Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
82 results about "Fat suppression" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
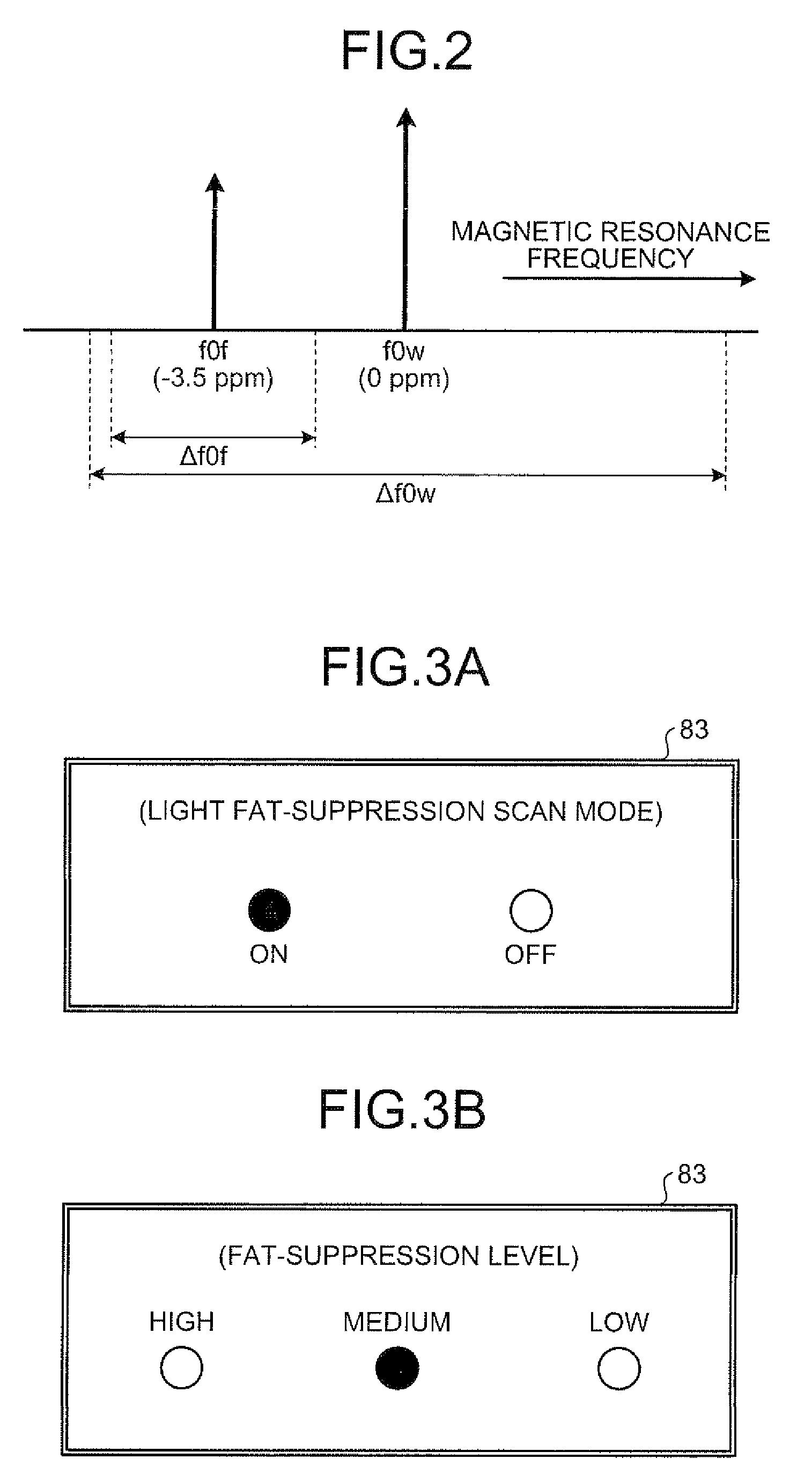
Fat suppression is used in routine magnetic resonance (MR) imaging for many purposes, but two main indications can be identified. First, fat suppression is used to suppress the signal from normal adipose tissue to reduce chemical shift artifact or improve visualization of uptake of contrast material.
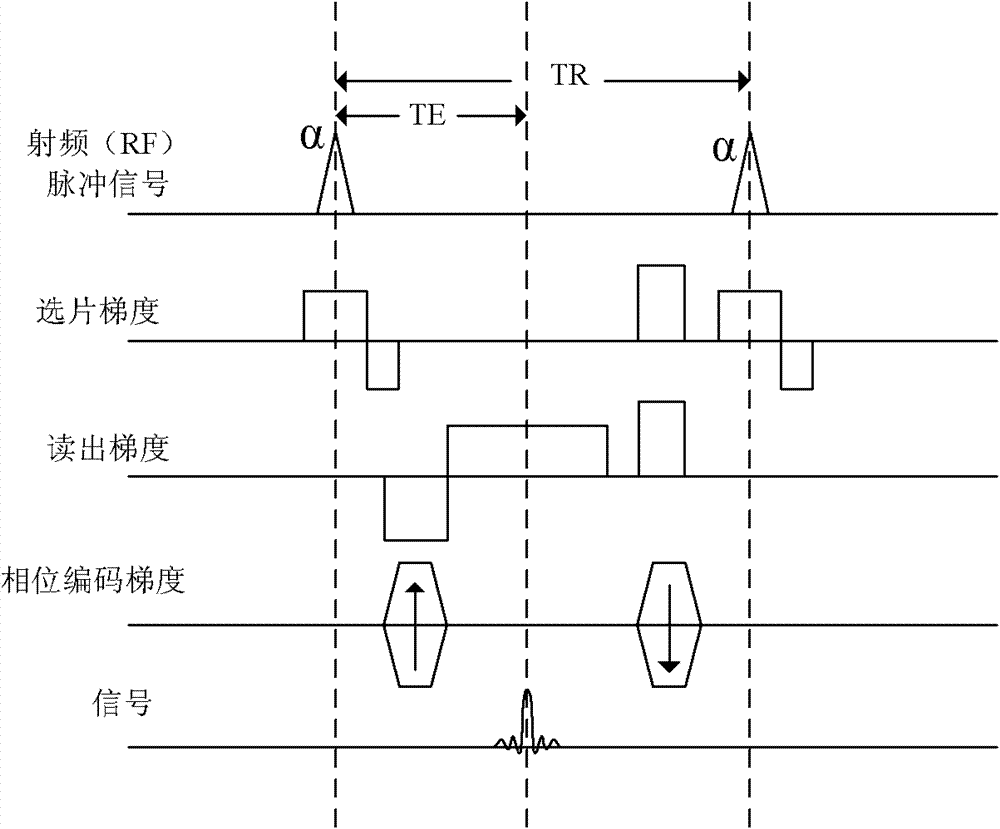
Method and system of MR imaging with simultaneous fat suppression and T1 inversion recovery contrast
ActiveUS7323871B2Suppressing signalImprove lesionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFat suppressionInversion recovery
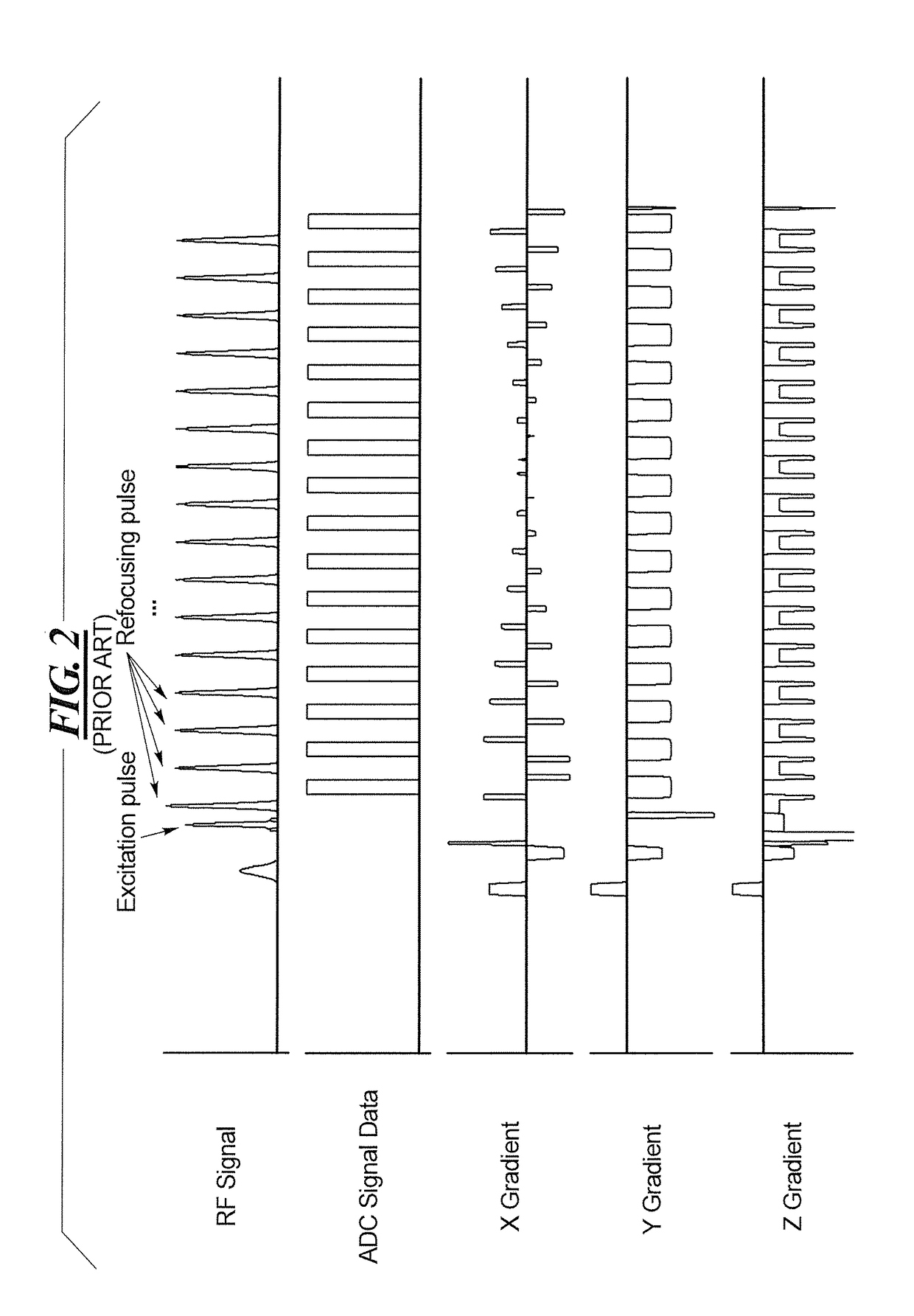
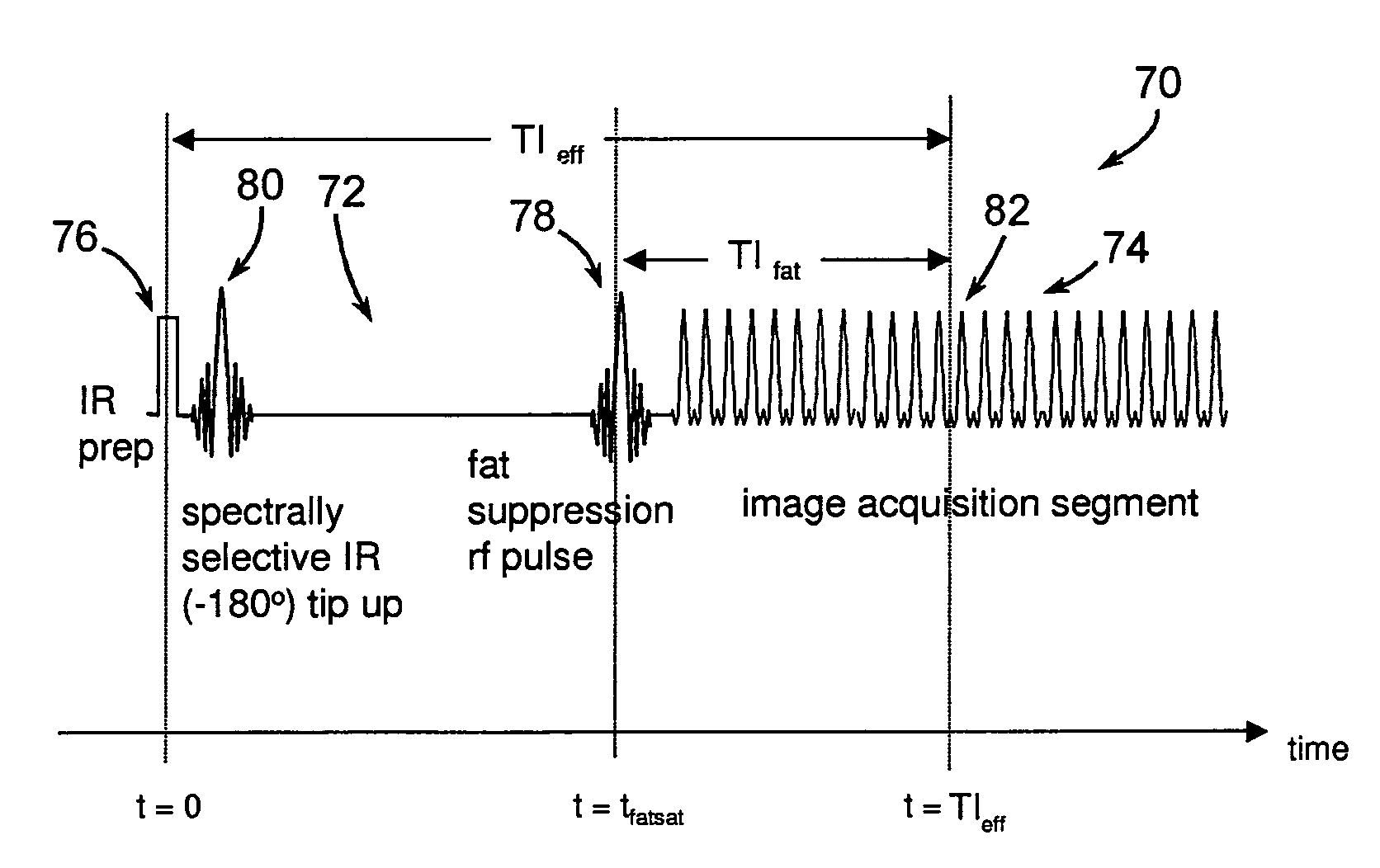
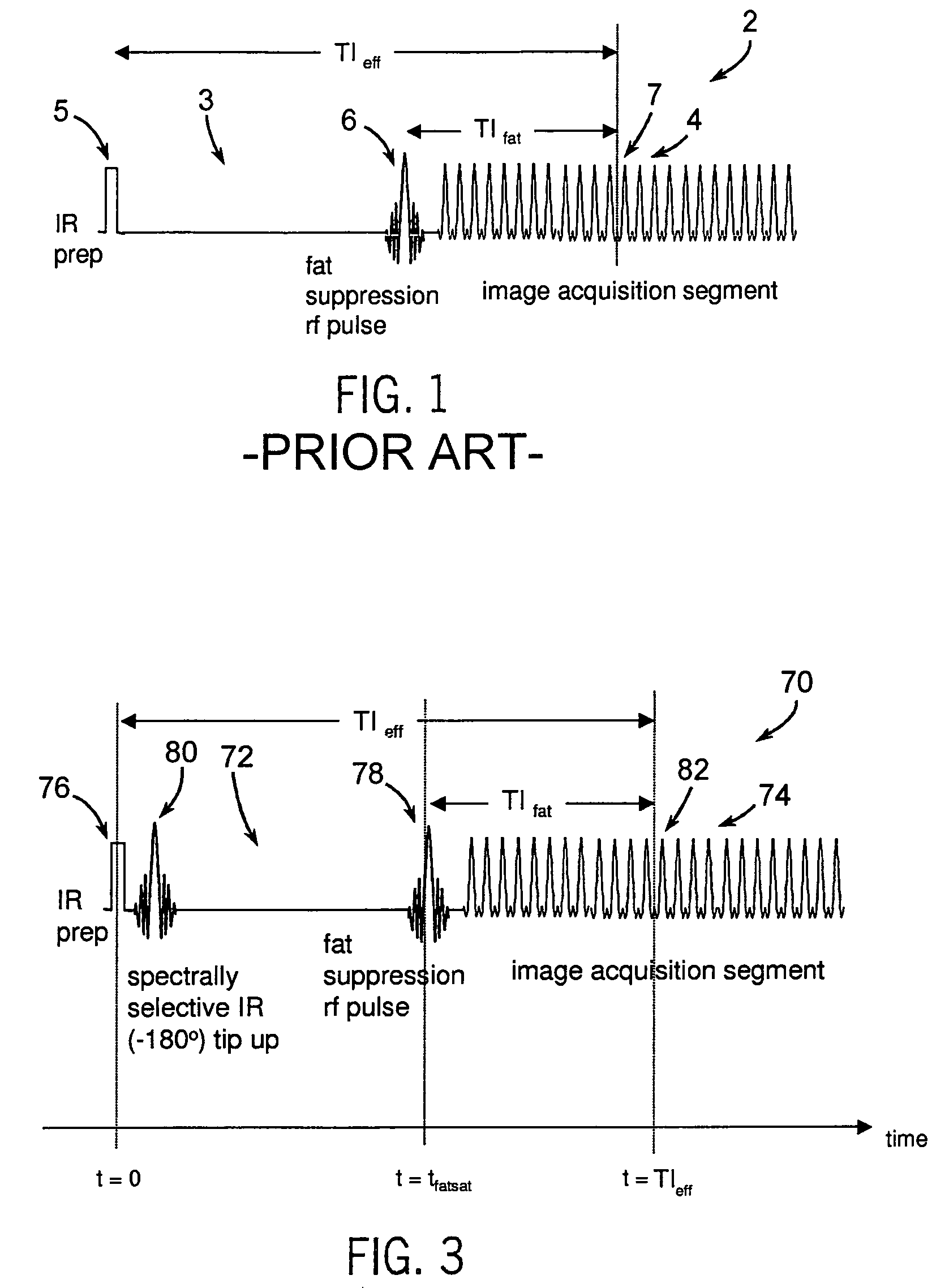
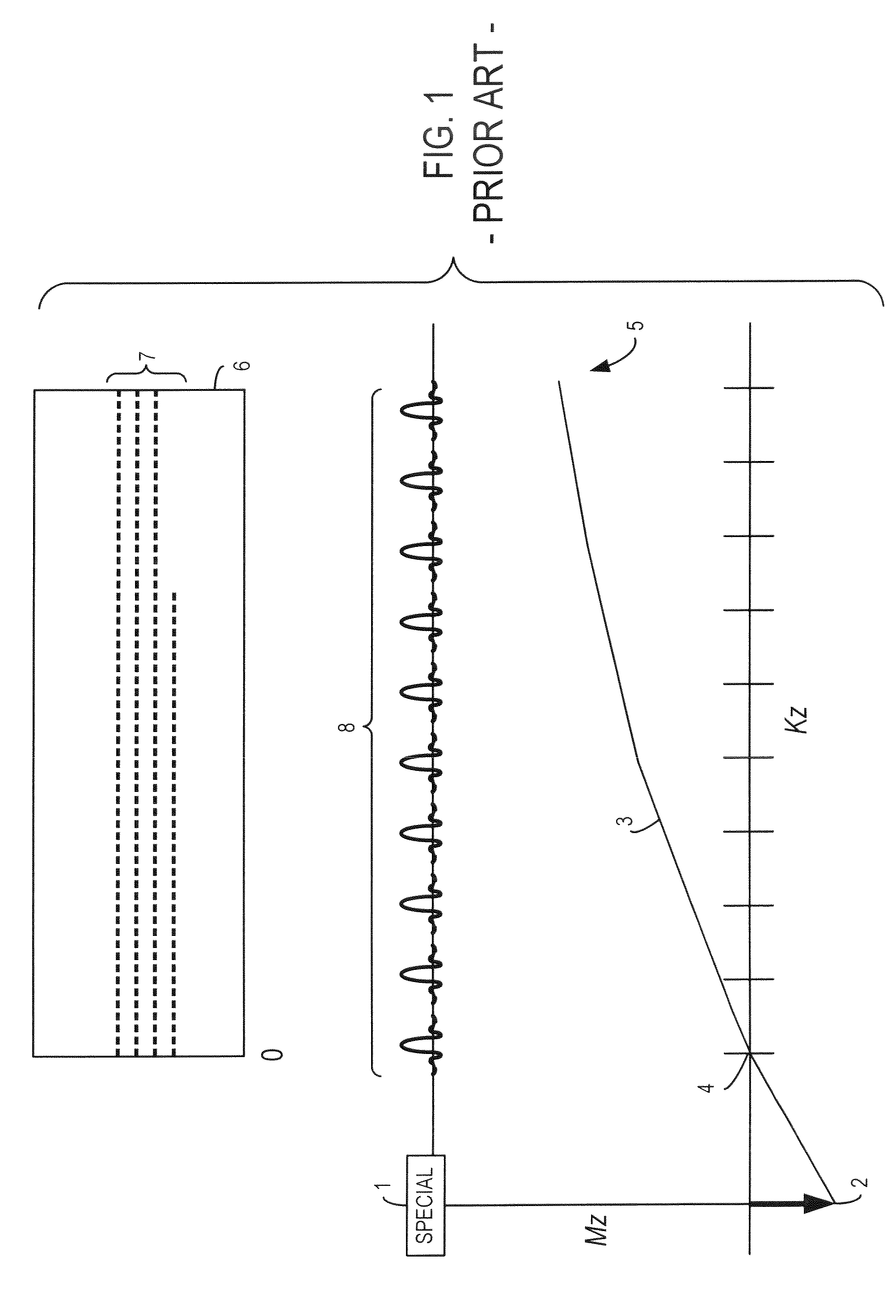
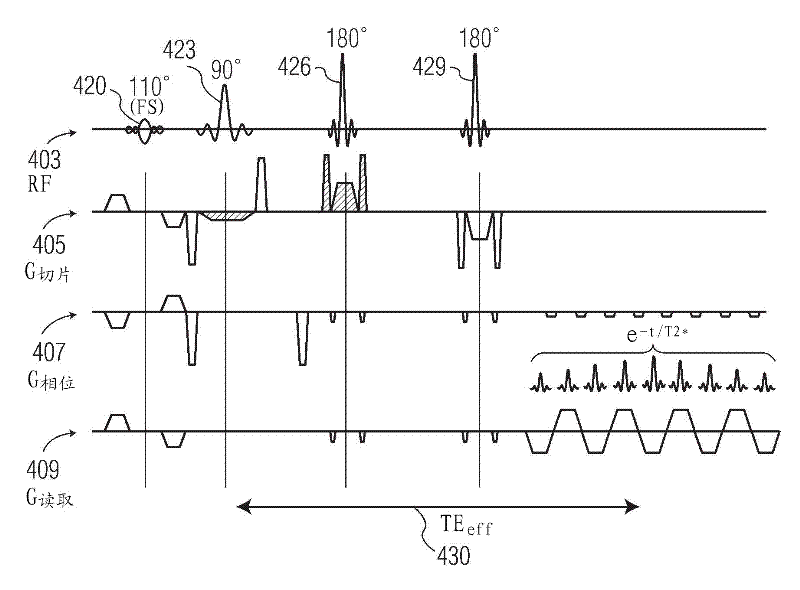
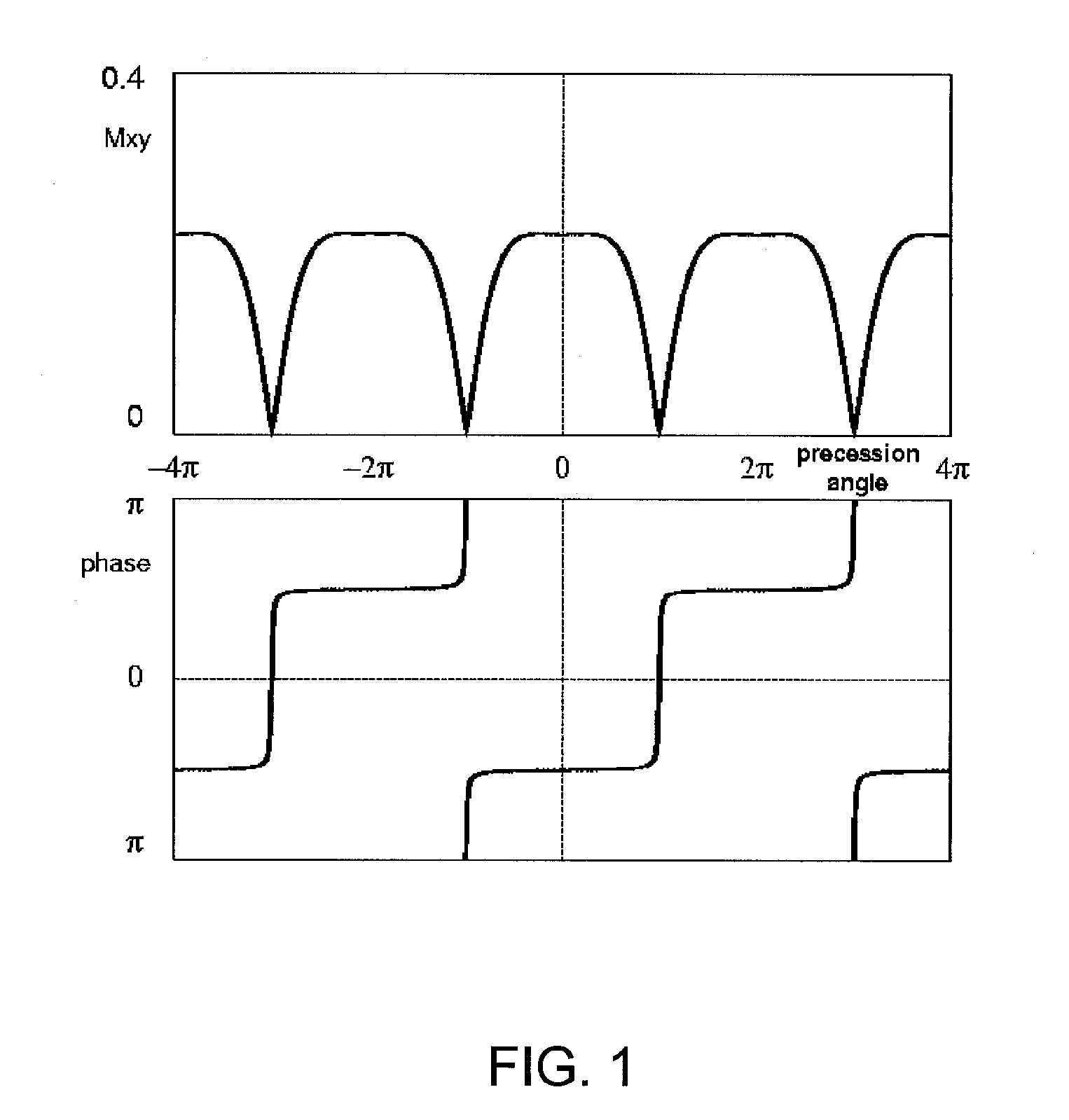
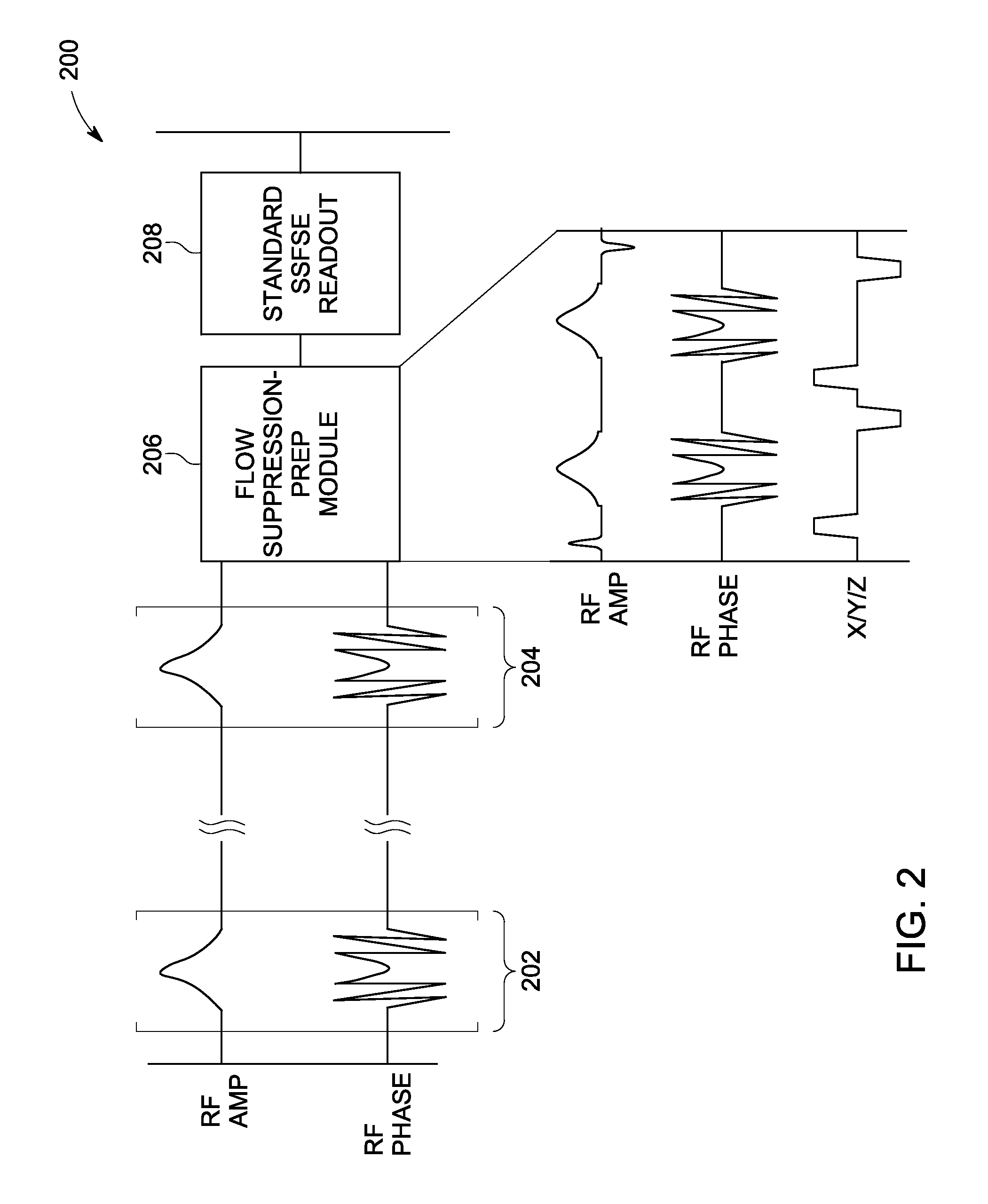
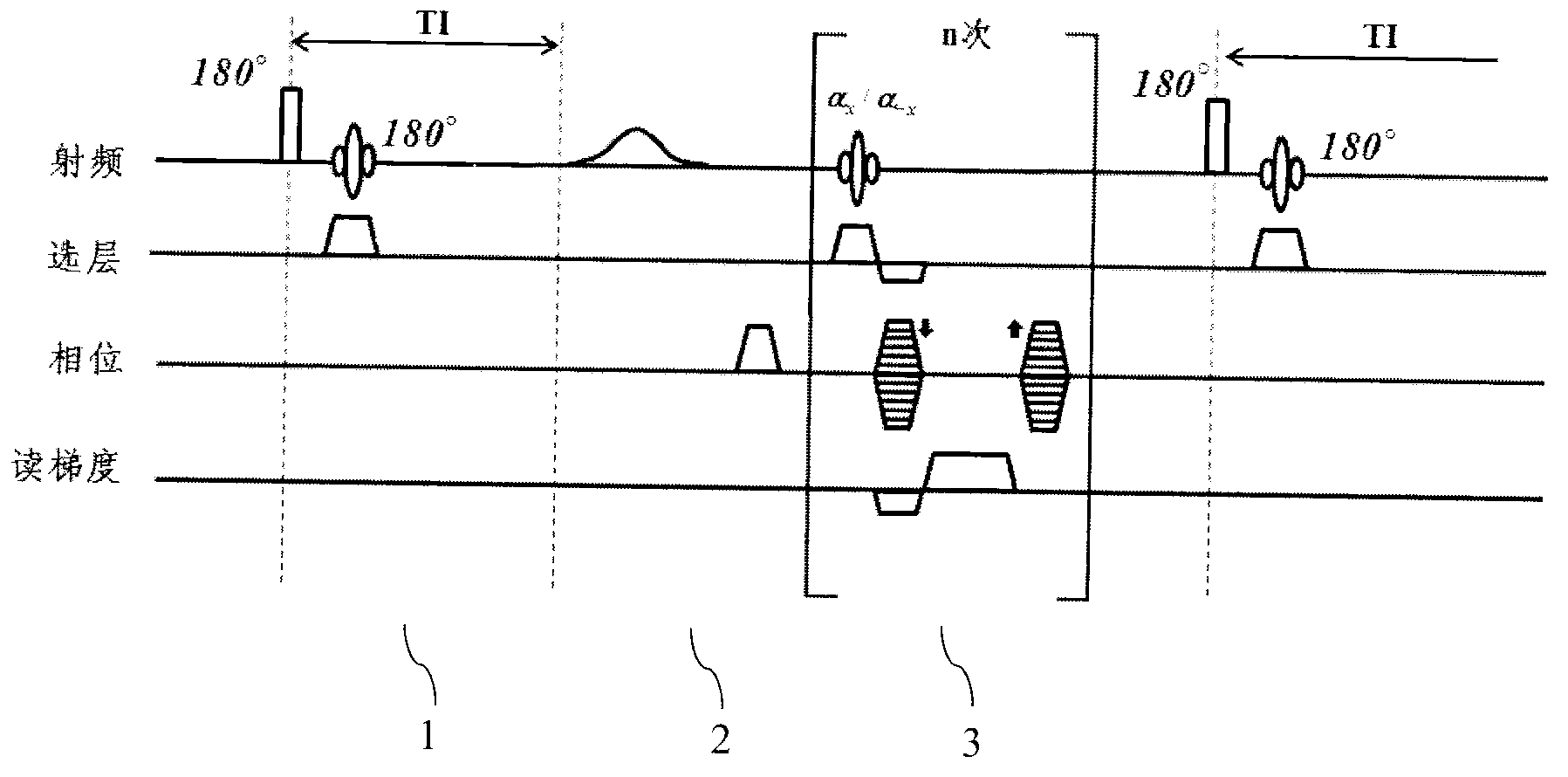
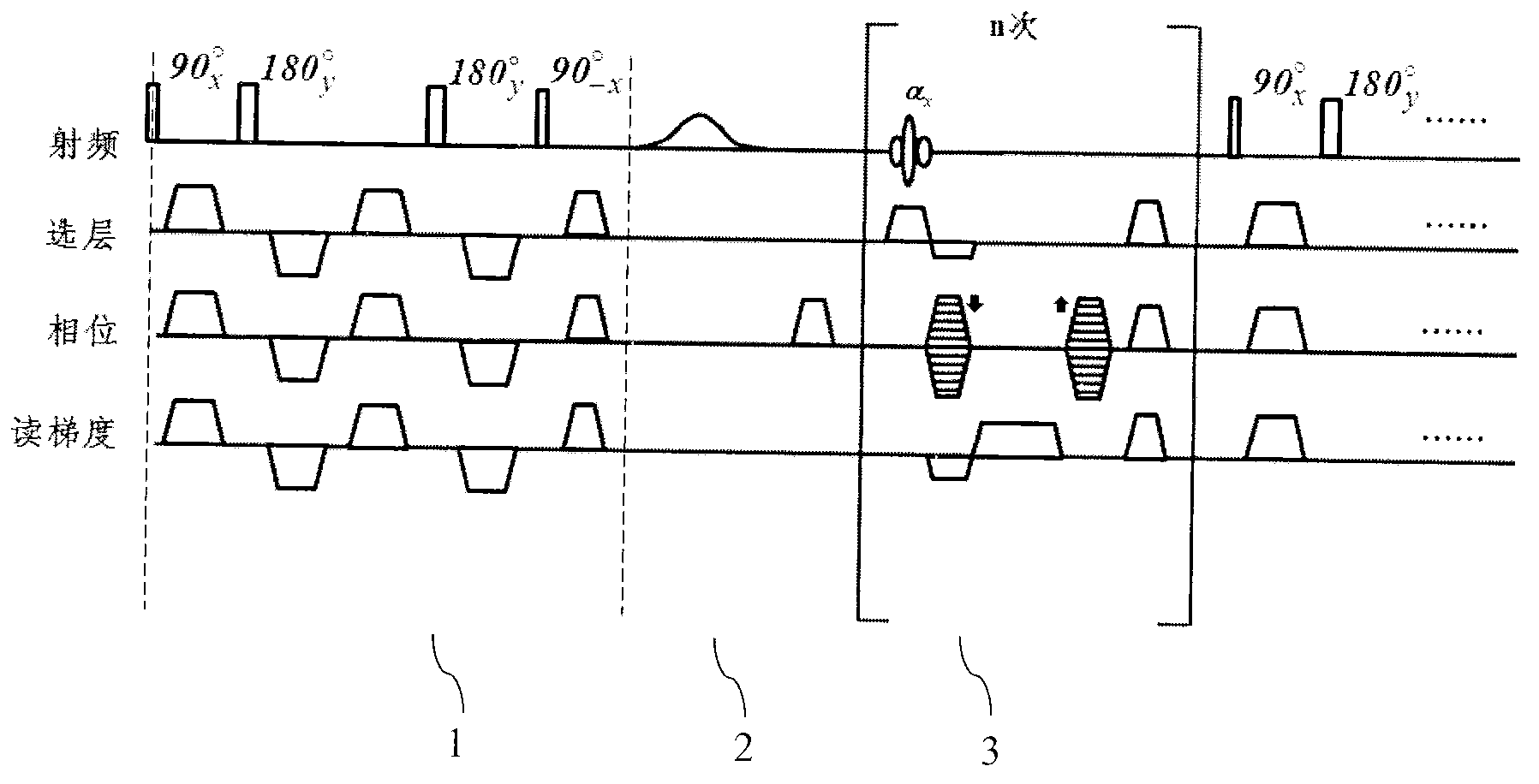
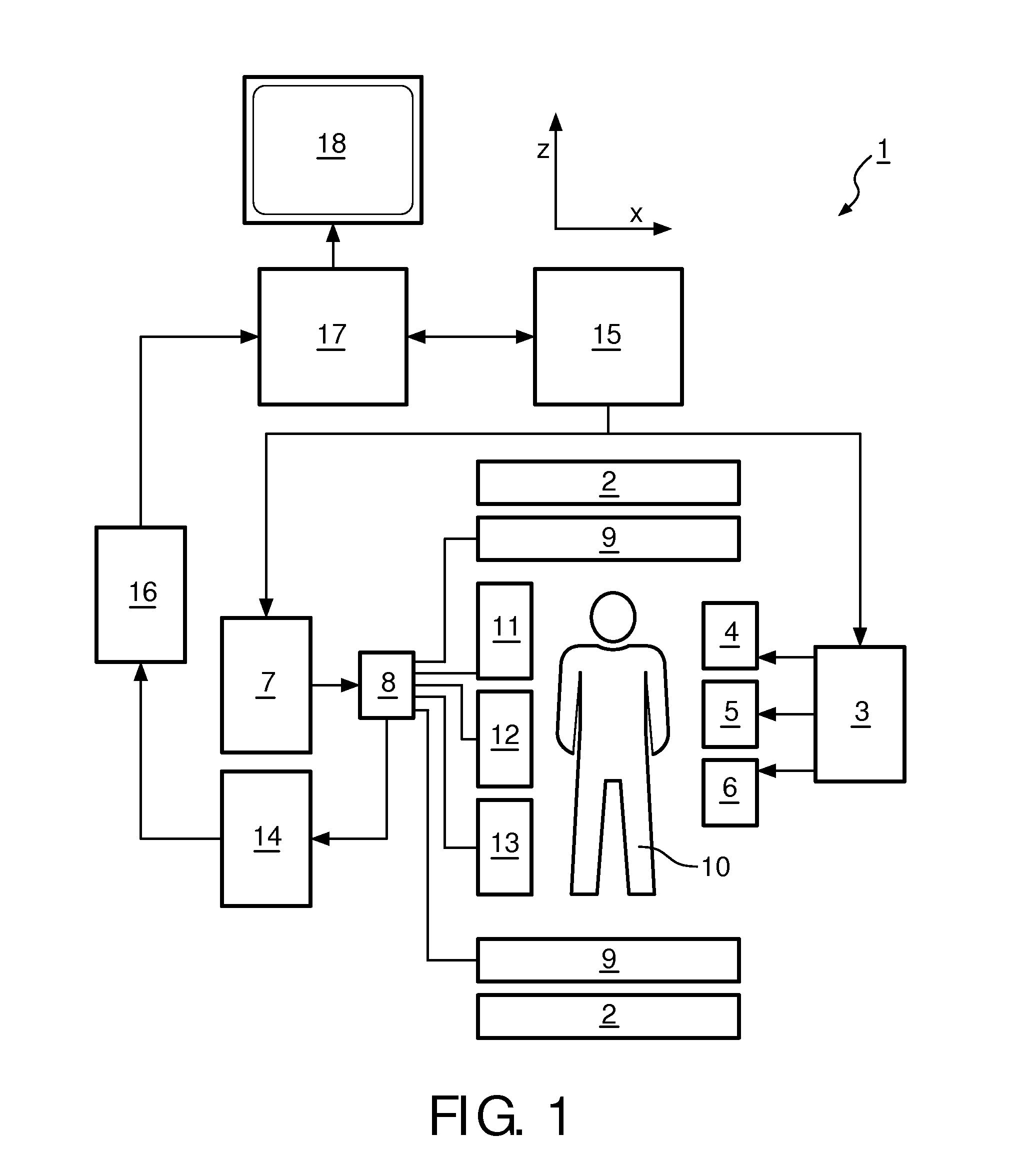
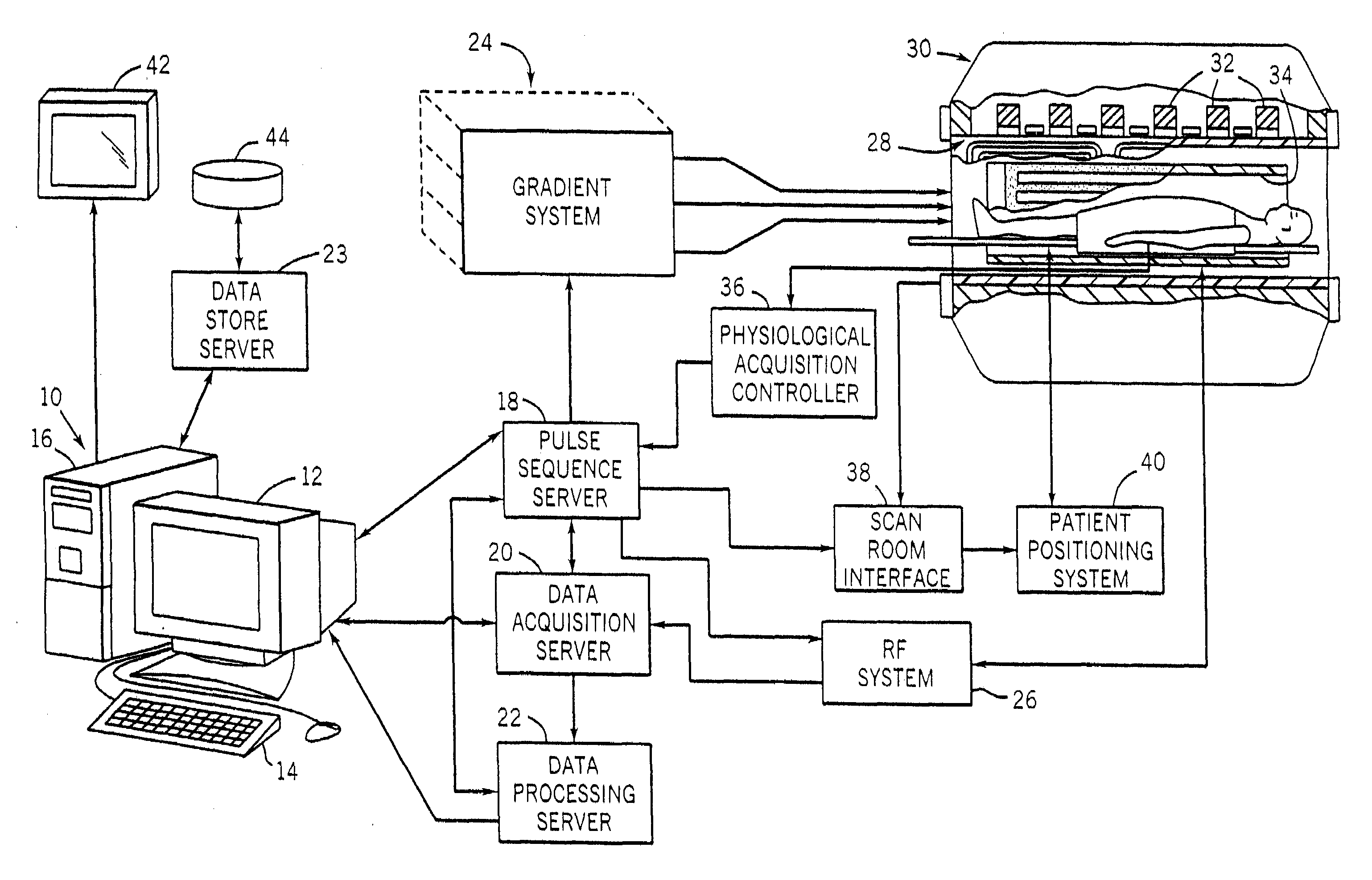
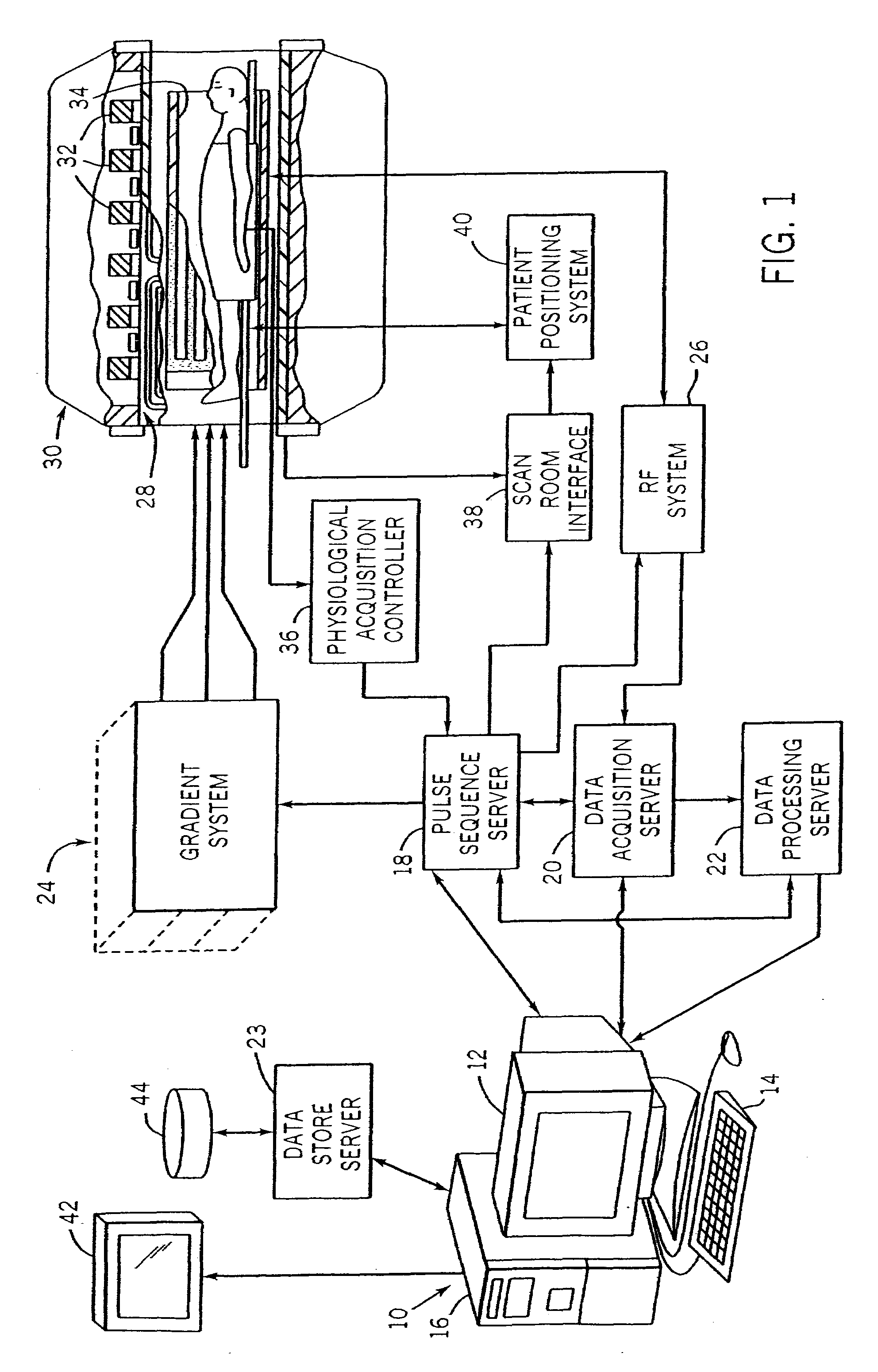
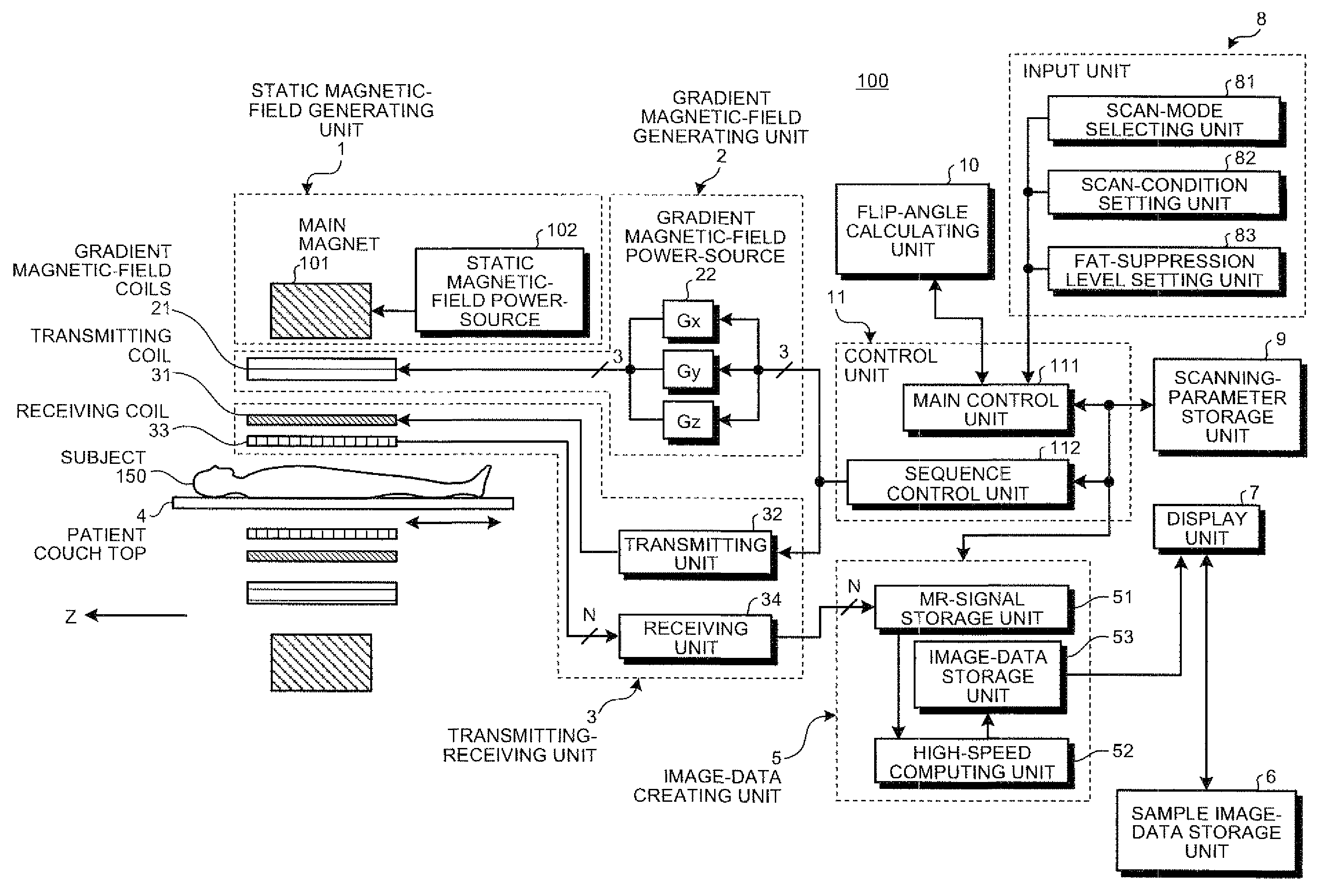
