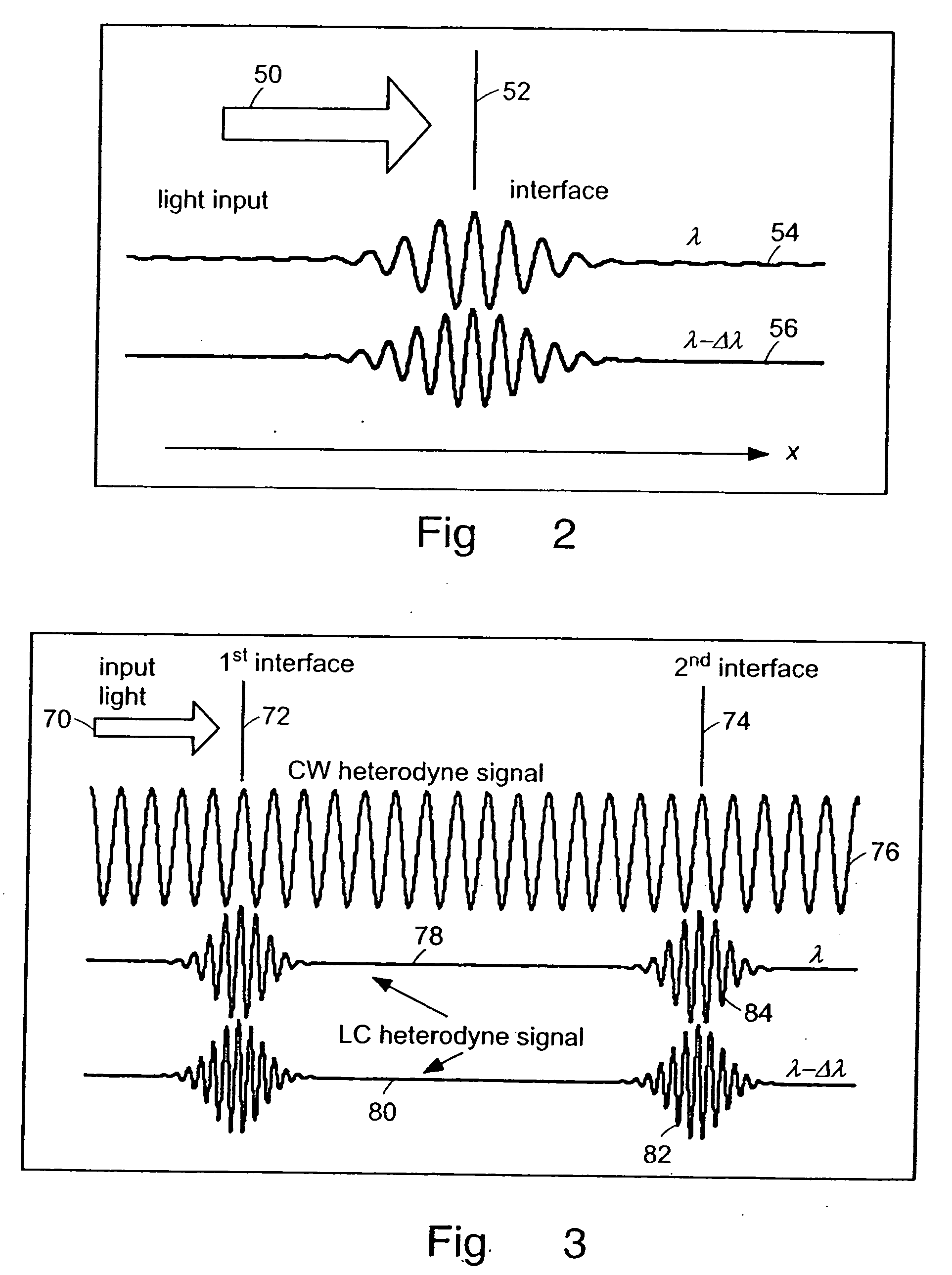
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
13657 results about "Performed Imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
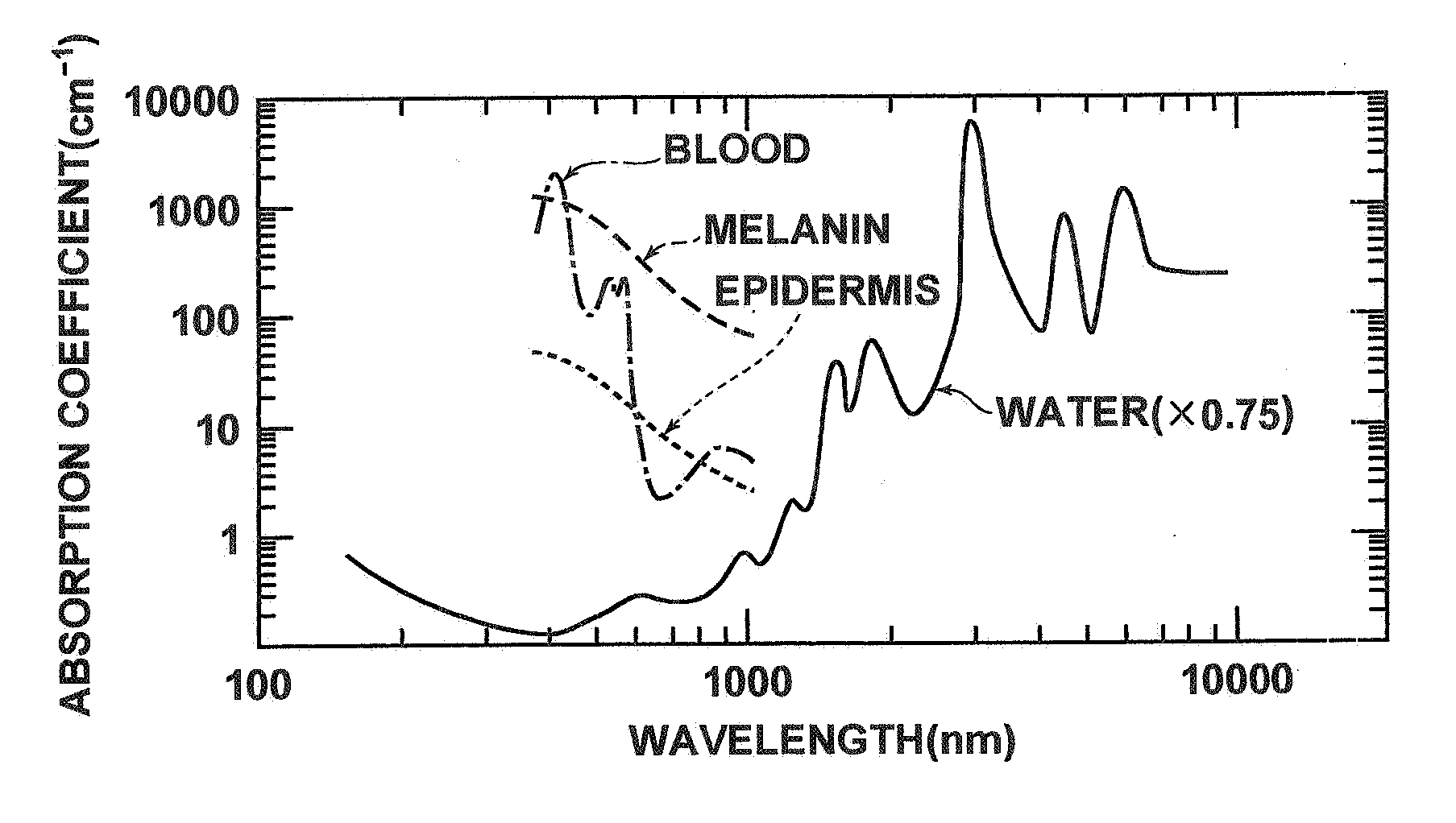
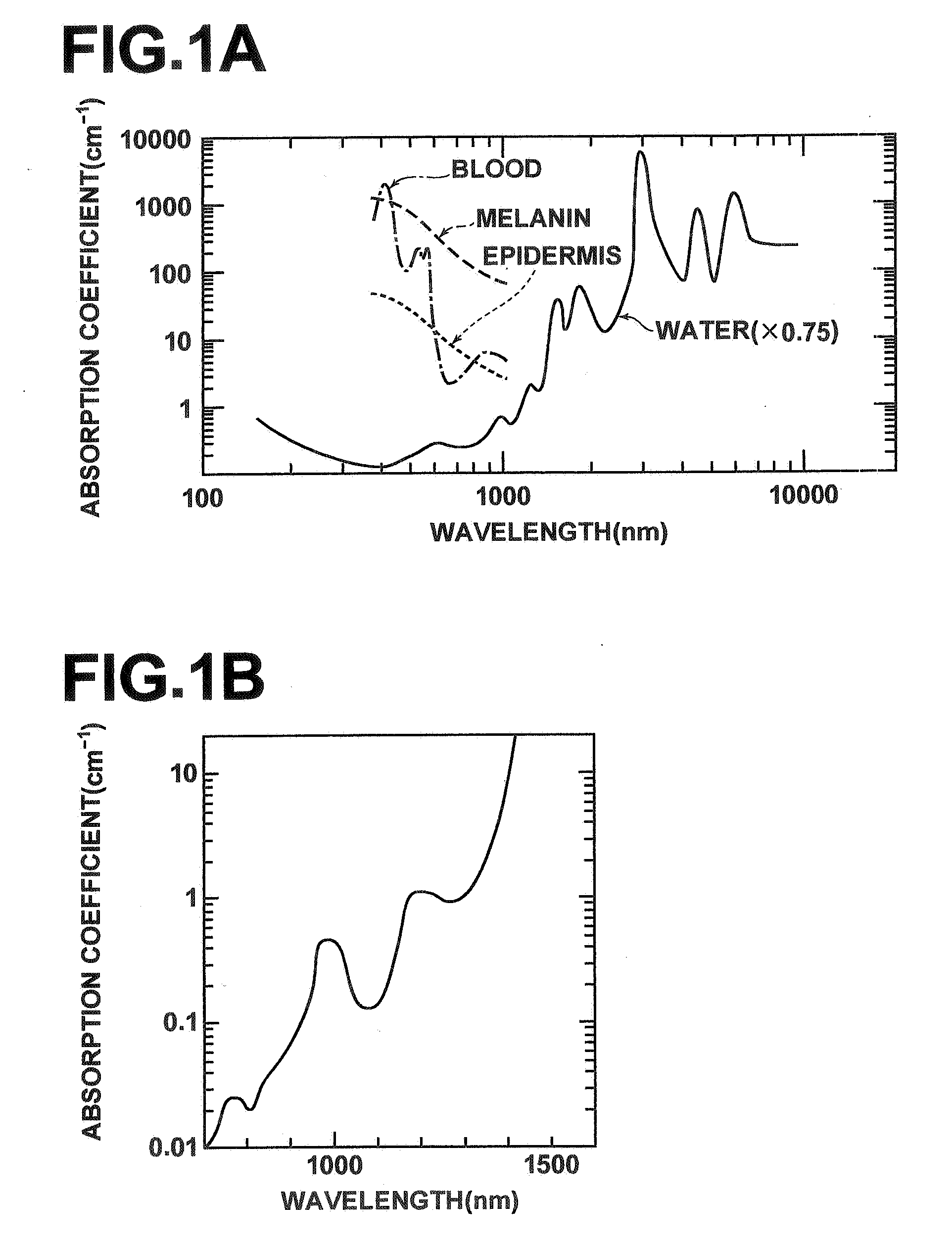
The completed action of obtaining pictures of the interior or exterior of the body usually for diagnostic reasons. EXAMPLE(S): X-ray, MRI, etc
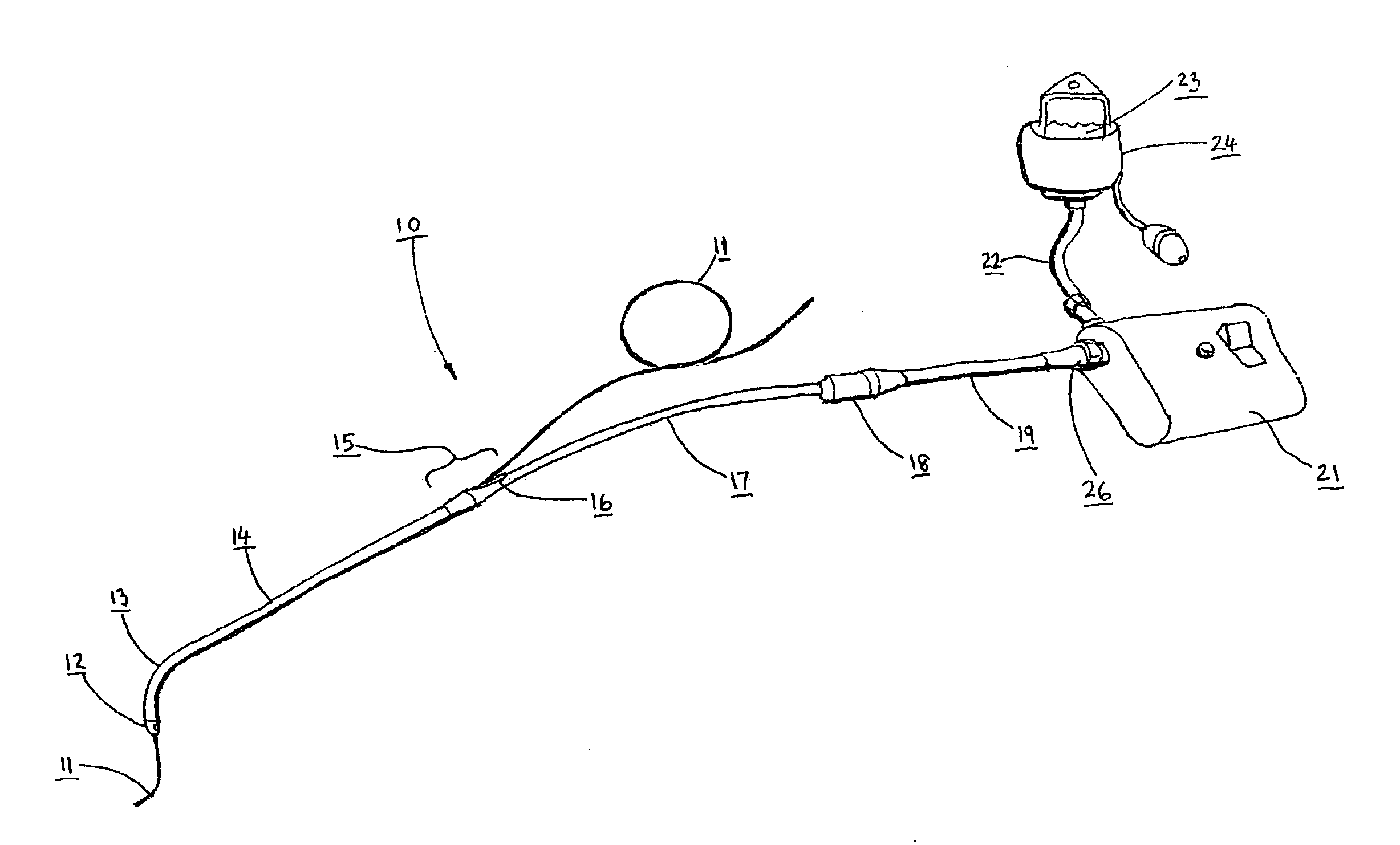
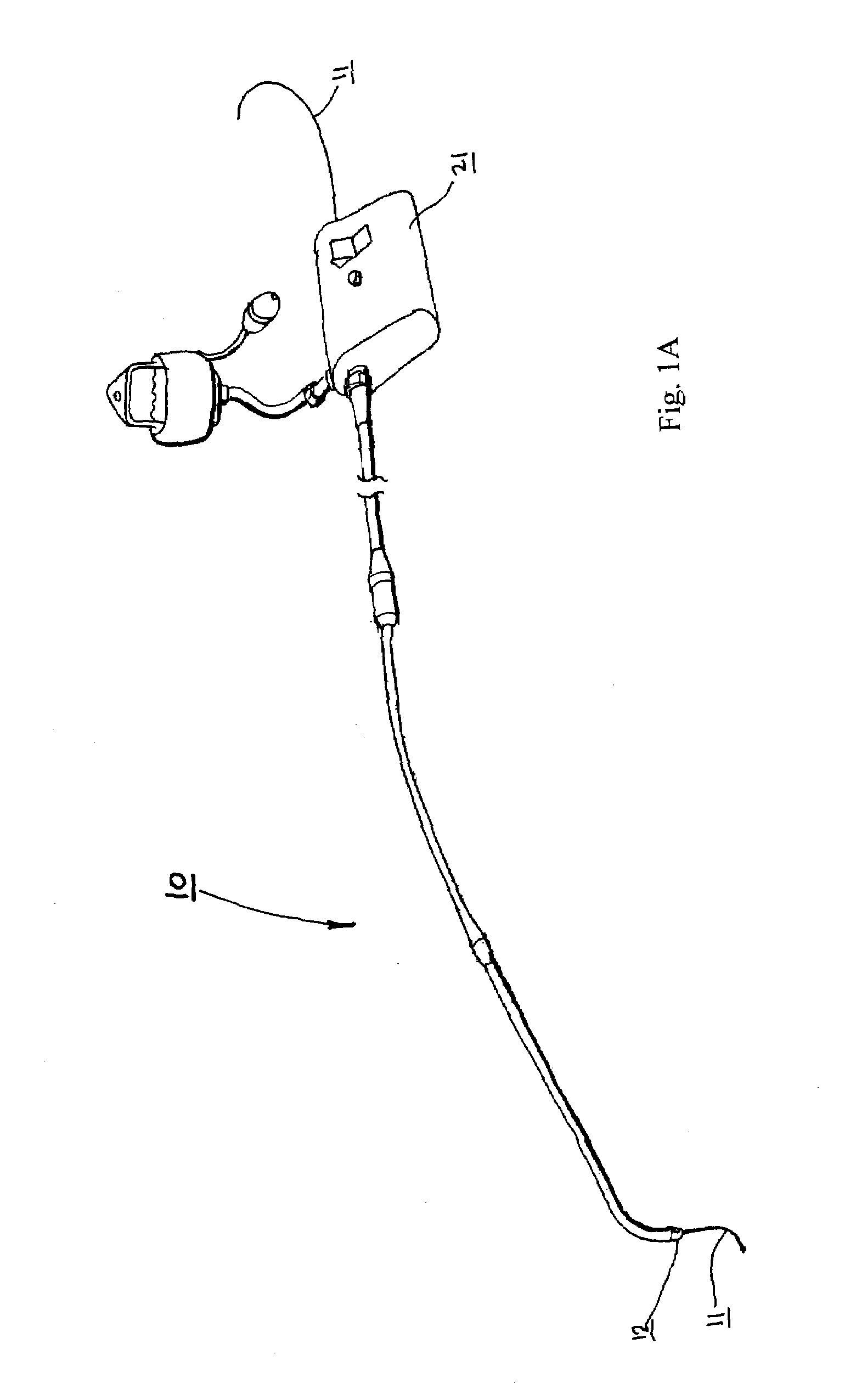
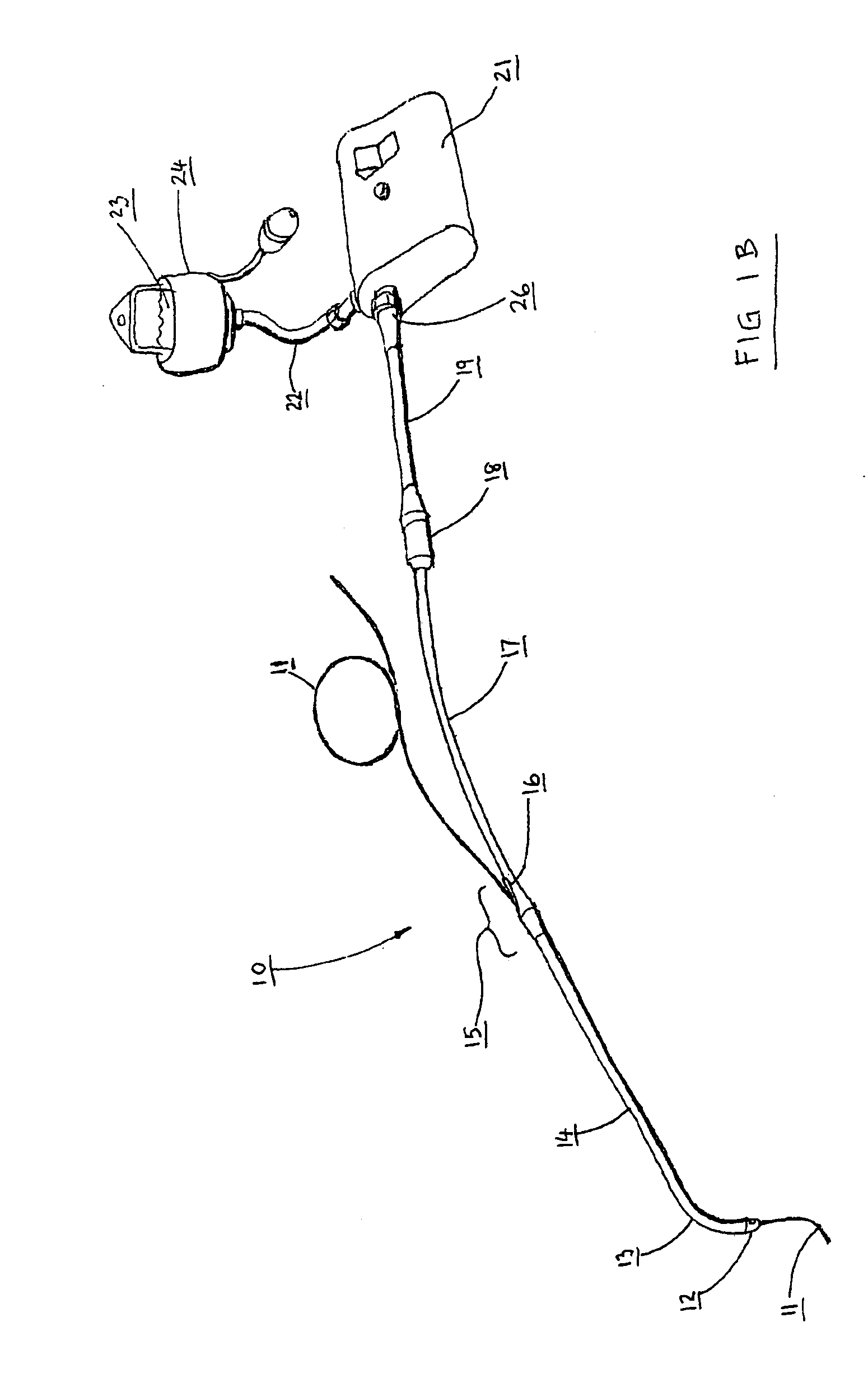
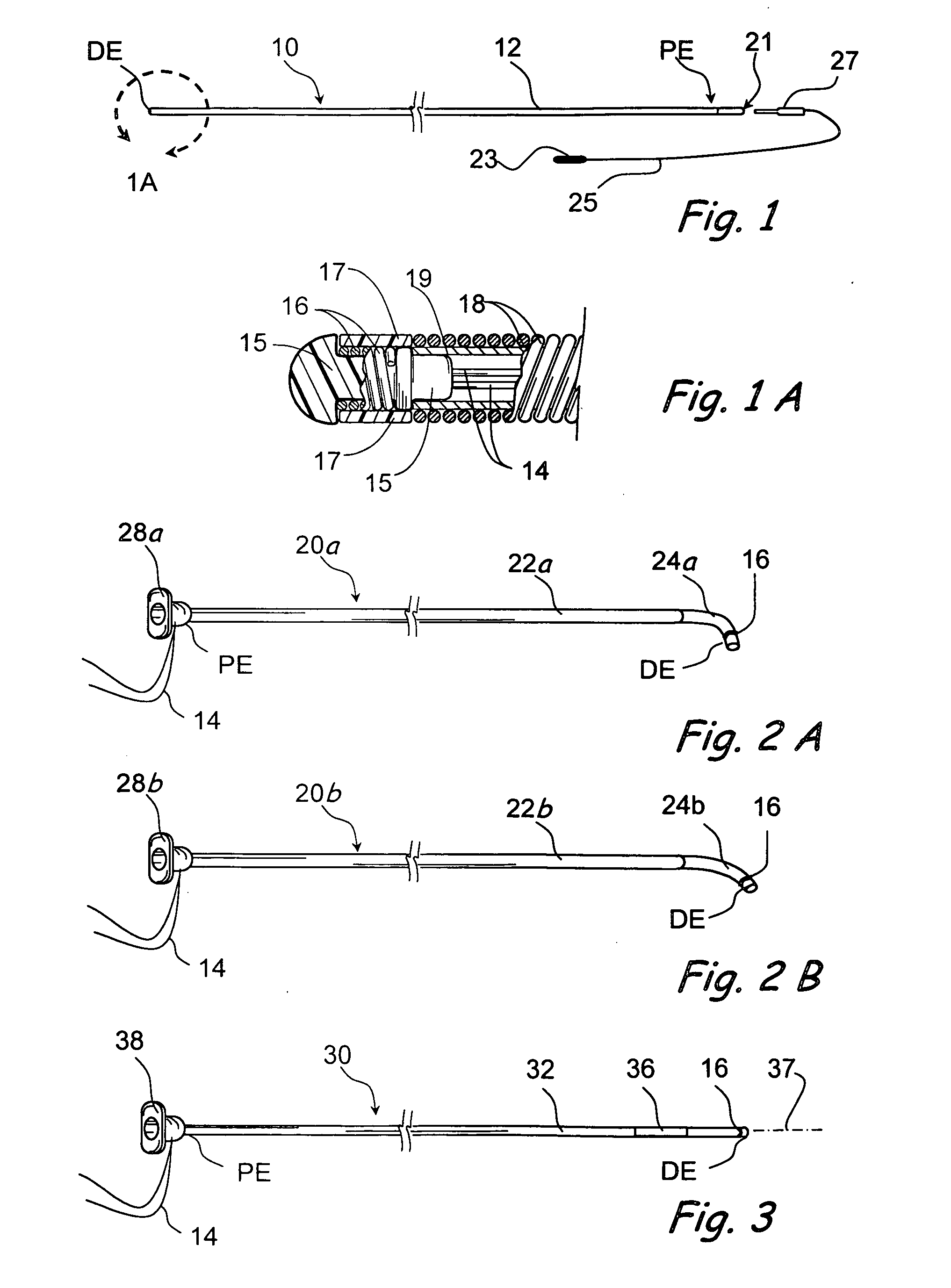
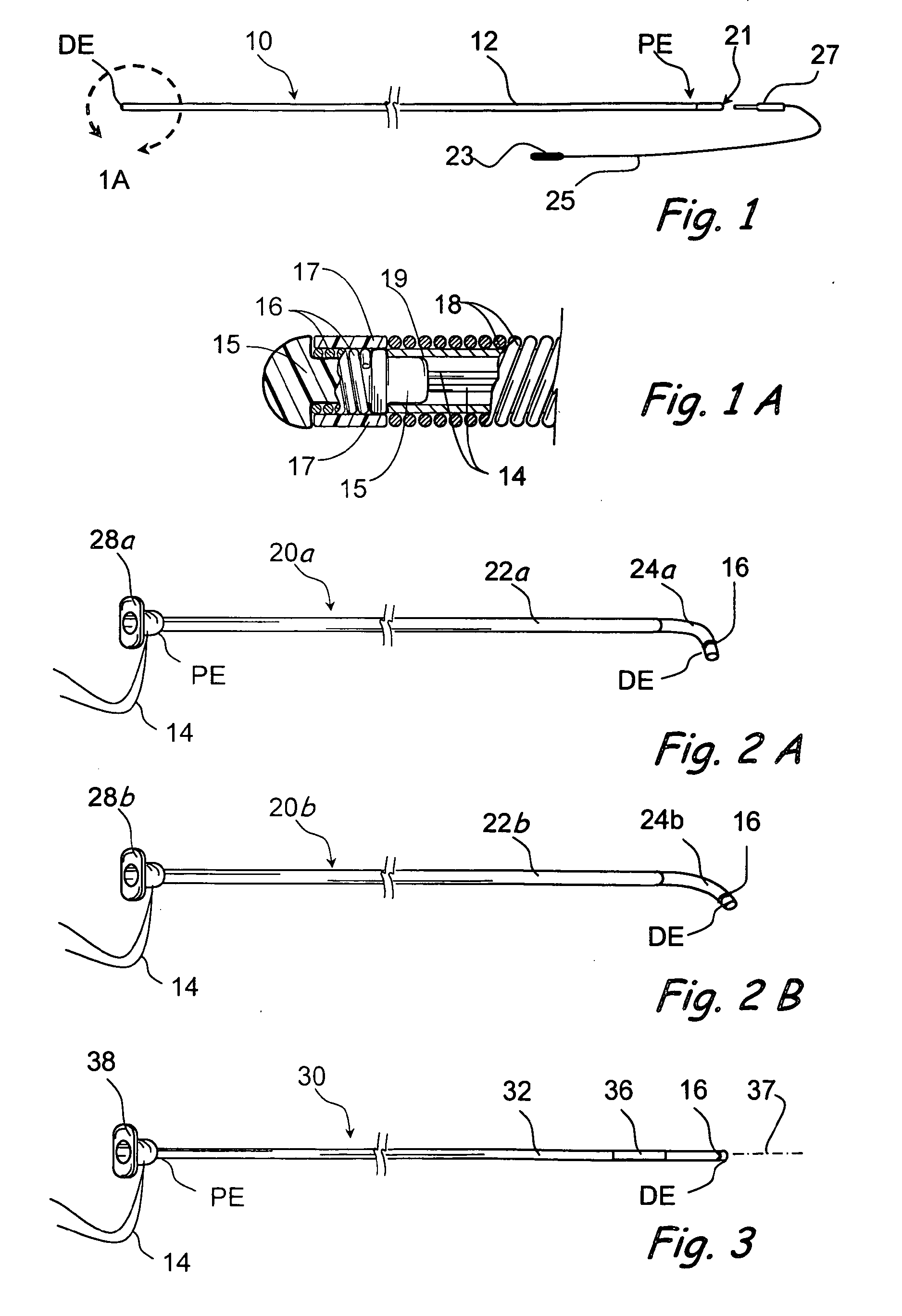
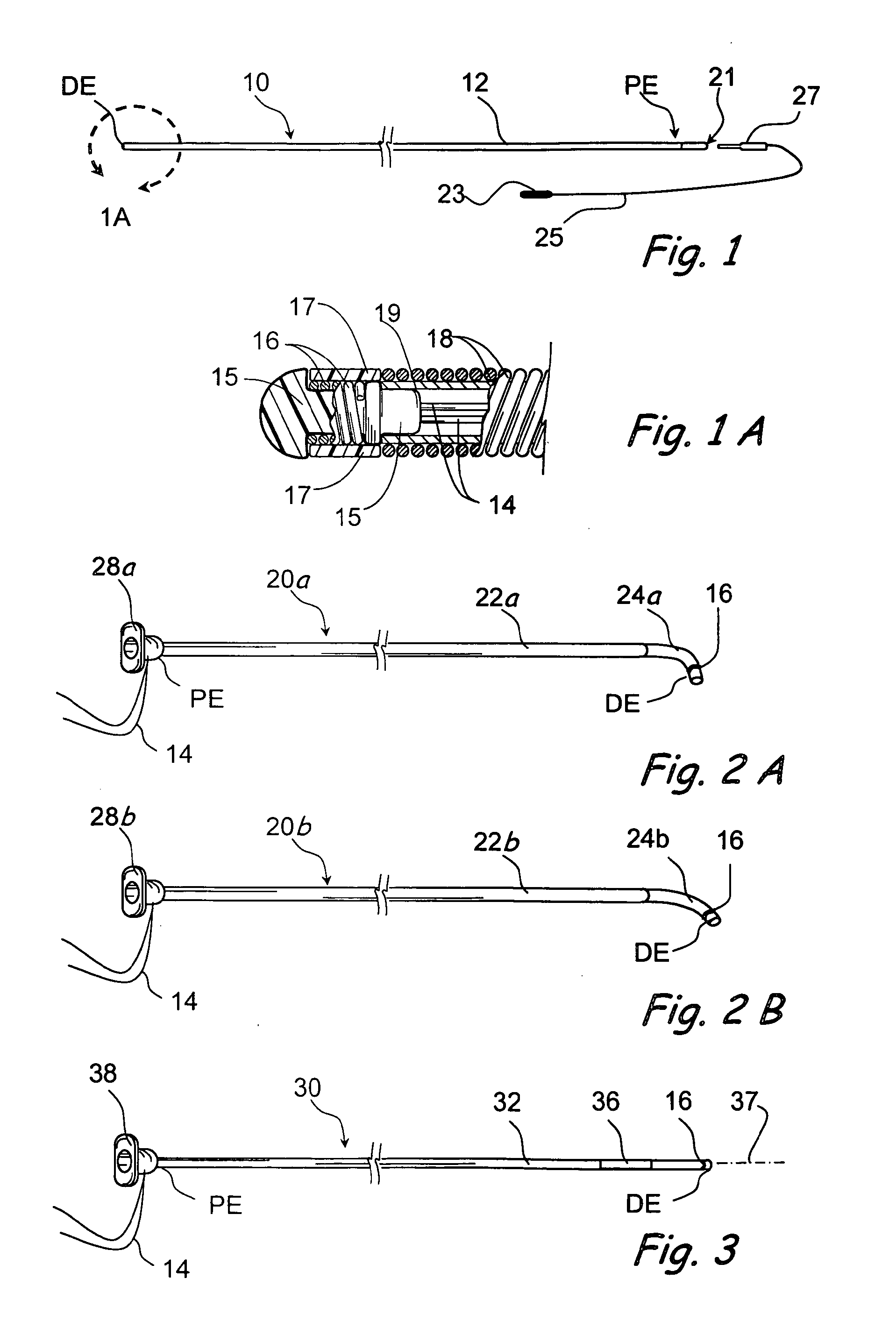
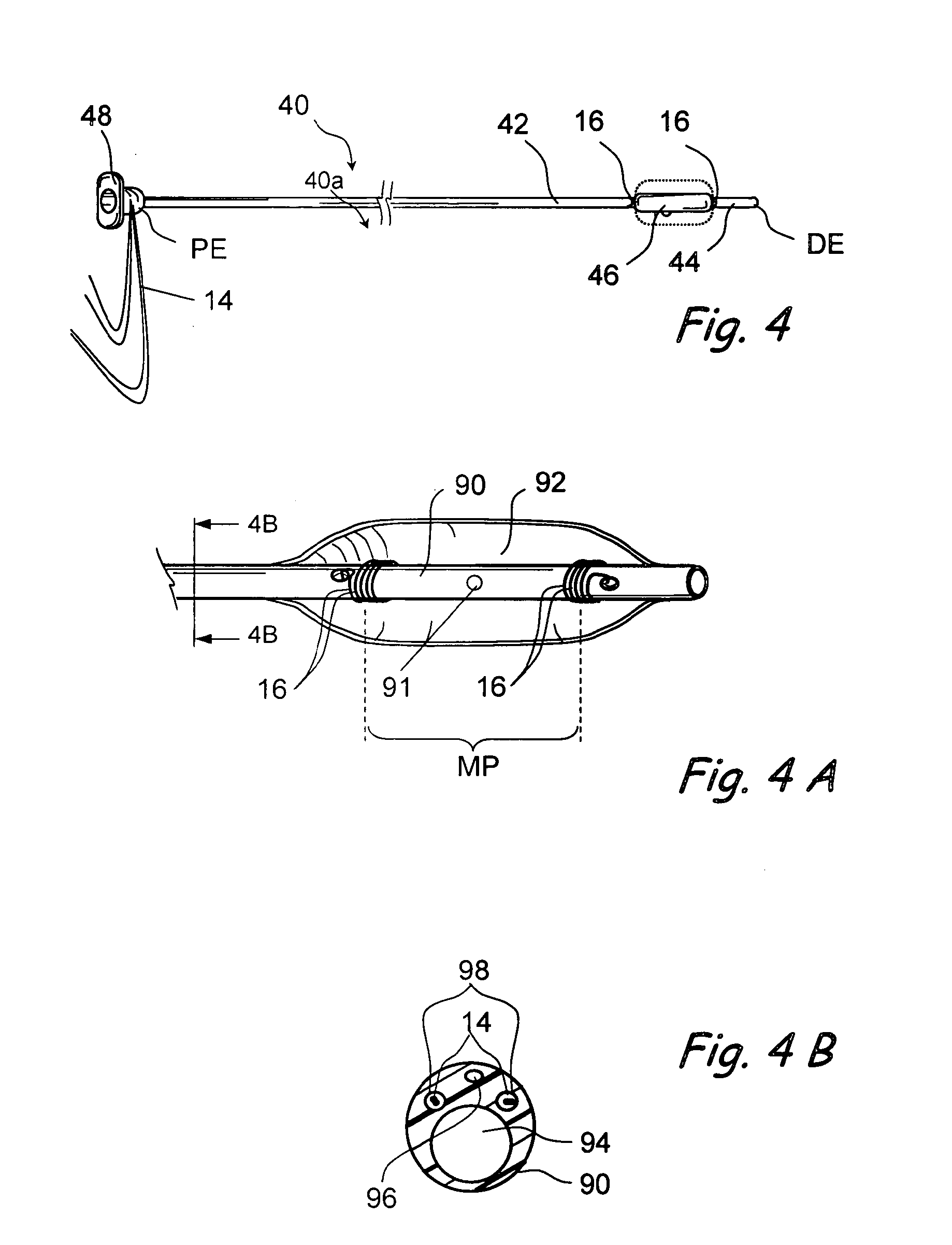
Catheter for conducting a procedure within a lumen, duct or organ of a living being
In an embodiment, the invention provides a catheter suitable for use in performing a procedure within a vessel, lumen or organ of a living having a distal end which is steerable, such as upon the application of compression. The catheter may be of the over the wire type, or alternatively may be a rapid exchange catheter. The catheter may provide for a rotating element which may be used to open a clogged vessel, or alternatively to provide information about adjacent tissues, such as may be generated by imaging or guiding arrangements using tissue detection systems known in the art, e.g., ultrasound, optical coherence reflectometry, etc. For rapid exchange catheters having a rotating element, there is provided an offset drive assembly to allow the rotary force to be directed from alongside the guidewire to a location coaxial to and over the guidewire.
Owner:KENSEY NASH CORP
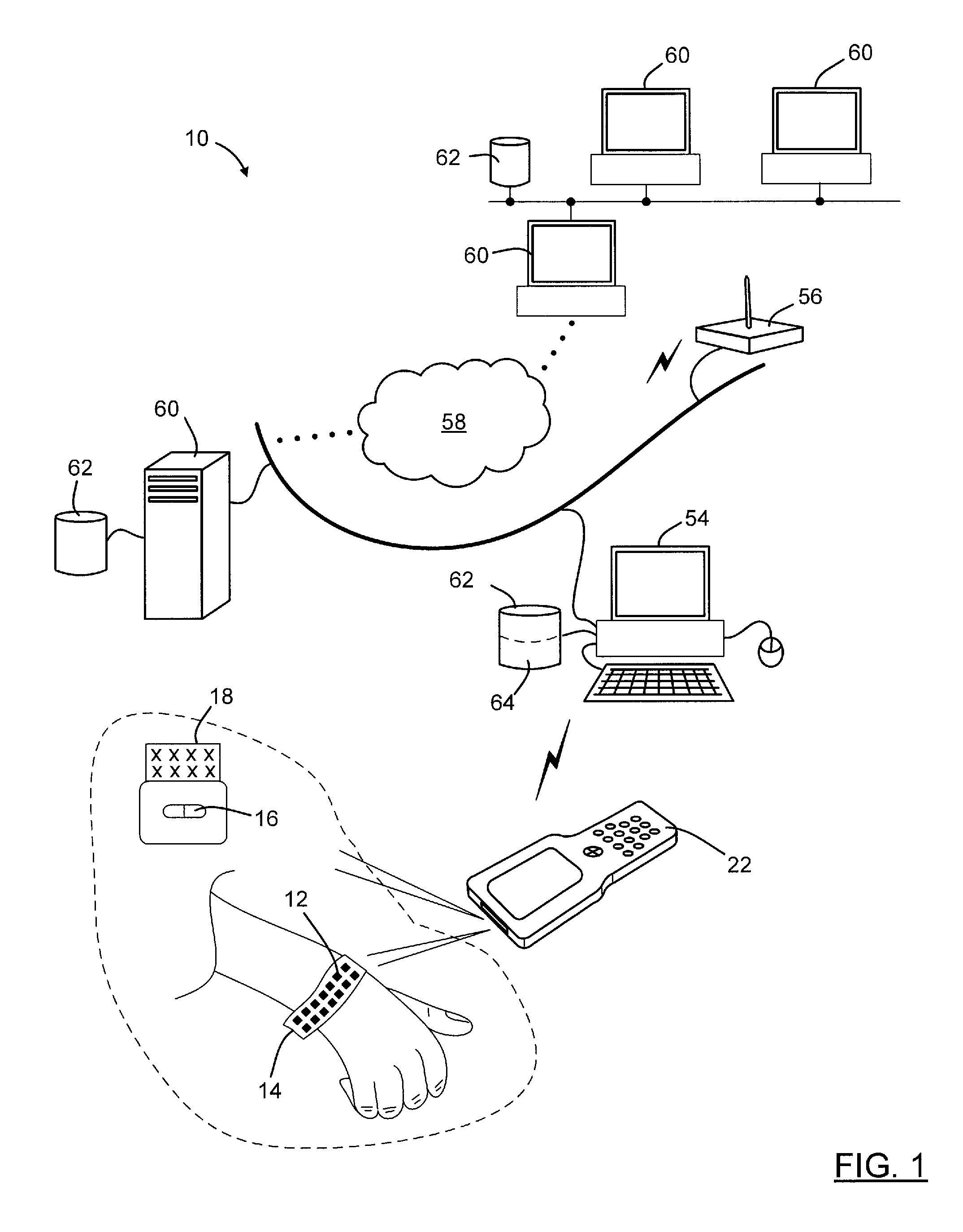
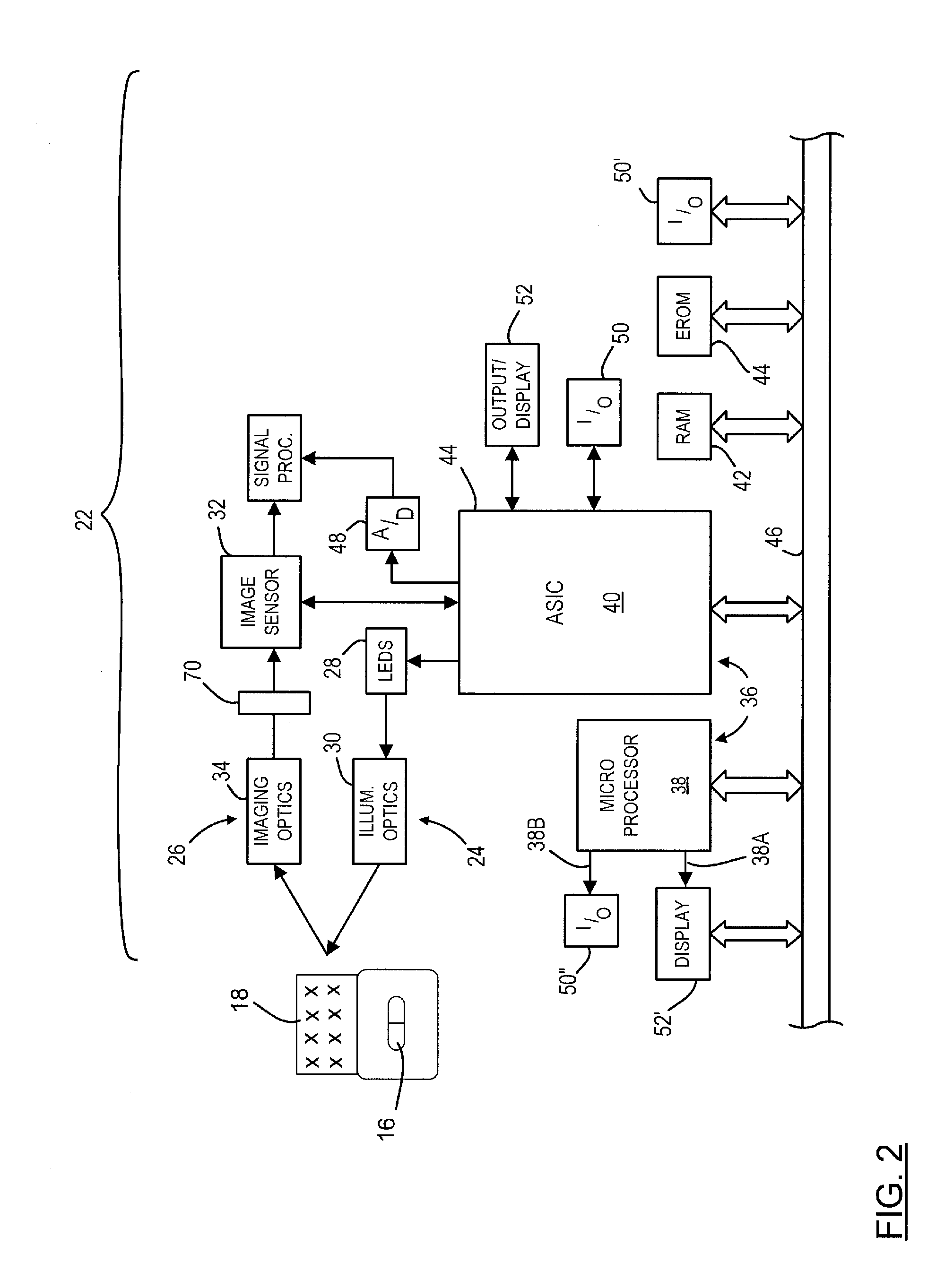
Optical imager and method for correlating a medication package with a patient
Owner:METROLOGIC INSTR
