Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
34 results about "Basal ganglia" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The basal ganglia (or basal nuclei) are a group of subcortical nuclei, of varied origin, in the brains of vertebrates, including humans, which are situated at the base of the forebrain and top of the midbrain. There are some differences in the basal ganglia of primates. Basal ganglia are strongly interconnected with the cerebral cortex, thalamus, and brainstem, as well as several other brain areas. The basal ganglia are associated with a variety of functions, including control of voluntary motor movements, procedural learning, habit learning, eye movements, cognition, and emotion.
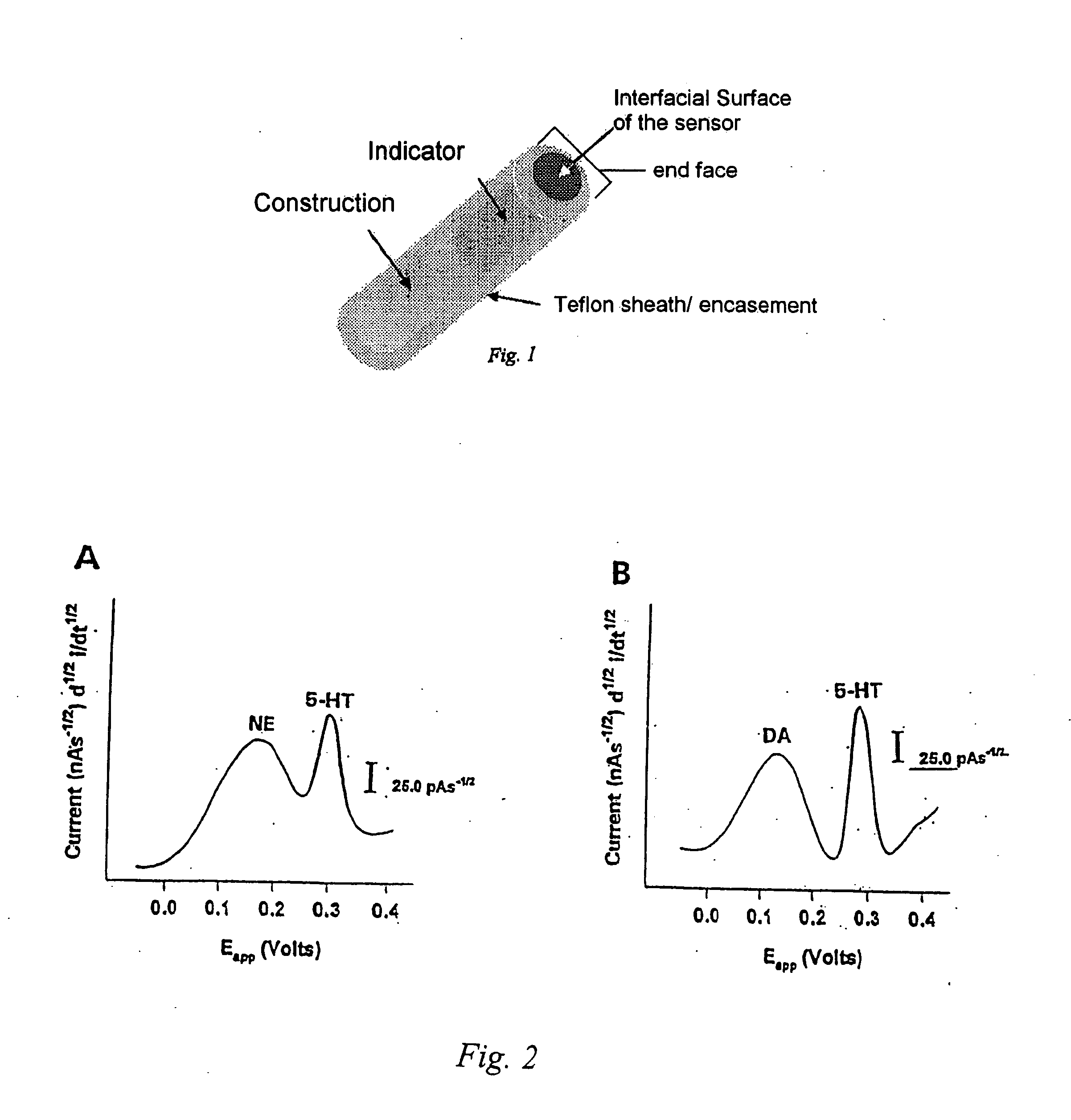
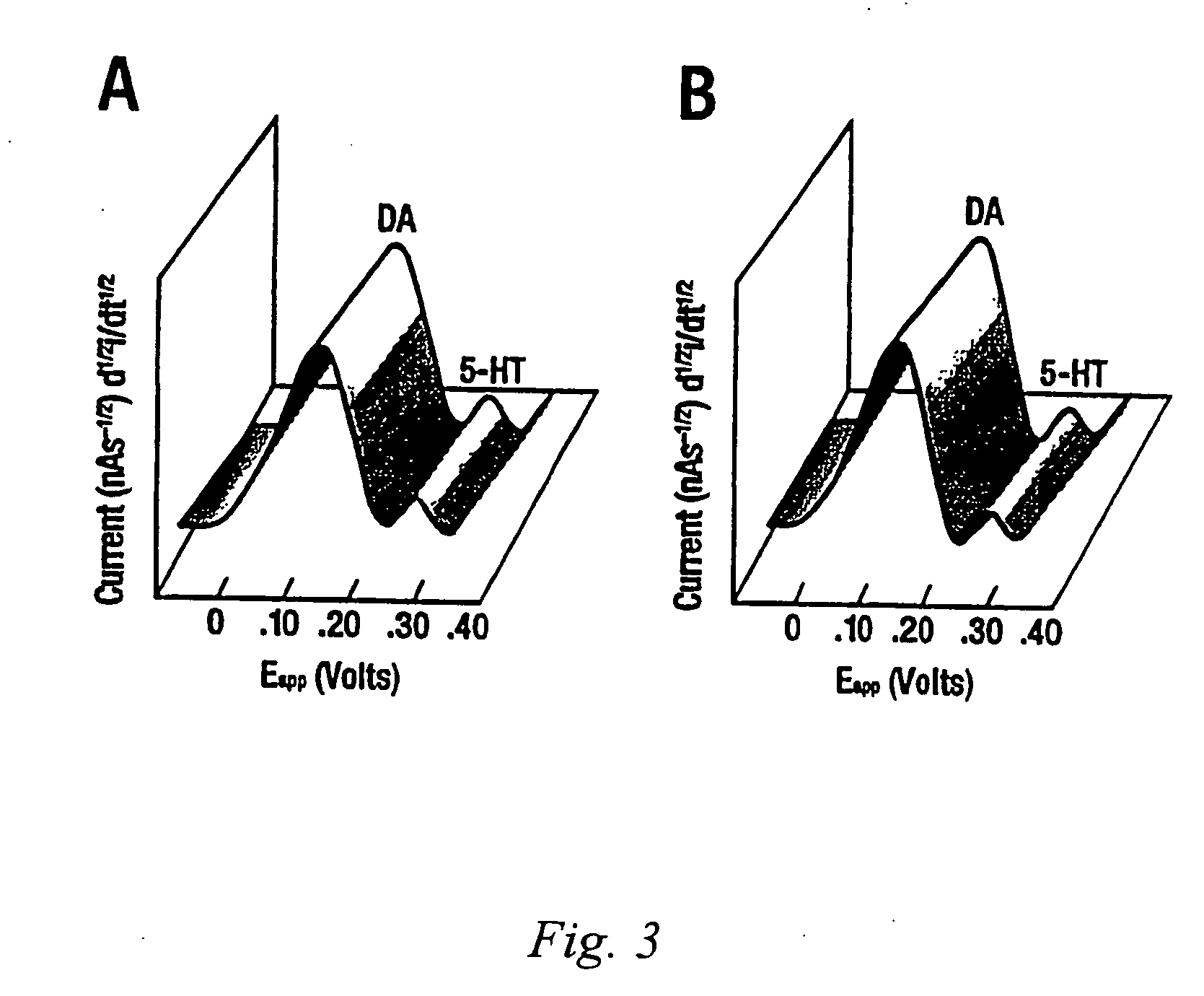
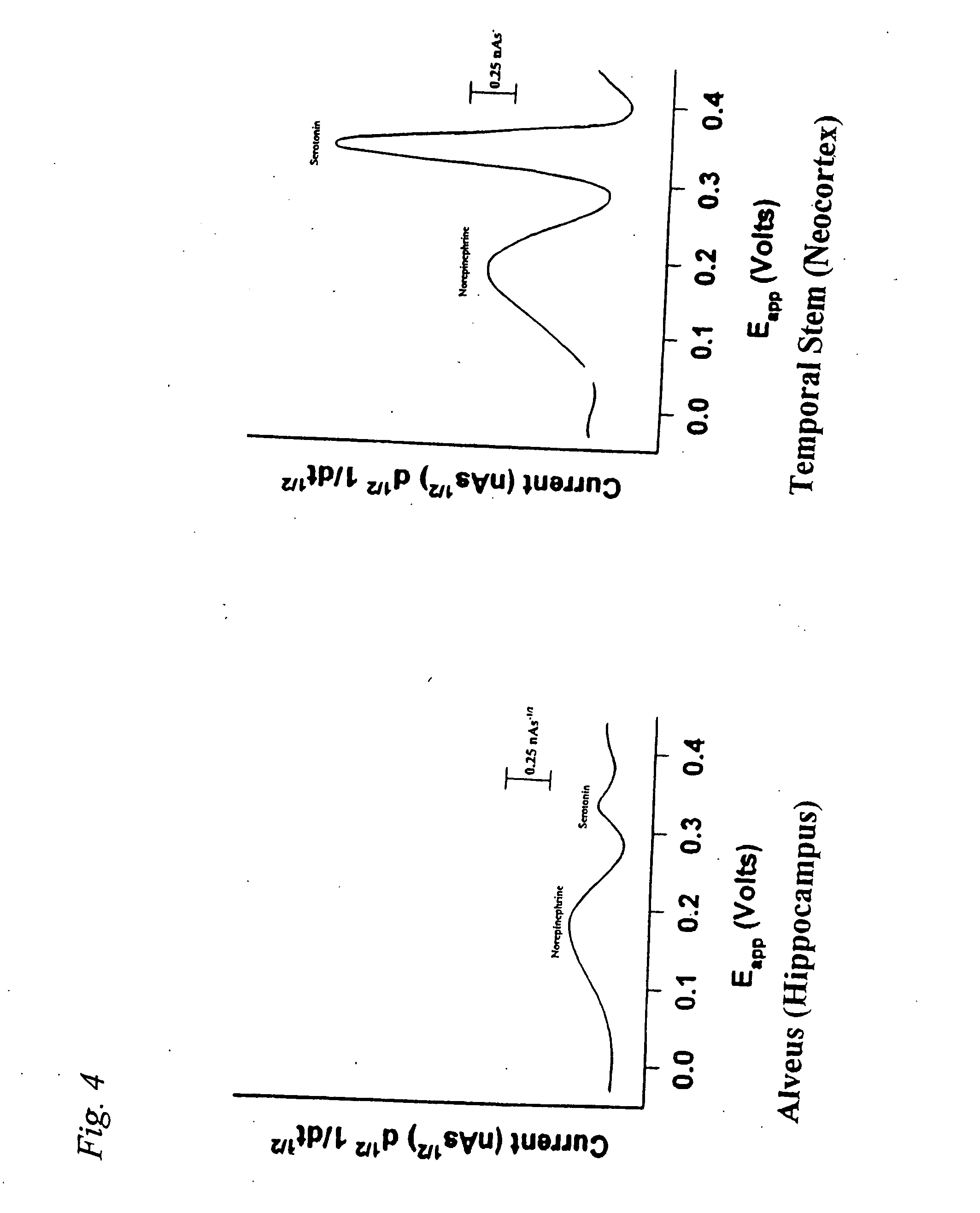
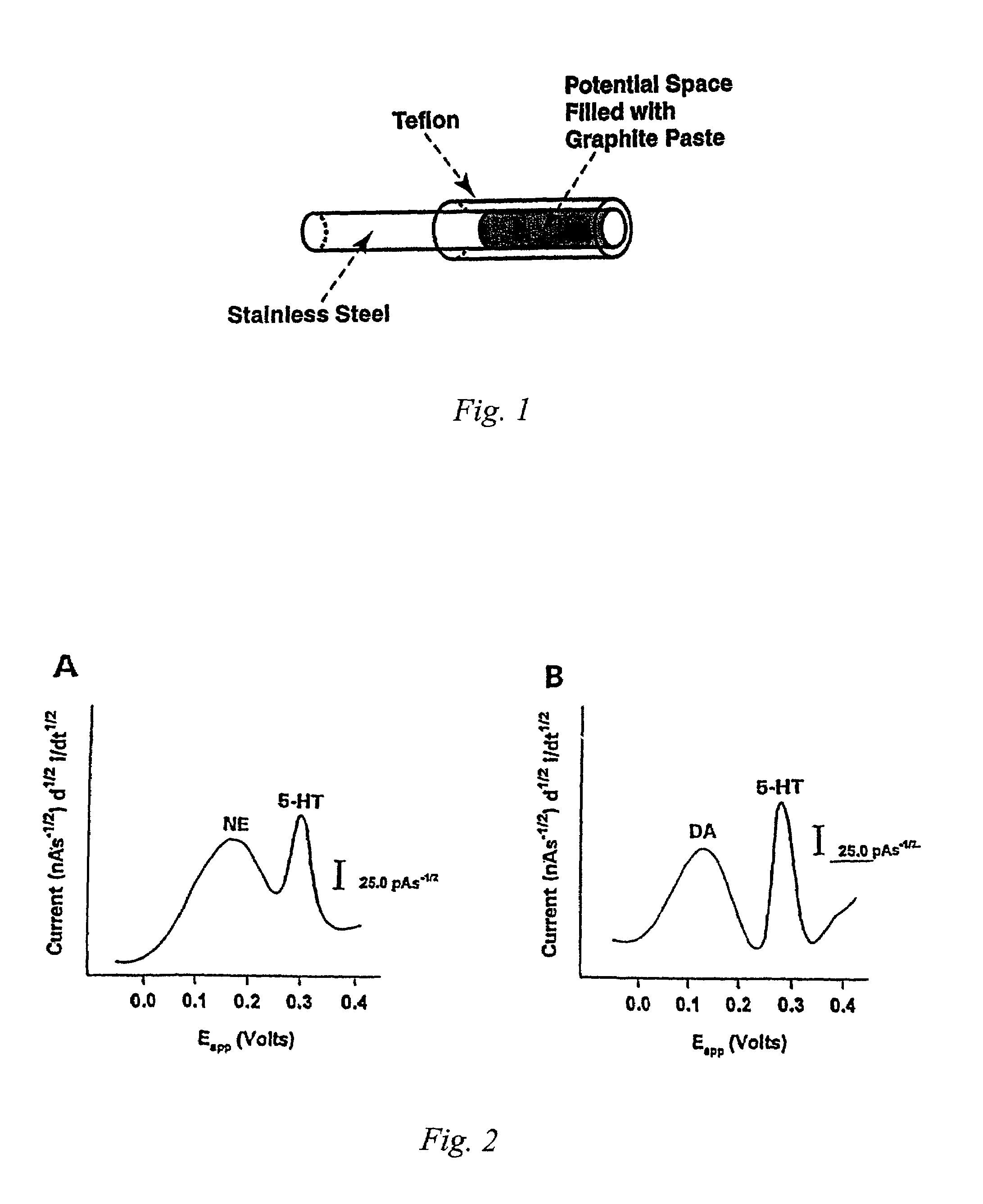
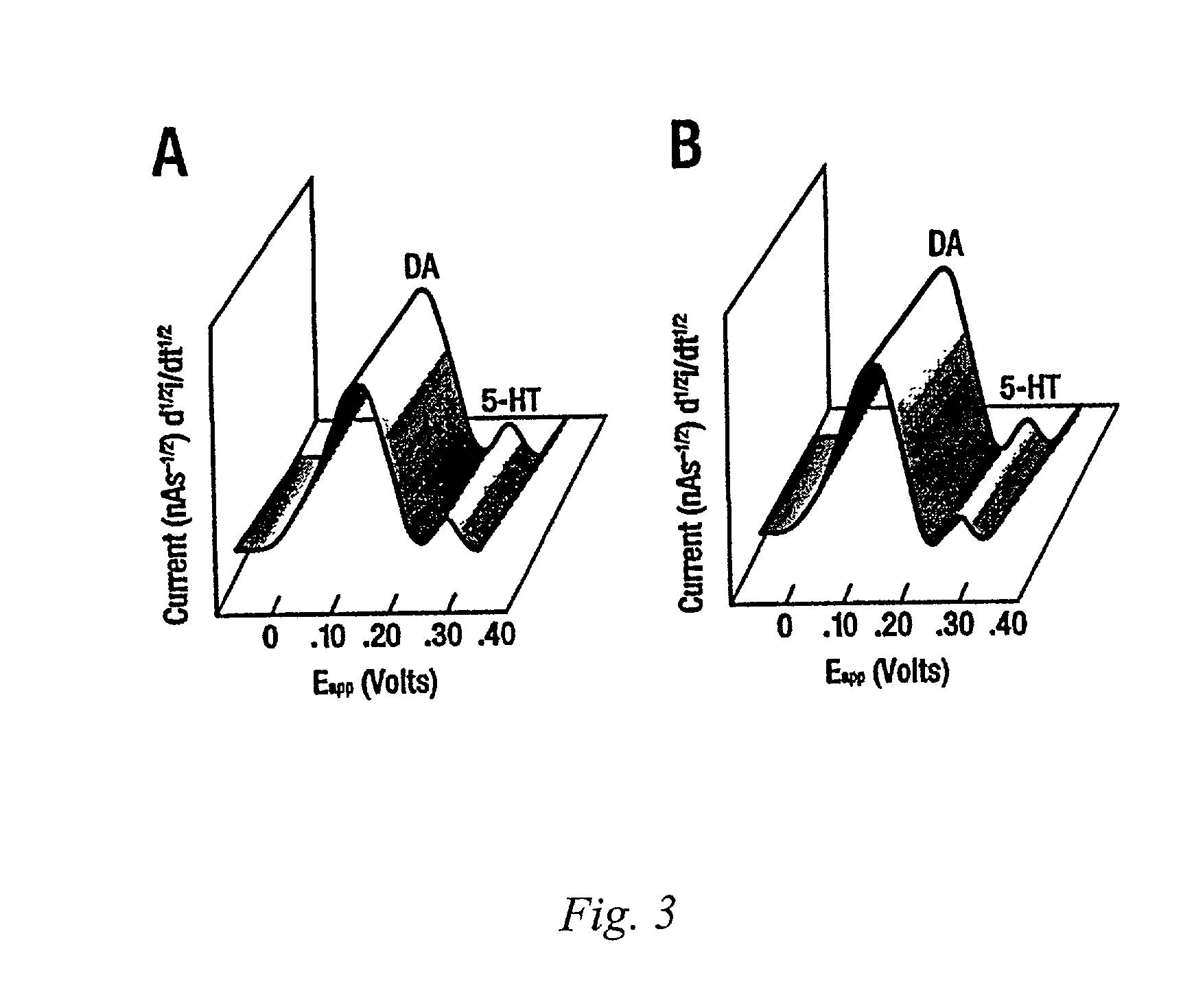
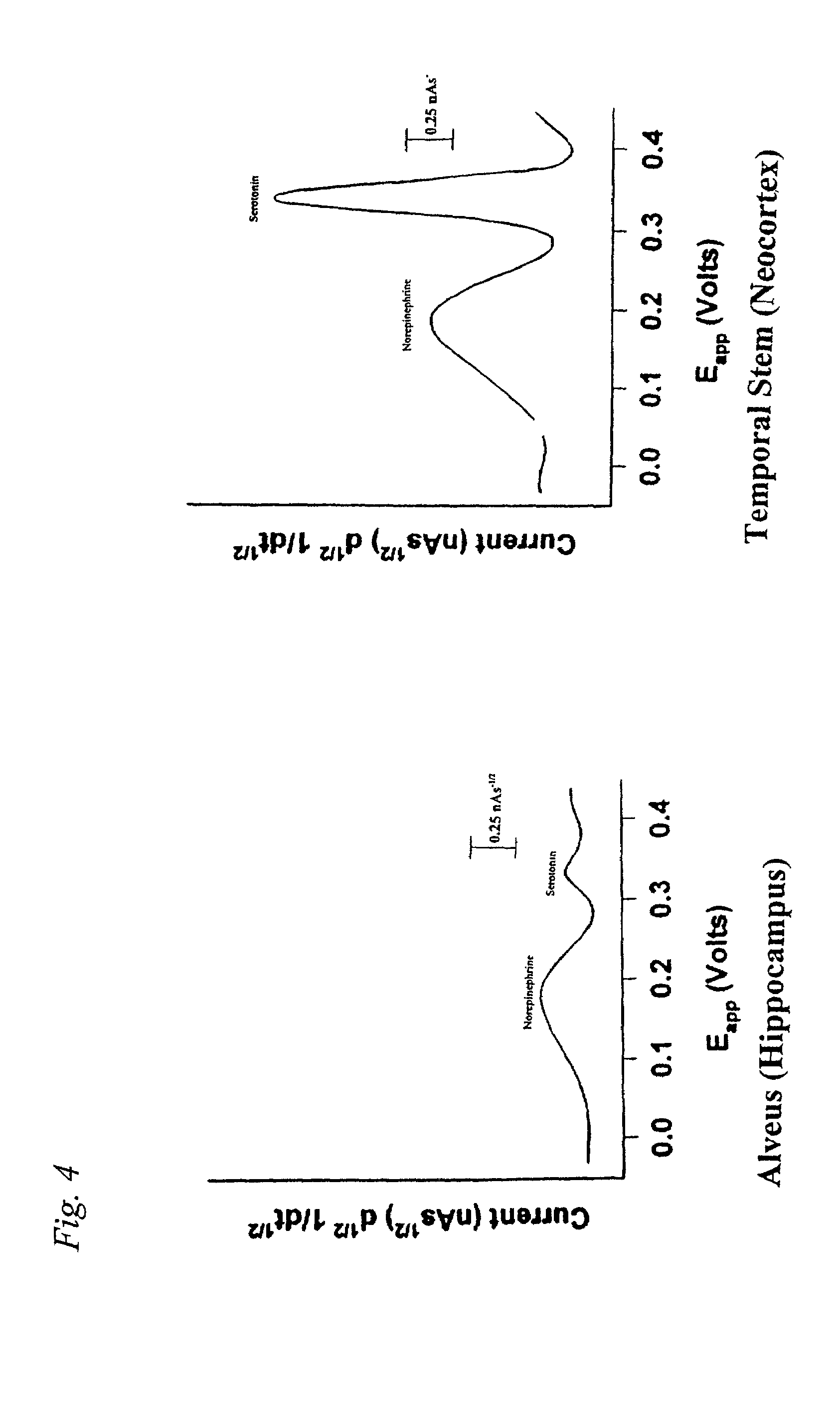
Identification, diagnosis, and treatment of neuropathologies, neurotoxicities, tumors, and brain and spinal cord injuries using electrodes with microvoltammetry
InactiveUS20070026440A1Microbiological testing/measurementVolume/mass flow measurementAbnormal tissue growthInjury brain
The present invention relates to devices and methods of use thereof for detection of biomolecules, in vitro, in vivo, or in situ. The invention relates to methods of diagnosing and / or treating a subject as having or being at risk of developing a disease or condition that is associated with abnormal levels of one or more biomolecules including, but not limited to, inter alia, epilepsy, diseases of the basal ganglia, athetoid, dystonic diseases, neoplasms, Parkinson's disease, brain injuries, spinal cord injuries, and cancer. The invention also provides methods of differentiating white matter from gray matter. In some embodiments, regions of the brain to be resected or targeted for pharmaceutical therapy are identified using sensors. The invention further provides methods of measuring the neurotoxicity of a material by comparing microvoltammograms of a neural tissue in the presence and absence of the material using the inventive sensors.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
Identification, diagnosis, and treatment of neuropathologies, neurotoxicities, tumors, and brain and spinal cord injuries using microelectrodes with microvoltammetry
InactiveUS7112319B2Reliable distinctionIn-vivo radioactive preparationsMicrobiological testing/measurementMetaboliteInjury brain
The present invention relates to devices and methods of use thereof for making semiderivative voltammetric and chronoamperometric measurements of chemicals, e.g. neurotransmitters, precursors, and metabolites, in vitro, in vivo, or in situ. The invention relates to methods of diagnosing and / or treating a subject as having or being at risk of developing a disease or condition that is associated with abnormal levels of one or more neurotransmitters including, inter alia, epilepsy, diseases of the basal ganglia, athetoid, dystonic diseases, neoplasms, Parkinson's disease, brain injuries, spinal cord injuries, and cancer. The invention provides methods of differentiating white matter from grey matter using microvoltammetry. In some embodiments, regions of the brain to be resected or targeted for pharmaceutical therapy are identified using Broderick probes. The invention further provides methods of measuring the neurotoxicity of a material by comparing Broderick probe microvoltammograms of a neural tissue in the presence and absence of the material.
