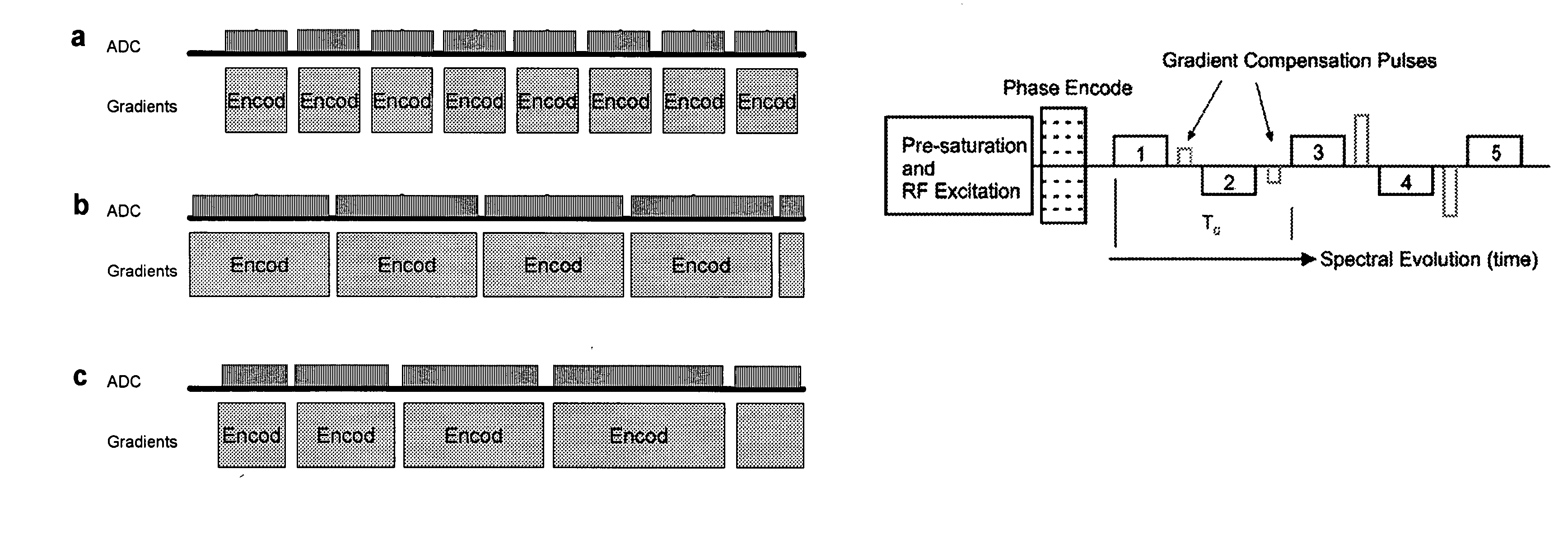
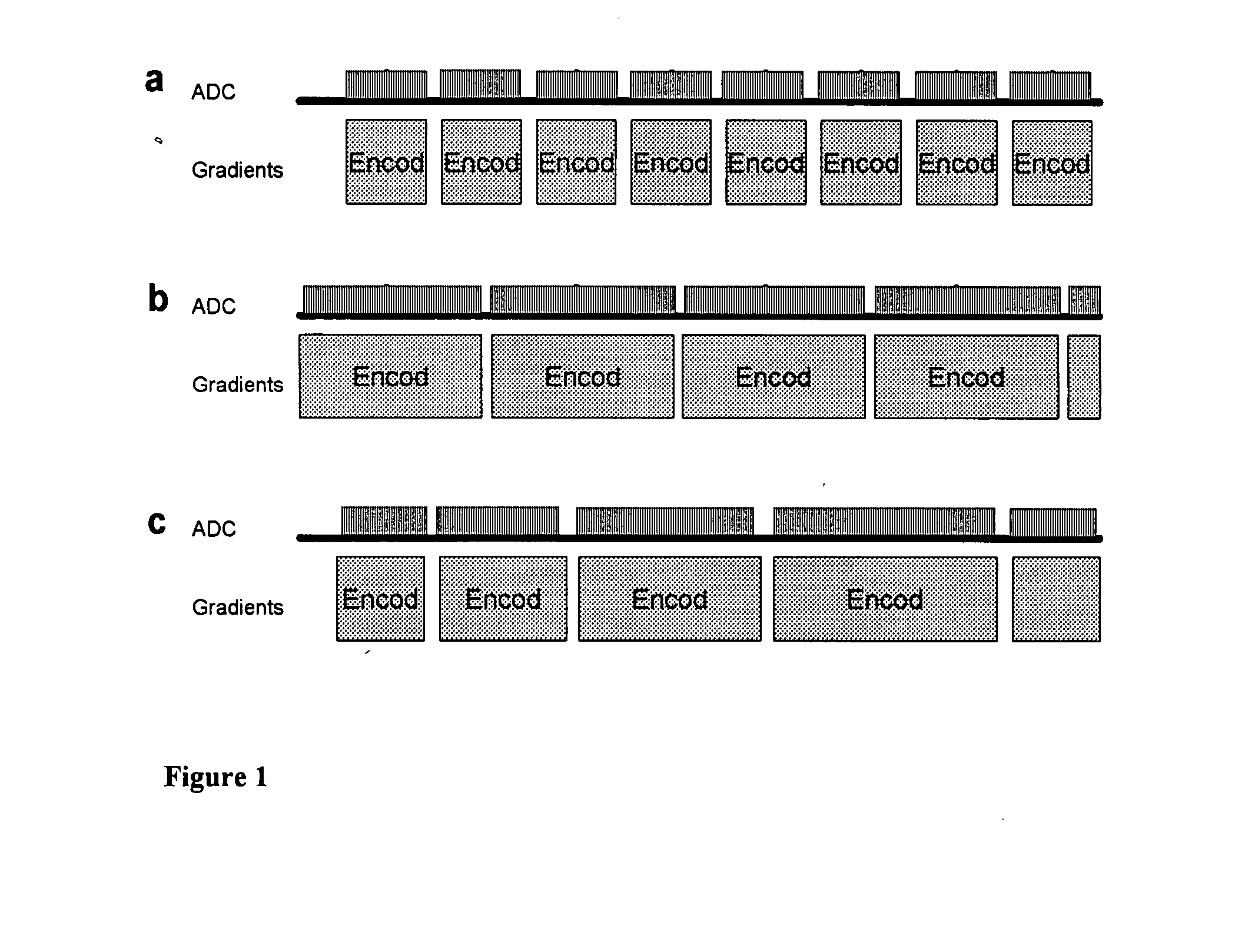
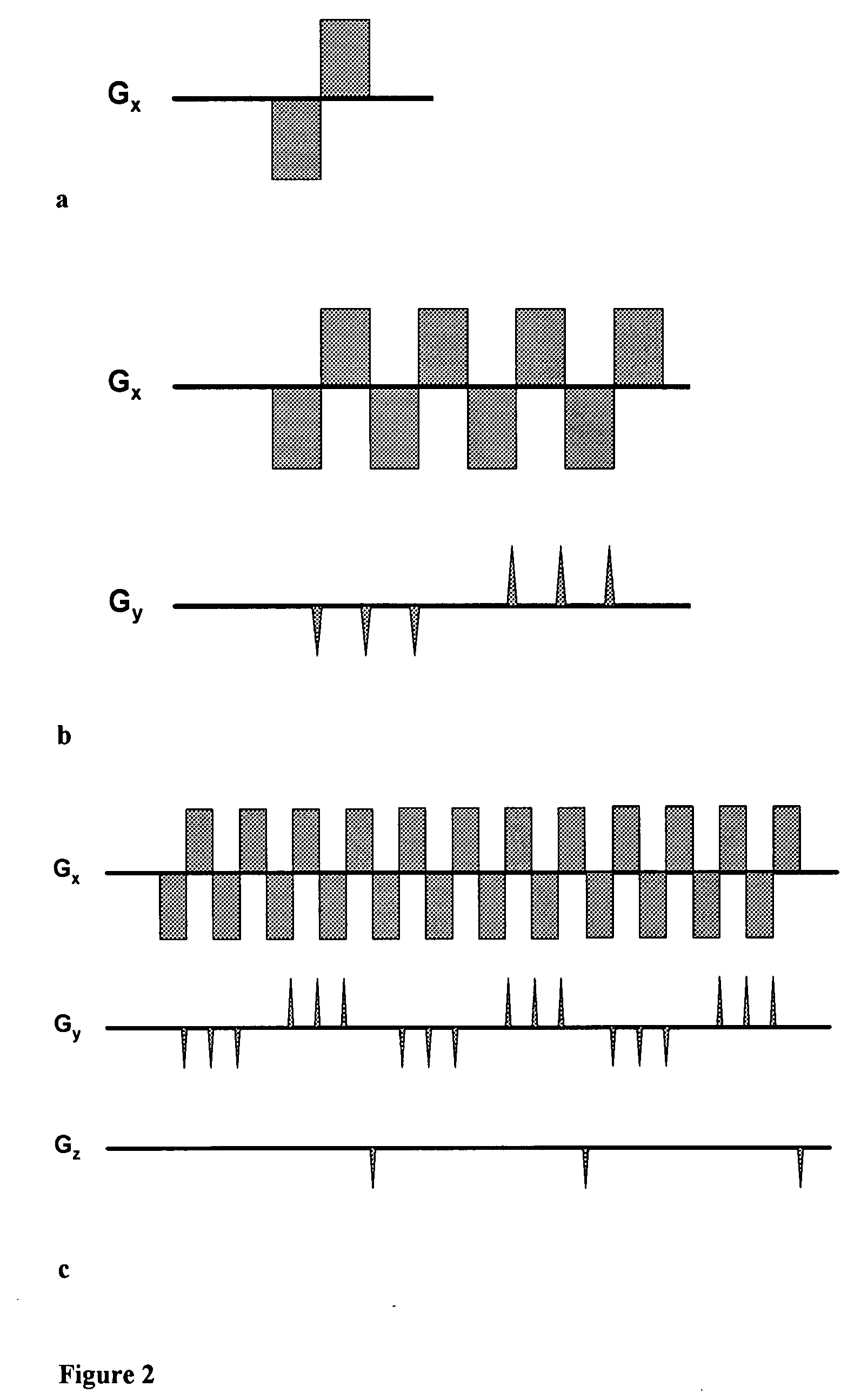
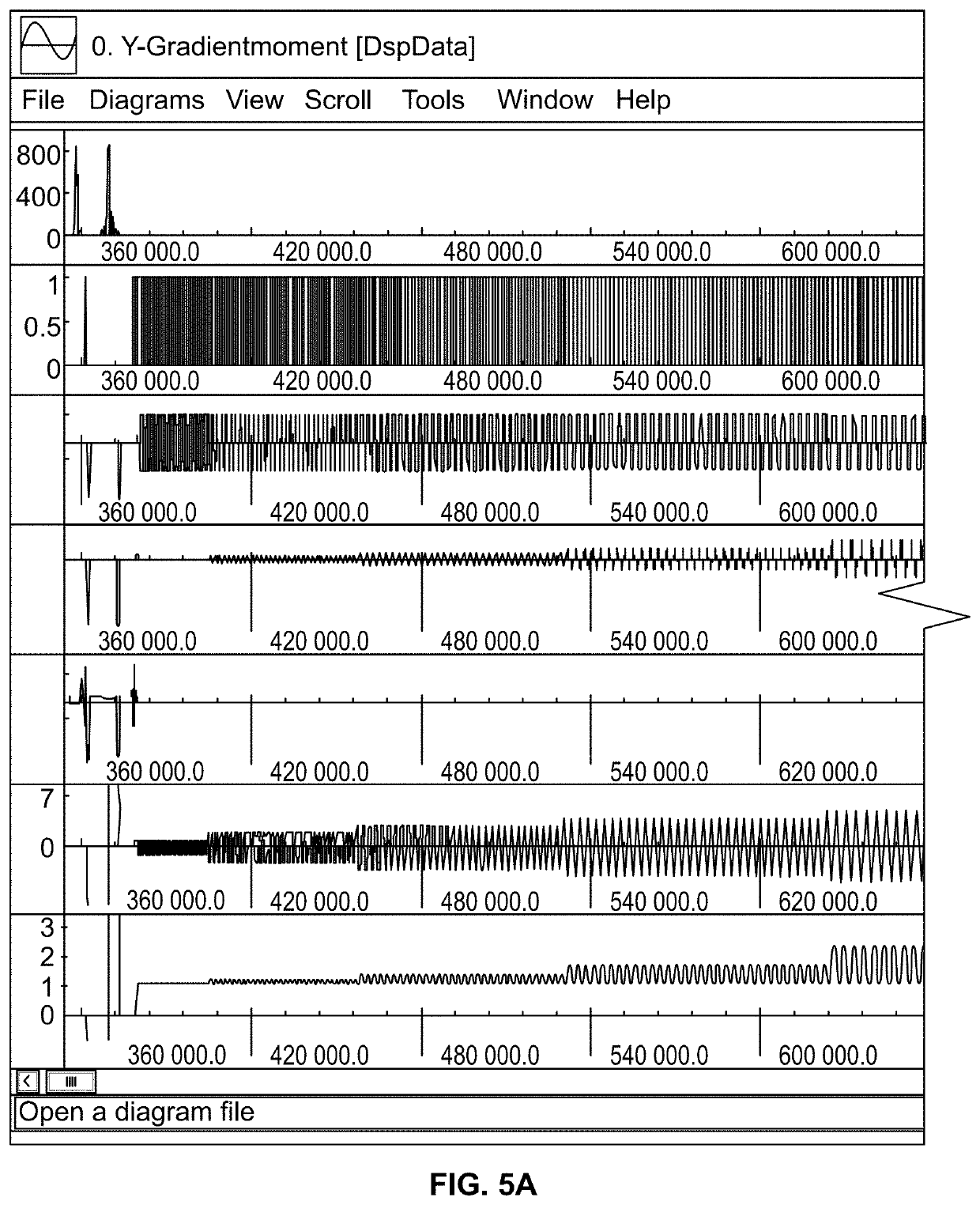
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
30 results about "Magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
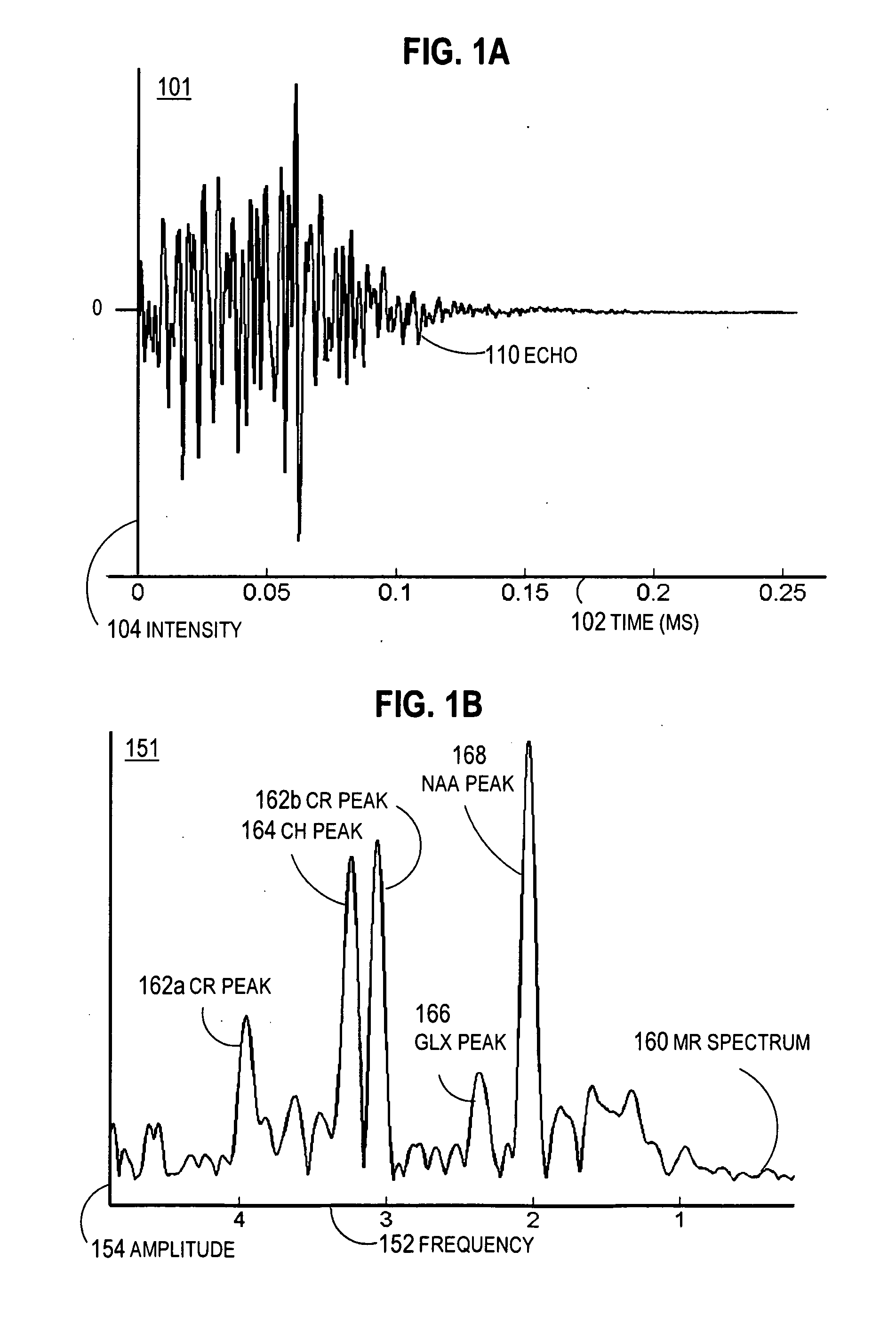
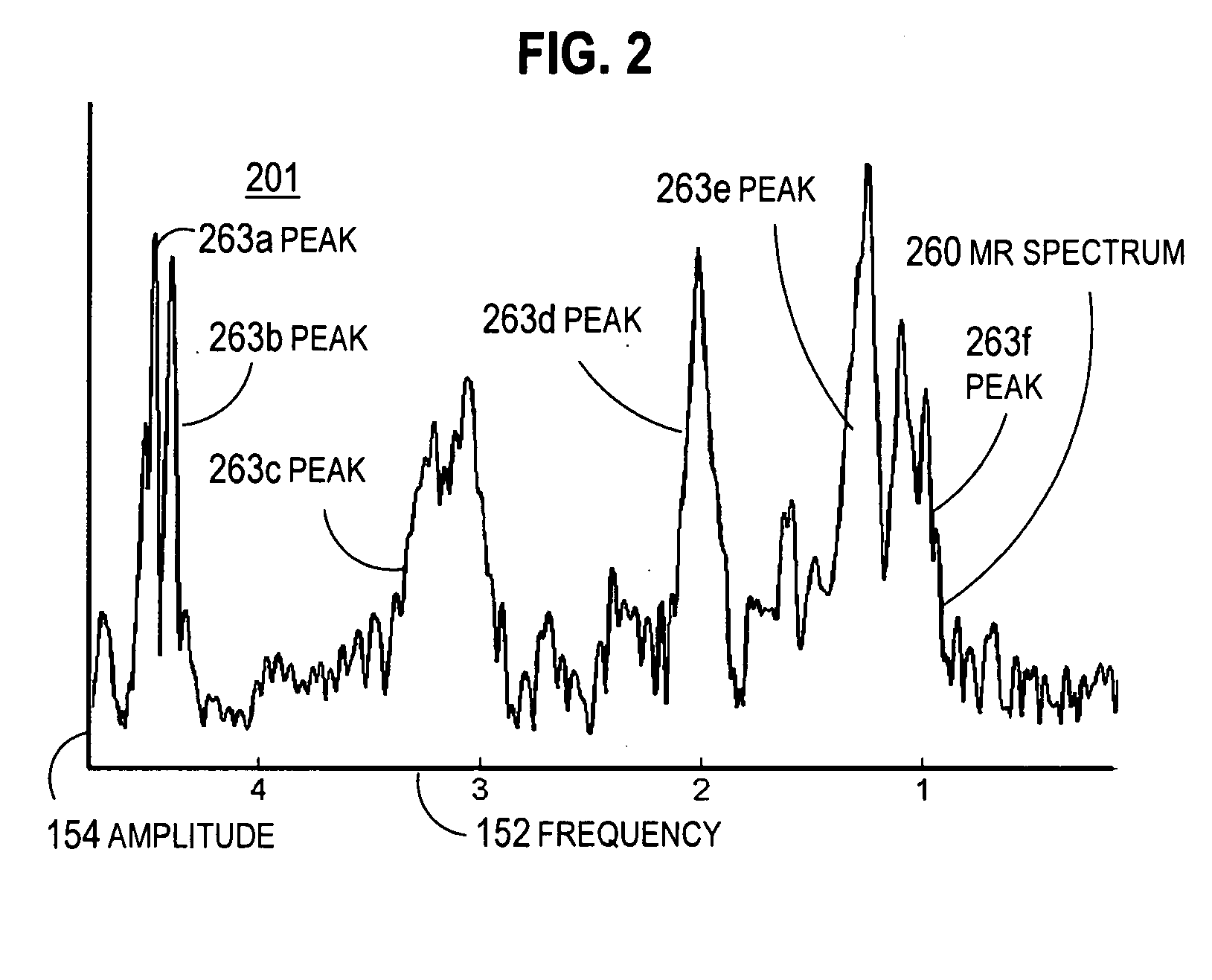
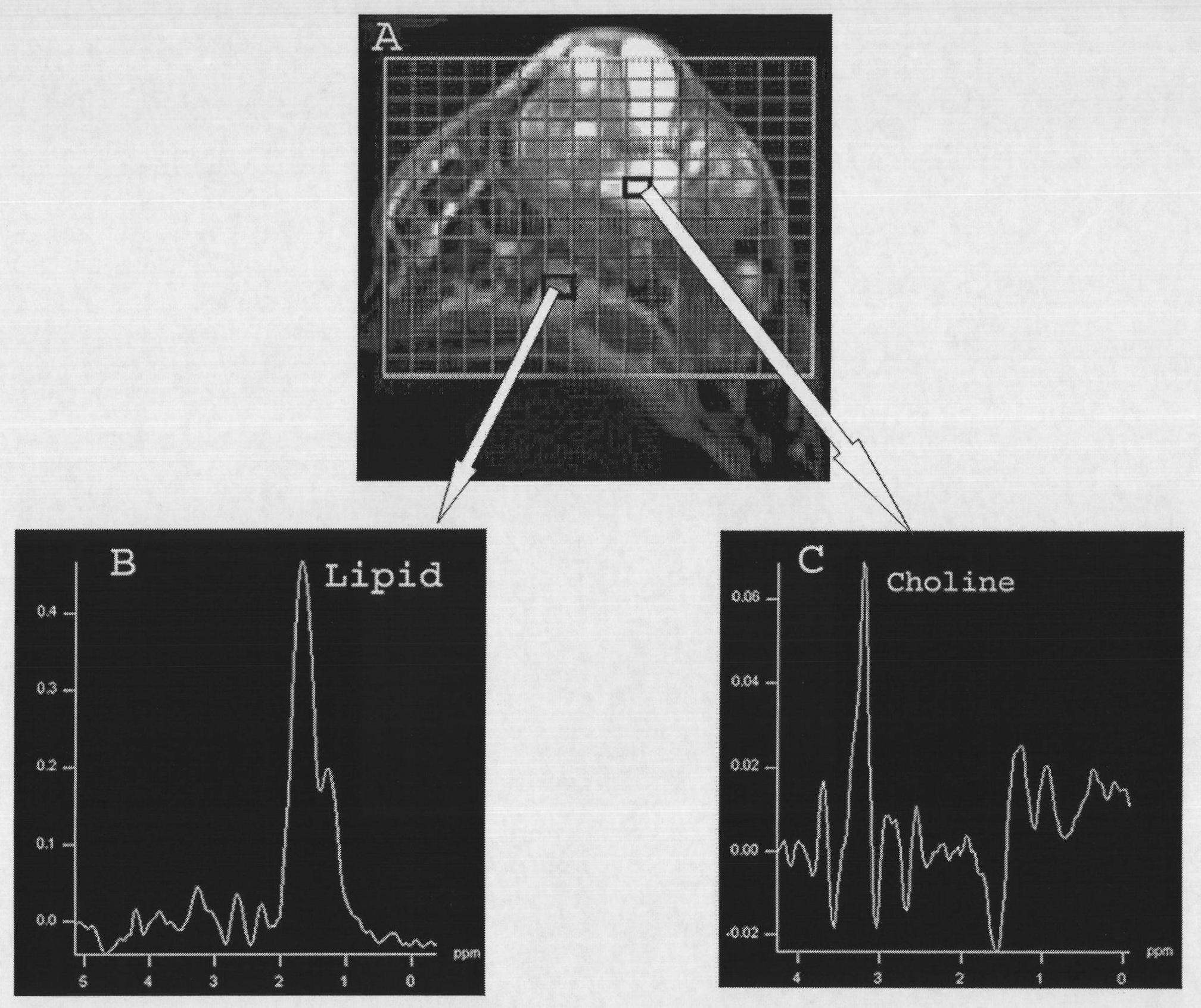
Magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) is a noninvasive imaging method that provides spectroscopic information in addition to the image that is generated by MRI alone. Whereas traditional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) generates a black-and-white image in which brightness is determined primarily by the T1 or T2 relaxation times of the tissue being imaged, the spectroscopic information obtained in an MRSI study can be used to infer further information about cellular activity (metabolic information). For example, in the context of oncology, an MRI scan may reveal the shape and size of a tumor, while an MRSI study provides additional information about the metabolic activity occurring in the tumor. MRSI can be performed on a standard MRI scanner, and the patient experience is the same for MRSI as for MRI. MRSI has broad applications in medicine, including oncology and general physiological studies.
