Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
409results about How to "Continuous measurement" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
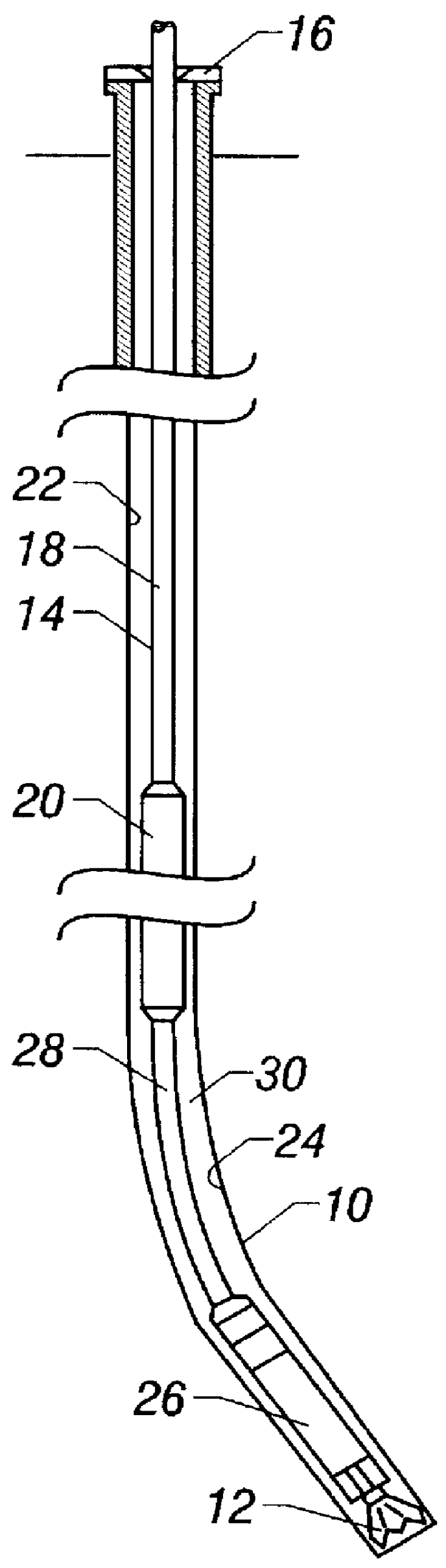
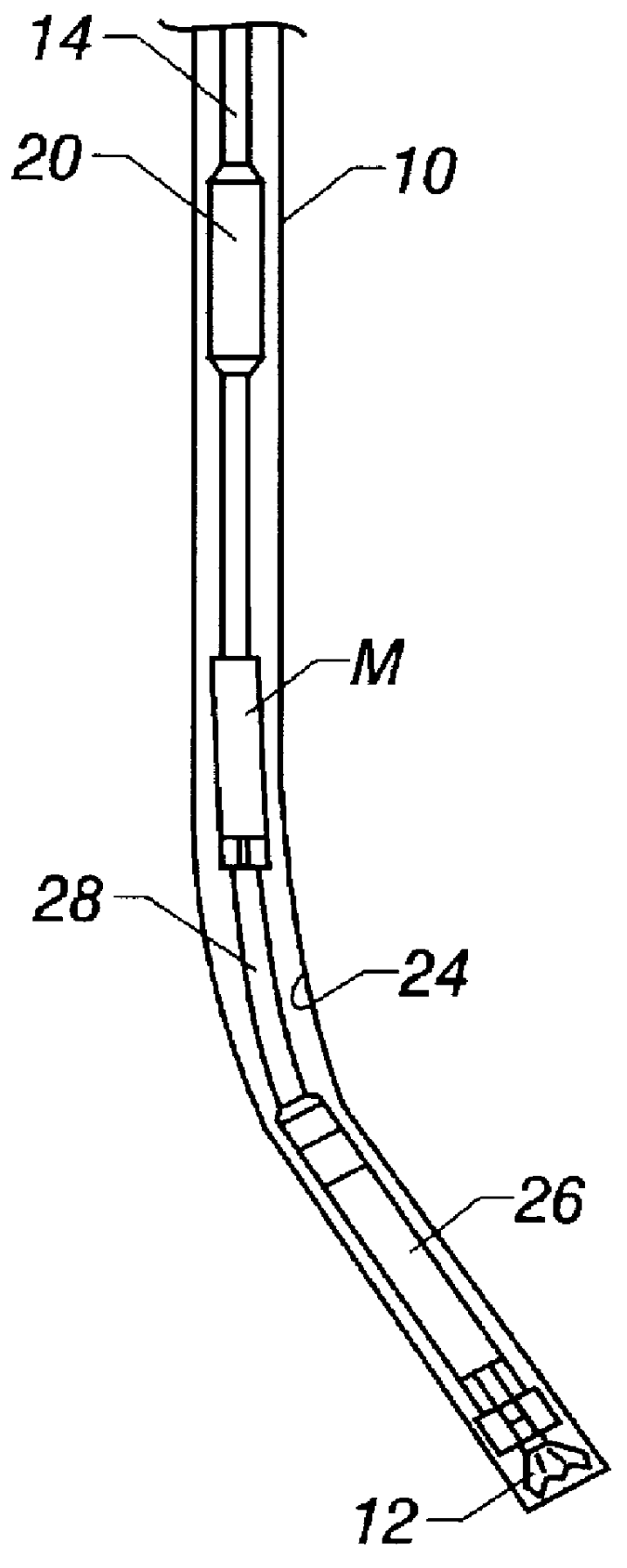
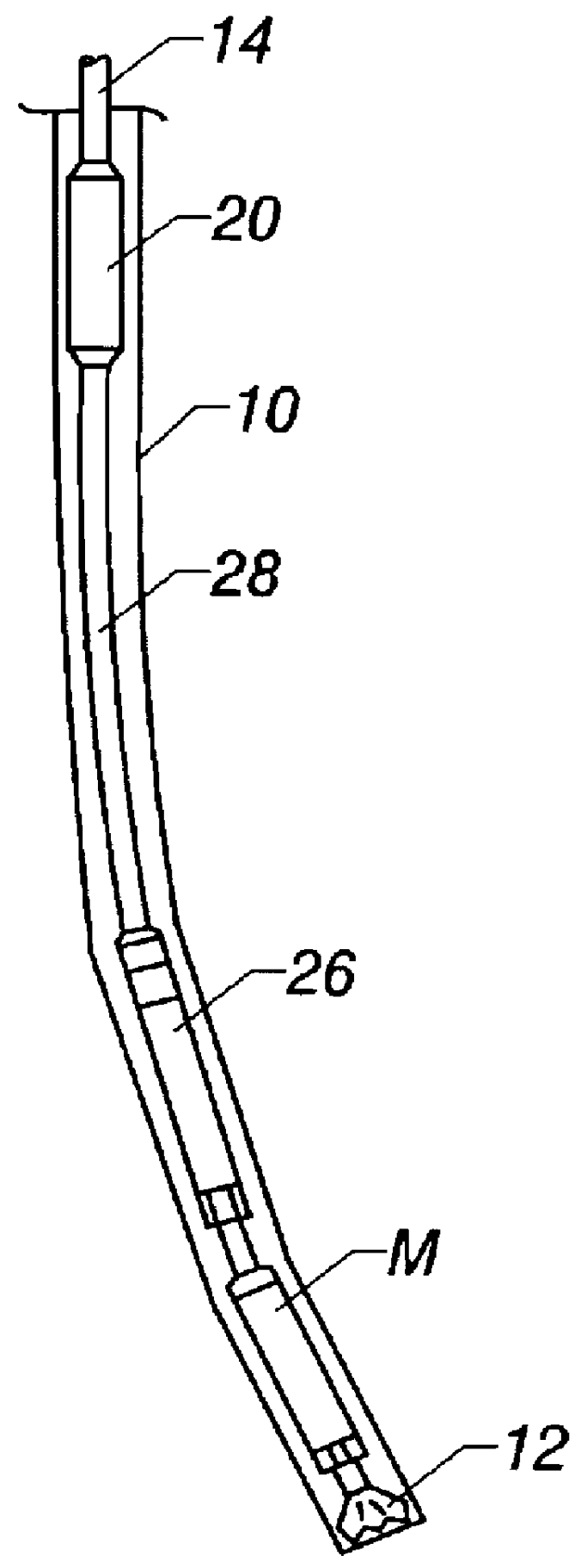
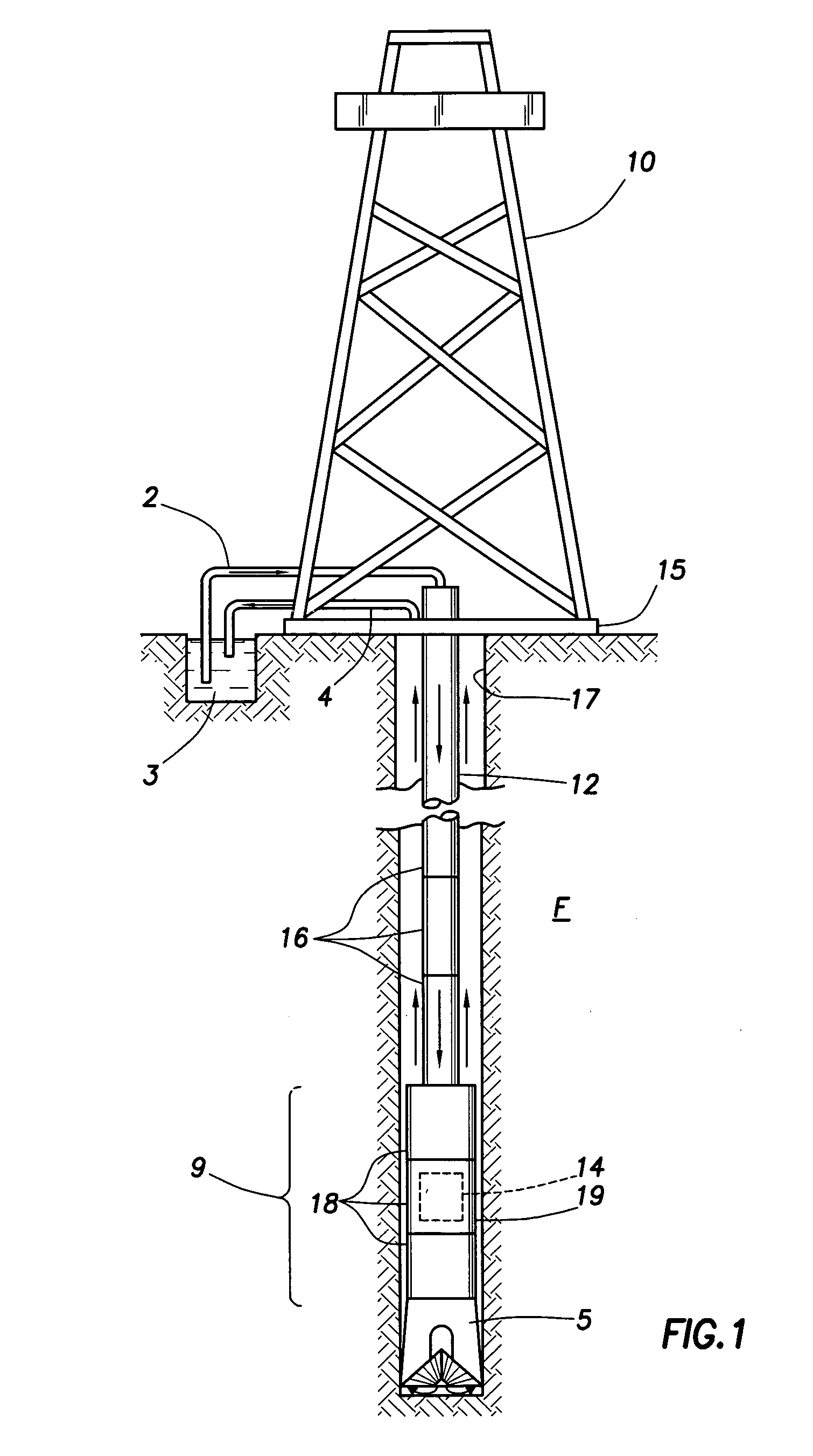
Actively controlled rotary steerable system and method for drilling wells
InactiveUS6092610AEfficient rotary speedPromote productionDrilling rodsConstructionsAccelerometerDirectional drilling
An actively controlled rotary steerable drilling system for directional drilling of wells having a tool collar rotated by a drill string during well drilling. A bit shaft has an upper portion within the tool collar and a lower end extending from the collar and supporting a drill bit. The bit shaft is omni-directionally pivotally supported intermediate its upper and lower ends by a universal joint within the collar and is rotatably driven by the collar. To achieve controlled steering of the rotating drill bit, orientation of the bit shaft relative to the tool collar is sensed and the bit shaft is maintained geostationary and selectively axially inclined relative to the tool collar during drill string rotation by rotating it about the universal joint by an offsetting mandrel that is rotated counter to collar rotation and at the same frequency of rotation. An electric motor provides rotation to the offsetting mandrel with respect to the tool collar and is servo-controlled by signal input from position sensing elements such as magnetometers, gyroscopic sensors, and accelerometers which provide real time position signals to the motor control. In addition, when necessary, a brake is used to maintain the offsetting mandrel and the bit shaft axis geostationary. Alternatively, a turbine is connected to the offsetting mandrel to provide rotation to the offsetting mandrel with respect to the tool collar and a brake is used to servo-control the turbine by signal input from position sensors.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
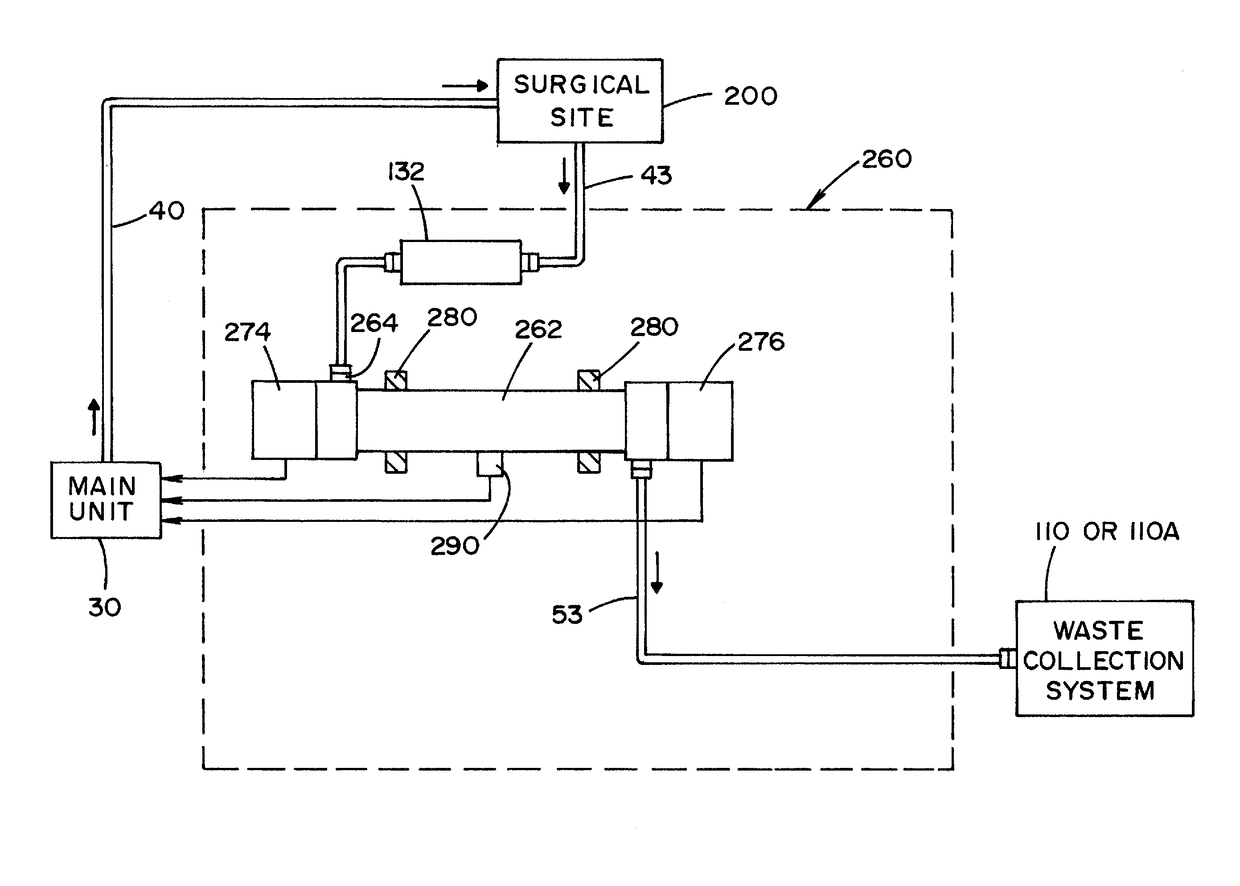
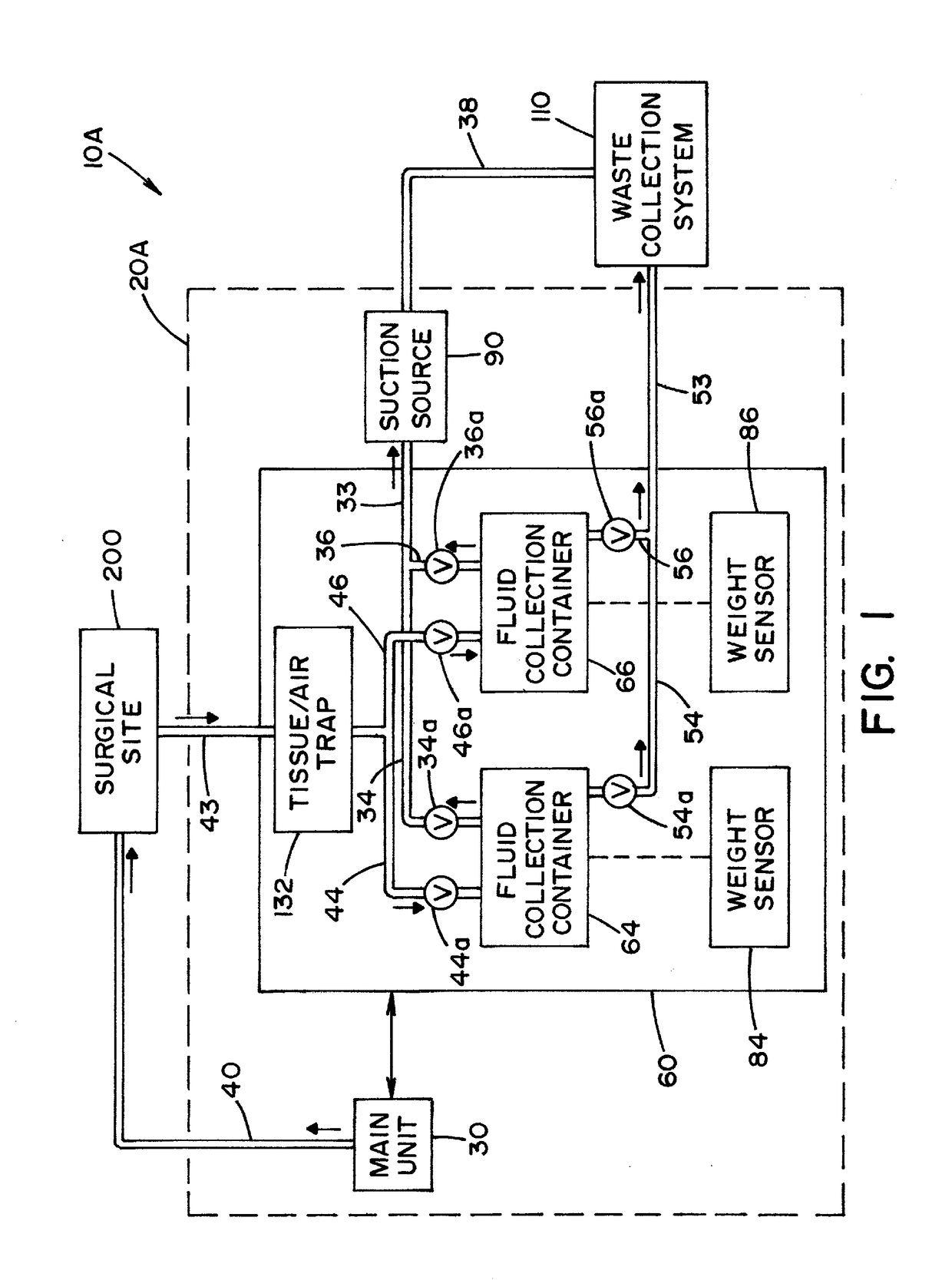
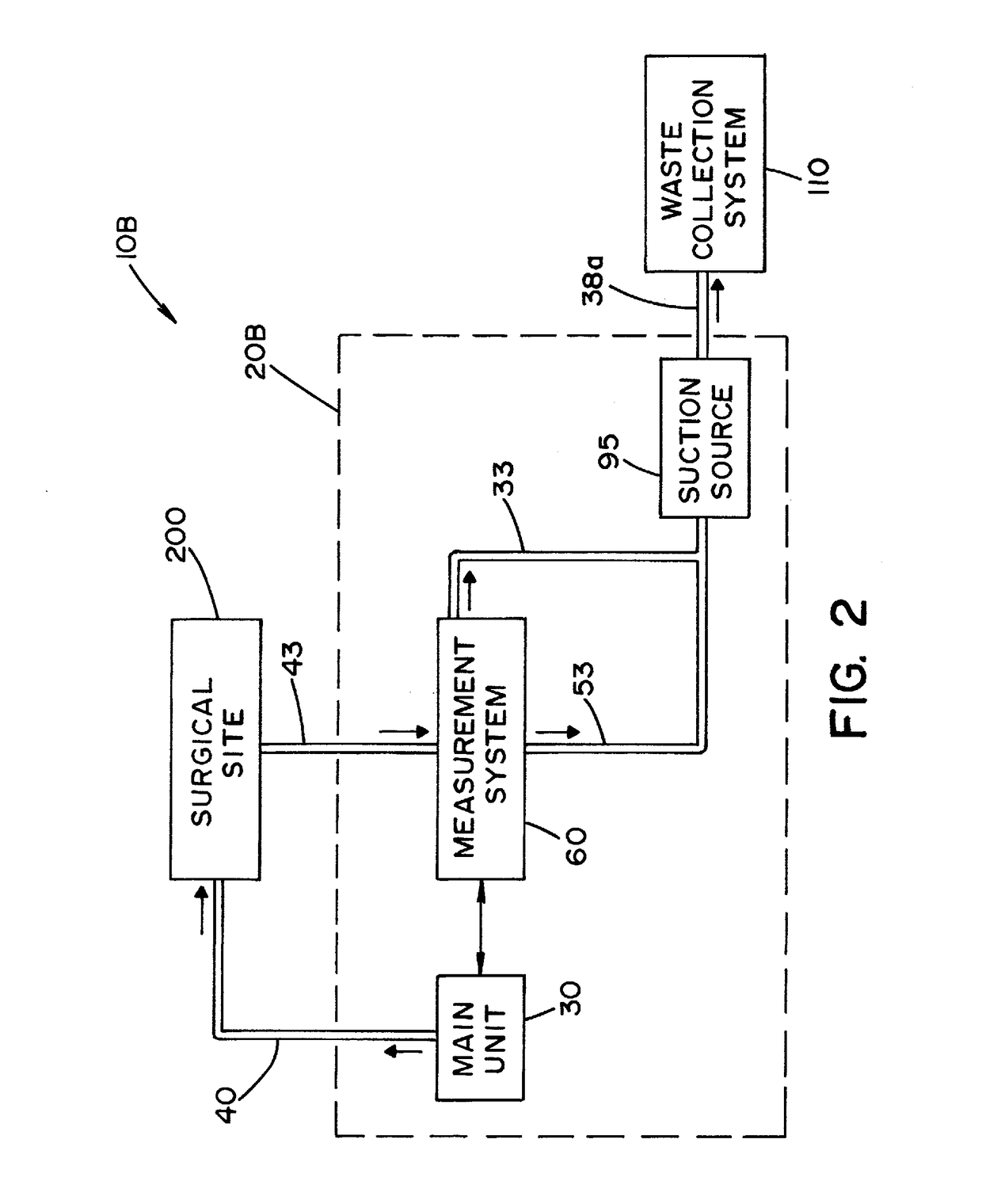
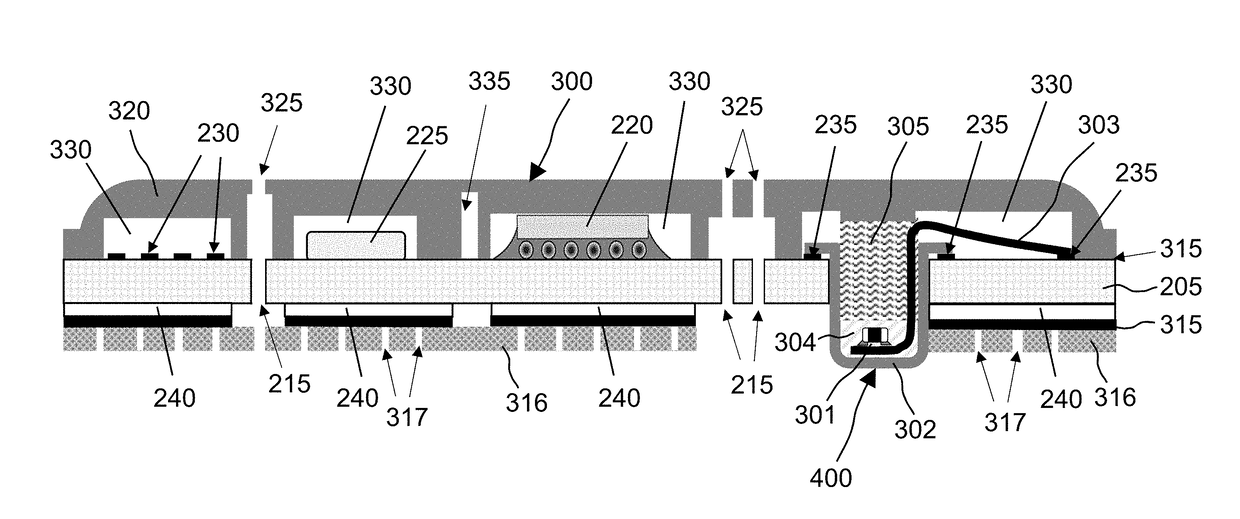
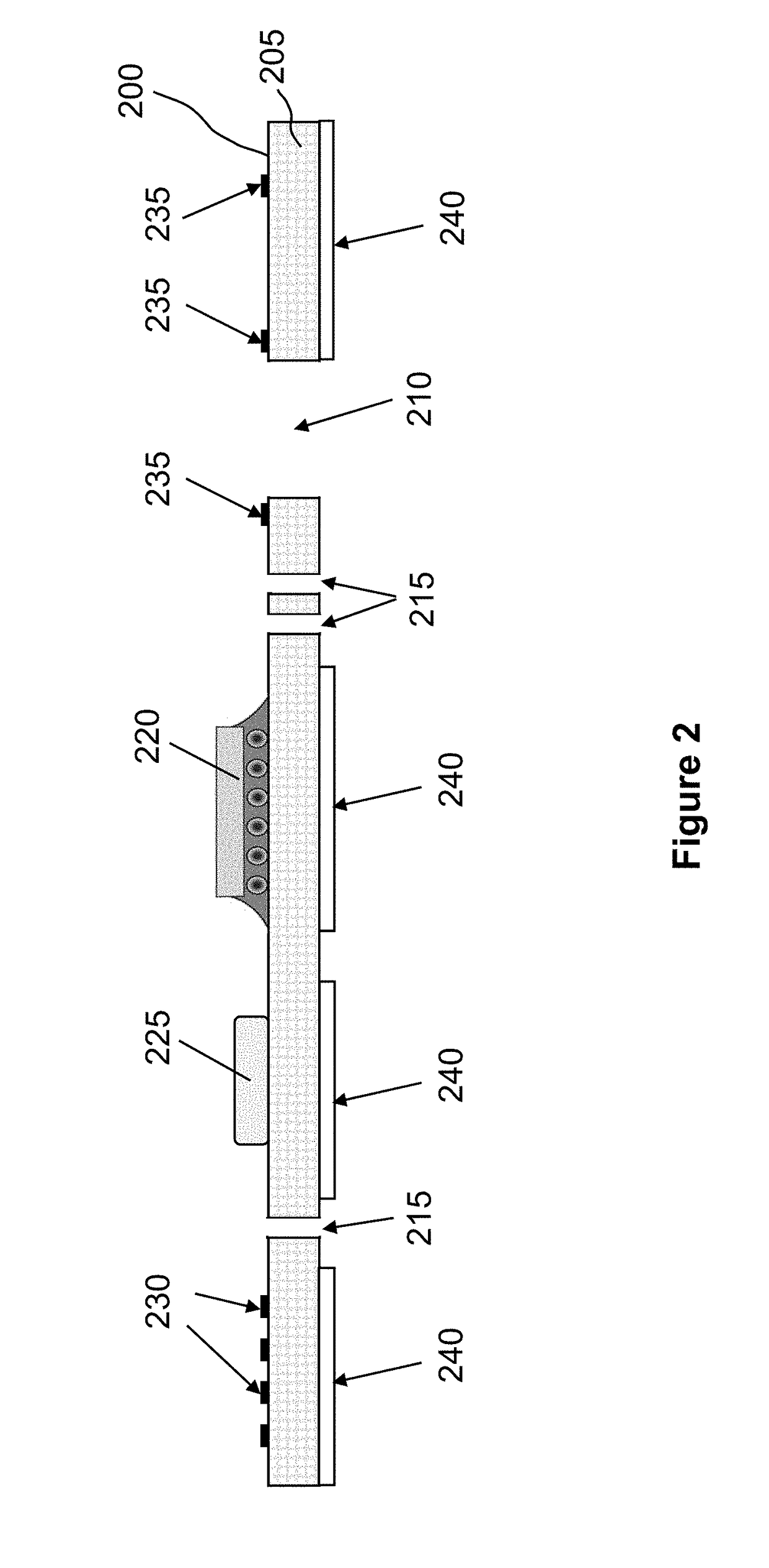
Fluid management system with pass-through fluid volume measurement
ActiveUS9770541B2Continuous measurementEliminate replacementMedical devicesIntravenous devicesContinuous measurementVolume measurements
A fluid management system including a pass-through fluid volume measurement system to provide continuous measurement of fluid returned from a surgical site during transit to a waste collection system. The pass-through fluid volume measurement system eliminates the need to physically replace full fluid collection containers during the medical procedure with new, empty fluid collection containers.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Implantable apparatus for sensing multiple parameters
ActiveUS20050148832A1Continuously measureContinuous measurementElectrotherapyCatheterBiomedical engineeringAnalyte
An apparatus for sensing multiple parameters includes an implantable housing and a plurality of implantable sensors disposed within the implantable housing. The plurality of implantable sensors sense parameters in a patient, such as biological or physiological parameters, for example, and each responds to an analyte in the patient. The plurality of implantable sensors may include, but is not limited to, electrochemical, potentiometric, current and optical sensors.
