Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
161 results about "Striatum" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
The striatum, or corpus striatum (also called the neostriatum and the striate nucleus) is a nucleus (a cluster of neurons) in the subcortical basal ganglia of the forebrain. The striatum is a critical component of the motor and reward systems; receives glutamatergic and dopaminergic inputs from different sources; and serves as the primary input to the rest of the basal ganglia.
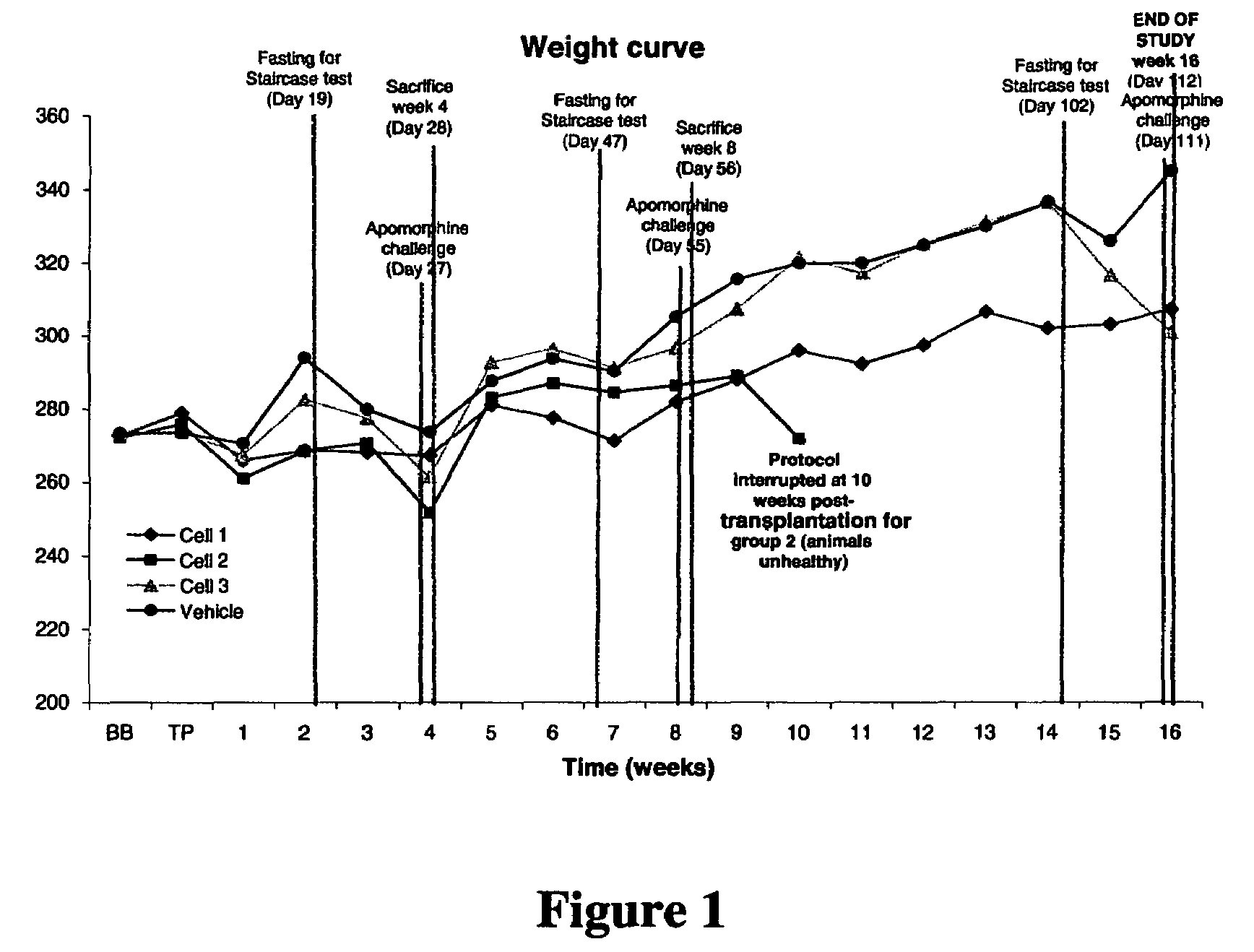
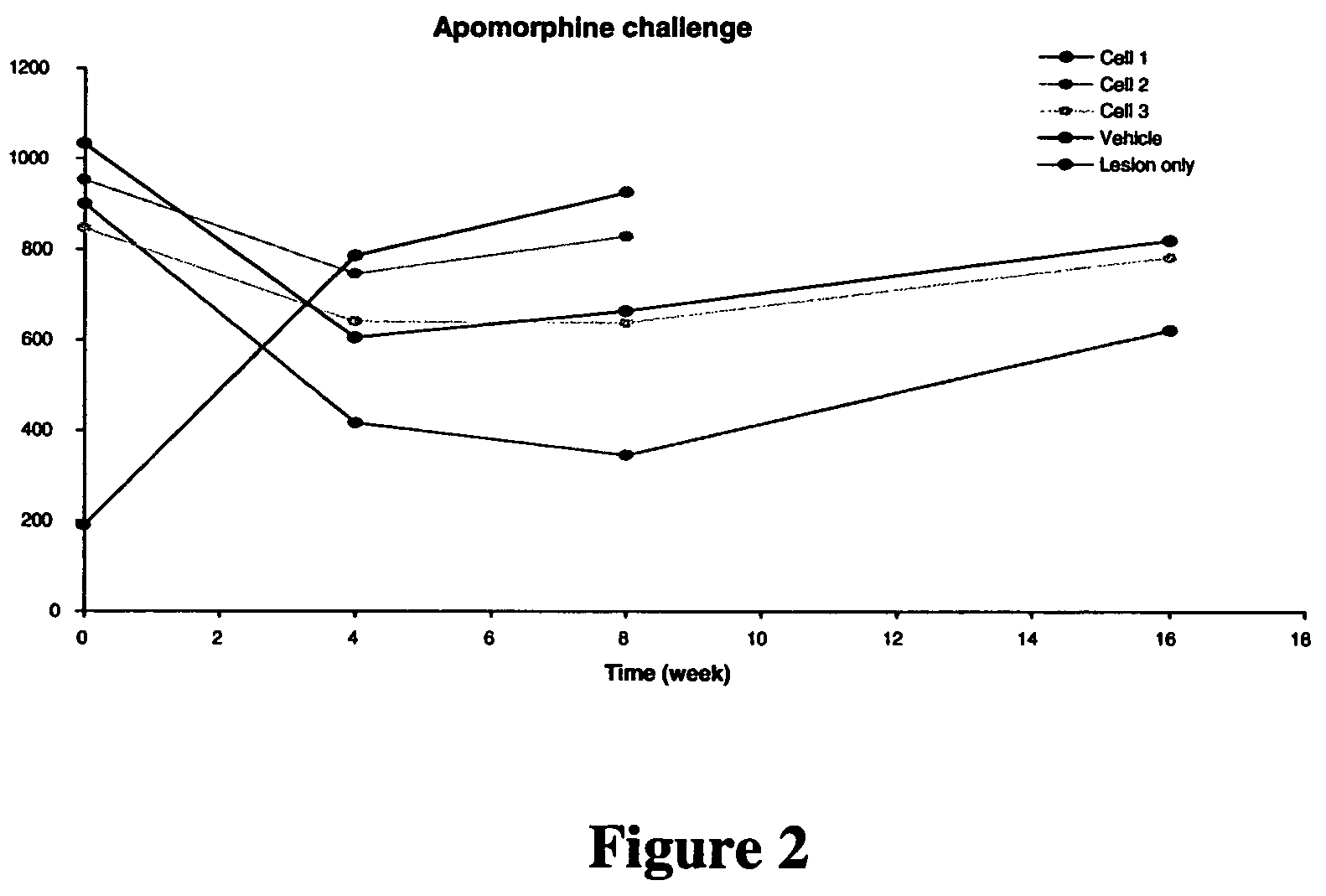
Treatment of Parkinson's disease and related disorders using postpartum derived cells
InactiveUS20060233766A1Convenient treatmentEffect is exertedBiocideNervous disorderPhysiologyPharmaceutical drug
Cells derived from postpartum tissue such as the umbilical cord and placenta, pharmaceutical compositions comprising such cells, and methods for using such cells and pharmaceutical compositions to treat patients having a neurodegenerative condition of the substantia nigra or striatum, such as Parkinson's disease, are provided.
