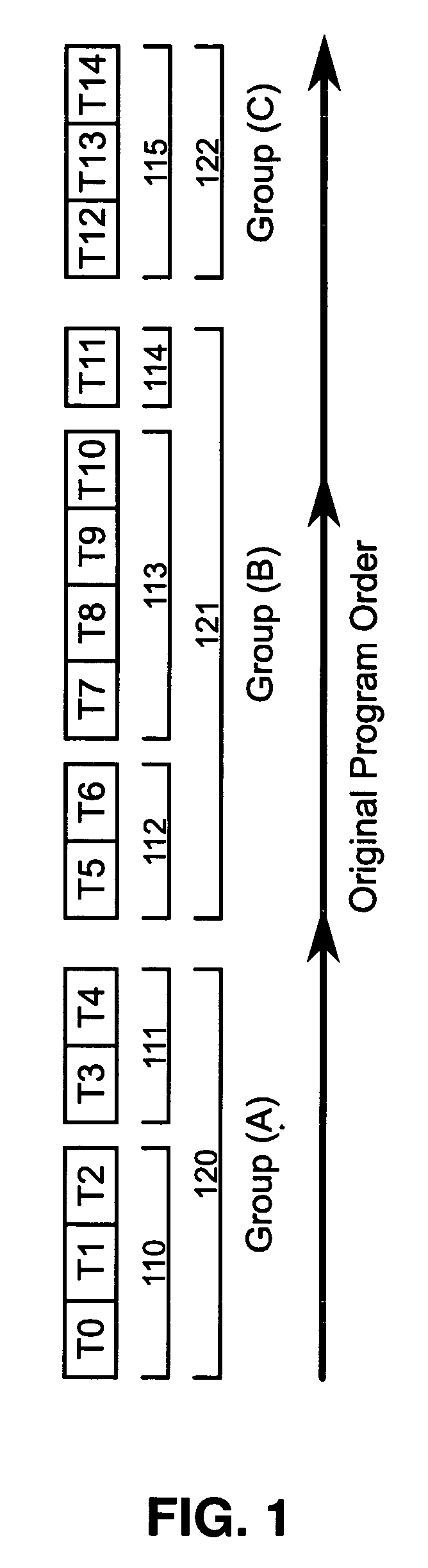
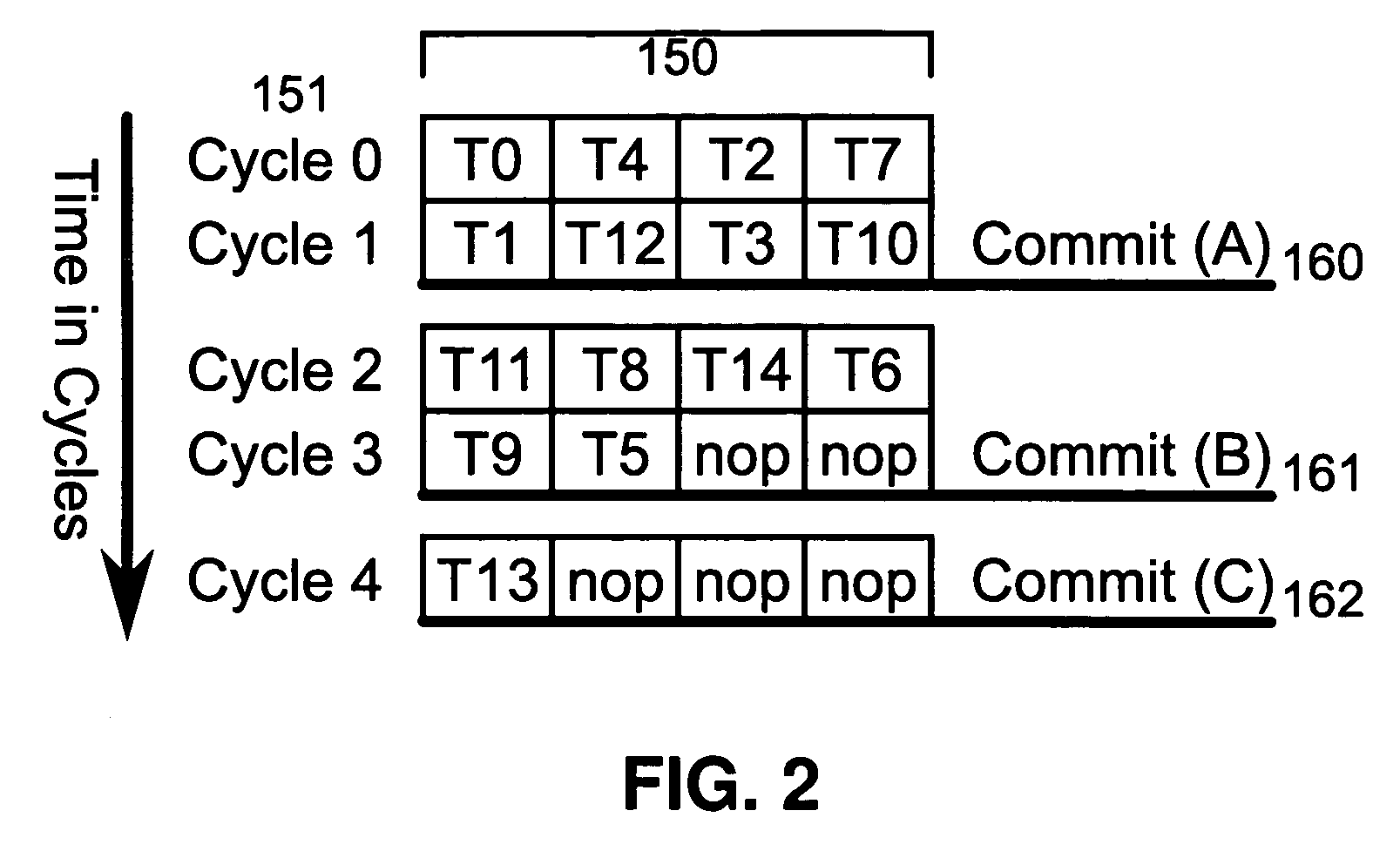
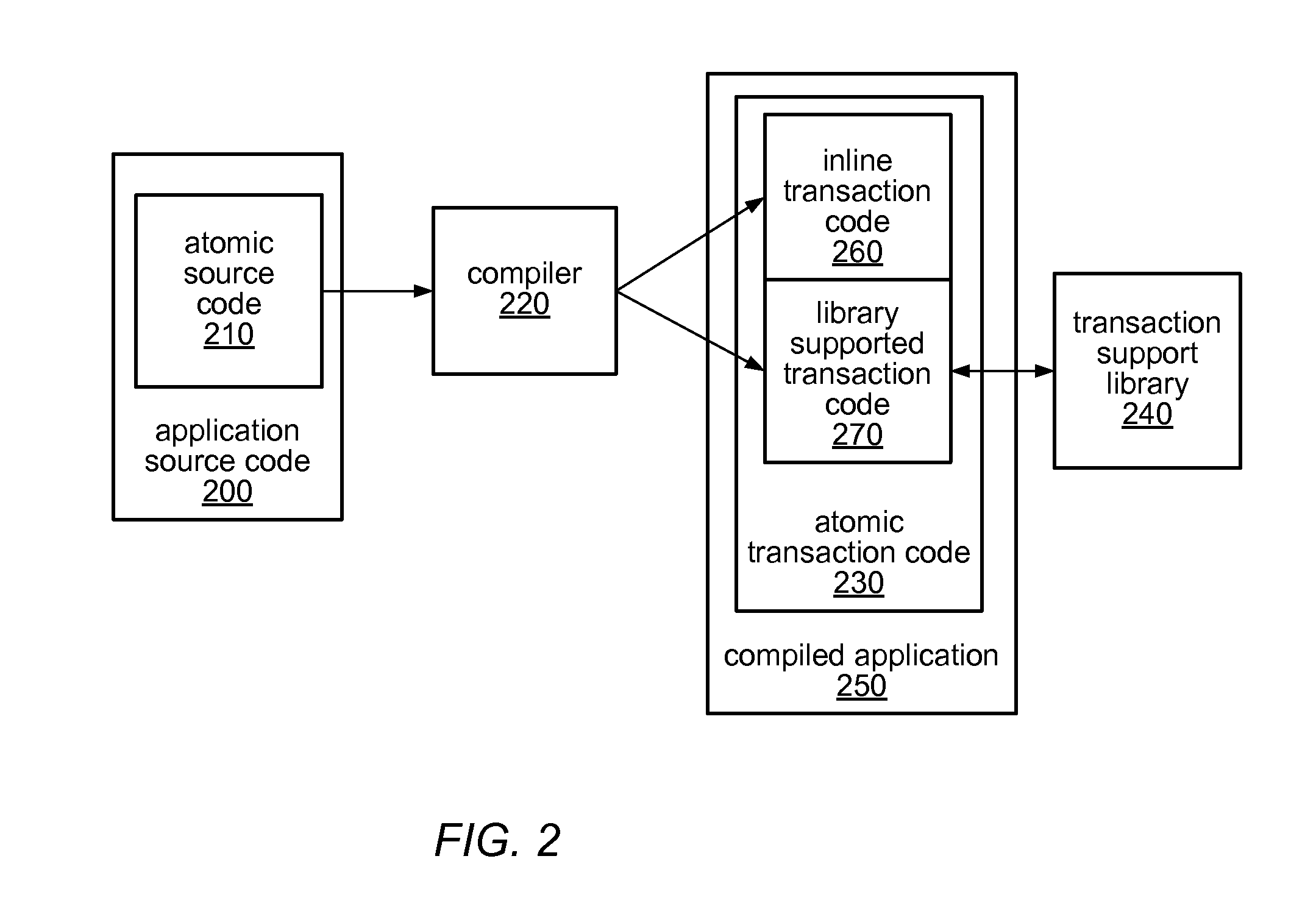
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
384 results about "Atomic operations" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Atomic operations are the foundation on which other synchronization methods are built, they provide instructions that execute atomically, without interruption. Atomic operators are indivisible instructions. The atomic increment can read and increment a variable by one in a single indivisible and uninterruptible step.
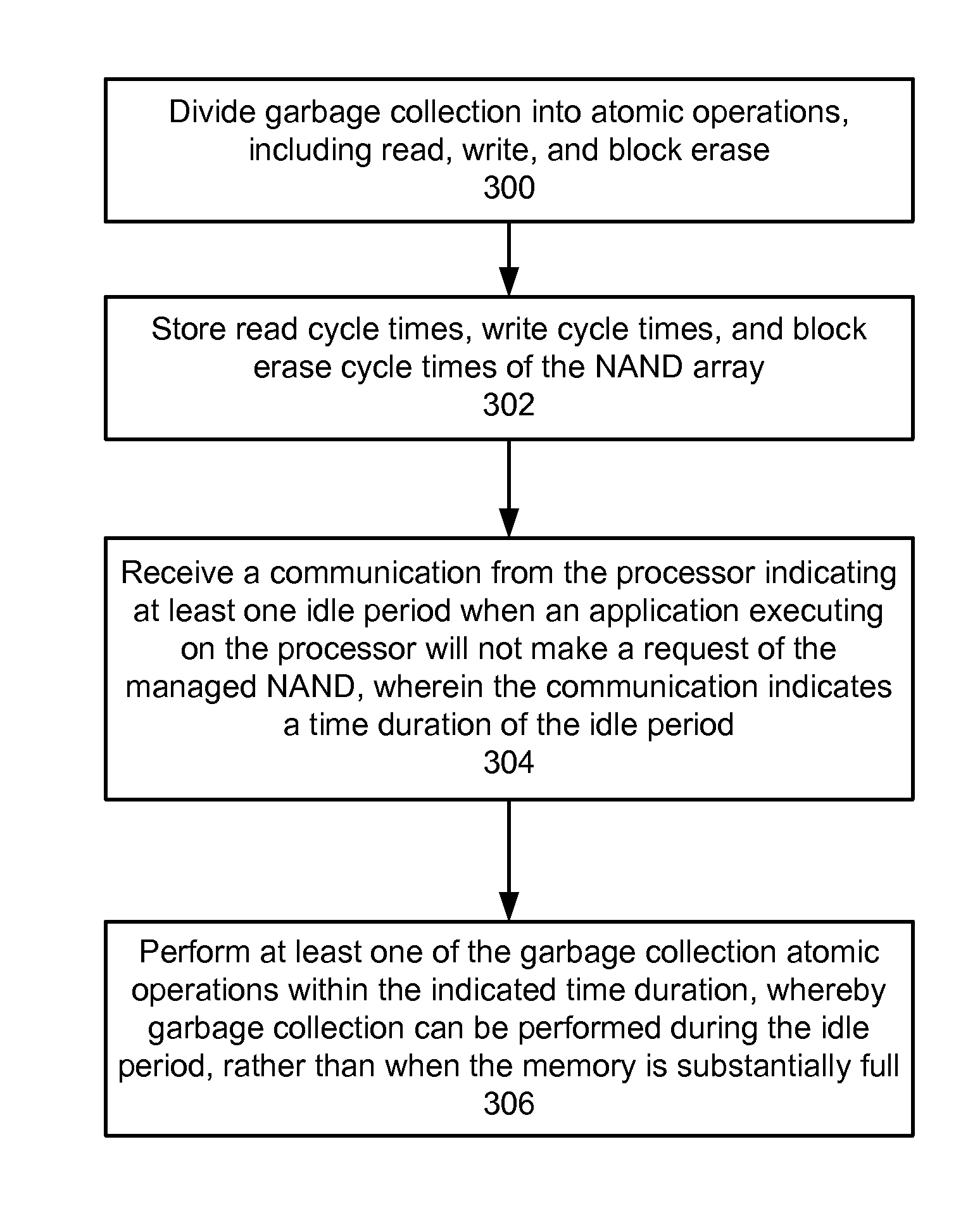
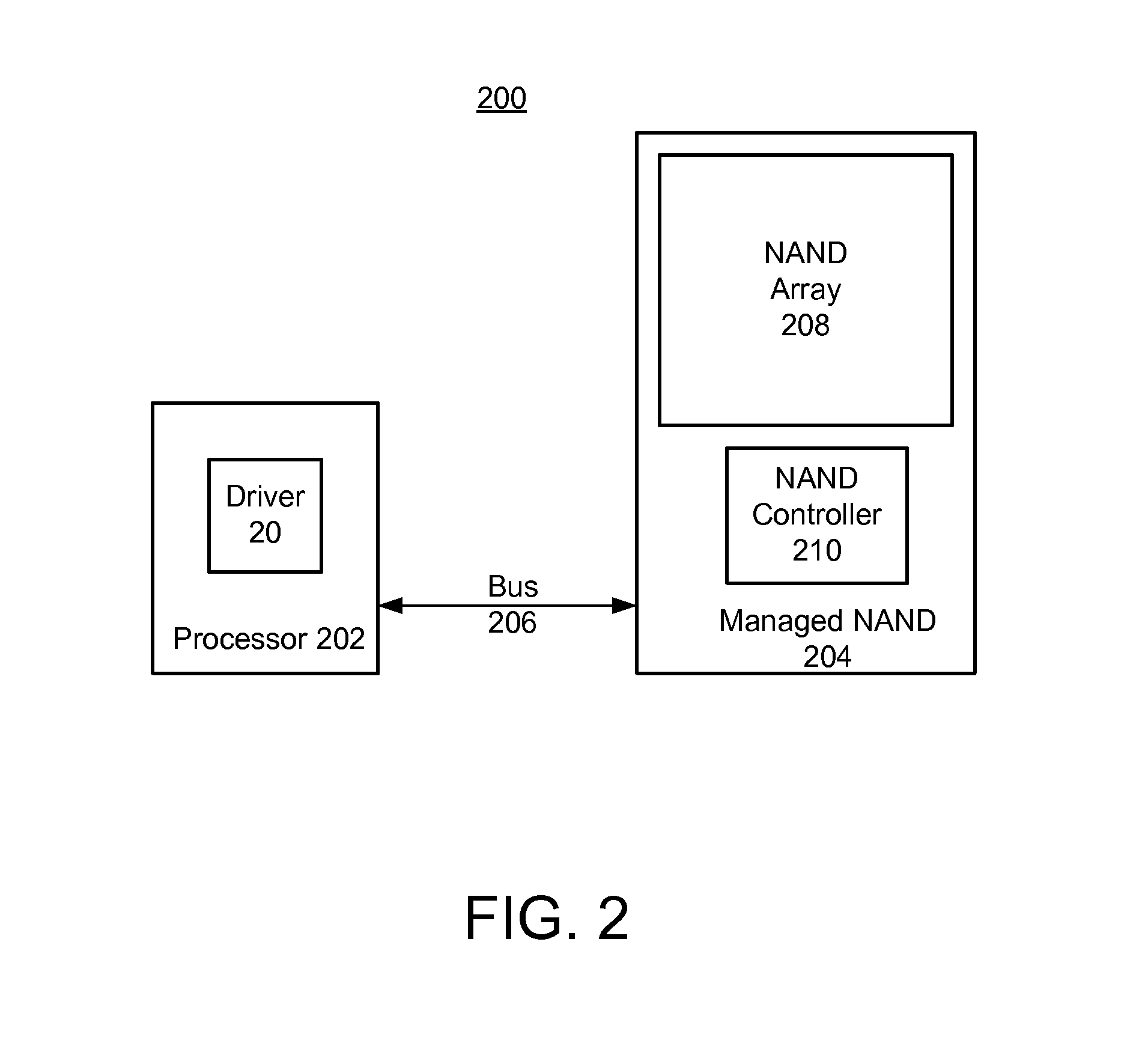
Demand-driven opportunistic garbage collection in memory components
A method and system for performing garbage collection in a memory is disclosed. Aspects of the exemplary embodiment include dividing garbage collection into atomic operations, including read, write, and block erase; storing read cycle times, write cycle times, and block erase cycle times of the memory; receiving a communication from a processor indicating at least one idle period when an application executing on the processor will not make a request of the memory, wherein the communication indicates a time duration of the at least one idle period; and in response, performing at least one of the garbage collection atomic operations within the time duration, whereby garbage collection can be performed during the at least one idle period, rather than when the memory is substantially full.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
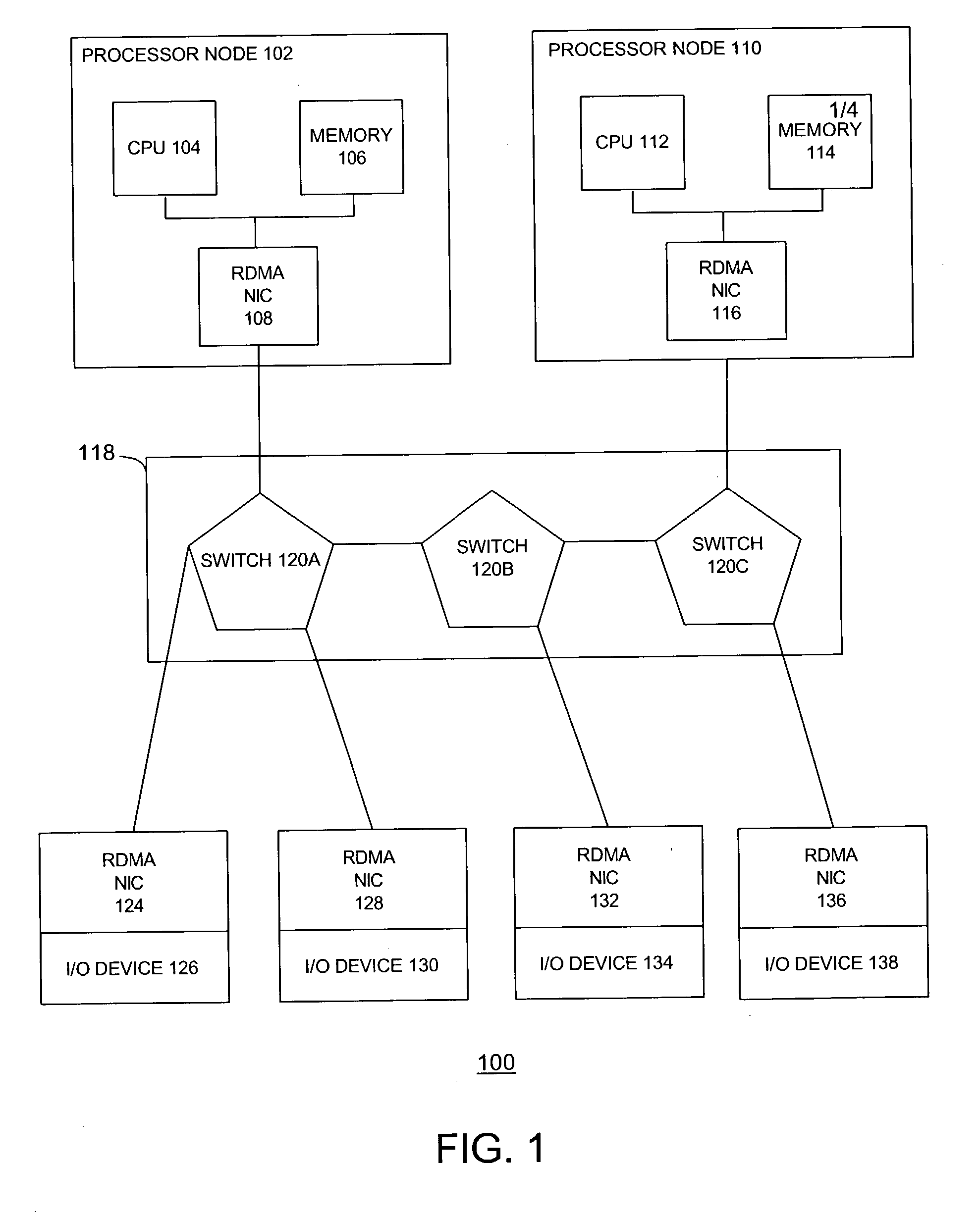
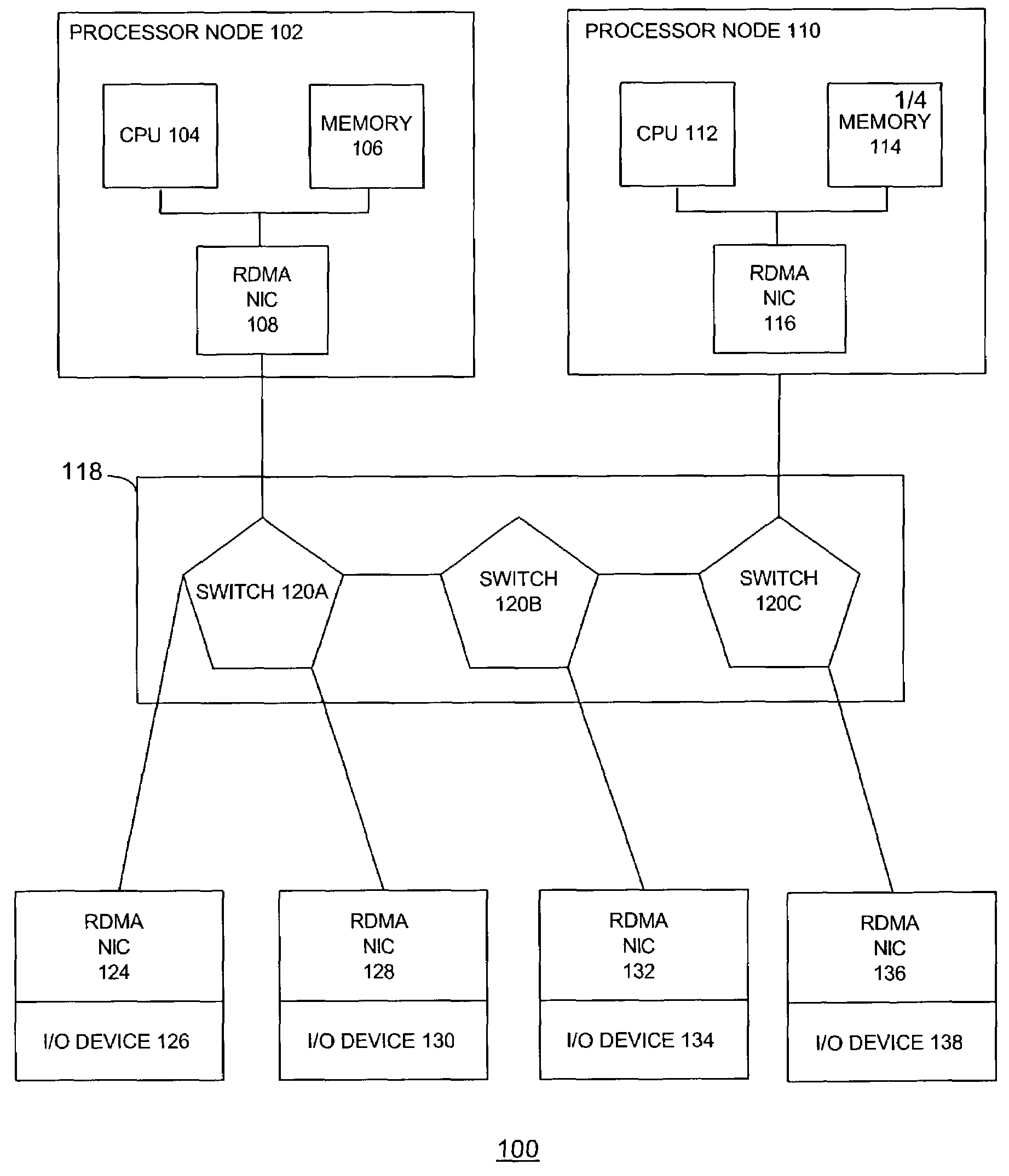
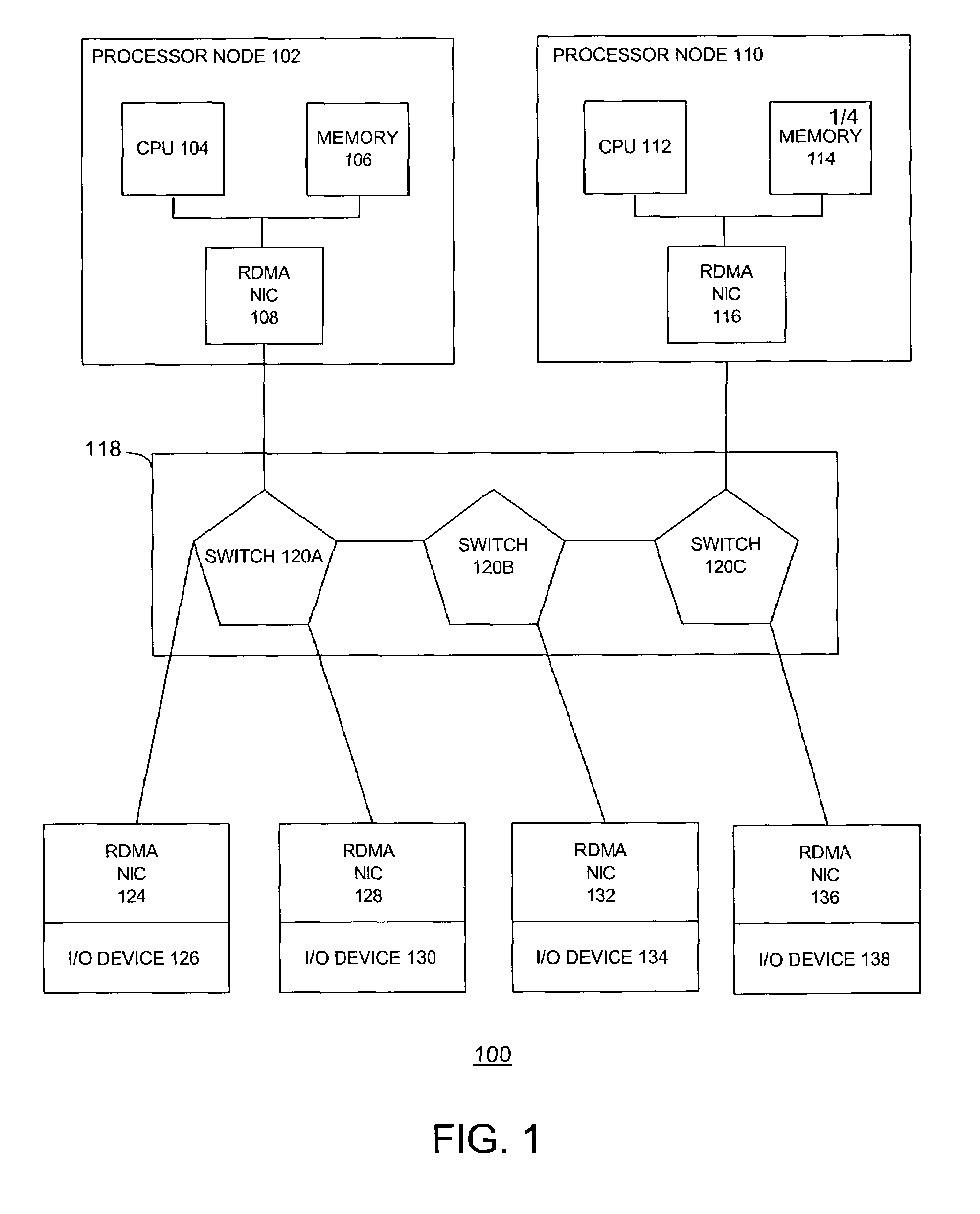
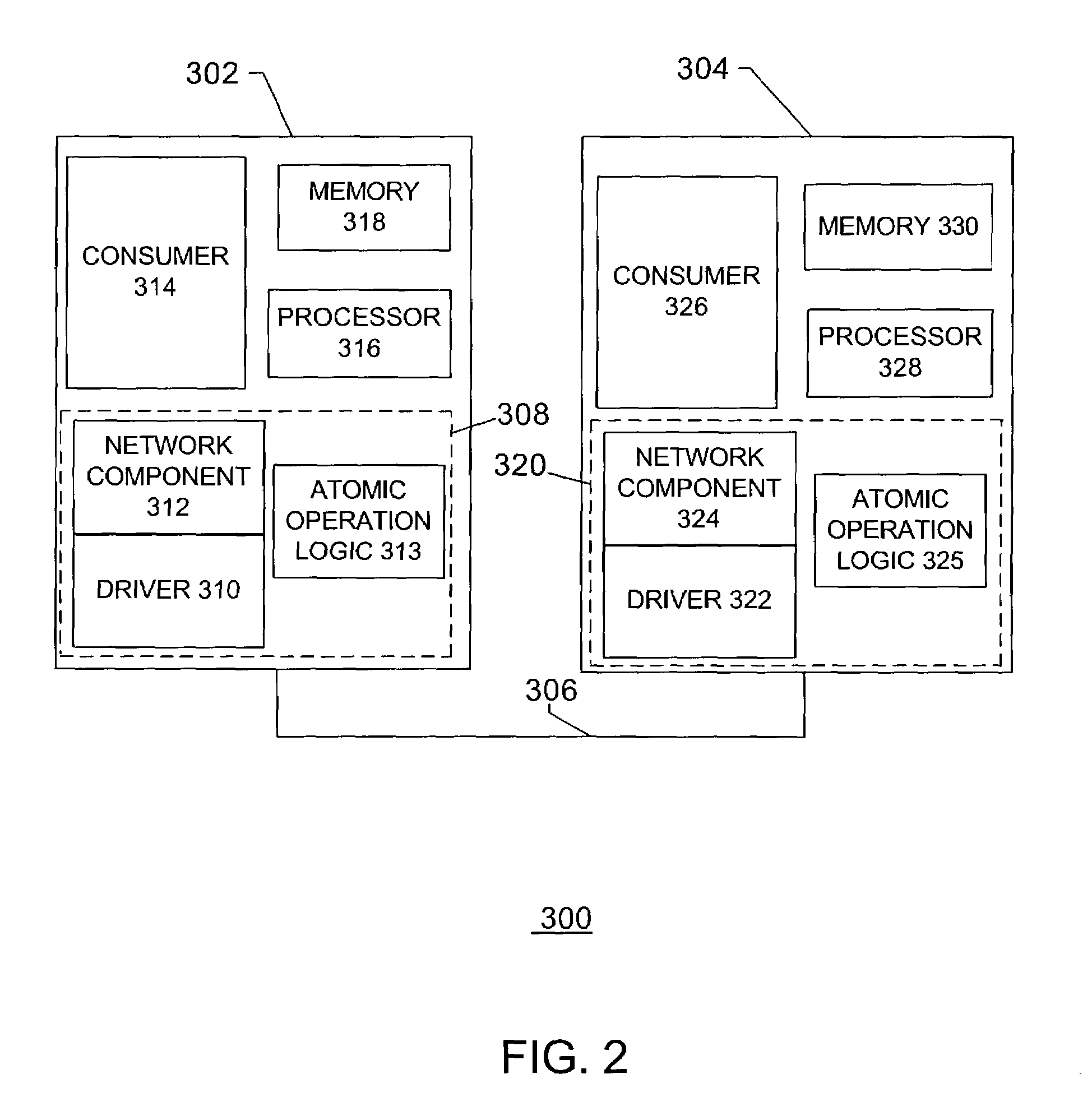
Atomic operations
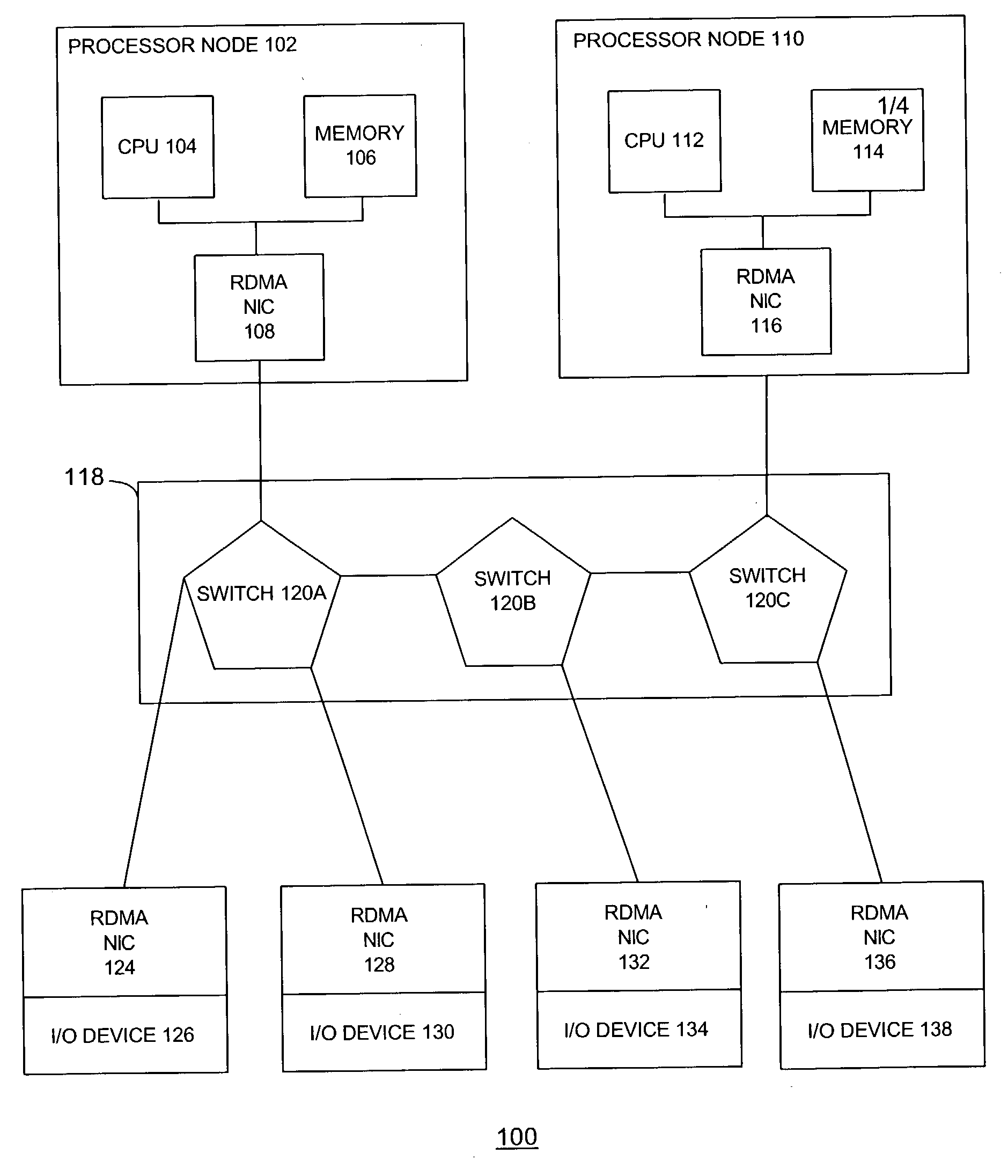
ActiveUS20040193734A1Multiple digital computer combinationsElectric digital data processingNetwork interface controllerCommunication device
The disclosed embodiments relate to a communication device for use in a node of a system having a plurality of nodes. Each of the plurality of nodes may include network interface controllers ("NICs") and each of the NICs may have an atomic operation logic device therewith. The atomic operation logic may receive from a requester a packet that contains a request to perform an atomic operation. Then the atomic operation logic may determine that the atomic operation is being requested from the information within the packet. The atomic operation logic may also respond to the requester to indicate whether the atomic operation has been performed.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
