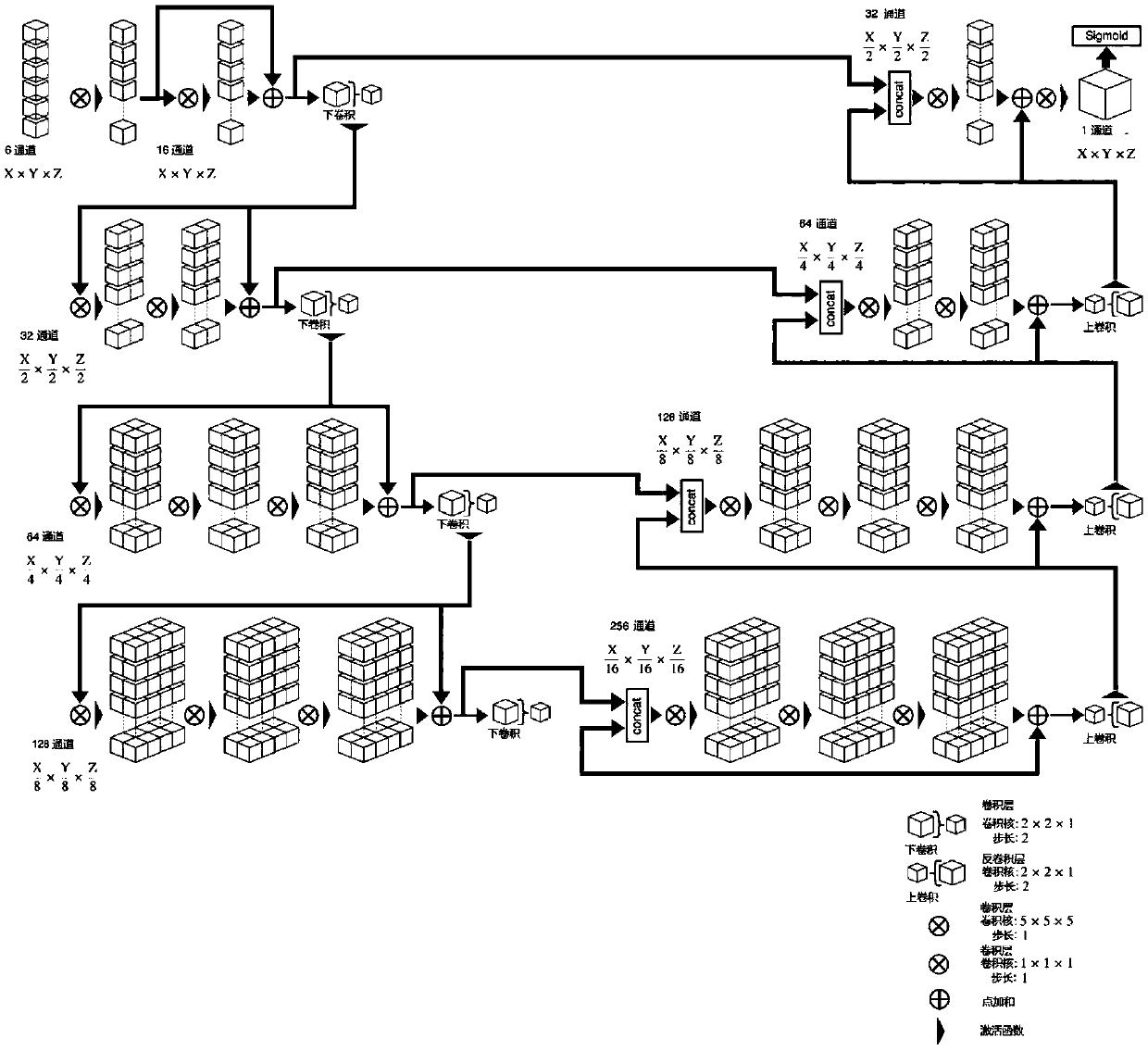
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
123 results about "T1 weighted" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
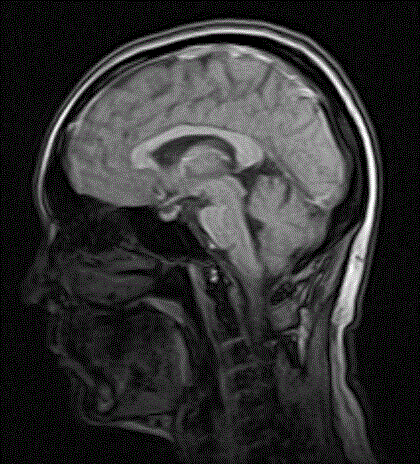
T1 weighted image (also referred to as T1WI or the "spin-lattice" relaxation time) is one of the basic pulse sequences in MRI and demonstrates differences in the T1 relaxation times of tissues. A T1WI relies upon the longitudinal relaxation of a tissue's net magnetization vector (NMV).
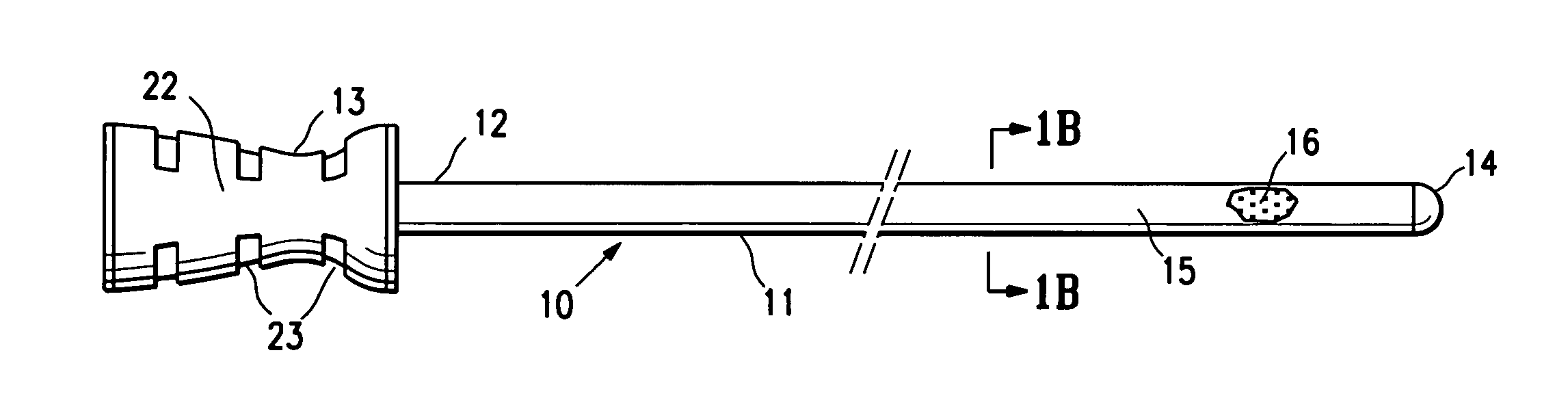
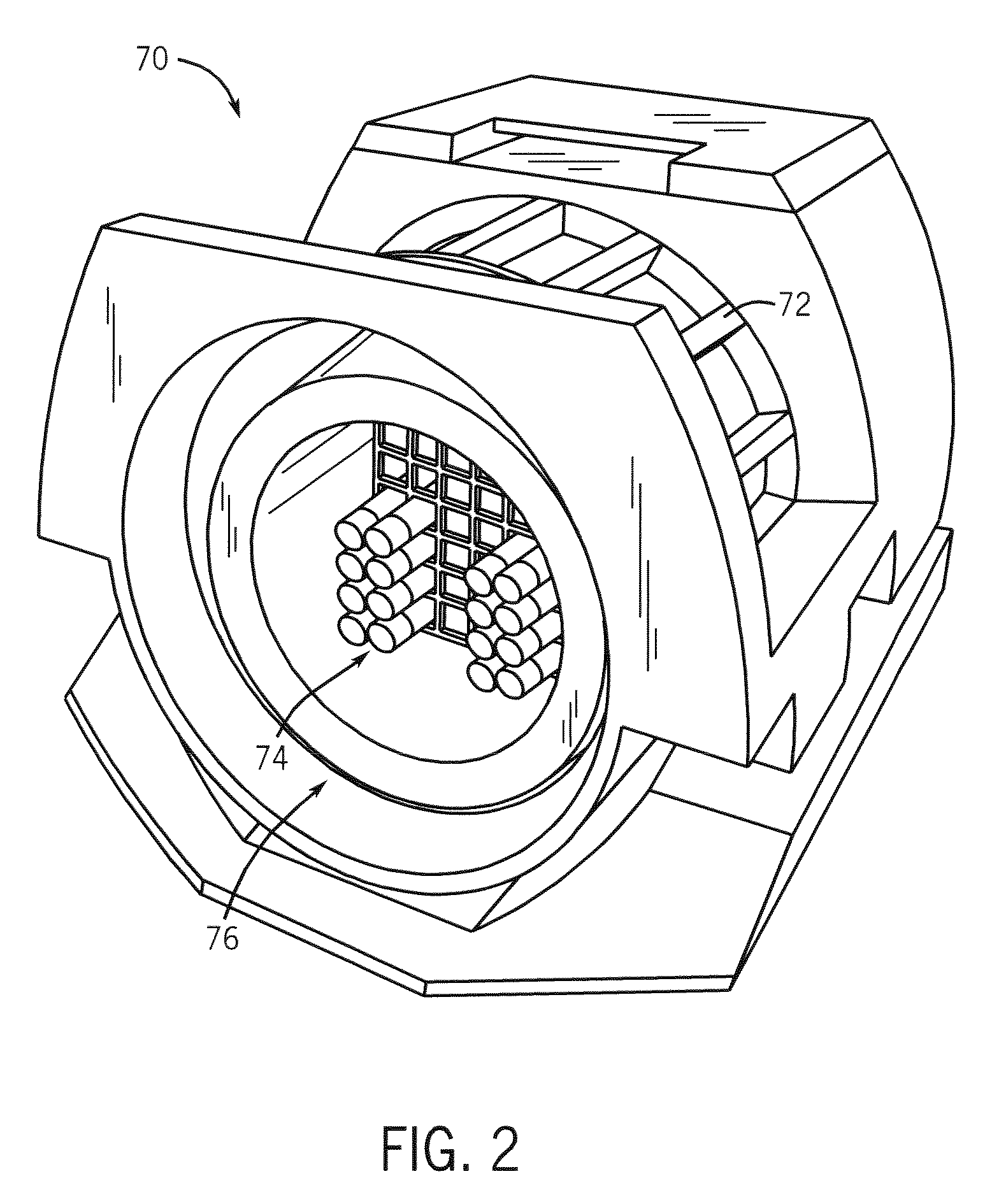
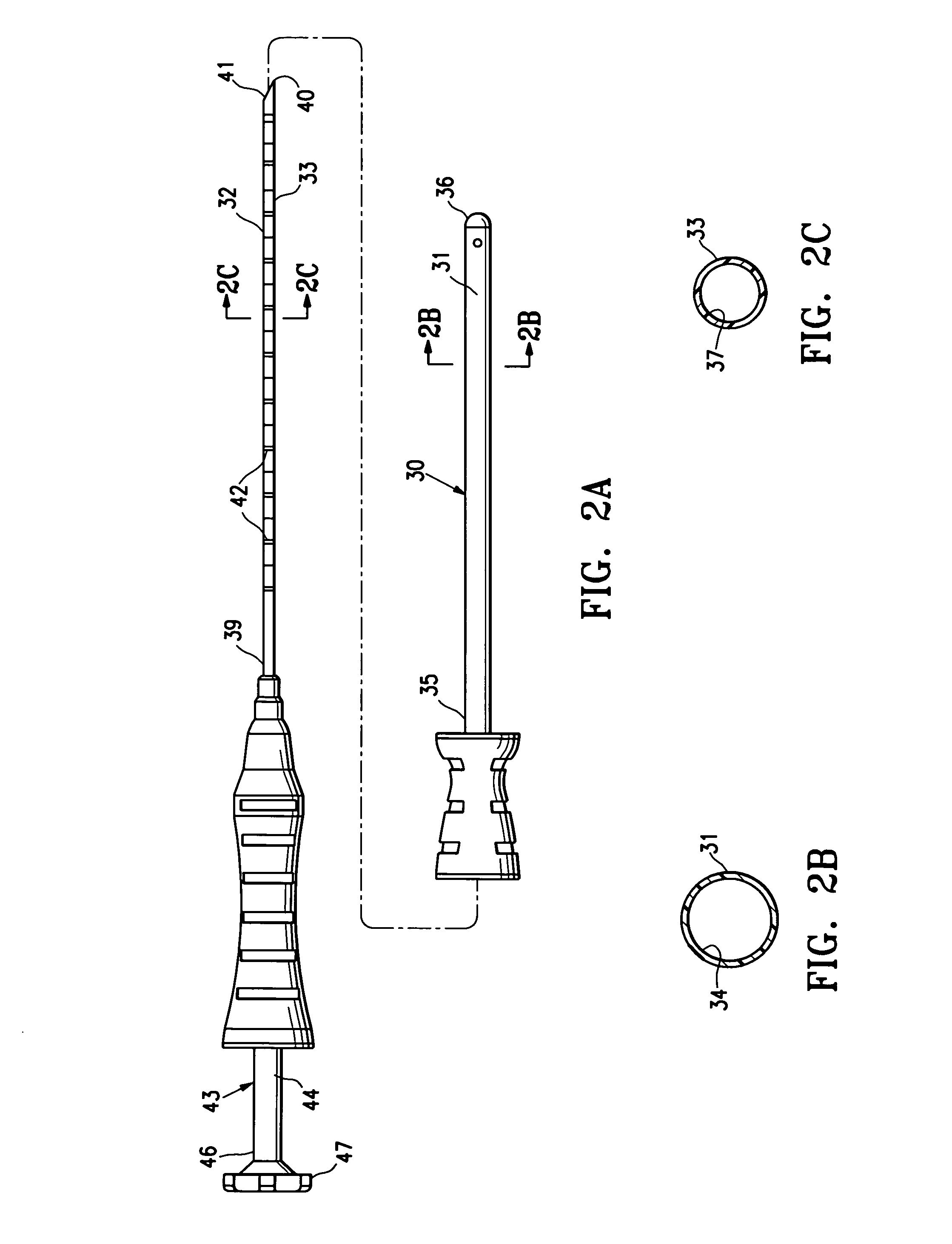
MRI detectable obturator
ActiveUS20080139928A1Prevents and minimizes backflowPreventing and minimizing entryCannulasSurgical needlesProximateT1 weighted
An obturator with an elongated shaft, a proximal end, a substantially closed distal end and a MRI detectable distal shaft portion, which does not interfere with magnetic resonance imaging of tissue proximate thereto. Preferably, the distal shaft portion has an effective MRI detectable mass so as to provide a clear, T1-weighted image within an outline of the distal shaft portion upon magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:SENORX
Apparatus to simulate MR properties of human brain for MR applications evaluation
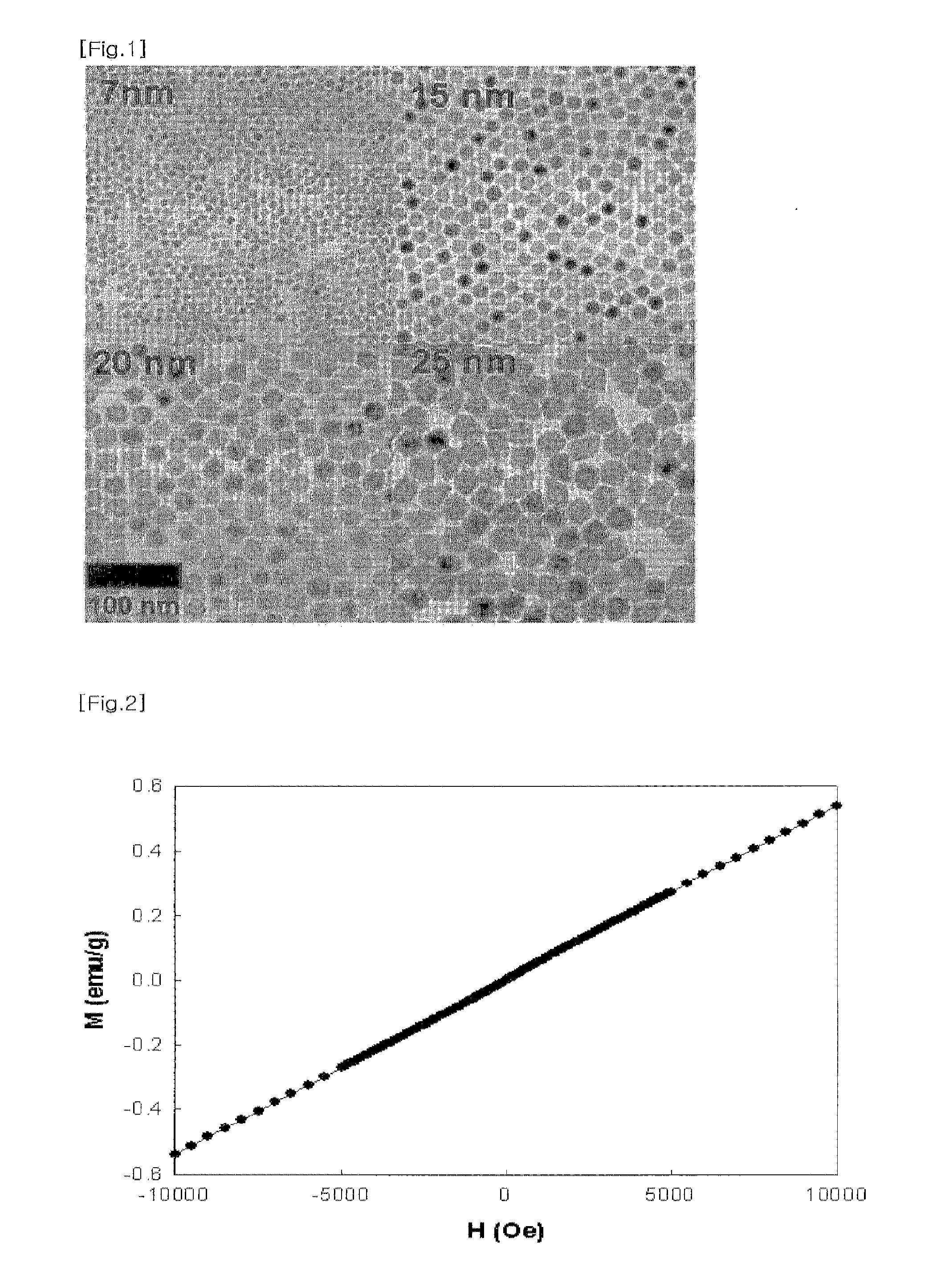
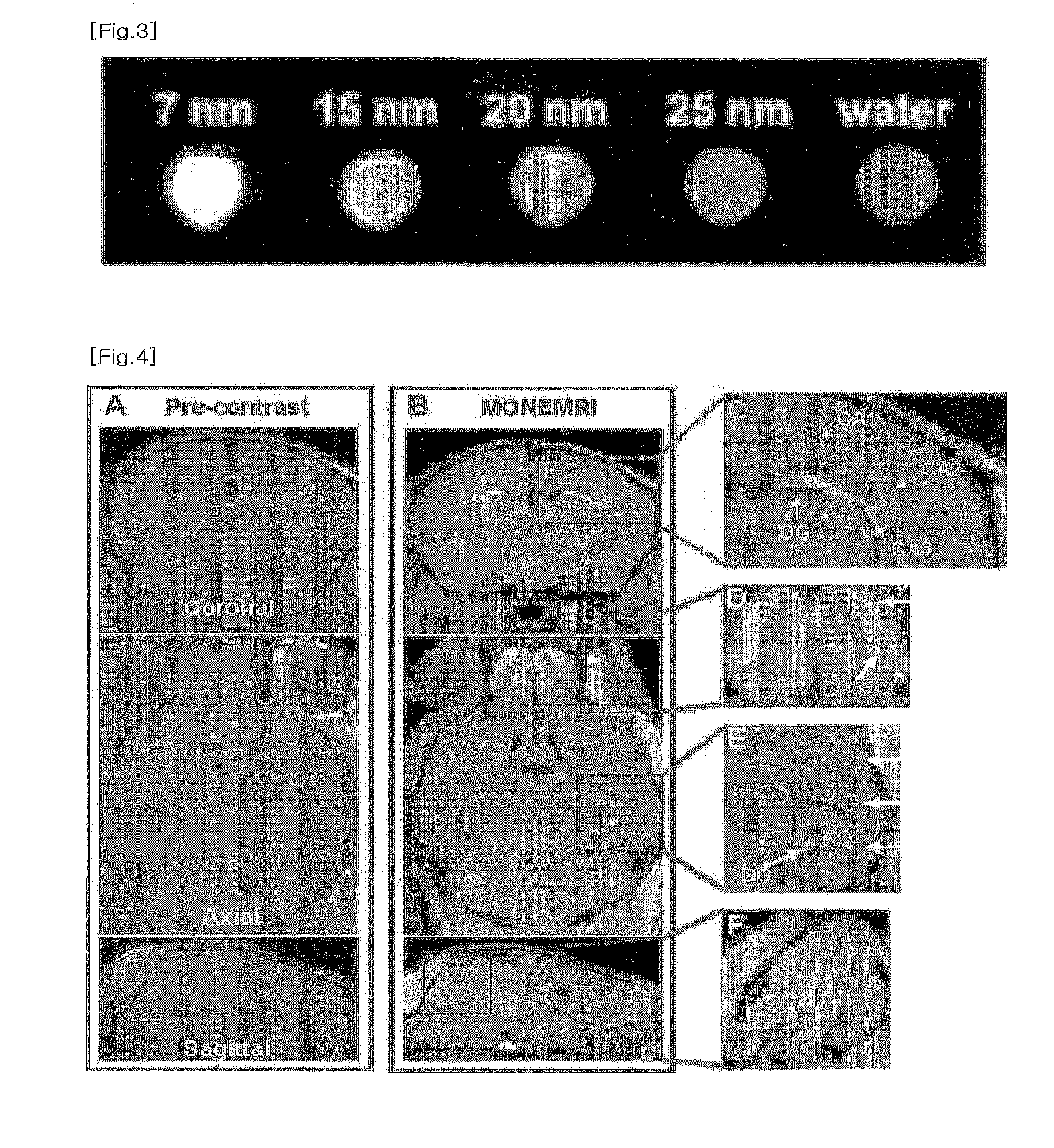
InactiveUS6965235B1Increase contrastImproves white matterMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionVolumetric Mass DensityT1 weighted
A system and method for mimicking a human brain for MR imaging at various magnetic field strengths is disclosed. A phantom is constructed of a structure having a number of sections. A first section contains a mixture of nickel chloride, agarose gel powder, potassium sorbate, deuterium oxide, and water such that the T1, T2, and proton density values of the first section mimic white matter of the human brain. A second section contains different amounts of the same components such that the T1, T2, and proton density values of the second section mimic gray matter of the human brain. As such, when the phantom is scanned in an MR imaging machine, an optimized flip angle for T1-weighted imaging to improve contrast between white matter and gray matter of the human brain that takes into account proton density differences therebetween can be determined.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Synchronous acquisition and calibration method for three-dimensional multi-parameter weighted magnetic resonance imaging
ActiveCN107271937AIncrease optionalityReduce dependenceMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsReconstruction methodT2 weighted
The invention discloses a synchronous acquisition and calibration method for three-dimensional multi-parameter weighted magnetic resonance imaging. A three-dimensional / two-dimensional fast multi-echo water-fat separation sequence and a signal debugging method, a pre-scanning method, a scanning method, a data preprocessing method and an image reconstruction method thereof can obtain a water-fat separation image and T2 weighted (T1 weighted or PD weighted) image by one-time scanning. The three-dimensional multi-parameter weighted synchronous scanning and calibration method can maximize the number of images obtained in a single scan, including, an in-phase image, a reverse-phase image, a fat image, a fat-pressed image water, a conventional T2 weighted (or T1 weighted / PD weighted ) image, and a T2weighted images, significantly shortens clinical scanning time and increases the selectivity of clinical scanning schemes, and has less reliance on the hardware performance of an MRI system.