A method and system for fat suppression with T1-weighted imaging includes a pulse sequence generally constructed to have a non-spectrally selective IR pulse that is played out immediately before a spectrally selective IR tip-up pulse. Thereafter, a fat suppression RF pulse is played out followed by the acquisition of fat-suppressed MR data. The pulse sequence maintains T1 contrast by not perturbing the non-fat signals from the IR preparation. The pulse sequence also ensures that the blood pool signal is homogeneously suppressed from the non-spectrally selective IR RF pulse. The pulse sequence also allows for increased fat suppression and provides flexibility for adjustment of the degree of fat suppression without affecting the view acquisition order for an image acquisition segment.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
MRI apparatus
ActiveCN101401723ADiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFat suppressionPulse sequence
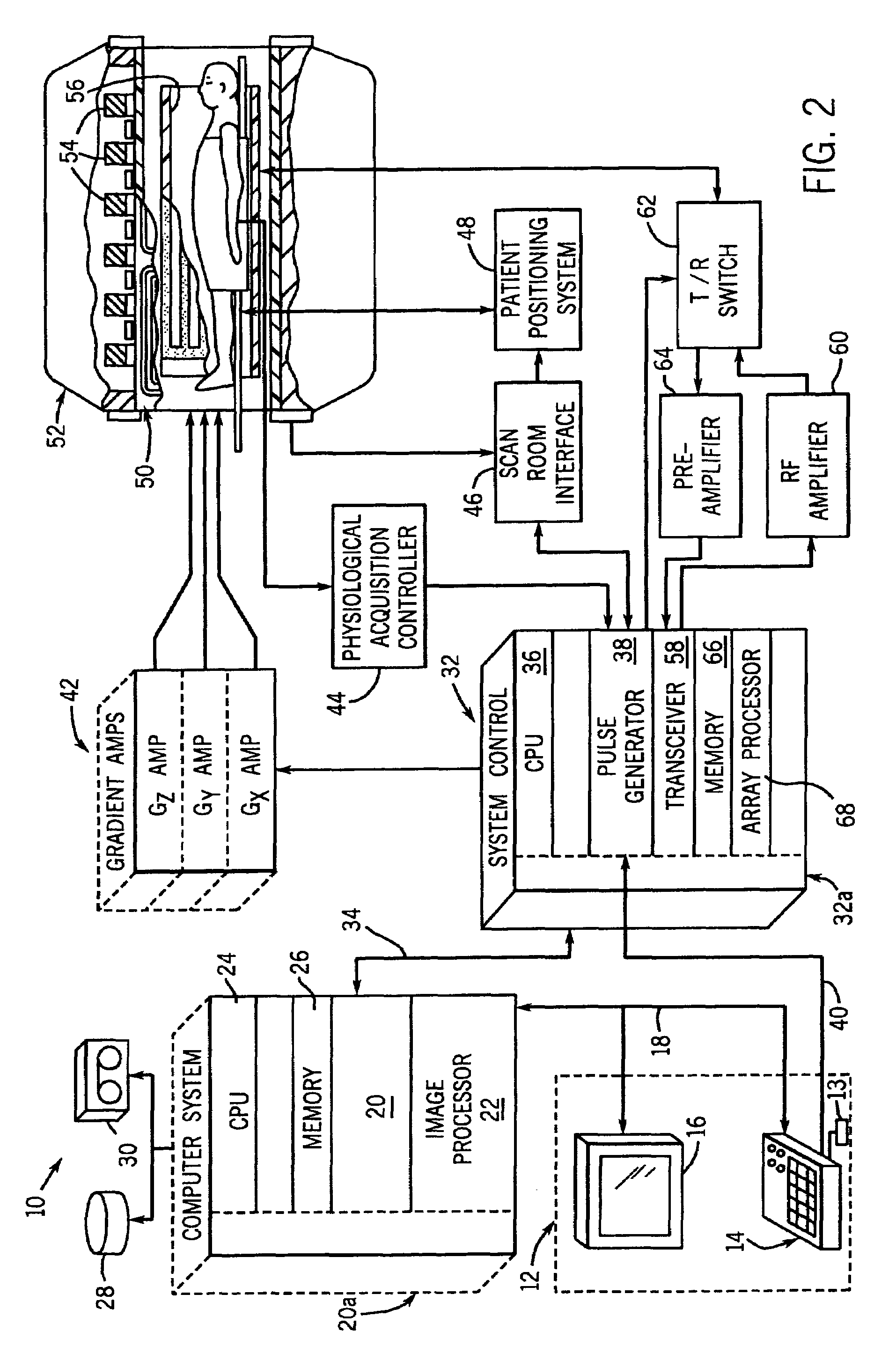
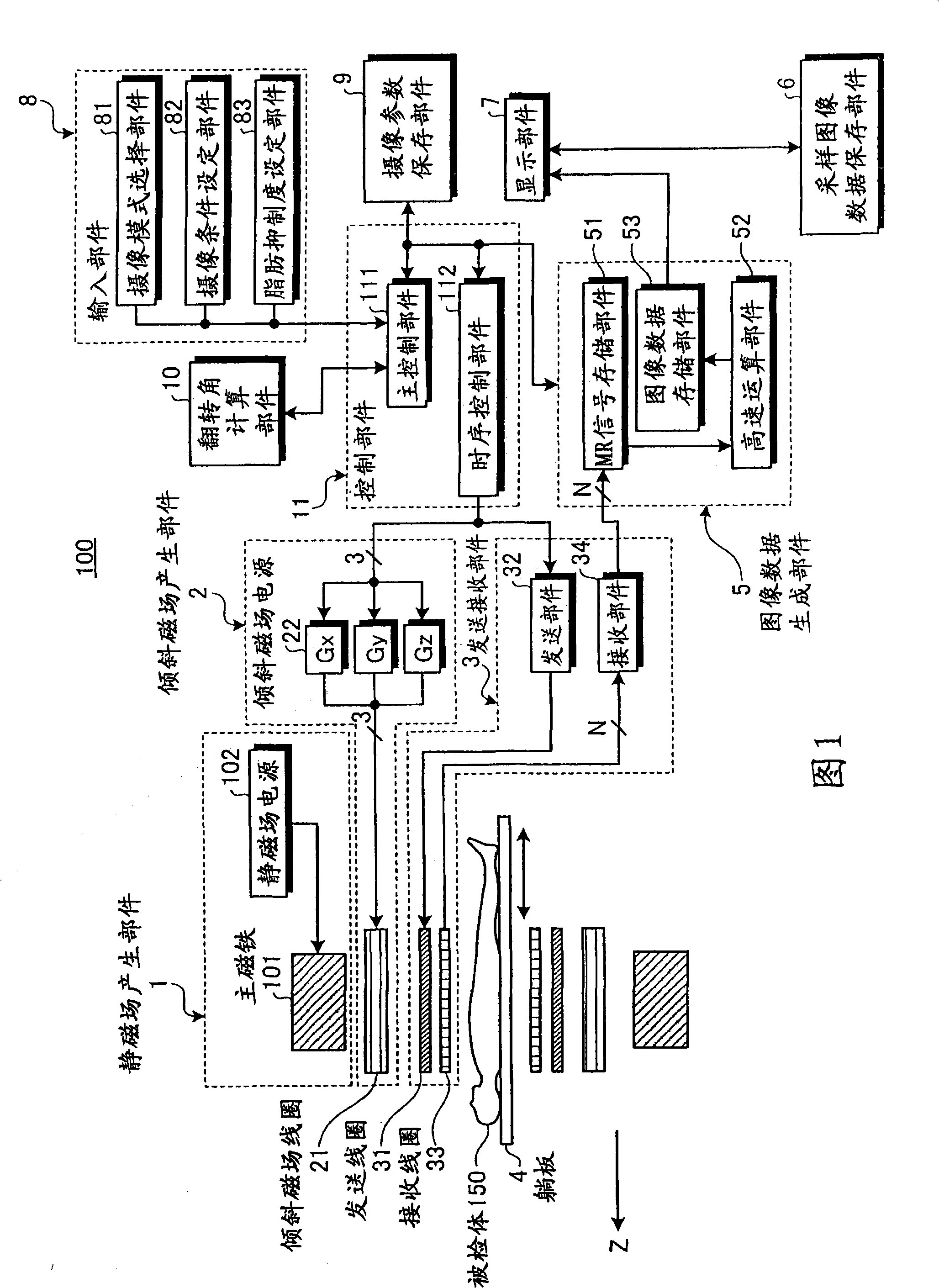
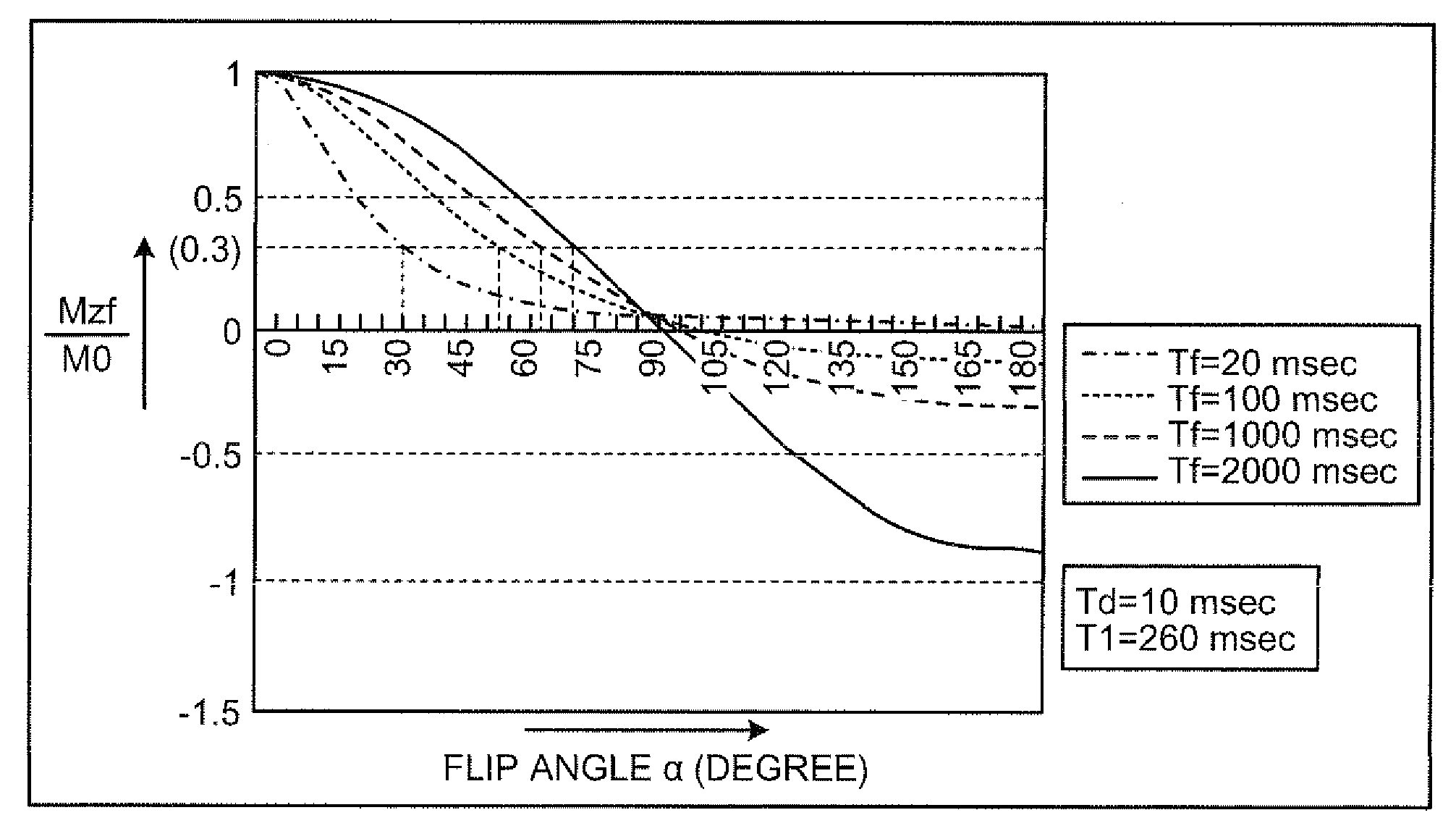
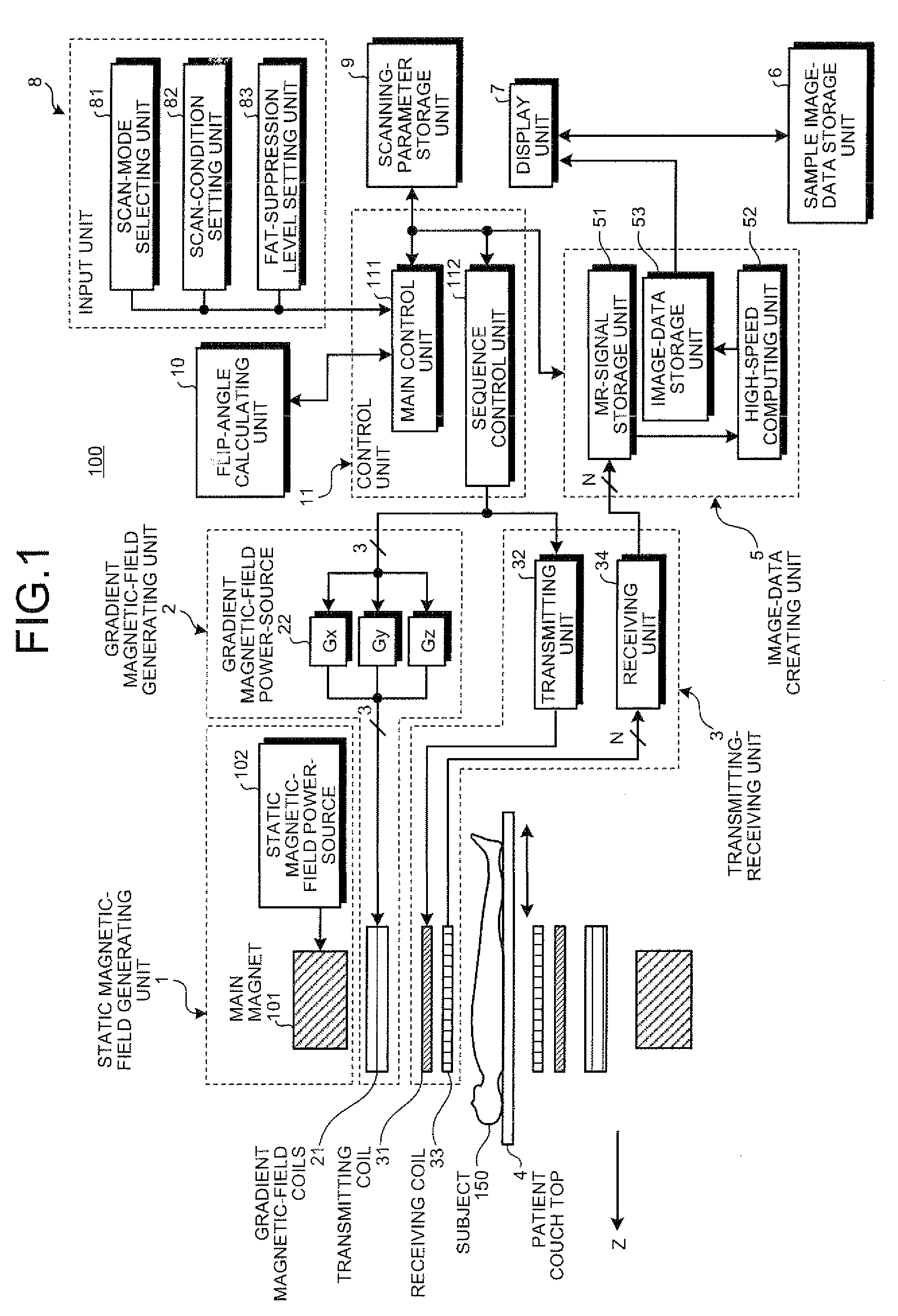
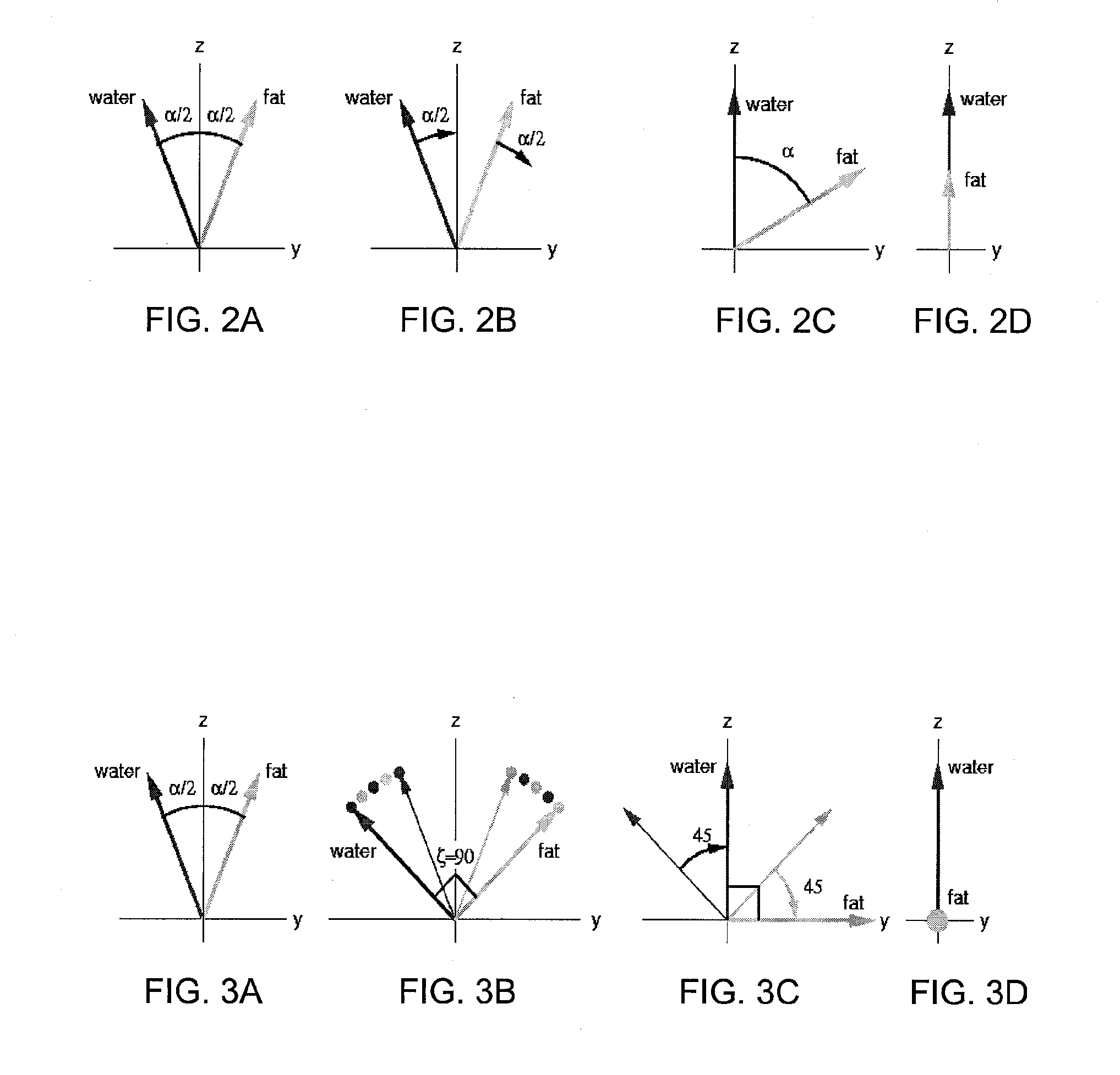
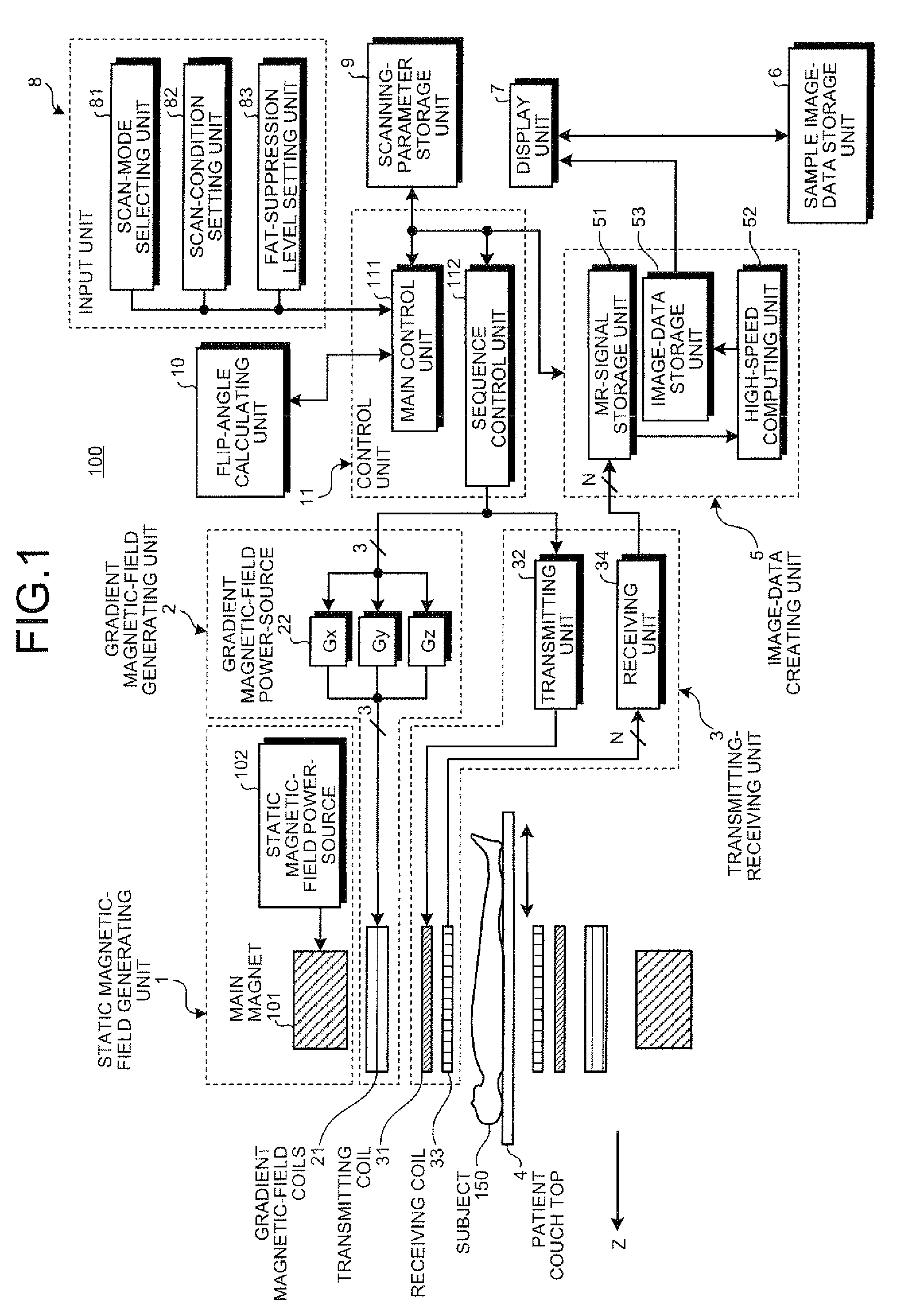
The present invention provides a MRI device, wherein, a flip-angle calculating unit calculates a flip angle of a fat-suppression pulse by inputting scanning parameters read from a scanning-parameter storage unit based on scanning conditions set by a scan-condition