Owner:RES FOUND THE CITY UNIV OF NEW YORK +1
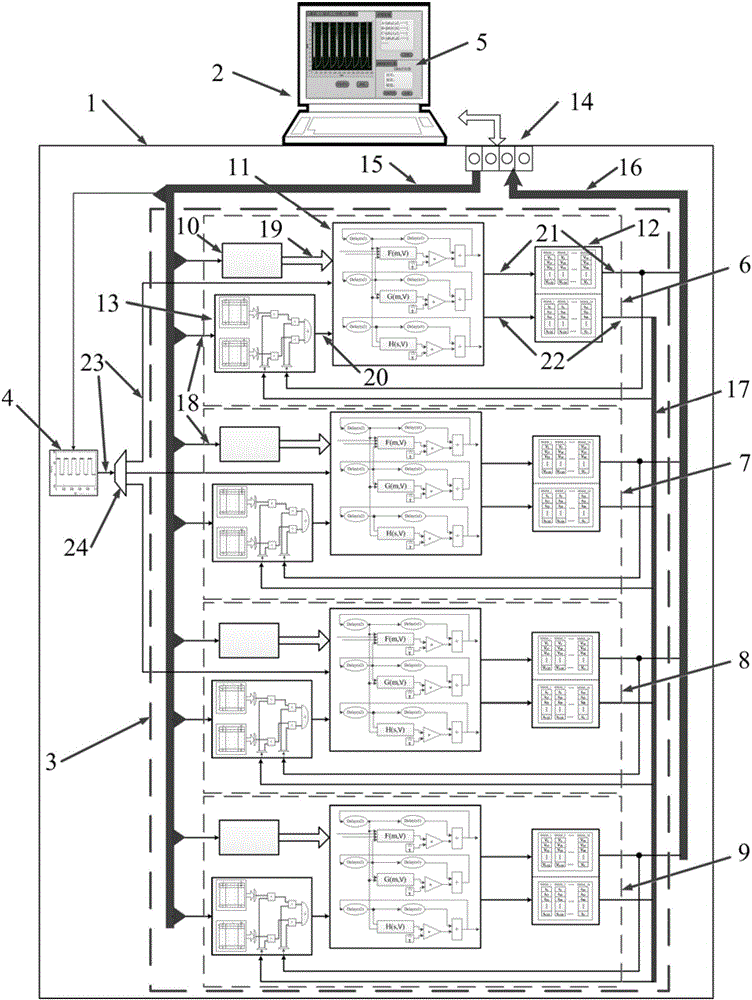
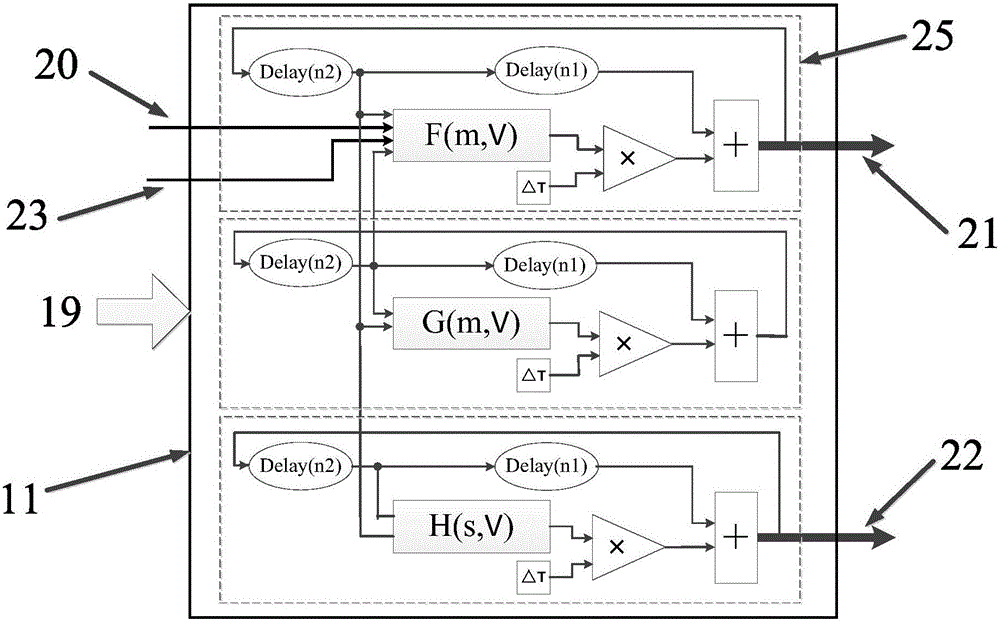
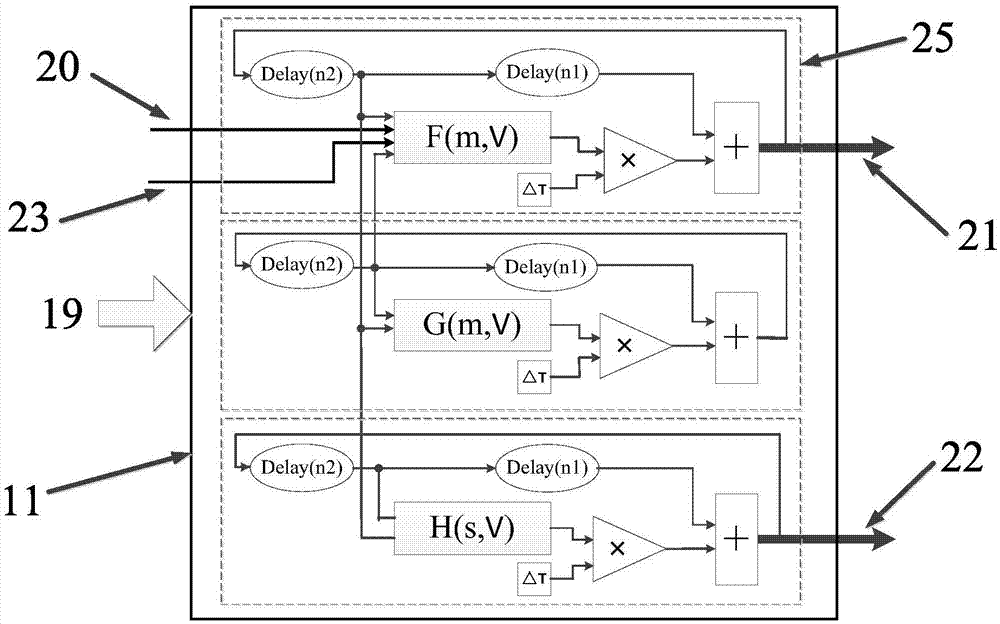
Deep brain stimulation FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array) experimental platform for basal ganglia and thalamencephalon network for parkinson's disease
The invention provides a deep brain stimulation FPGA experimental platform of a basal ganglia and thalamencephalon network for the parkinson's disease. The experimental platform comprises an FPGA development board and an upper computer, which are connected with each other; the FPGA development board is used for realizing a basal ganglia and thalamencephalonneuron network model and a deep brain stimulation controller; the upper computer is used for designing an upper computer software interface and being communicated with the FPGA development board. The experimental platform has the benefits that as an animal-free experiment means of a biological neural network, and on the basis of the high-speed computation FPGA neuron network, the experimental platform realizes the modeling of the neuron network of a complex parkinson's disease focus area, and the neuron network model can be consistent with real biological neuron on a time scale. The platform provides a visual research platform, closer to the real neuron network, for researching the discharging mechanism of the parkinson's disease and the abnormal discharging mode of the basal ganglia and thalamencephalonneuron network controlled by deep brain stimulation, and has a significant practical value in researching the treatment of the parkinson's disease.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
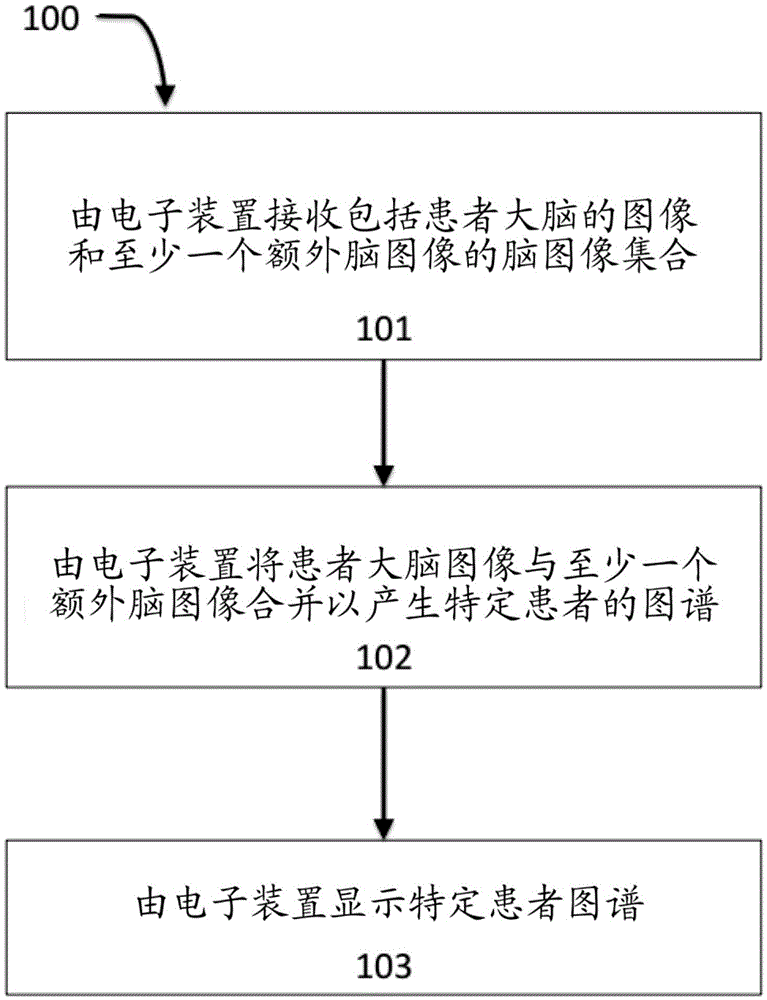
Method and system for a brain image pipeline and brain image region location and shape prediction
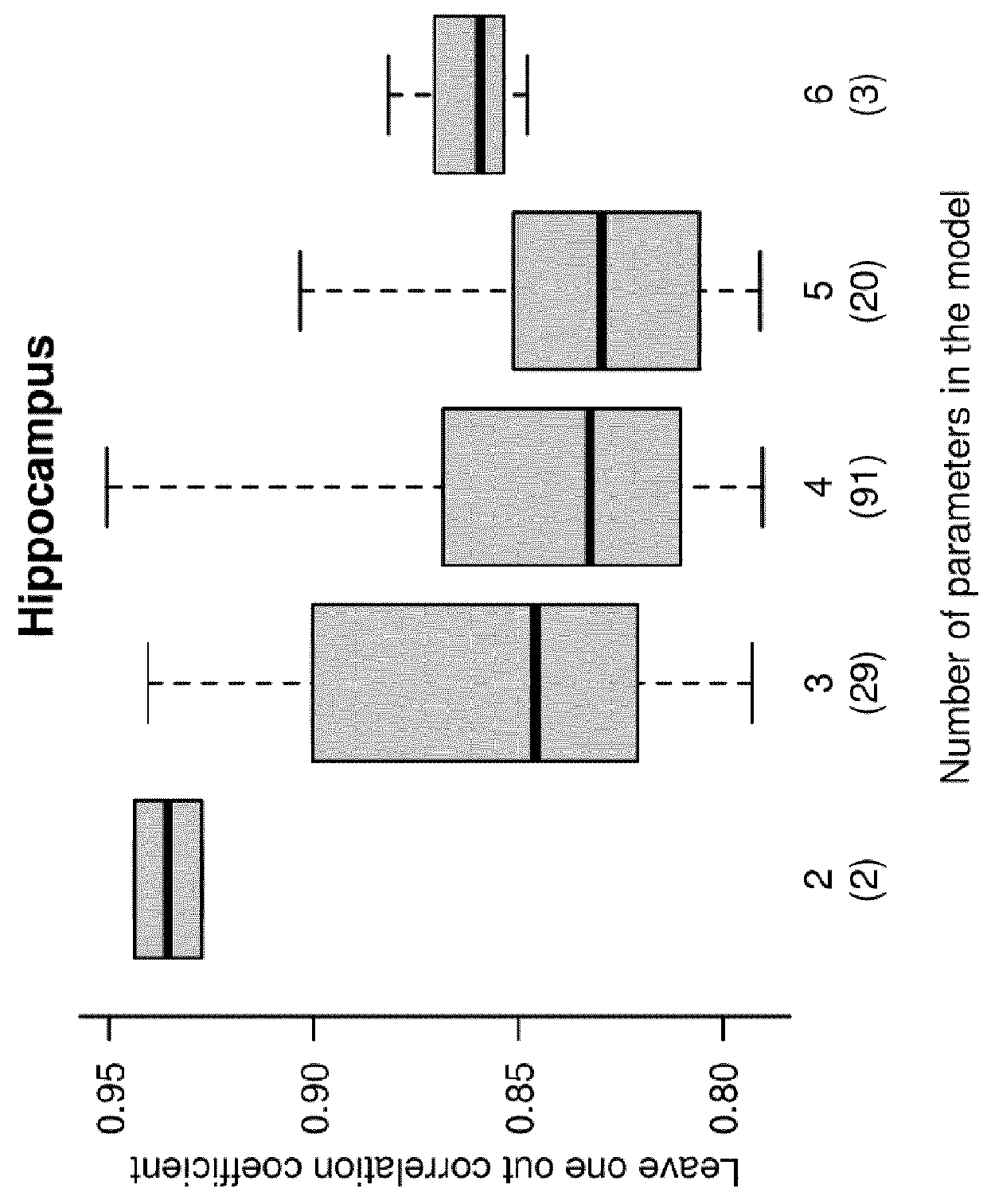
A volumetric segmentation method is disclosed for brain region analysis, in particular but not limited to, regions of the basal ganglia such as the subthalamic nucleus (STN). This serves for visualization and localization within the sub-cortical region of the basal ganglia, as an example of prediction of a region of interest for deep brain stimulation procedures. A statistical shape model is applied for variation modes of the STN, or the corresponding regions of interest, and its predictors on high-quality training sets obtained from high-field, e.g., 7T, MR imaging. The partial least squares regression (PLSR) method is applied to induce the spatial relationship between the region to be predicted, e.g., STN, and its predictors. The prediction accuracy for validating the invention is evaluated by measuring the shape similarity and the errors in position, size, and orientation between manually segmented STN and its predicted one.
Owner:オウルナビゲーションインコーポレイテッド
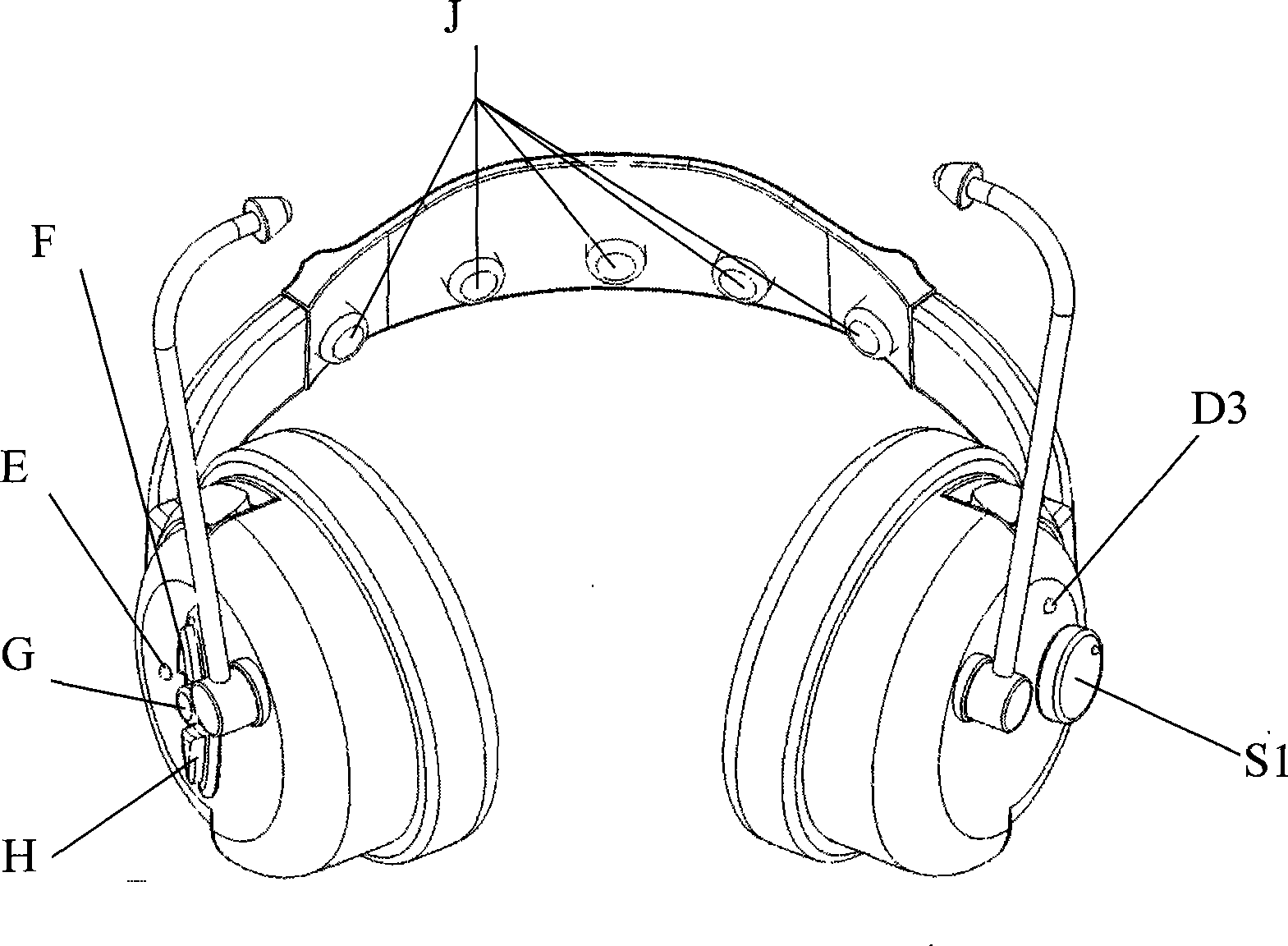
Transcranial magnetoelectric depression therapeutic apparatus
ActiveCN101530647AGood effectImprove performanceElectrotherapySleep inducing/ending devicesAuditory systemEngineering
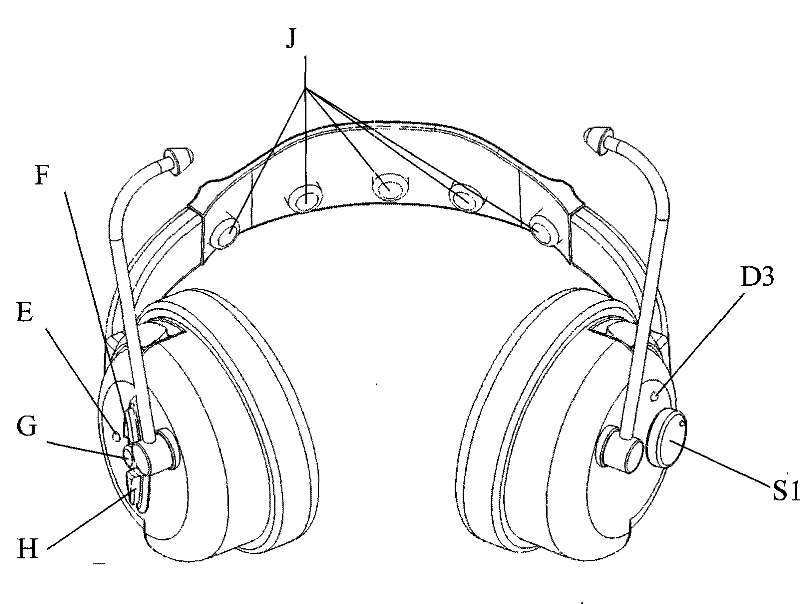
