Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4267 results about "Waste collection" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
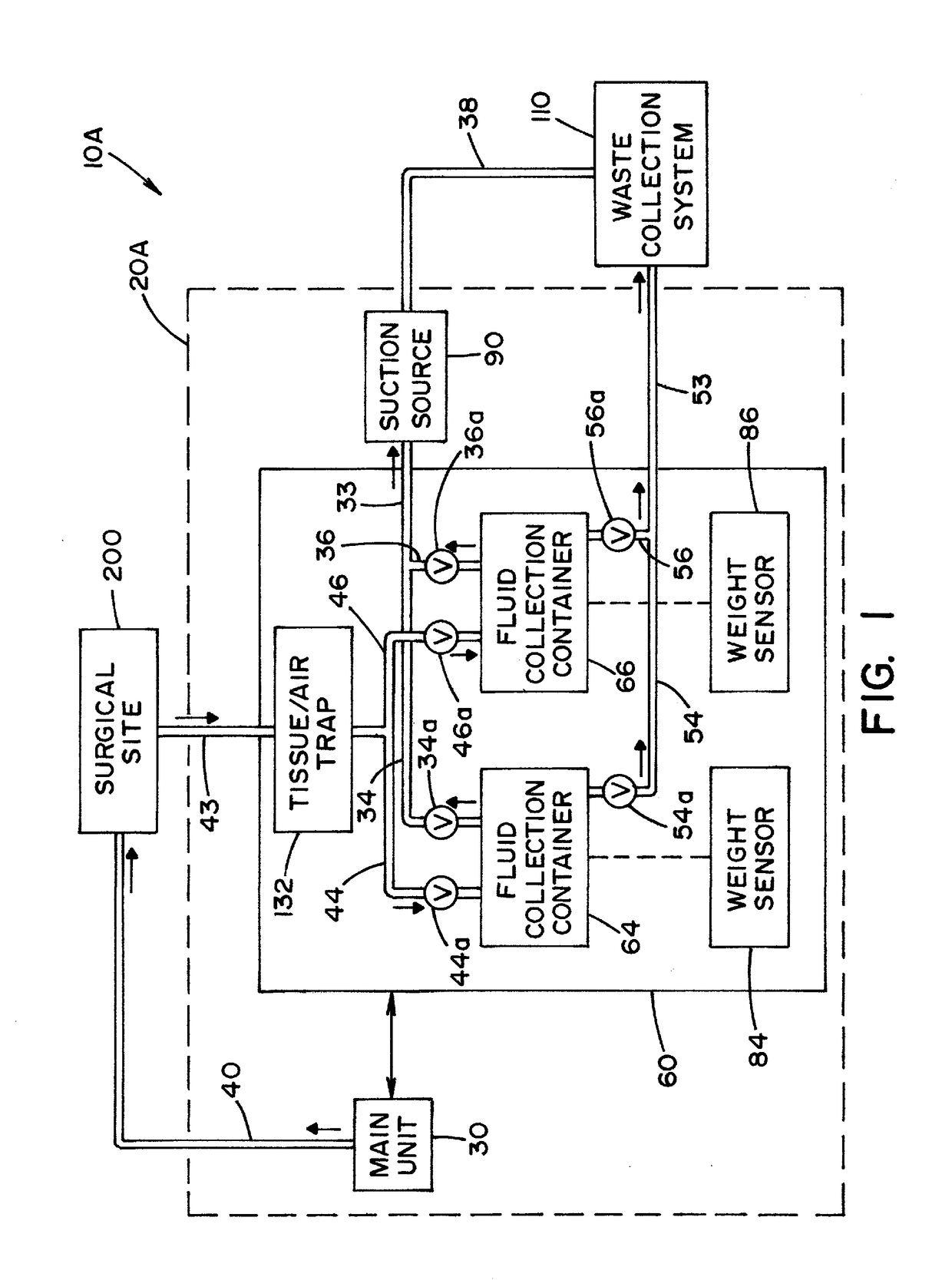
Waste collection is a part of the process of waste management. It is the transfer of solid waste from the point of use and disposal to the point of treatment or landfill. Waste collection also includes the curbside collection of recyclable materials that technically are not waste, as part of a municipal landfill diversion program.
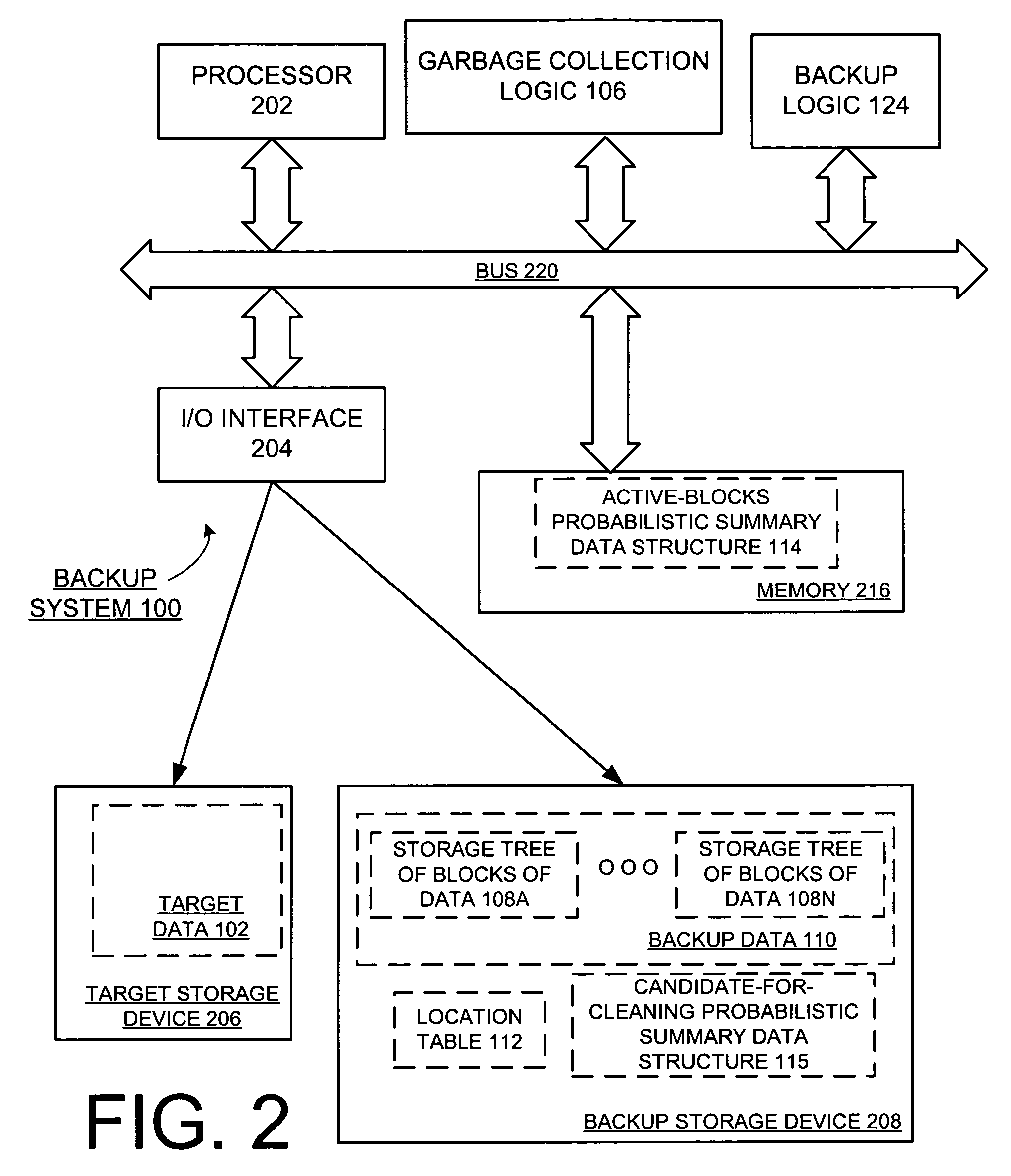
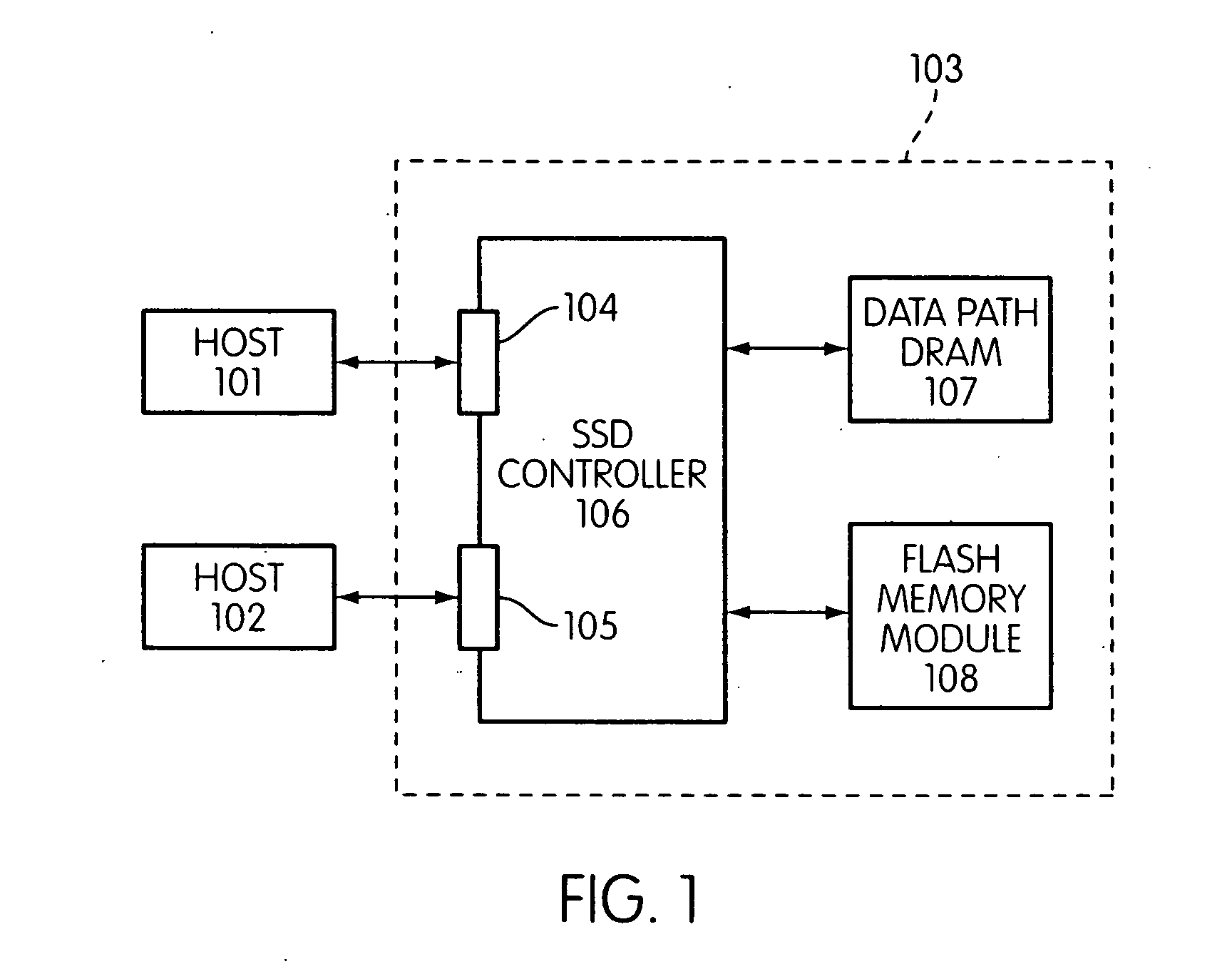
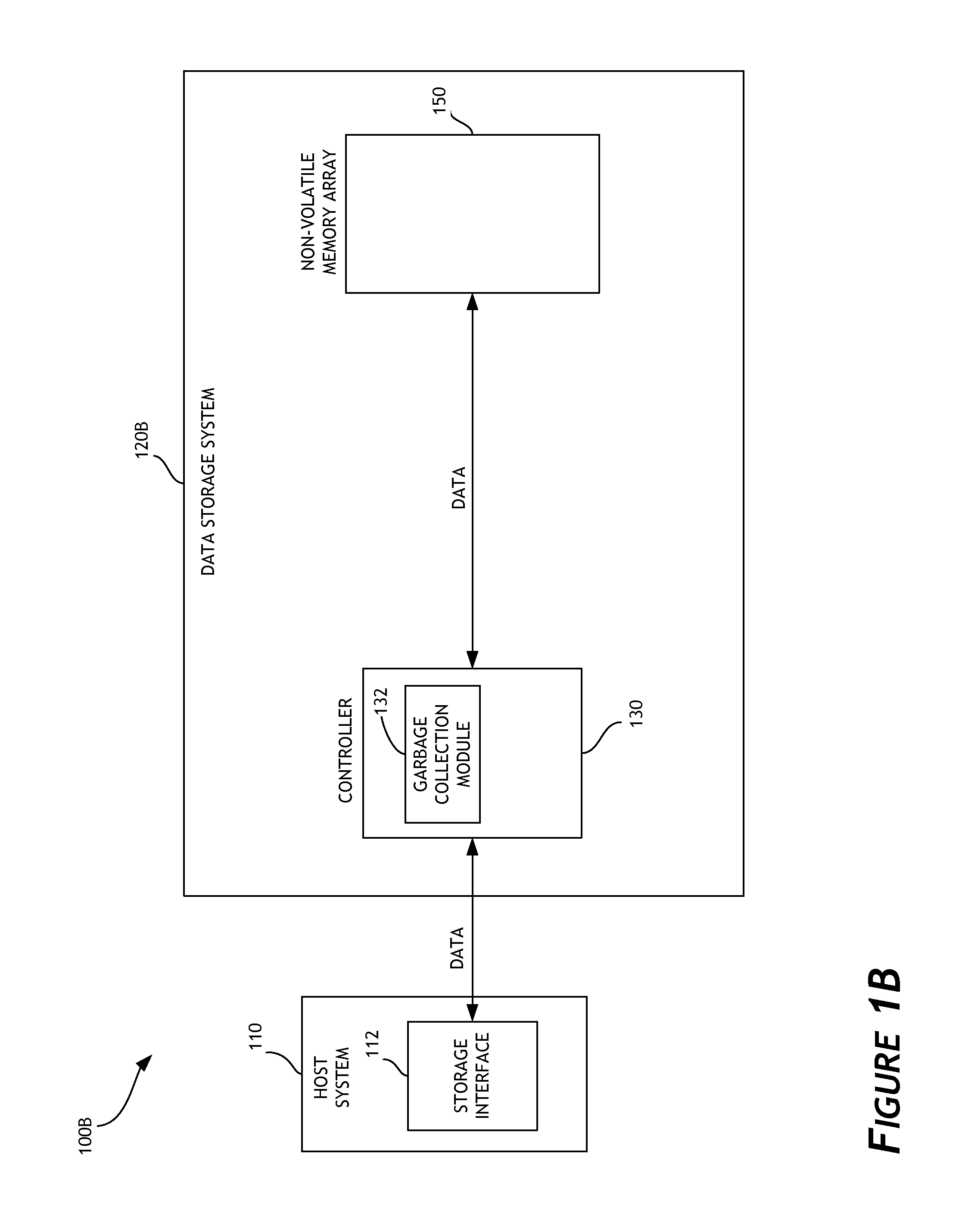
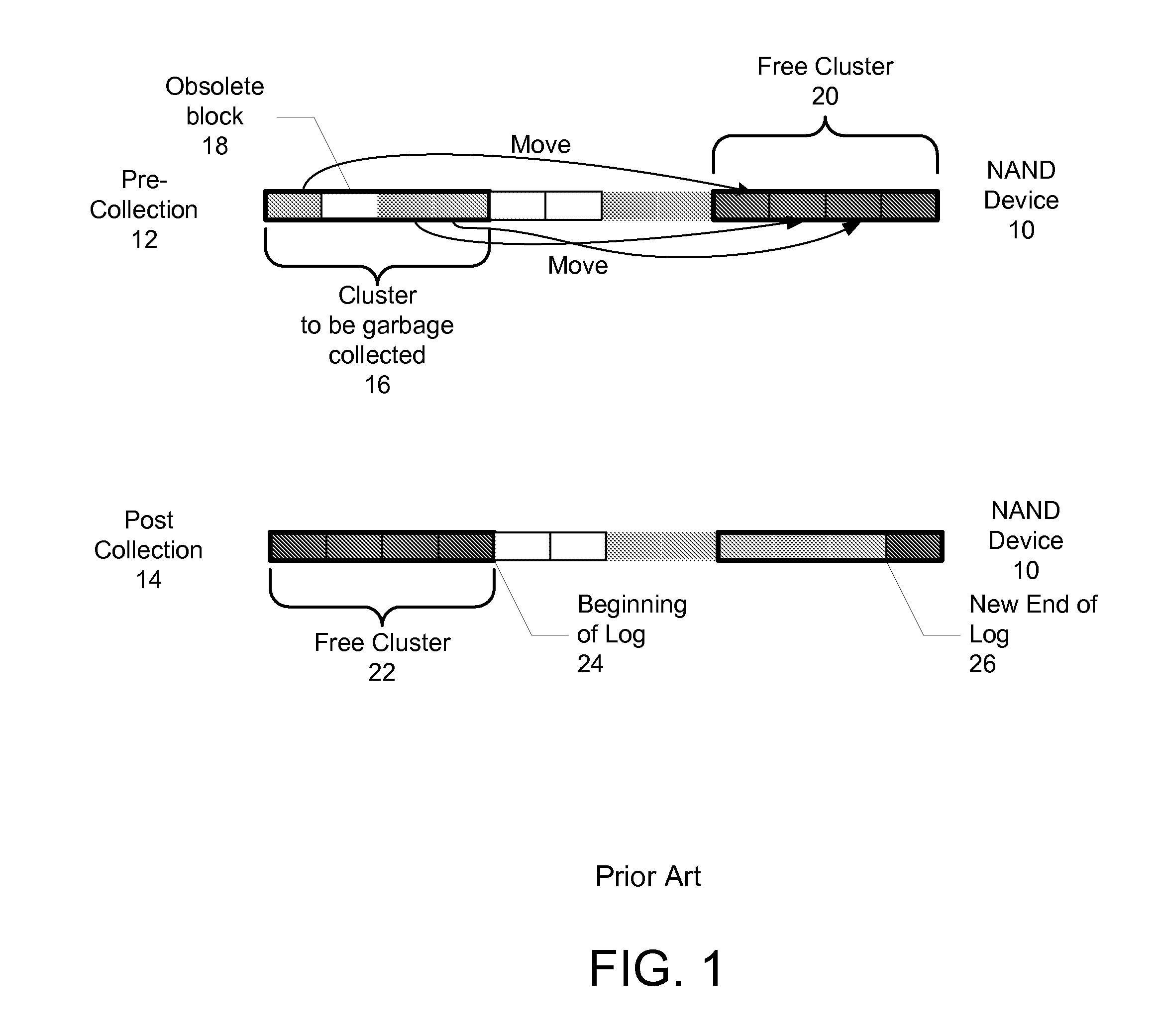
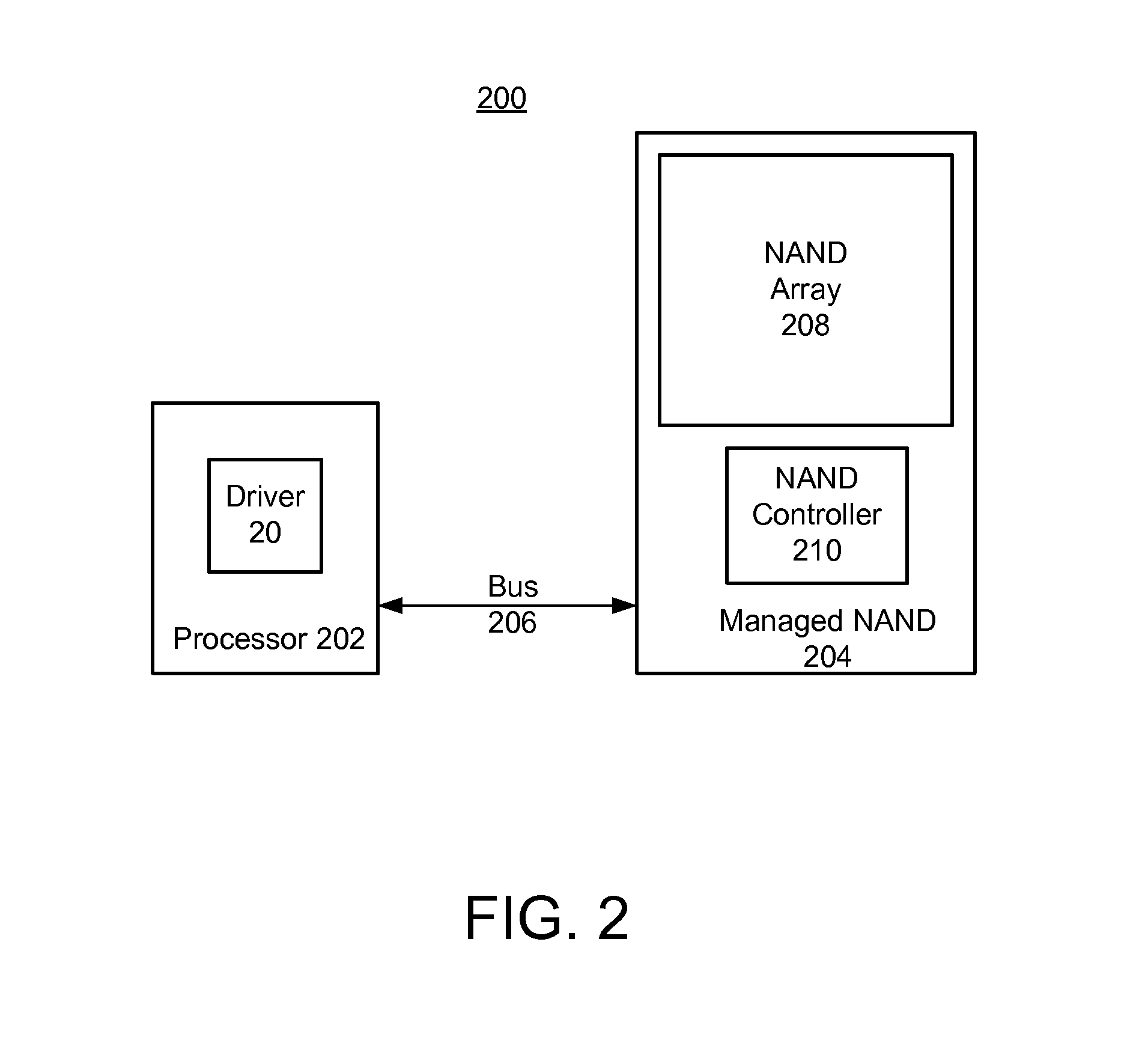
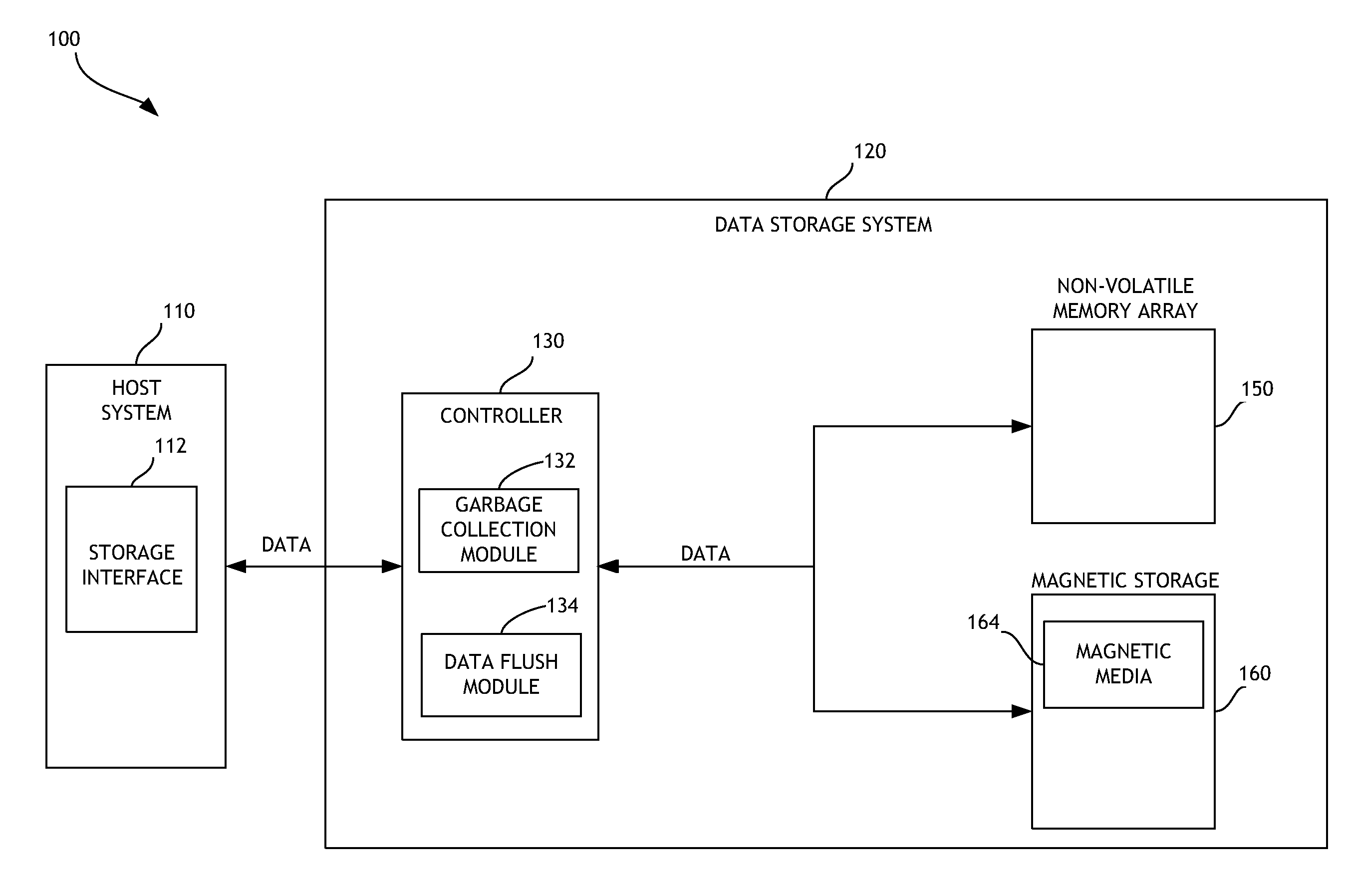
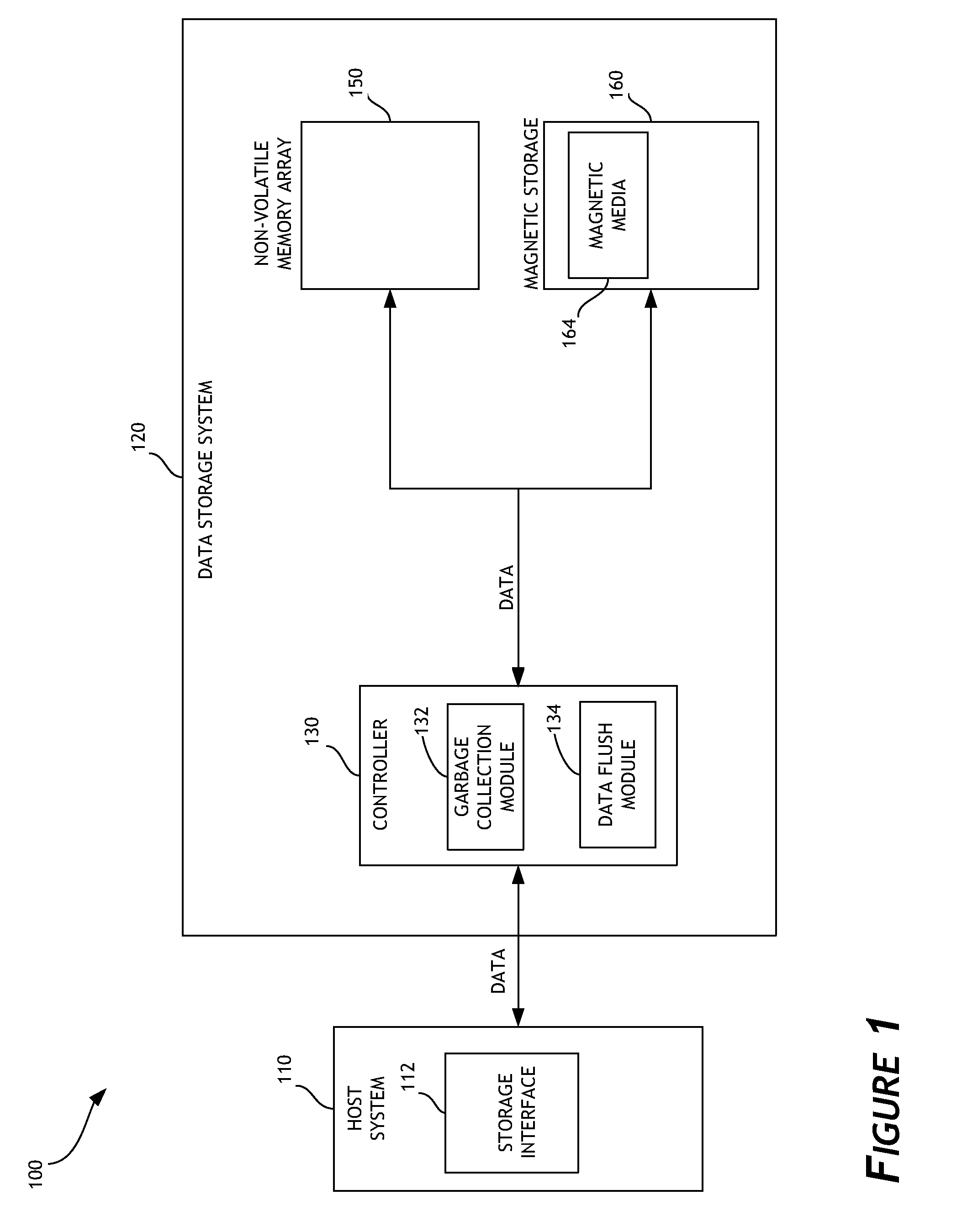
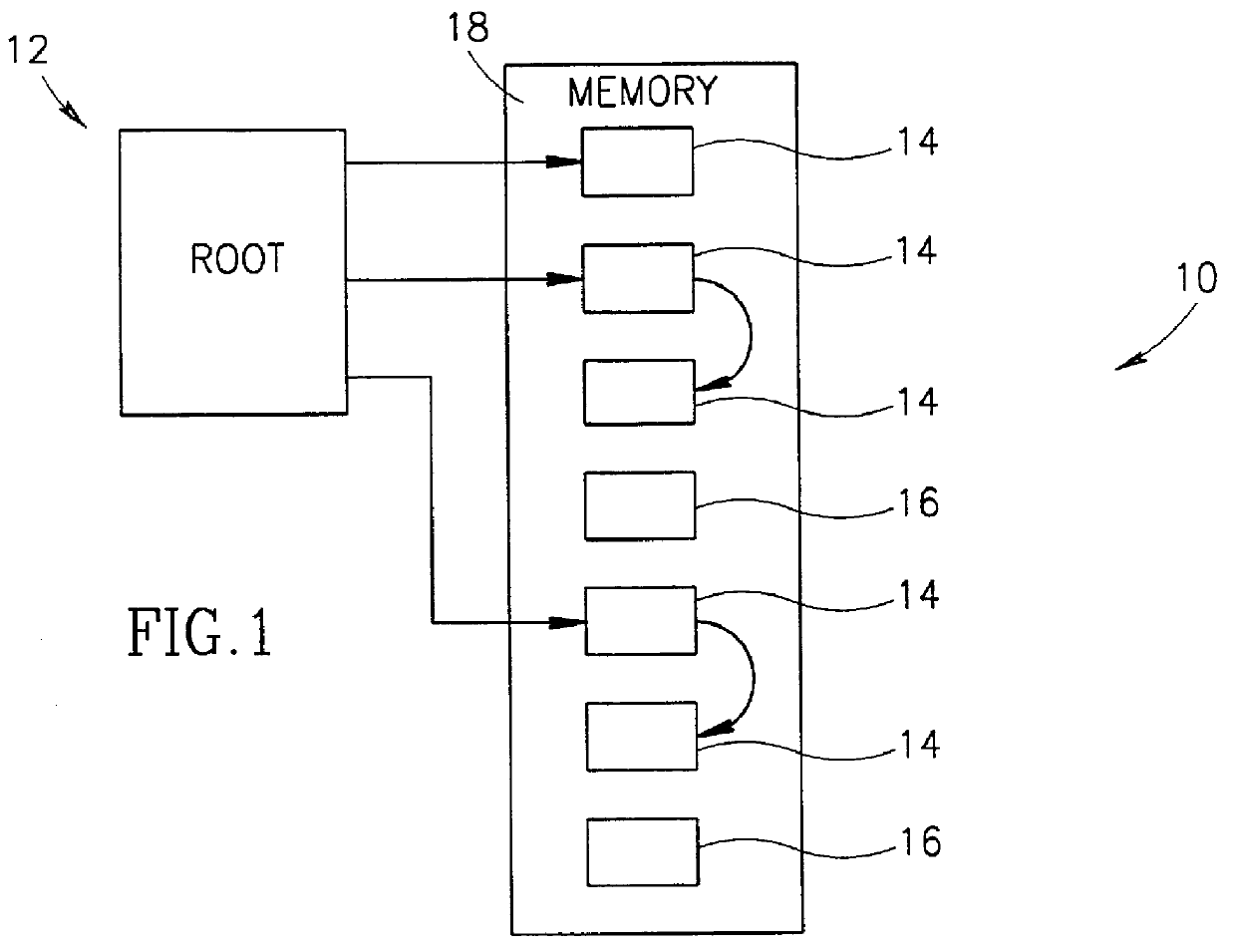
Garbage collection in a storage system
ActiveUS8527544B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data information retrievalRefuse collectionControl store
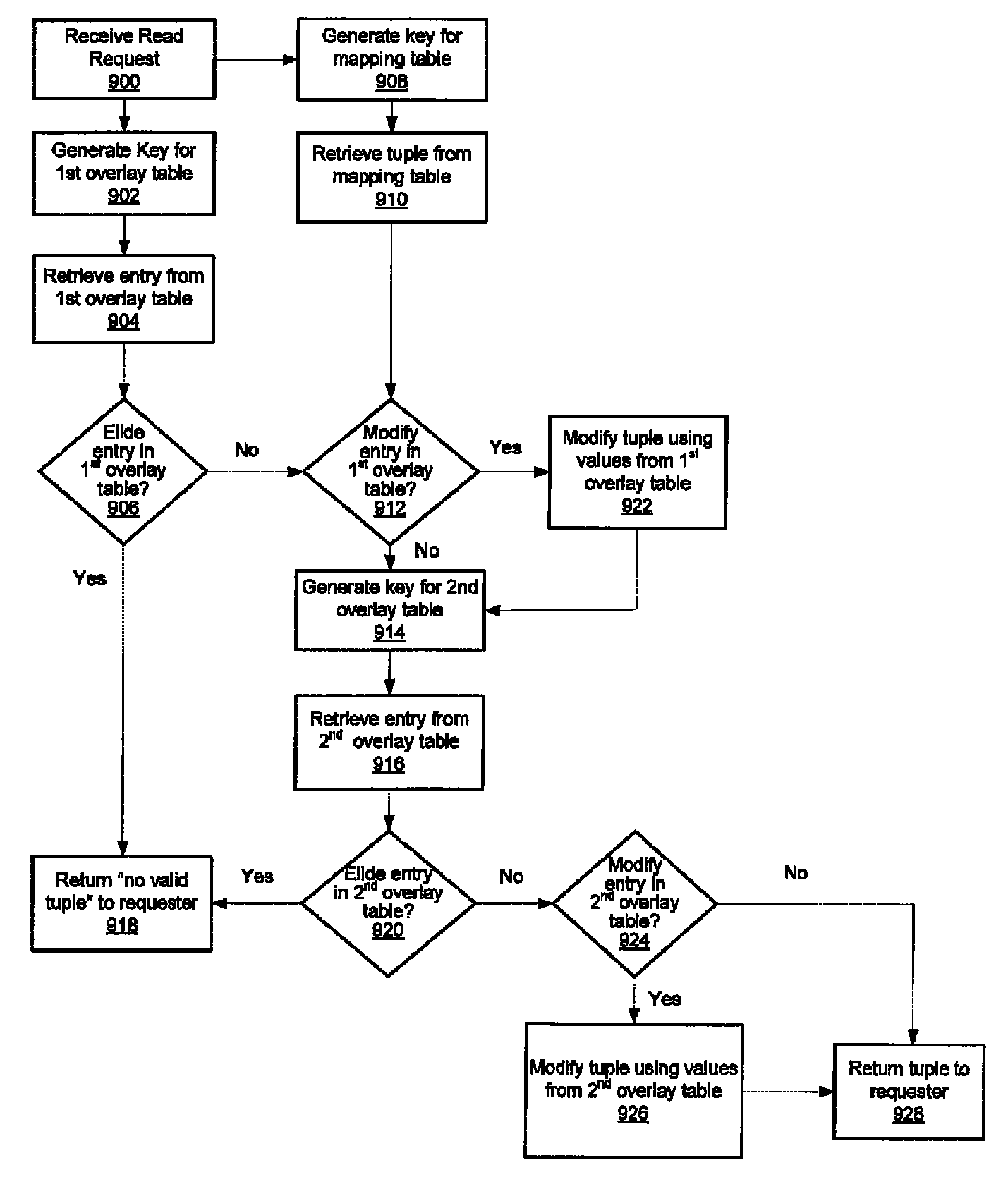
A system and method for performing garbage collection. A system includes a storage medium, a first table including entries which map a virtual address to locations in the storage medium, and a second table with entries which include a reverse mapping of a physical address in a data storage medium to one or more virtual addresses. A storage controller is configured to perform garbage collection. During garbage collection, the controller is configured to identify one or more entries in the second table which correspond to a segment to be garbage collected. In response to determining the first table includes a valid mapping for a virtual address included in an entry of the one of the one or more entries, the controller is configured to copy data from a first location identified in the entry to a second location in the data storage medium, and reclaim the first storage location.