Owner:MEDTRONIC MIMIMED INC
Equipment and Process for Measuring the Precision of Sun Tracking for Photovoltaic Concentrators
InactiveUS20080258051A1Down rateIncrease sampling ratePhotovoltaic supportsSolar heating energyElectricityEngineering
Mechanical sun trackers which have optical systems on their surface for concentrating direct solar radiation and its subsequent conversion into electricity through thermal or photovoltaic processes require precision solar tracking, which has to be all the more precise the greater the concentration factor used. Thus the precision required in these systems is generally less than a degree, and frequently of the order of a tenth of a degree. In view of the large dimensions of the surfaces, or apertures, of these trackers, currently in the approximate range of 20-250 m2, the difficulty of aligning these with the sun with such accuracy will be obvious. To achieve this objective a solar tracker must comply with strict rigidity specifications and its transmission must provide high resolution when positioning. In addition to this, equipment which is capable of controlling solar tracking with the specified precision at all times is required.
Owner:SOLFOCUS
Method and a device for monitoring nucleic acid amplification reactions
InactiveUS6310354B1Continuous measurementSimply performedBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsCuvetteMicroparticle
A method for quantitatively measuring nucleic acid amplification reactions, especially the polymerase chain reaction, employing microparticles as hybridization solid phase, a probe sequence labeled with a fluorescent label and a fluorescence detection system which is based on two-photon fluorescence excitation, contacting all the amplification reaction components and the solid phase simultaneously in a closed cuvette, performing the amplification reactions in the same cuvette, focusing a two-photon exciting laser beam into the cuvette during the amplification cycles and measuring the fluorescence signal emitted by the microparticles from one particle at a time when they randomly float through the focal volume of the laser beam. The features of this invention allow a method and device for performing a fast quantitative nucleic acid amplification assay of single or multiple target sequences in a very small closed sample volume.
Owner:SOINI ERKKI
Device and system for humor component detection
InactiveUS20050245798A1Fast learningContinuously carrying out measurement with accuracy for a long timeMicrobiological testing/measurementCatheterGenetically modified bacteriaEngineering
