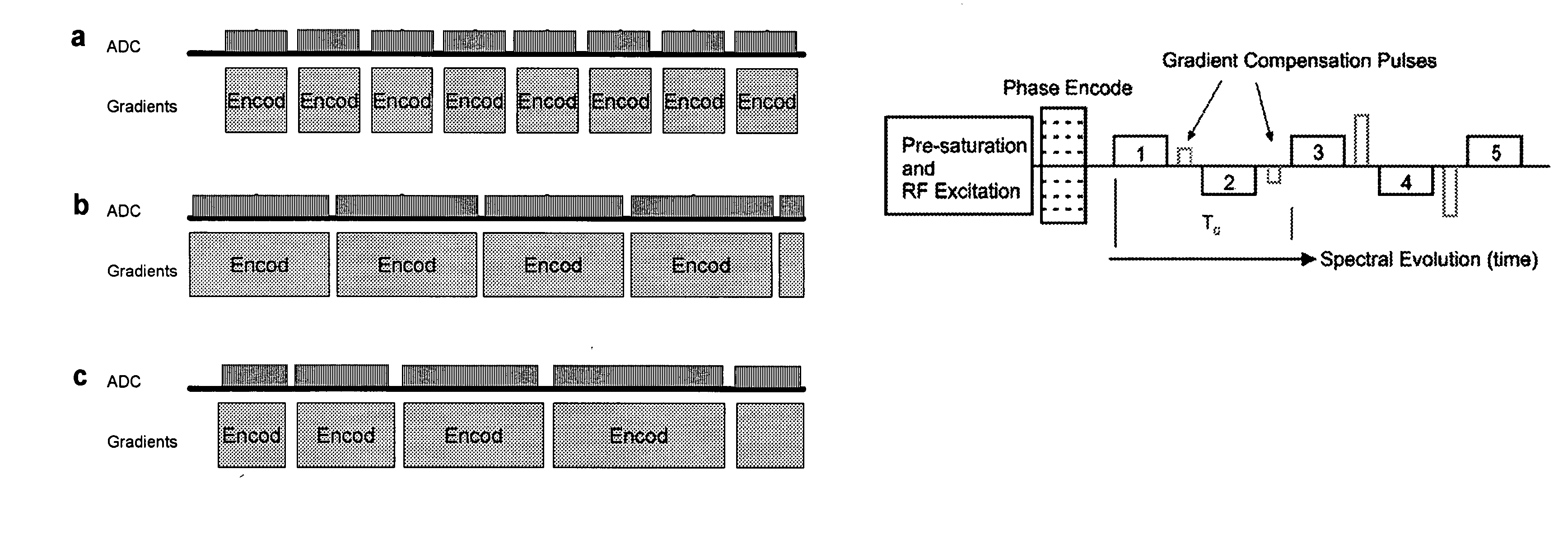
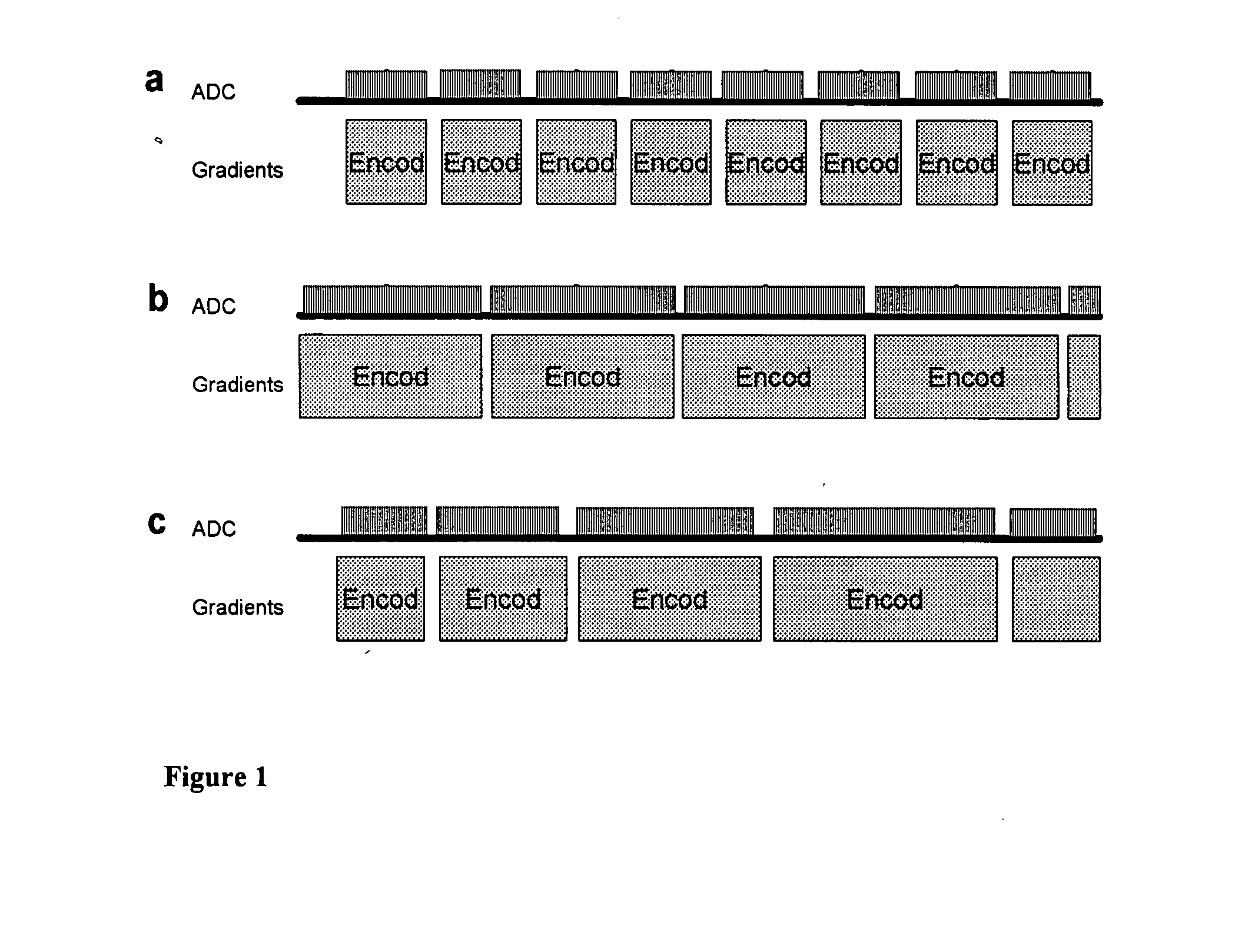
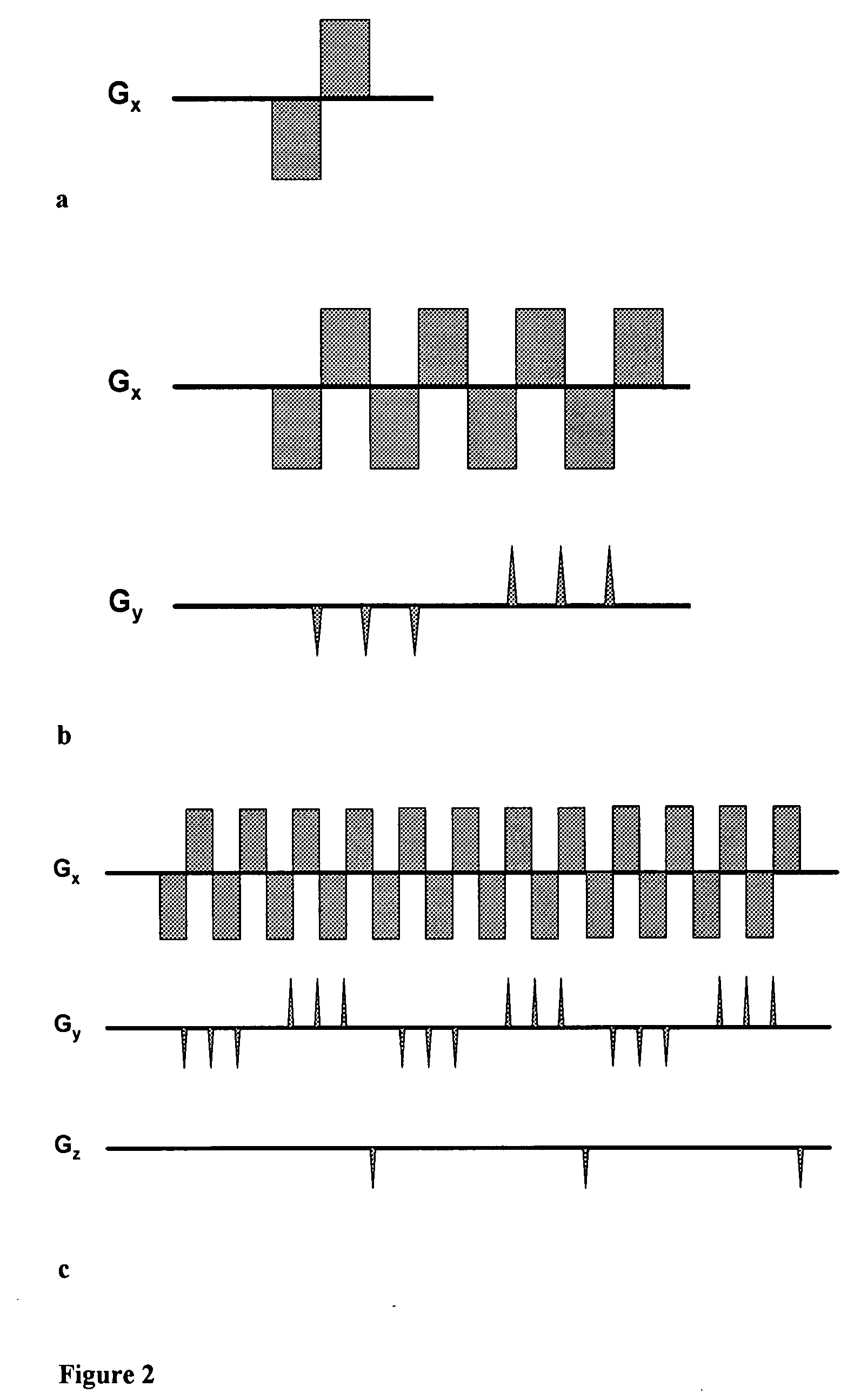
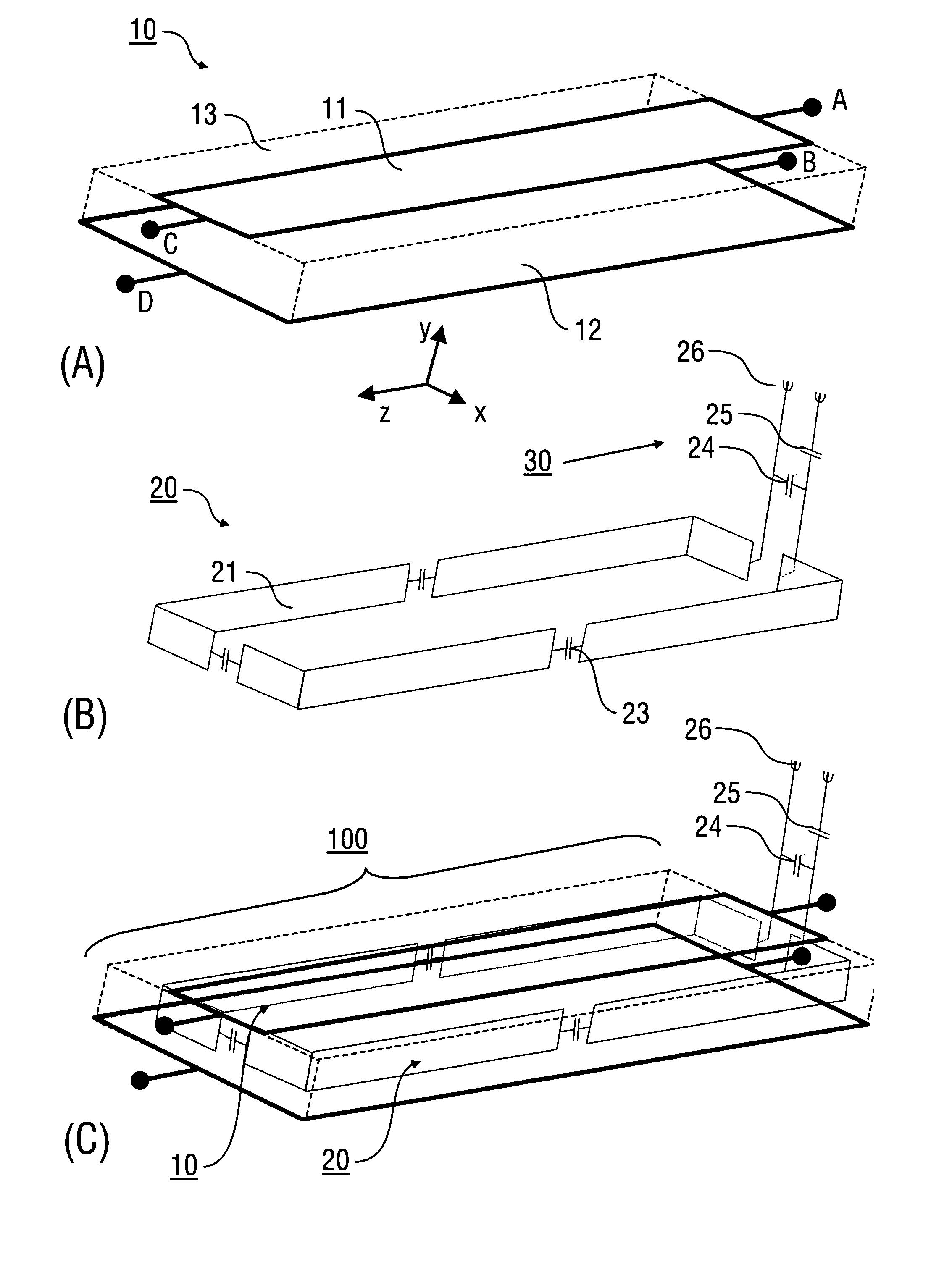
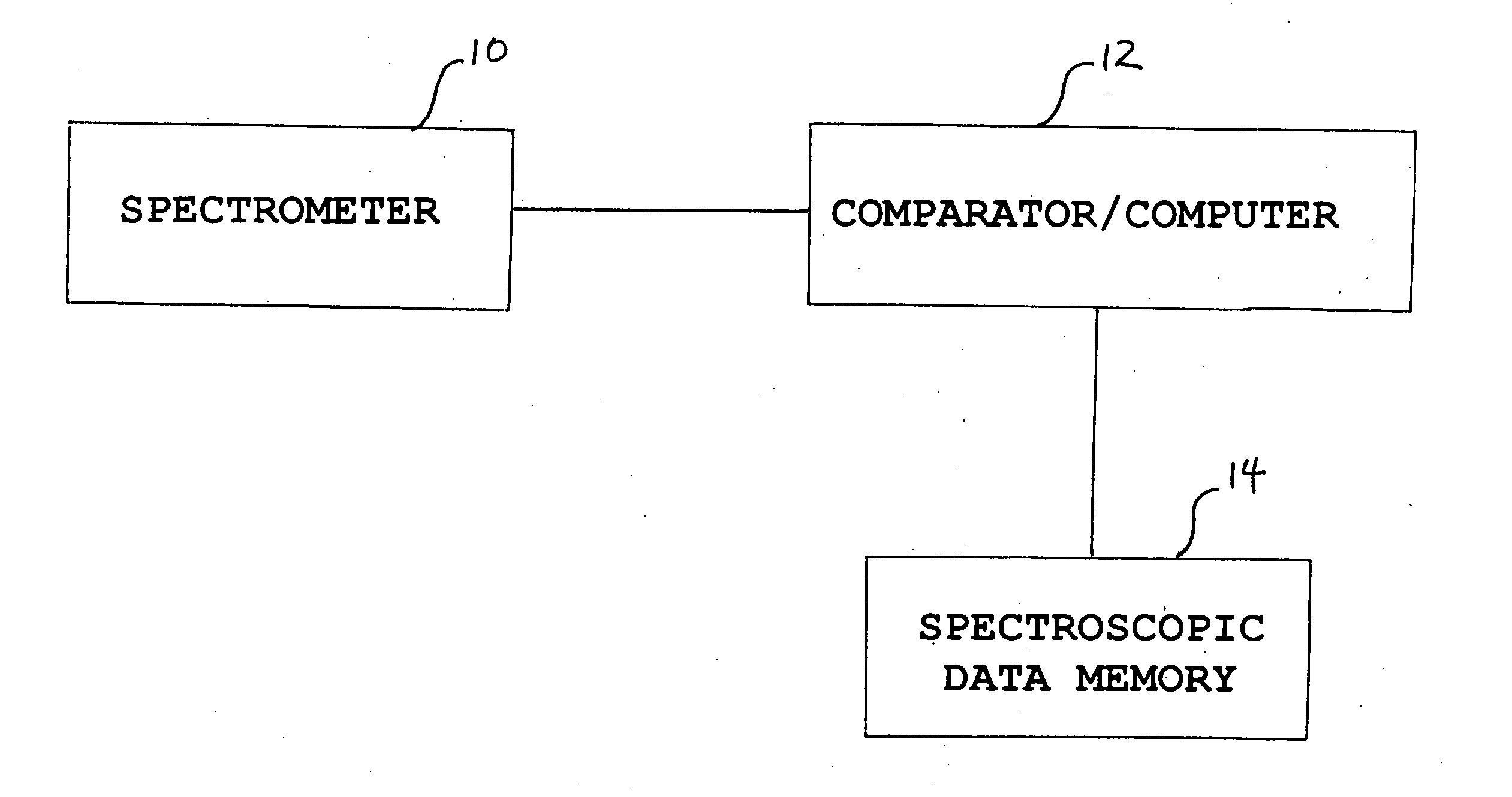
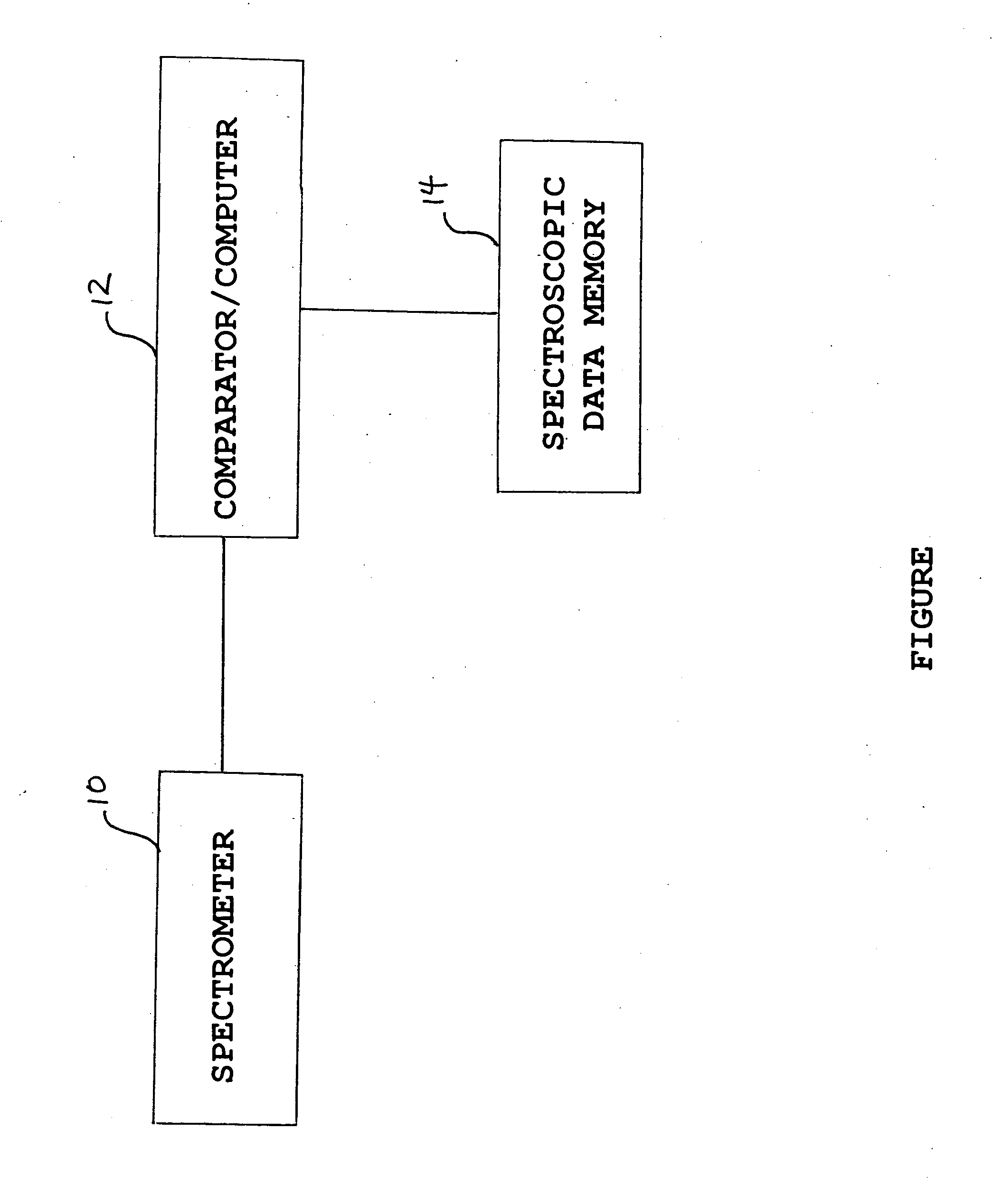
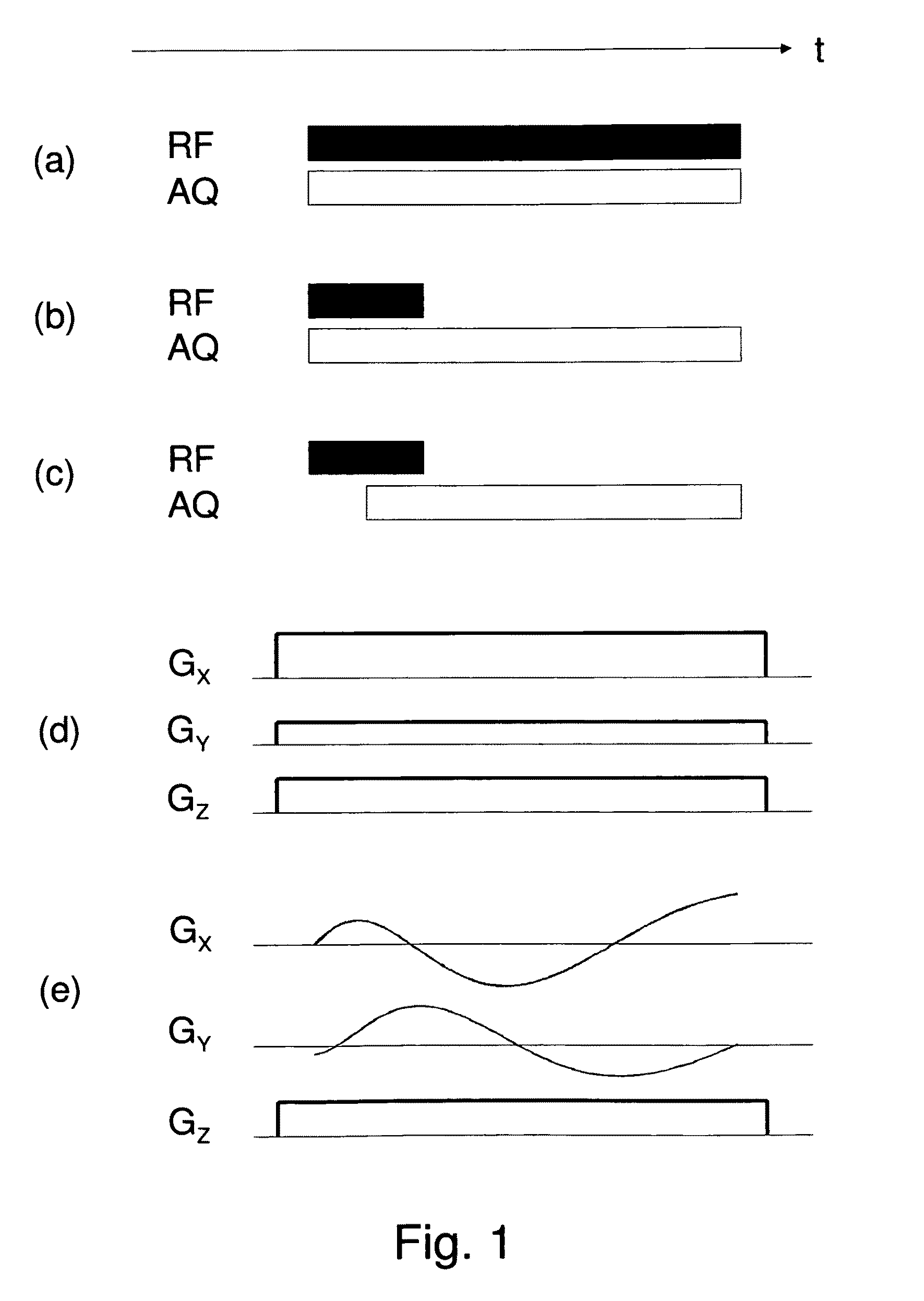
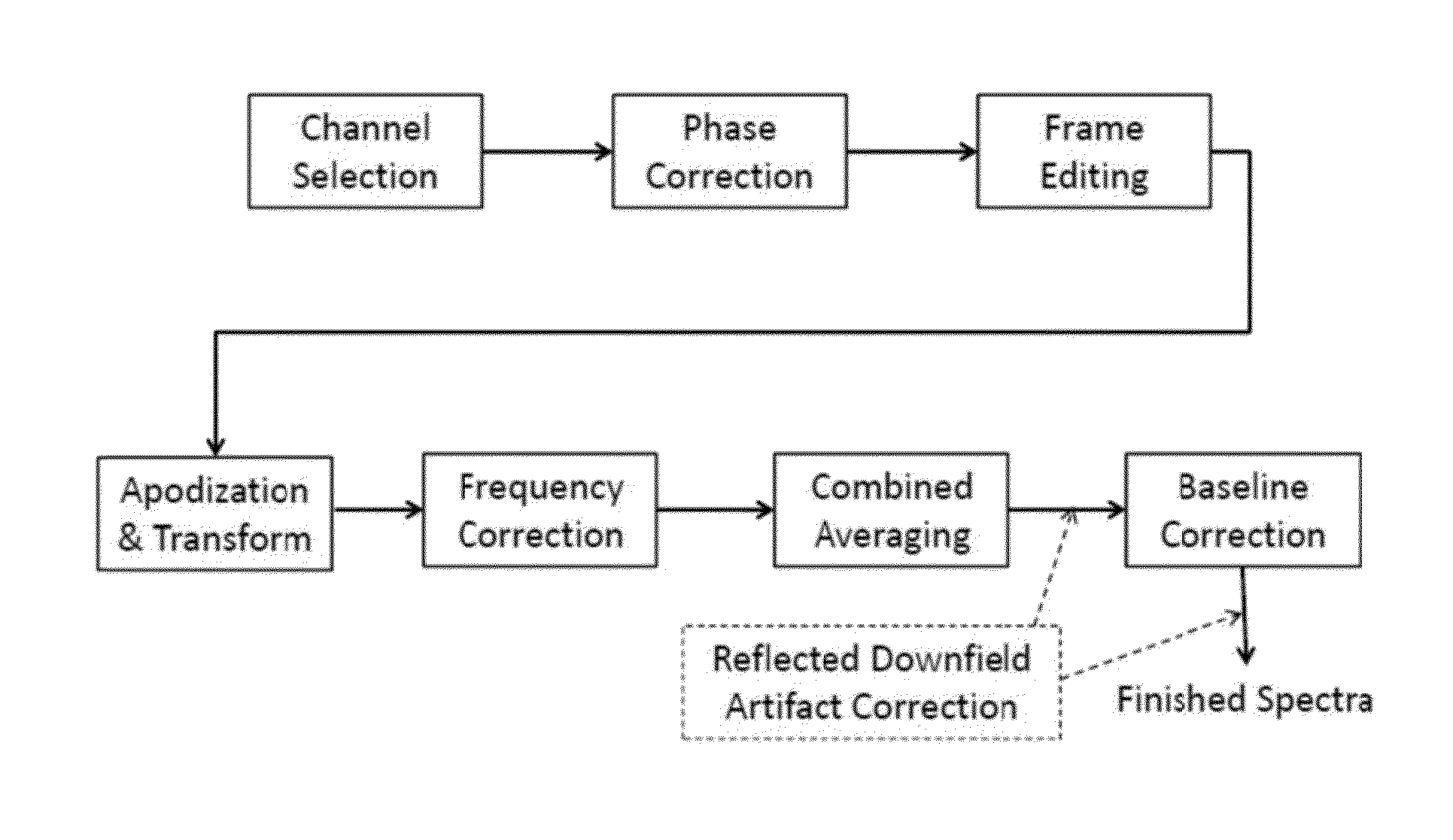
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
189 results about "Magnetic resonance spectrometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, most commonly known as NMR spectroscopy or magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS), is a spectroscopic technique to observe local magnetic fields around atomic nuclei.