Owner:PURE STORAGE
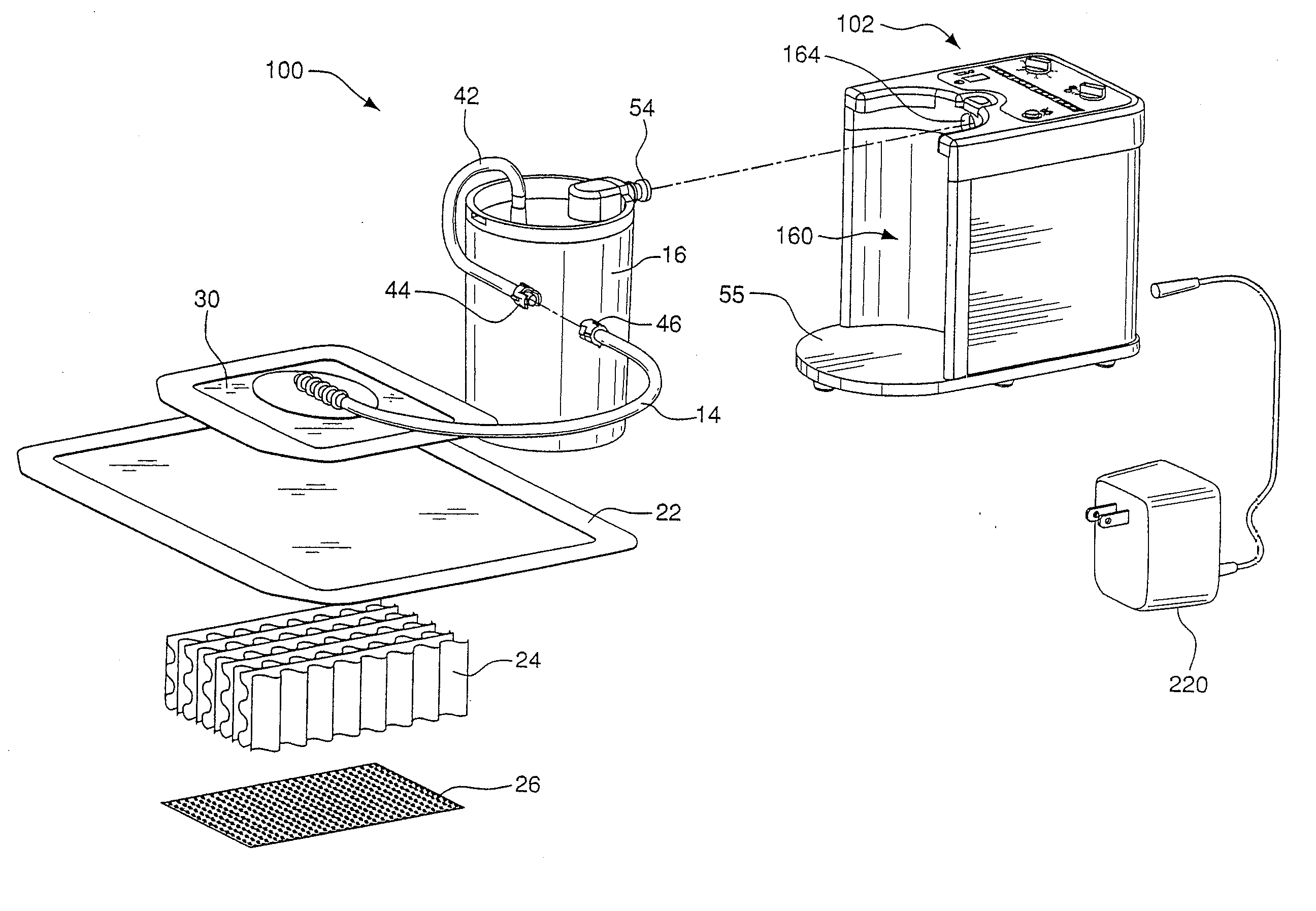
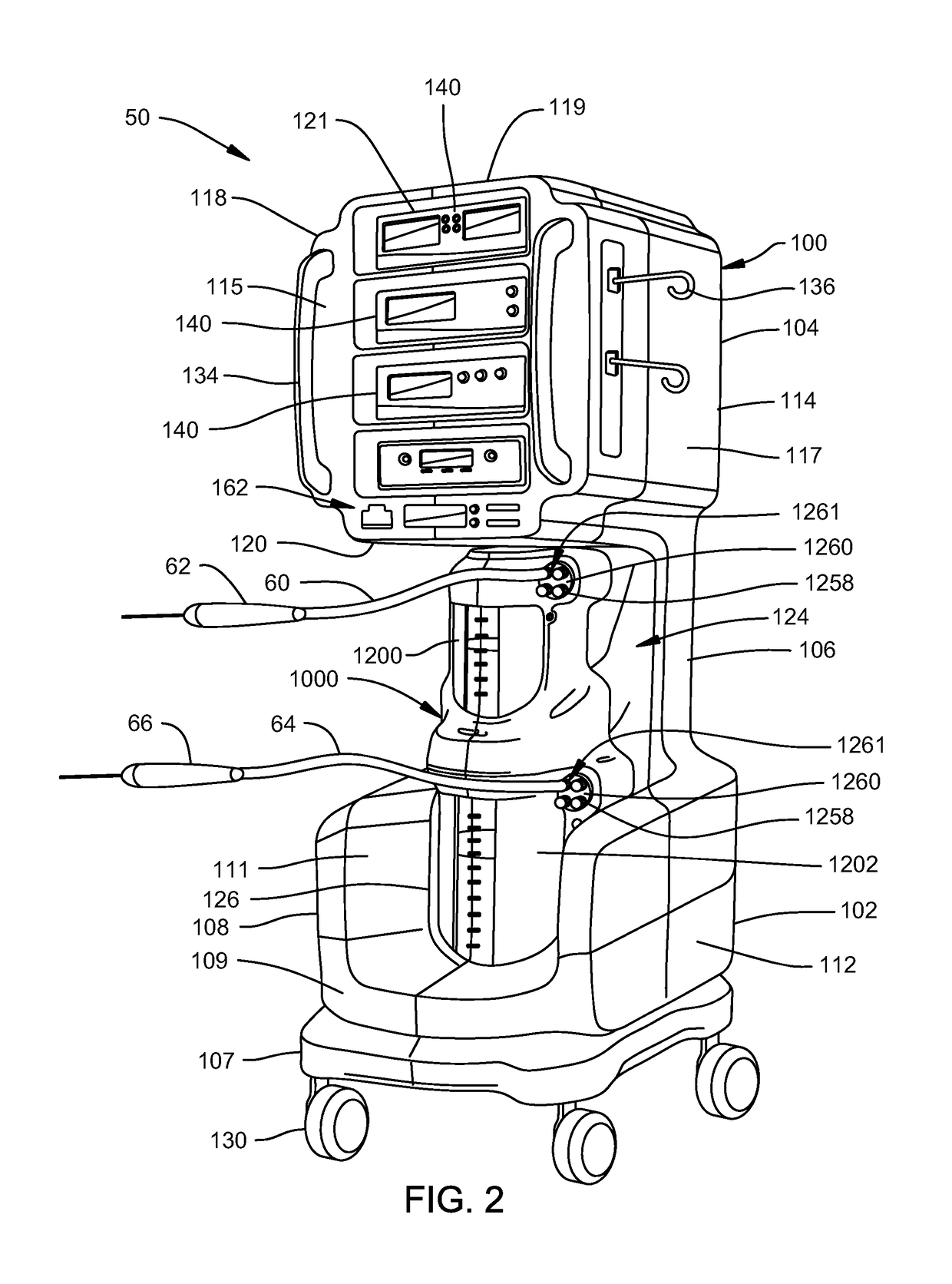
Pump system for negative pressure wound therapy
ActiveUS20070219532A1Reduce the possibilityTrend downWound drainsMedical devicesLevel sensorEngineering
A pump system for applying negative pressure to a wound, including a flow monitor capable of detecting a deviation from a reference airflow rate provided by a controlled leak to determine whether the system is operating normally or abnormally, and a flow status annunciator to indicate a normal operating condition or whether an abnormal condition is a leak or an occluded line in the system. The pump system further includes a pressure controller for regulating operation of a pump to control pressure in the system at a range around a user-selected setpoint. The pump system may also include a waste collector and a level sensor for detecting when the collector is full.
Owner:PAUL HARTMANN AG
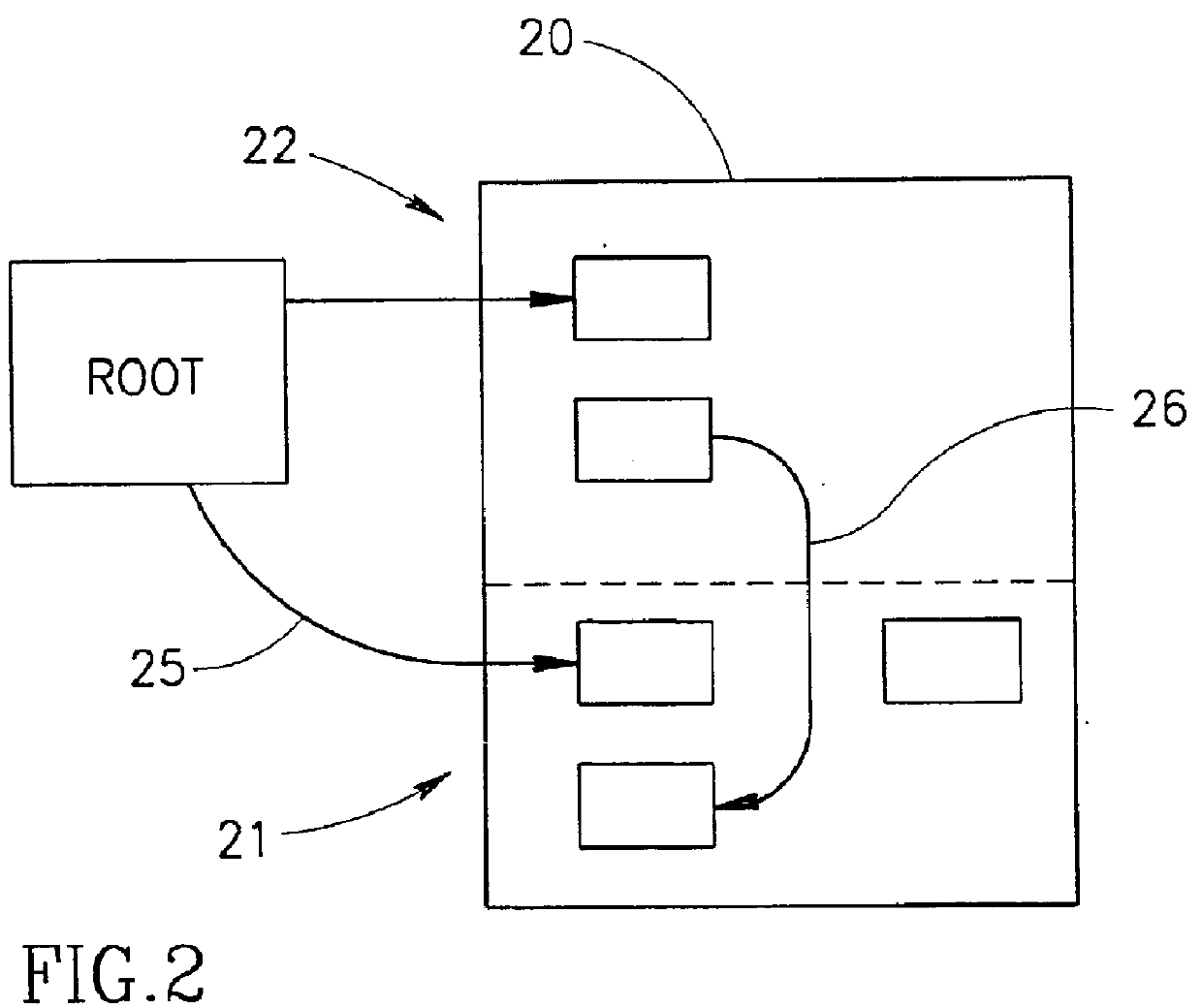
Specializing write-barriers for objects in a garbage collected heap
ActiveUS7089272B1Reduce in quantityWithout compromising garbage collector performanceData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsParallel computingWaste collection
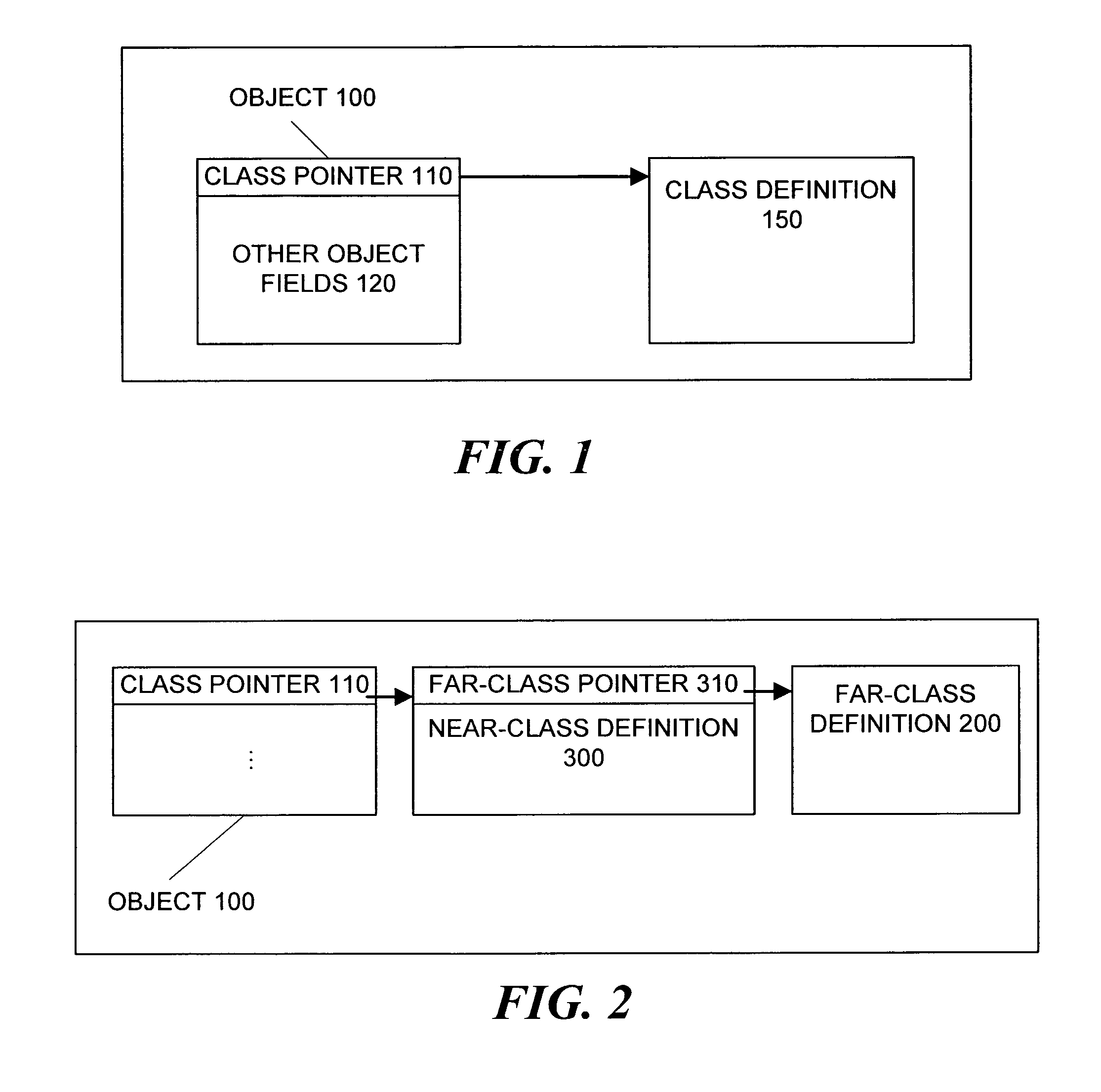
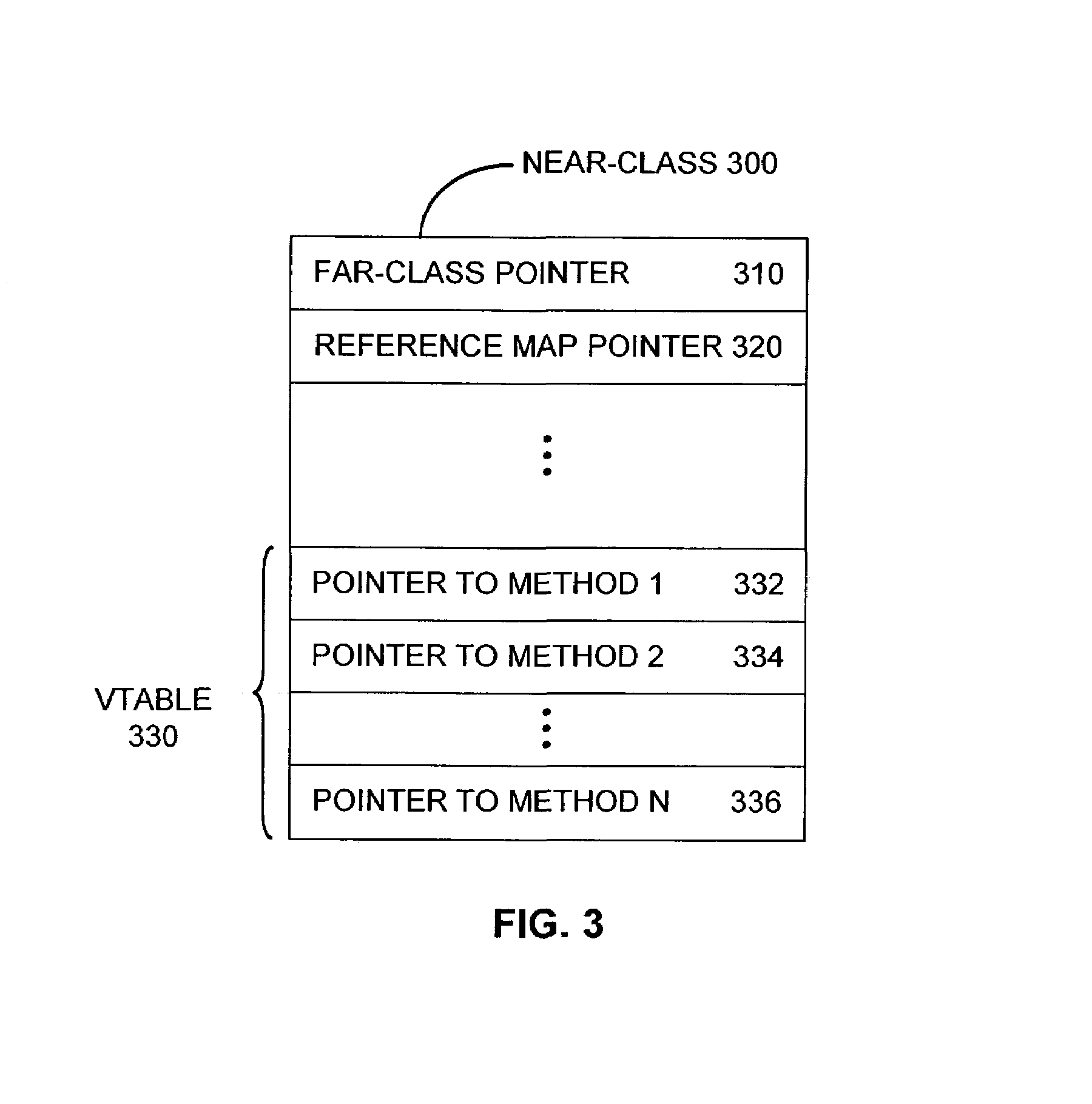
A technique is provided for reducing the number of write barriers executed in mutator code without compromising garbage collector performance. Advantageously, a compiler generates two forms of a mutator code—a first version with write barriers and a second version substantially without write barriers. In operation, the first version of the code may be accessed by a vtable in a “mature” near-class and the second version may be accessed by a vtable in a “nascent” near-class. According to the invention, mapping of functionally equivalent points in the first and second versions of the mutator code may be facilitated by an associated pcmap. Further, each of the first and second versions may also be associated with a respective nr_map that facilitates mapping functionally equivalent points within different branches of guard code sequences corresponding to reference-writes to non-receiver objects.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
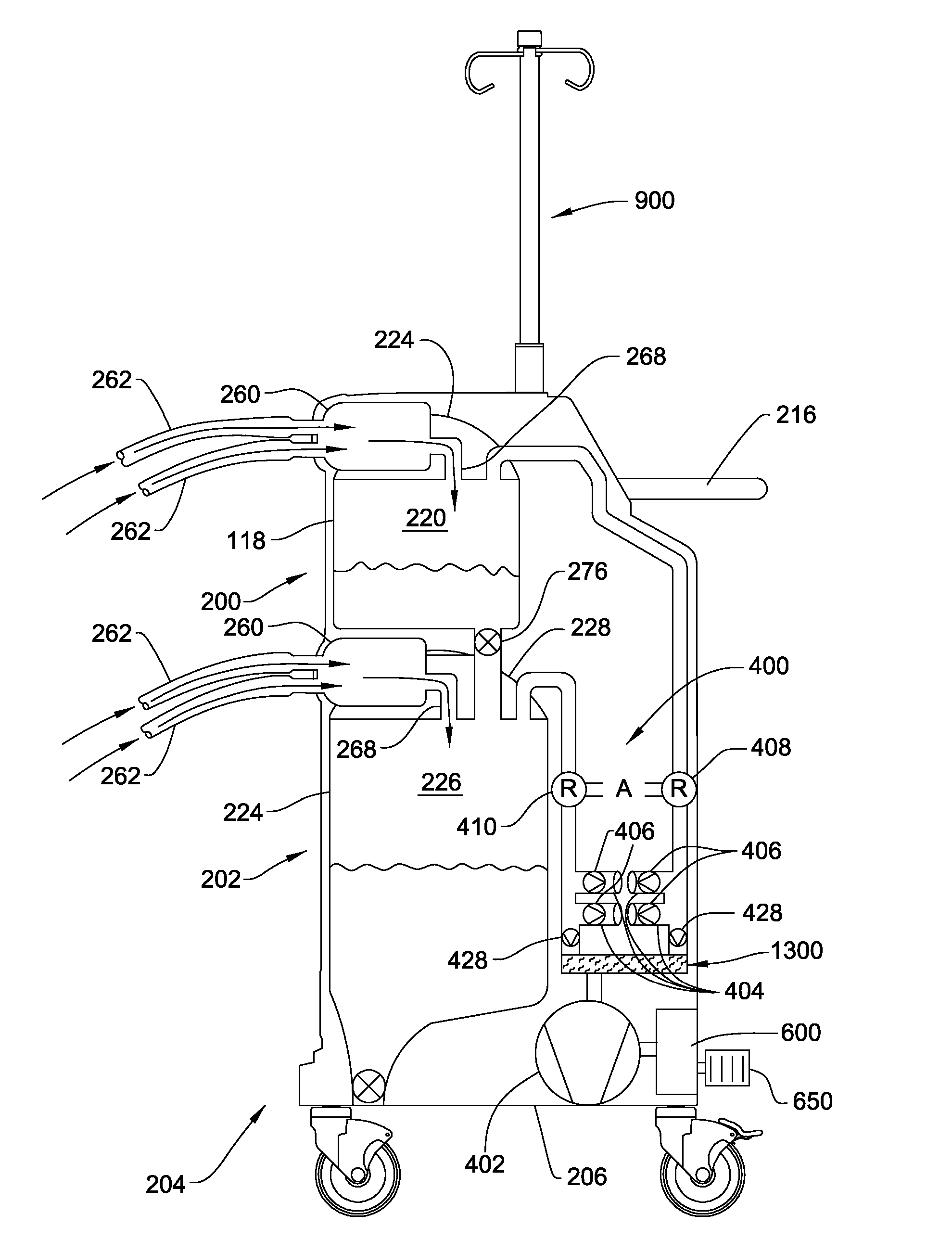
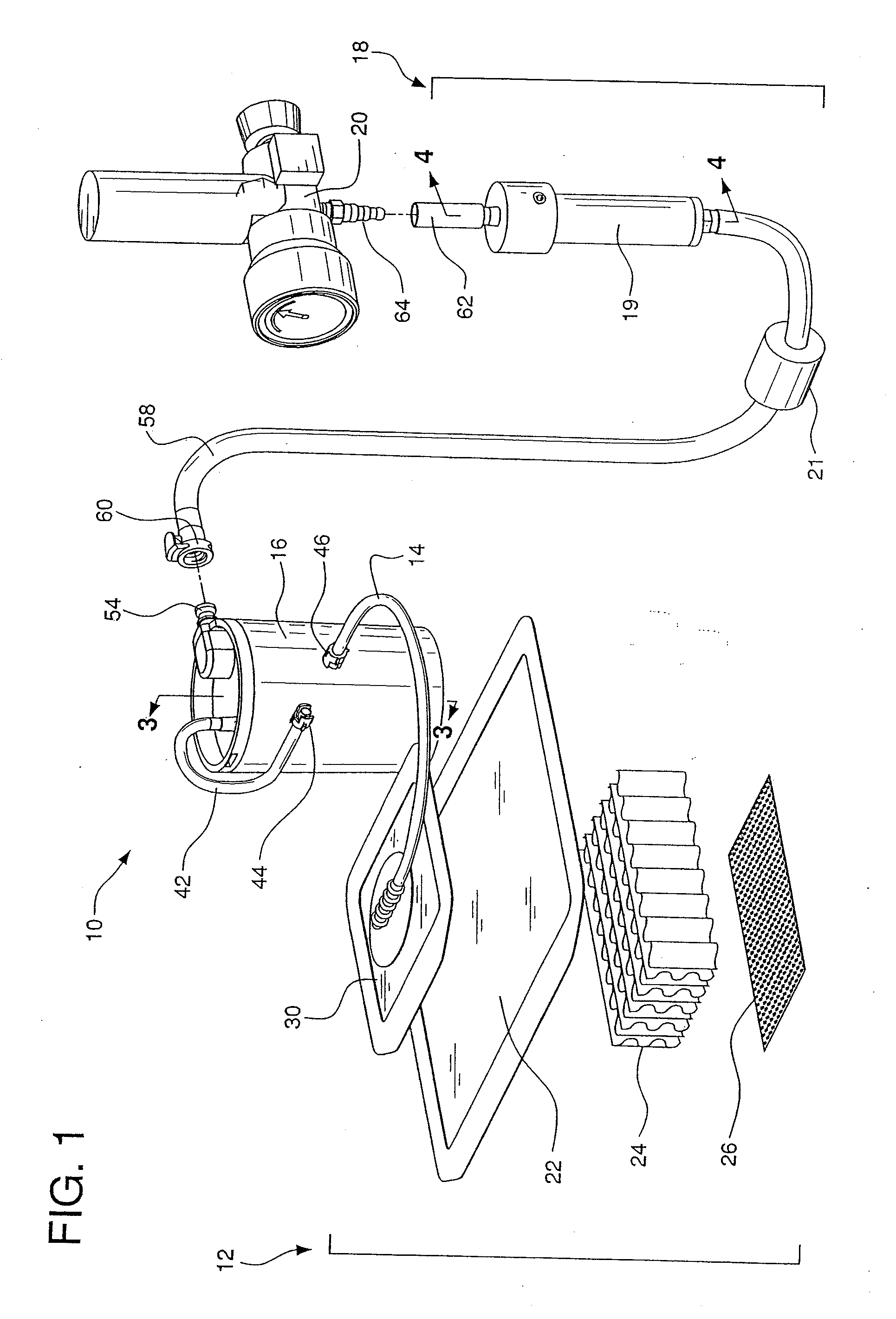
Medical/surgical waste collection unit including waste containers of different storage volumes with inter-container transfer valve and independently controlled vacuum levels
ActiveUS7621898B2Reduce in quantityLarge storage capacityMechanical apparatusDispersed particle filtrationDocking stationVacuum level
Owner:STRYKER CORP
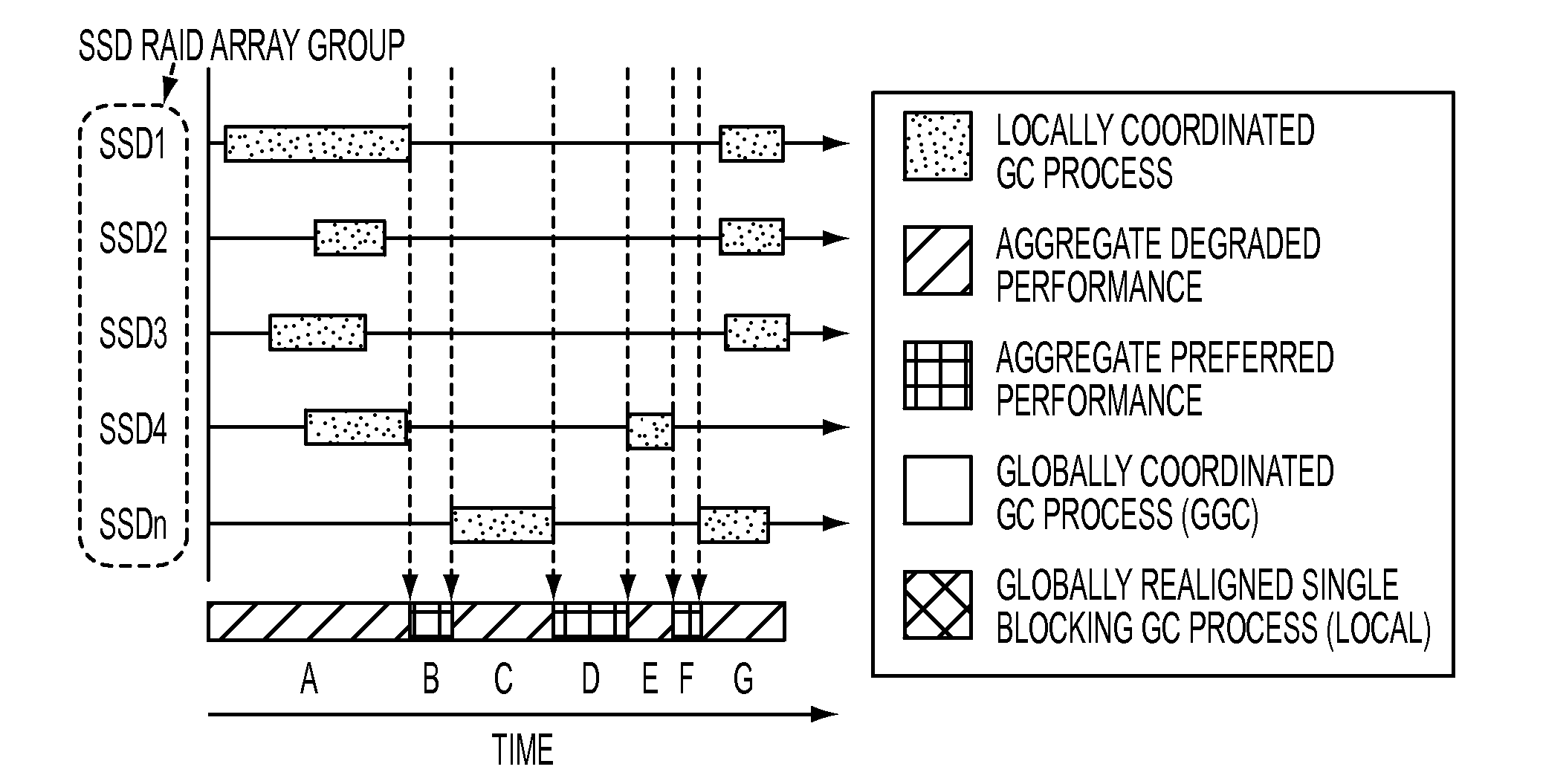
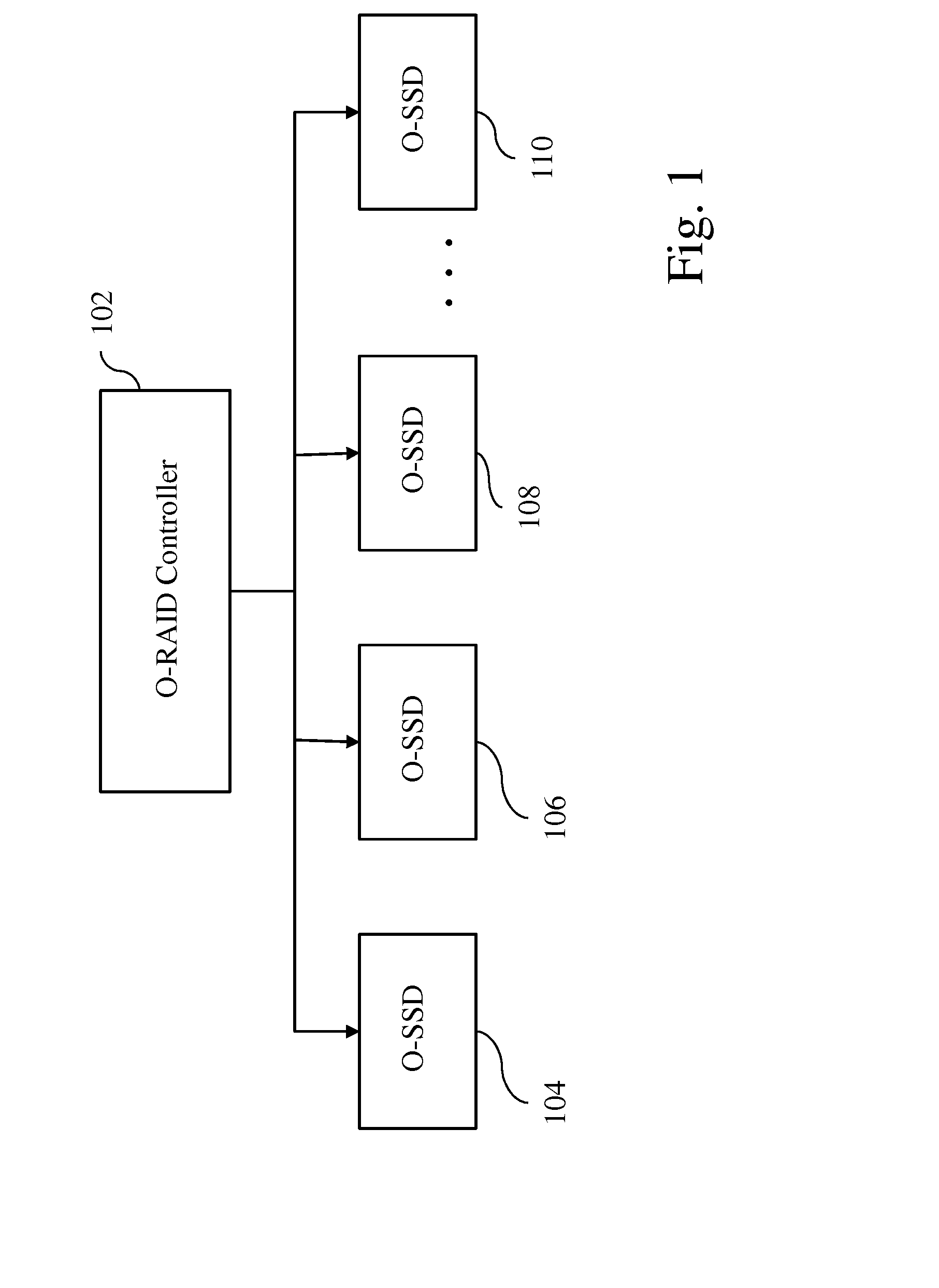
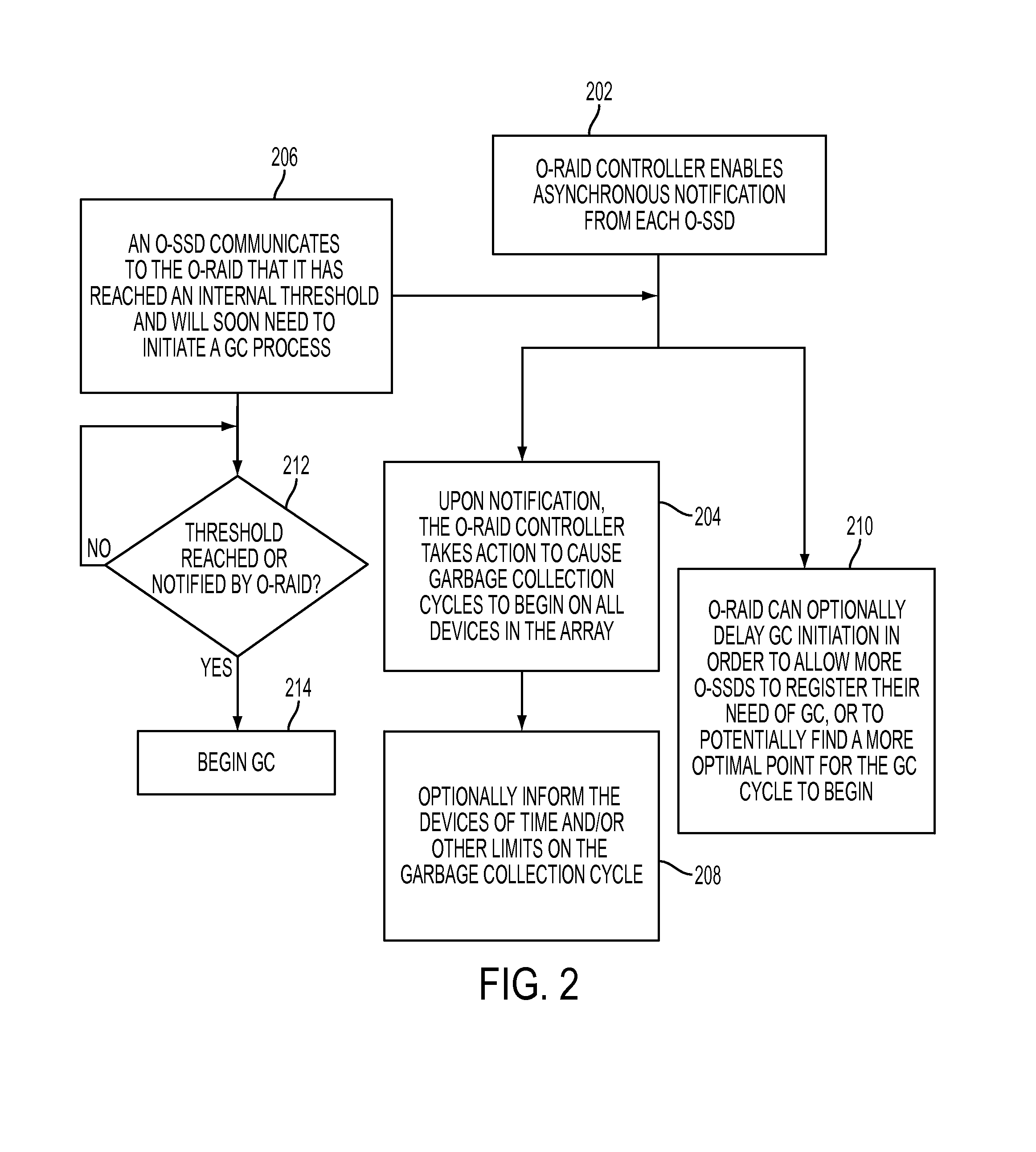
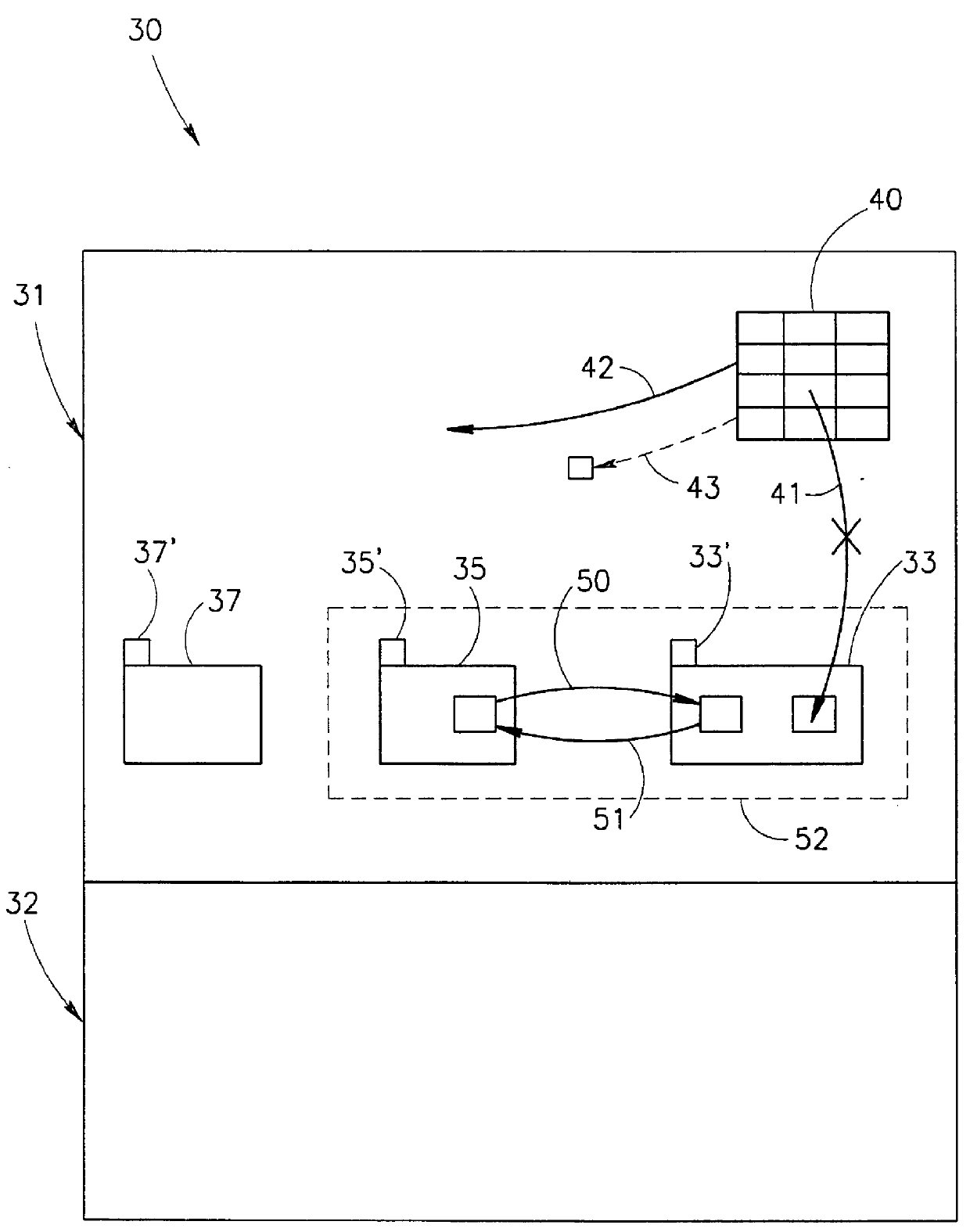
Coordinated garbage collection for raid array of solid state disks
ActiveUS20120036309A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationError detection/correctionRAIDWaste collection
An optimized redundant array of solid state devices may include an array of one or more optimized solid-state devices and a controller coupled to the solid-state devices for managing the solid-state devices. The controller may be configured to globally coordinate the garbage collection activities of each of said optimized solid-state devices, for instance, to minimize the degraded performance time and increase the optimal performance time of the entire array of devices.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