Owner:南京拓谱医疗科技有限公司
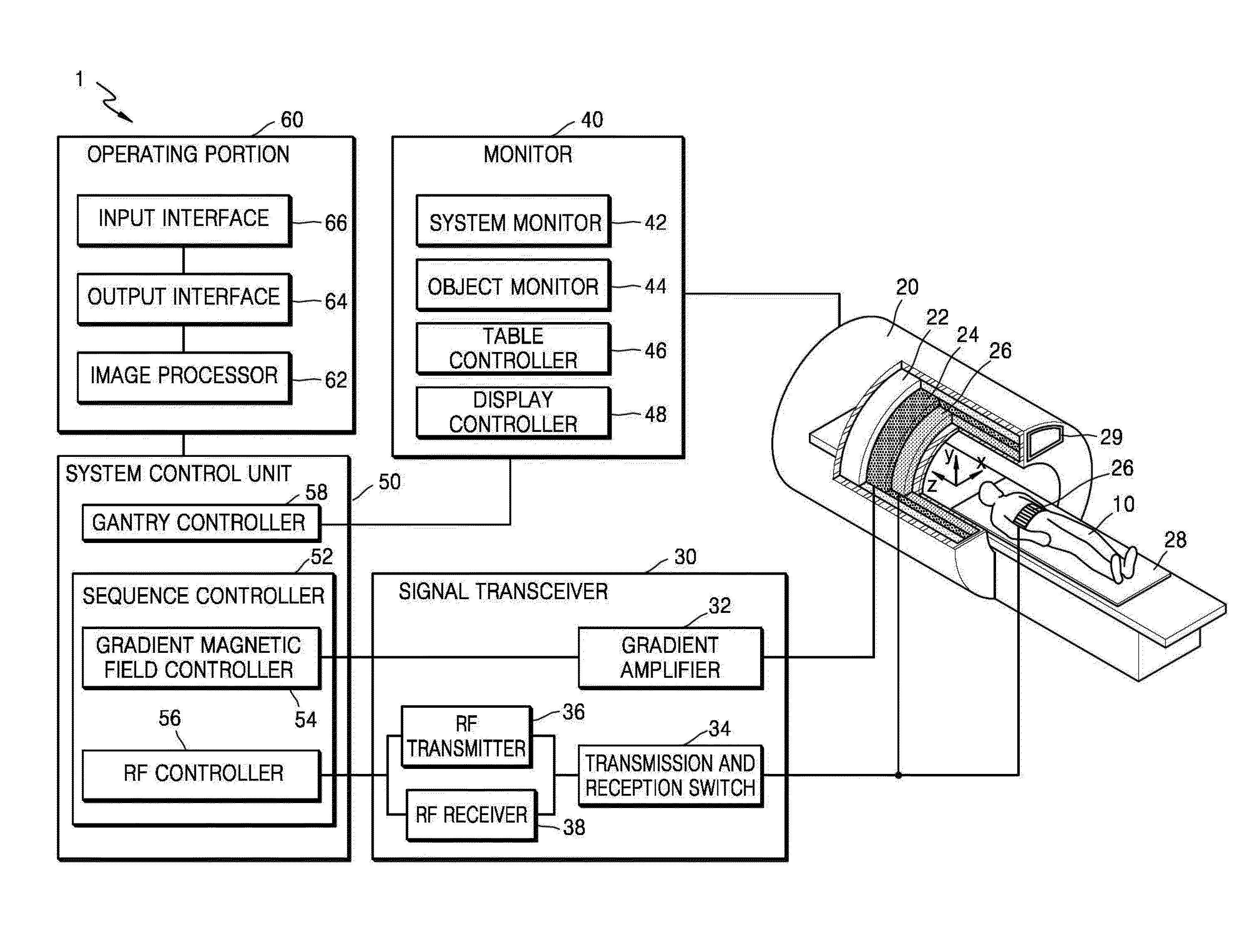
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus and method of processing mr image
ActiveUS20160110904A1Accurate detectionImage enhancementImage analysisFluid-attenuated inversion recoveryT1 weighted
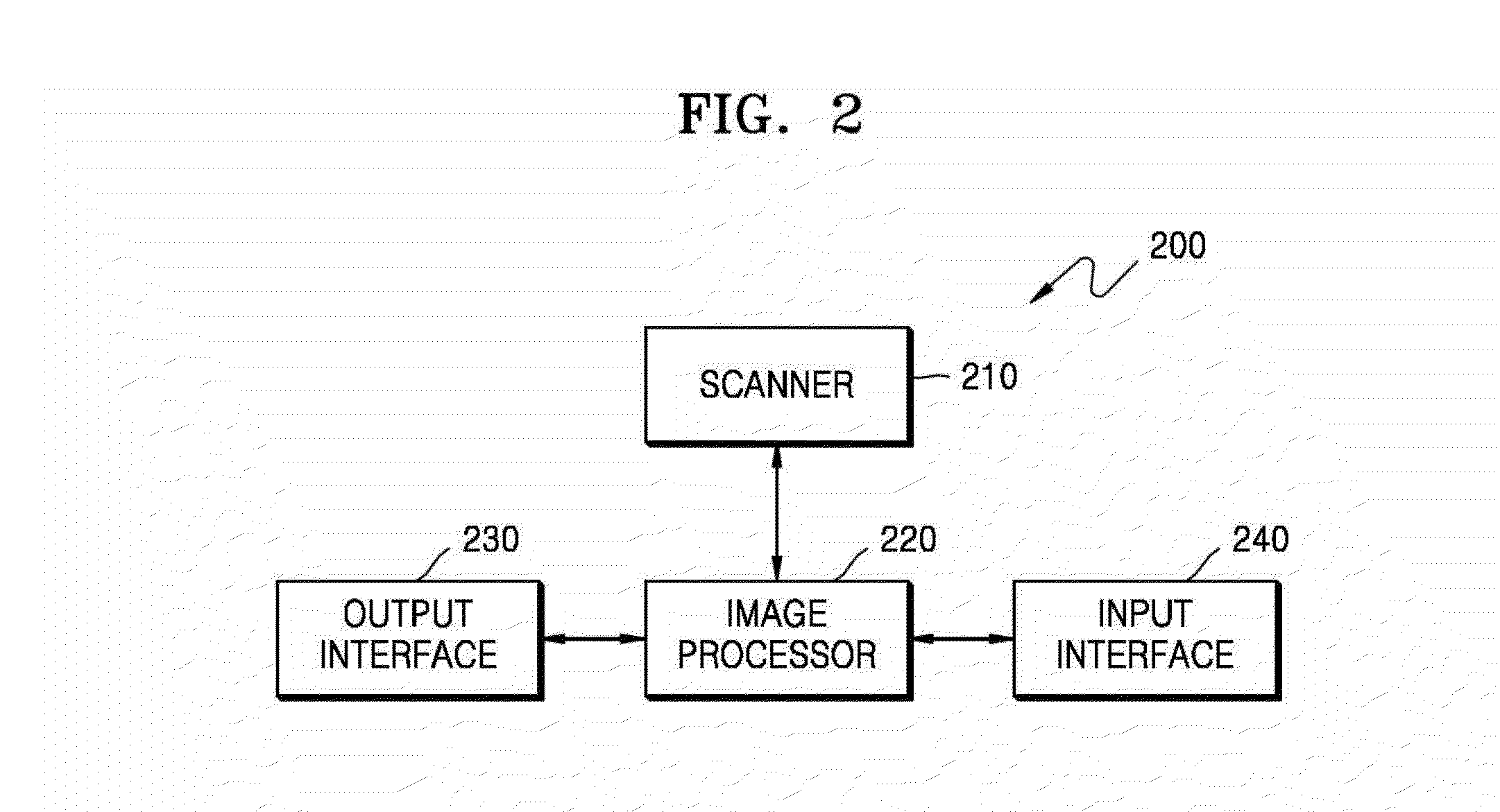
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) apparatus and a method of processing an MR image are provided. The MRI apparatus includes a scanner configured to acquire a first image that is a T1-weighted image and a second image that is a fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) image by performing an MRI scan on a brain. The MRI apparatus further includes an image processor configured to determine a white matter region in the second image based on the first image and the second image, and detect a white matter hyperintensity (WMH) region in the determined white matter region. The MRI apparatus further includes an output interface configured to display the detected WMH region and a change in the WMH region over time.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Method and System for Lymph Node Detection Using Multiple MR Sequences
ActiveUS20080171932A1Character and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringAnatomical landmarkResonance
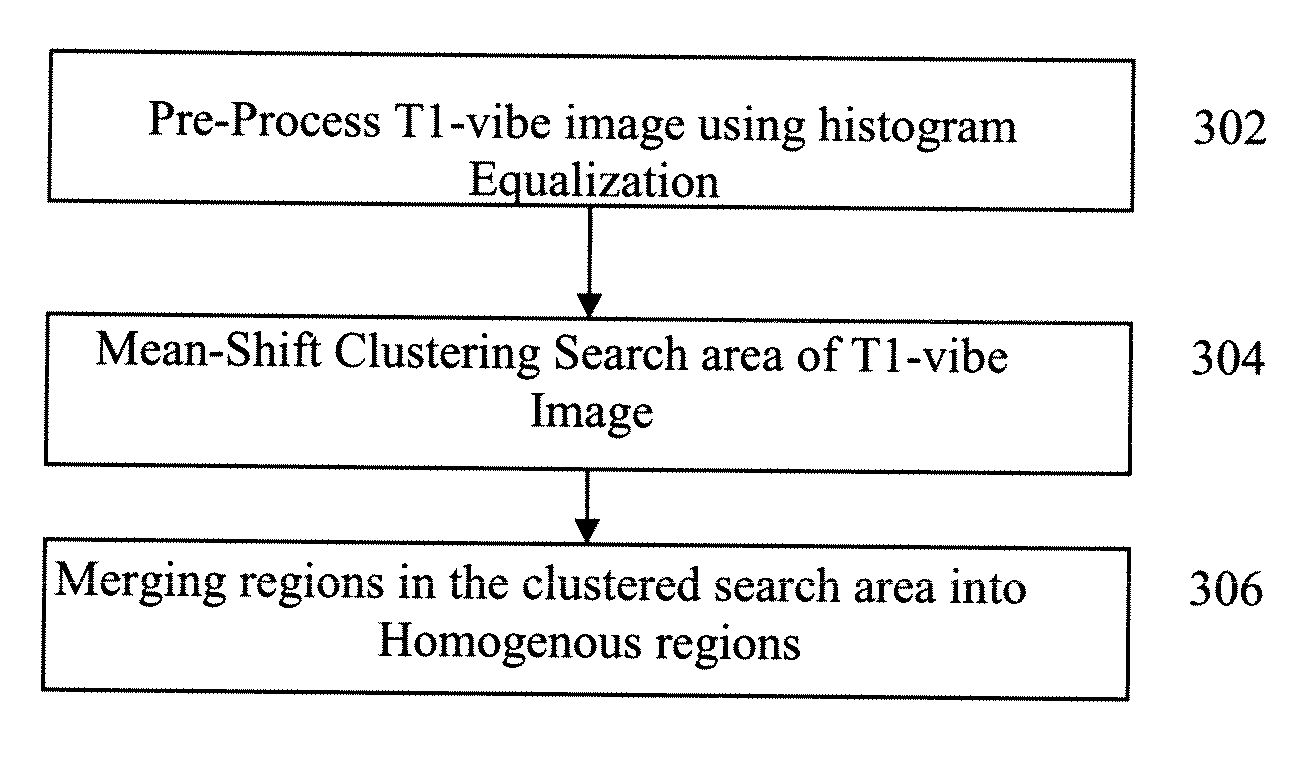
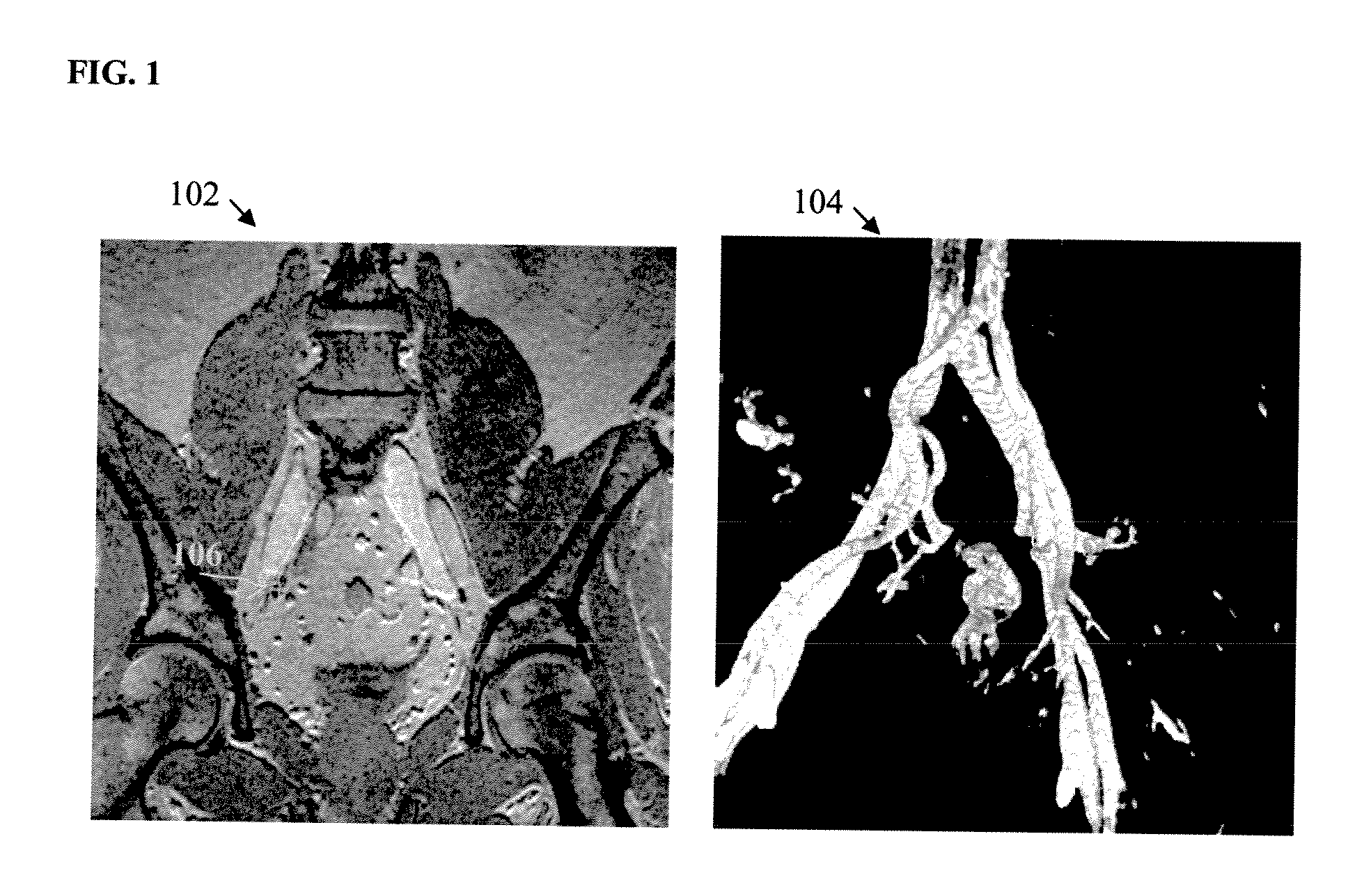
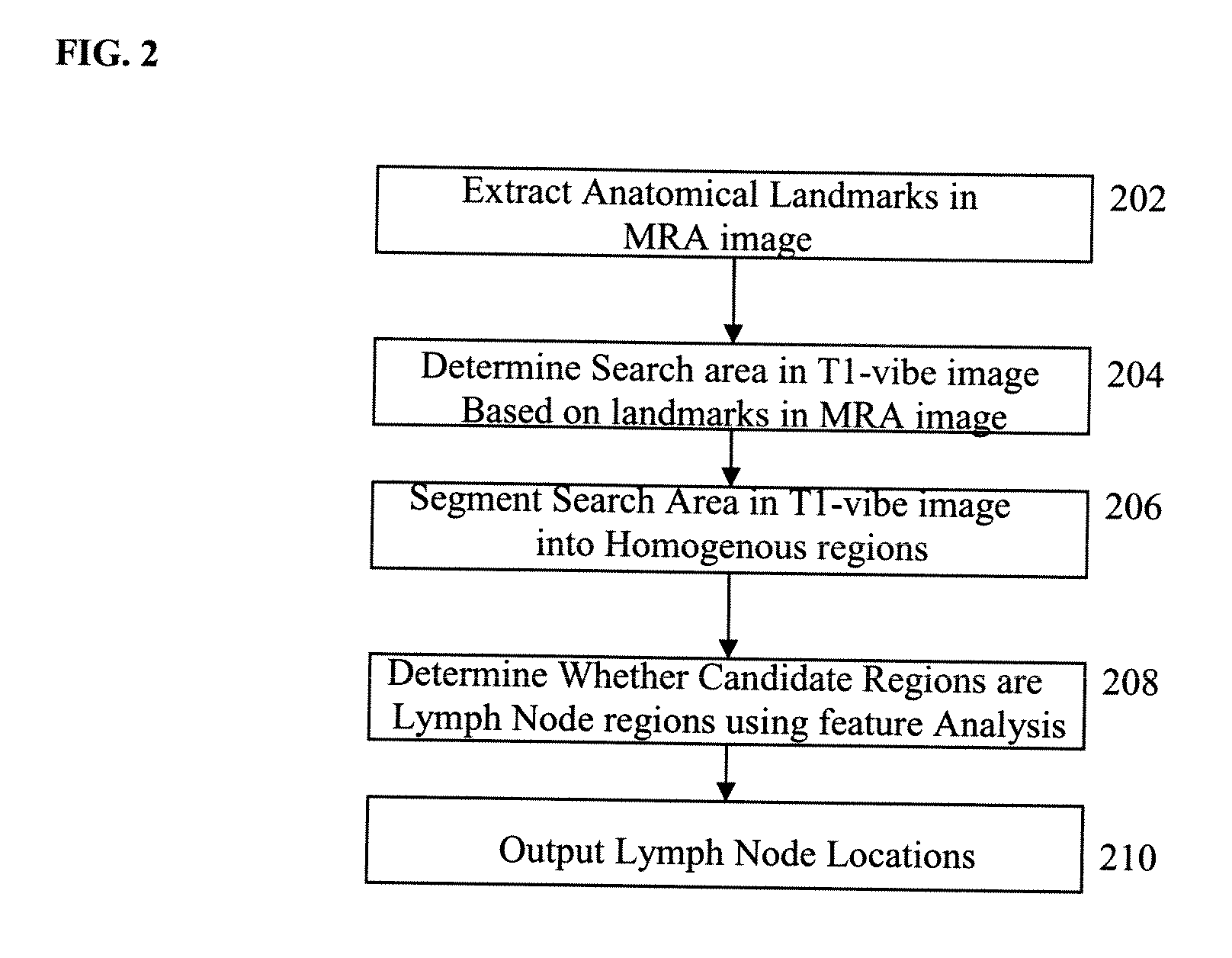
A method and system for detecting lymph nodes in multiple complementary magnetic resonance (MR) sequences is disclosed. Anatomical landmarks, such as blood vessels, are extracted in a first MR sequence, such as an MR angiography (MRA) image. A search area is defined in at least one second MR sequence, such as a T1 weighted VIBE image, based on the anatomical landmarks extracted the first MR sequence. Lymph nodes are then detected in the search area of the second MR sequence. The lymph nodes can be detected by segmenting the search area into homogenous regions and determining whether each region is a lymph node using feature analysis.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
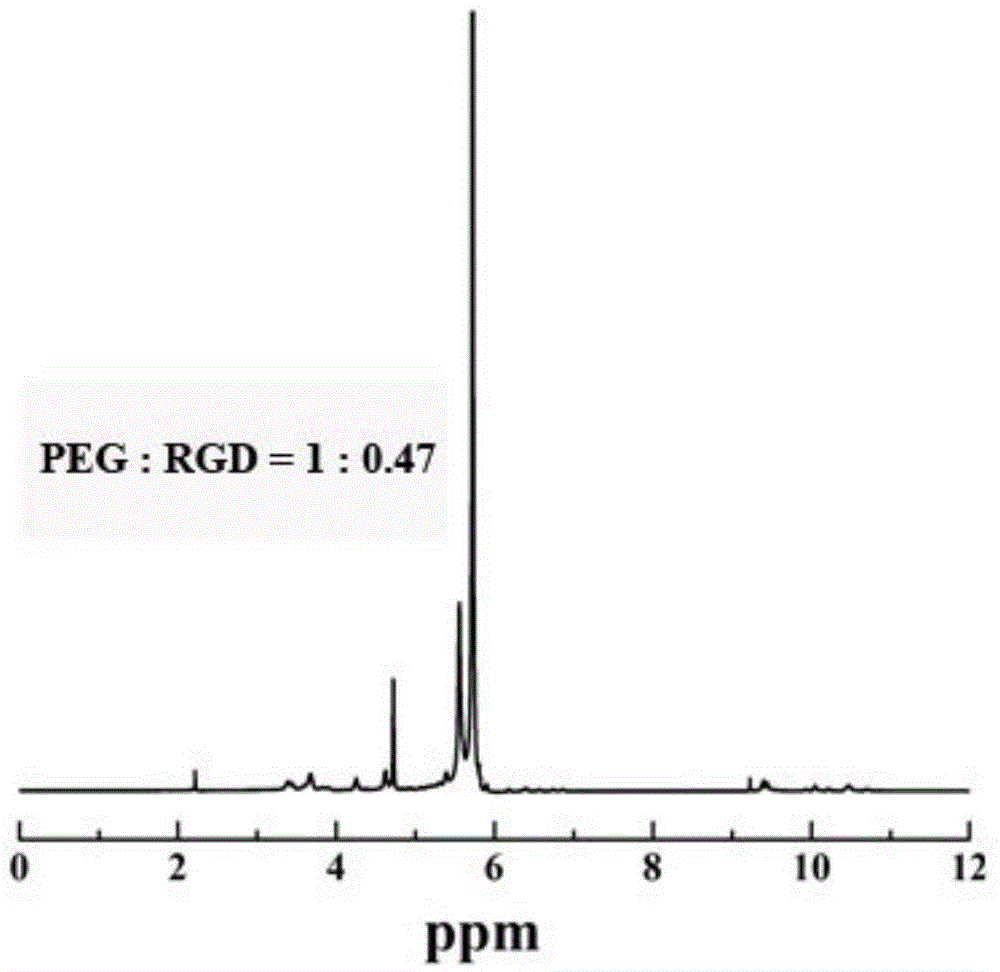
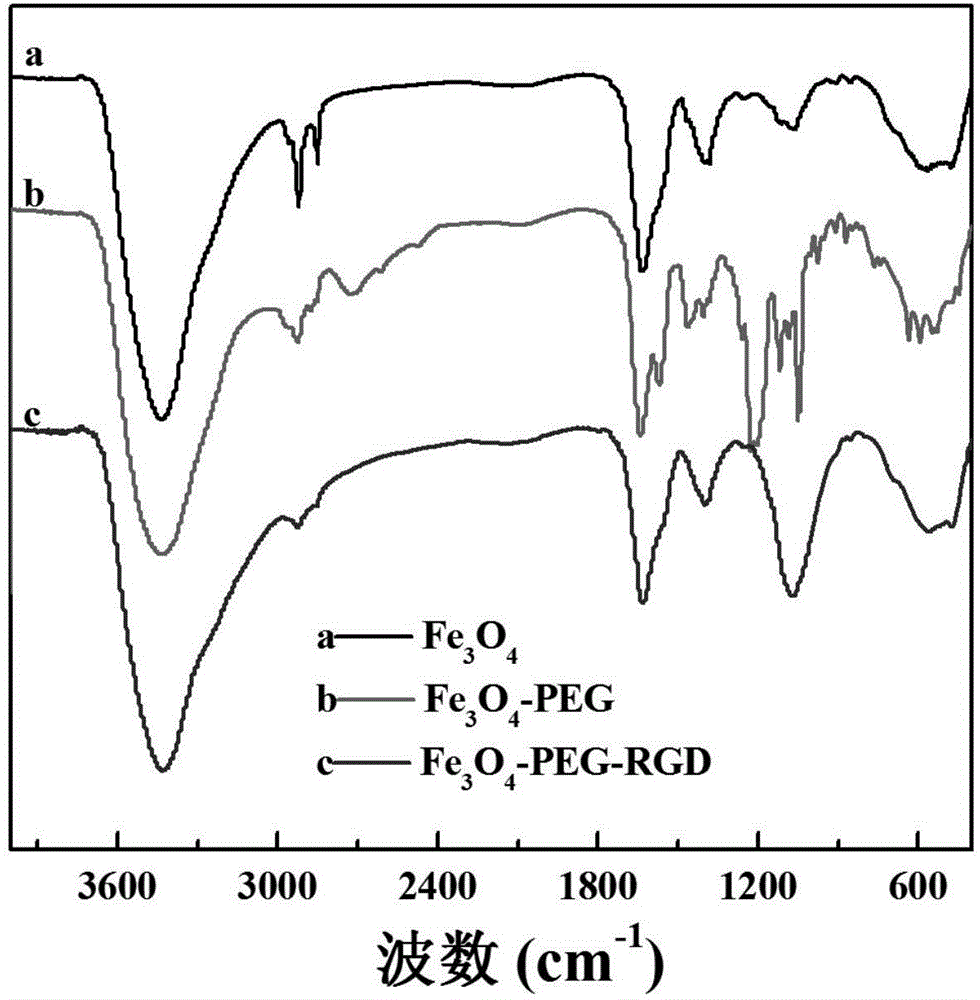
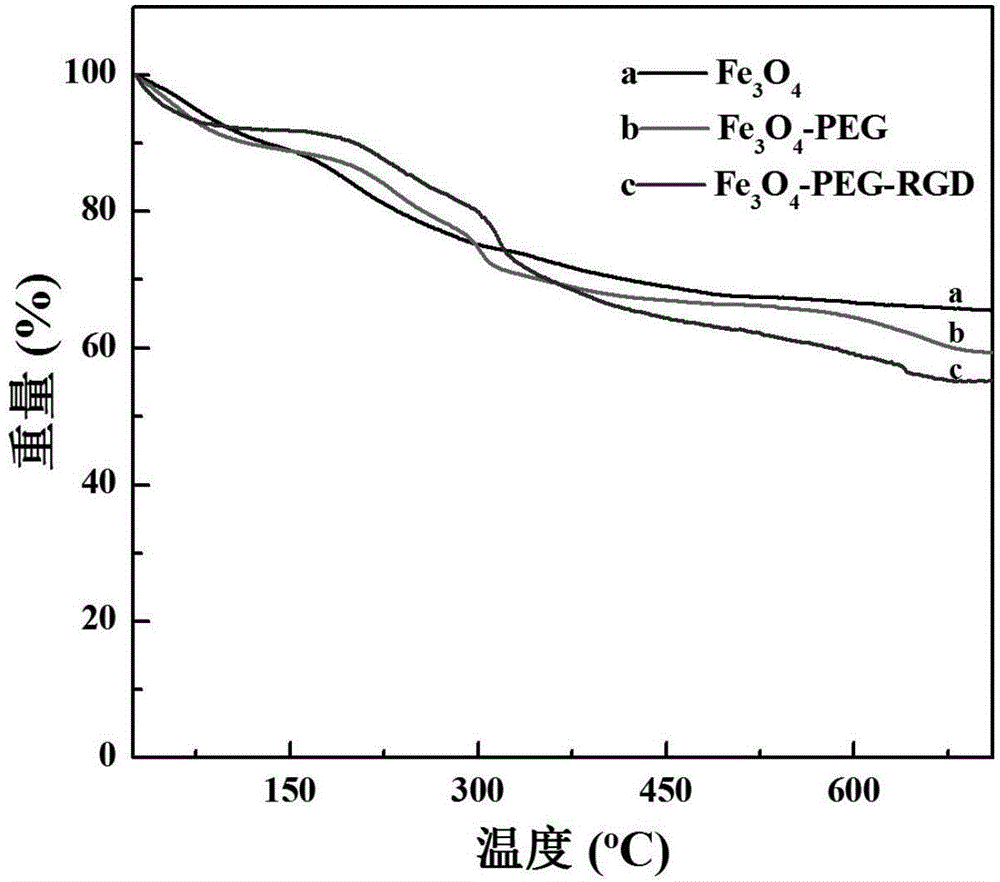
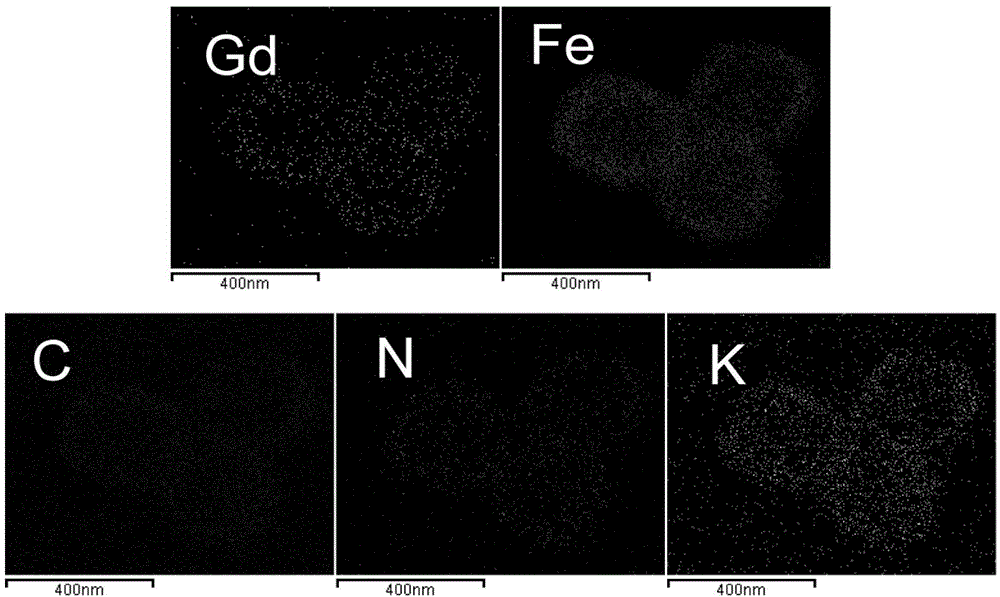
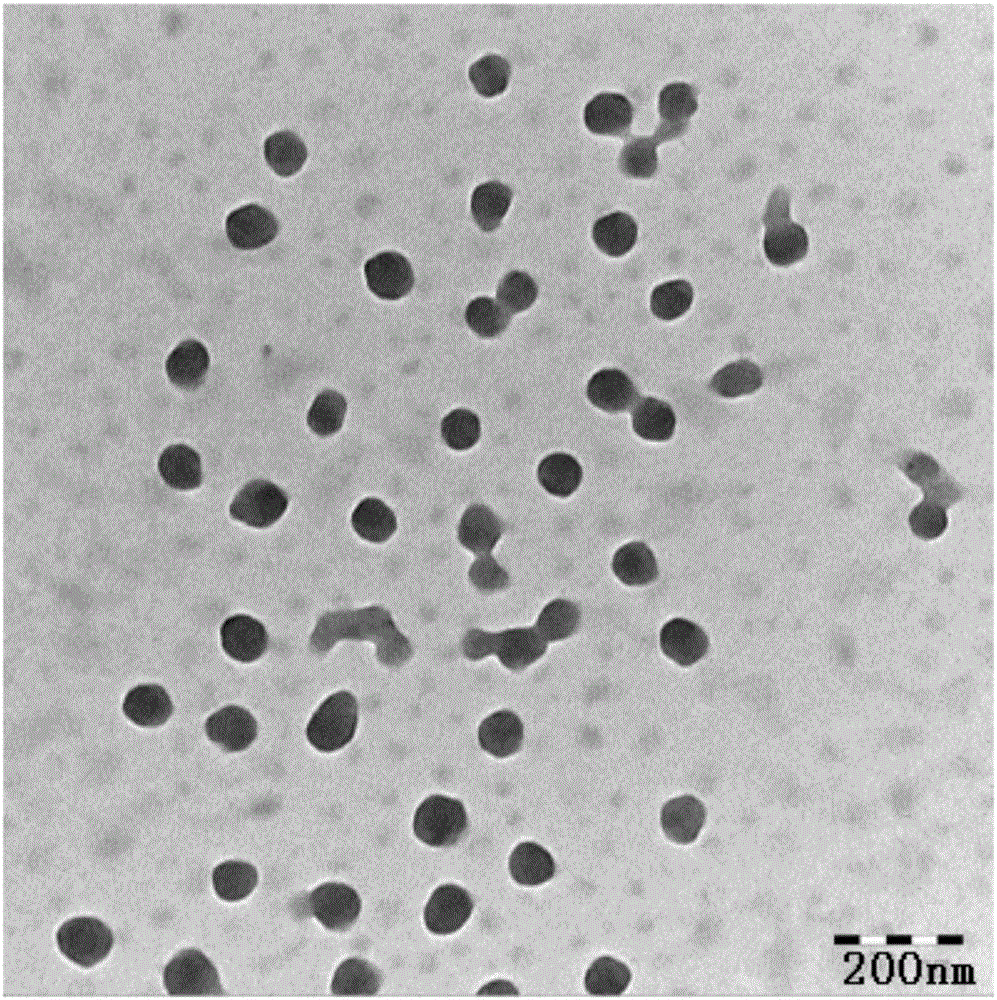
Preparation method and application of RGD-modified ultra-small magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles
ActiveCN104258425AStrong reducing propertiesHigh crystallinityNMR/MRI constrast preparationsEmulsion deliveryCyclic peptideActive agent
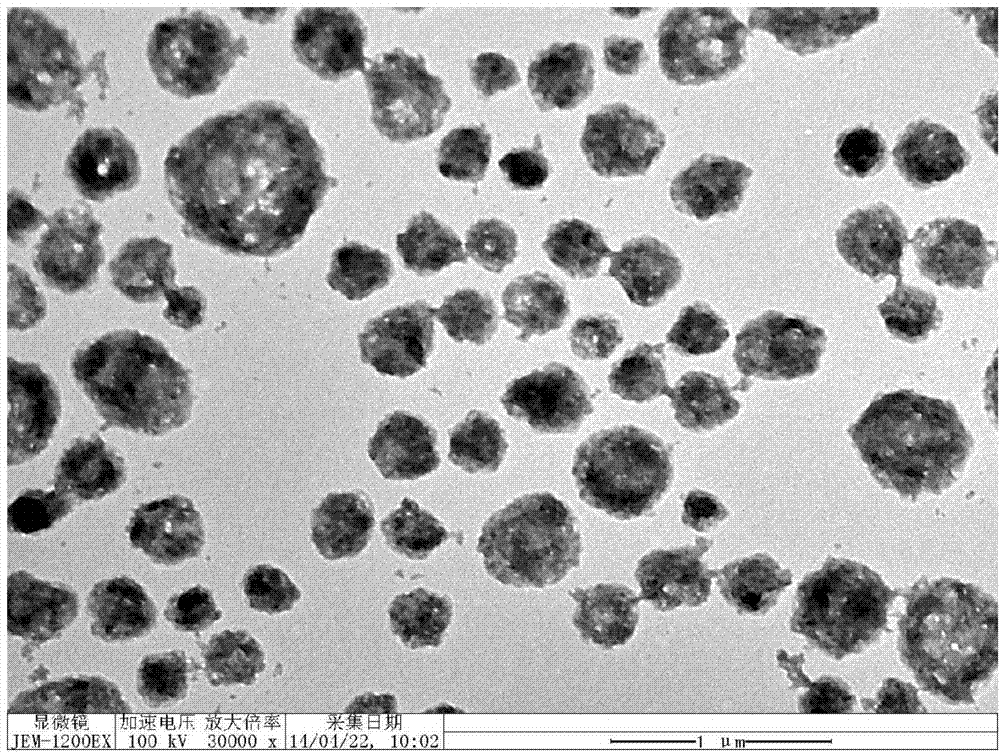
The invention discloses a preparation method of RGD-modified ultra-small magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. The preparation method comprises the following steps: preparing ultra-small magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles by taking ferric acetylacetonate as a reaction raw material and a precursor, taking oleylamine as a surfactant and a reducing agent and taking dibenzyl ether as a solvent; replacing oleylamine molecules wrapped on the surfaces of the nanoparticles by utilizing dopamine-modified HOOC-PEG-COOH to realize PEG-modification of the surfaces of the nanoparticles; and finally, chemically coupling RGD cyclic peptide by virtue of free carboxyl at the tail end of the PEG to obtain the RGD-modified ultra-small magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. The method of synthesizing the ultra-small magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles has the characteristics of a simple process, a high raw material conversion ratio, strong repeatability and the like. The synthesized magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles have the characteristics of a regular morphology, an ultra-small dimension, good stability, good monodispersity, high biocompatibility, and tumor specific targeting, and the like, and can be used as a T1-weighted imaging high-performance magnetic resonance imaging contrast agent with a tumor active targeting function.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
