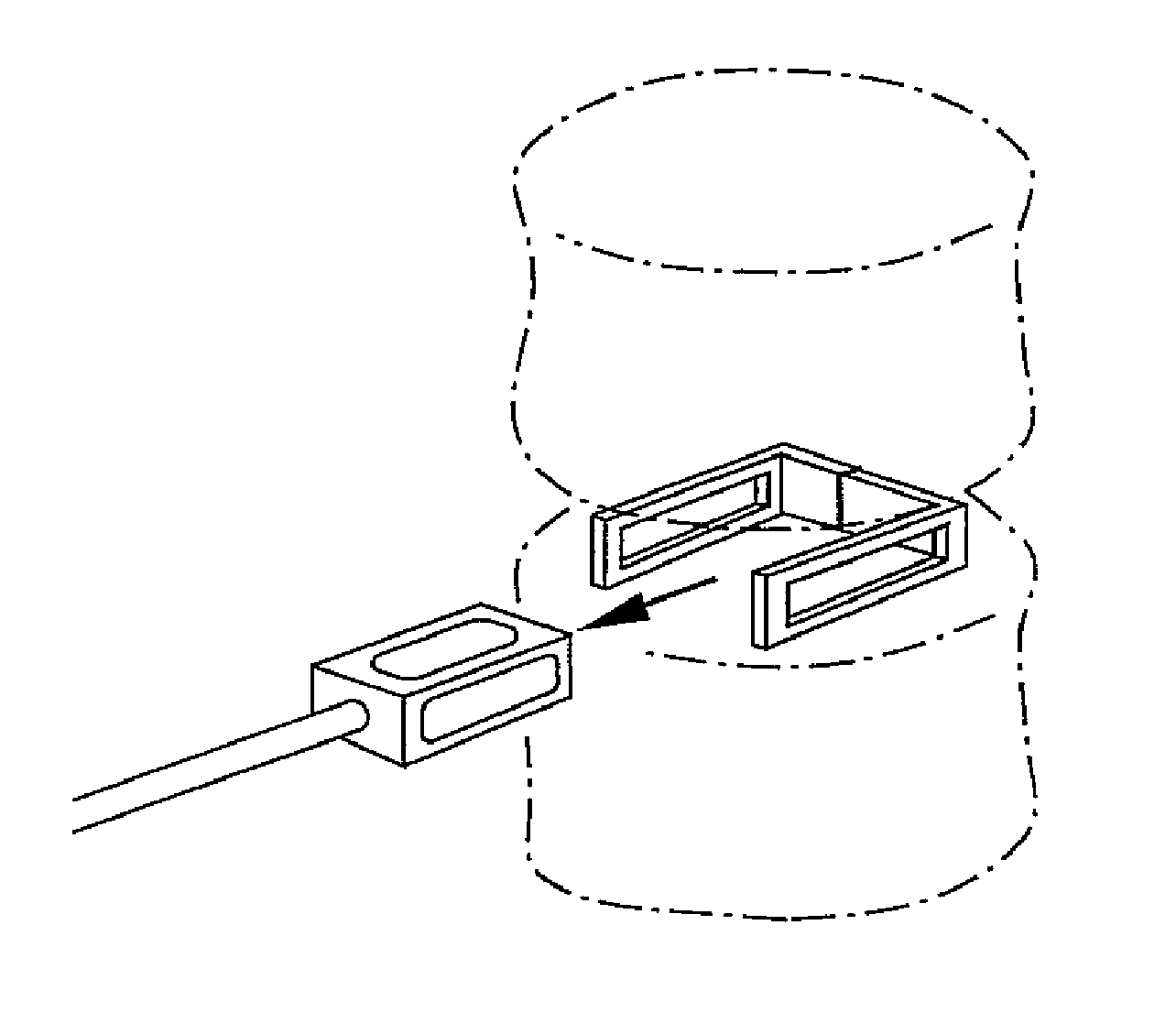
Apparatus for locating the position of a spinal implant during surgery
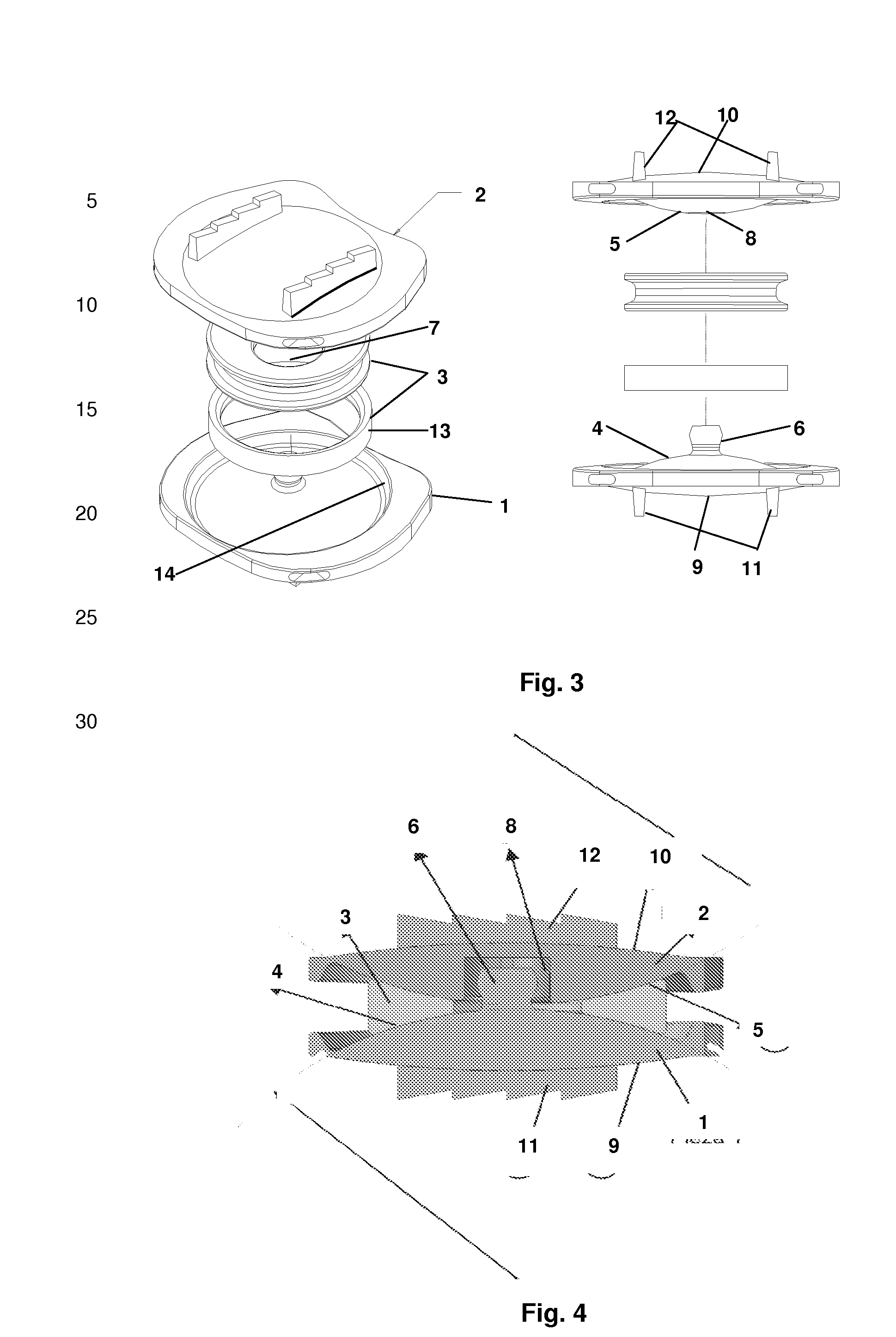
An apparatus and method for locating the position of a spinal implant in an intradiscal space patient during surgery, comprising a spinal implant formed of radiolucent material and a releasably attached inserter comprising a positioning element including thereon a marker of material more radiopaque than the material of the spinal implant. The positioning element extends into the implant such that the marker is positioned at a predetermined location within the implant, the positioning element with the radiopaque maker being removable from the spinal implant after insertion. In a particular method of locating the position of the spinal implant, the spinal implant is inserted from the lateral approach.