setting unit and a desired fat-suppression level, into a predetermined computing program. A control unit suppresses fat signals to a desired level by performing irradiation of a fat-suppression pulse having the calculated flip angle and application of a spoiler gradient magnetic field onto a scan target portion of a subject by controlling a gradient magnetic-field generating unit and a transmitting-receiving unit, and further performs irradiation of an RF pulse and application of a gradient magnetic field in accordance with a predetermined pulse sequence, thereby detecting water signals and suppressed fat signals as MR signals. An image-data creating unit creates image data by reconstructing the MR signals.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Magnetic resonance imaging device
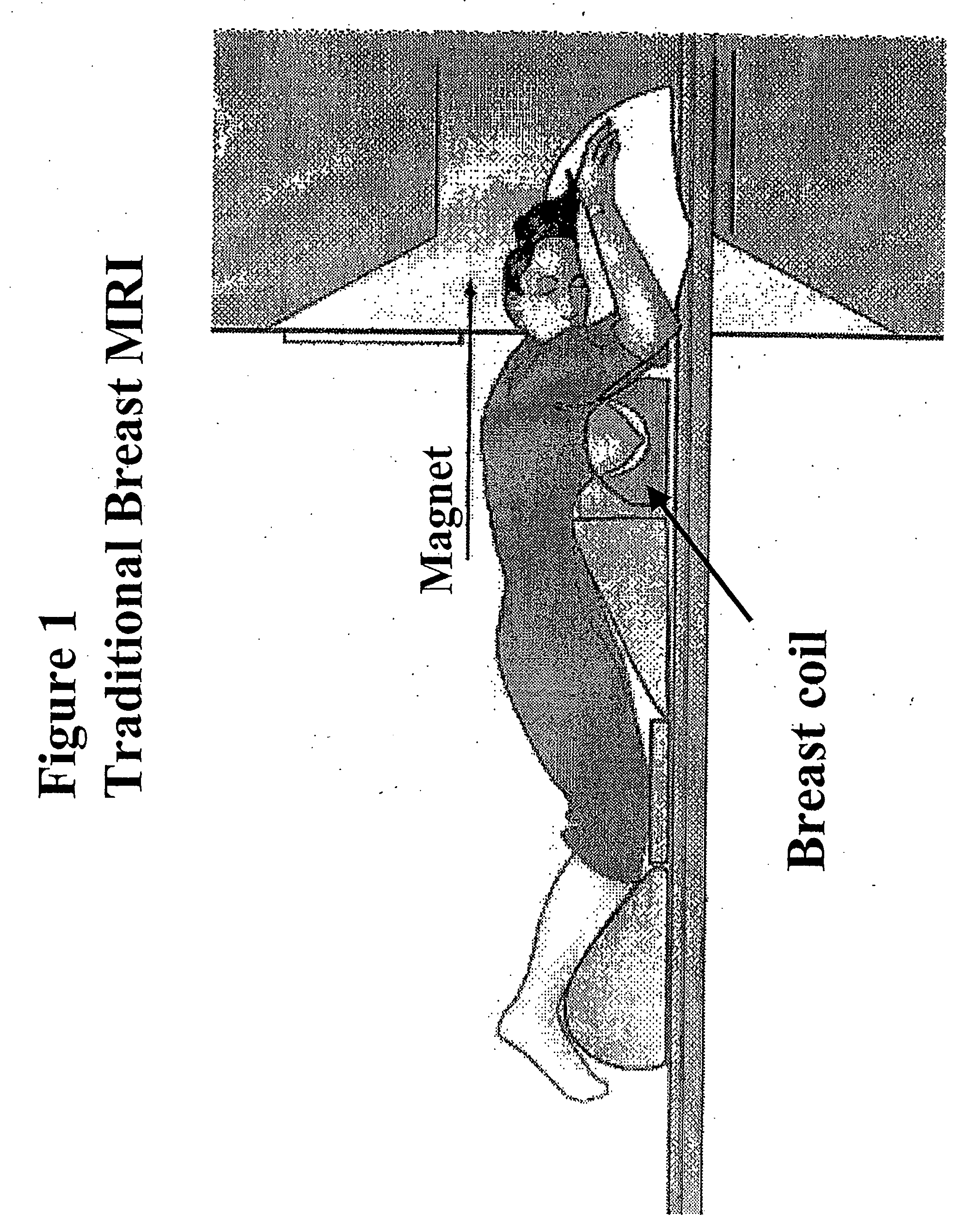
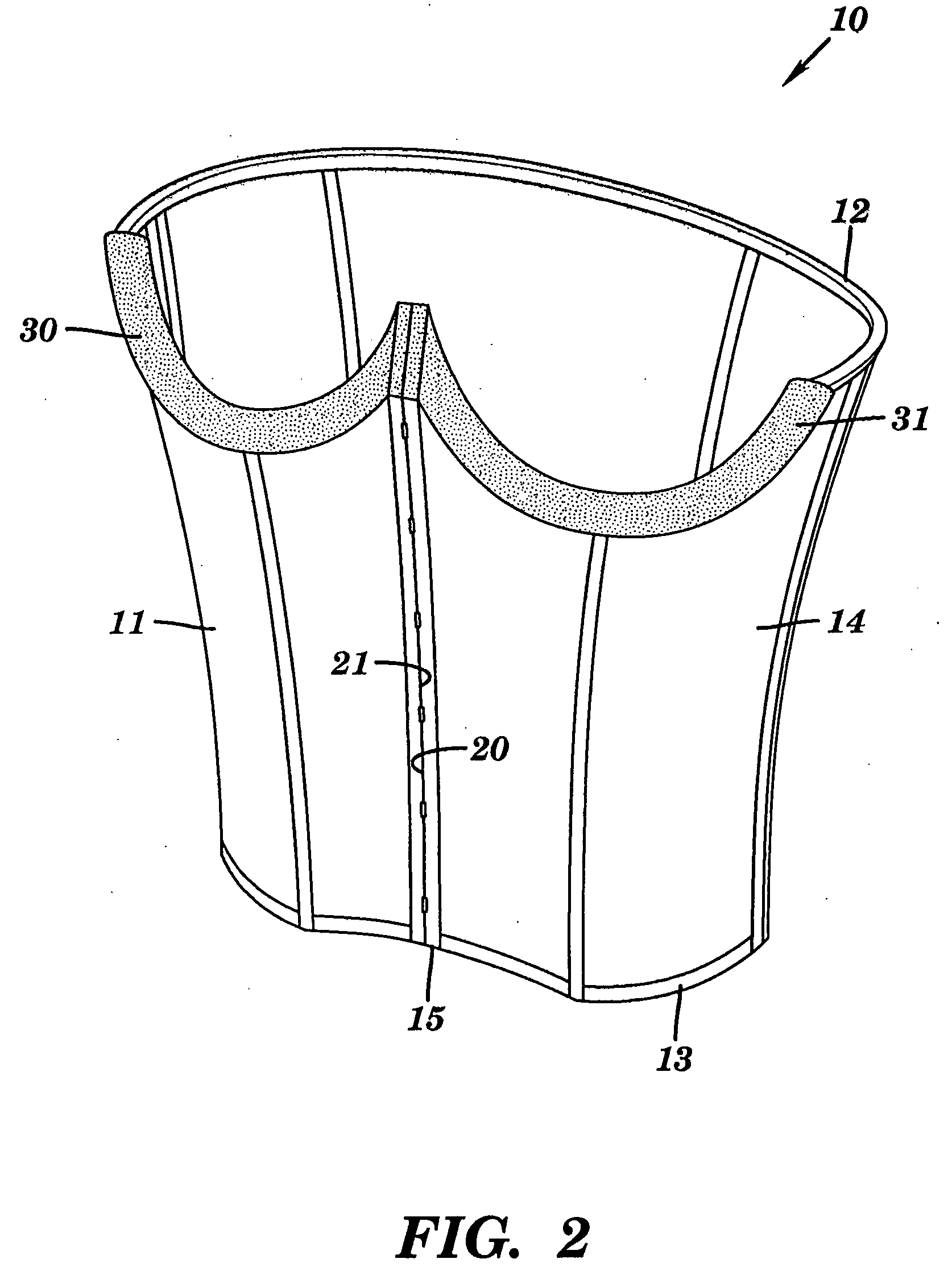
InactiveUS20060270930A1BrassieresDiagnostic recording/measuringFat suppressionMR - Magnetic resonance
The present invention provides a device for use in magnetic resonance imaging of a woman's breasts. The device has breast-supporting cups that comprise an enhanced fat saturation material to facilitate fat suppression during imaging. Significantly, the wearer can put the device on and position it with little or no assistance and without loss of dignity due to manipulation by a technician.