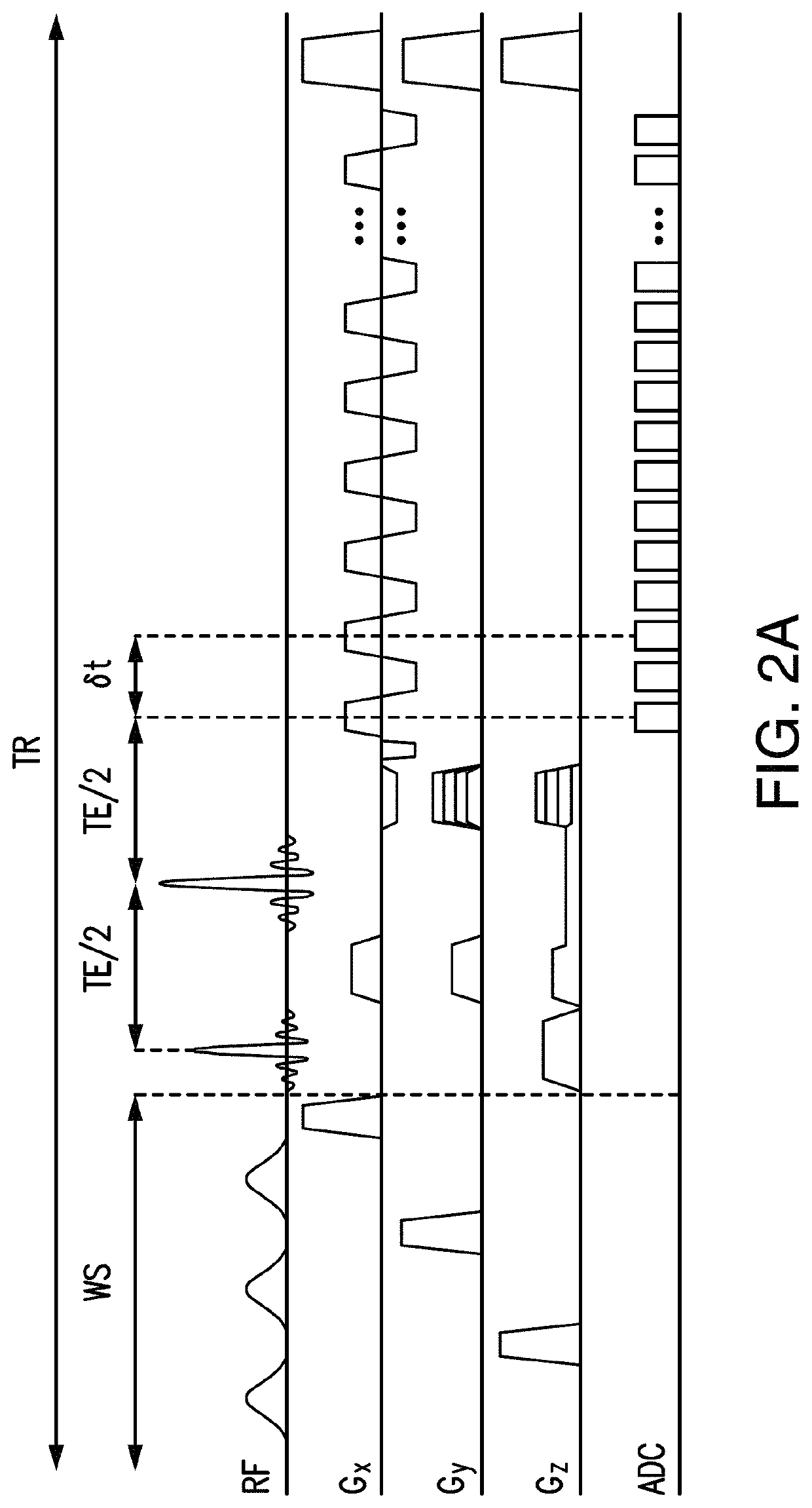
Method and device for magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
InactiveUS20120313641A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioAvoid disadvantagesMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionChemical speciesMirror image
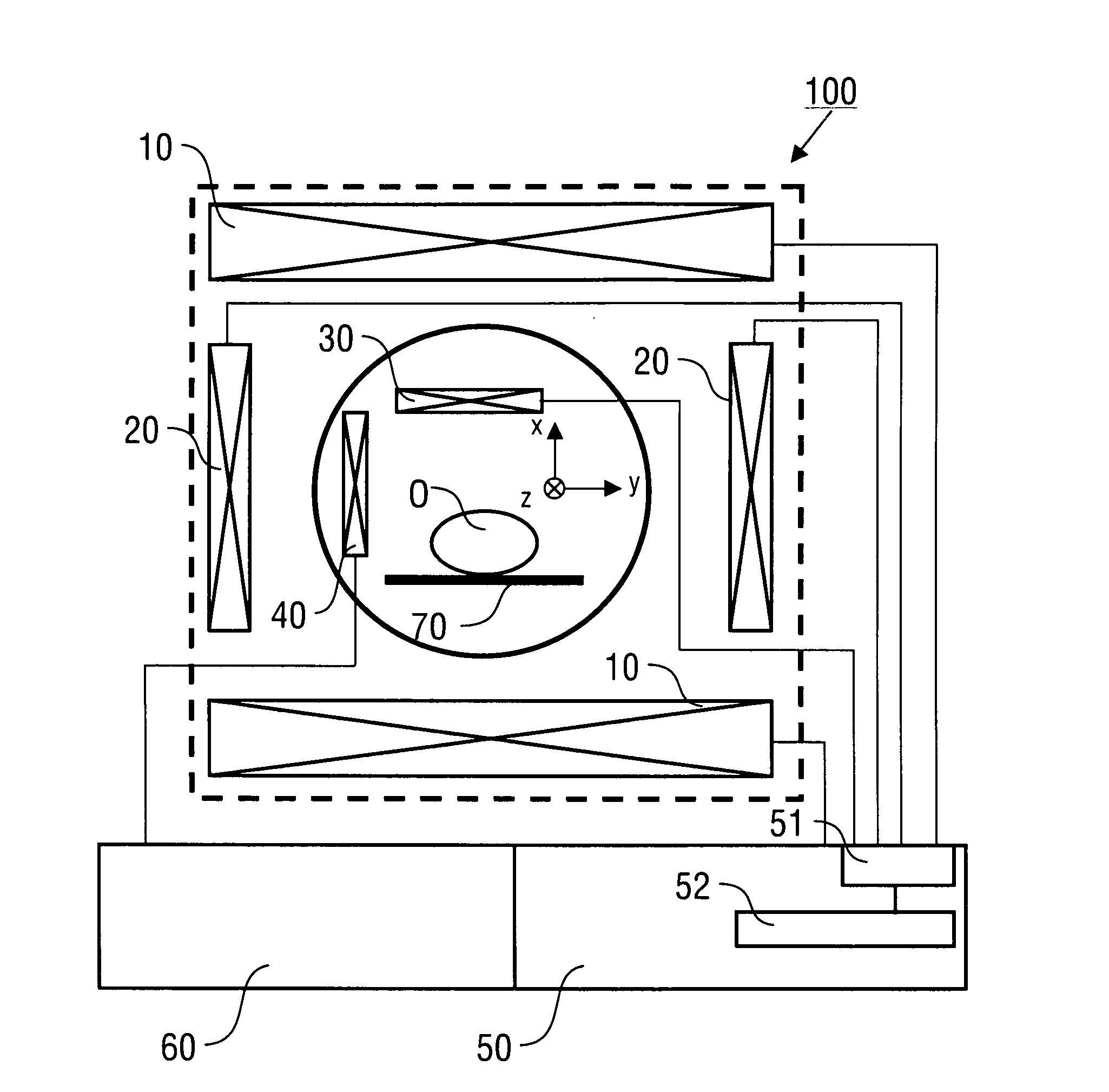
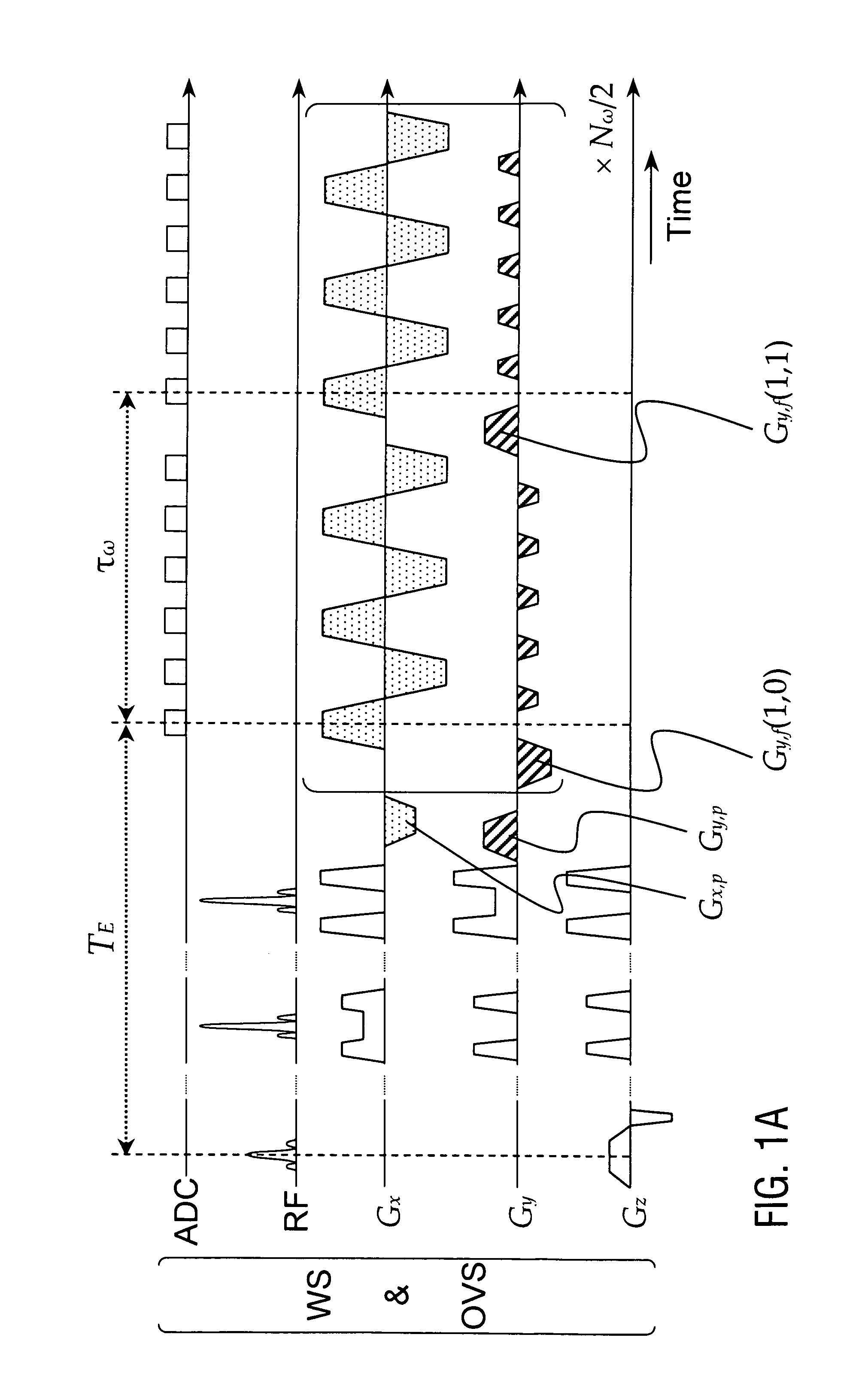
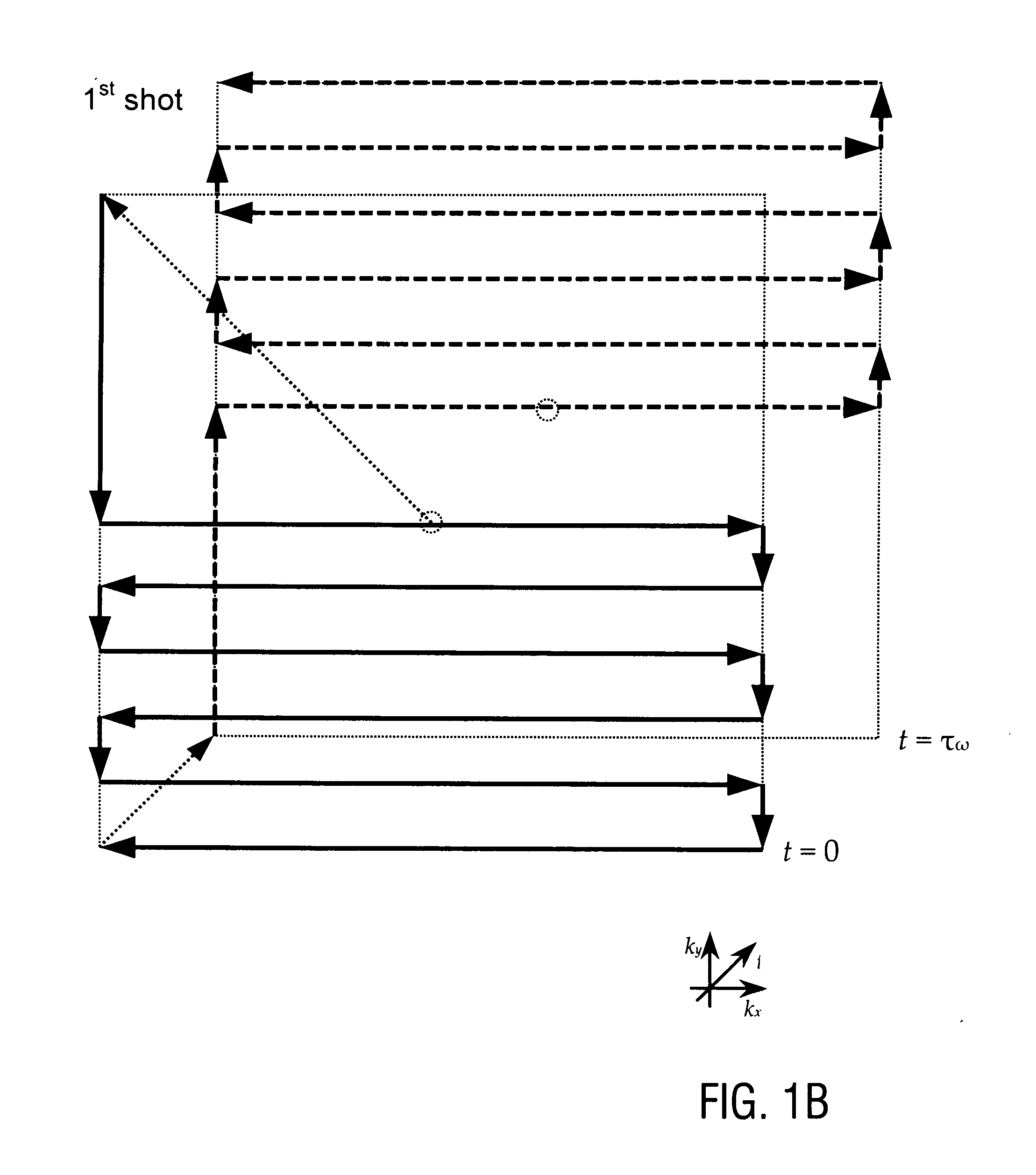
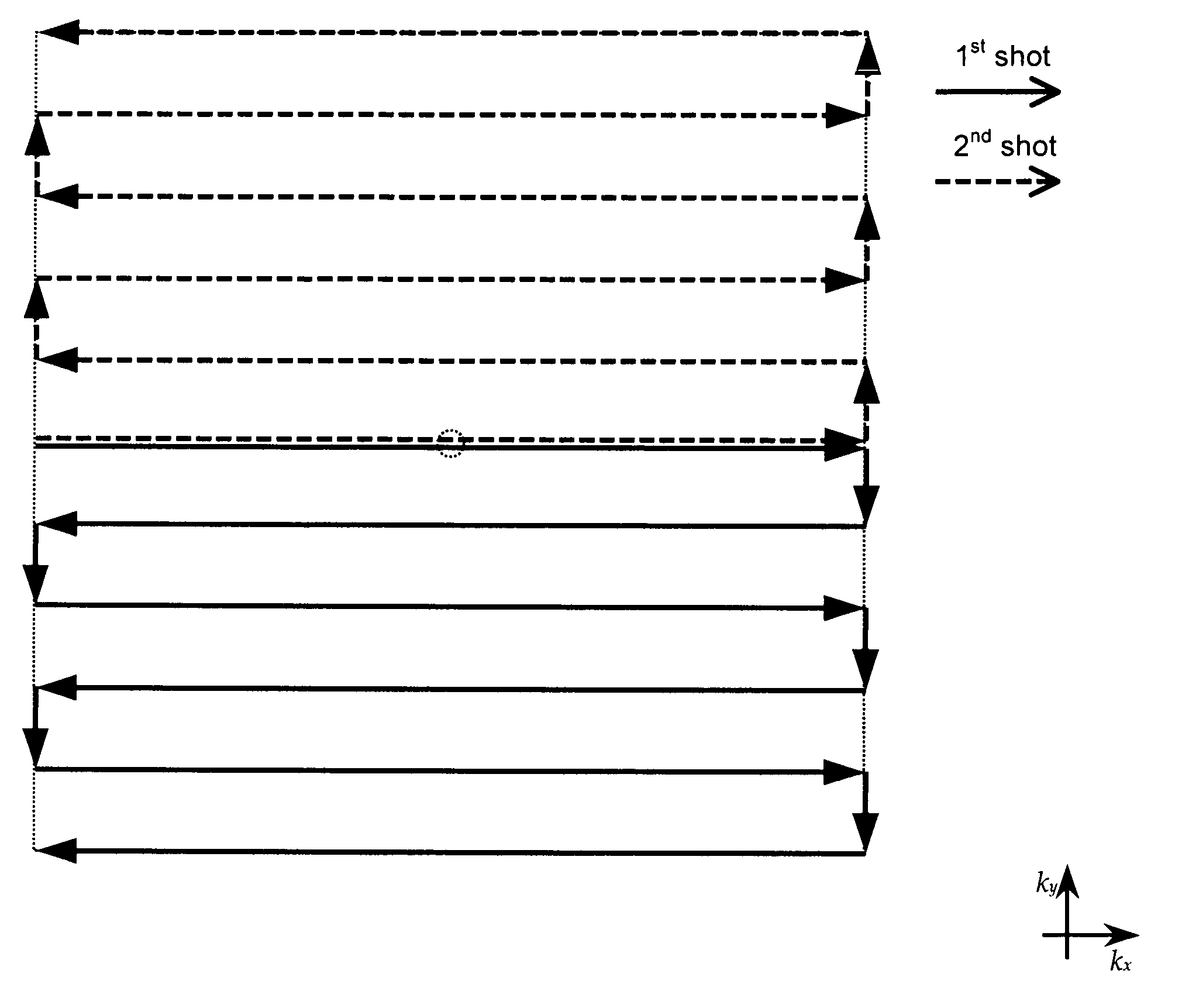
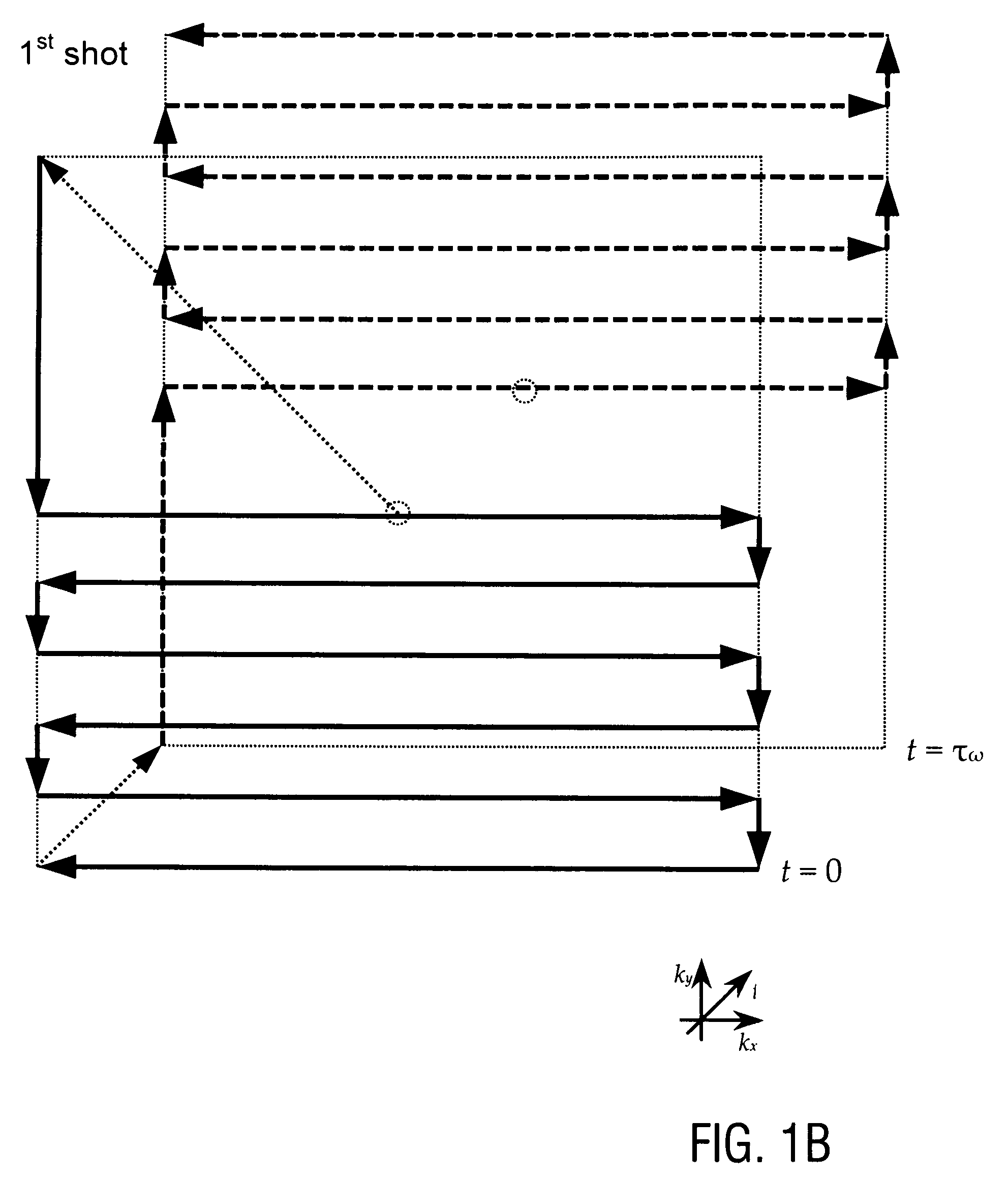
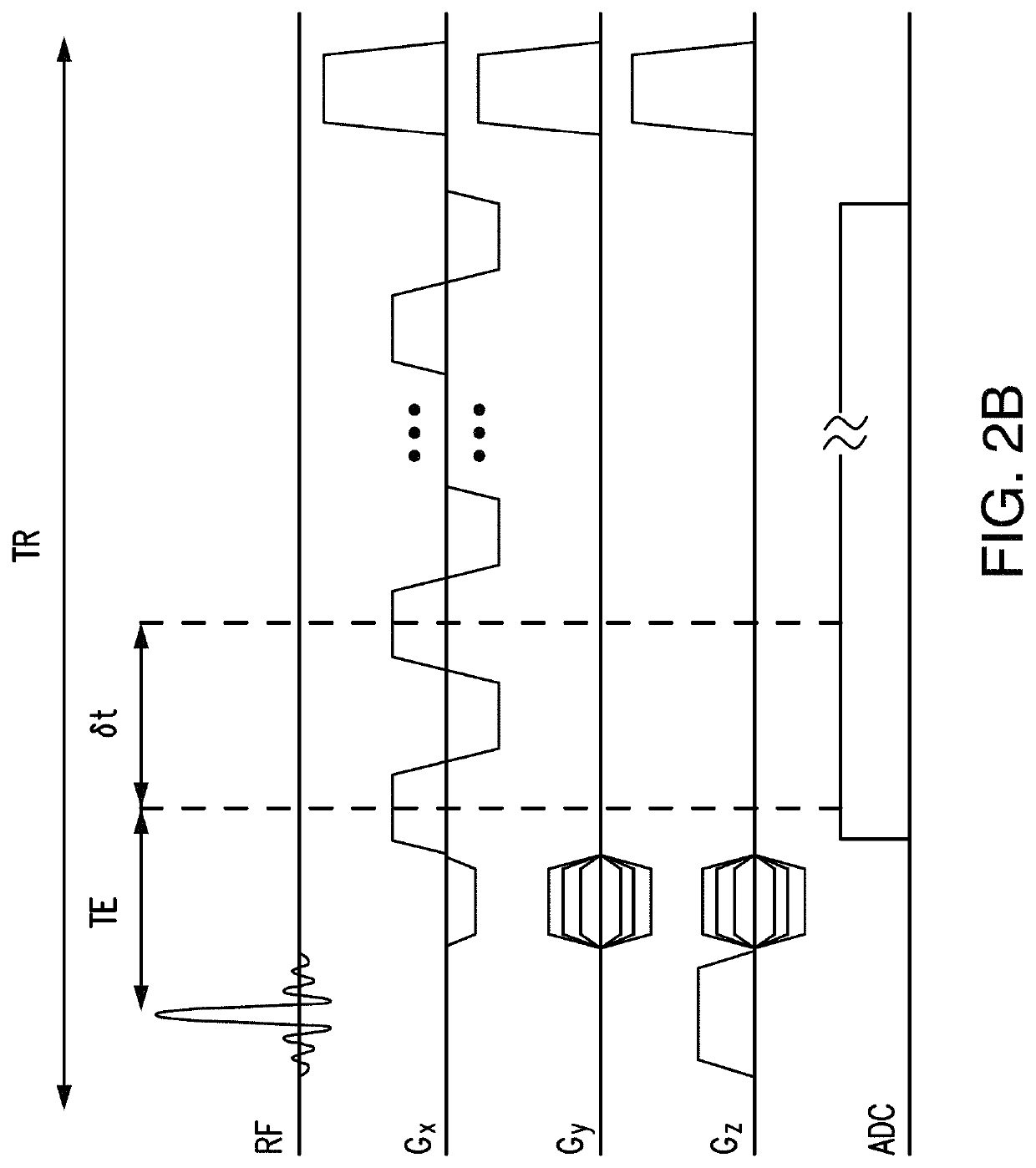
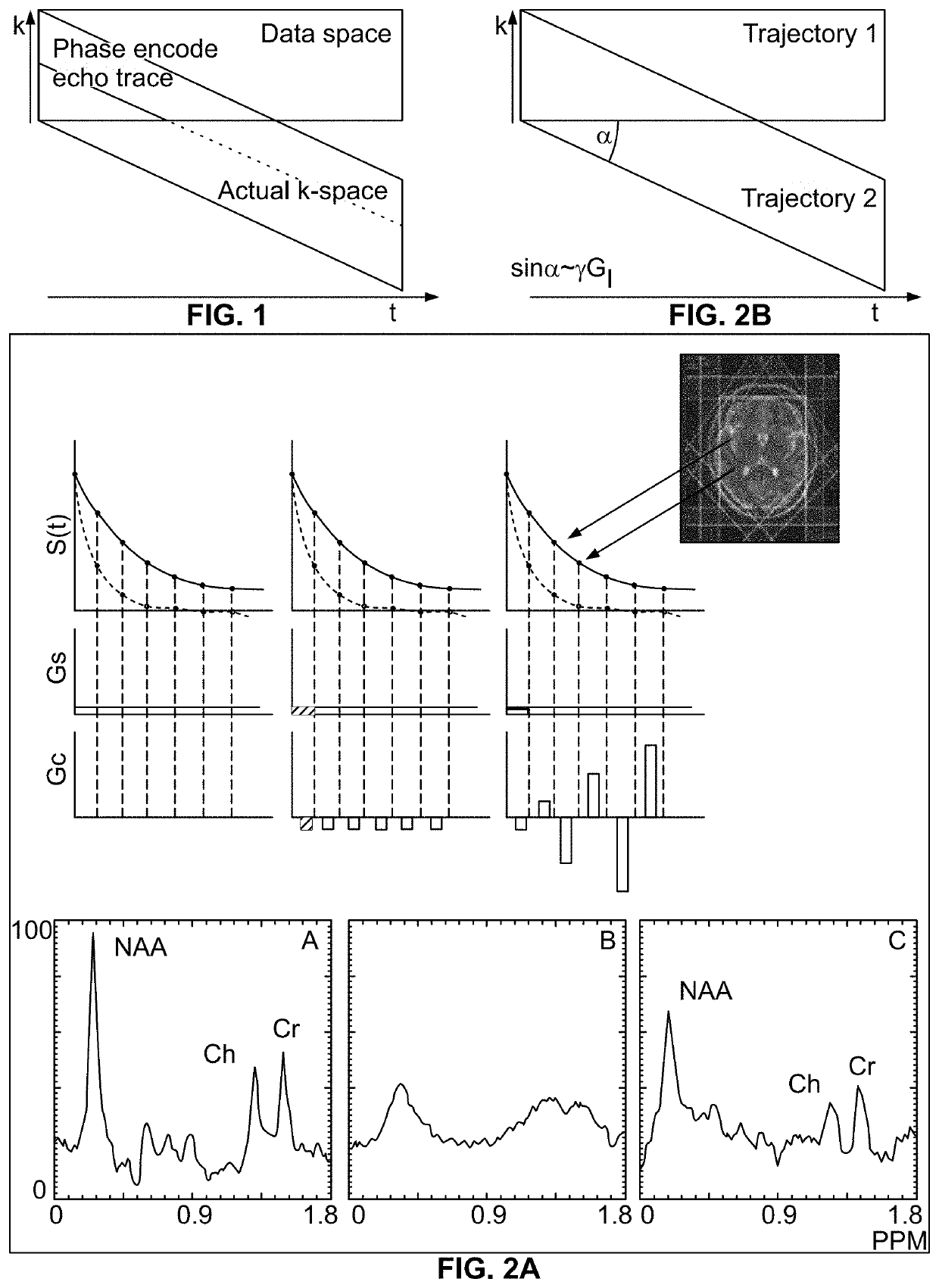
A method of magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging of an object (O) including at least one chemical species to be imaged, comprising sampling of the k-space such that a plurality of Nω first sampling trajectories through at least one k-space segment of the k-space is formed along a phase-encoding direction, each of said first sampling trajectories beginning in a central k-space region and continuing to a k-space border of the at least one k-space segment and having a duration equal to or below a spectral dwell time corresponding to the reciprocal spectral bandwidth, collecting at least one first set of gradient-echo signals obtained along said first sampling trajectories, collecting at least one second set of gradient-echo signals obtained along a plurality of Nω second sampling trajectories, said Nω second sampling trajectories and said Nω first sampling trajectories being mutually mirrored relative to a predetermined k-space line in the central k-space region.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Spectral resolution enhancement of magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
InactiveUS20100085050A1Spectral broadeningMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionTime domainMagnetic resonance spectroscopic
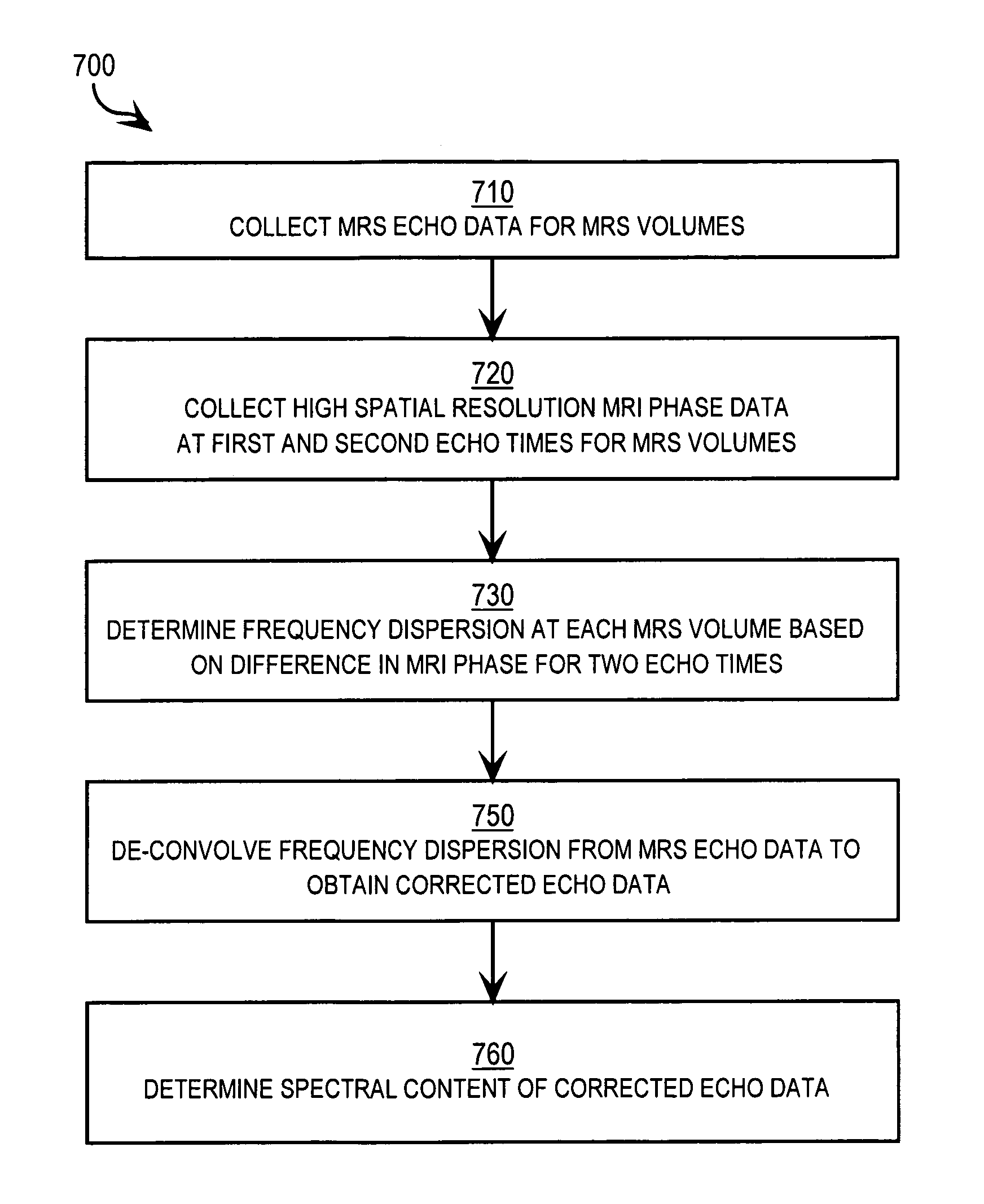
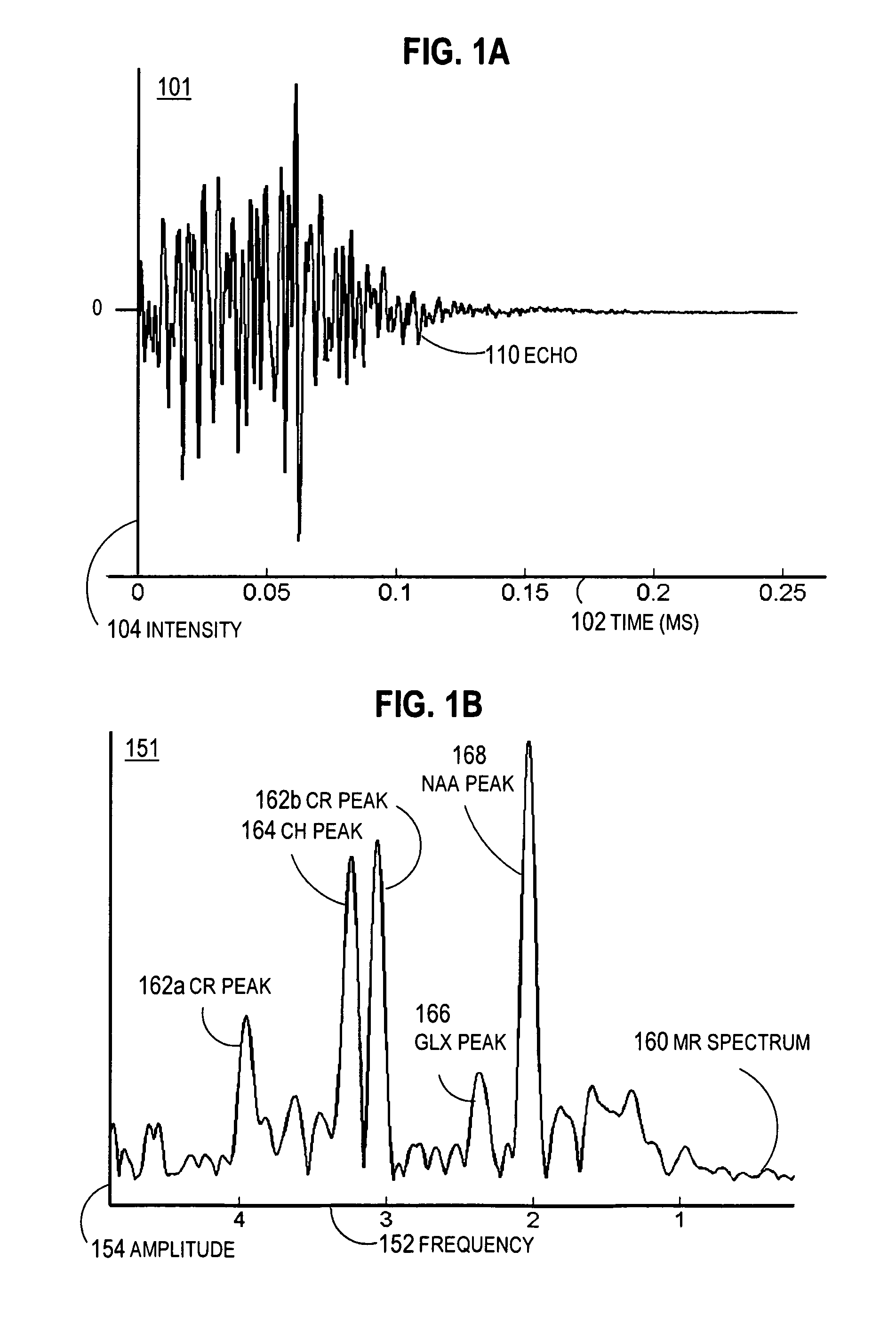
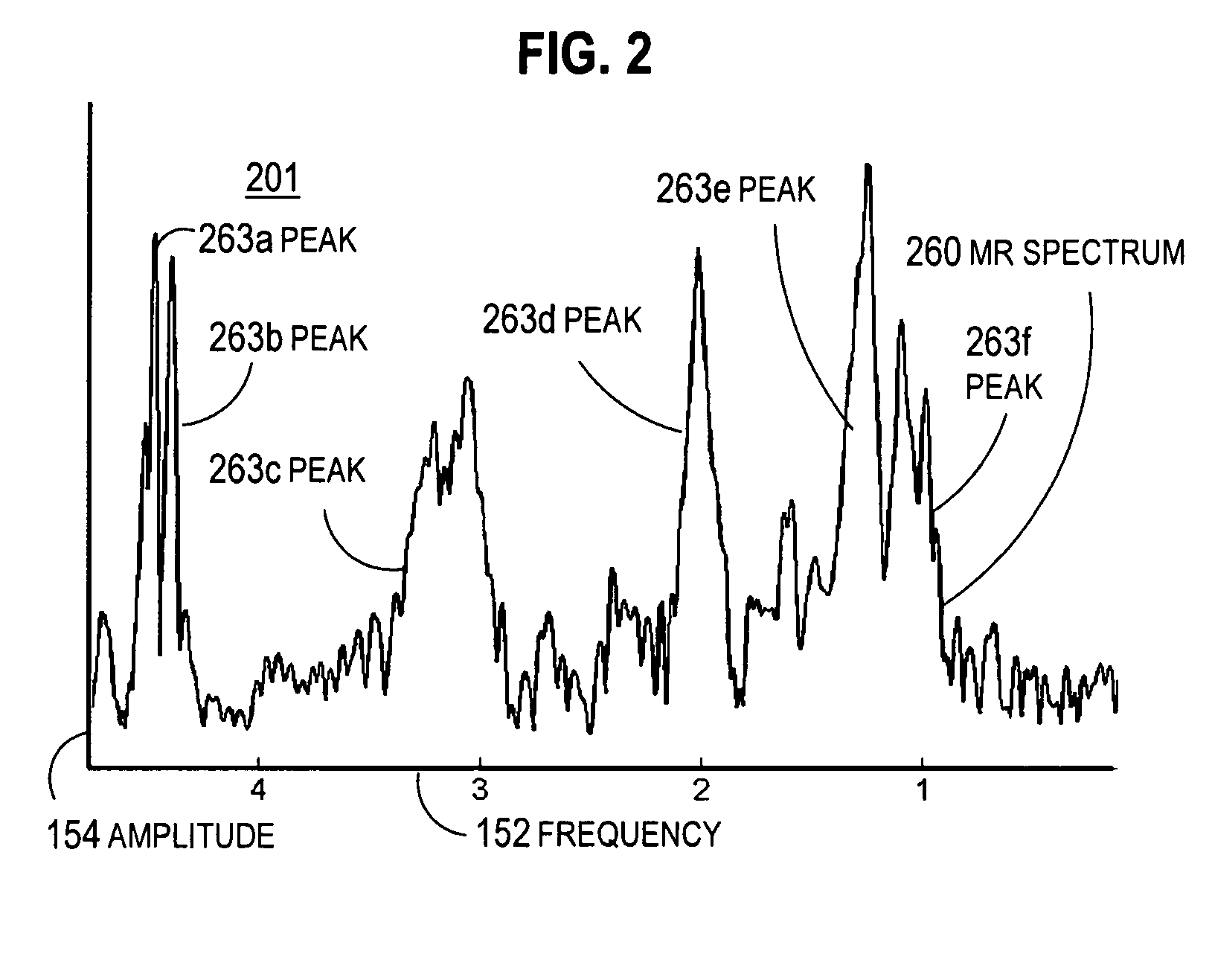
A method and apparatus for enhancing the spectral resolution of magnetic resonance spectroscopic (MRS) measurements include receiving time domain echo data from an MRS measurement for an MRS volume in a subject. Also received are high spatial resolution complex signal values within the MRS volume based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) measurements. Frequency-domain content is determined for the echo data based at least in part on the complex signal values. For example, in some embodiments, receiving complex signal values includes receiving high spatial resolution complex signal values within the MRS volume for each of two different echo time settings. The frequency-domain content of the echo data is corrected for a lineshape profile based on high resolution frequency dispersion values for the MRS volume determined from differences in the complex signal values for the two different echo time settings.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
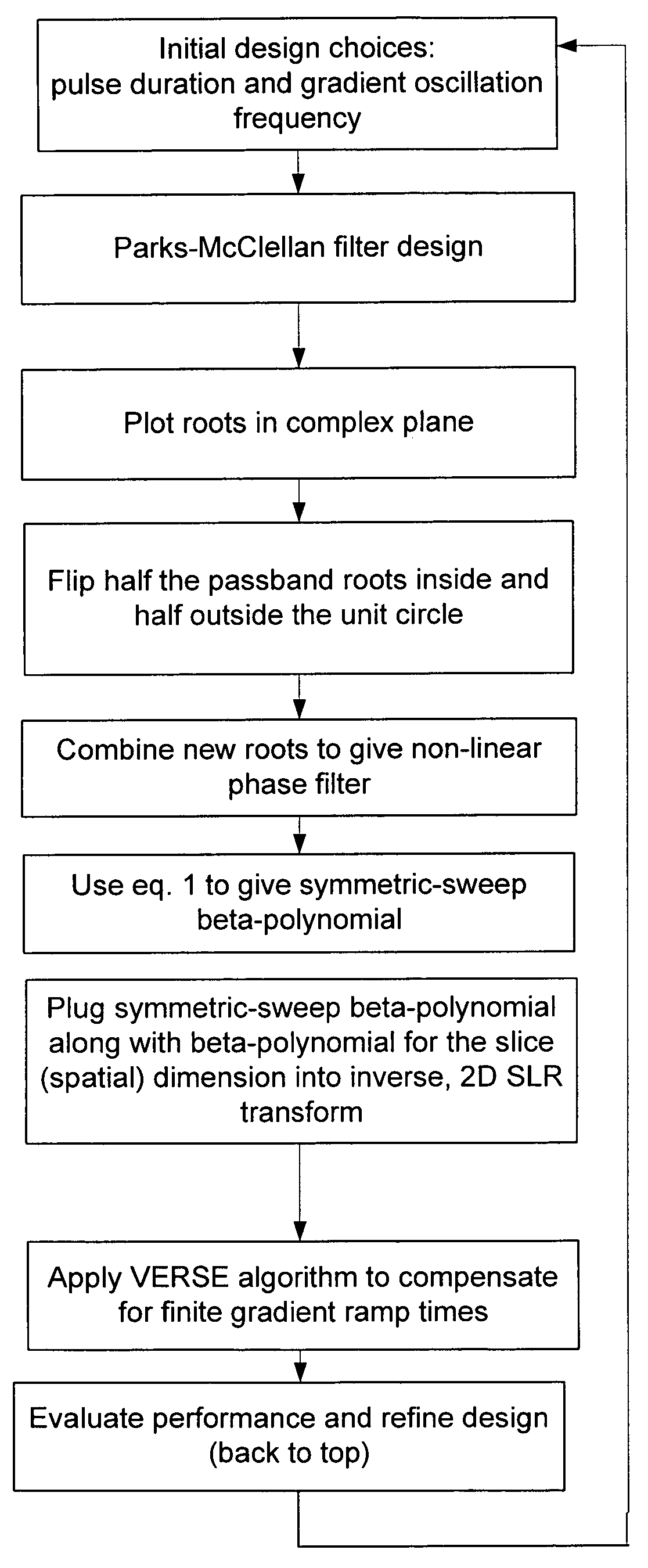
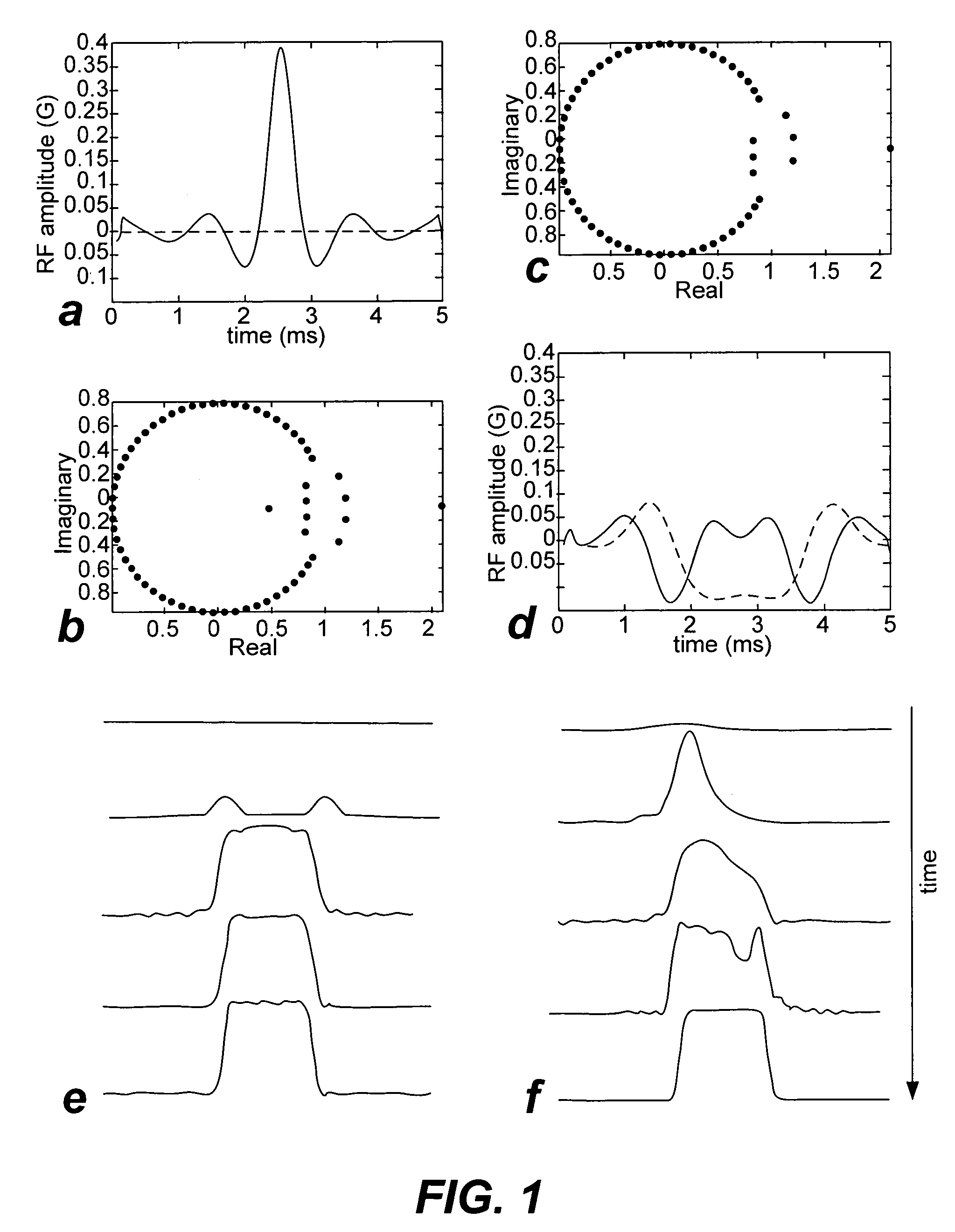
Non-linear symmetric sweep spectral-spatial RF pulses for MR spectroscopy
