Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
239 results about "Biopsy trephine" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
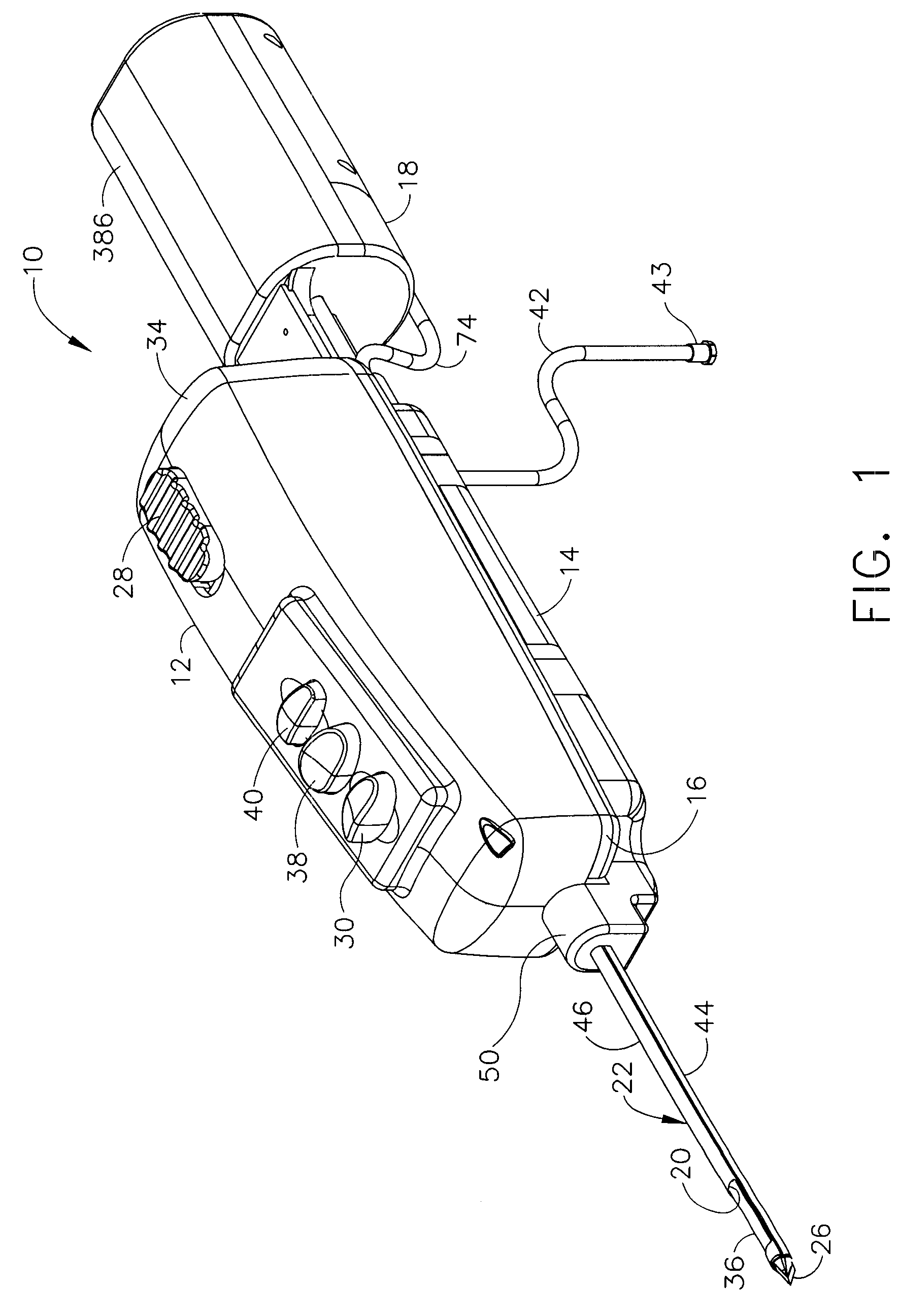
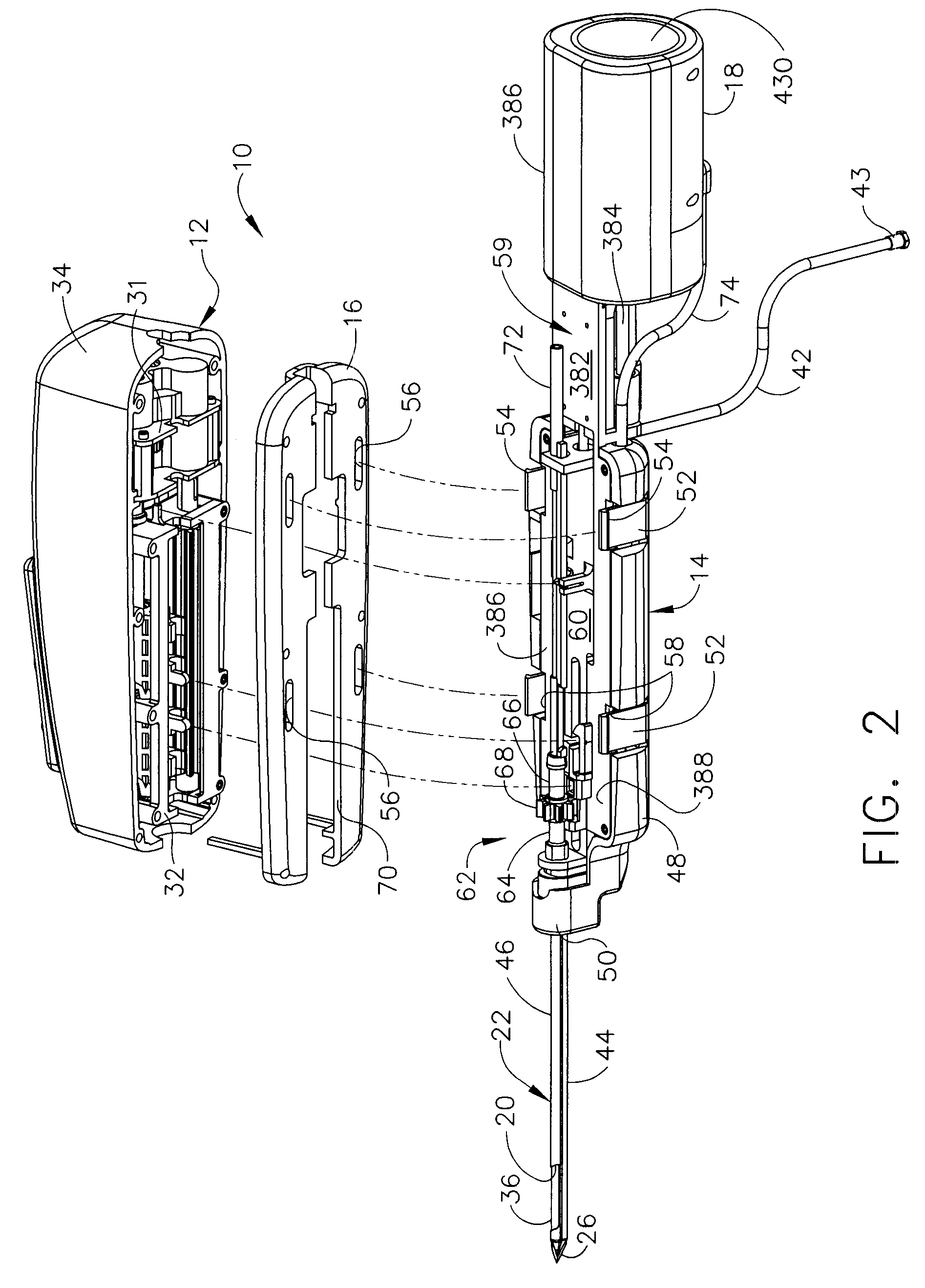
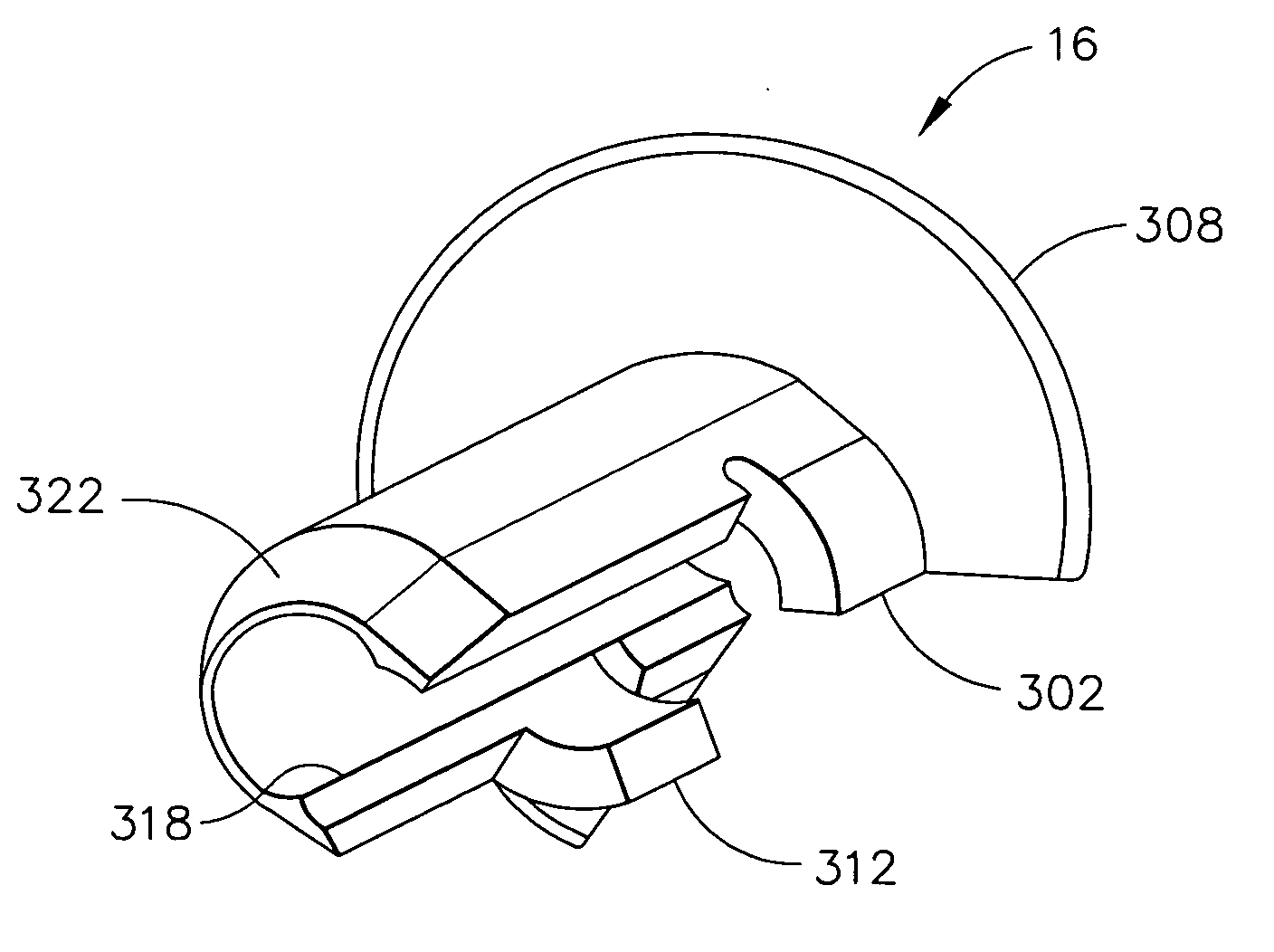
Core sampling biopsy device with short coupled MRI-compatible driver
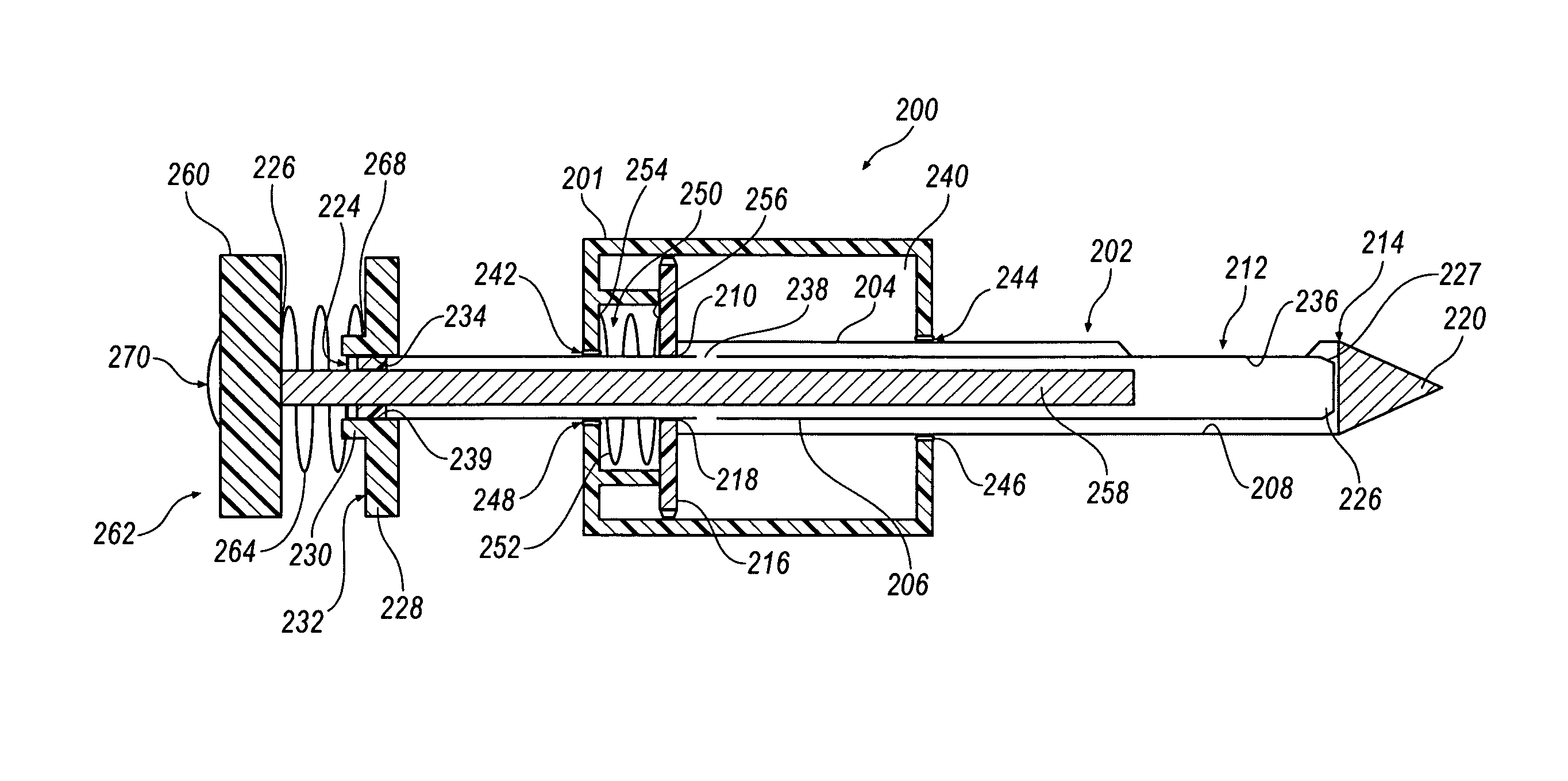
A core sampling biopsy device is compatible with use in a Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) environment by being driven by either a pneumatic rotary motor or a piezoelectric drive motor. The core sampling biopsy device obtains a tissue sample, such as a breast tissue biopsy sample, for diagnostic or therapeutic purposes. The biopsy device may include an outer cannula having a distal piercing tip, a cutter lumen, a side tissue port communicating with the cutter lumen, and at least one fluid passageway disposed distally of the side tissue port. The inner cutter may be advanced in the cutter lumen past the side tissue port to sever a tissue sample. A cutter drive assembly maintains a fixed gear ratio relationship between a cutter rotation speed and translation speed of the inner cutter regardless of the density of the tissue encountered to yield consistent sample size.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Multi-purpose catheter apparatus and method of use
InactiveUS20050010095A1Easy to adaptEfficiently and accurately deliverElectrocardiographySurgical needlesDistal portionSaline solutions
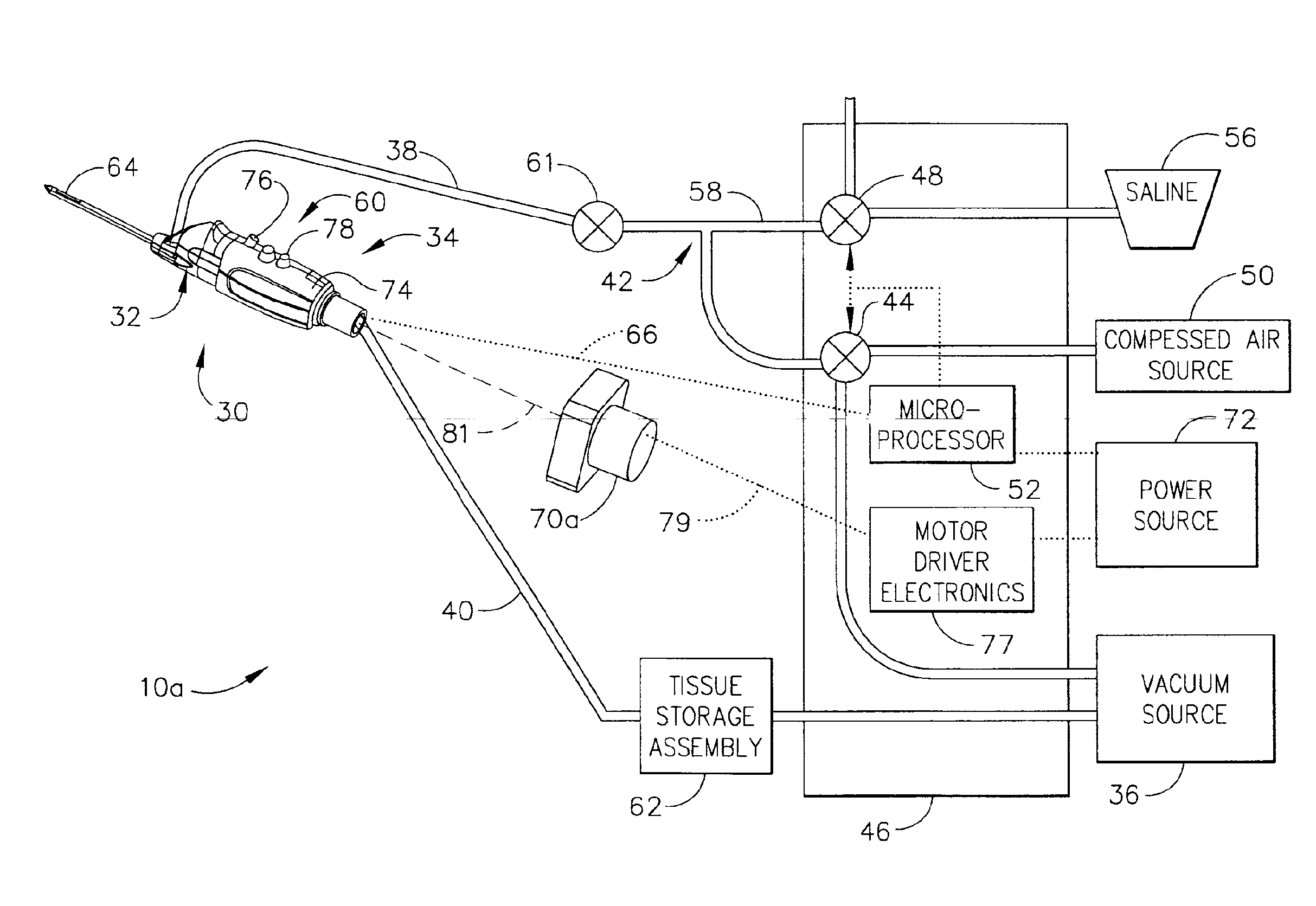
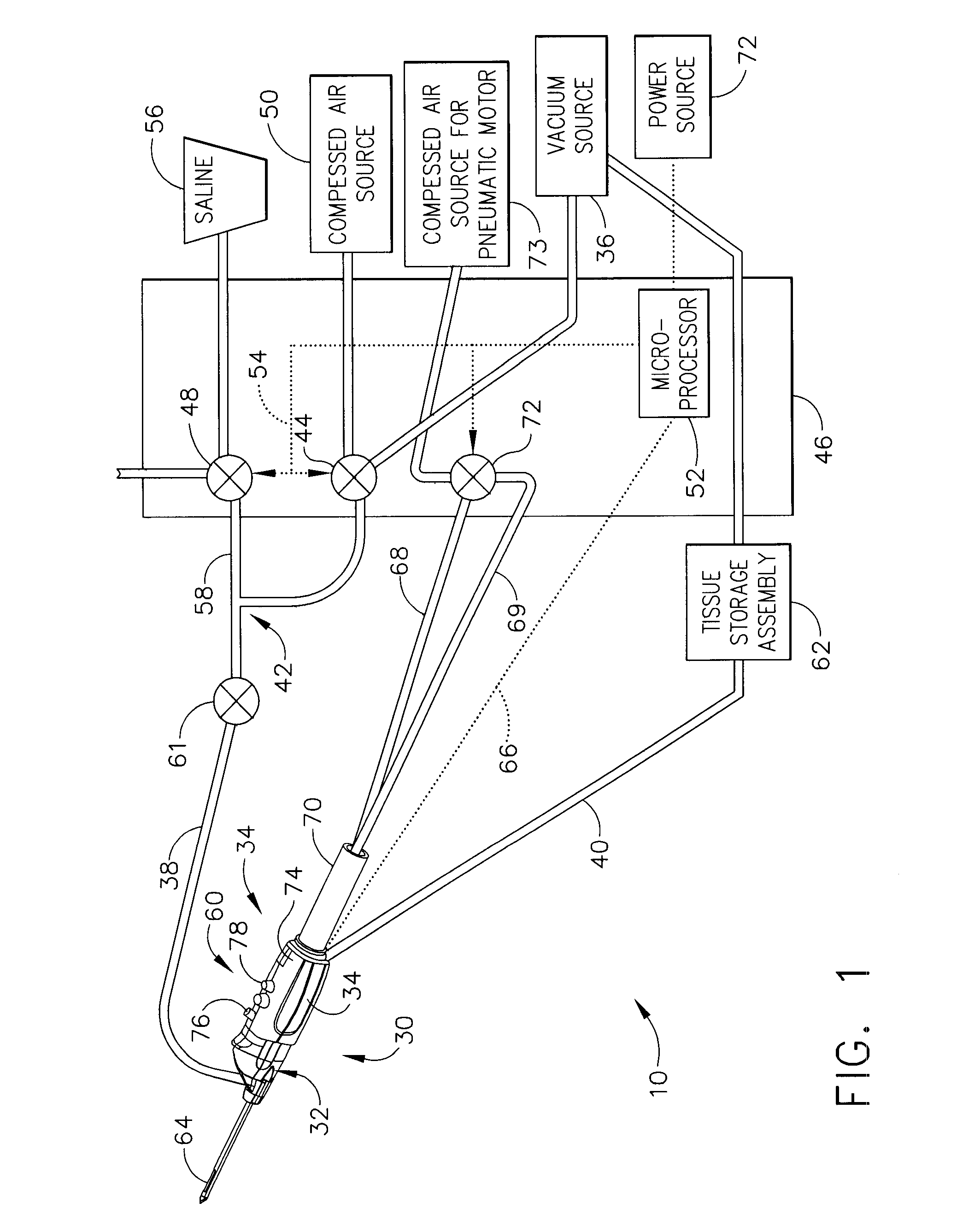
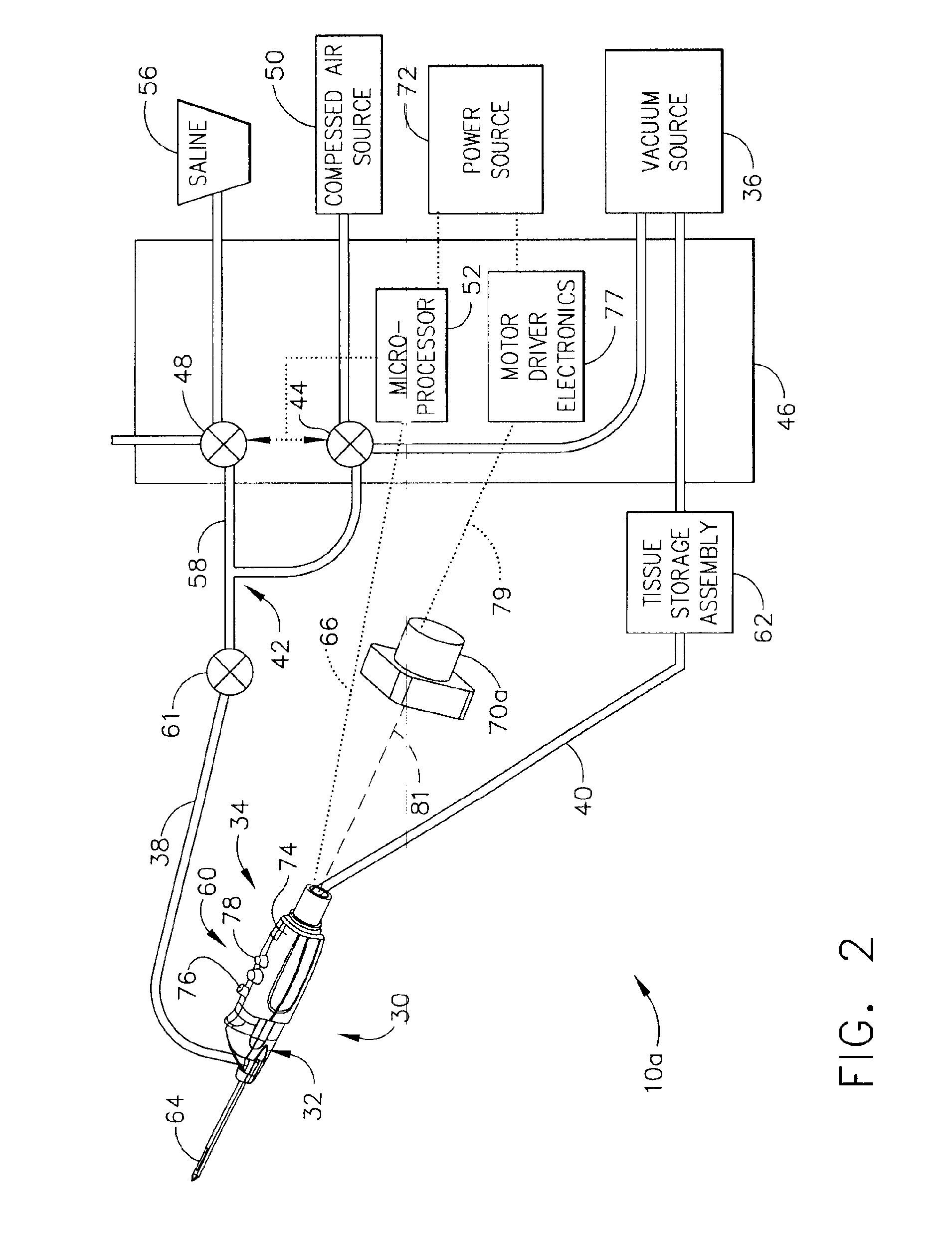
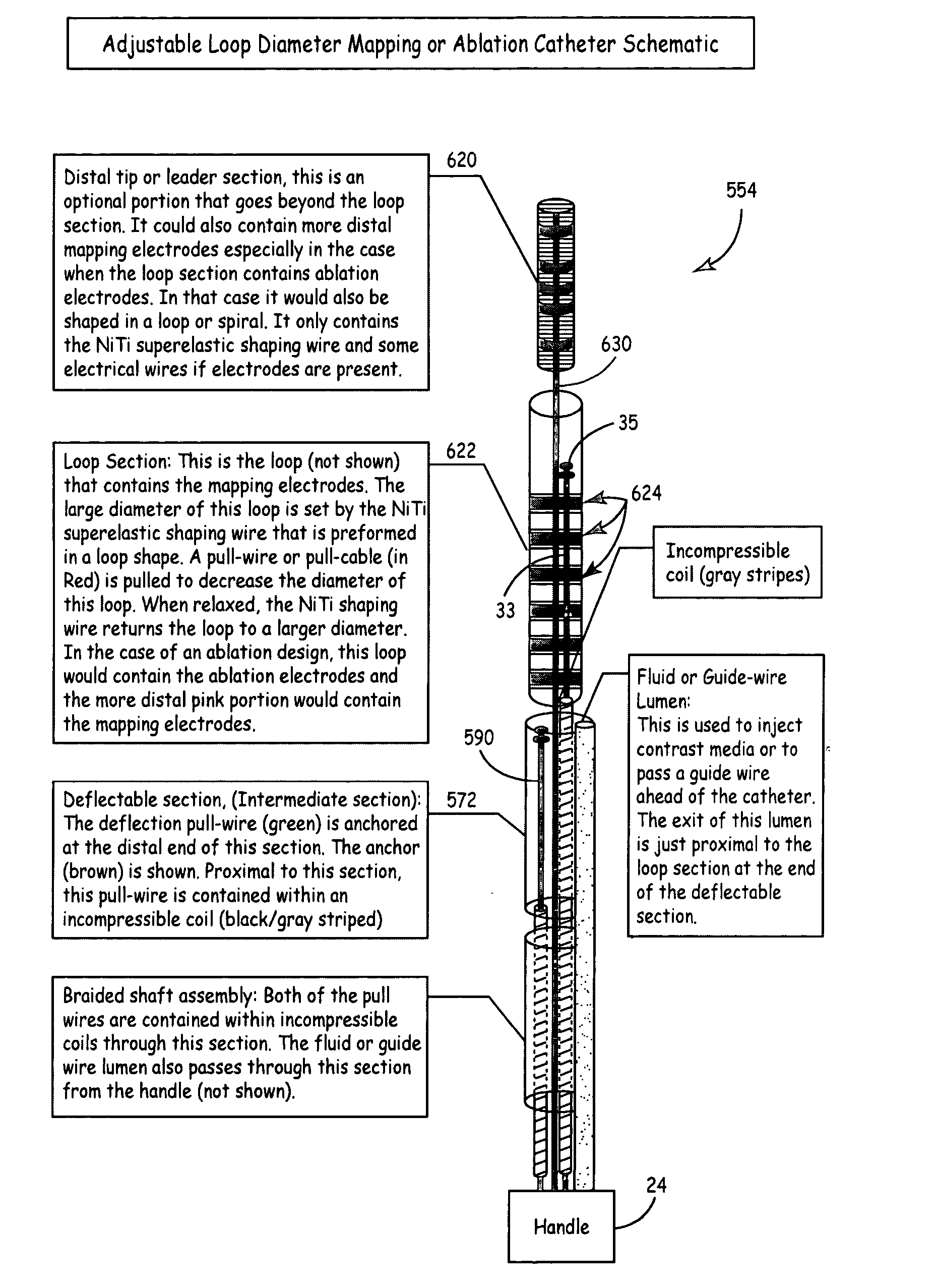
According to the present invention, a catheter having at least one multi-purpose lumen formed through the catheter terminates proximal a relatively complex-shaped distal portion thereof. In one form of this embodiment, the relatively complex-shaped distal portion comprises a looped portion having diagnostic- and / or ablation-type electrodes coupled thereto and an elongated diameter-adjusting member coupled proximal the distal end of the looped portion. The multi-purpose lumen may be used to alternately accommodate a variety of dedicated materials; such as, (i) a guide wire for initial deployment or later repositioning of the catheter, (ii) a volume or flow of a contrast media and the like, (iii) a deployable hollow needle or tube and the like used to biopsy adjacent tissue or dispense a therapeutic agent into a volume of tissue, and (iv) a cooling fluid, such as saline solution and the like dispensed at least during therapeutic tissue ablation procedures.
Owner:MEDTRONIC INC
Endoscopic apparatus with integrated multiple biopsy device
An imaging endoscope comprising a shaft having a proximal end adapted to be secured to a handle, and a distal end having a biopsy forceps disposed therein. The biopsy forceps includes one or more end-effector elements that are actuated with a control cable that may be connected to the handle. The endoscope shaft includes a biopsy sample lumen that is configured to receive a biopsy sample obtained from the forceps assembly. A sample collection apparatus is attached to the handle to capture multiple biopsy samples. In some embodiments, the endoscope is a single-use endoscope.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Biological sampler, collector and storage container