The invention provides a trabscranial magnetoelectric depression therapeutic apparatus, comprising a pair of earphones, a beam connected between the earphones, at least a magnet, at least a pair of electrodes and an internal circuit; wherein, the earphones and the electrodes are connected with the internal circuit. The technical proposal is as follows: trabscranial magnetoelectricity and audio signals directly act on heads and auditory systems of human; stereo superposition electric field formed in certain parts of brain by trabscranial magnet can ensure the parts to generate weak induced current so as to self stimulate the parts to secrete dopamine and restore the function of self secreting neurotransmitter such as dopamine by the parts; the trabscranial magnet directly stimulates neutral clusters of basal ganglia of thalamus, thus strengthening the effects of the trabscranial magnet; the audio signals with special rhythm act on the auditory systems of human, which can promote human to enter into meditation and tempt secretion of the neurotransmitter such as dopamine in the brain, thus further strengthening the effects of the trabscranial magnet. The trabscranial magnetoelectricity and audio signals integrate three effects into one, supplement and complement each other and promote each other, and the therapeutic effect on depression and insomnia is unreachable for any single function.
Owner:哈尔滨奥博医疗器械有限公司
Method and Use of Metabolites for the Diagnosis and Differentiation of Neonatal Encephalopathy
ActiveUS20140308687A1Appropriate and rapid and effective resuscitationSeizure controlElectrolysis componentsParticle separator tubesMetaboliteTreatment effect
Metabolites and signatures (panels) of metabolites are applicable as biomarkers in clinical diagnosis, in particular for neonatal encephalopathy. They are useful tools in differential clinical diagnosis for early detection of brain injury, determination of brain areas affected by the insults and prediction of adverse neurological outcome and may also be applied in diagnosing disease progression and treatment effect. An in vitro method for predicting the likelihood of neonatal encephalopathy of distinct brain areas, identification of affected brain area(s) of neonatal encephalopathy and risk of brain damage and prognosis and neurological outcome due to identification of the type and extent of damage of distinct brain tissues, in particular of hippocampus and / or basal ganglia, is provided.
Owner:INFANDX
Transcranial magnetic therapeutic instrument for computer diseases
ActiveCN101537228ASignificant effectAct as an intensifying stimulusElectrotherapyArtificial respirationDiseaseBrain pacemaker
The invention provides a transcranial magnetic therapeutic instrument for computer diseases, comprising a field effect cap which can be worn on head, field effect cap internally being distributed with electrodes and at least one electromagnet; the instrument further comprises an electroencephalographic simulative generator, and the electroencephalographic simulative generator is respectively connected with the electromagnet and the electrodes via conducting wires. In the invention, nerve cell nucleus of intracephalic basal ganglia part can be self-excited by a stereoscopic superposition alternating magnetic field transcranially magnetically formed at intracephalic deep part and a weak induced current formed at a specific part of intracephalic deep part; and the transcranial magnetic effect is strengthened when the nerve cell nucleus transcranially pass through basal ganglia part. The invention is not an interventional therapy but can achieve the functions of stimulating and recovering neurotransmitters of nerve cell nucleus of intracephalic basal ganglia part such as autocrine dopamine, and is applied to encephalopathic therapy such as Parkinson, encephalatrophy, epileptics and gork; the effects exceed that of a brain pacemaker, thereby overcoming the disadvantages of pharmacotherapy and surgical therapy; and the therapeutic instrument can be used in hospital, and is more applied to treatment of patients at home.