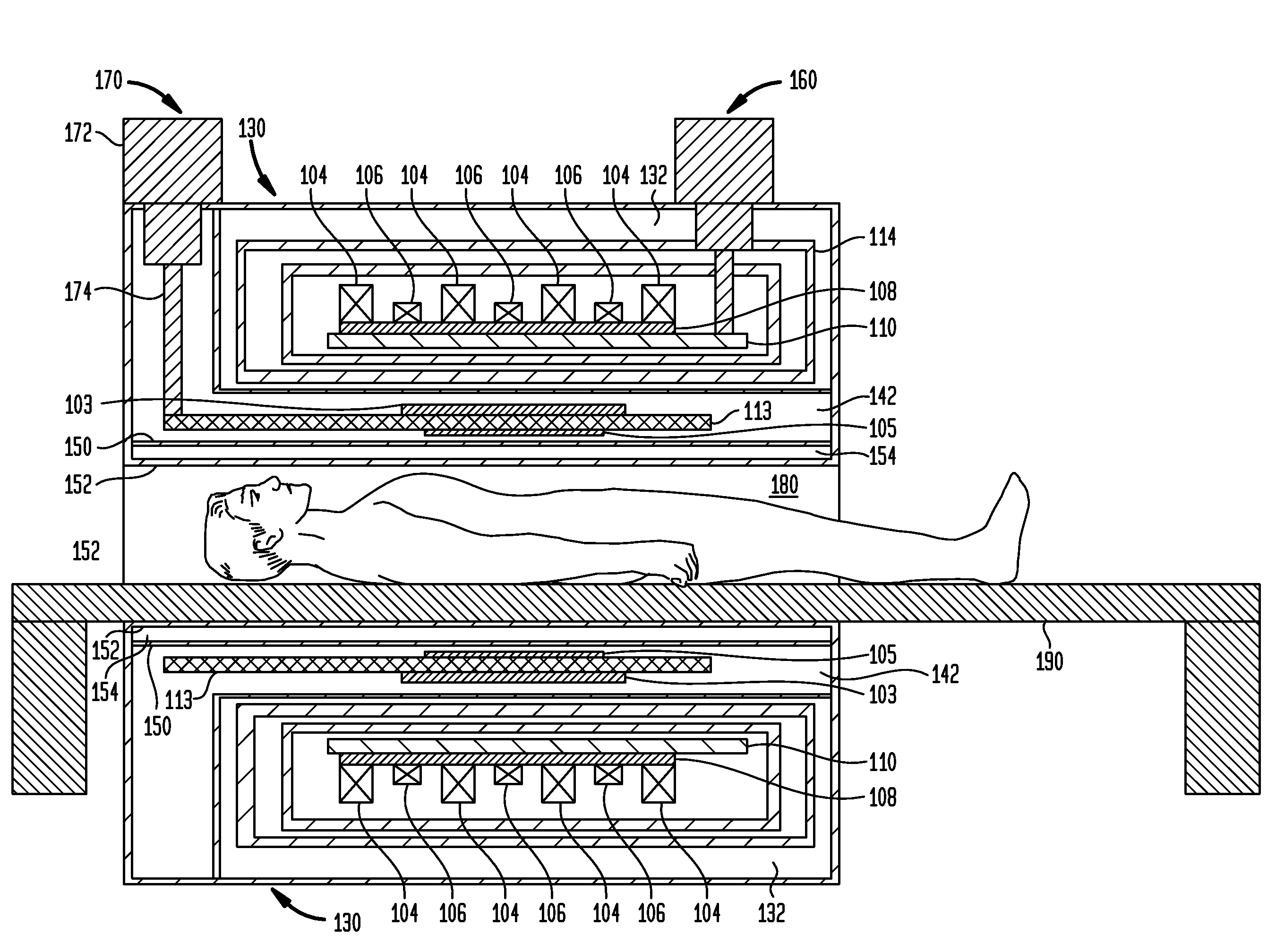
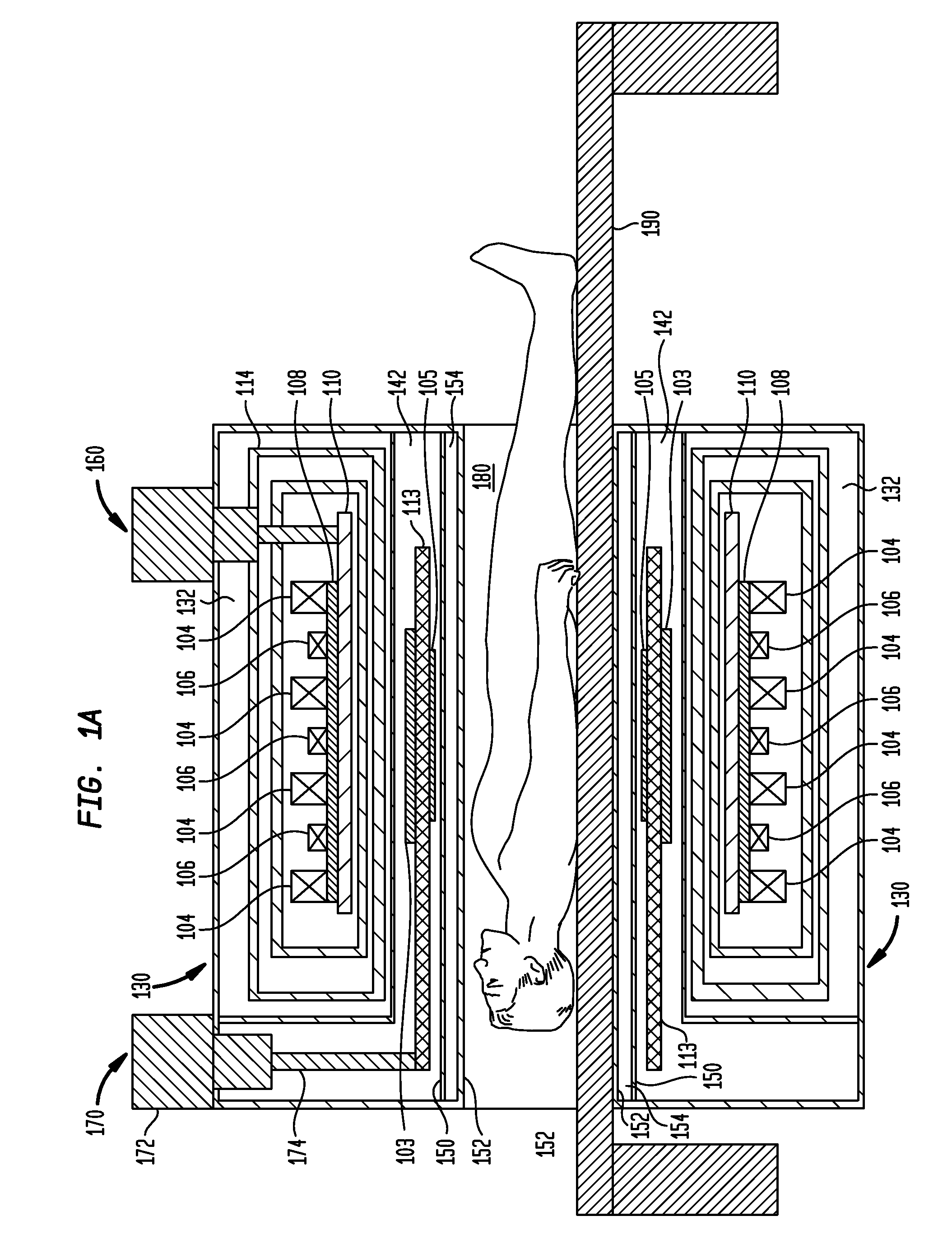
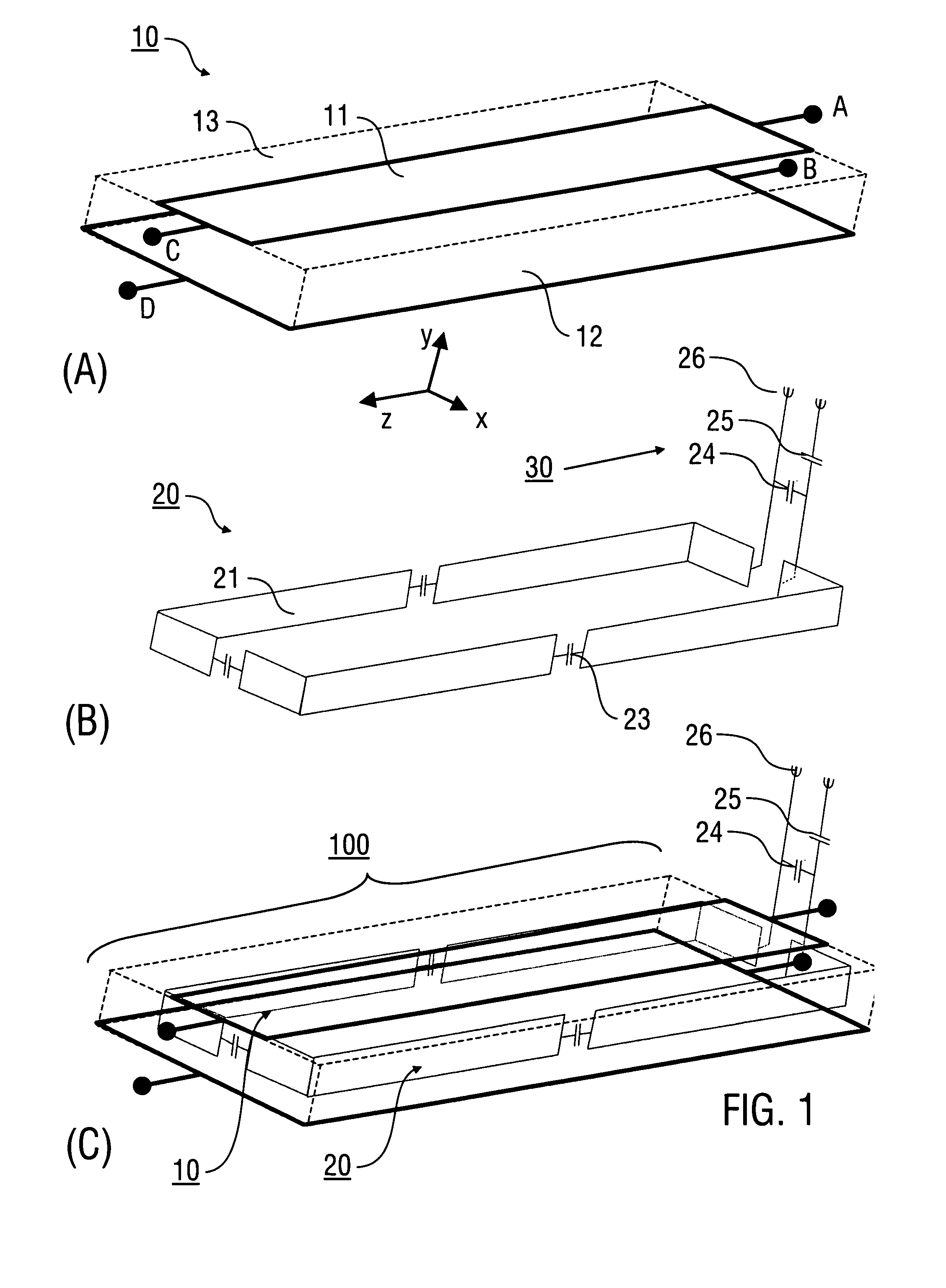
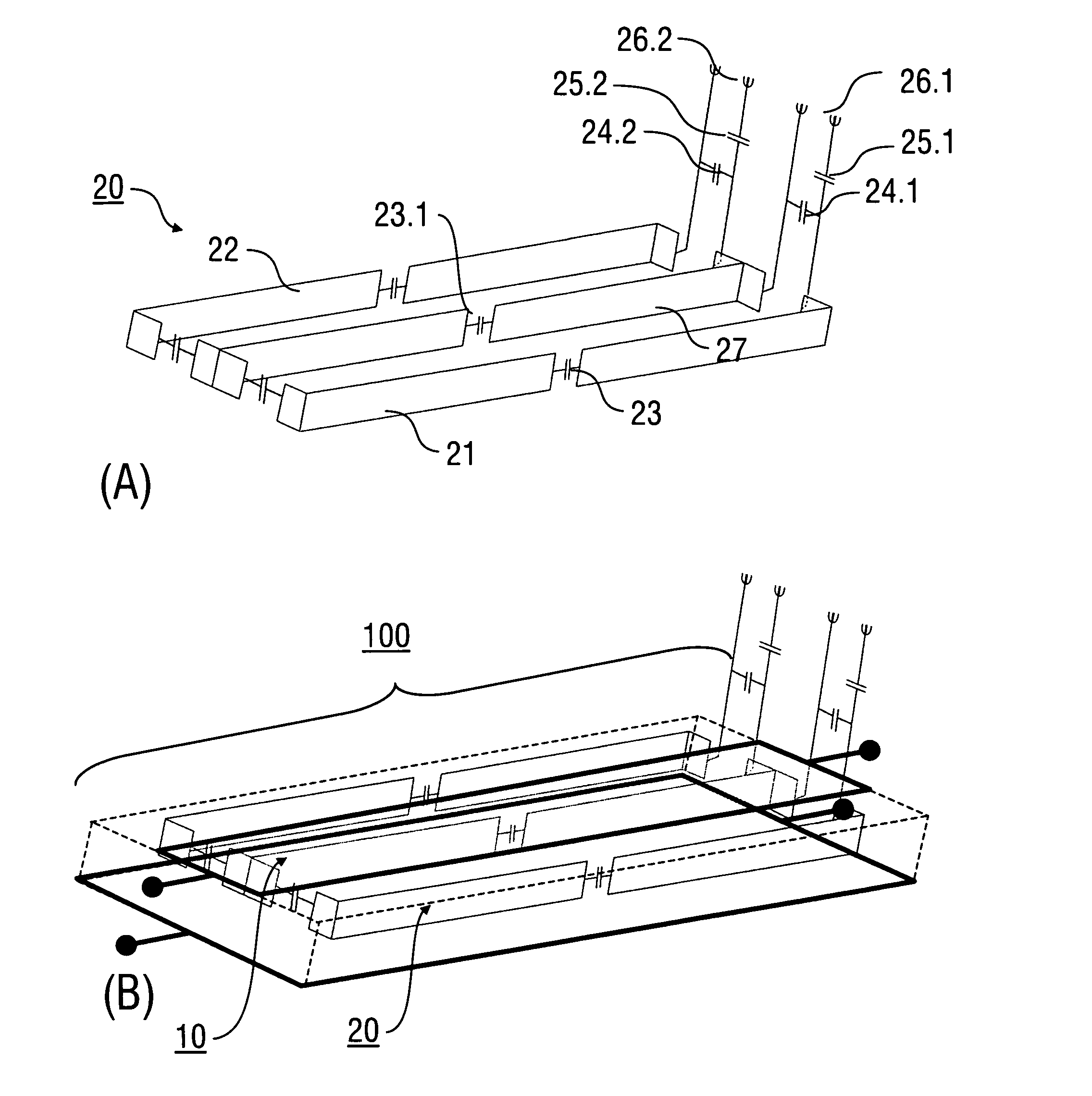
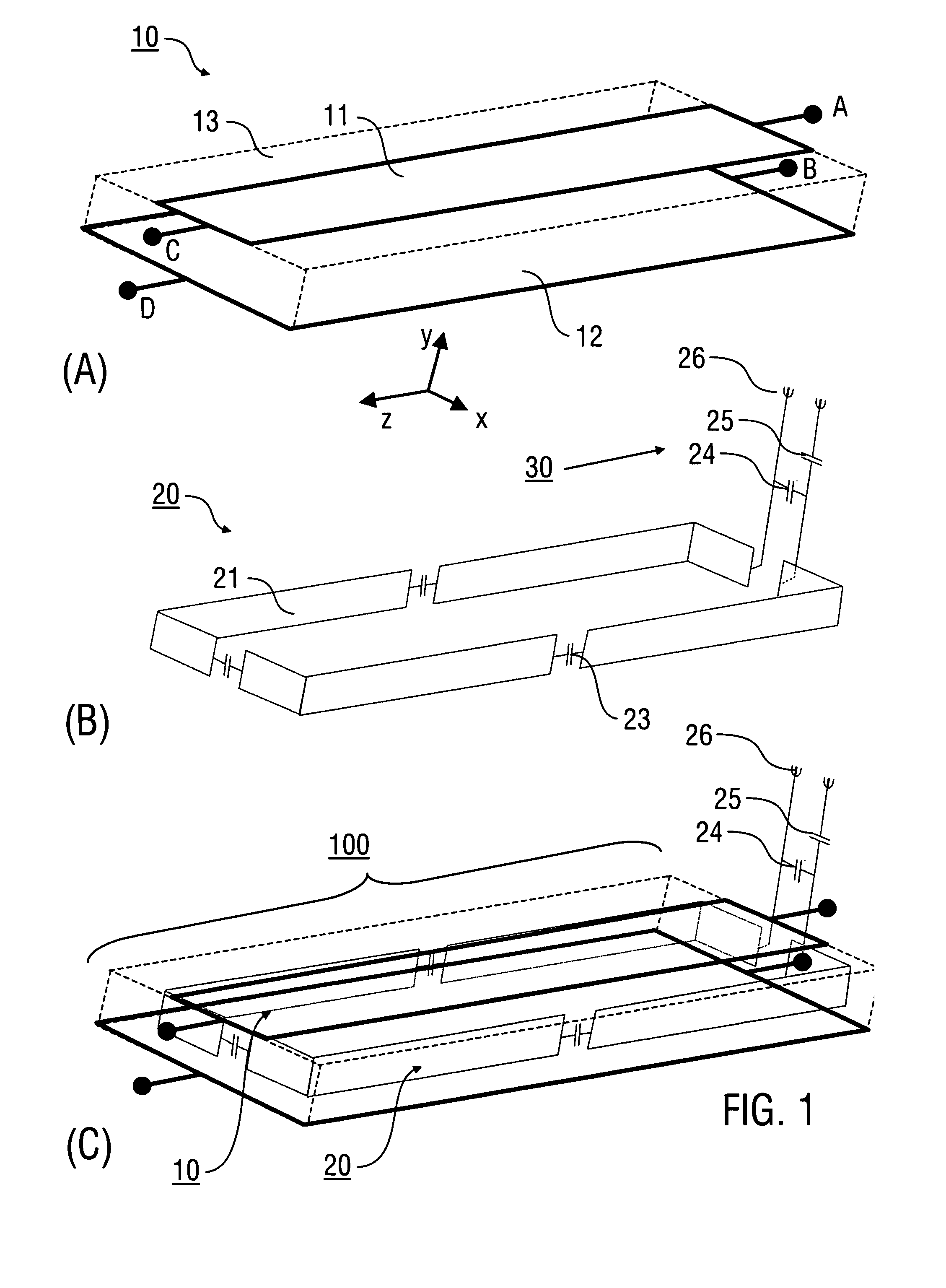
Antenna and antenna arrangement for magnetic resonance applications
InactiveUS20140197832A1Easy to manufactureAdjustabilityElectric/magnetic detectionLoop antennas with variable reactanceElectricityDielectric
An antenna (100), which is designed for exciting and / or detecting a magnetic resonance in an object (1) under investigation, comprises a conductor loop (10) with an inner conductor (11) and a primary shield conductor (12), which form at least one waveguide, wherein the primary shield conductor (12) is interrupted by a gap (13), and wherein a secondary shield conductor (14) is provided which surrounds the primary shield conductor (12), wherein a dielectric (15) is arranged between the primary shield conductor (12) and the secondary shield conductor (14) and at least the gap is covered by the secondary shield conductor (14). An antenna arrangement which comprises a plurality of such antennas, a magnetic resonance device, and a method for magnetic resonance imaging or magnetic resonance spectroscopy are also described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
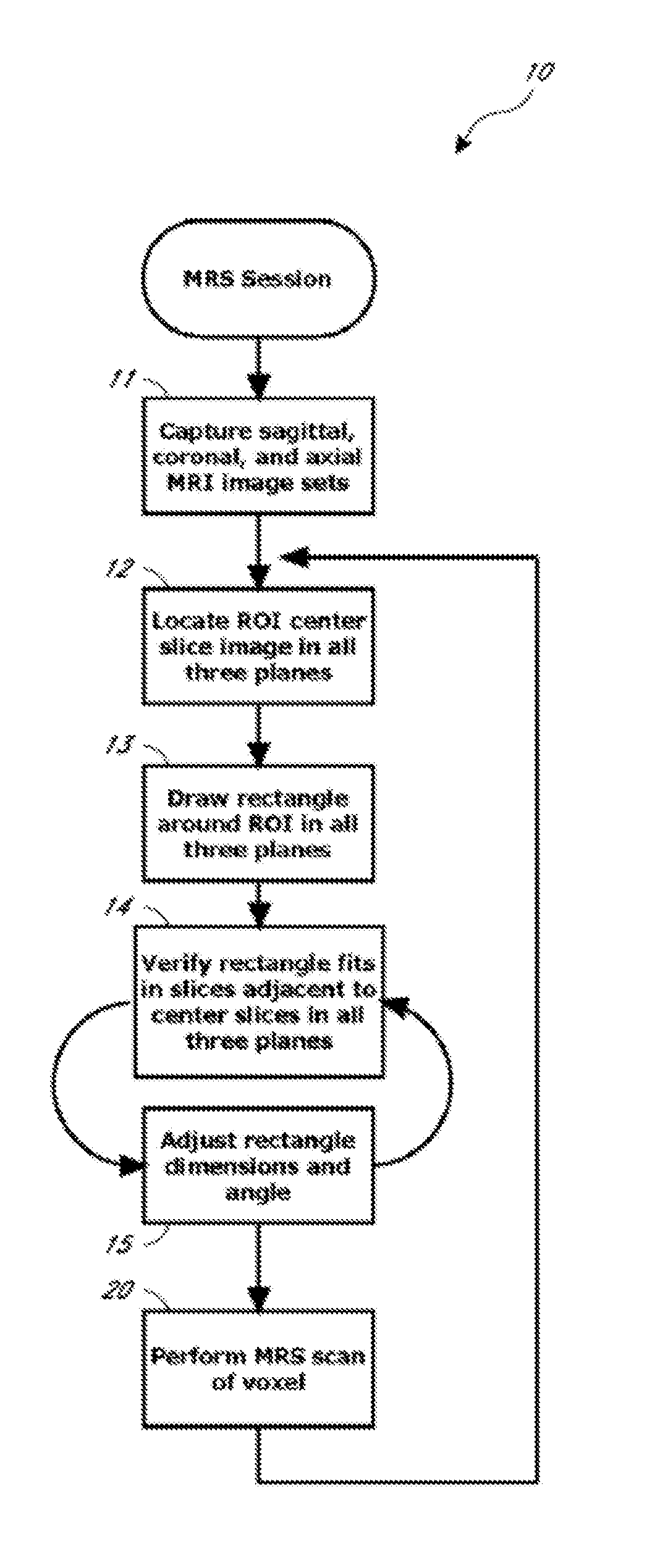
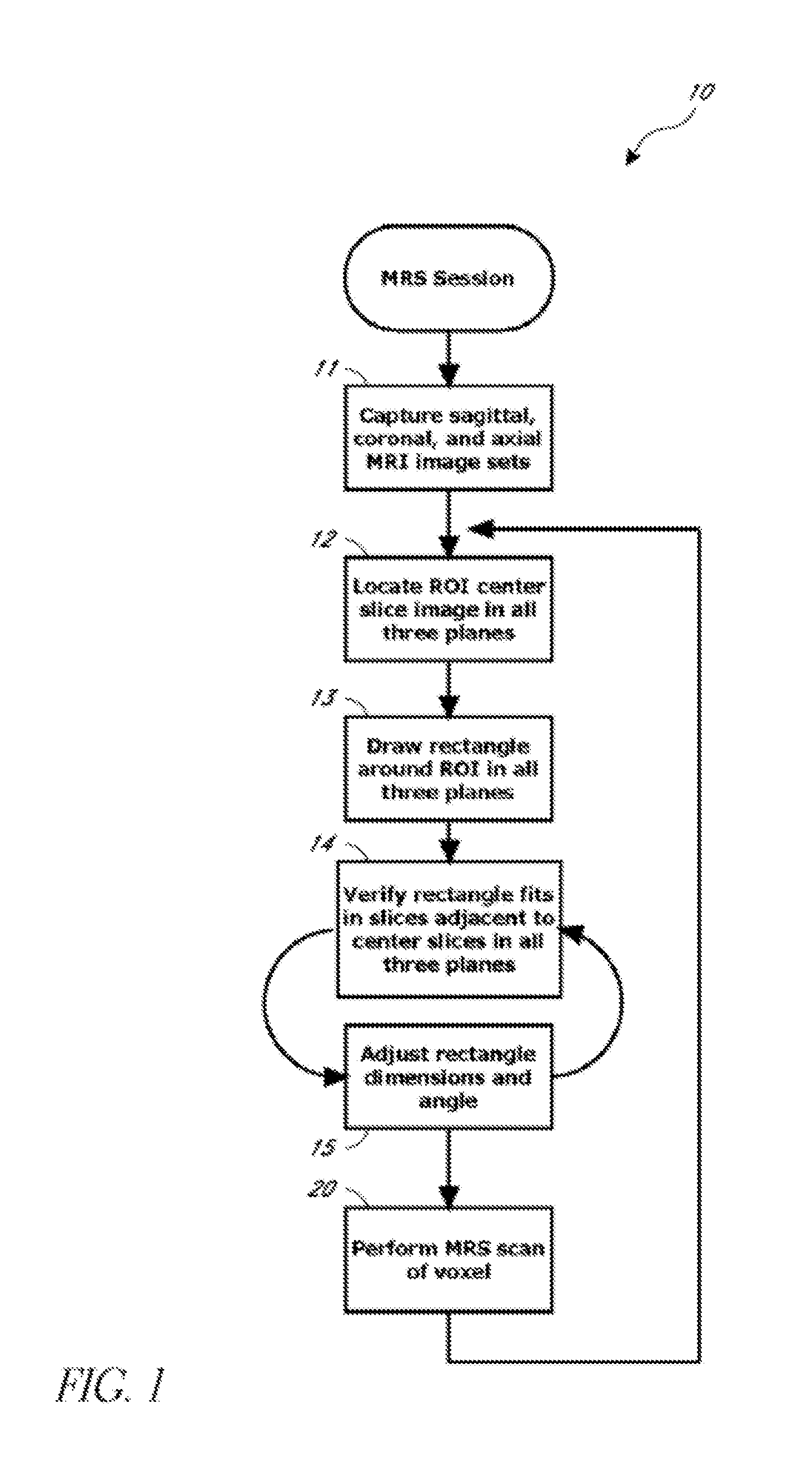
Systems and methods for automated voxelation of regions of interest for magnetic resonance spectroscopy
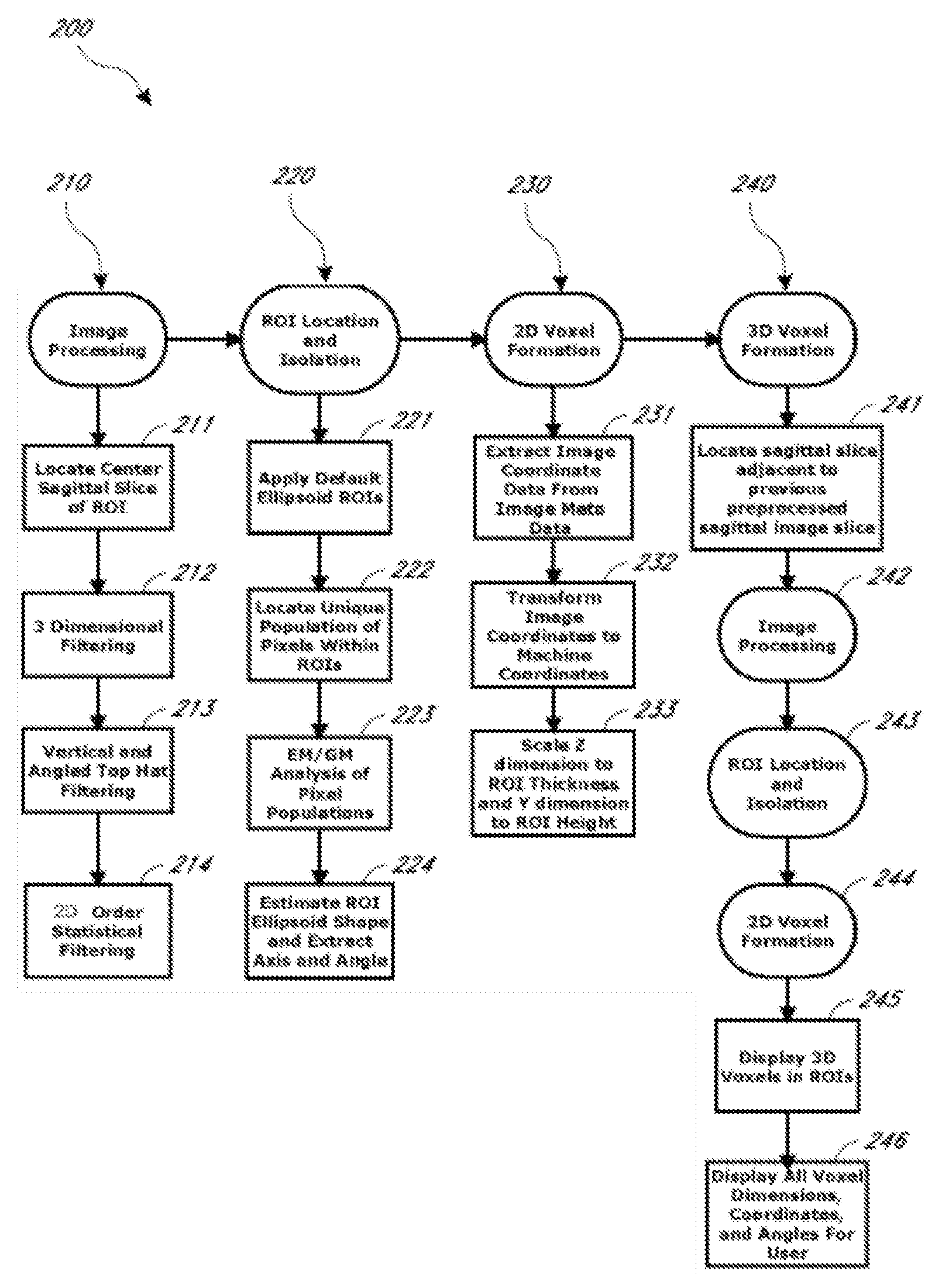
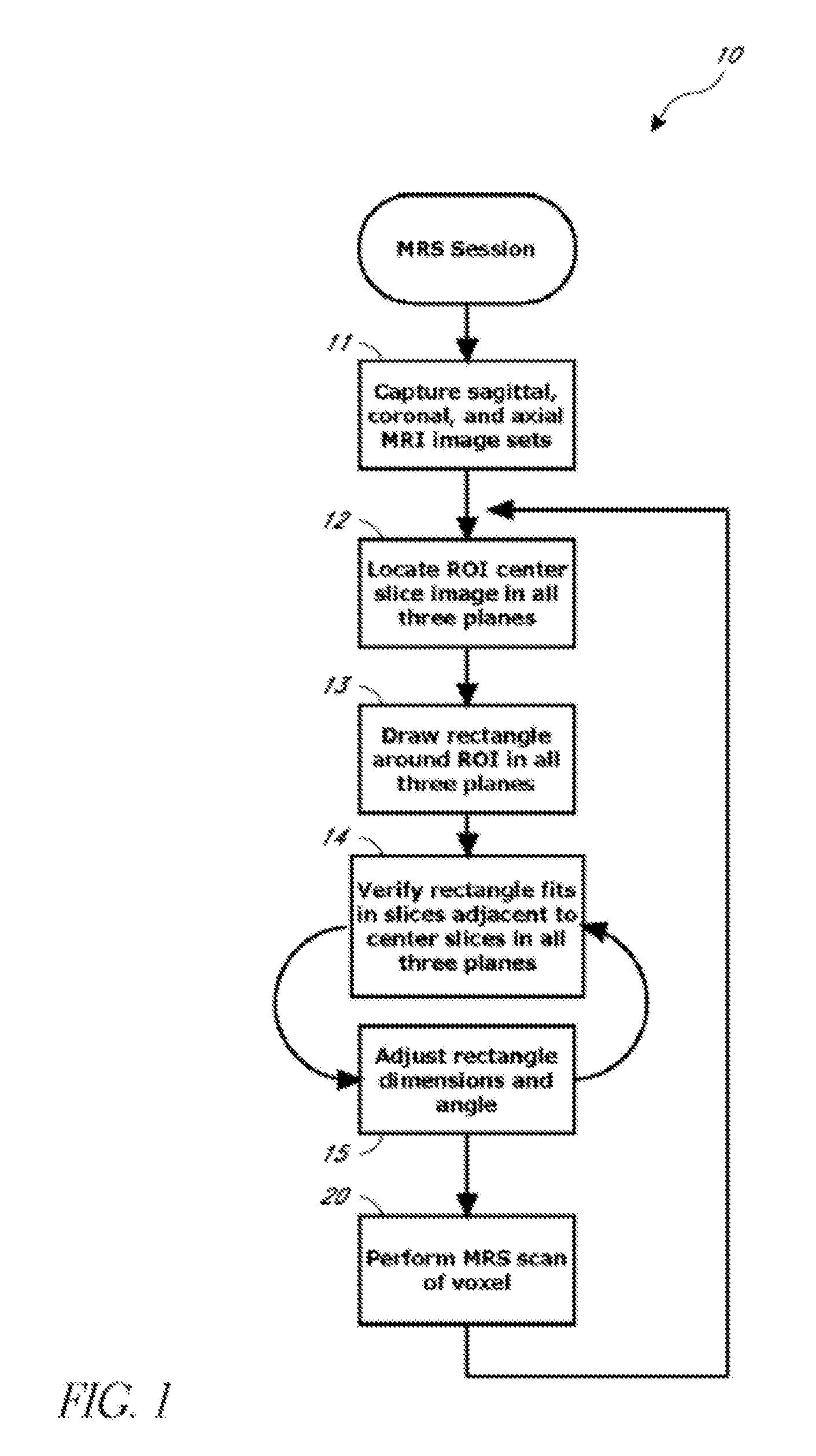
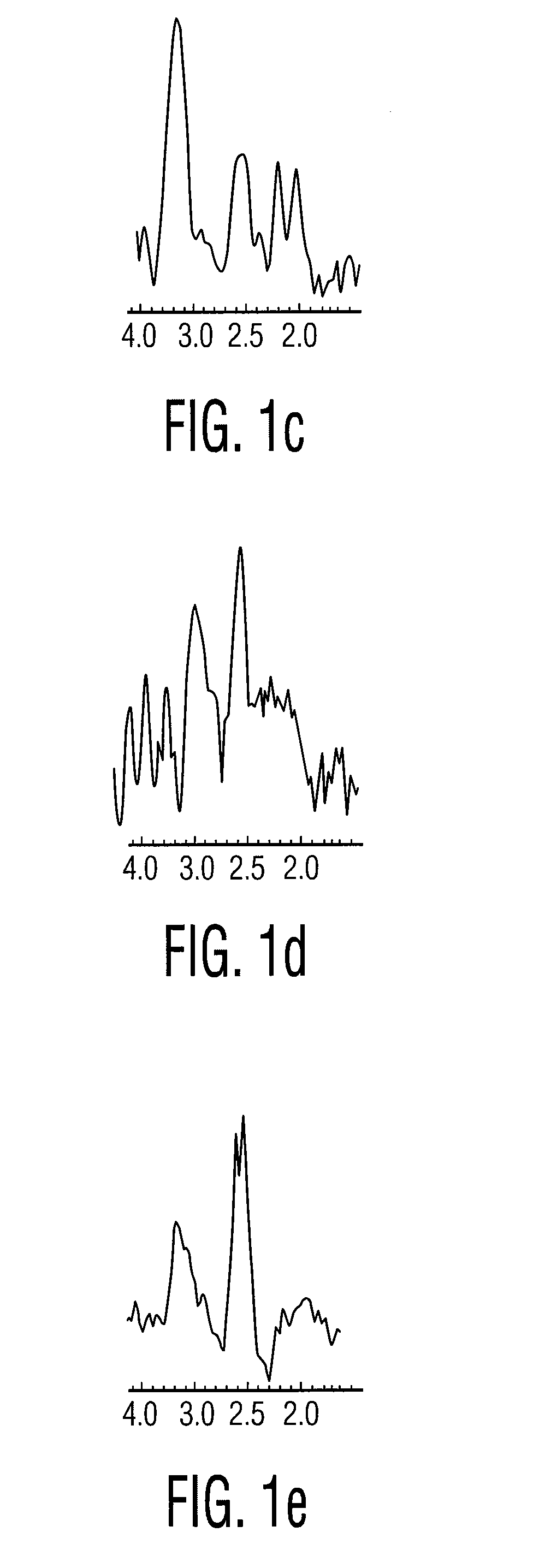
A system and method for automating an appropriate voxel prescription in a uniquely definable region of interest (ROI) in a tissue of a patient is provided, such as for purpose of conducting magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) in the ROI. The dimensions and coordinates of a single three dimensional rectilinear volume (voxel) within a single region of interest (ROI) are automatically identified. This is done, in some embodiments by: (1) applying statistically identified ROI search areas within a field of view (FOV); (2) image processing an MRI image to smooth the background and enhance a particular structure useful to define the ROI; (3) identifying a population of pixels that define the particular structure; (4) performing a statistical analysis of the pixel population to fit a 2D model such as an ellipsoid to the population and subsequently fit a rectilinear shape within the model; (5) repetiting elements (1) through (4) using multiple images that encompass the 3D ROI to create a 3D rectilinear shape; (6) a repetition of elements (1) through (5) for multiple ROIs with a common FOV. A manual interface may also be provided, allowing for override to replace by manual prescription, assistance to identify structures (e.g. clicking on disc levels), or modifying the automated voxel (e.g. modify location, shape, or one or more dimensions).