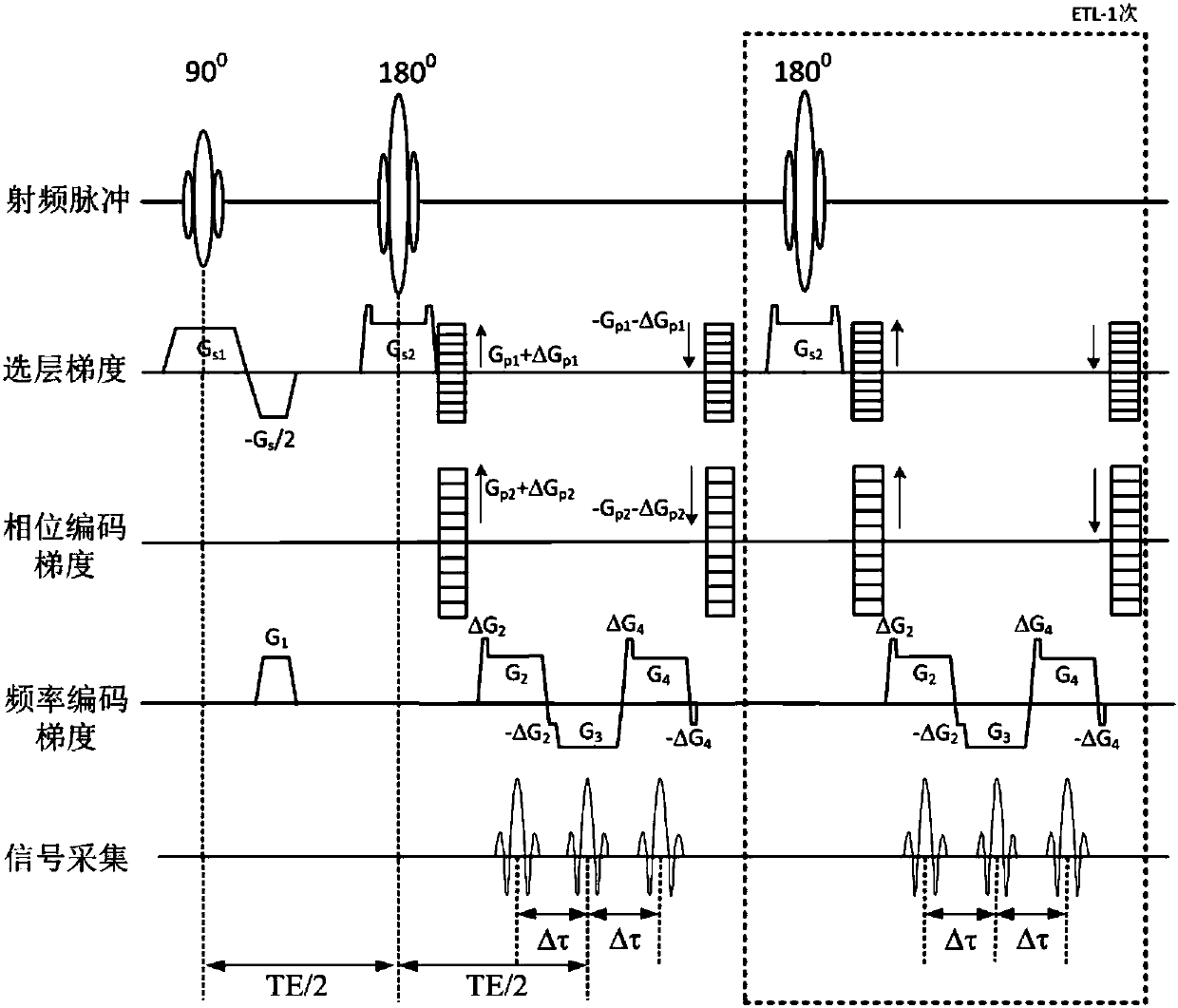
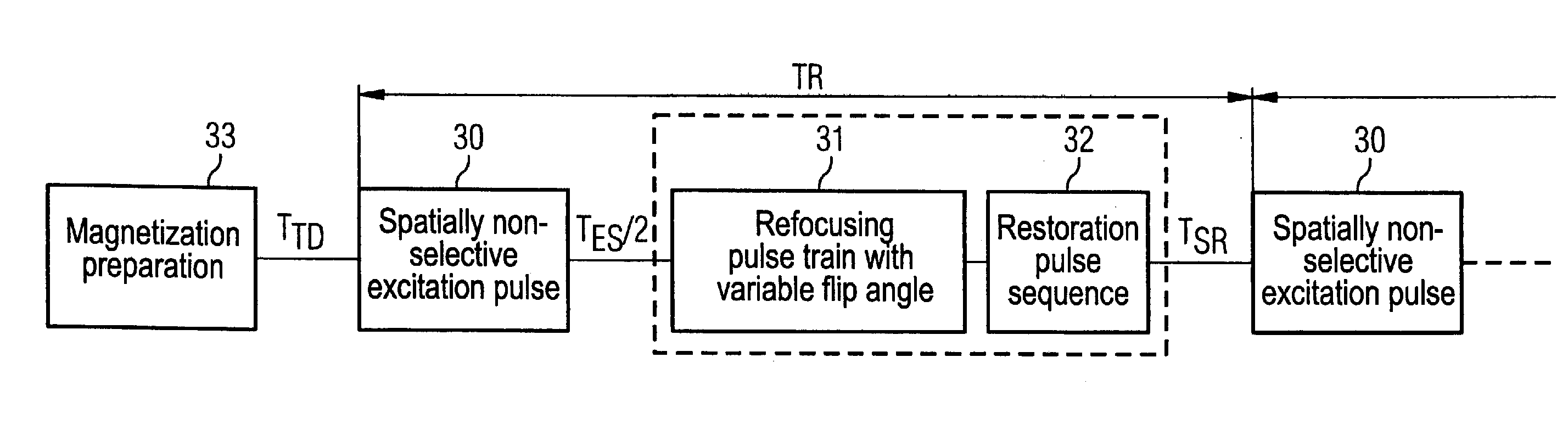
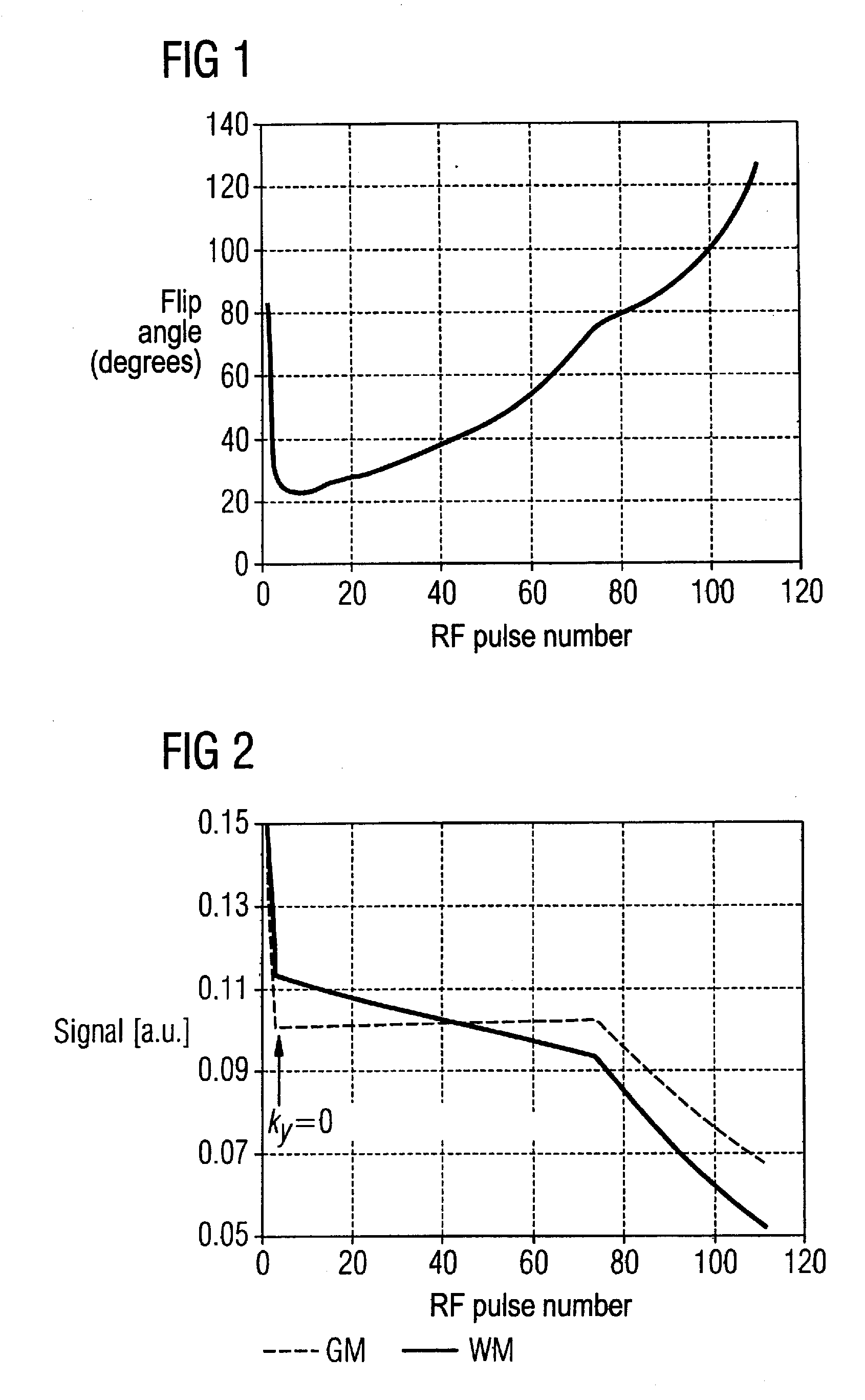
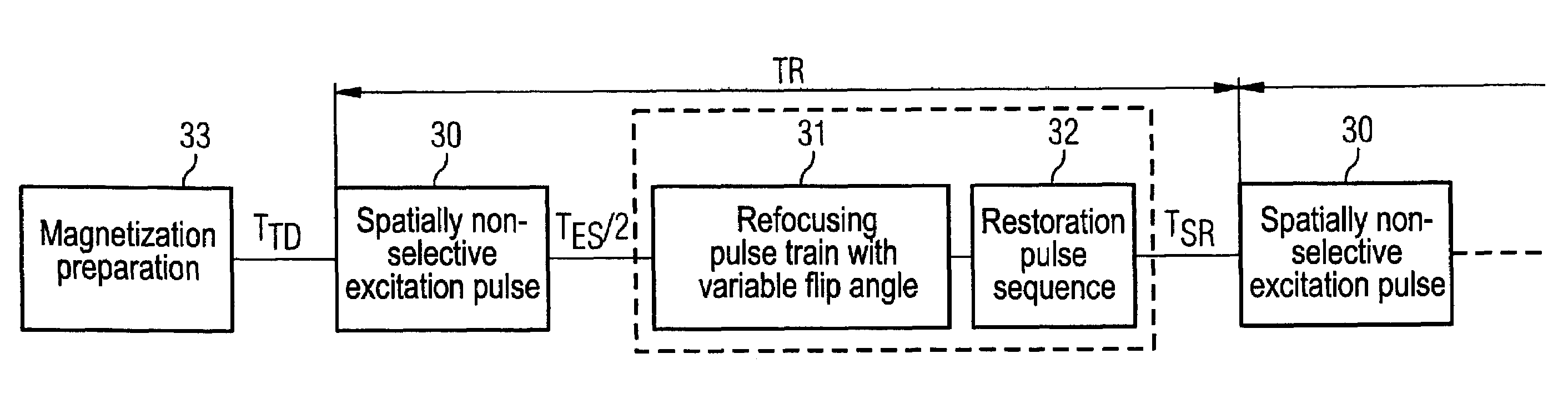
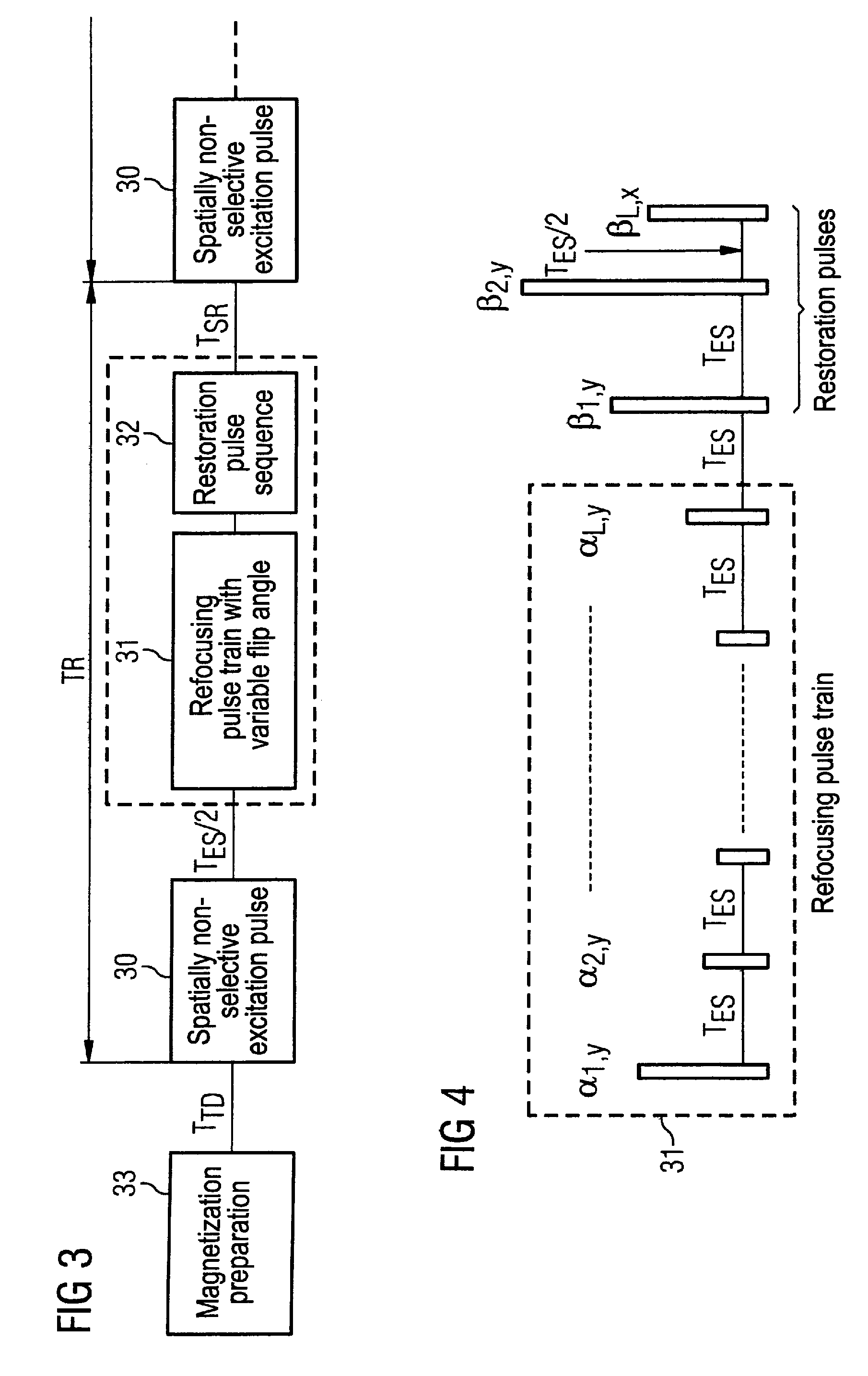
Turbospin echo imaging sequence with long echo trains and optimized t1 contrast
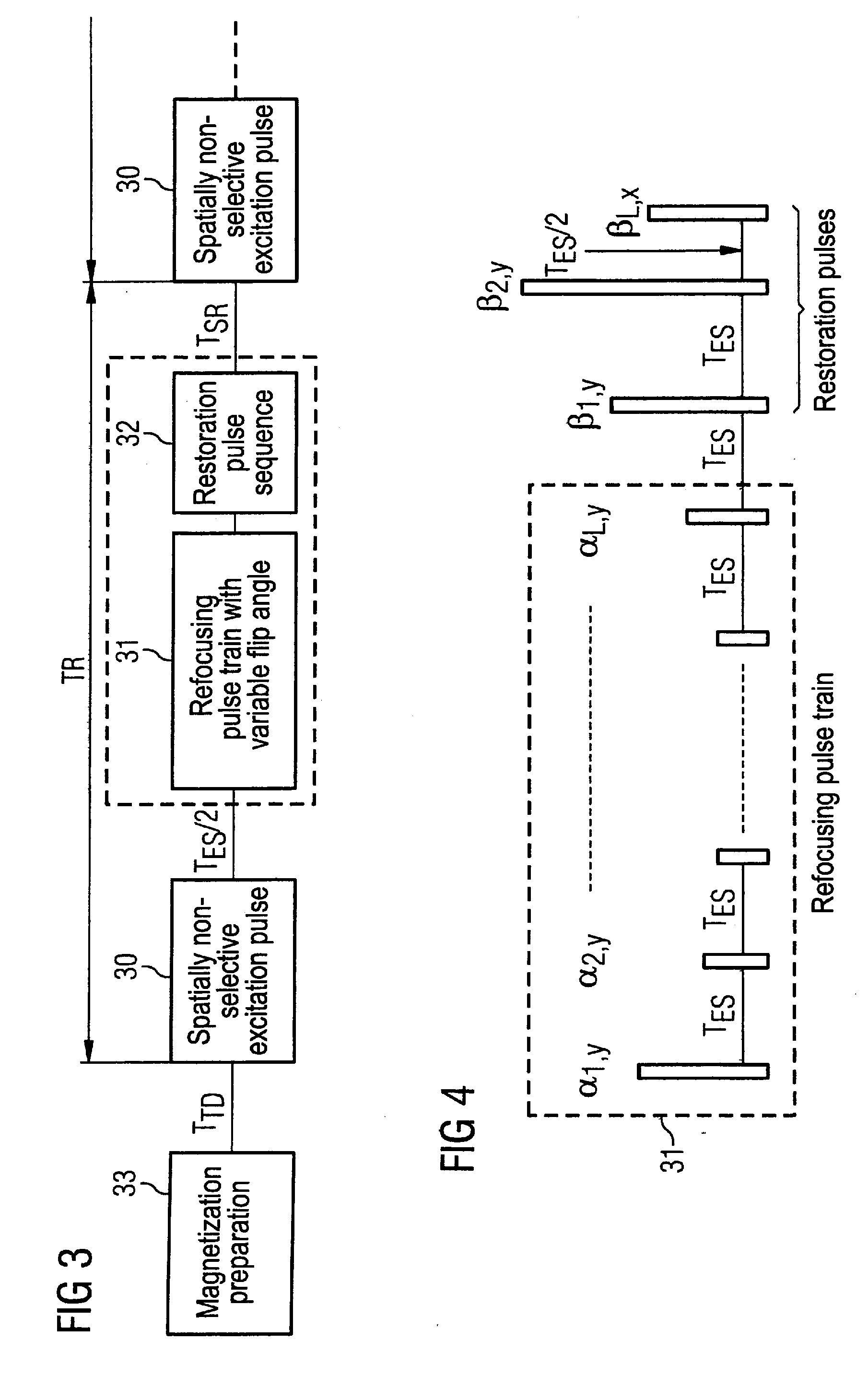
ActiveUS20080278159A1Minimize impactShorten the lengthMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionT1 contrastResonance
In a method in the form of a turbo spin echo imaging sequence with long echo trains and optimized T1 contrast for generation of T1-weighted images of an examination subject by magnetic resonance, magnetization in the examination subject is excited with an RF excitation pulse, a number N of RF refocusing pulses with variable flip angle are radiated to generate multiple spin echoes for an excitation pulse, a restoration pulse chain is activated after switching of the N refocusing pulses and before the next RF excitation pulse. The restoration pulse chain influences the magnetization such that the magnetization is aligned opposite to the direction of the basic magnetic field by the restoration pulse chain before the next RF excitation pulse.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
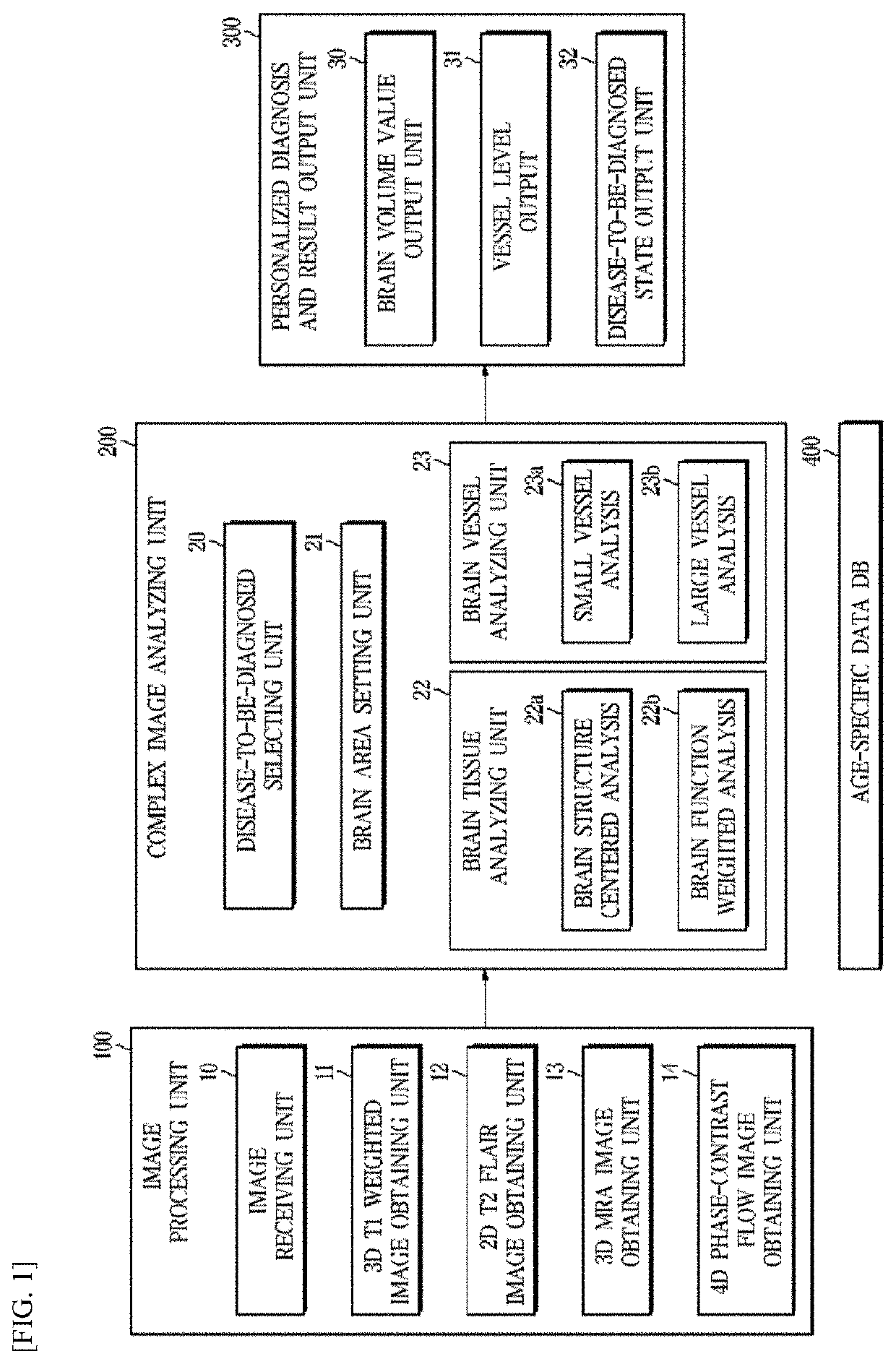
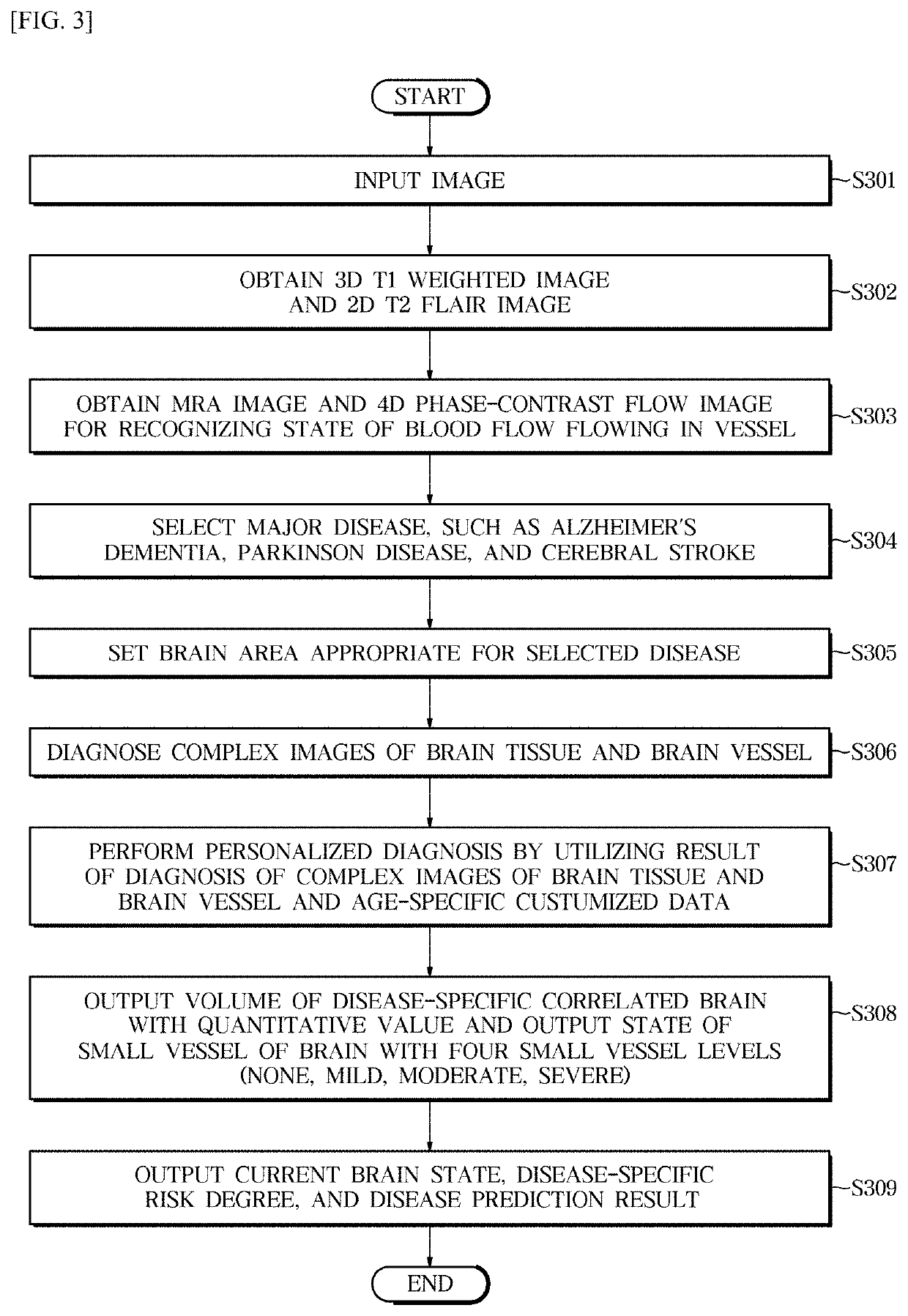
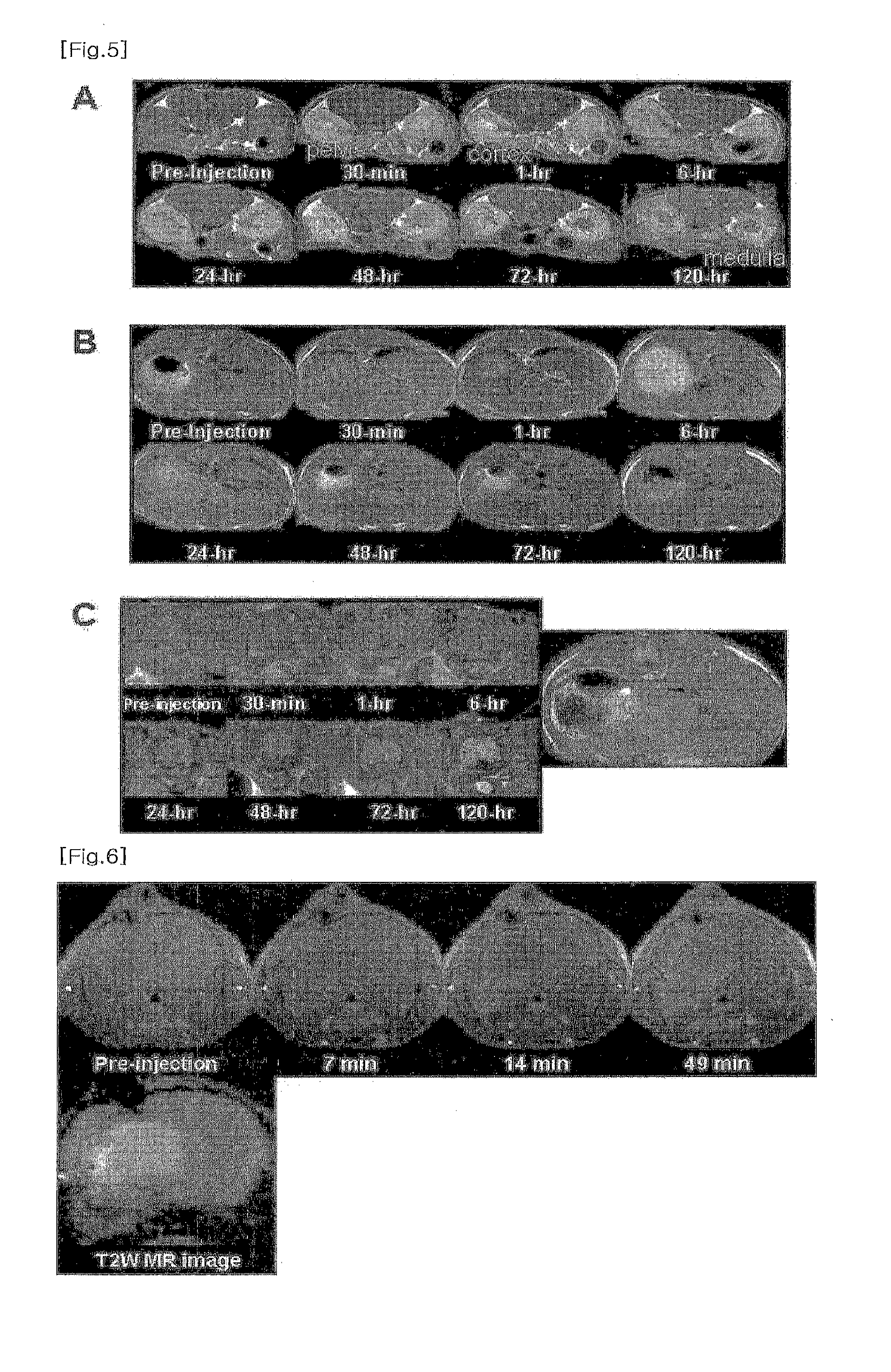
Medical image processing system and method for personalized brain disease diagnosis and status determination
InactiveUS20200315455A1Ensure correct executionEfficient analysisImage enhancementMedical imagingFluid-attenuated inversion recoveryImage manipulation
A system for processing a medical image for personalized brain disease diagnosis and status determination, includes: an image processing unit, which obtains a 3D T1 weighted image, a 2D T2 fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) image, a magnetic resonance angiogram (MRA) image, which images only a vessel for checking abnormality of a brain vessel, and a 4D phase-contrast flow image for recognizing a state of a blood flow in a vessel; a complex image analyzing unit, which selects a disease-to-be-diagnosed, sets a brain area according to the selected disease, and analyzes brain tissue and a brain vessel; and a personalized diagnosis and result output unit, which outputs a brain state, a disease-specific risk degree, a risk of disease, and a disease prediction result through a machine learning algorithm by utilizing an age-specific data DB.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO +1
Method for preparing RGD peptide targeted ultra-small ferriferrous oxide MRI positive nanoprobe
InactiveCN104826139ASimple operation processMild reaction conditionsIn-vivo testing preparationsCancer cellHuman glioma
The invention relates to a method for preparing an RGD peptide targeted ultra-small ferriferrous oxide MRI positive nanoprobe. The method comprises the steps of: conducting a one-step solvothermal synthesis method to obtain surface sodium citrate stabilized ultra-small Fe3O4 nanoparticles, then modifying NH2-PEG-RGD to the nanoparticle surface to obtain the RGD targeted ultra-small ferriferrous oxide MRI positive molecular probe. The PEG-RGD modified ultra-small ferriferrous oxide nanoprobe has long cycle time in mice, and realizes targeting T1-weighted enhancement MRI on the surface of cancer cells with alphavbeta3 integrin high expression (U87MG cells, human brain glioma cells) and subcutaneously transplanted tumor on animal level and cellular level. The Fe3O4 nanoparticles prepared by the invention can be in stably dispersed in an aqueous solution for a long time, and do not agglomerate. The preparation method provided by the invention has the advantages of simpleness, low cost and potential in industrialization and commercialization.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV +1