Owner:哈尔滨奥博医疗器械有限公司
Method
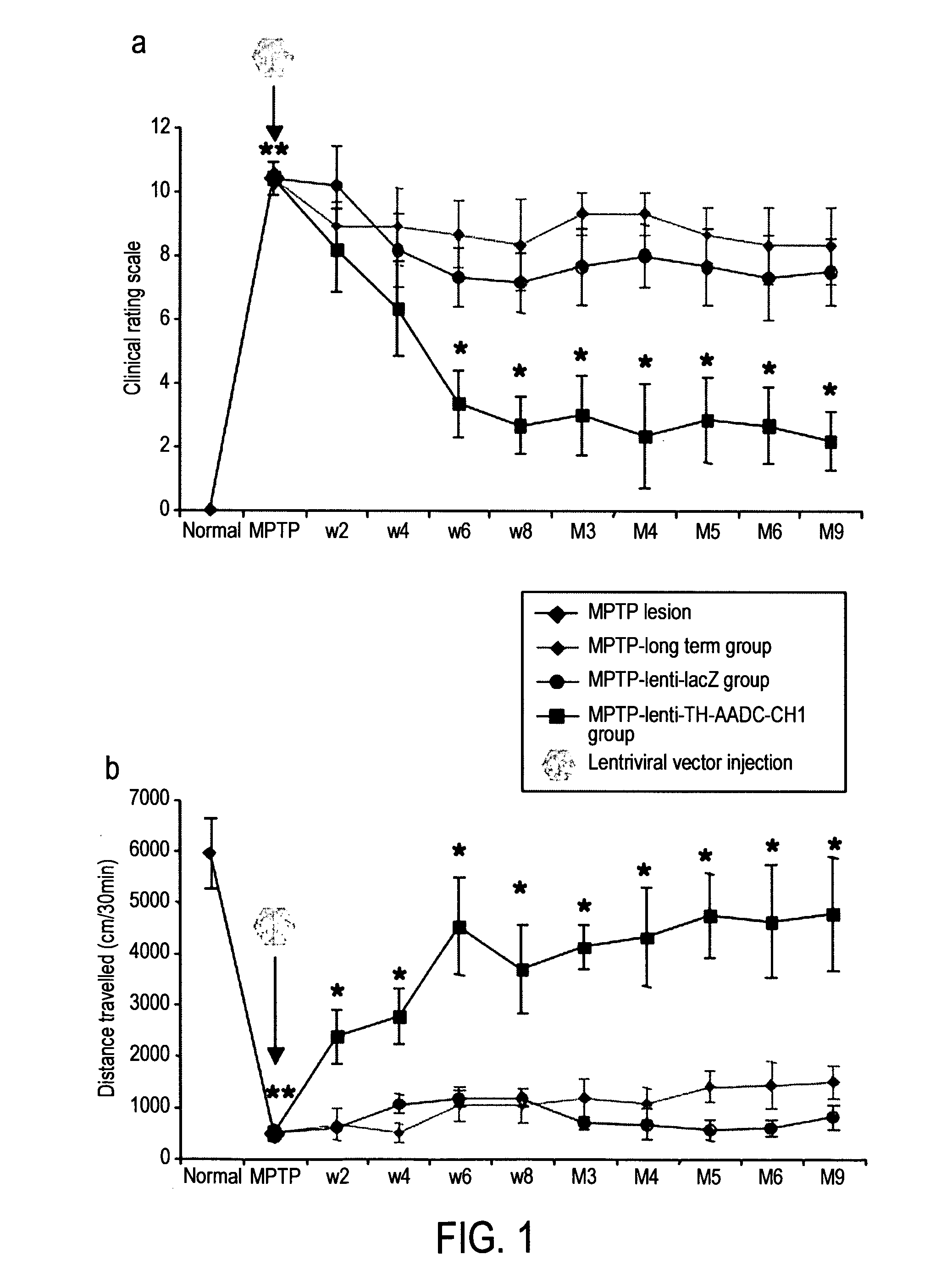
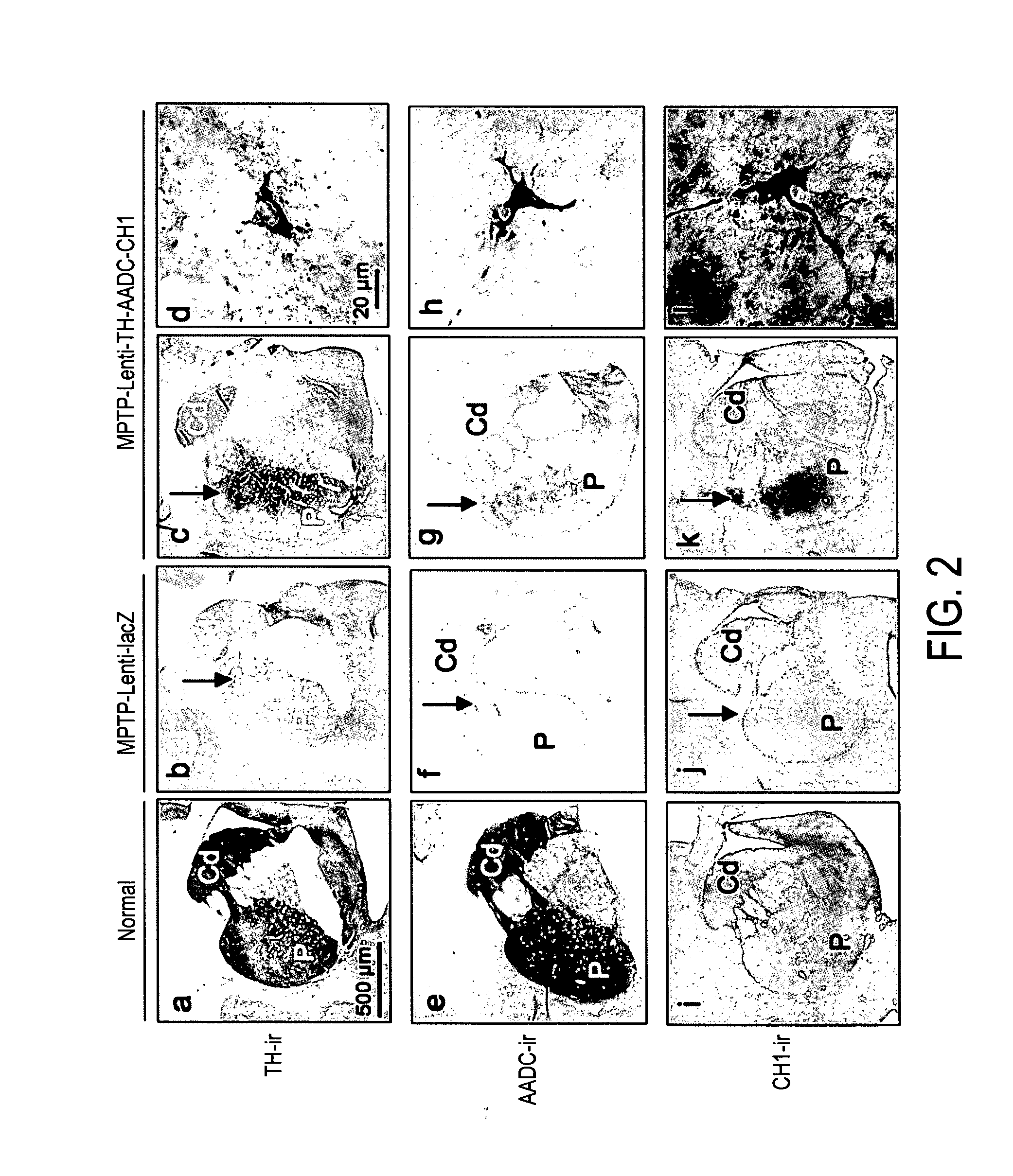
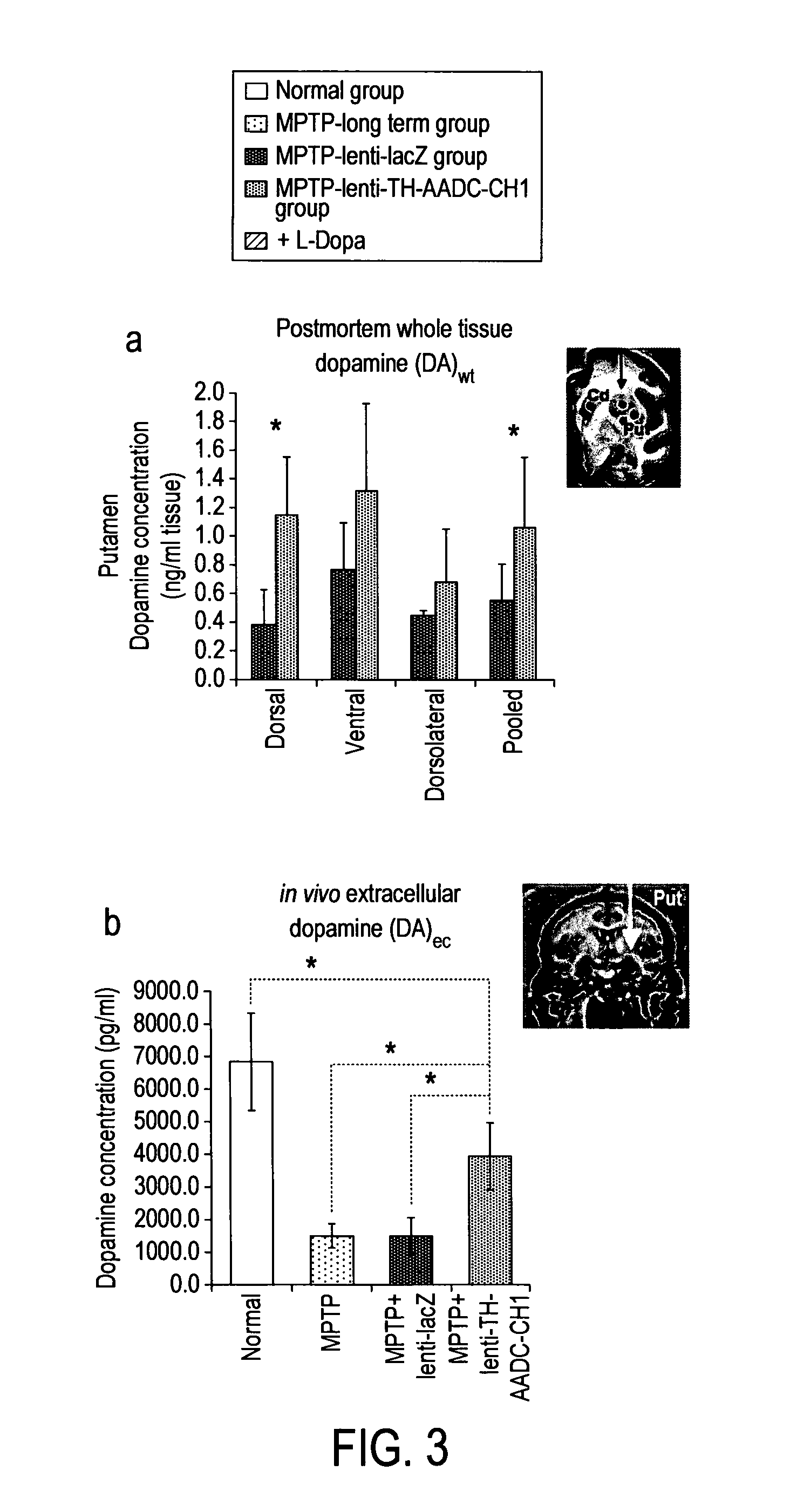
InactiveUS20110269826A1Good curative effectHigh expressionNervous disorderVirusesVector systemMedicine
The present invention provides methods for: (i) treating and / or preventing Parkinson's disease in a subject without causing cognitive impairment by using dopamine replacement gene therapy to maintain or restore constant physiological dopaminergic tone in both the dorsal and ventral striatum of the subject; (ii) normalising neuronal electrical activity in basal ganglia and / or subthalamic nucleus in a Parkinson's disease subject; and (iii) treating and / or preventing dyskinesias associated with oral L-dopa administration in a Parkinson's disease subject by administration of a vector system for dopamine replacement gene therapy to the subject.
Owner:OXFORD BIOMEDICA (UK) LTD
Transcranial multimodal electrical stimulation therapeutic apparatus and use method thereof
PendingCN110354385ARegulation of abnormally synchronized oscillationsEffective stimulation circuitElectrotherapyArtificial respirationElectricityTherapeutic effect
The invention provides a transcranial multimodal electrical stimulation therapeutic apparatus and a use method thereof. The therapeutic apparatus includes an electric stimulation signal control device, an electric stimulation signal generating device and a headset electric stimulation current output device, wherein the headset electric stimulation current output device is provided with two or moreelectrodes, and the electrodes on the headset electric stimulation current output device correspond to governor meridian acupoints of the head. The use method of the therapeutic apparatus includes the following steps that 1, the electric stimulation signal control device sets an electric stimulation signal parameter; 2, the electric stimulation signal generating device outputs an electric stimulation signal according to the signal parameter; 3, the headset electric stimulation current output device outputs the current. The therapeutic apparatus can achieve the treatment of non-invasive transcranial multimodal electrical stimulation, avoid surgical traumas and effectively regulate the abnormal synchronous oscillation of 'a cortex-basal ganglia loop', an effective stimulation loop is formed, and the good therapeutic effect is achieved.
