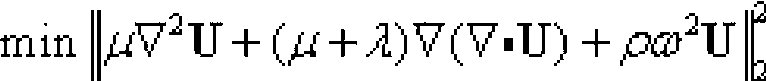Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73 results about "Magnetic resonance elastography" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
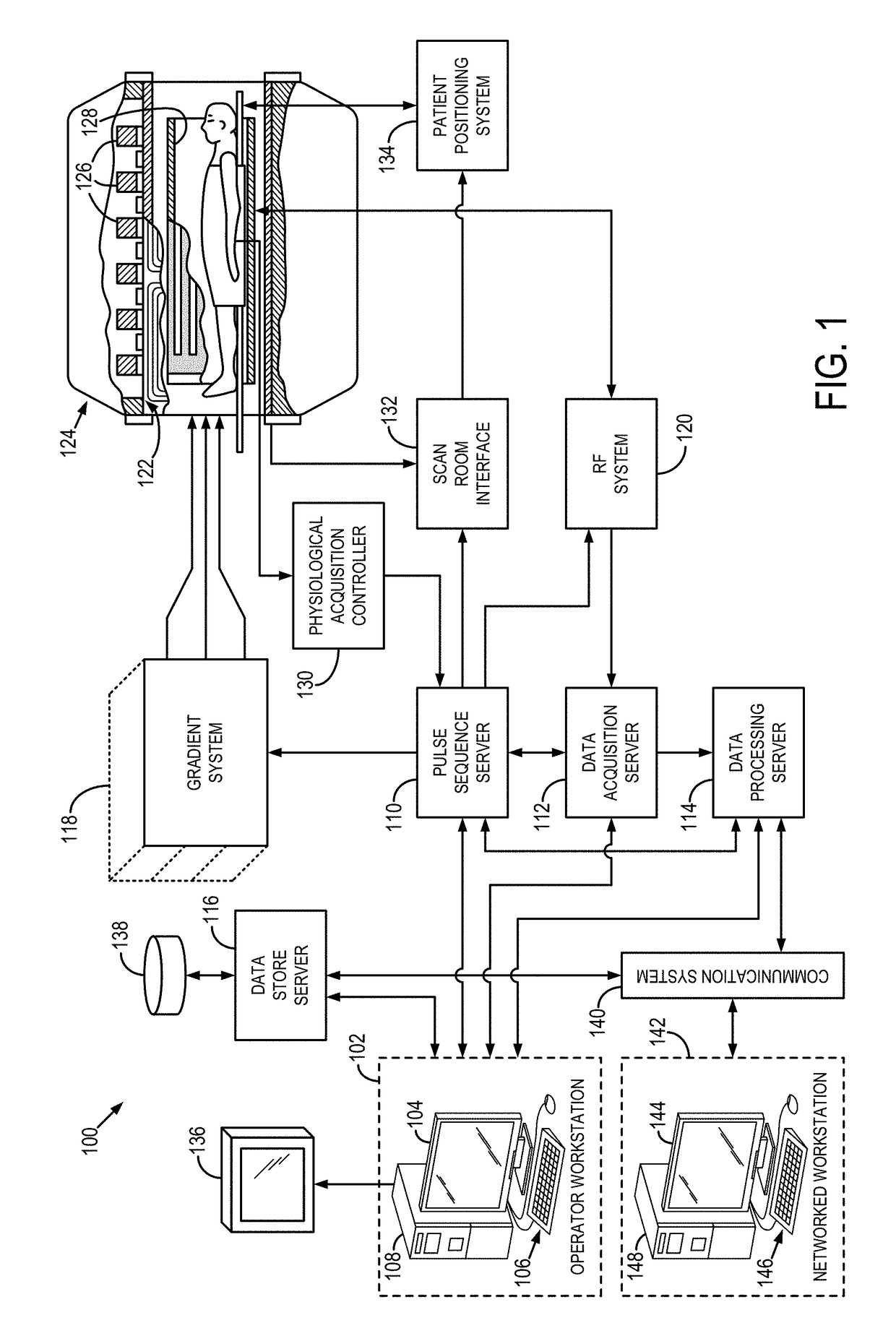
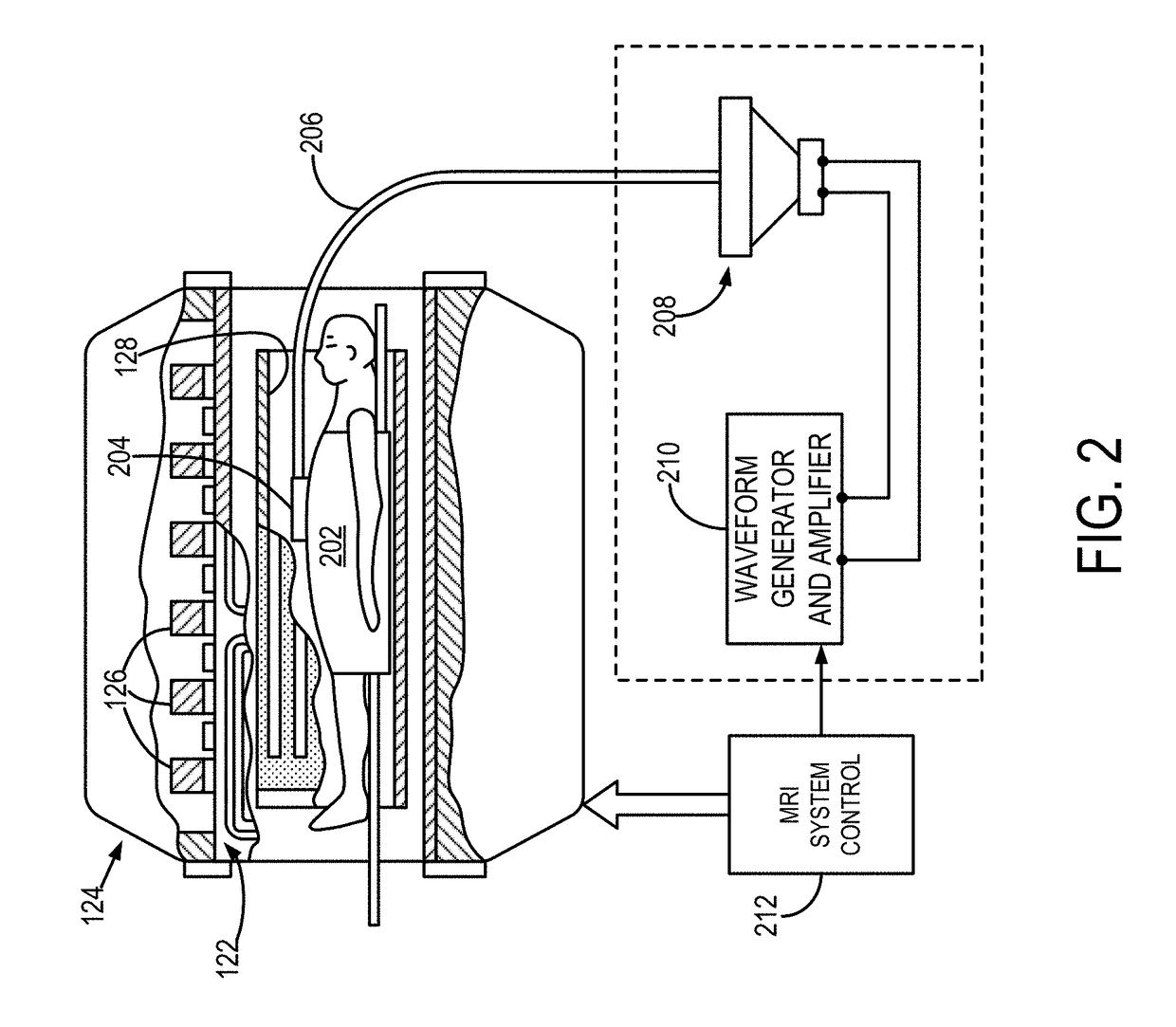
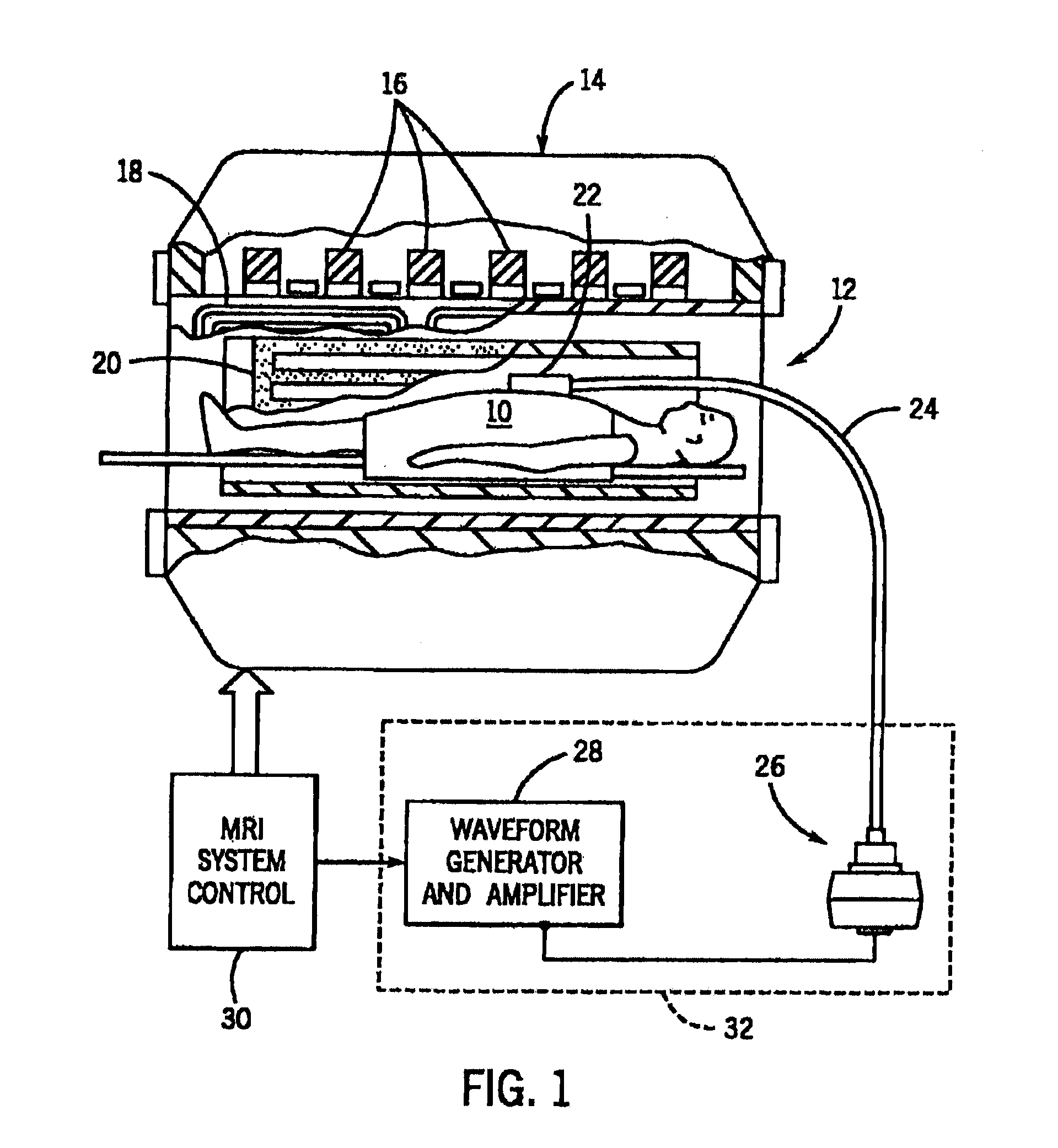
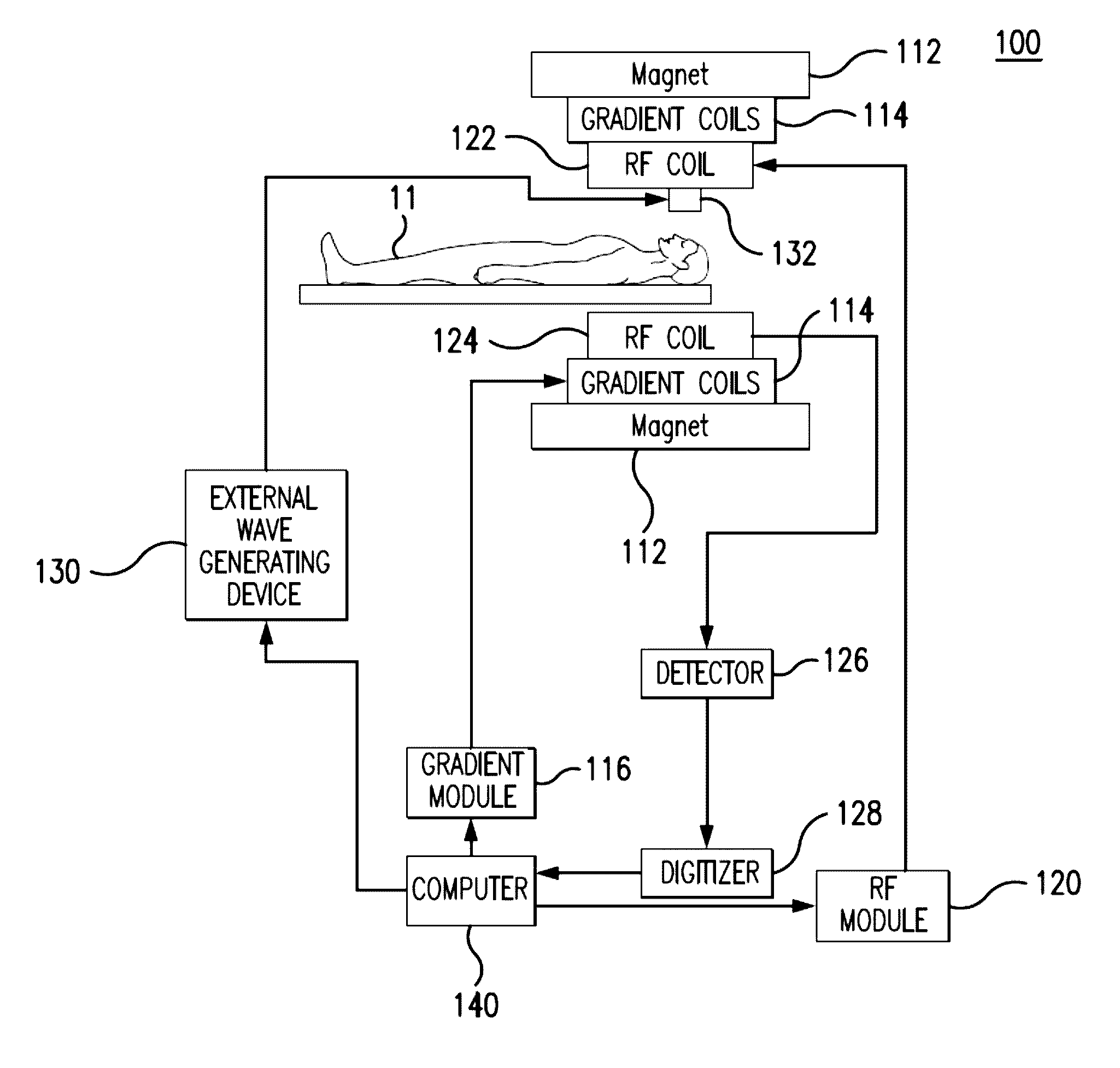
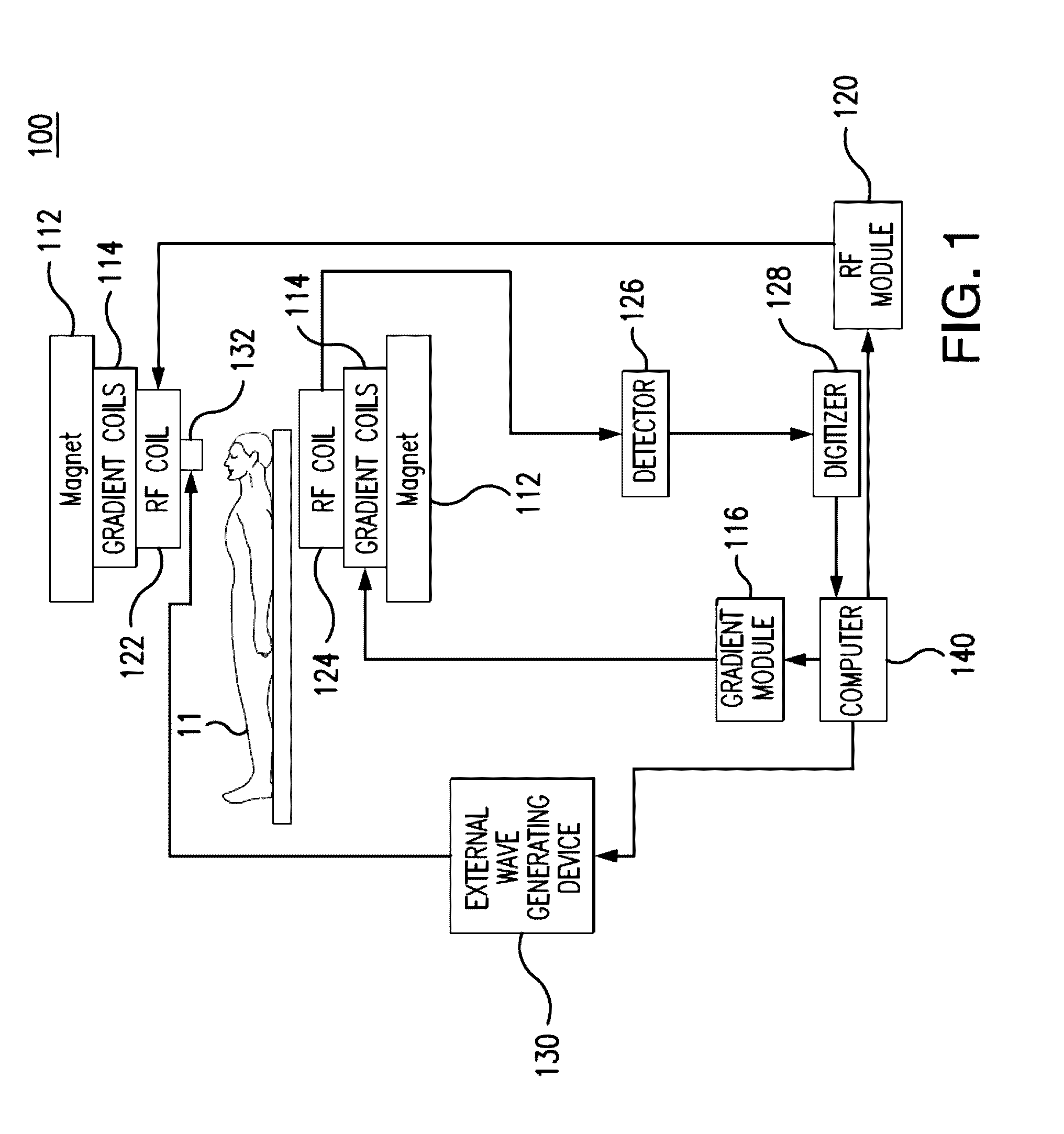
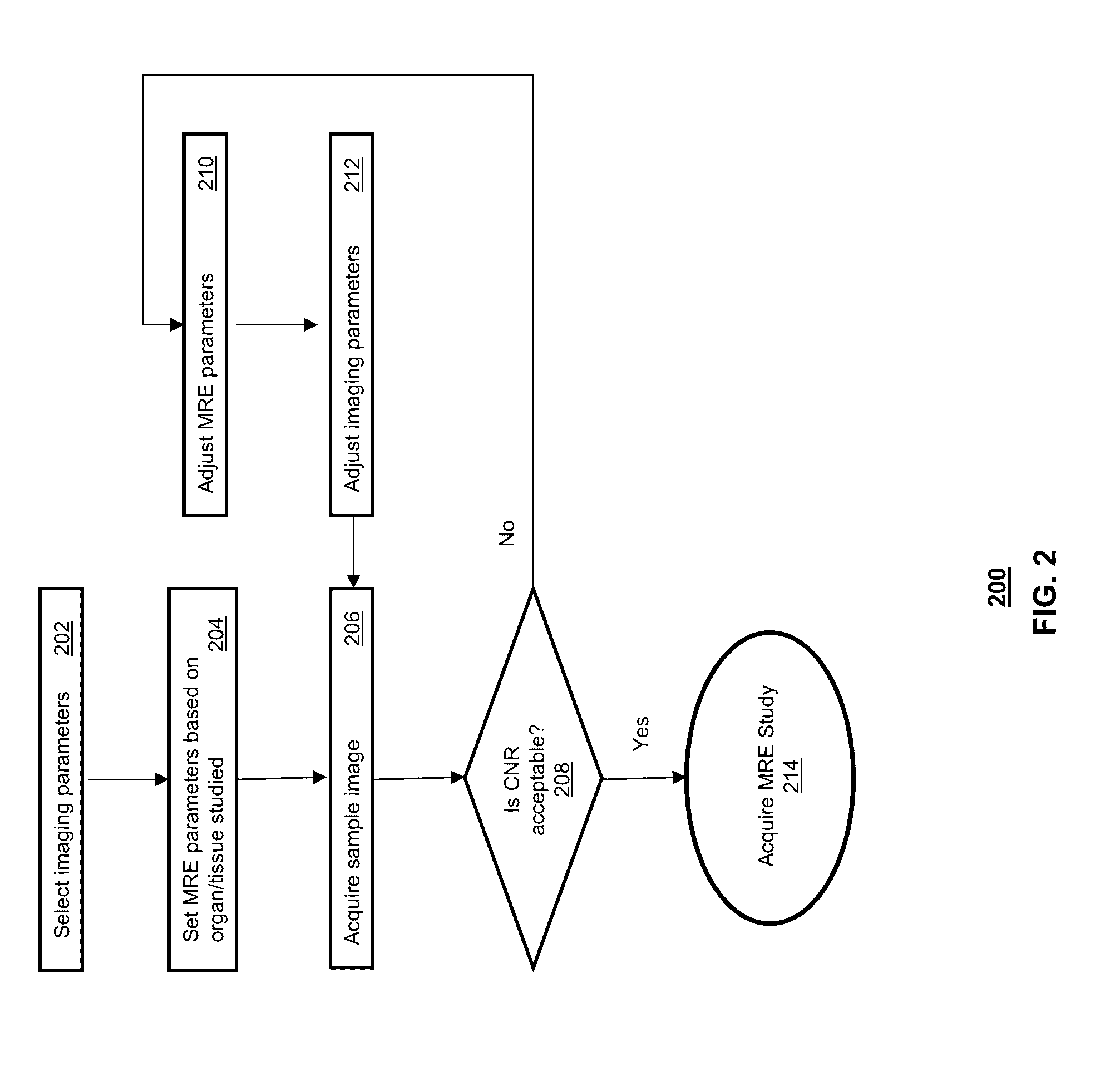
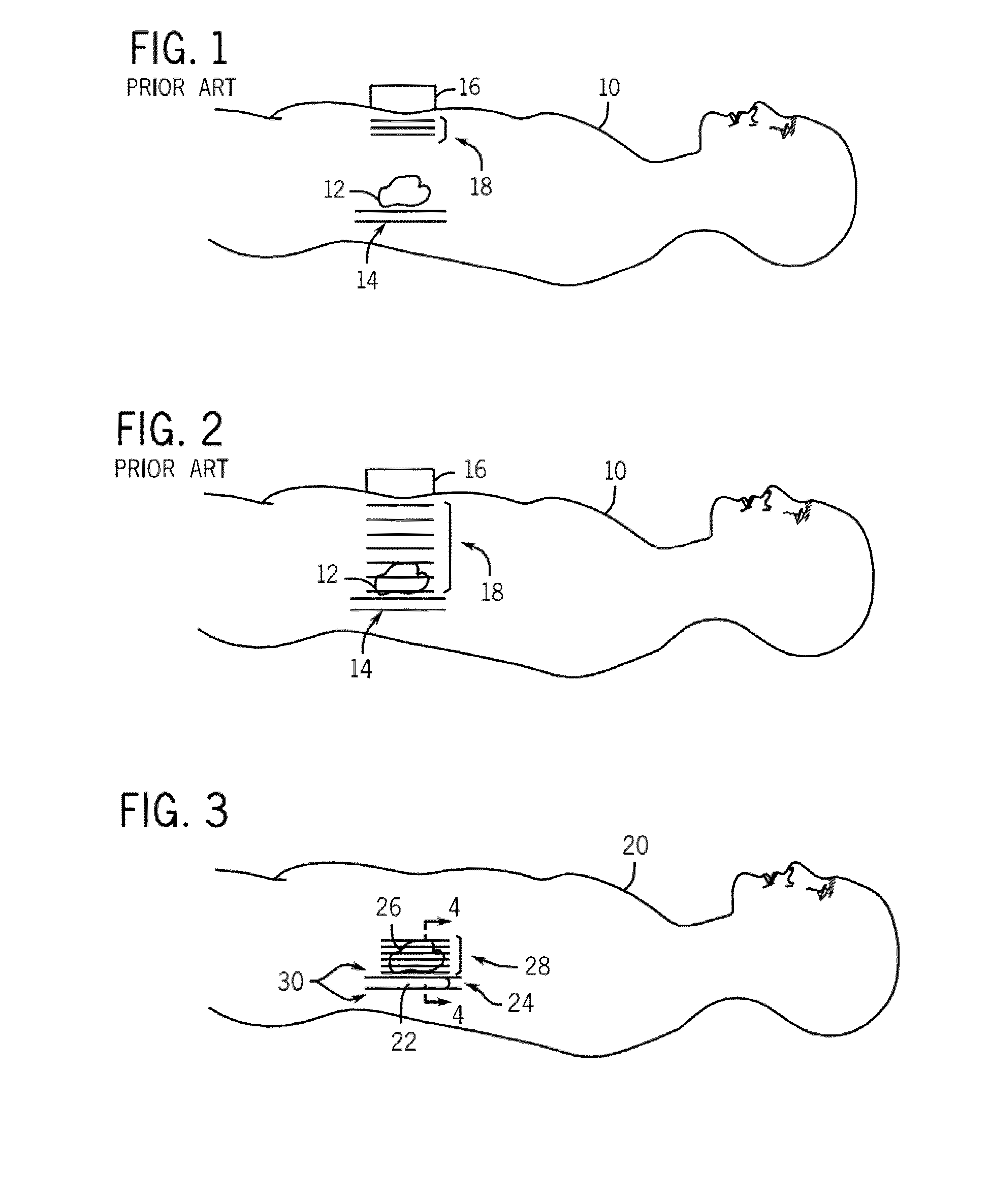
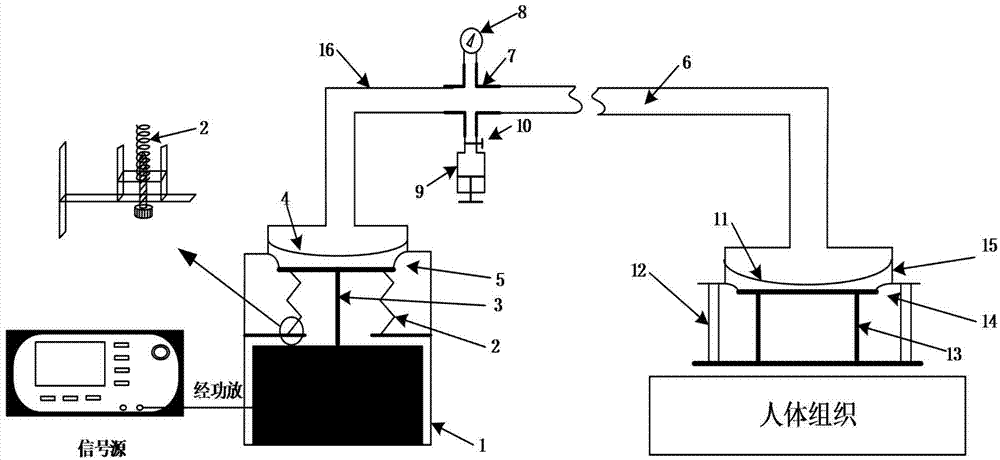
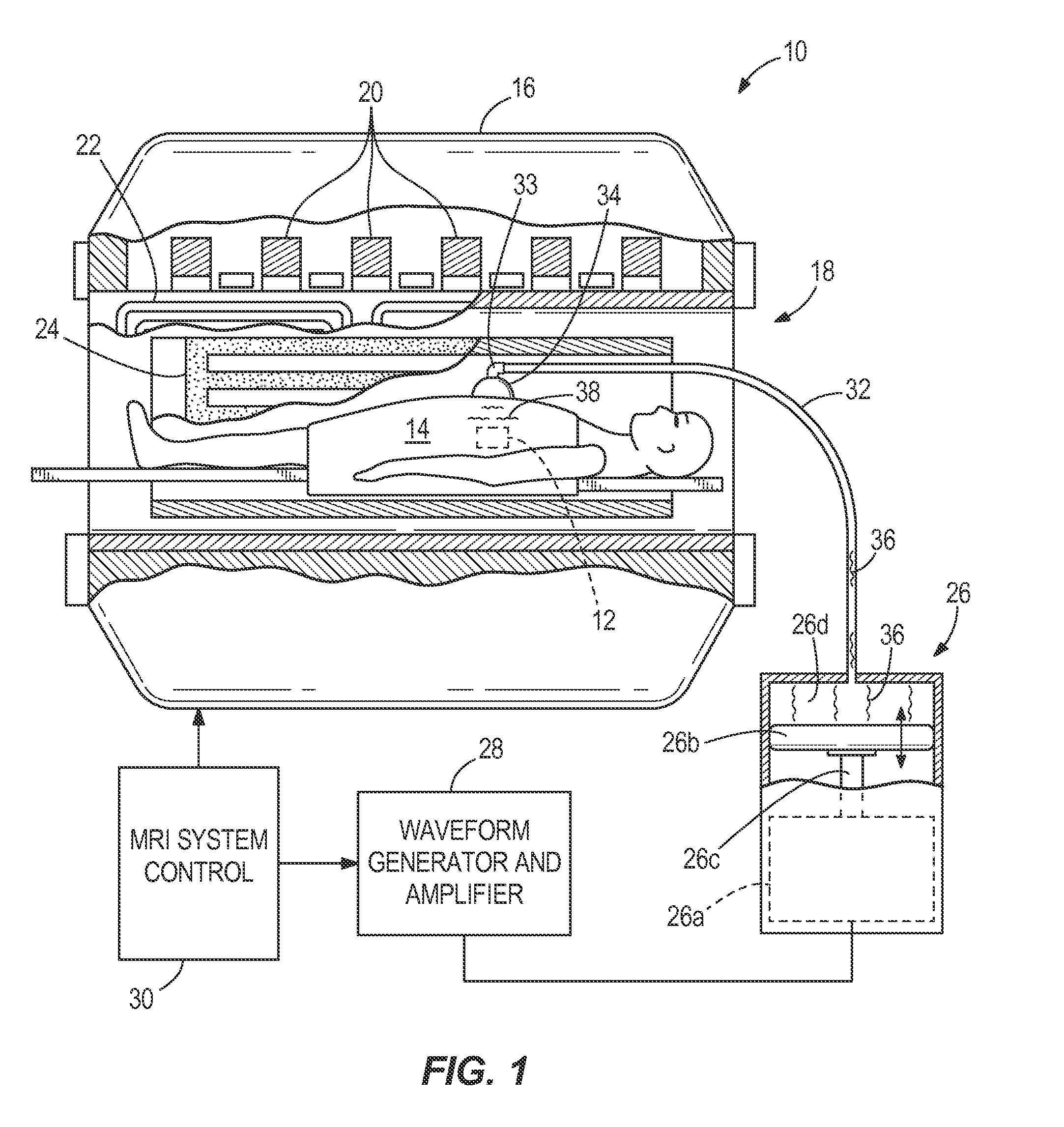
Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) is a non-invasive medical imaging technique that measures the stiffness of soft tissues by generating shear waves in tissue, imaging their propagation using MRI, and processing the images to generate a stiffness map (elastogram). It is one of the most commonly used elastography techniques.
