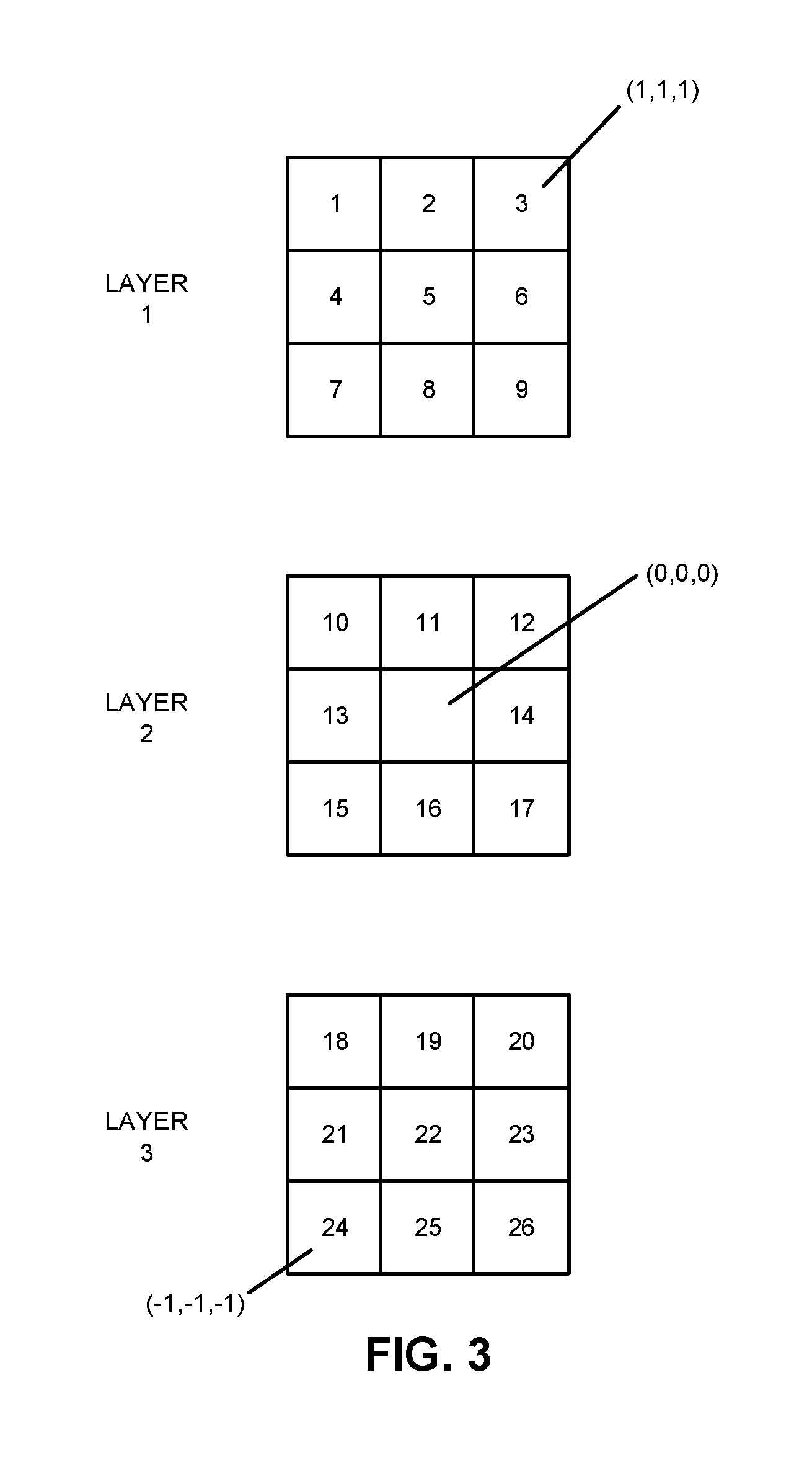
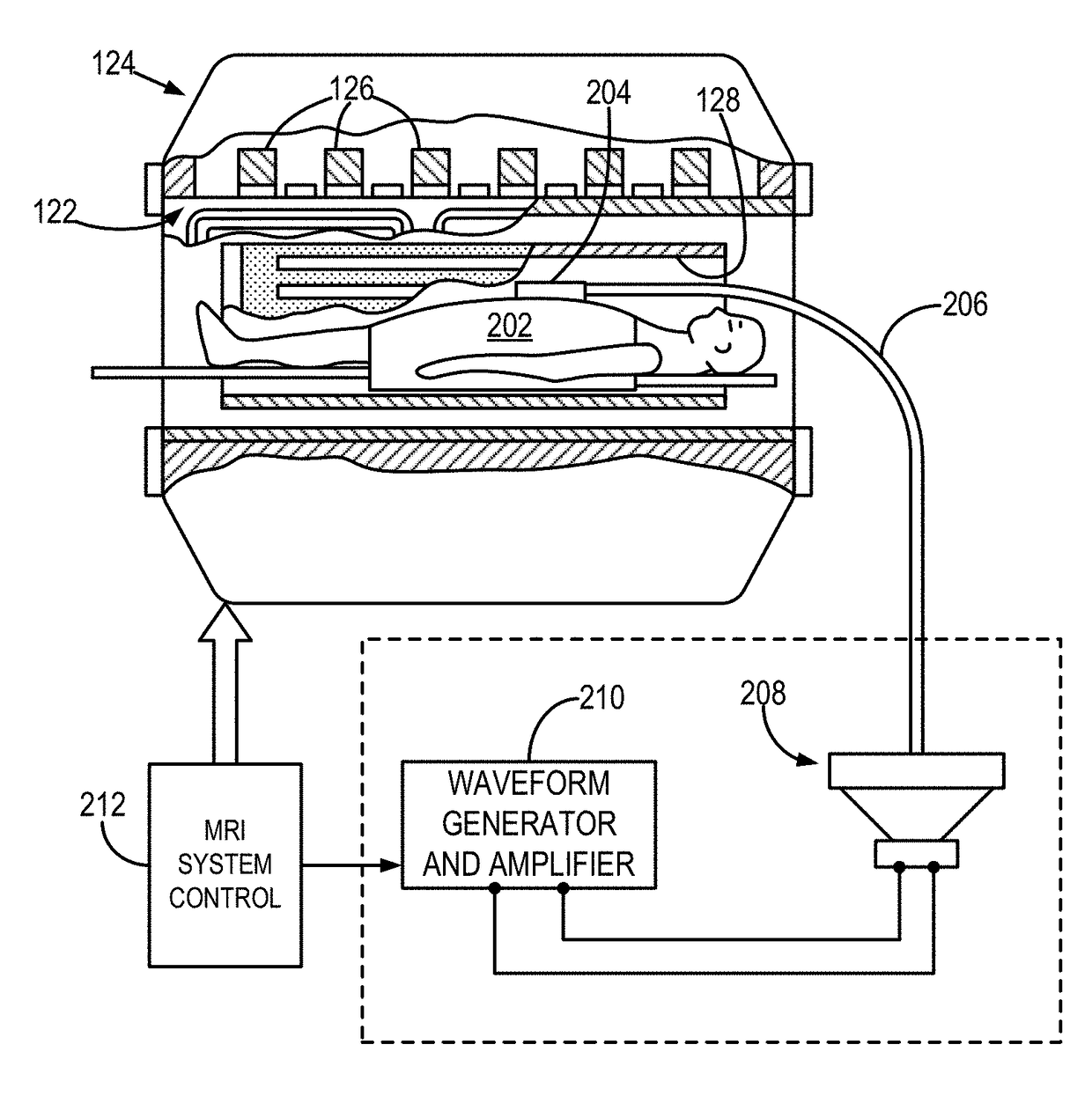
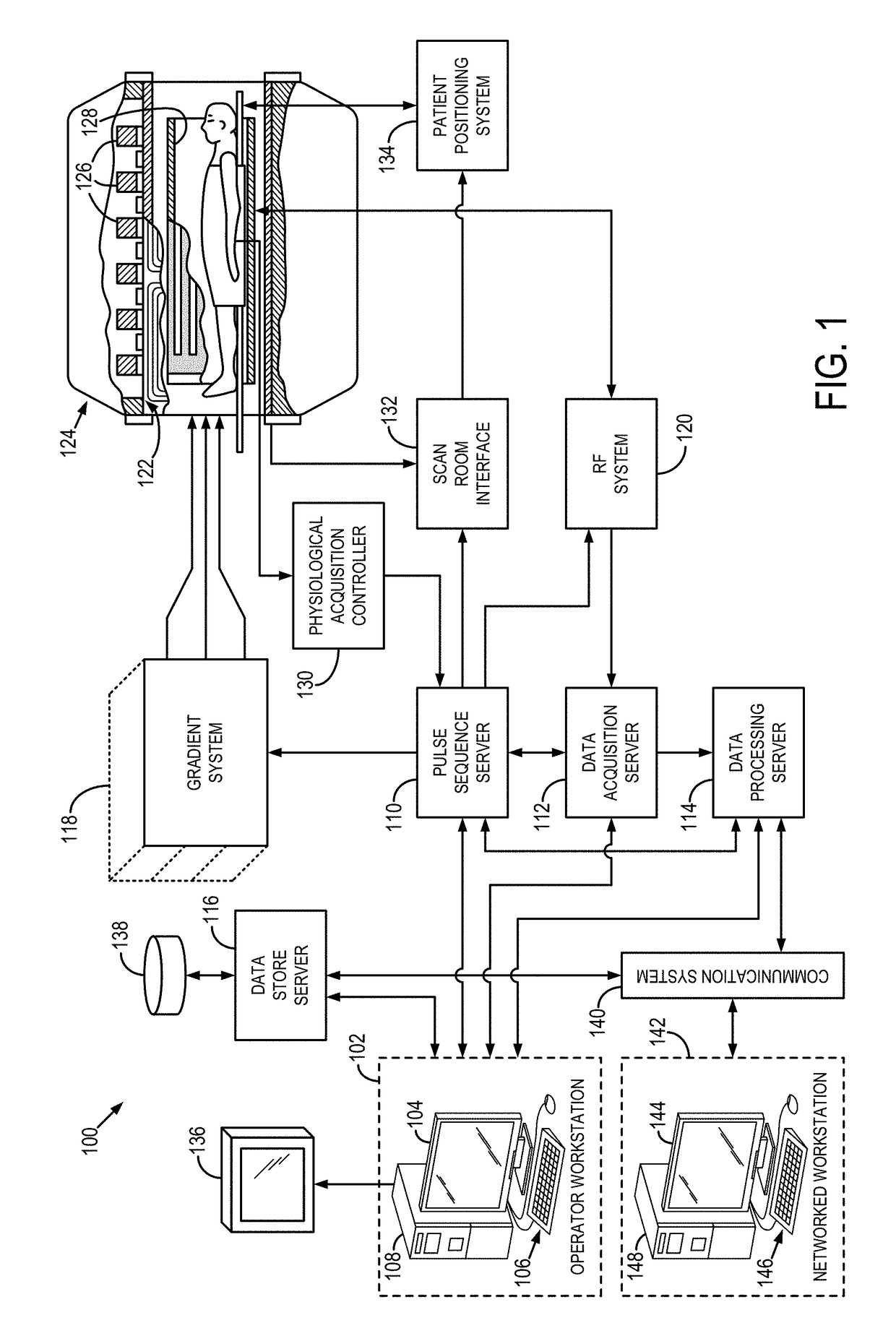
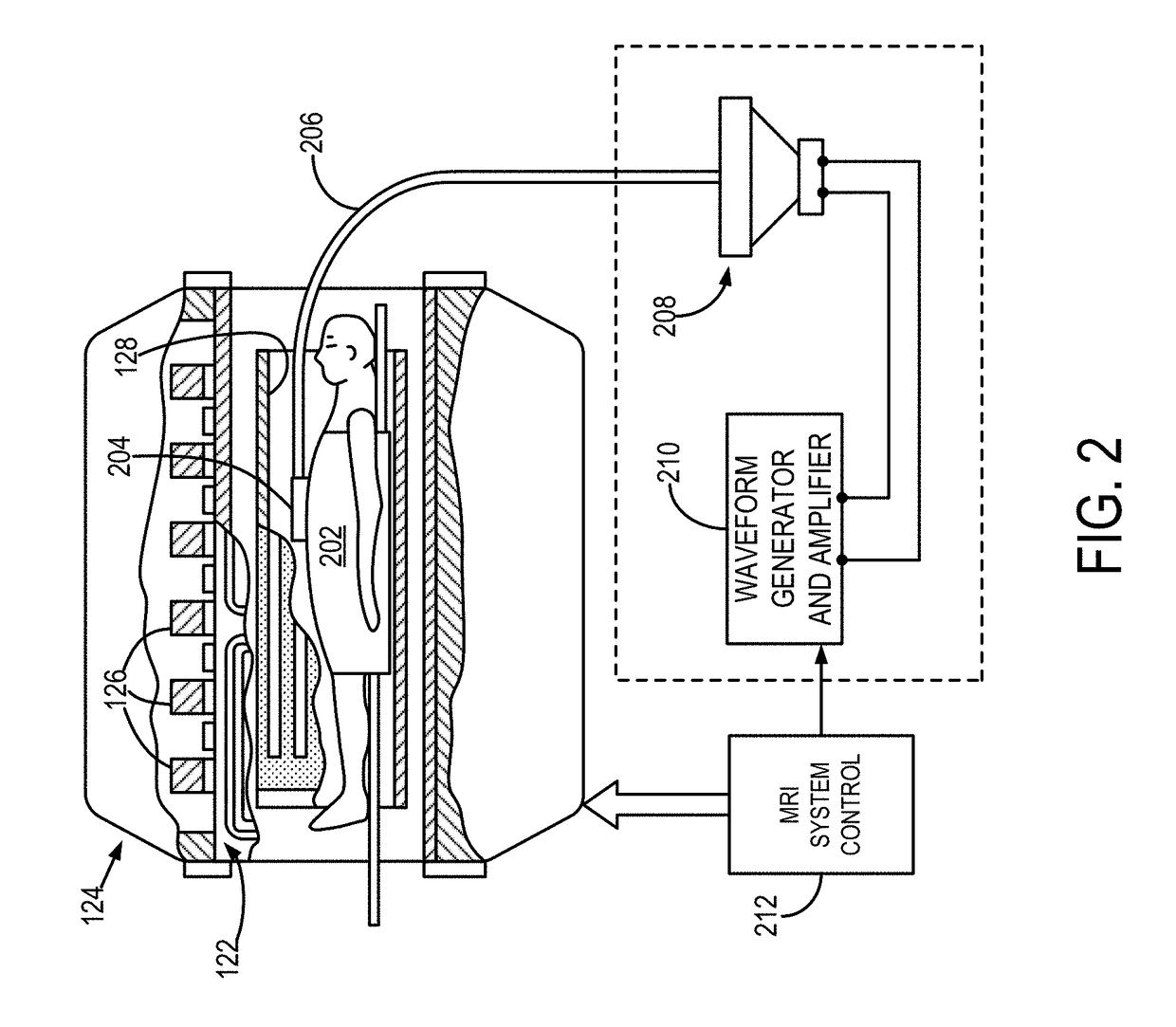
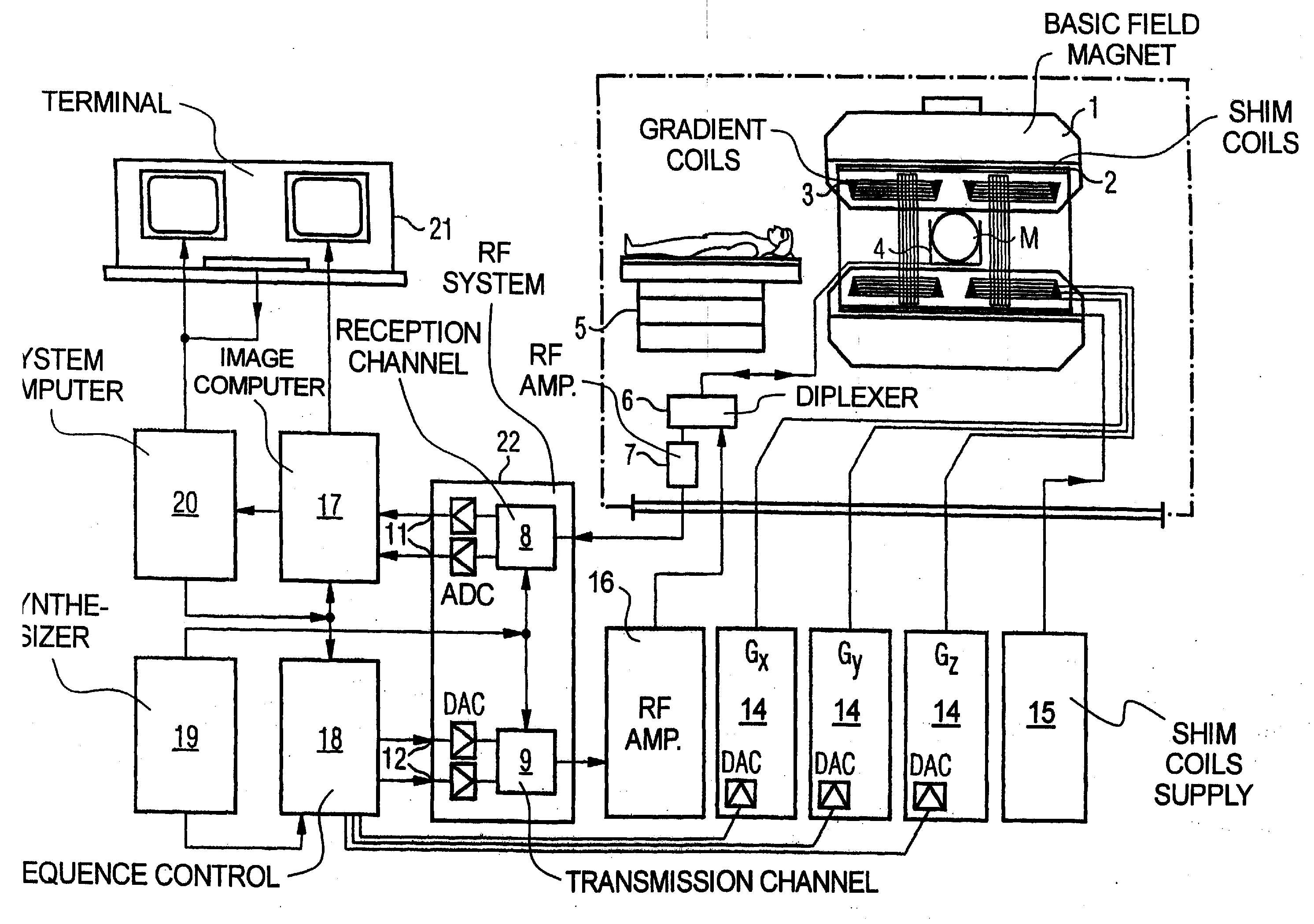
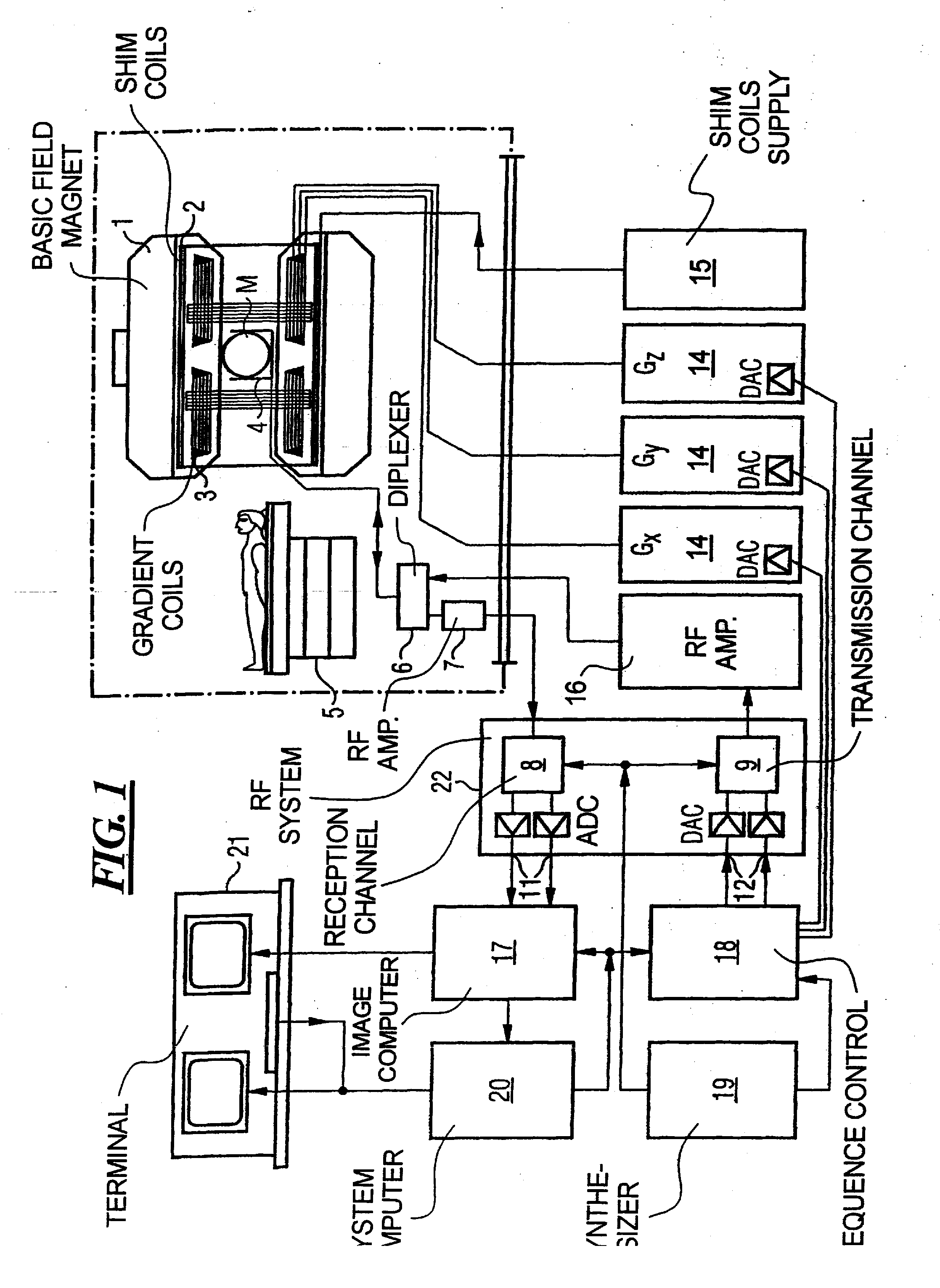
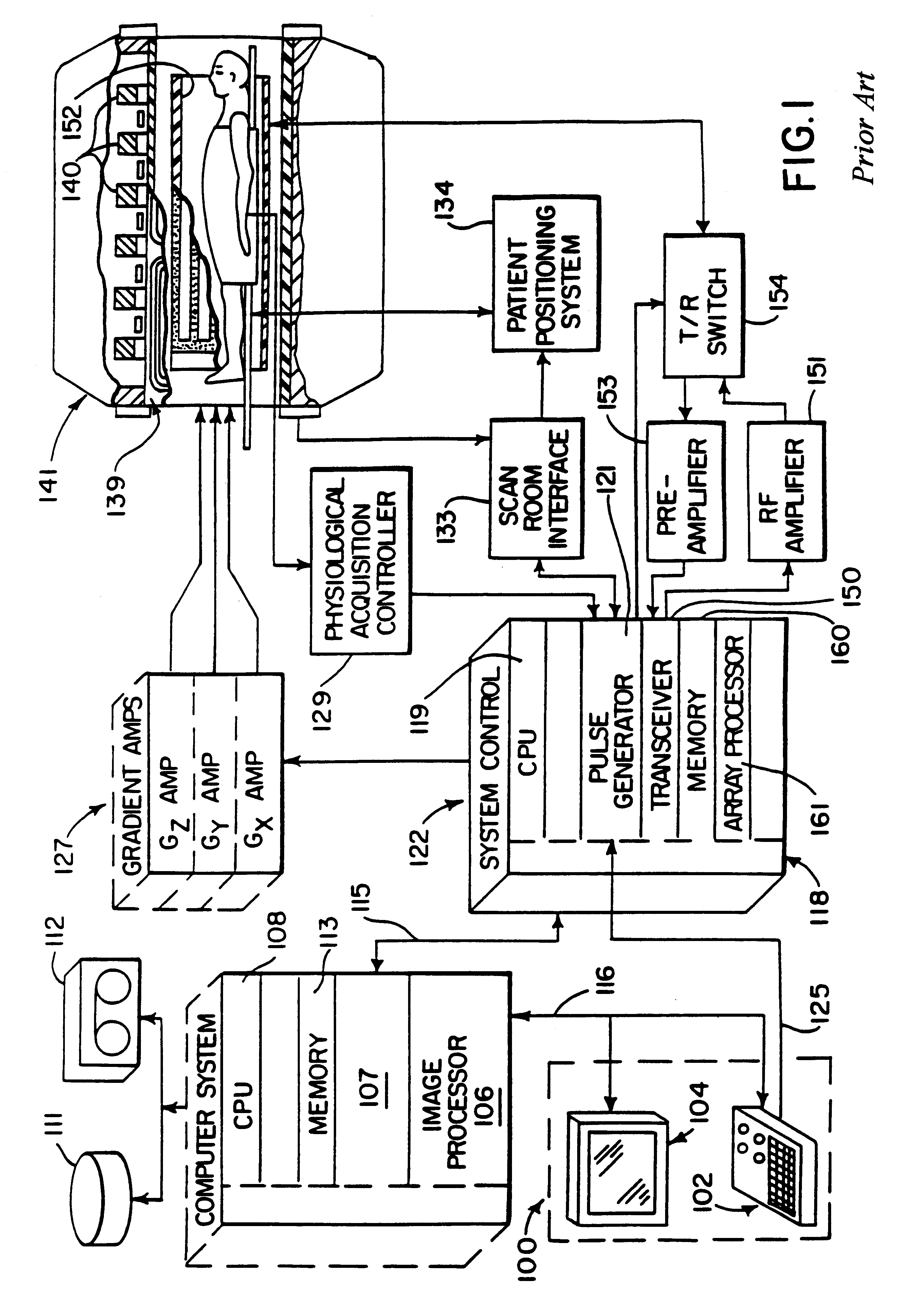
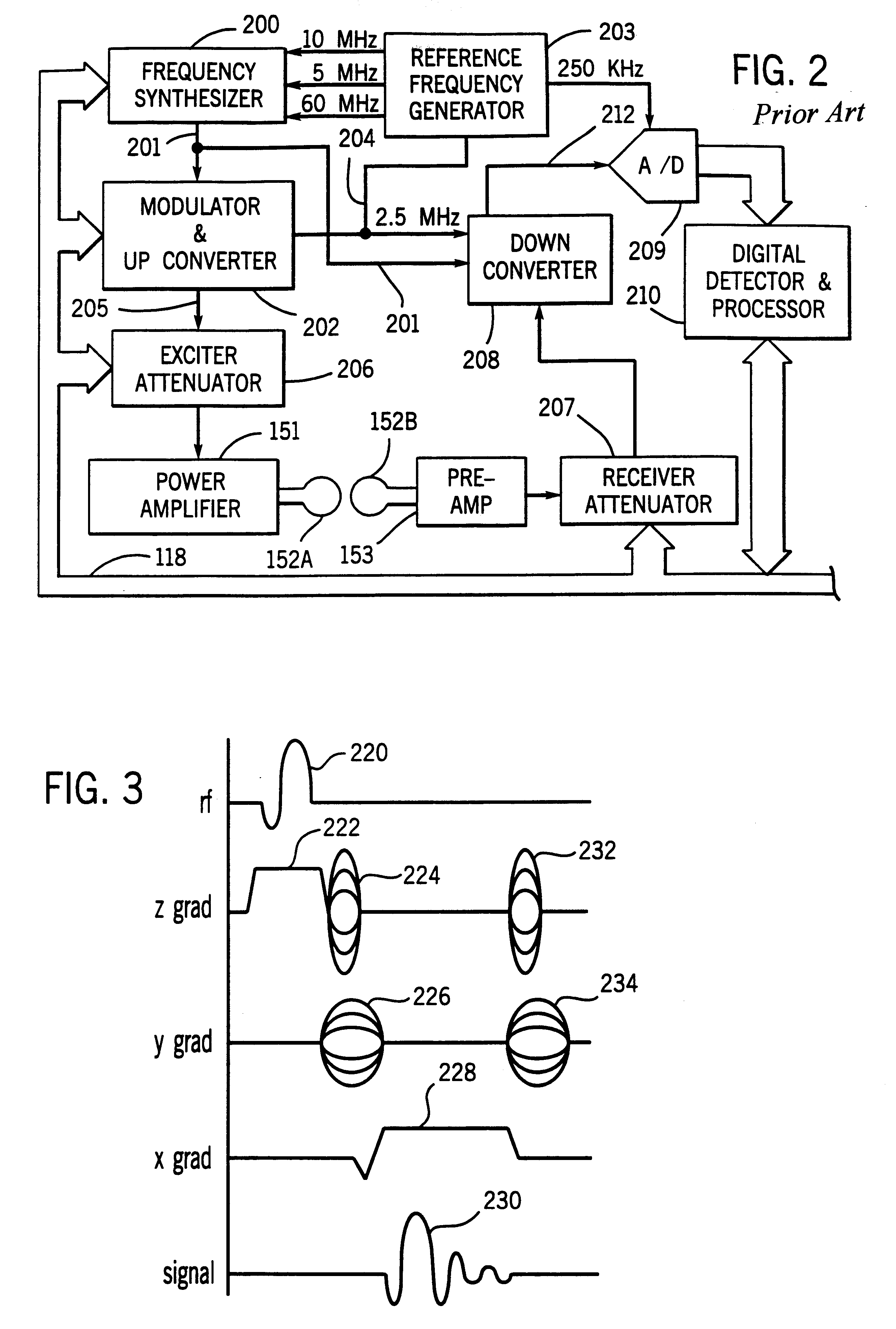
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
197 results about "Magnetic resonance angiography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
<ul><li>Normal results are inferred when the results do not show any blockages in the blood vessels.</li><li>If the results show any blockage or irregularity of blood flow in one or more blood vessels, further tests may be done to confirm the complications with heart function.</li></ul>
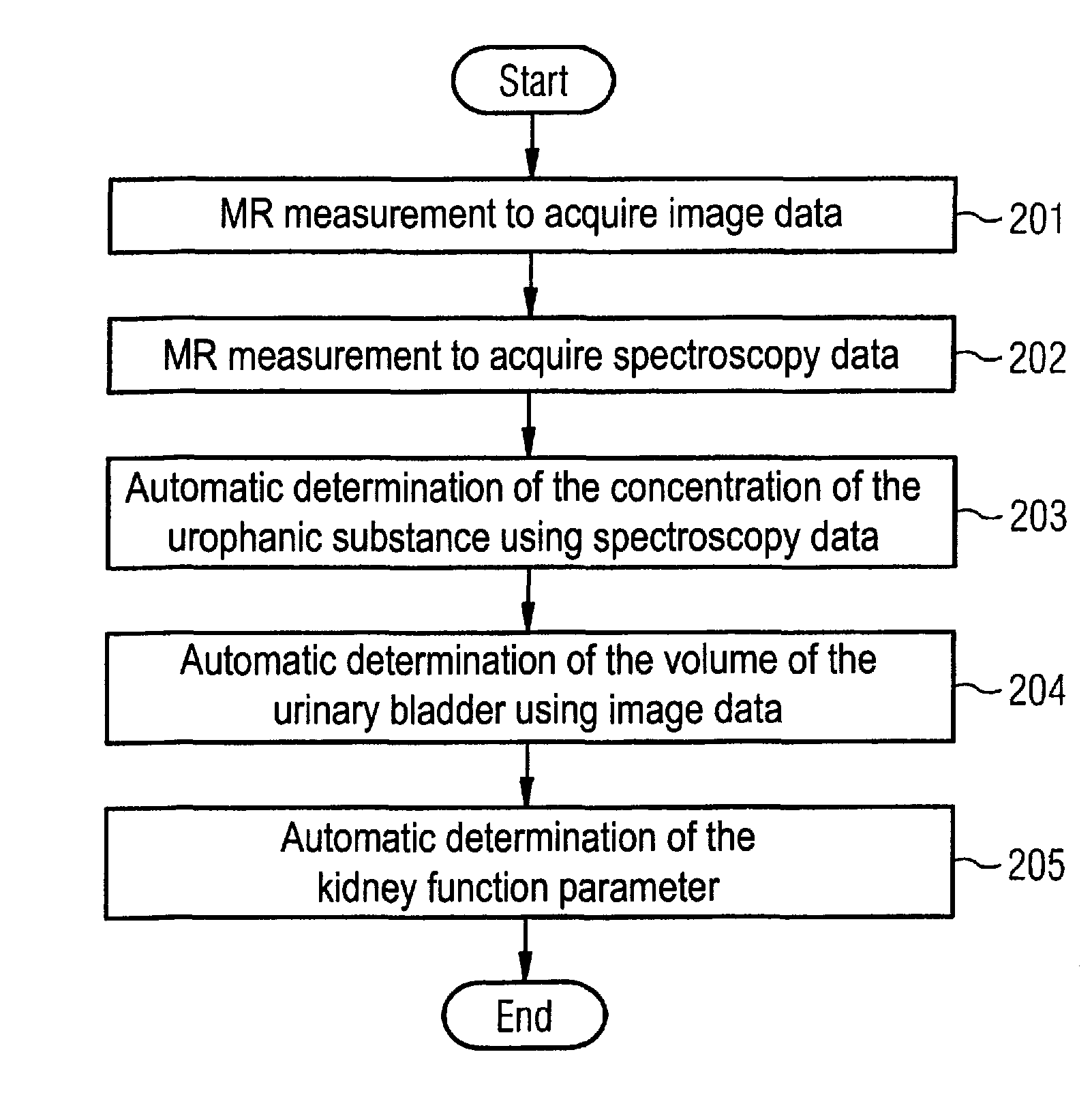
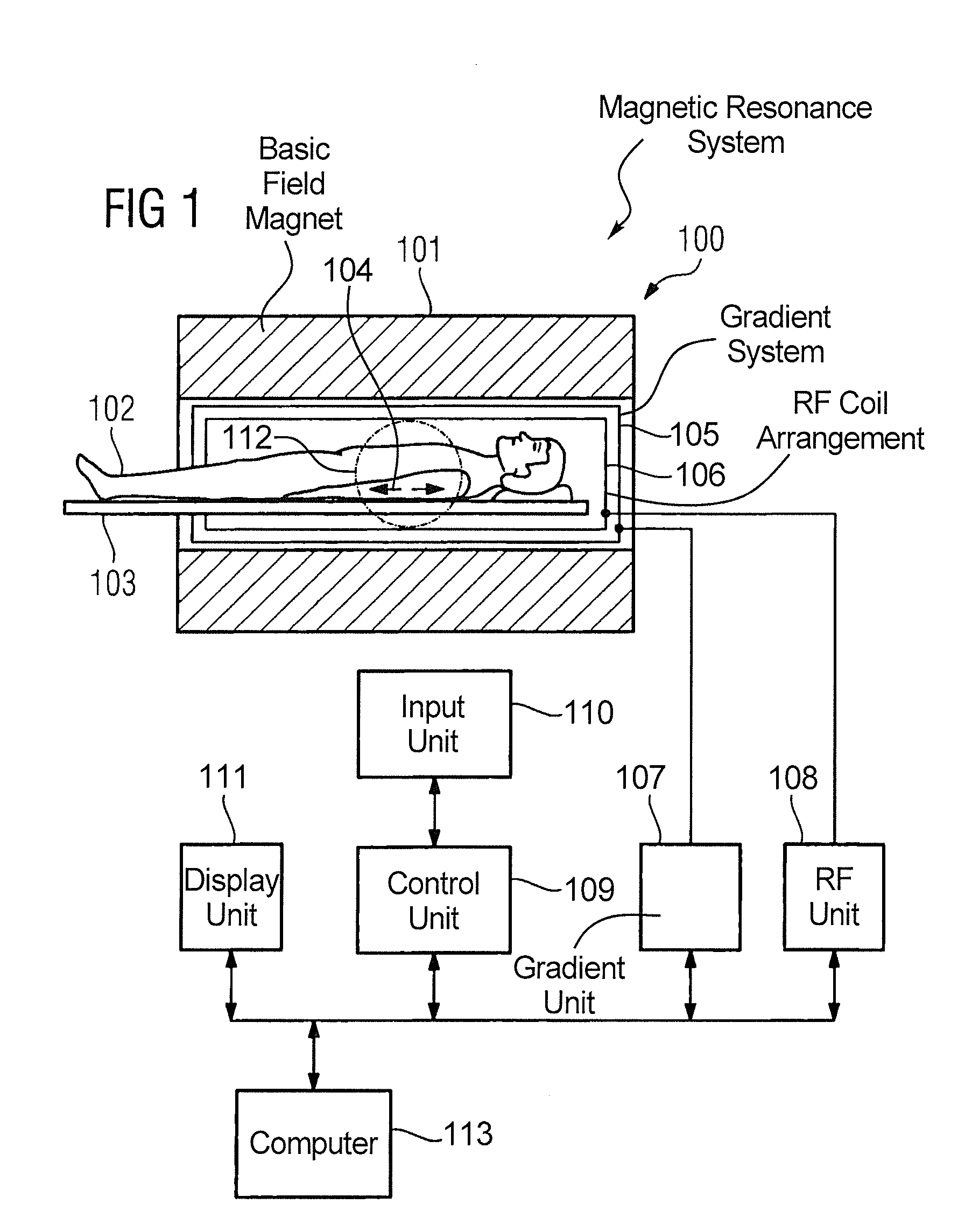
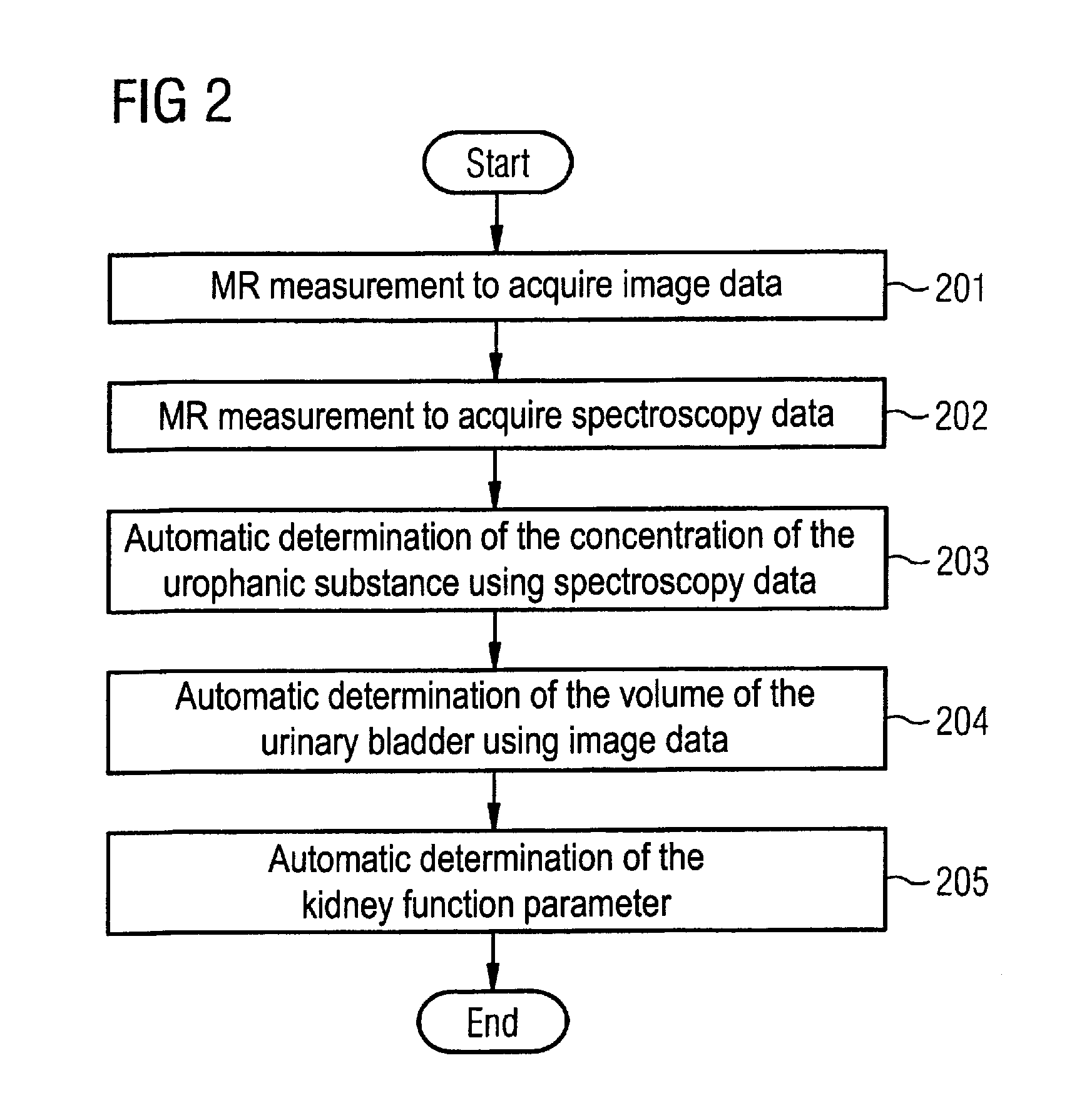
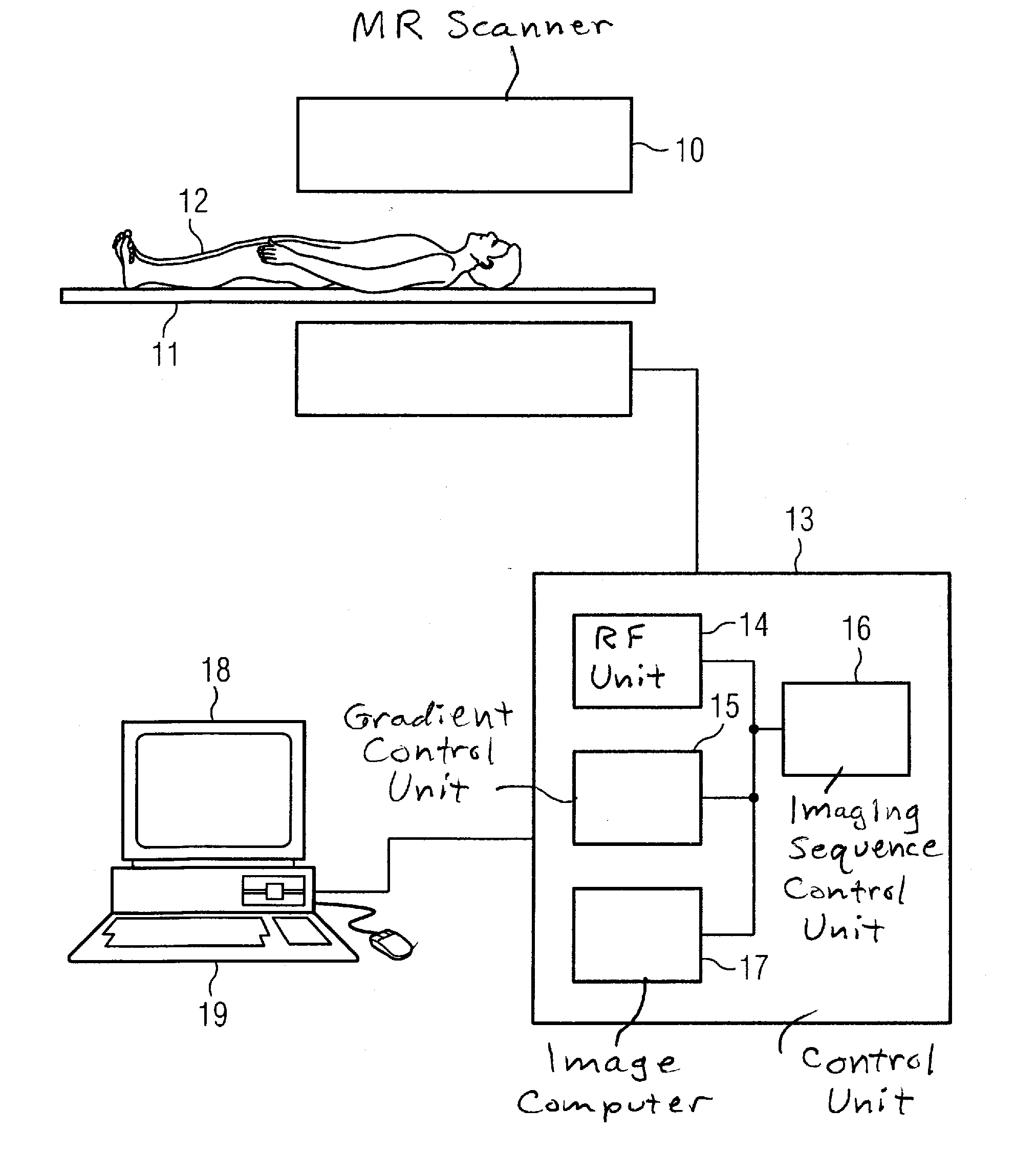
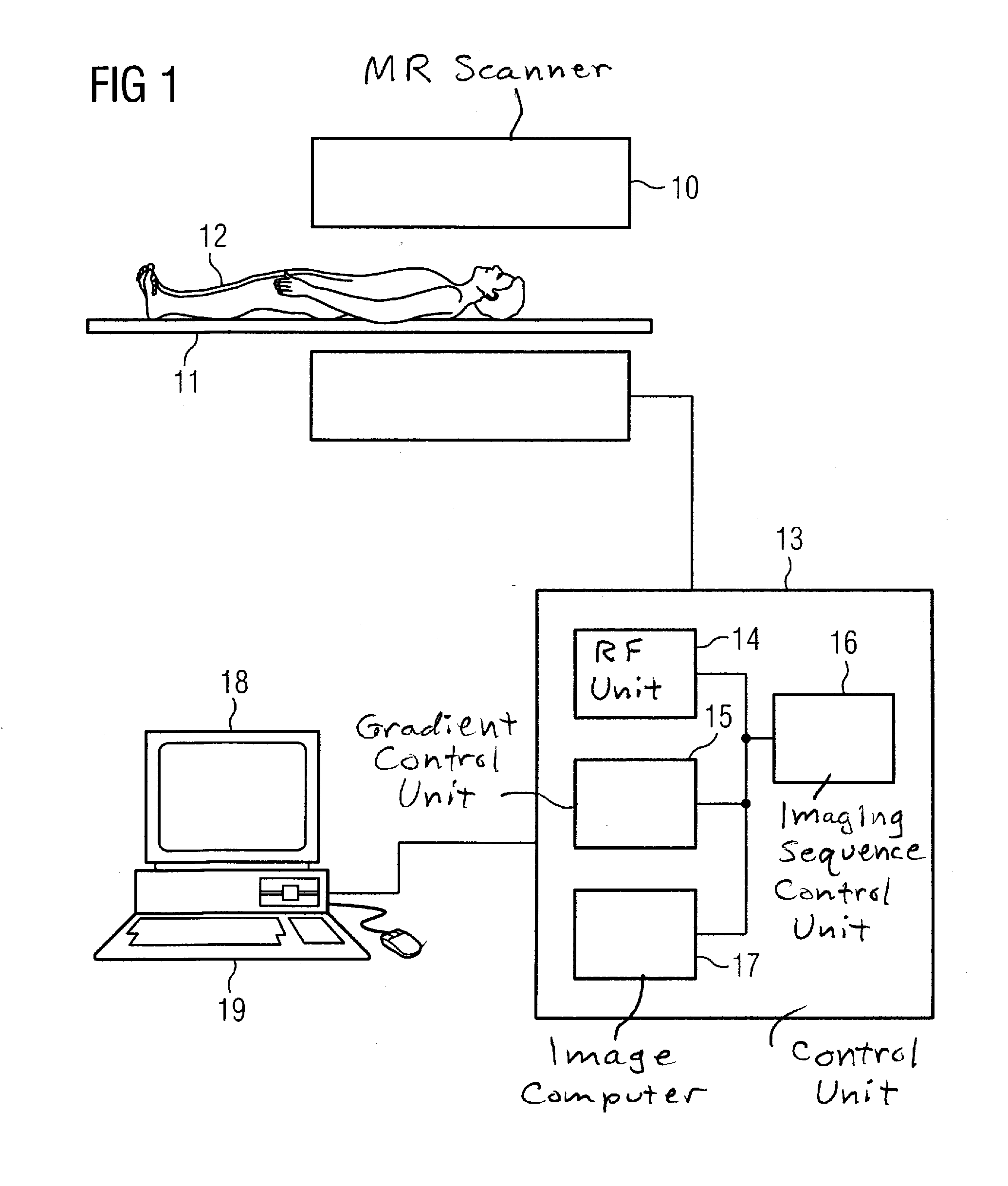
Magnetic resonance method and apparatus for determining a kidney function parameter
ActiveUS8260397B2Accurate measurementShort timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonance measurementRenal function
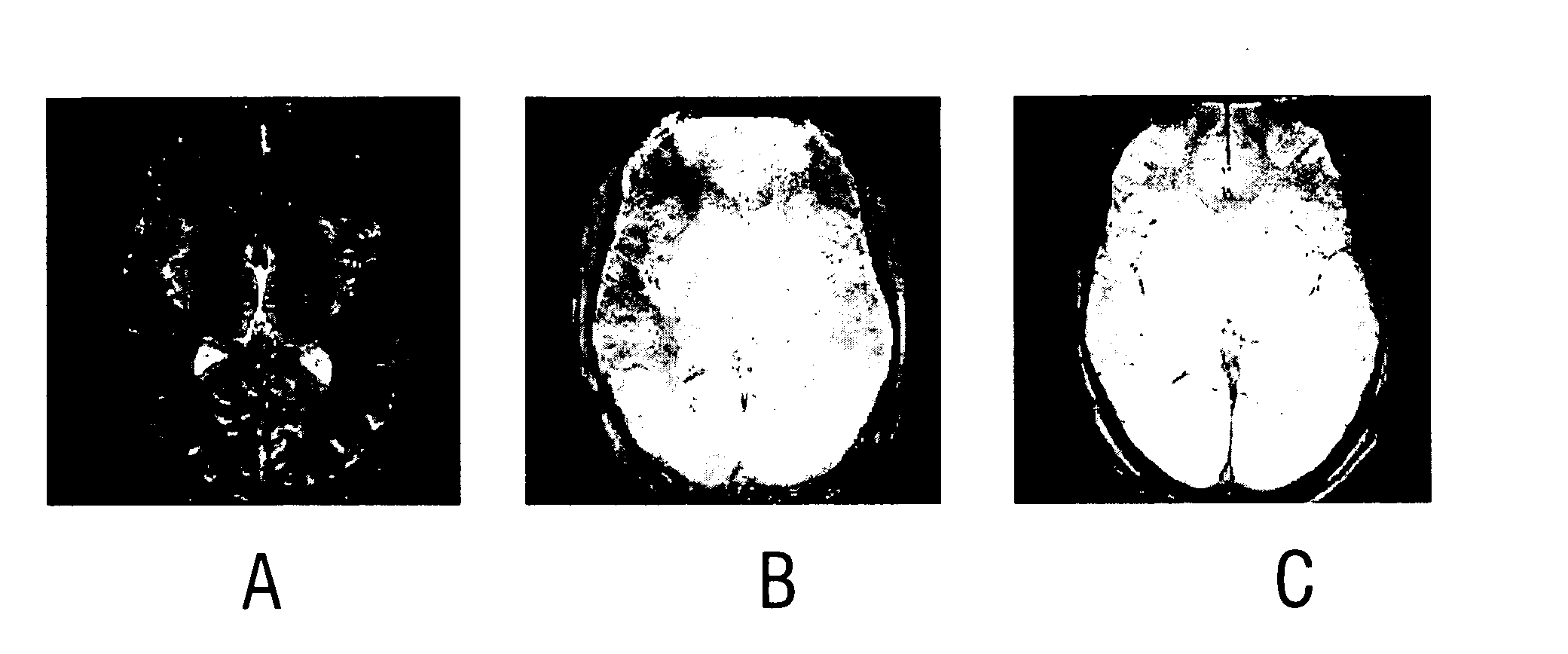
In a method to determine a kidney function parameter of kidneys of an examination person with the aid of magnetic resonance tomography, at least one magnetic resonance measurement is implemented for an examination region of the examination person that comprises a urinary bladder of the examination person, to acquire magnetic resonance data from the examination region that include at least image data. The concentration of a urophanic substance in the urinary bladder of the examination person is automatically determined based on the acquired magnetic resonance data. A volume of the urinary bladder is automatically determined based on the acquired image data. A kidney function parameter of the kidneys of the examination person is automatically determined on the basis of the determined concentration of the urophanic substance in the urinary bladder and of the specific volume of the urinary bladder.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Breast biopsy and therapy system for magnetic resonance imagers
The present invention describes a device for performing breast biopsies and / or therapy within magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems. The apparatus includes a RF receiver antenna for magnetic resonance imaging of the breast. The RF coil includes openings in the front and side to provide access to the breast during the procedure. Compression plates are integrated into the breast coil which compress the breast either laterally or in the head / feet direction as required for optimal access to the breast. The apparatus includes a mechanical device for positioning interventional instruments in the breast such as biopsy or therapy instruments. The mechanical positioning devices position the instrument along the desired trajectory to the target site and insert the instrument into the breast while the patient remains inside the MRI scanner. Real time MR images may be acquired during instrument alignment and insertion to verify the trajectory. The mechanical positioning devices allow manipulation of instruments in any type of MRI scanner, including high field MRI systems with cylindrical magnets. The positioning devices provide a means to overcome limited access to the patient in MRI scanners. The positioning devices may be manually operated by means of gears, drive shafts, cables or other mechanical means. Or they may be electronically controlled by means of MR compatible motorized drive systems. The devices may be remotely controlled from outside the magnet for MRI systems that have limited access to the patient in the magnet. An interface between the electronically controlled drivers and the MRI scanner computer can provide robotic control of the instrument.