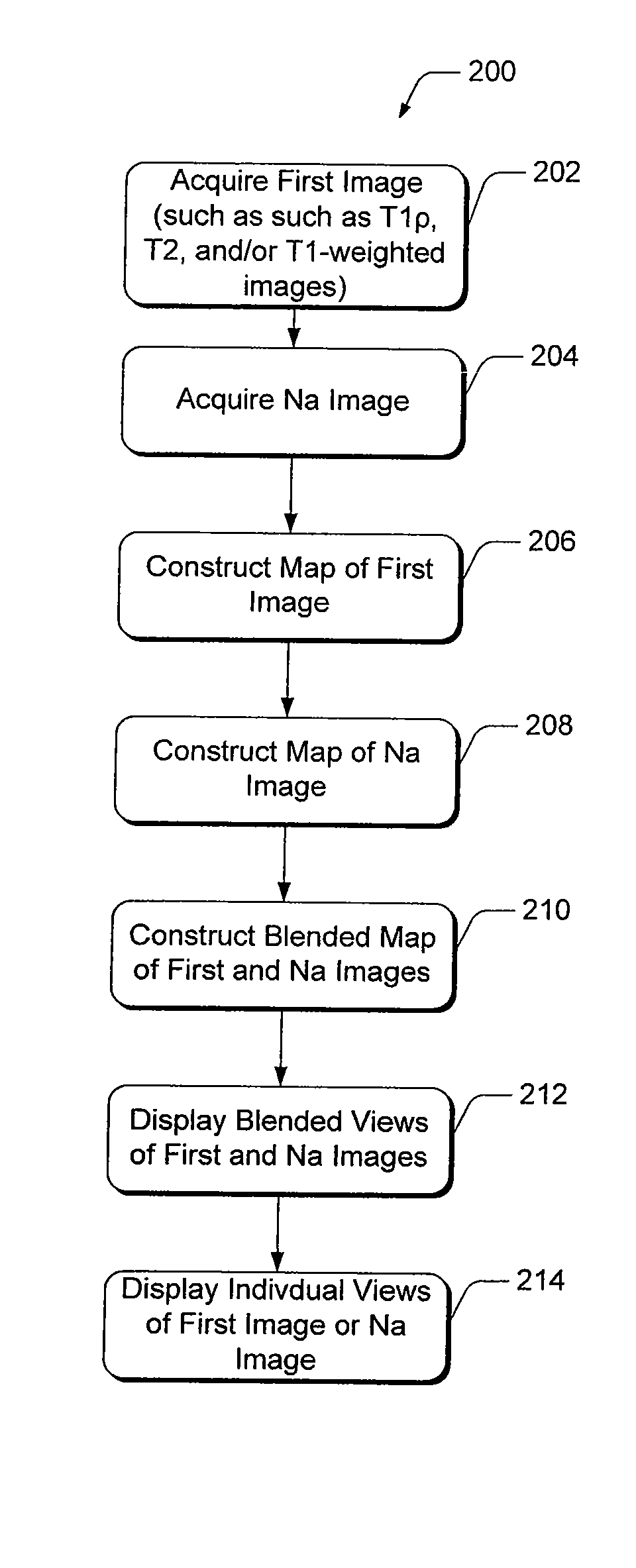
Magnetic Resonance Imaging For Diagnostic Mapping Of Tissues
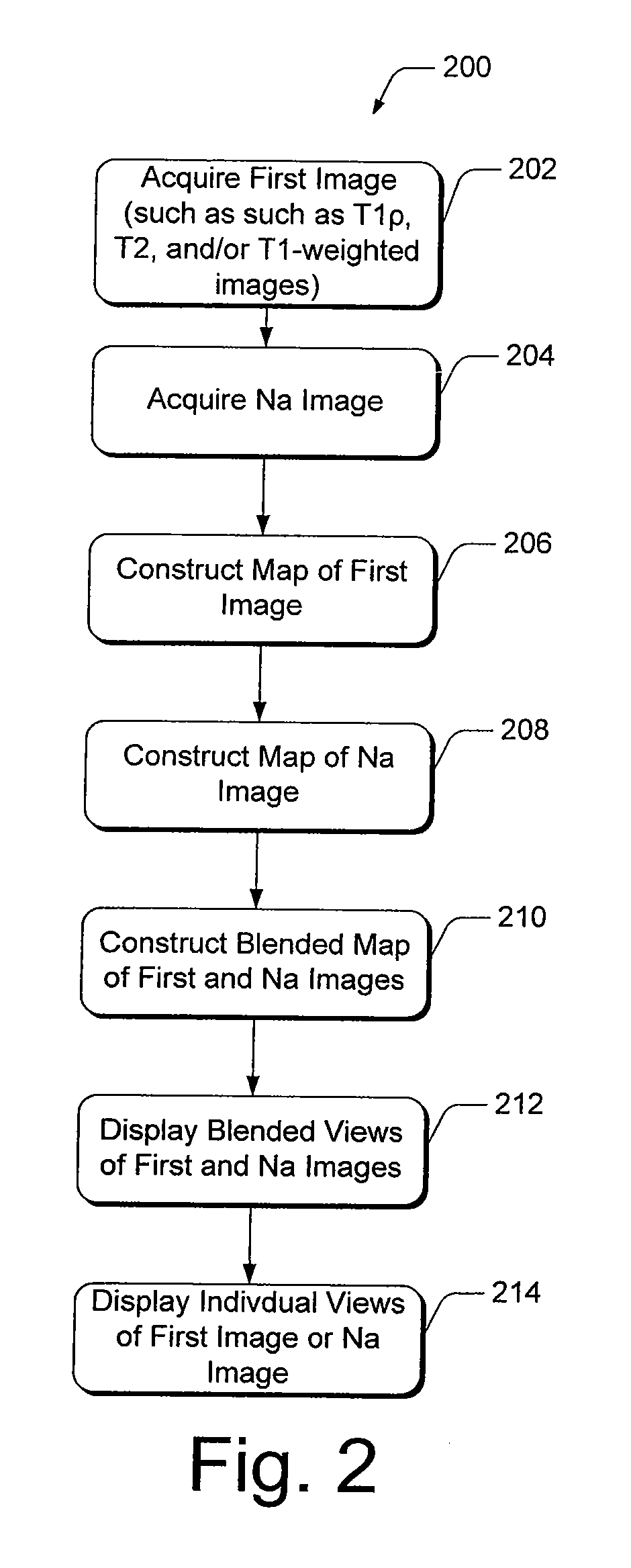
ActiveUS20100166278A1Effective diagnosisVerify efficacyCharacter and pattern recognitionDiagnostic recording/measuringResonanceT1 weighted
Methods of, and systems for, magnetic resonance imaging of diagnostic mapping of tissues, where sodium mapping is performed individually, as well as in combination with other images of tissue, such as T1ρ, T2, and / or T1-weighted images. In one method embodiment, a sodium image of the tissue is acquired during the same scanning session. Maps are constructed of each of the first and sodium images individually, and in combination, and further facilitate viewing in combination with each other as a single, blended image of the tissue. Maps of the images may be displayed individually or in combination with each other.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
Method for extracting microwave detection breast model based on medical magnetic resonance imaging
The invention belongs to the technical field of biomedical detection, and relates to a method for extracting a microwave detection breast model based on medical magnetic resonance imaging. The method includes the steps: acquiring a T1 weighted magnetic resonance image of a breast portion; enhancing a boundary; performing gray discrete processing; calculating the water content of a tissue corresponding to each pixel for a thoracic gland portion in the magnetic resonance image by the aid of an image gray value; comparing the water content of the tissue corresponding to each pixel with typical water content data of each tissue of a normal human body, determining tissue information of each pixel and defining the pixel as an islet if the tissue information of the pixel cannot be determined; giving the same gray value to the pixels with the determined tissue information and belonging to the same tissue, and normalizing the gray of the magnetic resonance image according to the tissue information; corroding small discrete islets; building the breast model. A breast structure can be really simulated by the method.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
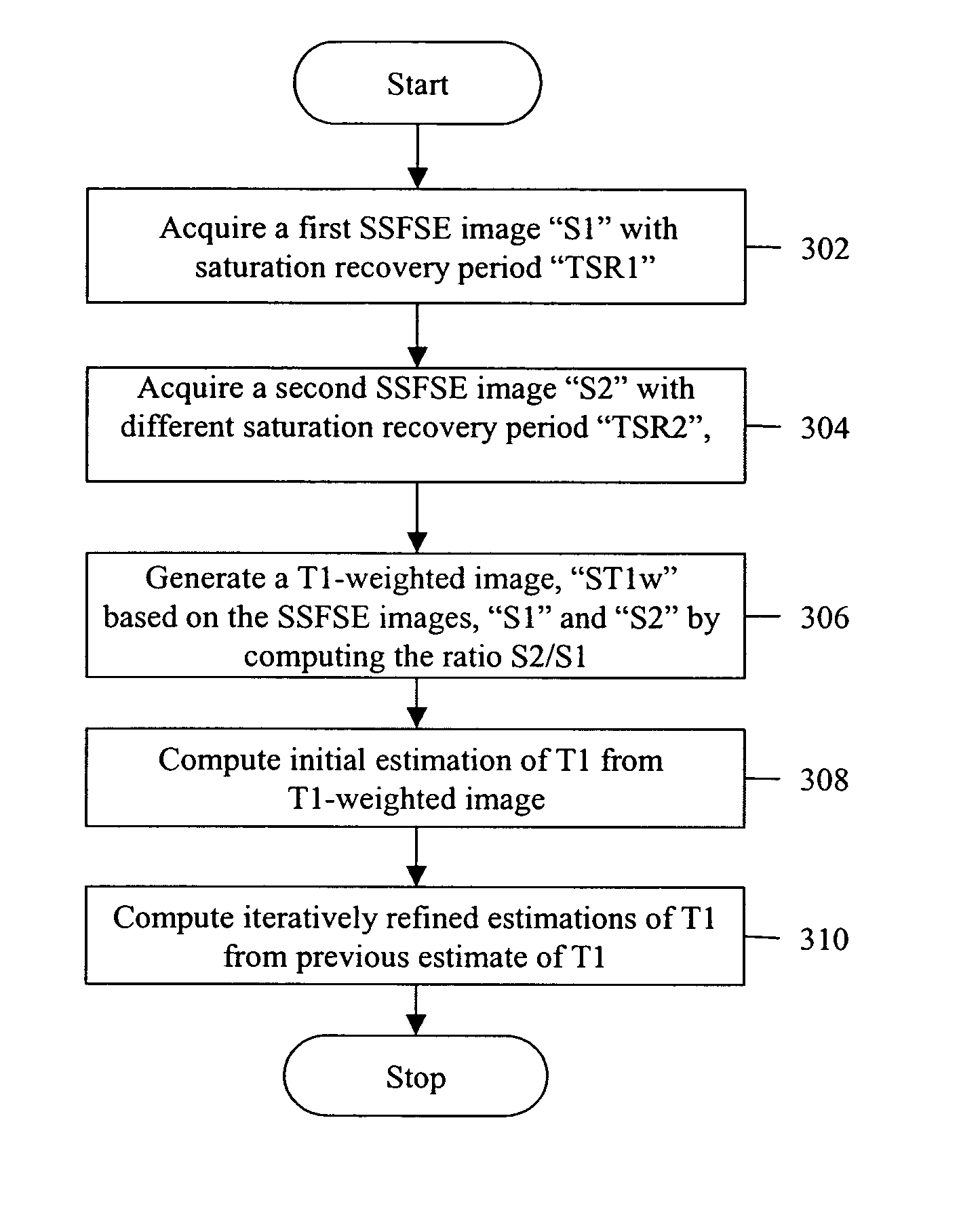
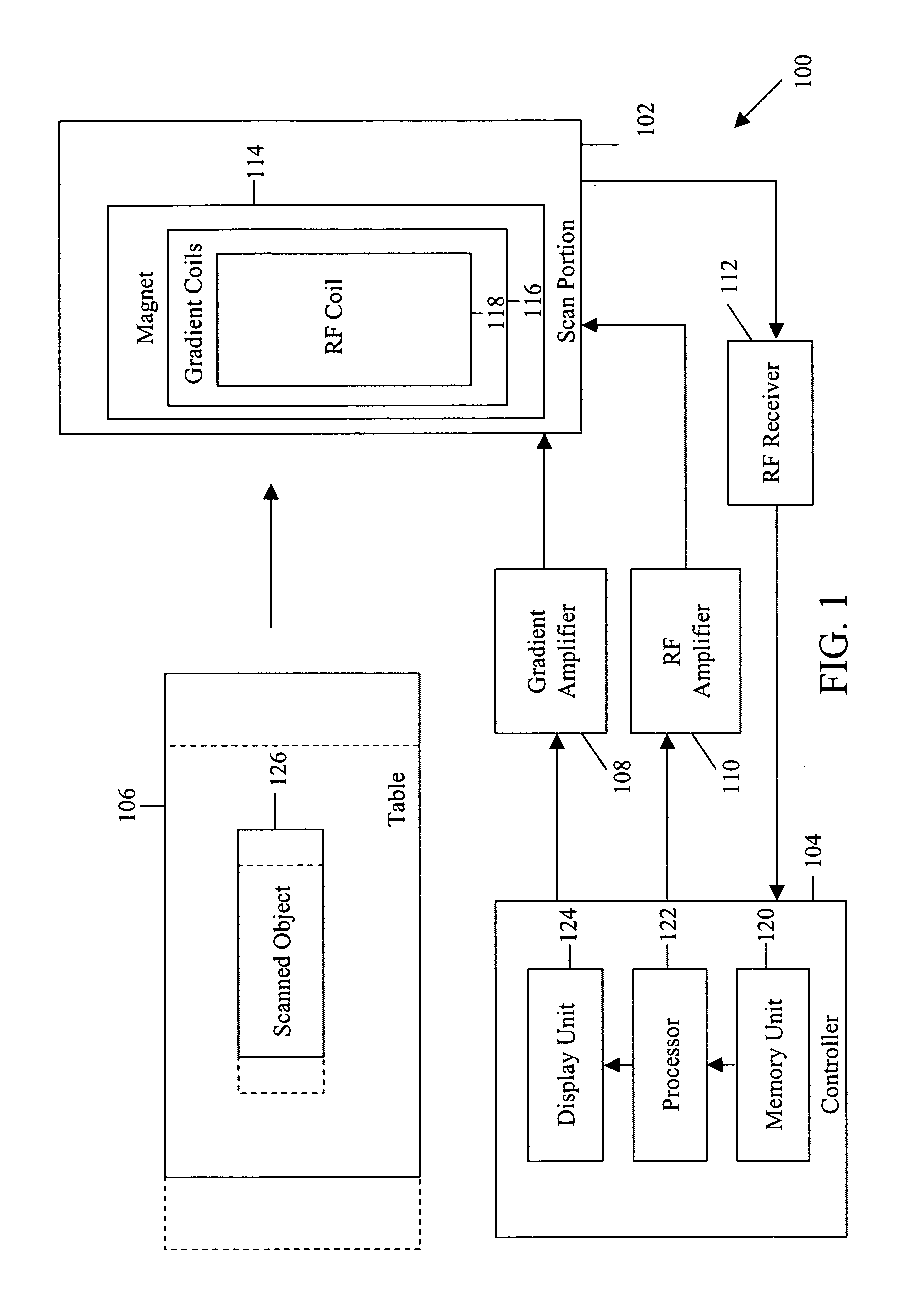
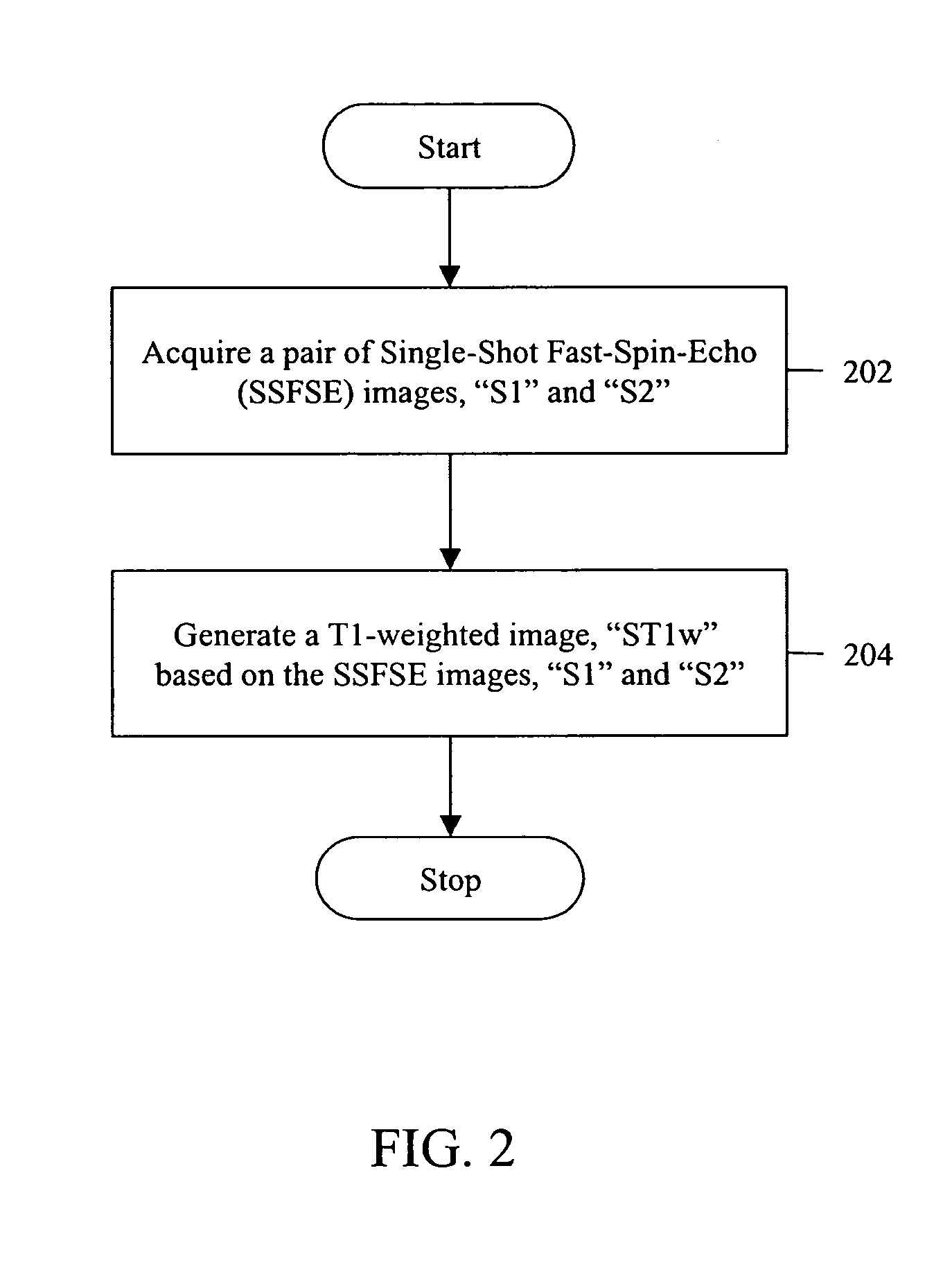
Method for generating T1-weighted magnetic resonance images and quantitative T1 maps
ActiveUS7276904B2Measurements using NMR imaging systemsElectric/magnetic detectionFast spin echoResonance
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
MRI t1 contrasting agent comprising manganese oxide nanoparticle
InactiveUS20120114564A1High intracellular uptakeBrighter imageBiocideGenetic material ingredientsT1 contrastRadiology
The present invention relates to the use of and method for using MnO nanoparticles as MRI T1 contrasting agents which reduces T1 of tissue. More specifically, the present invention is directed to MRI T1 contrasting agent comprising MnO nanoparticle coated with a biocompatible material bound to a biologically active material such as a targeting agent, for example tumor marker etc., and methods for diagnosis and treatment of tumor etc. using said MRI T1 contrasting agent, thereby obtaining more detailed images than the conventional MRI T1-weighted images. The MRI T1 contrasting agent of the present invention allows a high resolution anatomic imaging by emphasizing T1 contrast images between tissues based on the difference of accumulation of the contrasting agent in tissues. Also, the MRI T1 contrasting agent of the present invention enables to visualize cellular distribution due to its high intracellular uptake. The MRI T1 contrasting agent of the present invention can be used for target-specific diagnosis and treatment of various diseases such as tumor etc. when targeting agents binding to disease-specific biomarkers are conjugated to the surface of nanoparticles.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND