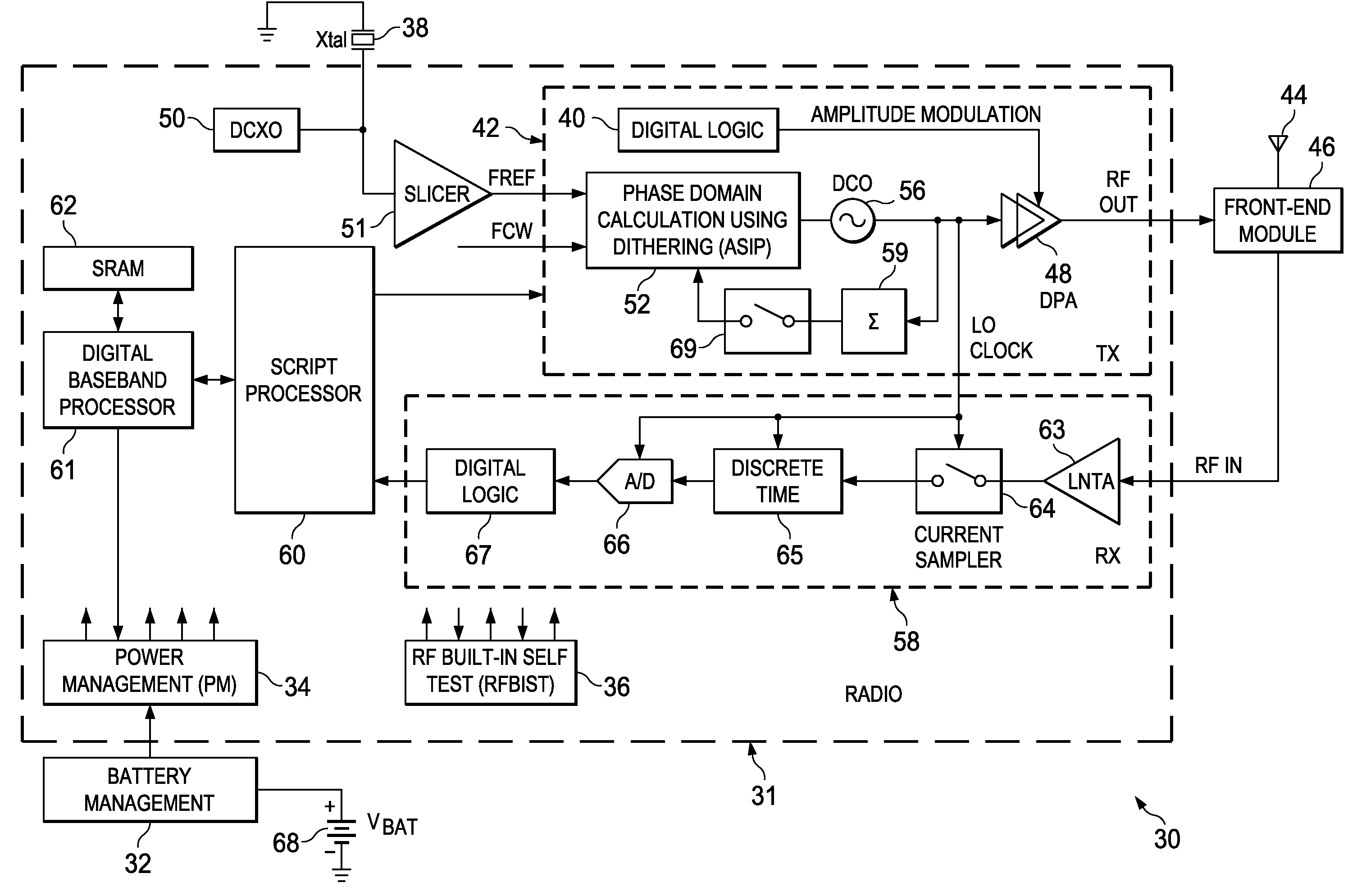
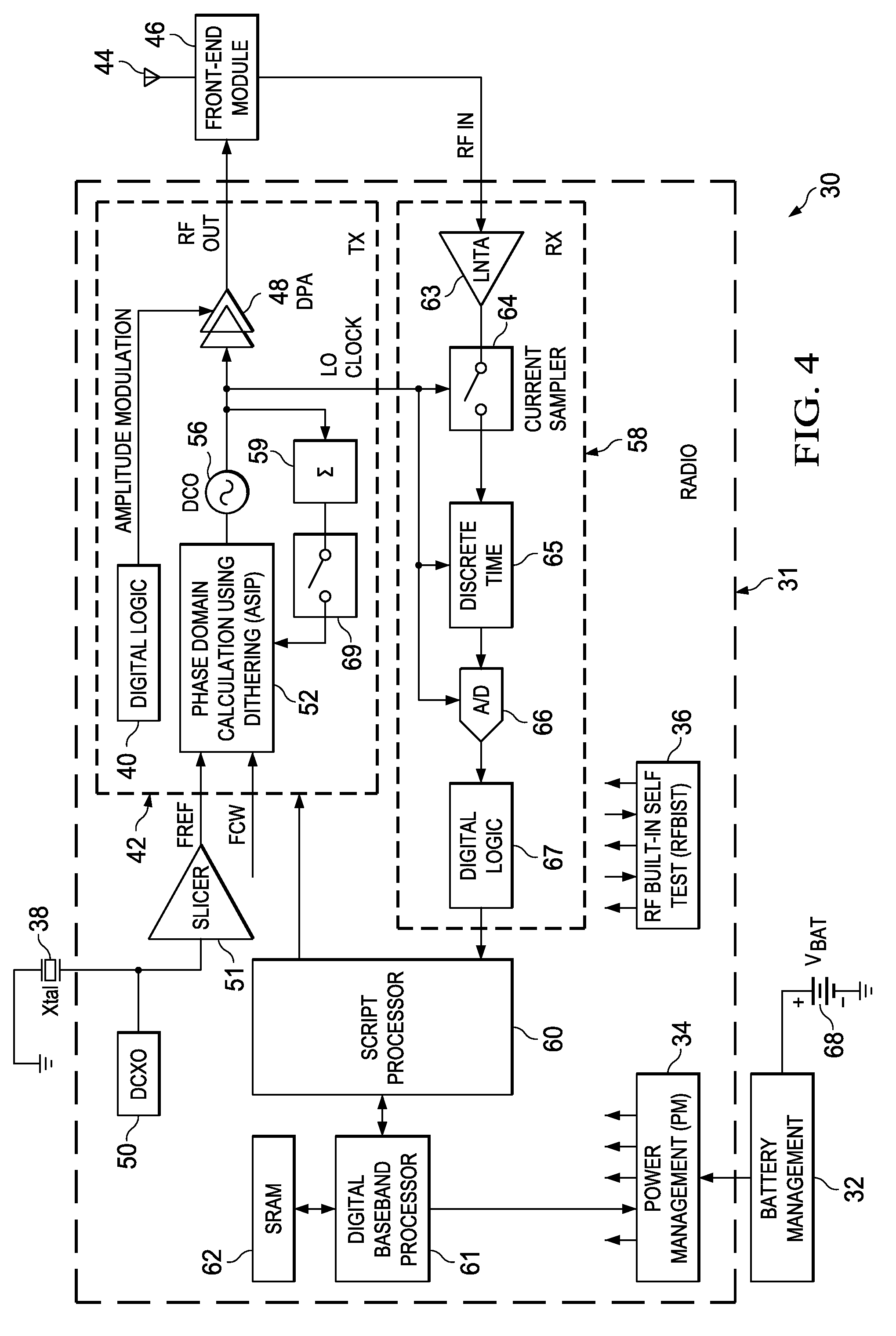
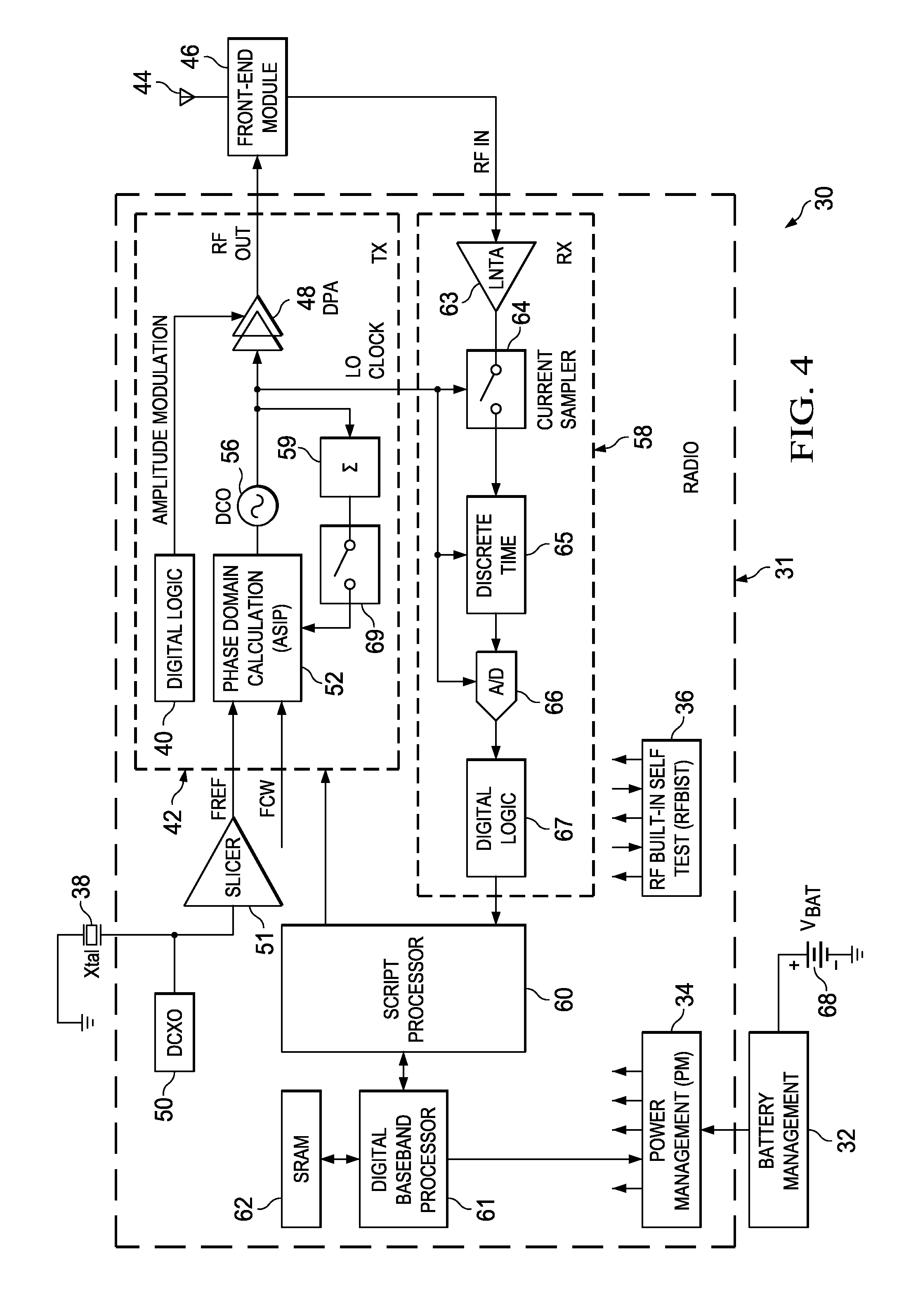
Computation spreading utilizing dithering for spur reduction in a digital phase lock loop
ActiveUS20090262877A1Easy to reconfigureReduce generationPulse automatic controlGenerator stabilizationFrequency spectrumClock rate
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of spur reduction using computation spreading with dithering in a digital phase locked loop (DPLL) architecture. A software based PLL incorporates a reconfigurable calculation unit (RCU) that is optimized and programmed to sequentially perform all the atomic operations of a PLL or any other desired task in a time sharing manner. An application specific instruction-set processor (ASIP) incorporating the RCU is adapted to spread the computation of the atomic operations out over a PLL reference clock period wherein each computation is performed at a much higher processor clock frequency than the PLL reference clock rate. This significantly reduces the per cycle current transient generated by the computations. The frequency content of the current transients is at the higher processor clock frequency which results in a significant reduction in spurs within sensitive portions of the output spectrum. Further reduction in spurs is achieved by dithering the duration of the software loop of atomic operations and / or by randomly shuffling one or more non-data dependent instructions within each iteration of the software loop.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
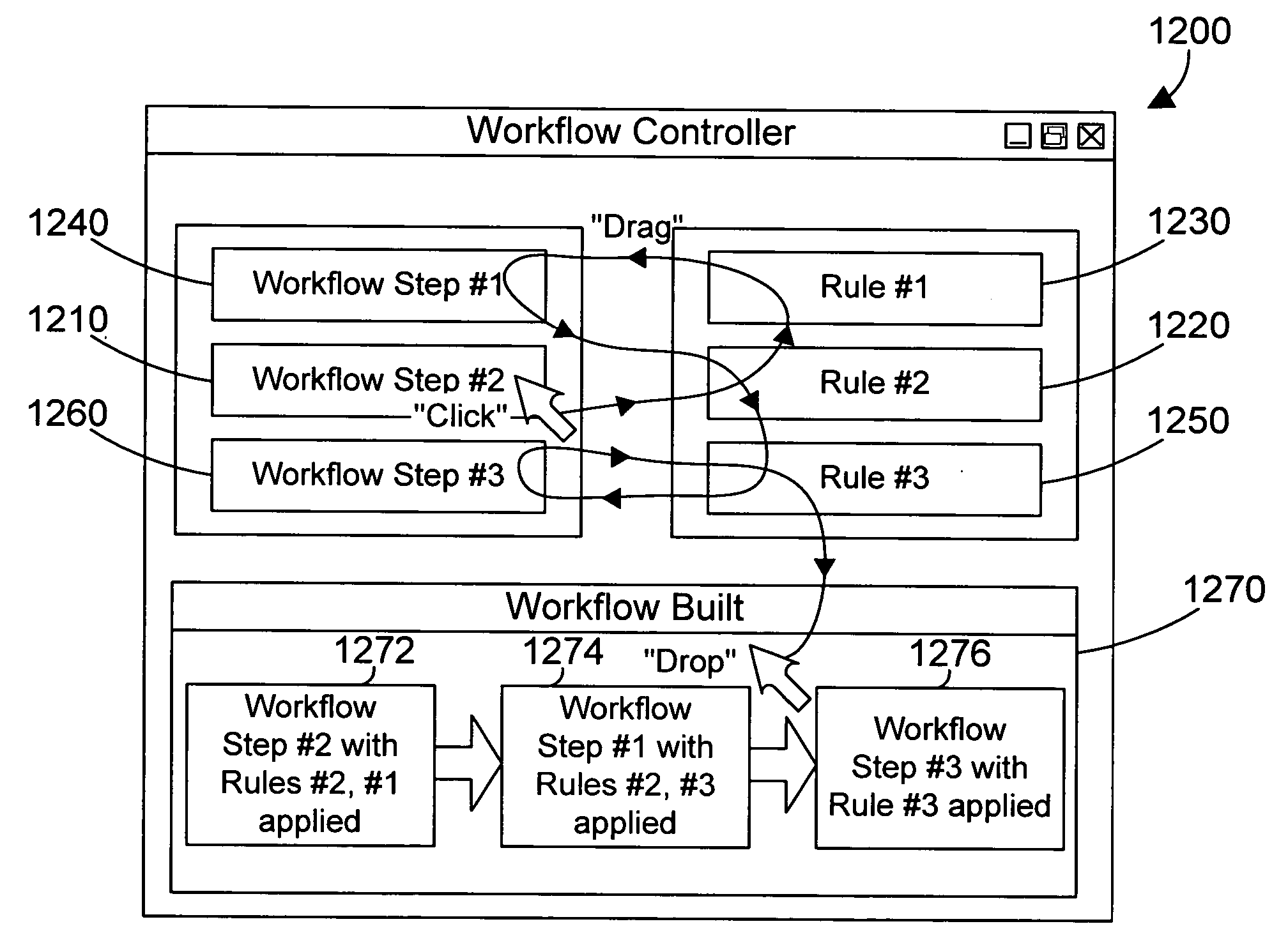
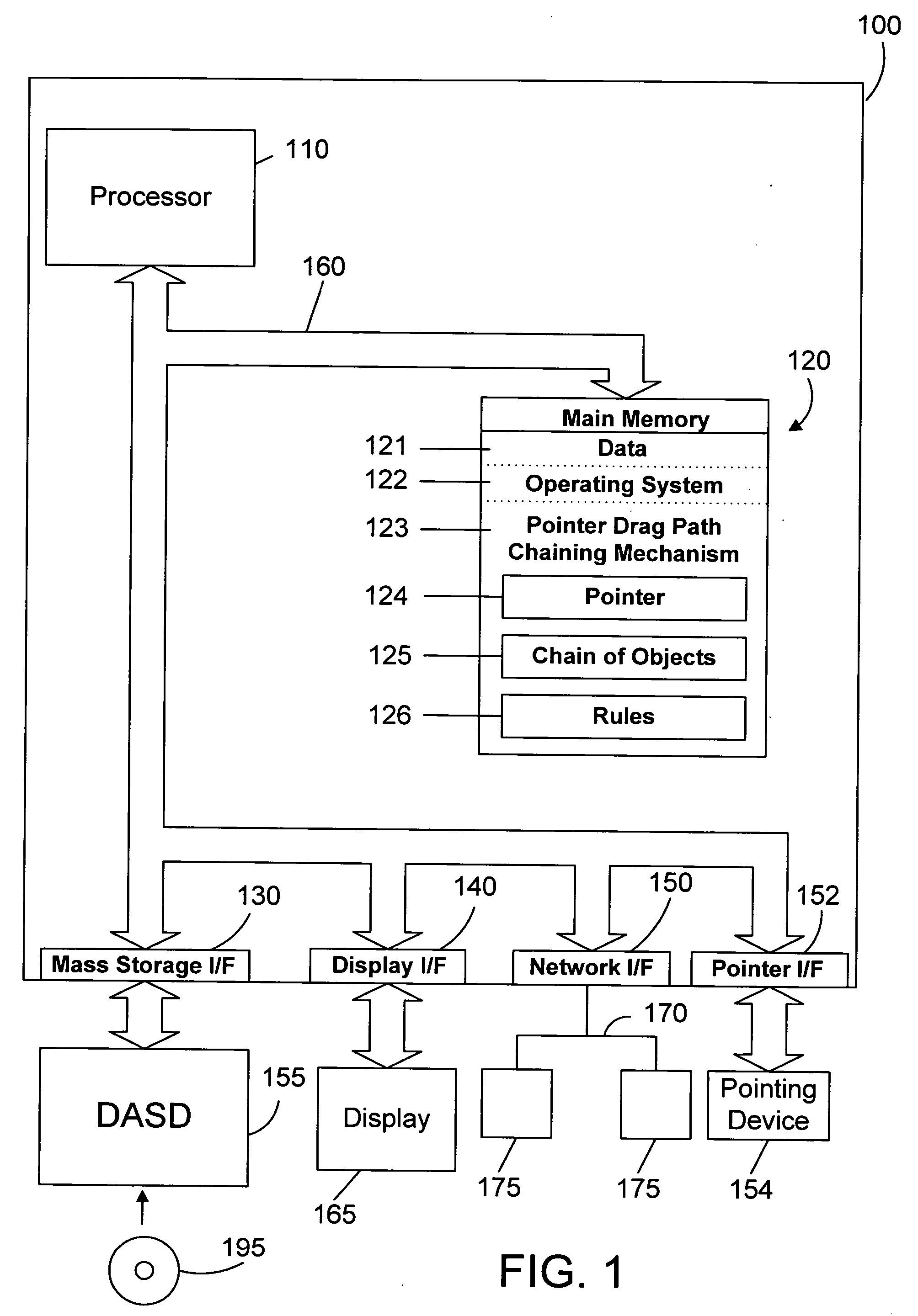
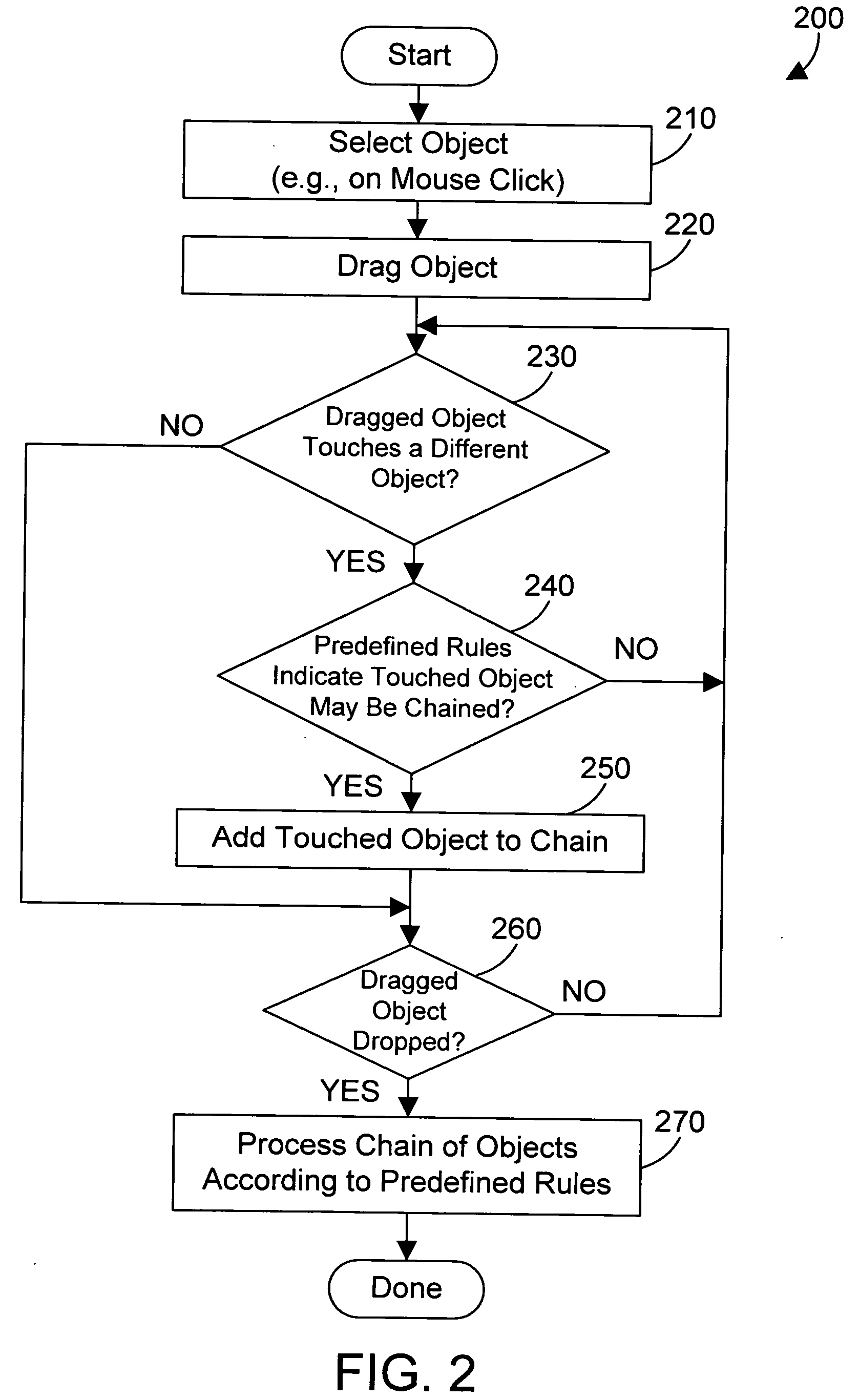
Apparatus and method for chaining objects in a pointer drag path
InactiveUS20060136833A1Improve user efficiencyReduce in quantityProgram controlMemory systemsGraphicsGraphical user interface
An apparatus and method for a graphical user interface allow performing operations simply by dragging a first object to touch a second object. The selection of the first object places a corresponding first object in a chain of objects. When the selected first object touches a second object, a corresponding second object is added to the chain of objects. This process may continue for the selection of many objects by merely touching each object with the selected first object, which causes a corresponding object to be added to the chain of objects. The chain of objects may then be processed as an atomic group of operations that may be rolled back if any of the operations in the group fail.
