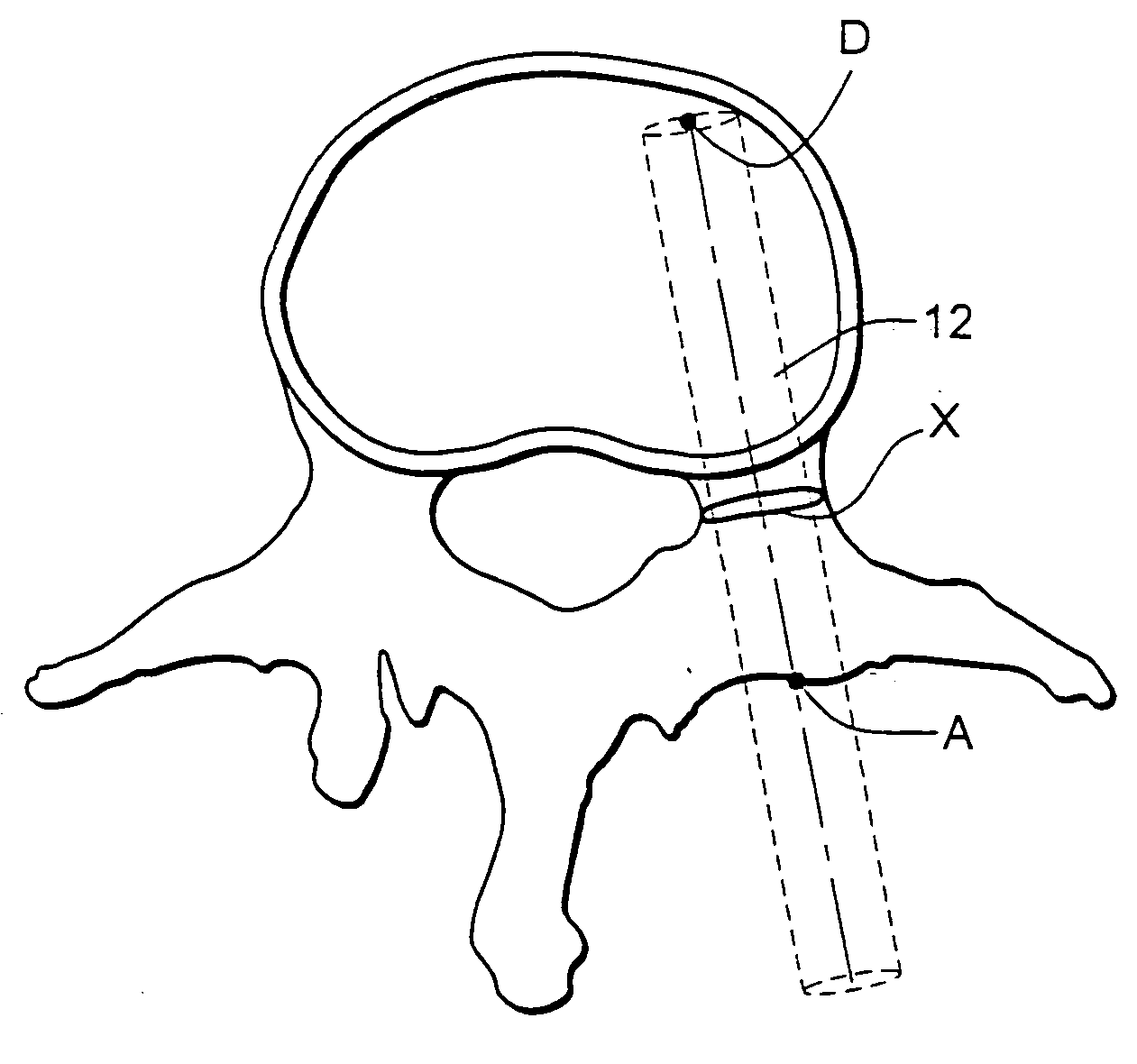
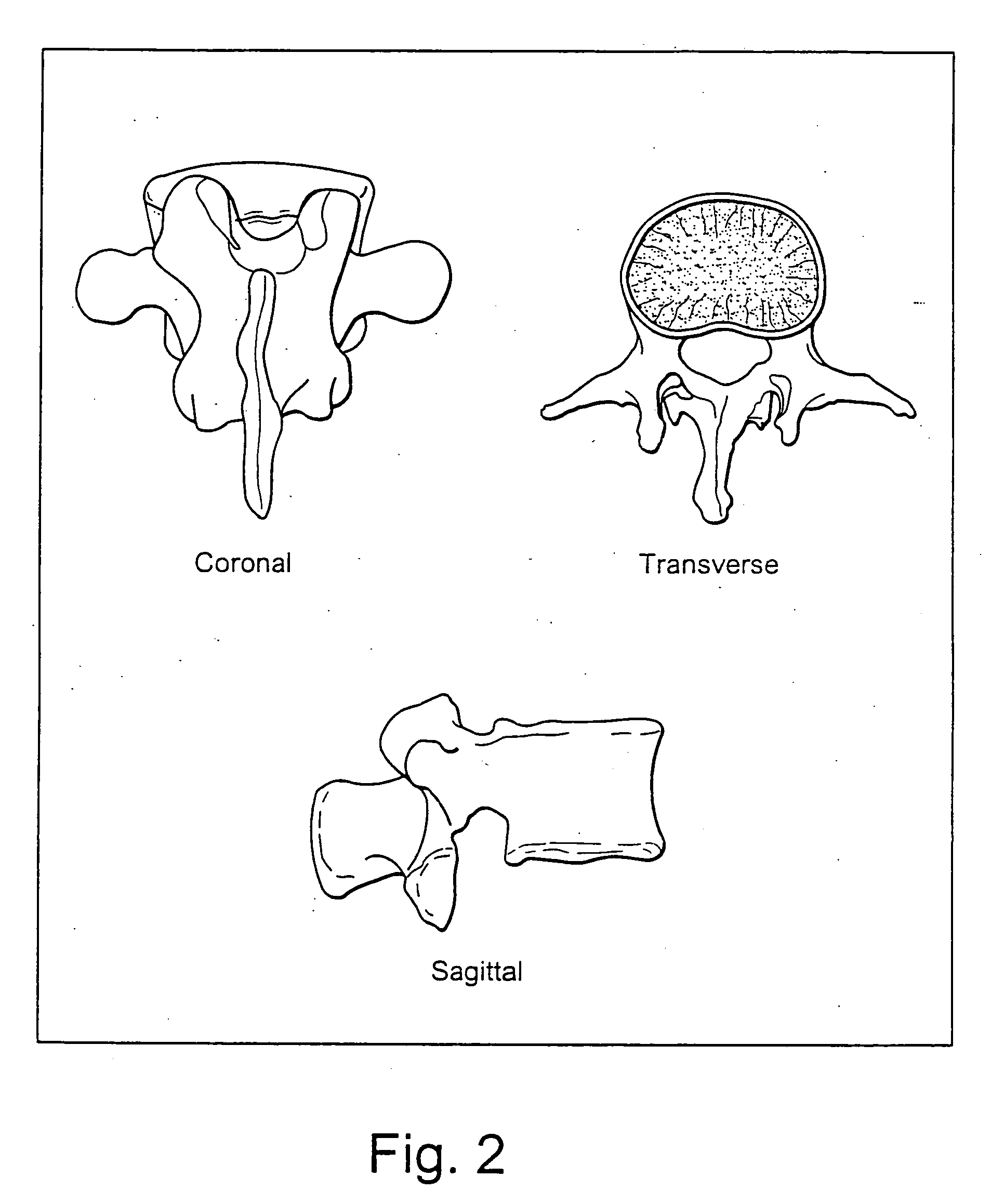
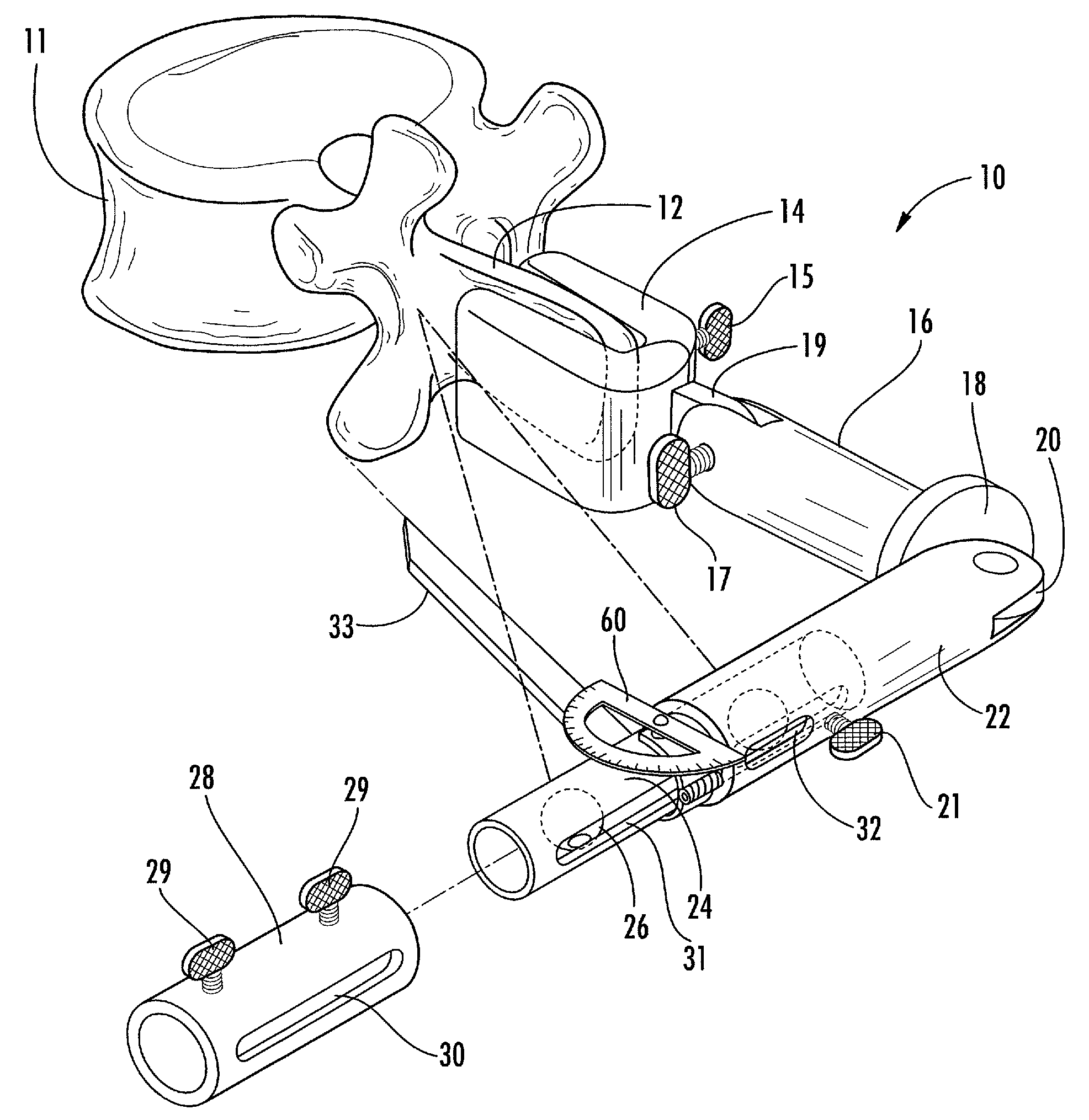
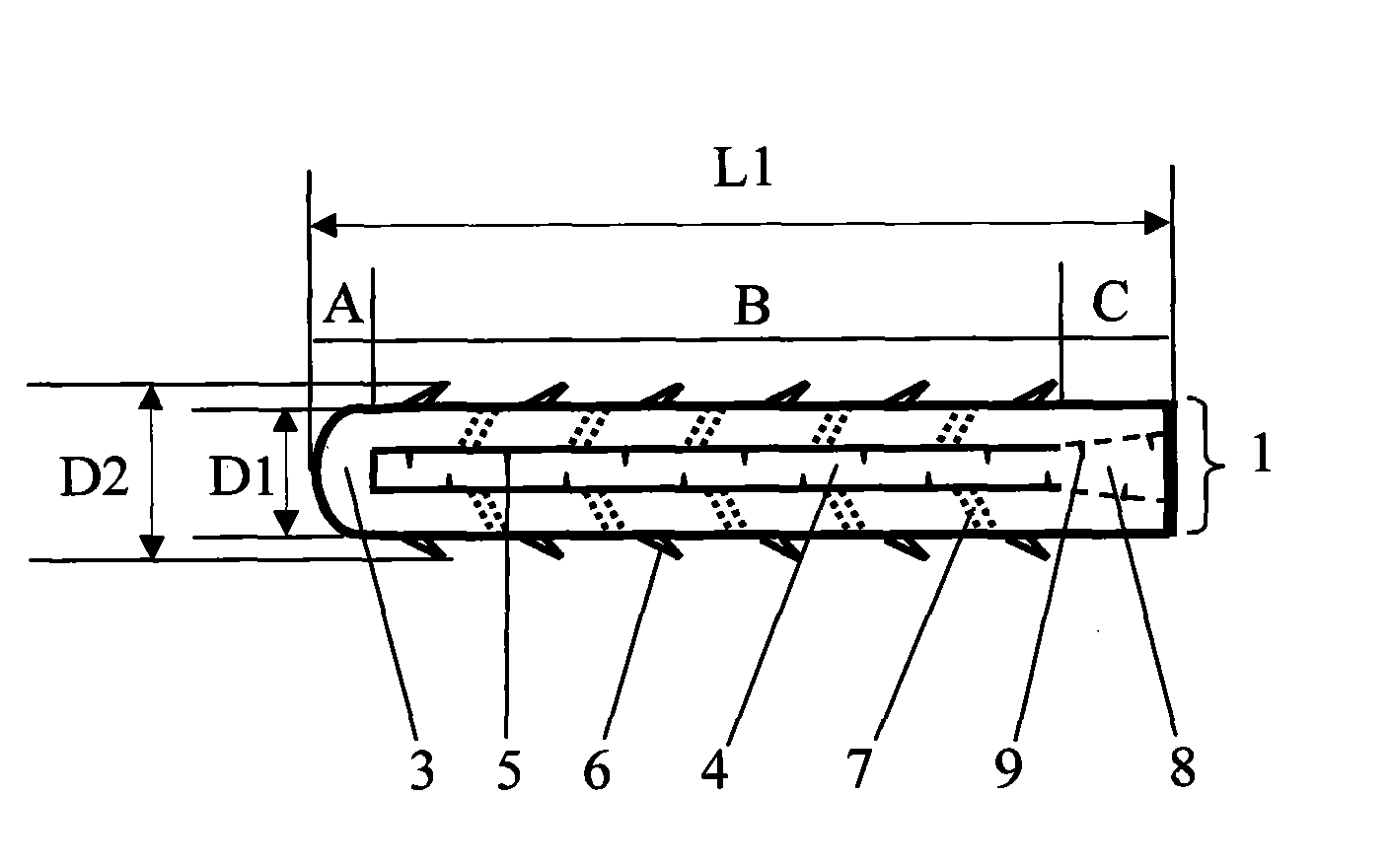
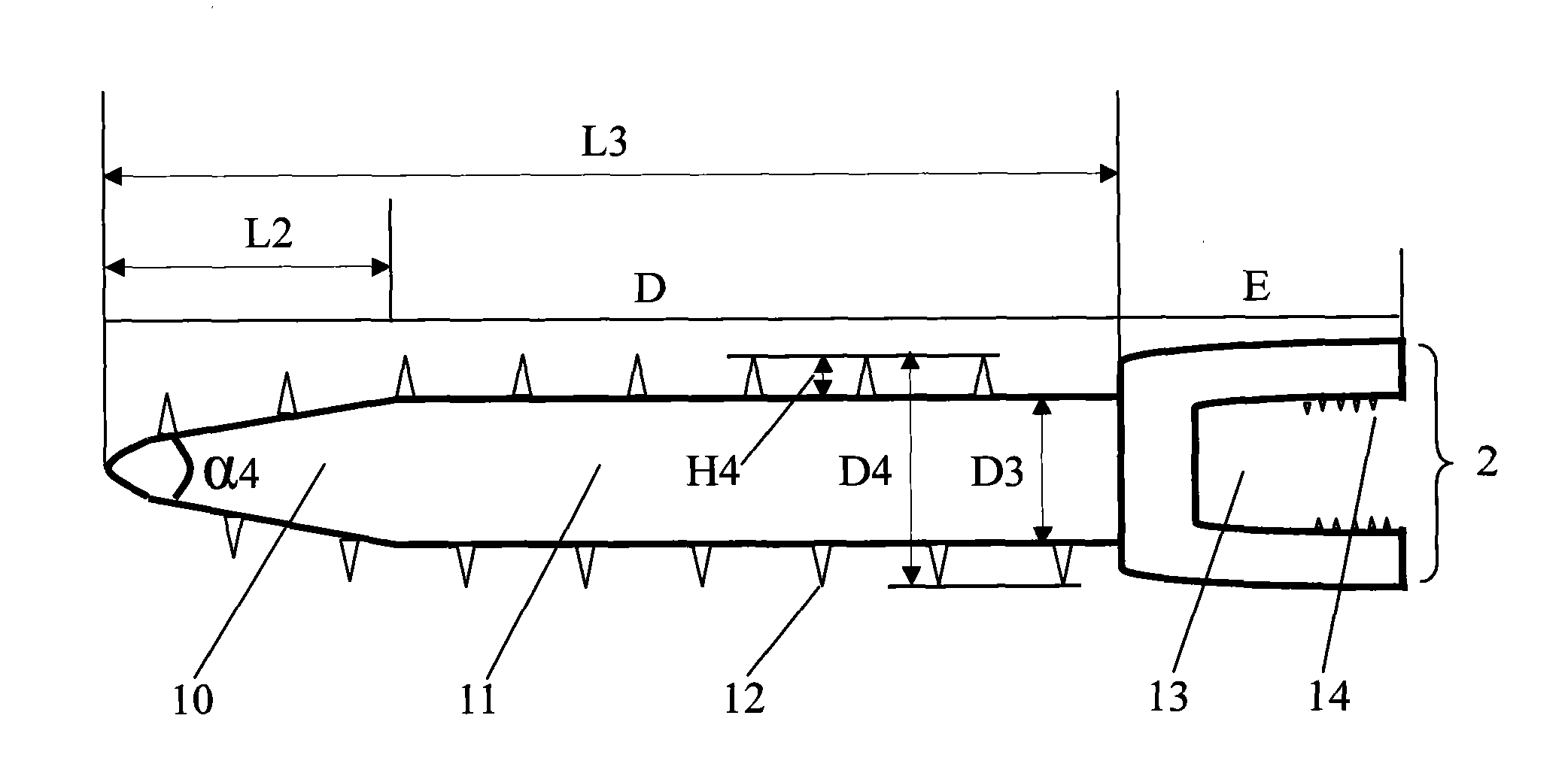
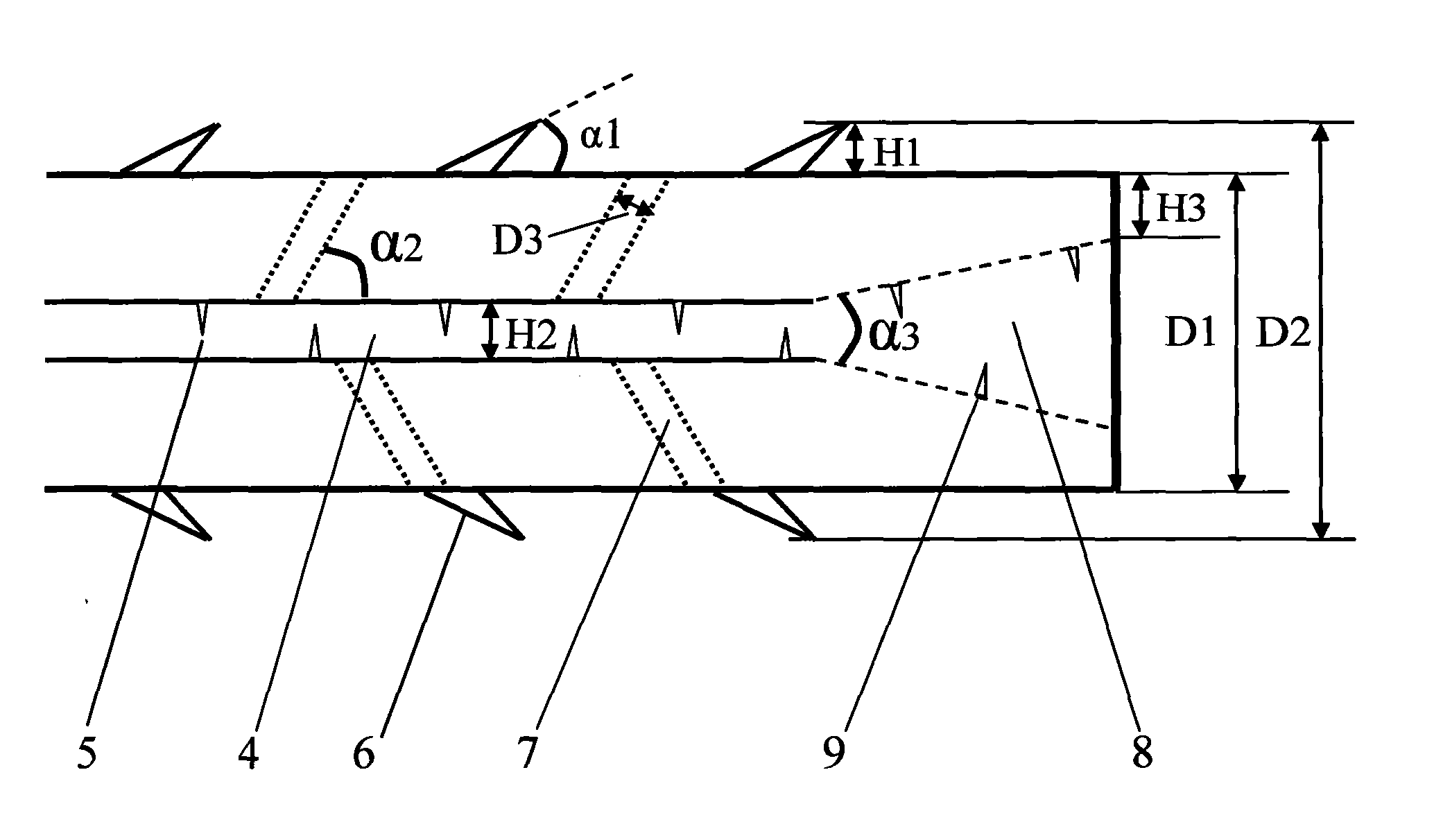
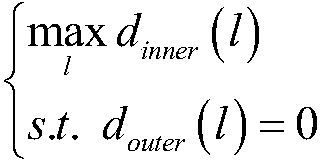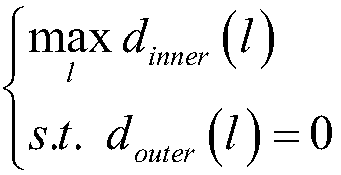Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
118 results about "Screw placement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
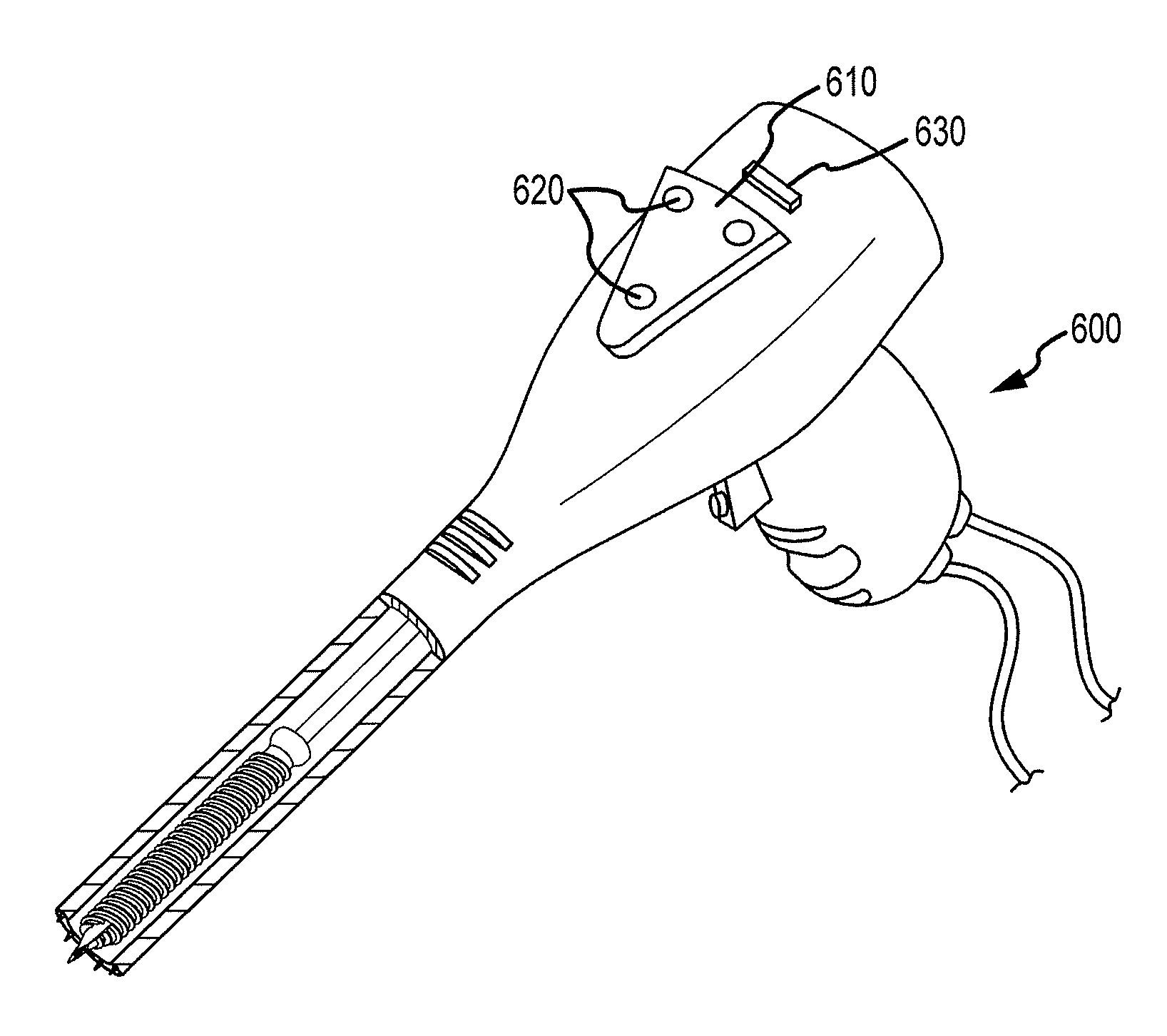
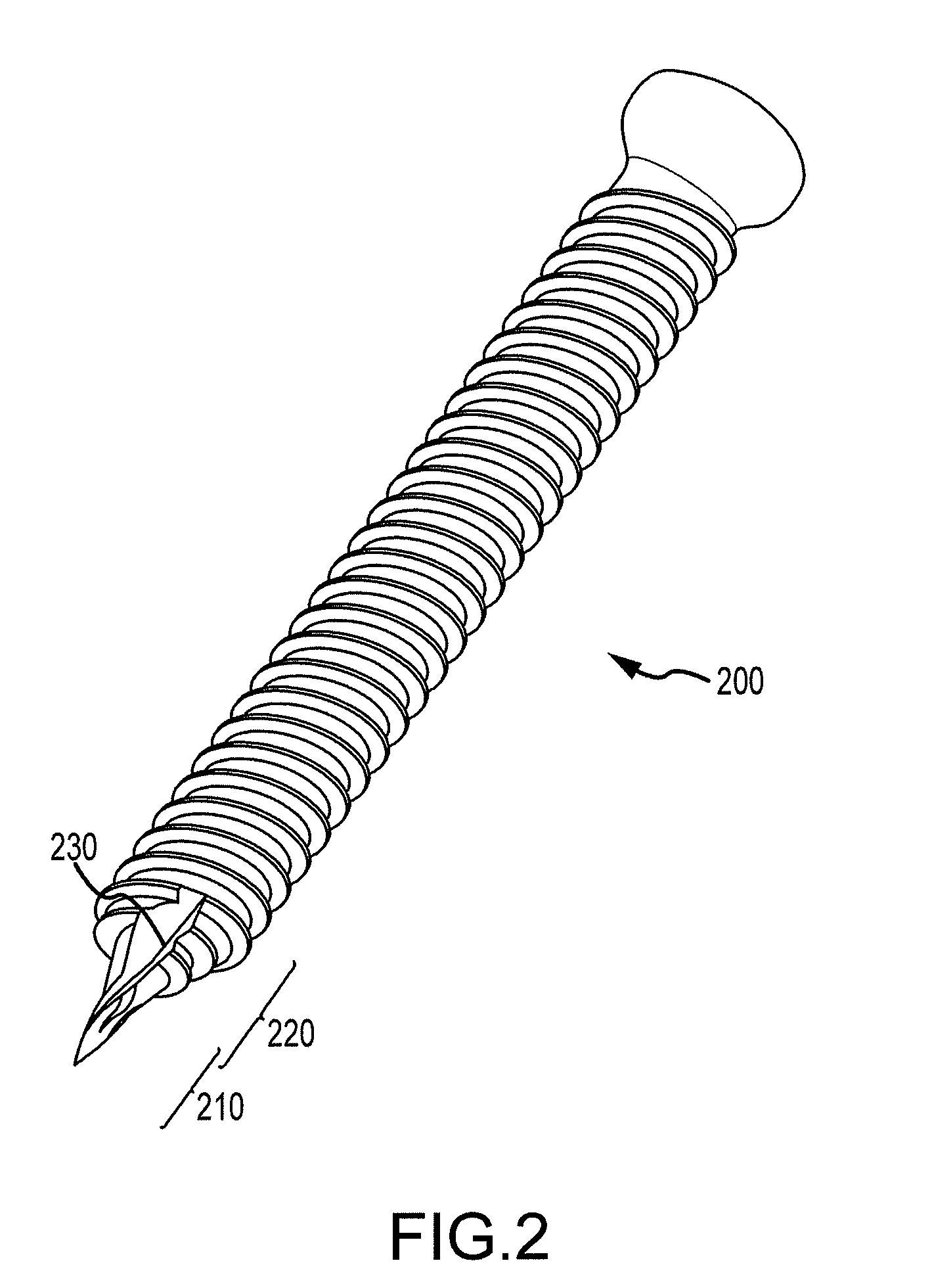
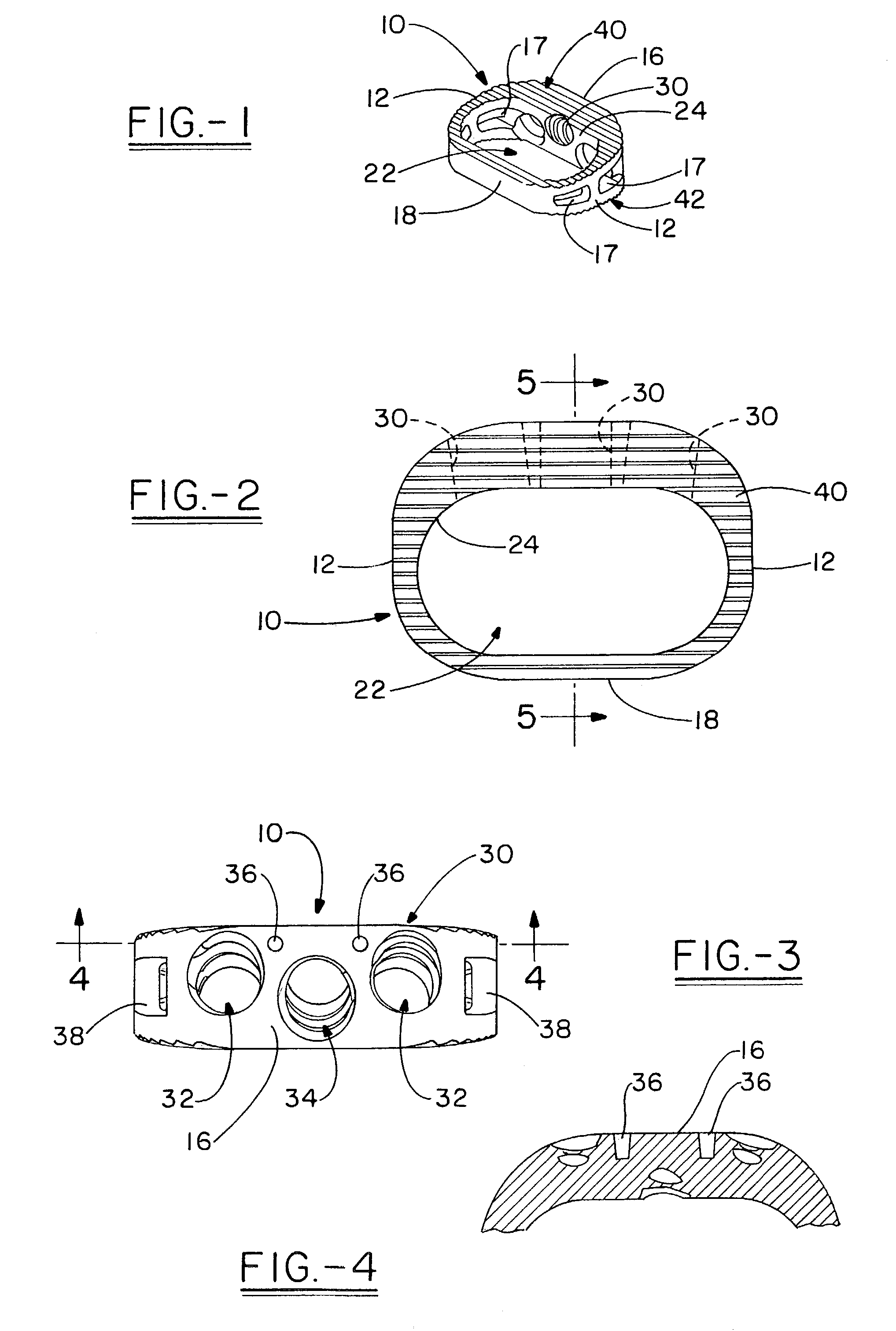
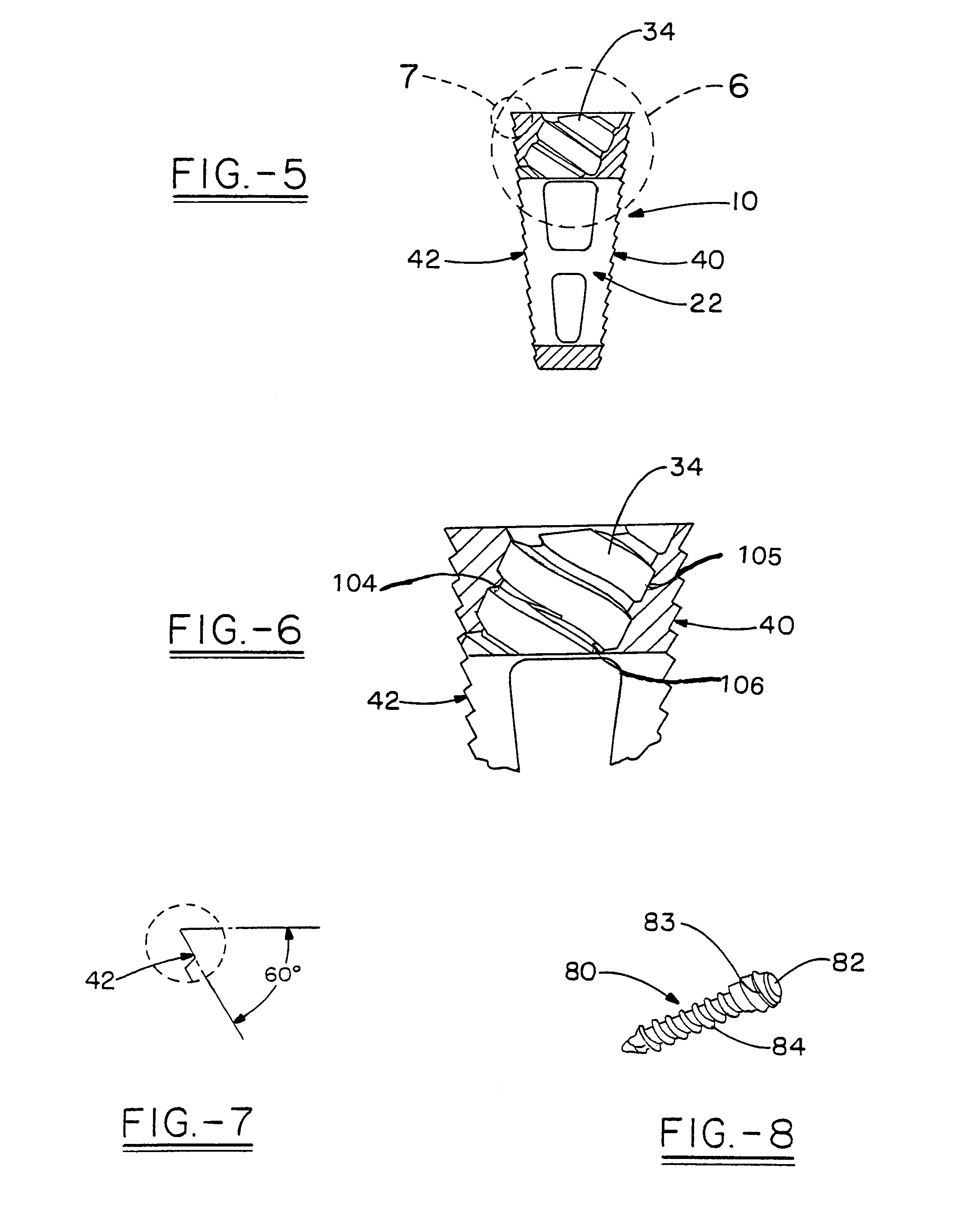
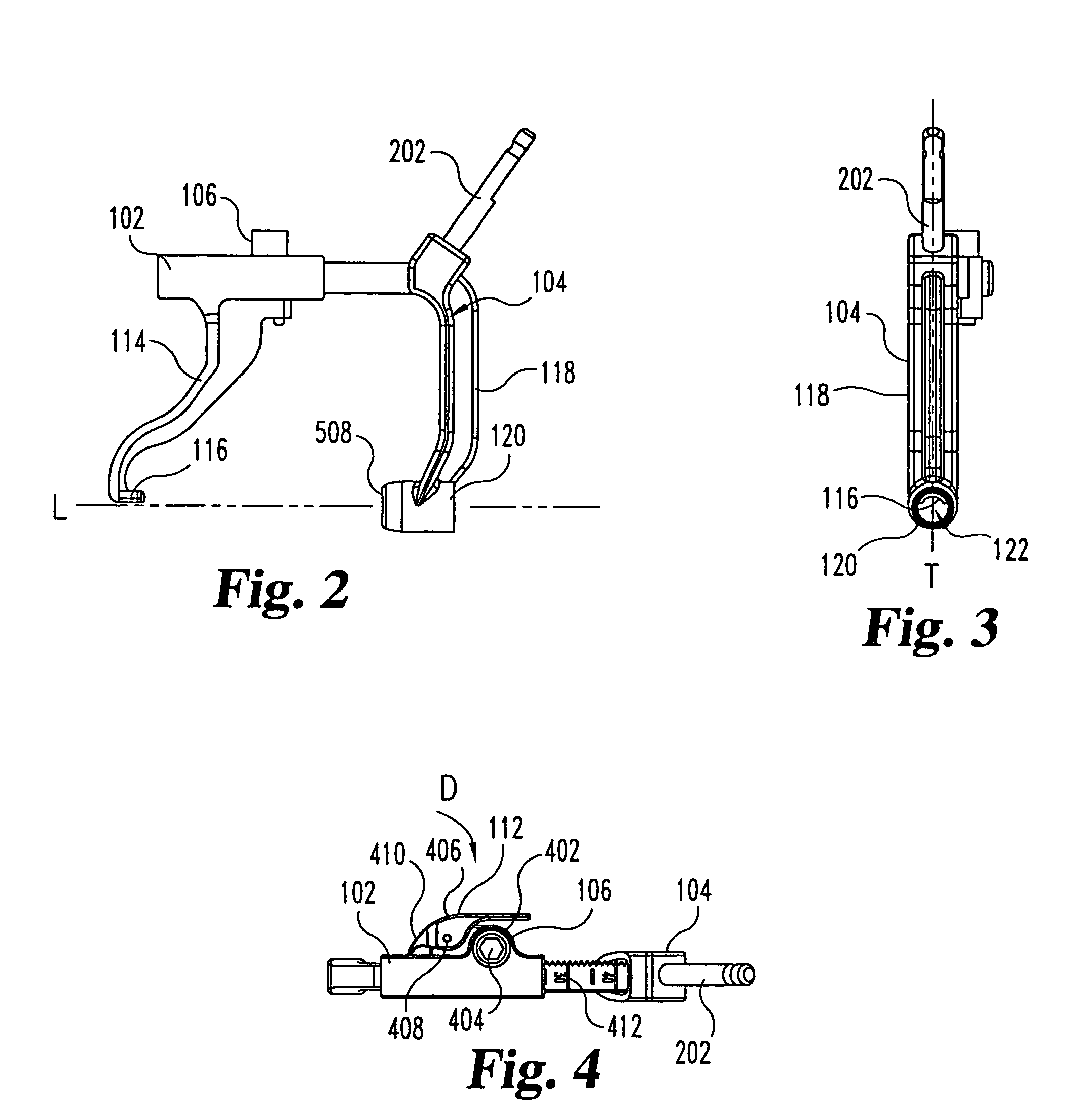
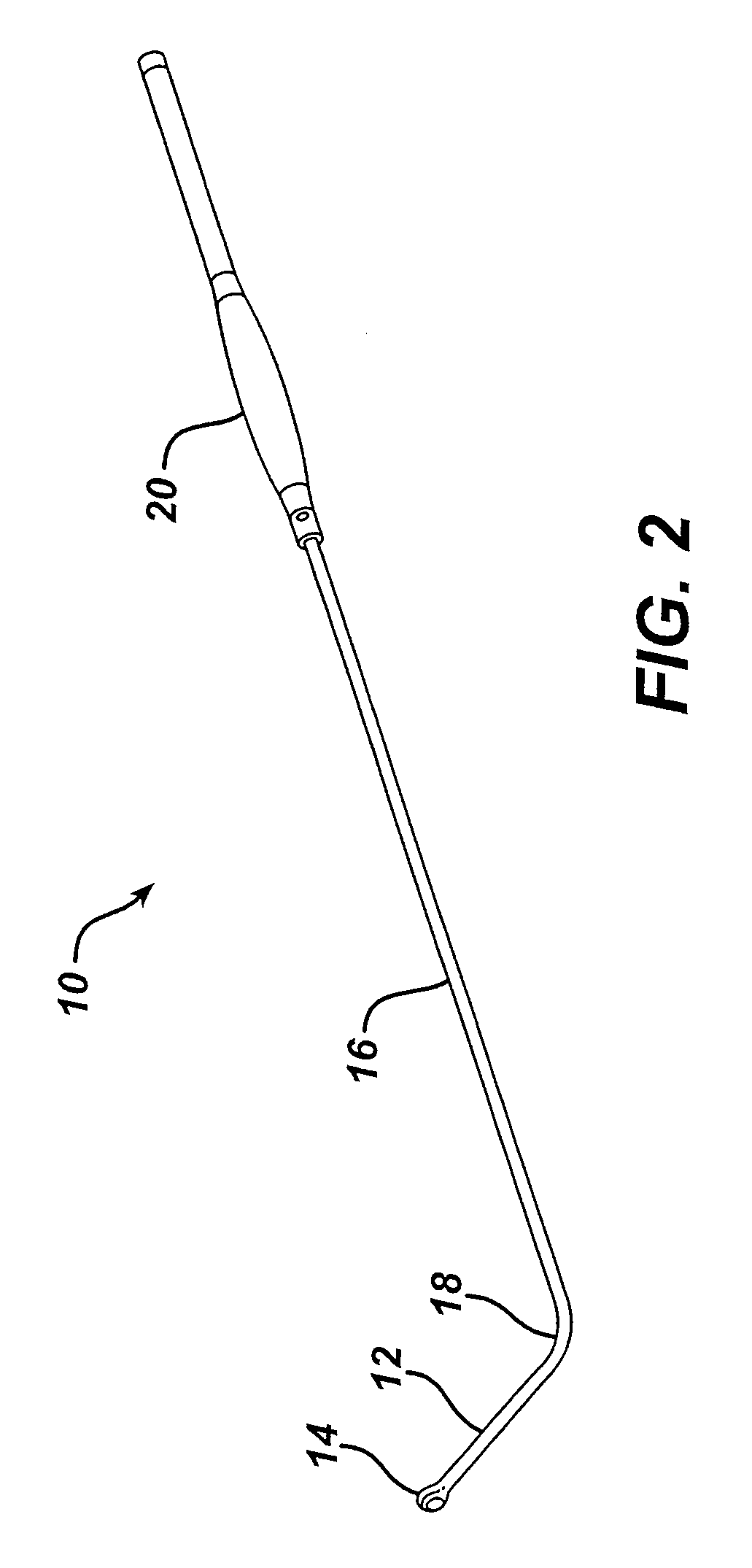
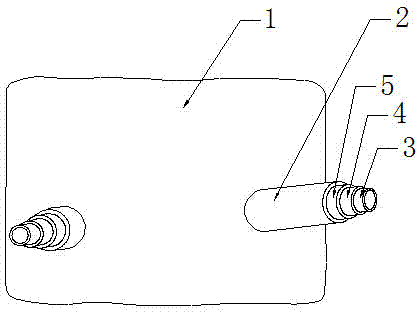
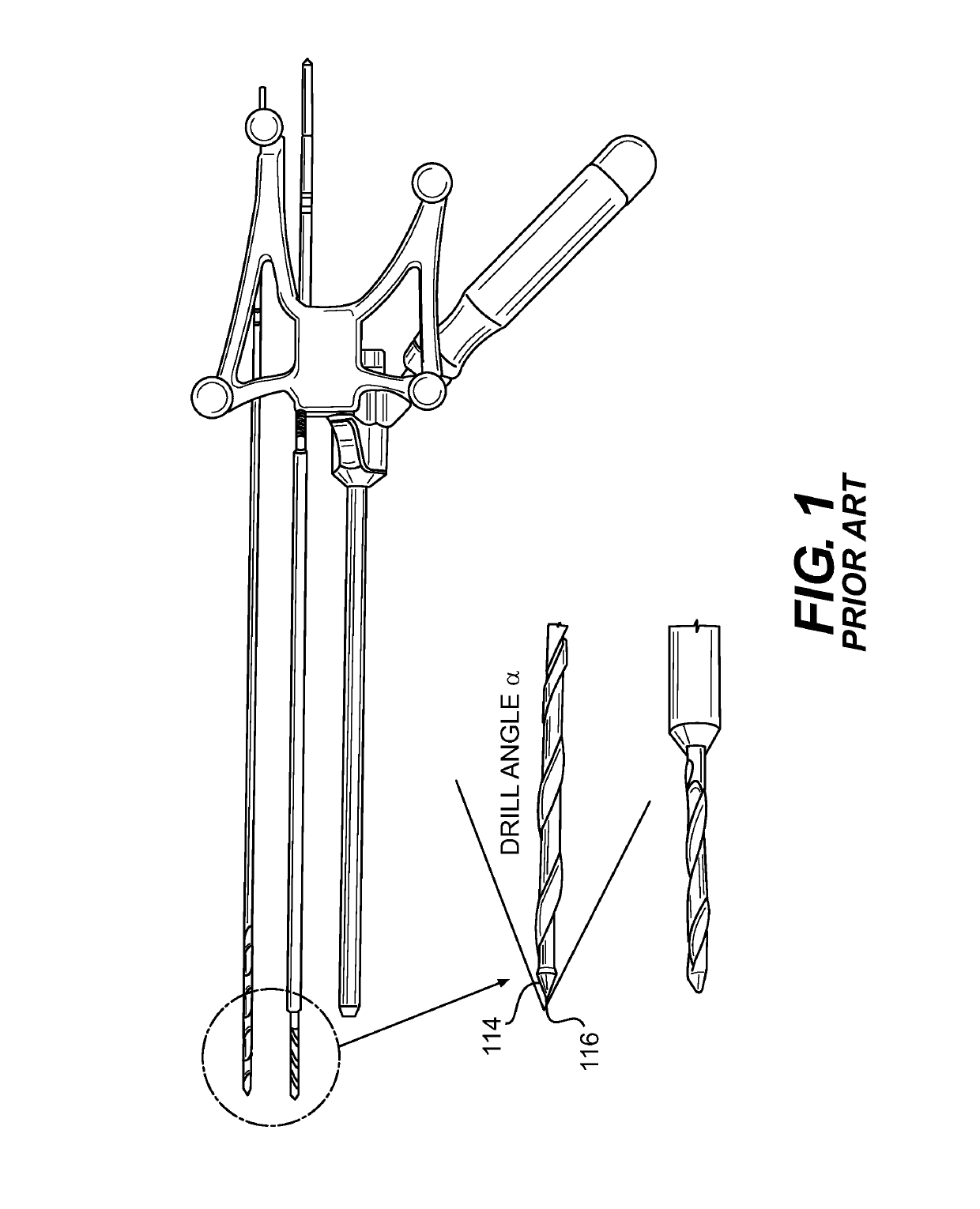
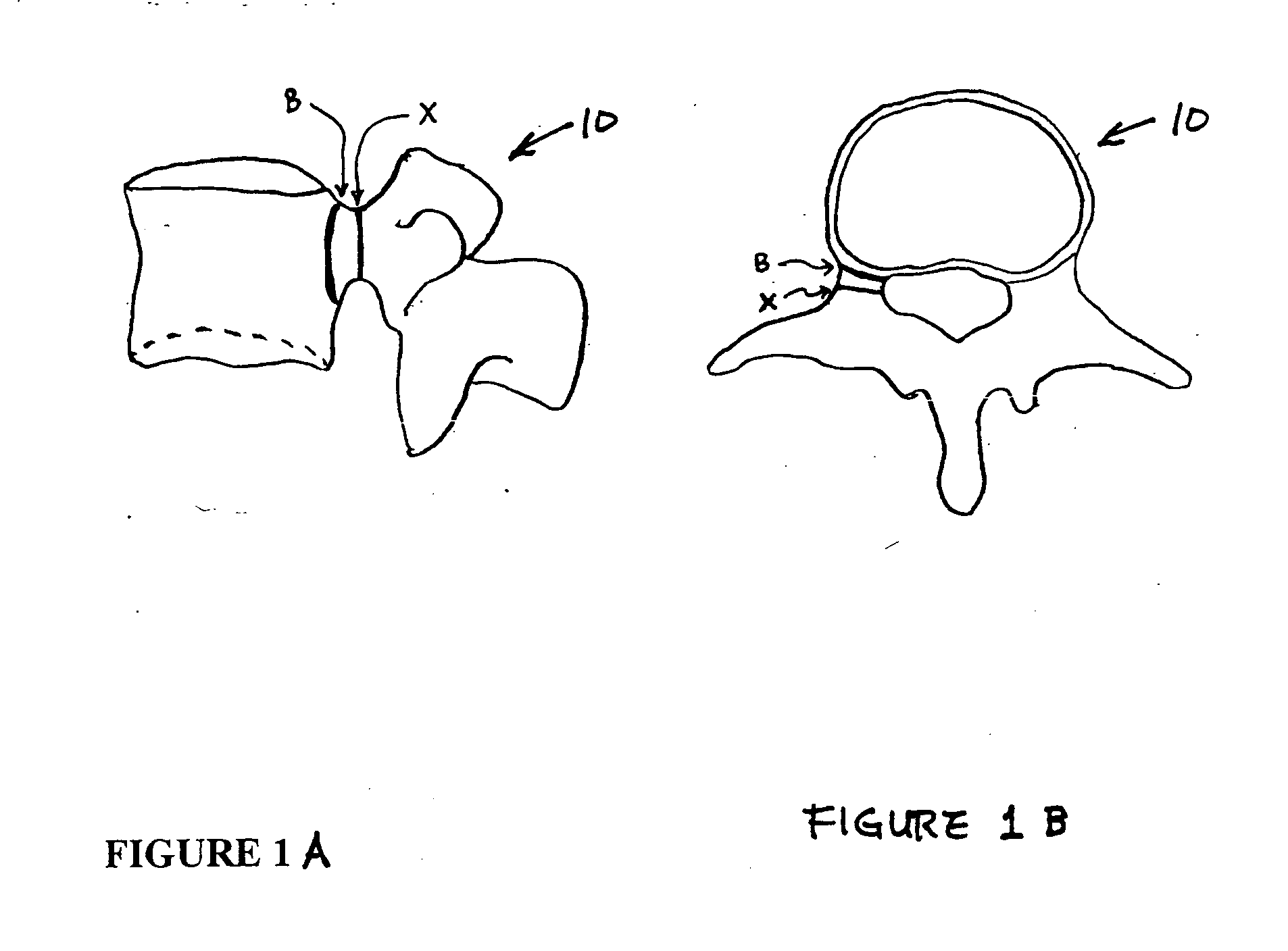
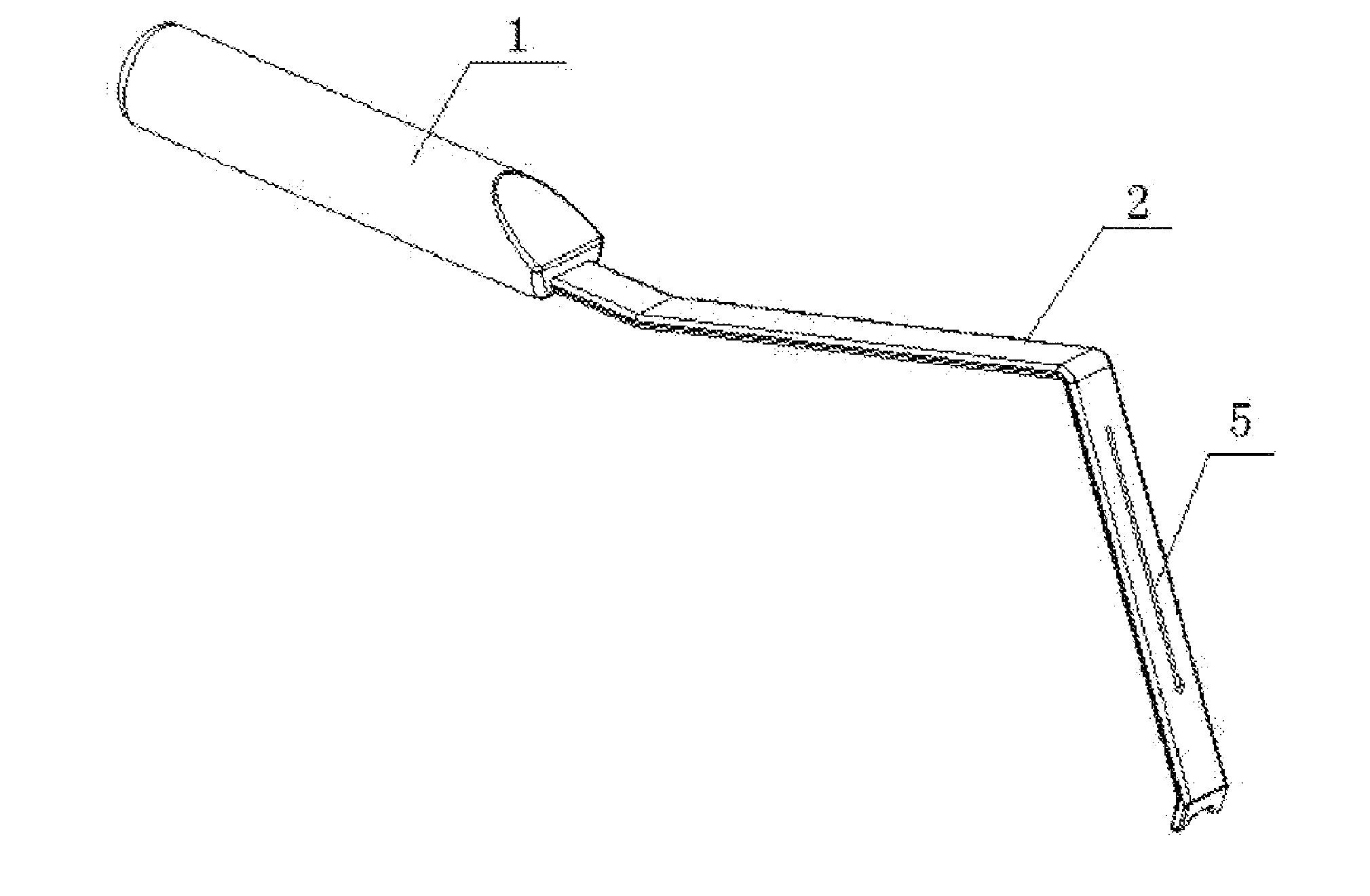
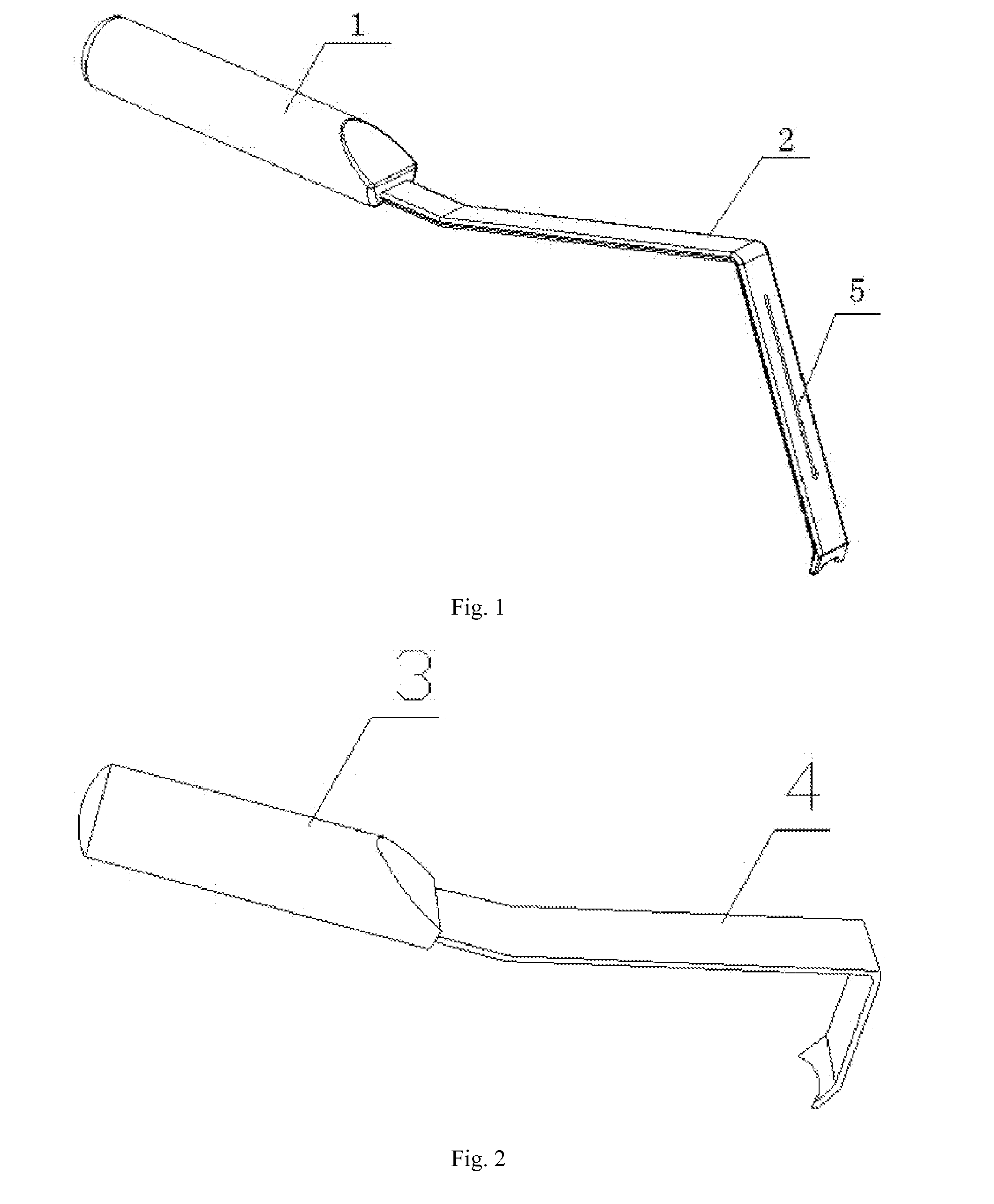
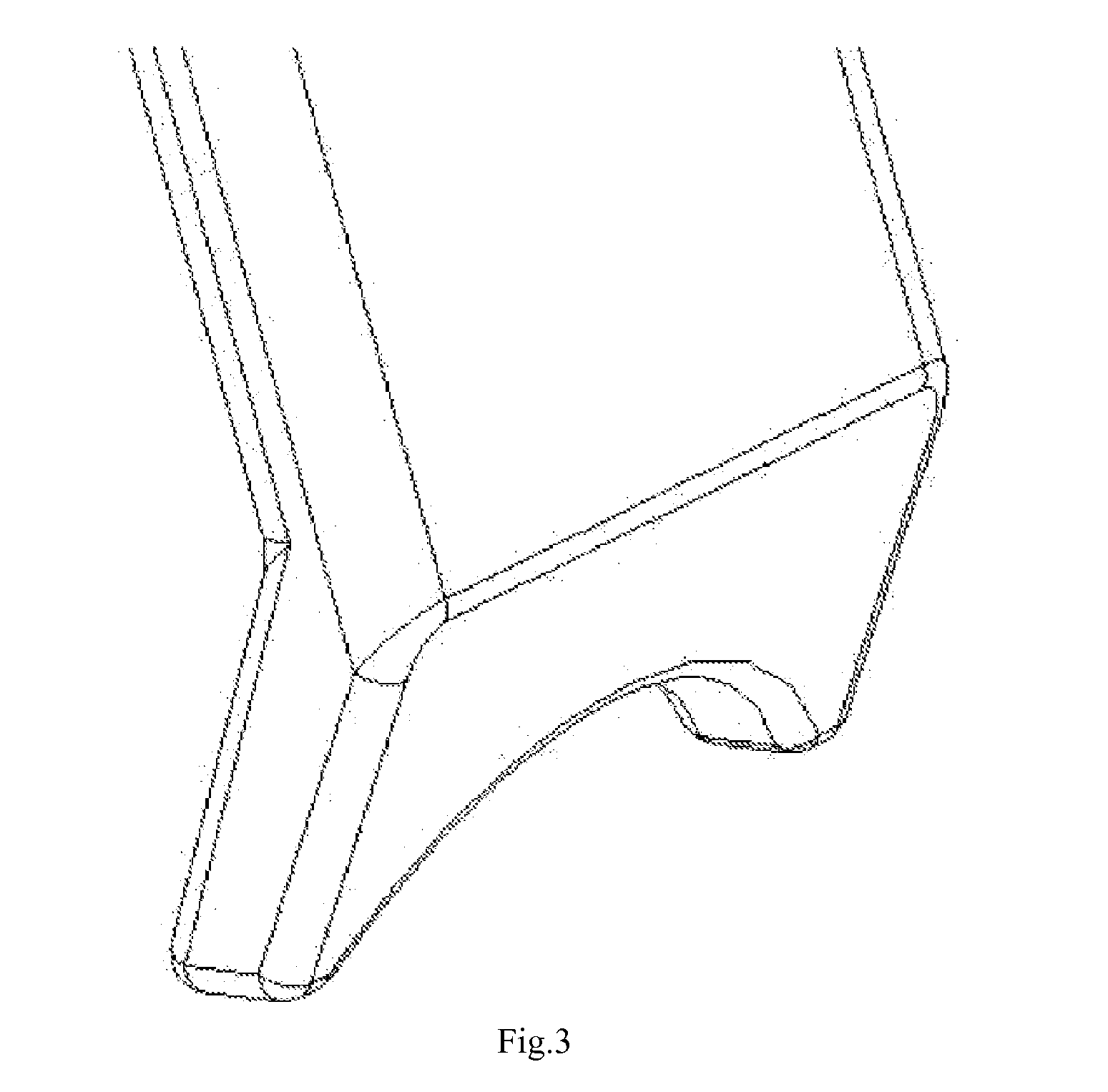
Image-guided minimal-step placement of screw into bone
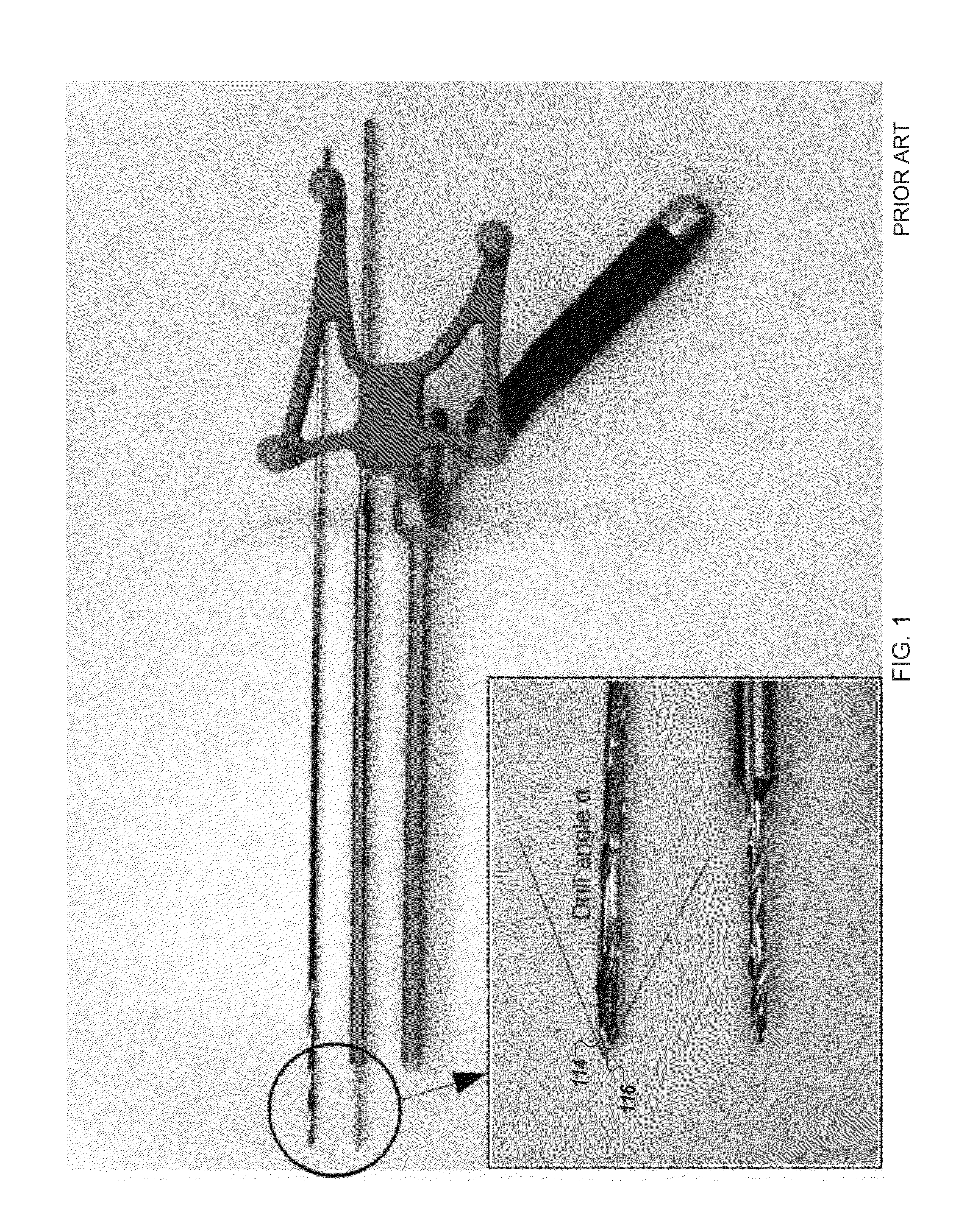
ActiveUS8366719B2Procedure is time-consumeImprove accuracyInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsScrew placementMonitoring system
The present disclosure describes a device and methods for safely and accurately placing screws into bones with a powered driving device. By employing multiple layers of fail-safe features and image-guidance systems, the powered driving device provides safe, accurate, and efficient screw placement. That is, the powered driving device may continuously monitor a screw advancement and placement and may automatically shutdown when improper placement is detected. Monitoring