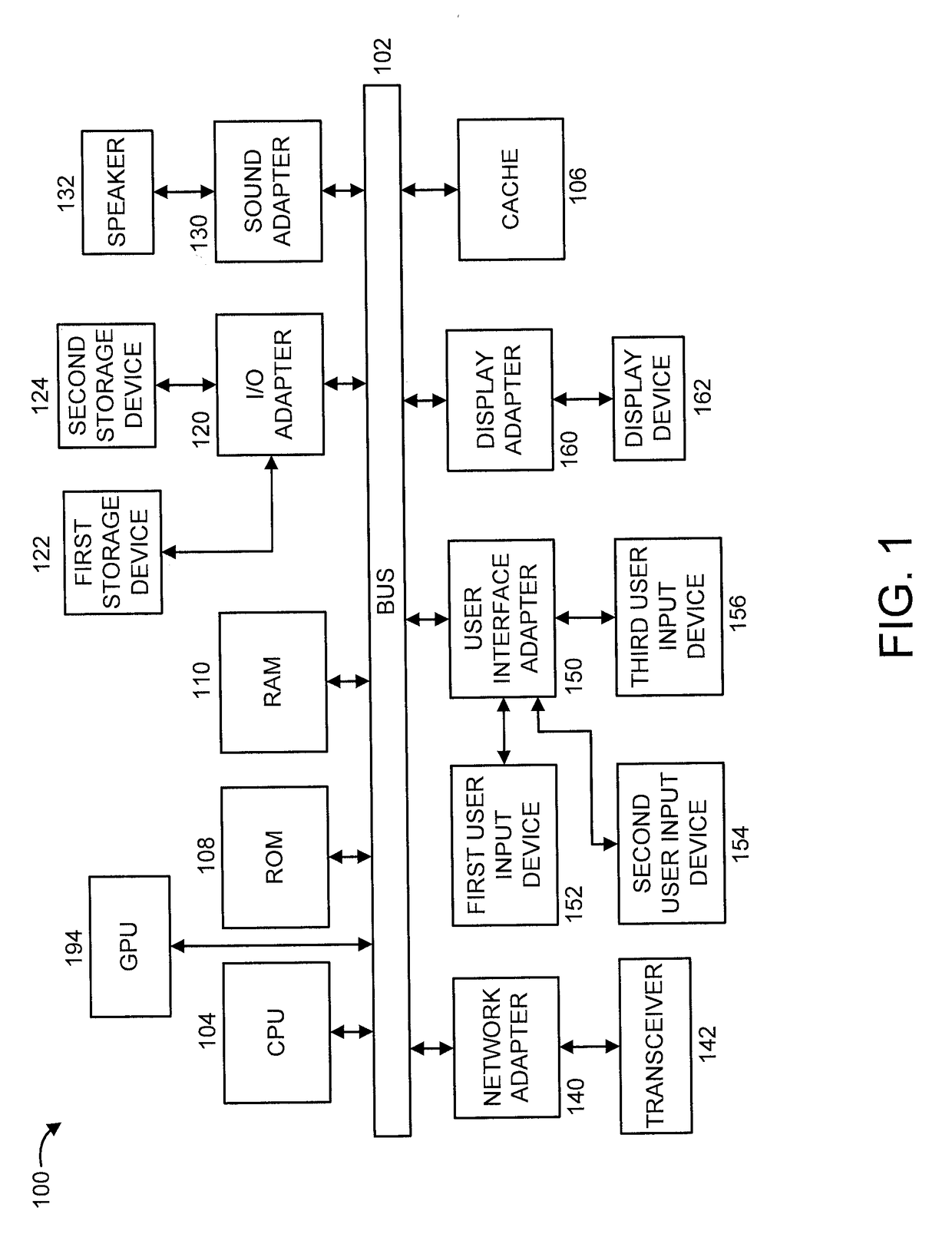
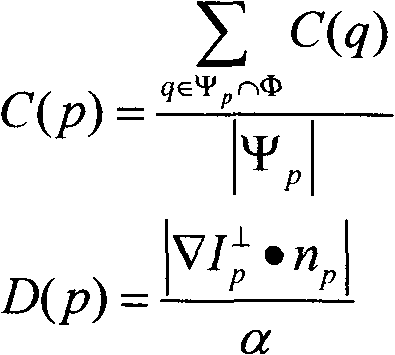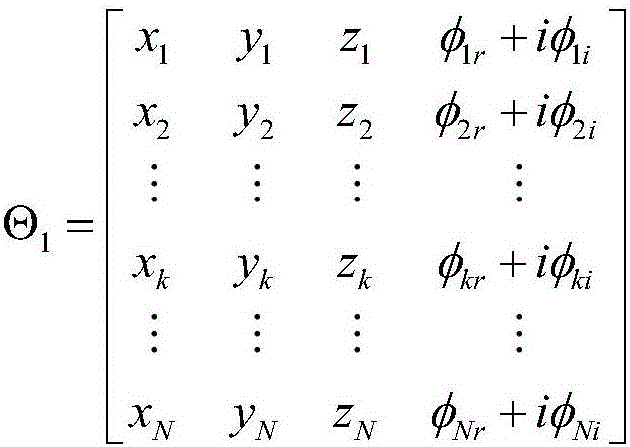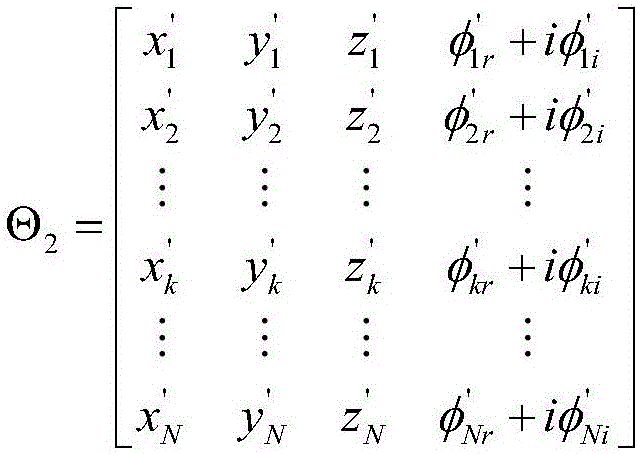Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
539 results about "Image domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Image domain is the domain in which the arrangement and relationship among different gray level intensities (pixels) are expressed.
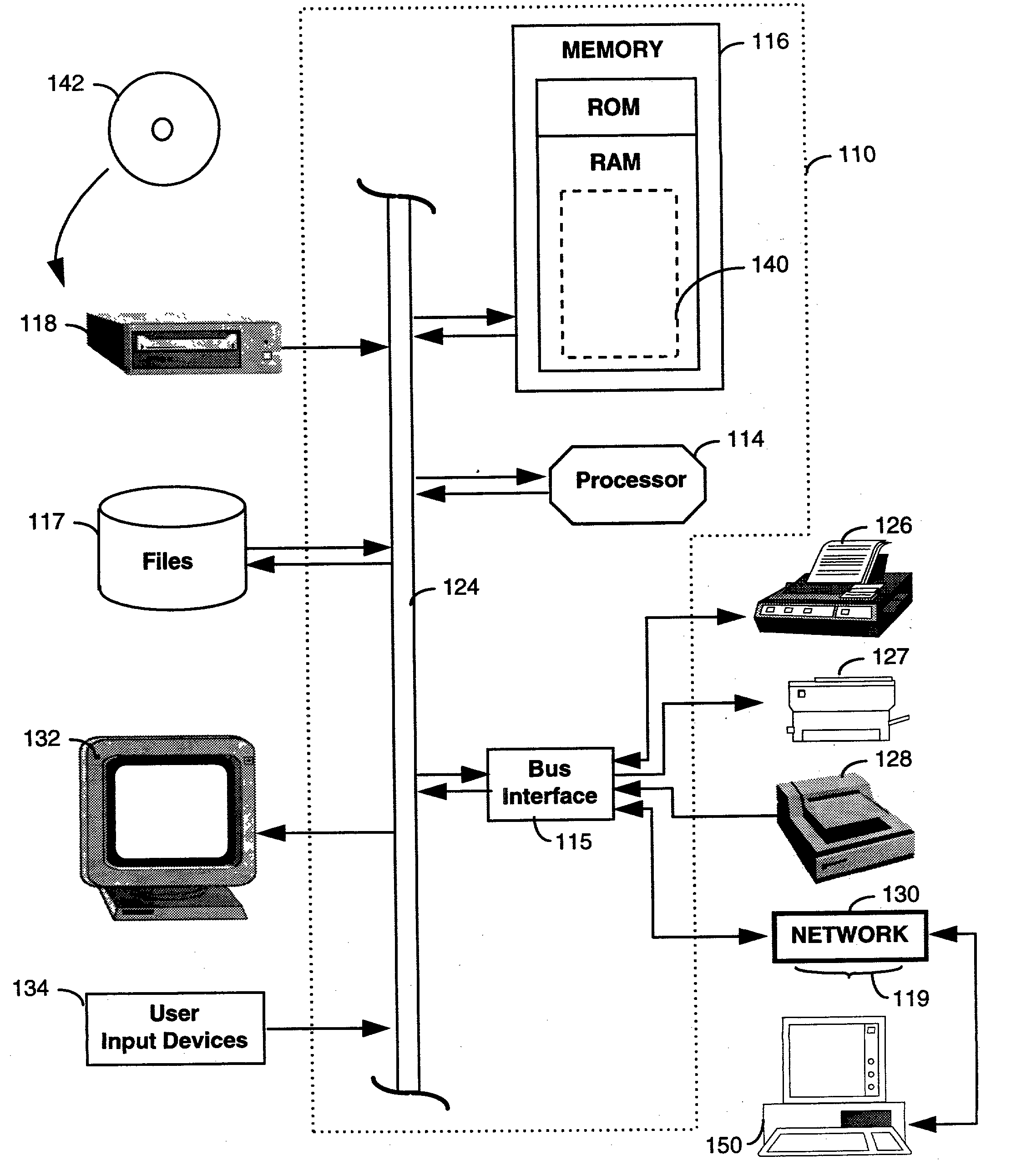
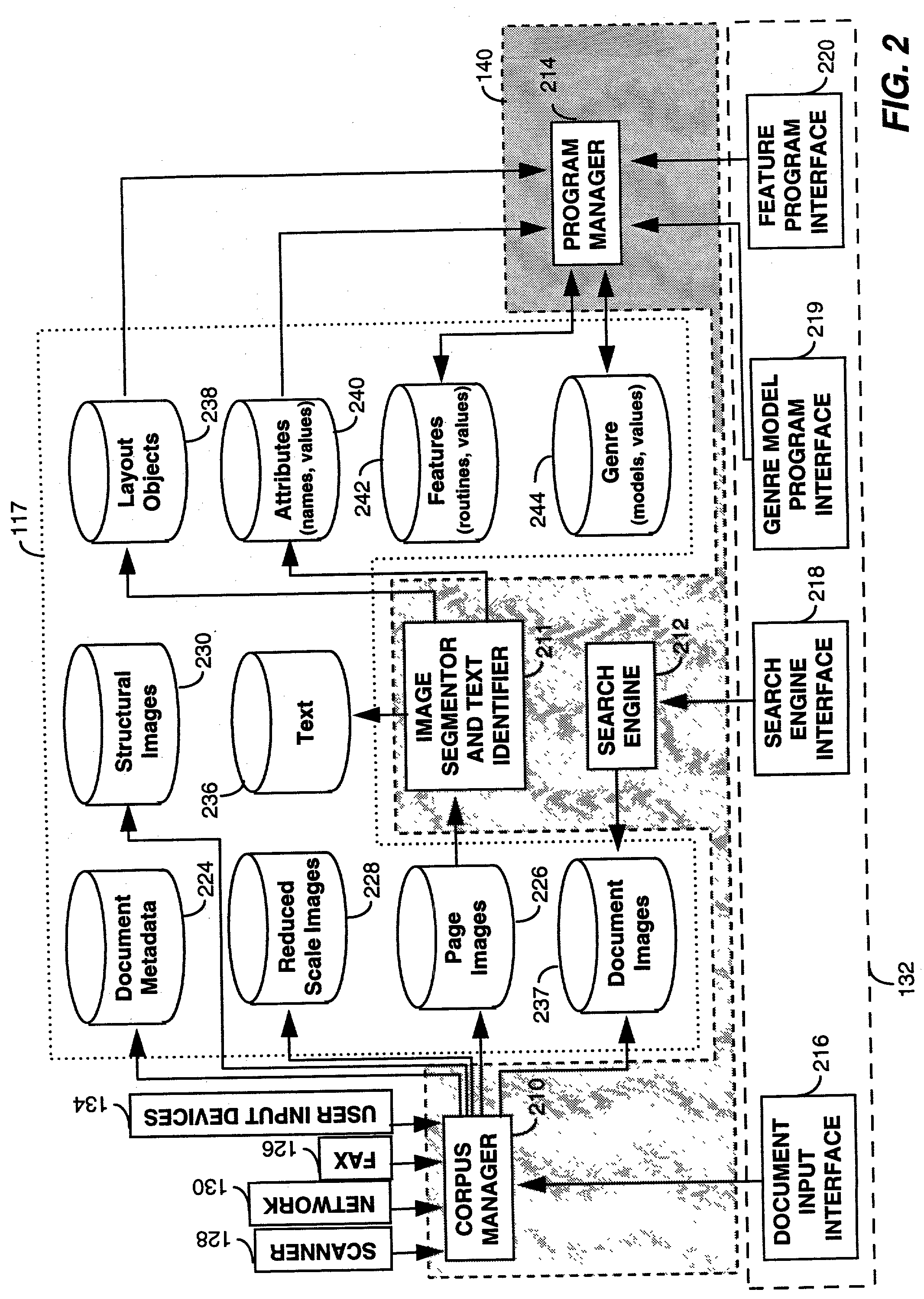
System for sorting document images by shape comparisons among corresponding layout components
A programming interface of document search system enables a user to dynamically specifying features of documents recorded in a corpus of documents. The programming interface provides category and format flexibility for defining different genre of documents. The document search system initially segments document images into one or more layout objects. Each layout object identifies a structural element in a document such as text blocks, graphics, or halftones. Subsequently, the document search system computes a set of attributes for each of the identified layout objects. The set of attributes are used to describe the layout structure of a page image of a document in terms of the spatial relations that layout objects have to frames of reference that are defined by other layout objects. Using the set of attributes a user defines features of a document with the programming interface. After receiving a feature or attribute and a set of document images selected by a user, the system forms a set of image segments by identifying those layout objects in the set of document images that make up the selected feature or attribute. The system then sorts the set of image segments into meaningful groupings of objects which have similarities and / or recurring patterns. In operation, the system sorts images in the image domain based on segments (or portions) of a document image which have been automatically extracted by the system. As a result, searching becomes more efficient because it is performed on limited portions of a document. Subsequently, document images in the set of document images are order and displayed to a user in accordance with the meaningful groupings.
Owner:XEROX CORP
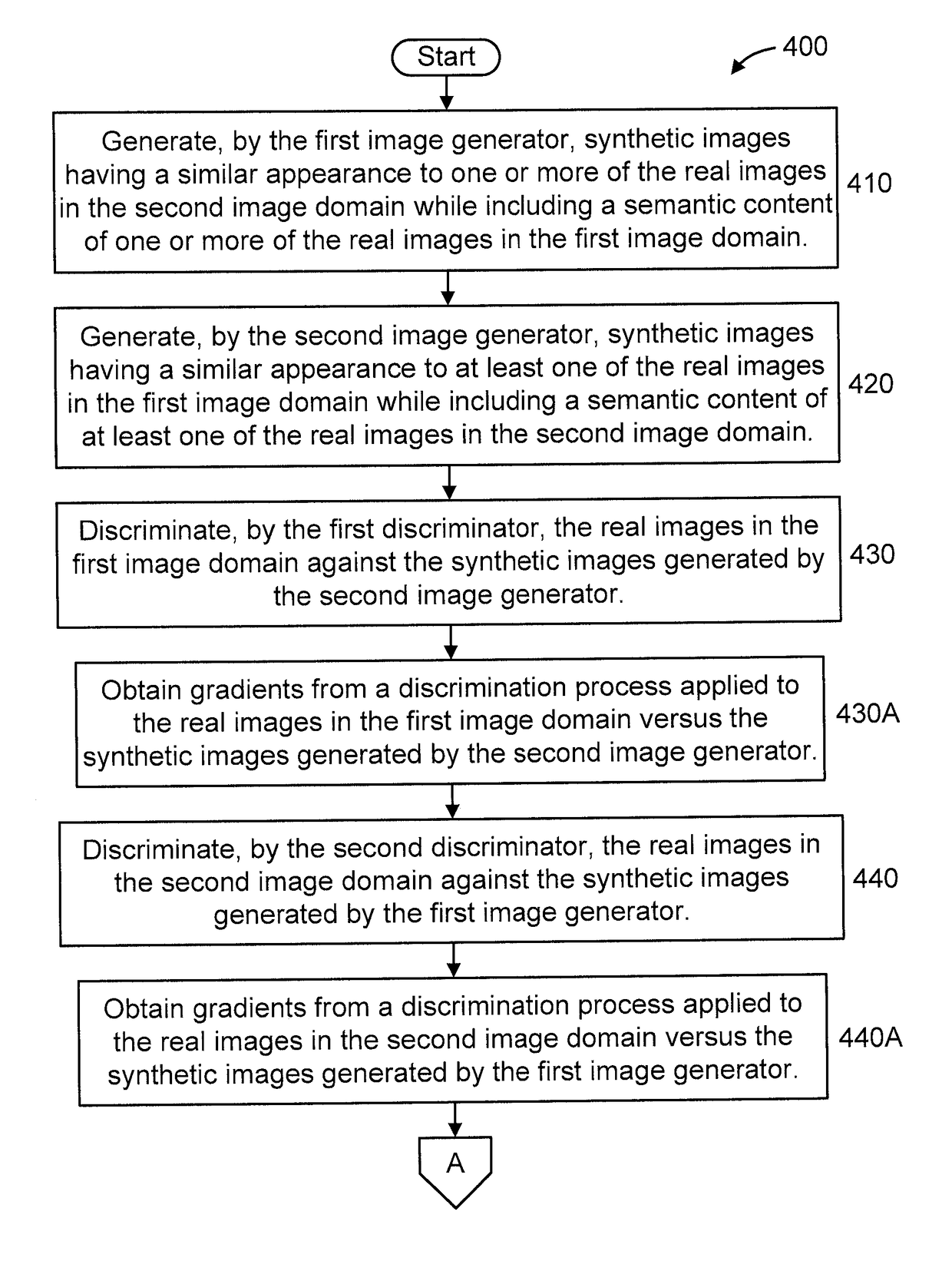
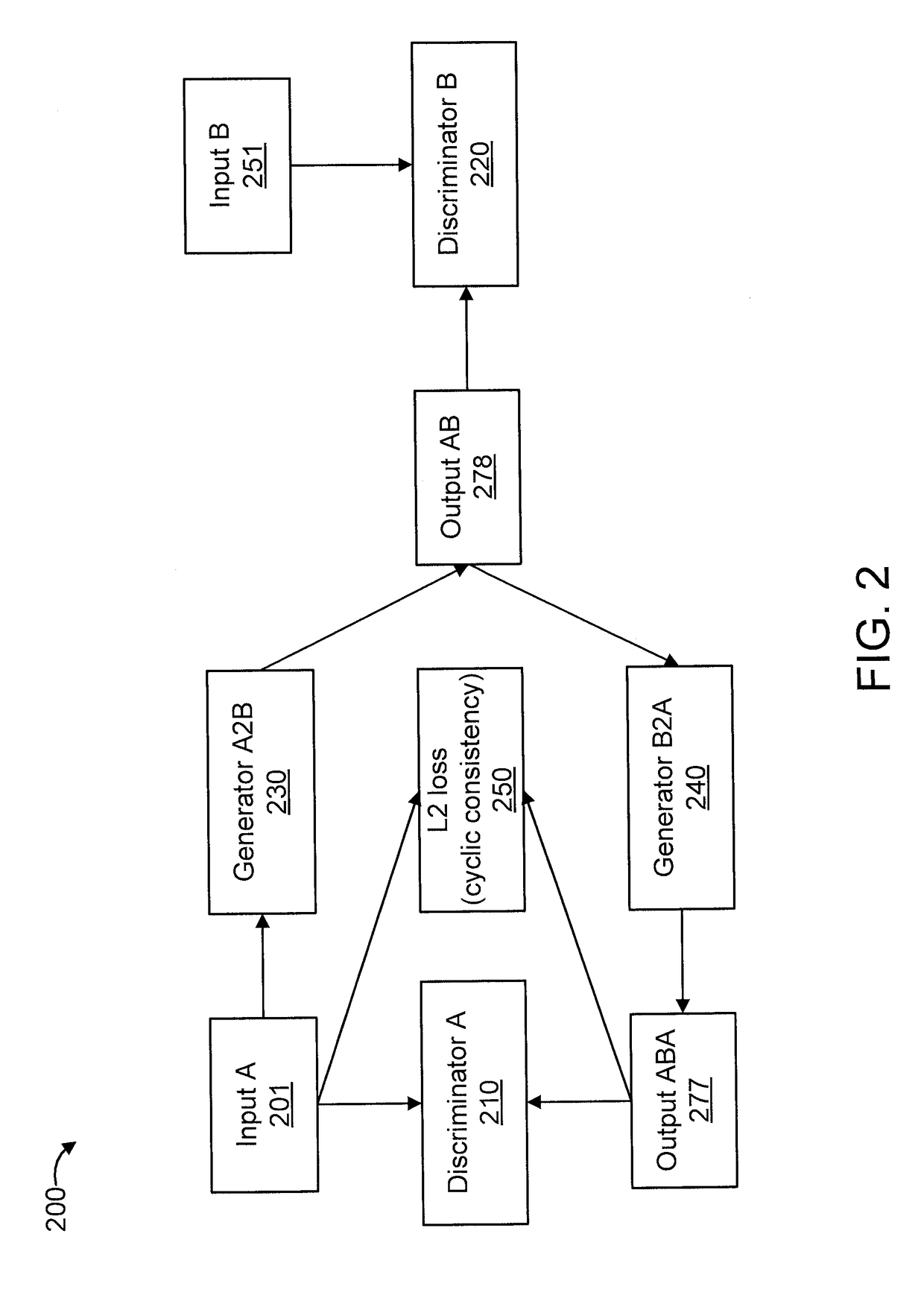
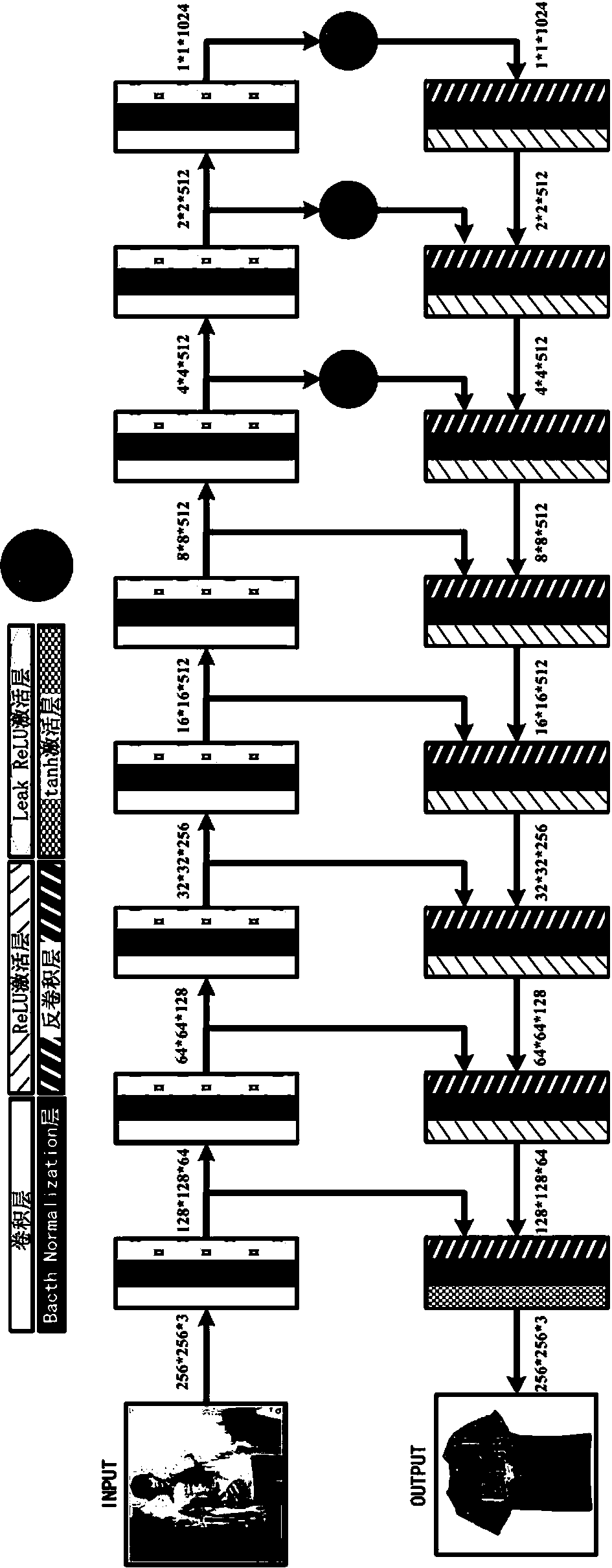
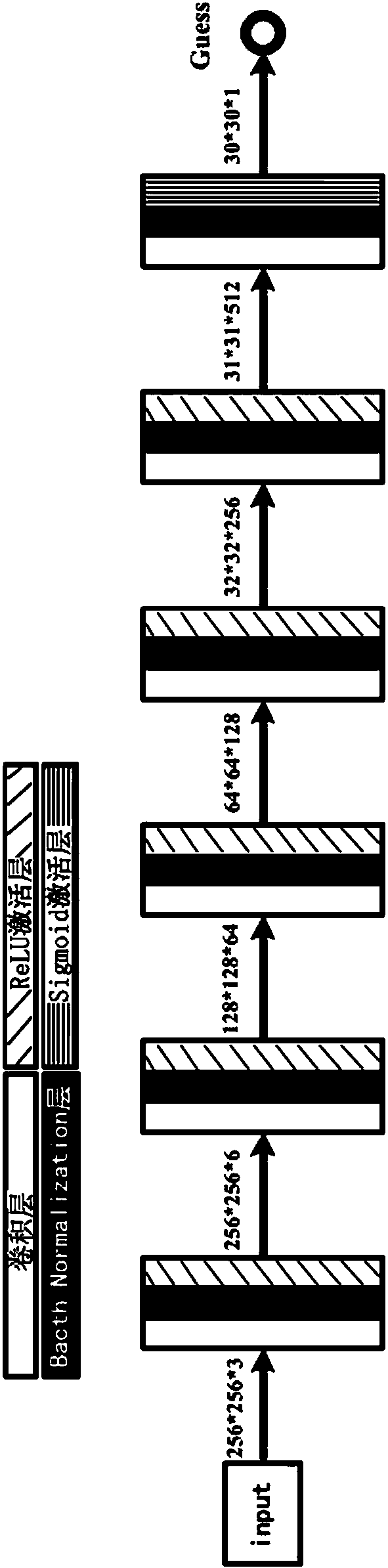
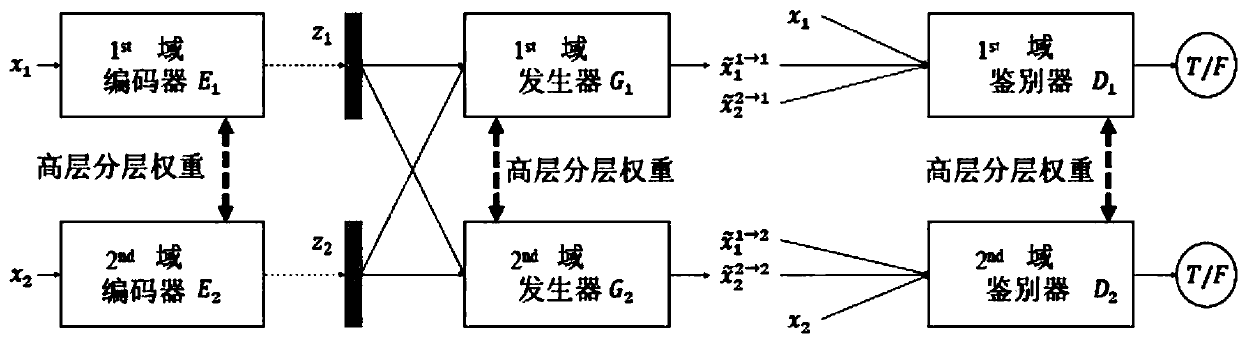
Cyclic generative adversarial network for unsupervised cross-domain image generation
ActiveUS20180307947A1Error rate of discriminativeQuality improvementTexturing/coloringCharacter and pattern recognitionGenerative adversarial networkAdversarial network
A system is provided for unsupervised cross-domain image generation relative to a first and second image domain that each include real images. A first generator generates synthetic images similar to real images in the second domain while including a semantic content of real images in the first domain. A second generator generates synthetic images similar to real images in the first domain while including a semantic content of real images in the second domain. A first discriminator discriminates real images in the first domain against synthetic images generated by the second generator. A second discriminator discriminates real images in the second domain against synthetic images generated by the first generator. The discriminators and generators are deep neural networks and respectively form a generative network and a discriminative network in a cyclic GAN framework configured to increase an error rate of the discriminative network to improve synthetic image quality.