ActiveUS7042214B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionSpectroscopyRadio frequency
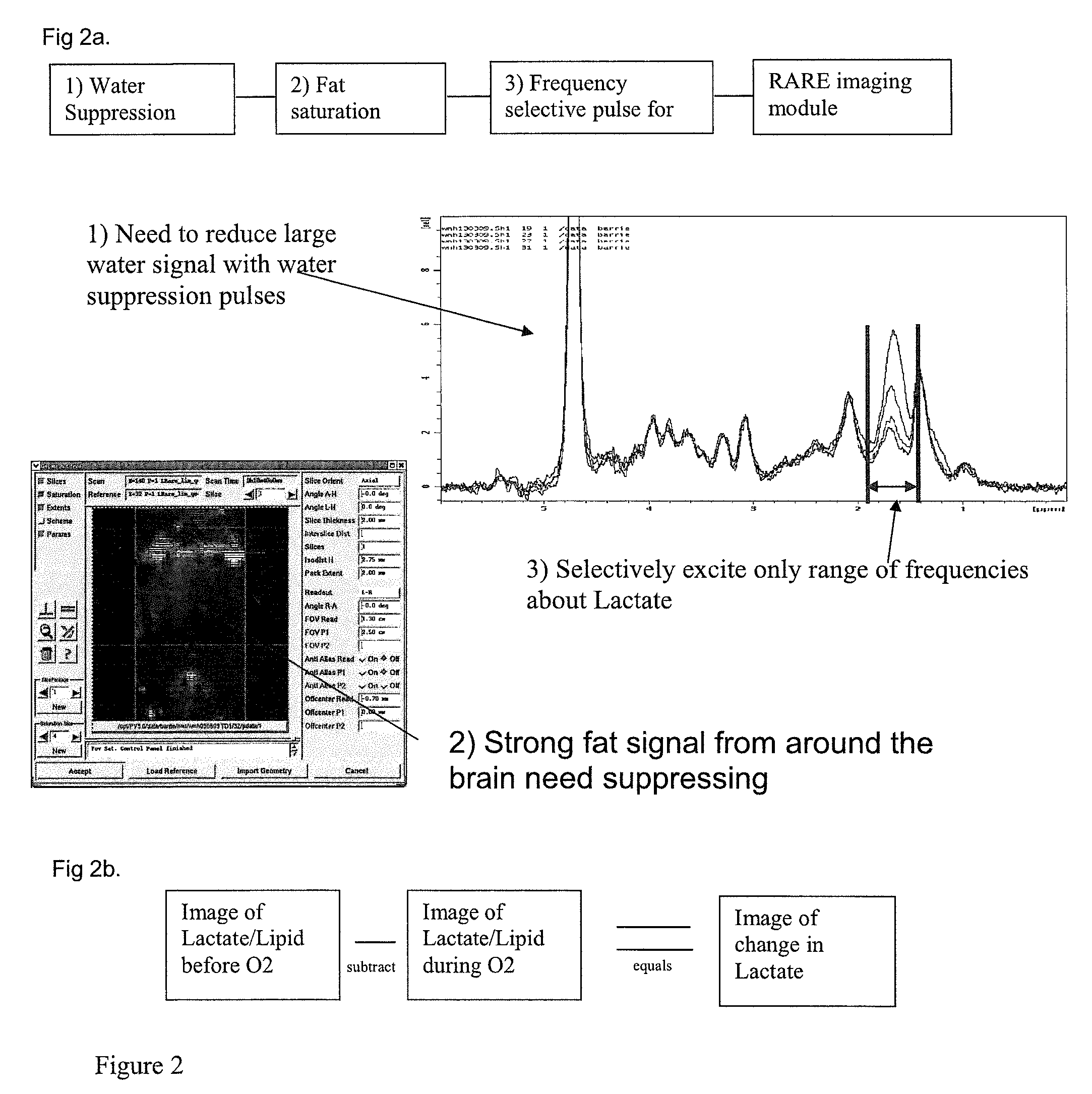
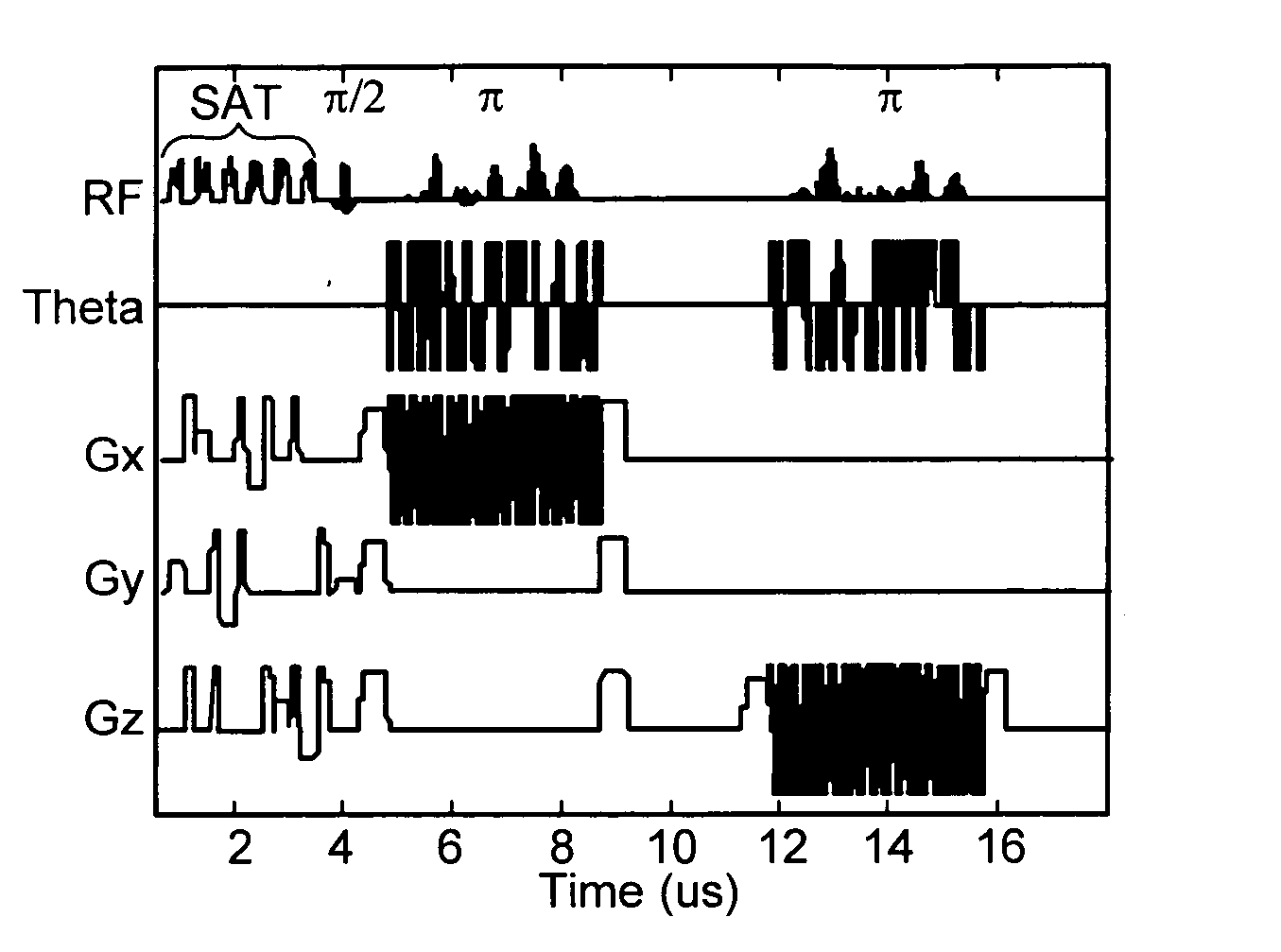
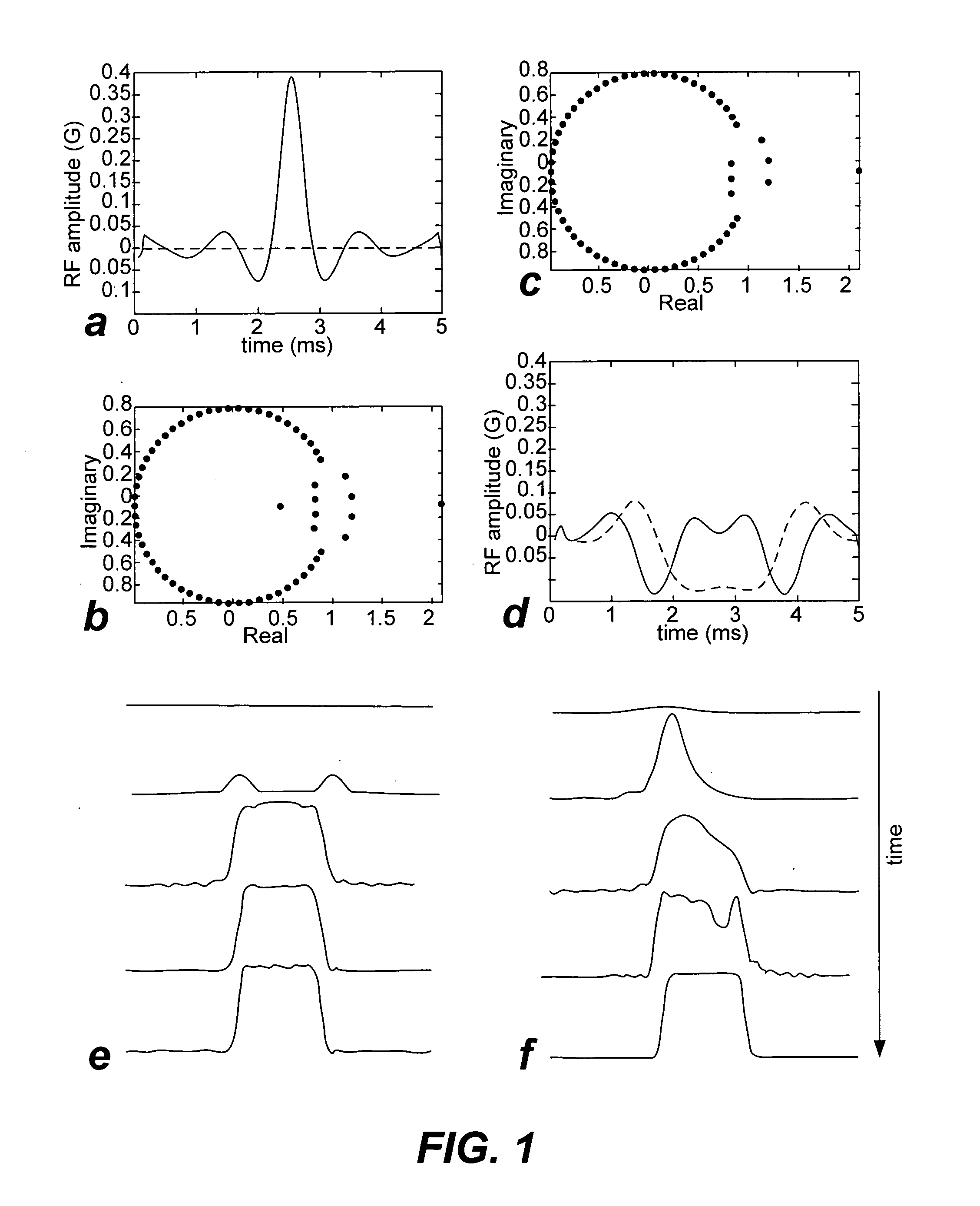
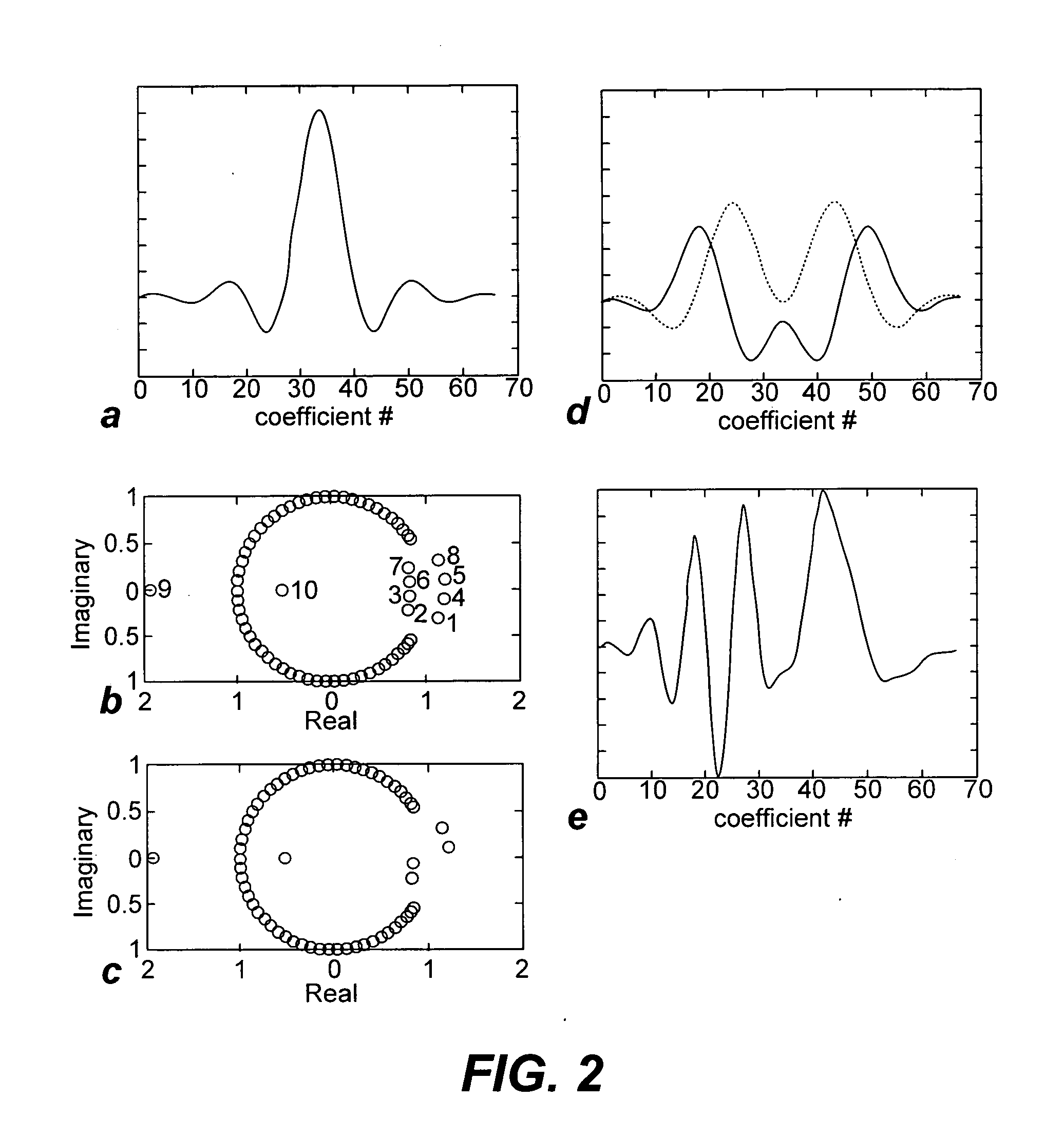
A method for designing non-linear phase 180° spectral-spatial radio frequency pulses that can be used for spectral editing in magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. A novel feature of the pulse is a symmetric sweep developed by the spectral profile from the outside edges of the spectral window towards the middle whereby coupled components are tipped simultaneously and over a short interval. Pulses have been designed for lactate editing at 1.5T and 3T. The spectral and spatial spin-echo profiles of the RF pulses can be measured experimentally and altered in an iterative manner. Spectral-spatial radio frequency (SSRF) pulses allow simultaneous selection in both frequency and spatial domains. These pulses are particularly important for clinical and research magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) applications for suppression of large water and lipid resonances.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy with sparse spectral sampling and interleaved dynamic shimming
InactiveUS7683614B2Maximize efficiencyMaximize sensitivityMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientSpectral dimension
The present invention relates to a magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) method, specifically to a magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging method with up to three spatial dimensions and one spectral dimension. Interleaving dynamically switched magnetic field gradients into the spectroscopic encoding scheme enables multi-region shimming in a single shot to compensate the spatially varying spectral line broadening resulting from local magnetic field gradients. The method also employs sparse spectral sampling with controlled spectral aliasing and nonlinear sampling density to maximize encoding speed, data sampling efficiency and sensitivity.
Owner:POSSE STEFAN
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy with sparse spectral sampling and interleaved dynamic shimming
InactiveUS20070252597A1Maximize encoding speedMaximize data sampling efficiencyMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientSpectral dimension
The present invention relates to a magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) method, specifically to a magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging method with up to three spatial dimensions and one spectral dimension. Interleaving dynamically switched magnetic field gradients into the spectroscopic encoding scheme enables multi-region shimming in a single shot to compensate the spatially varying spectral line broadening resulting from local magnetic field gradients. The method also employs sparse spectral sampling with controlled spectral aliasing and nonlinear sampling density to maximize encoding speed, data sampling efficiency and sensitivity.