System and method for generating nonalcoholic fatty liver disease activity score (NAS) using magnetic resonance elastography
The present disclosure relates to a system and method for non-invasively determining NAFLD activity scores (NAS) in patients using mechanical properties determined through magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) imaging. The non-invasively determined NAS score is then used to diagnose NFALD and NASH patients.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
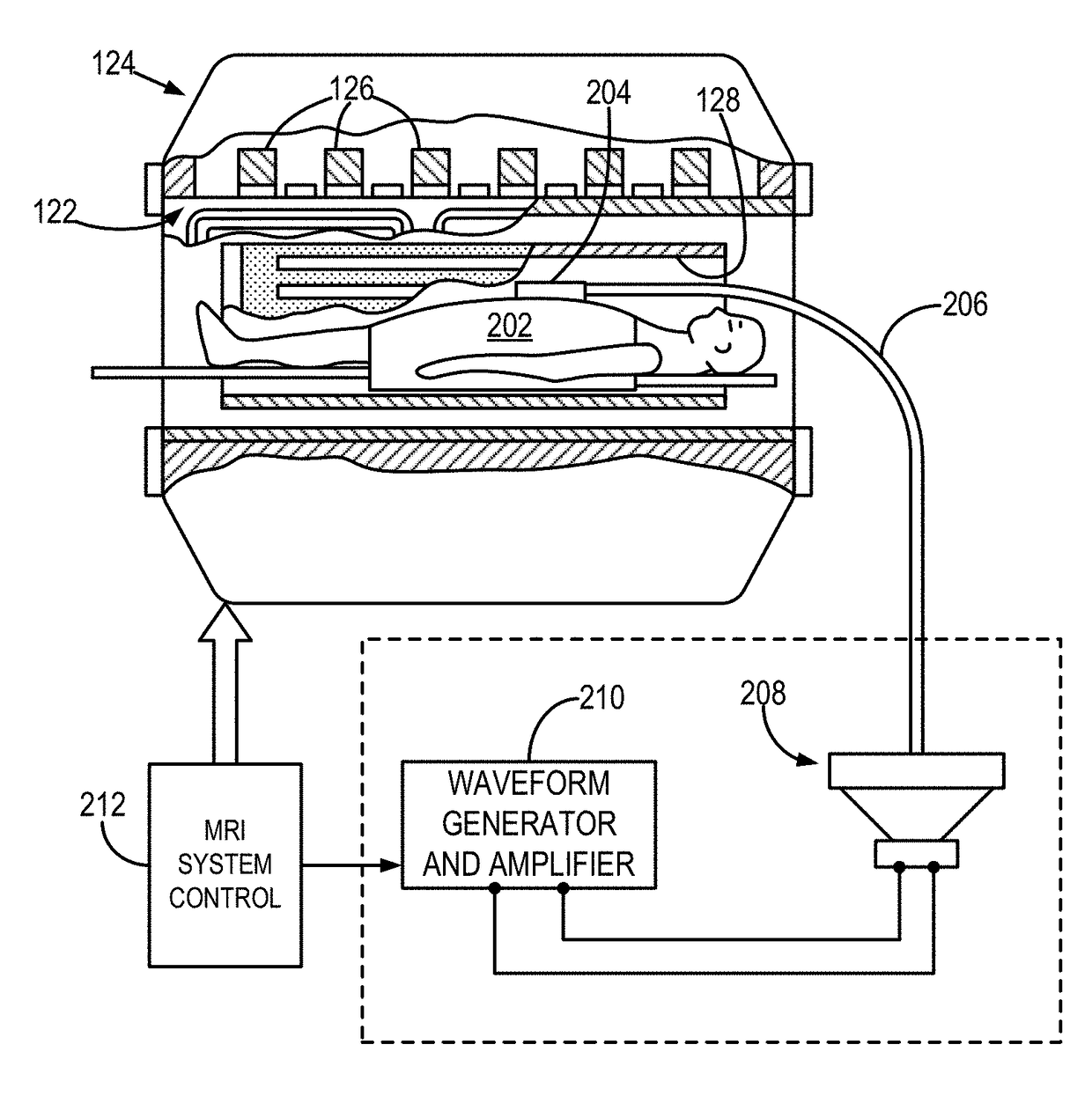
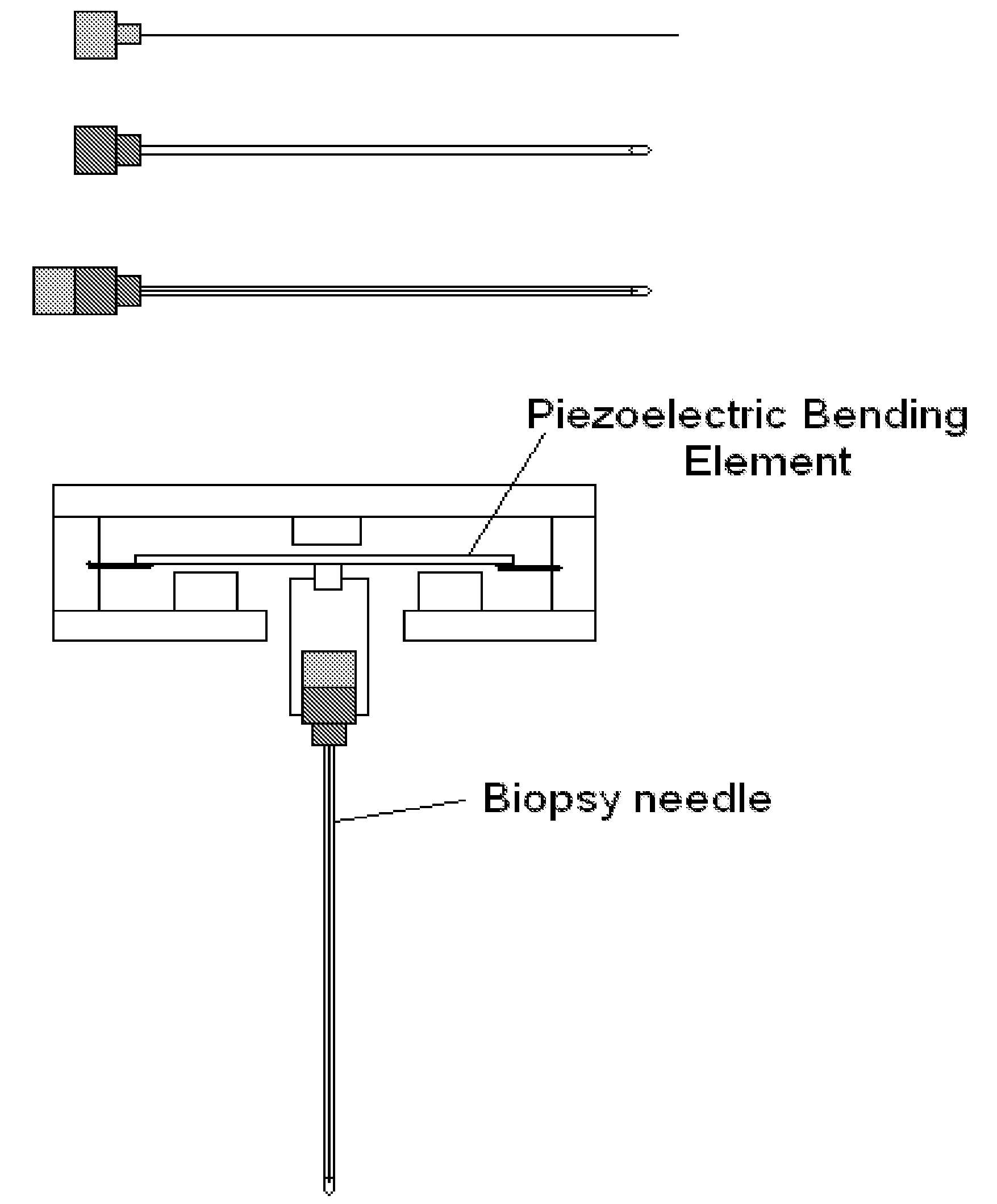
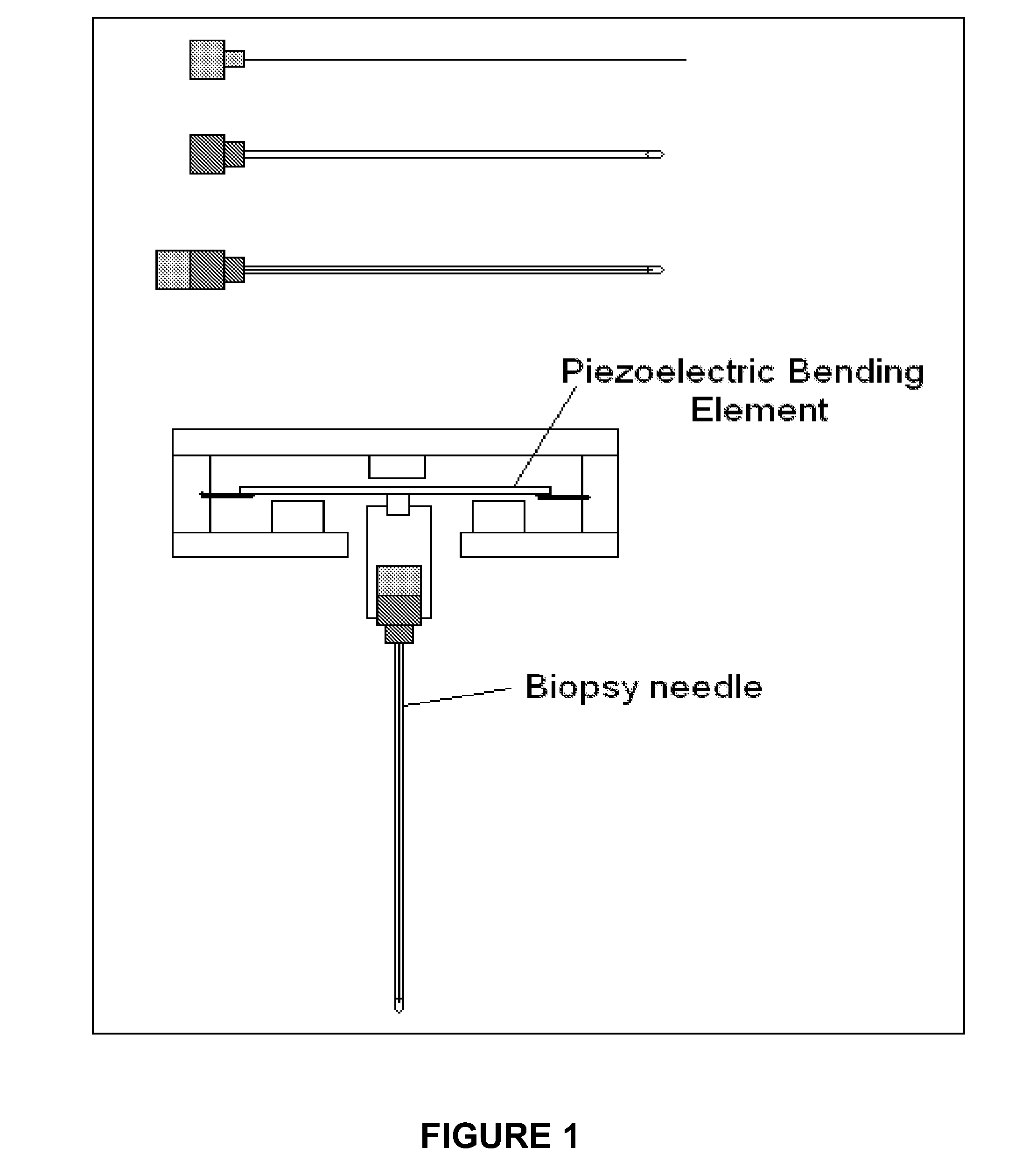
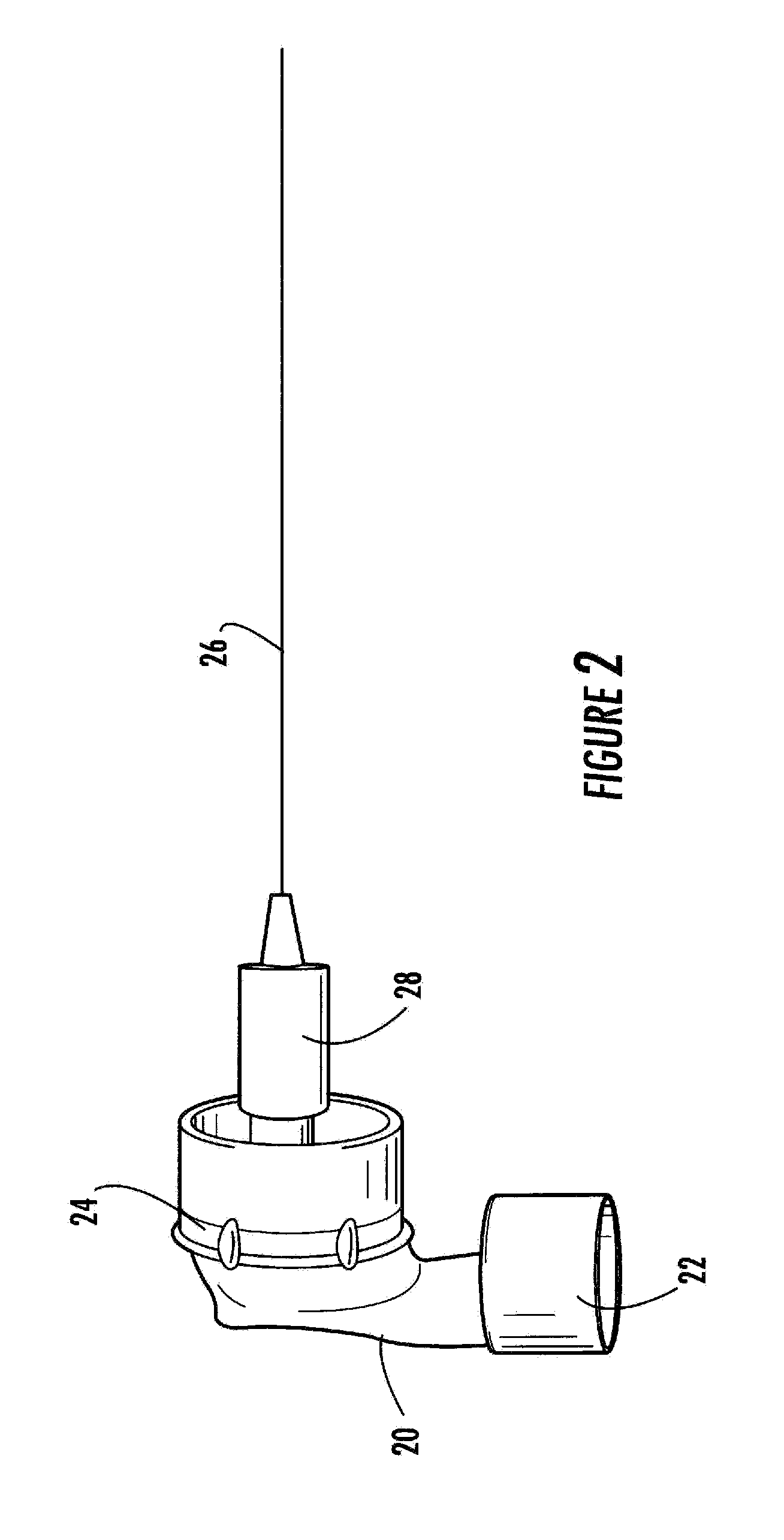
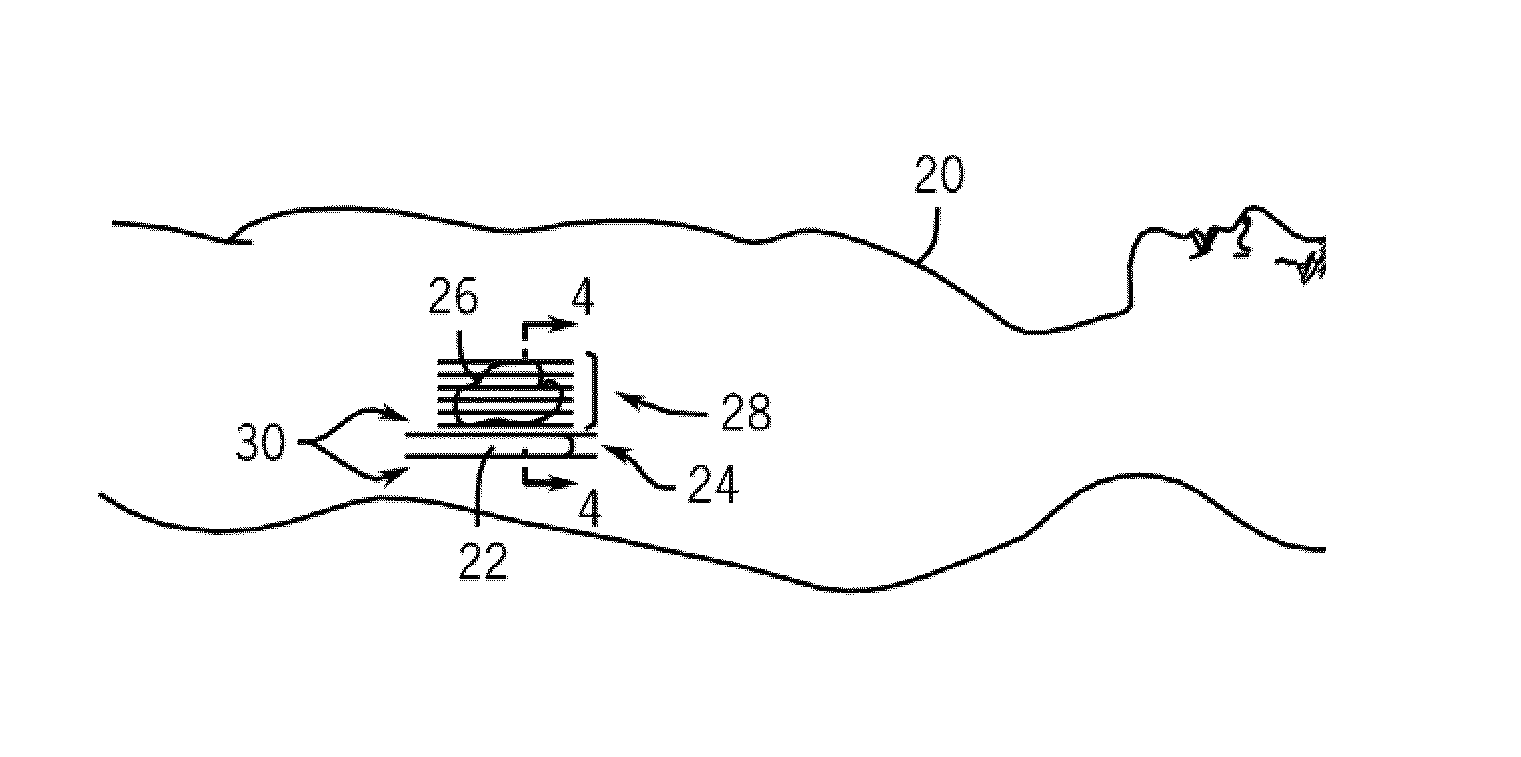
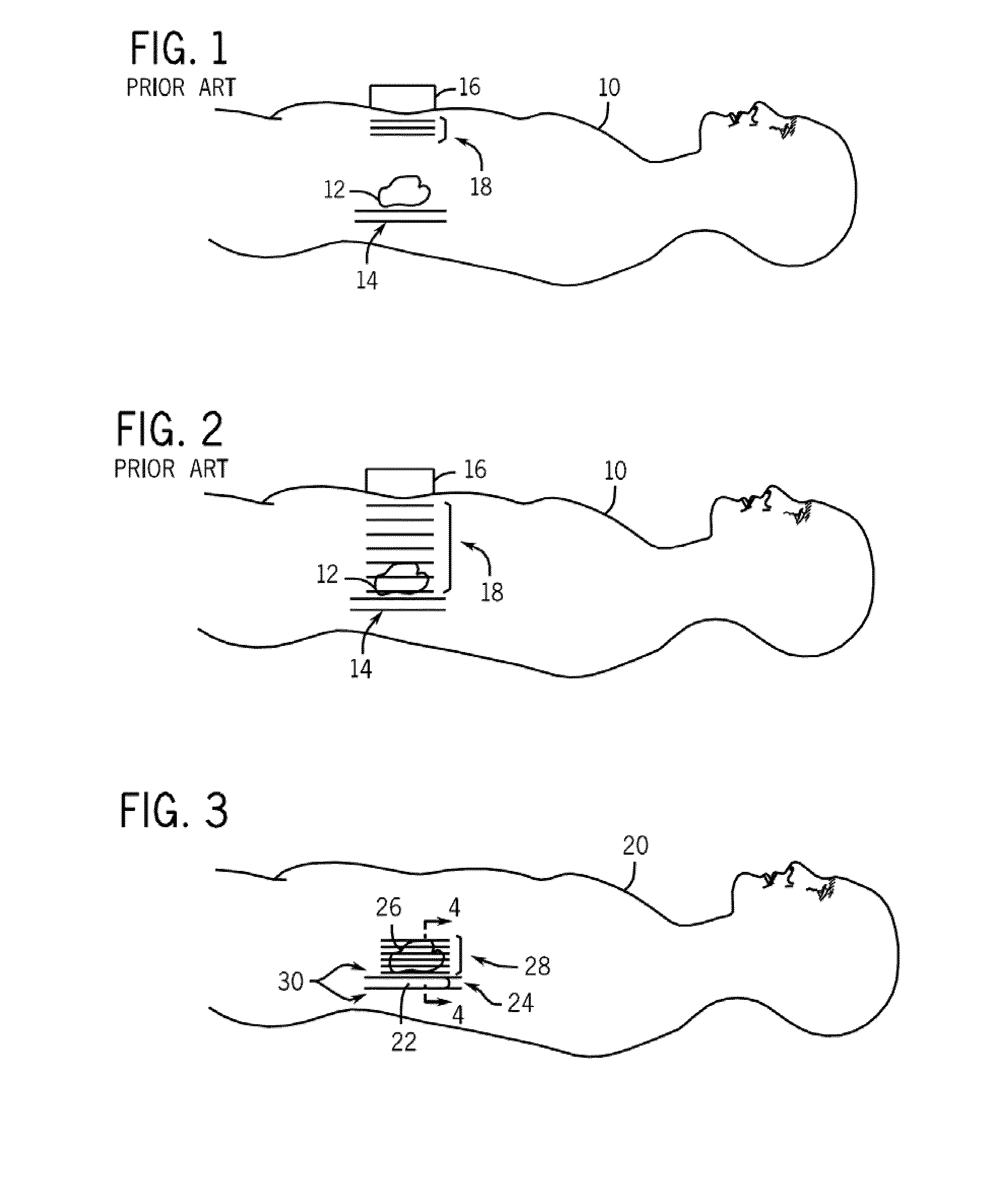
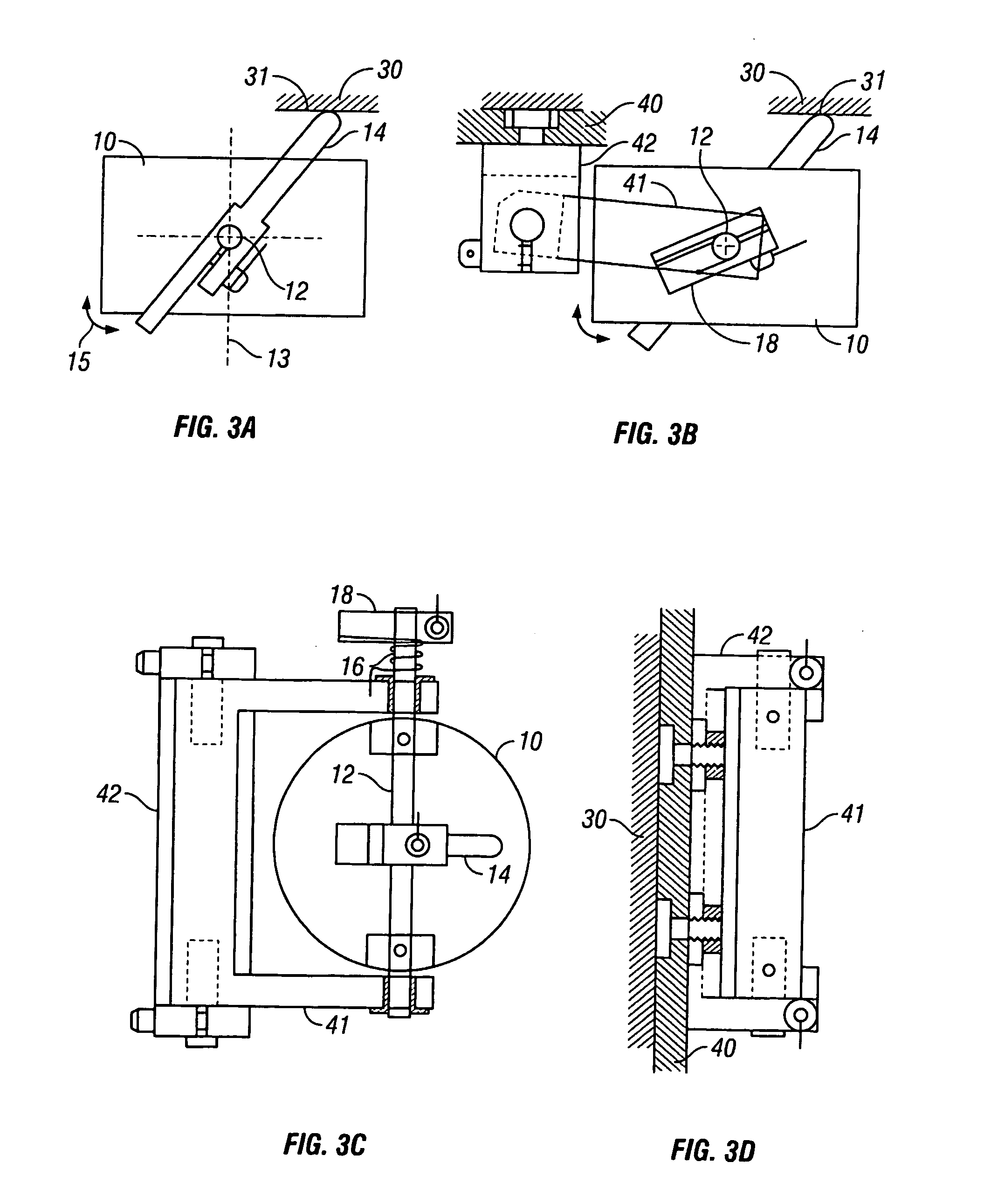
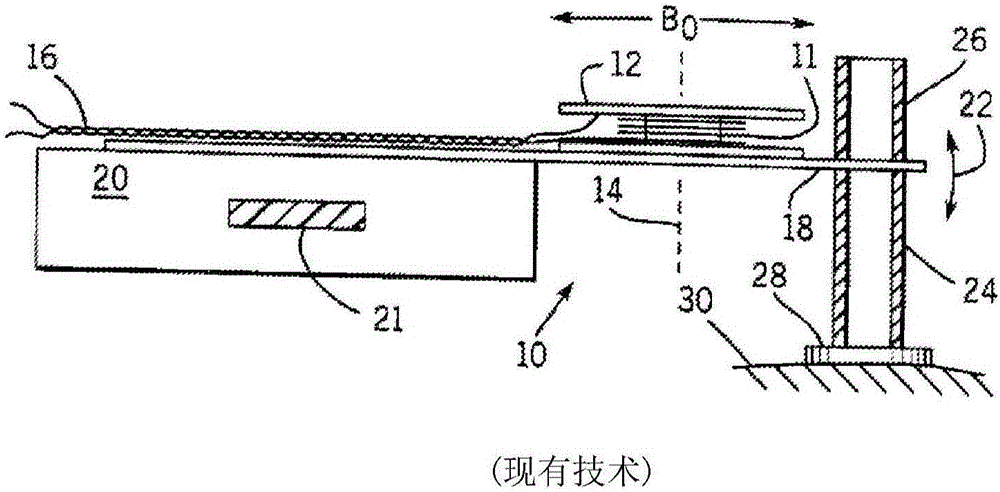
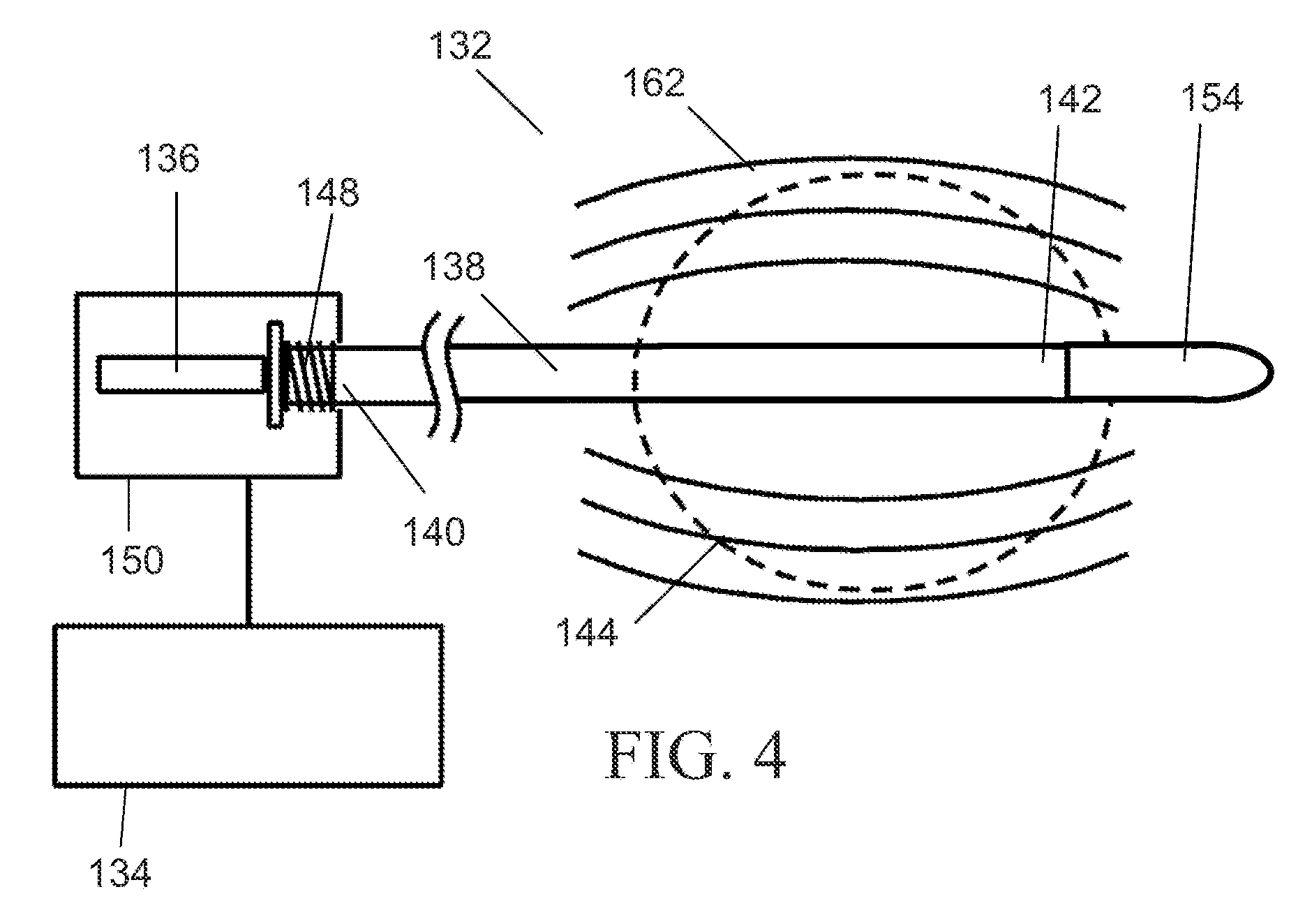
Novel needle driver for magnetic resonance elastography
ActiveUS20080255444A1Accurately determineReduce decreaseDiagnostics using vibrationsVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsAcupuncture needlesMild cognitive impairment (MCI)
Owner:LAWRENCE GROUP MEDICAL DEVICE TRUST
Magnetic resonance elastography detection system of liver fibrosis classification research and method thereof
InactiveCN101708123AImprove image qualityGood effectDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsPhase noiseLiver fibrosis
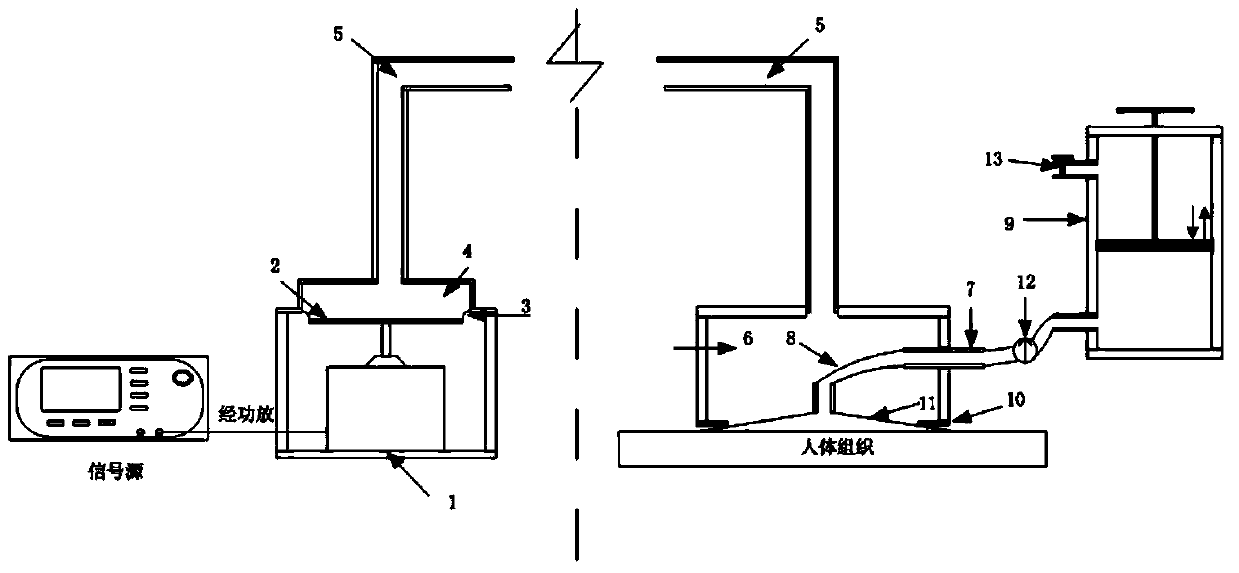
The invention relates to magnetic resonance elastography detection system and method thereof. The detection system comprises a high-field nuclear magnetic resonance whole body imaging system which can carry out liver imaging, and a shear wave excitation device. The detection method comprises the following steps of: (1) inner particle displacement on a phantom or a detected part; (2) magnetic resonance elastography forming; and (3) fibration classification. For preliminary experiments on the phantom as well as studies on background phase noise and experiment researches on the relationship between shear wave transmission and shear wave frequency, the invention has good image quality and obvious effect. The invention establishes a foundation for subsequent MRE researches on the liver tissue, and provides directions and references for elastic researches on other parts.
Owner:UNIV OF SHANGHAI FOR SCI & TECH
System and method for intracorporeal elastography
ActiveUS20100045289A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using vibrationsRadiologyMechanical energy