A device and a system for humor component detection are capable of continuously carrying out measurement with accuracy for a long time and are excellent from the aspect of good hygiene. The humor component detection system comprises the humor component detection device and an extra-corporeal sensing device. The humor component detection device comprises a biosensor, a microbe containing portion, and an outer shell. Here, the biosensor comprises a sensing element and an electronic device. The microbe containing portion includes a pouched microtube blanketing film into which the electrodes of the sensing element are inserted, a plurality of acinous polymer-filmed porous microcapsules contained inside the film, and GOD genetically-modified bacteria contained in the microcapsules.
Owner:DENSO CORP
Detecting cutaneous electrode peeling using electrode-skin impedance
ActiveUS20140296934A1Avoid riskReduce riskElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringElectrode arraySkin impedance
Apparatus for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in a user, the apparatus comprising:stimulation means for electrically stimulating at least one nerve;an electrode array connectable to said stimulation means, said electrode array comprising a plurality of electrodes for electrical stimulation of the at least one nerve, said electrodes having a pre-formed geometry and known electrode-skin contact area size when in complete contact with the user's skin;monitoring means electrically connected to said stimulation means for monitoring the impedance of the electrical stimulation through said electrode array; andanalysis means for analyzing said impedance to estimate a change in the electrode-skin contact area.
Owner:NEUROMETRIX
Detecting cutaneous electrode peeling using electrode-skin impedance
ActiveUS9474898B2Reduce riskContinuous measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsElectricityTranscutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
Apparatus for transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation in a user, the apparatus comprising:stimulation means for electrically stimulating at least one nerve;an electrode array connectable to said stimulation means, said electrode array comprising a plurality of electrodes for electrical stimulation of the at least one nerve, said electrodes having a pre-formed geometry and known electrode-skin contact area size when in complete contact with the user's skin;monitoring means electrically connected to said stimulation means for monitoring the impedance of the electrical stimulation through said electrode array; andanalysis means for analyzing said impedance to estimate a change in the electrode-skin contact area.
Owner:NEUROMETRIX INC
Biopsy device with acoustic element
InactiveUS20110066073A1Continuous measurementStrong absorption capacitySurgical needlesVaccination/ovulation diagnosticsRadiologyTransducer