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
Treatment of Parkinson's disease and related disorders using postpartum derived cells
InactiveUS7875273B2Convenient treatmentTrophic effect on the nervous system of the patientBiocideNervous disorderMedicinePlus disease
Owner:DEPUY SYNTHES PROD INC
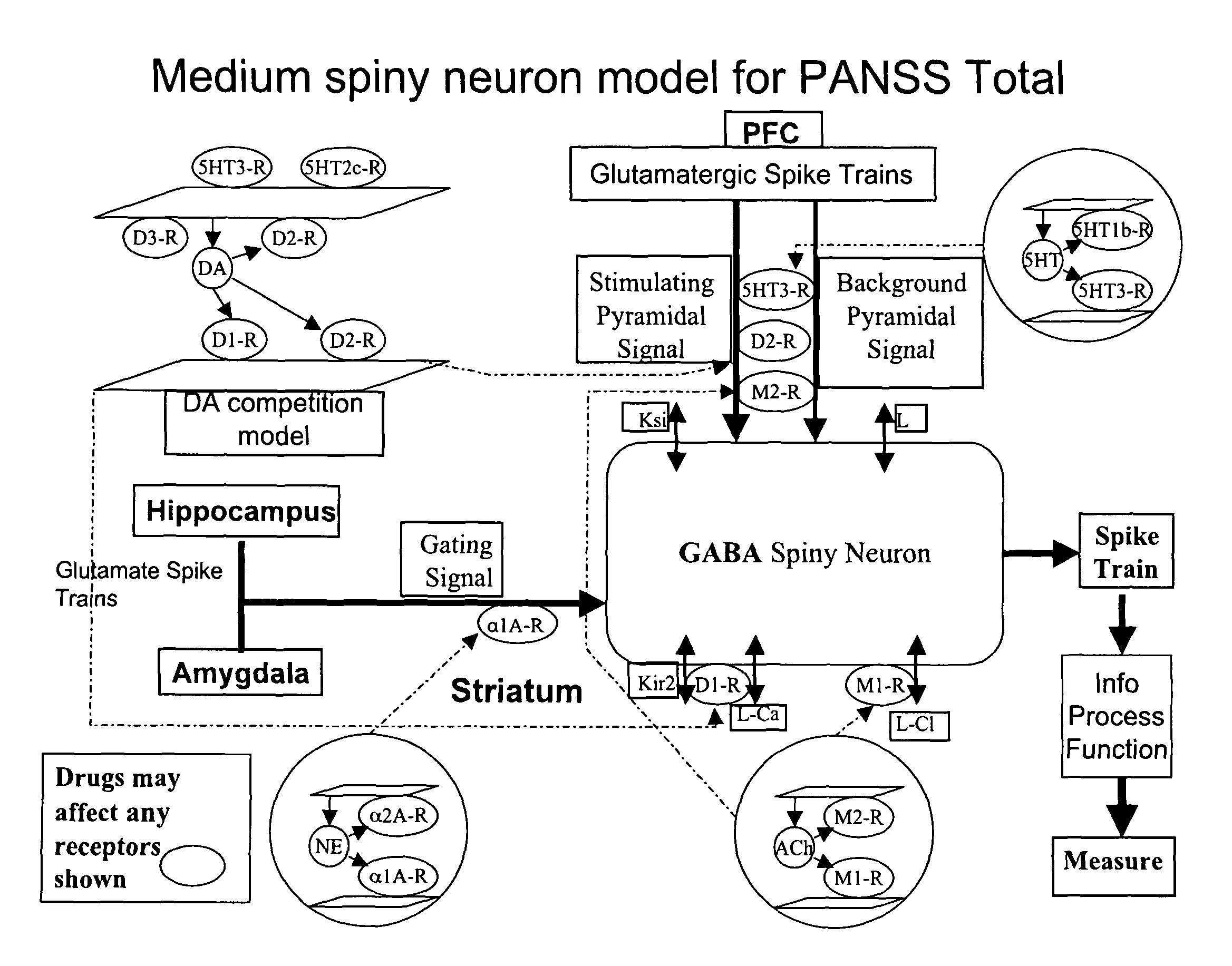
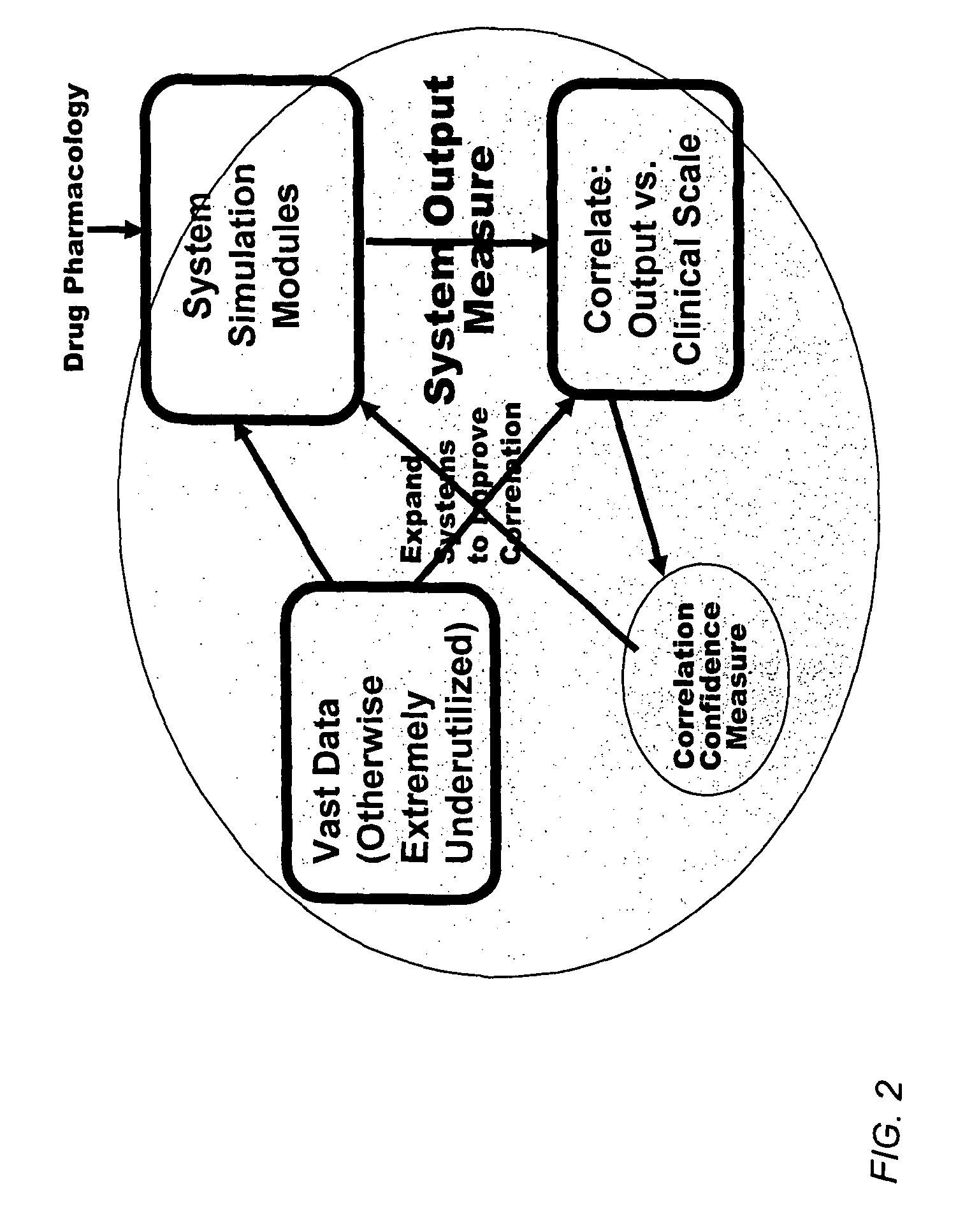
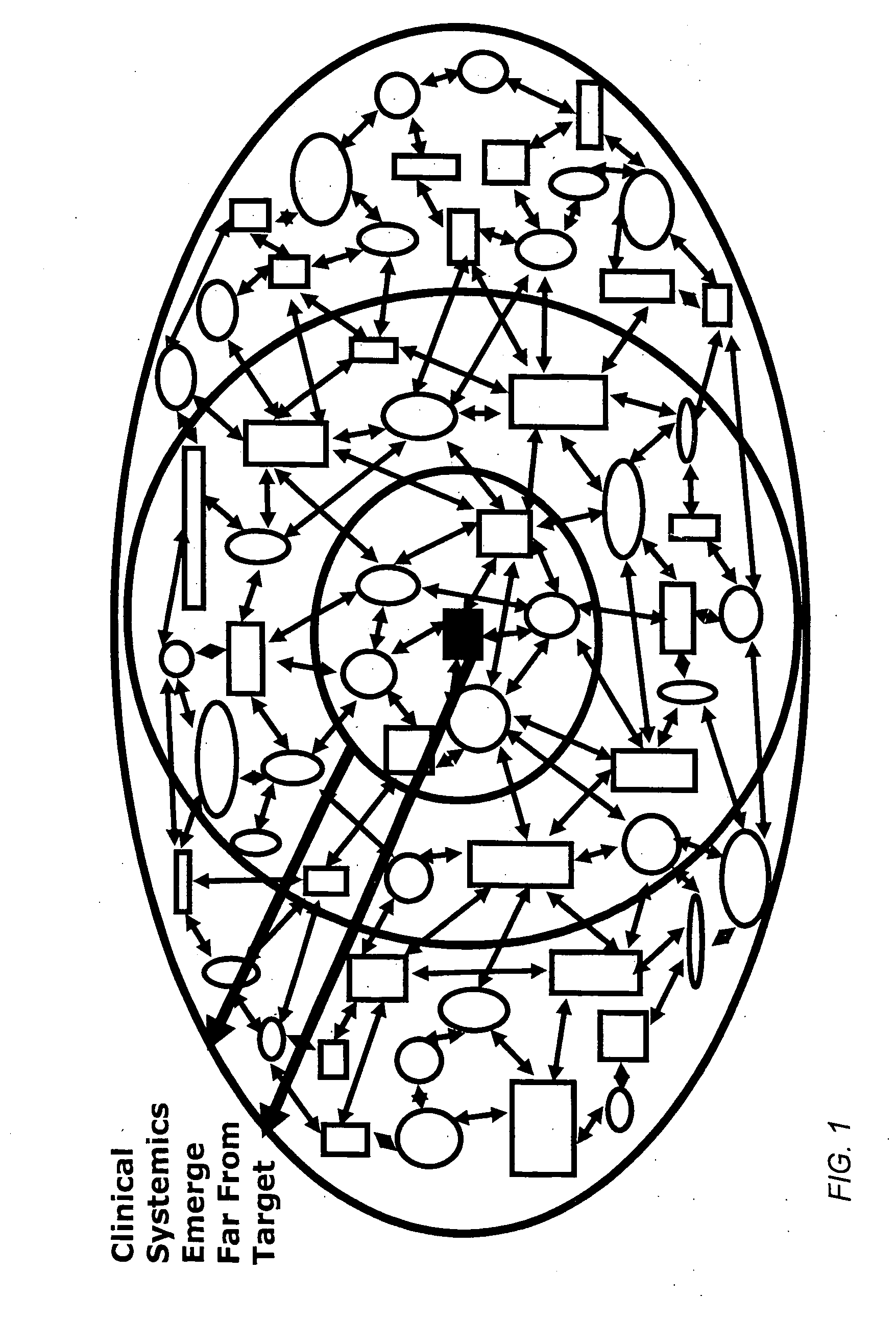
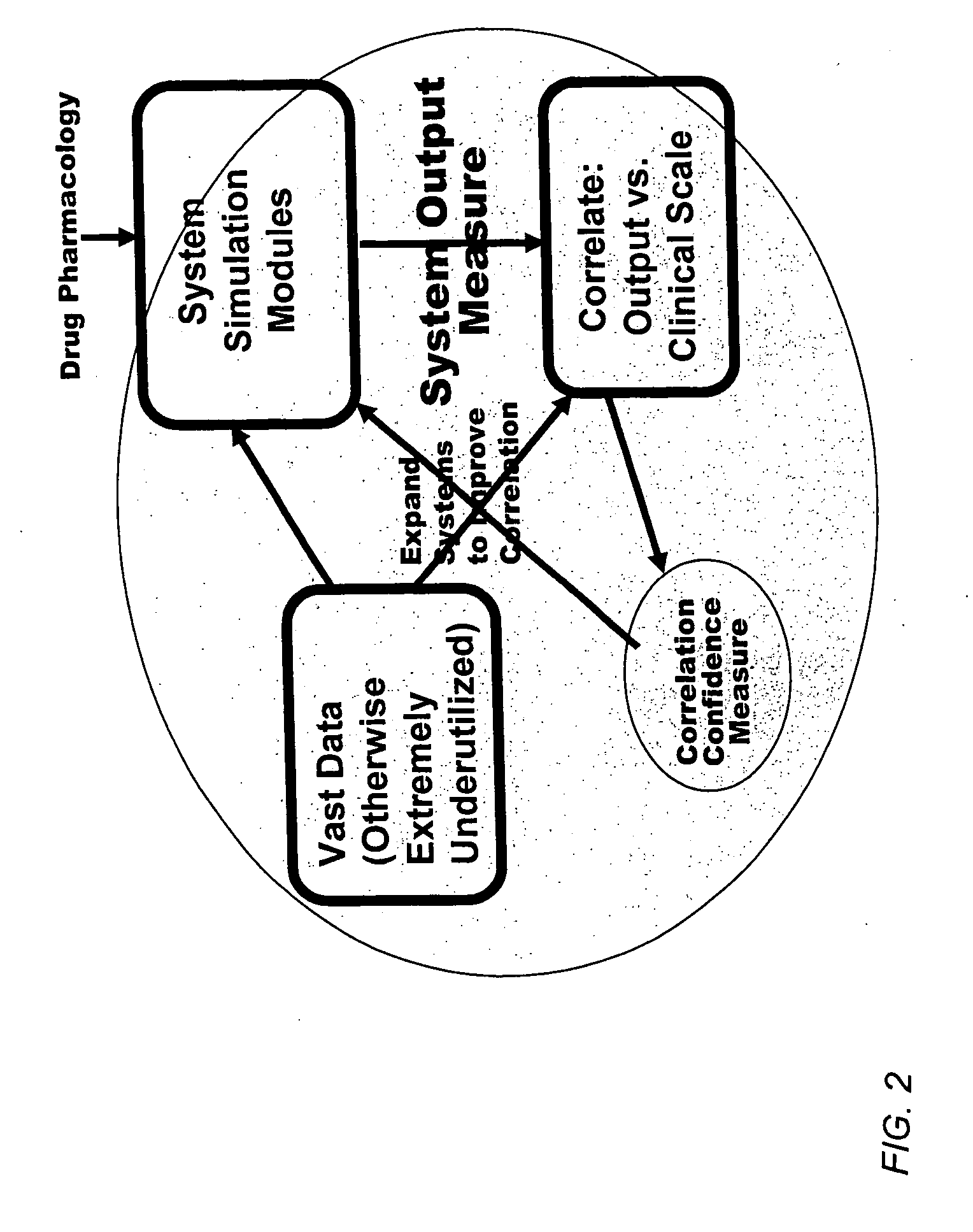
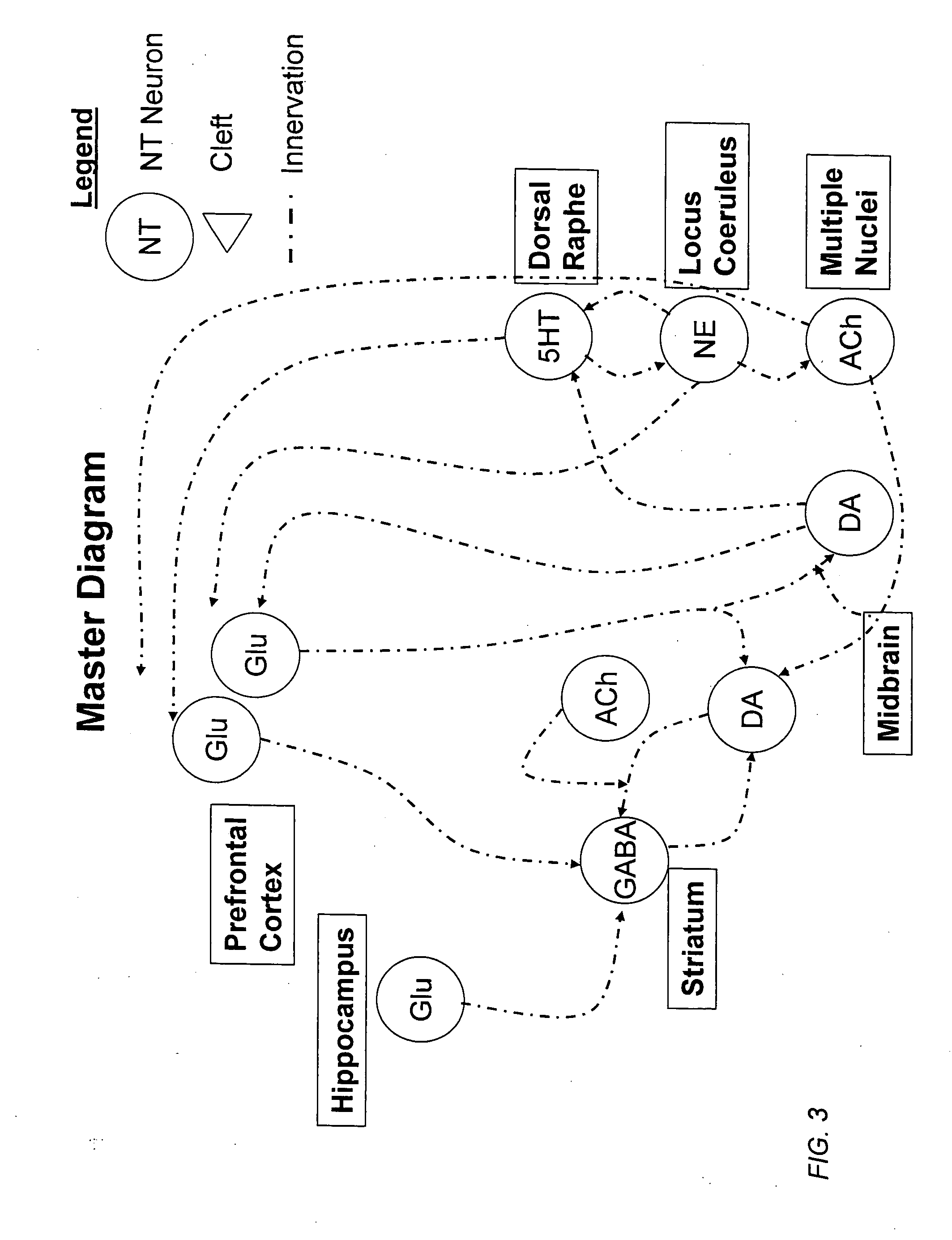
Method and apparatus for computer modeling of the interaction between and among cortical and subcortical areas in the human brain for the purpose of predicting the effect of drugs in psychiatric and cognitive diseases
ActiveUS8150629B2Easy to set upImprove clinical outcomesMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesSubstance abuserAmygdala
Computer modeling of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, for example in a normal and a pathological state resembling schizophrenia which pathological state has inputs representing the effects of a drug(s), for the purpose of using the outputs to predict the effect of drugs in psychiatric and cognitive diseases on one or more clinical scales. Diseases that can be modeled include psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depression, ADHD, autism, obsessive-compulsive disorder, substance abuse and cognitive deficits therein and neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Mild Cognitive impairment, Parkinson's disease, stroke, vascular dementia, Huntington's disease, epilepsy and Down syndrome. The computer model preferably uses the biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, to define the biological processes related to the biological state of the generic synapse model, the striatum, Locus Coeruleus, Dorsal raphe, hippocampus, amygdala and cortex, as well as certain mathematical relationships related to interactions among biological variables associated with the biological processes.
