Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
113 results about "Posterior approach" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
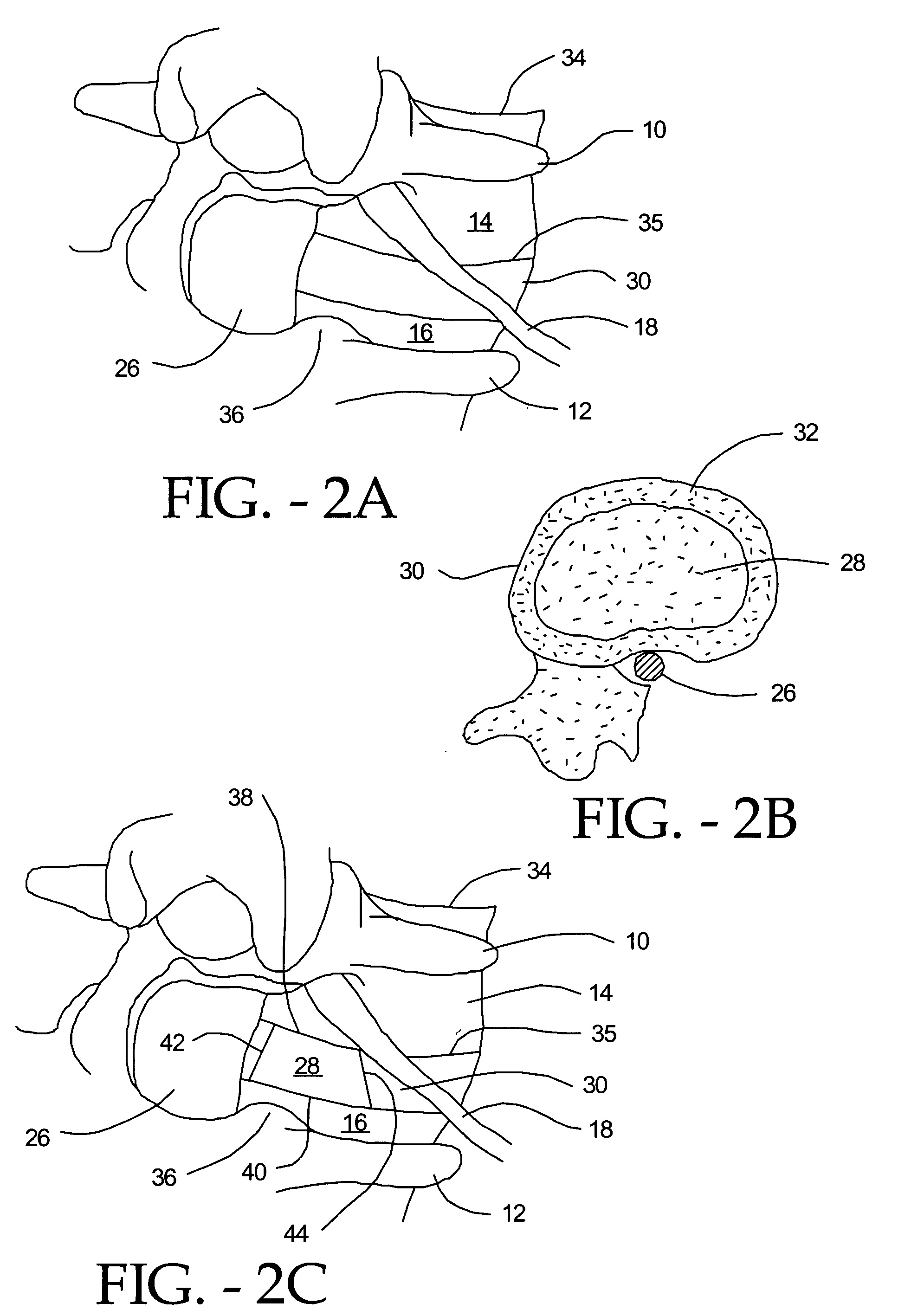
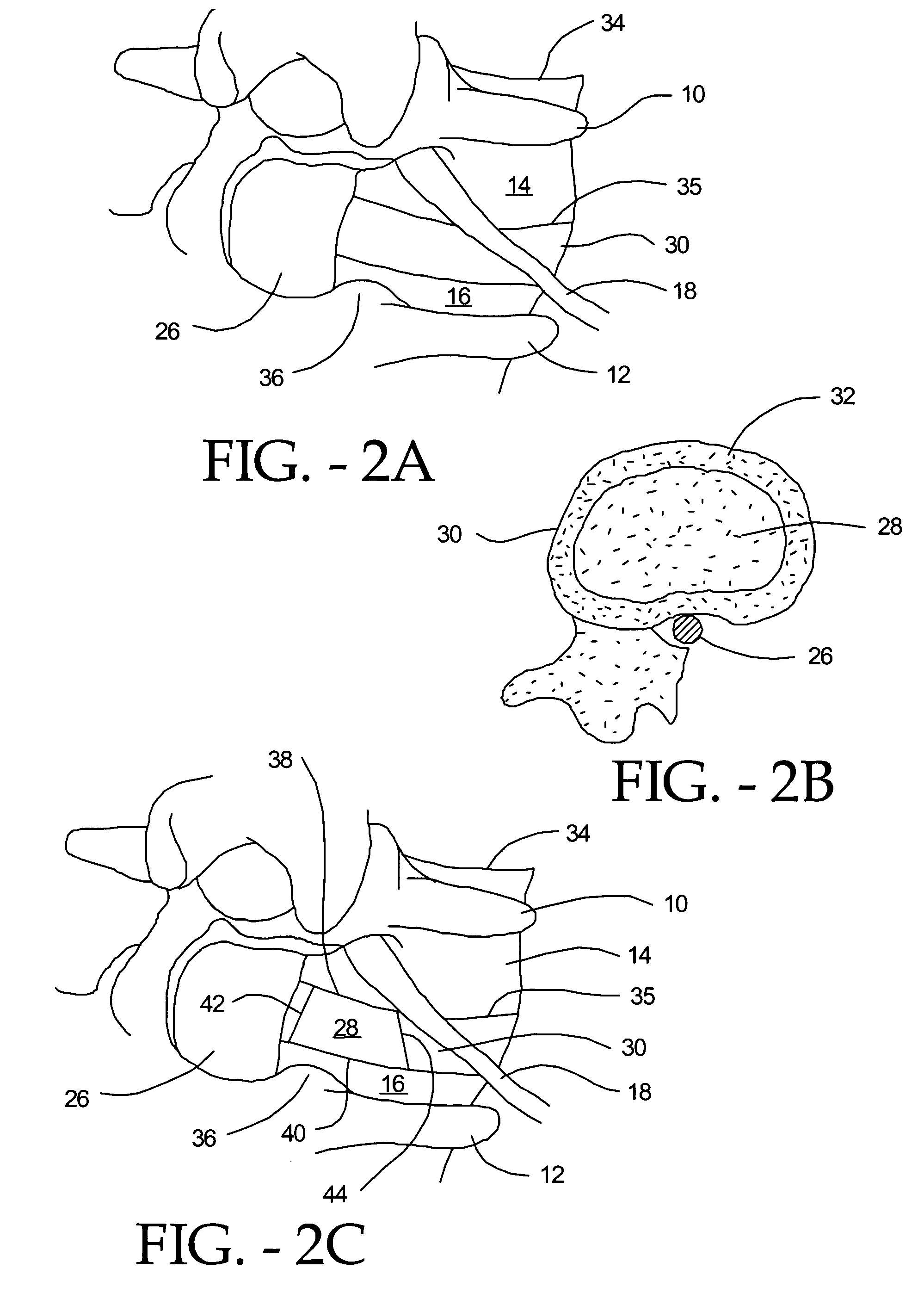
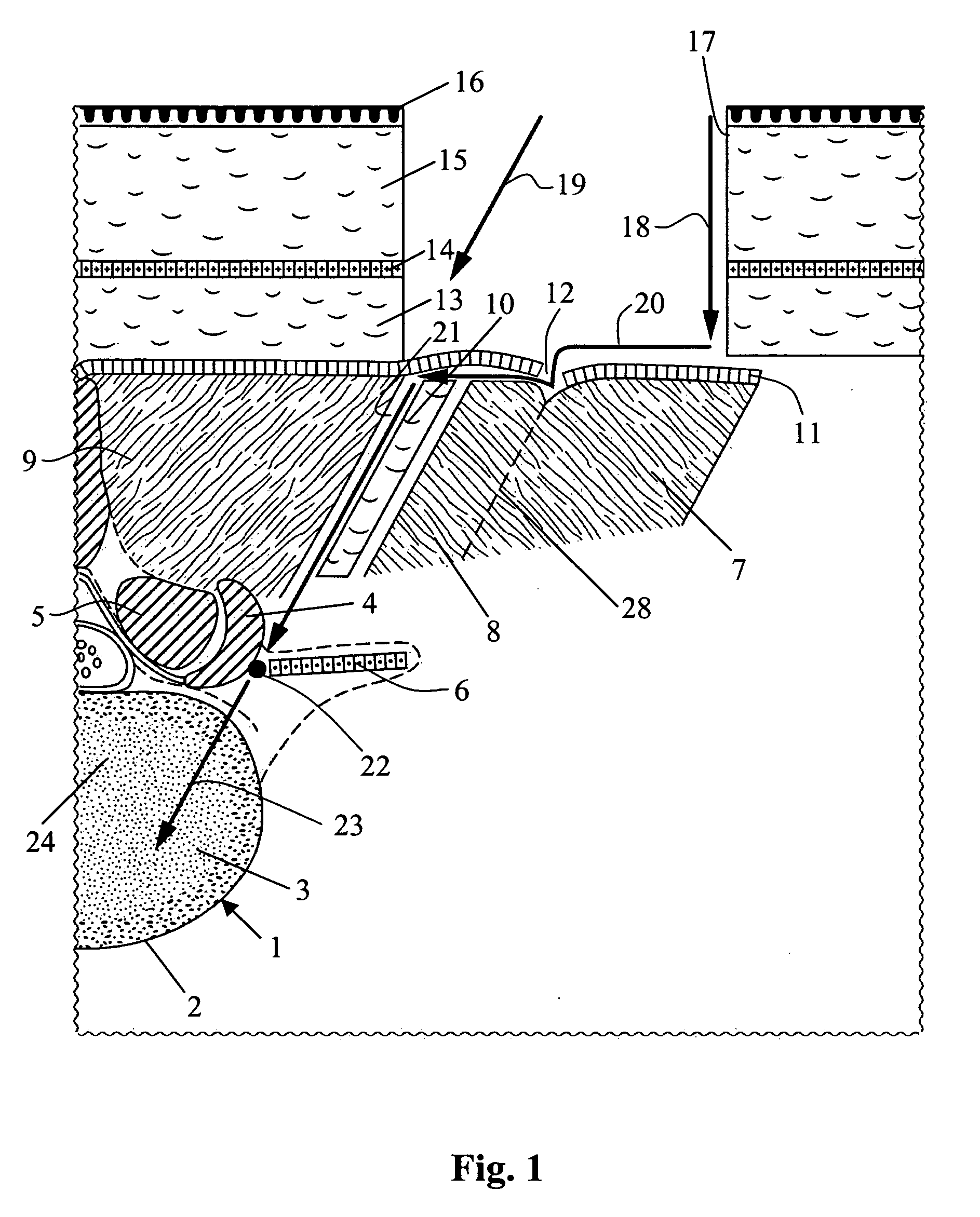
In the posterior approach, an incision is made beside or behind your hip joint. Your surgeon goes through muscle and detaches some of the muscles from the “ball and socket” of the hip joint. Next, your surgeon smoothes out the hip socket and removes cartilage and any debris such as damage to the bone from osteoarthritis.
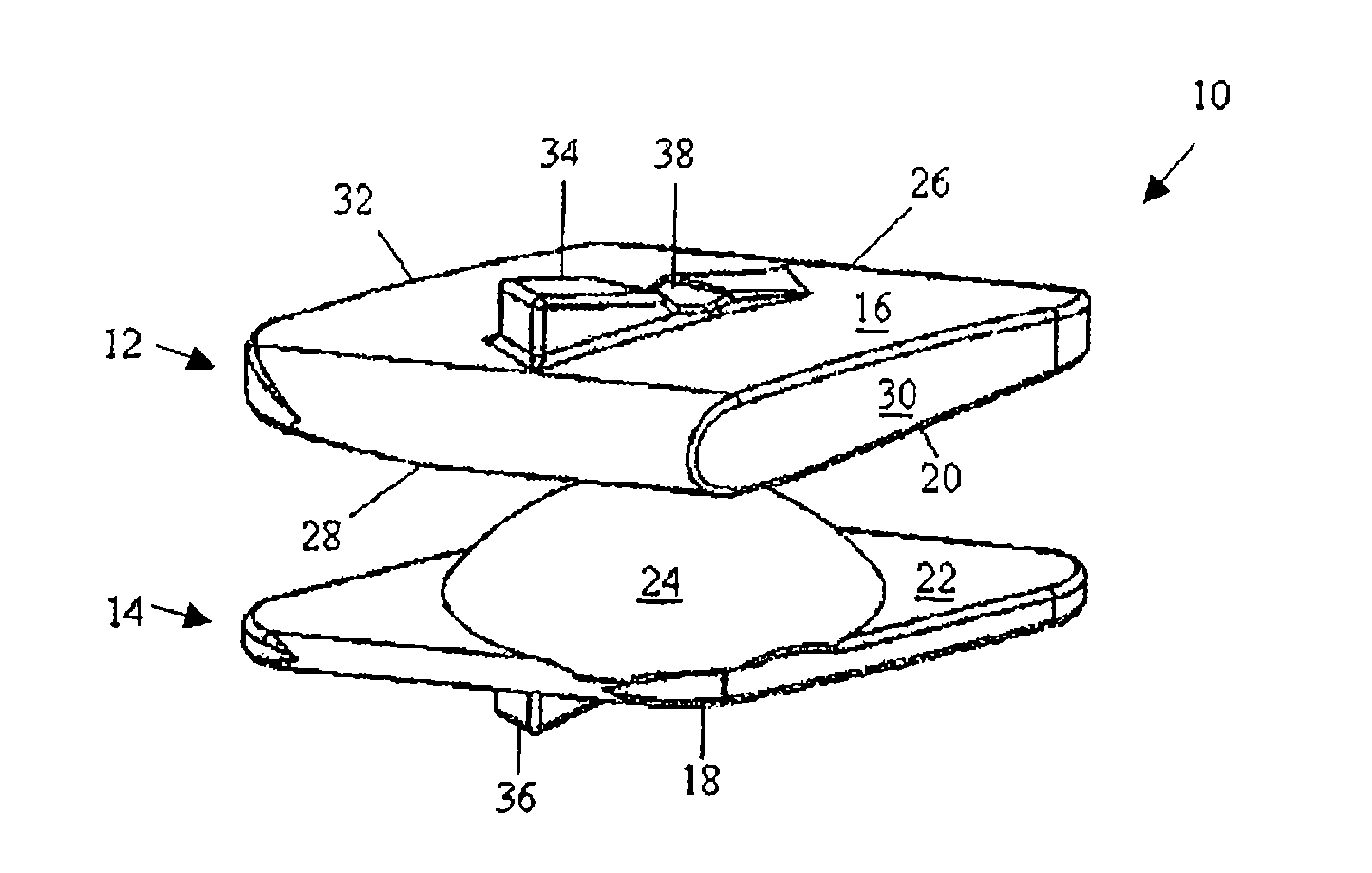
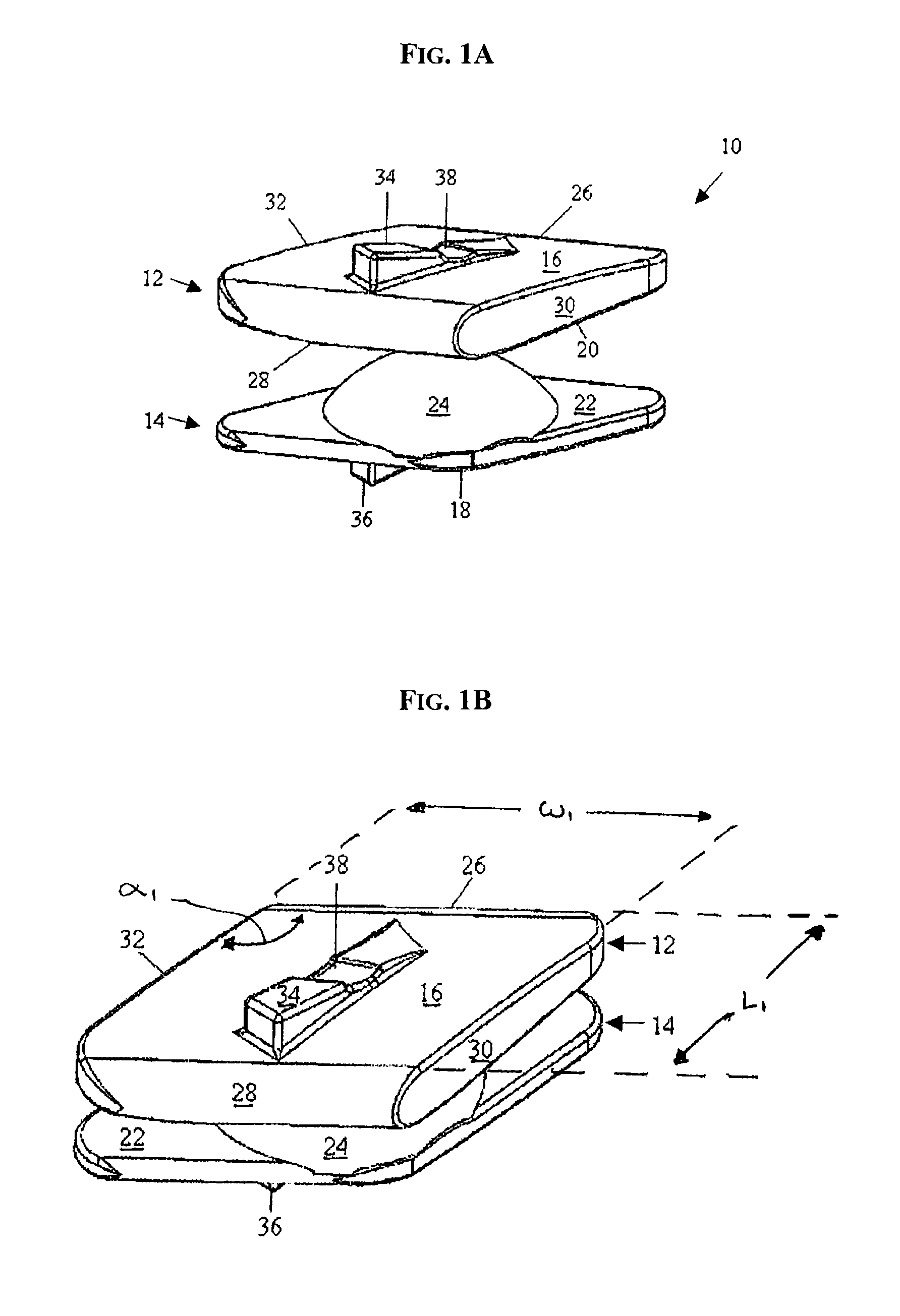
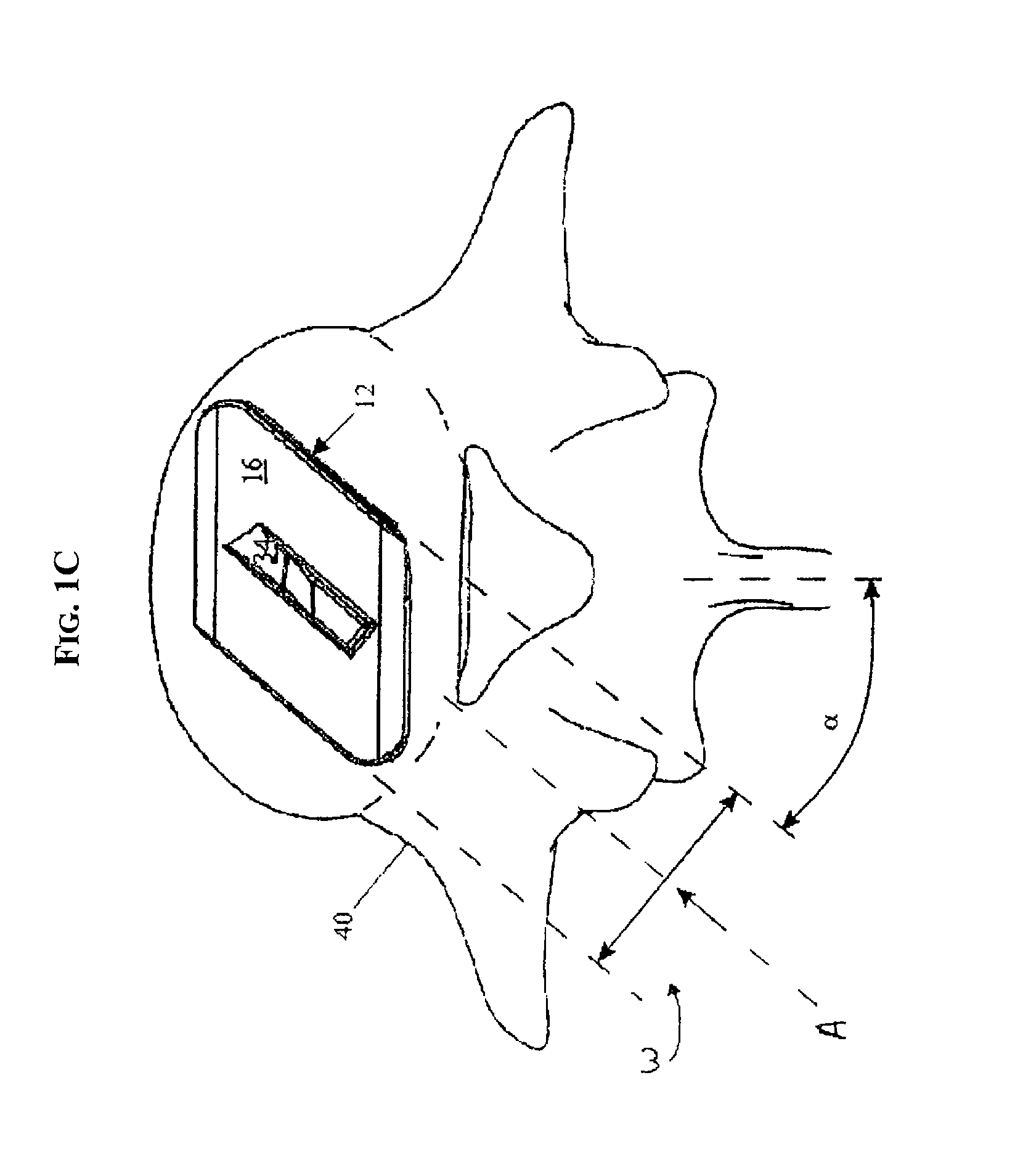
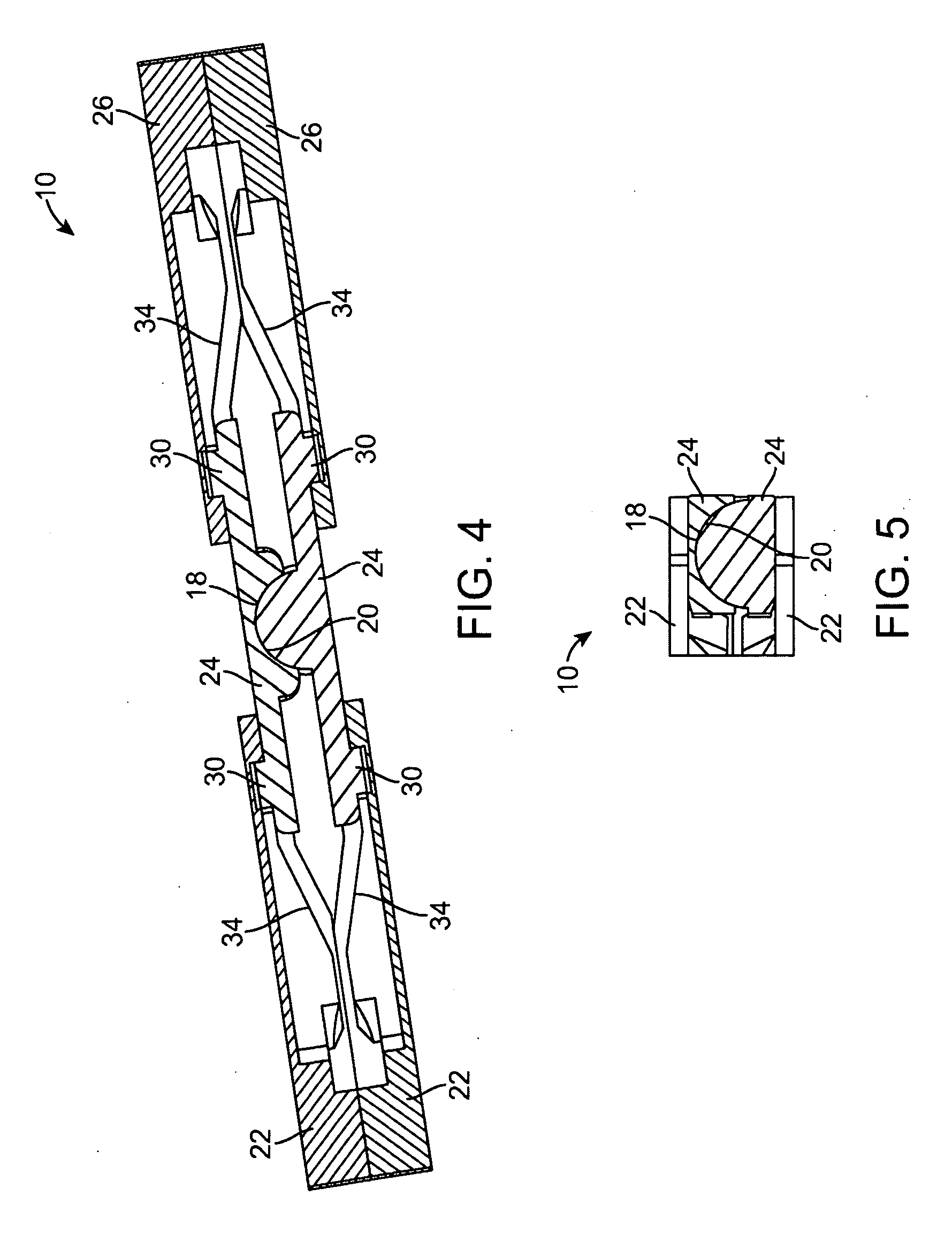
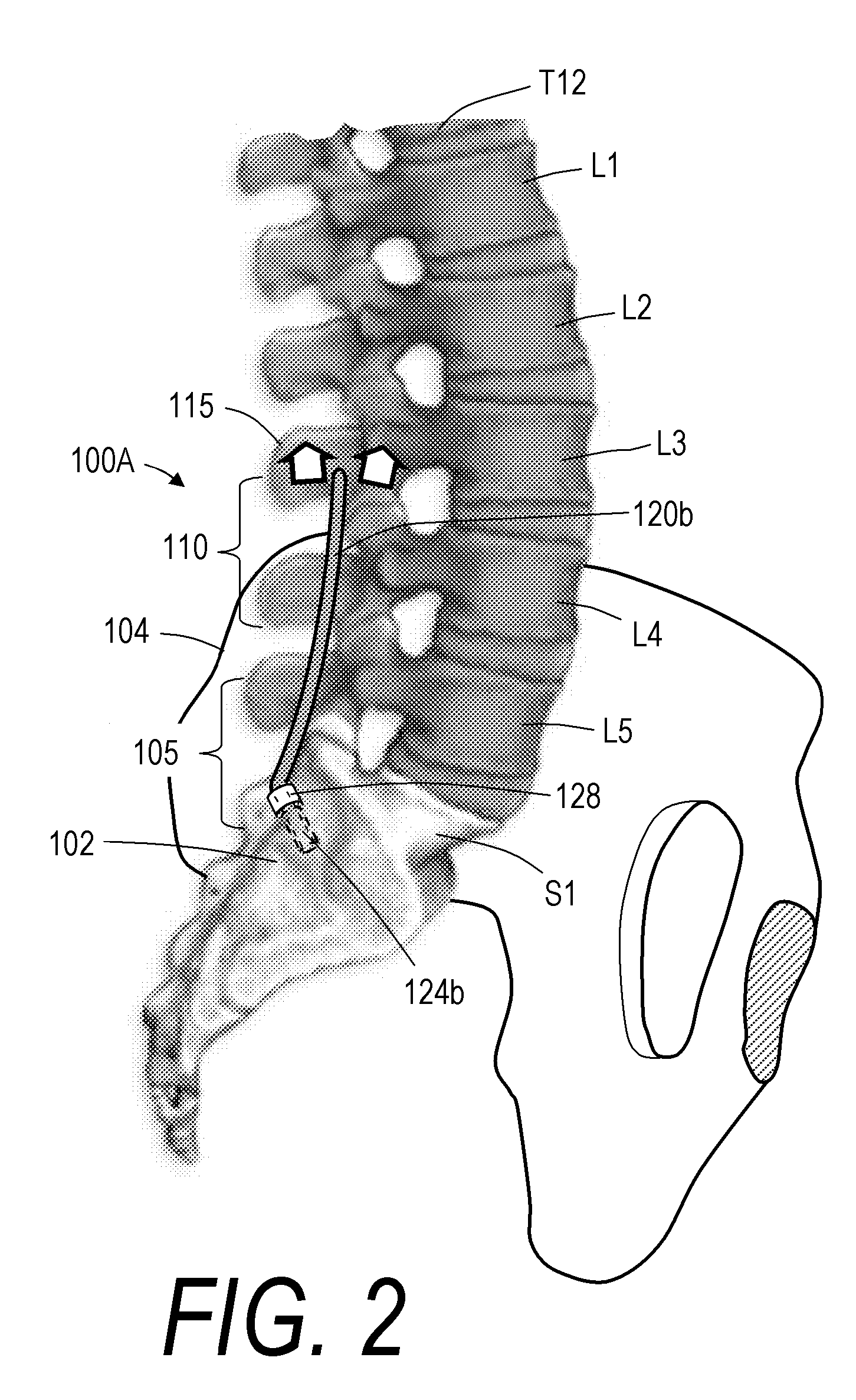
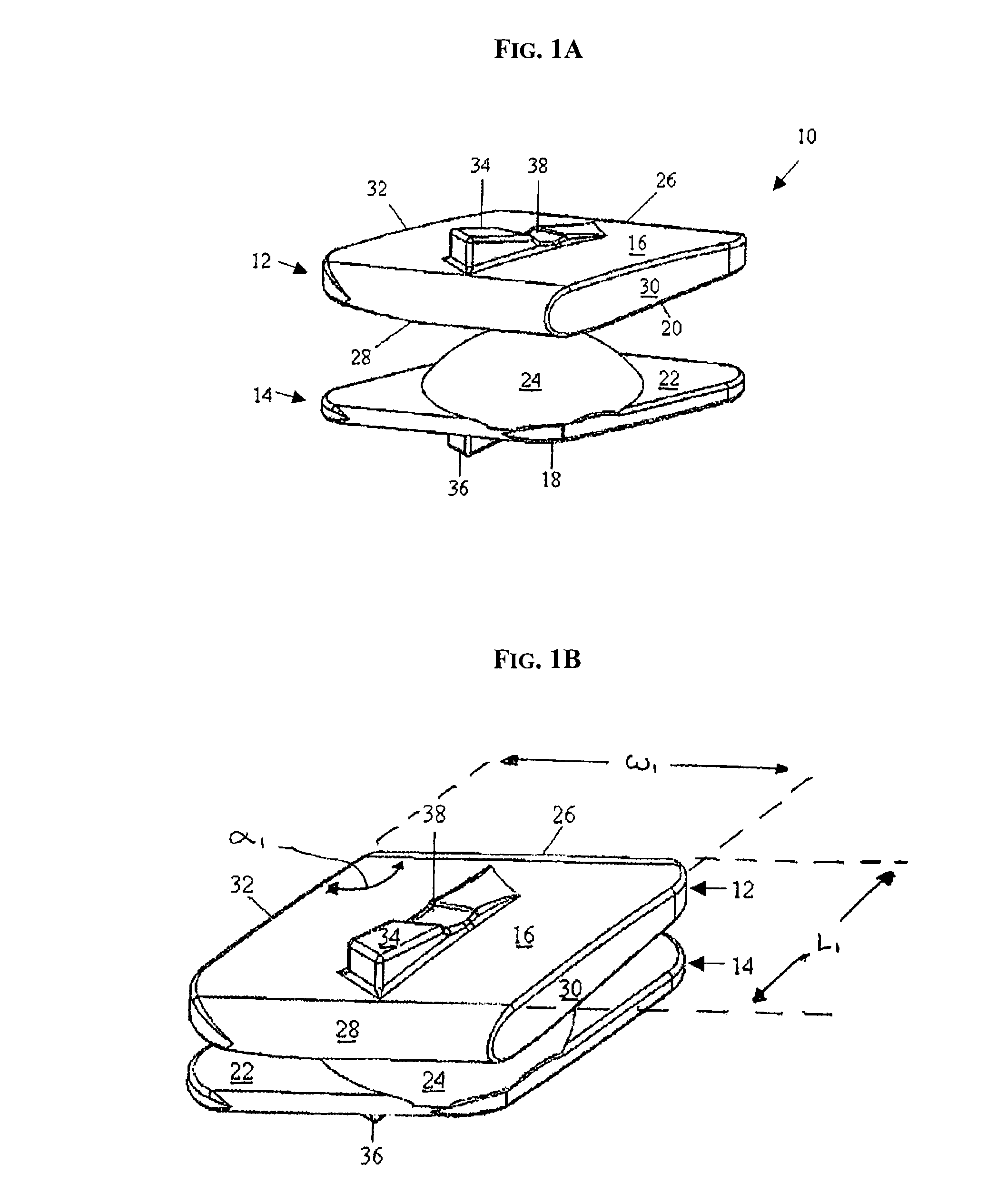
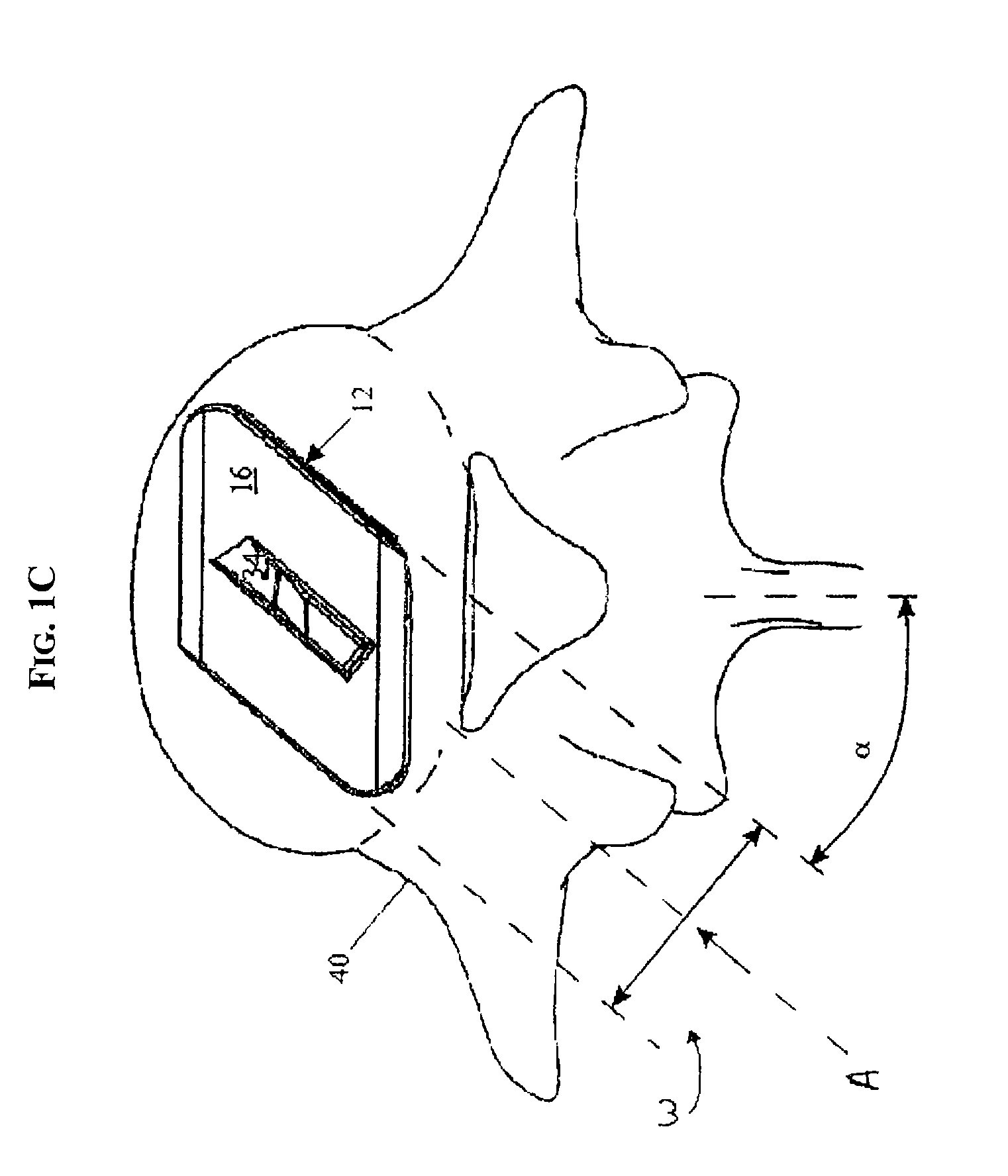
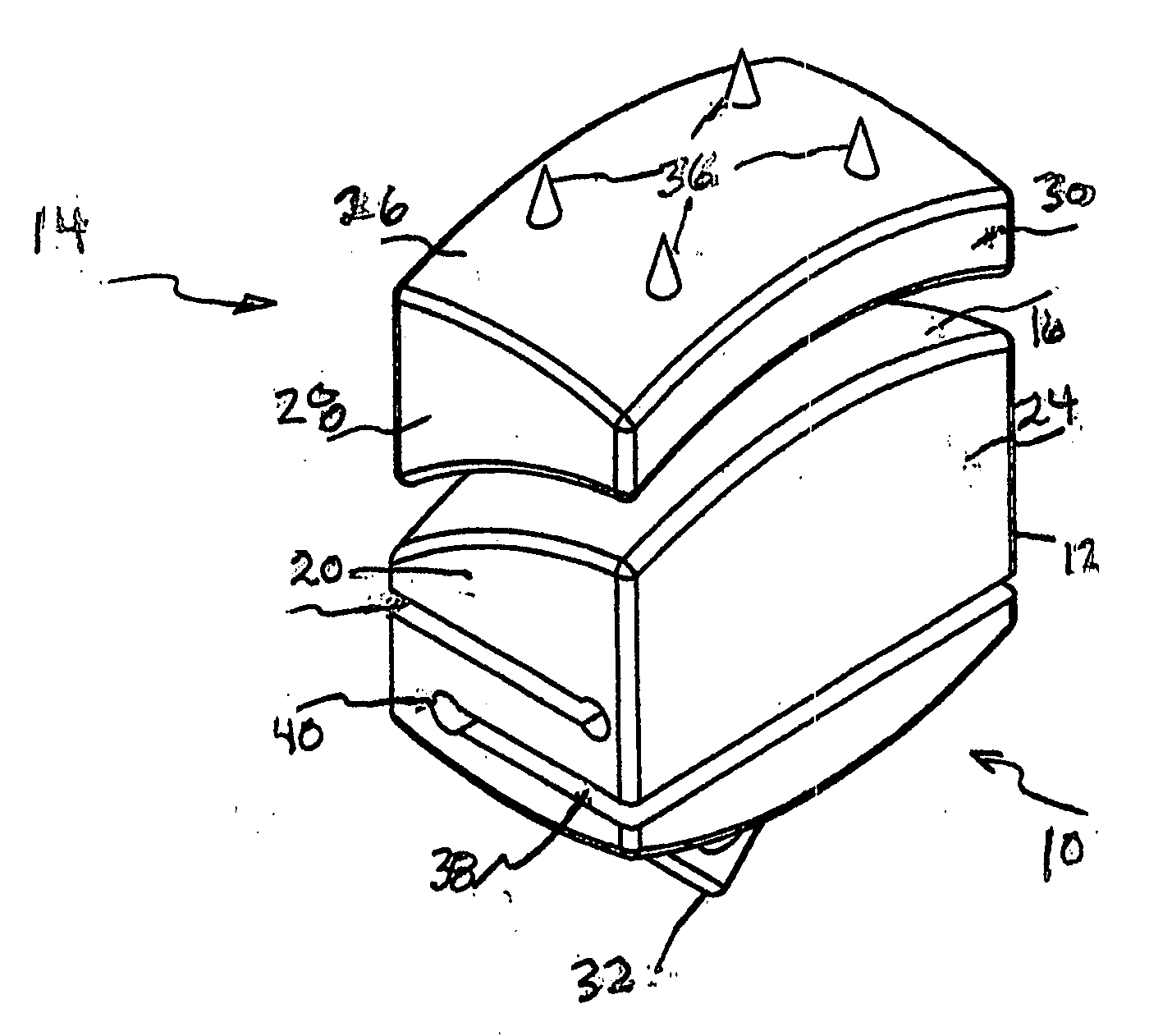
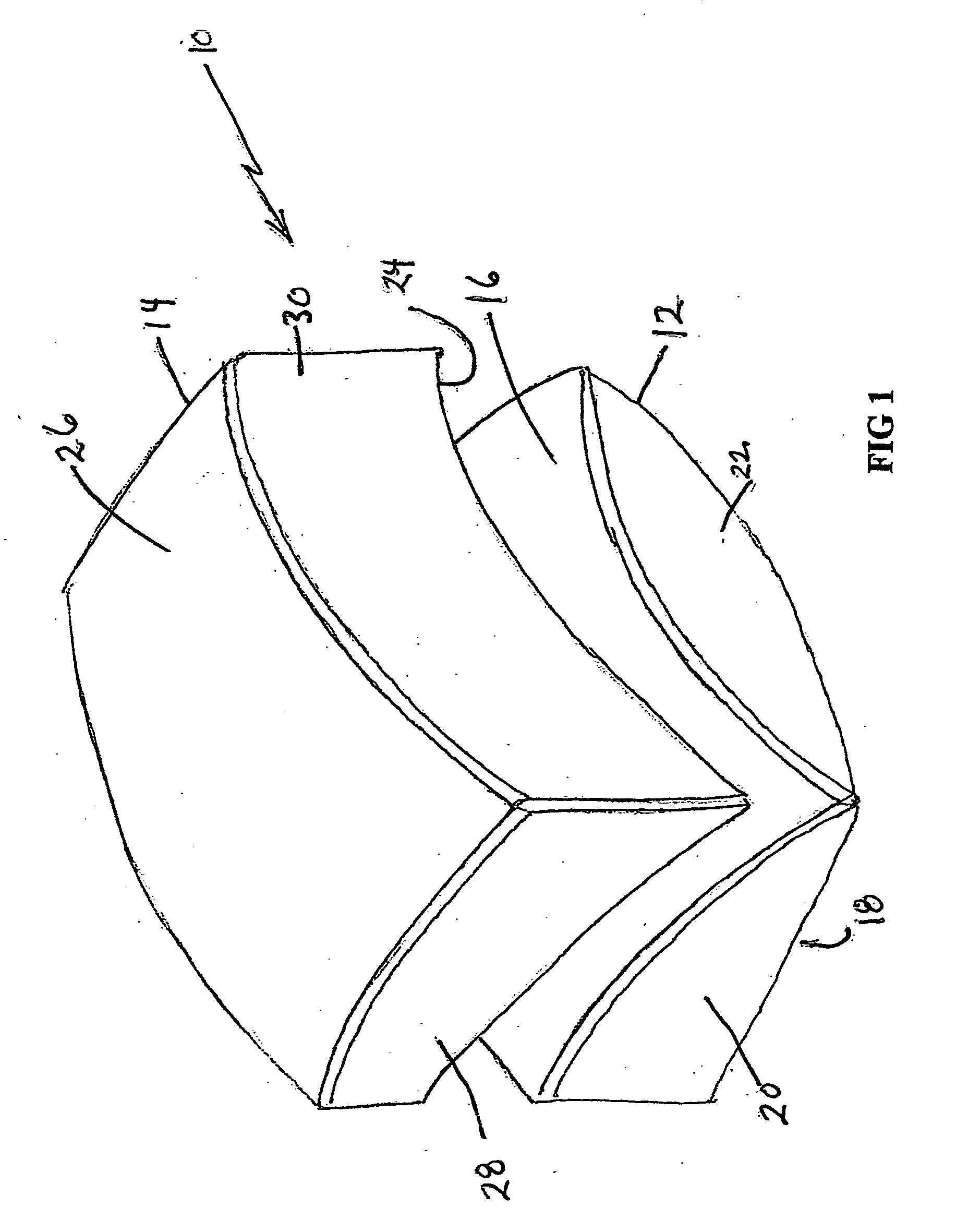
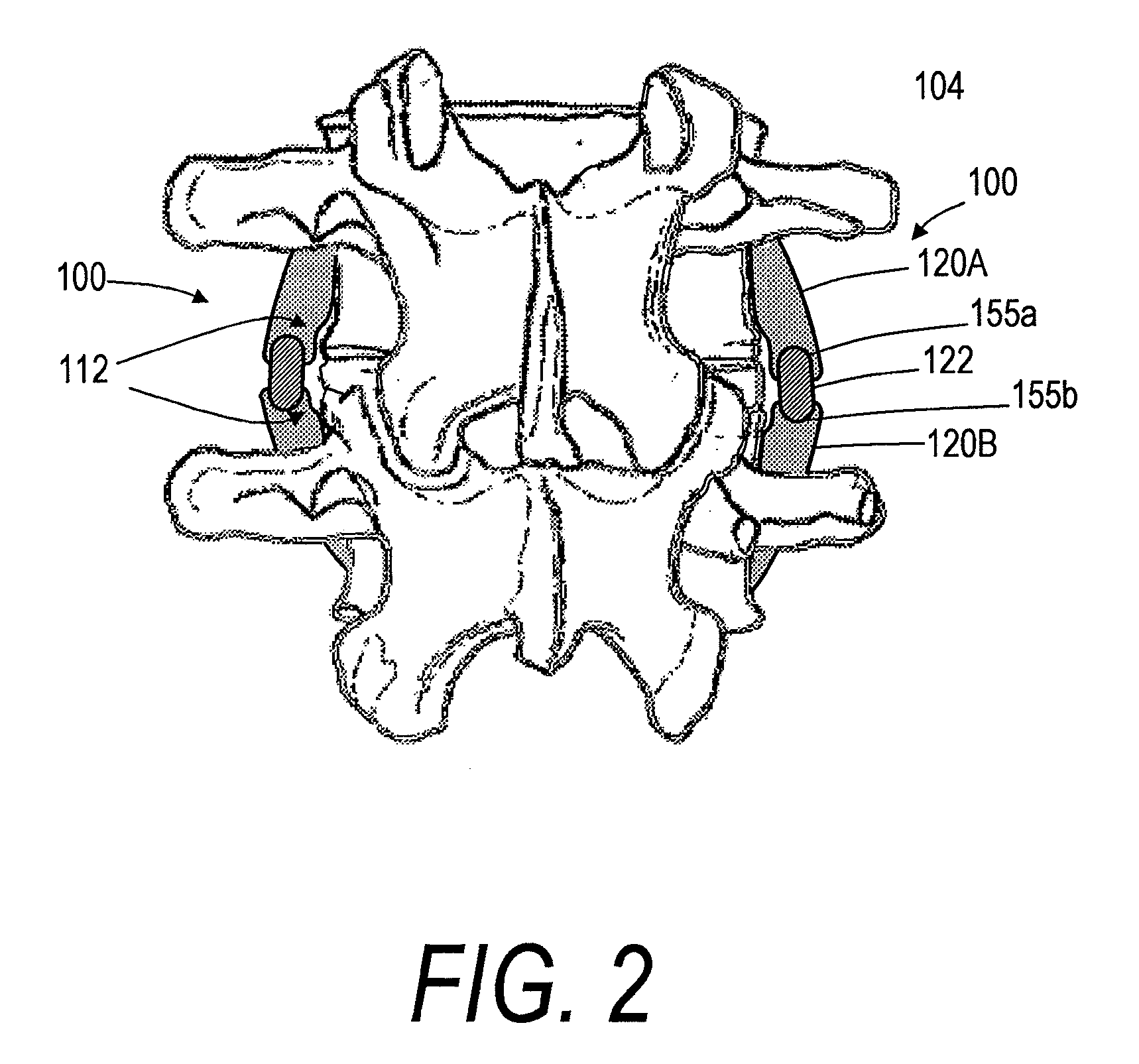
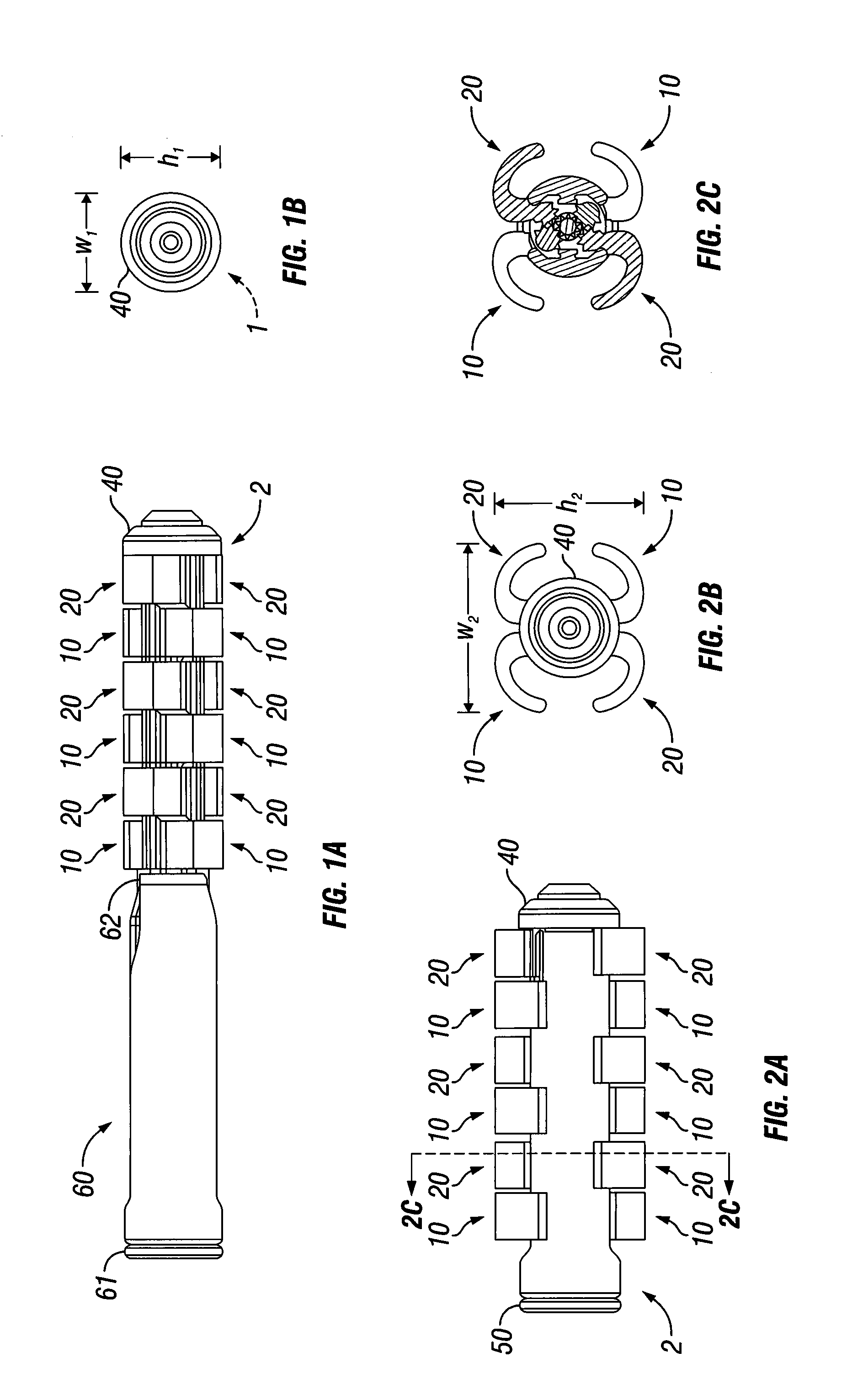
Artificial Disc Replacement Using Posterior Approach
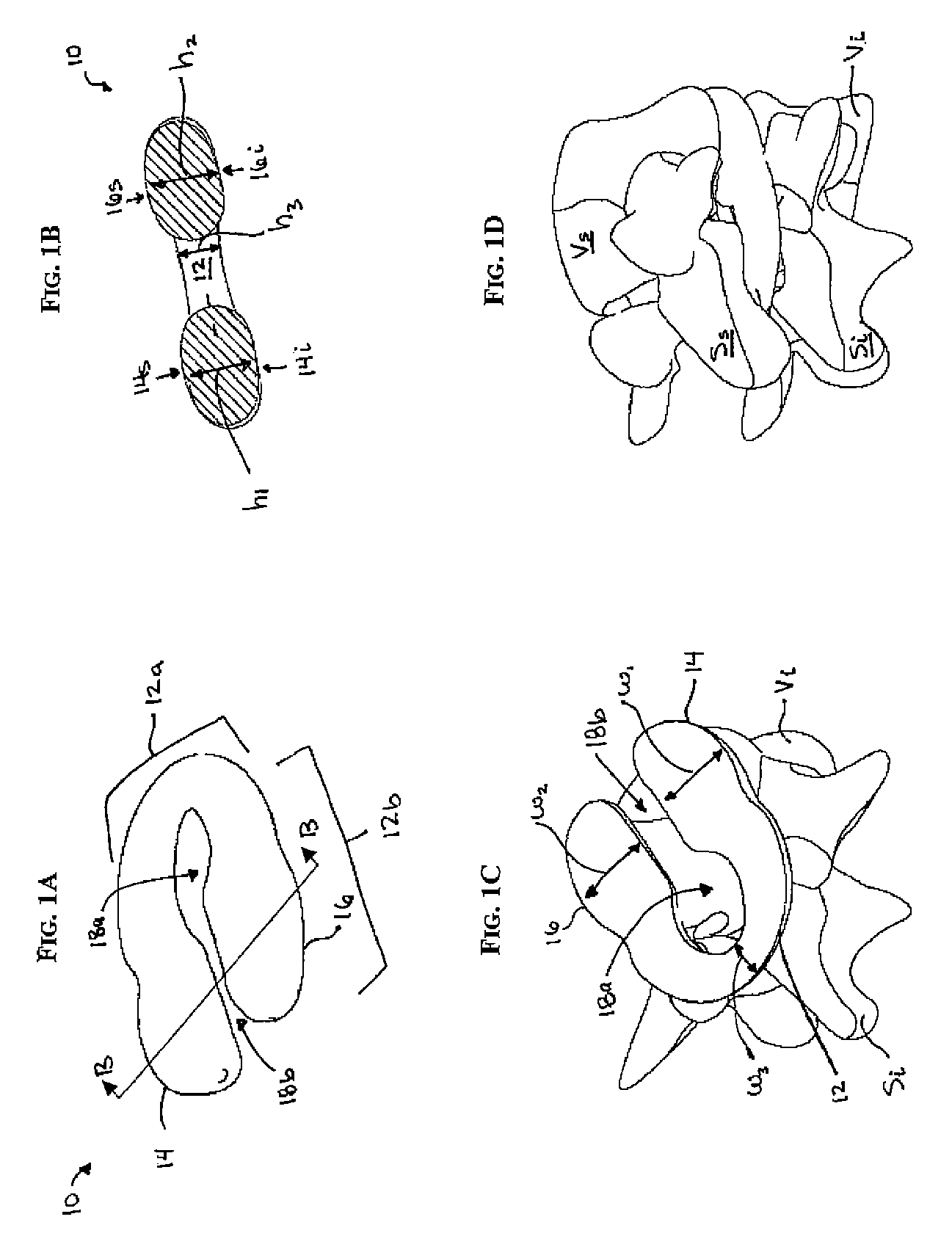
Methods and devices are provided for replacing a spinal disc. In an exemplary embodiment, artificial disc replacements and methods are provided wherein at least a portion of a disc replacement can be implanted using a posterolateral approach. With a posterolateral approach, the spine is accessed more from the side of the spinal canal through an incision formed in the patient's back. A pathway is created from the