Owner:POSSE STEFAN
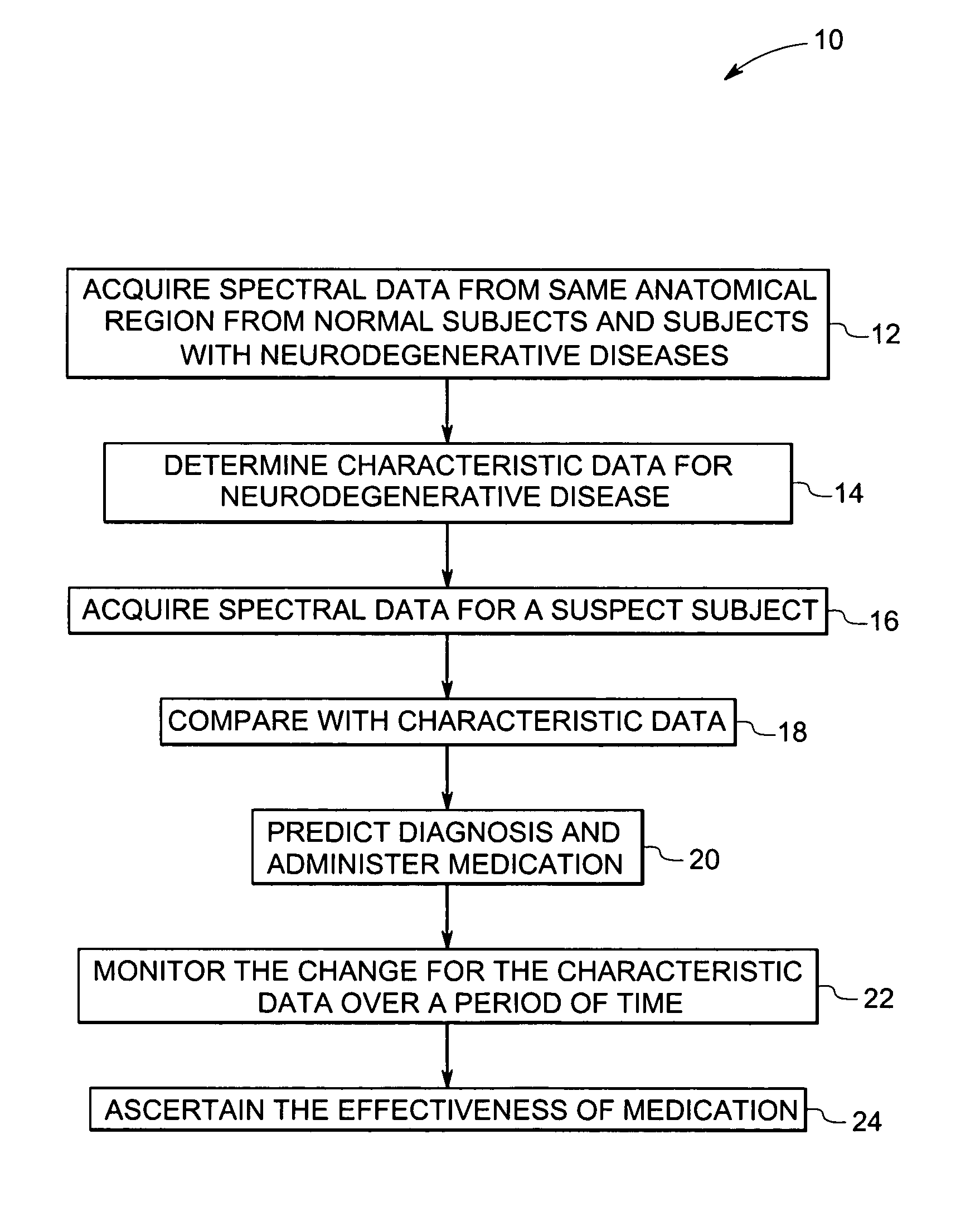
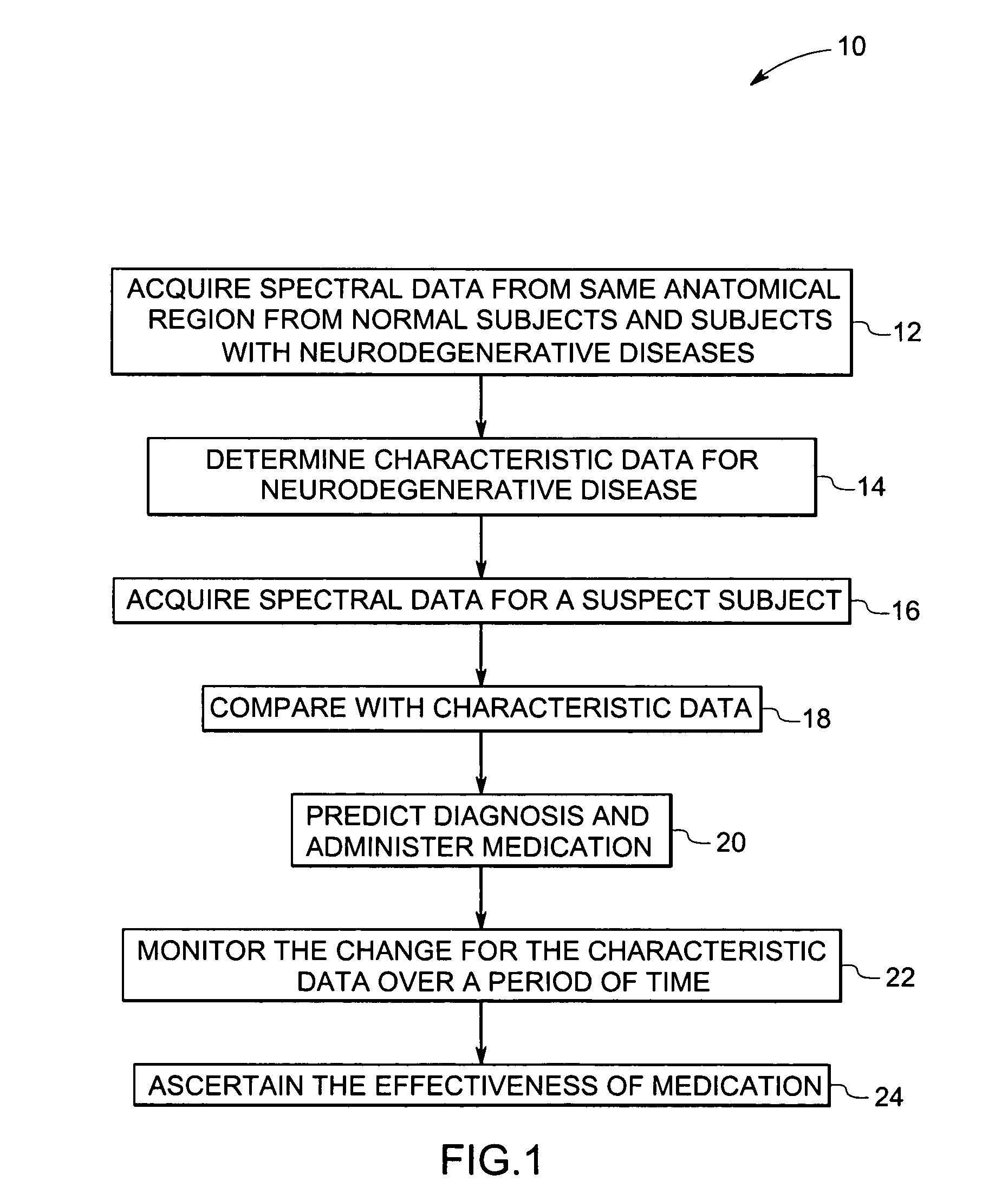
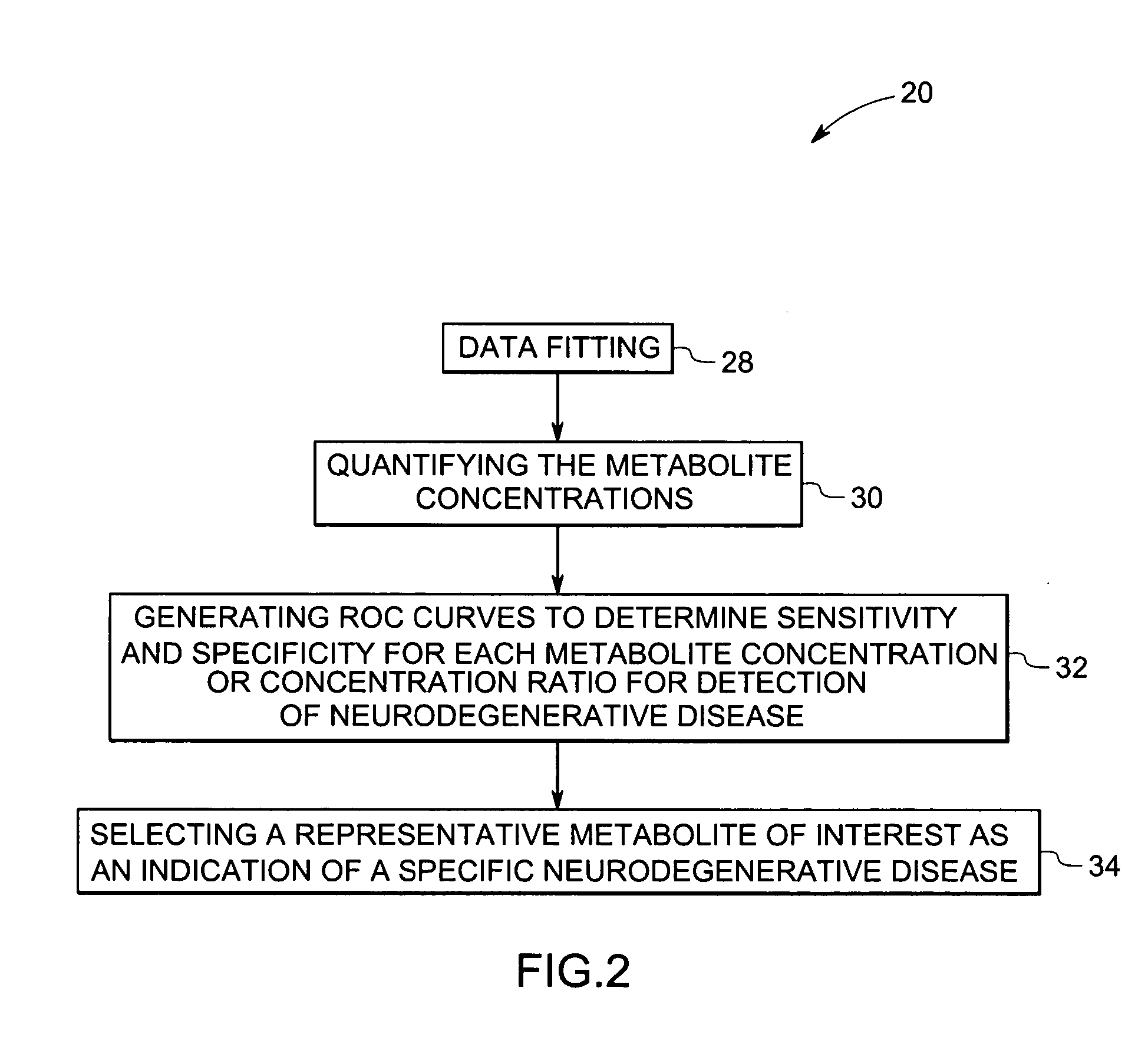
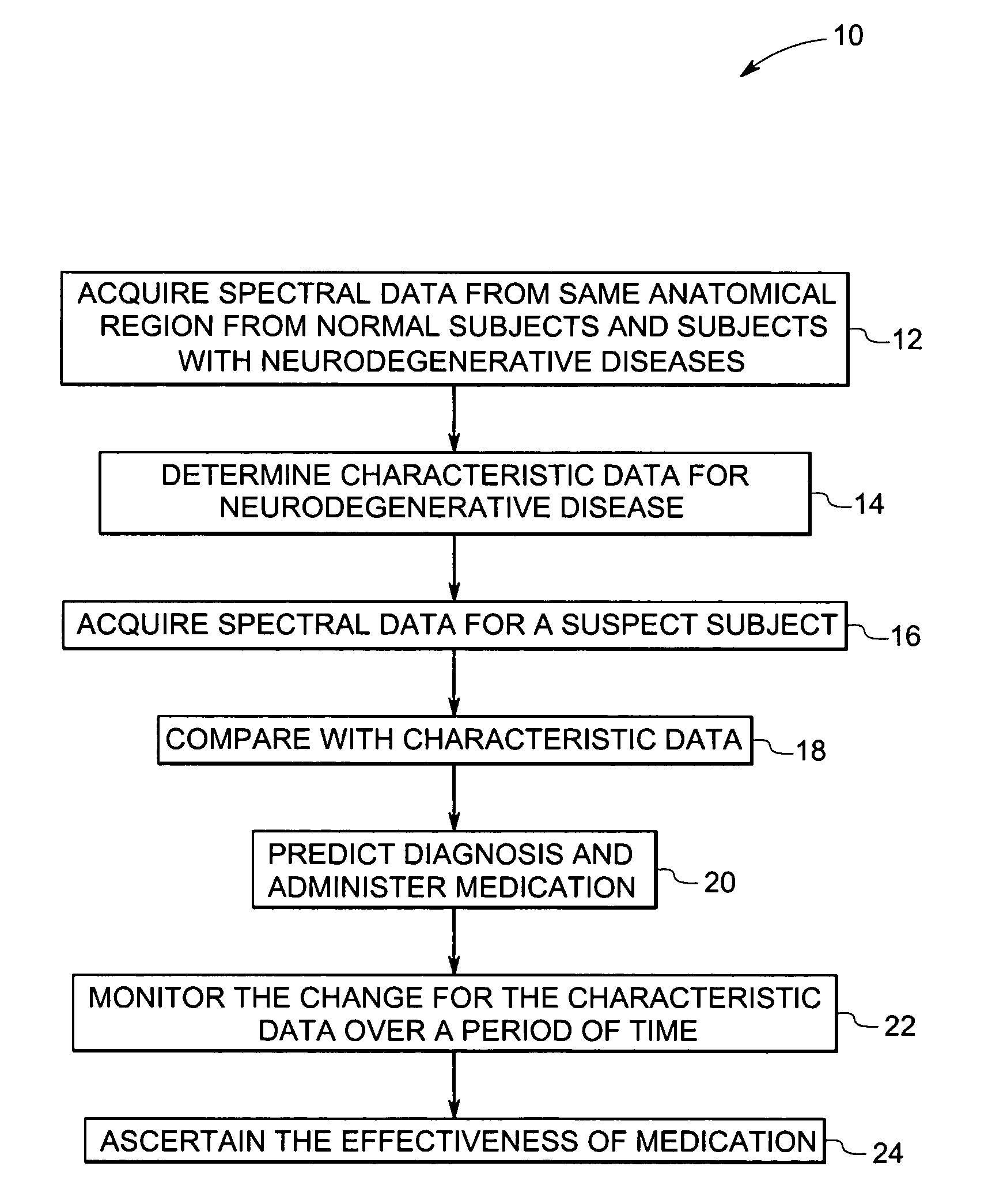
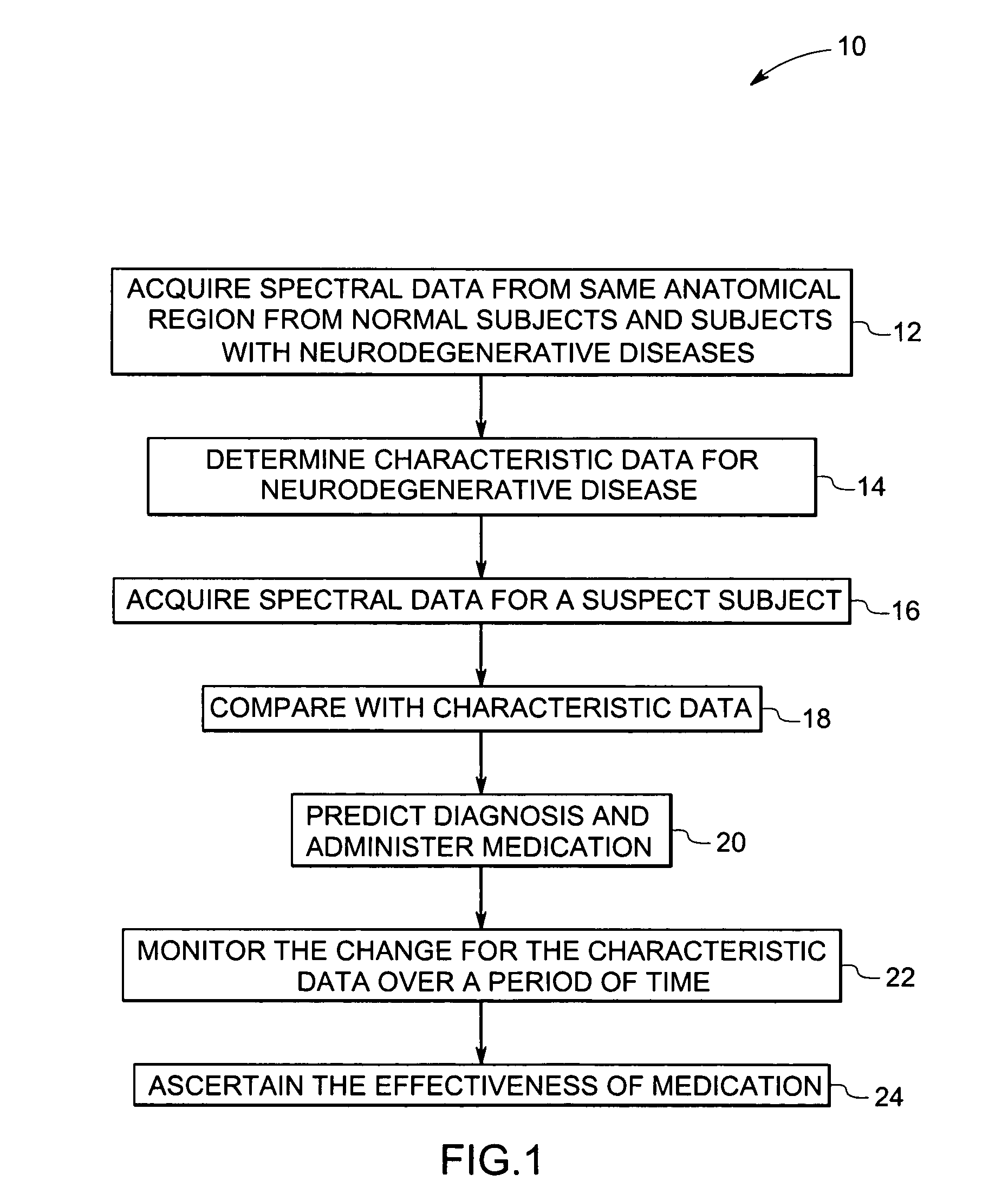
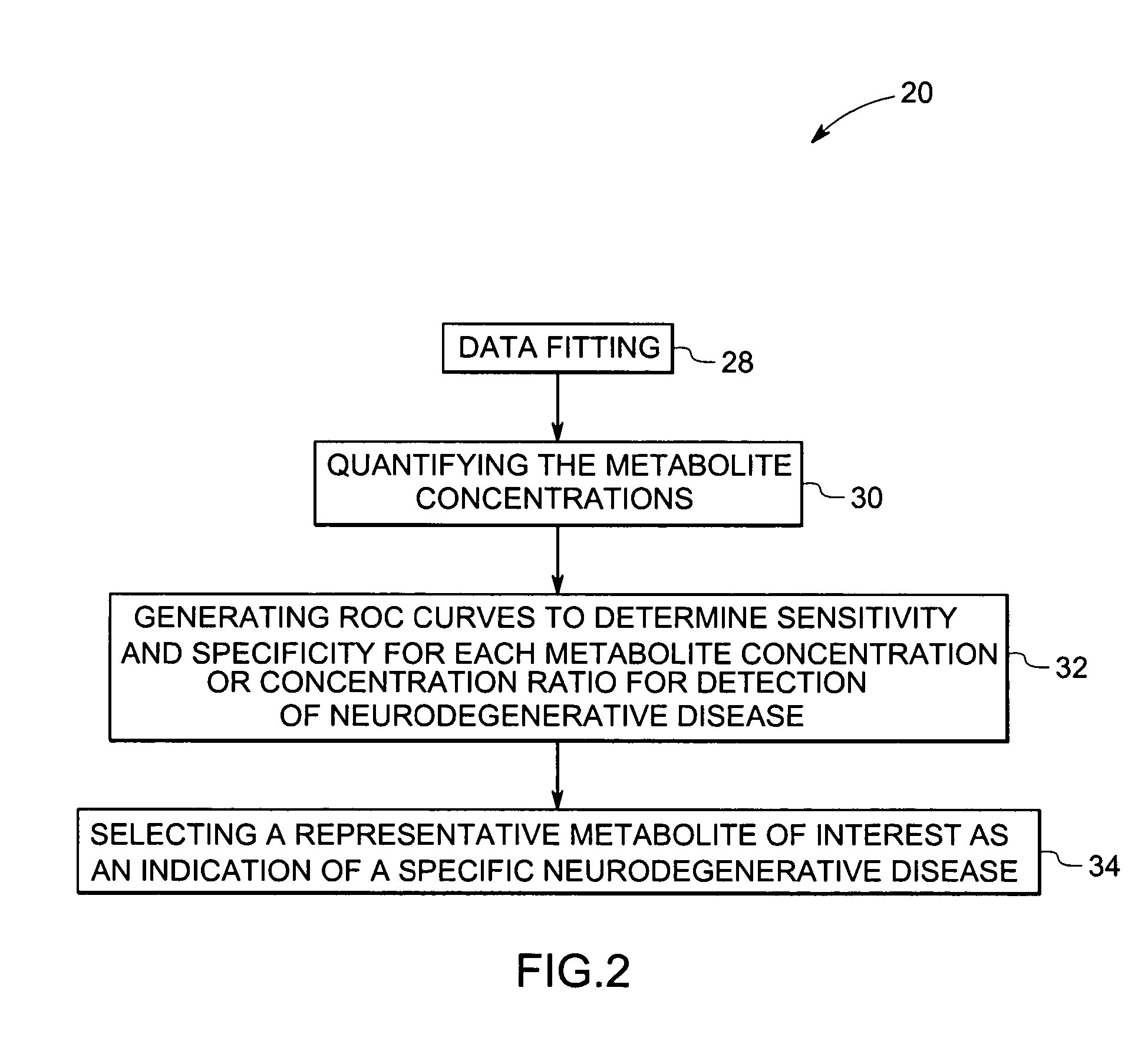
Methods and systems for detection and monitoring of neurodegenerative diseases using magnetic resonance spectroscopy
ActiveUS20050251025A1High sensitivityStrong specificityImage analysisDisease diagnosisMetaboliteConcentration ratio
A method for increasing sensitivity and / or specificity of a magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging technique for detecting a neurodegenerative disease is provided. The method includes acquiring magnetic resonance spectroscopy data from the brain of a subject, while suppressing certain metabolites in the spectrum via a data acquisition protocol, to improve quantification accuracy for the remaining metabolites, and quantifying a metabolite concentration or a metabolite concentration ratio from the spectral data as an indicator of the neurodegenerative disease.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy with real-time correction of motion and frequency drift, and real-time shimming
InactiveUS20070265520A1Suppress signalReduce sensitivityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSpectral patternObject motion
This invention relates to localized magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) and to magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) of the proton NMR signal, specifically to a magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) method to measure a single volume of interest and to a magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging method with at least one spectral dimension and up to three spatial dimensions. MRS and MRSI are sensitive to movement of the object to be imaged and to frequency drifts during the scan that may arise from scanner instability, field drift, respiration, and shim coil heating due to gradient switching. Inter-scan and intra-scan movement leads to line broadening and changes in spectral pattern secondary to changes in partial volume effects in localized MRS. In MRSI movement leads to ghosting artifacts across the entire spectroscopic image. For both MRS an MRSI movement changes the magnetic field inhomogeneity, which requires dynamic reshimming. Frequency drifts in MRS and MRSI degrade water suppression, prevent coherent signal averaging over the time course of the scan and interfere with gradient encoding, thus leading to a loss in localization. It is desirable to measure object movement and frequency drift and to correct object motion and frequency drift without interfering with the MRS and MRSI data acquisition.