placement may be conducted by a microcurrent-monitoring system, by an image-guidance system, or by any other appropriate sensory system. Additionally, upon detecting that screw insertion is complete, the powered driving device may be automatically shutdown. As screw placement is continuously simulated by image-guidance in real time, multiple redundant verification steps are eliminated, providing highly accurate screw placement while decreasing clinician error, device contamination, and surgical time, the decreased surgical time associated with decreased patient-recovery time and associated medical costs.
Owner:INTEGRATED SPINAL CONCEPTS
Vertebral interbody cage with translatable locking screw
A vertebral cage is provided for use in preserving the space between adjacent vertebral during the process of spinal fusion. In particular, this cage has an open modified oval peripheral shape with a continuous fluid anterior wall having angled screw passages accessible through co-planar openings to allow the construct to be stabilized between adjacent vertebral bodies through their endwalls. In addition, the cage has a back to front wedge taper with pull-out resistant ratchet surfaces. Further, in a second aspect of the invention, the screw passages have a unique locking mechanism provided by oversized internal threads in combination with a second locking thread on the head of the associated bone screws that allows for axial translation of the screws within the screw passages. This in turn permits play in the angulation of the screw relative to the anchoring bone in order to optimize the screw placement in the bone.
Owner:ZIMMER BIOMET SPINE INC
