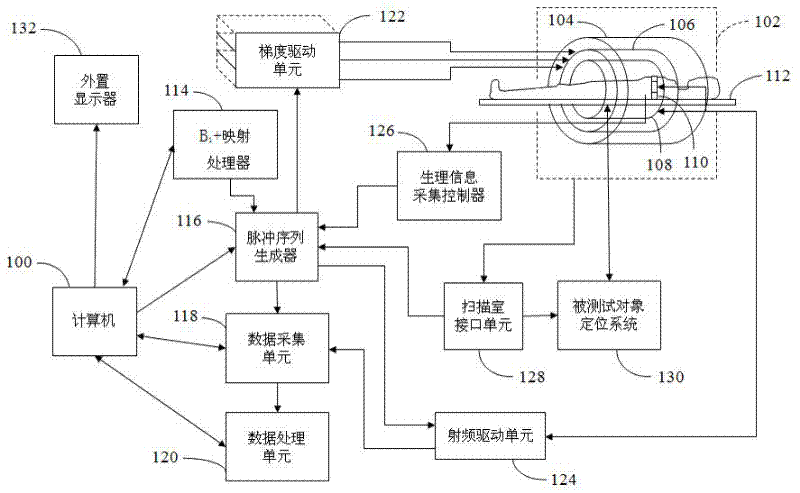
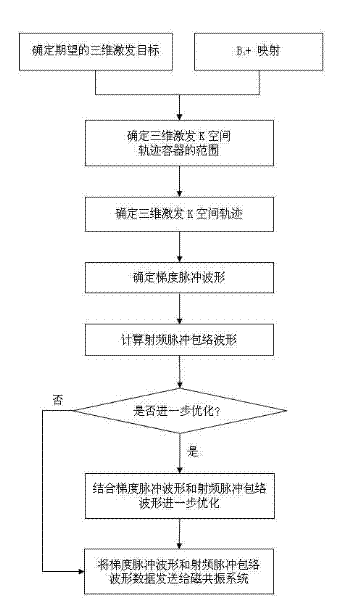
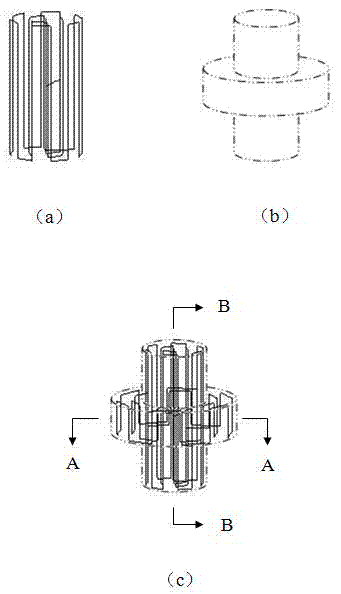
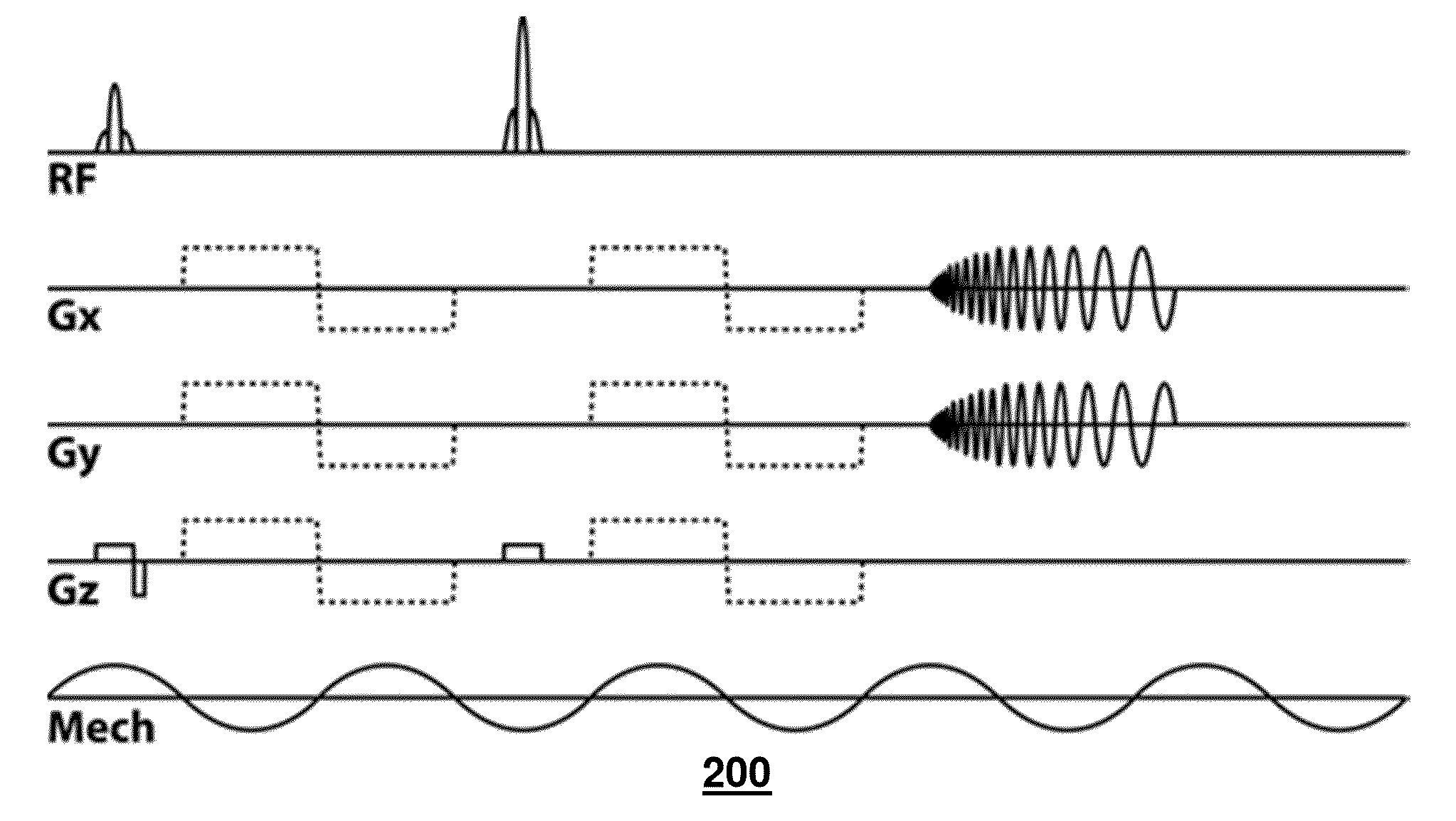
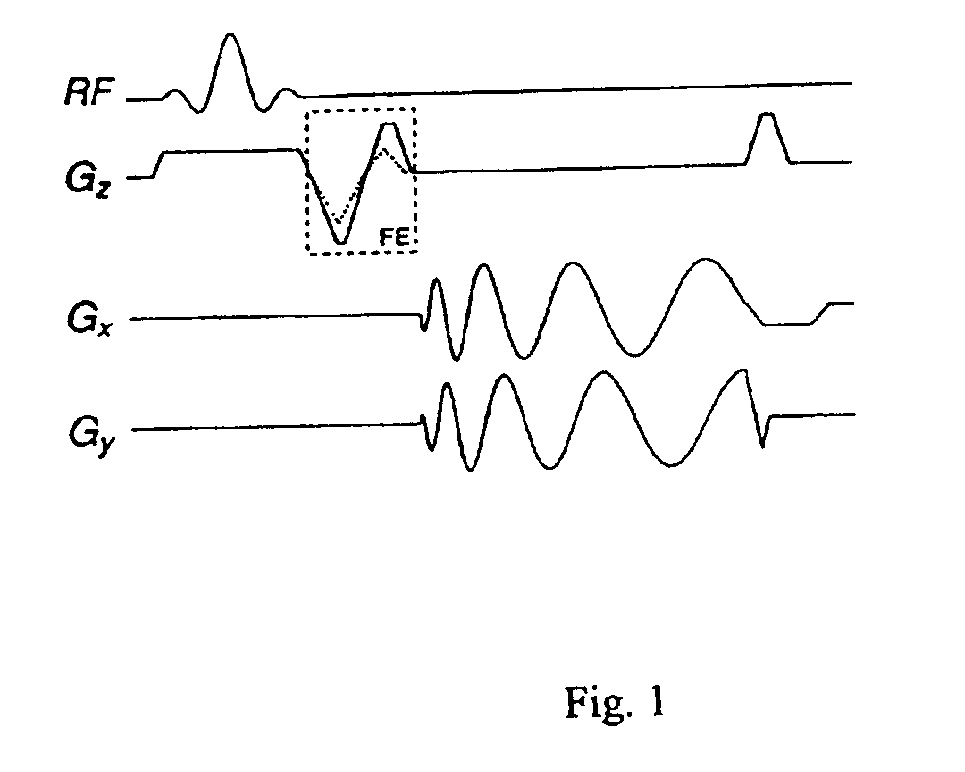
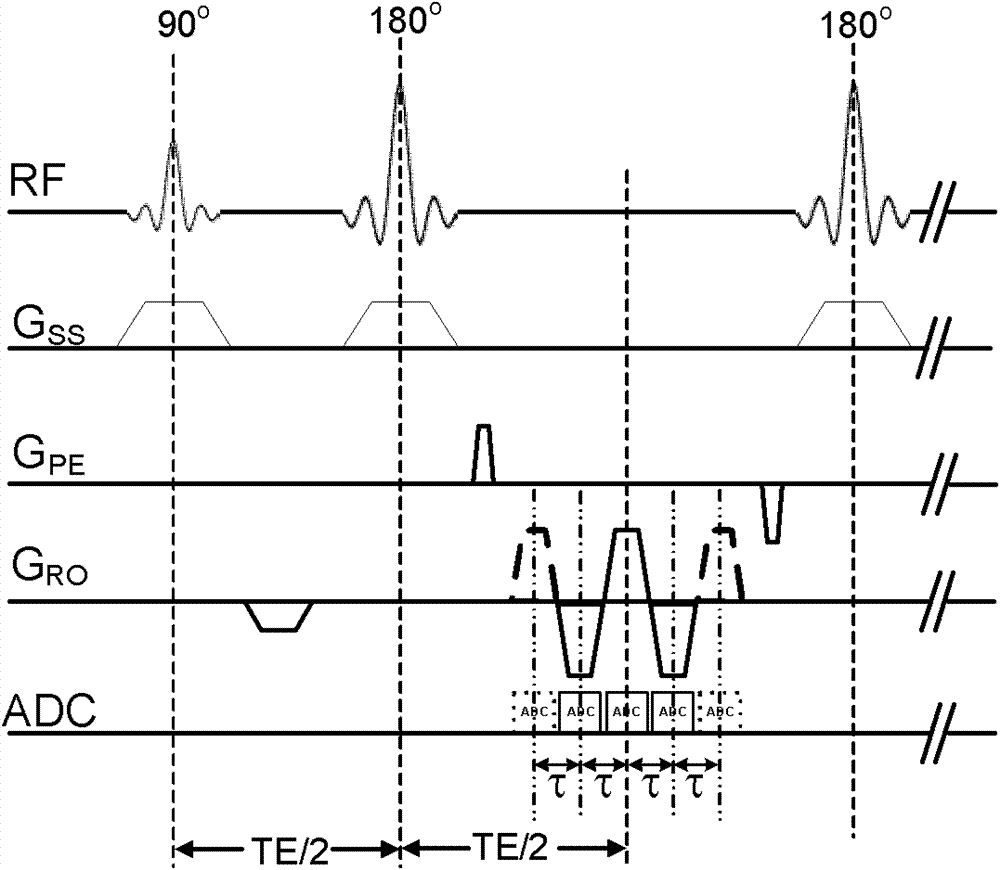
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
75 results about "K space trajectory" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Partially parallel magnetic resonance imaging using arbitrary k-space trajectories with image reconstruction based on successive convolution operations
ActiveUS7583082B1Uniform sensitivity profileMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionData setParallel magnetic resonance imaging
In a first step of image formation by MRI or the like, a gridding convolution is performed for each coil using a Kaiser-Bessel kernel, so that each coil channel now contains data on grid points. In the second step, another 2D convolution is performed on each of the gridded coil data sets in either k-space or image space, and all the convolutions are summed up to produce the composite k-space data set for the target coil. In the third step, the composite data set is then transformed to form an un-aliased image for that coil. In the fourth step, the un-aliased images for all the coils are combined using square-root-of-sum-of-squares to form the final reconstructed image.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND
K-space trajectory estimation in spiral MRI system and related method thereof
ActiveUS7888935B1The process is simple and effectiveReduce errorsMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionBaseline dataK space trajectory
First, benchmark data are collected on two thin slices of an object to get measured k-space trajectories. To find delays on different physical gradients, the root mean square error between estimated and measured k-space trajectories is minimized for different delays. To reduce the error further, an eddy current compensation is introduced along each physical gradient axis. A more accurate estimation of the k-space trajectory can be obtained to image the object.