incision to the disc space between adjacent vertebrae. Portions of the posterolateral annulus, and posterior lip of the vertebral body may be removed to access the disc space, leaving the remaining annulus and the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments in tact. The disc implant can be at least partially introduced using a posterolateral approach, yet it has a size that is sufficient to restore height to the adjacent vertebrae, and that is sufficient to maximize contact with the endplates of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Lumbar disc replacement implant for posterior implantation with dynamic spinal stabilization device and method
ActiveUS20080269904A1Resist shorteningReduce frictionInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsSpinal columnReplacement implant
The invention consists of disc replacement implant for the lumbar spine designed for insertion into the disc space via a posterior approach. The implant can be stabilized in the disc space by connection to the vertebra or can be connected to dynamic spinal stabilization device consisting of interconnected bullets nested in a spring nested in a woven sleeve. By controlling the limits of elongation and compression the device prevents movement beyond normal physiological limits. In the midrange of movement flexibility is allowed. A method for using the dynamic spinal stabilization device is also provided.
Owner:VOORHIES RAND M
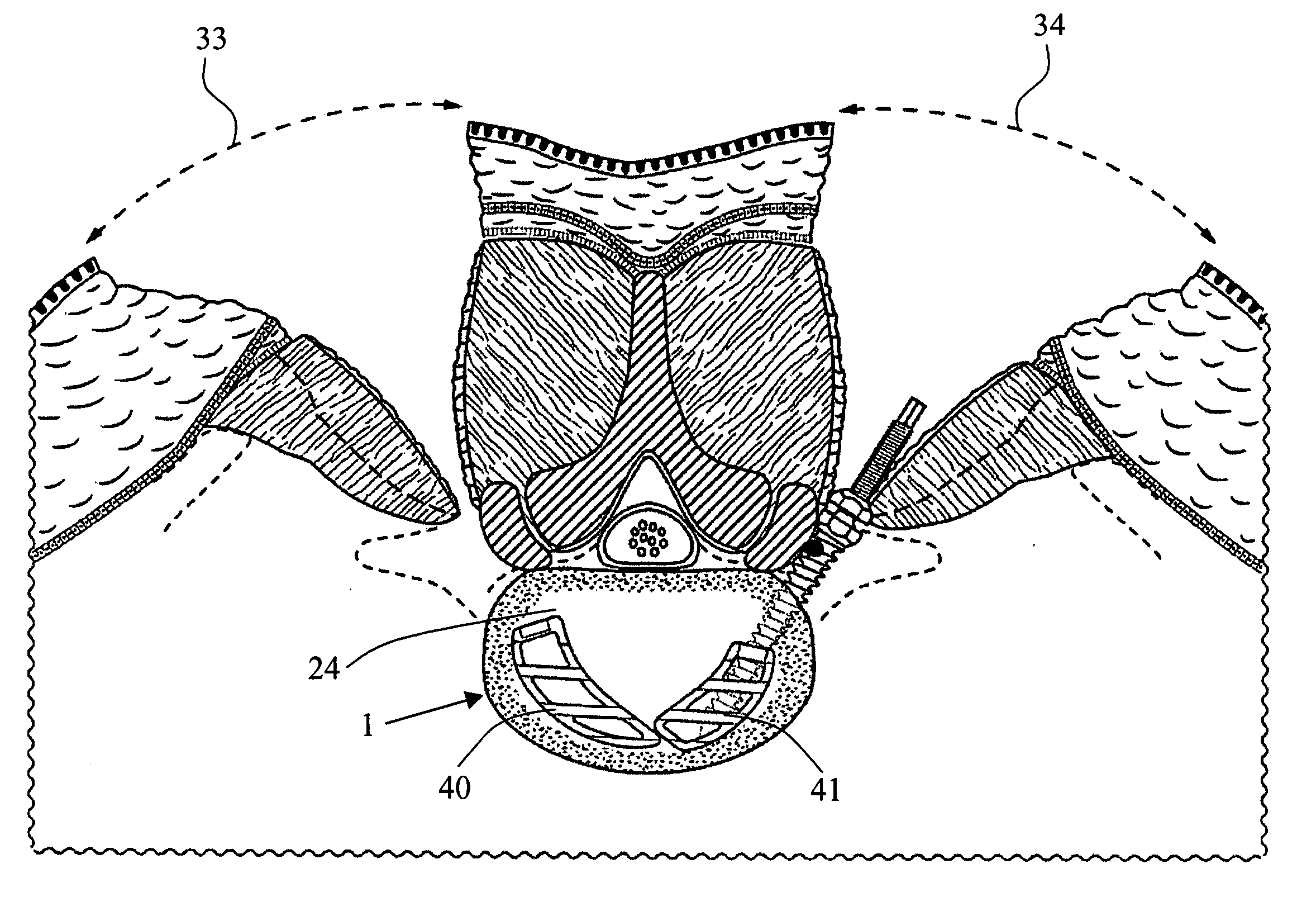
Posterior Prosthetic Intervertebral Disc
ActiveUS20100016973A1Increase disc heightIncrease heightJoint implantsSpinal implantsSpinal columnPosterior approach
A prosthetic intervertebral disc is formed of first and second end plates sized and shaped to fit within an intervertebral space and to be implanted from the back of the patient, thereby decreasing the invasiveness of the procedure. The posterior approach provides for a smaller posterior surgical incision and avoids important blood vessels located anterior to the spine particularly for lumbar disc replacements. The first and second plates are each formed of first, second and third parts are arranged in a first configuration in which the parts are axially aligned to form a low profile device appropriate for insertion through the small opening available in the TLIF or PLIF approaches described above. The three parts of both of the plates rotate and translate with respect to one another in situ to a second configuration or a deployed configuration in which the parts are axially unaligned with each other to provide a maximum coverage of the vertebral end plates for a minimum of insertion profile. Upon deployment of the disc, a height of the disc is increased.
Owner:SIMPLIFY MEDICAL PTY LTD
Multi-piece artificial spinal disk replacement device with selectably positioning articulating element
A posterior approach for intervertebral disk replacement is provided. This technique is particularly suited for assembling a multi-piece artificial spinal disk replacement device in situ in order to alleviate discomfort associated with the spinal column.