Owner:LAMPMAN DAVID A +1
Fast scaning based on magnetic resonance history
During operation, a system iteratively captures MR signals of one or more types of nuclei in one or more portions of a biological lifeform based on scanning instructions that correspond to a dynamic scan plan. The MR signals in a given iteration may be associated with voxels having associated sizes at three-dimensional (3D) positions in at least a corresponding portion of the biological lifeform. If the system detects a potential anomaly when analyzing the MR signals from the given iteration, the system dynamically modifies the scan plan based on the detected potential anomaly, a medical history and / or an MR-scan history. Subsequent measurements of MR signals may be associated with the same or different: types of nuclei, portions of the biological lifeform, voxels sizes and / or 3D positions.
Owner:Q BIO INC
System and method for generating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score (NAS) using magnetic resonance elastography
The present disclosure relates to a system and method for non-invasively determining NAFLD activity scores (NAS) in patients using mechanical properties determined through magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) imaging. The non-invasively determined NAS score is then used to diagnose NFALD and NASH patients.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Magnetic resonance imaging with improved imaging contrast
InactiveUS20120013336A1Minimize timeMinimal echo timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientObject based
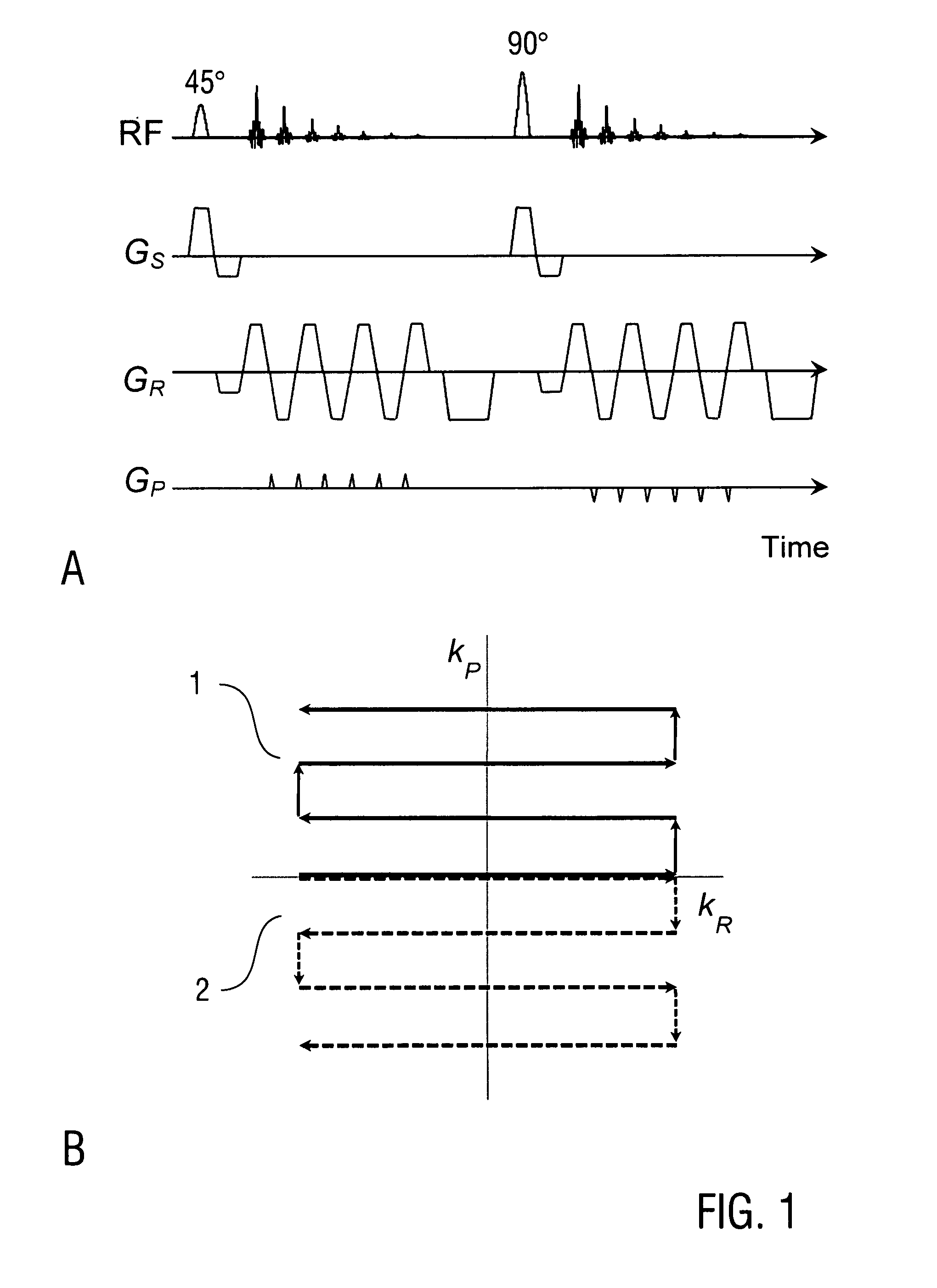
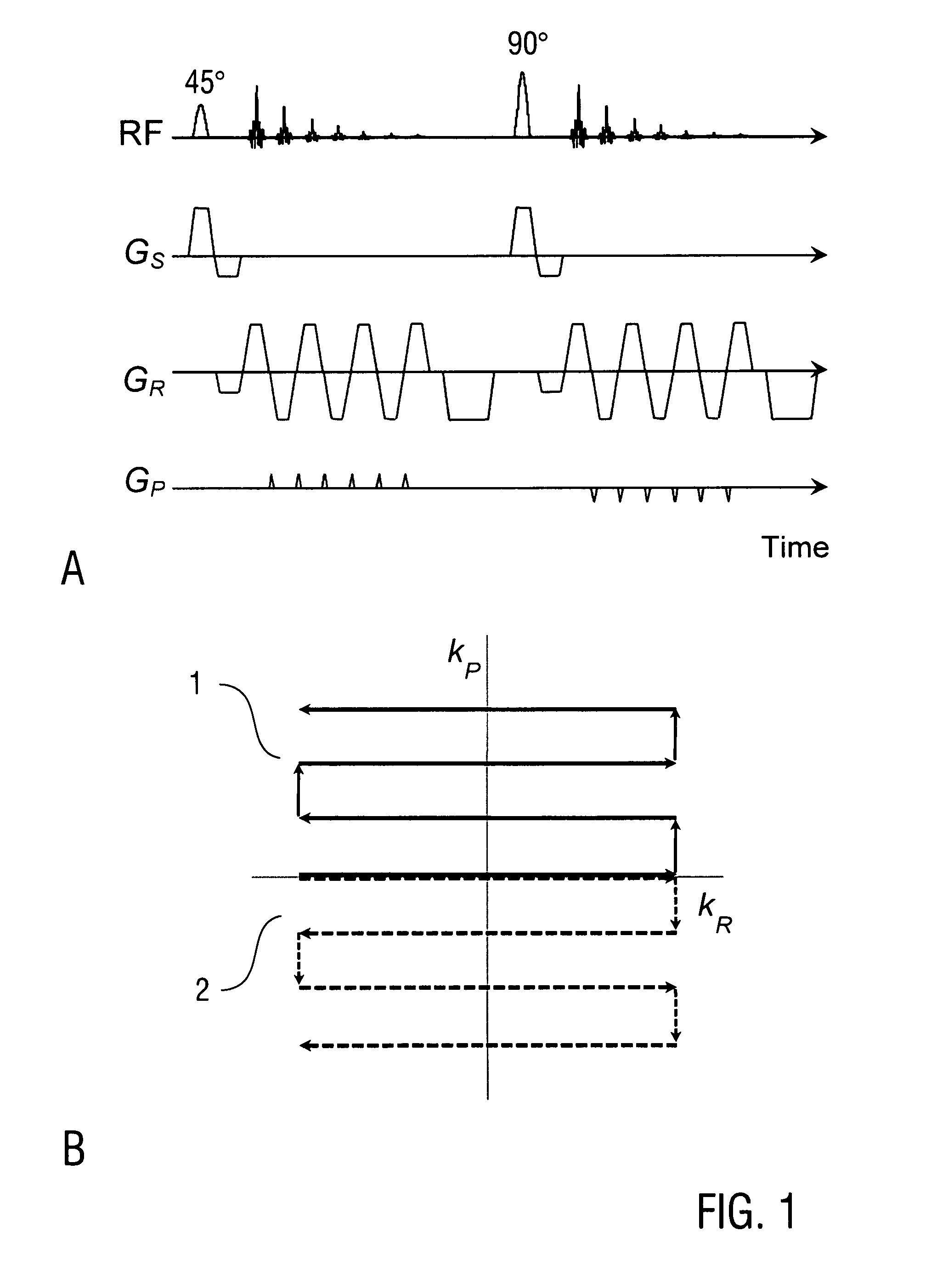
A method of magnetic resonance imaging of an object comprises the steps of arranging the object in a stationary magnetic field, subjecting the object to an excitation and encoding sequence of magnetic field gradients resulting in k-space sampling in two segments along the phase encoding direction, wherein the encoding sequence of the magnetic field gradients is selected such that the two segments in k-space are sampled along trajectories beginning with a central k-space line through the k-space center and continuing to opposite k-space borders of the two segments, collecting magnetic resonance signals created in the object, and reconstructing an image of the object based on the magnetic resonance signals, wherein one central k-space line is sampled in both of the two k-space segments, and intersegment phase and / or intensity deviations are corrected in both k-space segments using the magnetic resonance signals collected along the central k-space line. Furthermore, an imaging device for magnetic resonance imaging of an object is described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Method and apparatus for imaging abdominal aorta and aortic aneurysms
InactiveUS20060264741A1Eliminate riskIncrease contrastDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPre operativePathology diagnosis
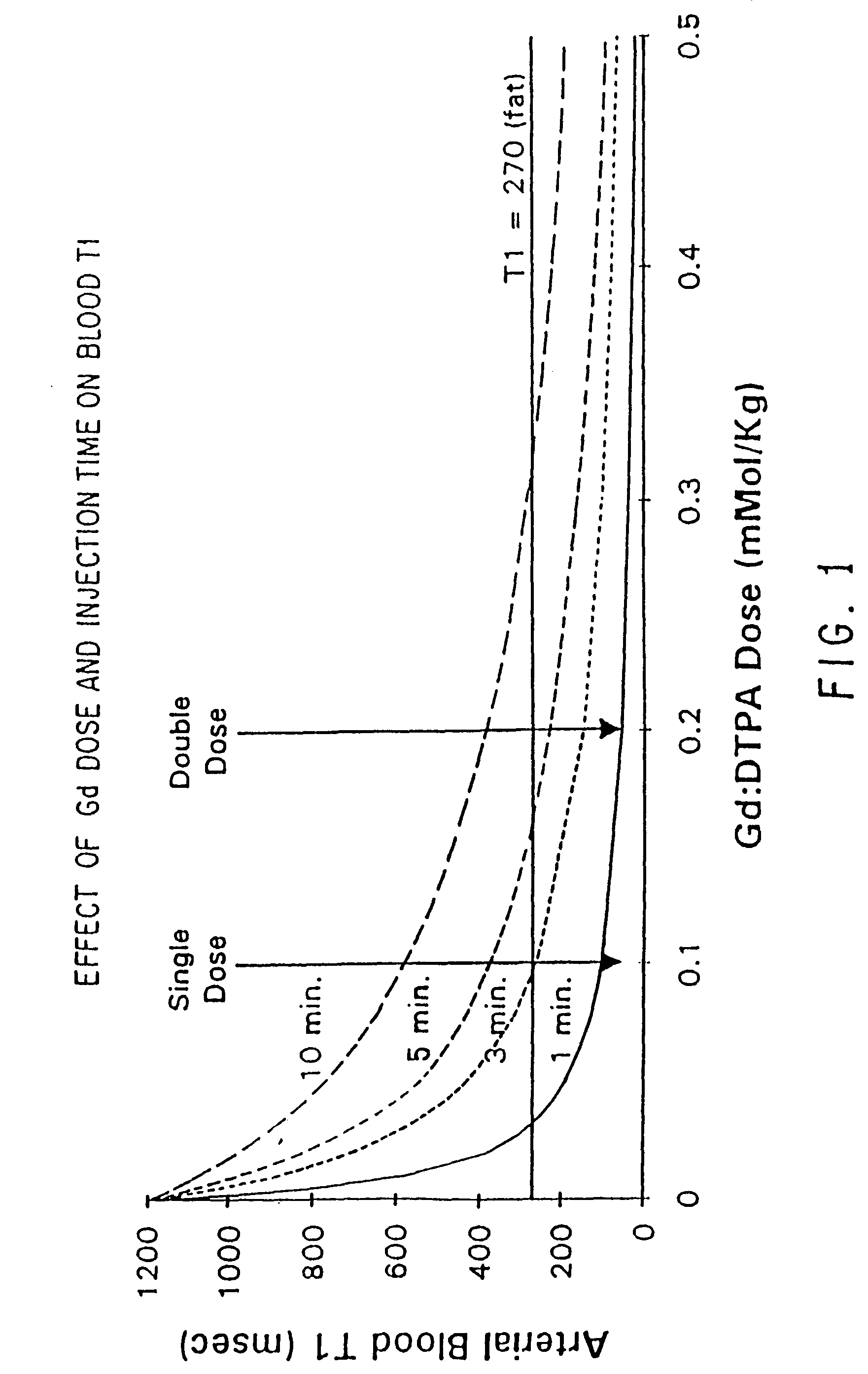
The present invention is a technique and apparatus for acquiring anatomic information used in diagnosing and characterizing abdominal aortic aneurismal disease and the like. This technique provides anatomic information, in the form of images, using a combination of a plurality of magnetic resonance angiography sequences, including a spin-echo and four contrast enhanced (e.g., gadolinium) magnetic resonance angiography sequences. The anatomic images may be used in, for example, pre-operative, operative and post-operative evaluation of aortic pathology, including aneurysms, atherosclerosis, and occlusive disease of branch vessels such as the renal arteries. The gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography provides sufficient anatomic detail to detect aneurysms and all relevant major branch vessel abnormalities seen at angiography operation. This technique and apparatus allows for imaging the aorta at a fraction of the cost of conventional aortography and without the risks of arterial catheterization or iodinated contrast.
Owner:PRINCE MARTIN R
Rapid magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance angiography of multiple anatomical territories
InactiveUS6493571B1Reduce osmotic pressureHigh resolutionBedsDiagnostic recording/measuringIodinated Contrast AgentSingle injection
A procedure and apparatus are provided which allow rapid positional change in the patient centering in order to facilitate the imaging of blood vessels in a series of different views. This procedure and apparatus can also facilitate the imaging of other tissues of the body at different spatial locations as well. The procedure and apparatus reduce the time required for obtaining the necessary images for a medical imaging examination using a single injection of an MRI or iodinated contrast agent.