Owner:ORGAMEND
Magnetic resonance imaging method
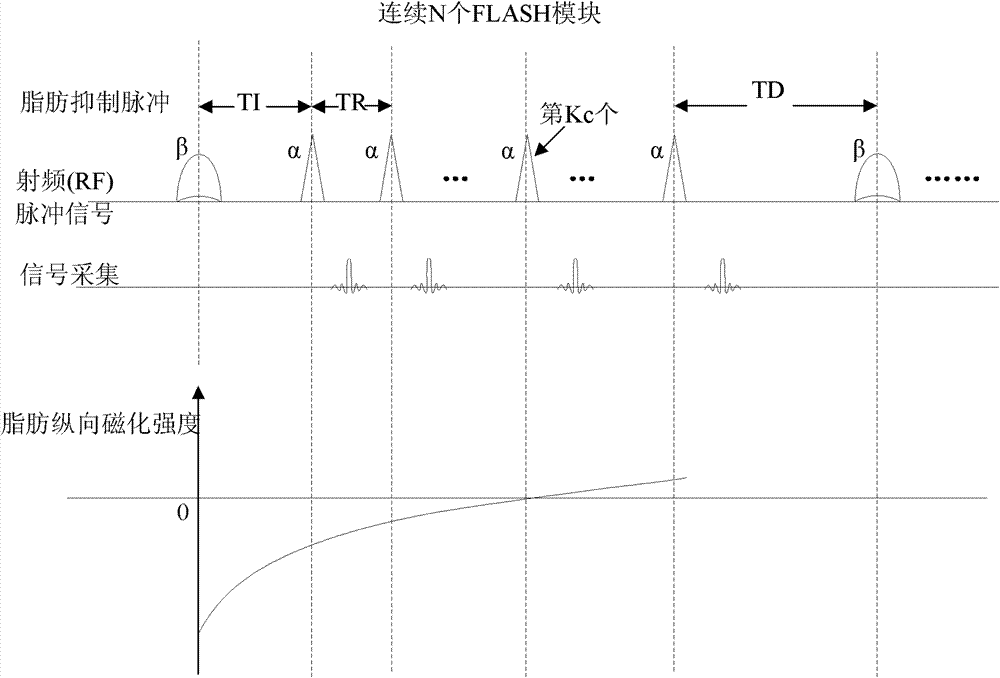
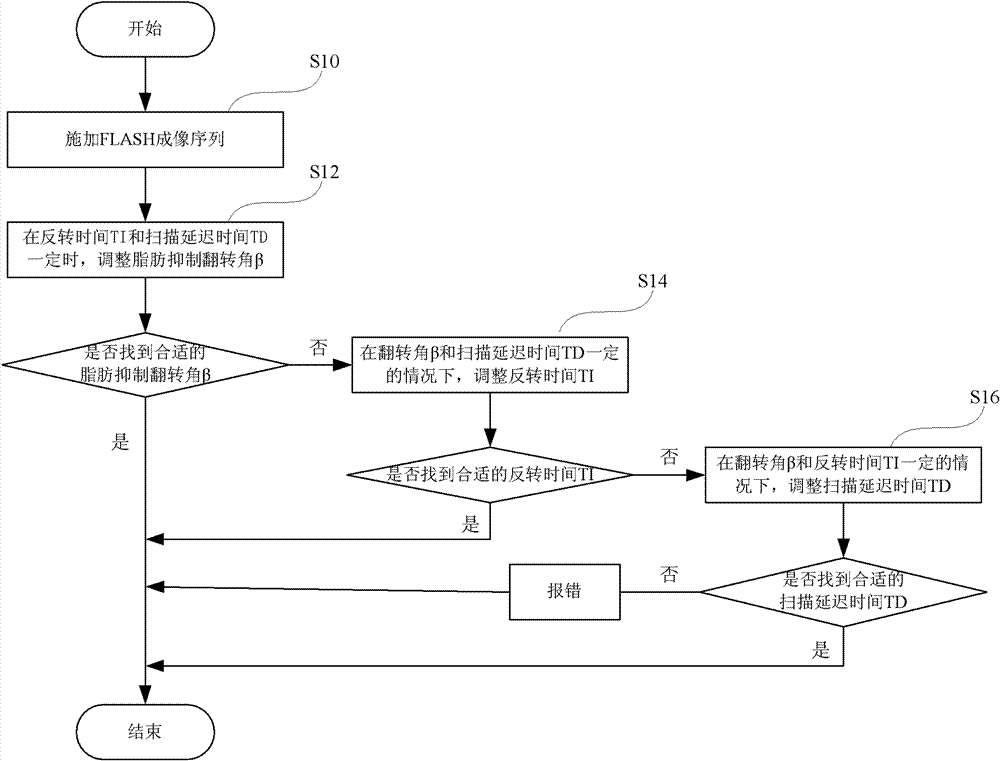
ActiveCN102772206AMeet the requirements of dynamic imagingAchieve any positionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFat suppressionDynamic contrast
The invention provides a magnetic resonance imaging method for dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging based on a three-dimensional pulse sequence of fast low angle shot FLASH. The method comprises the steps of: applying a FLASH imaging pulse sequence to an objected to be examined in a static magnetic field, wherein the FLASH imaging pulse sequence comprises radio frequency shot pulses a and fat inhibiting pulses b, and N radio frequency shot pulses a are comprised between two adjacent fat inhibiting pulses b; adjusting a fat inhibiting flip angle b with certain time of inversion T1 and time of scan delay TD to obtain the optimal fat inhibiting effect; and adjusting the time of inversion T1 and / or the time of scan delay TD to obtain the optimal fat inhibiting effect in a condition that the optimal fat inhibiting effect cannot be obtained by adjusting the fat inhibiting flip angle b. Compared with the prior art, the magnetic resonance imaging method provided by the invention has the advantages of good fat inhibiting effect and high imaging quality.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE CO LTD
MRI apparatus
ActiveUS20090091324A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFat suppressionSignal Repression
A flip-angle calculating unit calculates a flip angle of a fat-suppression pulse by inputting scanning parameters read from a scanning-parameter storage unit based on scanning conditions set by a scan-condition setting unit and a desired fat-suppression level, into a predetermined computing program. A control unit suppresses fat signals to a desired level by performing irradiation of a fat-suppression pulse having the calculated flip angle and application of a spoiler gradient magnetic field onto a scan target portion of a subject by controlling a gradient magnetic-field generating unit and a transmitting-receiving unit, and further performs irradiation of an RF pulse and application of a gradient magnetic field in accordance with a predetermined pulse sequence, thereby detecting water signals and suppressed fat signals as MR signals. An image-data creating unit creates image data by reconstructing the MR signals.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Methods for fat signal suppression in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS20080218169A1Shorten the timeReduce acquisition timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionData setFat suppression
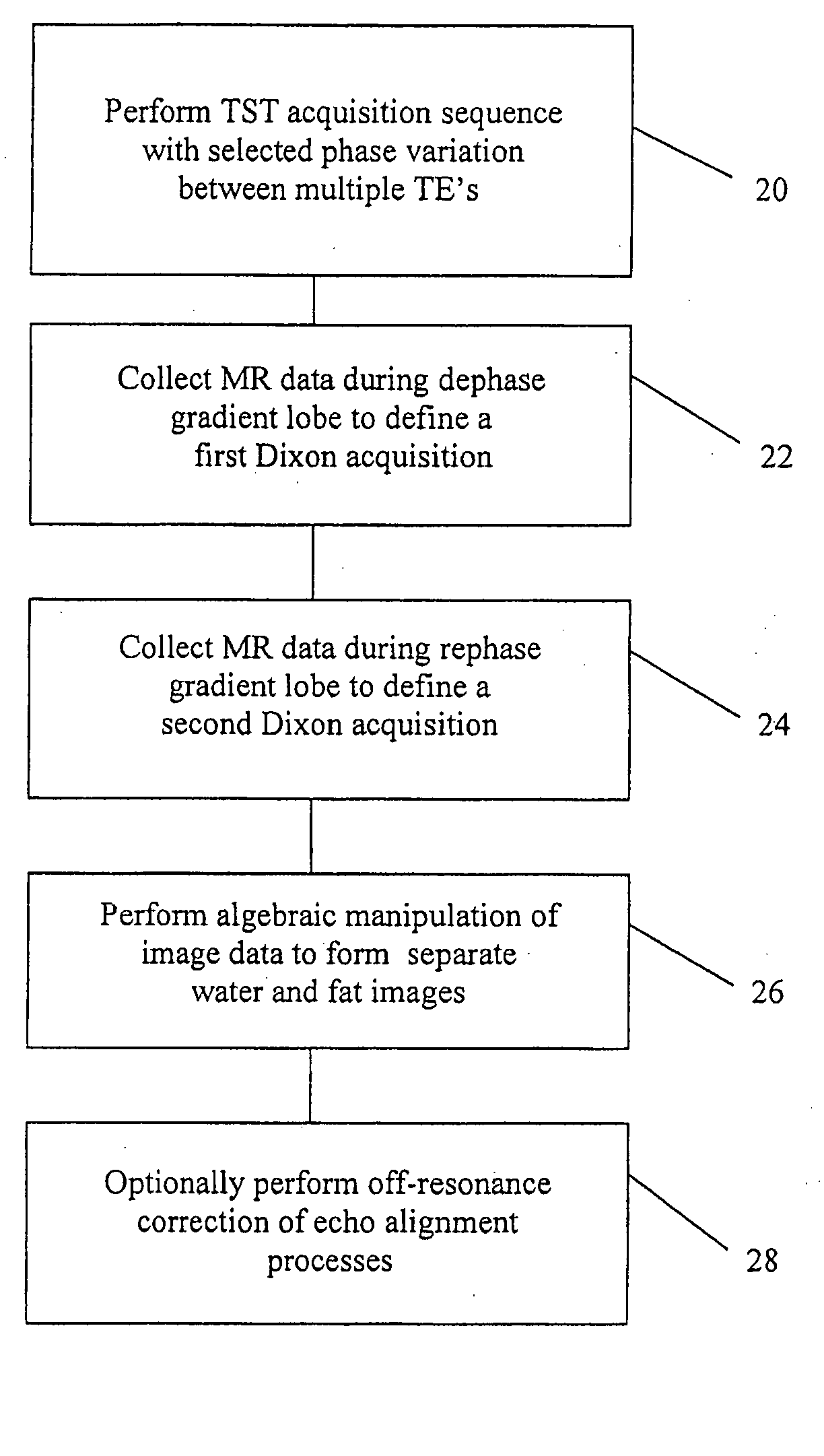
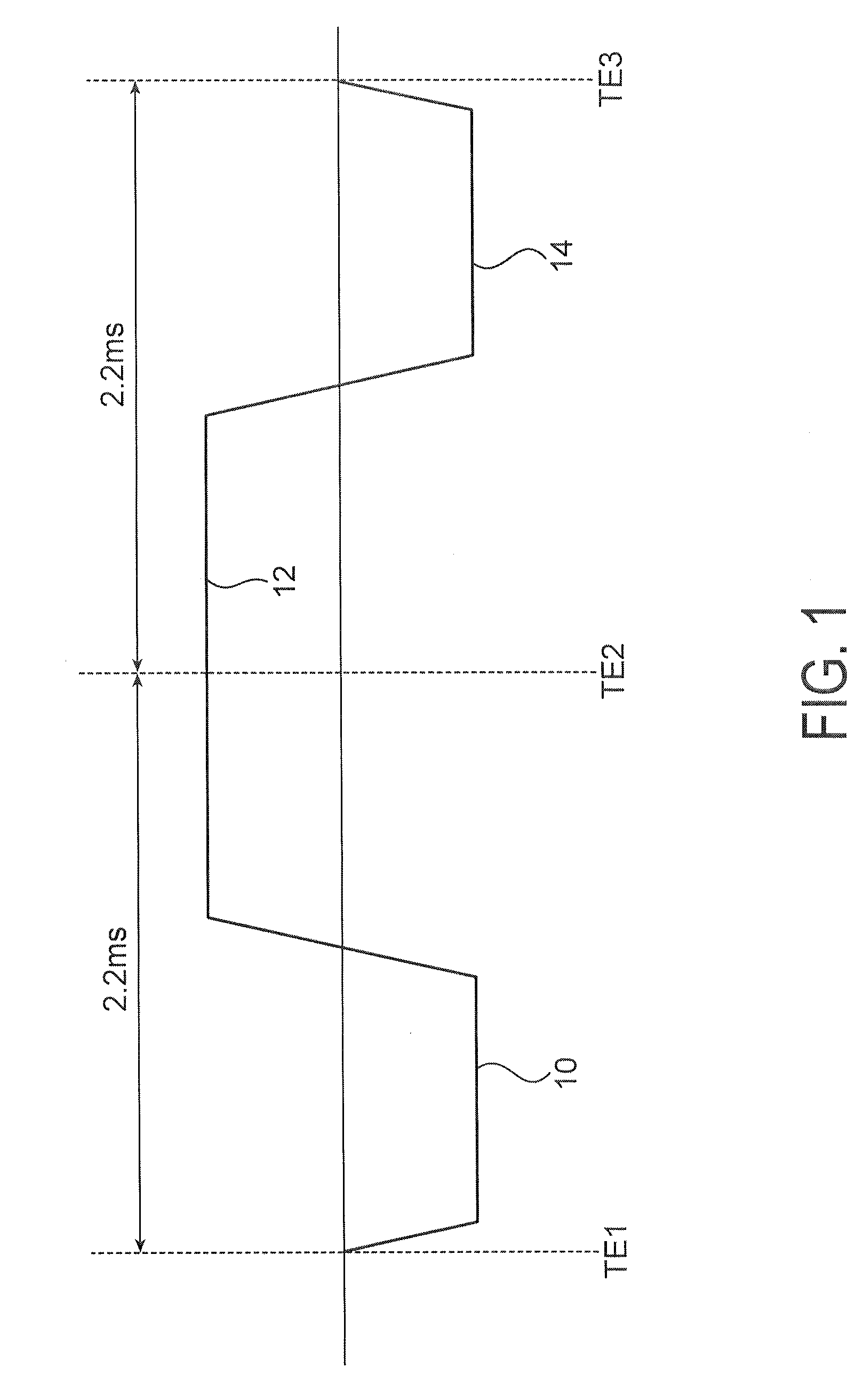
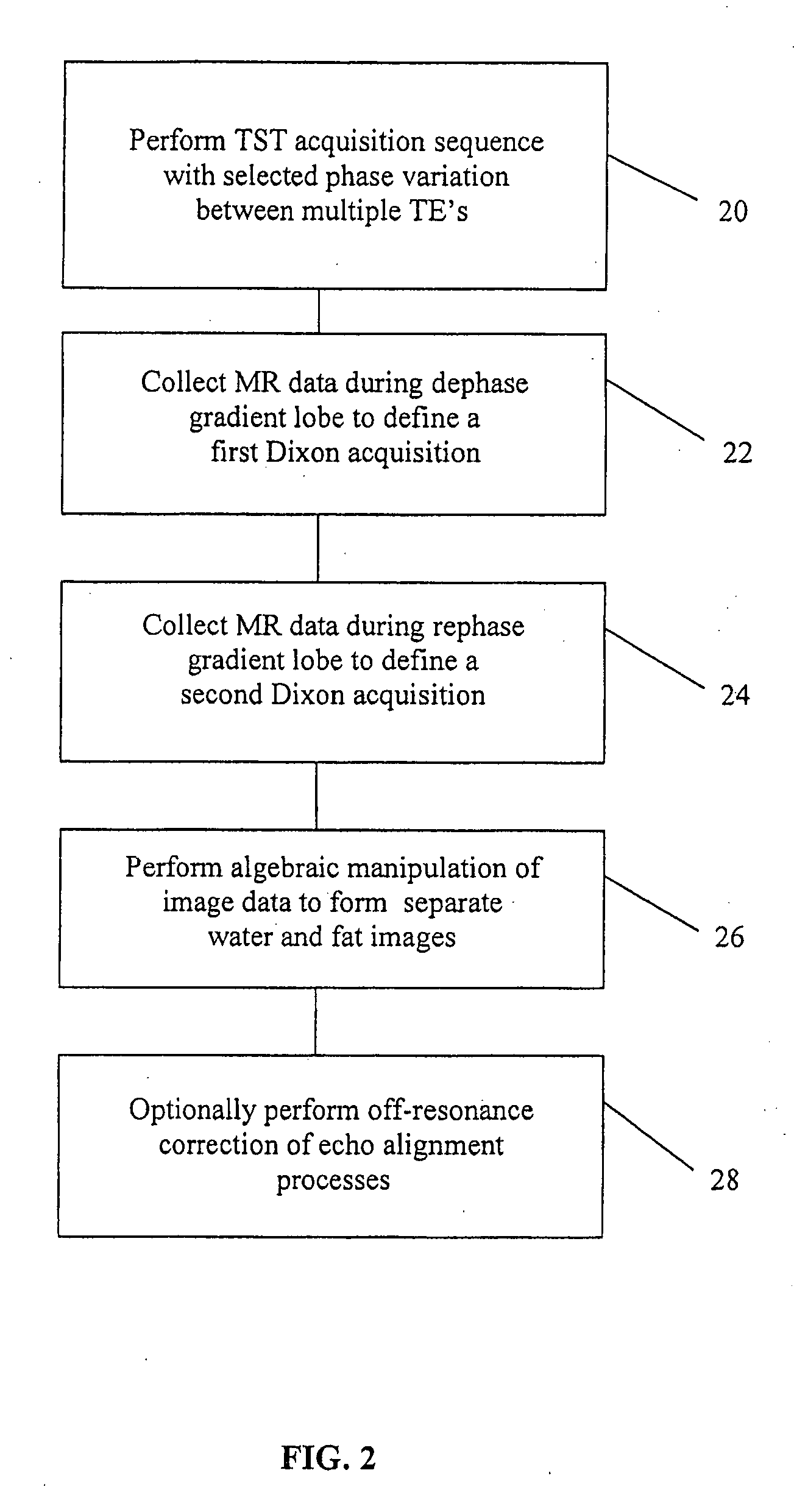
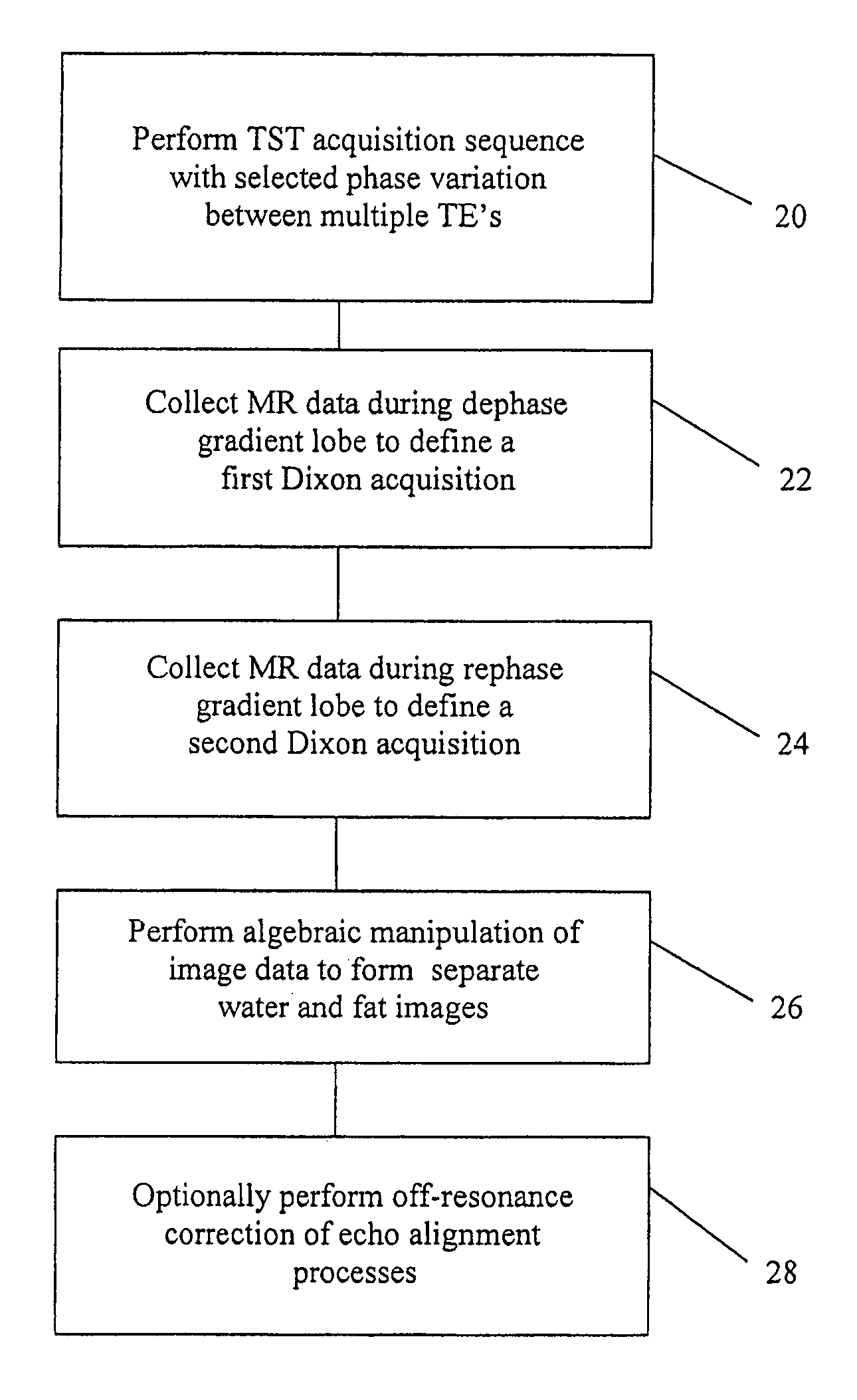
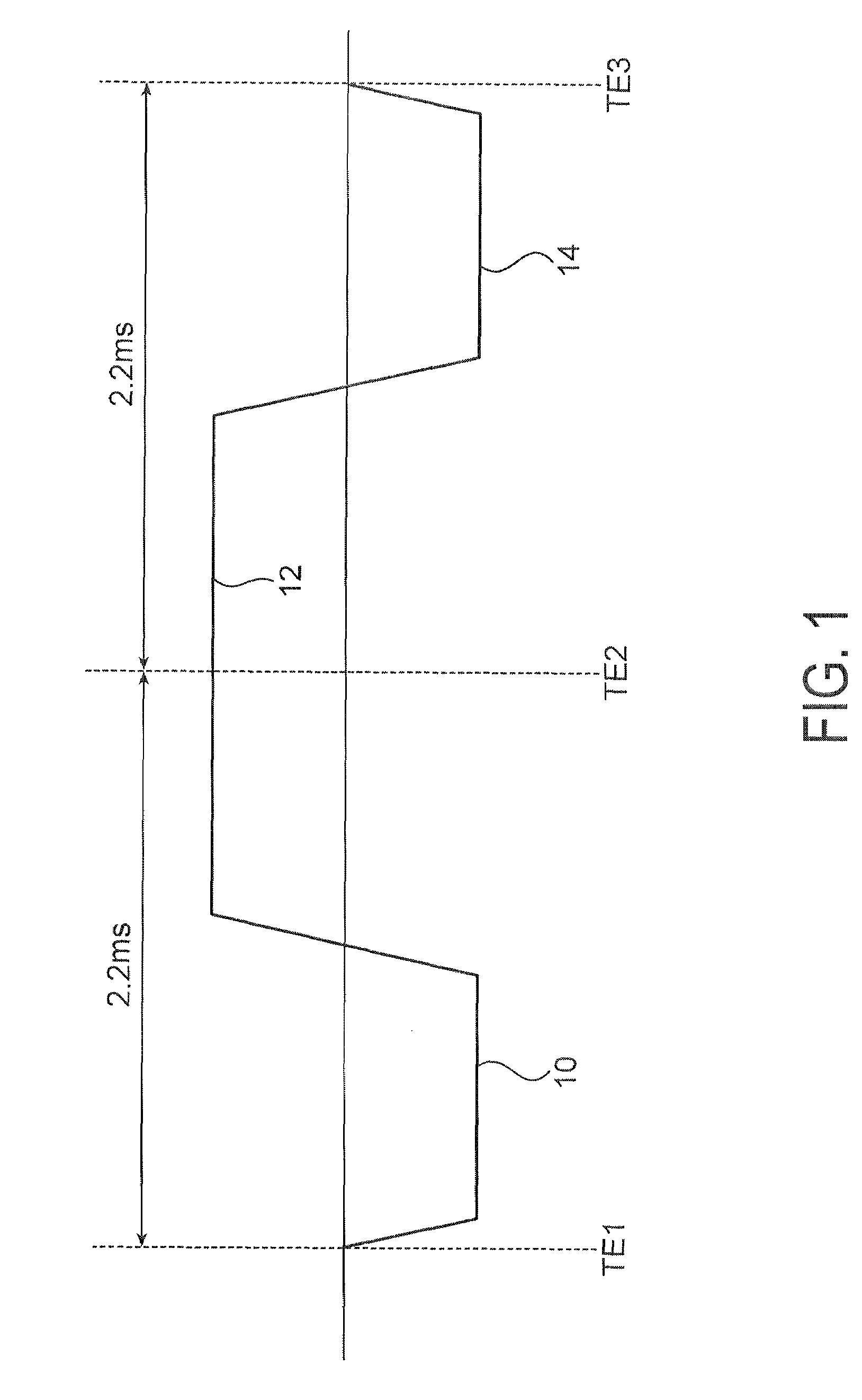
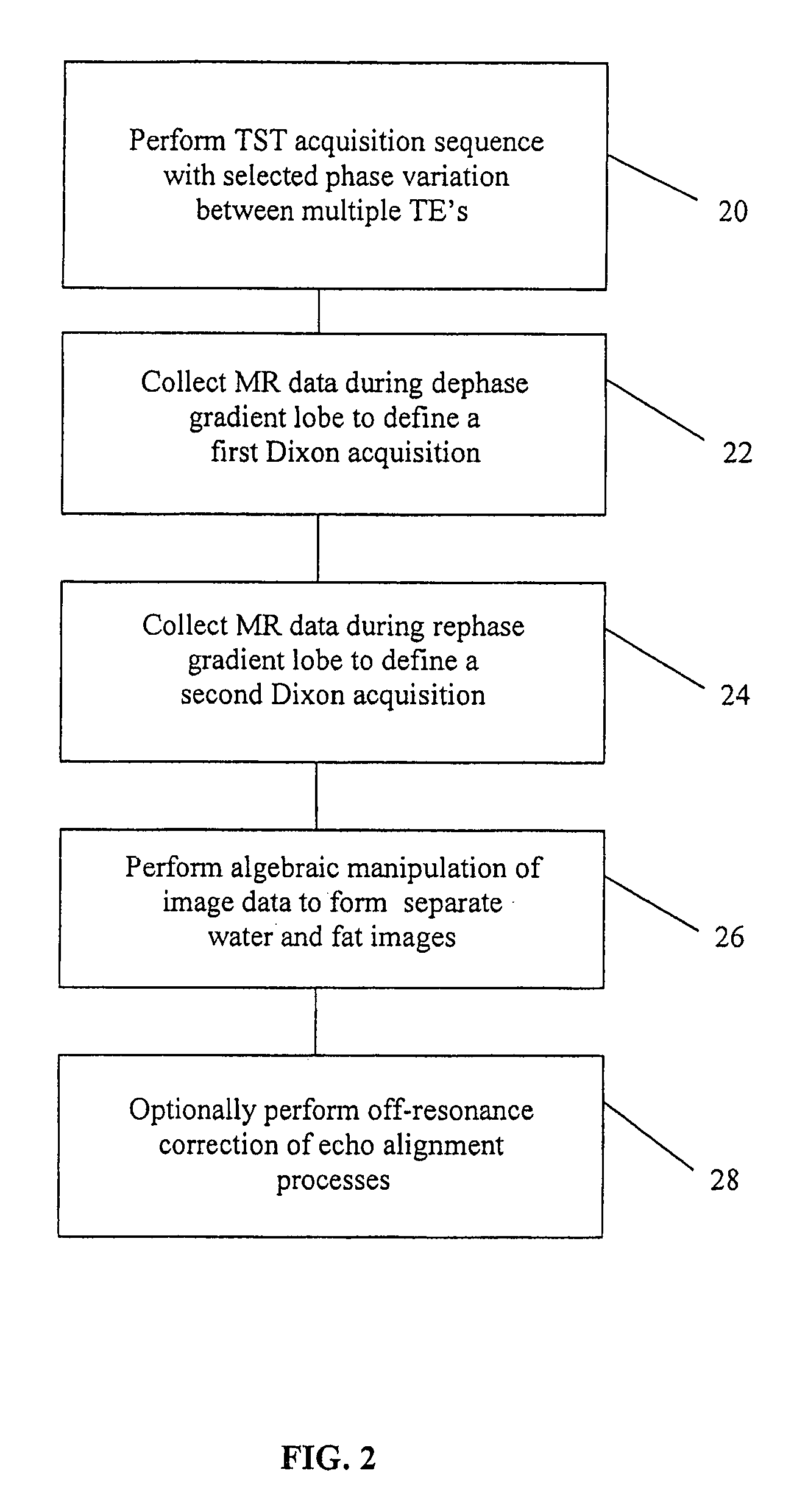
The present invention is directed to methods for chemical species signal suppression in magnetic resonance imaging procedures, wherein Dixon techniques are enhanced by continuously sampling techniques. In the invention, k-space data is acquired during the entire period of read gradient associated with a gradient echo pulse acquisition scheme. The invention utilizes a total sampling time (TST) acquisition during the entire read gradient, using three echoes of a TST data set to achieve chemical species separation in both homogenous fields as well as areas of field inhomogeneity. As an example, a continuously sampled rectilinearly FLASH pulse sequence is modified such that the time between echoes was configured to be 2.2 milliseconds, with TE selected to allow 180° phase variation in the fat magnetization between each of the three TE's (TE1, TE2, and TE3). Data collected during the dephase and rephase gradient lobes are defined as a first Dixon acquisition, with data collected by the read gradient lobe being defined as a second Dixon acquisition. Two point Dixon reconstruction techniques are used to form images for each chemical species, such as for generating water and fat images of the scanned object region. Other corrections, such as off-resonance correction may be applied on the image data.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
System And Method For Motion-Robust 3D Magnetic Resonance Imaging Of Vessel Walls
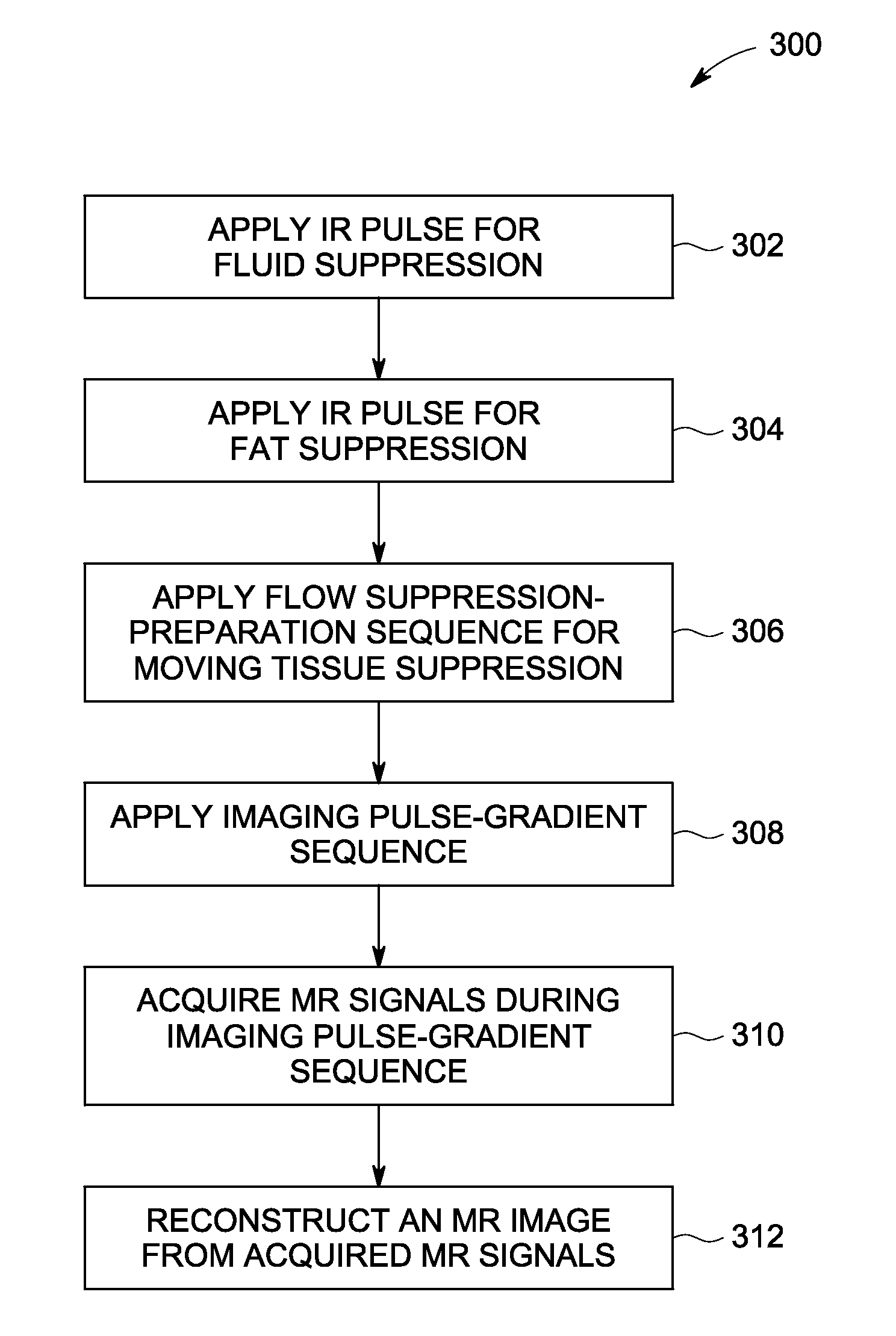
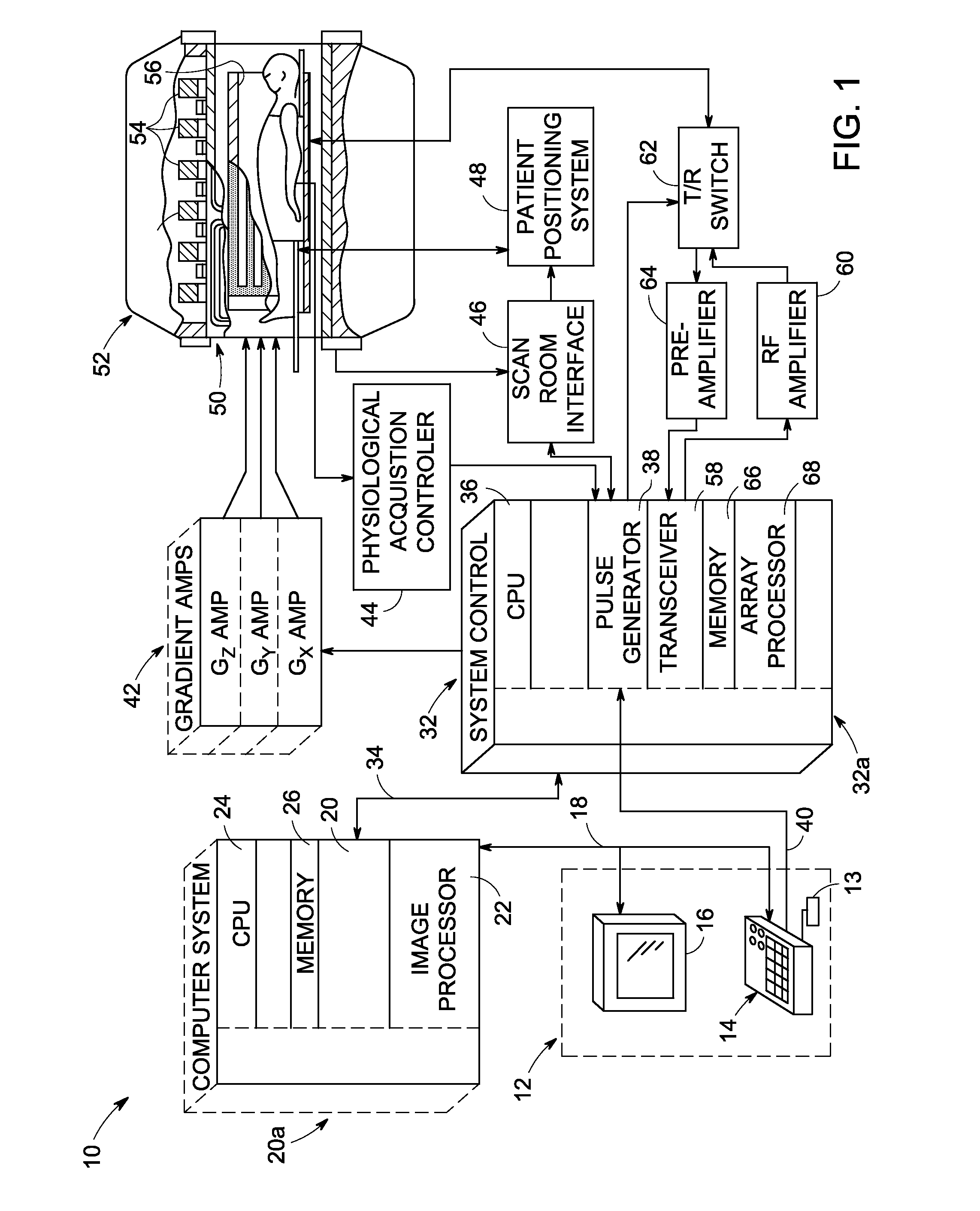
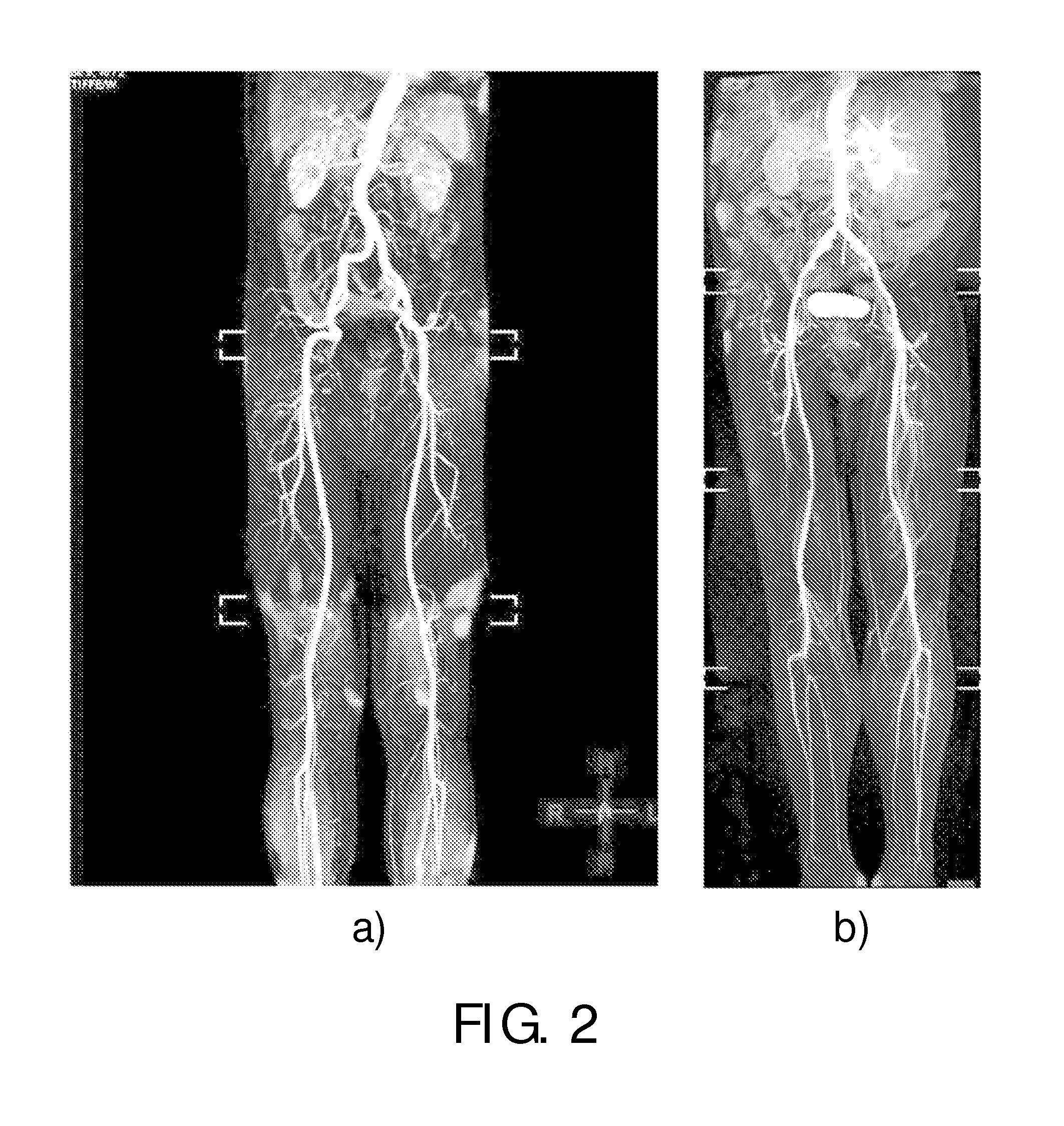
ActiveUS20160266223A1Optimal background suppressionReduce artifactsCatheterDiagnostic recording/measuringFat suppressionResonance
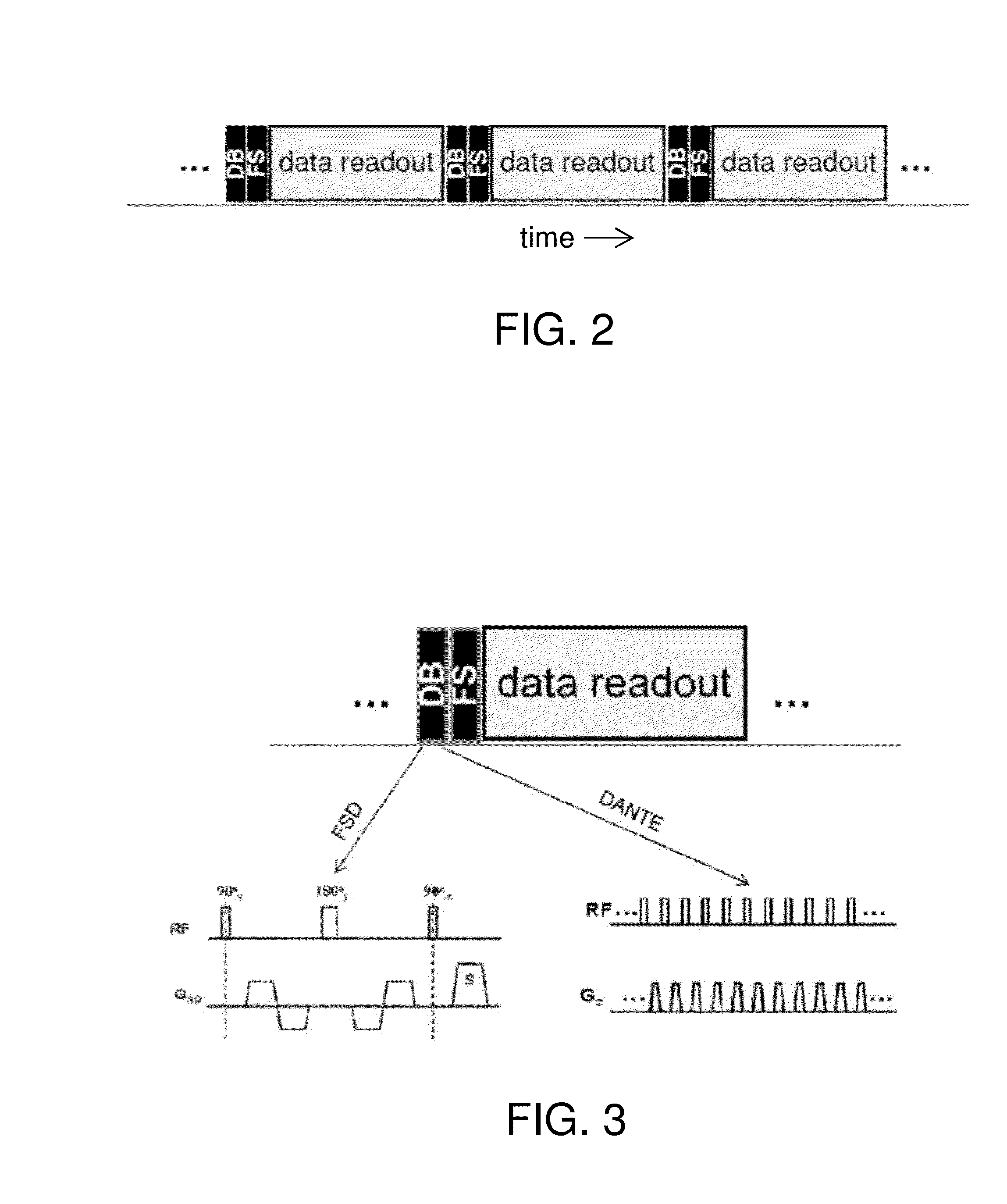
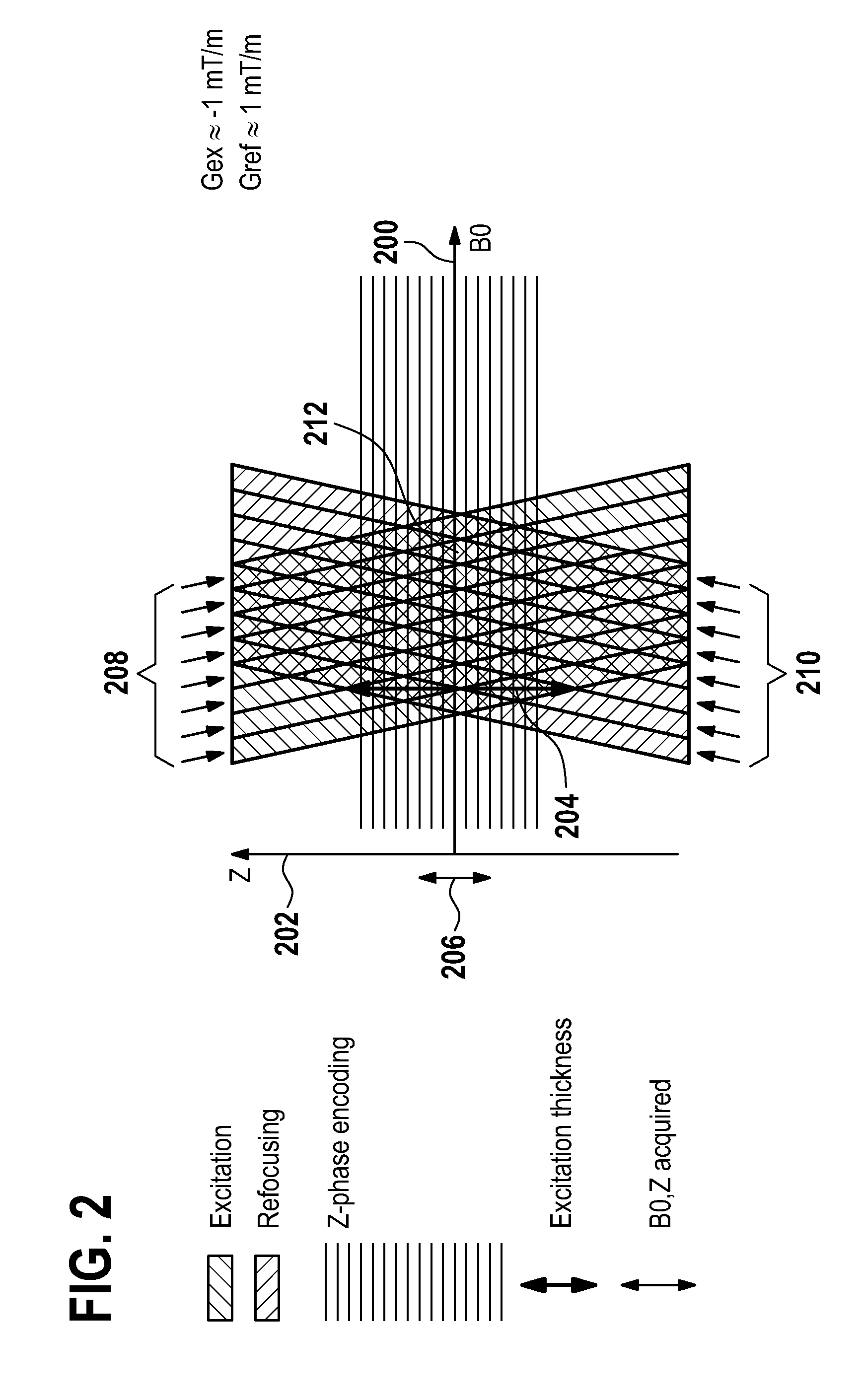
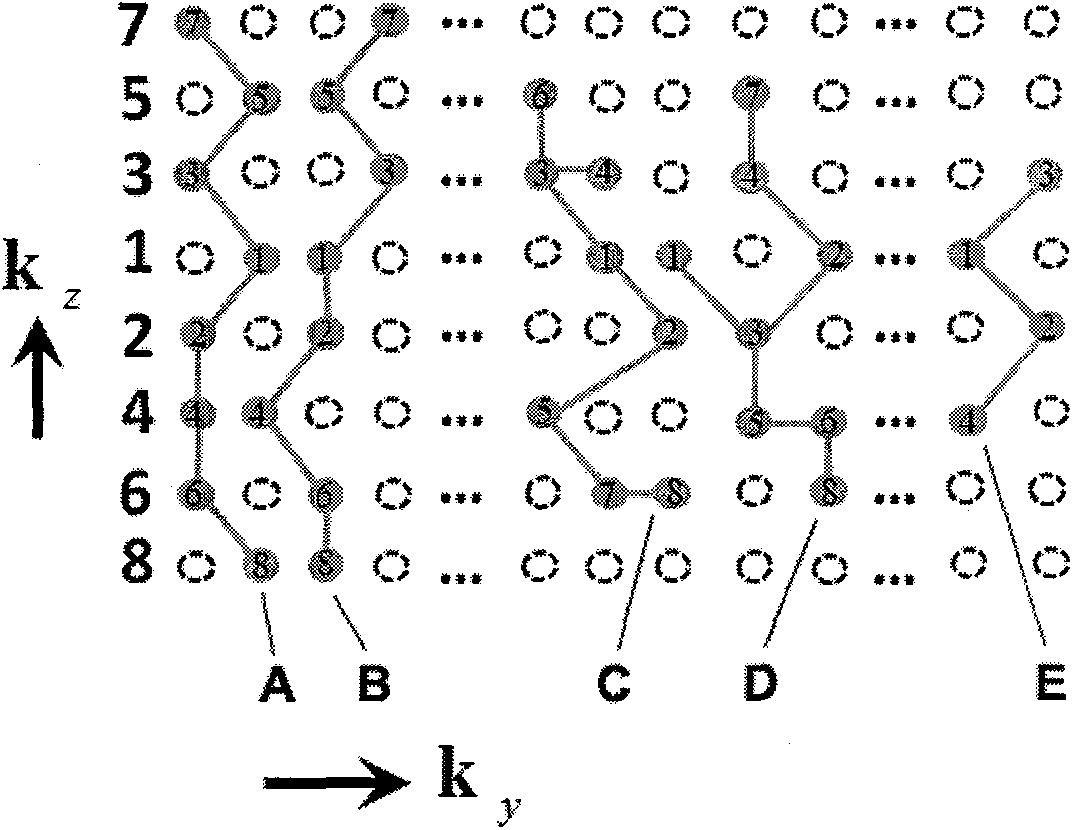
A magnetic resonance method and system are provided for providing improved 3D imaging of blood vessels and the like, which provides suppression of both blood and fat signals and is insensitive to subject motion, thereby facilitating improved visualization of vessel walls. The image data pulse sequence includes a plurality of pulse series, where each series includes a dark-blood sequence, a fat-suppression sequence, and a data readout sequence. Each data readout sequence samples a particular radial direction within each partition (Kz value) that passes through the Kz axis, and different radial orientations are sampled in subsequent series to provide a stack-of-stars sampling scheme.
Owner:CEDARS SINAI MEDICAL CENT +1
Fat/water separation and fat minimization magnetic resonance imaging systems and methods
ActiveUS7099499B2Reduced imaging timeEliminate needCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringExpectation–maximization algorithmWater based
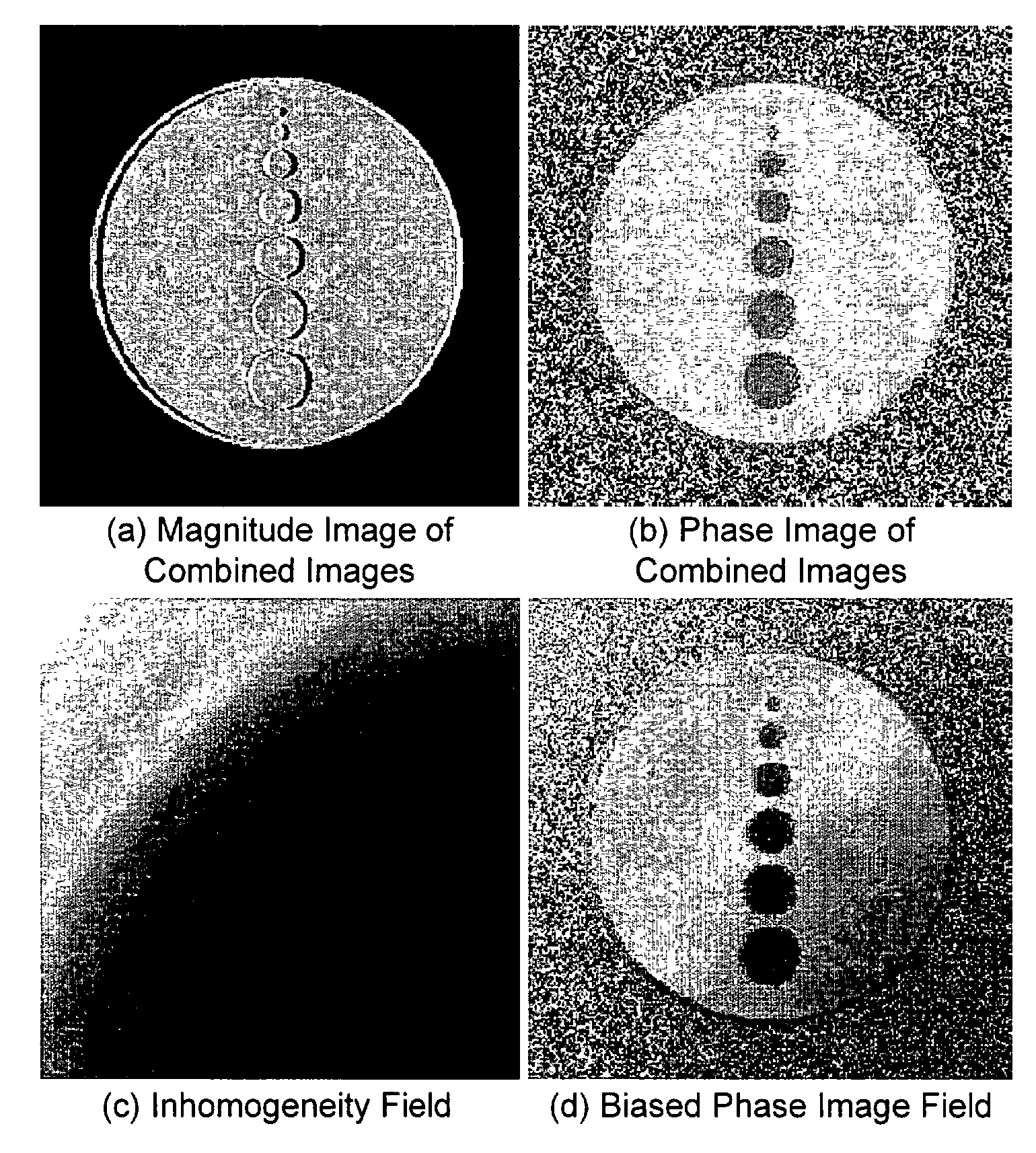