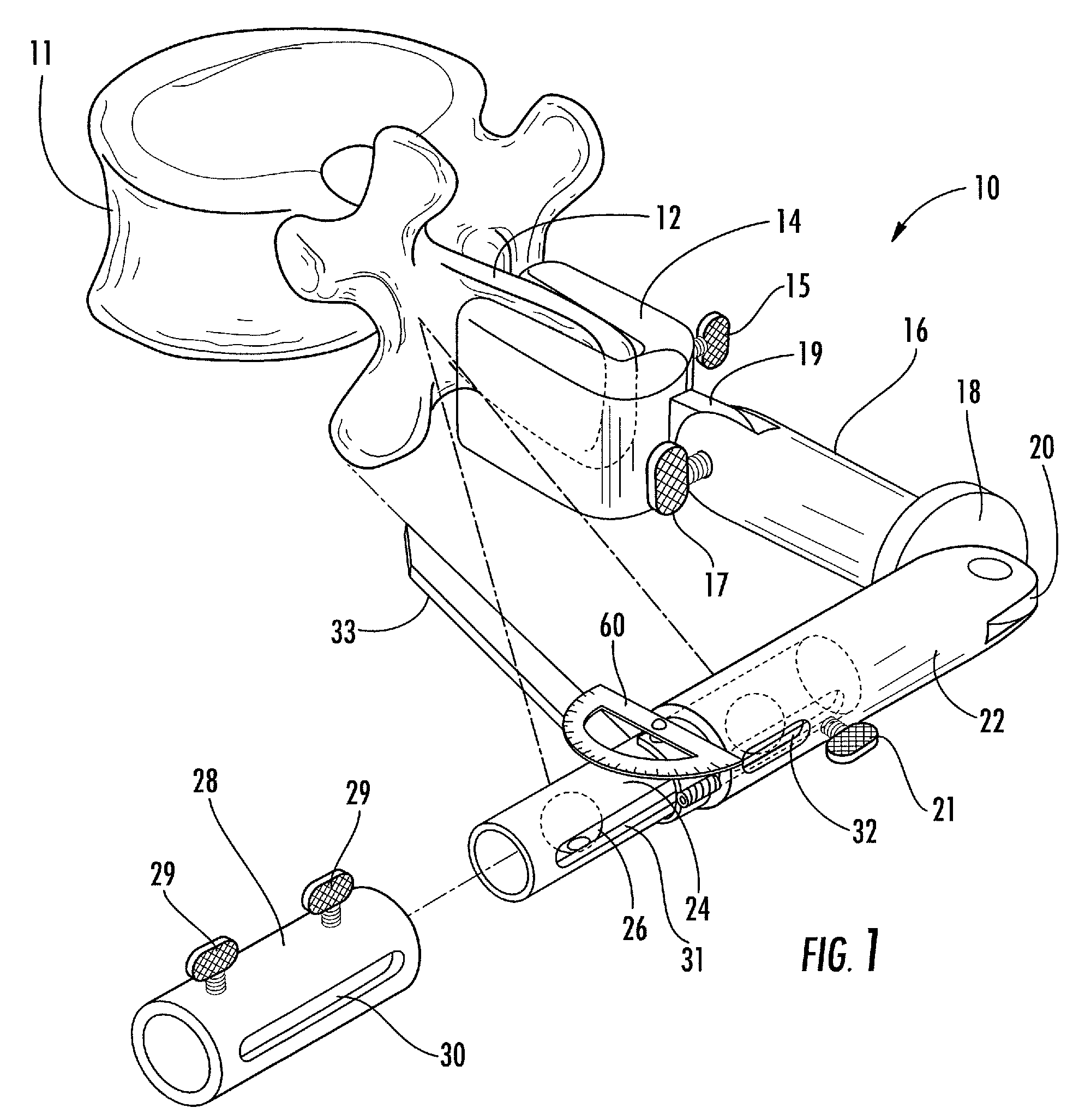
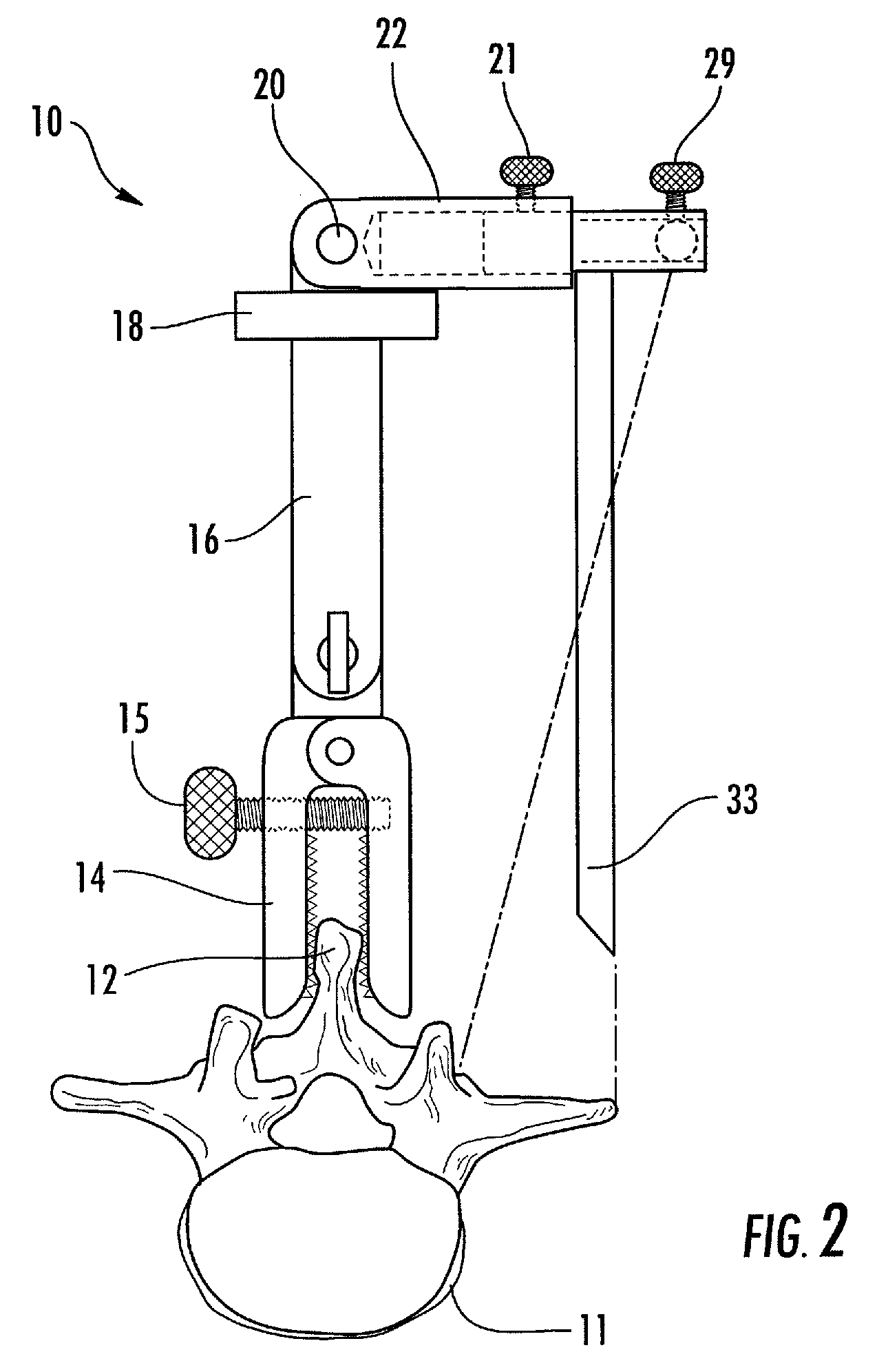
Vertebrae fastener placement guide
A screw placement guide includes a first member having a first guide adapted to contact a first vertebral bone portion and a second member having a second guide adapted to contact a second vertebral bone portion. A clamping mechanism provided on one of the members clamps the first guide and the second guide to the vertebral bone portions. The first guide and the second guide are aligned in order to indicate how a fastener will be aligned when fastened between adjacent vertebrae. A driver engages clamping mechanism to clamp the two members together.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
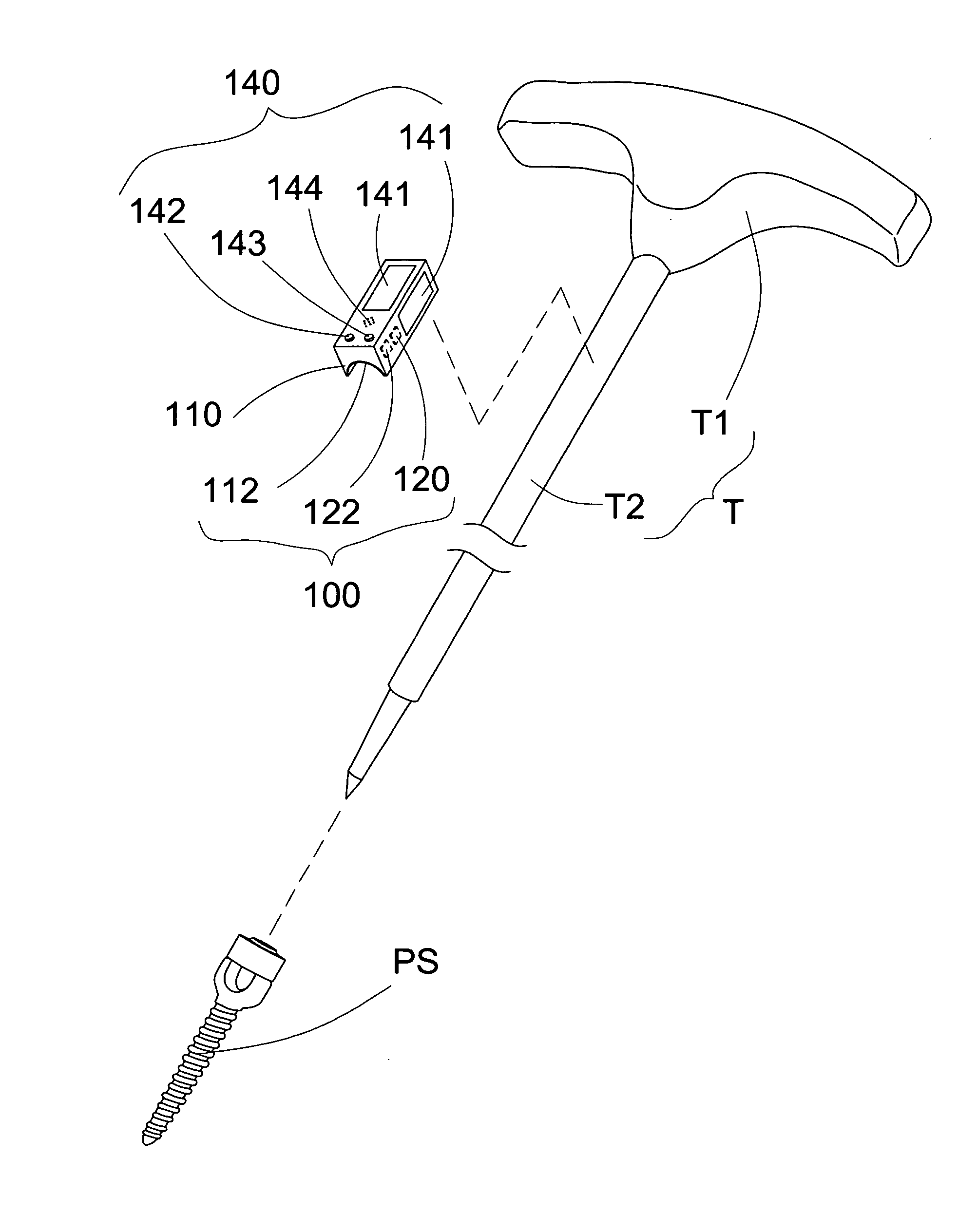
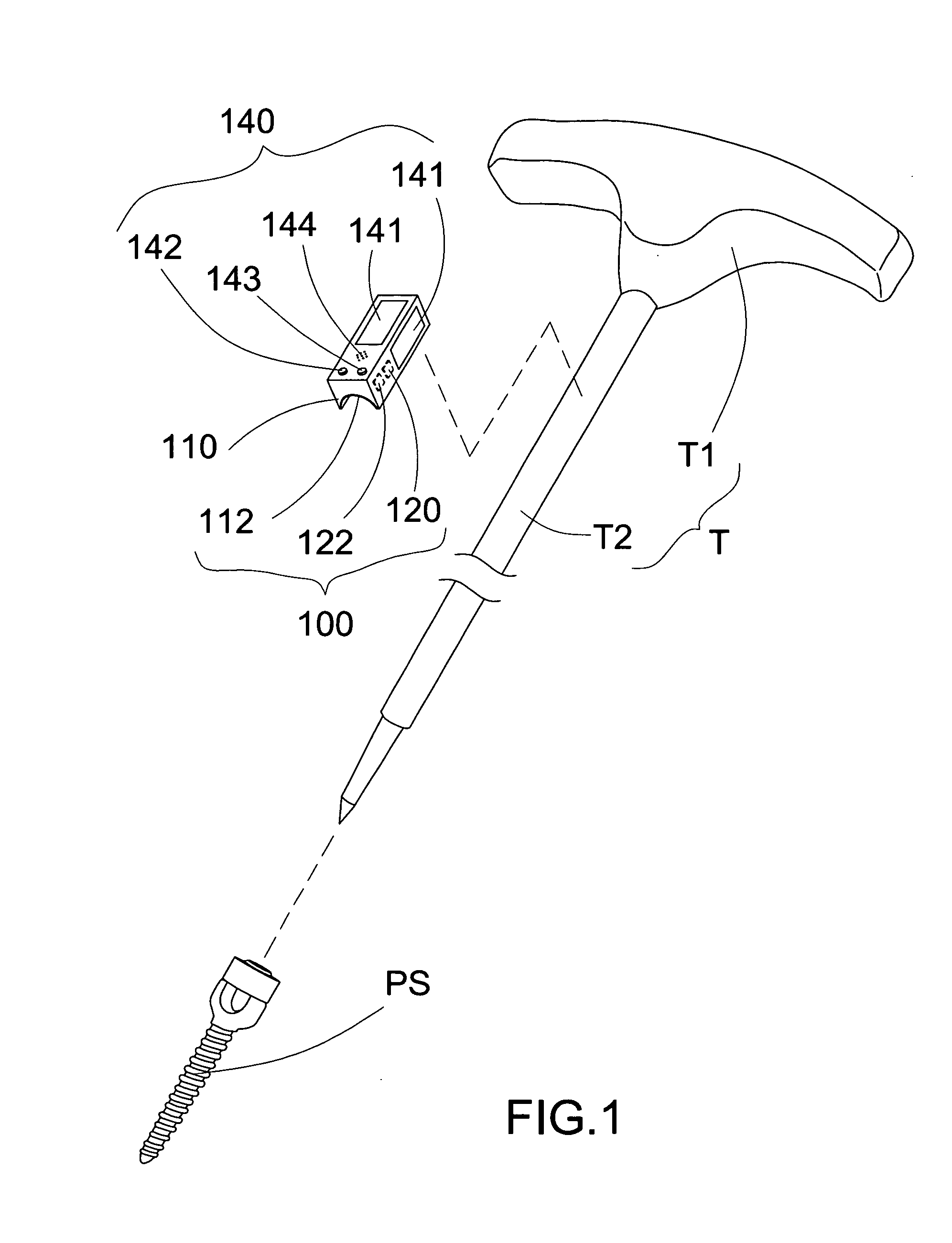
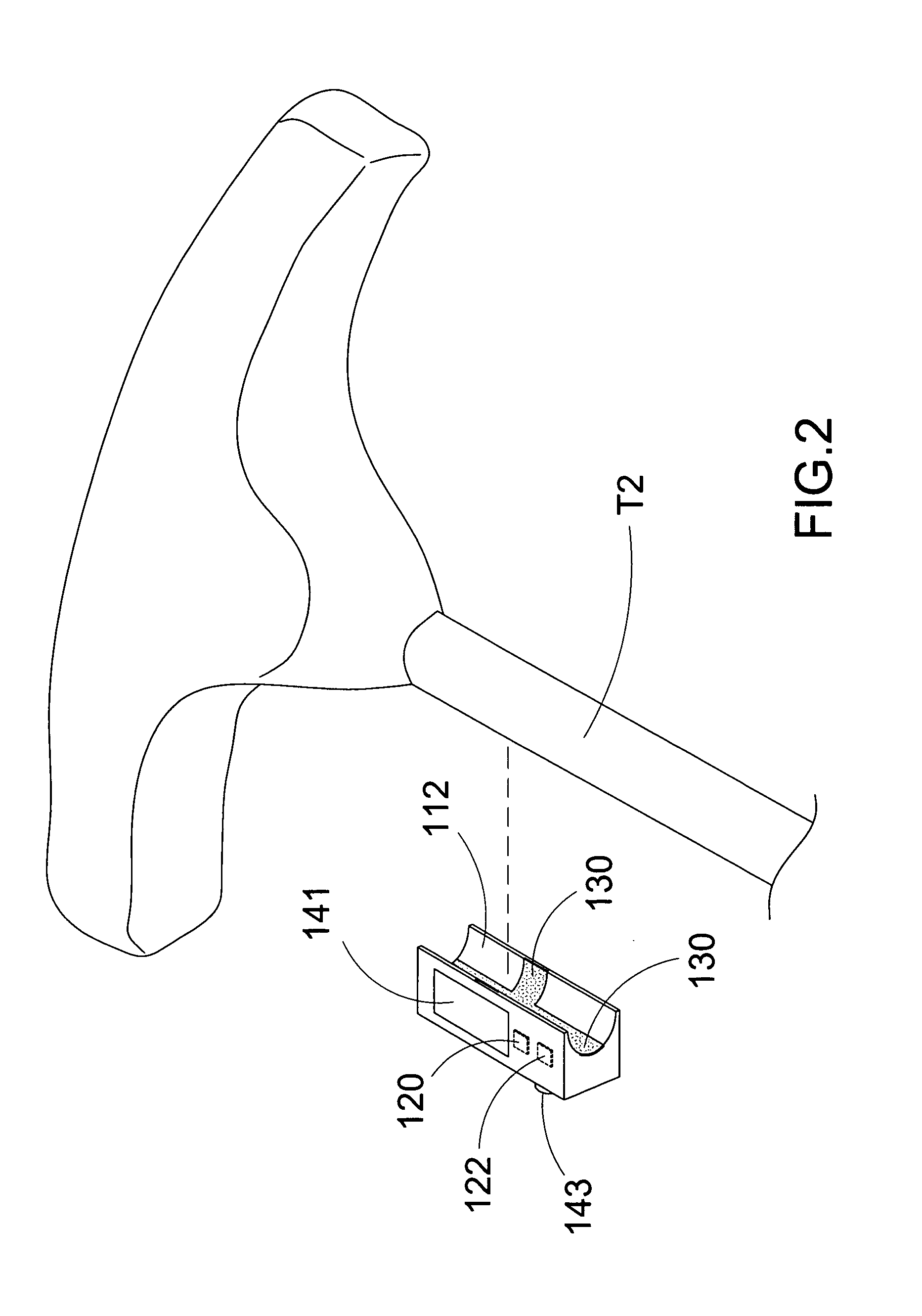
Surgical Angulation Measurement Instrument for Orthopedic Instumentation System
InactiveUS20130218166A1Improved surgical outcomeAccurate measurementInternal osteosythesisDiagnosticsScrew placementEngineering
A surgical angulation measurement instrument of the instant invention includes a positioning measurer and a positioning reader linked to the positioning measurer. The positioning measurer detachably couples with a tool which is used to implant the pedicle screw. In response to the orientation of the tool, the orientation of the pedicle screw is measured by the positioning measurer with respect to a pedicle axis of screw placement. The positioning reader indicates the orientation of the pedicle screw and notifies the orientation of the pedicle screw being aligned with the pedicle axis of screw placement.