The invention relates to a storage container to receive and store a biopsy sample of an organism, held by a biopsy sample collector. The storage container comprises a container body defining a containment region with an open or openable end. The storage container further comprises a container cap located at the open end. The container cap is able to be removed from the container body by displacement in a direction (herein after “removal direction”) away from said containment region. The cap includes a passage leading to the containment region the passage able to receive a sample retaining sample collector. The storage container additionally comprises a tamper evident sleeve about at least part of the cap and the container body. The sleeve comprises of two parts that are frangibly connected. The frangible connection is in a manner such that upon displacement of the cap in the removal direction, a first part of the sleeve travels with said cap and a second part of the sleeve is prevented from movement with the first part by said container body to thereby separate the first and second parts. The first and second parts may each include information matched to each other.
Owner:SNPSHOT TRUSTEE
Vacuum assisted biopsy needle set
A biopsy device having a cutting element is disclosed. The cutting element includes an inner cannula having a tissue receiving aperture disposed proximate a distal end thereof and an inner lumen. The inner cannula is slidably disposed within the inner lumen of an outer cannula. A vacuum chamber is disposed about at least a portion of the cutting element and is configured to create a vacuum in the cutting element during a biopsy procedure. The inner cannula is advanced distally outwardly and to cause the vacuum to be generated in the vacuum chamber. The vacuum is delivered to the cutting element whereby tissue is drawn into the tissue receiving aperture. The outer cannula is advanced distally outwardly after the inner cannula such that tissue drawn into the tissue cutting aperture is severed.
Owner:PROMEX TECH
Apparatus and method for harvesting and handling tissue samples for biopsy analysis
InactiveUS7156814B1Exemption stepsReduce the numberBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsTissue biopsyTissue fluid
A sectional cassette (10) for use in a process for harvesting and handling tissue samples for biopsy analysis is disclosed. In the procedure, a tissue biopsy sample is placed on a tissue trapping supporting material (A′) that can withstand tissue preparation procedures, and which can be cut with a microtome. The tissue is immobilized on the material, and the material and the tissue are held in the cassette (10) subjected to a process for replacing tissue fluids with wax. The tissue and supporting material are sliced for mounting on slides using a microtome. Harvesting devices and containers (200) using the filter material (202) are disclosed. An automated process is also disclosed.
Owner:BIOPATH AUTOMATION
Hybrid imaging method to monitor medical device delivery and patient support for use in the method
ActiveUS20050080333A1Easy procedureConvenient treatmentSurgical needlesStretcherLiver and kidneySurgical removal
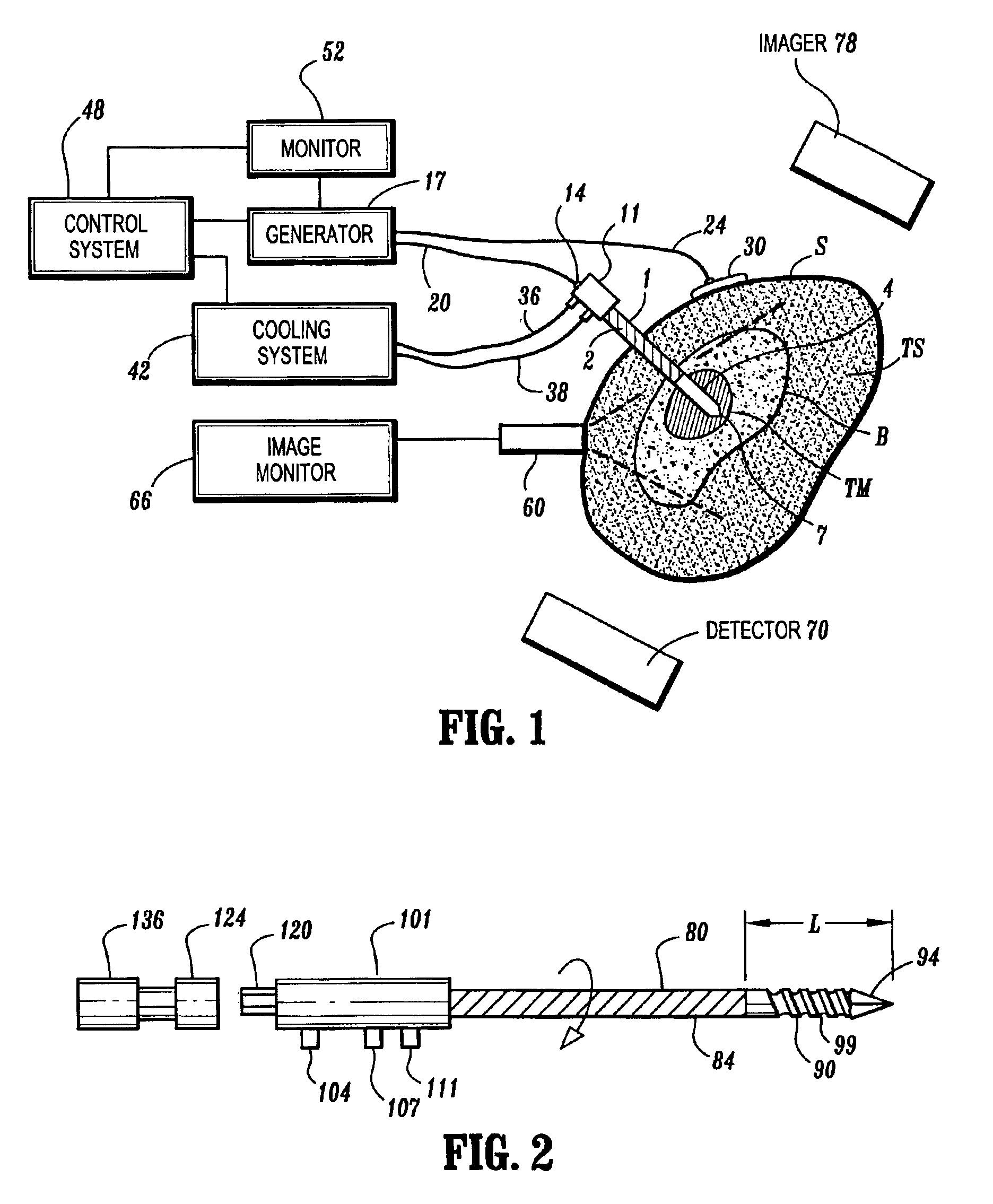
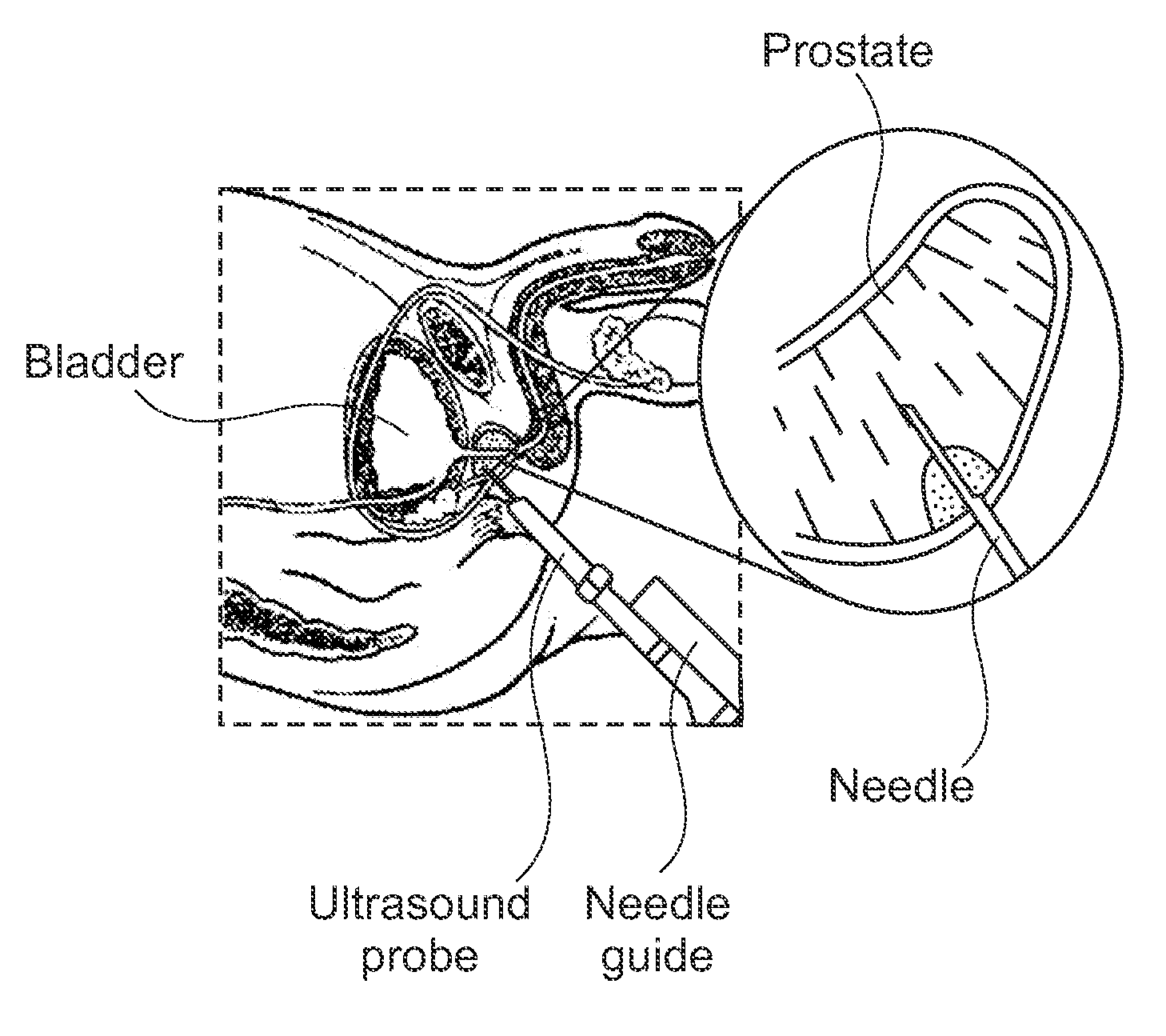
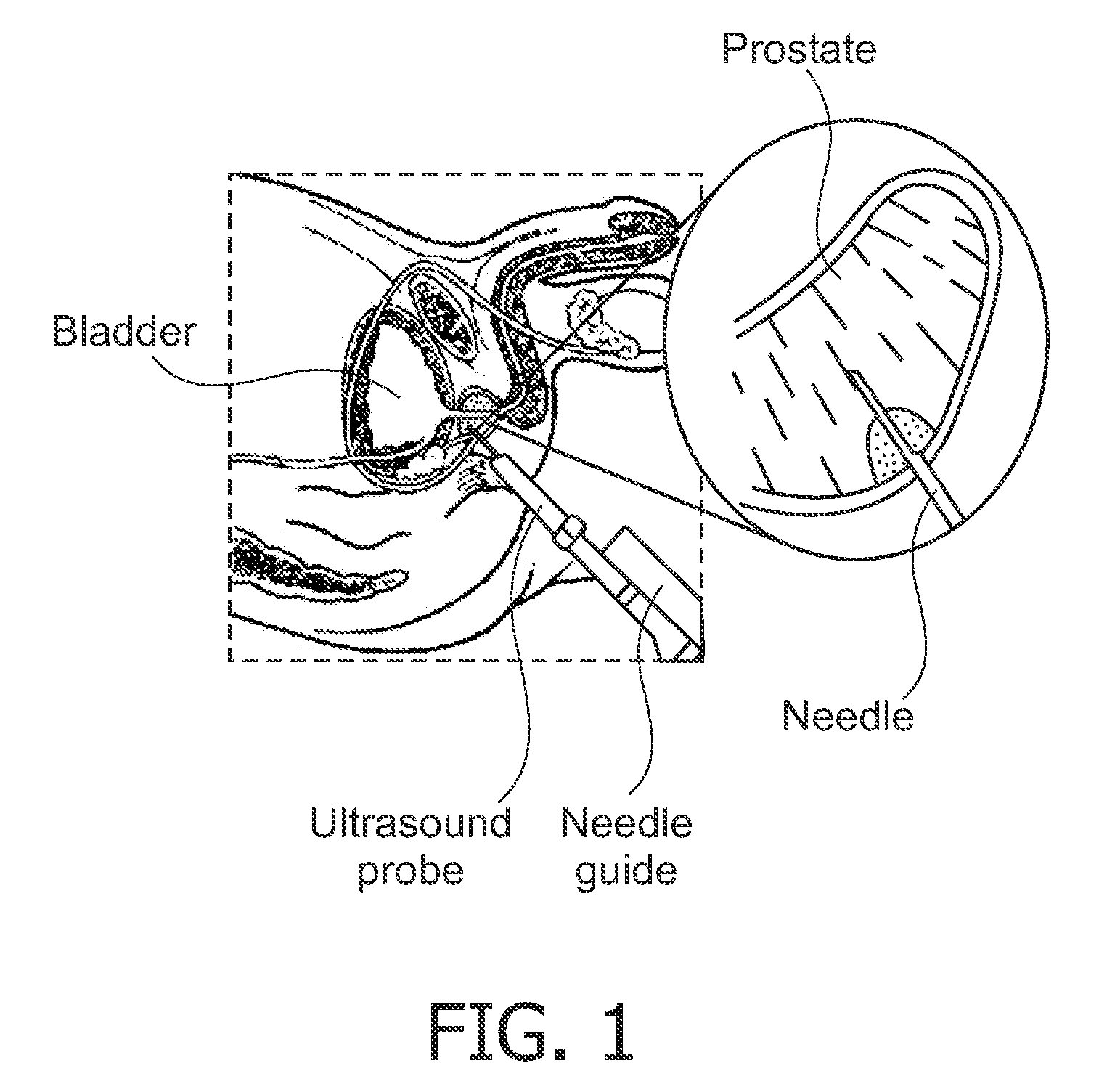
This invention discloses a method and apparatus to deliver medical devices to targeted locations within human tissues using imaging data. The method enables the target location to be obtained from one imaging system, followed by the use of a second imaging system to verify the final position of the device. In particular, the invention discloses a method based on the initial identification of tissue targets using MR imaging, followed by the use of ultrasound imaging to verify and monitor accurate needle positioning. The invention can be used for acquiring biopsy samples to determine the grade and stage of cancer in various tissues including the brain, breast, abdomen, spine, liver, and kidney. The method is also useful for delivery of markers to a specific site to facilitate surgical removal of diseased tissue, or for the targeted delivery of applicators that destroy diseased tissues in-situ.