Owner:POSSE STEFAN
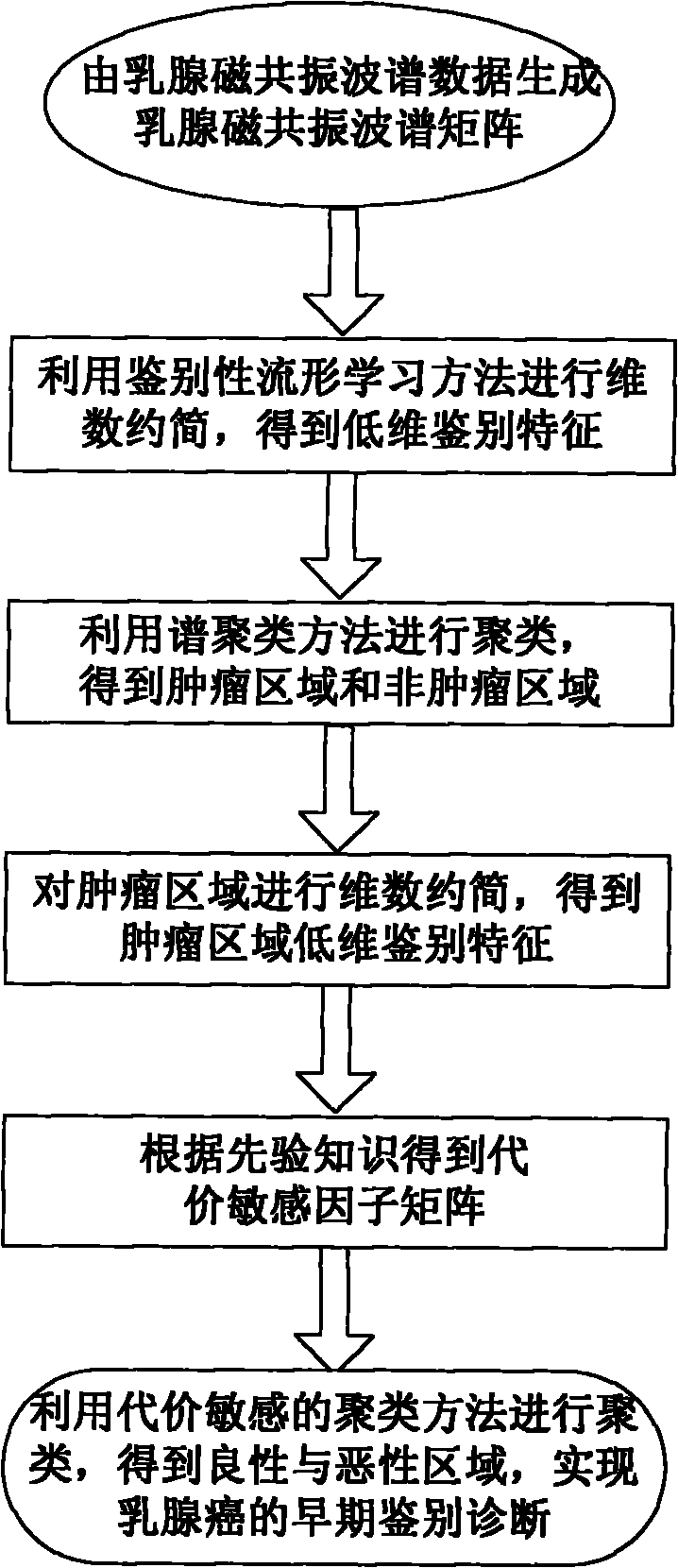
Breast tumor diagnosis system based on magnetic resonance spectrum imaging
InactiveCN101785672AAchieve early differential diagnosisKeep authentication informationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsBreast neoplasm diagnosisResonance spectrum
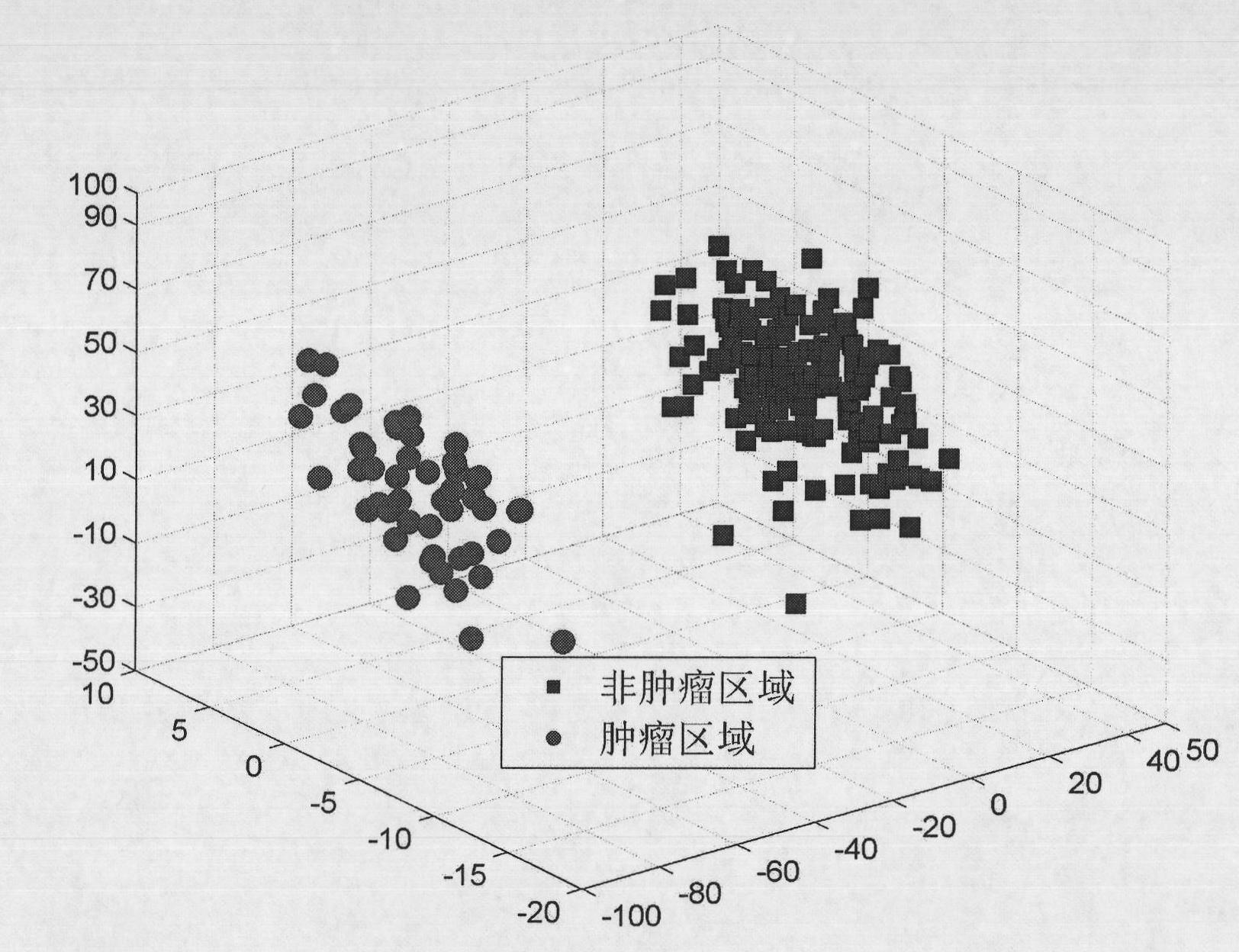
The invention provides a breast tumor diagnosis system based on magnetic resonance spectrum imaging, comprising a superconduction MR (Magneto Resistance) scanner and a computer system. Through a computer auxiliary detection measure, the breast tumor diagnosis system realizes the early identification diagnosis of a breast tumor and the further diagnosis of breast cancer. Mammary gland magnetic resonance spectrum data are studied by adopting a distinctive manifold study method and projected to a low dimension embedding space, thus not only a low dimension manifold structure hidden in a high dimension magnetic resonance spectrum space can be revealed, but also the identification information in the mammary gland magnetic resonance spectrum data can be efficiently kept; then optimization clustering is carried out on the low dimension identification characteristic by utilizing a clustering method so that data points without the similar identification characteristic are separated to the maximum; and further a cost sensitive mechanism is introduced to achieve misclassification total cost minimization and realize optimization diagnosis of the breast cancer.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
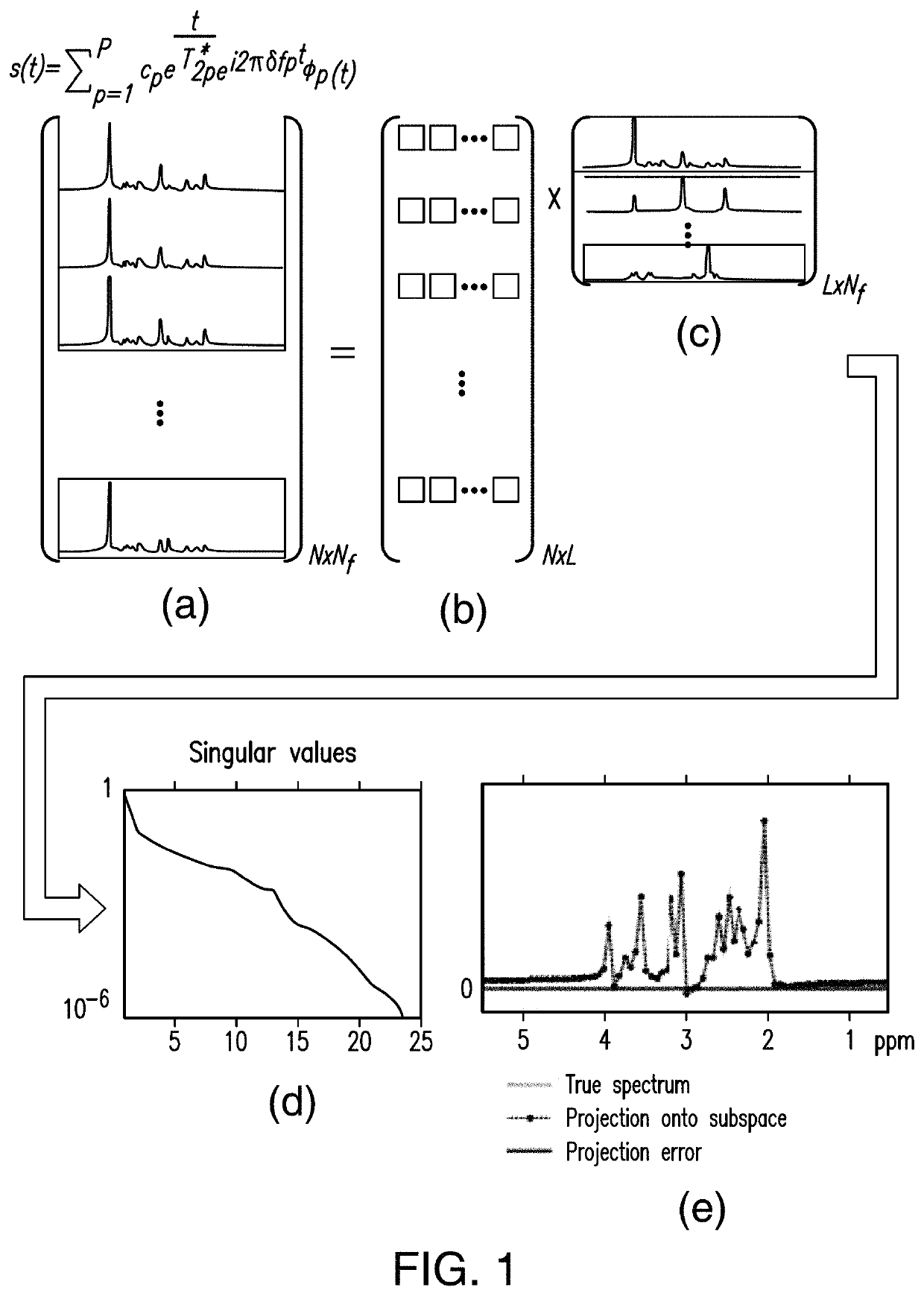
System and method for high-resolution spectroscopic imaging
ActiveUS20160202336A1Data acquisition time can be shortenedHigh resolutionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsBiological testingData setSubspace model
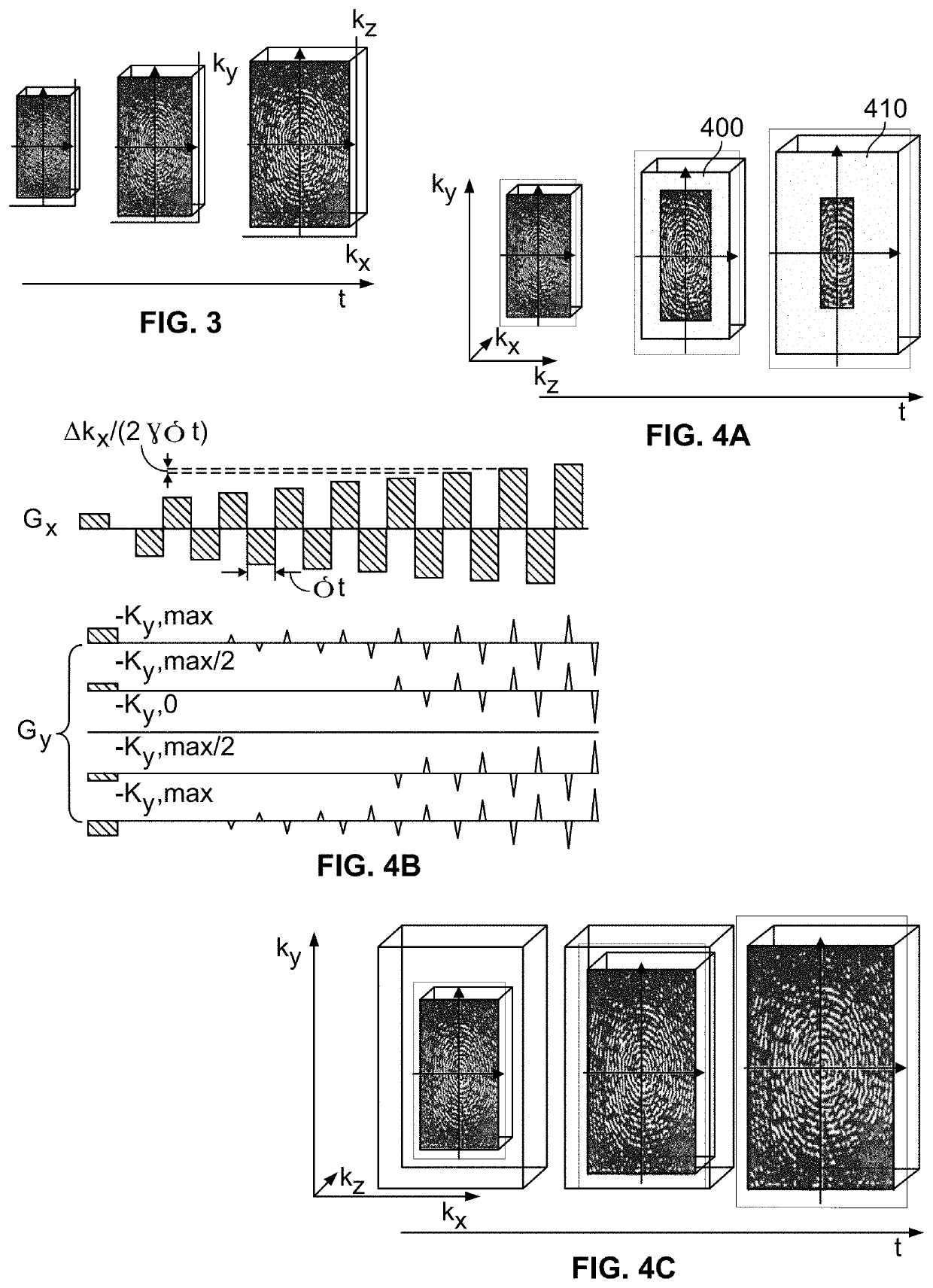
A new method is developed to accelerate high-resolution magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI). The method is built on a low-dimensional subspace model exploiting the partial separability of high-dimensional MRSI signals and uses this subspace model for data acquisition, processing, and image reconstruction. Specifically for two and three dimensional MRSI with one spectral dimension, this method sparsely samples the corresponding (k,t)-space in two complementary data sets, one with dense temporal sampling and high signal-to-noise ratio but limited k-space coverage and the other with sparse temporal sampling but extended k-space coverage. The reconstruction is then done by estimating a set of temporal / spectral basis functions and the corresponding spatial coefficients from these two data sets. The proposed subspace model can be further extended to incorporate multiple signal components for nuisance signal removal in 1H-MRSI and more generalized reconstruction methods. The resulting imaging technique can be used for high-resolution MRSI of different nuclei. It will be useful for high-resolution metabolic imaging with many exciting applications.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Method and device for magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
InactiveUS9234953B2Avoid disadvantagesIncrease contrastMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionChemical speciesGradient echo
A method of magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging of an object (O) including at least one chemical species to be imaged, comprising sampling of the k-space such that a plurality of Nω first sampling trajectories through at least one k-space segment of the k-space is formed along a phase-encoding direction, each of said first sampling trajectories beginning in a central k-space region and continuing to a k-space border of the at least one k-space segment and having a duration equal to or below a spectral dwell time corresponding to the reciprocal spectral bandwidth, collecting at least one first set of gradient-echo signals obtained along the first sampling trajectories, collecting at least one second set of gradient-echo signals obtained along a plurality of Nω second sampling trajectories, the Nω second sampling trajectories and the Nω first sampling trajectories being mutually mirrored relative to a predetermined k-space line in the central k-space region.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
System and method of performing magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
ActiveUS20140015529A1Measurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic resonance spectroscopicSpatial average
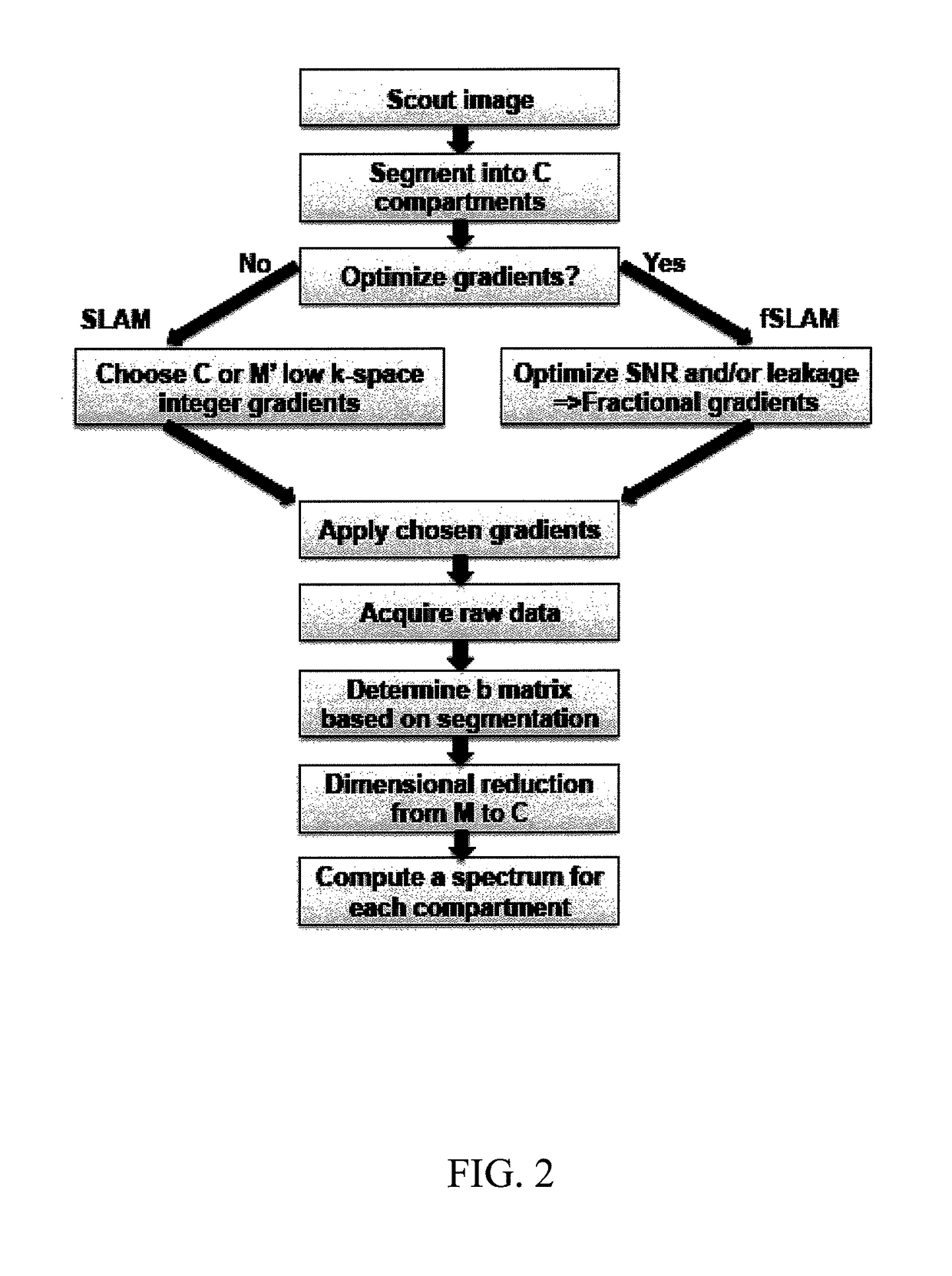
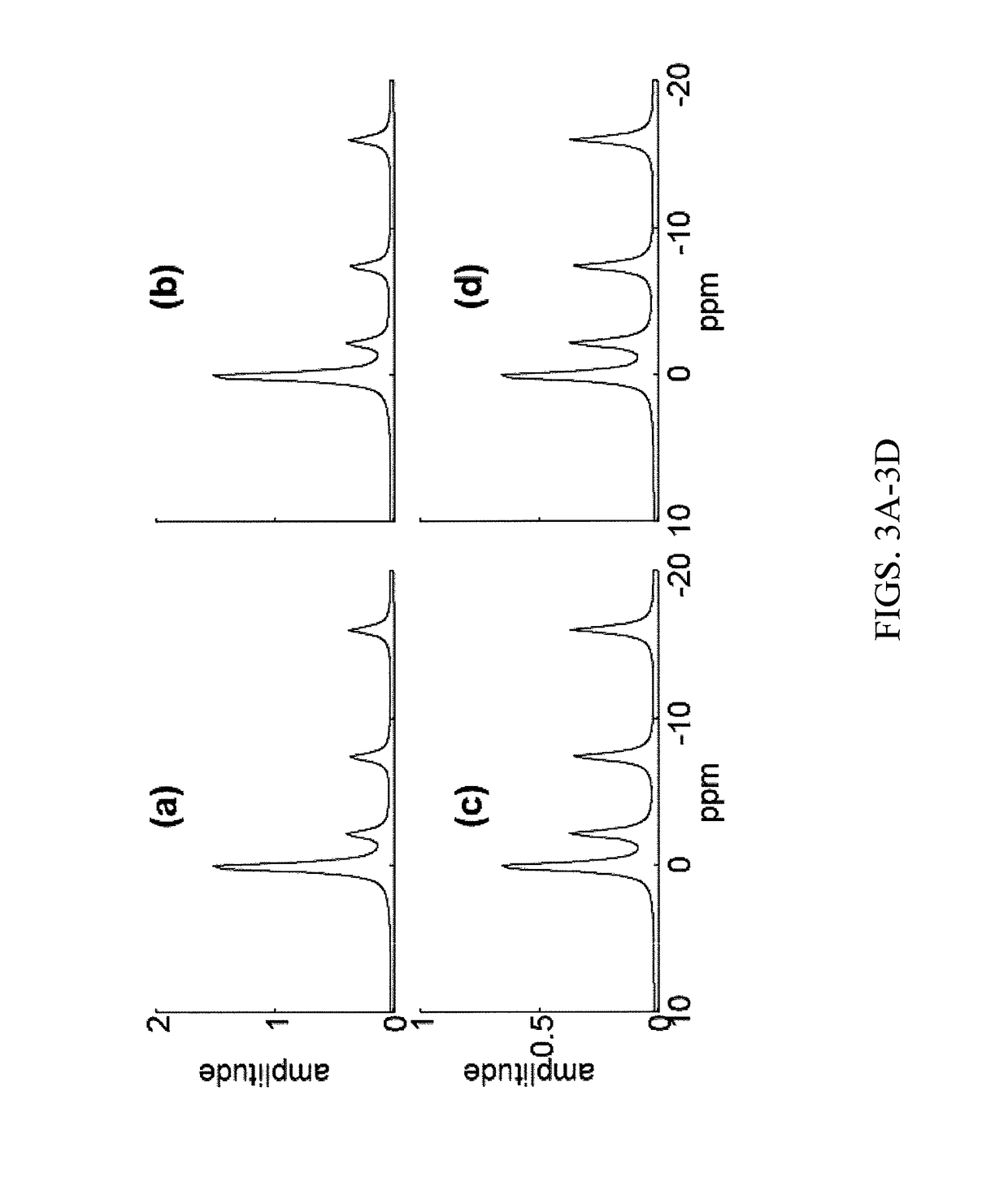
A method of performing spatially localized magnetic resonance spectroscopy includes receiving a magnetic resonance image of an object; identifying a plurality C of compartments that generate magnetic resonance spectroscopy signals in the object including at least one compartment of interest; segmenting in at least one spatial dimension the magnetic resonance image of the object into the C compartments; acquiring magnetic resonance spectroscopy signals from the compartments by applying a plurality of M′ phase encodings applied in the at least one spatial dimension, wherein M′≧C; calculating a spatially localized magnetic resonance chemical shift spectrum from the at least one compartment of interest; and rendering a spatially localized magnetic resonance spectrum that is substantially equal to a spatial average of magnetic resonance chemical shift spectra from the at least one compartment of interest. A magnetic resonance spectroscopy and imaging system is configured to perform the above method.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
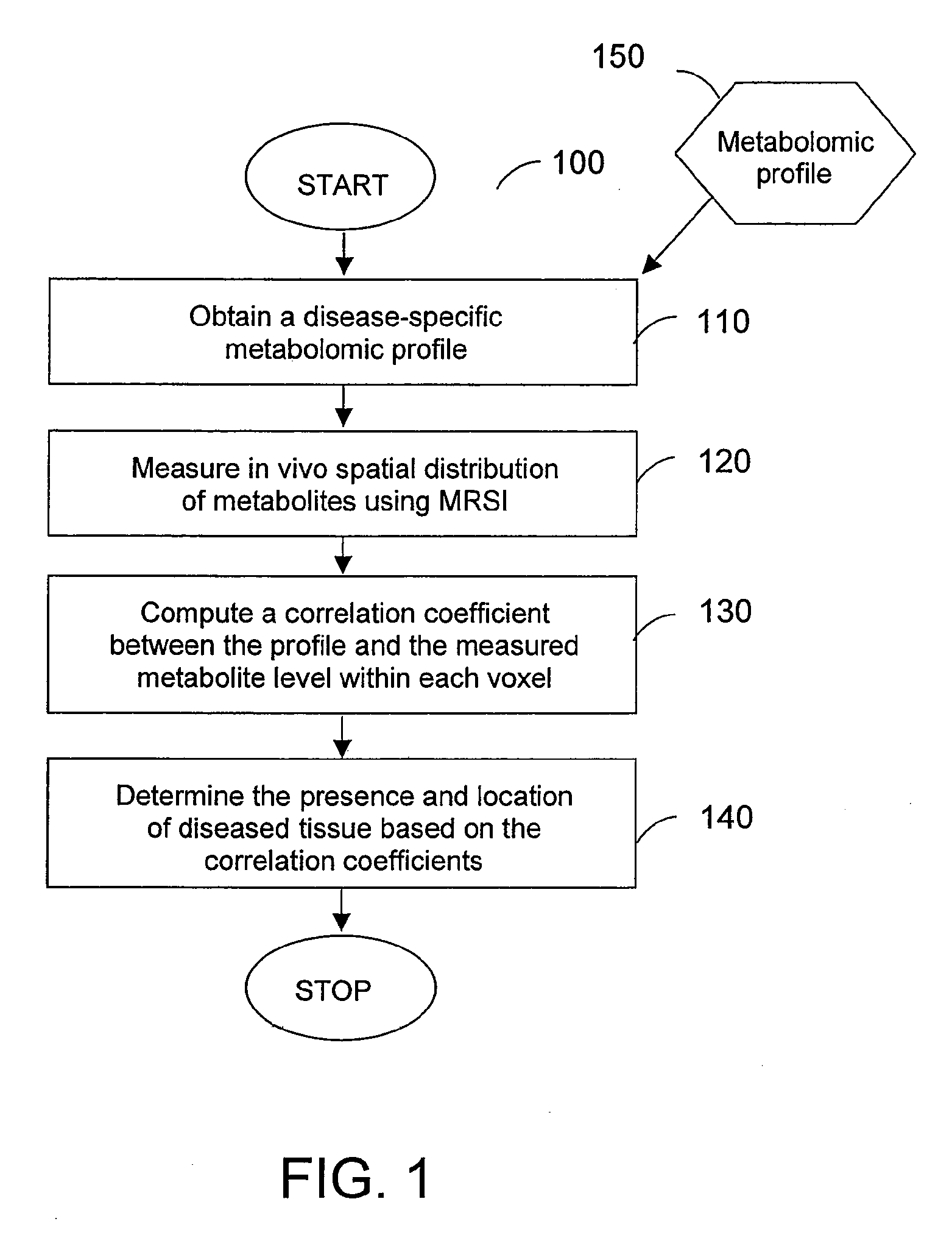
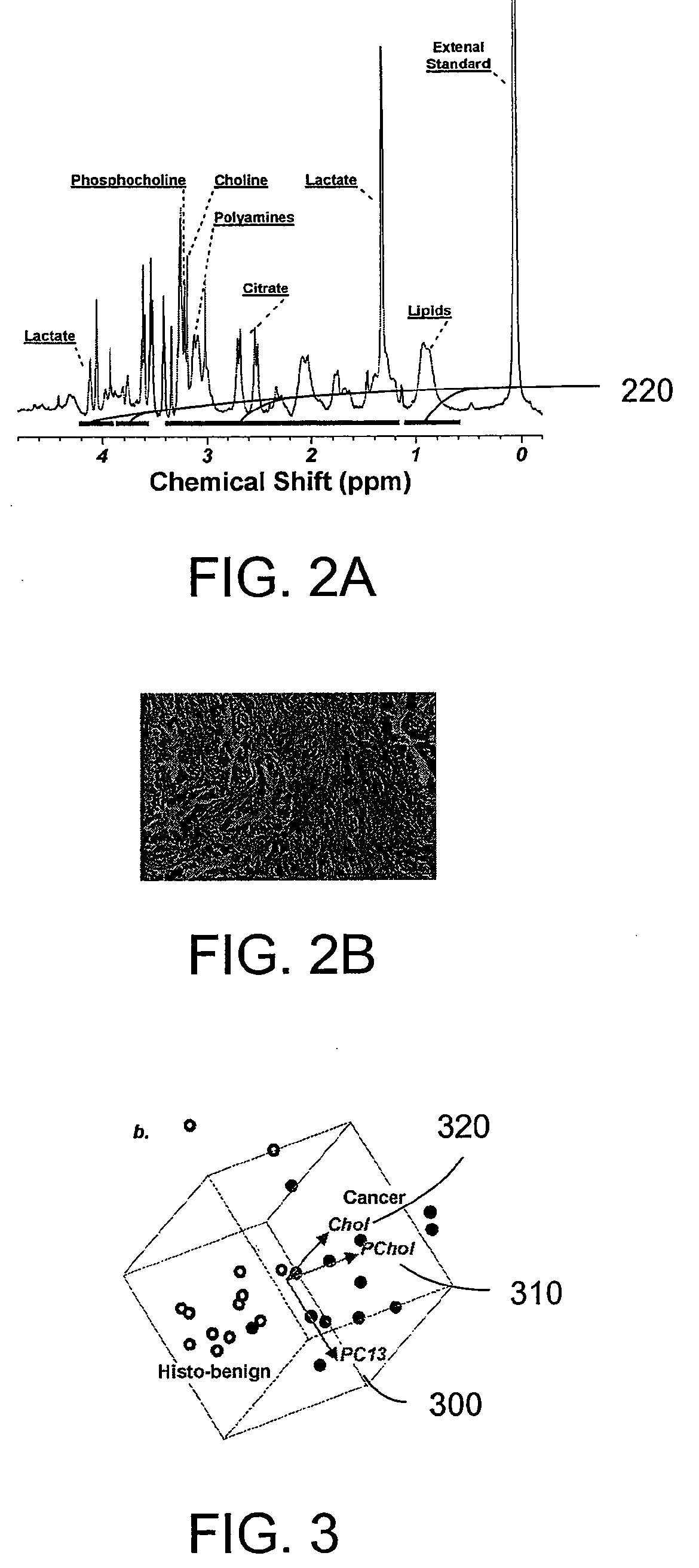
System, method and software arrangement for analyzing and correlating molecular profiles associated with anatomical structures
InactiveUS20090030618A1Accurate detection and diagnosisMagnetic measurementsBiological testingAnatomical structuresMetabolite
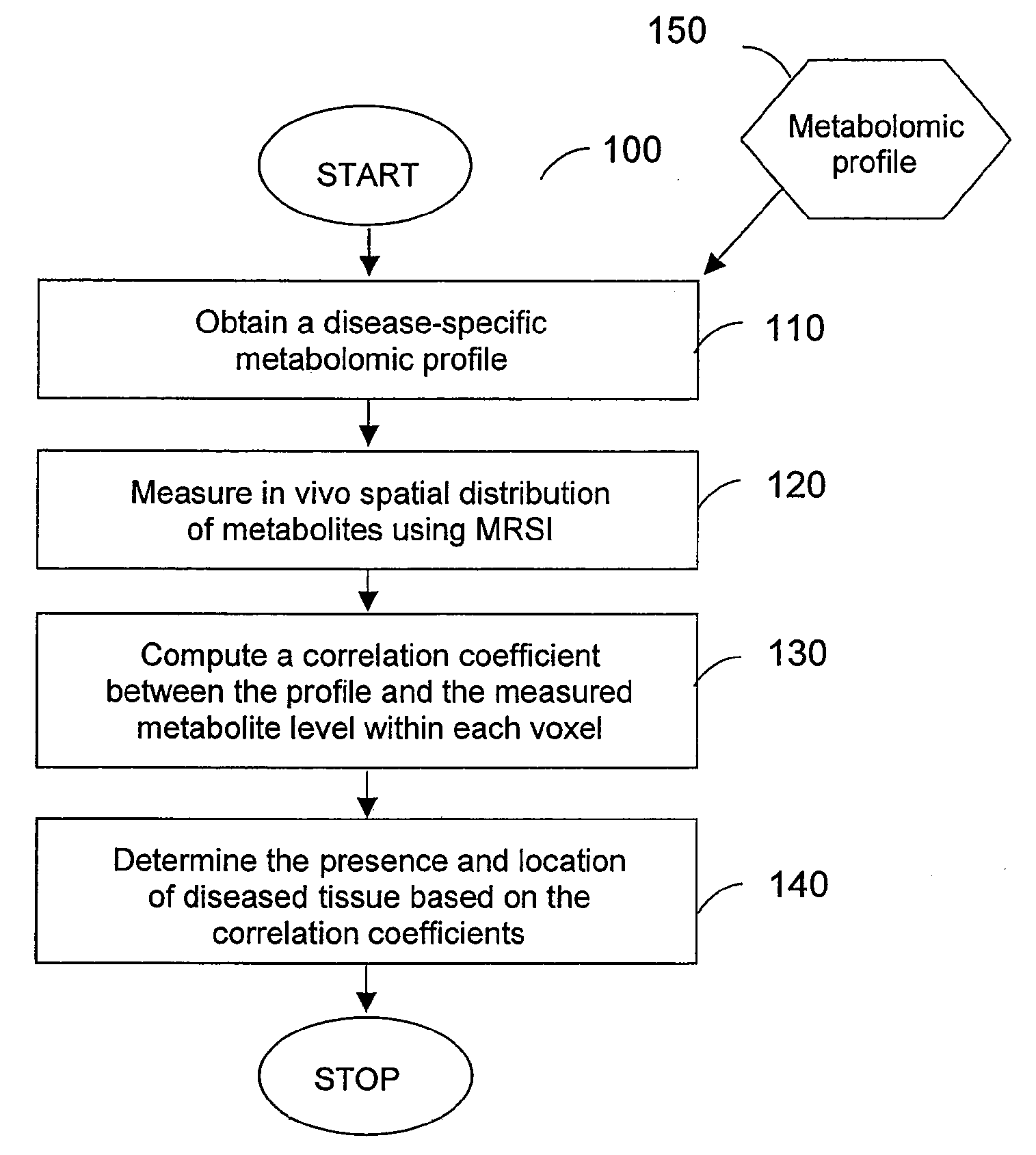
A system, method and software arrangement according to exemplary embodiments of the present invention are provided which can use molecular profiles obtained from unaltered human tissue specimens for clinical purposes including disease diagnoses and treatment evaluations. For example, spatial distributions of chemical species including metabolites within the tissue may be obtained using radiological techniques such as magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging. Disease-specific profiles may be obtained by comparing the distributions of chemical species obtained in ex vivo tissues with pathological observations made on them using statistical analysis. The disease-specific profiles may then be correlated with in vivo or ex vivo molecular profiles to obtain spatial maps that can provide a more sensitive and accurate detection of diseased tissue. Thus, such exemplary systems, methods and software arrangements can include the ability to receive information relating to the distribution of at least three chemical species in the tissue of interest, compare this information statistically to a predetermined profile and, based on the statistical correlation between the information and the profile, determine certain characteristics of the tissue of interest such as, e.g., the presence or absence of diseased tissue.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
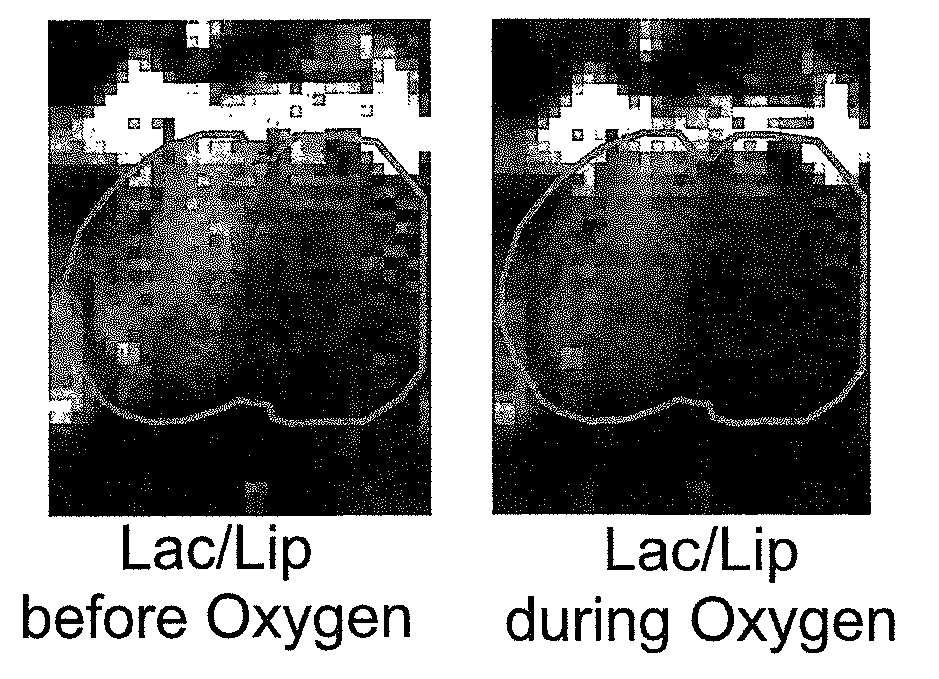
Method of determining metabolic function using magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
ActiveUS9322895B2Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic resonance spectroscopic imagingBiomedical engineering
The present invention provides a novel lactate difference imaging (LDI) technique, allowing assessment of the metabolic responses of tissue over a period of time. This approach utilizes lactate change over a time period as an indicator of viable tissue, and offers benefits in the management and treatment of the effects of many common diseases, in particular stroke.