Owner:ACLARION INC
Superconductor Magnetic Resonance Imaging System and Method (SUPER-MRI)
ActiveUS20100231215A1Improve conductivityMachines/enginesSuperconductor devicesMagnetic field gradientMagnetic resonance spectrometry
Methods and apparatuses for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and / or magnetic resonance spectroscopy comprising a superconducting main magnet operable to generate a uniform magnetic field in an examination region, at least one superconducting gradient field coil operable to apply a respective at least one magnetic field gradient within the examination region, and at least one RF coil that is operable to transmit and receive radio frequency signals to and from the examination region, and that is configured for cooling and comprises at least one of (i) a non-superconducting material that when cooled to a temperature below room temperature has a conductivity higher than that of copper at that temperature and (ii) a superconducting material. The main magnet, the gradient coils, and each of the at least one RF coil of a given system may each be implemented as high temperature superconductor materials.
Owner:TIME MEDICAL HLDG
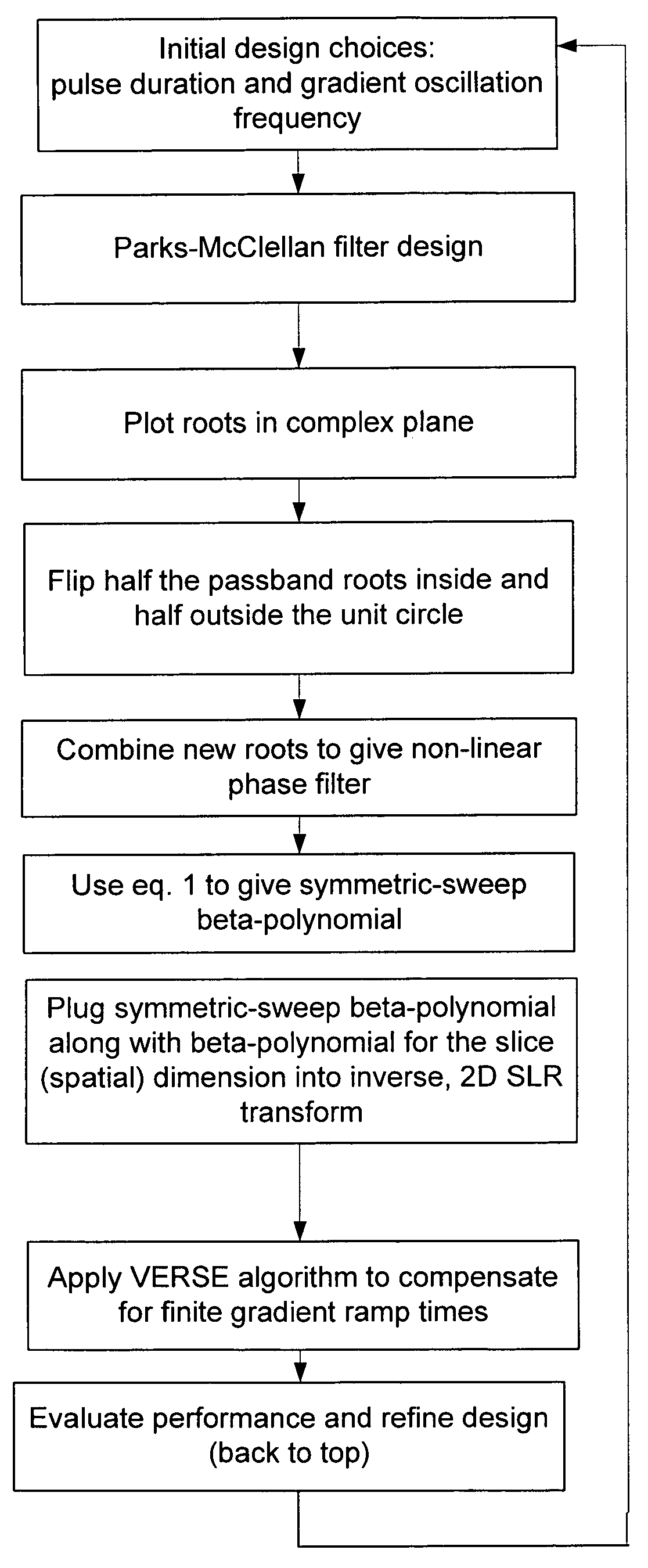
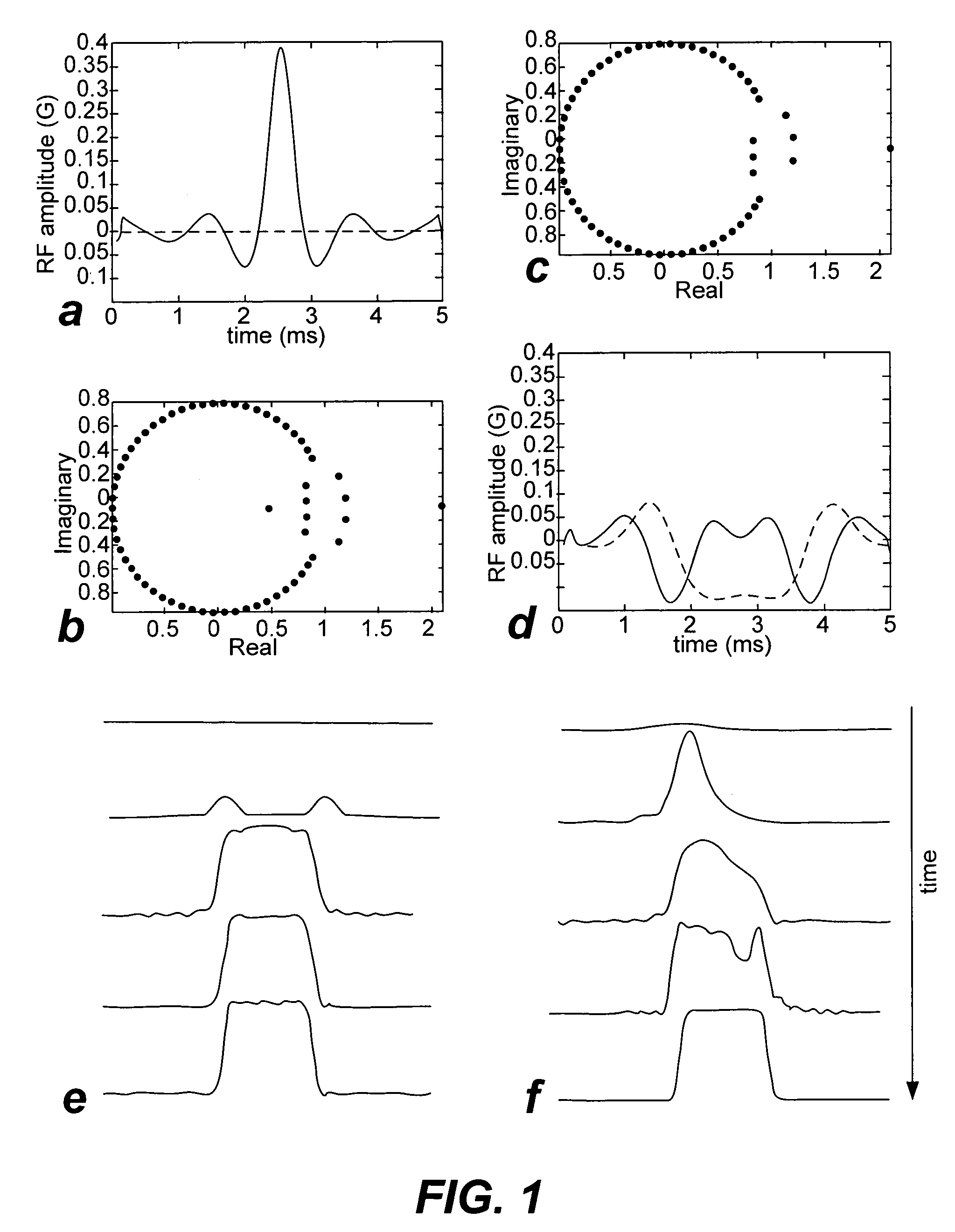
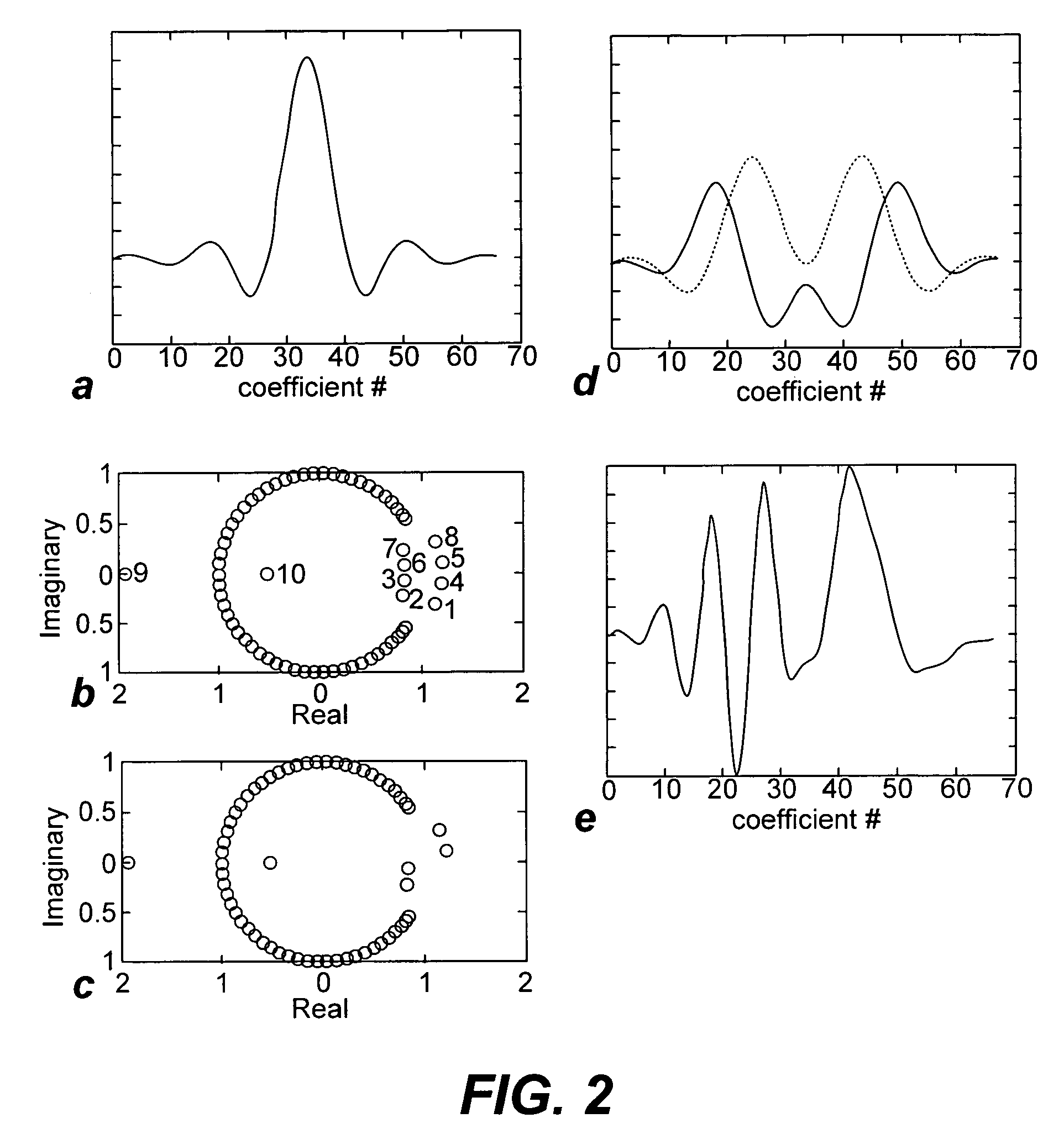
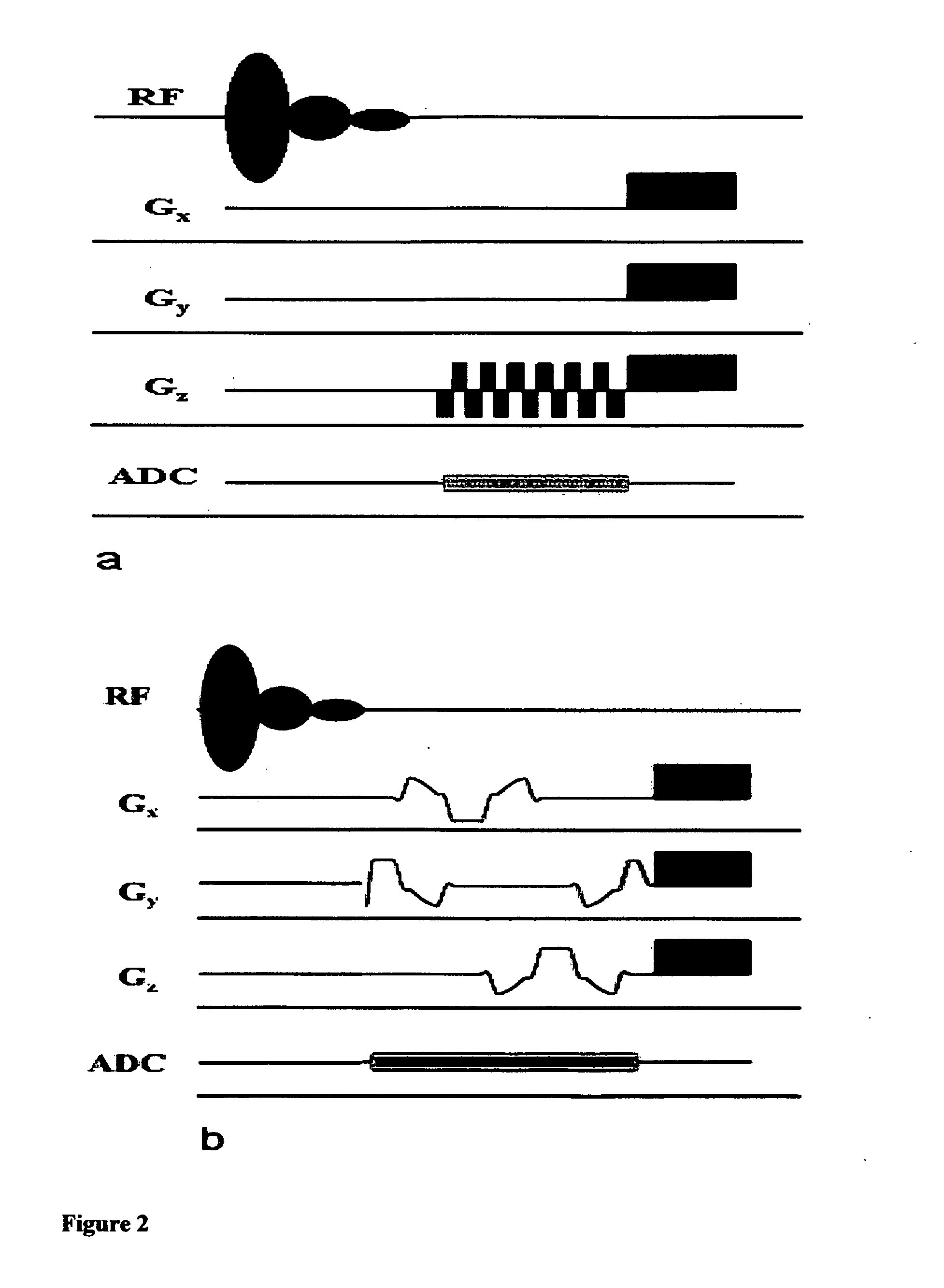
Non-linear symmetric sweep spectral-spatial RF pulses for MR spectroscopy
ActiveUS7042214B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionSpectroscopyRadio frequency
A method for designing non-linear phase 180° spectral-spatial radio frequency pulses that can be used for spectral editing in magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging. A novel feature of the pulse is a symmetric sweep developed by the spectral profile from the outside edges of the spectral window towards the middle whereby coupled components are tipped simultaneously and over a short interval. Pulses have been designed for lactate editing at 1.5T and 3T. The spectral and spatial spin-echo profiles of the RF pulses can be measured experimentally and altered in an iterative manner. Spectral-spatial radio frequency (SSRF) pulses allow simultaneous selection in both frequency and spatial domains. These pulses are particularly important for clinical and research magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) applications for suppression of large water and lipid resonances.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