Owner:INVIVO CORP
Ablation treatment of bone metastases
InactiveUS6881214B2Easily toleratedReduce the dependency of the patientDiagnosticsSurgical needlesElectrode placementHigh frequency power
Ablative treatment of metastatic bone tumors and relief of pain associated with metastatic bone tumors is achieved by heat ablation of the bone tumor or tissue near the bone tumor by an ablation probe. In one form the probe is an electrode coupled to a high frequency power supply to provide ablative heating of tissue proximate to an electrode that is placed in or near the bone tumor. Cooling of the electrode by fluid circulation from a cooling apparatus outside the patient's body may be used to enlarge the region of high frequency heating around the electrode. Image guidance of the electrode placement may be monitored by an imaging device. Tracking of the electrode by an image-guided navigator helps in placement of the electrode with respect to the configuration of the bone and bone metastasis. A set of tools accommodates biopsy and various shapes of electrodes according to clinical requirements. Several forms of electrodes, energy delivery and cooling apparatus and methods accommodate the specific objectives.
Owner:COVIDIEN AG
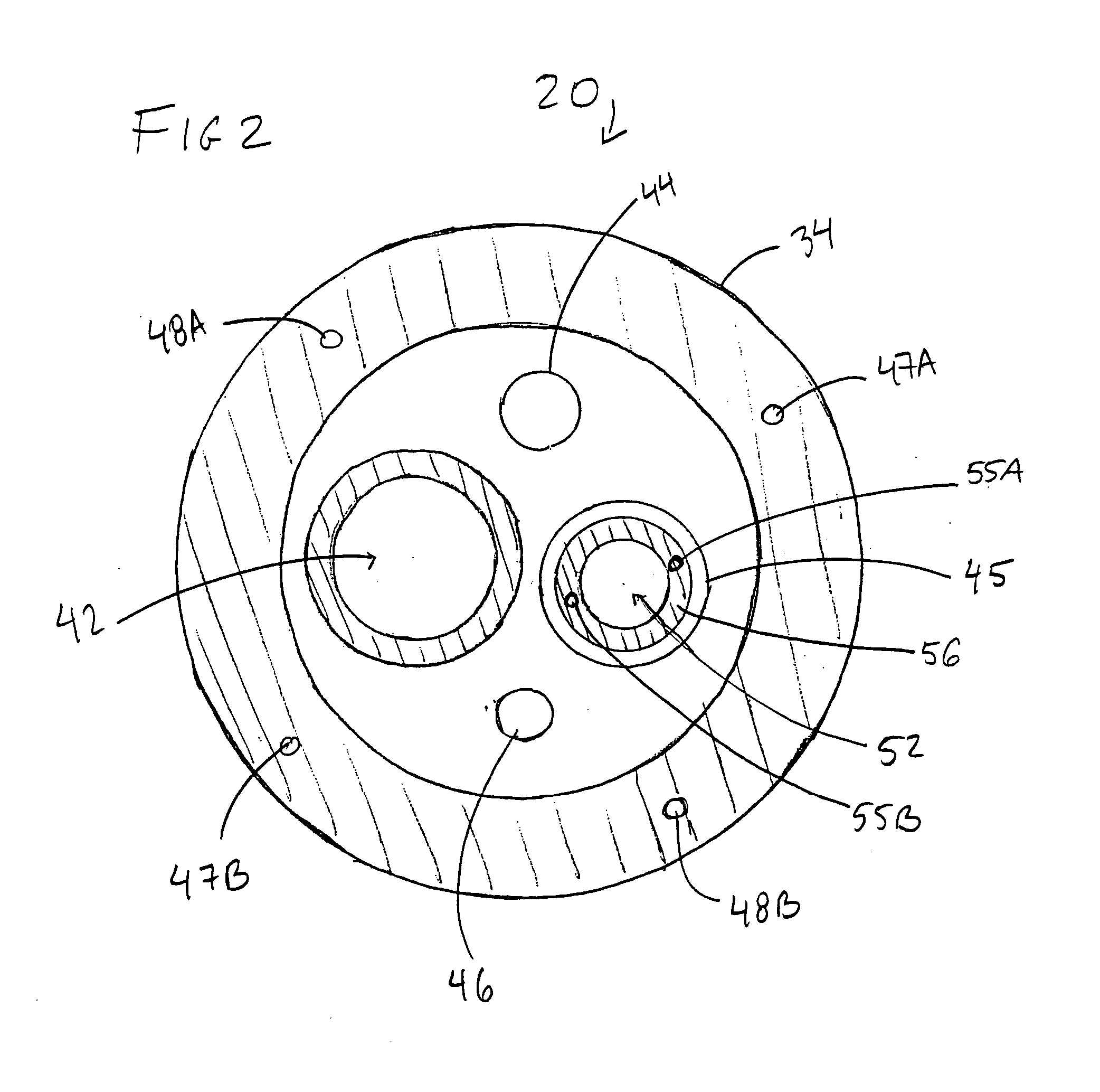
Rotational core biopsy device with liquid cryogen adhesion probe
ActiveUS7402140B2Avoid destructionReduces seedingSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsControl systemBody tissue
Owner:SCION MEDICAL
Hybrid imaging method to monitor medical device delivery and patient support for use in the method
ActiveUS7379769B2Easy procedureConvenient treatmentSurgical needlesStretcherLiver and kidneySurgical removal
Owner:INVIVO CORP
Marker device and method of deploying a cavity marker using a surgical biopsy device
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
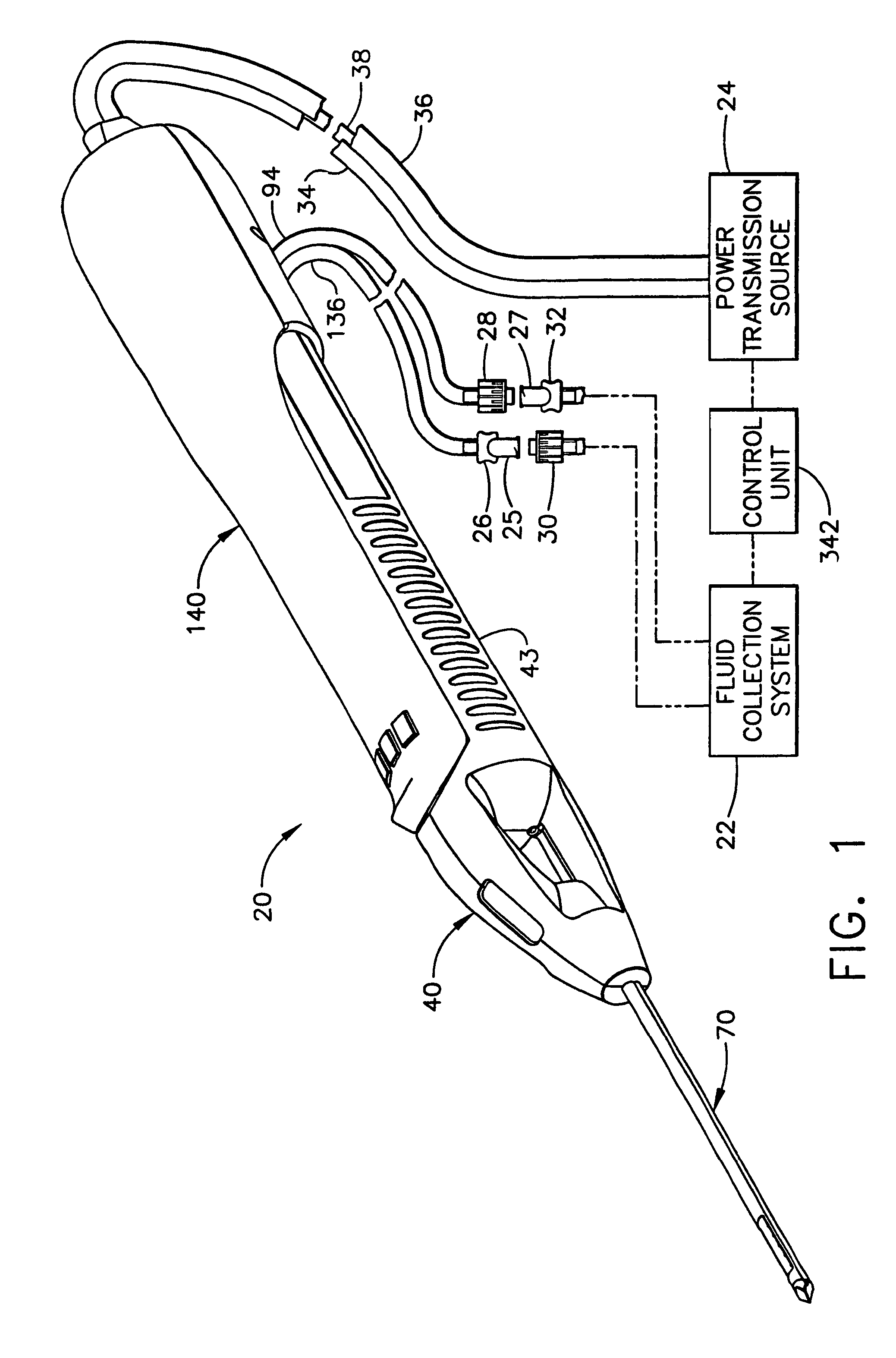
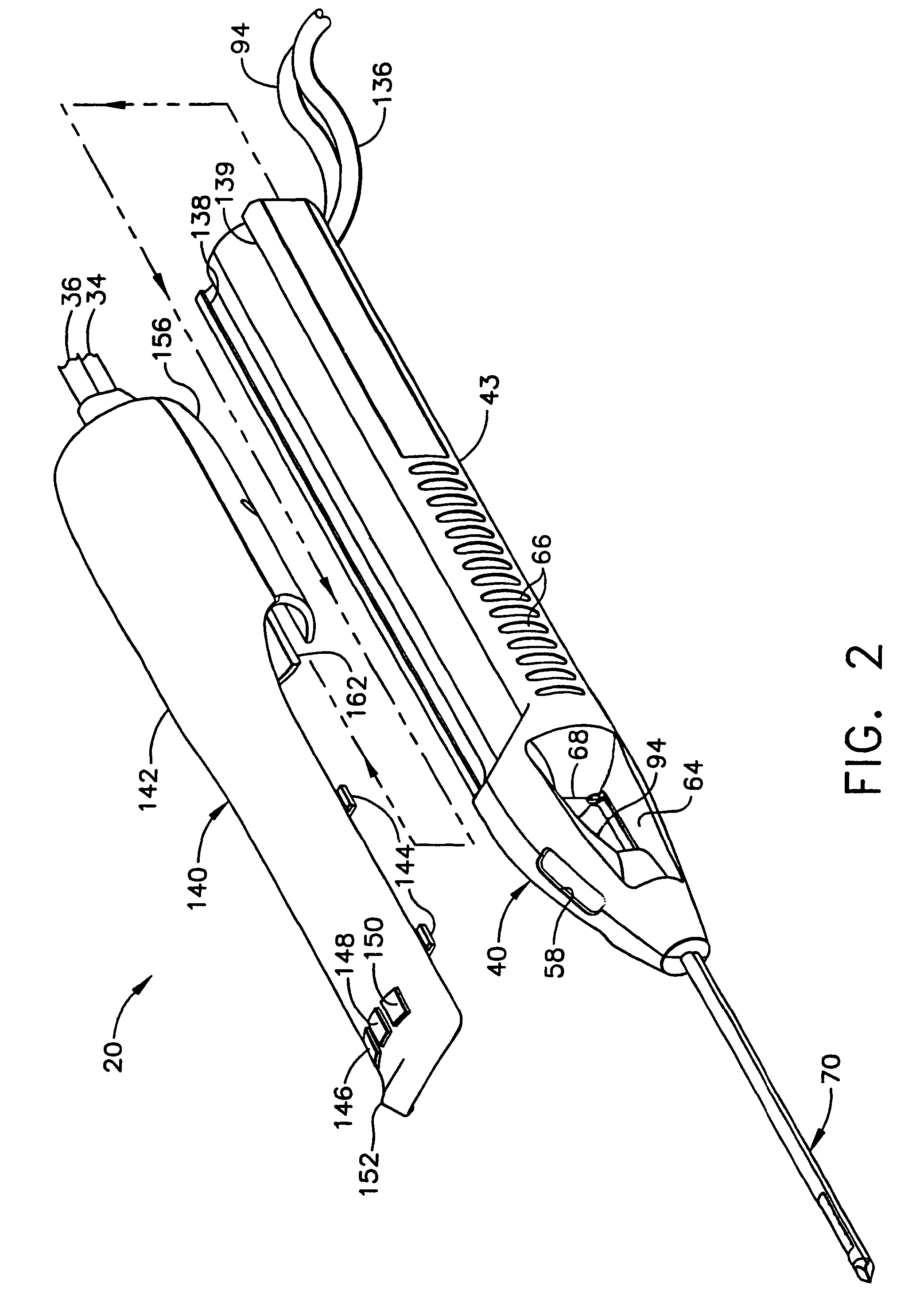
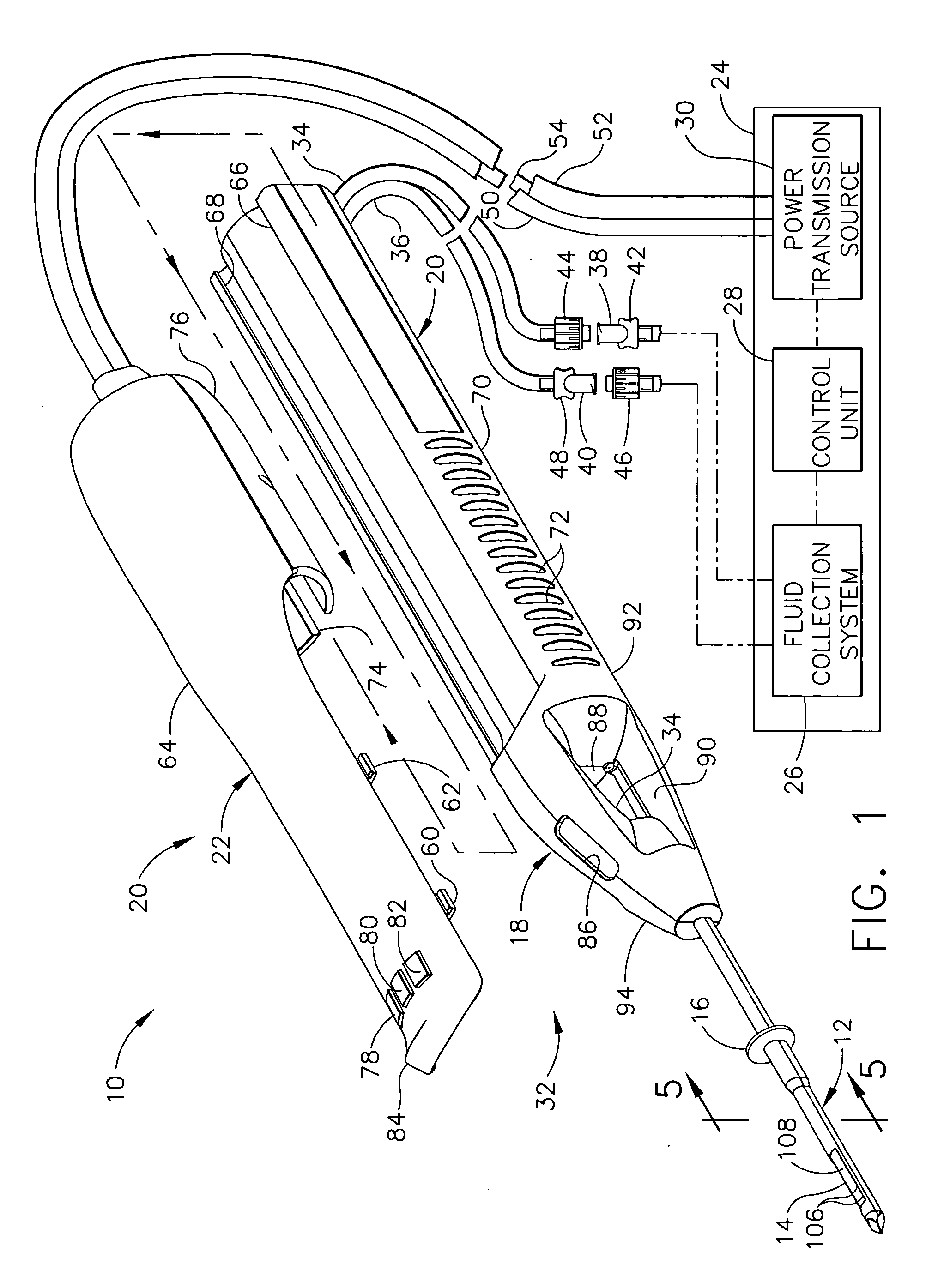
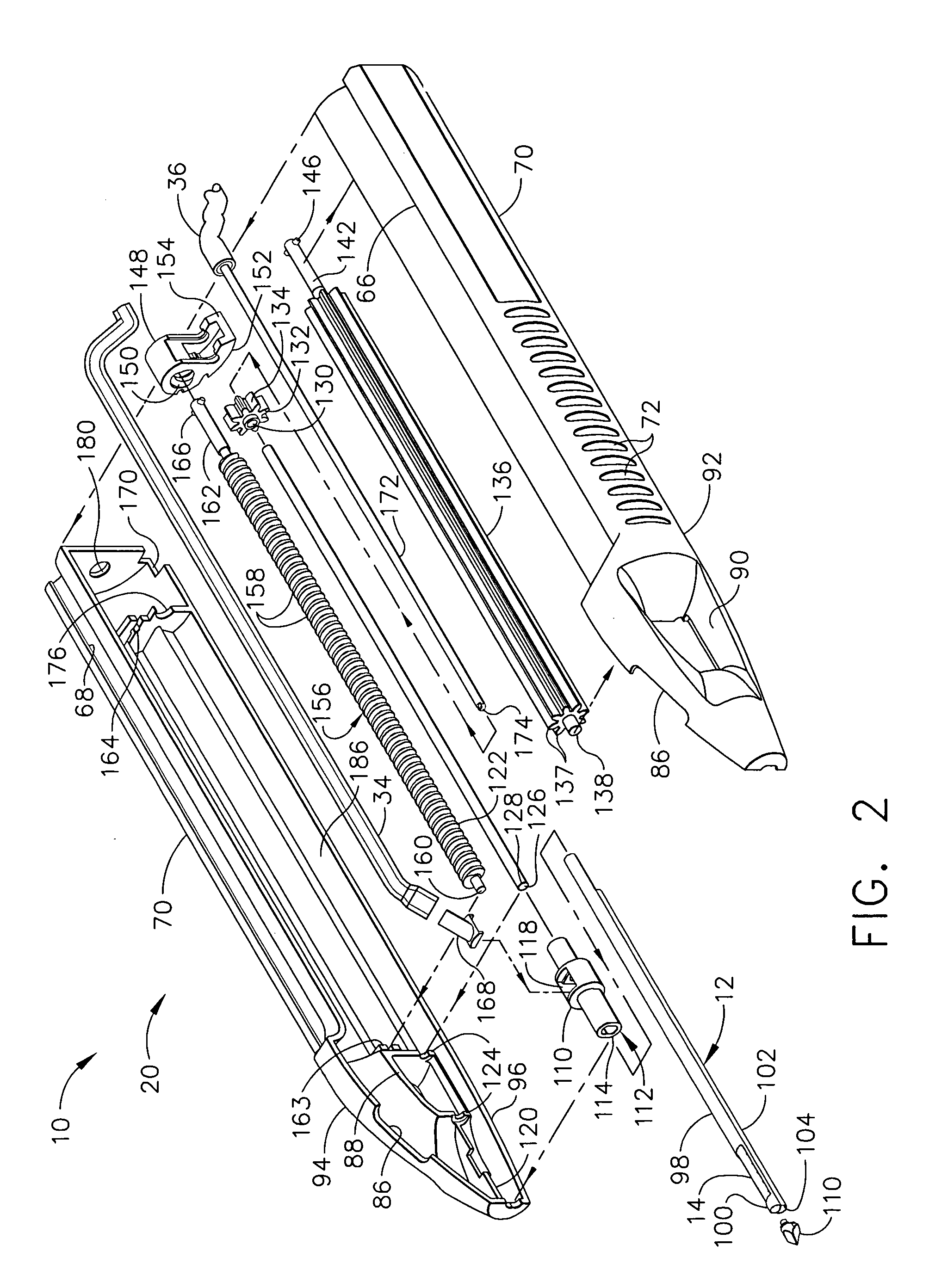
Surgical device for the collection of soft tissue
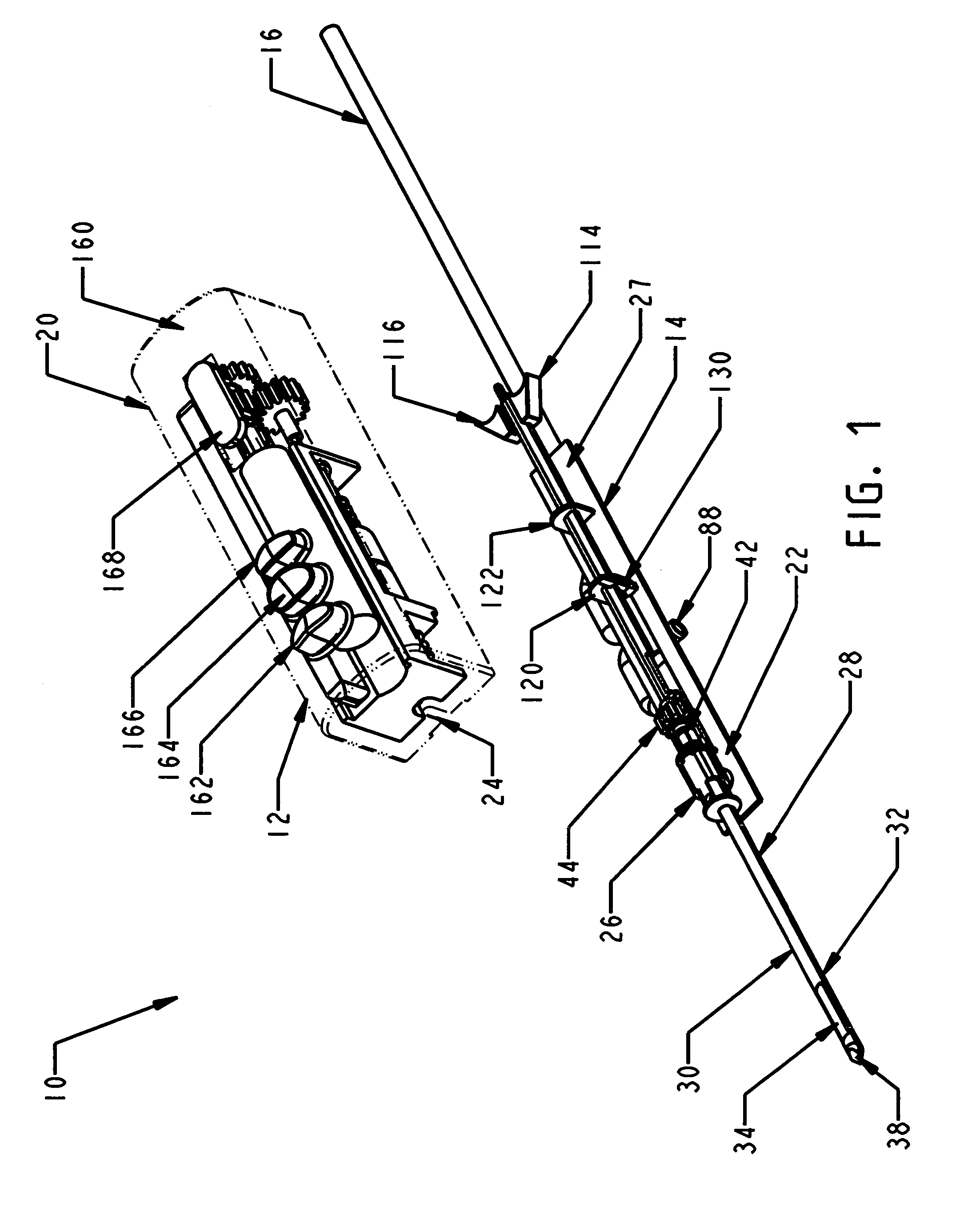
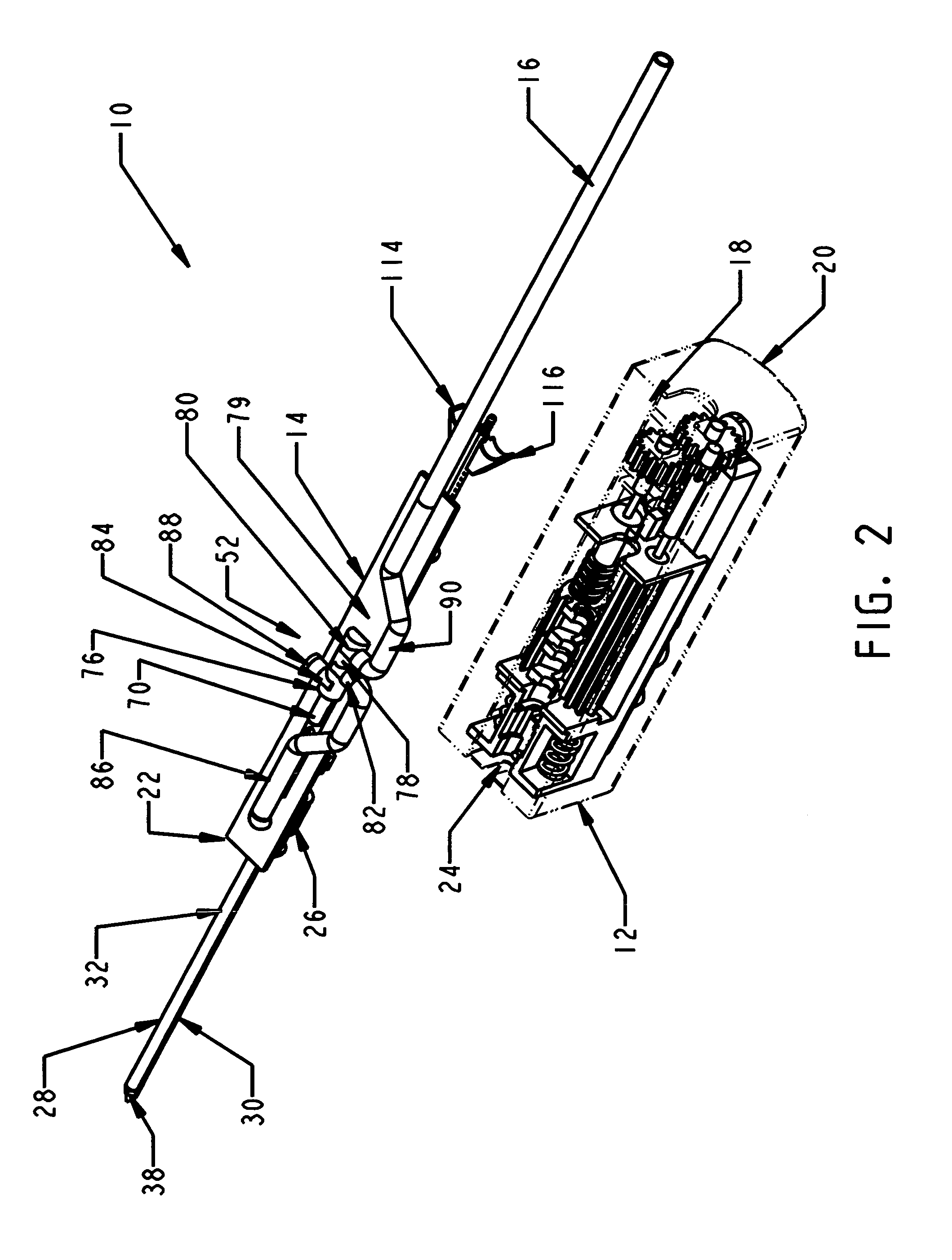
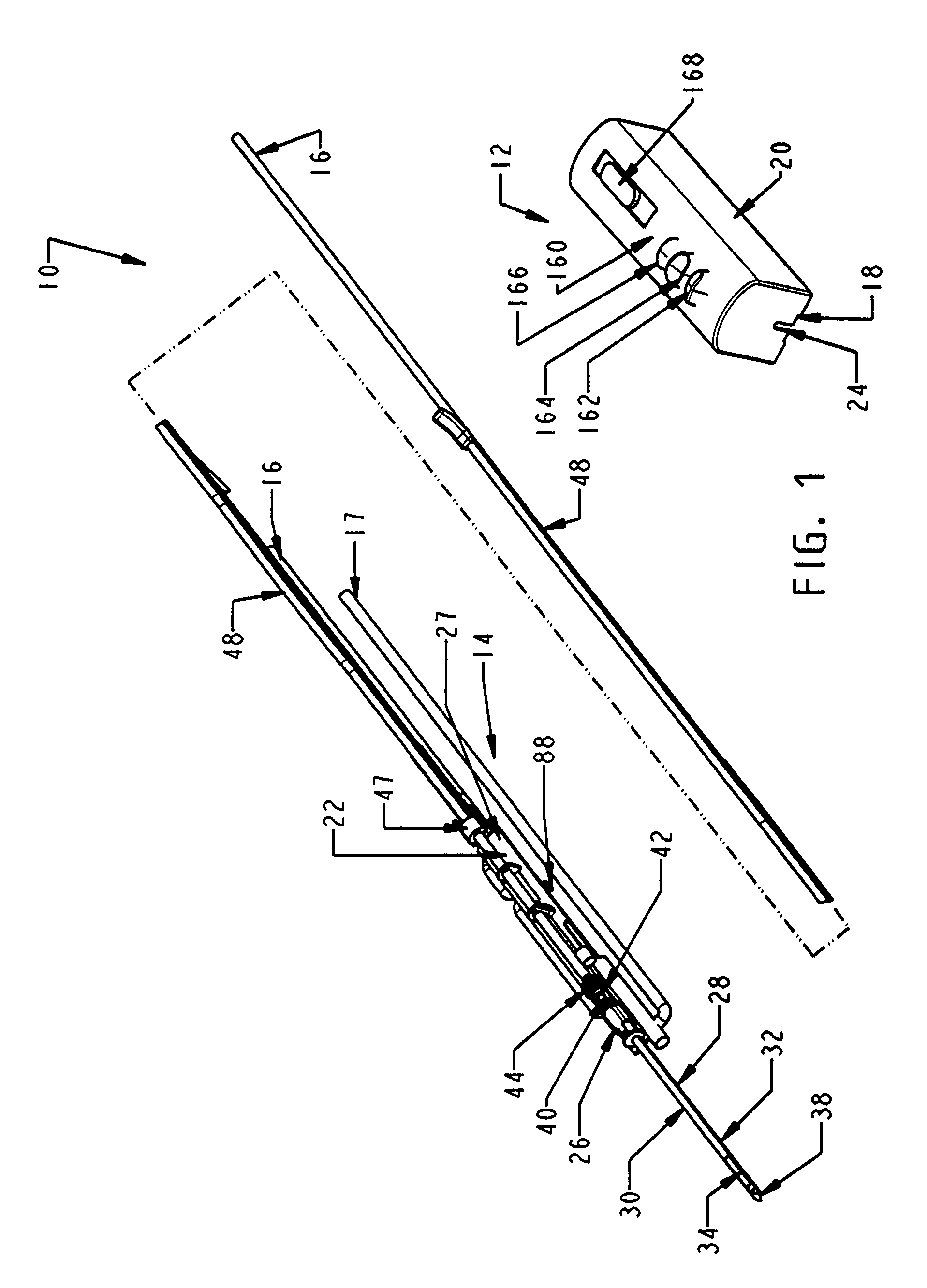
A handheld biopsy device is provided for the collection of soft tissue samples from a surgical patient. In a preferred embodiment, the biopsy device comprises a handpiece, a fluid collection system, and a power transmission source. The handpiece is configured for grasping by a single hand, and being independently manipulatable by hand for movement of the instrument toward and away from the patient. An elongated piercer extends from the distal end of the handpiece. The piercer has a sharpened distal end for entering the tissue and a port located proximal to the sharpened distal end for receiving a portion of tissue mass. An elongated cutter is disposed coaxially relative to a piercer lumen of the piercer. A distal blade of the cutter slides distally past the port of the piercer to severe the tissue portion drawn into the port by vacuum. The cutter is retracted to a most proximal position for removal of the tissue portion from a cutter lumen of the cutter. The handpiece further comprises a holster for detachably connecting a cutter rotational transmission and a cutter axial transmission to the power transmission source.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