A system and method for intracorporeal elastography include an intra-luminal vibratory member configured to be positioned within a lumen of an imaging subject and configured to impart mechanical energy into tissue of the lumen. In a preferred embodiment, an external piezoelectric energy source is included and coupled to the vibratory member and configured to cause the vibratory member to longitudinally vibrate, thereby generating shear waves for use with magnetic resonance elastography.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
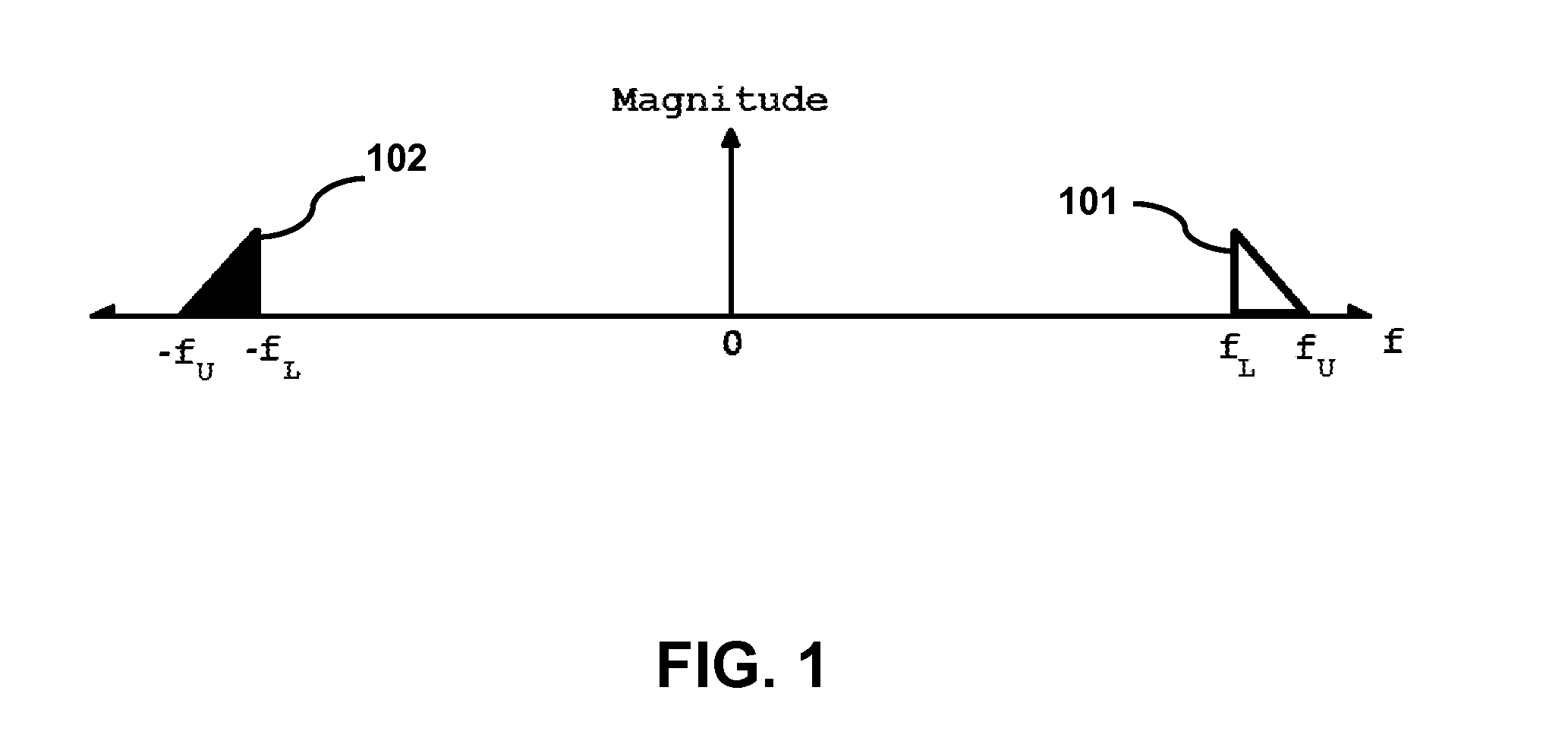
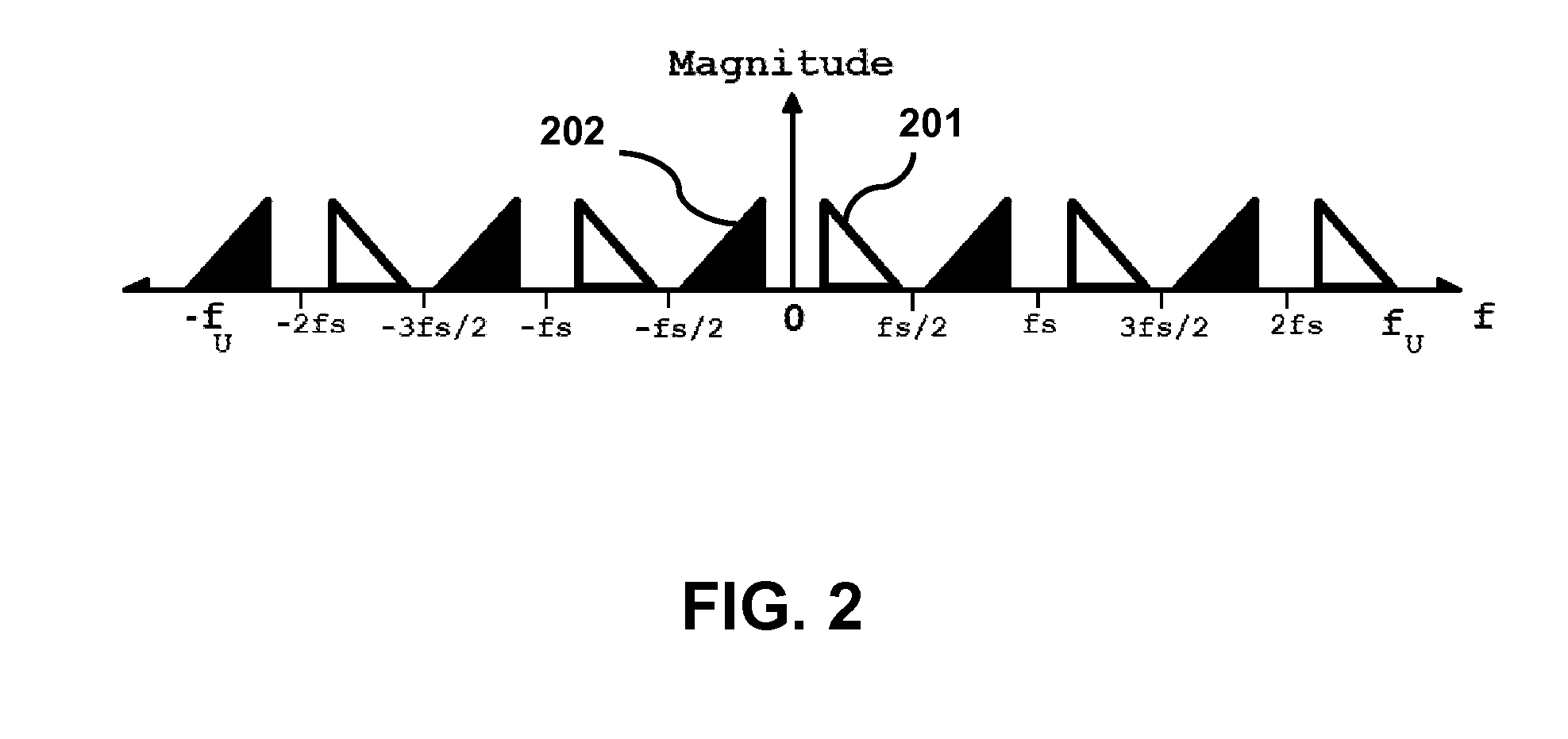
Bandpass sampling for elastography
ActiveUS8668647B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsWave based measurement systemsConventional medicineDiagnostic ultrasound
The characterization of tissue viscoelastic properties requires the measurement of tissue displacements over a region of interest at frequencies that exceed significantly the frame rates of conventional medical imaging devices. The present invention involves using bandpass sampling to track high-frequency tissue displacements. With this approach, high frequency signals limited to a frequency bandwidth can be sampled and reconstructed without aliasing at a sampling frequency that is lower than the Nyquist rate. With bandpass sampling, it is feasible to use conventional beam-forming on diagnostic ultrasound machines to perform high frequency dynamic elastography. The method is simple to implement as it does not require beam interleaving, additional hardware or synchronization and can be applied to magnetic resonance elastography.
Owner:THE UNIV OF BRITISH COLUMBIA IND LIAISON OFFICE
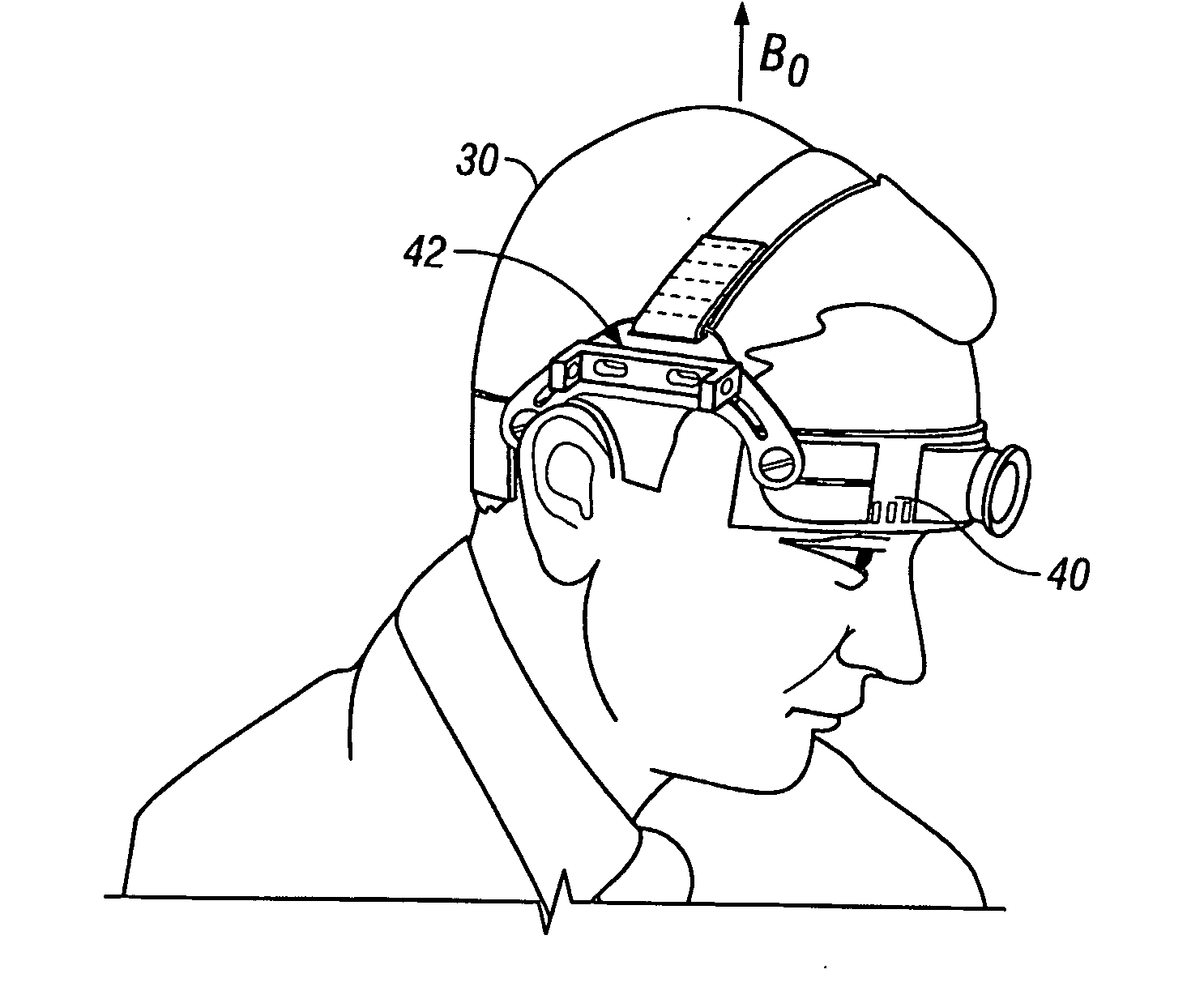
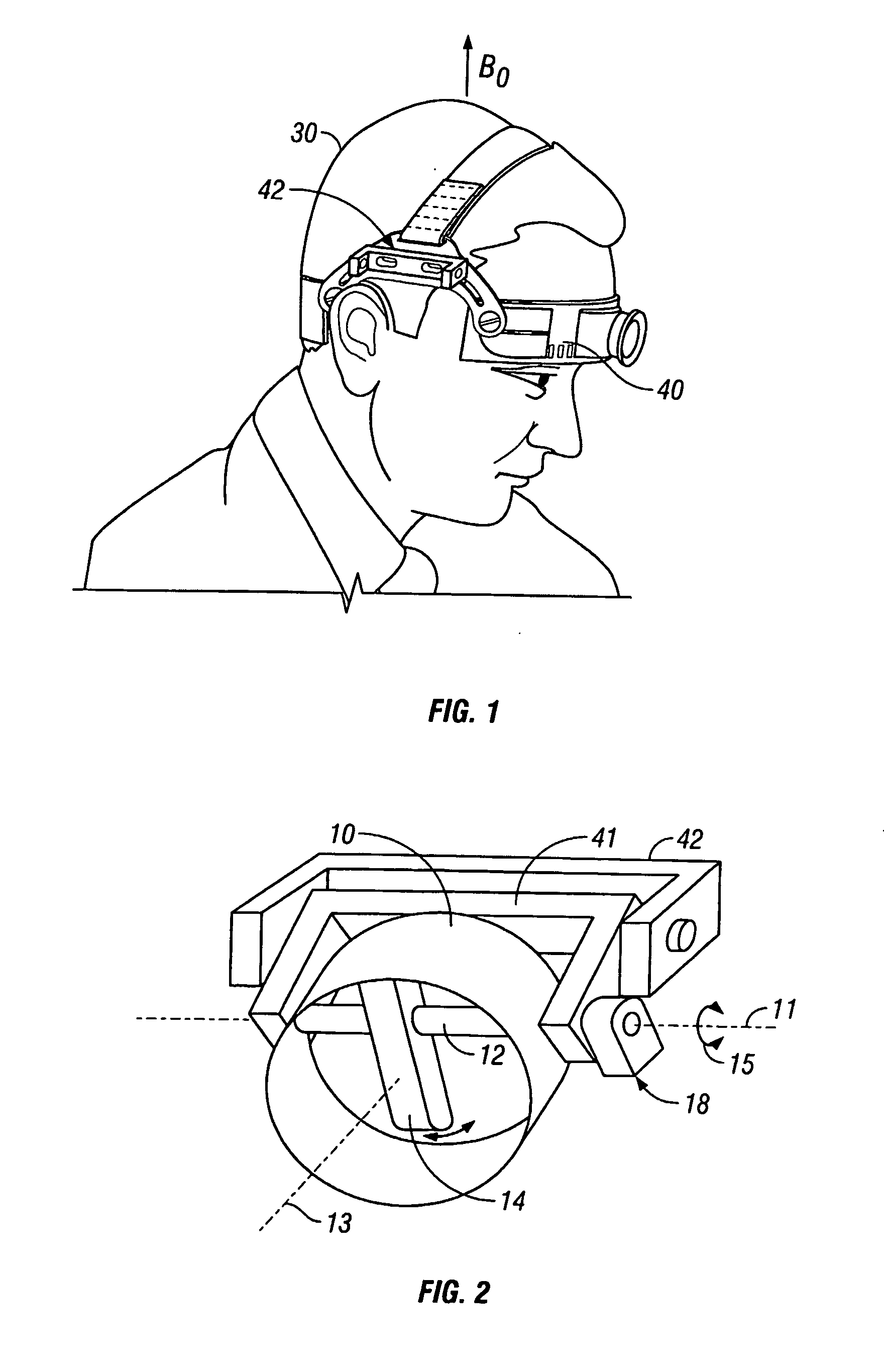
In vivo brain elasticity measurement by magnetic resonance elastography with vibrator coil
InactiveUS20070161891A1Altered mechanical propertyReduced patient functional outcomeMagnetic measurementsDiagnostics using vibrationsMagnetic field gradientVoxel
A vibrator coil (10) is applied to the skull (30) by adaptation of a commercially available transcranial Doppler monitoring harness (40) during MR applies mechanical waves in the acoustic waves through the skull to the brain. Utilizing magnetic resonance elastography (MRE), non-invasive estimation of tissue elastic properties in three dimensions occurs. The propagation of the acoustic waves through brain tissue, coupled to phase alteration of voxel isochromats in the presence of applies motion encoding magnetic field gradients allows measurements of brain elasticity.