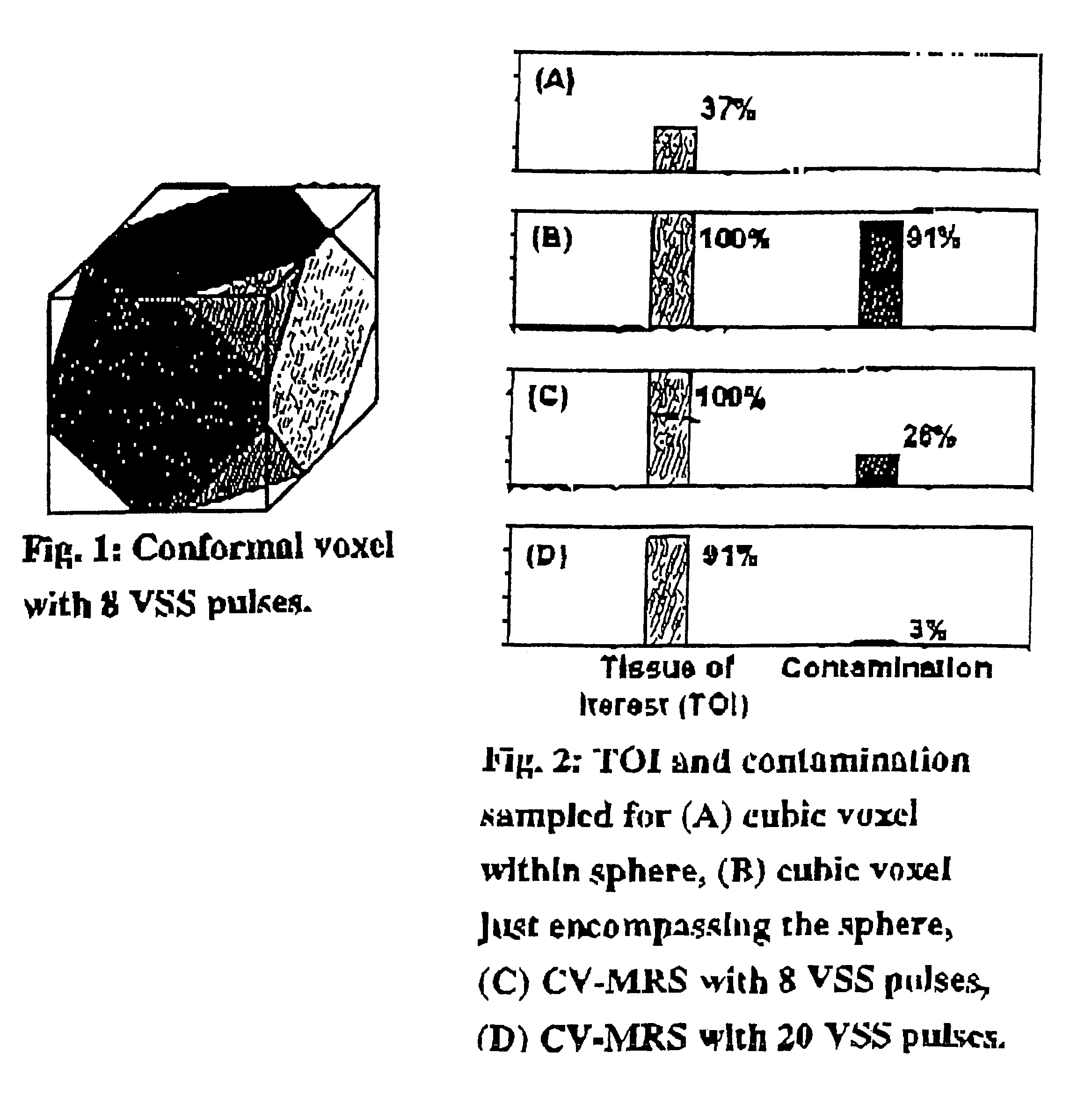
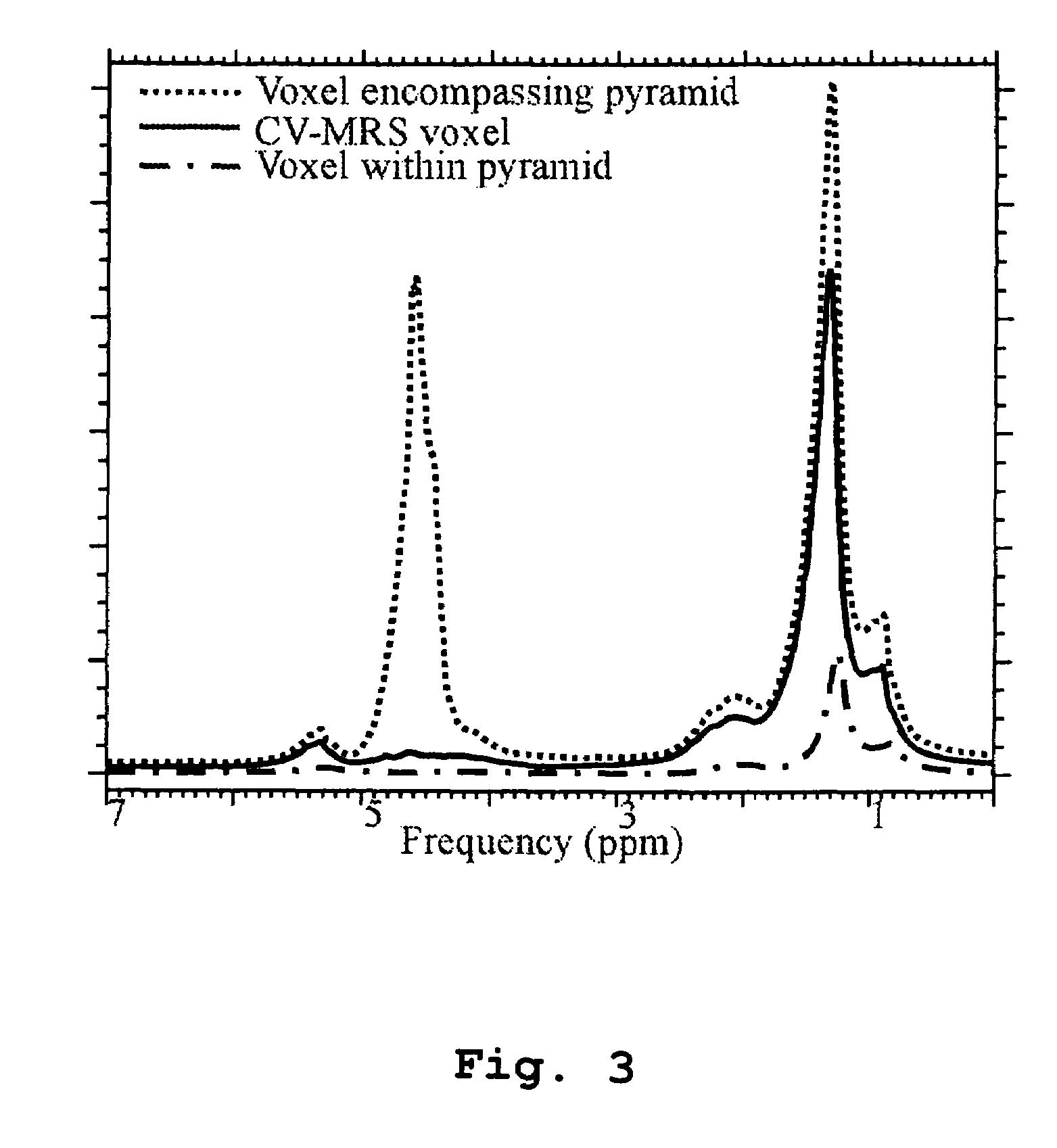
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy using a conformal voxel
InactiveUS7319784B2Improving prescriptionAdd featureMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionVoxelSelective excitation
The goal was to automate and optimize the shaping and positioning of a shape-specific / conformal voxel that conforms to any volume of interest, such as a cranial lesion, to allow conformal voxel magnetic resonance spectroscopy (CV-MRS). We achieved this by using a computer program that optimizes the shape, size, and location of a convex polyhedron within the volume of interest. The sides of the convex polyhedron are used to automatically prescribe the size and location of selective excitation voxels and / or spatial saturation slices. For a spherically-shaped, phantom-simulated lesion, CV-MRS increased the signal from the lesion by a factor of 2.5 compared to a voxel completely inside the lesion. CV-MRS reduces the voxel prescription time, operator subjectivity, and acquisition time.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
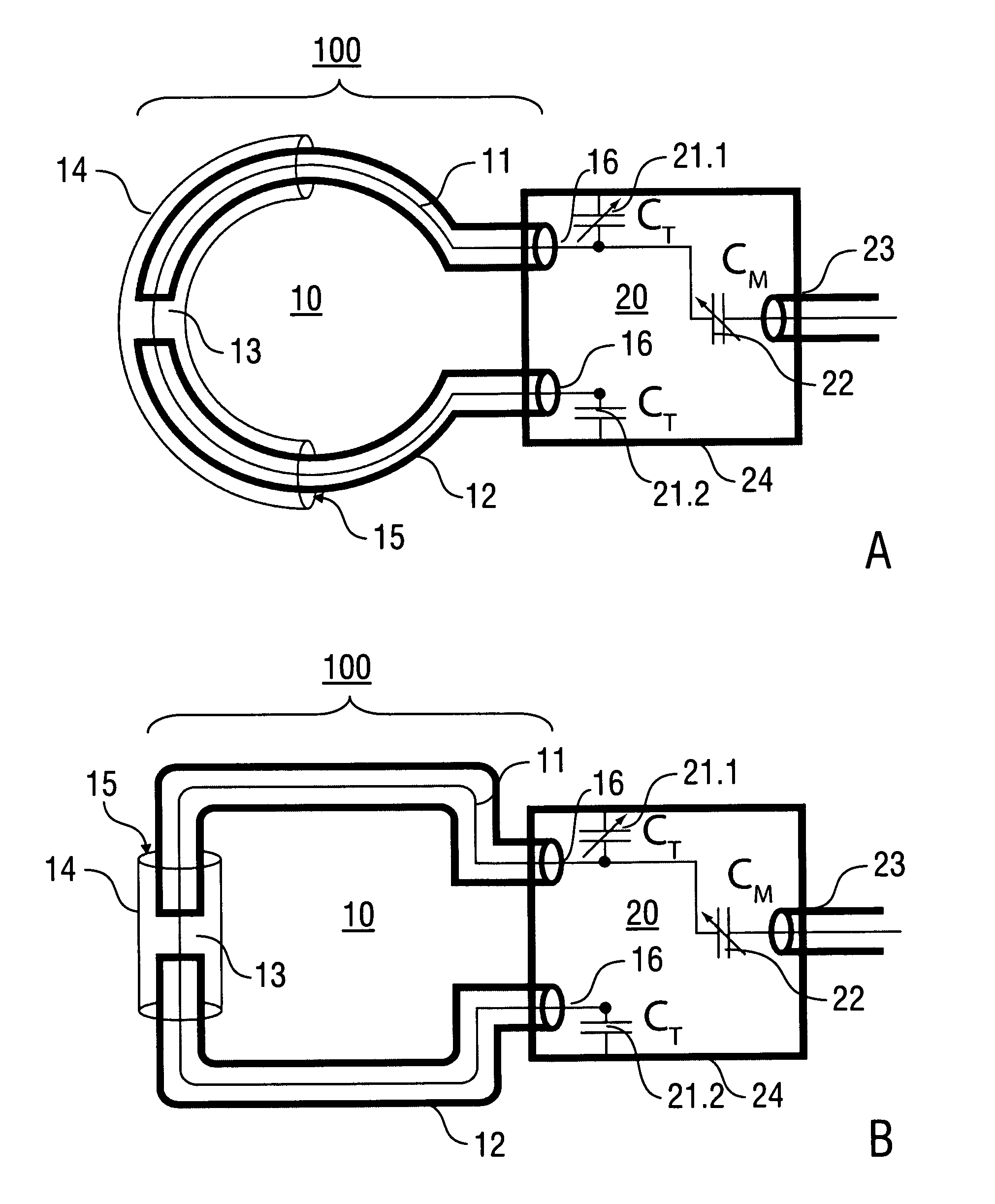
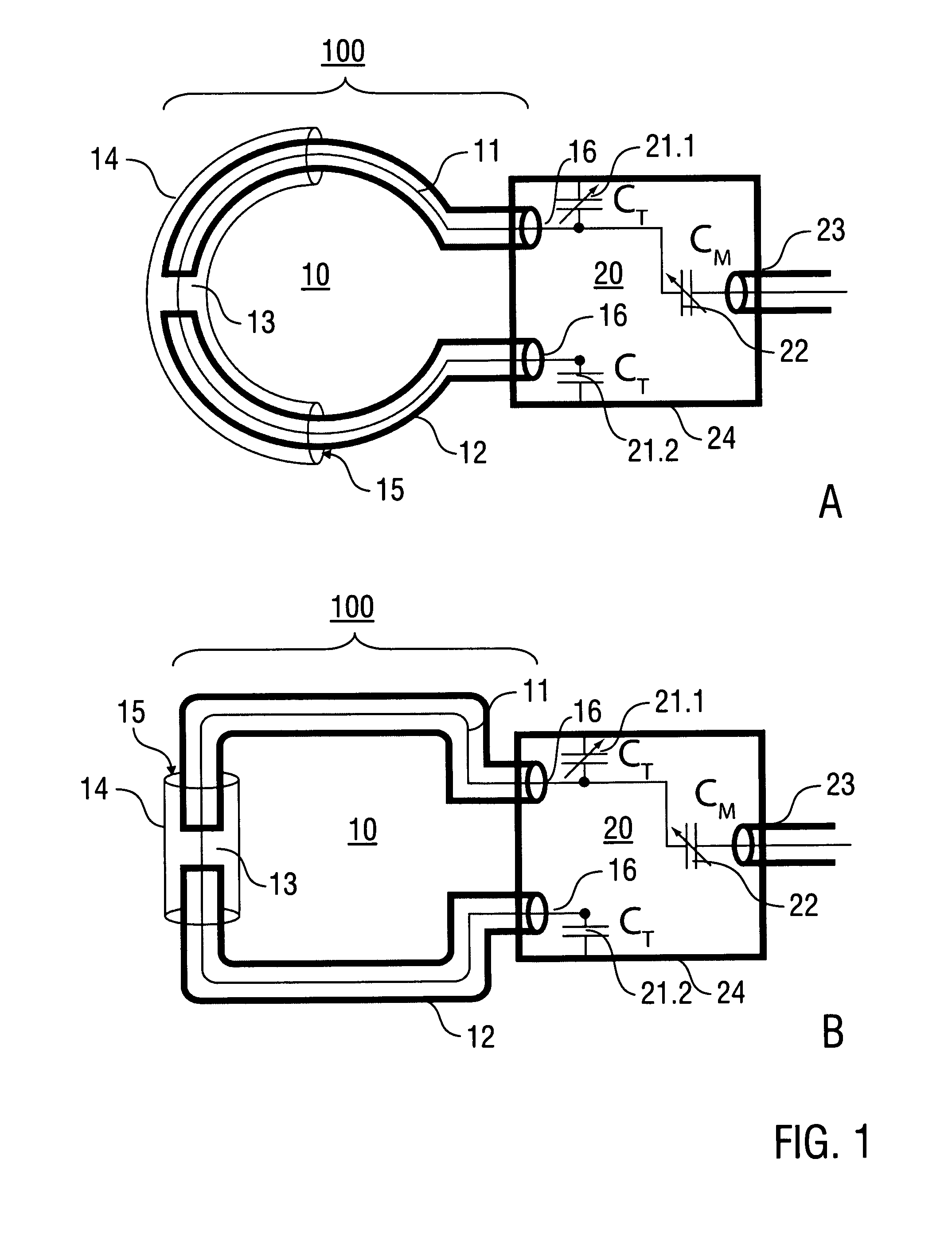
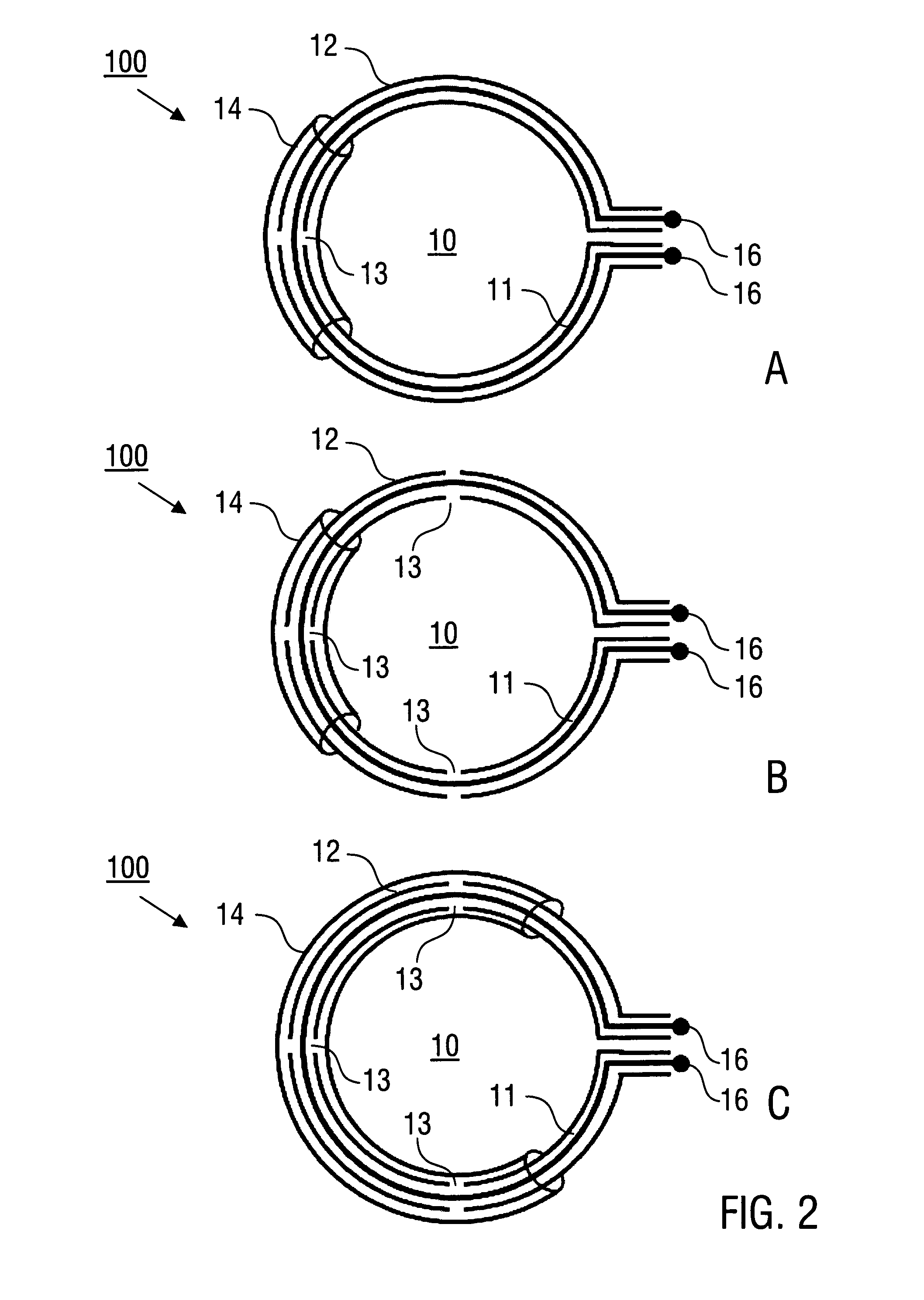
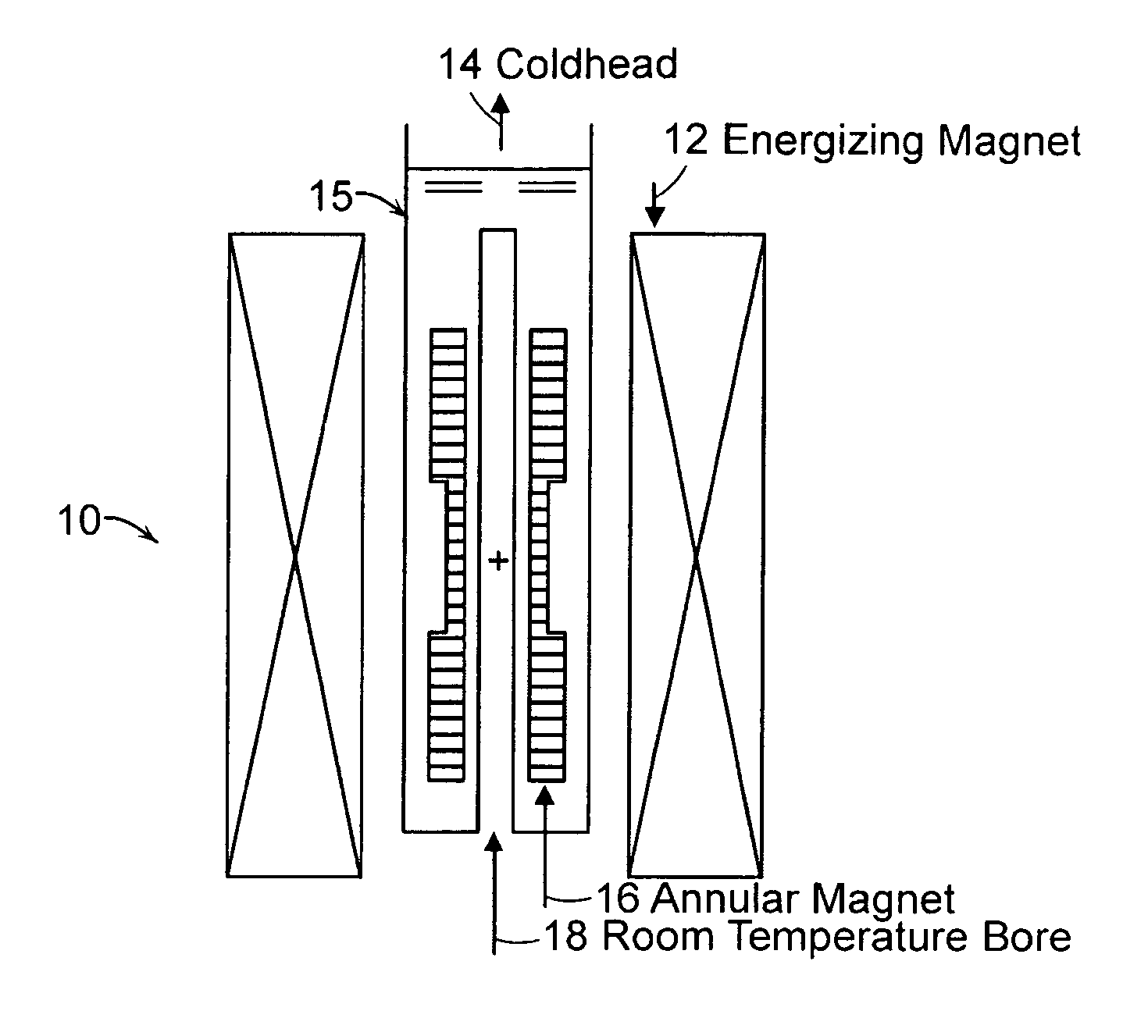
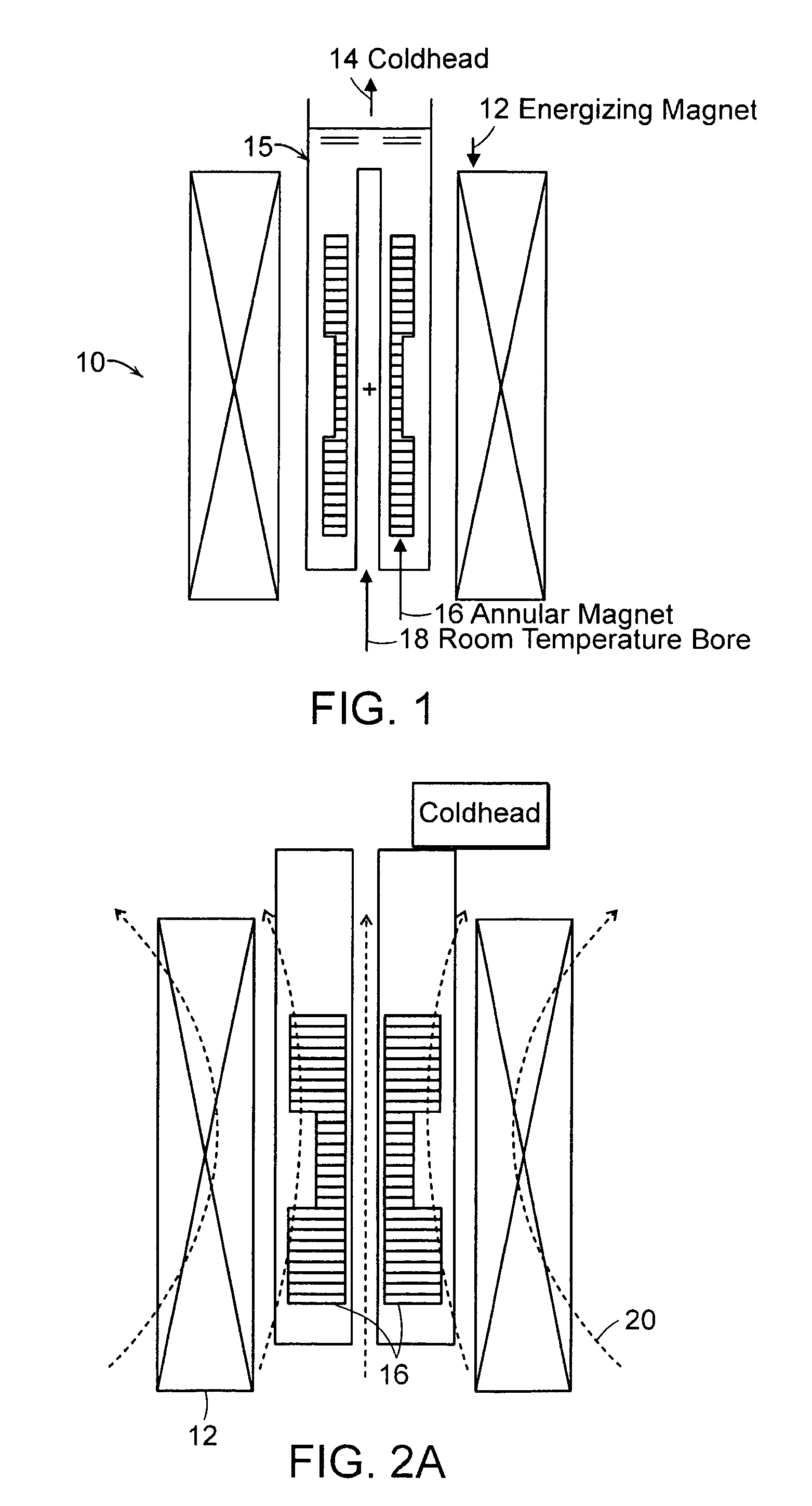
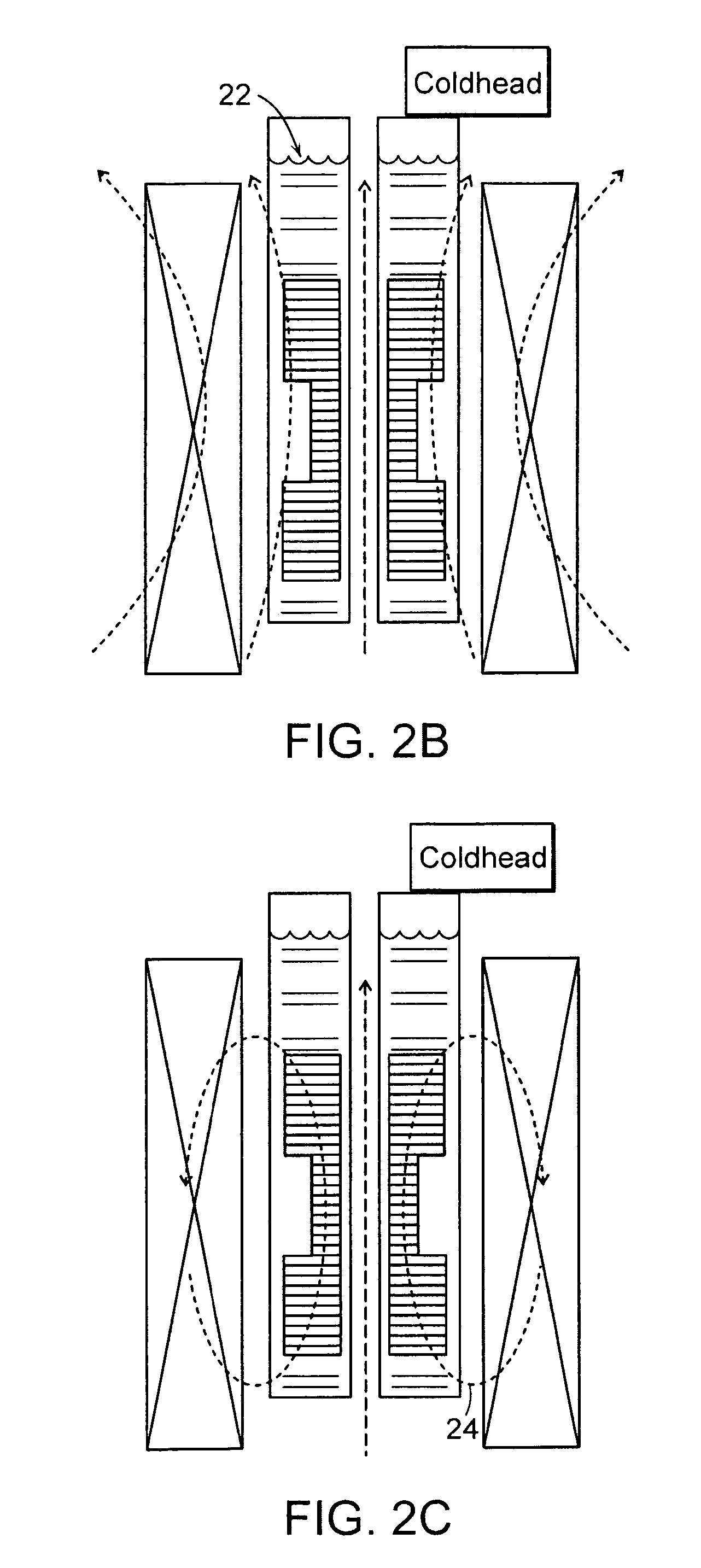
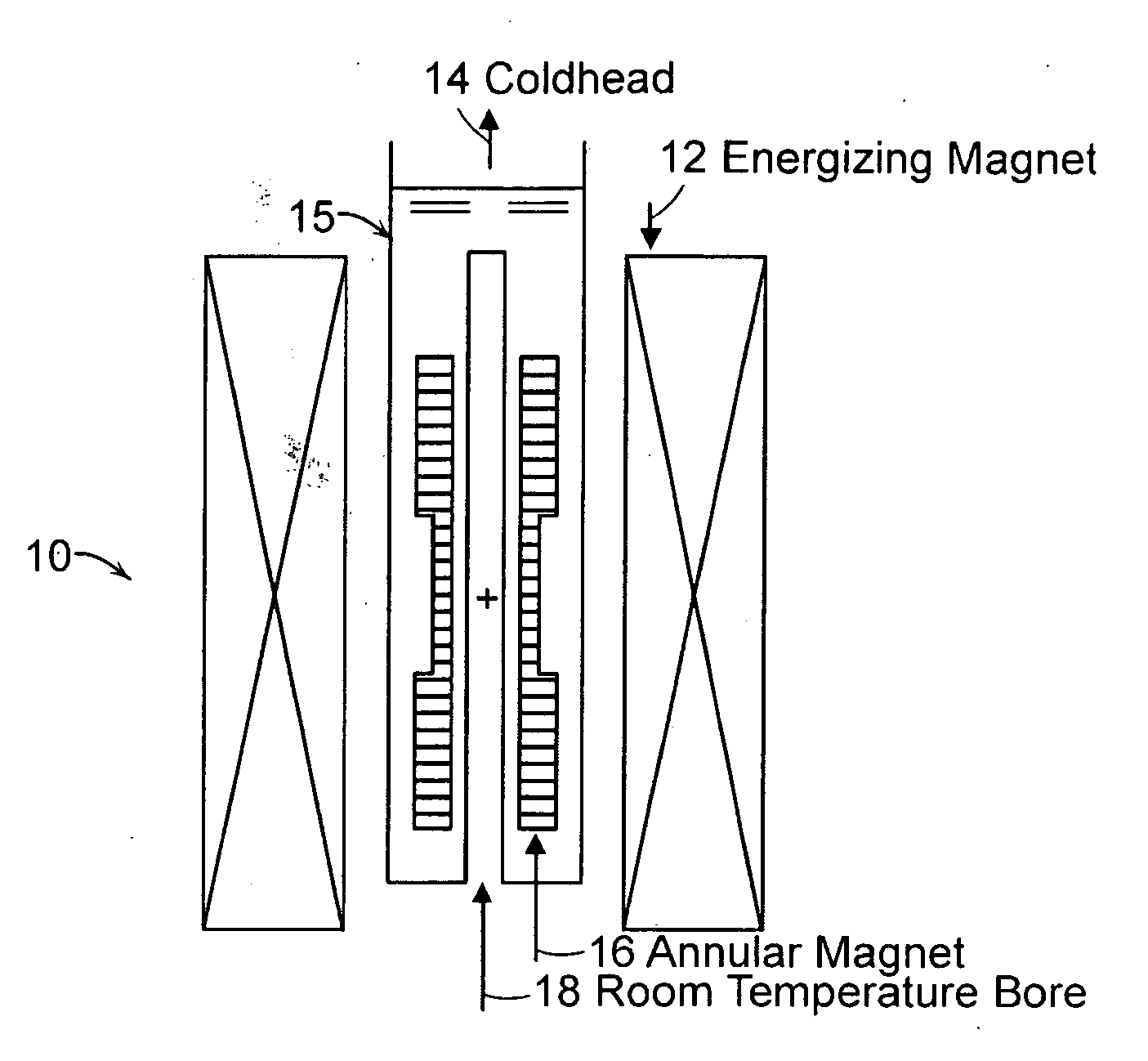
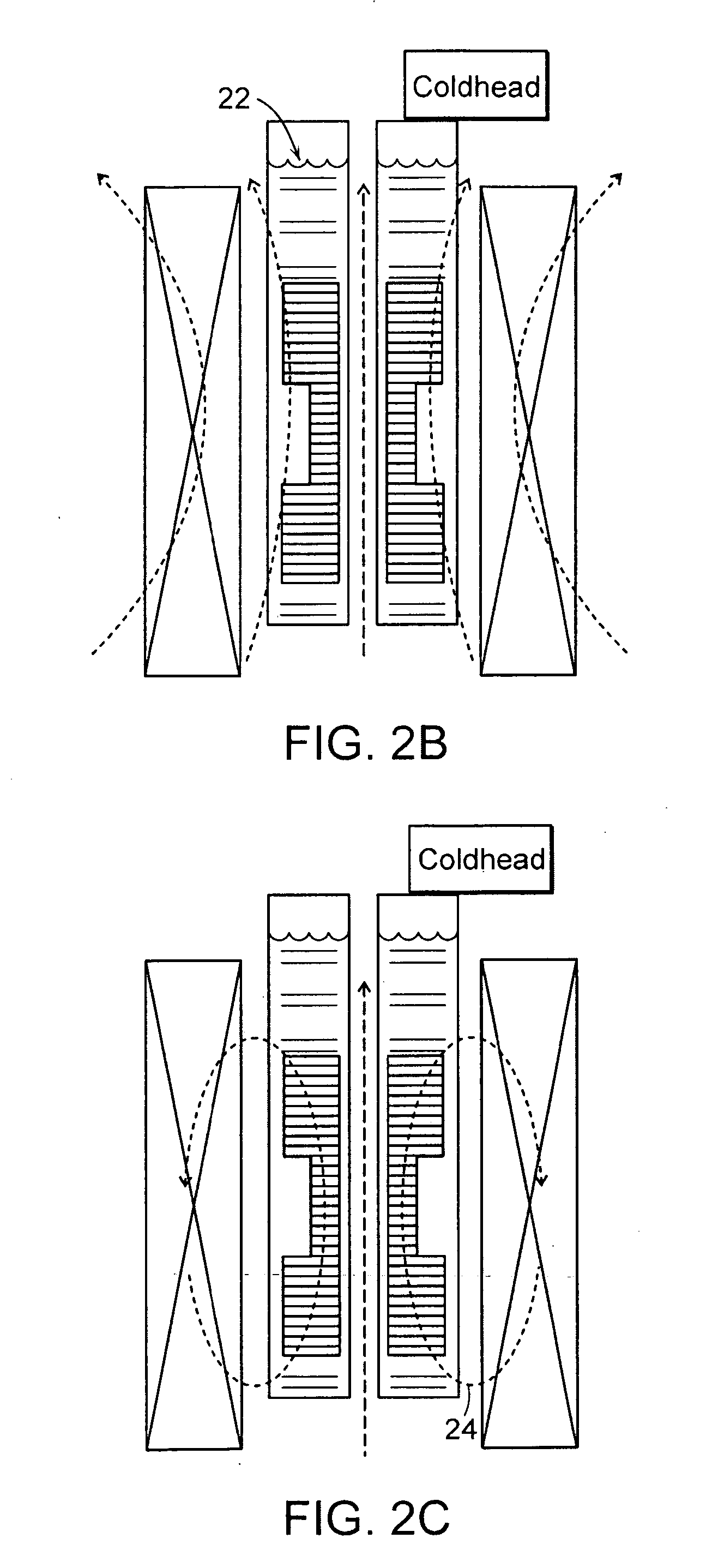
Annular magnet system for magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy with sparse spectral sampling and interleaved dynamic shimming
InactiveUS7683614B2Maximize efficiencyMaximize sensitivityMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientSpectral dimension
The present invention relates to a magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) method, specifically to a magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging method with up to three spatial dimensions and one spectral dimension. Interleaving dynamically switched magnetic field gradients into the spectroscopic encoding scheme enables multi-region shimming in a single shot to compensate the spatially varying spectral line broadening resulting from local magnetic field gradients. The method also employs sparse spectral sampling with controlled spectral aliasing and nonlinear sampling density to maximize encoding speed, data sampling efficiency and sensitivity.