Owner:AURUM BIOSCI LTD
Non-linear symmetric sweep spectral-spatial RF pulses for mr spectroscopy
ActiveUS20050225323A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionLipid formationFrequency spectrum
A method for designing non-linear phase 180° spectral-spatial radio frequency pulses that can be used for spectral editing in magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. A novel feature of the pulse is a symmetric sweep developed by the spectral profile from the outside edges of the spectral window towards the middle whereby coupled components are tipped simultaneously and over a short interval. Pulses have been designed for lactate editing at 1.5 T and 3 T. The spectral and spatial spin-echo profiles of the RF pulses can be measured experimentally and altered in an iterative manner. Spectral-spatial radio frequency (SSRF) pulses allow simultaneous selection in both frequency and spatial domains. These pulses are particularly important for clinical and research magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) applications for suppression of large water and lipid resonances.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Spectral resolution enhancement of magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
InactiveUS8143890B2Spectral broadeningMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionTime domainMagnetic resonance spectroscopic
A method and apparatus for enhancing the spectral resolution of magnetic resonance spectroscopic (MRS) measurements include receiving time domain echo data from an MRS measurement for an MRS volume in a subject. Also received are high spatial resolution complex signal values within the MRS volume based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) measurements. Frequency-domain content is determined for the echo data based at least in part on the complex signal values. For example, in some embodiments, receiving complex signal values includes receiving high spatial resolution complex signal values within the MRS volume for each of two different echo time settings. The frequency-domain content of the echo data is corrected for a lineshape profile based on high resolution frequency dispersion values for the MRS volume determined from differences in the complex signal values for the two different echo time settings.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
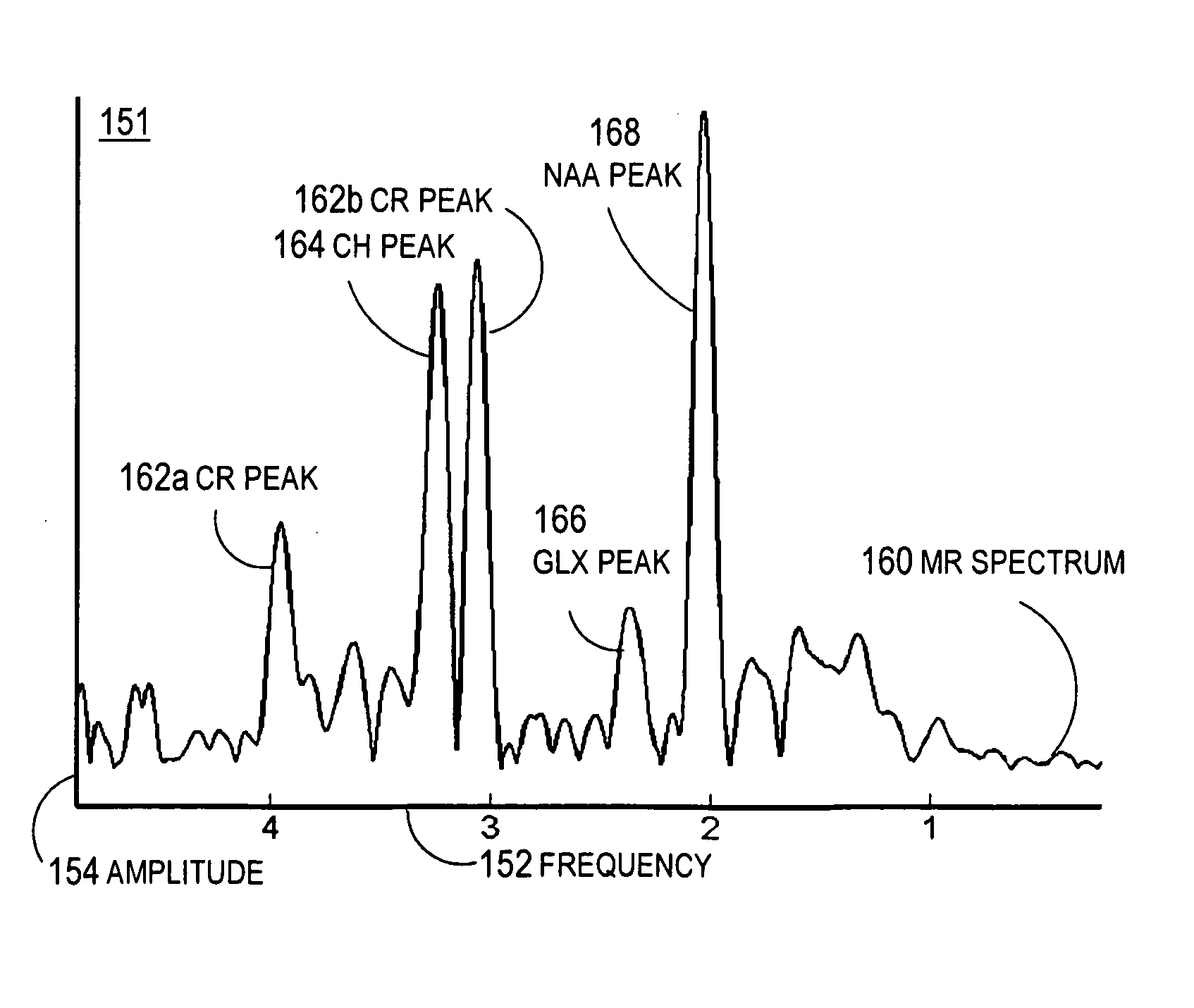
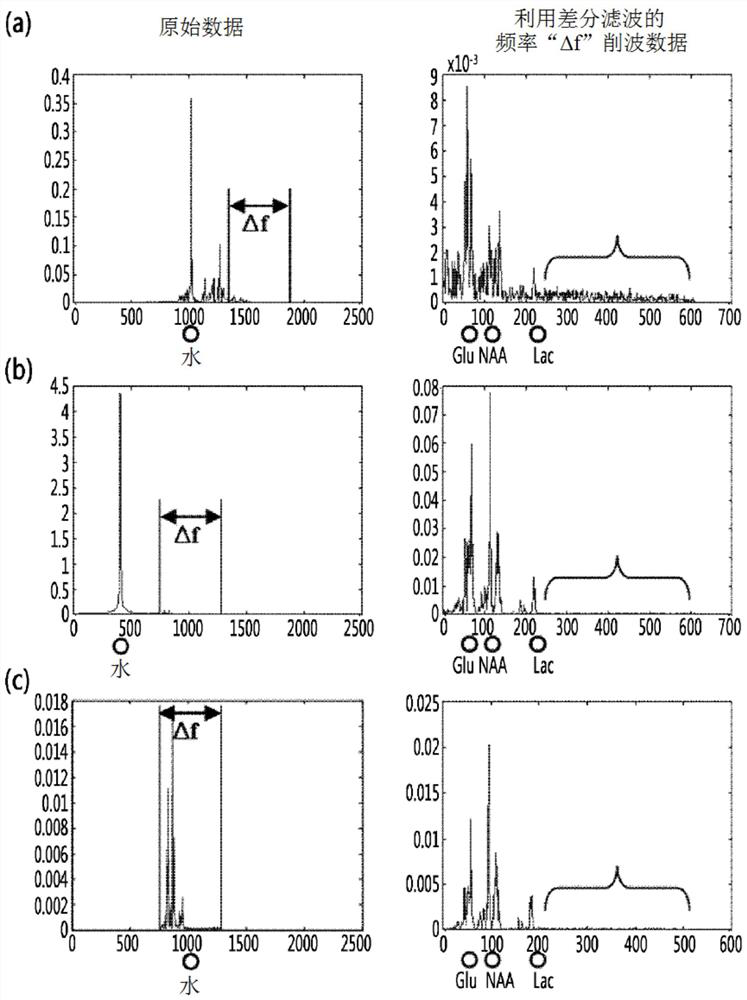
Frequency-domain-based method for lipid and water suppression treatment of magnetic resonance spectrum imaging data
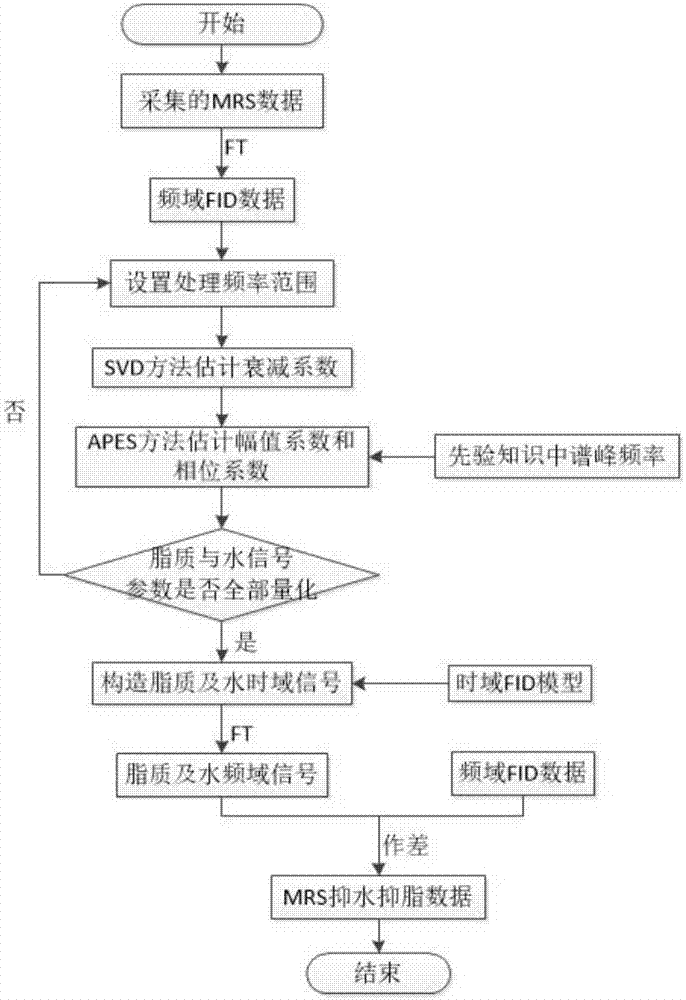
The invention belonging to the field of medical imaging provides a frequency-domain-based method for lipid and water suppression treatment of magnetic resonance spectrum imaging data. The method comprises: one-dimensional Fourier transform is carried out on collected single voxel magnetic resonance spectrum time-domain data to obtain a frequency-domain FID signal; according to prior knowledge, four lipid peaks and one water signal frequency range are determined; a nonlinear parameter attenuation coefficient in a spectrum time-domain model by using a singular value decomposition method; on the basis of a spectrum peak frequency in the prior knowledge and the attenuation coefficient obtained by quantification, the amplitude and phase of a linear parameter are estimated by using an amplitude-phase adaptive FIR filtering method; the frequency range is changed and the previous two steps are executed circularly until quantification of the four group of lipid and water signal parameters is completed; the time-domain FID model and the lipid and water signal quantification parameters form lipid and water time-domain signals; and one-dimensional Fourier transform is carried out on the time-domain signals, difference processing is carried out on the frequency domain and an original spectral signal, thereby obtaining magnetic resonance spectrum imaging data after lipid and water suppression treatment.
Owner:杭州全景医学影像诊断有限公司
System, method and computer accessible medium for magnetic resonance spectrocopic imaging
ActiveUS20090085564A1Improve signal-to-noise ratioRaise the ratioMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyMaterial analysis by using resonanceVoxelEngineering
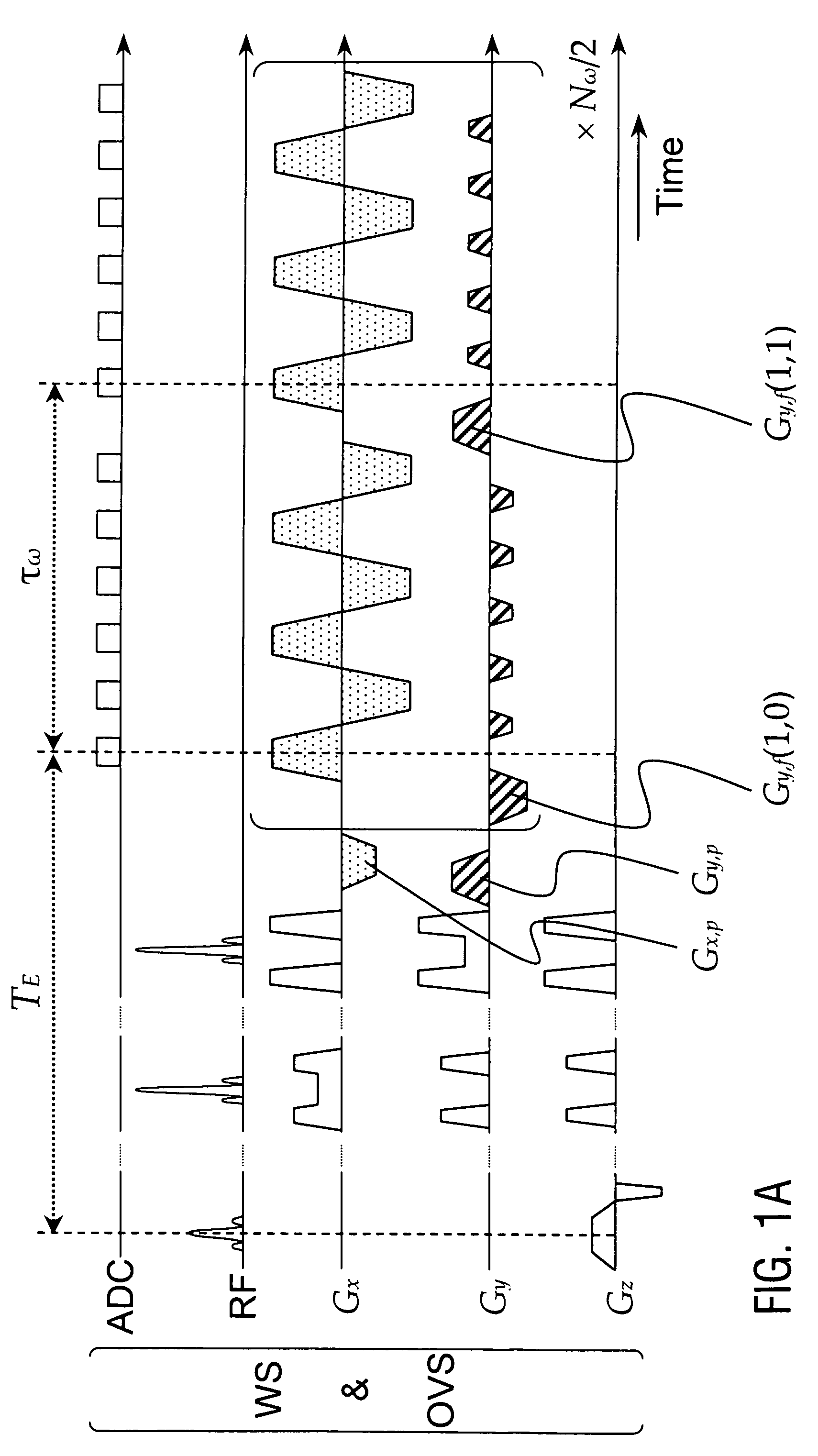
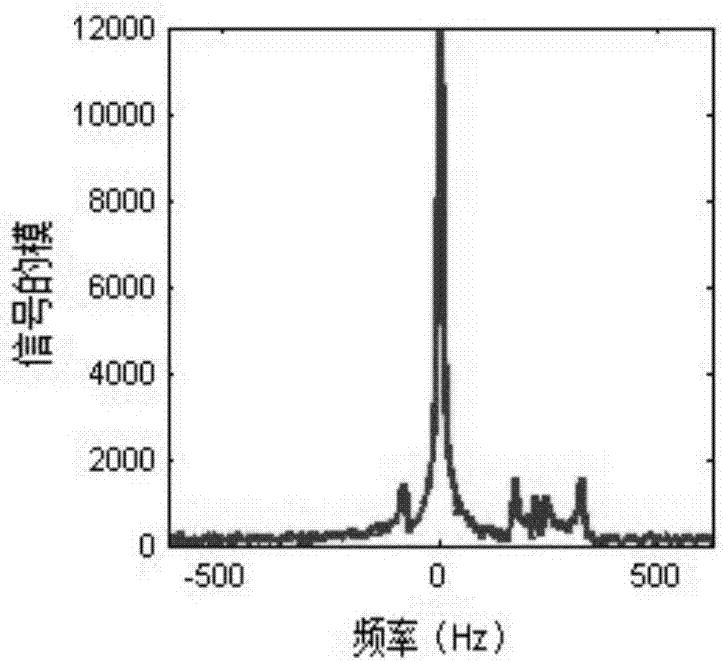
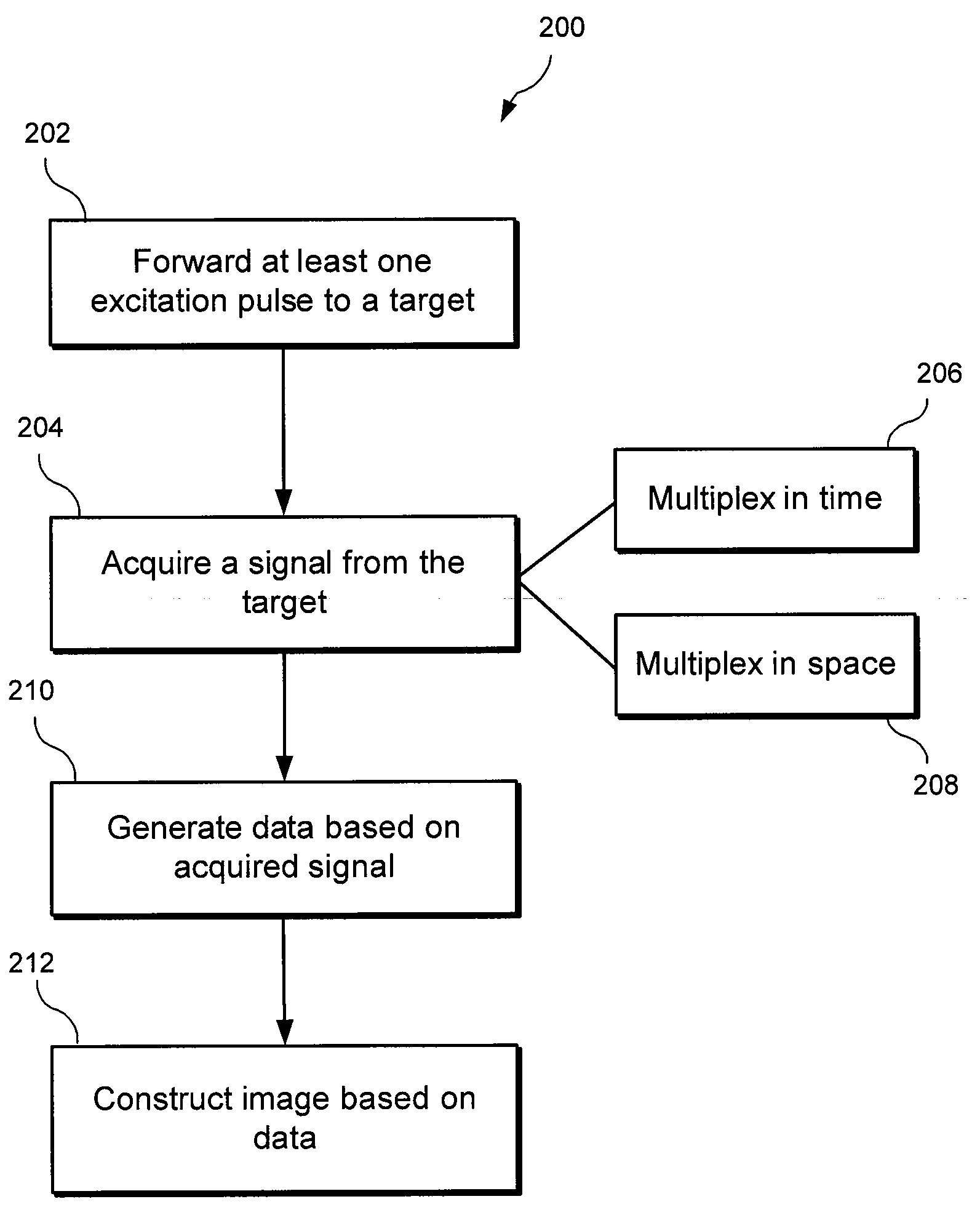
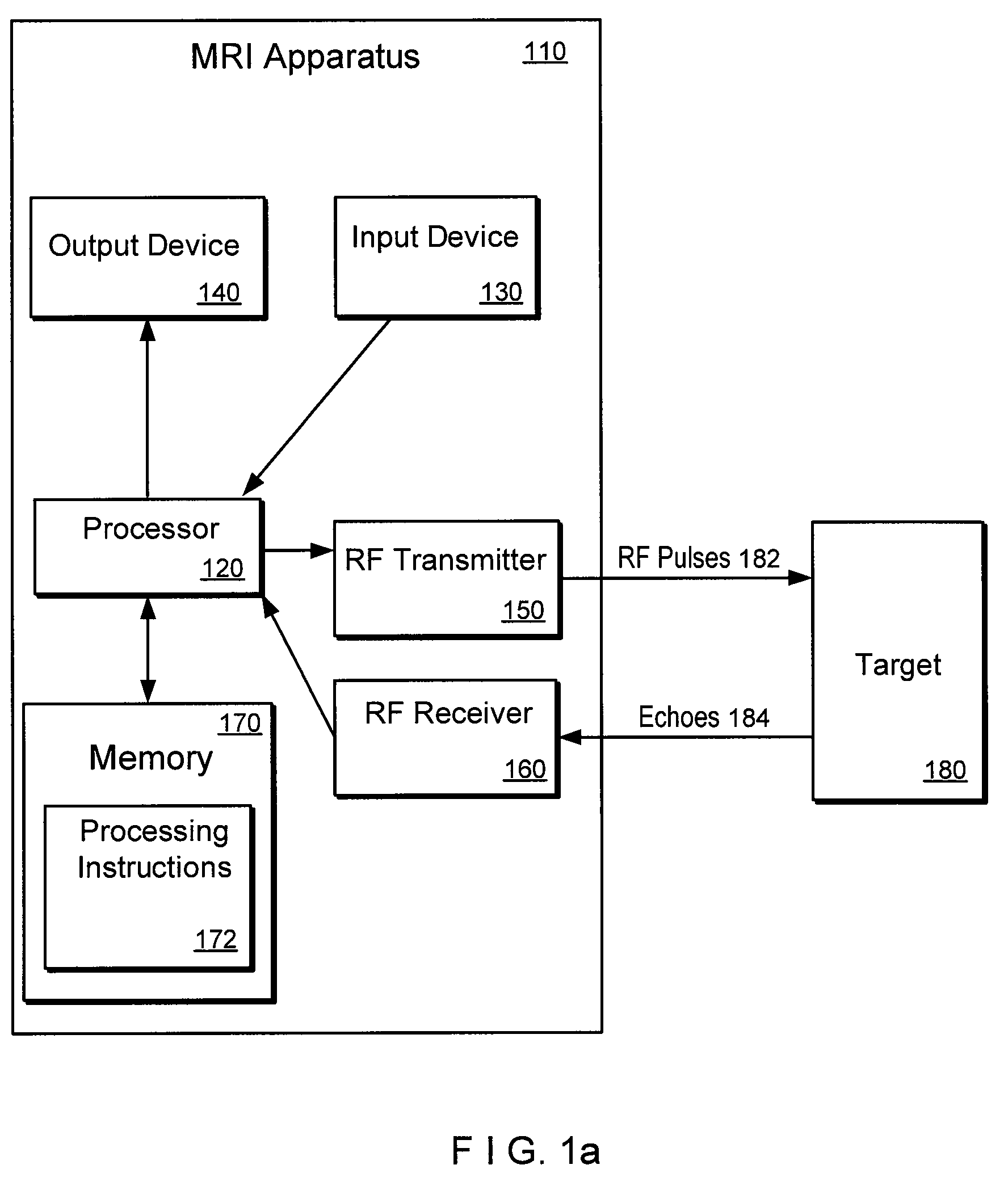
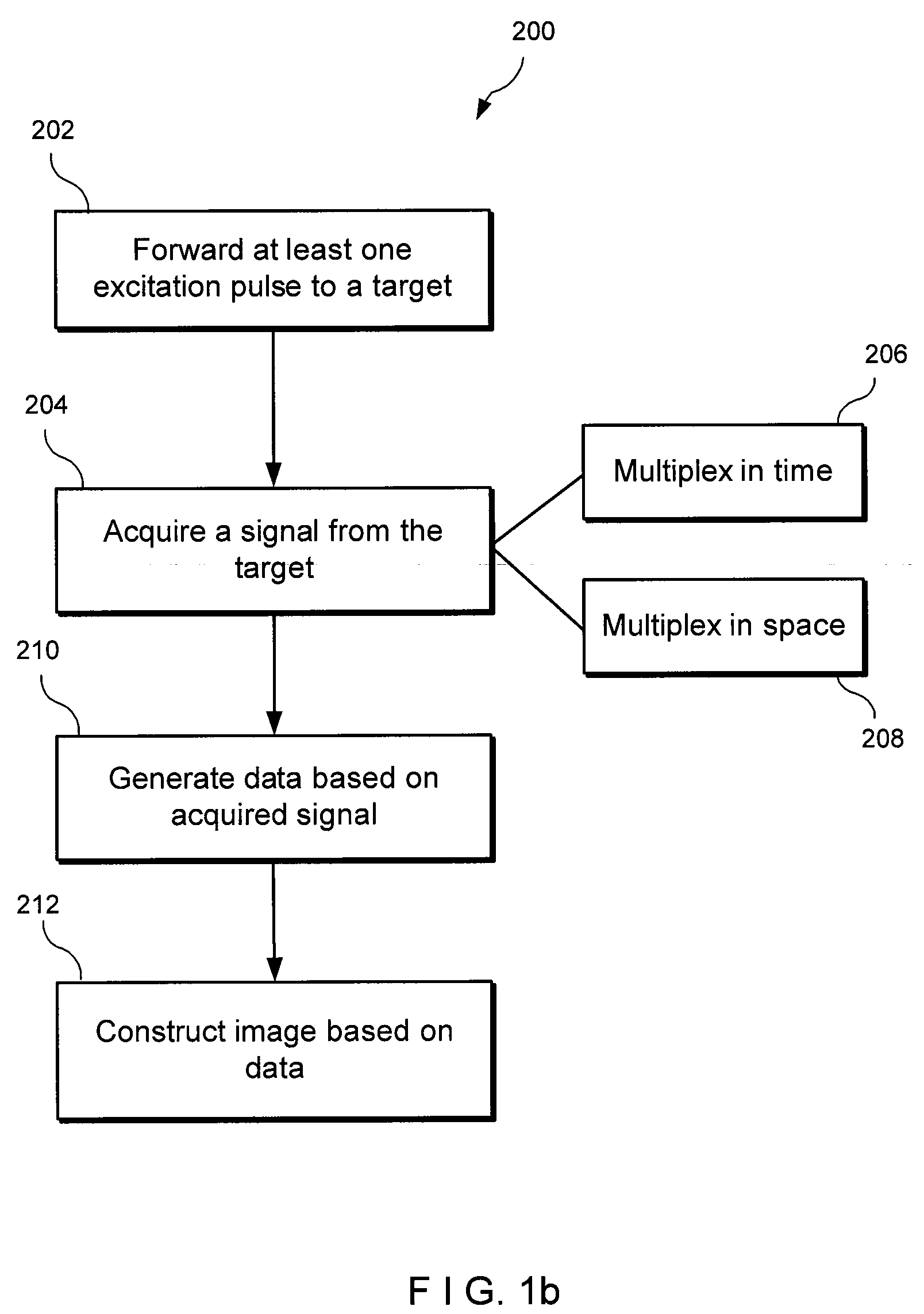
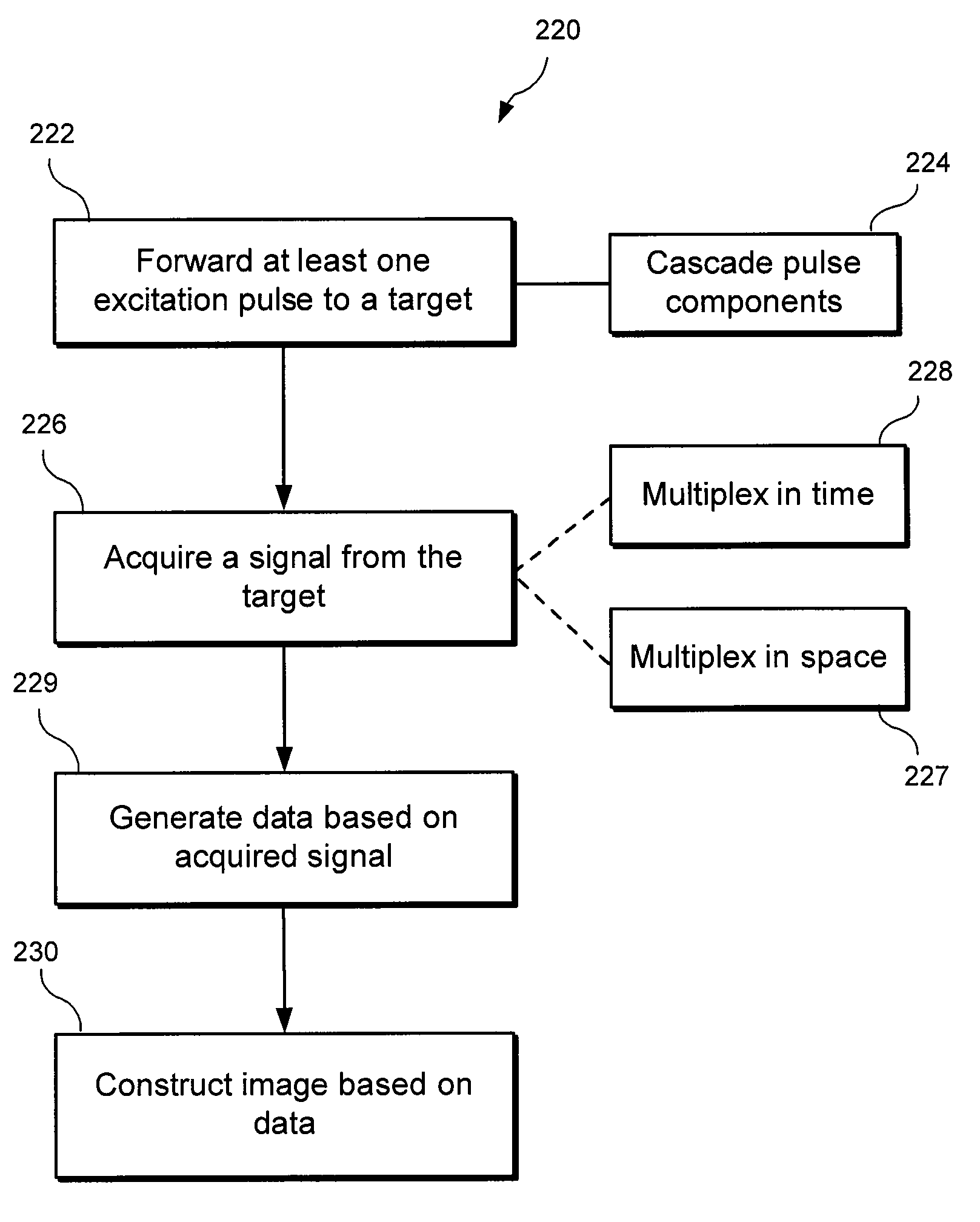
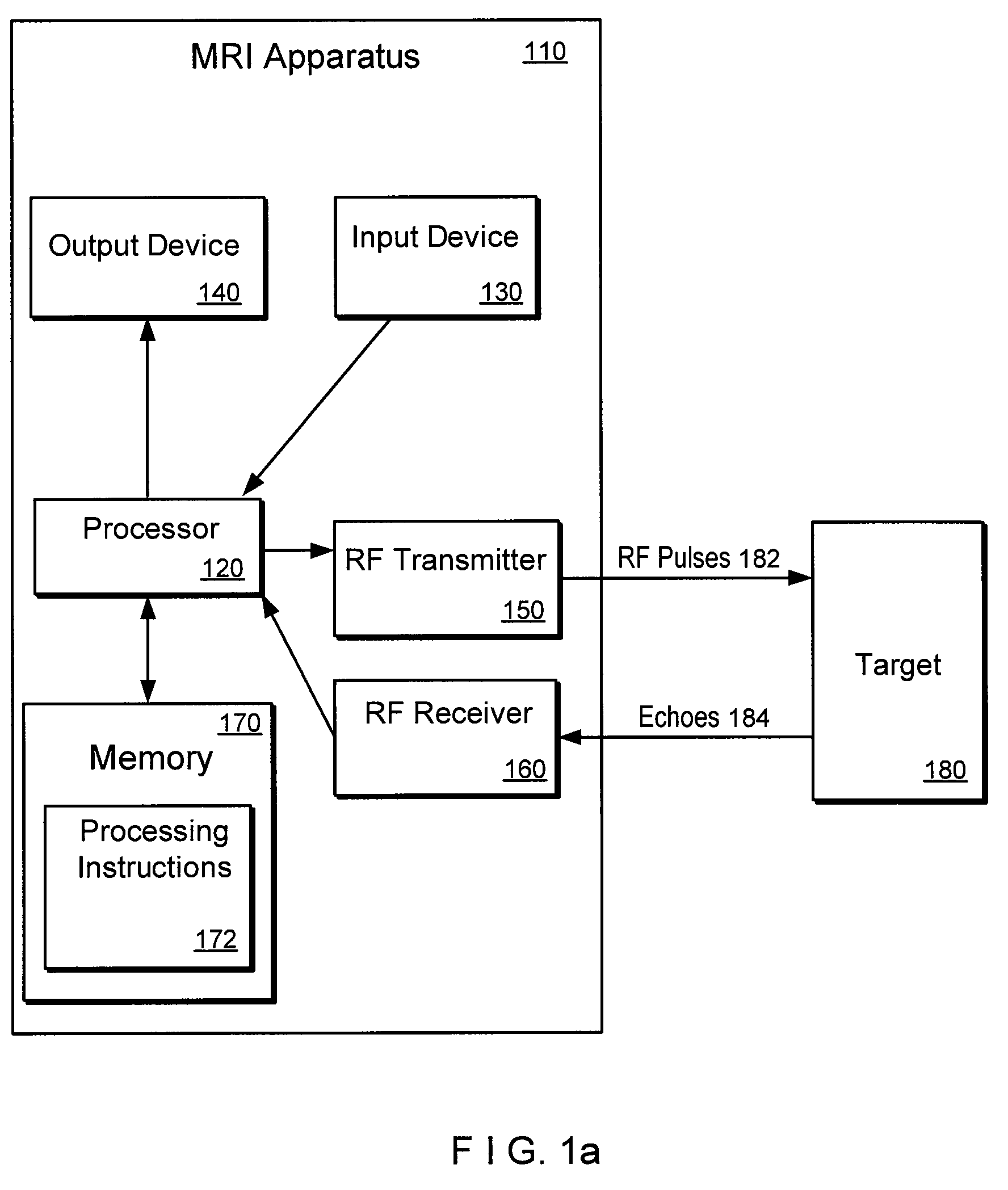
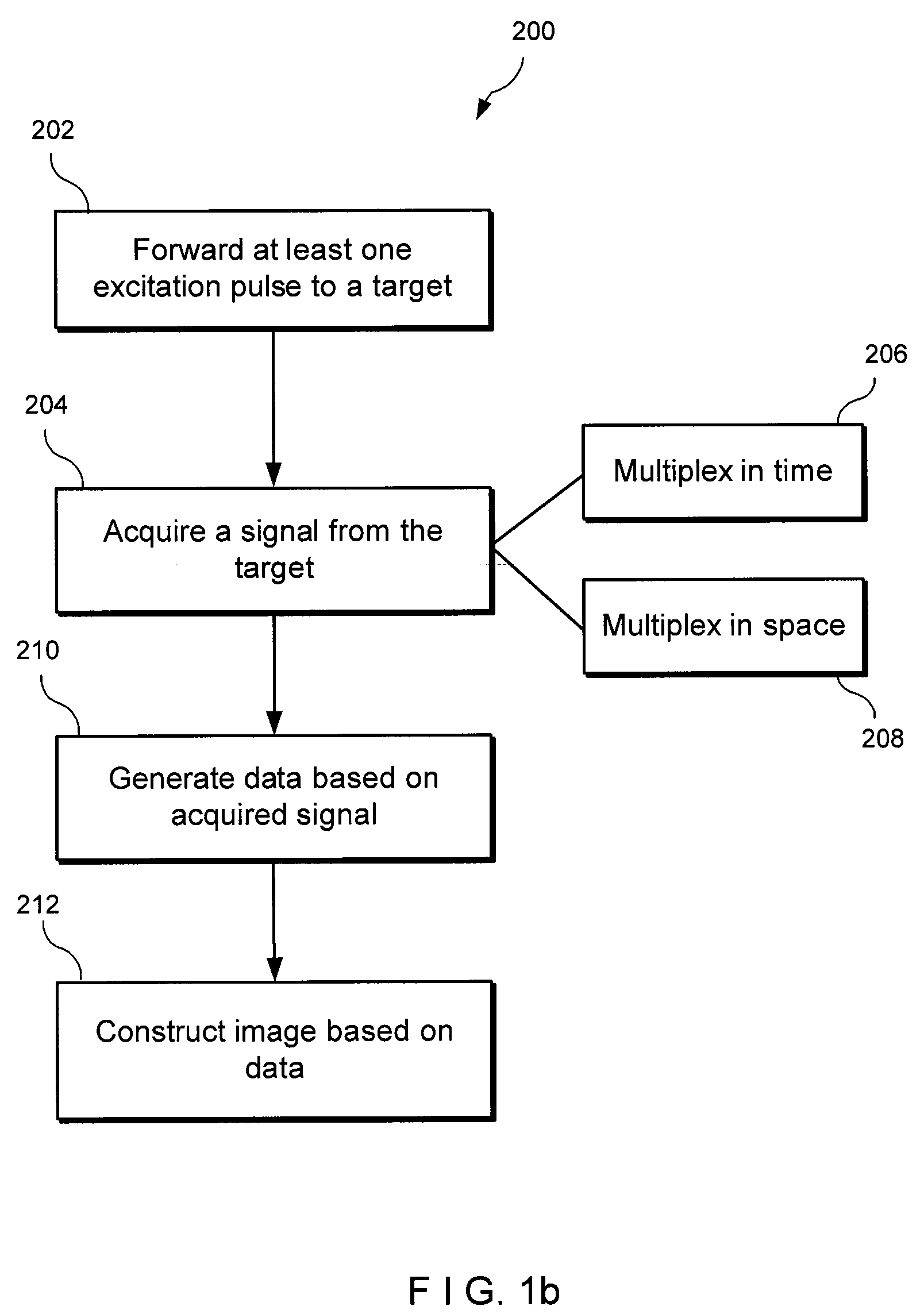