Owner:CERTARA USA INC
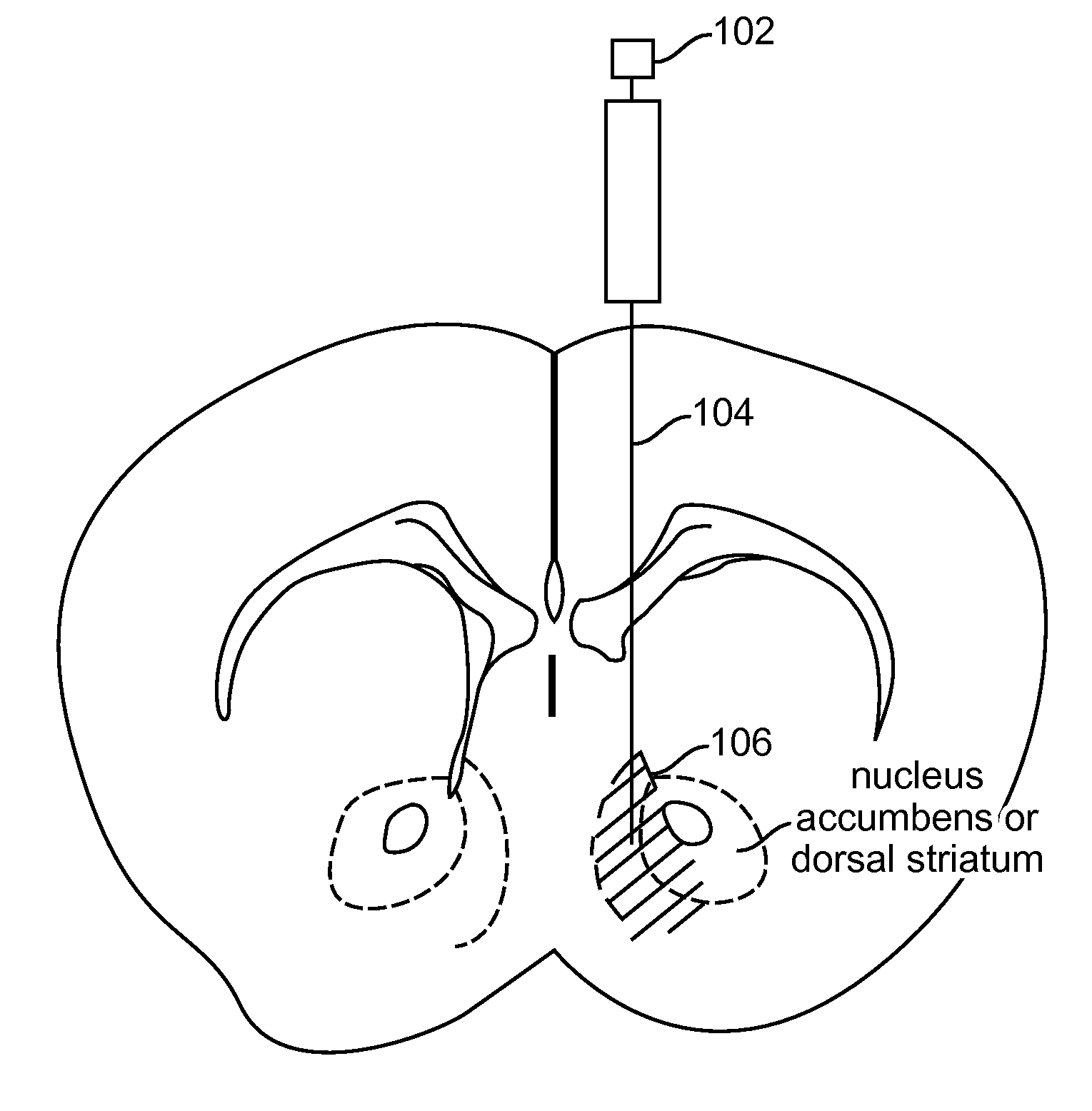
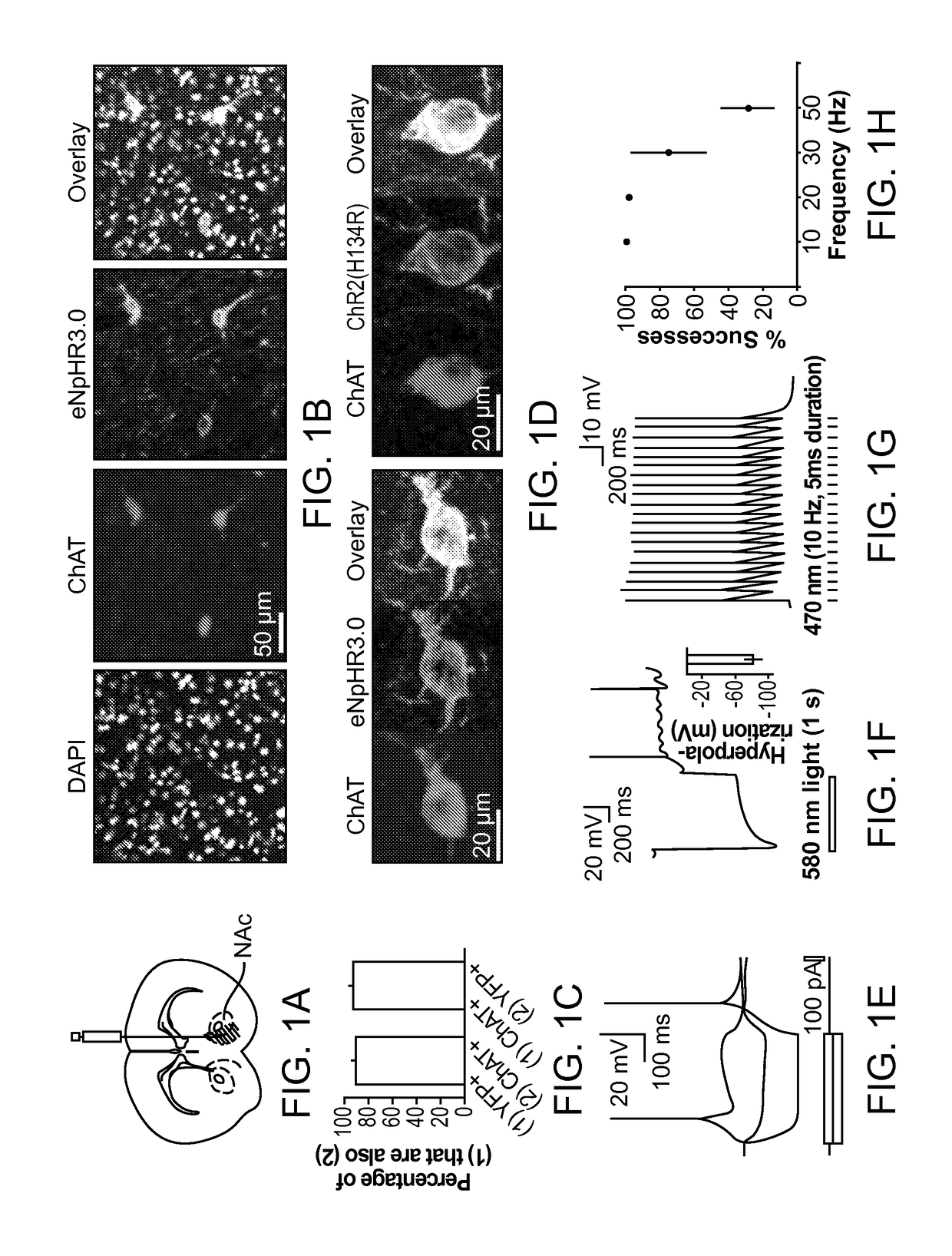
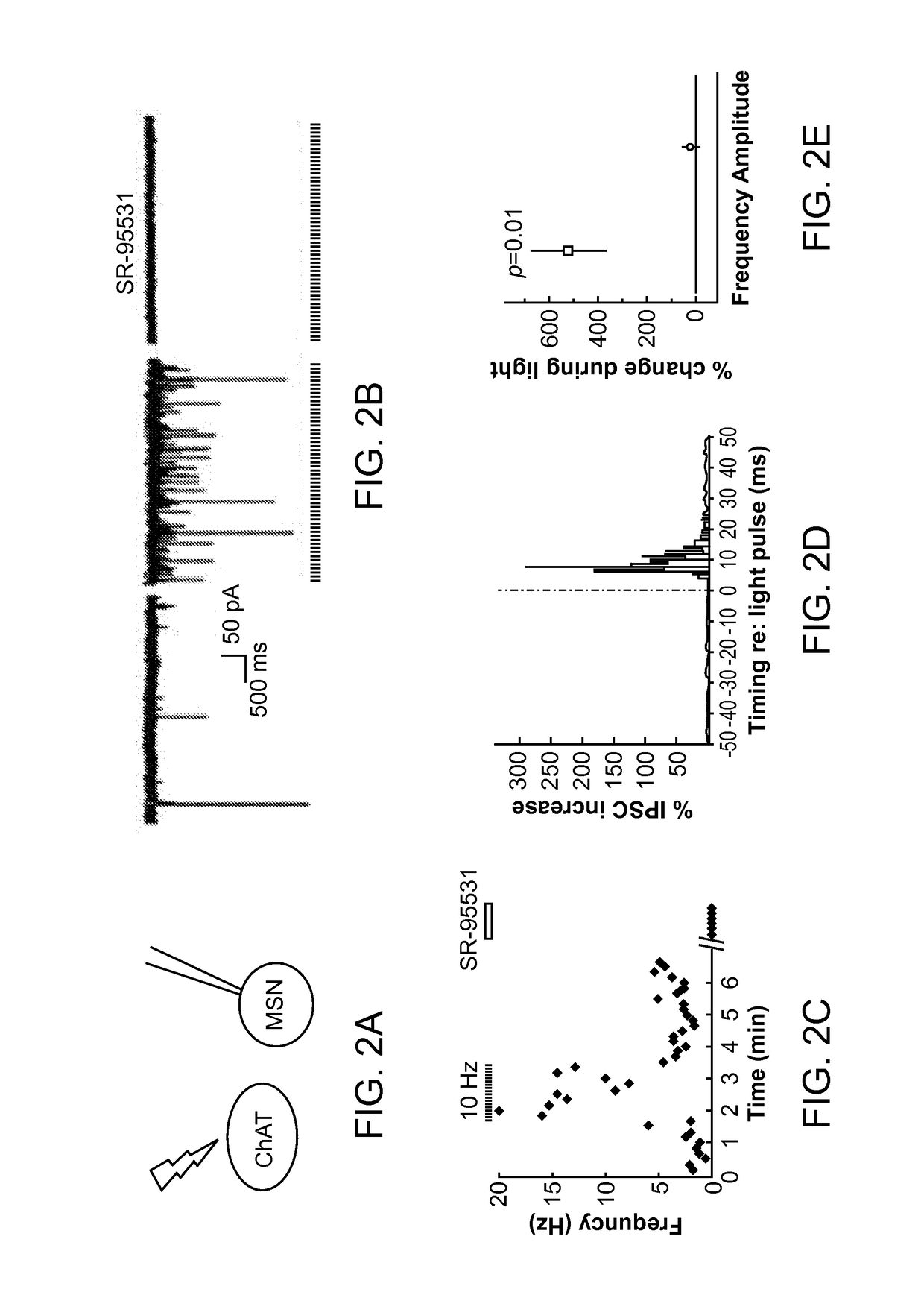
Optogenetic Control of Reward-Related Behaviors
ActiveUS20130317569A1Reduce and eliminate effectInhibition is effectiveNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsOptogeneticsInterneuron
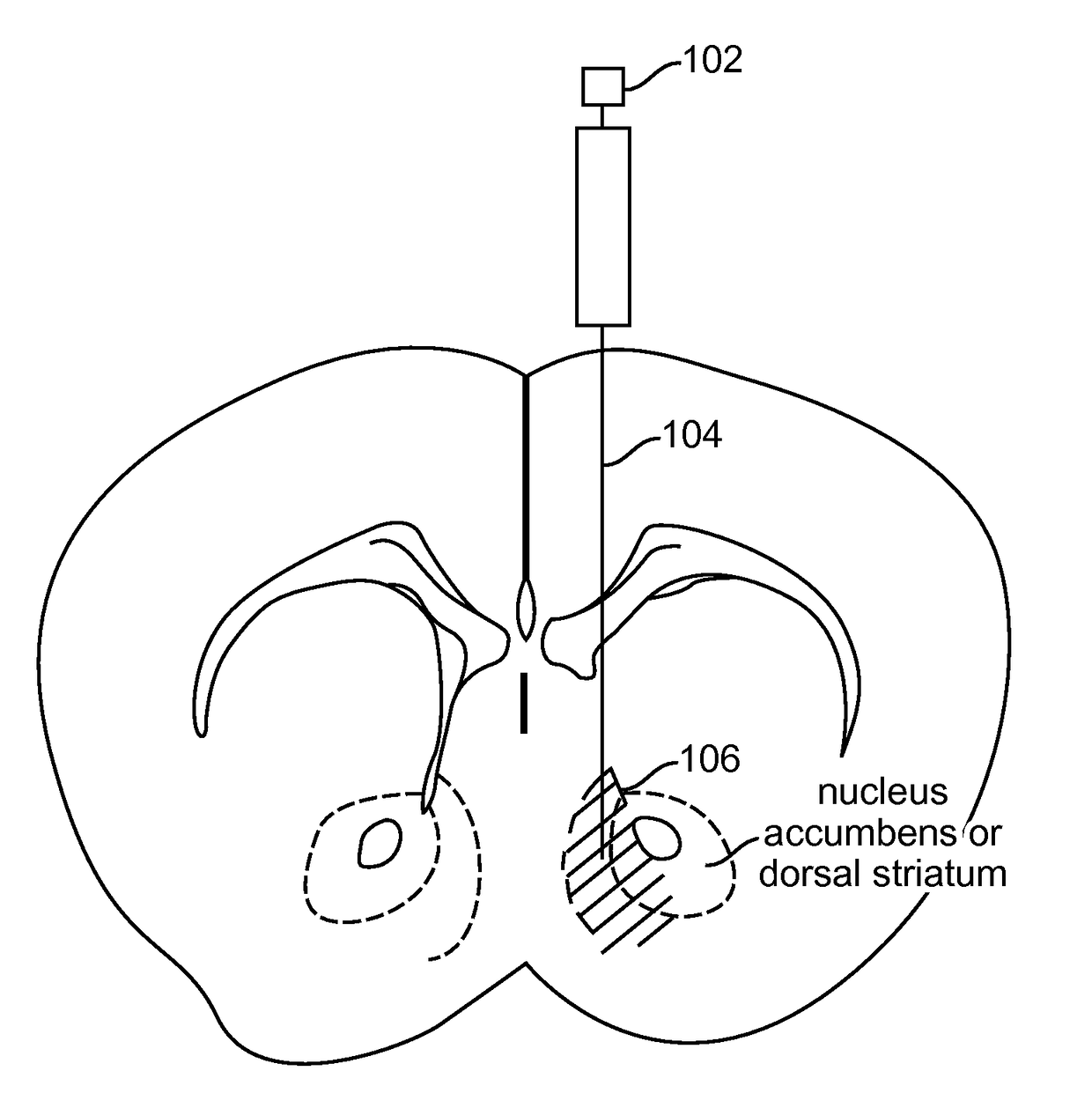
Provided herein are compositions and methods for disrupting at least one reward-related behavior in an individual through the use of light-responsive opsin proteins used to control the polarization state of the cholinergic interneurons of the nucleus accumbens or the striatum.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Method and apparatus for computer modeling of the interaction between and among cortical and subcortical areas in the human brain for the purpose of predicting the effect of drugs in psychiatric & cognitive diseases
ActiveUS20070106479A1Easy to set upImprove clinical outcomesMedical simulationAnalogue computers for chemical processesSubstance abuserHuntingtons chorea
Computer modeling of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, for example in a normal and a pathological state resembling schizophrenia which pathological state has inputs representing the effects of a drug(s), for the purpose of using the outputs to predict the effect of drugs in psychiatric and cognitive diseases. A method is provided for developing a computer model of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain which comprises the steps of identifying data relating to a biological state of a generic synapse model, the striatum, Locus Coeruleus, Dorsal raphe, hippocampus, amygdala and cortex; identifying biological processes related to the data, these identified biological processes defining at least one portion of the biological state of the generic synapse model, the striatum, Locus Coeruleus, Dorsal raphe, hippocampus, amygdala, and cortex; and combining the biological processes to form a simulation of the biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain. Diseases that can be modeled include psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, major depression, ADHD, autism, obsessive-compulsive disorder, substance abuse and cognitive deficits therein and neurological disorders such as Alzheimer's disease, Mild Cognitive impairment, Parkinson's disease, stroke, vascular dementia, Huntington's disease, epilepsy and Down syndrome. A resulting computer model is of the biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, comprising code to define the biological processes related to the biological state of the generic synapse model, the striatum, Locus Coeruleus, Dorsal raphe, hippocampus, amygdala and cortex, and code to define the mathematical relationships related to interactions among biological variables associated with the biological processes. At least two of the biological processes are associated with the mathematical relationships. A combination of the code to define the biological processes and the code to define the mathematical relationships define a simulation of the biological state of the interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain. Computer executable software code is provided comprised of code to define biological processes related to a biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain including code to define mathematical relations associated with the biological processes. A computer model of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain is provided, comprising a computer-readable memory storing codes and a processor coupled to the computer-readable memory, the processor configured to execute the codes. The memory comprises code to define biological processes related to the biological state of interactions between and among cortico and subcortical areas of the human brain, and code to define mathematical relationships related to interactions among biological variables associated with the biological processes.
Owner:CERTARA USA INC
Methods and kits for diagnosing and treating mental retardation