Owner:VIRGINIA UNIV OF
System and method for amplitude reduction in RF pulse design
InactiveUS20080284439A1Reduce SAROvercomes drawbackDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsK space trajectorySlew rate
A system and method are provided for adjusting RF pulses and gradient waveforms to reduce B1 field magnitude in MR imaging sequences. When an RF pulse is presented which has a high amplitude segment that would exceed a maximum B1 magnitude, the system and method provided herein can apply a variable slew rate design technique. A slew rate of at least one gradient waveform can be varied to reduce a B1 field magnitude during transmission of the high amplitude segment of the RF pulse. By controlling the slew rate of gradient waveforms for non-Cartesian k-space trajectories according to a calculated maximum allowable slew rate function, embodiments of the system and method can, in effect, reduce gradient amplitude.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
System and method for designing multi-channel RF pulses for MR imaging
ActiveUS7466131B1Improve image qualityImprove scanning efficiencyMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetizationEngineering
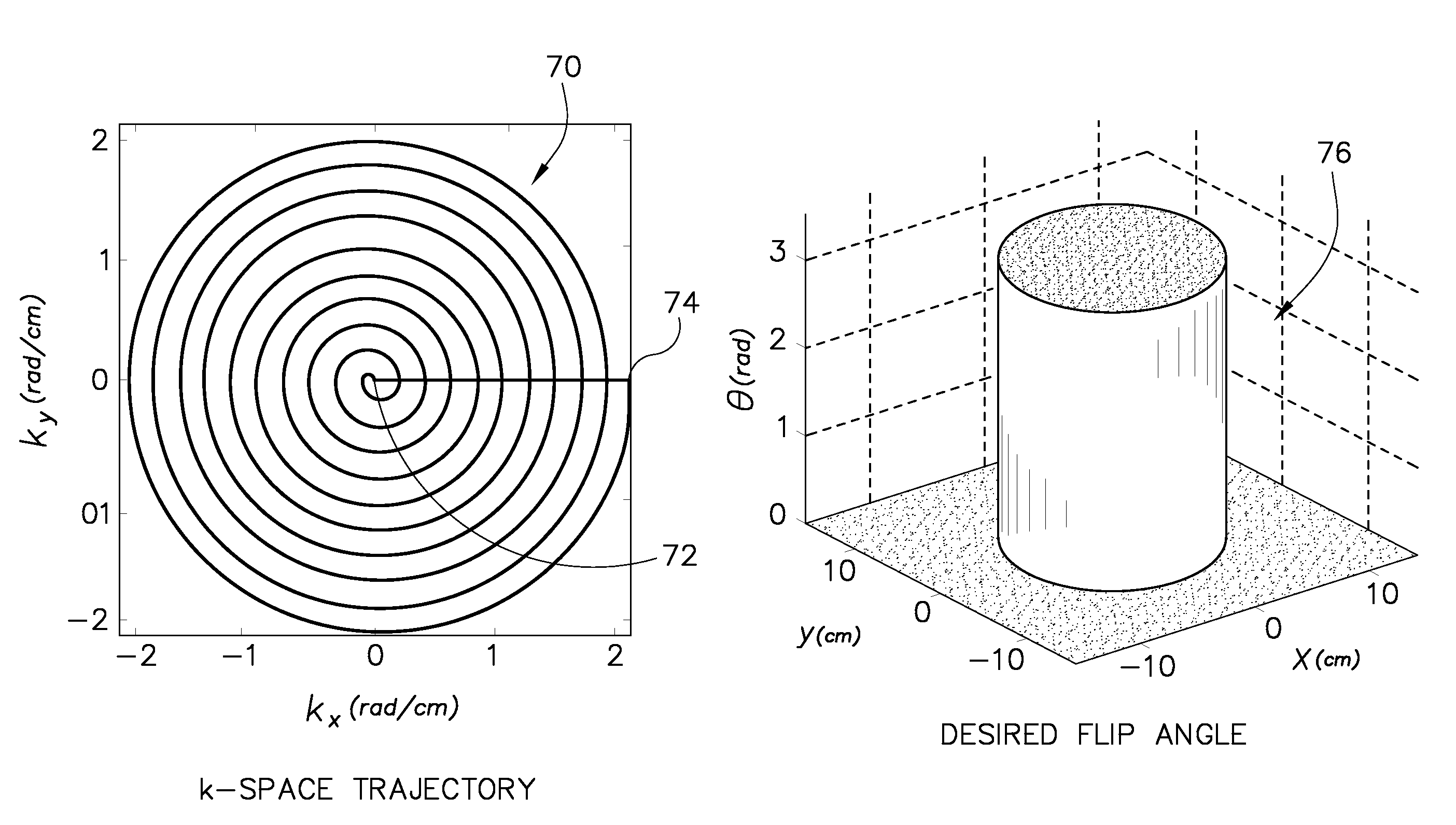
A system and method are provided for designing RF pulses for multi-channel and / or multi-dimensional spatially-selective applications using a linear approximation. Embodiments of the system and method may use a generalized linear-class large tip angle approximation to design RF pulses for multi-channel and parallel transmission. Further, some of these approximations allow for the design of arbitrarily large flip angles, irregularly-shaped flip angle profiles, or arbitrary initial magnetization values. Embodiments of the system and method may also provide for the design of k-space trajectories which aid in maintaining assumptions of the various linear class approximations.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF ILLINOIS AT URBANA--CHAMPAIGN +2
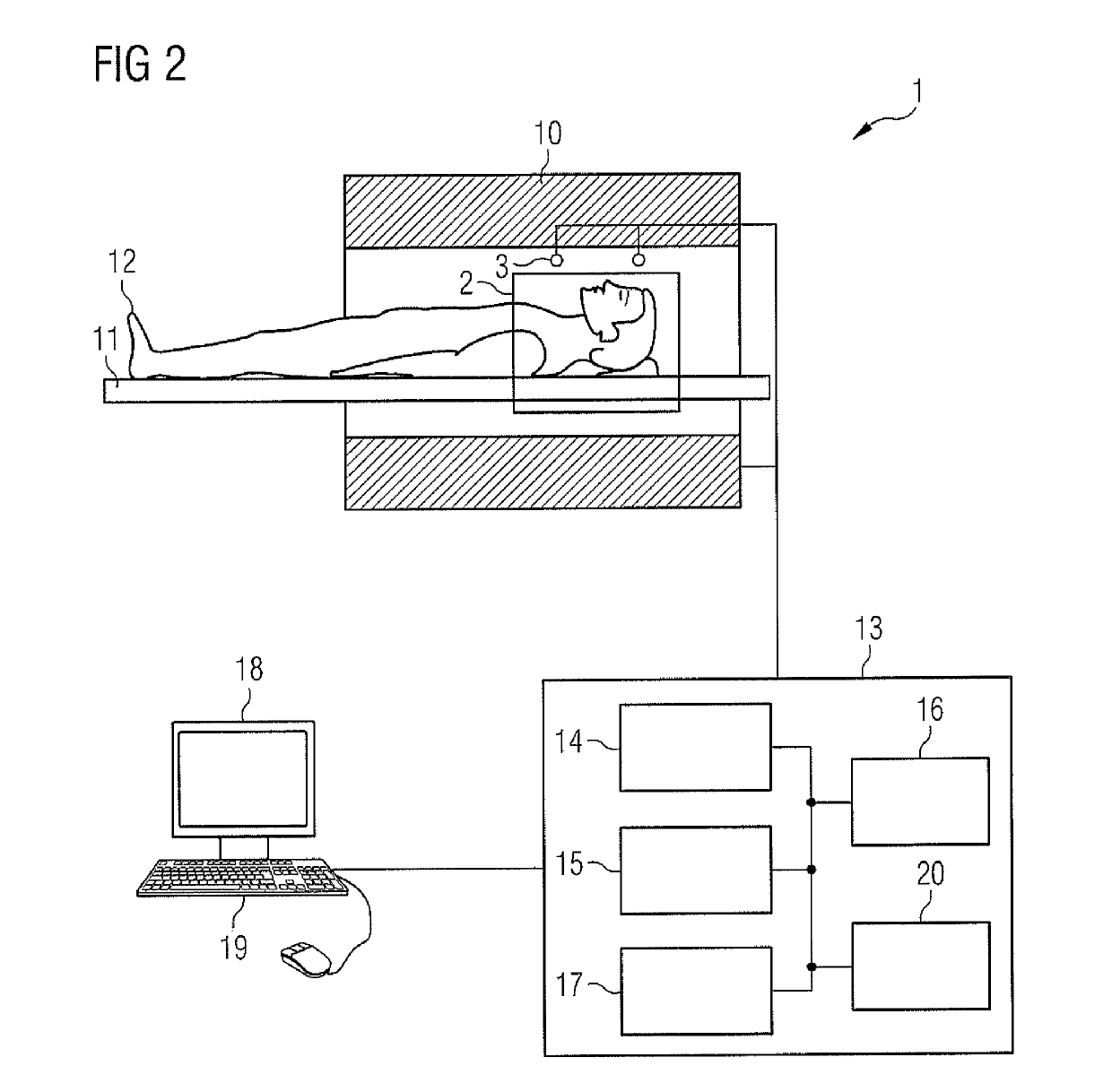
Method and device for reconstructing a sequence of magnetic resonance images
ActiveUS20110234222A1Degree of reductionEasy access to dataAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsOriginal dataResonance
A method for reconstructing a sequence of magnetic resonance (MR) images of an object under investigation, includes the steps of (a) providing a series of sets of image raw data including an image content of the MR images to be reconstructed, the image raw data being collected with the use of at least one radiofrequency receiver coil of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) device, wherein each set of image raw data includes a plurality of data samples being generated with a gradient-echo sequence, in particular a FLASH sequence, that spatially encodes an MRI signal received with the at least one radiofrequency receiver coil using a non-Cartesian k-space trajectory, each