Owner:POSSE STEFAN
Molecular chemotherapy enhancement of radiotherapy
InactiveUS6552005B1Tumour growth inhibitionCurrent is limitedBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsWhole bodyCytotoxicity
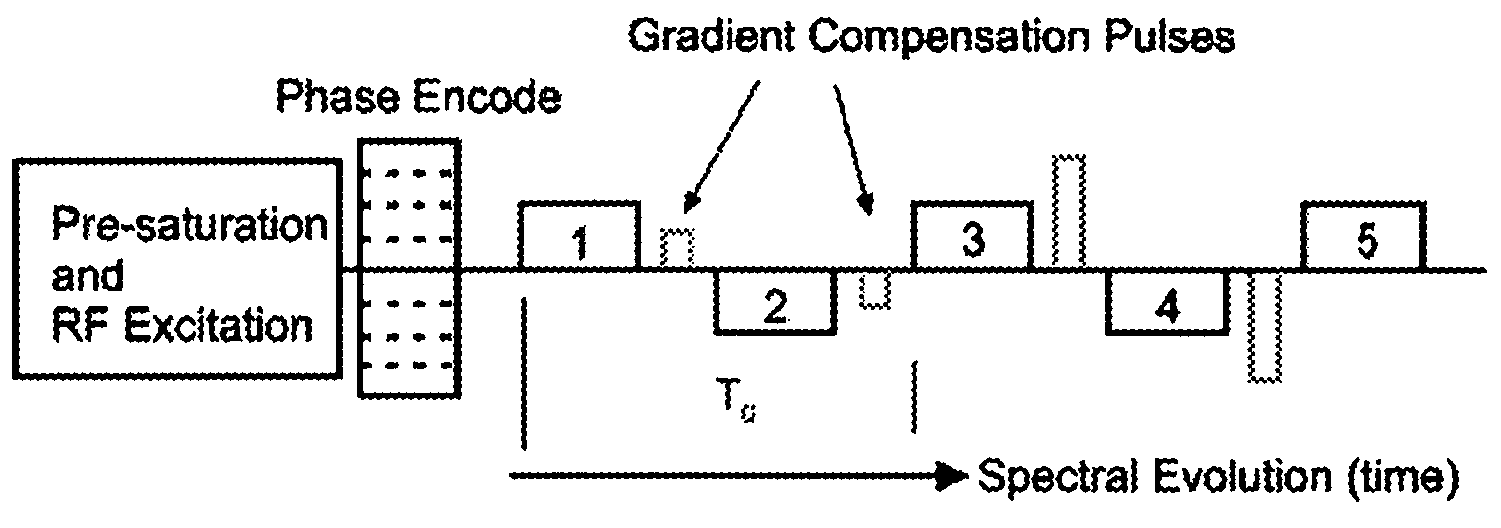
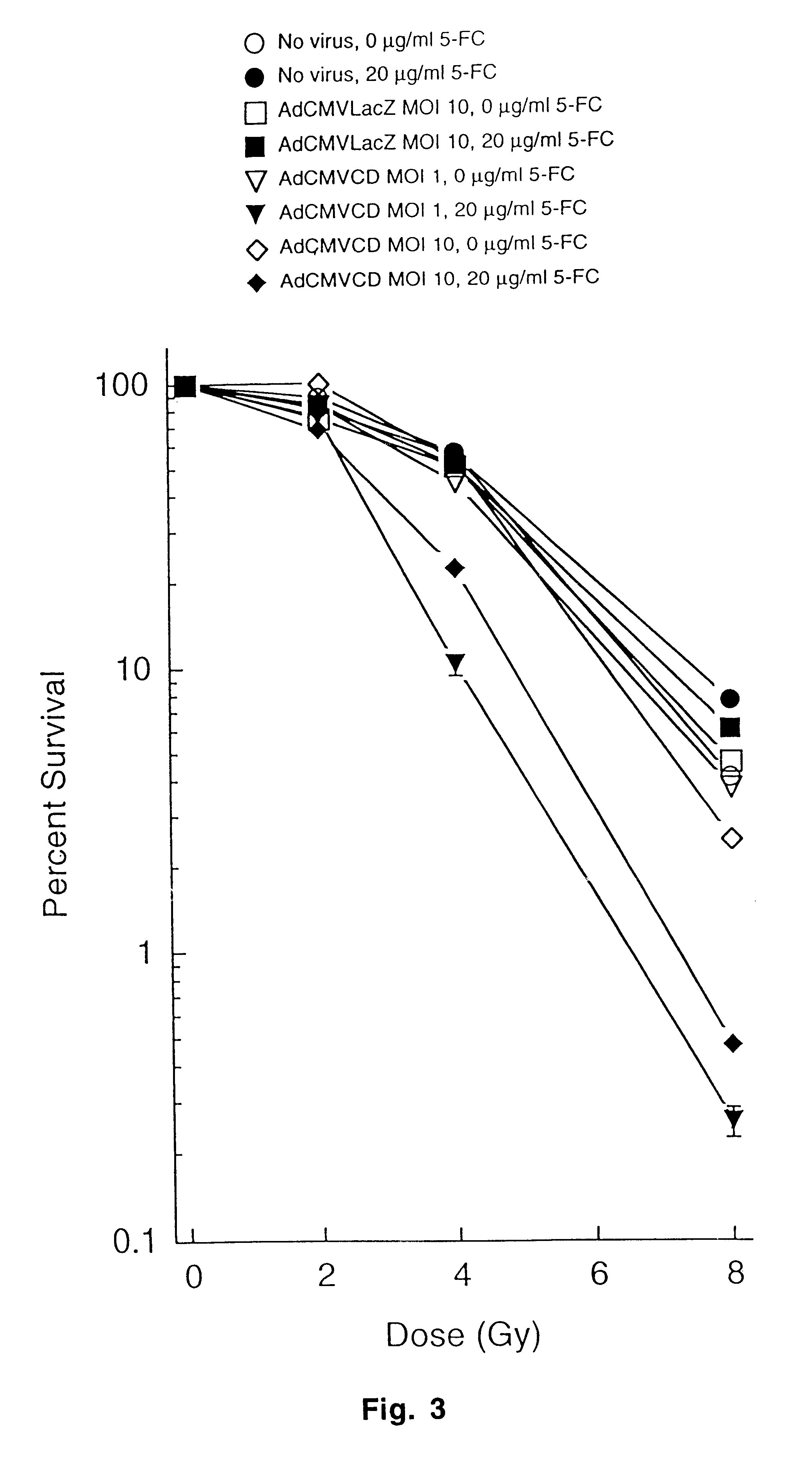
The present invention provides a new approach for cancer treatment by utilizing gene therapy combined with radiation therapy to enhance cytotoxicity in malignant cells. Specifically, the present invention demonstrates that molecular chemotherapy with the cytosine deaminase gene and 5-fluorocytosine is an effective radiosensitizing strategy which may lead to substantial improvement in tumor control, with less normal tissue toxicity than conventional systemic administration of 5-fluorouracil, that would translate into improved cure rates and better survival. A noninvasive method is described for continuous in vivo monitoring of 5-fluorouracil production via magnetic resonance spectroscopy. An adenovirus encoding cytosine deaminase gene which selectively replicates in tumor cells with a defective p53 pathway was constructed. Also provided is an adenovirus which encodes a fusion protein of cytosine deaminase and uracil phosphoribosyltransferase.
Owner:CDEPT
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy with sparse spectral sampling and interleaved dynamic shimming
InactiveUS20070252597A1Maximize encoding speedMaximize data sampling efficiencyMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientSpectral dimension
The present invention relates to a magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) method, specifically to a magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging method with up to three spatial dimensions and one spectral dimension. Interleaving dynamically switched magnetic field gradients into the spectroscopic encoding scheme enables multi-region shimming in a single shot to compensate the spatially varying spectral line broadening resulting from local magnetic field gradients. The method also employs sparse spectral sampling with controlled spectral aliasing and nonlinear sampling density to maximize encoding speed, data sampling efficiency and sensitivity.
Owner:POSSE STEFAN
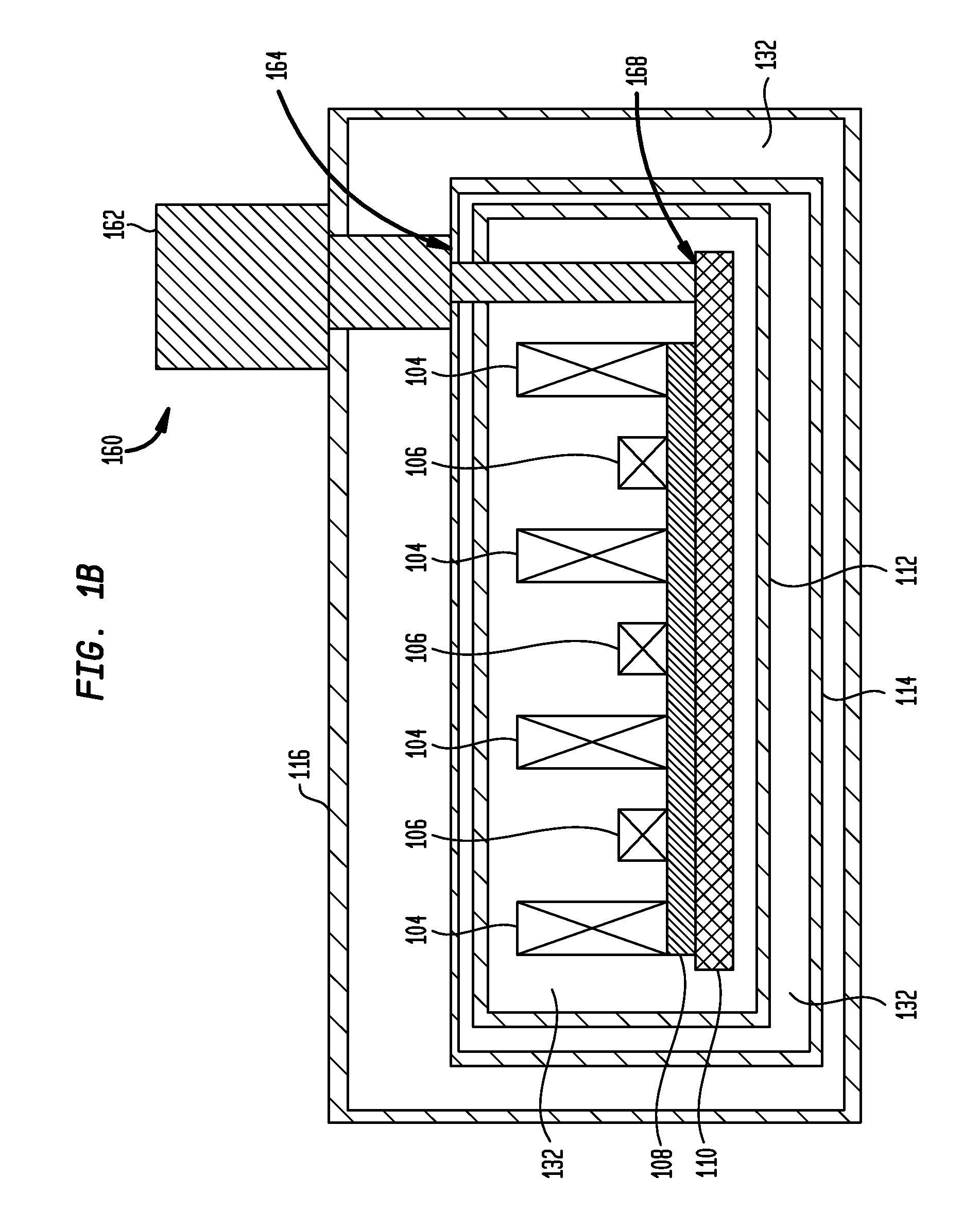
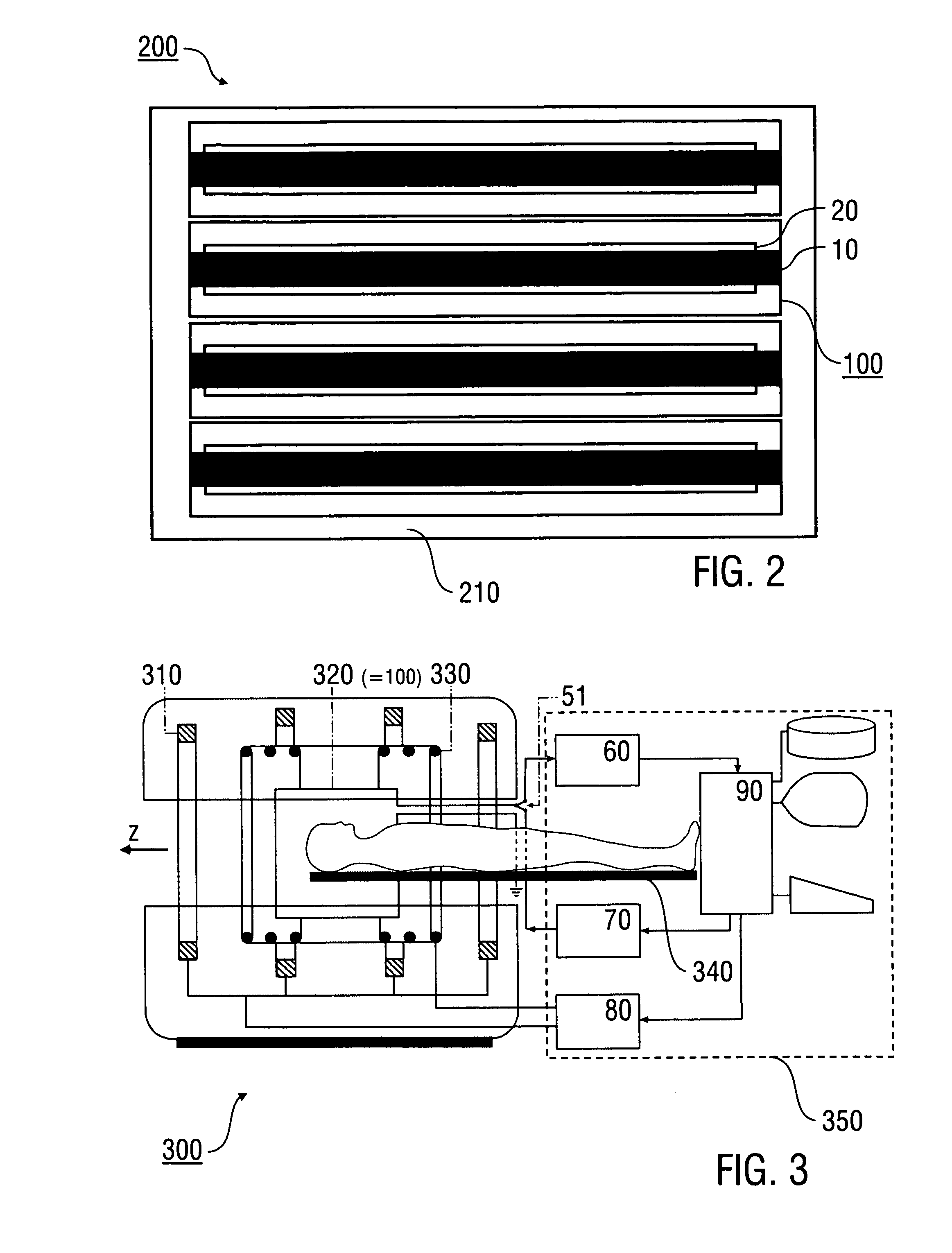
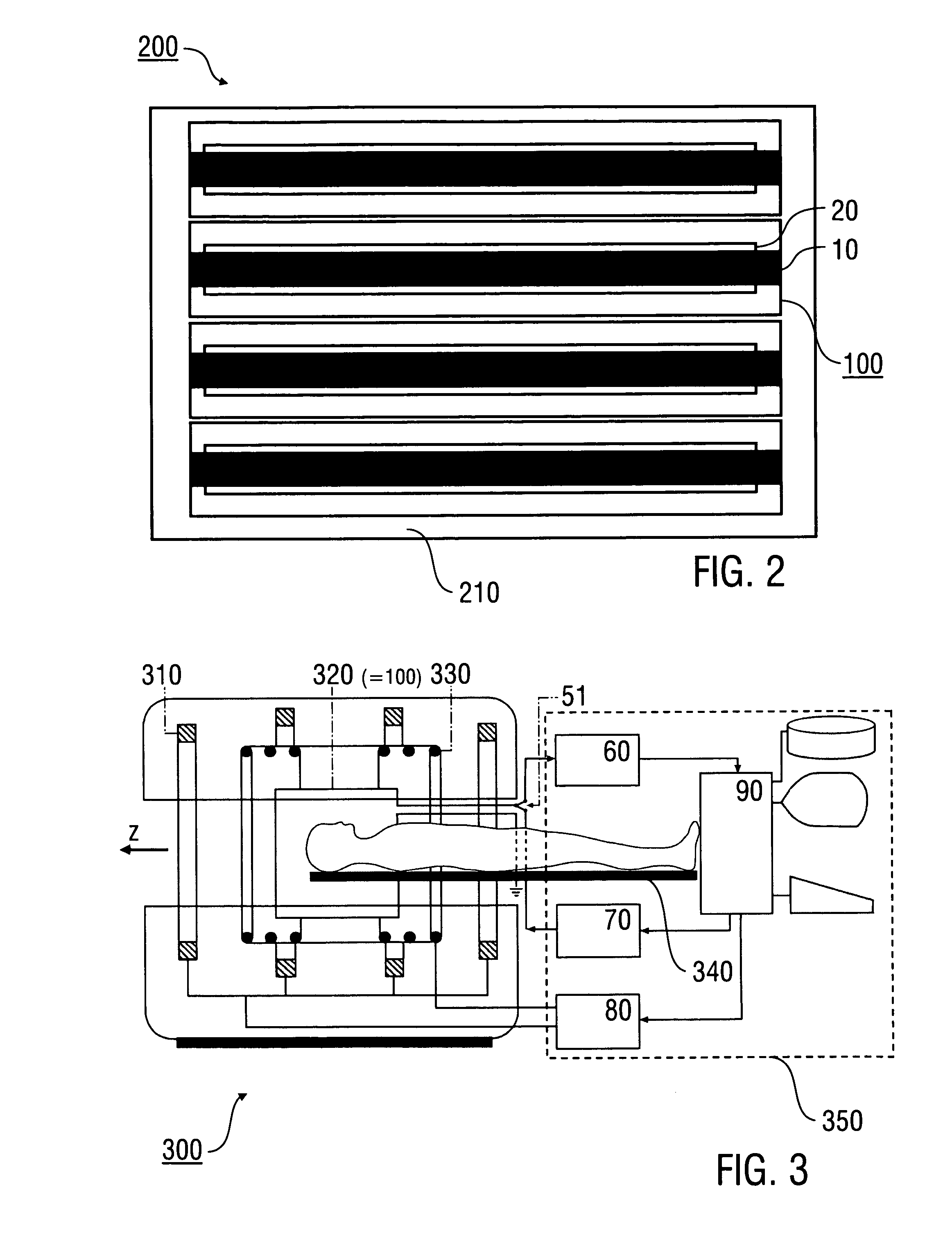
Stripline antenna and antenna array for a magnetic resonance device
InactiveUS20100213941A1Antenna structure is simpleSimple structureElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagnetic resonance spectroscopicStripline resonator
An antenna (100) for a magnetic resonance device has a predetermined sensitivity and is designed to excite and / or detect a magnetic resonance in an object under test. The antenna (100) includes a stripline resonator (10) that is equipped with at least one stripline (11), and a conductor loop arrangement (20) that adjoins the stripline resonator (10) and forms at least one conductor loop (21, 22, 28) which is interrupted by at least one capacitor (23). The sensitivity of the antenna (100) is formed by overlapping sensitivity profiles of the stripline resonator (10) and the conductor loop arrangement (20). Also described are an antenna array (200) including a plurality of antennas (100), a magnetic resonance device (300) including at least one antenna (100) or antenna array (200), and methods for magnetic resonance imaging or magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
System and method for detecting pain and its components using magnetic resonance spectroscopy
InactiveUS7676254B2Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMetaboliteAssessing Pain
Owner:SYDNEY UNIV OF +2
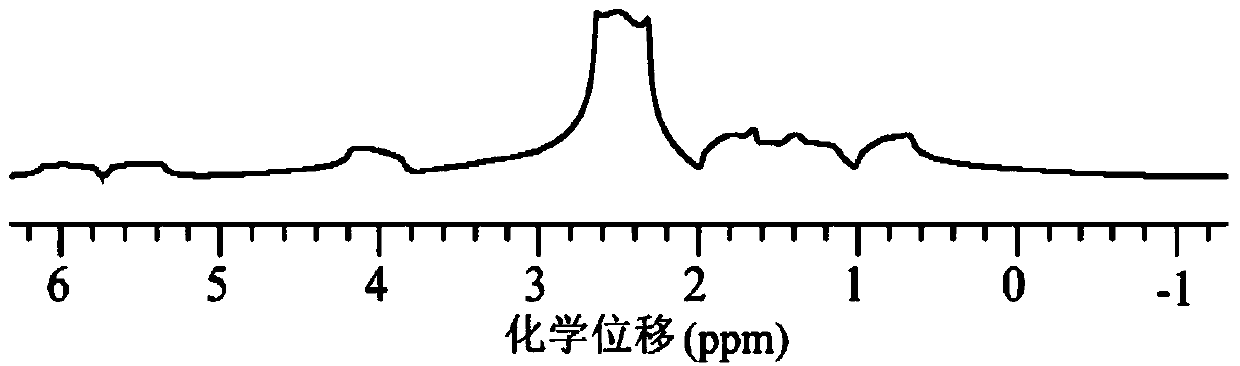
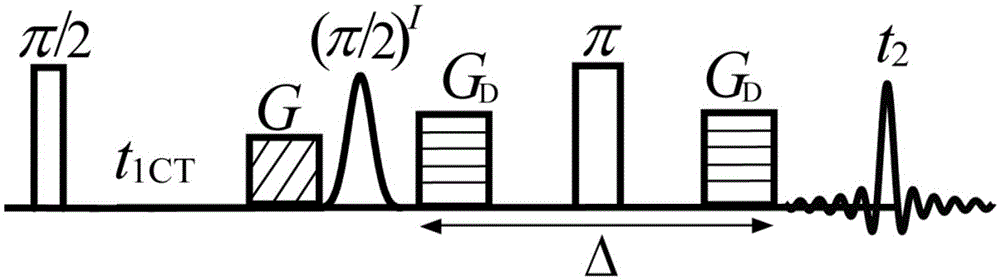
Method for obtaining high-resolution two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum
InactiveCN106093099AAvoid signal excitationAvoid applicabilityAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceDecompositionLine width
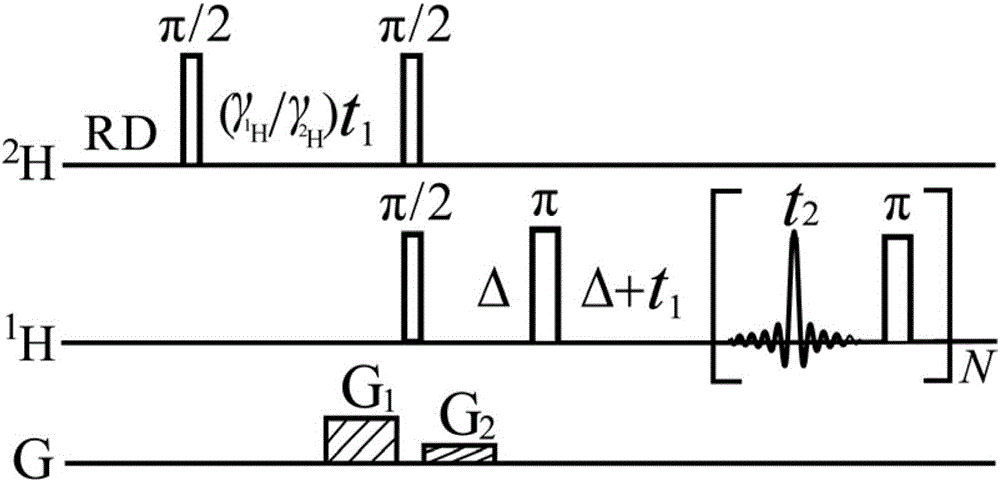
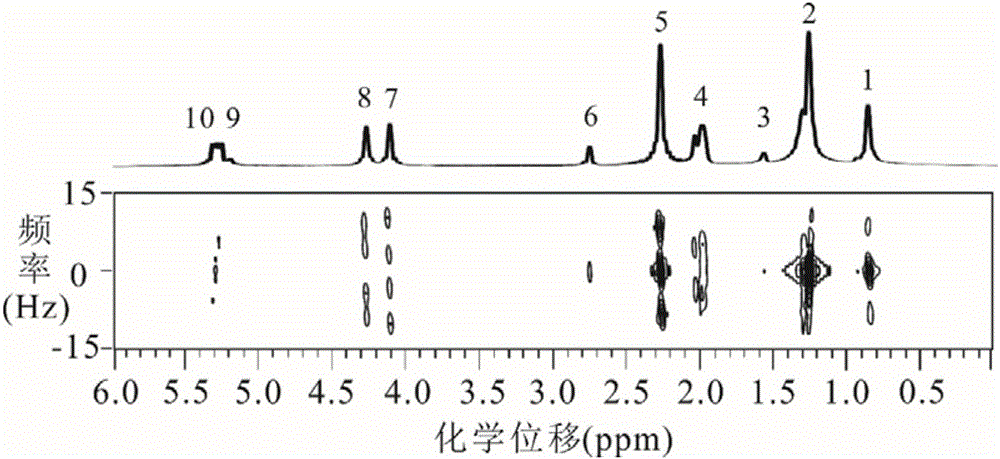
The invention provides a method for obtaining a high-resolution two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum, and relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy detection method. The method comprises: loading a sample to be detected into a standard nuclear magnetic test tube, and conveying into the detection chamber of a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer; sampling the one-dimensional hydrogen spectrum of the sample to be detected, and obtaining the signal peak distribution area and the spectral line width so as to provide the reference for the spectral width parameter setting, wherein the line width value reflects the magnetic field uniformity condition; measuring the pulse width of a radio frequency pulse required by excitation of the sample to be detected; introducing a compiled pulse sequence on the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer, opening the heteronuclear intermolecule multiple quantum coherent signal excitation module, the indirect dimensional evolving module, the spin echo fixed delay module and the J modulating fast sampling module of the pulse sequence, and setting the experiment parameters of various modules; skipping the artificial shimming operation process, and directly executing data sampling; and after completing the data sampling, calling data post-processing codes to carry out related data post-processing so as to obtain the high-resolution two-dimensional J decomposition spectrum being not affected by the inhomogeneous magnetic field.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
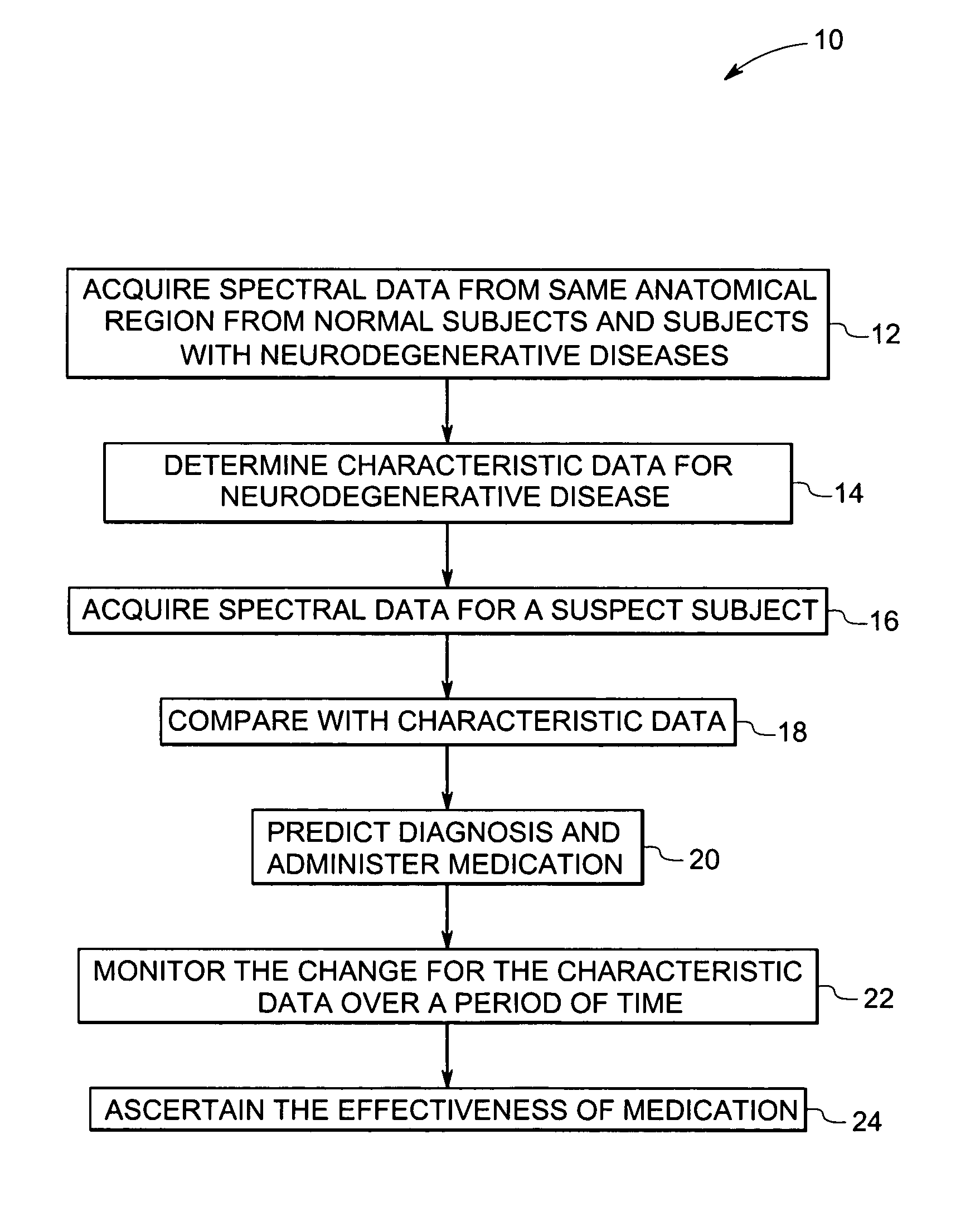
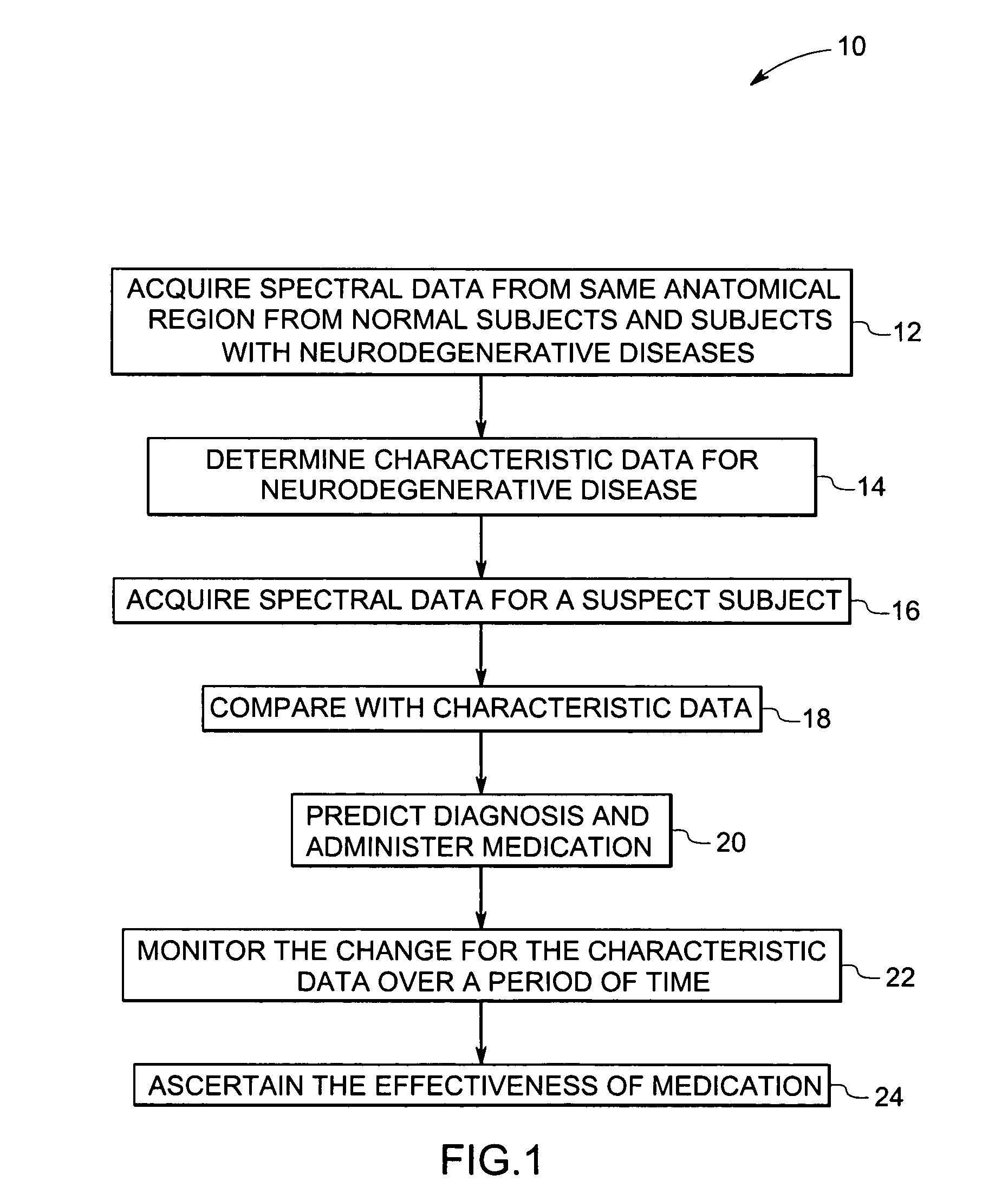
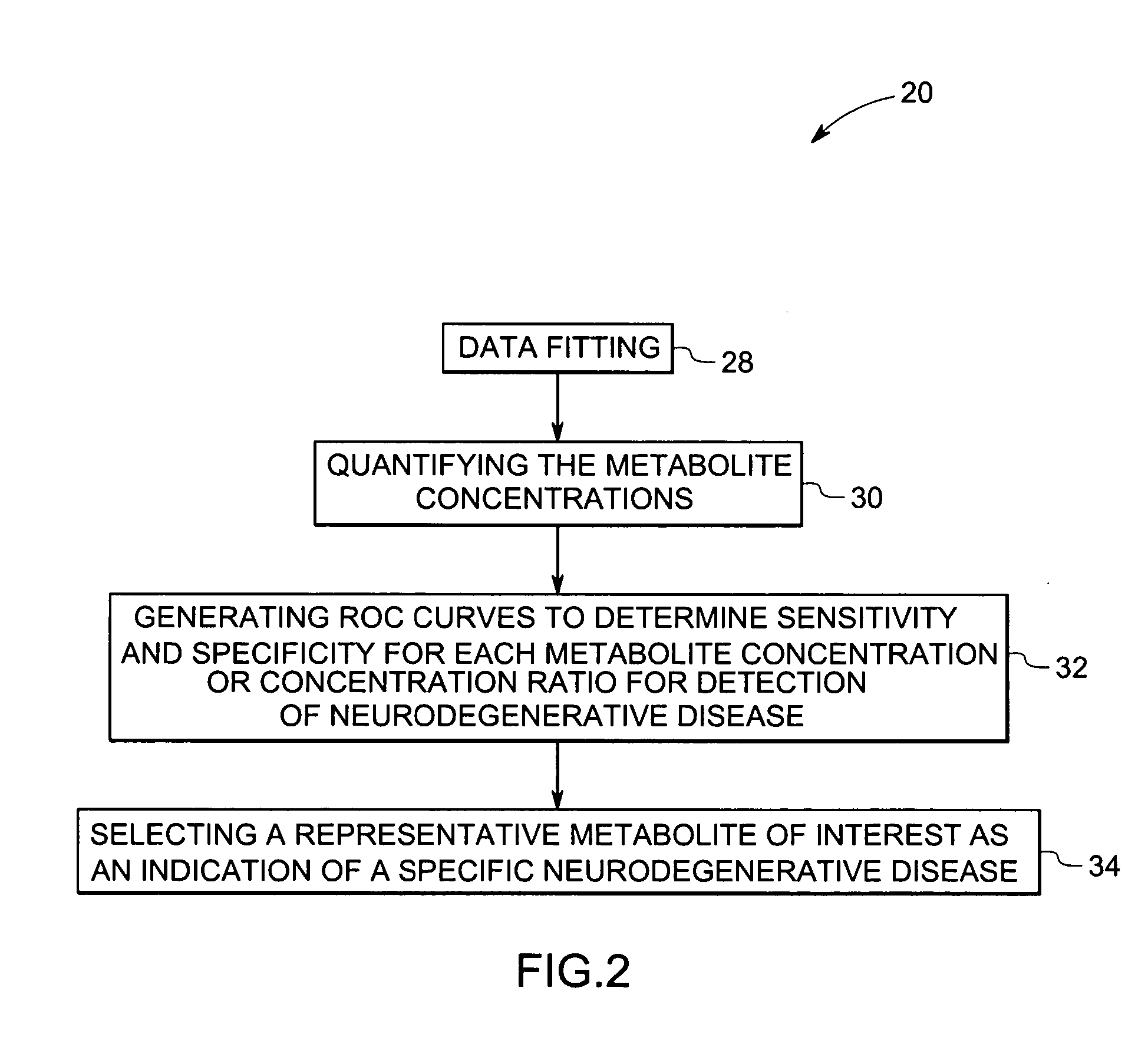
Methods and systems for detection and monitoring of neurodegenerative diseases using magnetic resonance spectroscopy