Owner:WILLIAM BEAUMONT HOSPITAL
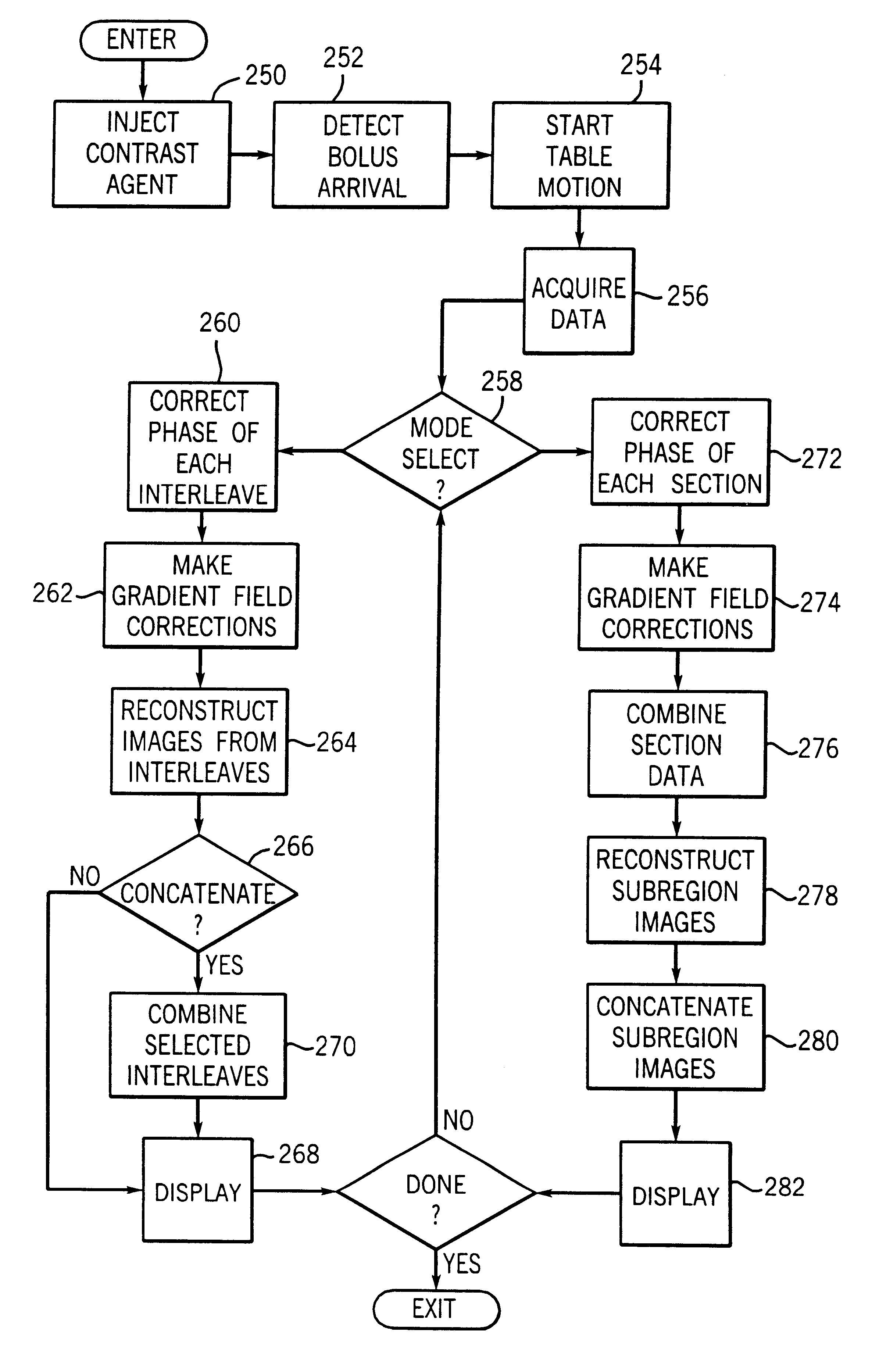
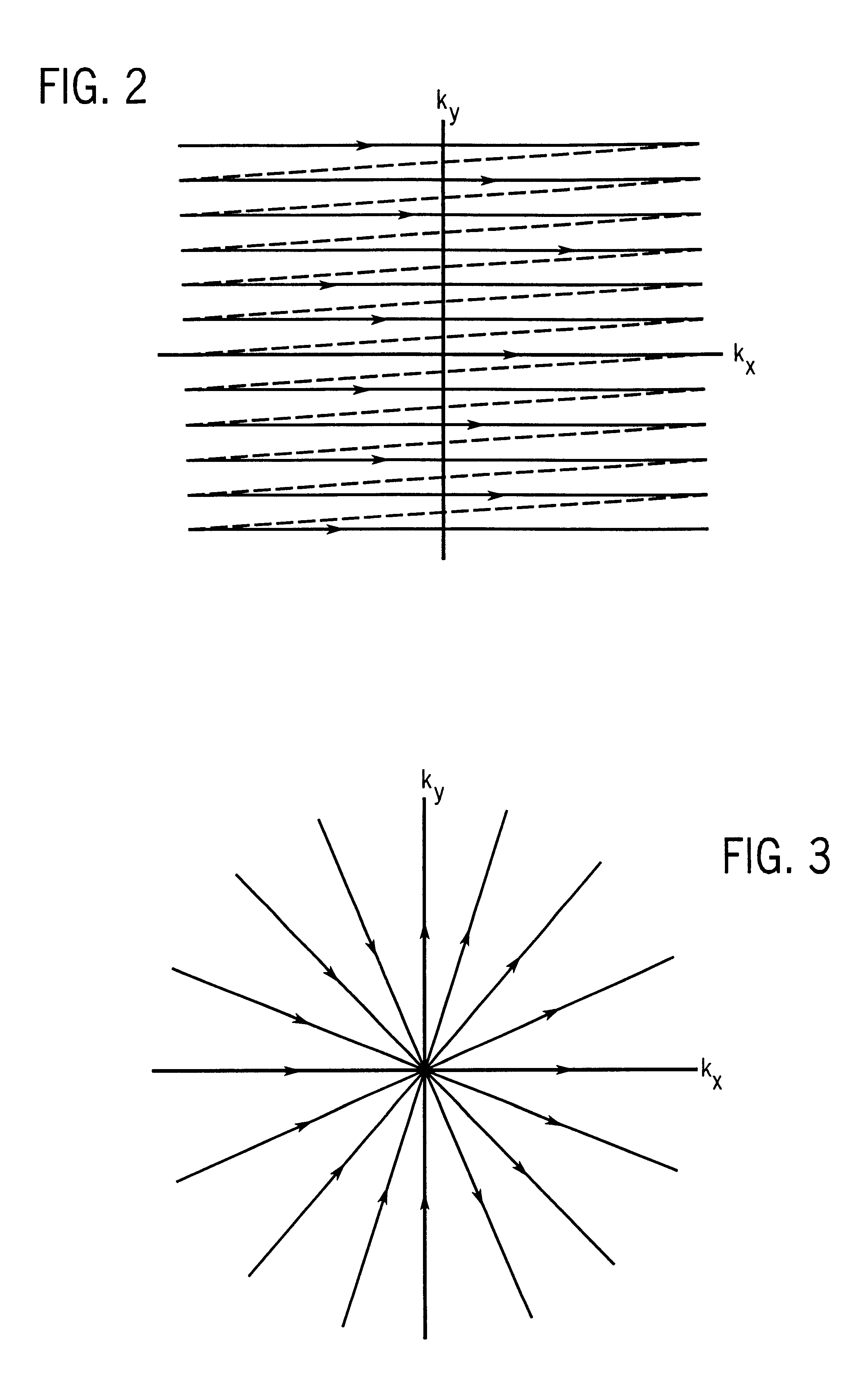
Magnetic resonance angiography using floating table projection imaging
InactiveUS6671536B2Quality improvementOptimal contrast enhancementSurgeryCharacter and pattern recognitionPhase correctionSingle image
A 3D projection reconstruction pulse sequence is employed to acquire CEMRA data as the subject is continuously moved through the field of view of the MRI system. The acquired k-space data is phase corrected to offset the table motion and the corrected data is used to reconstruct an image over a field of view that far exceeds the size of the MRI system field of view. In one embodiment the image is formed as a set of anatomic subregion images which are concatenated to form a single image and in another embodiment a series of images of each anatomic subregion are produced to depict the dynamic inflow of contrast agent.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
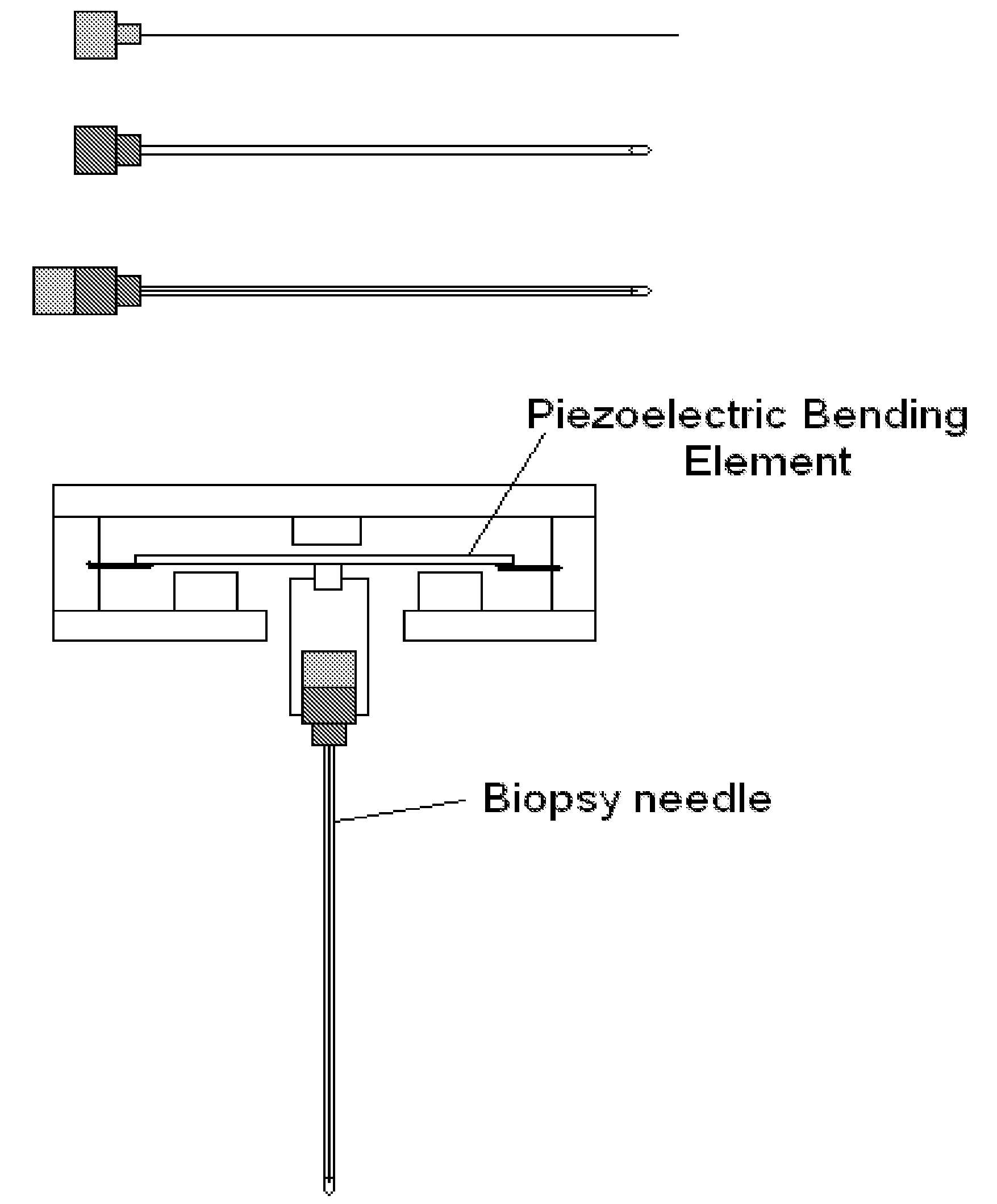
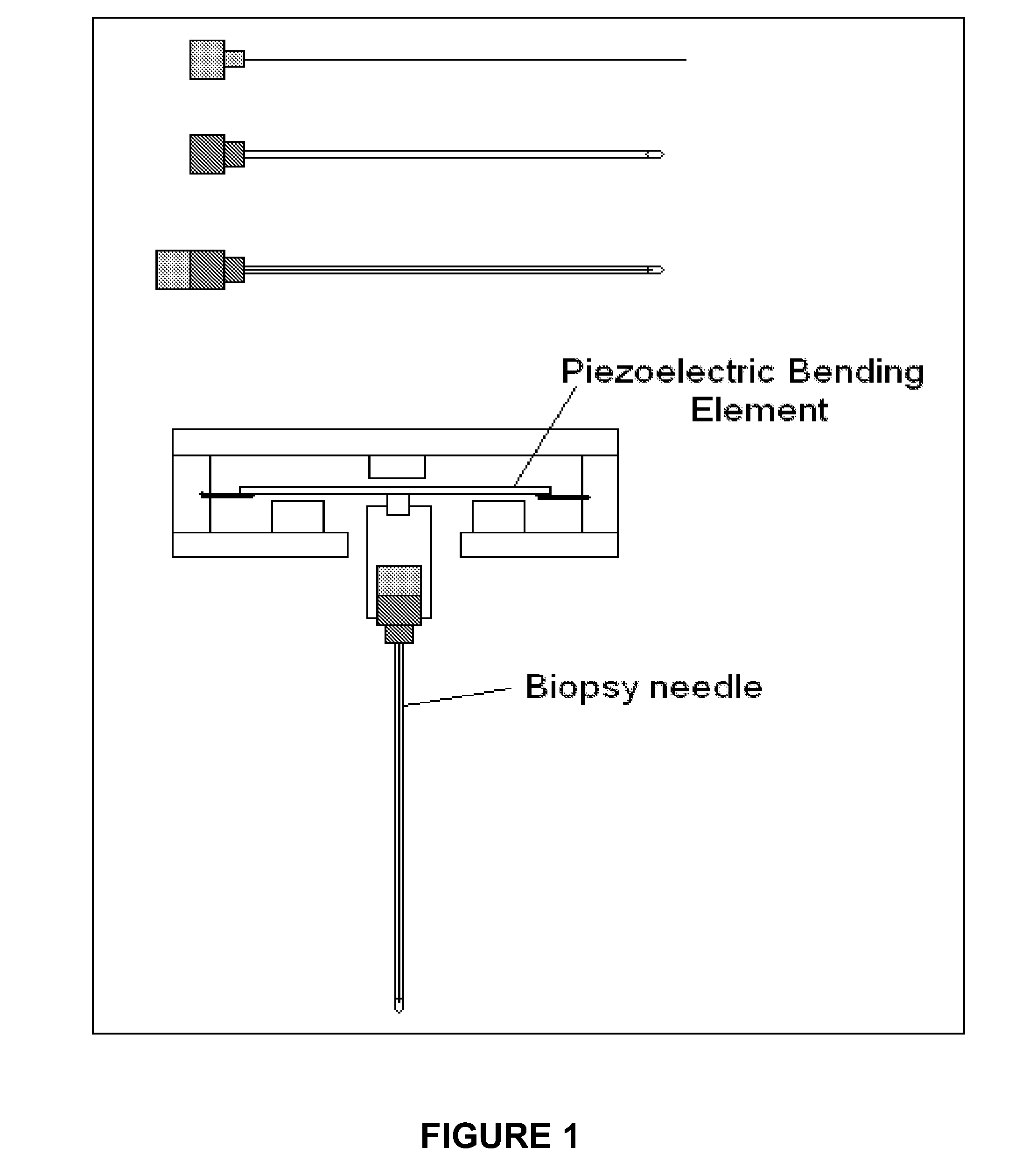
Novel needle driver for magnetic resonance elastography
ActiveUS20080255444A1Accurately determineReduce decreaseDiagnostics using vibrationsVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsAcupuncture needlesMild cognitive impairment (MCI)
Owner:LAWRENCE GROUP MEDICAL DEVICE TRUST
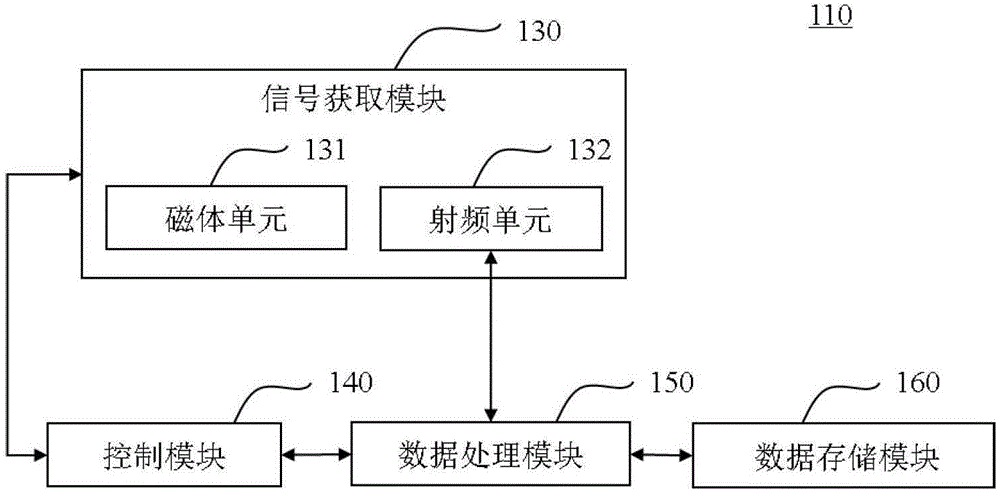
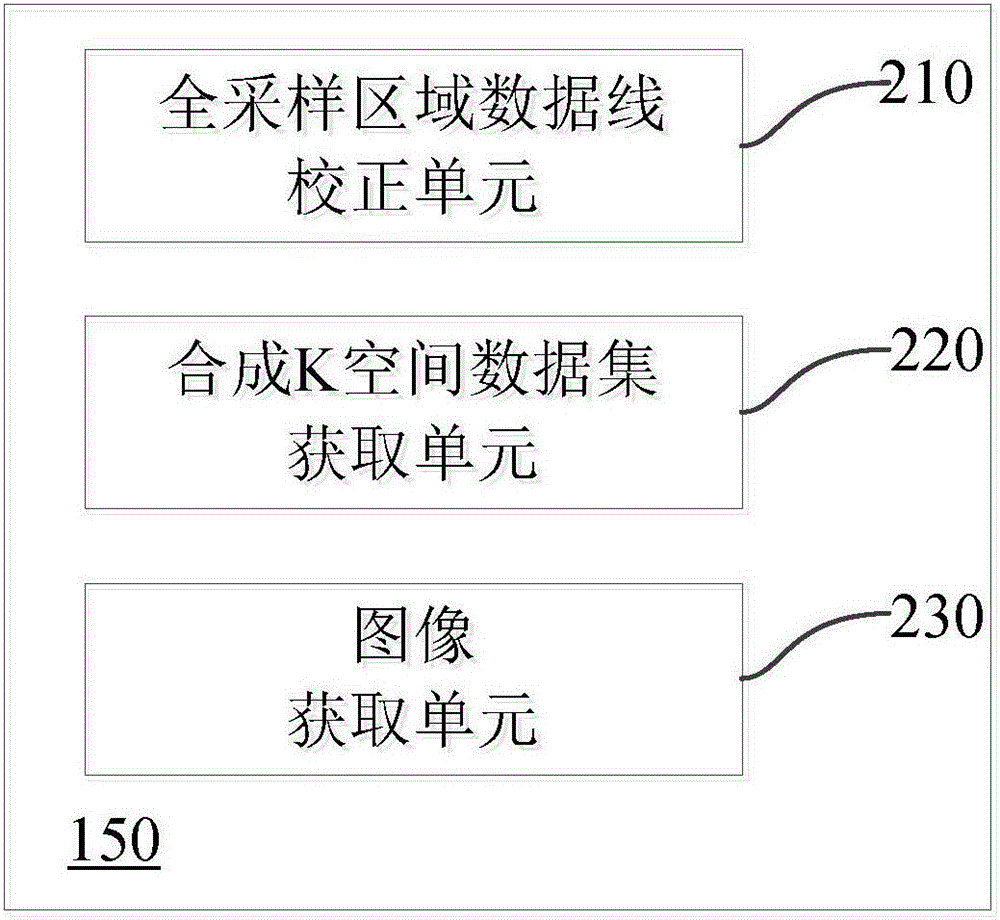
Magnetic resonance parallel imaging method and magnetic resonance imaging system
ActiveCN106597333AReduce mistakesInhibition Sensitive FunctionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringIntermediate imageImaging quality
The application discloses a magnetic resonance parallel imaging method. The method comprises: a target region is excited by using a radio-frequency pulse and a plurality of RF coils are used for collecting a magnetic resonance signal of the target region; phase coding is carried out on the magnetic resonance signal to obtain a plurality of data lines and K space is filled with the plurality of data lines, wherein the K space includes an all-sampling region and an under-sampling region; an intermediate image is obtained based on the data lines in the all-sampling region and pretreatment is carried out on the intermediate image; on the basis of the intermediate image after pretreatment, a correction data line in the all-sampling region is obtained; according to the correction data line in the all-sampling region, data lines of the under-sampling region are reconstructed and a synthesized K space data set is obtained; and according to the synthesized K space data set, a magnetic resonance image of a target region of a subject is obtained. With the method, the motion artifact can be suppressed; and the image quality can be improved. In addition, the application also provides a magnetic resonance imaging system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Magnetic resonance maps for analyzing tissue
ActiveUS20140270451A1High resolutionConvenient treatmentMedical simulationMedical imagingResonanceBrain mri
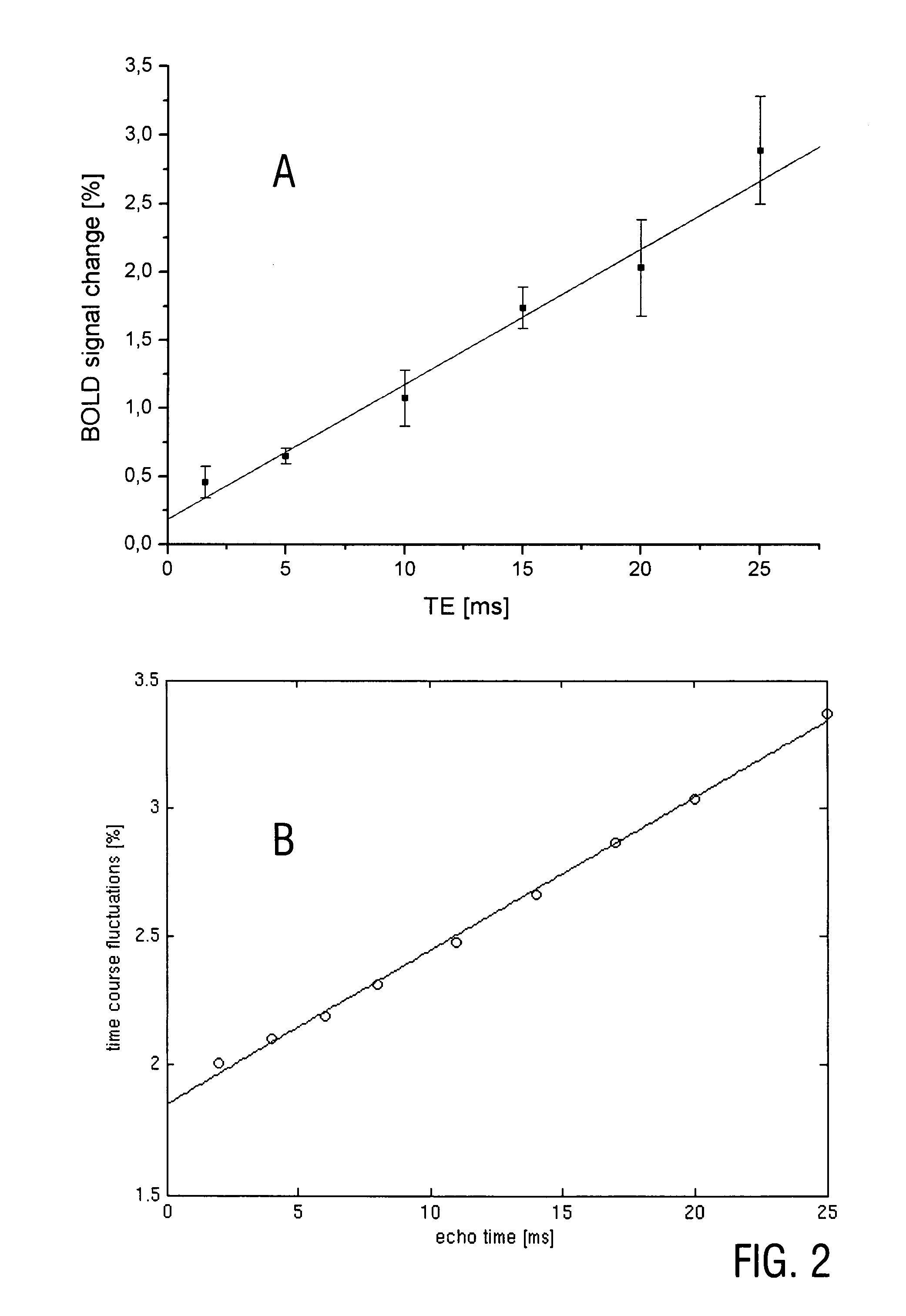
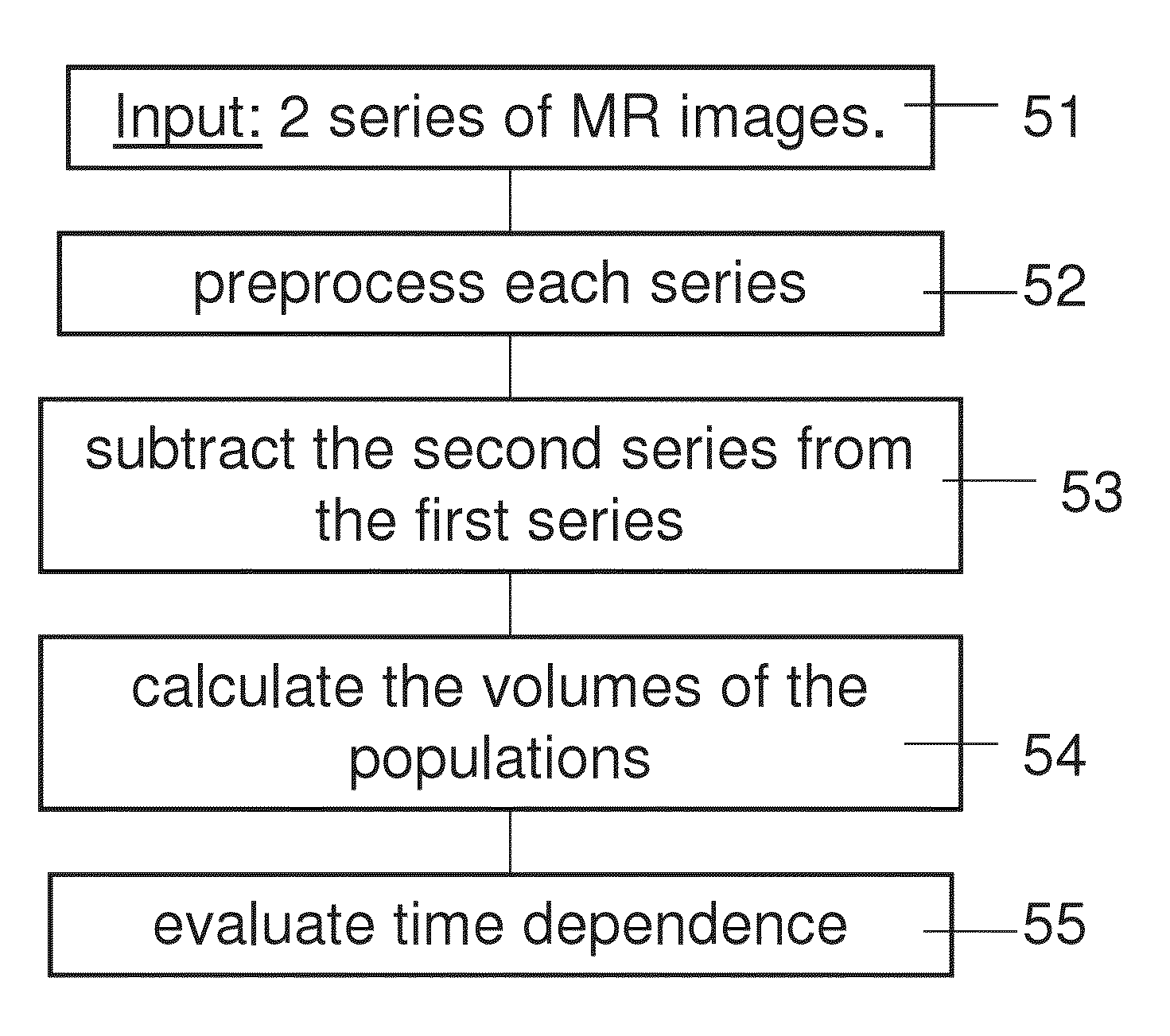
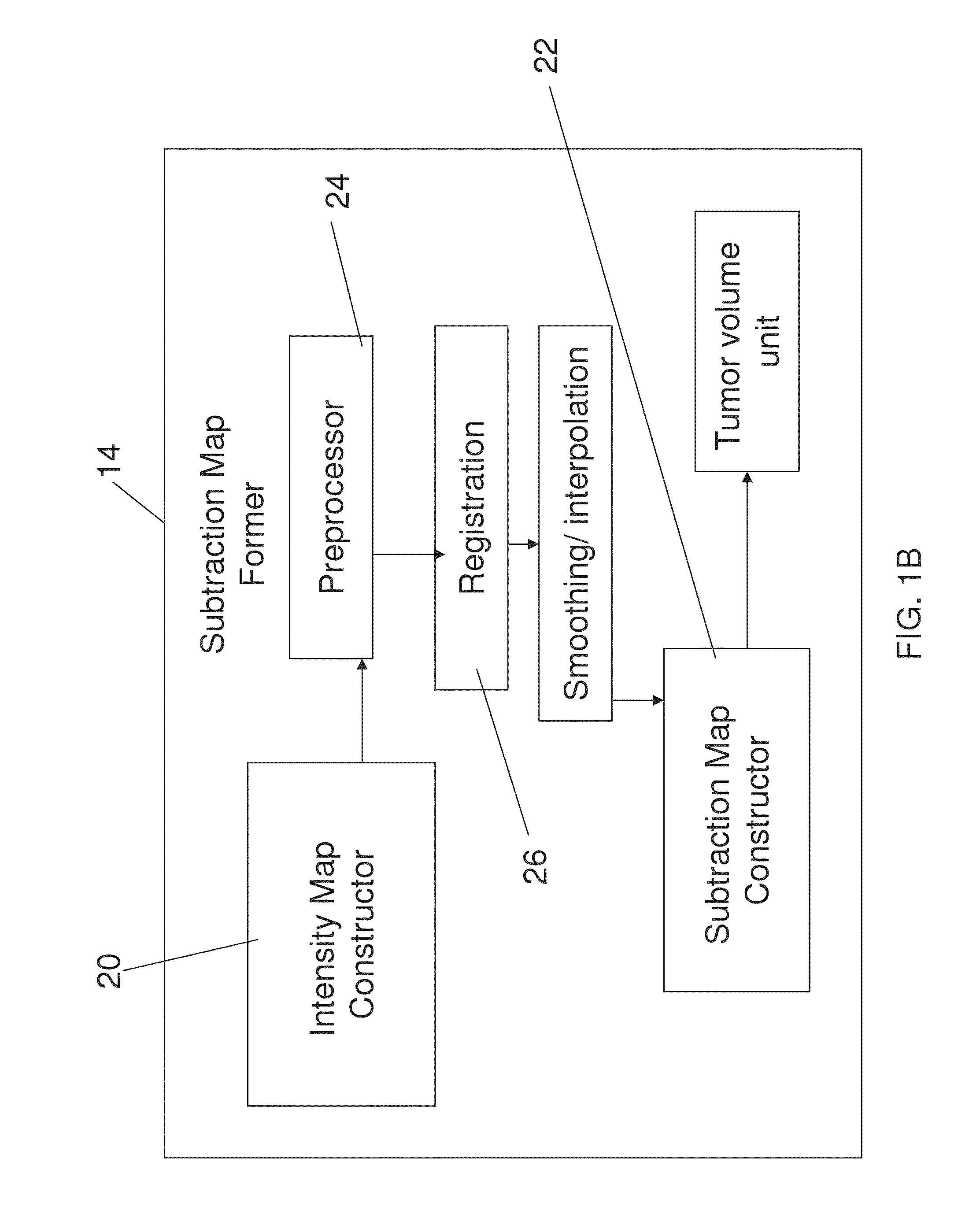
Apparatus for analyzing brain MRI, is disclosed. The apparatus comprises an input for receiving a first and a second MRI scans at the beginning and end of a predetermined time interval post contrast administration; a subtraction map former for forming a subtraction map from said first and said second MRI scans by analyzing said scans to distinguish between two primary populations, a slow population, in which contrast clearance from the tissue is slower than contrast accumulation, and a fast population in which clearance is faster than accumulation; and an output to provide an indication of distribution of said two primary populations, wherein said predetermined time period is at least twenty minutes.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD +1
Magnetic resonance imaging with improved imaging contrast
InactiveUS8664954B2Minimize timeMinimal echo timeMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetic field gradientObject based
A method of magnetic resonance imaging of an object comprises the steps of arranging the object in a stationary magnetic field, subjecting the object to an excitation and encoding sequence of magnetic field gradients resulting in k-space sampling in two segments along the phase encoding direction, wherein the encoding sequence of the magnetic field gradients is selected such that the two segments in k-space are sampled along trajectories beginning with a central k-space line through the k-space center and continuing to opposite k-space borders of the two segments, collecting magnetic resonance signals created in the object, and reconstructing an image of the object based on the magnetic resonance signals, wherein one central k-space line is sampled in both of the two k-space segments, and intersegment phase and / or intensity deviations are corrected in both k-space segments using the magnetic resonance signals collected along the central k-space line. Furthermore, an imaging device for magnetic resonance imaging of an object is described.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Method and device for real-time detection of moving electrocardiosignal QRS (magnetic resonance angiography) waves
InactiveCN103654770AReal-time uninterrupted detectionReduce complexityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalMobile device
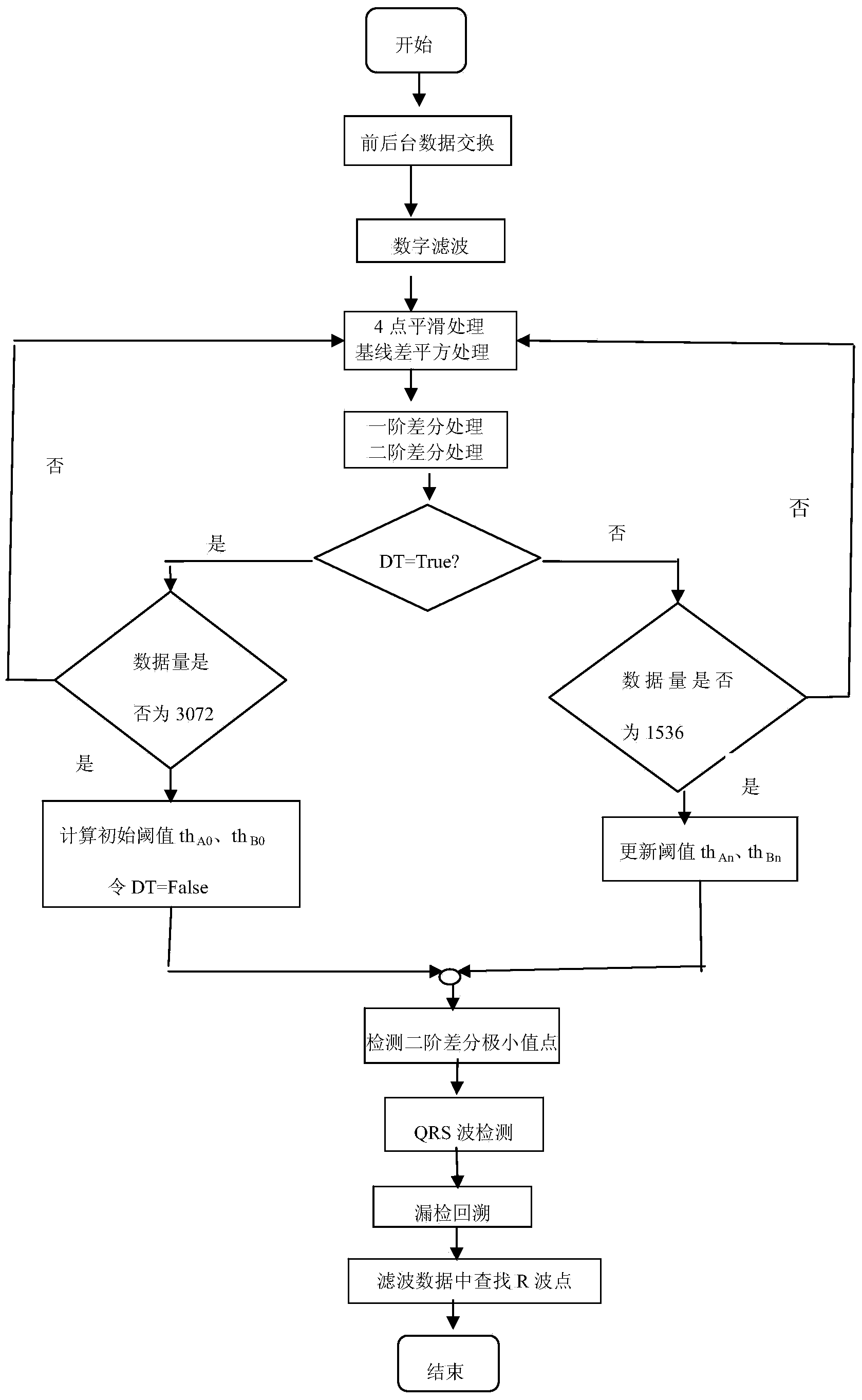
The invention discloses a method and a device for real-time detection of moving electrocardiosignal QRS (magnetic resonance angiography) waves. The method includes steps: performing four-point smoothing to electrocardiosignal data, subtracting a baseline by the smoothed data, and then performing square processing to the data in order to obtain a data sequence S; respectively performing first difference and second difference operations of the data sequence S to obtain data sequences D and E respectively; picking a certain amount of data from the data sequences D and E for calculating initial threshold values respectively, and updating the threshold values regularly; calculating and marking a second difference minimum value point meeting conditions of the threshold values as an R-type wave point; detecting a Q-type wave and an S-type wave near the R-type wave point, and excluding false detected QRS waves according to waveform features of the QRS waves; and finding a real R wave point in the electrocardiosignal data. By the aid of the method and the device, the QRS waves can be detected on a mobile device quickly and efficiently in real time.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