Owner:NEC CORP
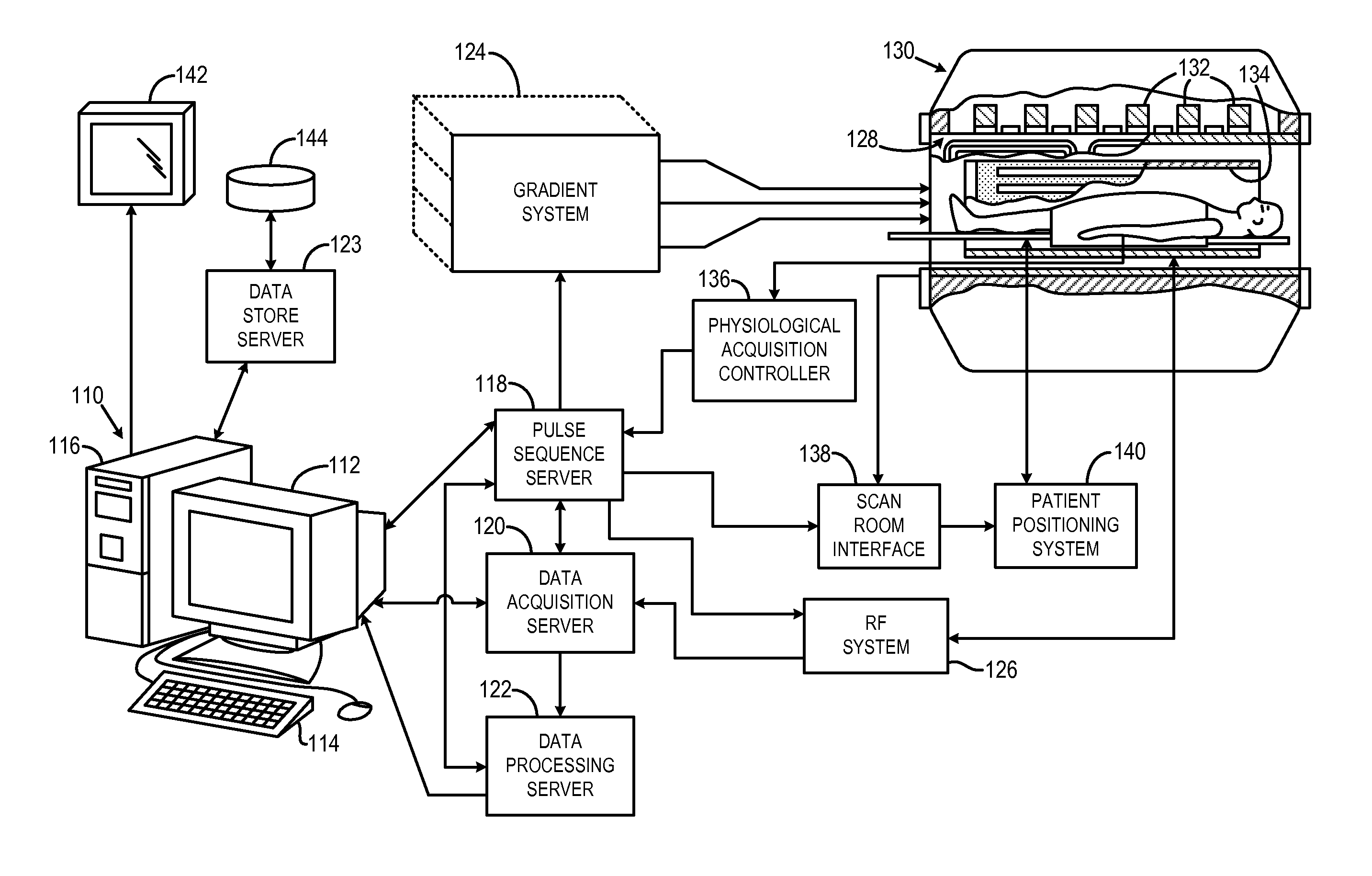
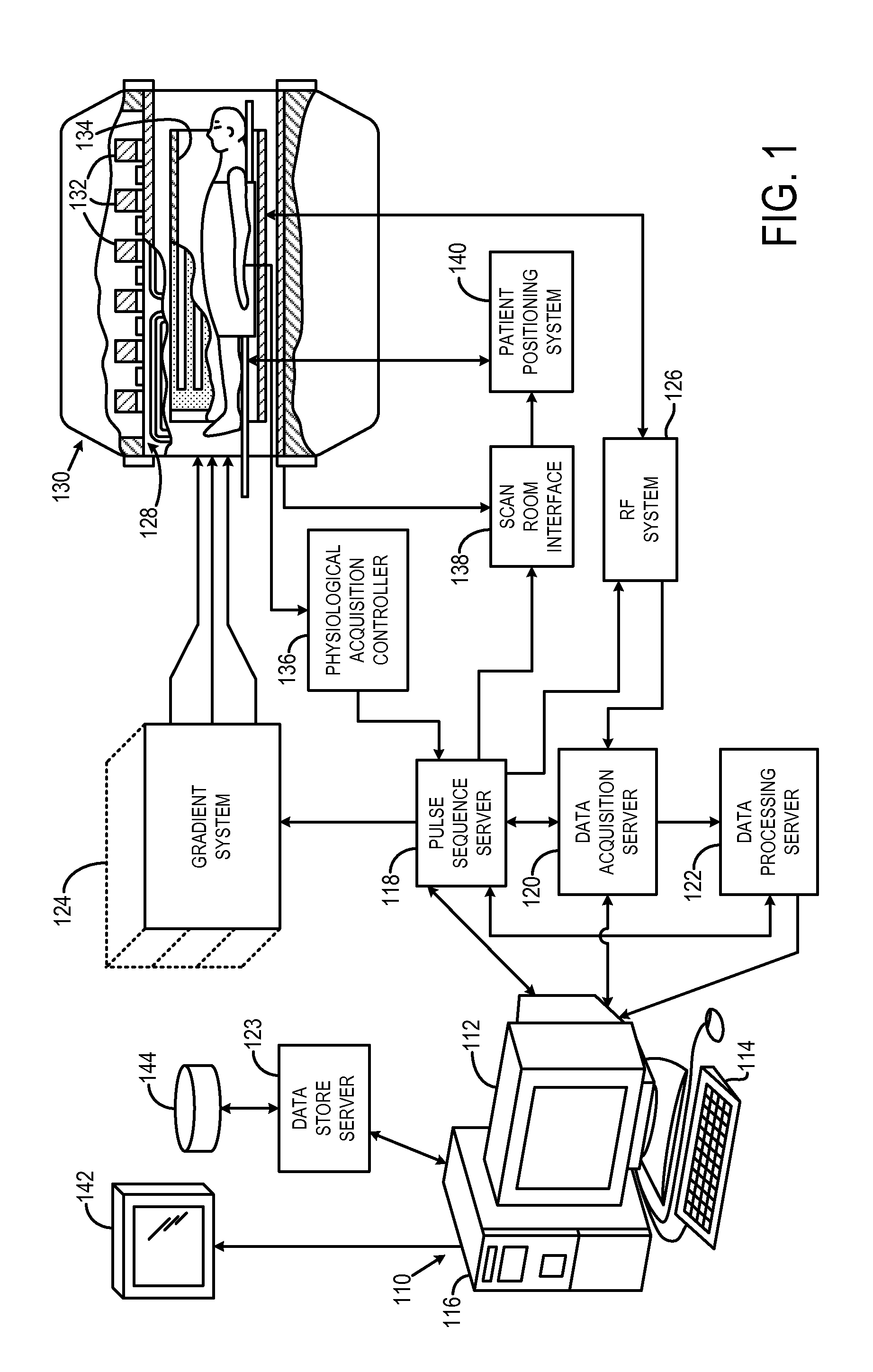
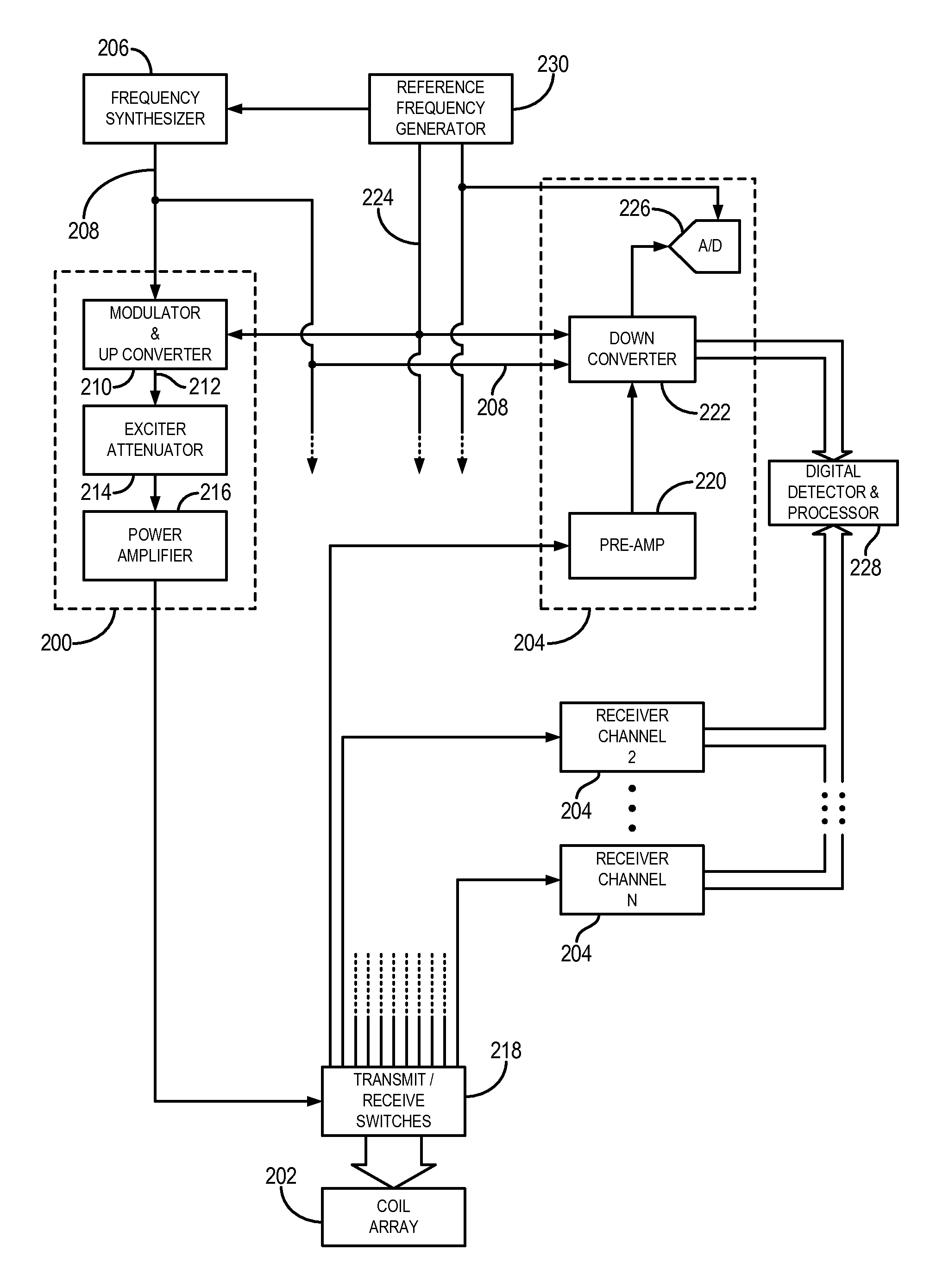
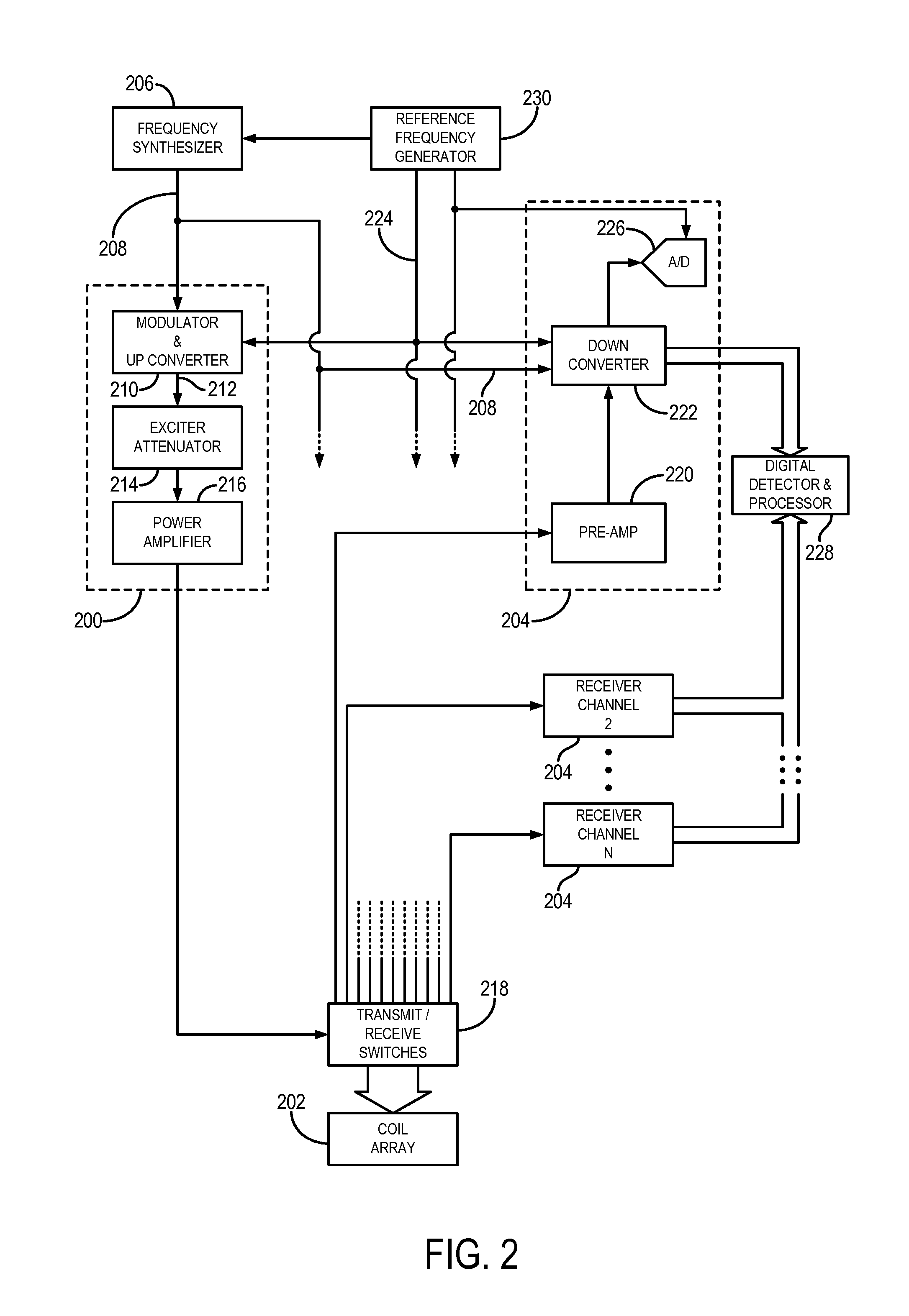
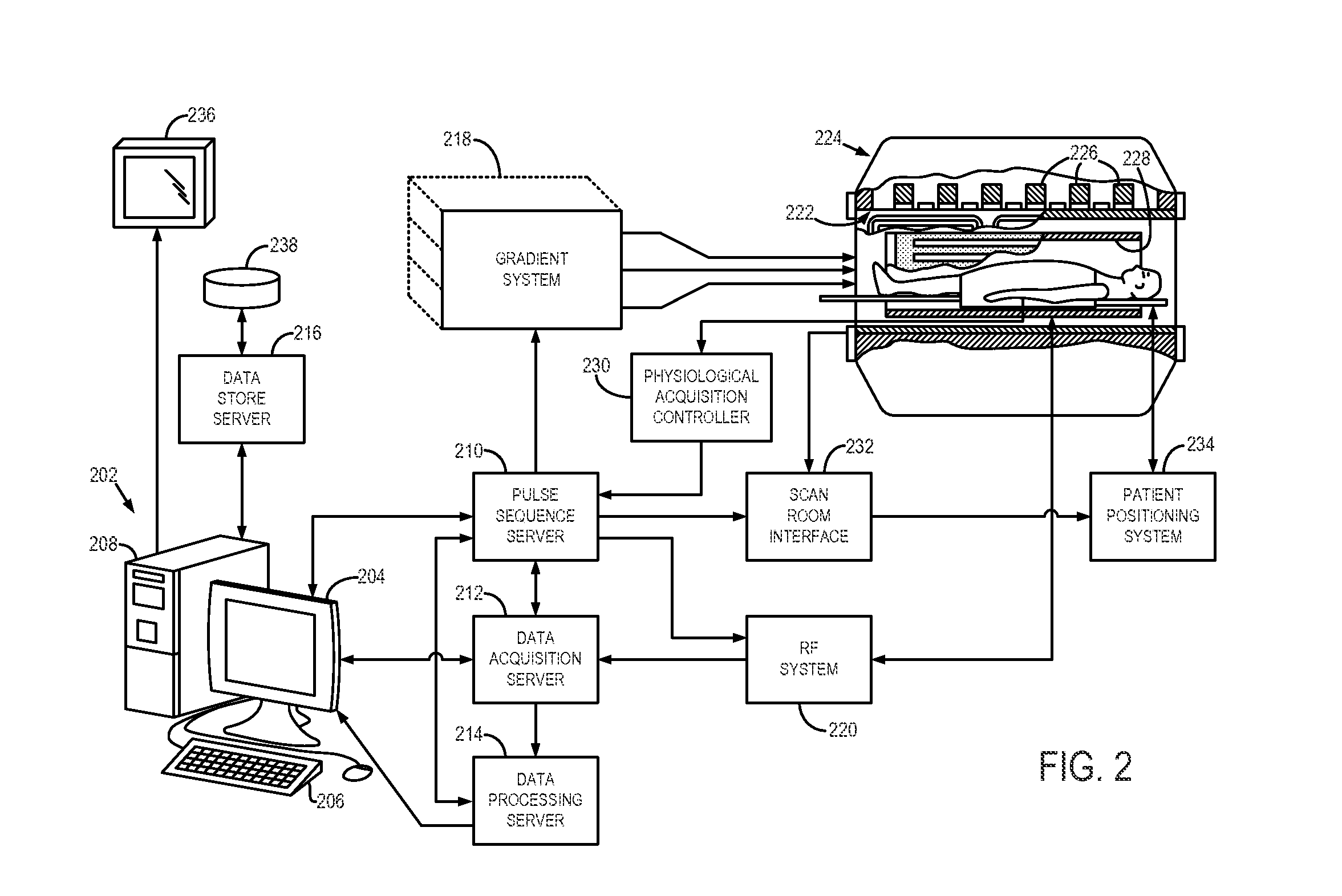
Method for simultaneous multi-slice magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20110254548A1Reliable separationLarge possible separationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientMulti slice
A method for multi-slice magnetic resonance imaging, in which image data is acquired simultaneously from multiple slice locations using a radio frequency coil array, is provided. By way of example, a modified EPI pulse sequence is provided, and includes a series of magnetic gradient field “blips” that are applied along a slice-encoding direction contemporaneously with phase-encoding blips common to EPI sequences. The slice-encoding blips are designed such that phase accruals along the phase-encoding direction are substantially mitigated, while providing that signal information for each sequentially adjacent slice location is cumulatively shifted by a percentage of the imaging FOV. This percentage FOV shift in the image domain provides for more reliable separation of the aliased signal information using parallel image reconstruction methods such as SENSE. In addition, the mitigation of phase accruals in the phase-encoding direction provides for the substantial suppression of pixel tilt and blurring in the reconstructed images.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
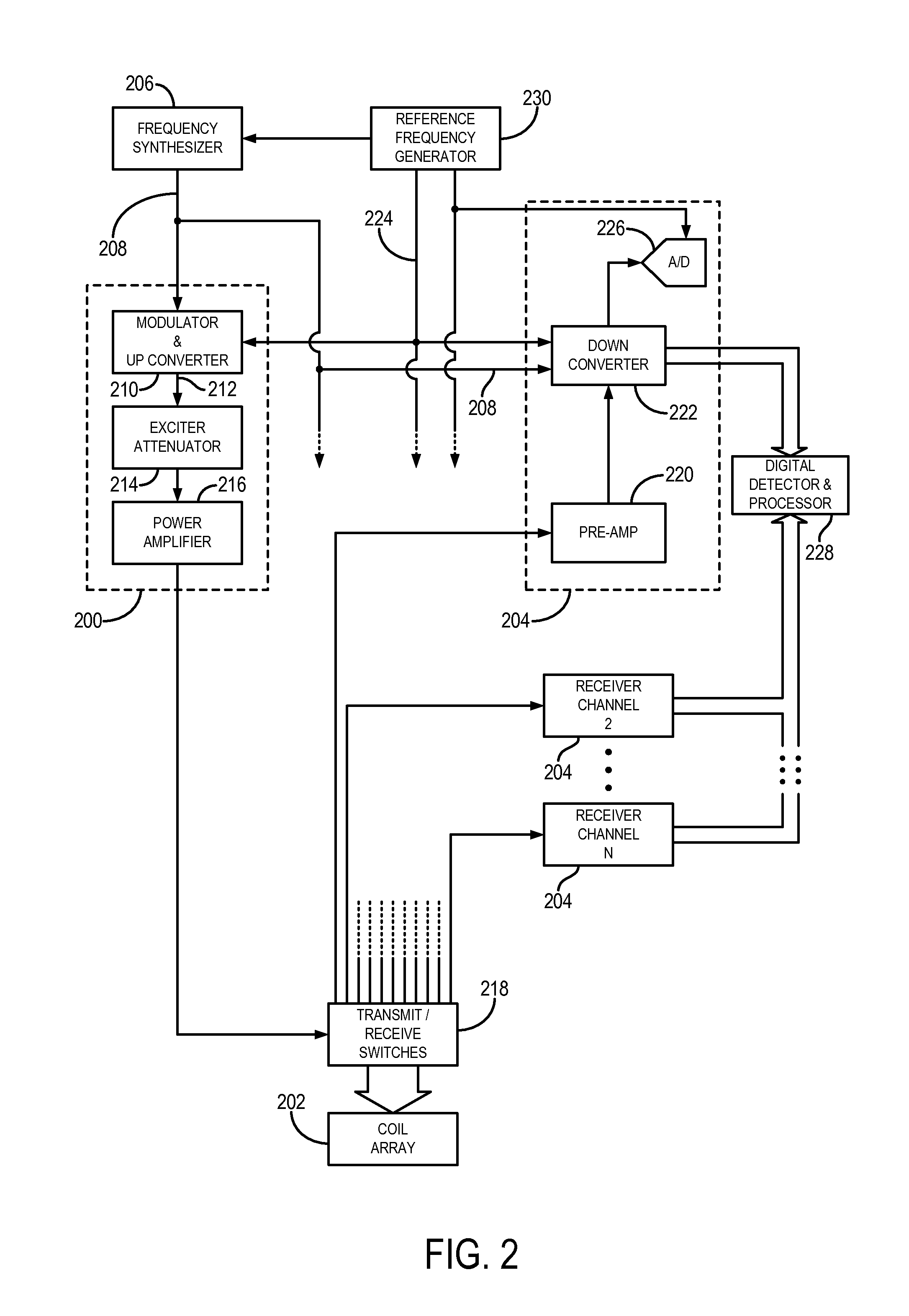
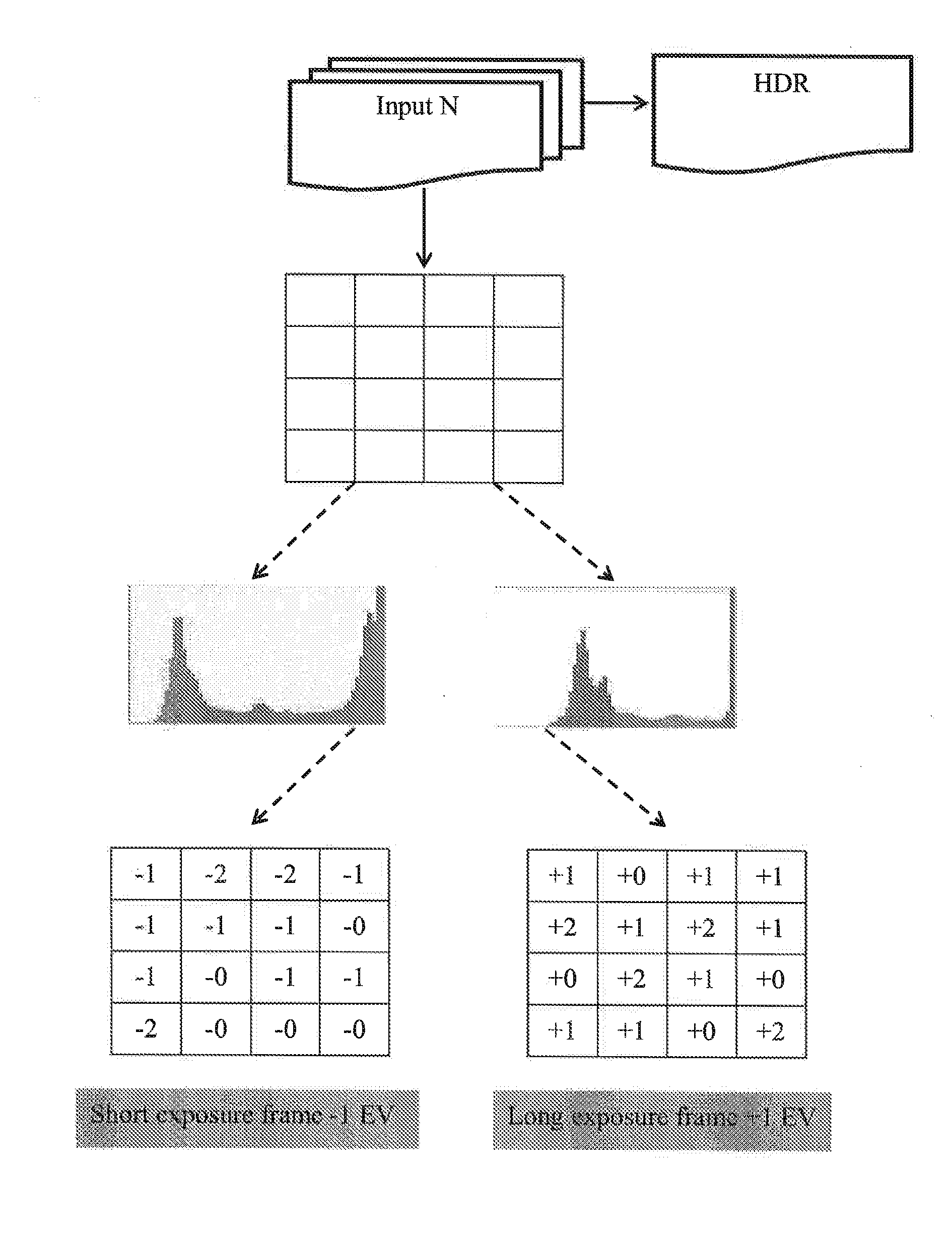
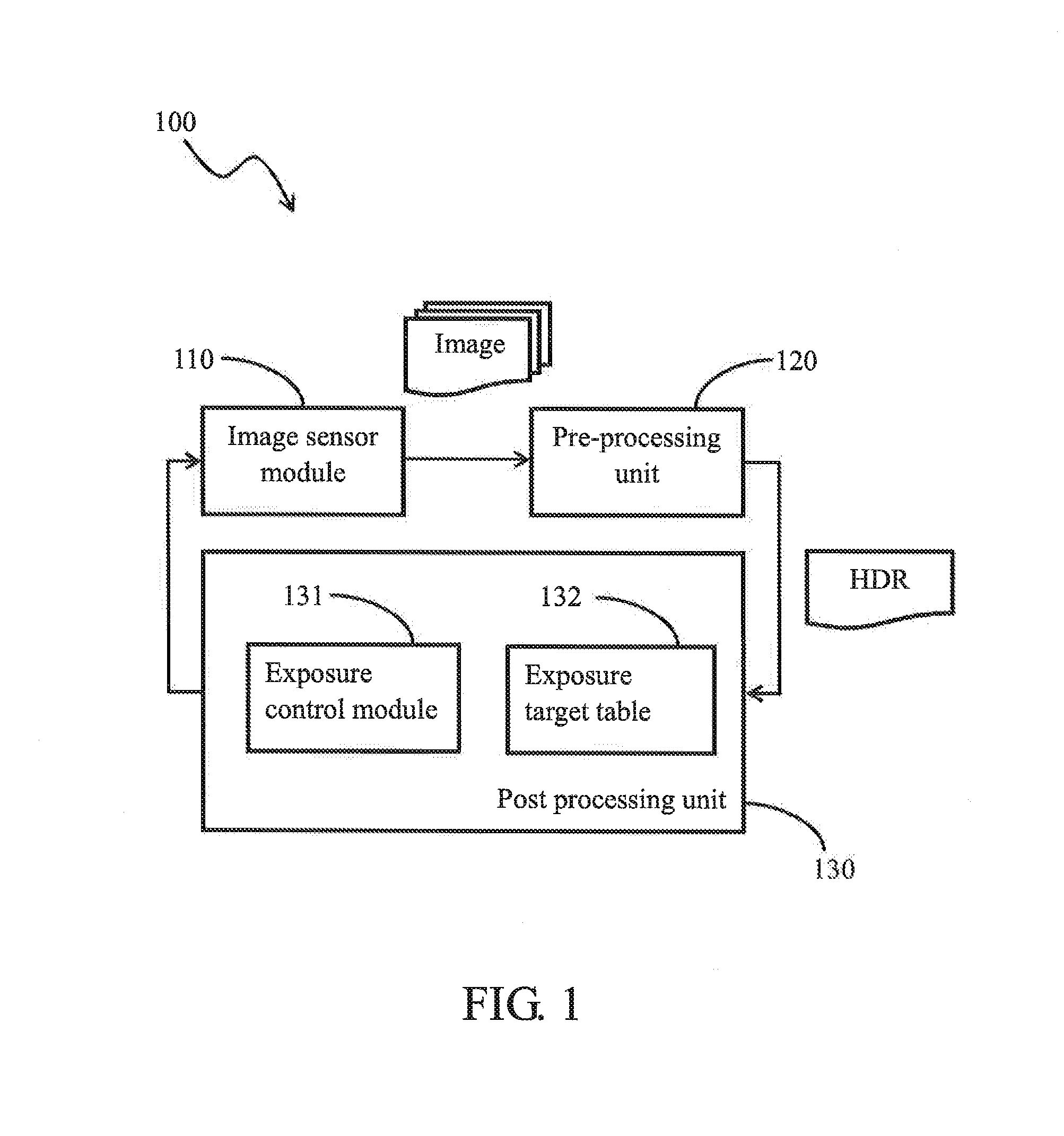
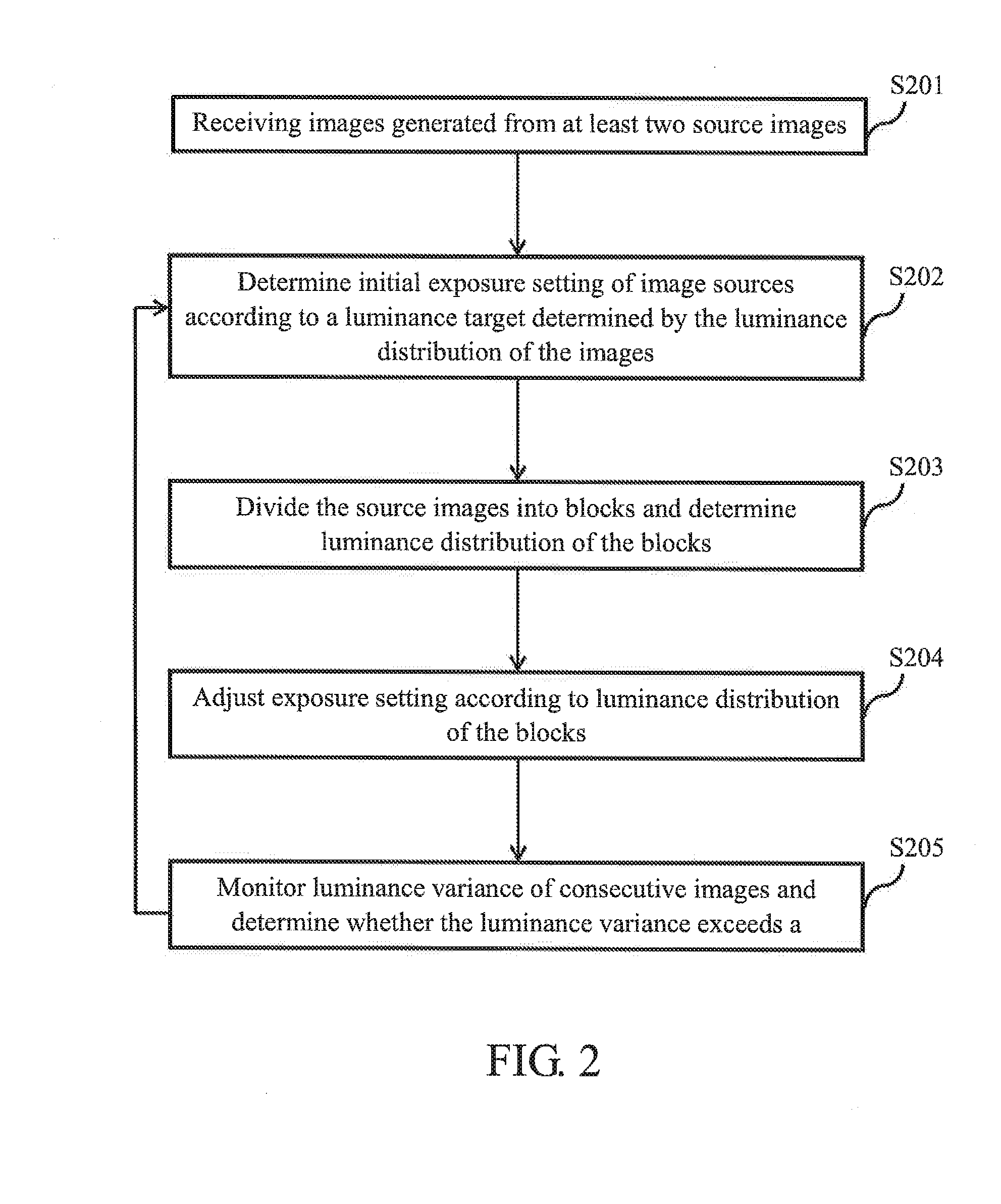
Automatic exposure control for sequential images
ActiveUS20140307117A1Television system detailsColor television detailsImage domainAutomatic exposure control
An exposure control method and an image processing system are provided. The image processing system comprises: an image sensor module, configured to provide at least two types of source images in parallel, each type of the source images has different exposure setting; a pre-processing unit, configured to determine luminance distribution of the source images on block basis, perform a first exposure control according to the luminance distribution of the two types of source images, and generate output images according to the source images in RAW image domain, and a post-processing unit, configured to determine luminance distribution of the output images, and perform a second exposure control according to the luminance distribution of the output images in normal image domain; wherein exposure settings of the image sensor module is adjusted according to the first exposure control and the second exposure control.