ActiveUS20050251025A1High sensitivityStrong specificityImage analysisDisease diagnosisMetaboliteConcentration ratio
A method for increasing sensitivity and / or specificity of a magnetic resonance spectroscopy imaging technique for detecting a neurodegenerative disease is provided. The method includes acquiring magnetic resonance spectroscopy data from the brain of a subject, while suppressing certain metabolites in the spectrum via a data acquisition protocol, to improve quantification accuracy for the remaining metabolites, and quantifying a metabolite concentration or a metabolite concentration ratio from the spectral data as an indicator of the neurodegenerative disease.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Control apparatus for controlling a therapeutic apparatus
InactiveUS20120035464A1Good effectReduced systemic side-effectsUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound therapyMagnetic resonance spectroscopicImaging processing
A control apparatus (106) for controlling a therapeutic apparatus (100), wherein the control apparatus comprises: —an ultrasound control interface (110) for controlling a therapeutic ultrasound system (102), —a magnetic resonance control interface (112) for controlling a magnetic resonance apparatus (104) adapted for acquiring magnetic resonance imaging data from a subject and for acquiring magnetic resonance spectroscopy data from a subject (244), —an image processing module (124, 126, 128) for generating at least one magnetic resonance imaging image (500) from the magnetic resonance imaging data and for generating at least one magnetic resonance spectroscopy map (502, 514, 516, 518, 520) from the magnetic resonance spectroscopy data, —a planning module (120) adapted for receiving the magnetic resonance imaging image and the magnetic resonance spectroscopy map and for outputting planning data (732), —a control module (122) adapted for controlling the therapeutic ultrasound system using the ultrasound control apparatus using the planning data, wherein the control module is further adapted for controlling the acquisition of the acquiring magnetic resonance imaging data and magnetic resonance spectroscopy data using the magnetic resonance control interface.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
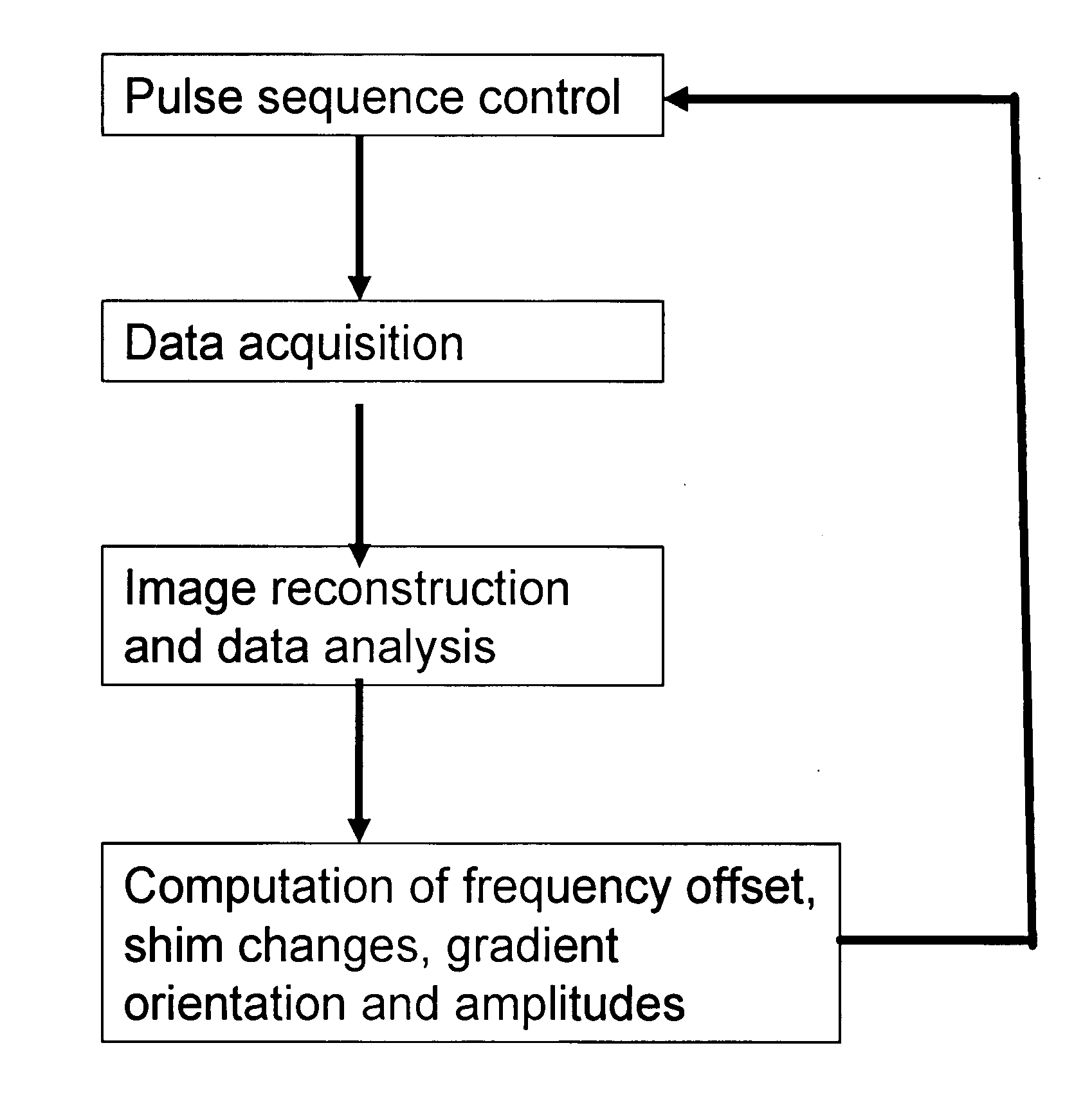
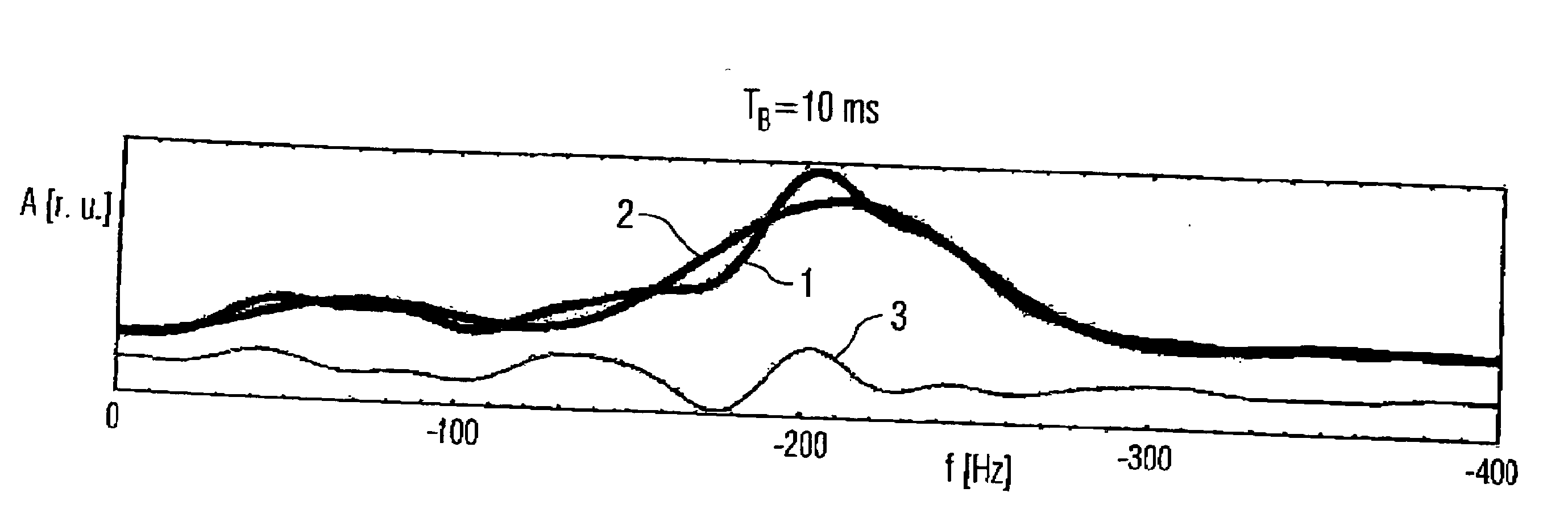
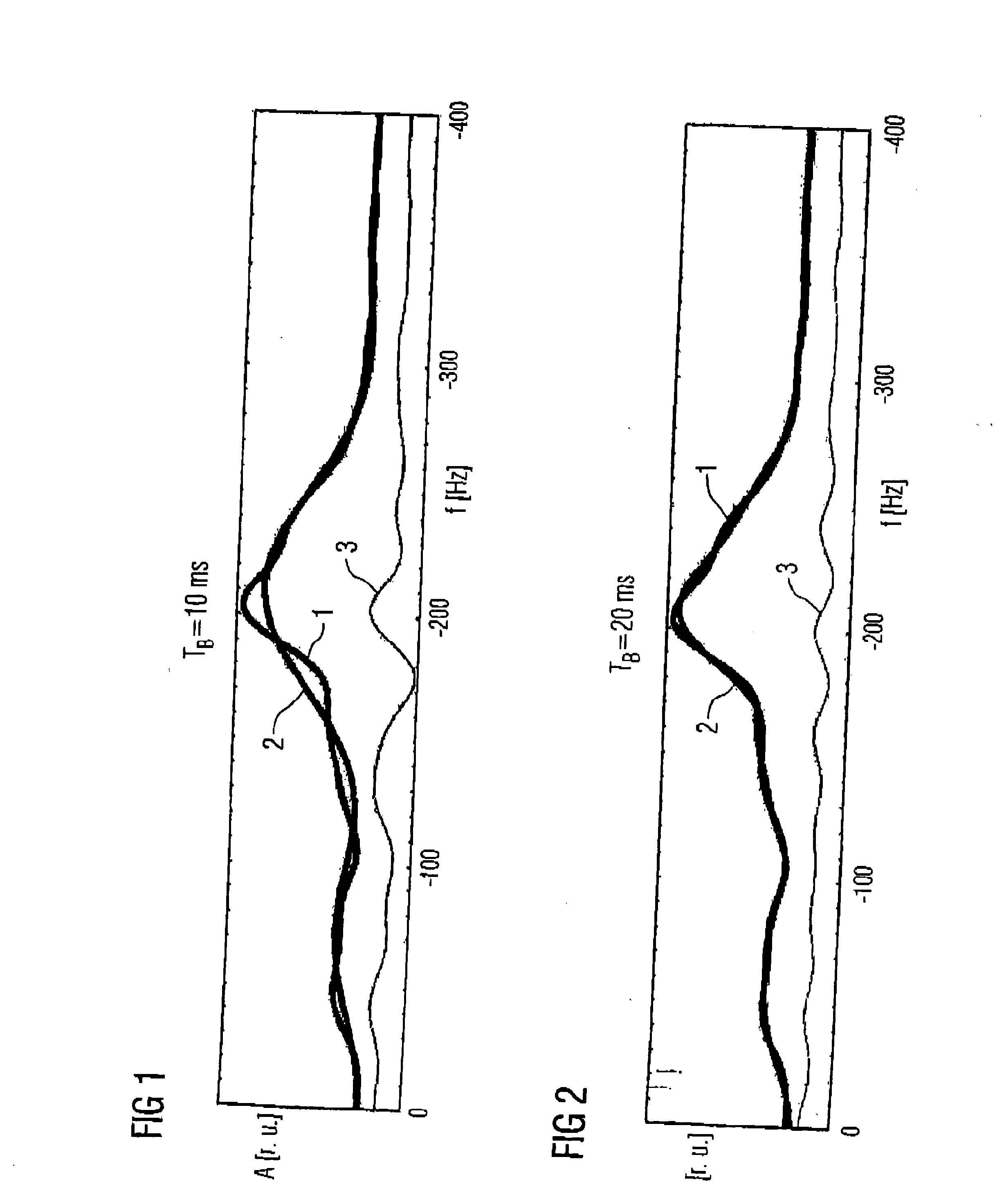
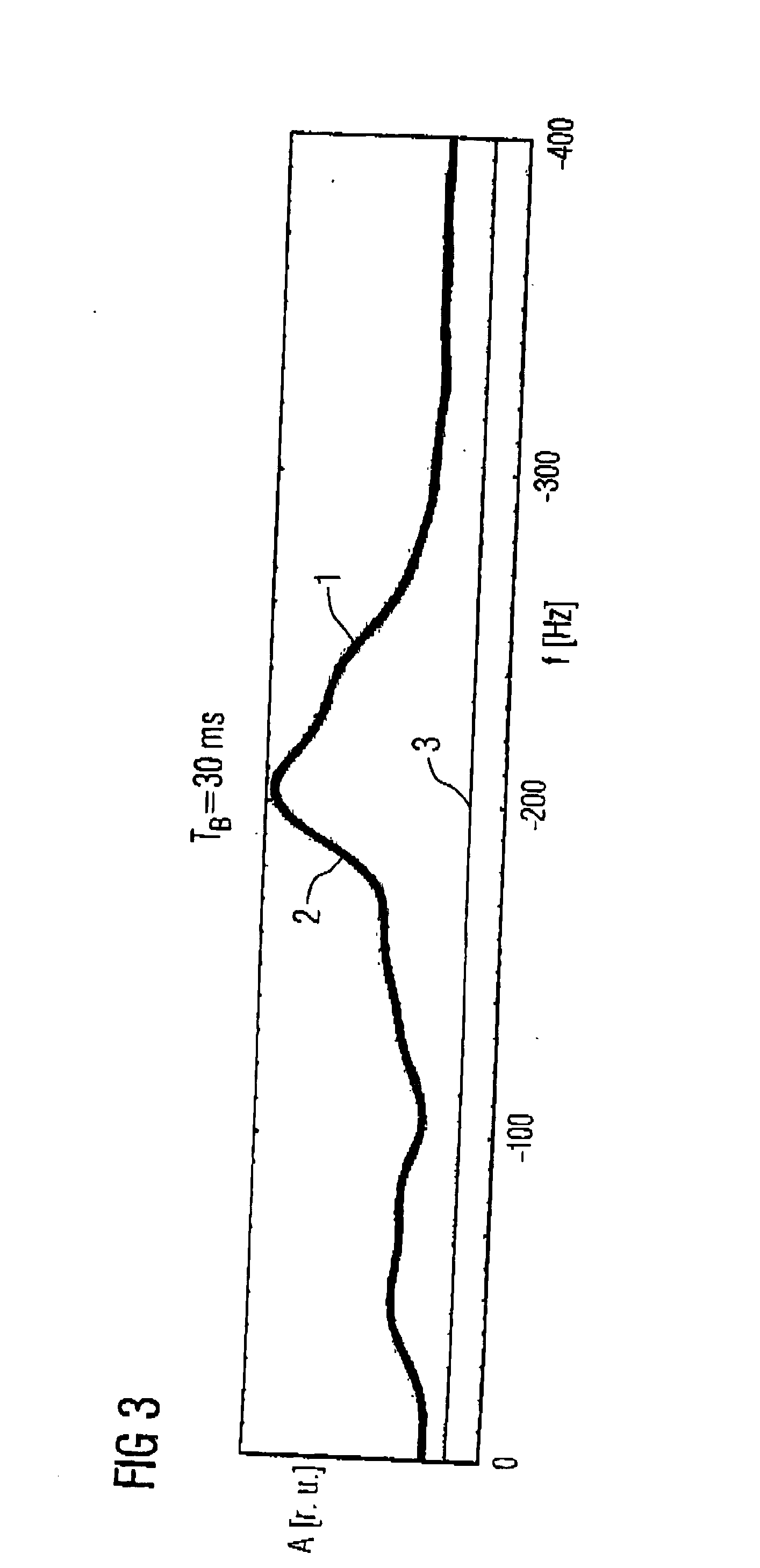
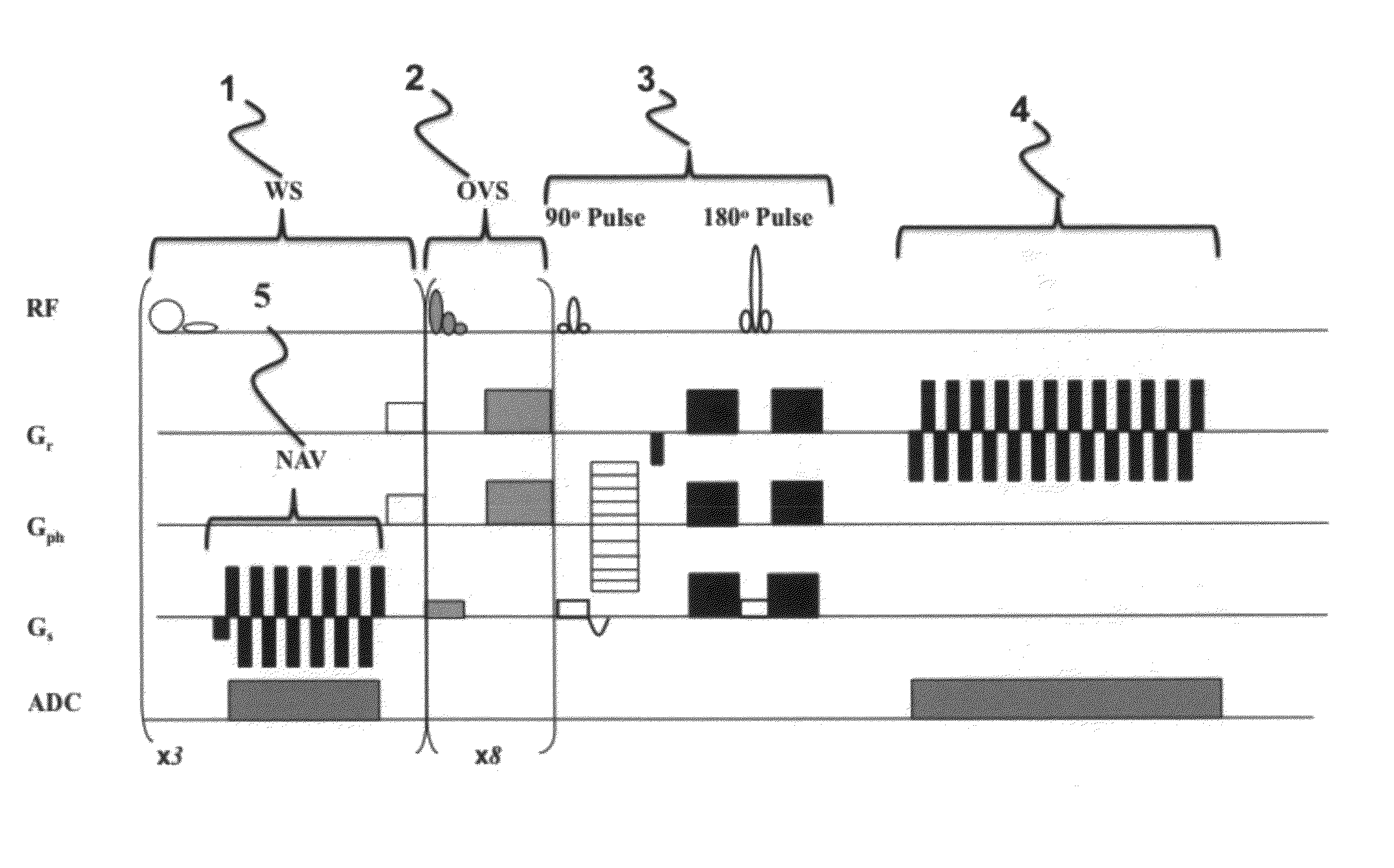
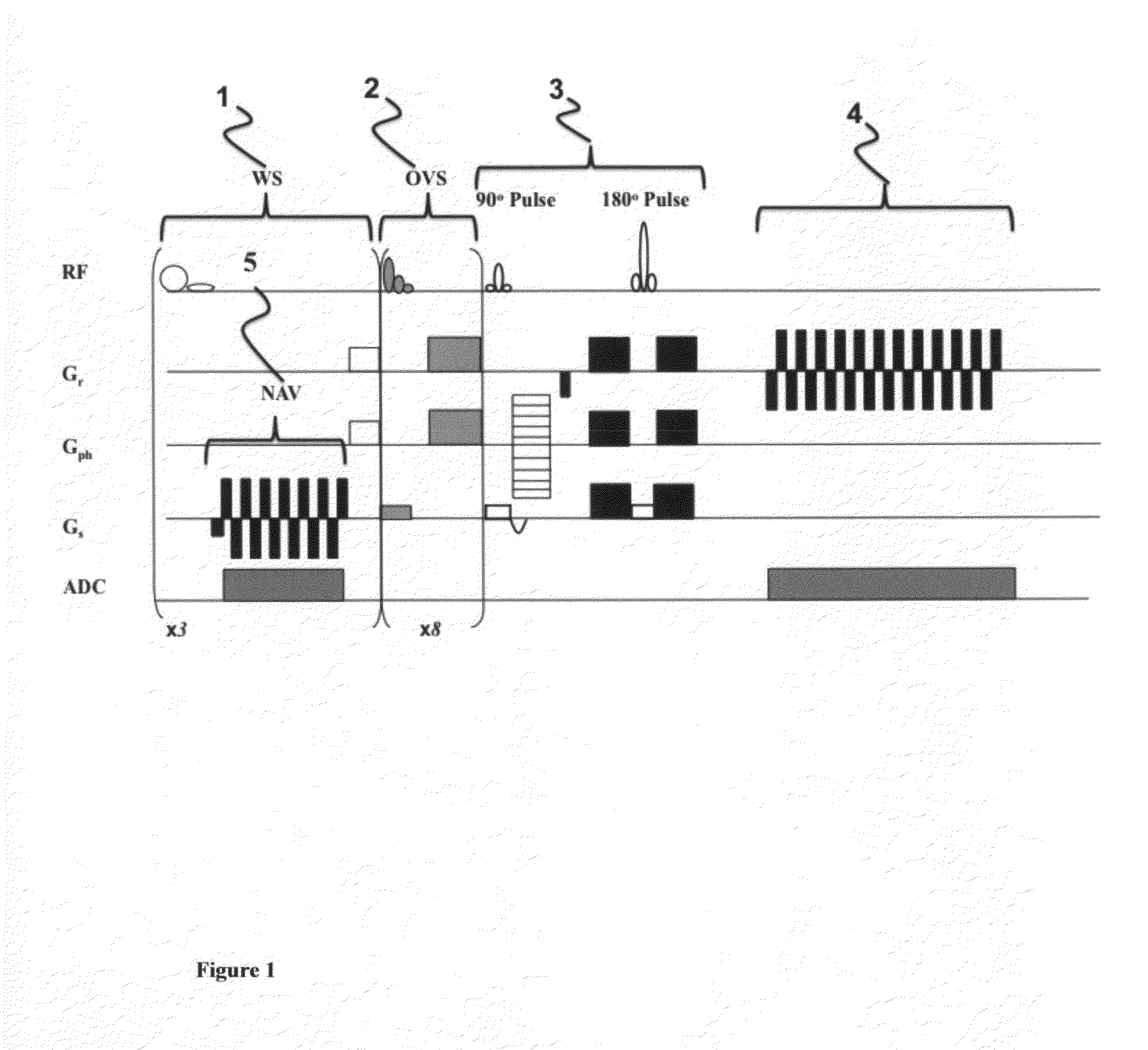
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy with real-time correction of motion and frequency drift, and real-time shimming
InactiveUS20070265520A1Suppress signalReduce sensitivityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSpectral patternObject motion
This invention relates to localized magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) and to magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) of the proton NMR signal, specifically to a magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) method to measure a single volume of interest and to a magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging method with at least one spectral dimension and up to three spatial dimensions. MRS and MRSI are sensitive to movement of the object to be imaged and to frequency drifts during the scan that may arise from scanner instability, field drift, respiration, and shim coil heating due to gradient switching. Inter-scan and intra-scan movement leads to line broadening and changes in spectral pattern secondary to changes in partial volume effects in localized MRS. In MRSI movement leads to ghosting artifacts across the entire spectroscopic image. For both MRS an MRSI movement changes the magnetic field inhomogeneity, which requires dynamic reshimming. Frequency drifts in MRS and MRSI degrade water suppression, prevent coherent signal averaging over the time course of the scan and interfere with gradient encoding, thus leading to a loss in localization. It is desirable to measure object movement and frequency drift and to correct object motion and frequency drift without interfering with the MRS and MRSI data acquisition.
Owner:POSSE STEFAN
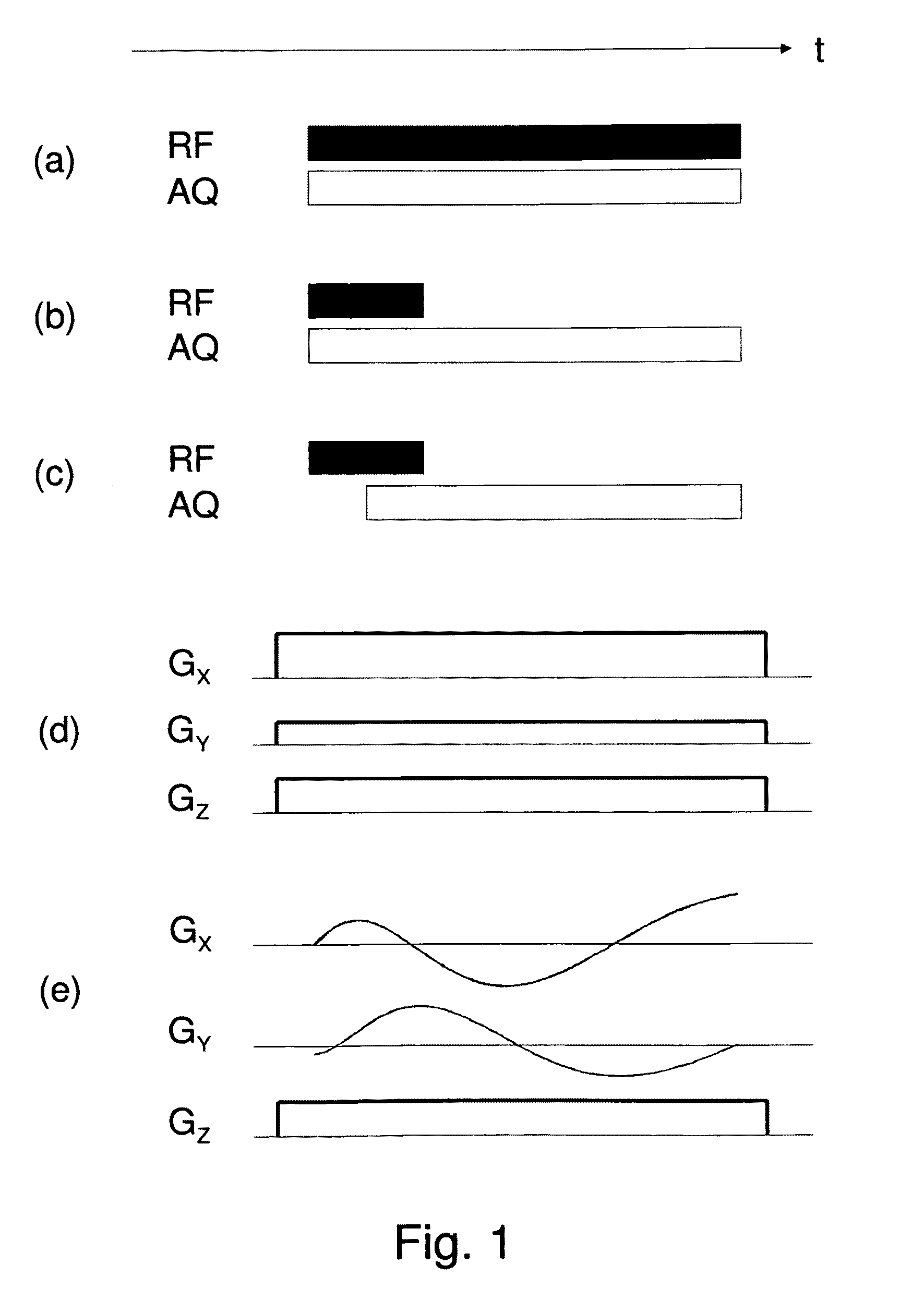
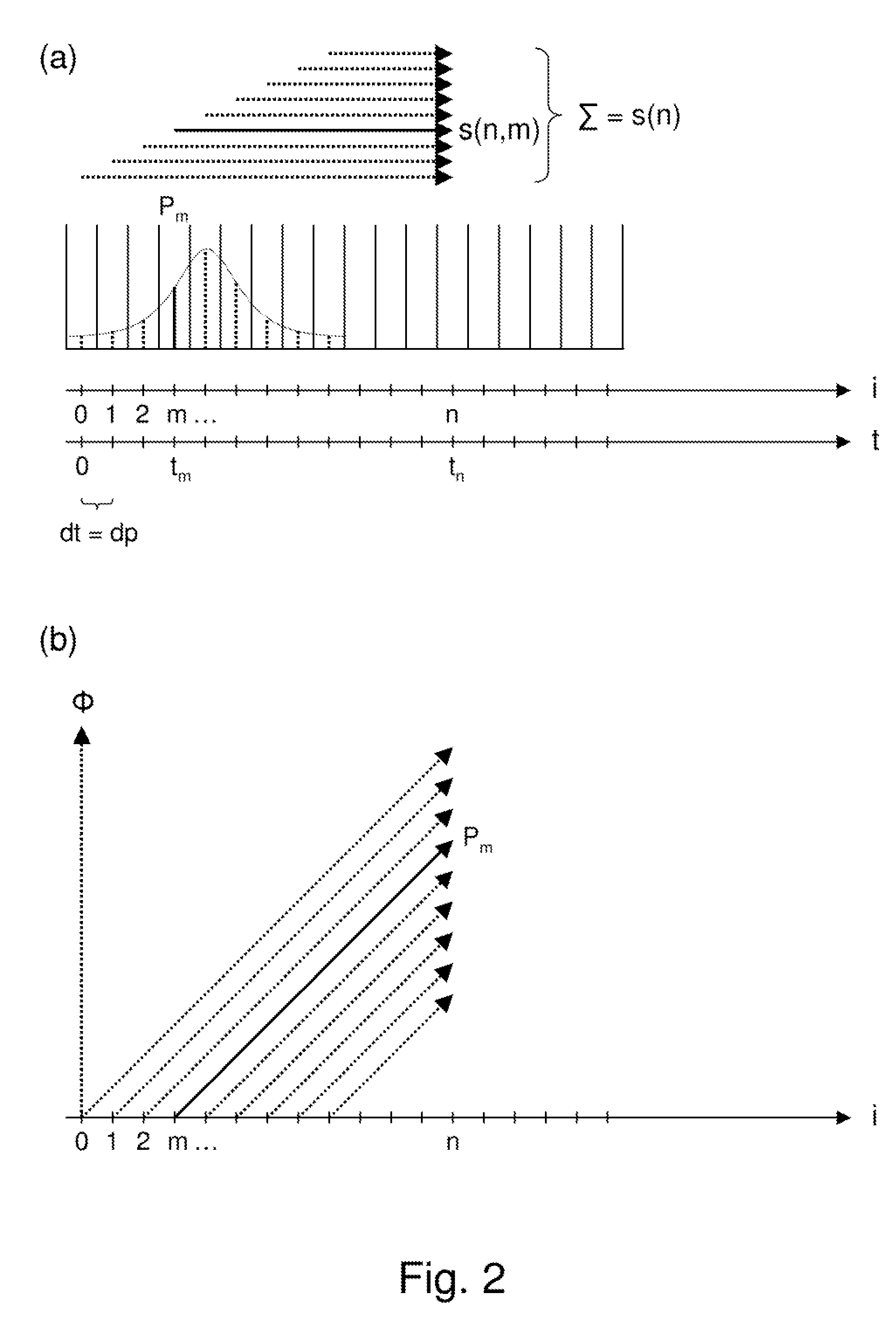
Simultaneous excitation and acquisition in magnetic resonance
ActiveUS20100244827A1Avoiding image intensity variationReduce data volumeDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFrequency spectrumMagnetic resonance spectrometry
A method for magnetic resonance spectroscopy (=MRS) or magnetic resonance imaging (=MRI) in which an NMR time-domain signal is created by an RF excitation pulse applied to an object in the presence of an applied magnetic field that may depend on spatial position and / or time, the time-domain signal being generated by an excited transverse nuclear magnetisation precessing about the applied magnetic field, whereby the RF excitation pulse is adapted to cover a whole range of NMR frequencies of interest present in the object, and time-domain signal acquisition takes place during, or during and after the application of the RF excitation pulse, is characterized in that spectral or image data are reconstructed by a matrix product of a reconstruction matrix and a vector of time-domain signal points, the reconstruction matrix being an inversion of an encoding matrix Anα whose elements are calculated using the formula:Anα=∑m=0n-1PmΦ(n,m,α),wherein n is the running number of a time-domain signal point, α is the running number of a discrete image or spectral element, Pm is the m-th discrete element of the RF excitation pulse in the time-domain, and Φ(n,m,α) is the phase accrued by the transverse nuclear magnetisation related to the discrete image or spectral element a in the time between the discrete RF excitation pulse element Pm and the time-domain signal point n under the influence of the applied magnetic field. An improved method for reconstructing spectral or image data from time-domain signal acquired as describe above is thereby provided which can be used more versatilely than conventional Fourier transform.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