InactiveUS20070015194A1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementINFANTILE BILATERAL STRIATAL NECROSISNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention provides methods, kits, isolated nucleic acid sequences, antibodies and addressable oligonucleotides microarrays which can be for analyzing sequence alterations and detecting the expression level of CC2D1A or nup62 in cells of an individual and thus diagnose nonsyndromic mental retardation (NSMR) and / or infantile bilateral striatal necrosis (IBSN) in the individual. In addition, the present invention provides methods and pharmaceutical compositions which can be used to treat pathologies associated with mental retardation such as NSMR or IBS.
Owner:RAMOT AT TEL AVIV UNIV LTD
Quinolinone PDE2 inhibitors
The present invention is directed to quinolinone compounds which are useful as therapeutic agents for the treatment of central nervous system disorders associated with phosphodiesterase 2 (PDE2). The present invention also relates to the use of such compounds for treating neurological and psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, psychosis or Huntington's disease, and those associated with striatal hypofunction or basal ganglia dysfunction.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
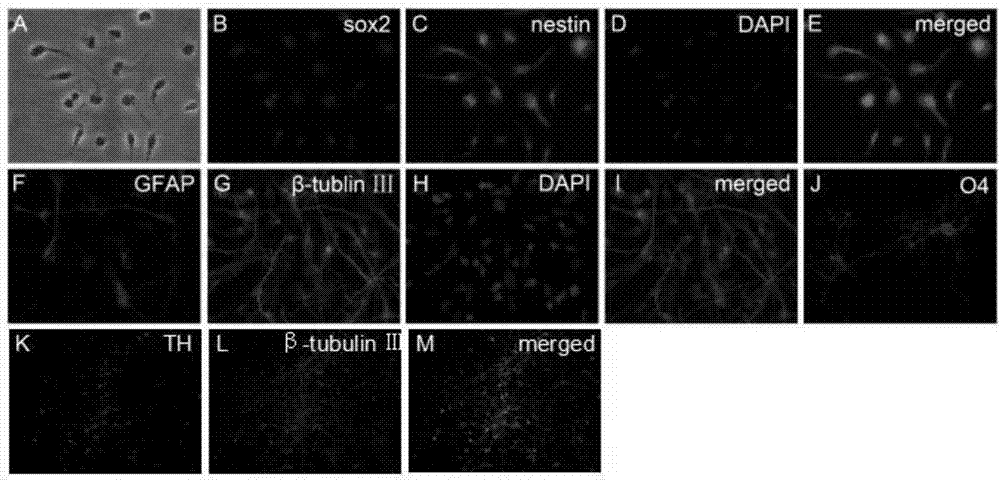
Method and application of induced neural stem cells
ActiveCN110396499AMaintain propertiesGuaranteed stabilitySsRNA viruses negative-senseNervous disorderNeural stem cellPrecursor cell
The invention discloses a method of induced neural stem cells and a composition. Through the method and the composition, peripheral blood mononuclear cells can be induced to form neural stem cells. The neural stem cells can express neural stem cell related genes, and can disintegrate out nerve cells, astroglia cells and oligodendrocyte. Dopaminergic nerve precursor cells formed through in vitro induction and disintegration of the neural stem cells are transplanted into the striatum corpora of a PD mouse model, no tumors are formed, the ethology of a mouse Parkinson 's disease model can be improved, and the process of the Parkinson 's disease can be delayed. The neural stem cell inducing and disintegrating method provided by the invention is simple and quick to operate, small in traumatic occlusion and good in safety, and is hopefully used for treating the Parkinson 's disease.
Owner:WISEHEART MEDICAL VALLEY CO LTD
Optogenetic control of reward-related behaviors
InactiveUS20170157269A1Reduce and eliminate effectBioreactor/fermenter combinationsNervous disorderOptogeneticsInterneuron
Provided herein are compositions and methods for disrupting at least one reward-related behavior in an individual through the use of light-responsive opsin proteins used to control the polarization state of the cholinergic intemeurons of the nucleus accumbens or the striatum.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Treatment of neurological deficits in the striatum or substanta nigra pars compacta
The present invention is directed to methods of treating neurological deficits resulting from injury or disease to the striatum or substanta nigra pars compacta of a human by administering human recombinant GDF5 to the striatum or substanta nigra pars compacta of a human in amounts effective to induce cell populations having the capacity to differentiate towards a dopaminergic phenotype to in fact differentiate towards a dopaminergic phenotype, and to neurotrophic compositions and matrices suitable for use in such treatments.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Treatment of Neurological Deficits in the Striatum or Substanta Nigra Pars Compacta
The present invention is directed to methods of treating neurological deficits resulting from injury or disease to the striatum or substanta nigra pars compacta of a human by administering BMP7 to the striatum or substanta nigra pars compacta of a human in amounts effective to induce cell populations having the capacity to differentiate towards a dopaminergic phenotype to in fact differentiate towards a dopaminergic phenotype, and to neurotrophic compositions and matrices suitable for use in such treatments.