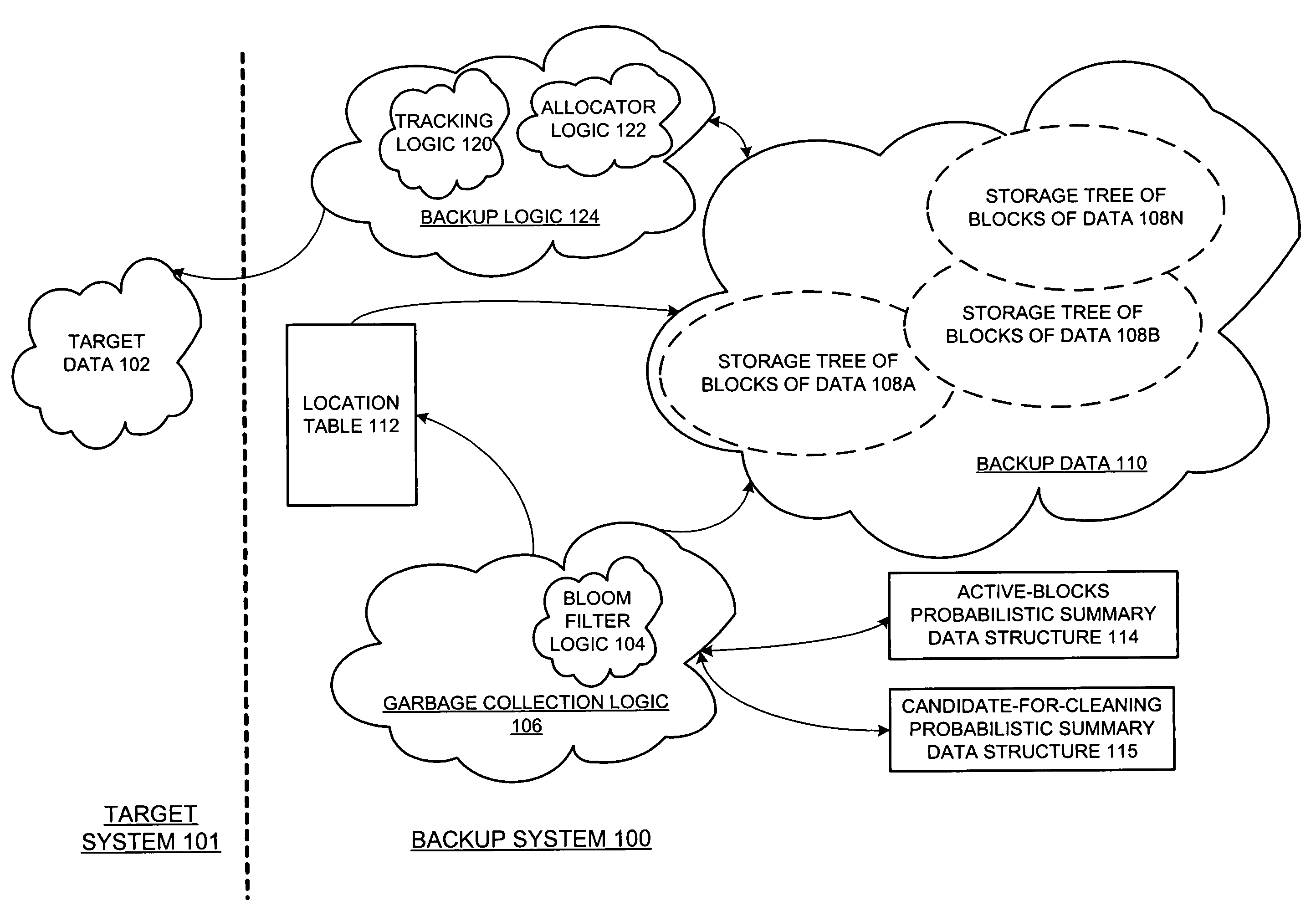
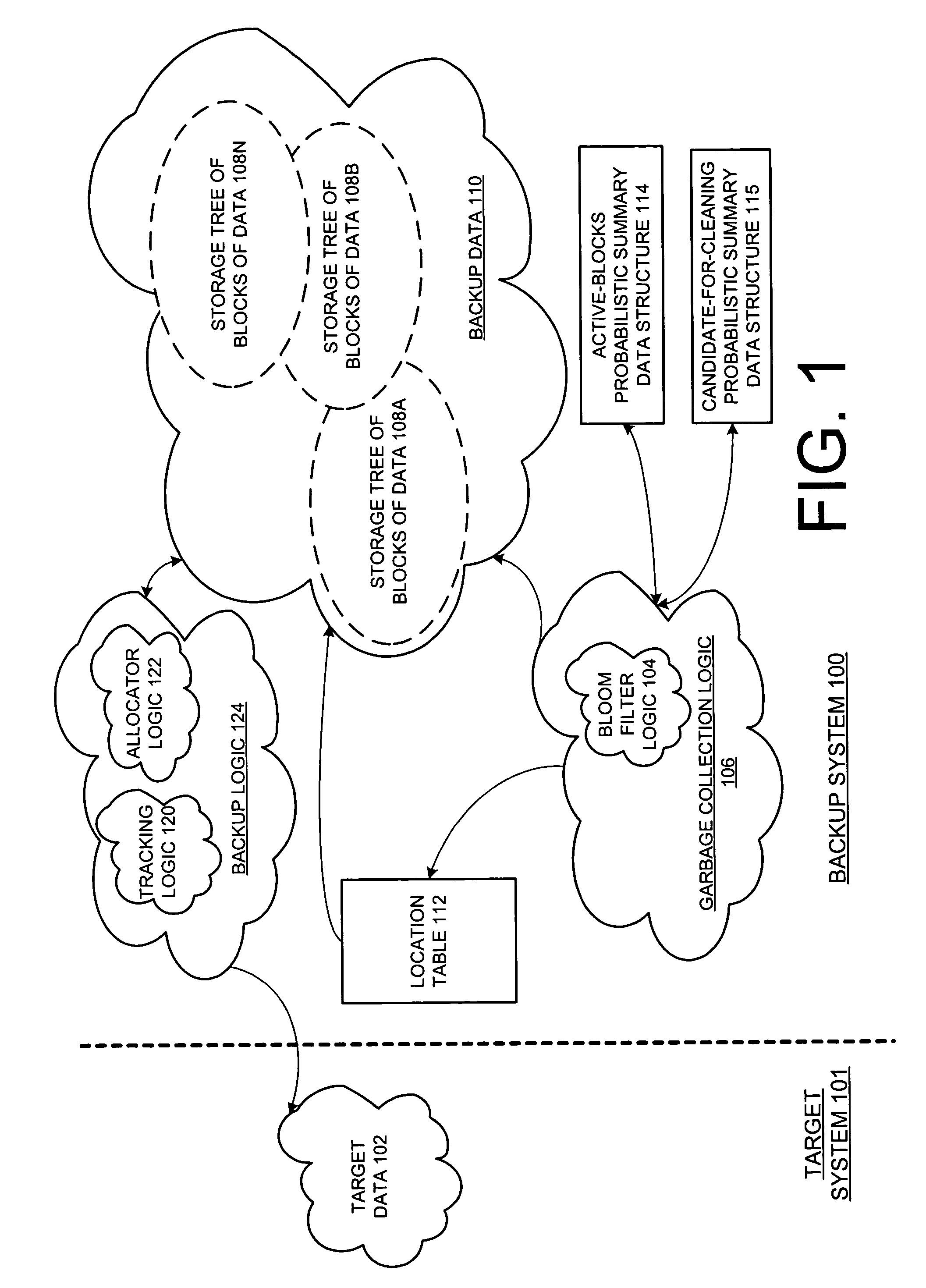
Probabilistic summary data structure based encoding for garbage collection
ActiveUS7424498B1Reduce data volumeIncrease the amount of dataData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsSummary dataWaste collection
A method and apparatus for different embodiments of probabilistic summary data structure based encoding for garbage collection are described. In one embodiment, a method comprises generating a probabilistic summary data structure that represents active blocks of data within a storage device based on identifications of the active blocks or the data within the active blocks. The method also includes performing garbage collection of at least a portion of the storage device based on the probabilistic summary data structure.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Medical/surgical waste collection and disposal system including waste containers of different storage volumes with inter-container transfer valve and independently controlled vacuum levels
ActiveUS20070135779A1Reduce the numberReduce tripsMechanical apparatusDispersed particle filtrationDocking stationWaste collection
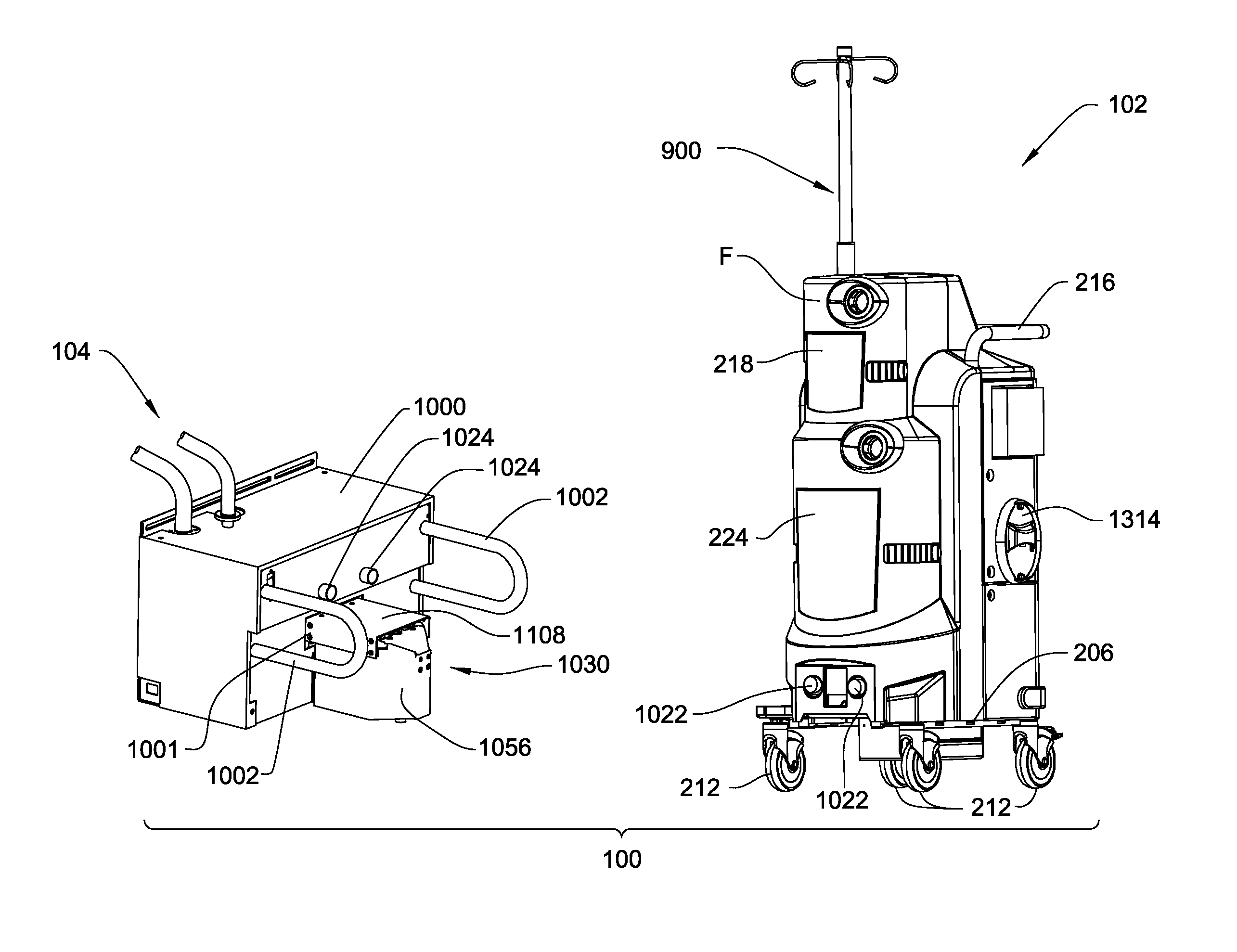
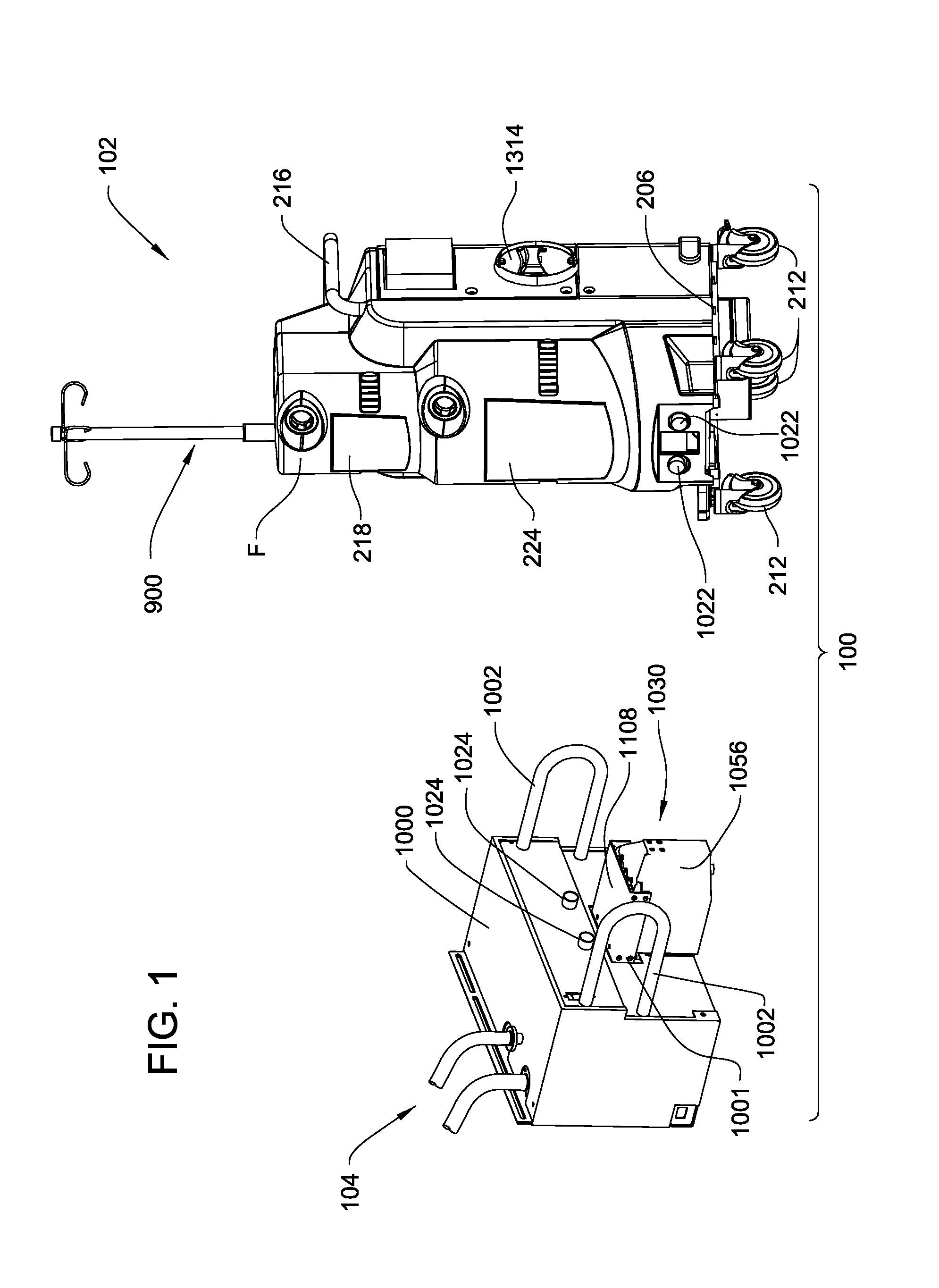
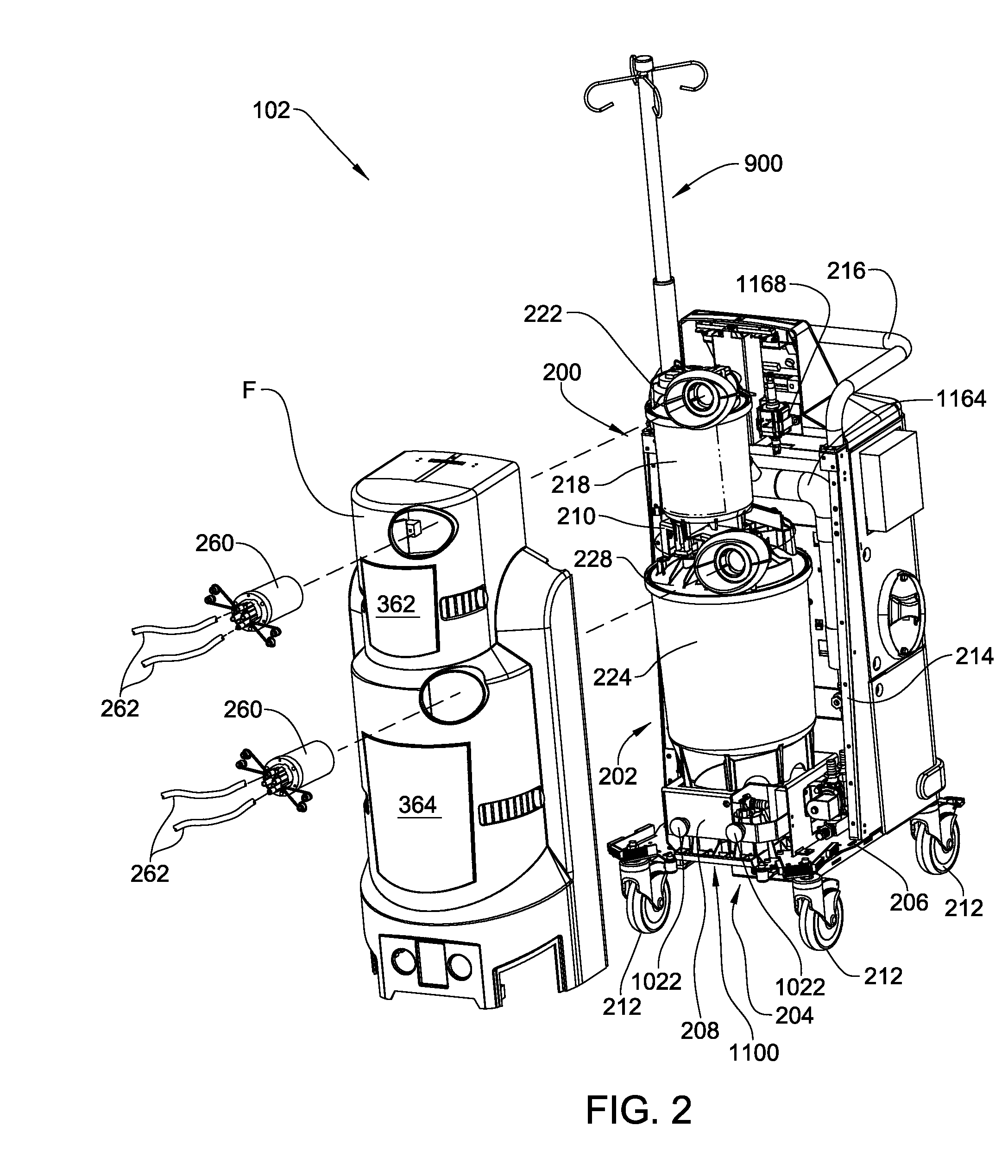
A waste collection and disposal system for use in health care facilities is provided. The system includes a mobile waste collection unit for moving between use areas in the health care facility to collect waste material generated during medical procedures including body fluids, body tissues, saline, etc. The waste collection unit includes stacked upper and lower waste containers for receiving the waste material. During use, the upper waste container can be emptied into the lower waste container for temporary storage. In addition, different vacuum levels can be provided in the waste containers during complex procedures. Once a user desires to empty the waste collection unit, the waste collection unit is wheeled to a docking station. At the docking station, the waste material is off-loaded to a waste drain and the waste collection unit is cleaned and rinsed for further use.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
Pump system for negative pressure wound therapy
InactiveUS20110077605A1Minimize the possibilityReduce the possibilityMedical devicesIntravenous devicesControl systemLevel sensor
A pump system for applying negative pressure to a wound, including a flow monitor capable of detecting a deviation from a reference airflow rate provided by a controlled leak to determine whether the system is operating normally or abnormally, and a flow status annunciator to indicate a normal operating condition or whether an abnormal condition is a leak or an occluded line in the system. The pump system further includes a pressure controller for regulating operation of a pump to control pressure in the system at a range around a user-selected setpoint. The pump system may also include a waste collector and a level sensor for detecting when the collector is full.