Owner:首都医科大学脑重大疾病研究中心 +1
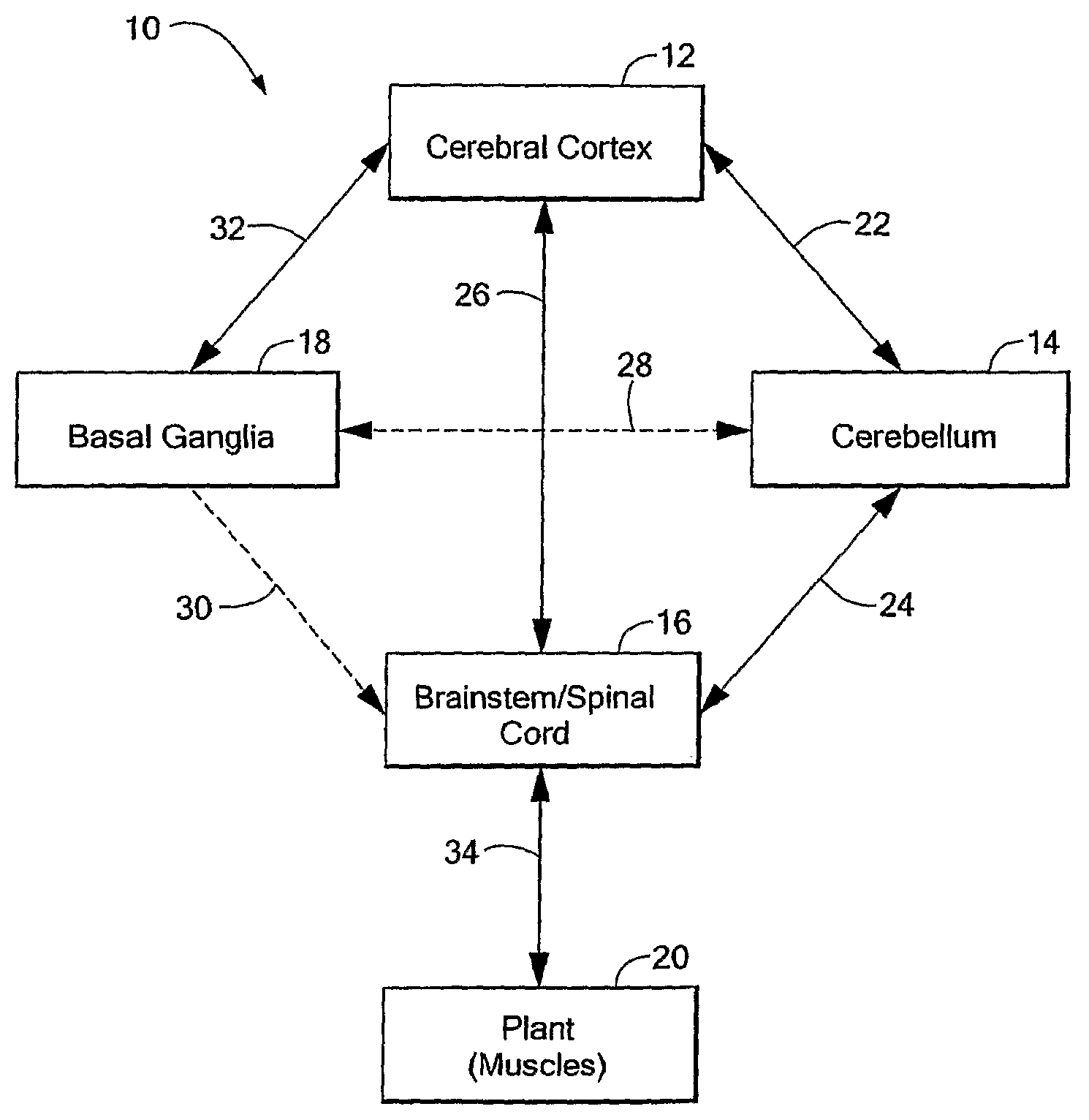
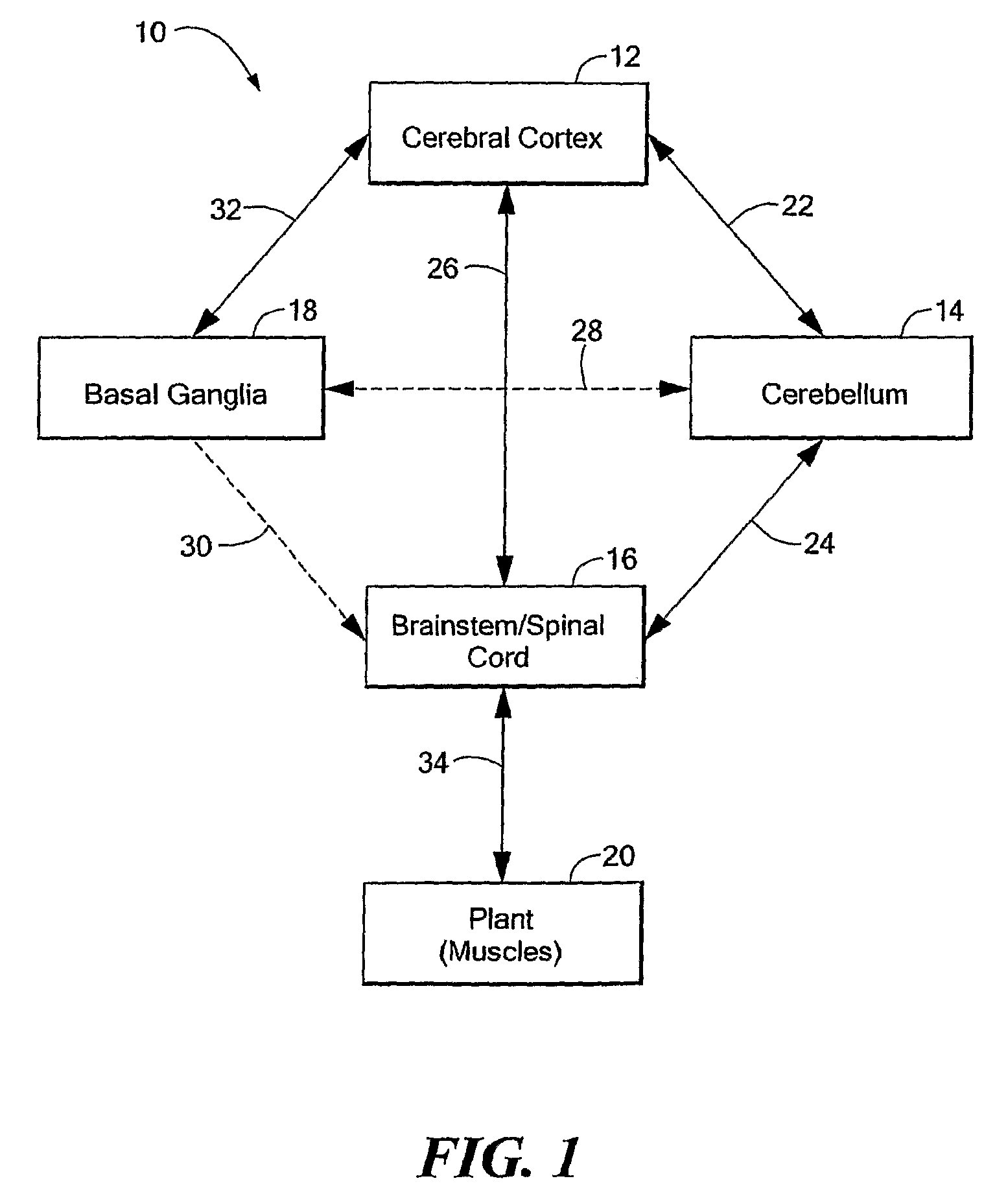
Computer-Implemented Model of the Central Nervous System
A computer-implemented model of the central nervous system includes at least one of a basal ganglia portion, a cerebral cortex portion coupled to the basal ganglia portion, or a cerebellum portion coupled to the cerebral cortex. Each one of the basal ganglia portion, the cerebral cortex portion, and the cerebellum portion is comprised of respective elements representative of real neuroanatomical structures of a central nervous system and the respective elements are adapted to perform functions representative of real neuroanatomical functions of the central nervous system. At least one of the basal ganglia portion, the cerebral cortex portion, or the cerebellum portion is adapted to control a plant.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Aminopyrazine compounds with A2A antagonist properties
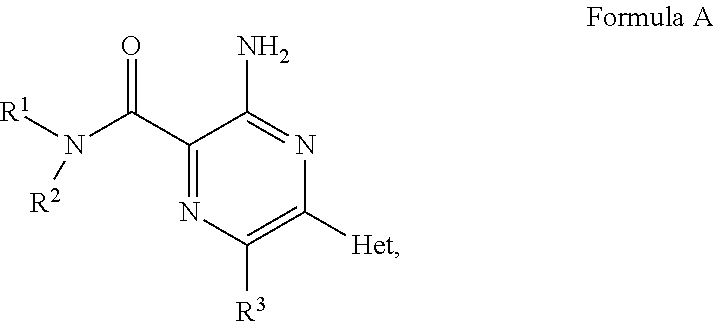
Disclosed are compounds of Formula A and Formula A-1, or a salt thereof, and pharmaceutical formulations (pharmaceutical compositions) comprising those compounds, or a salt thereof; wherein “R1”, “RA-1”, “R2”, “R3”, and “Het” are defined herein above, which compounds are believed suitable for use in selectively antagonizing the A2a receptors, for example, those found in high density in the basal ganglia. Such compounds and pharmaceutical formulations are believed to be useful in treatment or management of neurodegenerative diseases, for example, Parkinson's disease, or movement disorders arising from use of certain medications used in the treatment or management of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Fused tricyclic compounds as adenosine receptor antagonist
InactiveCN103261202AAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderVasopressin AntagonistsAdenosine a2a receptors
The present disclosure relates to fused tricyclic compounds of formula (I) or its tautomers, polymorphs, stereoisomers, prodrugs, solvate or a pharmaceutically acceptable salts, or pharmaceutical compositions containing them and methods of treating conditions and diseases that are mediated by thereof as A2A adenosine receptor antagonists. [Formula should be inserted here] The compounds of the present disclosure are useful in the treatment, prevention or suppression of diseases and disorders that may be susceptible to improvement by the mediation of adenosine A2A receptor.; Such conditions include, but are not limited to, Parkinsons disease, restless leg syndrome, Alzheimers disease, neurodegenerative disorder, inflammation, wound healing, dermal fibrosis, nocturnal myoclonus, cerebral ischaemia, myocardial ischemia, Huntington's disease, multiple system atrophy, corticobasal degeneration, Wilson's disease or other disorders of basal ganglia which results in dyskinesias, post traumatic stress disorder, hepatic cirrhosis, sepsis, spinal cord injury, retinopathy, hypertension, social memory impairment, depression, neuroprotection, narcolepsy or other sleep related disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, drug addiction, post traumatic stress disorder and vascular injury and the like. The present disclosure also relates to methods for the preparation of such compounds, and to pharmaceutical compositions containing them.
Owner:ADVINUS THERAPEUTICS PVT LTD
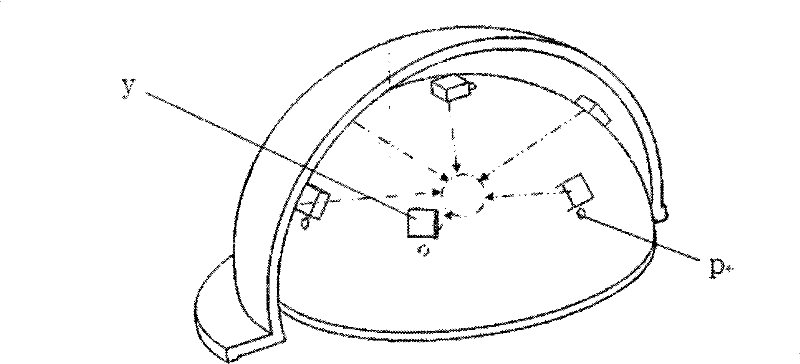
Optogenetic therapies for movement disorders
One embodiment is directed to a system for controllably managing motor function in the central nervous system of a patient having a targeted tissue structure that has been genetically modified to have light sensitive protein, comprising a light delivery element configured to direct radiation to at least a portion of a targeted tissue structure; a light source configured to provide light to the light delivery element; and a controller operatively coupled to light source; wherein the targeted tissue structure is a portion of the basal ganglia of the patient; and wherein the controller is configured to be automatically operated to illuminate the targeted tissue structure with radiation such that a membrane potential of cells comprising the targeted tissue structure is modulated at least in part due to exposure of the light sensitive protein to the radiation.
Owner:CIRCUIT THERAPEUTICS
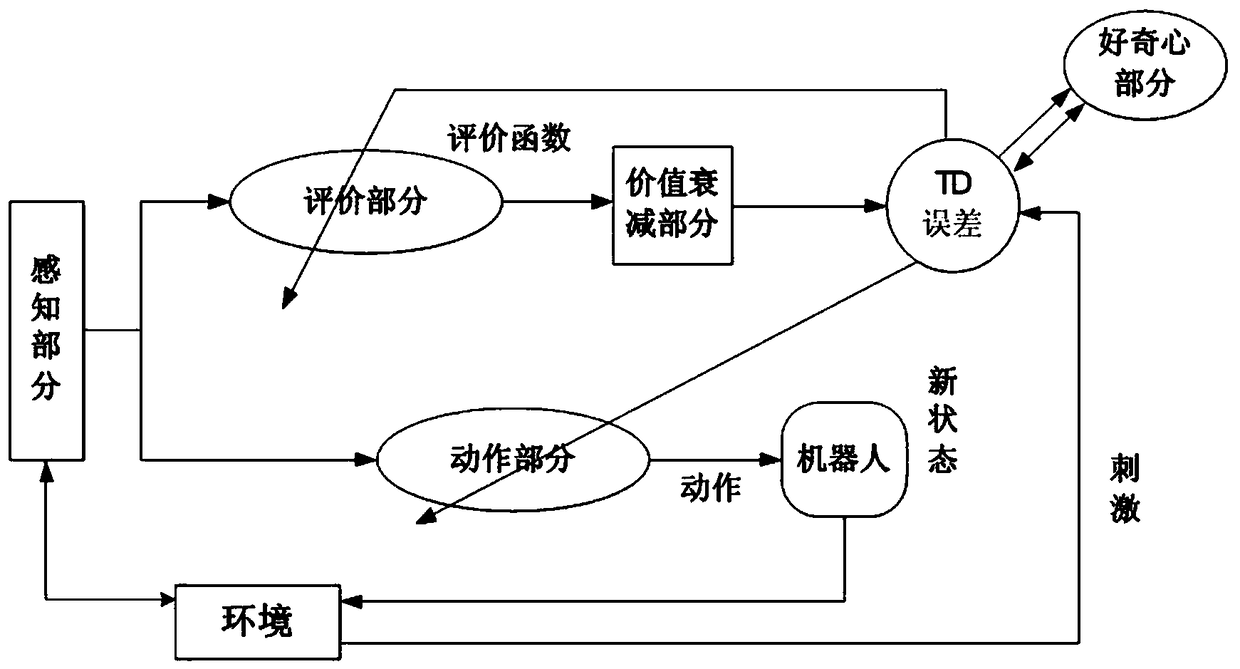
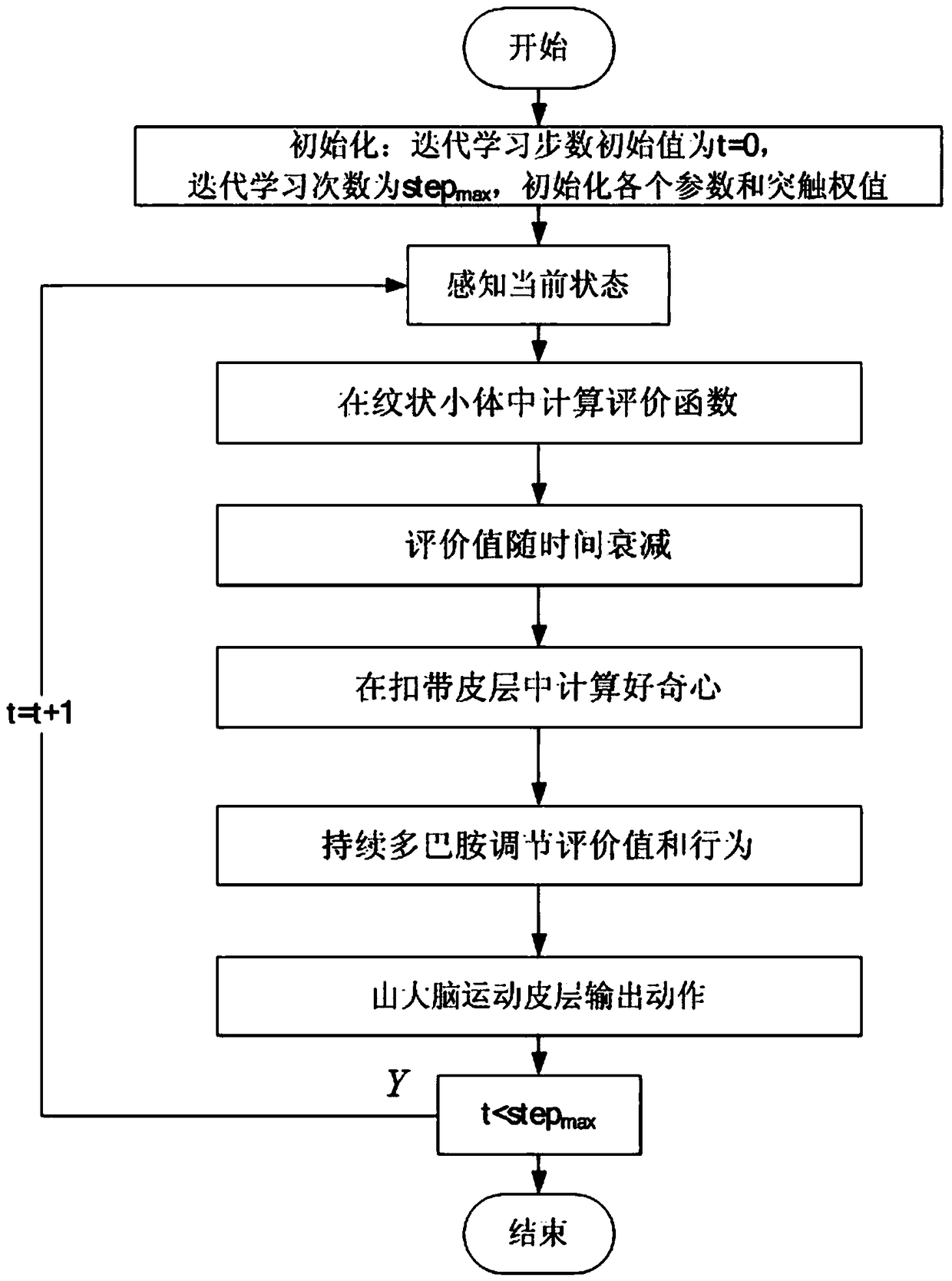
Bio-heuristic curiosity cognitive development system and operating method thereof
PendingCN109002887AImprove self-learningImprove adaptabilityPhysical realisationNerve networkOrganism
The invention relates to a bio-heuristic curiosity cognitive development system and an operating method thereof, belonging to the technical field of intelligent robots. The bio-heuristic curiosity cognitive development system is constructed by simulating the coordination mechanism of basal ganglia, cingulate cortex and the regulation mechanism of persistent dopamine, including a perceptual part, an evaluative part, a behavioral part, a value decreasing part, a curiosity part and a persistent dopamine regulation part. The invention provides an object-heuristic curiosity cognitive development system, and the problem of poor autonomous exploratory ability of robot in unknown environment is solved. Secondly, the mechanism of value attenuation is introduced, which can make the learned knowledgecontinuously affect the subsequent learning process of robot, make the robot reach the goal quickly, and solve the problem of low learning efficiency of traditional reinforcement learning.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Method for marking human body model map for diagnosis
InactiveCN106157774AAchieving Accurate DiagnosisOvercoming functional disordersEducational modelsHuman bodyThalamus
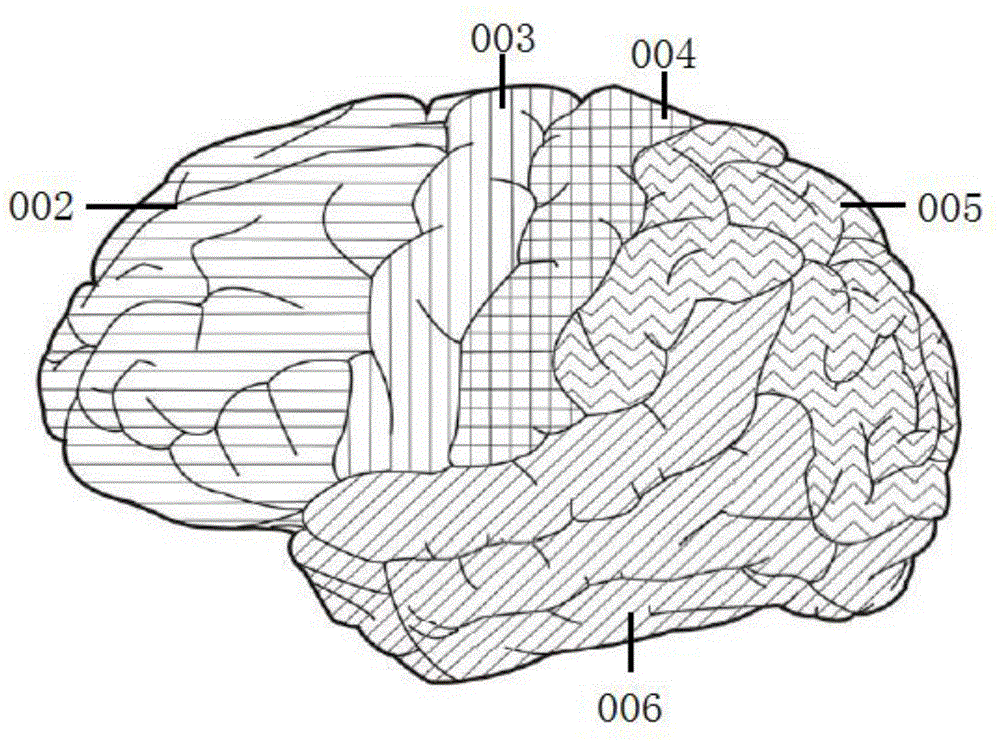
The invention provides a method for labeling human body model atlases for diagnosis. The method includes (1) dividing and labeling sub-regions, and dividing the central nervous system into the main sub-region of the telencephalon, the main sub-region of the hippocampus, the main sub-region of the basal nucleus, and the thalamus according to functional units. Main divisions, cerebellum main divisions, brainstem main divisions, spinal cord main divisions, further divide the nervous tissue into divisions or parts in the telencephalon main division, hippocampus main division, basal nucleus main division, thalamus main division and cerebellum main division, and then Partitions or parts are divided into several layers or blocks, and sub-regions are marked by layers and blocks. In the main spinal cord partition, the gray matter is first divided into 32 gray matter columns, and then each gray matter column is divided into upper and lower sections from different positions. (2) draw the atlas, divide the human body into 131 parts, and draw the corresponding position relationship diagram of the human body parts in each sub-division; (3) draw the atlas on each marked sub-division of the model above and marked.