set of image raw data includes a set of homogeneously distributed lines in k-space with equivalent spatial frequency content, the lines of each set of image raw data cross the center of k-space and cover a continuous range of spatial frequencies, and the positions of the lines of each set of image raw data differ in successive sets of image raw data, and (b) subjecting the sets of image raw data to a regularized nonlinear inverse reconstruction process to provide the sequence of MR images, wherein each of the MR images is created by a simultaneous estimation of a sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content and in dependency on a difference between a current estimation of the sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content and a preceding estimation of the sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
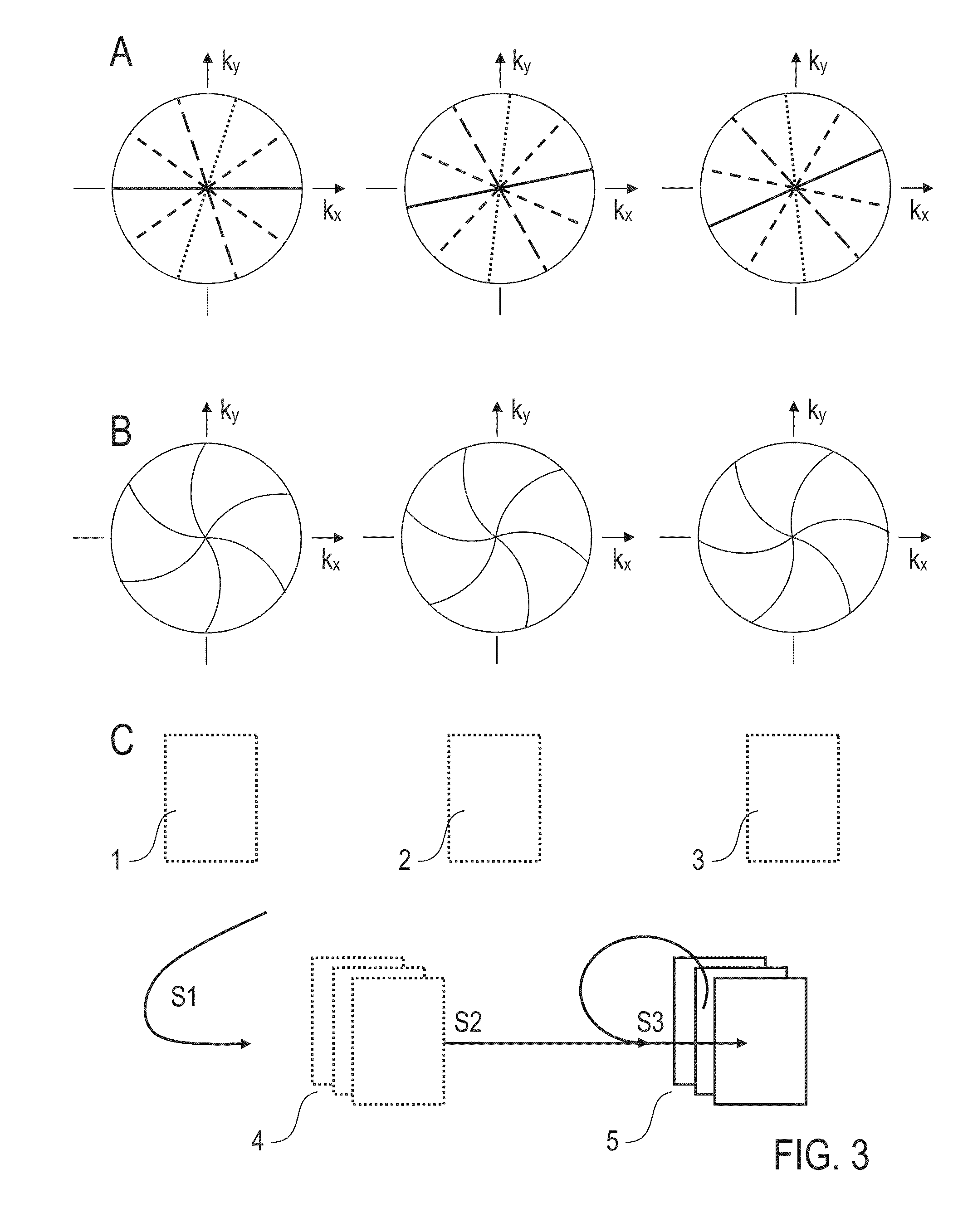
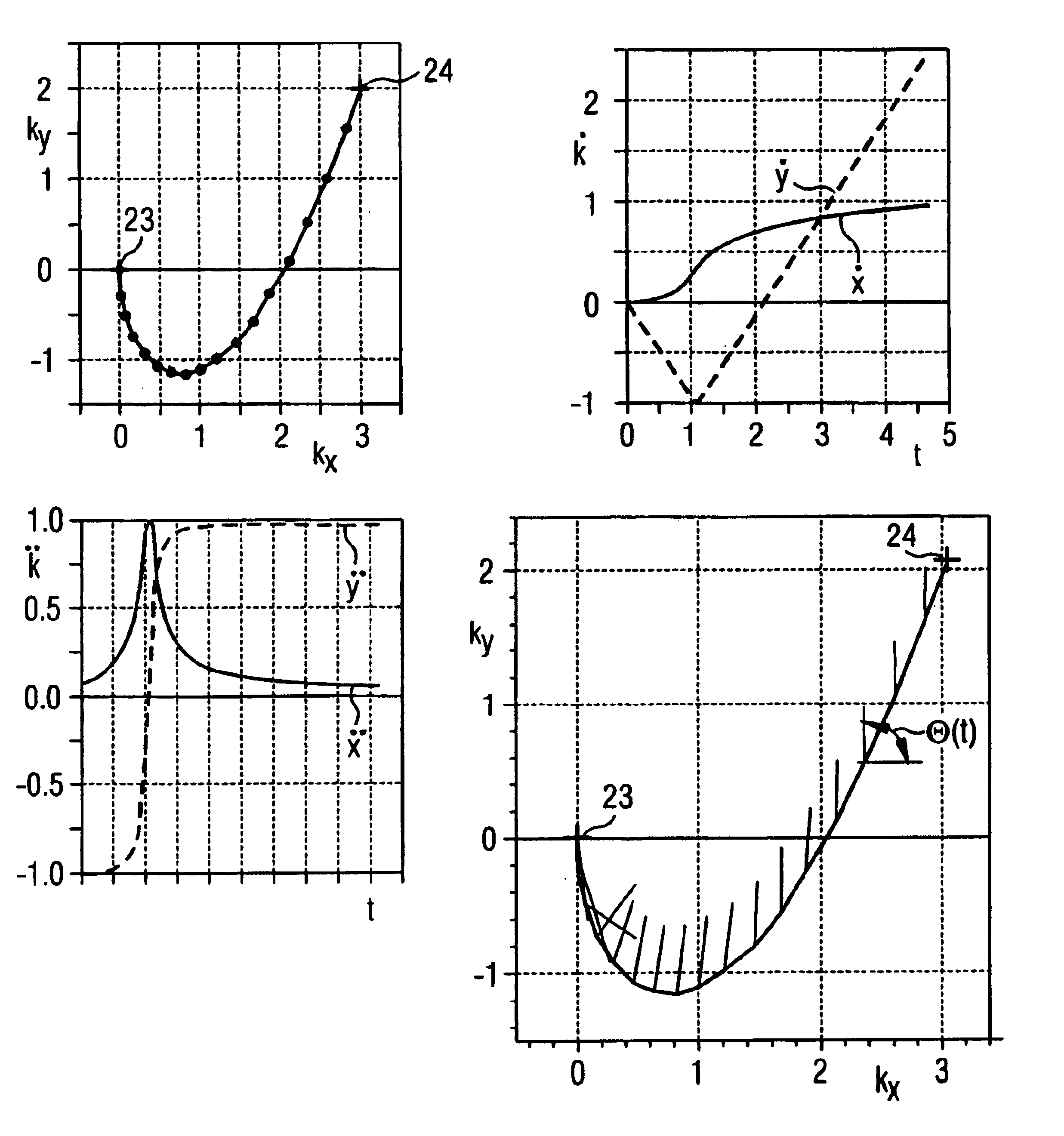
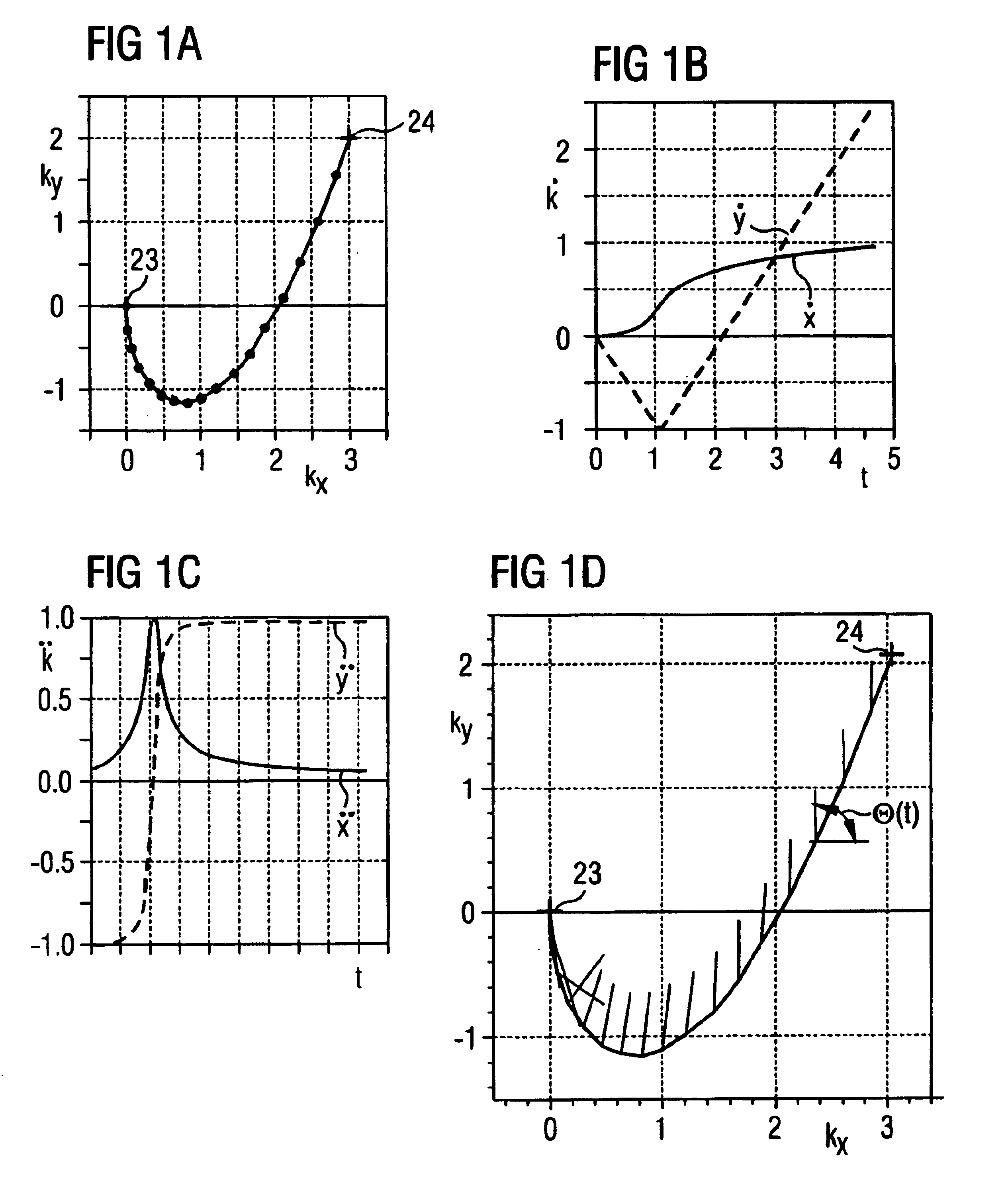
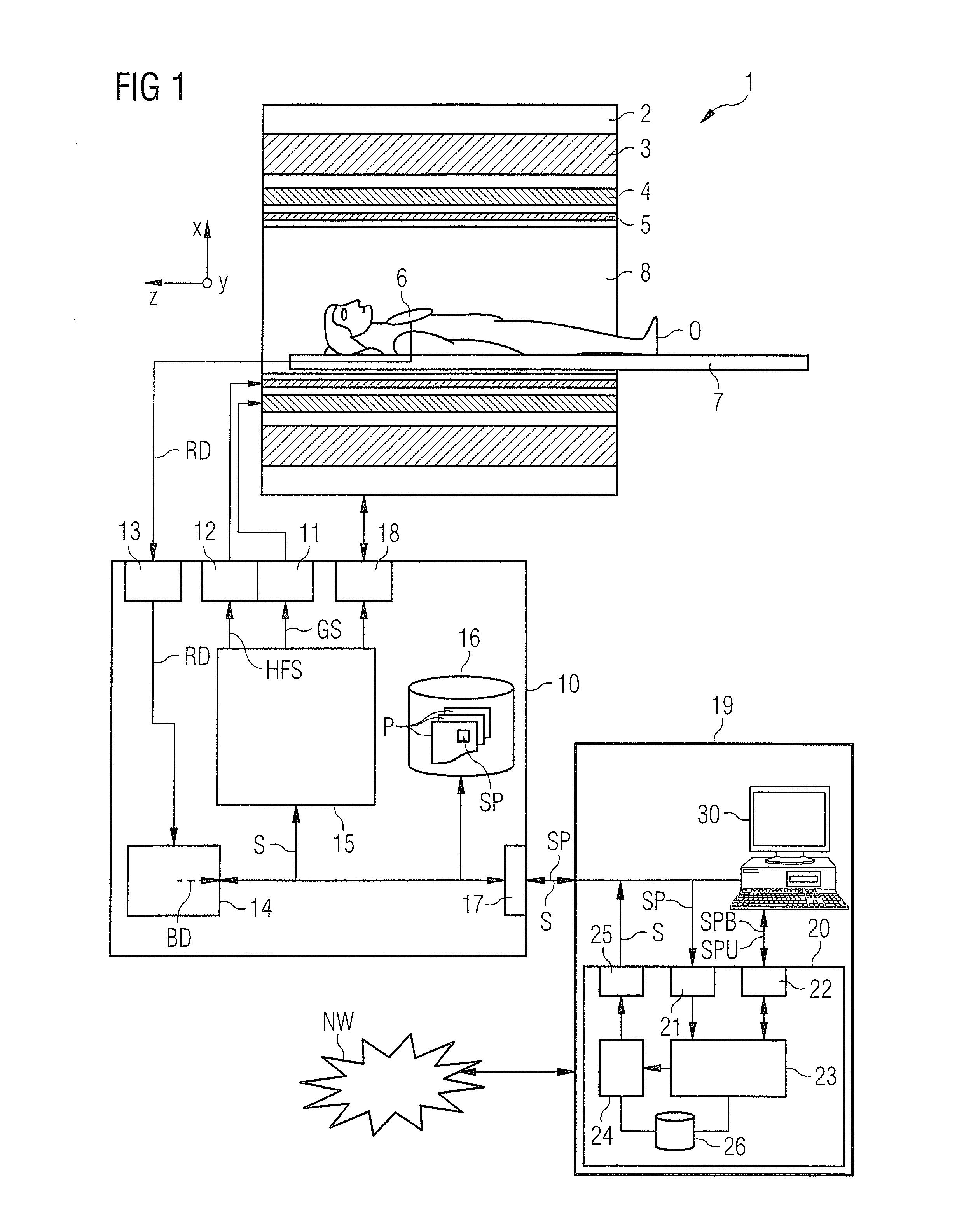
Method for optimizing the k-space trajectories in the location encoding of a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus
InactiveUS6937015B2Optimally fast samplingDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSequence controlResonance
In a method and apparatus for calculating the sampling path of the k-matrix under given boundary conditions for the examination of a subject by means of a magnetic resonance tomography apparatus having a gradient amplifier with appertaining gradient coils, an input-display terminal, a sequence controller and a system computer as well as an analog-to-digital converter, boundary conditions are entered into the sequence controller or into the system computer via the input-display terminal, the sampling path of the k-matrix is calculated taking the boundary conditions into consideration by the sequence controller or the system computer, and the gradient current curves are determined by the sequence controller or the system computer that lead to a sampling along the previously calculated sampling path when applied to the corresponding gradient coils with utilization of the ADC.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
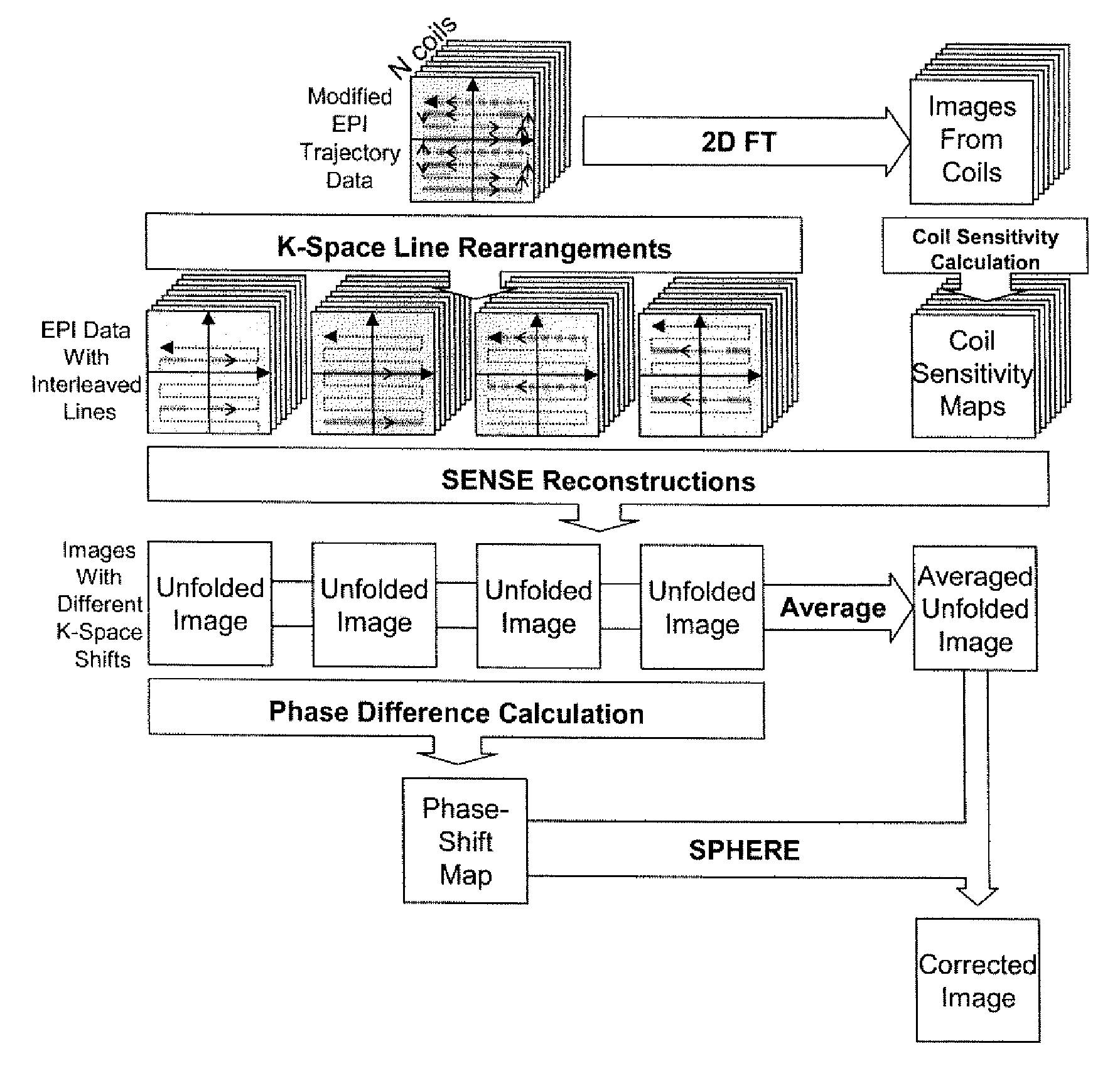
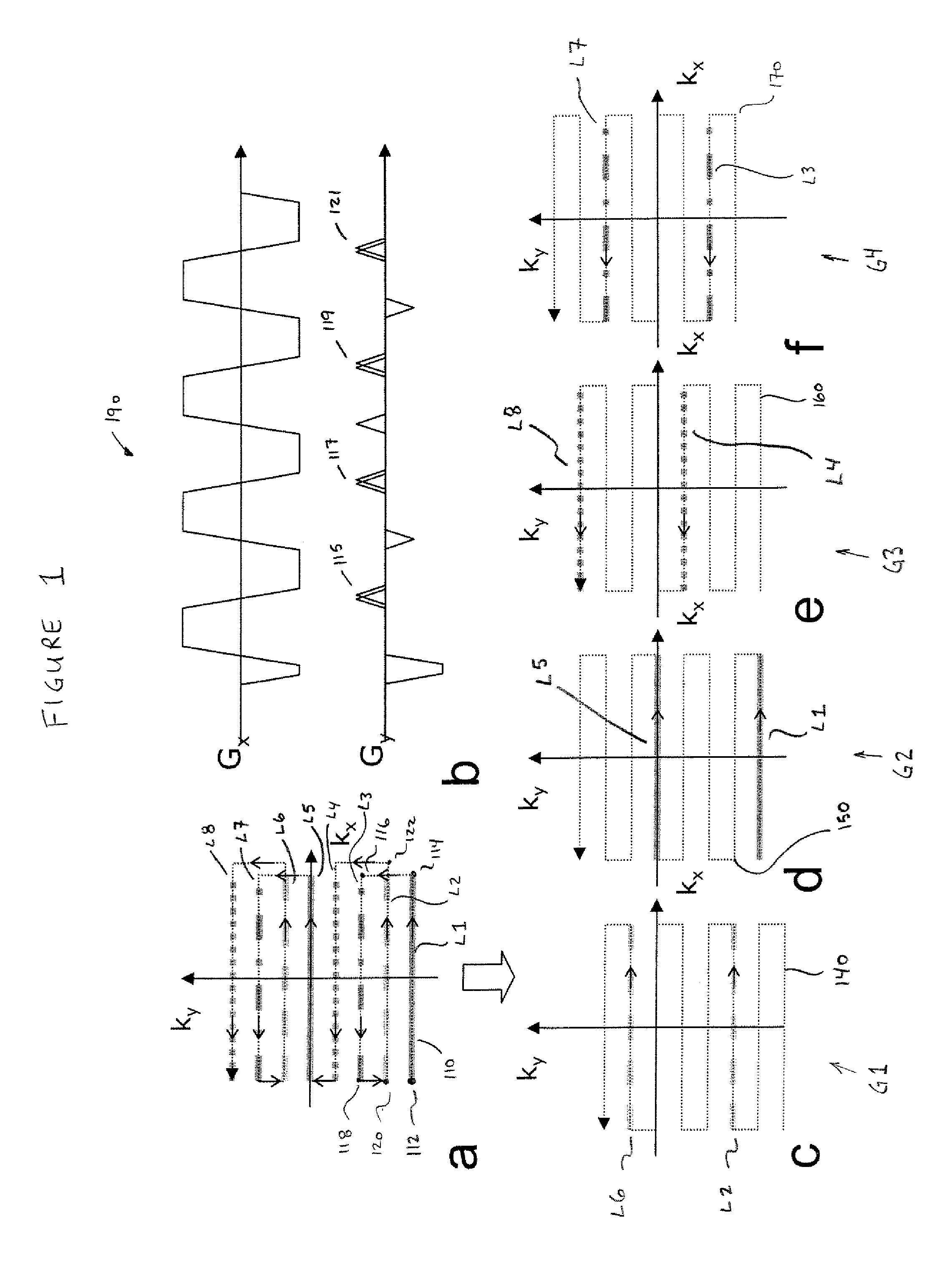
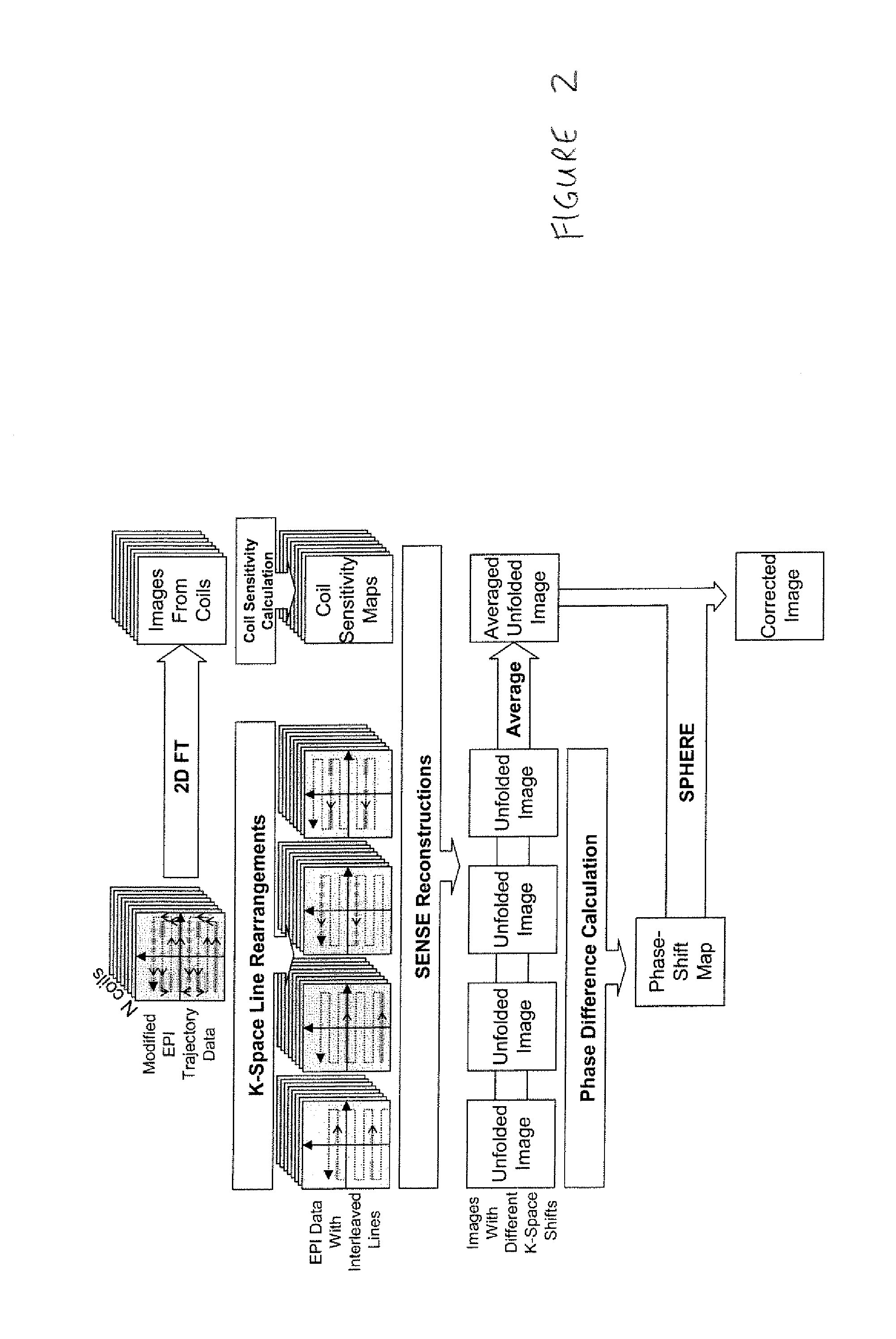
Phase labeling using sensitivity encoding: data acquisition and image reconstruction for geometric distortion correction in epi
InactiveUS20110260726A1Easy to pass to SPHERE calculationReduce artifactsMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionPhase shiftedData acquisition