Owner:IBM CORP
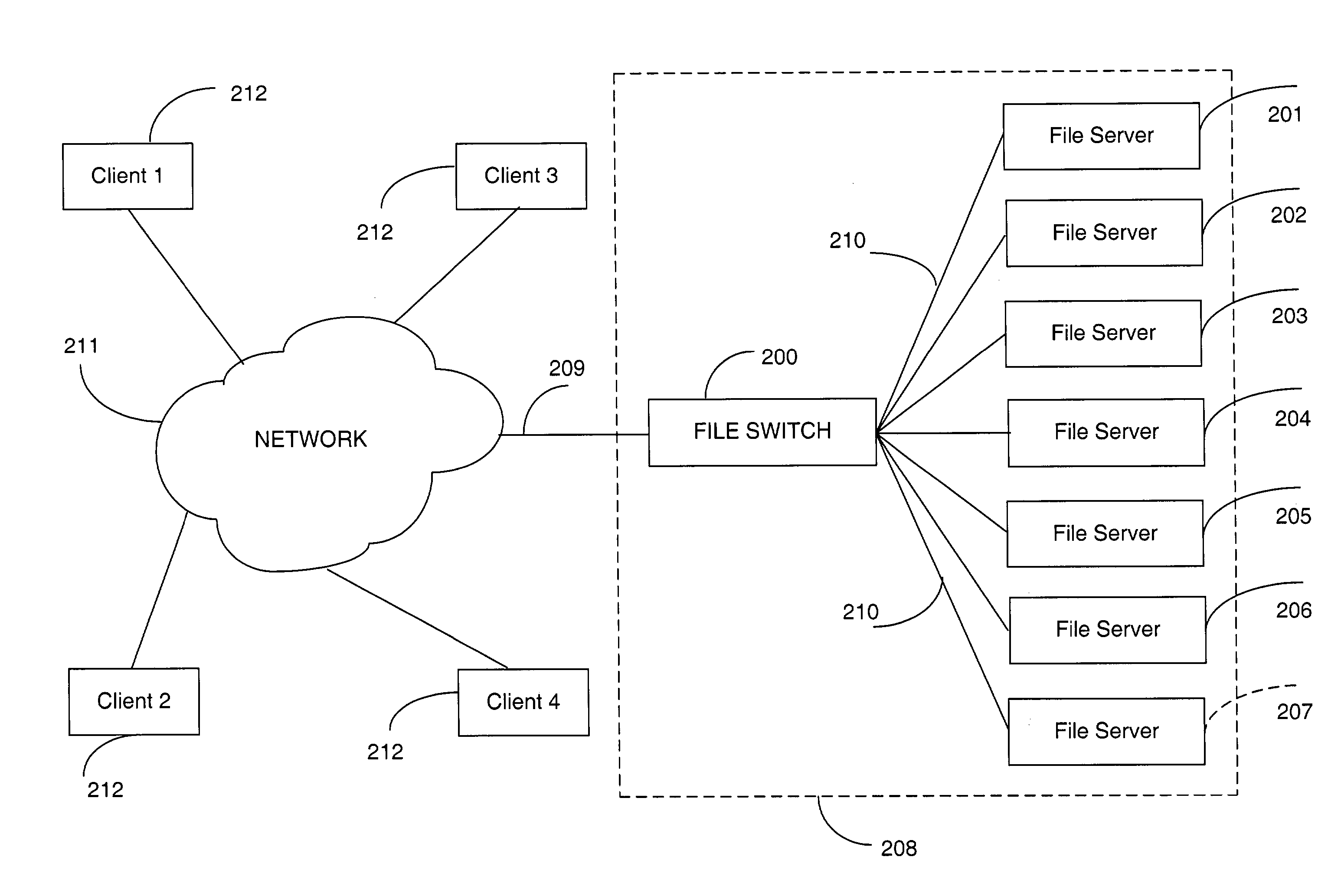
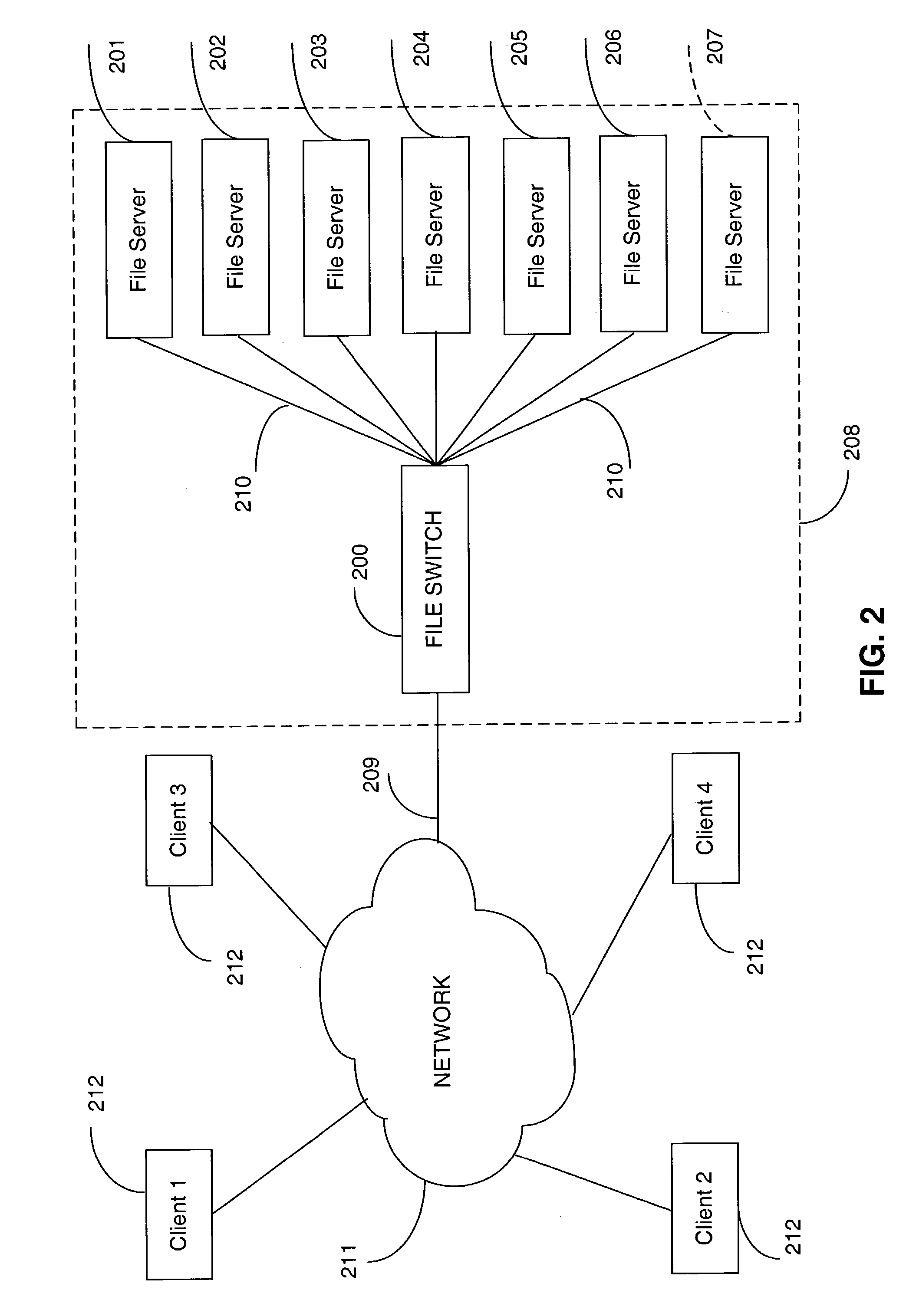
Aggregated lock management for locking aggregated files in a switched file system
InactiveUS20040133573A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsFile systemLocking mechanism
A switched file system, also termed a file switch, is logically positioned between client computers and file servers in a computer network. The file switch distributes user files among multiple file servers using aggregated file, transaction and directory mechanisms. The file switch ensures consistent and atomic behavior of the switched file system by aggregating in a deterministic way the transactions initiated by the client of multiple independent file switches so that only one of the multiple concurrent transactions attempted on the same aggregated data file may succeed, or so that the transactions are serialized so as to be performed as a sequence of atomic operations. In addition, the integrity of the aggregated data file is safeguarded by issuing locking requests on behalf of certain client applications that do not observe locking mechanism consistently.
Owner:RPX CORP
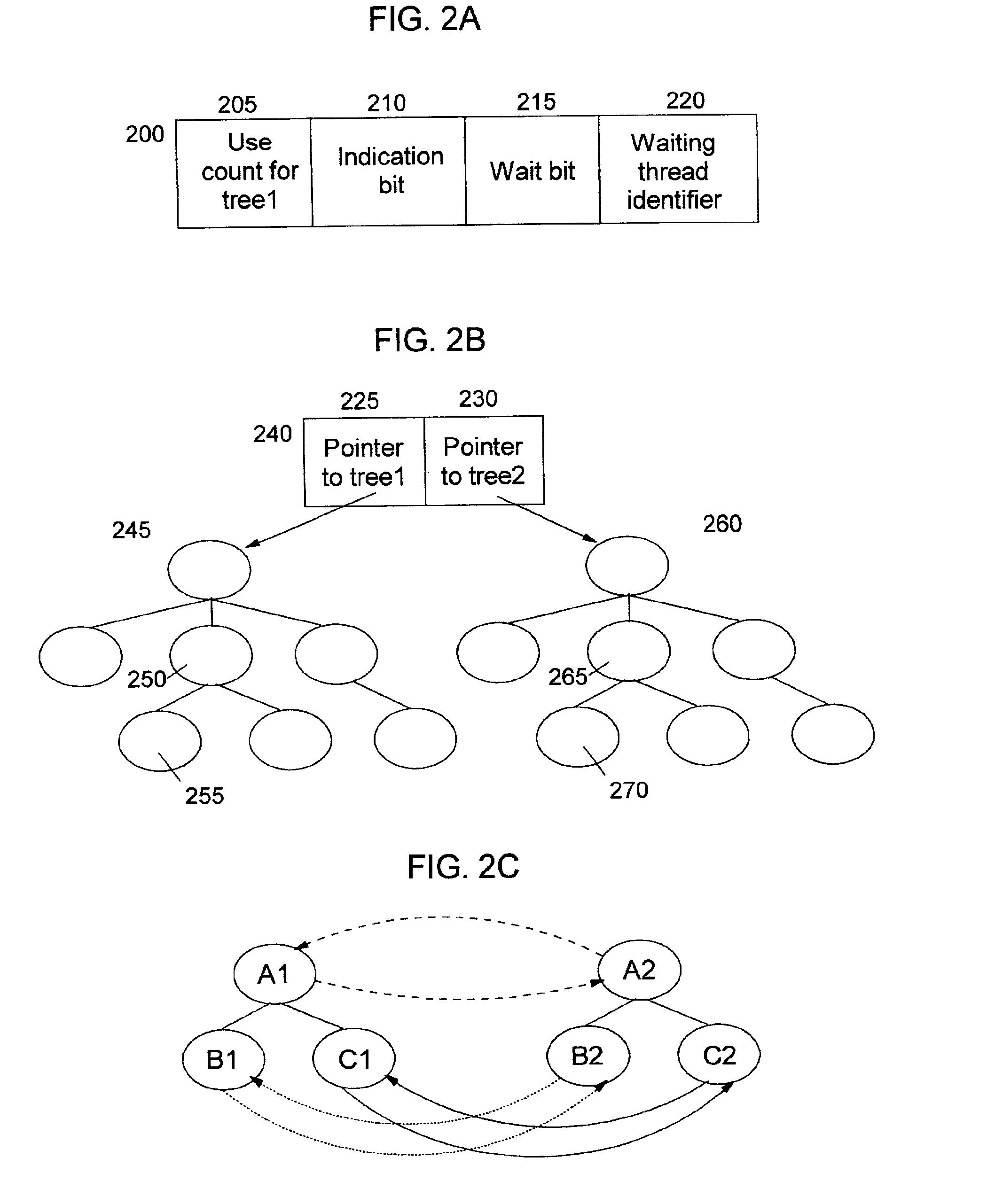
Technique for serializing data structure updates and retrievals without requiring searchers to use locks
InactiveUS6868414B2Use minimizedDigital data information retrievalData processing applicationsTheoretical computer scienceAtomic operations
The present invention provides a method, system, and computer program product for reliably and efficiently serializing access to data structures (i.e. updates and retrievals) without requiring searchers to use locks. The disclosed technique ensures that the contents of the data structure remain valid during access operations, yet does not require searchers to perform compute-intensive comparison operations to determine validity. Two trees are used at all times. Searches proceed against a first tree, while the second tree is used for performing updates. The steps required to carry out a particular update operation are stored as a queued transaction. When the update to the second tree completes, the trees are switched. The queued transaction is applied to the now-out-of-date tree, such that the nodes of this tree do not need to be searched or otherwise evaluated in order to perform the update, thereby optimizing the process of bringing this tree into synchronization with the tree that is now being used by the searchers. The two trees are repeatedly switched as additional update operations are performed. Atomic operations are used to ensure proper synchronization between the search and update processing on the trees.
Owner:IBM CORP
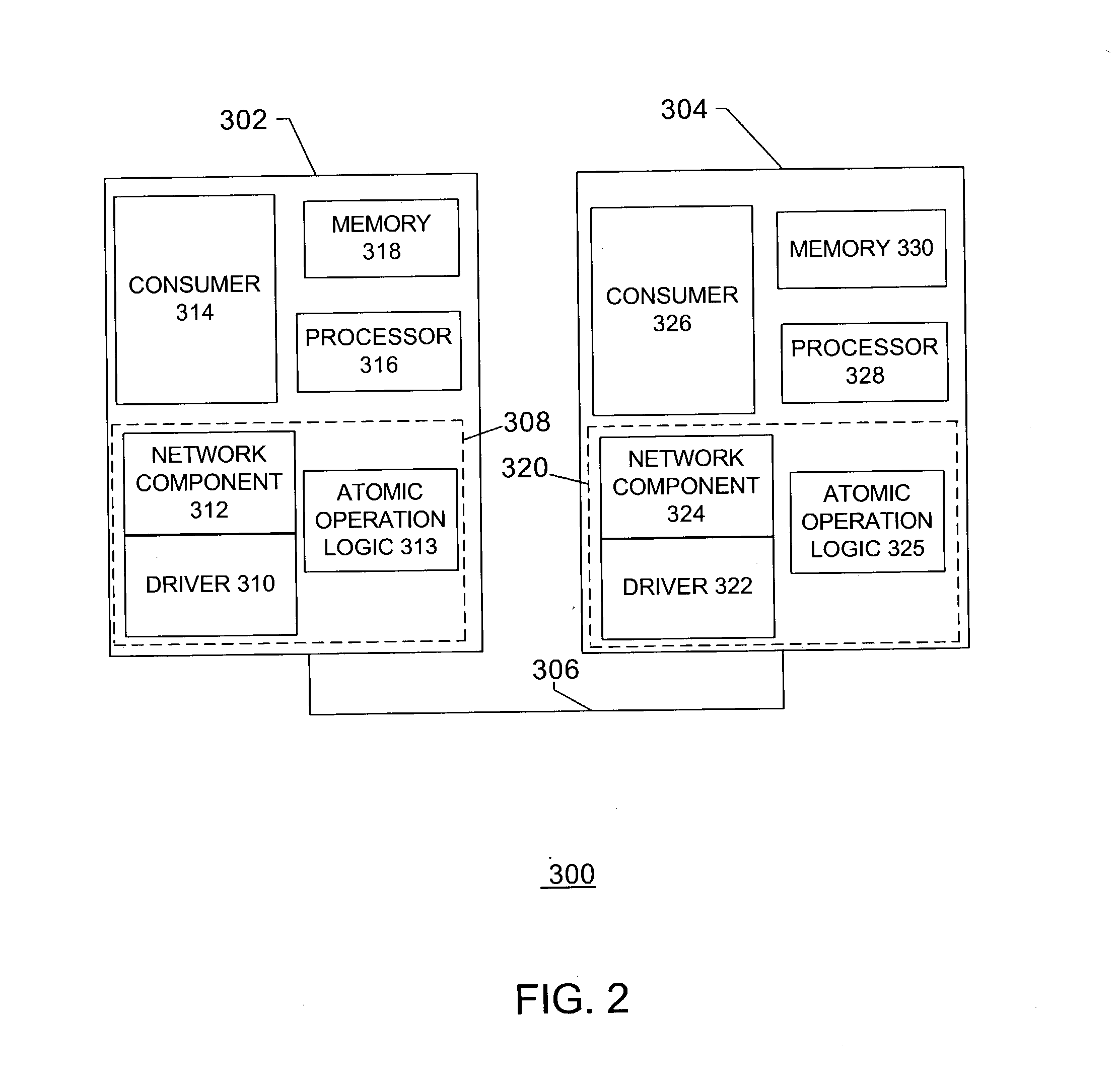
Atomic operations
ActiveUS7502826B2Minimized on demandMultiple digital computer combinationsElectric digital data processingNetwork interface controllerCommunication device
The disclosed embodiments relate to a communication device for use in a node of a system having a plurality of nodes. Each of the plurality of nodes may include network interface controllers (“NICs”) and each of the NICs may have an atomic operation logic device therewith. The atomic operation logic may receive from a requester a packet that contains a request to perform an atomic operation. Then the atomic operation logic may determine that the atomic operation is being requested from the information within the packet. The atomic operation logic may also respond to the requester to indicate whether the atomic operation has been performed.
Owner:HEWLETT-PACKARD ENTERPRISE DEV LP
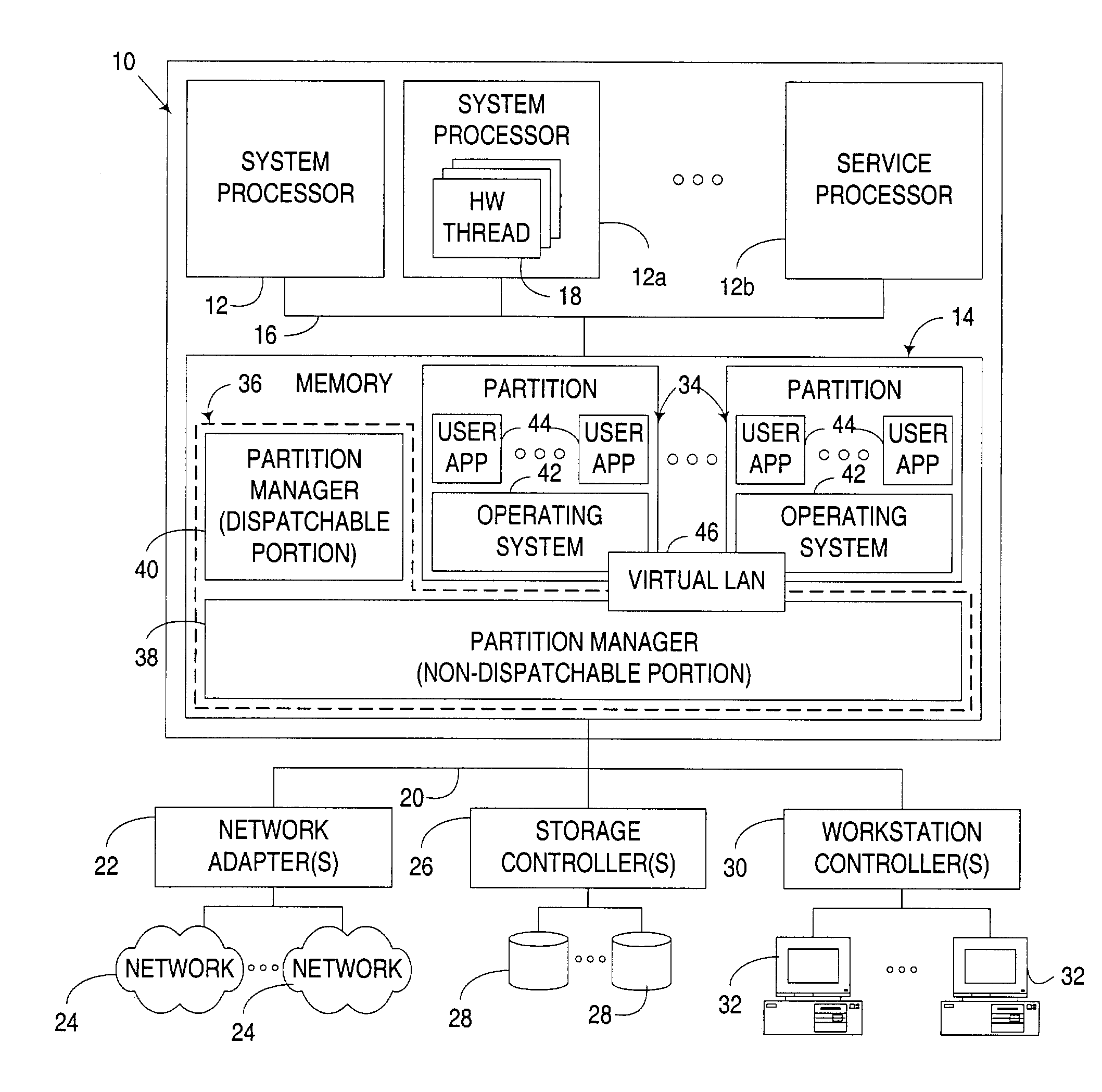
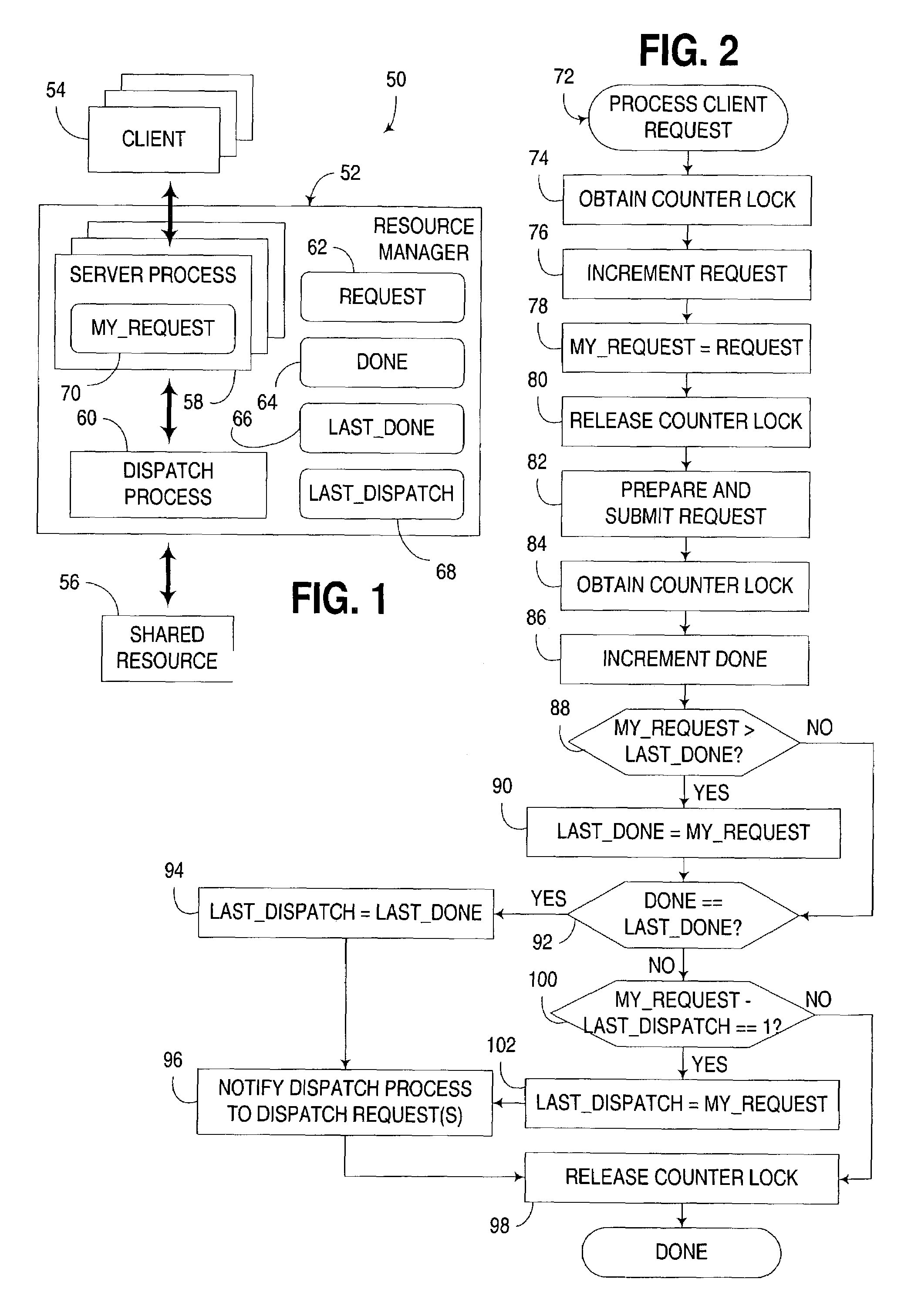
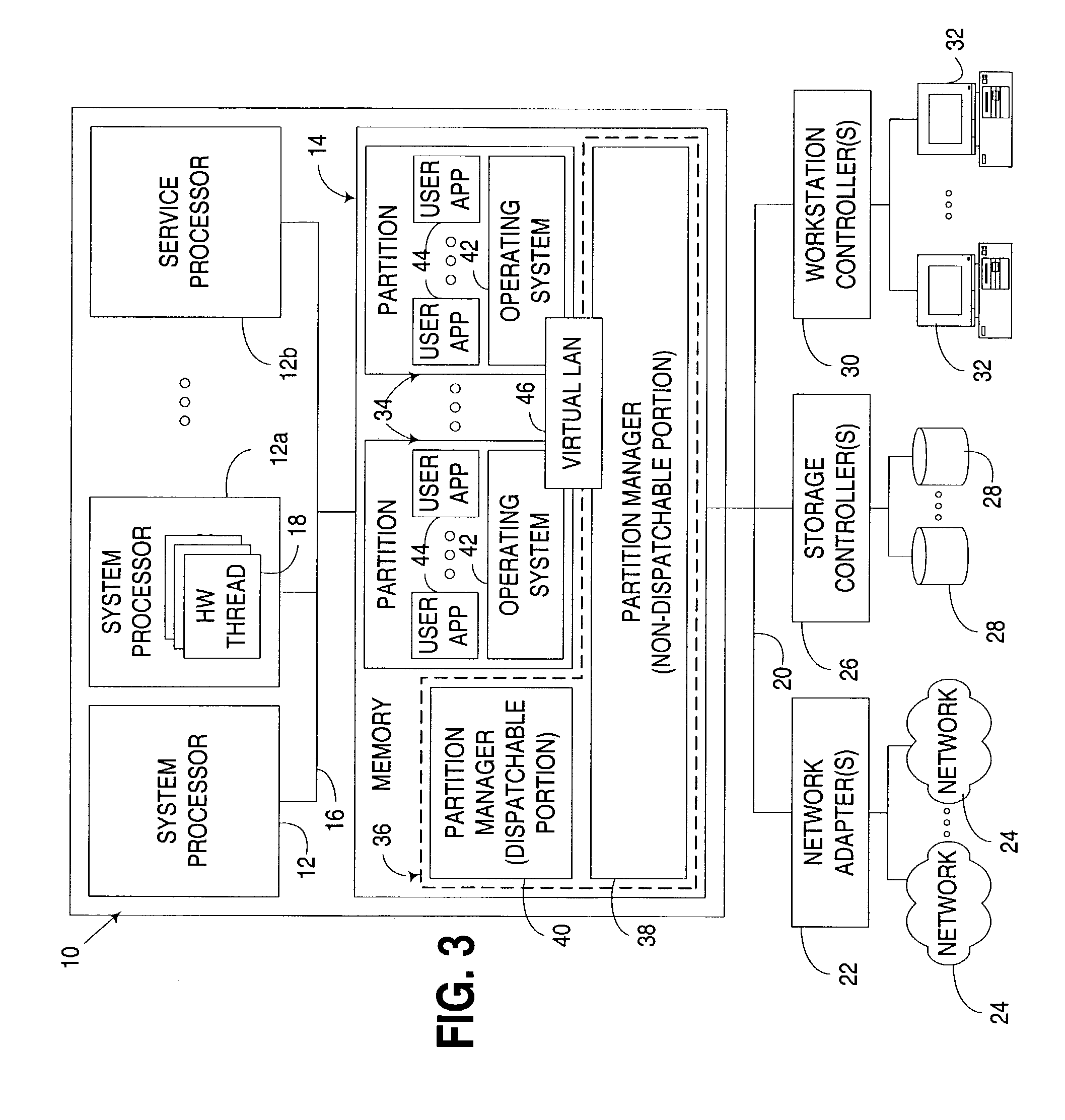
Concurrent access of shared resources utilizing tracking of request reception and completion order
ActiveUS7047337B2Reduce contentionLimited durationProgram synchronisationUnauthorized memory use protectionShared resourceDistributed computing
An apparatus, program product and method to manage access to a shared resource by a plurality of processes in a multithreaded computer via a collection of atomic operations that track both the order in which requests that use a shared resource are received, and the order in which processing of such requests are completed after they are received. Dispatching of requests is effectively deferred until processing of all non-dispatched requests that were received earlier than a most recently completed request has been completed. In many instances, completion of processing of requests can be performed non-atomically, thus reducing contention issues with respect to the shared resource. Furthermore, dispatching of requests may be batched to reduce the overhead associated with individual dispatch operations.