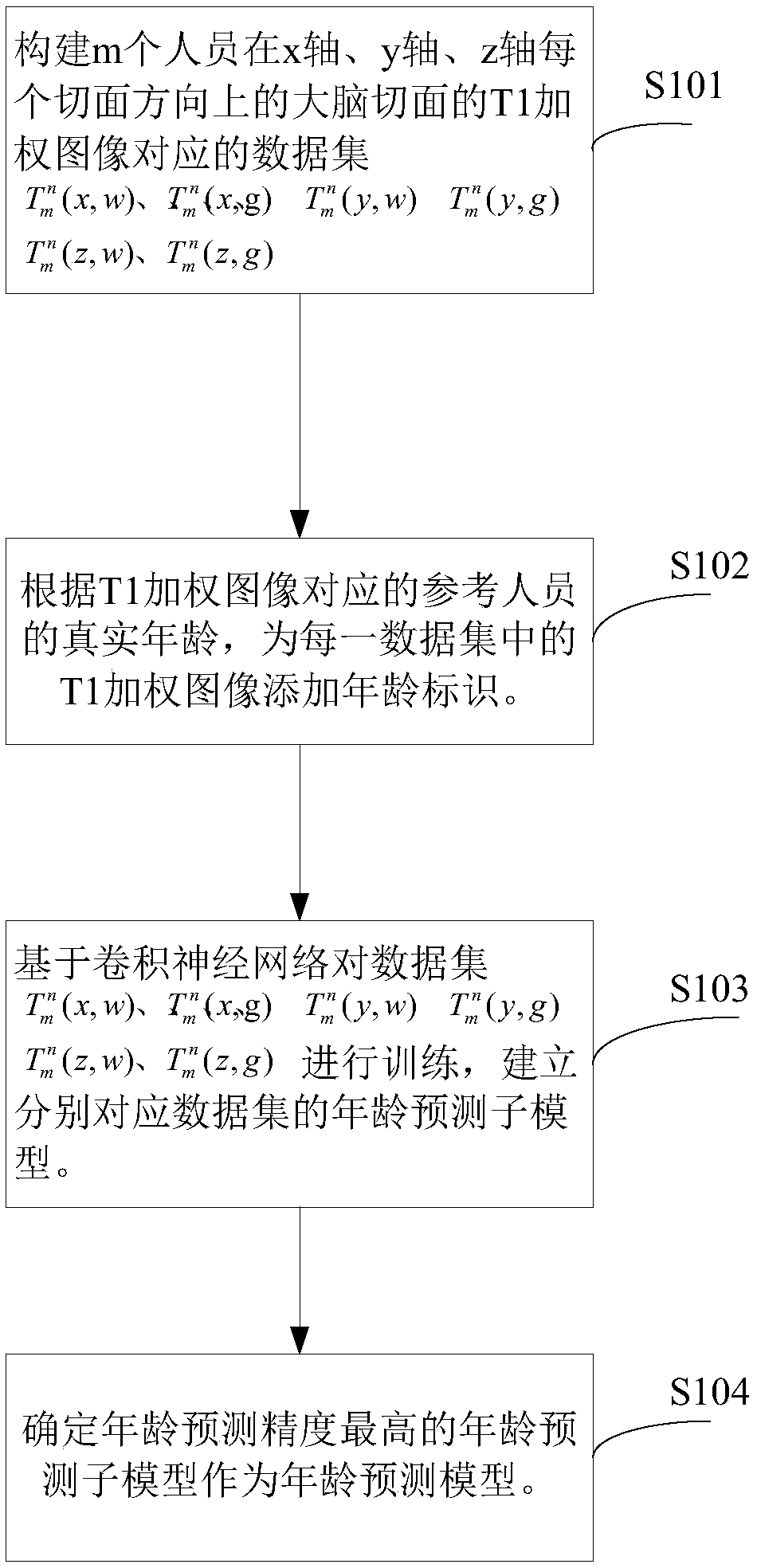
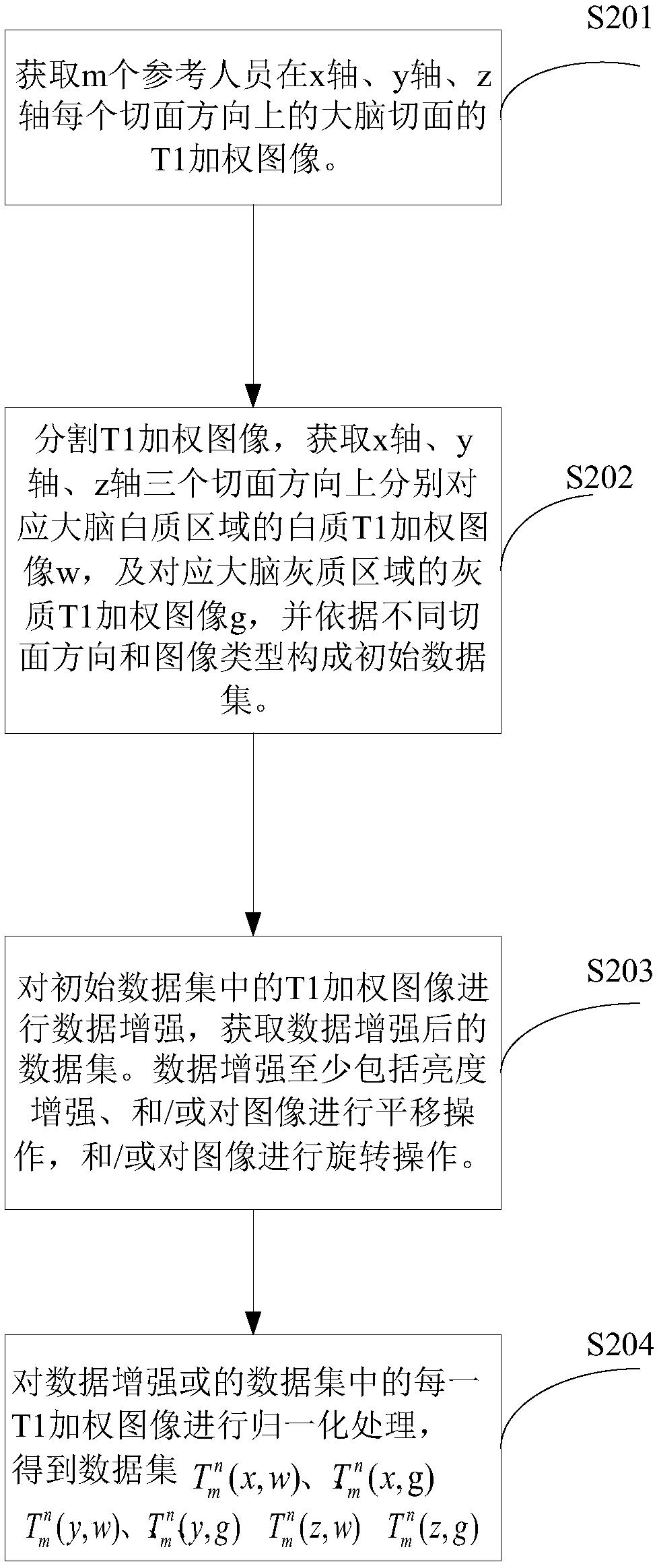
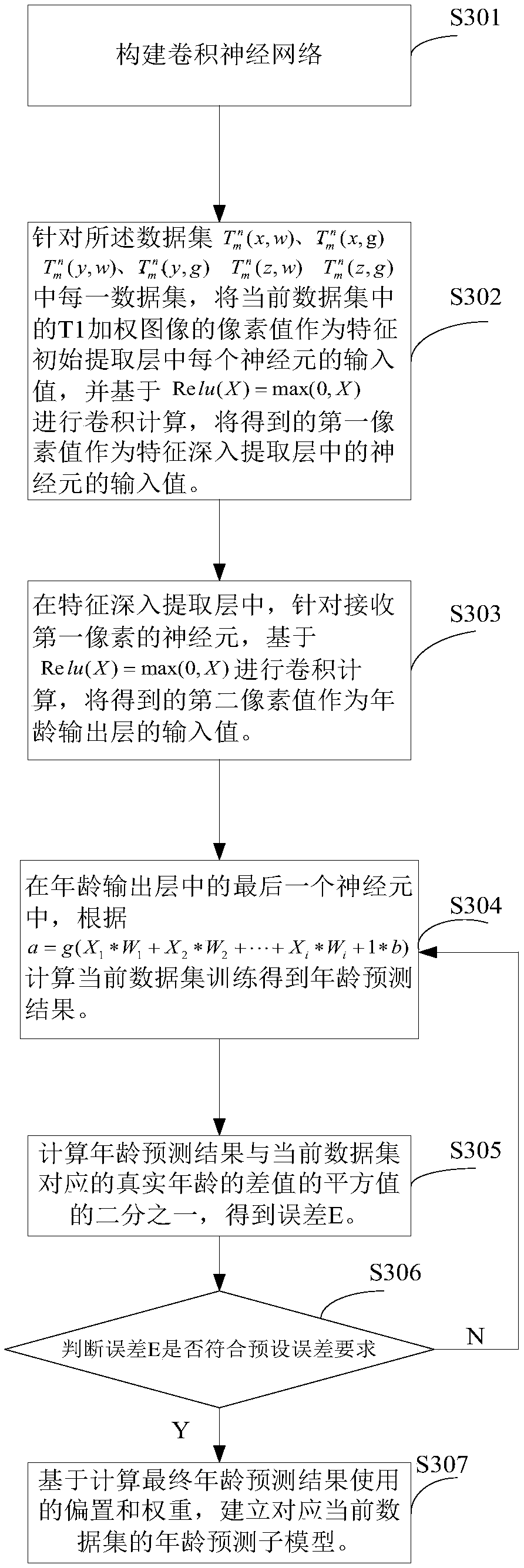
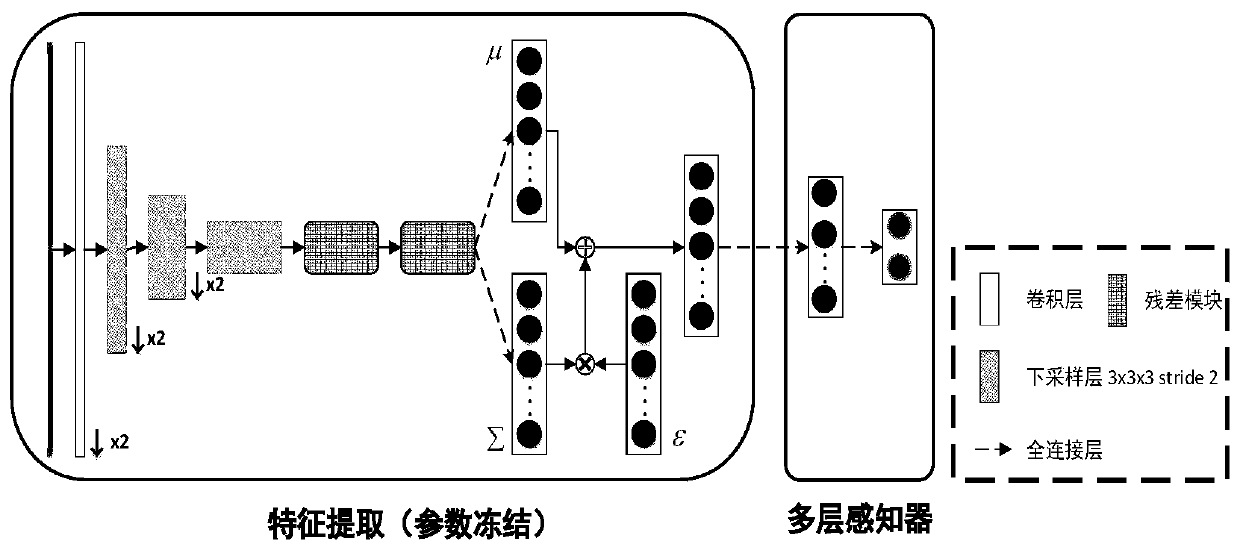
Method and device for establishing age prediction model, age prediction method and device
The invention provides a method and a device for establishing an age prediction model, an age prediction method and a device. The method comprises: building m references on the x-axis, y-axis, z-axisData sets (described in the description) corresponding to T1-weighted images of brain slices in each slice direction and T<n><n>(z, g), where w refers to the white matter T1-weighted image corresponding to the white matter region and g refers to the grey matter T1-weighted image corresponding to the grey matter region; n is the number of the reference person and n has a value ranging from 1 to m.According to the true age of the reference person corresponding to the T1-weighted image, age identification is added to the T1-weighted image in each data set. Convolution-based neural network pairdata sets (described in the description) and T<n><n>(z, g), corresponding data sets (described in the description)and <n><n>(z, g) are established. The age predictor model with the highest precision of age prediction is selected as the age predictor model.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
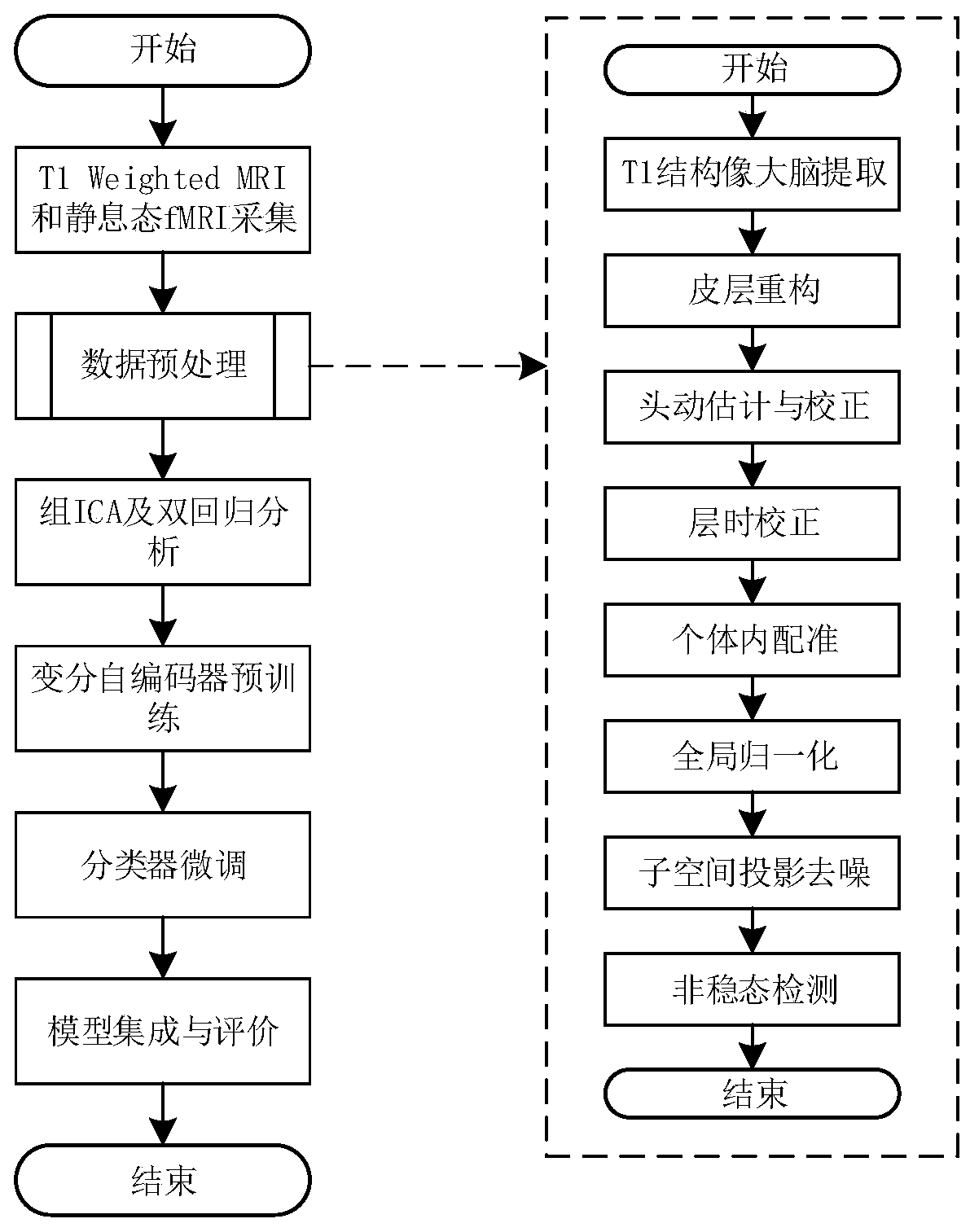
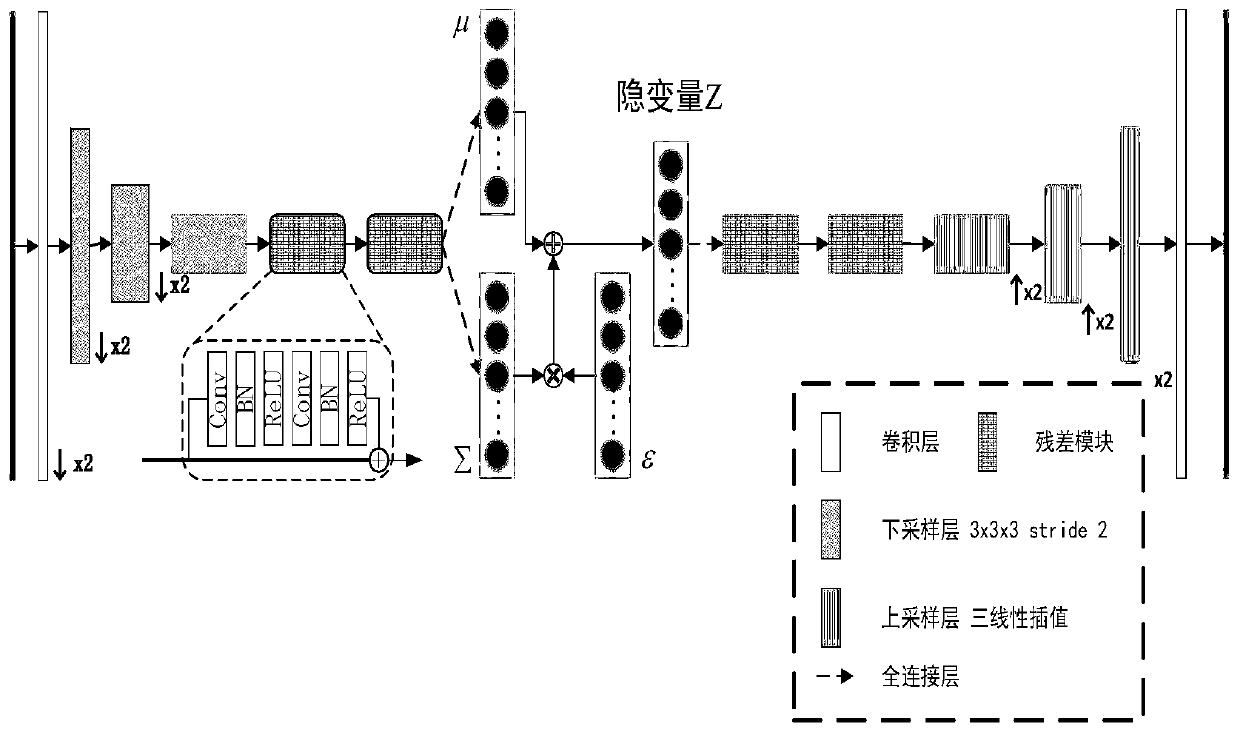
Brain function network classification method based on variational auto-encoder
ActiveCN110188836AImprove generalization abilityOvercome the disadvantage of poor fitting abilityCharacter and pattern recognitionNeural architecturesRegression analysisClassification methods
The invention discloses a brain function network classification method based on a variational autoencoder. The method comprises the following steps: The method comprises the following steps of: acquiring T1 weighted MRI and rs-fMRI of a plurality of normal people and patients with brain cognitive impairment; carrying out pretreatment; carrying out double regression analysis by taking the preprocessed rs-fMRI as a regression dependent variable and the brain function network as a regression independent variable to obtain an individual level brain function network; constructing a deep variationalautoencoder (VAE) model, taking the obtained individual level brain function network diagram as the input and output of the VAE, and taking the encoder part as a feature extraction module for obtaining the implicit code of the individual function network; constructing a multi-layer sensor network to classify the codes obtained by the VAE in the step 4; and deducing samples in the test set by using the trained classifiers for different brain function networks, and fusing deduction results of the classifiers to obtain a final classification result.acquiring T1 weighted magnetic resonance imagesT1 Weighted MRI and resting state functional magnetic resonance images rs-of a plurality of normal persons and patients with brain cognitive impairment; fMRI; carrying out pretreatment; pretreated rs- Performing double regression analysis by taking fMRI as a regression dependent variable and taking the brain function network as a regression independent variable to obtain an individual level brainfunction network; constructing a depth variation auto-encoder (VAE) model, taking the obtained individual level brain function network diagram as input and output of the VAE, and taking the encoder part as a feature extraction module for obtaining hidden codes of the individual function network; constructing a multi-layer perceptron network to classify the codes obtained by the VAE in the step 4;inferring samples in the test set by utilizing a plurality of trained classifiers for different brain function networks, and fusing inference results of the plurality of classifiers to obtain a finalclassification result; according According to the invention, the classification accuracy is improved.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