Owner:KYPHON
Spine treatment devices and methods
InactiveUS20070299445A1Limit extensionFlexible limitInternal osteosythesisProsthesisPosterior approachSacrum
Owner:DFINE INC
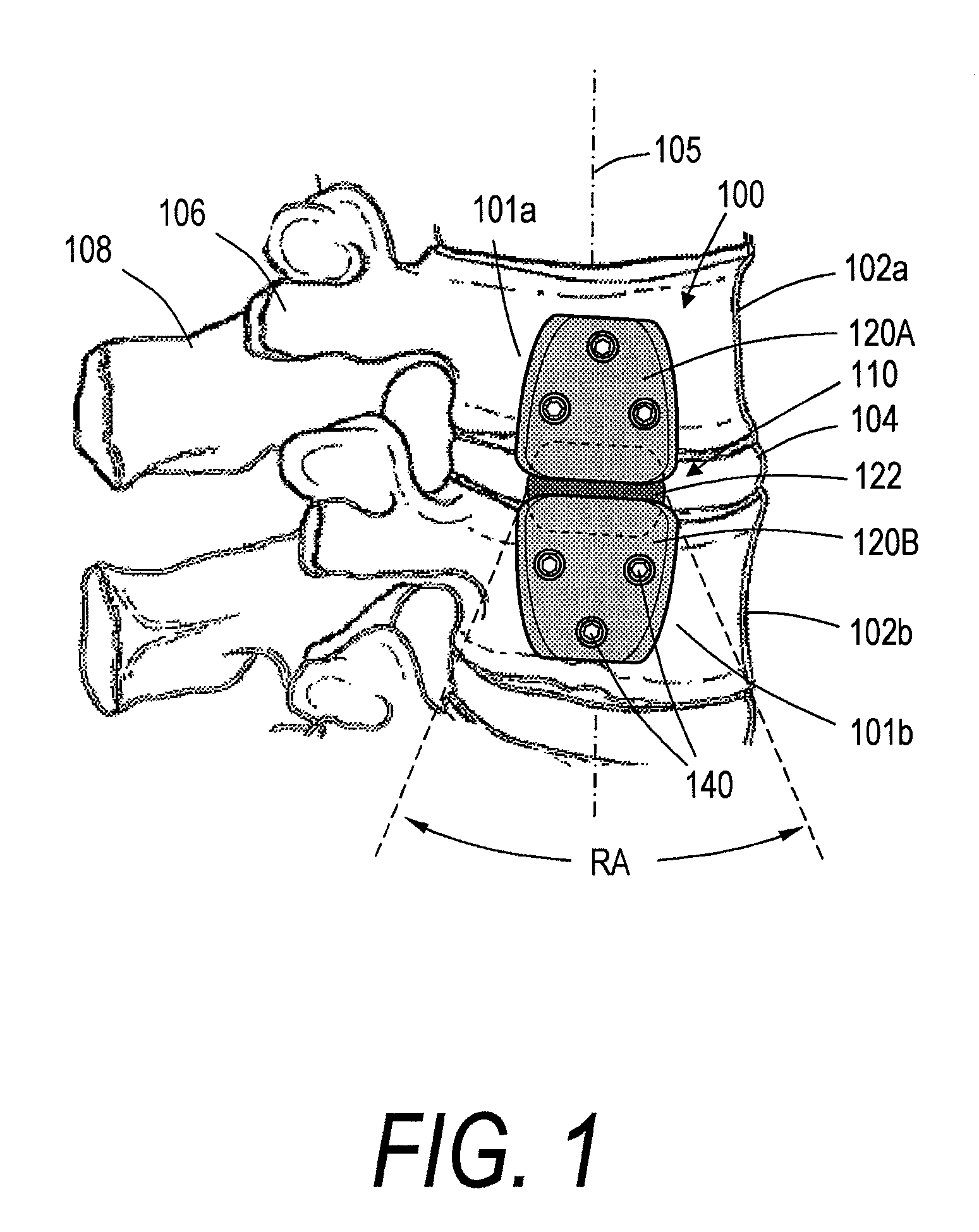
Surgical positioning assembly and associated spinal implant device and surgical methods
The present invention provides a surgical positioning assembly that is used to place a spinal implant device or the like within an intervertebral space or the like of a patient and associated surgical methods. Advantageously, the surgical positioning assembly allows access to the implantation site to be gained along a first axis, with the implant device subsequently being placed along a second axis that is disposed at an angle or substantially perpendicular to the first axis via the actuation of the surgical positioning assembly. Thus, for example, a surgeon may use an anterior or posterior approach to place an implant device laterally, or vice versa.
Owner:CTL MEDICAL CORP
Multi-piece artificial spinal disk replacement device with selectably positioning articulating element
A posterior approach for intervertebral disk replacement is provided. This technique is particularly suited for assembling a multi-piece artificial spinal disk replacement device in situ in order to alleviate discomfort associated with the spinal column.
Owner:KYPHON
Multi-piece artificial spinal disk replacement device with multi-segmented support plates
A posterior approach for intervertebral disk replacement is provided. This technique is particularly suited for assembling a multi-piece artificial spinal disk replacement device in situ in order to alleviate discomfort associated with the spinal column.
Owner:KYPHON
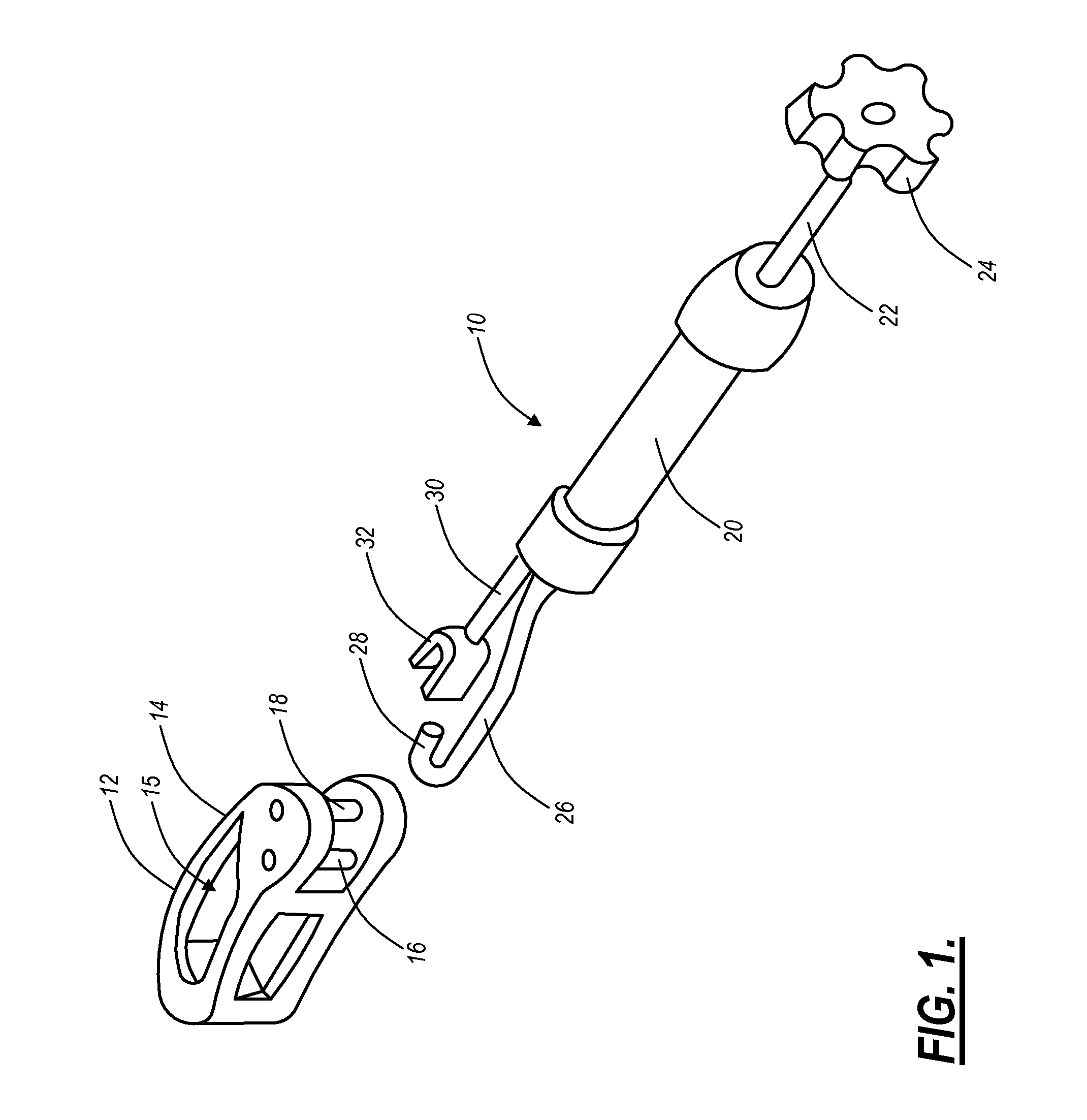
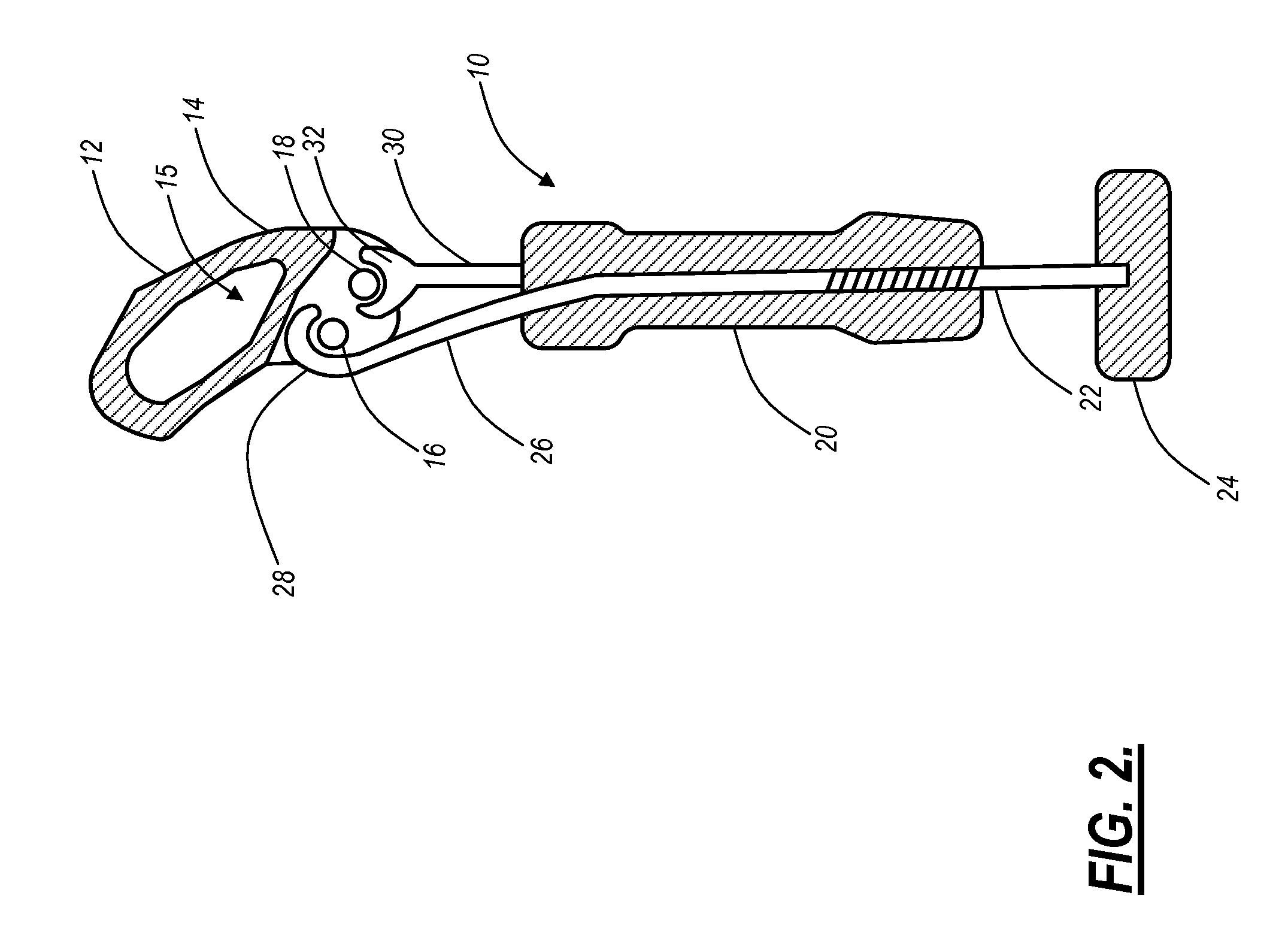
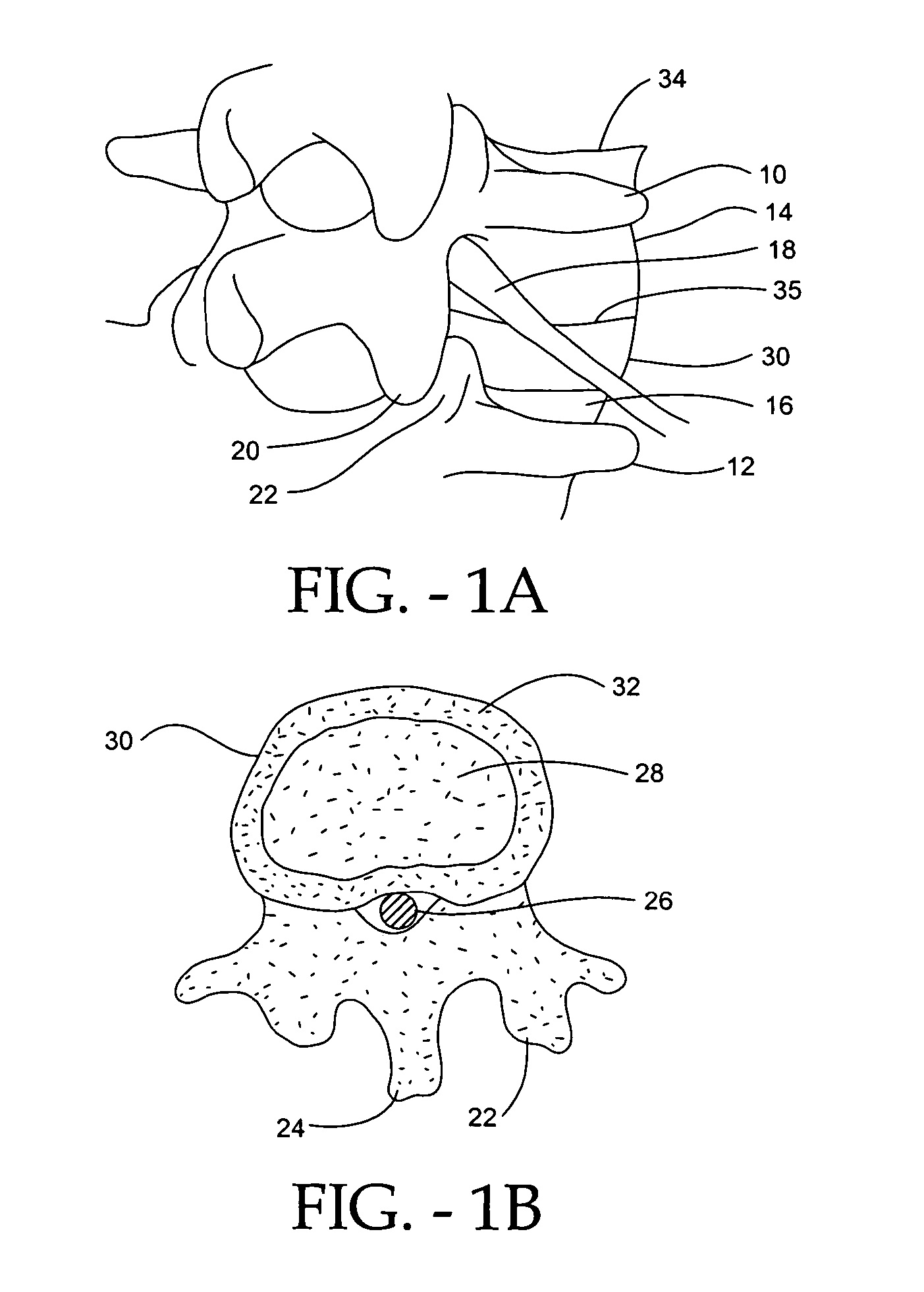
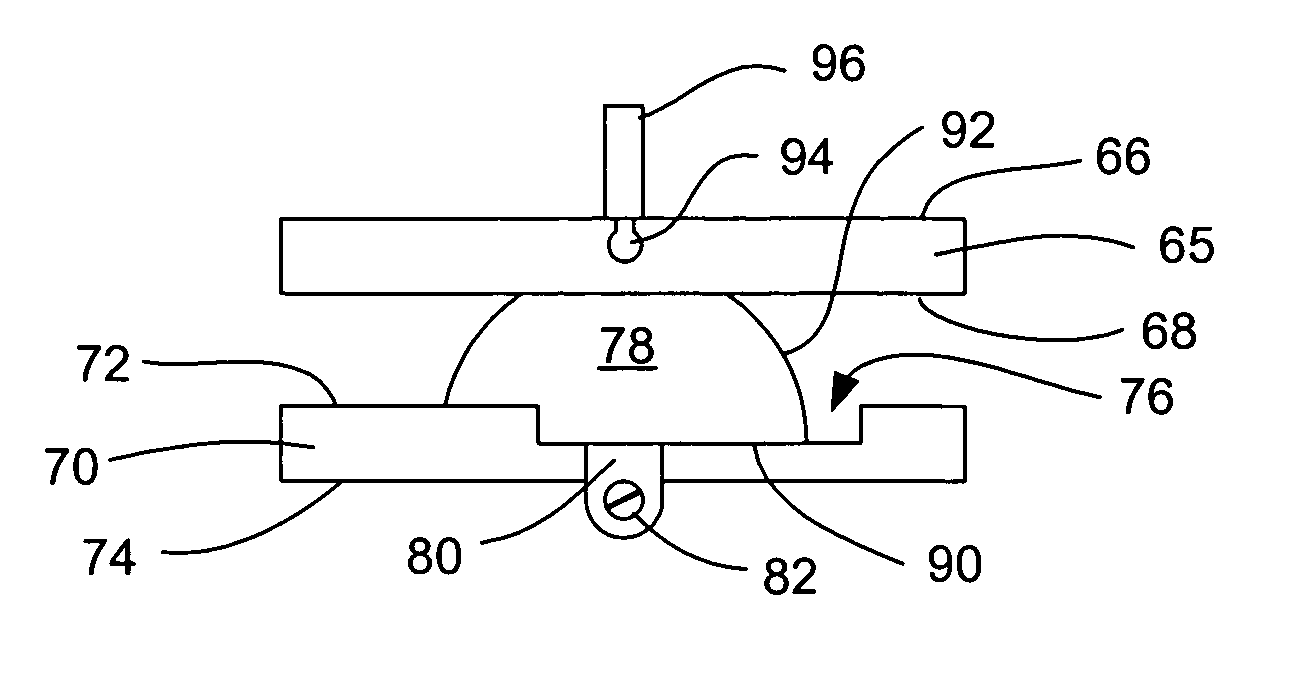
Geared spinal implant inserter-distractor
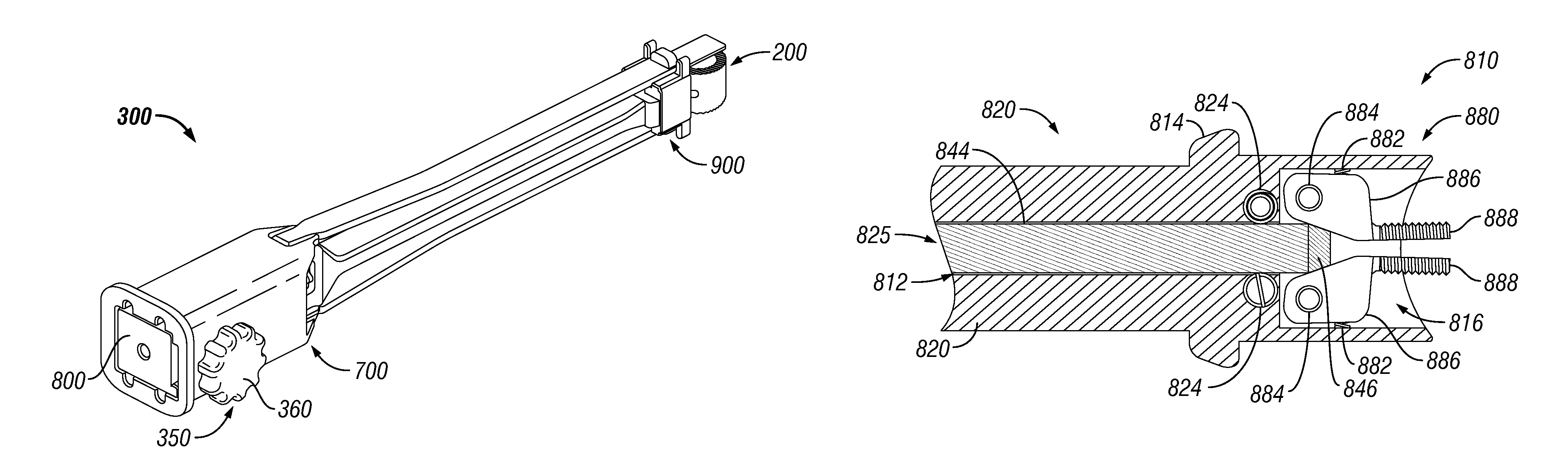
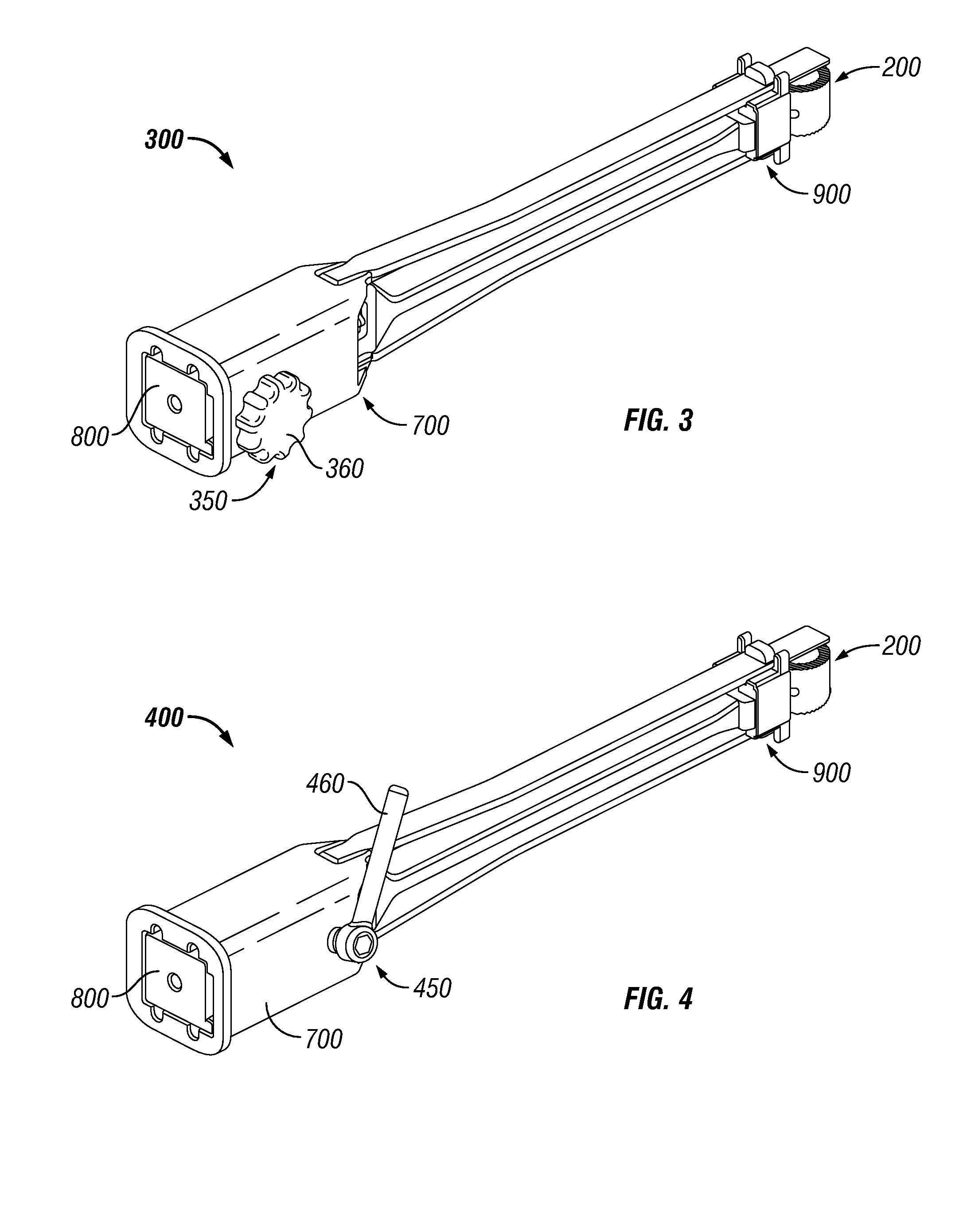
ActiveUS8114088B2Efficient and accurate deliveryGreat control and feedbackSpinal implantsOsteosynthesis devicesLinear motionPosterior approach
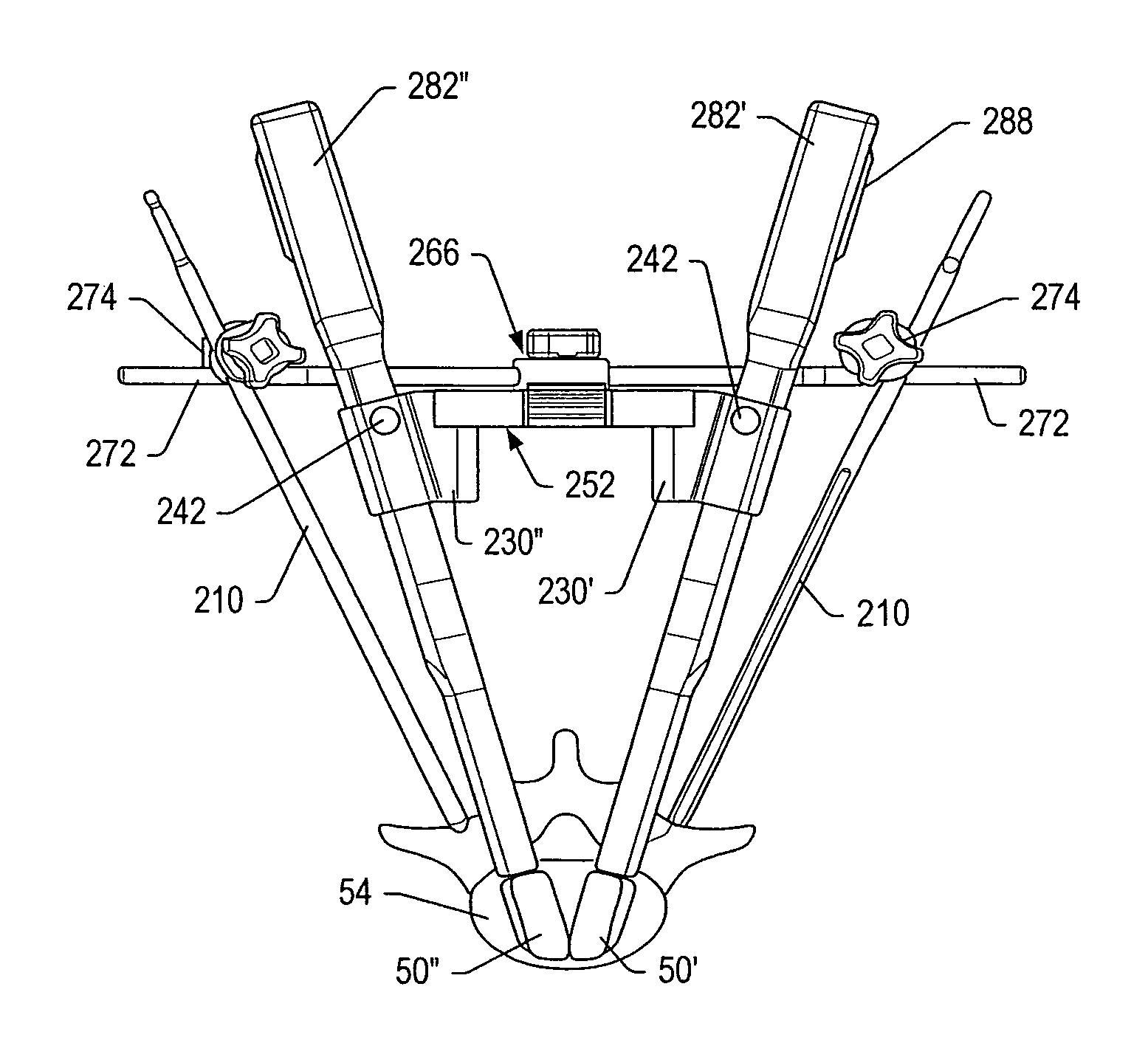
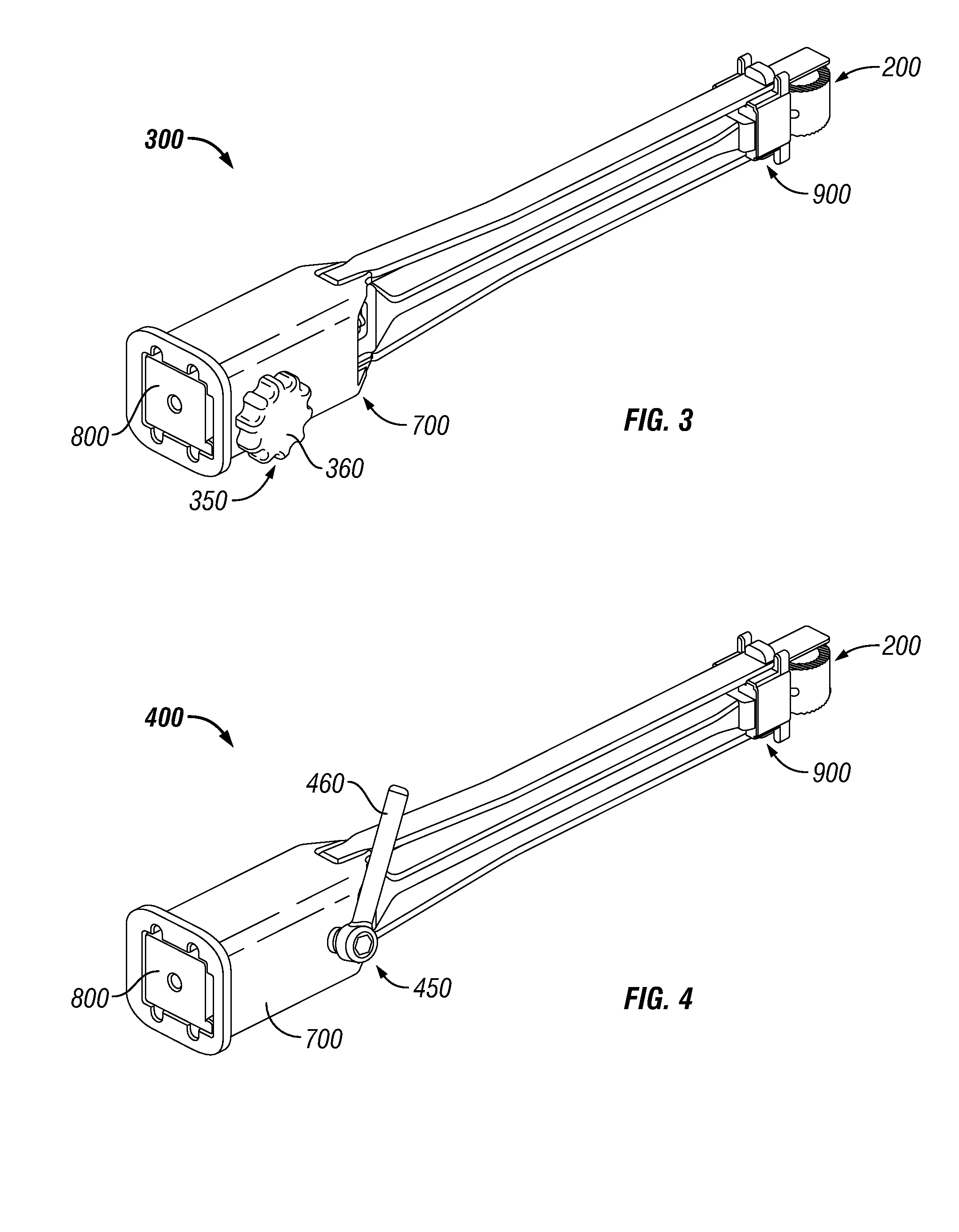
Embodiments of a geared spinal implant inserter-distractor disclosed herein provide a greater mechanical advantage in delivering an intervertebral implant via an anterior, anterior-lateral, or posterior approach. The geared spinal implant inserter-distractor comprises an inserter, a distractor structured to slidably receive the inserter with a collar and an intervertebral implant attached thereto, and a gear mechanism arranged to translate a surgeon's rotational motion into linear motion, allowing the surgeon to have a greater control and feedback when placing an implant within an intervertebral disc space. The gear arrangement comprises a pinion inside the distractor and a rack on the inserter. The pinion can be driven by a shaft connected to a knob or handle. With the gear mechanism, a surgeon can turn the knob or handle to drive the inserter in and out of the distractor in a quantifiable manner, which facilitates the desirable precision delivery of the intervertebral implant.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