Owner:LENOVO GLOBAL TECH INT LTD
Computation parallelization in software reconfigurable all digital phase lock loop
ActiveUS20090070568A1Easy to reconfigureReduce per cycle current transientPulse automatic controlGeneral purpose stored program computerData stream processingTime-sharing
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
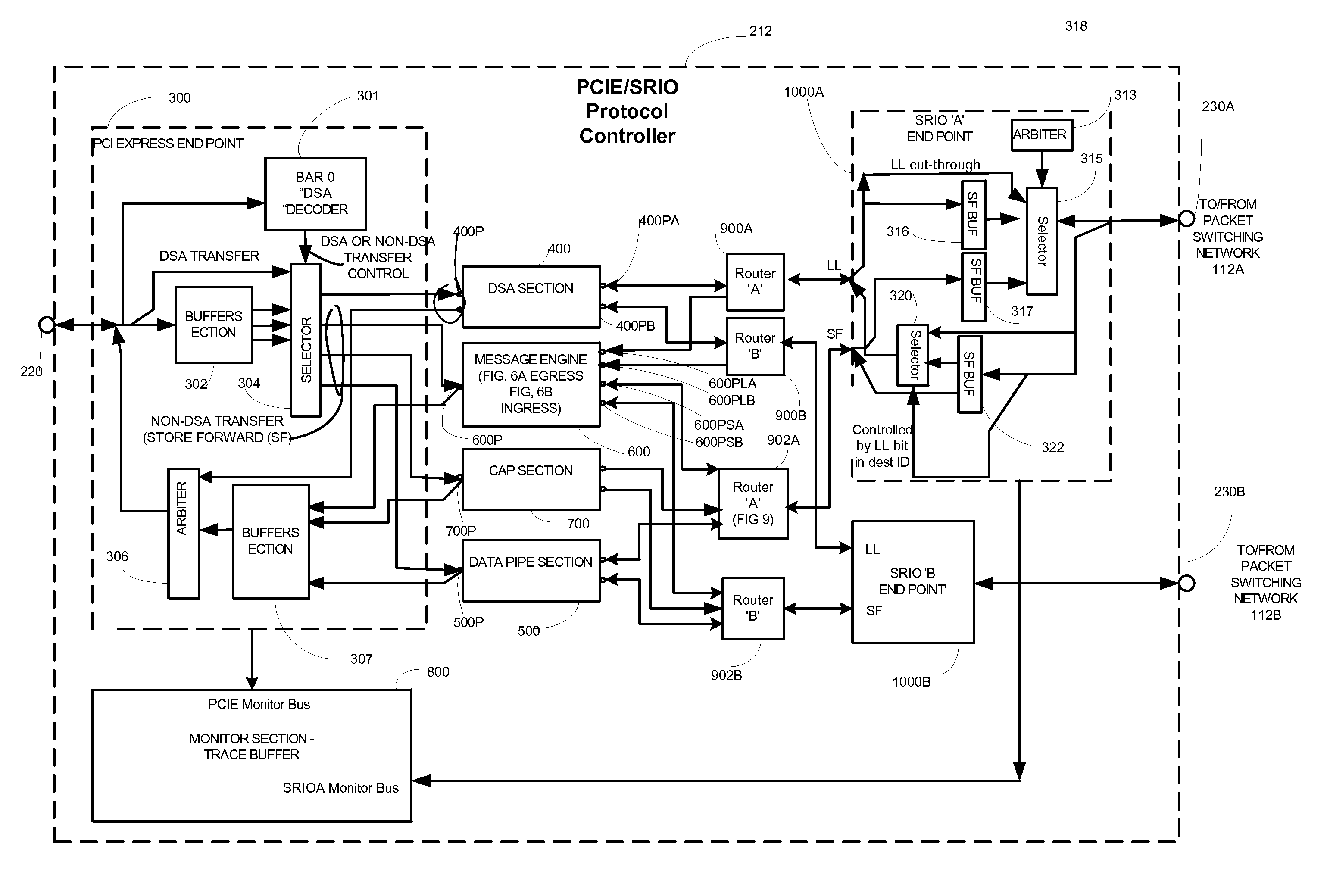
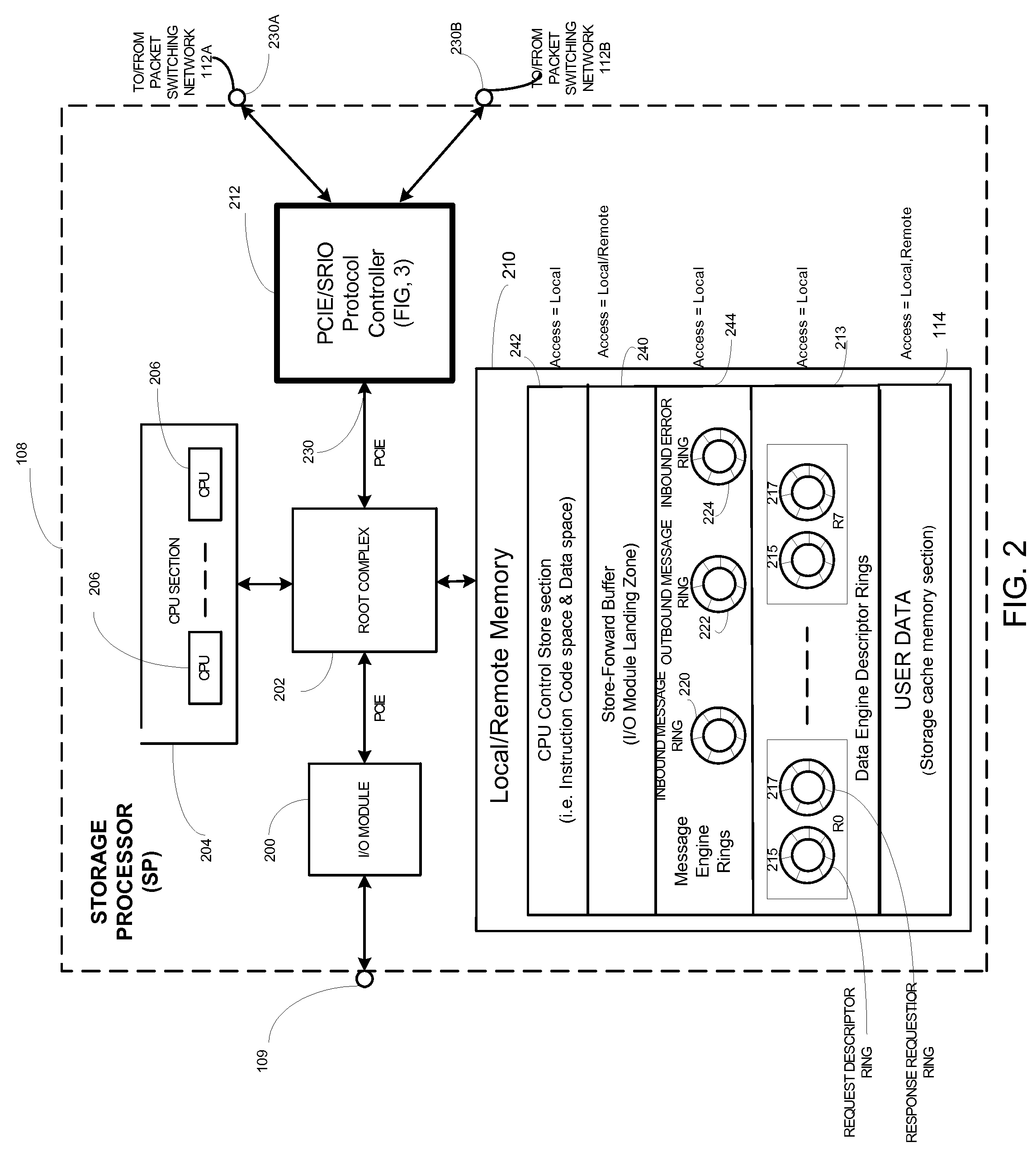
Protocol controller for a data storage system
ActiveUS7631128B1Lower latencyImprove throughputInput/output to record carriersMultiple digital computer combinationsData storeDistributed computing
A data storage system having protocol controller for converting packets between PCIE format used by a storage processor and Rapid IO format used by a packet switching network. The controller includes a PCIE end point for transferring atomic operation (DSA) requests, a data pipe section having a plurality of data pipes for passing user data; and a message engine section for passing messages among the plurality of storage processors. An acceleration path controller bypasses a DSA buffer in the absence of congestion on the network. Packets fed to the PCIE end point include an address portion having code indicating an atomic operation. An encoder converts the code from a PCIE format into the same atomic operation in SRIO format. Each one of a plurality of CPUs is adapted to perform a second DSA request during execution of a first DSA request.
Owner:EMC IP HLDG CO LLC
Aggregated lock management for locking aggregated files in a switched file system
InactiveUS7509322B2Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsFile systemLocking mechanism
Owner:RPX CORP
Device and method for testing a device through resolution of data into atomic operations
InactiveUS6457152B1Improve throughputElectronic circuit testingError detection/correctionClosed loopVerilog
A method of testing a device includes monitoring an output of the device, wherein the output is generated by the device in response to an applied test command; and resolving the output into atomic operations, wherein the atomic operations are substantially the smallest constituent operations which are substantially independent of the device. The method is used to provide a simple, comprehensive test environment that effectively tests 1394a and 1394-1995 designs, for example, in Verilog. The test environment contains rules which completely characterize the behavior of different 1394 bus protocols as defined by the IEEE specifications. The test environment provides portability between different devices under test and between different protocols, automated closed-loop reconciliation of test commands and protocol requirements, topology independence, and out-of-order execution of instructions or relative sequencing. The test environment further allows failure injection, and separate and independent design of the device and a test system.
Owner:SYNOPSYS INC
Method and apparatus for incremental commitment to architectural state in a microprocessor
InactiveUS20060112261A1Minimize overheadImprove performanceDigital computer detailsMemory systemsScheduling instructionsOperating system
Method and hardware apparatus are disclosed for reducing the rollback penalty on exceptions in a microprocessor executing traces of scheduled instructions. Speculative state is committed to the architectural state of the microprocessor at a series of commit points within a trace, rather than committing the state as a single atomic operation at the end of the trace.
Owner:VAN DIKE KORBIN S +2
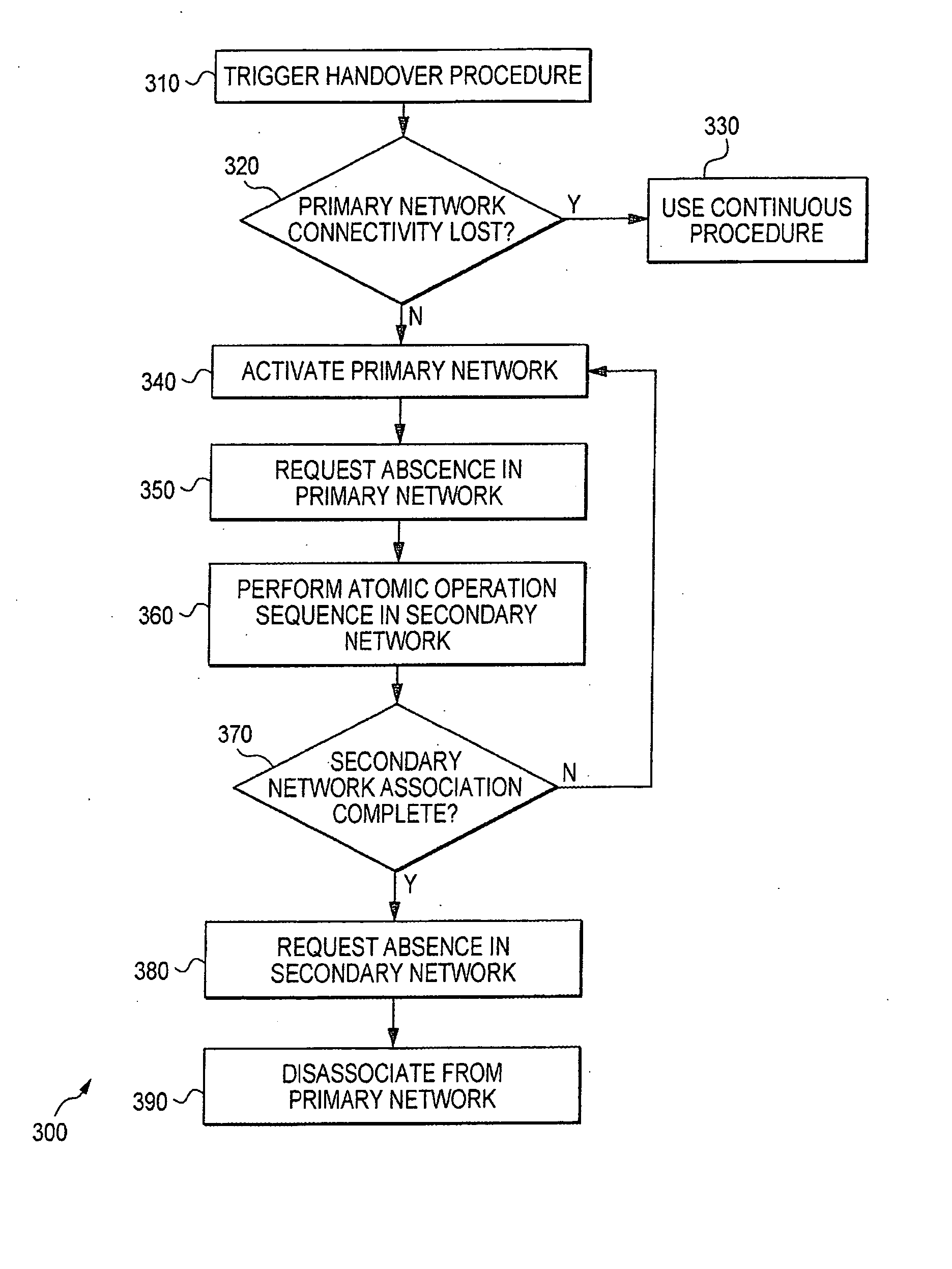
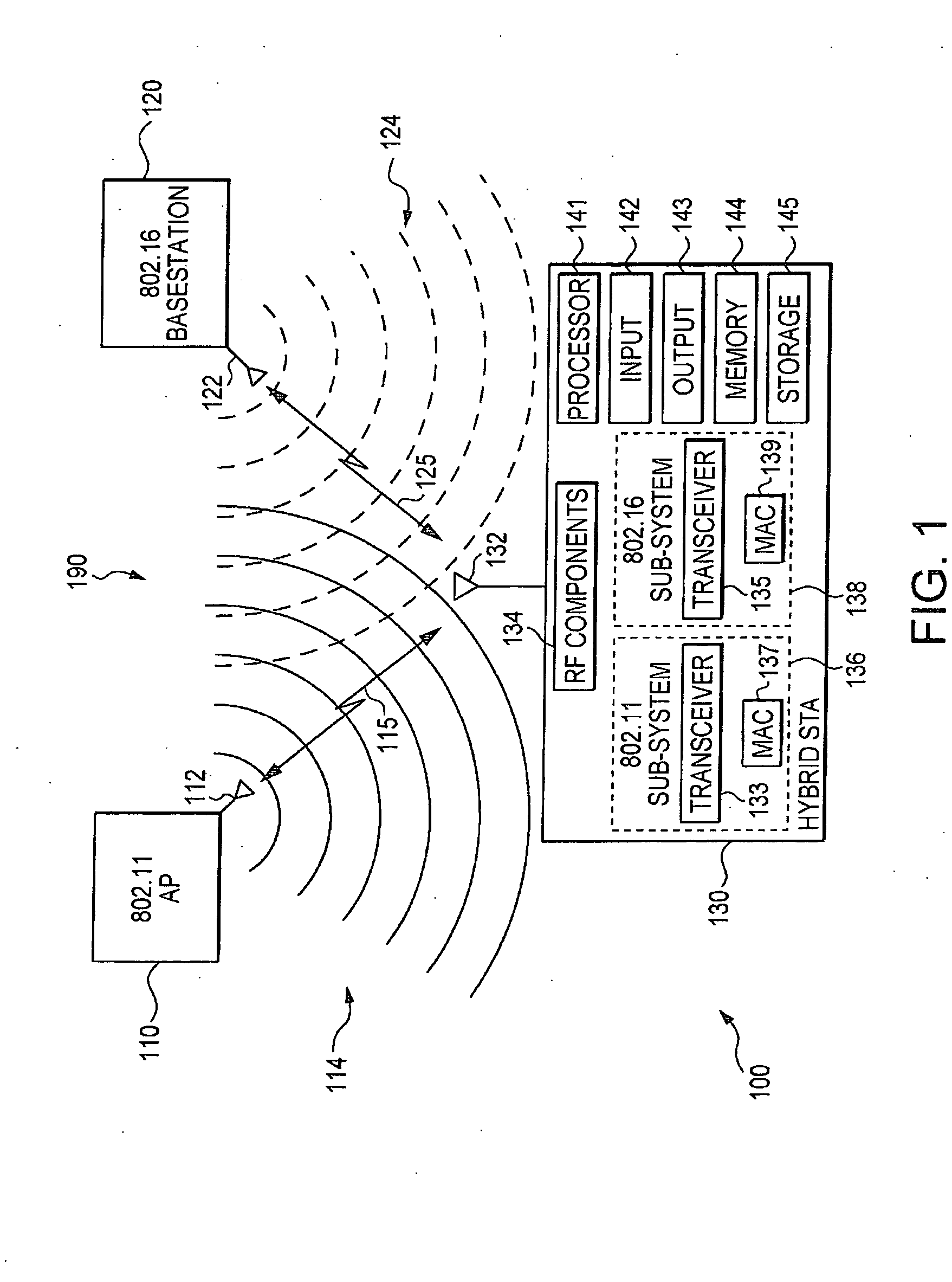
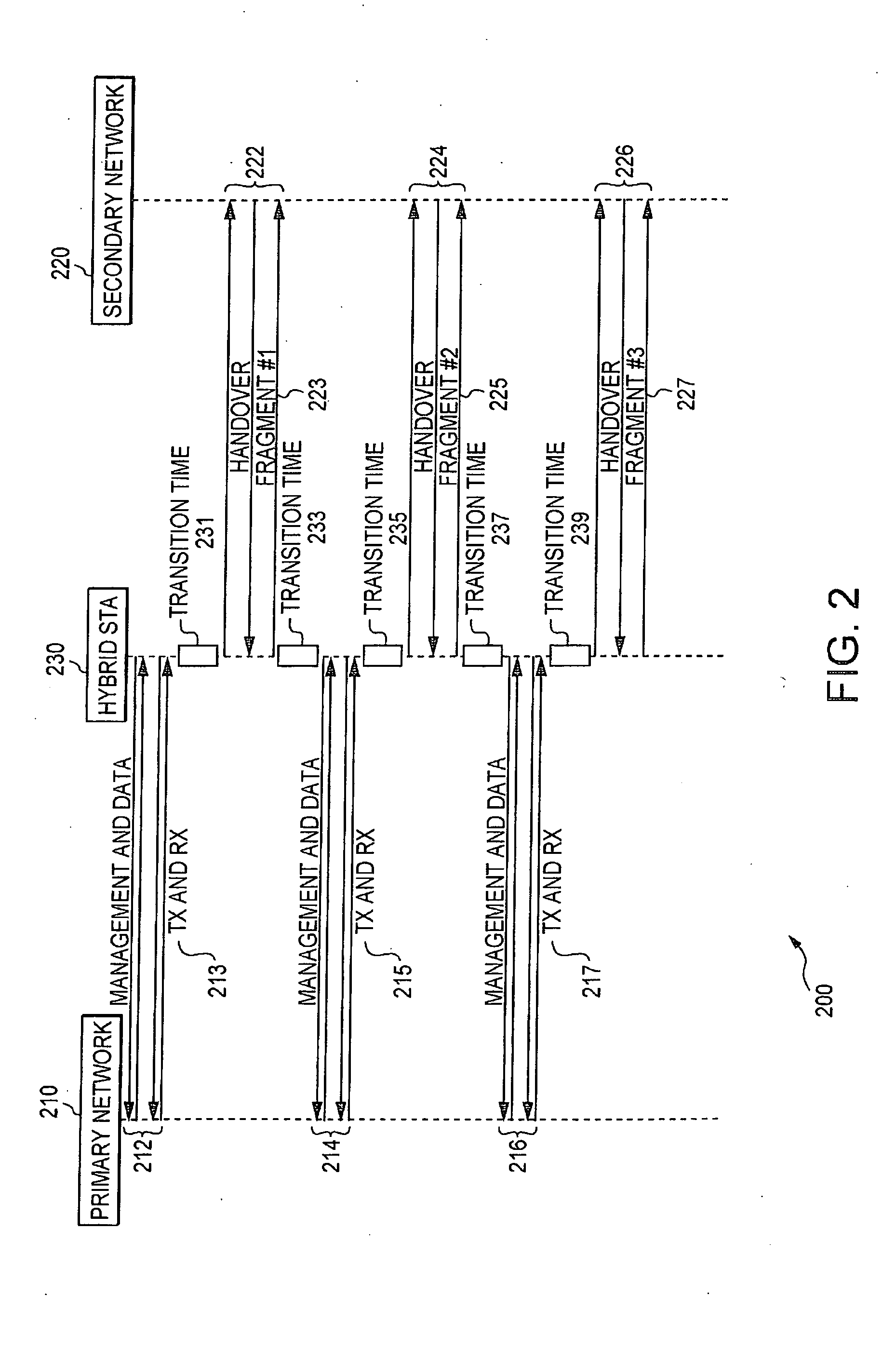
Device, system and method of layer 2 handover between heterogeneous networks
InactiveUS20070230401A1Wireless network protocolsRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransceiverWireless communication protocol
Embodiments of the present invention provide devices, systems and methods of seamless layer 2 handover between heterogeneous networks for a hybrid wireless communication device. For example, an apparatus includes a first wireless transceiver able to operate in accordance with a first wireless communication protocol, a second, collocated, wireless transceiver able to operate in accordance with a second wireless communication protocol, and possibly shared radio frequency components. A method includes a fragmented handover procedure in which a network entry procedure is divided into atomic operations which may be performed during short, orderly, absences from the active network. The method further includes orderly switching back to the active network for any data or connection-management transactions, until the fragmented handover is completed and layer 2 connections are established at the second network. Other features are described and claimed.