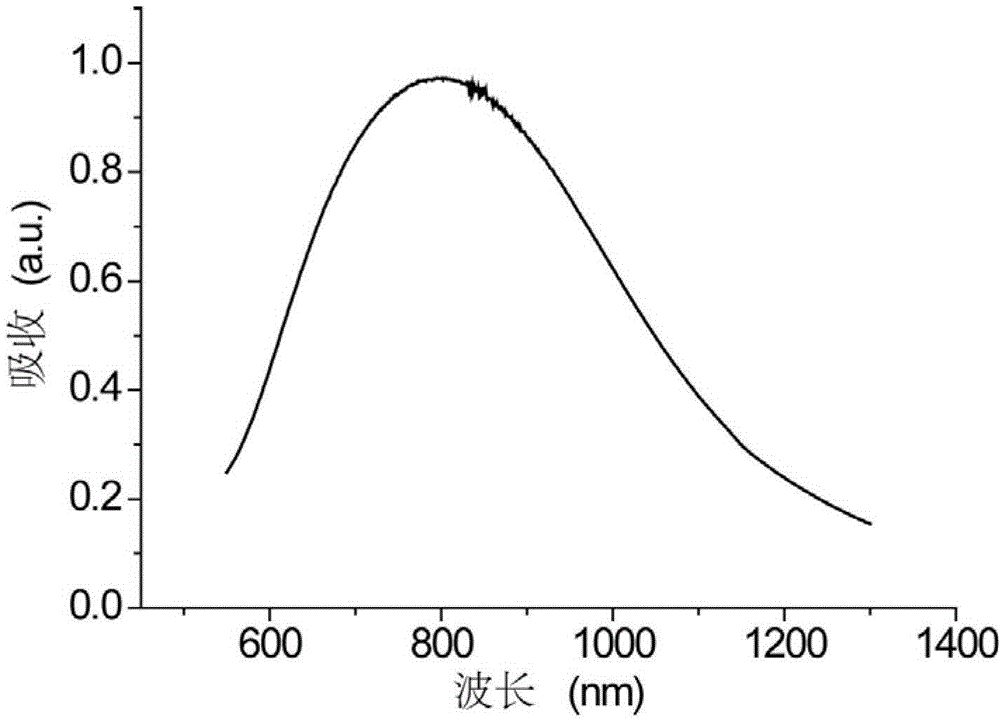
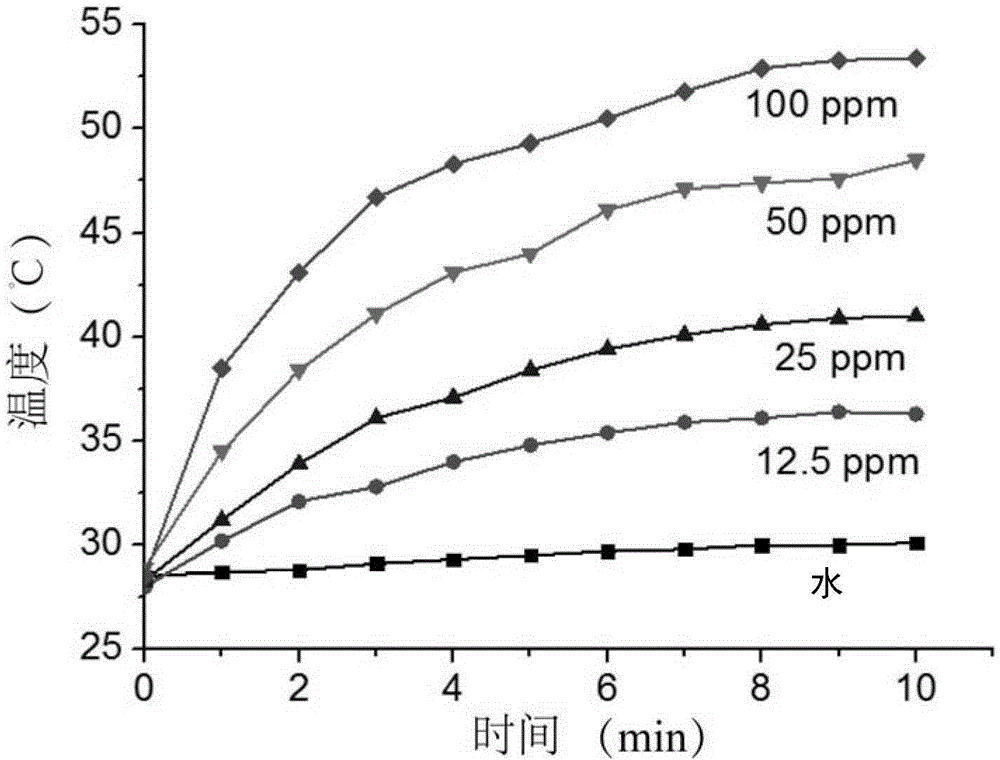
Multifunctional gadolinium-contained hollow mesoporous Prussian-blue nanometer treatment agent and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN105412948AGood biocompatibilityStrong absorption capacityEnergy modified materialsGeneral/multifunctional contrast agentsHigh absorptionMedicine
The invention relates to multifunctional gadolinium-contained hollow mesoporous Prussian-blue nanometer treatment agent and a preparation method and application thereof. The nanometer treatment agent is gadolinium-contained Prussian-blue nanometer particles which have mesopores and are hollow inside, wherein the molar ratio of iron to gadolinium is (0.8-200) to 1. The hollow mesoporous nanometer treatment agent is good in biocompatibility, T1 weighted magnetic resonance imaging performance is outstanding, and the nanometer treatment agent has high absorption and outstanding photothermal conversion performance in a near-infrared area and is improved in imaging and tumor treatment compared with other Prussian-blue nanometer particles.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF CERAMIC CHEM & TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
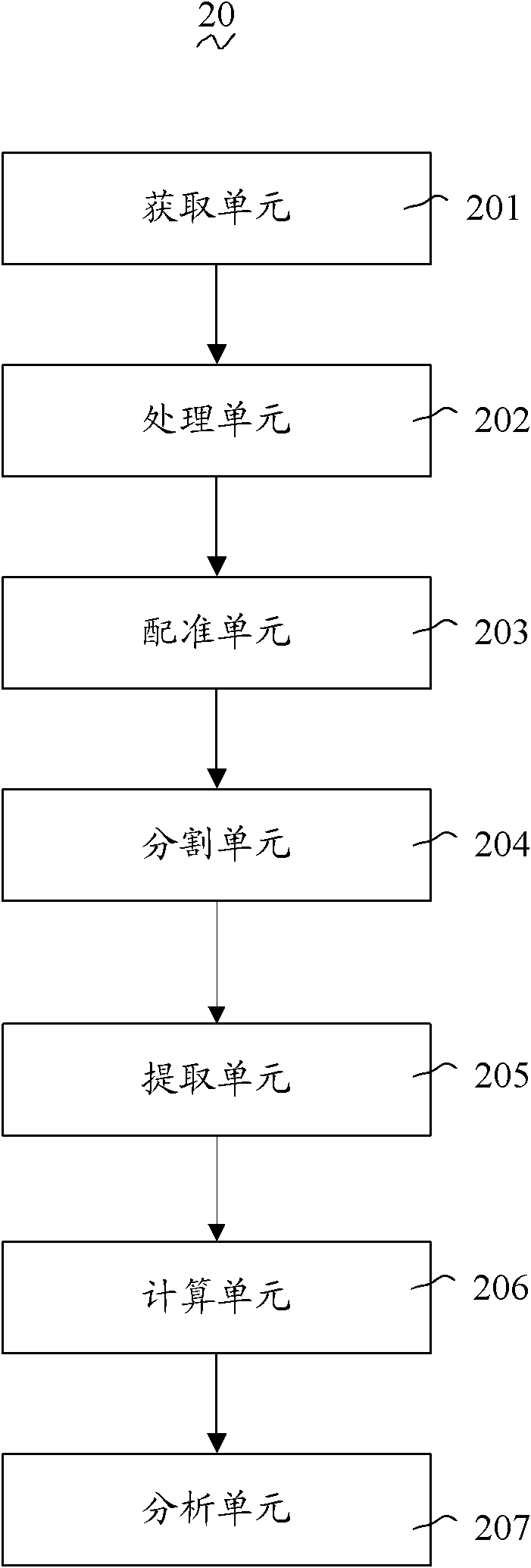
Image analysis method and system
The invention discloses an image analysis method, which comprises the steps of: obtaining a group of T1 weighted images including a control group image and an experimental group image, pre-processing all T1 weighted images, carrying out non-linear registration on preprocessed T1 weighted images into a preset template image, dividing the non-linear registered T1 weighted images to generate a plurality of interest regions, extracting at least one feature data of each interest region to obtain feature matrix information, calculating to obtain a reference value according to a preset Bayesian multi-layer model and the feature matrix information, and judging difference significance of the interest regions between the experimental group image and the control group image according to the relation between the reference value and a preset threshold value. The invention also provides a corresponding image analysis system. The image analysis method and the system can extract more and richer parameters to be analyzed and more diverse information in comparison with the conventional technology, and can simultaneously process multi-region multi-feature significance statistical test so that morphology analysis is more complete.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
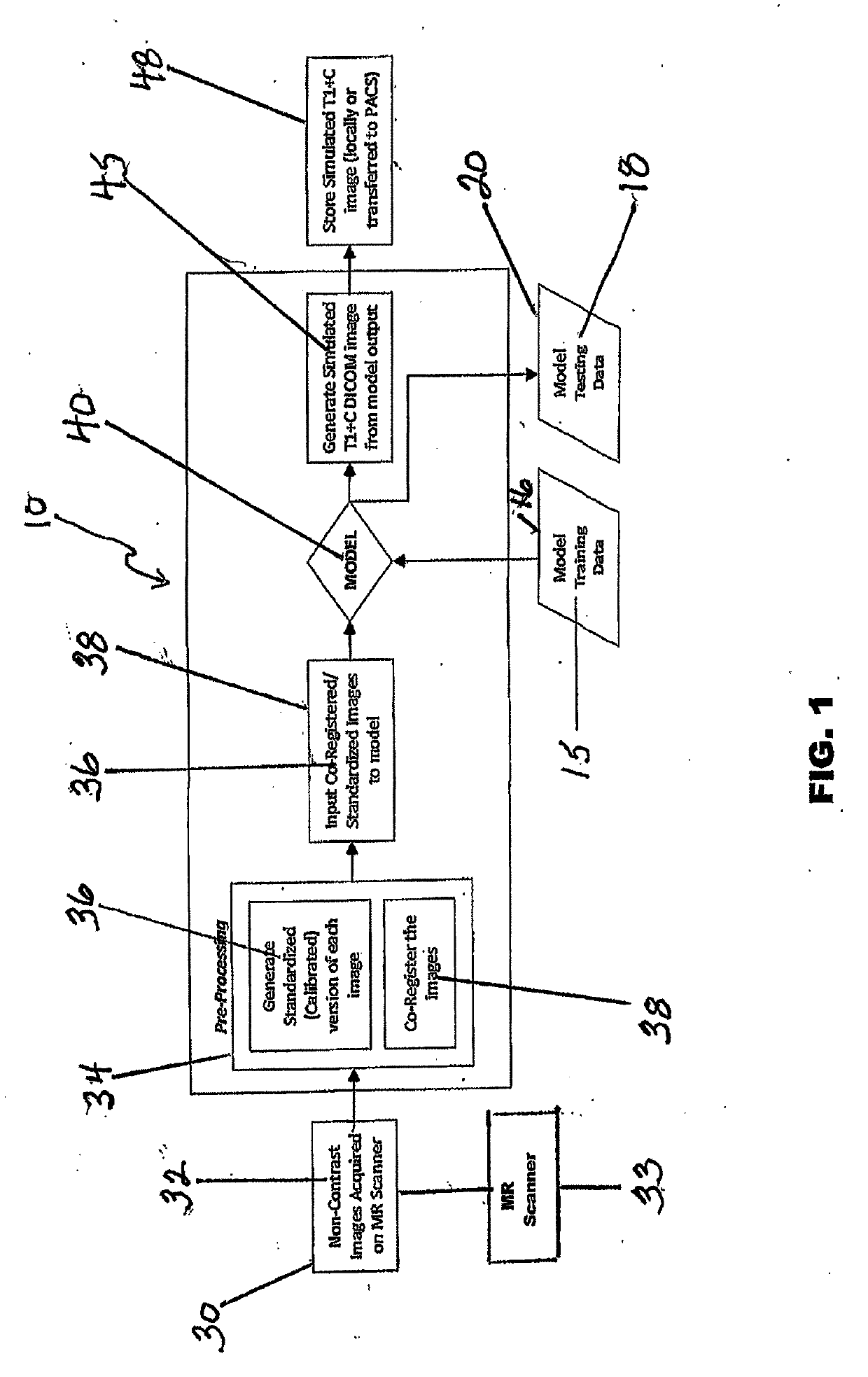
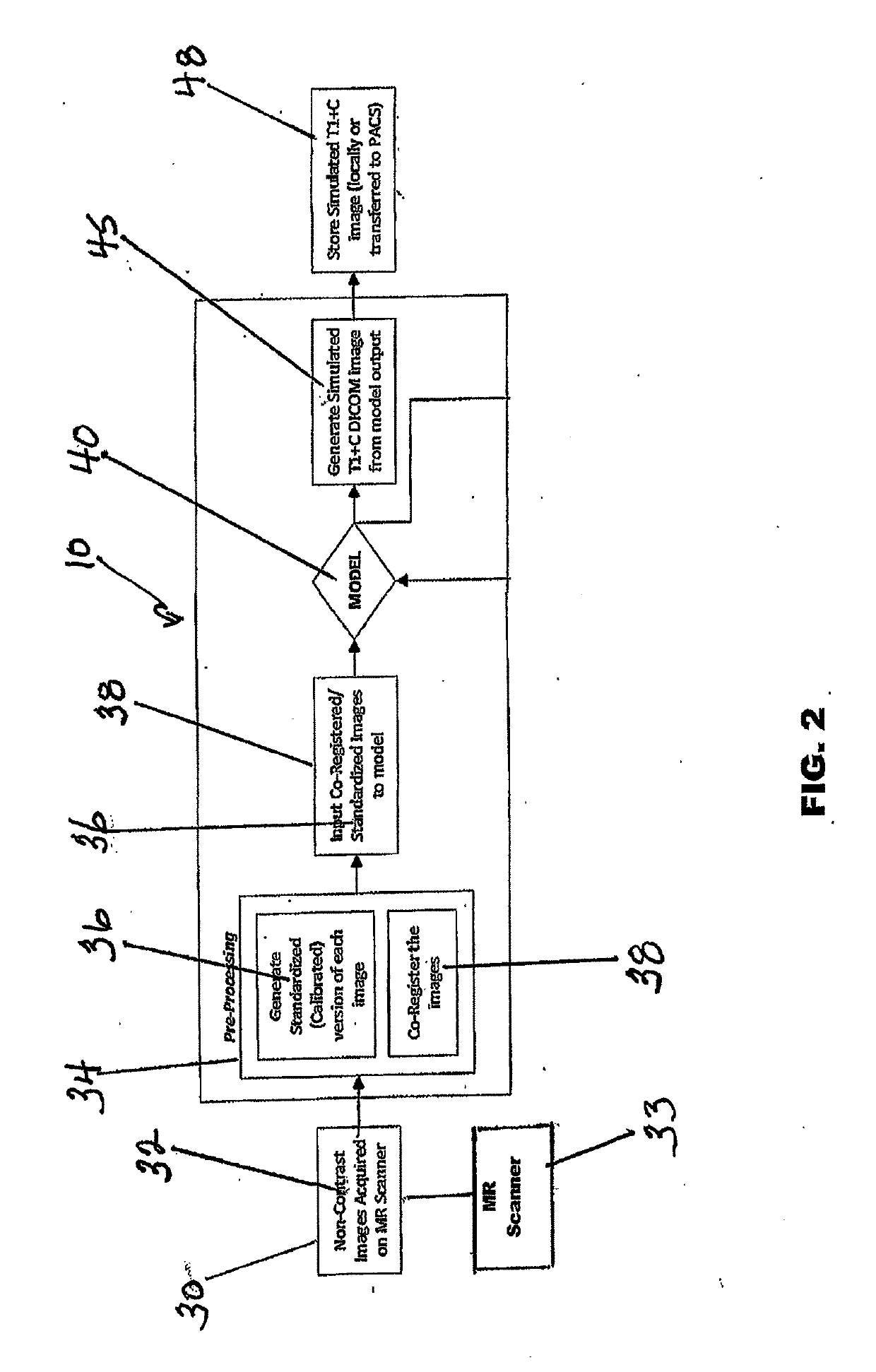
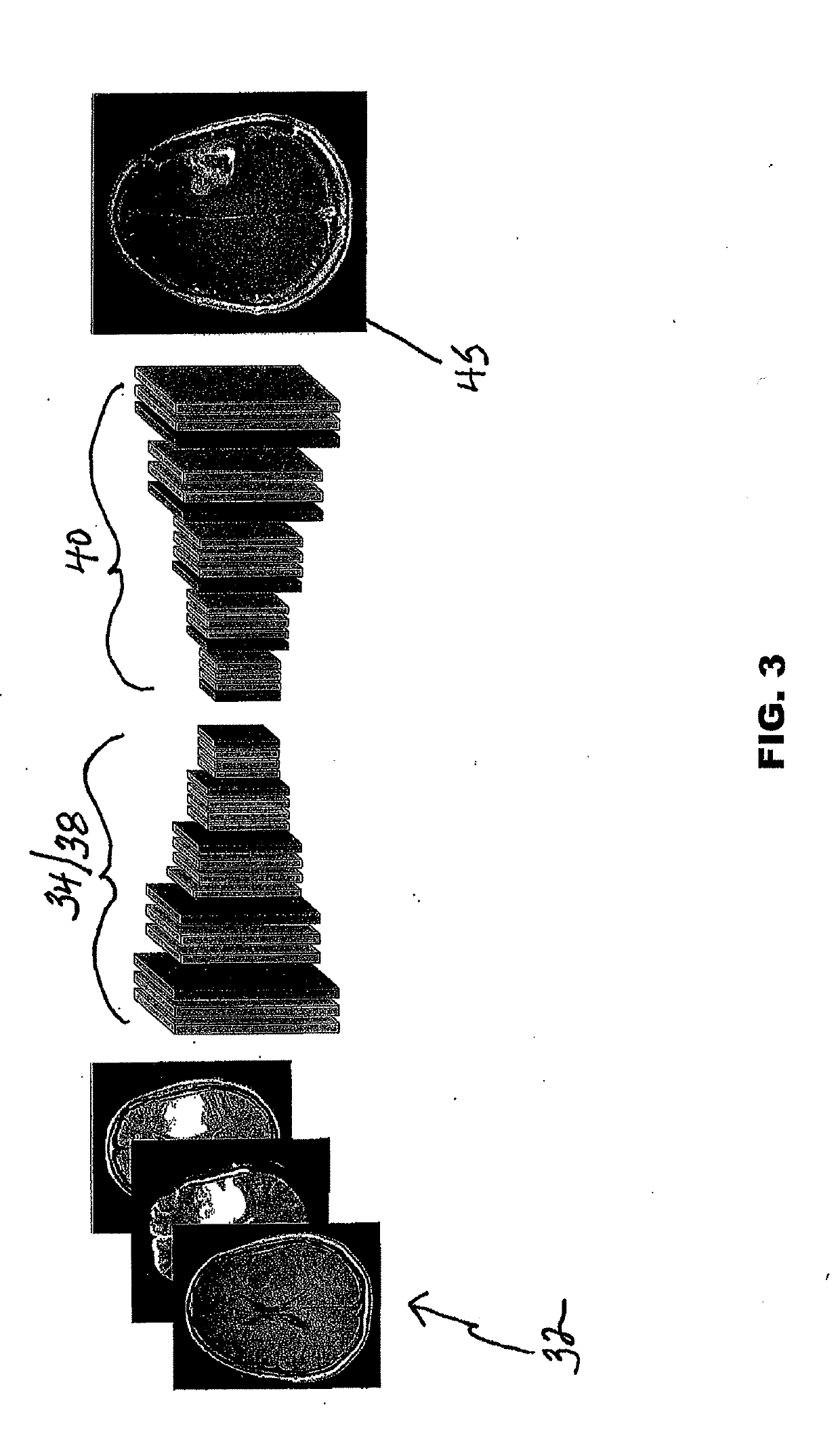
Simulated Post-Contrast T1-Weighted Magnetic Resonance Imaging
ActiveUS20190122348A1Eliminates common operationalEliminate errorsMedical simulationImage enhancementDiffusionInversion recovery
A system and method for generating simulated post-contrast T1-weighted magnetic resonance (MR) images without the use of exogenous contrast material based upon patient-specific non-contrast MR images using machine learning / artificial intelligence techniques to train the system to generate post-contrast T1-weighted magnetic resonance images based upon retrospectively collected non-contrast MR images of various sequence types including T1-weighted, T2-weighted, FLAIR (Fluid-Attenuated Inversion Recovery), and / or DWI (Diffusion-Weighted Imaging).
