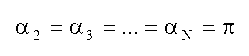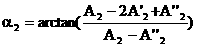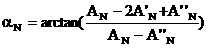Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
66 results about "Stimulated echo" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
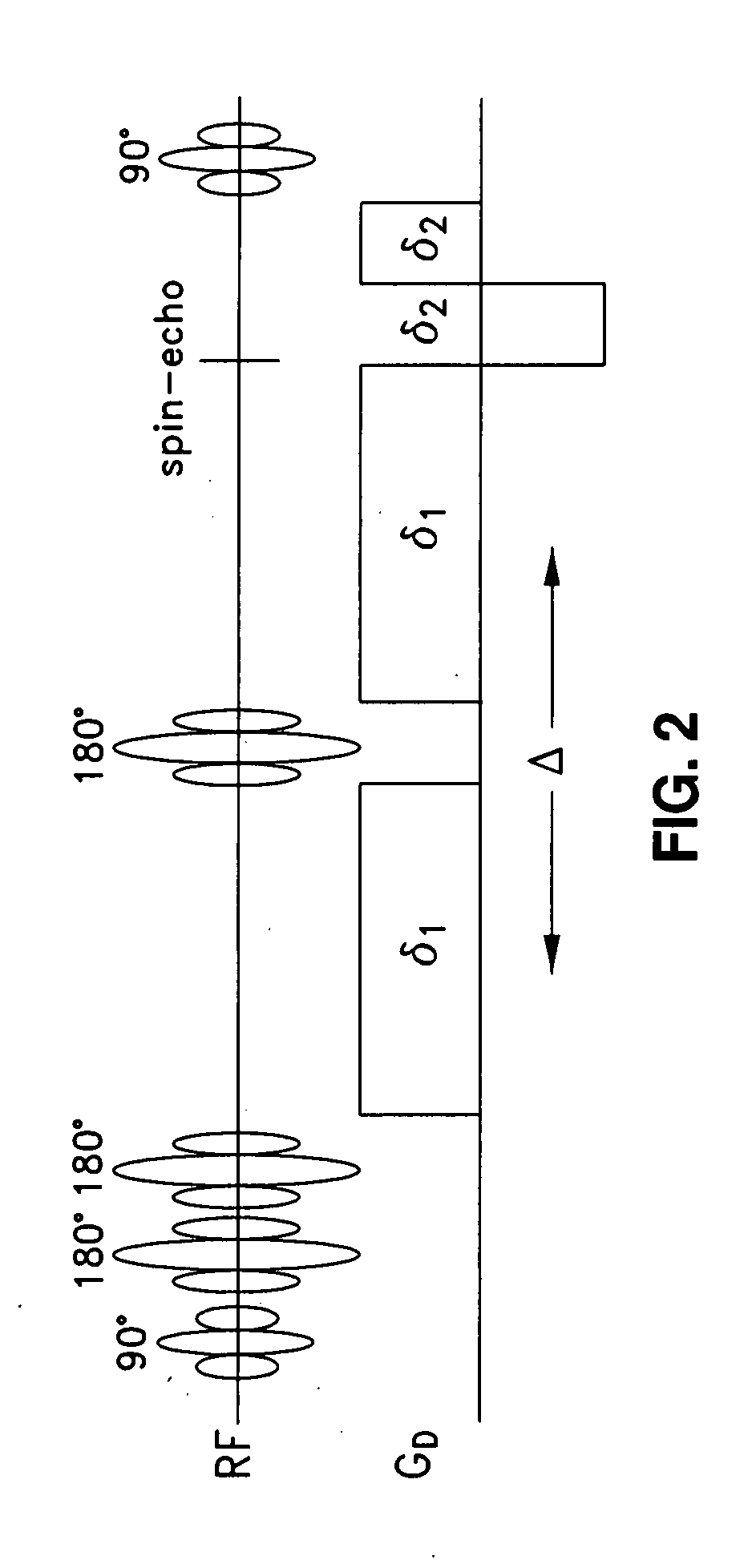
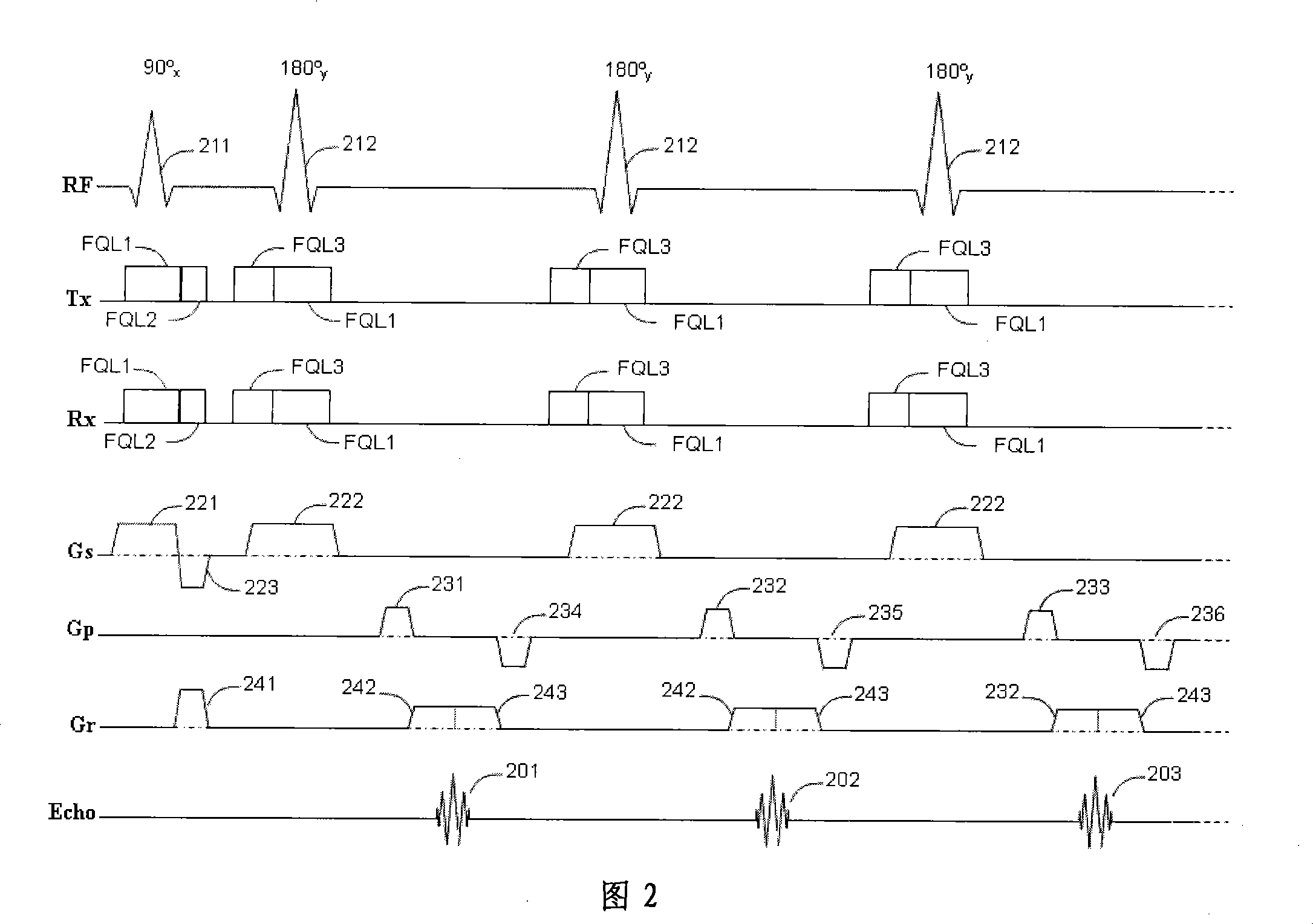
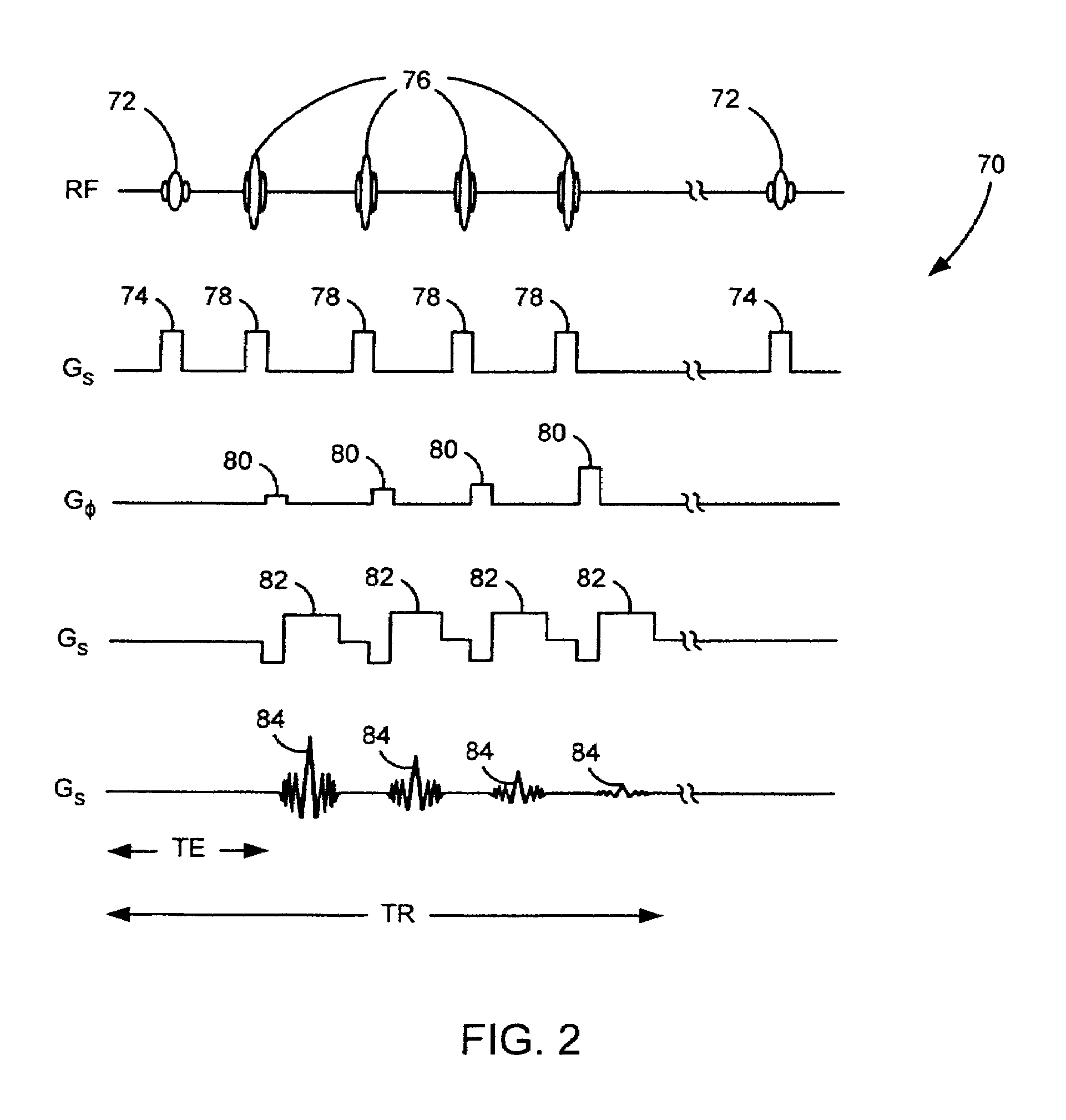
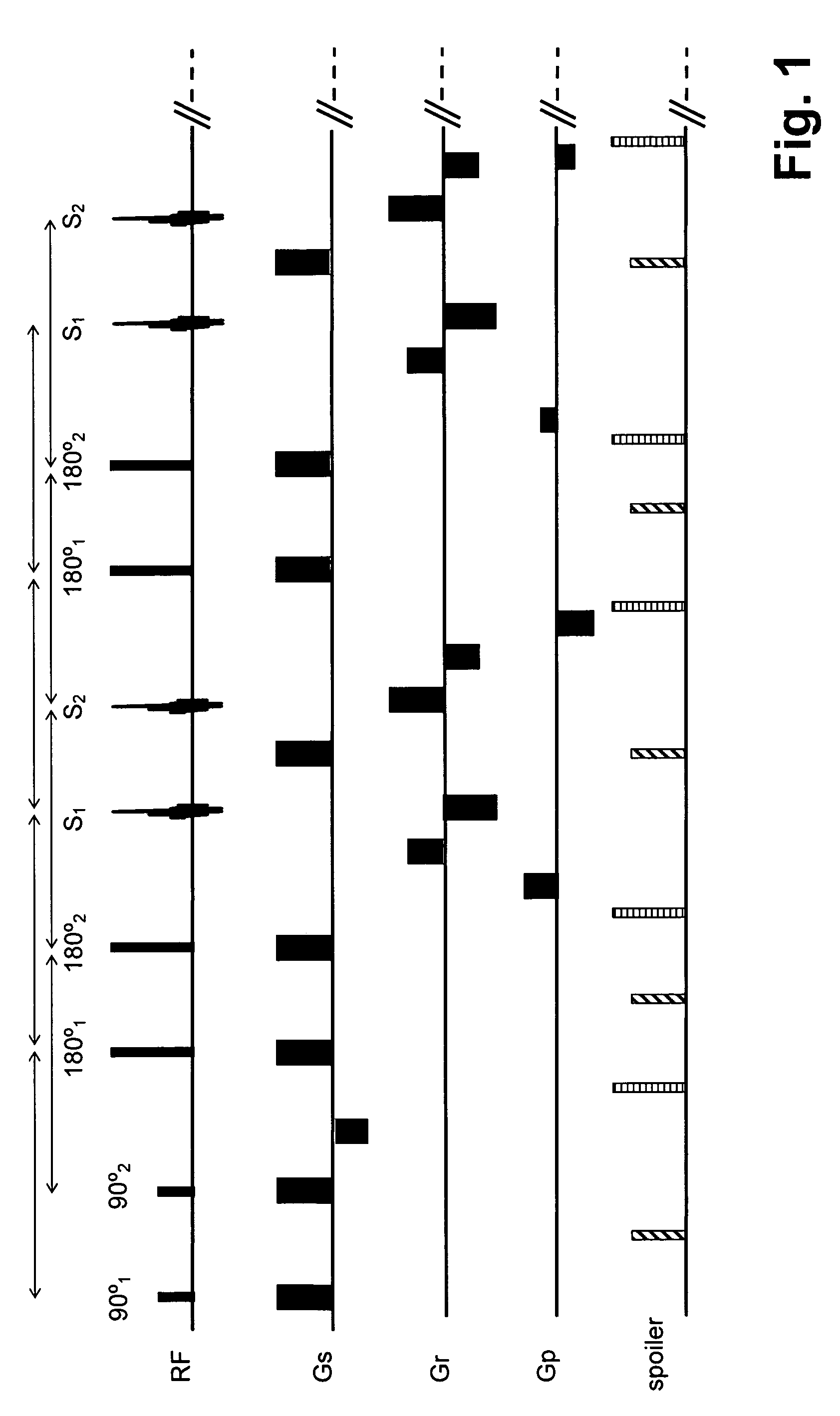
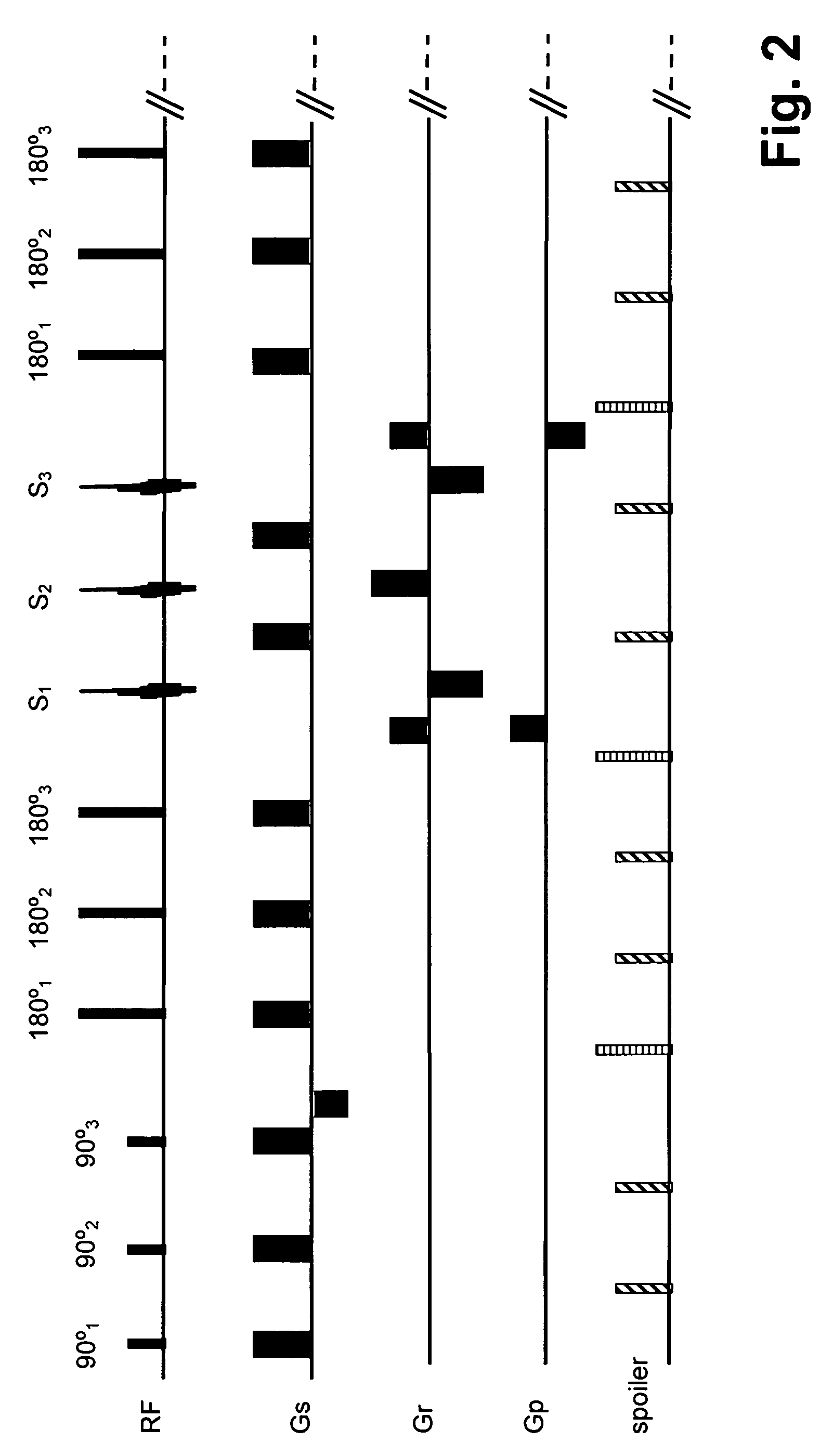
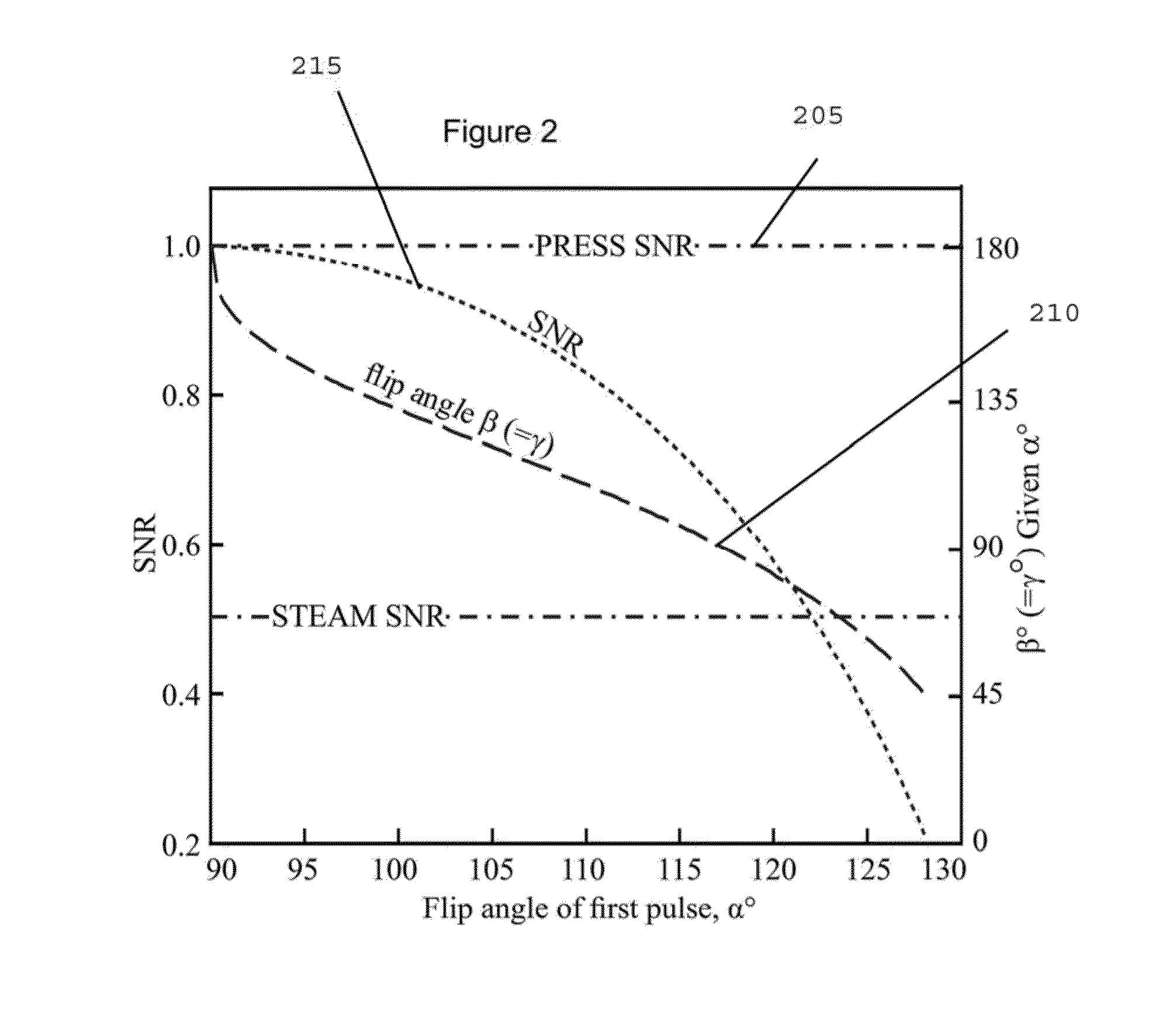
Stimulated Echo. A form of a spin echo produced by three pulse RF sequences, consisting of two RF pulses following an initial exciting RF pulse. The stimulated echo appears at a time delay after the third pulse equal to the interval between the first two pulses.