Owner:INTEL CORP
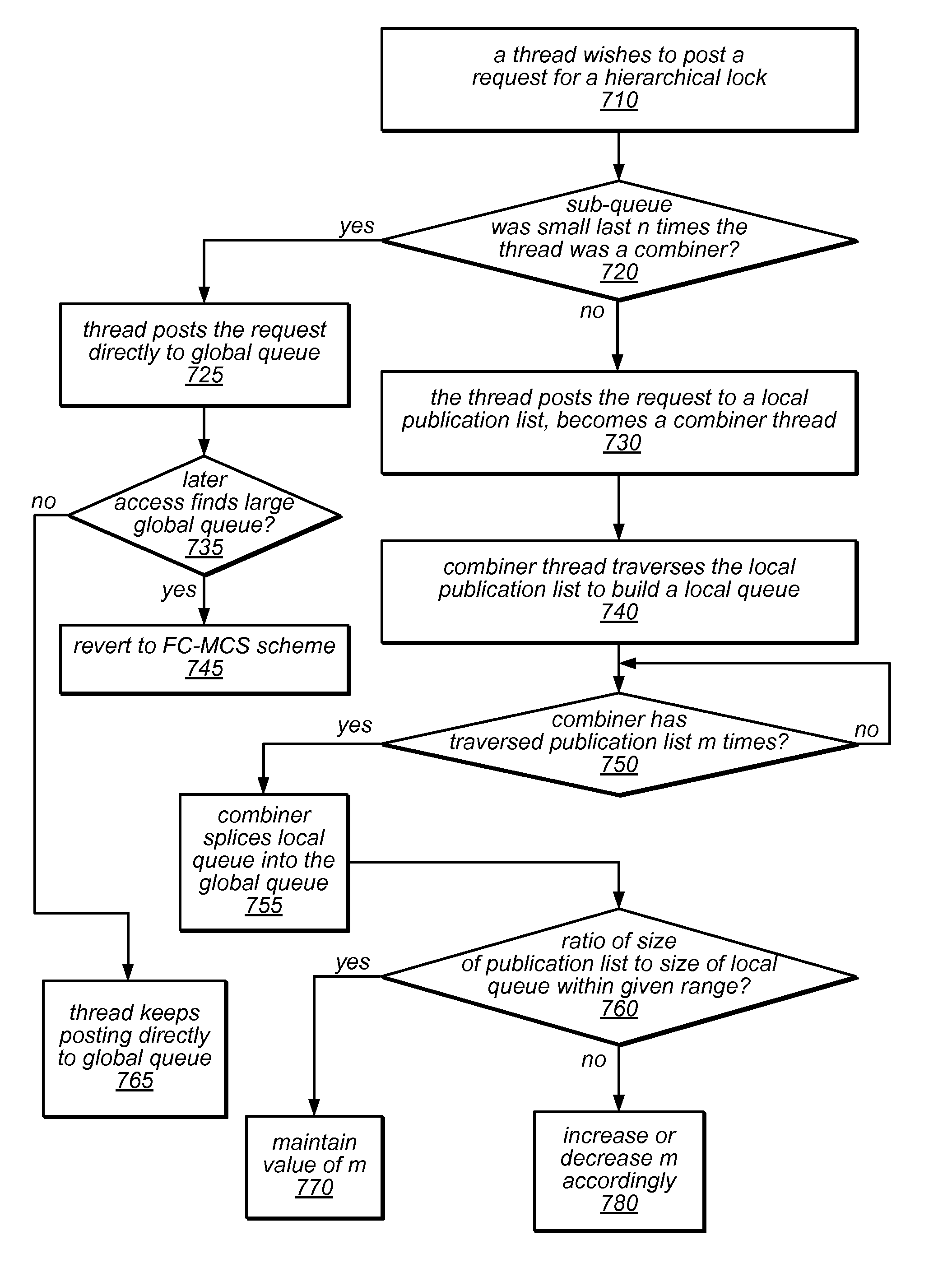
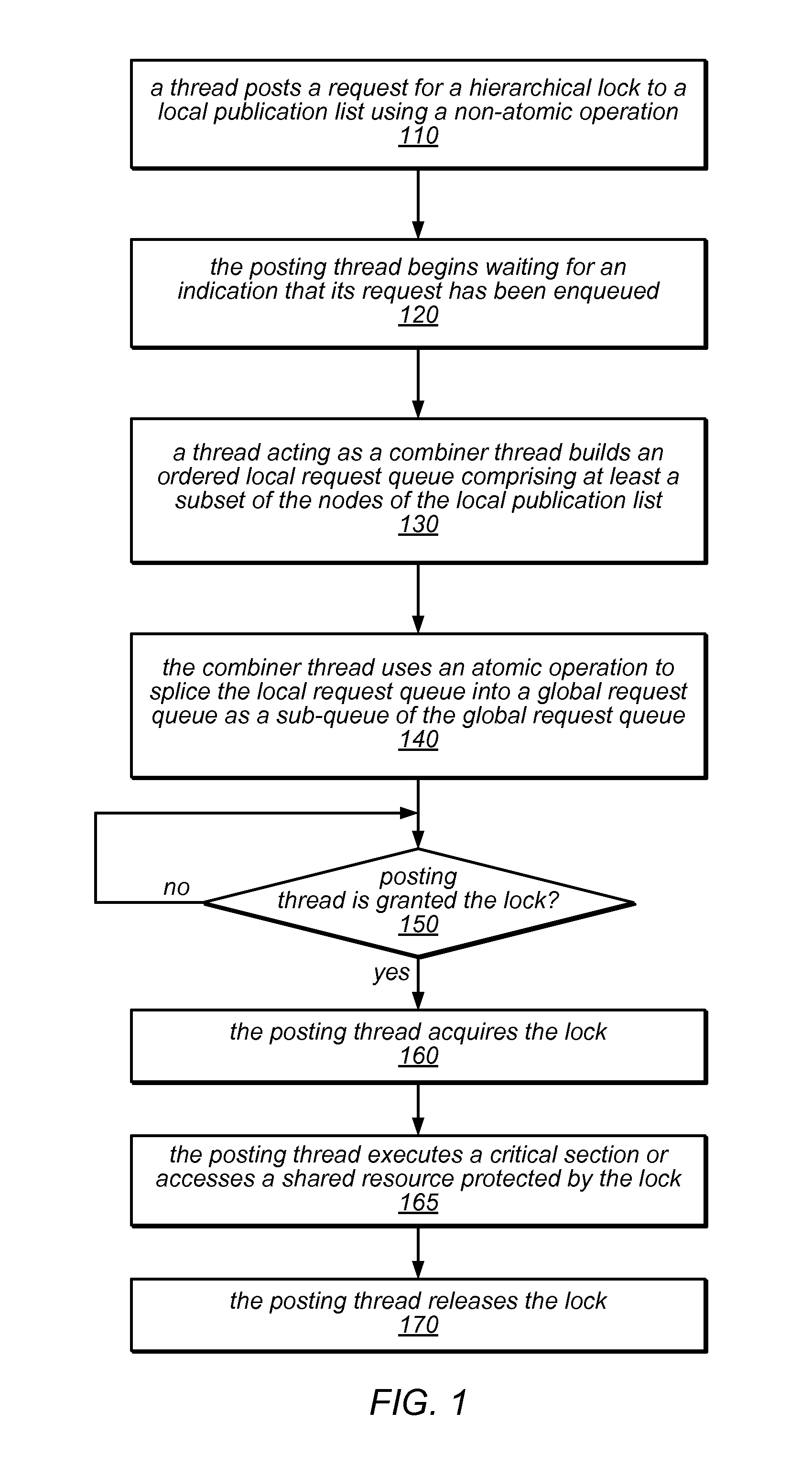
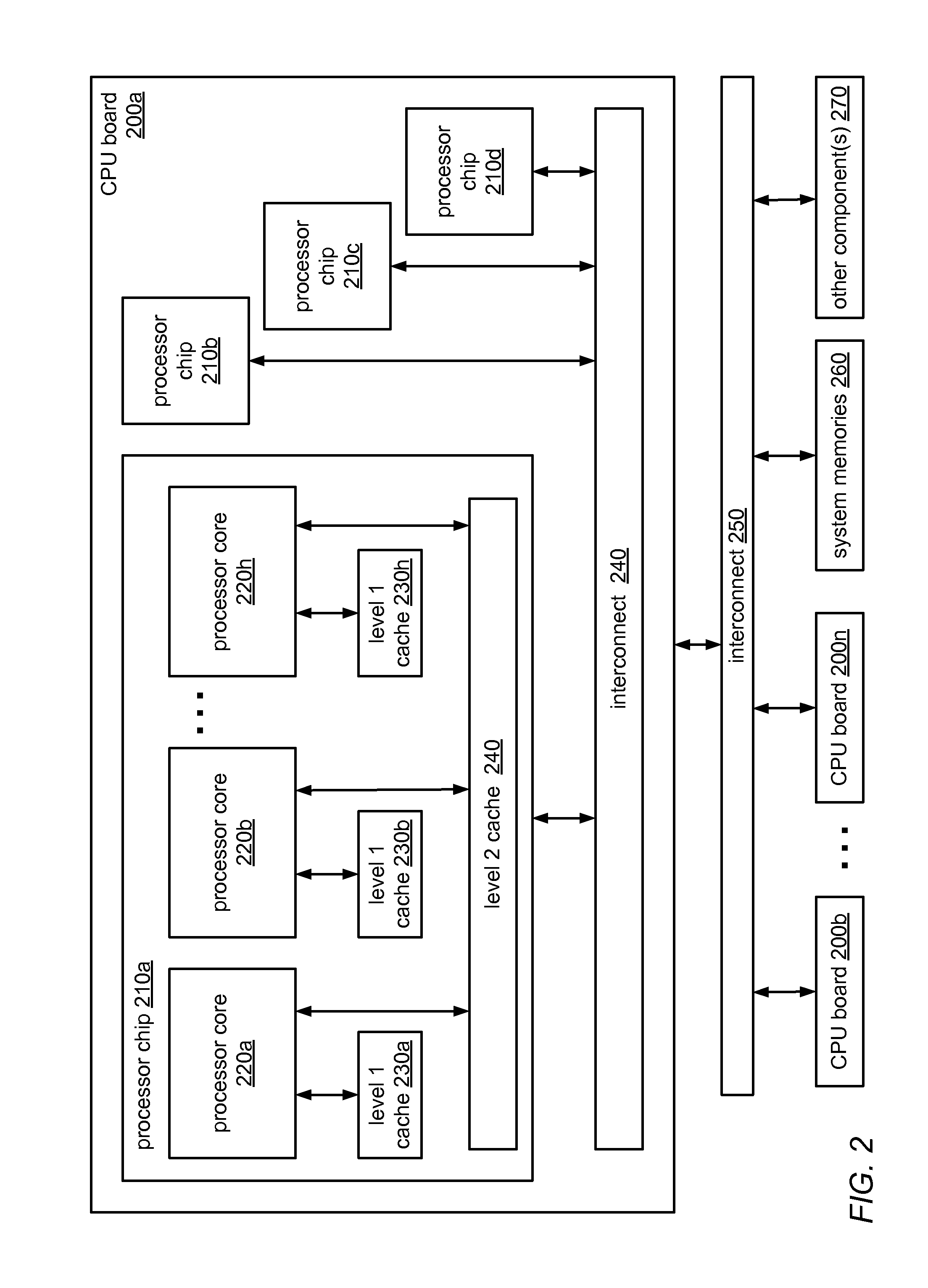
System and Method for Implementing Hierarchical Queue-Based Locks Using Flat Combining
ActiveUS20120311606A1Little interconnection trafficFew costly synchronization operationMultiprogramming arrangementsMemory systemsDistributed computingAtomic operations
The system and methods described herein may be used to implement a scalable, hierarchal, queue-based lock using flat combining. A thread executing on a processor core in a cluster of cores that share a memory may post a request to acquire a shared lock in a node of a publication list for the cluster using a non-atomic operation. A combiner thread may build an ordered (logical) local request queue that includes its own node and nodes of other threads (in the cluster) that include lock requests. The combiner thread may splice the local request queue into a (logical) global request queue for the shared lock as a sub-queue. A thread whose request has been posted in a node that has been combined into a local sub-queue and spliced into the global request queue may spin on a lock ownership indicator in its node until it is granted the shared lock.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
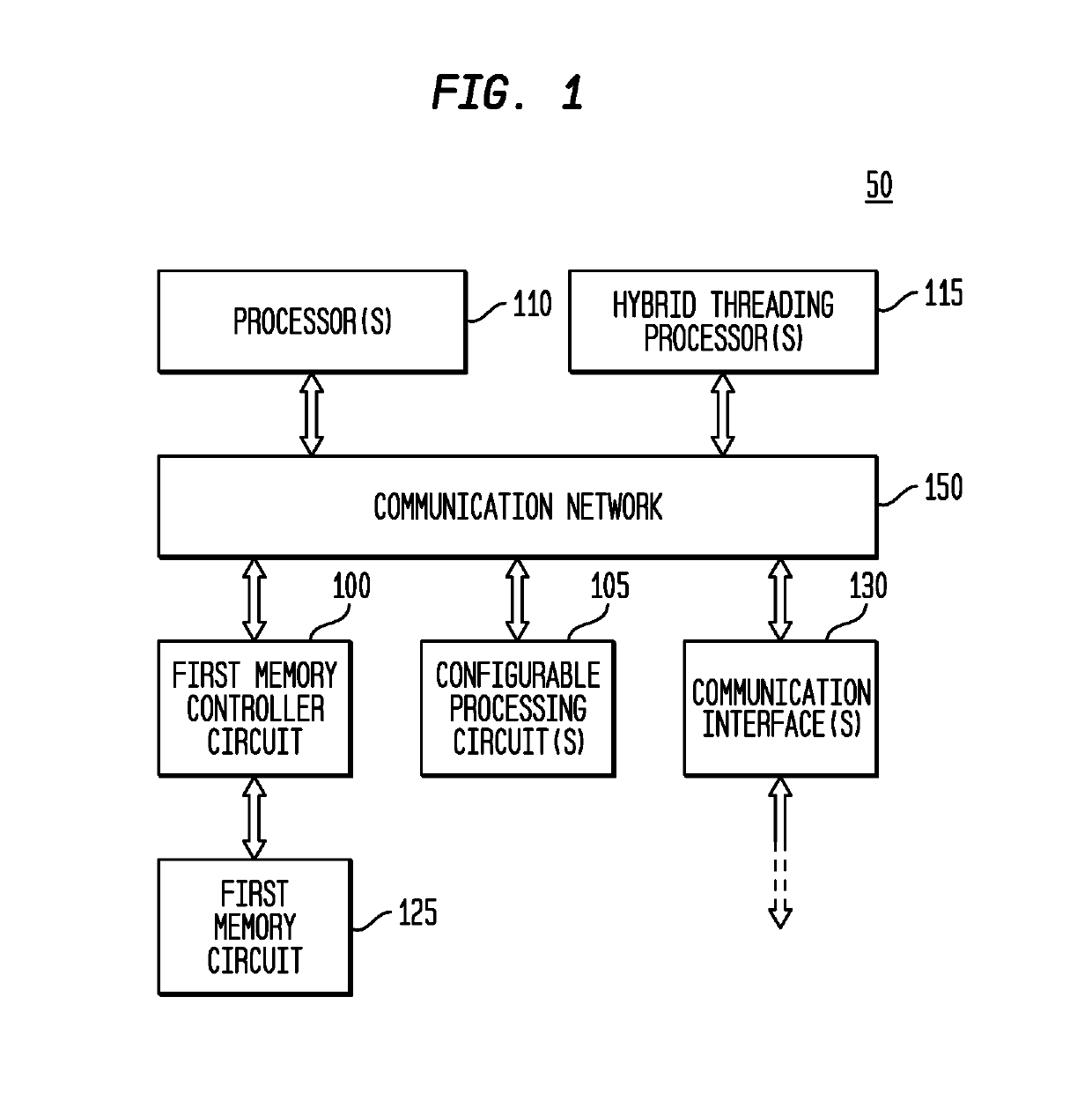
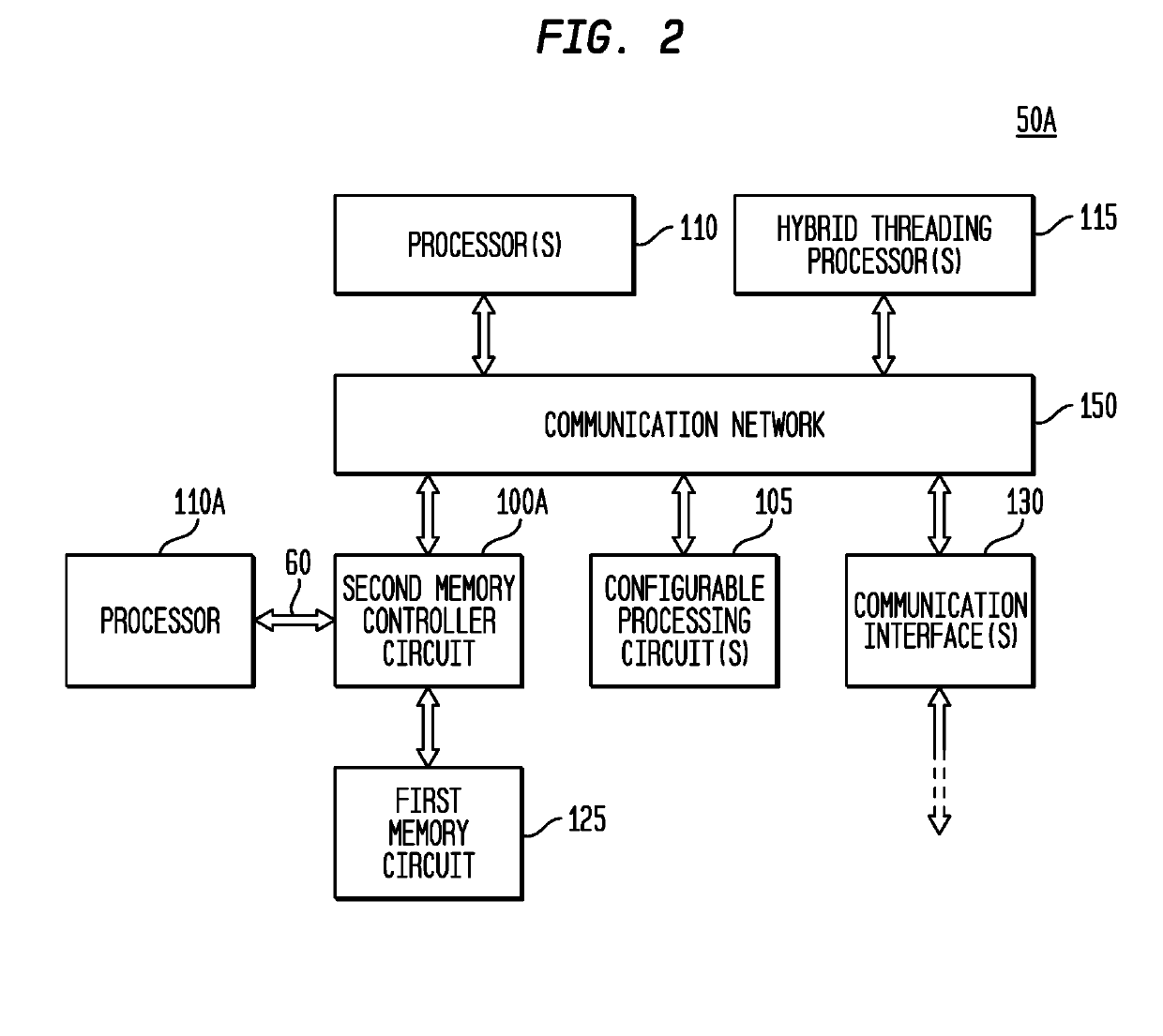
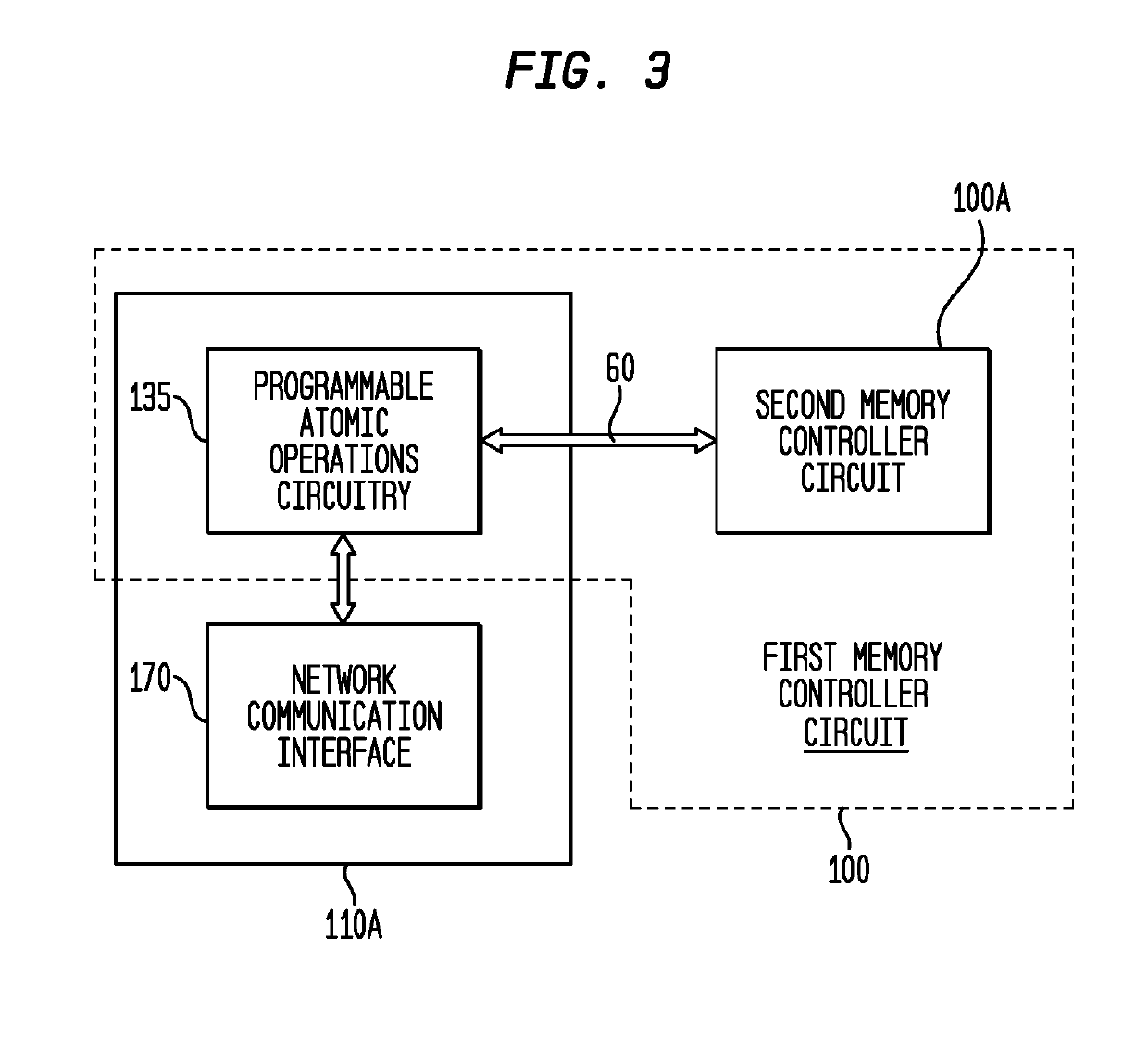
Memory Controller with Programmable Atomic Operations
ActiveUS20190324928A1Improve performanceEnergy efficiencyMemory architecture accessing/allocationProgram initiation/switchingMemory circuitsMemory controller
A memory controller circuit is disclosed which is coupleable to a first memory circuit, such as DRAM, and includes: a first memory control circuit to read from or write to the first memory circuit; a second memory circuit, such as SRAM; a second memory control circuit adapted to read from the second memory circuit in response to a read request read when the requested data is stored in the second memory circuit, and otherwise to transfer the read request to the first memory control circuit; predetermined atomic operations circuitry; and programmable atomic operations circuitry adapted to perform at least one programmable atomic operation. The second memory control circuit also transfers a received programmable atomic operation request to the programmable atomic operations circuitry and sets a hazard bit for a cache line of the second memory circuit.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Lock Mechanism to Enable Atomic Updates to Shared Memory
ActiveUS20090240860A1Reduce in quantityUnauthorized memory use protectionProgram controlLocking mechanismRead-modify-write
A system and method for locking and unlocking access to a shared memory for atomic operations provides immediate feedback indicating whether or not the lock was successful. Read data is returned to the requestor with the lock status. The lock status may be changed concurrently when locking during a read or unlocking during a write. Therefore, it is not necessary to check the lock status as a separate transaction prior to or during a read-modify-write operation. Additionally, a lock or unlock may be explicitly specified for each atomic memory operation. Therefore, lock operations are not performed for operations that do not modify the contents of a memory location.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
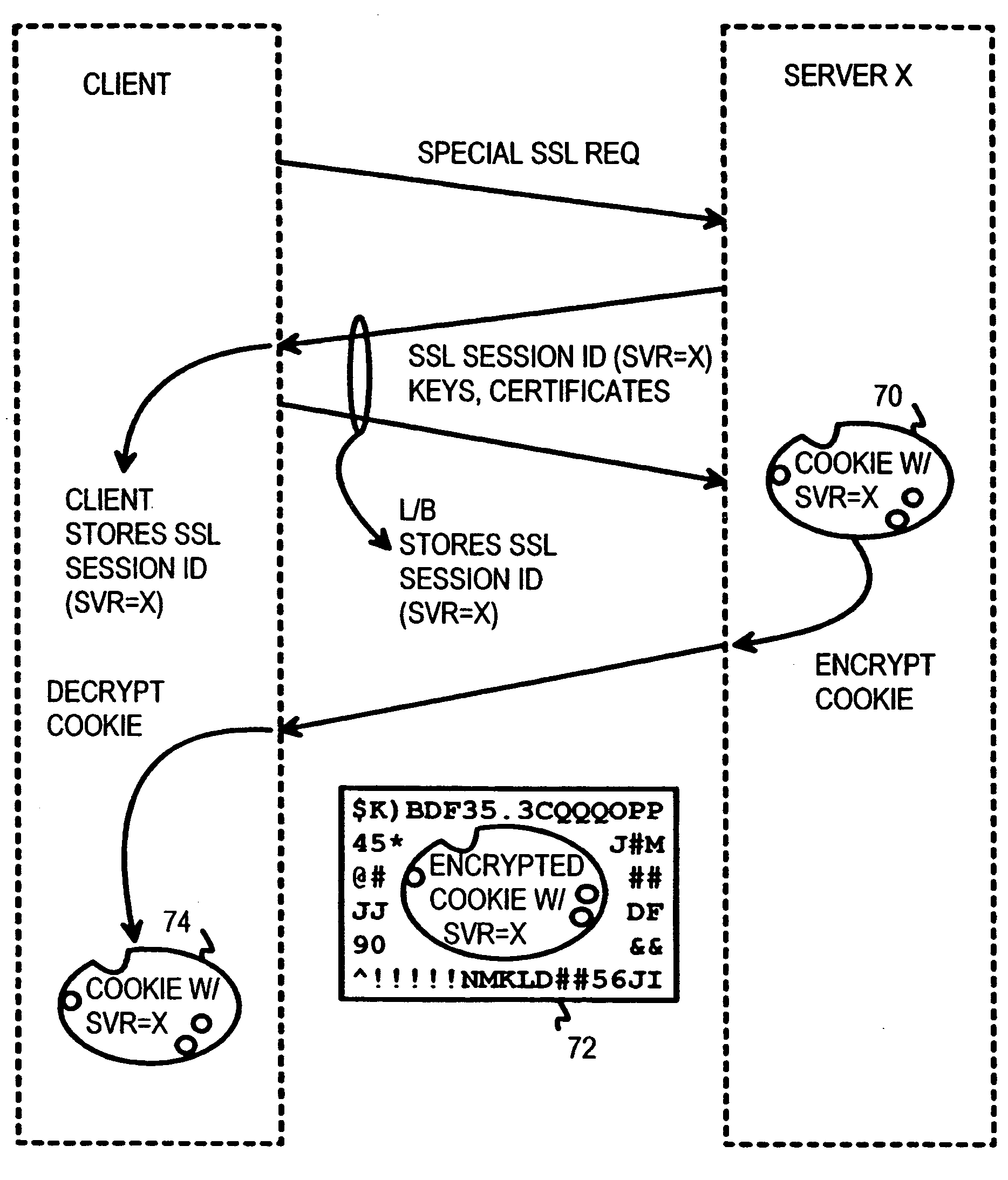
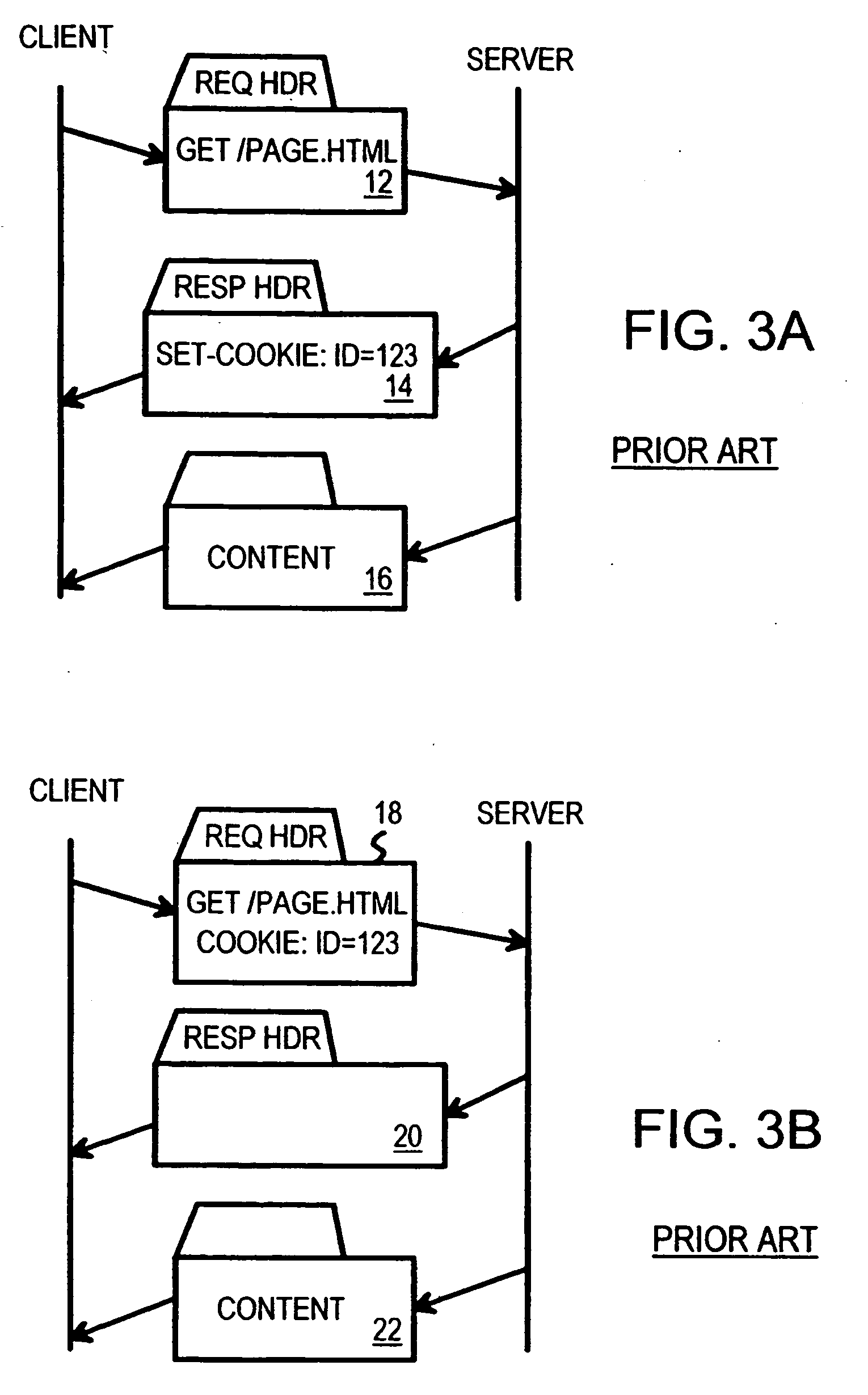
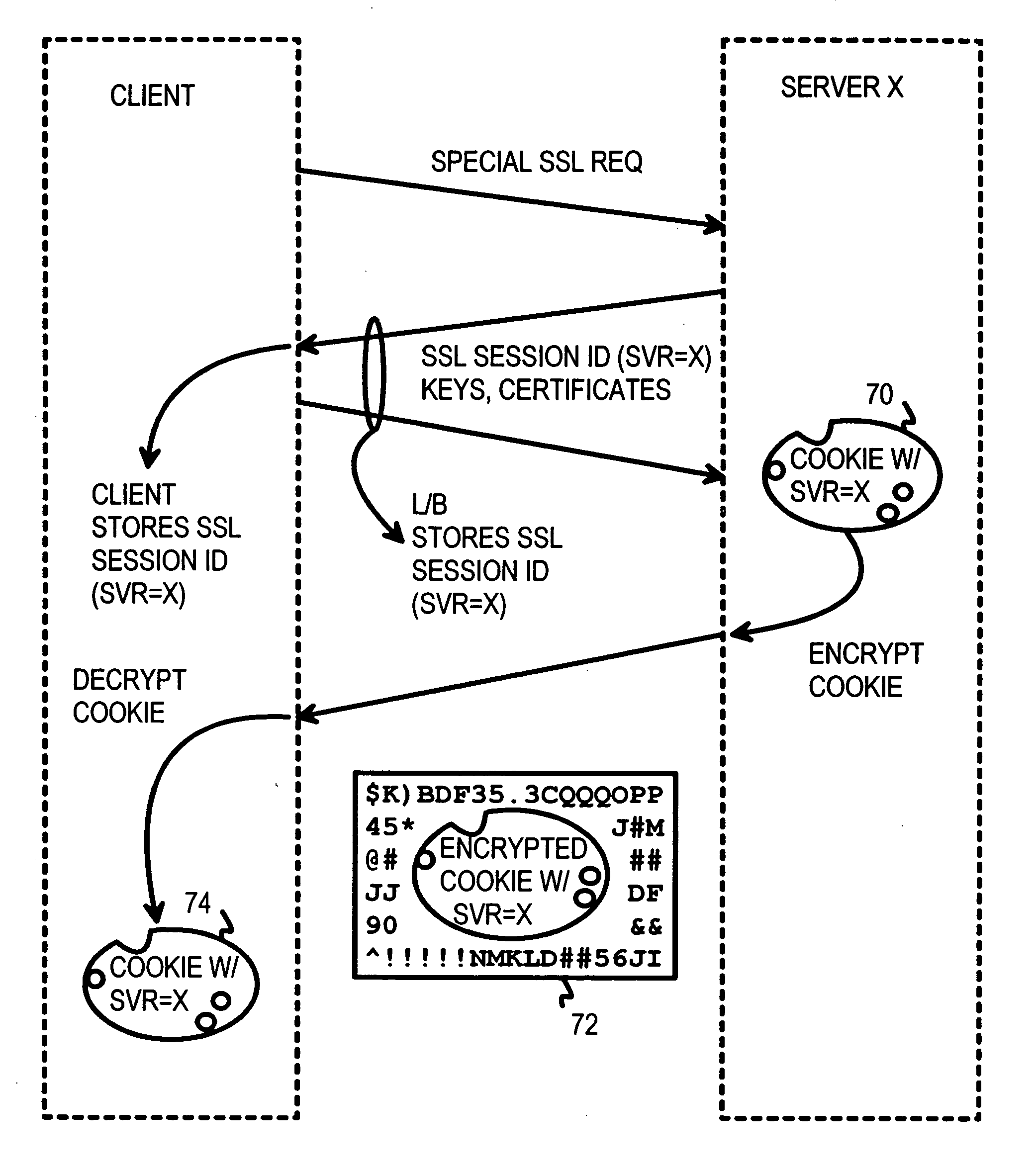
Atomic session-start operation combining clear-text and encrypted sessions to provide ID visibility to middleware such as load-balancers
InactiveUS20070094373A1Multiprogramming arrangementsMultiple digital computer combinationsVisibilityPlaintext