Owner:HTC CORP
Noise treatment of low-dose computed tomography projections and images
InactiveUS7187794B2Restore accuratelyReduce noiseImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionTomographyComputing tomography
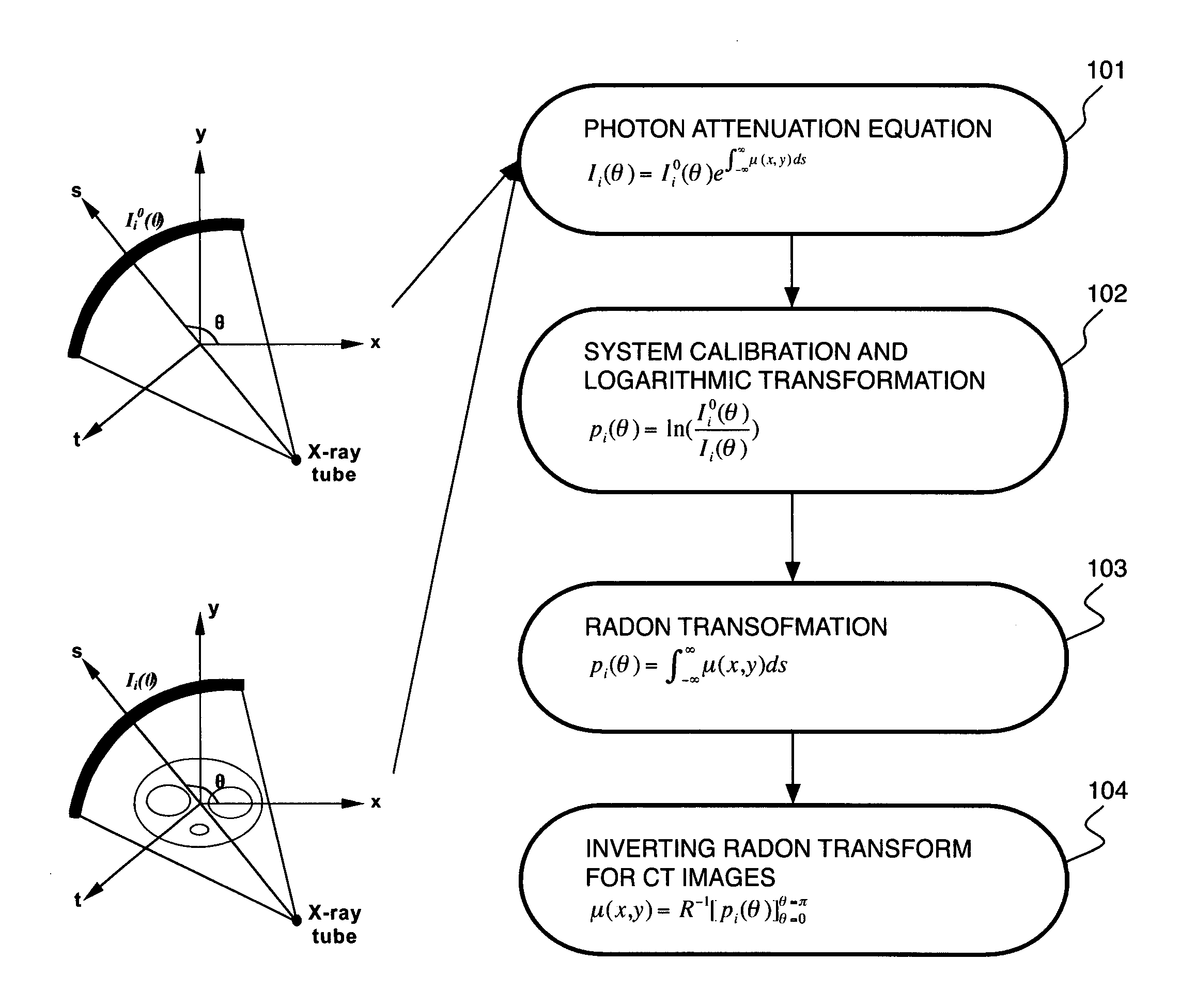
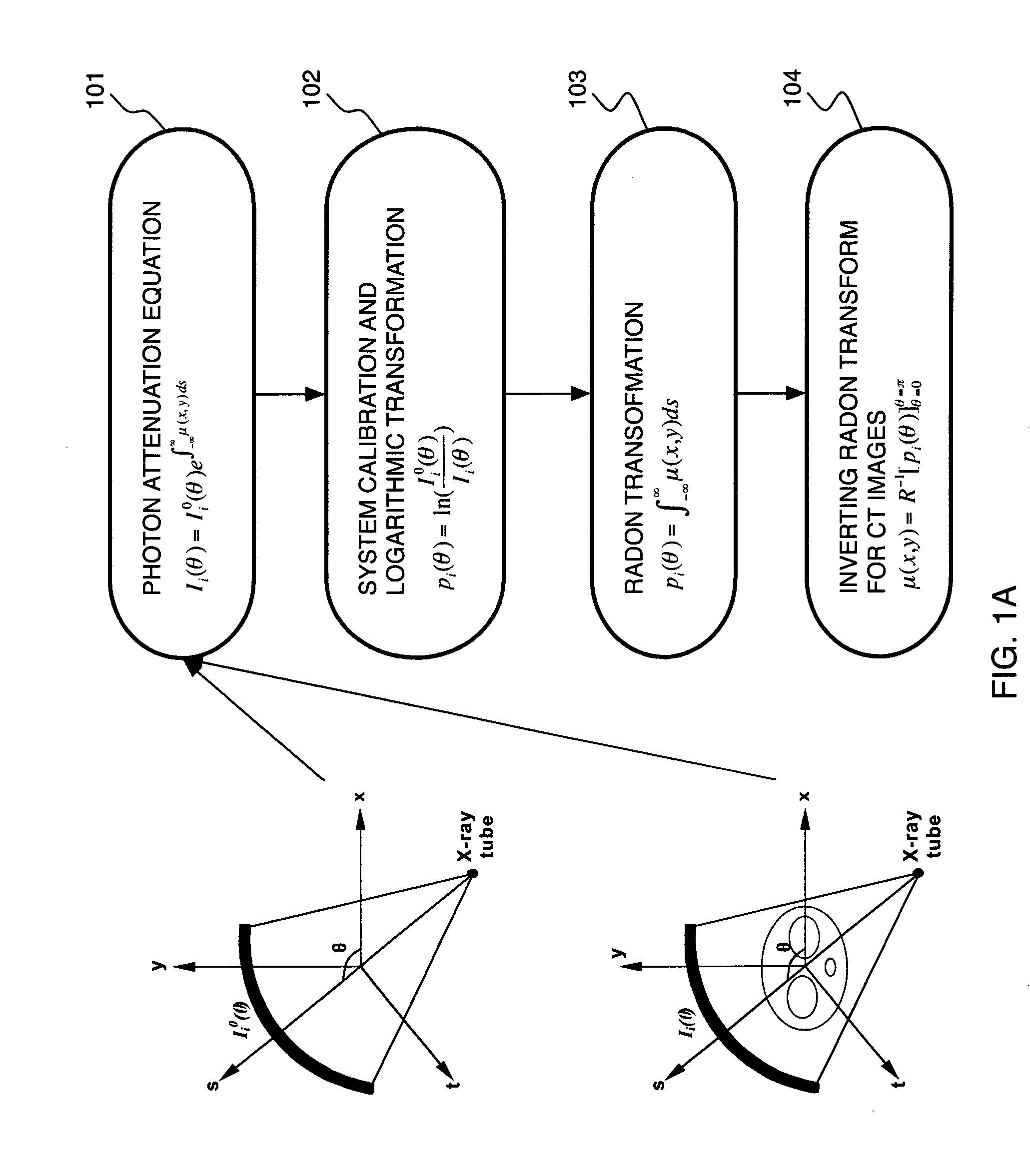
A method for treating noise in low-dose computed tomography projections and reconstructed images comprises acquiring raw data at a low mA value, applying a domain specific filter in a sinogram domain of the raw data, and applying an edge preserving smoothing filter in an image domain of the raw data after filtering in the sinogram domain.
Owner:NEW YORK RES FOUND OF STATE UNIV OF
Image domain conversion network based on generative adversarial networks (GAN) and conversion method
ActiveCN108171320AImprove conversion performanceImprove reliabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesGenerative adversarial networkNetwork model
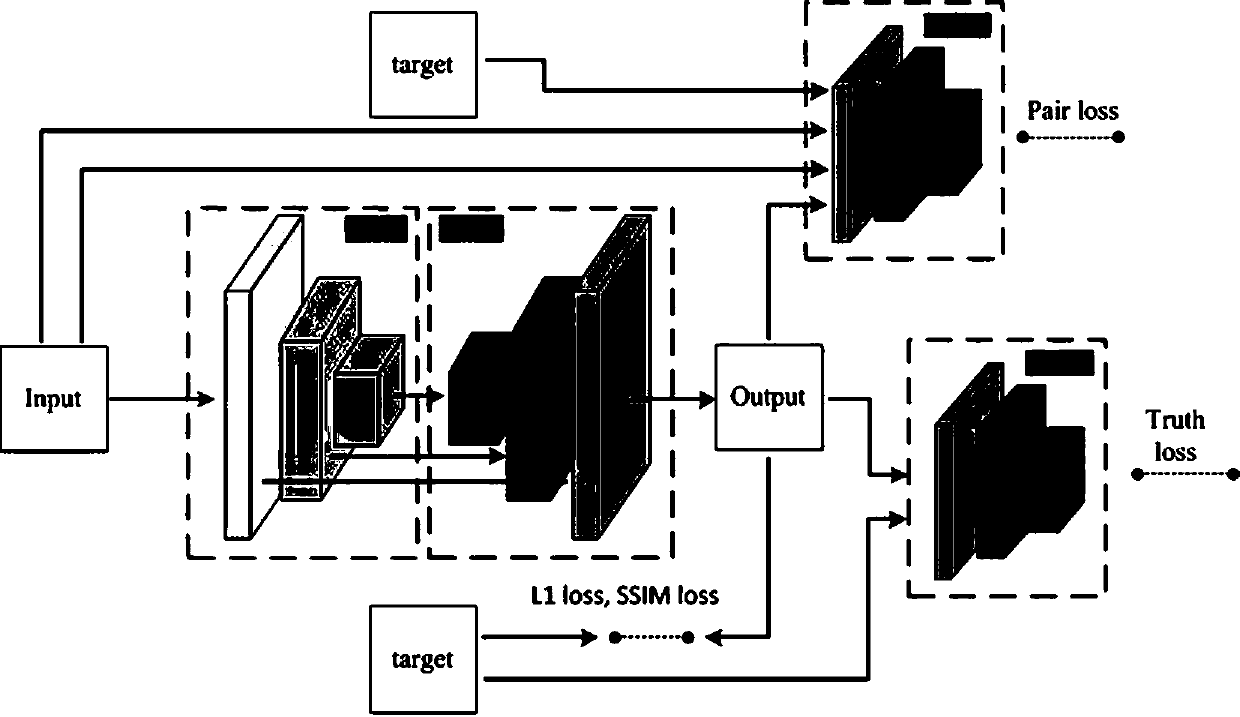
The invention discloses an image domain conversion network based on generative adversarial networks (GAN) and a conversion method. The image domain conversion network includes a U-shaped generative network, an authenticity authentication network and a pairing authentication network. An image domain conversion process mainly includes the following steps: 1) training the U-shaped generative network,and establishing a network model of the U-shaped generative network; and 2) normalizing a to-be-converted image, and then input the image into the network model established through the step 1) to complete image domain conversion of the to-be-converted image. According to the image domain conversion network, an image domain conversion task of a local region in the image can be achieved, image local-domain conversion quality is high, judgment ability of the network is high, stability of image conversion is high, and authenticity of a generated image is greatly improved.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
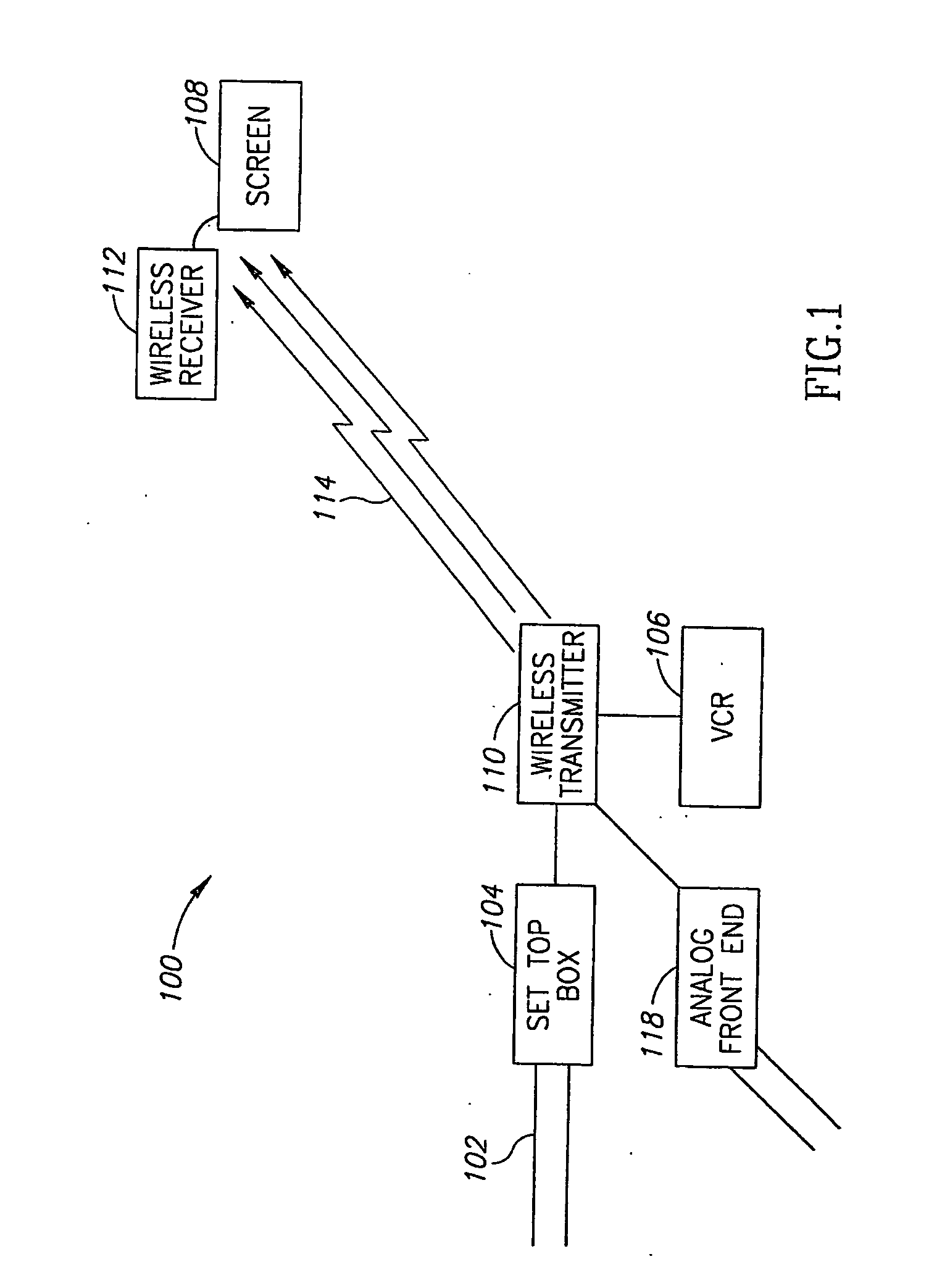
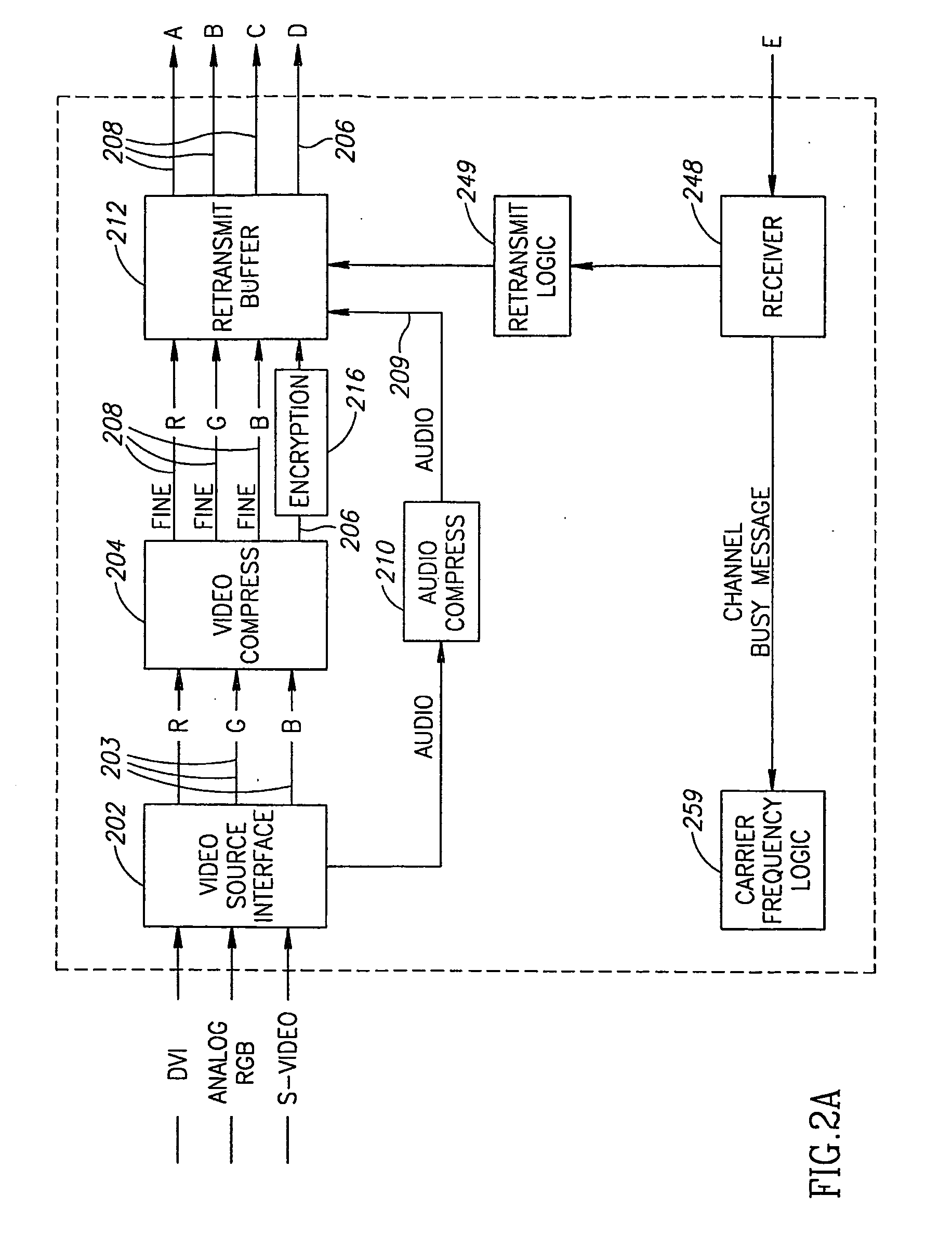
Wireless Transmission of High Quality Video
InactiveUS20080123739A1Simpler compression procedureEasy to compressSpatial transmit diversityPulse modulation television signal transmissionWireless transmissionComputer graphics (images)
A method of transmitting video images. The method includes providing a high definition video stream, compressing the video stream using an image domain compression method, in which each pixel is coded based on a vicinity of the pixel and transmitting the compressed video stream over a fading transmission channel.
Owner:AMIMON
Method for simultaneous multi-slice magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS8405395B2Reliable separationLarge possible separationMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic gradientMulti slice
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
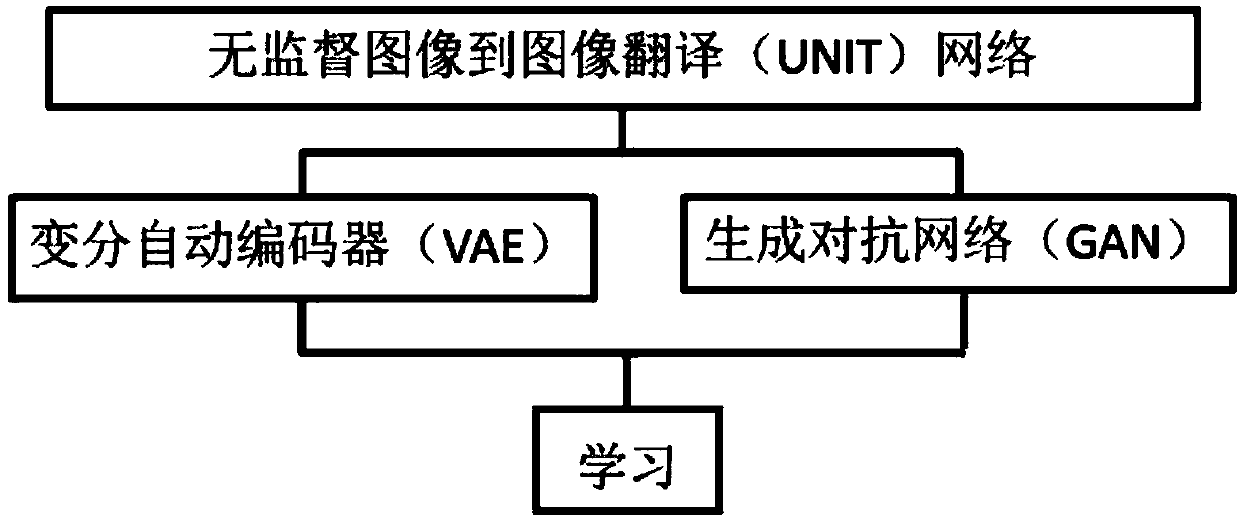
Image conversion method based on variation automatic encoder and generative adversarial network
The invention provides an image conversion method based on a variation automatic encoder and the generative adversarial network. The method is mainly characterized by comprising the variation automatic encoder (VAE), weight sharing, generating the generative adversarial network (GAN) and learning, in the process, a non-monitored image is utilized to learn a bidirectional conversion function between two image domains in an image conversion network framework (UNIT), VAE and VAE are comprised, modeling for each image domain is carried out through utilizing the VAE and the VAE, mutual action of an adversarial training target and a weight sharing constraint is carried out, corresponding images are generated in the two image domains, the conversion image is associated with an input image of each domain, and image reconstruction flow and image conversion flow problems can be solved through training network combination. The method is advantaged in that the non-monitoring image is utilized to the image conversion framework, images in the two domains having not any relations are made to accomplish conversion, a corresponding training data set formed by the images is not needed, efficiency and practicality are improved, and the method can be developed to non-monitoring language conversion.