System and method for combined time-resolved magnetic resonance angiography and perfusion imaging
A method for performing magnetic resonance angiography and perfusion imaging using the same pulse sequence is provided. Time-resolved image data is acquired as a contrast agent passes through a subject. This image data is acquired by sampling Cartesian points in k-space that are contained within either a central region of k-space, or one of a plurality of different sets of radial sectors extending outwards from the central region. The image data is combined to form individual image frame data sets that are then reconstructed to produce a time series of image frames. From this time series, MR angiograms and perfusion maps are produced. With the added acquisition of calibration data, T1 relaxation parameters are estimated and quantitative perfusion maps produced.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Switched protective device against electromagnetic interference
ActiveUS20110152972A1Eliminate disadvantagesOperational securityElectrotherapyResonanceElectromagnetic interference
A device and a method for working in the presence of electromagnetic fields, in particular fields occurring in magnetic resonance tomography (referred to below as “MRT” or “MRI”) imaging devices. More precisely, the invention relates to a medical device (MD) in which an electrode is in contact with bodily tissue, and for detection of electromagnetic interference fields the input characteristic of the MD is automatically modified by a switching device in such a way that the influences of the electromagnetic interference fields are minimized.
Owner:BIOTRONIK SE & CO KG
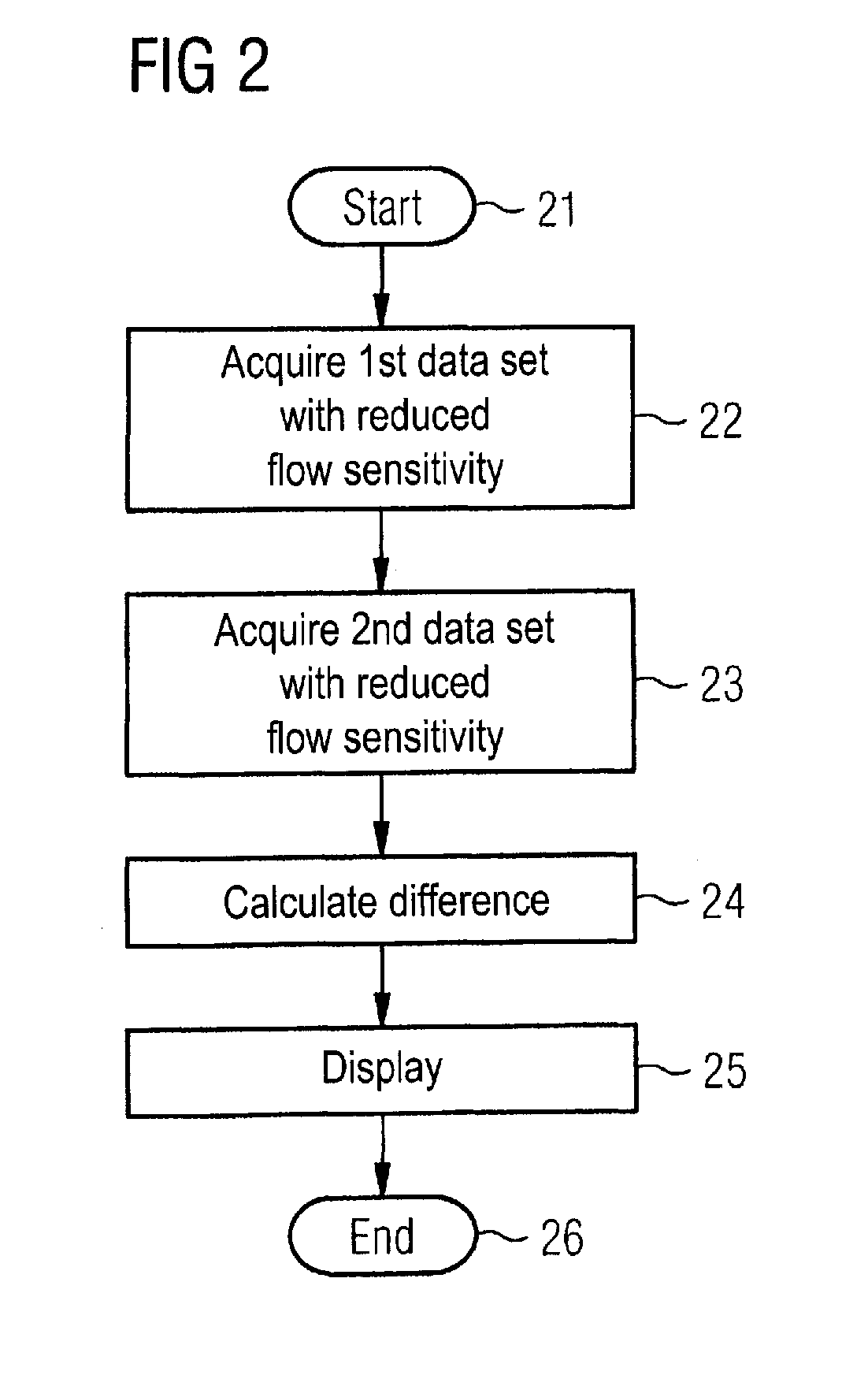
Magnetic resonance angiography with flow-compensated and flow-sensitive imaging
ActiveUS20100280357A1Increases flow sensitivityIncrease the differenceMagnetic measurementsCatheterHigh signal intensityData set
In a magnetic resonance angiography method with flow-compensated and flow-sensitive imaging and a magnetic resonance apparatus for implementing such a method, a first MR data set of the examination region is acquired with an imaging sequence in which vessels in the examination region are shown with high signal intensity, a second MR data set of the examination region with an imaging sequence in which the vessels in the examination region are shown with low signal intensity, and the angiographic magnetic resonance image is calculated in a processor by taking the difference of the first and second data set. The first data set is acquired with an imaging sequence with reduced flow sensitivity and the second data set is acquired with an imaging sequence with an increased flow sensitivity compared to the initial imaging sequence.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
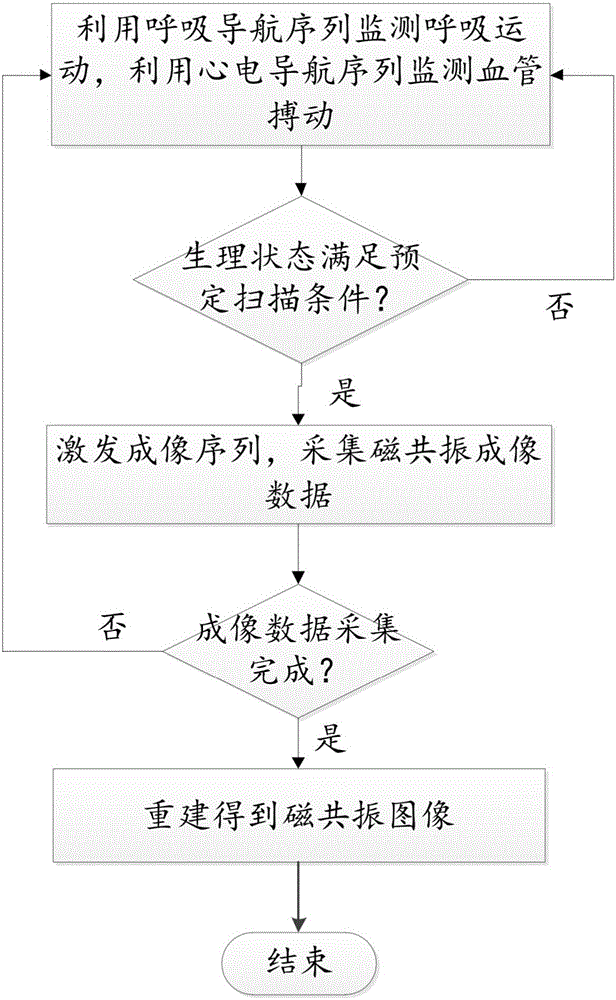
Magnetic resonance imaging method and system
ActiveCN106539584AAvoid homeostasis problemsReduce Motion ArtifactsRespiratory organ evaluationSensorsData acquisitionMri image
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance imaging method. The magnetic resonance imaging method comprises the steps of monitoring the respiratory movement of a subject through a respiratory navigation sequence, monitoring the cardiac motion of the subject through an electrocardio navigation sequence, and judging whether the physiological state meets the preset scanning condition or not, wherein the scanning condition is that the respiratory movement enters the expiratory end period and the cardiac motion enters the diastole; if the physiological state meets the scanning condition, motivating an imaging sequence in a to-be-imaged region, and acquiring the magnetic resonance imaging data; if the physiological state does not meet the scanning condition, continuing to monitor the physiological state of the subject till the physiological state meets the scanning condition; and after the imaging data is acquired, carrying out reestablishment to obtain a magnetic resonance image. According to the magnetic resonance imaging method, the physiological state of a human body is monitored through the respiratory navigation sequence and the electrocardio navigation sequence alternately, a magnetic resonance signal is acquired at a common interval of the expiratory end period and the diastole, and respiratory movement and cardiac motion artifacts can be effectively avoided. Besides, the invention further provides a magnetic resonance imaging system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Signal Transmitter for Pilot Tone Navigation
ActiveUS20170160367A1Convenient ArrangementInfluence is maximizedMeasurements using magnetic resonanceResonanceTomography
A transmitter for pilot tone navigation in a magnetic resonance tomography system includes a power supply and an antenna. The transmitter is configured to transmit a pilot tone signal via the antenna. The transmitter also includes a decoupling element in order to protect a transmitter output from signals that the antenna receives with excitation pulses of the magnetic resonance tomography system during a magnetic resonance tomography. In a method, movement-dependent changes to the pilot tone signal of the transmitter are identified by a controller of the magnetic resonance tomography system.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Channel pace-making signal detection method of electrocardiogram machine
ActiveCN102028459AThe test result is accurateAccurate methodDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsEcg signalNoise level
The invention discloses a channel pace-making signal detection method of an electrocardiogram machine, comprising the following steps: (1) carrying out sampling on original signals and carrying out differential processing on the sampled signals; (2) setting necessary conditions C1 for judging pace-making signals on the basis of a first threshold TH and a second threshold TH_Trail, detecting differential signals y(n) and filtering pulse spikes according to the necessary conditions C1; and (3) counting the number of spikes with high slope and low slope around the filtered pulse spikes, and carrying out noise evaluation on the filtered pulse spikes on the basis of the counted number. By utilizing the channel pace-making signal detection method, the noise and correct pace-making signals can be effectively distinguished, the accuracy of magnetic resonance angiography (QRS) detection and noise level evaluation is improved, therefore, the channel pace-making signal detection method can be conveniently applied on detection processing of channel pace-making signals of the 12-lead electrocardiogram machine, thus having good improvement effect in the process of detecting and analyzing electrocardiosignals.