Method for obtaining nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimension spin echo related spectrum under uneven magnetic field
ActiveCN103744042AOvercoming the influence of uneven magnetic fieldMagnetic measurementsLine widthPulse sequence
A method for obtaining a nuclear magnetic resonance two-dimension spin echo related spectrum under an uneven magnetic field relates to a nuclear magnetic resonance wave spectrum detection method and comprises the steps of using a normal one-dimension pulse sequence to sample a one-dimension spectrum, obtaining the line width of spectral lines, and providing a basis for spectrum width parameter setting, wherein the line width value also reflects the uniformity condition of a magnetic field; introducing well precompiled two-dimension spin echo related spectrum pulse sequences onto a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer; opening a multi-quantum coherent signal selection module, a three-dimension sampled indirect dimension evolution period t1 combination and indirect dimension evolution period t2 combination and an echo delay module among the two-dimension spin echo related spectrum pulse sequences; setting each experiment parameter of the two-dimension spin echo related spectrum pulse sequences; executing the two-dimension spin echo related spectrum pulse sequences, of which the experiment parameters are set, for data sampling; after the data sampling is finished, performing related data postprocessing to obtain the two-dimension spin echo related spectrum uninfluenced by the uneven magnetic field. The method has no need of shimming operation and is simple, convenient and effective.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Systems and methods for automated voxelation of regions of interest for magnetic resonance spectroscopy
A system and method for automating an appropriate voxel prescription in a uniquely definable region of interest (ROI) in a tissue of a patient is provided, such as for purpose of conducting magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) in the ROI. The dimensions and coordinates of a single three dimensional rectilinear volume (voxel) within a single region of interest (ROI) are automatically identified. This is done, in some embodiments by: (1) applying statistically identified ROI search areas within a field of view (FOV); (2) image processing an MRI image to smooth the background and enhance a particular structure useful to define the ROI; (3) identifying a population of pixels that define the particular structure; (4) performing a statistical analysis of the pixel population to fit a 2D model such as an ellipsoid to the population and subsequently fit a rectilinear shape within the model; (5) repetiting elements (1) through (4) using multiple images that encompass the 3D ROI to create a 3D rectilinear shape; (6) a repetition of elements (1) through (5) for multiple ROIs with a common FOV. A manual interface may also be provided, allowing for override to replace by manual prescription, assistance to identify structures (e.g. clicking on disc levels), or modifying the automated voxel (e.g. modify location, shape, or one or more dimensions).
Owner:ACLARION INC
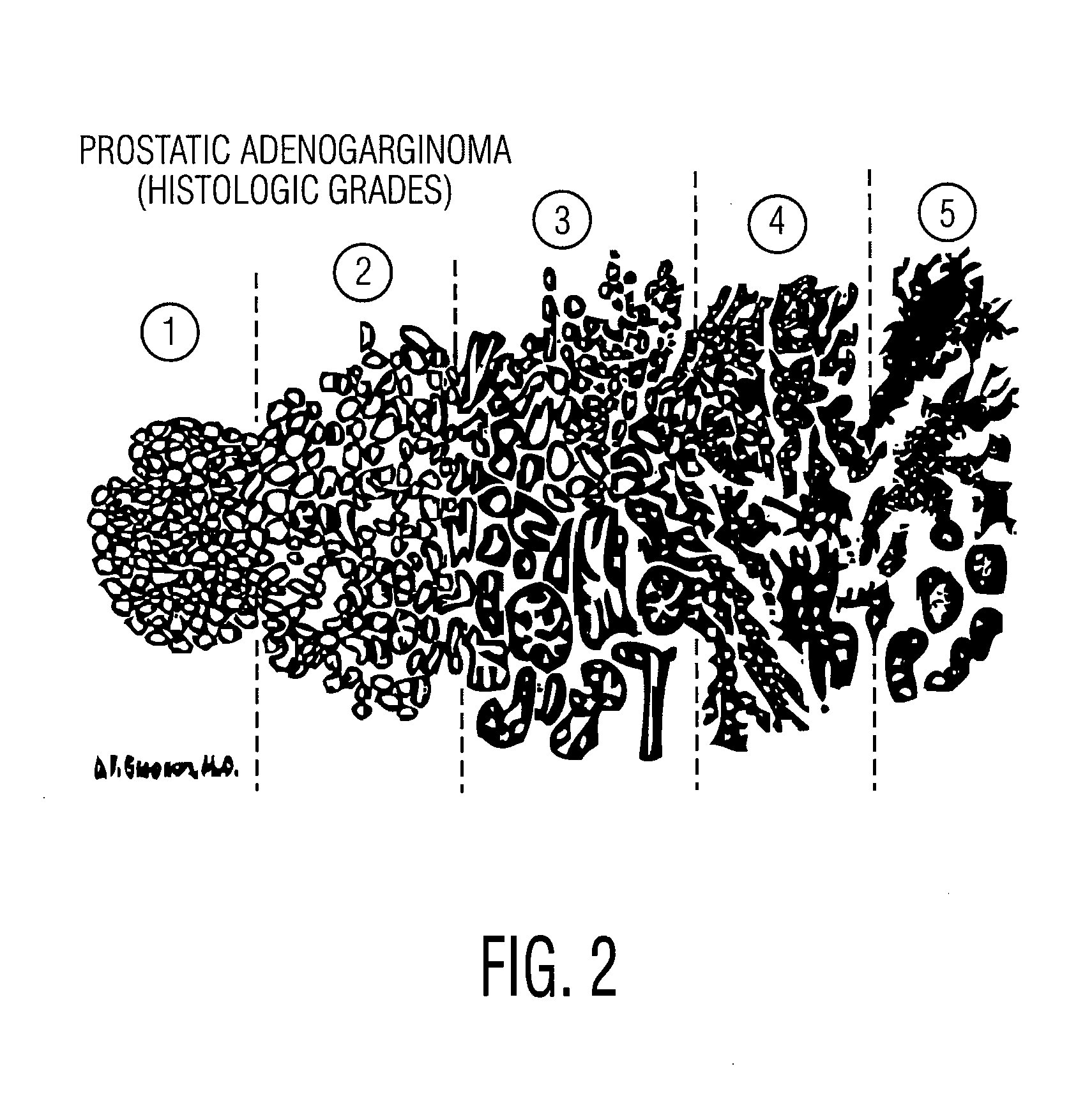
Defining quantitative signatures for different gleason grades of prostate cancer using magnetic resonance spectroscopy
InactiveUS20100169024A1Image enhancementImage analysisMagnetic resonance spectroscopicPattern recognition
A method for classifying a possible cancer from a magnetic resonance spectrographic (MRS) dataset includes extracting at least one feature from the MRS dataset as being identified with the possible cancer and embedding the extracted feature into a low dimensional space to form an embedded space. The method then clusters the embedded space into clusters representing a plurality of predetermined classes and spectrally decomposing the clusters to identify substantially significant independent metabolic signatures. The method then classifies the possible cancer as belong to one of at least two cancer classes based on the identified independent metabolic signatures.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA +1
Method for evaluating magnetic resonance spectroscopy data using a baseline model
ActiveUS20050137476A1Improve smoothnessGood precisionMeasurements using NMR spectroscopyDiagnostic recording/measuringTime domainMetabolite
In a method for evaluating data of a magnetic resonance signal, a baseline is modeled and at least one metabolite signal is modeled. The modeling of the baseline ensues based on magnetic resonance data in the time domain, and using only data that begins with the magnetic resonance signal and having a length that is shorter than the duration of the overall magnetic resonance signal.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System and method for detecting pain and its components using magnetic resonance spectroscopy
InactiveUS20050020905A1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMetaboliteMedicine
A system and method identifies different components of the pain experience (nociceptive (tissue damage), neuropathic (nerve damage) and psychological) and their relative contributions by the use of magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) to measure absolute and relative concentrations of metabolites in specific brain regions in the central nervous system or brain. The system and method can be used as a diagnostic tool for the assessment of the relative contribution of different aspects of the pain experience as well as monitoring of response to interventions directed at modifying these components.