Owner:THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF HEALTH & HUMAN
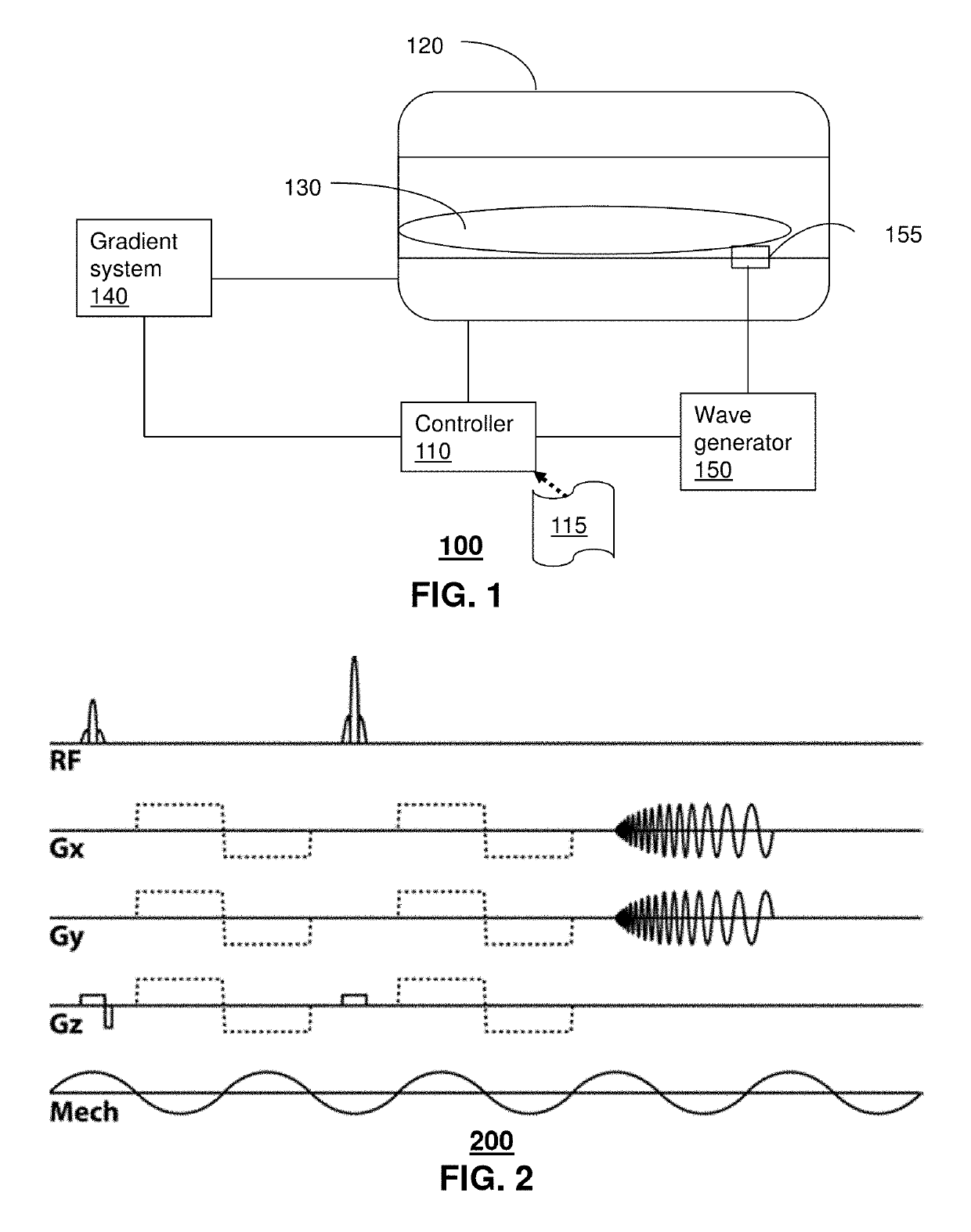
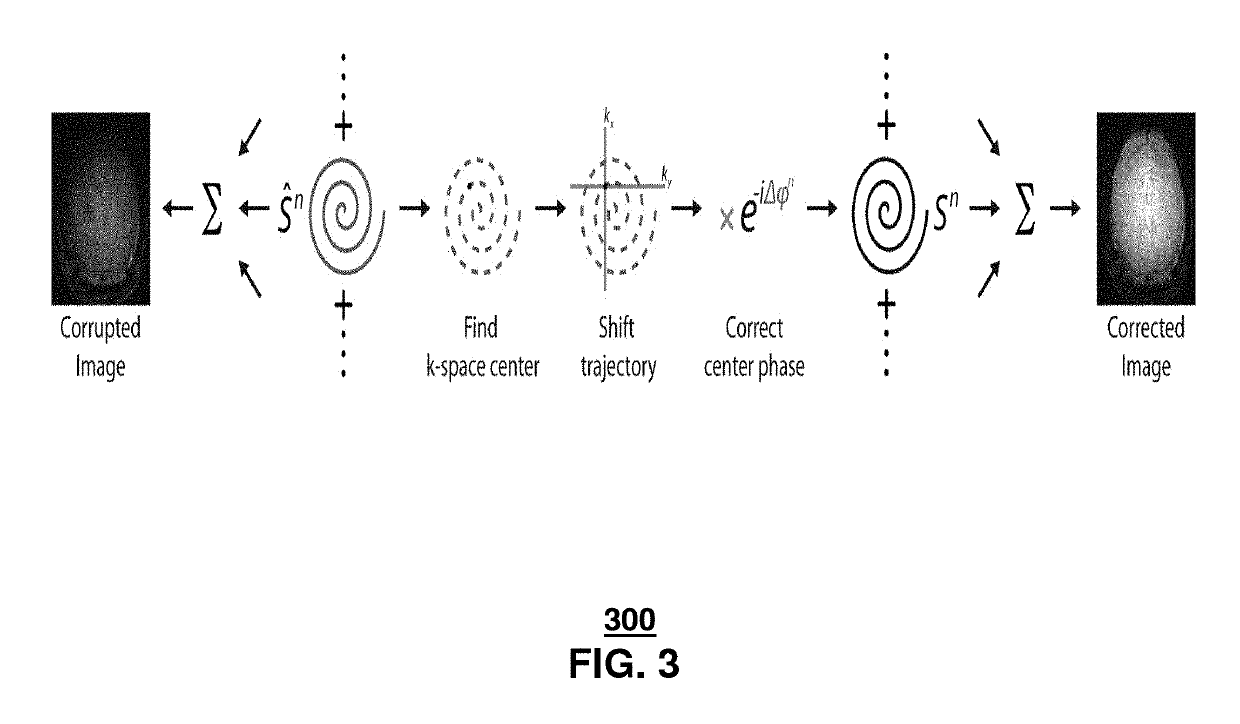
Method and system for multi-shot spiral magnetic resonance elastography pulse sequence
ActiveUS20140232395A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionK space trajectoryPulse sequence
Aspects of the subject disclosure may include, for example, a system that applies magnetic resonance elastography to a sample to obtain uncorrected k-space data where the magnetic resonance elastography utilizes a multi-shot spin-echo sequence with variable density spiral readout gradients, and adjusts the uncorrected k-space data to corrected k-space data by adjusting a k-space trajectory by shifting a center point for each shot to a new center point according to signal intensity and by adjusting a phase for each shot based on a phase offset that is determined according to the signal intensity. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
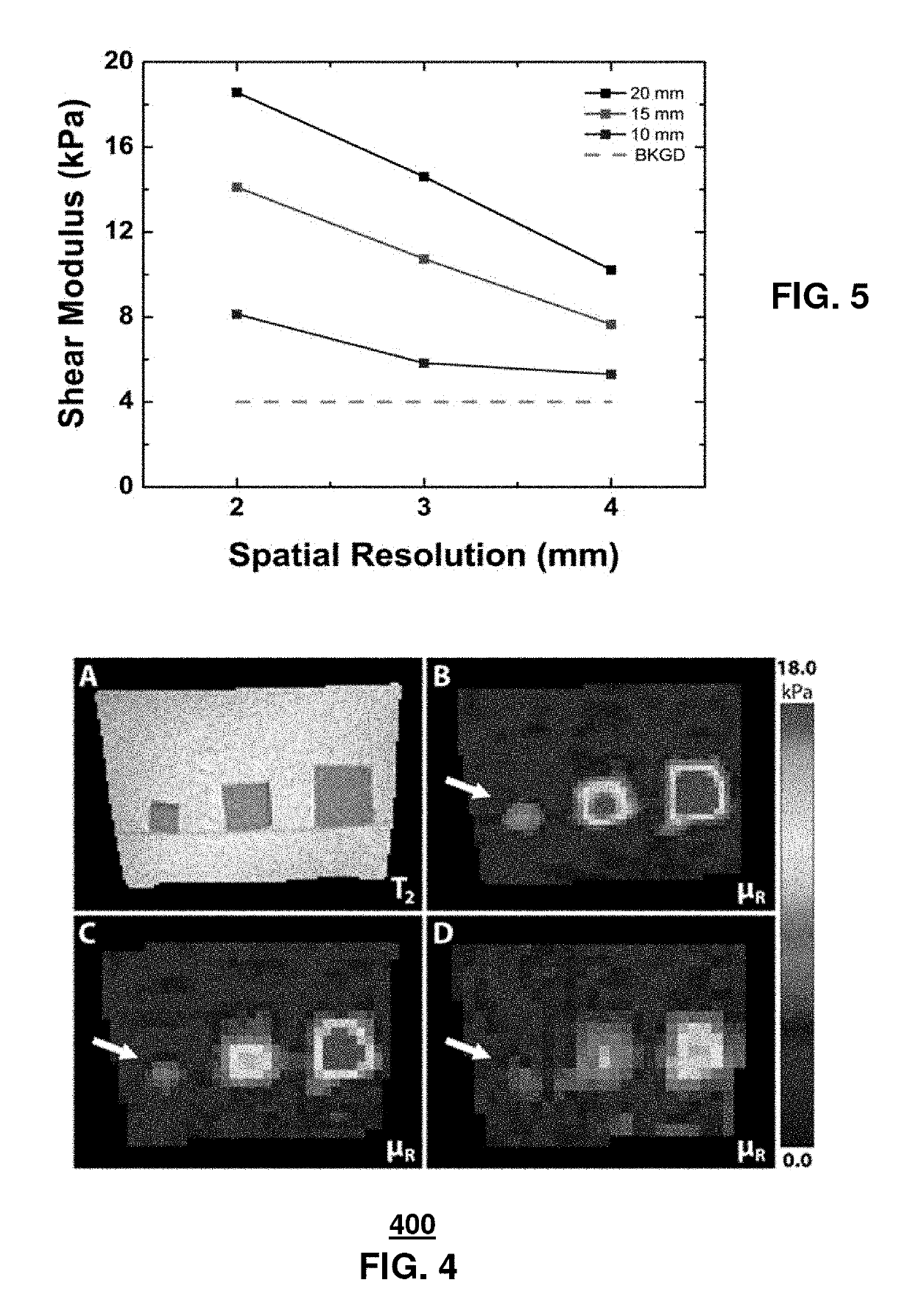
Method for assessing the probability of disease development in tissue
InactiveUS20110060210A1Prevent diseaseMagnetic measurementsDiagnostics using vibrationsDiseaseTissue stiffness
A method for detecting conditions in tissues that can lead to disease includes an in vivo measurement of the mechanical characteristics of the tissues using Magnetic Resonance Elastography (MRE). The deviation of mechanical characteristics such as tissue stiffness from a predetermined norm is determined and indicated on an image of the tissues.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
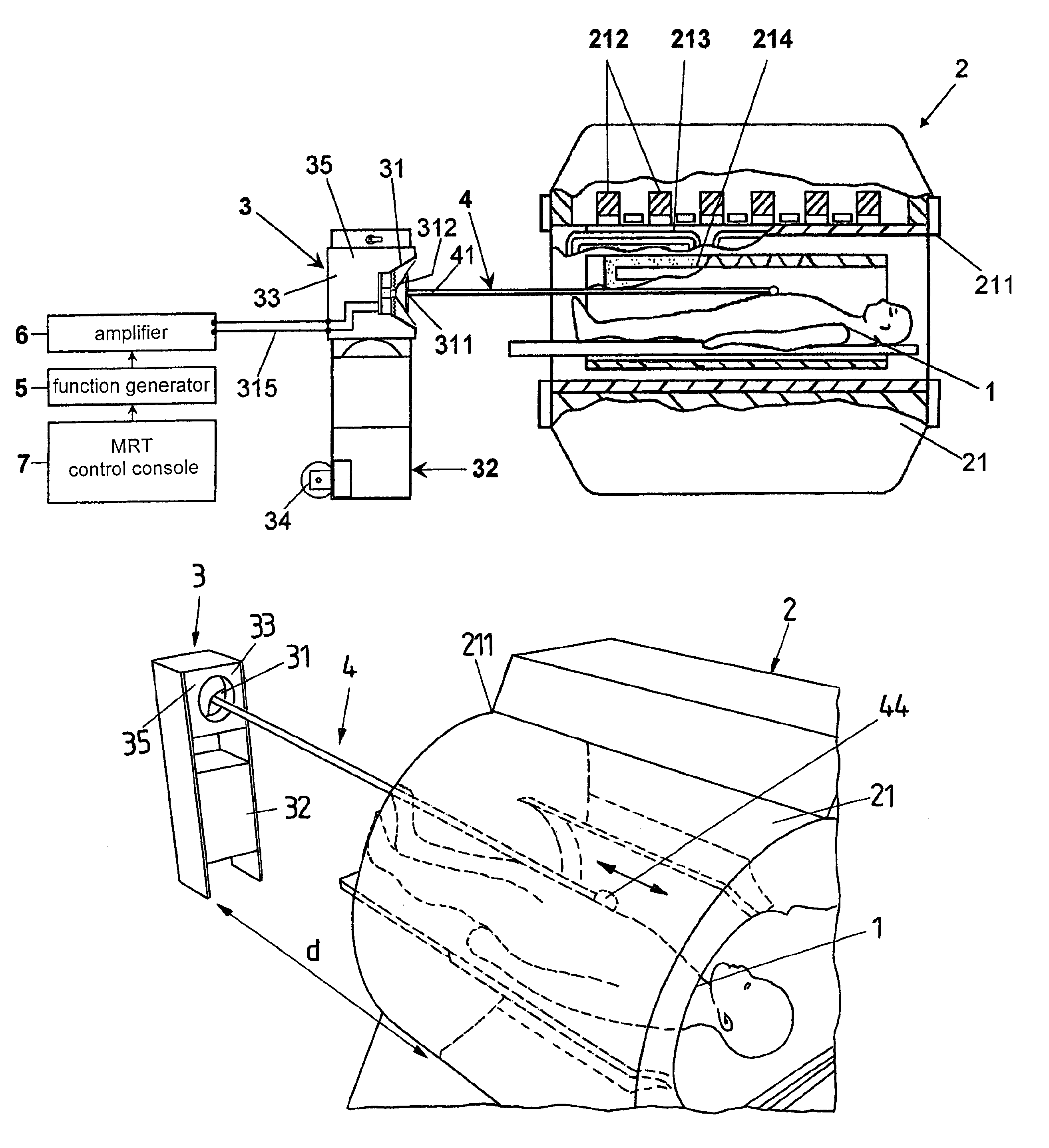
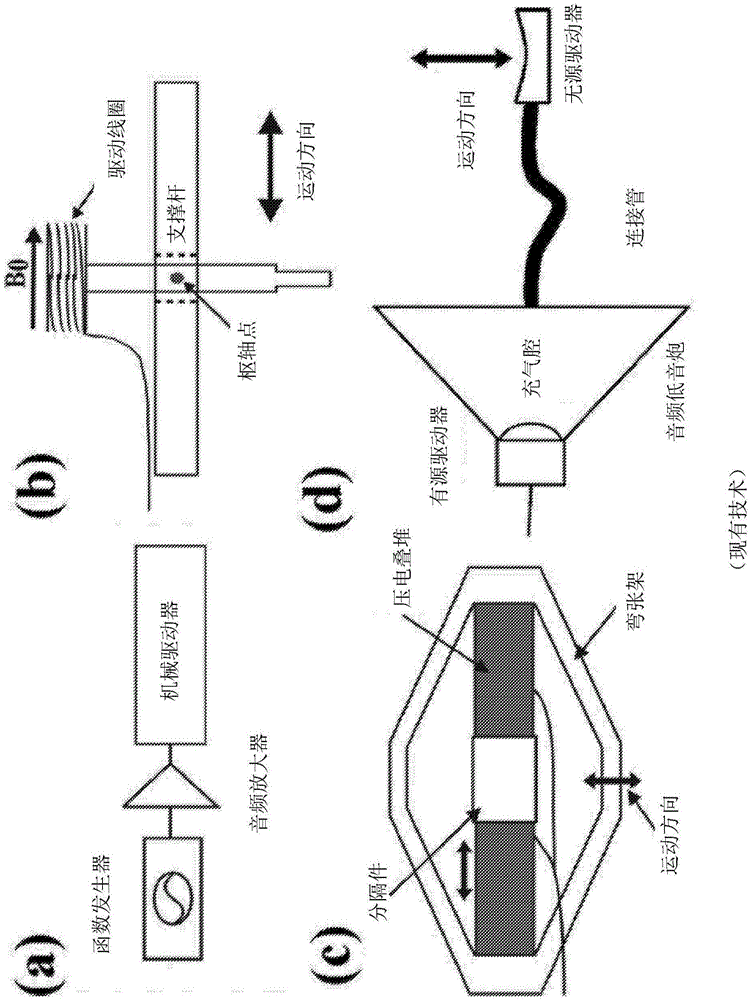
Device and method for generating mechanical oscillations in an examination object using magnetic resonance elastography
InactiveUS8305076B2Efficient inspectionEfficient executionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostics using vibrationsResearch ObjectEngineering
A device and method for producing mechanical oscillations in a research object using magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) with a membrane that can be set into periodic motion and a transmission element for the transmission of periodic motion of the membrane onto the research object, whereby the membrane is connected to the transmission element by means of a mounting medium in such a way that periodic motion of the membrane is transmitted over the mounting medium to the transmission element.