The invention relates to a biopsy device, particularly a biopsy device comprising a shaft with a transducer element for providing information about acoustic properties of a material to be analysed, a system of positioning a biopsy device and a method for positioning a biopsy device. The biopsy device may be adapted to take biopsies of different regions of the 5 human body for excluding or detecting abnormalities as cancerous lesions. The biopsy device may be used to measure acoustic properties of the material while inserting the tip portion of the biopsy device into the material to be analysed. The biopsy device may further allow measurement based on elastography.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
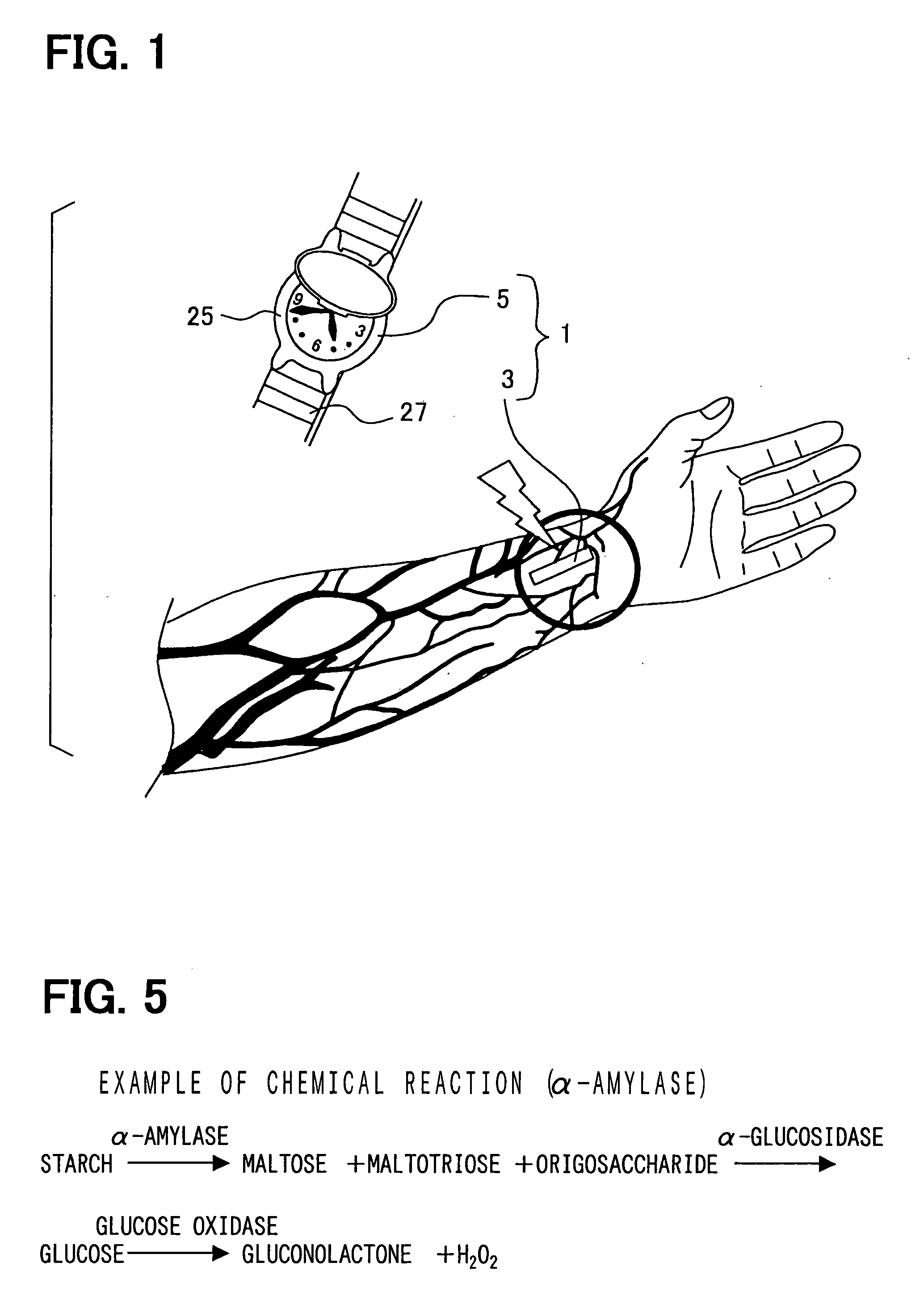
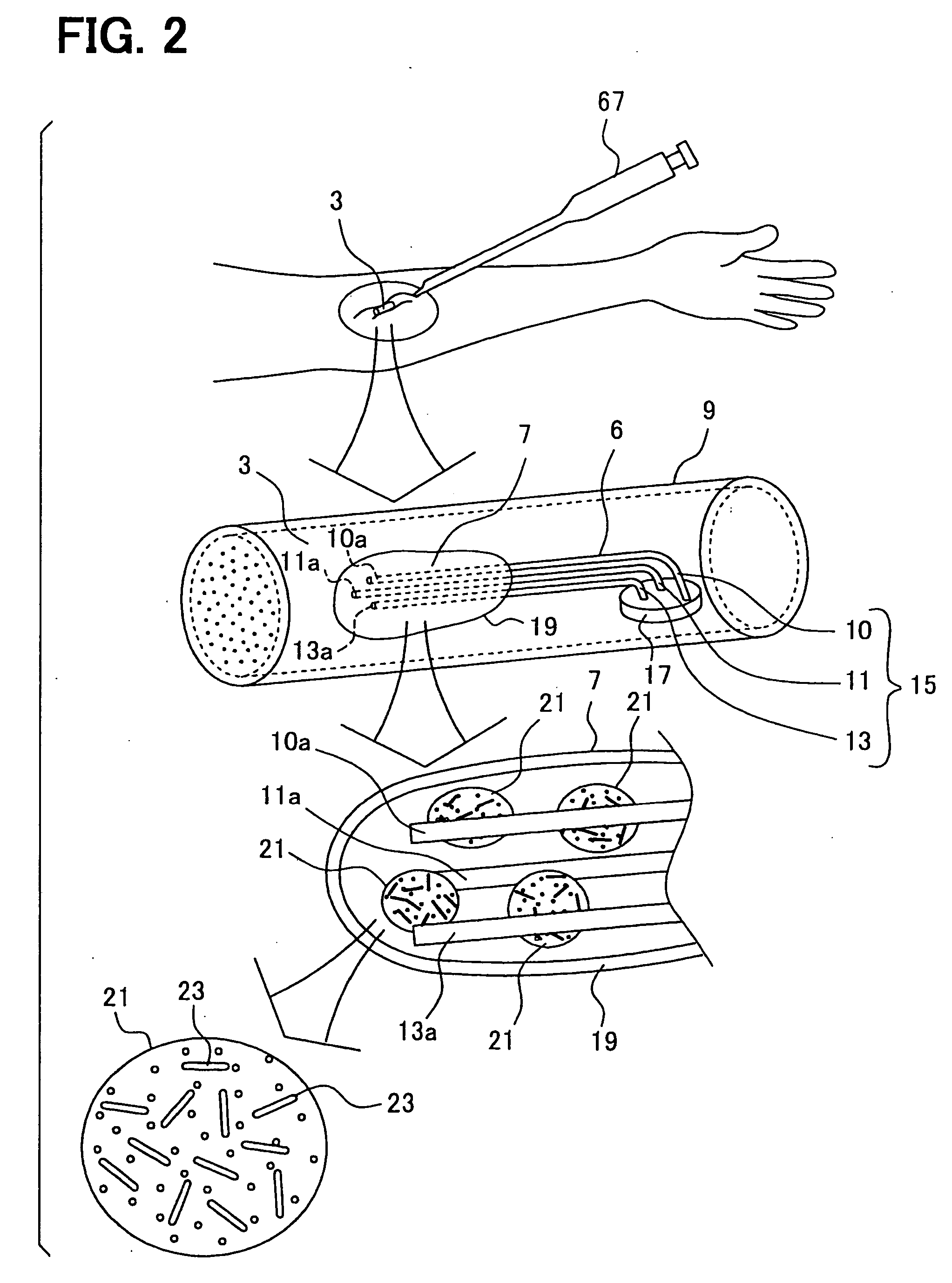
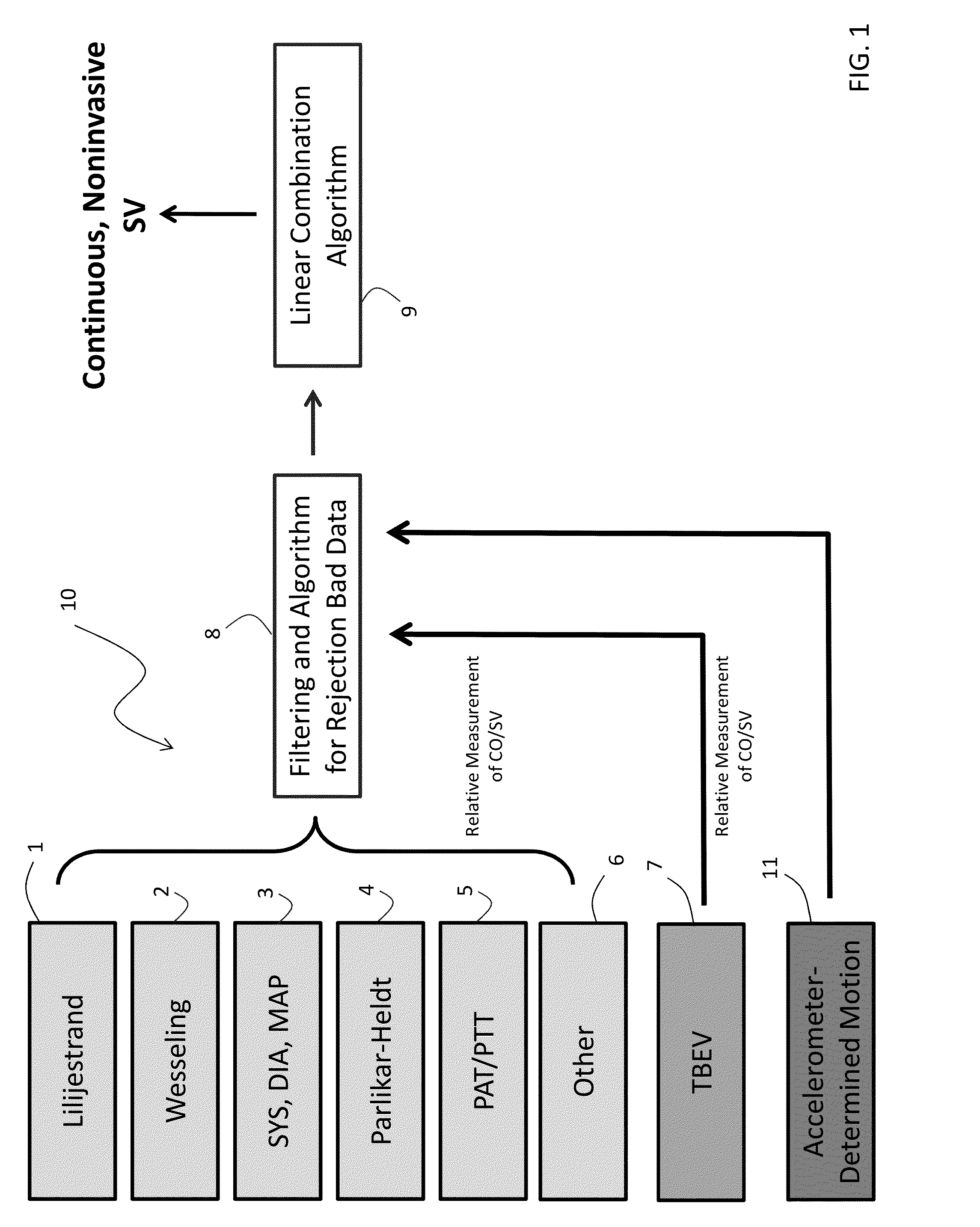
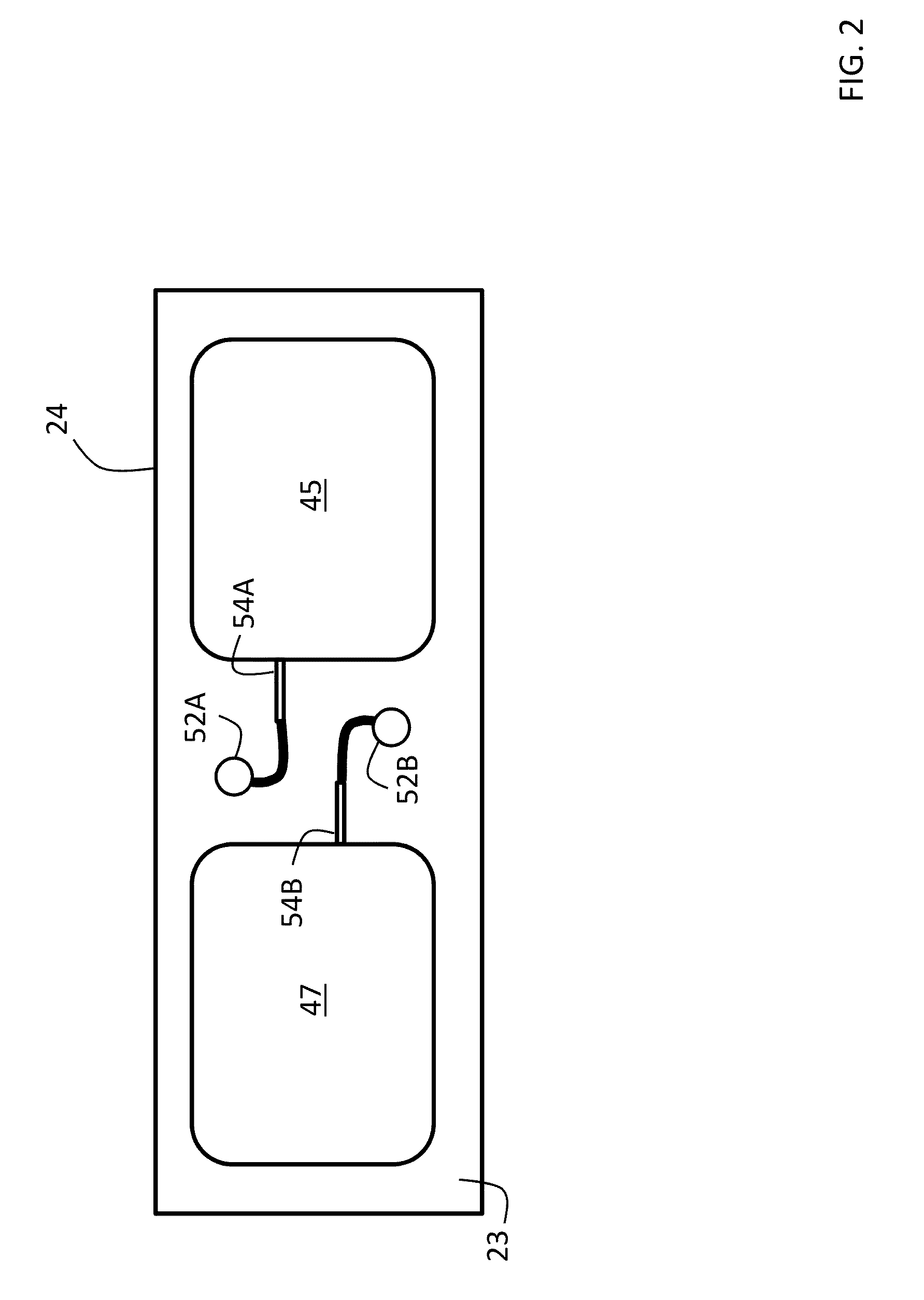
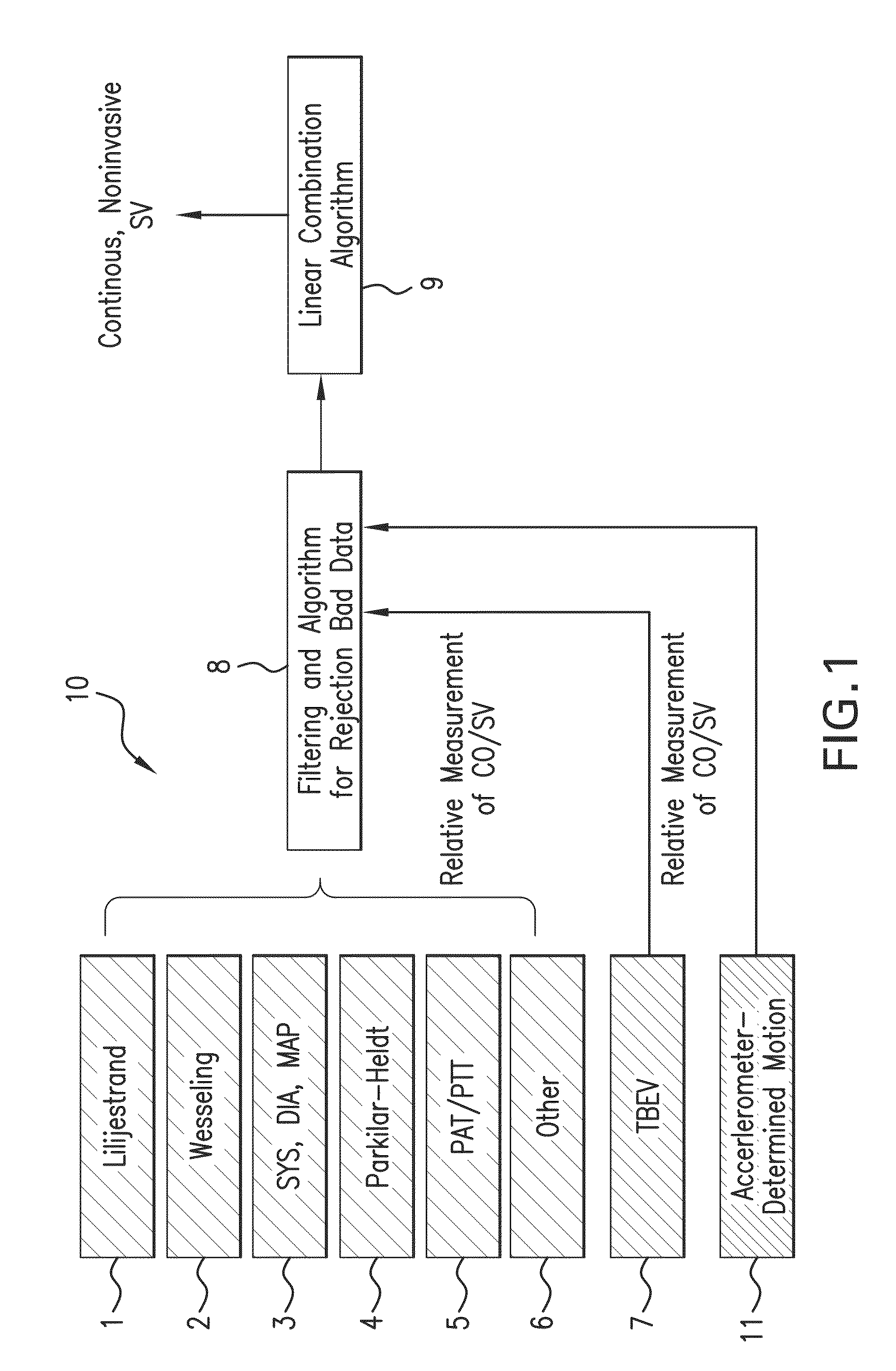
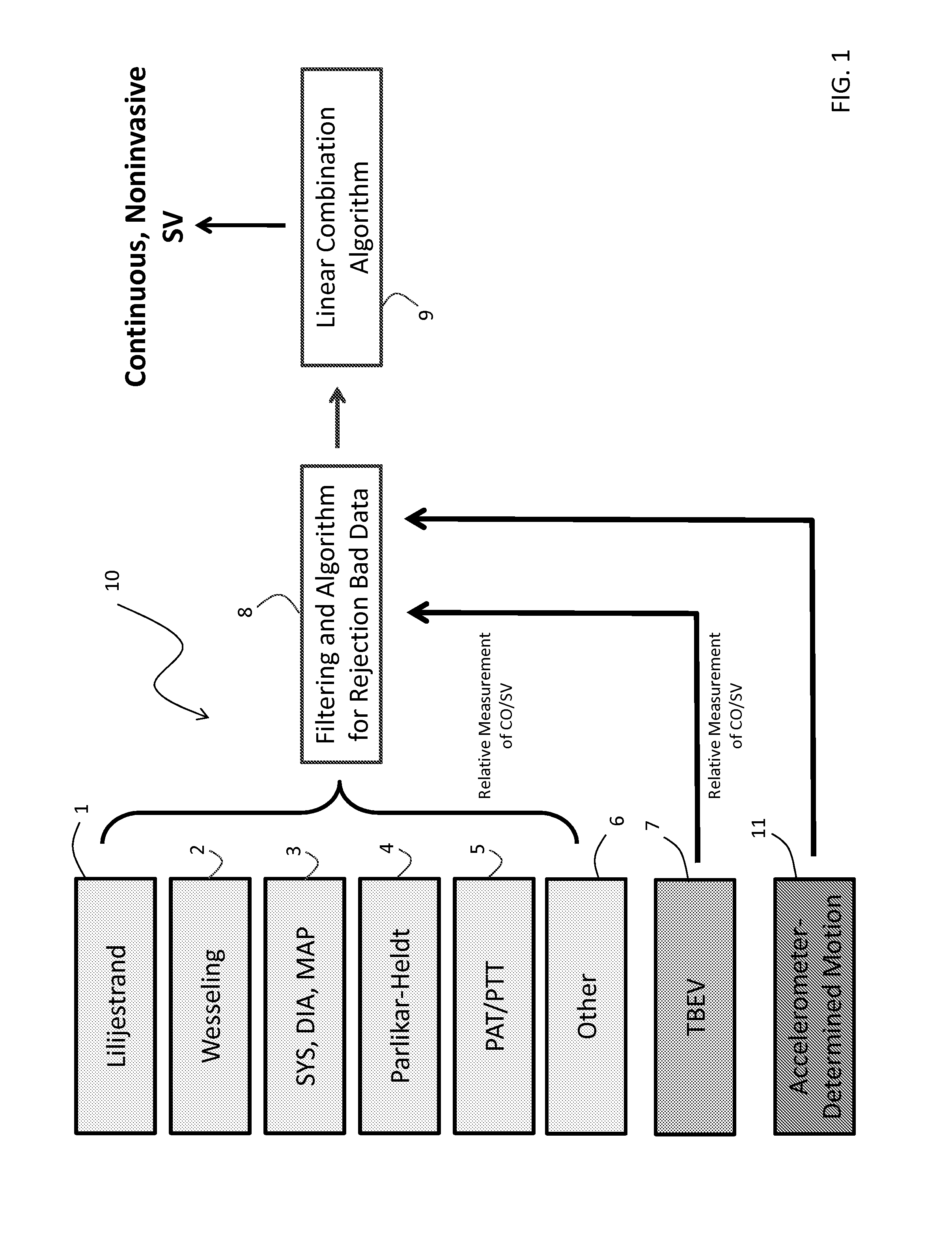
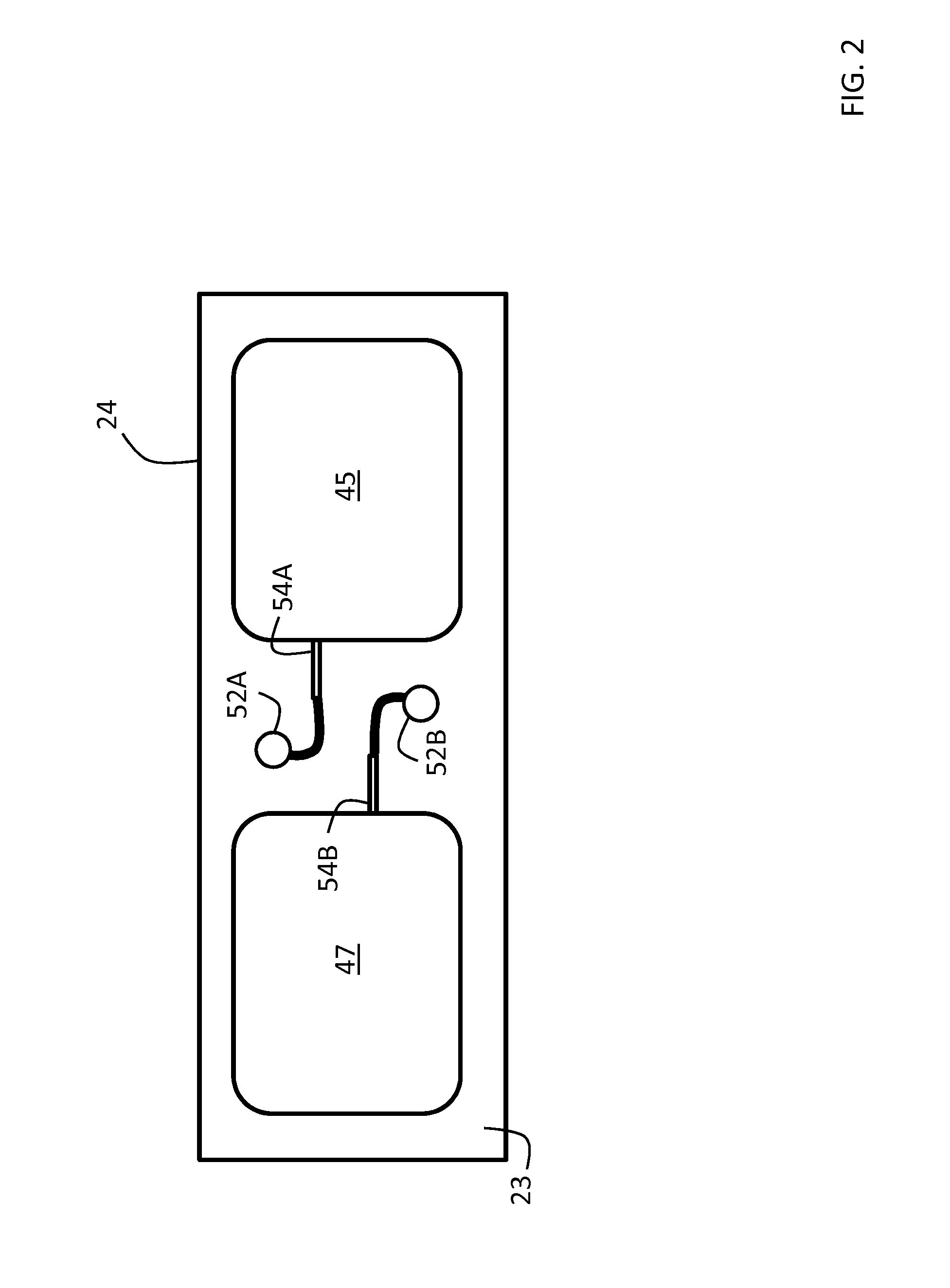
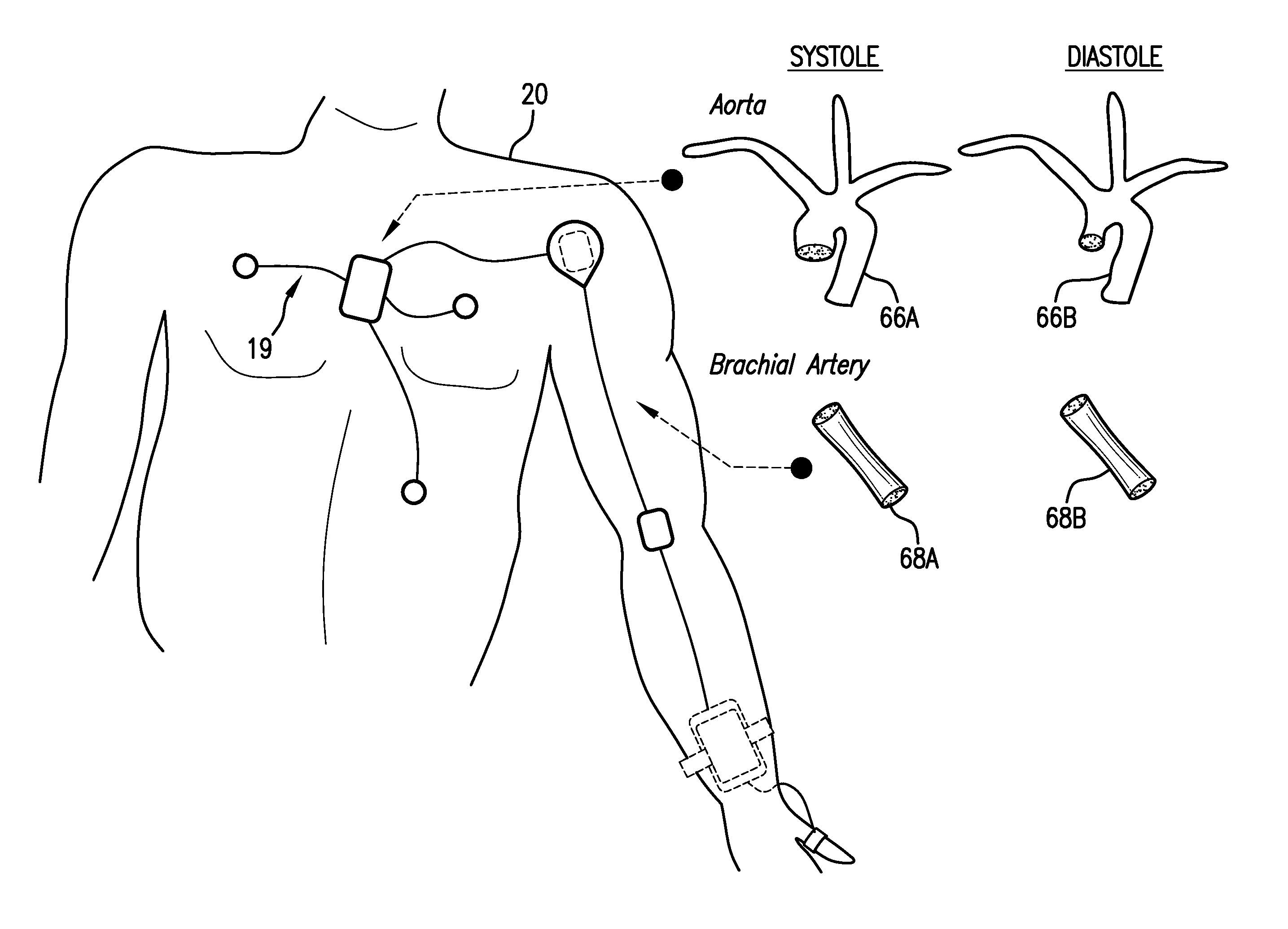
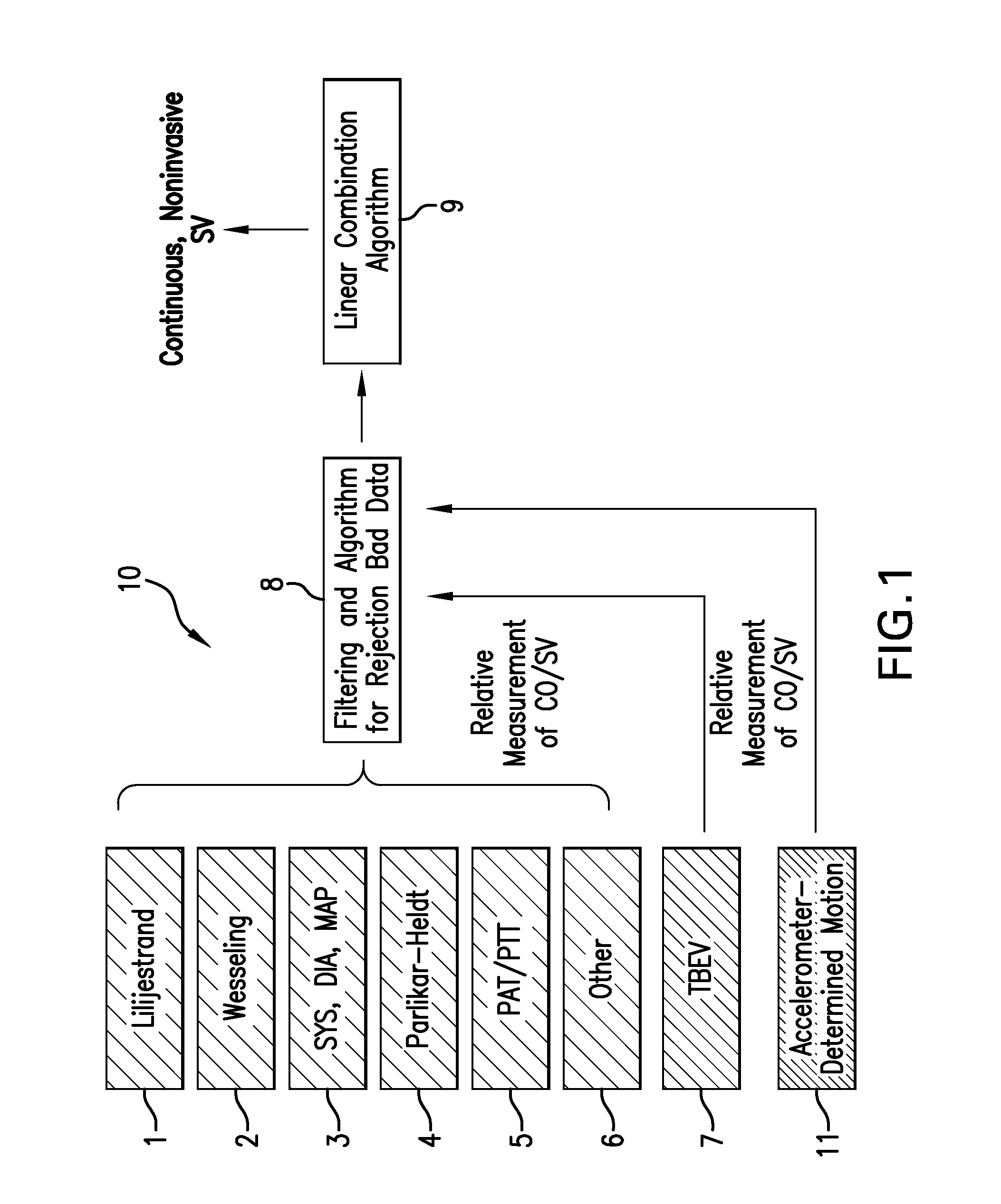
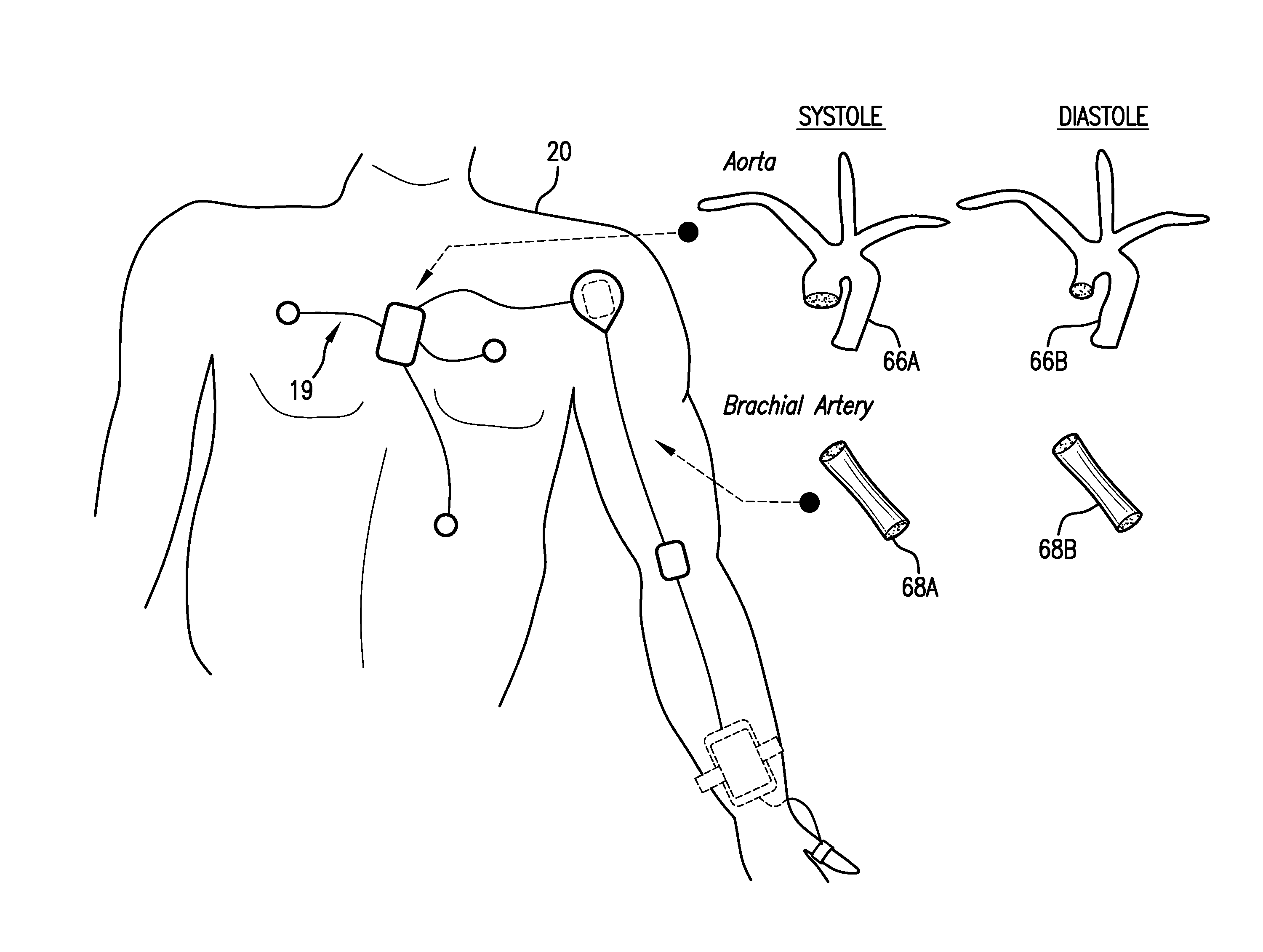
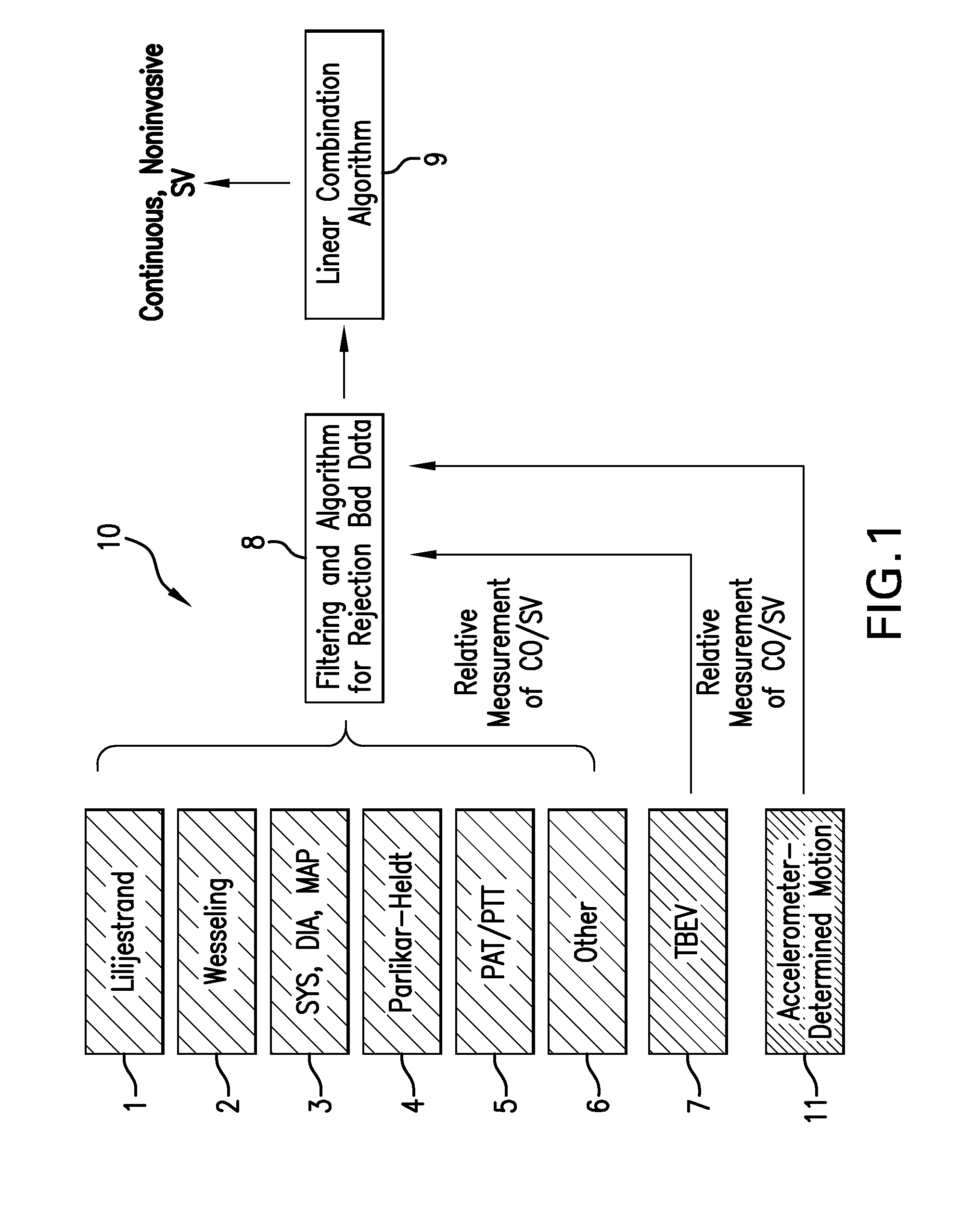
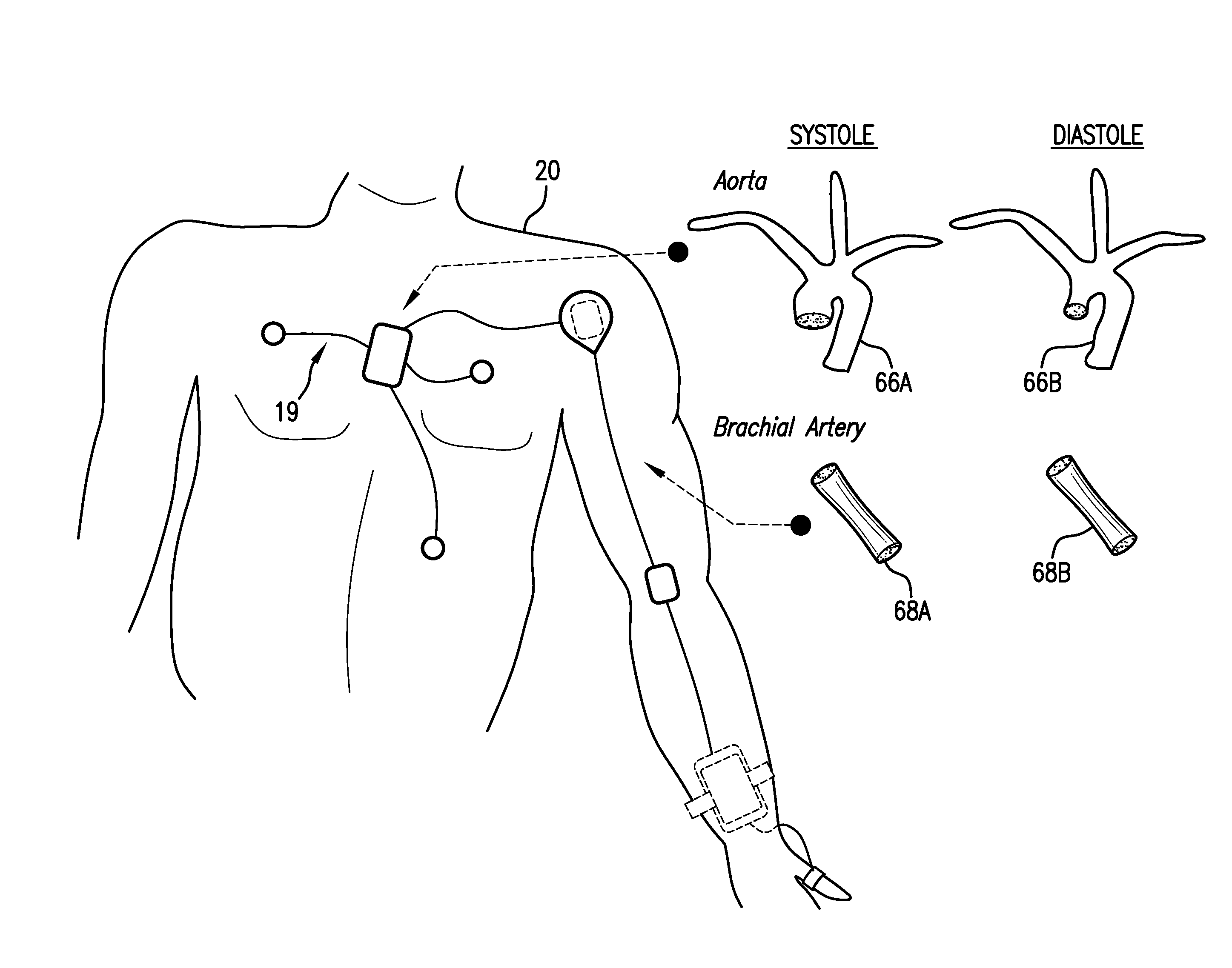
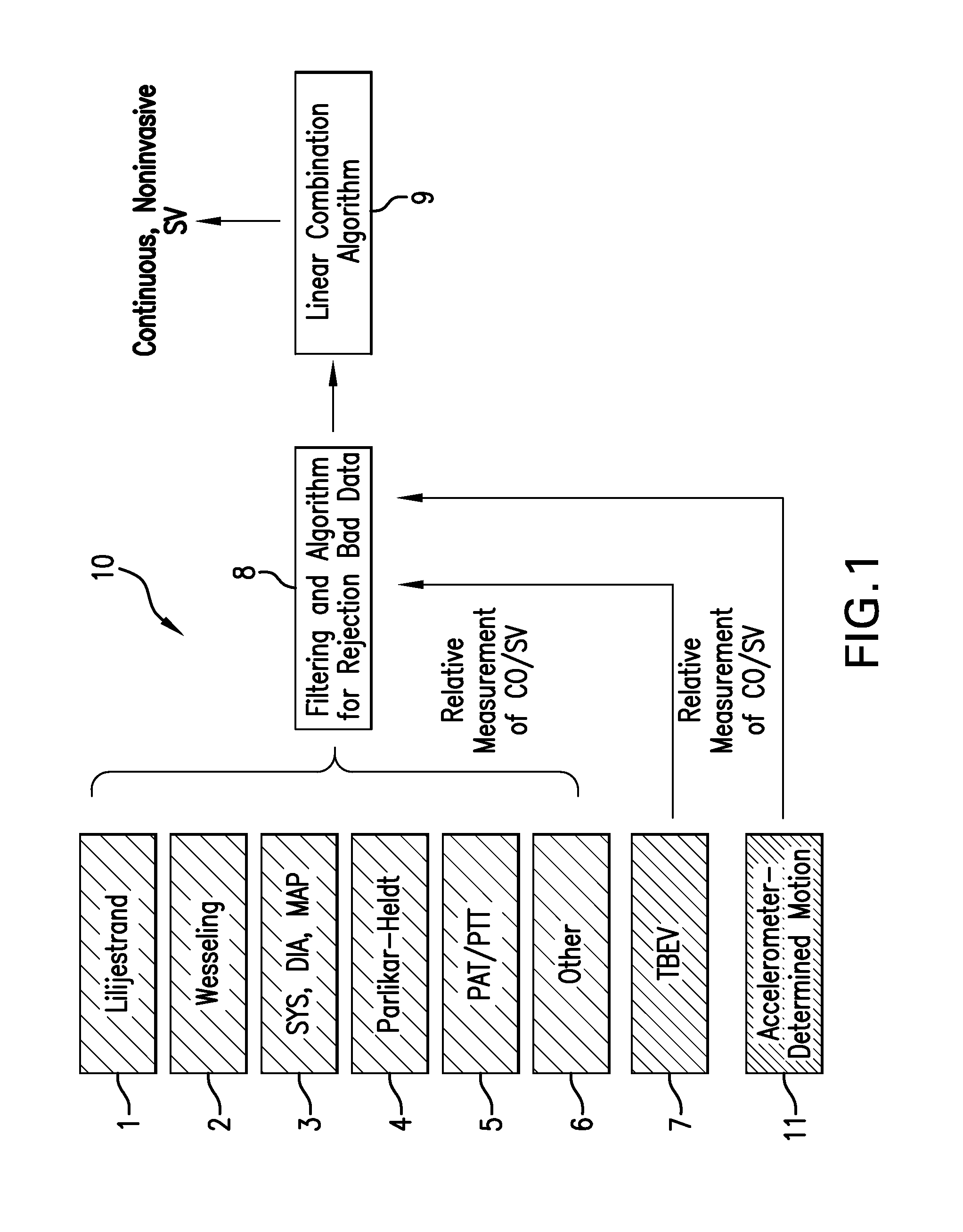
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS20140249431A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) an impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
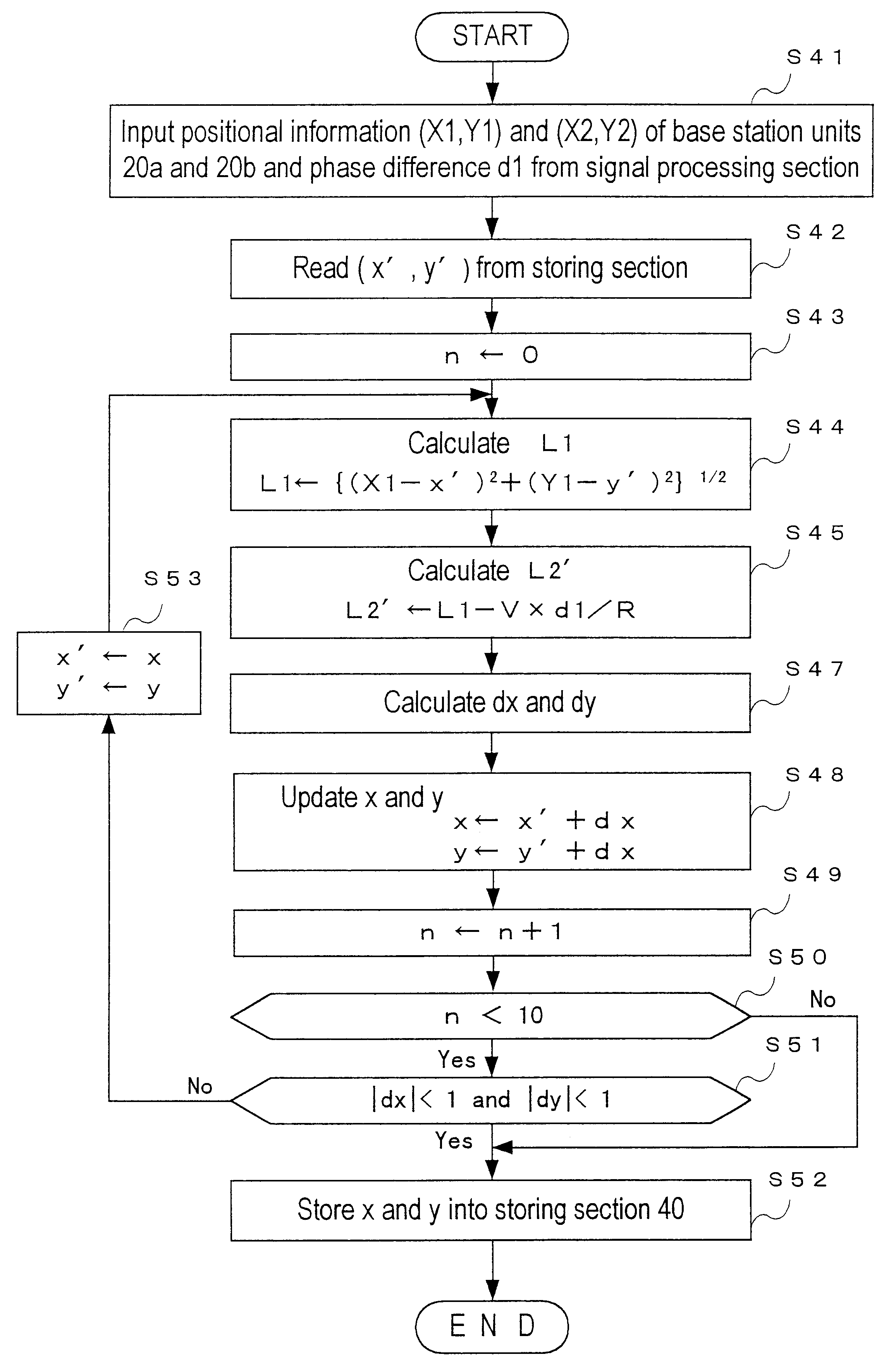
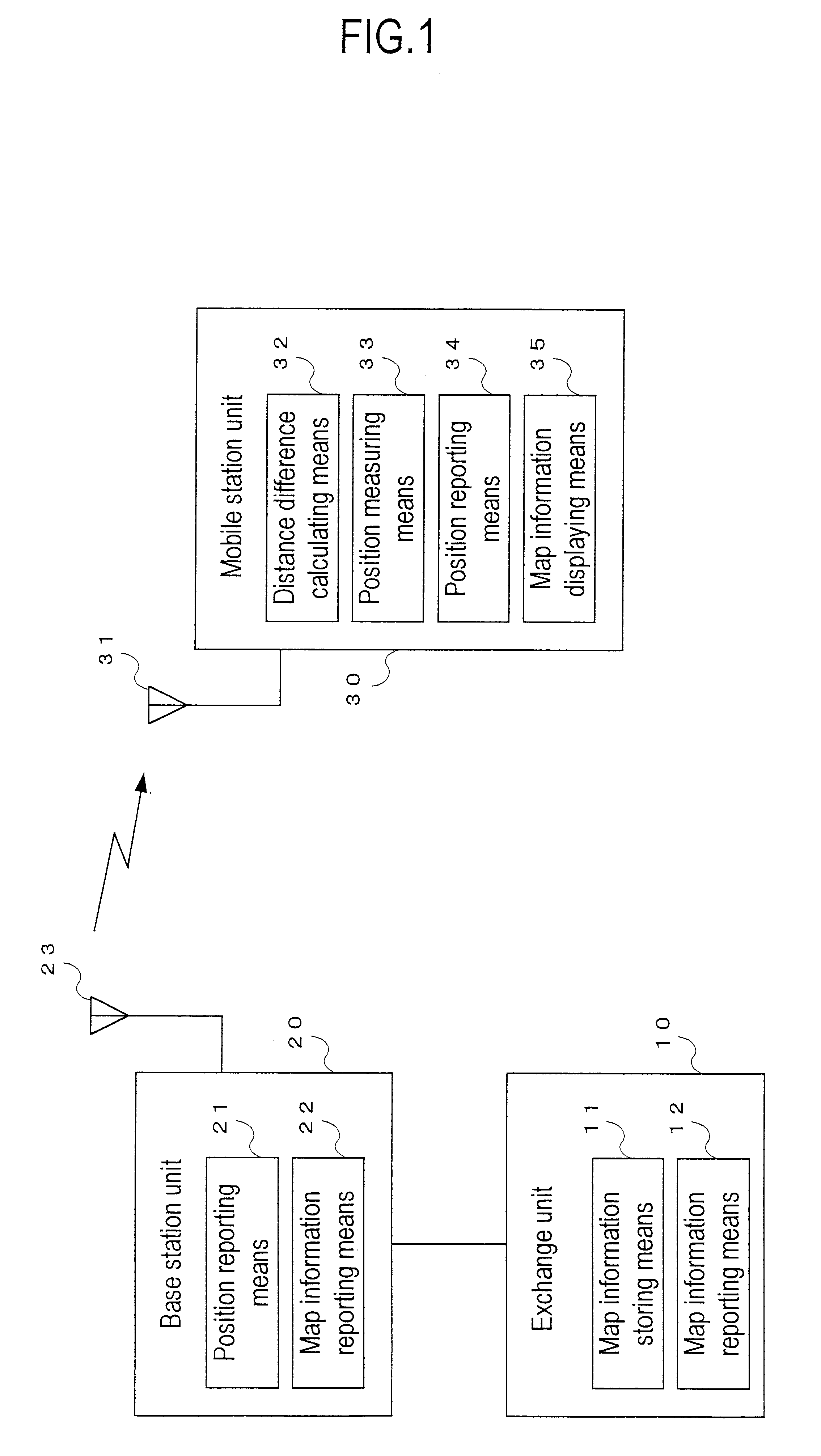
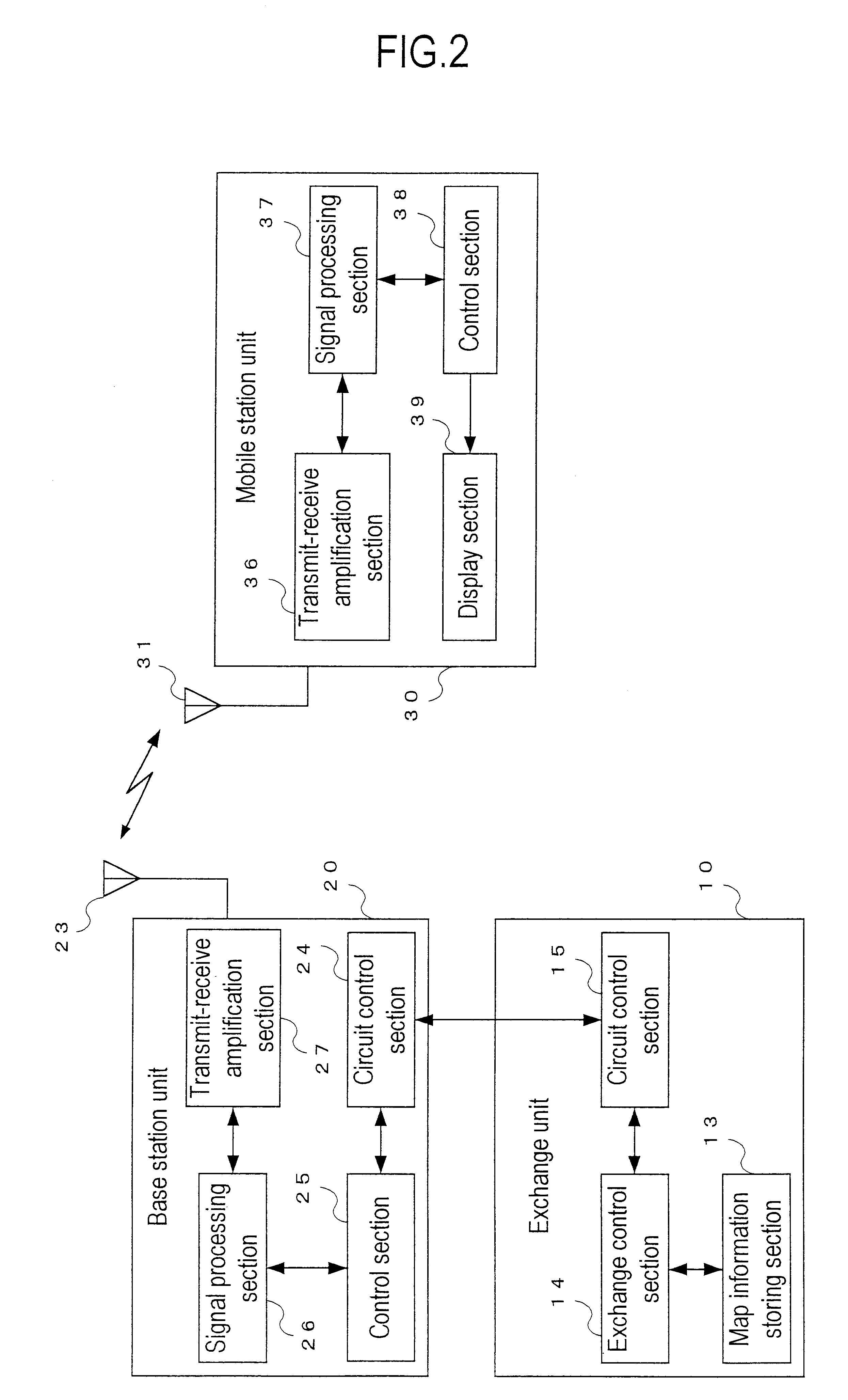
Positioning system and position calculating method in mobile communication system
InactiveUS6845239B1Easy to useAccurate calculationDirection finders using radio wavesRoad vehicles traffic controlReal-time computingMobile station
A positioning system and a position calculating method in a mobile communication system for specifying a position of a mobile station unit on the basis of positional information from three base station units and for displaying related map information on the mobile station unit to utilize the positional information effectively, the position system and the position calculating method in which a position reporting means of a base station unit reports positional information, a distance difference calculating means of the mobile station unit calculates differences in distance between the mobile station unit and three base station units on the basis of the positional information from the three base station units, measures a position of the mobile station unit on the basis of the positional information and the distance differences by using a position measuring means, reports the measured position to an exchange unit by using a position reporting means, and a map information displaying means of the mobile station unit displays related map information reported from the exchange unit.