Artificial functional spinal unit system and method for use
Insertion methods for placing dynamic interbody devices between a first vertebra and a second vertebra using a posterior approach are provided. In an embodiment, the insertion method may be based on the first vertebra. A bridge assembly may be attached to tap shafts positioned in the first vertebra. The bridge assembly may establish an insertion angle of implants into a disc space between the vertebrae. In an embodiment, the insertion method may be based on the position of expandable trials positioned between the vertebrae. The trials may be positioned and a bridge assembly may be coupled to the expandable trials and taps positioned in the first vertebra. One or more posterior stabilization systems may be coupled to the vertebrae after insertion of the dynamic interbody devices between the vertebrae.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE INC
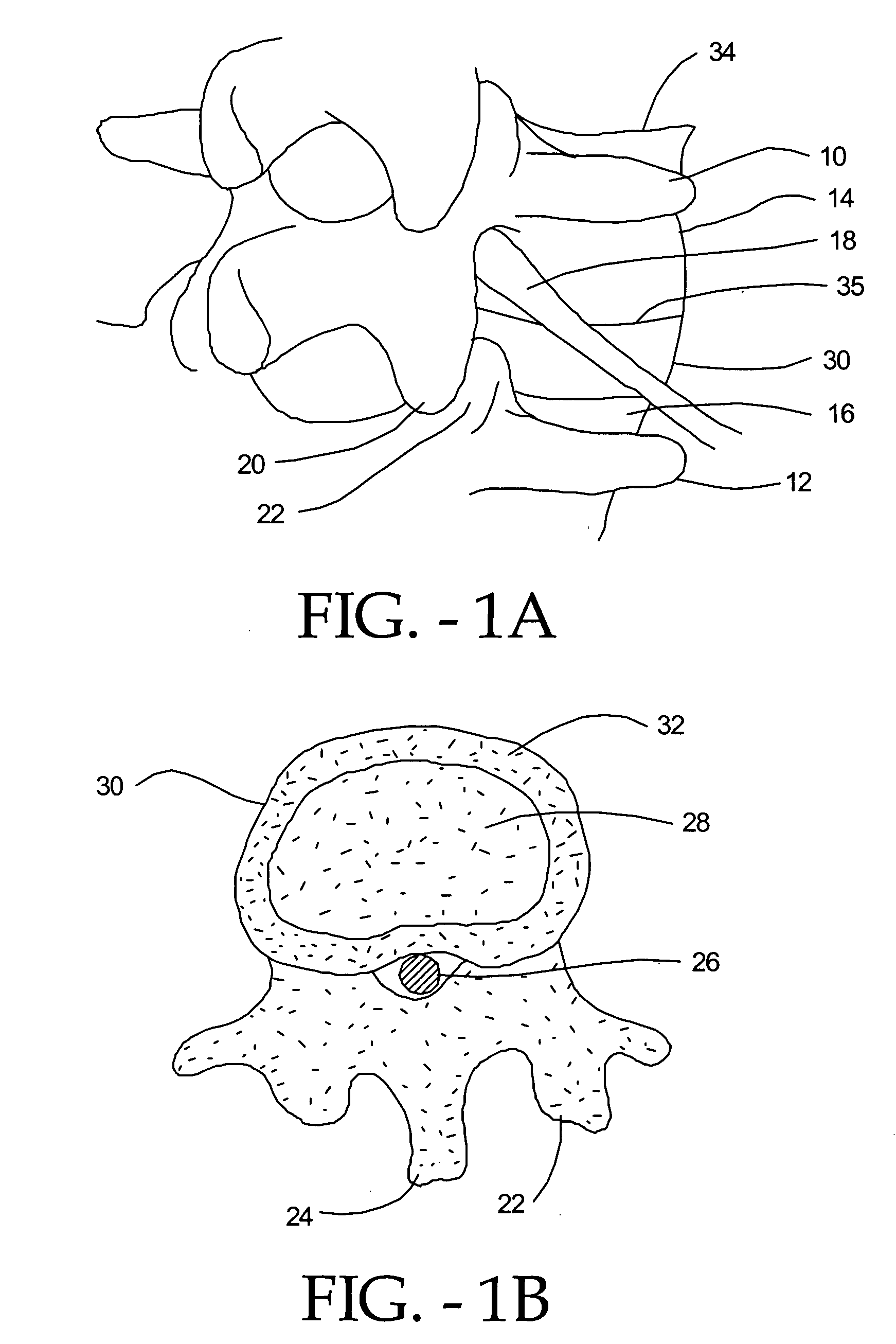
Artificial Disc Replacement Using Posterior Approach
Methods and devices are provided for replacing a spinal disc. In an exemplary embodiment, artificial disc replacements and methods are provided wherein at least a portion of a disc replacement can be implanted using a posterolateral approach. With a posterolateral approach, the spine is accessed more from the side of the spinal canal through an incision formed in the patient's back. A pathway is created from the incision to the disc space between adjacent vertebrae. Portions of the posterolateral annulus, and posterior lip of the vertebral body may be removed to access the disc space, leaving the remaining annulus and the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments in tact. The disc implant can be at least partially introduced using a posterolateral approach, yet it has a size that is sufficient to restore height to the adjacent vertebrae, and that is sufficient to maximize contact with the endplates of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
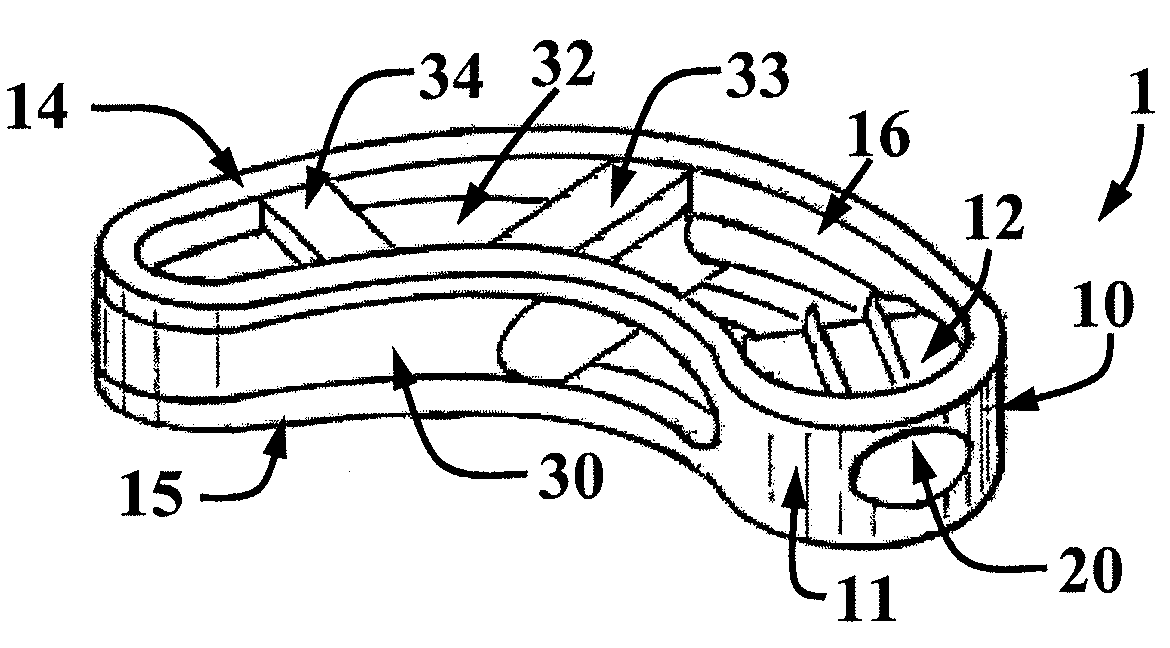
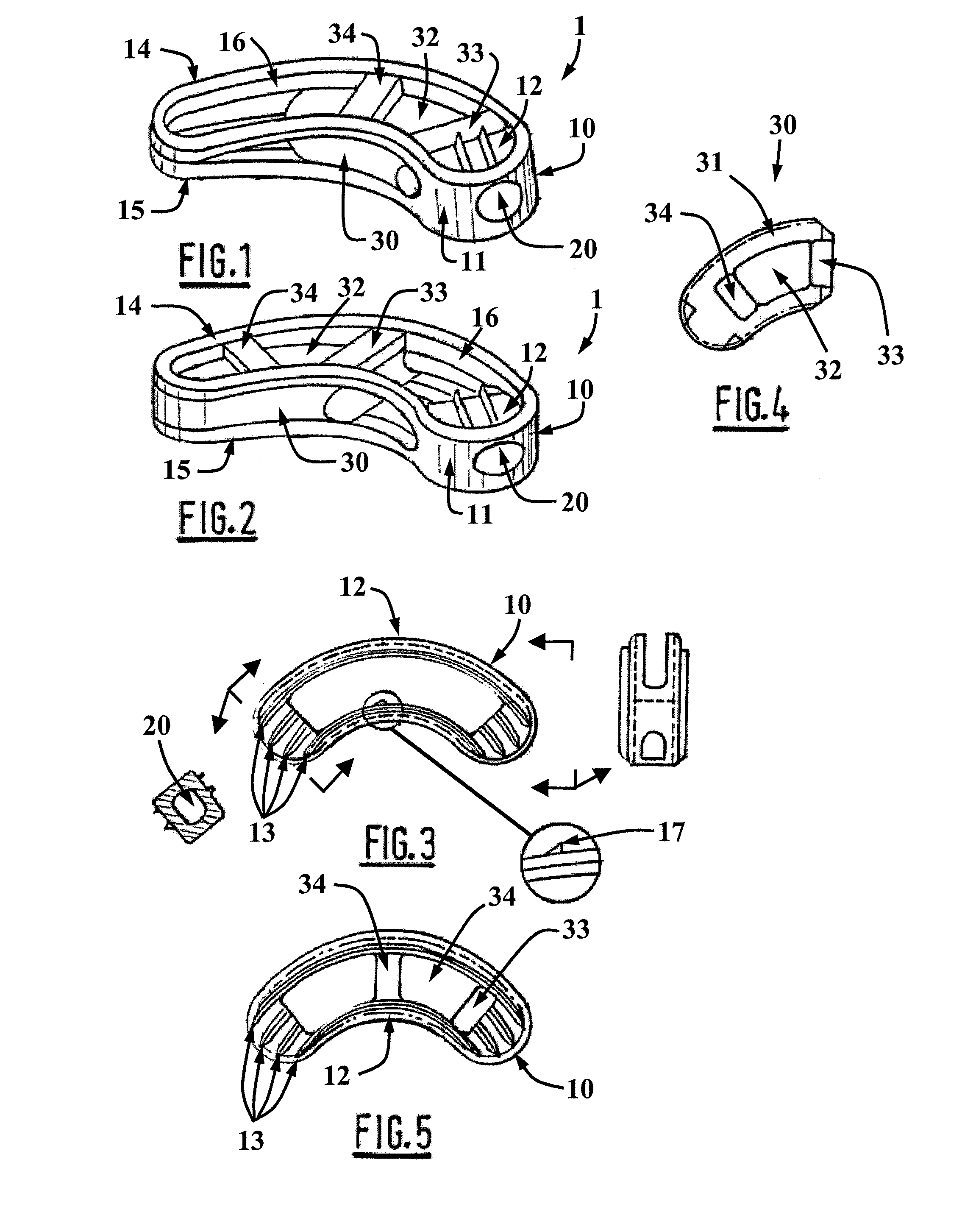
Posterior approach implant method for assembly of multi-piece artificial spinal disk replacement device in situ
A posterior approach for intervertebral disk replacement is provided. This technique is particularly suited for assembling a multi-piece artificial spinal disk replacement device in situ in order to alleviate discomfort associated with the spinal column.