Contact printing using a magnified mask image
InactiveUS20050068639A1Avoid stickingPhotomechanical exposure apparatusMicrolithography exposure apparatusRefractive indexOff-axis illumination
Improvements in the fabrication of integrated circuits are driven by the decrease of the size of the features printed on the wafers. Current lithography techniques limits have been extended through the use of phase-shifting masks, off-axis illumination, and proximity effect correction. More recently, liquid immersion lithography has been proposed as a way to extend even further the limits of optical lithography. This invention described a methodology based on contact printing using a projection lens to define the image of the mask onto the wafer. As the imaging is performed in a solid material, larger refractive indices can be obtained and the resolution of the imaging system can be increased.
Owner:APPLIED MATERIALS INC
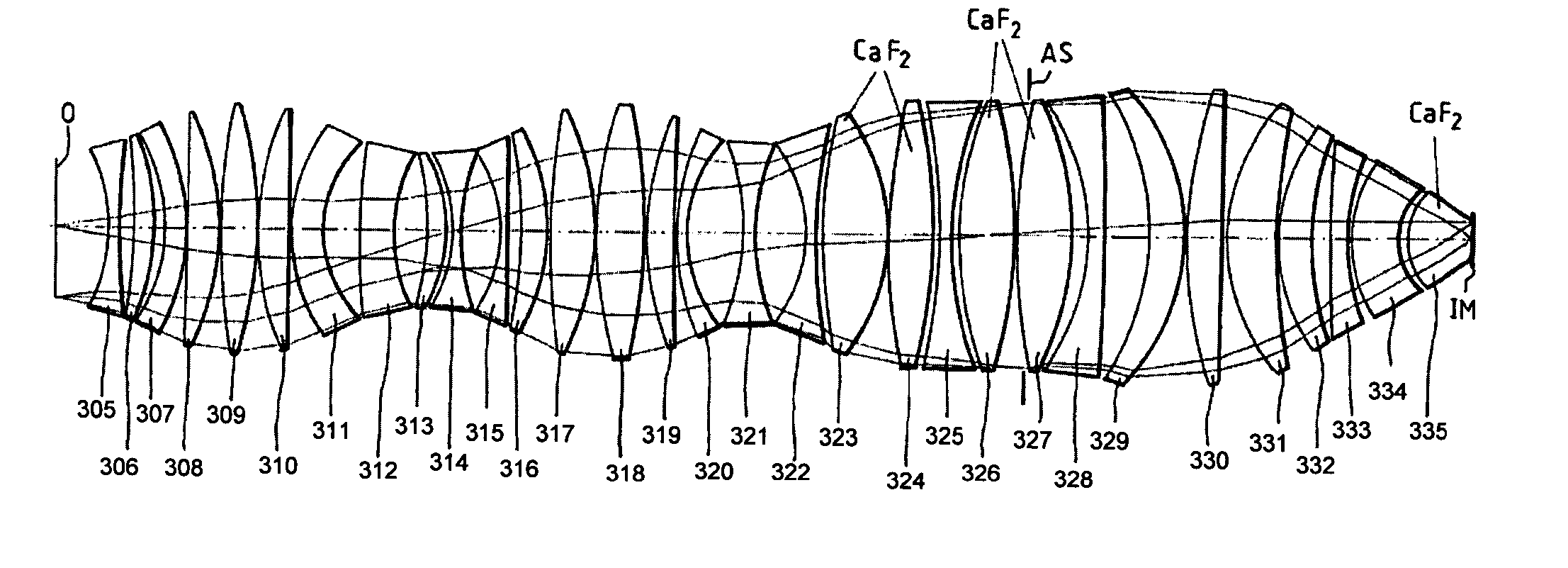
Very high-aperture projection objective
InactiveUS20050141098A1Guaranteed true stateIncrease the number ofSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMicroscopesSpherical shapedOptic system
A very high-aperture, purely refractive projection objective having a multiplicity of optical elements has a system diaphragm (5) arranged at a spacing in front of the image plane. The optical element next to the image plane (3) of the projection objective is a planoconvex lens (34) having a substantially spherical entrance surface and a substantially flat exit surface. The planoconvex lens has a diameter that is at least 50% of the diaphragm diameter of the system diaphragm (5). It is preferred to arrange only positive lenses (32, 33, 34) between the system diaphragm (5) and image plane (3). The optical system permits imaging in the case of very high apertures of NA≧0.85, if appropriate of NA≧1.