Owner:王智
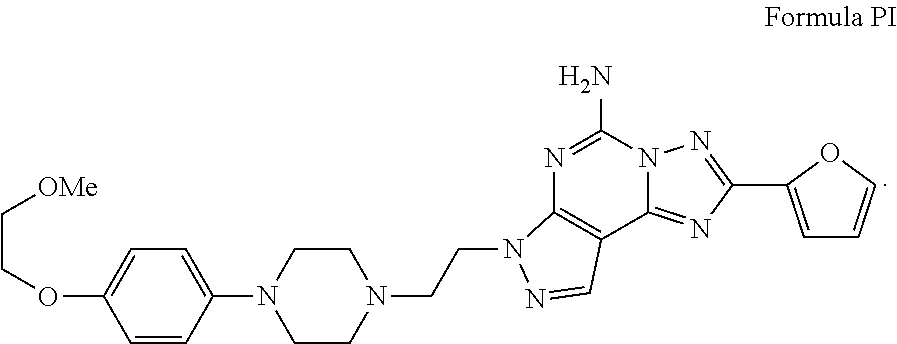
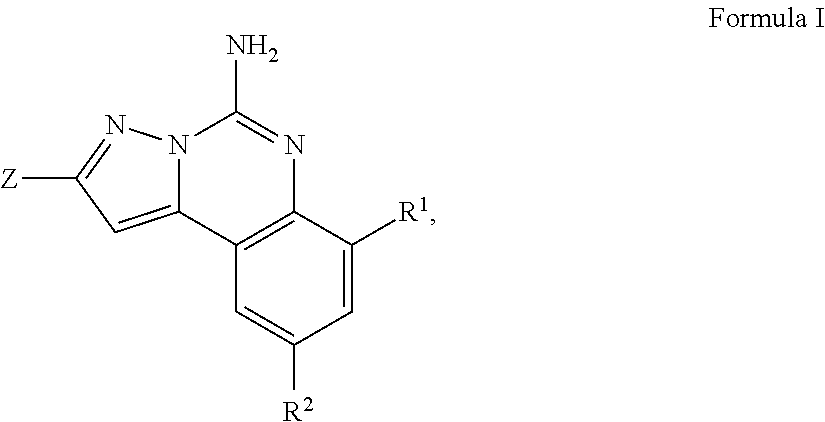
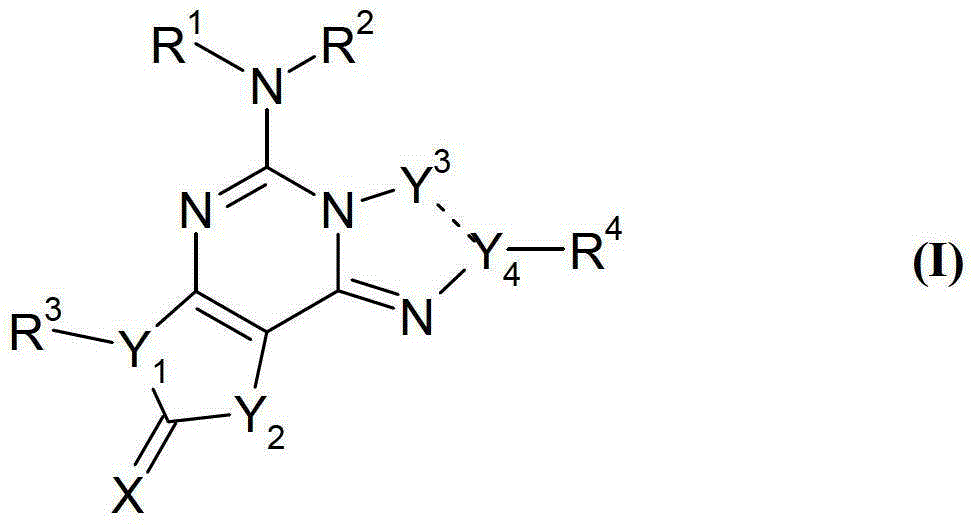
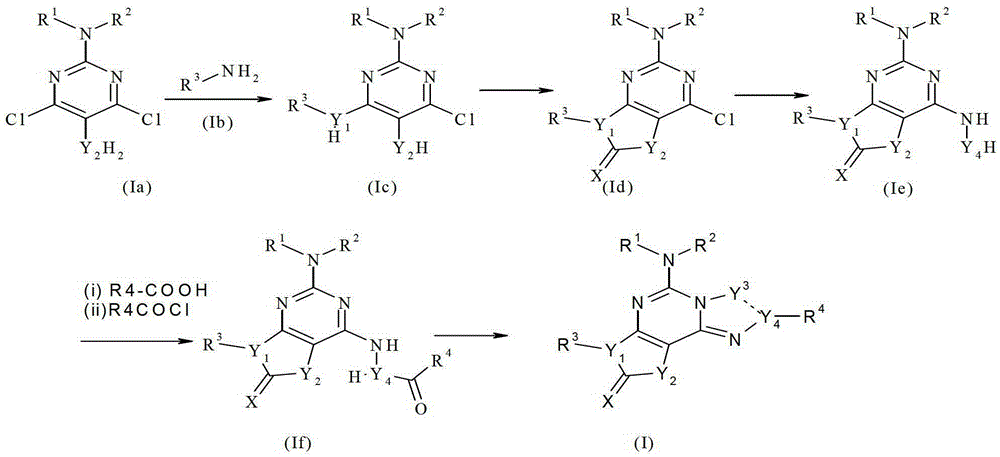
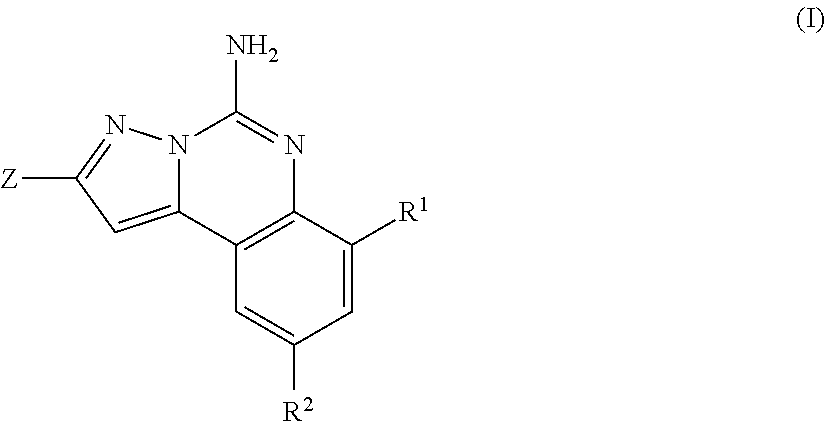
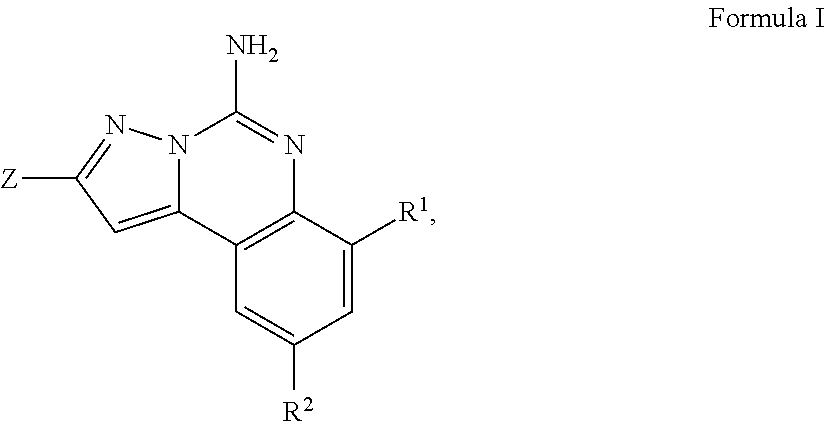
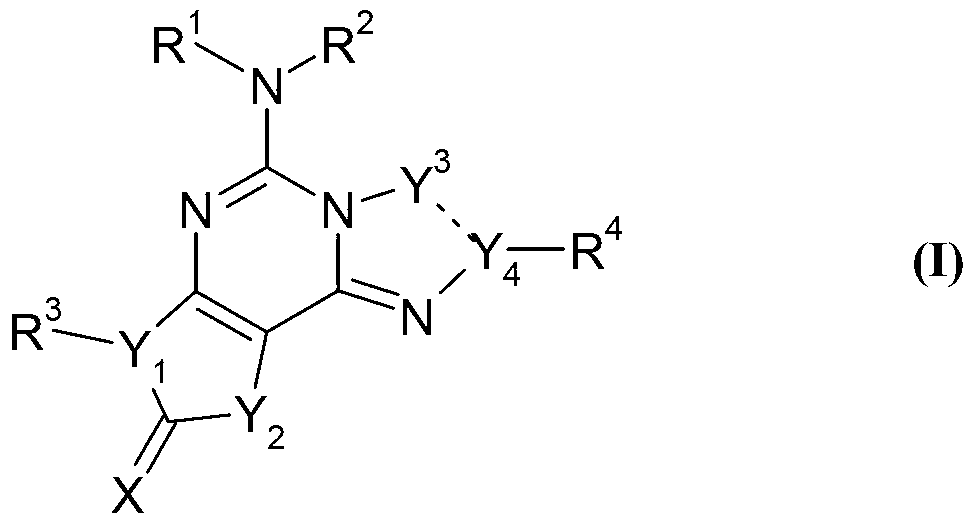
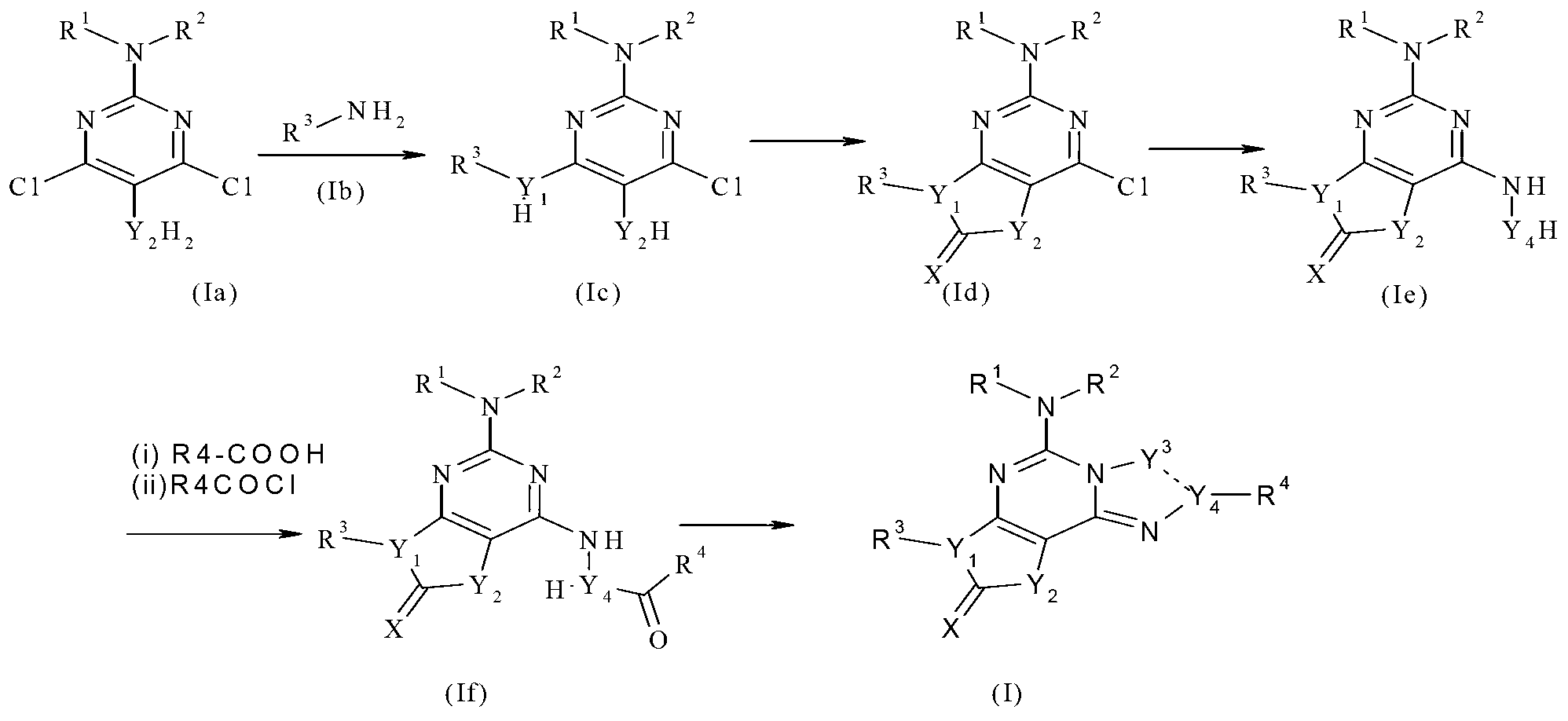
Imidazo[1,2-c]quinazolin-5-amine compounds with a2a antagonist properties
Disclosed are compounds having the structure of Formula I, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of any thereof: wherein: “Z” and R1 are defined herein, which compounds are believed suitable for use in selectively antagonizing the A2a receptors, for example, those found in high density in the basal ganglia. Such compounds and pharmaceutical formulations are believed to be useful in treatment or management of neurodegenerative diseases, for example, Parkinson's disease, or movement disorders arising from use of certain medications used in the treatment or management of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
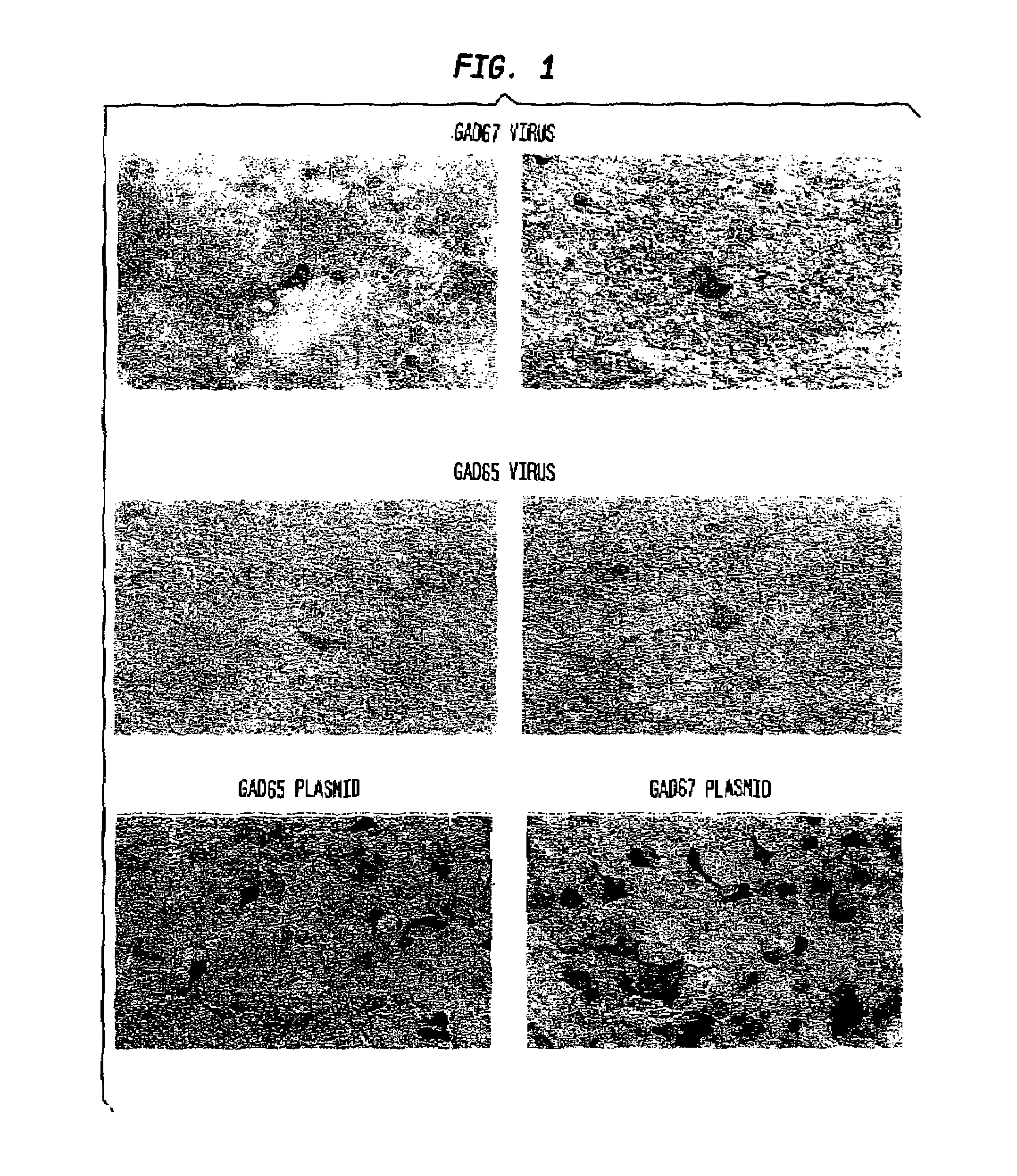
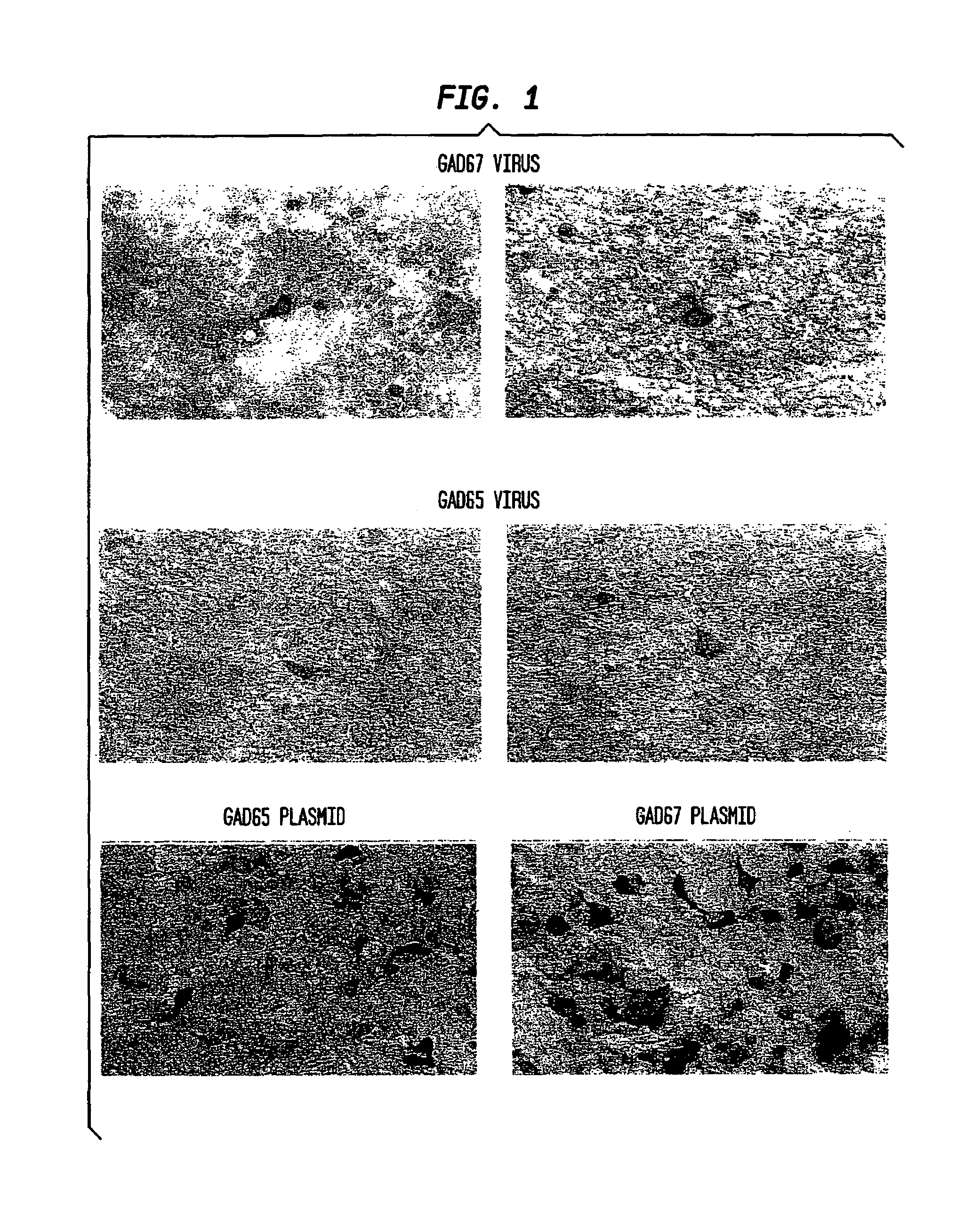
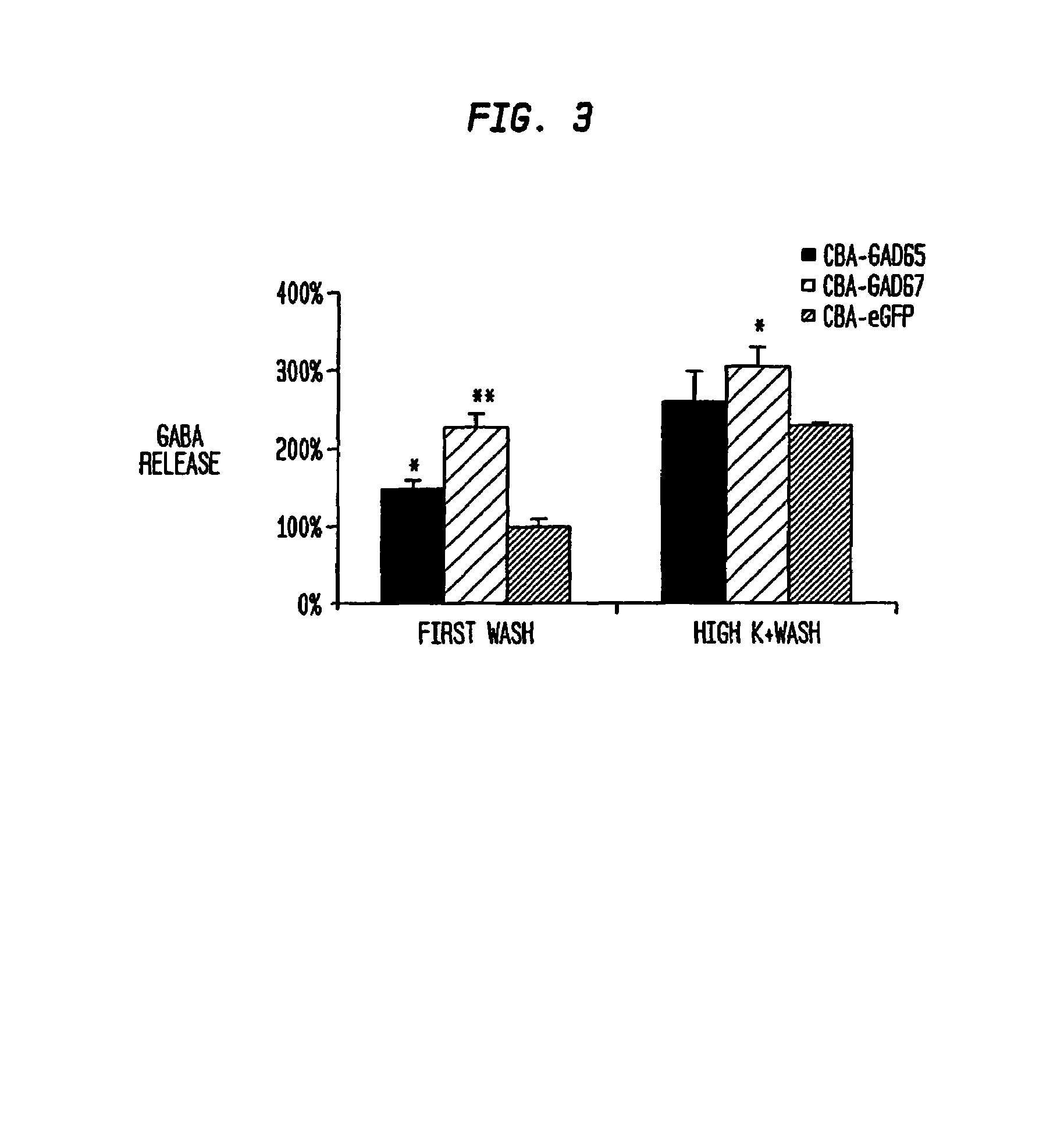
Glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) based delivery system
The invention provide methods and compositions for localized delivery of a vector comprising a therapeutic agent to a specific region of the brain that is overstimulated in neurodegenerative diseases. In particular, the invention provides methods and compositions used to deliver an adeno-associated virus vector (AAV) comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) to cells in the subthalmic nucleus of the basal ganglia, mesaphilia and thalamus.
Owner:VECTOR NEUROSCIENCES INC
Transcranial magnetic therapeutic instrument for computer diseases
ActiveCN101537228BSignificant effectAct as an intensifying stimulusElectrotherapyArtificial respirationDiseaseBrain pacemaker
The invention provides a transcranial magnetic therapeutic instrument for computer diseases, comprising a field effect cap which can be worn on head, field effect cap internally being distributed with electrodes and at least one electromagnet; the instrument further comprises an electroencephalographic simulative generator, and the electroencephalographic simulative generator is respectively connected with the electromagnet and the electrodes via conducting wires. In the invention, nerve cell nucleus of intracephalic basal ganglia part can be self-excited by a stereoscopic superposition alternating magnetic field transcranially magnetically formed at intracephalic deep part and a weak induced current formed at a specific part of intracephalic deep part; and the transcranial magnetic effect is strengthened when the nerve cell nucleus transcranially pass through basal ganglia part. The invention is not an interventional therapy but can achieve the functions of stimulating and recoveringneurotransmitters of nerve cell nucleus of intracephalic basal ganglia part such as autocrine dopamine, and is applied to encephalopathic therapy such as Parkinson, encephalatrophy, epileptics and gork; the effects exceed that of a brain pacemaker, thereby overcoming the disadvantages of pharmacotherapy and surgical therapy; and the therapeutic instrument can be used in hospital, and is more applied to treatment of patients at home.