Owner:KYPHON
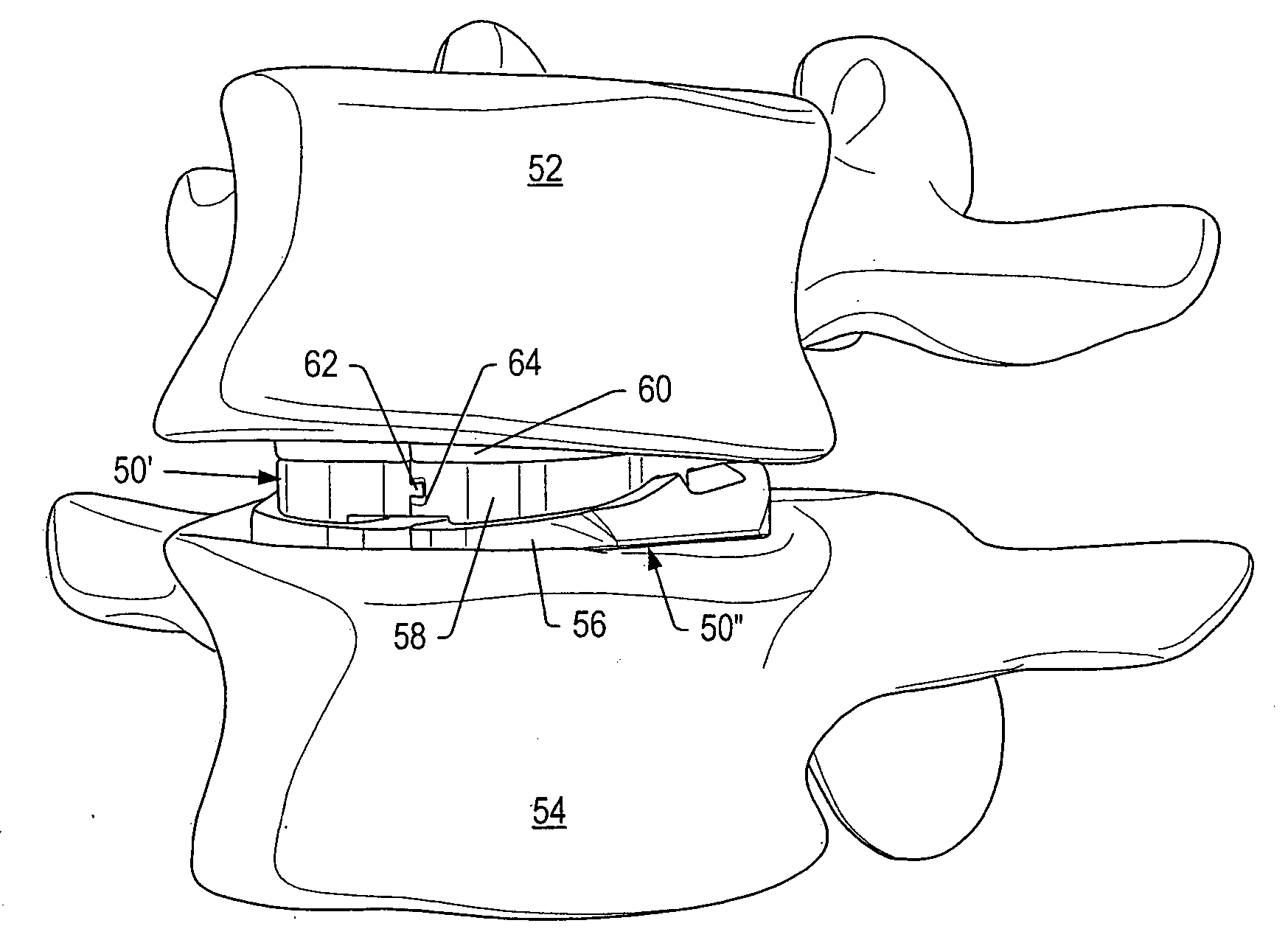
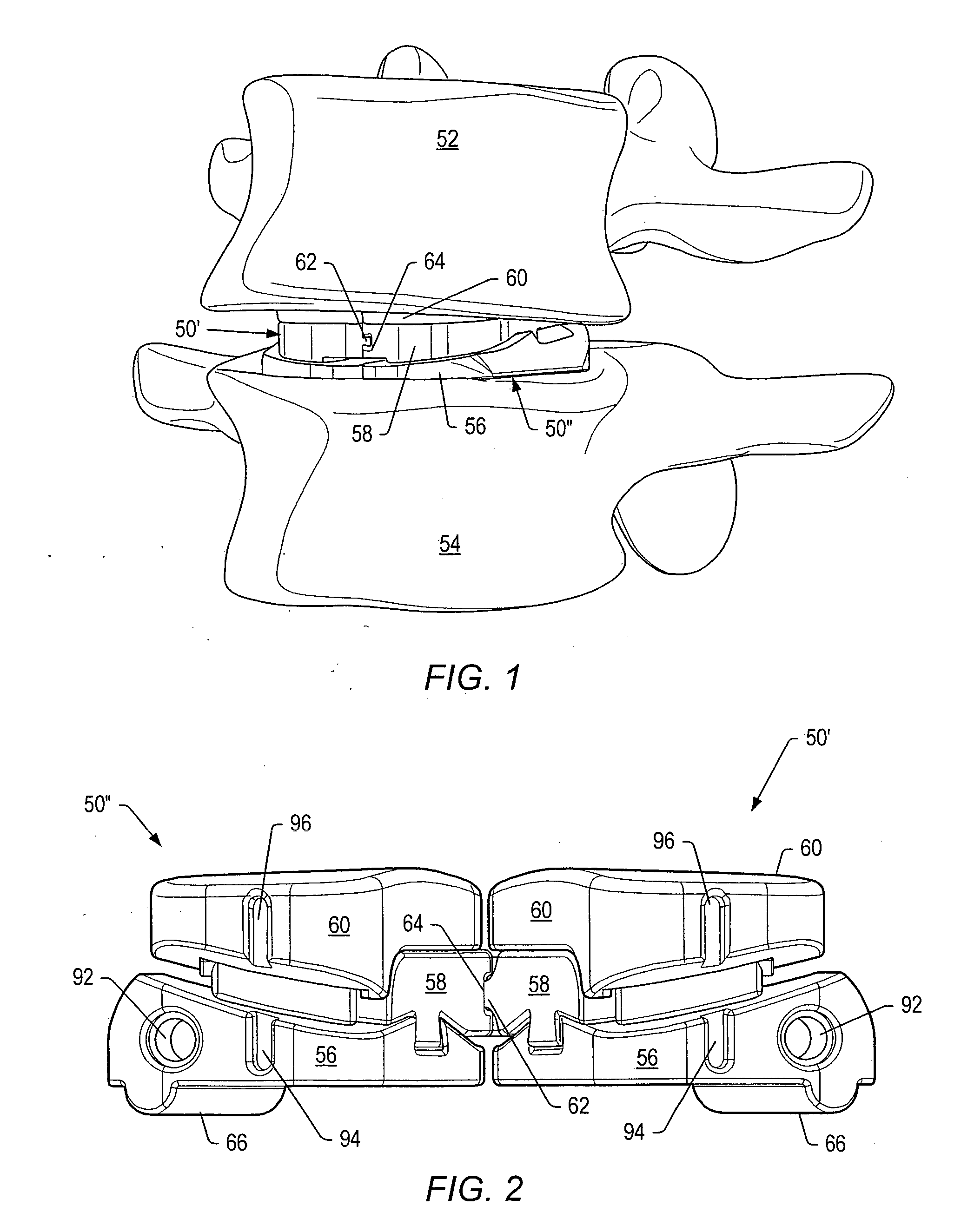
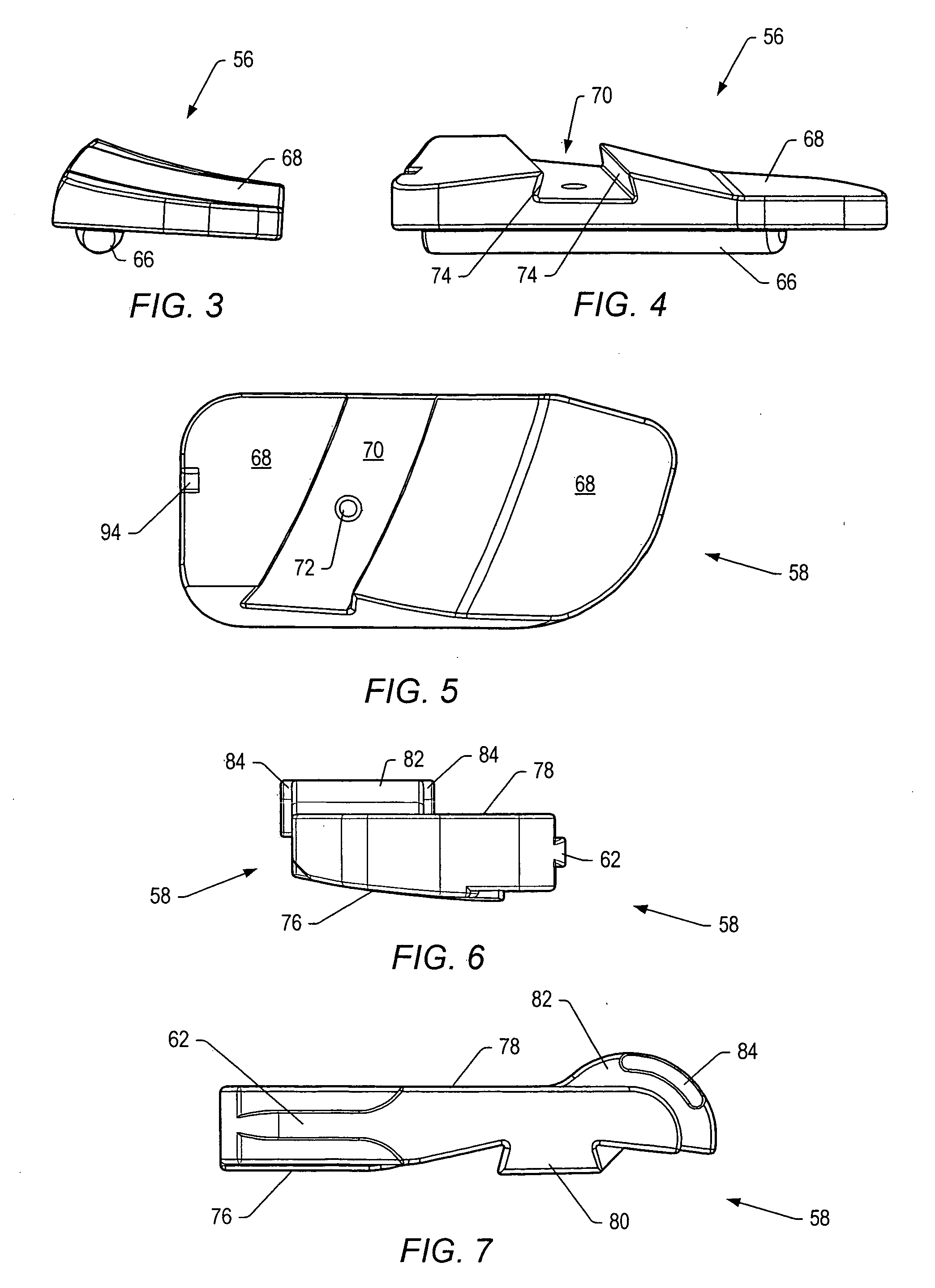
Dynamic interbody devices
A stabilization system for a human spine is provided. The stabilization system may include two dynamic interbody devices and / or one or more dynamic posterior stabilization systems. The dynamic interbody devices may be inserted into a disc space using a posterior approach. A first portion of a dynamic interbody device may contact a lower vertebra. A second portion of the dynamic interbody device may contact an upper vertebra. The first portion may be wider than the second portion to facilitate a large contact area against the lower vertebra and to facilitate insertion of the dynamic interbody device in the available space. The dynamic interbody devices may allow for coupled axial rotation and lateral bending of vertebrae adjacent to the dynamic interbody devices. The dynamic posterior stabilization systems may provide resistance to movement that mimics the resistance provided by a normal functional spinal unit.