A phase labeling using sensitivity encoding system and method for correcting geometric distortion caused by magnetic field inhomogeneity in echo planar imaging (EPI) uses local phase shifts derived directly from the EPI measurement itself, without the need for extra field map scans or coil sensitivity maps. The system and method employs parallel imaging and k-space trajectory modification to produce multiple images from a single acquisition. The EPI measurement is also used to derive sensitivity maps for parallel imaging reconstruction. The derived phase shifts are retrospectively applied to the EPI measurement for correction of geometric distortion in the measurement itself.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Method and device for reconstructing a sequence of magnetic resonance images
ActiveUS8384383B2Degree of reductionReduce in quantityAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceDigital computer detailsOriginal dataResonance
A method for reconstructing a sequence of magnetic resonance (MR) images of an object under investigation, includes the steps of (a) providing a series of sets of image raw data including an image content of the MR images to be reconstructed, the image raw data being collected with the use of at least one radiofrequency receiver coil of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) device, wherein each set of image raw data includes a plurality of data samples being generated with a gradient-echo sequence, in particular a FLASH sequence, that spatially encodes an MRI signal received with the at least one radiofrequency receiver coil using a non-Cartesian k-space trajectory, each set of image raw data includes a set of homogeneously distributed lines in k-space with equivalent spatial frequency content, the lines of each set of image raw data cross the center of k-space and cover a continuous range of spatial frequencies, and the positions of the lines of each set of image raw data differ in successive sets of image raw data, and (b) subjecting the sets of image raw data to a regularized nonlinear inverse reconstruction process to provide the sequence of MR images, wherein each of the MR images is created by a simultaneous estimation of a sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content and in dependency on a difference between a current estimation of the sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content and a preceding estimation of the sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
Generalized Method for MRI Chemical Species Separation Using Arbitrary k-space Trajectories
ActiveUS20080048659A1Eliminate the effects ofMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionData setChemical species
A method for producing images of a subject containing M spin species using a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system includes obtaining N k-space data matrices from N k-space data sets acquired with the MRI system using a pulse sequence with an individual associated echo time. The k-space data matrices each include corresponding data at the same plurality of k-space locations and time stamps are tracked for each k-space location. For each k-space location, a set of linear equations in k-space is solved. The set of linear equations relates corresponding data from the N k-space data matrices, echo times and time stamps to desired calculated k-space data. Calculated data in k-space which is corrected for chemical shift is produced corresponding to each k-space location and aggregated to obtain a k-space calculated data set. The k-space calculated data set is transformed to image space to obtain a corresponding image.