Owner:MESSINA DARIN J +1
Treatment of neurological deficits in the striatum or substanta nigra pars compacta
InactiveUS20060069009A1Efficient inductionNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsP PHENOTYPEDisease cause
The present invention is directed to methods of treating neurological deficits resulting from injury or disease to the striatum or substanta nigra pars compacta of a human by administering BMP7 to the striatum or substanta nigra pars compacta of a human in amounts effective to induce cell populations having the capacity to differentiate towards a dopaminergic phenotype to in fact differentiate towards a dopaminergic phenotype, and to neurotrophic compositions and matrices suitable for use in such treatments.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Quinolinone PDE2 Inhibitors
The present invention is directed to quinolinone compounds which are useful as therapeutic agents for the treatment of central nervous system disorders associated with phosphodiesterase 2 (PDE2). The present invention also relates to the use of such compounds for treating neurological and psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, psychosis or Huntington's disease, and those associated with striatal hypofunction or basal ganglia dysfunction.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Gene necessary for striatal function, uses thereof, and compounds for modulating same
InactiveUS20040152106A1Tetracycline active ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseHuntingtons chorea
PDE10A, a gene that is normally highly expressed in mammalian striatum and elsewhere, has been found to decrease in expression during the development of CAG repeat disorders such as Huntington's disease. The invention teaches a method for detecting the presence of or the predisposition for a CAG repeat disorder. Compounds which modulate CAG repeat disorders and their uses are taught. Methods for screening for further compounds to modulate CAG repeat disorders are also taught.
Owner:NOVANEURON
Enhanced delivery of viral particles to the striatum and cortex
Provided herein are novel methods for delivering recombinant adeno-associated viral (rAAV) particles to the central nervous system of a mammal (e.g., a human). In aspects, the methods involve administering rAAV particles containing a heterologous nucleic acid to the striatum and causing expression of the heterologous nucleic acid in at least the cerebral cortex and the striatum of the mammal.
Owner:GENZYME CORP
Characterisation of progressive system dysfunction
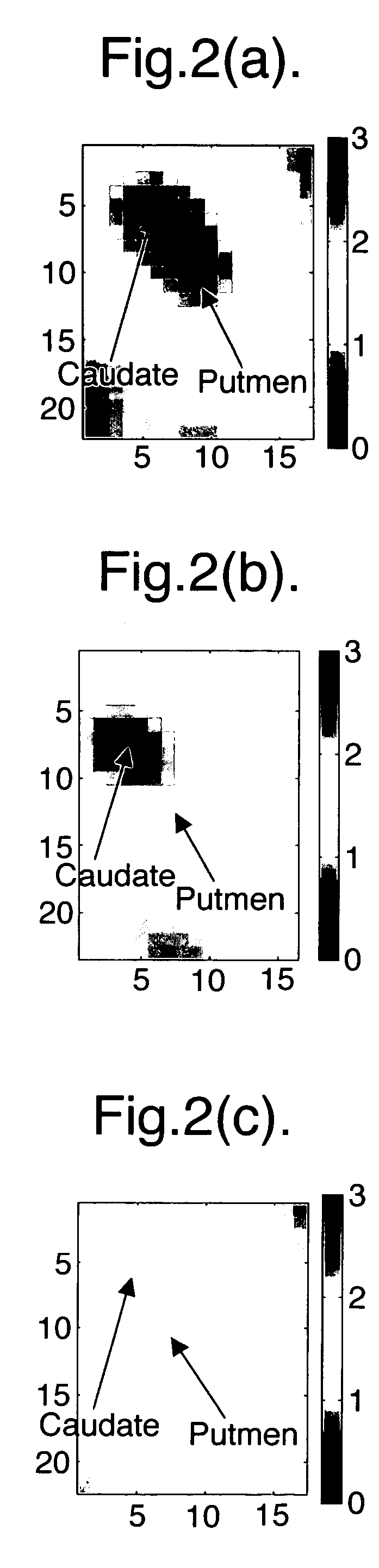
A technique for assessing the progression of multilateral dysfunction, e.g. bilateral diseases is described. The process consists of two stages: firstly, a ‘health measure’ is computed for each of the features of the multi-lateral dysfunction. One example is in terms of the progression of Parkinson's disease by applying it to the uptake of imaging agent in the two striata of the brain, which can be viewed using SPECT imaging. In this example, a characteristic graph for each striatum is matched to a family of such graphs in order to quantify the state of each striatum as a health measure. Then the lower health measure is plotted against the higher health measure. This point is then projected onto a previously computed disease progression trajectory which is used to assign a percentage to the progression of the disease, from 0% normal to 100% extreme progression of the disease. In addition to the disease progression percentage, the technique also provides a confidence measure of the accuracy of this estimation. The invention is applicable to other forms of multilateral dysfunction, including other human or animal conditions and dysfunction in non-biological systems such as mechanical, electrical or electronic systems.
Owner:SIEMENS MEDICAL SOLUTIONS USA INC
Neural stem cell preparation for treating Parkinson's disease through nasal delivery
InactiveCN106924286AEasy to useGood curative effectNervous disorderPharmaceutical delivery mechanismNasal cavityDisease
The invention belongs to the field of biological medicine and specifically relates to a neural stem cell preparation for treating a Parkinson's disease through nasal delivery as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: cultivation and purification of seed cells; cultivation of P6-P8 generation cells; cultivation of a working cell repository; preparation of a preparation for treating the Parkinson's disease. According to the preparation as well as the preparation method and the application thereof, after the preparation is dropped or injected into a nasal cavity, the preparation can quickly form a solid membrane shape under a body temperature condition and can be adsorbed on the nasal cavity for slow absorption, and the preparation cannot enter an oral cavity or lungs along with breathing, so that the preparation can be used by patients and doctors conveniently and fast; in addition, test data indicate that the preparation has better curative effect and safety compared with a traumatic corpus striatum delivery. The preparation can be used for treating the Parkinson's disease, and an immunosuppressive agent is not needed.
Owner:SHANGHAI ANGECON BIOTECH
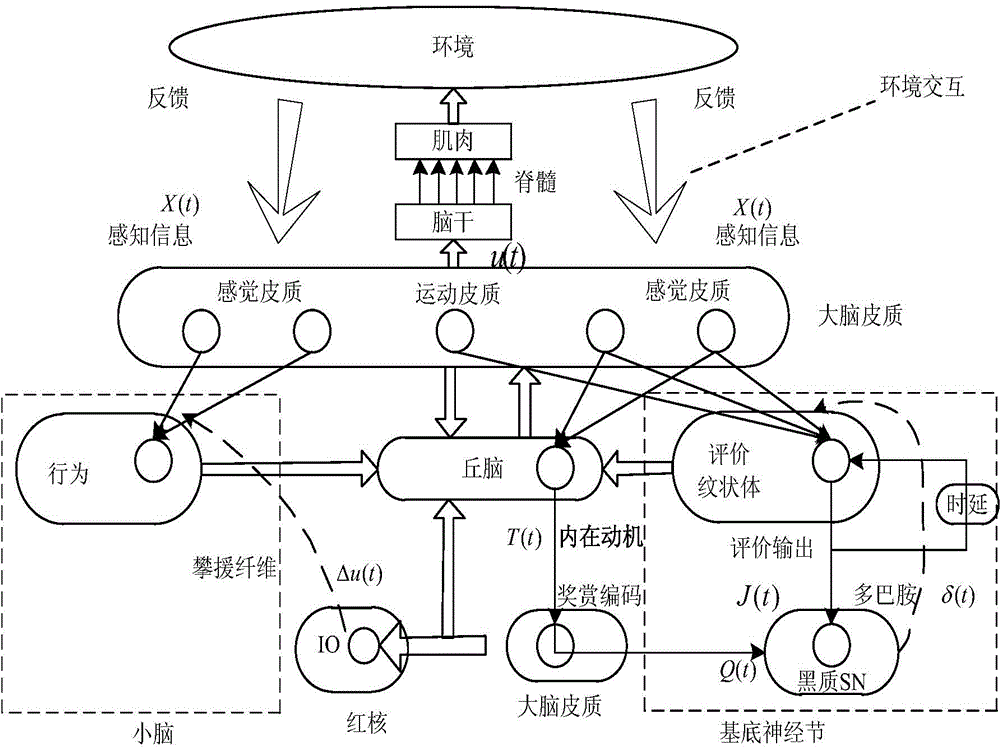
Intrinsic motivation based self-cognition system for motion balance robot and control method
InactiveCN104992059ASolve self-awareness problemsSolve the "conversion" problemSpecial data processing applicationsRoboticsIntrinsics
The invention discloses an intrinsic motivation based self-cognition system for a motion balance robot and a control method. The system comprises an intrinsic motivation based cognition model composed of behavior generation, behavior evaluation and orientation mechanism; the behavior generation is the formation of a 'perception-motion' loop; the behavior evaluation is the formation of a 'motion-result' loop; and the orientation mechanism is used for connecting the behavior generation with the behavior evaluation. The method comprises the steps that: a cortex-cerebellum system calculates action output amount according to sensory cortex information fed back by an intelligent body; a cortex-striatum system in a basal ganglion obtains an evaluation value by utilizing the sensory cortex information fed back by the intelligent body and motor cortex information calculated by cerebellum; and the cortex-striatum system and the cortex-cerebellum system are subjected to synaptic modification. According to the system and the method, neurophysiology, cognitive psychology and robotology are combined, a cognition mechanism is described and realized in a mathematic mode, and the self-cognition problem of the robot is solved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF TECH & EDUCATION TEACHER DEV CENT OF CHINA VOCATIONAL TRAINING & GUIDANCE