An exemplary embodiment of system, method, and computer accessible medium for magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging for improving signal-to-noise ratio per unit time and optimizing duty cycle in MRSI and / or for reducing chemical-shift artifacts can be provided. One exemplary embodiment includes forwarding an excitation pulse to the target and acquiring a signal from the target by multiplexing in time and space. Multiplexing in time may involve segmenting a field of view of the at least one portion of the target into a predetermined number of slabs that are acquired sequentially during each repetition time. Multiplexing in space may involve acquiring multiple voxels. Data may be generated based on the acquired signal. A further exemplary embodiment includes providing an excitation pulse to the target and acquiring a signal from the target. The excitation pulse can be a series of cascaded Hadamard pulse components. Data may be generated based on the acquires signal.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Interferometric techniques for magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS9811924B2Less timeEnhance the imageElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingReconstruction from projectionComputer scienceMagnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
System and method for high-resolution spectroscopic imaging
Various embodiments accelerate high-resolution magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI). Various embodiments are built on a low-dimensional subspace model exploiting the partial separability of high-dimensional MRSI signals. For two and three dimensional MRSI with one spectral dimension, various embodiments sparsely sample the corresponding (k,t)-space in two complementary data sets, one with dense temporal sampling and high signal-to-noise ratio but limited k-space coverage and the other with sparse temporal sampling but extended k-space coverage. The reconstruction is then done by estimating a set of temporal / spectral basis functions and the corresponding spatial coefficients from these two data sets. The imaging technique of various embodiments can be used for high-resolution MRSI of different nuclei.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
System, method and computer accessible medium for magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
ActiveUS7982462B2Improve signal-to-noise ratioRaise the ratioMagnetic measurementsMaterial analysis by using resonanceVoxelEngineering
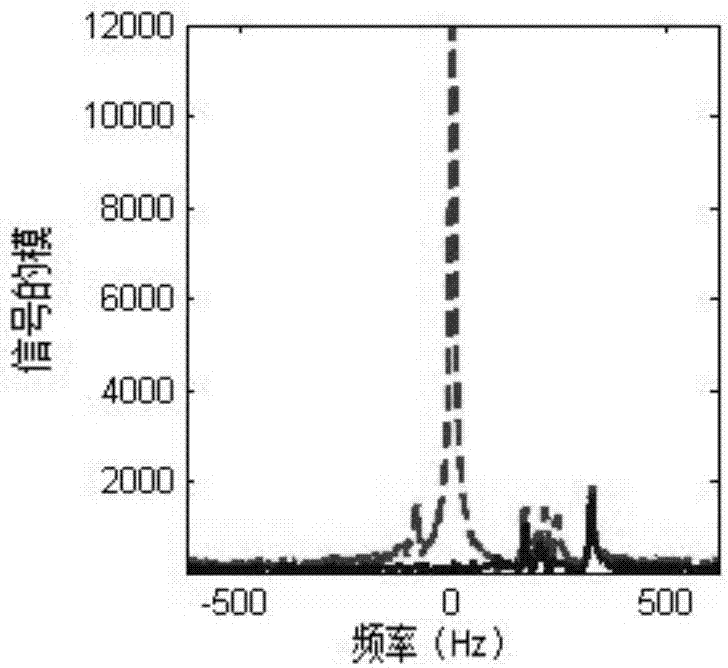
An exemplary embodiment of system, method, and computer accessible medium for magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging for improving signal-to-noise ratio per unit time and optimizing duty cycle in MRSI and / or for reducing chemical-shift artifacts can be provided. In one exemplary embodiment, an excitation pulse can be forwarded to the target and acquiring a signal from the target by multiplexing in time and space. The multiplexing procedure in time can involve (i) a segmentation of a field of view of the at least one portion of the target into a predetermined number of slabs that are acquired sequentially during each repetition time, and / or (ii) an acquisition of multiple voxels. Data can be generated based on the acquired signal. According to another exemplary embodiment, an excitation pulse can be provided to the target, and a signal can be acquired from the target. The excitation pulse can be a series of cascaded Hadamard pulse components. Data can be generated based on the acquired signal.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Interferometric Magnetic Resonance Imaging System and Related Method
ActiveUS20140044335A1Accuracy and efficiencyEnhance the imageElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingReconstruction from projectionComputer scienceMagnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
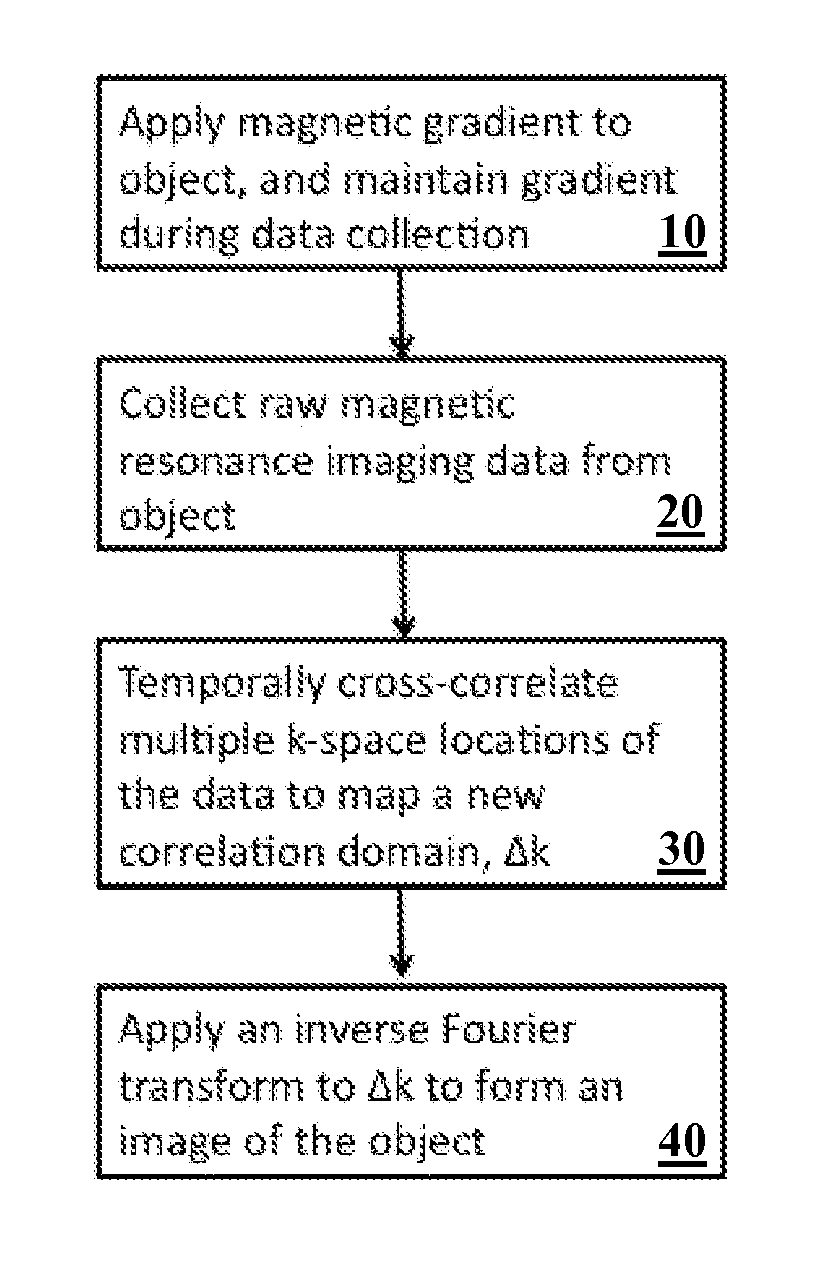
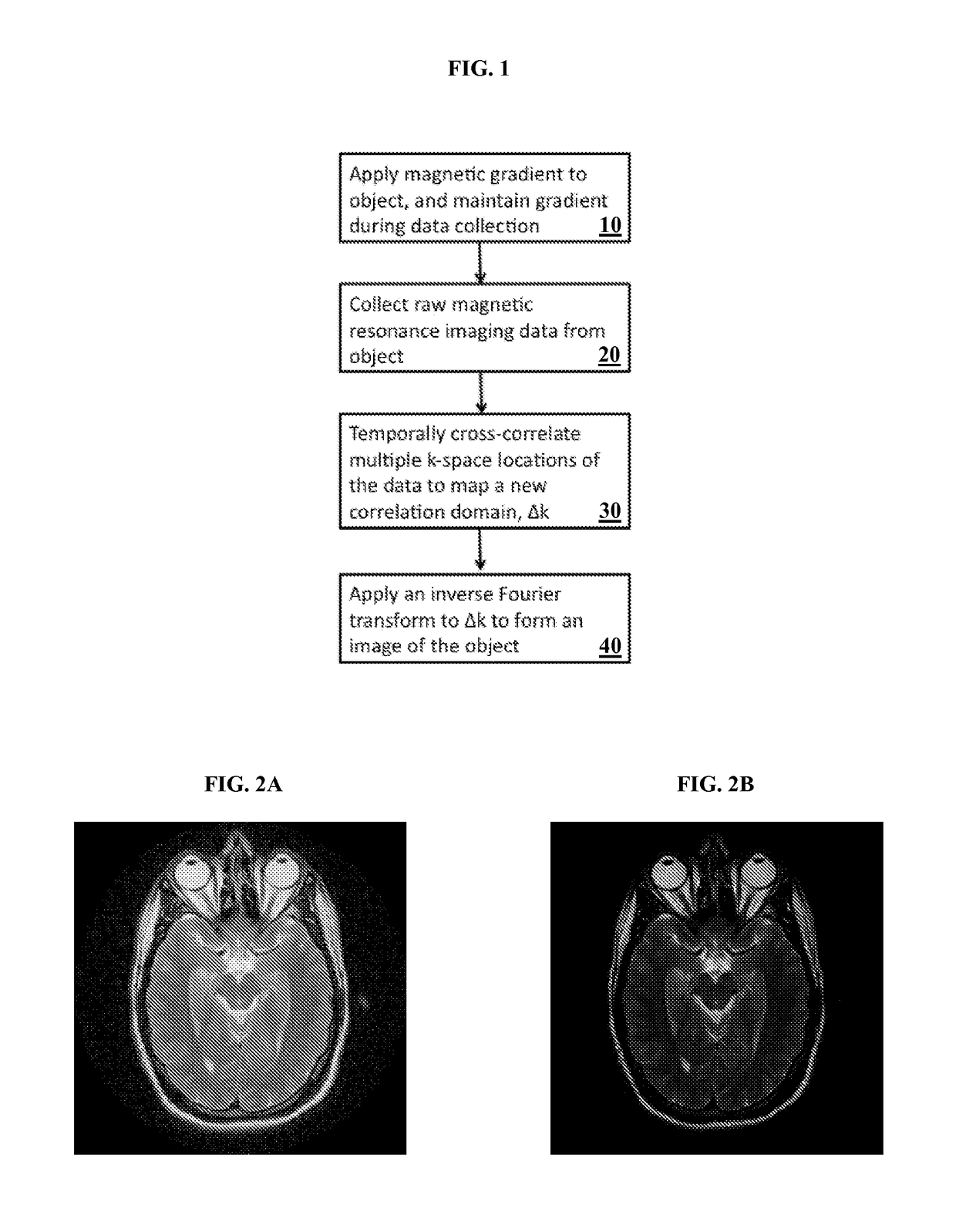
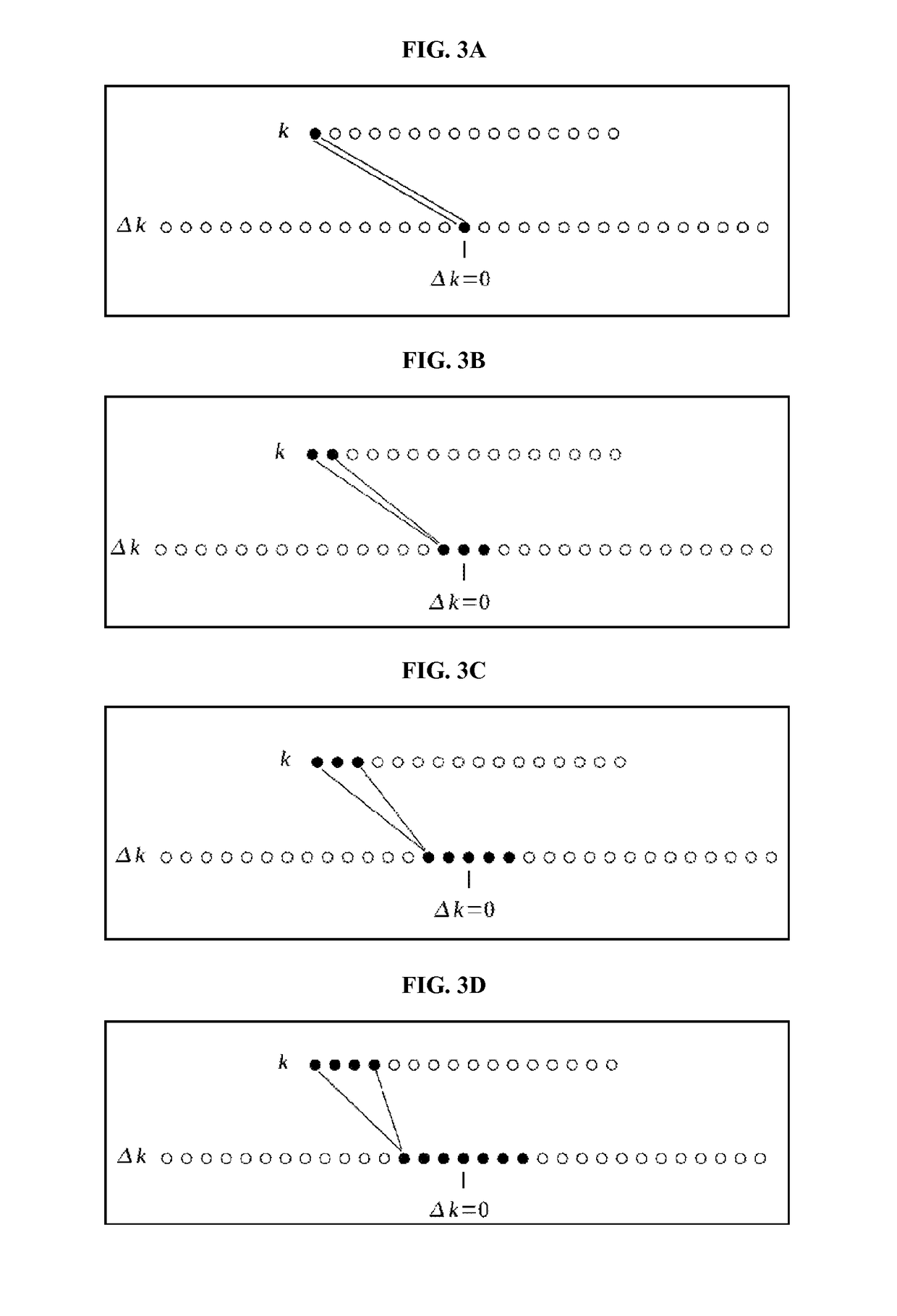
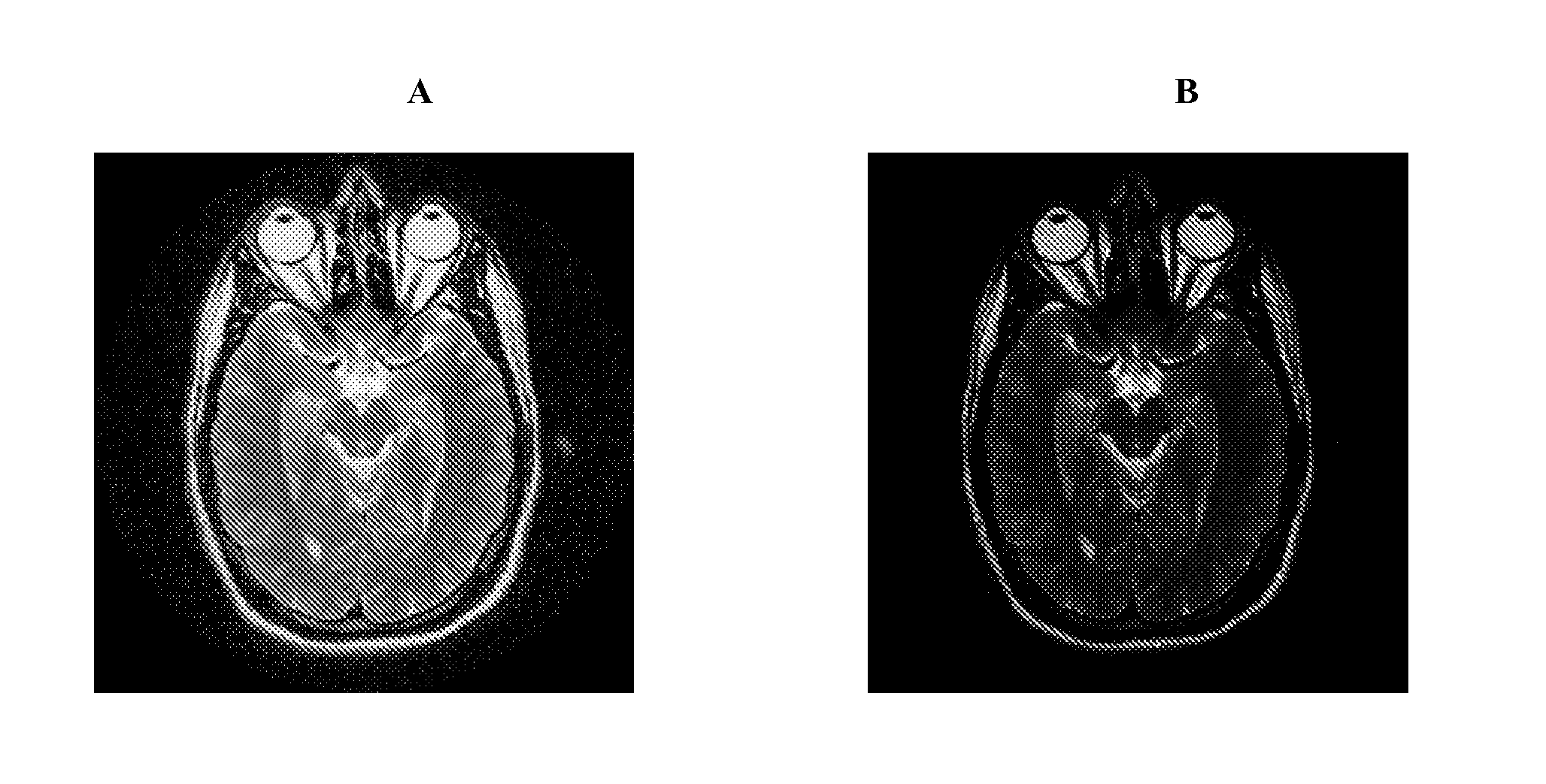
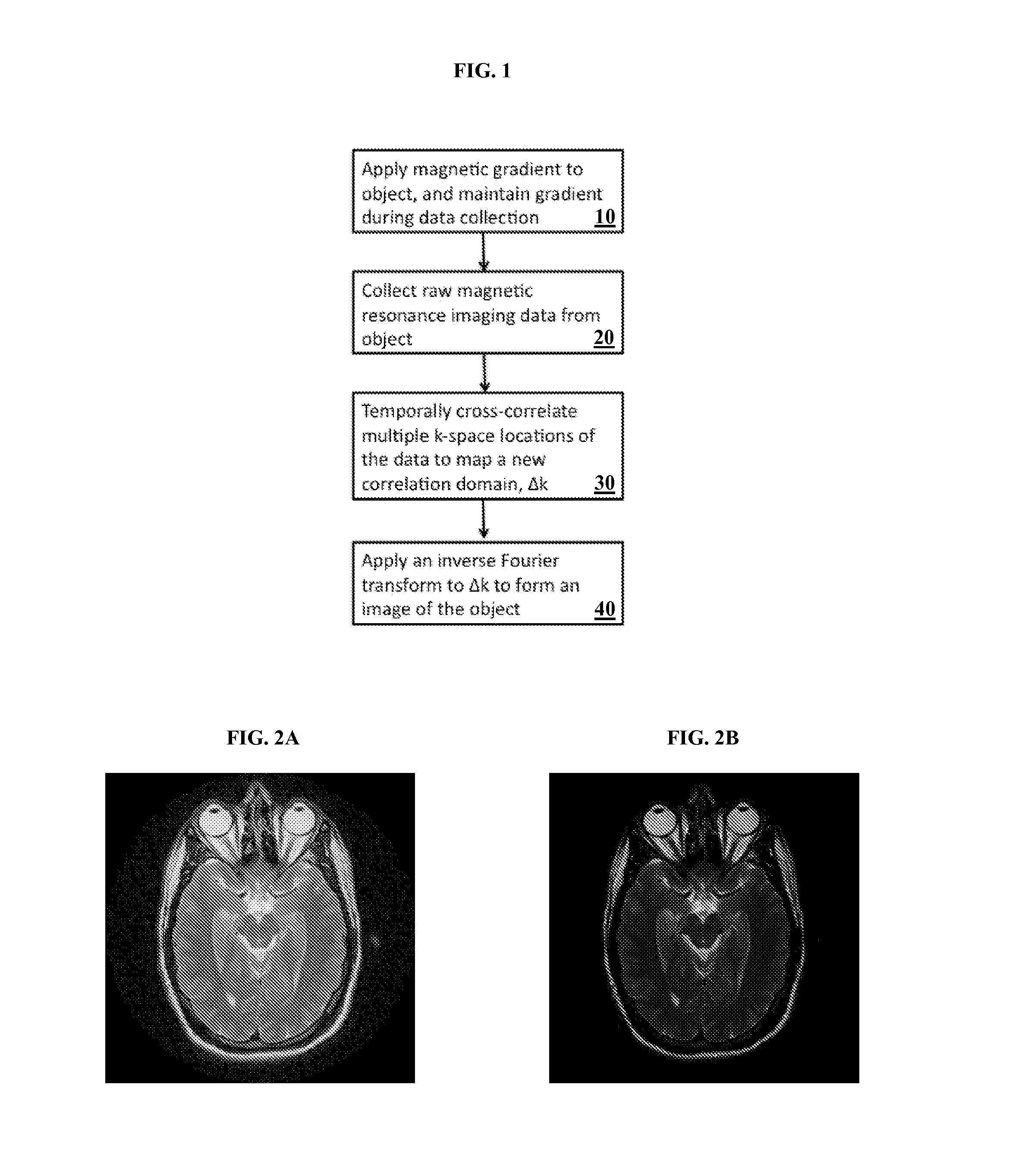
A method and system for providing a fast image reconstruction of magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) data based on applying, at least in part, interferometric techniques using a single receiver element. The images are reconstructed through temporally cross-correlating spacially incoherent k-space locations.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
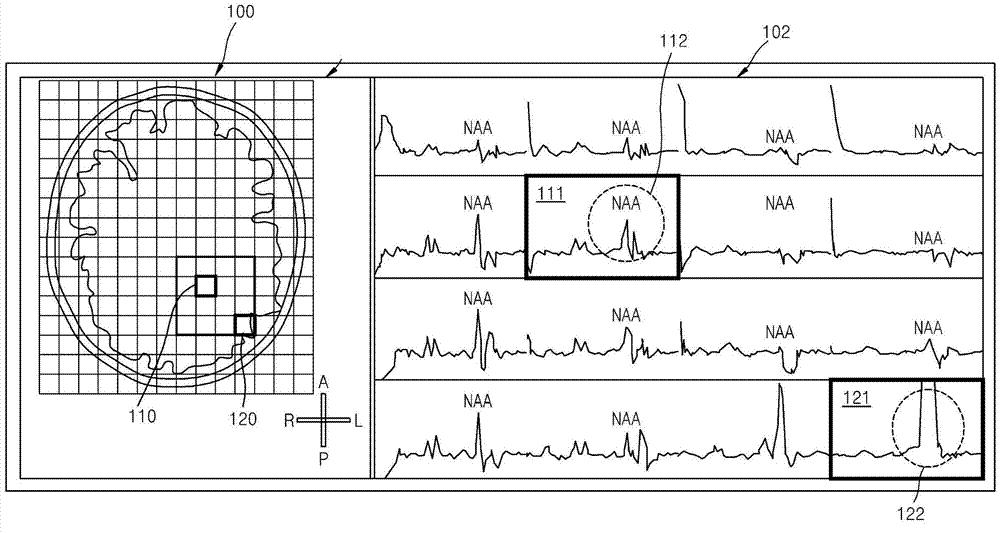
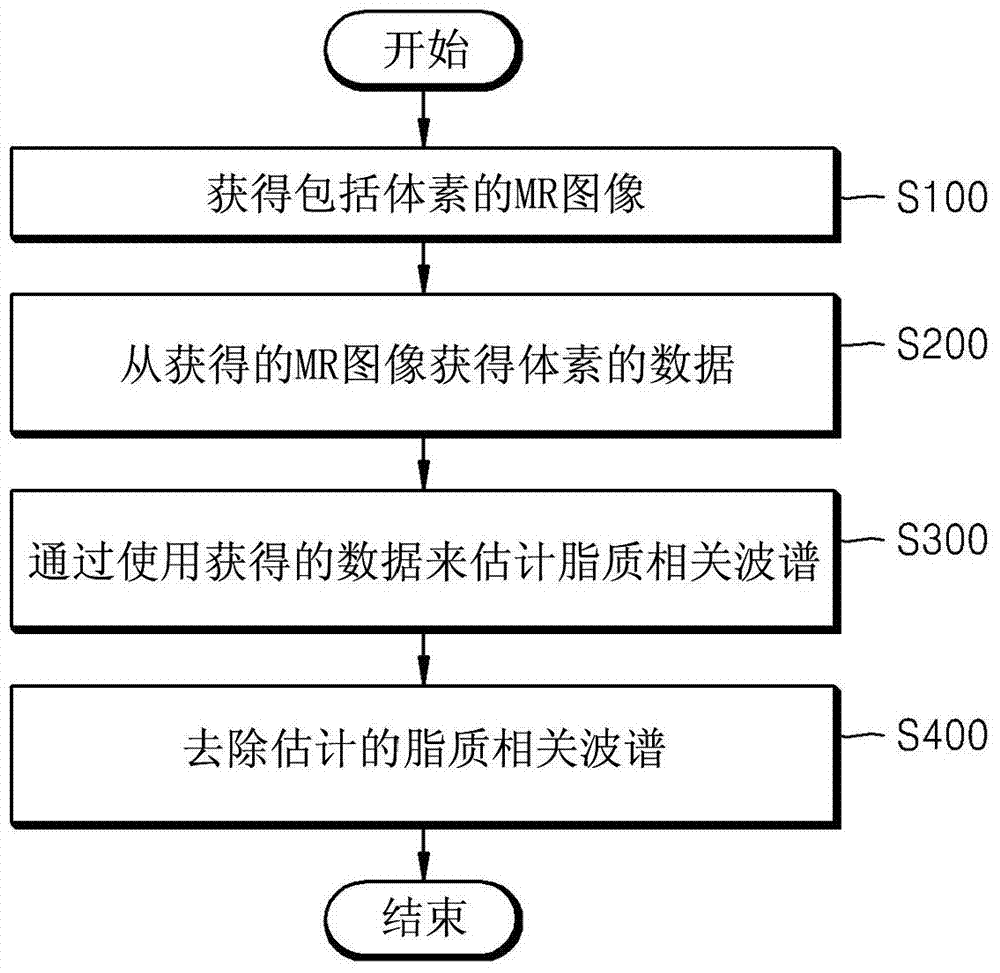
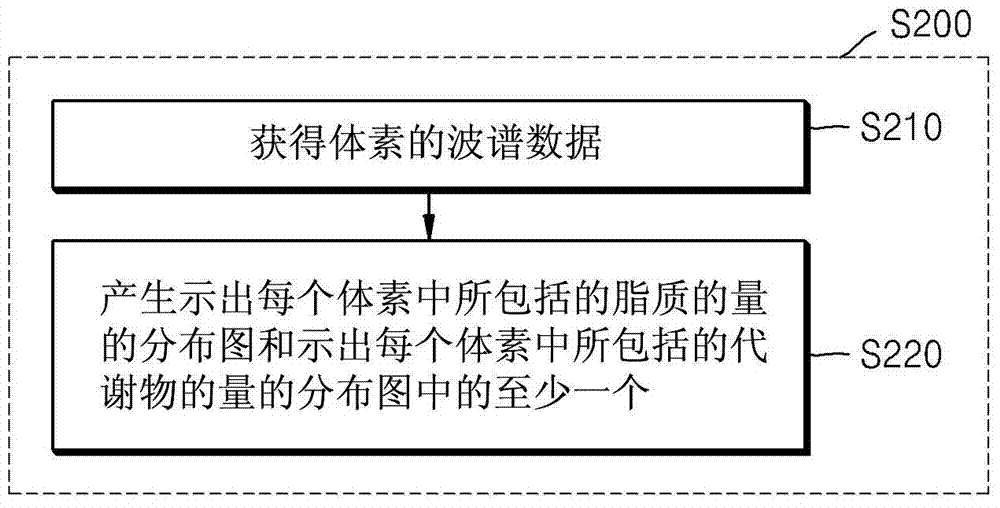
Method and apparatus for removing distortion by lipids from magnetic resonance spectroscopic image
The invention provides a method and an apparatus for removing distortion by lipids from a magnetic resonance spectroscopic image. The method of removing distortion by lipids from an MR image includes obtaining an MR image including voxels, obtaining data of the voxels from the obtained MR image, estimating a lipid-related spectrum by using the obtained data, and removing the estimated lipid-related spectrum from the obtained data. The method may be used in the context of magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI).