Owner:GUANGDONG BIOLIGHT MEDITECH CO LTD
Method for contrast-agent-free angiographic imaging in magnetic resonance tomography
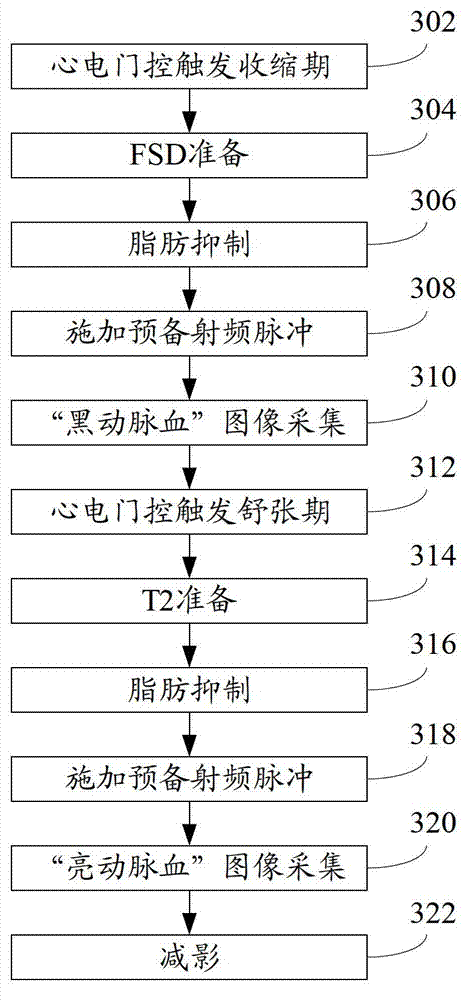
A method for contrast-agent-free non-triggered angiographic imaging in magnetic resonance tomography that includes the steps of (S1) 2D or 3D measurement of a bodily region having a flow of blood, using a flow-insensitive SSFP sequence, (S2) measurement of the same bodily region using a flow-sensitive SSFP sequence, (S3) registration of the measurement results obtained in steps S1 and S2 to one another, (S4) unweighted or self-weighted subtraction of the registered measurement result obtained in step S2 from the registered measurement result obtained in step S1, (S5) execution of a 2D or 3D image correction of the image obtained in step S4 by removing image distortions caused by gradient field inhomogeneities and / or magnetic basic field inhomogeneities, and (S6) representation of the angiogram obtained in step S5 in the form of an MIP or segmented 2D or 3D vessel tree representation.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
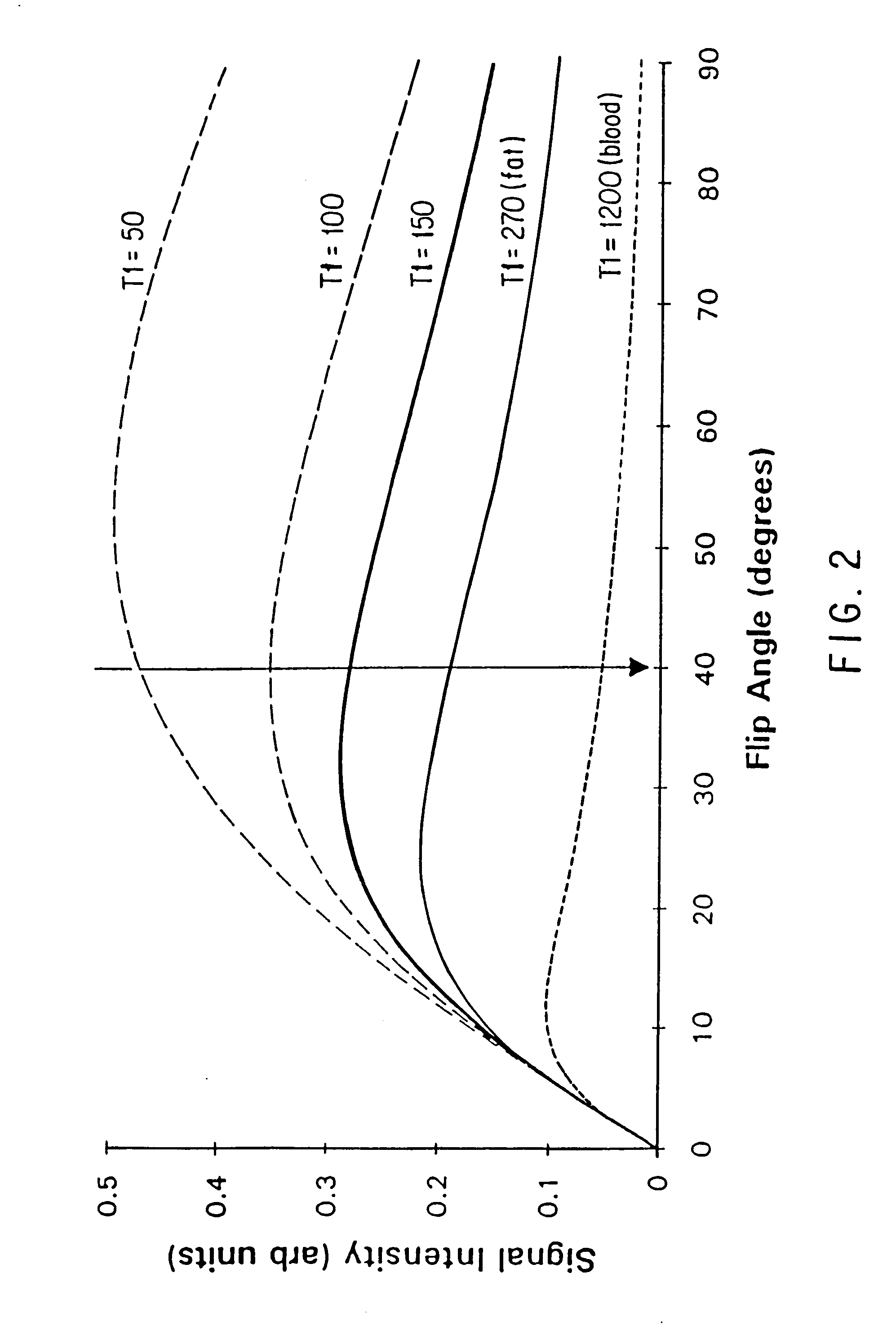
Flip angle modulated magnetic resonance angiography
InactiveUS6198960B1Improvement in signal enhancementEnhanced signalDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPulse sequenceMR - Magnetic resonance
A dynamic MRA study of a subject is performed using a 3D fast gradient-recalled echo pulse sequence after the subject is injected with a contrast agent. The flip angle of an rf excitation pulse in the pulse sequence is modulated during the acquisition as a function of contrast agent concentration in the region of interest. In one embodiment the flip angle is updated by interleaving measurement pulse sequences which measure in real-time contrast agent concentration. In another embodiment the contrast concentration profile is determined in advance and a corresponding table of optimal flip angles are calculated and played out during the image acquisition.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
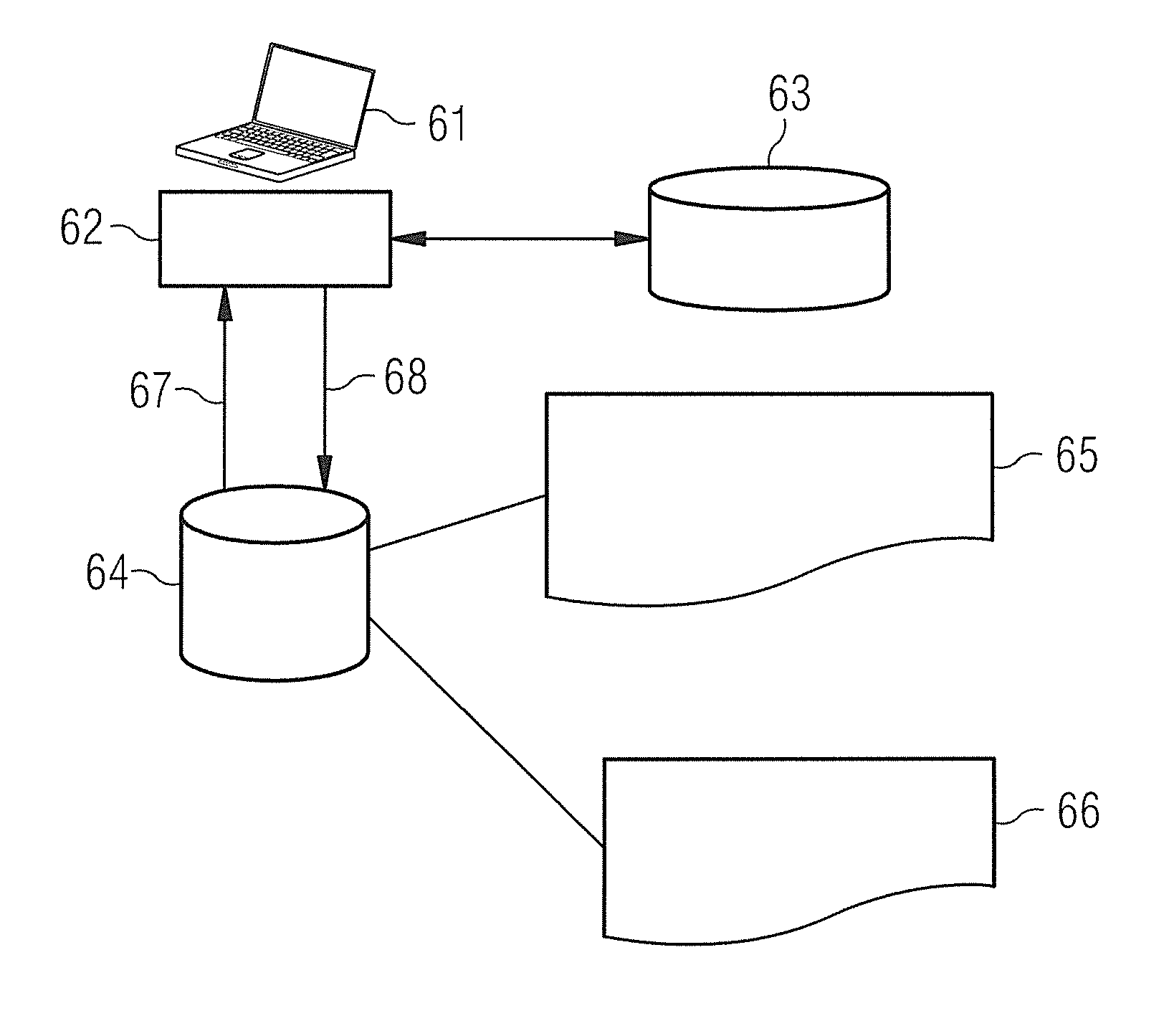
Method to configure an imaging device
InactiveUS20120041909A1Reduces time and cost and tendency toward errorAutomatic conversion of the protocolsMagnetic measurementsDigital computer detailsTraining phaseProgram planning
A database contains variants of protocols for the operation of magnetic resonance tomographs as well as different types of magnetic resonance tomographs. Each variant contains parameter values and is associated with one of the types. In a training phase, relationships are determined between the parameters among one another and / or between the parameters and the associated types and are stored as patterns in a knowledge base. A protocol plan for the operation of a new magnetic resonance tomograph is created later in an application phase using the determined pattern. The method offers the advantage that the efficiency and quality of the automatic conversion of the protocols is improved. The improved quality of the protocol plan reduces operating time and costs for a manual post-processing of the protocols. Furthermore, a higher consistency of the protocols among one another is achieved both between product families and between individual configurations.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
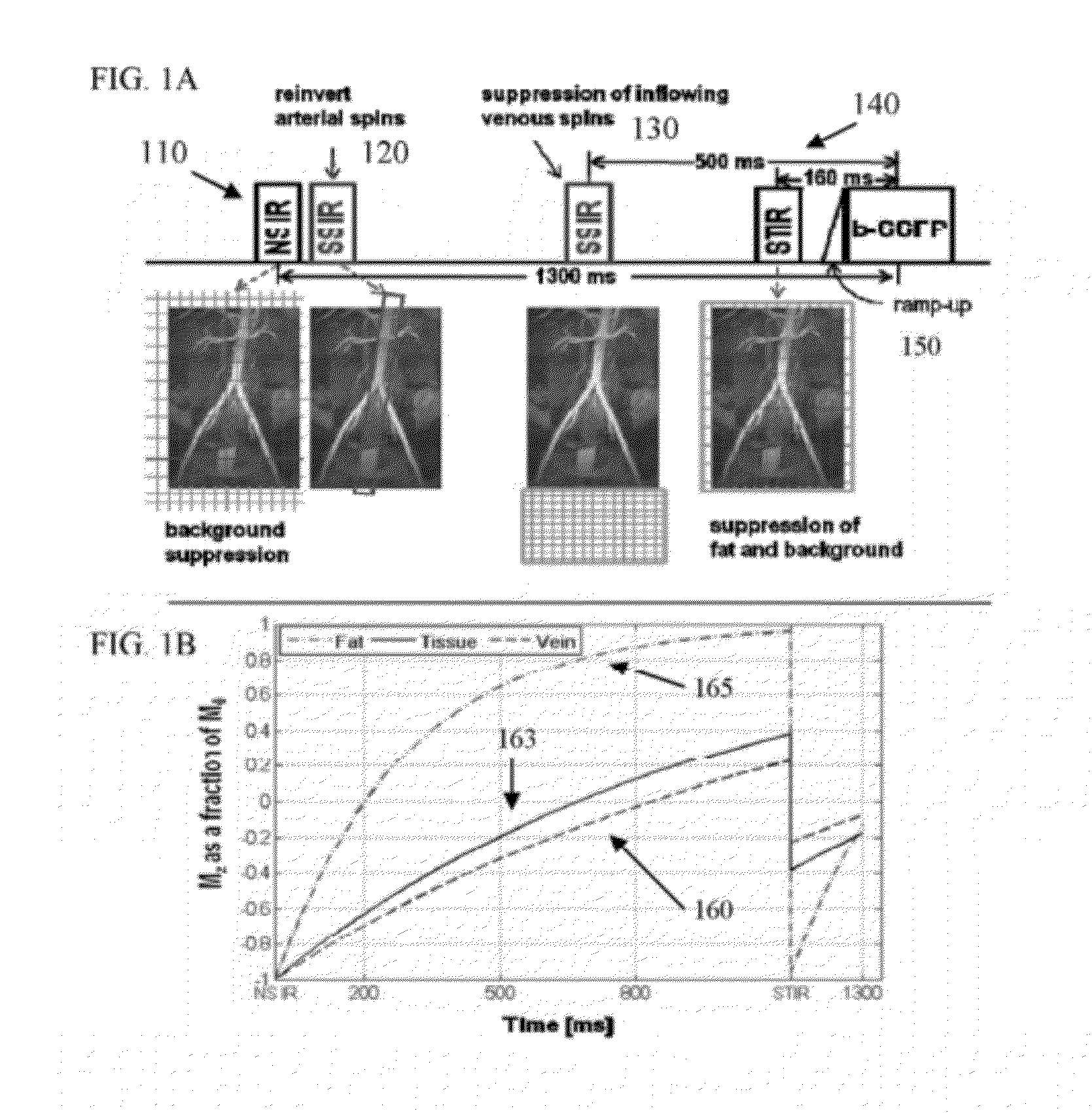
Apparatus and Method of Non-Contrast Magnetic Resonance Angiography of Abdominal and Pelvic Arteries
InactiveUS20120296199A1FocusMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringInversion TimeArtery organ
Exemplary method and apparatus can be provided for generating information regarding at least one tissue. Using such exemplary method and apparatus, it is possible to generate a plurality of inversion recovery (IR) radio frequency (RF) pulses that are configured to establish an identifier of an element associated with at least one portion of the tissue(s). It is also possible to determine an inversion time associated with at least one of the RF pulses. Further, it is possible to generate, e.g., with a computing arrangement, the information regarding the tissue(s) based on the inversion time.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
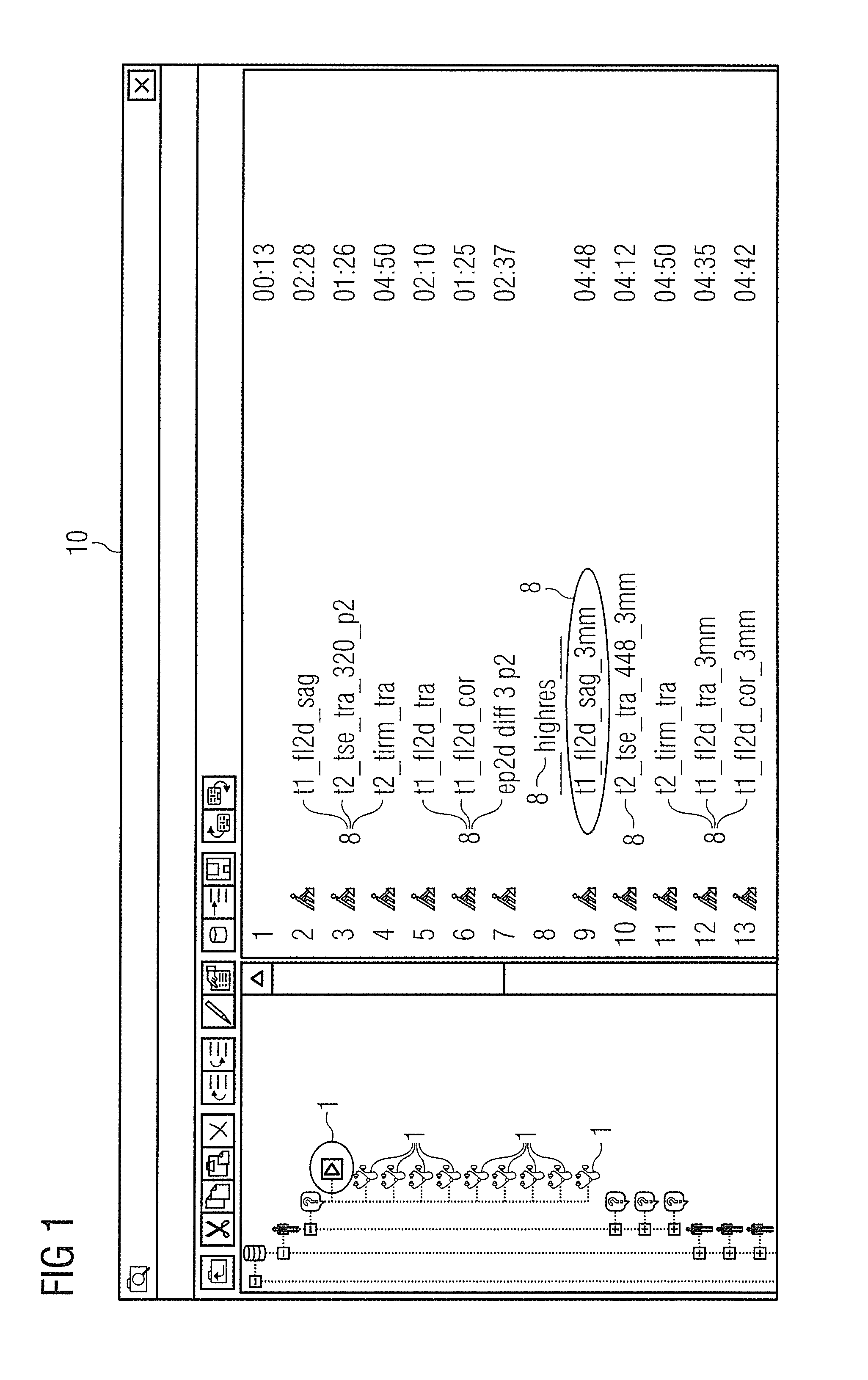
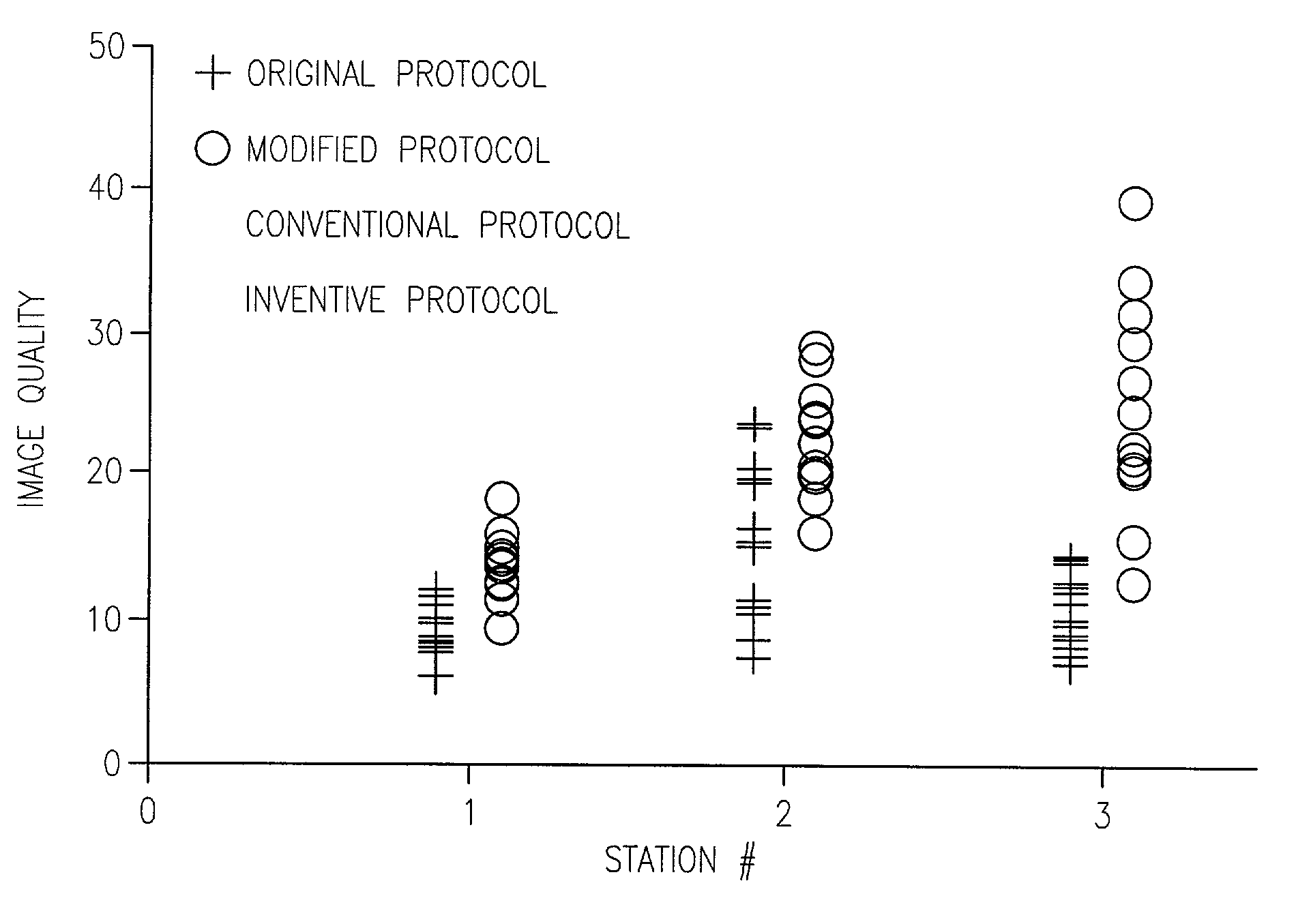
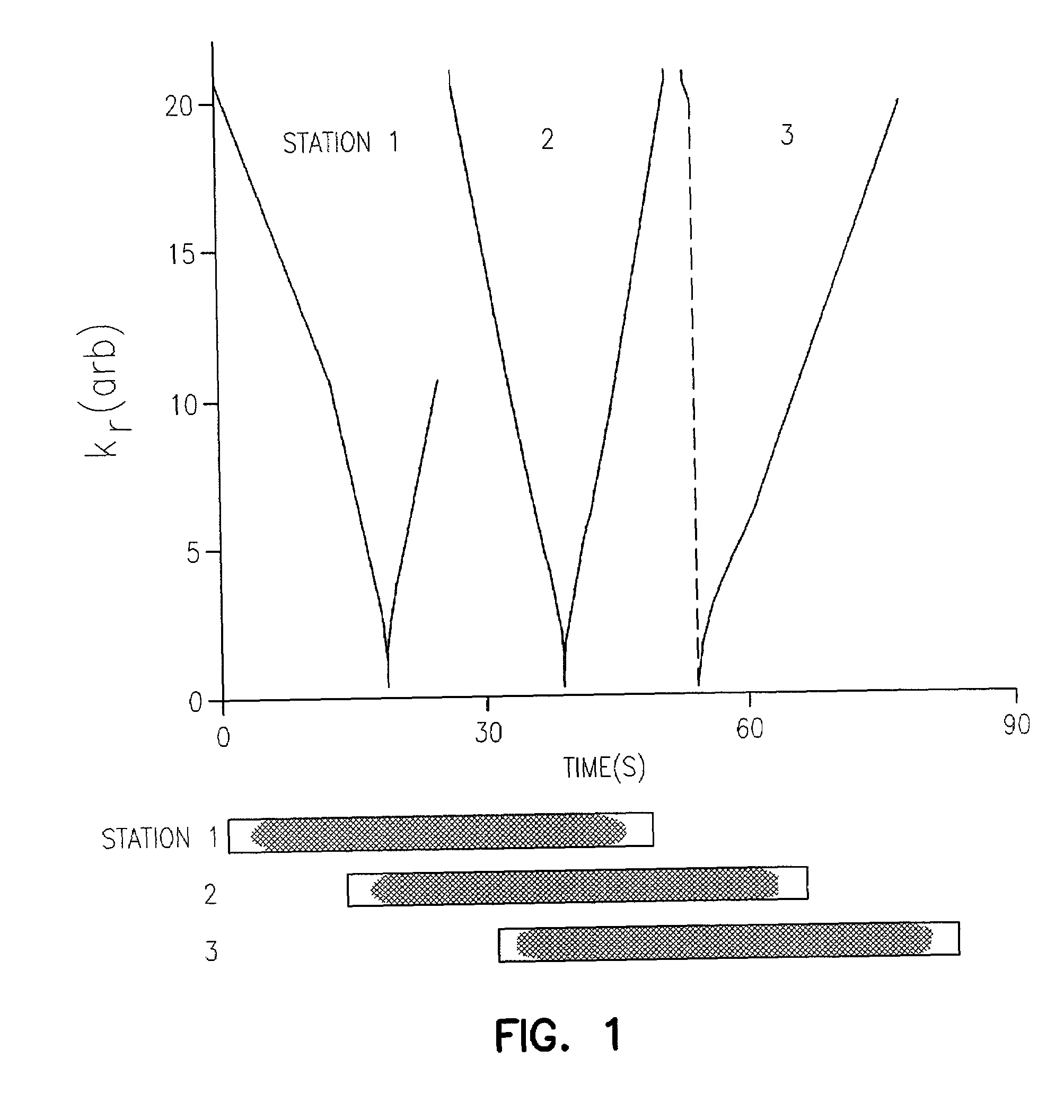
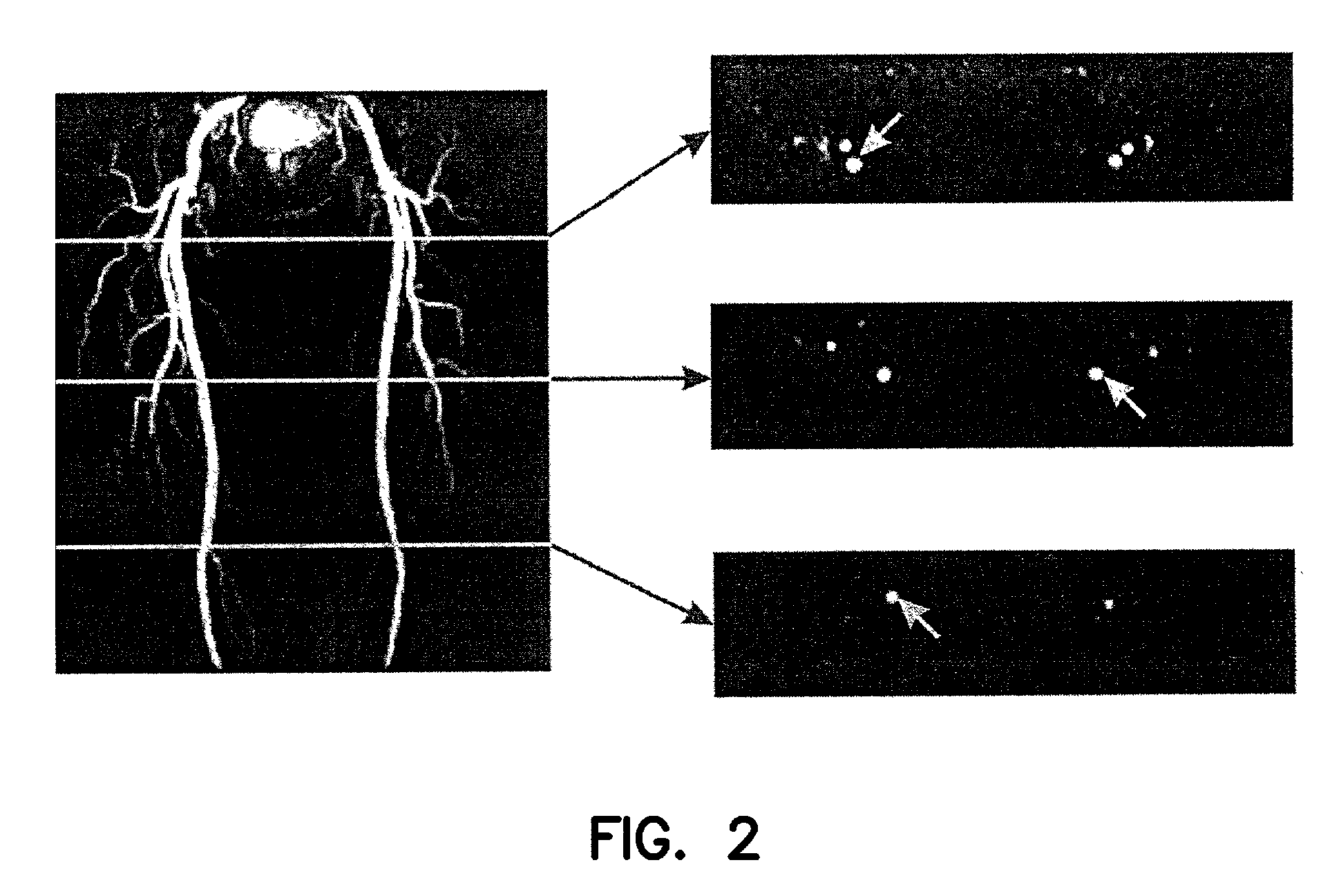
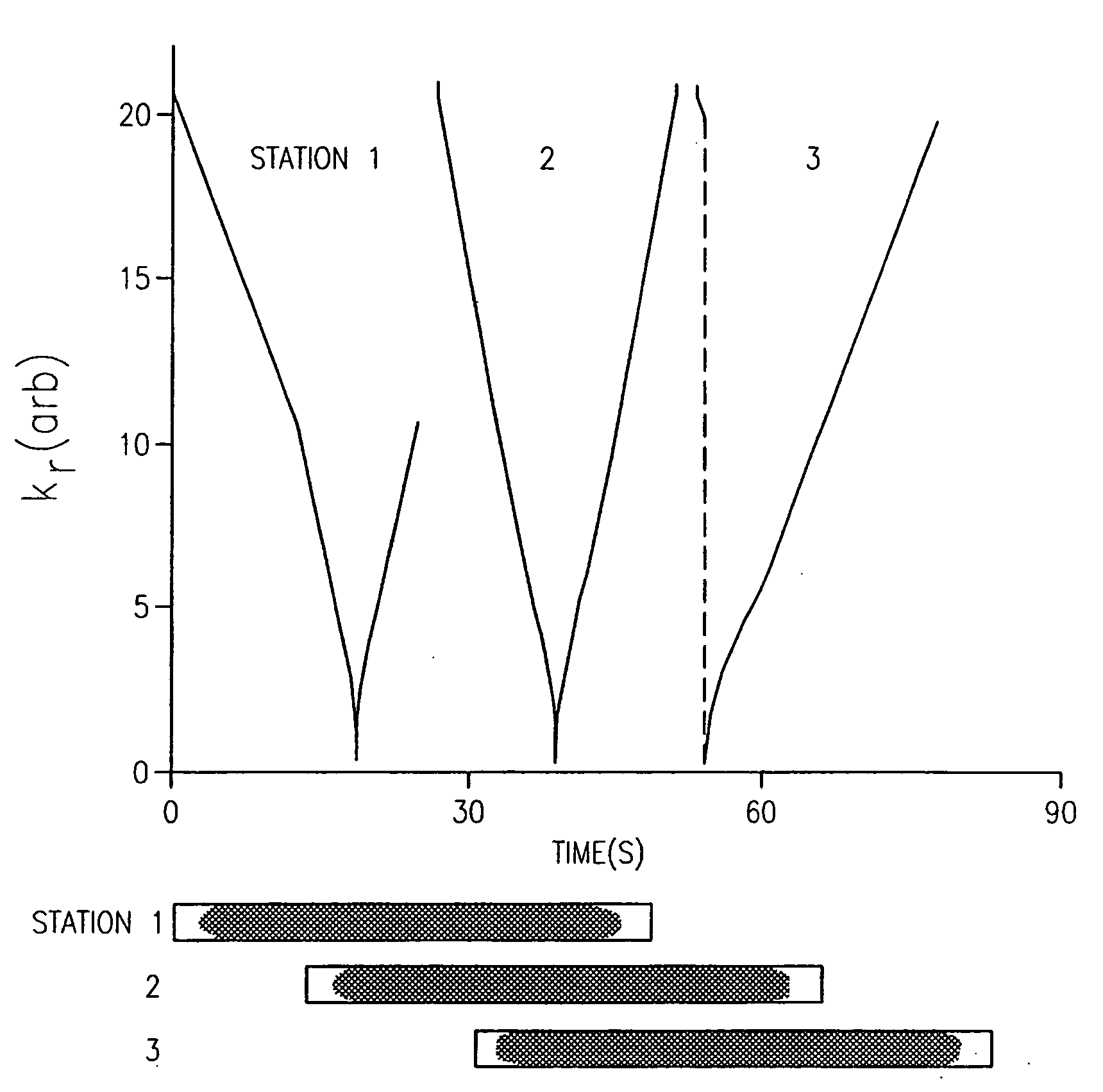
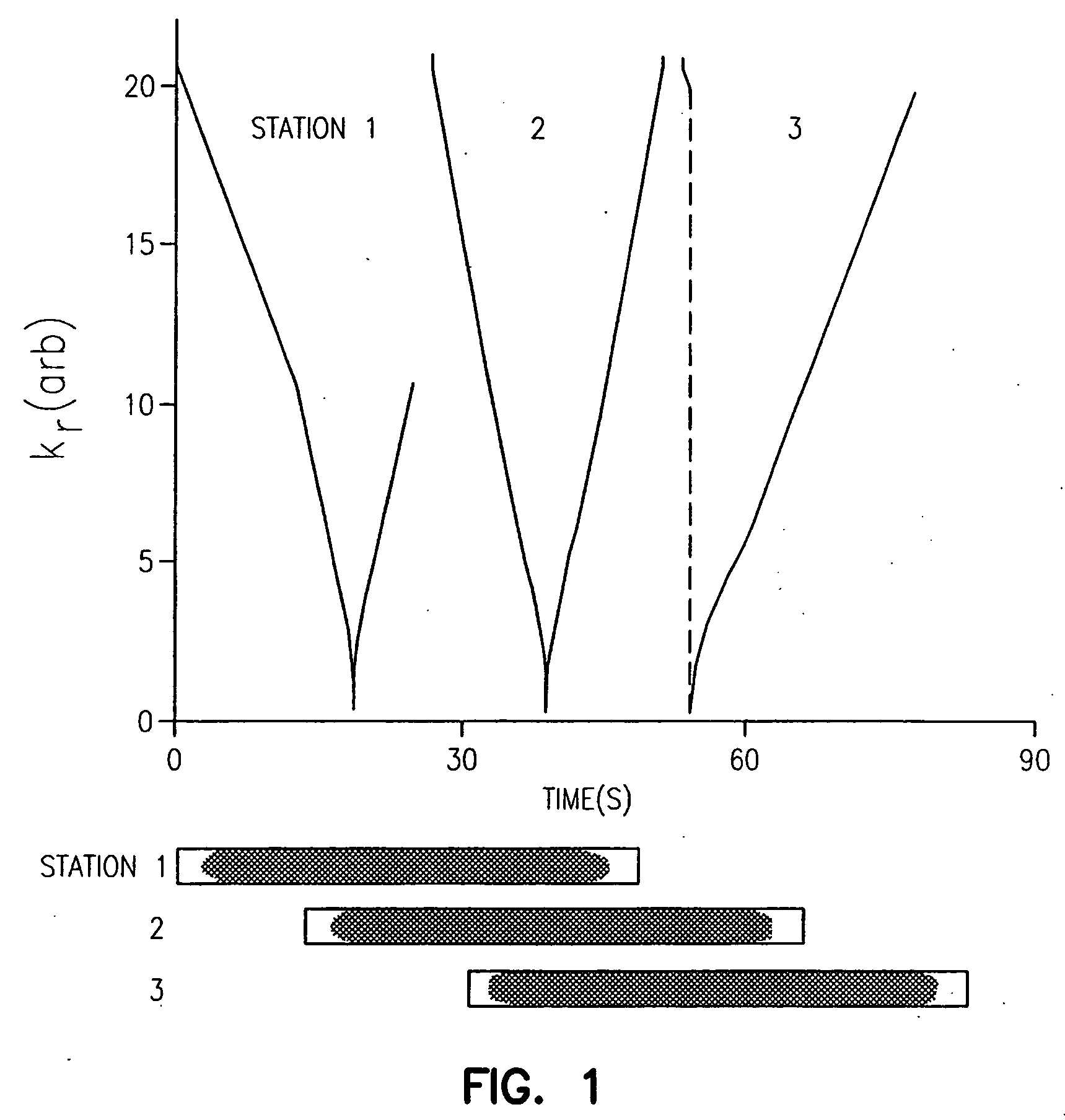
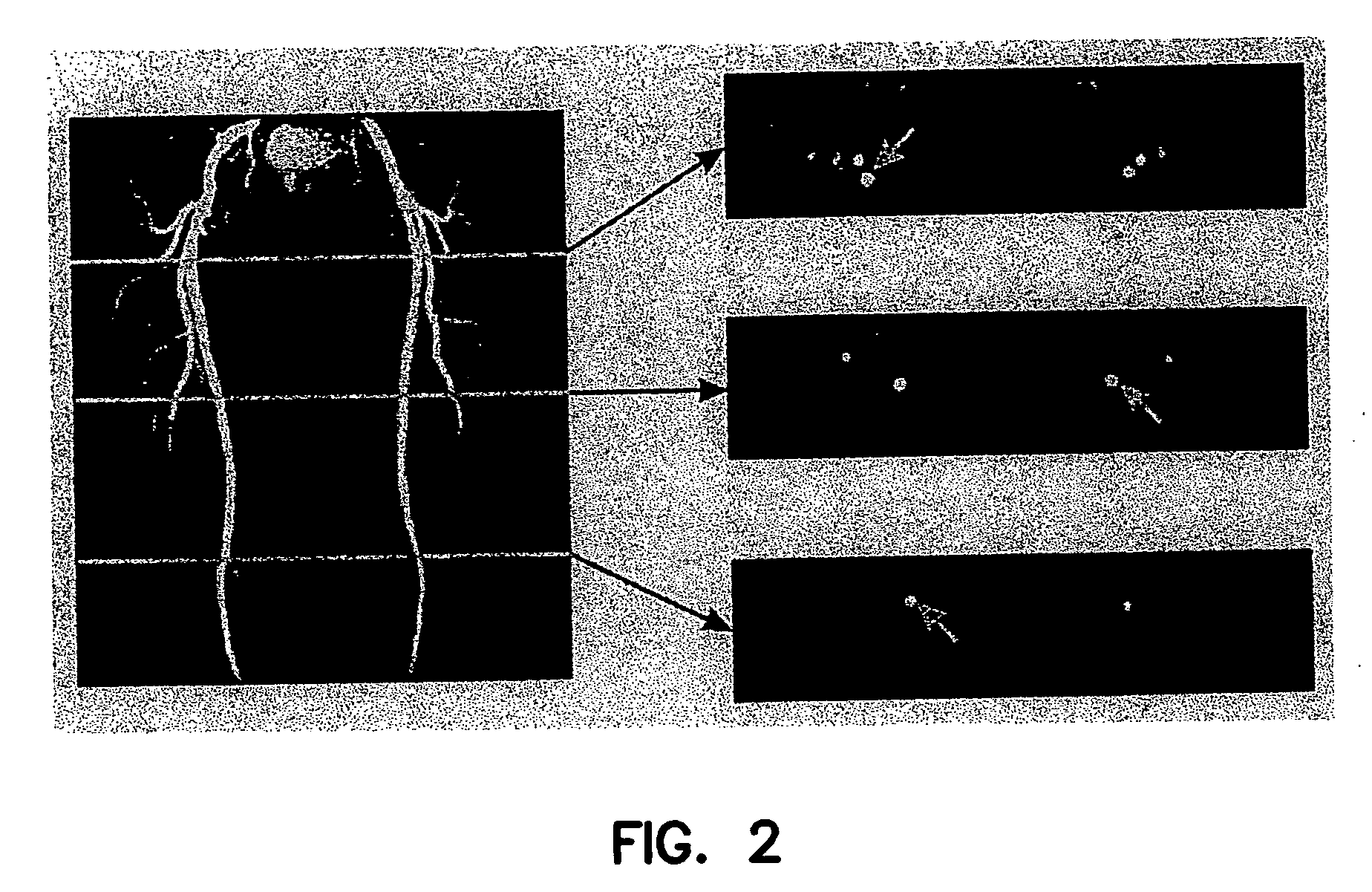
Method and apparatus for anatomically tailored k-space sampling and recessed elliptical view ordering for bolus-enhanced 3D MR angiography
InactiveUS7003343B2Increasing dose sharingMinimize timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImaging qualityBlood vessel
Current bolus chase magnetic resonance angiography is limited by the imaging time for each station. Tailoring the density of k-space sampling along the anterior-posterior direction of the coronal station allows a substantial decrease in scan time that leads to greater contrast bolus sharing among stations and consequently a significant improvement in image quality. Fast arterial-venous transit in the carotid arteries requires accurate, reliable timing of the acquisition to the bolus transit to maximize arterial signal and minimize venous artifacts. The rising edge of the bolus is not utilized in conventional elliptical-centric view ordering because the critical k-space center must be acquired with full arterial enhancement. The invention provides a recessed elliptical-centric view ordering scheme is introduced in which the k-space center is acquired a few seconds following scan initiation. The recessed view ordering is shown to be more robust to timing errors in a patient studies.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Method and apparatus for accelerated phase contrast magnetic resonance angiography and blood flow imaging