Owner:ELMORE RANELL
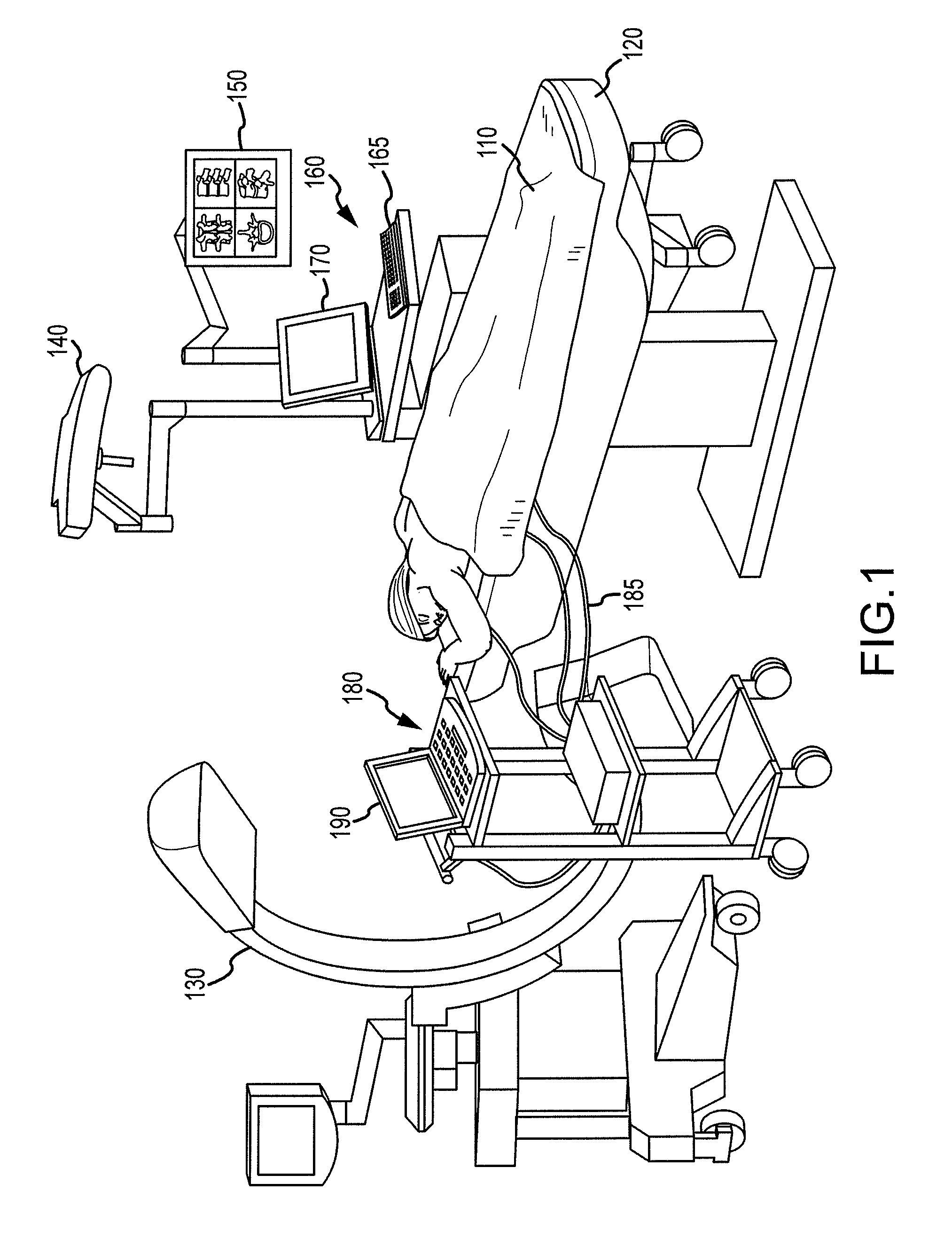
System and methods for improved access to vertebral bodies for kyphoplasty, vertebroplasty, vertebral body biopsy or screw placement
ActiveUS20060235338A1Easy to installSurgical navigation systemsPerson identificationSpinal columnAnterior cortex
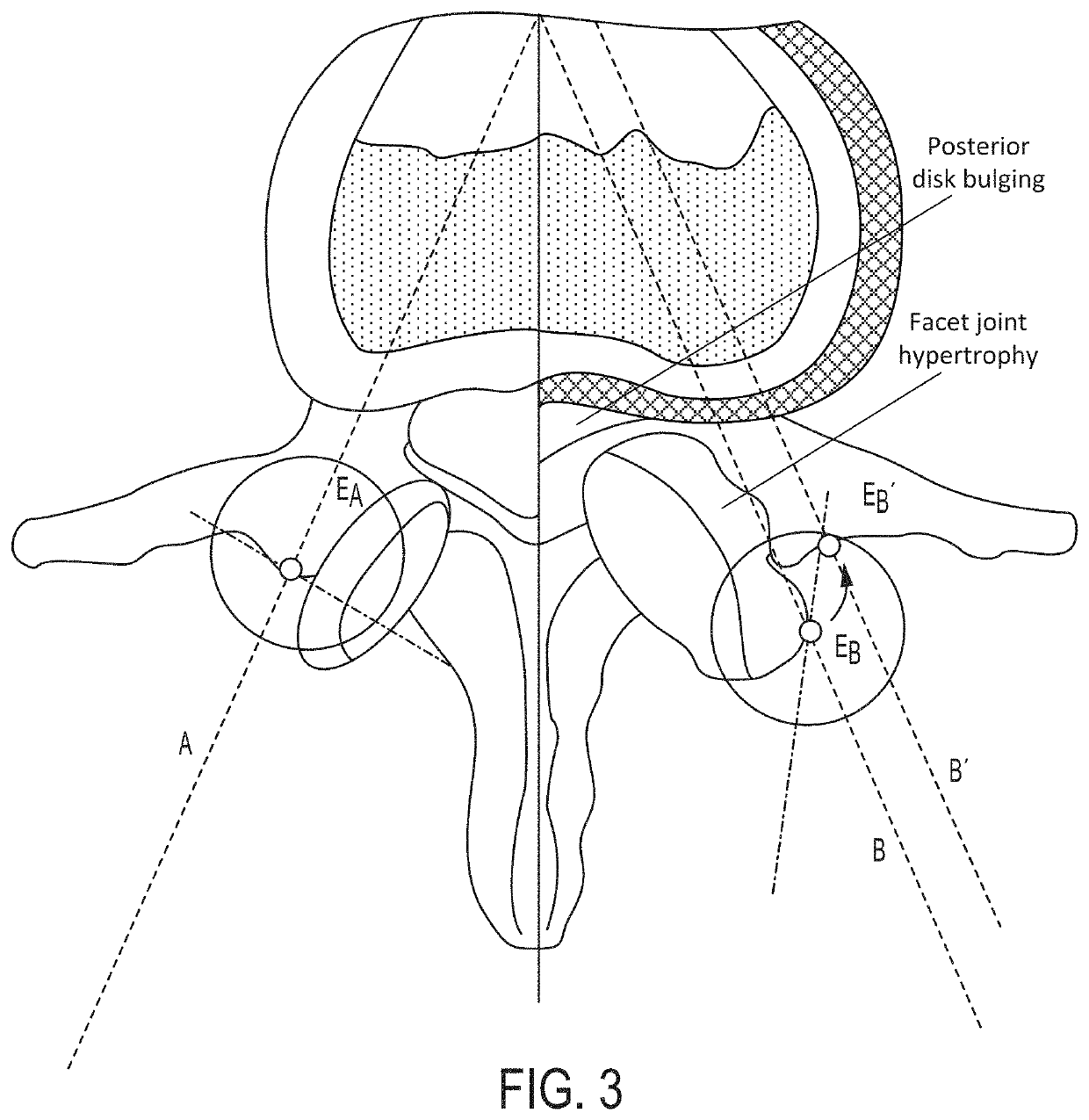
A method of determining the size and / or placement of screws or other instruments in pedicles during surgery in a selected spinal area, comprising generating a dimensionally true three-dimensional image of the bony spine in the selected spinal area; hollowing out the vertebra in the three-dimensional image with cortical wall thicknesses selected by a surgeon performing the surgery; determining the narrowest cross section (isthmus) within each pedicle; generating a straight line starting at the center of the isthmus and extending inwardly to a point centered within the anterior cortex so that it is positioned concentrically within the pedicle without touching the walls thereof, the line terminating inside the vertebral body a predetermined distance from the anterior inner cortical wall and extending outwardly in the opposite direction to penetrate the posterior pedicle cortex; expanding the line concentrically and radially to a cross sectional size that is less than that of the isthmus, the line being expanded into a cylinder that stops growing when any portion thereof contacts the inner cortical wall of the hollowed out vertebral body, with the exception of the posterior pedicle cortex; and calculating the ideal pedicle screw or instrument diameter, length and / or trajectory based on the dimensions and trajectory of the cylinder generated for each pedicle. Also, a new and improved method for providing access to the interior of a pedicle for a desired transpedicular procedure, and a new and improved pedicle cannula construction are disclosed herein.
Owner:LEUCADIA 6 LLC
Spinous process fixated bilateral drilling guide
InactiveUS20100023018A1Precise positioningAccurate and repeatable drilling and screw placementProsthesisOsteosynthesis devicesAnatomical landmarkCoronal plane
The application describes a bilateral drilling and screw placement guide adapted for fixation to the spinous process of a vertebral body. The positioning and surgical guiding instrument is adapted for use during a spinal surgical procedure in conjunction with a drilling tool, fastening device, e.g. a pedicle screw, K-wire or the like. The guide includes an engagement device for attachment to a region of the spinous process, to which an adjustably attached support member is affixed. This allows for immobilizing the guide upon the spinous process anatomical landmark, in a specific orientation with respect thereto. The guide includes a bilaterally adjustable drill guide assembly for precise anatomical positioning of the drill and screw placement guides bilaterally about the sagittal, axial and coronal planes so as to enable the defining of a plurality of drilling axes extending toward the vertebral body. The device further provides for adjustment to account for anatomical variations in width along the axial plane, and includes pointing and angular positioning functionality to insure repeatable and reliable pilot hole and screw placement along a plurality of angles.
Owner:ALPHA GUIDE HLDG LLC
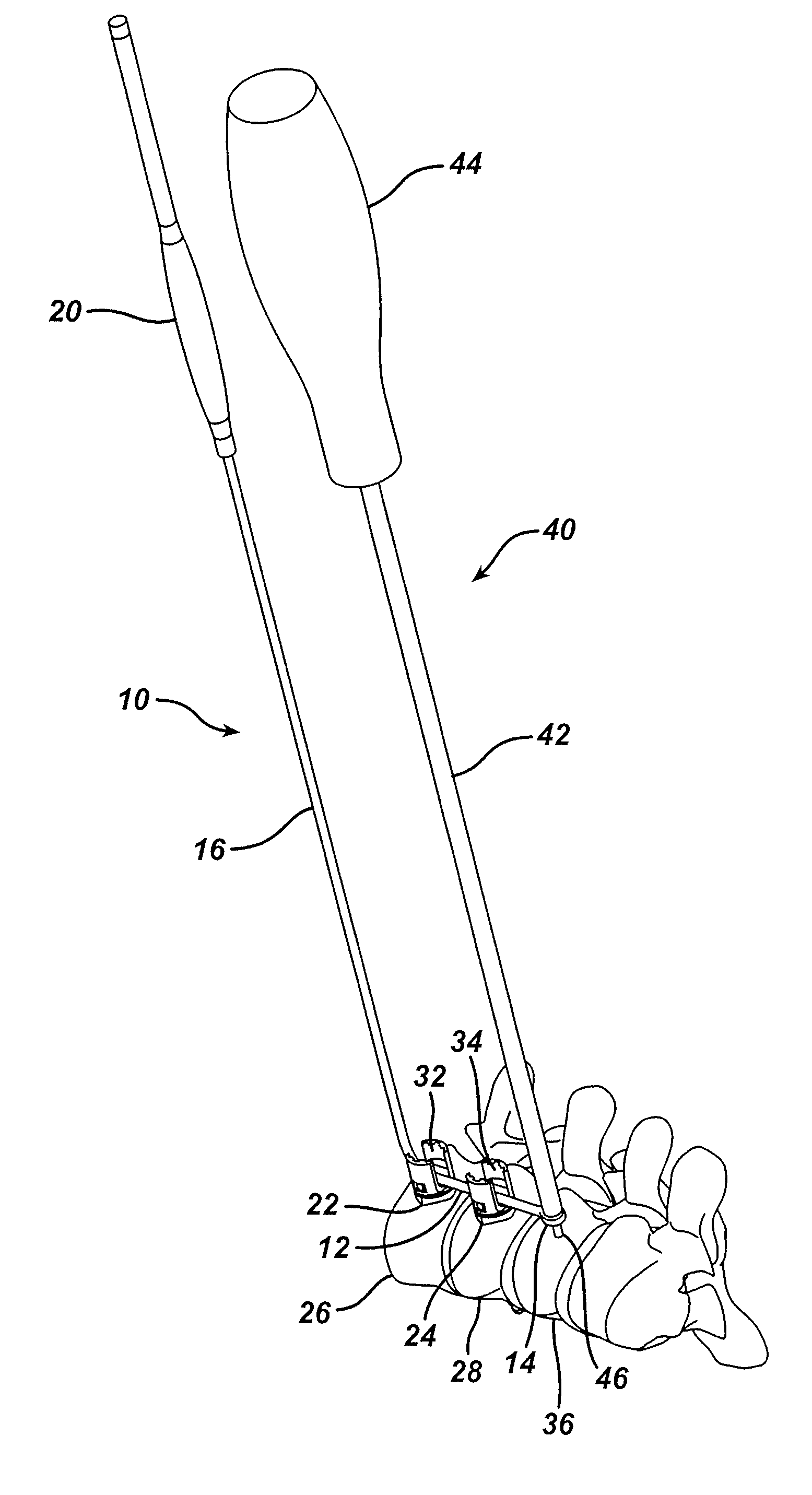
Screw placement guide
ActiveUS7981117B2Accurate placementProsthesisOsteosynthesis devicesLess invasive surgeryScrew placement
A screw placement guide tool for use in minimally invasive surgery has a proximal handle portion, an extension member extending distally from the handle portion, and an alignment element connected transversely to a distal portion of the extension member and having a screw placement guide located thereon. In this aspect of the invention, the tool is configured so that a surgeon may operate the tool using the handle portion external to a patient's body to align the alignment element with implanted screws so that the screw placement guide indicates a desired position for implantation of an additional screw. Systems and methods for placing a rod receiving screw are also provided.
Owner:DEPUY SPINE INC (US)
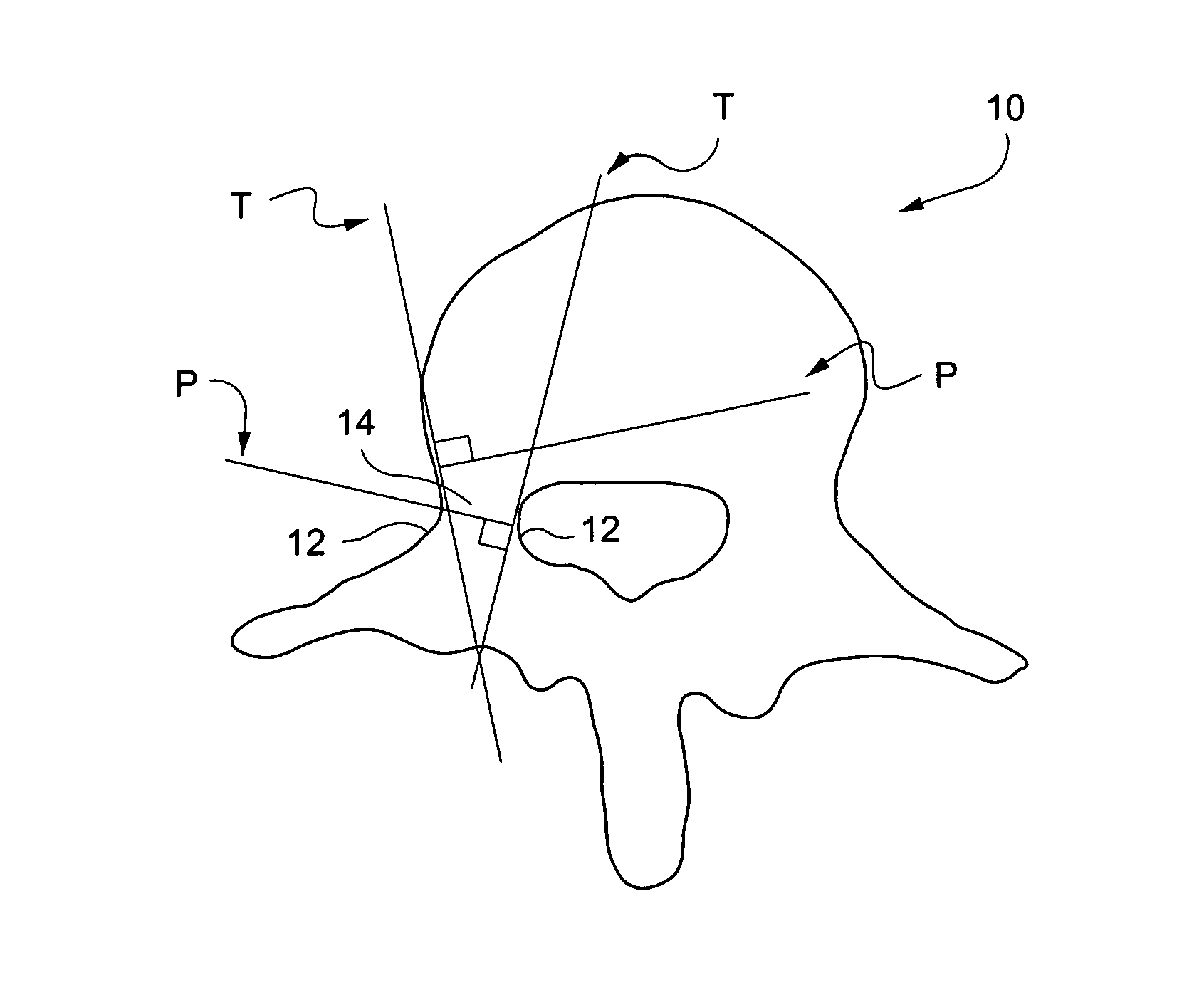
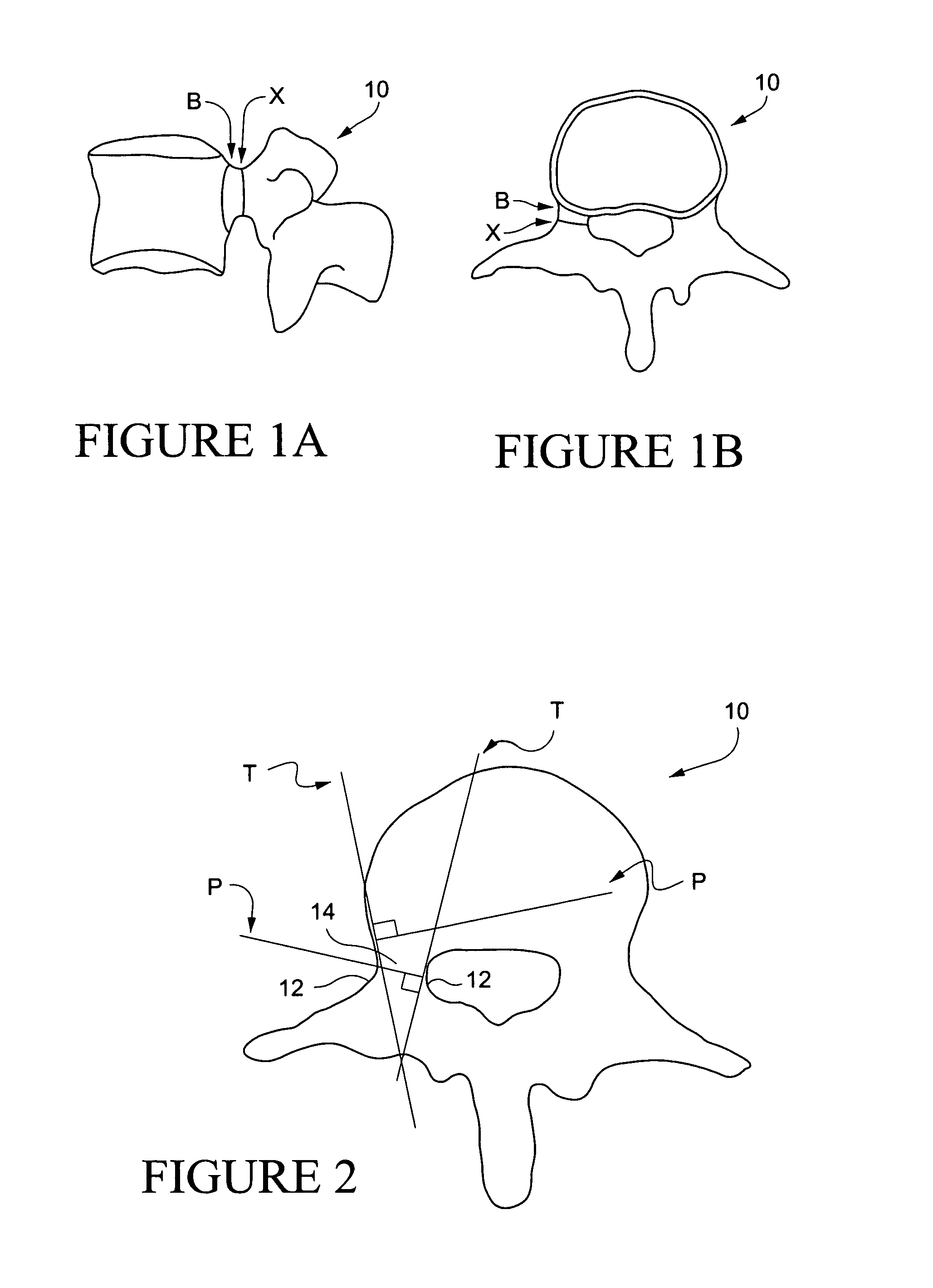
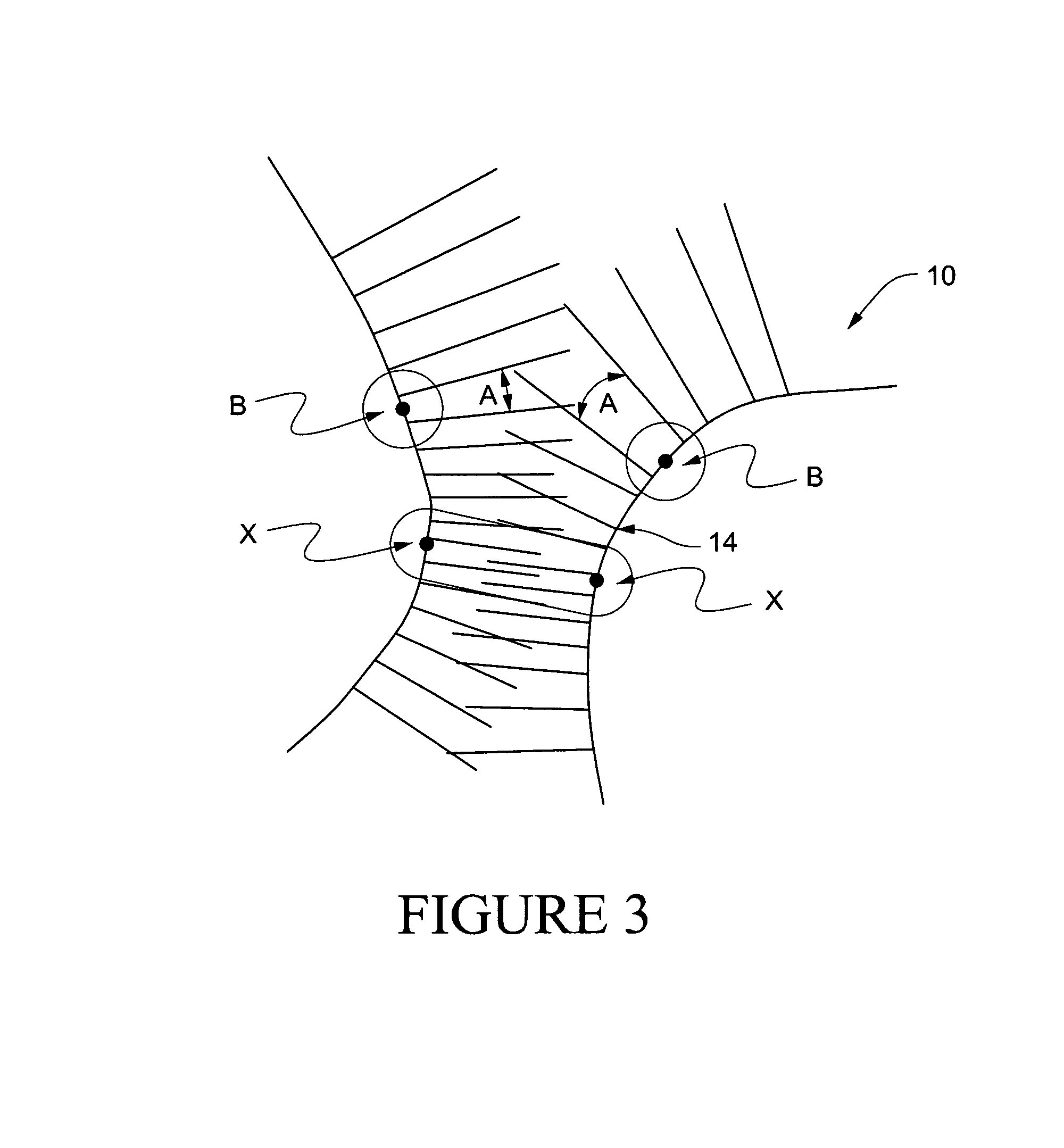
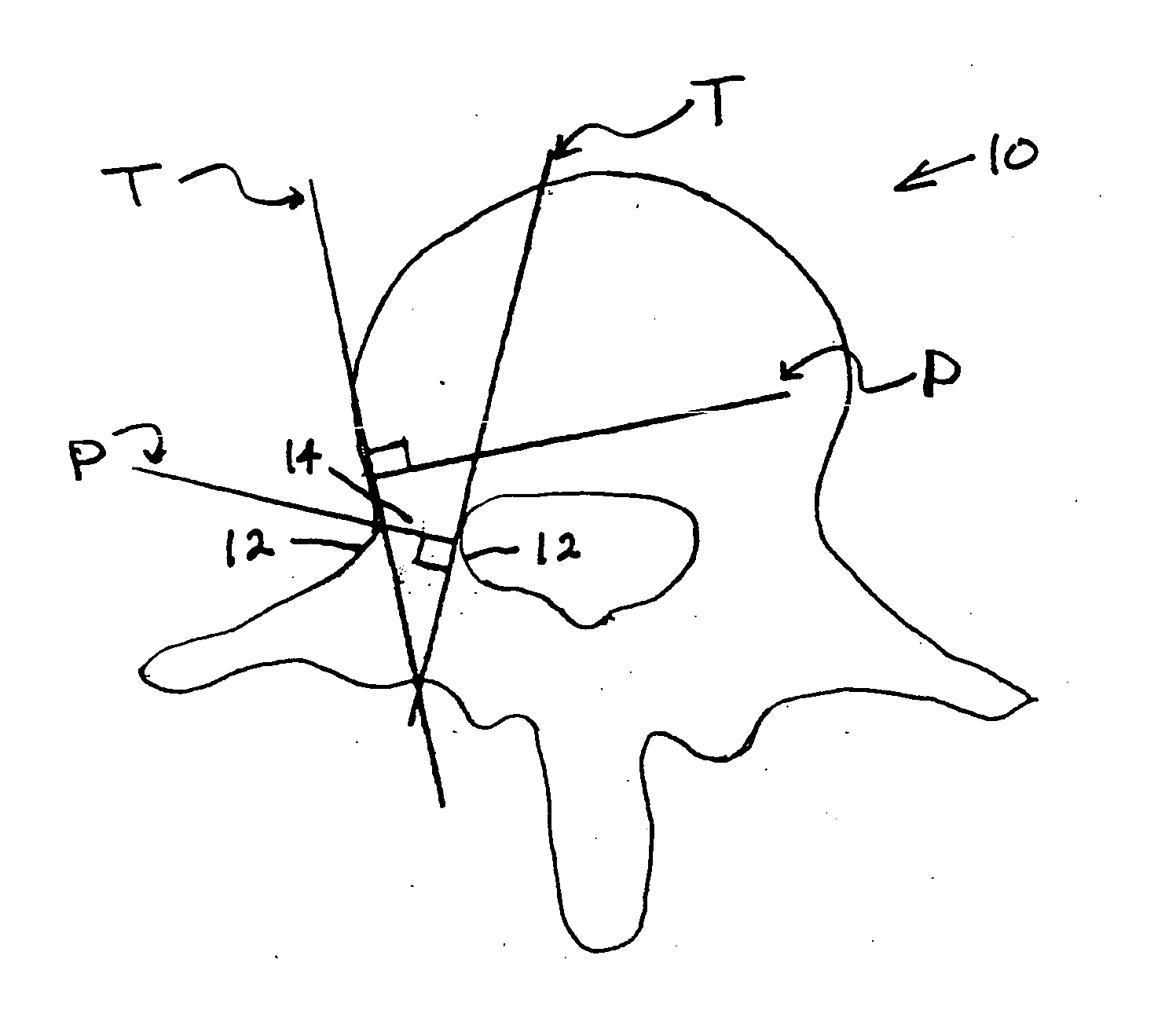
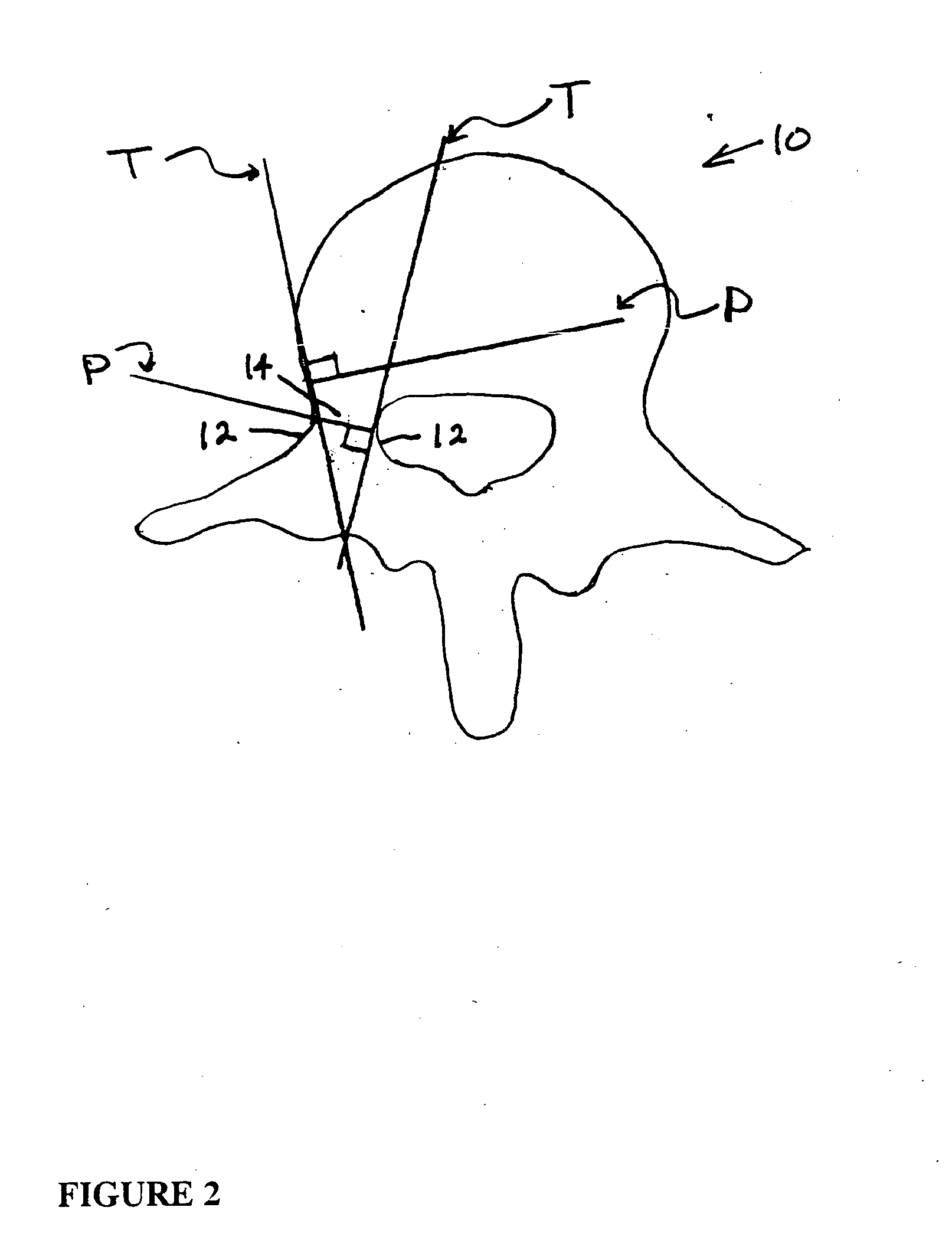
Methods for determining pedicle base circumference, pedicle isthmus and center of the pedicle isthmus for pedicle screw or instrument placement in spinal surgery
A method of determining the pedicle base circumference and the pedicle isthmus to facilitate screw placement in a pedicle of a vertebral body during spinal surgery, comprising providing a series of first lines tangential to the outer cortical surface of the vertebral body in and near the pedicle on a transverse section from a three-dimensional image of the vertebral body, providing a series of second lines extending through the vertebral body in and near the pedicle thereof in perpendicular relation to the series of first lines, identifying the pedicle base circumference as the areas of the outer cortical surface where adjacent second lines are at the greatest angle with respect to one another, and identifying the pedicle isthmus as the areas of the outer cortical surface where the second lines that are opposed to each other are closest to being parallel to one another.