A load-balancer assigns incoming requests to servers at a server farm. An atomic operation assigns both un-encrypted clear-text requests and encrypted requests from a client to the same server at the server farm. An encrypted session is started early by the atomic operation, before encryption is required. The atomic operation is initiated by a special, automatically loaded component on a web page. This component is referenced by code requiring that an encrypted session be used to retrieve the component. Keys and certificates are exchanged between a server and the client to establish the encrypted session. The server generates a secure-sockets-layer (SSL) session ID for the encrypted session. The server also generates a server-assignment cookie that identifies the server at the server farm. The server-assignment cookie is encrypted and sent to the client along with the SSL session ID. The Client decrypts the server-assignment cookie and stores it along with the SSL session ID. The load-balancer stores the SSL session ID along with a server assignment that identifies the server that generated the SSL session ID. When other encrypted requests are generated by the client to the server farm, they include the SSL session ID. The load-balancer uses the SSL session ID to send the requests to the assigned server. When the client sends a non-encrypted clear-text request to the server farm, it includes the decrypted server-assignment cookie. The load balancer parses the clear-text request to find the server-assignment cookie. The load-balancer then sends the request to the assigned server.
Owner:ZARBANA DIGITAL FUND +1
Interlocked Increment Memory Allocation and Access
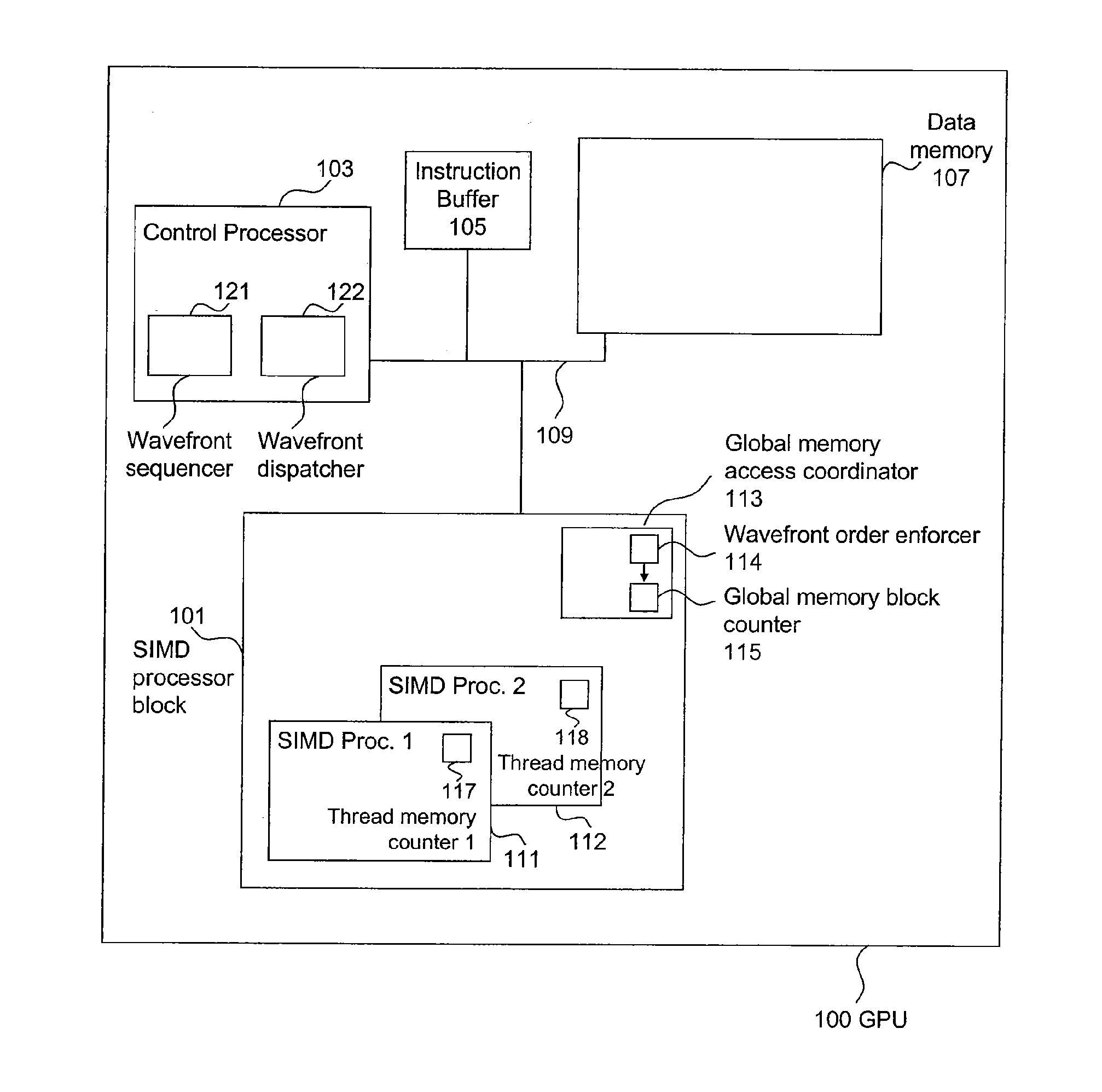
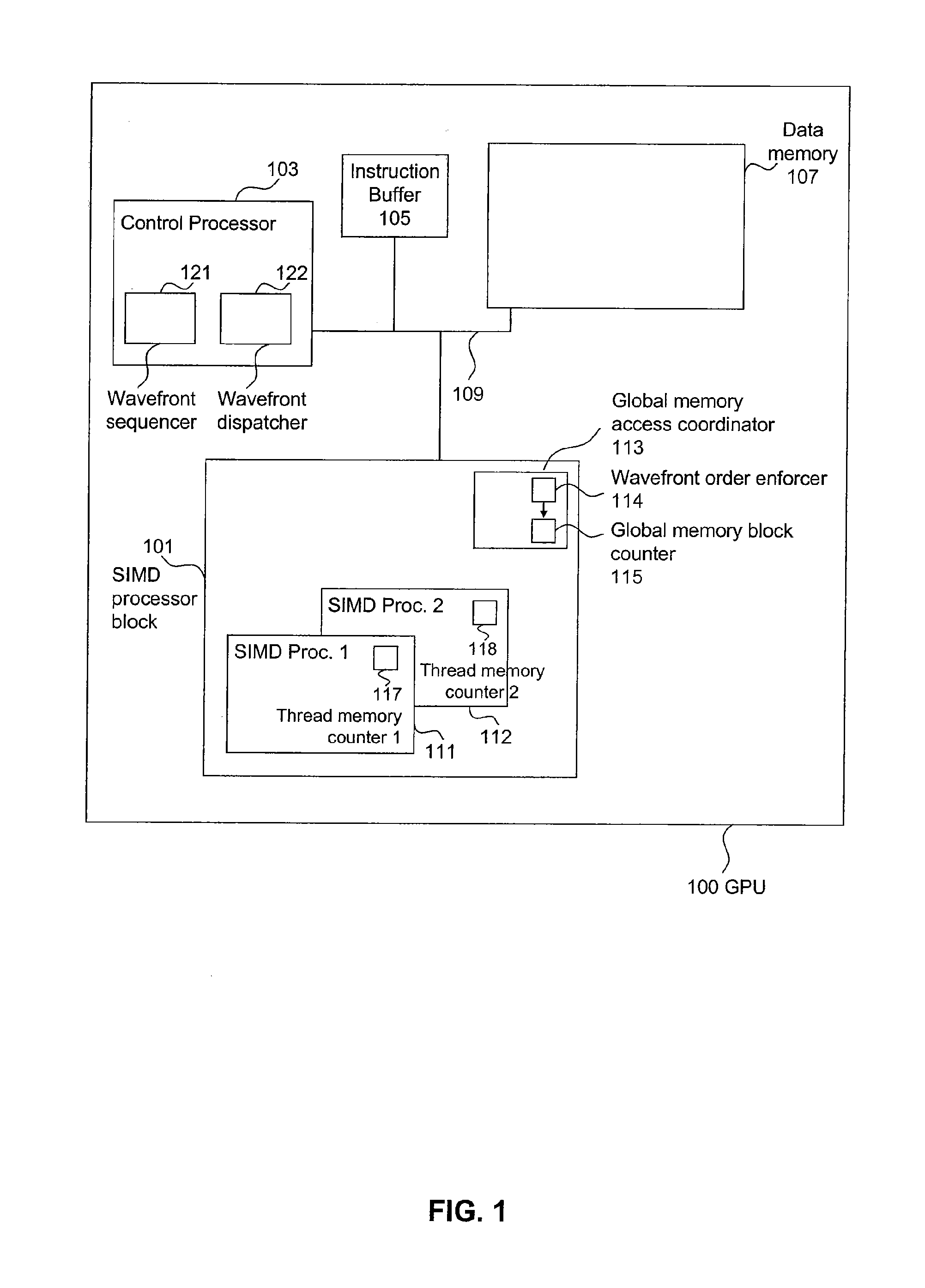
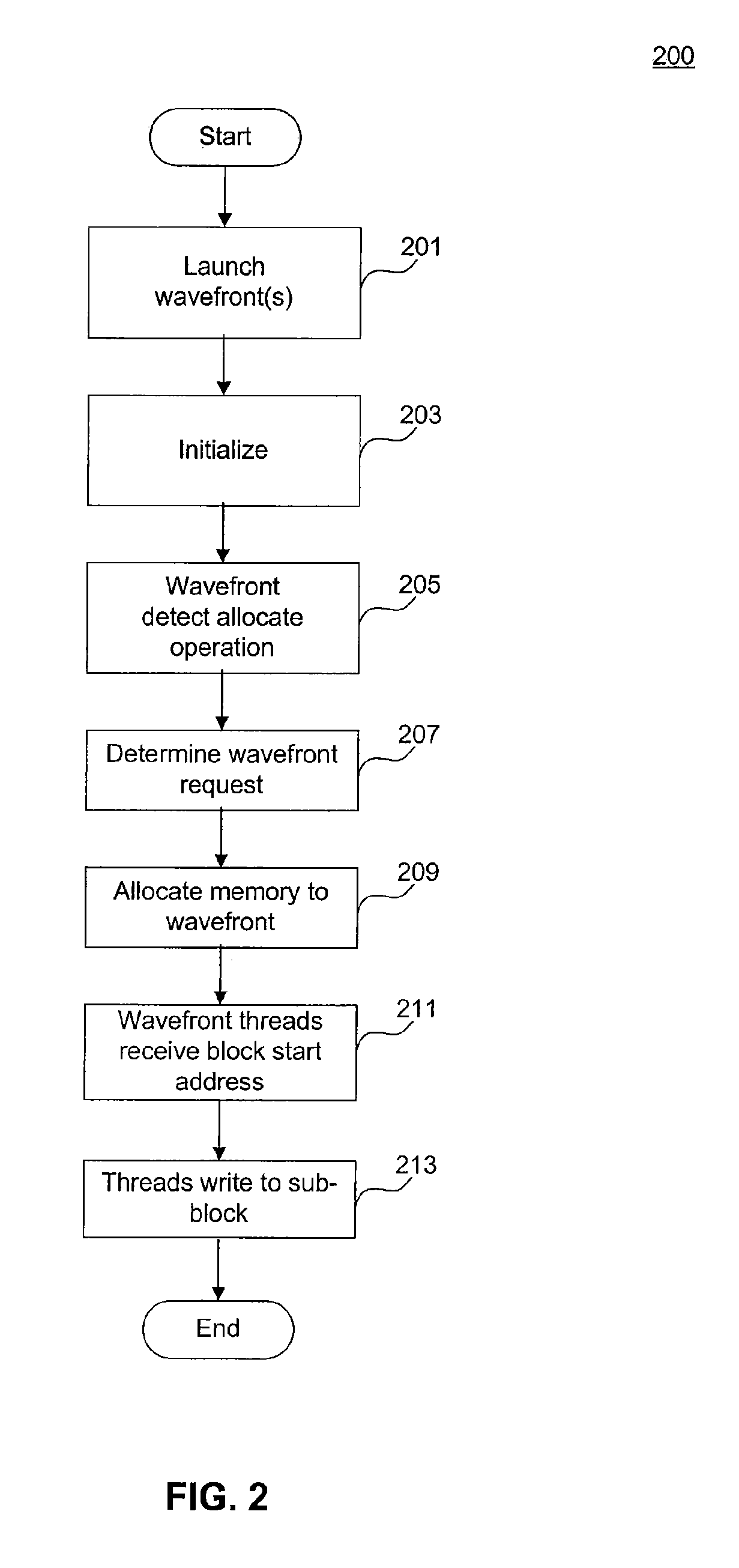
ActiveUS20110055511A1Increase profitMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMultiprogramming arrangementsWavefrontAtomic operations
A method of allocating a memory to a plurality of concurrent threads is presented. The method includes dynamically determining writer threads each having at least one pending write to the memory; and dynamically allocating respective contiguous blocks in the memory for each of the writer threads. Another method of allocating a memory to a plurality of concurrent threads includes launching the plurality of threads as a plurality of wavefronts, dynamically determining a group of wavefronts each having at least one thread requiring a write to the memory, and dynamically allocating respective contiguous blocks in the memory for each wavefront from the group of wavefronts. A corresponding method of assigning a memory to a plurality of reader threads includes determining a first number corresponding to a number of writer threads having a block allocated in said memory, launching a first number of reader threads, entering a first wavefront of said reader threads from said group of wavefronts to an atomic operation, and assigning a first block in the memory to the first wavefront during the corresponding atomic operation, where the first block is contiguous to a previously allocated block dynamically allocated to another wavefront from said group of wavefronts. Corresponding system embodiments and computer program product embodiments are also presented.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
Method and Apparatus for Performing a Geometric Transformation on Objects in an Object-Oriented Environment using a Multiple-Transaction Technique
InactiveUS20130212505A1Saving informationObject oriented databasesConstraint-based CADEnterprise engineeringDatabase
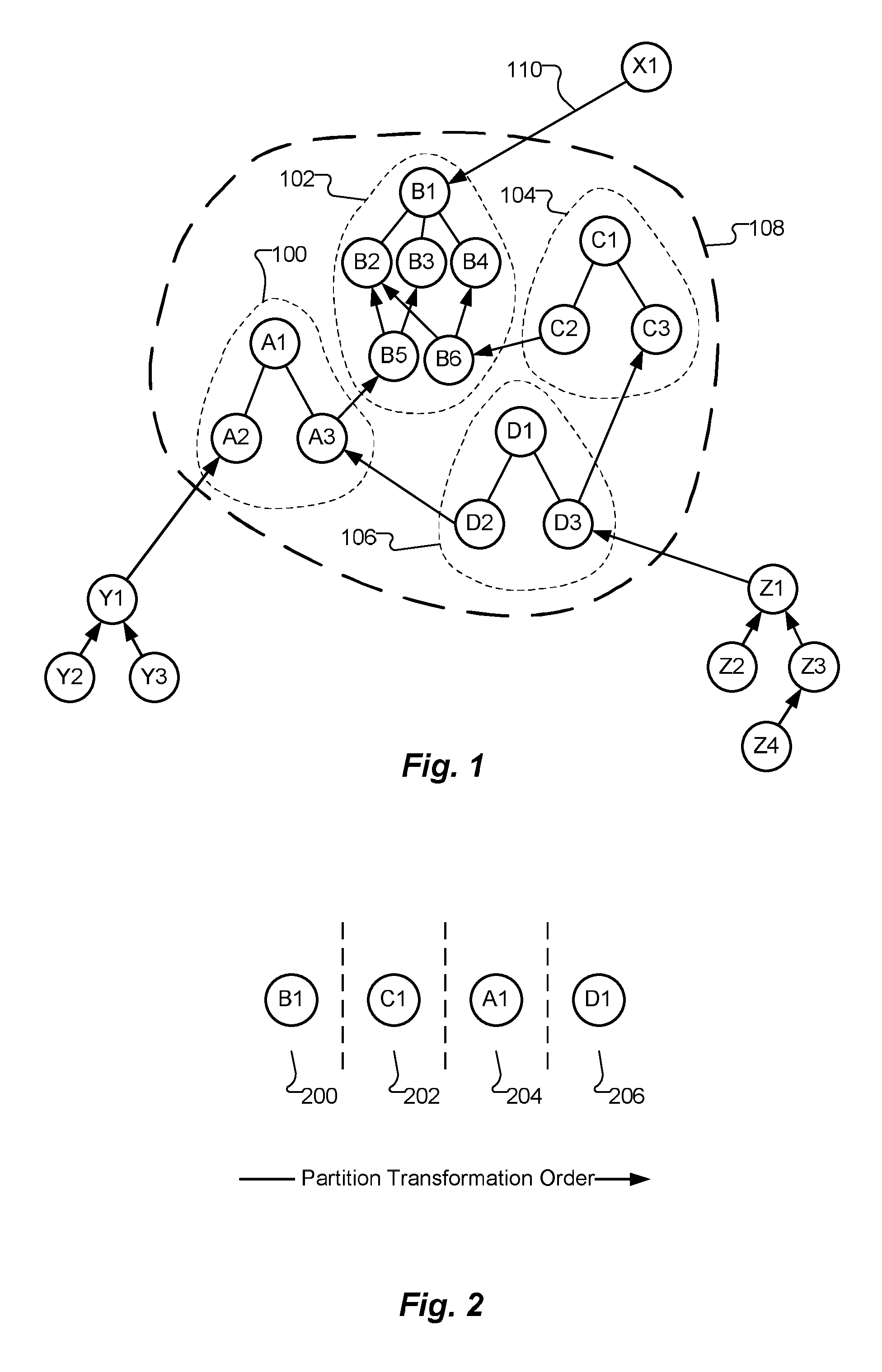
A large number of objects, such as objects representing beams and columns in an object-oriented enterprise engineering system, may be geometrically transformed in a model database by dividing the objects according to criteria into a number of ordered partitions and transforming the objects in each partition as an atomic operation. Objects that are to be transformed are organized into the ordered partitions, and the partitions are transformed in sequential order, such that all predecessors of a given object are transformed before, or in the same operation as, the given object. If a large transformation operation abnormally terminates before all the small transformation operations have been completed, the model database is, nevertheless, left in a consistent state. The transformation operation may be resumed from the point of interruption. Furthermore, the number of objects that may be transformed is not constrained by the amount of memory available in the system.