Owner:CARL ZEISS SMT GMBH
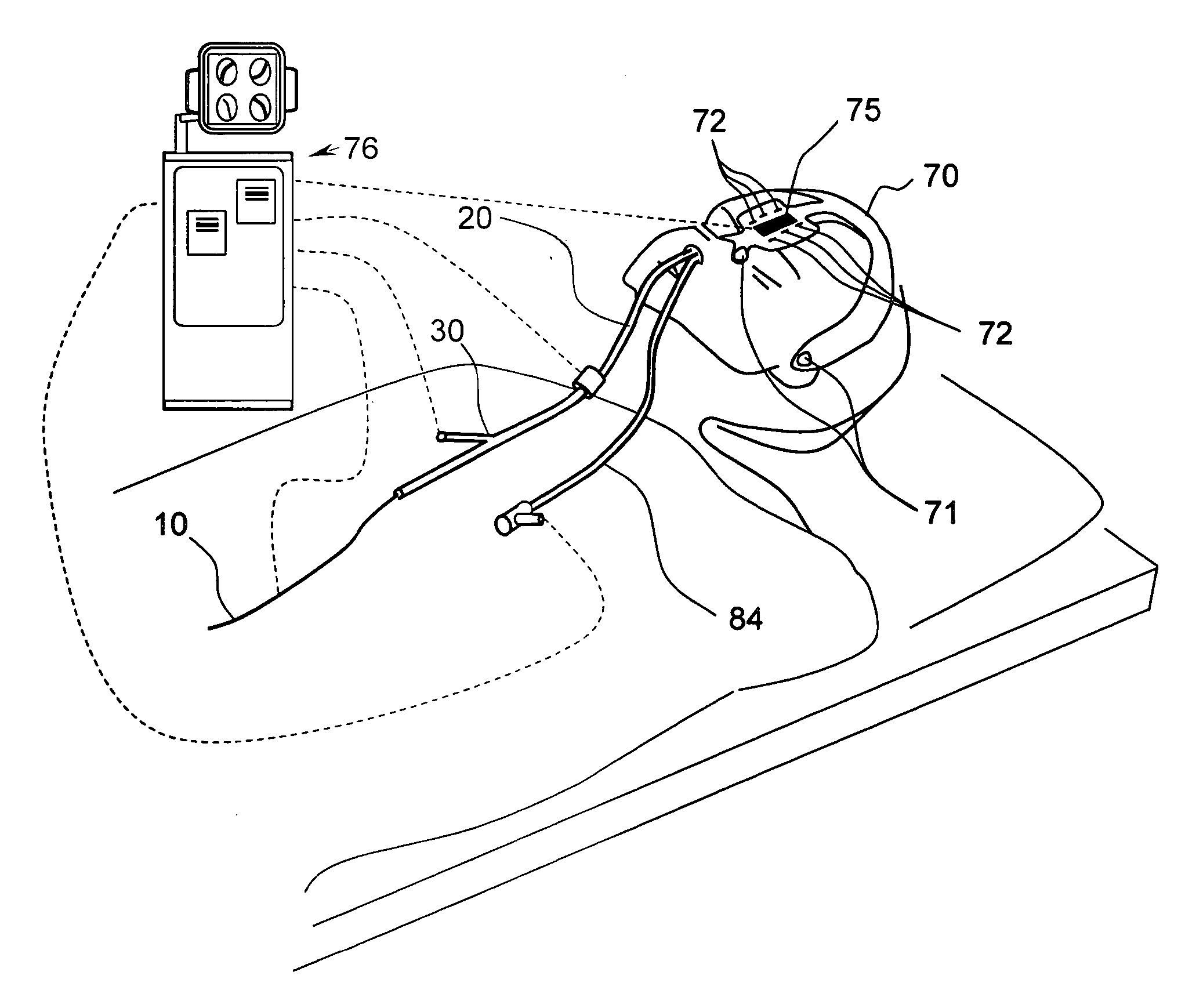
Systems and methods for performing image guided procedures within the ear, nose, throat and paranasal sinuses
Devices, systems and methods for performing image guided interventional and surgical procedures, including various procedures to treat sinusitis and other disorders of the paranasal sinuses, ears, nose or throat.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
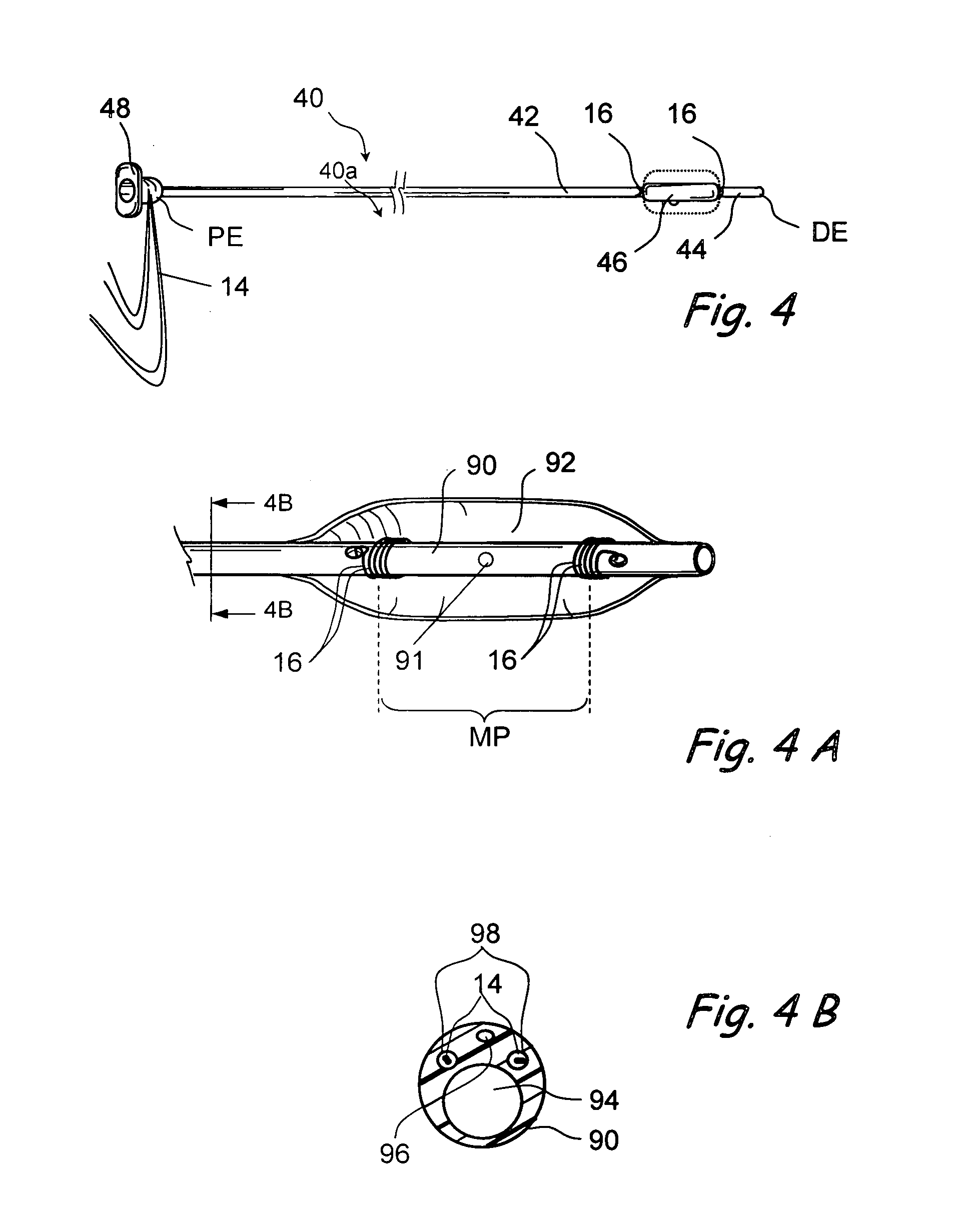
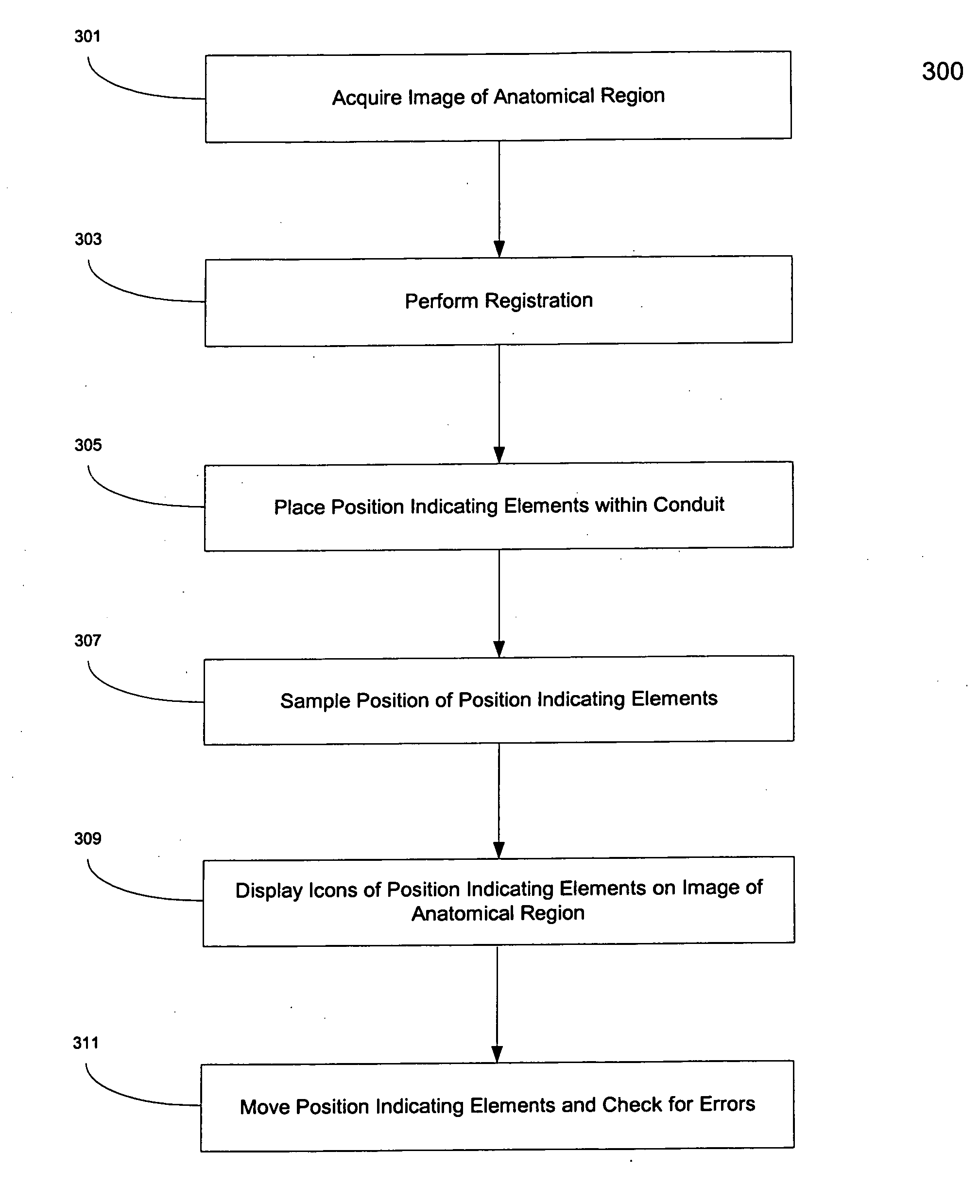
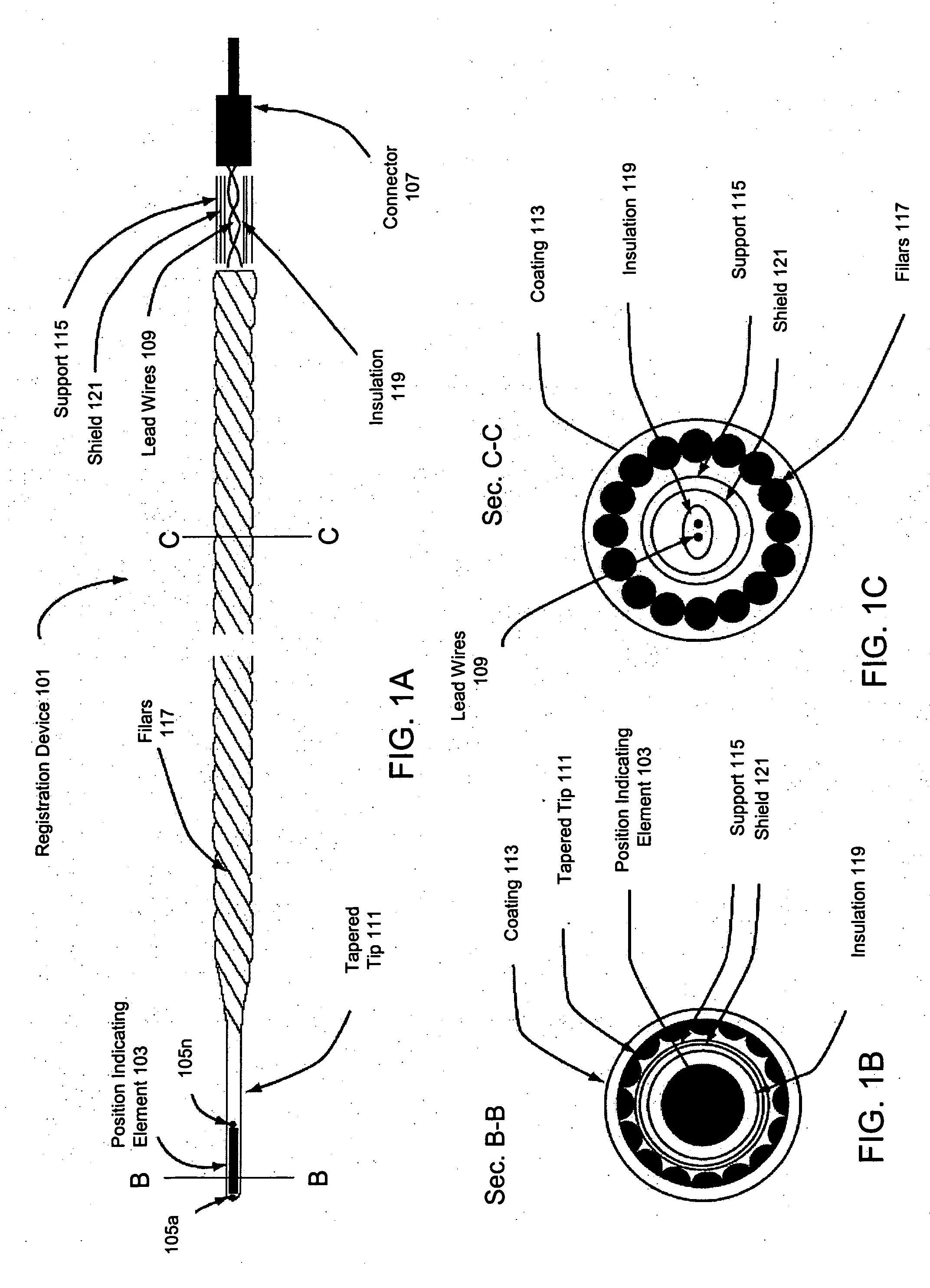
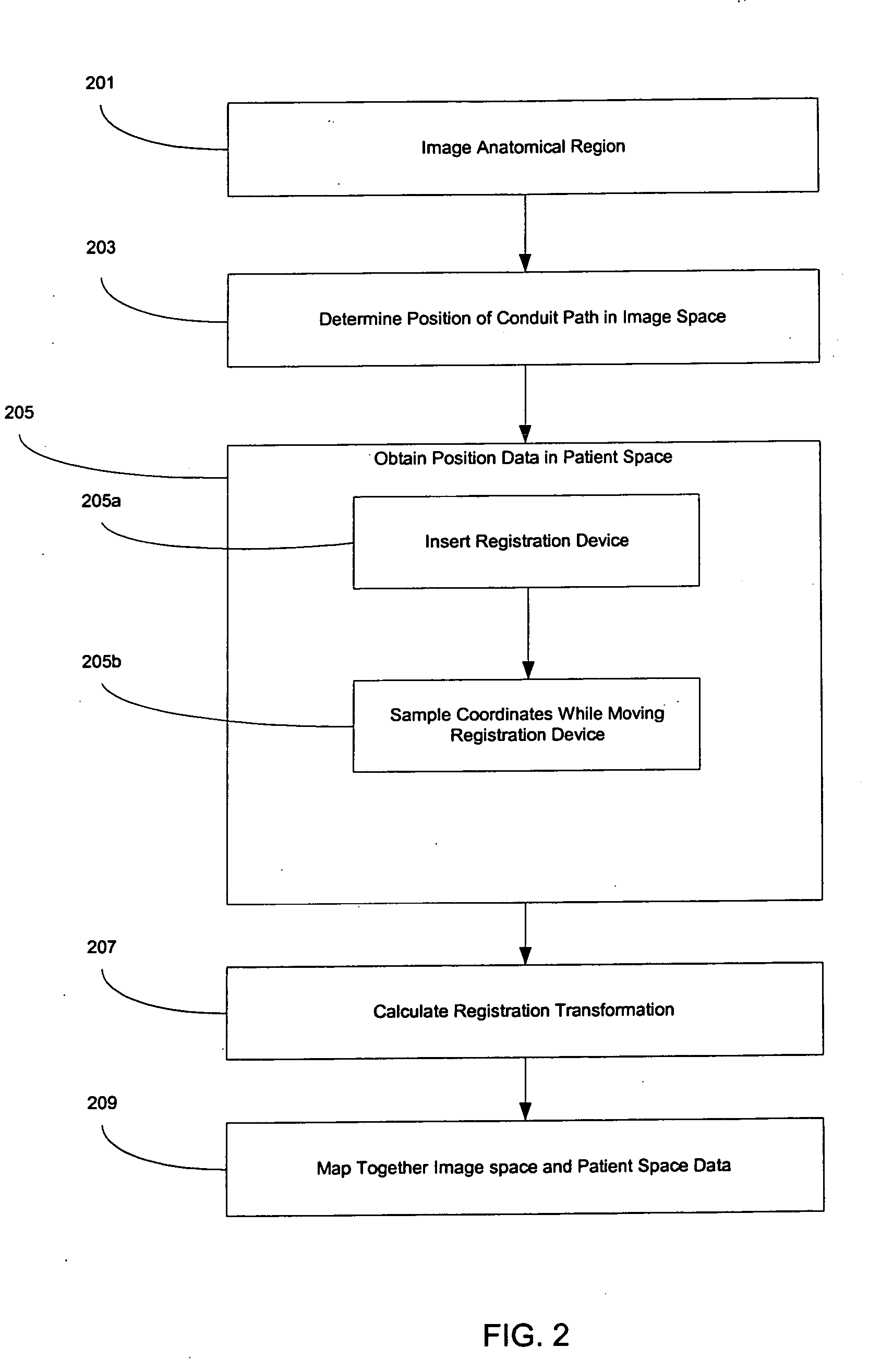
Method and apparatus for registration, verification, and referencing of internal organs
InactiveUS20050182319A1Sufficient informationPrevent material seeping into the deviceAudiometeringCatheterOrgan systemBiomedical engineering
Systems and methods for registering, verifying, dynamically referencing, and navigating an anatomical region of interest of a patient are provided. In one embodiment, the anatomical region of interest is imaged using an imaging device such as, for example, an x-ray device. A tracked registration device may then be removably inserted in a conduit within the anatomical region and the position of the registration device may be sampled by a tracking device as the registration device is moved within the anatomical region through the catheter. The sampled position data is registered to the image data to register the path of the conduit to the anatomical region of interest. The same or a similar device may be used to dynamically reference the movements affecting the anatomical region and modify the registration in real time. The registration may also be verified.
Owner:PHILIPS ELECTRONICS LTD
Methods and devices for performing procedures within the ear, nose, throat and paranasal sinuses
Devices, systems and methods for performing image guided interventional and surgical procedures, including various procedures to treat sinusitis and other disorders of the paranasal sinuses, ears, nose or throat.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
Tool tracking systems and methods for image guided surgery
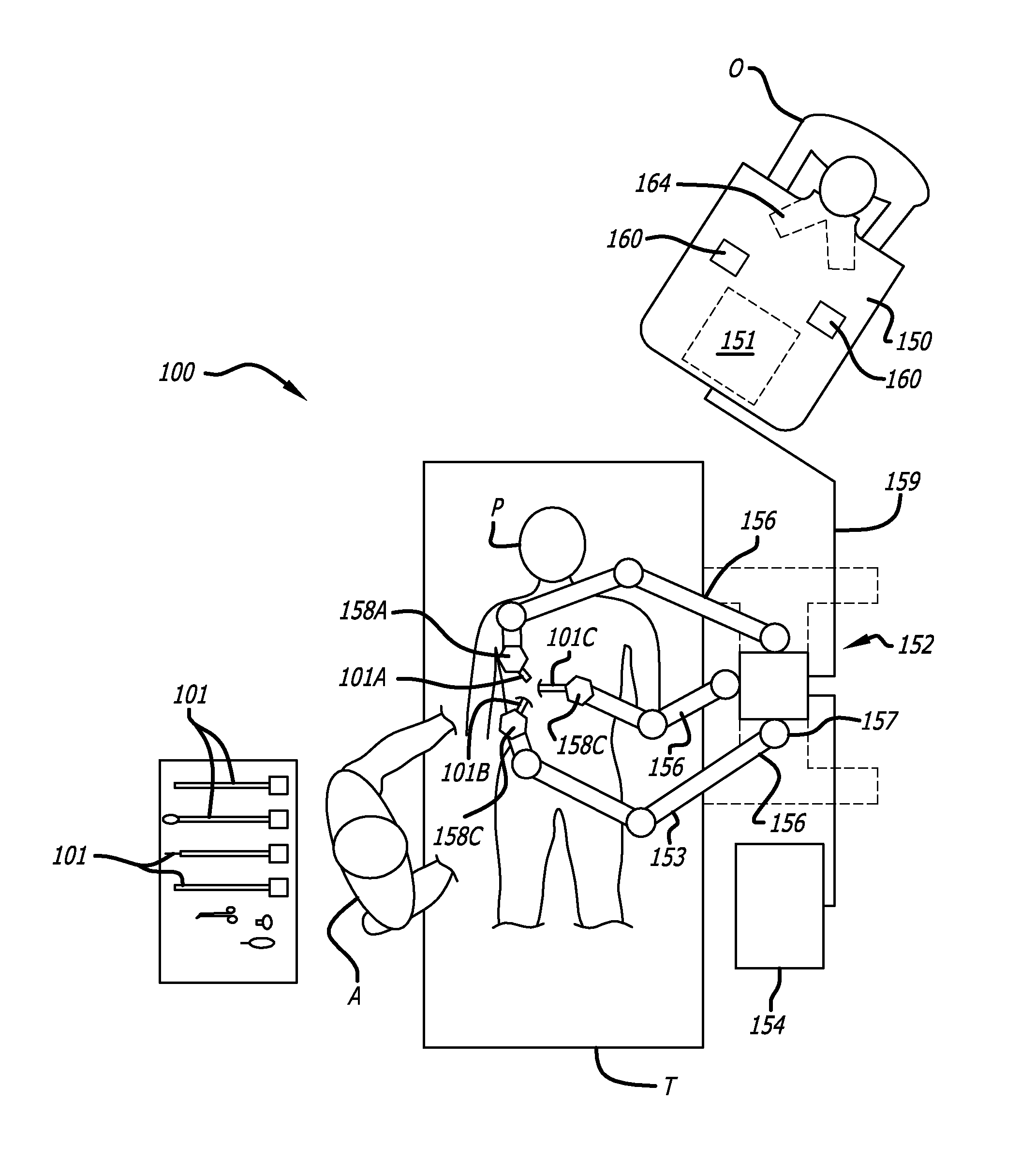
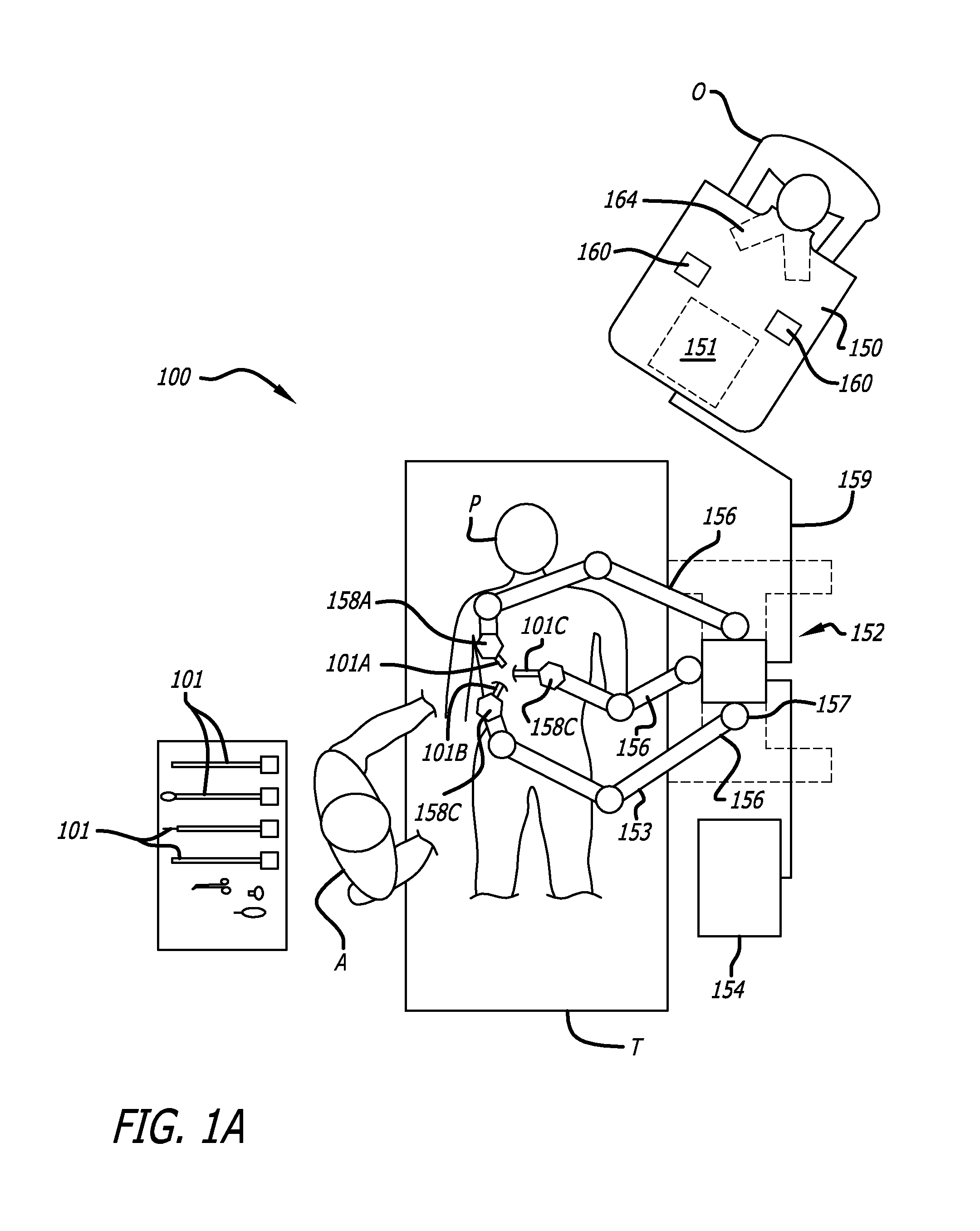
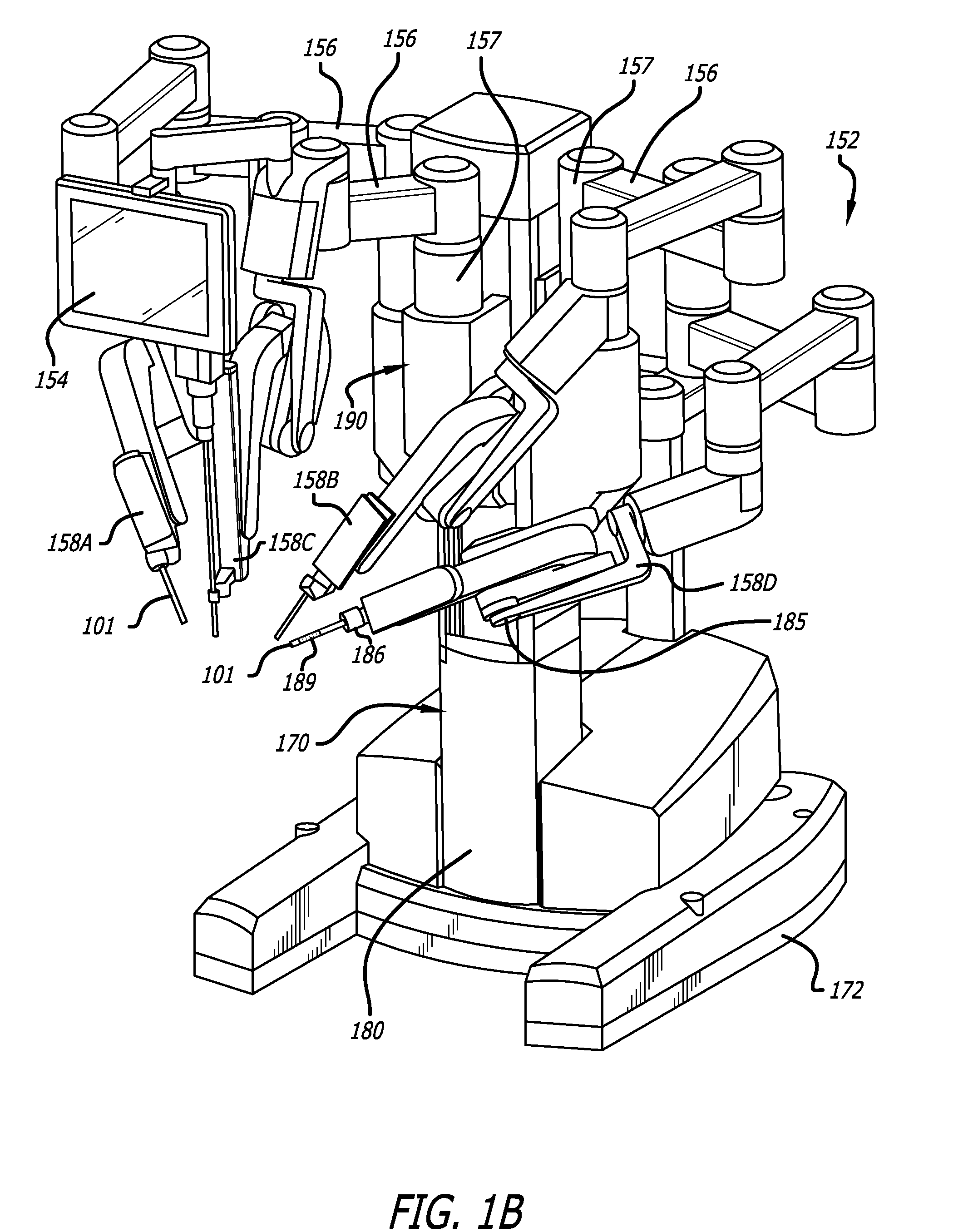
ActiveUS20090088634A1Improve performanceUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsProgramme-controlled manipulatorPostural orientationPerformed Imaging
In one embodiment of the invention, a tool tracking system is disclosed including a computer usable medium having computer readable program code to receive images of video frames from at least one camera and to perform image matching of a robotic instrument to determine video pose information of the robotic instrument within the images. The tool tracking system further includes computer readable program code to provide a state-space model of a sequence of states of corrected kinematics information for accurate pose information of the robotic instrument. The state-space model receives raw kinematics information of mechanical pose information and adaptively fuses the mechanical pose information and the video pose information together to generate the sequence of states of the corrected kinematics information for the robotic instrument. Additionally disclosed are methods for image guided surgery.