Owner:PAUL HARTMANN AG
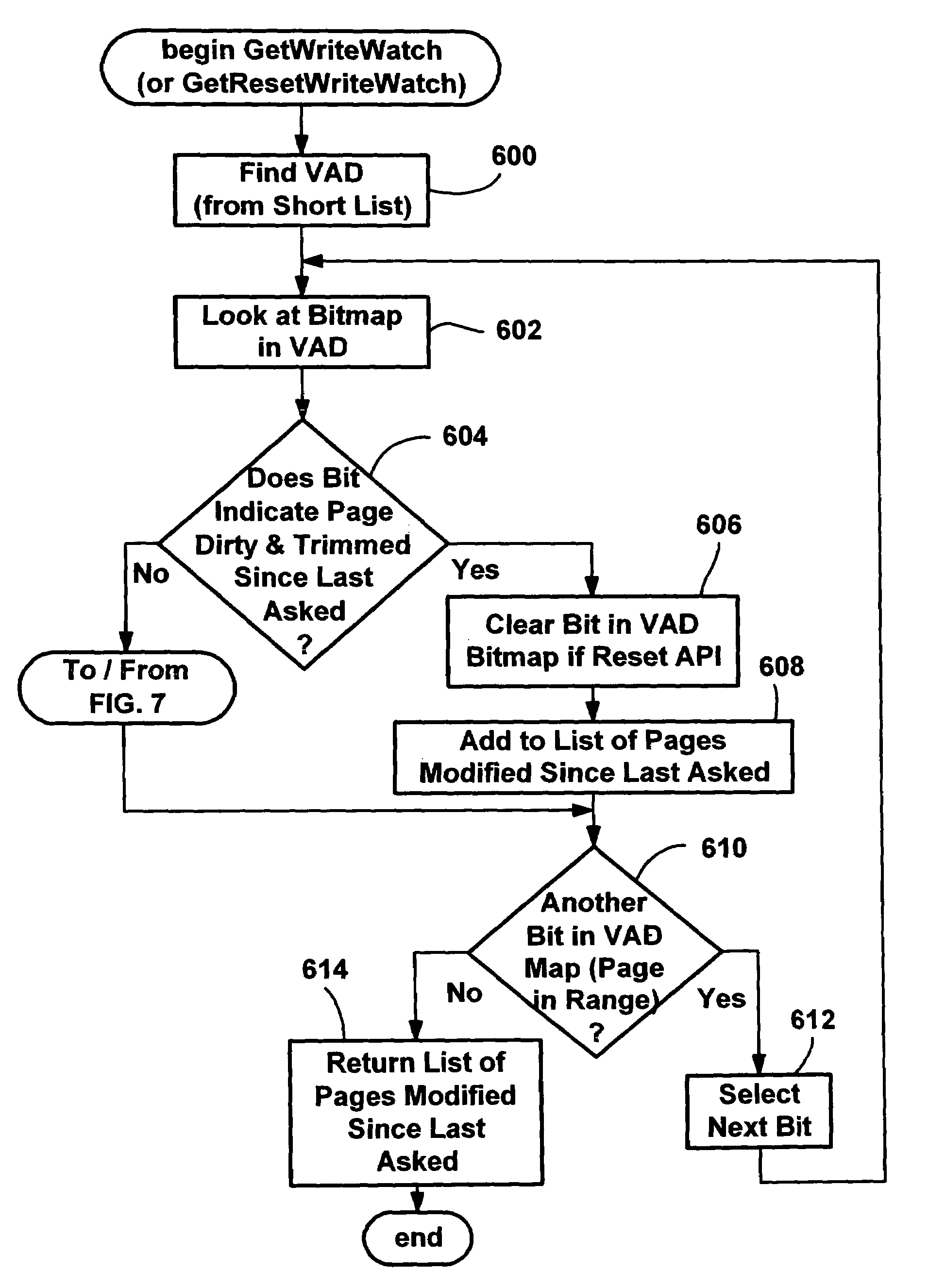
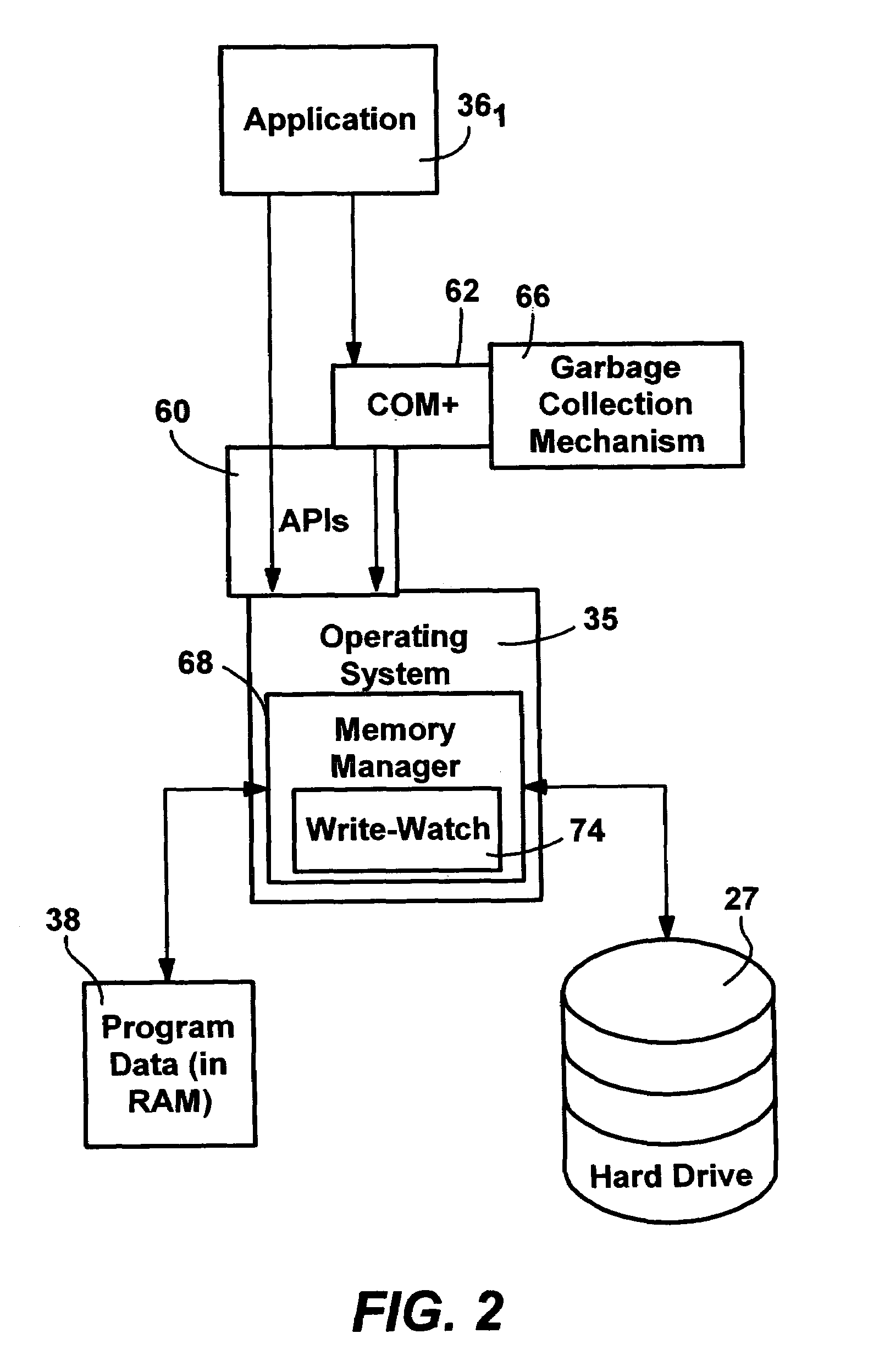
Efficient write-watch mechanism useful for garbage collection in a computer system
InactiveUS7065617B2Efficient write-watchReduce performanceData processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationComputerized systemWaste collection
An efficient write-watch mechanism and process. A bitmap is associated with the virtual address descriptor (VAD) for a process, one bit for each virtual page address allocated to a process having write-watch enabled. As part of the write-watch mechanism, if a virtual address is trimmed to disk and that virtual address page is marked as modified, then the corresponding bit in the VAD is set for that virtual address page. In response to an API call (e.g., from a garbage collection mechanism) seeking to know which virtual addresses in a process have been modified since last checked, the memory manager walks the bitmap in the relevant VAD for the specified virtual address range for the requested process. If a bit is set, then the page corresponding to that bit is known to have been modified since last asked. If specified by the API, the bit is cleared in the VAD bitmap so that it will reflect the state since this time of asking. If the bit is not set, to determine if the page was modified, the page table entry (PTE) is checked for that page, and if the PTE indicates the page was modified, the page is known to be modified, otherwise that page is known to be unmodified since the last call. One enhancement uses page directory tables to locate a series of trimmed pages, sometimes avoiding the need to access the PTE.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
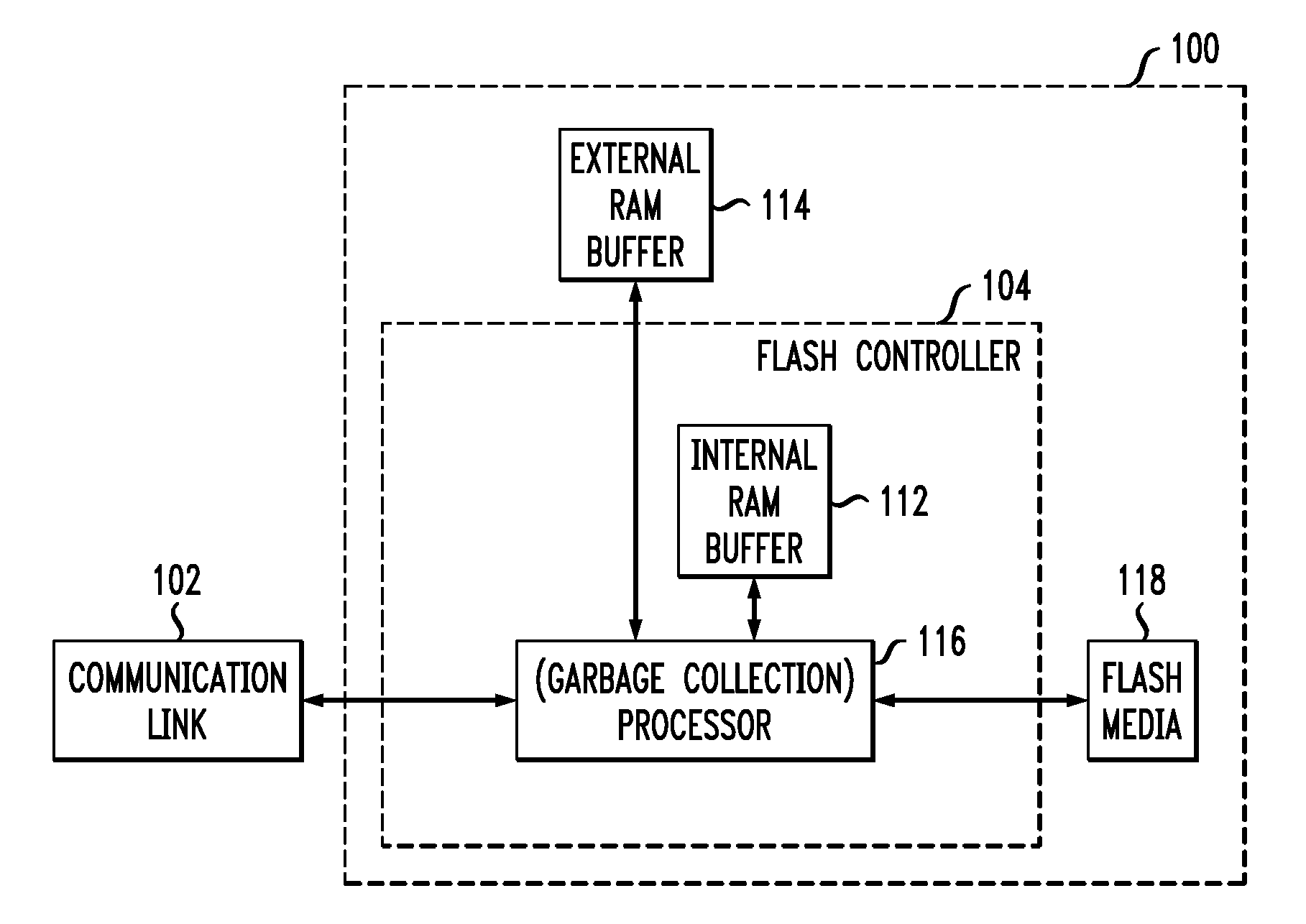
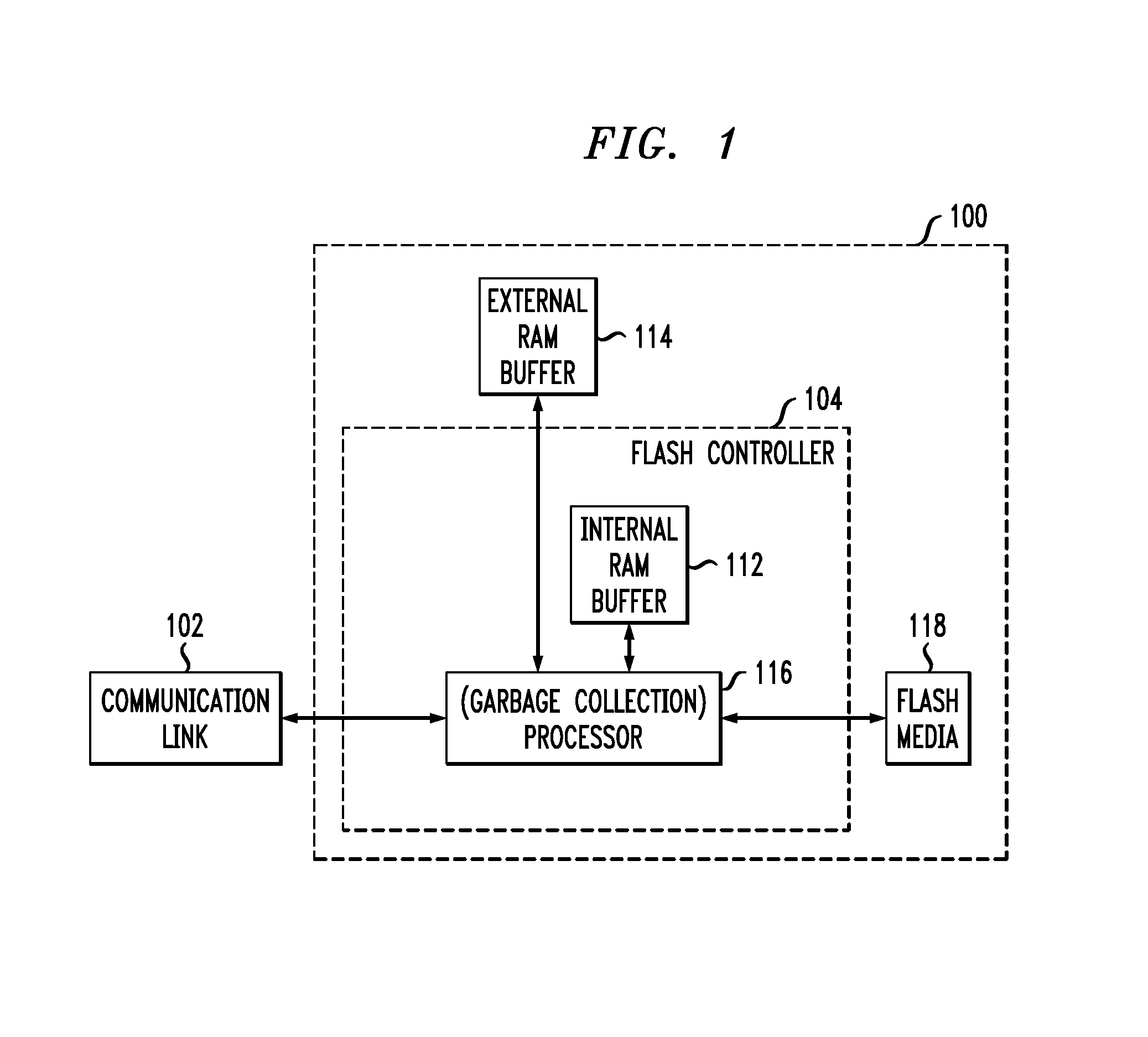
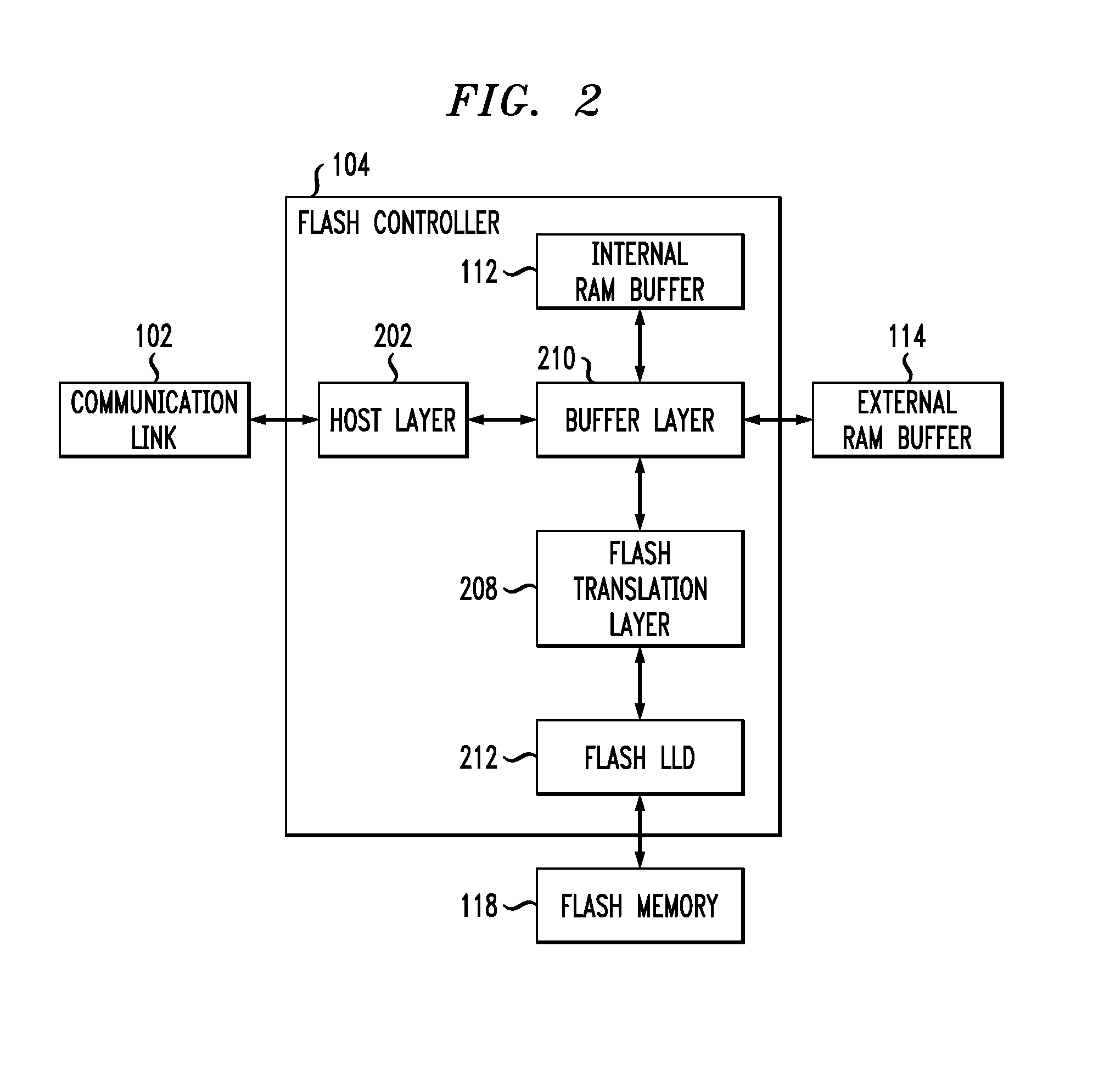
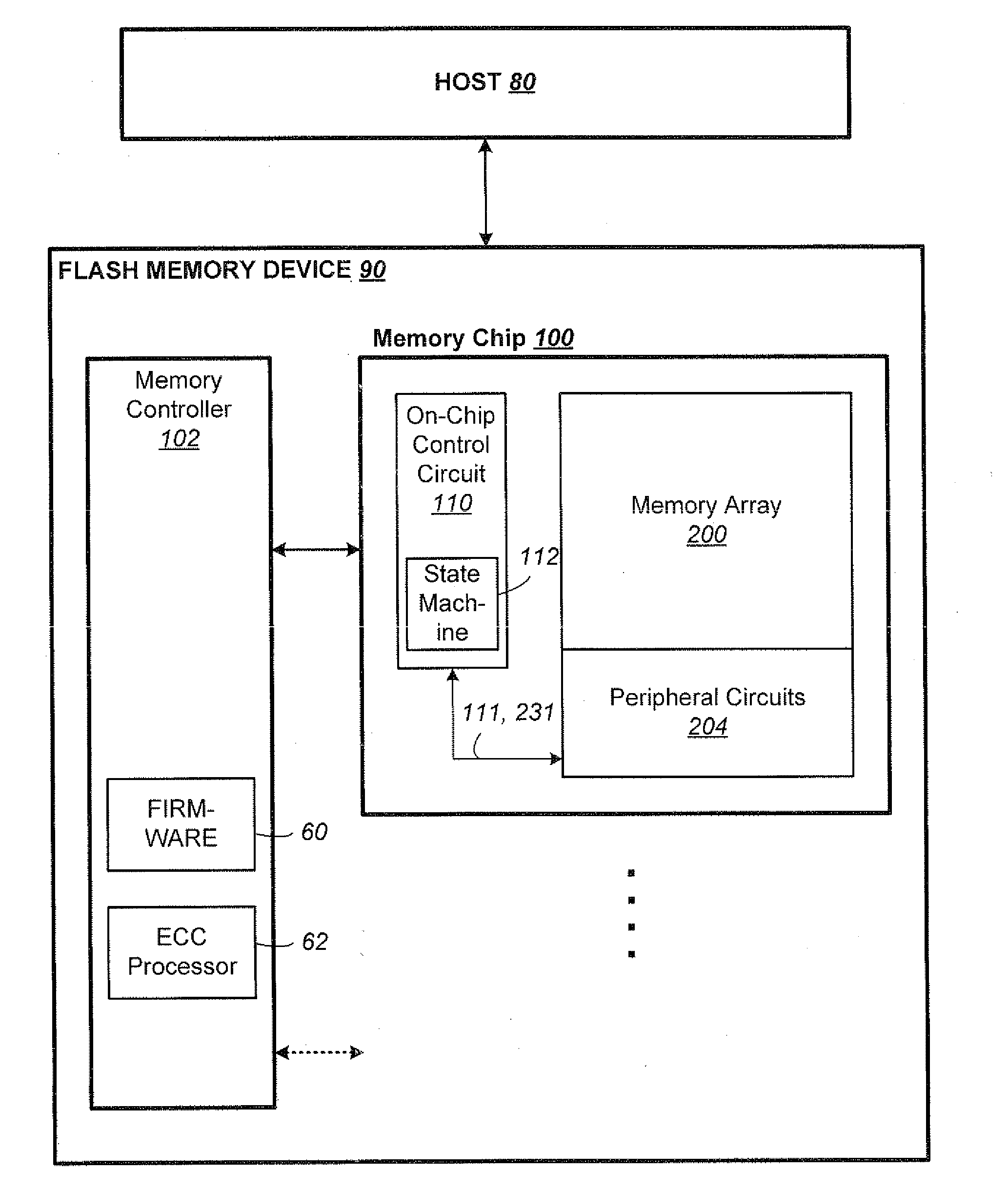
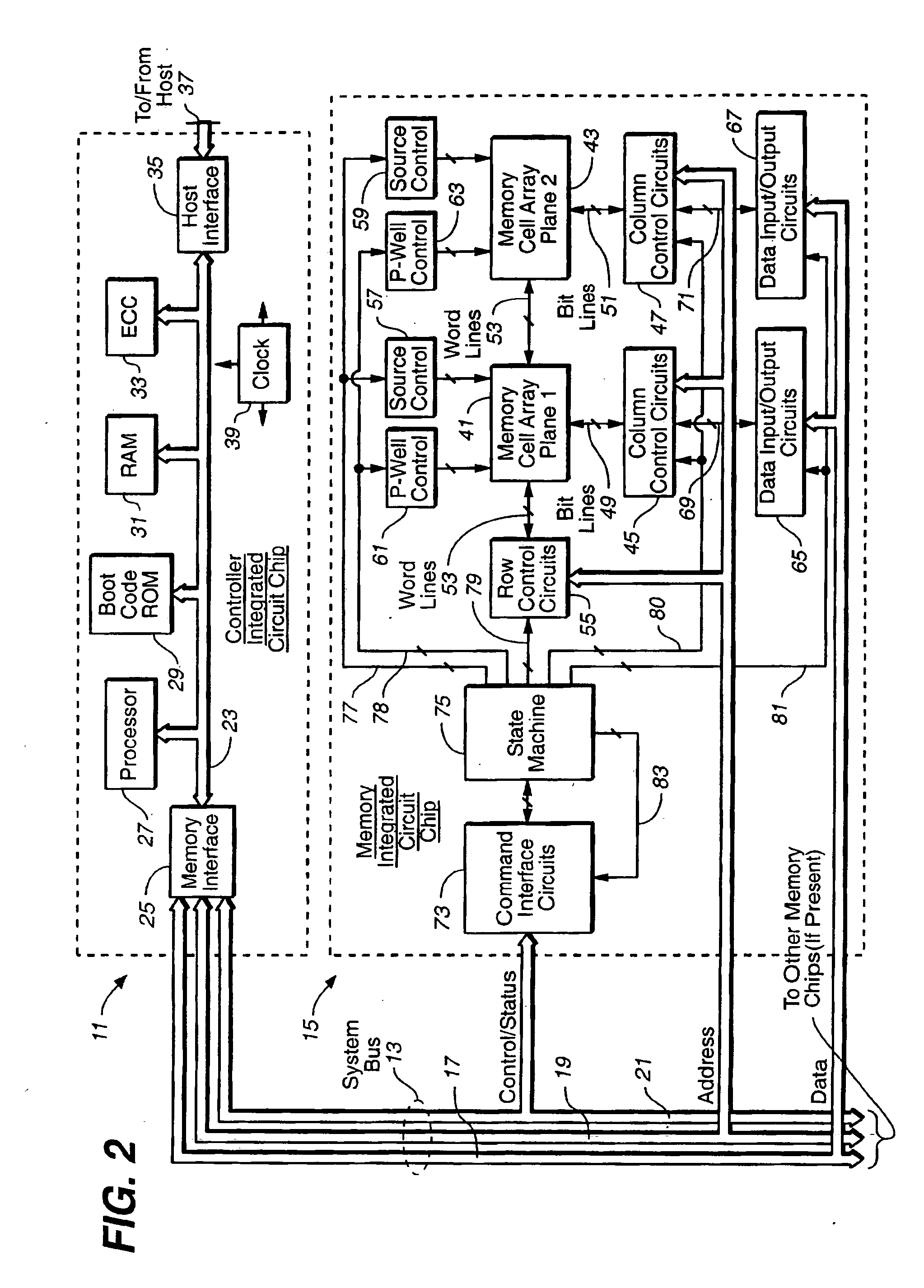
Flash memory controller garbage collection operations performed independently in multiple flash memory groups
ActiveUS20090172258A1Affect performanceMaximize useMemory architecture accessing/allocationRead-only memoriesWaste collectionFlash memory controller
A flash memory controller connected to multiple flash memory groups performs independent garbage collection operations in each group. For each group, the controller independently determines the amount of free space and performs garbage collection operations if the amount falls below a threshold.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
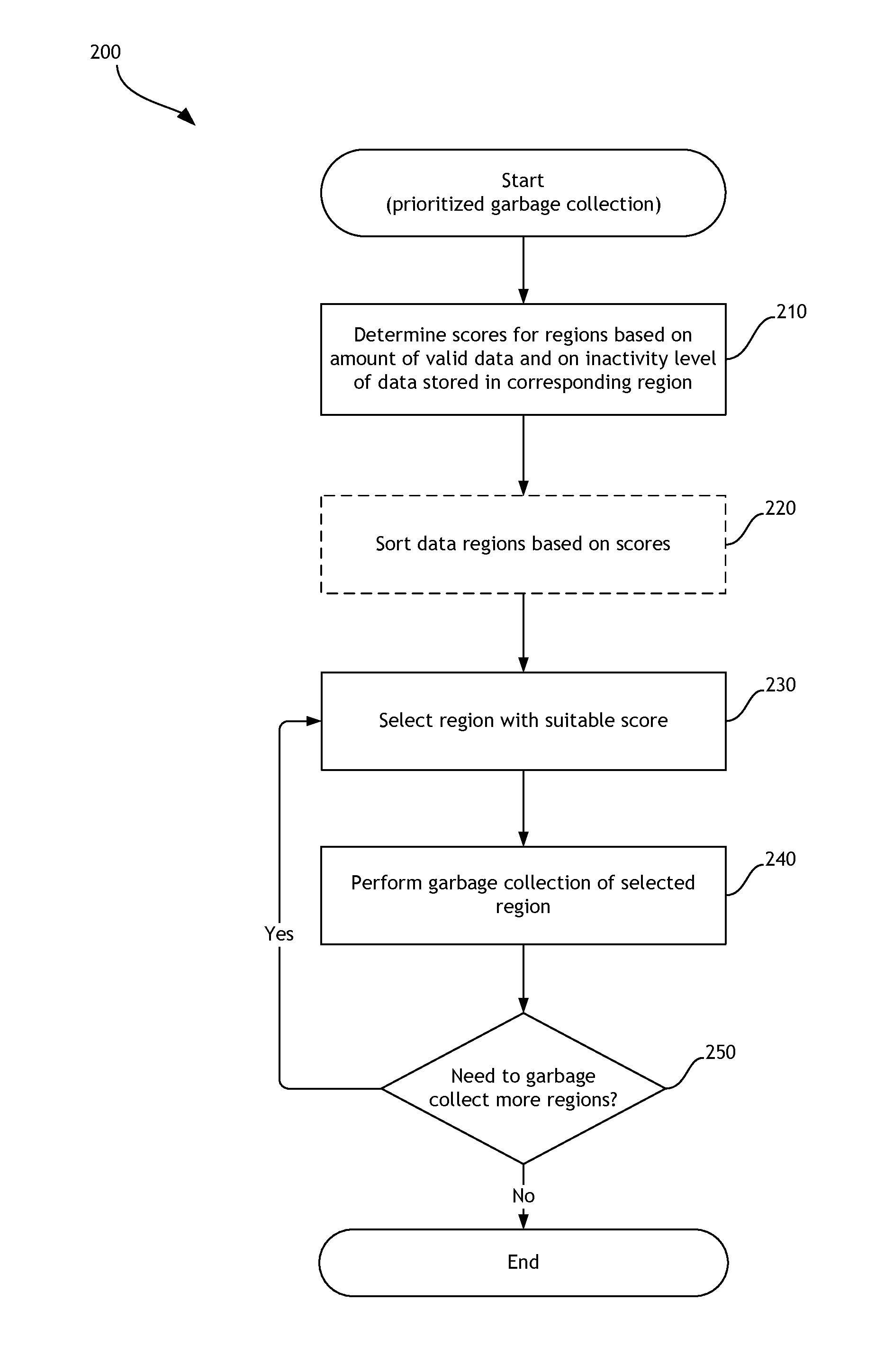
Garbage collection based on the inactivity level of stored data
ActiveUS8788778B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationInput/output to record carriersWrite amplificationWaste collection
A data storage system implements garbage collection based on the inactivity level of stored data. In one embodiment, the inactivity level of data stored in regions of a data storage system is taken into account when prioritizing regions for garbage collection. Inactivity level of memory regions can be compared to an inactivity threshold. The threshold can be adjusted during operation of the data storage system. Garbage collection can be delayed until data stored in a particular region is unlikely to be updated. Write amplification associated with garbage collection is reduced, and improved performance is attained.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Garbage Collection for Solid State Disks
ActiveUS20110022778A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationPage countRefuse collection
Described embodiments provide a method of recovering storage space on a solid state disk (SSD). An index and valid page count are determined for each block of a segment of an SSD. If the valid page count of at least one block in the segment is zero, a quick clean is performed. A quick clean deallocates blocks having zero valid pages and places them in a queue for erasure. Otherwise, a deep clean is performed. A deep clean determines a compaction ratio, N-M, wherein N is a number of partially valid blocks and M is a number of free blocks required to compact the valid data from the N partially valid blocks into M entirely valid blocks. At least one data structure of the SSD is modified to refer to the M entirely valid blocks, and the N partially valid blocks are placed in the queue for erasure.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Non-Volatile Memory and Method Having Block Management with Hot/Cold Data Sorting
ActiveUS20120297122A1Minimize rewriteIncrease probabilityMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHigh probabilityWaste collection