Owner:SHENZHEN WEITESHI TECH
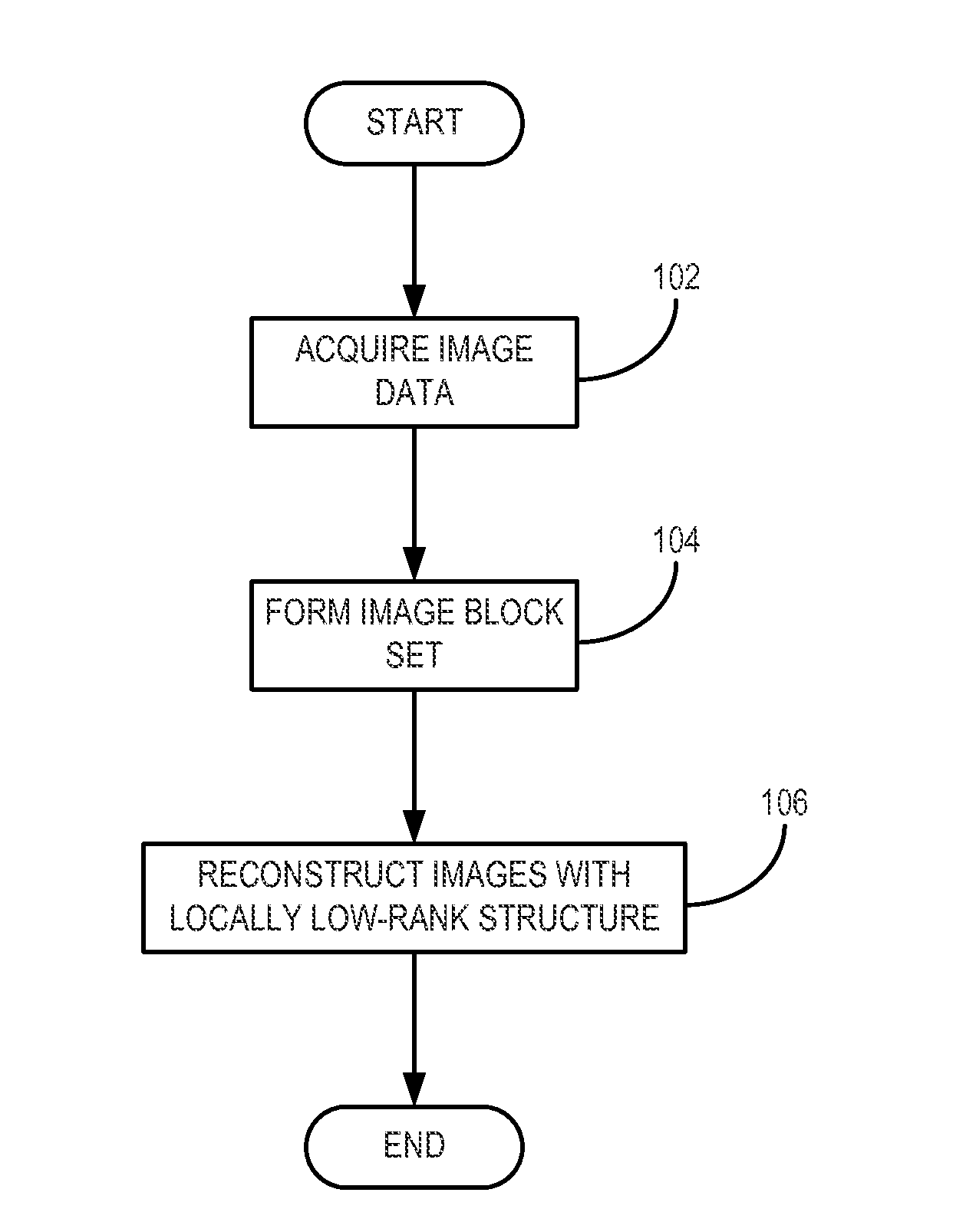
System and method for medical image reconstruction and image series denoising using local low rank promotion
ActiveUS20130182930A1Simple structureOvercomes drawbackReconstruction from projectionCharacter and pattern recognitionMedical imagingNuclear medicine
A method for reconstructing a time series of images from data acquired with a medical imaging system is provided. Data is acquired with the medical imaging system, and a set of image blocks that defines the location and size of each of a plurality of image blocks in the image domain is then selected. The acquired data and selected image block set are then used to jointly estimate a plurality of images that form a time series of images while promoting locally-low rank structure in the images.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
High-speed weak target flight path detection method of image field
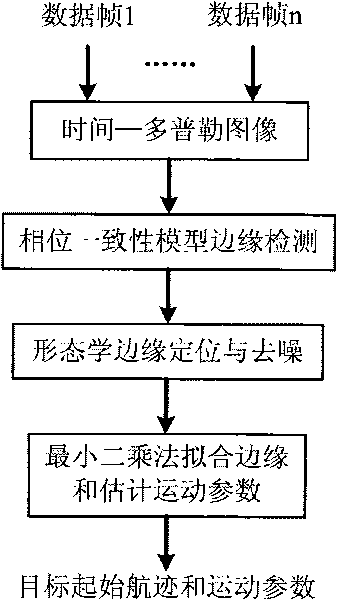
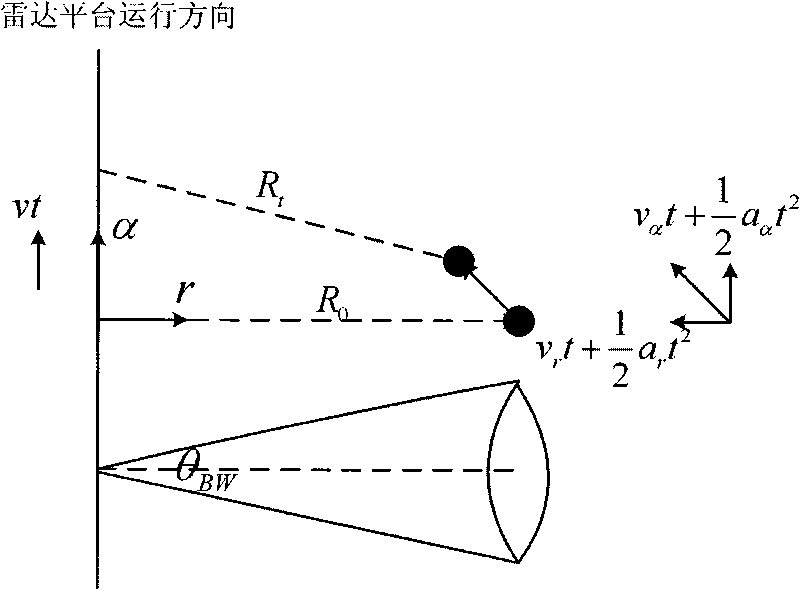
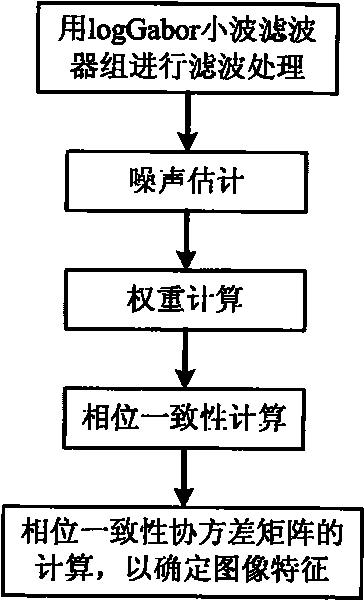
InactiveCN101718870AReduce the impactPrecise positioningRadio wave reradiation/reflectionMethod of imagesSkeletonization
The invention discloses a high-speed weak target flight path detection method of an image field, relating to the field of moving object tracking, and mainly solving the problem of extracting a moving object flight path and a target kinematic parameter from data with a low signal-to-noise ratio. The detection process is as follows: firstly, obtaining a time-Doppler image by mixing and accumulating target multiframe data; carrying out edge extracting on the basis of phase equalization model; carrying out skeletonization and binary image de-noising treatment on the edge detection result with a morphology method to realize edge center positioning as well as noise inhibition; and finally, using a least square method to detect the target flight path and estimate a target parameter. The invention can accurately estimate the advantages of a curve flight path parameter, and can be used for the data processing field for monitoring systems, such as radars and the like to realize high-speed weak target detection and tracking.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
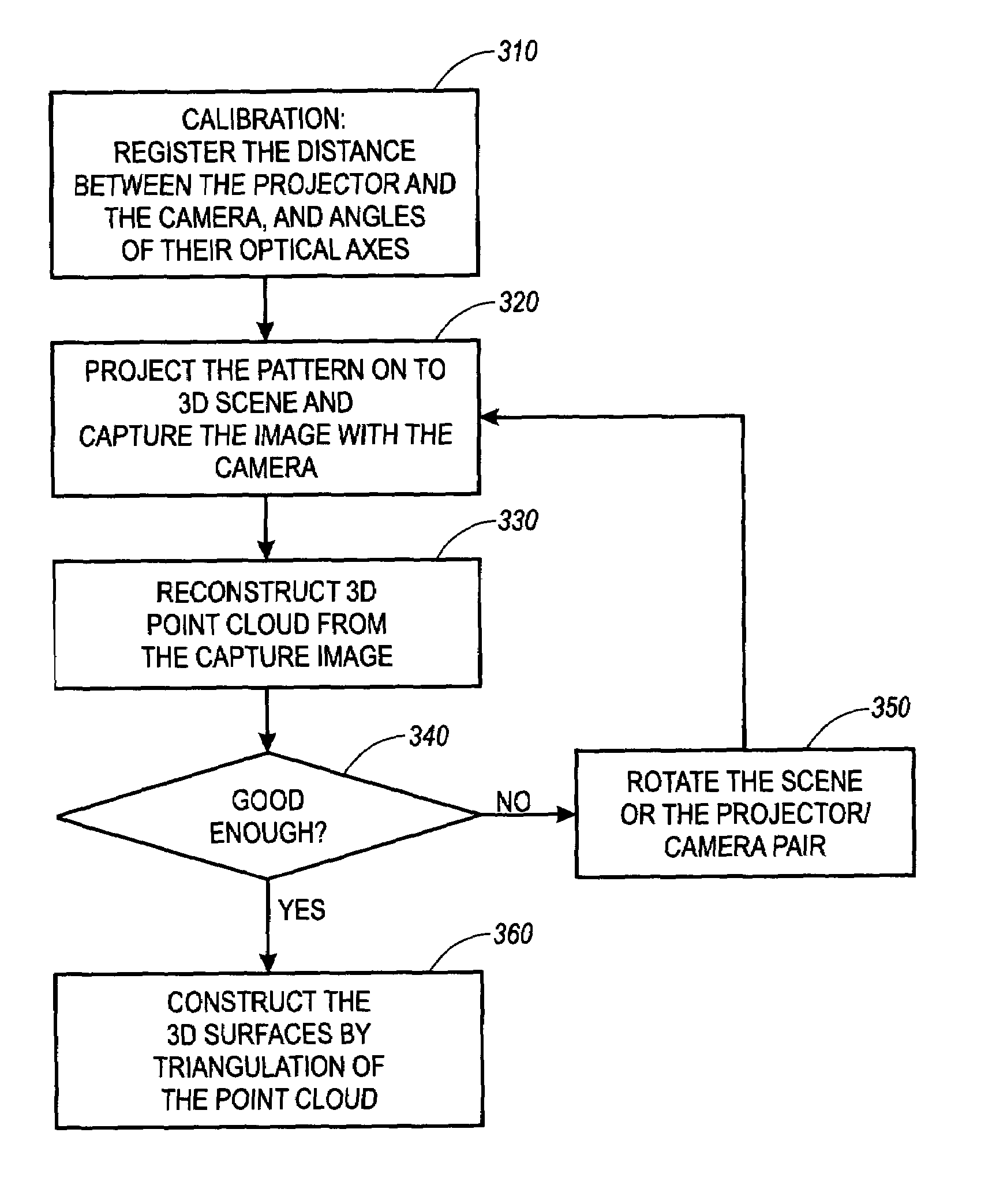
Three-dimensional active vision with glyph address carpet
A method for reconstructing three dimensional shapes from two dimensional image domains uses glyph address carpets as a structured light pattern. The glyph address carpet includes a glyph encoding scheme in which the coordinates of any given point can be computed by looking at the glyph marks in a small neighborhood. The method includes calibrating at least one projecting device and at least one image detecting device and projecting a glyph address carpet pattern onto a three dimensional figure. The projected glyph address carpet pattern is detected and used to reconstruct the three dimensional coordinates for each readable glyph mark within the projected glyph address carpet pattern.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
Image enhancement and partition method
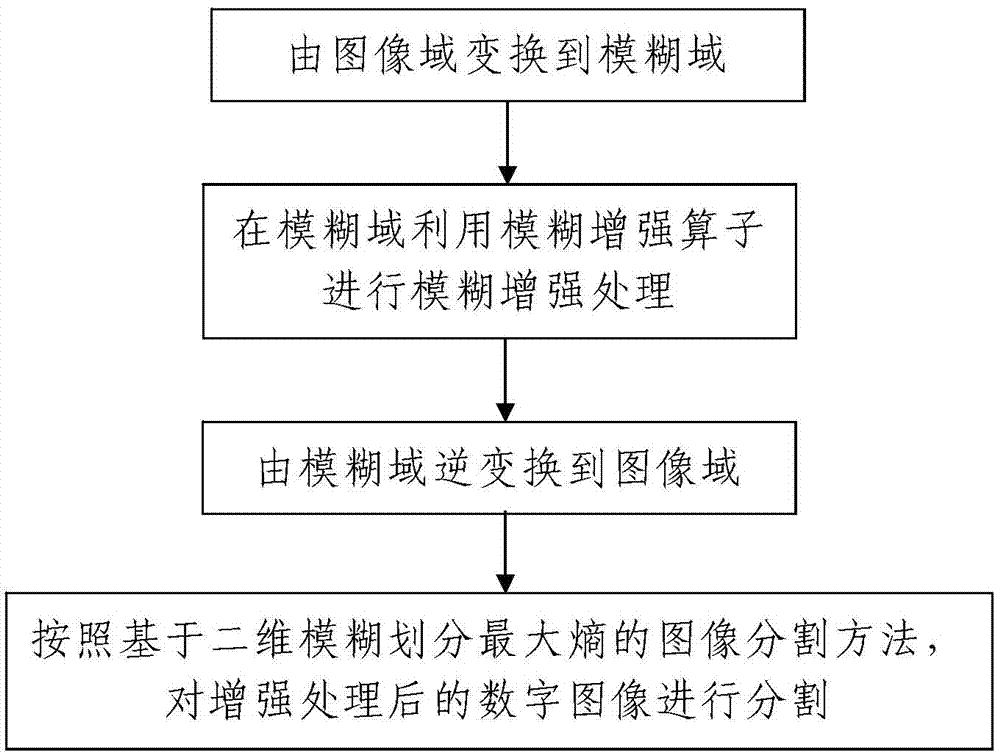
InactiveCN103871029AThe method steps are simpleReasonable designImage enhancementImage analysisGradationImage segmentation
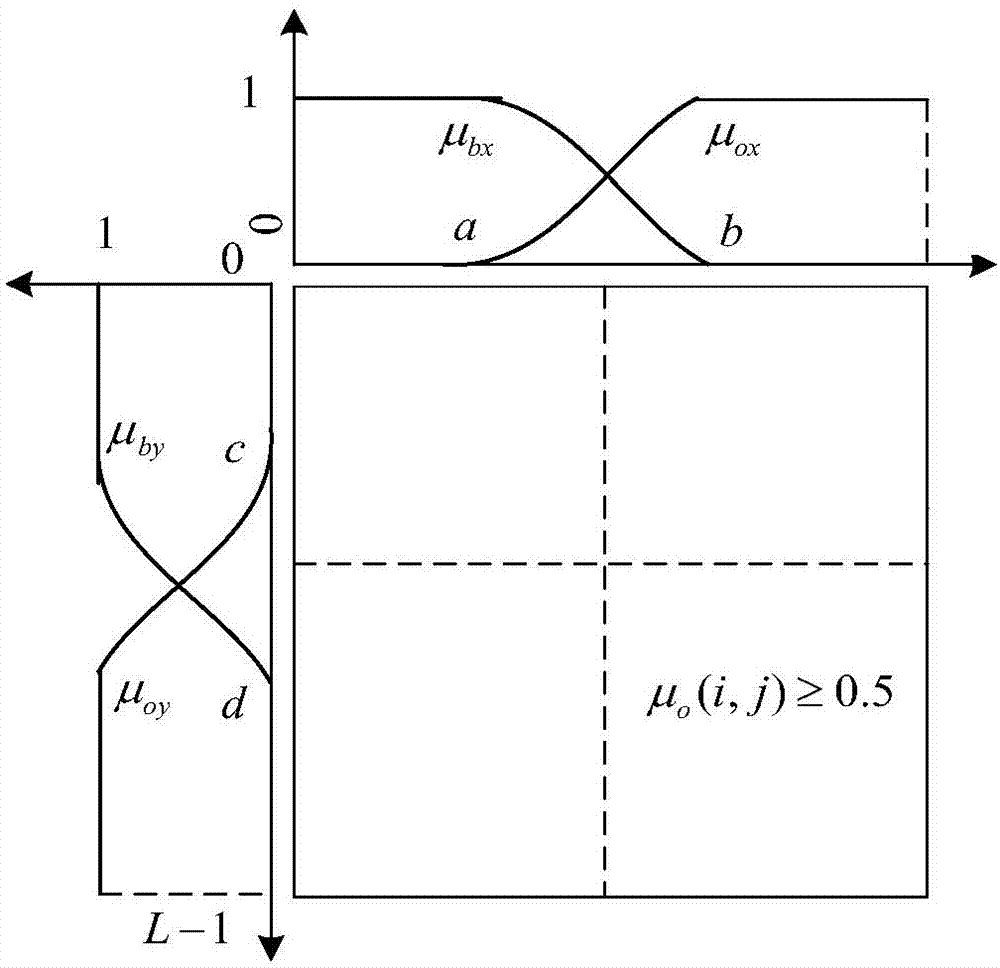
The invention discloses an image enhancement and partition method, which comprises the following steps of I, image enhancement: a processor and an image enhancement method based on fuzzy logic are adopted for performing enhancement processing on an image needing to be processed, and the process is as follows: i, converting from an image domain to a fuzzy domain: mapping the grey value of each pixel point of the image needing to be processed to a fuzzy membership degree of a fuzzy set according to a membership function (shown in the specifications); ii, performing fuzzy enhancement processing by utilizing a fuzzy enhancement operator in the fuzzy domain; iii, converting from the fuzzy domain to the image domain; II, image partition: partitioning a digital image subjected to enhancement processing, i.e. a to-be-partition image, according to an image partition method based on a three-dimensional fuzzy division maximum entropy. The method is simple in steps, reasonable in design, convenient to realize, good in processing effect and high in practical value, and an image enhancement and partition process can be simply, conveniently and quickly completed with high quality.
Owner:XIAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
MR image reconstruction method and MR apparatus using propeller imaging
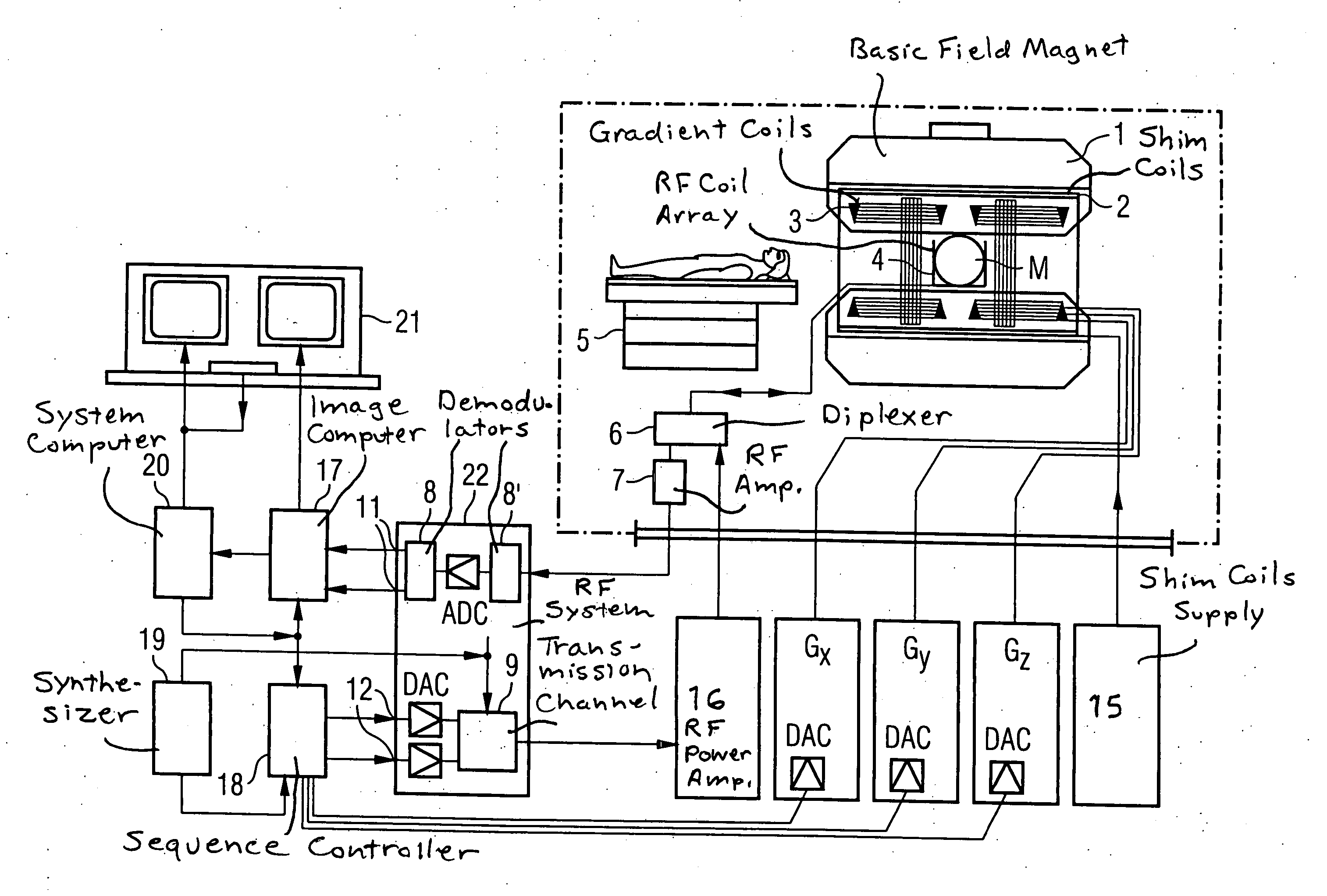
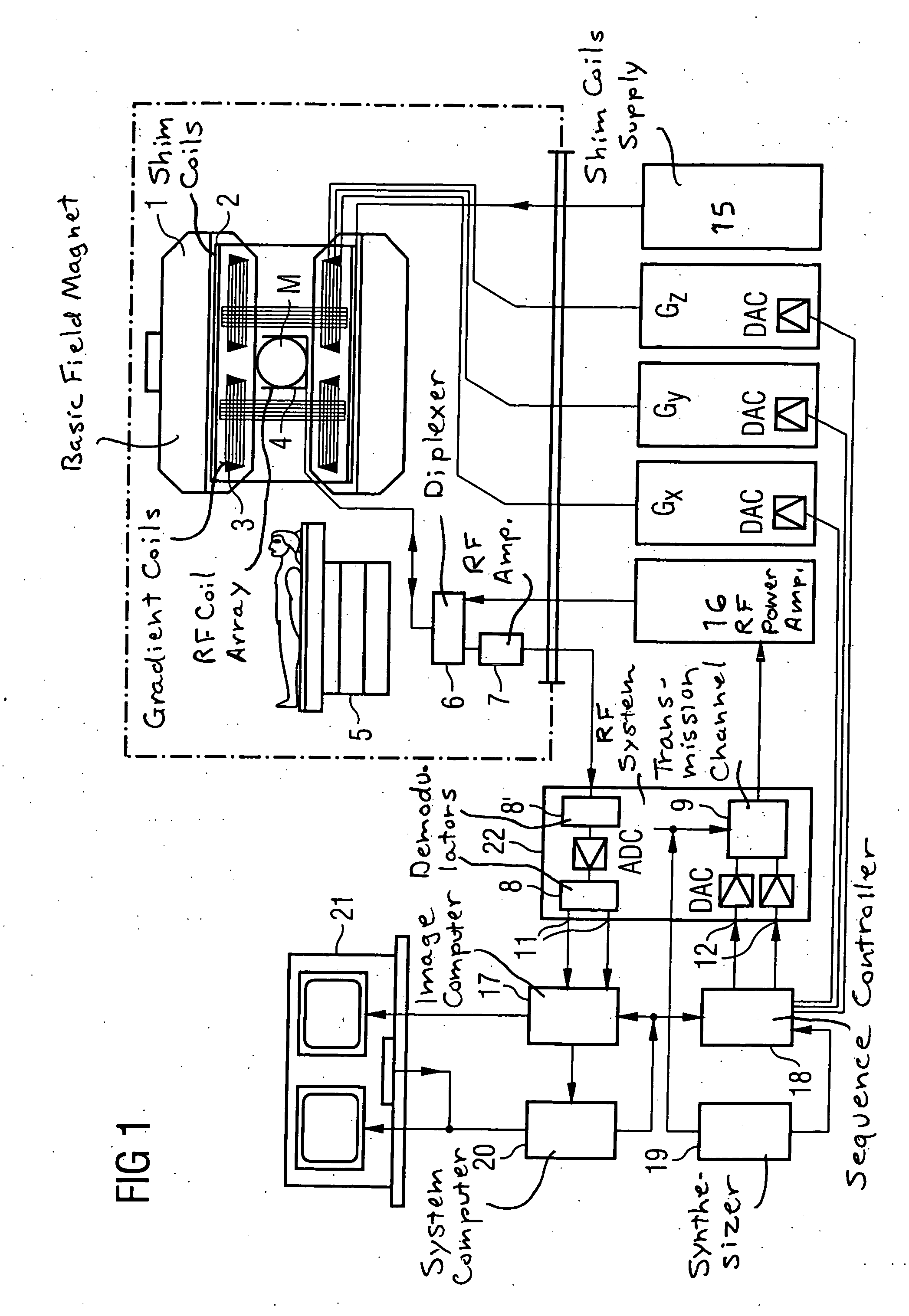
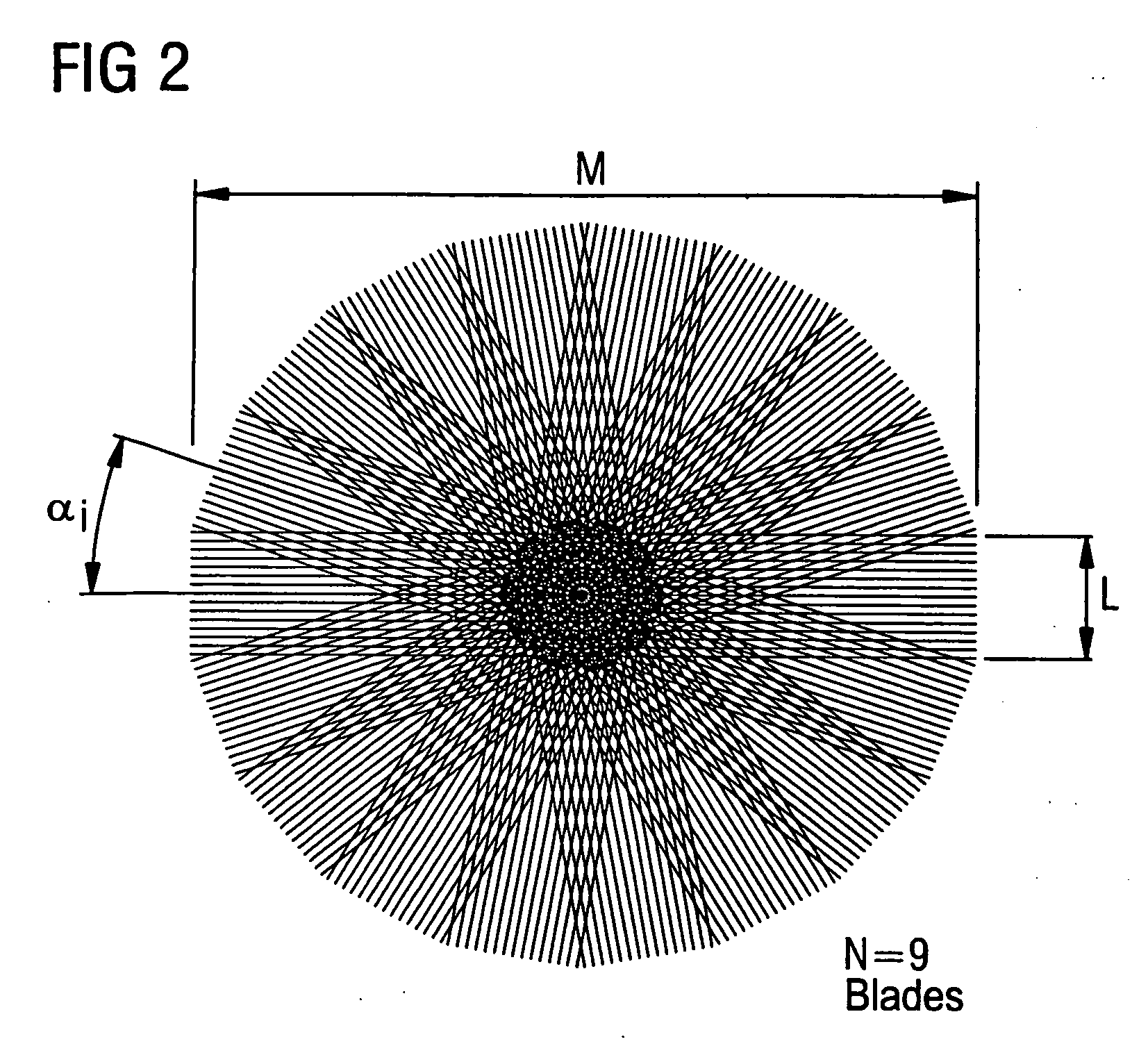
ActiveUS20060264735A1Simple (andReconstructed imageMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringData setResonance
In a magnetic resonance (MR) image reconstruction method and MR apparatus, for raw MR data are acquired with the propeller technique, and k-space sampling ensues in sub-data sets. The sample points of each sub-data set correspond to grid points of a Cartesian initial grid and the Cartesian initial grid of the sub-data sets can be brought into congruence by rotation: A Cartesian final grid is selected, and a calculation-based transfer of the data points of each sub-data set ensues to a respective new grid that exhibits the orientation of the respective sub-data set and the grid constants of the final grid, if the grid constants of the output grid differ from those of the final grid. A calculation-based transfer of the data points of each sub-data set, or the data points of a respective new grid (if obtained) ensures to the final grid by the application of a rotation module followed by transformation of the acquired data into the image domain.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Shadow Removal in an Image Captured by a Vehicle-Based Camera for Clear Path Detection
InactiveUS20120008021A1Reduce shadowsImage enhancementImage analysisVision based systemsVision based
A method for is provided for creating a shadow-reduced image from a captured image for distinguishing a clear path of travel. Each pixel of a captured input image is plotted according to a two dimensional logarithmic graph. A specific color set relating to an associated color value of a clear path. A linear illumination-invariant axis is determined as a function of the specific color set. An illumination direction for the linear illumination-invariant axis is determined. A log-chromaticity value of each plotted pixel of the specific color set is projected on the axis. Edges in the input image and the illumination-invariant image domain are identified. The identified edges of the input image are compared to identify edges in the illumination-invariant image domain. A determination is made whether a shadow edge is present in response to comparing the edges. A shadow-reduced image is generated for scene analysis by a vehicle vision-based system.