Owner:哈尔滨奥博医疗器械有限公司
Glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) based delivery system
The invention provide methods and compositions for localized delivery of a vector comprising a therapeutic agent to a specific region of the brain that is overstimulated in neurodegenerative diseases. In particular, the invention provides methods and compositions used to deliver an adeno-associated virus vector (AAV) comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) to cells in the hippocampus, subthalamic nucleus of the basal ganglia, mesaphilia and thalamus.
Owner:VECTOR NEUROSCIENCES INC +1
An FPGA experimental platform for deep brain stimulation of the basal ganglia-thalamus network in Parkinson's disease
The invention provides a deep brain stimulation FPGA experimental platform of a basal ganglia and thalamencephalon network for the parkinson's disease. The experimental platform comprises an FPGA development board and an upper computer, which are connected with each other; the FPGA development board is used for realizing a basal ganglia and thalamencephalonneuron network model and a deep brain stimulation controller; the upper computer is used for designing an upper computer software interface and being communicated with the FPGA development board. The experimental platform has the benefits that as an animal-free experiment means of a biological neural network, and on the basis of the high-speed computation FPGA neuron network, the experimental platform realizes the modeling of the neuron network of a complex parkinson's disease focus area, and the neuron network model can be consistent with real biological neuron on a time scale. The platform provides a visual research platform, closer to the real neuron network, for researching the discharging mechanism of the parkinson's disease and the abnormal discharging mode of the basal ganglia and thalamencephalonneuron network controlled by deep brain stimulation, and has a significant practical value in researching the treatment of the parkinson's disease.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
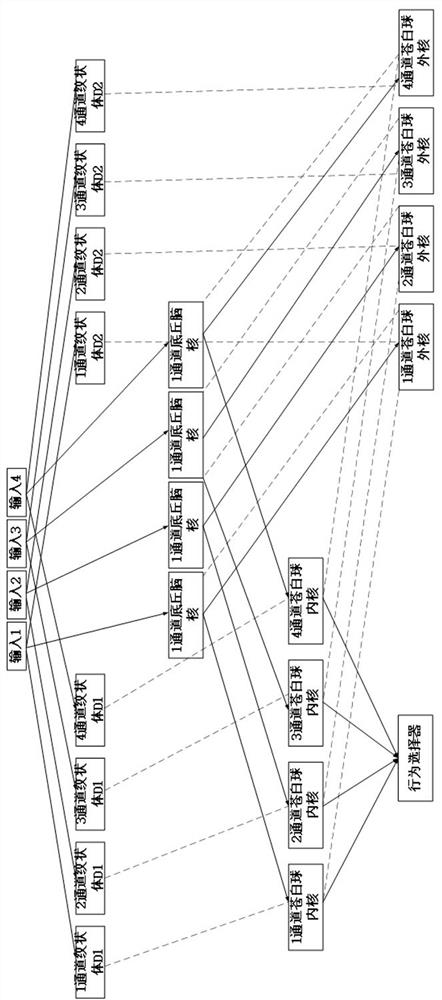
A multi-agent formation method based on behavior selection
The invention discloses a multi-agent formation method based on behavior selection, which comprises the following steps: Step 1, setting a position-related detection revenue calculation method; Step 2, defining specific behaviors of multiple agents; Step 3, determining The number of channels of the basal ganglia, establishing a channel model of the basal ganglia, and initializing relevant parameters; Step 4, correcting the channel model parameters of the basal ganglia. Through the above method, the multi-agent formation method based on behavior selection of the present invention introduces a dynamic agent formation method based on behavior selection, which effectively solves the problem of poor robustness and reliability in existing formation detection methods. Weakness and other disadvantages, through the opening of parameters and various weight modification channels, the technical solution of this application has wider versatility, and the introduction of target detection income variables can improve the income of multi-agent detection tasks as a whole.