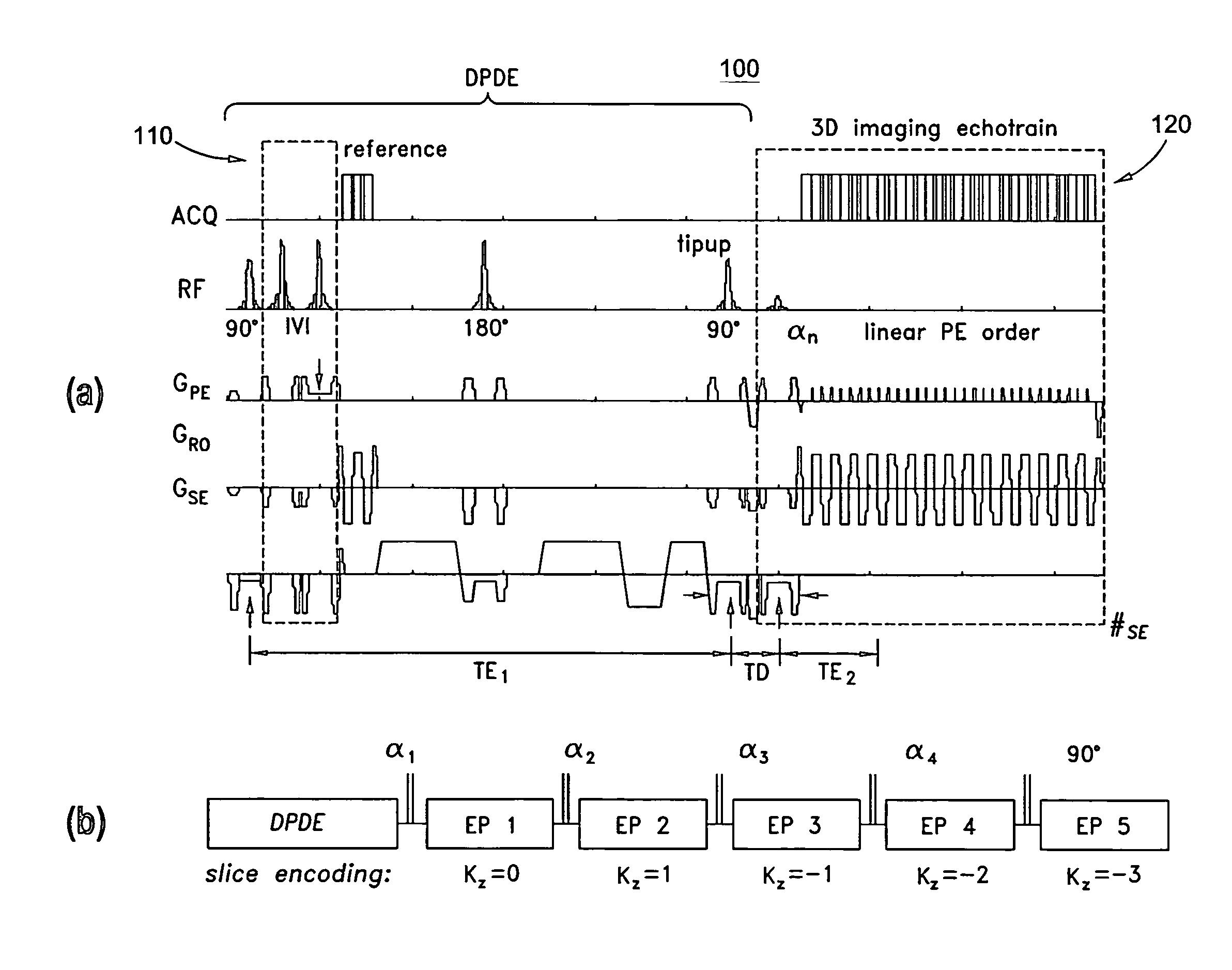
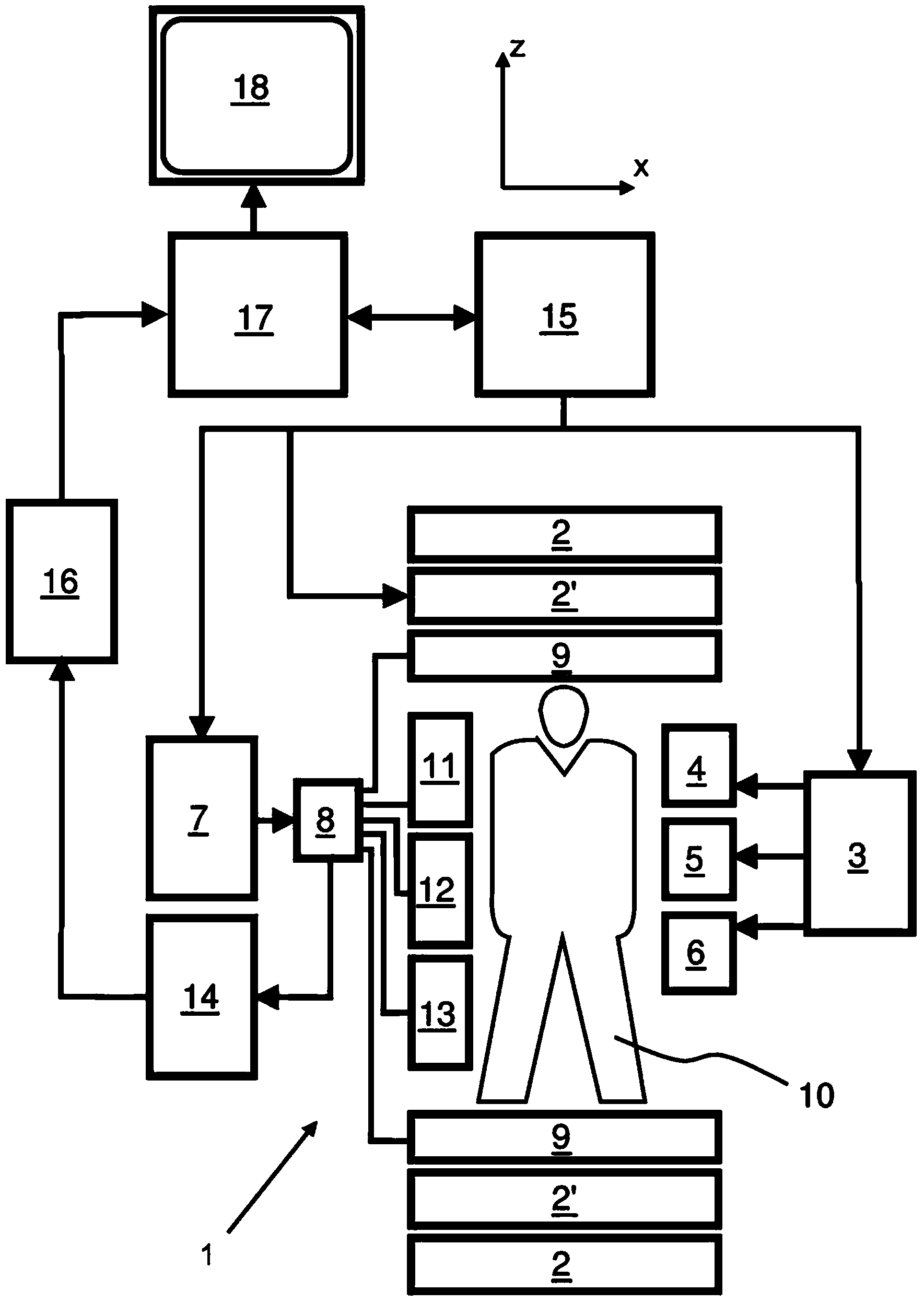
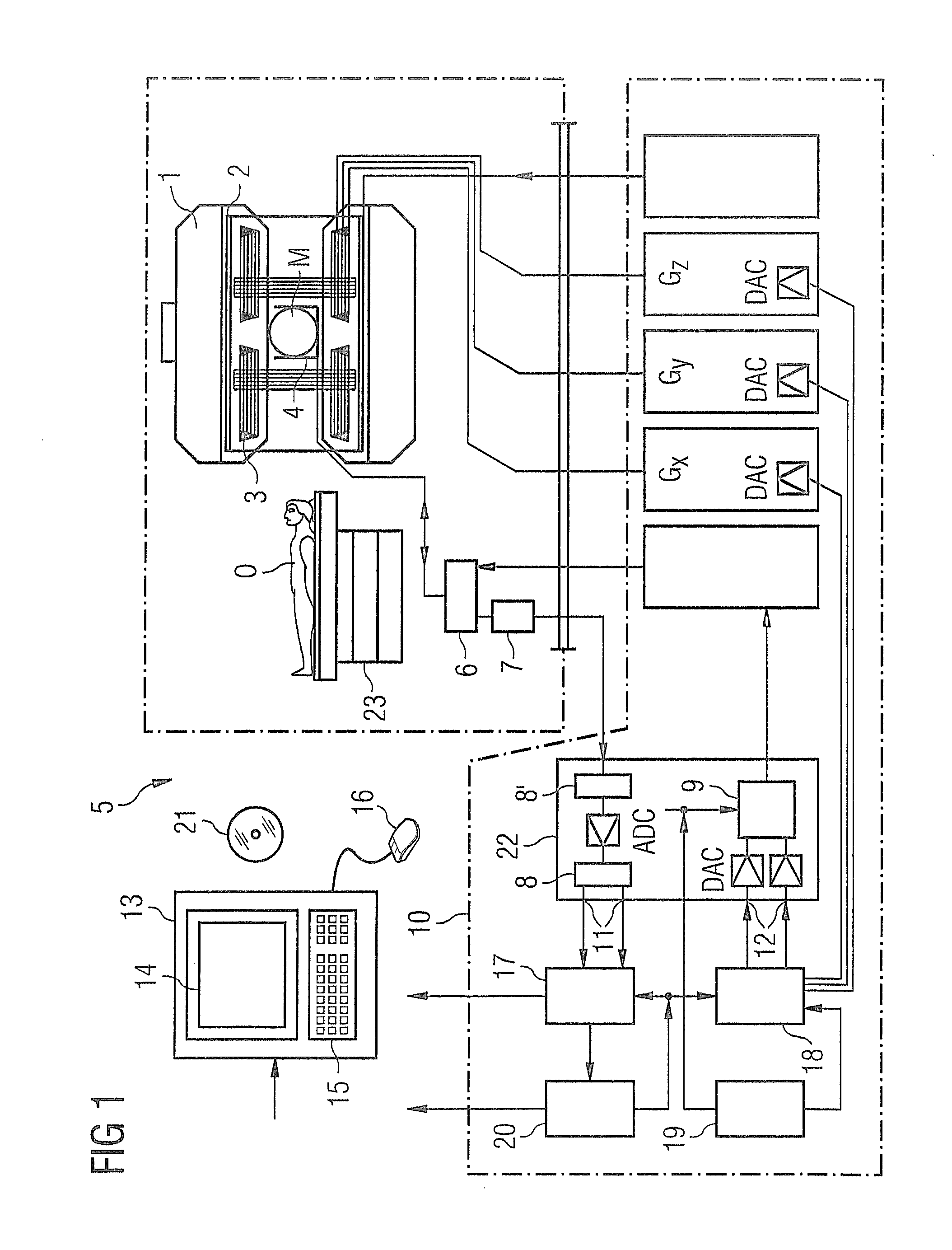
Systems and methods for magnetic resonance imaging
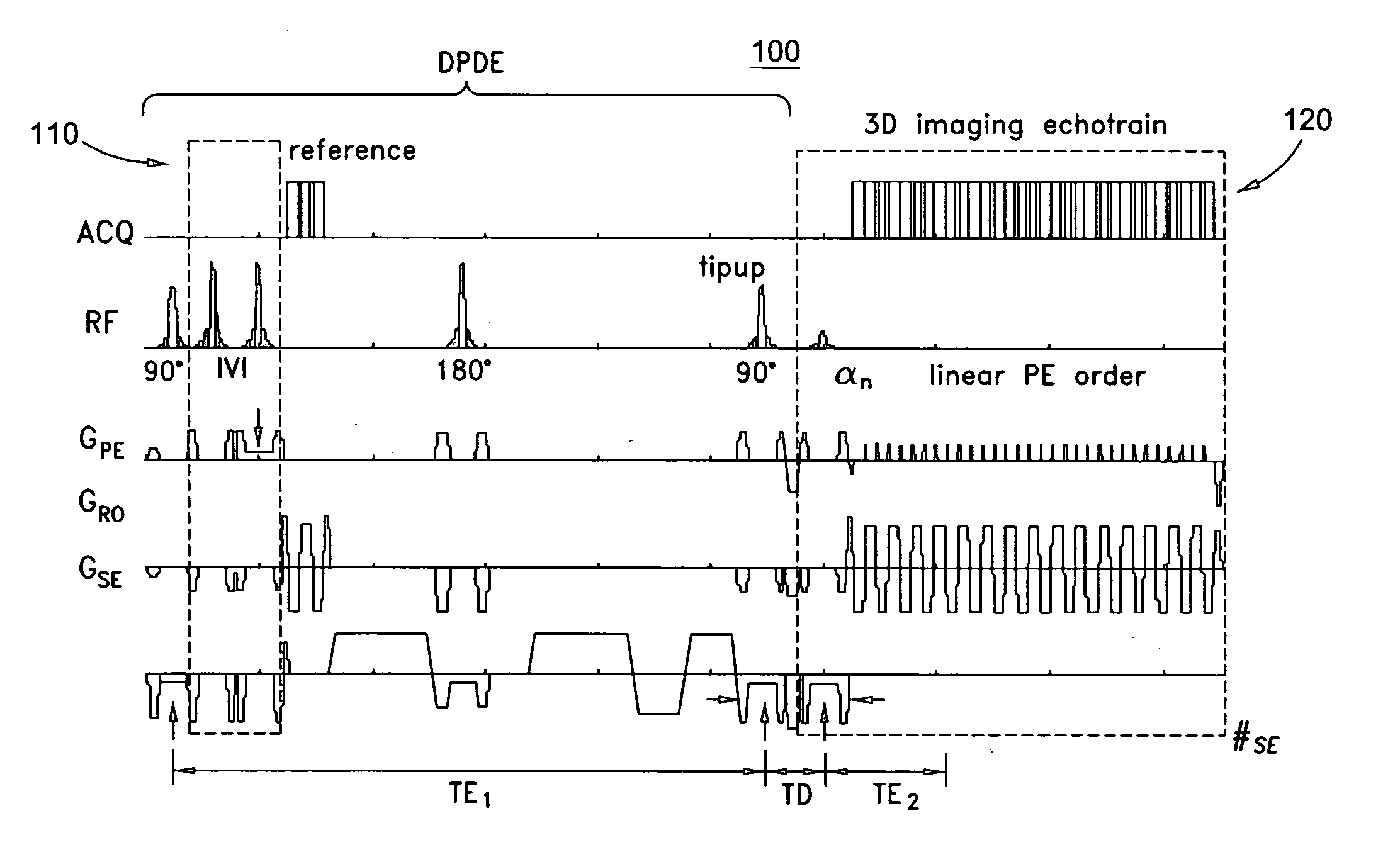
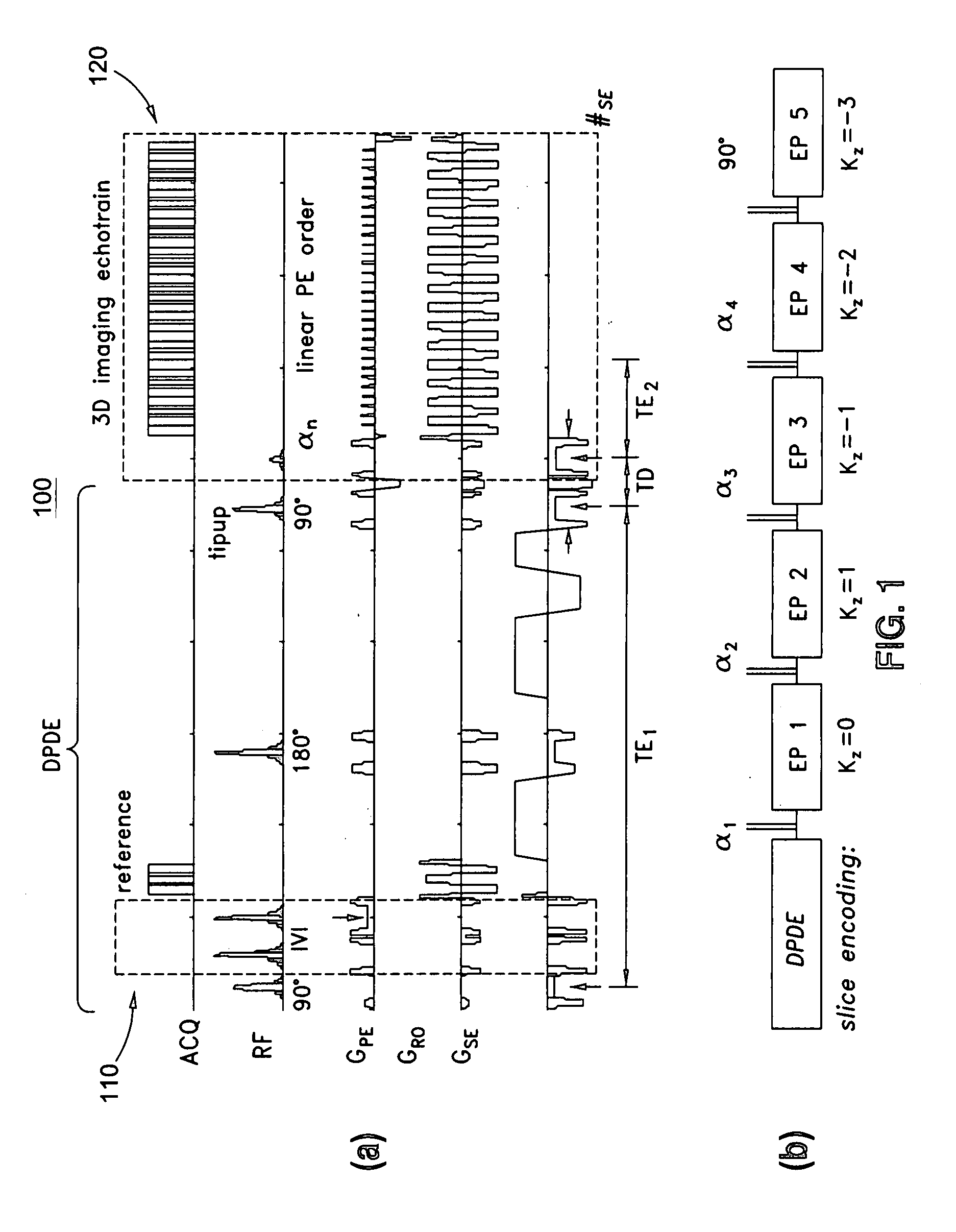
Methods and apparatus for operating an MRI system is provided. The disclosure provides a diffusion-prepared driven-equilibrium preparation for an imaging volume and acquiring 3-dimensional k-space data from said prepared volume by a plurality of echoplanar readouts of stimulated echoes. An excitation radio-frequency signal and first and second inversion RF signals are provided to define a field-of-view (FOV).