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
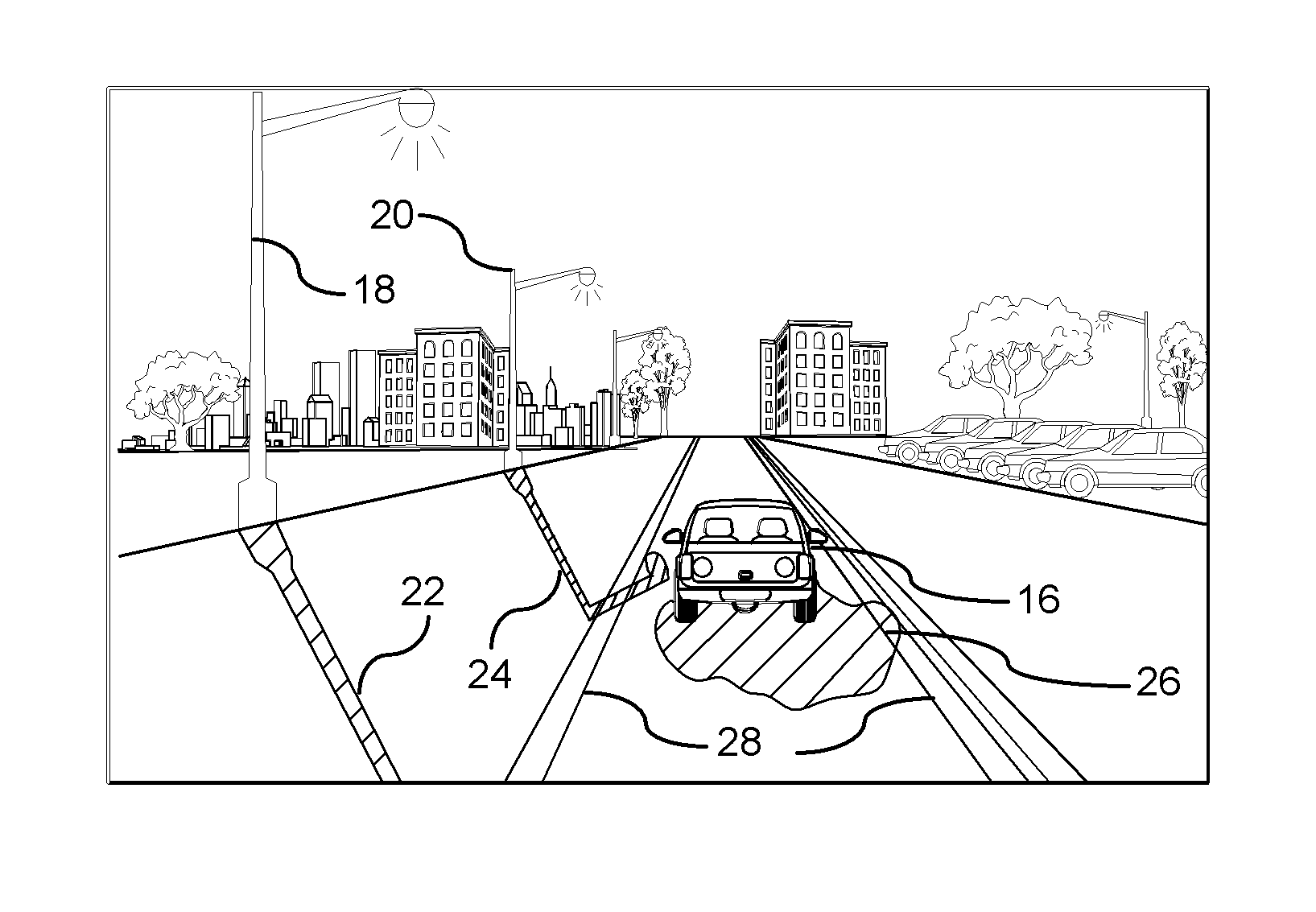
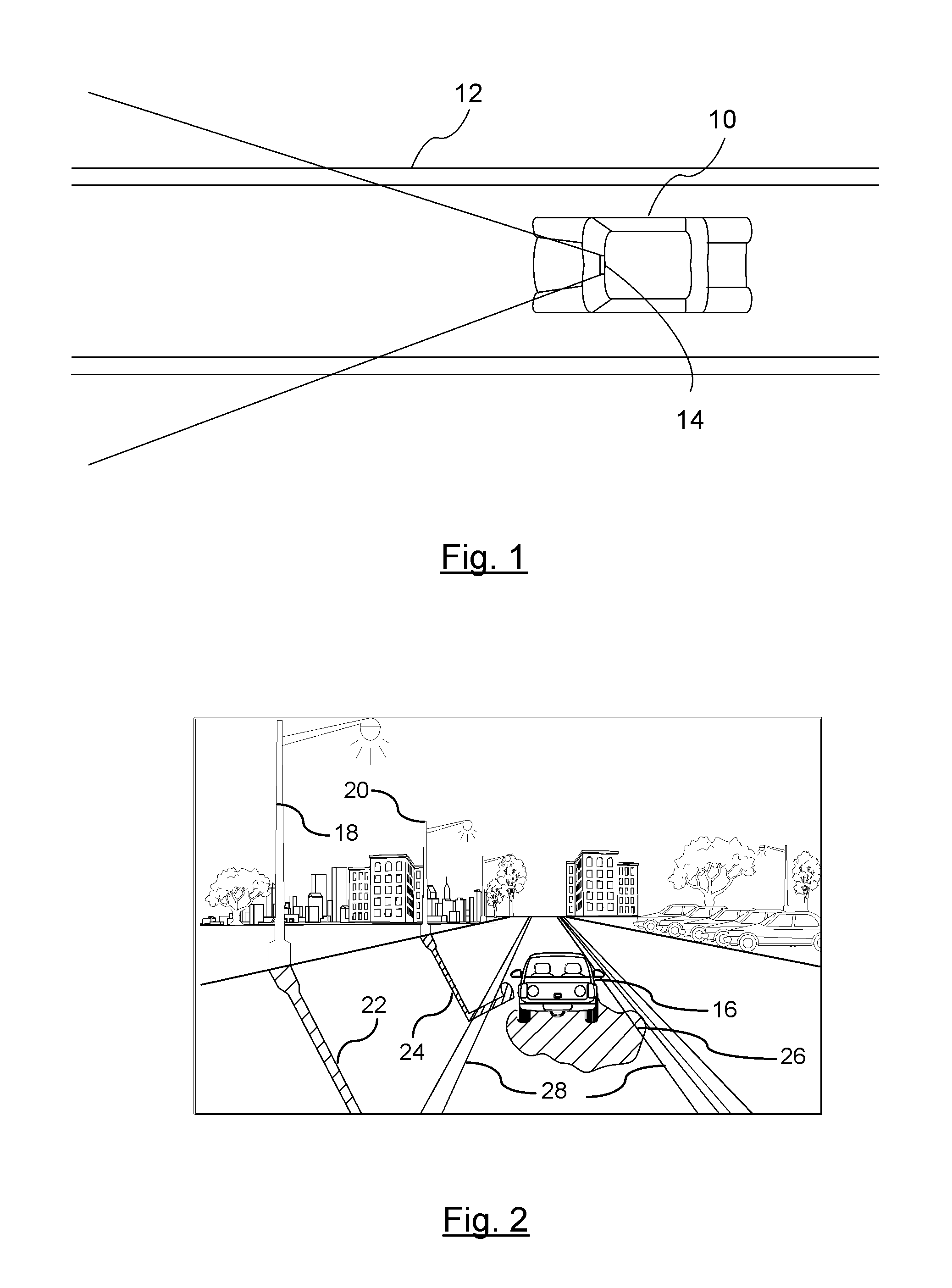
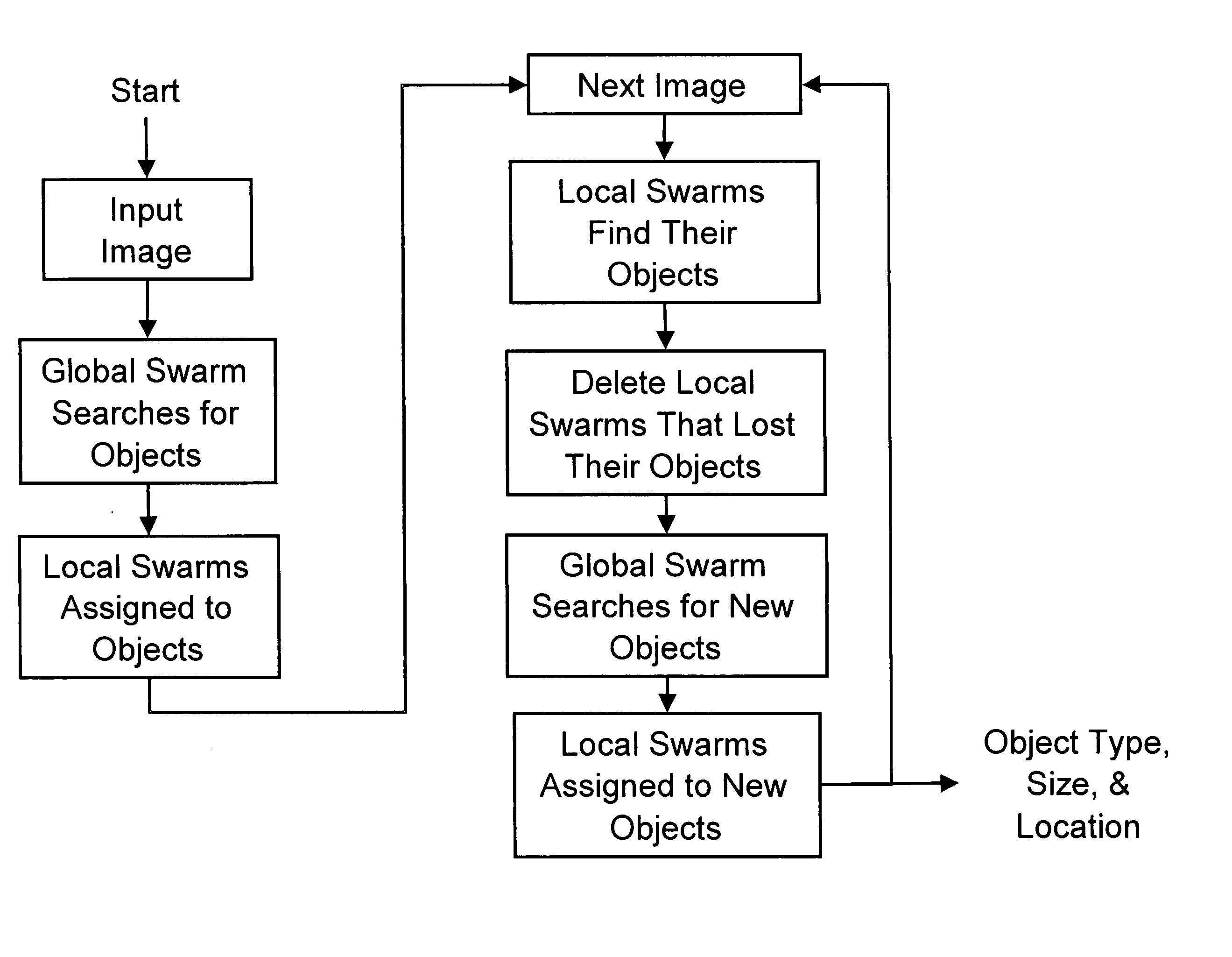
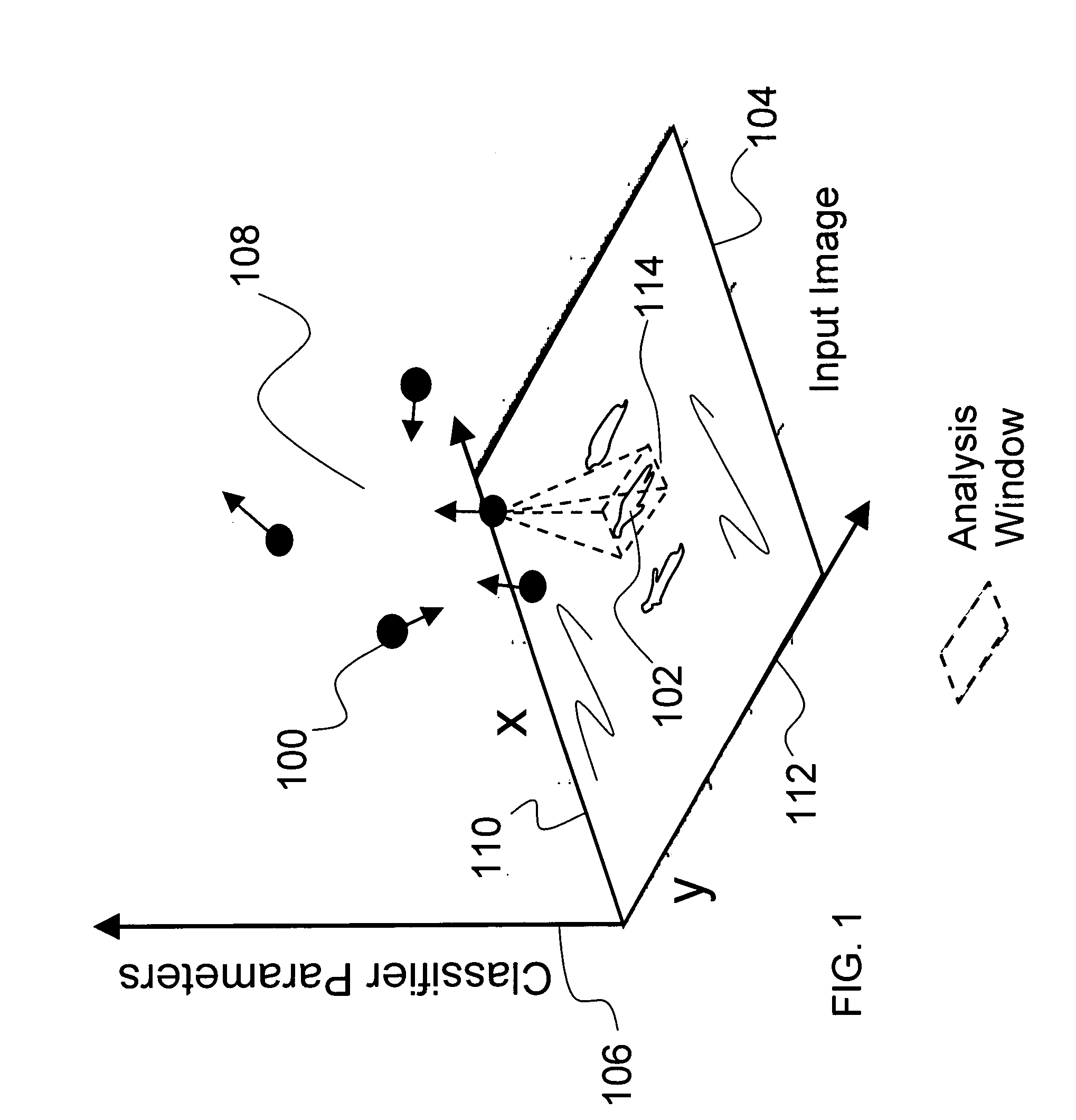
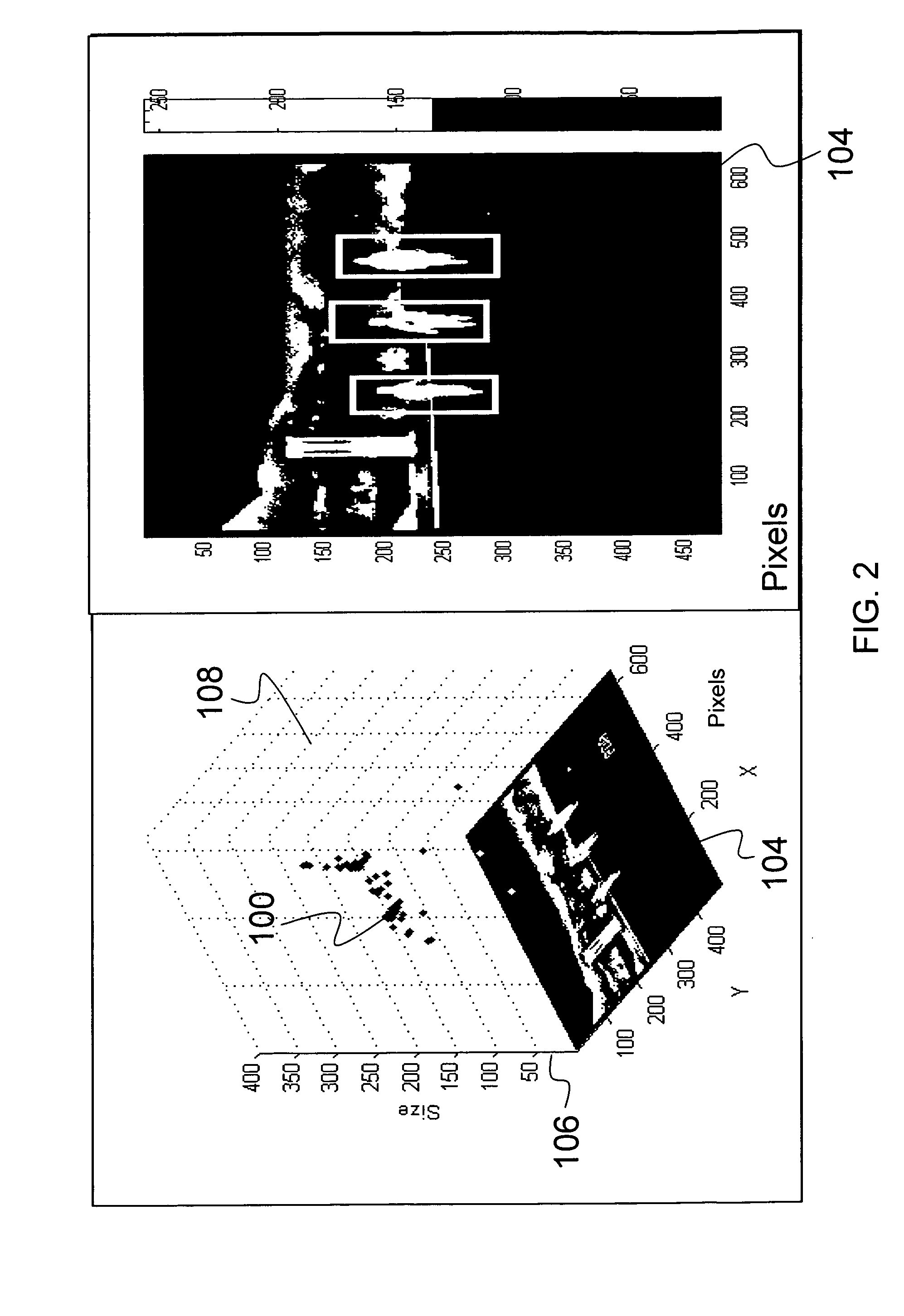
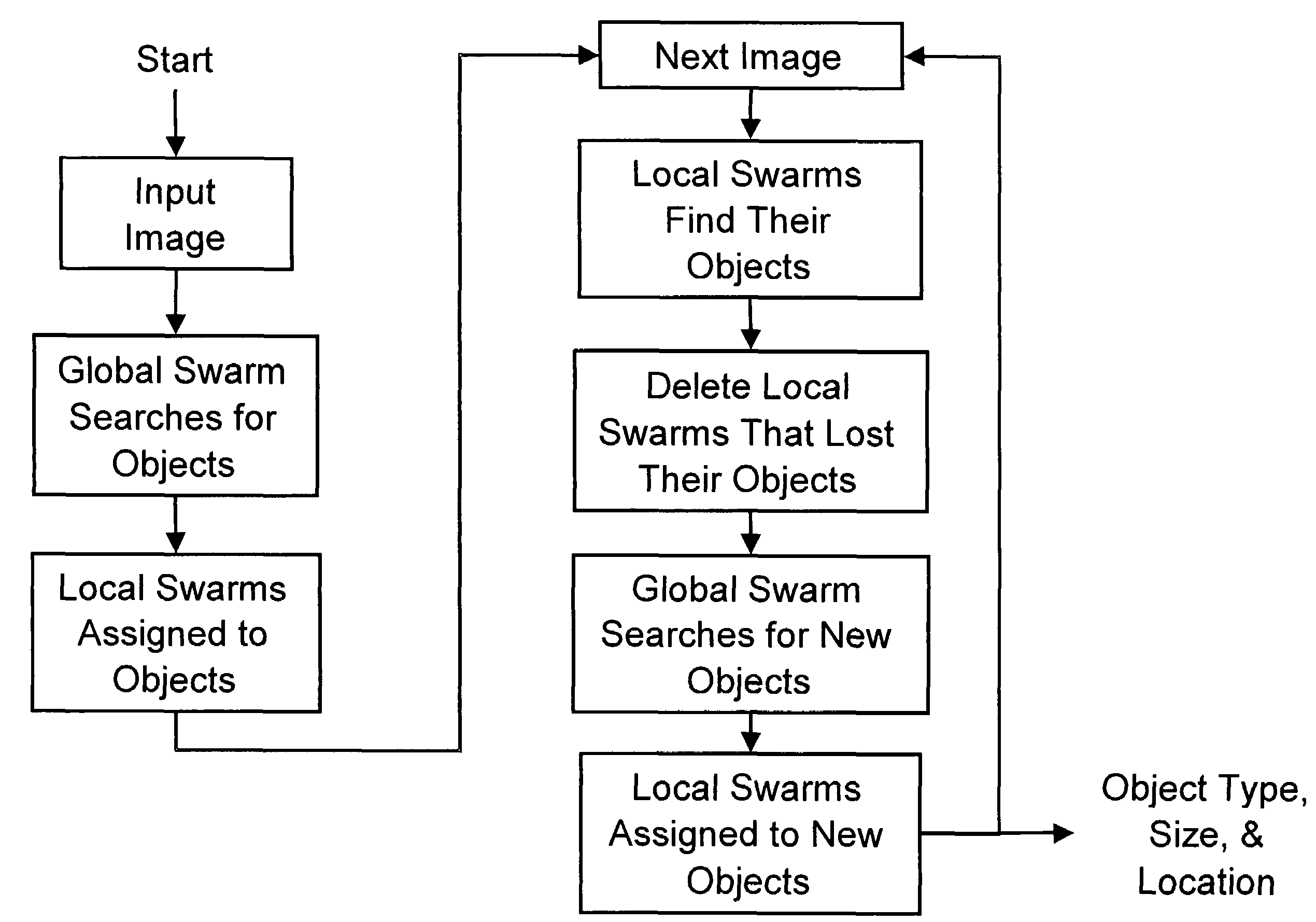
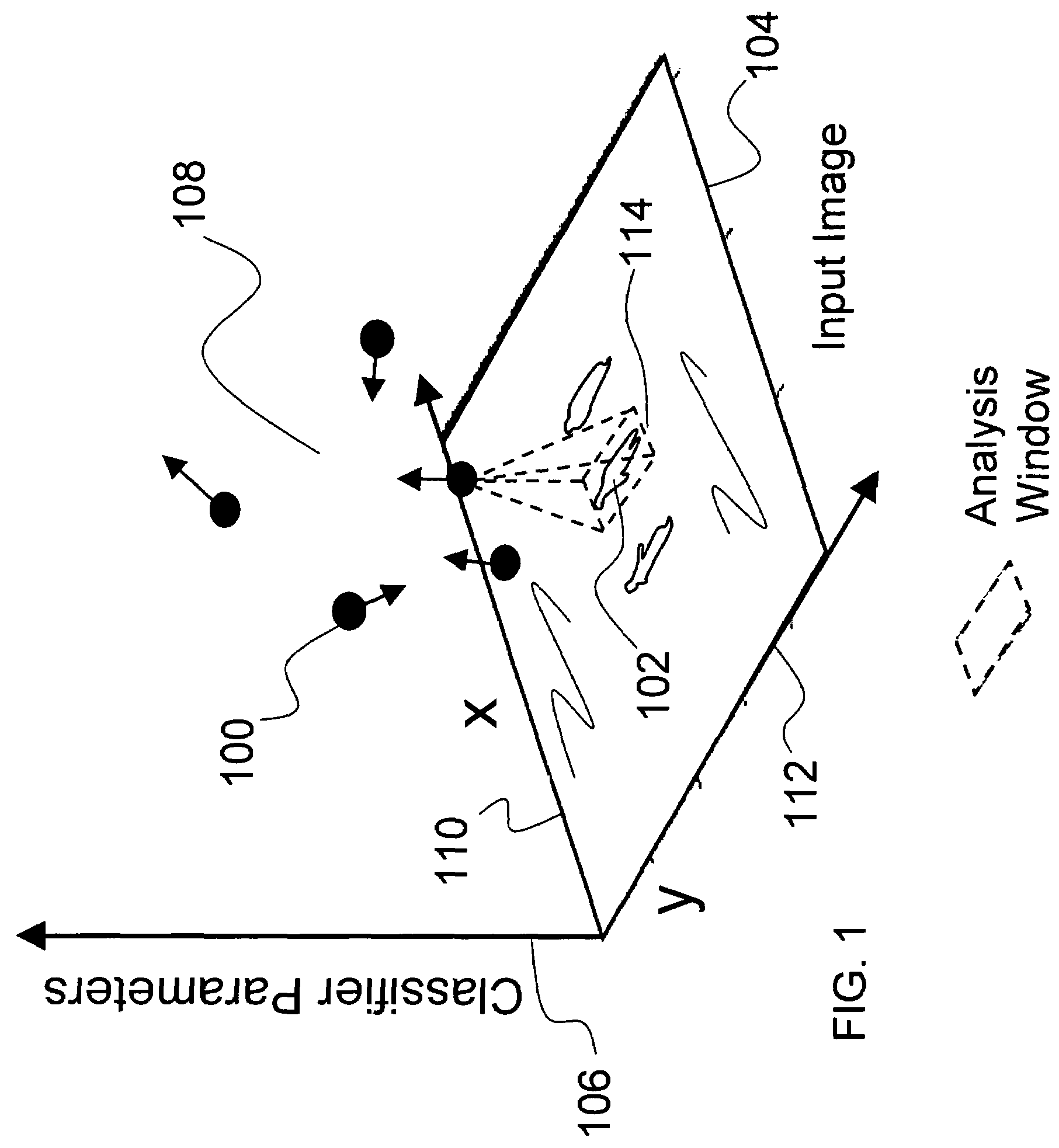
Object recognition using a congnitive swarm vision framework with attention mechanisms
InactiveUS20070019865A1Avoid clustersPrevents unnecessary classifier evaluationCharacter and pattern recognitionMulti dimensionalSoftware agent
An object recognition system is described that incorporates swarming classifiers with attention mechanisms. The object recognition system includes a cognitive map having a one-to-one relationship with an input image domain. The cognitive map records information that software agents utilize to focus a cooperative swarm's attention on regions likely to contain objects of interest. Multiple agents operate as a cooperative swarm to classify an object in the domain. Each agent is a classifier and is assigned a velocity vector to explore a solution space for object solutions. Each agent records its coordinates in multi-dimensional space that are an observed best solution that the agent has identified, and a global best solution that is used to store the best location among all agents. Each velocity vector thereafter changes to allow the swarm to concentrate on the vicinity of the object and classify the object when a classification level exceeds a preset threshold.