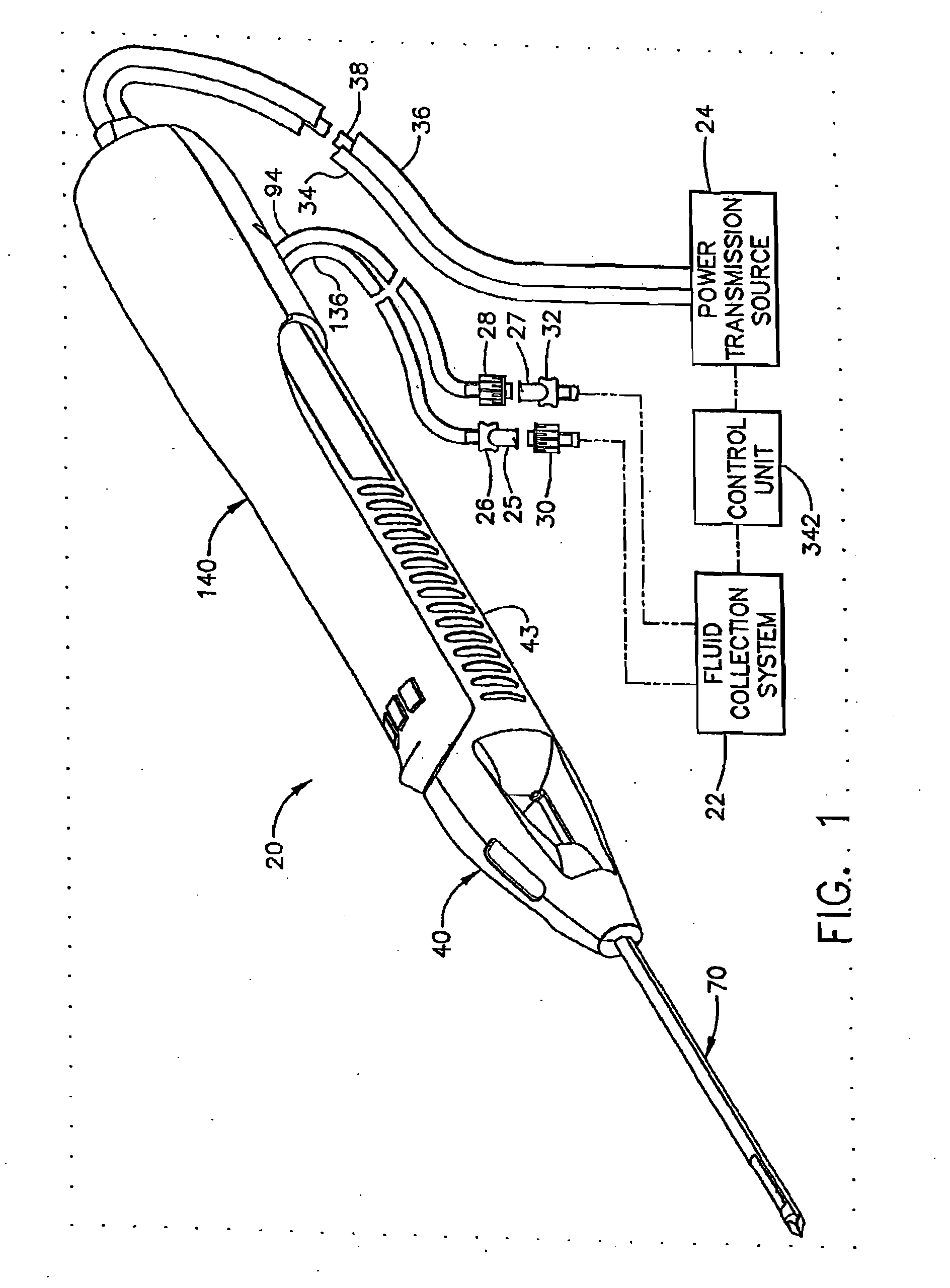
Surgical Device for The Collection of Soft Tissue
A handheld biopsy device is provided for the collection of soft tissue samples from a surgical patient. In a preferred embodiment, the biopsy device comprises a handpiece, a fluid collection system, and a power transmission source. The handpiece is configured for grasping by a single hand, and being independently manipulatable by hand for movement of the instrument toward and away from the patient. An elongated piercer extends from the distal end of the handpiece. The piercer has a sharpened distal end for entering the tissue and a port located proximal to the sharpened distal end for receiving a portion of tissue mass. An elongated cutter is disposed coaxially relative to a piercer lumen of the piercer. A distal blade of the cutter slides distally past the port of the piercer to severe the tissue portion drawn into the port by vacuum. The cutter is retracted to a most proximal position for removal of the tissue portion from a cutter lumen of the cutter. The handpiece further comprises a holster for detachably connecting a cutter rotation transmission and a cutter axial transmission to the power transmission source.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
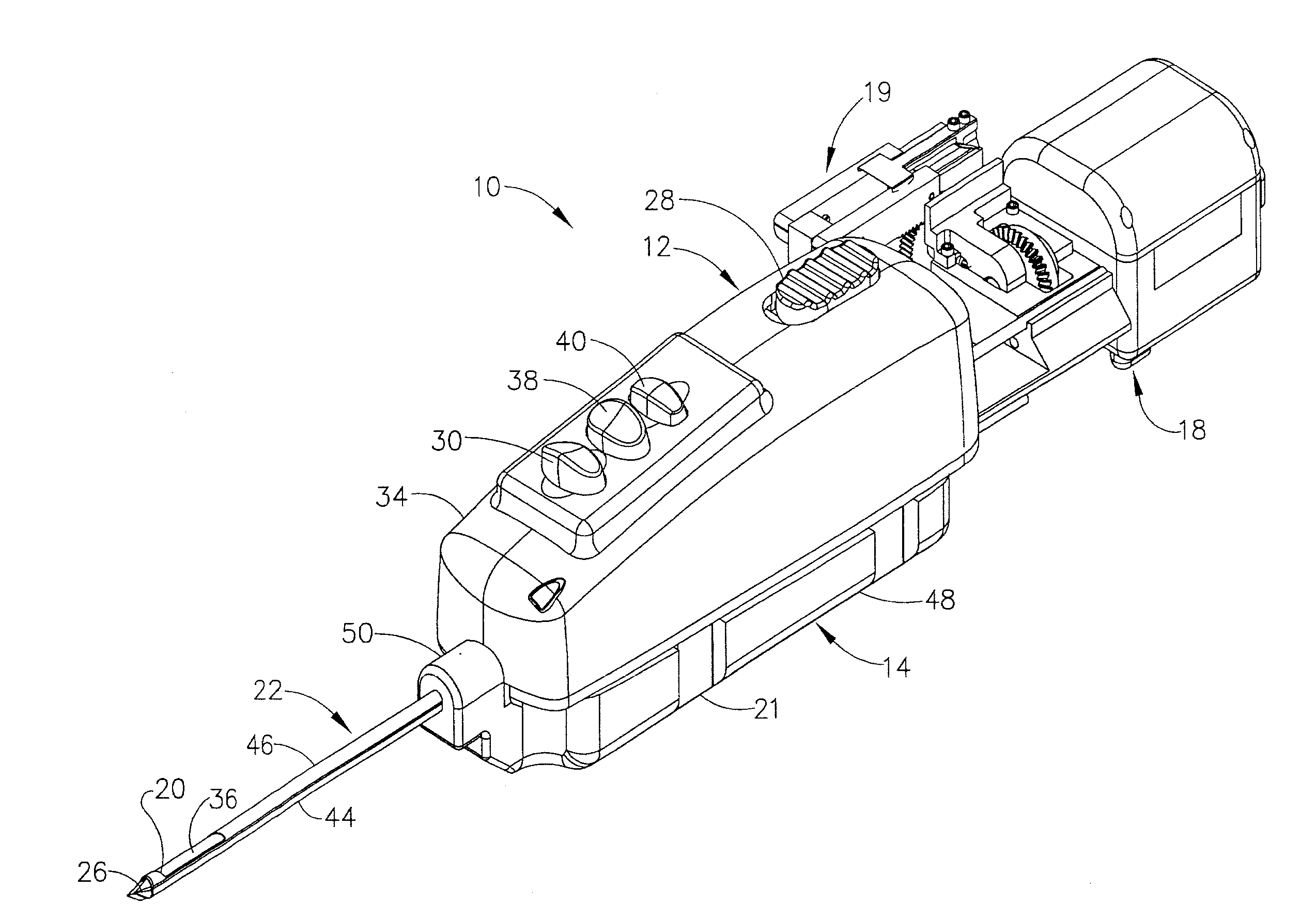
Method of conducting a needle biopsy procedure
InactiveUS7008383B1Reduce harmReduce frictionSurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsBiopsy procedureReciprocating motion
A vibration assisted needle device is disclosed for use in medical procedures such as needle aspiration biopsies. Reciprocation of the needle, such as a biopsy needle, eases the advance of the needle through tissue, penetration of the site of interest and the collection of sample at a site of interest. The device comprises a housing defining a chamber, a needle support external to the chamber for supporting a needle and a mechanism in the chamber for causing reciprocatory motion of the needle support. The needle support is preferably external to the housing. A syringe support may be connected to the housing for supporting a syringe. The reciprocatory mechanism may comprise means for converting rotational motion into reciprocating motion, such as a bearing or a rotor with a circumferential, angled groove on its surface, coupled to the needle support. The bearing or the rotor may be driven by a rotational motor, preferably located outside of the housing, or by a hydraulically driven turbine within the housing. Alternatively, the reciprocatory mechanism means may comprise a stationary solenoid and a movable solenoid for being coupled to the needle. Preferably, a second stationary solenoid is provided and the moving solenoid is between the two stationary solenoids. Energization of the stationary solenoid or solenoids by an alternating current for example, and energization of the movable solenoid by a direct current, or vice versa, attracts and repulses the movable solenoid, causing reciprocation of the needle. Methods and systems using the vibration assisted needle device are also disclosed.