Owner:JIANGSU JIANGRONG INTELLIGENT TECH
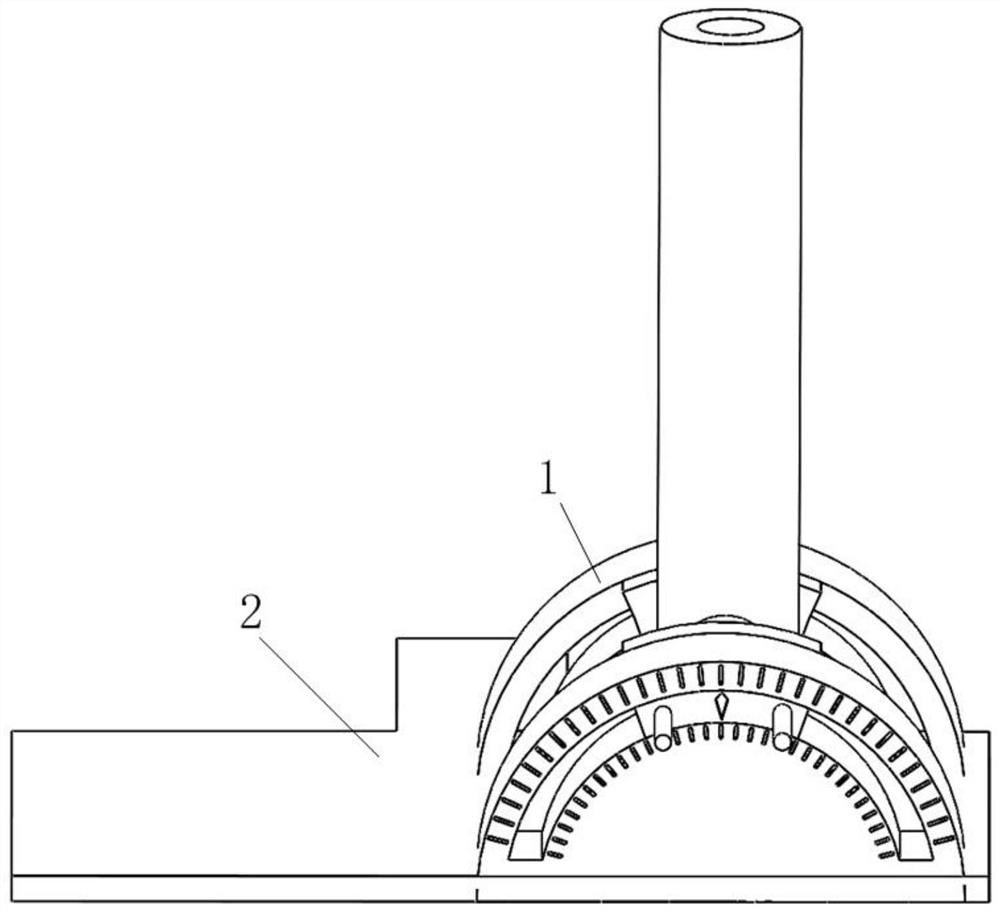
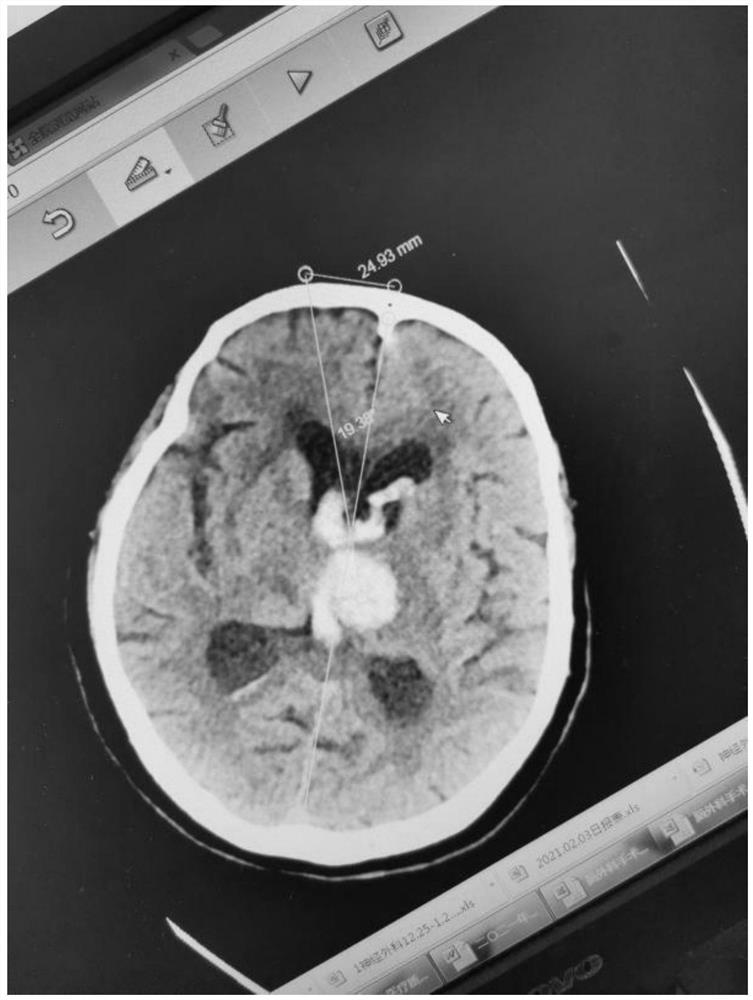
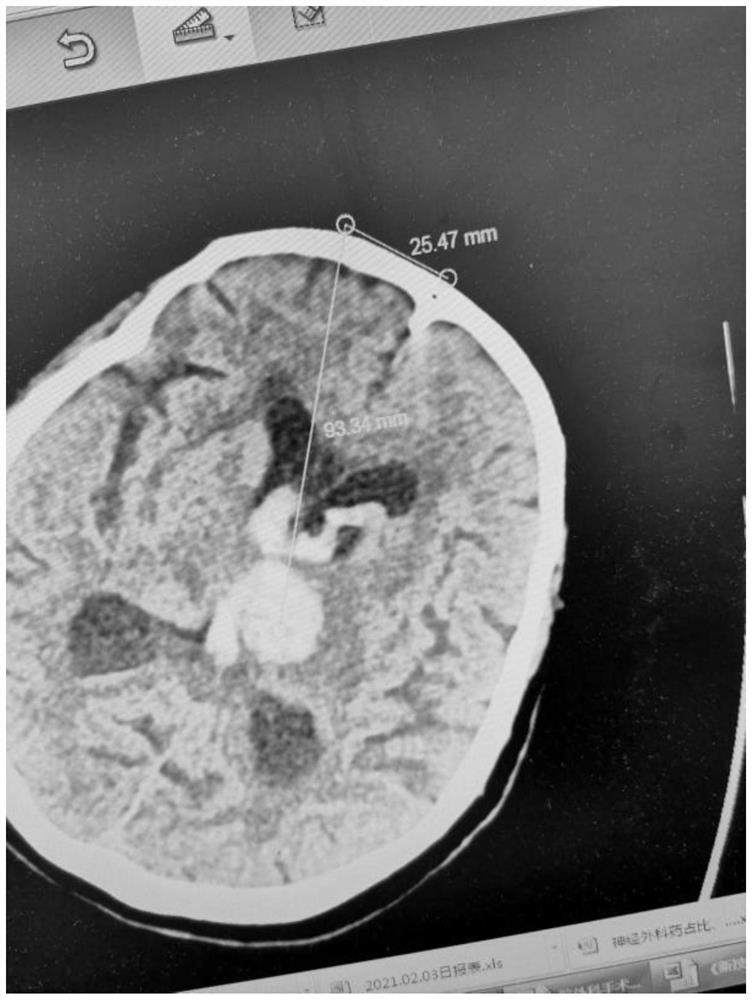
3D improved multifunctional minimally invasive surgery auxiliary guide plate, design method and operation method
InactiveCN113040875AMeet the diverse needs of clinicalRealize personalized hematoma punctureSurgical needlesTrocarLess invasive surgeryThalamus
The invention belongs to the technical field of 3D minimally invasive surgery equipment, and discloses a 3D improved multifunctional minimally invasive surgery auxiliary guide plate, a design method and an operation method. A puncture guide plate base and an angle-adjustable puncture channel with an angle ruler are designed by taking a puncture point as the center; and the puncture base and the puncture channel are integrated, and a basal ganglia region cerebral hemorrhage and thalamic hemorrhage transfrontal puncture guide plate is determined and printed through a 3D conversion technology. The 3D improved multifunctional minimally invasive surgery auxiliary guide plate comprises the angle-adjustable puncture channel with the angle ruler; and the puncture channel is fixed on the puncture guide plate base. The inner diameter of the puncture channel is 5mm. According to the invention, the 3D improved multifunctional minimally invasive puncture surgery guide plate is designed and prepared by utilizing the 3D printing conversion technology, so that the requirements of a cerebral hemorrhage emergency minimally invasive surgery are met, and the clinical diversified requirements are met.
Owner:QINGDAO CITY CHENGYANG DISTRICT PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Aminopyrazine compounds with a2a antagonist properties
Disclosed are compounds having the structure of Formula I, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of any thereof, wherein: “Z”, R1 and R2 are defined herein, which compounds are believed suitable for use in selectively antagonizing the A2a receptors, for example, those found in high density in the basal ganglia. Such compounds and pharmaceutical formulations are believed to be useful in treatment or management of neurodegenerative diseases, for example, Parkinson's disease, or movement disorders arising from use of certain medications used in the treatment or management of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Transcranial magnetoelectric depression therapeutic apparatus
ActiveCN101530647BGood effectImprove performanceElectrotherapySleep inducing/ending devicesAuditory systemTherapeutic effect
The invention provides a trabscranial magnetoelectric depression therapeutic apparatus, comprising a pair of earphones, a beam connected between the earphones, at least a magnet, at least a pair of electrodes and an internal circuit; wherein, the earphones and the electrodes are connected with the internal circuit. The technical proposal is as follows: trabscranial magnetoelectricity and audio signals directly act on heads and auditory systems of human; stereo superposition electric field formed in certain parts of brain by trabscranial magnet can ensure the parts to generate weak induced current so as to self stimulate the parts to secrete dopamine and restore the function of self secreting neurotransmitter such as dopamine by the parts; the trabscranial magnet directly stimulates neutral clusters of basal ganglia of thalamus, thus strengthening the effects of the trabscranial magnet; the audio signals with special rhythm act on the auditory systems of human, which can promote human to enter into meditation and tempt secretion of the neurotransmitter such as dopamine in the brain, thus further strengthening the effects of the trabscranial magnet. The trabscranial magnetoelectricity and audio signals integrate three effects into one, supplement and complement each other and promote each other, and the therapeutic effect on depression and insomnia is unreachable for any single function.
Owner:哈尔滨奥博医疗器械有限公司
Glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) based delivery systems
The invention provide methods and compositions for localized delivery of a vector comprising a therapeutic agent to a specific region of the brain that is overstimulated in neurodegenerative diseases. In particular, the invention provides methods and compositions used to deliver an adeno-associated virus vector (AAV) comprising a nucleotide sequence encoding glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) to cells in the hippocampus, subthalamic nucleus of the basal ganglia, mesaphilia and thalamus.
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV +1
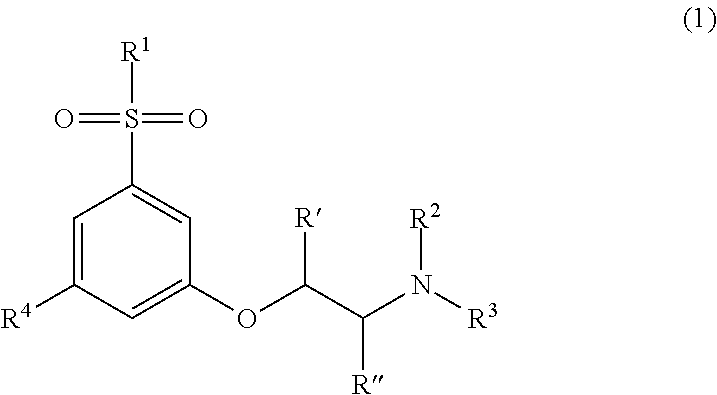
Novel modulators of cortical dopaminergic- and nmda-receptor-mediated glutamatergic neurotransmission
ActiveUS20140128360A1Decreased locomotor activityBiocideNervous disorderNR1 NMDA receptorDopaminergic
The present invention relates to novel substituted phenoxyethylamine derivatives, useful as modulators of cortical and basal ganglia dopaminergic and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor-mediated glutamatergic neurotransmission. In other aspects the invention relates to the use of these compounds in a method for therapy and to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of the invention.
Owner:INTEGRATIVE RES LAB SWEDEN
Fused tricyclic compounds as adenosine receptor antagonists
InactiveCN103261202BAntibacterial agentsSenses disorderVasopressin AntagonistsAdenosine a2a receptors
The present disclosure relates to fused tricyclic compounds of formula (I) or its tautomers, polymorphs, stereoisomers, prodrugs, solvate or a pharmaceutically acceptable salts, or pharmaceutical compositions containing them and methods of treating conditions and diseases that are mediated by thereof as A2A adenosine receptor antagonists. The compounds of the present disclosure are useful in the treatment, prevention or suppression of diseases and disorders that may be susceptible to improvement by the mediation of adenosine A2A receptor. Such conditions include, but are not limited to, Parkinsons disease, restless leg syndrome, Alzheimers disease, neurodegenerative disorder, inflammation, wound healing, dermal fibrosis, nocturnal myoclonus, cerebral ischaemia, myocardial ischemia, Huntington's disease, multiple system atrophy, corticobasal degeneration, Wilson's disease or other disorders of basal ganglia which results in dyskinesias, post traumatic stress disorder, hepatic cirrhosis, sepsis, spinal cord injury, retinopathy, hypertension, social memory impairment, depression, neuroprotection, narcolepsy or other sleep related disorders, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, drug addiction, post traumatic stress disorder and vascular injury and the like. The present disclosure also relates to methods for the preparation of such compounds, and to pharmaceutical compositions containing them.
Owner:ADVINUS THERAPEUTICS PVT LTD
Diagnosis and treatment of neonatal encephalopathy
ActiveUS10514383B2Accurate and rapid and sensitive prediction and diagnosisMaterial analysis by electric/magnetic meansDisease diagnosisMetaboliteInjury brain
Metabolites and signatures (panels) of metabolites are applicable as biomarkers in clinical diagnosis, in particular for neonatal encephalopathy. They are useful tools in differential clinical diagnosis for early detection of brain injury, determination of brain areas affected by the insults and prediction of adverse neurological outcome and may also be applied in diagnosing disease progression and treatment effect. An in vitro method for predicting the likelihood of neonatal encephalopathy of distinct brain areas, identification of affected brain area(s) of neonatal encephalopathy and risk of brain damage and prognosis and neurological outcome due to identification of the type and extent of damage of distinct brain tissues, in particular of hippocampus and / or basal ganglia, is provided.
Owner:INFANDX
Aminopyrazine compounds with A2A antagonist properties
Disclosed are compounds having the structure of Formula I, or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt of any thereof, wherein: “Z”, R1 and R2 are defined herein, which compounds are believed suitable for use in selectively antagonizing the A2a receptors, for example, those found in high density in the basal ganglia. Such compounds and pharmaceutical formulations are believed to be useful in treatment or management of neurodegenerative diseases, for example, Parkinson's disease, or movement disorders arising from use of certain medications used in the treatment or management of Parkinson's disease.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Modulators of cortical dopaminergic- and NMDA-receptor-mediated glutamatergic neurotransmission
The present invention relates to novel substituted phenoxyethylamine derivatives, useful as modulators of cortical and basal ganglia dopaminergic and N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor-mediated glutamatergic neurotransmission. In other aspects the invention relates to the use of these compounds in a method for therapy and to pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds of the invention.
Owner:INTEGRATIVE RESEARCH LABORATORIES SWEDEN AB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com


















![Imidazo[1,2-c]quinazolin-5-amine compounds with a2a antagonist properties Imidazo[1,2-c]quinazolin-5-amine compounds with a2a antagonist properties](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b679afc8-e11b-44df-afbf-b1f742fb121e/US20210053973A1-C00001.png)
![Imidazo[1,2-c]quinazolin-5-amine compounds with a2a antagonist properties Imidazo[1,2-c]quinazolin-5-amine compounds with a2a antagonist properties](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b679afc8-e11b-44df-afbf-b1f742fb121e/US20210053973A1-C00002.png)
![Imidazo[1,2-c]quinazolin-5-amine compounds with a2a antagonist properties Imidazo[1,2-c]quinazolin-5-amine compounds with a2a antagonist properties](https://images-eureka-patsnap-com.libproxy1.nus.edu.sg/patent_img/b679afc8-e11b-44df-afbf-b1f742fb121e/US20210053973A1-C00003.png)