Owner:INTUITIVE SURGICAL OPERATIONS INC
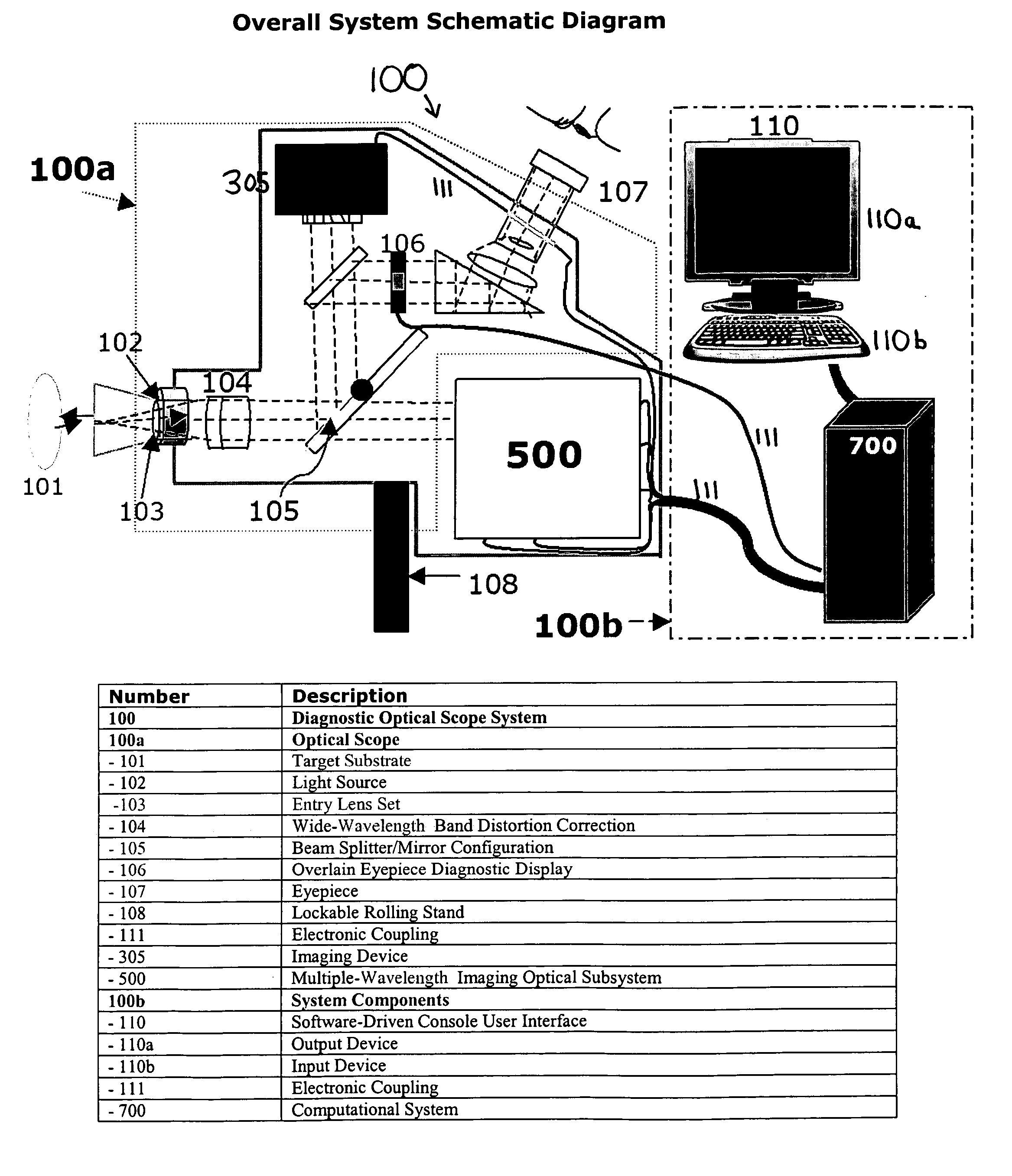
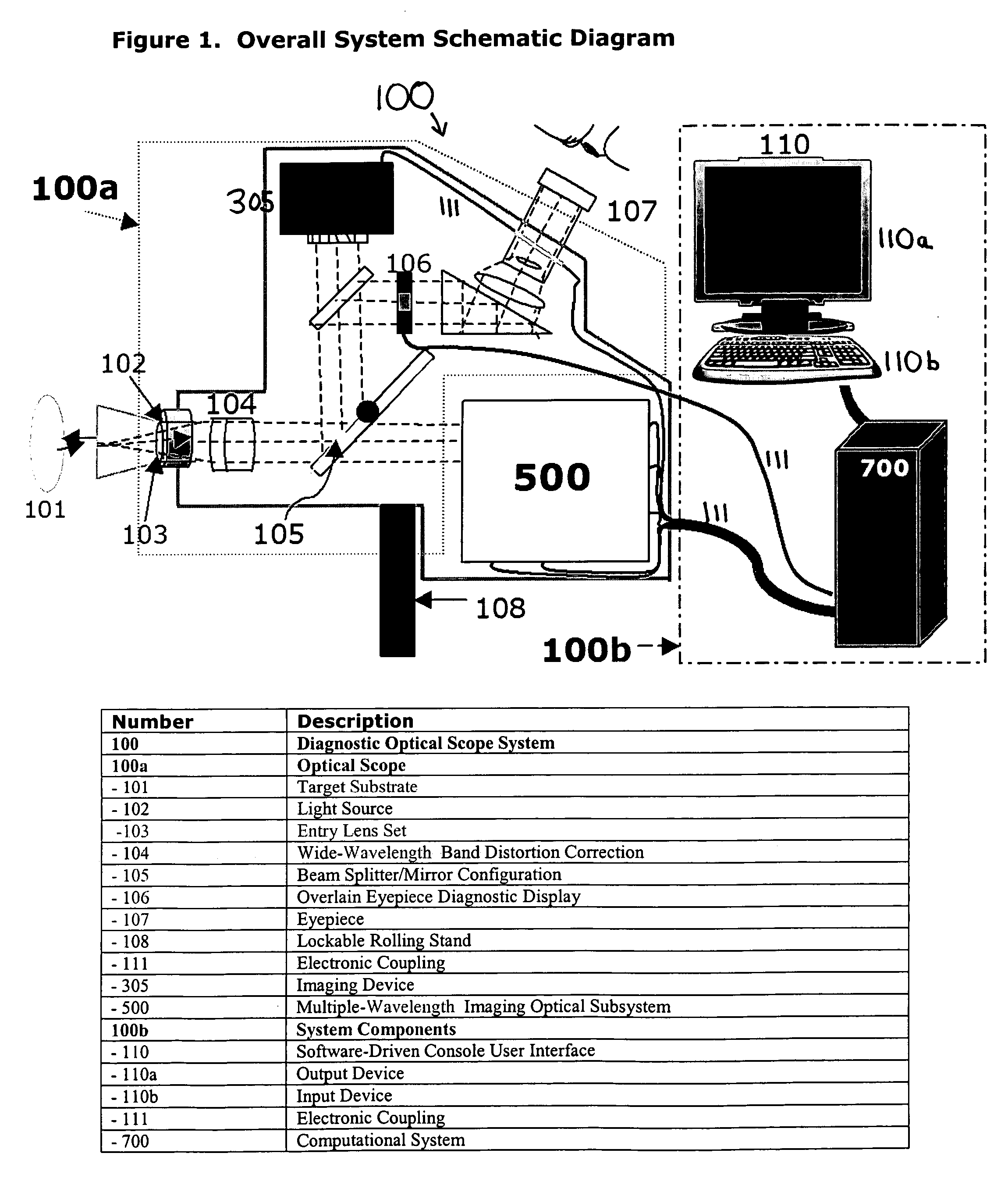
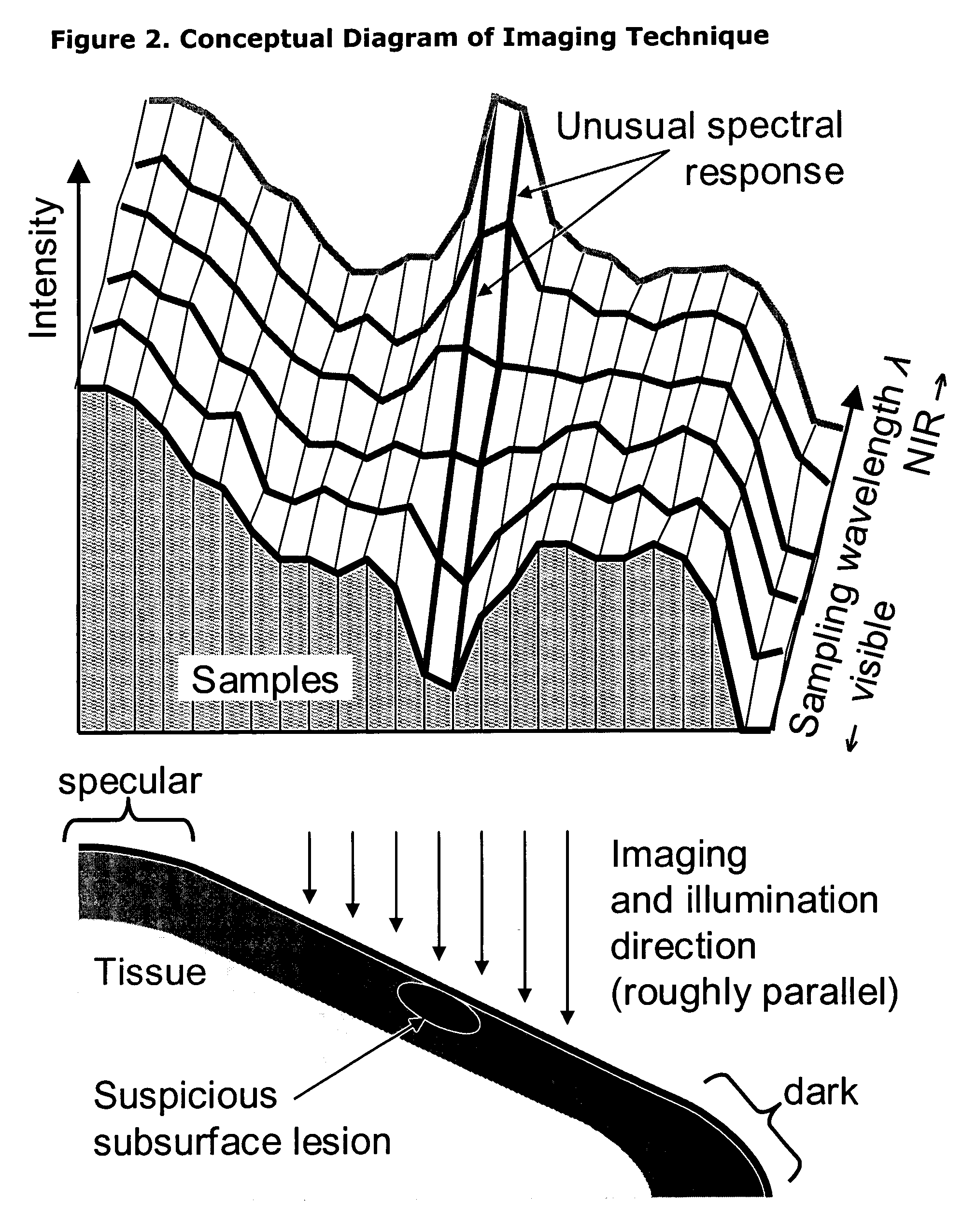
Apparatus, system and method for optically analyzing a substrate
InactiveUS20060184040A1Quality improvementDiagnostics using lightScattering properties measurementsLength waveLight filter
An apparatus for optically analyzing a substrate. The apparatus includes: (a) a light source for directing light onto the substrate; (b) optics for creating an optical path from light reflected from the substrate; and (c) a multiple wavelength imaging optical subsystem positioned in the optical path. The multiple wavelength imaging optical subsystem includes: (i) one or more filters which are capable of one or both of: (1) being alternatively or sequentially interposed in the optical path to extract one or more of wavelengths or wavelength bands of interest; or (2) having their wavelength selectivity adjusted to extract one or more wavelengths or wavelength bands of interest; and (ii) one or more imaging devices positioned to image the extracted wavelengths or wavelength bands of interest from the one or more filters; (d) an imaging device positioned in the optical path. Also a method is included, making use of the apparatus for analysis of a substrate.
Owner:INNEROPTIC TECH
Object and spatial level quantitative image analysis
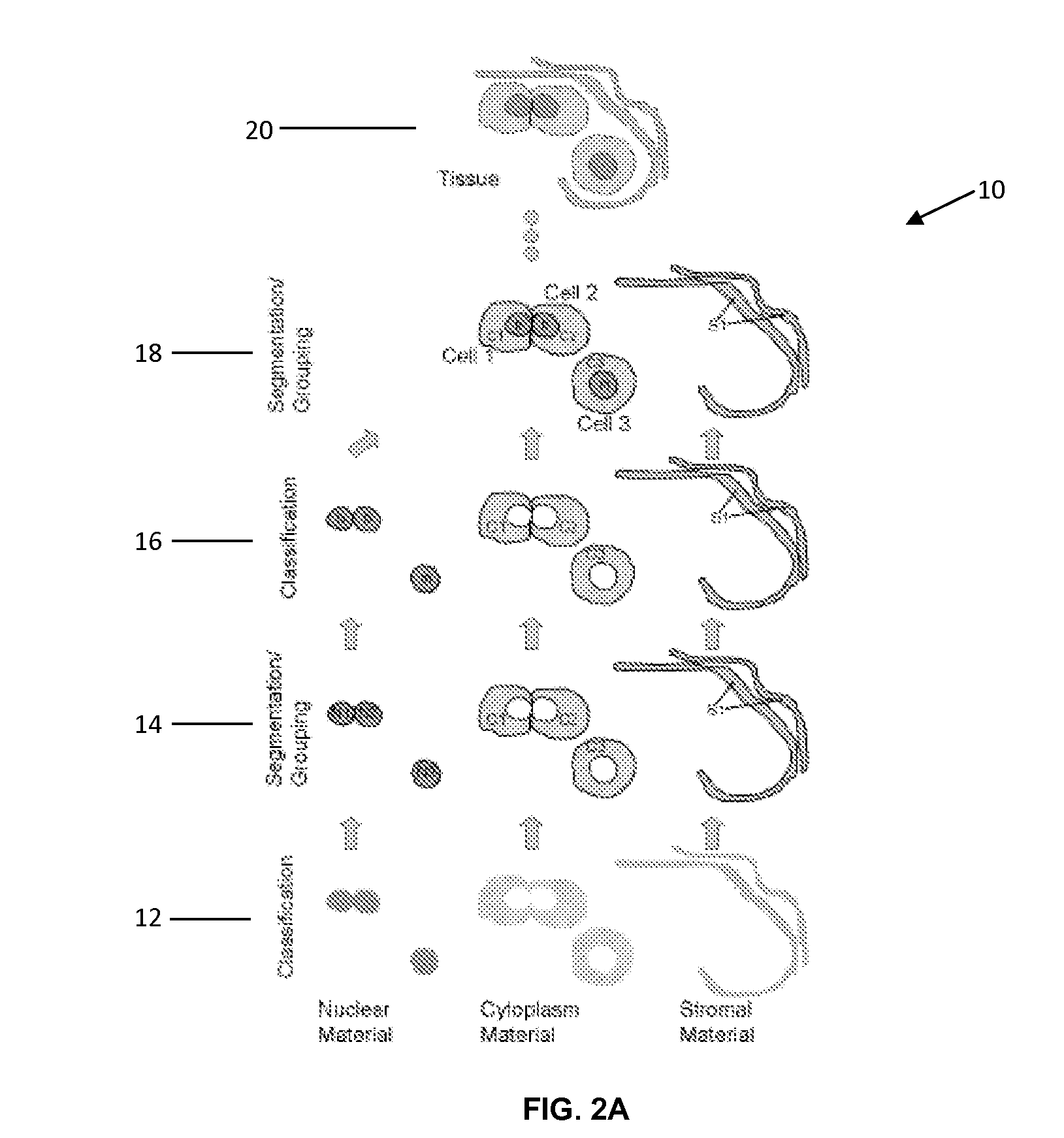
InactiveUS20100111396A1Improve classification effectImprove classification performanceImage enhancementImage analysisGraphicsGraphical user interface
Quantitative object and spatial arrangement-level analysis of tissue are detailed using expert (pathologist) input to guide the classification process. A two-step method is disclosed for imaging tissue, by classifying one or more biological materials, e.g. nuclei, cytoplasm, and stroma, in the tissue into one or more identified classes on a pixel-by-pixel basis, and segmenting the identified classes to agglomerate one or more sets of identified pixels into segmented regions. Typically, the one or more biological materials comprises nuclear material, cytoplasm material, and stromal material. The method further allows a user to markup the image subsequent to the classification to re-classify said materials. The markup is performed via a graphic user interface to edit designated regions in the image.
Owner:TRIAD NAT SECURITY LLC
Imaging probe with combined ultrasounds and optical means of imaging
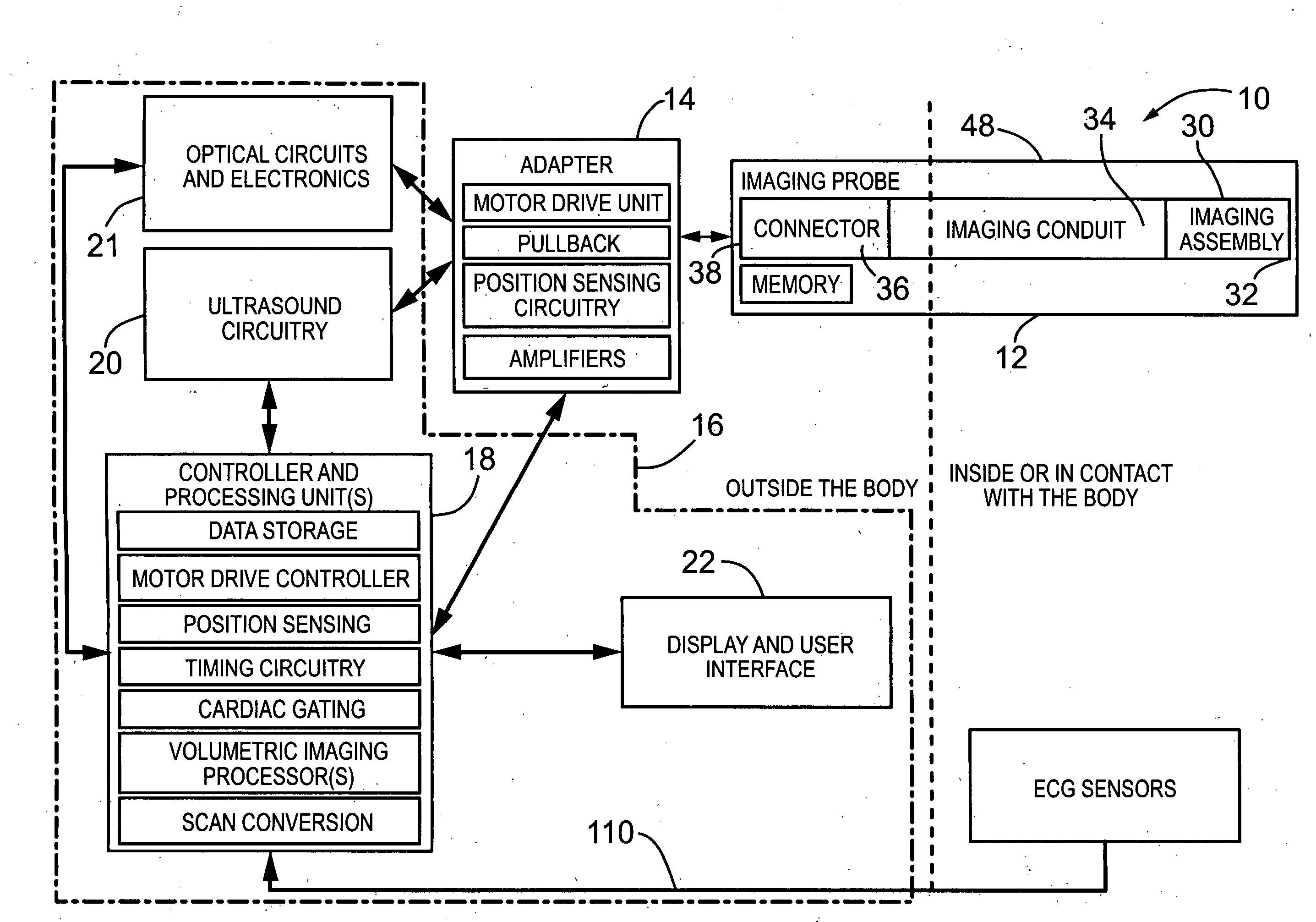
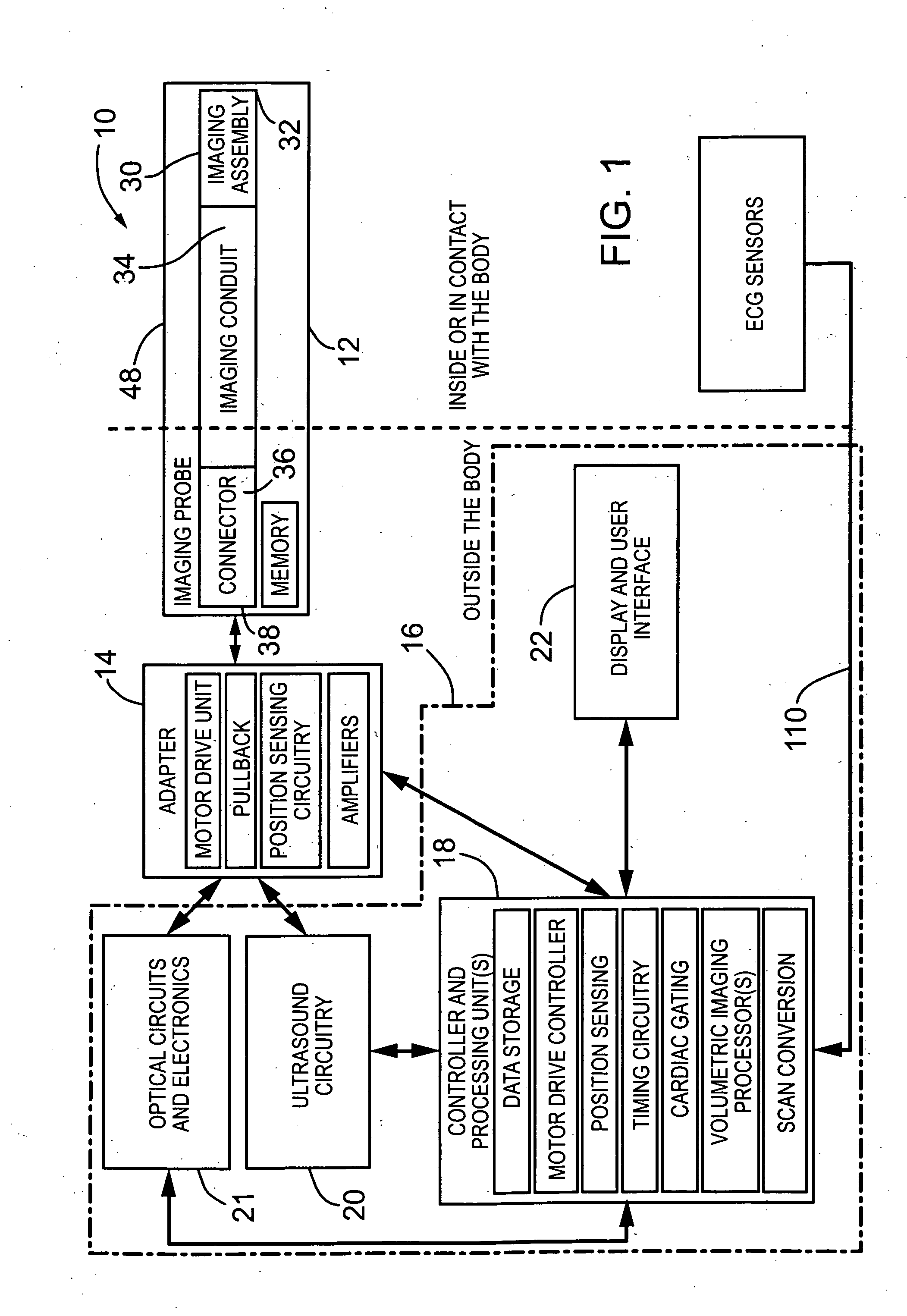
ActiveUS20080177183A1Provide goodFacilitates simultaneous imagingUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryHigh resolution imagingMammalian tissue
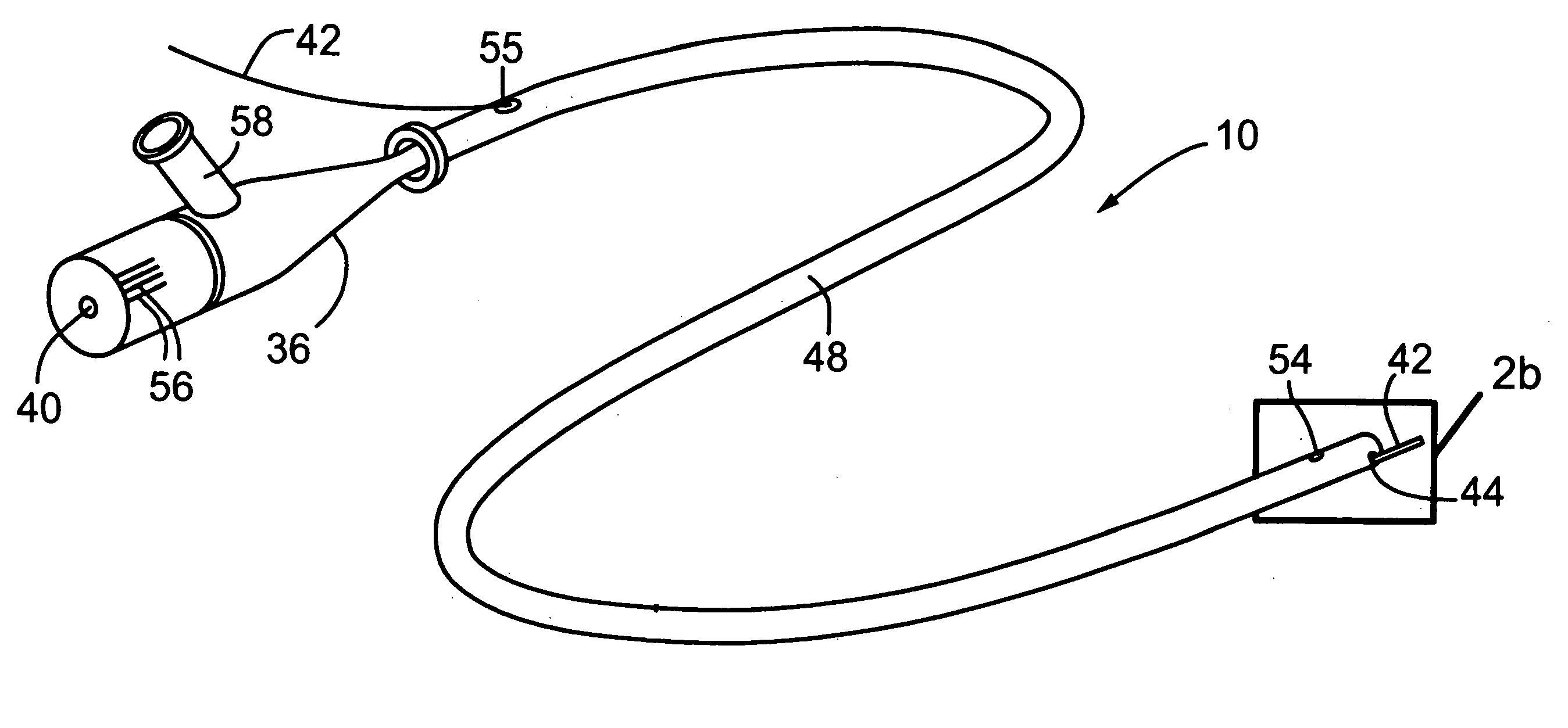
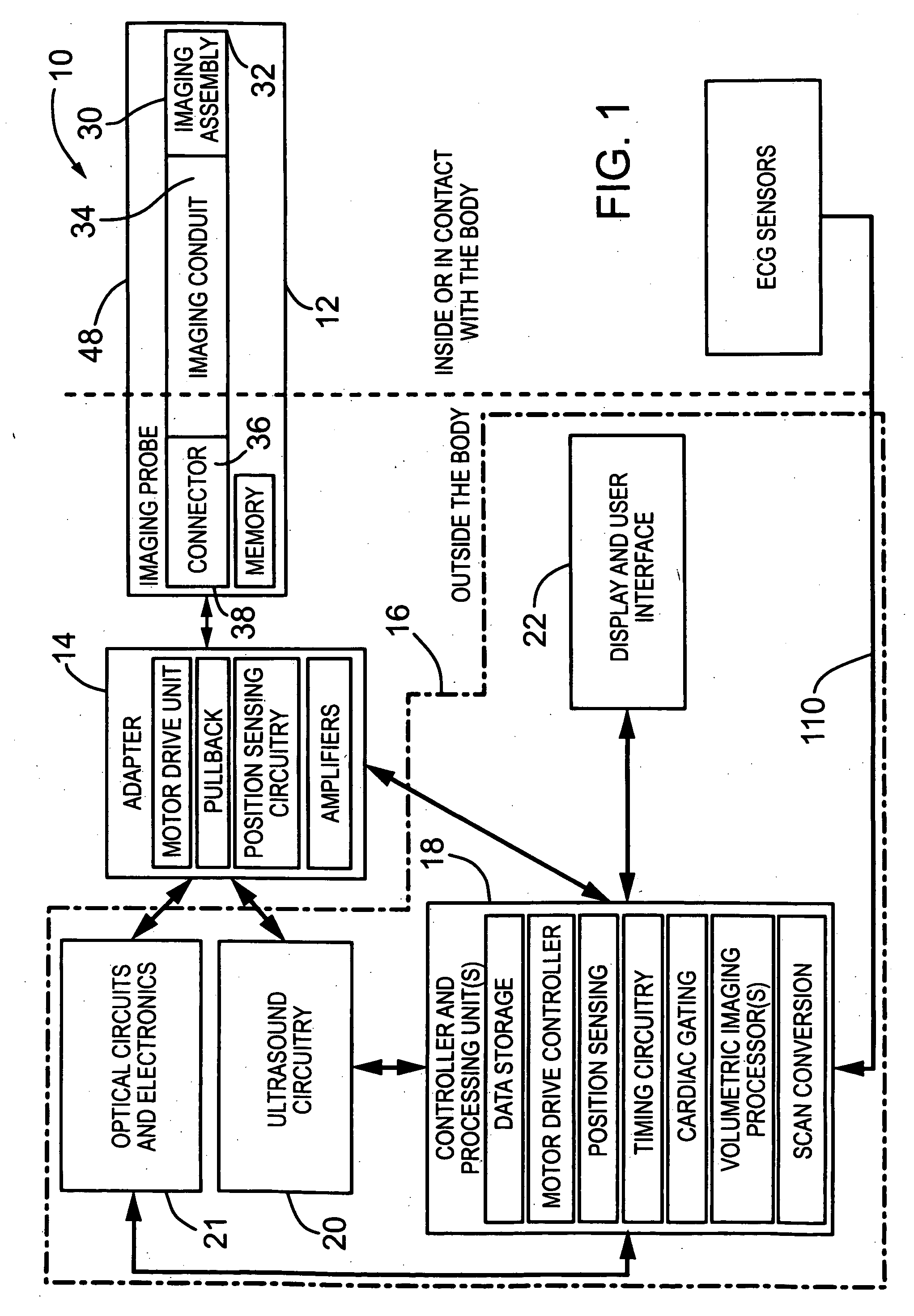
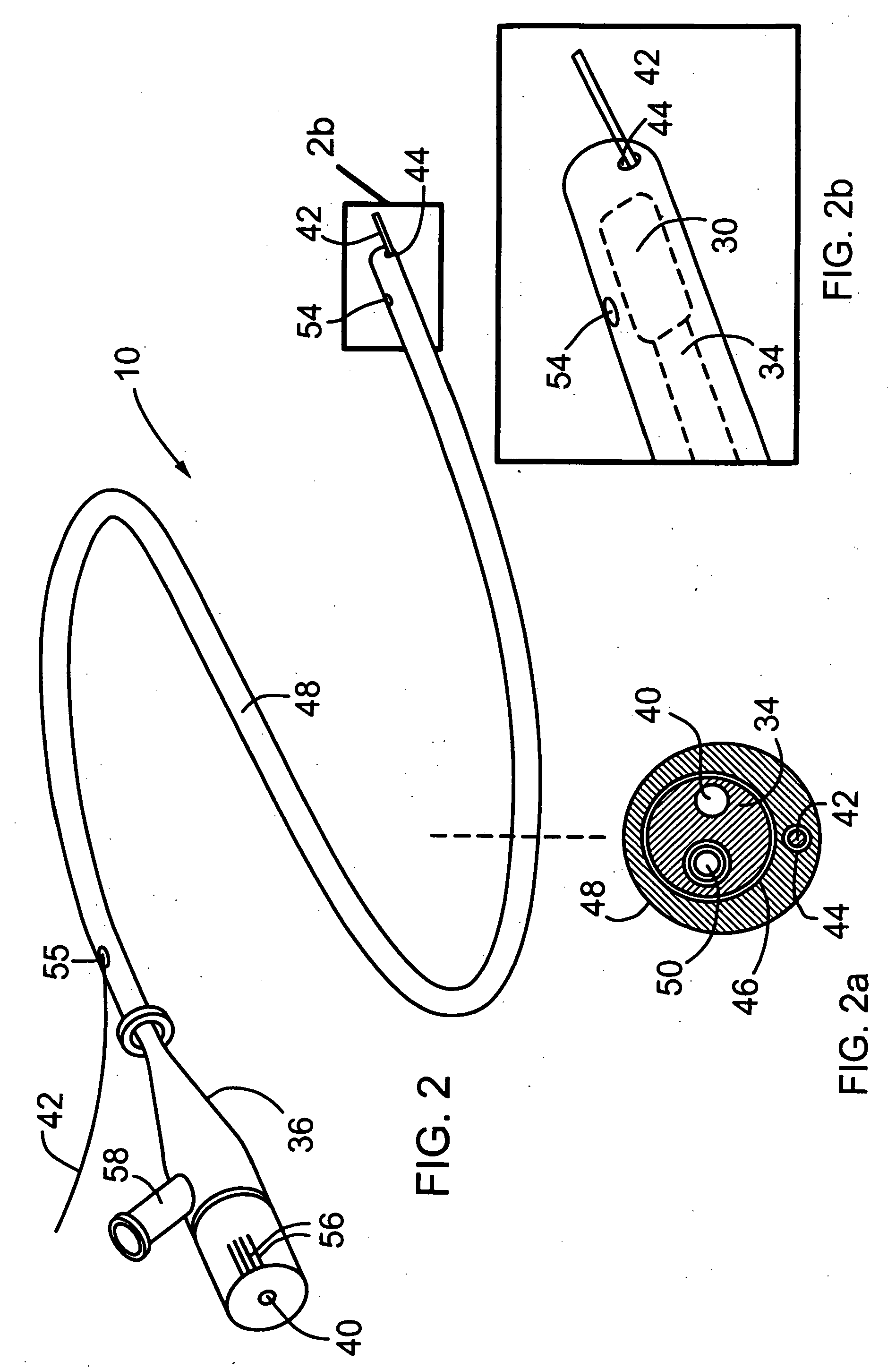