Owner:FONAR
Vacuum assisted biopsy device
A biopsy device is disclosed that comprises a cutting element mounted to a handpiece and a vacuum chamber. The cutting element comprises a stylet assembly and an outer cannula assembly. The stylet assembly includes a stylet that includes an open proximal end and a tissue opening at a distal end thereof. The tissue receiving opening is in communication with a lumen extending through the stylet. The outer cannula assembly includes an outer cannula that is slidably mounted over the stylet and has an open distal end with a cutting edge formed thereon. The vacuum chamber is in communication with the lumen of the stylet. The stylet is selectively advanced distally outwardly with respect to outer cannula to expose the tissue opening to targeted tissue. The outer cannula is selectively advanced over the tissue opening to sever tissue, while vacuum is generated in the vacuum chamber and delivered to the tissue opening through the lumen. The vacuum causes tissue to be drawn into and maintained in the tissue opening while the outer cannula severs tissue to obtain a biopsy core.
Owner:PROMEX TECH
Sealant Plug Delivery Methods
InactiveUS20050228309A1High precisionReduce the overall diameterSurgical needlesMedical devicesBiopsy procedureSkin surface
A bioabsorbable sealant plug that expands in response to contact with moisture in a mammalian body is optimally positioned in a biopsy tract to seal the biopsy tract when a biopsy procedure is completed. In a first method, the leading end of the sealant plug is advanced through the lumen of a coaxial needle by a plunger until a leading end of a supporting leg abuts the patient's skin surface. A second method is performed with a pistol-shaped tool having a trigger that enables adjustment of the plunger. A third embodiment includes a plunger having a bifurcated end that grasps the plug. A fourth embodiment has a turning nut that causes compression of a gasket that clamps down on the plug. A supporting rod and coaxial needle are in parallel relation to one another in a fifth embodiment.
Owner:MEDICAL DEVICE TECH
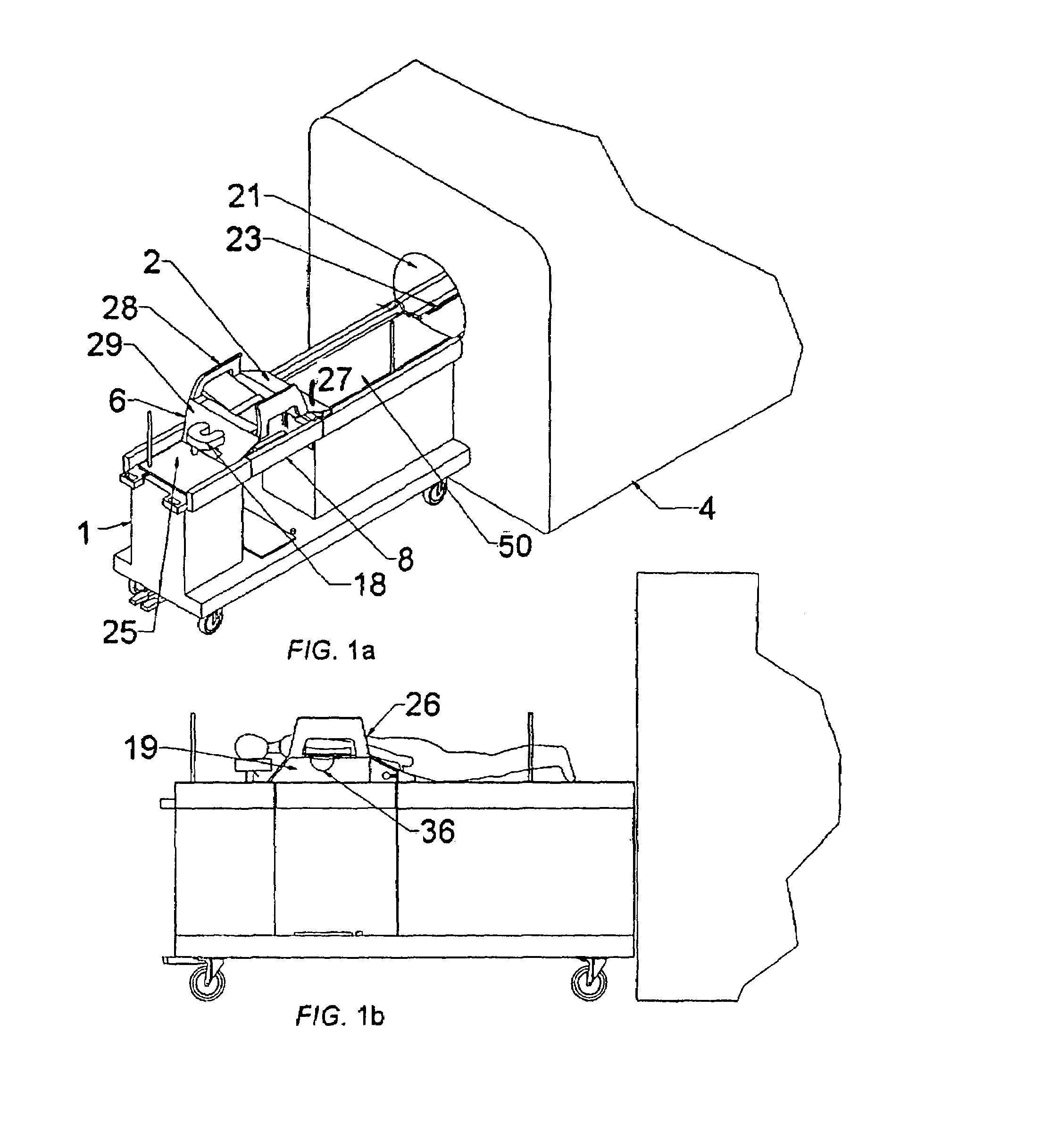
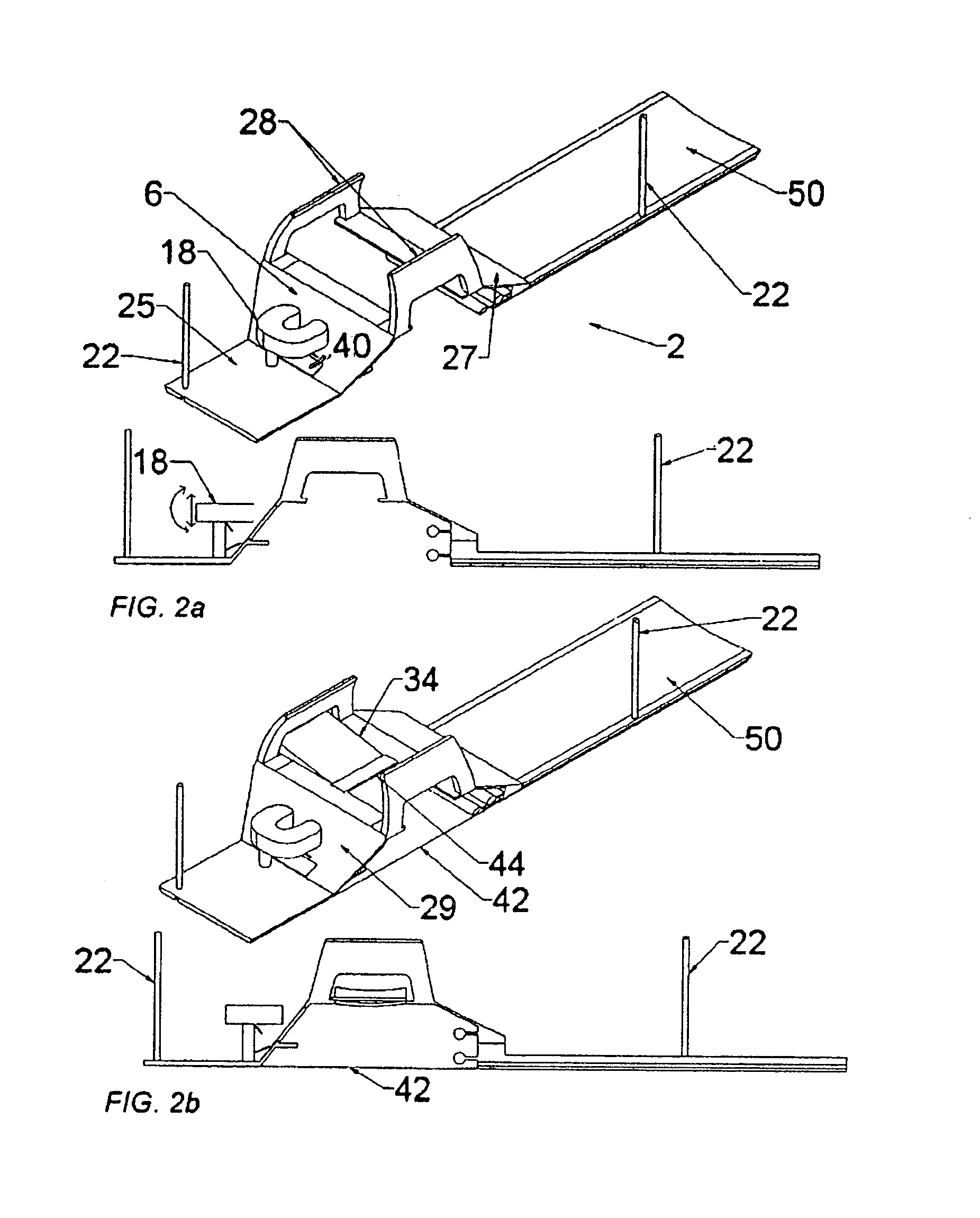
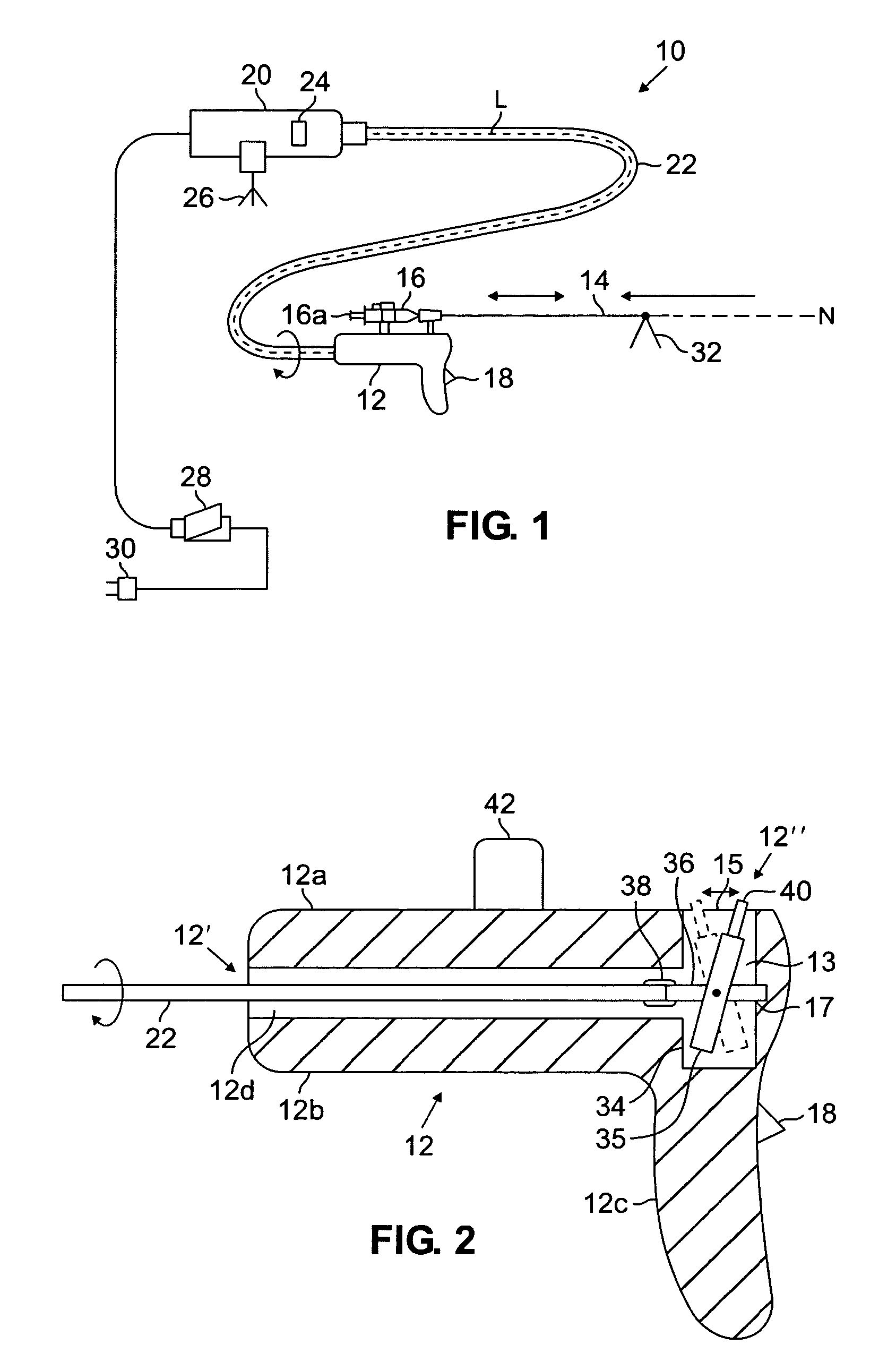
Breast biopsy and therapy system for magnetic resonance imagers
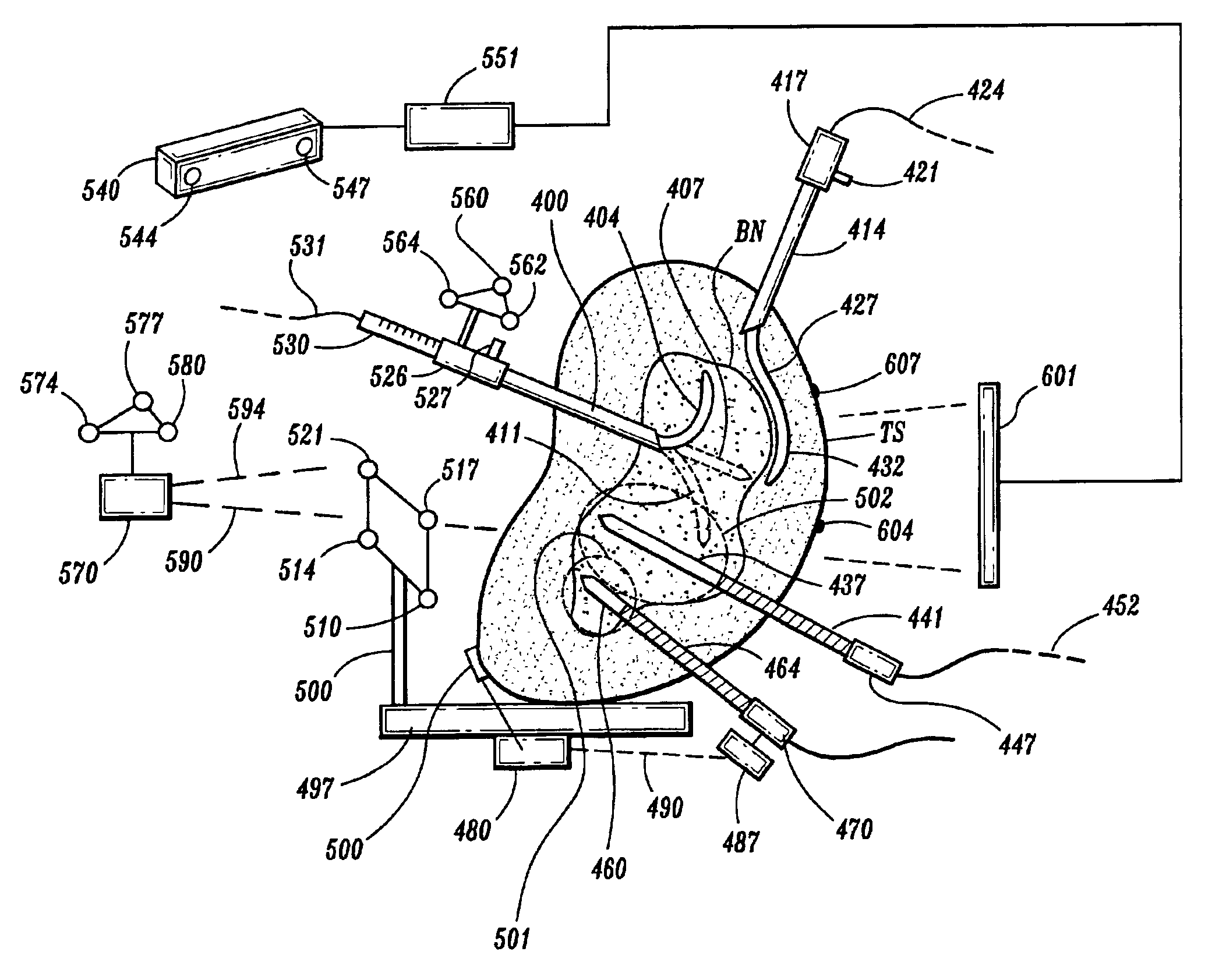
The present invention describes a device for performing breast biopsies and / or therapy within magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) systems. The apparatus includes a RF receiver antenna for magnetic resonance imaging of the breast. The RF coil includes openings in the front and side to provide access to the breast during the procedure. Compression plates are integrated into the breast coil which compress the breast either laterally or in the head / feet direction as required for optimal access to the breast. The apparatus includes a mechanical device for positioning interventional instruments in the breast such as biopsy or therapy instruments. The mechanical positioning devices position the instrument along the desired trajectory to the target site and insert the instrument into the breast while the patient remains inside the MRI scanner. Real time MR images may be acquired during instrument alignment and insertion to verify the trajectory. The mechanical positioning devices allow manipulation of instruments in any type of MRI scanner, including high field MRI systems with cylindrical magnets. The positioning devices provide a means to overcome limited access to the patient in MRI scanners. The positioning devices may be manually operated by means of gears, drive shafts, cables or other mechanical means. Or they may be electronically controlled by means of MR compatible motorized drive systems. The devices may be remotely controlled from outside the magnet for MRI systems that have limited access to the patient in the magnet. An interface between the electronically controlled drivers and the MRI scanner computer can provide robotic control of the instrument.
Owner:LAMPMAN DAVID A +1
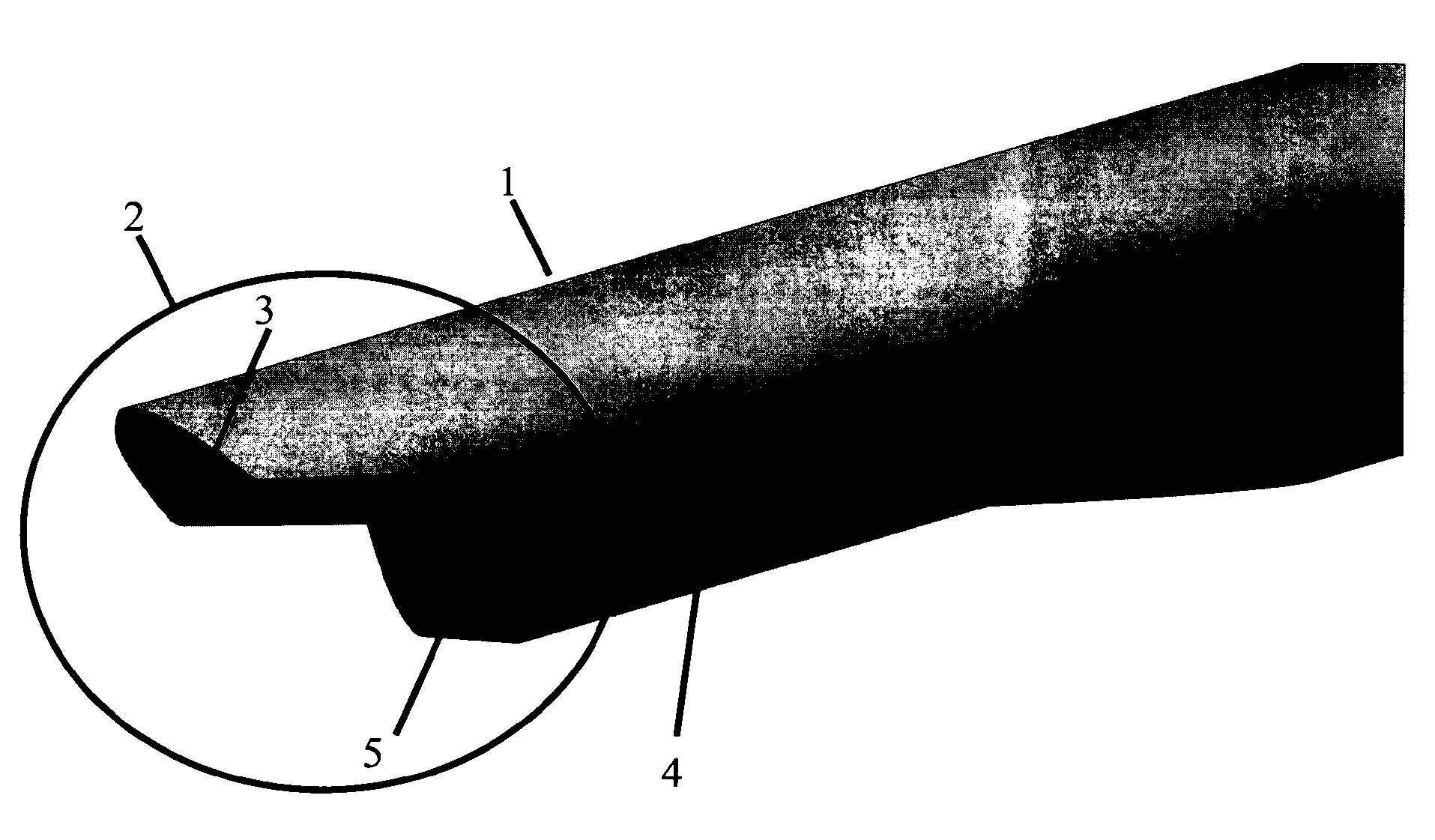
Sutureless guided skin biopsy system
A skin biopsy system covers all aspects of the biopsy procedure from initial incision to final closure. The system includes a flexible closure consisting of 4 elongated rigid members interconnected by flexible hinges. The opening within the closure is initially diamond-shaped, approximating an ellipse, which is then deformed or pinched to a narrow linear opening when the wound is closed. Included with the system is a knife which interacts with the closure to yield a guided incision of constant depth. The path of the knife is guided by interference between the blade and the inside faces of the closure while the depth is limited by interference of the handle proximal the blade and the top faces of the closure.