Owner:FLEXUSPINE INC
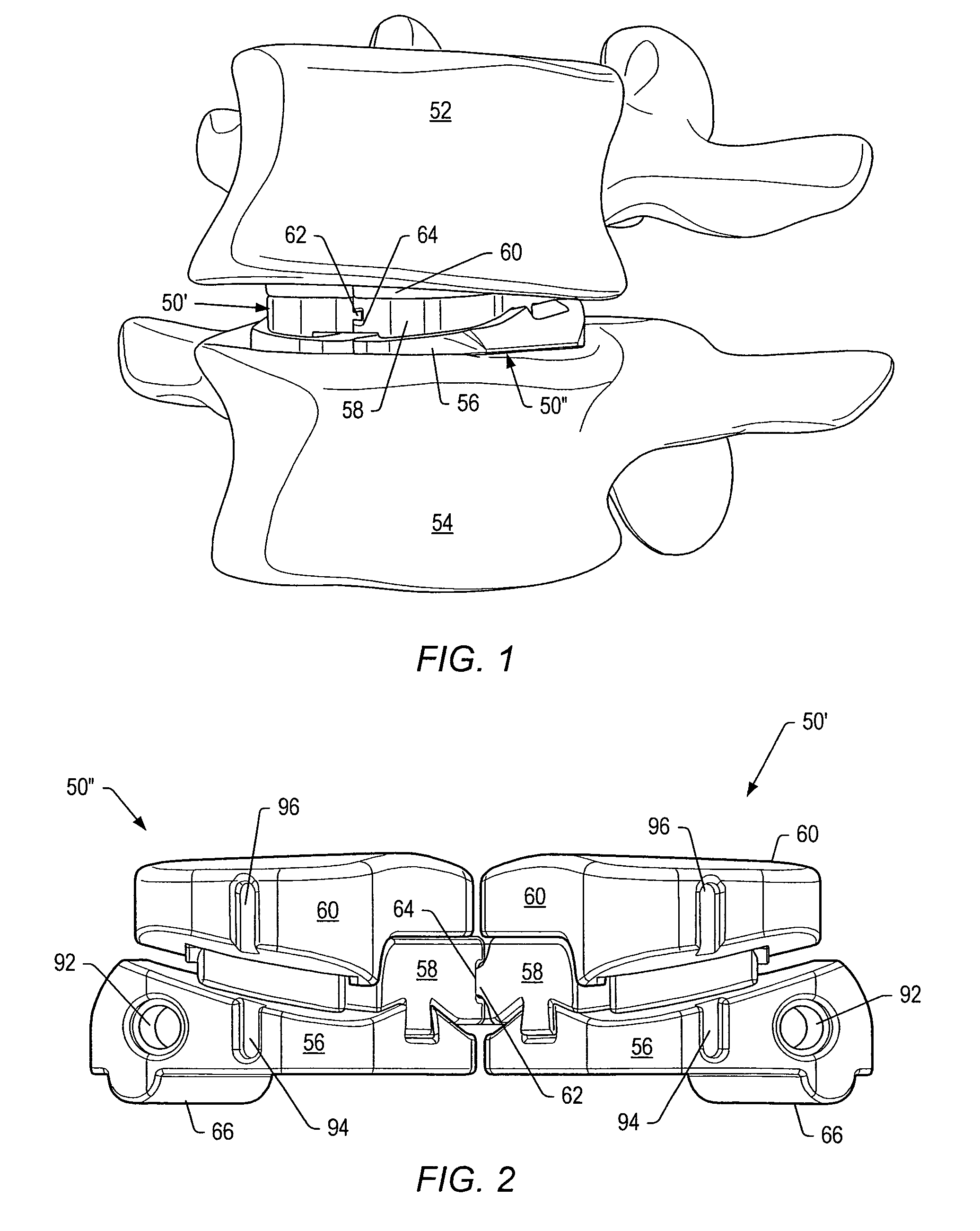
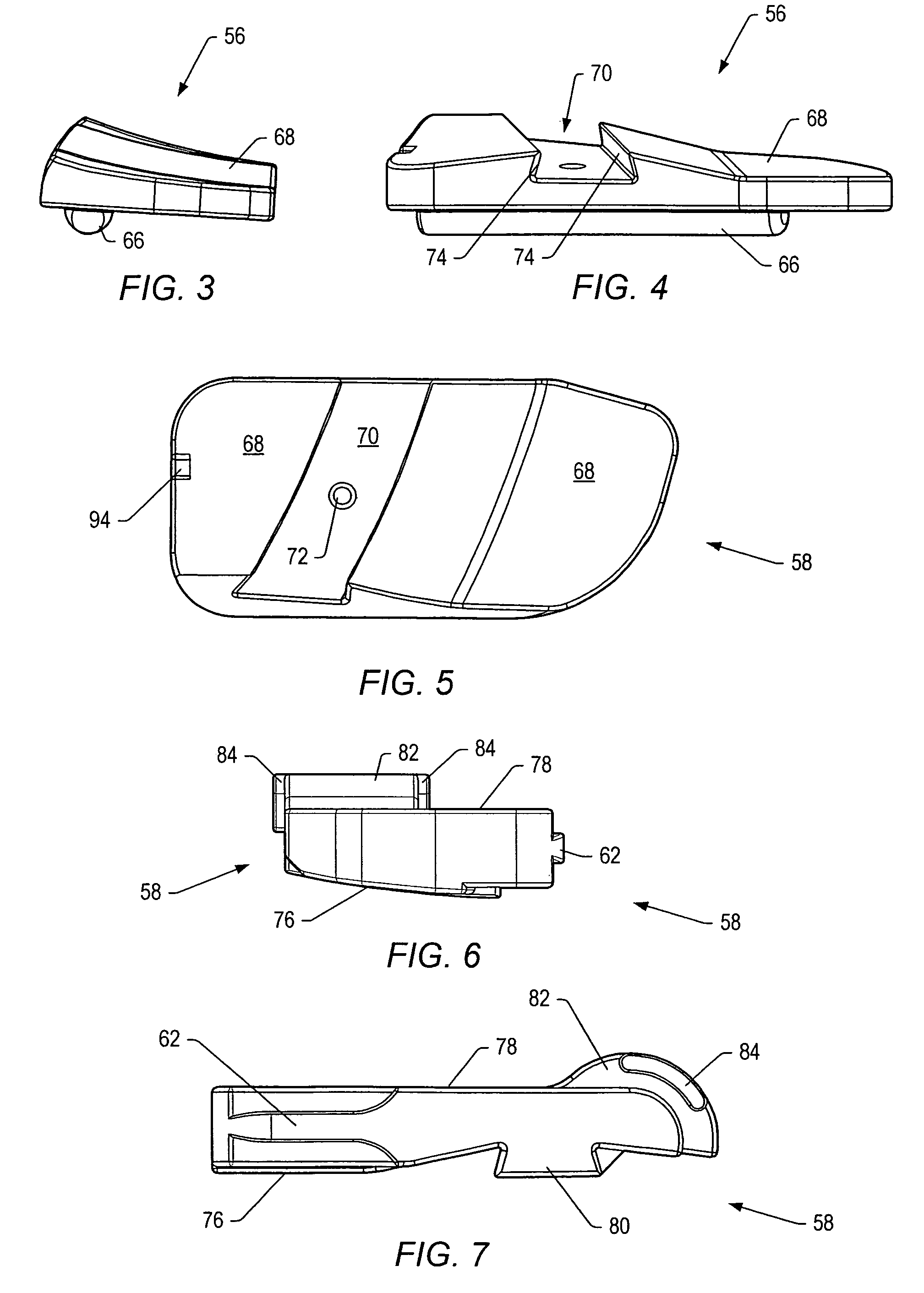
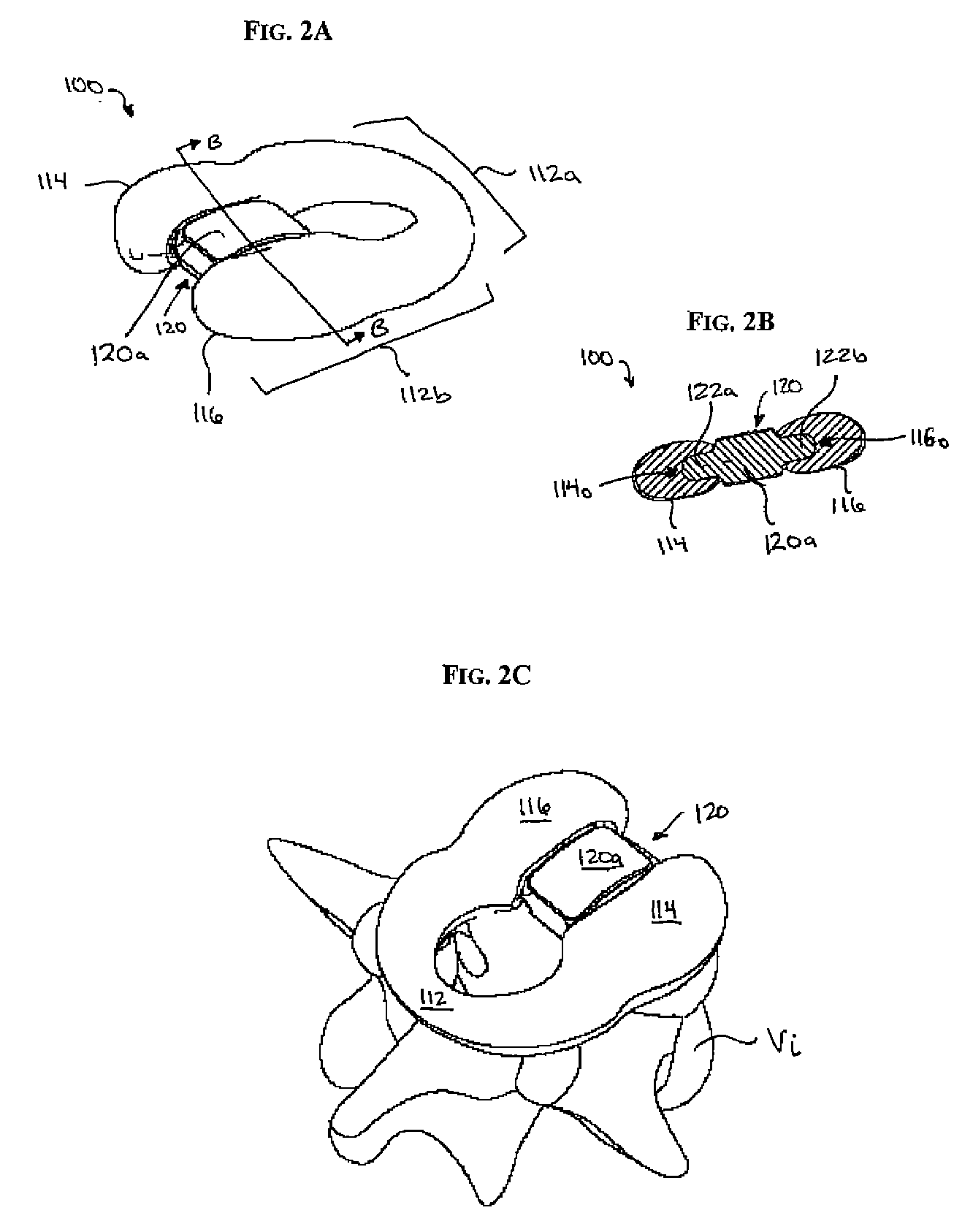
Posterior metal-on-metal disc replacement device and method
ActiveUS20070083267A1Reduce frictionJoint implantsSpinal implantsArticular surfacesPosterior approach
Provided is a device and method for replacing a diseased or damaged intervertebral disc in the spine of a patient. The device provided having at least two units, each of the units having an articulation surface and a bone contacting surface, the articulation surfaces of each of the at least two being in articulating opposition one to the other, one of which having a convex articulation surface and the other having a complementary concave articulation surface. The bone contacting surfaces being provided with bone implantation securing elements such as keel type or spike type protrusions. Also provided is a method of implanting the device into an intervertebral space from a posterior approach.
Owner:K2M
C-shaped disc prosthesis
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Spinal fusion implant for oblique insertion
Intervertebral spinal fusion implants for interbody fusion of the anterior column of the spine are described. The implants have a substantially bi-convex or a substantially offset bi-convex shape. The implants are placed through a transforaminal or posterior approach at an oblique insertion angle. The implants have an outermost point on the superior convex surface and an outermost point on the inferior convex surface and four edges of differing heights. The outermost superior and inferior points of the implants are connected with the four edges with convex surfaces of different curvatures. The curvatures of the convex surfaces of the implants are designed to match the curvatures of concave vertebral surfaces when the implants are inserted at an oblique insertion angle.
Owner:CAMBER SPINE TECH
Spine treatment devices and methods
InactiveUS20080208260A1Reduce compressionRelieve painInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsPosterior approachBiomedical engineering
A modular implant system and method is provided for the dynamic stabilization of a spine segment and that can be implanted in a posterior approach. The implant system can include first and second support bodies configured for fixation to outward or lateral surfaces of first and second vertebrae, respectively. The implant system can also comprise a resilient portion. The method can comprise fixating first and second support bodies to first and second vertebrae respectively.
Owner:DFINE INC
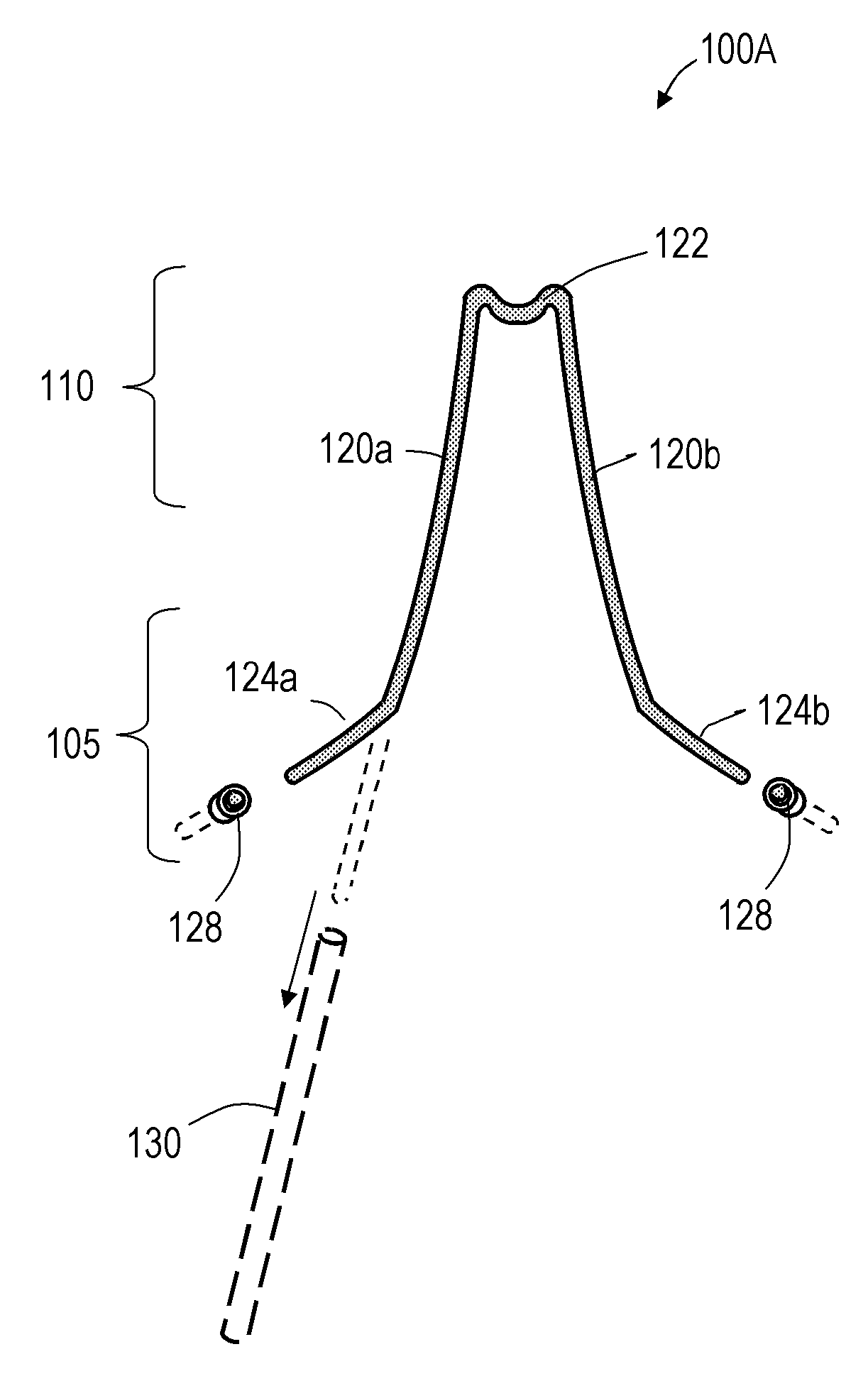
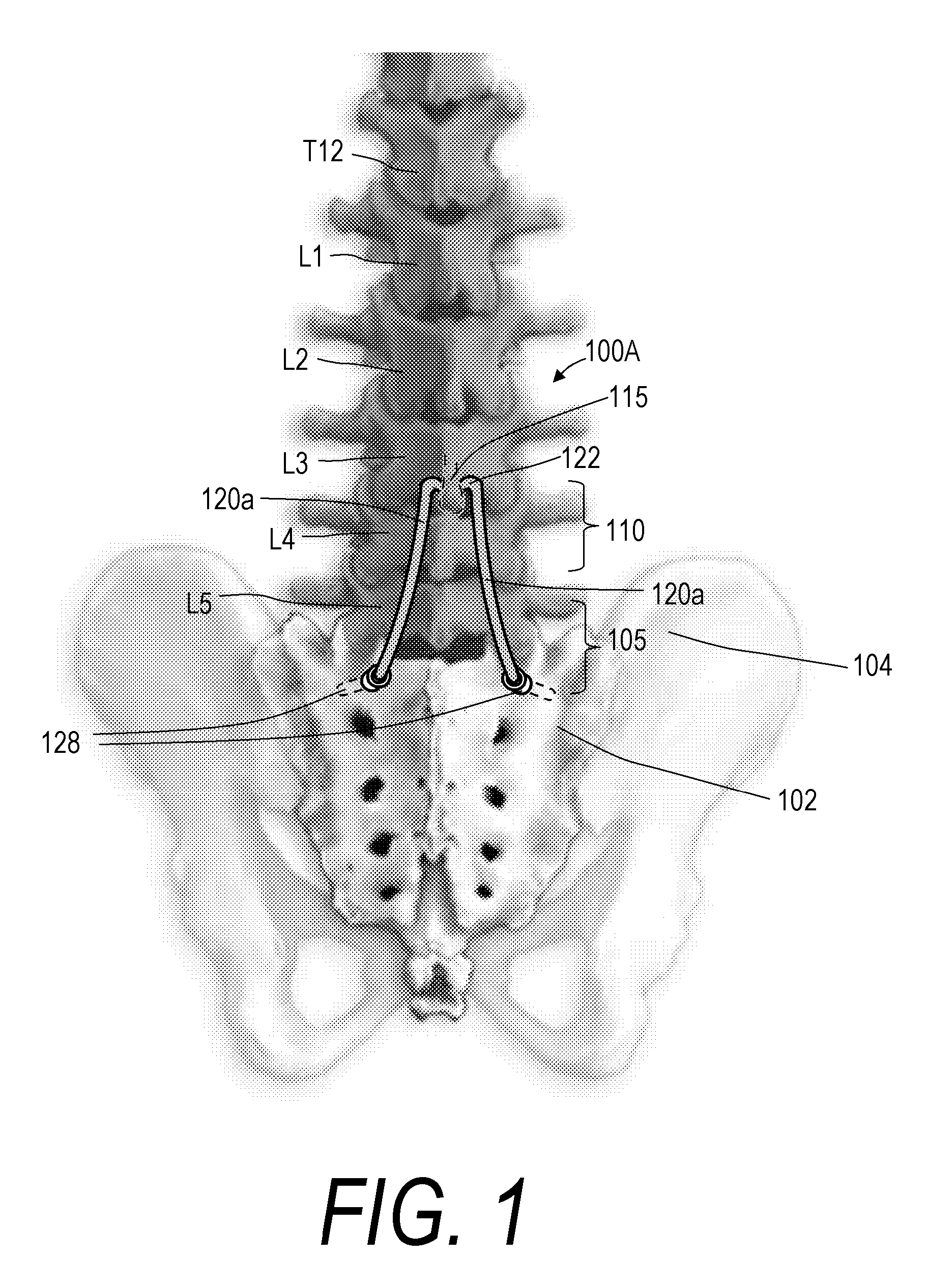
Expandable intervertebral spacer and method of posterior insertion thereof
An expandable intervertebral spacer has a plurality of arms. The arms can be retracted or extended. The spacer has a width that is narrower than the width between the nerve roots near the posterior approach to an intervertebral space. Once inserted into the intervertebral space, the arms can be deployed. The deployed arms expand the height and width of the spacer. Once deployed, the spacer stabilizes two adjacent vertebrae. The arms are interconnected mechanically to deploy simultaneously.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Lateral mass fixation implant
InactiveUS20150342648A1Easy to insertInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsPosterior approachLess invasive
The various embodiments described herein provide lateral mass and facet fixation implants, which may be inserted and applied via a posterior approach, using minimally invasive or less invasive techniques. The embodiments described below generally include an intrafacet implant (or “facet implant”) and a lateral mass fixation member attached to or attachable to the facet implant. The lateral mass fixation member can include one or more tabs extending from a middle portion and configured to secure the lateral mass fixation member to lateral masses of adjacent vertebrae. The tabs may be flexible, semi-rigid, or rigid, and may be collapsible to facilitate insertion of the device. Methods for delivering the lateral mass and facet fixation implants are also described.
Owner:PROVIDENCE MEDICAL TECH
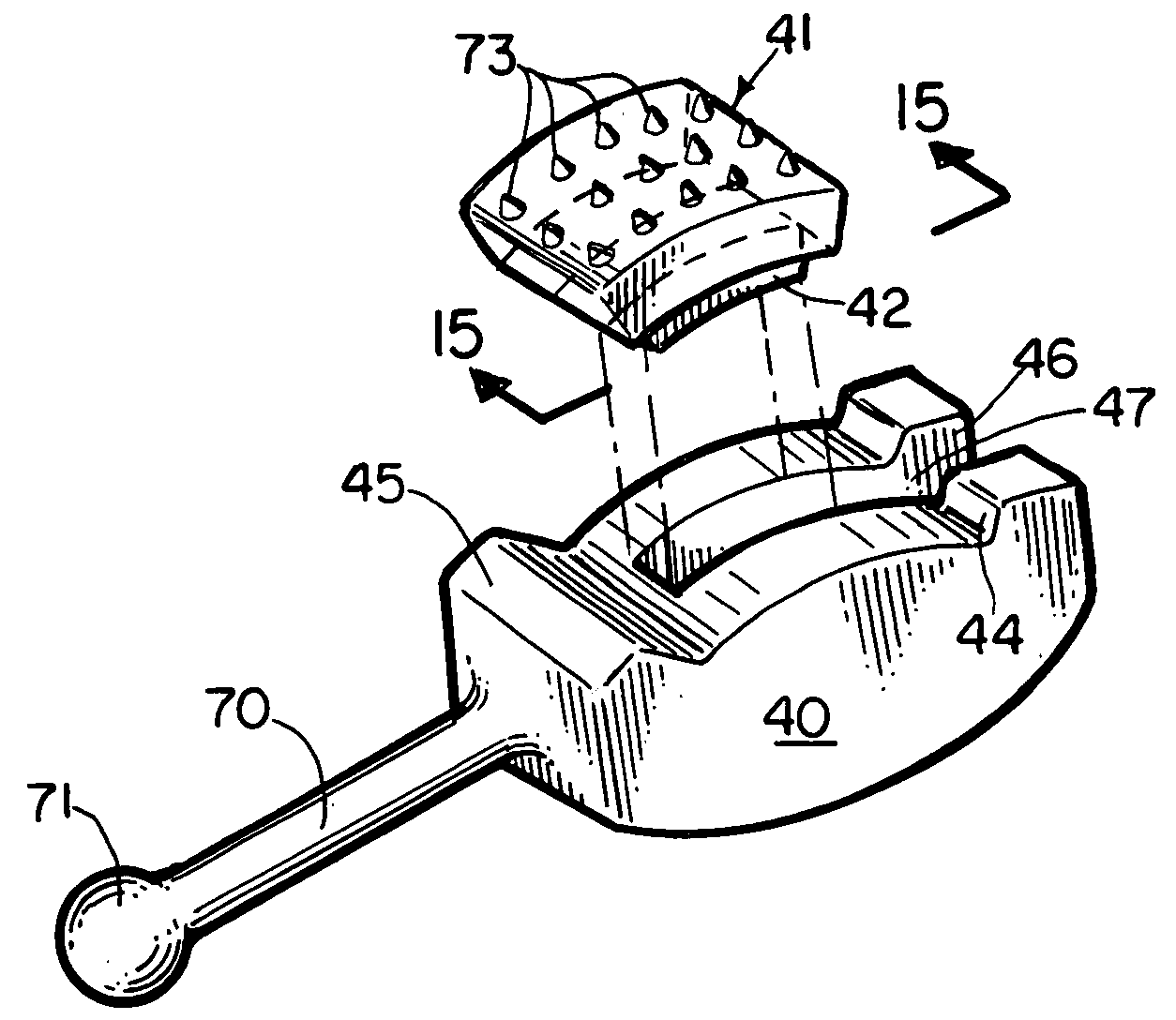
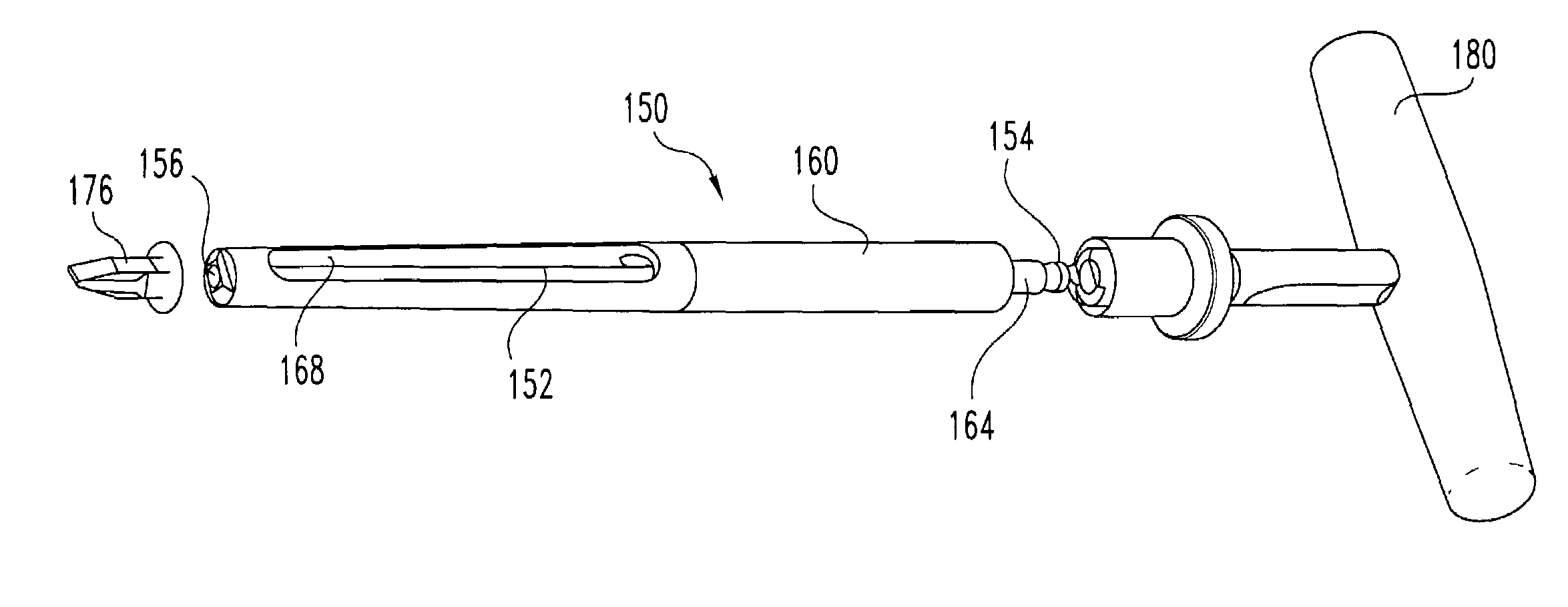
Method and instrumentation for posterior interbody fusion
InactiveUS7722618B2Limiting pivotal movementEasy to markDiagnosticsJoint implantsSpinal columnPosterior approach
A method and instrumentation for spinal interbody fusion is disclosed. The instruments and methods are particularly adapted for interbody fusion from a posterior approach to the spine. One instrument is a retractor having a lockable pivotally mounted handle. Another instrument is a template for straddling the dura. A modular distractor is also provided and preferably includes a tapered shaft with a visualization window disposed therein. Yet another instrument is a depth gauge to verify bone opening depth and dimension, preferably including a radiopaque portion. A method contemplates the use of these instruments to prepare a disc space to receive an implant.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
Expandable Intervertebral Spacer and Method of Posterior Insertion Thereof
ActiveUS20120046748A1Increase heightIncrease widthSpinal implantsPosterior approachIntervertebral space
An expandable intervertebral spacer has a plurality of arms. The arms can be retracted or extended. The spacer has a width that is narrower than the width between the nerve roots near the posterior approach to an intervertebral space. Once inserted into the intervertebral space, the arms can be deployed. The deployed arms expand the height and width of the spacer. Once deployed, the spacer stabilizes two adjacent vertebrae. The arms are interconnected mechanically to deploy simultaneously.