Method to isolate, identify, and use embryonic stem cells directed to forebrain interneuron fate
The present invention relates to methods of isolating a purified or enriched population of cortical or striatal immature interneuron progenitor cells and the isolated purified or enriched population of immature interneuron progenitor cells. Methods of treating a condition mediated by a loss or deficiency of interneuron function using the purified or enriched population of immature interneuron progenitor cells are also disclosed.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY +1
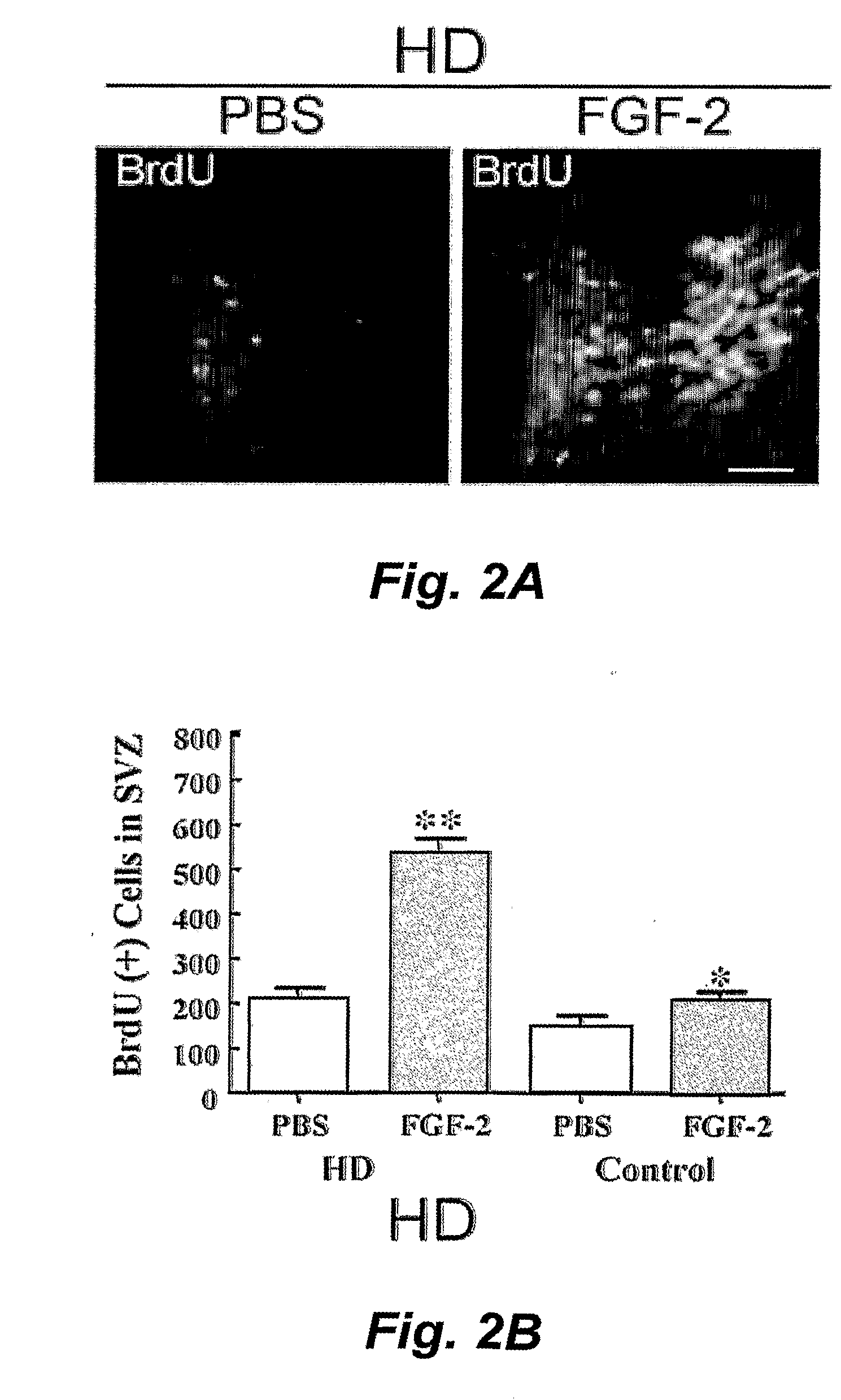
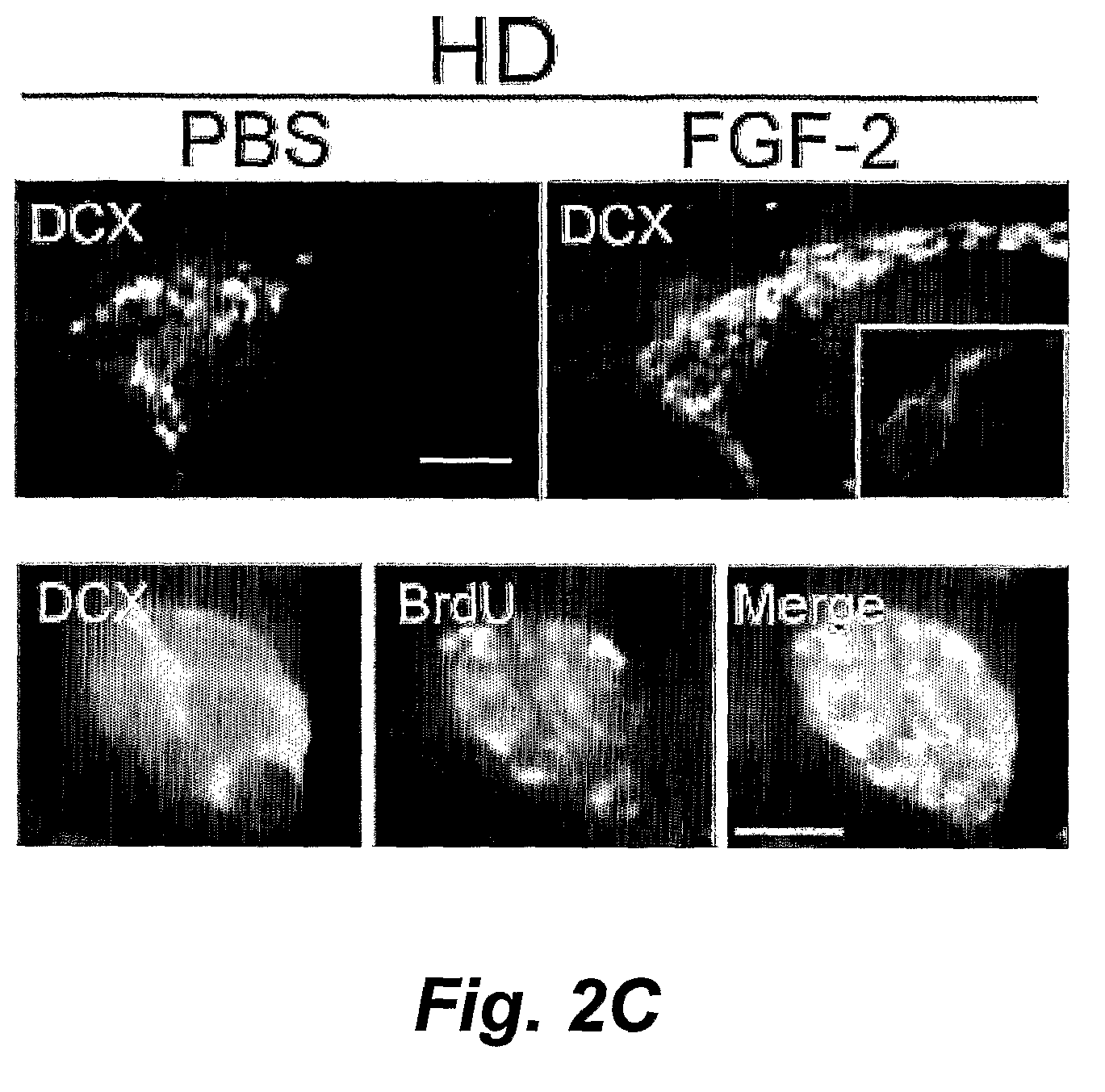
Fibroblast growth factor-2 promotes neurogenesis and neuroprotection and prolongs survival in huntington's disease
InactiveUS20090111748A1Reduce neuronal lossIncrease neurogenesisPeptide/protein ingredientsHuntingtons choreaNeurogenesis
This invention pertains to the discovery that fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) stimulates neurogenesis, induces migration of newborn cells into the striatum and cortex, is neuroprotective, and significantly extends the lifespan mammals suffering from neurodegenerative conditions (e.g., Huntington's disease, Parkinson's disease, etc.). In certain embodiments this invention provides a method of promoting neurogenesis, neuroprotection and / or survival in a mammal having a neurodegenerative disease by upregulating expression or availability of endogenous fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) in said mammal; and / or administering FGF2 or an FGF2 mutein to the mammal in an amount sufficient to promote neurogenesis, neuroprotection and / or survival of the mammal.
Owner:THE BUCK INST FOR RES ON AGING
Preparation method of corn cervi pantotrichum extract, and related products
InactiveCN106333966ARelieve symptomsIncrease the number ofNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseAfter treatment
Owner:EXPERIMENTAL RES CENT CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
Aryl aminopyridine pde10 inhibitors
The present invention is directed to aryl aminopyridine compounds which are useful as therapeutic agents for the treatment of central nervous system disorders associated with phosphodiesterase 10 (PDE10). The present invention also relates to the use of such compounds for treating neurological and psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, psychosis or Huntington's disease, and those associated with striatal hypofunction or basal ganglia dysfunction.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Application of HIF-1 alpha micromolecule activator FG-4592 for Parkinson's diseases
InactiveCN107468692AReduce apoptosisIncrease vitalityOrganic active ingredientsNervous disorderMetaboliteMitochondrial membrane permeability transition
The invention relates to a new application of FG-4592, a small molecule activator of HIF-1α, which belongs to the technical field of biomedicine, that is, the application of FG-4592 in the preparation of drugs for treating Parkinson's disease. Its advantages are as follows: the compound is in the third phase of clinical trials, and there is no need to explore its clinical pharmacology and human safety evaluation, which is conducive to the transformation of results. The present invention finds through research in Parkinson's disease cells and animal models that, compared with the model group, the FG-4592 pretreatment group can increase neuron cell viability, reduce cell apoptosis, and can partially reverse the mitochondrial membrane damage caused by neurotoxic drugs. The decrease of electric potential, the decrease of ATP content and the decrease of respiratory function can reduce the damage of MPTP to the dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra and striatum of mice, increase the secretion of dopamine and its metabolites in the damaged area, and finally achieve the relief of its movement. Reduced level of function.
Owner:SHANGHAI FIRST PEOPLES HOSPITAL
Isoindoline pde10 inhibitors
The present invention is directed to isoindolinone compounds which are useful as therapeutic agents for the treatment of central nervous system disorders associated with phosphodiesterase 10 (PDE10). The present invention also relates to the use of such compounds for treating neurological and psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, psychosis or Huntington's disease, and those associated with striatal hypofunction or basal ganglia dysfunction.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Pyrazolopyrimidine PDE 10 inhibitors
The present invention is directed to pyrazolopyrimidine compounds which are useful as therapeutic agents for the treatment of central nervous system disorders associated with phosphodiesterase 10 (PDE10). The present invention also relates to the use of such compounds for treating neurological and psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, psychosis or Huntington's disease, and those associated with striatal hypofunction or basal ganglia dysfunction.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Methods for treating parkinson's disease and other disorders of dopaminergic neurons of the brain
A specific clinical protocol for use toward therapy of defective, diseased and damaged neurons in the mammalian brain, of particular usefulness for treatment of neurodegenerative conditions such as Parkinson's disease. The protocol is practiced by directly delivering a definite concentration of a nerve growth factor via delivery of the protein, an expression vector operably encoding the nerve growth factor, or grafting a donor cell containing such an expression vector into the substantia nigra and preferably also the striatum. The method stimulates growth of targeted neurons, and reversal of functional deficits associated with the neurodegenerative disease being treated.