Systems and methods for identifying the relative contribution of fat and water signals in a magnetic resonance (“MR”) image including an algorithm operable for selecting an image signal model, selecting a scan parameter, forming a bias field estimate, applying a bias correction to a phase image, estimating the signal fraction of fat and water at each of a plurality of voxels, and forming a fat-suppressed image, a water-suppressed image, or a combination of a fat-based image and a water-based image. The (“MRI”) fat suppression systems and methods requiring only a single image acquisition including an algorithm operable for selecting a relative phase of approximately θ=π / 2 or another suitable relative phase, employing an expectation maximization algorithm to classify the phase of the complex image, and projecting complex vectors into fat and water components to obtain fat and water images.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Restriction of the imaging region for MRI in an inhomogeneous magnetic field
ActiveUS20140002080A1Avoid distortionReduce noiseMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFat suppressionParallel imaging
The invention relates to magnetic resonance imaging in the vicinity of a metallic object (like, for instance, a metal implant) where severe spatial perturbations of the static magnetic field occur. In order to suppress the back-folding of distant off-resonant signals into the region of interest, the imaging volume is spatially restricted by means of selection gradients applied concurrently with the excitation and the refocusing RF pulses in a spin echo sequence. The selection gradient applied during the excitation pulse has an amplitude and / or a polarity different from that of the selection gradient applied during the refocusing pulse so that the respectively selected slices in an off-resonance frequency versus spatial coordinate diagram become tilted with respect to one another. The applied imaging technique may of the SEMAC or MAVRIC type and may incorporate compressed sensing, parallel imaging, fat suppression and / or SVD-based noise reduction.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and method for MR data acquisition with uniform fat suppression
InactiveUS7706855B1Reduce scan timeIncrease patient throughputMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionFat suppressionDynamic contrast
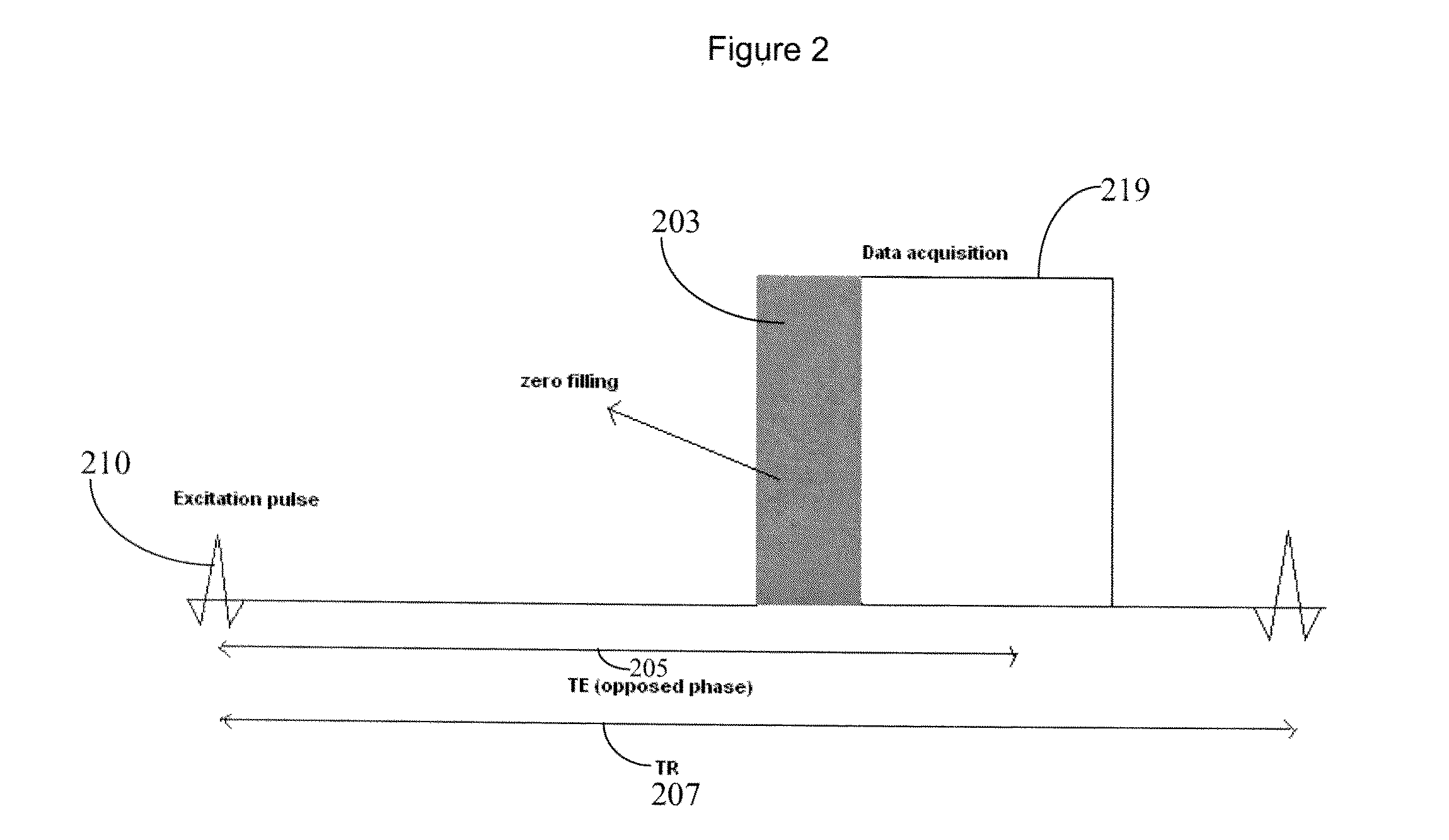
A system and method of MR imaging is disclosed that includes reconstruction of MR images with uniform or homogeneous fat suppression. An imaging process is performed using partial asymmetric acquisitions in conjunction with zero-filling of k-space for dynamic contrast-enhanced imaging. Data acquisition is carried out in a relatively short period of time which reduces scan time, reduces the likelihood of subject discomfort and motion-induced artifacts, and increases patient throughput.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and method of simultaneous fat suppression, magnetization transfer contrast, and spatial saturation for 3D time-of-flight imaging
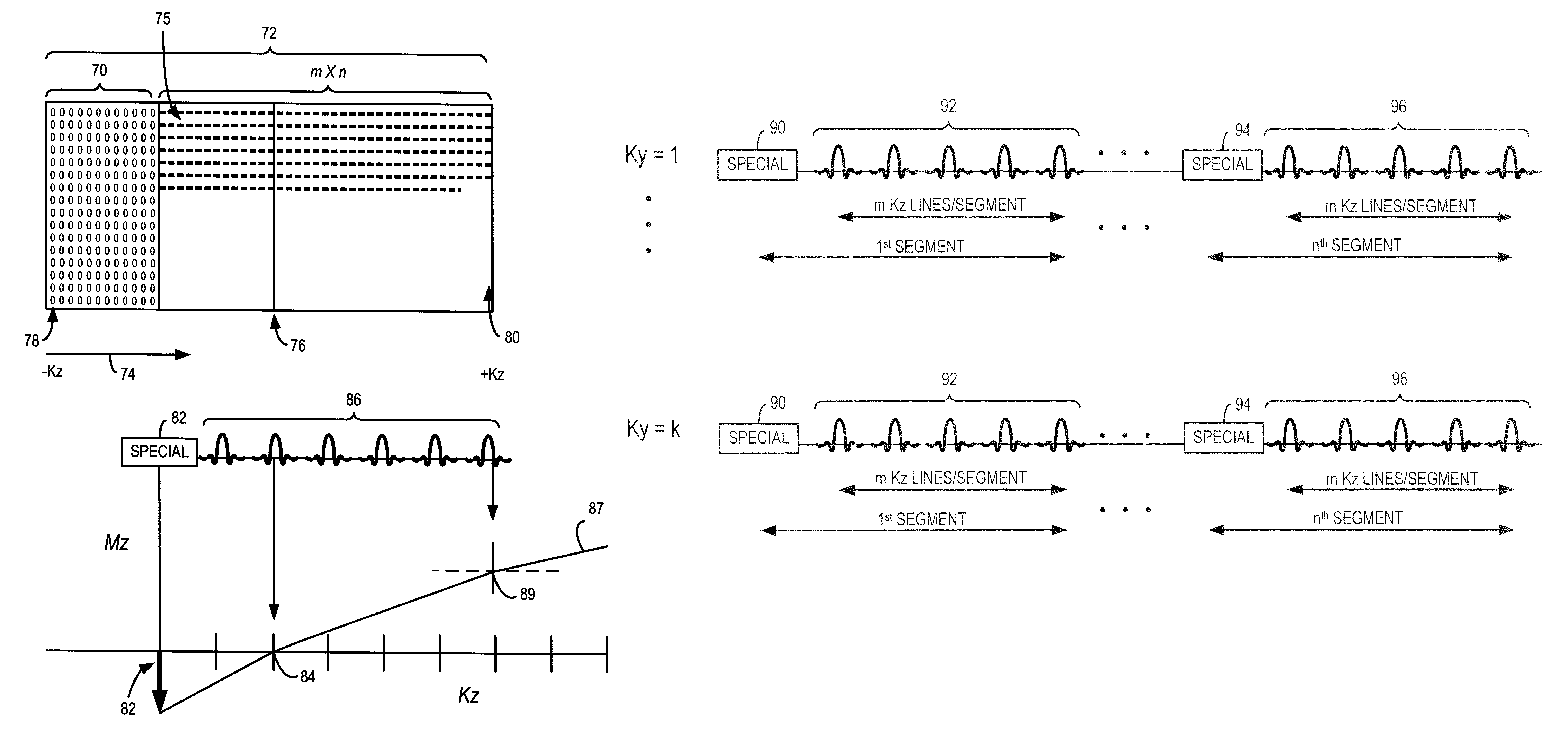
ActiveUS7330028B2Improve image qualityIncrease contrastMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionFat suppressionImaging quality
A pulse sequence for time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) includes a fatsat segment, a magnetization transfer segment, and a spatial saturation segment that are applied by an MR apparatus to acquire MR data for image reconstruction with improved image quality. The pulse sequence is constructed such that at the beginning of each iteration of the inner loop of a 3D acquisition, a fatsat pulse is applied. After the fatsat pulse, MR data is acquired in a series of imaging segments with well-suppressed fat signal. Effective fat suppression is achieved by sampling central k-space data first, before signal from fat relaxes back to a pre-saturation level. Each imaging segment is immediately preceded by one of a MT pulse or a spatial saturation pulse and immediately followed by the other one of the MT pulse or the spatial saturation pulse.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
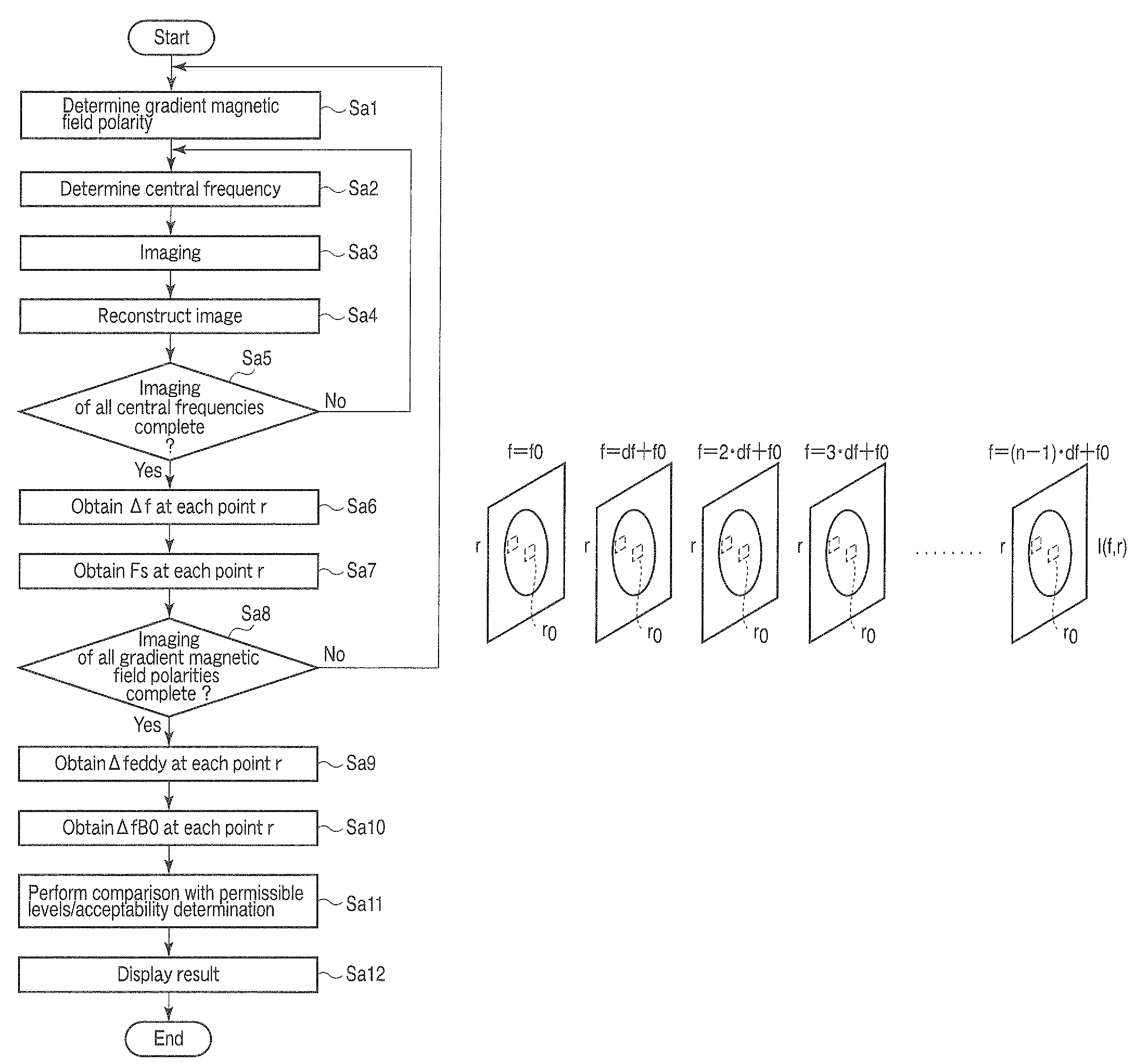
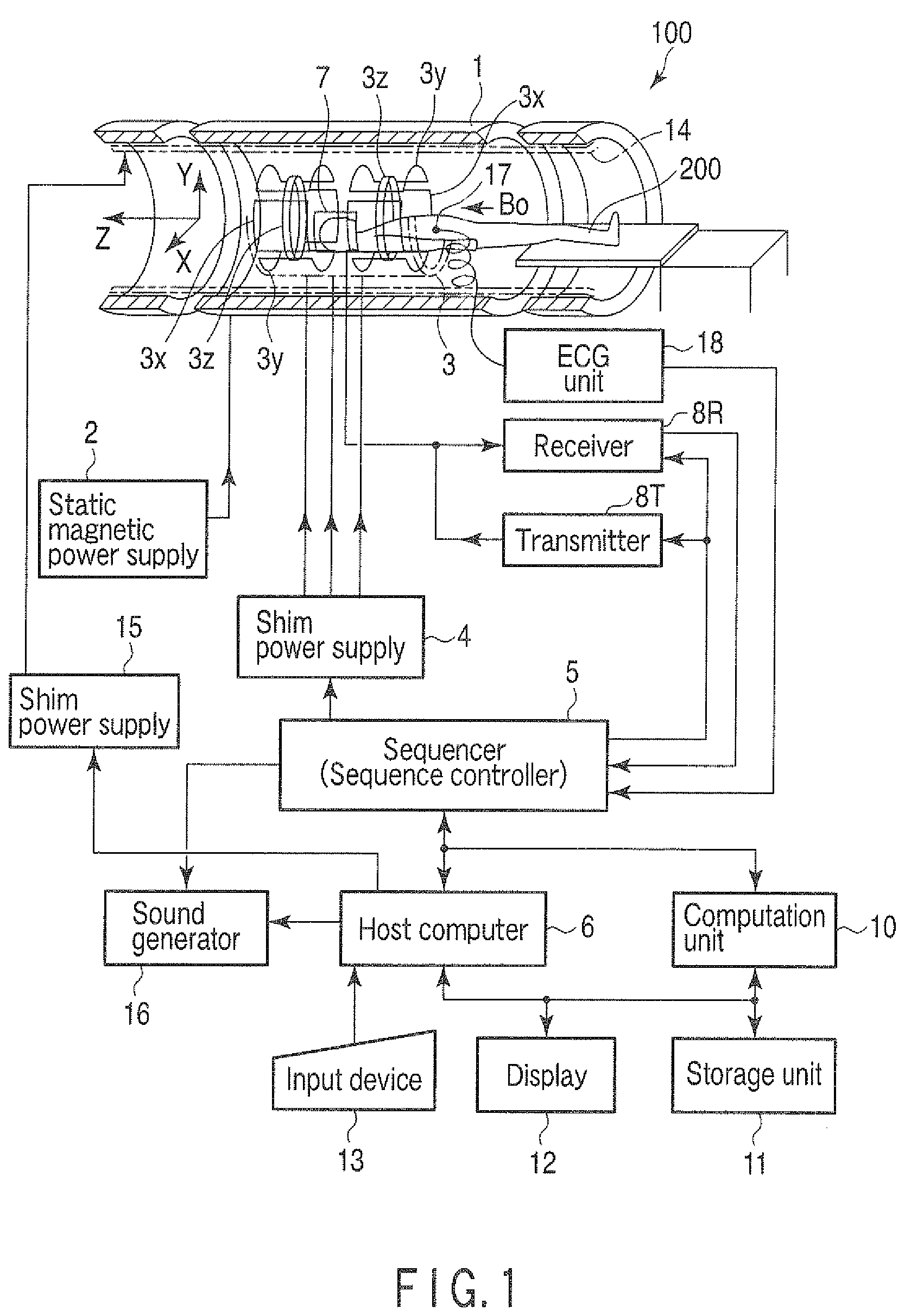
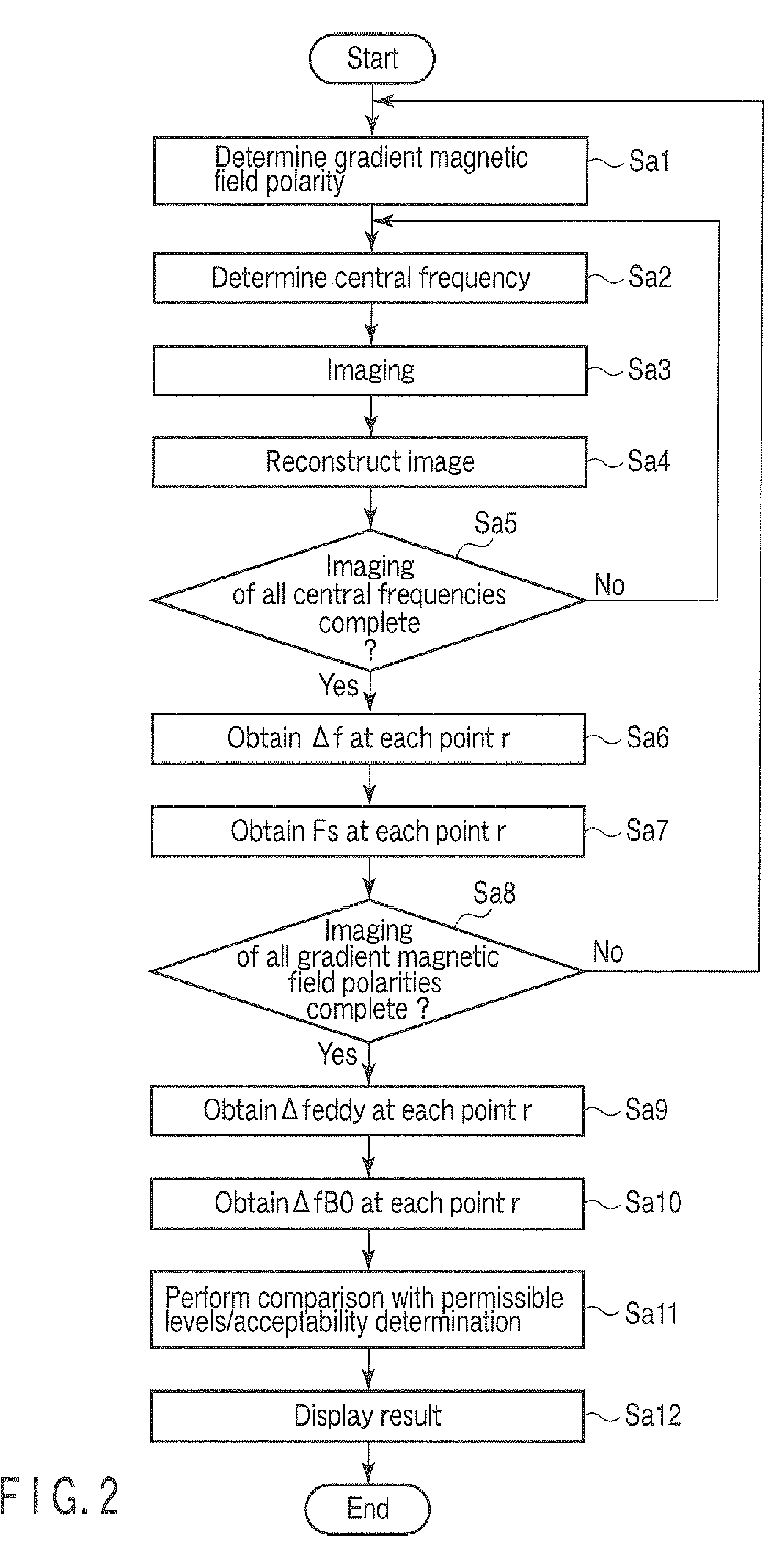
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and analysis method for fat suppression effect in magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
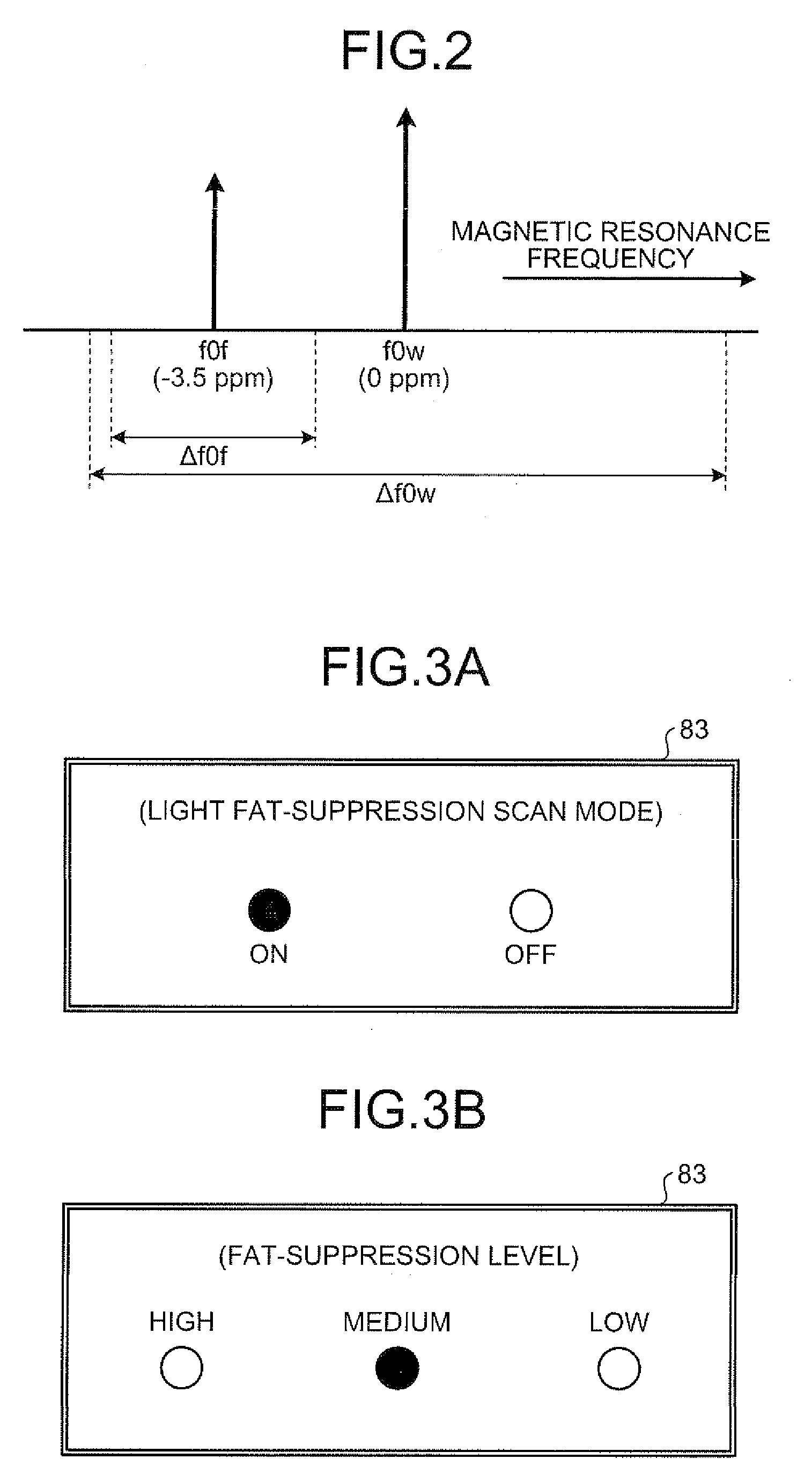
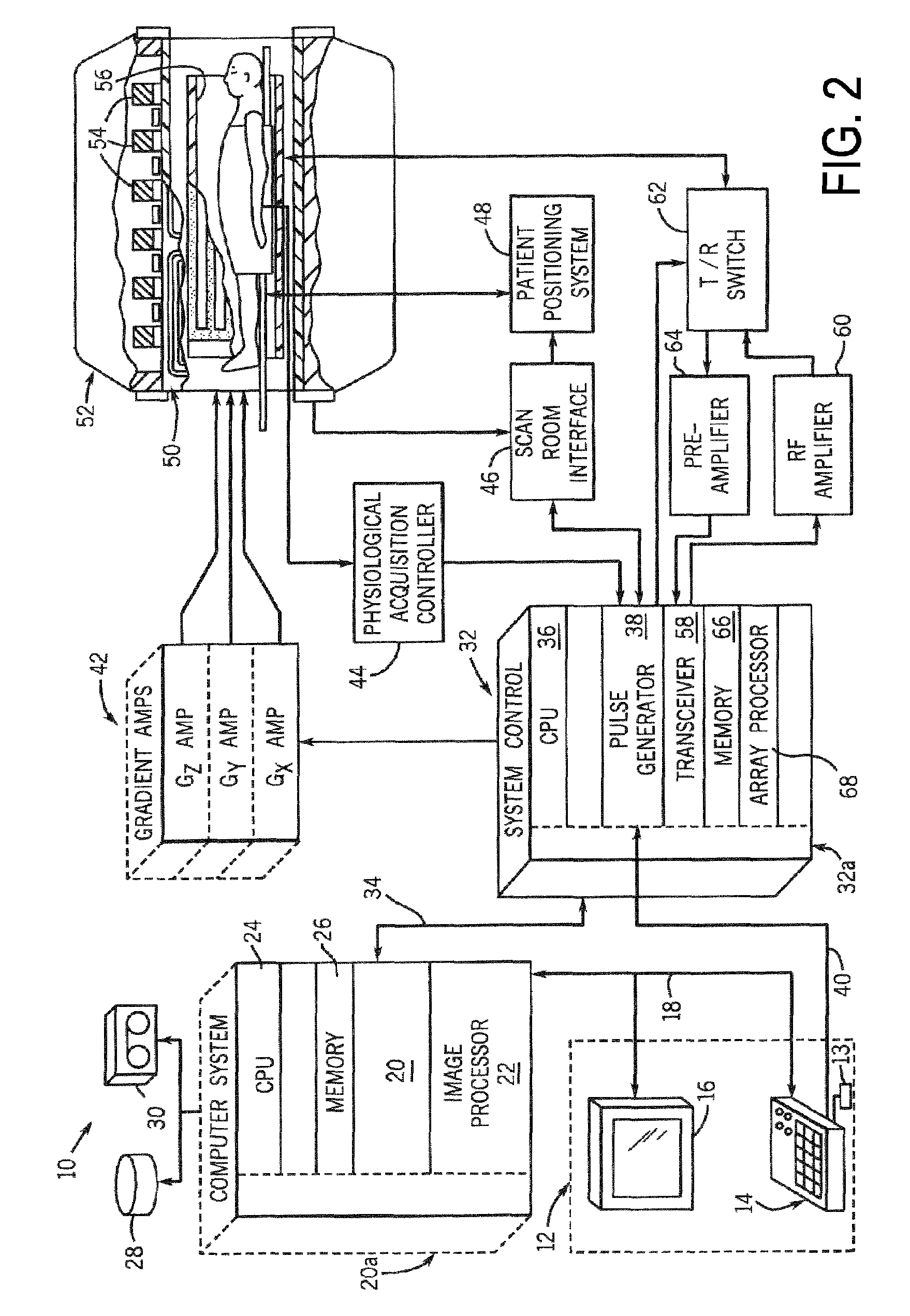
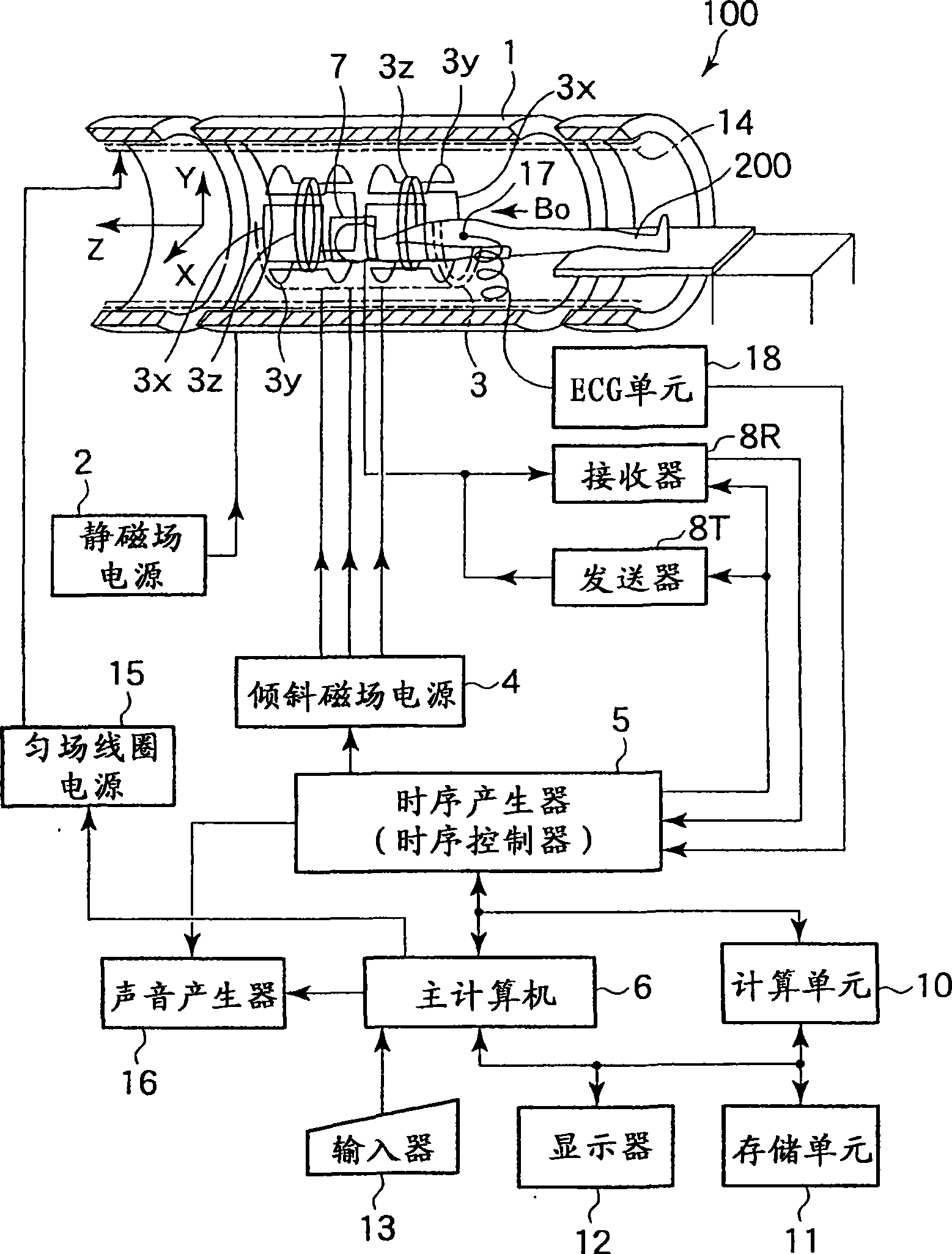
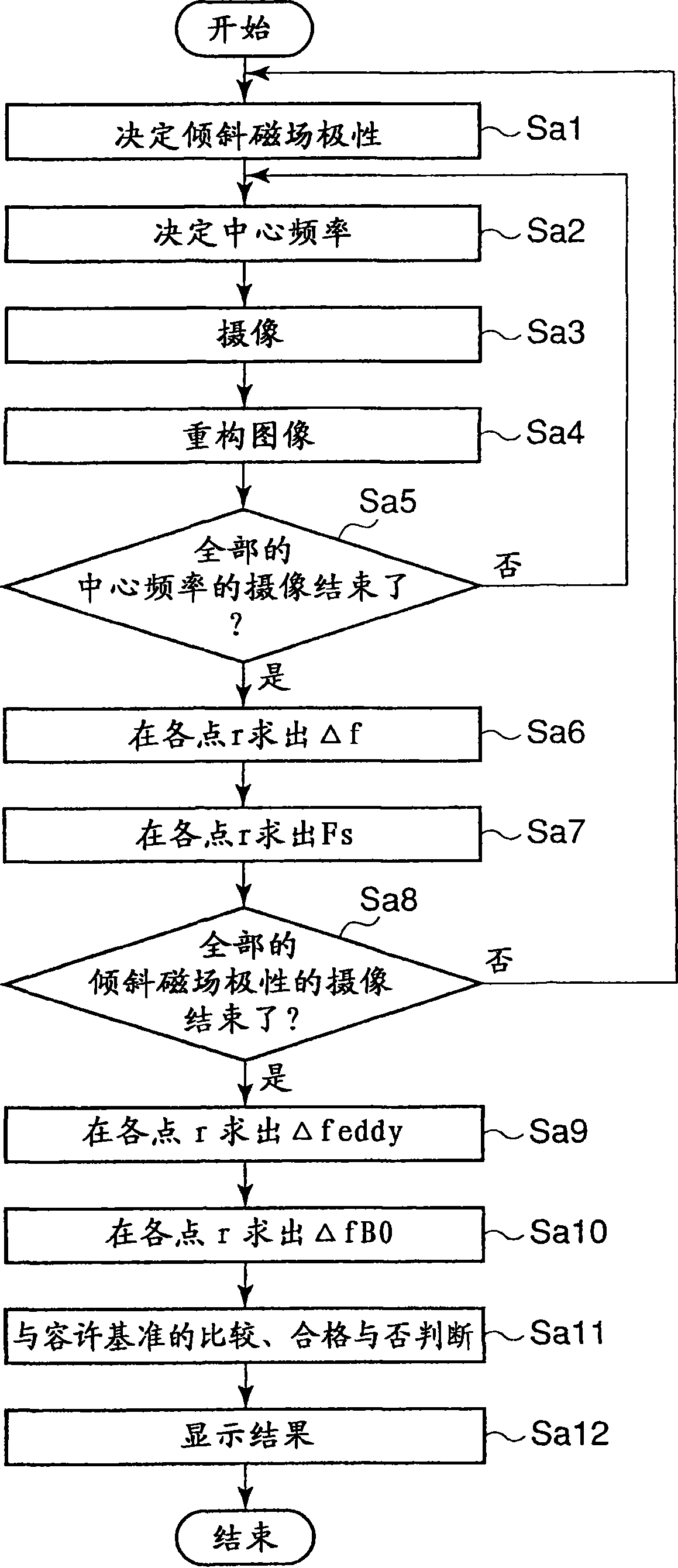
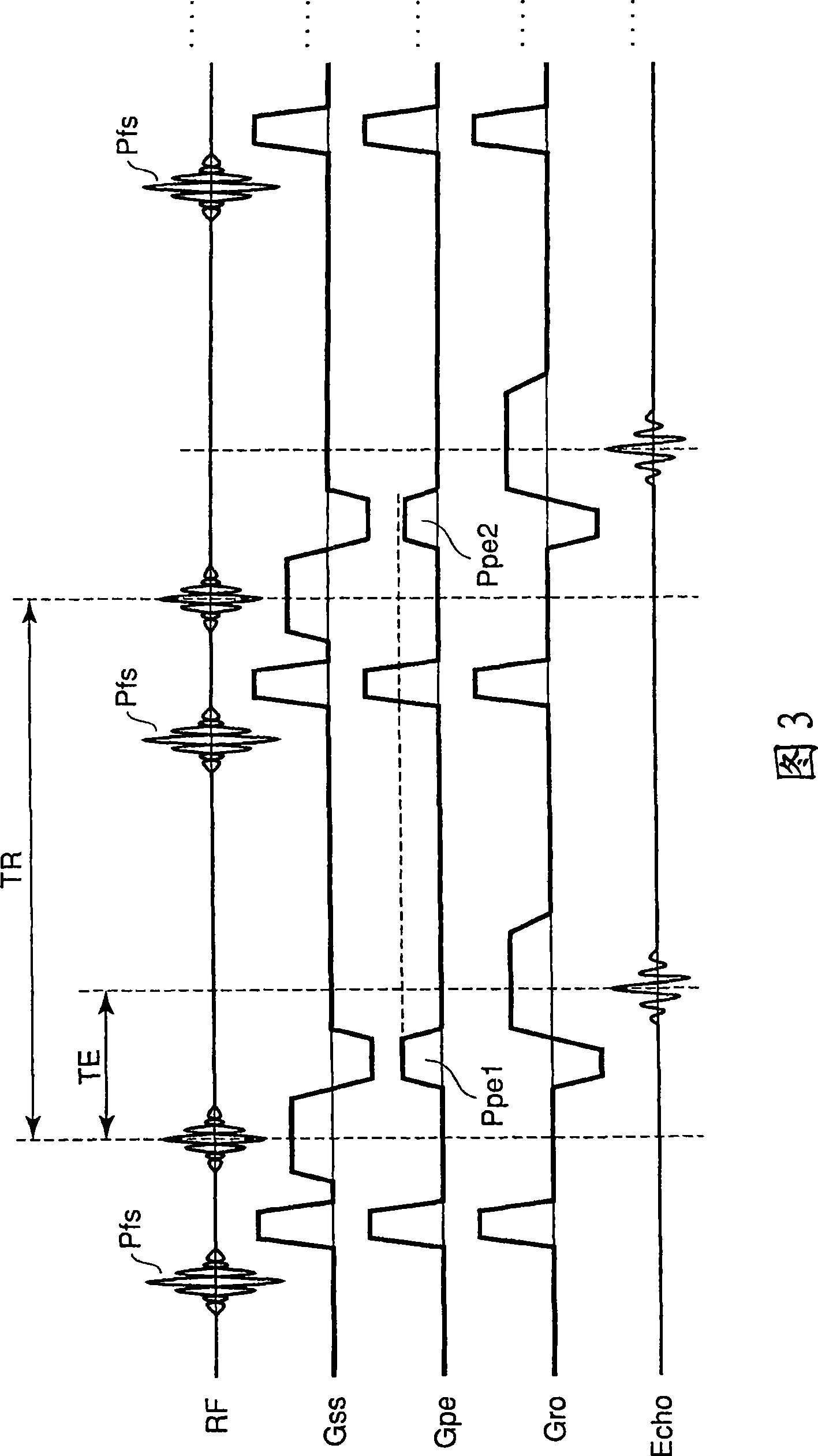
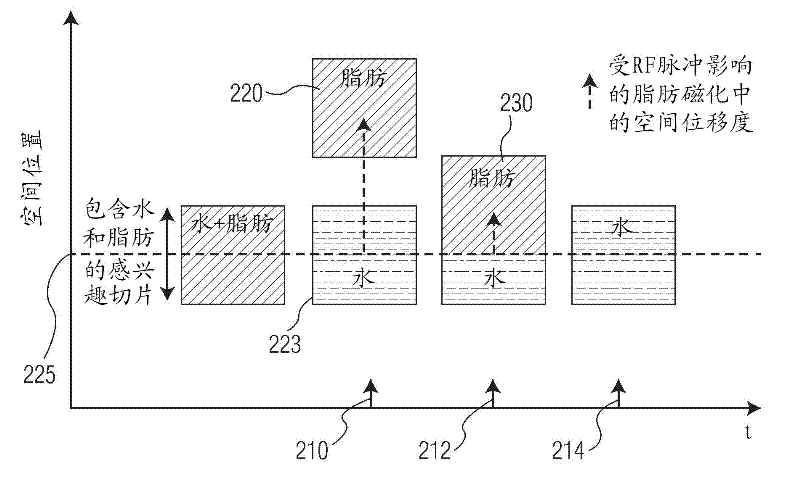
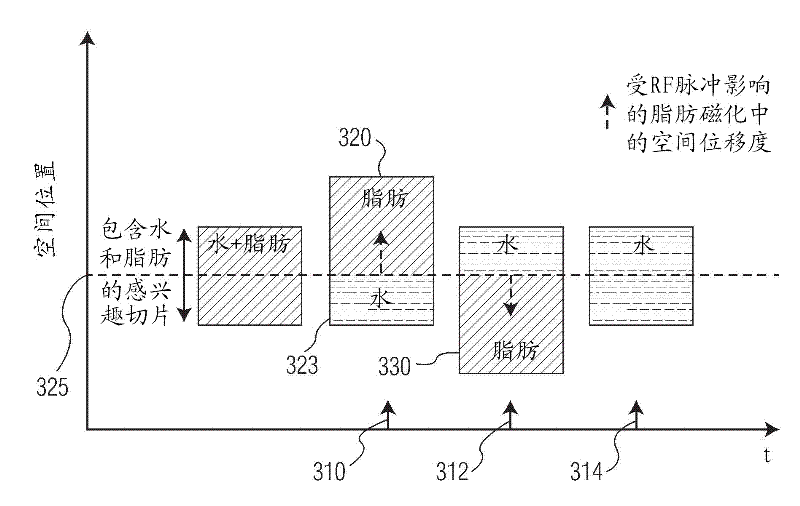
A magnetic resonance imaging apparatus includes an imaging unit which performs imaging more than once with respect to an imaging target while changing a central frequency of a fat suppression pulse, a generation unit which generates a plurality of images based on magnetic resonance signals obtained by imaging performed more than once, and a calculation unit which calculates factor information of spatial inhomogeneity of a fat suppression effect based on the plurality of images.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
System for fat suppression in obtaining of MR image
ActiveCN102188245AGet suppressedDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetic field gradientFat suppression
The invention relates to a system for fat suppression in obtaining of MR image, comprising: an RF signal generator for generating the RF pulses in an MR pulse sequence, including an RF excitation pulse and an RF re-focusing pulse after the RF excitation pulse, using one or more RF pulses for an echo signal structure. A magnetic field slice selection gradient generator generates two different slice selection magnetic field gradients to be used together with the RF excitation pulse and the RF re-focusing pulse correspondingly, wherein the first and second slice selection magnetic field gradients are substantially different in amplitude. An MR imaging control unit controls the obtaining of MR imaging data substantially suppressed in fat signal using the generated RF signals and the differentslice selection magnetic field gradients.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