Owner:HRL LAB
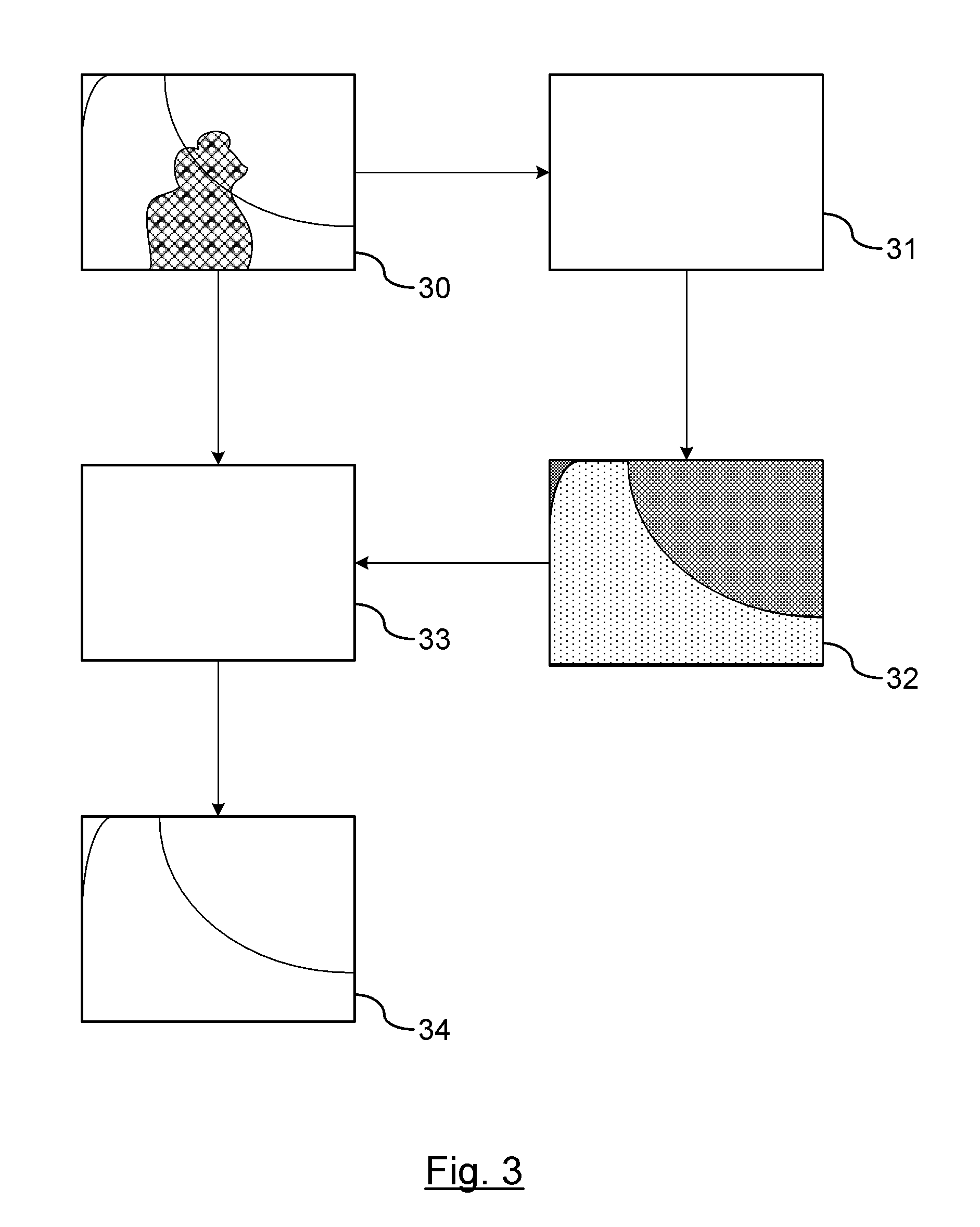
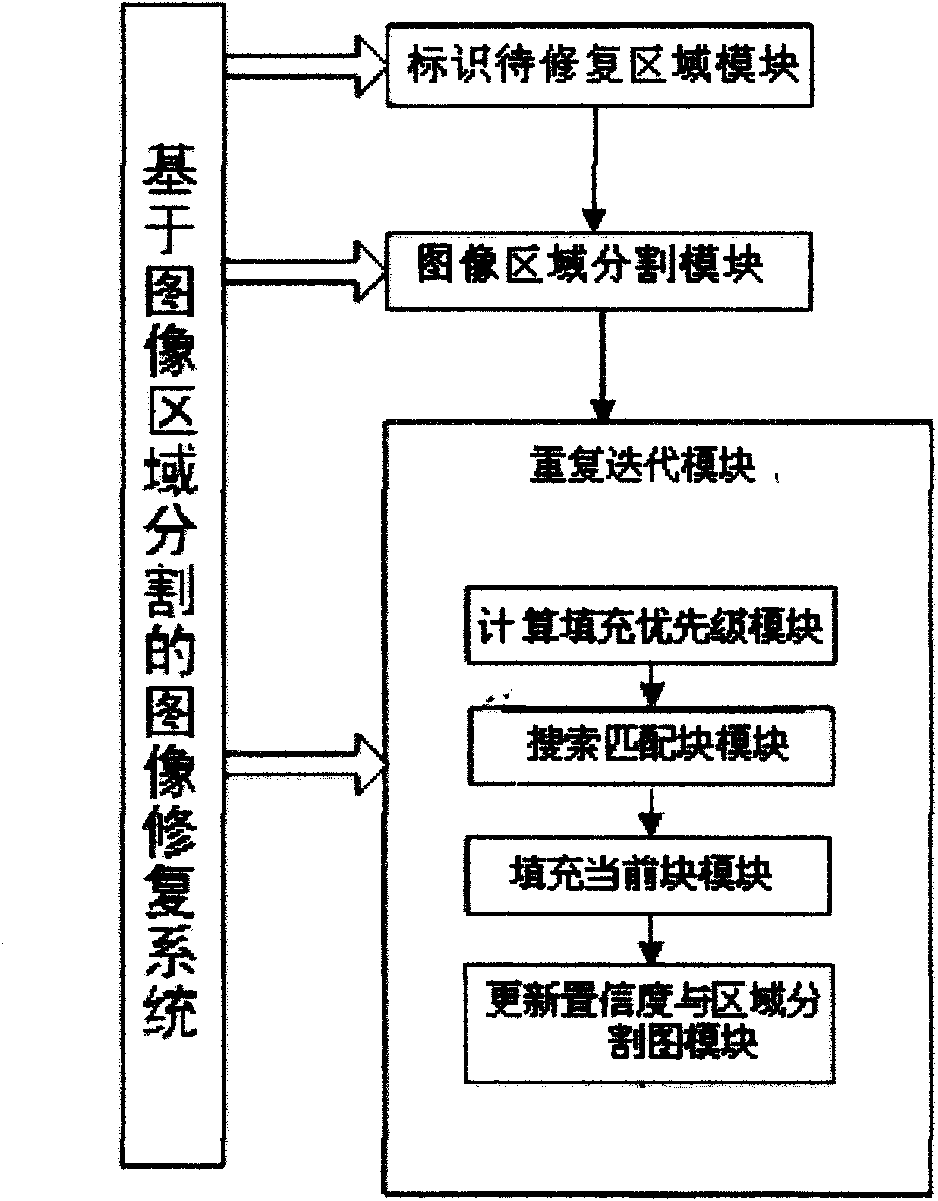
Image restoration method based on image segmentation, and system therefor
InactiveCN101661613AOvercoming the matching phenomenonGuaranteed Priority Patching OrderImage enhancementImage analysisMean-shiftDecomposition
The invention discloses an image restoration method based on image segmentation, and a system therefor; the method comprises: firstly, manually selecting and marking the area to be restored in image by a user; then, carrying out image domain decomposition by mean shift algorithm, and dividing the image into a number of areas; finally, carrying out repeated iterative operation on the area to be restored until all pixels in the area to be restored is filled to be full. The method optimizes the calculation of priority in image restoration algorithm, thus effectively preventing the over expansionof the restored image from a high-texture area to a low-texture area; furthermore, matched block searching standard based on the image domain decomposition can be formulated on that basis, so that anerroneous block can be avoided being introduced; compared with the original image restoration method based on the sample, the effect of the method is more in accordance with the visual expectation ofhuman beings; furthermore, at present, the method is successfully applied to large size area restoration of various images with complex texture and structural characteristics as well as the aspects such as wiping off characters, removing target objects and the like.
Owner:BEIJING JIAOTONG UNIV
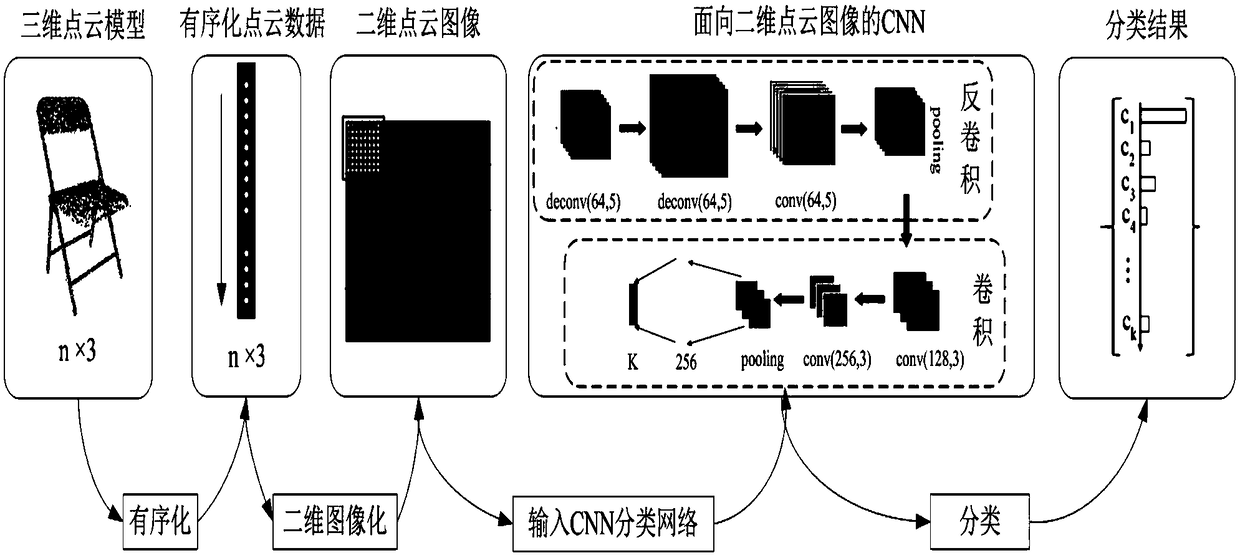
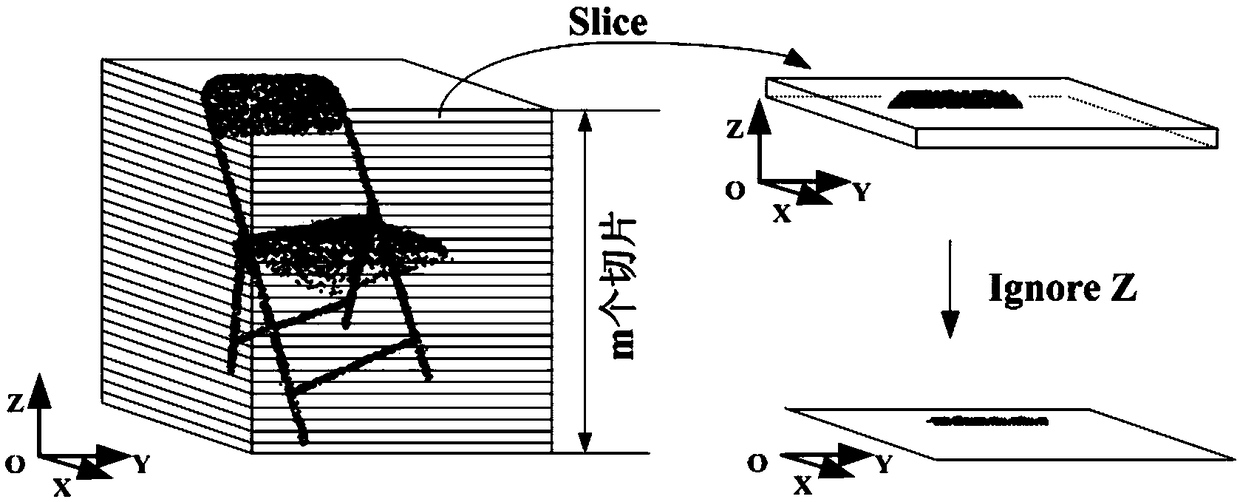
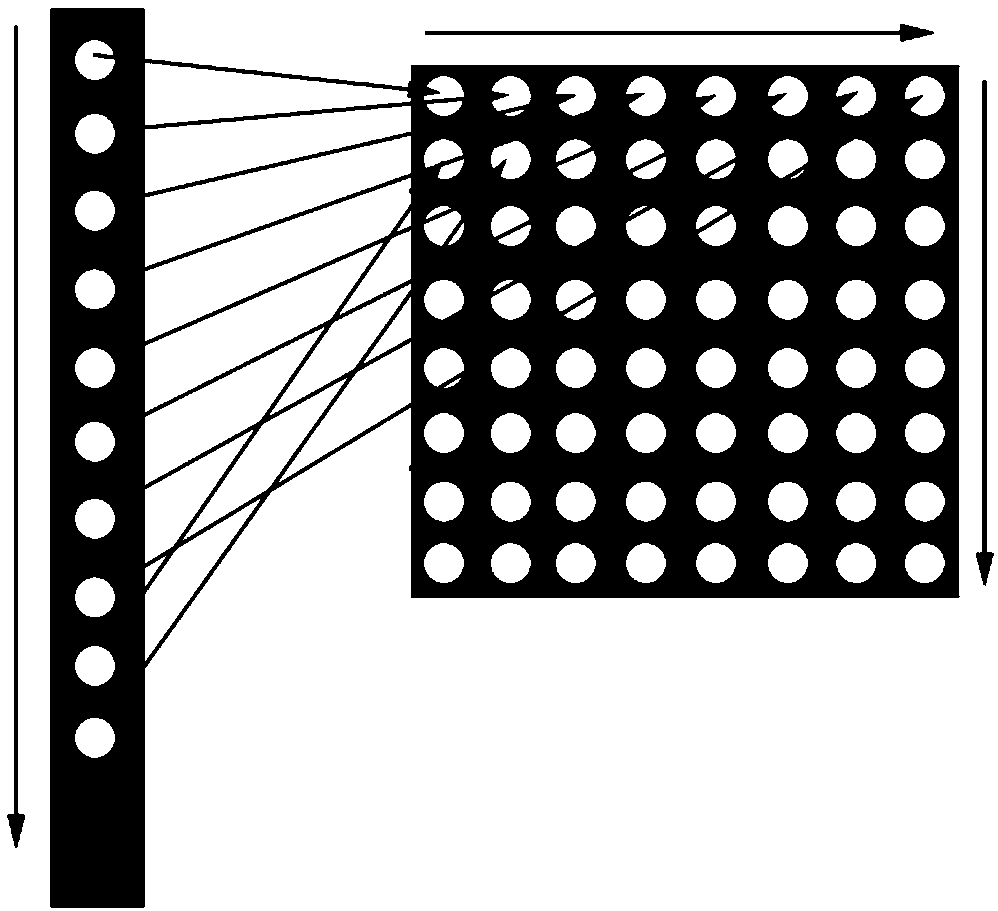
=Three-dimensional point cloud model classification method based on convolution neural network
ActiveCN109063753AEffective classificationOvercoming disorderCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesPoint cloudData set
The invention discloses a three-dimensional point cloud model classification method based on convolution neural network, includes selecting Princeton ModelNet to generate training set and data set from training data and test data by selecting required number of models from official website according to ModelNet 10 and ModelNet 40 respectively, selecting training data and test data from official website according to Princeton ModelNet, selecting Princeton ModelNet to generate training set and data set according to model Net 10 and ModelNet 40 respectively, and selecting Princeton ModelNet to generate training data and test data. 2, carry out feature analysis on that point cloud model and constructing a classification framework; S3, ordering the point cloud; S4, two-dimensional visualizing the ordered point cloud data; S5, Constructing CNN network for two-dimensional point cloud image. The invention applies the CNN in the image field directly to the classification of the three-dimensional point cloud model for the first time, 93.97% and 89.75% classification accuracy were obtained on ModelNet 10 and ModelNet 40 respectively, Experimental results show that it is feasible to classify 3D point cloud model by using CNN in image domain. PCI2CNN proposed in this paper can capture 3D feature information of point cloud model effectively and is suitable for classification of 3D point cloud model.
Owner:BEIFANG UNIV OF NATITIES
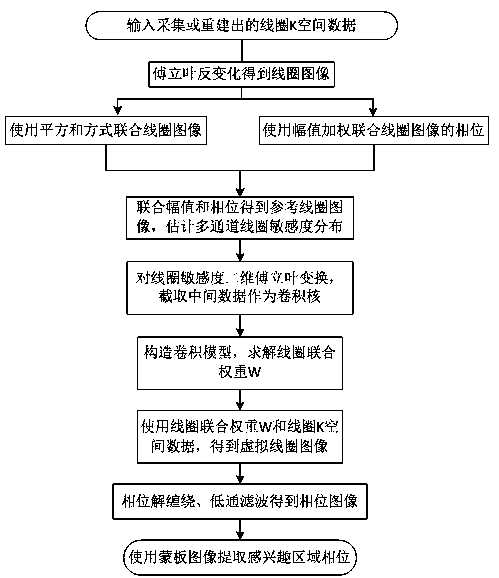
Phase processing method for parallel magnetic resonance imaging
InactiveCN104749538AAvoid noiseAvoid the effects of aliasing artifactsMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsImage domainMR - Magnetic resonance
The invention discloses a phase processing method for parallel magnetic resonance imaging. The phase processing method comprises the following steps of performing Fourier inverse transformation on K spacial data acquired by multi-channel coils in the parallel magnetic resonance imaging to obtain amplitudes and phases of all coil images; constructing a reference coil image, and estimating the spatial sensitivity distribution of all the coils in multiple channels; performing two-dimensional Fourier transformation on the spatial sensitivity distribution of the reference coil image, and intercepting an intermediate matrix as a convolution kernel; constructing a K spacial data convolution model, and solving a joint weight W of the coils; obtaining a K spacial value of a virtual coil and performing Fourier inverse transformation to obtain a virtual coil image; unwrapping a phase and removing the phase of the background of the virtual coil image; extracting the phase of a region of interest by using a mask image. According to the phase processing method disclosed by the invention, phase information of the image is acquired by combining K space with coil data, and the phenomenon that a phase information acquisition algorithm based on an image domain is influenced by noise and aliasing artifact in the reconstruction of the parallel magnetic resonance imaging under the condition of accelerated sampling is avoided.
Owner:ZHENGZHOU UNIVERSITY OF LIGHT INDUSTRY
Quick generalized partially parallel acquisition(GRAPA) image reconstruction algorithm for magnetic resonance imaging(MRI)
InactiveCN1799498AHigh speedEasily compare SNR lossesMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Resonance
The invention provides an algorism of magnetic resonance imaging fast and generalized self-aligning and collecting image for reconstructing, which combines the data fitting and channel merging to one step linear operation, the parameter of which can be counted out in advance and stored, which can increase the image reconstructing speed greatly, and solve the problem of long reconstructing time in current GRAPPA algorism; the algorism can also compare the image signal-to-noise ratio loss caused by different reconstructing method base on image domain and frequency domain by using weighting matrix.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHINEERS LTD
DIXON water-fat separation method in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveCN103513202AIncrease flexibilityReduce restrictionsMagnetic measurementsPhase differenceFourier transform on finite groups
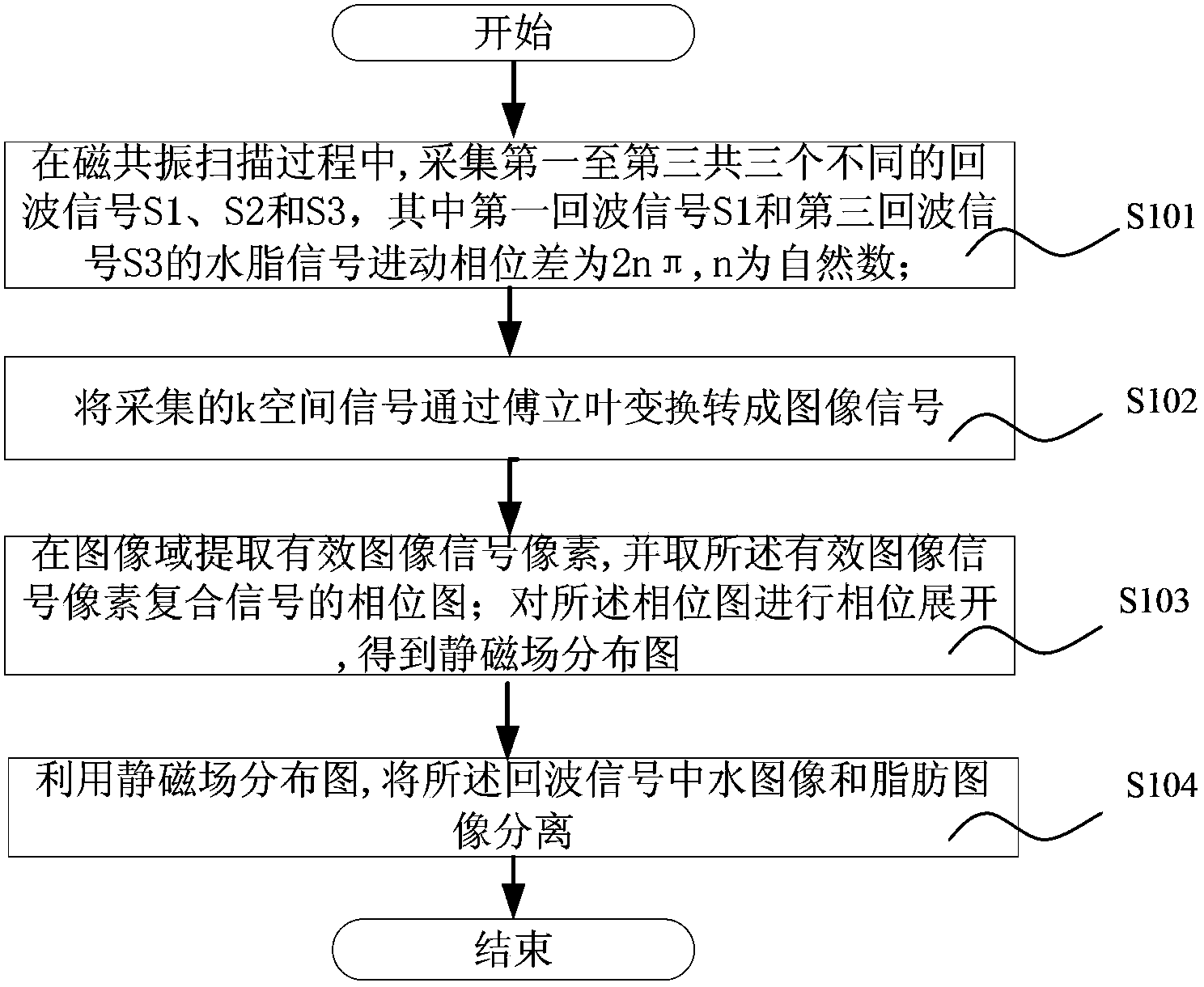
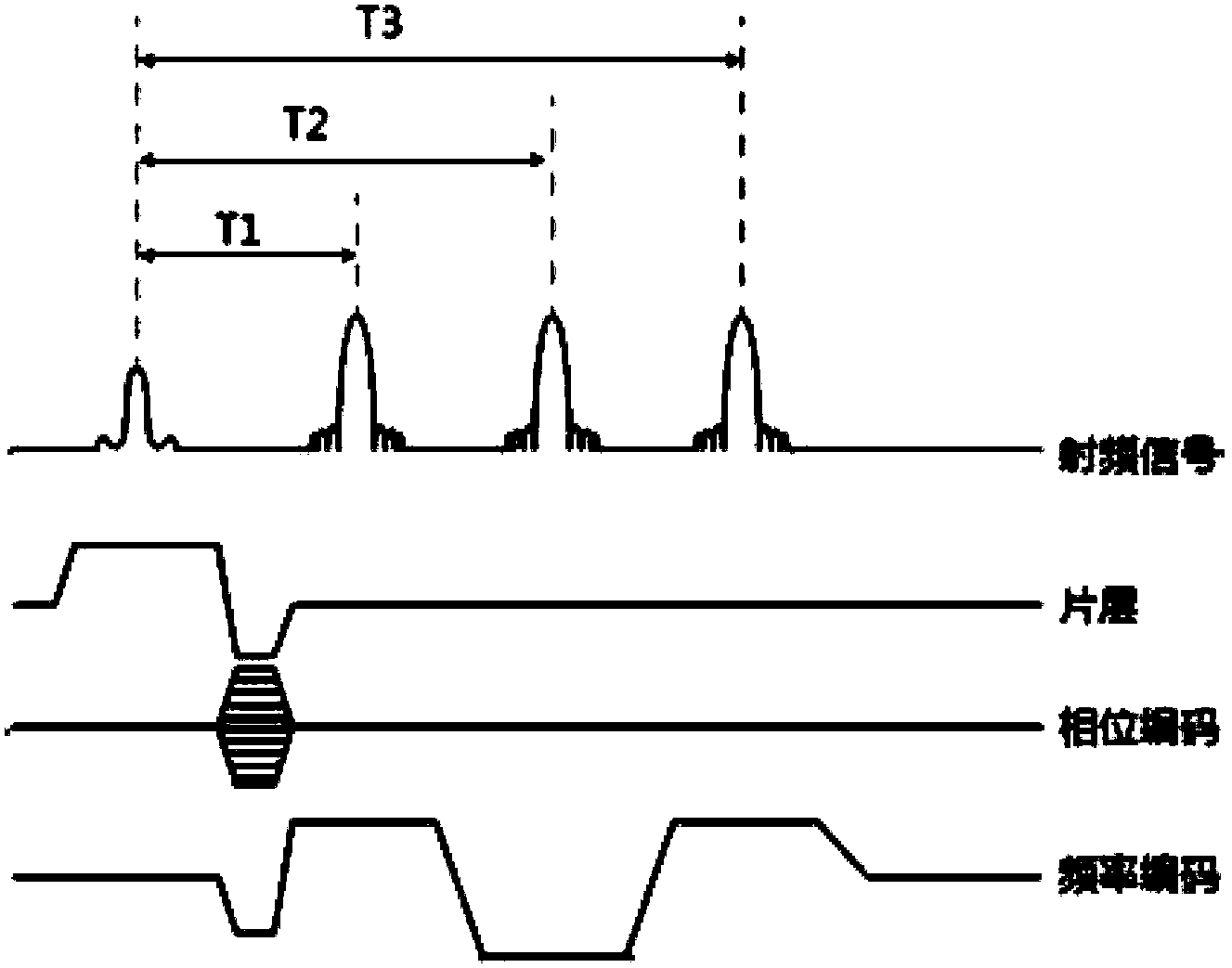