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
SAR reduction in parallel transmission by k-space dependent RF pulse selection
InactiveUS20120019247A1Improve image qualityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionImaging qualityExcitation pattern
When generating an MR image using a multi-channel transmit coil arrangement, SAR is reduced by employing a number of different RF pulses in a single scan. Each RF pulse exhibits a different performance and / or accuracy, resulting in different RF pulse-specific SAR values. As a result, the RF pulses differ slightly in actual excitation pattern, B1 waveform and / or k-space trajectory, etc. The average SAR over a single scan is thus reduced compared to a fixed RF pulse, without compromising image quality.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Rapid parallel reconstruction for arbitrary k-space trajectories containing GRAPPA operator
InactiveCN103384836AMinimize parallel imagingReconstruction from projectionMagnetic measurementsPattern recognitionMissing data
An imaging method comprises acquiring an undersampled magnetic resonance partially parallel imaging (MR-PPI) dataset using a plurality of radio frequency receive coils and reconstructing the under-sampled MR-PPI dataset to generate a reconstructed magnetic resonance (MR) image. The reconstructing includes: (i) using a generalized auto-calibrating partially parallel acquisition (GRAPPA) operator or direct convolution to fill in at least some missing data of the undersampled MR-PPI data-set so as to generate an enhanced dataset; and (ii) using an algorithm other than a GRAPPA operator and other than direct convolution to reconstruct the enhanced dataset or to reconstruct the undersampled MR-PPI dataset using the enhanced dataset as an initialization dataset for an iterative reconstruction algorithm. In some embodiments the MR-PPI dataset is a non-Cartesian dataset and a GRAPPA operator for wider radial bands (GROWL) is used in the operation (i).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
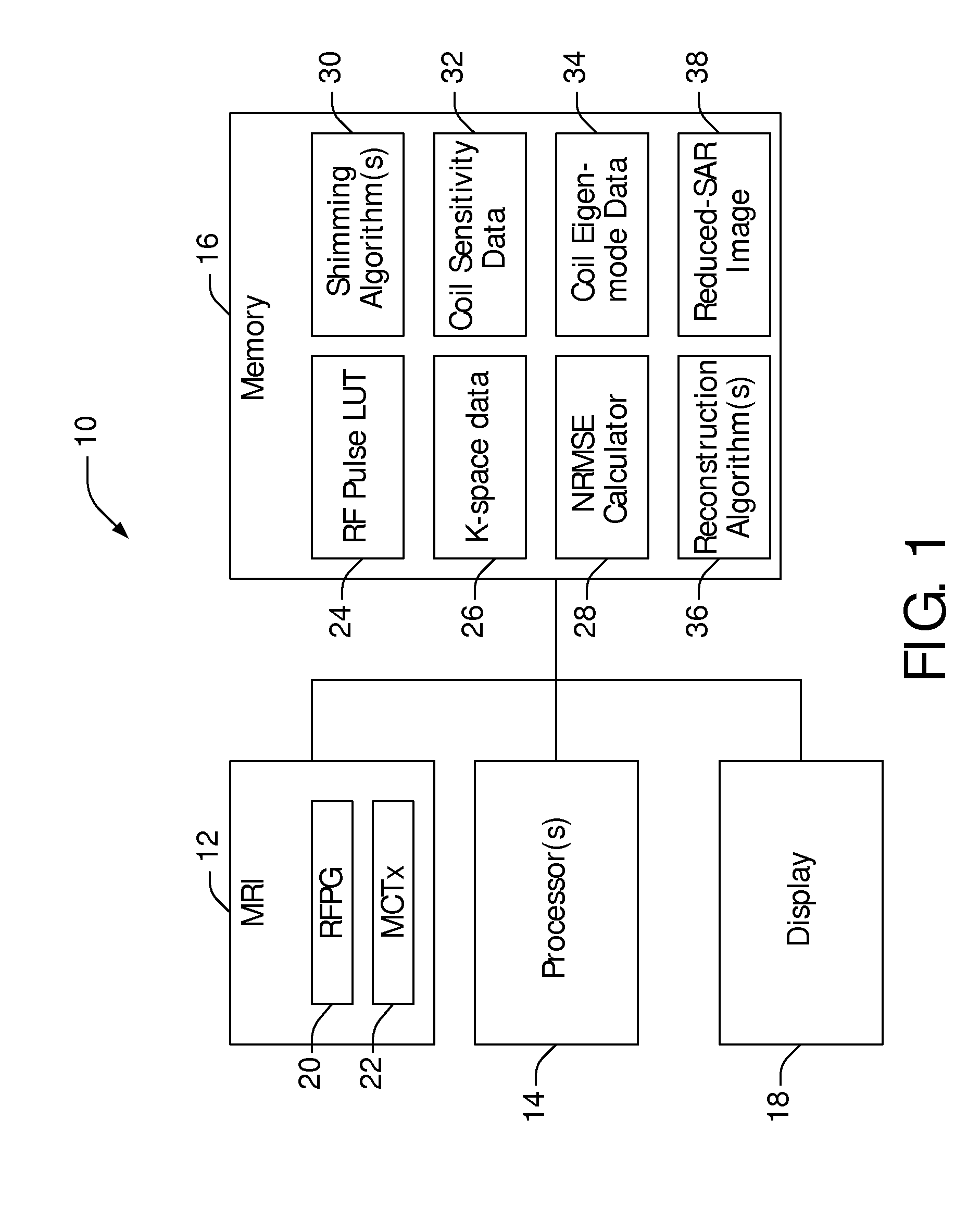
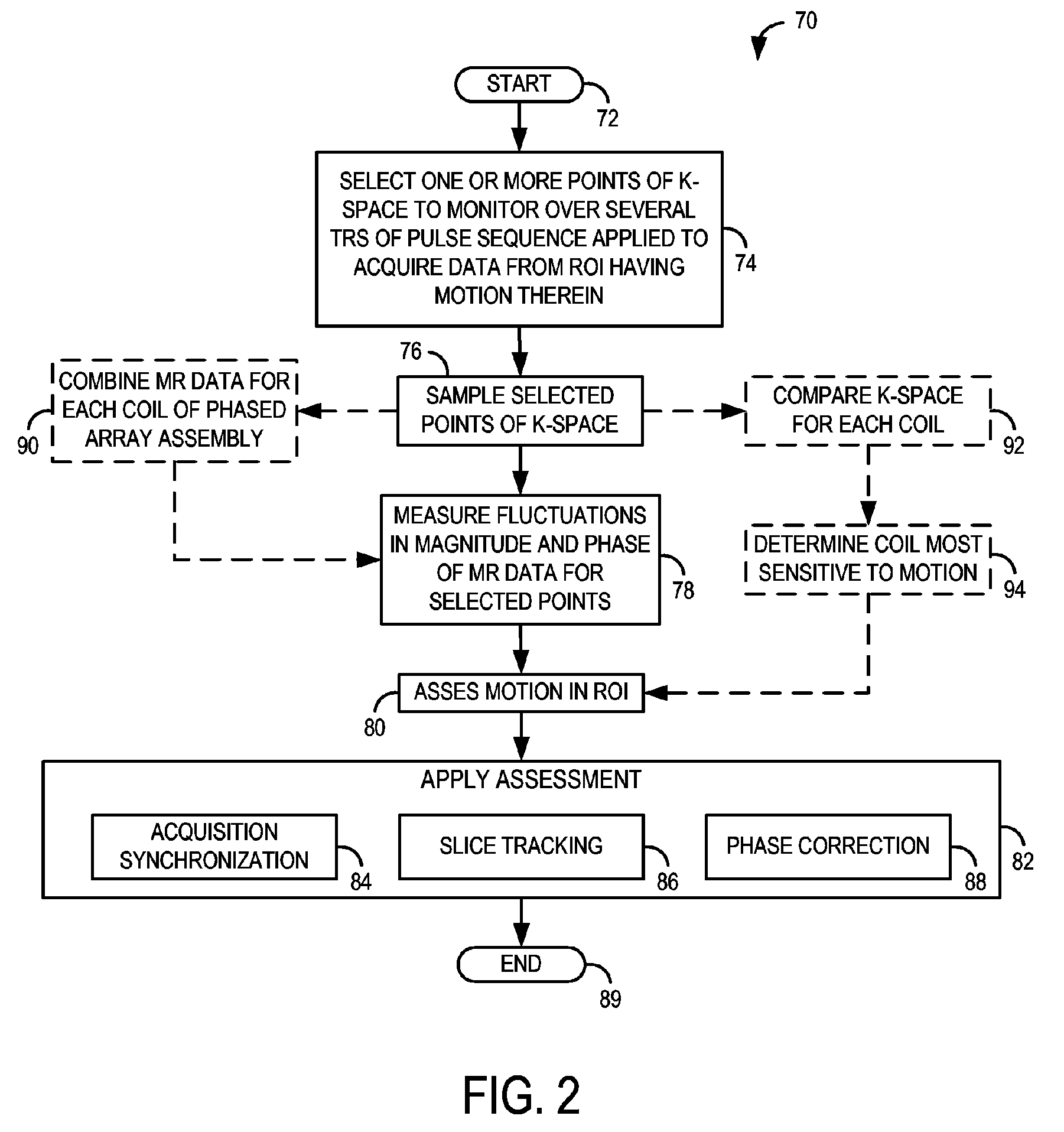
Method and system of determining motion in a region-of-interest directly and independently of k-space trajectory
ActiveUS7693569B1Good synchronizationAccurate assessmentImage enhancementImage analysisK space trajectoryRegion of interest
A system and method for determining motion in a region-of-interest directly from MR data acquired from the region-of-interest and independently of k-space trajectory are disclosed.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