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
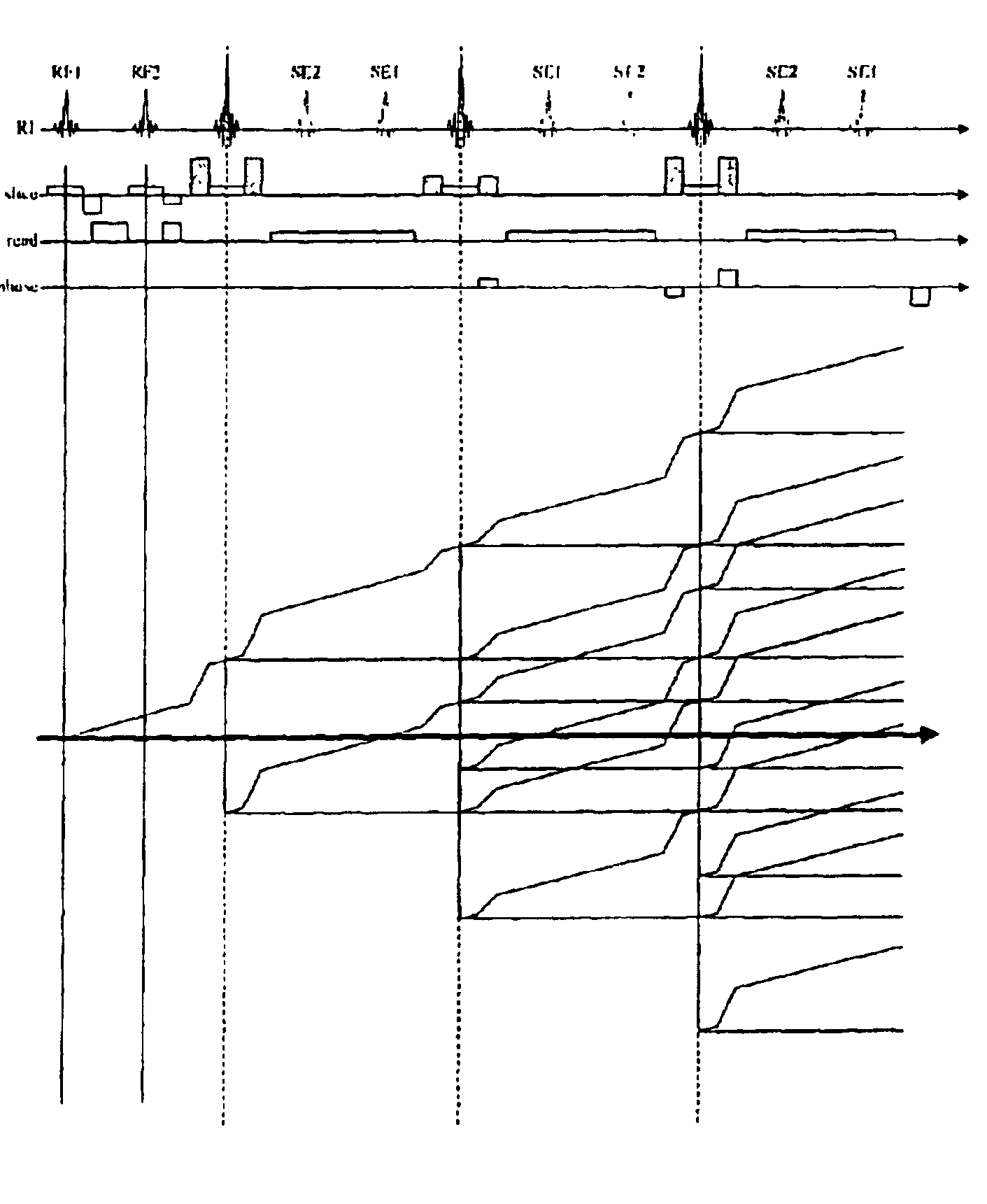
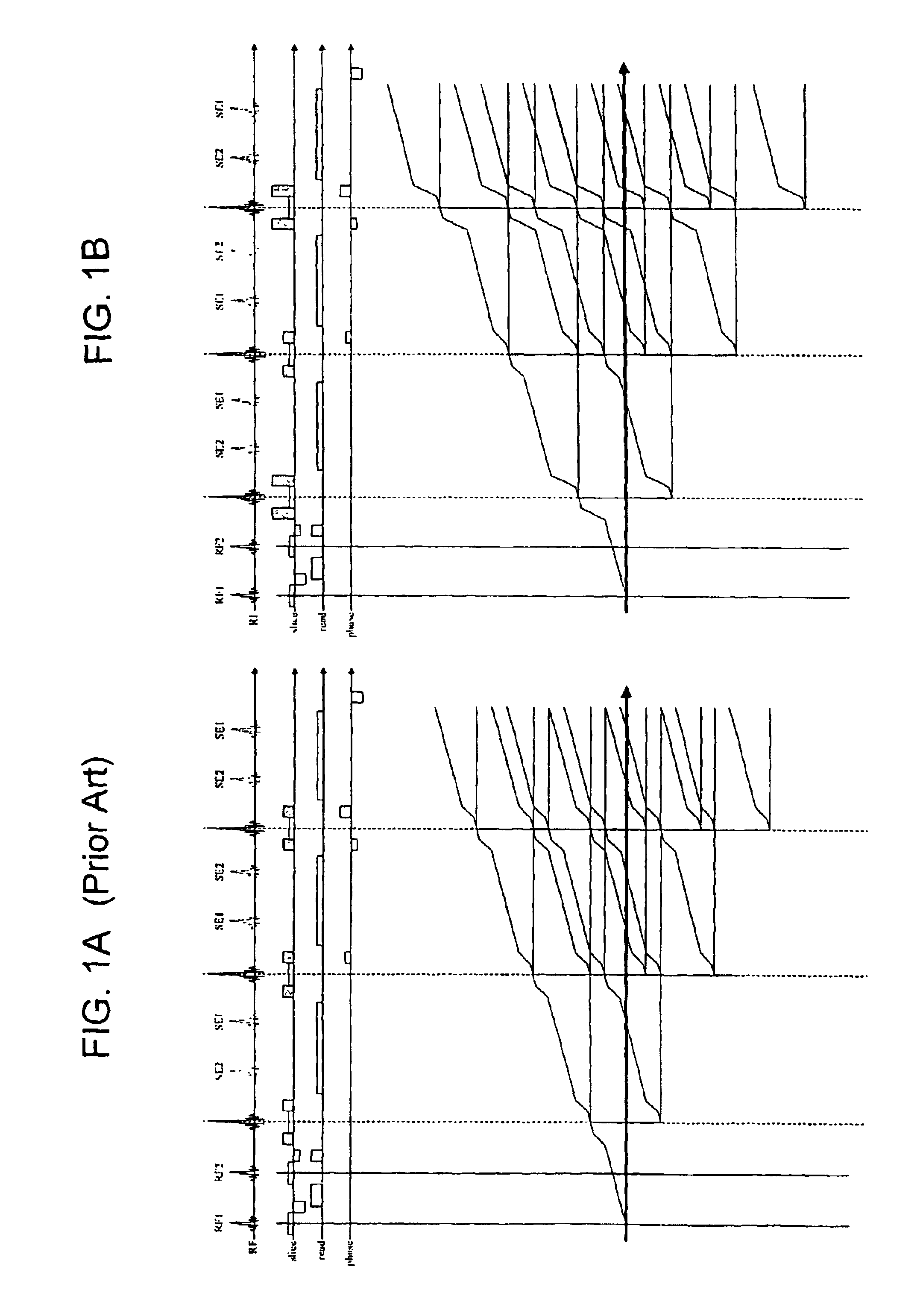
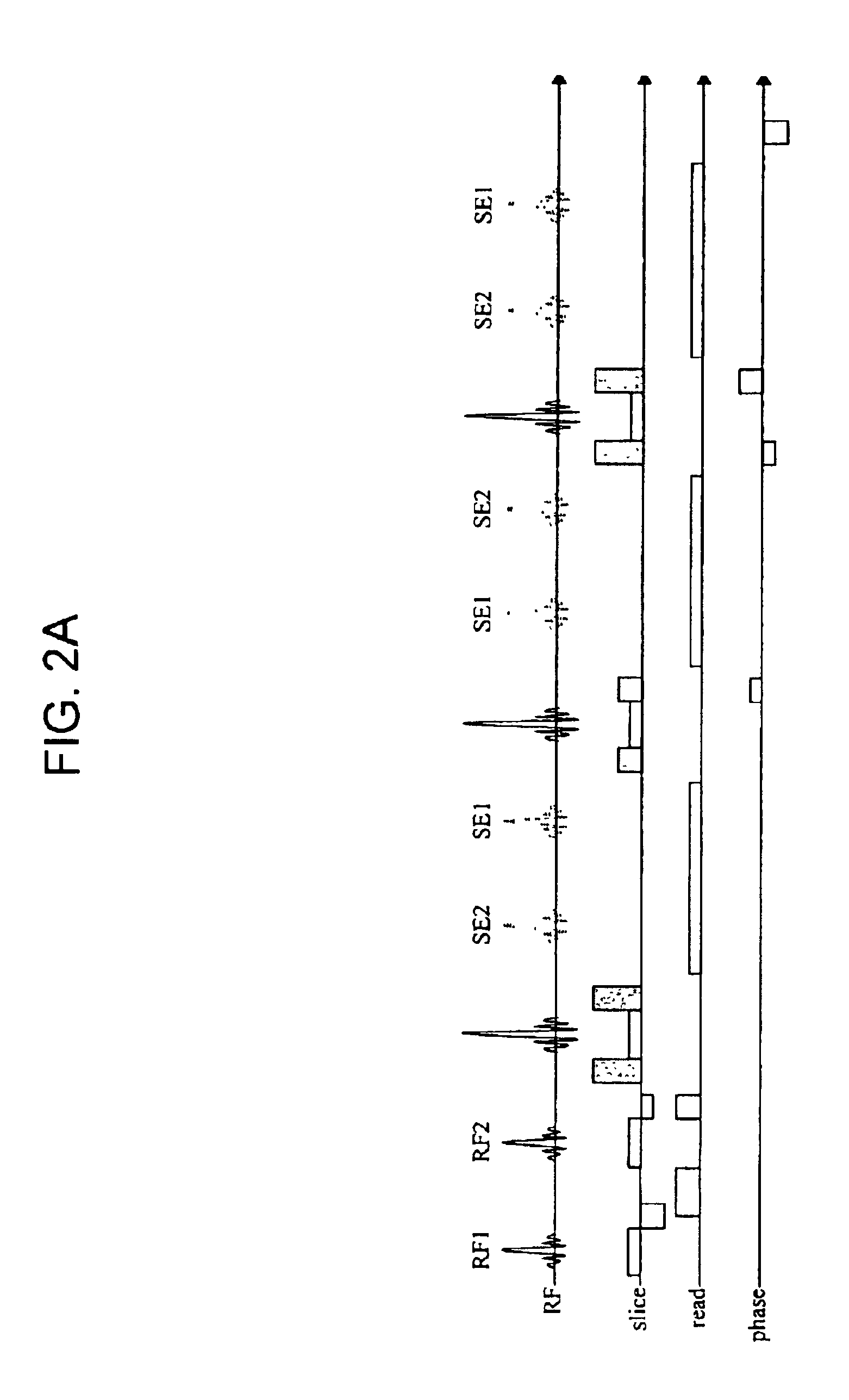
Correcting method for quick-speed spin echo pulse sequence and uses thereof
InactiveCN101162262AResolve ArtifactsEliminate image quality effectsMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringFast spin echoStimulated echo
The invention provides a method for correcting fast spin echo sequence, aiming at solving the problem that the prior FSE images have the factors of an imaging system such as artifacts, magnetic field stability, eddy current, etc. which have impact on the quality of images. The method can be used to correct the parameter of the fast spin echo (FSE) sequence of a magnetic resonance diagnostic, in particular to correct the parameter of the fast spin echo (FSE) sequence of a magnetic resonance diagnostic which can switch frequence of a transmitter and a receiver. The method for correcting fast spin echo sequence of the invention eliminates the impact of the factors of the imaging system such as artifacts, magnetic field stability, eddy current, etc. on the quality of the images; and as the parameter which is obtained by the correcting method and used in the pre-scanning is the optimal parameter, thereby solving the problem of artifacts of the prior FSE images.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
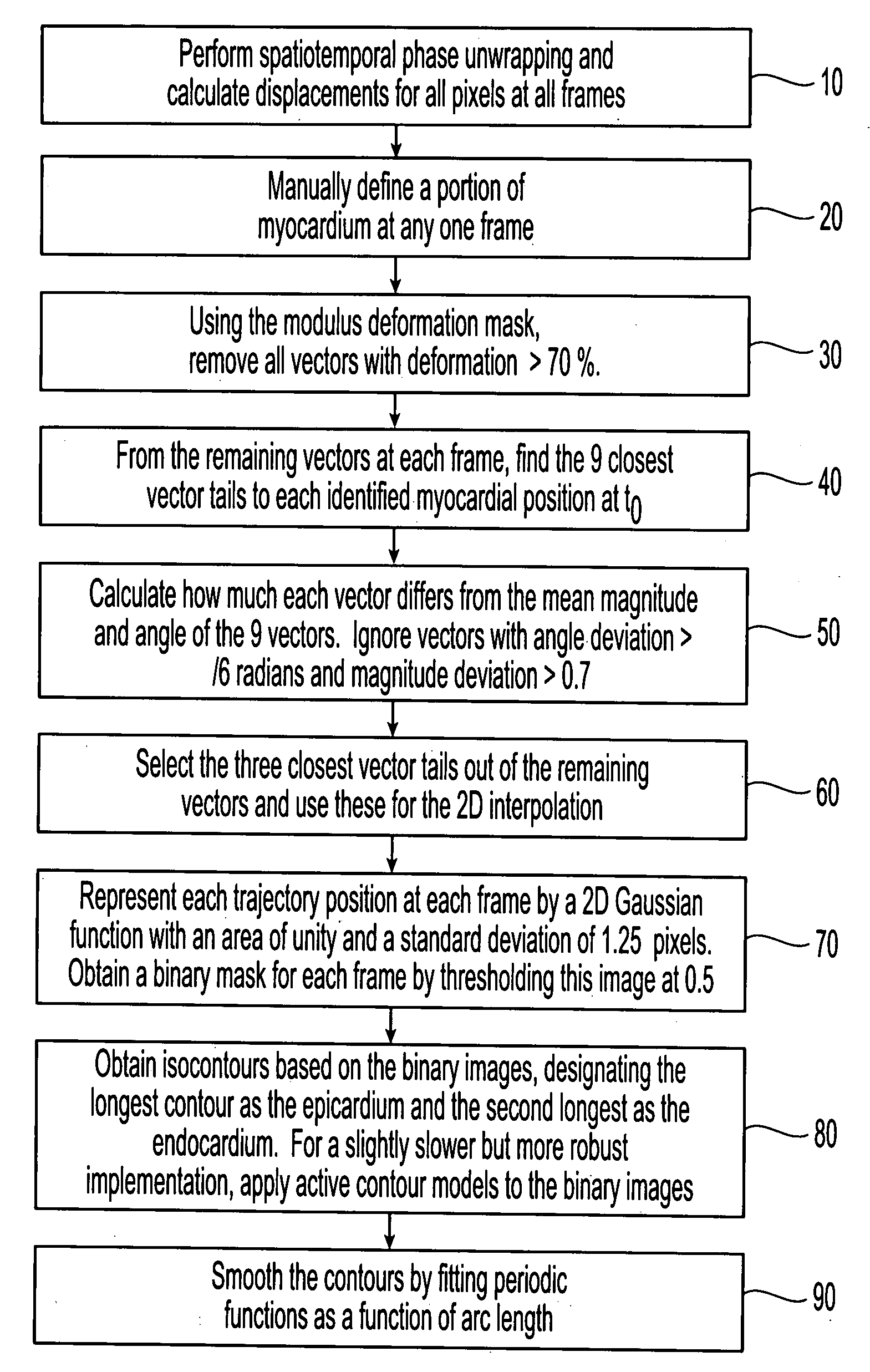
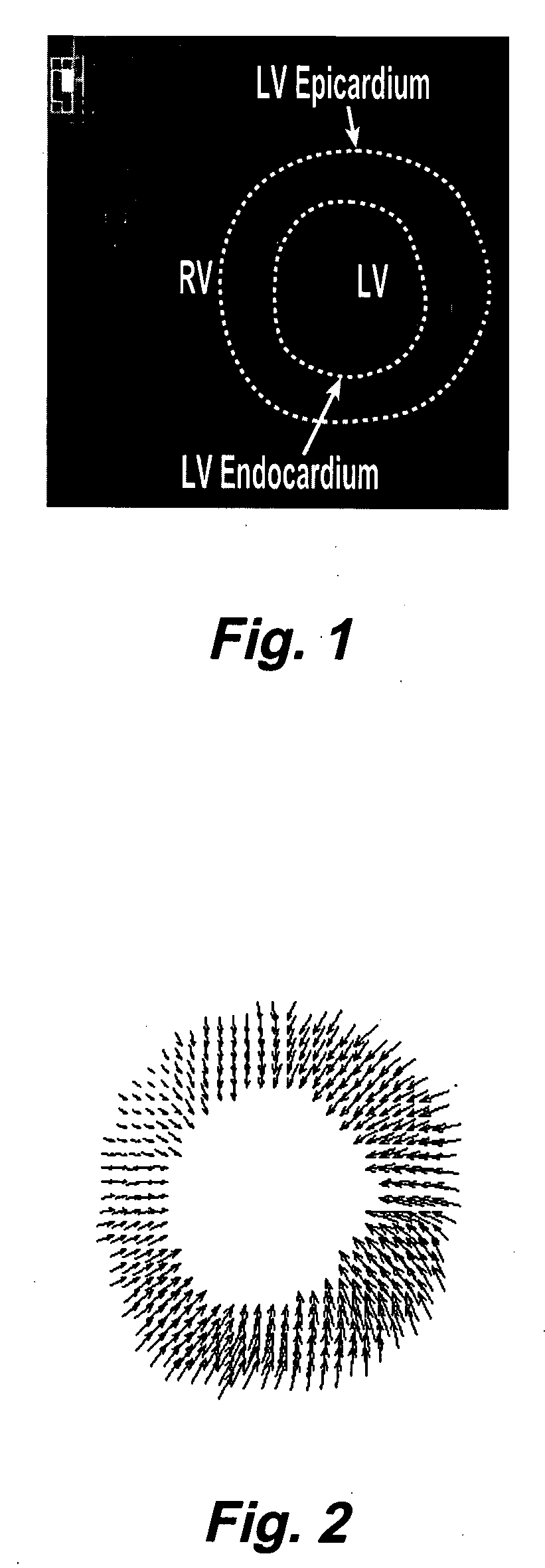
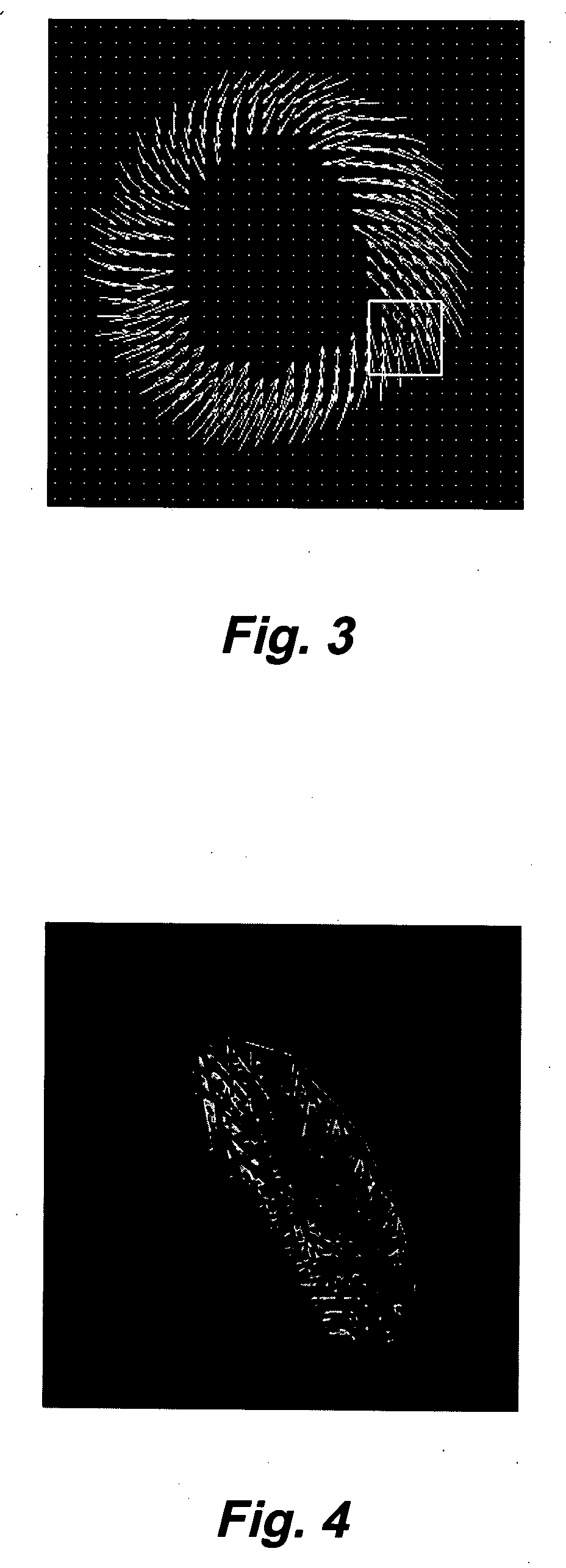
Motion-guided segmentation for cine dense images
Myocardial tissue tracking techniques are used to project or guide a single manually-defined set of myocardial contours through time. Displacement encoding with stimulated echoes (DENSE), harmonic phase (HARP) and speckle tracking is used to encode tissue displacement into the phase of complex MRI images, providing a time series of these images, and facilitating the non-invasive study of myocardial kinematics. Epicardial and endocardial contours need to be defined at each frame on cine DENSE images for the quantification of regional displacement and strain as a function of time. The disclosed method presents a novel and effective two dimensional semi-automated segmentation technique that uses the encoded motion to project a manually defined region of interest through time. Contours can then easily be extracted for each cardiac phase.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND +2
Simultaneous excitation and acquisition of signal from multiple slices in the RARE sequence (multiplex RARE)
InactiveUS20100259260A1Improve efficiencyEasy to useMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionStimulated echoSelective excitation
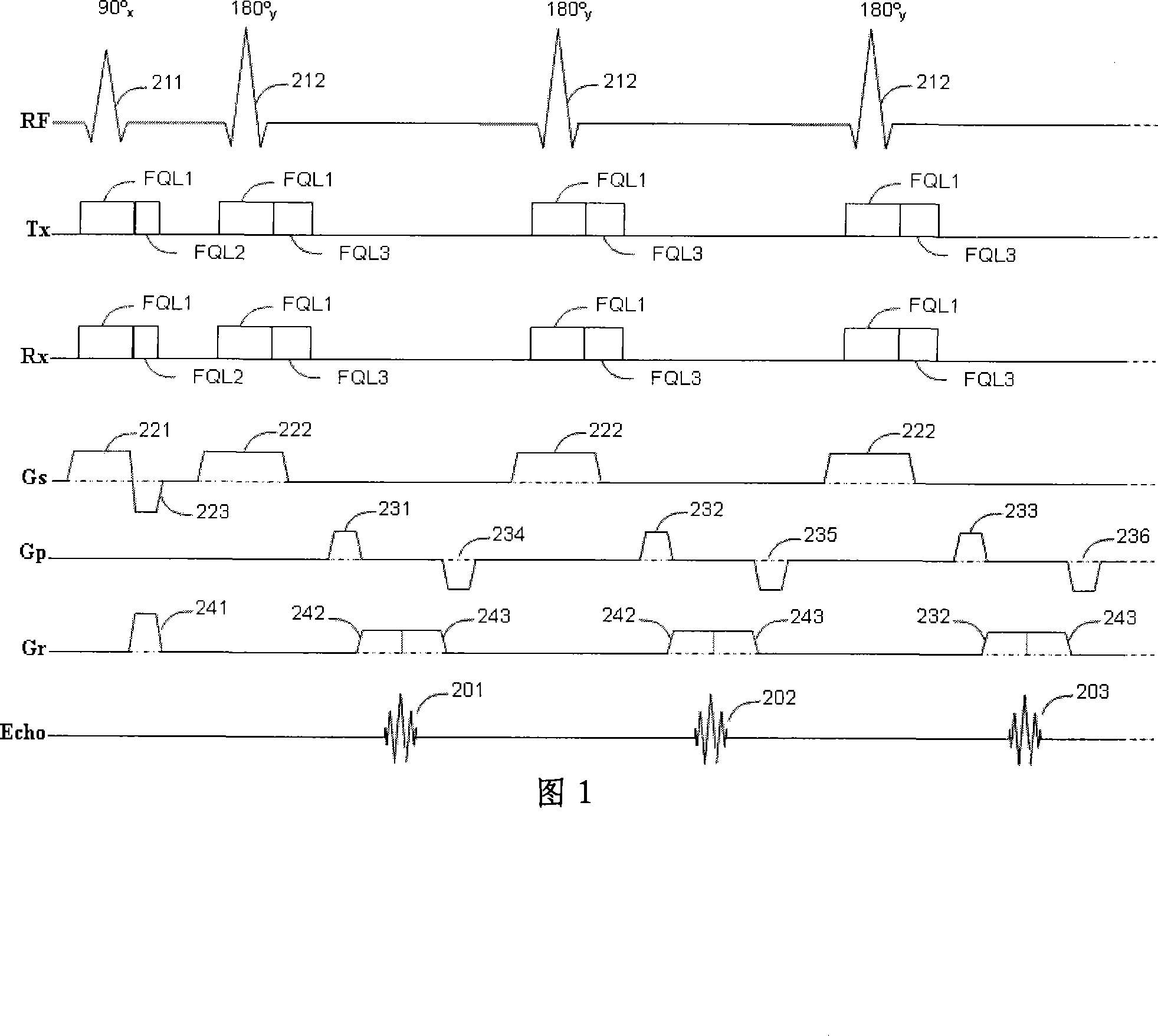
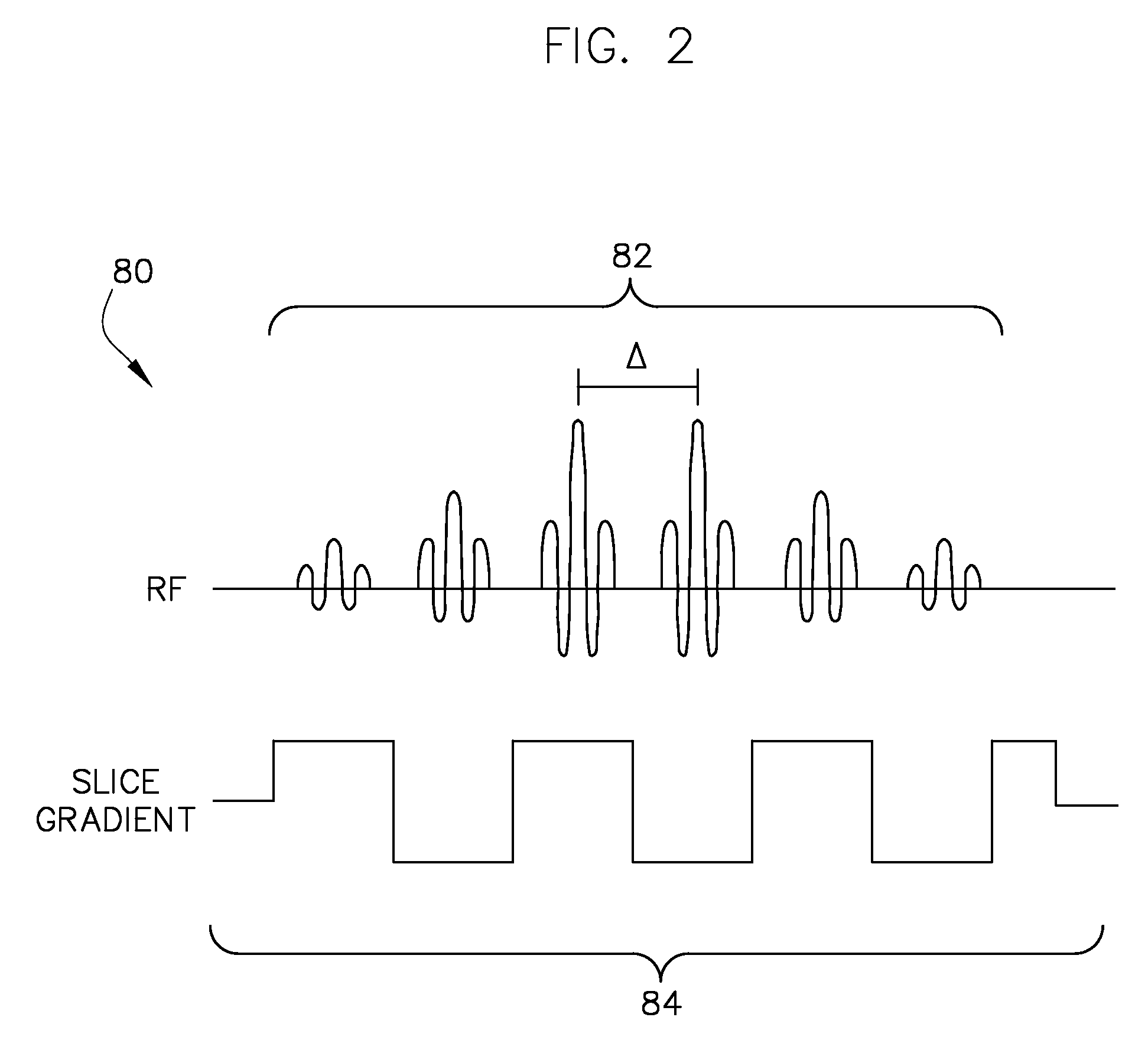
A method for RARE magnetic resonance imaging comprising slice selective excitation of two or more slices and of one or more nuclei, followed by refocusing of these slices and application of gradient pulses which cause a diversion of the signal into spin echoes and stimulated echoes, is characterized by application of refocusing slice selective RF pulses, which are placed to fulfill the echo-spacing CPMG condition for each slice and by arrangement of gradient pulses which cause the phase accumulated by spins in each slice between two consecutive refocusing RF pulses corresponding to that slice to be equal, thus fulfilling the CPMG phase accumulation condition. Thereby, the obtainable signal can be increased and stabilized.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
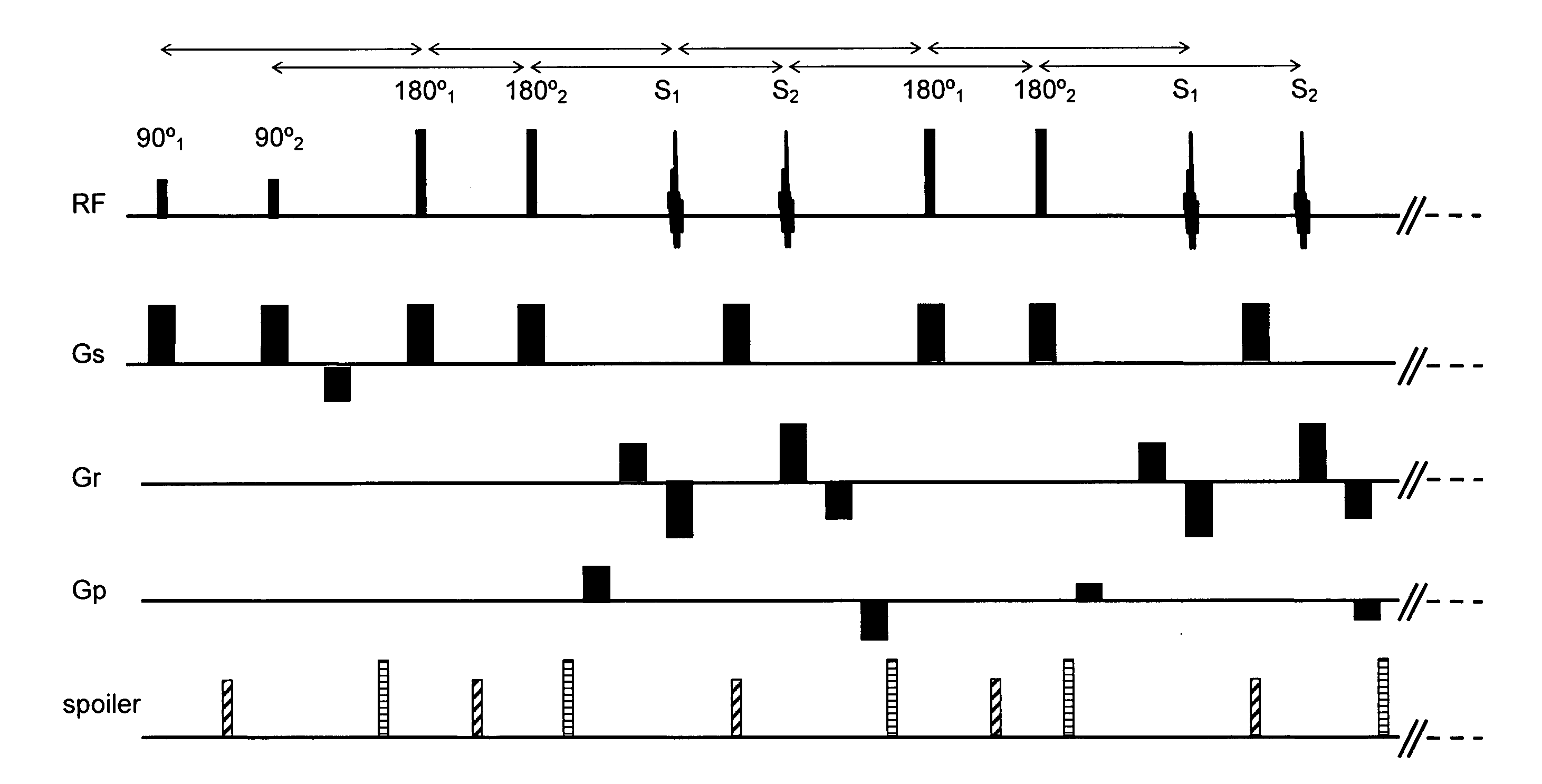
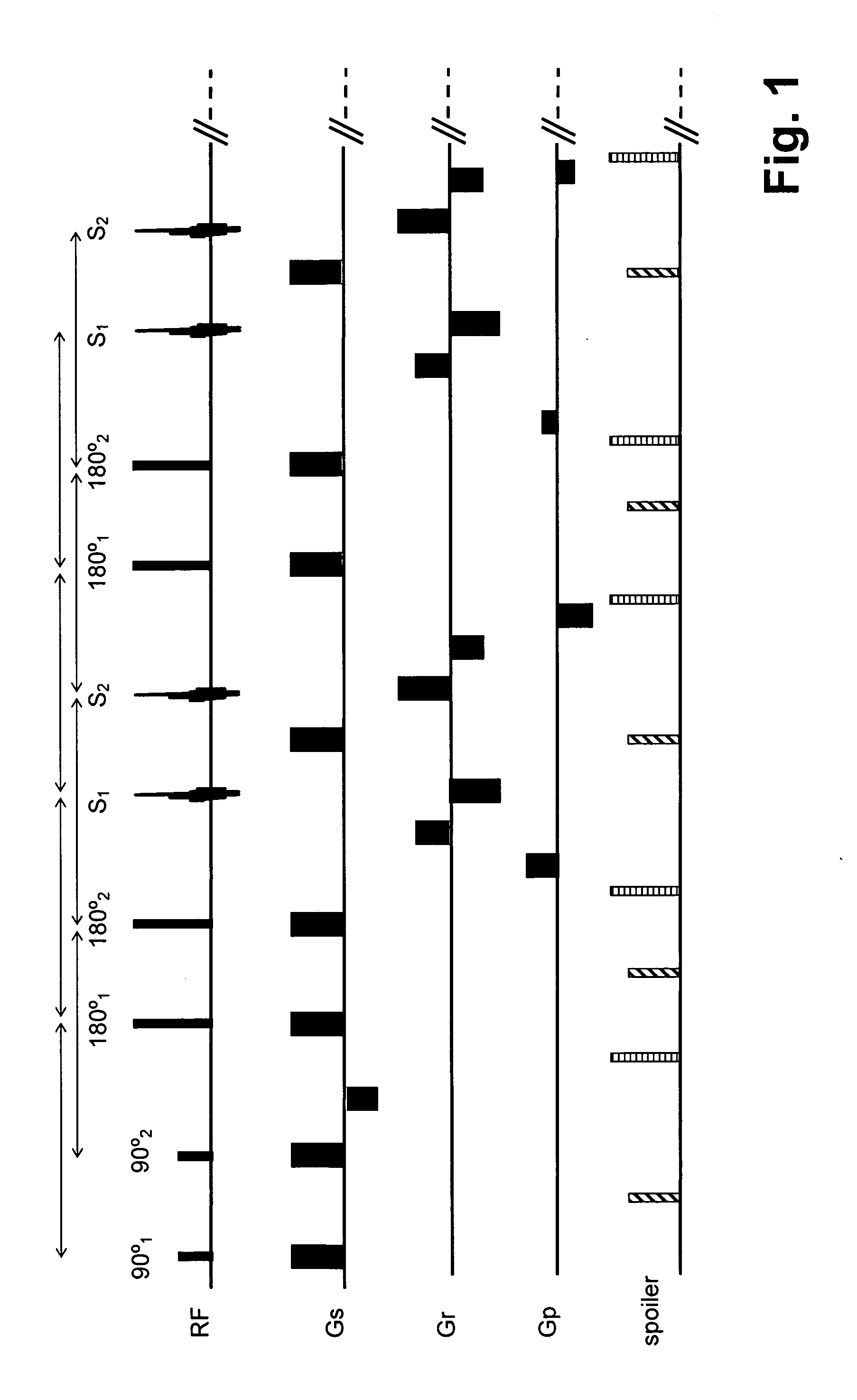
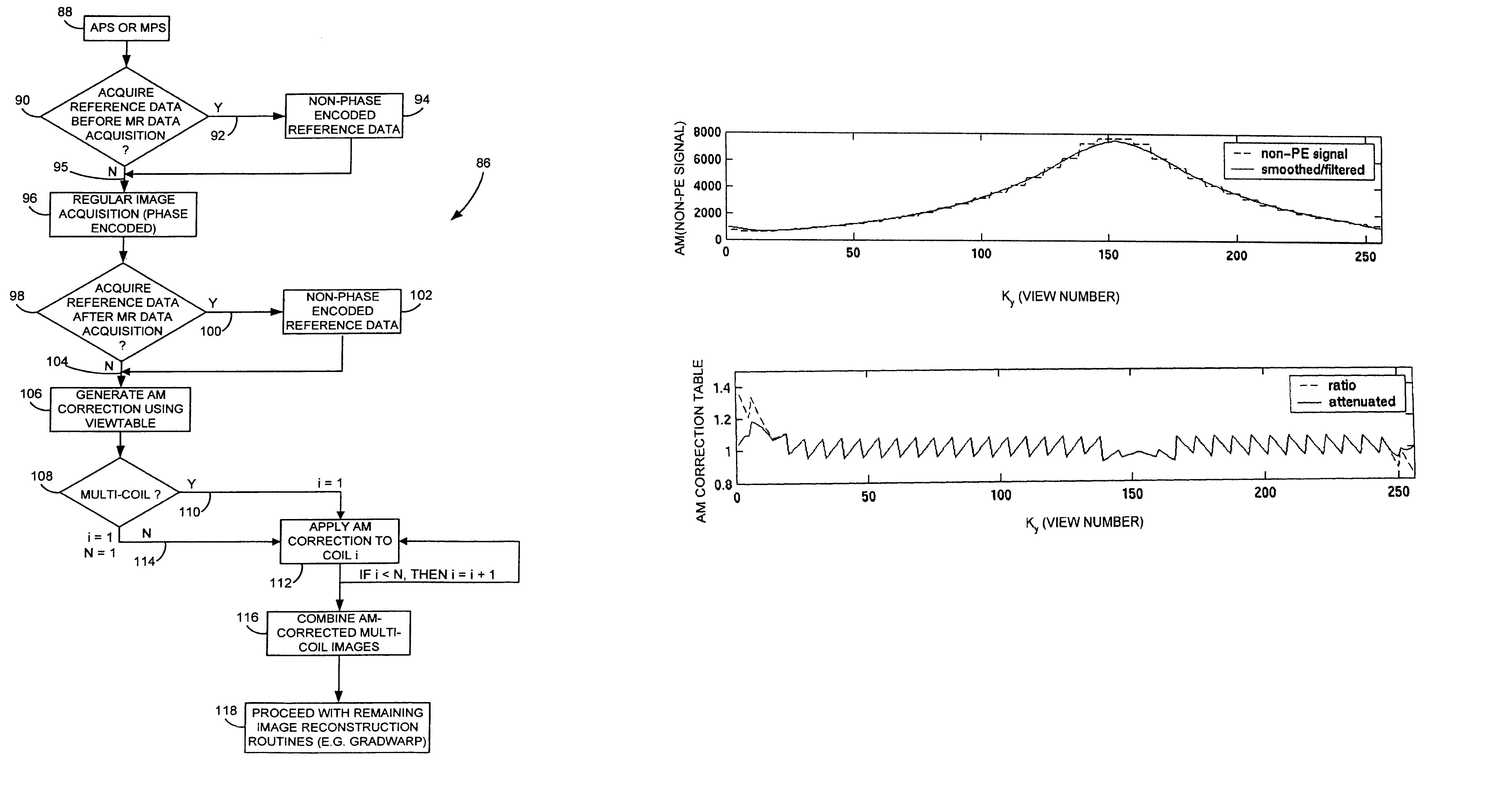
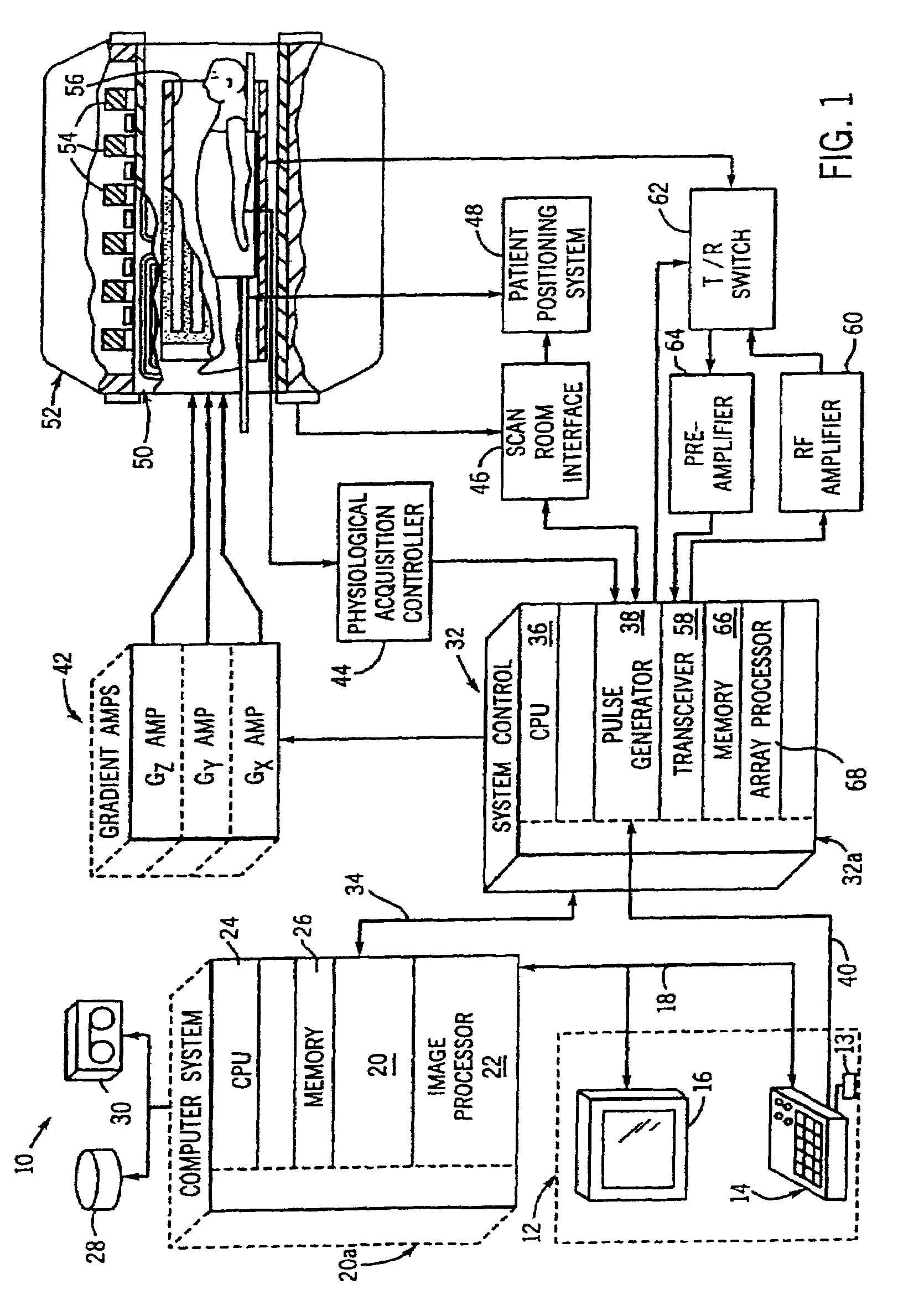
Method and apparatus to correct amplitude modulation in multi-echo magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveUS7075299B1Reduce ghostingImprove image qualityElectrocardiographyMagnetic measurementsStimulated echoImaging quality
An imaging technique is disclosed for multi-echo, magnetic resonance imaging that addresses amplitude modulations, such as those caused by T2 decay and stimulated echo refocusing, in acquired MR data. Acquired MR data is corrected by non-phase encoded data such that amplitude modulations in the echo signal are addressed. Reducing the effects of amplitude modulations in the echo signal reduces ghosting and thereby improves image quality.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Method and apparatus for removing specific stimulated echoes in simultaneous image refocusing