Owner:CHARITE UNIVS MEDIZIN BERLIN
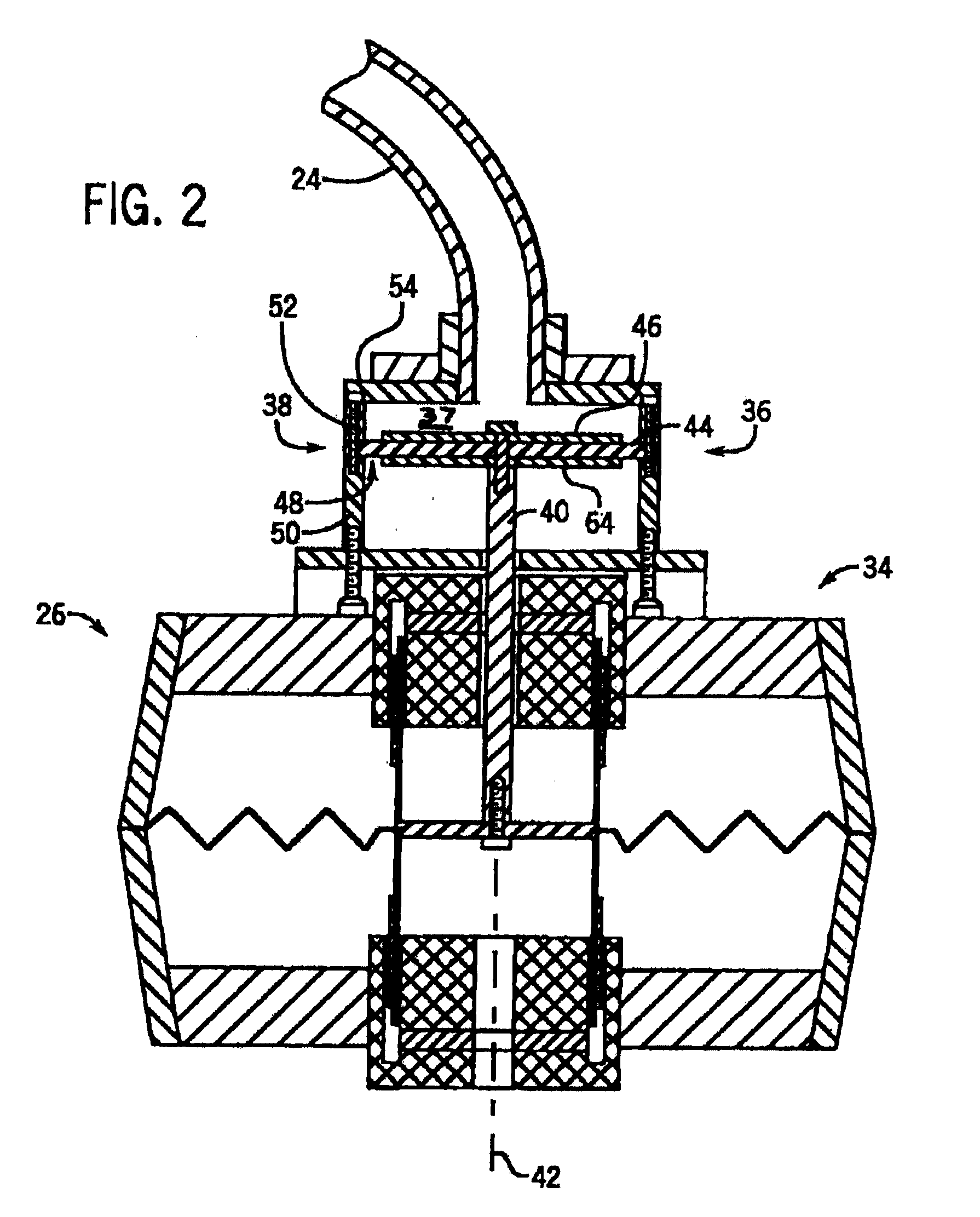
Shear mode pressure-activated driver for magnetic resonance elastography
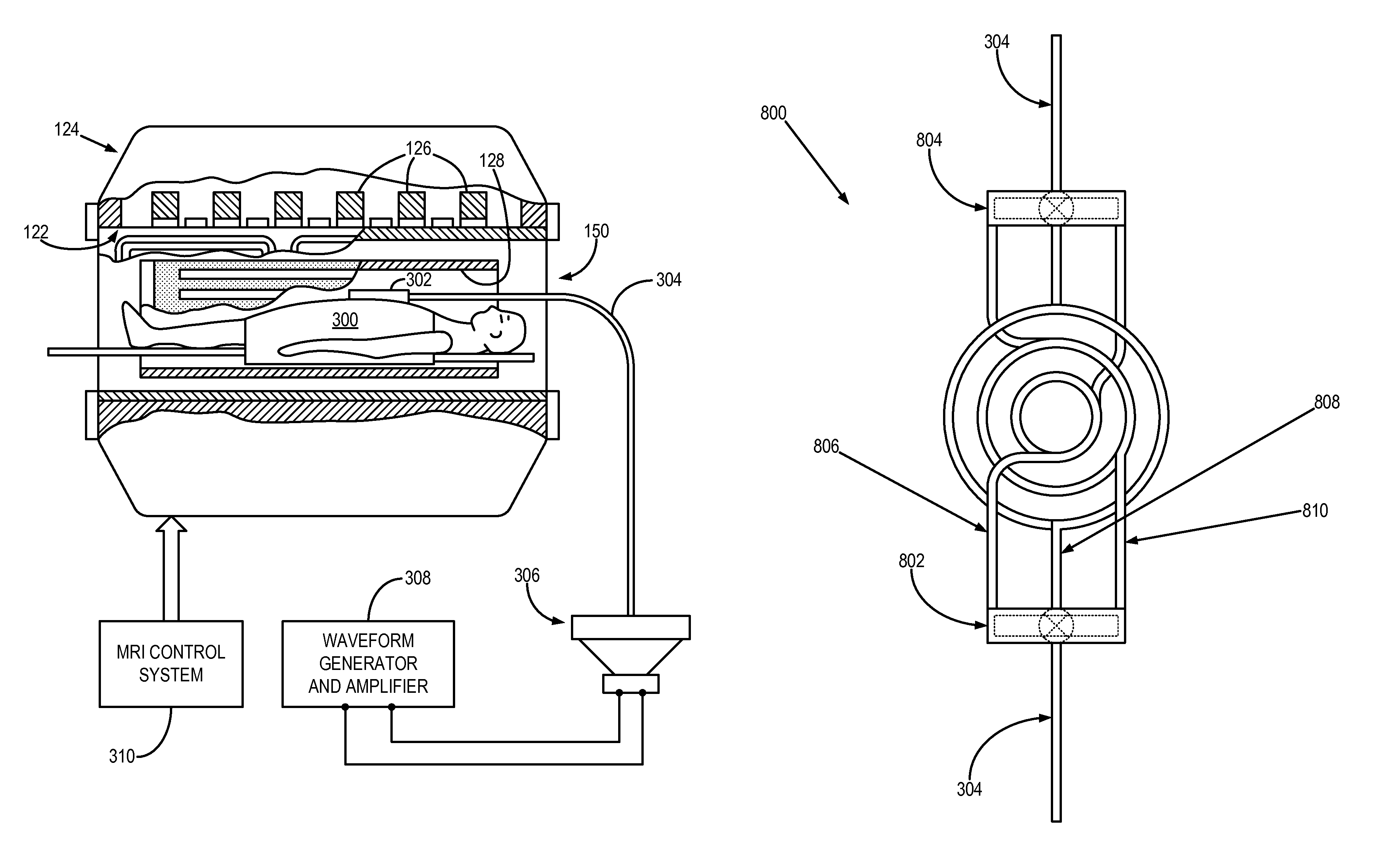
A magnetic resonance elastography (“MRE”) driver that can produce shear waves in a subject without relying on mode conversion of longitudinal waves is disclosed. More specifically, the MRE driver includes a pneumatic driver located remotely from a magnetic resonance imaging (“MRI”) system which is operable in response to an applied electrical current to oscillate, a pressure-activated driver that is positioned on a subject in the MRI system, and a tube that is in fluid communication, at one end, with the pneumatic driver. The pressure-activated driver includes a base plate and a driver plate having a region between them that receives the tube. Oscillations of the pneumatic driver produce a pressure wave in the tube that causes the driver plate to vibrate. The driver plate rests against the subject of interest to apply a corresponding shear oscillatory force to the subject during the MRE examination.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
Flexible Passive Acoustic Driver for Magnetic Resonance Elastography
ActiveUS20120271150A1Improve the patient comfortPoint is avoidedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using vibrationsCouplingEngineering
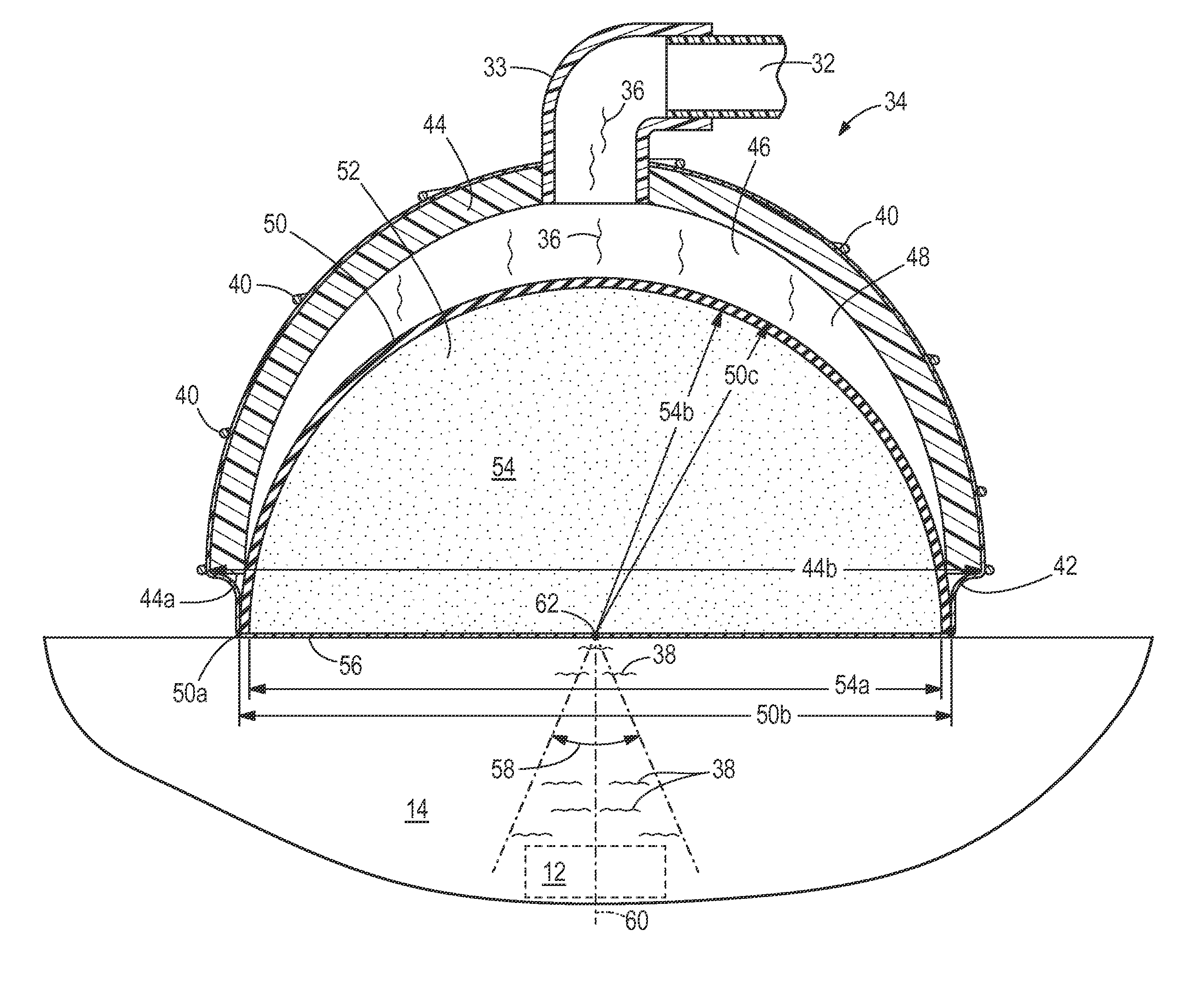
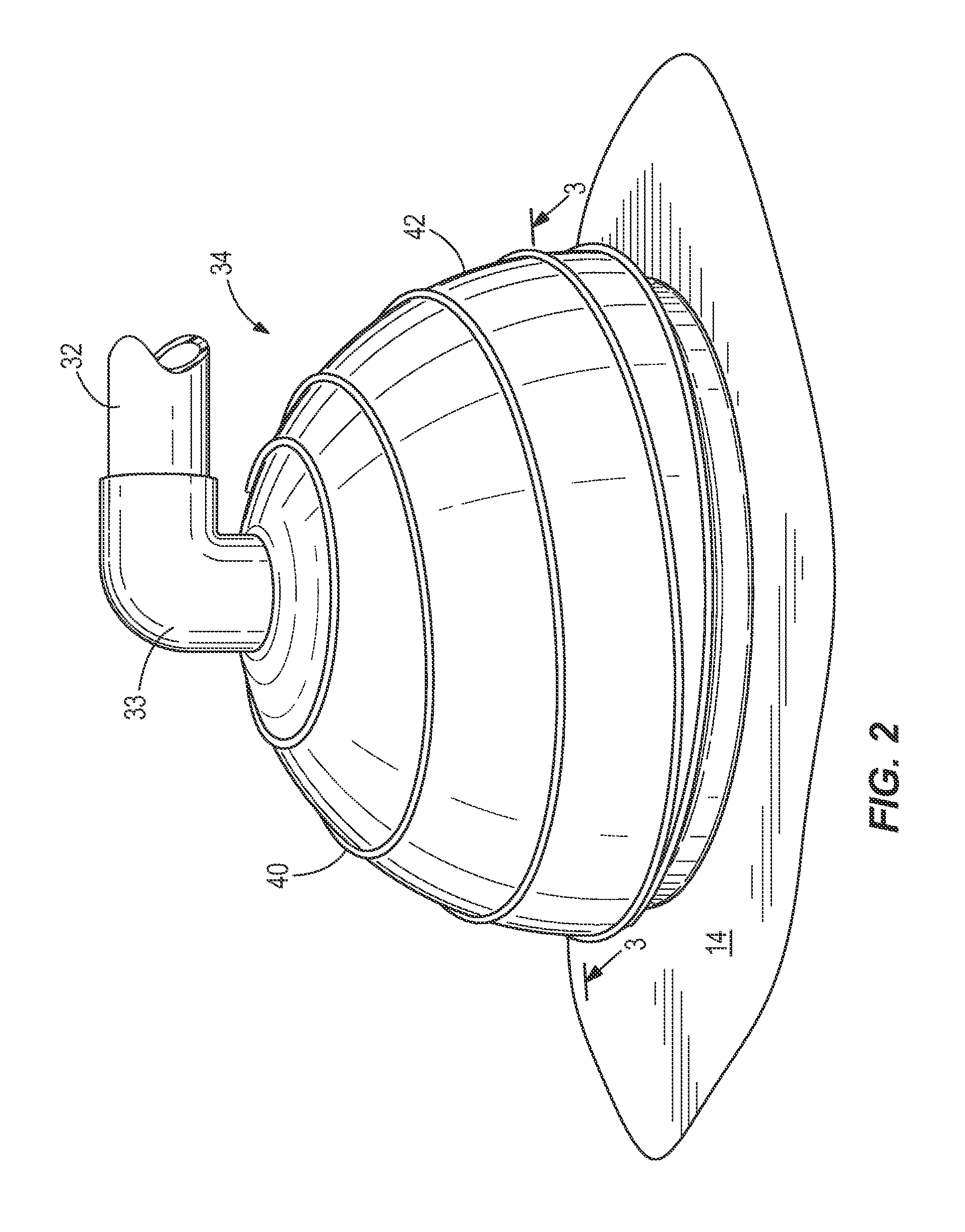
A flexible passive acoustic driver for use in an acoustic driver system which applies an oscillating stress to a subject undergoing a magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) examination which includes receiving acoustic pressure waves from an active driver through a tube and imparts pressure waves to a subject of an imaging procedure. In one configuration, the passive driver includes a flexible bag that forms the walls of an acoustic cavity, and a structure filling material located inside the acoustic cavity provides support for the flexible bag. The flexible bag conforms to the shape of the subject and may be held in place by an elastic band. The passive driver can have an integrated or detachable non-active push-on compartment which is rigid or semi-flexible to improve the human-driver mechanical coupling and the driver energy efficiency of converting acoustic pressure to mechanical vibration applied to a subject.
Owner:MAYO FOUND FOR MEDICAL EDUCATION & RES
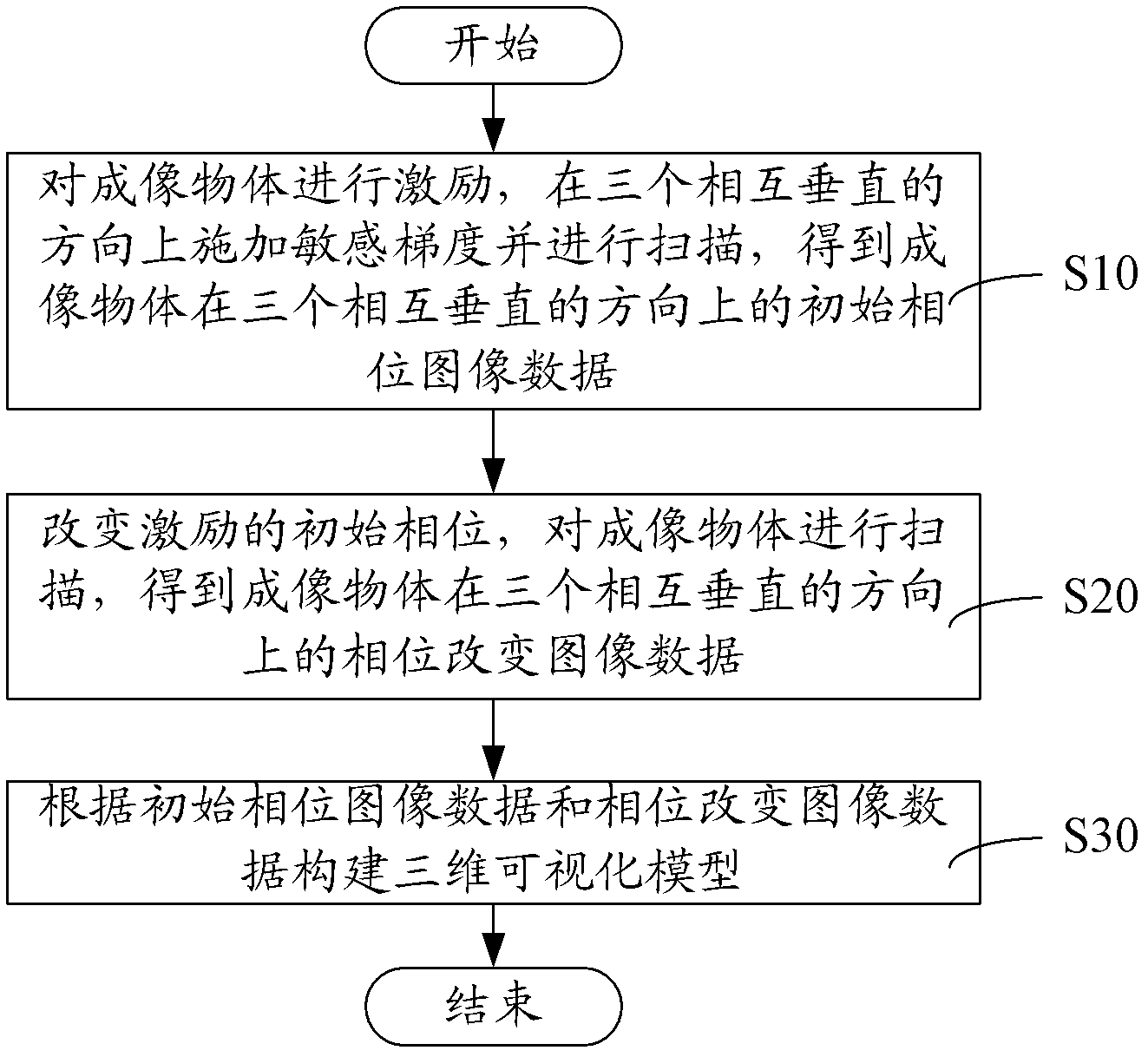
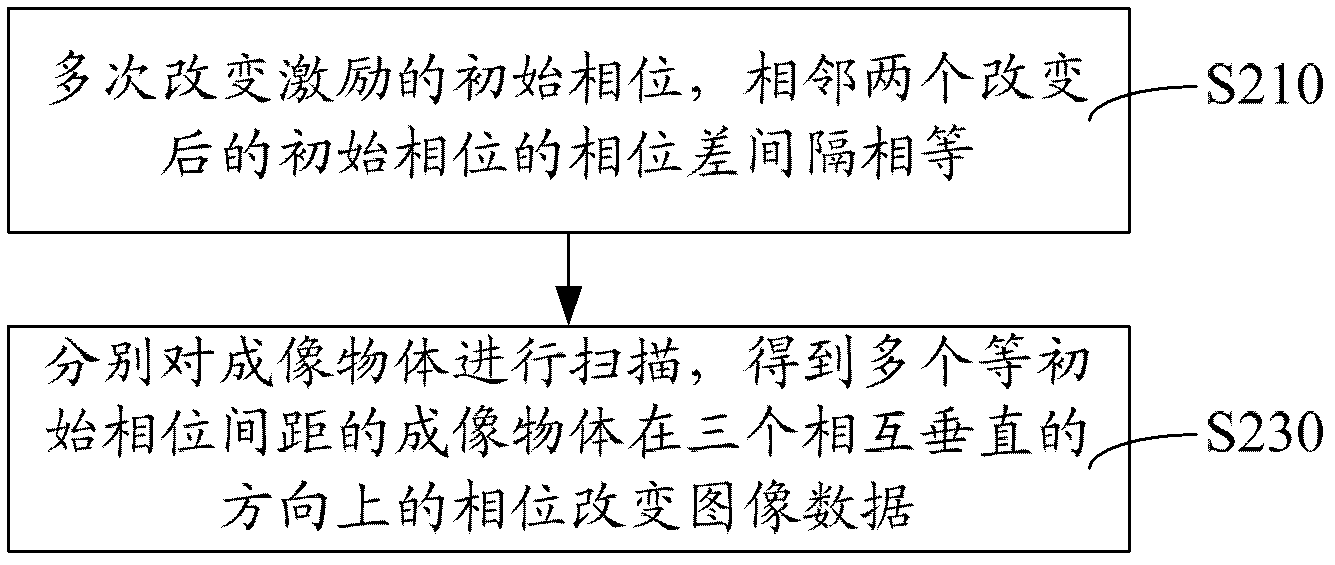
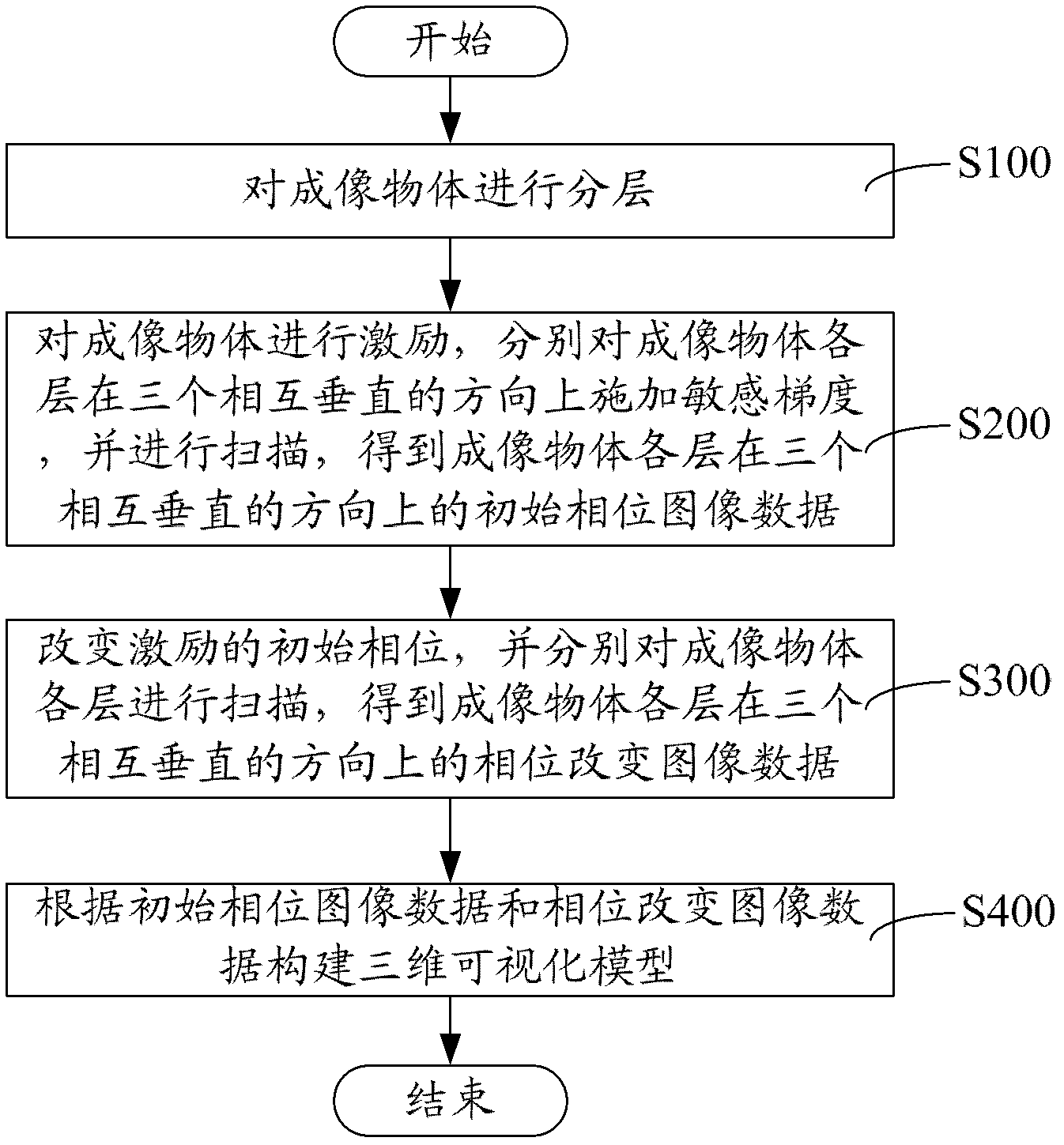
Three-dimensional visualization method and system of magnetic resonance elastography
ActiveCN102631196ARealize 3D visualizationMagnetic property measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringVisualization modelPhase change
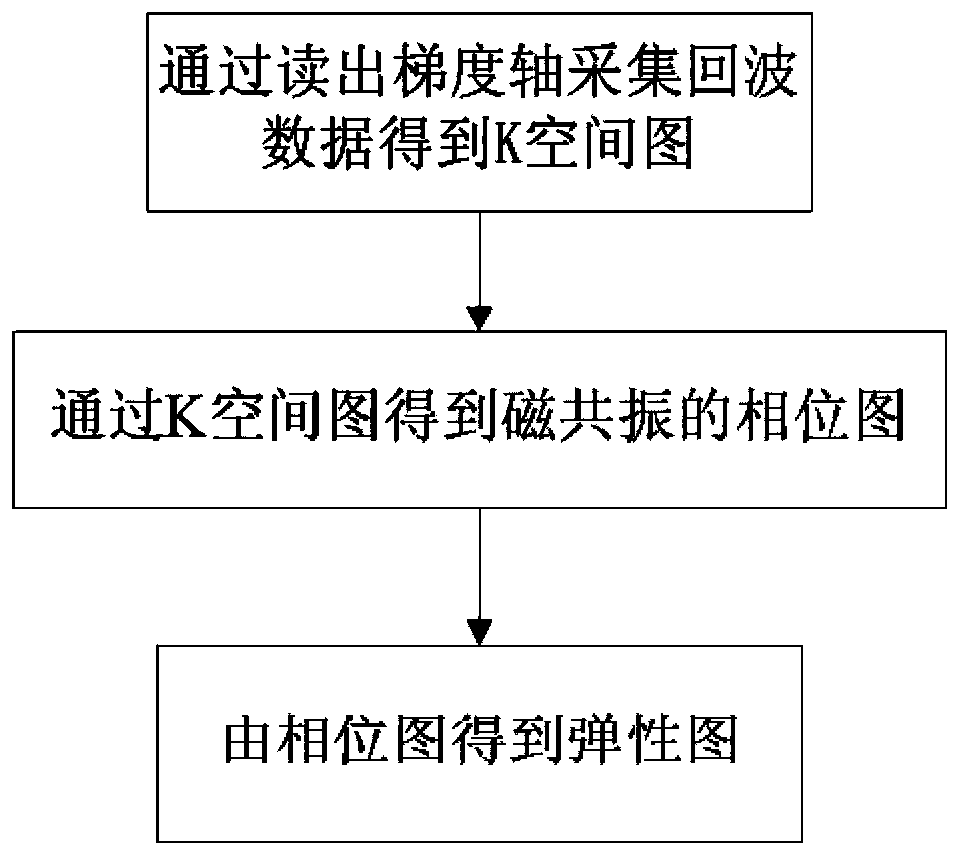
The invention discloses a three-dimensional visualization method of magnetic resonance elastography, comprising the following steps: stimulating an imaged object, applying sensitive gradient on three mutually perpendicular directions and scanning to obtain the initial phase image data of the imaged object at the three mutually perpendicular directions; changing the initial phase of the stimulation and scanning the imaged object to obtain the phase change image data of the imaged object at the three mutually perpendicular directions; constructing a three-dimensional visual model according to the initial phase image data and the phase change image data and setting up an image. In the three-dimensional visualization method of magnetic resonance elastography, the initial phase image data and the phase change image data, namely the three-dimensional image data along with variation of time, are obtained by changing the initial phase of the stimulation, which means so as to construct the three-dimensional visual model of the magnetic resonance elastography to realize three-dimensional visualization of the magnetic resonance elastography. In addition, a system for three-dimensional visualization of magnetic resonance elastography is provided.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
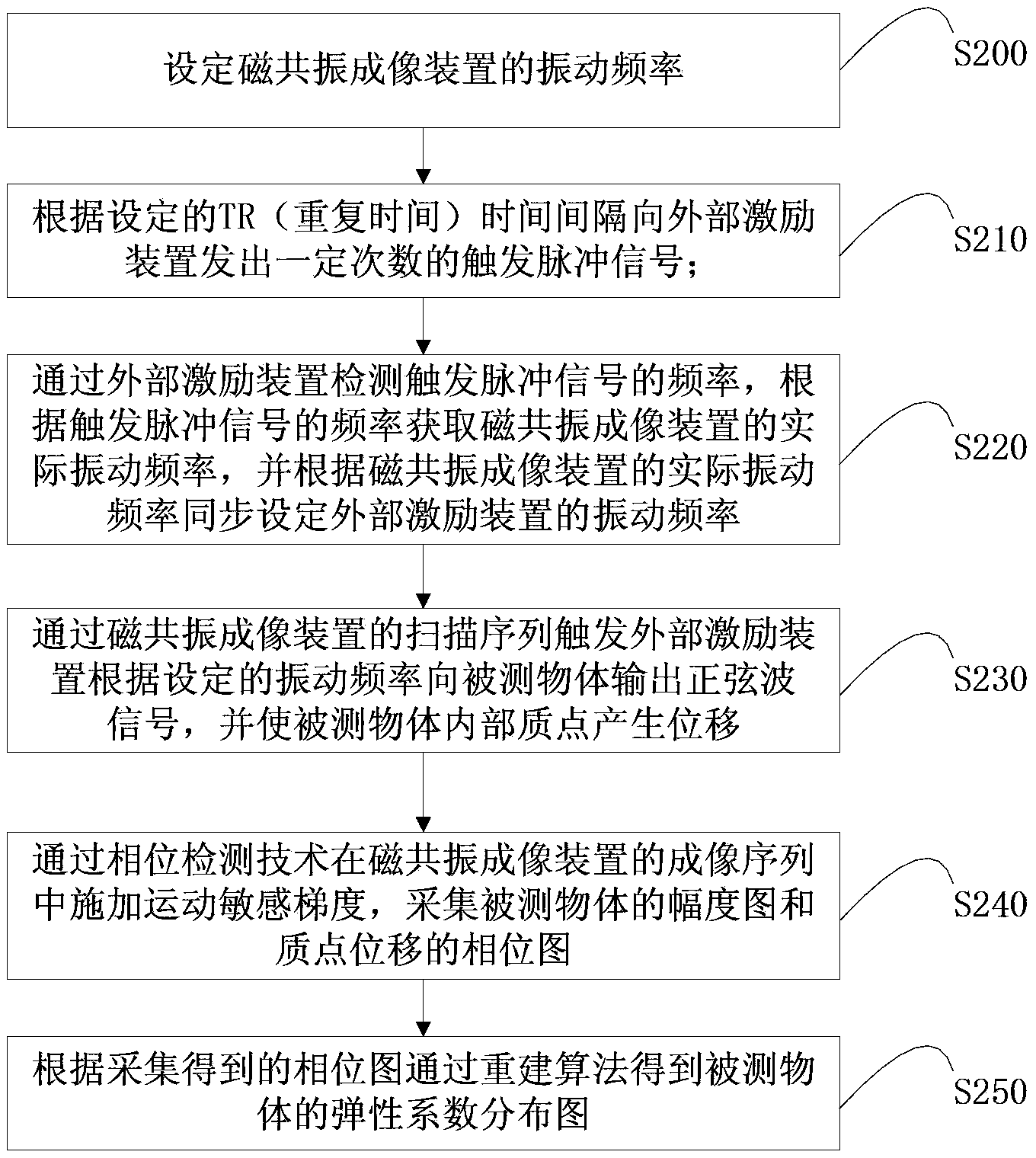
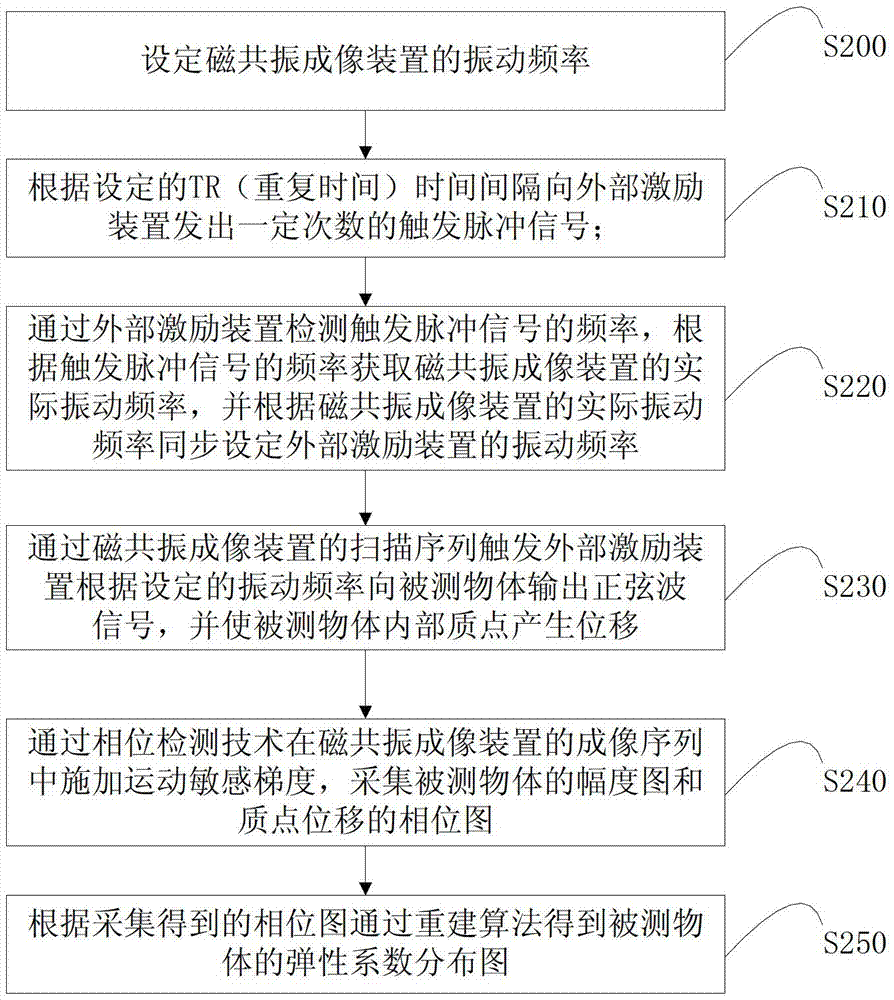
Magnetic resonance elasticity imaging method and system