Owner:KOKUSA ELECTRIC CO LTD
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS9364158B2Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) an impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors. The processing system analyzes the ECG, TBEV and optical signals to determine SV, and further analyzes SV and HR determined from an ECG sensor to determine CO.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
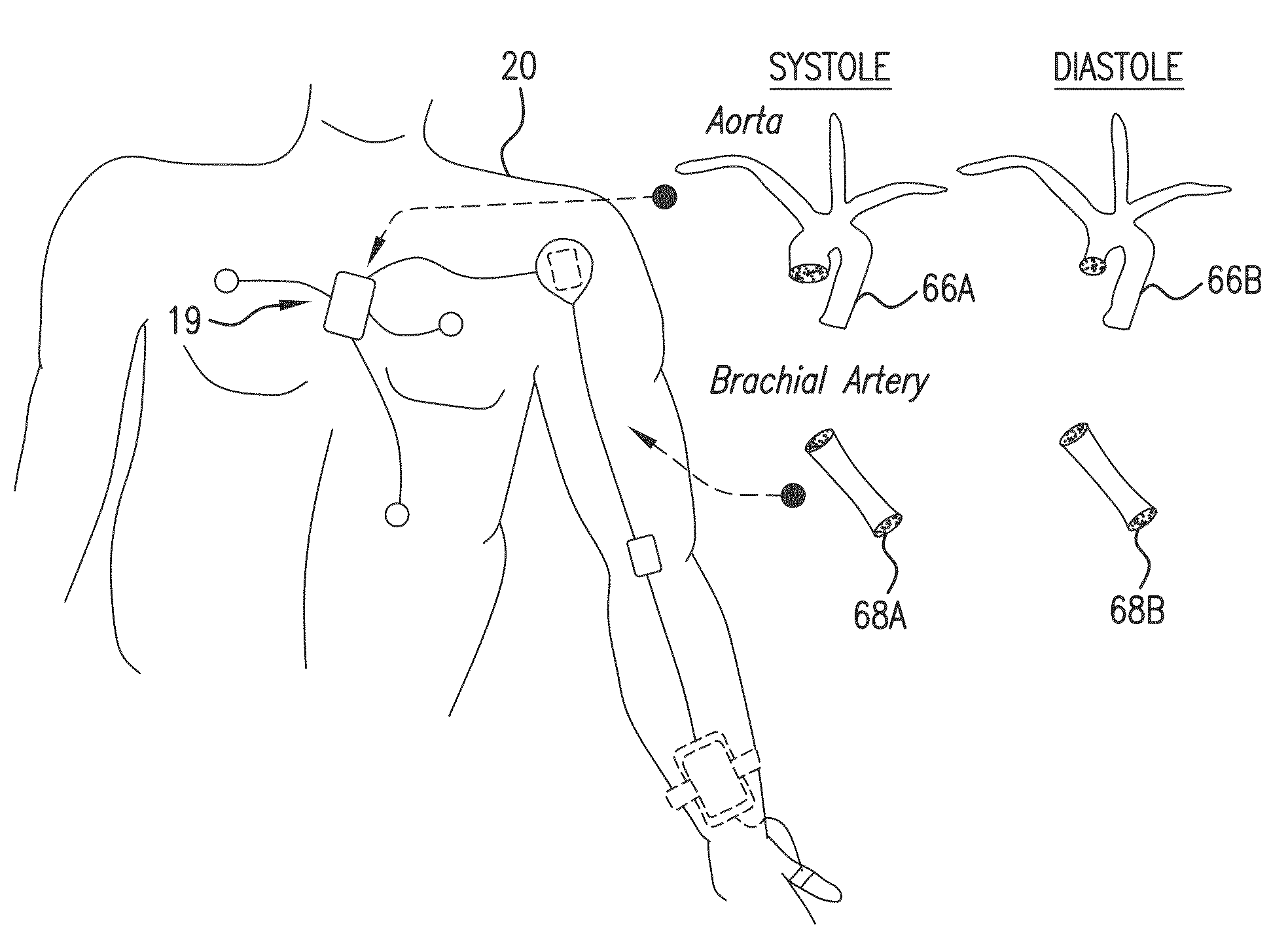
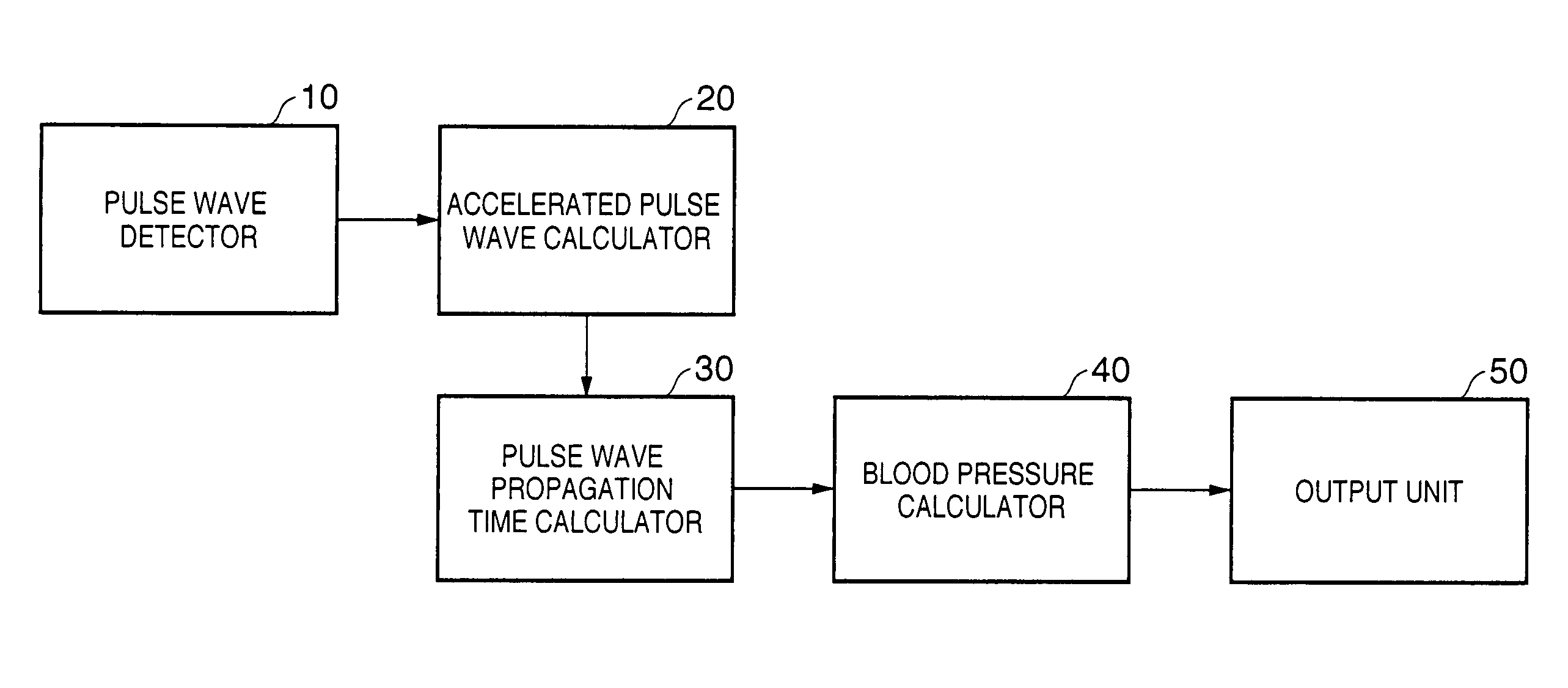
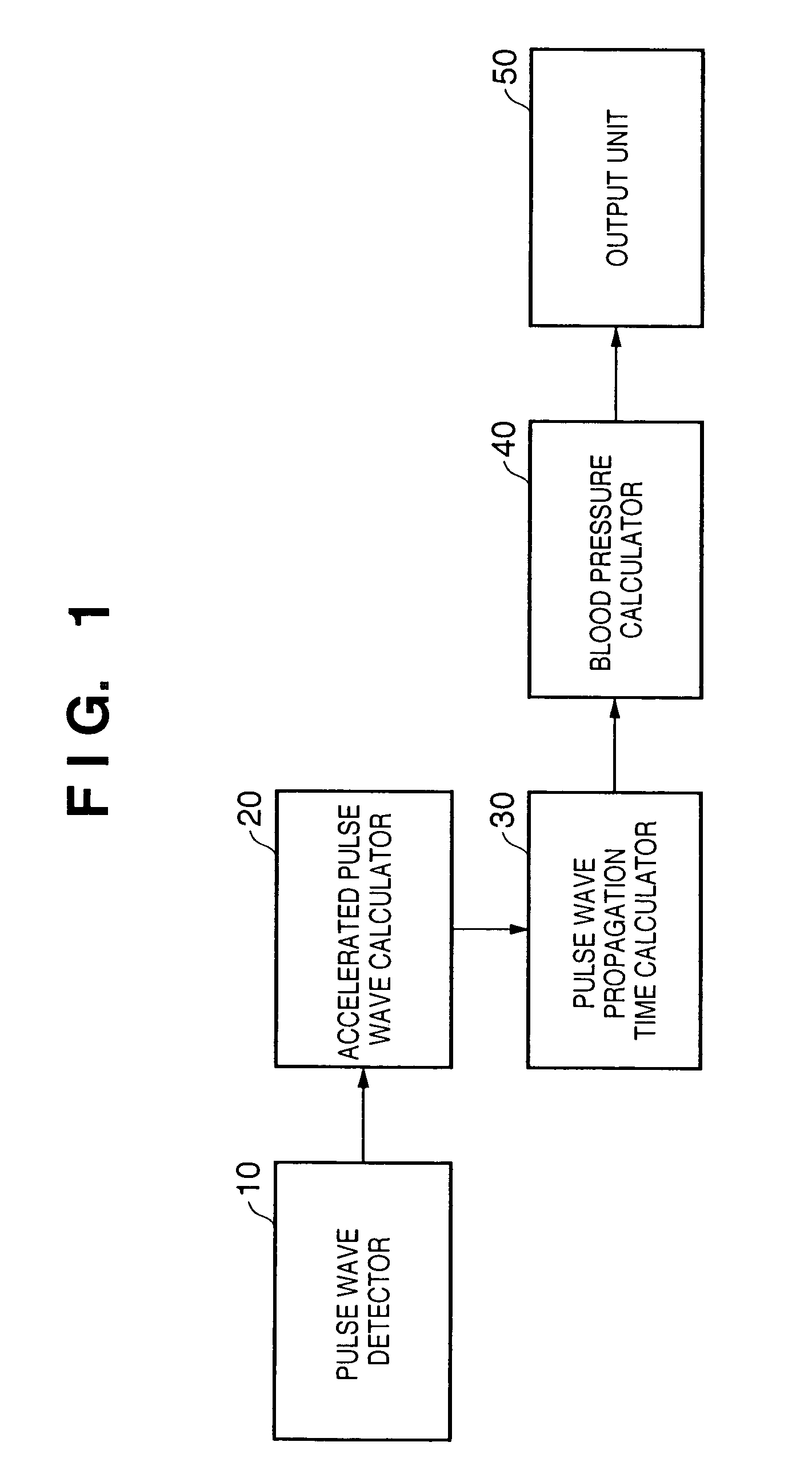
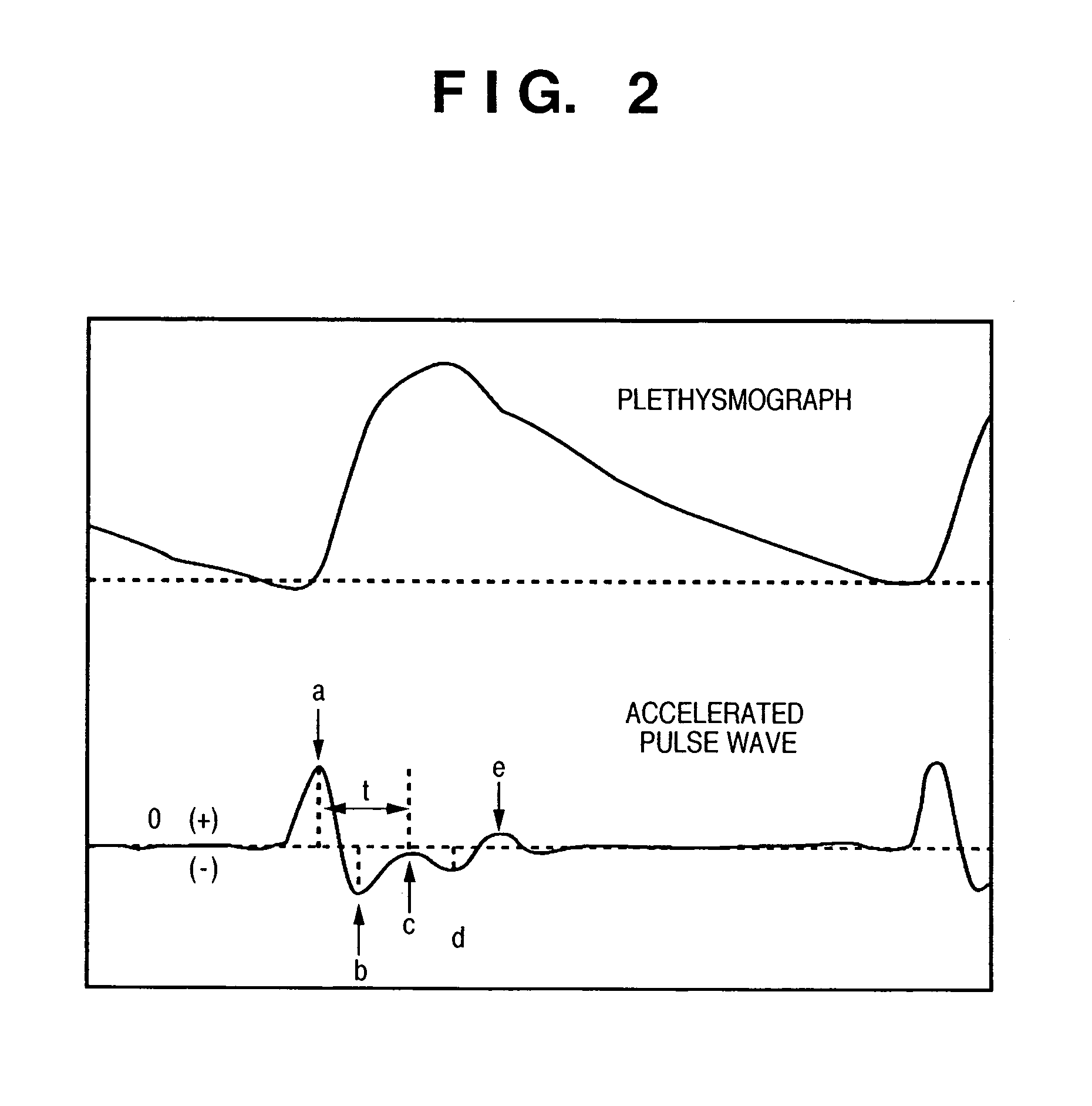
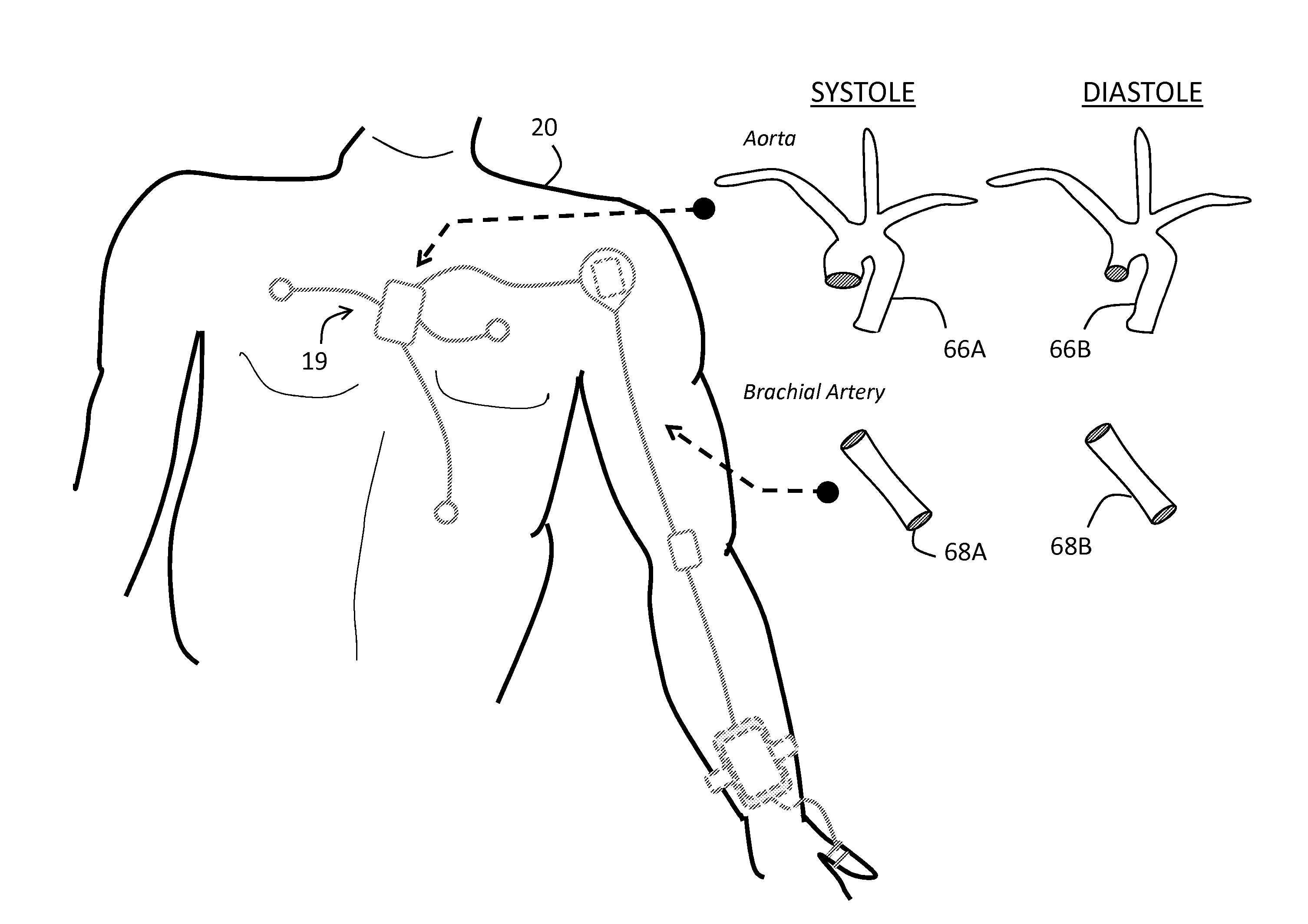
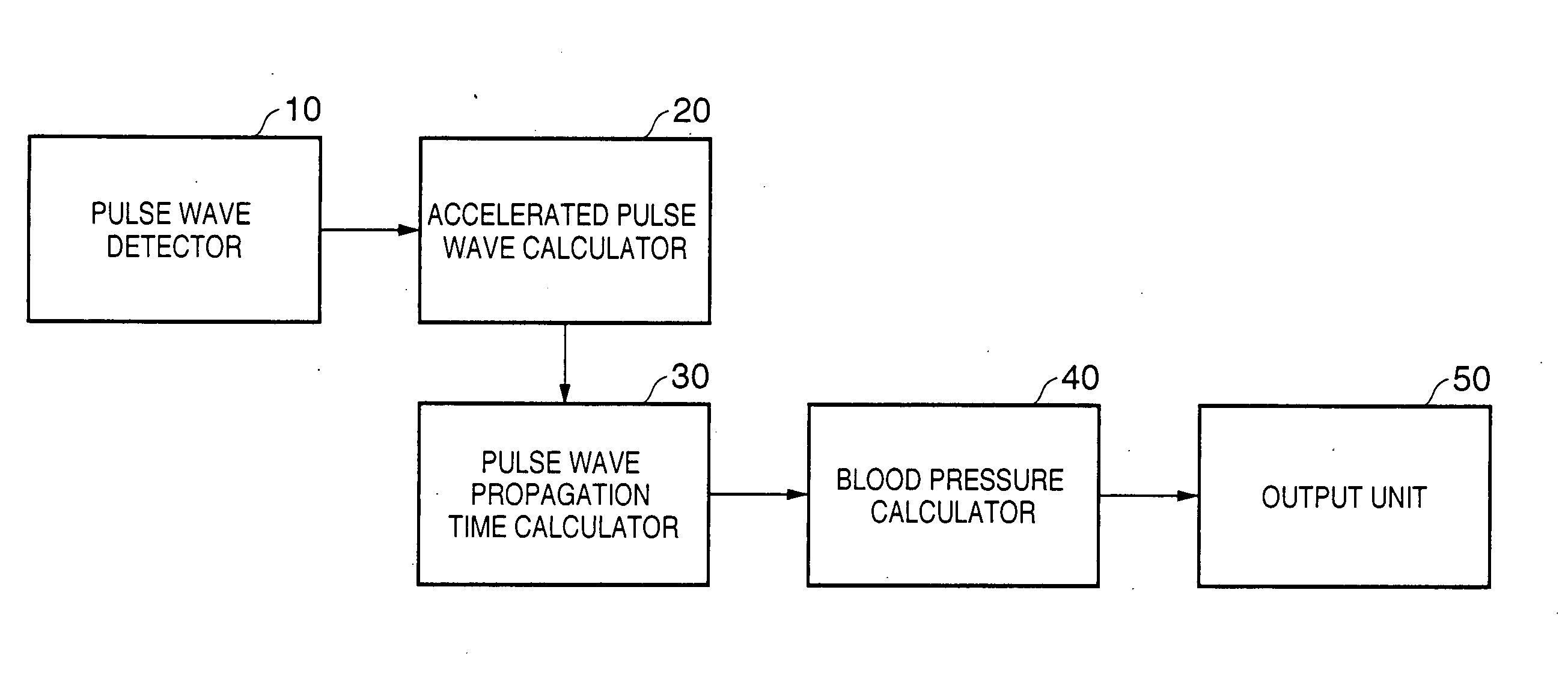
Blood pressure measuring apparatus
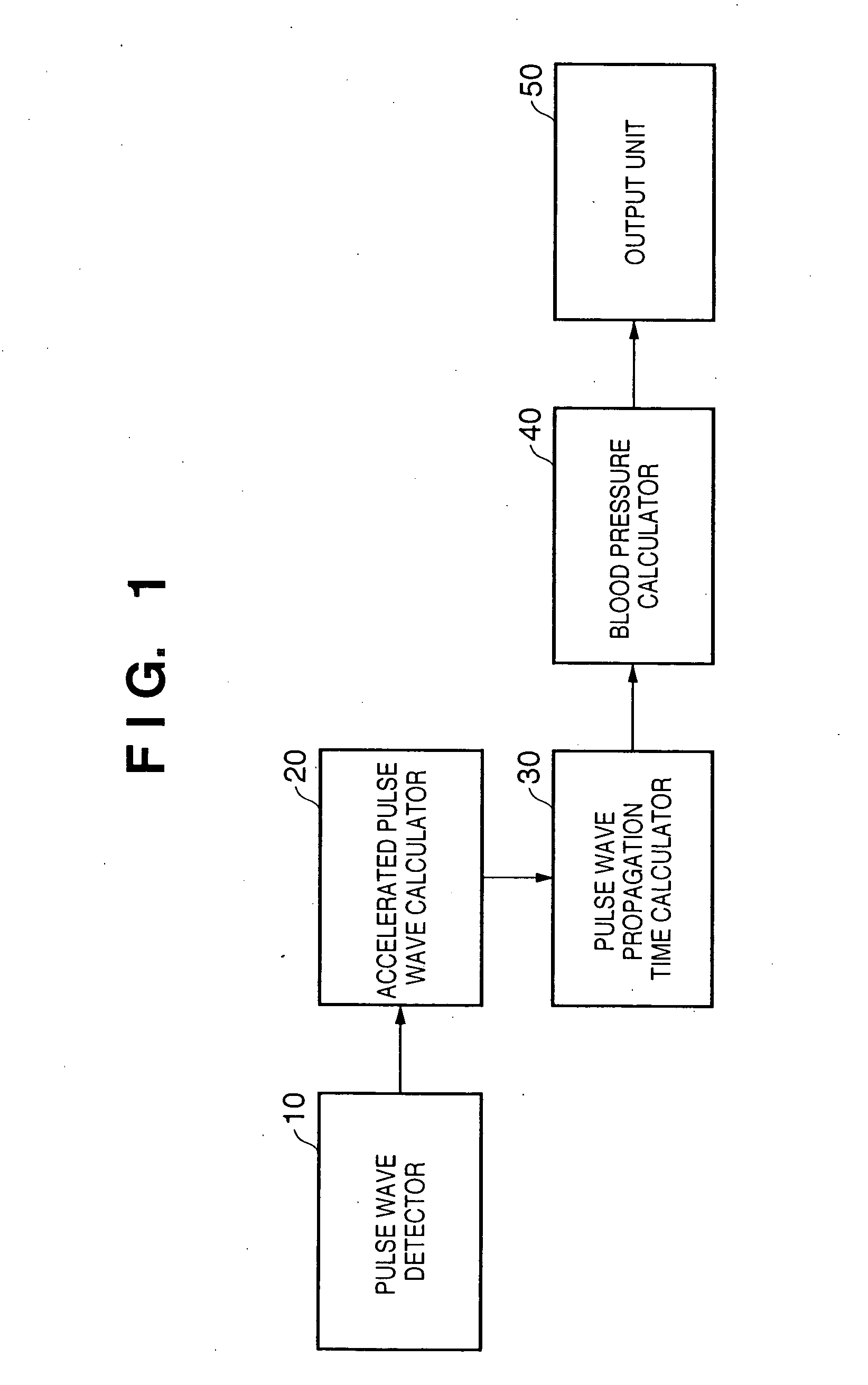
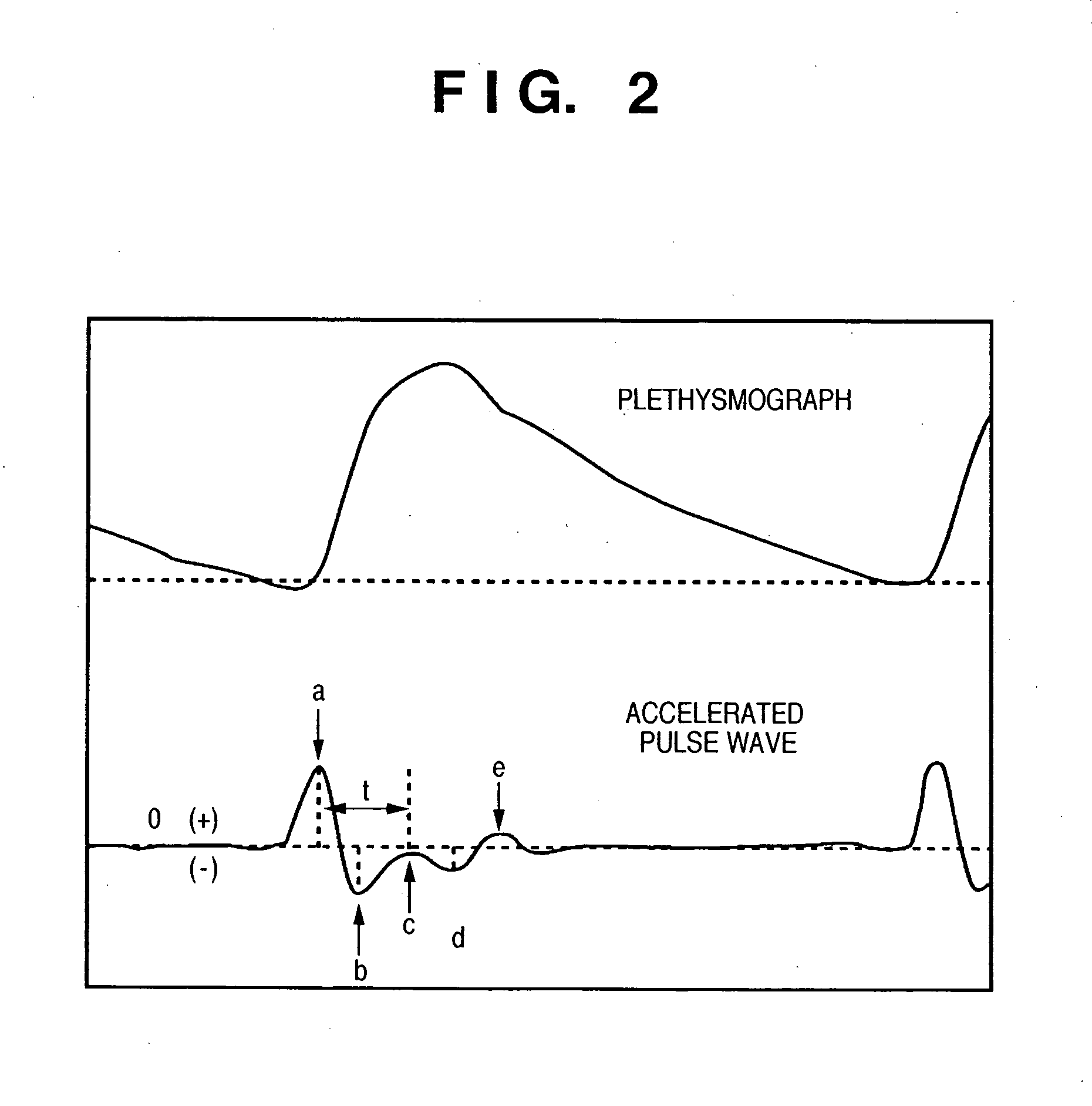
ActiveUS7390300B2Continuous measurementSimple methodEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterBlood pressureReflected waves
A pulse wave is detected in a predetermined location of a living body, and the progressive wave component and reflected wave component are extracted from the pulse wave. The pulse wave propagation time is calculated from the progressive wave component and reflected wave component, and blood pressure is calculated on the basis of this pulse wave propagation time. The use of this method provides blood pressure measuring apparatus capable of continuously measuring blood pressure with a simple method.