Owner:IMAGING BIOMETRICS
Magnetic nanoparticle, and preparation method and application thereof
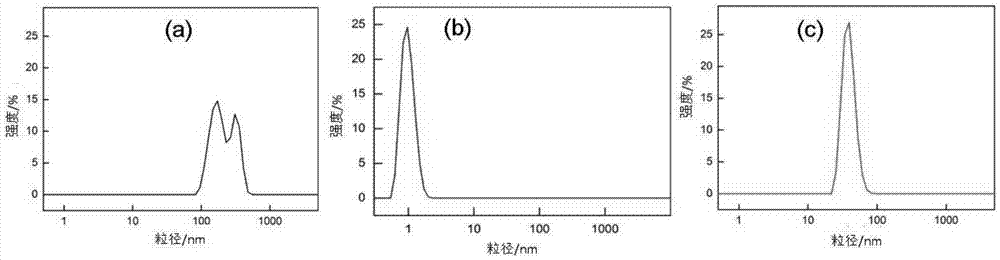
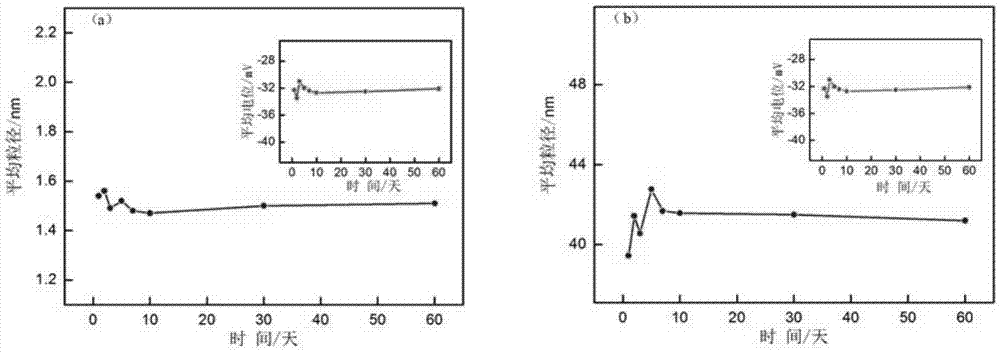
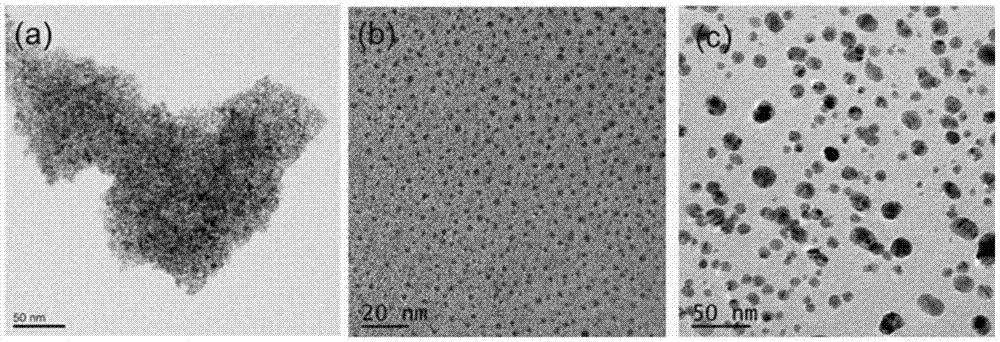
ActiveCN106913885ASmall particle sizeConcentrated particle size distributionInorganic non-active ingredientsEmulsion deliveryDiseaseMRI contrast agent
The invention relates to a magnetic nanoparticle, and a preparation method and application thereof. Specifically, the magnetic nanoparticle has the characteristics that 1) the magnetic nanoparticle is ferrite; 2) the magnetic nanoparticle has a particle size of 0.1 to 30 nm; 3) the relaxation rate r1 of the magnetic nanoparticle is no less than 1.2 m / M / s; 4) a ratio of a relaxation rate r2 to the relaxation rate r1 of the magnetic nanoparticle is no more than 3.5 and no less than 1.05; and 5) the T1 weighted signal intensity of 0.5mM of the magnetic nanoparticle is no less than 70. The invention also discloses the preparation method and application of the magnetic nanoparticle. When the magnetic nanoparticle is applied to magnetic resonance imaging, a high-quality MRI contrast agent with substantial and excellent imaging performance, high magnetosensitivity and rich T1 signals can be obtained, and the MRI contrast agent is improved in discovery and detection of tumors, cardio-cerebrovascular diseases and other serious diseases, so medical detection and treatment cost can be substantially lowered.
Owner:NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Magnetic resonance imaging method and system
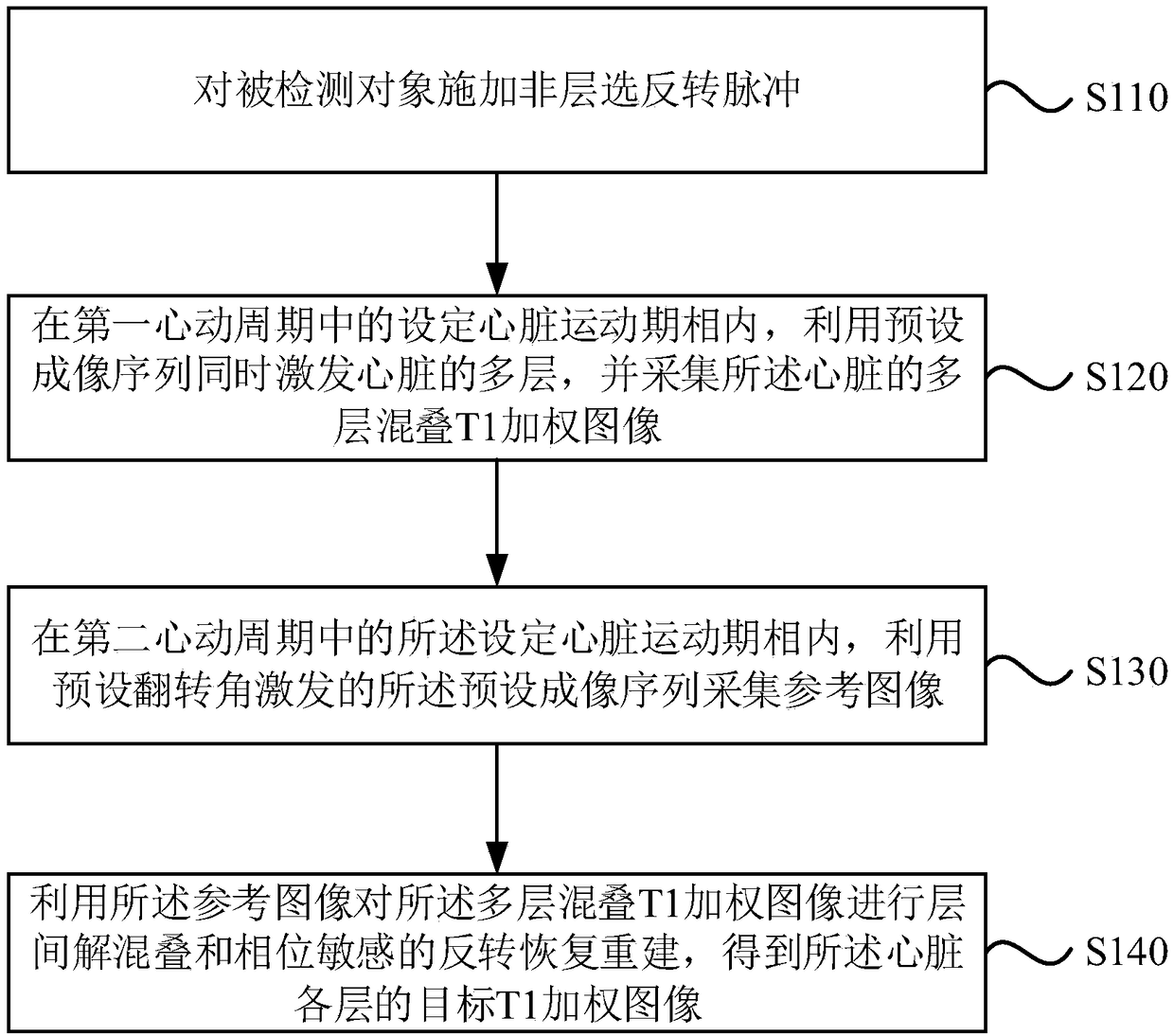
ActiveCN109507622AReduce the number of acquisitionsImprove data collection efficiencyDiagnostic recording/measuringMeasurements using NMR imaging systemsInversion recoveryImaging quality
Embodiments of the invention disclose a magnetic resonance imaging method and system. The method comprises the following steps: applying non-layering inverse pulses to a detected object; simultaneously stimulating multiple layers of a heart by using a preset imaging sequence in a set heart movement phase in a first heartbeat period, and acquiring a multilayer aliasing T1 weighted image of the heart; acquiring a reference image by using a preset imaging sequence stimulated by a preset overturning angle in a set heart movement phase in a second heartbeat period, wherein the first heartbeat period and the second heartbeat period correspond to a same breath-holding and are two adjacent heartbeat periods, and the reference image corresponds to one layer of the multiple layers; and performing the interlayer de-aliasing and phase-sensitive reverse restoration re-establishment for the multilayer aliasing T1 weighted image by using the reference image to obtain a target T1 weighted image of each layer of the heart. By virtue of the technical scheme, on the premise of ensuring the image quality, the magnetic resonance data acquisition efficiency can be improved.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
Imaging method and system applied to neurosurgery
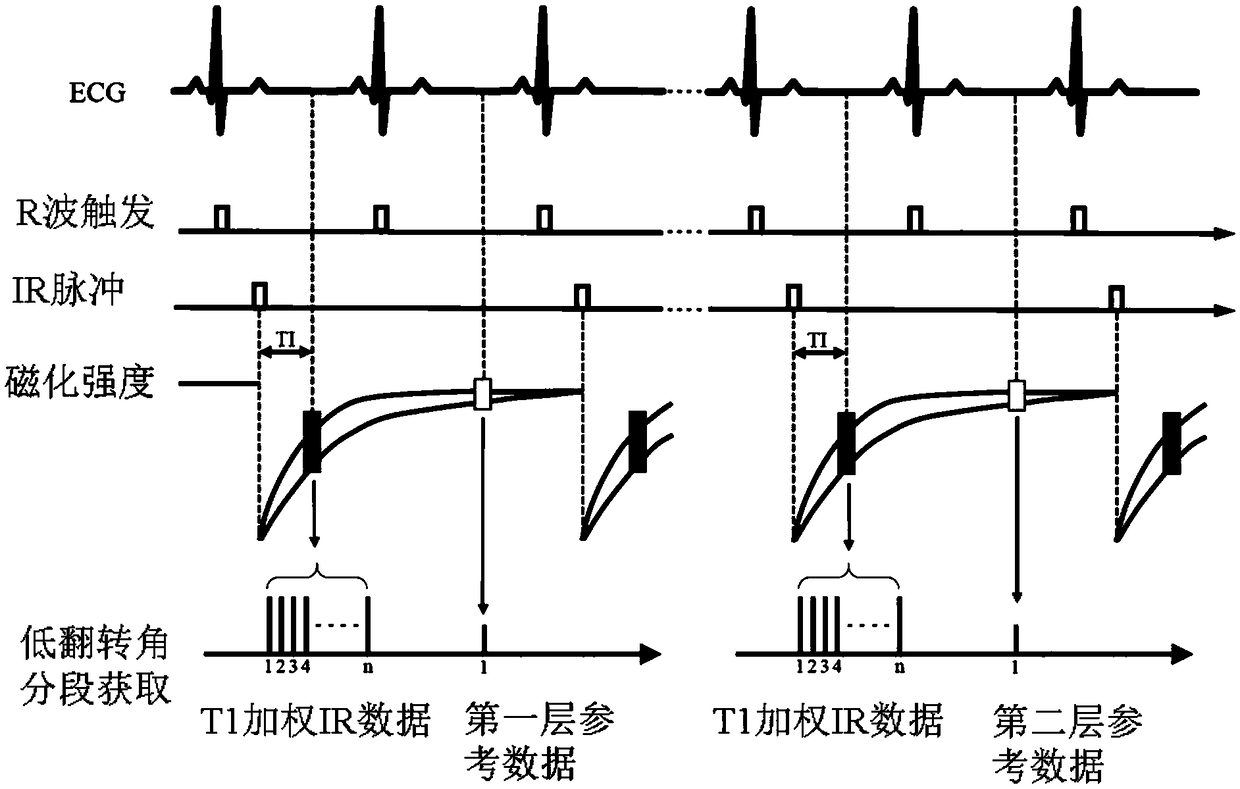
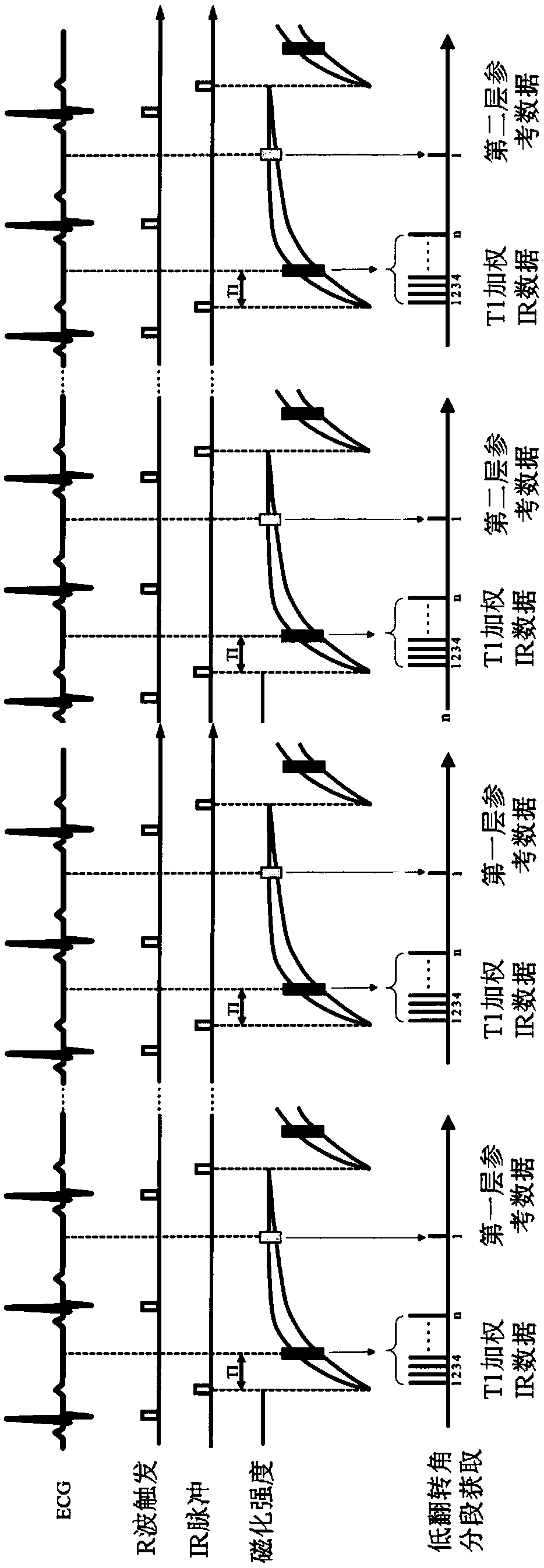
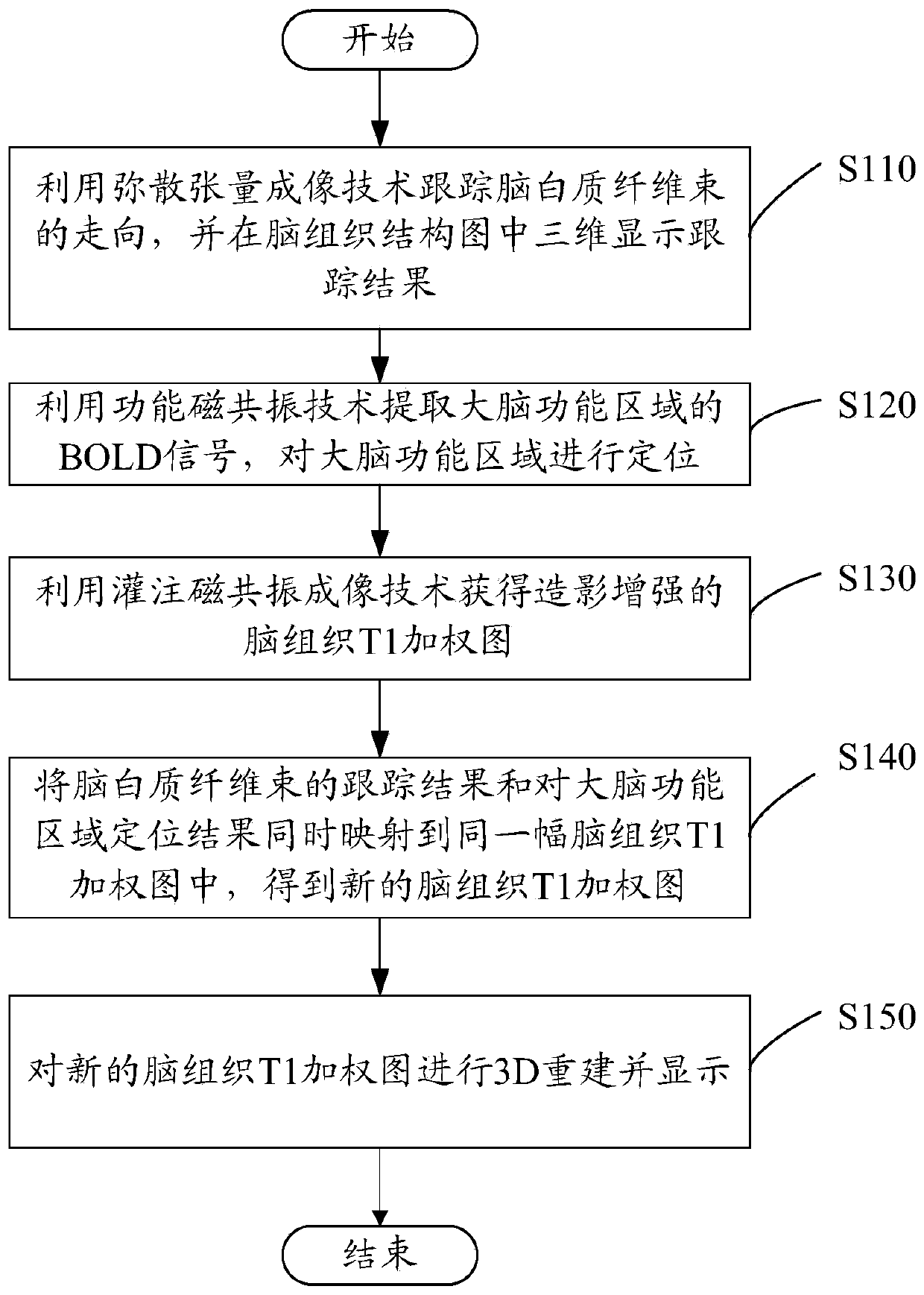
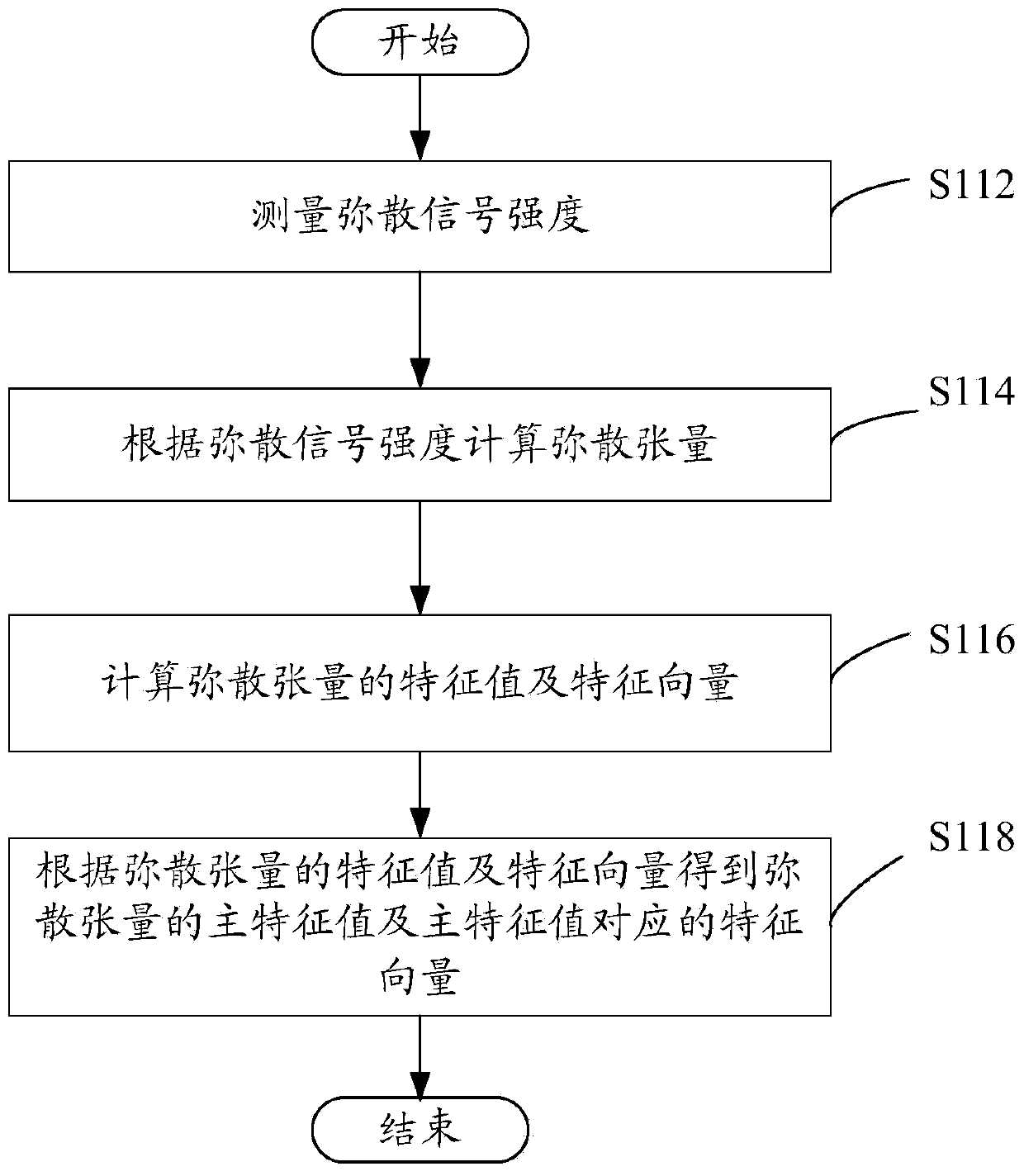
ActiveCN103462606AEasy to implementReflect the distributionMagnetic measurementsDiagnostic recording/measuringT1 weightedNeurosurgical Procedure
The invention relates to an imaging method applied to a neurosurgery. The method includes the following steps: utilizing a diffusion tensor imaging technology to track the moving trend of brain white matter fiber bundles, displaying a tracking result in a three-dimensional mode in a brain tissue structure graph, utilizing a functional magnetic resonance technology to extract BOLD signals in brain functional regions to locate the brain functional regions, utilizing a filling magnetic resonance imaging technology to obtain a brain tissue T1 weighted graph obtained through contract enhancement, and mapping the tracking result of the brain white matter fiber bundles and a location result of the brain functional regions into the same brain tissue T1 weighted graph simultaneously to obtain a new brain tissue T1 weighted graph. By means of the imaging method applied to the neurosurgery, the tracking result of the brain white matter fiber bundles and the location result of the brain functional regions are mapped into the same brain tissue T1 weighted graph simultaneously, and distribution conditions of the brain functional regions and the white matter fiber bundles connecting the functional regions can be reflected clearly and visually. In addition, an imaging system applied to the neurosurgery is further provided.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
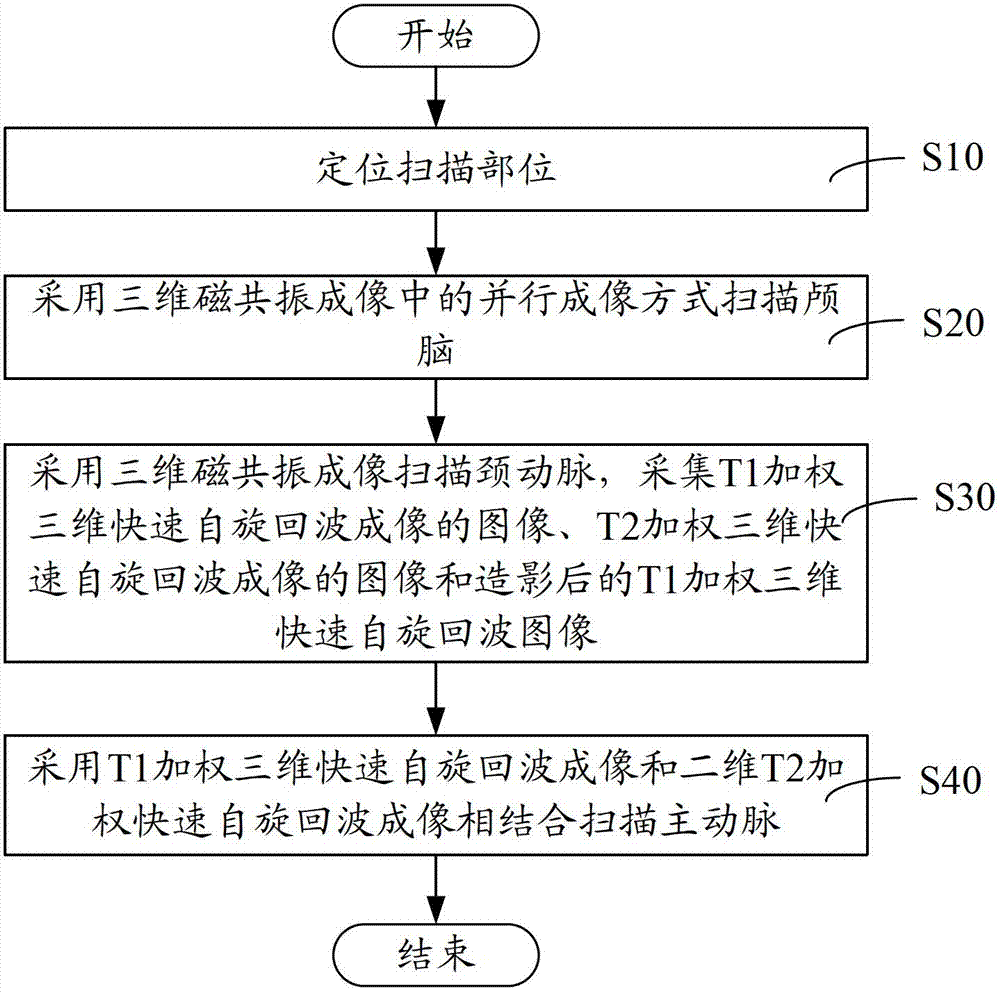
Brain, carotid artery and aorta three-in-one scanning method and scanning system
ActiveCN102727206AReduce scan timeImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringFast spin echoRapid imaging
The invention relates to a brain, carotid artery and aorta three-in-one scanning method, comprising the following steps of: positioning a scanning part; scanning a brain by utilizing parallel imaging of three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging; scanning a carotid artery by utilizing the three-dimensional magnetic resonance imaging and collecting a T1 weighted three-dimensional rapid spin echo imaged image, a T2 weighted three-dimensional rapid spin echo imaged image and a radiographed T1 weighted three-dimensional rapid spin echo image; and scanning a carotid artery by utilizing T1 weighted three-dimensional rapid spin echo imaging and T2 weighted three-dimensional rapid spin echo imaging which are combined. The brain, carotid artery and aorta three-in-one scanning method and system disclosed by the invention firstly adopt the steps of firstly positioning the scanning part and directly scanning the brain, the carotid artery and the aorta; the positioning and the scanning do not need to be repeated so that the scanning time is shortened; the brain is scanned by using a rapid imaging method by parallel imaging so that the scanning time is reduced; and three-dimensional T1 weighted imaging and two-dimensional T2 weighted imaging are combined to scan the carotid artery so that the scanning time is further shortened.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNITED IMAGING HEALTHCARE
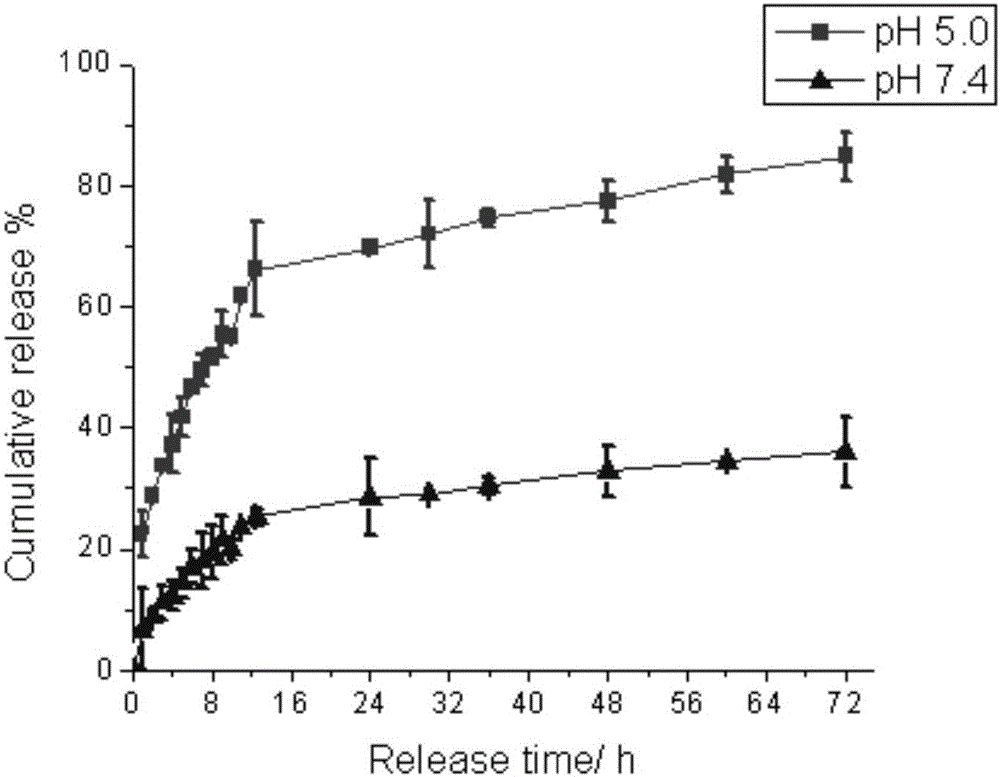
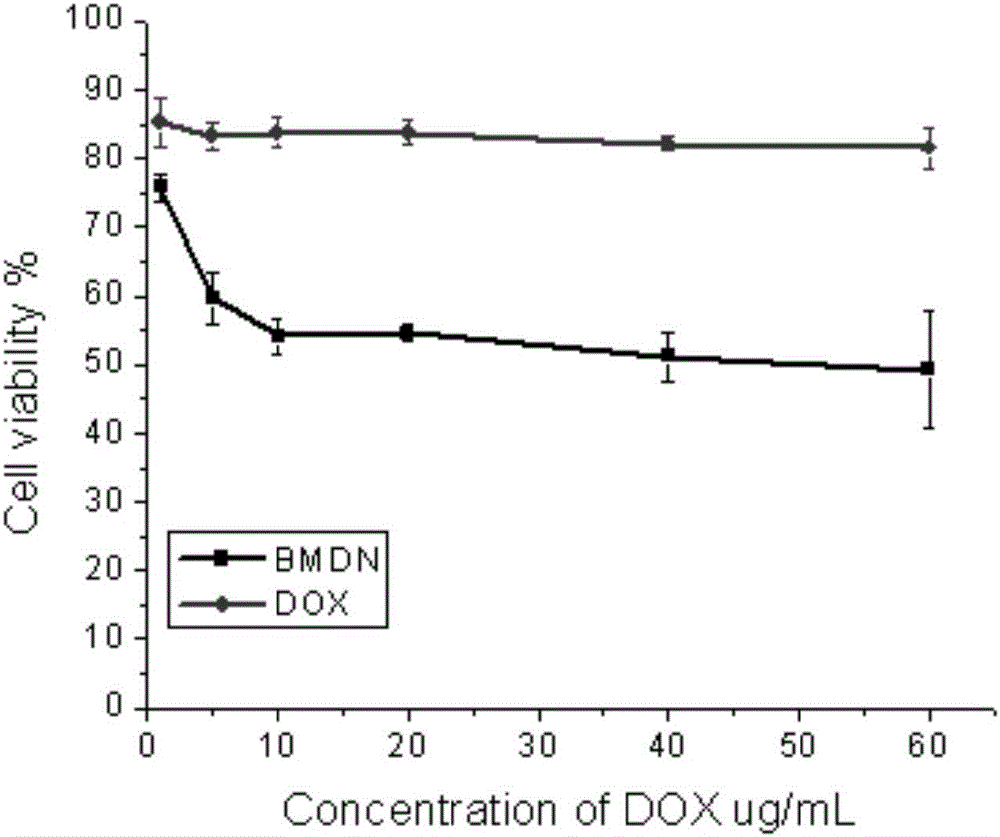
Albumin nanoparticles realizing co-delivery of antitumor drug and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) contrast medium and preparation method of albumin nanoparticles
ActiveCN105879045AAchieve releaseRealize the combination of diagnosis and treatmentOrganic active ingredientsPowder deliveryMRI contrast agentT1 weighted
The invention discloses albumin nanoparticles realizing co-delivery of an antitumor drug and an MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) contrast medium and a preparation method of the albumin nanoparticles and further provides an albumin nanoparticle vector containing the MRI contrast medium, and drug loading is realized through electrostatic adsorption and coordination between the drug and the vector as well as crosslinking of amino acid residues of the vector. The invention further discloses an optimal preparation technology of the albumin nanoparticles realizing co-delivery of the antitumor drug and the MRI contrast medium and a function of the albumin nanoparticles in diagnosis and treatment combination of tumors. According to the albumin nanoparticles realizing co-delivery of the antitumor drug and the MRI contrast medium, the drug uptake ratio of cells can be increased, and drug efflux caused by drug-resistant cells is reduced, so that drug resistance is reversed, and efficient delivery of the drug is realized; the albumin nanoparticles realizing co-delivery of the antitumor drug and the MRI contrast medium have excellent T1 weighted imaging capability and an effective means is provided for the diagnosis and treatment combination of the tumors.
Owner:CHINA PHARM UNIV
Method and system for automatically extracting magnetic resonance image corpus callosum
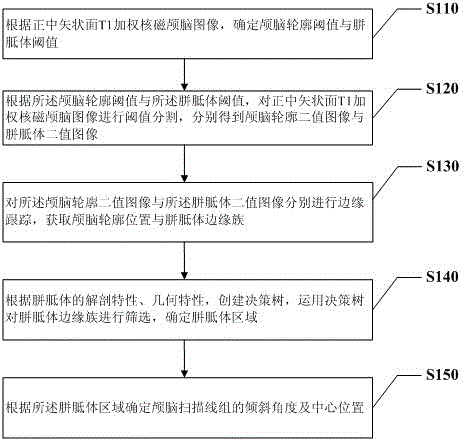
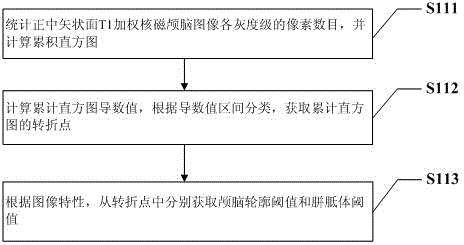
ActiveCN104083170ARealize automatic adjustmentImprove scanning efficiencyImage analysisDiagnostic recording/measuringDecision takingT1 weighted