Owner:GLOBUS MEDICAL INC
Modular disc for spinal arthroplasty through a small posterior exposure with intradiscalor intervertebral assembly in-situ
A prosthetic nucleus replacement comprises modules about 10-13 mm in width of various heights that can be placed via a posterior approach and assembled intradiscalor intervertebral
Owner:LAWSON INC
Assembled disc spacers
InactiveUS20060004454A1Reduce pressureImproves upon disc spacers (DS)Joint implantsSpinal implantsPosterior approachLamina terminalis
Disc spacers (DS) are assembled within a disc space, allowing them to be inserted through smaller openings in the Annulus Fibrosus (AF). The large size of the assembled DS decreases the pressure on the vertebral endplates. Embodiments of the invention may be used in the cervical, thoracic, or lumbar spine. The DS may be inserted through an anterior, lateral, or posterior approach to the spine using annulus preserving techniques. The devices are preferably made of biocompatible materials such as titanium, chrome cobalt, and ceramic. Alternative materials, including materials with shape memory properties, such as Nitinol, may be used to form one or more components of the device.
Owner:FERREE BRET A +1
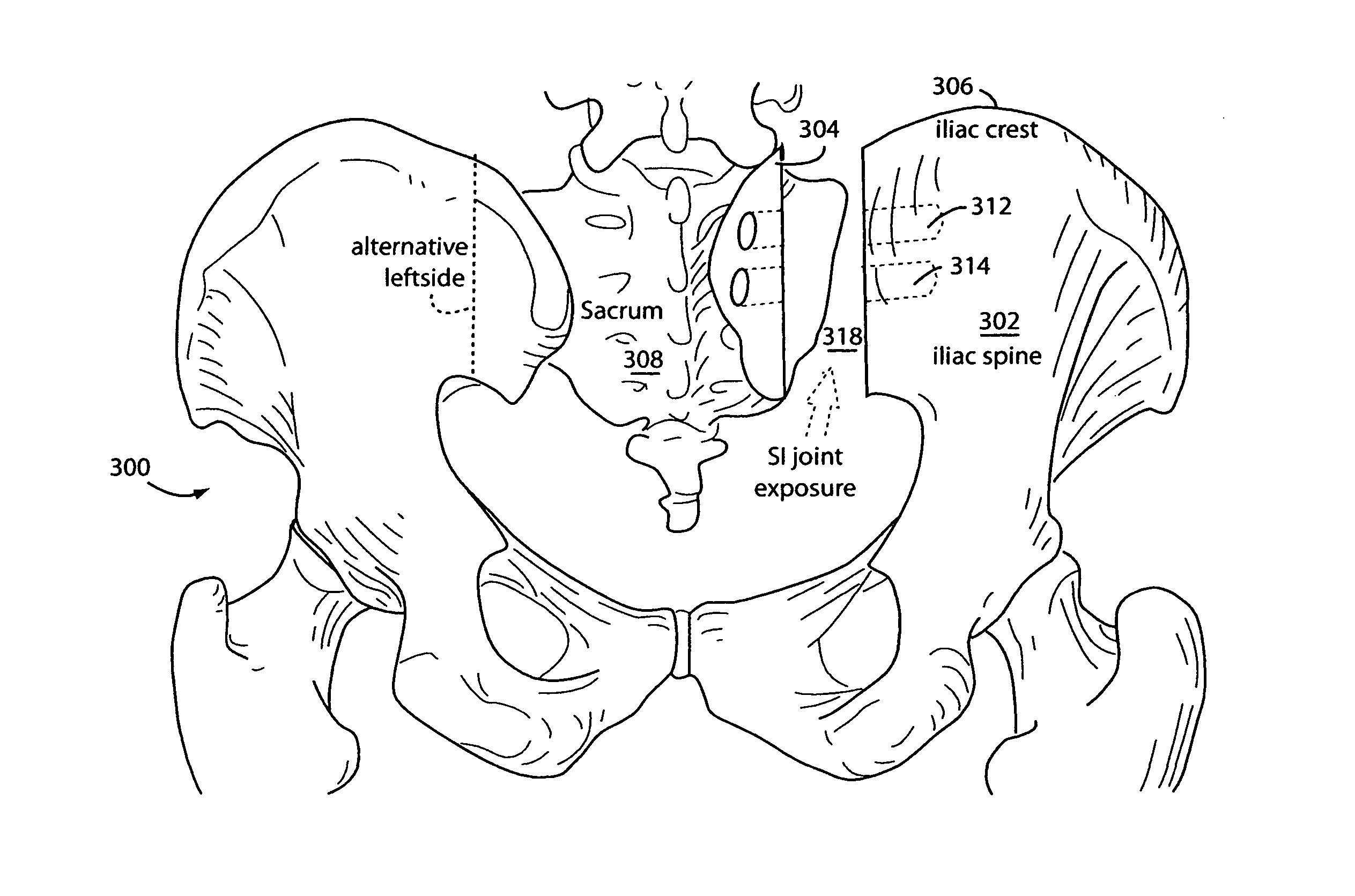
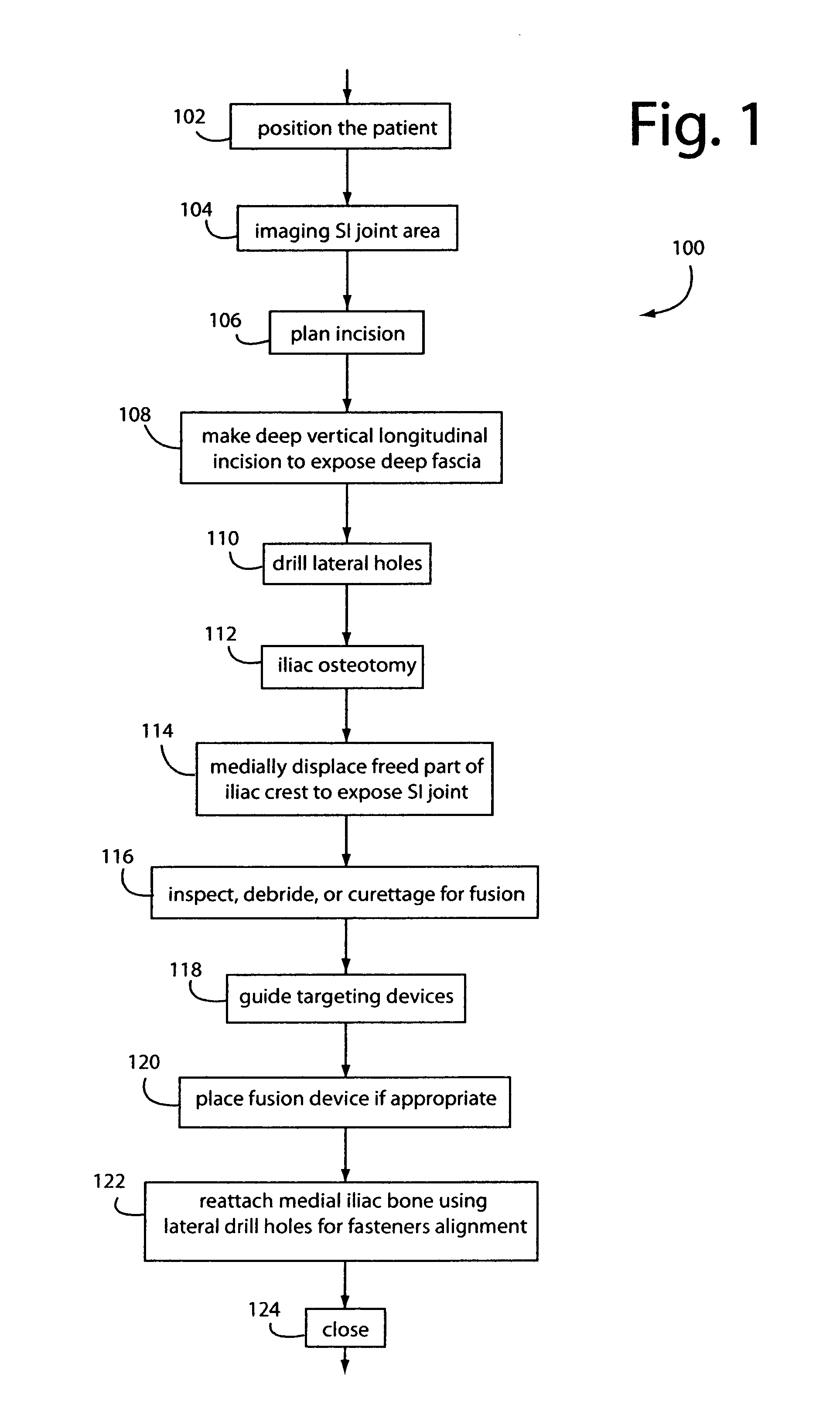
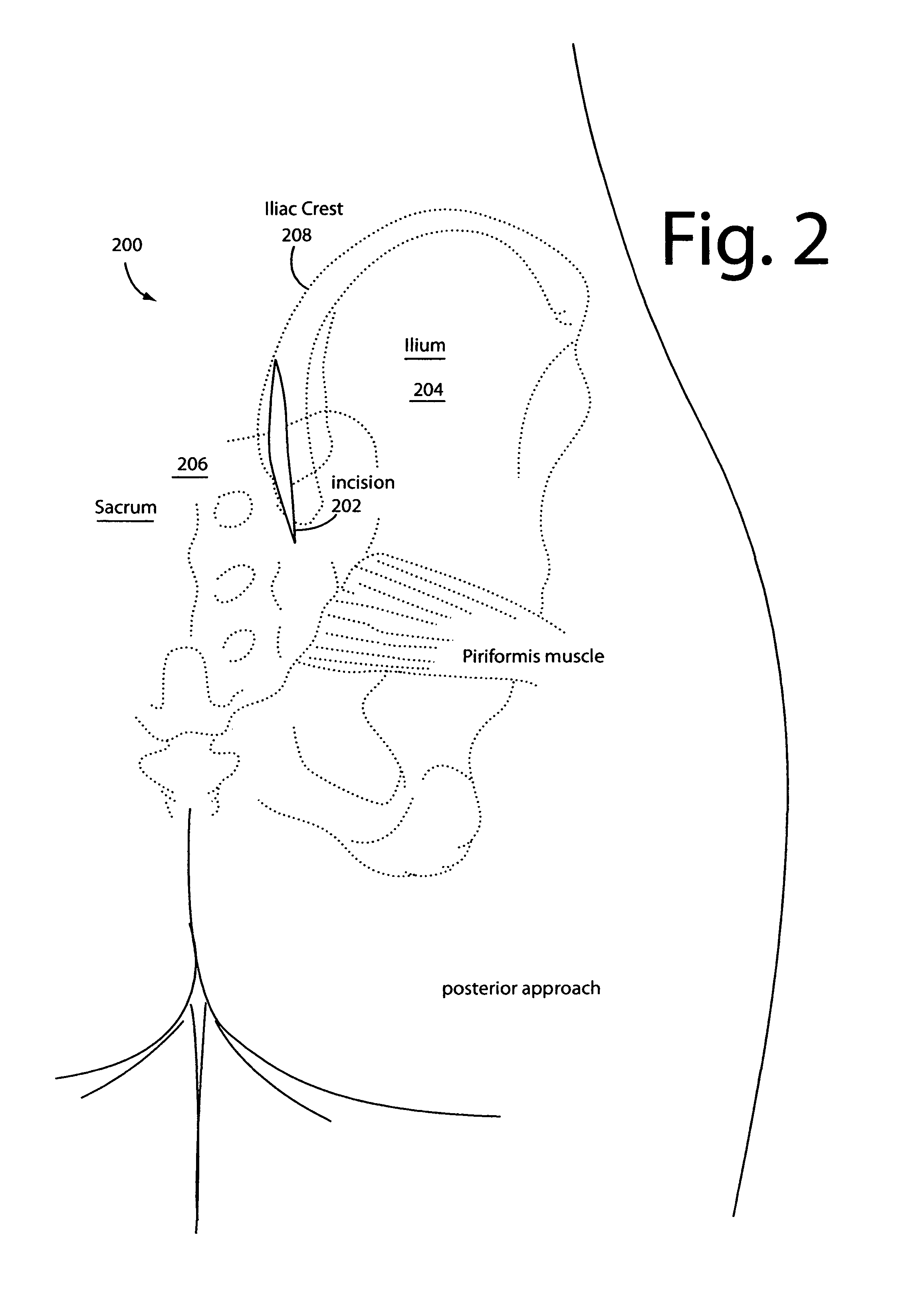
Sacroiliac joint exposure, fusion, and debridement
InactiveUS9452065B1Closure and subsequent healing are facilitatedEasy to placeJoint implantsSpinal implantsPosterior approachSacrum
A surgical method for exposure of the sacroiliac joint using a posterior approach begins with a longitudinal incision over the posterior iliac crest, centered on the posterior iliac spine. Holes which will be used to repair the iliac osteotomy are made obliquely from the medial to lateral to cross the plane of exposure. A cut through the bone is made lateral to the drill holes and centered over the sacroiliac complex with the aid of fluoroscope or radiograph imaging. The medial part of the iliac crest is freed from the back of the sacrum and displaced medially for the sacroiliac joint complex to be inspected, debrided, or curettaged for fusion. The closure and subsequent healing are facilitated by the predrilled oblique holes. These are used to re-attach the medial iliac bone to the remaining lateral ilium.
Owner:HILL ROBERT CHARLES
Geared spinal implant inserter-distractor
ActiveUS20100076557A1Efficient and accurate deliveryGreat control and feedbackSpinal implantsOsteosynthesis devicesLinear motionPosterior approach
Embodiments of a geared spinal implant inserter-distractor disclosed herein provide a greater mechanical advantage in delivering an intervertebral implant via an anterior, anterior-lateral, or posterior approach. The geared spinal implant inserter-distractor comprises an inserter, a distractor structured to slidably receive the inserter with a collar and an intervertebral implant attached thereto, and a gear mechanism arranged to translate a surgeon's rotational motion into linear motion, allowing the surgeon to have a greater control and feedback when placing an implant within an intervertebral disc space. The gear arrangement comprises a pinion inside the distractor and a rack on the inserter. The pinion can be driven by a shaft connected to a knob or handle. With the gear mechanism, a surgeon can turn the knob or handle to drive the inserter in and out of the distractor in a quantifiable manner, which facilitates the desirable precision delivery of the intervertebral implant.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
Spinal implant
InactiveUS20080039942A1Less invasiveEasy to disassembleSurgerySpinal implantsPosterior approachIntervertebral disk
A spinal implant that includes a plurality of components adapted for use as an implant in a disc. Each component is configured to be inserted into a void of a disc and each component complimentarily abuts at least one other component to form the implant. A method treating a spinal disc that includes creating a port from a posterior approach into the disc space of a spinal disc; and inserting components that form a spinal implant into the disc space through the port to form the spinal implant. A method of forming a modular spinal implant, comprising: preparing a plurality of components that are shaped for insertion into a disc, wherein each component abuts at least one other component in the disc.
Owner:ZIMMER SPINE INC +1
Expandable cage for vertebral surgery involving lumbar intersomatic fusion by a transforaminal posterior approach
An implant of the intersomatic cage type, for fusion of vertebral bodies by a transforaminal approach, is disclosed that comprises a body with a curved profile that is designed to be implanted between the vertebral plates of two adjacent vertebrae. According to the invention, said body of curved profile comprises a posterior maneuvering part and an anterior attack part, said anterior attack part being composed of a lower tongue and of an upper tongue that are designed to receive between them a spacer element that can slide between a position of introduction, in which it is situated near said posterior maneuvering part, and a spacing position, in which it is situated near the end of said anterior attack part, thus increasing the thickness of the latter by spreading the tongues apart, said spacer element comprising a receiving seat that is open at the top and bottom.
Owner:SCHAUMBURG GERALD +1
Method for repair of a spine and intervertebral implant
Repair of a spine from a posterior approach especially for locating an implant between a lower and upper human vertebra includes making an incision in the skin lateral to the midline, making an incision through the Erector Spinae Aponeurosis (ESA) following the ELIF groove, separating the ESA from the Longissimus Thoracis Pars Lumborum (LTPL), atraumatic separating the Multifidus from the LTPL using the interfascial boundary between the Multifidus and the LTPL, and creating a surgical plane having an angle of 20°-60°.
Owner:LIGNE
Artificial disc replacement using posterior approach
Methods and devices are provided for replacing a spinal disc. In an exemplary embodiment, artificial disc replacements and methods are provided wherein at least a portion of a disc replacement can be implanted using a posterolateral approach. With a posterolateral approach, the spine is accessed more from the side of the spinal canal through an incision formed in the patient's back. A pathway is created from the incision to the disc space between adjacent vertebrae. Portions of the posterolateral annulus, and posterior lip of the vertebral body may be removed to access the disc space, leaving the remaining annulus and the anterior and posterior longitudinal ligaments in tact. The disc implant can be at least partially introduced using a posterolateral approach, yet it has a size that is sufficient to restore height to the adjacent vertebrae, and that is sufficient to maximize contact with the endplates of the adjacent vertebrae.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
Expandable Intervertebral Prosthesis Device for Posterior Implantation and Related Method Thereof
A method and device for the insertion of a vertebral cage that may be done through a posterior approach that is minimally traumatic and does not require retraction of the spinal cord, dural sac or spinal nerves. The insertion of the cage may therefore be parallel to the spinal cord and the cage will be rotated ninety degrees (or as desired or required) in the vertebral body defect or as applicable to achieve its proper positioning before expansion.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com