InactiveUS6853188B2Increase spacingReduce penetrationMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionStimulated echoSpins
Owner:ADVANCED MRI TECH
System and method for tissue specific MR imaging of metabolites using spectral-spatially formed stimulated echo
A system for magnetic resonance (MR) spectroscopy includes a plurality of gradient coils positioned about a bore of a magnet and an RF coil assembly coupled to a pulse generator to emit RF pulse sequences and arranged to receive resulting MR signals from a subject of interest. A system control is also included in the MR spectroscopy system and is coupled to the plurality of gradient coils and the RF coil assembly. The system control is programmed to cause the RF coil assembly to emit a first RF pulse and a second RF pulse, wherein at least one of the first and second RF pulses is spectrally selective and at least one of the first and second RF pulses is spatially selective. The system control is also programmed to cause the RF coil assembly to emit a third RF pulse after a pre-defined time delay to generate a stimulated echo and detect MR signals resulting from the stimulated echo.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Magnetic resonance system and imaging method thereof
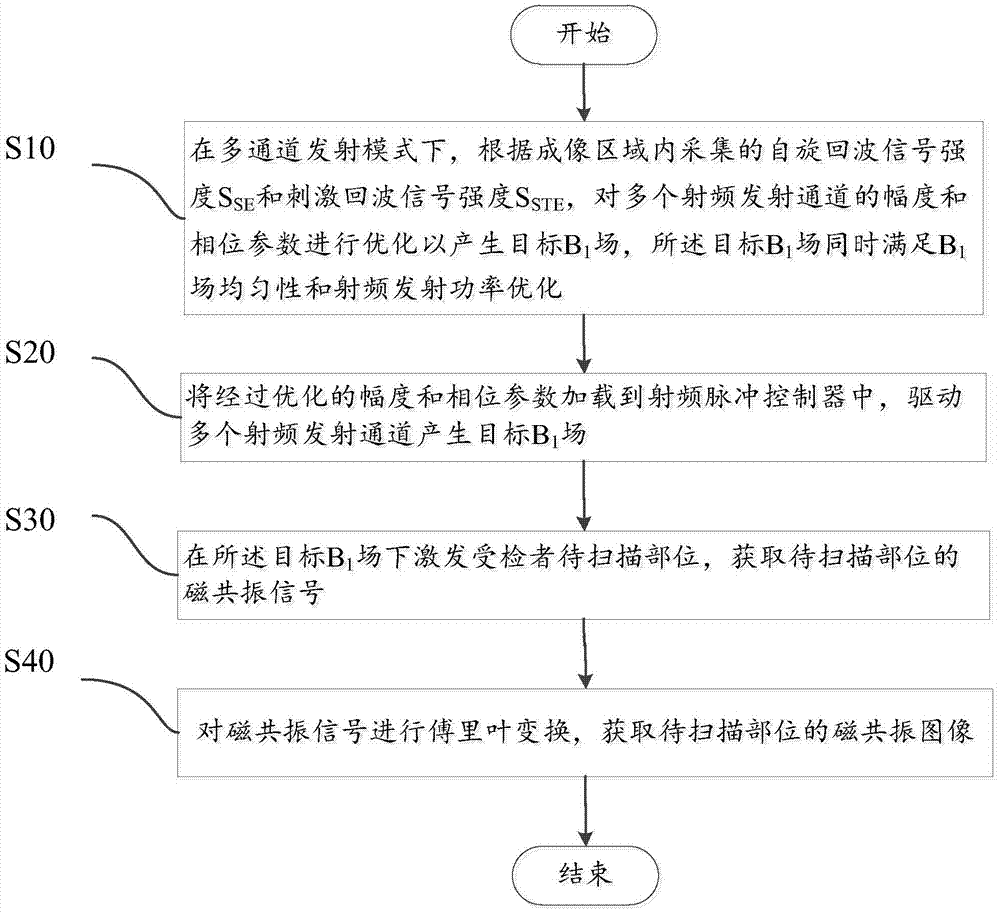
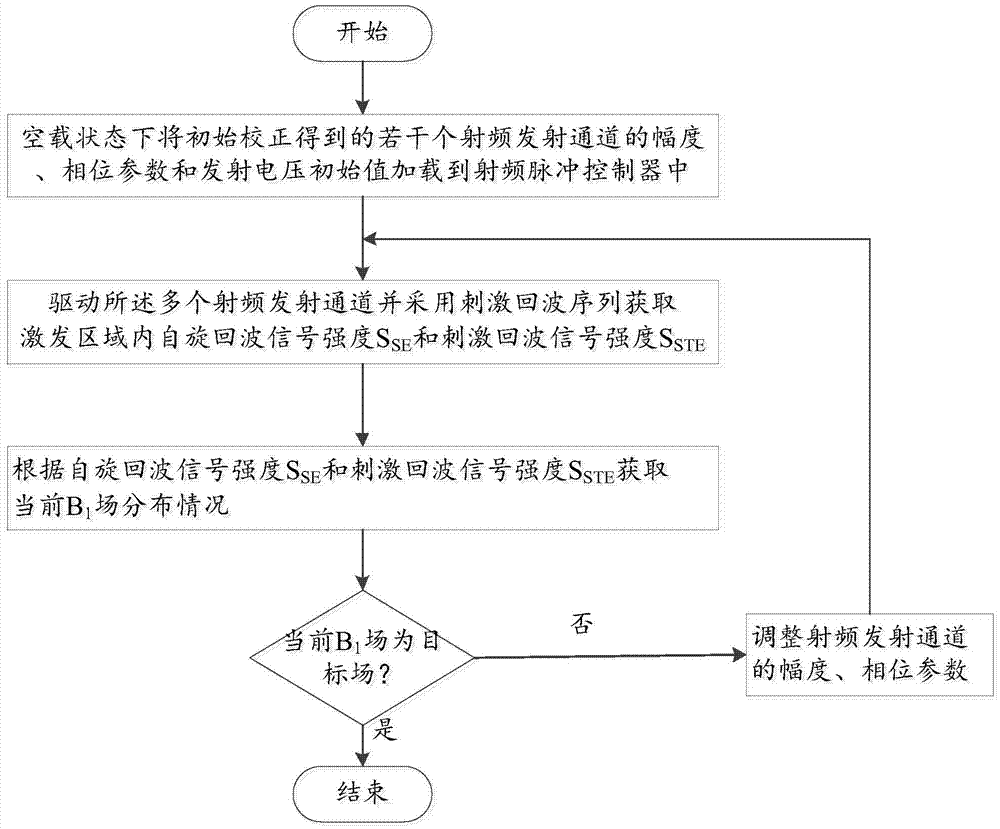
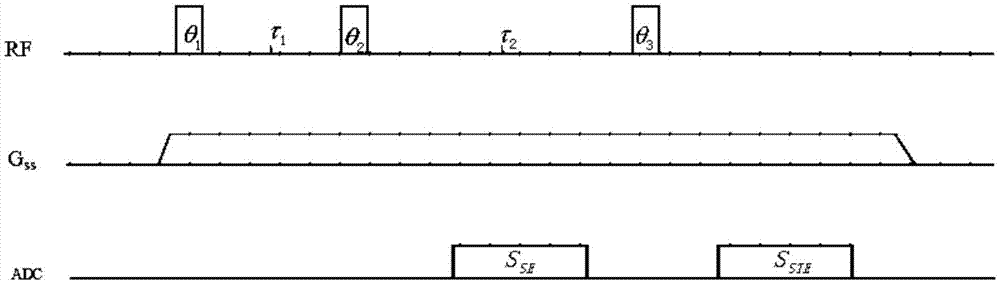
The invention discloses a magnetic resonance system imaging method, which comprises the following steps: under a multichannel emission mode, according to spin echo signal intensity SSE and stimulated echo signal intensity SSTE, carrying out optimization on amplitude and phase parameters of a plurality of radio frequency emission channels to generate a target B1 field, wherein the target B1 field meets B1 field uniformity and radio frequency emission power optimization simultaneously; loading the optimized amplitude and phase parameters to a radio frequency pulse controller, and driving the plurality of radio frequency emission channels to generate the target B1 field; under the target B1 field, exciting a part to be scanned of a subject to obtain a magnetic resonance signal of the part to be scanned; and carrying out Fourier transform on the magnetic resonance signal to obtain a magnetic resonance image of the part to be scanned. The spin echo signal intensity and the stimulated echo signal intensity are collected to reflect distribution of the B1 field; and fast correction can be carried out to obtain a uniform B1 field, and radio frequency emission power can be corrected. The invention also provides a magnetic resonance system.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Method for optimizing radio frequency impulse phases in fast spin echo impulse sequence
ActiveCN103278785AReduce dependencyImprove optimization efficiencyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFast spin echoStimulated echo
The invention provides a method for optimizing radio frequency impulse phases in a fast spin echo impulse sequence. According to the method, a spin echo and an excited echo are separated through the difference of effects of the spin echo and the excited echo according to spoiled gradients so as to ensure that the spin echo coincide with the excited spin echo more accurately; an optimized inversion impulse phase can be acquired through simple calculation according to the phase relation of the spin echo and an inversion impulse and the relation of the excited echo and the inversion impulse. The method for optimizing the radio frequency impulse phases in the fast spin echo impulse sequence can reduce the affect of unsatisfactory factors of instrument hardware on an FSE sequence parameter optimization process and the degree of dependence of the optimal parameter searching process on the phase step precisions, and therefore optimizing efficiency is improved.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV +1
Systems and methods for magnetic resonance imaging
Methods and apparatus for operating an MRI system is provided. The disclosure provides a diffusion-prepared driven-equilibrium preparation for an imaging volume and acquiring 3-dimensional k-space data from said prepared volume by a plurality of echoplanar readouts of stimulated echoes. An excitation radio-frequency signal and first and second inversion RF signals are provided to define a field-of-view (FOV).