A non-volatile memory organized into flash erasable blocks sorts units of data according to a temperature assigned to each unit of data, where a higher temperature indicates a higher probability that the unit of data will suffer subsequent rewrites due to garbage collection operations. The units of data either come from a host write or from a relocation operation. The data are sorted either for storing into different storage portions, such as SLC and MLC, or into different operating streams, depending on their temperatures. This allows data of similar temperature to be dealt with in a manner appropriate for its temperature in order to minimize rewrites. Examples of a unit of data include a logical group and a block.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Generation isolation system and method for garbage collection
InactiveUS6098089AData processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationProgramming languageWaste collection
Architectural support for generation isolation is provided through trapping of intergenerational pointer stores. Identification of pointer stores as intergenerational is performed by a store barrier responsive to an intergenerational pointer store trap matrix that is programmably encoded with store target object and store pointer data generation pairs to be trapped. The write barrier and intergenerational pointer store trap matrix provide a programmably-flexible definition of generation pairs to be trapped, affording a garbage collector implementer with support for a wide variety of generational garbage collection methods, including remembered set-based methods, card-marking type methods, write barrier based copying collector methods, etc., as well as combinations thereof and combinations including train algorithm type methods to managing mature portions of a generationally collected memory space. Pointer specific store instruction replacement allows implementations in accordance with this invention to provide an exact barrier to not only pointer stores, but to the specific intergenerational pointer stores of interest to a particular garbage collection method or combination of methods.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Medical/surgical waste collection unit with a light assembly separate from the primary display, the light assembly presenting information about the operation of the system by selectively outputting light
ActiveUS10420865B2Easily determine informationSure easyMedical devicesIntravenous devicesLine tubingDisplay device
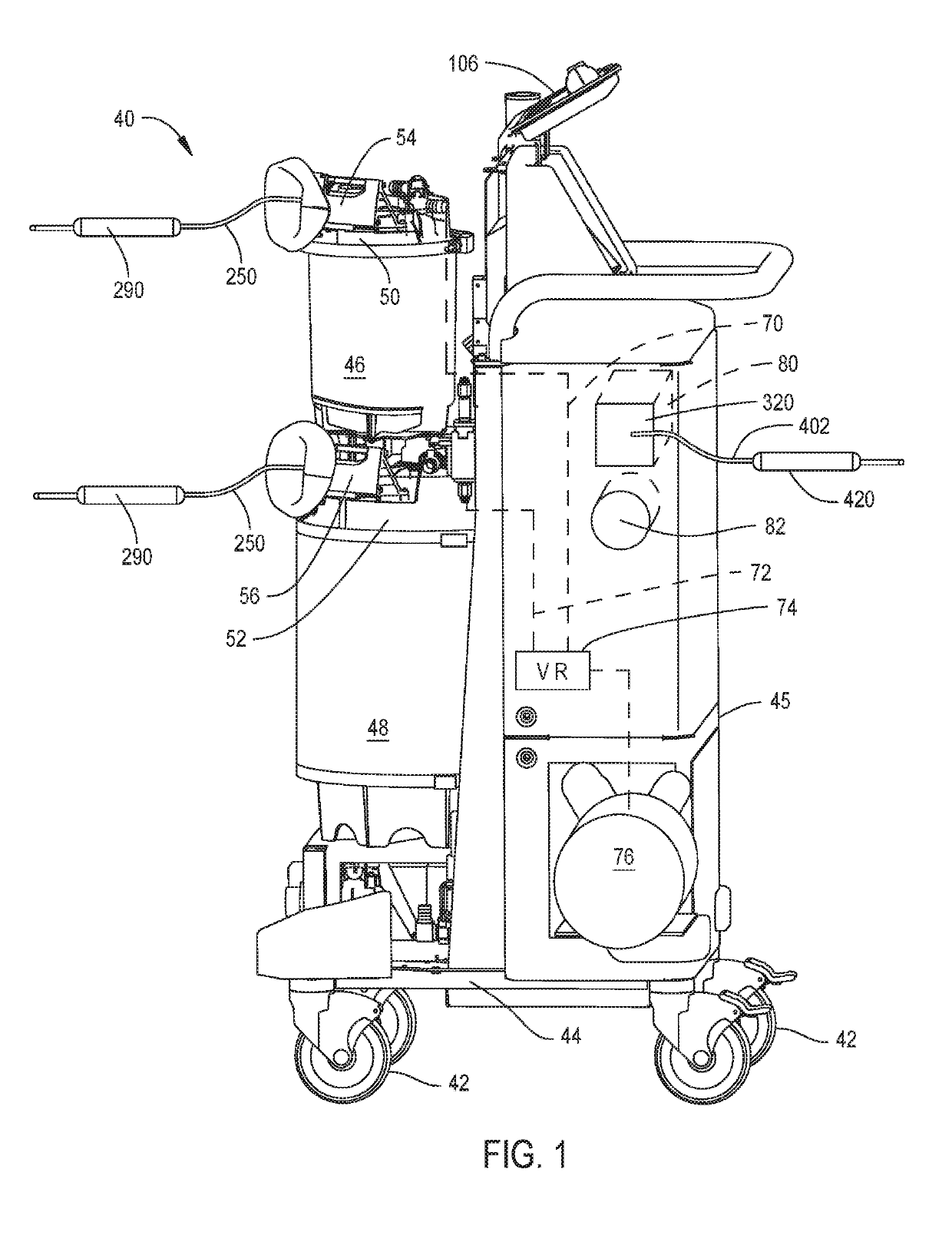
A waste collection unit (40) with a primary display (106) on which information about the operation of the unit is presented. In addition to the primary display there is a light assembly (662) adjacent the fitting (614) to which a suction line is attached. The light assembly emits light of selectively colors or in a selected pattern based on an operation state of the waste collection unit.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
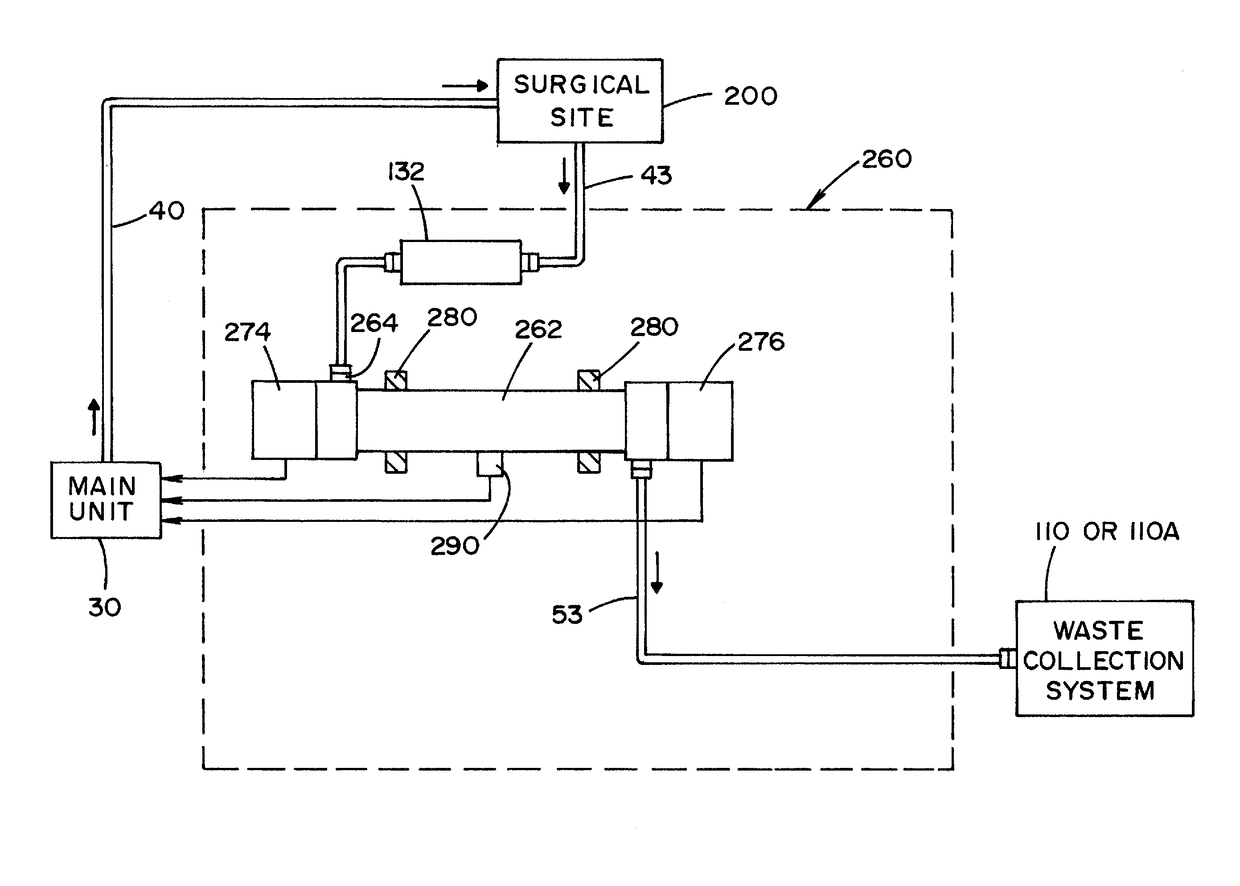
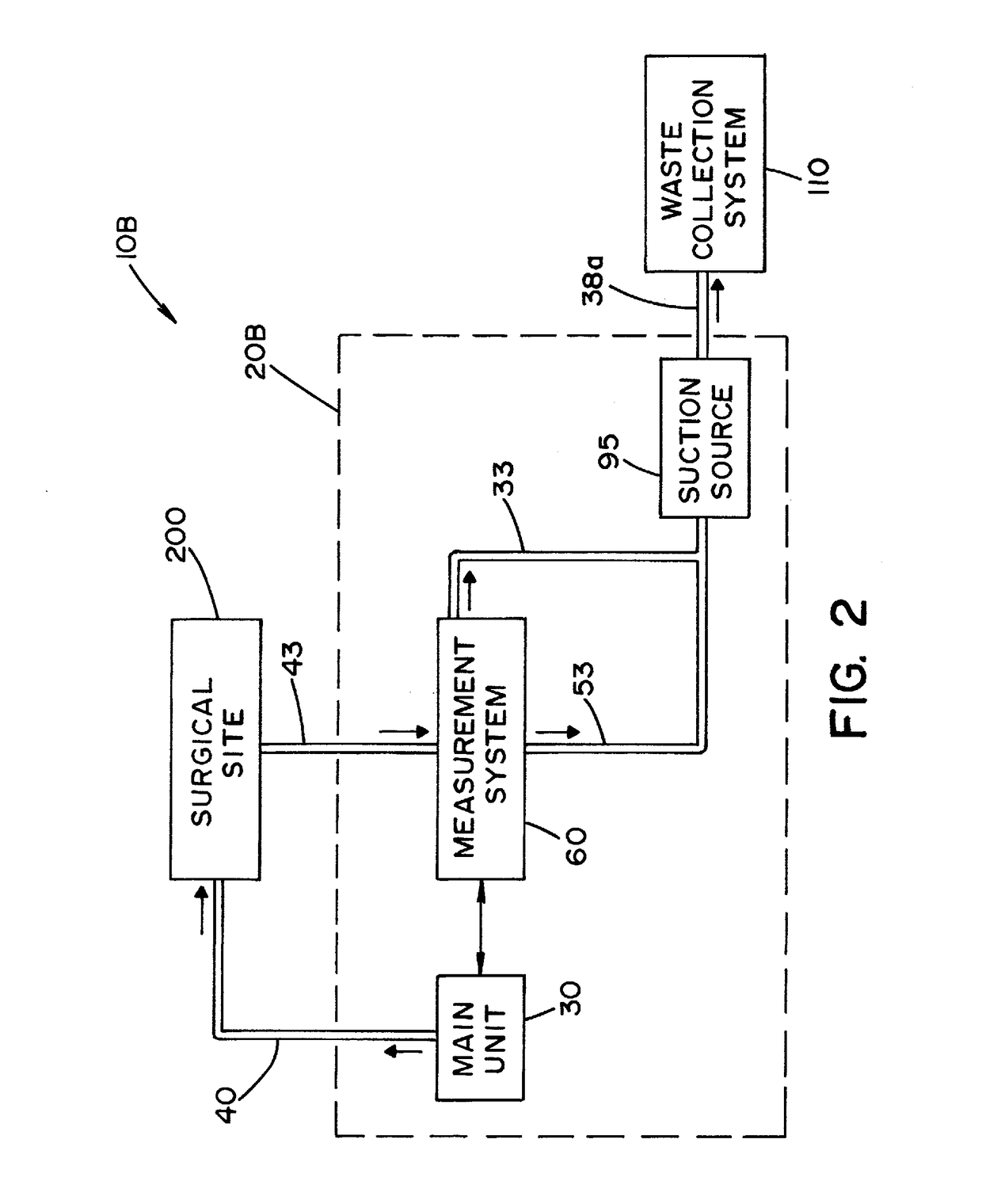
Fluid management system with pass-through fluid volume measurement
ActiveUS9770541B2Continuous measurementEliminate replacementMedical devicesIntravenous devicesContinuous measurementVolume measurements
A fluid management system including a pass-through fluid volume measurement system to provide continuous measurement of fluid returned from a surgical site during transit to a waste collection system. The pass-through fluid volume measurement system eliminates the need to physically replace full fluid collection containers during the medical procedure with new, empty fluid collection containers.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
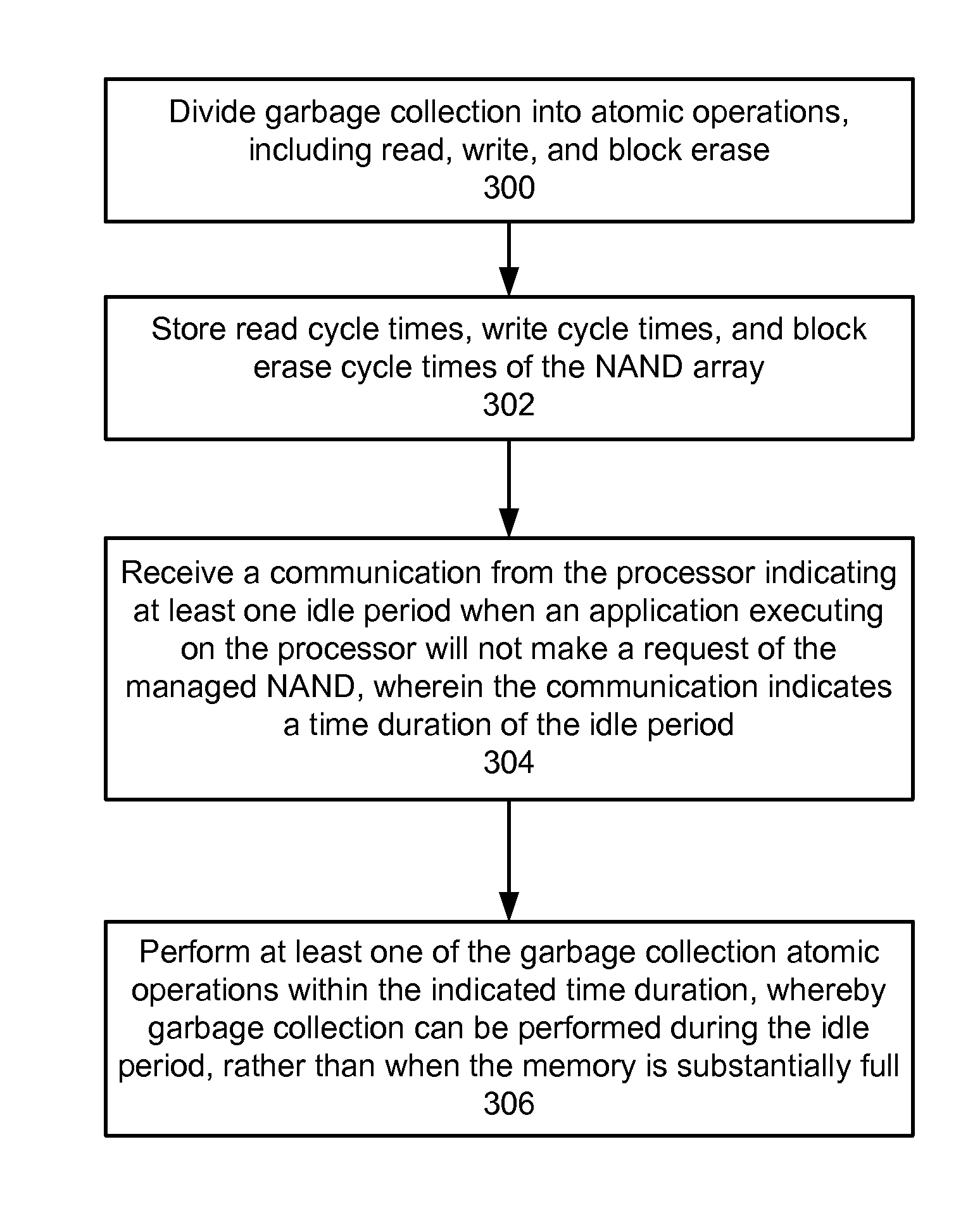
Demand-driven opportunistic garbage collection in memory components
A method and system for performing garbage collection in a memory is disclosed. Aspects of the exemplary embodiment include dividing garbage collection into atomic operations, including read, write, and block erase; storing read cycle times, write cycle times, and block erase cycle times of the memory; receiving a communication from a processor indicating at least one idle period when an application executing on the processor will not make a request of the memory, wherein the communication indicates a time duration of the at least one idle period; and in response, performing at least one of the garbage collection atomic operations within the time duration, whereby garbage collection can be performed during the at least one idle period, rather than when the memory is substantially full.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
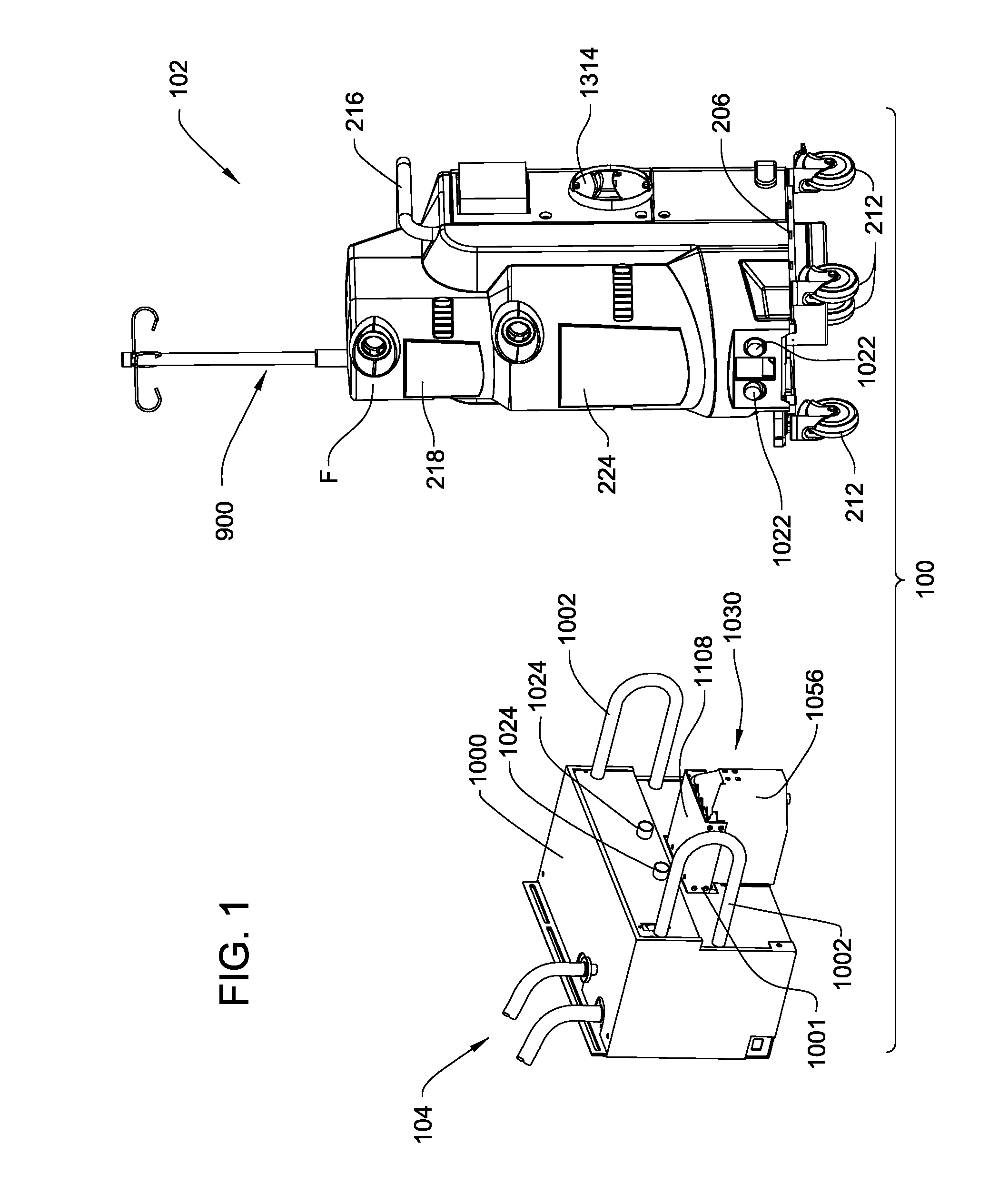