The invention discloses a method and system for automatically extracting the extracting magnetic resonance image corpus callosum. The method comprises the steps of according to a midsagittal plane T1 weighted nuclear magnetism brain image, determining a brain outline threshold value and a corpus callosum threshold value; performing threshold segmentation on the image according to the brain outline threshold value and the corpus callosum threshold value to respectively obtain a brain outline binary image and a corpus callosum binary image; respectively performing margin tracing on the brain outline binary image and the corpus callosum binary image to acquire a brain outline position and a corpus callosum margin cluster; establishing a decision tree, and screening marginal information to determine a corpus callosum region; determining an angle of inclination and a central position of a brain scanning line set according to the corpus callosum region. By means of the method and system, the corpus callosum in the midsagittal plane T1 weighted nuclear magnetism brain image can be extracted automatically, automatic regulation of the scanning line set during brain scanning can be completed according to information on the corpus callosum and the like, scanning efficiency is increased, no manual regulation is needed, time and labor are saved, an strong practicability is achieved.
Owner:SHENZHEN ANKE HIGH TECH CO LTD
Image segmentation method, image segmentation apparatus and electronic device
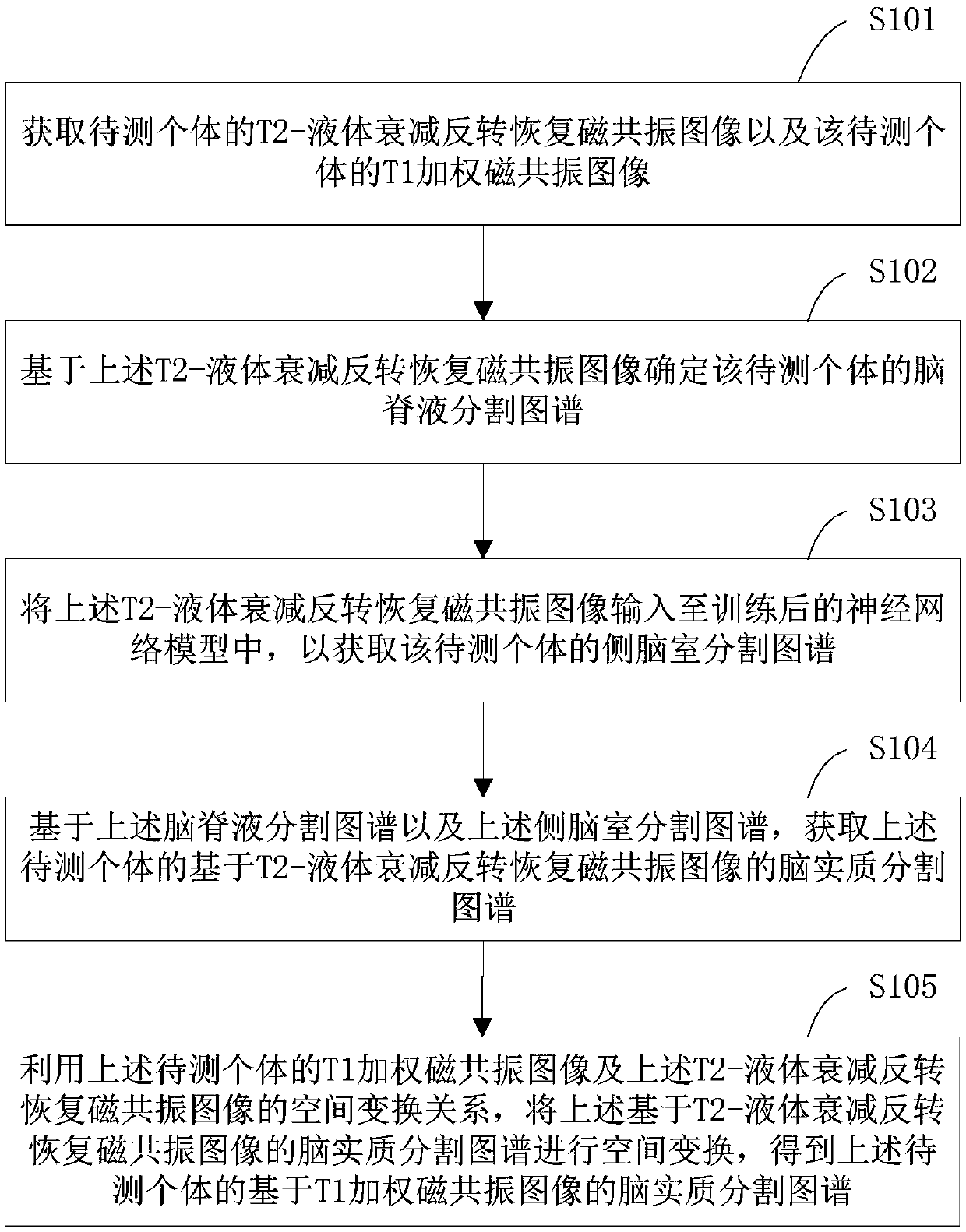
ActiveCN108765447AAccurate divisionAccurately Segment AtlasesImage enhancementImage analysisParenchymaInversion recovery
The invention provides an image segmentation method, an image segmentation apparatus and an electronic device. The method comprises the steps of acquiring a T2-fluid attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance image and a T1 weighted magnetic resonance image of a to-be-tested individual; based on the T2-fluid attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance image, determining a cerebrospinalfluid segmentation graph; inputting the T2-fluid attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance image to a neural network model, thereby obtaining a lateral ventricle segmentation graph; on the basis of the cerebrospinal fluid segmentation graph and the lateral ventricle segmentation graph, obtaining a brain parenchyma segmentation graph based o the T2-fluid attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance image; and by utilizing a spatial conversion relationship between the T1 weighted magnetic resonance image and the T2-fluid attenuated inversion recovery magnetic resonance image, obtaining a brain parenchyma segmentation graph based on the T1 weighted magnetic resonance image. According to the technical scheme, a cerebrospinal fluid part and a non-cerebrospinal fluid part can be moreaccurately divided, so that the more accurate brain parenchyma segmentation graphs can be obtained.
Owner:SHENZHEN BRAINNOW MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Turbospin echo imaging sequence with long echo trains and optimized T1 contrast
ActiveUS7639010B2Shorten the lengthMinimize impactMagnetic measurementsElectric/magnetic detectionResonanceT1 contrast
In a method in the form of a turbo spin echo imaging sequence with long echo trains and optimized T1 contrast for generation of T1-weighted images of an examination subject by magnetic resonance, magnetization in the examination subject is excited with an RF excitation pulse, a number N of RF refocusing pulses with variable flip angle are radiated to generate multiple spin echoes for an excitation pulse, a restoration pulse chain is activated after switching of the N refocusing pulses and before the next RF excitation pulse. The restoration pulse chain influences the magnetization such that the magnetization is aligned opposite to the direction of the basic magnetic field by the restoration pulse chain before the next RF excitation pulse.
Owner:SIEMENS HEALTHCARE GMBH
Double-functional nano-composite spheres based on metal ion-inducing polypeptide self-assembly and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN104758954ANo toxicityLower synthesis costEnergy modified materialsEmulsion deliveryCancer cellSynthesis methods
The invention discloses a double-functional nano-composite spheres based on metal ion-inducing polypeptide self-assembly and a preparation method thereof. In the invention, by means of a one-step reaction synthesis method, with [alpha]-lactalbumin hydrolyzed polypeptide as a carrier, the nano spheres are self-assembled under induction by Ca<2+> and Gd<3+> together, wherein the nano spheres, during self-assembly, are wrapped by a photosensitive agent, rose Bengal. The particle size of the nano-composite spheres can be adjusted and controlled in the range of 100-500 nm. The Gd<3+> which participates in the inductive sphere forming is used as a contrast medium unit of magnetic resonance imaging and the T1-weighted nuclear magnetic resonance signal response can be effectively increased so that the magnetic resonance imaging diagnosis to a tumor site can be performed. The rose Bengal wrapping the nano-composite spheres can release singlet oxygen to kill tumor cells under excitation illumination at 550 nm, thereby achieving the effect of photodynamic treatment. The nano-composite spheres are toxic-free without illumination. Meanwhile, the treatment process allows tracing through the magnetic resonance imaging. In addition, the nano-composite spheres are low in preparation cost, are simple in processes, and have a potential wide application prospect in the bio-medicinal field.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
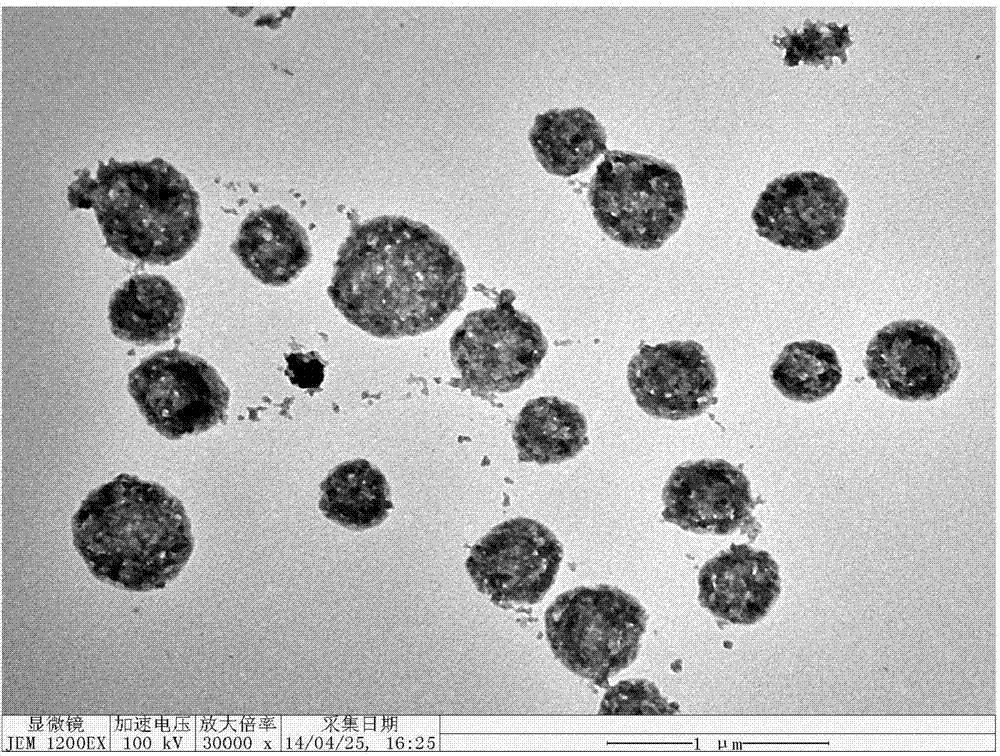
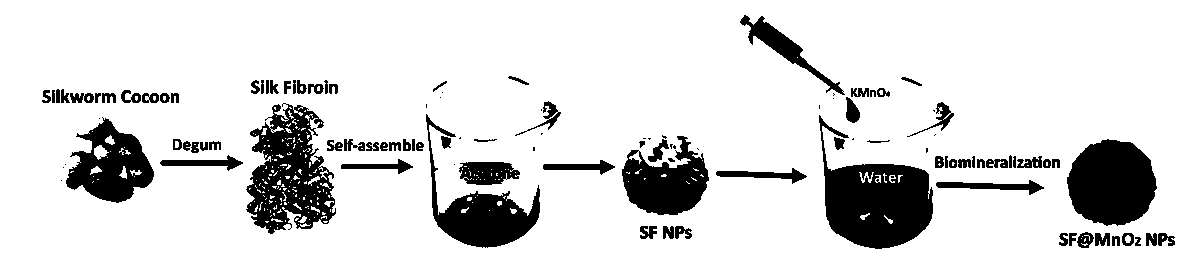
Preparation of silk fibroin nanoparticles coated with manganese dioxide
PendingCN110054697AHigh biosecurityExcellent photothermal performancePeptide preparation methodsCarrier-bound/immobilised peptidesT1 weightedCatalase
The invention relates to the field of synthesis of nanomaterials, in particular to a method for synthesizing silk fibroin nanoparticles and a method for rapidly and gently encapsulating manganese dioxide onto the surfaces of silk fibroin nanoparticles inspired by biomineralization. The method specifically includes the following steps: (1) silk fibroin extraction and silkworm cocoon degumming; (2)self-assembly of the silk fibroin nanoparticles in an acetone solution; (3) utilizing silk fibroin balls as both a template and a reducing agent to react with a potassium permanganate solution to produce manganese dioxide in situ on the surfaces of the silk fibroin nanoparticles. A resulting multifunctional nano platform has photothermal performances, drug delivery capabilities, catalytic activitysimilar to catalase and T1-weighted nuclear magnetic resonance imaging capabilities. The preparation has great potential for application in the fields of biomedicine and other areas of social economy.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
MRI detectable obturator
InactiveUS20080139925A1Prevents and minimizes backflowPreventing and minimizing entryMagnetic measurementsSurgeryProximateDistal portion
An obturator with an elongated shaft, a proximal end, a substantially closed distal end and a MRI detectable distal shaft portion, which does not interfere with magnetic resonance imaging of tissue proximate thereto. Preferably, the distal shaft portion has an effective MRI detectable mass so as to provide a clear, T1-weighted image within an outline of the distal shaft portion upon magnetic resonance imaging.
Owner:SENORX
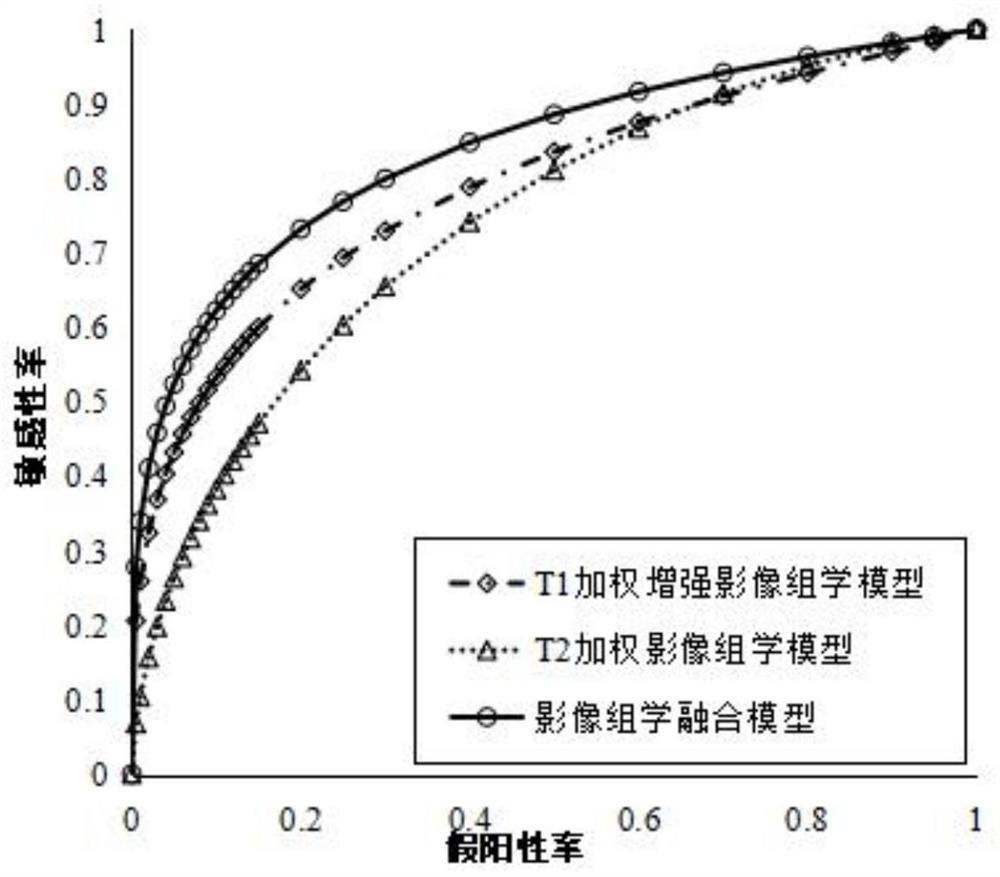
High-grade serous ovarian cancer recurrence risk prediction system based on imaging omics
ActiveCN111862079AAchieve early predictionEnable early detectionMedical simulationImage enhancementFeature extractionRadiology
The invention discloses a high-grade serous ovarian cancer recurrence risk prediction system based on imaging omics. A method comprises the steps of T1 weighted enhanced imaging omics processing, T2 weighted imaging omics processing and information fusion. The image omics processing mainly comprises the steps of three-dimensional tumor segmentation, image standardization, image omics feature extraction, feature normalization, feature screening, SMOTE resampling and classifier training; the information fusion is mainly used for fusing recurrence risk prediction probabilities output by T1 and T2image omics processing, so the risk prediction accuracy is further improved.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV SHANGHAI CANCER CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com