Owner:FUKUDA DENSHI CO LTD
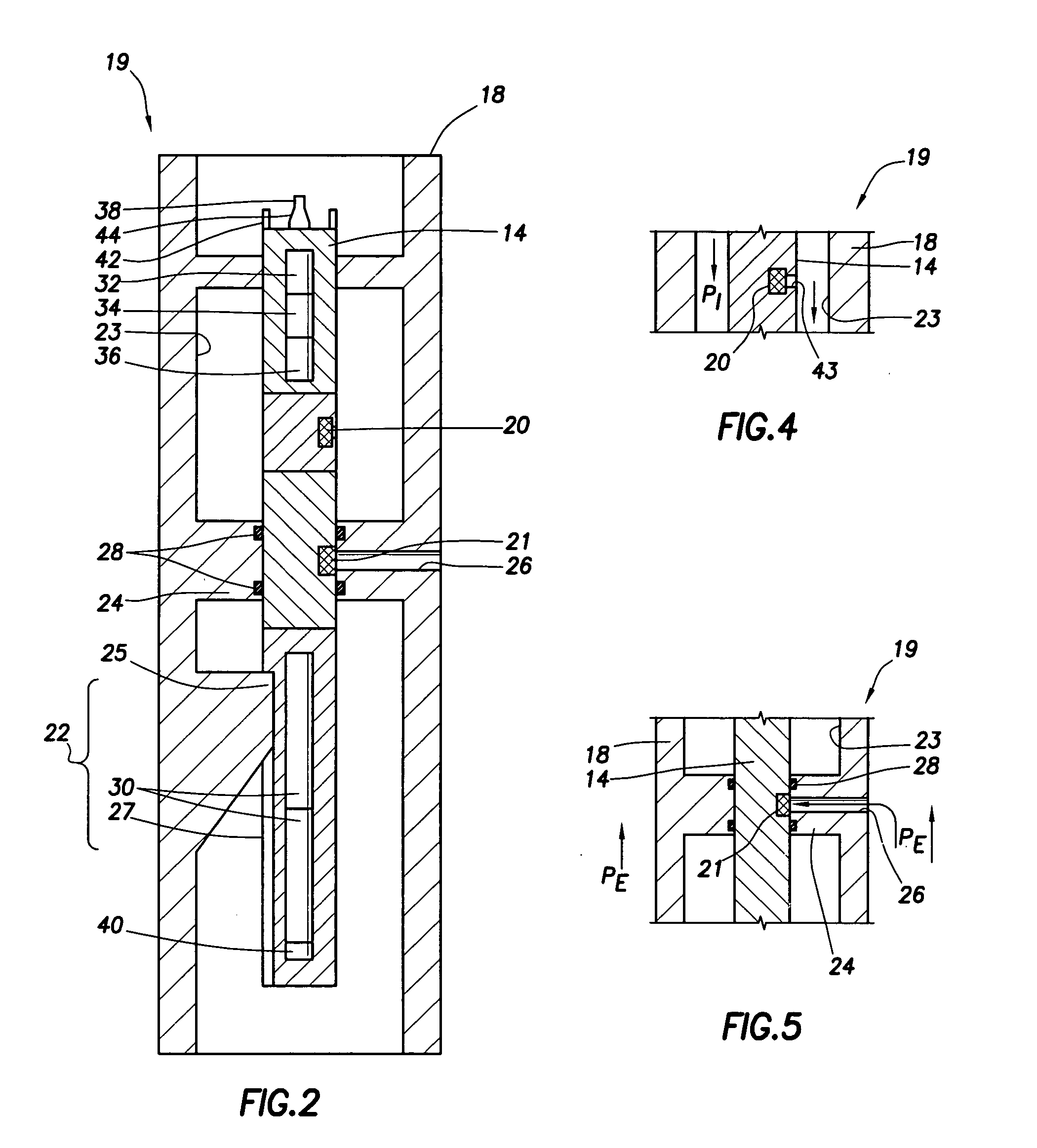
While drilling system and method
A while drilling system and method for determining annular pressure while drilling is provided. The system is positioned in a drilling tool suspended from a drilling rig via a drill string. The system includes at least one drill collar, a while drilling tool and at least one external sensor. The drill collar has a tubular sidewall defining a passage therein for the flow of drilling mud therethrough. The while drilling tool is supported in the passage of the at least one drill collar and selectively retrievable therefrom. The external sensor is positioned in the sidewall of the drill collar and isolated from the passage. The sensor is exposed to the wellbore for measurement thereof and adapted to wirelessly communicate with the while drilling tool. The system is preferably adapted for use in high temperature and pressure environments.
Owner:SCHLUMBERGER TECH CORP
System for fall prevention and a method for fall prevention using such a system
InactiveUS20100049096A1Easy to useDisadvantage of known is minimizedPerson identificationSensorsLower riskEngineering
System for fall prevention for a user, comprising a number of sensors (2) attachable to at least one lower body segment (3), wherein said sensors (2) are adapted to measure movement of said at least one lower body segment (3) and to translate the movement into a signal (S), the system further comprising a control (12) adapted to receive the signal (S) from said respective sensors (2), wherein in use the control (12) observes the signal (S) as an actual sequence of postures of said at least one lower body segment (3) and compares the actual sequence with a predetermined sequence of postures as a function of time, (the predetermined sequence relating to a low risk of falling,) wherein the control (12) is adapted to determine a high risk of falling when the actual sequence deviates from the predetermined sequence (to a certain degree). The invention further relates to a method for fall prevention using such a system for fall prevention.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Exhaust gas component analyzer
ActiveUS20060236752A1High measurement accuracySave electricityAnalysing fluids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesInternal-combustion engine testingEngineeringInternal combustion engine
An exhaust gas analyzer includes a main flow path and at least one sub-flow path. Exhaust gas from an internal combustion engine is introduced to the main flow path; sub-flow paths are parallel to the main flow path. Plural kinds of analyzers are mounted on the main flow path and sub-flow paths to measure concentration of multiple components in the exhaust gas. Actual measurement values of the concentration for the measured components are obtained. A deviance from a true value generated to an actual measurement value due to a mutual influence of the measured components is corrected based on at least one actual measurement value.
Owner:HORIBA LTD
Wearable thermometer patch capable of measuring human skin temperature at high duty cycle
InactiveUS20180028072A1Faster respond timeImprove accuracyBody temperature measurementSensorsElectricityHuman skin
A wearable thermometer patch for continuous wearing by a user includes a circuit substrate that includes an electric circuit, a battery holder mounted in the circuit substrate, and a detachable cover layer on the battery holder. The battery holder can hold a replaceable battery to supply power to the electric circuit. A temperature probe unit in connection with the electric circuit includes one or more temperature sensors in electric connection with the electric circuit in the circuit substrate. The one or more temperature sensors each can measure temperatures near the user's skin to produce one or more temperature values.
Owner:VIVALNK
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
InactiveUS20140249434A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) an impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
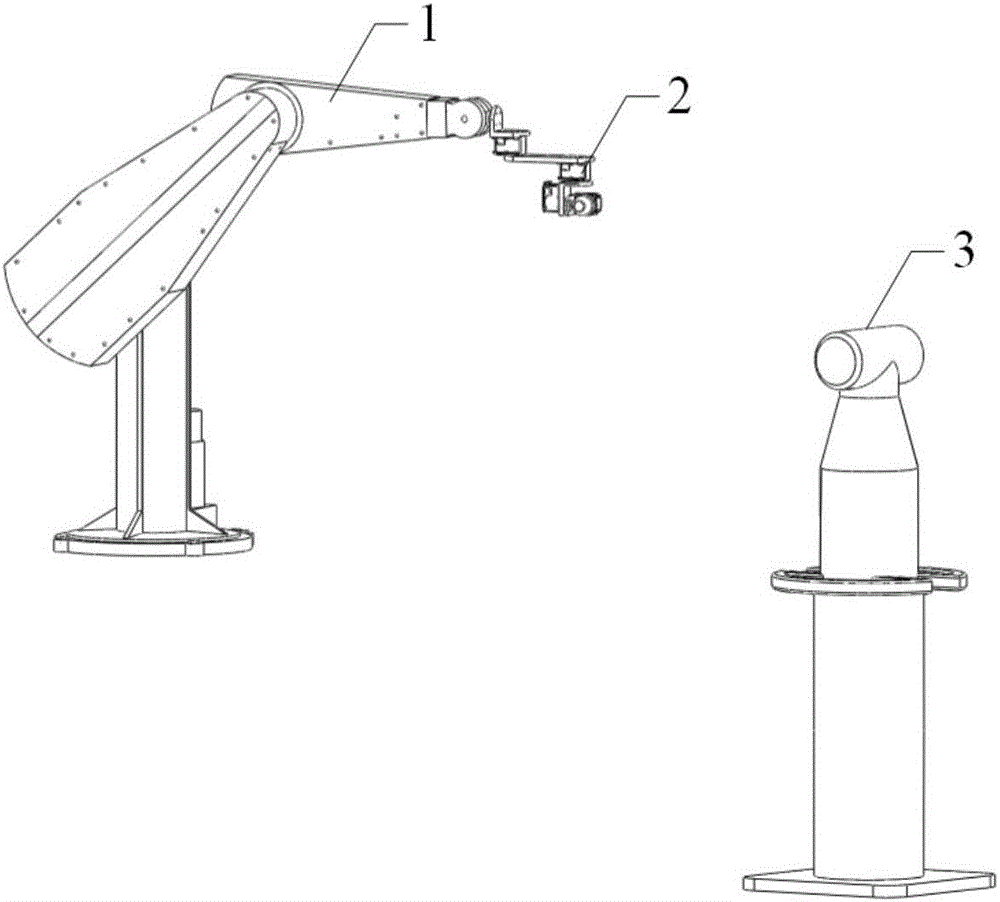
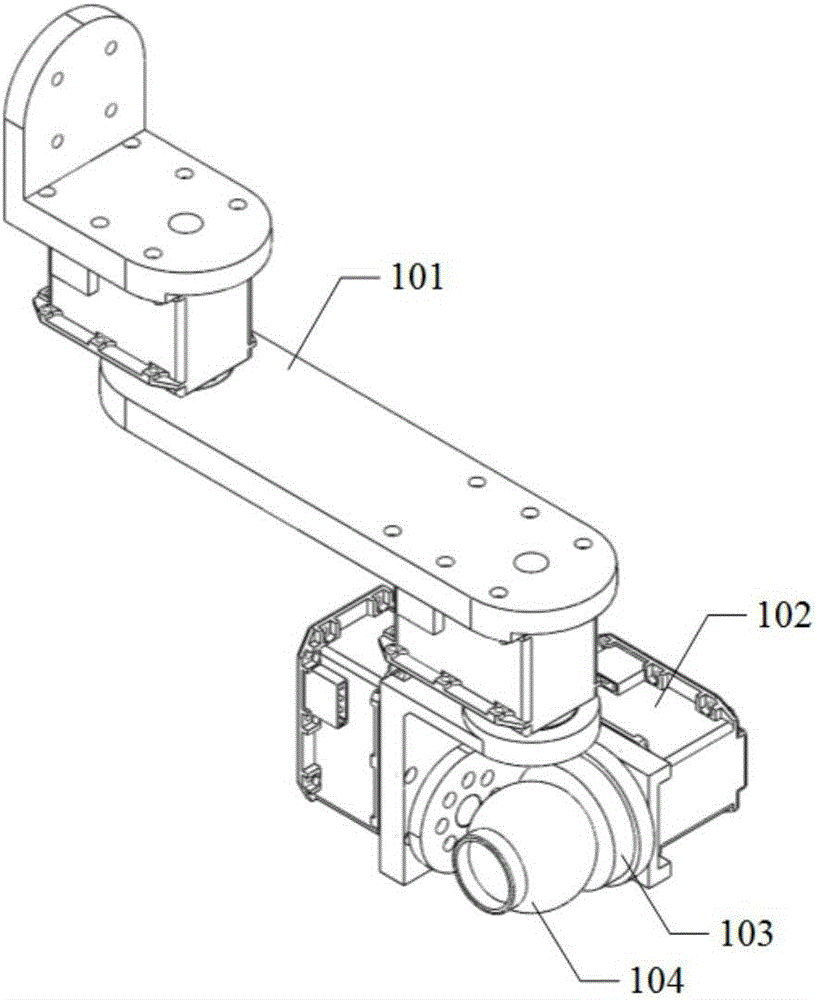
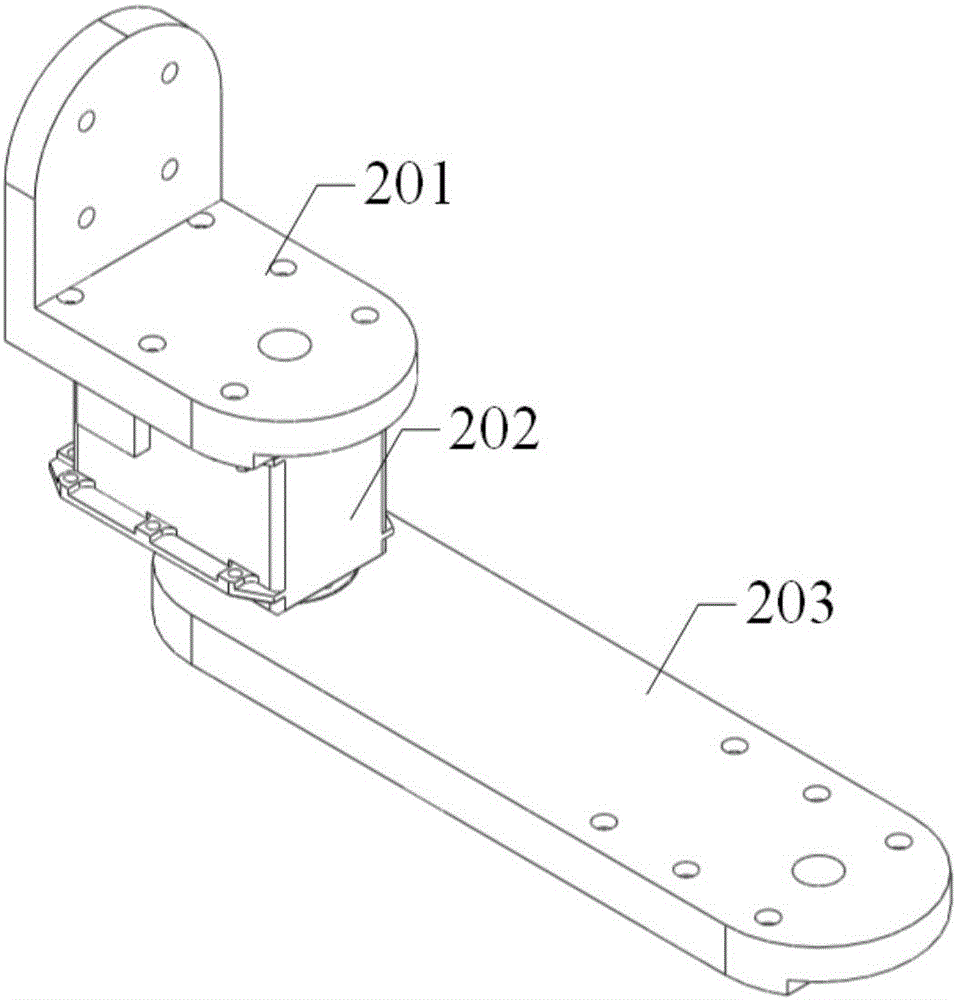
Rapid industrial robot tail end pose measuring device and measuring method thereof
ActiveCN106705956ARealize pose data measurementImprove efficiencyNavigation instrumentsTotal factory controlFast measurementMeasurement point
The invention discloses a rapid industrial robot tail end pose measuring device and a measuring method thereof. The rapid industrial robot tail end pose measuring device is characterized by comprising a planar rotating device, a concentric triaxial adjusting device, a magnetic base and a target ball. Firstly, an industrial robot is controlled to move to a point to be measured, then, the planar rotating device is controlled to drive the target ball to do circling motion, the position of the target ball is measured through a laser tracker, the concentric triaxial adjusting device can actively adjusts the direction of the target ball according to the motion of the planar rotating device to ensure that the target ball can reflect laser rays; according to a rotating plane and a trajectory circle center are fit according to measuring point data, a coordinate system (E) of the rapid tail end pose measuring device is established, a tail end pose in a measurement coordinate system (S) can be calculated; an expression of a flange pose in the measurement coordinate system (S) is further obtained through conversion matrix between a flange coordinate system (N) and the coordinate system (E) of the rapid tail end pose measuring device, and accordingly pose measurement of an industrial robot tail end is achieved.