InactiveUS20140056496A1Improve accuracyImprove processing speedCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringReconstruction methodOutput device
An apparatus and method process magnetic resonance image (MRI) data and other data from a subject, including image data corresponding to at least one of angiographic data, four-dimensional blood flow, neurological blood flow, abdominal blood flow, and peripheral blood flow in the subject, and applies a compressed sensing (CS) reconstruction method utilizing a complex difference of the image data as a sparsifying transform for imaging of at least one of blood flow and magnetic resonance angiography to output a reconstructed image of the blood flow and magnetic resonance angiography, in the subject with increased processing speed and having high accuracy. The apparatus receives the MRI data of the fluid flow from an MRI device. The processor operates predetermined software, receives the MRI data, and applies the CS reconstruction method to generate the reconstructed image. An output device outputs the reconstructed image of the fluid flow.
Owner:BETH ISRAEL DEACONESS MEDICAL CENT INC
Method and apparatus for anatomically tailored k-space sampling and recessed elliptical view ordering for bolus-enhanced 3D MR angiography
InactiveUS20050203377A1Increasing dose sharingMinimize timeDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImaging qualityImage quality
Current bolus chase magnetic resonance angiography is limited by the imaging time for each station. Tailoring the density of k-space sampling along the anterior-posterior direction of the coronal station allows a substantial decrease in scan time that leads to greater contrast bolus sharing among stations and consequently a significant improvement in image quality. Fast arterial-venous transit in the carotid arteries requires accurate, reliable timing of the acquisition to the bolus transit to maximize arterial signal and minimize venous artifacts. The rising edge of the bolus is not utilized in conventional elliptical-centric view ordering because the critical k-space center must be acquired with full arterial enhancement. The invention provides a recessed elliptical-centric view ordering scheme is introduced in which the k-space center is acquired a few seconds following scan initiation. The recessed view ordering is shown to be more robust to timing errors in a patient studies.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
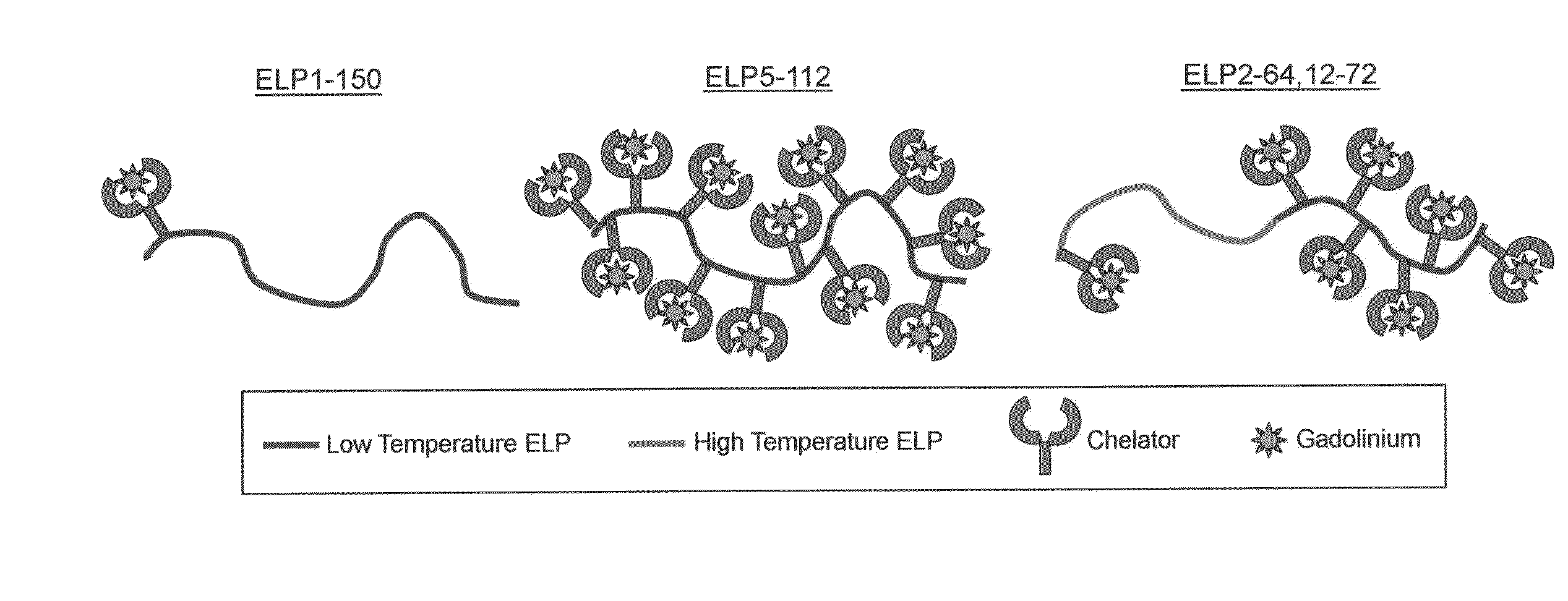
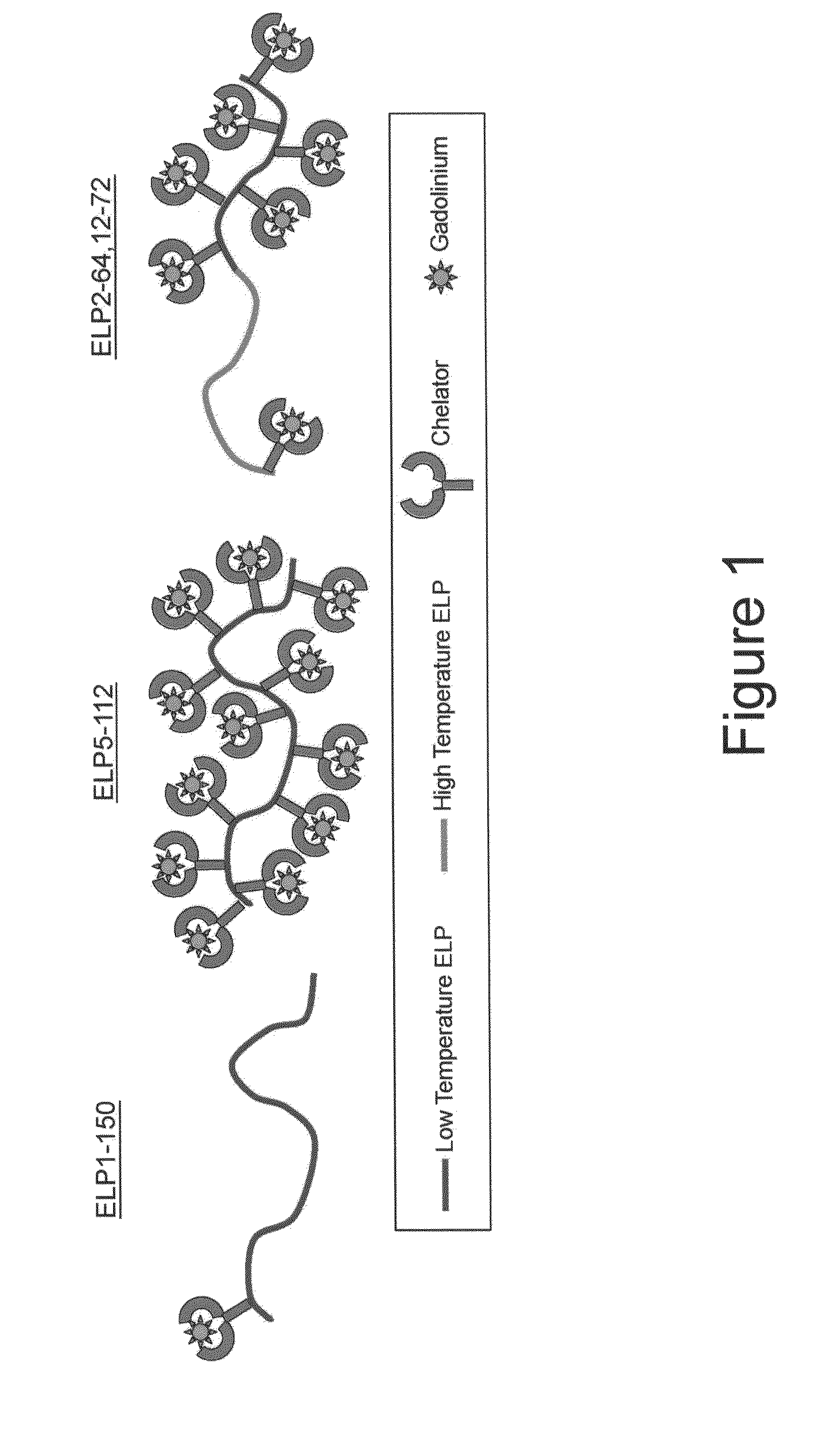
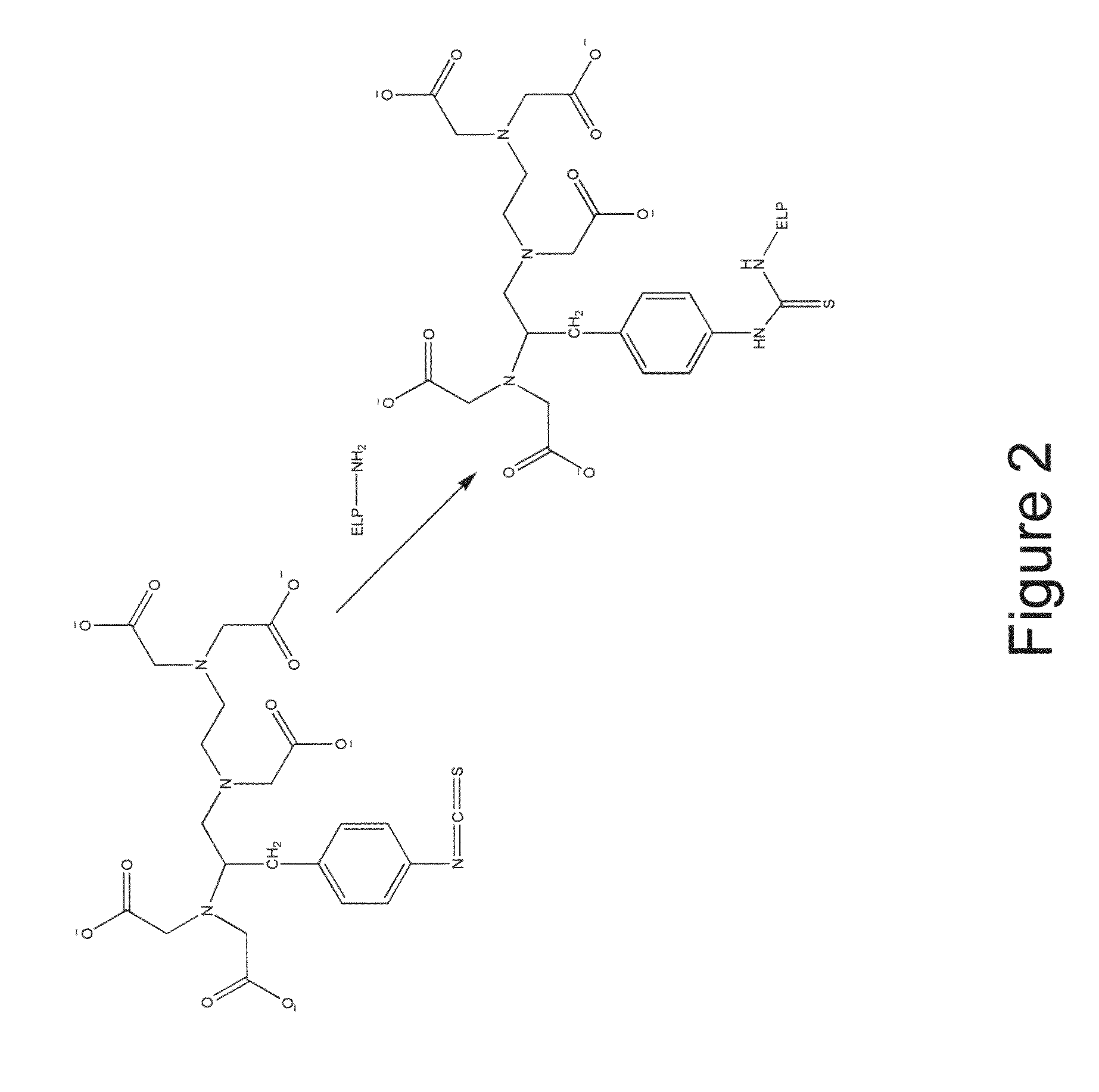
Elastin-like polypeptide and gadolinium conjugate for magnetic resonance imaging
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) contrast enhancement agent comprising an elastin-like polypeptide (ELP) and one or more paramagnetic metal ions is disclosed. Also disclosed are methods of preparing ELP MRI contrast enhancement agents, formulations comprising ELP MRI contrast enhancement agents, and methods of using ELP MRI contrast enhancement agents to image biological samples and to image and deliver therapeutic agents to targeted sites in vivo. In some embodiments, the ELP MRI agents can be used in methods related to blood volume determination, in magnetic resonance angiography (MRA), and in vascular transport determinations. The ELP MRI contrast agents can also provide information on the expression of various proteins through affinity targeting or enzymatic crosslinking in order to aid in diagnosis and in the spatial definition of pathologic tissue.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
Method for imaging an artery using a magnetic resonance contrast agent
InactiveUS7110806B2Eliminate riskReduction in flow artifactBiocideDiagnostic recording/measuringPathology diagnosisDisease cause
The present invention is a technique and apparatus for acquiring anatomic information used in diagnosing and characterizing abdominal aortic aneurismal disease and the like. This technique provides anatomic information, in the form of images, using a combination of a plurality of magnetic resonance angiography sequences, including a spin-echo and four contrast enhanced (e.g., gadolinium) magnetic resonance angiography sequences. The anatomic images may be used in, for example, pre-operative, operative and post-operative evaluation of aortic pathology, including aneurysms, atherosclerosis, and occlusive disease of branch vessels such as the renal arteries. The gadolinium-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography provides sufficient anatomic detail to detect aneurysms and all relevant major branch vessel abnormalities seen at angiography operation. This technique and apparatus allows for imaging the aorta at a fraction of the cost of conventional aortography and without the risks of arterial catheterization or iodinated contrast.