Owner:INTERGRAPH
System and Method for Split Hardware Transactions
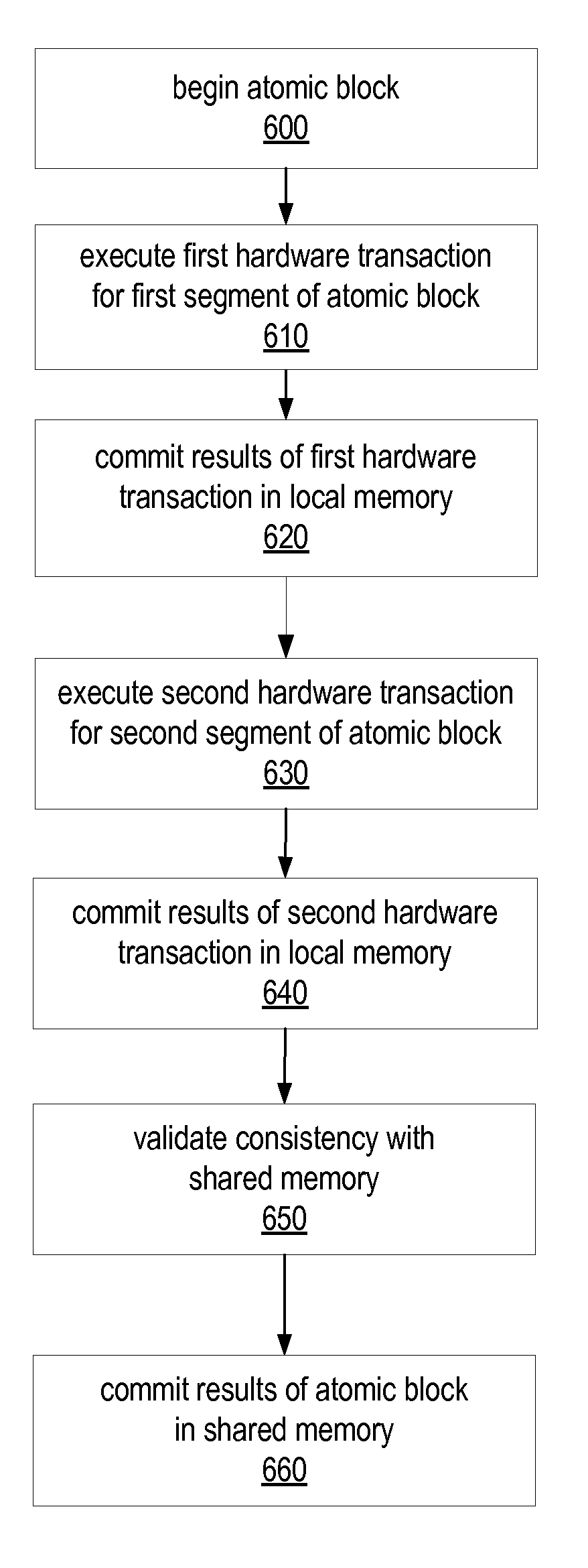
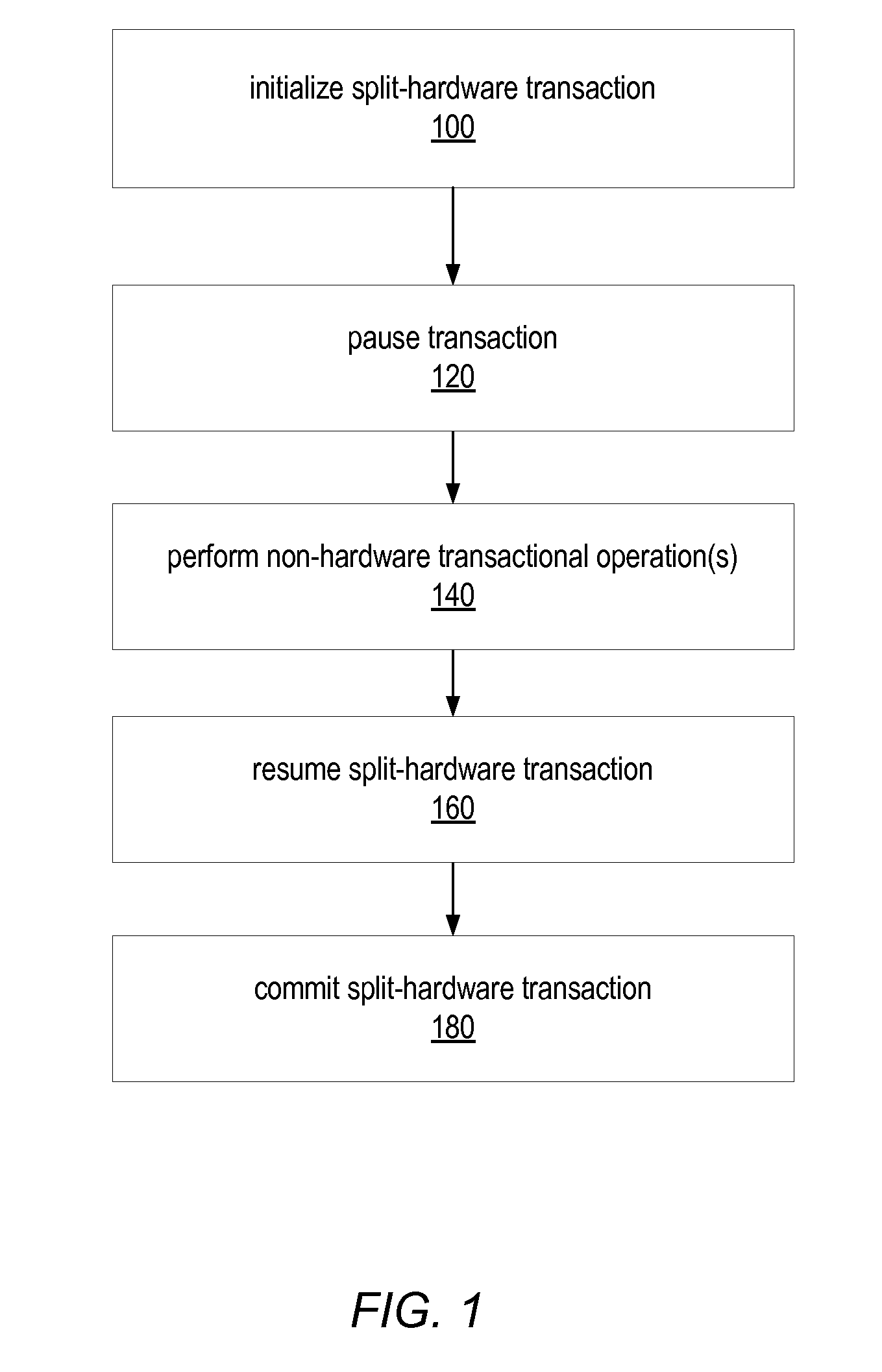
ActiveUS20090031309A1Reduce difficultyError detection/correctionMemory systemsComputer scienceLocal memories
A split hardware transaction may split an atomic block of code to be executed using multiple hardware transactions, while logically taking effect as a single atomic transaction. A split hardware transaction may use software to combine the multiple hardware transactions into one logically atomic operation. In some embodiments, a split hardware transaction may allow execution of atomic blocks including non-hardware-transactionable (NHT) operations without resorting to exclusively software transactions. A split hardware transaction may maintain a thread-local buffer logs all memory accesses performed by the split hardware transaction. A split hardware transaction may use a hardware transaction to copy values read from shared memory locations into a local memory buffer. To execute a non-hardware-transactionable operation, the split hardware transaction may commit the active hardware transaction, execute the non-hardware-transactionable operation, and then initiate a new hardware transaction to execute the rest of the atomic block.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Atomic session-start operation combining clear-text and encrypted sessions to provide ID visibility to middleware such as load-balancers
InactiveUS20050010754A1Reducing local network trafficSimplifying web-site architectureDigital computer detailsMultiprogramming arrangementsPlaintextLoad Shedding
A load-balancer assigns incoming requests to servers at a server farm. An atomic operation assigns both un-encrypted clear-text requests and encrypted requests from a client to the same server at the server farm. An encrypted session is started early by the atomic operation, before encryption is required. The atomic operation is initiated by a special, automatically loaded component on a web page. This component is referenced by code requiring that an encrypted session be used to retrieve the component. Keys and certificates are exchanged between a server and the client to establish the encrypted session. The server generates a secure-sockets-layer (SSL) session ID for the encrypted session. The server also generates a server-assignment cookie that identifies the server at the server farm. The server-assignment cookie is encrypted and sent to the client along with the SSL session ID. The Client decrypts the server-assignment cookie and stores it along with the SSL session ID. The load-balancer stores the SSL session ID along with a server assignment that identifies the server that generated the SSL session ID. When other encrypted requests are generated by the client to the server farm, they include the SSL session ID. The load-balancer uses the SSL session ID to send the requests to the assigned server. When the client sends a non-encrypted clear-text request to the server farm, it includes the decrypted server-assignment cookie. The load balancer parses the clear-text request to find the server-assignment cookie. The load-balancer then sends the request to the assigned server.
Owner:HANGER SOLUTIONS LLC +1
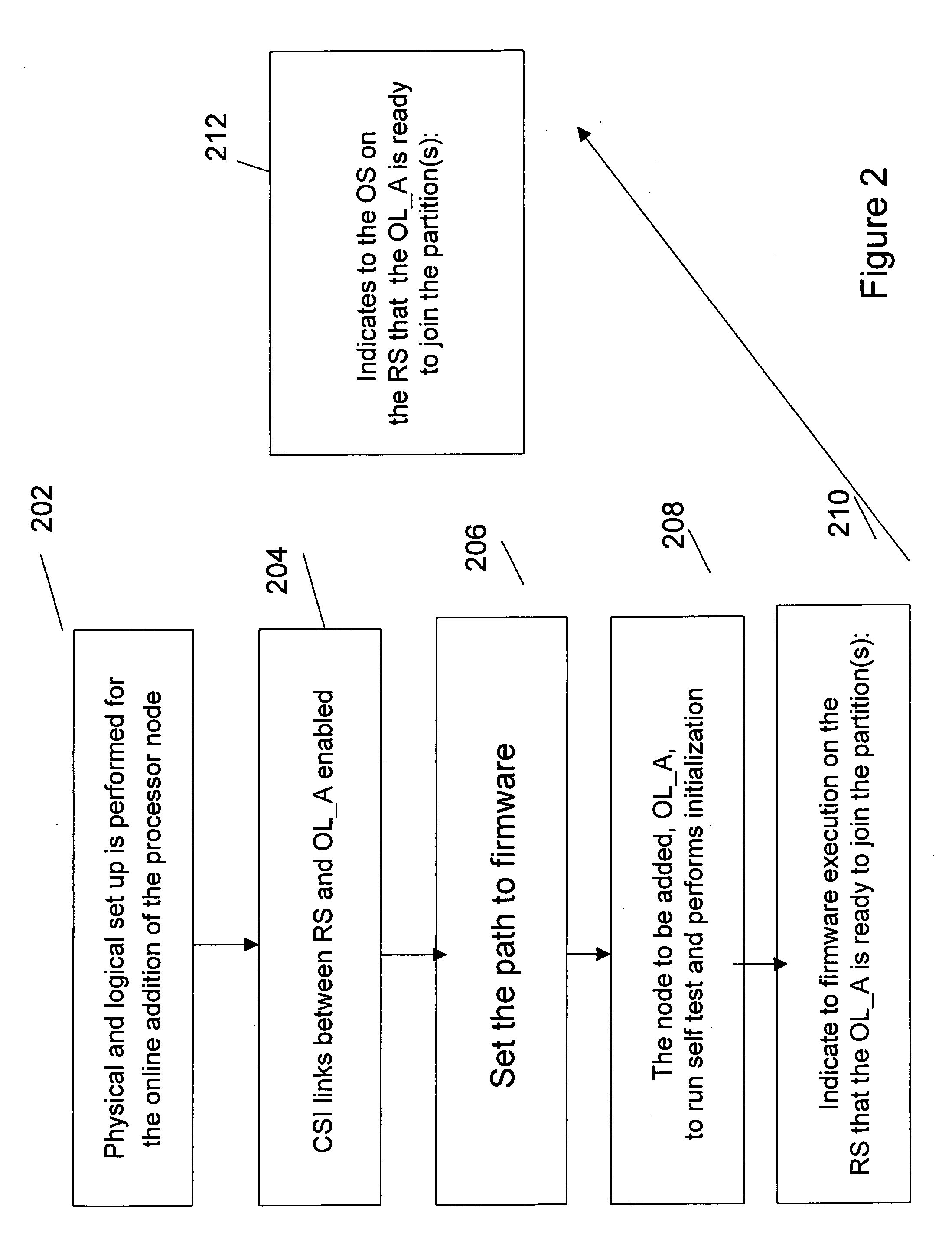
Method, system, and apparatus for dynamic reconfiguration of resources
InactiveUS20060184480A1Facilitates dynamic allocationResource allocationDigital computer detailsAddress decoderRouting table
A dynamic reconfiguration to include on-line addition, deletion, and replacement of individual modules of to support dynamic partitioning of a system, interconnect (link) reconfiguration, memory RAS to allow migration and mirroring without OS intervention, dynamic memory reinterleaving, CPU and socket migration, and support for global shared memory across partitions is described. To facilitate the on-line addition or deletion, the firmware is able to quiesce and de-quiesce the domain of interest so that many system resources, such as routing tables and address decoders, can be updated in what essentially appears to be an atomic operation to the software layer above the firmware.
Owner:INTEL CORP
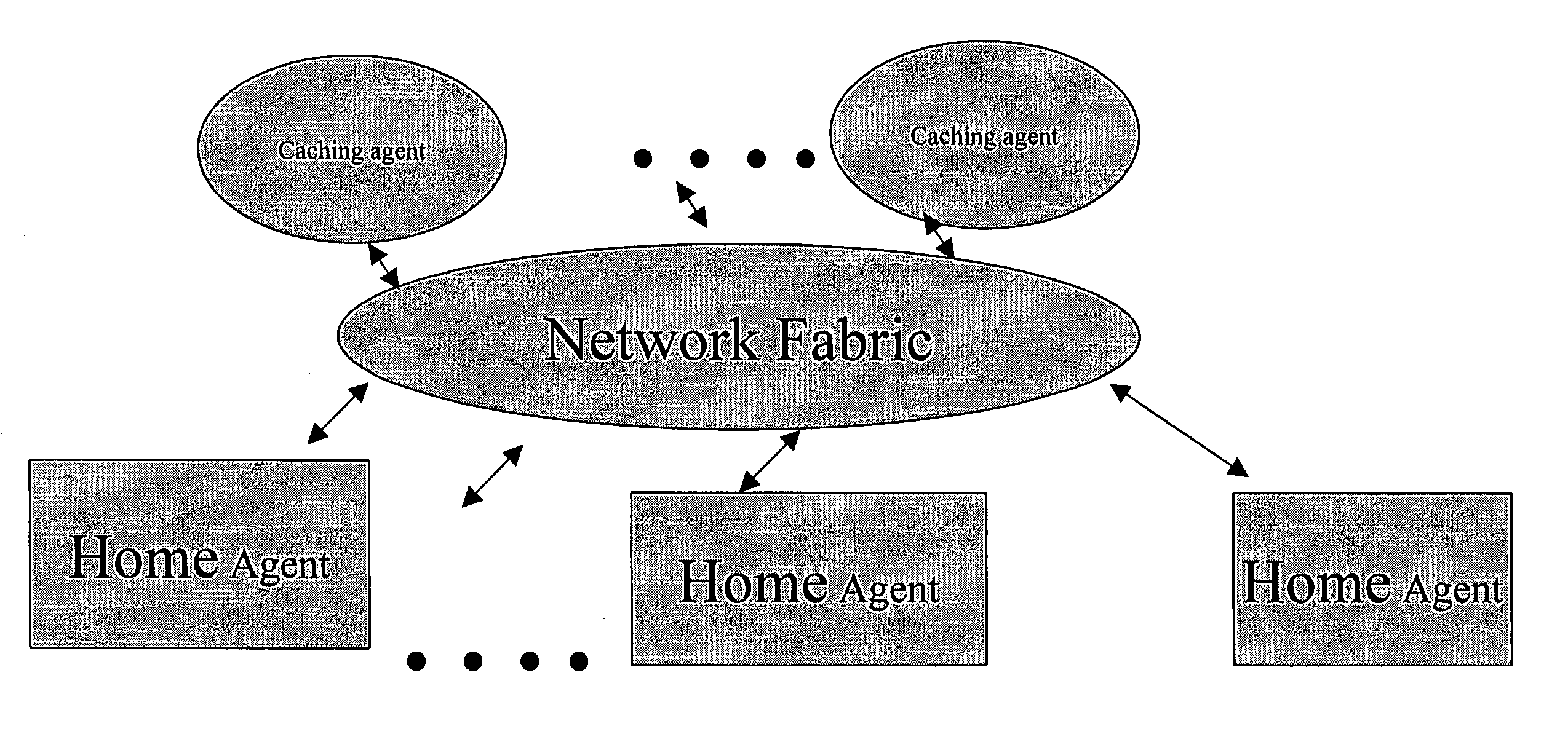
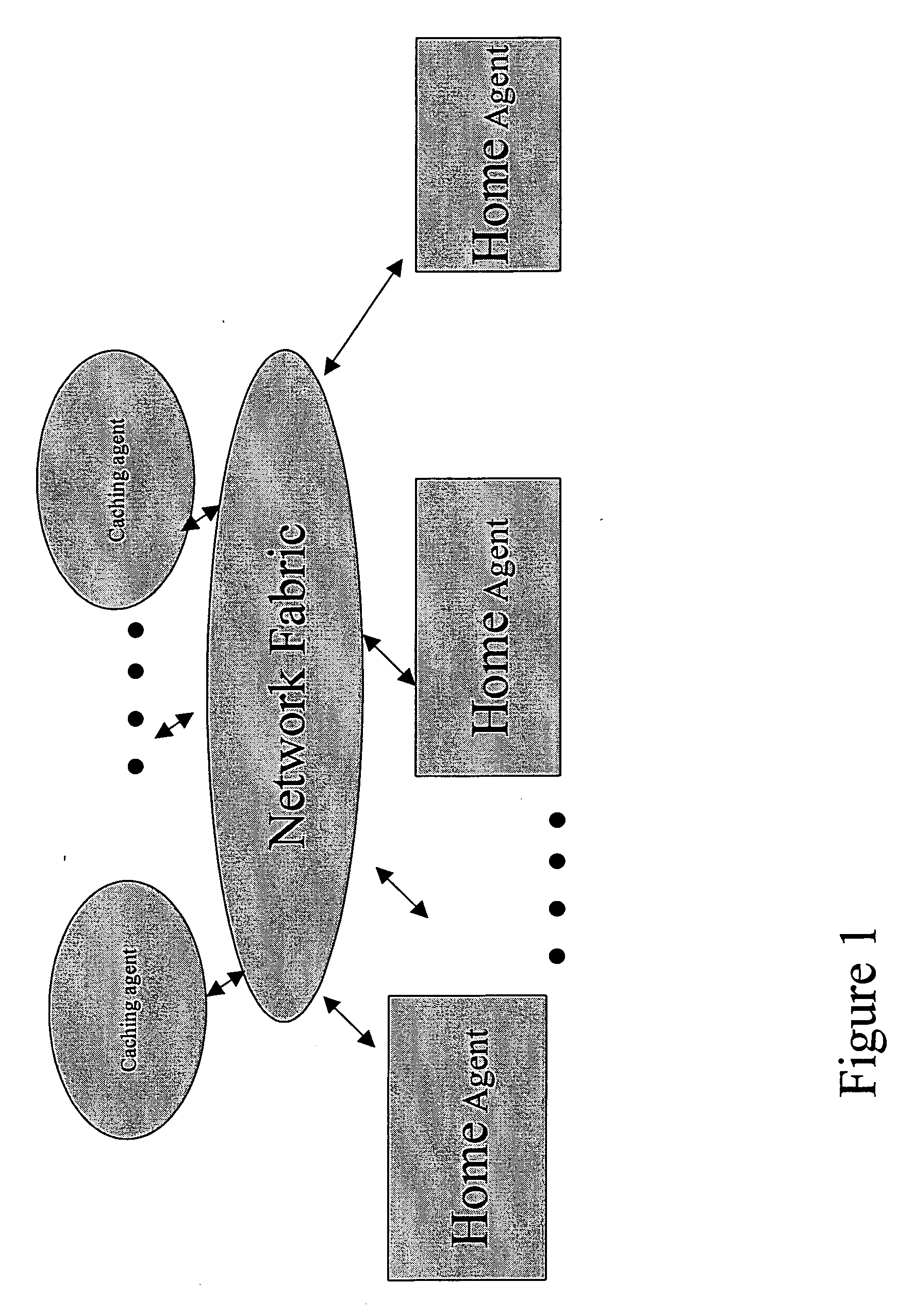
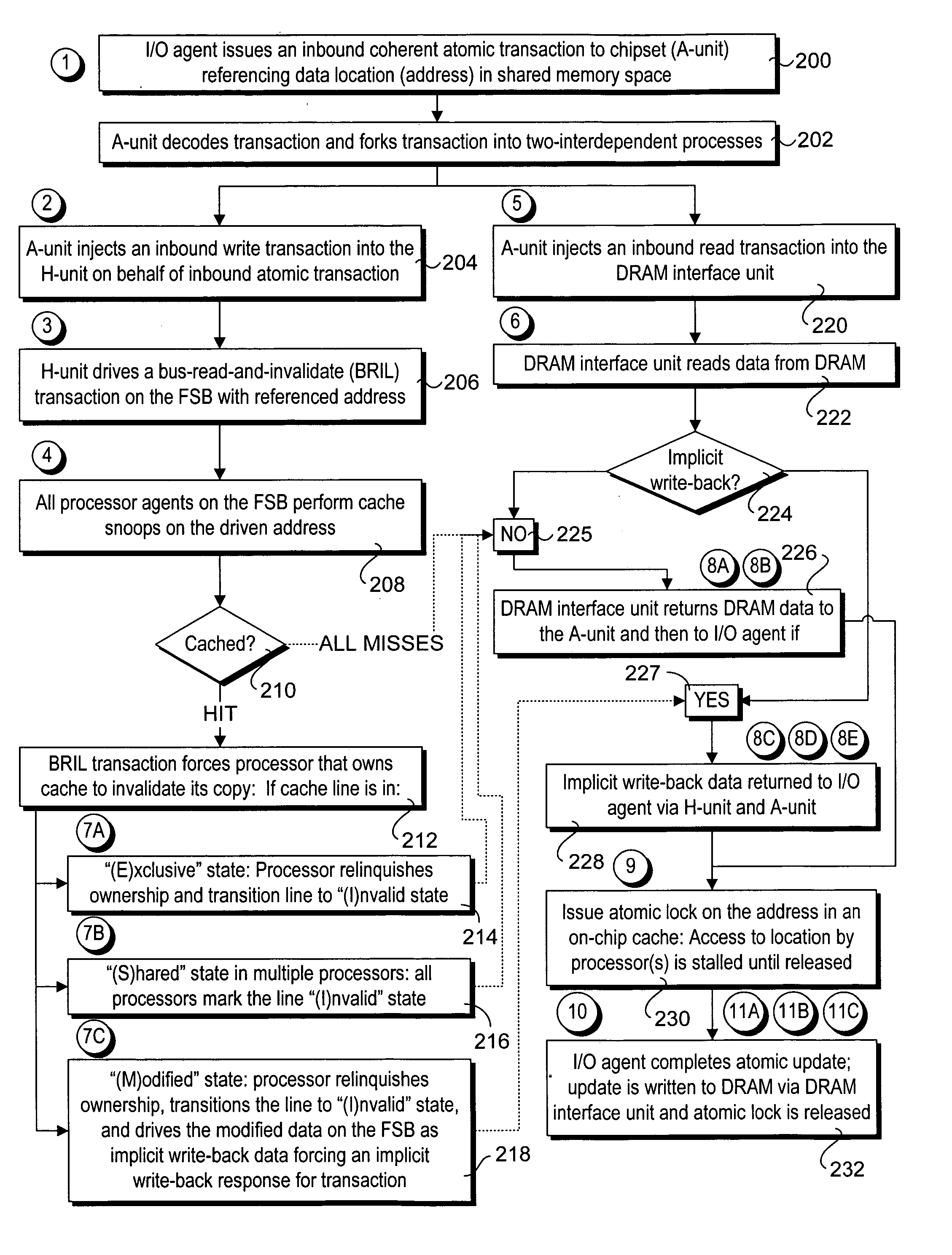
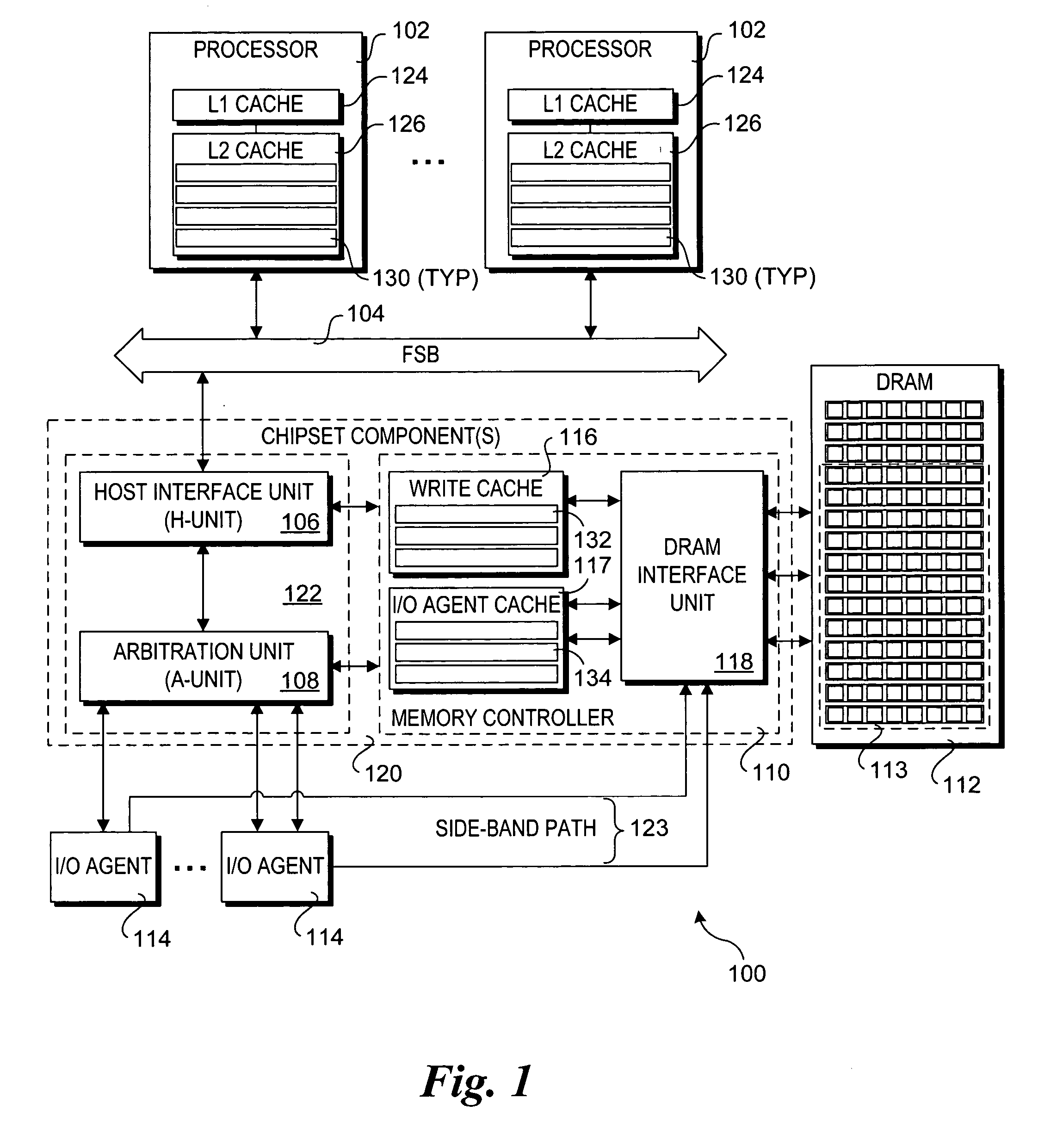
Method and apparatus to enable I/O agents to perform atomic operations in shared, coherent memory spaces
Method and apparatus to enable I / O agents to perform atomic operations in shared, coherent memory spaces. The apparatus includes an arbitration unit, a host interface unit, and a memory interface unit. The arbitration unit provides an interface to one or more I / O agents that issue atomic transactions to access and / or modify data stored in a shared memory space accessed via the memory interface unit. The host interface unit interfaces to a front-side bus (FSB) to which one or more processors may be coupled. In response to an atomic transaction issued by an I / O agent, the transaction is forked into two interdependent processes. Under one process, an inbound write transaction is injected into the host interface unit, which then drives the FSB to cause the processor(s) to perform a cache snoop. At the same time, an inbound read transaction is injected into the memory interface unit, which retrieves a copy of the data from the shared memory space. If the cache snoop identifies a modified cache line, a copy of that cache line is returned to the I / O agent; otherwise, the copy of the data retrieved from the shared memory space is returned.