The present invention provides an imaging probe for imaging mammalian tissues and structures using high resolution imaging, including high frequency ultrasound and optical coherence tomography. The imaging probes structures using high resolution imaging use combined high frequency ultrasound (IVUS) and optical imaging methods such as optical coherence tomography (OCT) and to accurate co-registering of images obtained from ultrasound image signals and optical image, signals during scanning a region of interest.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
Color image sensor having imaging element array forming images on respective regions of sensor elements
The color image sensor generates a color image signal representing a subject and includes an optical substrate and a light sensor. The optical substrate includes spatially-separated imaging elements. Each of the imaging elements is configured to image light of a respective color. The light sensor includes regions of sensor elements disposed opposite respective ones of the imaging elements. The sensor elements in each of the regions are operable to generate a component of the color image signal in response to the light of the respective color incident on them.
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Systems and Methods for Performing Image Guided Procedures Within the Ear, Nose, Throat and Paranasal Sinuses
Devices, systems and methods for performing image guided interventional and surgical procedures, including various procedures to treat sinusitis and other disorders of the paranasal sinuses, ears, nose or throat.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
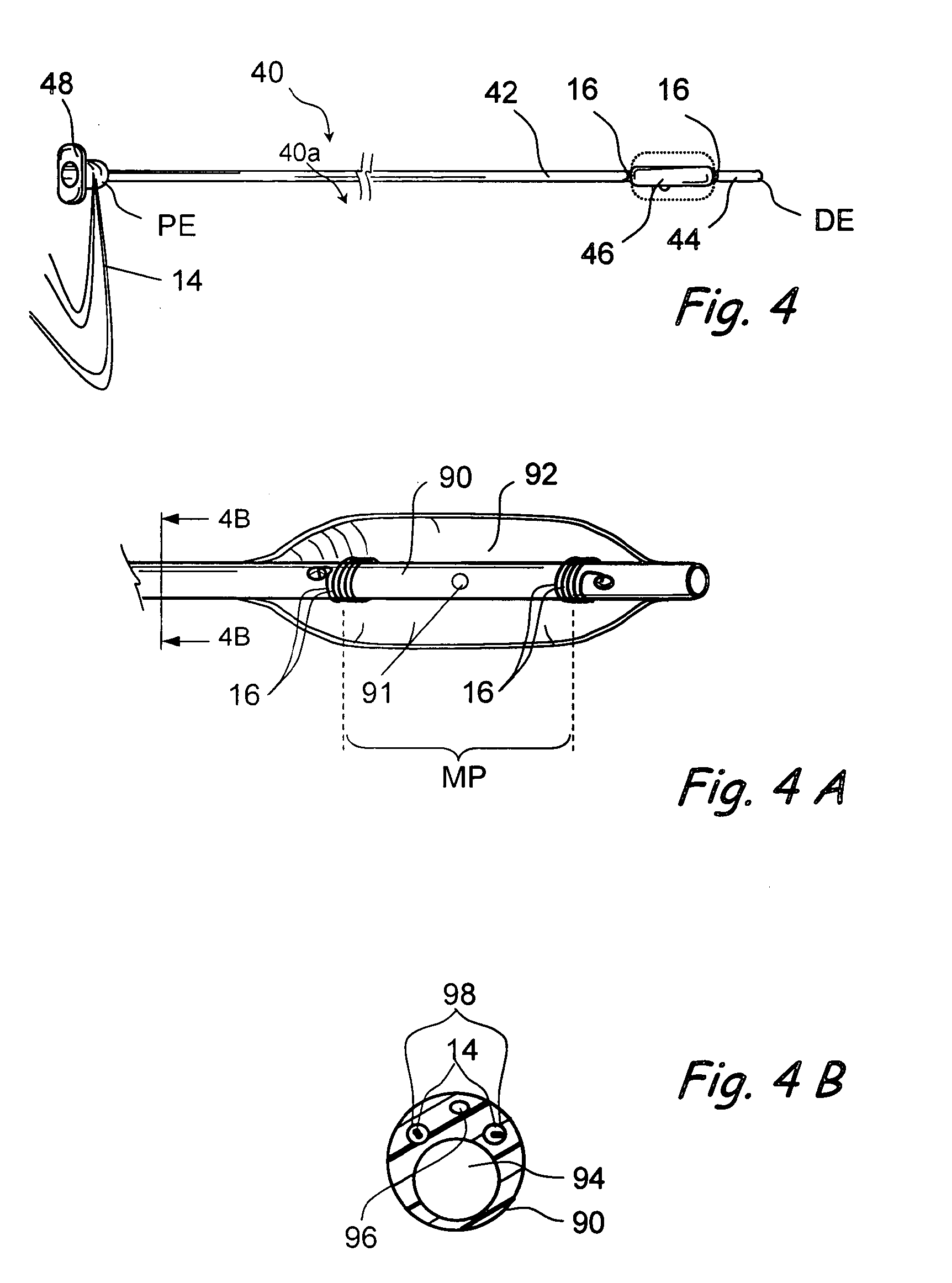
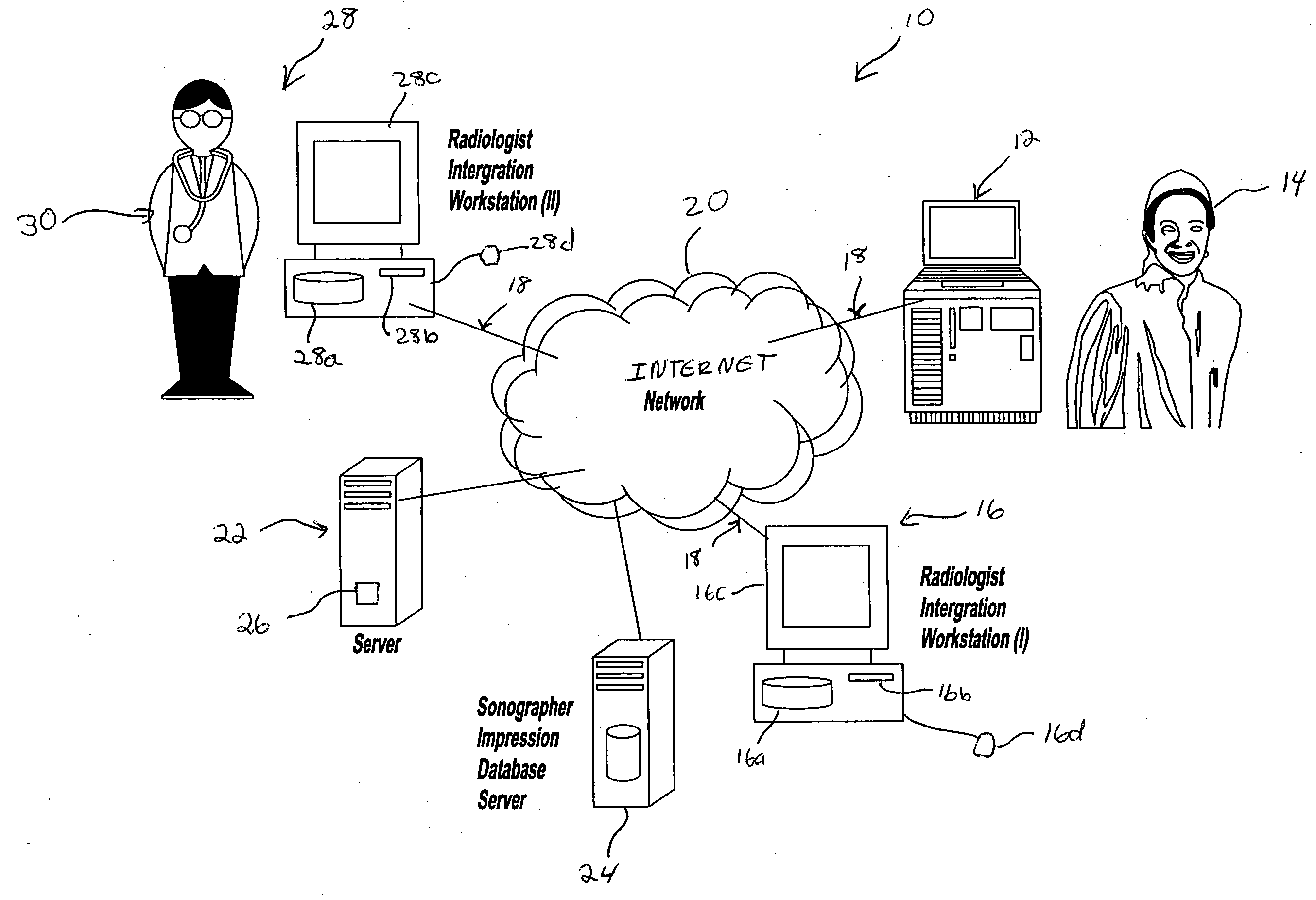
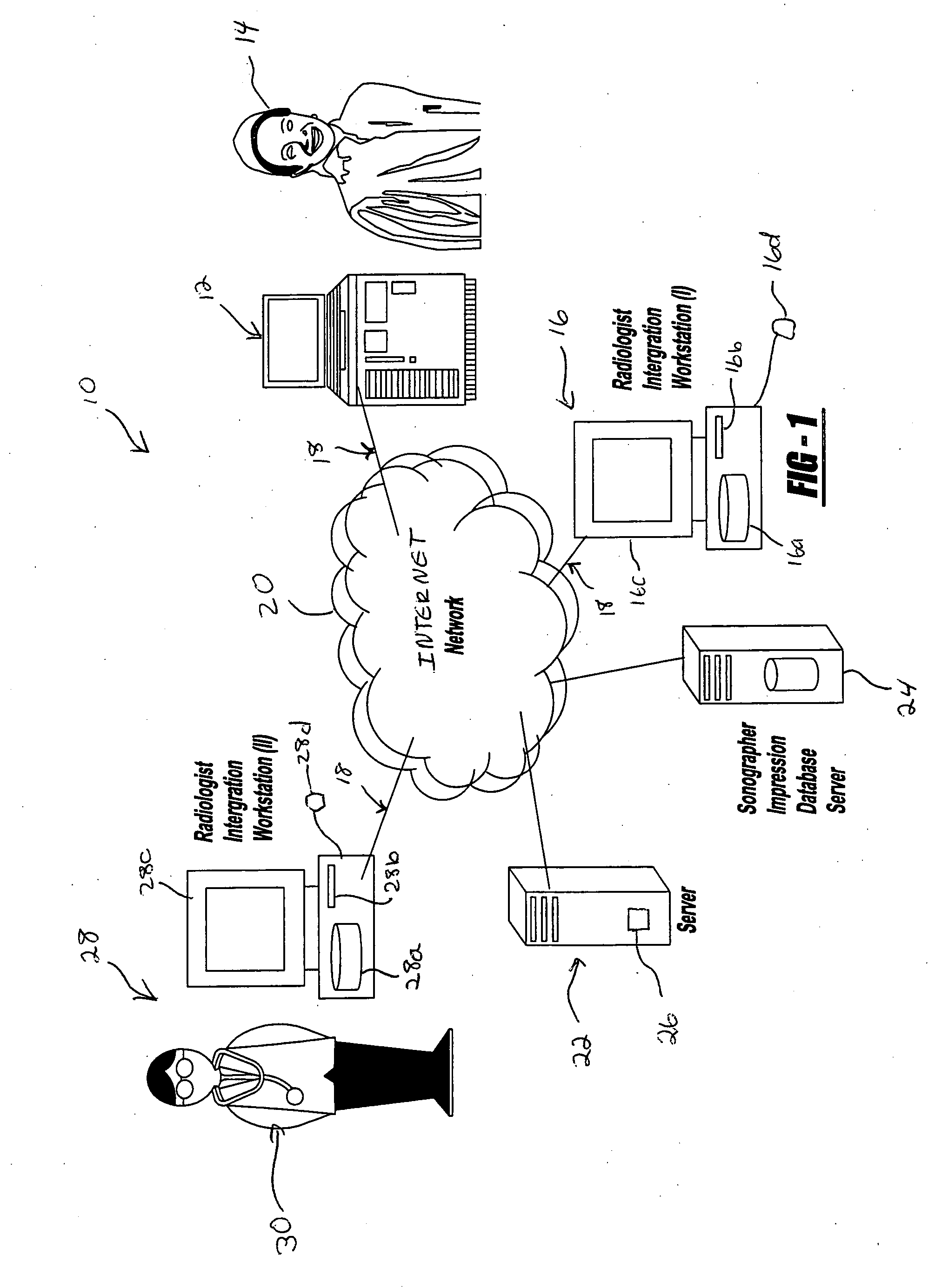
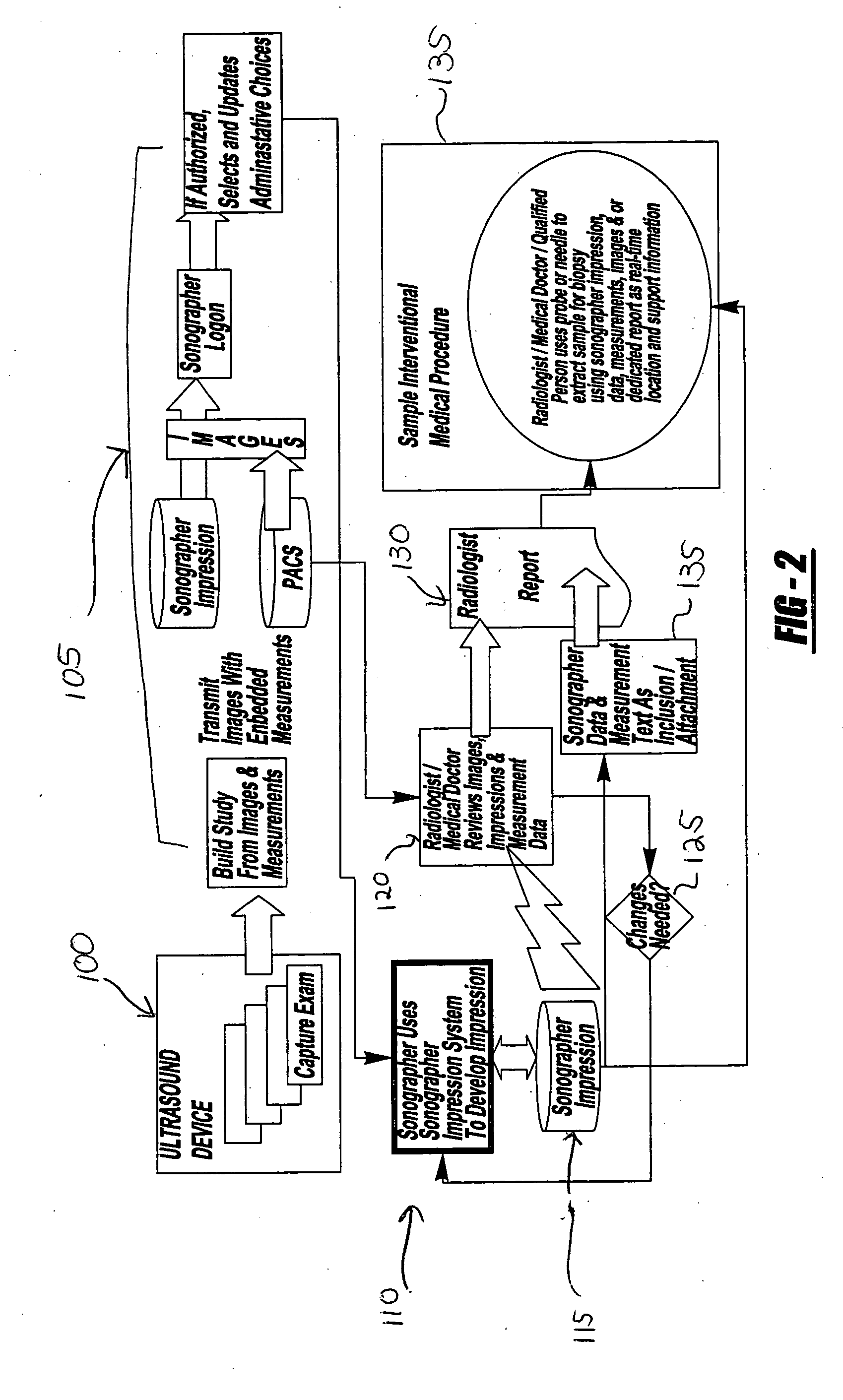
System and method of capturing and managing information during a medical diagnostic imaging procedure
InactiveUS20050065438A1Improve accuracyAmount of timeUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsUltrasound imagingMedical diagnosis
A system and method of capturing and managing the medical information obtained during an imaging procedure is provided. The system includes a sonogram imaging device operated by a technician, and a technician computer system in communication with the imaging device via a communications network. A computer server communicates with the technician computer system, and includes a medical diagnostic imaging software program. A healthcare provider computer system is operatively in communication with the computer server via the communications network. The method includes the steps of conducting the imaging procedure and building a study from the generated image and captured impression of the real-time observations of the generated image and measurement data by the technician. The study is stored in the database associated with a computer server and is accessible by a healthcare professional using a healthcare provider computer system for preparing a medical diagnosis.