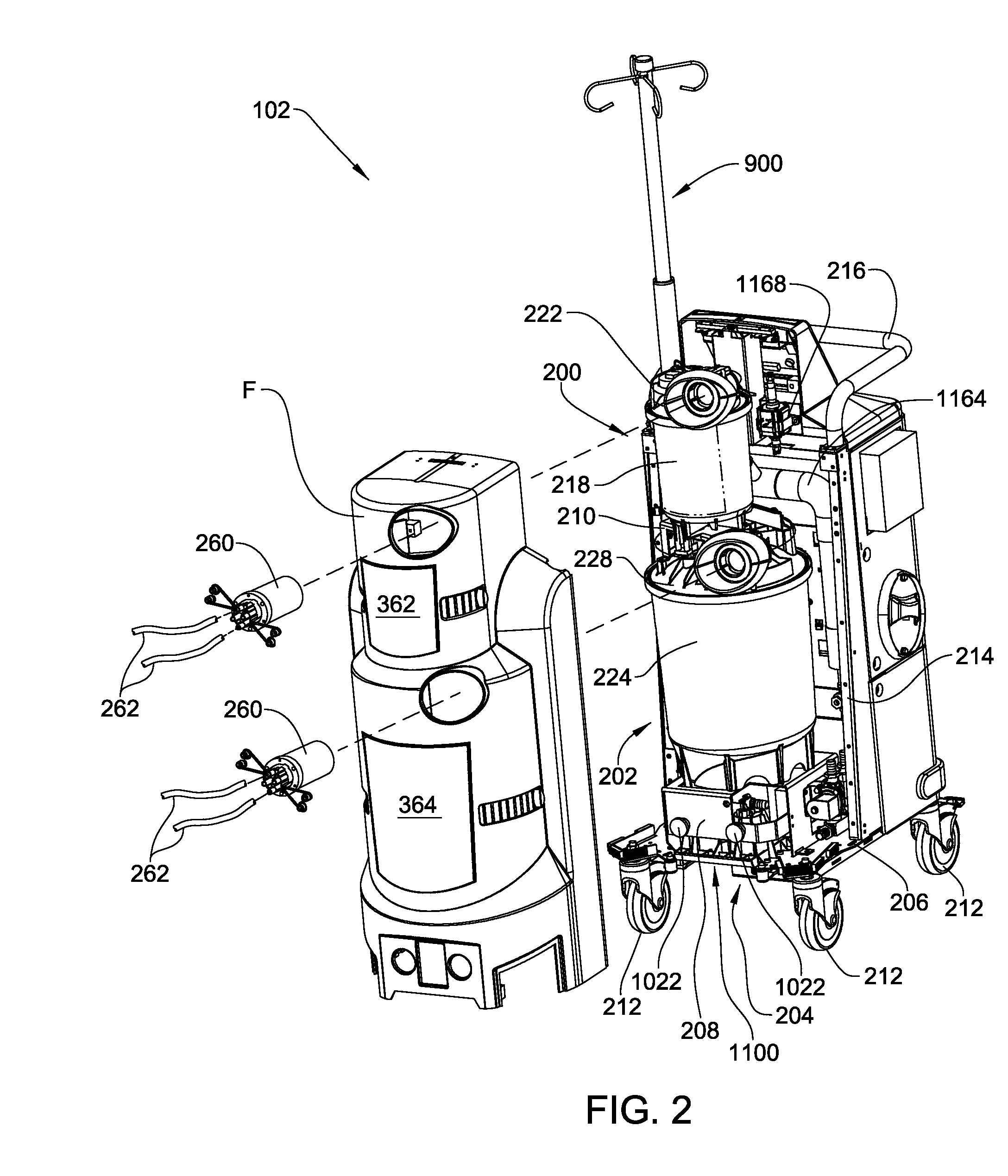
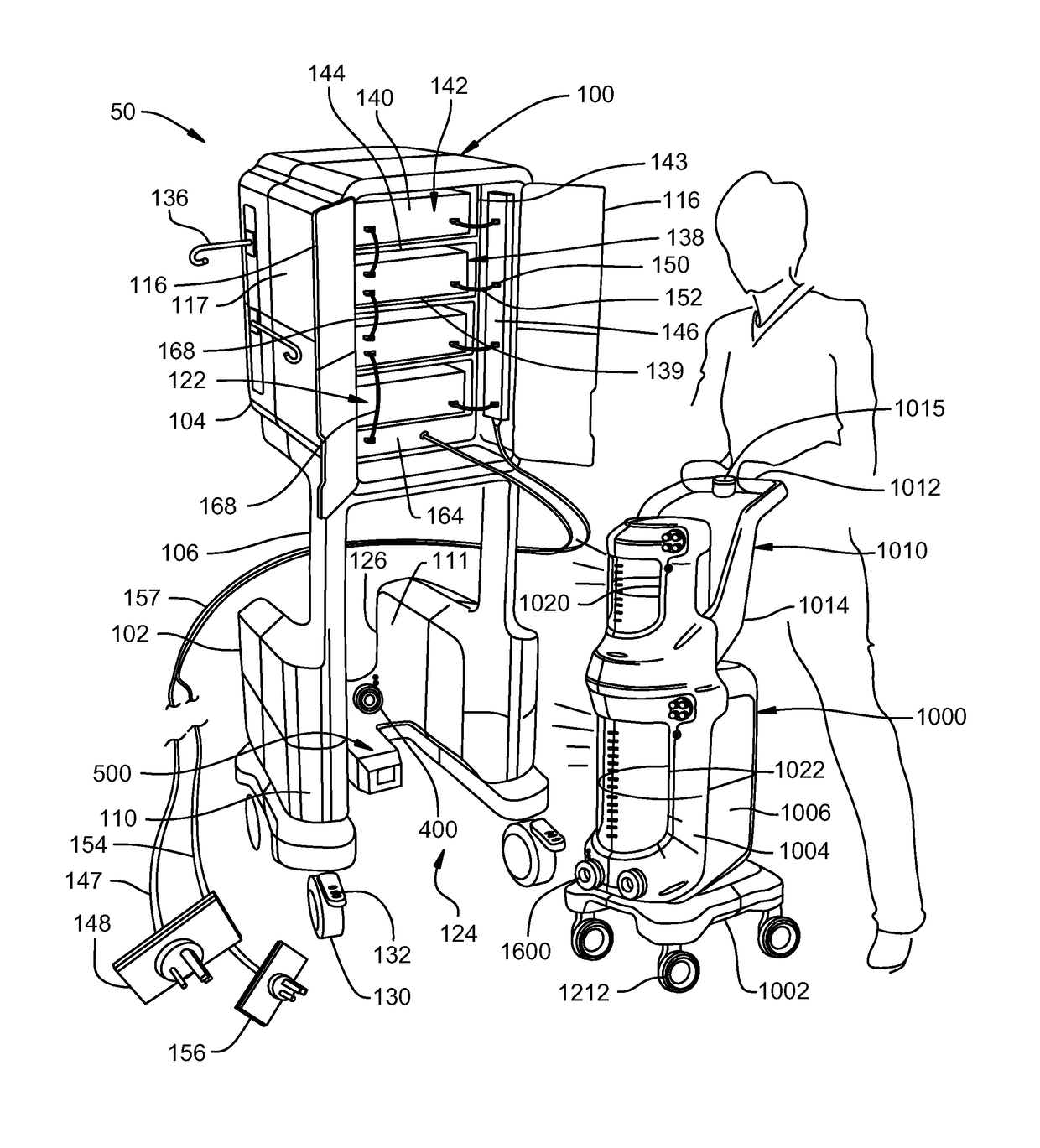
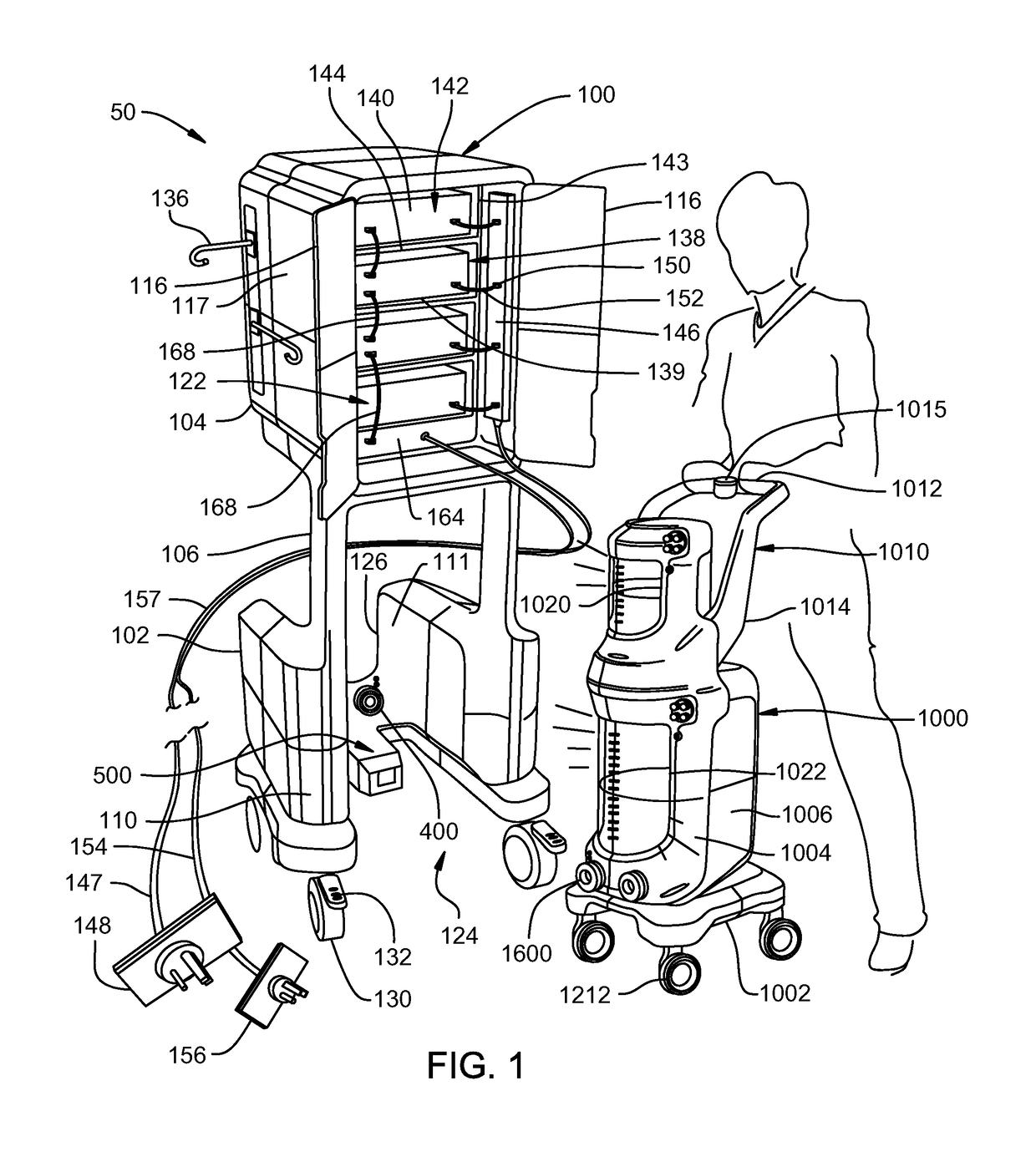
Mobile instrument assembly for use as part of a medical/surgical waste collection system, the assembly including a vacuum source to which a mobile waste collection cart can be releasably attached
ActiveUS10105470B2Reduces weight and sizeReduced footprintSurgical furnitureMedical devicesWaste collectionVacuum pump
A waste collection system for collecting waste during medical / surgical procedures including a mobile container cart with a waste container. A container cart is selectively coupled to a suction cart that includes a vacuum pump. The connection of the carts results in the connection of the vacuum pump to the waste container. The vacuum pump draws a vacuum that results in waste being drawn through a suction line into the waste container. The container cart holds instruments that can be removably attached to the container cart. This facilitates the configuration of the container cart for the specific procedure for which it is necessary to draw a suction.
Owner:STRYKER CORP
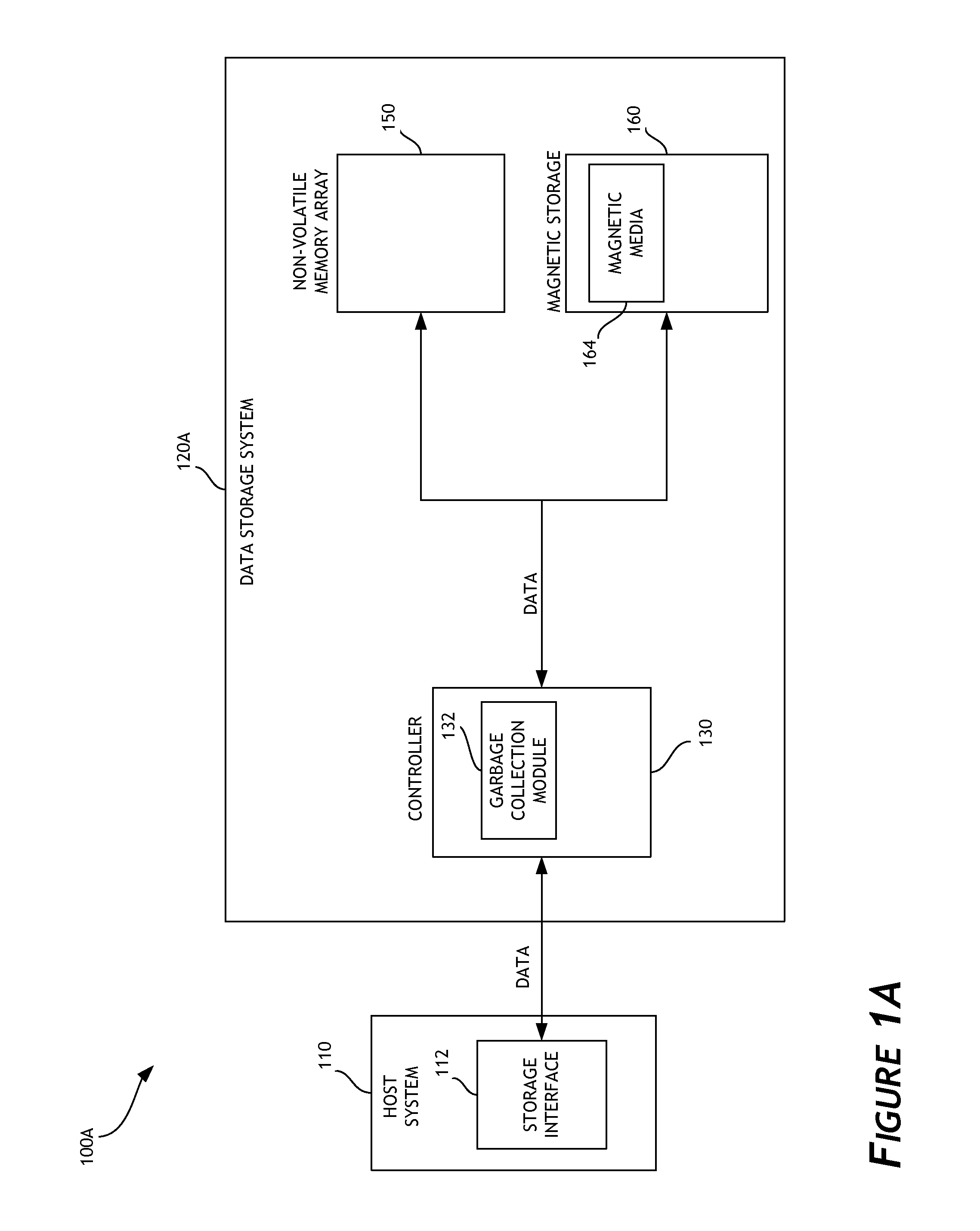
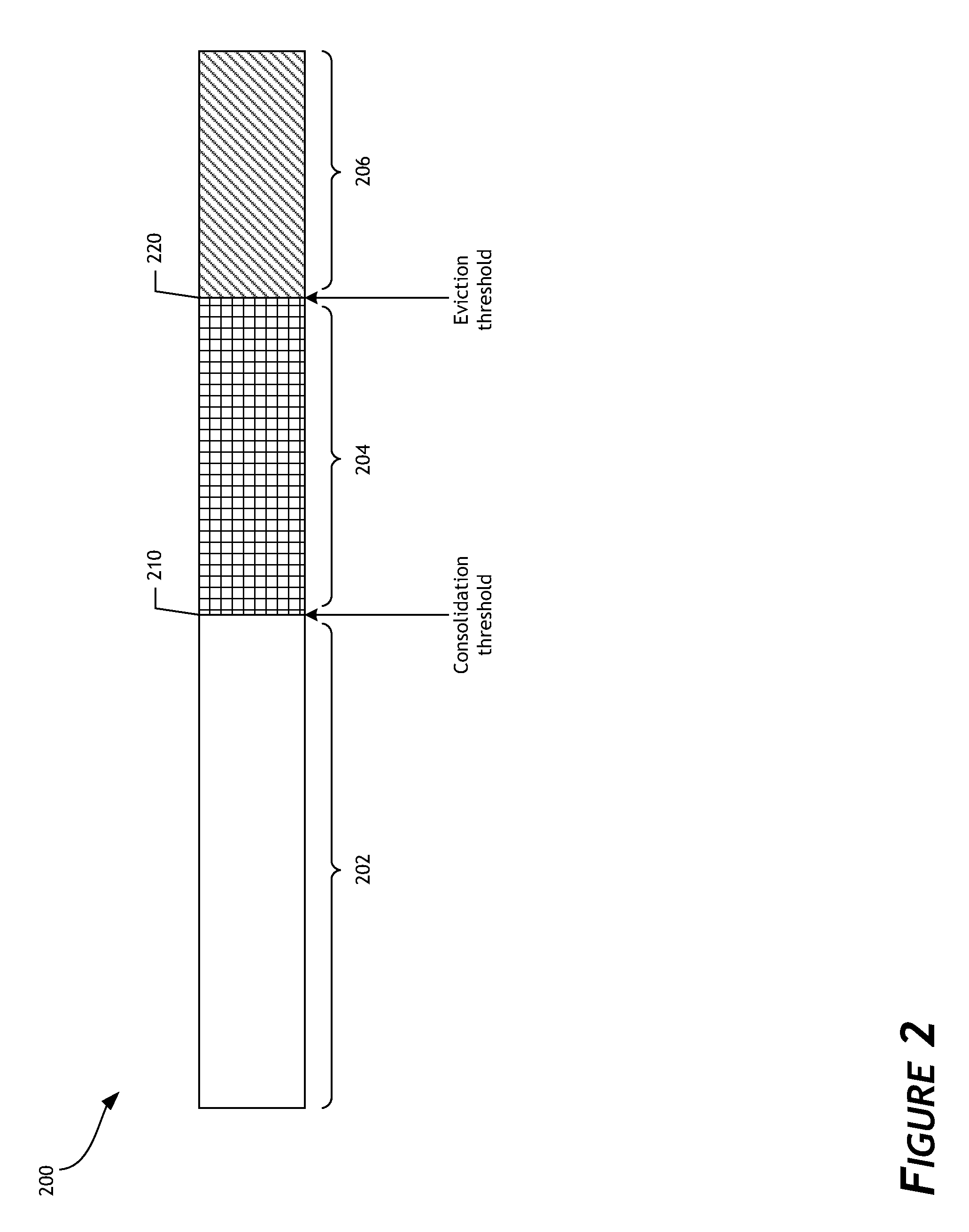
Priority-based garbage collection for data storage systems
ActiveUS20140181432A1Increased longevityImprove performanceMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationWrite amplificationWaste collection
Priority-based garbage collection utilizes attributes of data stored in the non-volatile memory array in order to improve efficiency of garbage collection and of the overall data storage system. A set of low priority data can be selectively evicted from a non-volatile memory array. This can, for example, reduce write amplification associated with garbage collection. Another set of low priority data can be regrouped or consolidated in a different region of the non-volatile memory array. In addition, flushing of data can be performed in order to enhance or optimize garbage collection. Performance and endurance can thereby be improved.
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
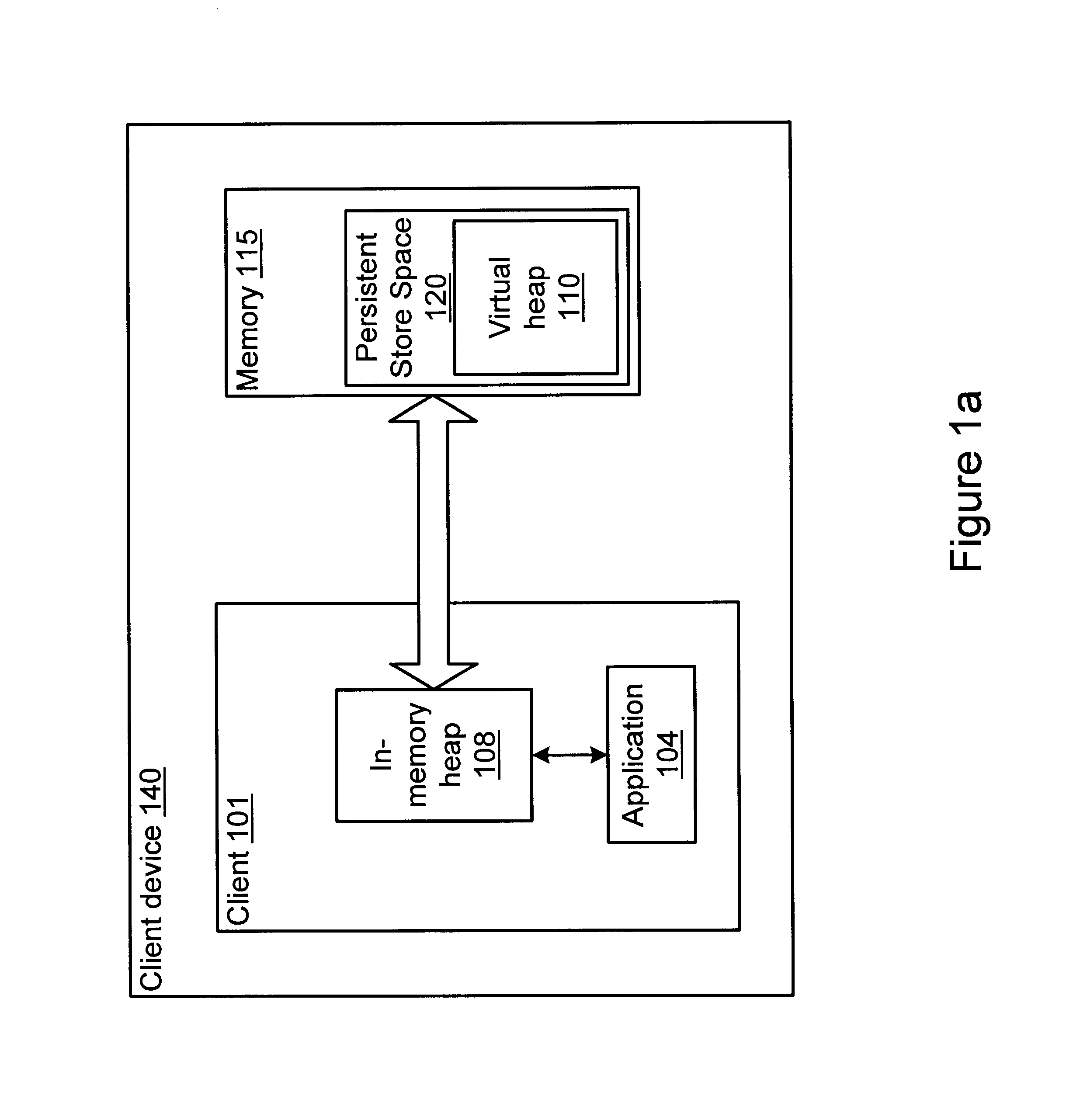
Garbage collector for a virtual heap
InactiveUS6865657B1Memory architecture accessing/allocationData processing applicationsObject copyingRefuse collection
A method and system for performing generational garbage collection on a virtual heap in a virtual machine is provided. The garbage collection method is suited for use with small consumer and appliance devices that have a small amount of memory and may be using flash devices as persistent storage. The garbage collection method may provide good performance where only a portion of the virtual heap may be cached in the physical heap. The virtual heap may use a single address space for both objects in the store and the in-memory heap. In one embodiment, a single garbage collector is run on the virtual heap address space. The garbage collection method may remove non-referenced objects from the virtual heap. The garbage collection method may also include a compaction phase to reduce or eliminate fragmentation, and to improve locality of objects within the virtual heap. In one embodiment, the garbage collector for the virtual heap may be implemented as a generational garbage collector using working sets in the virtual heap, where each generation is confined to a working set of the heap. The generational garbage collector may allow the flushing of changes after each garbage collection cycle for each working set region. Heap regions with different flushing policies may be used. An object nursery region without flushing where objects are initially created may be used. When a garbage collection cycle is run, objects truly referenced in the object nursery may be copied back into heap regions to be flushed, while short-lived objects no longer referenced may be deleted without flushing.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP +1
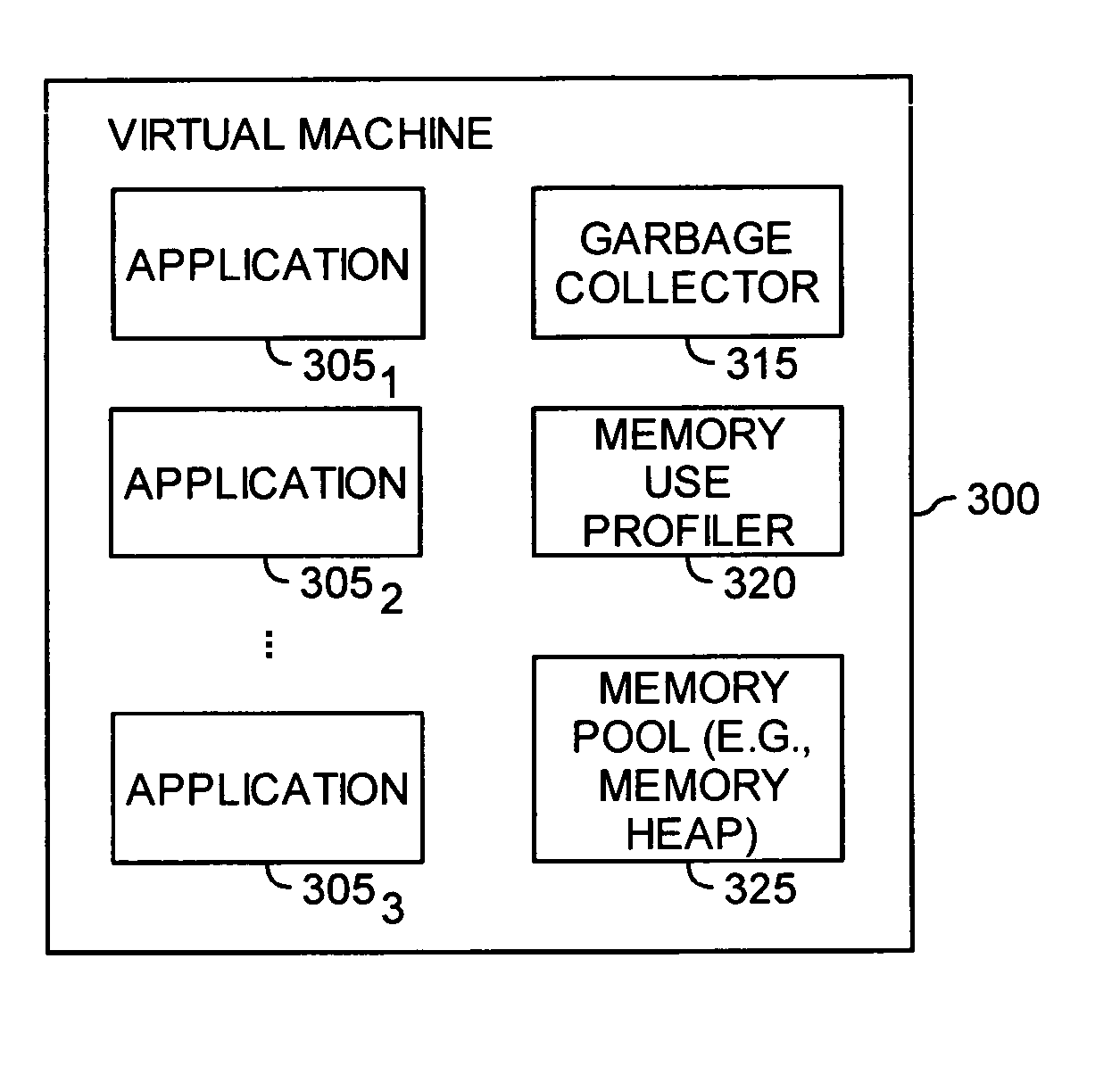
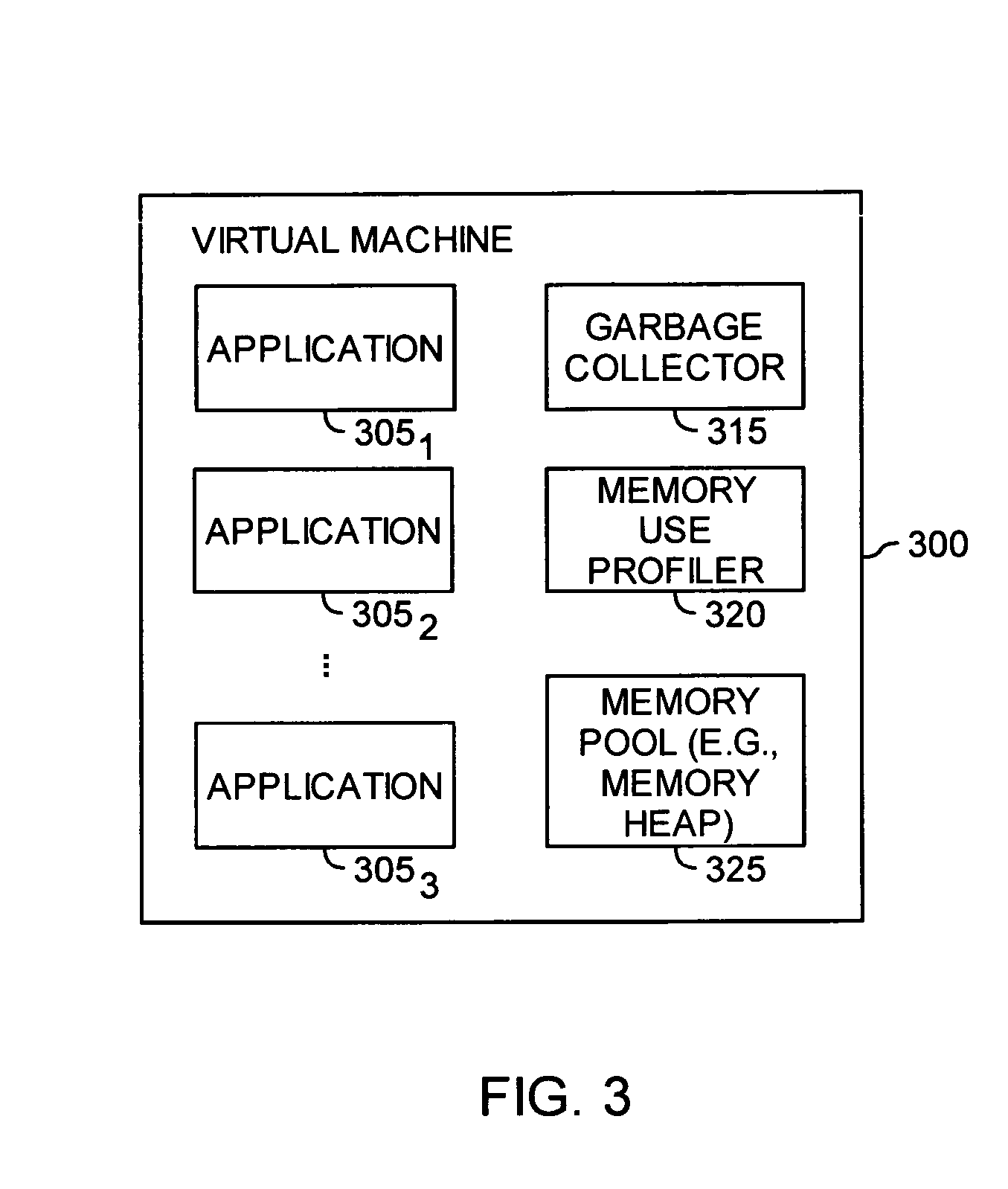
Automatic prediction of future out of memory exceptions in a garbage collected virtual machine
InactiveUS20070136402A1Special data processing applicationsMemory systemsOut of memoryParallel computing
A method, article of manufacture and apparatus for automatically predicting out of memory exceptions in garbage collected environments are disclosed. One embodiment provides a method of predicting out of memory events that includes monitoring an amount of memory available from a memory pool during a plurality of garbage collection cycles. A memory usage profile may be generated on the basis of the monitored amount of memory available, and then used to predict whether an out of memory exception is likely to occur.