The invention discloses a DIXON water-fat separation method in magnetic resonance imaging. The method comprises the following steps: a) in the magnetic resonance scanning process, three different echo signals including the first echo signal S1, the second echo signal S2 and the third echo signal S3 are acquired, wherein the water-fat signal procession phase difference of the first echo signal S1 and the third echo signal S3 is 2npi, and n is a natural number; b) the acquired k space signals are converted into image signals through Fourier transform; c) effective image signal pixels are extracted in a image domain, the phase diagram of the effective image signal pixel composite signal is extracted, and phase unwrapping is performed on the phase diagram to obtain a static magnetic field distribution diagram delta B0; d) and the water image and the fat image in the echo signals are separated by utilizing the static magnetic field distribution diagram delta B0. According to the DIXON water-fat separation method provided in the invention, the echo time can be set flexibly according to a magnetic resonance imaging sequence and application requirements, so not only data can be processed by applying the conventional DIXON algorithm, and but also the limitation on imaging sequence parameter setting can be reduced at the same time.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Imaging spectroscopy based on multiple pan-chromatic images obtained from an imaging system with an adjustable point spread function
ActiveUS7385705B1Avoid introduction of noiseHigh resolutionRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryData setDiffusion function
Generating a multispectral or hyperspectral image of an image source with an optical system having an adjustable, wavenumber-dependent point spread function, by collecting panchromatic images of the image source, each of which corresponds to a selected point spread function and includes a measured intensity data set corresponding to a range of wavelengths, transforming the panchromatic images into the spatial frequency domain by using a Fourier transform, solving a matrix equation at each spatial frequency, in which a vector of the transformed panchromatic images is equal to the product of a predetermined matrix of discrete weighting coefficients and a vector representing a wavenumber content of the image source at each spatial frequency, resulting in a determined wavenumber content of the image source in the spatial frequency domain, and inverse transforming the determined wavenumber content of the image source from the spatial frequency domain into the image domain, resulting in the multispectral or hyperspectral image.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Highly-scalable image reconstruction using deep convolutional neural networks with bandpass filtering
ActiveUS20190257905A1Improve networking flexibilityMinimization requirementsImage enhancementImage analysisBandpass filteringField of view
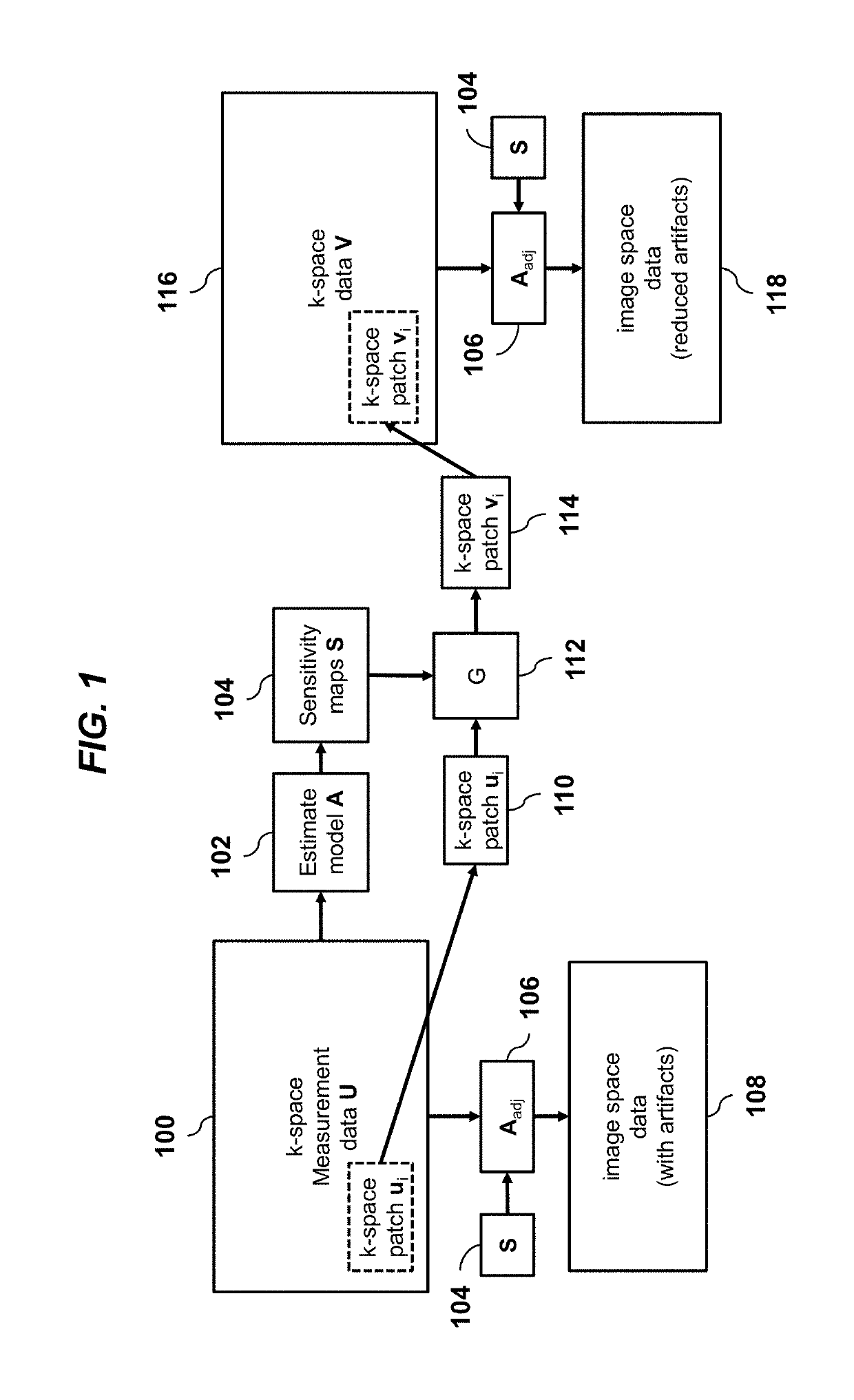
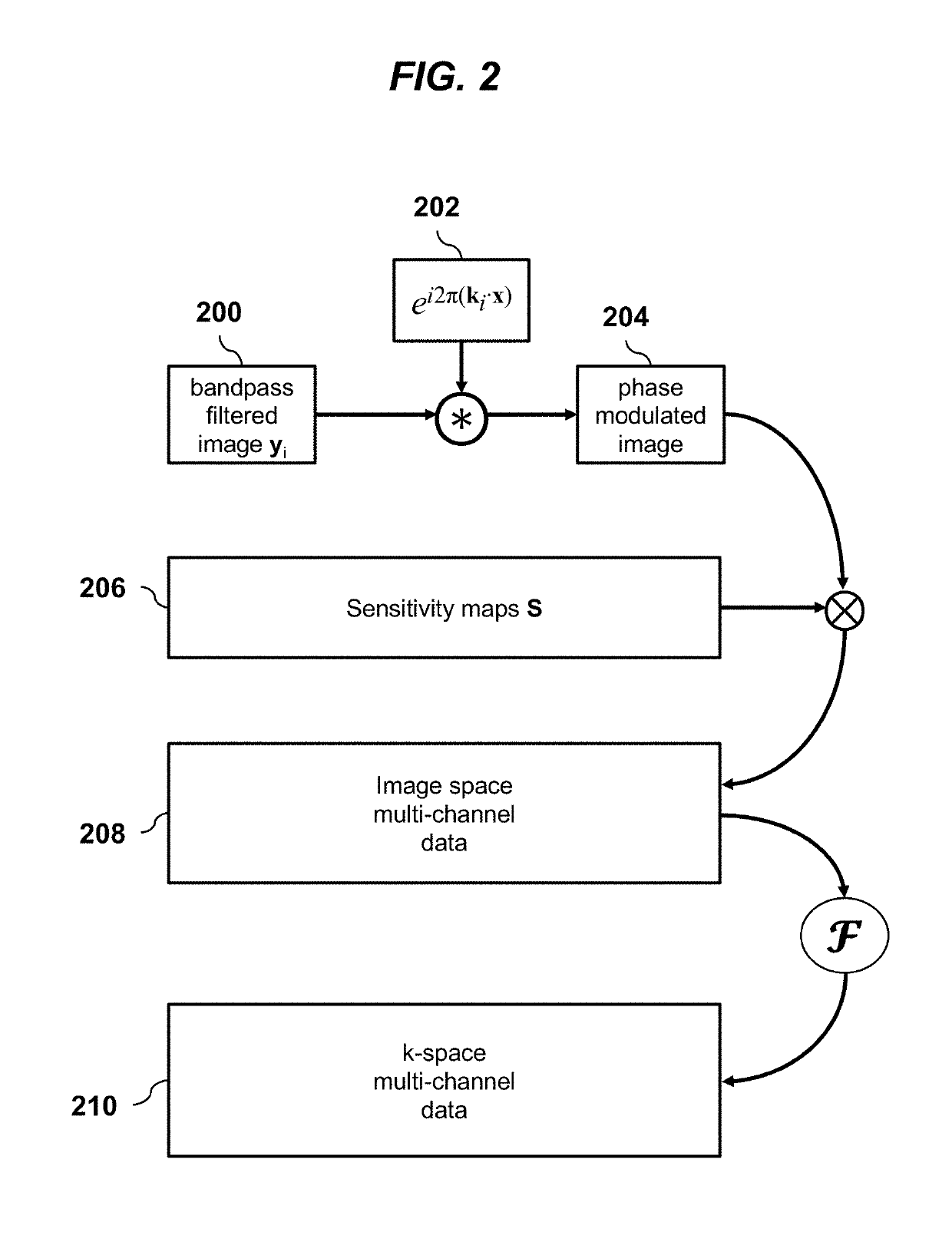
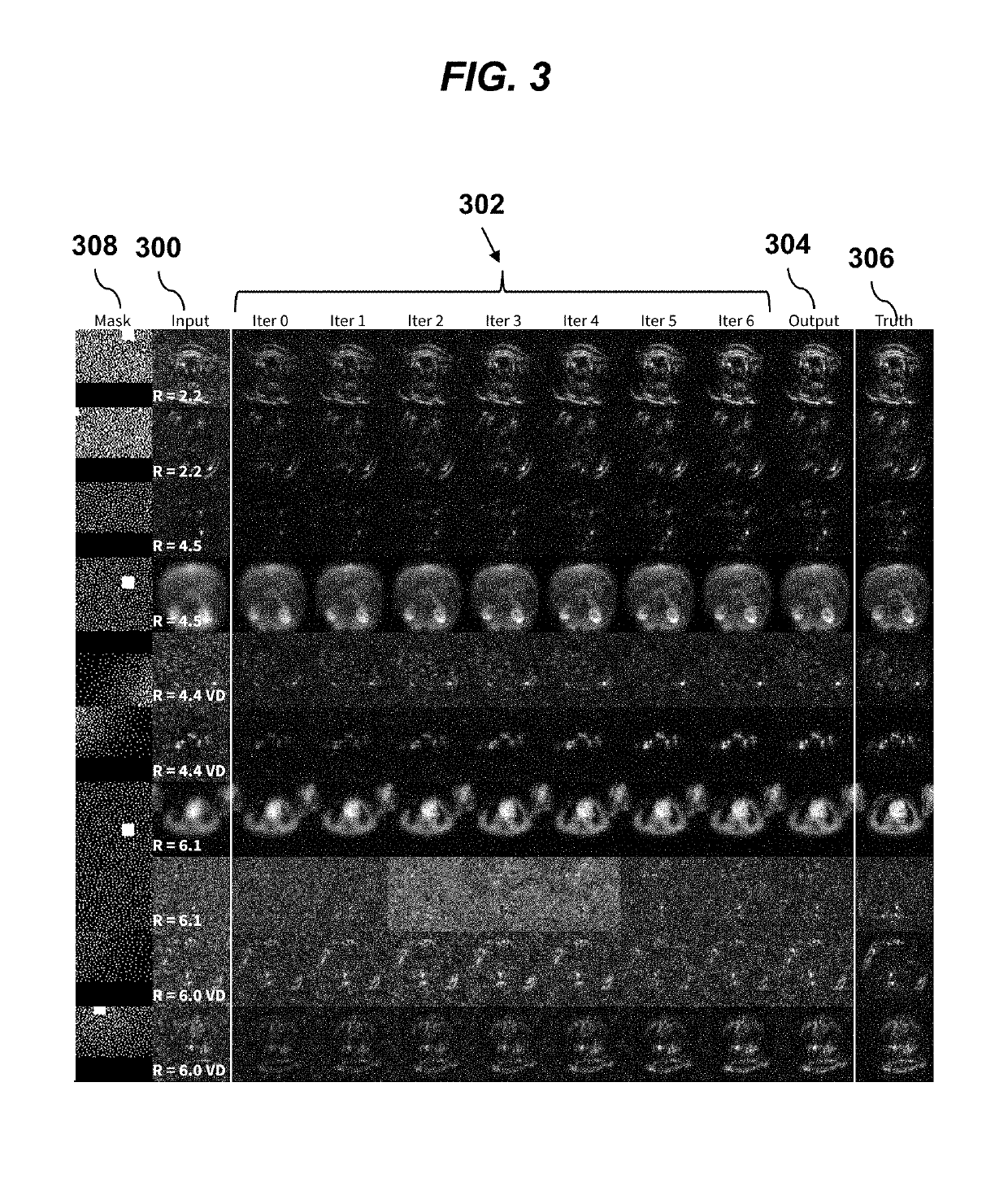
A method for magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans a field of view and acquires sub-sampled multi-channel k-space data U. An imaging model A is estimated. Sub-sampled multi-channel k-space data U is divided into sub-sampled k-space patches, each of which is processed using a deep convolutional neural network (ConvNet) to produce corresponding fully-sampled k-space patches, which are assembled to form fully-sampled k-space data V, which is transformed to image space using the imaging model adjoint Aadj to produce an image domain MRI image. The processing of each k-space patch ui preferably includes applying the k-space patch ui as input to the ConvNet to infer an image space bandpass-filtered image yi, where the ConvNet comprises repeated de-noising blocks and data-consistency blocks; and estimating the fully-sampled k-space patch vi from the image space bandpass-filtered image yi using the imaging model A and a mask matrix.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
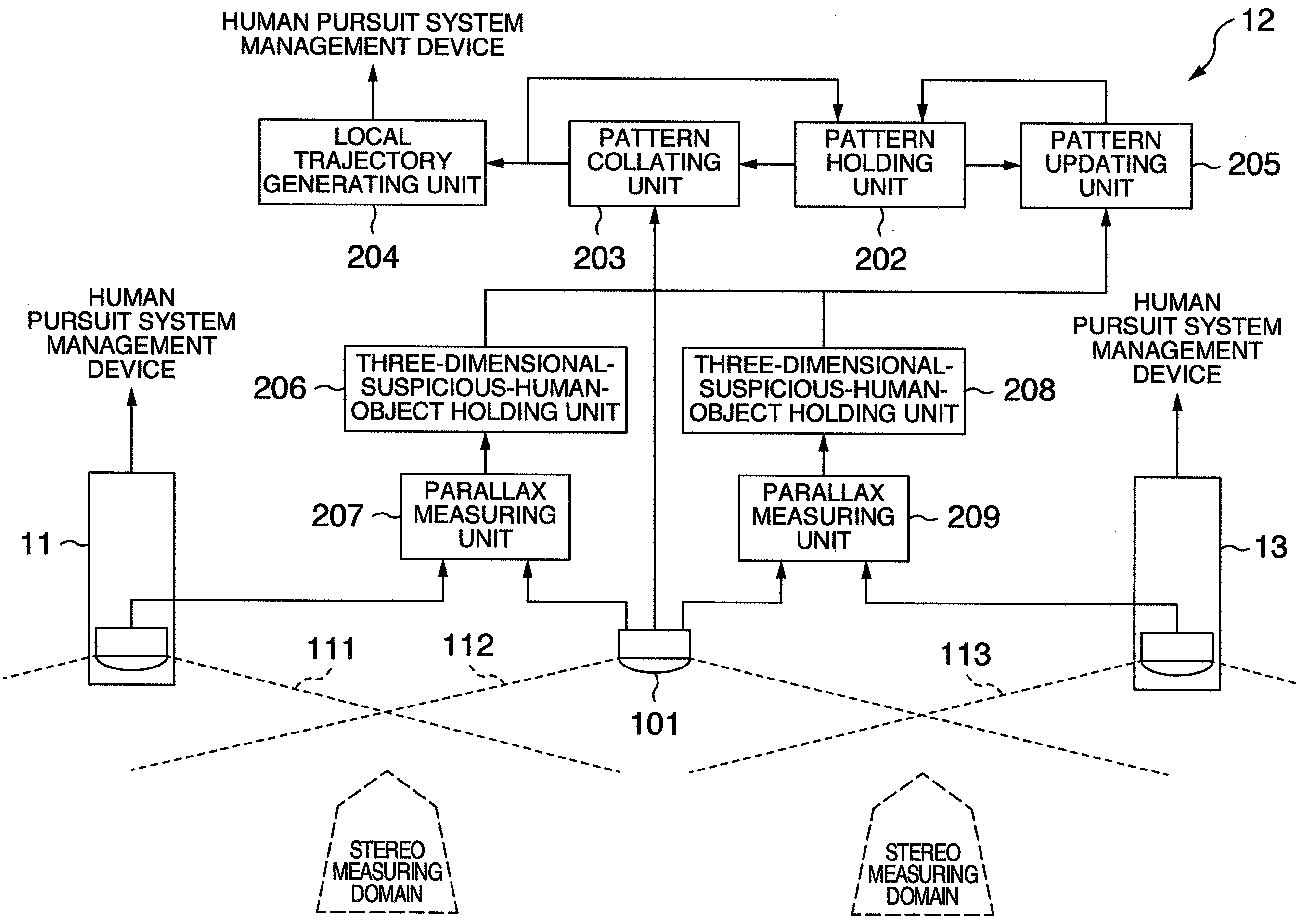
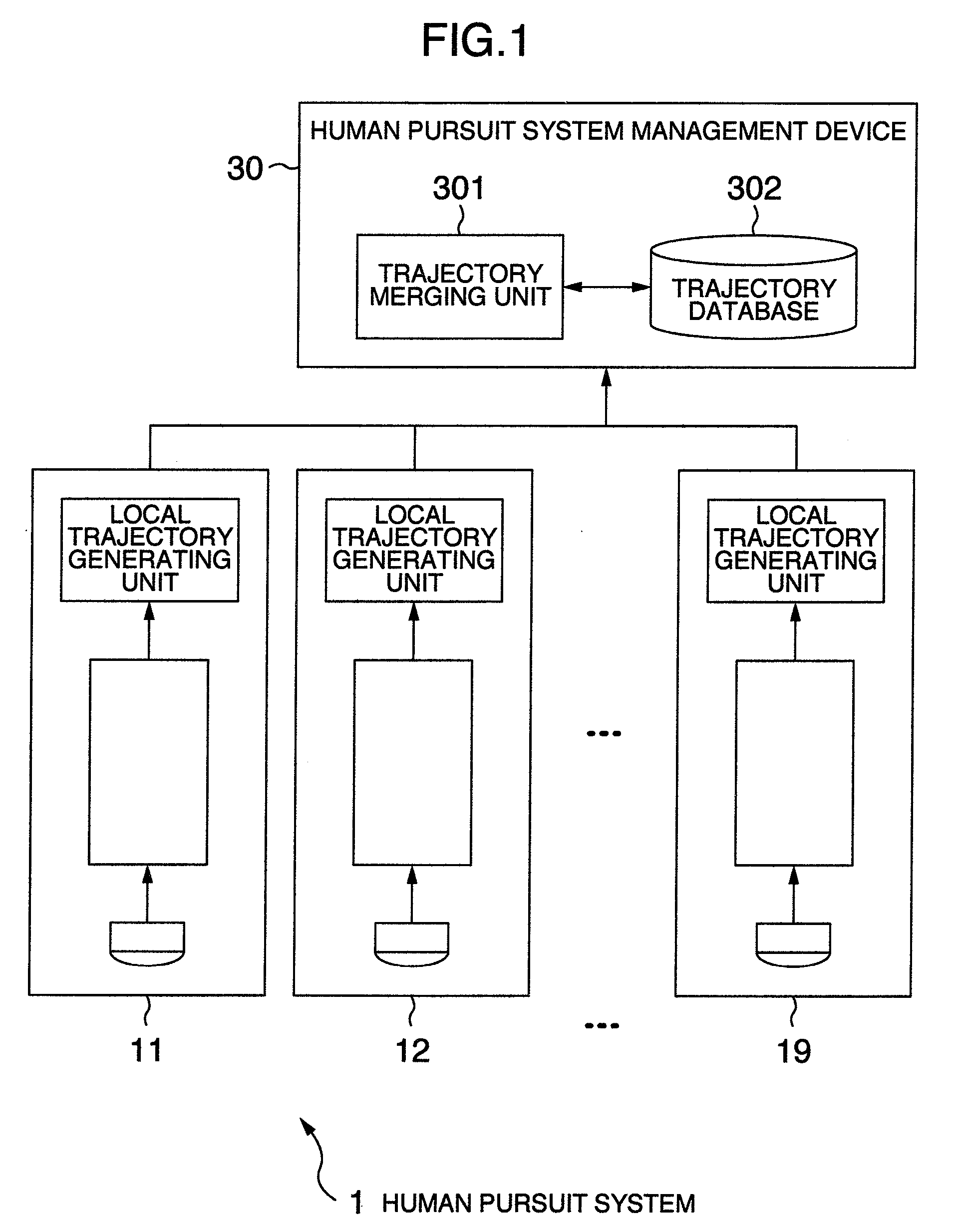
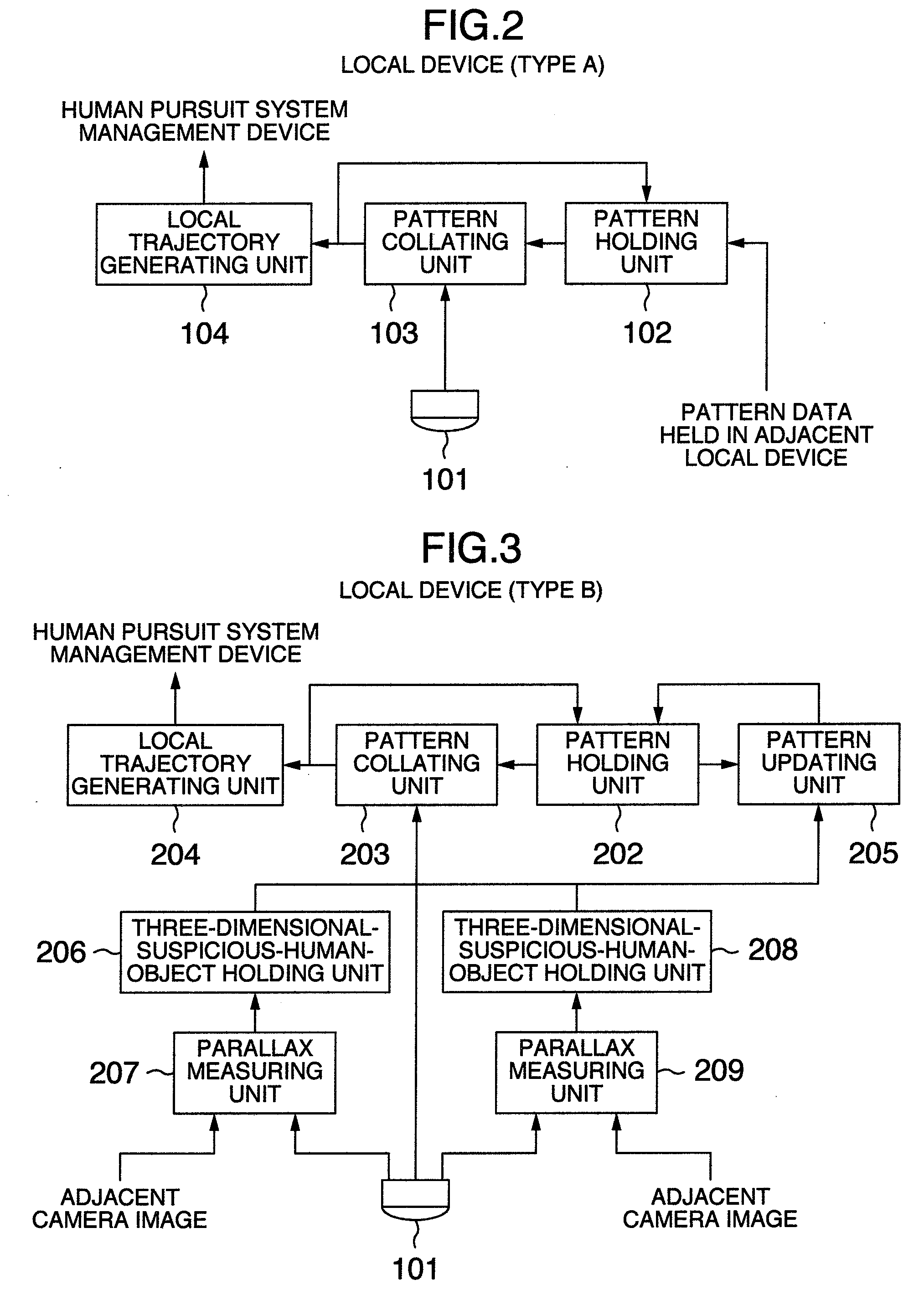
Human pursuit system, human pursuit apparatus and human pursuit program
ActiveUS20090052739A1Improve accuracyRelatively small errorCharacter and pattern recognitionParallaxPattern matching
A human pursuit system includes a plurality of cameras, shooting directions of which are directed toward a floor, are installed on a ceiling, a parallax of an object reflected in an overlapping image domain is calculated on the basis of at least a portion of the overlapping image domain where images are overlapped among shot images shot by the plurality of cameras, the object equal to or greater than a threshold value predetermined by the calculated parallax is detected as a human, a pattern image including the detected human object is extracted, and a pattern matching is applied to the extracted pattern image and the image shot by the camera to thereby pursue a human movement trajectory.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
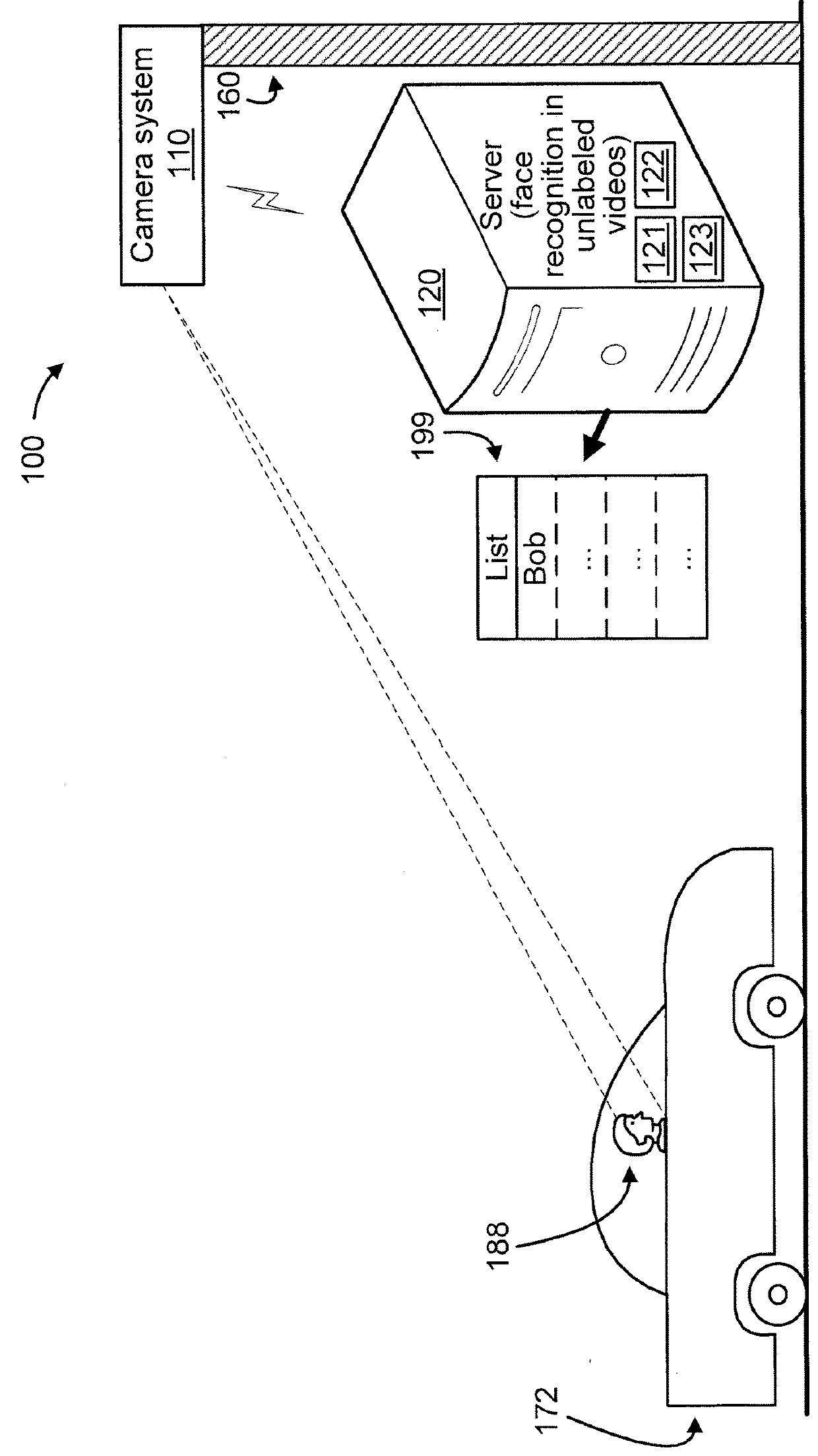
Face recognition system for face recognition in unlabeled videos with domain adversarial learning and knowledge distillation
A face recognition system is provided that includes a device configured to capture a video sequence formed from a set of unlabeled testing video frames. The system includes a processor configured to pre-train a face recognition engine formed from reference CNNs on a still image domain that includes labeled training still image frames of faces. The processor adapts the face recognition engine to a video domain to form an adapted engine, by applying non-reference CNNs to domains including the still image and video domains and a degraded image domain. The degraded image domain includes labeled synthetically degraded versions of the frames included in the still image domain. The video domain includes random unlabeled training video frames. The processor recognizes, using the adapted engine, identities of persons corresponding to at least one face in the video sequence to obtain a set of identities. A display device displays the set of identities.