Owner:ALLEN MICHAEL E +1
Endoscopic apparatus with integrated multiple biopsy device
An imaging endoscope comprising a shaft having a proximal end adapted to be secured to a handle, and a distal end having a biopsy forceps disposed therein. The biopsy forceps includes one or more end-effector elements that are actuated with a control cable that may be connected to the handle. The endoscope shaft includes a biopsy sample lumen that is configured to receive a biopsy sample obtained from the forceps assembly. A sample collection apparatus is attached to the handle to capture multiple biopsy samples. In some embodiments, the endoscope is a single-use endoscope.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Vacuum syringe assisted biopsy device
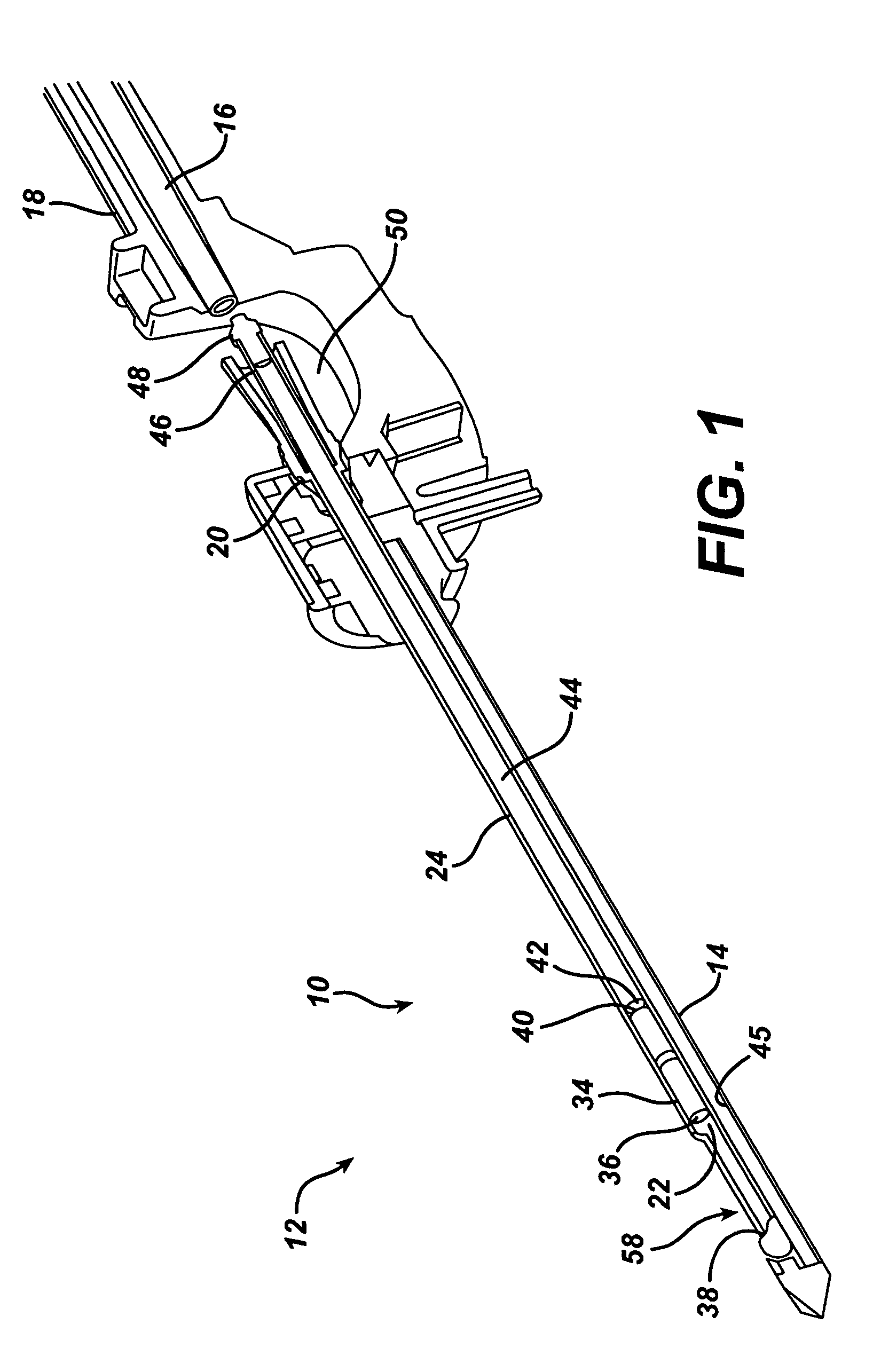
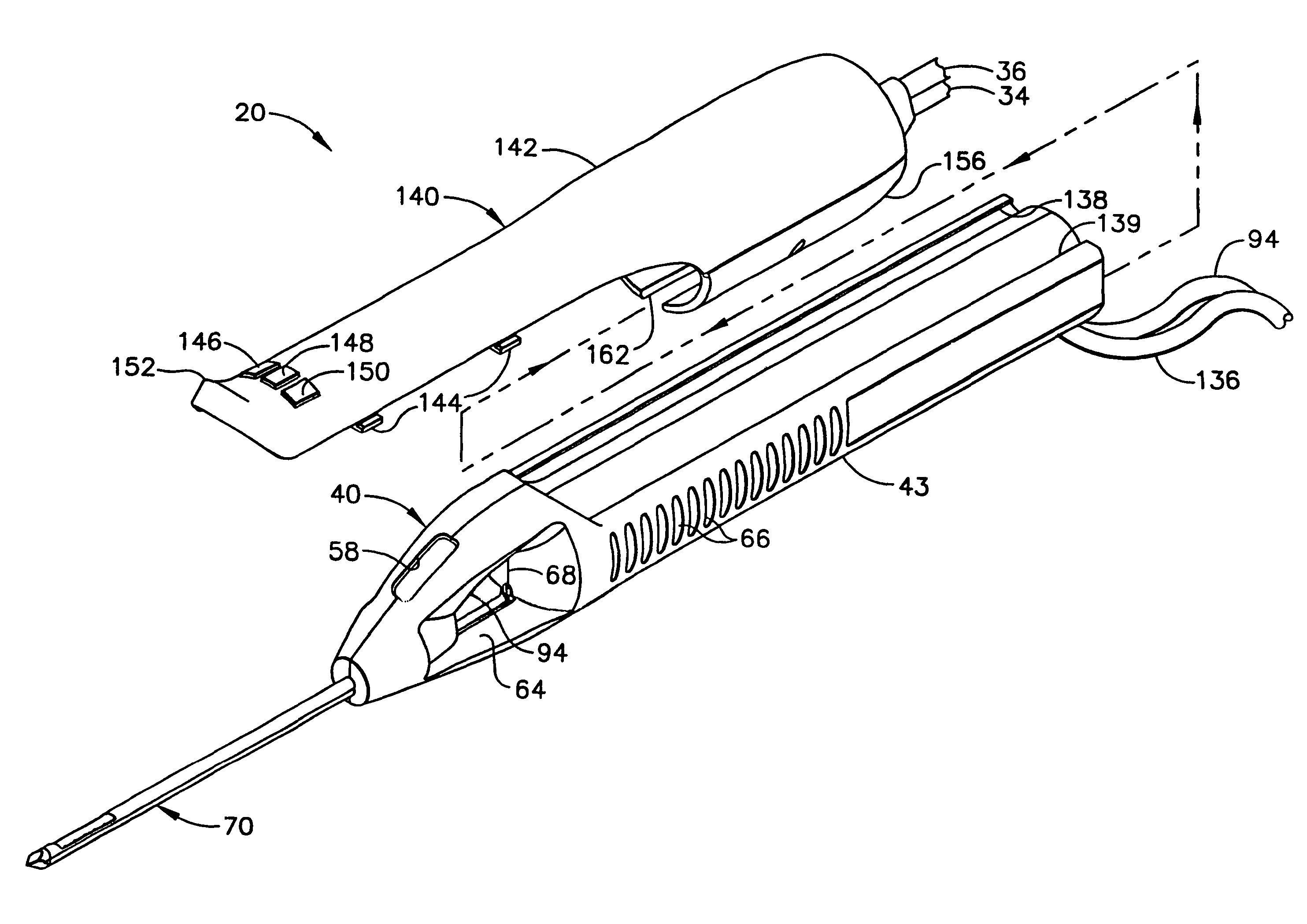
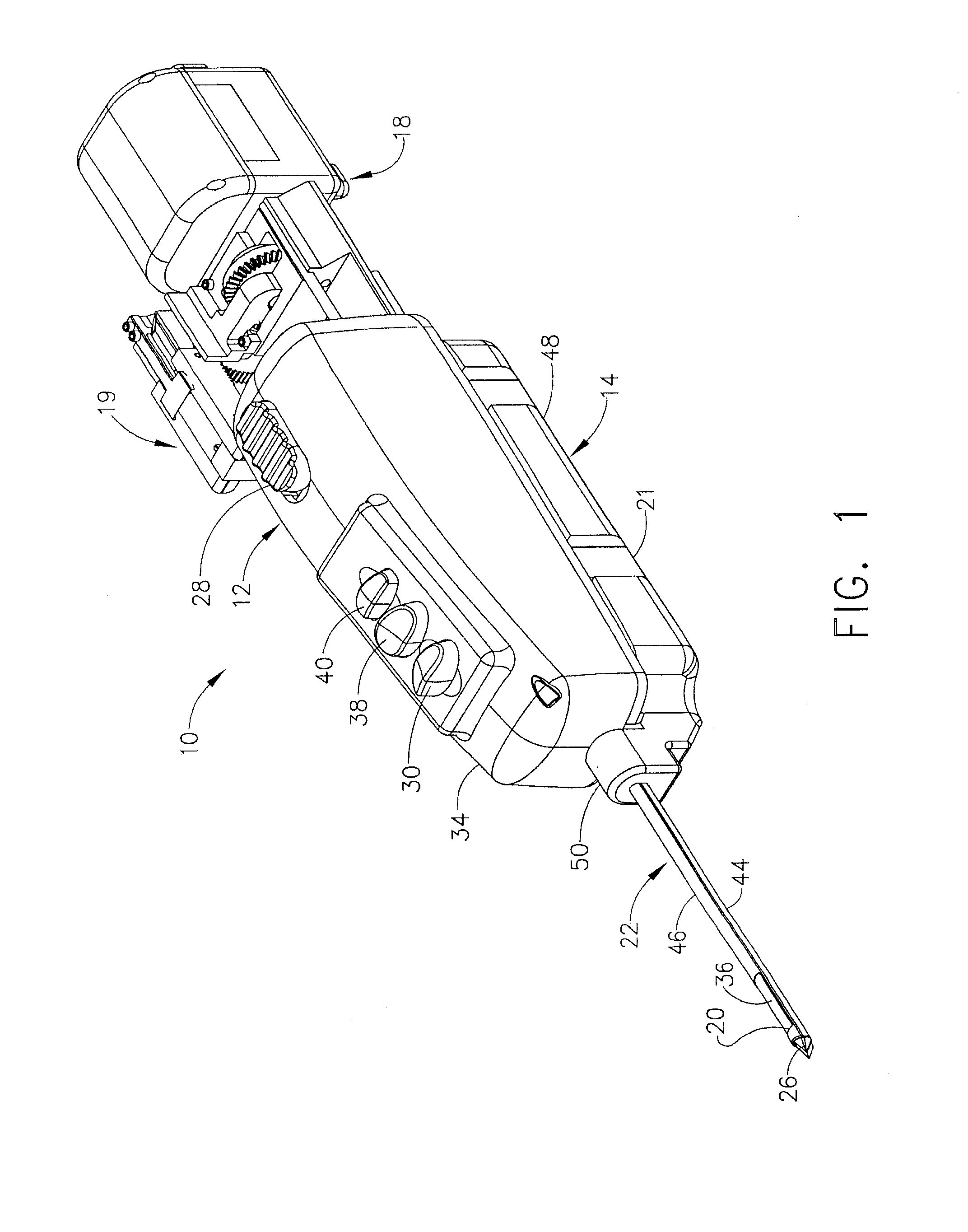
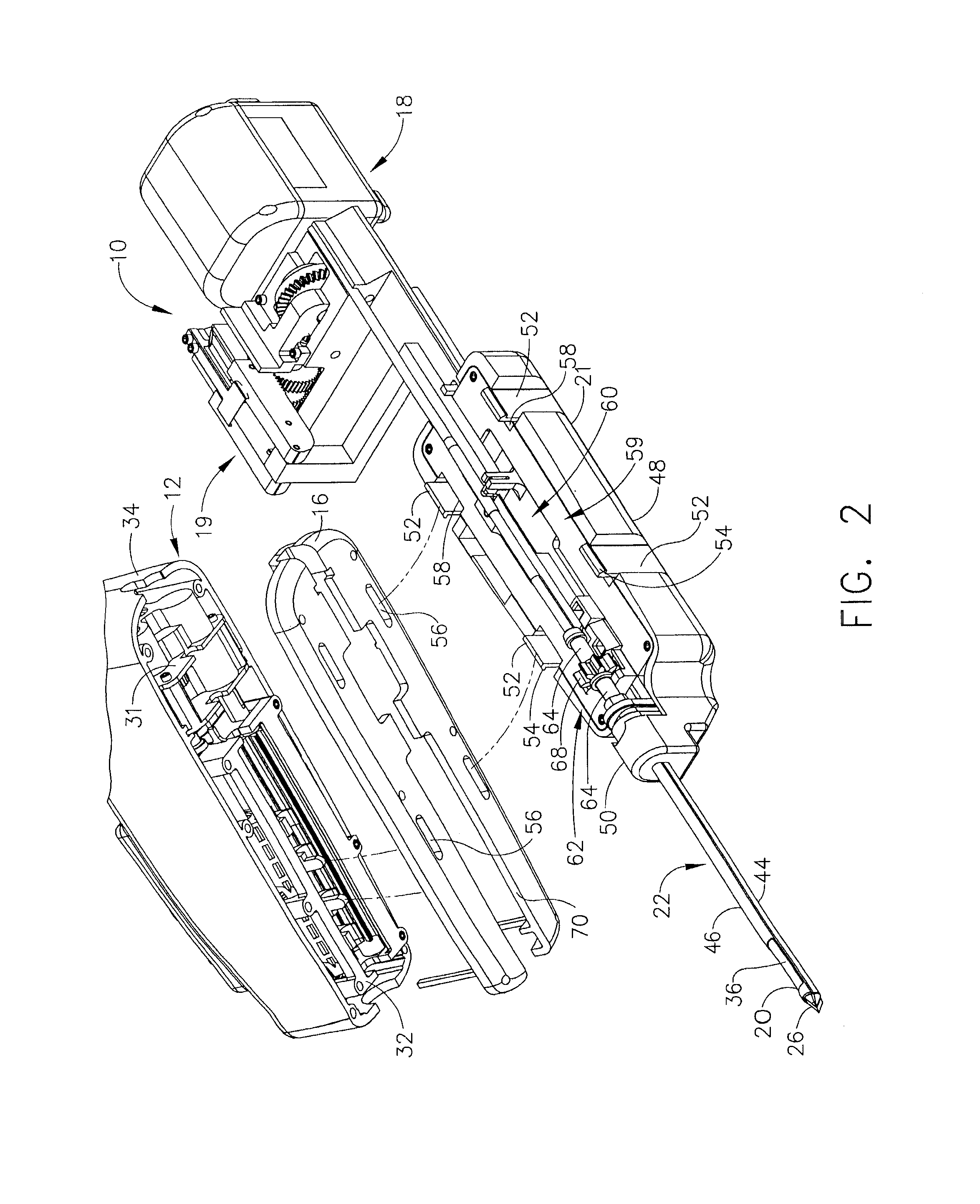
A biopsy device and method are provided for obtaining a tissue sample, such as a breast tissue biopsy sample. The biopsy device includes a disposable probe assembly with an outer cannula having a distal piercing tip, a cutter lumen, and a cutter tube that rotates and translates past a side aperture in the outer cannula to sever a tissue sample. The biopsy device also includes a reusable handpiece with an integral motor and power source to make a convenient, untethered control for use with ultrasonic imaging. The reusable handpiece