Owner:IBM CORP
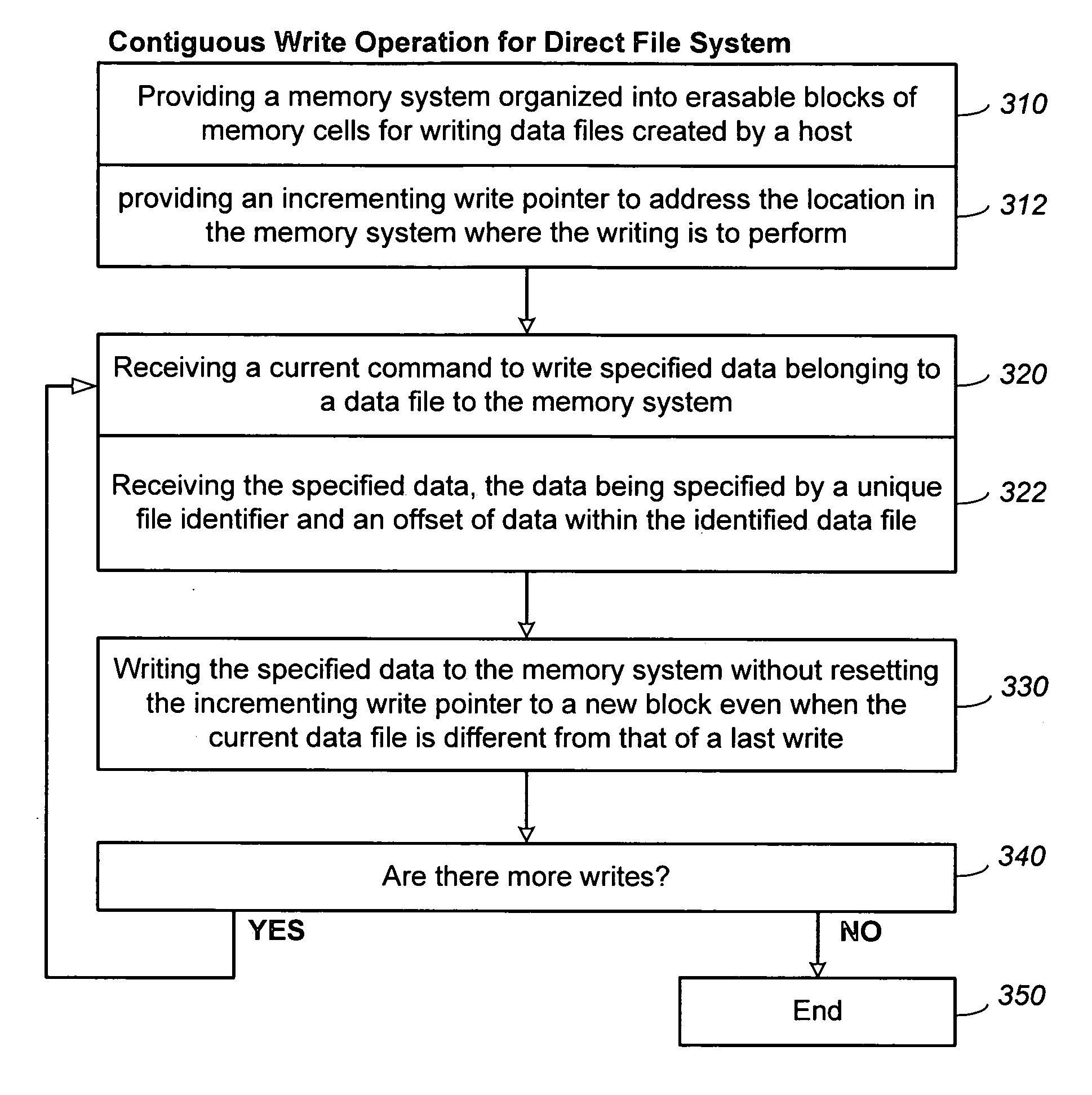
Methods for adaptive file data handling in non-volatile memories with a directly mapped file storage system
InactiveUS20070143561A1Promote high performanceImprove performanceMemory systemsData compressionWaste collection
In a memory system with a file storage system, an optimal file handling scheme is adaptively selected from a group thereof based on the attributes of the file being handled. The file attributes may be obtained from a host or derived from a history of the file had with the memory system. In one embodiment, a scheme for allocating memory locations for a write operation is dependent on an estimated size of the file to be written. In another embodiment, a scheme for allocating memory locations for a relocation operation, such as for garbage collection or data compaction, is dependent on an estimated access frequency of the file in question. In this way, the optimal handling scheme can be used for the particular file at any time.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
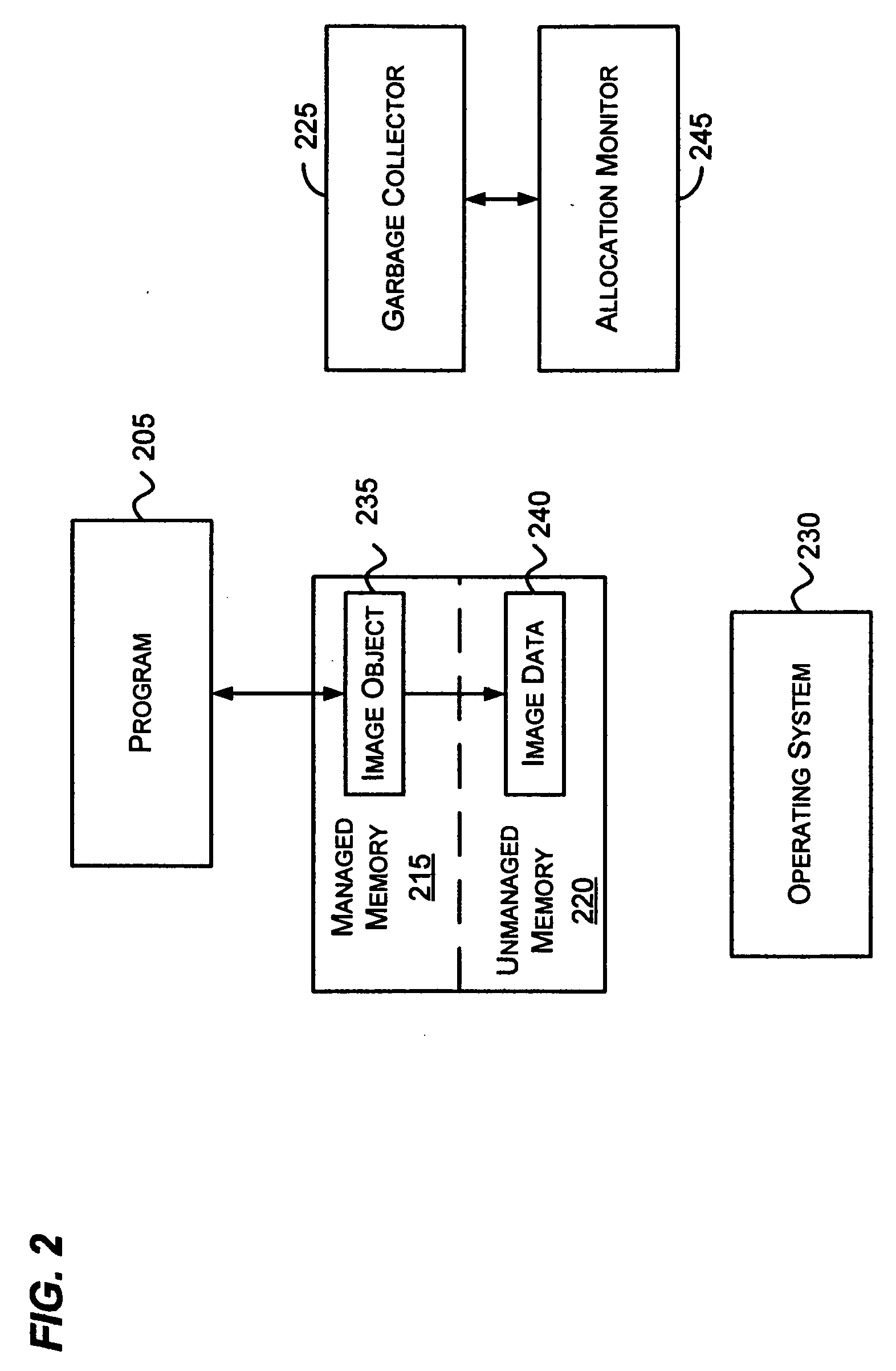
Implementation for collecting unmanaged memory
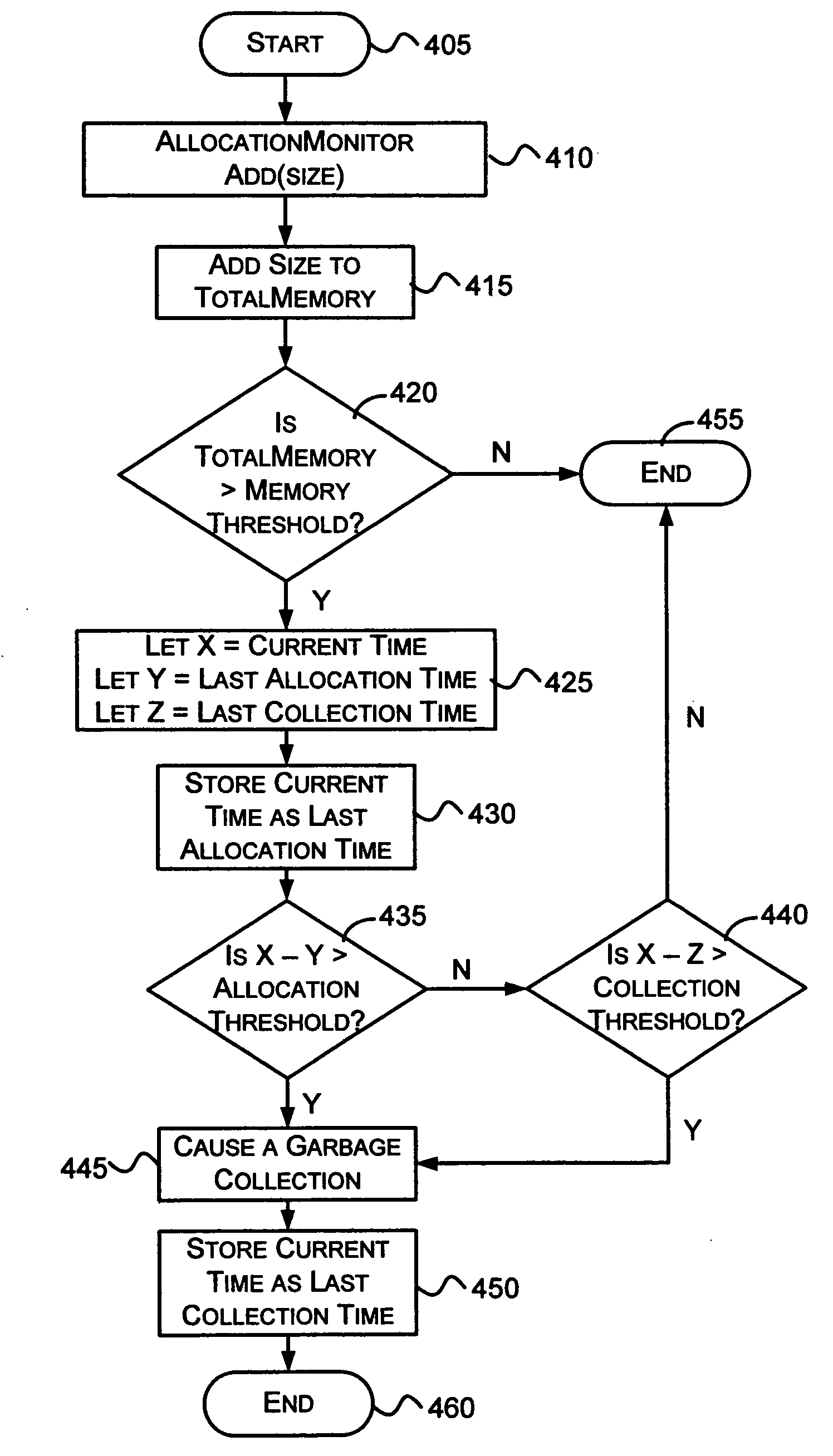
InactiveUS20060259528A1Data processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsParallel computingWaste collection
A method and system for garbage collecting managed and unmanaged memory that is no longer referenced. The time between allocations is compared with a threshold to determine if the garbage collector needs to collect unused memory. Unmanaged memory referenced by objects in the unused managed memory may be freed during the collection.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method for predicting and avoiding danger in execution environment
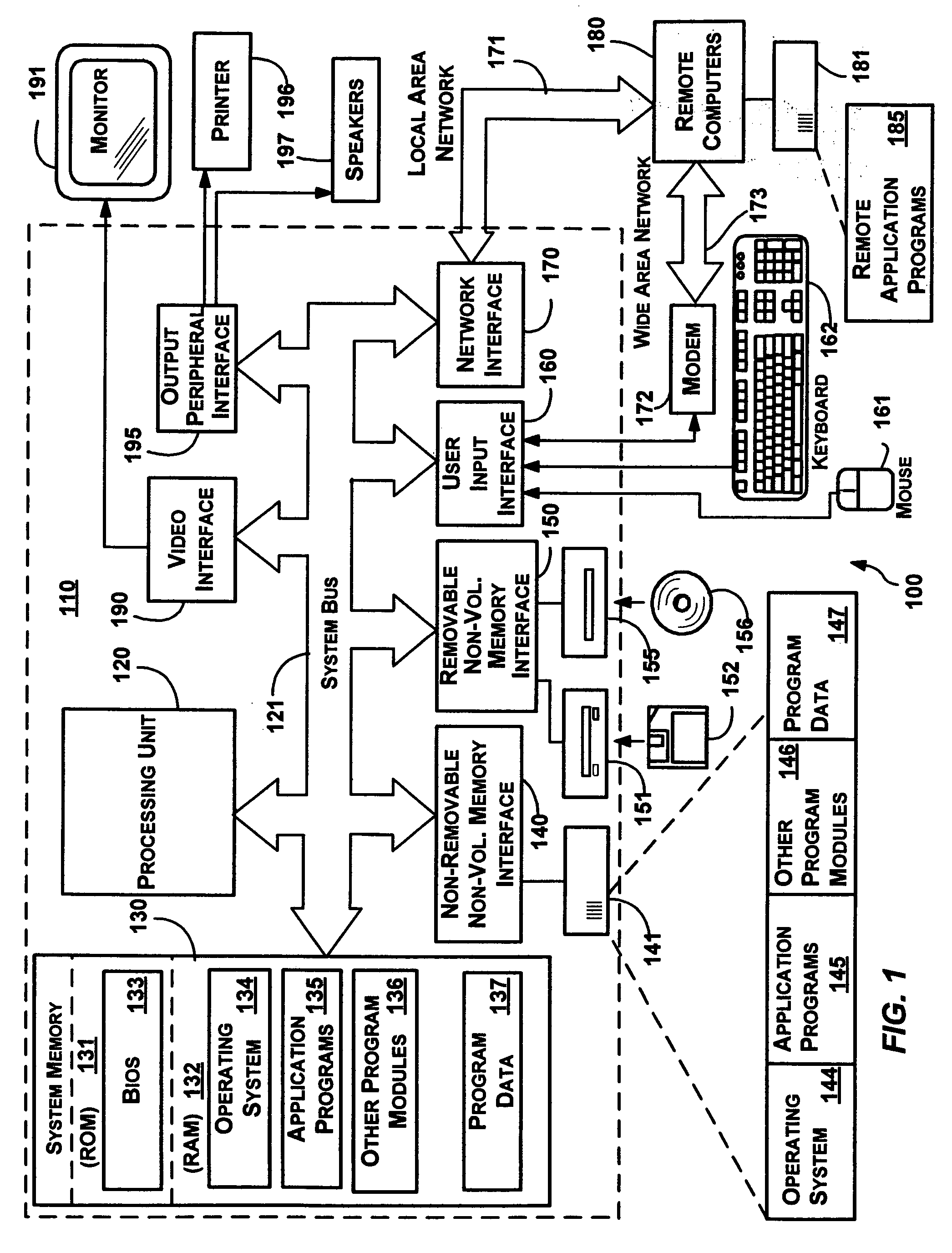
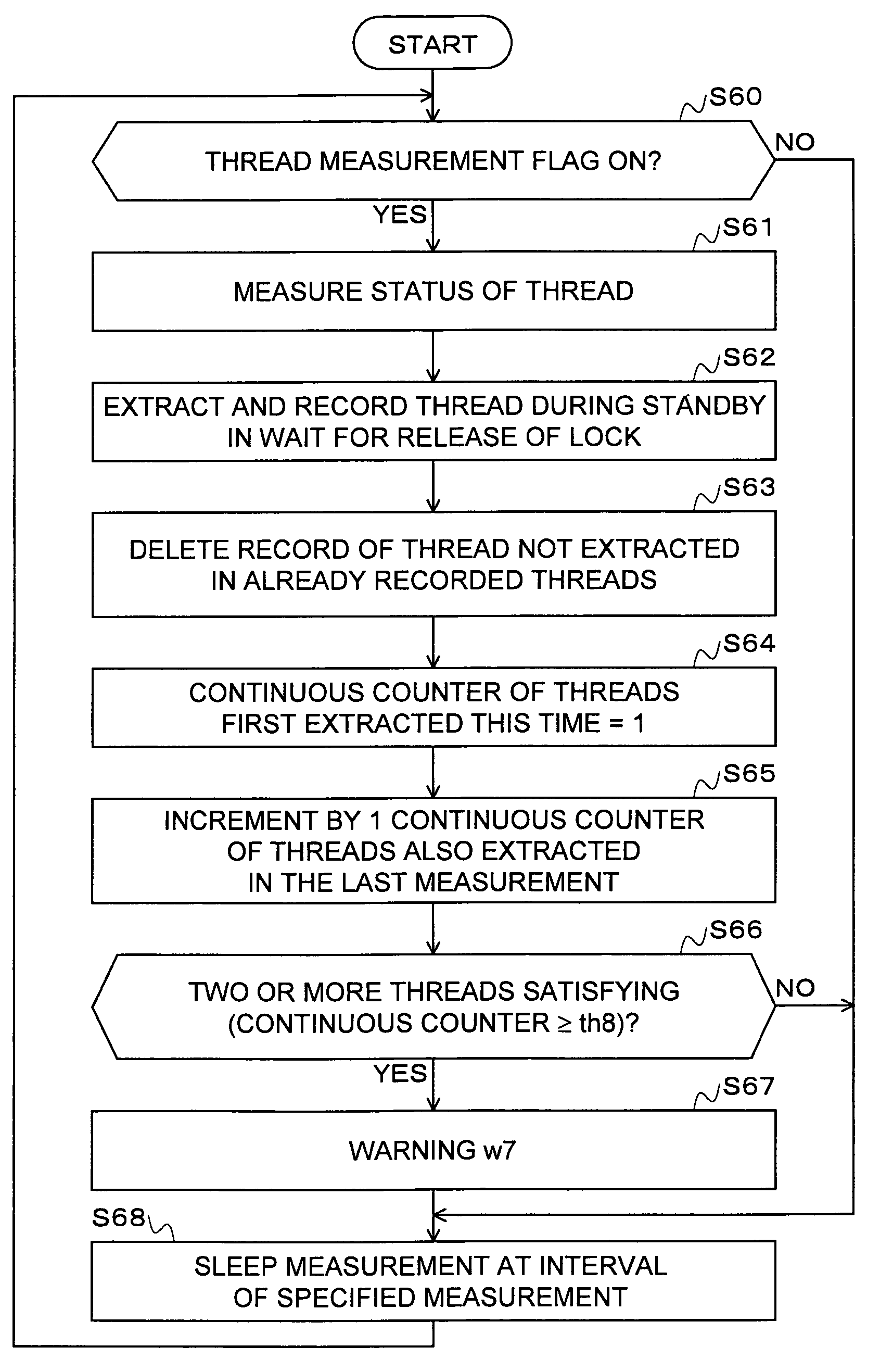
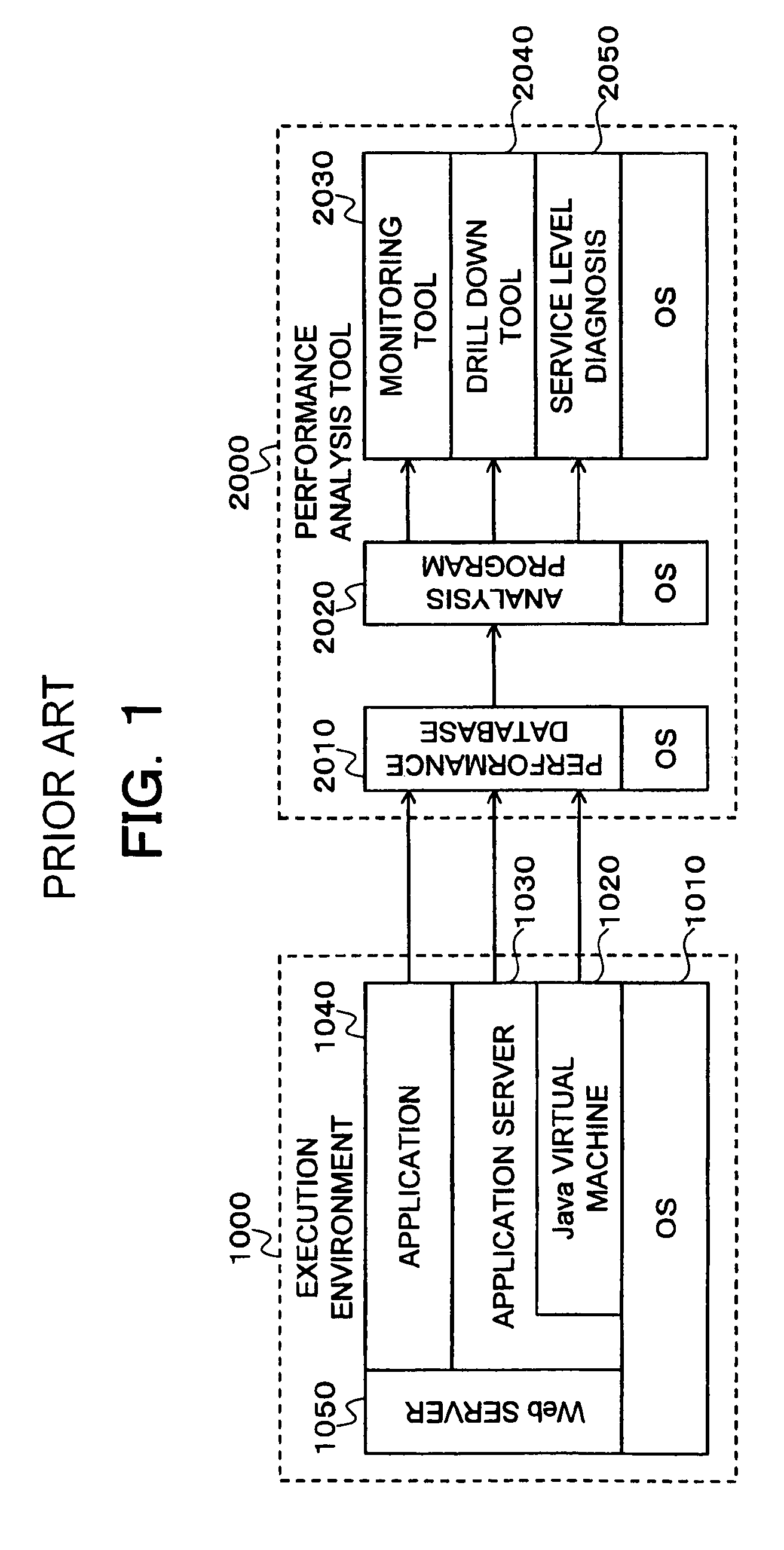
InactiveUS7516292B2Reduce loadShort timeData processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationApplication serverParallel computing
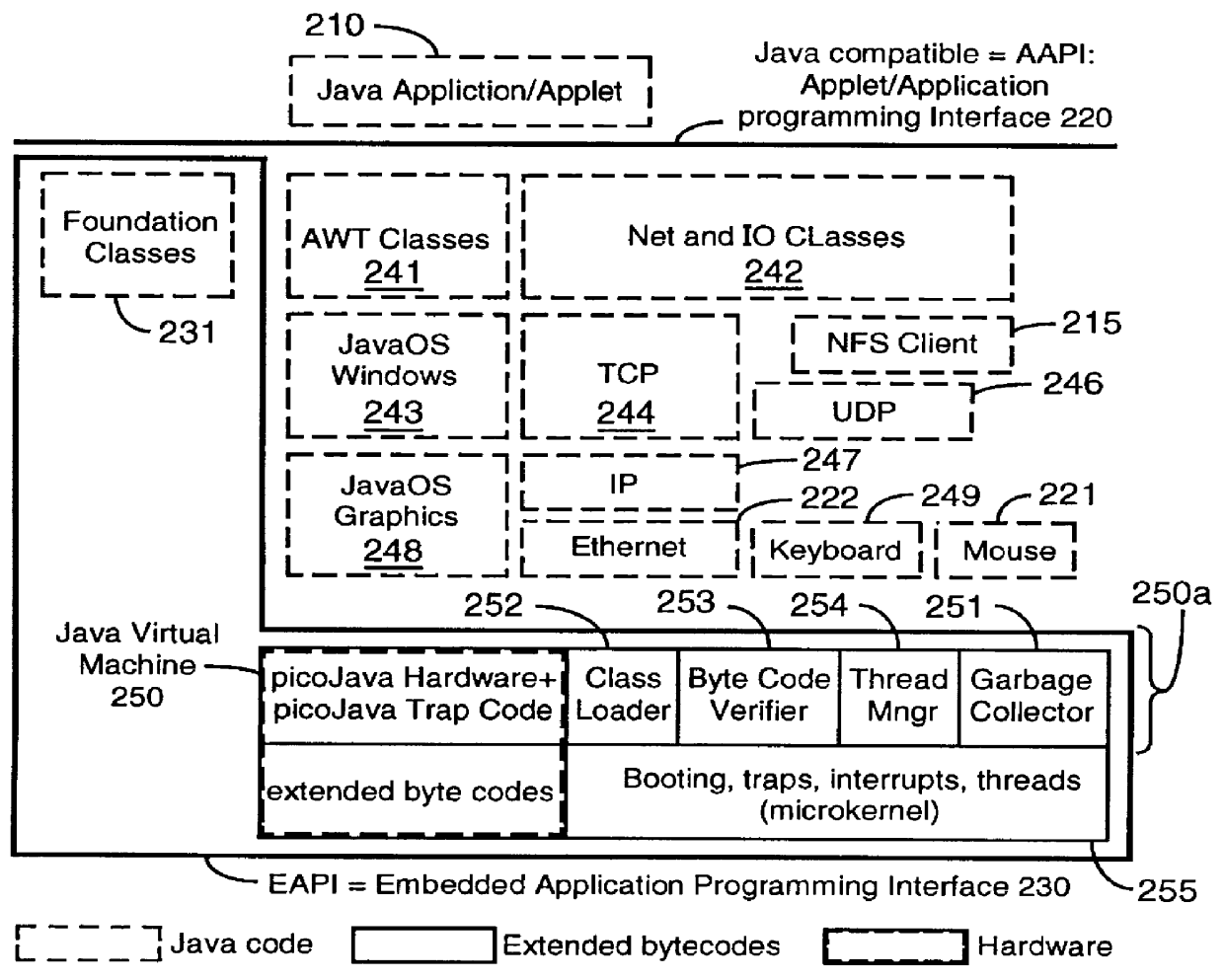
Measurement / analysis unit in a Java virtual machine has the function of measuring data when an event of garbage collection occurs, and the function of periodically measuring data. The measurement / analysis unit analyzes the measured data and predicts a danger of a memory shortage, and predicts a danger using an algorithm depending on the type of garbage collection used by the Java virtual machine. An application server is notified of a warning of the predicted danger of a memory shortage by an analysis result notification means by an inter-process communication, or the like. The measurement / analysis unit calculates a memory capacity required to avoid the predicted danger of a memory shortage, and the calculated memory capacity is transmitted to the application server by the analysis result notification means by an inter-process communication, or the like in the same way as the warning.