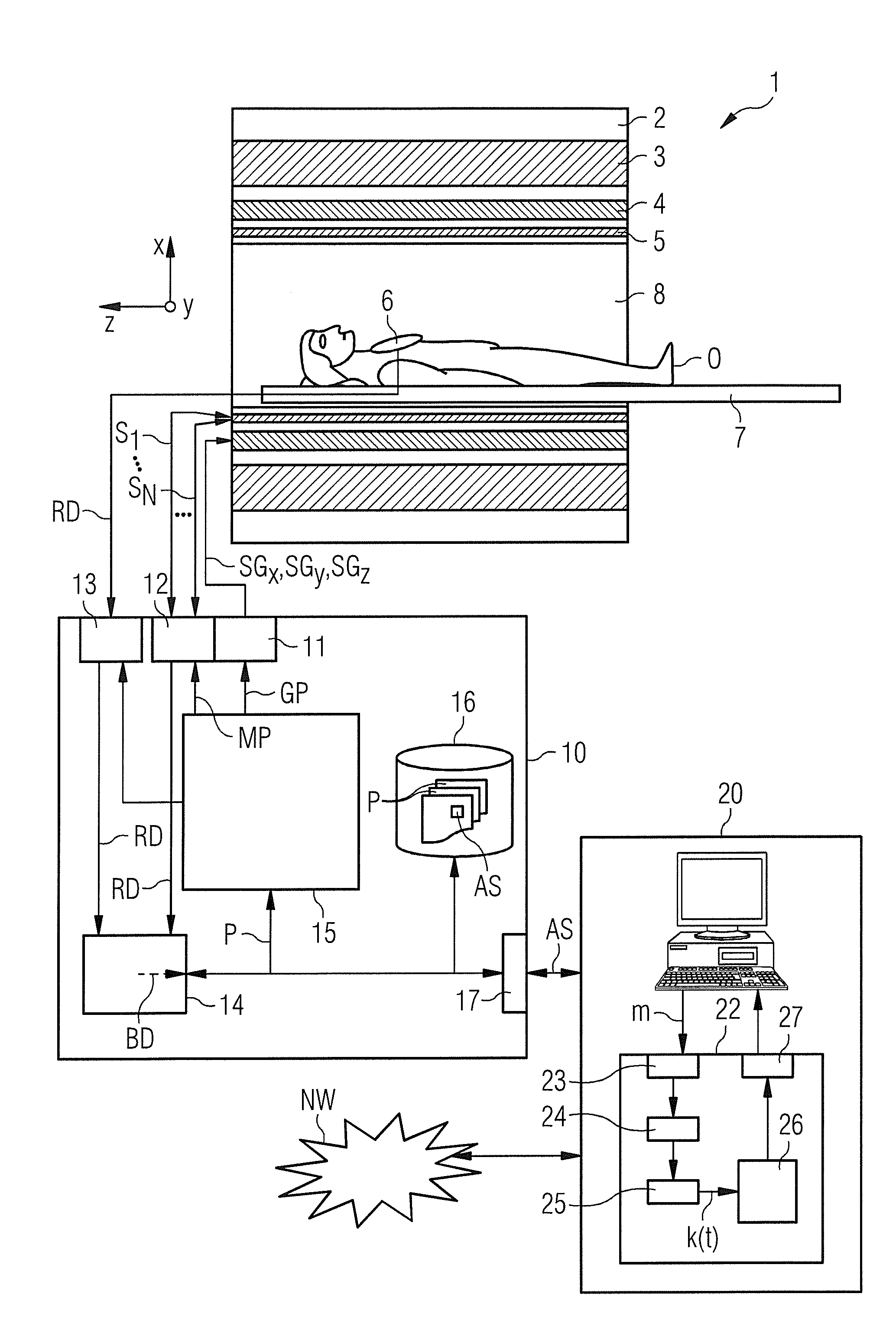
Determination of a magnetic resonance system control sequence
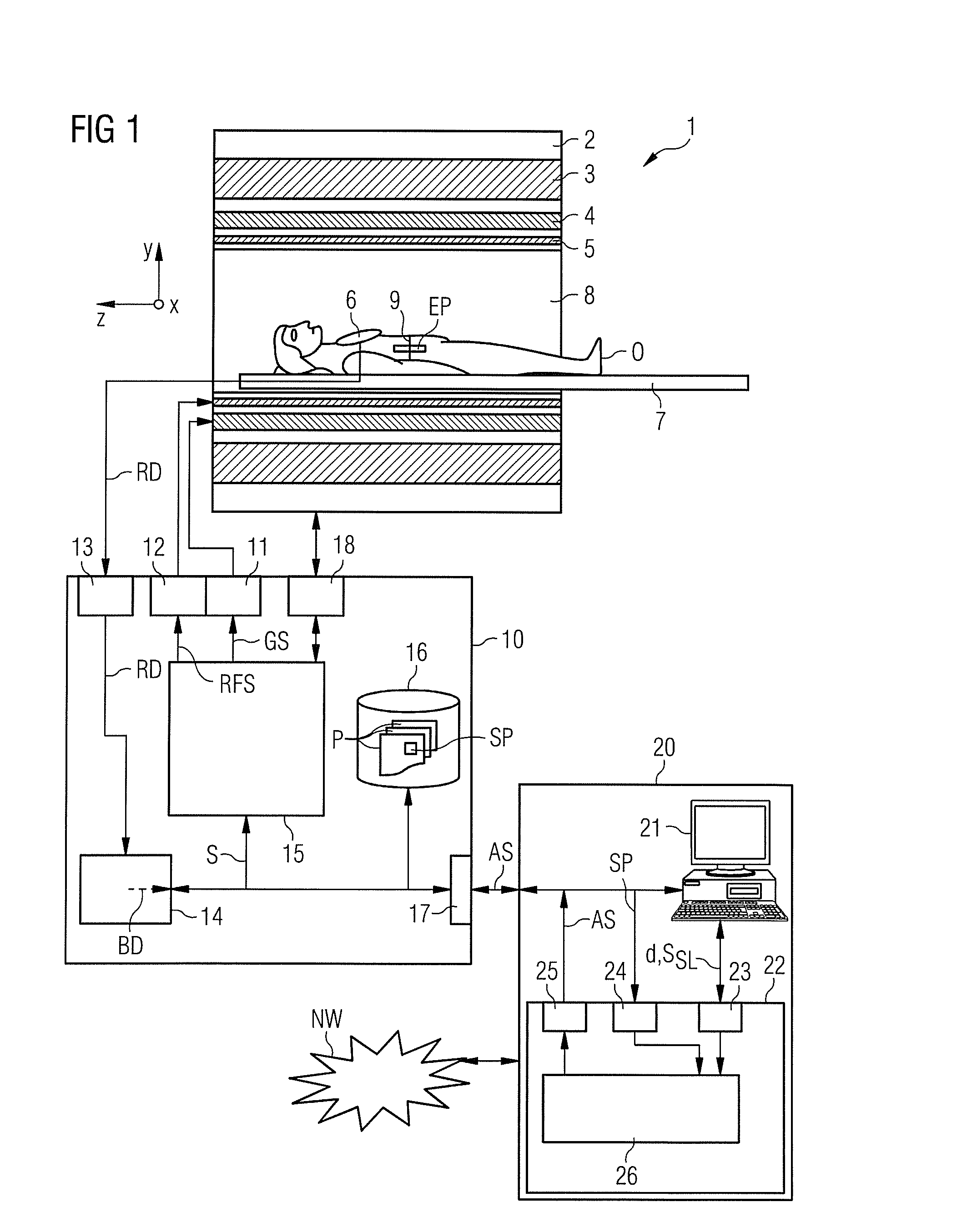
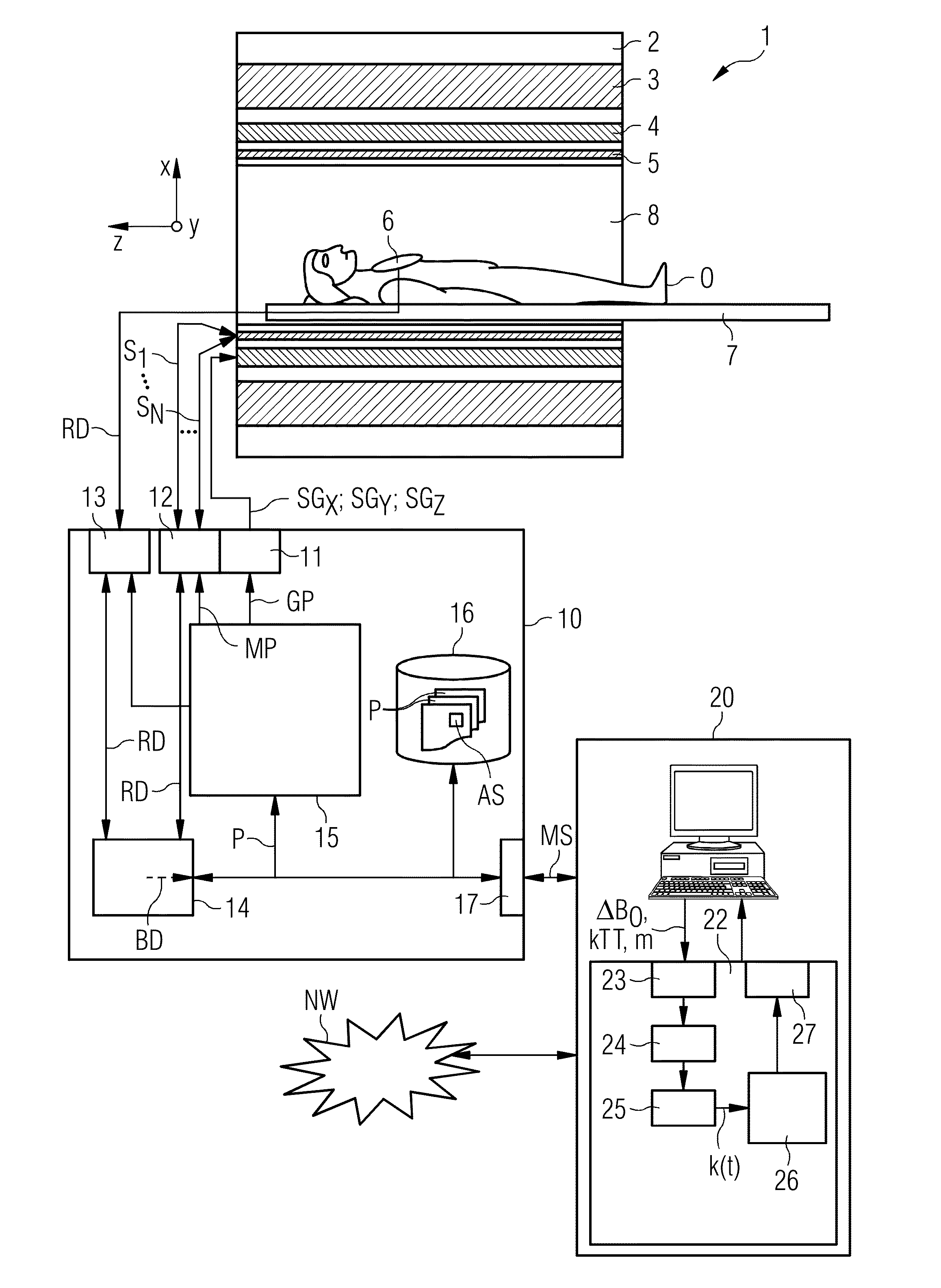
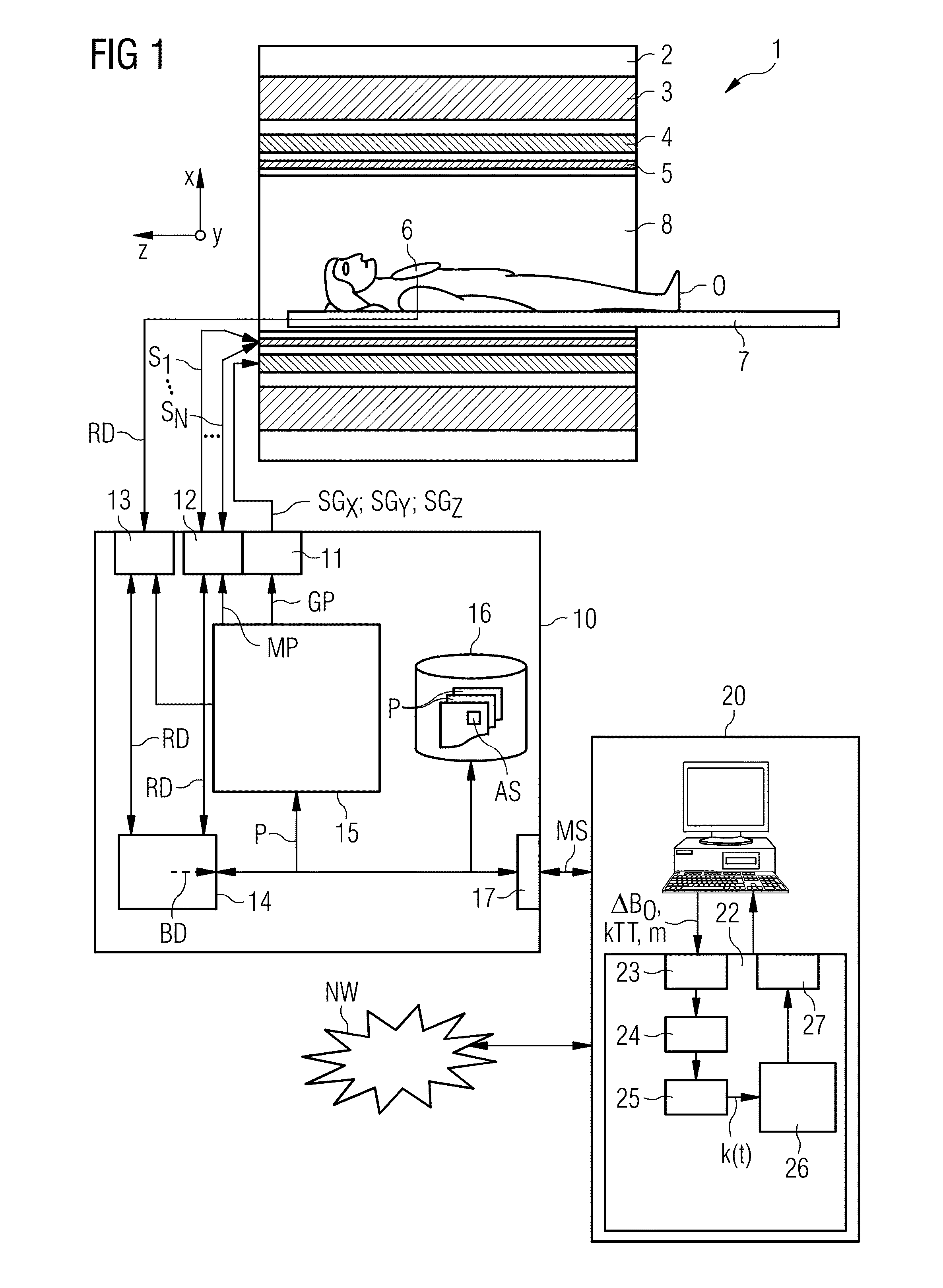
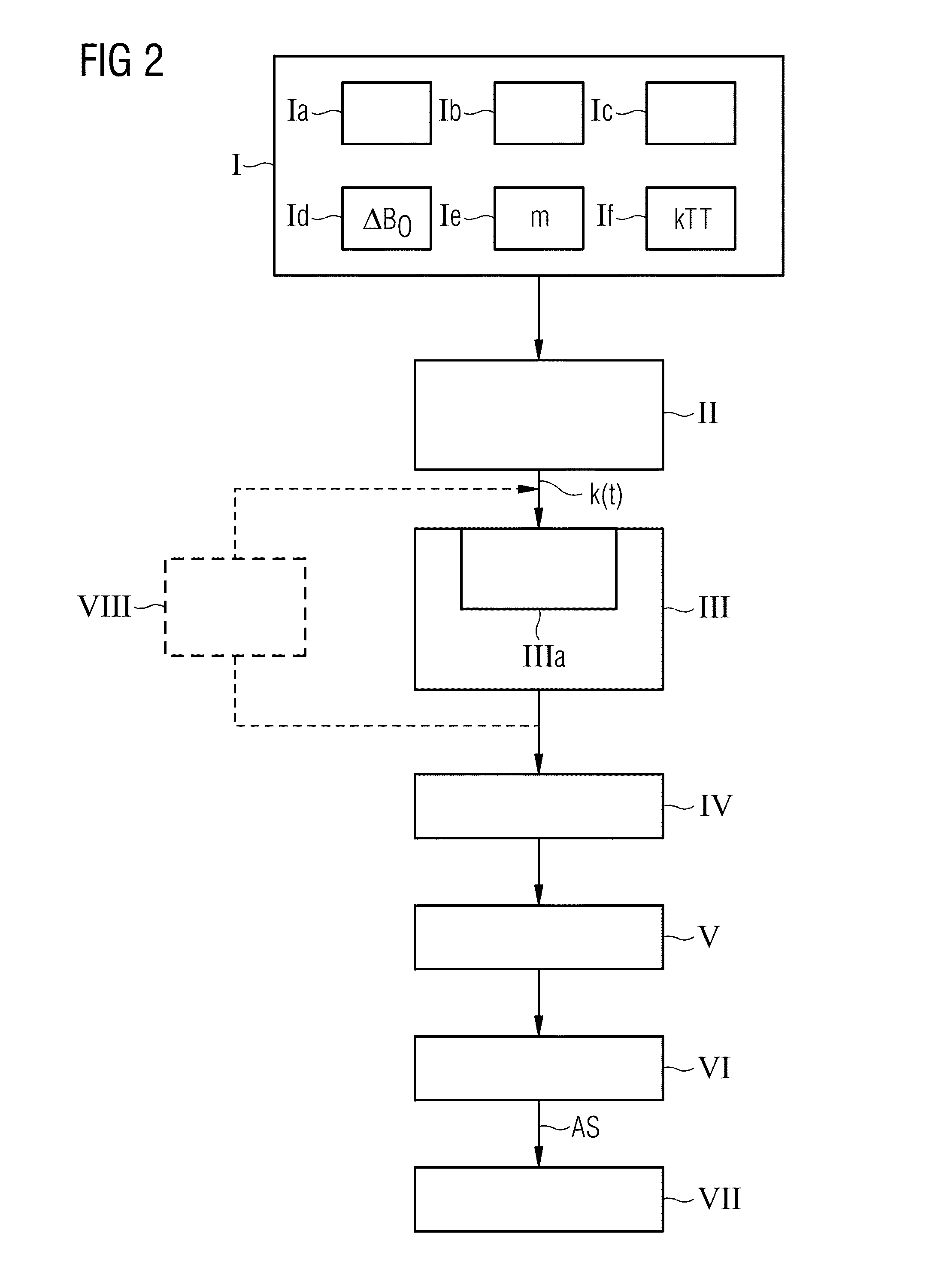
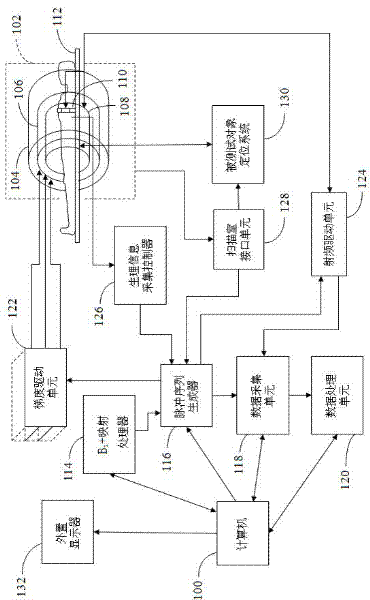
ActiveUS20130249549A1Fast and optimally robust calculationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsBiological testingResonanceMagnetization
In method and a control sequence determination device to determine a magnetic resonance system control sequence that includes at least one radio-frequency pulse train to be emitted by a magnetic resonance system, a target magnetization (m) is initially detected, and an energy distribution function in k-space is determined on the basis of the target magnetization. A k-space trajectory is then determined under consideration of the energy distribution function in k-space, for which the radio-frequency pulse train is then determined in an RF pulse optimization method. The method is suitable for operation of a magnetic resonance system, and a magnetic resonance system includes such a control sequence determination device.
Owner:SIEMENS HEATHCARE GMBH
Method and device for reconstructing a sequence of mr images using a regularized nonlinear inverse reconstruction process
A method for reconstructing a sequence of magnetic resonance (MR) images of an object under investigation, comprises the steps of (a) providing a series of sets of image raw data including an image content of the MR images to be reconstructed, said image raw data being collected with the use of at least one radiofrequency receiver coil of a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) device, wherein each set of image raw data includes a plurality of data sampies being generated with a gradient-echo sequence, in particular a FLASH sequence, that spatially encodes an MRl signal received with the at least one radiofrequency receiver coil using a non-Cartesian k-space trajectory, each set of image raw data comprises a set of homogeneously distributed lines in k-space with equivalent spatial frequency content,; the lines of each set of image raw data cross the center of k-space and cover a continuous range of spatial frequencies, and the positions of the lines of each set of image raw data differ in successive sets of image raw data, and (b) subjecting the sets of image raw data to a regularized nonlinear inverse reconstruction process to provide the sequence of MR images, wherein each of the MR images is created by a simultaneous estimation of a sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content and in dependency on a difference between a current estimation of the sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content and a preceding estimation of the sensitivity of the at least one receiver coil and the image content.