Owner:NANJING INST OF TECH
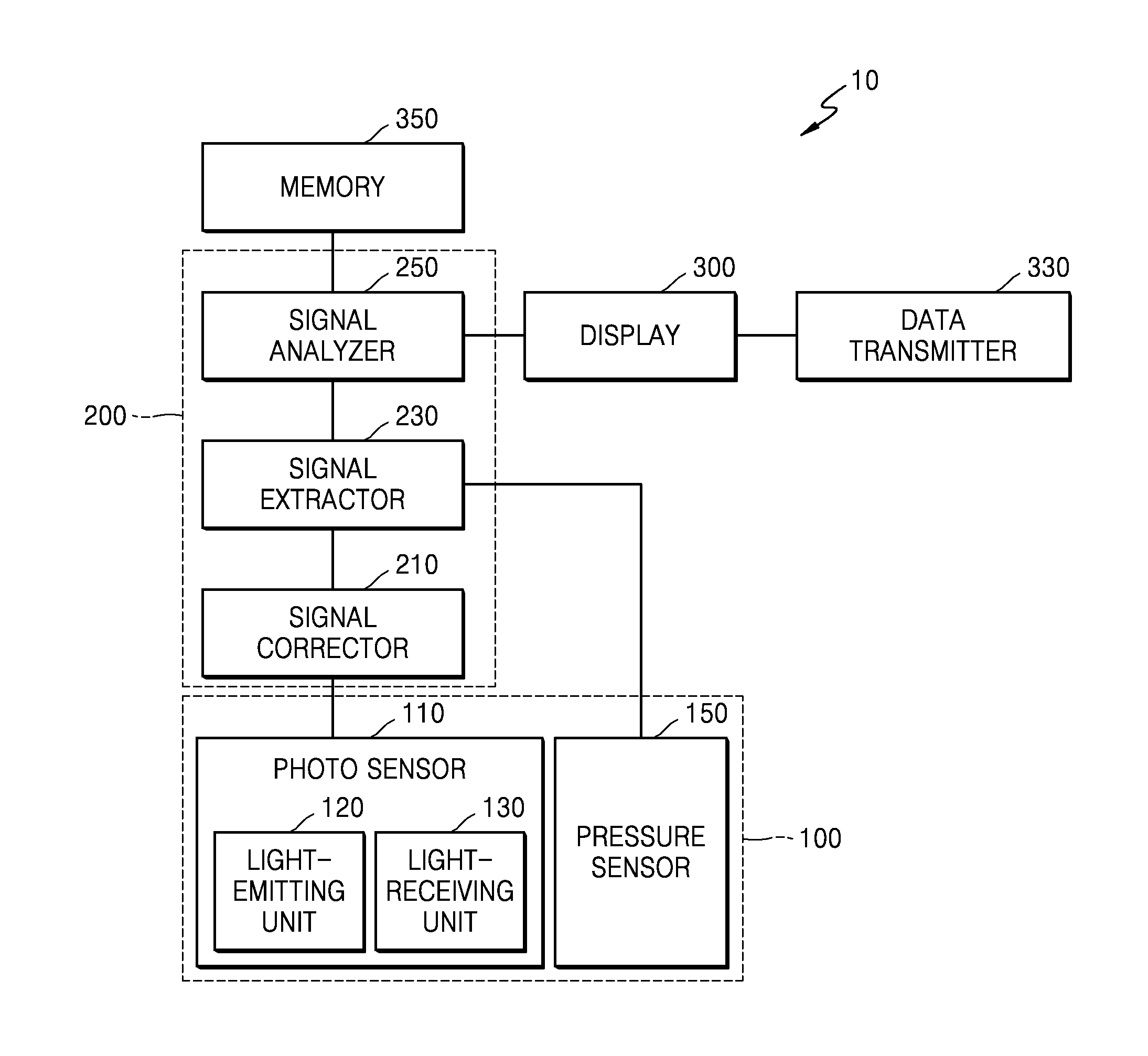
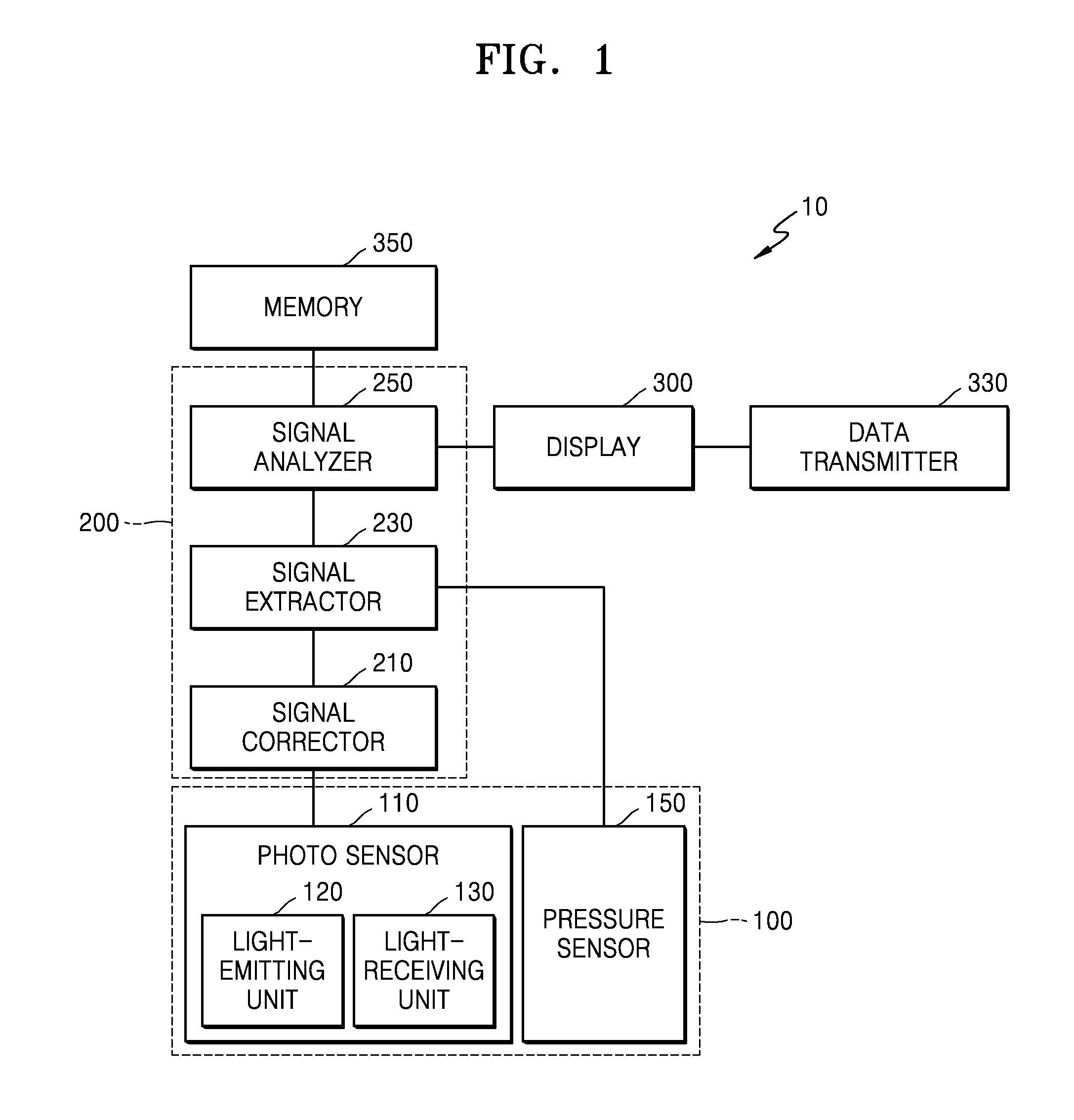
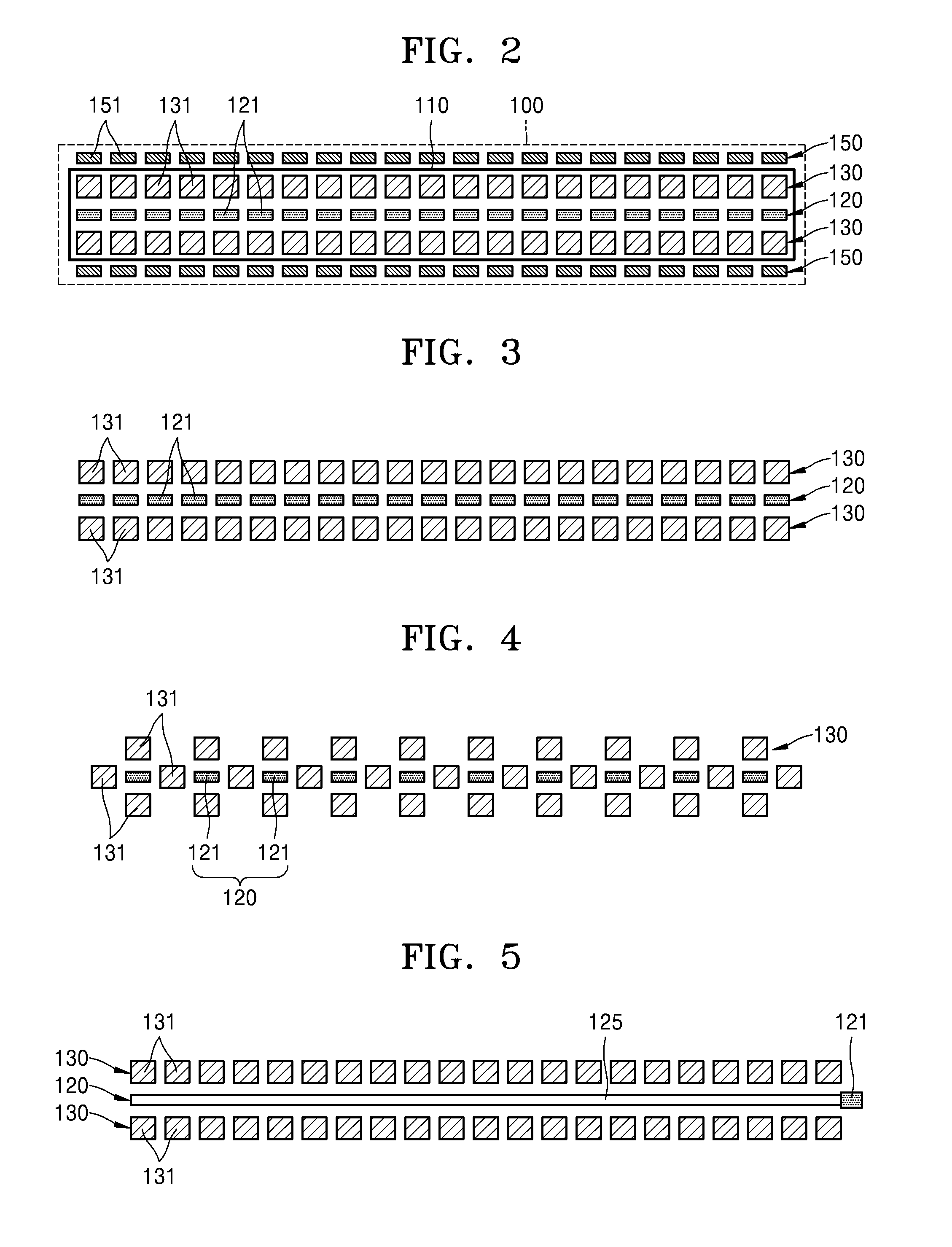
Apparatus and method for detecting biometric information of a living body
An apparatus for detecting biometric information includes a photo sensor configured to acquire a first signal by detecting a change in an optical signal with respect to an object; a pressure sensor configured to acquire a second signal by detecting a change of a pressure with respect to the object; a signal extractor configured to extract a waveform signal from at least one from among the first signal and the second signal based on signal sensitivities of the first and second signals; and a signal analyzer configured to analyze biometric information from the extracted waveform signal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and system for switched beam antenna communications
ActiveUS20110026418A1Increase rangeReduce transmit powerError preventionTransmission systemsPhase shiftedAntenna element
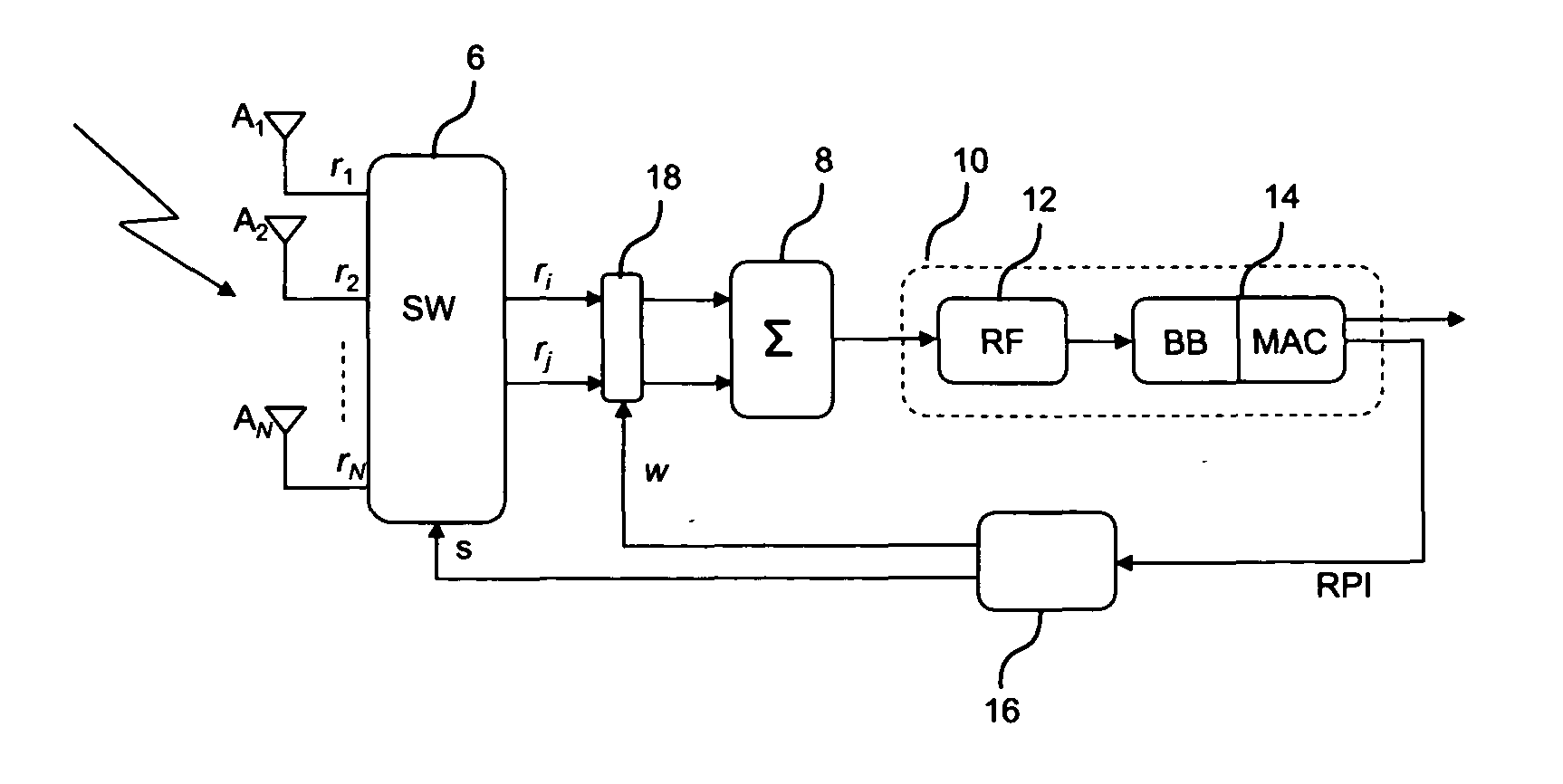
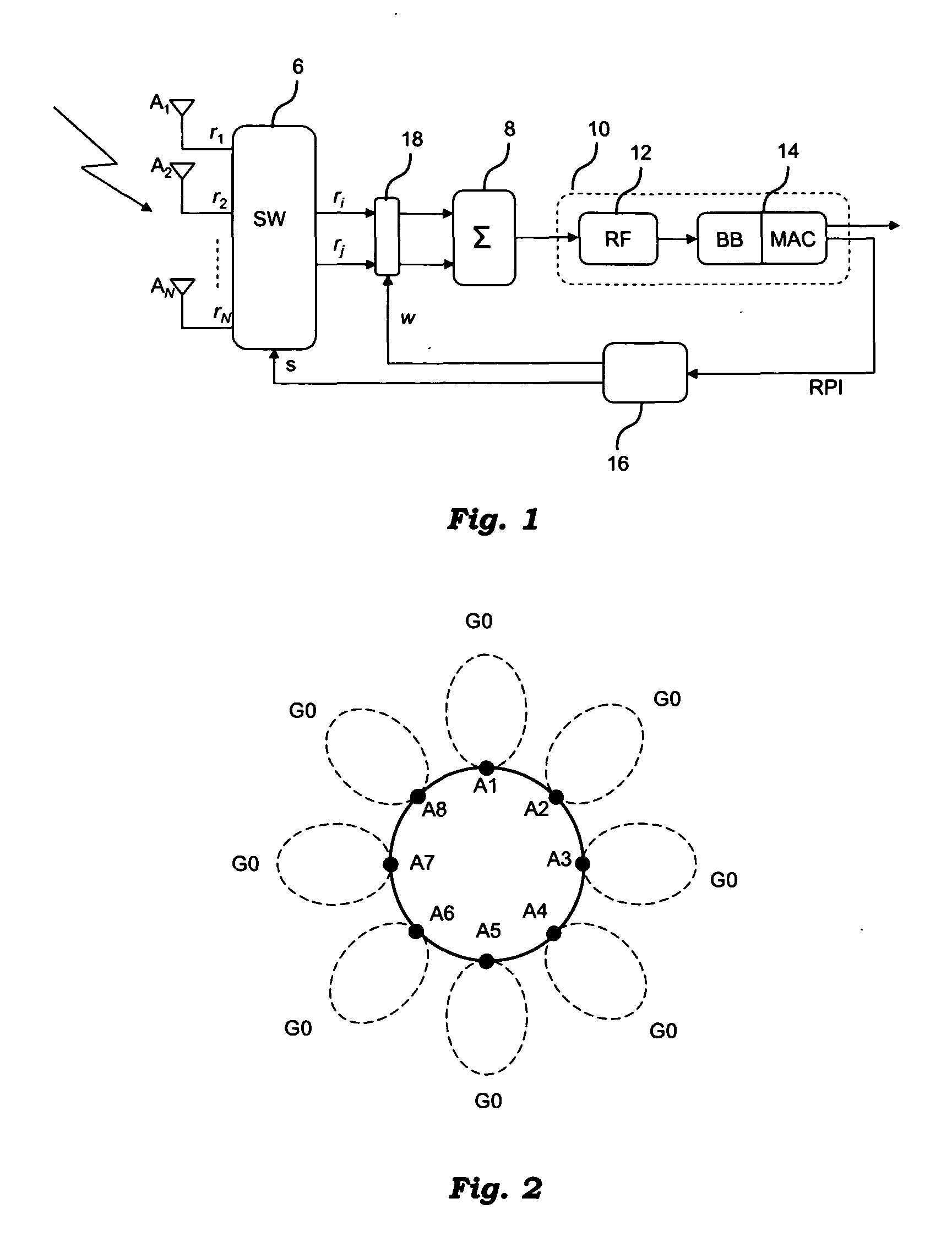
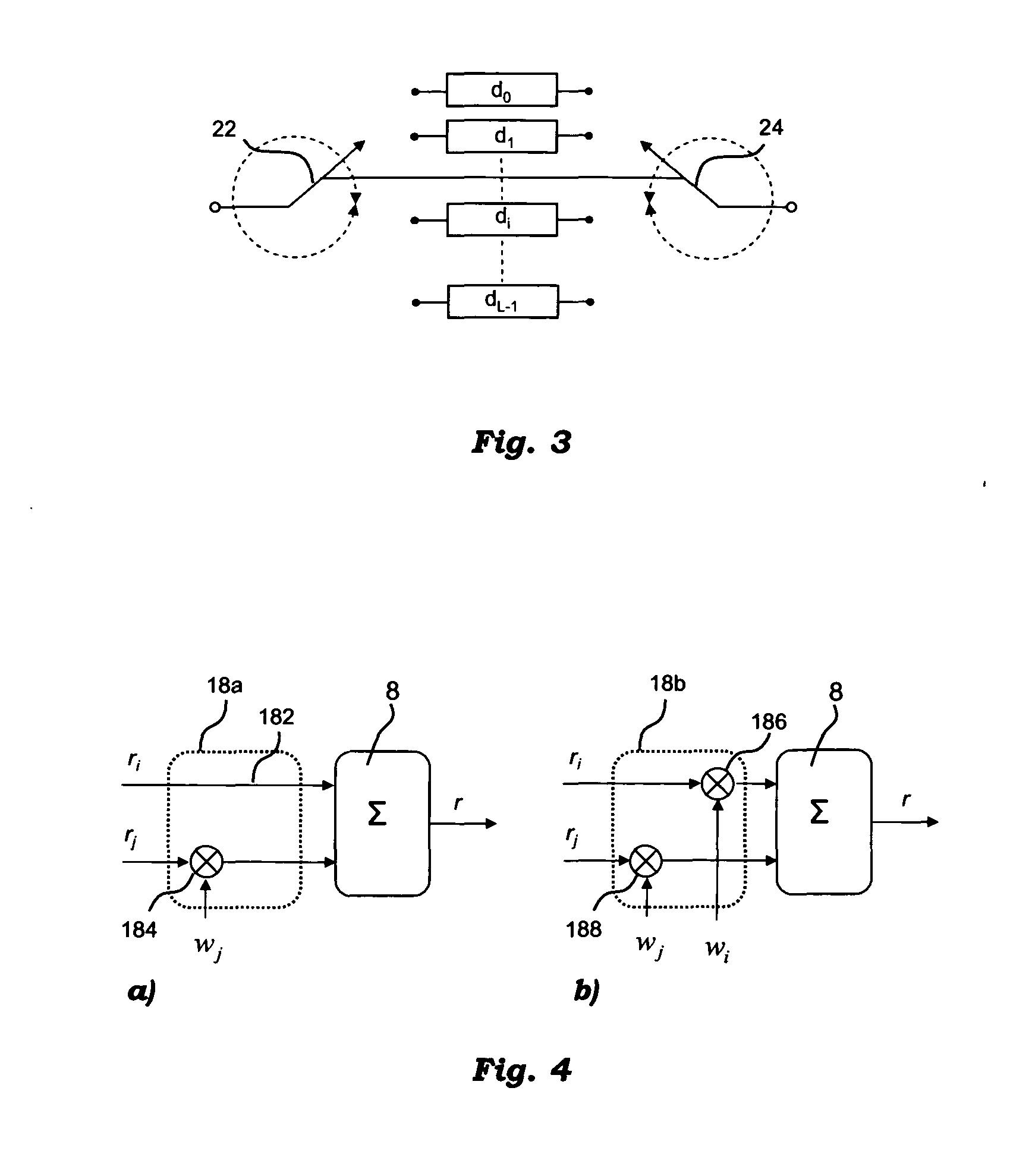
A system for processing an RF signal received via a plurality of antenna elements includes a connection arrangement for selecting a sub-set of a given number of RF signals received from the antenna elements as well as a processing arrangement for combining the received RF signals of the selected sub-set into a single RF signal for demodulation. The system includes an RF phasing circuit for producing selective combinations of the received RF signals by applying relative RF phase shift weights to the RF signals that are combined; each combination includes RF signals received from a number of adjacent antenna elements equal to the number of the RF signals in the sub-set to be selected. A radio performance estimator generates for each selective combination of RF signals at least one non-RF radio performance indicator representative of the quality of the RF signals in the combination. A decision block identifies the sub-set of received RF signals to be selected as a function of the one radio performance indicator generated for the selective combinations of the received RF signals.