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD +1
Methods and systems for detection and monitoring of neurodegenerative diseases using magnetic resonance spectroscopy
ActiveUS7742800B2High sensitivityStrong specificityImage analysisDisease diagnosisMetaboliteConcentration ratio
A method for increasing sensitivity and / or specificity of a magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging technique for detecting a neurodegenerative disease is provided. The method includes acquiring magnetic resonance spectroscopy data from the brain of a subject, while suppressing certain metabolites in the spectrum via a data acquisition protocol, to improve quantification accuracy for the remaining metabolites, and quantifying a metabolite concentration or a metabolite concentration ratio from the spectral data as an indicator of the neurodegenerative disease.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for ultrafast magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging using learned spectral features
ActiveUS11079453B2Measurements using NMR spectroscopyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMetaboliteSubspace model
A new method is developed for ultrafast, high-resolution magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) using learned spectral features. The method uses Free Induction Decay (FID) based ultrashort-TE and short-TR acquisition without any solvent suppression pulses to generate the desired spatiospectral encodings. The spectral features for the desired molecules are learned from specifically designed “training” data by taking into account the resonance structure of each compound generated by quantum mechanical simulations. A union-of-subspaces model that incorporates the learned spectral features is used to effectively separate the unsuppressed water / lipid signals, the metabolite signals, and the macromolecule signals. The unsuppressed water spectroscopic signals in the data can be used for various purposes, e.g., removing the need of additional auxiliary scans for calibration, and for generating high quality quantitative tissue susceptiability mapping etc. Simultaneous spatiospectral reconstructions of water, lipids, metabolite and macromolecule can be obtained using a single 1H-MRSI scan.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Breast tumor diagnosis system based on magnetic resonance spectrum imaging
InactiveCN101785672BAchieve early differential diagnosisKeep authentication informationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsCost sensitiveComputerized system
The invention provides a breast tumor diagnosis system based on magnetic resonance spectrum imaging, comprising a superconduction MR (Magneto Resistance) scanner and a computer system. Through a computer auxiliary detection measure, the breast tumor diagnosis system realizes the early identification diagnosis of a breast tumor and the further diagnosis of breast cancer. Mammary gland magnetic resonance spectrum data are studied by adopting a distinctive manifold study method and projected to a low dimension embedding space, thus not only a low dimension manifold structure hidden in a high dimension magnetic resonance spectrum space can be revealed, but also the identification information in the mammary gland magnetic resonance spectrum data can be efficiently kept; then optimization clustering is carried out on the low dimension identification characteristic by utilizing a clustering method so that data points without the similar identification characteristic are separated to the maximum; and further a cost sensitive mechanism is introduced to achieve misclassification total cost minimization and realize optimization diagnosis of the breast cancer.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
System and method of performing magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
ActiveUS10209330B2Measurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringMagnetic resonance spectroscopicSpatial average
A method of performing spatially localized magnetic resonance spectroscopy includes receiving a magnetic resonance image of an object; identifying a plurality C of compartments that generate magnetic resonance spectroscopy signals in the object including at least one compartment of interest; segmenting in at least one spatial dimension the magnetic resonance image of the object into the C compartments; acquiring magnetic resonance spectroscopy signals from the compartments by applying a plurality of M′ phase encodings applied in the at least one spatial dimension, wherein M′≥C; calculating a spatially localized magnetic resonance chemical shift spectrum from the at least one compartment of interest; and rendering a spatially localized magnetic resonance spectrum that is substantially equal to a spatial average of magnetic resonance chemical shift spectra from the at least one compartment of interest. A magnetic resonance spectroscopy and imaging system is configured to perform the above method.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
Method of suppressing water signal and enhancing metabolite signal by adjusting excitation signal frequency band center frequency and receiving bandwidth in mrs imaging method
ActiveCN108700638BNo loss of frequency resolutionDoes not increase shooting timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic resonance spectrometryCenter frequency
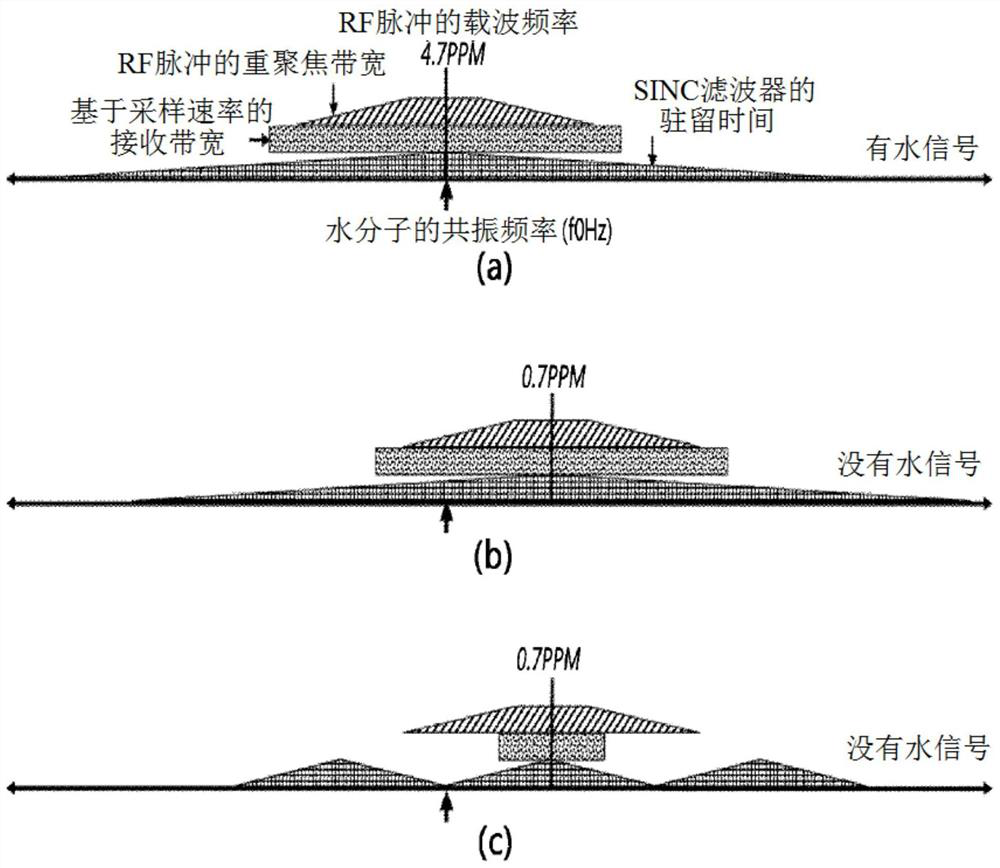
The invention discloses a method for suppressing water signals and enhancing metabolite signals by adjusting the central frequency and receiving bandwidth of excitation signal frequency bands in magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) imaging technology. According to an embodiment of the water signal suppression and metabolite signal enhancement method, an excitation signal adjusted to have a center frequency lower than the resonance frequency of water is applied, and the size of the receiving bandwidth is adjusted to match the resonance frequency of the water and the resonance frequency of the water. The center frequency difference is the same.
Owner:GIL MEDICAL CENT +1
Compensation of magnetic field inhomogeneity in MR spectroscopic imaging using dynamic k-space expansion in combination with parallel imaging
ActiveUS11221388B1Extension of timeHigh gradientMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSensorsParallel imagingMagnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging
A method for the compensation of magnetic field inhomogeneity in magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging comprising the steps of using dynamic k-space expansion in combination with parallel imaging.
Owner:UNM RAINFOREST INNOVATIONS
Fat pressing method for magnetic resonance spectrum imaging
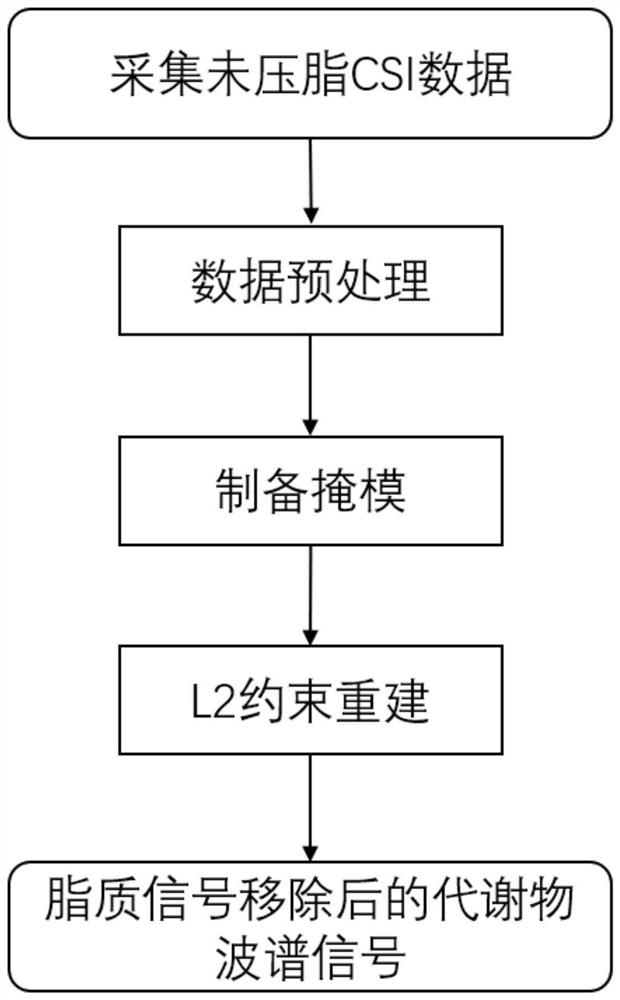
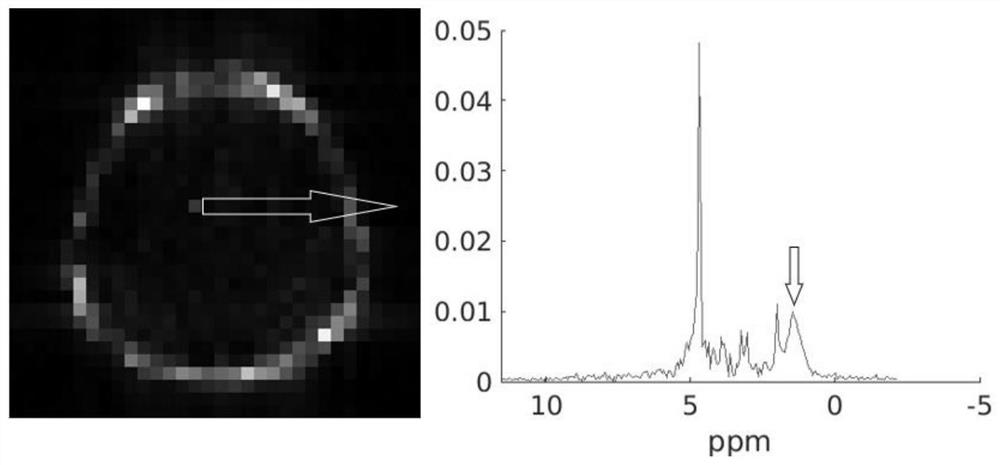
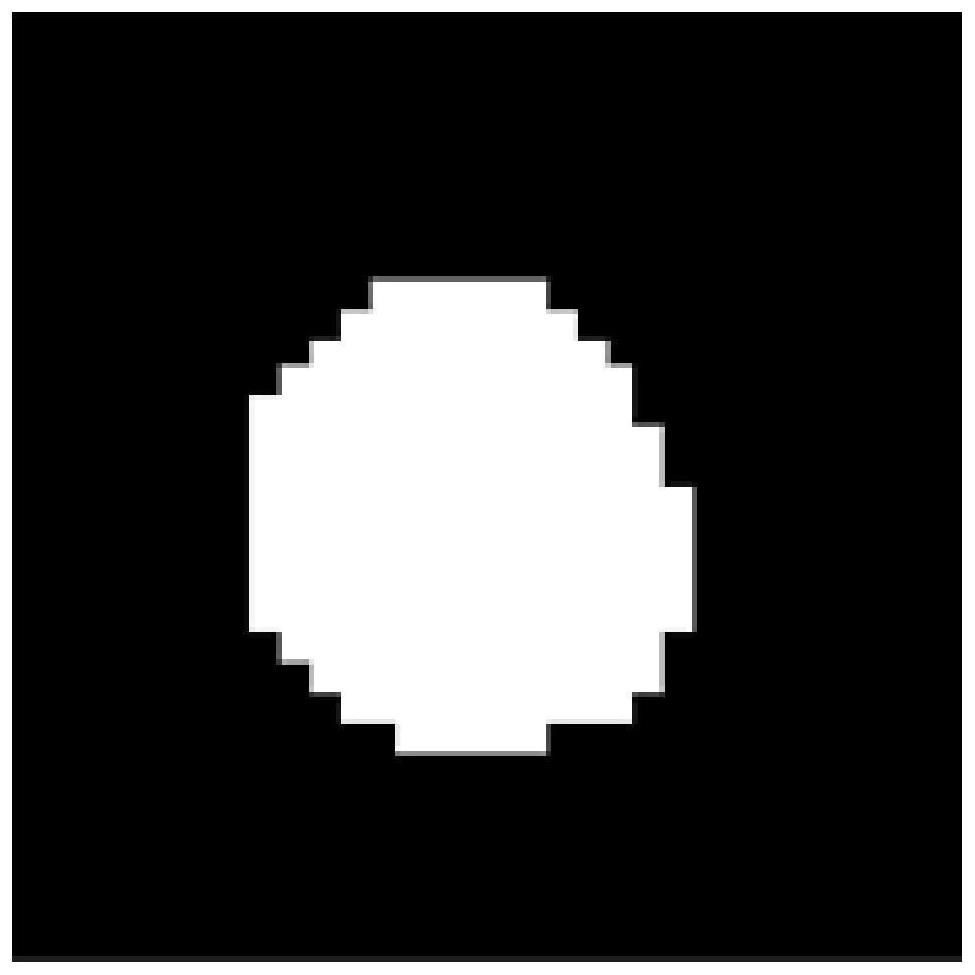
ActiveCN113933332ANo need for multiple acquisitionsData collection time is shortWater resource assessmentMaterial analysis by using resonanceChannel state informationMedicine
The invention discloses a fat pressing method for magnetic resonance spectrum imaging. The fat pressing method comprises the following steps of: acquiring non-fat-pressing spectrum imaging data: acquiring the non-fat-pressing spectrum imaging data by adopting a CSI (Channel State Information) sequence; preprocessing the data: preprocessing the non-fat-pressing wave spectrum imaging data to obtain data XCSI; preparing masks: preparing a lipid signal mask MIipid and a metabolite signal mask Mtrain; performing double-weight signal reconstruction to obtain a double-weight signal Xdual; and performing L2 constraint reconstruction to obtain metabolite spectrum signals X with lipid signals removed. The data acquisition sequence adopted by the method is a clinical common sequence and does not need to be acquired for multiple times, so that the data acquisition time is short; lots of prior information is not needed; and lipid signals can be quickly and robustly removed, and metabolite signals can be retained.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Magnetic resonance spectrum imaging method and device, computer equipment and storage medium
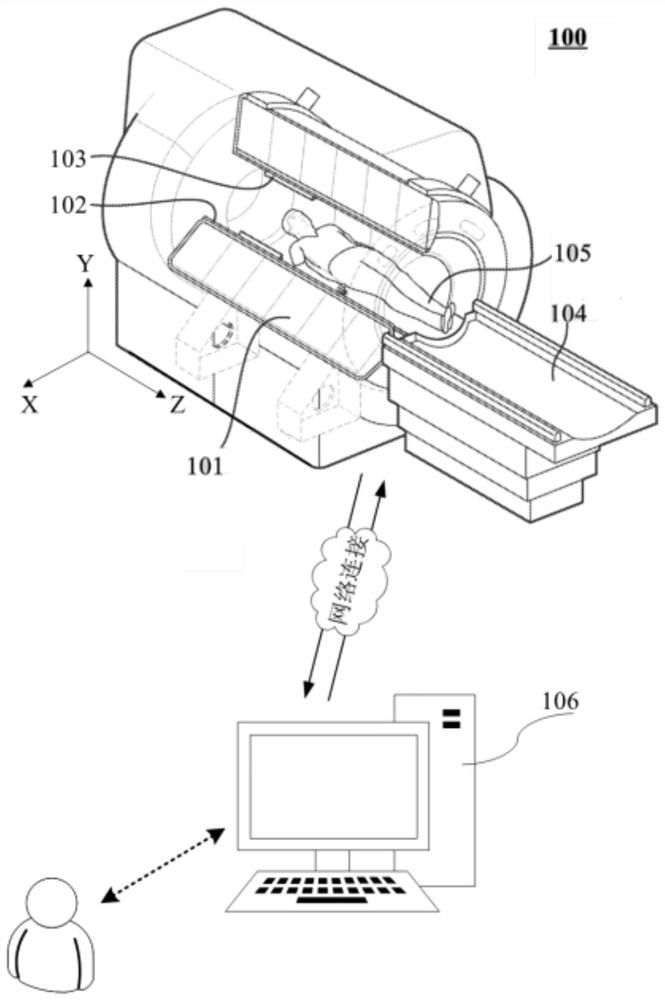
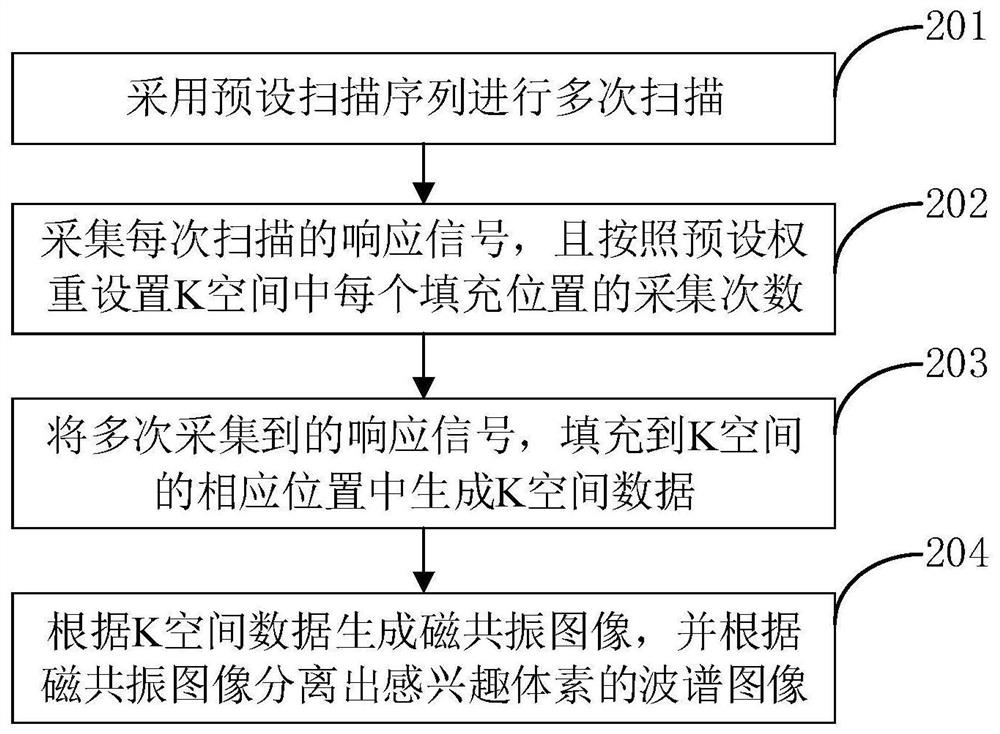
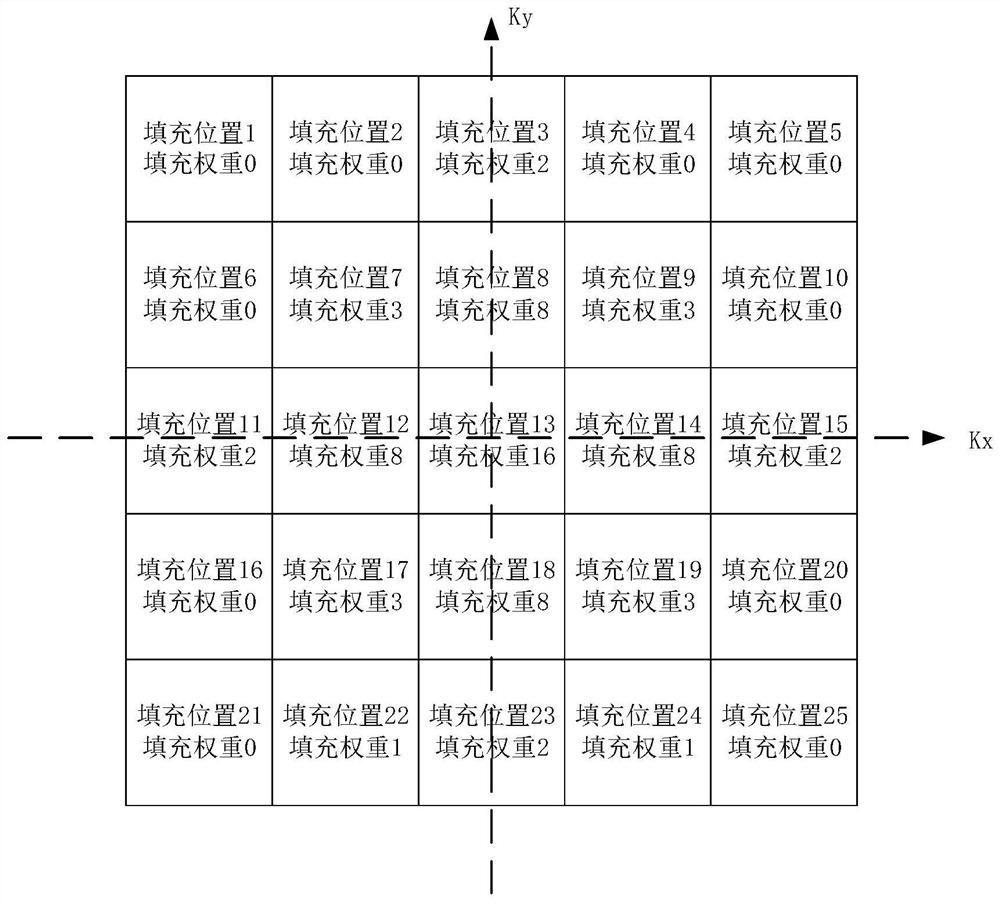
The invention relates to a magnetic resonance spectrum imaging method and device, computer equipment and a storage medium. The method comprises the steps of scanning for multiple times by adopting a preset scanning sequence, wherein the preset scanning sequence comprises an excitation pulse and a spatial positioning coding gradient, the excitation pulse comprises three mutually perpendicular layer selection pulses, and the three mutually perpendicular layer selection pulses are matched with the corresponding spatial positioning gradients to determine voxels of interest; acquiring a response signal of each scanning, and setting the acquisition times of each filling position in the K space according to a preset weight; filling the response signals acquired for multiple times into corresponding positions of the K space to generate K space data; and generating a magnetic resonance image according to the K space data, and separating a spectrum image of the voxel of interest according to the magnetic resonance image. By adopting the method, the spectrum image of the voxel of interest can be accurately separated.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com