Owner:SPINEWAVE
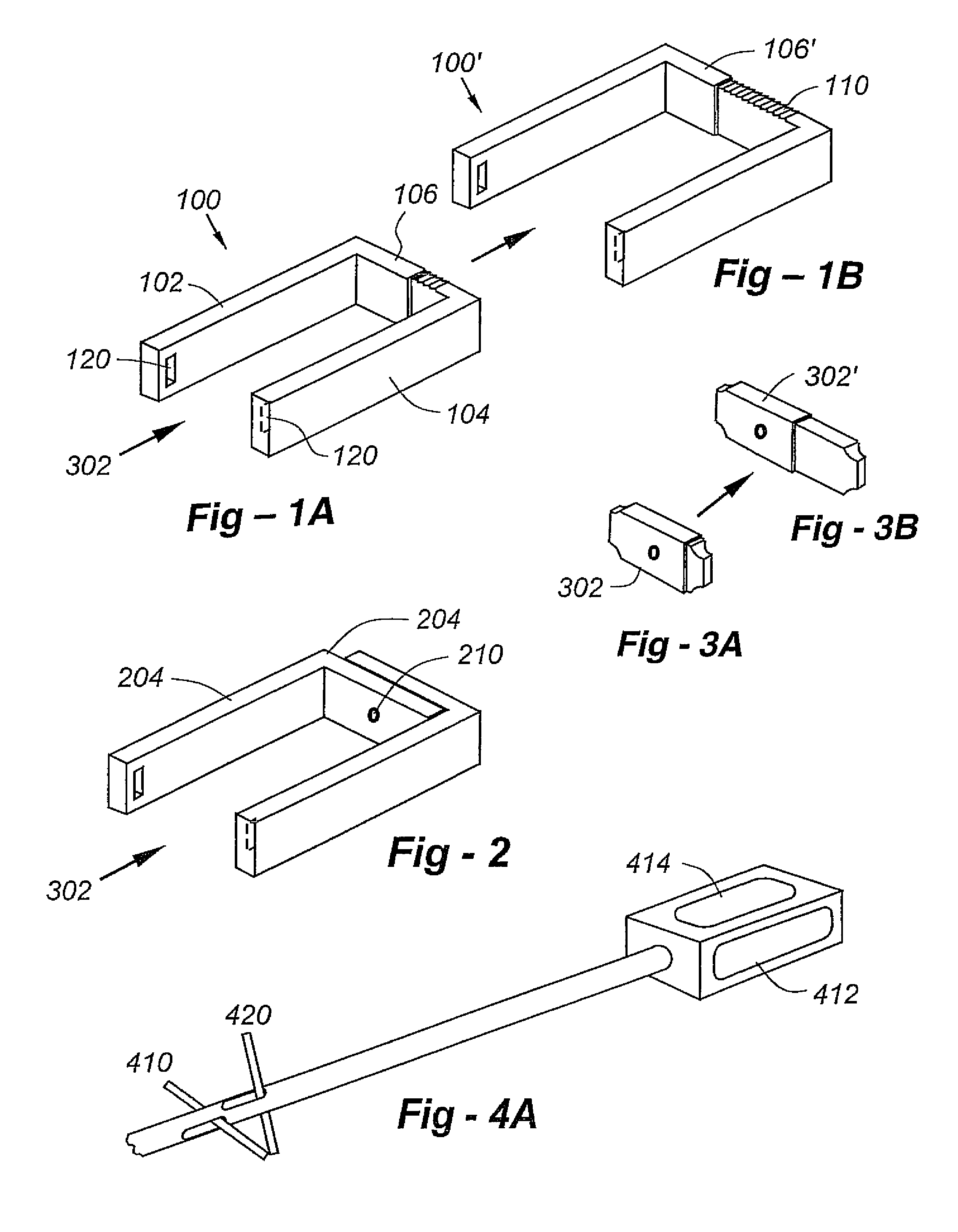
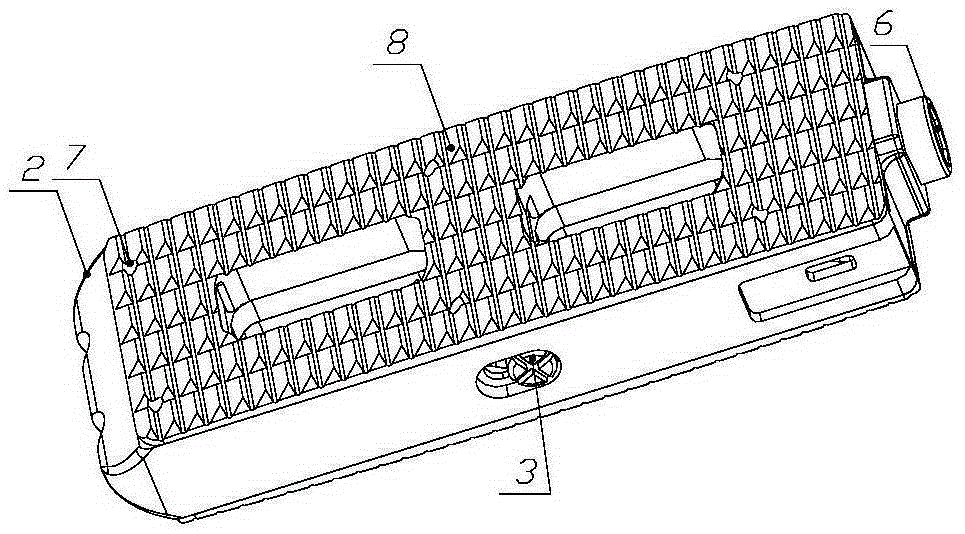
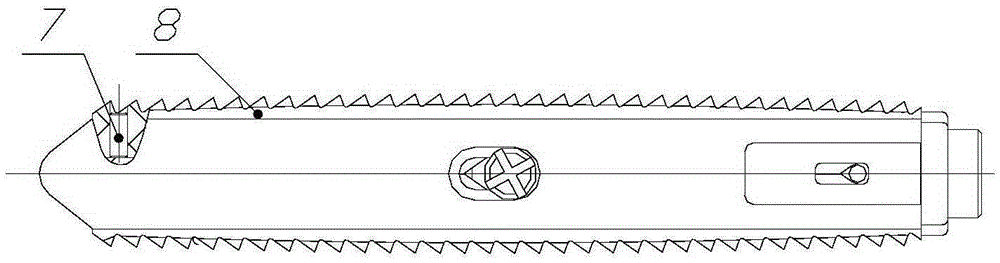
Opening type interbody fusion cage
The invention provides an opening type interbody fusion cage. The opening type interbody fusion cage comprises a fusion cage body, a push block, a jackscrew and two end covers. The fusion cage body is in a rectangular frame shape, the push block is installed in the fusion cage body, the two end covers are arranged at the top and the bottom of the fusion cage body respectively, a rectangular boss is arranged on one end face of the fusion cage body, the other end of the fusion cage body is in a transitional sharp corner shape, the jackscrew is arranged in the middle of the rectangular boss and connected with the rectangular boss through threads, and wedge-shaped protrusions are arranged at the two ends and the middle poison of the push block respectively. In a working state, the ends, close to the jackscrew, of the wedge-shaped protrusions are platforms, and a first round hole matched with the jackscrew in installation is formed in the platform of the wedge-shaped protrusion, close to the jackscrew, of the push block. Tooth-shaped protrusions are evenly distributed on the upper surfaces of the end covers, and wedge-shaped grooves