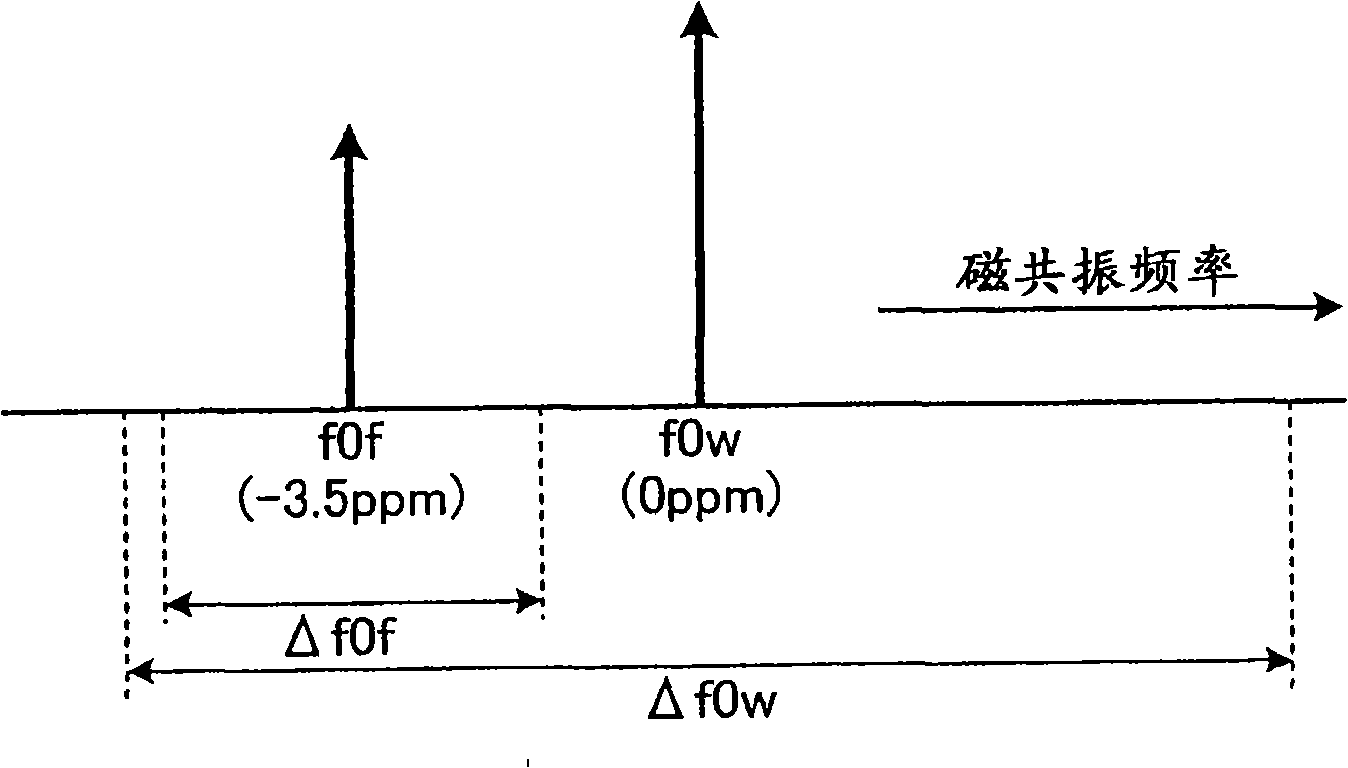
Transmitting frequency calibration method for chemical saturation in MRI and MRI system
ActiveCN101744616ARobust suppressionSaturation emission frequency is goodDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFat suppressionImaging quality
The invention relates to a transmitting frequency calibration method for chemical saturation in MRI and a MRI system. The invention provides a transmitting frequency calibration method for chemical saturation, which relates to the chemical saturation imaging technology of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) technology. The method of the invention adopts the decrease of water signal amplitude as standard to judge that the fat is fully saturated, therefore obtaining the transmitting frequency of fat saturation. And in addition, the invention also can confirm the best saturation transmitting frequency through combining with other prescan method. With the method of the invention, the fat-suppression effect is stable than before, and the method is less rely on the experience of the operator, and the image quality of chemical saturation (particularly the image quality of chemical saturation in low field MRI) is improved.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Spectrally selective suppression with steady-state free precession
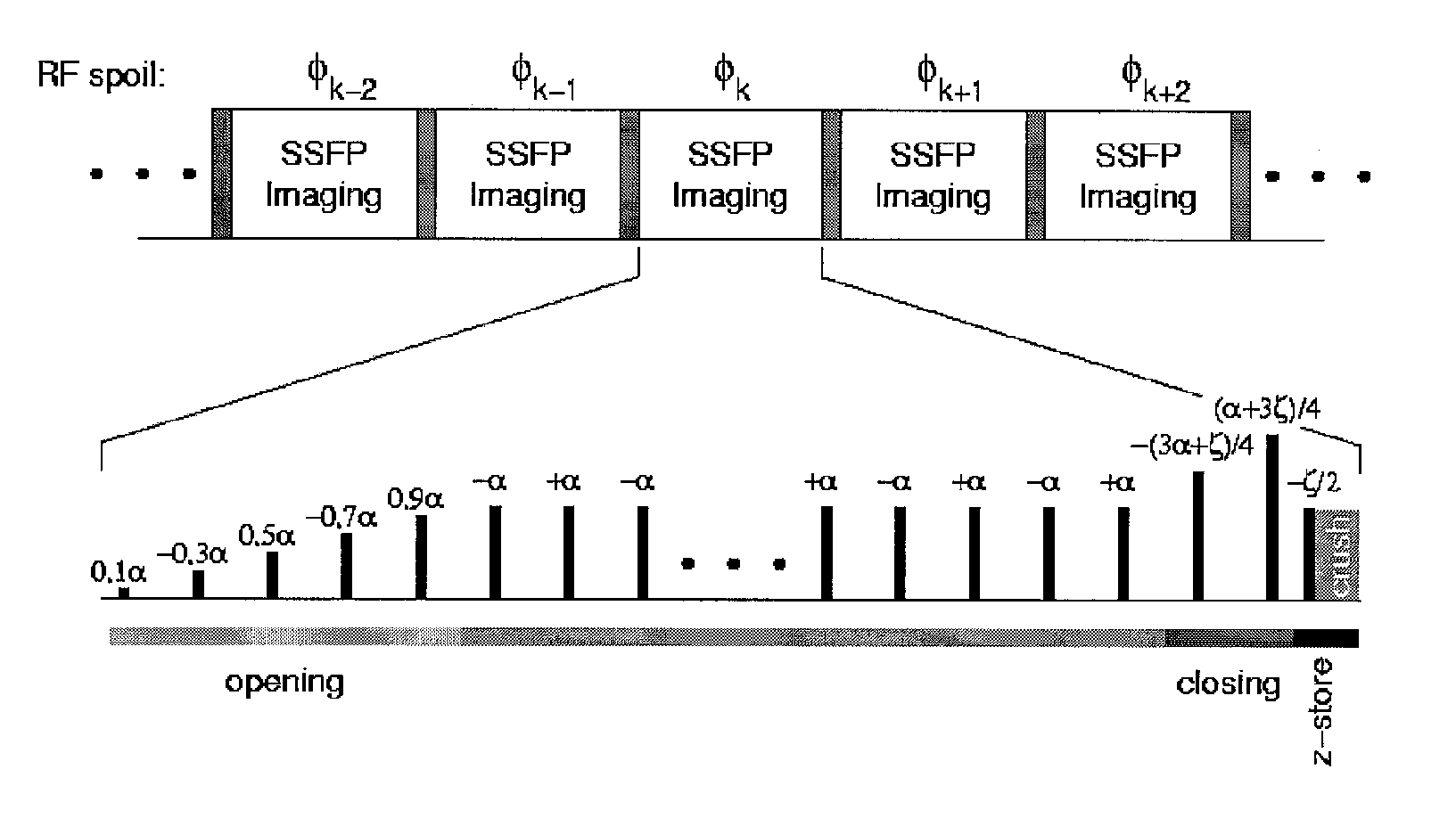
ActiveUS20070225591A1Effective imagingEnhanced inhibitory effectMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFrequency spectrumFat suppression
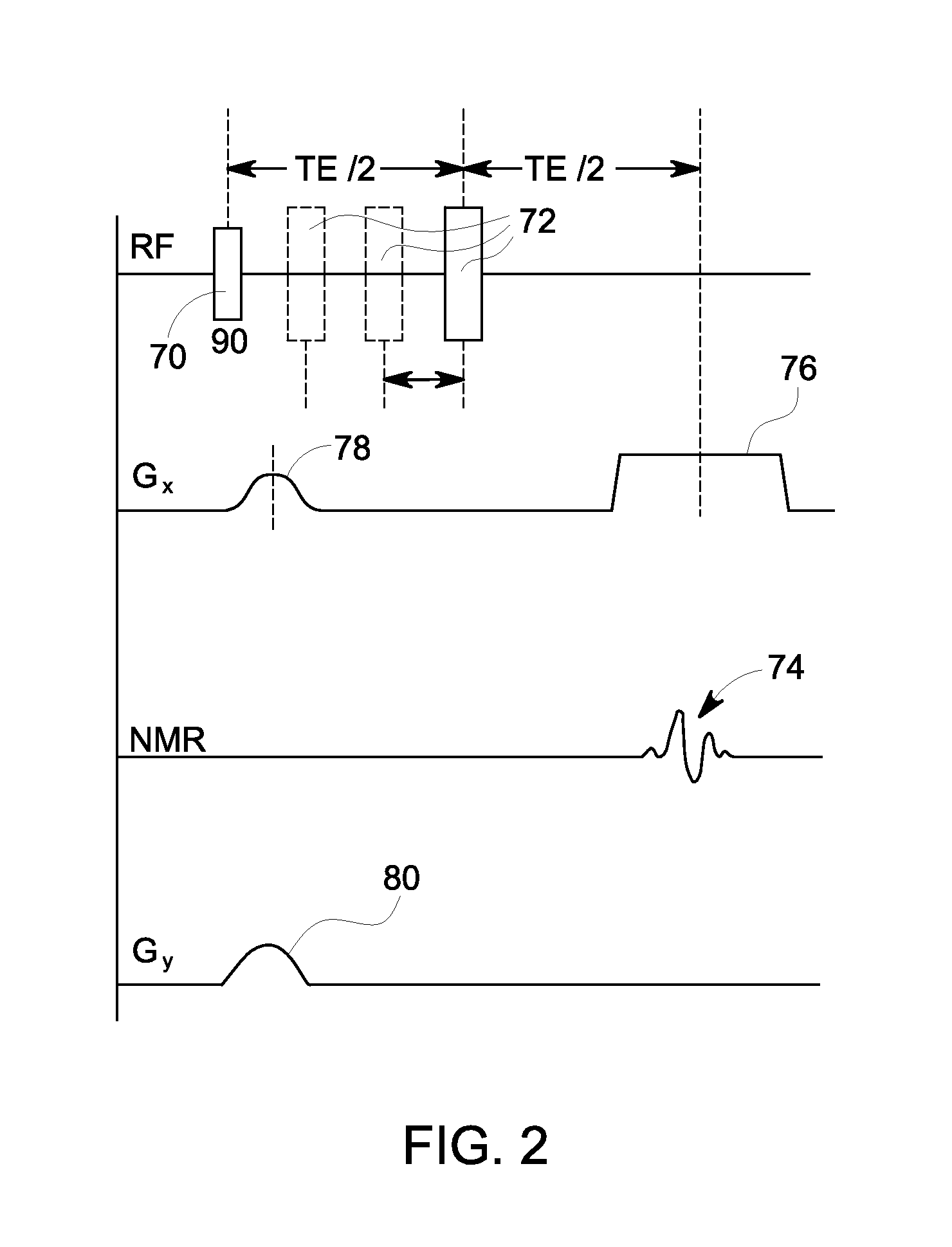
A method for fat-suppressed imaging is disclosed. Such a method may include storing a first spectral component of an echo signal formed at TR / 2 from a sample, suppressing a second spectral component of the echo signal at TR / 2, re-exciting the stored spectral component after suppressing the second spectral component, and producing an image of the sample based on the re-excited stored spectral component.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
System and method of high signal-to-noise ratio magnetic resonance imaging screening
ActiveUS20120262175A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFat suppressionTransceiver
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC +1
System and method for fat suppression in chemical shift based water-fat separated mr imaging
ActiveUS20120176131A1Character and pattern recognitionMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsVoxelFat suppression
An apparatus and method for separating the NMR signal contributions from a plurality of different species having different chemical shifts is disclosed. The apparatus acquires MR image data sets including a first species signal and a second species signal, generates a first species image from the acquired MR image data, and generates a second species image from the acquired MR image data. The apparatus also identifies voxels in the second species image representative of only the second species and, for voxels identified as being representative of only the second species, calculates a fraction of the second species signal appearing in the first species image. The apparatus generates a modified first species image based on the fraction of the second species signal appearing in the first species image, with the modified first species image having a different fraction of the second species as compared to the first species image.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC +1
Three dimensional vascular wall imaging sequence with rapid high isotropy resolution ration
InactiveCN103300858AFast and high isotropic resolutionImprove image qualityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsFat suppressionReconstruction method
The invention has the advantages that the signal to noise ration of the three dimensional magnetic resonance vascular wall imaging is improved effectively, and meanwhile, high isotropy resolution ratio is obtained. The invention provides a three dimensional vascular wall imaging sequence with rapid high isotropy resolution ration as shown in figure 1. The three dimensional vascular wall imaging sequence with rapid high isotropy resolution ration comprises a motion-sensitizing driven equilibrium prepulse part 1, a fat suppressed sequence part 2, a three dimensional rapid gradient echo sequence part 3 and a signal relaxation part 4. When the sequences are carried out, the four parts must be carried out in sequence. According to three dimensional vascular wall imaging sequence with rapid high isotropy resolution ration, when the three dimensional rapid gradient echo scanning is carried out, a sub-sampling method of compressed sensing is adopted to carry out sampling to the three dimensional K space, meanwhile, in order to effectively control a blood signal during the sampling, the sampling is carried out according to the pseudo intermediate sequence, after the sampling is accomplished, the data is recovered effectively by adopting nonlinear reconstruction method on the basis of sub-sampling data, so that the high quality three dimensional vascular wall image is obtained.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Contrast enhanced magnetic resonance angiography with chemical shift encoding for fat suppression
ActiveUS20140043022A1Rapid and reliable mannerEfficiently signaledDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFat suppressionData set