Owner:CEREGENE
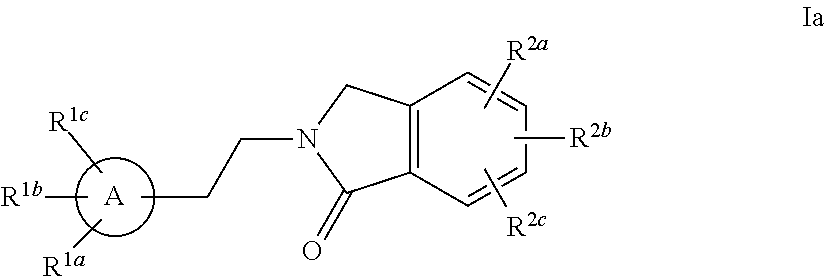
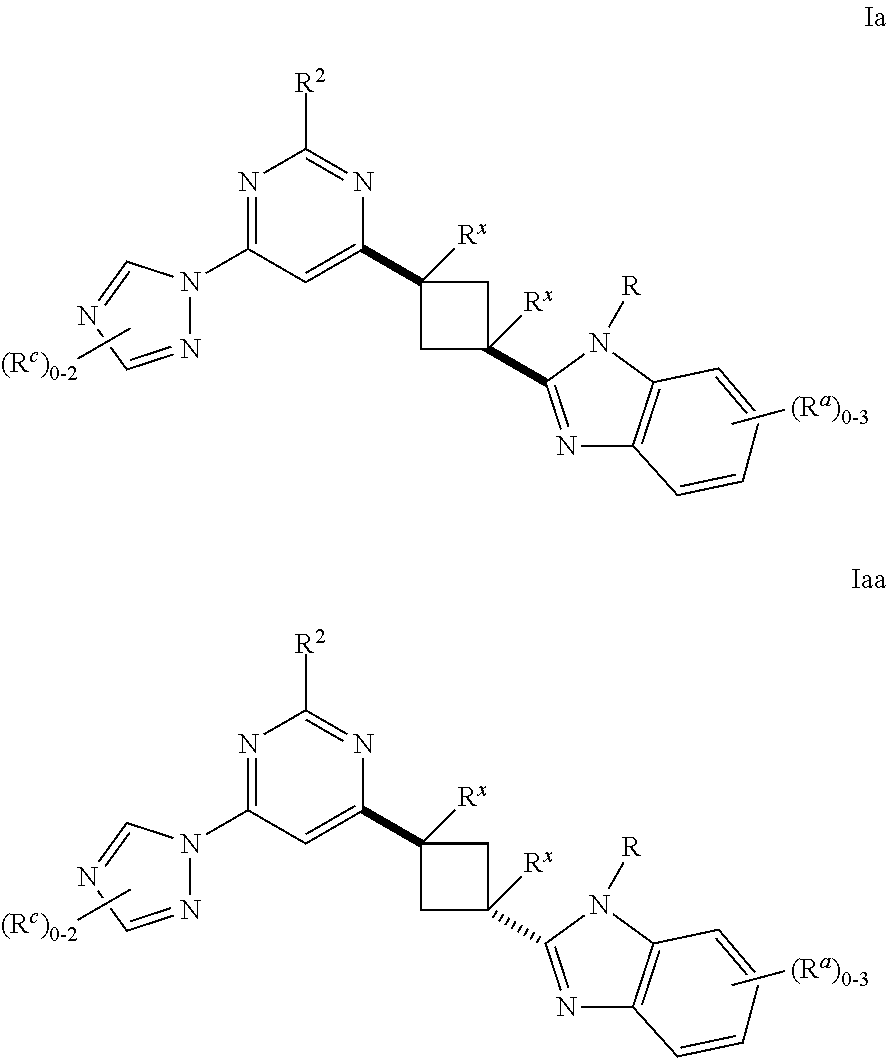
Cyclobutyl benzimidazoles as PDE 10 inhibitors
ActiveUS20150307479A1Useful in therapyBiocideOrganic active ingredientsBasal ganglia dysfunctionPhosphodiesterase
The present invention is directed to substituted cyclobutyl benzimidazole compounds which are useful as therapeutic agents for the treatment of central nervous system disorders associated with phosphodiesterase 10 (PDE10). The present invention also relates to the use of such compounds for treating neurological and psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, psychosis or Huntington's disease, and those associated with striatal hypofunction or basal ganglia dysfunction.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
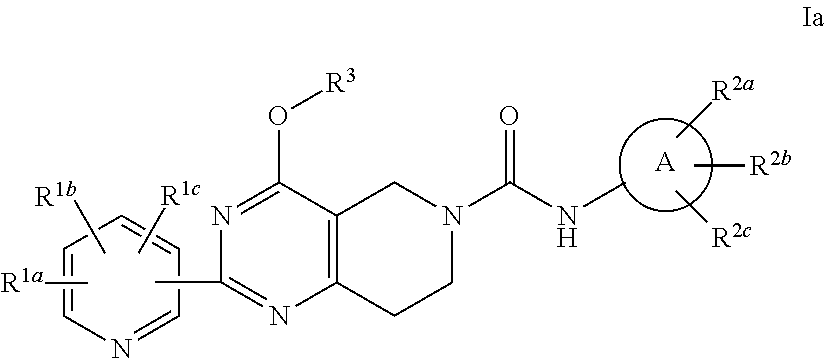
Alkoxy tetrahydro-pyridopyrimidine pde10 inhibitors
The present invention is directed to alkoxy tetrahydro-pyridopyrimidine compounds which are useful as therapeutic agents for the treatment of central nervous system disorders associated with phosphodiesterase 10 (PDE10). The present invention also relates to the use of such compounds for treating neurological and psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, psychosis or Huntington's disease, and those associated with striatal hypofunction or basal ganglia dysfunction.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Alkoxy pyrimidine PDE10 inhibitors
The present invention is directed to 2-alkoxy pyrimidine compounds which are useful as therapeutic agents for the treatment of central nervous system disorders associated with phosphodiesterase 10 (PDE10). The present invention also relates to the use of such compounds for treating neurological and psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, psychosis or Huntington's disease, and those associated with striatal hypofunction or basal ganglia dysfunction.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
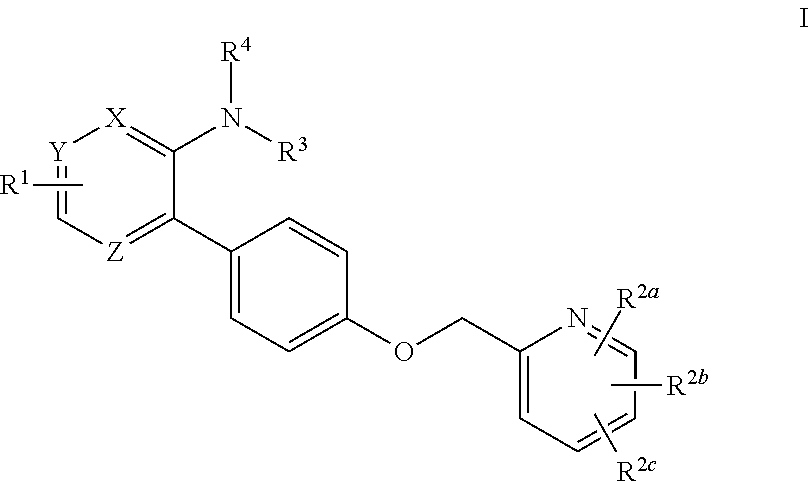
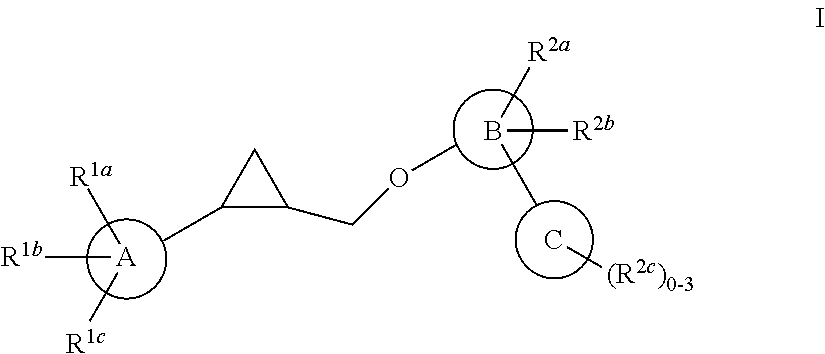
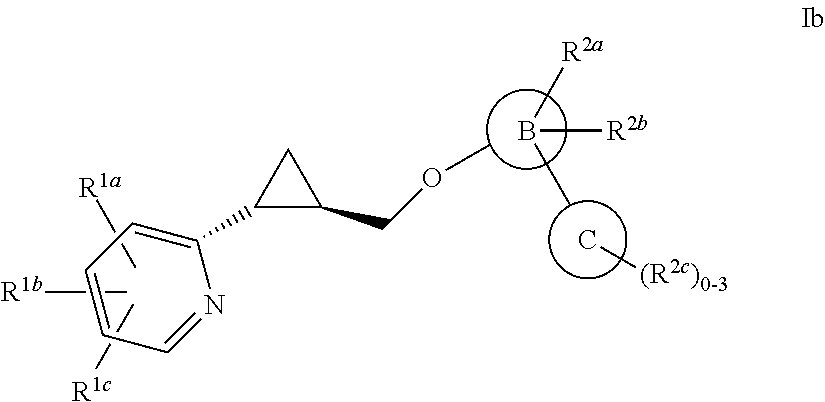
Aryloxmethyl cyclopropane derivatives as PDE10 inhibitors
The present invention is directed to aryloxymethyl cyclopropane derivatives which are useful as therapeutic agents for the treatment of central nervous system disorders associated with phosphodiesterase 10 (PDE10). The present invention also relates to the use of such compounds for treating neurological and psychiatric disorders, such as schizophrenia, psychosis or Huntington's disease, and those associated with striatal hypofunction or basal ganglia dysfunction.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME LLC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com