Owner:UNIV OF UTAH RES FOUND
Mr imaging with b1 mapping
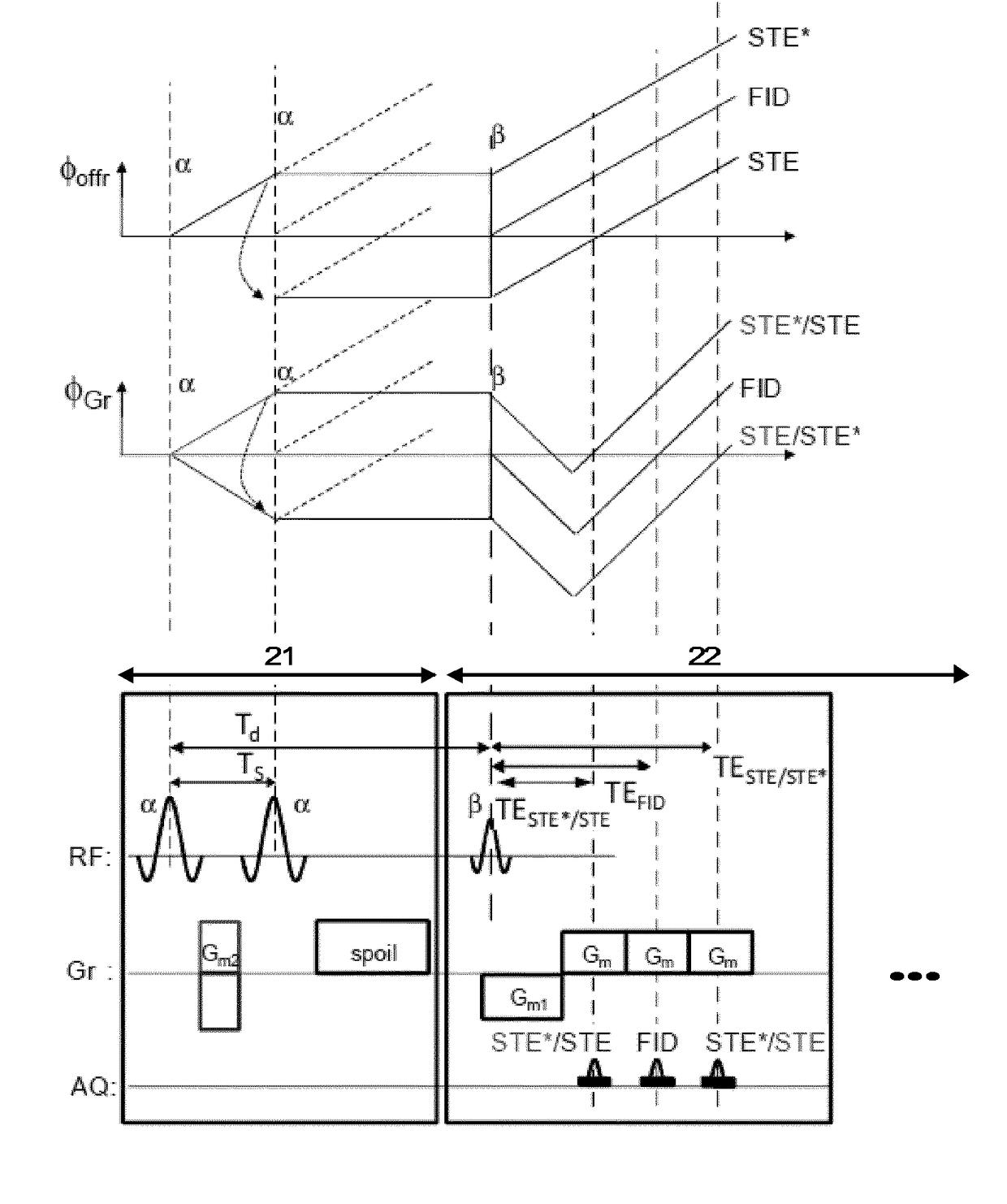
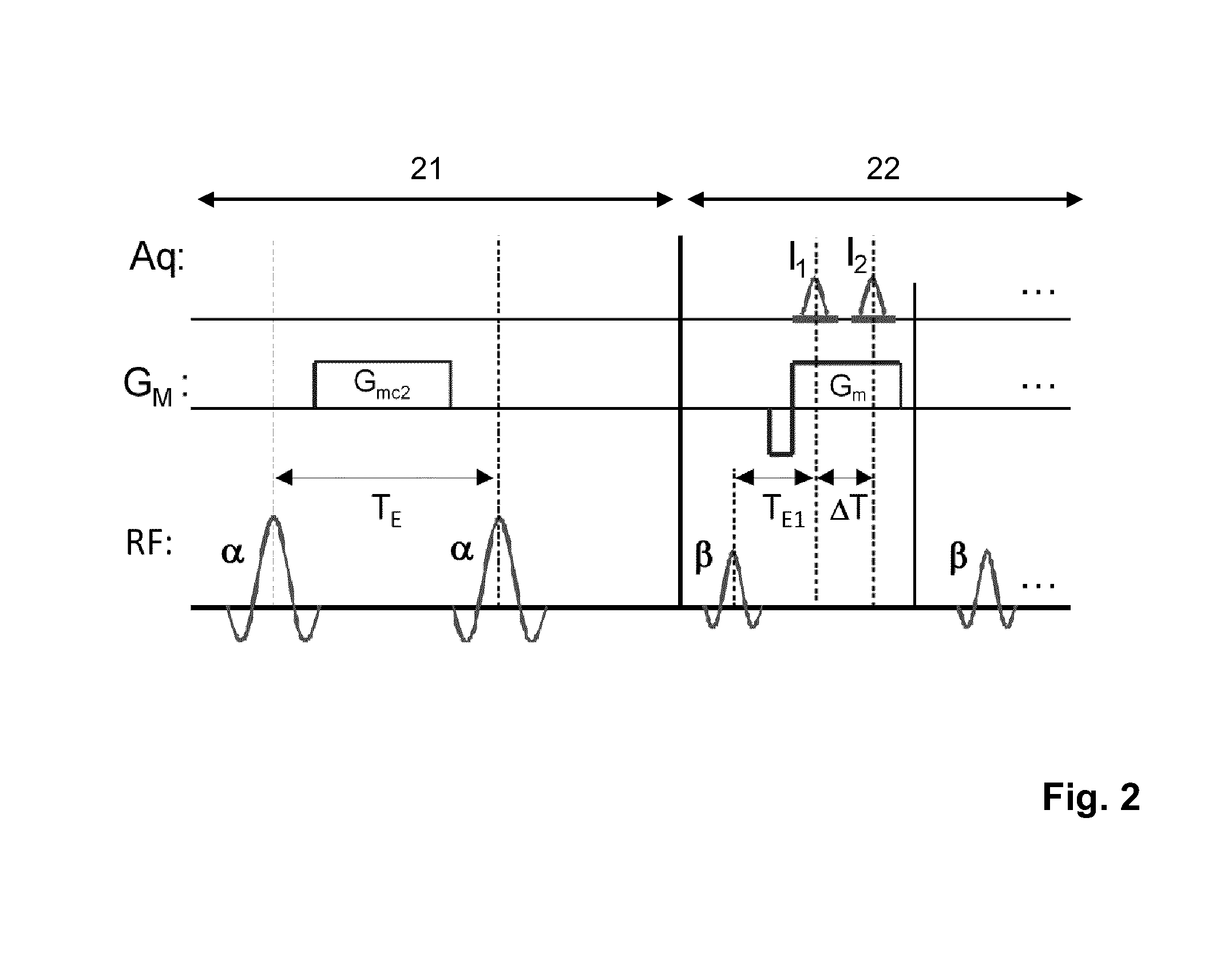
ActiveUS20150042335A1Avoid artifactsFast readoutSensorsBlood flow measurementMagnetic field gradientStimulated echo
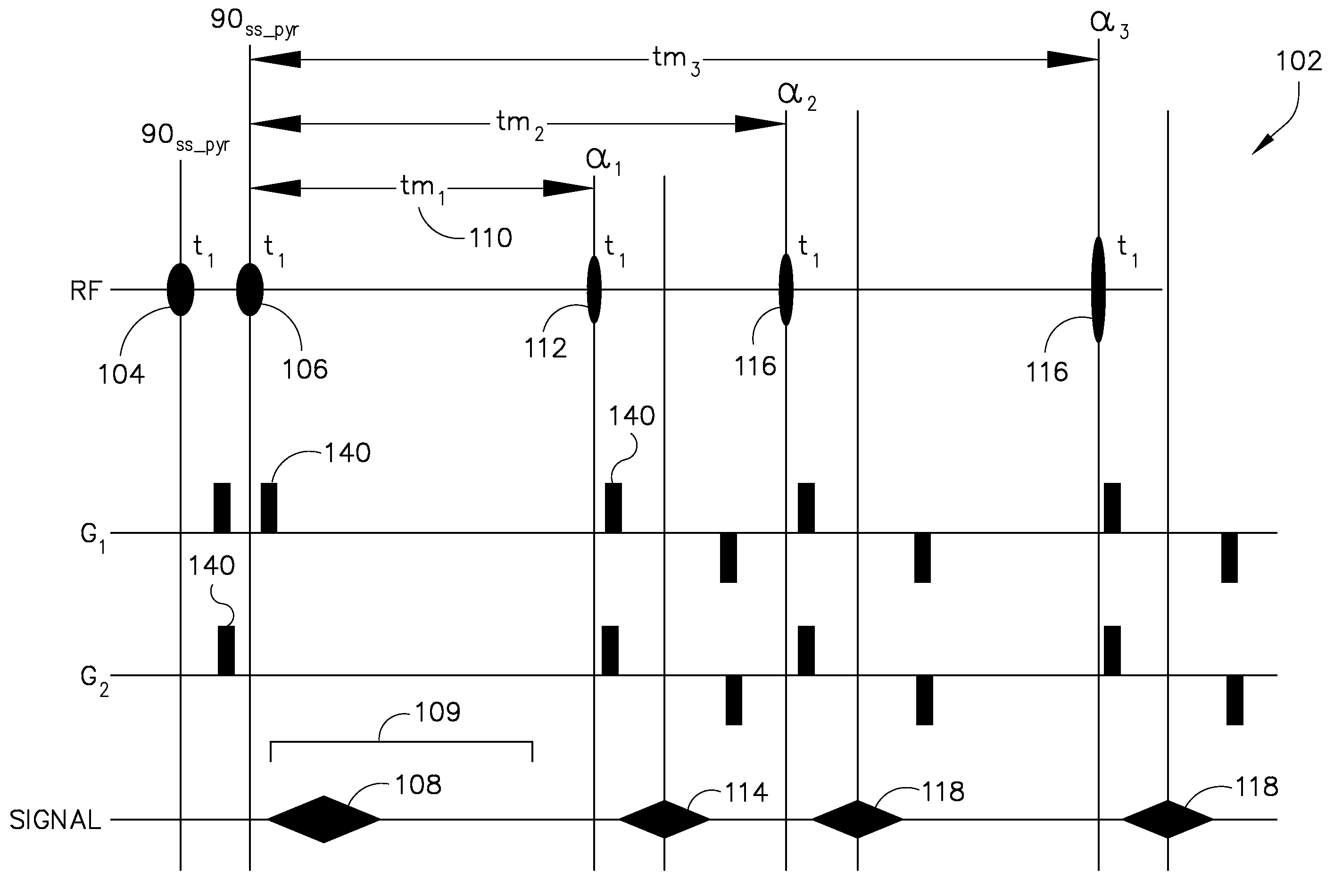
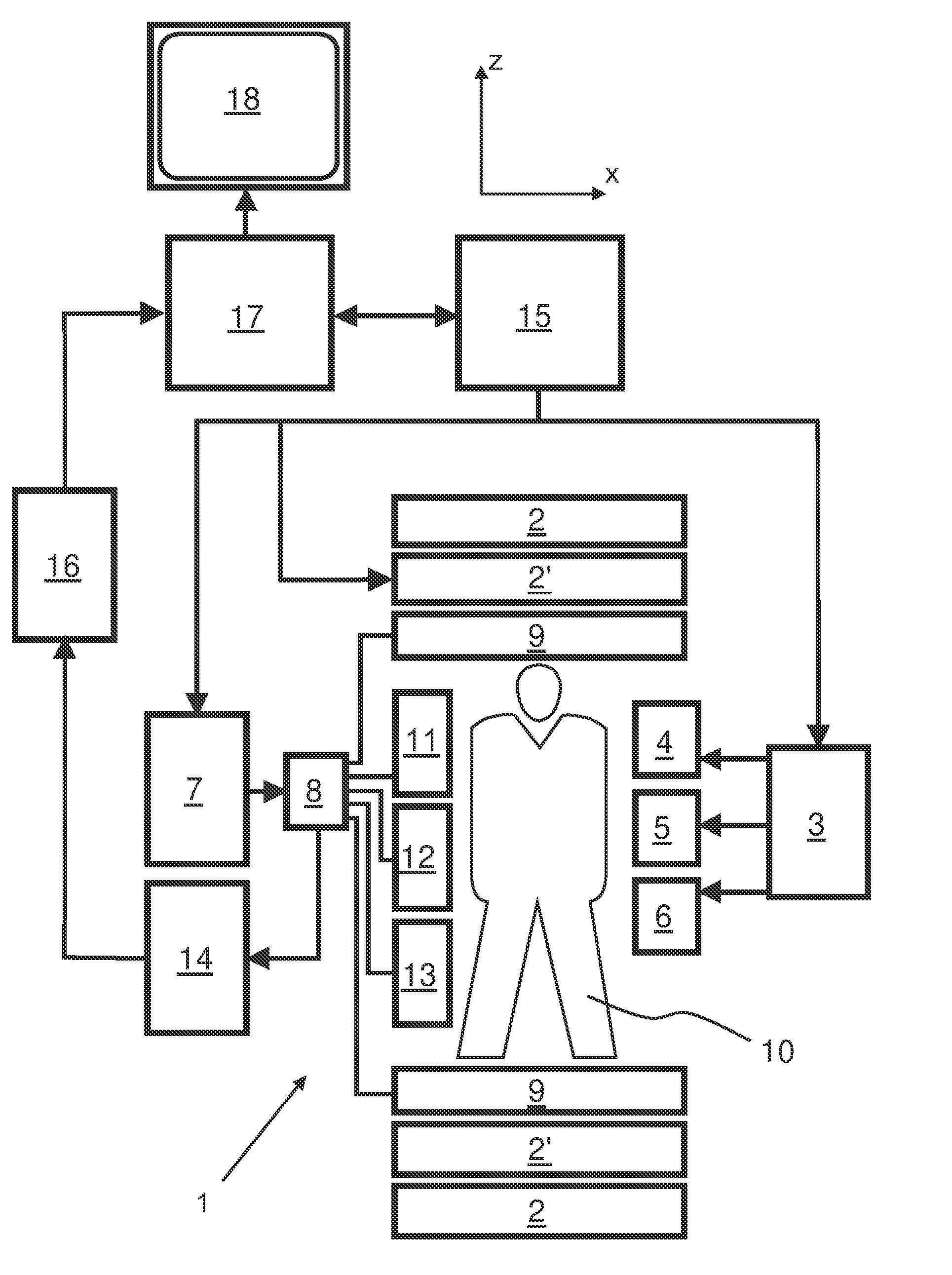
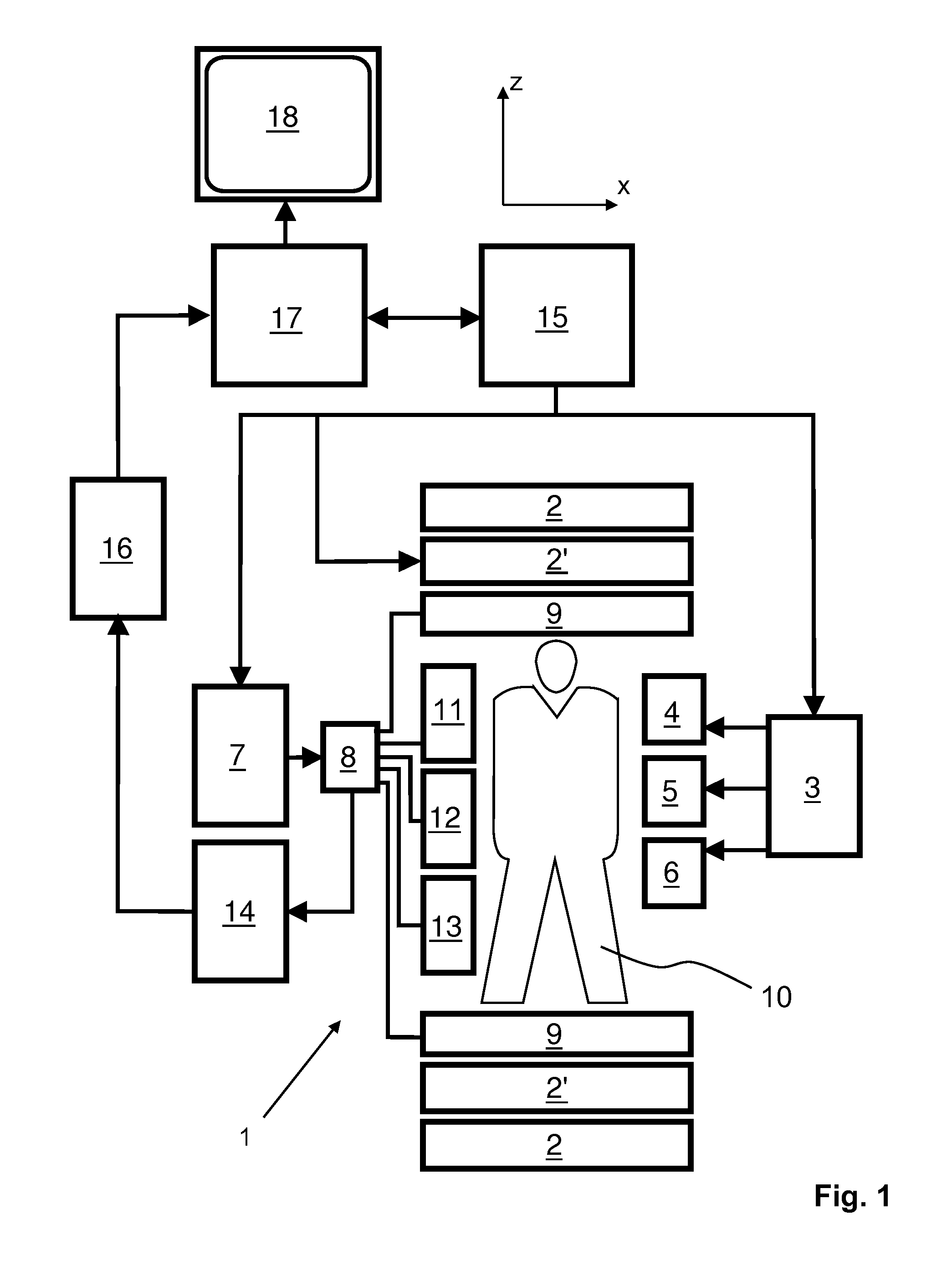
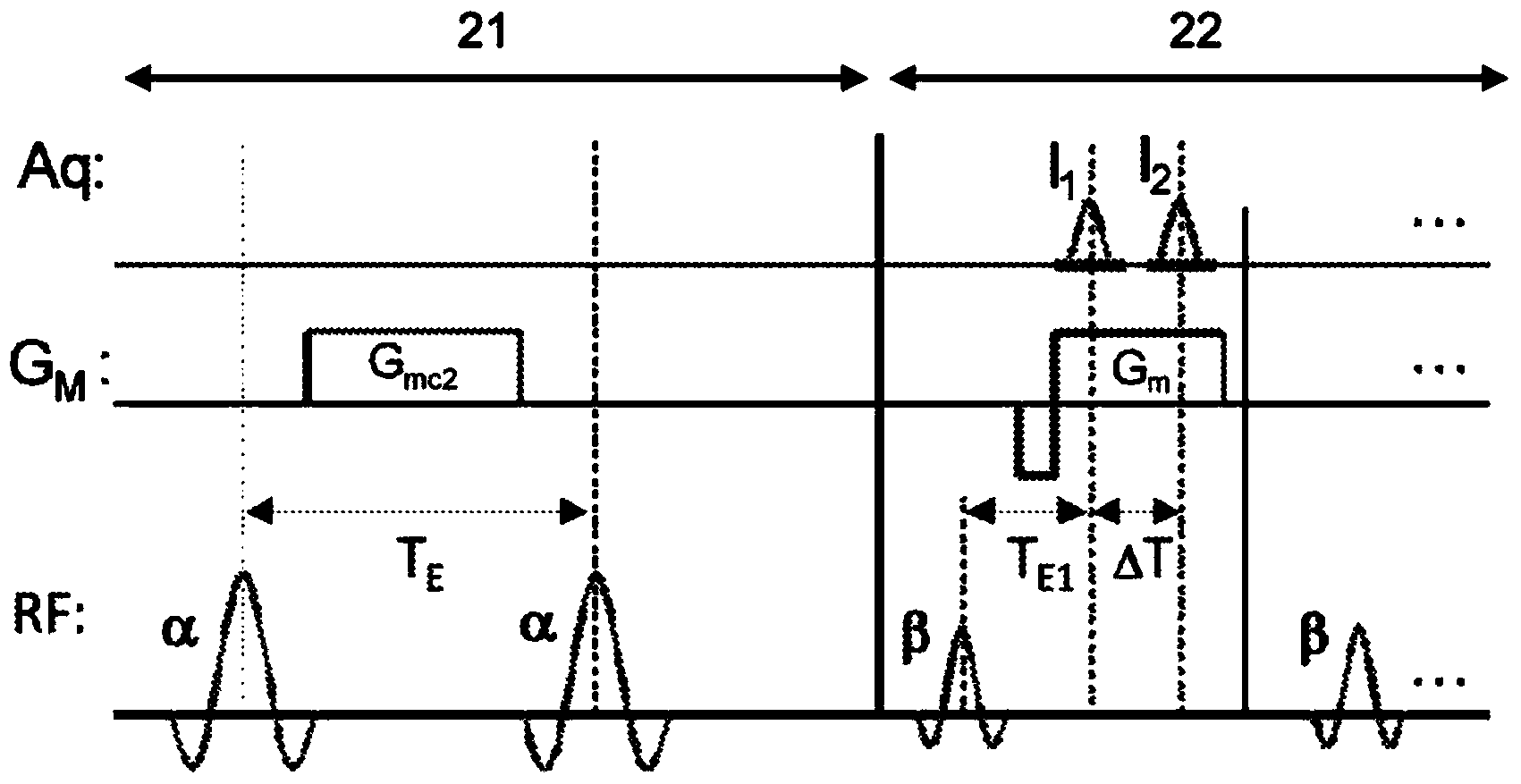
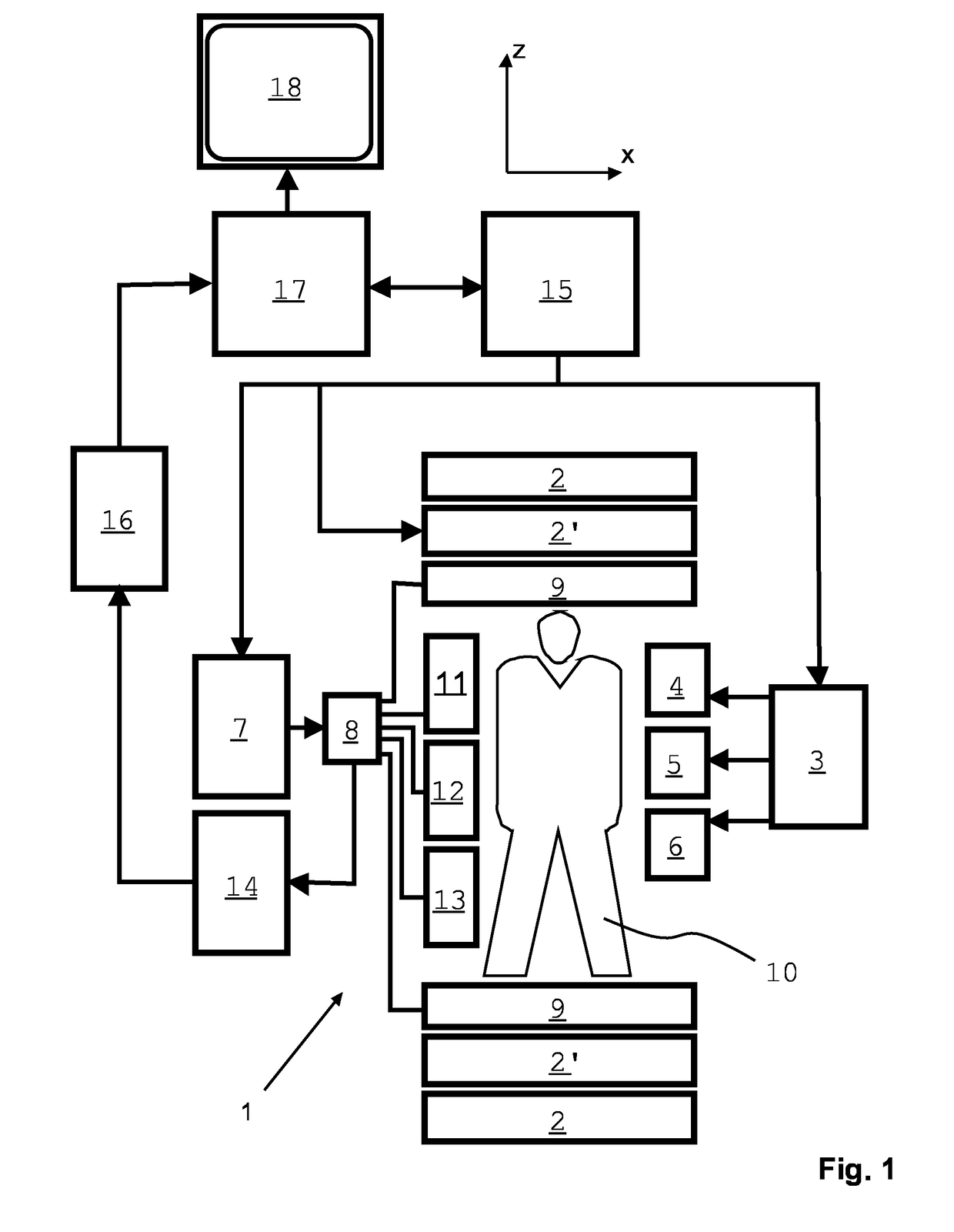
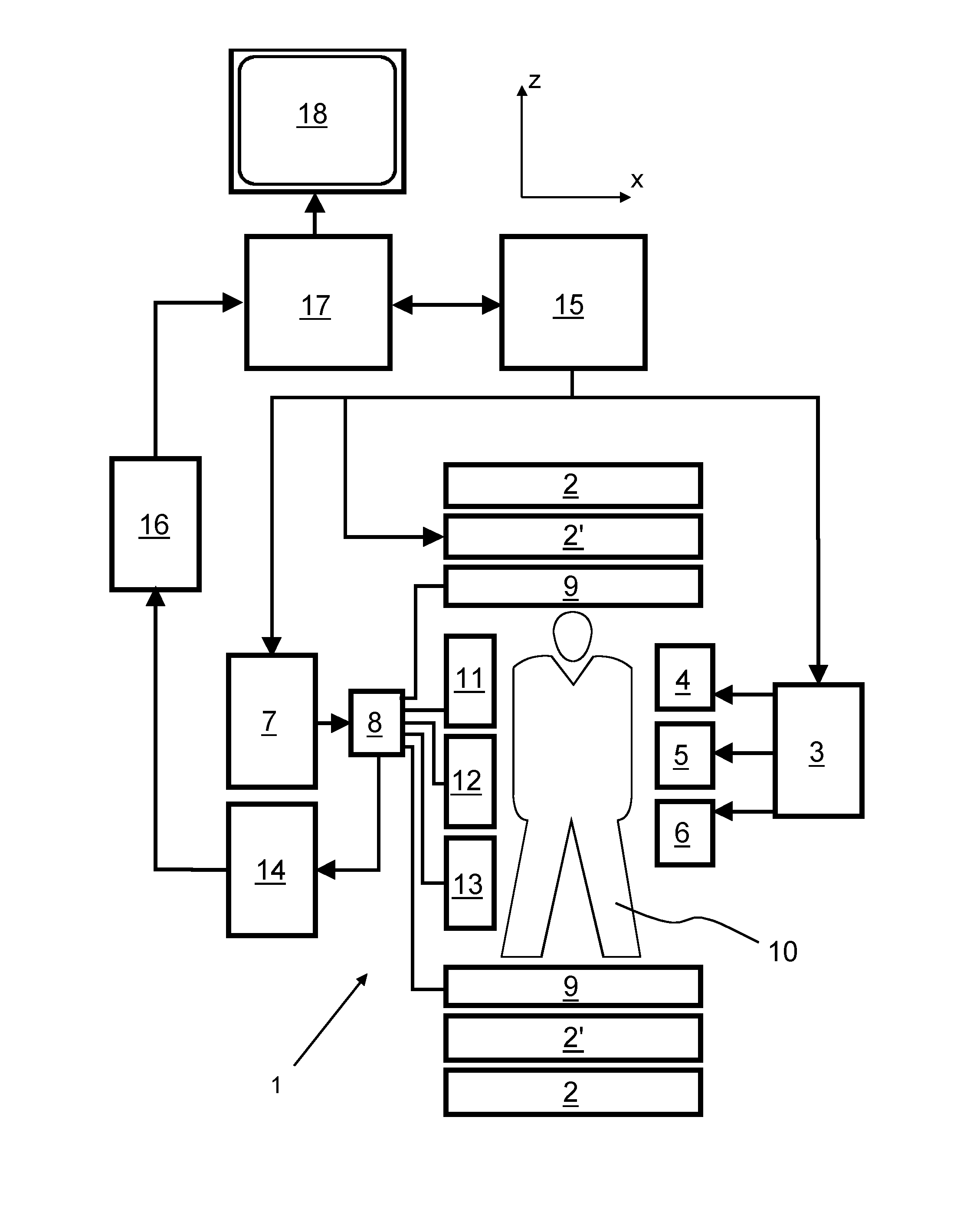
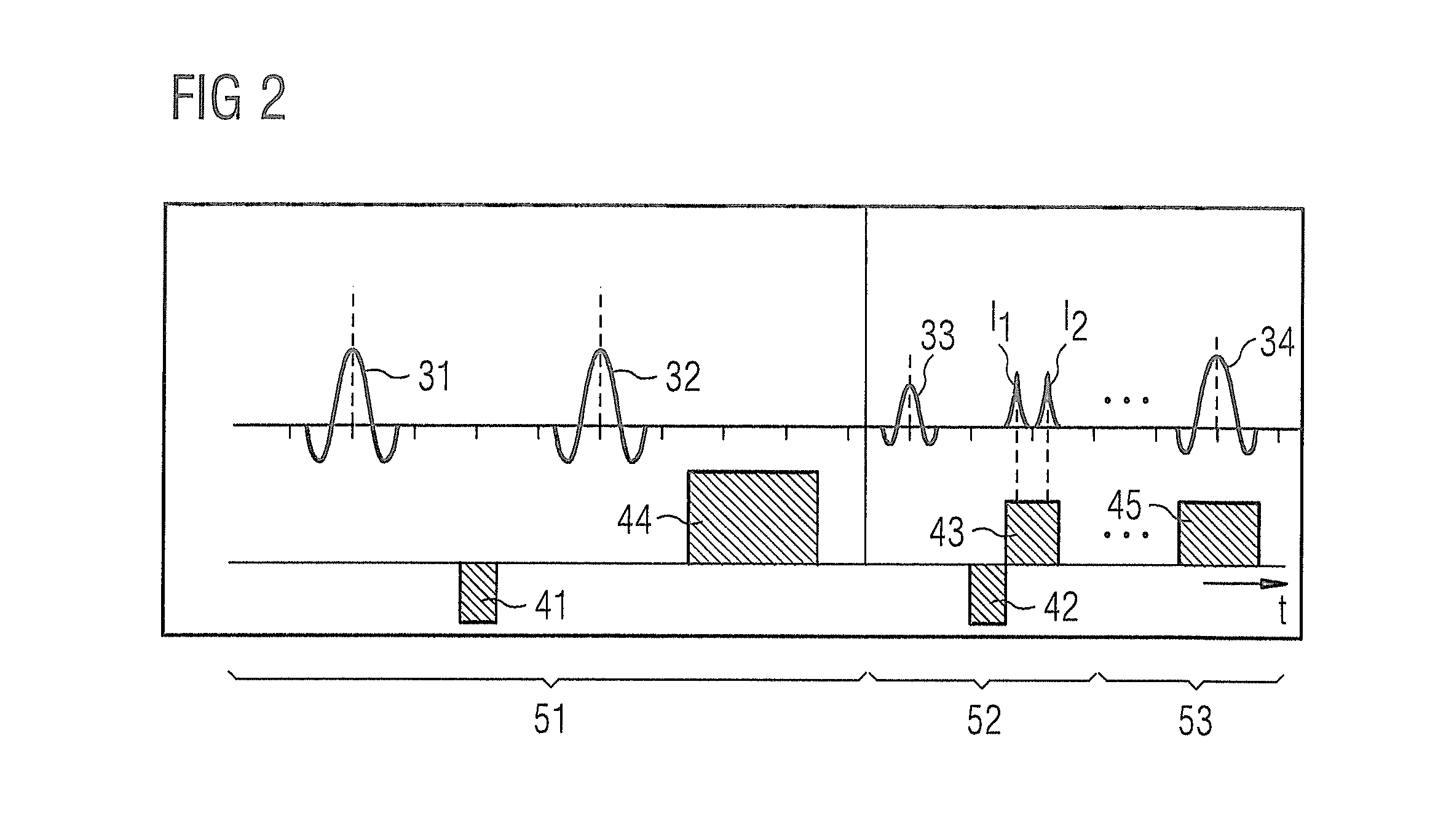
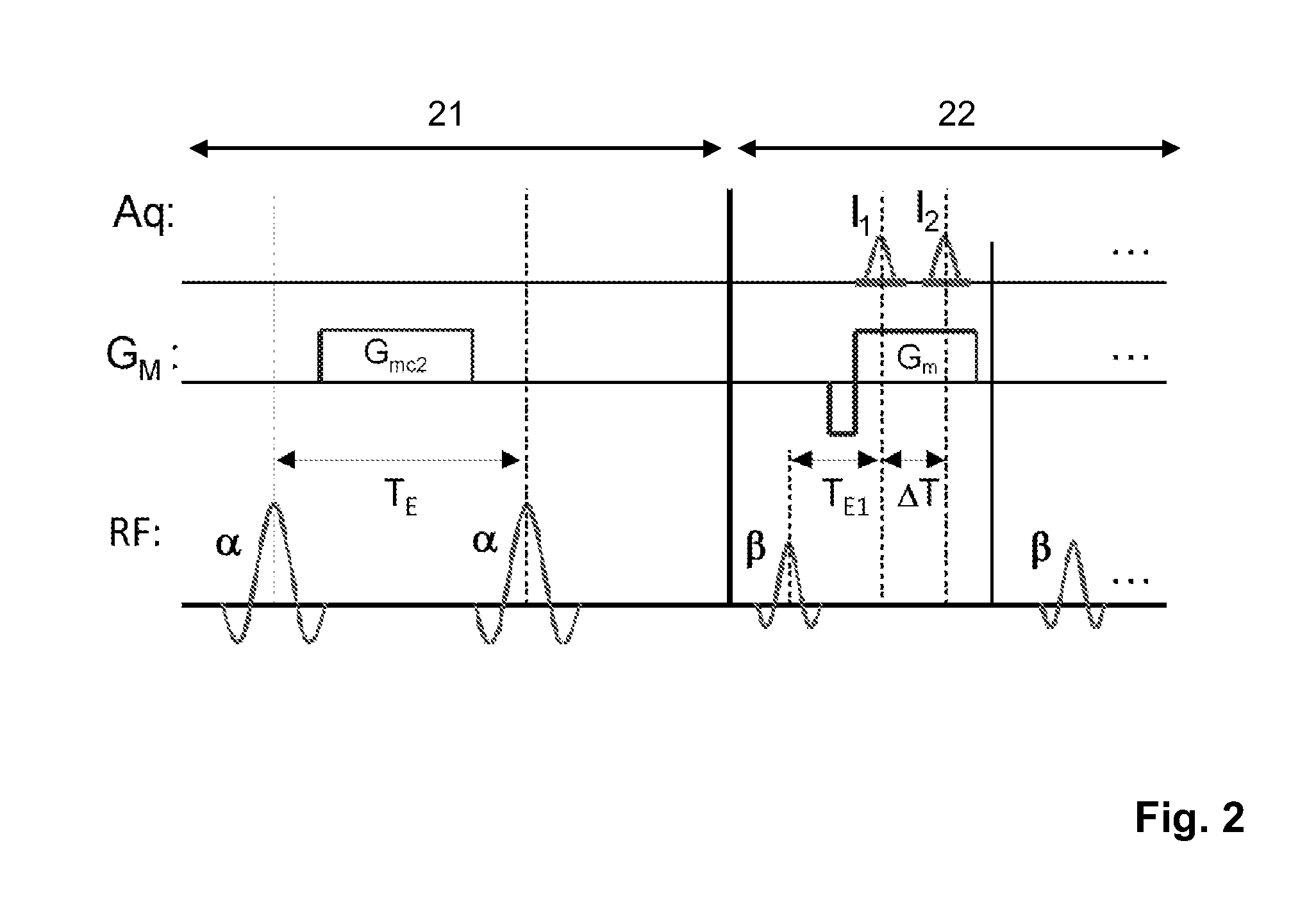
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging, wherein a portion of a body (10) placed in the examination volume of a MR device (1) is subjected to an imaging sequence (IMG) of RF pulses and switched magnetic field gradients. The imaging sequence (IMG) is a stimulated echo sequence including i) at least two preparation RF pulses (α) radiated toward the portion of the body (10) during a preparation period (21), and ii) one or more reading RF pulses (β) radiated toward the portion of the body (10) during an acquisition period (22) temporally subsequent to the preparation period (21). One or more FID signals (I1) and one or more stimulated echo signals (I2) are acquired during the acquisition period (22). A B1 map indicating the spatial distribution of the RF field of the RF pulses within the portion of the body (10) is derived from the acquired FID (I1) and stimulated echo (I2) signals. It is an object of the invention to provide an improved B1 mapping method which can be applied in magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) and, in particular, in cardiac imaging, where the acquisition of a complete B1 map needs to be performed within the diastolic phase of the heartbeat. The invention proposes that the portion of the body (10) is subjected to a suppression sequence (BB) for suppression of MR signals emanating from blood prior to the imaging sequence (IMG). Moreover, the invention relates to a MR device (1) and to a computer program for a MR device (1).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Mr imaging with b1 mapping
InactiveUS20140070805A1Accurate and effective B mapping techniqueIncrease the magnetic field strengthElectric/magnetic detectionMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientStimulated echo
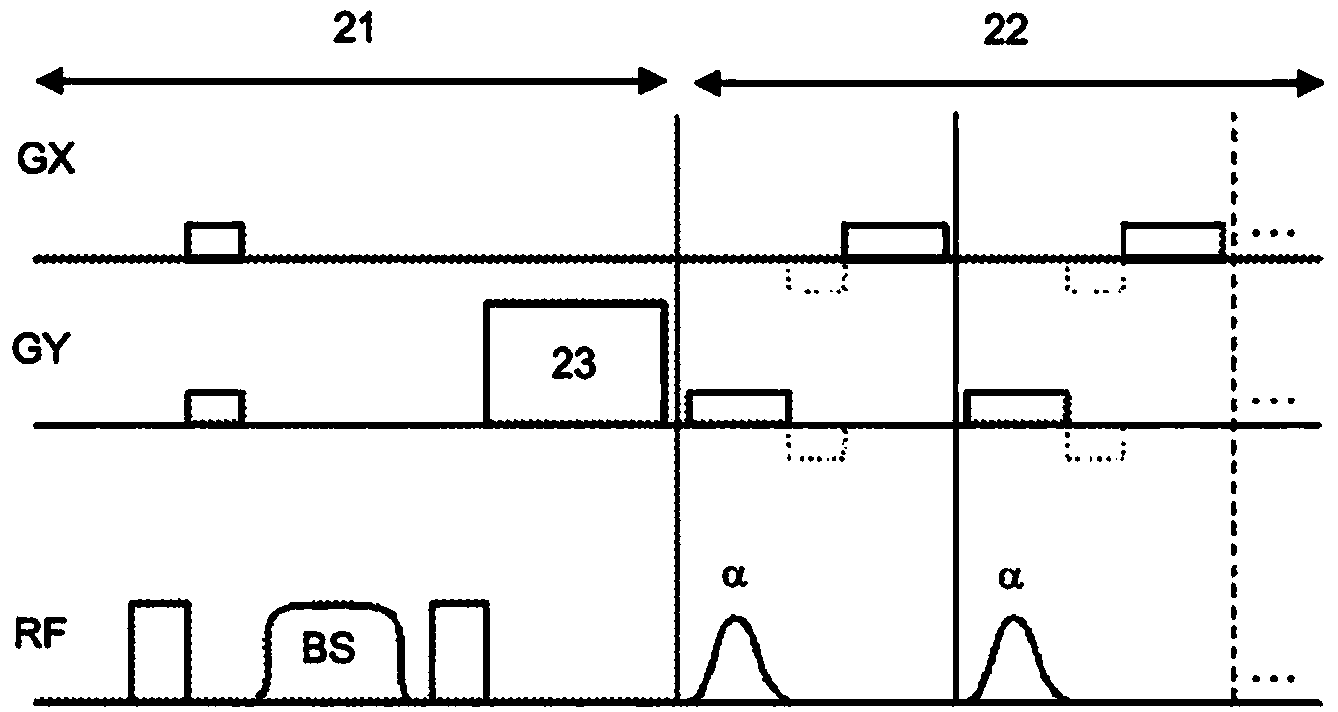