The invention relates to a method of performing contrast enhanced first pass magnetic resonance angiography, the method comprising: acquiring (302) magnetic resonance datasets of a region of interest using a single- or multi-echo data acquisition technique, wherein the echo times of the one or multiple echoes are flexible, wherein at the time of the data acquisition the region of interest comprises fat, water and a contrast agent, processing (304) the datasets using a generalized Dixon water-fat separation technique to eliminate the signal originating from the fat from the background for reconstruction of an image data set.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Accelerated Shells Trajectory MRI Acquisition
ActiveUS20080045828A1Shorter TR and signal readout durationReduce contributionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFat suppressionPulse sequence
An MRI k-space data set is acquired using a series of shell k-space sampling trajectories of different radii. Off-resonance effects are reduced and fat-suppression can be improved by using a shorter TR for pulse sequences that sample at smaller radii. At larger radii sampling is repeated with the central axis of the shell sampling trajectory tilted such that the polar regions of shells acquired at the same radii are sampled by the other shell.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Apparatus and method of simultaneous fat suppression, magnetization transfer contrast, and spatial saturation for 3D time-of-flight imaging
ActiveUS20070069724A1Improve image qualityEffective applicationMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionFat suppressionImaging quality
A pulse sequence for time-of-flight (TOF) magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) includes a fatsat segment, a magnetization transfer segment, and a spatial saturation segment that are applied by an MR apparatus to acquire MR data for image reconstruction with improved image quality. The pulse sequence is constructed such that at the beginning of each iteration of the inner loop of a 3D acquisition, a fatsat pulse is applied. After the fatsat pulse, MR data is acquired in a series of imaging segments with well-suppressed fat signal. Effective fat suppression is achieved by sampling central k-space data first, before signal from fat relaxes back to a pre-saturation level. Each imaging segment is immediately preceded by one of a MT pulse or a spatial saturation pulse and immediately followed by the other one of the MT pulse or the spatial saturation pulse.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
MRI apparatus
ActiveUS7990140B2Magnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionFat suppressionNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
A flip-angle calculating unit calculates a flip angle of a fat-suppression pulse by inputting scanning parameters read from a scanning-parameter storage unit based on scanning conditions set by a scan-condition setting unit and a desired fat-suppression level, into a predetermined computing program. A control unit suppresses fat signals to a desired level by performing irradiation of a fat-suppression pulse having the calculated flip angle and application of a spoiler gradient magnetic field onto a scan target portion of a subject by controlling a gradient magnetic-field generating unit and a transmitting-receiving unit, and further performs irradiation of an RF pulse and application of a gradient magnetic field in accordance with a predetermined pulse sequence, thereby detecting water signals and suppressed fat signals as MR signals. An image-data creating unit creates image data by reconstructing the MR signals.
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
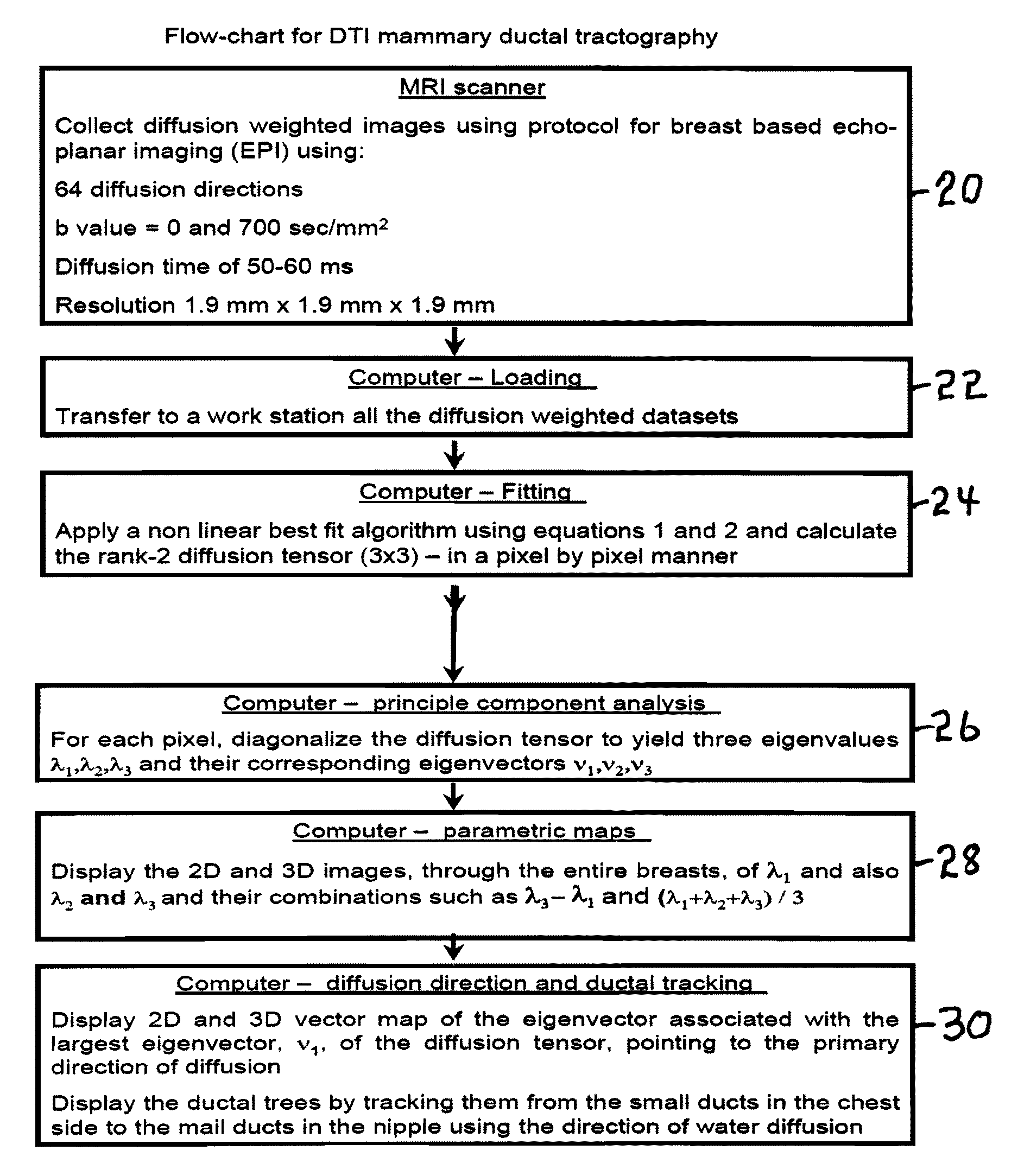
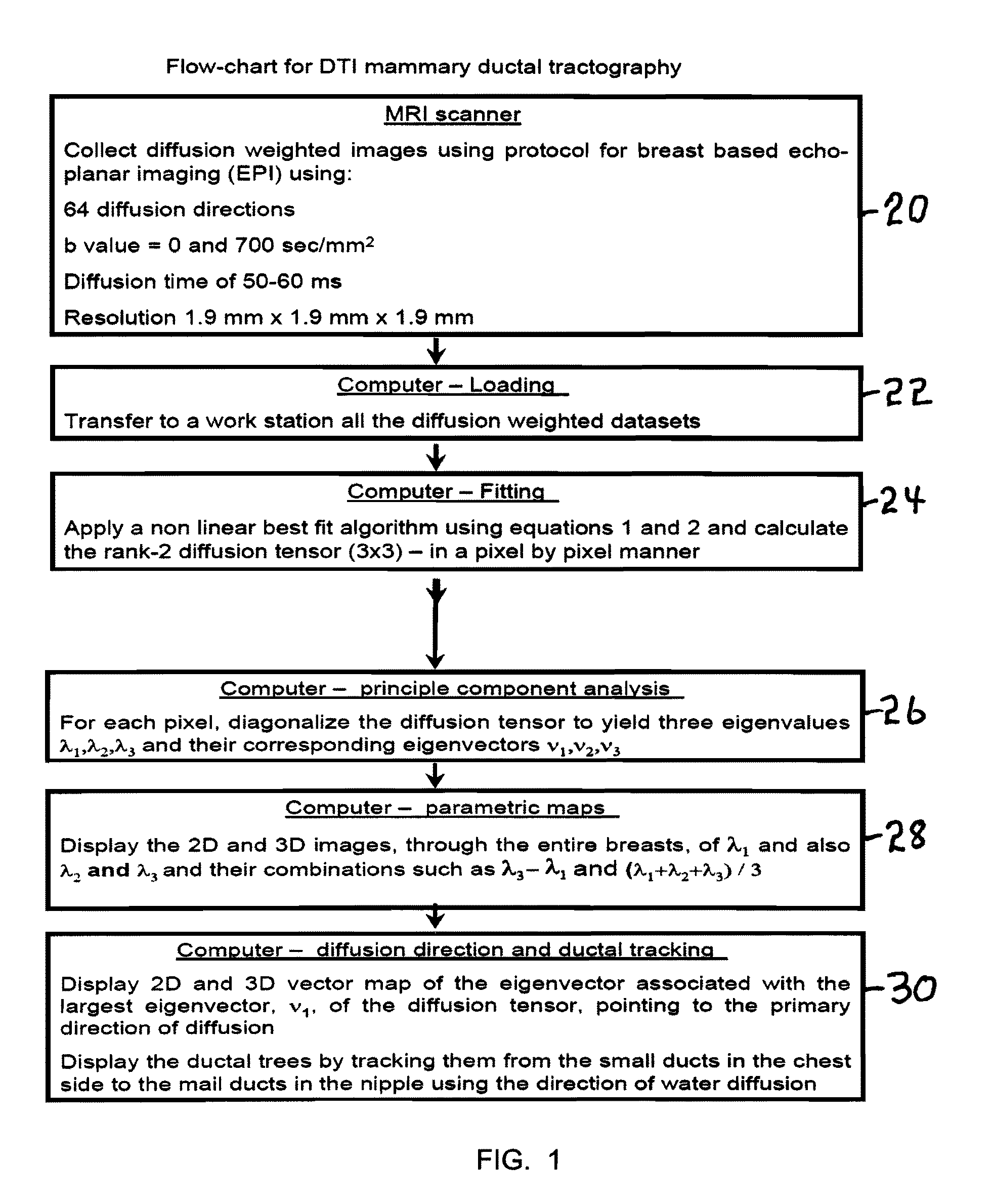
Method and apparatus for ductal tube tracking imaging for breast cancer detection and diagnosis, and product
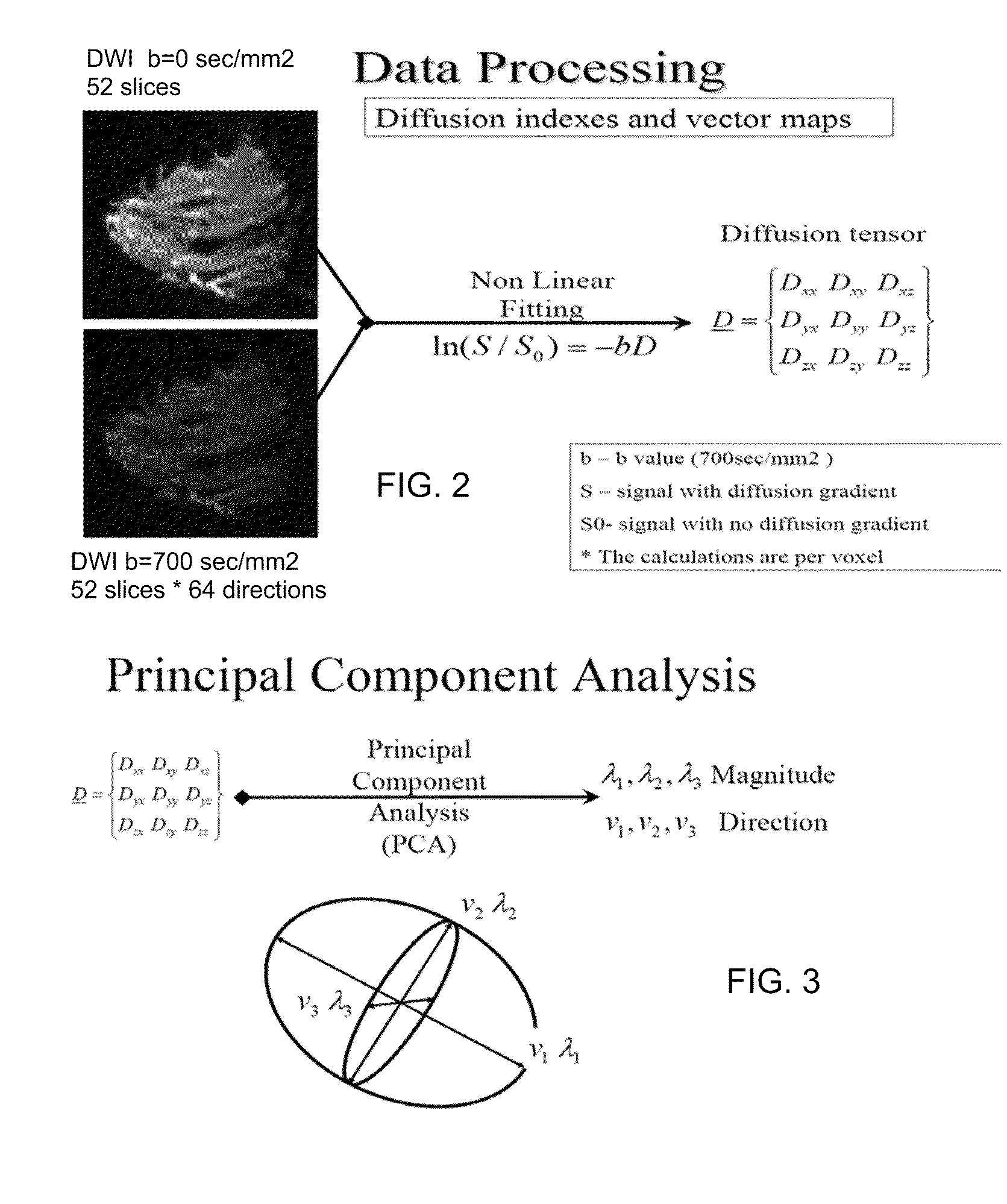
ActiveUS20110038521A1Low costEliminate discomfortMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionVoxelFat suppression
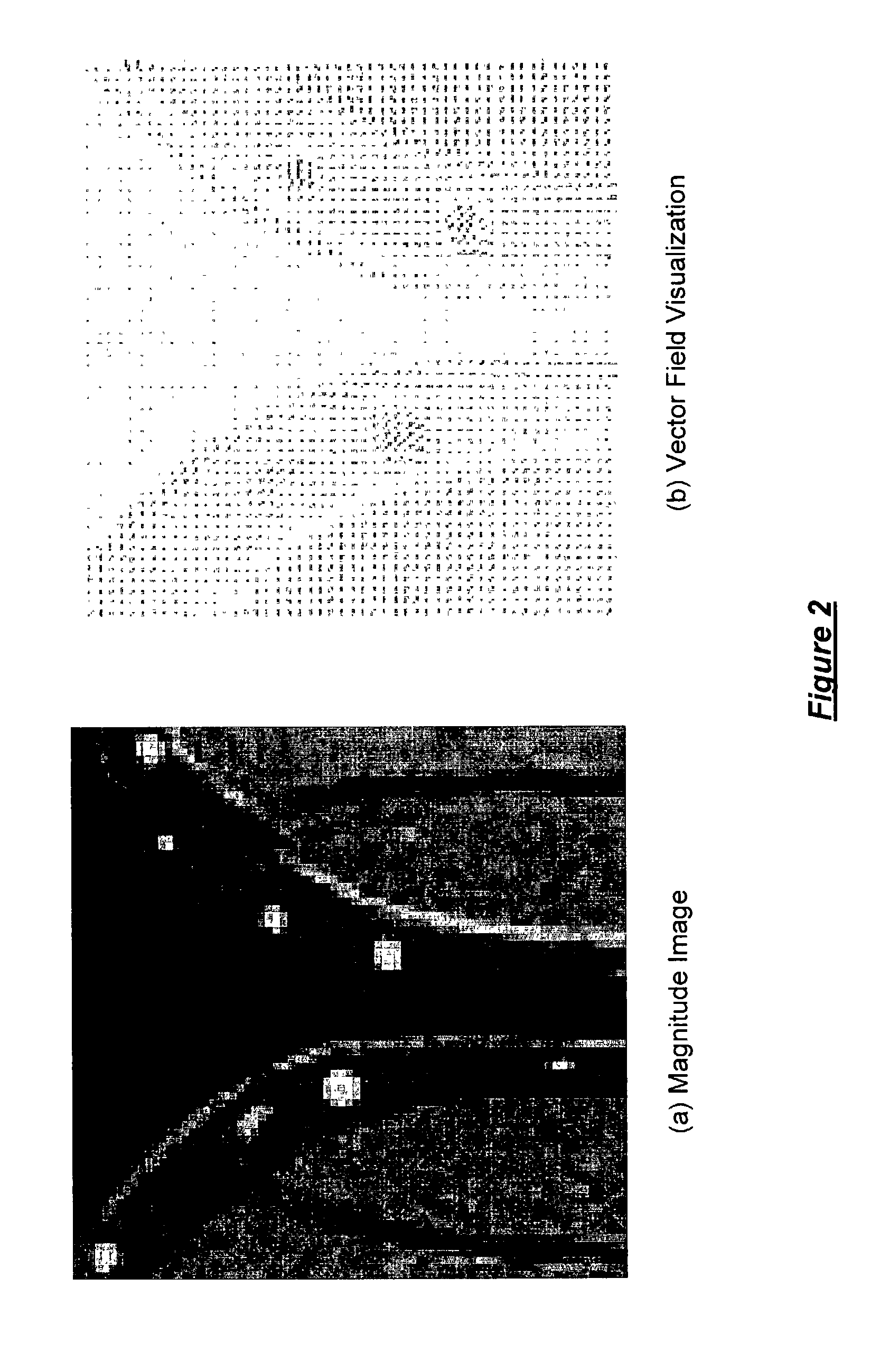
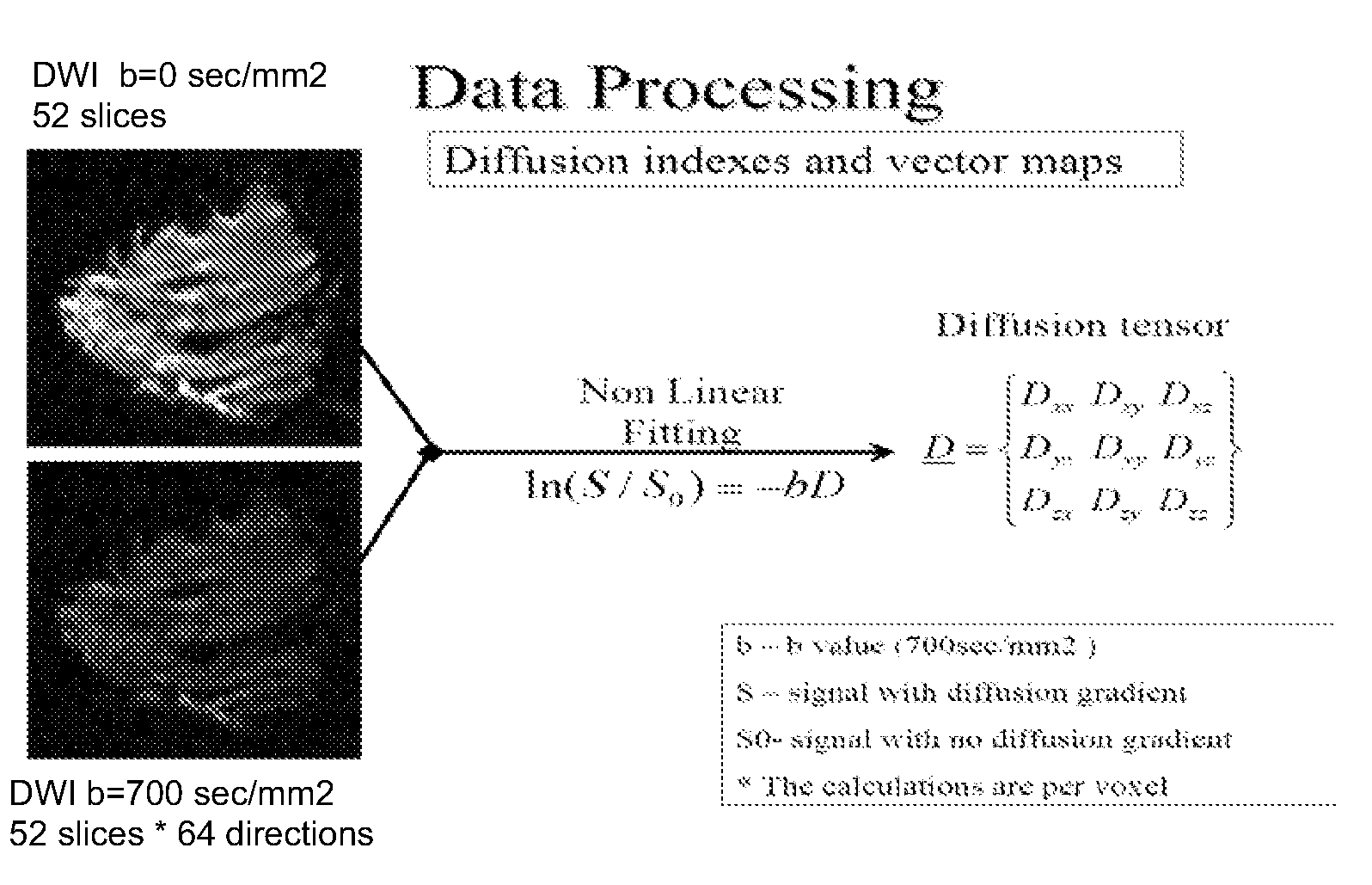
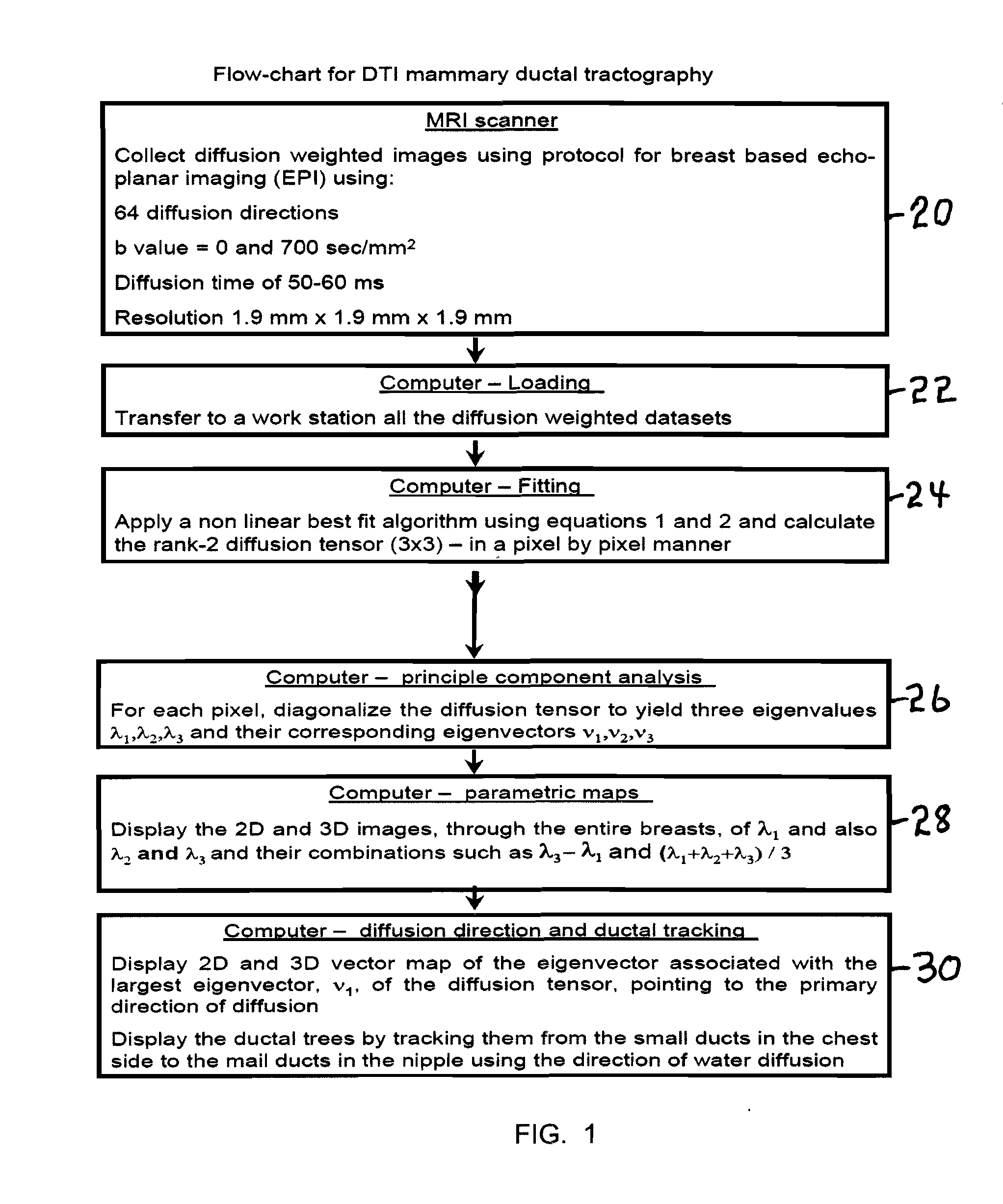
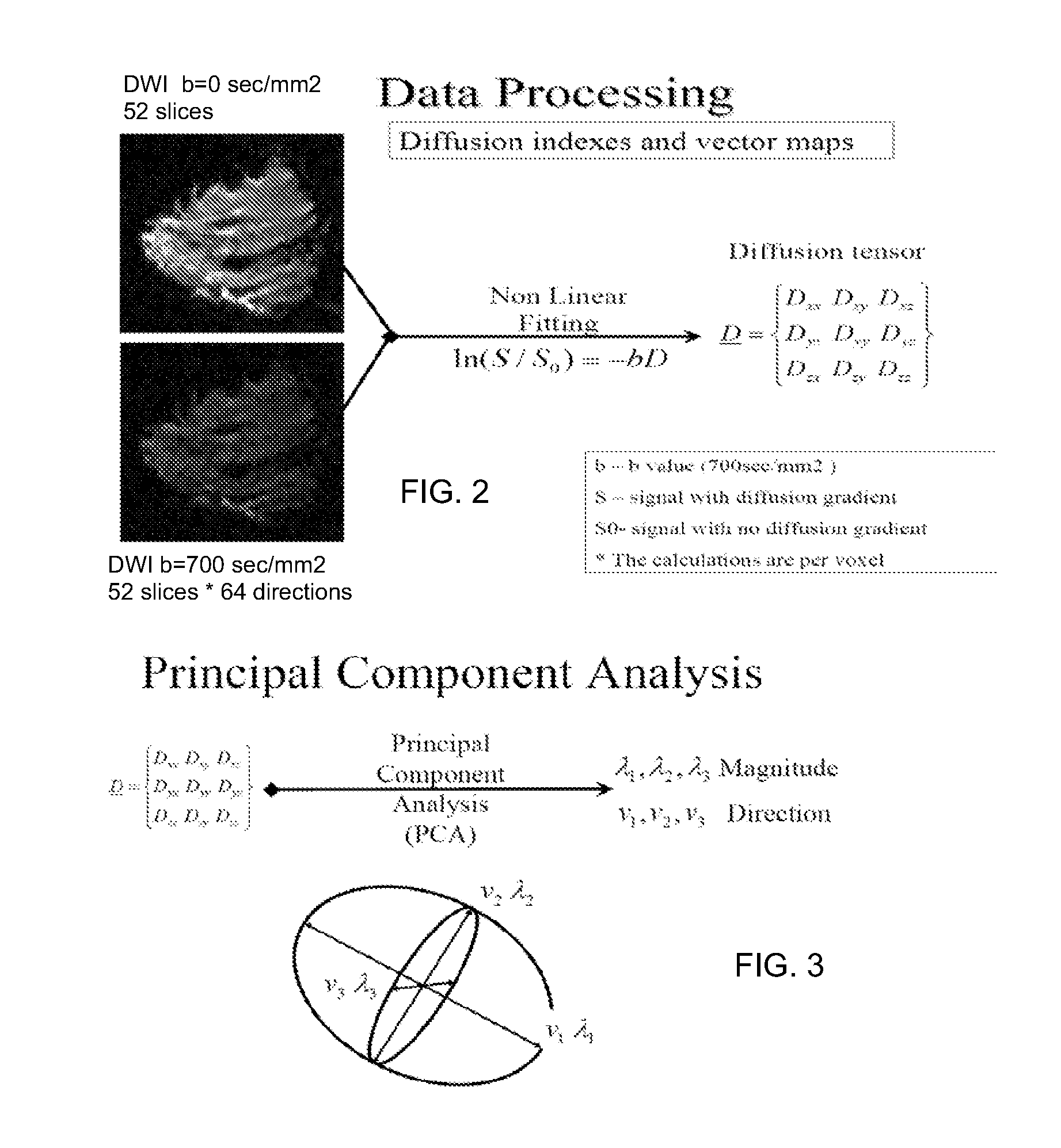
A method apparatus and computer product for imaging a human breast to map the breast ductal tree is disclosed. First, a breast is diffusion tensor imaged with high spatial resolution. Then the breast ductal tree is tracked using a protocol for breast based on echo-planar imaging (EPI) diffusion designed for optimizing diffusion weightings (b values), number of non-collinear directions for tensor calculations, diffusion, echo and repetition times, spatial resolution, signal to noise, scanning time and a sequence for fat suppression. The diffusion tensor is calculated by a non-linear best fit algorithm and then diagonalized with principal component analysis to three eigen vectors and their corresponding eigen values. A vector field map is obtained for tracking of breast ducts of the ductal trees along the direction of the 1st eigenvector v1 and the ductal tree is displayed on a voxel by voxel basis in parametric images using color coding and vector pointing.
Owner:DDE MRI SOLUTIONS LTD
Method and magnetic resonance imaging apparatus for spatial fat suppression in multi-contrast SMS imaging
ActiveUS20180074146A1Reduce peak powerSuppression spaceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMulti bandProton magnetic resonance
In a method and imaging apparatus for acquiring multi-contrast magnetic resonance (MR) data, a data acquisition scanner is operated in a simultaneous multislice data acquisition sequence to radiate at least one single-band binomial radio-frequency (RF) pulse, that excites fat protons in at least some slices of an examination subject from which MR raw data are to be acquired simultaneously, and leaving water in a longitudinal plane for those at least some slices, and leaving all spin species in a longitudinal plane in others of the slices that are to be acquired simultaneously. A spoiler gradient is subsequently activated that dephases the fat protons that were excited. The scanner is then operated to execute an MR data acquisition sequence with excitation by radiation of multi-band RF pulses. MR raw data resulting from excitation of the fat protons, and MR raw data acquired with said multi-band RF excitation, are compiled in respective data files.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