ActiveCN103349551AGuaranteed accuracyGuarantee stabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsAcquisition timeResonance
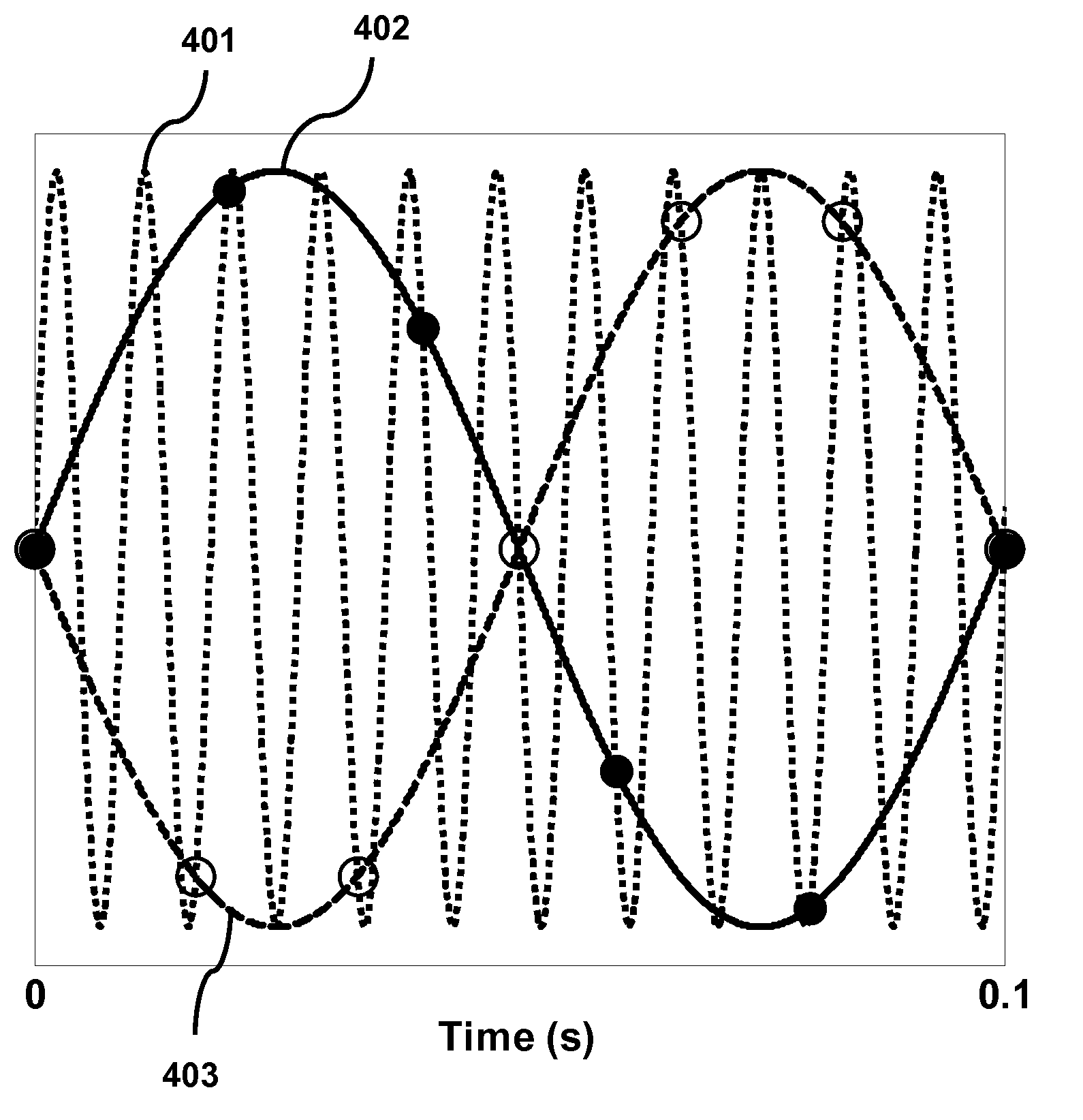
The invention belongs to the technical field of magnetic resonance imaging, and particularly relates to a magnetic resonance elasticity imaging method and system. The magnetic resonance elasticity imaging method comprises the following steps: a, sending a trigger pulse signal through a magnetic resonance imaging device; b, detecting the frequency of the trigger pulse signal through an external excitation device, and setting the vibration frequency of the external excitation device according to the frequency of the trigger pulse signal, wherein the set vibration frequency of the external excitation device and the vibration frequency of the magnetic resonance imaging device are synchronous; c, outputting a signal to a tested object through the mode that the magnetic resonance imaging device triggers the external excitation device, and obtaining elasticity images of the tested object. Due to the fact that the magnetic resonance imaging device sends the trigger pulse signal to the external excitation device in advance, the vibration frequency of the magnetic resonance imaging device and the vibration frequency of the external excitation device are synchronous automatically through the trigger pulse signal, manual operation for regulating the vibration frequency is saved, collection time is shortened, and collection efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
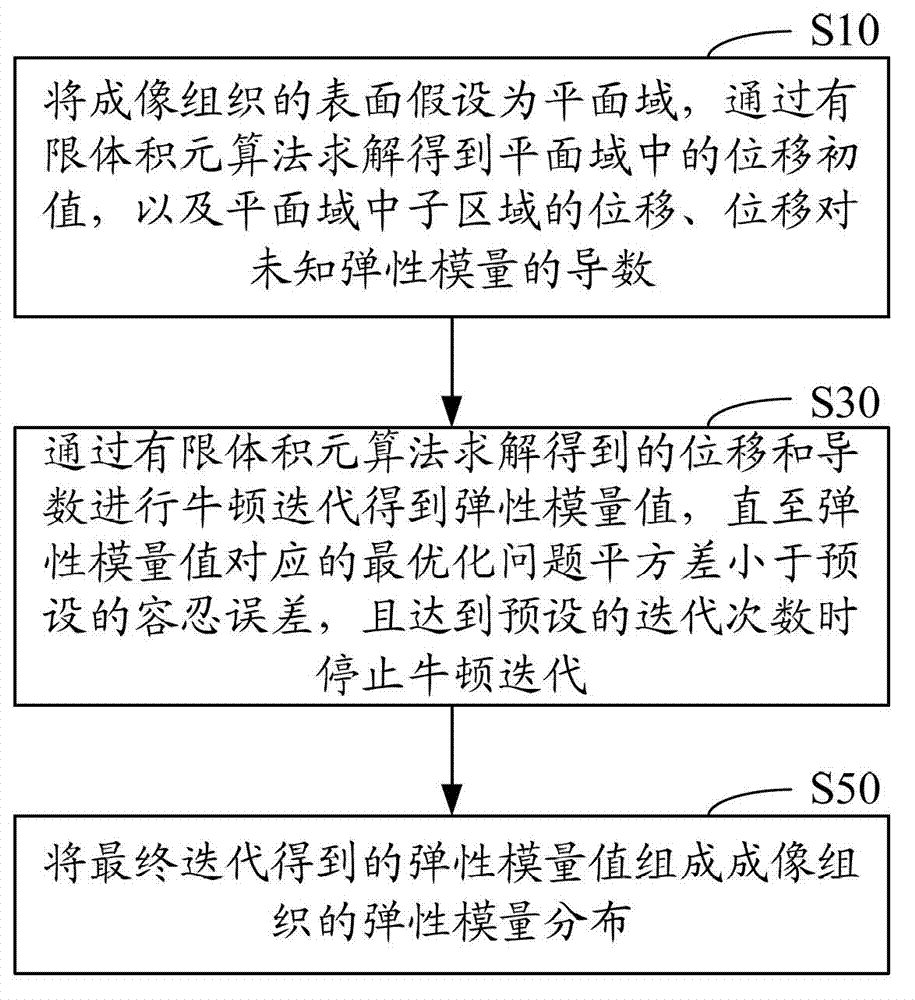
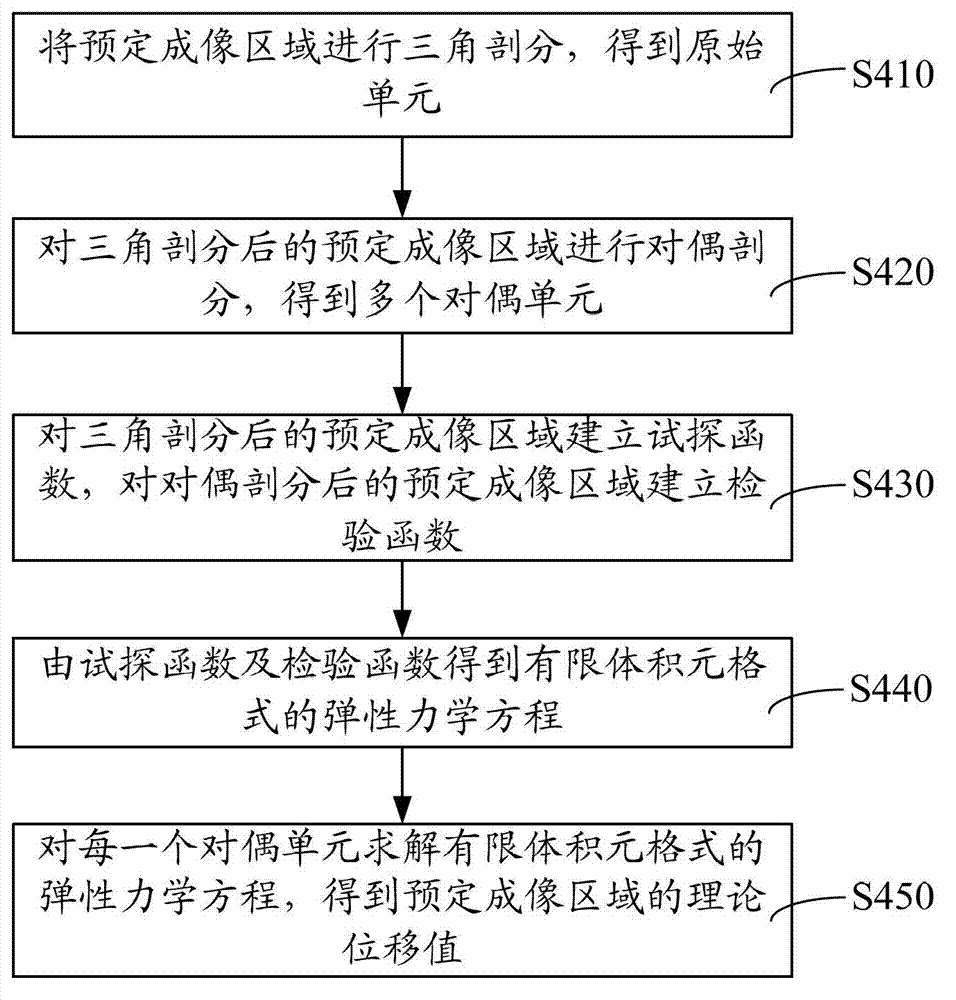
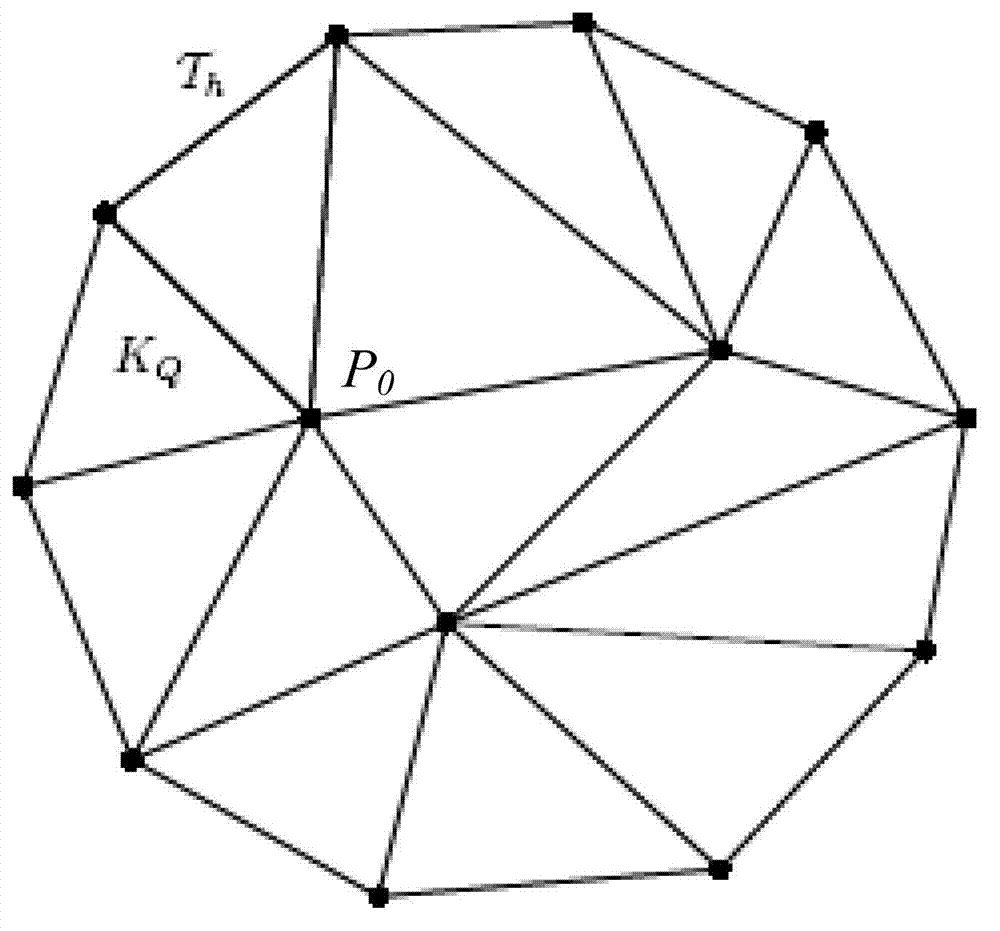
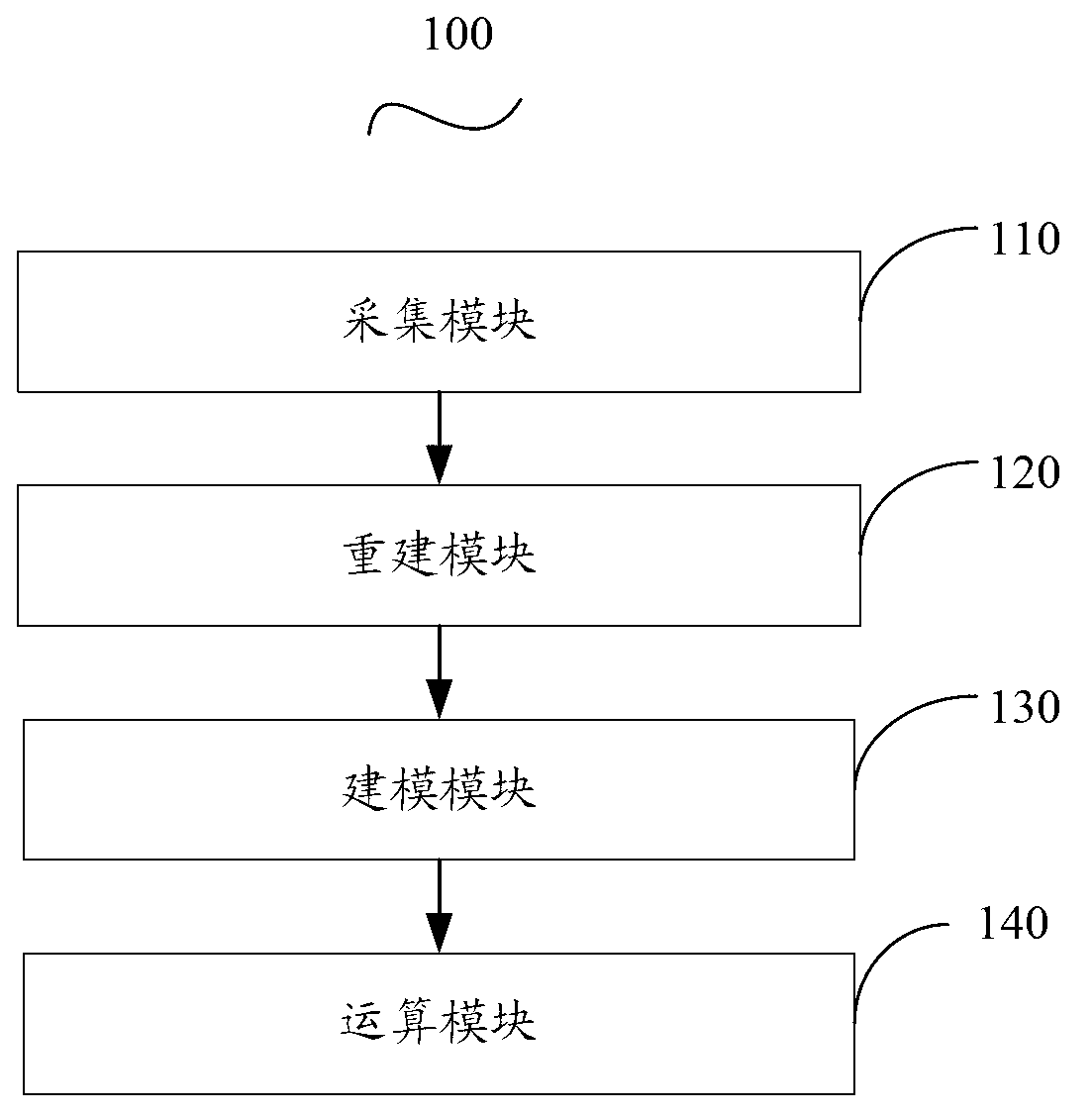
Elasticity modulus reconstruction method and system for magnetic resonance elastography
ActiveCN103049663AGuaranteed calculation accuracySmall amount of calculationSpecial data processing applicationsReconstruction methodErrors and residuals
The invention provides elasticity modulus reconstruction method and system for magnetic resonance elastography. The method includes: assuming the surface of image issue as a plane domain, and solving by finite volume element algorithm to obtain a displacement initial value in the plane domain, displacement of subdomains in the plane domain, and derivatives of the displacement to unknown elasticity modulus; subjecting the displacement and derivatives obtained by solving by the finite volume element algorithm to Newton iteration to obtain an elasticity modulus value, and stopping Newton iteration until an optimization problem square difference corresponding to the elasticity modulus value is smaller than a preset tolerated error and a preset number of iterations reaches; and composing the elasticity modulus values obtained by final iteration into elasticity modulus distribution of the image tissue. Calculated amount can be reduced by the use of the method and system.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Magnetic resonance elasticity imaging pillow style excited by electromagnetism device
InactiveCN101406395AConsider comfortConsider securityDiagnostics using vibrationsSensorsAudio power amplifierResonance
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance elastography head pillow-type electromagnetic excitation device, which comprises a table frame; a support shaft is fixed on the table frame; the support shaft can be rotationally provided with at least one driving plate, one end of the driving plate positioned on one side of the support shaft is provided with an electromagnetic coil on which a copper wire is used to be connected with an output interface of a low frequency sinusoidal signal amplifier of the magnetic resonance elastography device, and one end of the driving plate positioned on the other side of the support shaft forms a head pillowing part. The excitation device has the advantages that the excitation device sufficiently considers the clinical practicability, has good comfort, so that a patient is easy to accept; during inspection, the head of an inspected person can be substantially contacted with the vibrational excitation device, so the inspected person has no adverse reaction even if receiving the inspection for a longer period, and the device can complete routine MRI inspection and MRE inspection at one time.