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging, wherein a portion of a body is subjected to an imaging sequence of RF pulses and switched magnetic field gradients, which imaging sequence is a stimulated echo sequence including an off-resonant Bloch-Siegert RF pulse (BS) radiated during a preparation period (21) of the stimulated echo sequence. A B1 map is derived from the acquired stimulated echo MR signals. Moreover, the invention relates to a method of MR imaging, wherein a portion of a body is subjected to a first imaging sequence, which comprises a first composite excitation RF pulse consisting of two RF pulse components having essentially equal flip angles and being out of phase by essentially 90°. Further, the portion of the body is subjected to a second imaging sequence, wherein a B1 map is derived from signal data acquired by means of the first and second imaging sequences.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and method for tissue specific mr imaging of metabolites using spectral-spatially formed stimulated echo
A system for magnetic resonance (MR) spectroscopy includes a plurality of gradient coils positioned about a bore of a magnet and an RF coil assembly coupled to a pulse generator to emit RF pulse sequences and arranged to receive resulting MR signals from a subject of interest. A system control is also included in the MR spectroscopy system and is coupled to the plurality of gradient coils and the RF coil assembly. The system control is programmed to cause the RF coil assembly to emit a first RF pulse and a second RF pulse, wherein at least one of the first and second RF pulses is spectrally selective and at least one of the first and second RF pulses is spatially selective. The system control is also programmed to cause the RF coil assembly to emit a third RF pulse after a pre-defined time delay to generate a stimulated echo and detect MR signals resulting from the stimulated echo.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Mr imaging with b1mapping
InactiveCN103649765AMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsMeasurements using magnetic resonanceMagnetic field gradientStimulated echo
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Motion-guided segmentation for cine DENSE images
Myocardial tissue tracking techniques are used to project or guide a single manually-defined set of myocardial contours through time. Displacement encoding with stimulated echoes (DENSE), harmonic phase (HARP) and speckle tracking is used to encode tissue displacement into the phase of complex MRI images, providing a time series of these images, and facilitating the non-invasive study of myocardial kinematics. Epicardial and endocardial contours need to be defined at each frame on cine DENSE images for the quantification of regional displacement and strain as a function of time. The disclosed method presents a novel and effective two dimensional semi-automated segmentation technique that uses the encoded motion to project a manually defined region of interest through time. Contours can then easily be extracted for each cardiac phase.