Owner:LEUCADIA 6 LLC
3D printing percutaneous vertebral pedicle guide plate, preparation method of 3D printing percutaneous vertebral pedicle guide plate, and using method of 3D printing percutaneous vertebral pedicle guide plate
ActiveCN104287815ASimple structureEasy to manufactureInternal osteosythesisScrew placementVertebral pedicle
The invention discloses a 3D printing percutaneous vertebral pedicle guide plate, a preparation method of the 3D printing percutaneous vertebral pedicle guide plate, and a using method of the 3D printing percutaneous vertebral pedicle guide plate. The guide plate comprises a wavy panel which can be attached to the spine of a human body, the panel is provided with two hollow input sleeves used for pedicle screws to penetrate through, and a first layer sleeve, a second layer sleeve and a third layer sleeve are sequentially arranged inside each inlet sleeve from inside to outside. The preparation method of the 3D printing percutaneous vertebral pedicle guide plate comprises the steps of the building of a three-dimensional geometrical model, the determination of pedicle screw channels, the generation of the guide plate, 3D printing and sleeve installation. The 3D printing percutaneous vertebral pedicle guide plate is simple in structure and convenient to prepare. In the preparation process of the guide plate, machining is carried out on the designed guide plate in advance according to a body surface mark so that locking can be achieved for body surface positioning, it is guaranteed that the inlet sleeves and the pedicle screw channels are coaxially arranged, displacement is prevented, and it is guaranteed that the direction of puncturing and the direction of screw placement are accurate; through the guide plate, the placement depth is accurate, fluoroscopy does not need to be carried out repeatedly, surgical accuracy is improved, and surgical time is shortened.
Owner:江苏舟可医疗器械科技有限公司
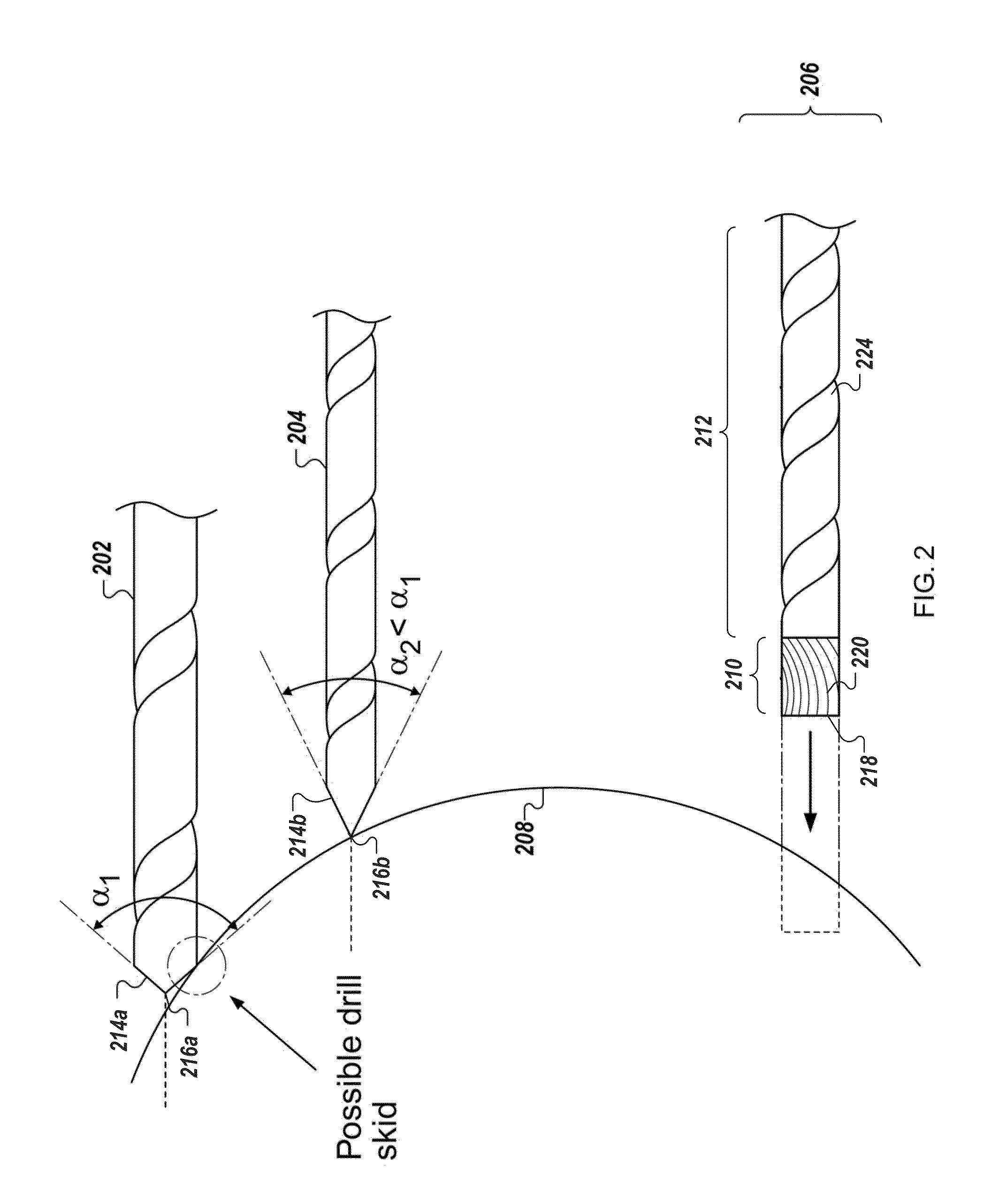
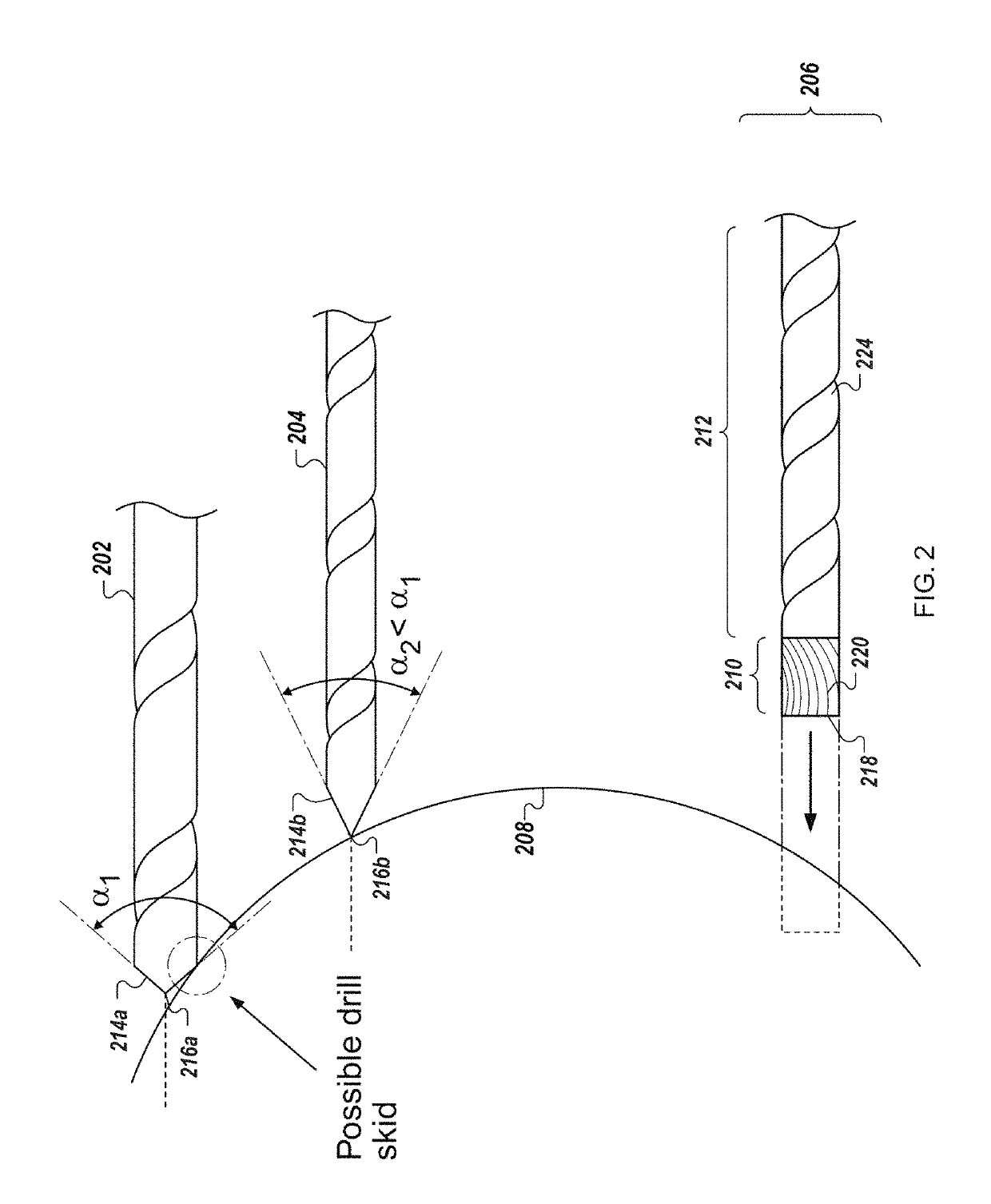
Anti-skid surgical instrument for use in preparing holes in bone tissue
ActiveUS20160008011A1Precise holeHigh precisionDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsScrew placementBone tissue
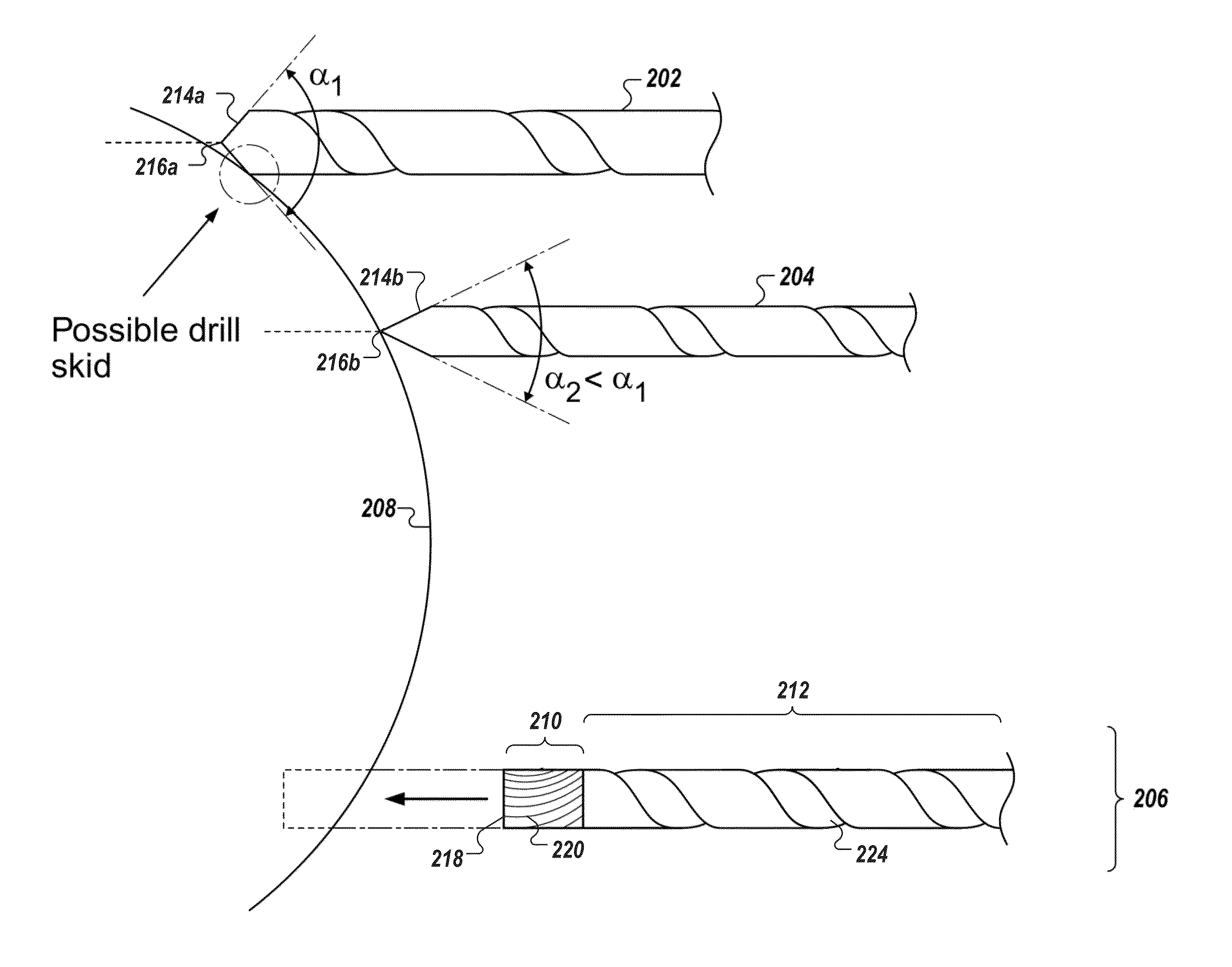
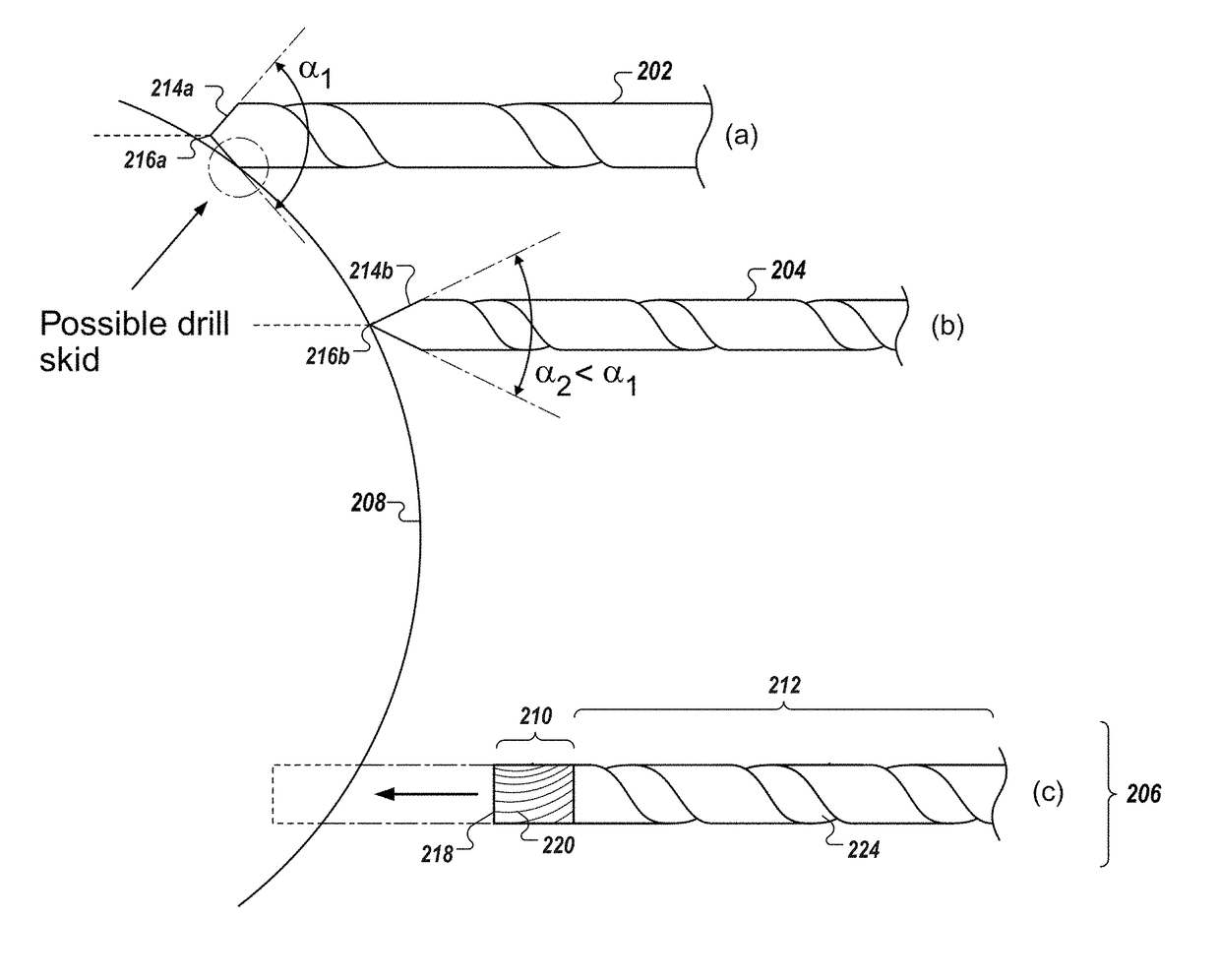
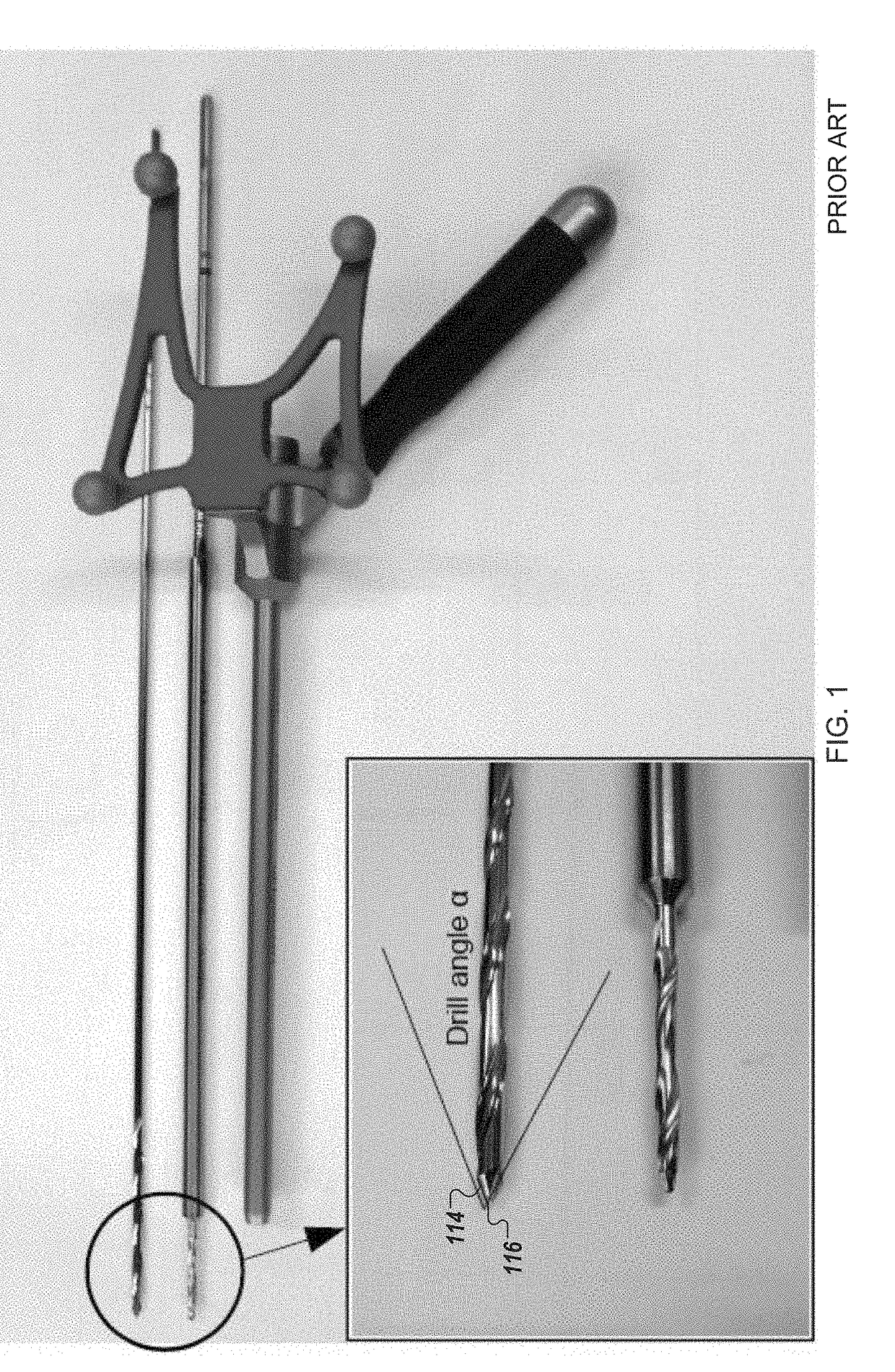
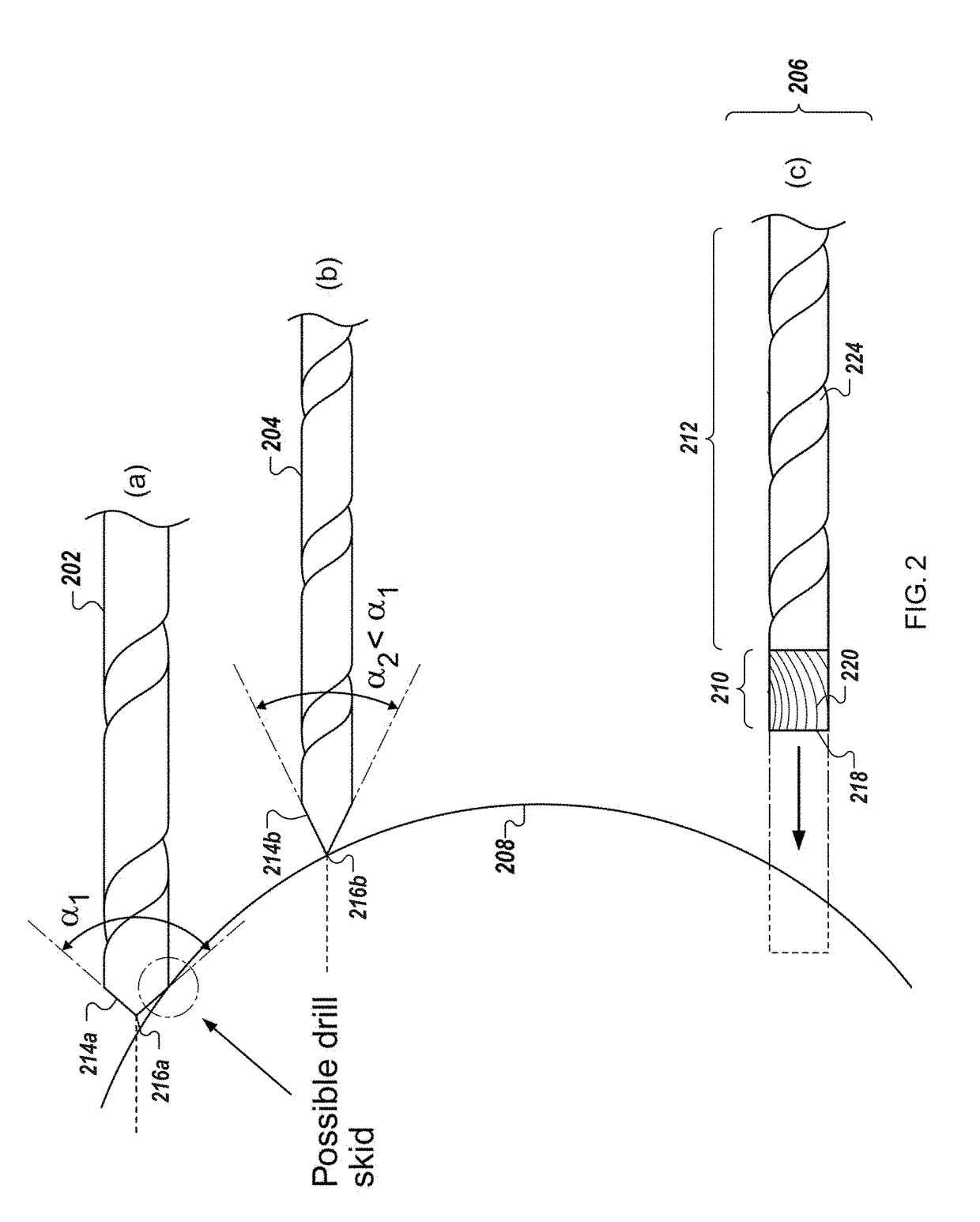
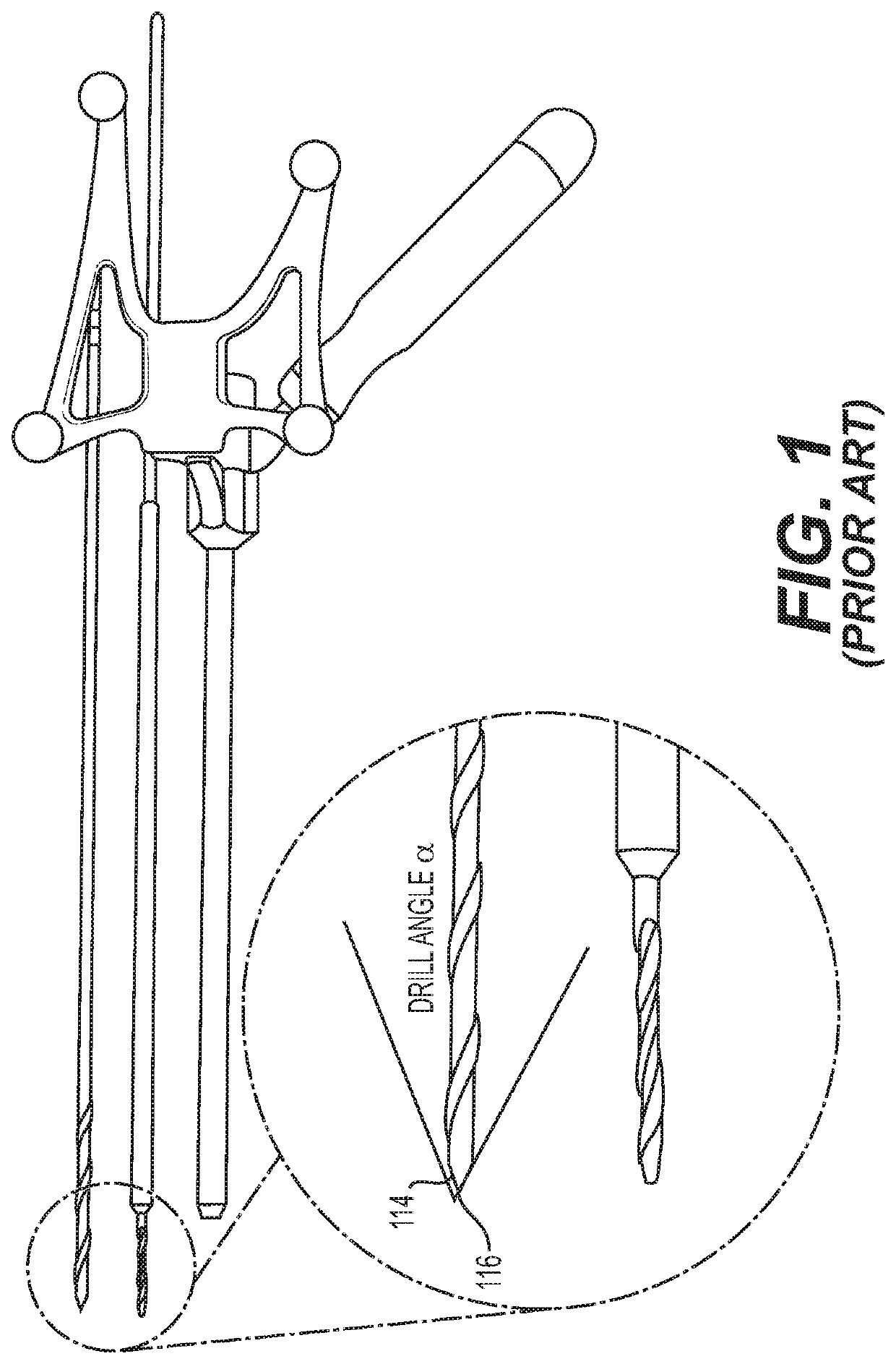
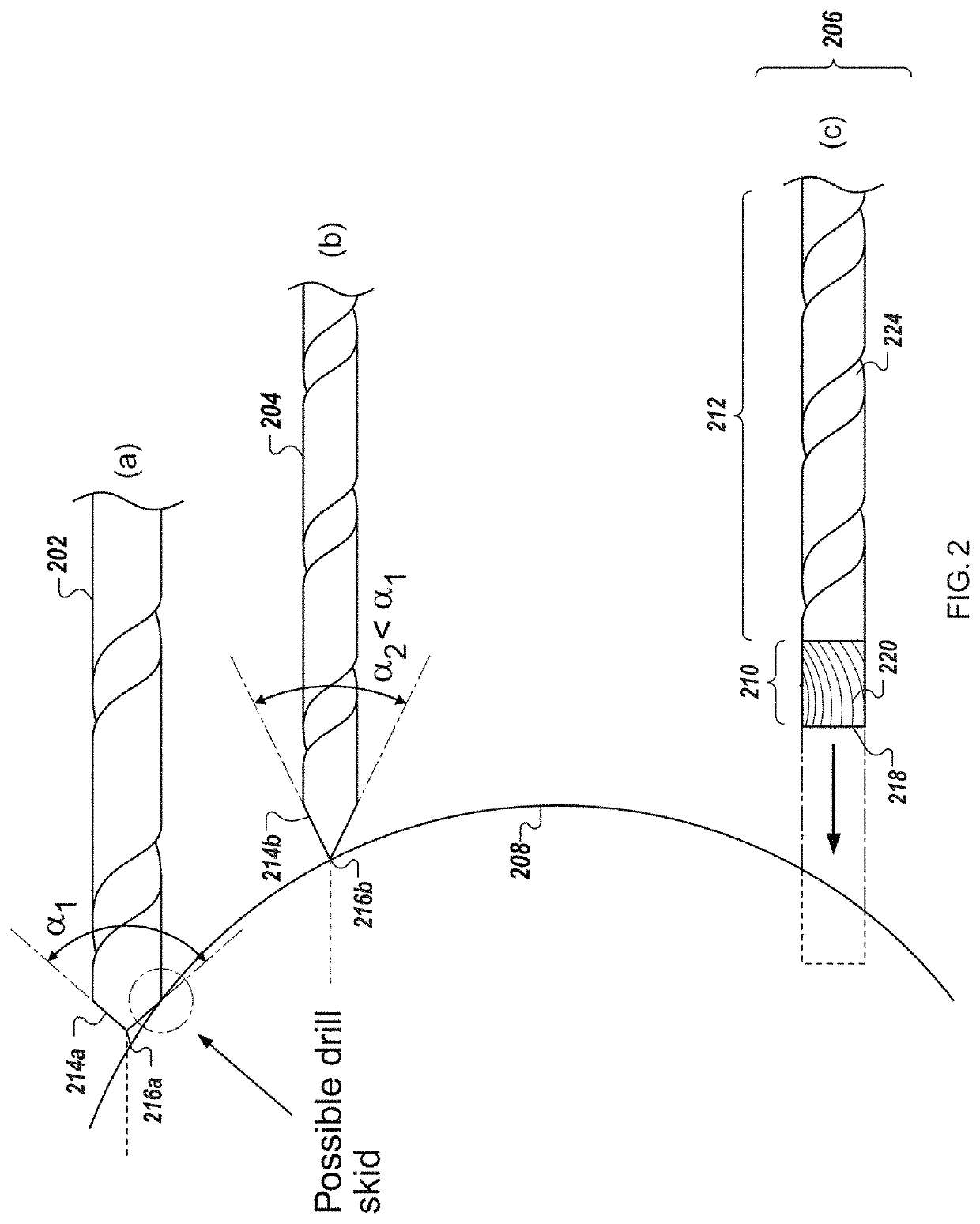
Described herein is an anti-skid surgical instrument for use in preparing holes in bone tissue. The disclosed surgical instrument provides the ability to prepare a precise hole in bone tissue during surgery (e.g., spinal surgeries and pedicle screw placement, intramedullary screw placement). The disclosed surgical instrument accomplishes precise hole placement regardless of whether the angle between the drill axis and surface of the bone tissue is perpendicular. The disclosed technology includes a flat drilling surface which is perpendicular to the surface of the body of the surgical instrument. This reduces the likelihood of the surgical instrument skidding on the surface of the bone tissue and thereby increases the precision of the hole.
Owner:KB MEDICAL SA
Percutaneous minimally invasive pedicle screw/rod internal fixation system
The invention provides a percutaneous minimally invasive pedicle screw / rod internal fixation system. The system comprises a pedicle screw, a longitudinal connecting rod, a locating needle tube, a guide needle, a dilating core, a placed screw guide sleeve, a screw loader, a rod holder, a distraction pressurizer, arm fracture devices and a screw loading base, wherein the locating needle tube and the guide needle are used for determining the position of a placed screw; the dilating core is used for dilating a screw placement channel; the arm fracture devices are used for fracturing long arms of the pedicle screw; the pedicle screw comprises a screw body, a screw base, two fracturable long arms and a plug screw; the screw body is connected with the screw base; the two fracturable long arms are oppositely and fixedly connected to the screw base to form a U-shaped structure in which the longitudinal connecting rod can be embedded; the two fracturable long arms extend out of the skin incision; and the plug screw is screwed in the U-shaped structure formed by the two fracturable long arms so as to compress the longitudinal connecting rod. By utilizing the system provided by the invention in the posterior thoracolumbar minimally invasive surgery, the trauma is little, and the haemorrhage is less; and the system is simple and flexible to operate and can achieve the effect of open surgery.
Owner:贺新宁
System and methods for improved access to vertebral bodies for kyphoplasty, vertebroplasty, vertebral body biopsy or screw placement
Owner:LEUCADIA 6 LLC
Anti-skid surgical instrument for use in preparing holes in bone tissue
ActiveUS20170224358A1Precise holeHigh precisionDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsScrew placementBone tissue
Described herein is an anti-skid surgical instrument for use in preparing holes in bone tissue. The disclosed surgical instrument provides the ability to prepare a precise hole in bone tissue during surgery (e.g., spinal surgeries and pedicle screw placement, intramedullary screw placement). The disclosed surgical instrument accomplishes precise hole placement regardless of whether the angle between the drill axis and surface of the bone tissue is perpendicular. The disclosed technology includes a flat drilling surface which is perpendicular to the surface of the body of the surgical instrument. This reduces the likelihood of the surgical instrument skidding on the surface of the bone tissue and thereby increases the precision of the hole.