Owner:NEC CORP
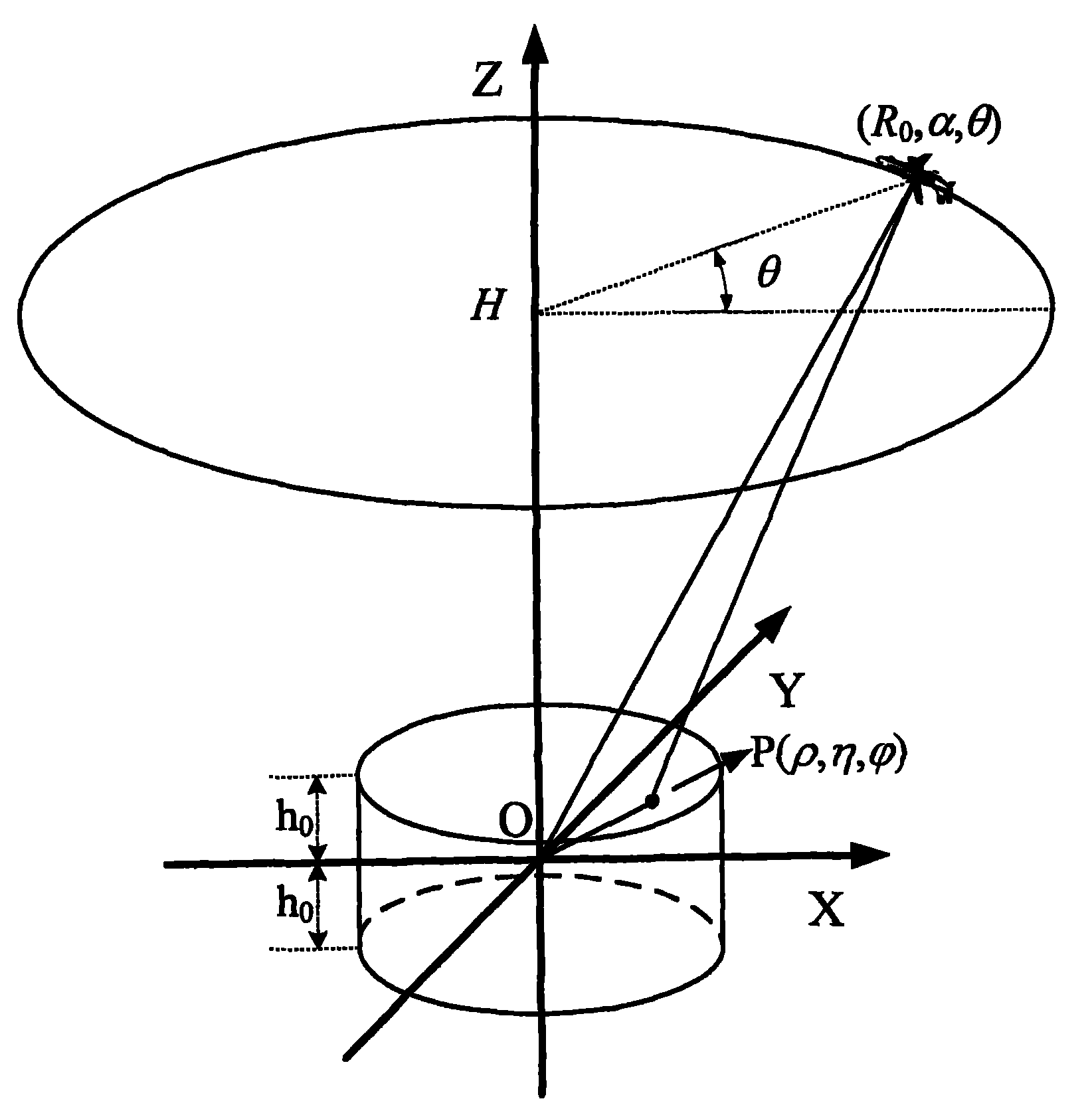
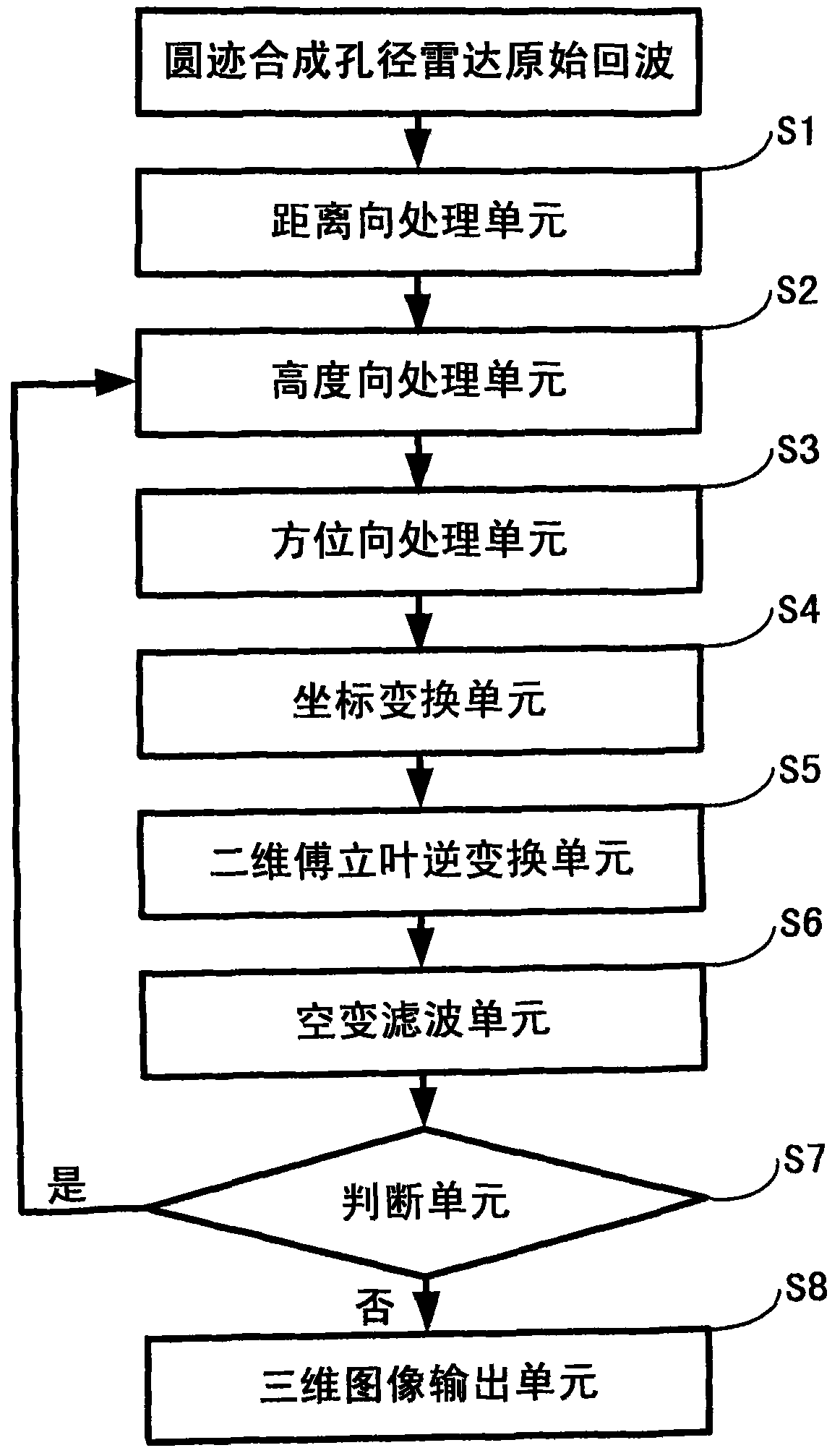
Three-dimensional imaging method in widefield polar format for circular synthetic aperture radar
The invention discloses a three-dimensional imaging method in a widefield polar format for a circular synthetic aperture radar. The traditional polar format imaging method for a spotlight synthetic aperture radar is developed into the three-dimensional imaging method suitable for the circular synthetic aperture radar. The traditional polar format imaging method only corrects a migration term of a range cell once, and plane wave approximation of the method causes range curvature distortion, so the method only can image a narrow field. The three-dimensional imaging method in the widefield polar format for the circular synthetic aperture radar removes a migration term of a secondary range cell through twice correction of secondary filtration of an azimuth frequency domain and the space variant filtration of an image domain based on the conventional polar format imaging method, and has more accurate three-dimensional imaging for a wider field compared with the traditional polar format imaging method.
Owner:INST OF ELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Synthetic aperture radar anti-deceptive-interference method based on shadow characteristics
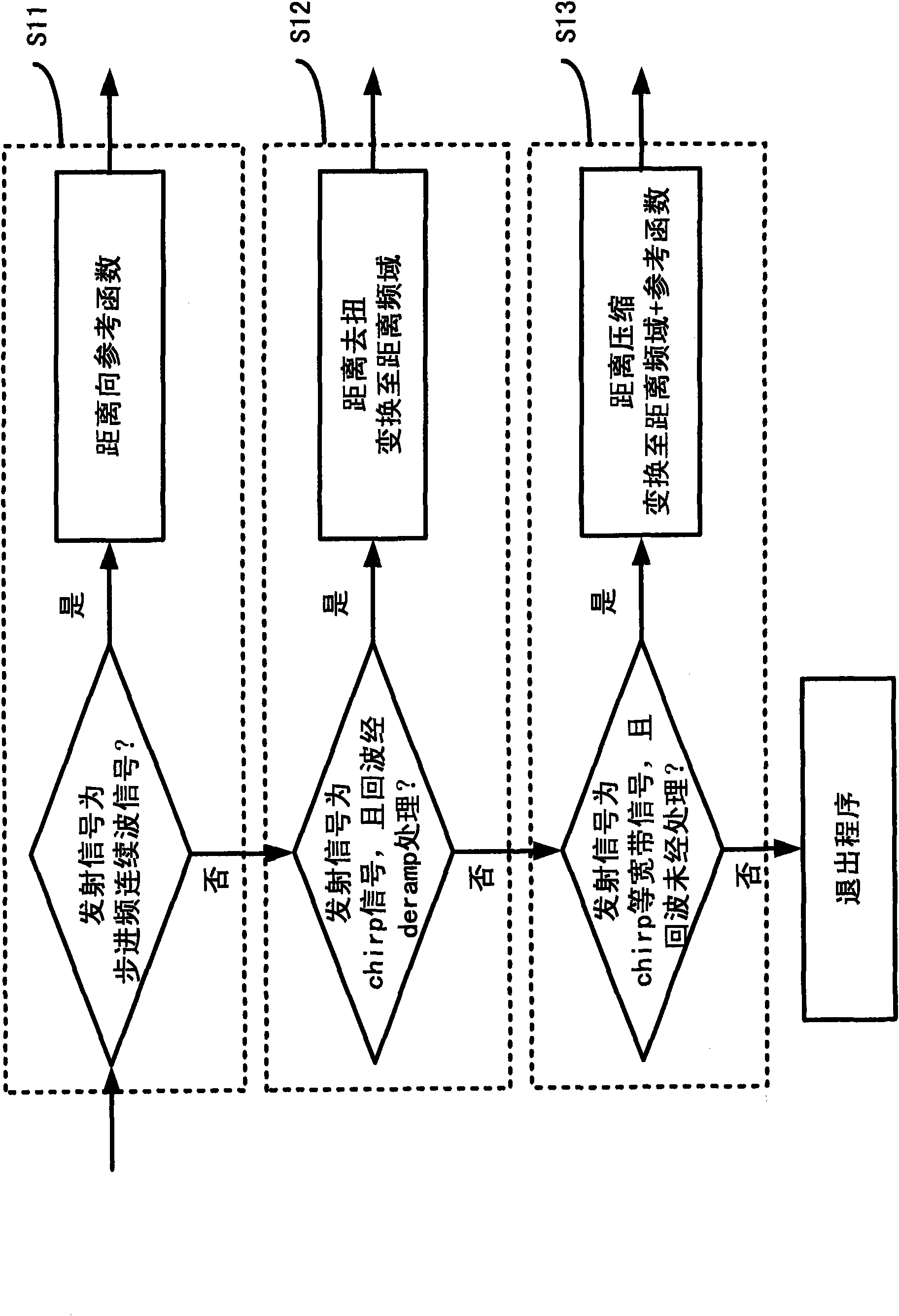
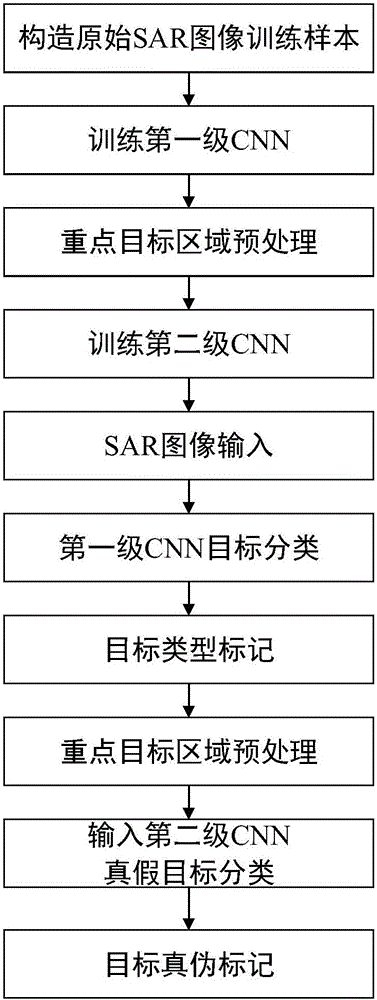
InactiveCN106228201AAchieve anti-spoofing jammingFast convergenceCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural learning methodsSynthetic aperture radarClassification methods
The invention provides a synthetic aperture radar anti-deceptive-interference method based on shadow characteristics. Firstly, SAR images with and without shadows of several types of targets under different postures are obtained by using a synthetic aperture radar imaging method and an electromagnetic scattering simulation method. The SAR images obtained at different radar incident angles are used as training samples and test samples for a convolutional neural network. In order to overcome the disadvantage of poor shadow characteristic identification effect of the convolutional network, a first-level convolutional neural network is used to classify the targets and the backgrounds to obtain targets and backgrounds of different types, a standard threshold segmentation method and multi-value processing are employed for key target images to obtain multi-value images after target regions are segmented, and real targets and deceptive targets are distinguished by a convolutional neural network classification method. The functions of SAR automatic target identification and interference target identification are realized, and high-performance SAR anti-deceptive-interference in the image domain is achieved.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
System and method for median fusion of depth maps
InactiveUS6868191B2Accurate representationImage analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionGraphicsComputer science
The present invention is directed toward providing a system for constructing a graphical representation of an image, as perceived from a desired view, from a plurality of calibrated views. An optimum, median fused depth map of a new, desired view of an object or a scene is constructed from a plurality of depth maps of the object or scene, utilizing median values for each of the image pixels within the image domain of the new view. Each of the known depth maps are rendered into the new view, and the pixels of the rendered image are processed one at a time until a median value for each pixel in the new view of the image of the object or scene is calculated. The calculated median values are then assembled into a median fused depth map of the new view of the object or scene, with the median fused depth map available to construct a new two or three dimension images and models of the object or scene as perceived from the new view.
Owner:TELEFON AB LM ERICSSON (PUBL)
Optical writing unit, a driving method thereof, and an image forming apparatus
InactiveUS7068295B2Optimize volumeVisual representatino by photographic printingPrintingProperty valueWhite stripe
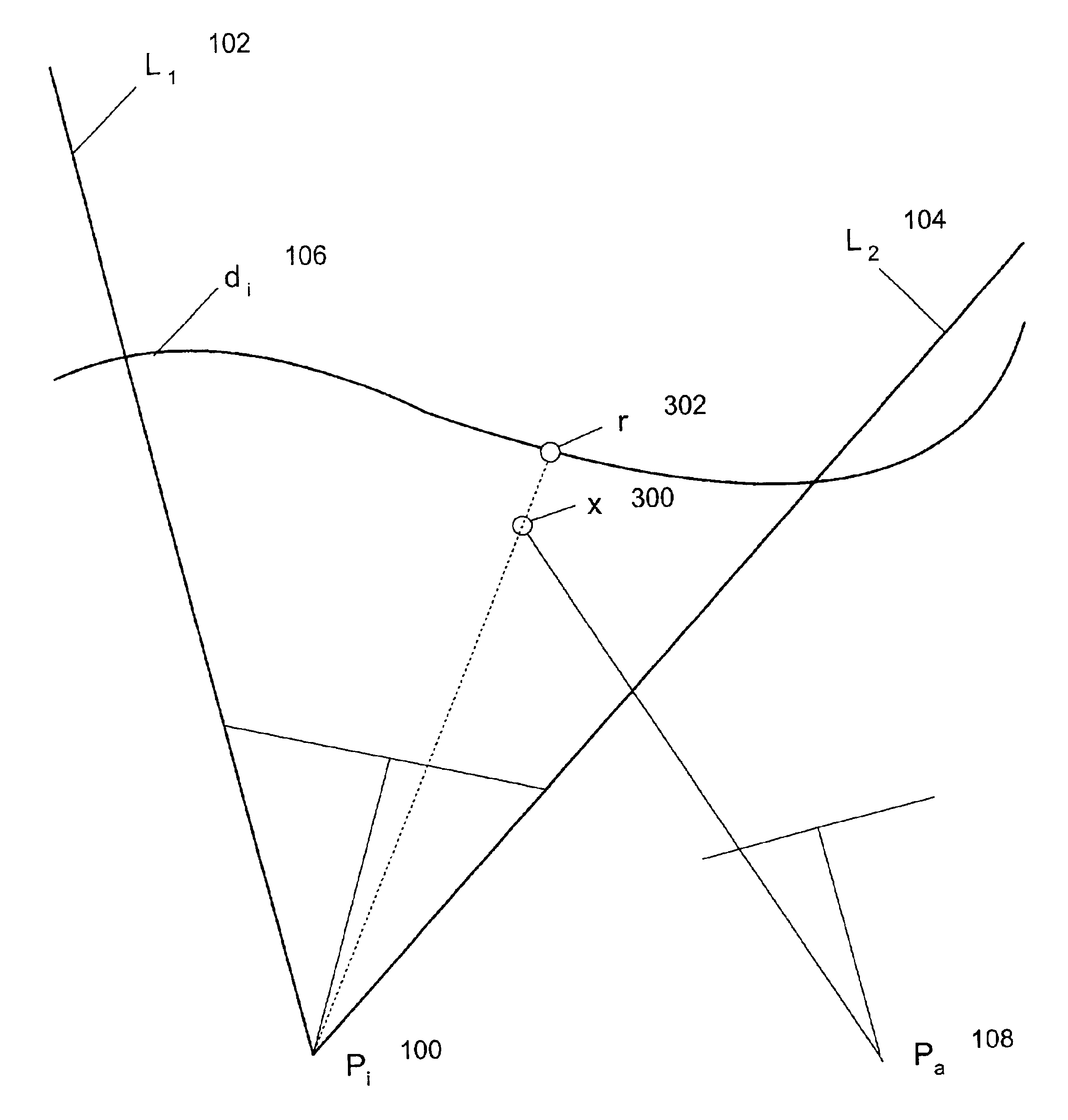
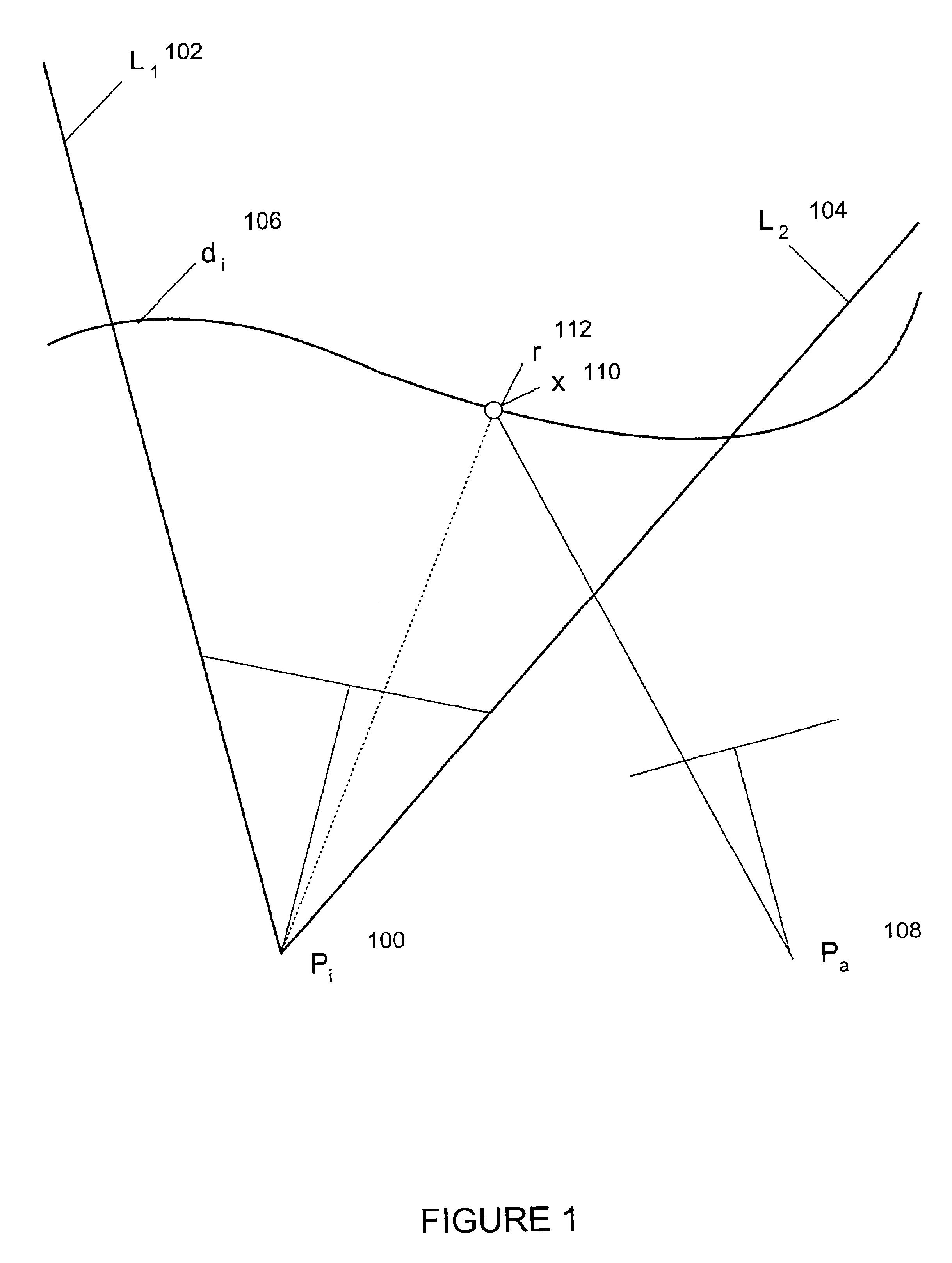
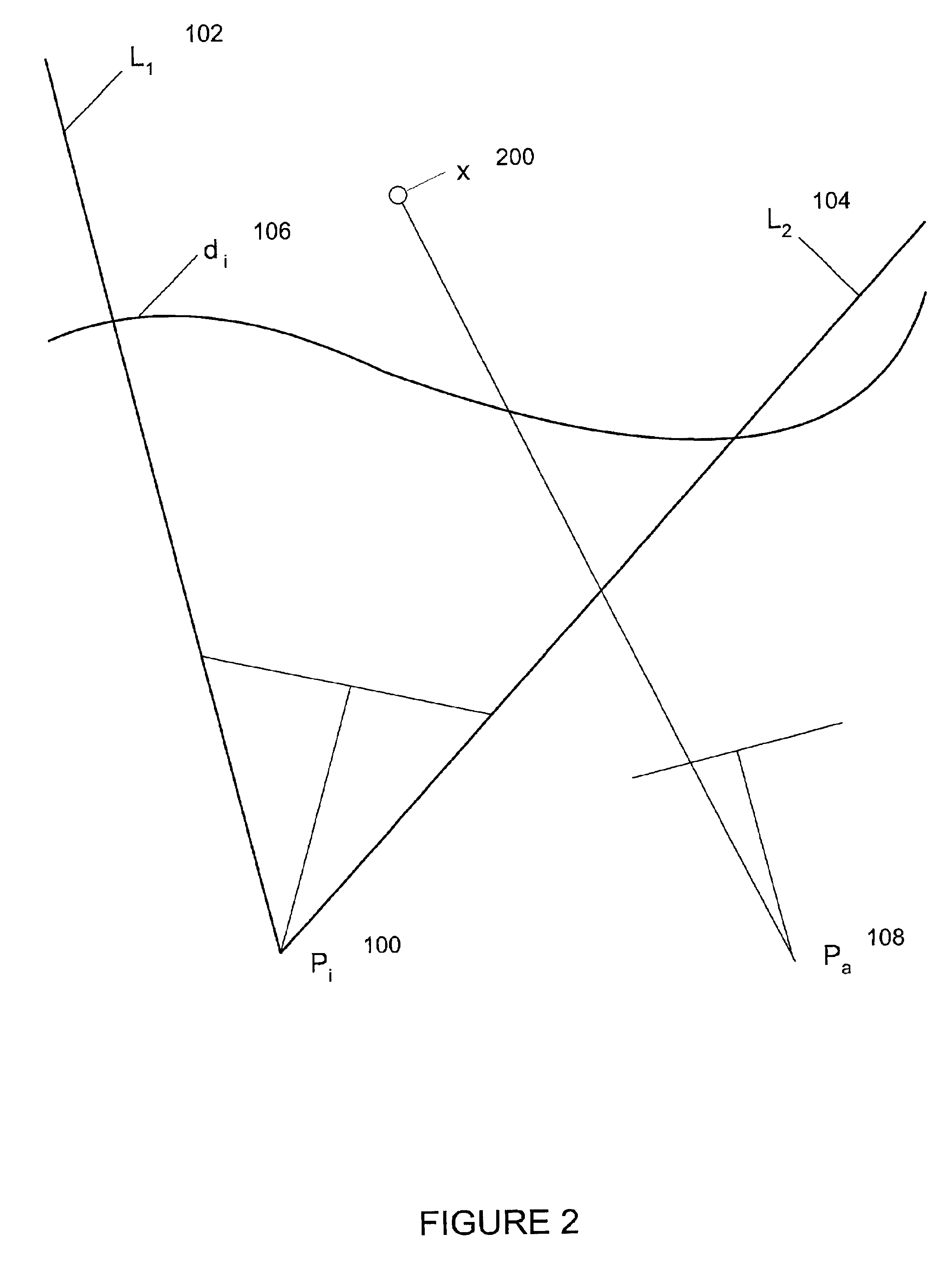
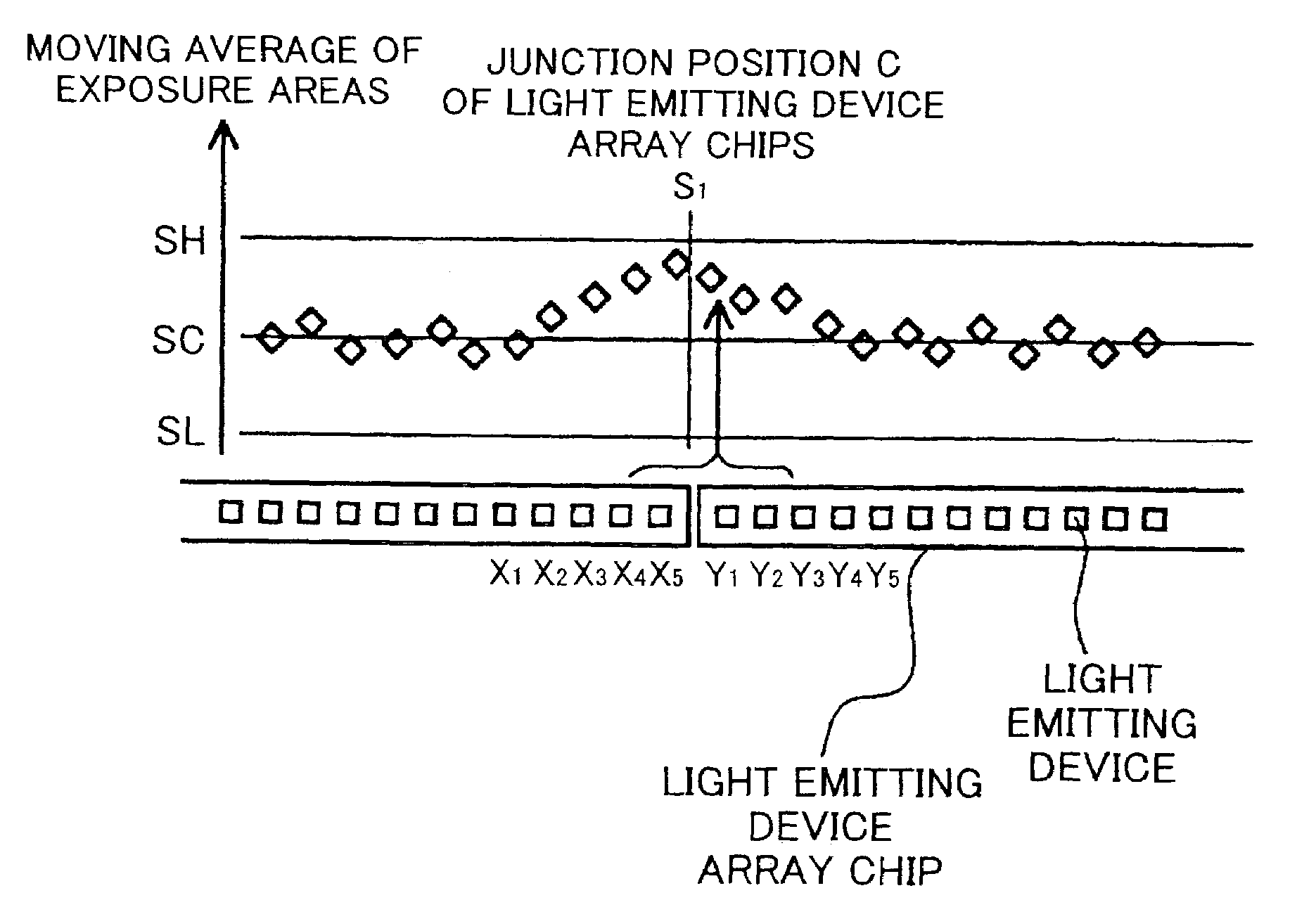
An optical writing unit is capable of producing a high-quality image in which the formation of white stripes and black stripes, due to uneven intervals between light emitting devices, is suppressed. The unevenness, often occurring at the junction part of two-light emitting diode array chips, is compensated for by increasing or decreasing the light volume of light emitting devices that are located on and near the edge of a light emitting device array chip, such that a property value concerning an exposure intensity distribution falls within a predetermined range for an effective image domain in its entirety.
Owner:RICOH KK
Object recognition using a cognitive swarm vision framework with attention mechanisms
InactiveUS7599894B2Avoid clustersPrevents unnecessary classifier evaluationDigital computer detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionMulti dimensionalSoftware agent
An object recognition system is described that incorporates swarming classifiers with attention mechanisms. The object recognition system includes a cognitive map having a one-to-one relationship with an input image domain. The cognitive map records information that software agents utilize to focus a cooperative swarm's attention on regions likely to contain objects of interest. Multiple agents operate as a cooperative swarm to classify an object in the domain. Each agent is a classifier and is assigned a velocity vector to explore a solution space for object solutions. Each agent records its coordinates in multi-dimensional space that are an observed best solution that the agent has identified, and a global best solution that is used to store the best location among all agents. Each velocity vector thereafter changes to allow the swarm to concentrate on the vicinity of the object and classify the object when a classification level exceeds a preset threshold.
Owner:HRL LAB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com