Owner:UNIV OF VIRGINIA ALUMNI PATENTS FOUND +2
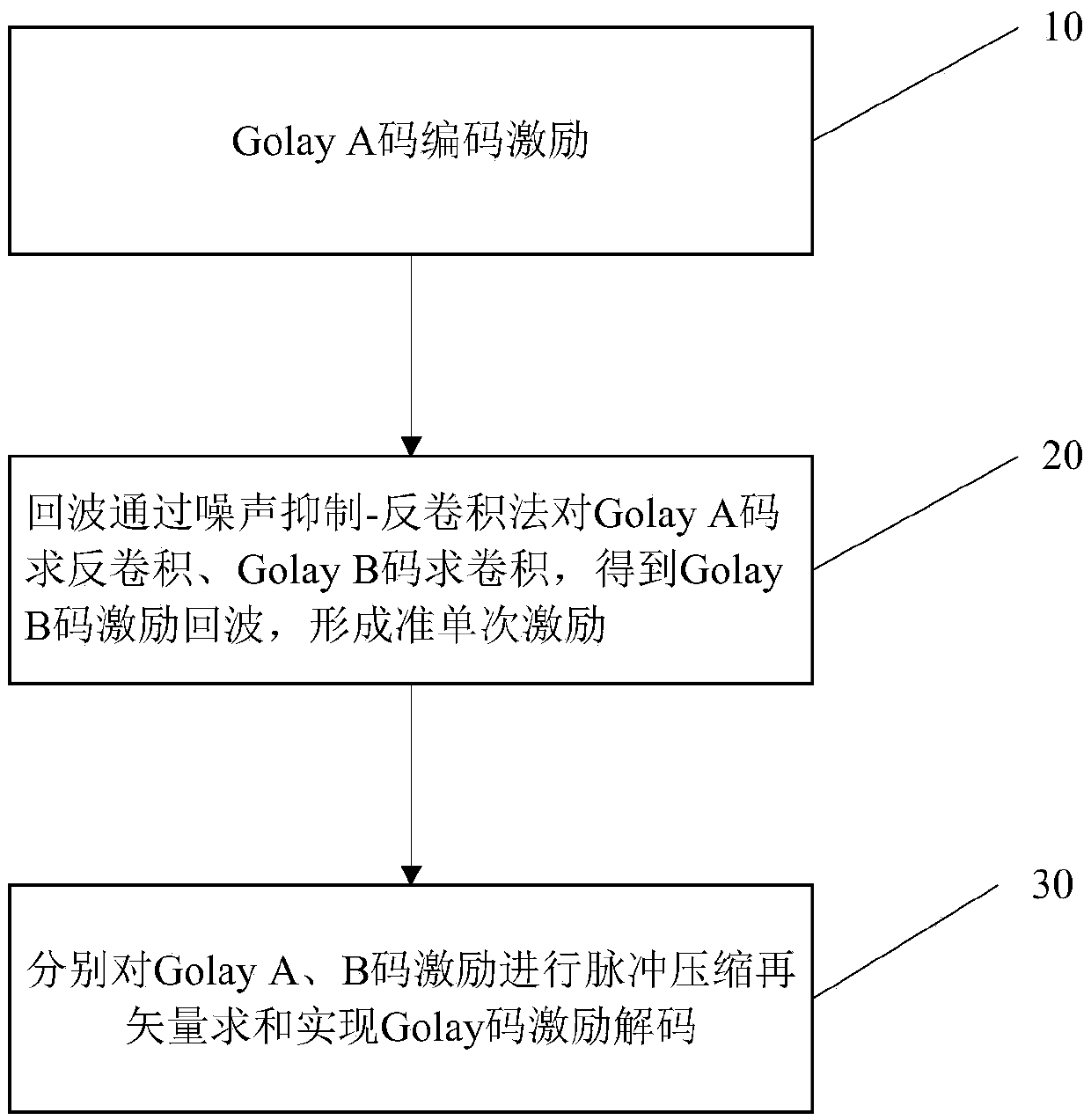
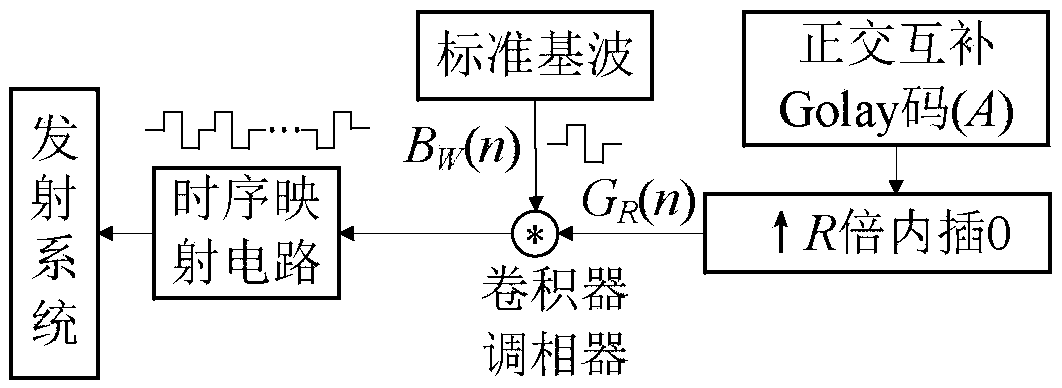
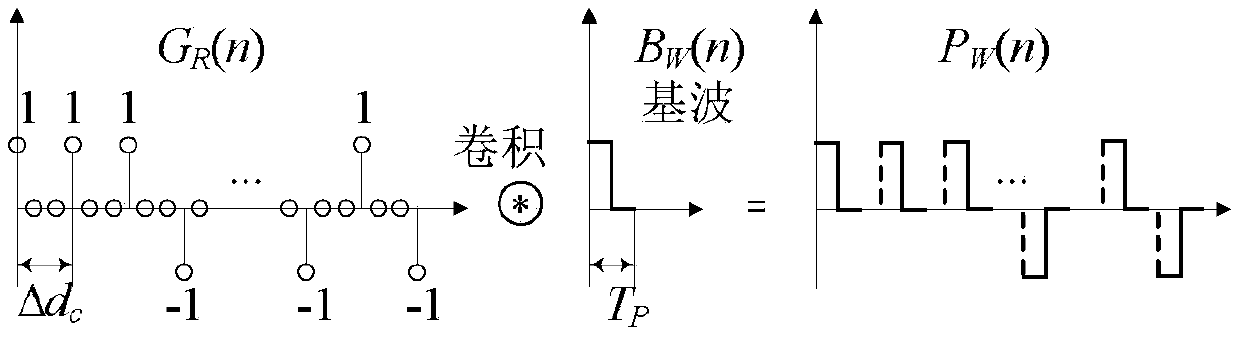
Quasi one-time orthogonal complementary Golay (A,B) code ultrasonic phased array coded excitation method
ActiveCN105548373AGrowth inhibitionImprove scanning efficiencyUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic wave generationSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)Stimulated echo
The invention discloses a quasi one-time orthogonal complementary Golay (A,B) code ultrasonic phased array coded excitation method. The method comprises the following steps: coded excitation is carried out by Golay A code; Golay A to B code excitation transition of received echo is realized by software algorithm, and twice stimulated echoes of Golay A,B are obtained (orthogonal complementary Golay coded excitation condition is formed); pulse compression is carried out, decoding is realized by summarizing vectors, so that quasi one-time orthogonal complementary Golay coded excitation technology is realized, and replaces the traditional double-emission scheme with physical hardware. An effective noise inhibition-deconvolution algorithm is used, FPGA(Field Programmable Gate Array) is used for realizing excitation transition algorithm of sequence Golay A code excitation to Golay B code, in order to realize the purpose of quasi one-time excitation; the traditional Golay A,B code separated excitation scheme is improved, operation efficiency of the phased array system is increased by 50%, signal to noise ratio (related to coding length Lc) is greatly improved, the problem of decoding effect influenced by inconsistent received waveforms due to position changes of twice emissions in some dynamic scanning processes is avoided, and the method has an important application value in practical engineering.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Simultaneous excitation and acquisition of signal from multiple slices in the RARE sequence (multiplex RARE)
InactiveUS8395385B2Improve efficiencyEasy to useMagnetic property measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionStimulated echoSelective excitation
A method for RARE magnetic resonance imaging comprising slice selective excitation of two or more slices and of one or more nuclei, followed by refocusing of these slices and application of gradient pulses which cause a division of the signal into spin echoes and stimulated echoes, is characterized by application of refocusing slice selective RF pulses, which are placed to fulfill the echo-spacing CPMG condition for each slice and by arrangement of gradient pulses which cause the phase accumulated by spins in each slice between two consecutive refocusing RF pulses corresponding to that slice to be equal, thus fulfilling the CPMG phase accumulation condition. Thereby, the obtainable signal can be increased and stabilized.
Owner:UNIVERSITATSKLINIKUM FREIBURG
Magnetic resonance imaging apparatus and method
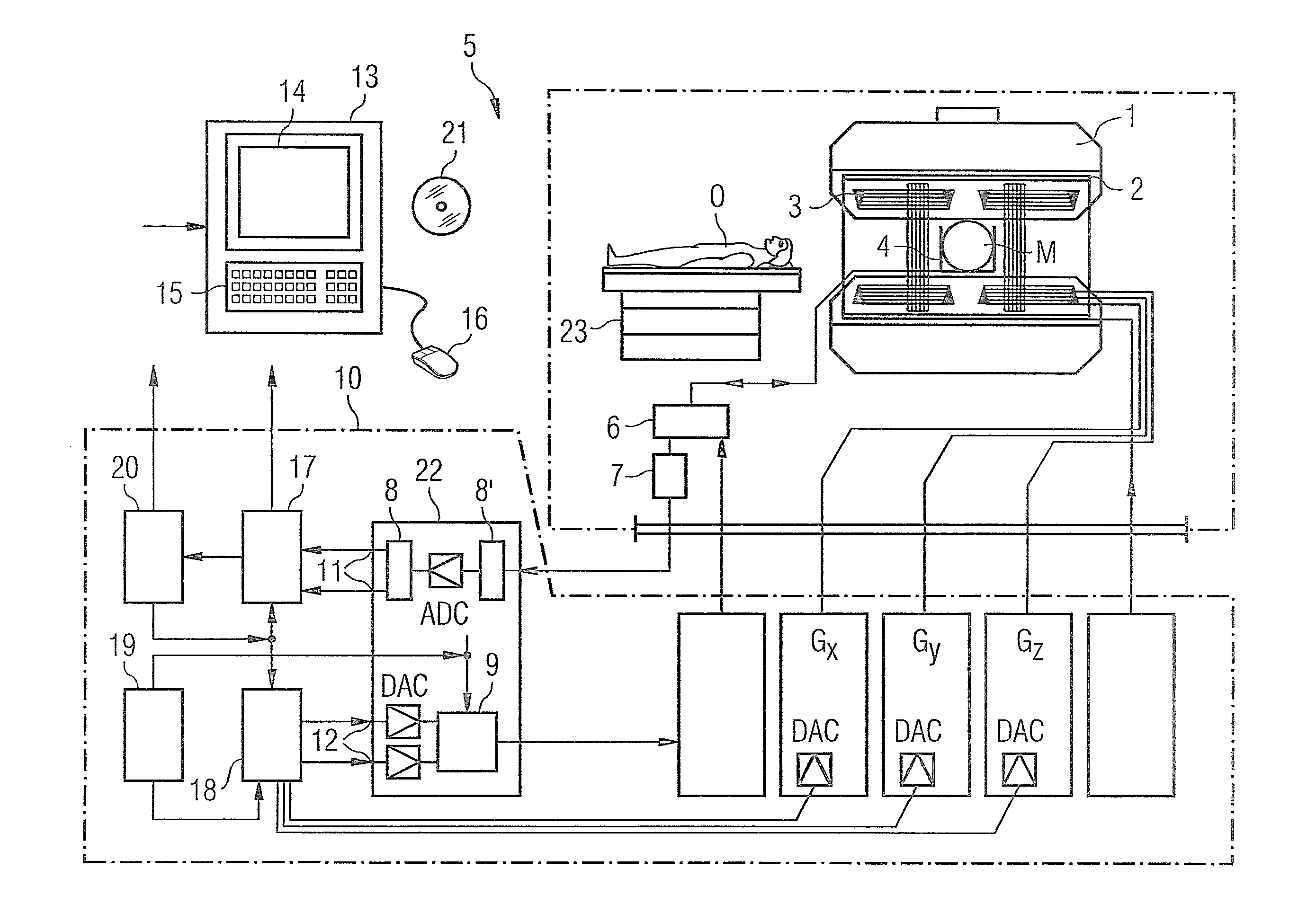
ActiveUS20190154784A1Faster MR scanning timeSimple methodMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsPhase correctionStimulated echo
Magnetic resonance (MR) data are acquired by applying magnetic fields to an examination region concurrent with stimulated echo signals, such that trajectories, which are not straight lines, are generated in k-space. For this purpose, sequence of RF pulses is applied to generate the stimulated echo signals in the examination object, undersampled MR measurement data are detected during reception of the stimulated echo signals in the at least two receiving coils, along the curved k-space trajectories, and fully sampled MR measurement are generated from the undersampled MR measurement data using sensitivity information of the at least two receiving coils. Alternatively, the MR measurement data are fully sampled in a central region of k-space, and a region outside the central region is not fully sampled, and a phase correction with a Partial Fourier technique is executed on the MR measurement data using fully sampled MR measurement data from the central region of k-space.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Method and device for accurate quantification of t2 relaxation times based on fast spin-echo nmr sequences
ActiveUS20150355298A1Accurate modelingIncrease the number ofDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsFast spin echoNMR - Nuclear magnetic resonance
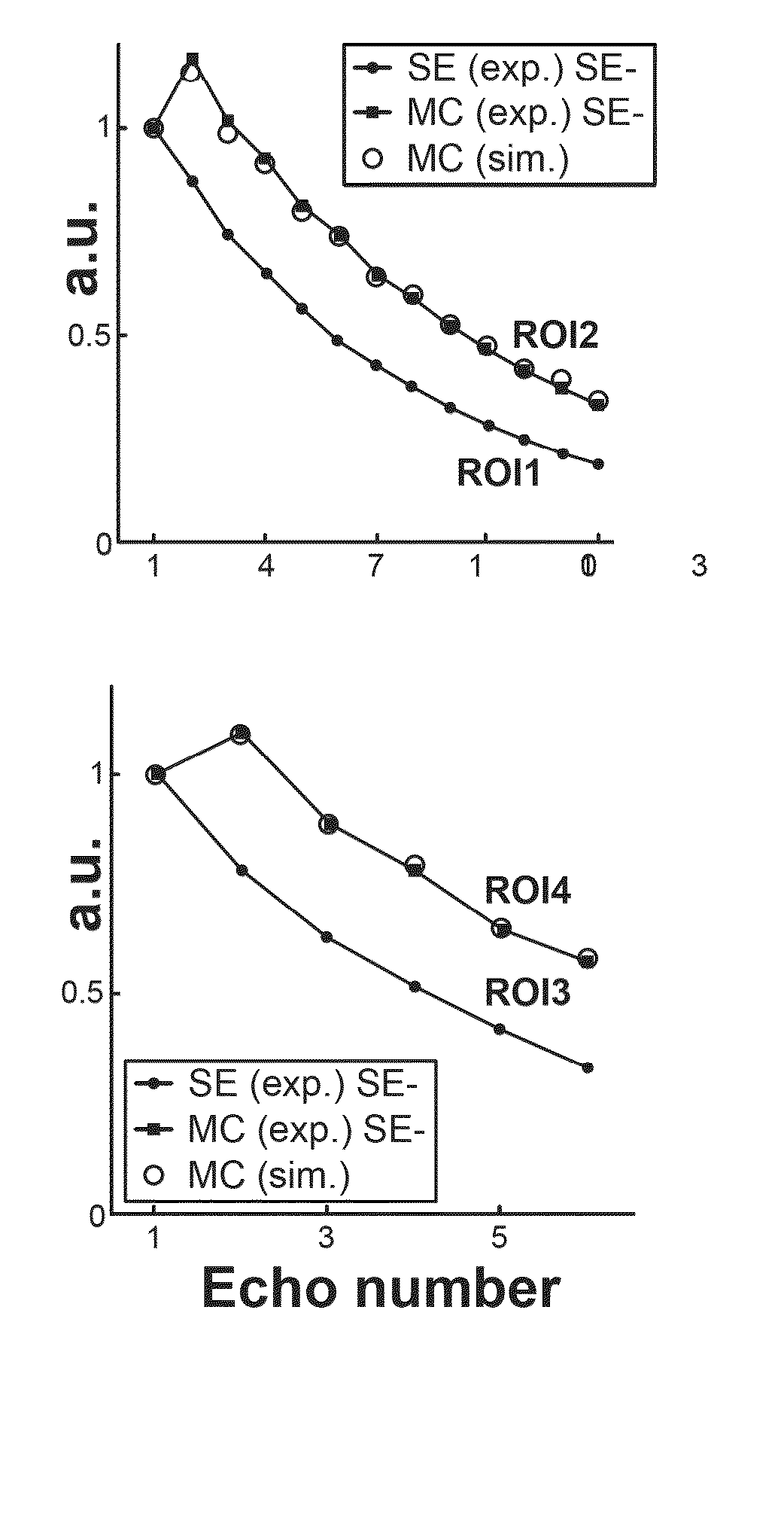
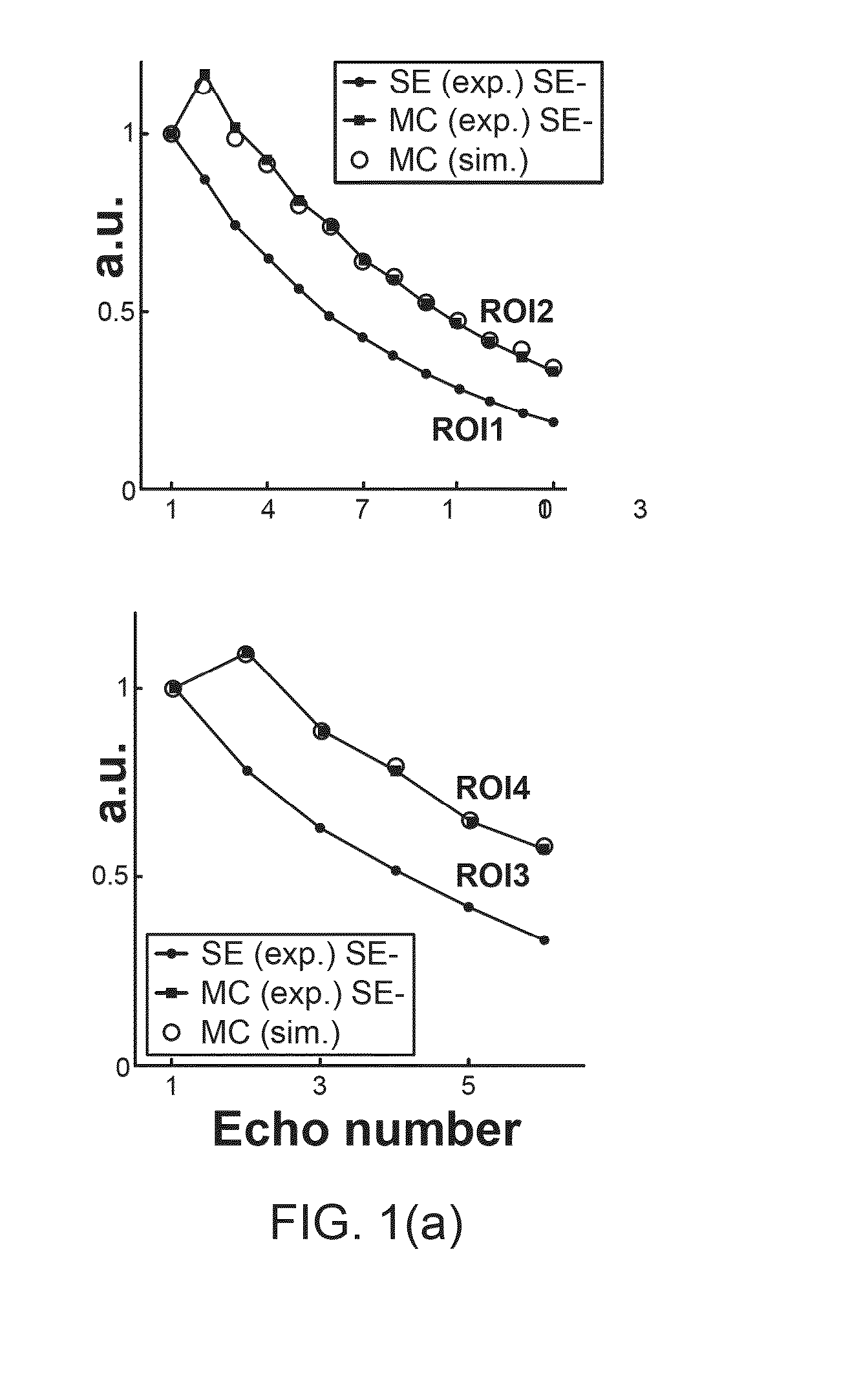
A method and a device are provided that improve quantification of the spin-spin relaxation (“T2”) time of an image in nuclear magnetic resonance (“NMR”) applications using fast multi spin-echo sequences. The method employs time-efficient computer simulations for exact modeling of spurious stimulated echoes in multi-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging (“MRI”) runs. The method employs Bloch simulations and can use a plurality of parameters to produce echo modulation curves prior to correcting distorted experimental data based on pre-calculated simulation values.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
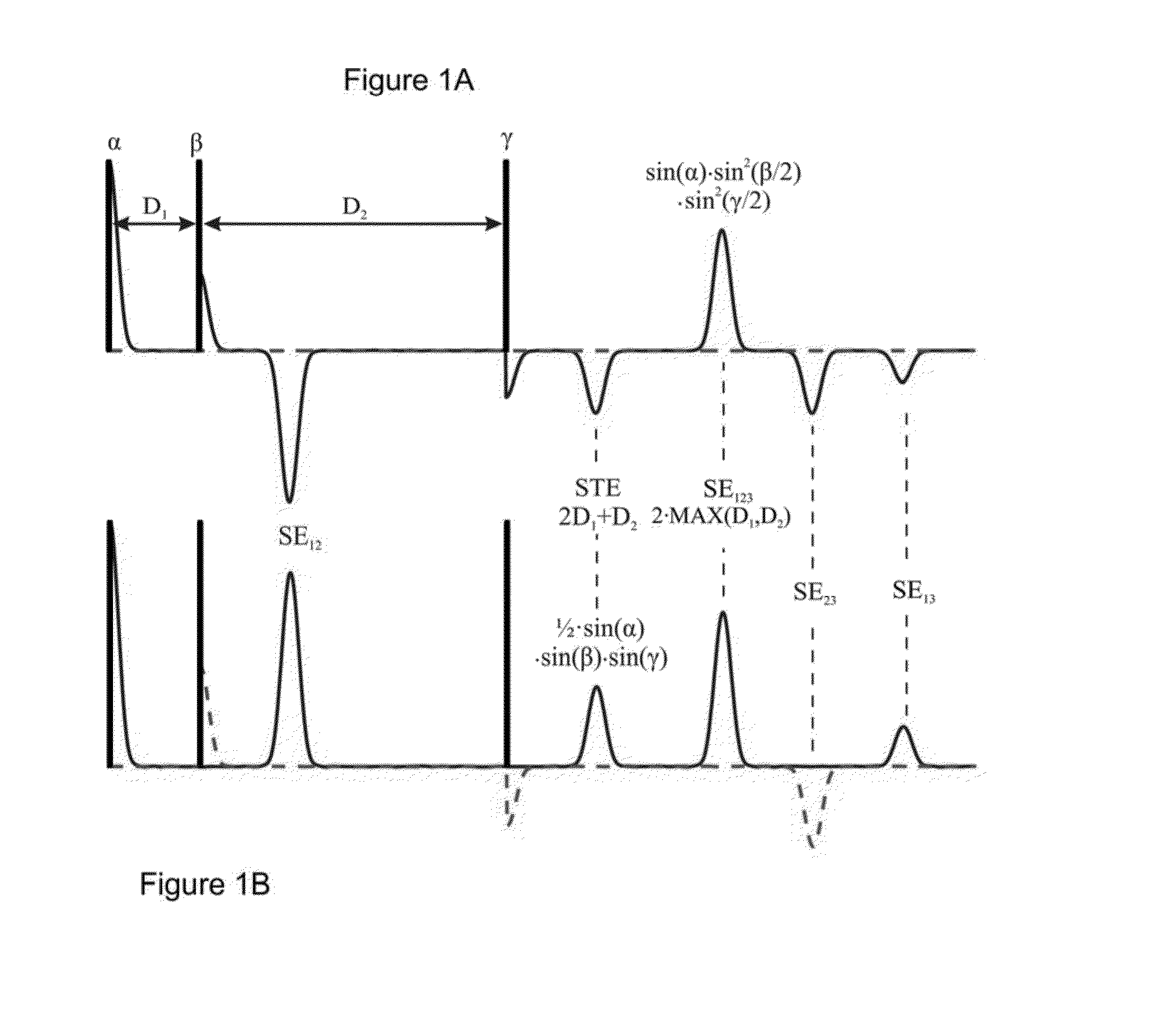
System, method and computer-accessible medium for spectroscopic localization using simultaneous acquisition of double spin and stimulated echoes
ActiveUS20150285878A1Measurements using NMR spectroscopyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsStimulated echoSpins
Method, system and non-transitory computer-accessible medium can be provided for performing magnetic resonance spectroscopy for at least one structure. For example, with such method and / or computer-accessible medium, it is possible to receive information related to a substantially simultaneous acquisition of a stimulated echo pathway and a double spin echo associated with at least one portion of the at least one structure.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
MR imaging with B1 mapping
ActiveCN104081219ARobust resistanceImprove mapping speedMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsMagnetic field gradientStimulated echo
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging. A portion of a body placed in the examination volume of an MR device is subjected to an imaging sequence of RF pulses and switched magnetic field gradients. The imaging sequence is a stimulated echo sequence including i) two preparation RF pulses (alpha) radiated toward the portion of the body during a preparation period (21), and ii) reading RF pulses (beta) radiated toward the portion of the body during an acquisition period (22) temporally subsequent to the preparation period (21). FID signals (I1) and one or more stimulated echo signals I2) are acquired during the acquisition period (22) with equal T2*-weighting. A B1 map indicating the spatial distribution of the RF field of the preparation RF pulses within the portion of the body is derived from the acquired FID (I1) and stimulated echo (I2) signals.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Method and magnetic resonance system to acquire mr data and to determine a b1 magnetic field
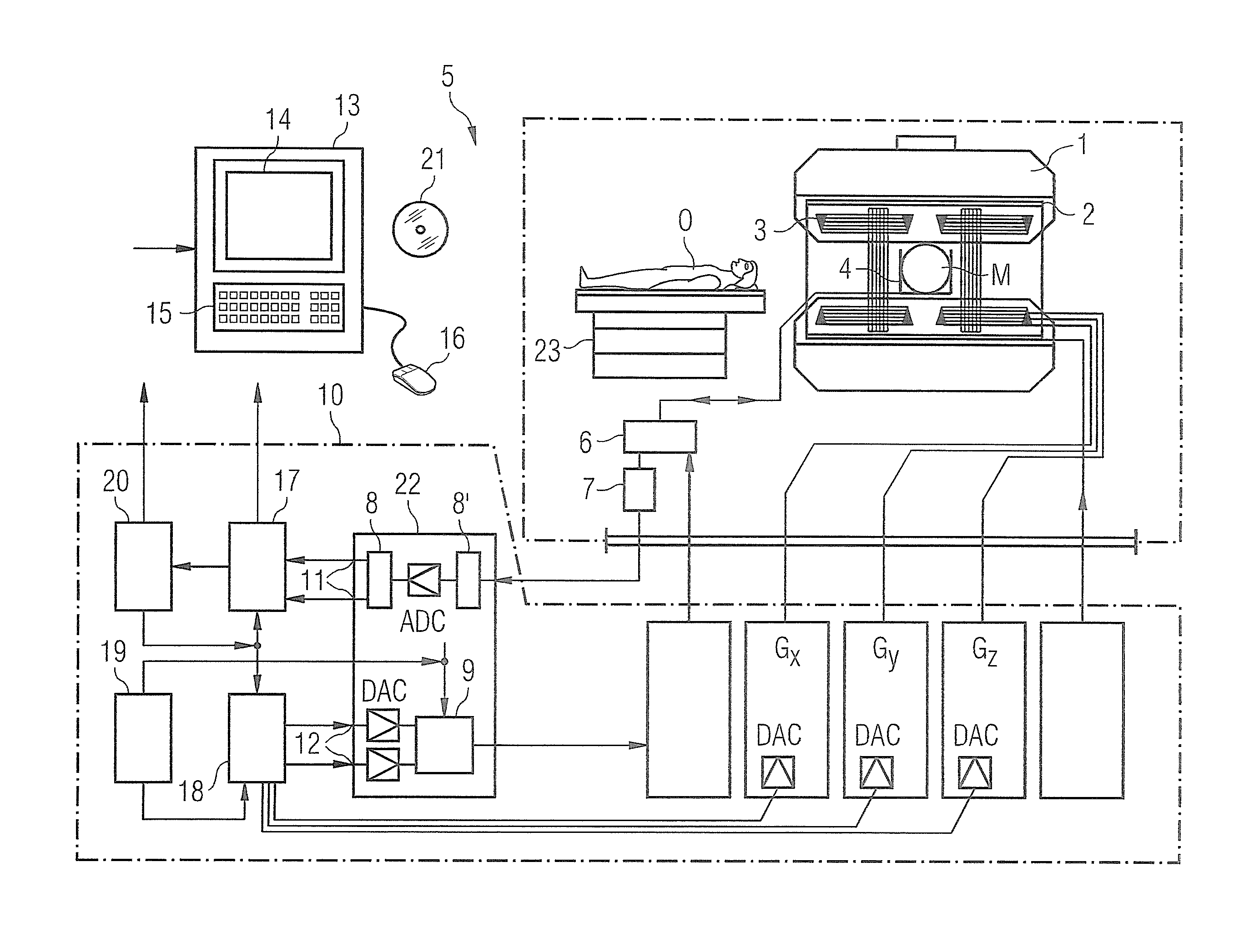
In a method to acquire magnetic resonance (MR) data within a volume segment with a magnetic resonance system, the MR data are repeatedly acquired with a sequence that includes radiating a first resonant RF pulse, radiating a second resonant RF pulse, applying a dephasing first gradient after the first resonant RF pulse and before the second resonant RF pulse, radiating a third resonant RF pulse after the second resonant RF pulse, applying a second gradient after the third RF pulse in order to refocus a stimulated echo of a magnetization component prepared by the first gradient, and read out MR data. At least one of the first gradient and / or the second gradient is / are different in a respective repetition of the sequence and an additional repetition of the sequence that directly follows the respective repetition.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Brand-new nuclear magnetic resonance echo mechanism based magnetic resonance imaging method
ActiveCN108196210AReduce relaxation decayRaise the image signal-to-noise ratioMeasurements using NMRLongitudinal planeTransverse plane
The invention discloses a brand-new nuclear magnetic resonance echo mechanism based magnetic resonance imaging method. The method includes: turning dispersion-phase spins to a longitudinal plane, andsubstituting transverse relaxation with longitudinal relaxation to reduce signal relaxation attenuation; combining with a brand-new echo generating mechanism to obtain completely gathered echo on a transverse plane to keep signals as far as possible, so that a signal-to-noise ratio of an imaging sequence is substantially increased. The method has advantages that the defect of respective signal loss of traditional echo sequences (spin echoes and stimulated echoes) is overcome, optimal echo signals are formed, sequence schemes comprehensively superior to the spin echoes and the stimulated echoesare provided for echo sequence applying diffusion imaging and flow imaging, the signal-to-noise ratio of images is increased to obtain high-quality images, and accordingly an accurate and reliable quantitative measurement method is provided for magnetic resonance in bulk diffusion and flow imaging, and a promising application prospect in biological medical research and clinical diagnosis is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING HANSHI MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Parallel mr imaging with RF coil sensitivity mapping