Owner:KB MEDICAL SA
Fixing device used for surgical operation
InactiveCN107811712AReduce the burden onNo risk of contamination of the surgical fieldInstruments for stereotaxic surgeryScrew placementEngineering
The invention discloses a fixing device for surgical operations, which comprises a bottom plate. A chute is provided on the bottom plate. A clamping block is slidably connected in the chute. One end of the clamping block is screw-connected with a sliding rod, and the outer end of the sliding rod is threaded. There is a rotating rod, the side wall of one end of the rotating rod is screwed with a handle, the other end of the sliding rod is riveted with a first slider, the side wall of one end of the first slider is fixedly connected with a second connecting rod, and the other end of the second connecting rod The side wall is fixedly connected with a connecting shaft, the upper side wall of the fixed plate is riveted with a bracket, the other end of the bracket is screwed with a table board, the upper side wall of the table board is screwed with a push rod motor, and one end of the push rod motor is slidingly connected to the side wall There is a retractable rod, and the other end of the retractable rod is screwed with a placement block. The device can easily adjust the height of the device, and can also be used for different types of surgical operations, reducing the workload of medical staff.
Owner:廖仁良
Medical pedicle screw component with telescopic double thread and capable of resisting pullout
InactiveCN104287819AImprove fixation stabilityEasy to useInternal osteosythesisFastenersScrew placementEngineering
The invention relates to a medical pedicle screw component with a telescopic double thread and capable of resisting pullout. The medical pedicle screw component with the telescopic double thread and capable of resisting the pullout is characterized in that a thread control shaft is arranged in a hollow cavity of a nail body, the thread control shaft is matched with connection rods, the connection rods are connected with telescopic screws, and the telescopic screws are arranged in a plurality of holes formed in the outer wall at the front end of the nail body. Furthermore, the cross section of the thread control shaft is of a butterfly structure, the thread control shaft comprises a middle shaft and a first support body and a second support body which are symmetrically arranged along the center line of the middle shaft, two slide pieces matched with the connection rods are fixed on the outer side of each of the first support body and the second support body, the cross section of each slide piece is in a crescent shape, the two slide pieces on each of the first support body and the second support body are oppositely arranged, and therefore rising and falling of the telescopic screws are adjusted by rotating the thread control shaft, unscrewing of threads is achieved by rotating the thread control shaft, stability of internal fixation of a spine is improved when bone rarefaction is cured or secondary screw placement is performed for revision, and occurrence rate of loosening or even detachment is reduced.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Simple pedicle screw placement navigator
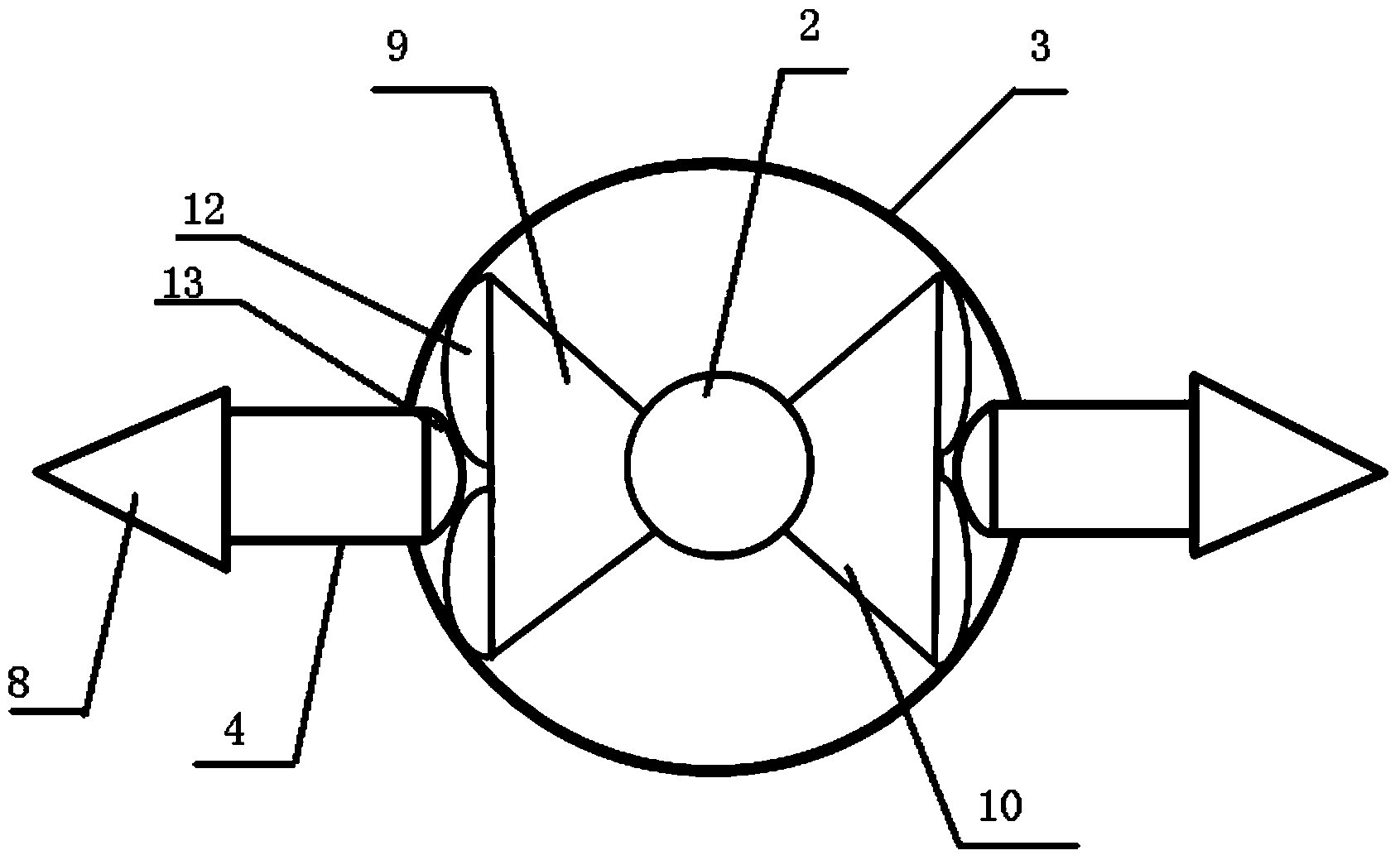
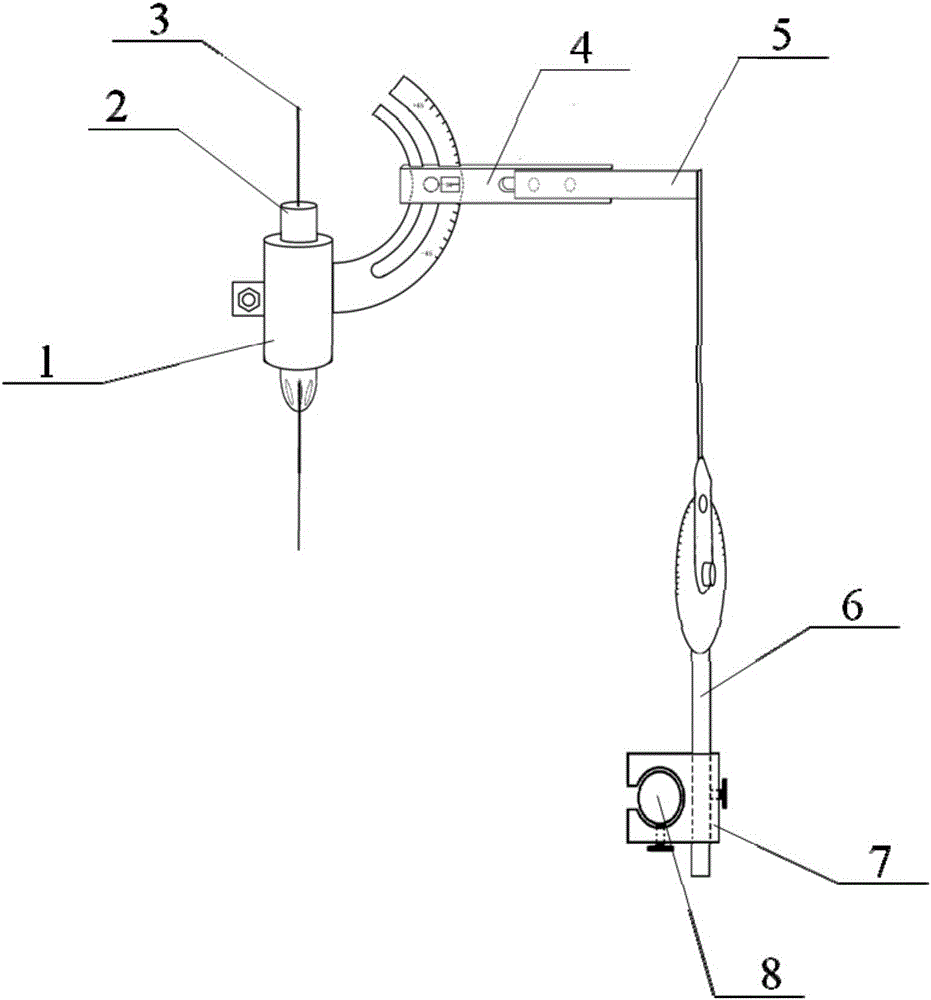
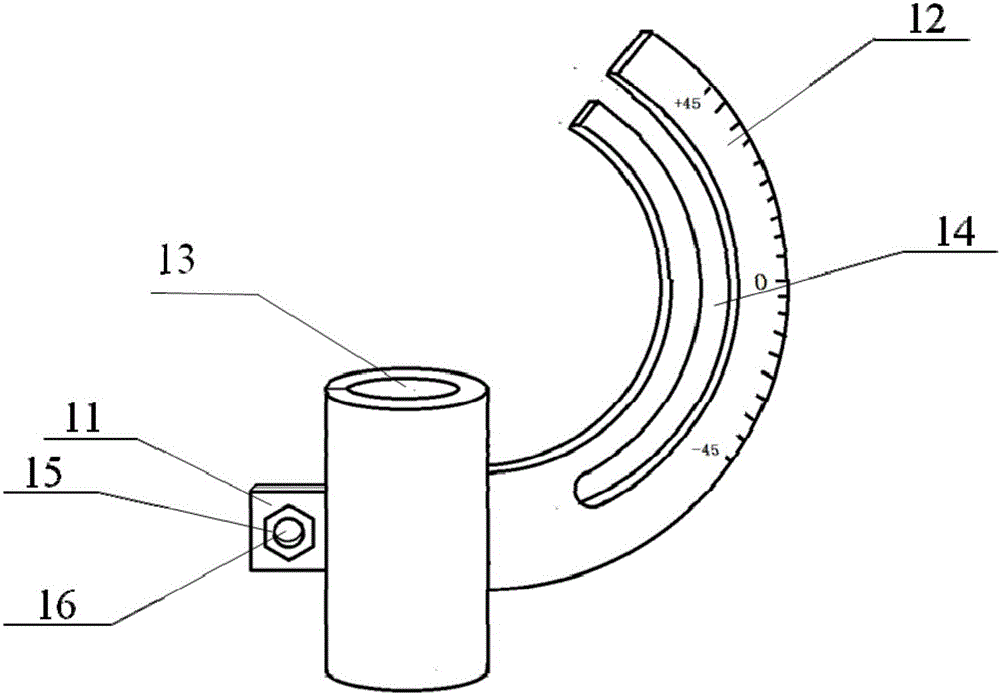
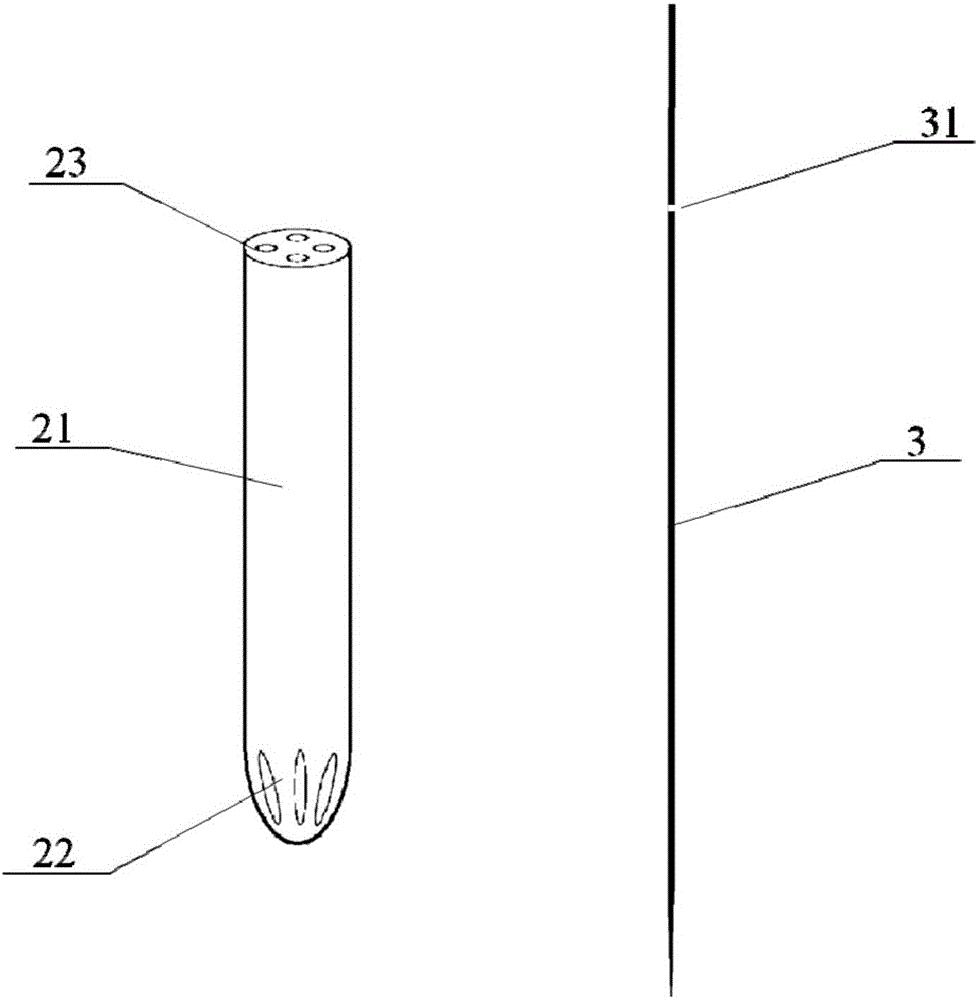
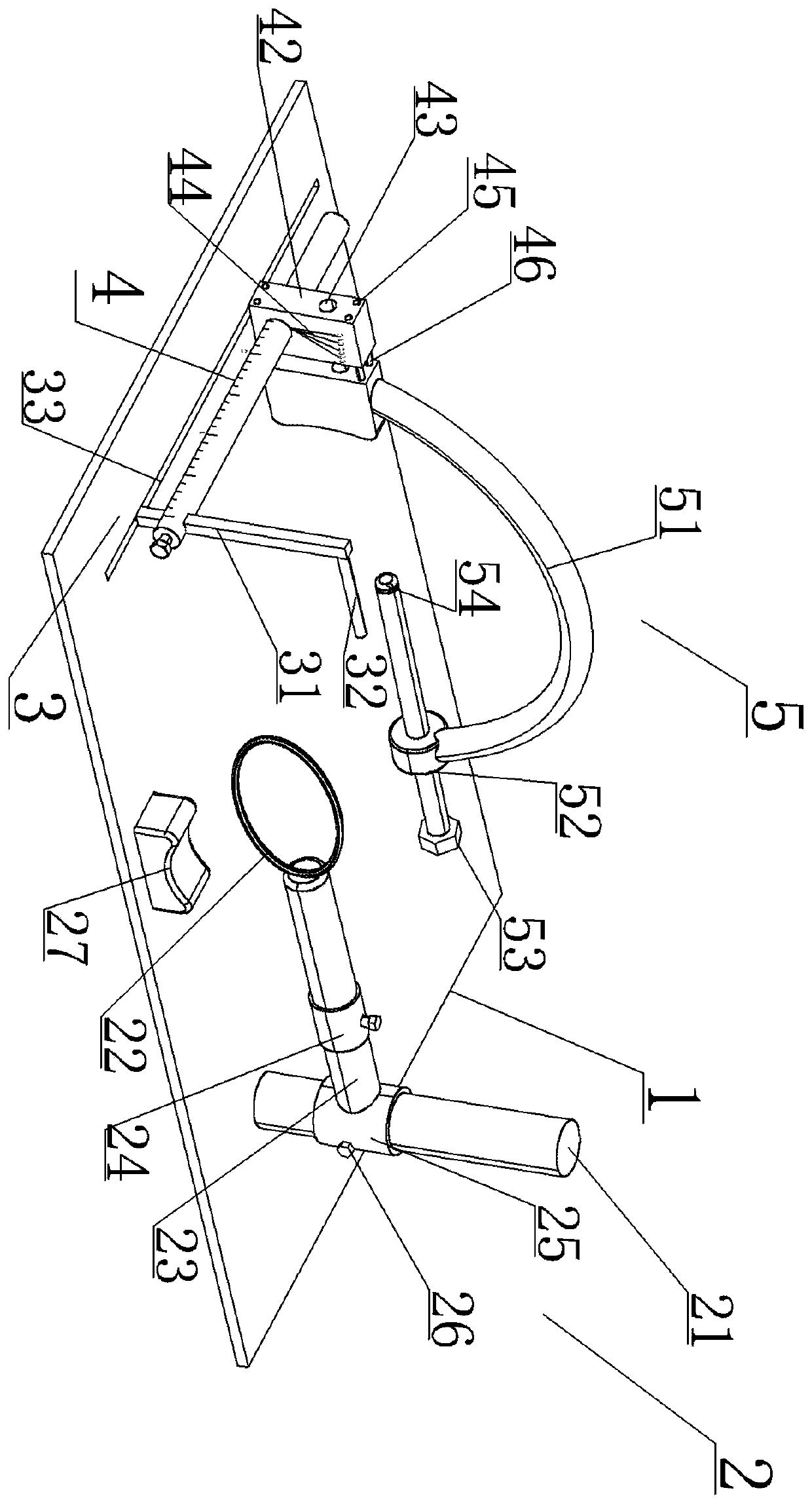
InactiveCN105935313AOvercoming expensiveOvercome time-consuming and other disadvantagesInternal osteosythesisOperating tablesProtractorScrew placement
The present invention relates to a simple pedicle screw placement navigator. The simple pedicle screw placement navigator comprises a guide sleeve, a guide tube, a guide pin, a transverse link rod, a right-angle swing rod, a lifting bar and a sliding block; the guide tube is fixed by the guide sleeve; the guide pin is positioned in the guide tube; one side of the guide sleeve is provided with a protractor, and the protractor can slide on the transverse link rod in an arc direction to achieve a specific abduction angle; the other end of the transverse link rod is slidably connected with a transverse main body of the right-angle swing rod and capable of achieving left and right translation; the tail end of a longitudinal main body of the right-angle swing rod is connected with a dial at an upper end of the lifting bar, and the longitudinal main body can rotate around the center of the dial to achieve head inclination or tail inclination with a specific angle; and a lower end of the lifting bar is connected with a sliding bar through the sliding block, so that the whole device can translate on the sliding bar. Compared with the prior art, the abduction angle and the head inclination or tail inclination angle of pedicle screw placement can be rapidly quantified after a screw entering point is determined, compared with a screw placement technology by hand, precision can be largely increased, and the expensive and time-consuming disadvantages of a large-scale navigation device are also overcome.