Owner:MILLER LANDON C G
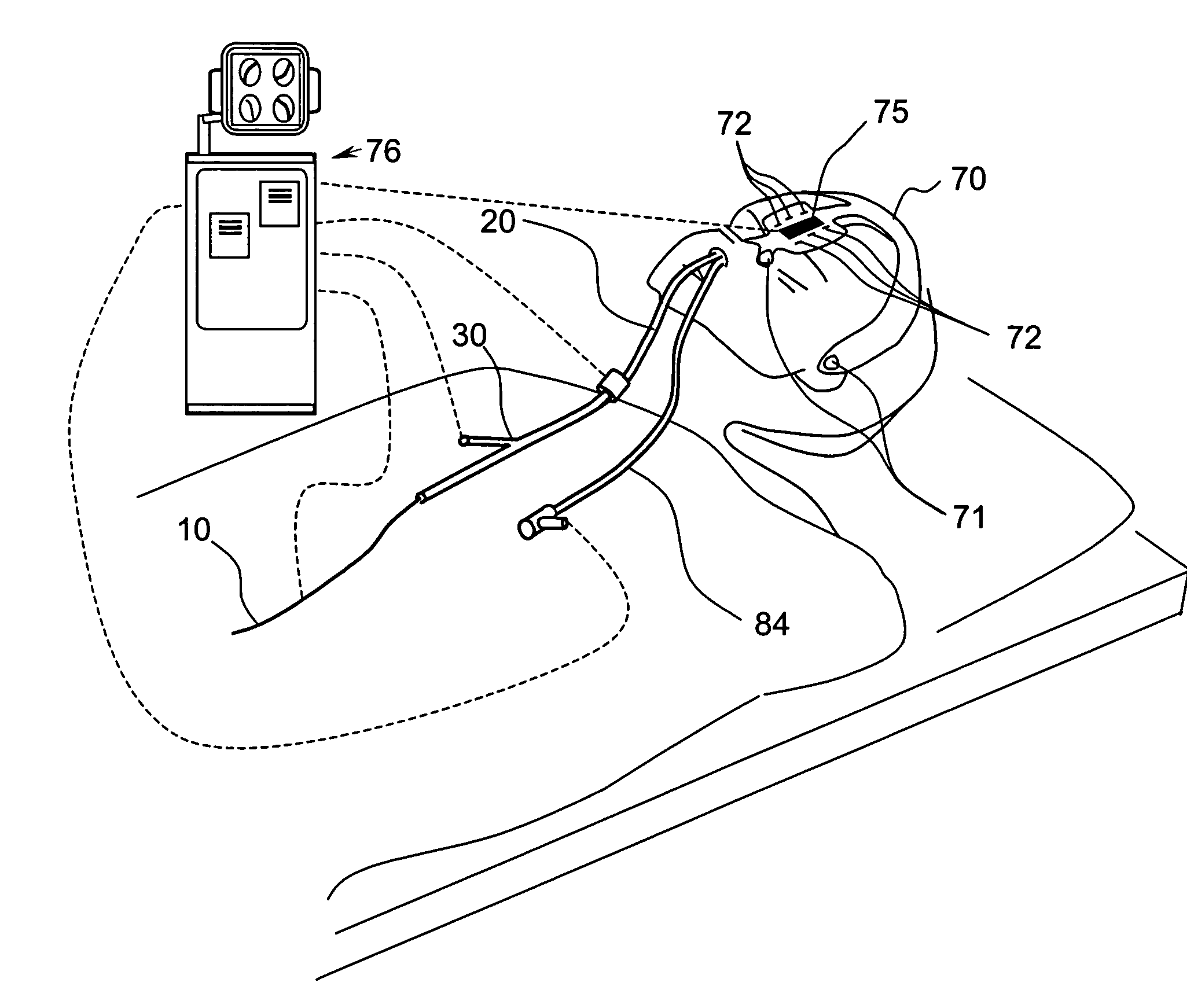
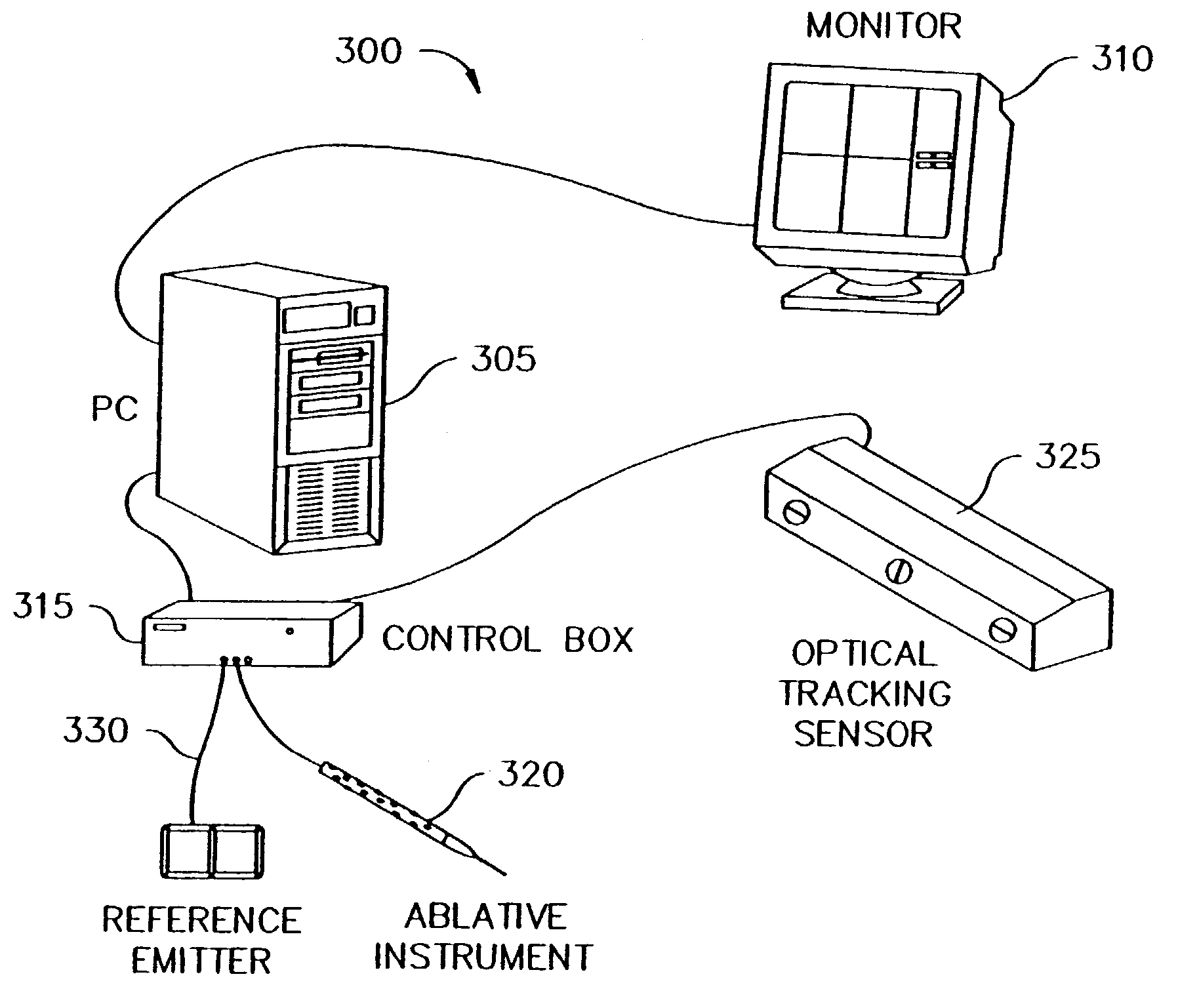
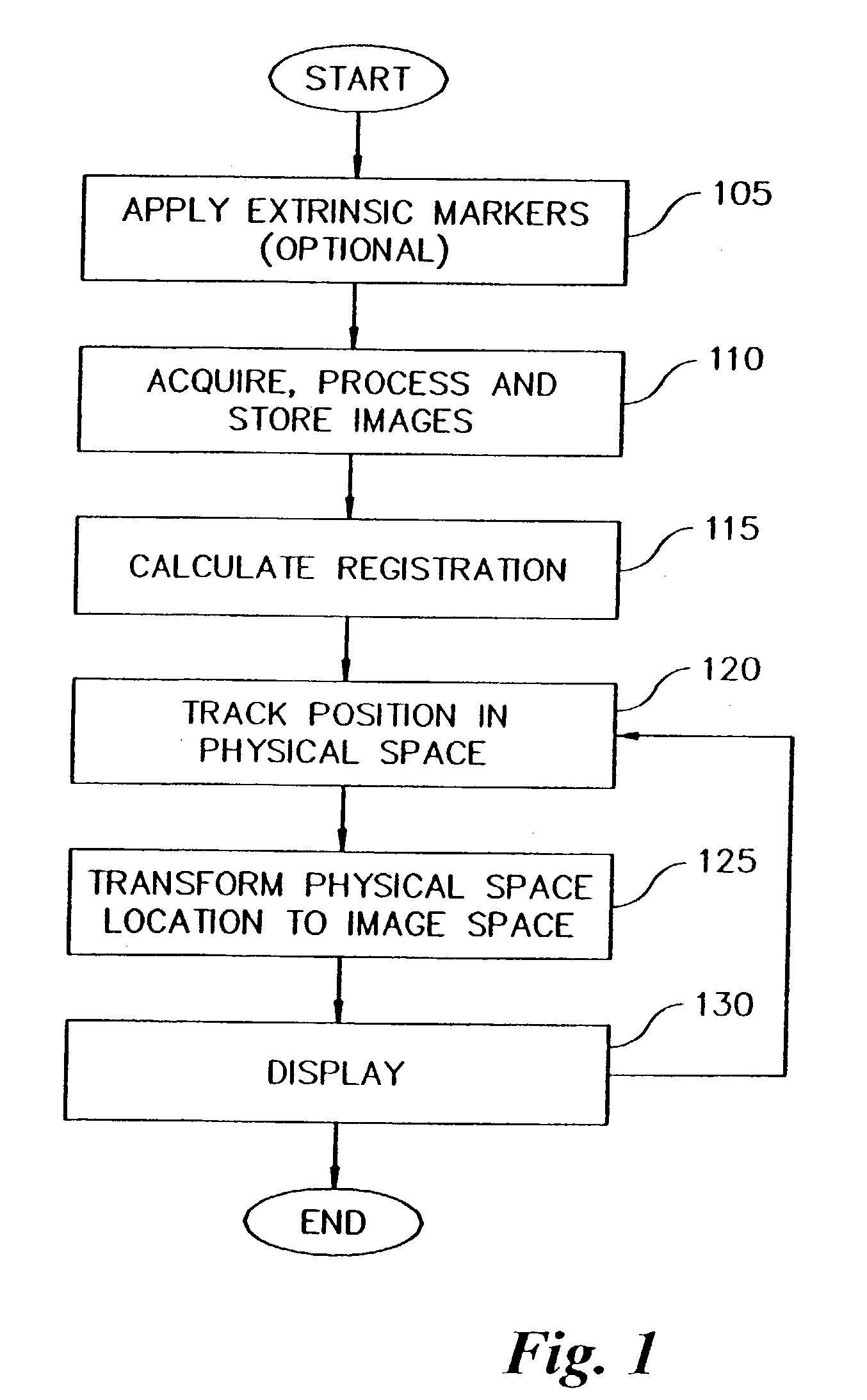
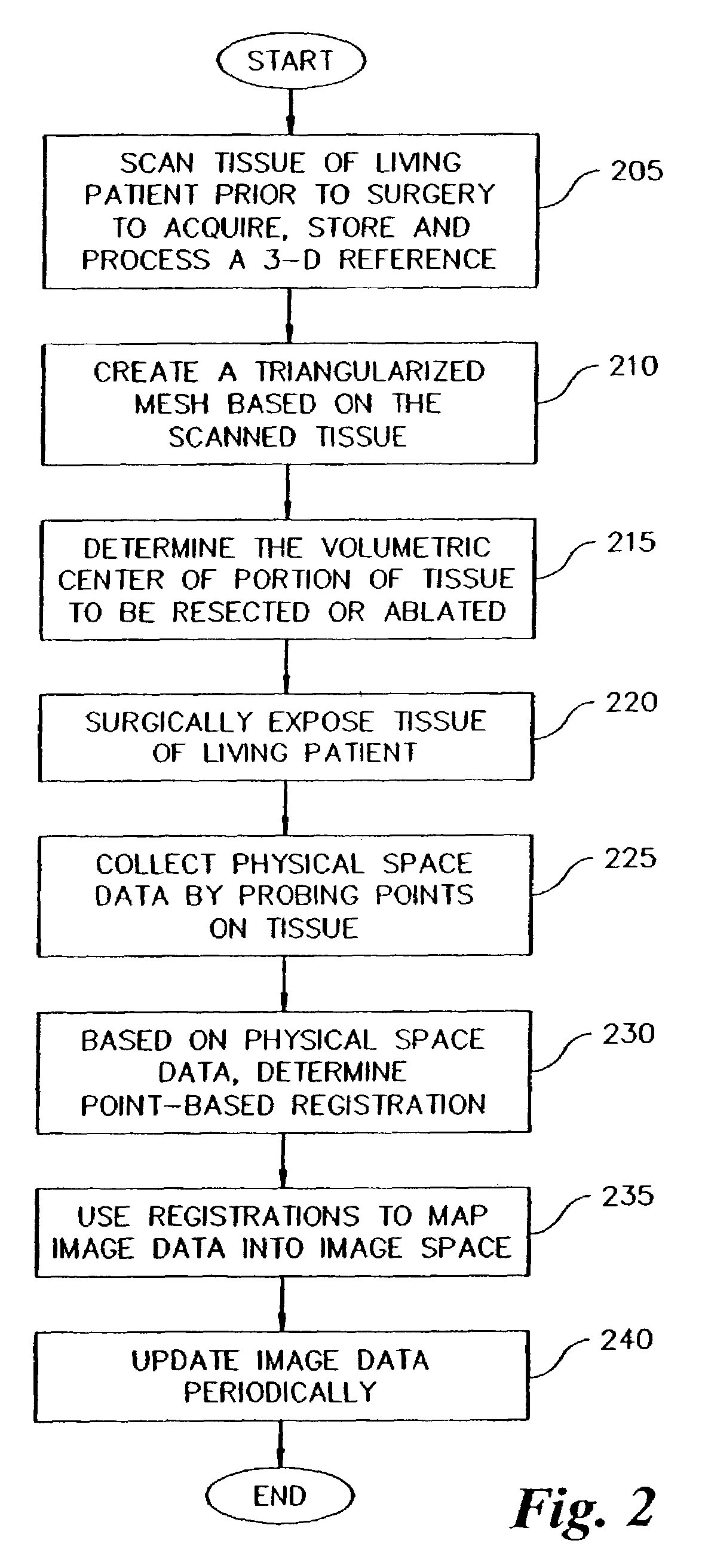
Method and apparatus for collecting and processing physical space data for use while performing image-guided surgery
InactiveUS7072707B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgical navigation systemsPhysical spaceLaser light
A method and apparatus for collecting and processing physical space data used while performing image-guided surgery is disclosed. Physical space data is collected by probing physical surface points of surgically exposed tissue. The physical space data provides three-dimensional (3-D) coordinates for each of the physical surface points. Based on the physical space data collected, point-based registrations used to indicate surgical position in both image space and physical space are determined. In one embodiment, the surface of surgically exposed tissue of a living patient is illuminated with laser light. Light reflected from the illuminated surface of the exposed tissue is received and analyzed. In another embodiment, one or more magnetic fields of known shape and size are established in the proximity of the exposed tissue. Data associated with the strength of the magnetic fields is acquired and analyzed.
Owner:VANDERBILT UNIV
Systems and methods for performing image guided procedures within the ear, nose, throat and paranasal sinuses
Devices, systems and methods for performing image guided interventional and surgical procedures, including various procedures to treat sinusitis and other disorders of the paranasal sinuses, ears, nose or throat.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
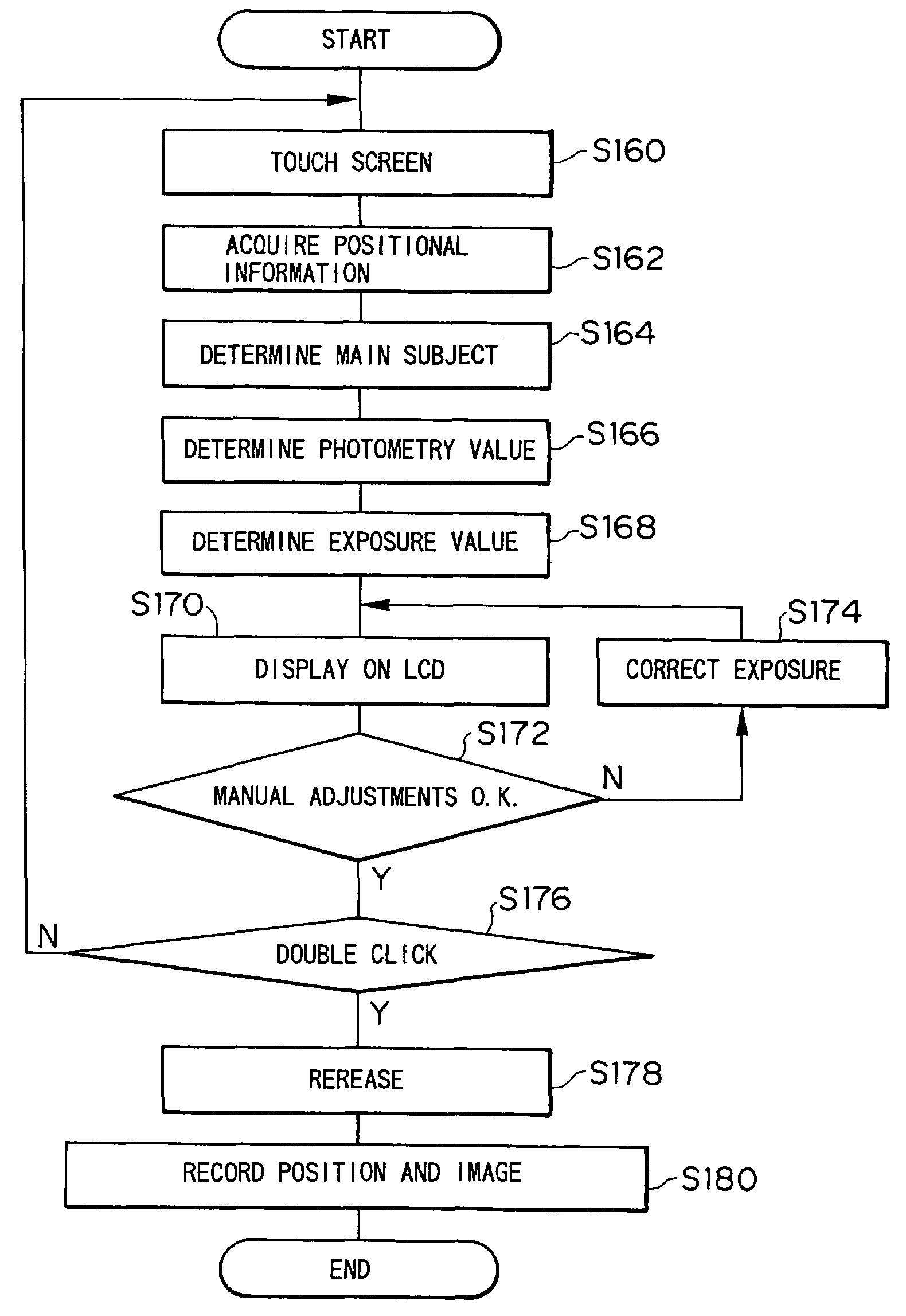
Camera provided with touchscreen
InactiveUS7034881B1Easy to specifySmall sizeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsExternal storageTouchscreen
An electronic camera is provided with a touchscreen. When a cameraman touches the touchscreen on a principal subject in a captured image shown on the touchscreen, the touched portion is determined and the focus and exposure are adjusted in conformity with the principal subject. When the image is designated to be stored, positional information on the principal subject as well as image information is stored into a built-in memory or a detachable external memory. For this reason, wherever the principal subject is located on the image, the image-capturing is performed with favorable results. The positional information on the principal subject is utilized for printing or reproducing the image so as to perform image tone corrections such as correction of brightness and skin pigmentation in an area including the principal subject, so that a high-quality image can be printed or reproduced.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Devices, Systems and Methods For Diagnosing and Treating Sinusitis and Other Disorders of the Ears, Nose and/or Throat
Sinusitis, enlarged nasal turbinates, tumors, infections, hearing disorders, allergic conditions, facial fractures and other disorders of the ear, nose and throat are diagnosed and / or treated using minimally invasive approaches and, in many cases, flexible catheters as opposed to instruments having rigid shafts. Various diagnostic procedures and devices are used to perform imaging studies, mucus flow studies, air / gas flow studies, anatomic dimension studies, endoscopic studies and transillumination studies. Access and occluder devices may be used to establish fluid tight seals in the anterior or posterior nasal cavities / nasopharynx and to facilitate insertion of working devices (e.g., scopes, guidewires, catheters, tissue cutting or remodeling devices, electrosurgical devices, energy emitting devices, devices for injecting diagnostic or therapeutic agents, devices for implanting devices such as stents, substance eluting devices, substance delivery implants, etc.
Owner:ACCLARENT INC
Optical tomography apparatus
ActiveUS20070019208A1High resolutionMaintain good propertiesMaterial analysis by optical meansCatheterMultiplexingDiffusion
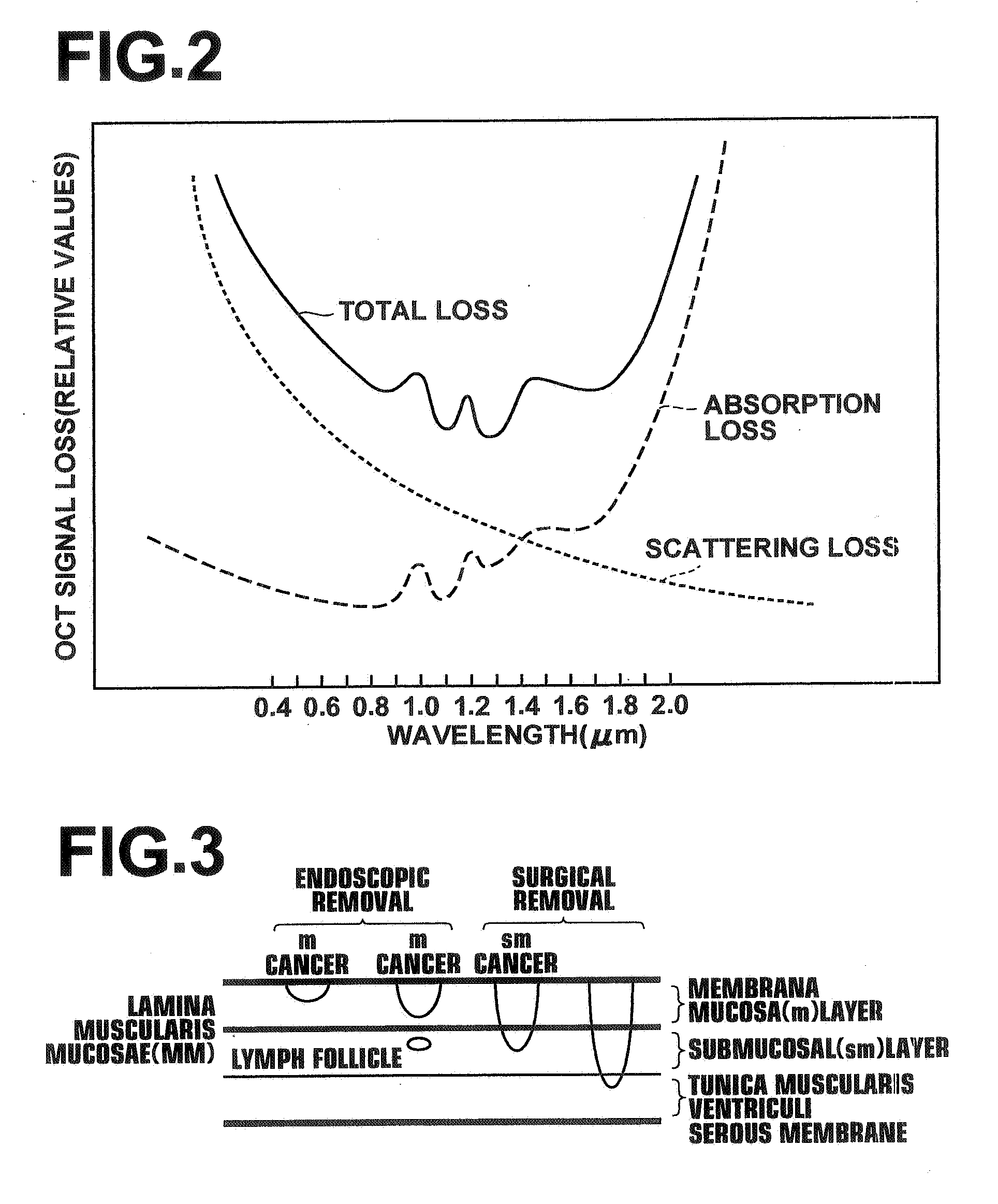
Low coherence light having a central wavelength λc of 1.1 μm and a full width at half maximum spectrum Δλ of 90 nm is emitted. The low coherence light has wavelength properties suited for the light absorbing properties, the diffusion properties, and the dispersion properties of living tissue. A light dividing means divides the low coherence light into a measuring light beam, which is irradiated onto a measurement target via an optical probe, and a reference light beam that propagates toward an optical path length adjusting means. A multiplexing means multiplexes a reflected light beam, which is the measuring light beam reflected at a predetermined depth of the measurement target, and the reference light beam, to form coherent light. A coherent light detecting means detects the optical intensity of the multiplexed coherent light. An image obtaining means performs image processes, and displays an optical tomographic image on a display apparatus.