Owner:MAX PLANCK GESELLSCHAFT ZUR FOERDERUNG DER WISSENSCHAFTEN EV
A Sequence Design Method for Three-Dimensional Spatially Selective Excitation for Magnetic Resonance Imaging
InactiveCN102283649AImprove sampling efficiencyImprove securityDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsSequence designPulse envelope
The invention discloses a selective excitation sequential design method for magnetic resonance imaging in a three-dimensional space. According to the sequential design method disclosed by the invention, a proper excitation K space track is optimally determined according to space sensitive conditions of an excitation target and a plurality of transmitting channels of a radio-frequency coil, thereby a gradient pulse waveform and a radio frequency pulse envelope waveform corresponding to each transmitting channel are determined. A gradient driving unit and a radio-frequency driving unit in a magnetic resonance system can be used for generating gradient pulse and radio frequency pulse according to the radio frequency pulse envelope waveform and the gradient pulse waveform and driving a gradient coil and the radio frequency coil to apply the gradient pulse and radio frequency pulse in a scanning space, thereby the expected selective excitation target in the three-dimensional space is realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method and system for multi-shot spiral magnetic resonance elastography pulse sequence
ActiveUS20140232395A1Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionK space trajectoryPulse sequence
Aspects of the subject disclosure may include, for example, a system that applies magnetic resonance elastography to a sample to obtain uncorrected k-space data where the magnetic resonance elastography utilizes a multi-shot spin-echo sequence with variable density spiral readout gradients, and adjusts the uncorrected k-space data to corrected k-space data by adjusting a k-space trajectory by shifting a center point for each shot to a new center point according to signal intensity and by adjusting a phase for each shot based on a phase offset that is determined according to the signal intensity. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF ILLINOIS
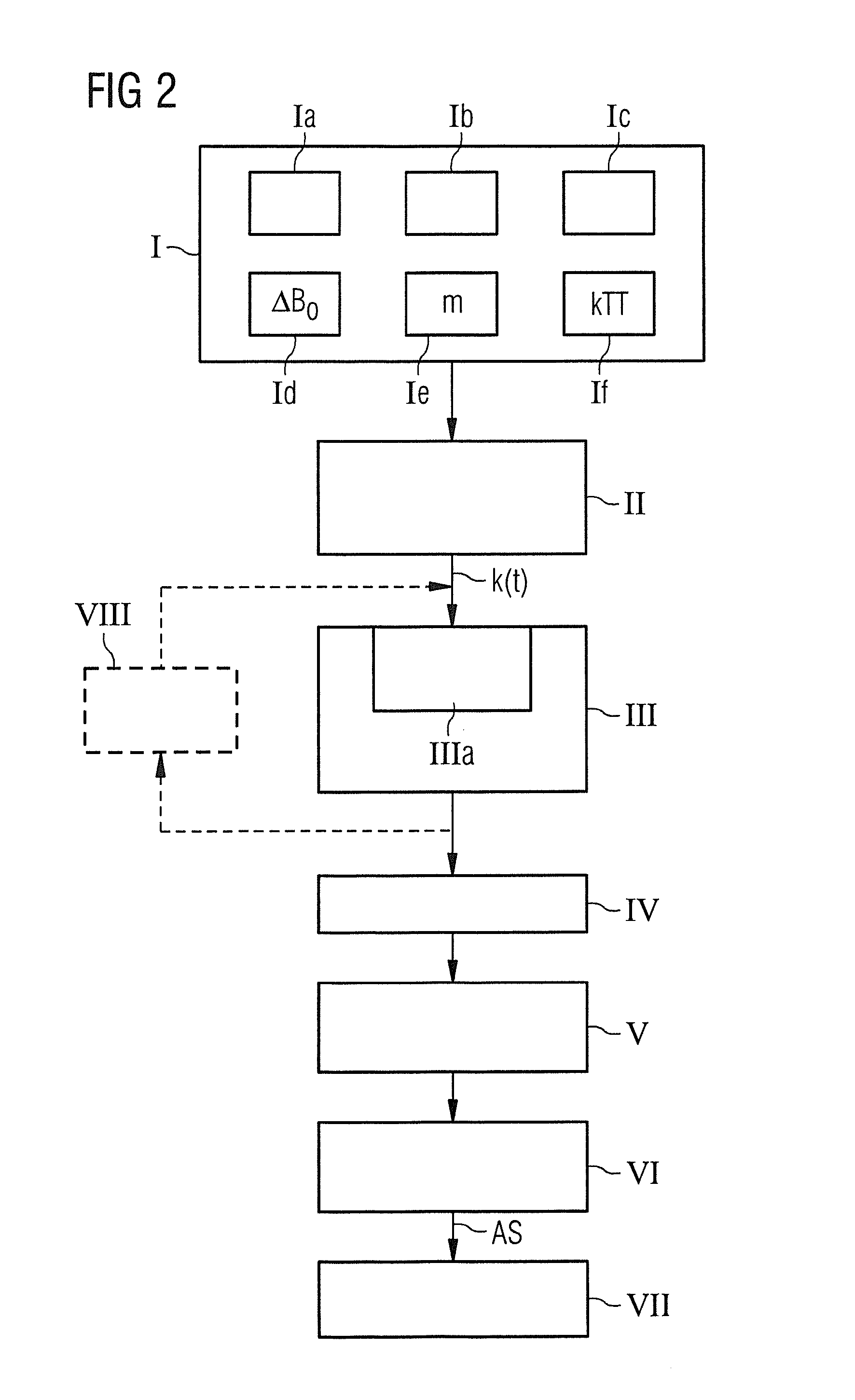
Method and device for determination of a magnetic resonance control sequence
ActiveUS20150035531A1Minimize durationShort timeMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectrical measurementsResonanceK space trajectory
A magnetic resonance control sequence with a pulse arrangement that acts selectively in at least two spatial directions in order to excite a limited rotationally symmetrical excitation profile within an examination subject has an RF excitation pulse formed as a sequence of multiple partial RF pulses, and gradient pulses in the two spatial directions that are coordinated with the partial RF pulses so that the RF energy introduction of different partial RF pulses in transmission k-space occurs on circular k-space transmission trajectories that are concentric to one another. The amplitude of the RF envelope of the partial RF pulses is constant during the duration of a traversal of each circular k-space trajectory. The control sequence can also be used in a calibration of a magnetic resonance system.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Determination of a Magnetic Resonance System Activation Sequence
InactiveUS20130253876A1Rapid and robust calculationQuick calculationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsResonanceMagnetization
A method and a control sequence determination device for the determination of a magnetic resonance system activation sequence including at least one high-frequency pulse sequence to be transmitted by a magnetic resonance system are provided. A current B0 map and optionally a target magnetization are acquired. In addition, a k-space trajectory type is determined. An error density is calculated in a k-space based on the current B0 map and optionally based on the target magnetization using an analytic function. This analytic function defines an error density in the k-space as a function of the current B0 map and optionally the target magnetization. Taking account of the error density in the k-space, a k-space trajectory of the specified k-space trajectory type is determined. The high-frequency pulse sequence is determined for the k-space trajectory in an HF pulse optimization process.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Rapid measurement of time-averaged blood flow using ungated spiral phase-contrast MRI
ActiveUS6957097B2Rapid quantitationReduce the impactSensorsBlood flow measurementCardiac cycleBlood flow
Pulsatile flow is measured using magnetic resonance imaging without cardiac gating using a phase-contrast excitation method to rapidly quantify blood flow and using a spiral k-space trajectory for image data read-out to mitigate deleterious effects of pulsatility. Post-processing of the read-out data provides a cumulative-average velocity plot from which a period of a cardiac cycle is obtained. Time-averaged blood flow rates can be rapidly and robustly measured and is more repeatable than conventional gated techniques.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Dual gradient echo pulse sequence using interleaved spiral-out spiral-in k-space trajectories
ActiveUS20060062731A1Avoids saturation effectMore sensitivityMagnetic measurementsNMR/MRI constrast preparationsMagnetic susceptibilityBlood flow
Measurements of functional, hemographic, and blood flow parameters use a multiple echo or spin echo gradient pulse sequence whereby an early echo is acquired near the beginning of the pulse sequence which avoids saturation effects and a later echo near the end of the pulse sequence which can provide information with more sensitivity to a contrast agent for a susceptibility weighted image.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Generalized method for MRI chemical species separation using arbitrary k-space trajectories
ActiveUS7619411B2Eliminate the effects ofMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionData setChemical species
A method for producing images of a subject containing M spin species using a magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) system includes obtaining N k-space data matrices from N k-space data sets acquired with the MRI system using a pulse sequence with an individual associated echo time. The k-space data matrices each include corresponding data at the same plurality of k-space locations and time stamps are tracked for each k-space location. For each k-space location, a set of linear equations in k-space is solved. The set of linear equations relates corresponding data from the N k-space data matrices, echo times and time stamps to desired calculated k-space data. Calculated data in k-space which is corrected for chemical shift is produced corresponding to each k-space location and aggregated to obtain a k-space calculated data set. The k-space calculated data set is transformed to image space to obtain a corresponding image.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
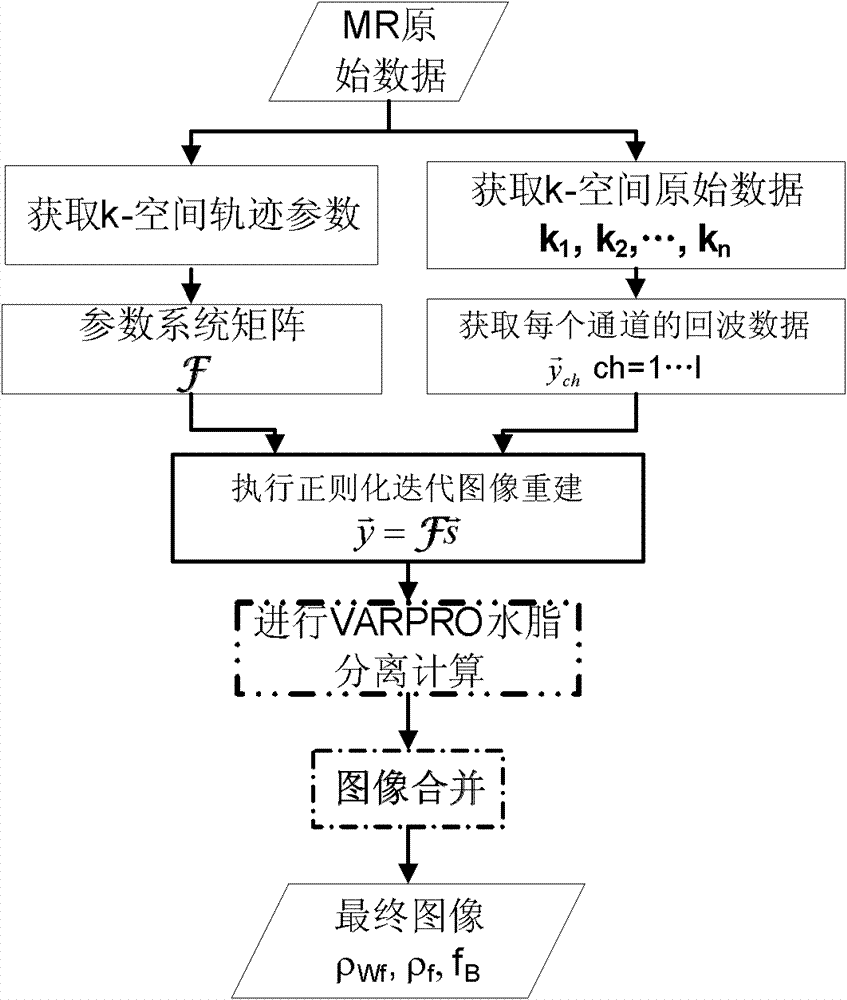
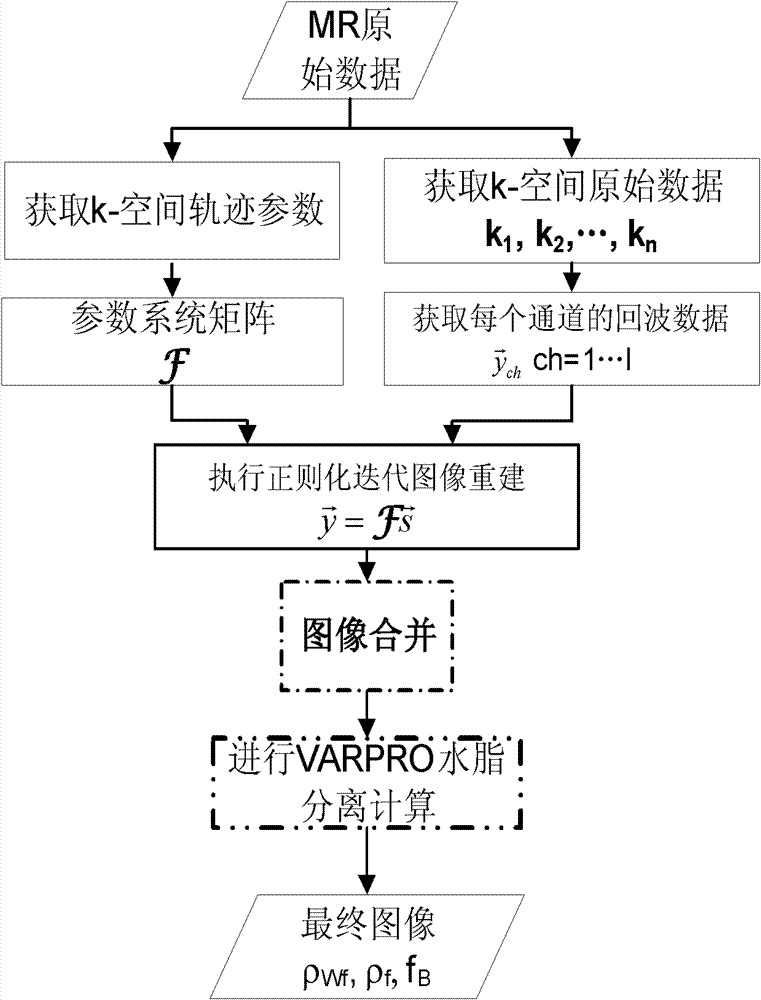
Water and fat separation method based on under-sampling k-space data
ActiveCN102779327AConvenience to mergeReduce the amount of calculationImage enhancementSystem matrixResonance
The invention discloses a water and fat separation method based on under-sampling k-space data. The method includes steps of, step one, respectively acquiring k-space trajectory parameters and k-space raw data according to magnetic resonance (MR) raw data; step two, selecting a parameter system matrix according to the k-space trajectory parameters; step three, acquiring echo data of each channel according to the k-space raw data; step four, executing regularization iteration image reconstruction by using the parameter system matrix and the echo data of each channel; and step five, subjecting reconstructed images to variable projection (VARPRO) water and fat separation calculating to obtain a final image. The water and fat separation method based on the under-sampling k-space data is applicable to more scanning tracks, and by means of a VARPRO water and fat separation algorithm, a phase diagram, a B0 field image, a water image and a fat image which are irrelevant to main magnetic field inhomogeneity are separated; the water and fat separation method based on the under-sampling k-space data has advantages of VARPRO iteration field image calculating and is insensitive to seed points; and the water and fat separation method based on the under-sampling k-space data is smaller in calculated amount and fewer in calculating requirements, image merging is easier to finish, and a system function which is capable of achieving parallel imaging can be introduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE CO LTD
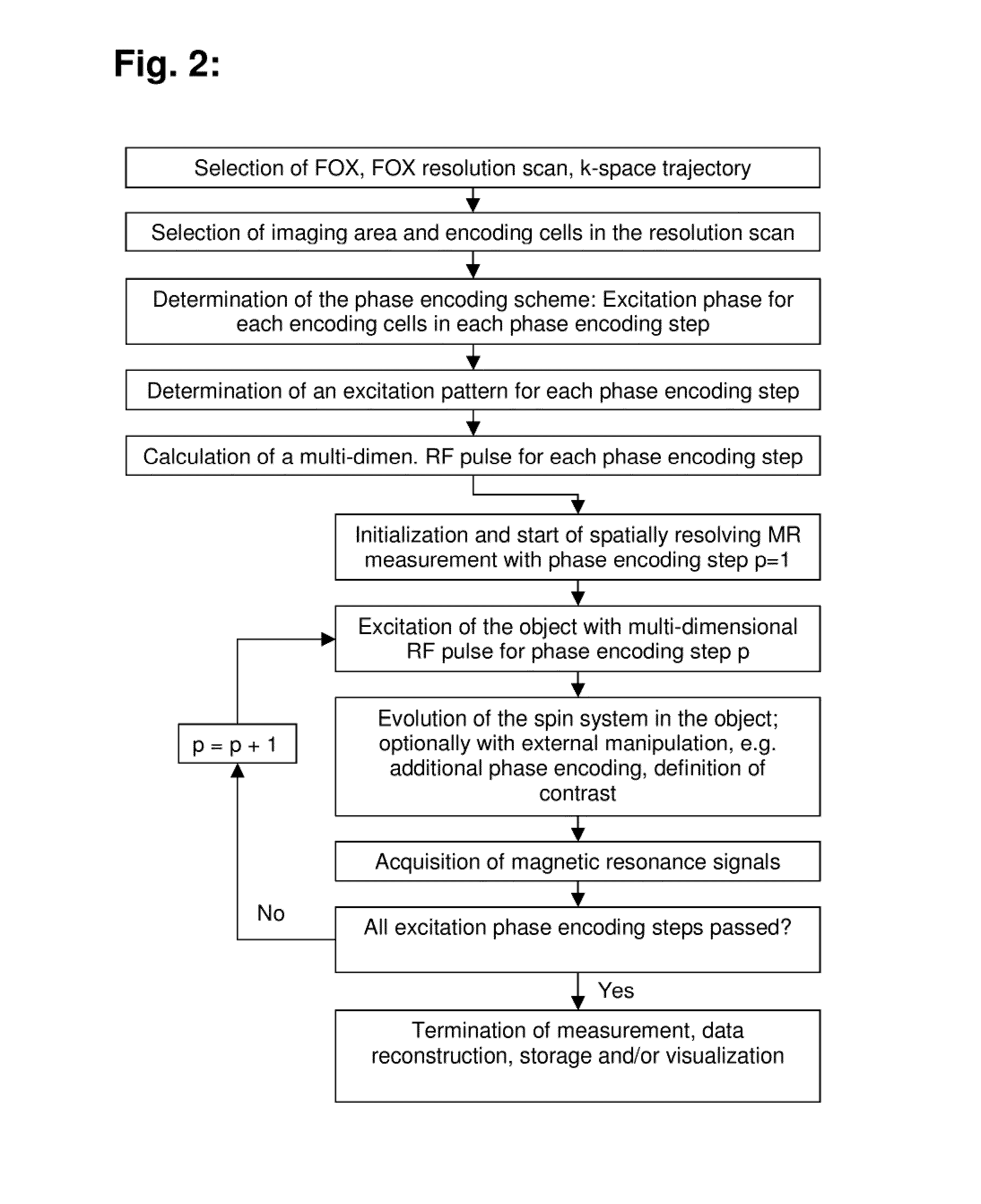
Method for determining the spatial distribution of magnetic resonance signals through multi-dimensional RF excitation pulses
ActiveUS8082127B2Short relaxation timeEliminate delaysUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAmplifier modifications to reduce noise influenceSpatial encodingMulti dimensional
A method for determining the spatial distribution of magnetic resonance signals from an imaging area, wherein nuclear spins are excited in a spatially encoded fashion through multi-dimensional RF pulses, is characterized in that in a definition step, a resolution grid with resolution grid cells is predetermined, and in accordance with a predetermined phase encoding scheme, an excitation pattern is defined for each phase encoding step, in which the amplitudes within the imaging area are set in accordance with a predetermined distribution identically for each phase encoding step. In a preparatory step, the amplitude and phase behavior of the RF pulses to be irradiated is calculated in accordance with a predetermined k-space trajectory for each defined complex excitation pattern.