incorporates a probe oscillation mode to assist when inserting the distal piercing tip into tissue. The motor also actuates a vacuum syringe in coordination with movement of the cutter tube to provide vacuum assistance in prolapsing tissue and retracting tissue samples.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
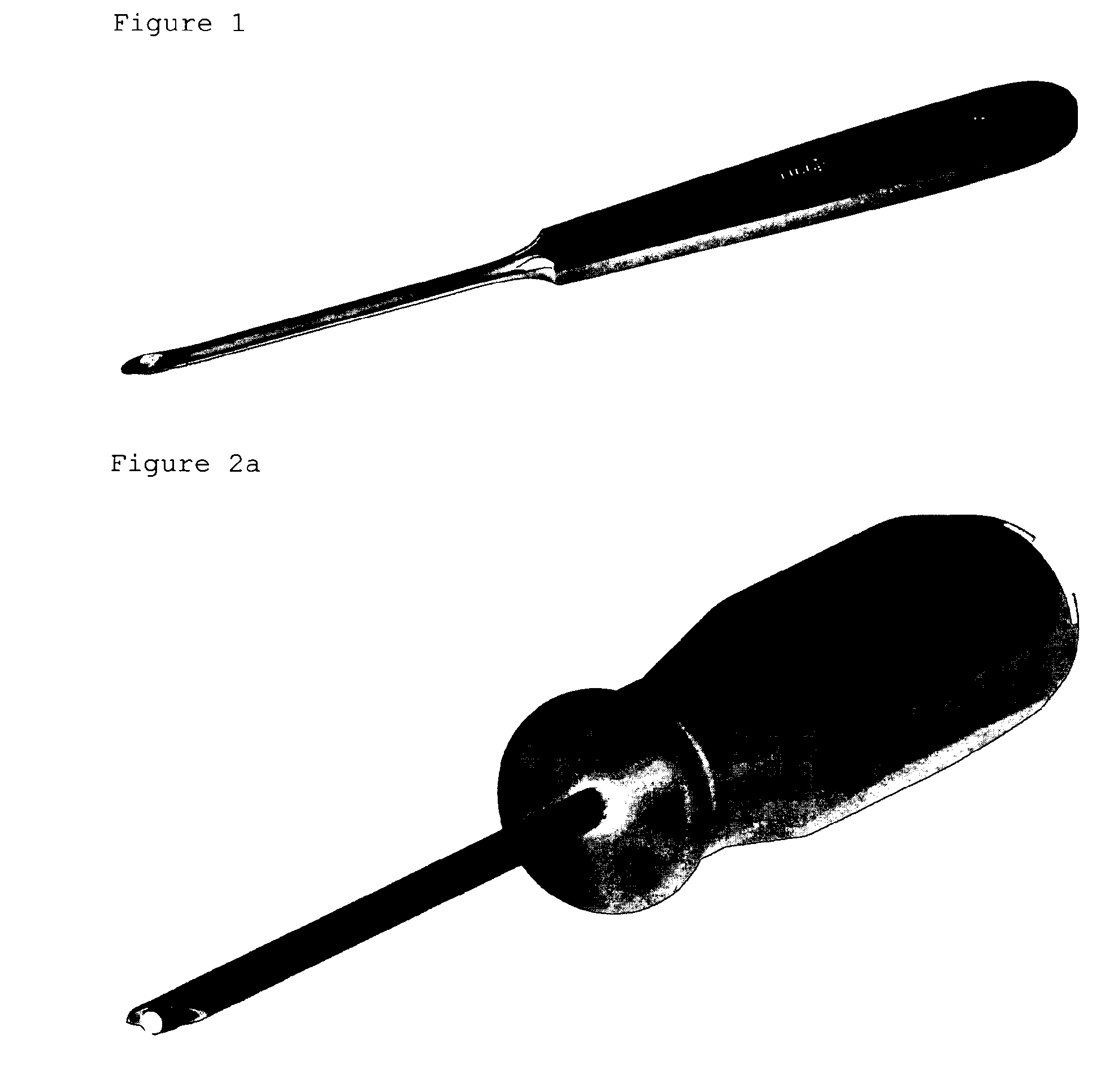
Biopsy device
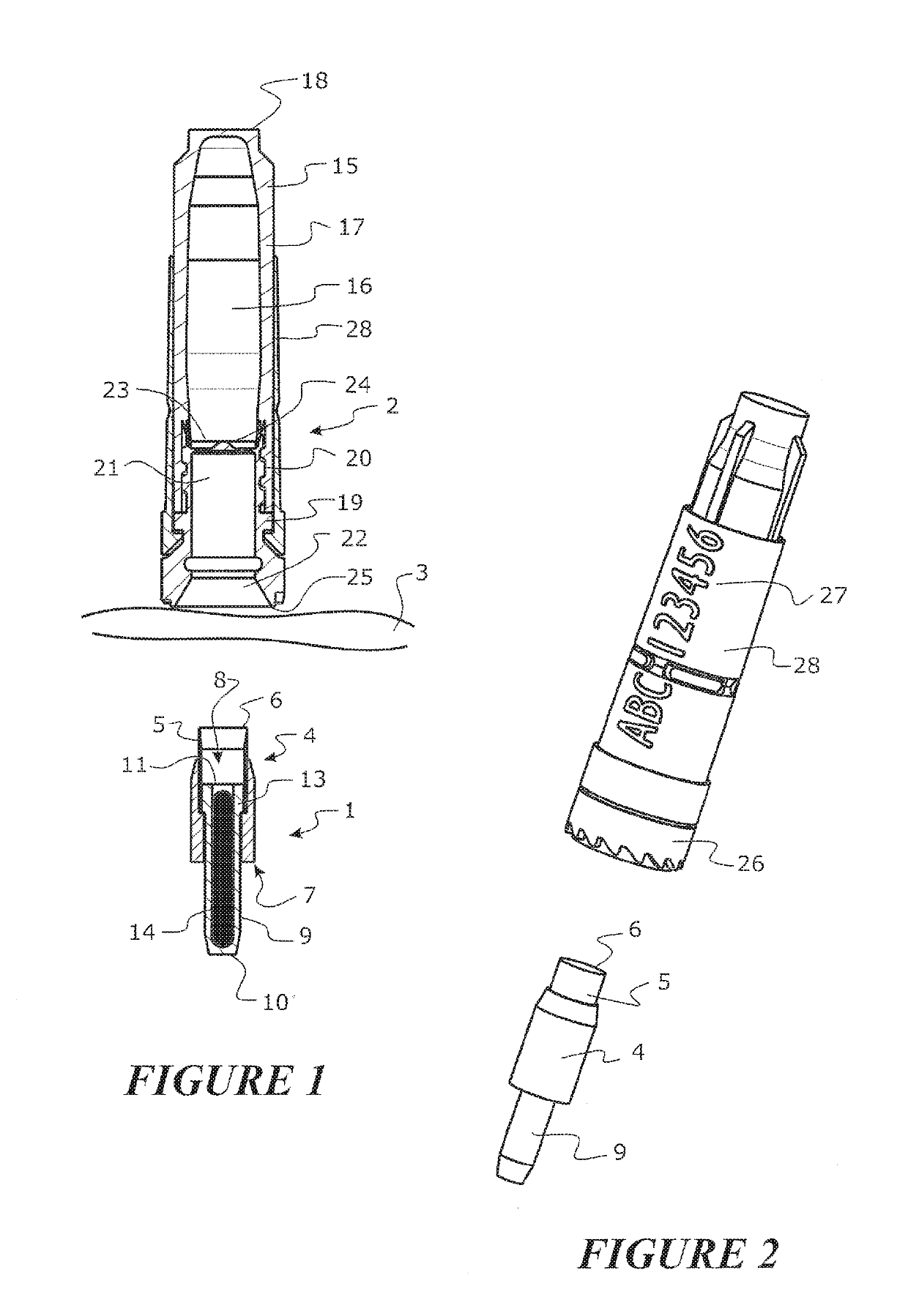
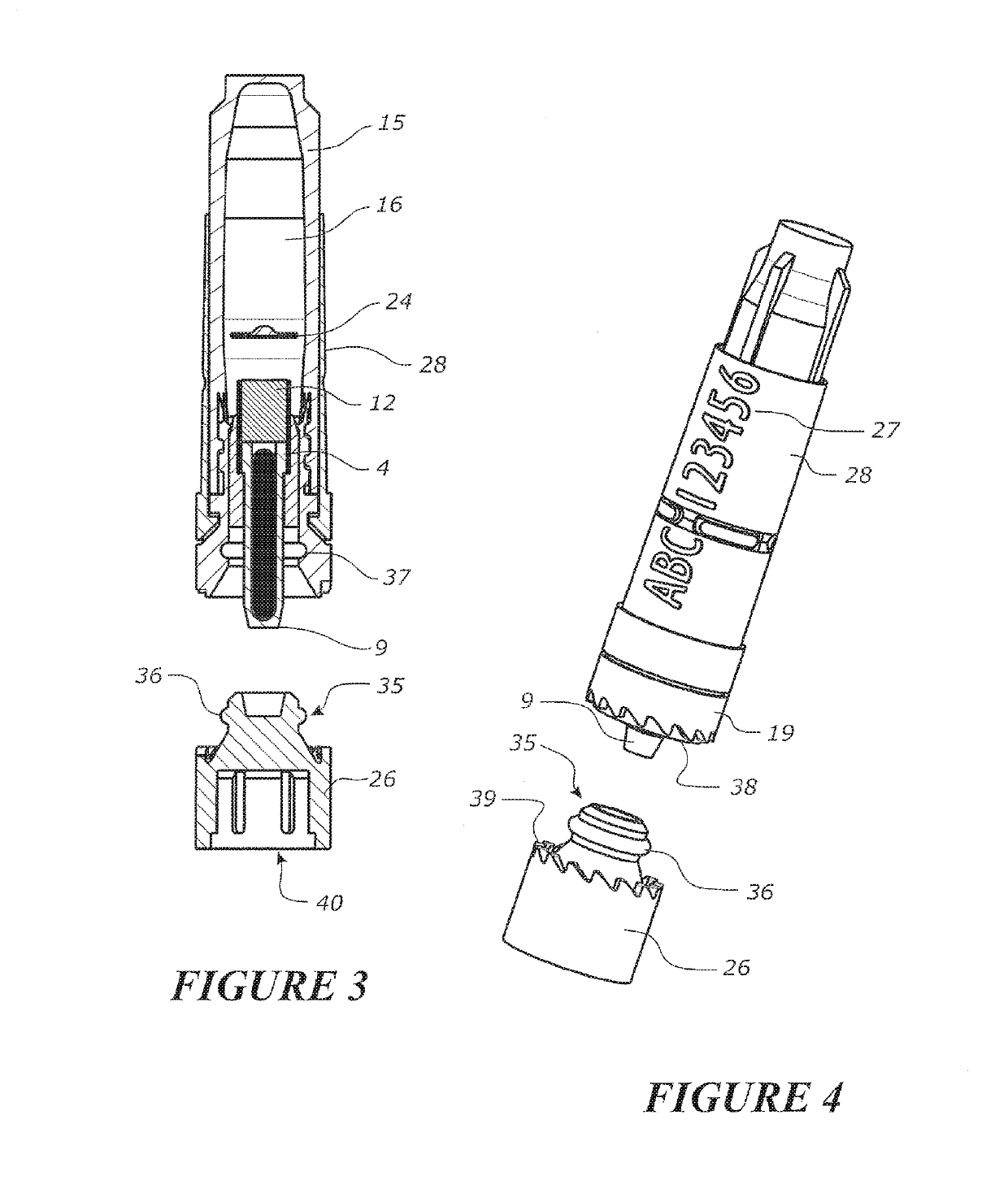
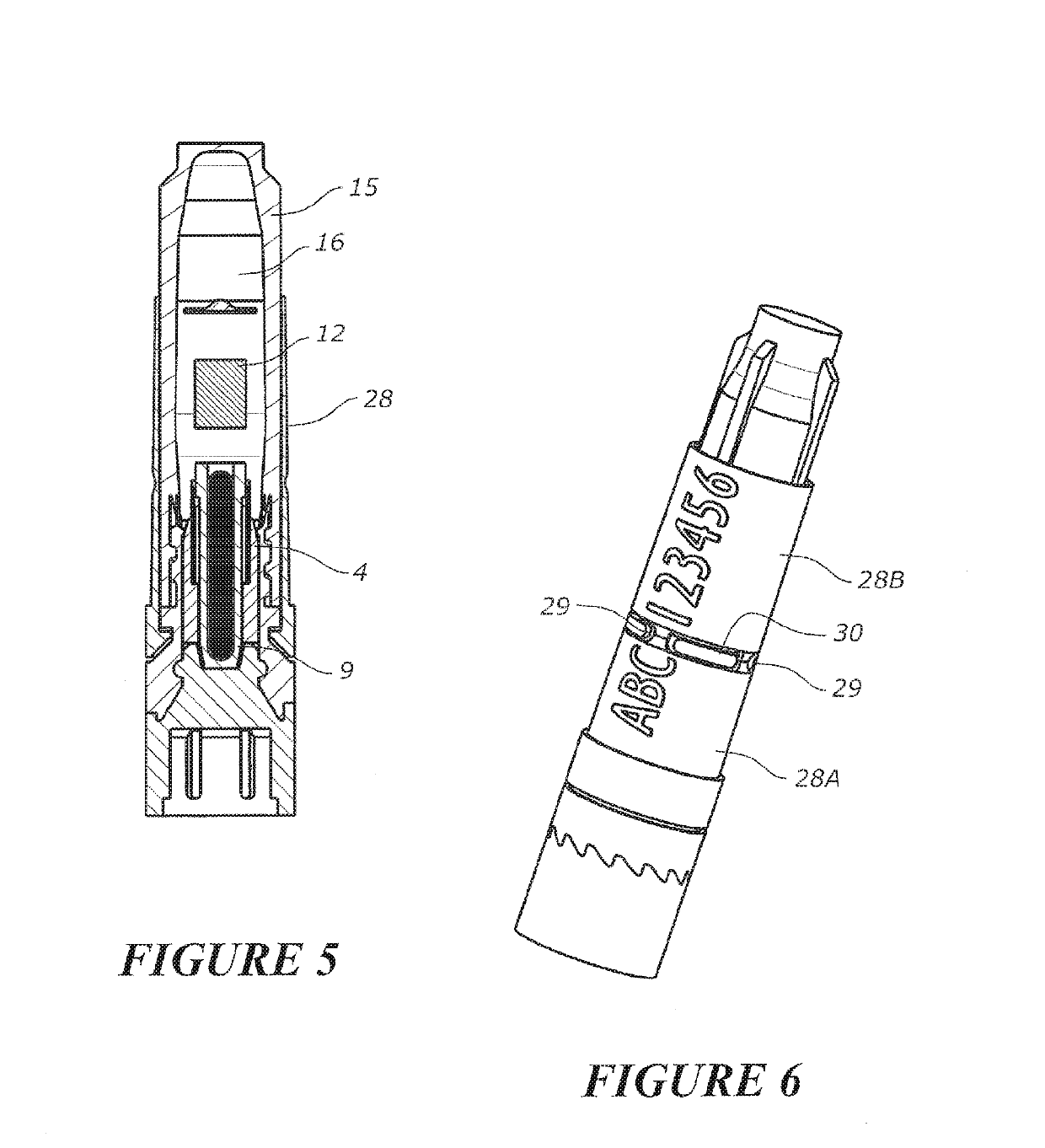
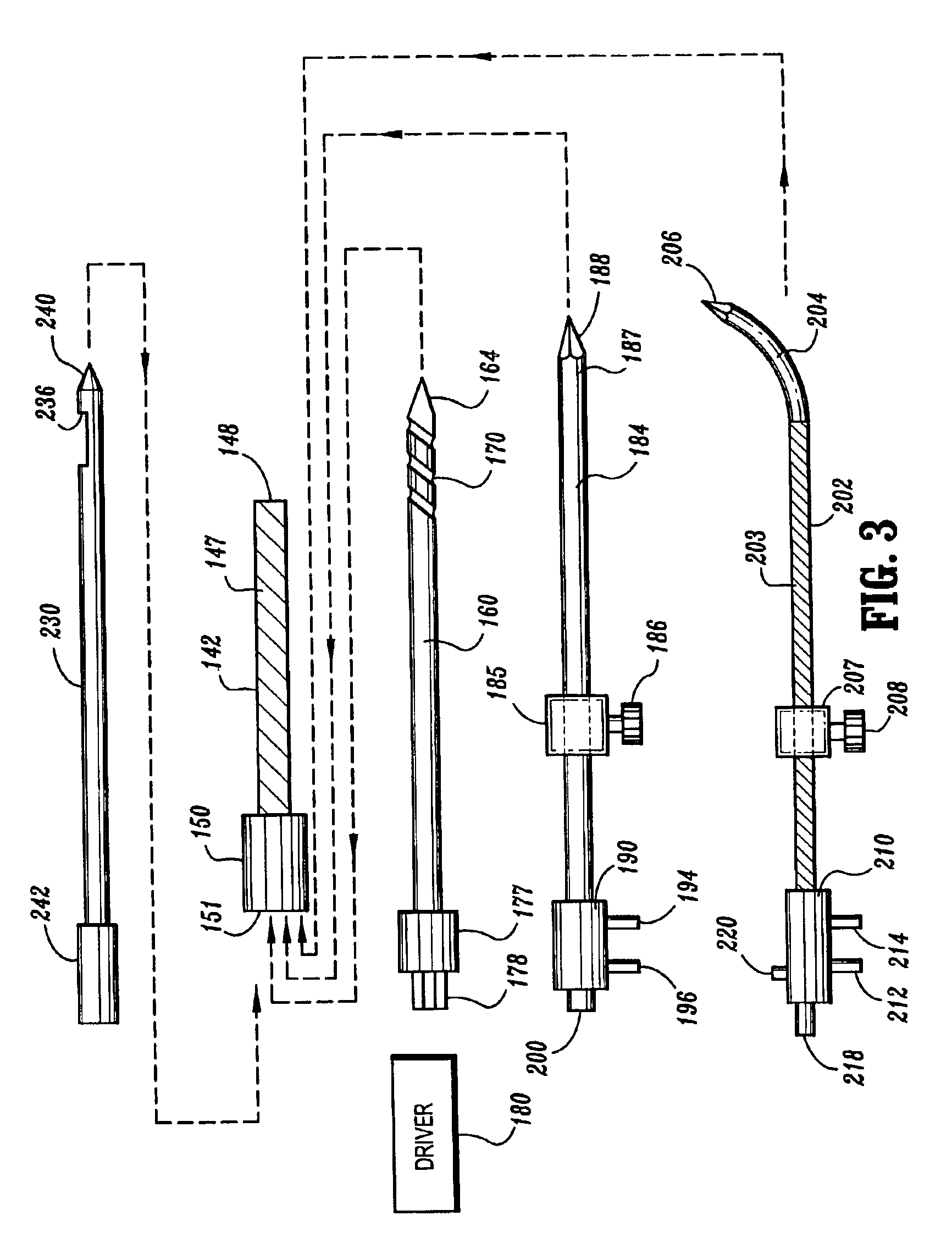
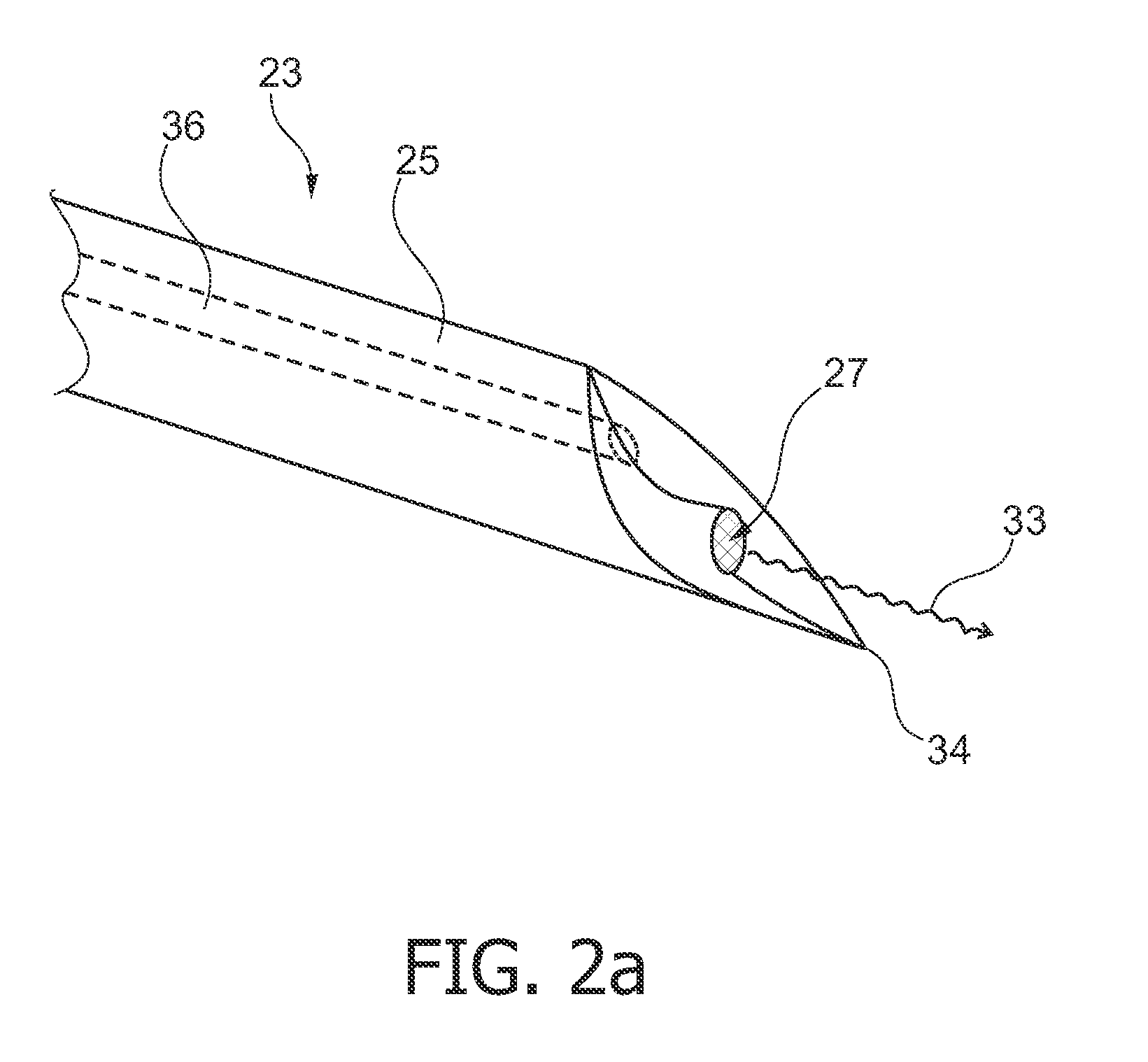
This invention relates to a biopsy device consisting of an inner cannula (4) and an outer hollow tube (1), a handle (7) which may be removably attached to the outer hollow tube, a locking system to secure the inner cannula and / or the attenuator in the outer hollow tube, and characterized in that the tip of the outer hollow tube is ellipse shaped and extends beyond the inner cannula, the latter ending in a blunt edge. The blunted tip of the outer hollow tube together with the sharpened ending of the inner cannula determines the cutting edge of the device. In combination the distal ends of inner cannula and outer hollow tube determine the biopsy depth size and shape of the biopsy sample in a reproducible way. In one embodiment of the present invention, the length of the inner cannula can be controlled, allowing varying the aforementioned sample parameters as desired.