Owner:ADVANCED DIGITAL BROADCAST +1
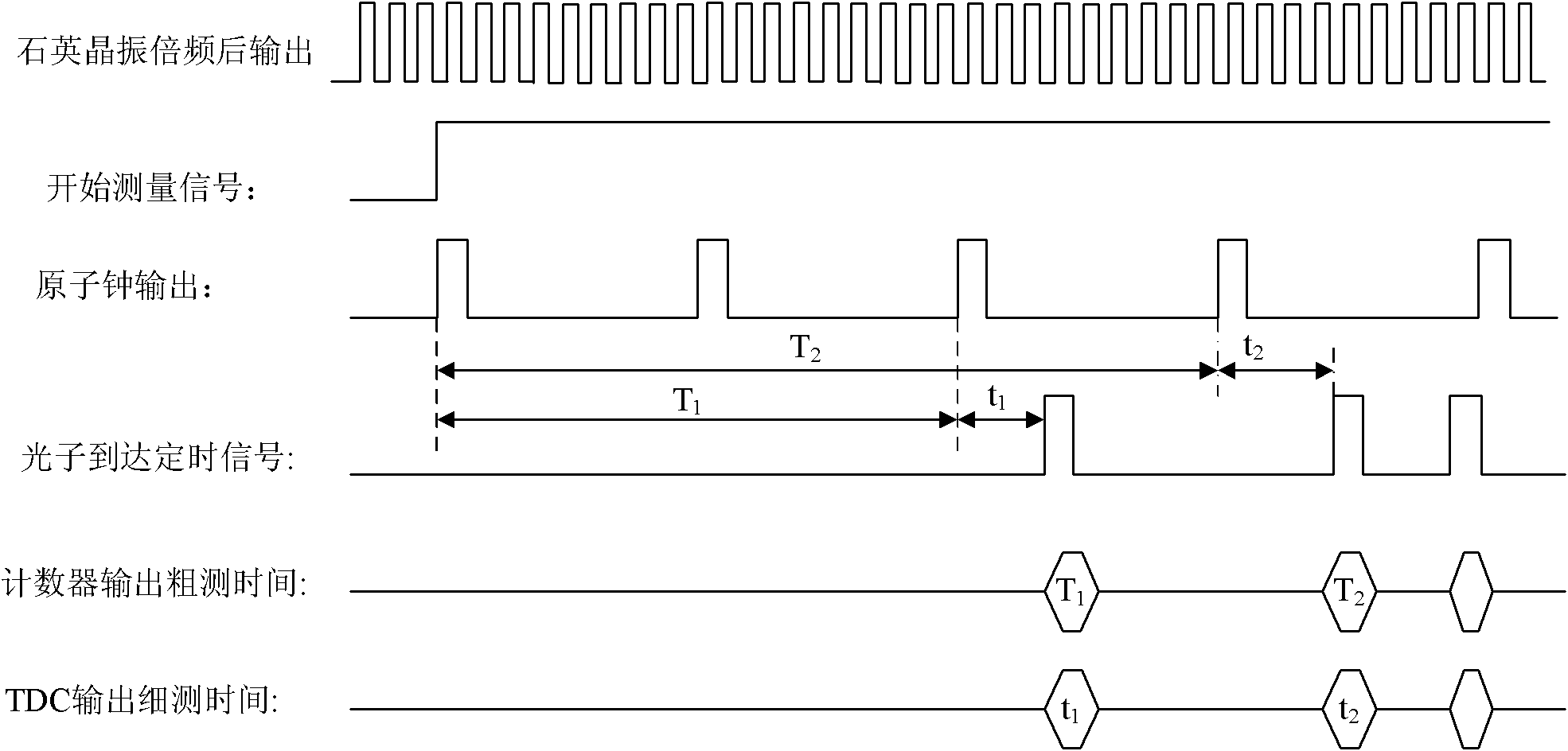
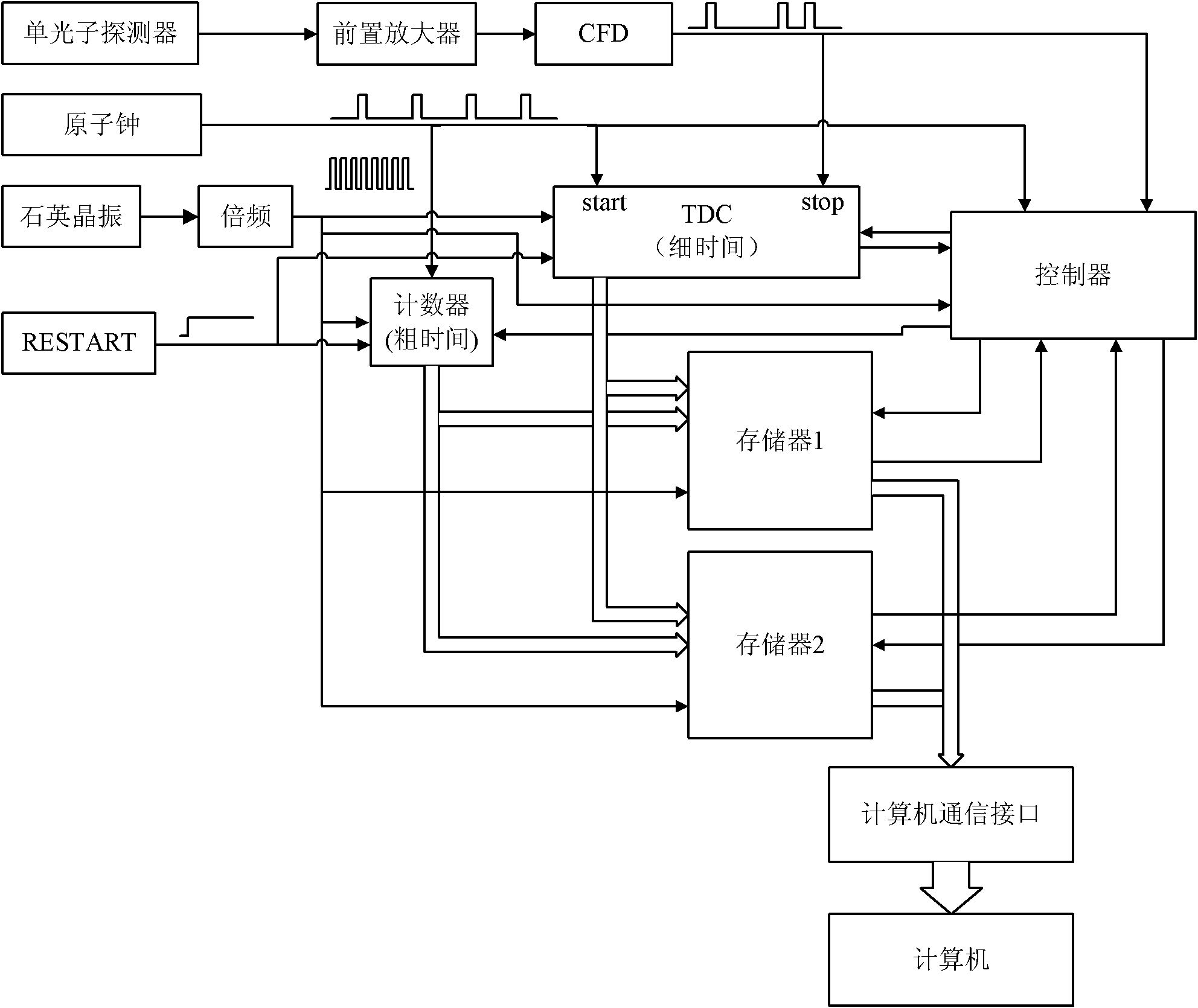
Device and method for continuously measuring arrival time of photon sequence
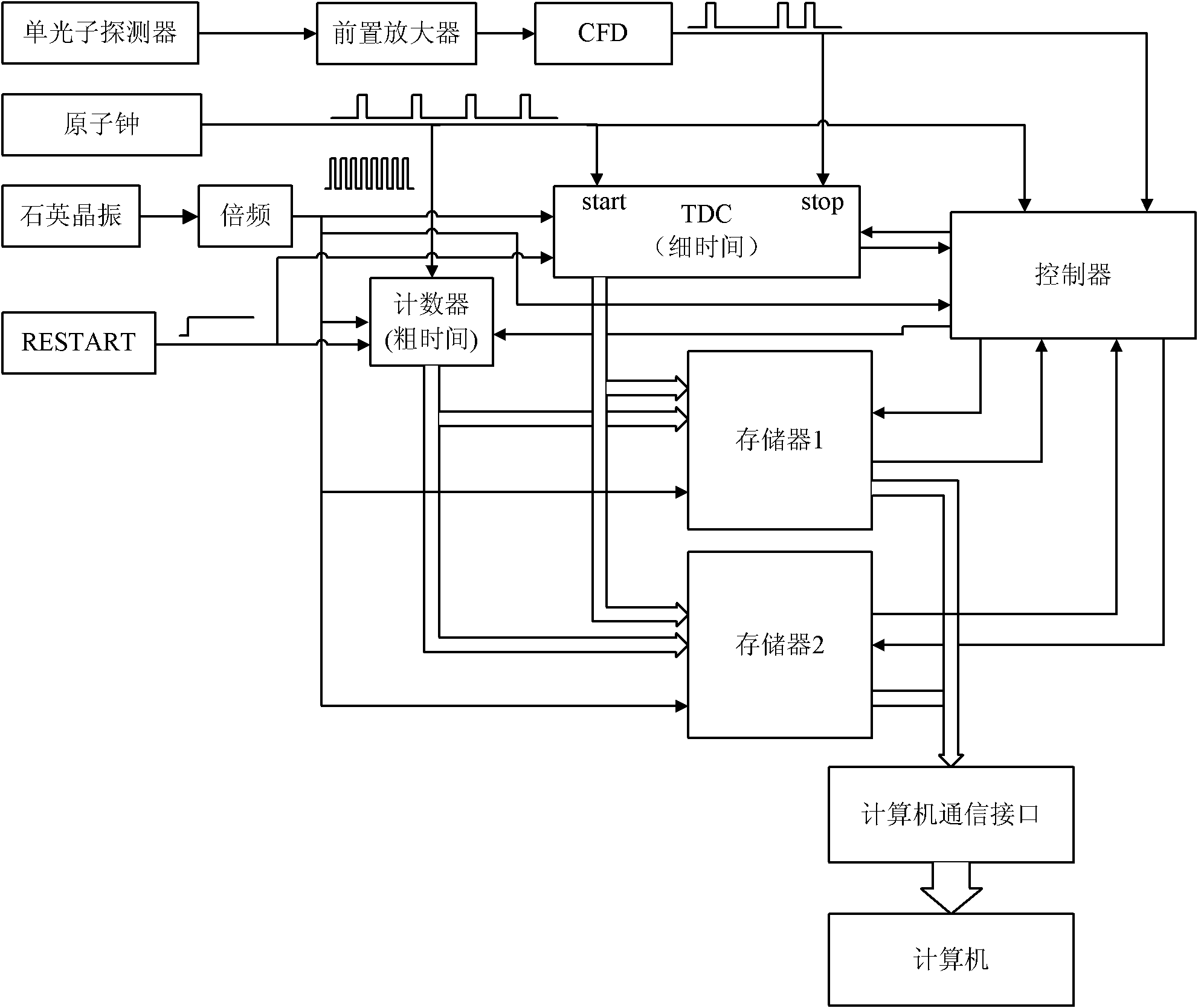
InactiveCN102141772ALarge measuring rangeImprove stabilityApparatus using atomic clocksContinuous measurementDiscriminator
The invention relates to a device and a method for continuously measuring the arrival time of a photon sequence. The device comprises a single photon detector, a preamplifier, a constant ratio discriminator, an atomic clock, a counter, a time-to-digital converter, a controller, a memory unit and a computer, wherein the output end of the constant ratio discriminator is connected with the controller; a square-wave pulse output by the atomic clock is used as a counting object of the counter and is transmitted into the time-to-digital converter; the rising edge of the square-wave pulse is used as a start signal of the time-to-digital converter, and the rising edge of a digital pulse signal is used as a stop signal of the time-to-digital converter; and the control end of the controller is respectively connected with the counter, a digit converter and the memory unit and used for controlling the synchronous storage of rough measuring time and fine measuring time into the memory unit. The invention solves the technical problems of continuous measurement incapability, narrow measurement range and limited application range of a traditional photon sequence arrival time measuring device, and the device has a wide measurement range and high accuracy in measuring the photon arrival time.
Owner:XI'AN INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Alignment plate apparatus and system and method of use
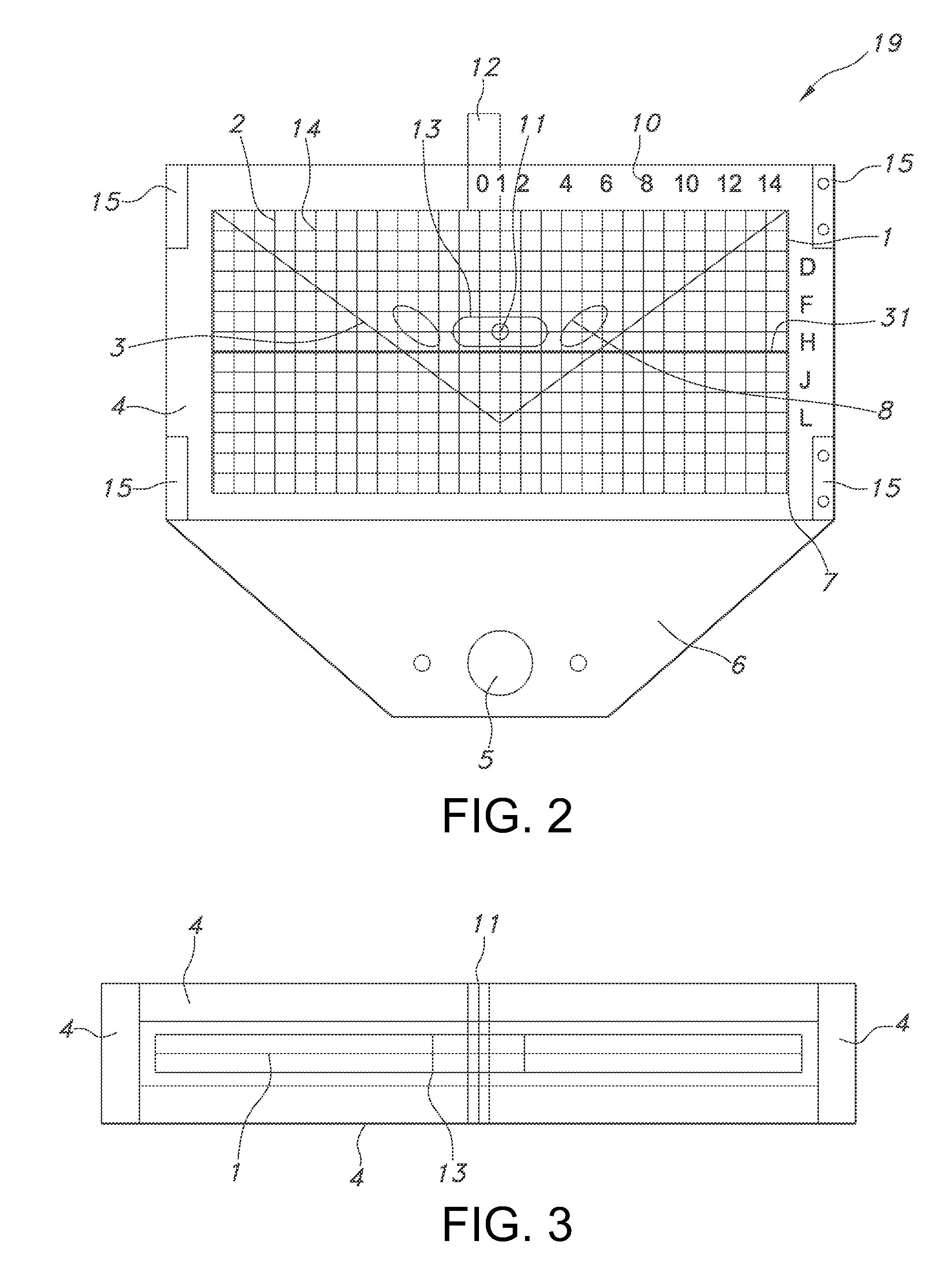
ActiveUS20150257846A1Easy to installContinuous measurementImage enhancementImage analysisFracture reductionLeg length
A computer implemented system for adjusting the placement of an implant in a patient through the use of a dimensioned grid template placed relative to patient anatomy on a fluoroscopic machine and a method to digitally quantify alignment parameters is provided. This system can be used for determining: 1) leg length, offset, and cup position during arthroplasty replacement surgery; 2) fracture reduction / correction position during trauma procedures and 3) an apparatus to be used for deformity correction planning is provided; 4) placement and positioning of instruments and implants relative to bone and anatomical architecture; 5) bone anatomy boundary parameter identification relative to reaming and cutting landmarks of bone.
Owner:ORTHOGRID SYST HLDG LLC
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS20140249440A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS20140249433A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on the patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
Blood pressure measuring apparatus
ActiveUS20070016085A1Continuous measurementSimple methodEvaluation of blood vesselsCatheterReflected wavesBlood pressure
A pulse wave is detected in a predetermined location of a living body, and the progressive wave component and reflected wave component are extracted from the pulse wave. The pulse wave propagation time is calculated from the progressive wave component and reflected wave component, and blood pressure is calculated on the basis of this pulse wave propagation time. The use of this method provides blood pressure measuring apparatus capable of continuously measuring blood pressure with a simple method.
Owner:FUKUDA DENSHI CO LTD
Carbon nanotube biofet with a local amplifier in a system array for analysis of biomarkers and method of analysis of same
ActiveUS20160238553A1Reliable measurementHigh affinitySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansElectronic transmissionCarbon nanotube
A bioFET cell for measuring a time dependent characteristic of an analyte bearing fluid includes a source, a drain, a semiconductive single wall carbon nanotube network layer extending between the source and drain electrodes and electrically coupled there between, a gate insulatively spaced from and disposed over and extending between the source and drain electrodes, a layer of at least one selected antibody disposed on and linked to the polymer layer to functionalize the semiconductive single wall carbon nanotube network layer to a selected target biomarker corresponding to the at least one selected antibody so that electron transport into the semiconductive single wall carbon nanotube network layer is facilitated, where the source, drain and gate electrodes with the carbon nanotube network layer form a defined channel through which the analyte bearing fluid may flow, and a high impedance source follower amplifier coupled to the source electrode.
Owner:SENSOR KINESIS
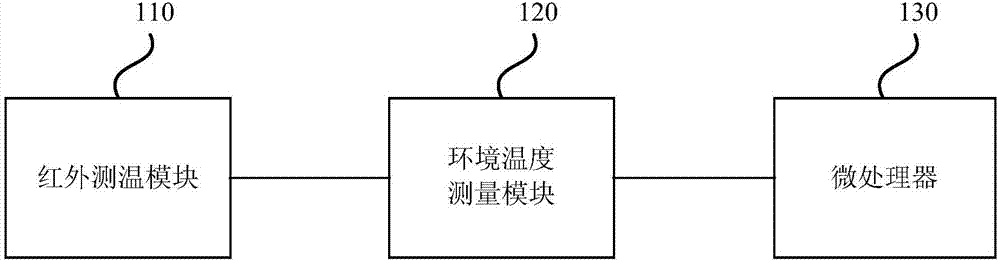
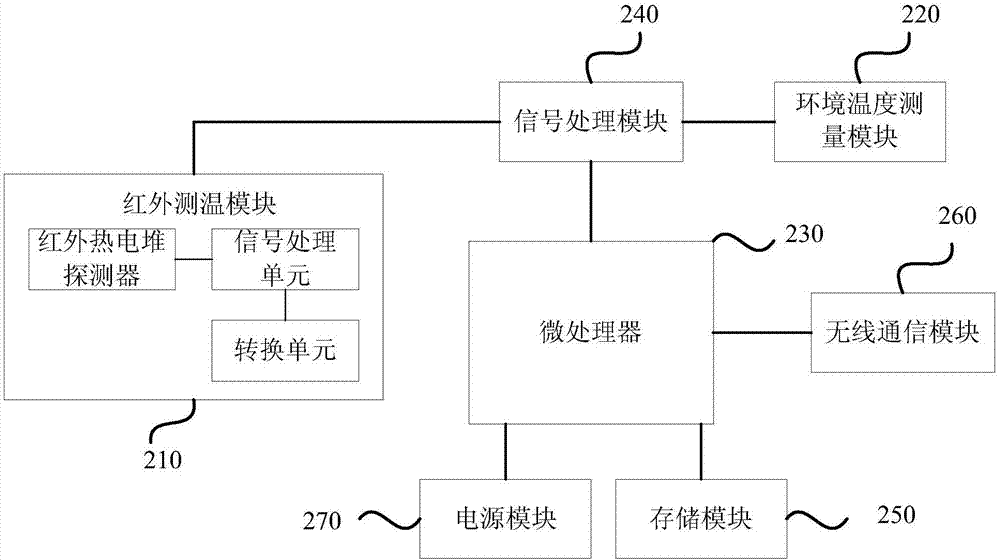
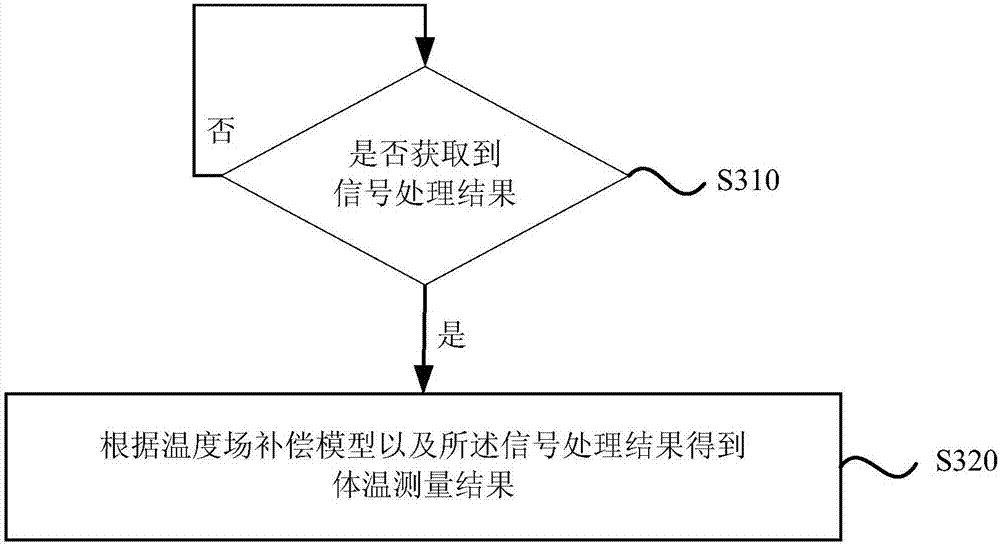
Temperature measurement equipment, method and device
InactiveCN107576421AContinuous measurementAccurate acquisitionRadiation pyrometryDiagnostic recording/measuringHuman bodyBody temperature measurement
The invention discloses a temperature measurement equipment, method and device. The equipment comprises an infrared temperature measurement module, an environment temperature measurement module and amicro processor, wherein the infrared temperature measurement module is used for measuring human body temperature according to an infrared signal radiated by a human body and sending acquired infraredtemperature measurement data to the micro processor, the environment temperature measurement module is used for measuring temperature of the surrounding environment of the human body and sending acquired environment temperature measurement data to the micro processor, the micro processor is used for constructing a temperature field compensation model and acquiring the human body temperature measurement result according to the temperature field model when receiving the infrared temperature measurement data and the acquired environment temperature measurement data. The equipment is advantaged in that the body temperature data of a measurement object can be acquired through the temperature field compensation model, measurement accuracy is high, the measurement time is short, efficiency is high, the measurement process is simple and convenient, and user experience is effectively improved.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM +1
Body-worn system for continuous, noninvasive measurement of cardiac output, stroke volume, cardiac power, and blood pressure
ActiveUS20140249435A1Accurate estimateEffective monitoringDiagnostic signal processingEvaluation of blood vesselsEcg signalBlood pressure kit
The invention provides a system for measuring stroke volume (SV), cardiac output (CO), and cardiac power (CP) from a patient that features: 1) an impedance sensor connected to at least two body-worn electrodes and including an impedance circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure an impedance signal (e.g. a TBEV waveform); 2) an ECG sensor connected to at least two chest-worn electrodes and including an ECG circuit that processes analog signals from the electrodes to measure and ECG signal; 3) an optical sensor connected to a body-worn optical probe and including an optical circuit that processes signals from the probe to measure at least one optical signal (e.g. a PPG waveform) from the patient; 4) a processing system, typically worn on patient's wrist and connected through a wired interface to the optical sensor, and through either a wired or wireless interface to the TBEV and ECG sensors.
Owner:SOTERA WIRELESS
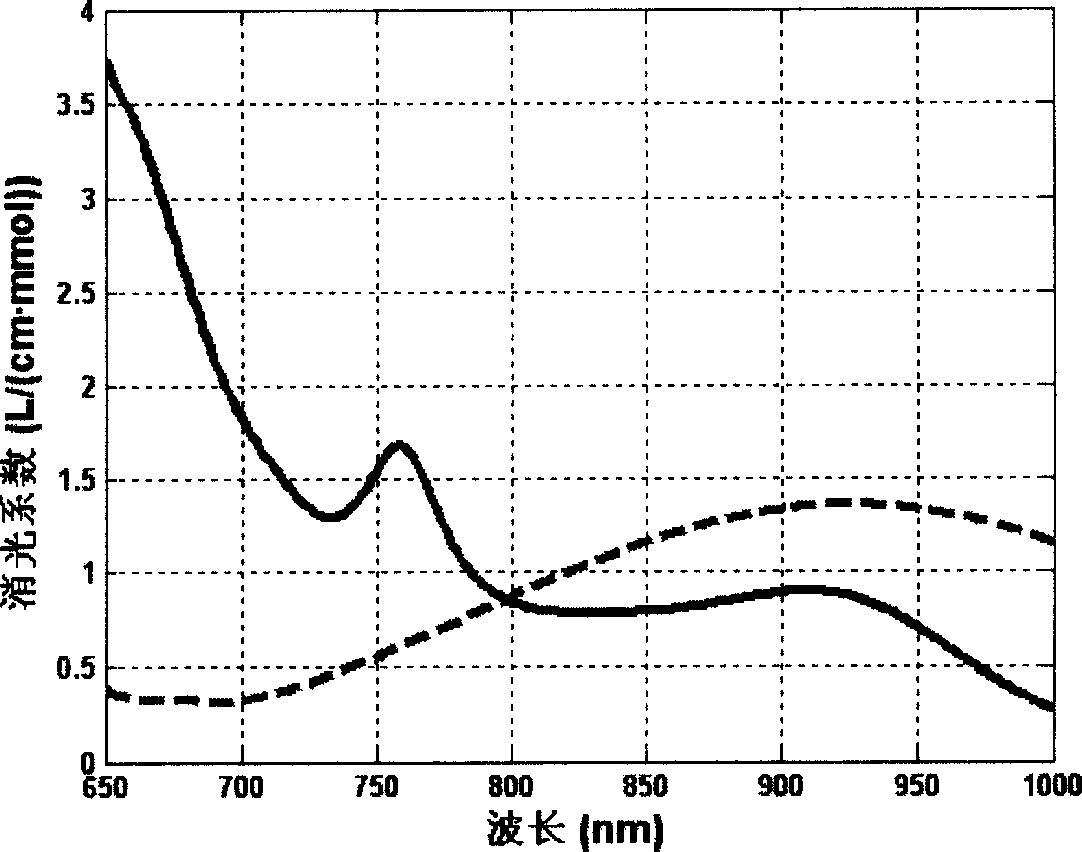
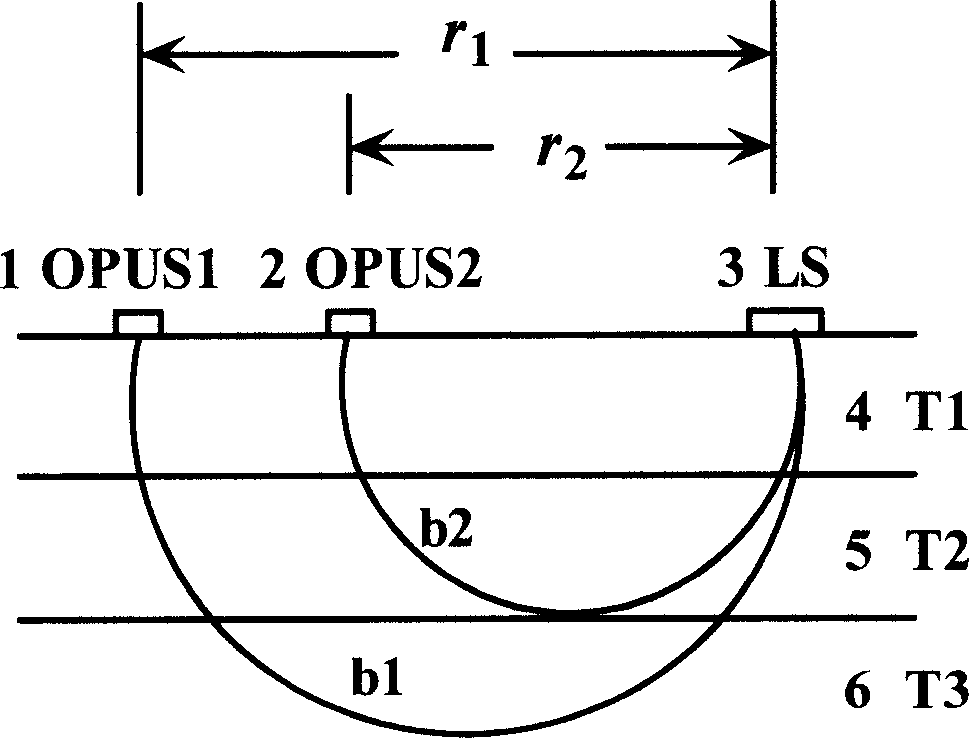
Method for testing absolute volume of concentration of oxidized hemoglobin and reduced hemoglobin in human tissue
ActiveCN1911172AHelp to understand blood volumeUnderstanding blood volumeMaterial analysis by optical meansDiagnostic recording/measuringHemoglobin FHEMOGLOBIN I
A method for measuring the absolute concentration of oxygenated and reduced hemoglobin in human tissue features that its sensor is composed of 2 photoelectric receiving tubes and at least 3 light sources with different wavelengths, which are arranged on a straight line at intervals. Said absolute concentration can be calculated out. Said light source can emit respectively red light and near infrared light.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com