Owner:BRUKER BIOSPIN MRI
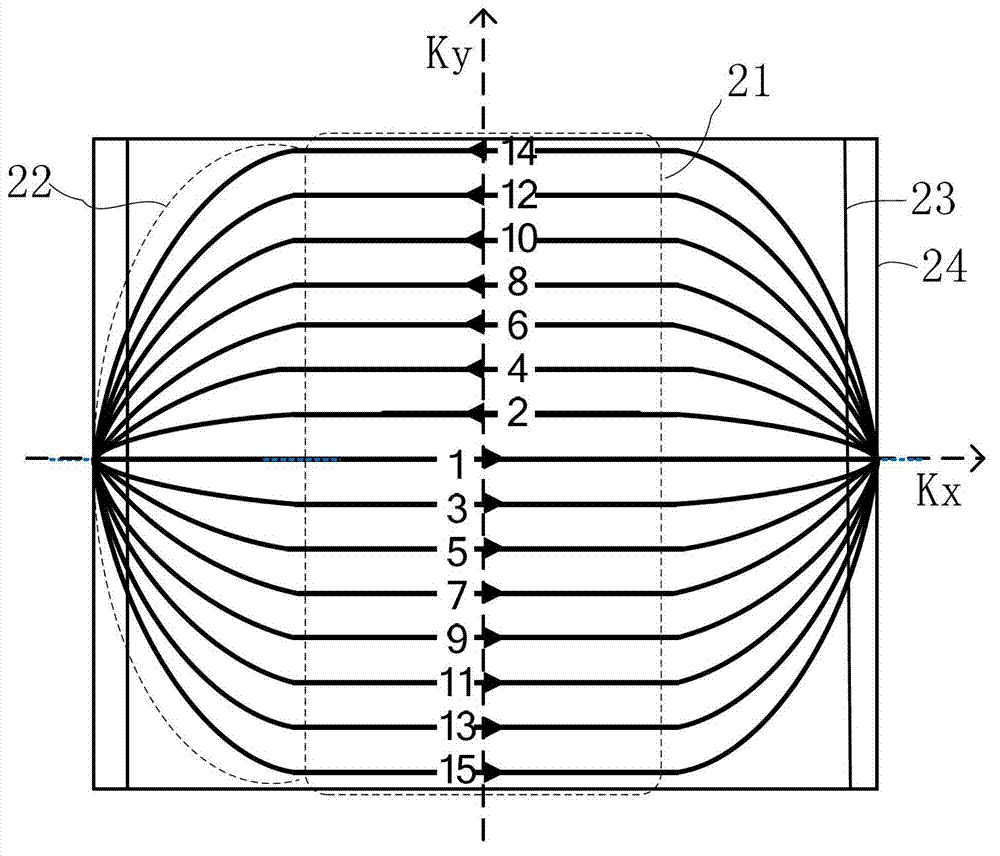
Inside-out echo-planar imaging method for shortening echo time
InactiveCN102890255AShortened echo timeImprove signal-to-noise ratioMagnetic measurementsSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Arterial spin labeling
The invention discloses an inside-out echo-planar imaging method for shortening echo time. The method is characterized in that: a k-space trajectory extends to the outer side of a phase encoding direction from the center, wherein a gradient for generating the trajectory is composed of reading-out gradients which switch between forward and reverse directions and phase encoding gradients which switch between forward and reverse directions and gradually increases from zero. The method further comprises a step that: in order to accommodate the phase encoding gradients of which the area increases gradually without adding an echo spacing, the phase encoding gradient and a data collecting window are permitted to be overlapped. According to the method disclosed by the invention, an effective echo time in a sequence is located in the center of a first echo, the echo time is shortened greatly, and the signal to noise ratio is increased; since the contrast ratio of an image depends on signals of a k-space centre, and data of the k-space center are from an initial echo, T2 or T2* weighing of the obtained image is very small; and in diffusion imaging and arterial spin labeling imaging, the decreasing of the T2 or the T2* weighing is beneficial to improving the quality of the image.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Determination of a pulse sequence for a magnetic resonance system
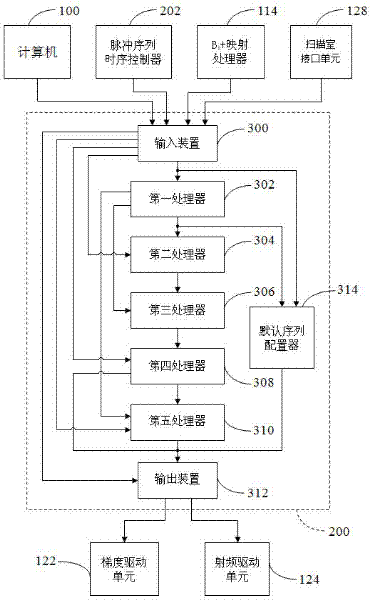
InactiveUS20140232397A1Facilitates sequence programmingLess effortMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceK space trajectory
In a method and a pulse sequence determination device to determine a pulse sequence for a magnetic resonance system, control protocol parameter values are initially acquired. A determination of k-space trajectory node points within k-space then takes place in a processor on the basis of the control protocol parameter values. The determination of the pulse sequence then takes place on the basis of the k-space trajectory node points. A method for operating a magnetic resonance system uses such a pulse sequence, and a magnetic resonance system embodies such a pulse sequence determination device.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Excitation Pulse Sequence Generator for Magnetic Resonance Systems
InactiveCN102288929AImprove sampling efficiencyShorten the durationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsSelective excitationResonance
The invention provides an excitation pulse sequence generator for a magnetic resonance system. An excitation pulse sequence generated by the excitation pulse sequence generator is applied to the magnetic resonance system, so that optimized three-dimensional space selective excitation based on a parallel excitation technology can be realized. By using the excitation pulse sequence generator, an appropriate excitation K space track can be determined in an optimized way according to an excitation target and the space sensitivity situation of a plurality of transmitting channels of a radiofrequency coil, so that a gradient pulse waveform and a radiofrequency pulse envelope waveform corresponding to each transmitting channel are determined. A gradient driving unit and a radiofrequency driving unit of the magnetic resonance system are used for generating gradient pulses and radiofrequency pulses accordingly and driving a gradient coil and the radiofrequency coil to apply the gradient pulsesand the radiofrequency pulses to a scanning space, so that the aim of selectively exciting in a desired three-dimensional space is fulfilled.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and method
ActiveUS20190154784A1Faster MR scanning timeSimple methodMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPhase correctionStimulated echo
Magnetic resonance (MR) data are acquired by applying magnetic fields to an examination region concurrent with stimulated echo signals, such that trajectories, which are not straight lines, are generated in k-space. For this purpose, sequence of RF pulses is applied to generate the stimulated echo signals in the examination object, undersampled MR measurement data are detected during reception of the stimulated echo signals in the at least two receiving coils, along the curved k-space trajectories, and fully sampled MR measurement are generated from the undersampled MR measurement data using sensitivity information of the at least two receiving coils. Alternatively, the MR measurement data are fully sampled in a central region of k-space, and a region outside the central region is not fully sampled, and a phase correction with a Partial Fourier technique is executed on the MR measurement data using fully sampled MR measurement data from the central region of k-space.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Low-noise magnetic resonance imaging using low harmonic pulse sequences
ActiveUS20150309148A1Electric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceLow noiseHarmonic
Systems and method for magnetic resonance imaging are disclosed which utilize sinusoidal gradient waveforms to drive gradient coils in an MRI system. The sinusoidal gradient waveforms may be applied on all two or more (e.g. three) gradient axes to produce a relatively pure acoustic tone. In certain embodiments, gradient directions may be spiraled in three-dimensions to generate a radial pin-cushion k-space trajectory
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
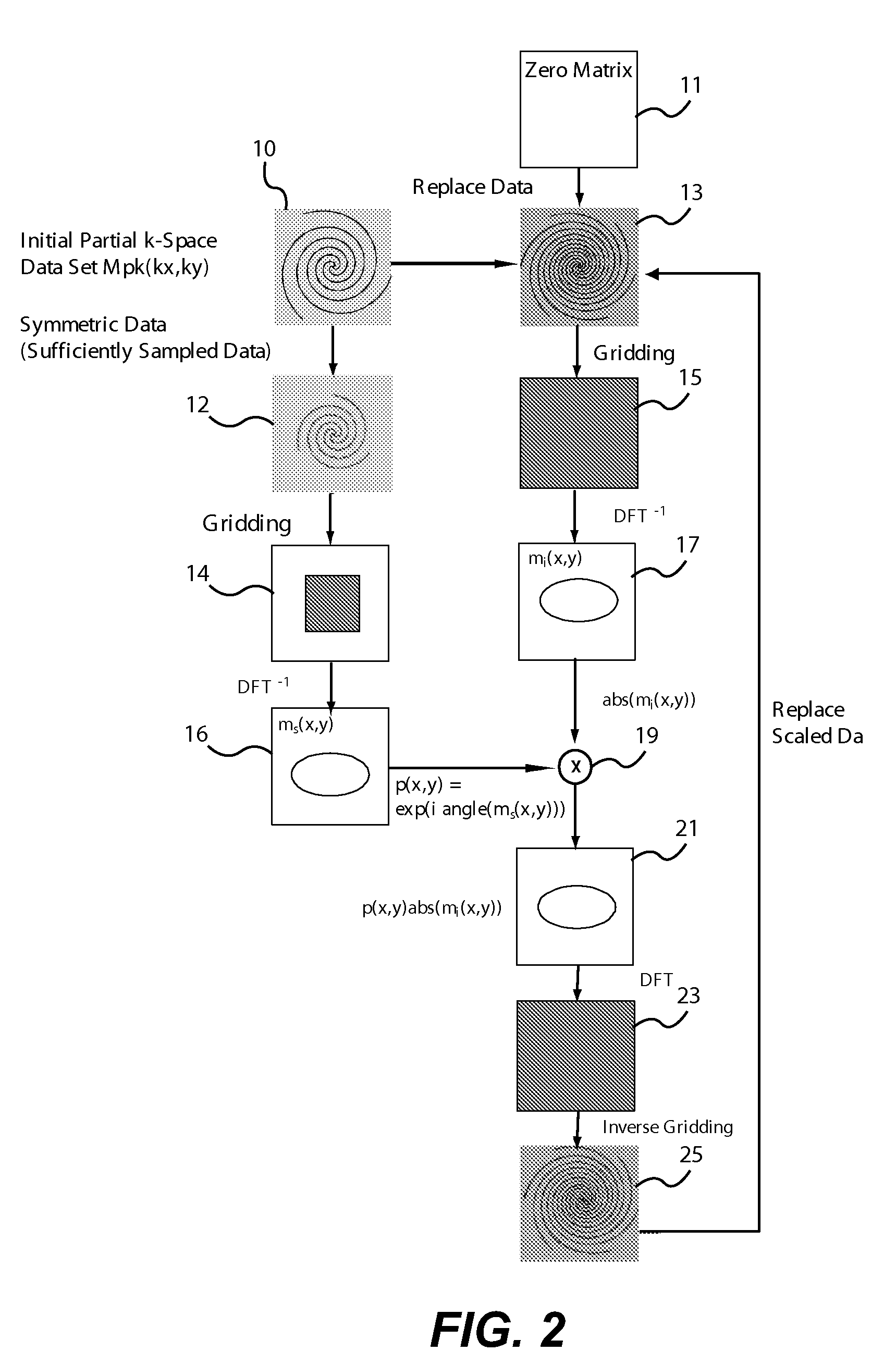
Partial k-space reconstruction for radial k-space trajectories in magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS7277597B2Minimal aliasing artifactAccurate compensationMagnetic measurementsCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmK space trajectory
A modified projection on convex sets (POCS) algorithm and method for partial k-space reconstruction using low resolution phase maps for scaling full sets of reconstructed k-space data. The algorithm can be used with partial k-space trajectories in which the trajectories share a common point such as the origin of k-space, including variable-density spiral trajectories, projection reconstruction trajectories with a semicircle region acquisition, and projection reconstruction trajectories with every other spike acquired.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Mr imaging with an RF pulse producing reduced magnetization transfer
ActiveUS20070236216A1Reduce and limit amountMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionMagnetizationK space trajectory
A system and method are provided herein for designing and transmitting RF pulses which cause a reduced off-resonance magnetization transfer saturation. An RF pulse shape may be optimized according to a set of Bloch solutions defining a desired magnetization profile. An RF pulse may be transmitted according to this optimized shape according to a k-space trajectory which traverses a high amplitude portion of the RF pulse more times than one or more low amplitude portions. In addition, a generally alternating slice select gradient may be applied during transmission of the RF pulse.
Owner:DIGNITY HEALTH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com