Owner:高培毅
Detecting method of magnetic resonance elastography accuracy
ActiveCN102920457AHigh precisionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMR - Magnetic resonanceElastic modulus
The invention discloses a detecting method of magnetic resonance elastography accuracy, comprising the following steps: obtaining an imaging displacement value at a predetermined imaging area generated by the magnetic resonance elastography under a predetermined external force; obtaining the predetermined external force and the elasticity modulus of the predetermined imaging area; according to the predetermined external force, obtaining the stress of the predetermined imaging area; based on the stress of the predetermined imaging area and the elasticity modulus, obtaining a theoretical displacement value of the predetermined imaging area; comparing the theoretical displacement value of the predetermined imaging area with the imaging displacement value generated by the magnetic resonance elastography, and detecting the accuracy of the magnetic resonance elastography. The detecting method of magnetic resonance elastography accuracy is to adopt a finite volume element method, is based on the stress of the predetermined imaging area and the elasticity modulus, and obtains the theoretical displacement value, which provides references for solving the elasticity modulus of the imaging area by inverse calculation after obtaining the displacement diagram of the magnetic resonance elastography.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
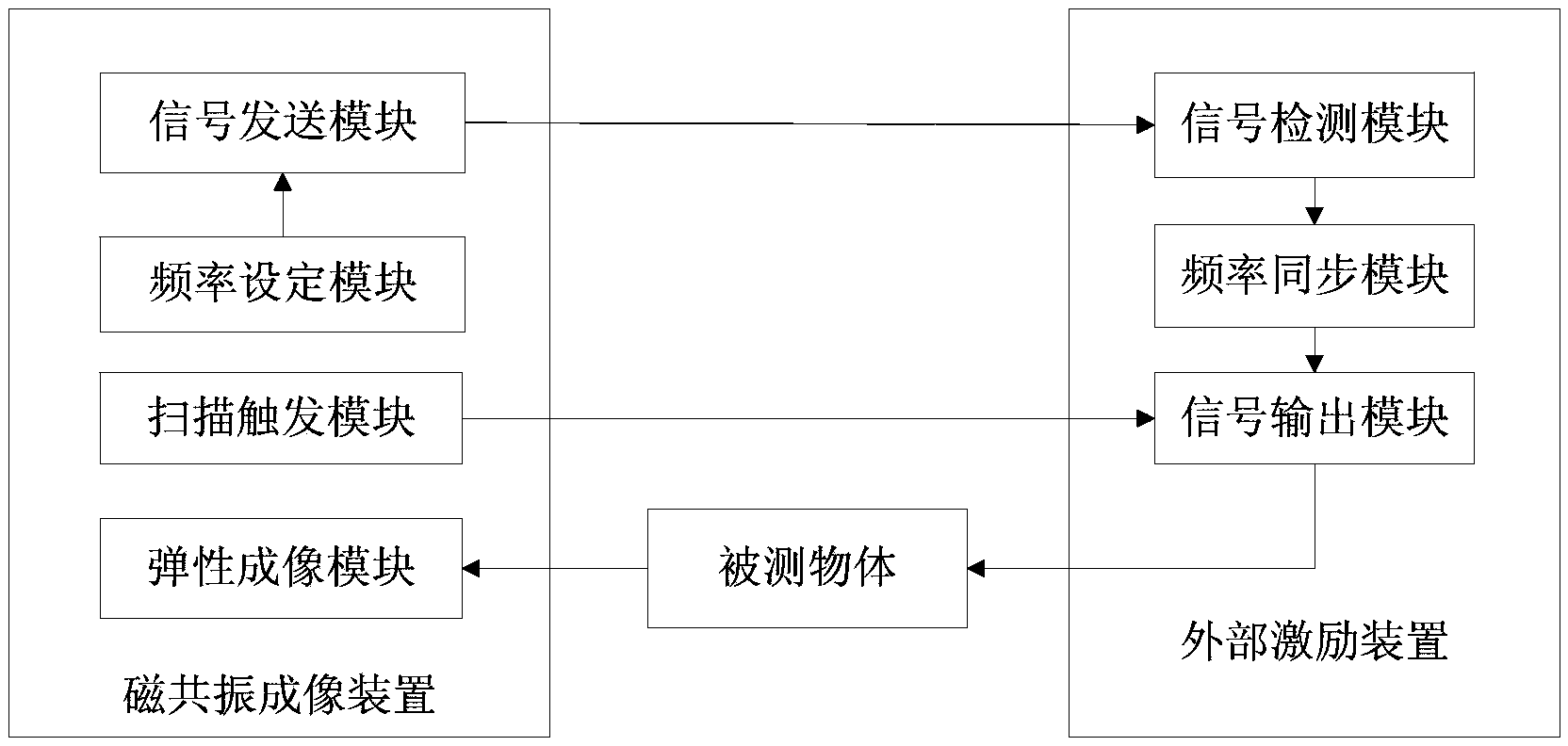
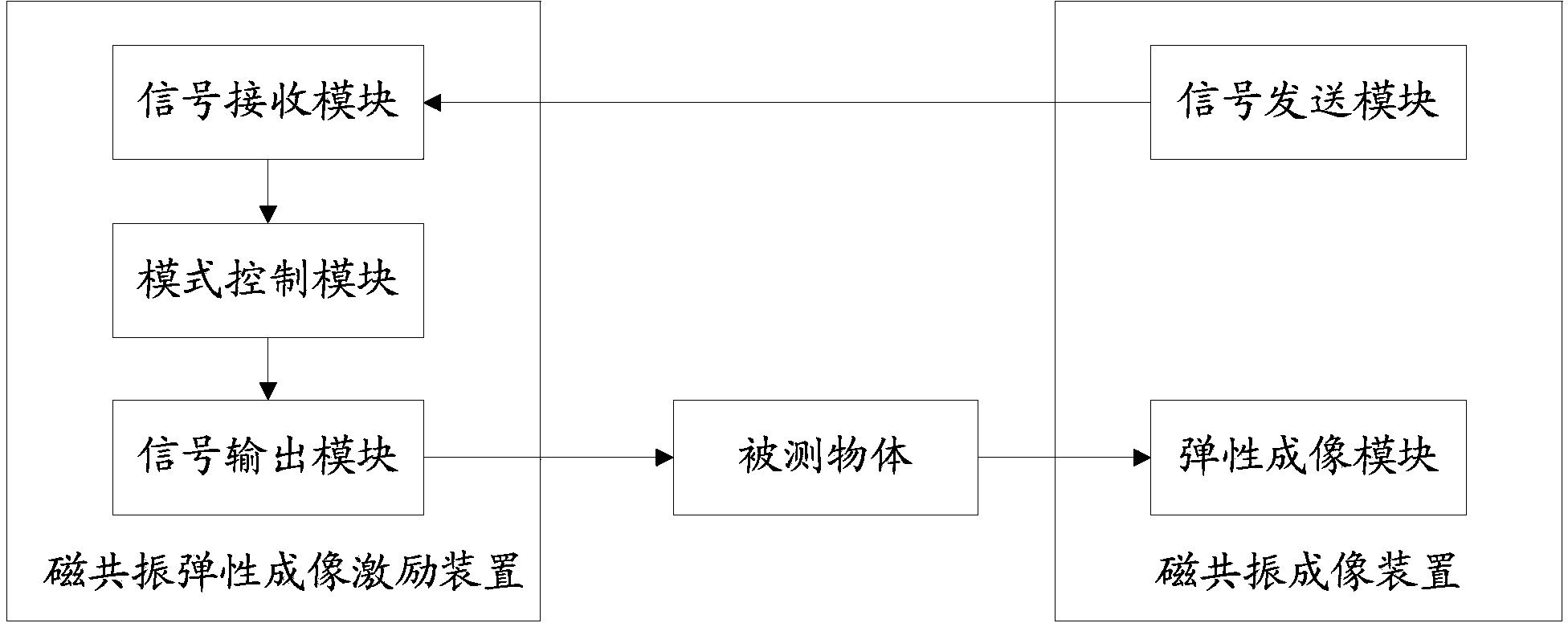
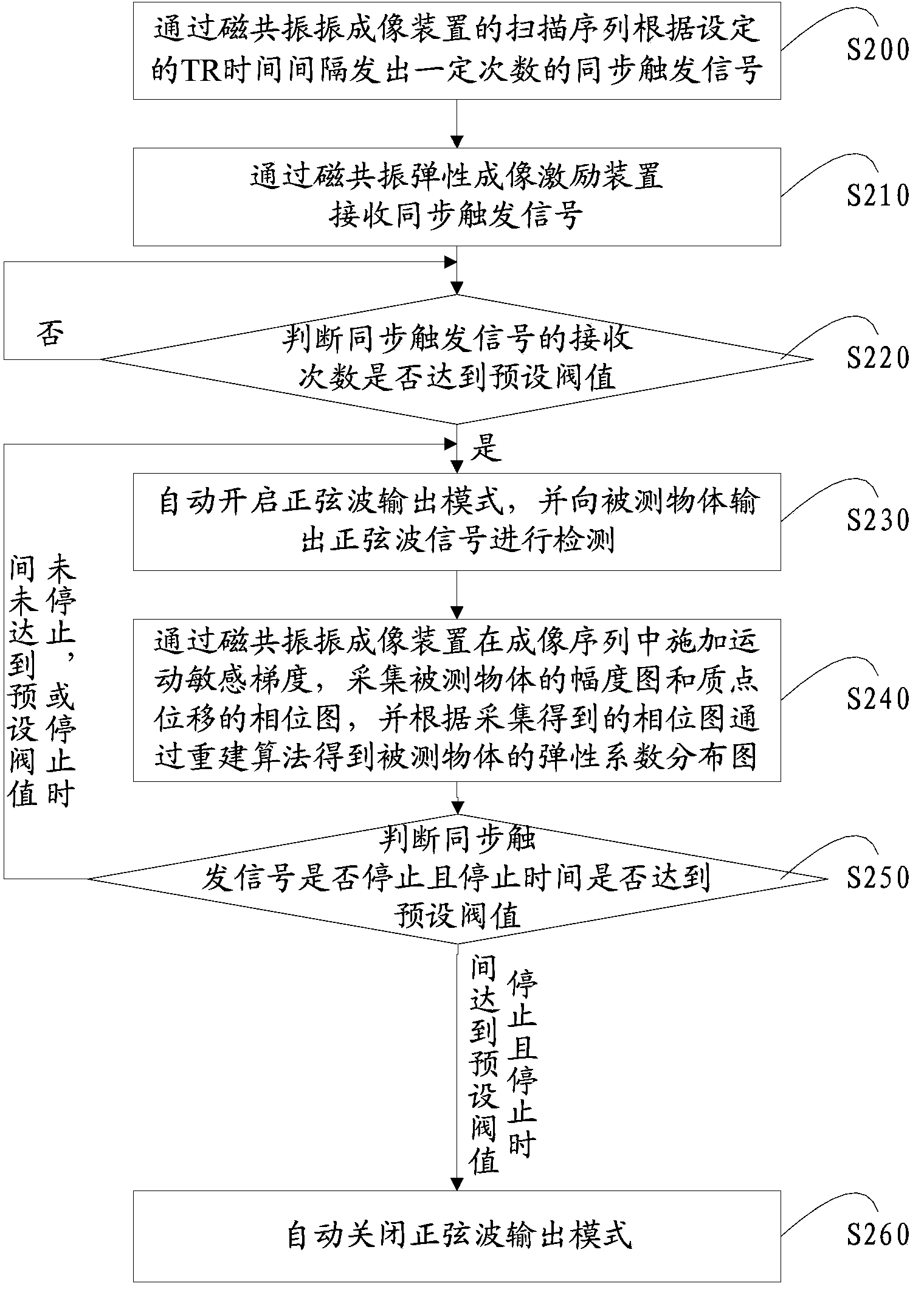
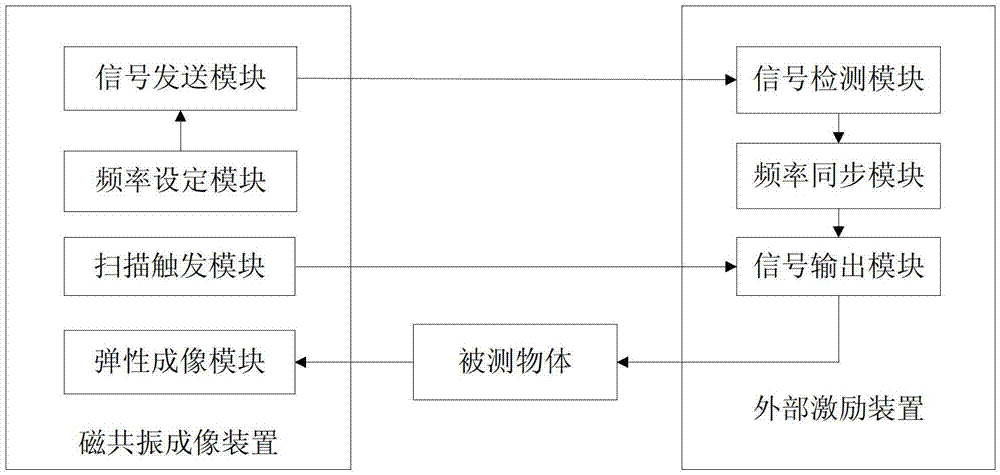
Medical image configuration system and method
ActiveCN103356192AAvoid failureSave the inconvenience of manual operationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonanceMode control
The invention relates to a medical image configuration system and method. The medical image configuration system comprises an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) device and a magnetic resonance elastic imaging exciting device, wherein the MRI device comprises an elastic imaging module; the magnetic resonance elastic imaging exciting device comprises a signal receiving module, a mode control module and a signal output module; the signal receiving module receives synchronous trigging signals given out by the MRI device; the mode control module opens a sine wave output mode automatically according to the synchronous trigging signals receiving frequency of the signal receiving module, and closes the sine wave output mode automatically according to the synchronous trigging signals receiving stopping; the signal output module detects the sine wave signal outputted by a to-be-detected object. The sine wave signal output of the magnetic resonance elastic imaging exciting device is automatically opened or closed through detecting the synchronous trigging signals given out by the MRI device, so that the manual operation inconvenience is removed, and the acquisition efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Magnetic resonance elastography active adsorption type bridging exciter
InactiveCN104000591AImprove conversion efficiencyDo not interfere with deliveryDiagnostics using vibrationsSensorsTissue strainExternal source
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance elastography active adsorption type bridging exciter which is characterized by comprising a vibration generator and an active adsorption type bridging mechanism, the vibration generator comprises a minitype vibrating table, a vibrating end airtight air chamber and a T-shaped push rod, and the active adsorption type bridging mechanism comprises a bridging end airtight air chamber, a concave adsorption surface and an air extractor. The bridging exciter with the active adsorption function is capable of achieving bidirectional exciting, defects of unidirectional exciting are overcome, phase and frequency consistency between external source driving and tissue strain is achieved, elastic wave driving and tissue strain are coordinated, and elastic wave conversion efficiency is improved.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Needle driver for magnetic resonance elastography
InactiveUS7979109B2High shear elasticityImprove sensitivity and specificityDiagnostics using vibrationsVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsMild cognitive impairment (MCI)Acupuncture treatment
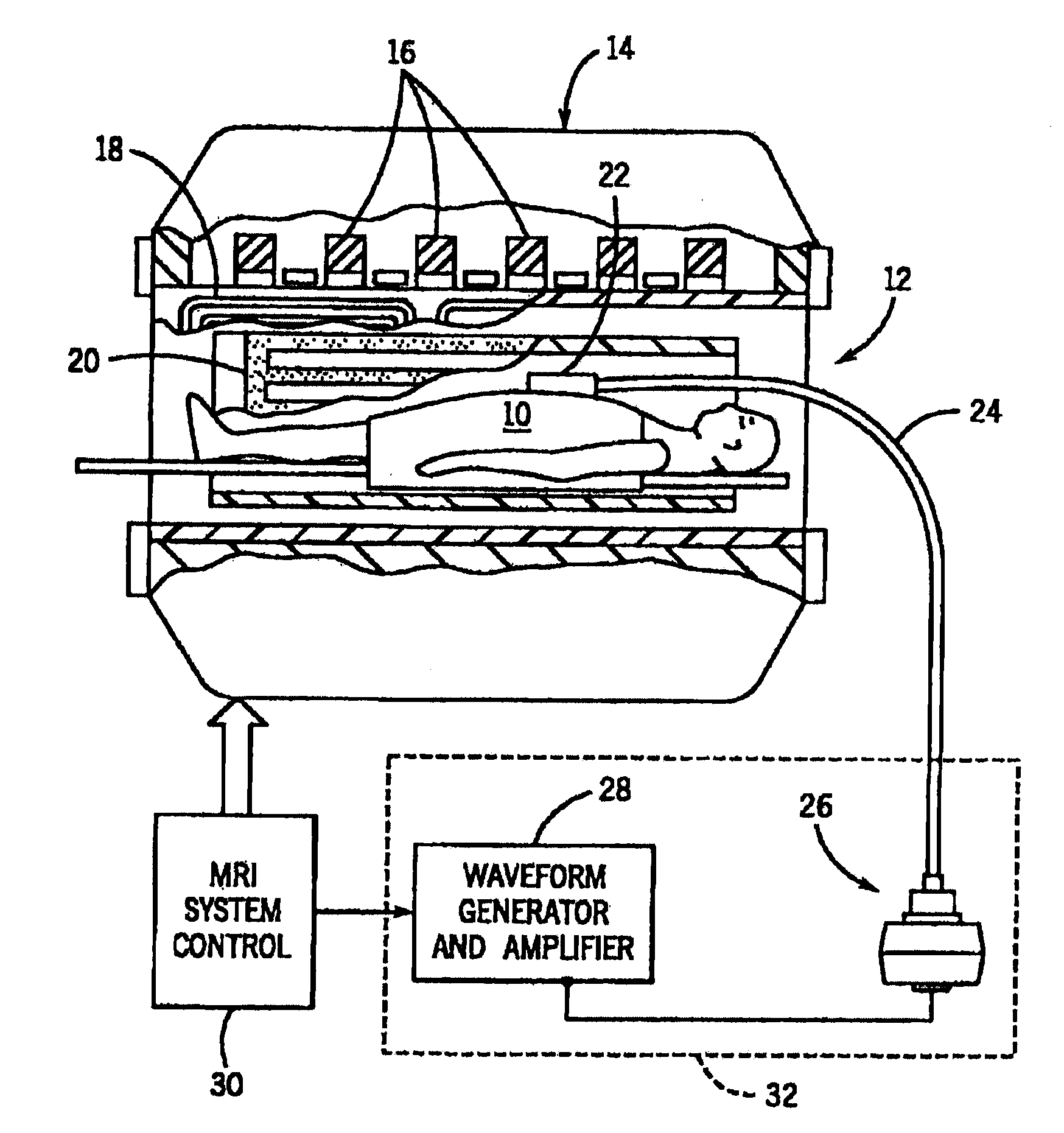
The present invention is directed toward an acoustic, piezoelectric, electric, electro-mechanical or pneumatically driven surface drum driver, in mechanical engagement with a biopsy or acupuncture needle device and a method for its use for diagnosis of small e.g. 100 microns, tumors via the production of magnetic resonance elastographic images (MRE), without artifact production, in a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machine. In a second embodiment, the invention is directed toward an acoustically, pneumatically, piezoelectrically, electrically and / or electro-mechanically driven acupuncture needle, useful for simulating manual single-needle acupuncture treatments via a non-manually manipulated acupuncture needle; and further to a device and process for determination, using twin pneumatically driven surface drivers, of organ stiffness, e.g. brain stiffness, which can be quantified so as to be useful in elucidating and quantifying brain cognitive state, e.g. normal, mild cognitive impairment (MCI) or Alzheimer's dementia (AD).
Owner:LAWRENCE GROUP MEDICAL DEVICE TRUST
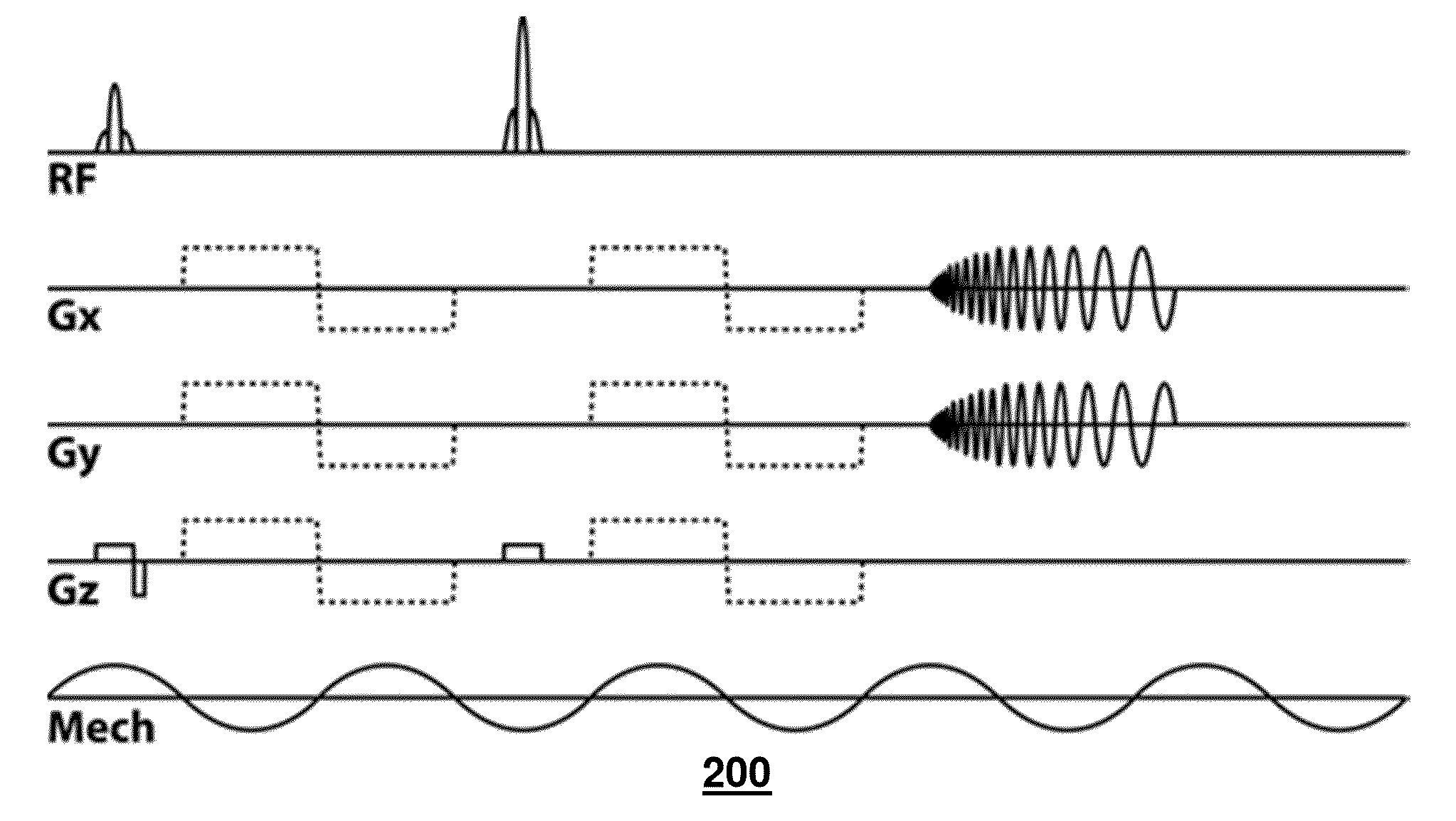
Echo-planar imaging magnetic resonance elastography pulse sequence
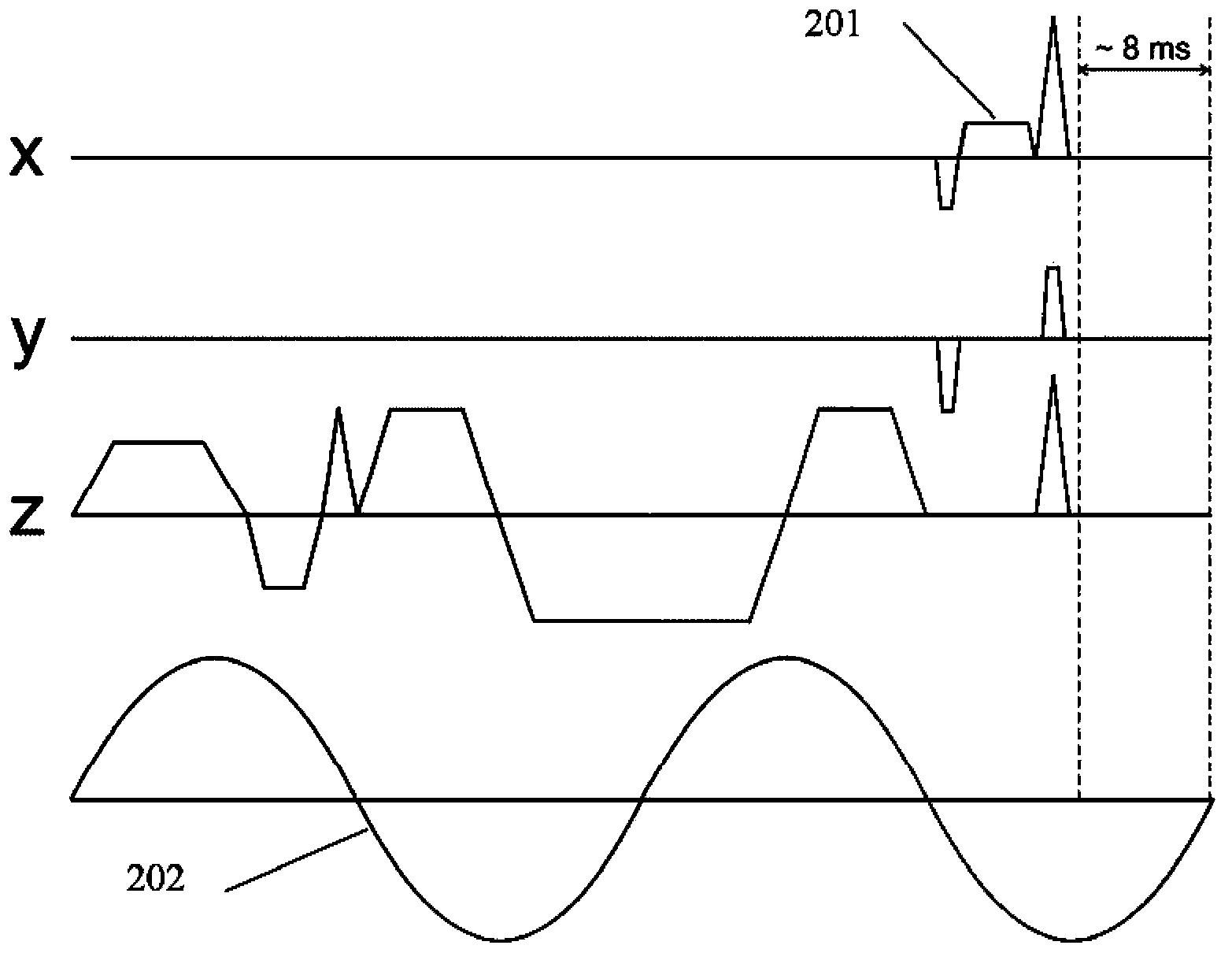
Magnetic resonance elastography (MRE) is an imaging technique for estimating the stiffness of tissues non-invasively. Shear waves are generated via external mechanical actuation and the tissue imaged with a specially designed MR pulse sequence. The resulting images are used to calculate the underlying properties. The application provides methods for acquiring MRE data using a single shot, echo planar imaging readout. The purpose of the developed sequence is to acquire MRE data using a single-shot, echo-planar imaging readout, avoiding to need for off-line image processing.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
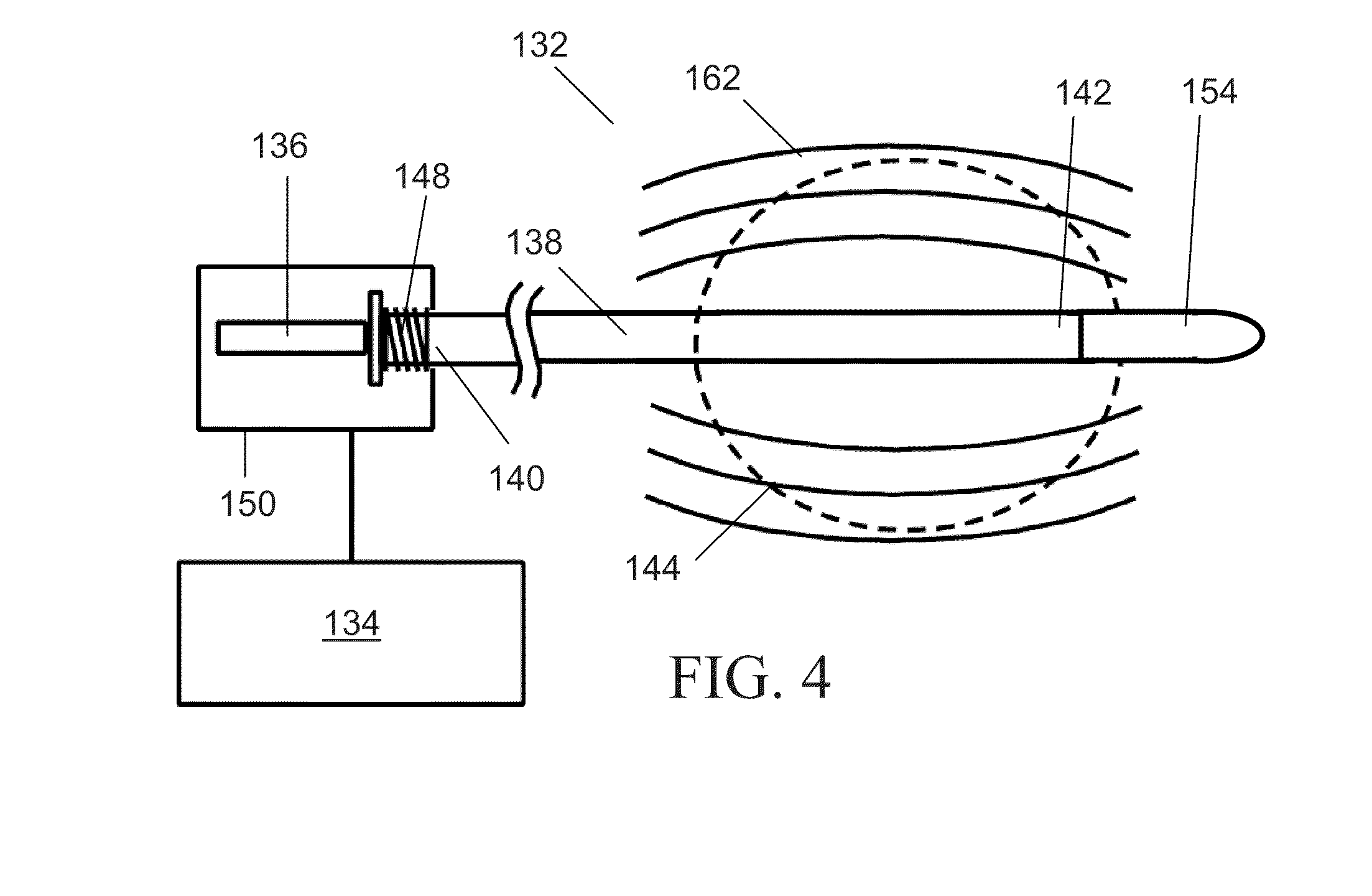
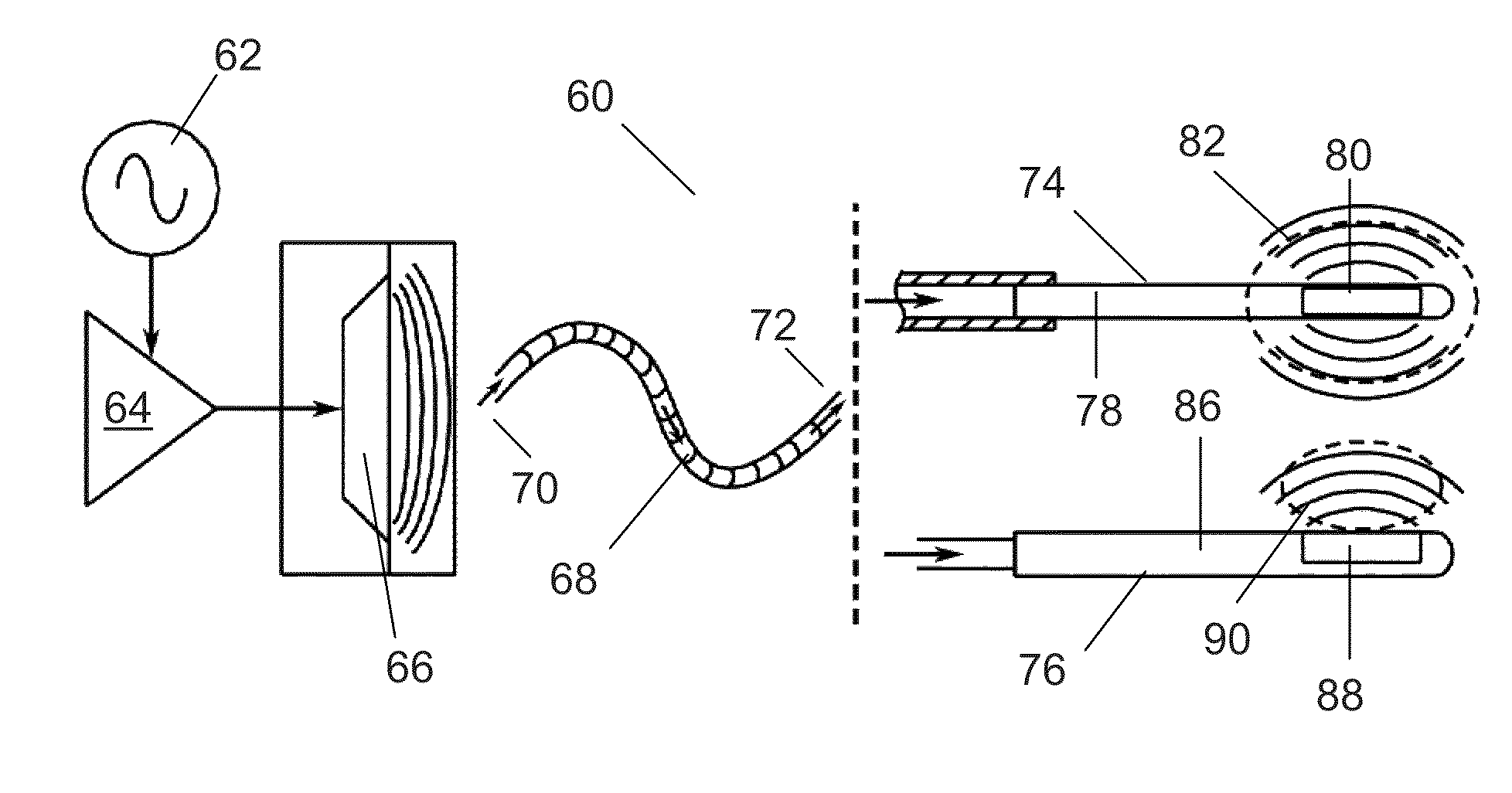
Vibration inducing apparatus for magnetic resonance elastography
Embodiments of the invention provide a magnetic resonance (MR) compatible transducer for magnetic resonance elastography applications having a cantilevered drive element a free end of which is arranged in use to move reciprocally, and a flexible non-conductive connection rod slidably disposed within a flexible non-conductive sleeve. The connection rod is affixed at a proximal end to the cantilevered drive element via a proximal flexible connection piece that in use accommodates the slight rotational movement of the cantilevered drive element as it reciprocates about its secured end, whilst translating the rotational reciprocation of the cantilevered drive element into a pure translational reciprocation of the connection rod within the sleeve. The distal end of the connection rod is affixed against a protrusion connected to another cantilevered driven element, upon which is mounted a piston element that in use contacts the subject. The distal end of the connection rod is provided with a distal flexible connection piece that forms the connection between the end of the connection rod and the cantilevered driven element, again to account for the pure translational movement of the rod being converted to rotational movement of the cantilevered driven element about its cantilever pivot point.