Owner:FUJIFILM HLDG CORP +1
Scanning mechanisms for imaging probe
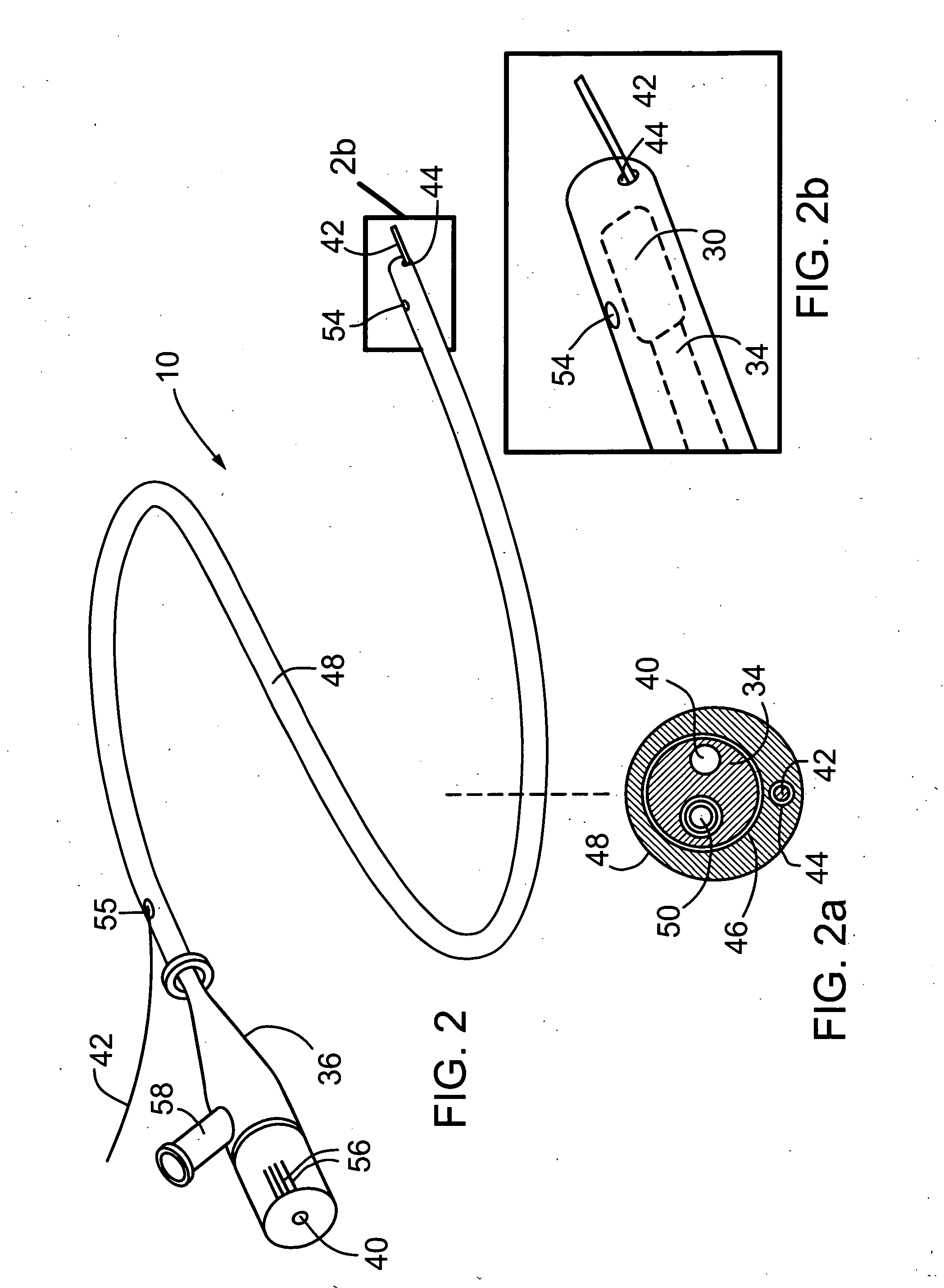
ActiveUS20080177138A1High resolutionQuantity minimizationUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgeryPhysicsMammalian tissue
The present invention provides scanning mechanisms for imaging probes using for imaging mammalian tissues and structures using high resolution imaging, including high frequency ultrasound and / or optical coherence tomography. The imaging probes include adjustable rotational drive mechanism for imparting rotational motion to an imaging assembly containing either optical or ultrasound transducers which emit energy into the surrounding area. The imaging assembly includes a scanning mechanism having including a movable member configured to deliver the energy beam along a path out of said elongate hollow shaft at a variable angle with respect to said longitudinal axis to give forward and side viewing capability of the imaging assembly. The movable member is mounted in such a way that the variable angle is a function of the angular velocity of the imaging assembly.
Owner:SUNNYBROOK HEALTH SCI CENT
Imaging system and method for providing extended depth of focus, range extraction and super resolved imaging
InactiveUS7646549B2Improving geometrical resolutionIncrease depth of focusSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffraction gratingsImaging lensField of view
An imaging system is presented for imaging objects within a field of view of the system. The imaging system comprises an imaging lens arrangement, a light detector unit at a certain distance from the imaging lens arrangement, and a control unit connectable to the output of the detection unit. The imaging lens arrangement comprises an imaging lens and an optical element located in the vicinity of the lens aperture, said optical element introducing aperture coding by an array of regions differently affecting a phase of light incident thereon which are randomly distributed within the lens aperture, thereby generating an axially-dependent randomized phase distribution in the Optical Transfer Function (OTF) of the imaging system resulting in an extended depth of focus of the imaging system. The control unit is configured to decode the sampled output of the detection unit by using the random aperture coding to thereby extract 3D information of the objects in the field of view of the light detector unit.
Owner:BRIEN HOLDEN VISION INST (AU)
Method and apparatus for imaging a sample on a device
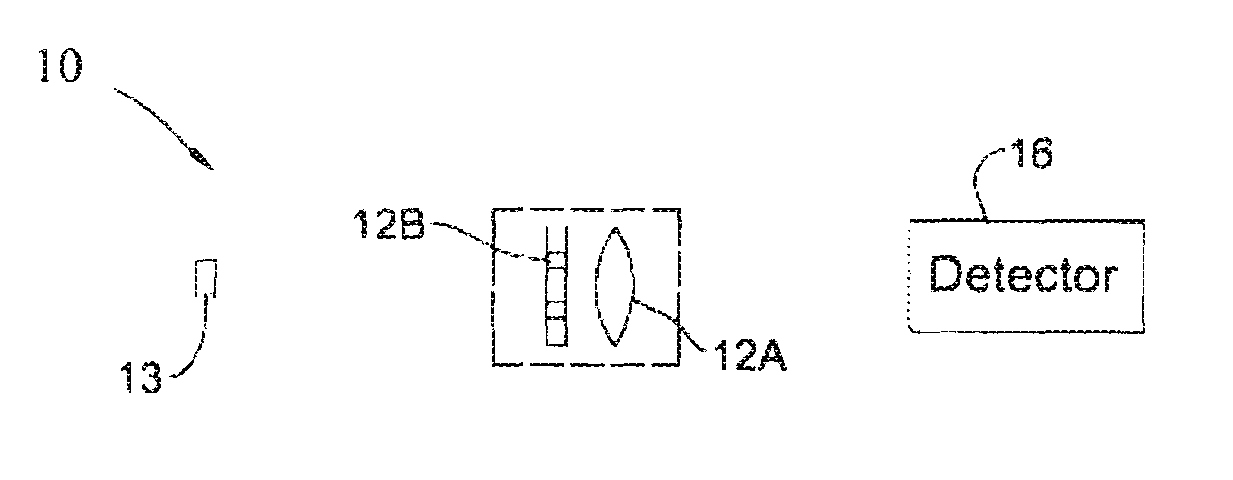
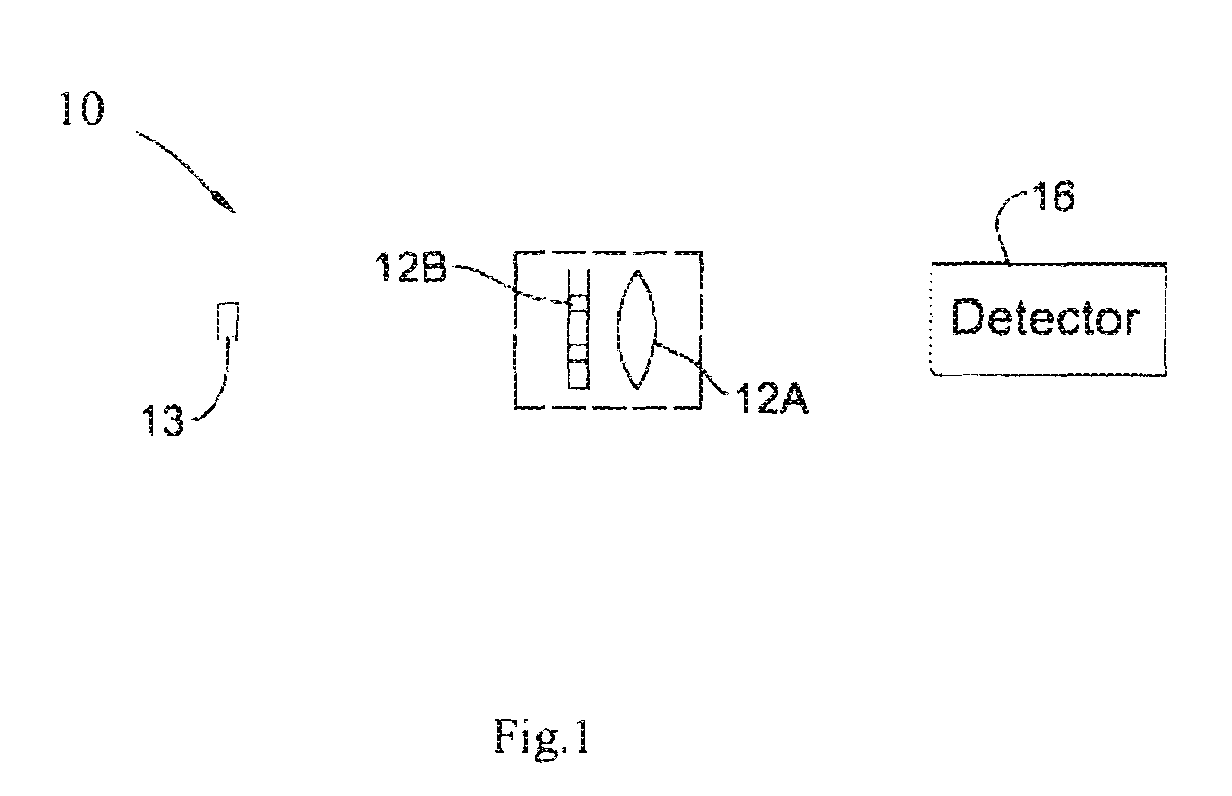
InactiveUS20030152490A1Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsPhotometry using reference valuePolymerPerformed Imaging
Labeled targets on a support synthesized with polymer sequences at known locations according to the methods disclosed in U.S. Pat. No. 5,143,854 and PCT WO 92 / 10092 or others, can be detected by exposing selected regions of sample 1500 to radiation from a source 1100 and detecting the emission therefrom, and repeating the steps of exposition and detection until the sample is completely examined.
Owner:TRULSON MARK +4
OCT using spectrally resolved bandwidth
The present invention is related to a system for optical coherence tomographic imaging of turbid (i.e., scattering) materials utilizing multiple channels of information. The multiple channels of information may be comprised and encompass spatial, angle, spectral and polarization domains. More specifically, the present invention is related to methods and apparatus for utilizing optical sources, systems or receivers capable of providing (source), processing (system) or recording (receiver) a multiplicity of channels of spectral information for optical coherence tomographic imaging of turbid materials. In these methods and apparatus the multiplicity of channels of spectral information that can be provided by the source, processed by the system, or recorded by the receiver are used to convey simultaneously spatial, spectral or polarimetric information relating to the turbid material being imaged tomographically. The multichannel optical coherence tomographic methods can be incorporated into an endoscopic probe for imaging a patient. The endoscope comprises an optical fiber array and can comprise a plurality of optical fibers adapted to be disposed in the patient. The optical fiber array transmits the light from the light source into the patient, and transmits the light reflected by the patient out of the patient. The plurality of optical fibers in the array are in optical communication with the light source. The multichannel optical coherence tomography system comprises a detector for receiving the light from the array and analyzing the light. The methods and apparatus may be applied for imaging a vessel, biliary, GU and / or GI tract of a patient.
Owner:BOARD OF RGT THE UNIV OF TEXAS SYST
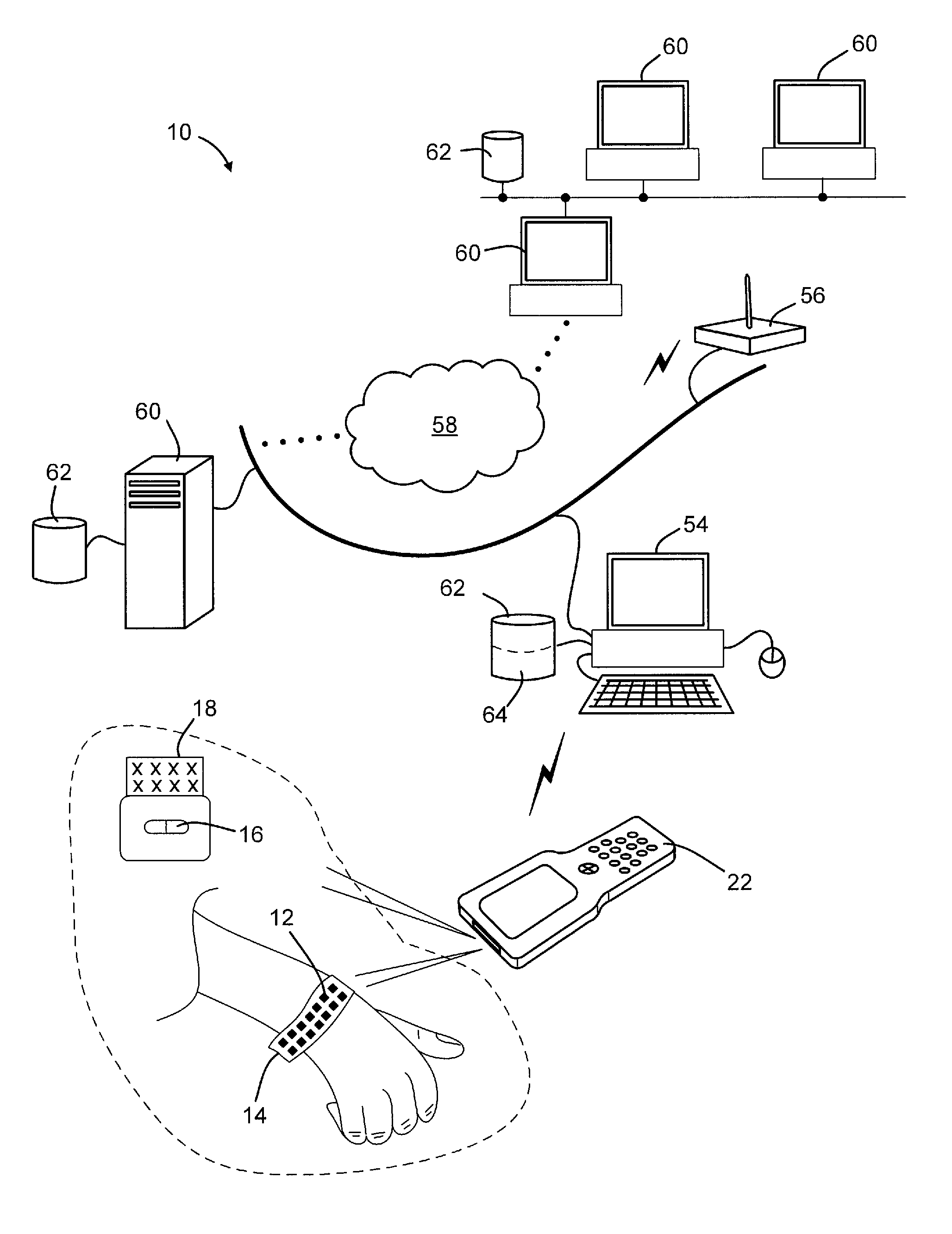
Optical displacement sensor for infusion devices
InactiveUS7498563B2Other blood circulation devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDetector arrayEngineering
An optical sensor for a delivery device having a piston that displaces a substance, such as a fluid, from a reservoir. The optical sensor has a light source and a detector array for imaging encoding features disposed along a plunger rod coupled to the piston. By virtue of the pattern of encoding features, an absolute position of the plunger rod relative to a fiducial position may be determined uniquely. Thus, the volume of fluid remaining in the reservoir, the rate of fluid delivery, and proper loading of the reservoir may be accurately ascertained. Additionally, the encoding may serve to uniquely identify a version of the reservoir which may be supplied in various versions corresponding, for example, to differing concentrations of a therapeutic agent to be dispensed.
Owner:EUGLY DIABETES CARE LLC
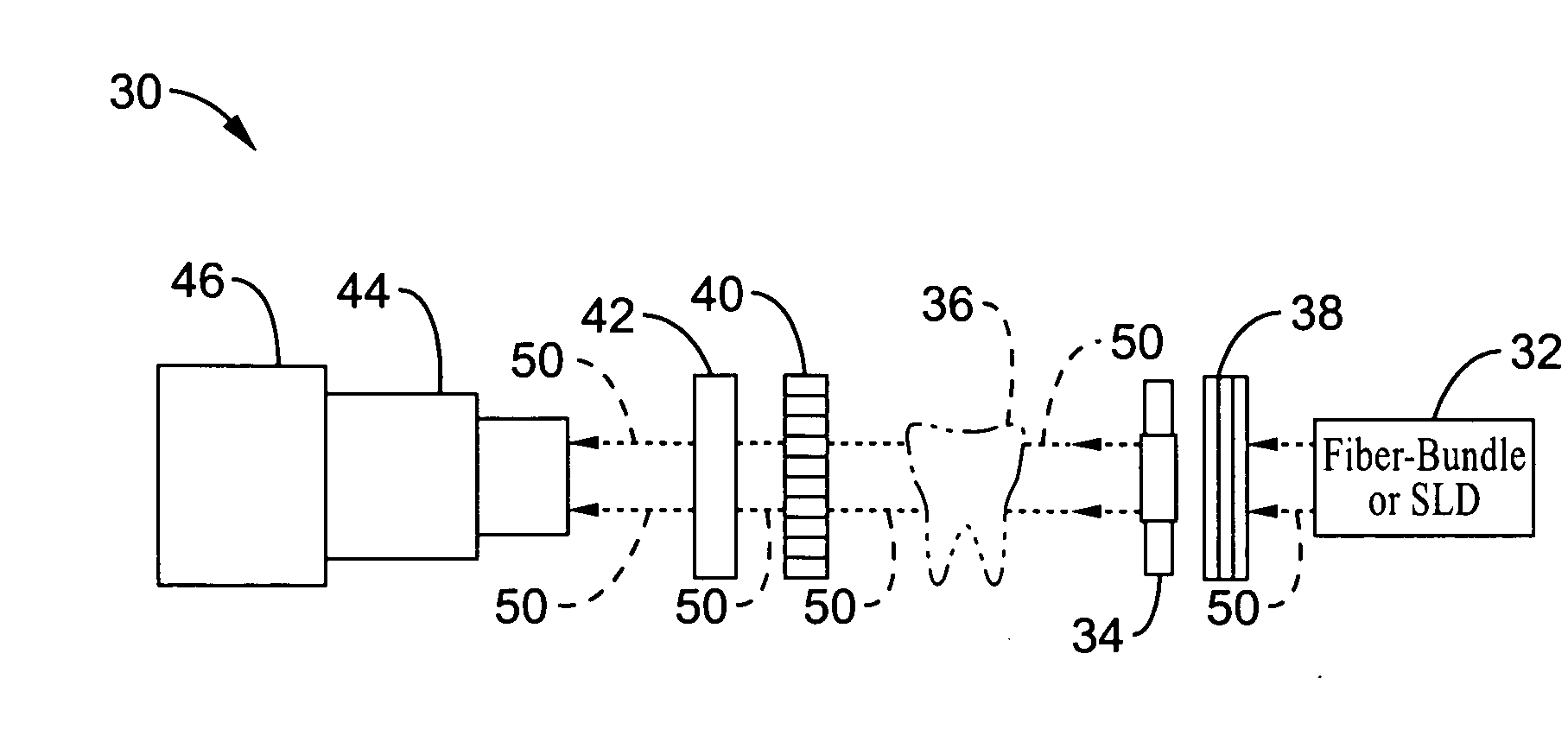
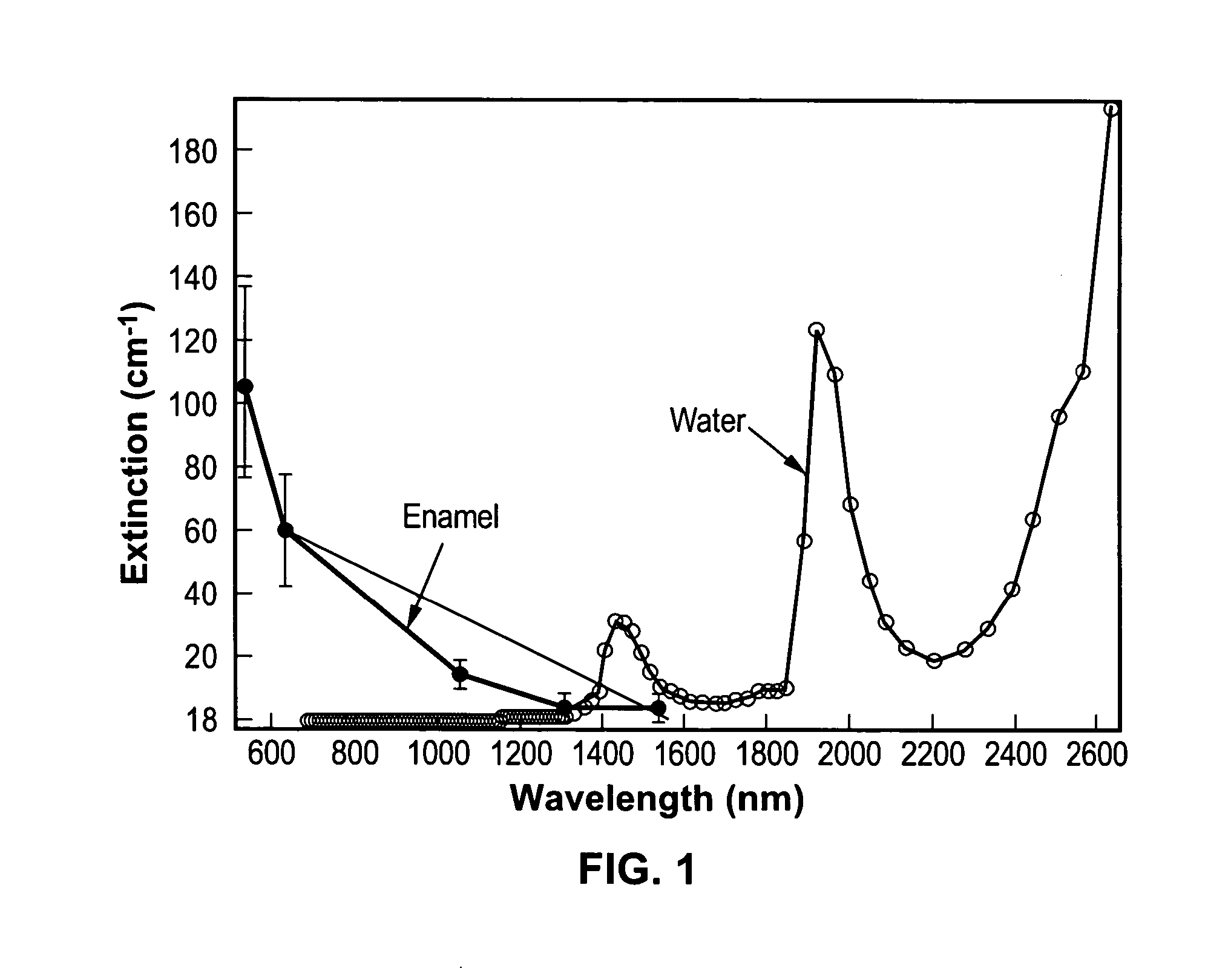
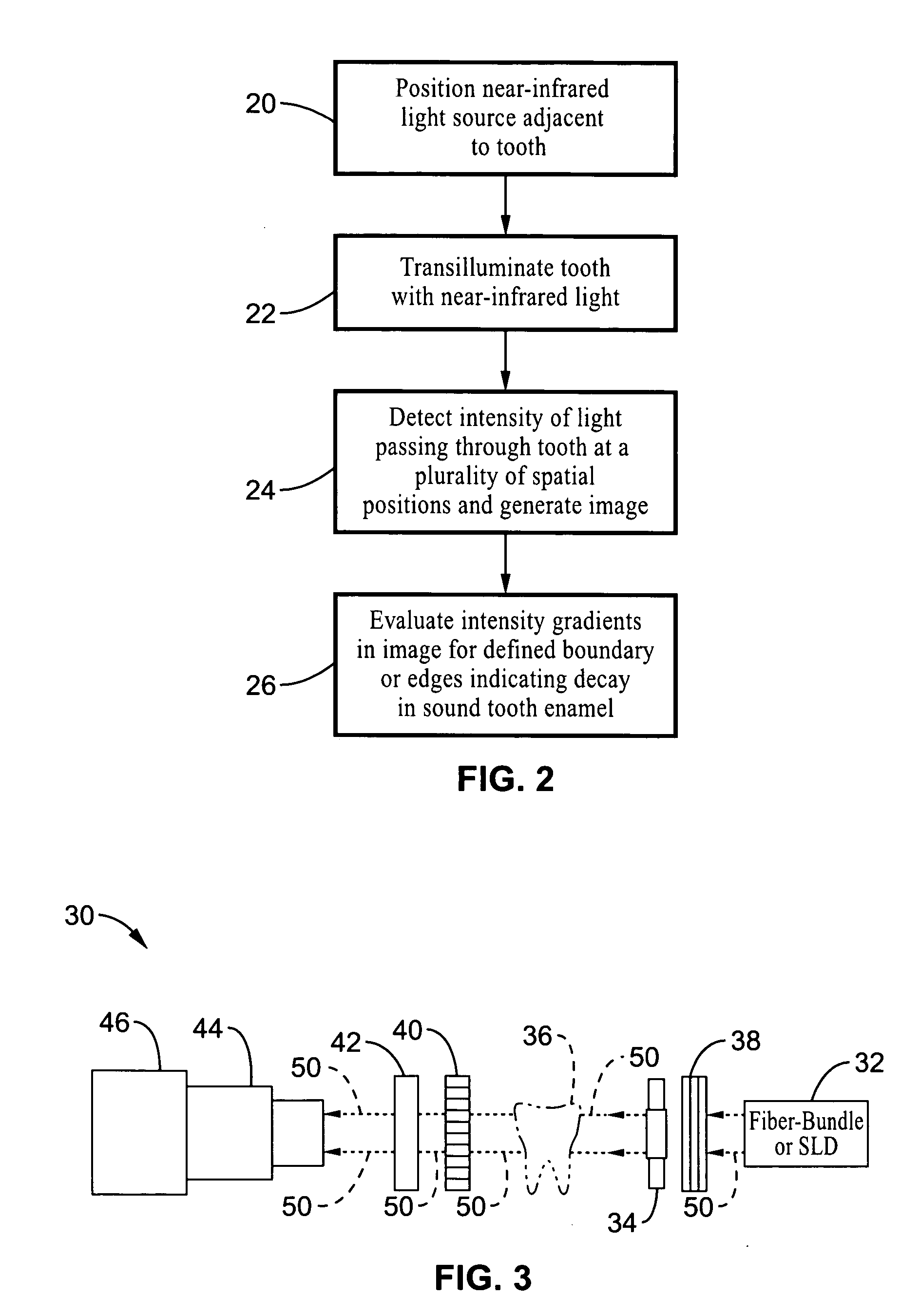
Near-infrared transillumination for the imaging of early dental decay
A method for detecting tooth decay and other tooth anomalies wherein a tooth is transilluminated with a near-infrared light source preferably in the range from approximately 795-nm to approximately 1600-nm, more preferably in the range from approximately 830-nm to approximately 1550-nm, more preferably in the range from approximately 1285-nm to approximately 1335-nm, and more preferably at a wavelength of approximately 1310-nm, and the light passing through the tooth is imaged for determining an area of decay in the tooth. The light source is a fiber-optic bundle coupled to a halogen lamp or more preferably a superluminescent diode, and the imaging device is preferably a CCD camera or a focal plane array (FPA).