Owner:INTEL CORP
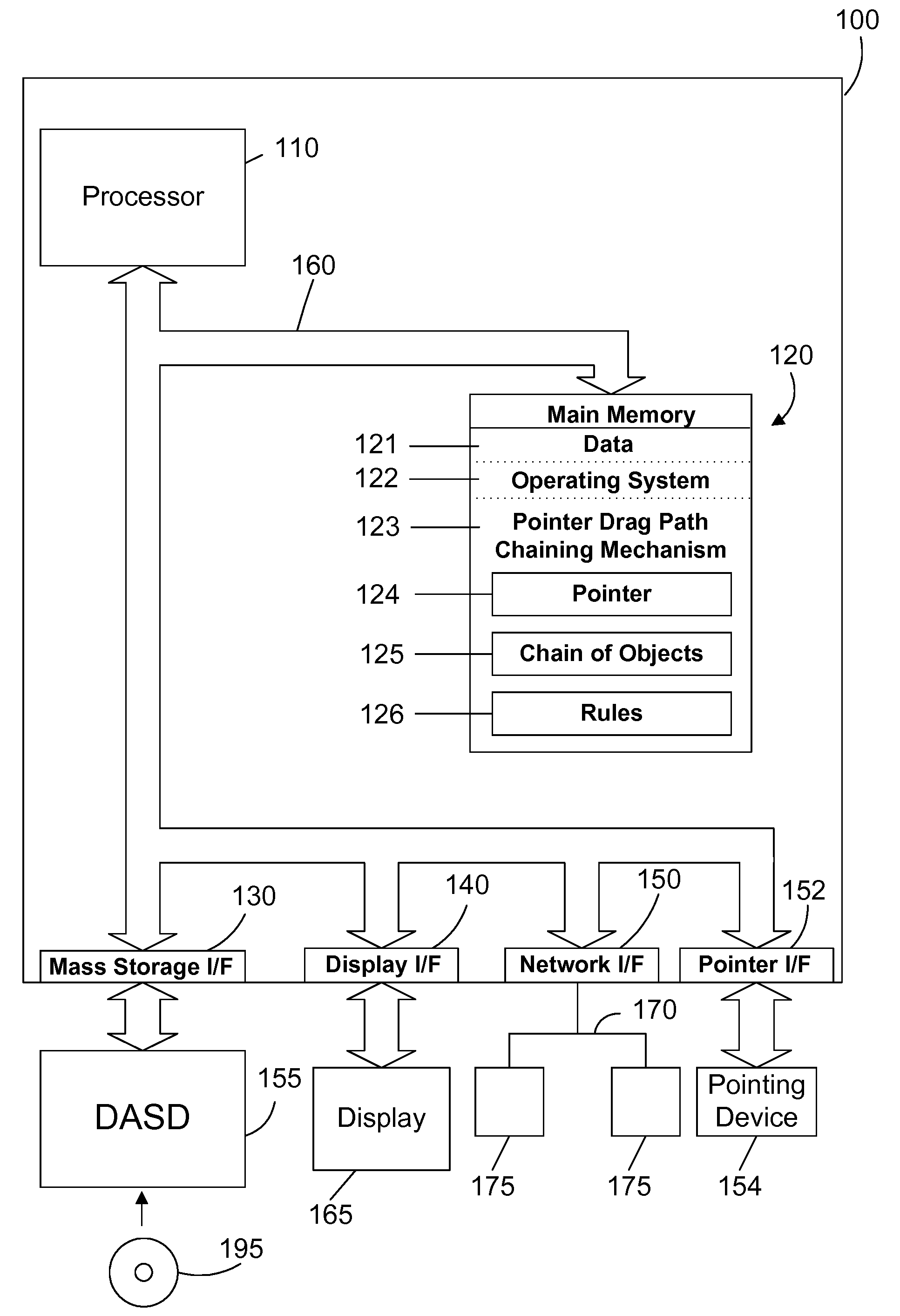
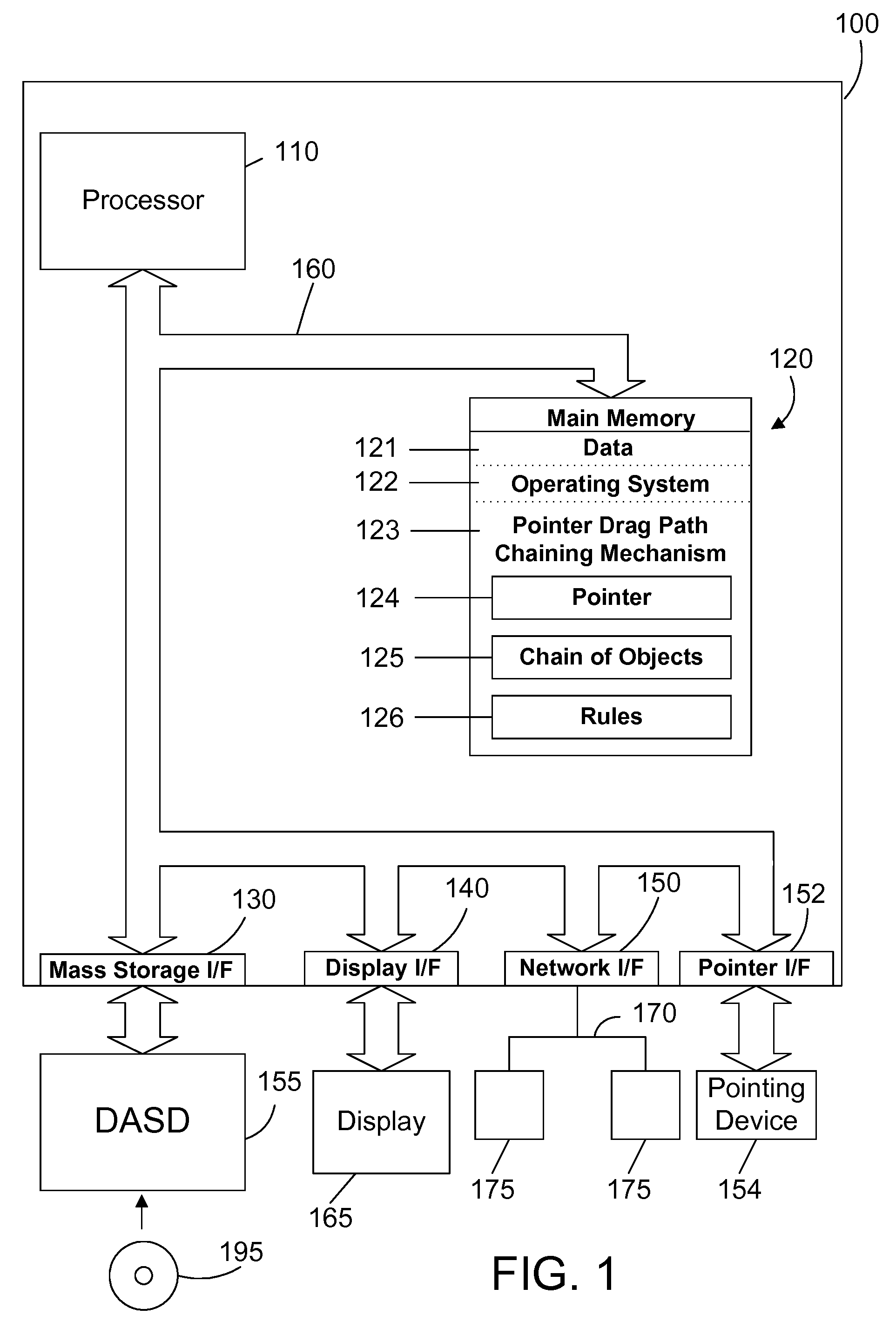
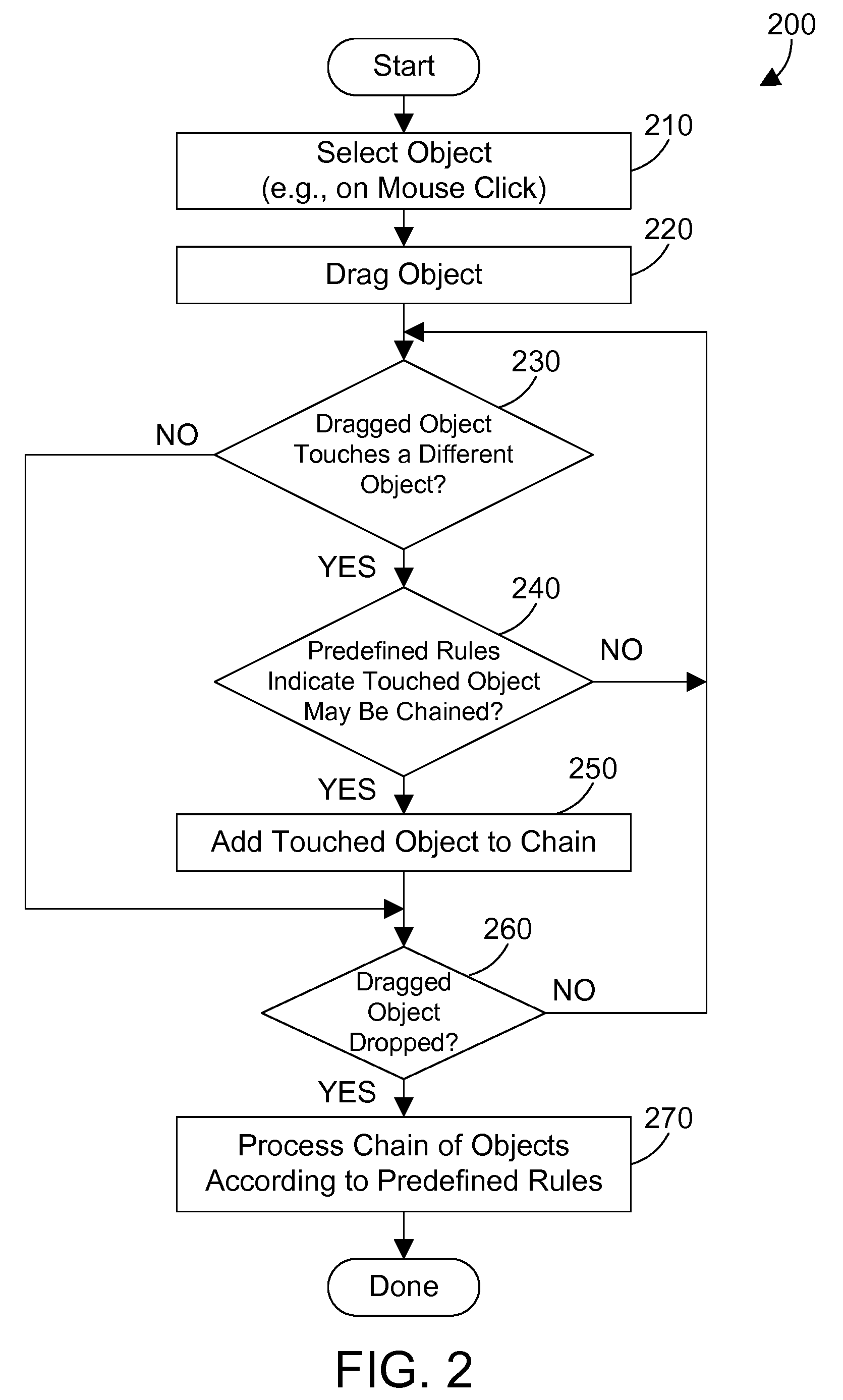
Chaining objects in a pointer drag path
ActiveUS20080235610A1Improve user efficiencyReduce in quantityInput/output for user-computer interactionGraph readingGraphicsGraphical user interface
An apparatus and method for a graphical user interface allow performing operations simply by dragging a first object to touch a second object. The selection of the first object places a corresponding first object in a chain of objects. When the selected first object touches a second object, a corresponding second object is added to the chain of objects. This process may continue for the selection of many objects by merely touching each object with the selected first object, which causes a corresponding object to be added to the chain of objects. The chain of objects may then be processed as an atomic group of operations that may be rolled back if any of the operations in the group fail.
Owner:WRP IP MANAGEMENT LLC
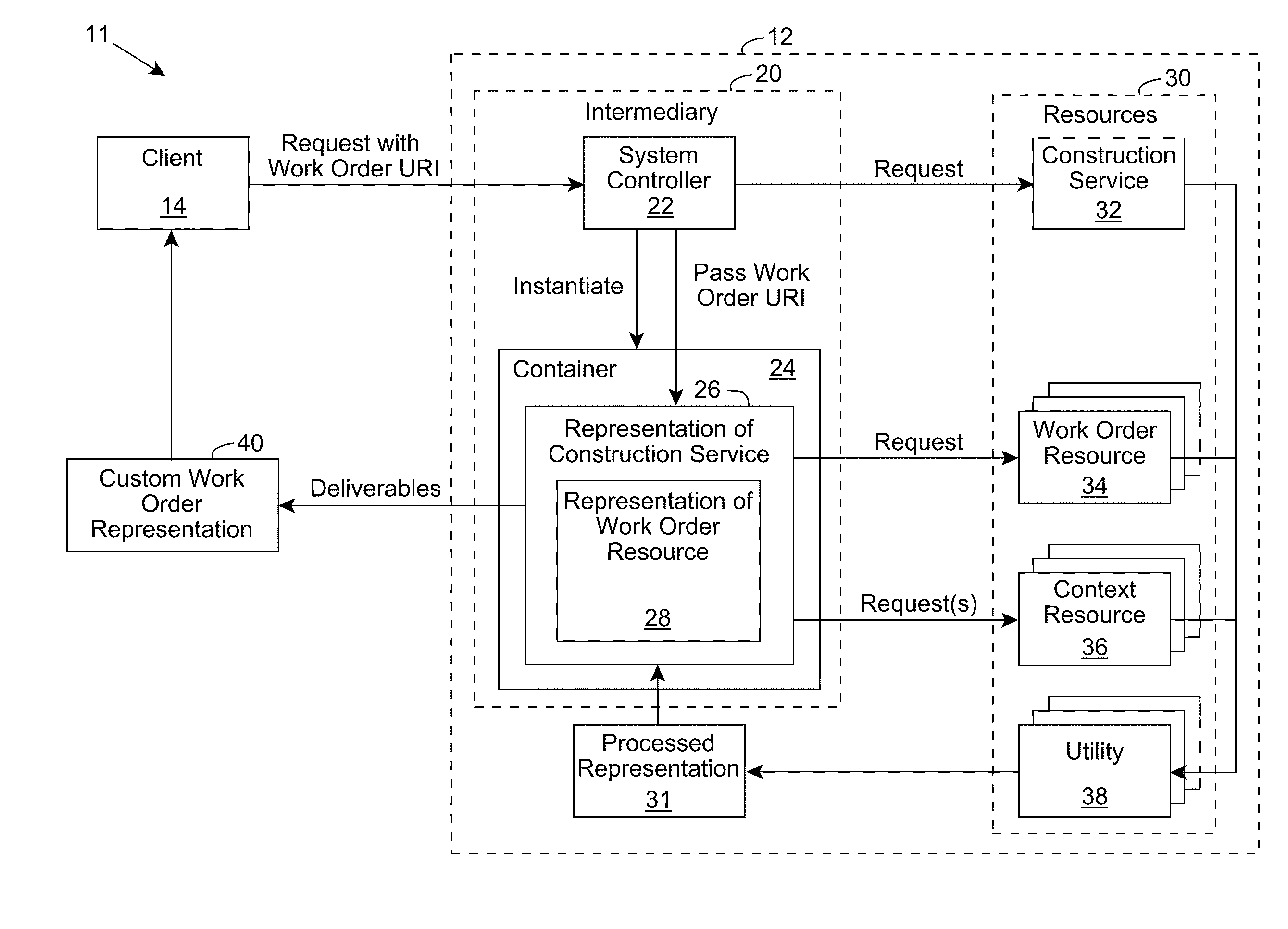
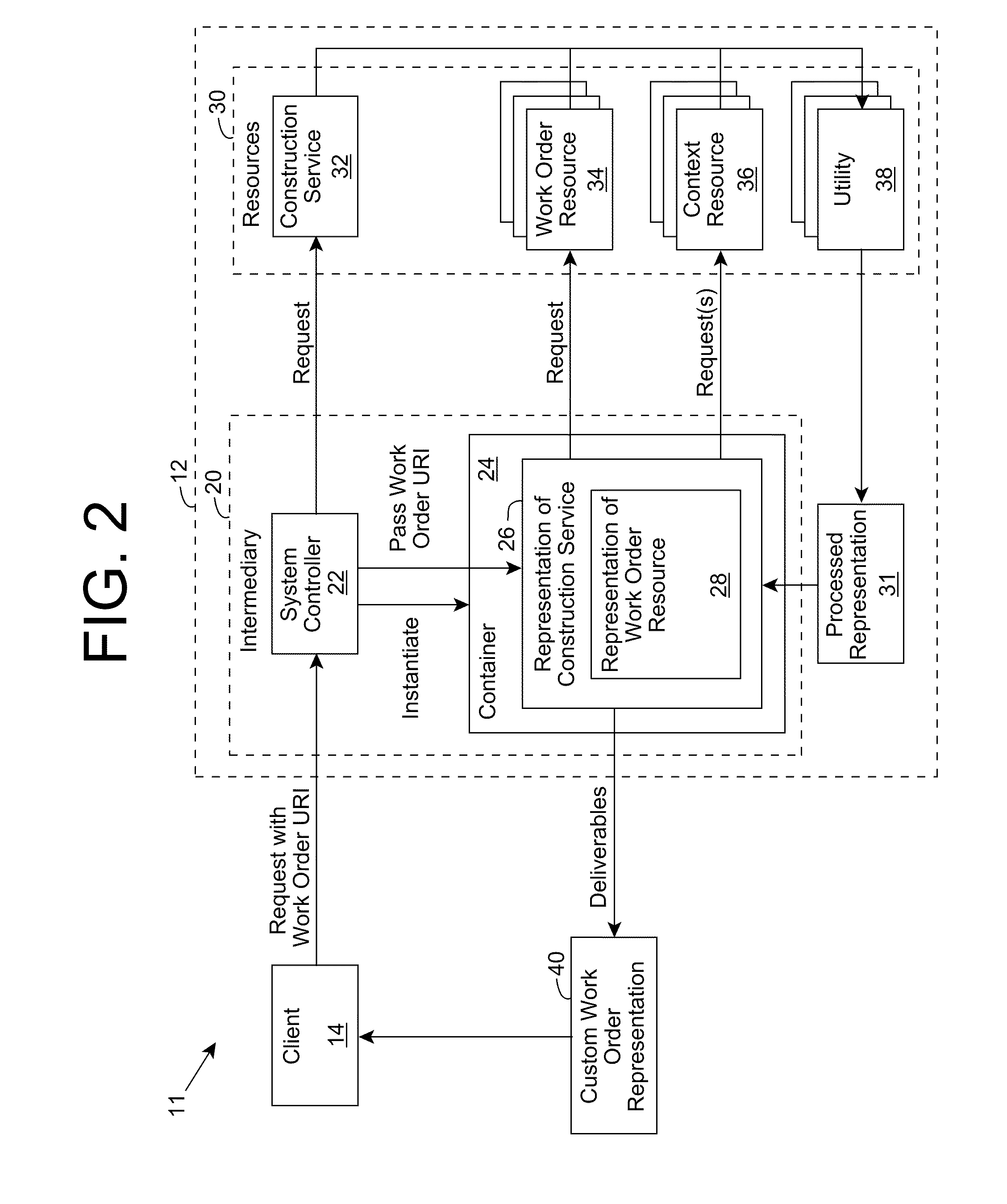
Resource processing using an intermediary for context-based customization of interaction deliverables
A software application includes work order resources, each of which defines an atomic operation for the software application, and a construction service resource, which processes the work order resources in response to all interaction requests for the software application. Each interaction request is received from a client and identifies a corresponding work order, which the construction service processes to dynamically construct a set of deliverables, which can include a custom representation of the work order. While processing the interaction request, the construction service, as directed by the work order, can make one or more requests to context resources for context information corresponding to an activity for which the interaction was requested to construct the set of deliverables. The work order resource can comprise a reflective program that enables the construction service to dynamically determine and construct the set of deliverables, including the next appropriate interaction(s) using the context information, thereby directing a set of atomic operations as part of an activity being performed and enabling the dynamic context-based construction of interaction deliverables.
Owner:ENTERPRISEWEB
Accelerating unbounded memory transactions using nested cache resident transactions
ActiveUS20110145802A1Well formedMemory adressing/allocation/relocationTransaction processingAtomic operationsSoftware
Using cache resident transaction hardware to accelerate a software transactional memory system. The method includes identifying a plurality of atomic operations intended to be performed by a software transactional memory system as transactional operations as part of a software transaction. The method further includes selecting at least a portion of the plurality of atomic operations. The method further includes attempting to perform the portion of the plurality of atomic operations as hardware transactions using cache resident transaction hardware.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Computation spreading for spur reduction in a digital phase lock loop
ActiveUS20080069286A1Easy to reconfigureReduce generationPulse automatic controlDigital computer detailsClock rateTime-sharing
A novel and useful apparatus for and method of spur reduction using computation spreading in a digital phase locked loop (DPLL) architecture. A software based PLL incorporates a reconfigurable calculation unit (RCU) that is optimized and programmed to sequentially perform all the atomic operations of a PLL or any other desired task in a time sharing manner. An application specific instruction-set processor (ASIP) incorporating the RCU is adapted to spread the computation of the atomic operations out over and completed within an entire PLL reference clock period. Each computation being performed at a much higher processor clock frequency than the PLL reference clock rate. This functions to significantly reduce the per cycle current transient generated by the computations. Further, the frequency content of the current transients is at the higher processor clock frequency. This results in a significant reduction in spurs within sensitive portions of the output spectrum.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Integrated Circuit and Metod for Issuing Transactions
InactiveUS20070234006A1Shorten the timeReduce loadData switching by path configurationArchitecture with single central processing unitFinancial transactionEmbedded system
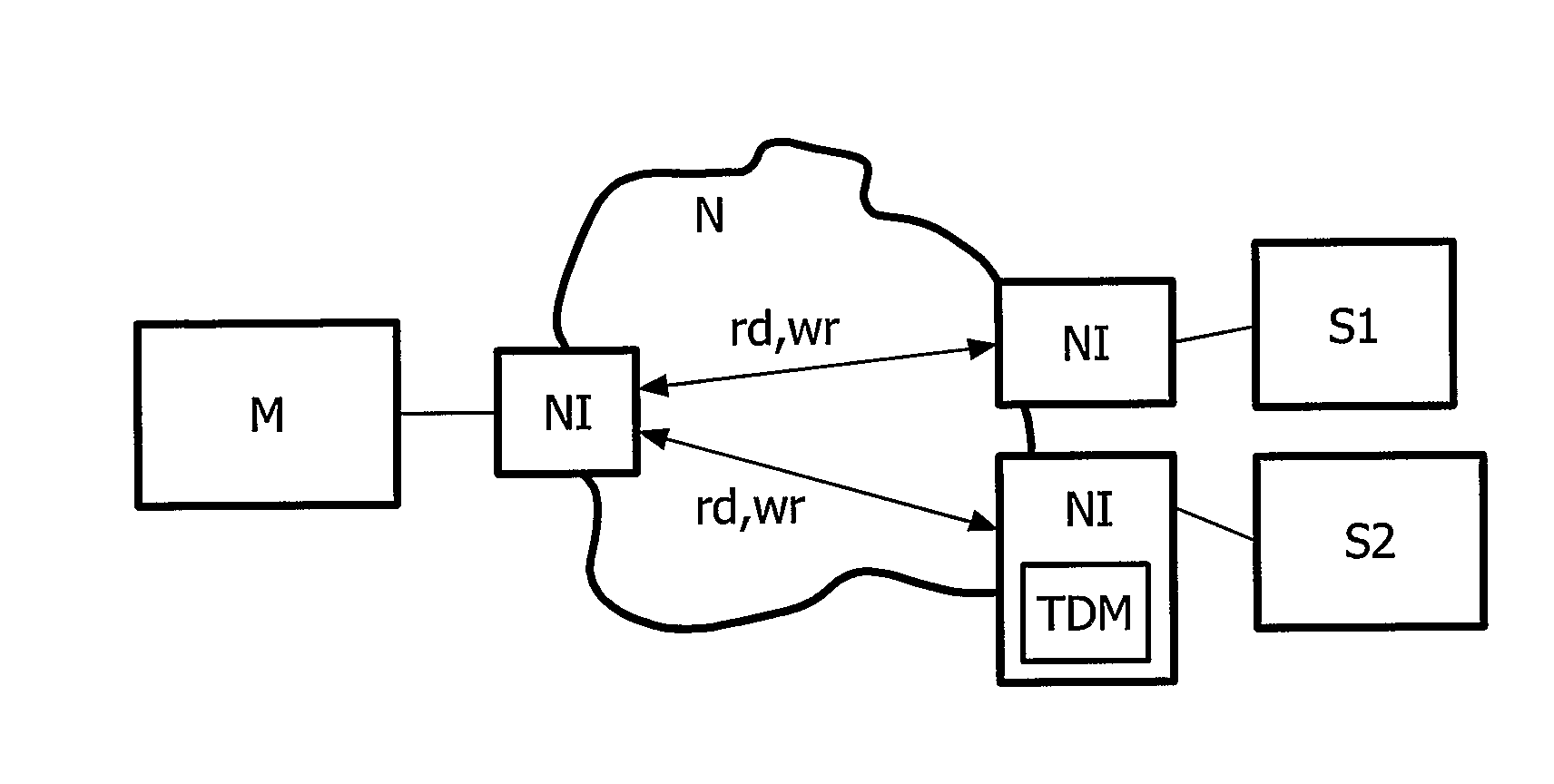
An integrated circuit is provided comprising a plurality of processing modules (M, S) and a network (N) arranged for coupling said processing modules (M, S). Said integrated circuit comprises a first processing module (M) for encoding an atomic operation into a first transaction and for issuing said first transaction to at least one second processing module (S) . In addition, a transaction decoding means (TDM) for decoding the issued first transaction into at least one second transaction is provided.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Global Stores and Atomic Operations
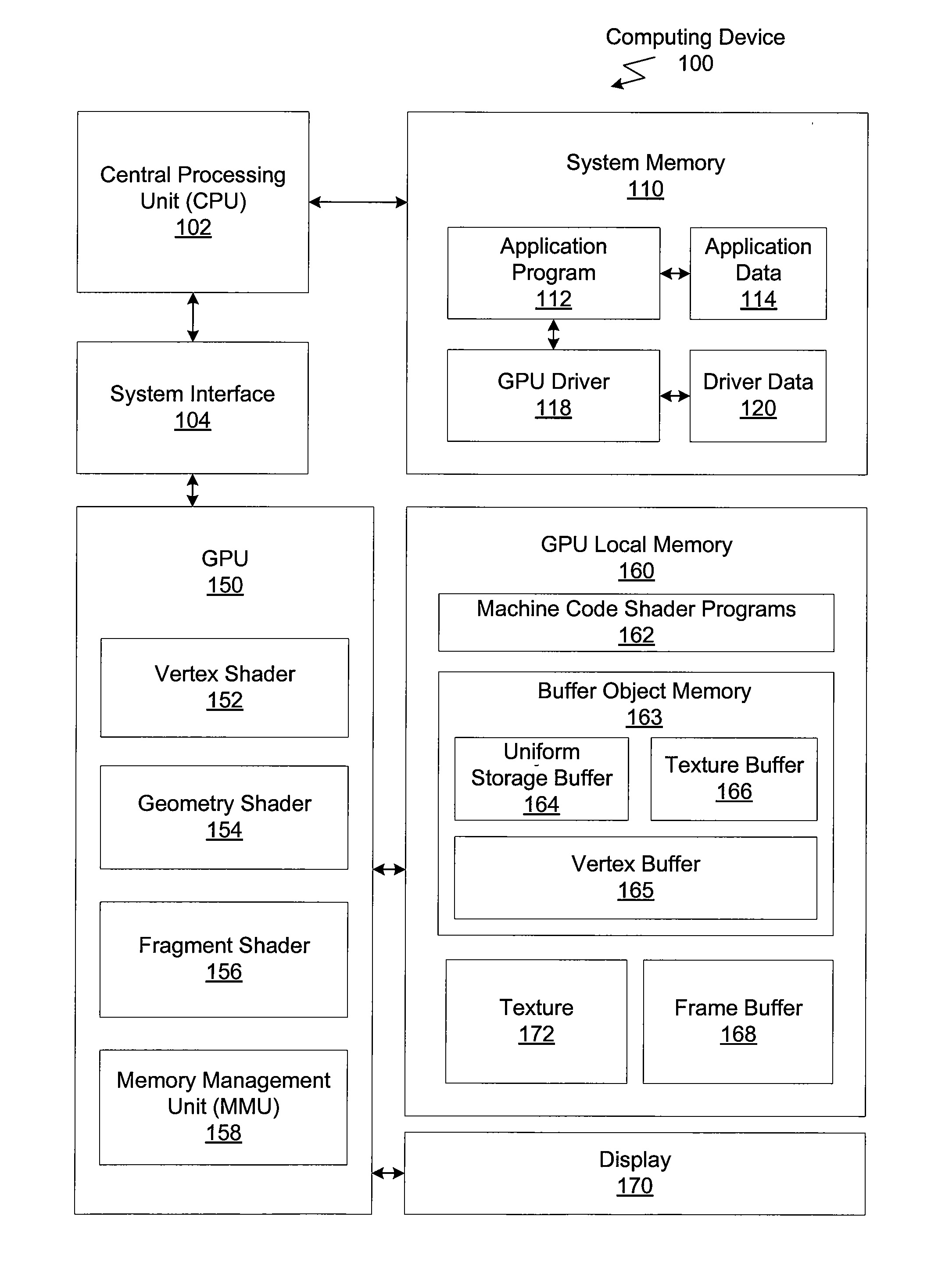
ActiveUS20110063296A1Dramatic performance increaseCathode-ray tube indicatorsProcessor architectures/configurationObject storeData store
One embodiment of the present invention sets forth a method for storing processed data within buffer objects stored in buffer object memory from within shader engines executing on a GPU. The method comprises the steps of receiving a stream of one or more shading program commands via a graphics driver, executing, within a shader engine, at least one of the one or more shading program commands to generate processed data, determining from the stream of one or more shading program commands an address associated with a first data object stored within the buffer memory, and storing, from within the shader engine, the processed data in the first data object stored within the buffer memory.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com