Owner:SYDNEY UNIV OF +2
Simultaneous excitation and acquisition in magnetic resonance
ActiveUS8432165B2Reduce complexityMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFrequency spectrumData acquisition
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy pulse sequence, acquisition, and processing system and method
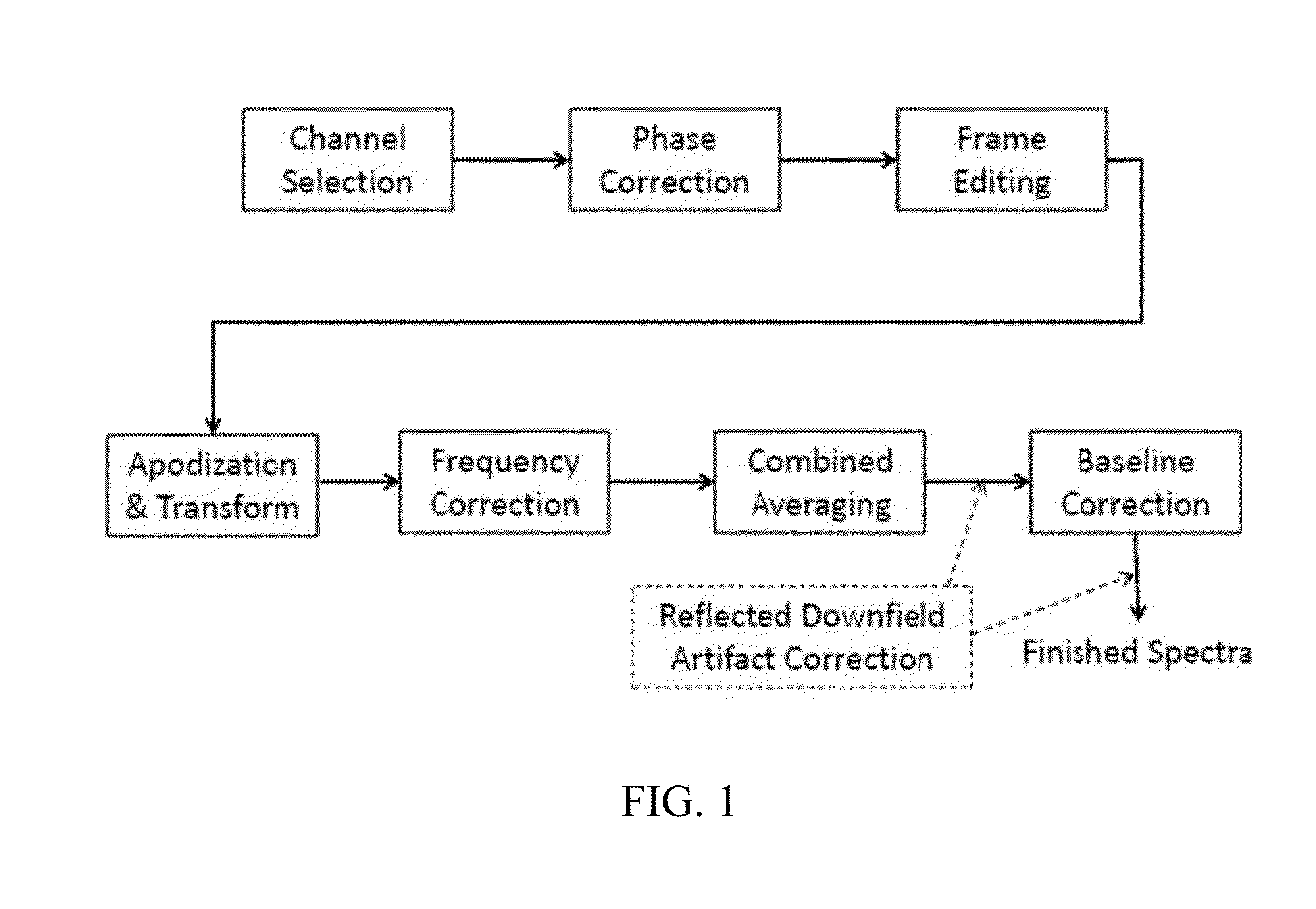
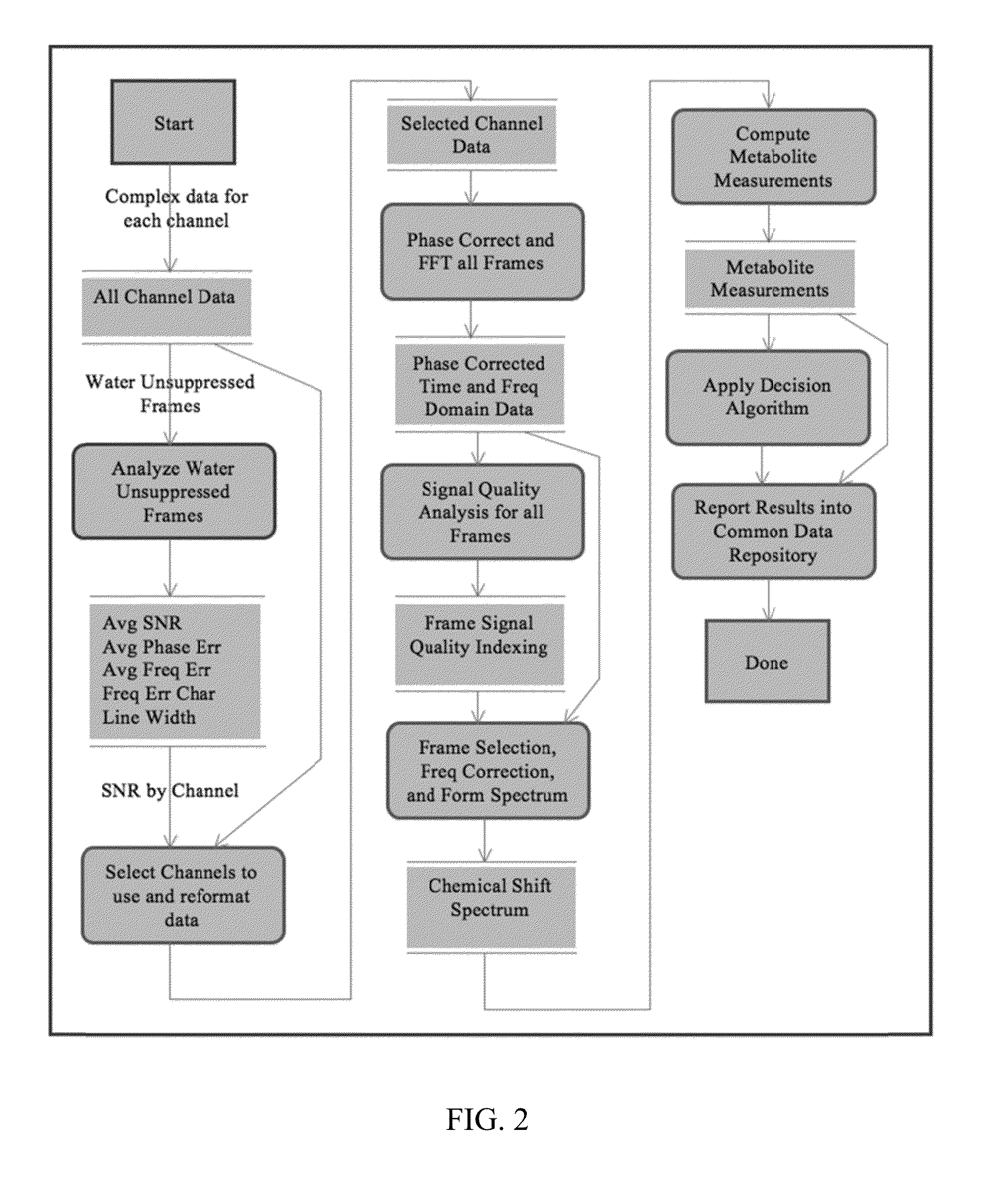
ActiveUS8965094B2Enhanced frequency shift artifact correctionEliminate the effects ofImage analysisDiagnostics using spectroscopyMagnetic resonance spectroscopicMultiple frame
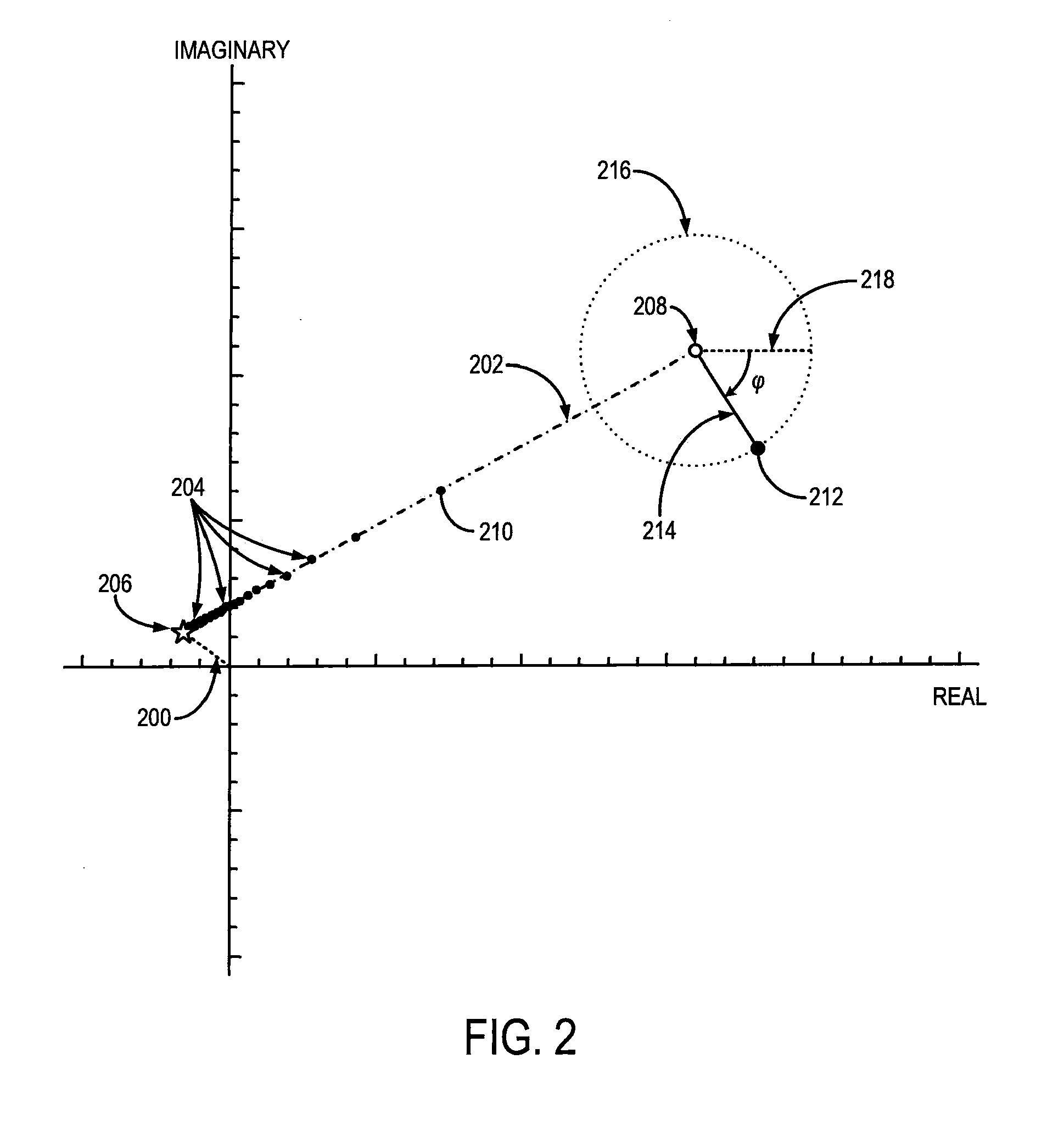
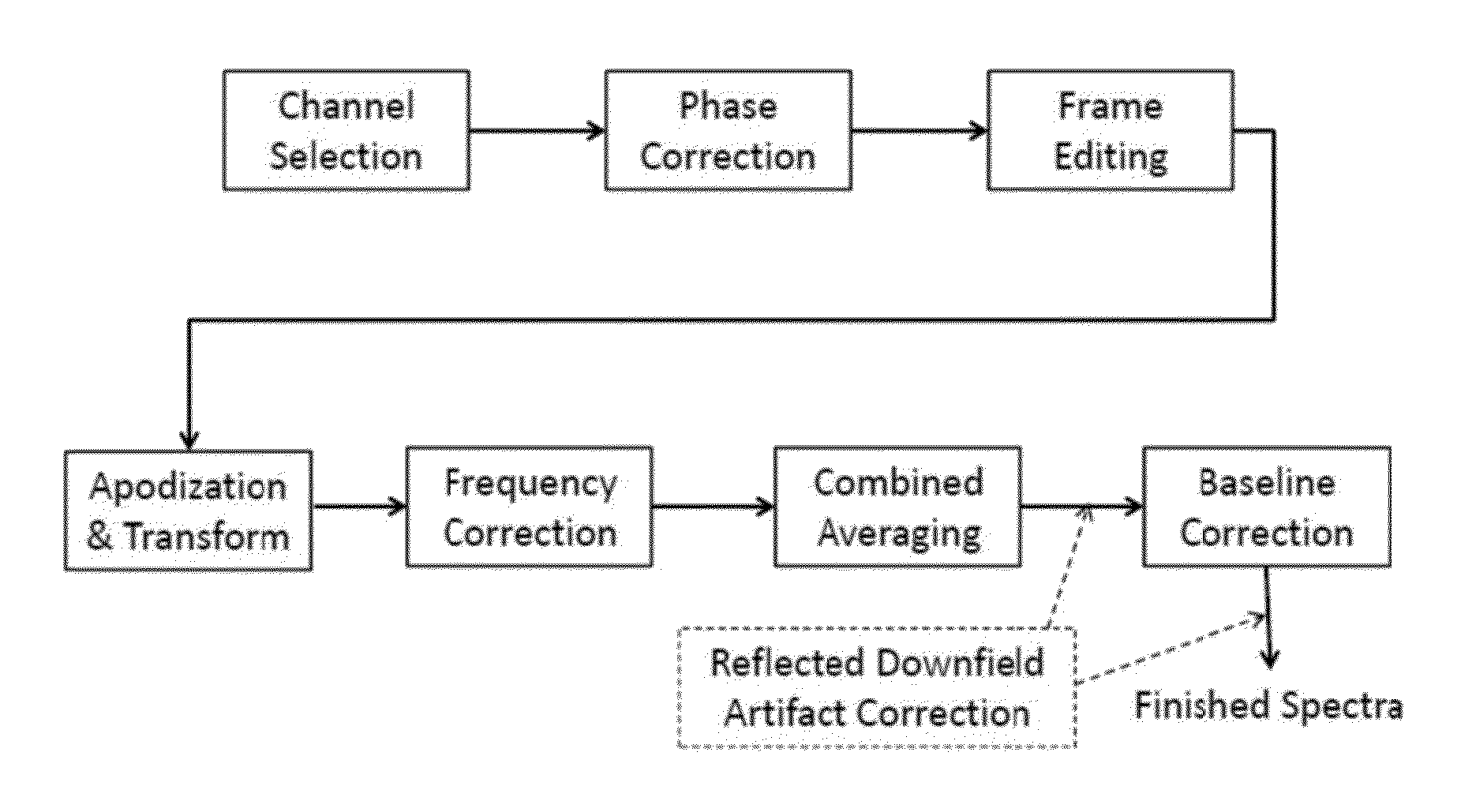
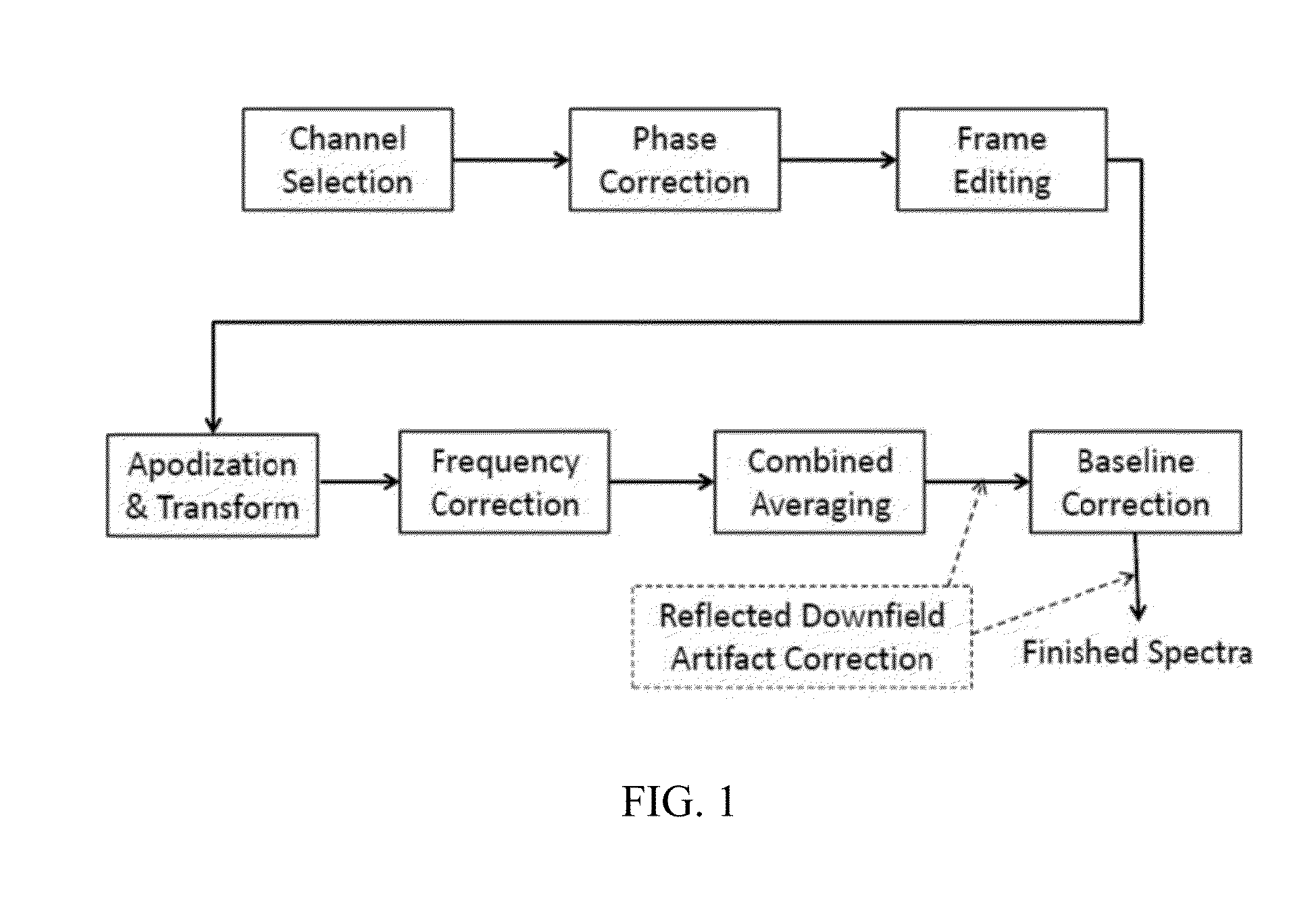
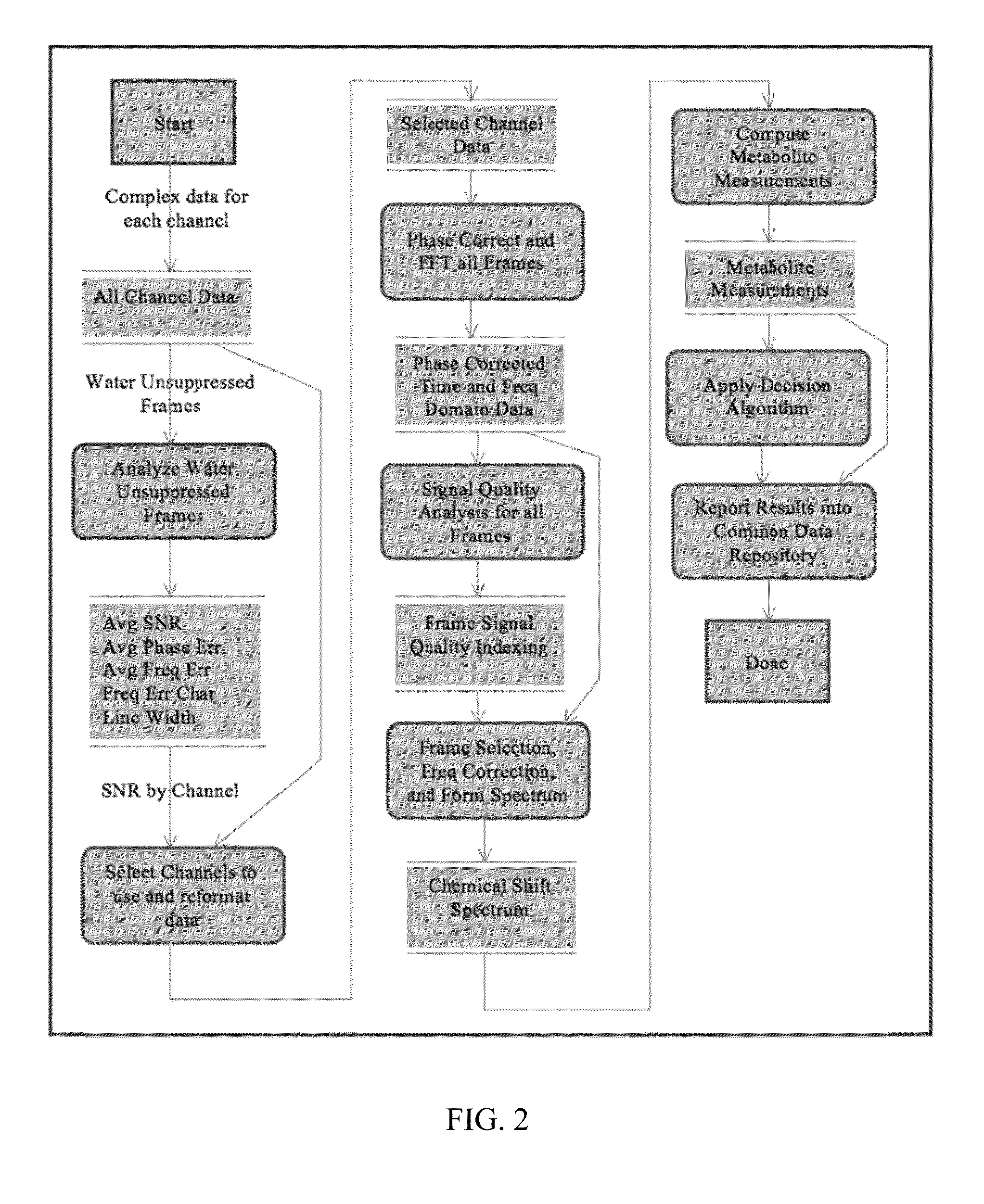
Systems and methods are provided for processing a set of multiple serially acquired magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) free induction decay (FID) frames from a multi-frame MRS acquisition series from a region of interest (ROI) in a subject, and for providing a post-processed MRS spectrum. Processing parameters are dynamically varied while measuring results to determine the optimal post-processed results. Spectral regions opposite water from chemical regions of interest are evaluated and used in at least one processing operation. Frequency shift error is estimated via spectral correlation between free induction decay (FID) frames and a reference spectrum. Multiple groups of FID frames within the acquired set are identified to different phases corresponding with a phase step cycle of the acquisition. Baseline correction is also performed via rank order filter (ROF) estimate and a polynomial fit. Sections of the ROF may be excluded from the polynomial fit, such as for example sections determined to be associated with relevant spectral peaks.
Owner:ACLARION INC
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy with real-time correction of motion and frequency drift, and real-time shimming
InactiveUS20110221439A1Diagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSpectroscopyData acquisition
Disclosed are MR Spectroscopy and MR Spectroscopic Imaging (MRSI) methods comprising the sequential steps of water suppression, spatial prelocalization and spatial-spectral encoding, wherein the water suppression is modified to additionally measure and correct the frequency drift, the change in magnetic field inhomogeneity in the volume of interest, and the object movement. By inserting between the water suppression RF pulse and the dephasing gradient pulses either a phase sensitive MRI encoding module, or a 1D, 2D or 3D high-speed MRSI encoding module with simultaneous acquisition of the decaying water signal it is possible to measure frequency drift, magnetic field inhomogeneity and object movement. This information is used to dynamically change the synthesizer frequency of the scanner, the shim settings and to rotate the encoded k-space. In the preferred implementation this information is computed in real-time during the ongoing scan and via feeback loop downloaded to the acquisition control unit to update the aforementioned parameters before the subsequent data acquisition.
Owner:POSSE STEFAN
Method of Utilization of High Dielectric Constant (HDC) Materials for Reducing SAR and Enhancing SNR in MRI
ActiveUS20110152670A1Reduce transmit powerImprove image signal-to-noise ratioDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Image contrast
Layers or coats of materials with high dielectric constant or permittivity with very low conductivity are inserted in between radiofrequency (RF) coil or coil's conductive elements and the sample to enhance the signal to noise ratio (SNR), improve image contrast, and reduce the specific absorption rate (SAR) of magnetic resonance imaging or magnetic resonance spectroscopy instruments. The embodiments of the present invention can be used as an auxiliary device to the standard pre-constructed RF coils or incorporated with RF coil constructions for enhancing RF coil performances in both transmission and reception.
Owner:YANG QING X
Annular magnet system for magnetic resonance spectroscopy
InactiveUS20070171014A1Increase current densityEasy manufacturabilityMagnetsMagnetic materialsHelmholtz coilMicro coil
A persistent-mode magnet, assembled from superconducting annuli, provides a micro coil NMR, in which compactness and manufacturability are provided for a variety of applications. An annular magnet for micro NMR can include a YBCO-annulus Helmholtz coil, for example, that can energized by a magnet system and then transported for use at a second location with an operating system.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH +1
System and method for phase offset and time delay correction in magnetic resonance spectroscopy data
ActiveUS20110066025A1High resolutionImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringData setFrequency spectrum
A method is provided for producing, with a magnetic resonance (MR) system, a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum that has been corrected for errors arising from phase offsets and time shifts in the acquired spectroscopic data. A spectroscopic data set includes temporal information indicative of the underlying phase offsets and time shifts. In general, this temporal information is utilized to correct for errors in the acquired data. As a result, a plurality of acquired spectroscopic data sets are more accurately combined by first individually correcting each spectroscopic data set for such errors. Exemplary sources of the phase offsets and time shifts include the physical separation between a volume of interest and the detectors in the MRI system. Using the temporal information, T2 decay in the produced spectrum is also corrected.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy pulse sequence, acquisition, and processing system and method
ActiveUS20140064586A1Enhanced frequency shift artifact correctionEliminate the effects ofImage analysisDiagnostics using spectroscopyPulse sequenceHandling system
Systems and methods are provided for processing a set of multiple serially acquired magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) free induction decay (FID) frames from a multi-frame MRS acquisition series from a region of interest (ROI) in a subject, and for providing a post-processed MRS spectrum. Processing parameters are dynamically varied while measuring results to determine the optimal post-processed results. Spectral regions opposite water from chemical regions of interest are evaluated and used in at least one processing operation. Frequency shift error is estimated via spectral correlation between free induction decay (FID) frames and a reference spectrum. Multiple groups of FID frames within the acquired set are identified to different phases corresponding with a phase step cycle of the acquisition. Baseline correction is also performed via rank order filter (ROF) estimate and a polynomial fit. Sections of the ROF may be excluded from the polynomial fit, such as for example sections determined to be associated with relevant spectral peaks.
Owner:ACLARION INC
Stripline antenna and antenna array for a magnetic resonance device
InactiveUS8581588B2Antenna structure is simpleSimple structureMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic resonance spectroscopicElectrical conductor
An antenna (100) for a magnetic resonance device has a predetermined sensitivity and is designed to excite and / or detect a magnetic resonance in an object under test. The antenna (100) includes a stripline resonator (10) that is equipped with at least one stripline (11), and a conductor loop arrangement (20) that adjoins the stripline resonator (10) and forms at least one conductor loop (21, 22, 28) which is interrupted by at least one capacitor (23). The sensitivity of the antenna (100) is formed by overlapping sensitivity profiles of the stripline resonator (10) and the conductor loop arrangement (20). Also described are an antenna array (200) including a plurality of antennas (100), a magnetic resonance device (300) including at least one antenna (100) or antenna array (200), and methods for magnetic resonance imaging or magnetic resonance spectroscopy.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
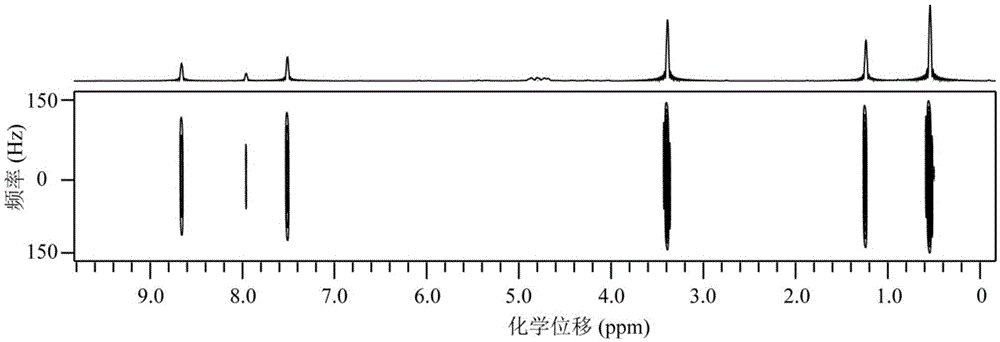
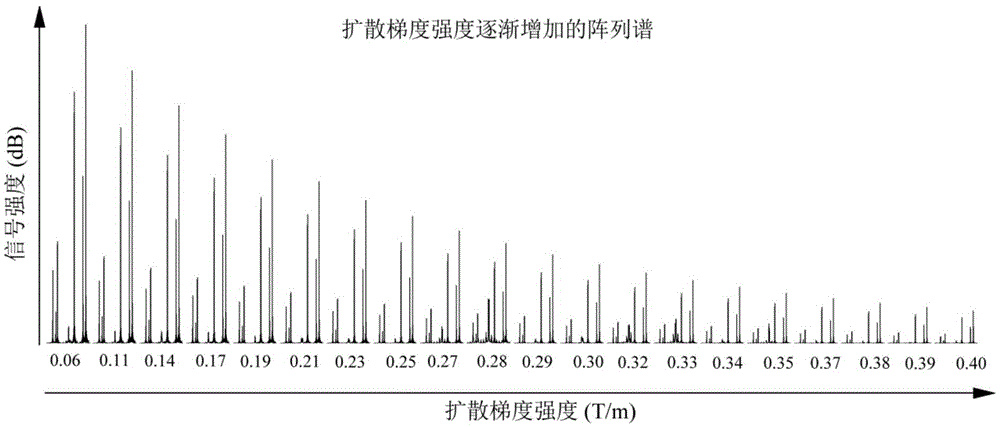
Two-dimensional diffusion-ordered nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy method used for any magnetic field environments
ActiveCN105651803ABreak through limitationsAchieve separationAnalysis using nuclear magnetic resonanceLiquid separationSpectroscopySolvent
The invention discloses a two-dimensional diffusion-ordered nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy method used for any magnetic field environments and relates to nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy detection methods. The method includes the steps of 1), measuring pi / 2 nonselective radiofrequency pulse width and (pi / 2) solvent selective radiofrequency pulse width required by sample stimulation; 2), importing a nuclear magnetic resonance pulse sequence on a nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometer; 3), turning on an intermolecular zero-quantum coherence signal selection module, a time-invariant evolution module and a diffusion order module of the nuclear magnetic resonance pulse sequence and setting experiment parameters of all modules; 4), executing data sampling; 5), performing data post-processing to obtain high-resolution two-dimensional diffusion-ordered spectroscopy. The two-dimensional diffusion-ordered nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy method used for any magnetic field environments does not need any shimming operation, a sample preprocessing process and any special hardware devices, is simple, convenient and feasible and is applicable to any conventional nuclear magnetic resonance spectrometers.
Owner:XIAMEN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com