Owner:TONGJI UNIV
Anti-skid surgical instrument for use in preparing holes in bone tissue
ActiveUS10357257B2Precise holeHigh precisionDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsScrew placementBone tissue
Owner:KB MEDICAL SA
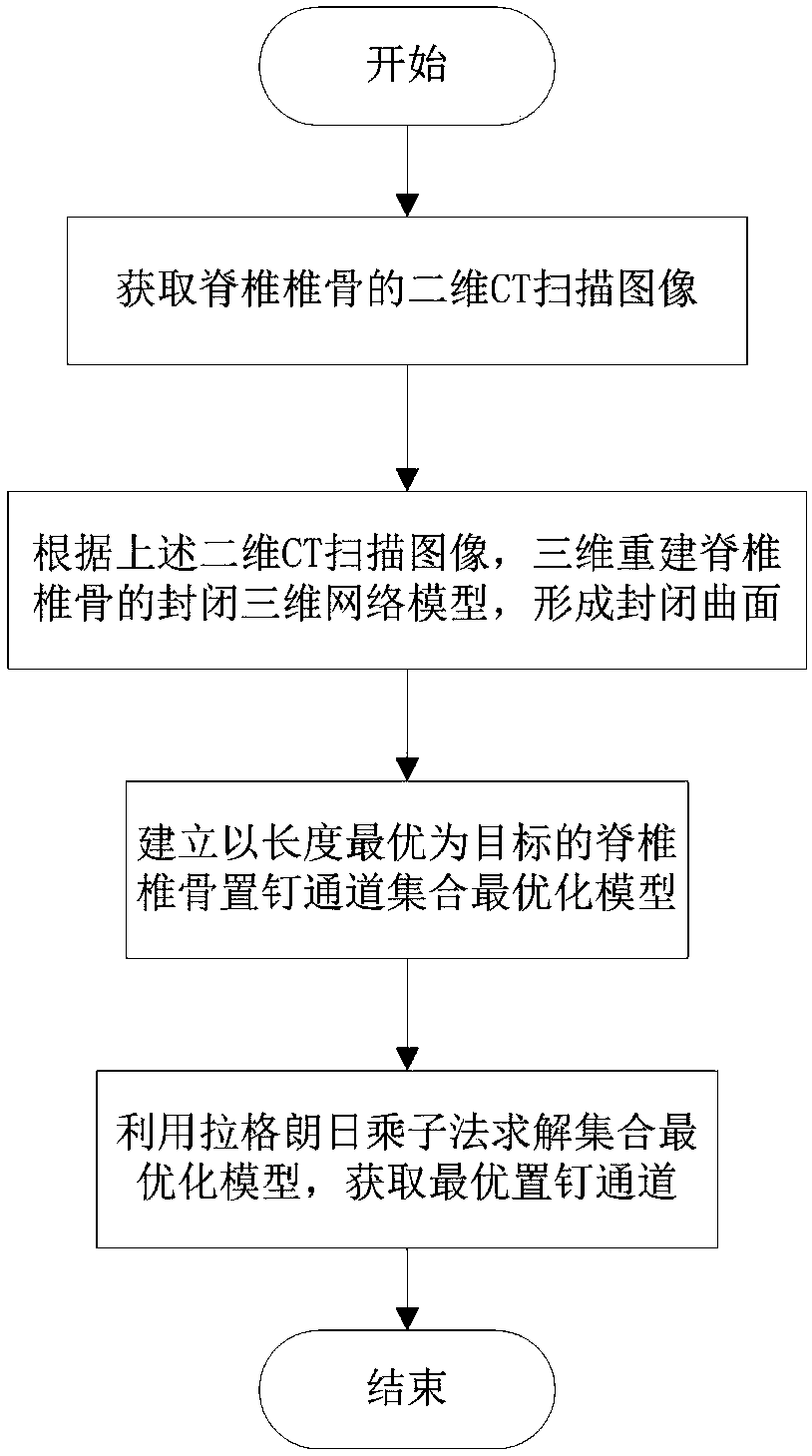
Pedicle operation guide plate optimal screw placement path intelligent generation method
ActiveCN107647914ASolve the problem of automatic generationEnsure surgical safetyInternal osteosythesisComputer-aided planning/modellingScrew placementPath generation
The invention provides a pedicle operation guide plate optimal screw placement path intelligent generation method. The method comprises the steps: S1, a two-dimensional CT scanning image for vertebrais acquired; S2, according to the two-dimensional CT scanning image, a closed three-dimensional network model for the vertebra is rebuilt in a three-dimensional mode, and a closed curved surface is formed; S3, a vertebra screw placement path set optimal model with the optimal length as a target is built; and S4, the set optimal model is solved by using a Lagrange multiplier method, and the optimalscrew placement path is acquired. According to the pedicle screw placement path generation method provided by the invention, the automatic optimal screw placement path generation problem is solved, and as for a given vertebra three-dimensional digital geometric model, based on the user requirements, on the premise of ensuring the operation safety, the longest screw placement path can be generatedautomatically.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF TECH ZHEJIANG UNIV ZHEJIANG
Medical vertebral pedicle strengthening screw
InactiveCN101632601AImprove pullout strengthEasy to take outInternal osteosythesisFastenersFailure rateInternal fixation
The invention discloses a medical vertebral pedicle strengthening screw consisting of a screw sleeve and a self-tapping screw in mutual fit, wherein, the screw sleeve is made from medical absorbable materials and has certain mechanical strength and toughness; the medical absorbable materials can effectively maintain the mechanical strength in vivo for 2 to 3 months; the screw sleeve is divided into a head end, a middle section and a tail end, wherein, the head end of the screw sleeve is sealed up and in a hemispherical shape, the middle section is provided with a longitudinal crack, and a cone-shaped hollow cavity is formed at the tail end thereof; and the self-tapping screw is made of medical titanium alloy and consists of a thread section and a tail part, wherein, the thread section is formed by connecting a cone-shaped tip part and a cylinder in external-thread design, a U-shaped groove penetrating in a radial direction is formed at the tail part, and internal threads are formed on the inner wall of the U-shaped groove. The invention is able to improve the stability of internal fixation in the process of the primary screw placement in an osteoporosis situation and reduce the incidence that the pedicle screw becomes loosened or even prolapsed, thus enhancing the stability and reliability of the internal fixation of spines and lowering the failure rate of operations.
Owner:FOURTH MILITARY MEDICAL UNIVERSITY
Anti-skid surgical instrument for use in preparing holes in bone tissue
ActiveUS10765438B2Precise holeHigh precisionDiagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsSpinal columnScrew placement
Described herein is an anti-skid surgical instrument for use in preparing holes in bone tissue. The disclosed surgical instrument provides the ability to prepare a precise hole in bone tissue during surgery (e.g., spinal surgeries and pedicle screw placement, intramedullary screw placement). The disclosed surgical instrument accomplishes precise hole placement regardless of whether the angle between the drill axis and surface of the bone tissue is perpendicular. The disclosed technology includes a flat drilling surface which is perpendicular to the surface of the body of the surgical instrument. This reduces the likelihood of the surgical instrument skidding on the surface of the bone tissue and thereby increases the precision of the hole.
Owner:KB MEDICAL SA
Tibiofibular syndesmosis reduction and screw placement guide device
InactiveCN109875673AHigh precisionImprove the effect of surgical treatmentOsteosynthesis devicesScrew placementSurgical treatment
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, in particular to a tibiofibular syndesmosis reduction and screw placement guide device. The guide device comprises a base disc andan ankle neutral fixing assembly, an ankle joint horizontal marking rod assembly, a tibiofibular screw placement spacing and angle assembly and a tibiofibular syndesmosis pressurizing reduction assembly which are arranged on the base disc. By means of the tibiofibular syndesmosis reduction and screw placement guide device, tibiofibular screws can be placed reasonably with the placement position accuracy to 1mm and 1 degree, so that the tibiofibular screw placement accuracy is greatly improved, the surgical treatment effect is greatly improved, the occurrence of medical technical accidents is avoided, and the guide device is suitable for popularization and application in clinical medicine.
Owner:青岛山大齐鲁医院(山东大学齐鲁医院(青岛))
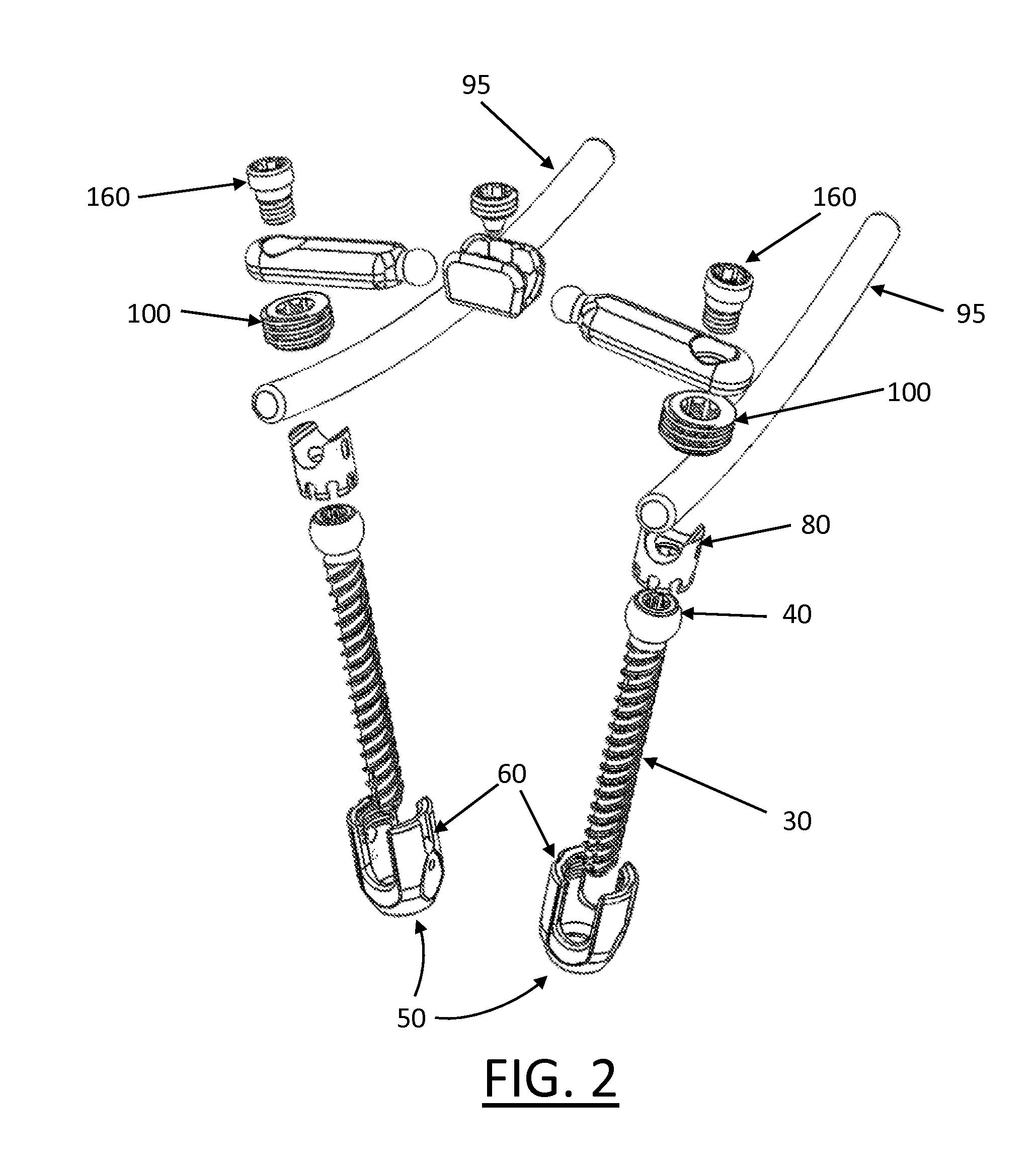
Threaded Setscrew Crosslink
InactiveUS20160128734A1Convenient to accommodateIncreased torsional stiffnessInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsScrew placementEngineering
Devices, systems and methods for connecting surgical screws together, which can be utilized to attach surgical screws in a variety of configurations, such as where the screws and / or attached tulip head components are not parallel or where a significant amount of anatomical variation creates widely divergent screw placement. Also disclosed are low profile crosslink arrangements having a high degree of strength and capable of providing an extremely strong connection to various components of a surgical screw.
Owner:INTREPID ORTHOPEDICS
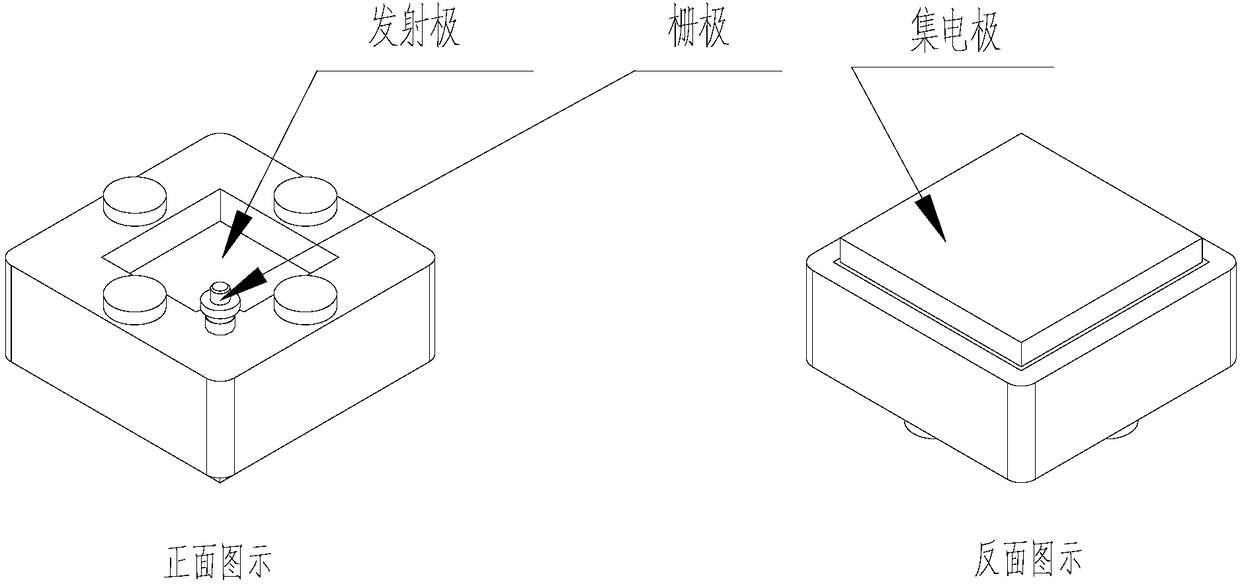
Testing device and method for sub-module of crimping type IGBT (Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor) module
ActiveCN109298305ASimple structureEasy to useBipolar transistor testingElectrical measurement instrument detailsScrew placementEngineering
The invention discloses a testing device and a method for a sub-module of a crimping type IGBT module. The device comprises an emitter lead-out end, a gate lead-out end, a collector lead-out end, a pressure block, a test chamber, and a screw. The upper surface of the pressure block is configured with a screw contact portion, and the lower surface of the pressure block is configured with a gate contact portion and a protruding pressure head of the pressure block. The gate contact portion is connected to the gate lead-out end. The pressure head of the pressure block is connected to the emitter lead-out end. The top of the inside of the test chamber is configured with a threaded screw placement opening, and the bottom of the inside of the test chamber corresponding to the screw placement opening is configured with a placement portion for arranging the sub-module to be tested of the IGBT module. The screw has the threads, and is matched with the screw placement opening. The device of the invention is matched with the sub-module of the crimping type IGBT module, can assist existing test equipment to test the sub-module of the crimping type IGBT module. Compared with the equipment in theprior art, the device of the invention has the advantages of simple structure, simple use, and high practical value.
Owner:ZHUZHOU CRRC TIMES SEMICON CO LTD
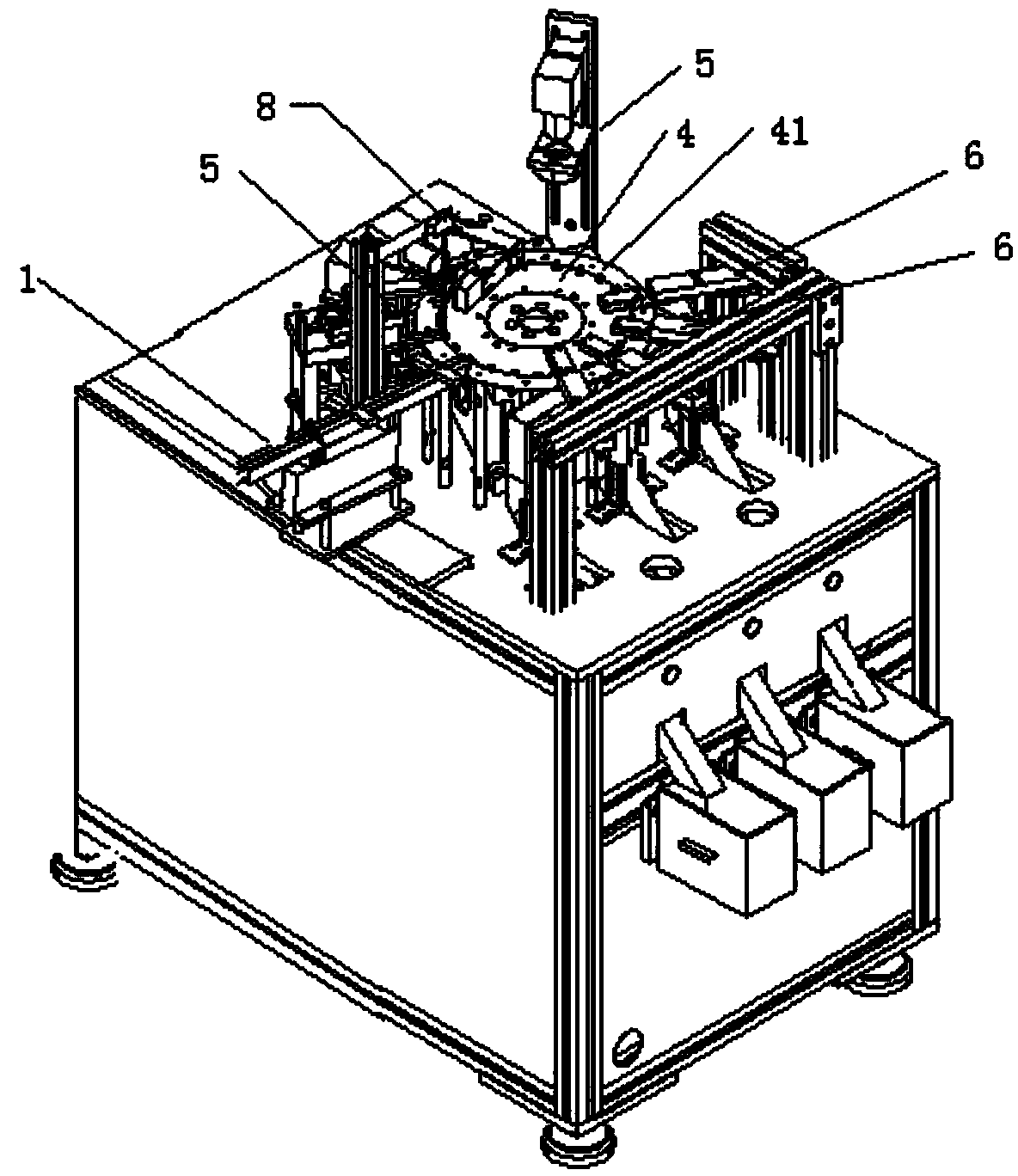
Screw testing machine
InactiveCN104076045AImprove versatilityImprove the diversity of defect detectionOptically investigating flaws/contaminationScrew positionScrew placement
The invention relates to a screw testing machine which comprises a screw loading mechanism, a rotary table, a plurality of screw defect detectors, a plurality of screw recovery mechanisms and a screw position correction mechanism, wherein the screw loading mechanism is used for loading screws onto the rotary table; the screws to be tested are respectively arranged in screw placement holes in the rotary table by the screw loading mechanism; the rotary table is used for sending the screws into the corresponding testing positions by rotation; the plurality of screw defect detectors are used for carrying out defect detection on the screws which are rotated to the corresponding positions by the rotary table; the plurality of screw recovery mechanisms comprise at least one defective screw recovering mechanism and at least one accepted screw recovering mechanism; the screw position correction mechanism comprises a screw pressing mechanism and a lifting mechanism, wherein the lifting mechanism is linked with a cam divider of the rotary table; the screw pressing mechanism is connected with the lifting mechanism; when the rotary table rotates and the screws are sent into the correction potions of the screw position correction mechanism, the screw pressing mechanism is driven to press the screws positioned at the corresponding correction potions by the lifting mechanism.