System for Image Acquisition With Fast Magnetic Resonance Gradient Echo Sequences
ActiveUS20100052675A1Reduce acquisition timeReduces RF pulse repetition timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFat suppressionData acquisition
A system uses a three-dimensional spoiled gradient recalled echo sequence for fat suppression with reduced total acquisition time suitable for acquiring image data under breath-hold conditions using a reversed asymmetry during data acquisition on an opposed phase echo. A system reduces RF pulse repetition time in an MR imaging pulse sequence in an MR imaging device. The system includes an RF pulse generator for generating an RF excitation pulse sequence having a pulse repetition interval. A read-out gradient magnetic field generator generates an asymmetric read-out gradient magnetic field having a readout gradient mid-point occurring prior to an RF echo pulse peak. The RF echo pulse peak is received in response to a generated RF excitation pulse.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH +1
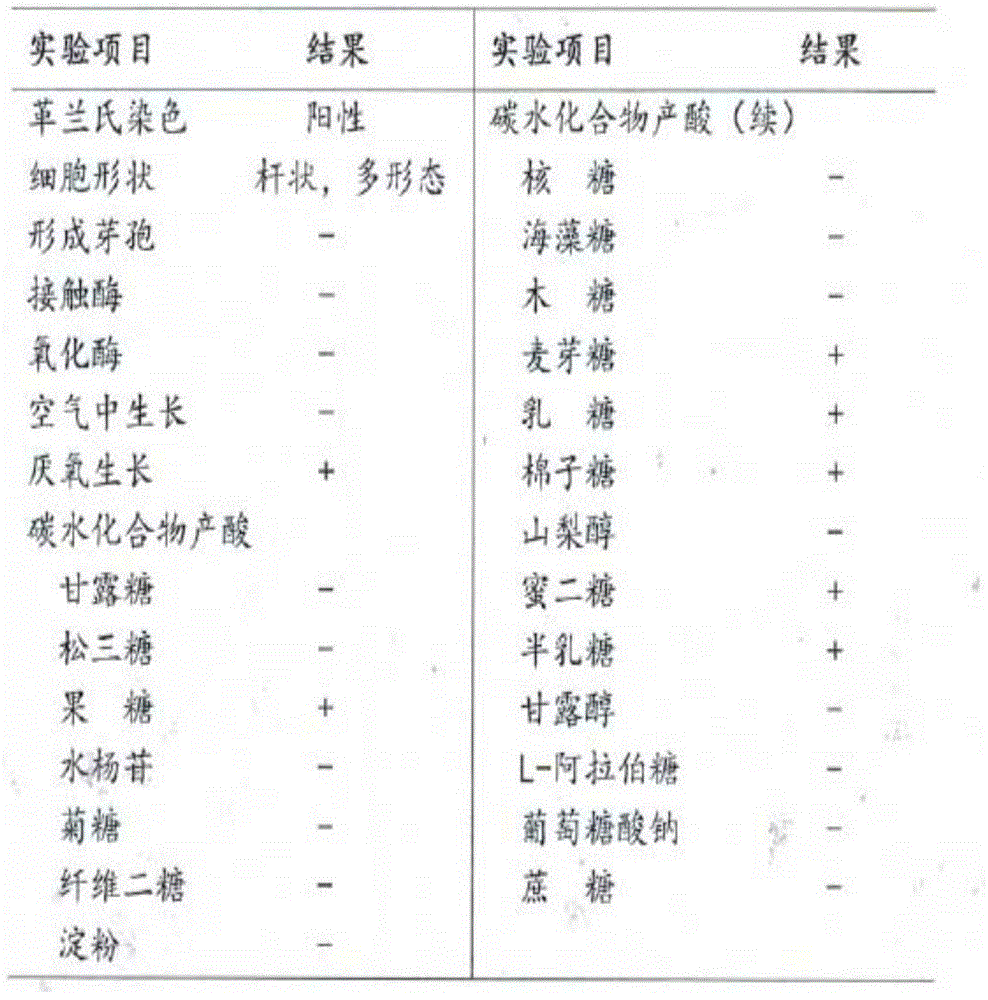
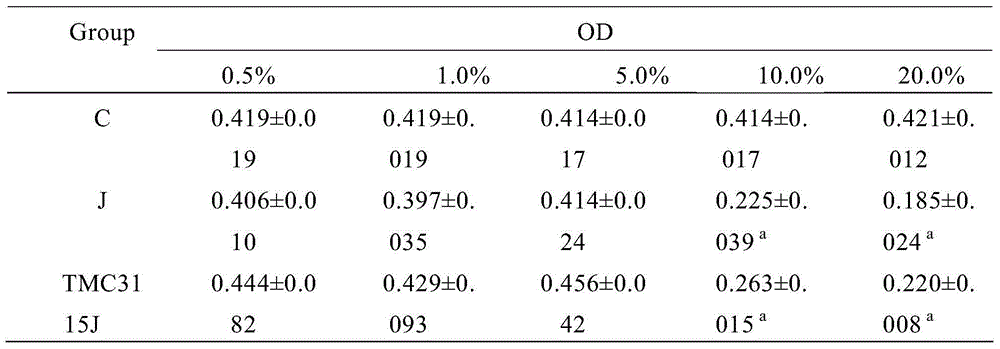
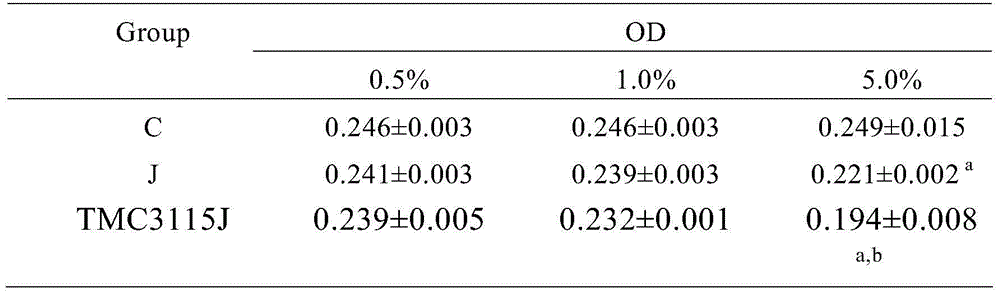
Bifidobacterium bifidum strain TMC3115 with fat suppression cells and application therepof
The invention relates to a bifidobacterium bifidum strain TMC3115 and an application of the bifidobacterium bifidum strain TMC3115. The bifidobacterium bifidum strain TMC3115 has the obvious function of suppressing fat cells. The invention also relates to an application of the bifidobacterium bifidum strain TMC3115 to preparation of milk products and probiotic products containing the strain.
Owner:河北一然生物科技股份有限公司
Method and apparatus for ductal tube tracking imaging for breast cancer detection and diagnosis, and product
ActiveUS8526698B2Less expensiveShort timeMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionVoxelFat suppression
A method apparatus and computer product for imaging a human breast to map the breast ductal tree is disclosed. First, a breast is diffusion tensor imaged with high spatial resolution. Then the breast ductal tree is tracked using a protocol for breast based on echo-planar imaging (EPI) diffusion designed for optimizing diffusion weightings (b values), number of non-collinear directions for tensor calculations, diffusion, echo and repetition times, spatial resolution, signal to noise, scanning time and a sequence for fat suppression. The diffusion tensor is calculated by a non-linear best fit algorithm and then diagonalized with principal component analysis to three eigen vectors and their corresponding eigen values. A vector field map is obtained for tracking of breast ducts of the ductal trees along the direction of the 1st eigenvector v1 and the ductal tree is displayed on a voxel by voxel basis in parametric images using color coding and vector pointing.
Owner:DDE MRI SOLUTIONS LTD
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and analysis method for fat suppression effect in magnetic resonance imaging apparatus
Owner:TOSHIBA MEDICAL SYST CORP
Methods for fat signal suppression in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS7646198B2Shorten the timeReduce acquisition timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionData setFat suppression
The present invention is directed to methods for chemical species signal suppression in magnetic resonance imaging procedures, wherein Dixon techniques are enhanced by continuously sampling techniques. In the invention, k-space data is acquired during the entire period of read gradient associated with a gradient echo pulse acquisition scheme. The invention utilizes a total sampling time (TST) acquisition during the entire read gradient, using three echoes of a TST data set to achieve chemical species separation in both homogenous fields as well as areas of field inhomogeneity. As an example, a continuously sampled rectilinearly FLASH pulse sequence is modified such that the time between echoes was configured to be 2.2 milliseconds, with TE selected to allow 180° phase variation in the fat magnetization between each of the three TE's (TE1, TE2, and TE3). Data collected during the dephase and rephase gradient lobes are defined as a first Dixon acquisition, with data collected by the read gradient lobe being defined as a second Dixon acquisition. Two point Dixon reconstruction techniques are used to form images for each chemical species, such as for generating water and fat images of the scanned object region. Other corrections, such as off-resonance correction may be applied on the image data.
Owner:CASE WESTERN RESERVE UNIV
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveUS20100156418A1Image degradationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMulti sliceFat suppression
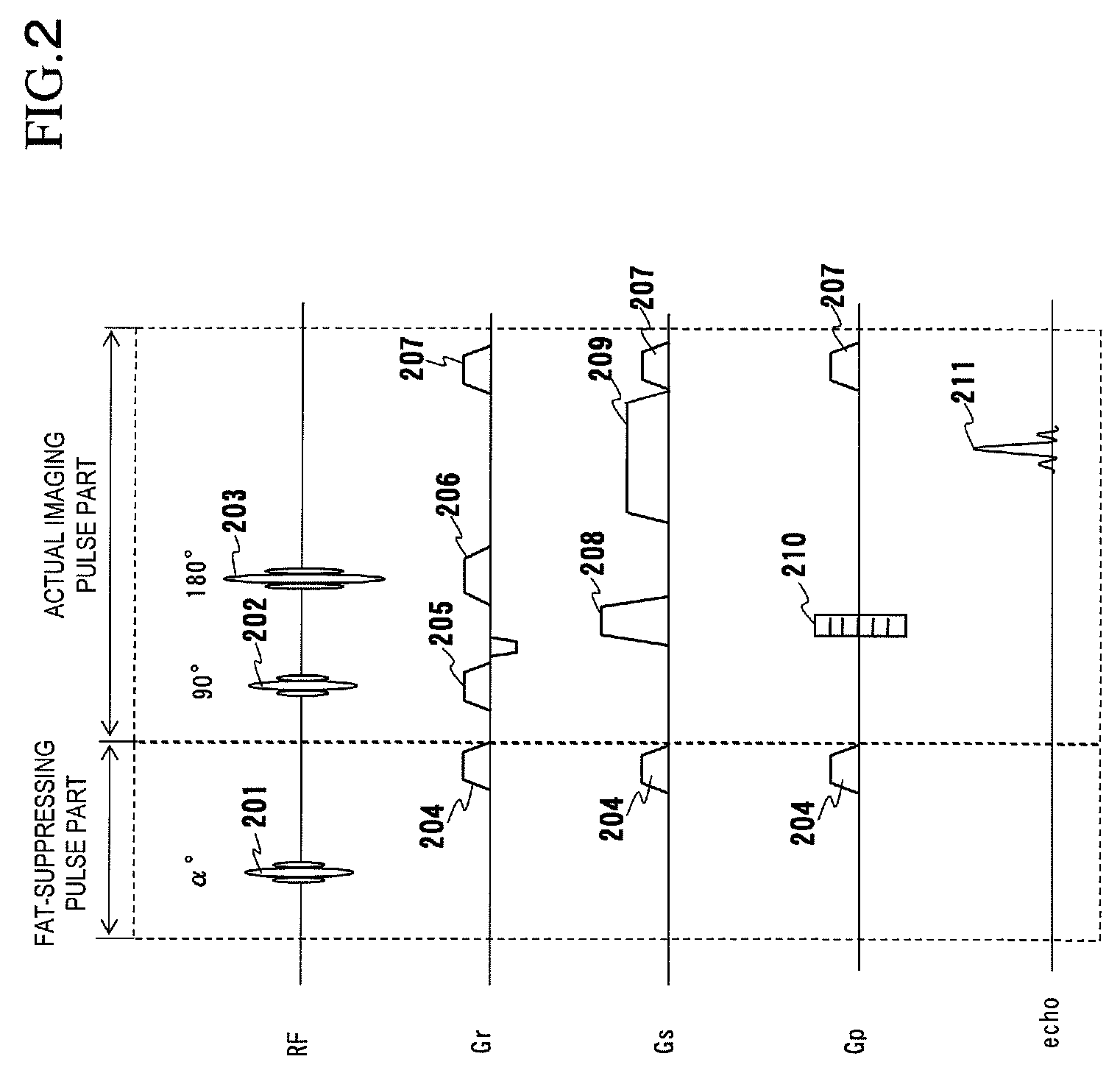
In order to stably obtain an even fat-suppressed image without reduction of an imaging efficiency and without being affected by unevenness of irradiation magnetic field of an RF pulse, when an imaging sequence having a first sequence part for suppressing a signal from a desired component of an examinee by applying a CHESS pulse and a second sequence part for measuring an echo signal from the examinee is repeated, the flip angle of the CHESS pulse is changed at plural times. In the case of multi-slice imaging, the flip angle of the CHESS pulse is changed in at lest two slice imaging.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com