Owner:FUJITSU LTD
Method and apparatus for efficient virtual memory management
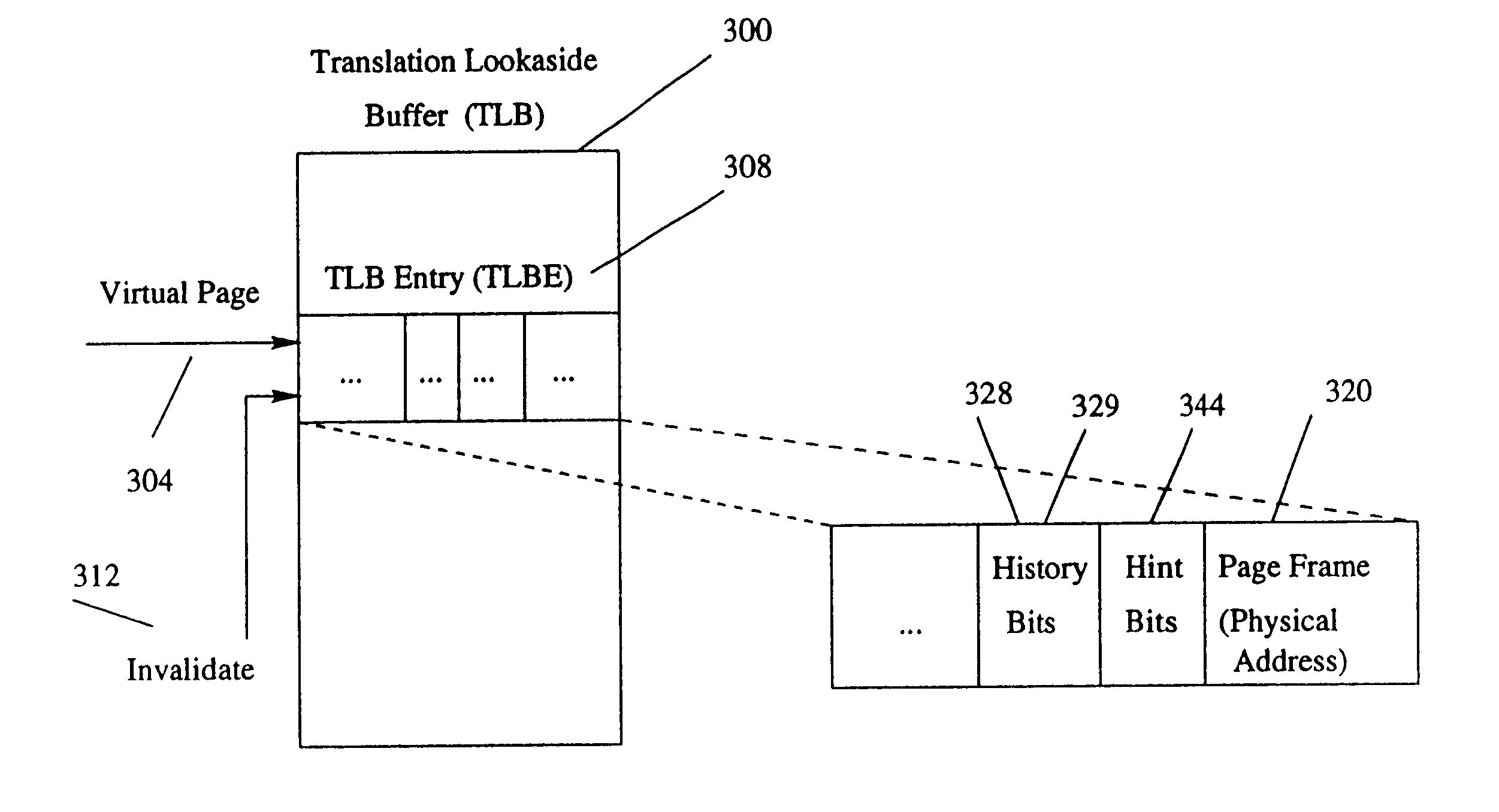
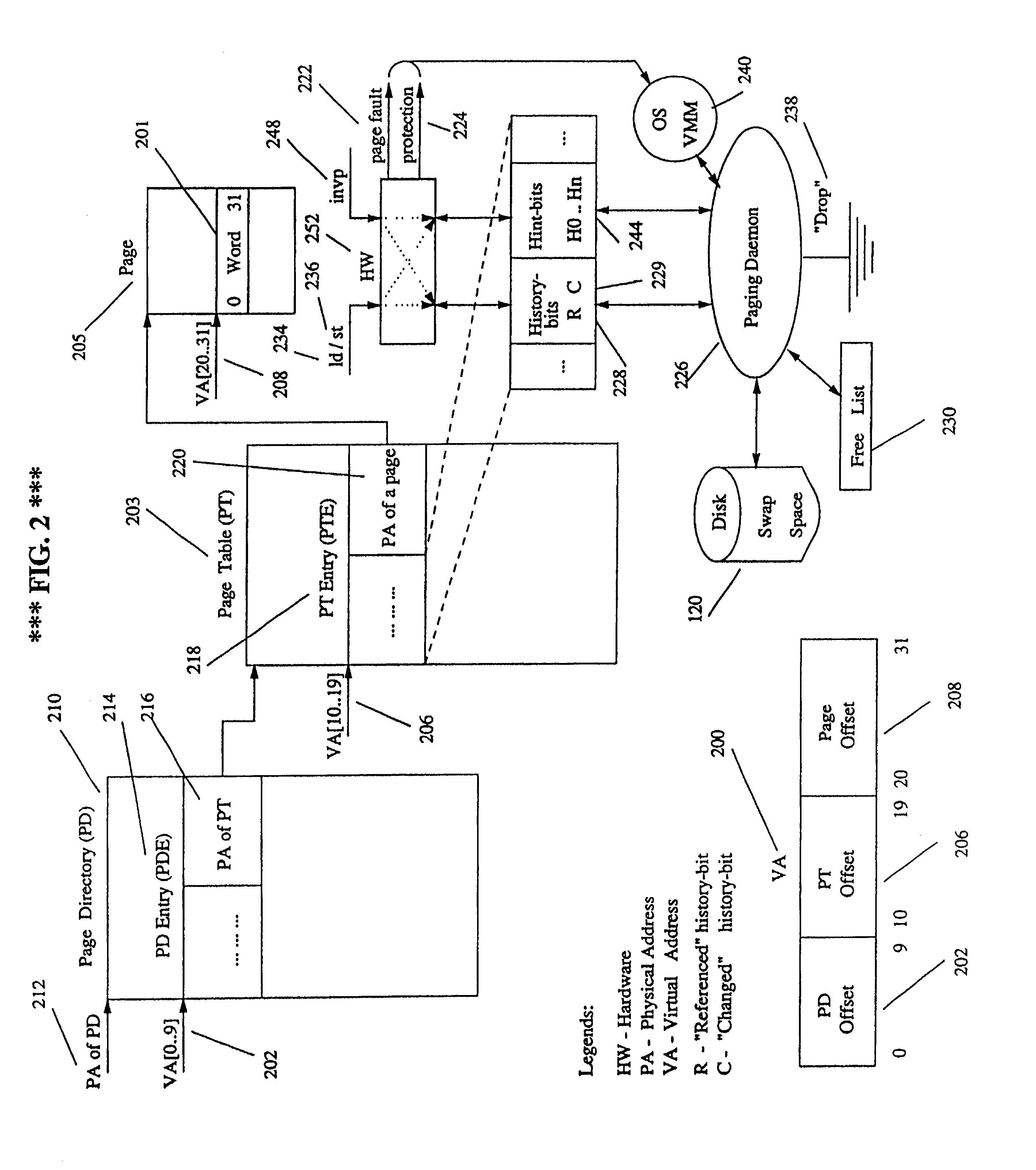
InactiveUS6886085B1Reduce the amount of dataReduce the number of dataMemory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationWaste collectionVirtual memory management
A method and an apparatus that improves virtual memory management. The proposed method and apparatus provides an application with an efficient channel for communicating information about future behavior of an application with respect to the use of memory and other resources to the OS, a paging daemon, and other system software. The state of hint bits, which are integrated into page table entries and TLB entries and are used for communicating information to the OS, can be changed explicitly with a special instruction or implicitly as a result of referencing the associated page. The latter is useful for canceling hints. The method and apparatus enables memory allocators, garbage collectors, and compilers (such as those used by the Java platform) to use a page-aligned heap and a page-aligned stack to assist the OS in effective management of memory resources. This mechanism can also be used in other system software.
Owner:IBM CORP
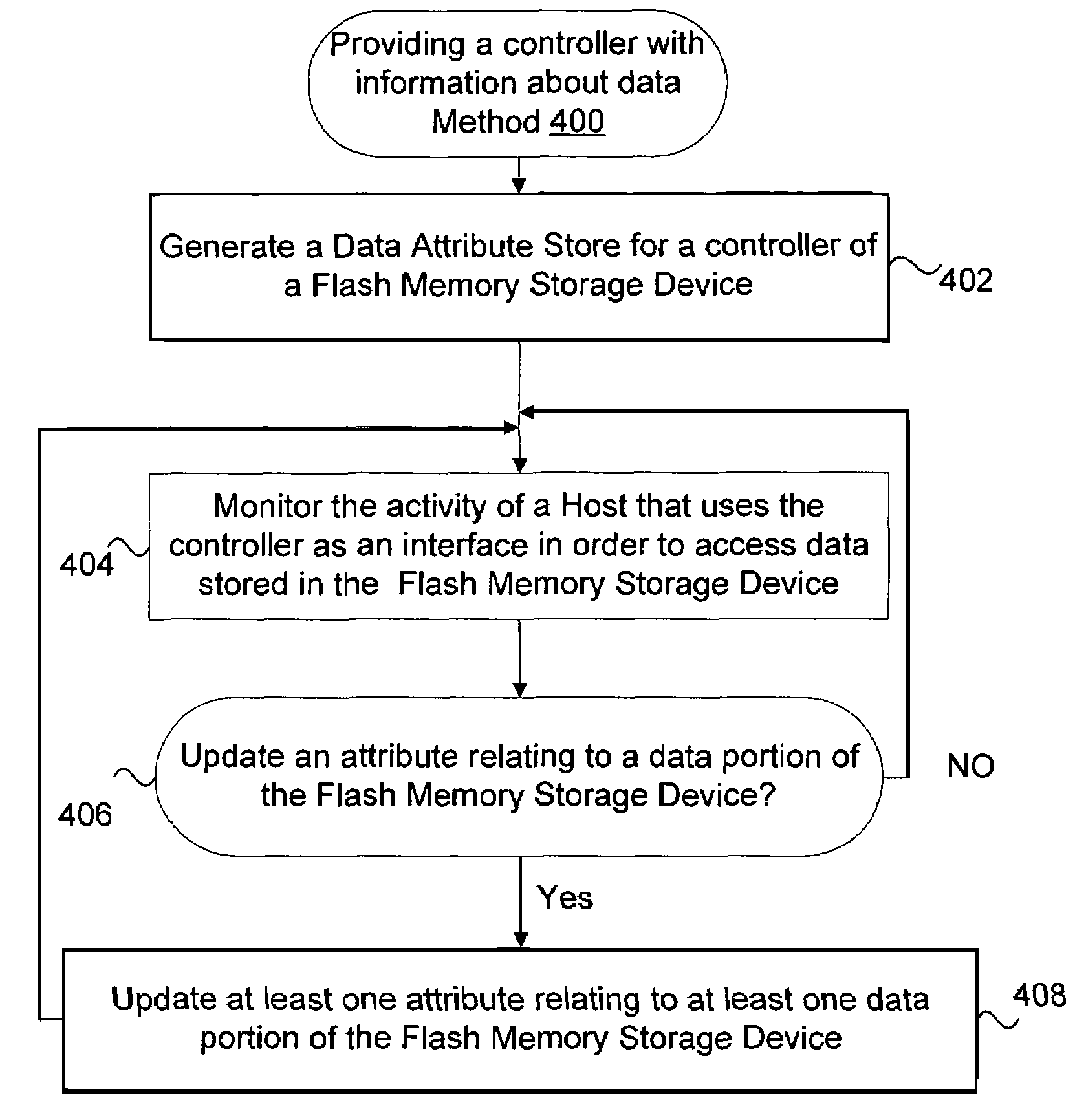
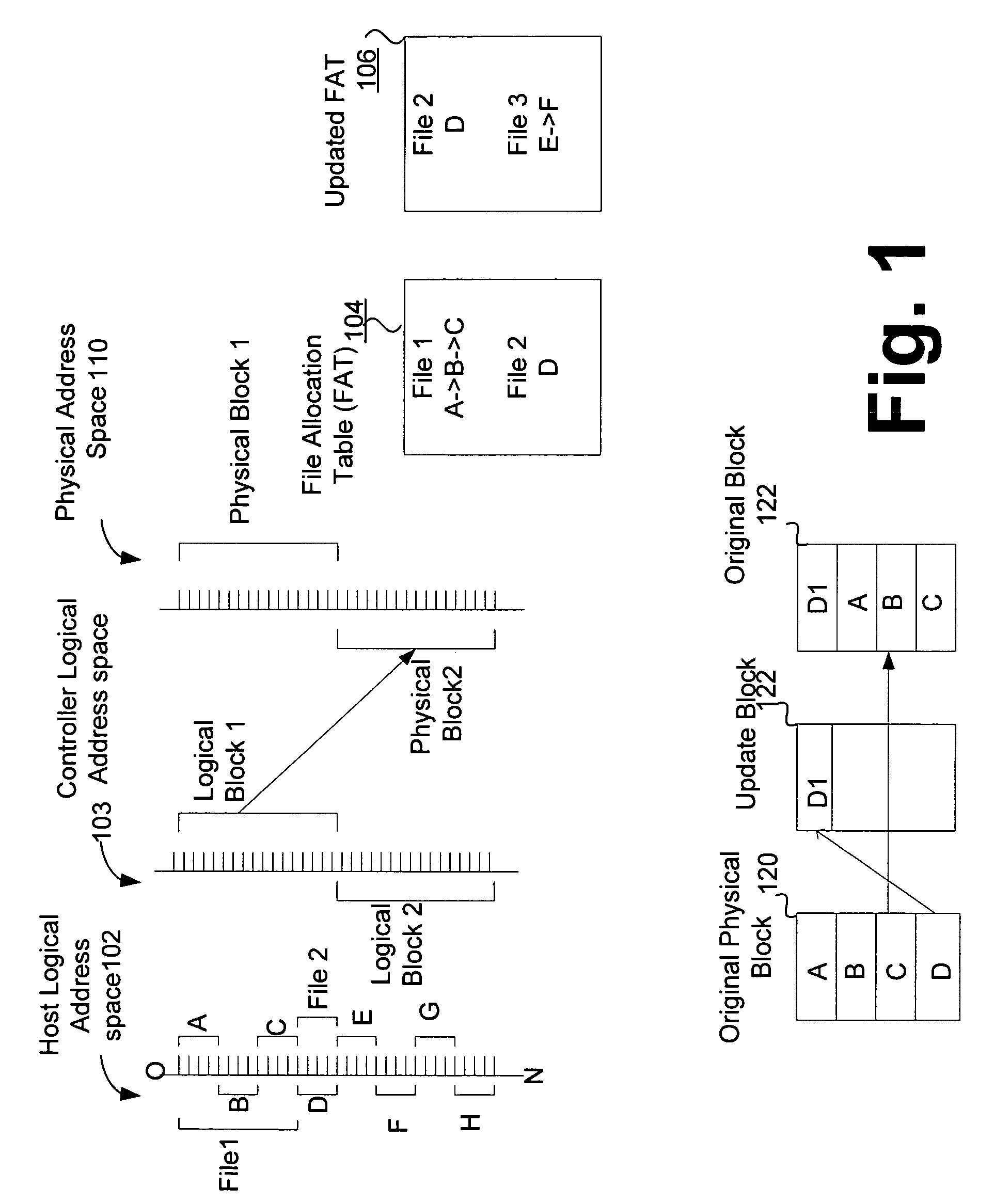
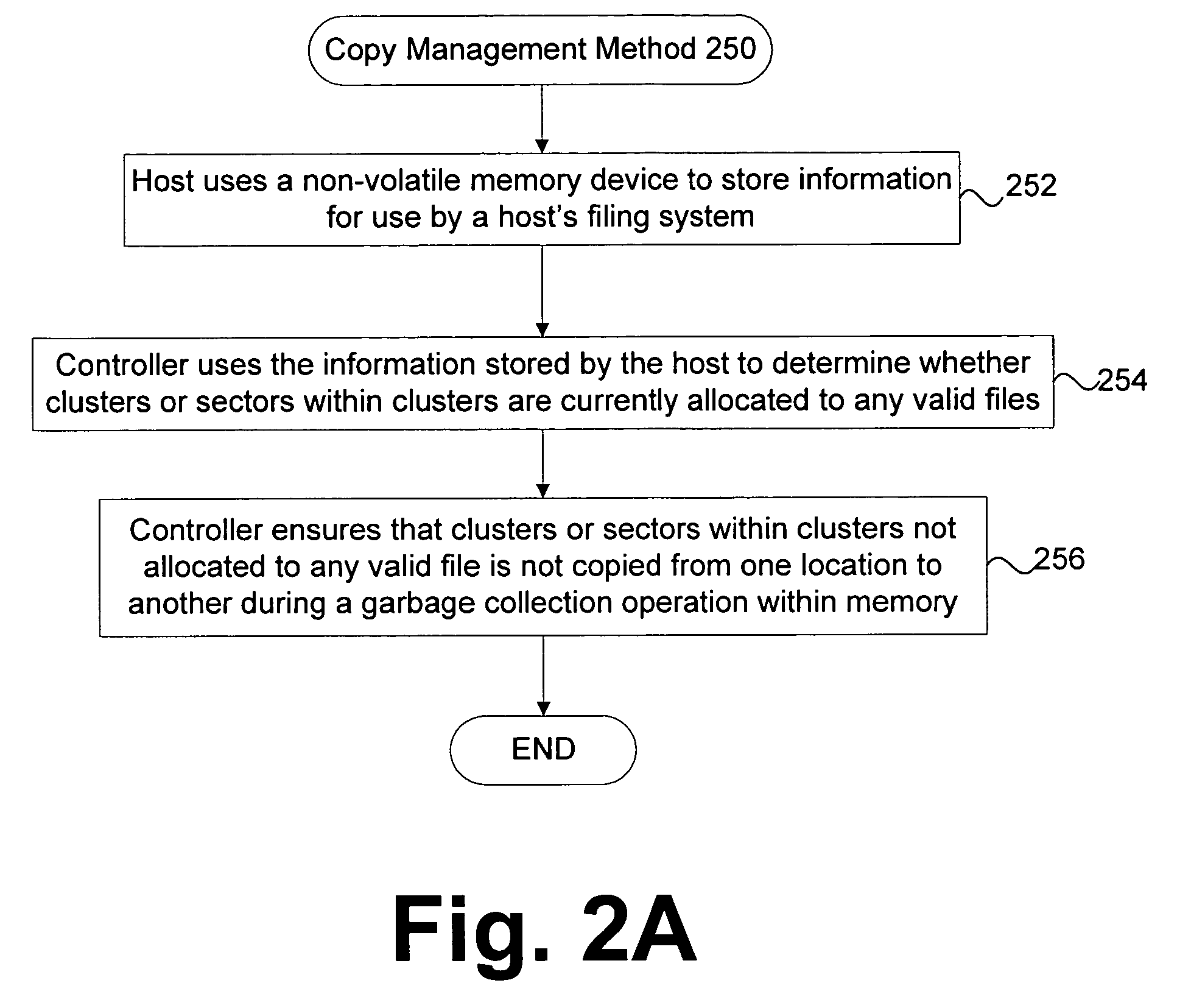
Method and apparatus for maintaining data on non-volatile memory systems
ActiveUS7395384B2Improve system performanceEasy to manageMemory architecture accessing/allocationData processing applicationsWaste collectionCopying
Techniques for managing data in a non-volatile memory system (e.g., Flash Memory) are disclosed. A controller can use information relating to a host's filing system, which is stored by the host on non-volatile memory, to determine if one or more clusters (or sectors with clusters) are currently allocated. The controller can use the information relating to the host's filing system to ensure that one or more clusters (or one or more sectors within a cluster) are not copied from one location to another location in the memory during a garbage collection cycle. As a result, some unnecessary operations (e.g., copying data) which are conventionally performed can be avoided and system performance can be enhanced.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
System and method for computer automatic memory management
ActiveUS20070203960A1Ensure correct executionEfficient memory usageData processing applicationsSpecial data processing applicationsImmediate releaseWaste collection
The present invention is a method and system of automatic memory management (garbage collection). An application automatically marks up objects referenced from the “extended root set”. At garbage collection, the system starts traversal from the marked-up objects. It can conduct accurate garbage collection in a non-GC language, such as C++. It provides a deterministic reclamation feature. An object and its resources are released immediately when the last reference is dropped. Application codes automatically become entirely GC-safe and interruptible. A concurrent collector can be pause-less and with predictable worst-case latency of micro-second level. Memory usage is efficient and the cost of reference counting is significantly reduced.
Owner:GUO MINGNAN
Method for combining card marking with remembered sets for old area of a memory heap
InactiveUS6148310AData processing applicationsMemory adressing/allocation/relocationWaste collectionMemory object
A system for garbage collection of memory objects in a memory heap. The system includes memory heap that is partitioned into respective old and young areas. The old area is partitioned into cars and is further associated with card markings and remembered sets data structures. The card markings include for each card, a card time stamp that represents the time that the card was updated. The car includes, for each car, a car time entry stamp that represents the time the remembered set of the car was updated. The system further includes a processor communicating with the memory, and being capable of identifying all cards that were updated later than the remembered set of a selected car. In response to the event, it performs identifying change in pointers that refer from the card to a memory object in the selected car and in response to identified change in pointers, updating the remembered set of the car with the identified pointers. The process is further capable of updating the car time stamp of the selected car.
Owner:IBM CORP
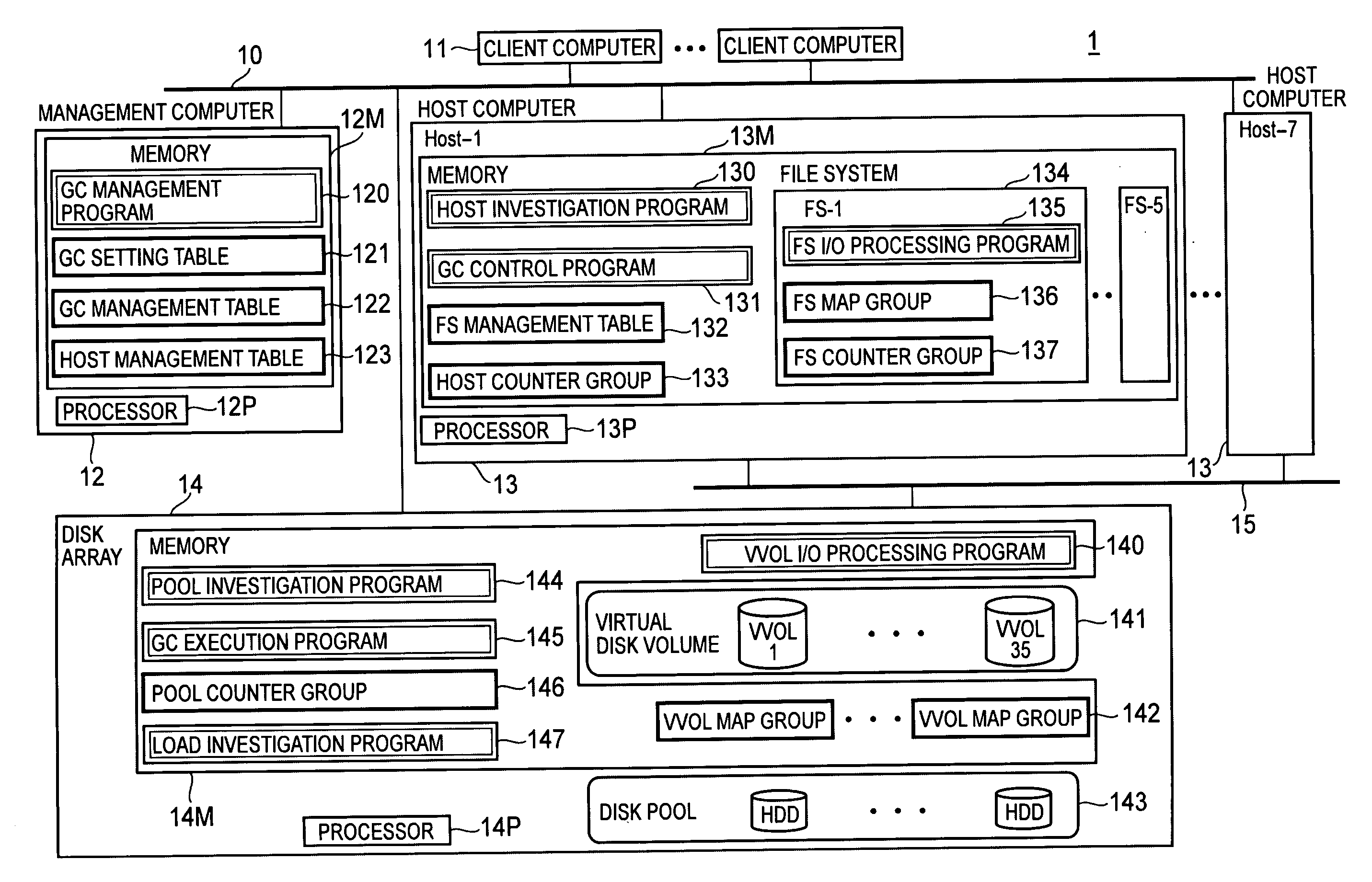
Computer system and garbage collection method of disk space
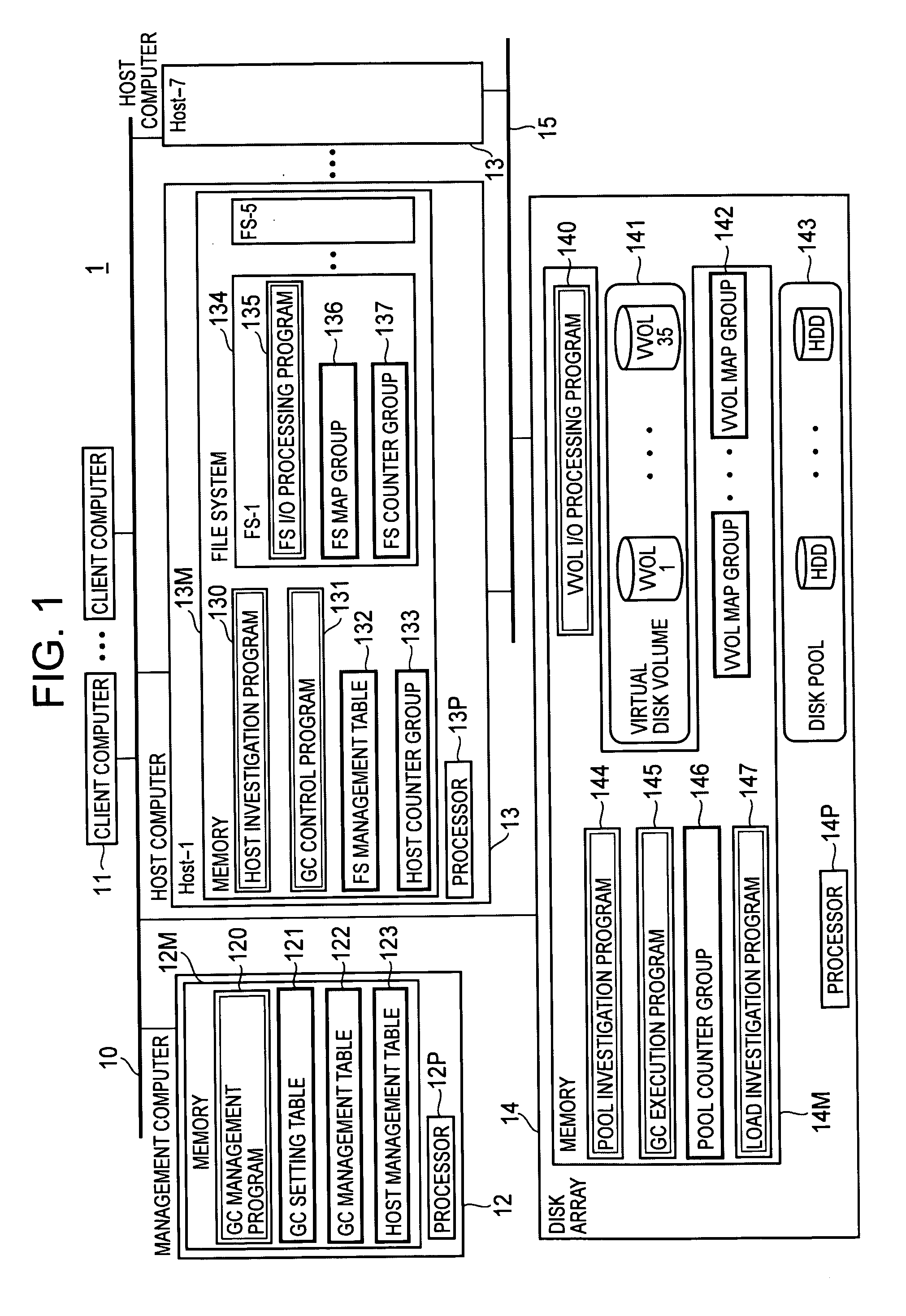
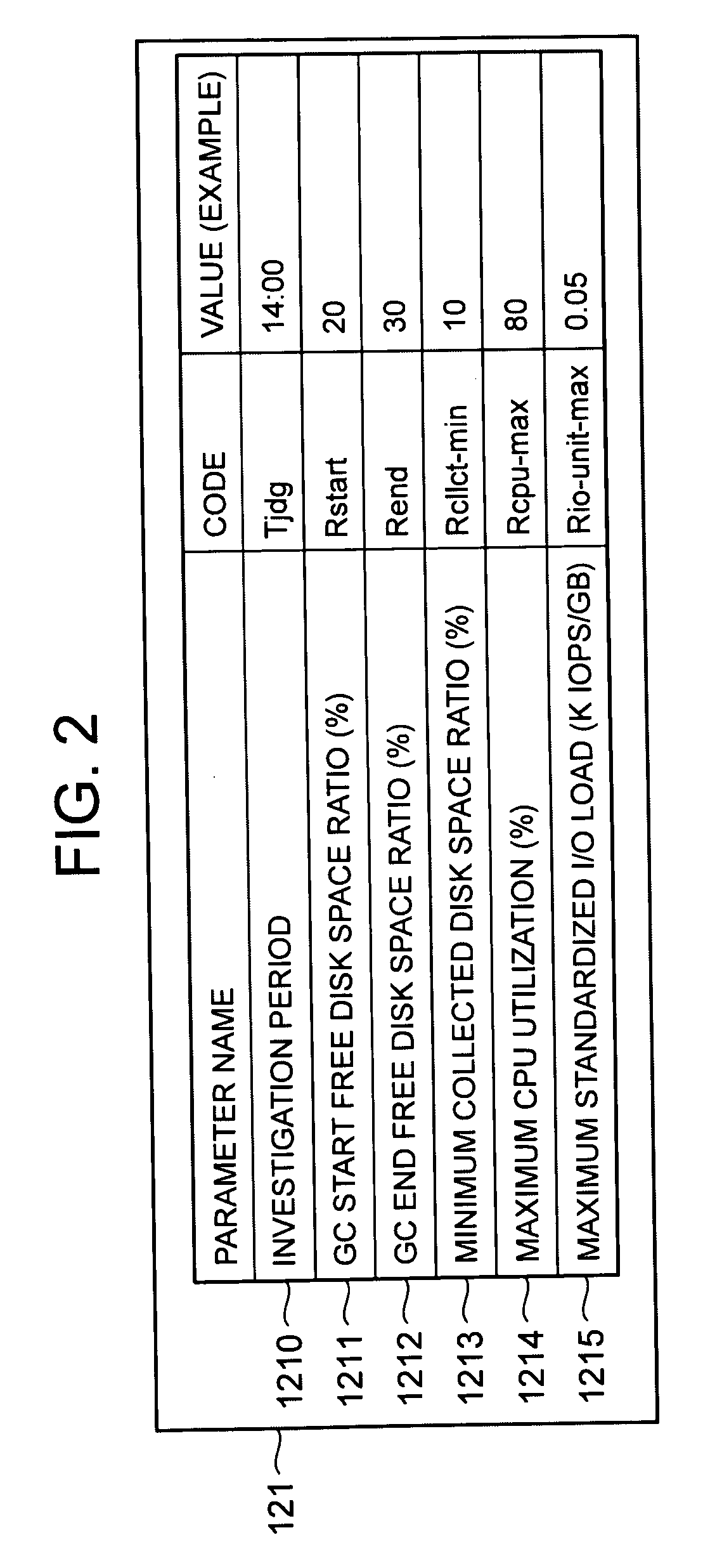
InactiveUS20090198946A1Avoid processing inefficienciesMemory systemsInput/output processes for data processingComputerized systemWaste collection
A processor of a management computer acquires the free disk space amount of a disk pool, acquires the invalid disk space amount from a plurality of host computers, determines a host computer to which the instruction for the physical disk space collection is issued on the basis of the invalid disk space amount, and judges that the free disk space amount is smaller than a predetermined threshold value before transmitting a GC control request to the determined host computer; another processor generates and transmits invalid disk space position information indicating the position of the invalid disk space in a virtual volume in cases where a host investigation request is received; and the other processor collects the physical disk space of a physical disk allocated to the storage disk space of the virtual volume in the disk pool.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Tracking and Handling of Super-Hot Data in Non-Volatile Memory Systems
ActiveUS20130024609A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationHigh probabilityParallel computing
A non-volatile memory organized into flash erasable blocks sorts units of data according to a temperature assigned to each unit of data, where a higher temperature indicates a higher probability that the unit of data will suffer subsequent rewrites due to garbage collection operations. The units of data either come from a host write or from a relocation operation. Among the units more likely to suffer subsequent rewrites, a smaller subset of data super-hot is determined. These super-hot data are then maintained in a dedicated portion of the memory, such as a resident binary zone in a memory system with both binary and MLC portions.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com