Owner:DONGGUAN POLYTECHNIC
Methods for determining pedicle base circumference, pedicle isthmus and center of the pedicle isthmus for pedicle screw or instrument placement in spinal surgery
A method of determining the pedicle base circumference and the pedicle isthmus to facilitate screw placement in a pedicle of a vertebral body during spinal surgery, comprising providing a series of first lines tangential to the outer cortical surface of the vertebral body in and near the pedicle on a transverse section from a three-dimensional image of the vertebral body, providing a series of second lines extending through the vertebral body in and near the pedicle thereof in perpendicular relation to the series of first lines, identifying the pedicle base circumference as the areas of the outer cortical surface where adjacent second lines are at the greatest angle with respect to one another, and identifying the pedicle isthmus as the areas of the outer cortical surface where the second lines that are opposed to each other are closest to being parallel to one another. The center of the pedicle isthmus is identified from a cross-section thereof as the intersection of two lines derived from the centers of infinitesimal orthogonal second perpendicular lines from the outer cortical surface.
Owner:LEUCADIA 6 LLC
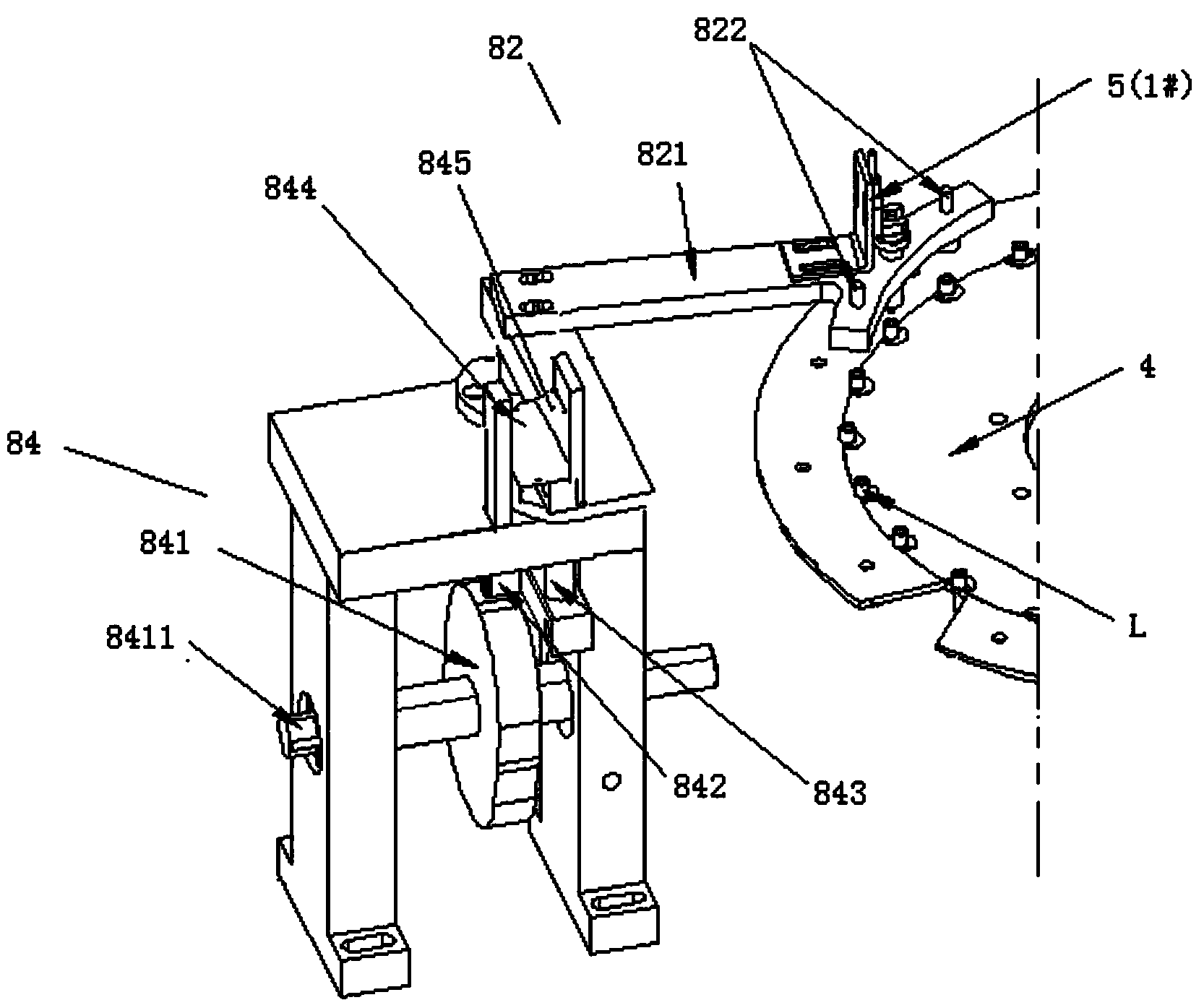
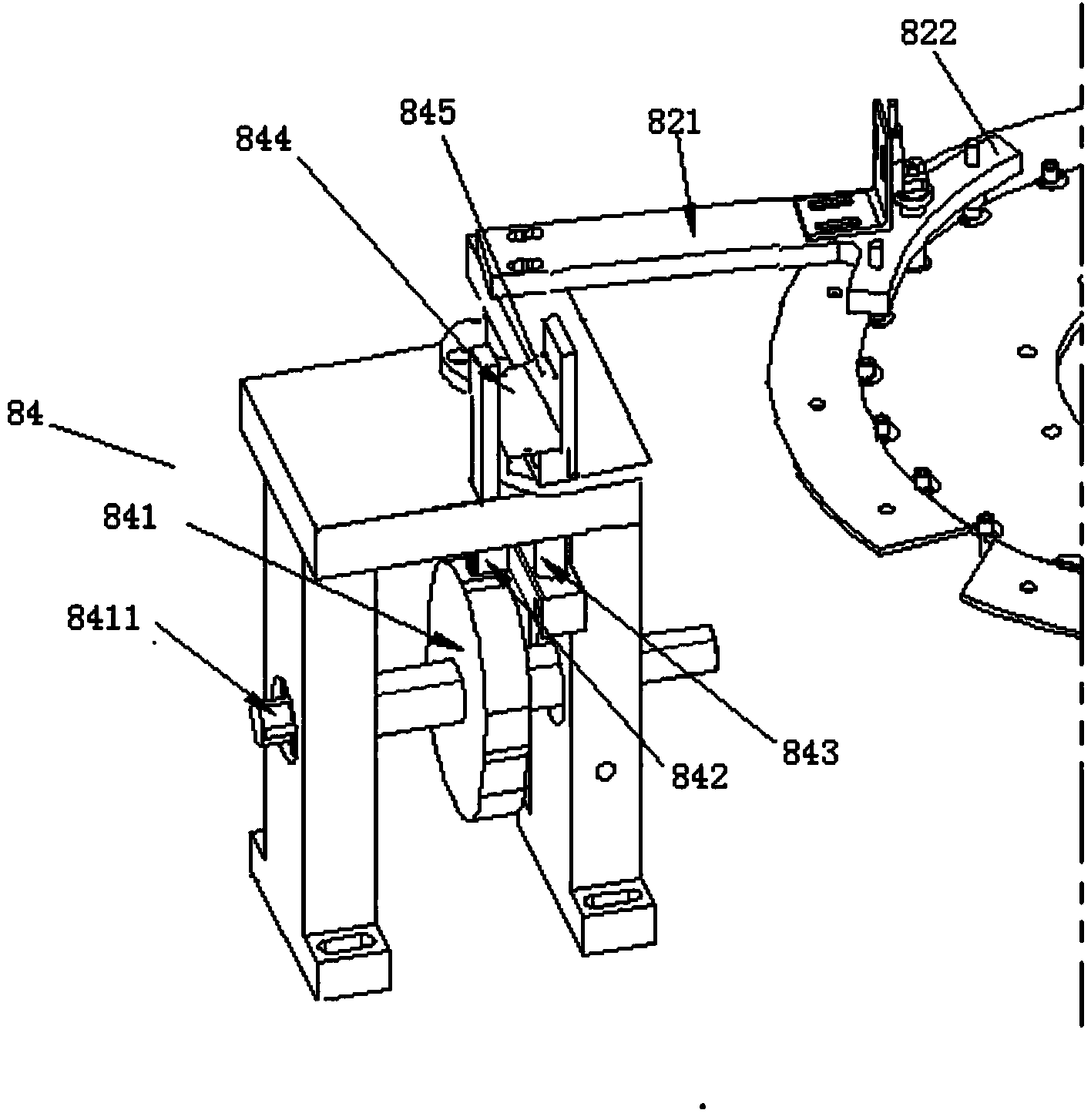
Tibial talocalcaneal joint fusion screw placement guider and application method thereof
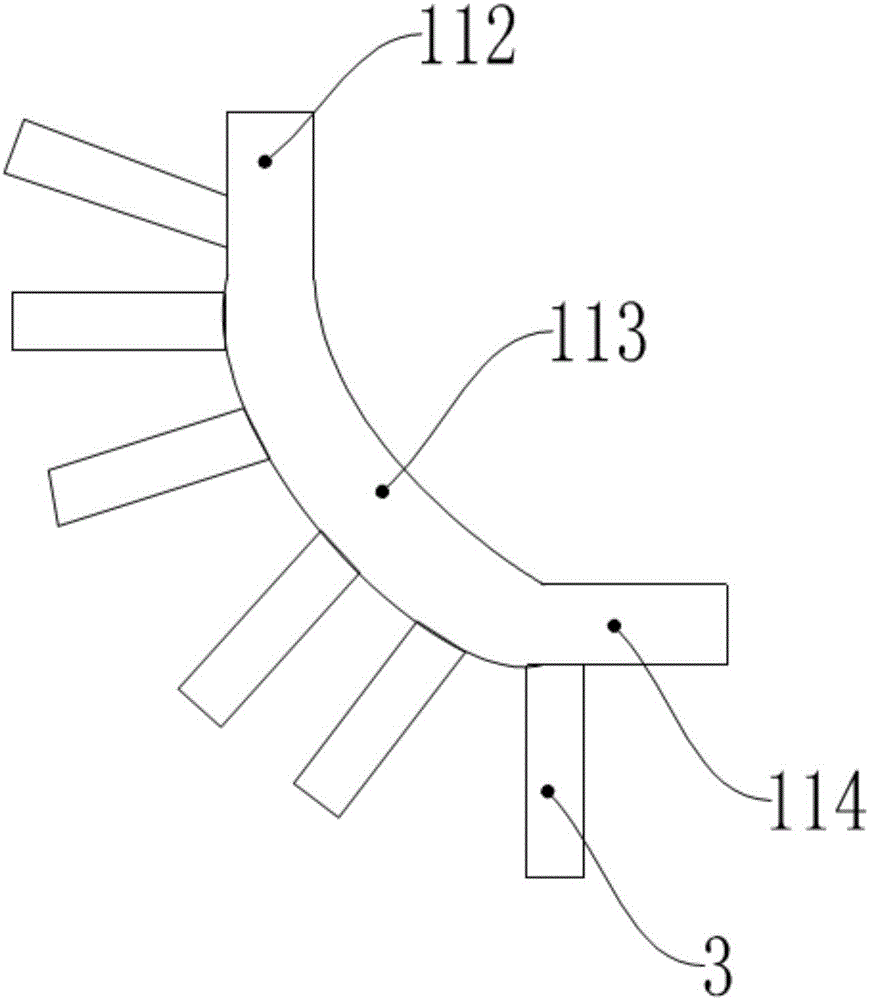
The invention relates to a tibial talocalcaneal joint fusion screw placement guider which comprises a screw placement guider, wherein the screw placement guider comprises a guide plate and a mounting support; the guide plate is an arc-shaped strip plate, the guide plate comprises a front guide section, a middle arc-shaped section and a rear guide section, a 90-degree angle is kept between the front guide section and the rear guide section, the two ends of the middle arc-shaped section respectively bend for 90 degrees and are connected with the front guide section and the rear guide section, and screw placement mounting holes distributed in one row are distributed at the middle part of a plate; and the mounting support is U-shaped, and two tail ends of the U-shaped mounting support are hinged with the two sides of the guide plate. The guider provided by the invention can carry out accurate positioning on the bone surface of calcaneus, the operation is convenient, the tibia, ankle bone and calcaneus can be accurately connected together, and thus the operation success rate is improved.
Owner:朱永展 +3
First-accurate-type central axis minimally invasive mechanical navigation system for femoral neck surgery
PendingCN111772771AReduce incidenceAvoid easily causing iatrogenic accidentsInternal osteosythesisDiagnostic markersOrthopedics surgeryScrew placement
The invention belongs to the technical field of orthopedic surgery equipment, and relates to a first-accurate-type central axis minimally invasive mechanical navigation system for femoral neck surgery. The system comprises a femoral neck positioning hook connecting component, an adapter, a porous positioning guide plate, a positioning guider, a sliding rod right-angle adapter and a central axis positioning guide component, the femoral neck positioning hook connecting component is connected to the adapter through the vertical connecting rod, the porous positioning guide plate is arranged on theadapter, the sliding rod right-angle adapter is connected to the porous positioning guide plate and the positioning guider, and the central axis positioning guide component is arranged on the positioning guider. The system can be objectively, accurately and completely matched with the neck shaft angle, the front inclination angle and the front torsion angle, passes through the center of the femoral neck, guarantees the accuracy of the central axis of the femoral neck surgery, and achieves initial accurate screw placement with high accuracy. Meanwhile, a detachable structure is adopted, disinfection and repeated use after an operation are facilitated, the structure is simple, and functions are diversified.
Owner:邓迎生
Exposure apparatus for posterior spinal minimally invasive screw placement surgery
InactiveUS20150366549A1Accurately and quickly and conveniently conductEasy to placeDiagnosticsSurgeryMultifidus muscleScrew placement
An exposure apparatus for posterior spinal minimally invasive screw placement surgery includes a transverse process refractor and a facet joint retractor, is provided. The apparatus separates a gap between a multifidus muscle and a longissimus muscle, easily and atraumatically reach a screw placement position on a pedicle, accurately place the retractors, and thereafter locally form a screw placement tunnel space that externally extends 10 to 15 degrees. During a screw placement operation, the distal end of the transverse process refractor can straddle above the transverse process and is antagonistically tractive with the facet joint retractor so as to leave a sufficient space for the screw placement operation and to prompt a needle inlet point and direction for placing a pedicle screw. The distal end of the refractor employs a design of a recessed crescent type, protects local soft tissues during traction, and prevents the tissues from damage.
Owner:JIANGSU PROVINCE HOSPITAL
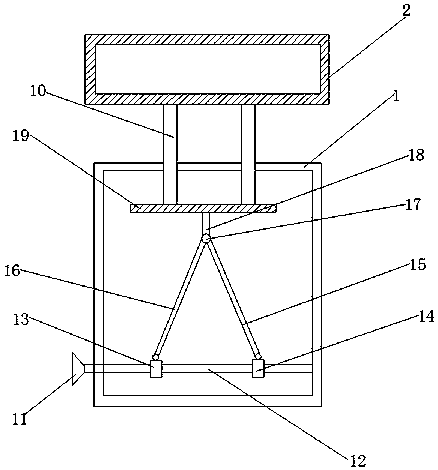
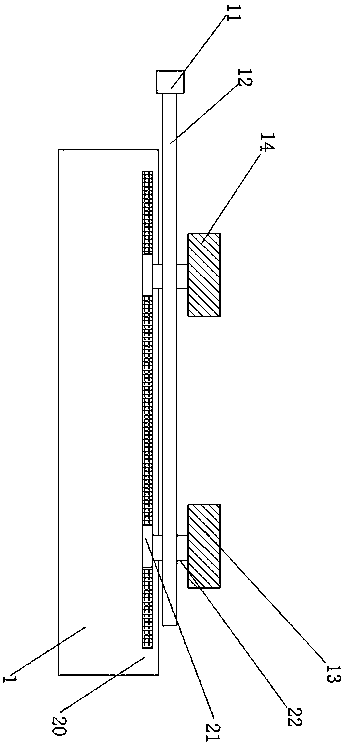
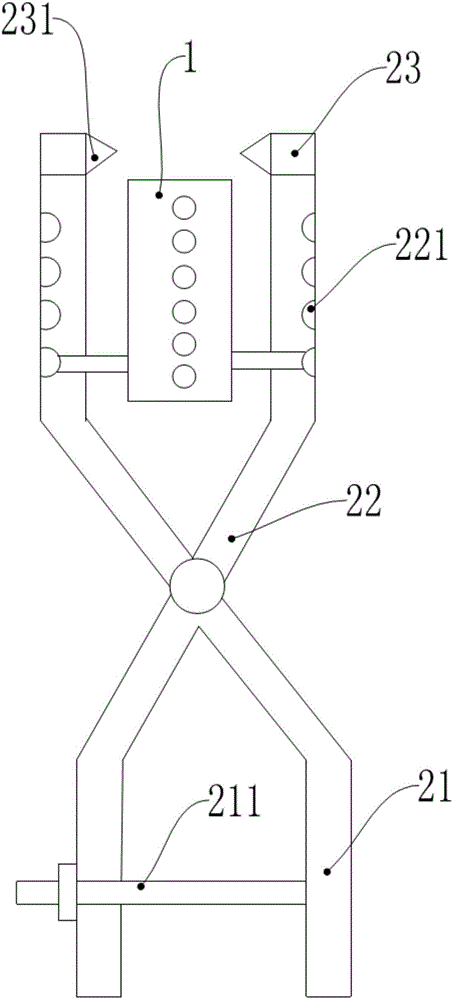
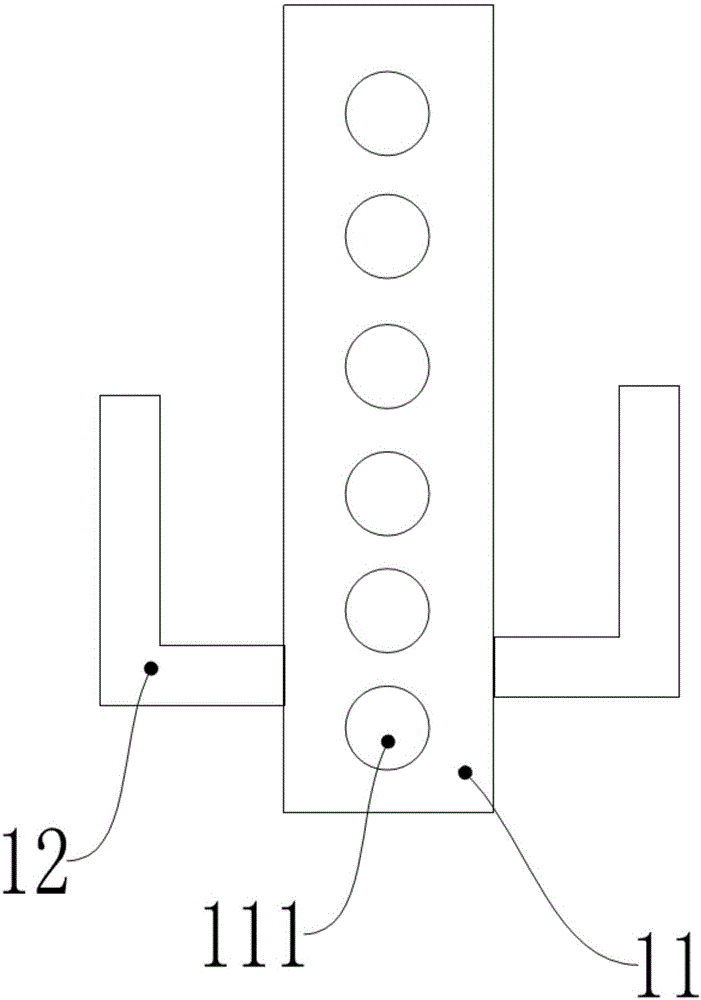
Screw placement box
The present invention discloses a screw placement box which comprises a support column, rotating members arranged on the support column, and placement boards which are connected to the rotating members and are provided with through holes for placing screws. The through holes are internally provided with elastic rings. The invention provides the screw placement box suitable for all models of screws, the end part of each column of placement boxes is labeled, a user can write models, the finding of a suitable screw is facilitated, the screws are placed and are perpendicular to a ground plane, thus the user can use an electric screwdriver to take the screws conveniently, multiple placement plates are arranged, and thus a small occupation space and a large placement quantity are realized.
Owner:苏州金牛精密机械有限公司
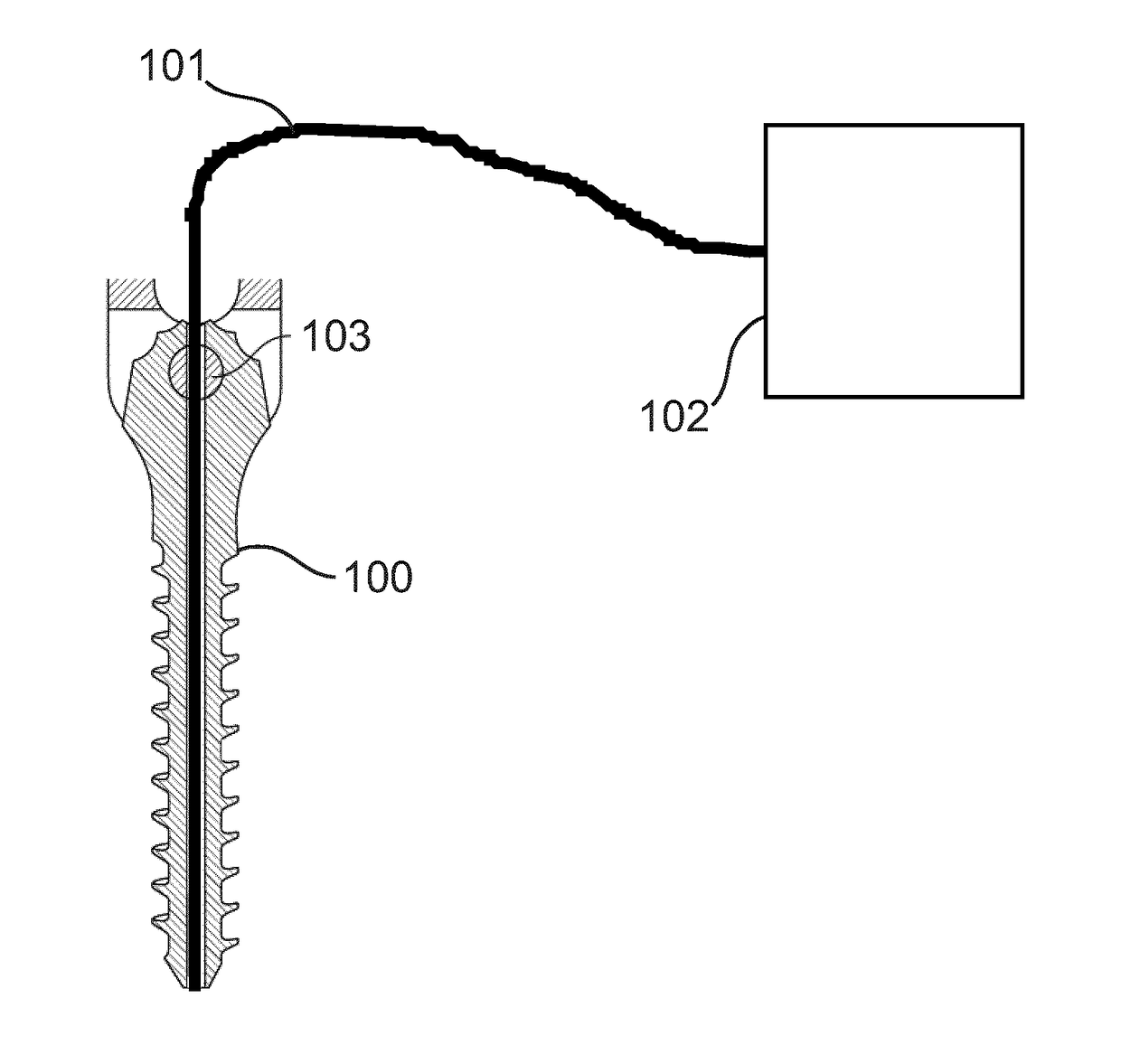
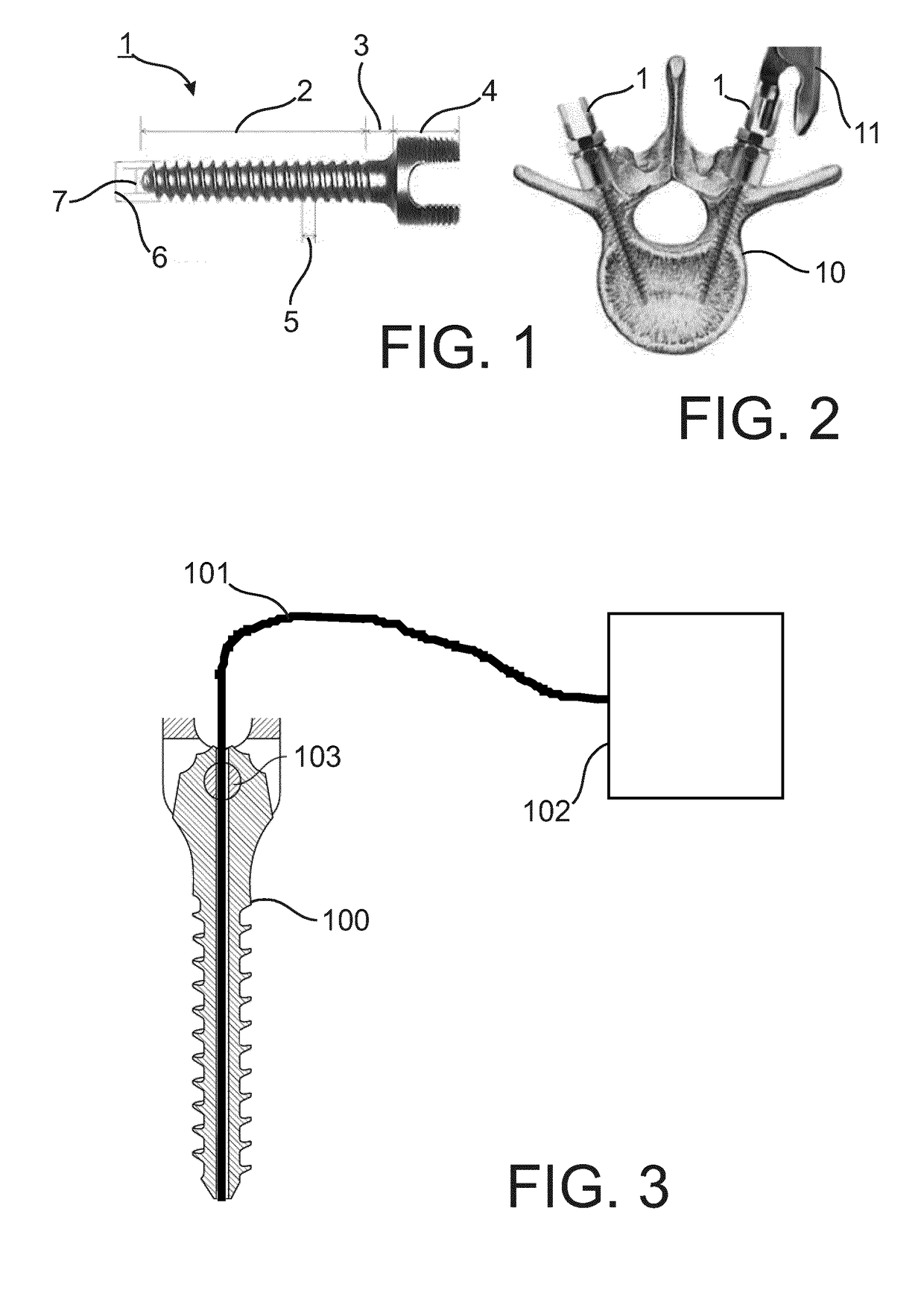
System for implanting in bone tissue
ActiveUS20180280065A1Improved implantAccurate placementInternal osteosythesisFastenersScrew placementBone tissue
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com