matched with the wedge-shaped protrusions are formed in the two ends and the middle of the bottoms of the end covers. The jackscrew is rotated to drive the push block to move to one end, and the wedge-shaped protrusions are made to slide along the slopes of the wedge-shaped grooves to open the end covers in parallel. A lateral approach implantation method can be adopted, surgery is simple, damage to the spine is very small, and higher stability is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING FULE SCI & TECH DEV +1
Surgical probe incorporating a dilator
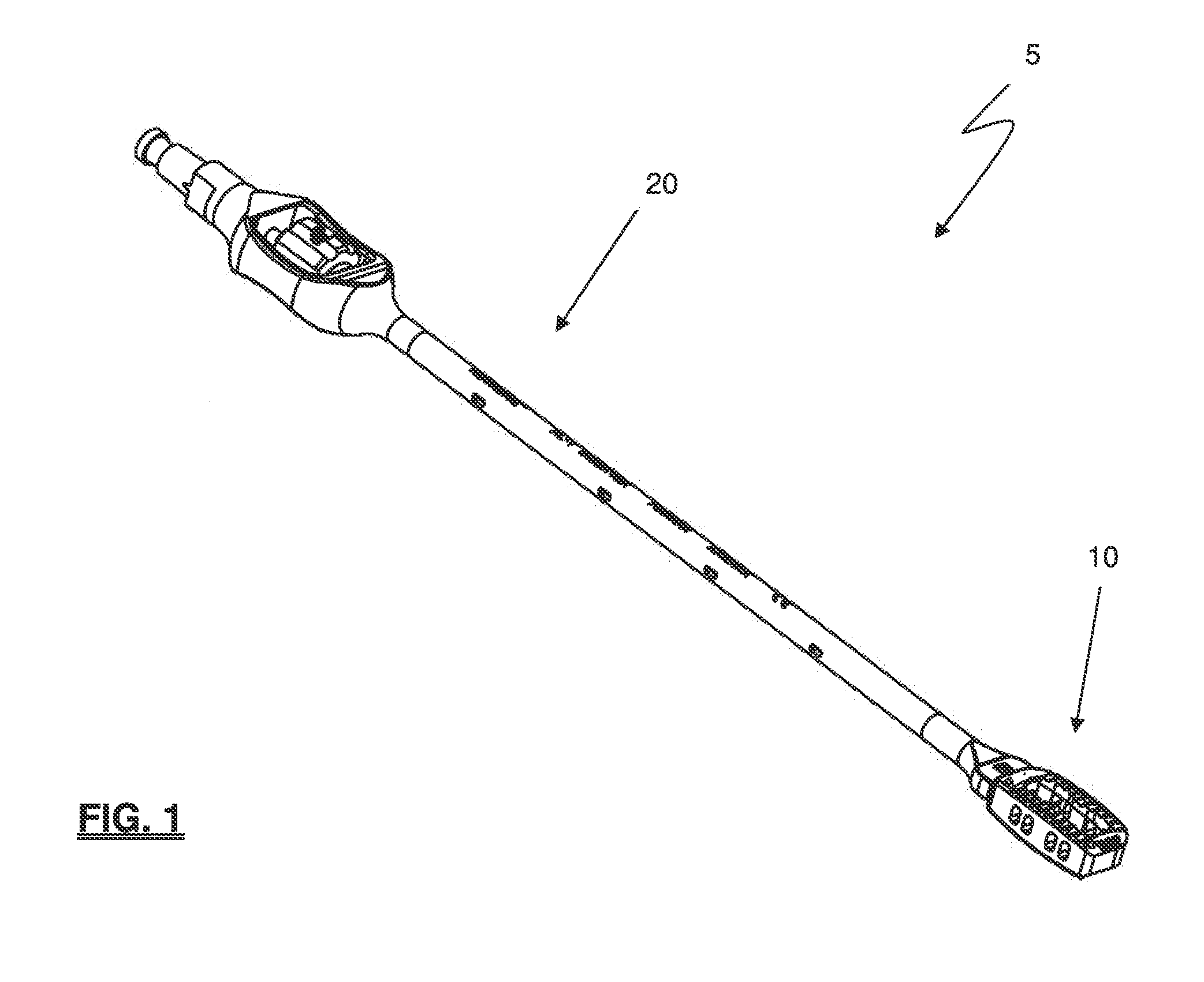
A surgical probe and a method for forming and enlarging an access opening through a psoas muscle to provide for minimally invasive lateral approach for surgical access to a lumber intervertebral disc. A distal end portion of the probe is equipped with an electrode useful for confirming proper location of the probe and includes an inflatable dilator body for enlarging an access opening through tissue adjacent to a spinal column. The probe includes a cannula through which a K wire can be extended to anchor the probe to a patient.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Transosseous spine core approach method implant and instrumentation
InactiveUS7637927B2Simple procedureShorten the timeInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsSpinal columnSurgical approach
The transosseous spinal core approach (TOSCA) represents a novel approach to the interior of the spine or disc space by removing a core from a first bone and performing a procedure, and / or making further enlargements and cuts in the first bone and performing a procedure, and / or making another cut into an adjacent disc space from the first bone hole and performing a procedure and / or continuing by cutting into another second bone and performing a procedure. The process can be further extended into additional spine levels by extending the cutting process. A core can be made at more than one level. The preferred surgical approach is a posterior lateral approach. An anterior surgical approach can be used as well. Any practical surgical approach or any combination of surgical approaches can be utilized to gain access to the first bone. Once the surgical soft tissue access to the first bone is completed TOSCA can be used to gain access to the interior of a vertebral body or disc space. After the procedure is completed in a vertebral body or disc space, usually at least a portion of the bone core is replaced to fill in the core hole.
Owner:HYDE JR EDWARD R
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com