Owner:KINGS COLLEGE LONDON
System and method for intracorporeal elastography
ActiveUS8222901B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostics using vibrationsMechanical energyRadiology
A system and method for intracorporeal elastography include an intra-luminal vibratory member configured to be positioned within a lumen of an imaging subject and configured to impart mechanical energy into tissue of the lumen. In a preferred embodiment, an external piezoelectric energy source is included and coupled to the vibratory member and configured to cause the vibratory member to longitudinally vibrate, thereby generating shear waves for use with magnetic resonance elastography.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
Method and system for multi-shot spiral magnetic resonance elastography pulse sequence
ActiveUS10261157B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionK space trajectoryPulse sequence
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
Pneumatic supercharging excitation device and method oriented to magnetic resonance elasticity imaging
ActiveCN104771170ASpread fastReduce lossesDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsImaging qualityResonance
The invention discloses a pneumatic supercharging excitation device and method oriented to magnetic resonance elasticity imaging. The pneumatic supercharging excitation device comprises a vibration generator and a bridging mechanism, wherein the vibration generator comprises a T-type push rod, the edge of a round face of the T-type push rod is connected with a vibrating end airtight air bin through a vibrating end supporting film in a sealed mode, a vibrating end sealing film is arranged in the vibrating end airtight air bin, and opposite balance springs are arranged below the round face of the T-type push rod; the bridging mechanism comprises a miniature air cylinder, an air pressure gauge and a bridging head, a bridging end sealing film is arranged in the bridging head, the lower edge of the bridging head is connected with the edge of an upper round face of an I-type push rod through a bridging end supporting film, and tension springs are arranged at the two sides of the I-type push rod. As the pressure intensity of air in a guide pipe is increased, propagation speed of mechanical waves in the guide pipe is higher, and energy loss of the mechanical waves is smaller. Excitation on tissue in the human body is enhanced, and therefore elasticity imaging quality is higher.
Owner:HEFEI UNIV OF TECH
Curved Passive Acoustic Driver for Magnetic Resonance Elastography
An acoustic driver system includes an active acoustic driver and a passive acoustic driver. The active acoustic driver is configured to produce oscillating acoustic energy. The passive acoustic driver is acoustically connected to the active acoustic driver and is configured to receive the oscillating acoustic energy and to convert it into shear waves. The passive acoustic driver includes a housing member and a vibrating member. The housing member includes a housing member cavity. The vibrating member is disposed at least partially within the housing member cavity. The vibrating member permanently retains a curved shape while disposed within the housing member cavity.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN UNIV
Method and device for acquiring echoes of magnetic resonance elastography
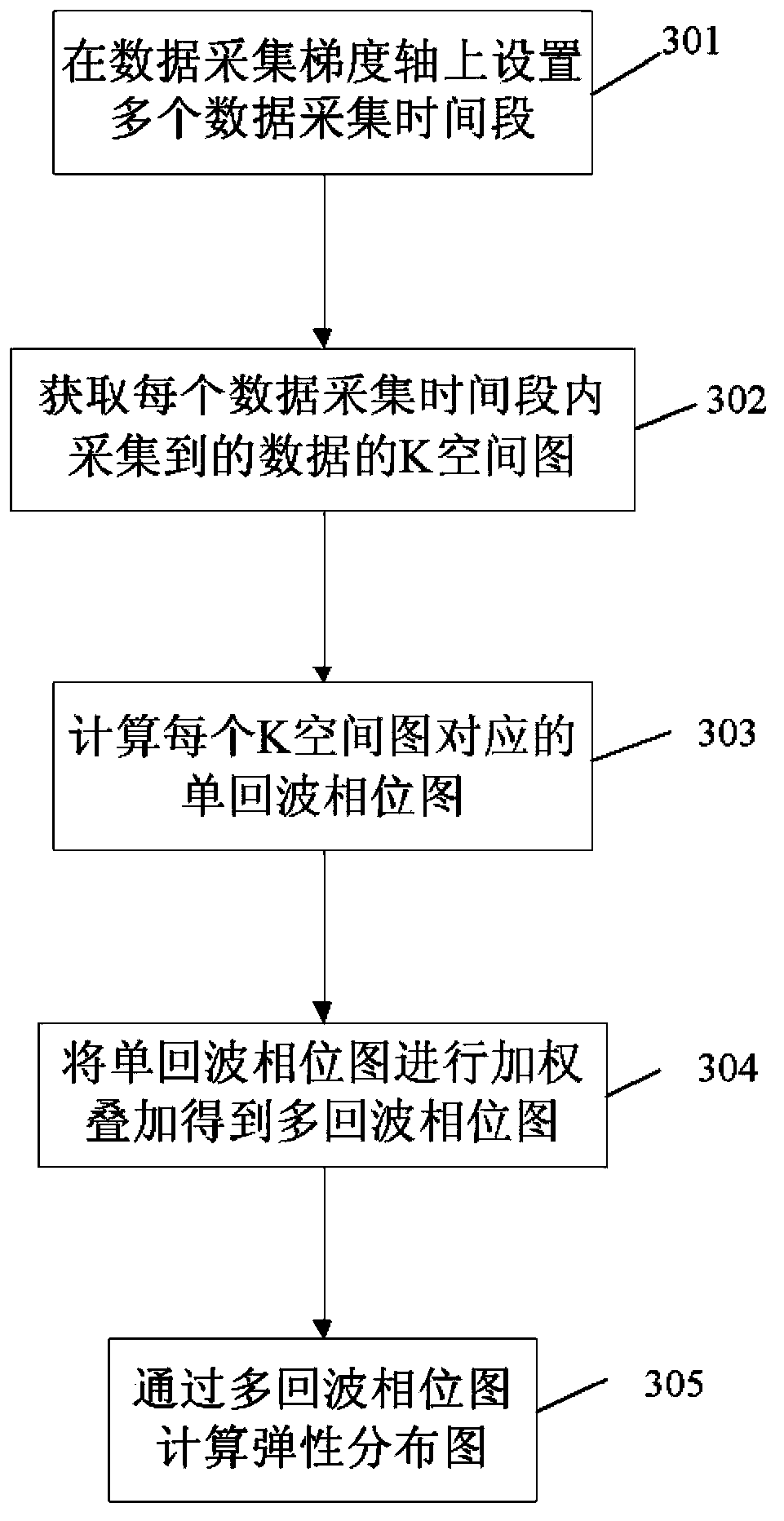
ActiveCN104068857ATake advantage ofImprove signal-to-noise ratioDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Idle time
The invention discloses a method and a device for acquiring echoes of magnetic resonance elastography. The method includes setting a plurality of data acquisition periods on a data acquisition gradient axis. The method and the device for acquiring the echoes of magnetic resonance elastography have the advantages that idle time which is not utilized in the prior art can be sufficiently utilized, accordingly, the scanning time can be shortened, and the signal-to-noise ratio of echo signals can be increased.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Method for predicting obesity related disease using images of the subcutaneous adipose tissue or the epididymal adipose tissue
InactiveUS20200335214A1Less invasive techniqueBest accuracy in predictionMedical simulationImage enhancementDiseaseDynamic contrast
The present invention relates to obesity related diseases, such as cancer of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). Tissue perfusion is currently investigated by using dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging which is an invasive technique and does not provide enough accuracy. As a result, the inventors worked on post-processing images of subcutaneous adipose tissue or the epididymal adipose tissue taken with a magnetic resonance imaging technique and a multifrequency magnetic resonance elastography technique to obtain parameters such as loss modulus and storage modulus which are more accurate for a diagnosing purpose. This post-processing method may be applied for a method for predicting that a subject is at risk of suffering from said disease, identifying a therapeutic target or a biomarker and screening compounds useful as medicine.
Owner:INST NAT DE LA SANTE & DE LA RECHERCHE MEDICALE (INSERM) +2
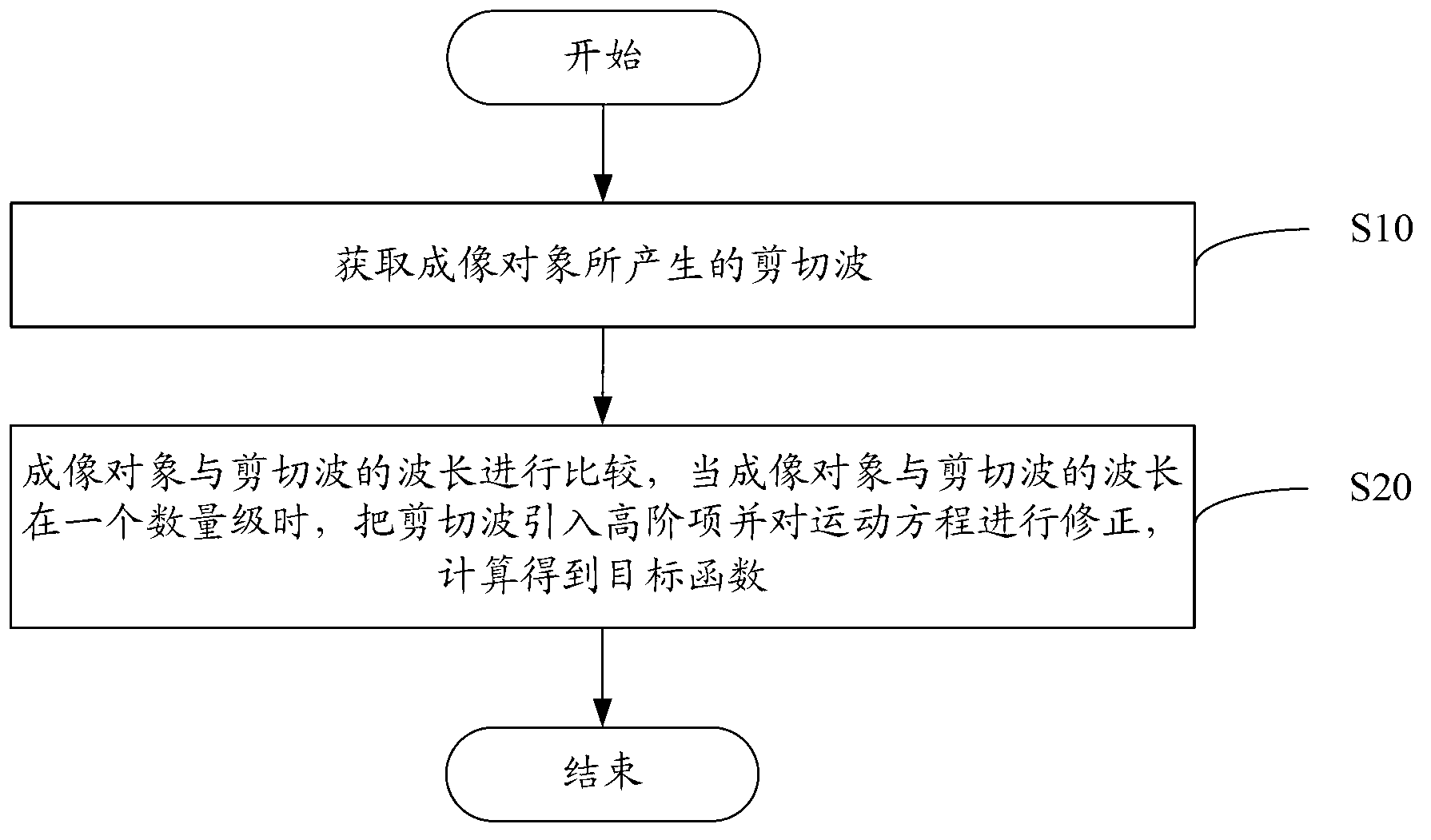
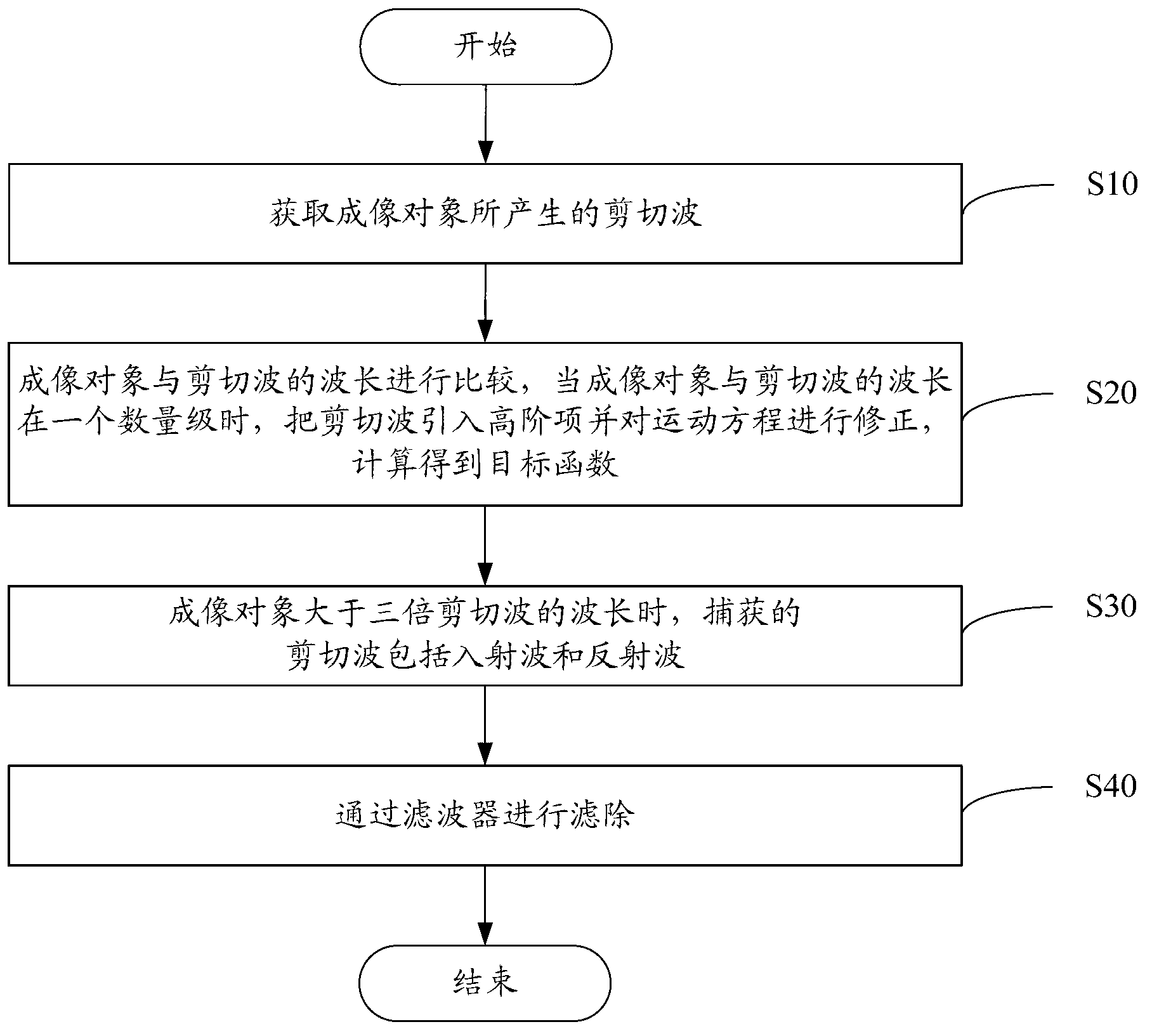
Correcting method and correcting system for elastic rebuilding of magnetic resonance elastography (MRE)
ActiveCN103064047AElastic Rebuild AccurateMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMedium densityLength wave
The invention relates to a correcting method and correcting system for elastic rebuilding of magnetic resonance elastography (MRE). The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a shear wave generated by an imaging object; comparing the size of the imaging object with the wavelength of the shear wave, and when the size of the imaging object and the wavelength of the shear wave are of an identical order of magnitude, the shear wave is introduced into a higher order term to correct an equation of motion and then obtain an objective function through calculation, wherein according to the objective function, gamma is the correction factor, mu is the lame constant, rho is the medium density, omega is the angular frequency of an incentive, and U is the displacement vector of a medium. According to the correcting method and correcting system for the elastic rebuilding of the MRE, through acquisition of the shear wave generated by the imaging object, comparison of the wavelength of the shear wave with the size of the imaging object and then adoption of an algorithm of the objective function, the elastic rebuilding can be relatively accurately achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
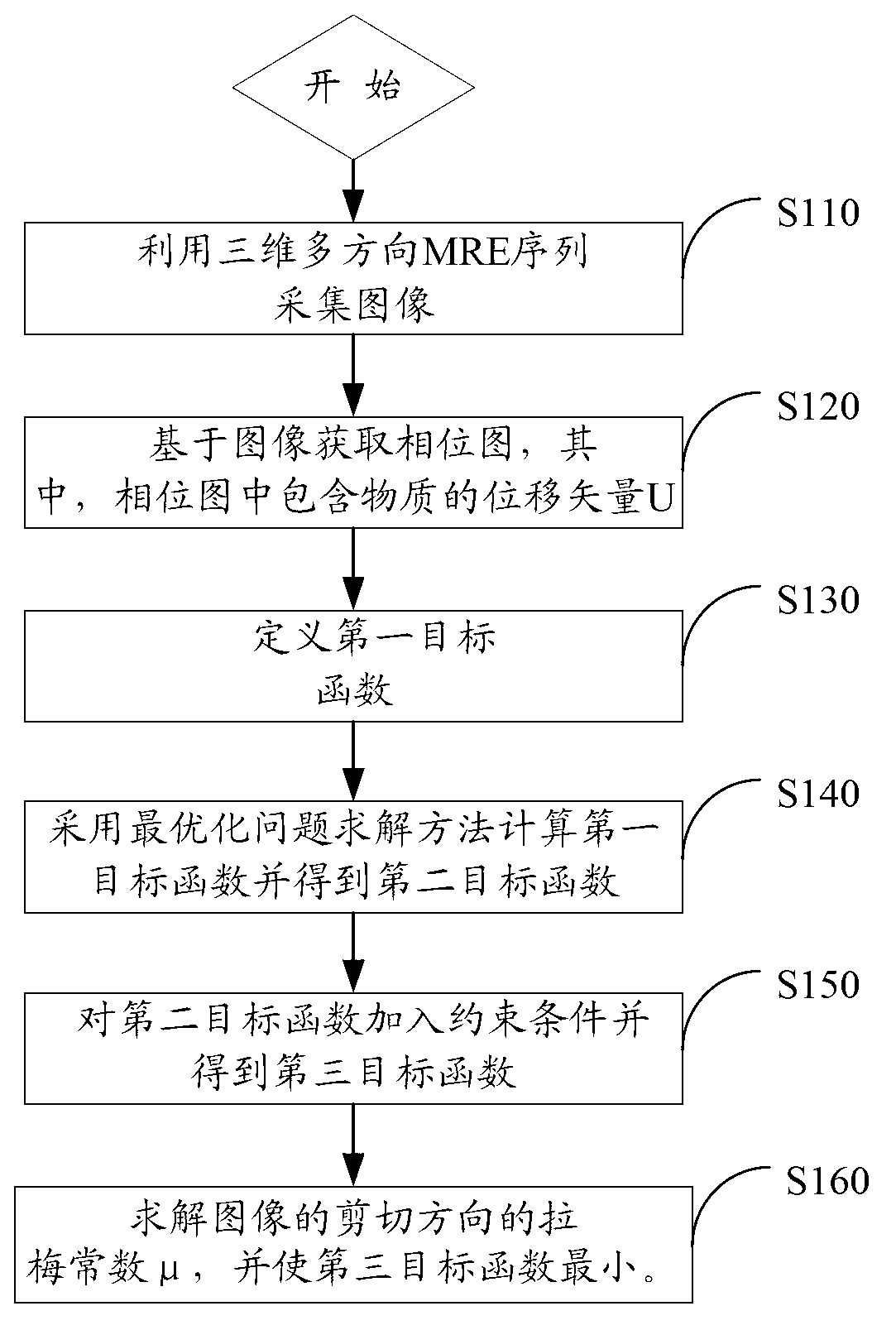
Magnetic-resonance elastic imaging reconstruction method and imaging system
ActiveCN103006216AImprove accuracyEasy to operateDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonanceMedium density
The invention relates to a magnetic-resonance elastic imaging reconstruction method which comprises the following steps: collecting images by a three-dimensional multidirectional MRE (mean relative error) sequence; acquiring a phase image based on the images, wherein the phase image contains the displacement vector U of an object; defining a first objective function in which U is the displacement vector, lambda and mu respectively are the lame constants in the longitudinal direction and the shearing direction, rho is the medium density, and omega is the angular frequency of excitation; calculating the first objective function to obtain a second objective function by an optimized problem solution method; and then adding constraint conditions to the second objective function to obtain a third objective function; solving the lame constant mu of the image in the shearing direction, and ensuring that the third objective function is the minimum. In addition, the invention also provides a magnetic-resonance elastic imaging system. The magnetic-resonance elastic imaging reconstruction method has high precision, the elastic distribution of tissues reappears precisely, and the precision of the elastic measurement is improved obviously.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Magnetic resonance elastography method and system
ActiveCN103349551BGuaranteed accuracyGuarantee stabilityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonanceAcquisition time
The invention belongs to the technical field of magnetic resonance imaging, and particularly relates to a magnetic resonance elasticity imaging method and system. The magnetic resonance elasticity imaging method comprises the following steps: a, sending a trigger pulse signal through a magnetic resonance imaging device; b, detecting the frequency of the trigger pulse signal through an external excitation device, and setting the vibration frequency of the external excitation device according to the frequency of the trigger pulse signal, wherein the set vibration frequency of the external excitation device and the vibration frequency of the magnetic resonance imaging device are synchronous; c, outputting a signal to a tested object through the mode that the magnetic resonance imaging device triggers the external excitation device, and obtaining elasticity images of the tested object. Due to the fact that the magnetic resonance imaging device sends the trigger pulse signal to the external excitation device in advance, the vibration frequency of the magnetic resonance imaging device and the vibration frequency of the external excitation device are synchronous automatically through the trigger pulse signal, manual operation for regulating the vibration frequency is saved, collection time is shortened, and collection efficiency is improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com