Owner:PRINCE MARTIN R
Magnetic resonance angiography method and magnetic resonance angiography system
InactiveCN103110420AQuality improvementImprove clinical utilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsArteriolar VasoconstrictionPhase gradient
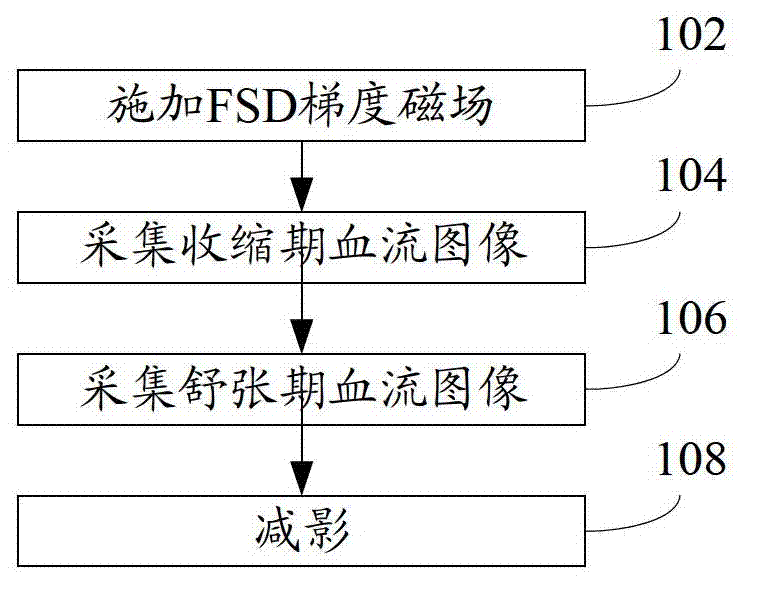
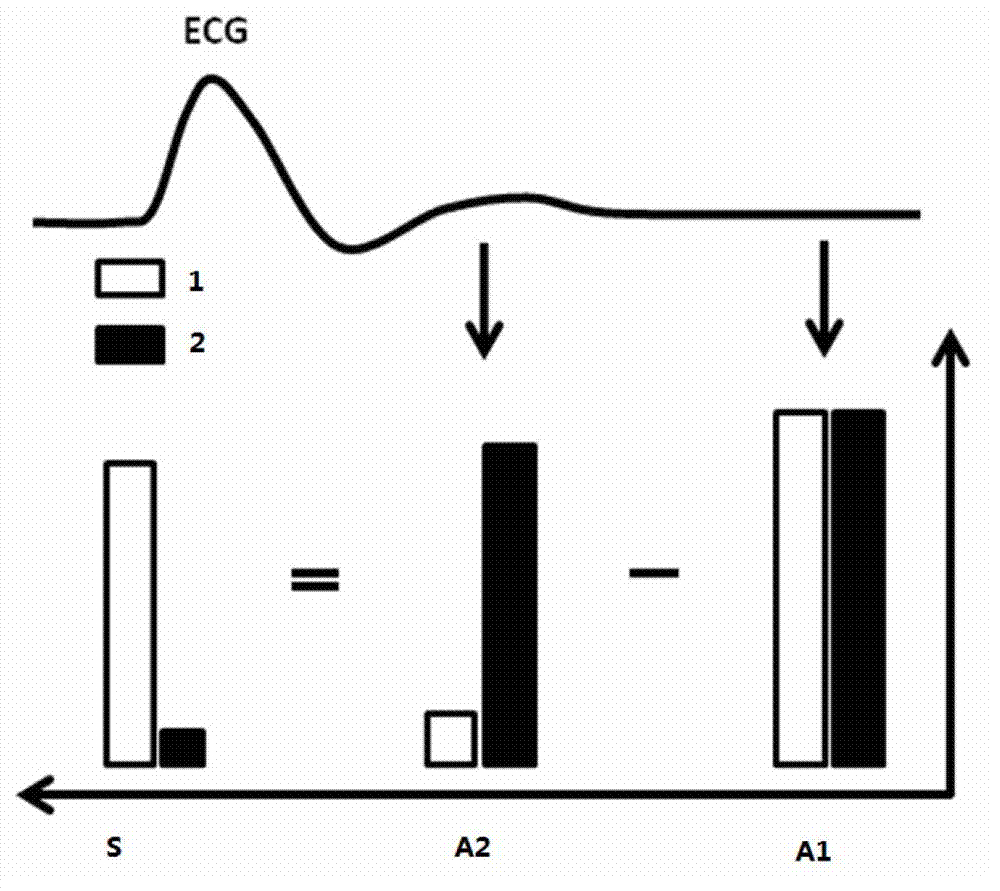
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance angiography method. The magnetic resonance angiography method includes applying a flowing sensitive dispersed phase gradient magnetic field in the readout direction and / or the phase encoding direction and / or the layer selection direction in a vasoconstriction period and then applying a residual magnetic moment removing gradient magnetic field after the flowing sensitive dispersed phase gradient magnetic field is applied; collecting blood flow images in the vasoconstriction period; collecting blood flow images in a vasodilatation period; and carrying out subtraction on the blood flow images in the vasoconstriction period and the blood flow images in the vasodilatation period to obtain blood flow images. The invention further discloses a magnetic resonance angiography system. According to the magnetic resonance angiography method and the magnetic resonance angiography system, in the specific implementation method, the flowing sensitive dispersed phase is used in the vasoconstriction period imaging process, so that intra-arterial self-spin dispersed phase can significantly lower arterial blood signals, and therefore the influence on imaging due to the velocity and the direction of blood flow can be reduced, high-quality peripheral arterial images can be obtained, and clinical practicability of the non-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography technology is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
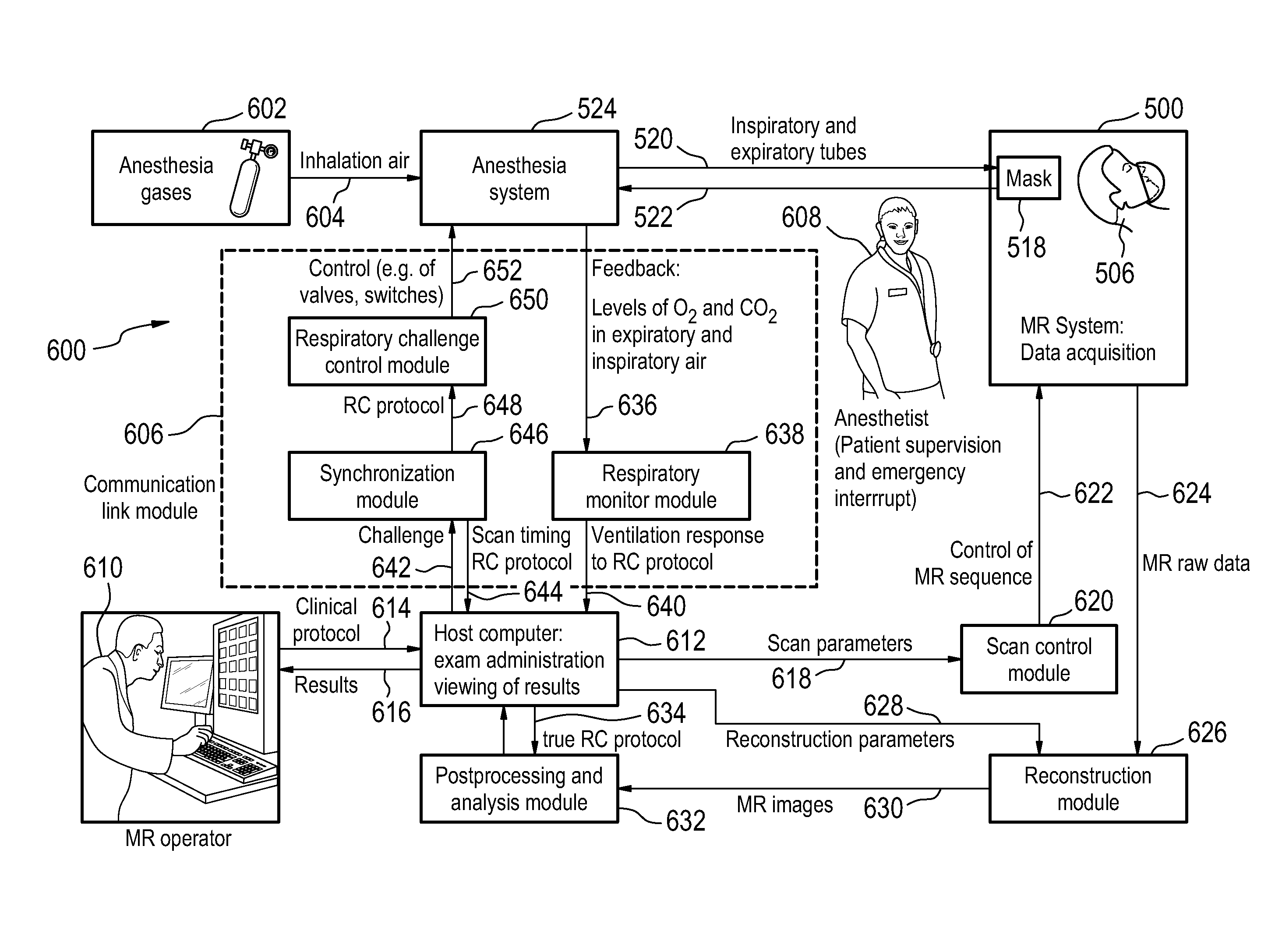
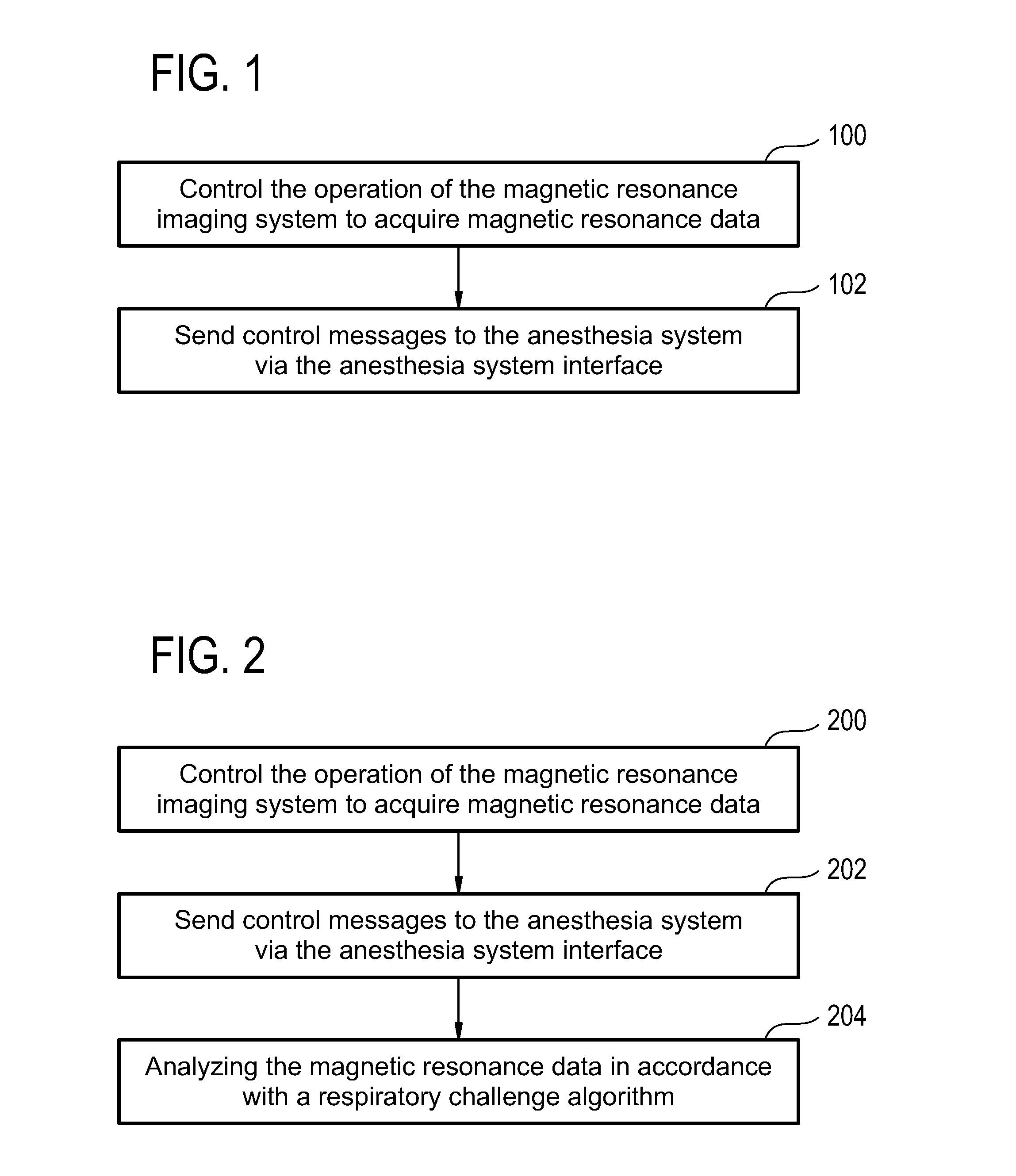
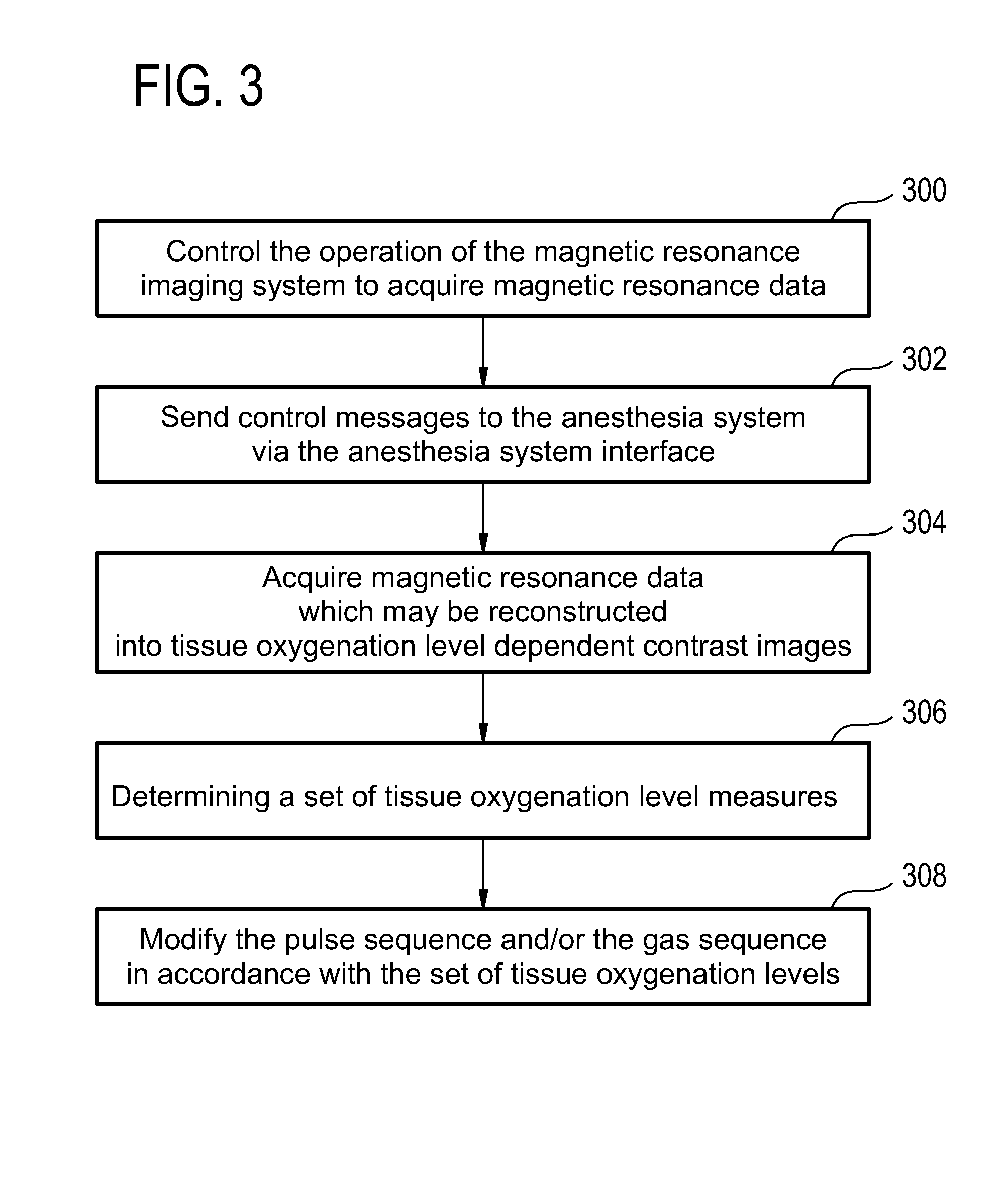
Magnetic resonance imaging system, computer system, and computer program product for sending control messages to an anesthesia system
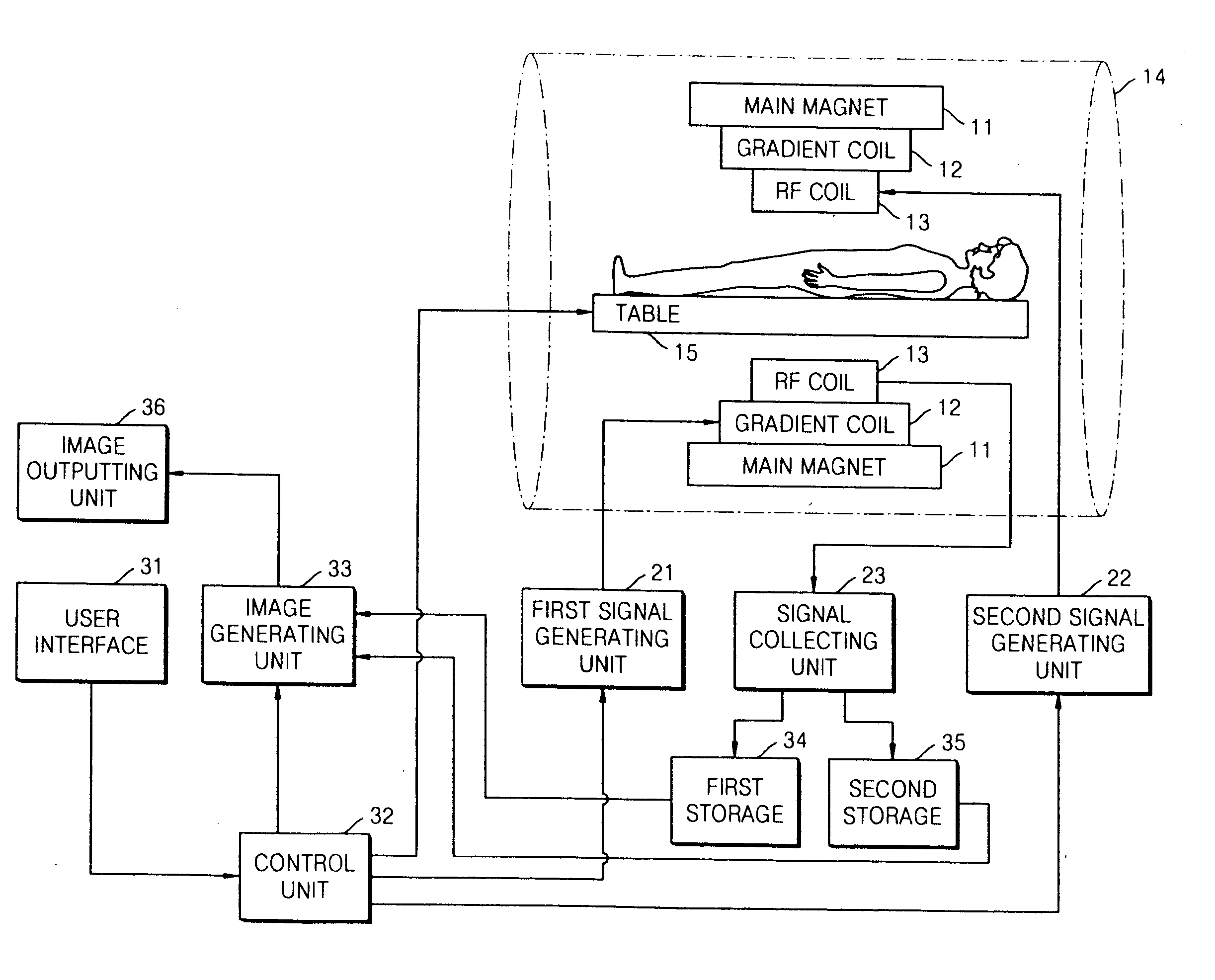
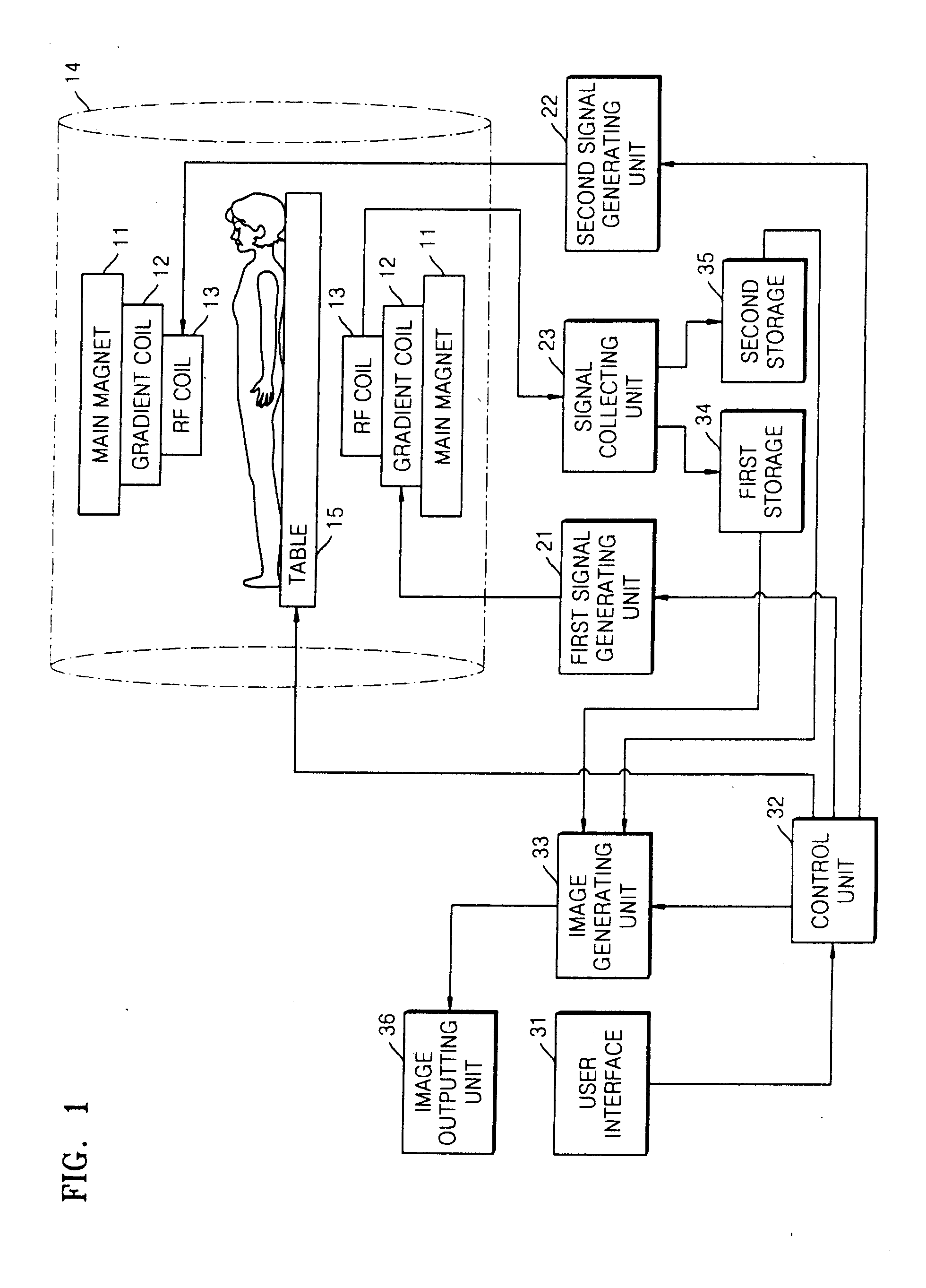
InactiveUS20130225978A1Sufficient changeOptimized and robust useRespiratorsMedical devicesMagnetic field gradientSpatial encoding
A magnetic resonance imaging system (500) comprising: a magnet (502) for generating a magnetic field; a radio frequency system (516) for acquiring magnetic resonance data; a magnetic field gradient coil (510) for spatial encoding of the magnetic spins of nuclei within the imaging volume; a magnetic field gradient coil power supply (512) for supplying current to the magnetic field gradient coil; an anesthesia system interface (532) for sending control messages to an anesthesia system (524) for controlling the delivery of inhalation gases to a subject and a computer system comprising a processor (534) and a memory (538, 540), wherein the memory contains instructions (542, 544, 546, 548, 550, 552) for execution by the processor, wherein execution of the instructions causes the processor to: control (100, 200, 300, 400) the operation of the magnetic resonance imaging system to acquire magnetic resonance data, and to send (102, 202, 302, 402) control messages to the anesthesia system via the anesthesia system interface.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com