Owner:DOKTER YVES FORTEMS
Method for stimulating an immune response
InactiveUS6977073B1Stimulating directed immune responseStimulate immune responseBiocideArtificial cell constructsAbnormal tissue growthHematopoietic cell
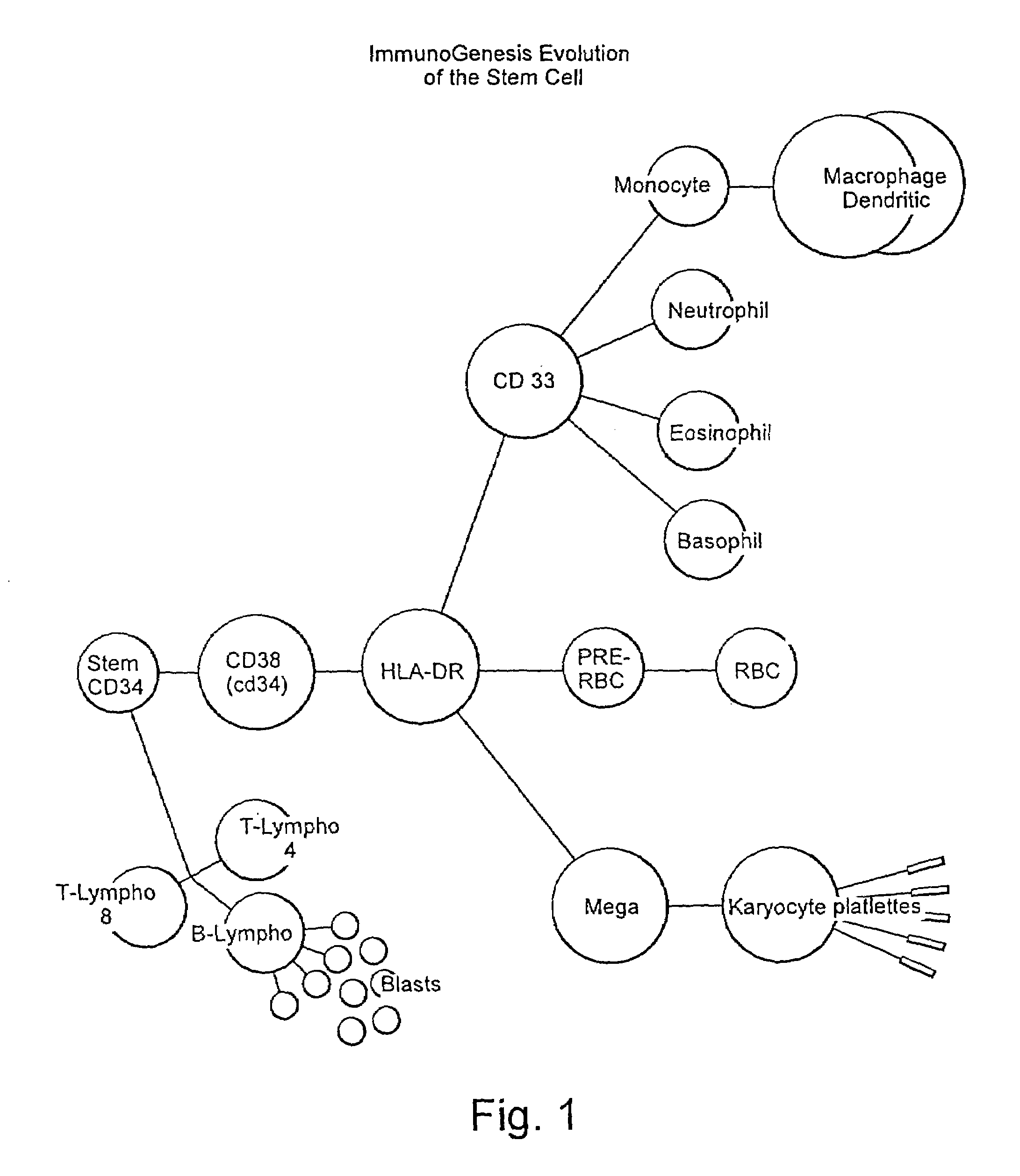
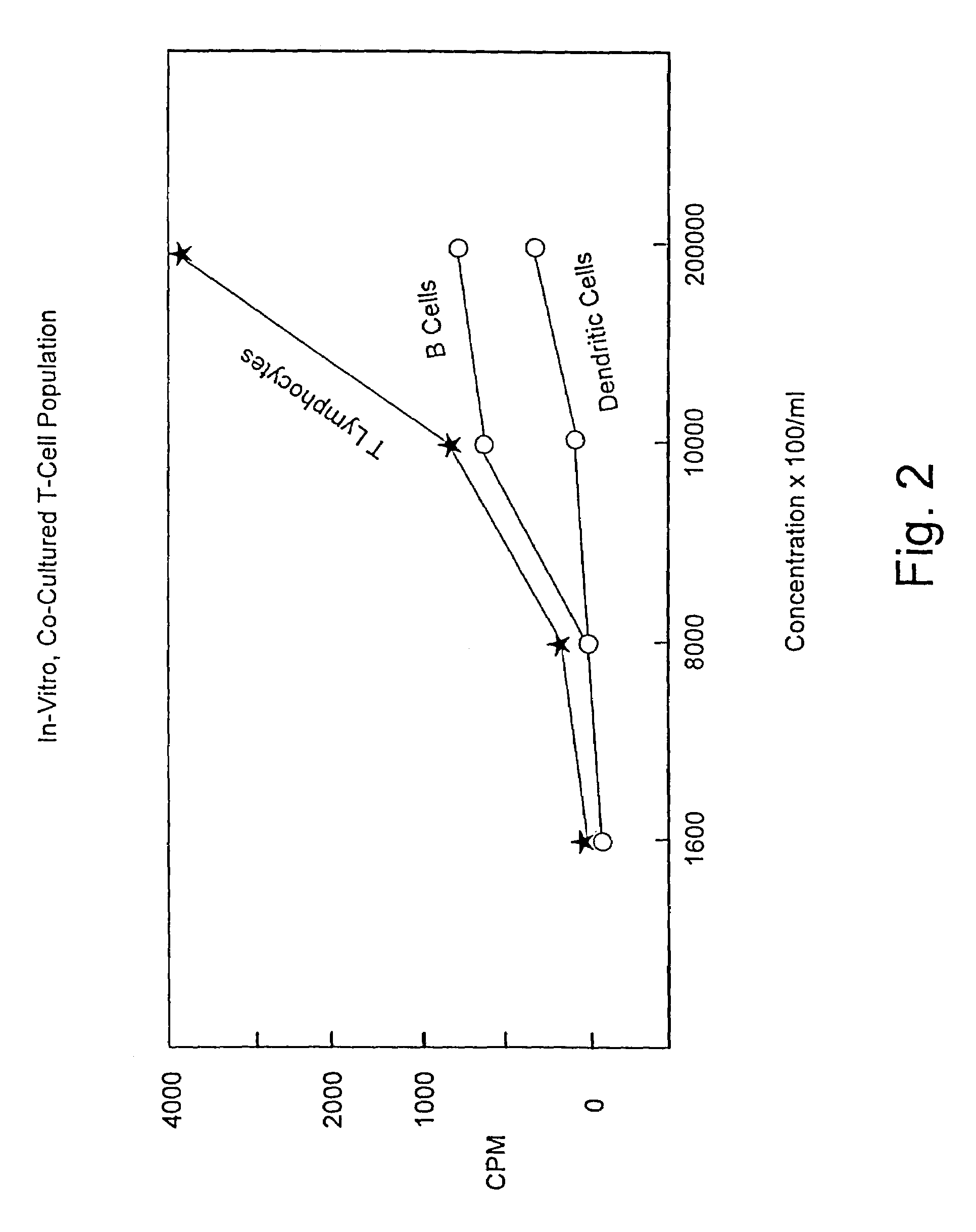
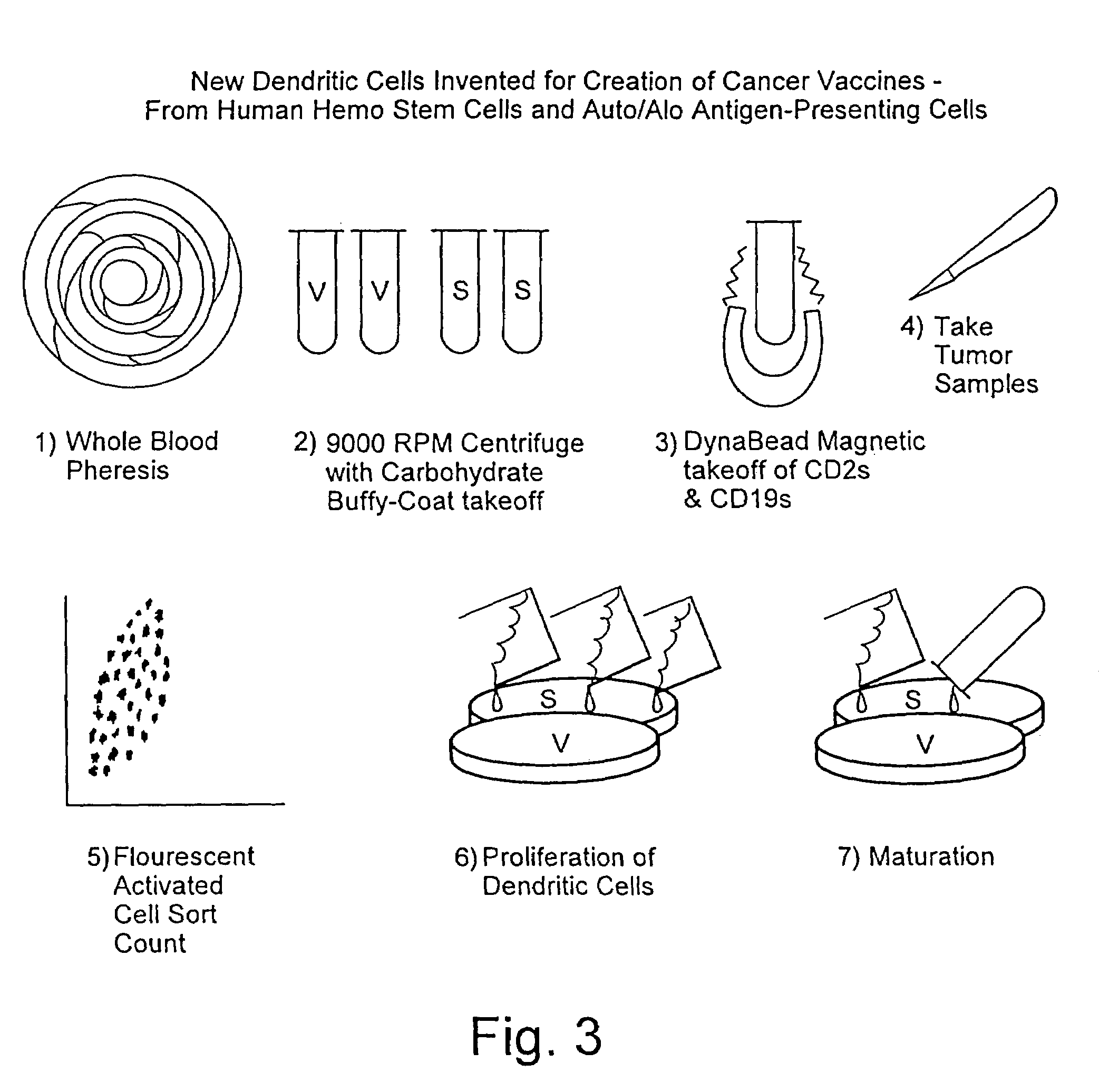
A method is described whereby dendritic cells derived from the CD34+ and CD 34−hematopoietic cell lineages are directed to become programmable antigen presenting cells. The programmed cells may be pulsed with tumor cell RNA or tumor cell RNA expression products. The protocol provides for directing the maturation of dendritic cells to become antigen presenting cells. The protocol further provides for isolating tumor cell RNA from biopsy material that has been prepared in paraffin block storage. The directed dendritic cell is provided with a plurality of tumor markers by using tumor RNA in toto, the poly A+RNA fraction or the expression product of such RNA. Once activated the dendritic cells are incubated with T4 and T8 lymphocytes to stimulate and sensitize the T lymphocytes which upon introduction either into a donor host or a nondonor recipient will provide immune response protection.
Owner:CEZAYIRLI CEM
Biopsy device incorporating an adjustable probe sleeve
InactiveUS20060200042A1Discomfort and disfiguring scarring is avoidedSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsTissue sampleRadiology
A biopsy device and method are provided for obtaining a tissue sample, such as a breast tissue biopsy sample. The biopsy device may include an outer cannula having a distal piercing tip, a cutter lumen, a side tissue port communicating with the cutter lumen, and at least one fluid passageway disposed distally of the side tissue port. The inner cutter may be advanced in the cutter lumen past the side tissue port to sever a tissue sample. After the tissue sample is severed, and before the inner cutter is retracted proximally of the side tissue port, the cutter may be used to alternately cover and uncover the fluid passageway disposed distally of the side tissue.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Biopsy Device with Rotatable Tissue Sample Holder
A biopsy device comprises a probe body, a cannula extending distally from the probe body, a cutter moveable relative to the cannula to sever tissue, and a tissue sample holder coupled with the probe body. The tissue sample holder comprises a rotatable member and at least one removable member secured about the exterior of the rotatable member. The at least one removable member defines a plurality of tissue sample compartments. Each tissue sample compartment is configured to receive one or more tissue samples captured by the cutter. In some versions, the at least one removable member comprises a belt and a plurality of vials.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Device for needle biopsy with integrated needle protection
ActiveUS20100121218A1Enhance maneuverability and operationEnhance echogenicitySurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsDistal portionSurgery
A device for needle biopsy is presented. The device includes a handle member having proximal and distal portions. A proximal handle member is disposed to the proximal portion of the handle member and a distal handle member is disposed to the distal portion of the handle member. A sheath lumen is disposed within the handle member and extends from the distal portion of the handle member. A needle housing member is partially disposed to the proximal portion of the handle member and a needle is disposed within the sheath lumen. A plurality of protrusions is disposed upon the needle. A needle protection member is partially disposed to the distal portion of the needle housing member. The needle protection member includes a needle protection hub and a needle protection shaft.
Owner:TYCO HEALTHCARE GRP LP
Biopsy forceps for endoscope
A biopsy forceps for an endoscope has a flexible sheath and a control wire axially movably inserted in the sheath. A control part is connected to the proximal end of the sheath. The control wire is advanced or retracted at the control part to open or close a pair of forceps cups pivotally provided at the distal end of the sheath. The sheath is formed from a member that does not twist in at least one direction about an axis thereof. A rotation control member is provided on or near the control part to rotate the sheath about the axis in a direction in which the sheath does not twist.
Owner:ASAHI KOGAKU KOGYO KK
Biopsy device with acoustic element
InactiveUS20110066073A1Continuous measurementStrong absorption capacitySurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsRadiologyTransducer
The invention relates to a biopsy device, particularly a biopsy device comprising a shaft with a transducer element for providing information about acoustic properties of a material to be analysed, a system of positioning a biopsy device and a method for positioning a biopsy device. The biopsy device may be adapted to take biopsies of different regions of the 5 human body for excluding or detecting abnormalities as cancerous lesions. The biopsy device may be used to measure acoustic properties of the material while inserting the tip portion of the biopsy device into the material to be analysed. The biopsy device may further allow measurement based on elastography.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Biopsy device with replaceable probe and incorporating vibration insertion assist and static vacuum source sample stacking retrieval
InactiveUS7867173B2Inexpensively incorporatedSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsUltrasonic imagingTissue sample
A biopsy device and method are provided for obtaining a tissue sample, such as a breast tissue biopsy sample. The biopsy device includes a disposable probe assembly with an outer cannula having a distal piercing tip, a cutter lumen, and a cutter tube that rotates and translates past a side aperture in the outer cannula to sever a tissue sample. The biopsy device also includes a reusable hand piece with an integral motor and power source to make a convenient, untethered control for use with ultrasonic imaging. The reusable hand piece incorporates a probe oscillation mode to assist when inserting the distal piercing tip into tissue. A straw stacking assembly is automatically positioned by the reusable hand piece to retract multiple samples with a single probe insertion as well as giving a visual indication to the surgeon of the number of samples that have been taken.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
Biopsy device with replaceable probe incorporating static vacuum source dual valve sample stacking retrieval and saline flush
InactiveUS7662109B2Small sizeInexpensively incorporatedSurgeryVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsSaline flushUltrasonic imaging
A biopsy device and method are provided for obtaining a tissue sample, such as a breast tissue biopsy sample. The biopsy device includes a disposable probe assembly with an outer cannula having a distal piercing tip, a cutter lumen, and a cutter tube that rotates and translates past a side aperture in the outer cannula to sever a tissue sample. The biopsy device also includes a reusable hand piece with an integral motor and power source to make a convenient, untethered control for use with ultrasonic imaging. The reusable hand piece incorporates a probe oscillation mode to assist when inserting the distal piercing tip into tissue. A saline valve positioned by the reusable hand piece communicates a saline supply through the probe assembly to perform saline flush of the cutter tube and outer cannula.
Owner:DEVICOR MEDICAL PROD
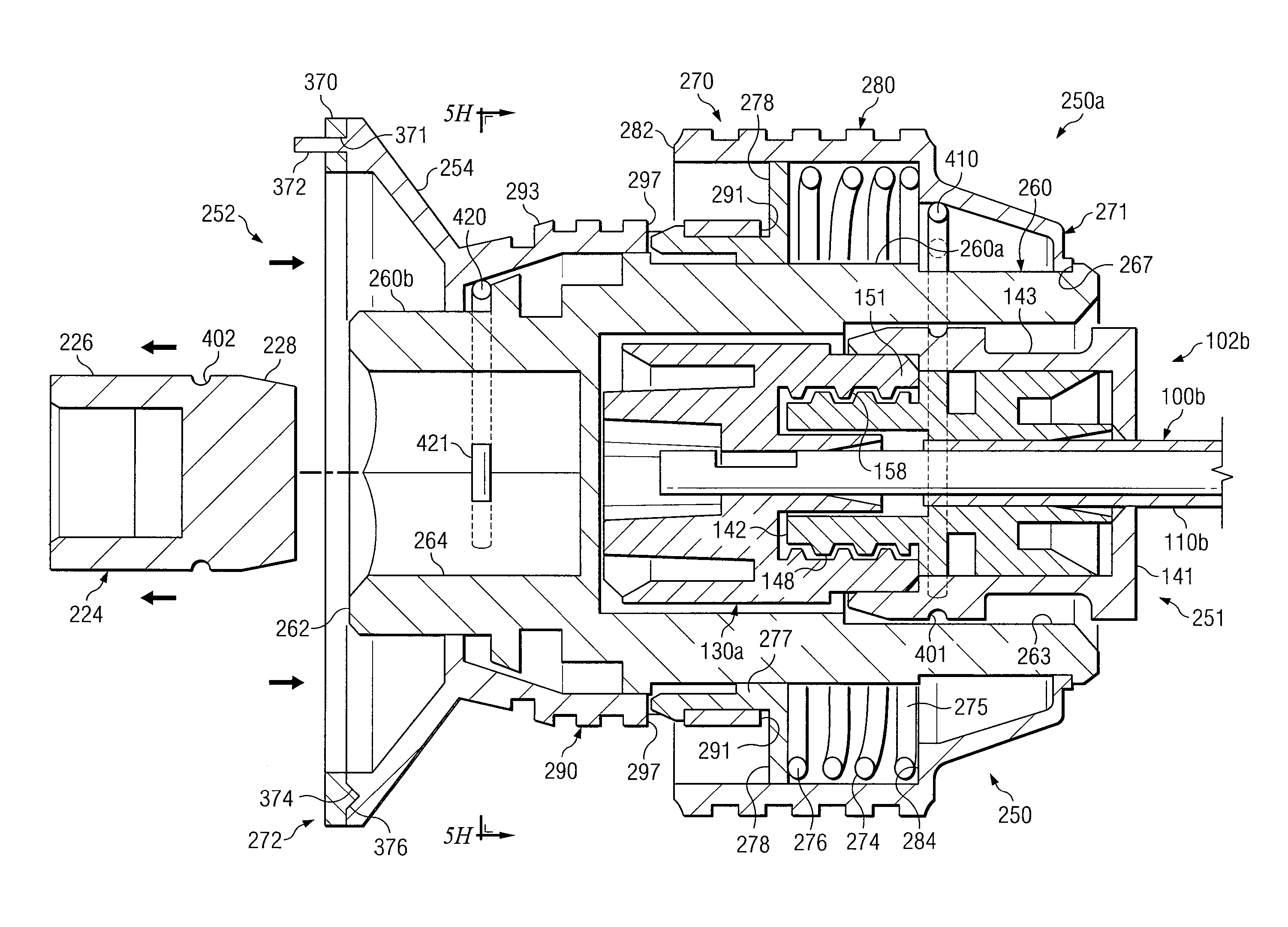
Assembly for coupling powered driver with intraosseous device
ActiveUS8668698B2Easy to captureIncrease speedSurgical furnitureThread cutting machinesCatheterTransplant Procedure
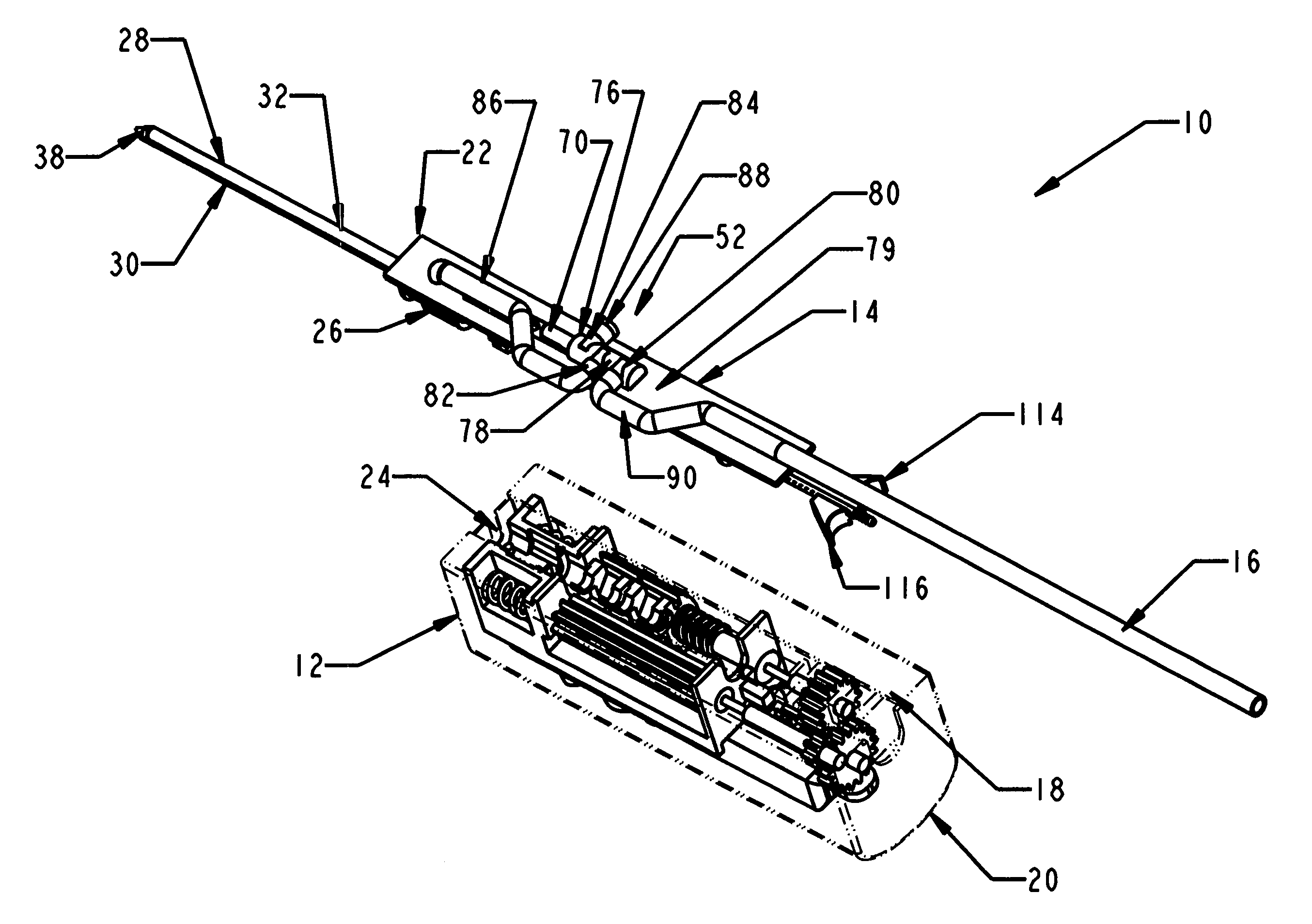
Apparatus and methods are provided to remove biopsy specimens from a bone and / or associated bone marrow using a powered drive and an intraosseous (IO) needle set. The powered driver may rotate the IO needle set at an optimum speed to obtain a biopsy sample of bone and / or bone marrow. Apparatus and methods may also be provided for aspiration of bone marrow and / or stem cell transplant procedures. The apparatus may include a powered driver, a coupler assembly, a containment bag or sterile sleeve and various IO needles and IO needle sets with associated hubs and / or hub assemblies. Each IO needle set may include a cannula or catheter and an associated trocar stylet with respective tips operable to penetrate a bone and / or bone marrow with minimum trauma to a patient. Each hub assembly may be used to releasably dispose a respective stylet within an associated generally hollow cannula. Some coupler assemblies and / or hub assemblies may also be used with manual drivers.
Owner:TELEFLEX LIFE SCI LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com