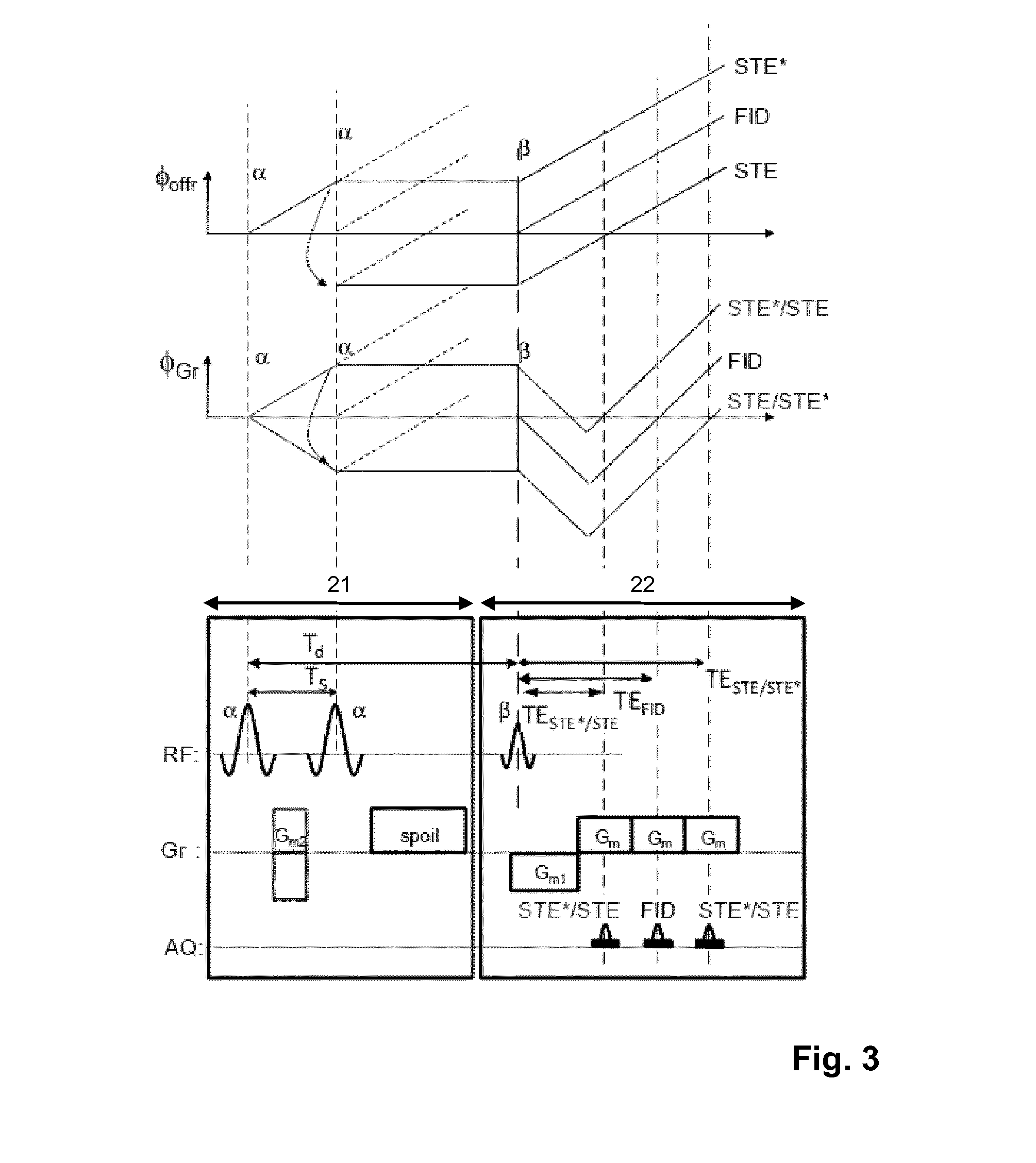
ActiveUS20180120402A1Reducing undesirable phase wrappingHigh sensitivityMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnitude/direction of magnetic fieldsStimulated echoCondensed matter physics
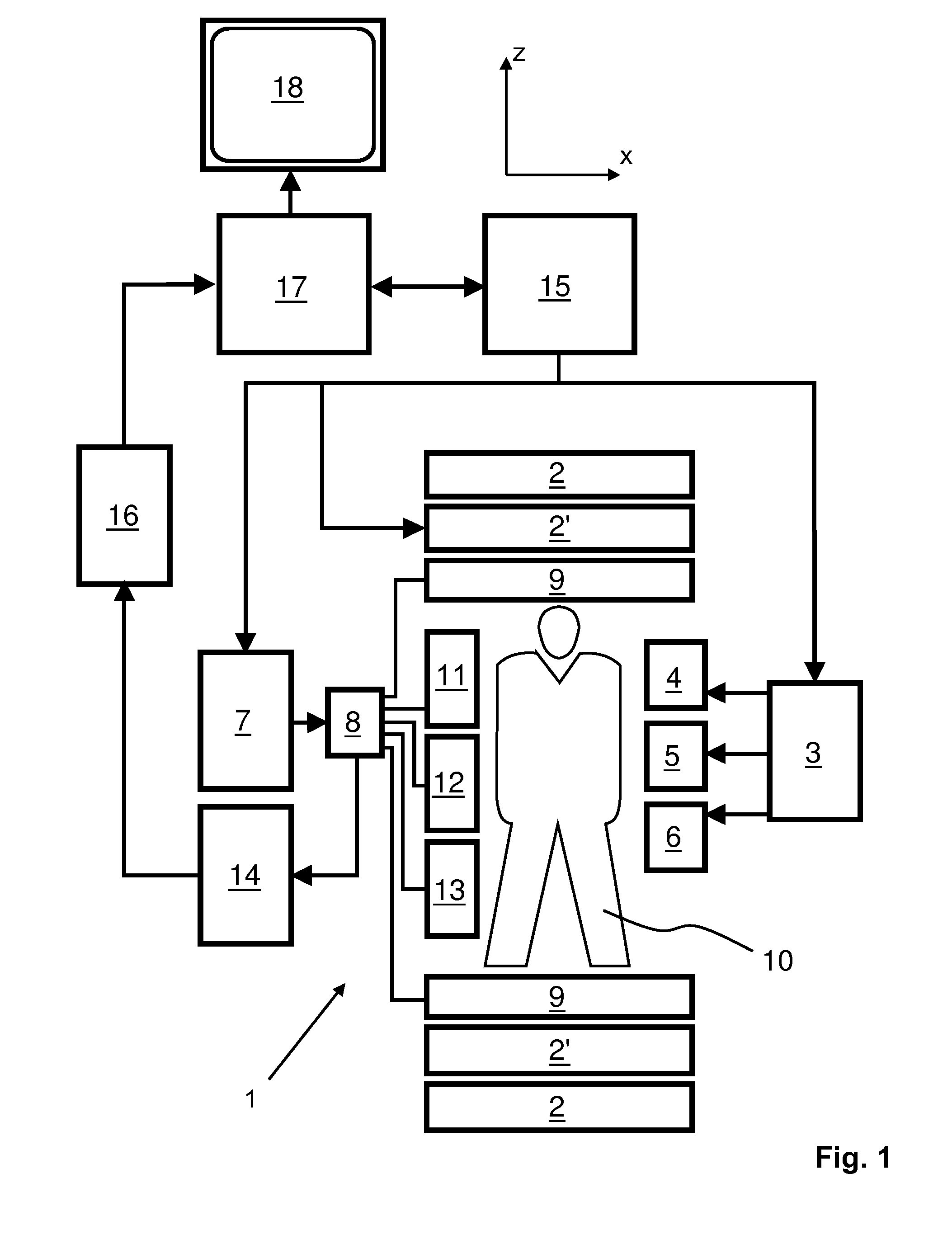
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging of an object (10). The problem of the invention is to provide an improved MR imaging technique that enables fast and robust determination of spatial sensitivity profiles of RF receiving antennas (11, 12, 13) used in parallel imaging as well as B1 and / or B0 mapping. The method of the invention comprises subjecting the object (10) to a stimulated echo sequence. Two or more stimulated echo signals (STE, STE*) are acquired, namely a direct stimulated echo signal (STE) and a conjugated stimulated echo signal (STE*), wherein at least one of the stimulated echo signals (STE, STE*) is received in parallel via an array of two or more RF receiving antennas (11, 12, 13) having different spatial sensitivity profiles, and wherein at least another one of the stimulated echo signals (STE, STE*)is received via a body RF coil (9) having an essentially homogeneous spatial sensitivity profile. Sensitivity maps indicating the spatial sensitivity profiles of the individual RF receiving antennas (11, 12, 13) of the array are derived by comparing the stimulated echo signals (STE, STE*) received via the array of RF receiving antennas (11, 12, 13) with the stimulated echo signals (STE, STE*) received via the body RF coil (9). Moreover, the invention relates to a MR device (1) and to a computer program for a MR device (1).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Metal resistant mr imaging
ActiveUS20160223635A1Easy accessSensitive to susceptibility effectMagnetic measurementsMagnetic field gradientStimulated echo
The invention relates to a method of parallel MR imaging which comprises the steps of: —subjecting a portion of a body (10) to a first imaging sequence (21,22) of RF pulses and switched magnetic field gradients, wherein first MR signals (11,12) are acquired via at least two RF coils having different spatial sensitivity profiles within the examination volume, —deriving the spatial sensitivity profiles of the at least two RF coils from the acquired first MR signals, —subjecting the portion of the body to a second imaging sequence of RF pulses and switched magnetic field gradients, wherein second MR signals are acquired by parallel acquisition via the at least two RF coils with sub-sampling of k-space, and —reconstructing a MR image from the acquired second MR signals and from the spatial sensitivity profiles of the at least two RF coils. According to the invention, the type and / or parameters of the first imaging sequence are selected automatically depending on the presence of a metal implant in the body. The selection of the type of the first imaging sequence is made between a gradient echo sequence, if no metal implants are present, and a spin echo sequence or a stimulated echo sequence, if a metal implant is present.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Magnetic resonance system and method to acquire mr data and to determine a b1 magnetic field
InactiveUS20140218022A1Reduce decreaseImprove efficiencyMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionStimulated echoResonance
In a method and magnetic resonance (MR) system to acquire MR data within a volume segment, the MR data are repeatedly acquired with a sequence that which includes the following steps. A first resonant RF pulse is radiated and a second resonant RF pulse is radiated. A dephasing first gradient is applied after the first resonant RF pulse and before the second resonant RF pulse. A third resonant RF pulse is radiated after the second resonant RF pulse. A second gradient is applied after the third RF pulse in order to refocus a stimulated echo of a magnetization component prepared by the first gradient. MR data are read out, and a fourth resonant RF pulse is radiated after the readout of the MR data, to reduce the longitudinal magnetization.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Metal resistant mr imaging reference scan
ActiveUS20150253406A1Avoid potential slice cross-talkEase signal evaluationDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsMagnetic susceptibilityStimulated echo
The invention relates to a method of parallel MR imaging, wherein a reference scan is performed by means of a stimulated echo sequence including i) at least two preparation RF pulses (a) radiated toward a portion of a body (10) during a preparation period (21), and ii) one or more reading RF pulses 03) radiated toward the portion of the body (10) during an acquisition period (22) temporally subsequent to the preparation period (21). One or more FID signals (I1) and one or more stimulated echo signals (I2) are acquired during the acquisition period (22). The spatial receive and / or—if applicable—transmit4 sensitivity profiles of at least two RF coils (11, 12, 13) are derived from the acquired FID signals (I1) and / or from the acquired stimulated echo signals (I2). The parameters of the stimulated echo sequence are selected such that it is robust against susceptibility-induced artefacts. Moreover, 10 the invention relates to a MR device (1) and to a computer program for a MR device (1).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Mr imaging with temperature mapping
ActiveUS20160252595A1Good temperature sensitivityLong effective PRF encoding timeDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsMagnetic field gradientStimulated echo
The invention relates to a method of MR imaging of an object (10) placed in the examination volume of a MR device (1). It is the object of the invention to provide an improved MR-based temperature mapping method. The method of the invention comprises the steps of: subjecting the object (10) to an imaging sequence of RF pulses and switched magnetic field gradients, which imaging sequence is a stimulated echo sequence including: a) at least two preparation RF pulses (a) radiated toward the object (10) during a preparation period (21), and b) one or more reading RF pulses (β) radiated toward the object (10) during an acquisition period (22) temporally subsequent to the preparation period (21); acquiring at least two MR signals during the acquisition period (22), wherein the two MR signals are either (i) a FID signal (I1, FID) and a stimulated echo signal (I2) or (ii) two stimulated echo signals (STE, STE*); and deriving a temperature map indicating the spatial distribution of the temperature within the object (10) from the at least two acquired MR signals. Moreover, the invention relates to a MR device (1) and to a computer program for a MR device (1).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
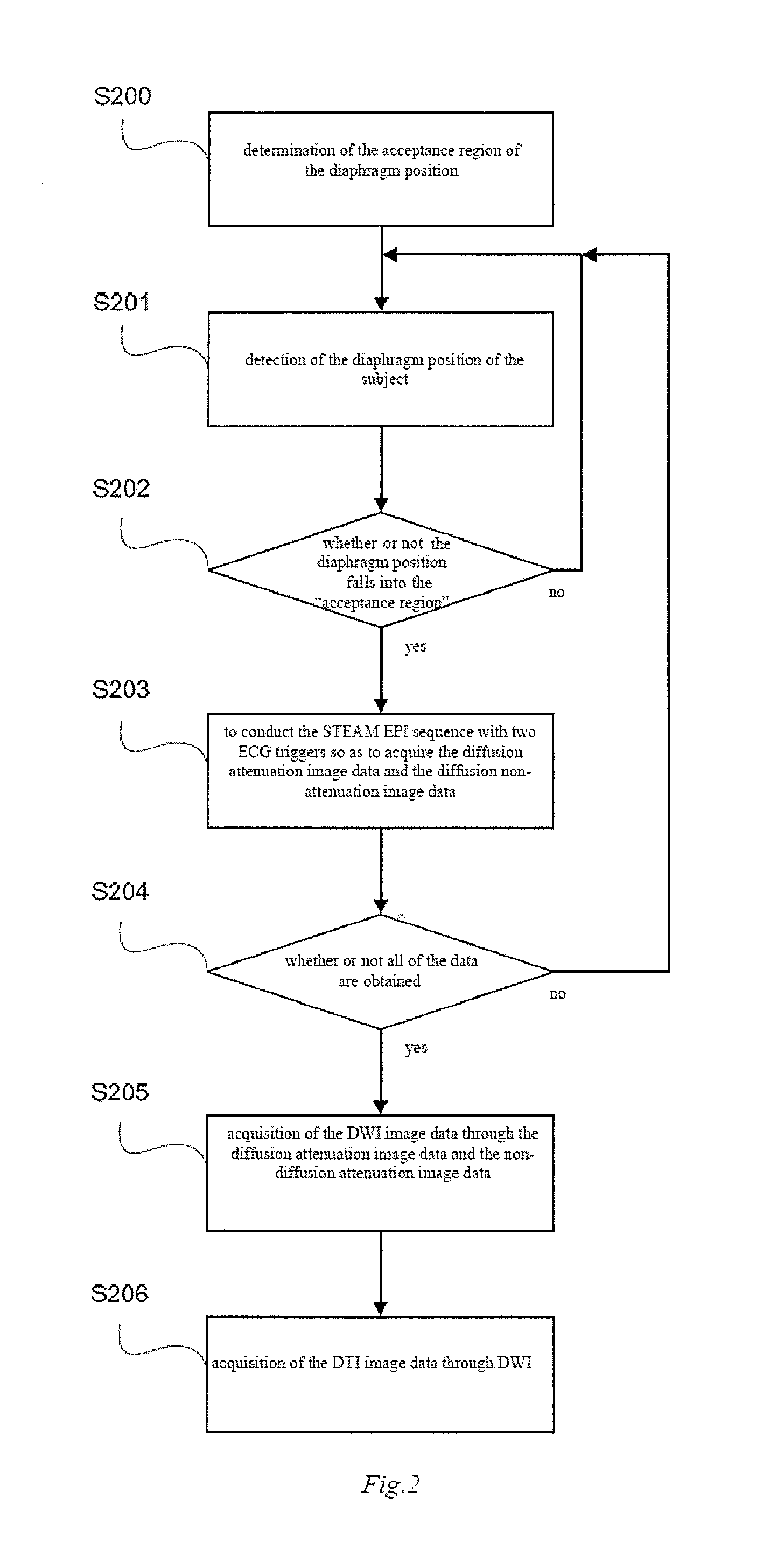
Diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging method
InactiveUS20130338486A1Reduce the impactReduce scan timeMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringStimulated echoMyocardial fiber
In a diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging method for imaging a myocardial fiber structure, the diaphragm position of a subject is detected and a determination is made as to whether the diaphragm position of the subject falls into the acceptance region or not. If it does not, continue the diaphragm position of the examination subject is continued to be detected. If and when the diaphragm position is in the acceptance region, an echo planar imaging sequence with stimulated echo is executed with two electrocardiogram triggers, so as to acquire diffusion tensor image data of the myocardial fiber structure. The cardiac DTI image data thus can be obtained under free respiration of the subject, and the influence of respiratory movement is reduced and the scanning time is shortened.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Systems and methods for measuring cardiac strain
A method for rapid computation of three-dimensional displacement and Lagrange strain in a high resolution filed of phase data obtained with Displacement Encoding with Stimulated Echoes (DENSE) in magnetic resonance images of the myocardium. The method includes semi-automated segmentation of a region of a heart, phase unwrapping the images in three dimensions, and a custom radial point interpolation method (RPIM). The RPIM is a meshfree numerical analysis method that uses radial basis functions and polynomial functions to calculate the Lagrange strain of DENSE displacement data acquired from the myocardium.
Owner:WASHINGTON UNIV IN SAINT LOUIS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com