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Method of correcting nonuniformity of pixels in an OLED
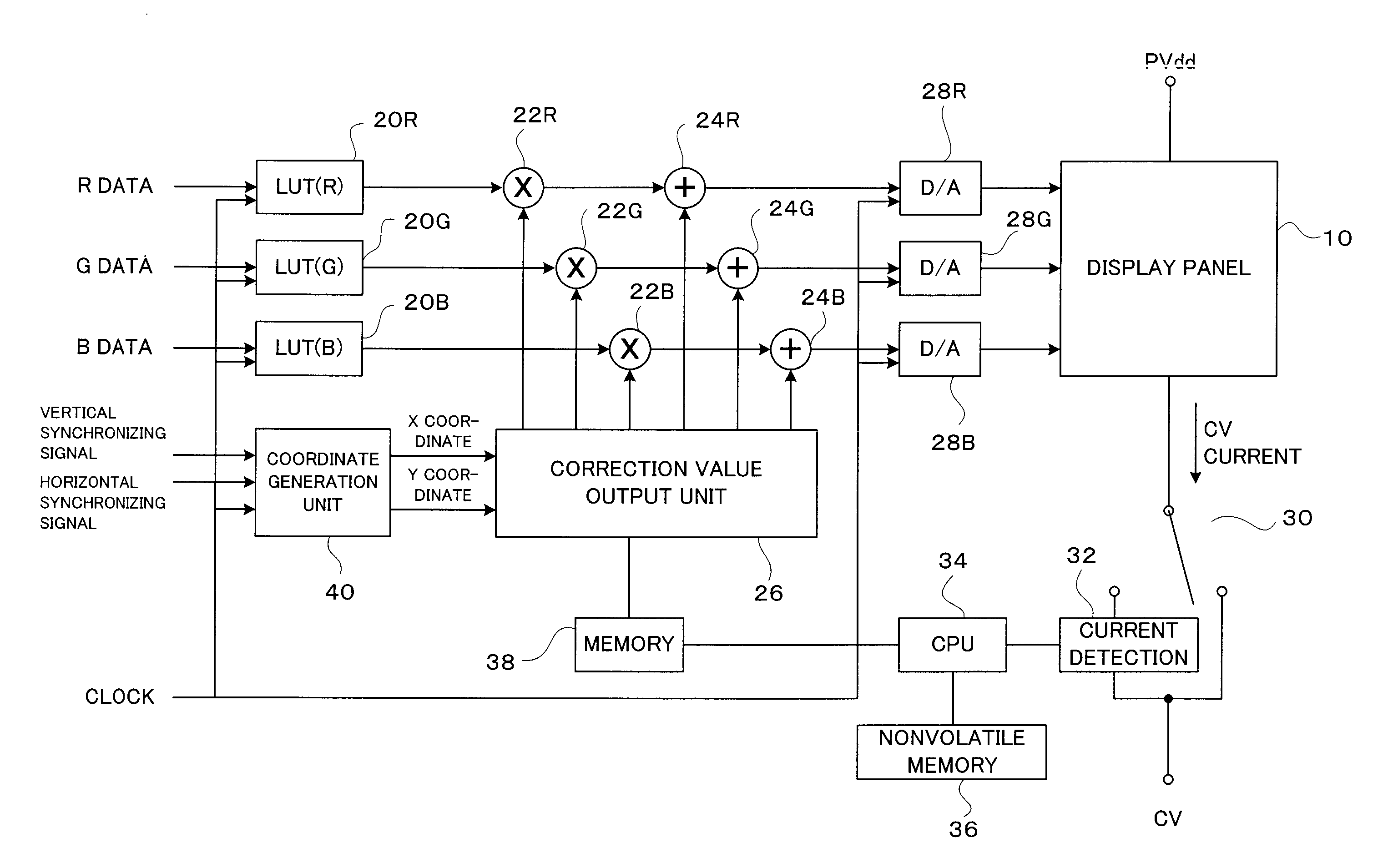
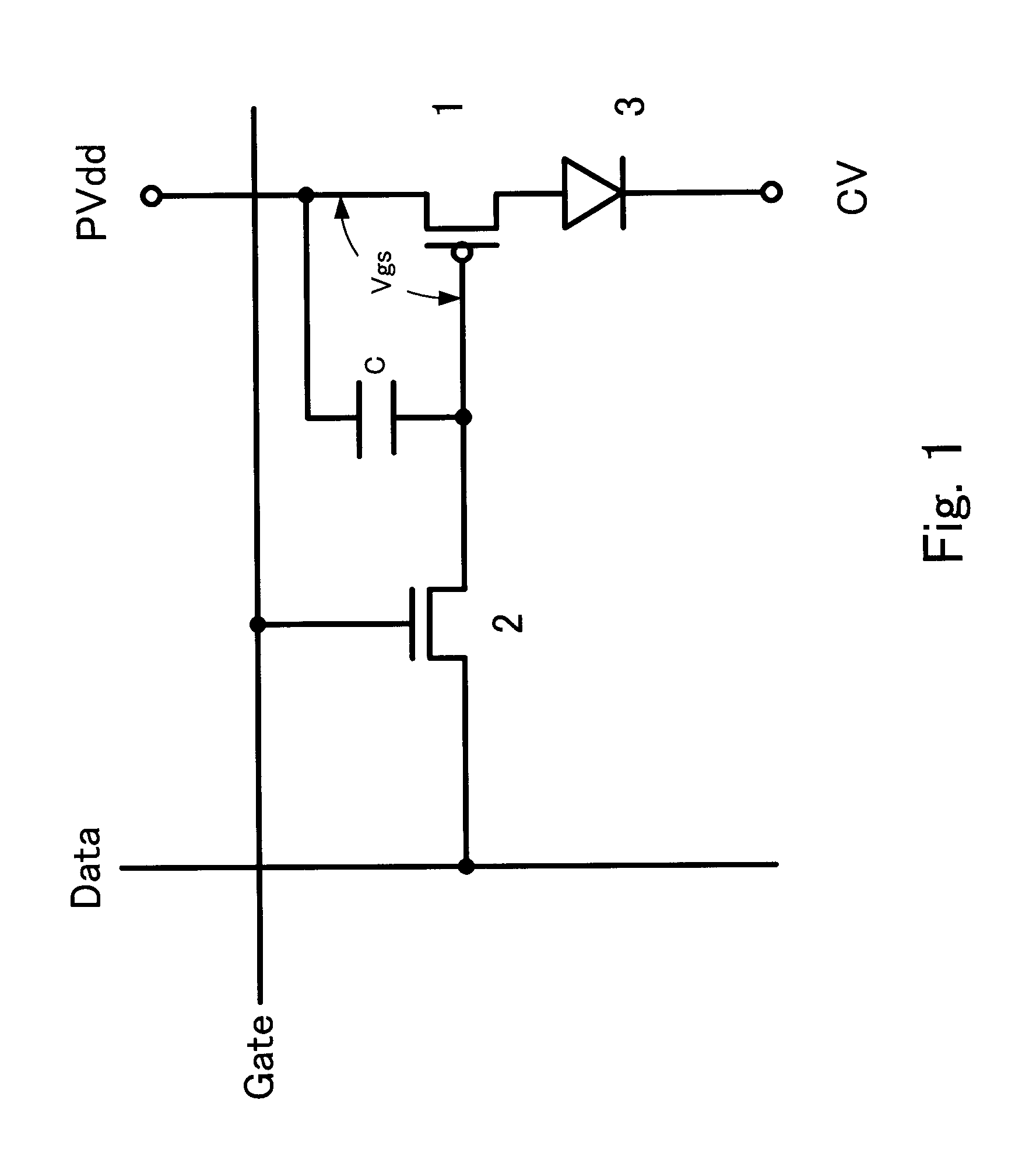
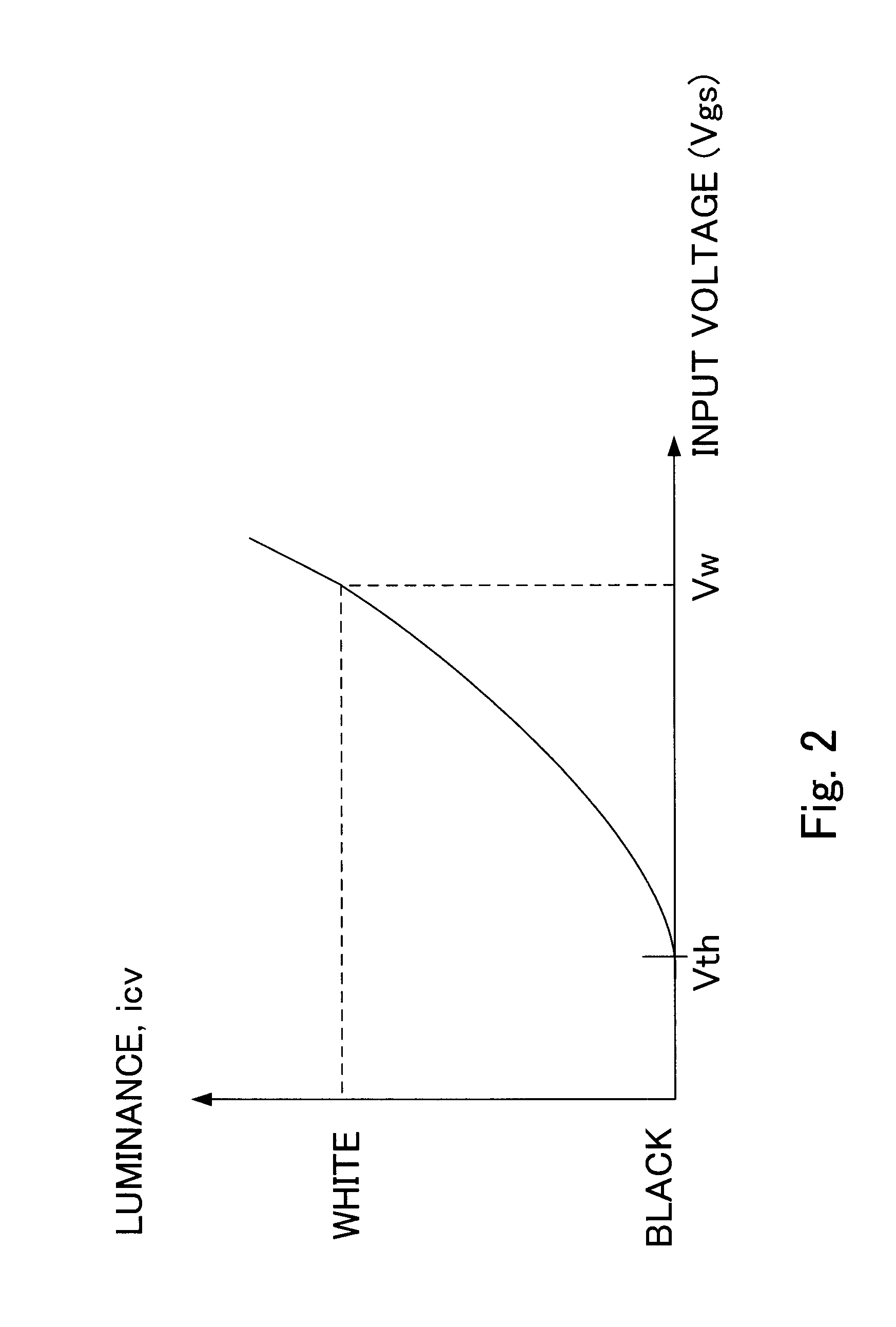
ActiveUS20070008251A1Accurate correction dataShorten the timeCathode-ray tube indicatorsInput/output processes for data processingImaging processingDisplay device
Nonuniformity in an organic EL display device is effectively detected. All display pixels of an organic EL panel are turned on and the display is photographed with a digital camera. A computer performs image processing of the photographed image to detect an area in which unevenness exists. Then, a V-I curve of each pixel in the area is measured to calculate necessary correction values. The calculated correction values are stored in a memory for use in correcting a signal input to the organic EL panel.
Owner:GLOBAL OLED TECH
Compensator for multiple surface imaging
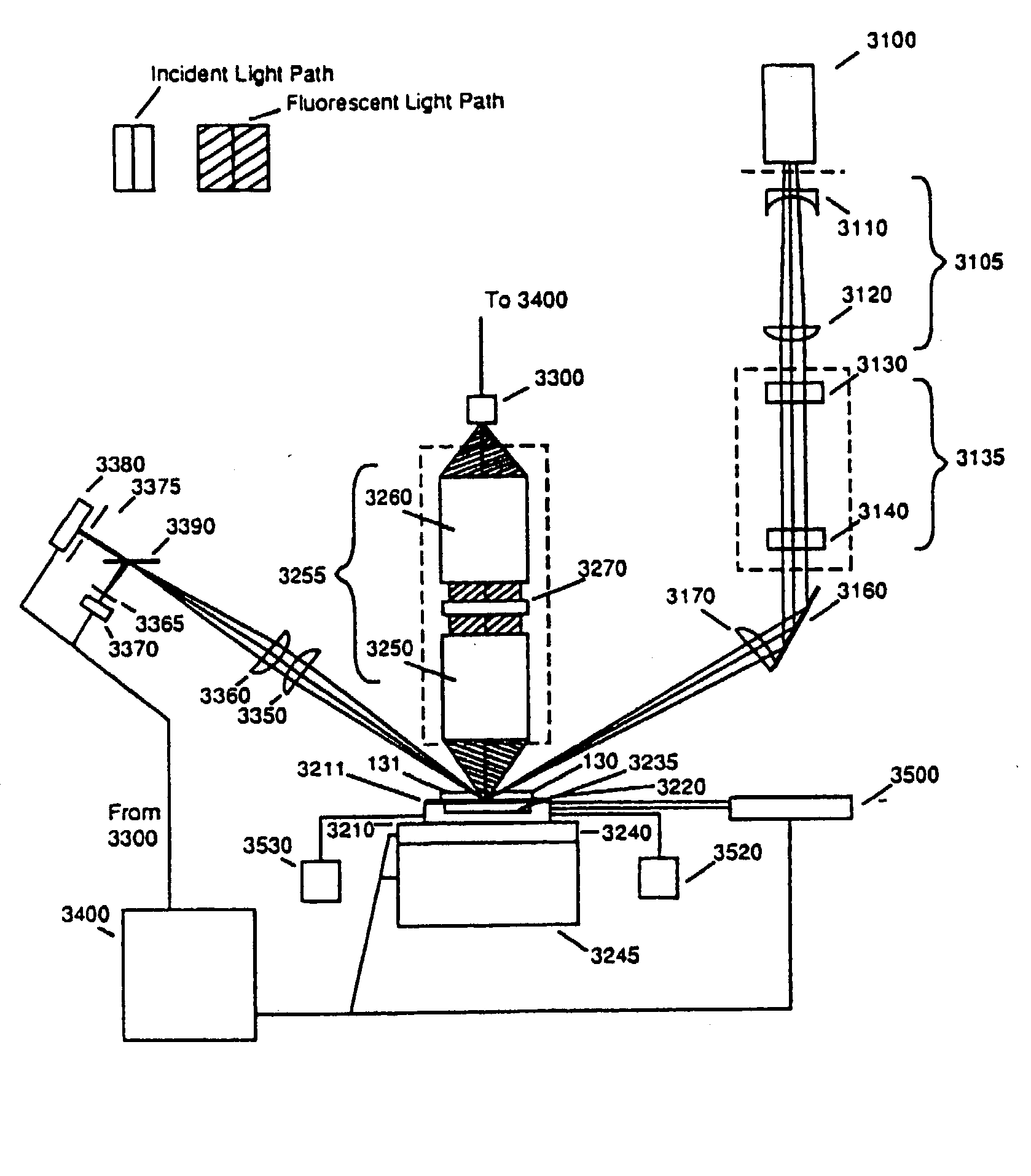
ActiveUS20090272914A1Reduce aberrationScattering properties measurementsLuminescent dosimetersTotal internal reflectionFluorescence
A system and method for imaging biological samples on multiple surfaces of a support structure are disclosed. The support structure may, for instance, be a flow cell through which a reagent fluid is allowed to flow and interact with the biological samples. Excitation radiation from at least one radiation source may be used to excite the biological samples on multiple surfaces. In this manner, fluorescent emission radiation may be generated from the biological samples and subsequently captured and detected by detection optics and at least one detector. The captured and detected fluorescent emission radiation may then be used to generate image data. This imaging of multiple surfaces may be accomplished either sequentially or simultaneously. In addition, the techniques of the present invention may be used with any type of imaging system. For instance, both epifluorescent and total internal reflection (TIR) methods may benefit from the techniques of the present invention. In addition, the biological samples imaged may be present on the surfaces of the support structure in a random special pattern and need not be at known locations in order for the imaging to be performed.
Owner:ILLUMINA INC
Systems and methods for phase measurements
InactiveUS20050105097A1Efficient collectionNo loss of precisionOptical measurementsInterferometersCellular componentPhase noise
Preferred embodiments of the present invention are directed to systems for phase measurement which address the problem of phase noise using combinations of a number of strategies including, but not limited to, common-path interferometry, phase referencing, active stabilization and differential measurement. Embodiment are directed to optical devices for imaging small biological objects with light. These embodiments can be applied to the fields of, for example, cellular physiology and neuroscience. These preferred embodiments are based on principles of phase measurements and imaging technologies. The scientific motivation for using phase measurements and imaging technologies is derived from, for example, cellular biology at the sub-micron level which can include, without limitation, imaging origins of dysplasia, cellular communication, neuronal transmission and implementation of the genetic code. The structure and dynamics of sub-cellular constituents cannot be currently studied in their native state using the existing methods and technologies including, for example, x-ray and neutron scattering. In contrast, light based techniques with nanometer resolution enable the cellular machinery to be studied in its native state. Thus, preferred embodiments of the present invention include systems based on principles of interferometry and / or phase measurements and are used to study cellular physiology. These systems include principles of low coherence interferometry (LCI) using optical interferometers to measure phase, or light scattering spectroscopy (LSS) wherein interference within the cellular components themselves is used, or in the alternative the principles of LCI and LSS can be combined to result in systems of the present invention.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
Optical lens system and method for microfluidic devices
ActiveUS20060006067A1Less complexProblem is reduced and eliminatedSludge treatmentVolume/mass flow measurementFluorescenceEngineering
An apparatus for imaging one or more selected fluorescence indications from a microfluidic device. The apparatus includes an imaging path coupled to least one chamber in at least one microfluidic device. The imaging path provides for transmission of one or more fluorescent emission signals derived from one or more samples in the at least one chamber of the at least one microfluidic device. The chamber has a chamber size, the chamber size being characterized by an actual spatial dimension normal to the imaging path. The apparatus also includes an optical lens system coupled to the imaging path. The optical lens system is adapted to transmit the one or more fluorescent signals associated with the chamber.
Owner:STANDARD BIOTOOLS INC
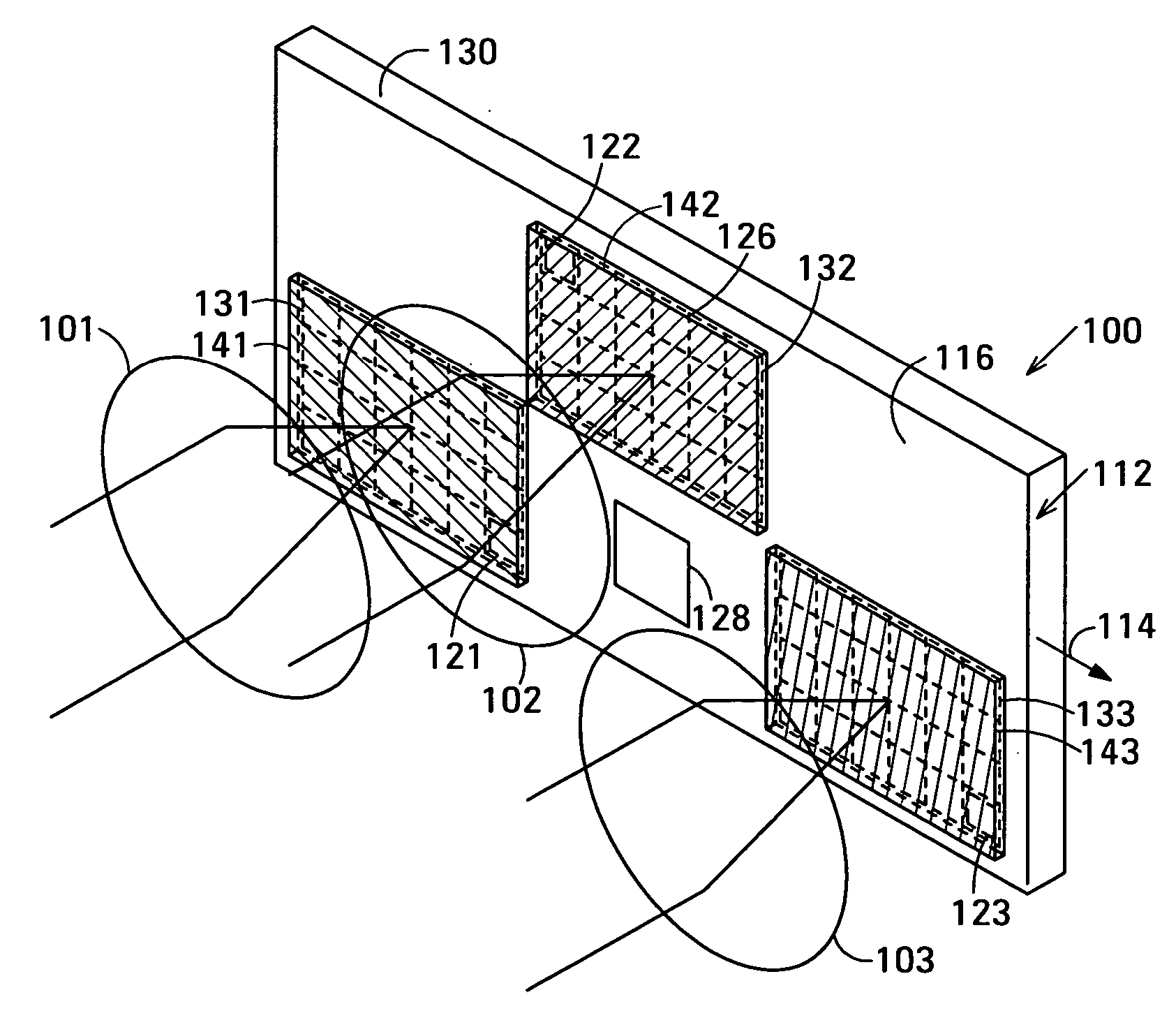
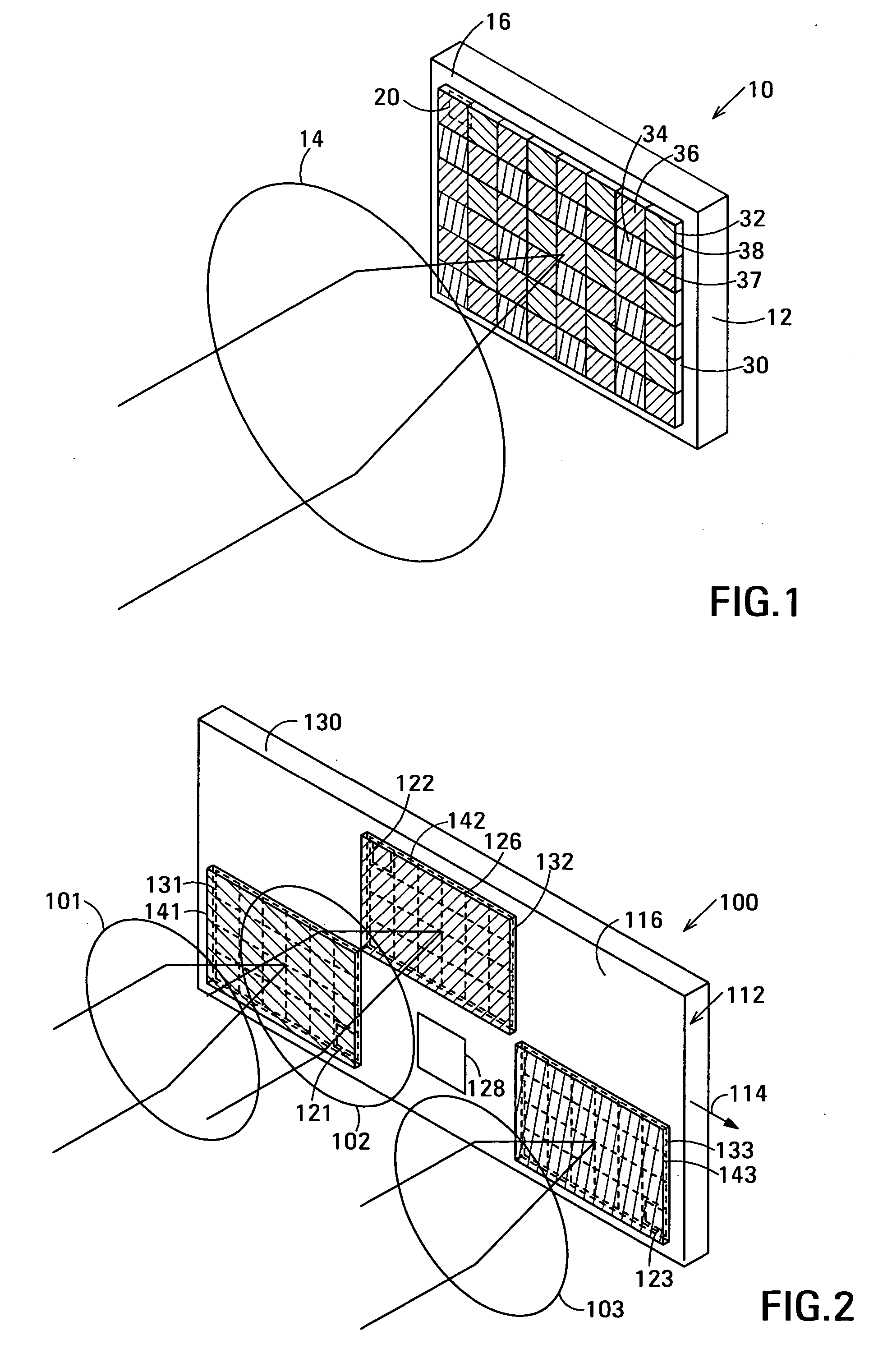
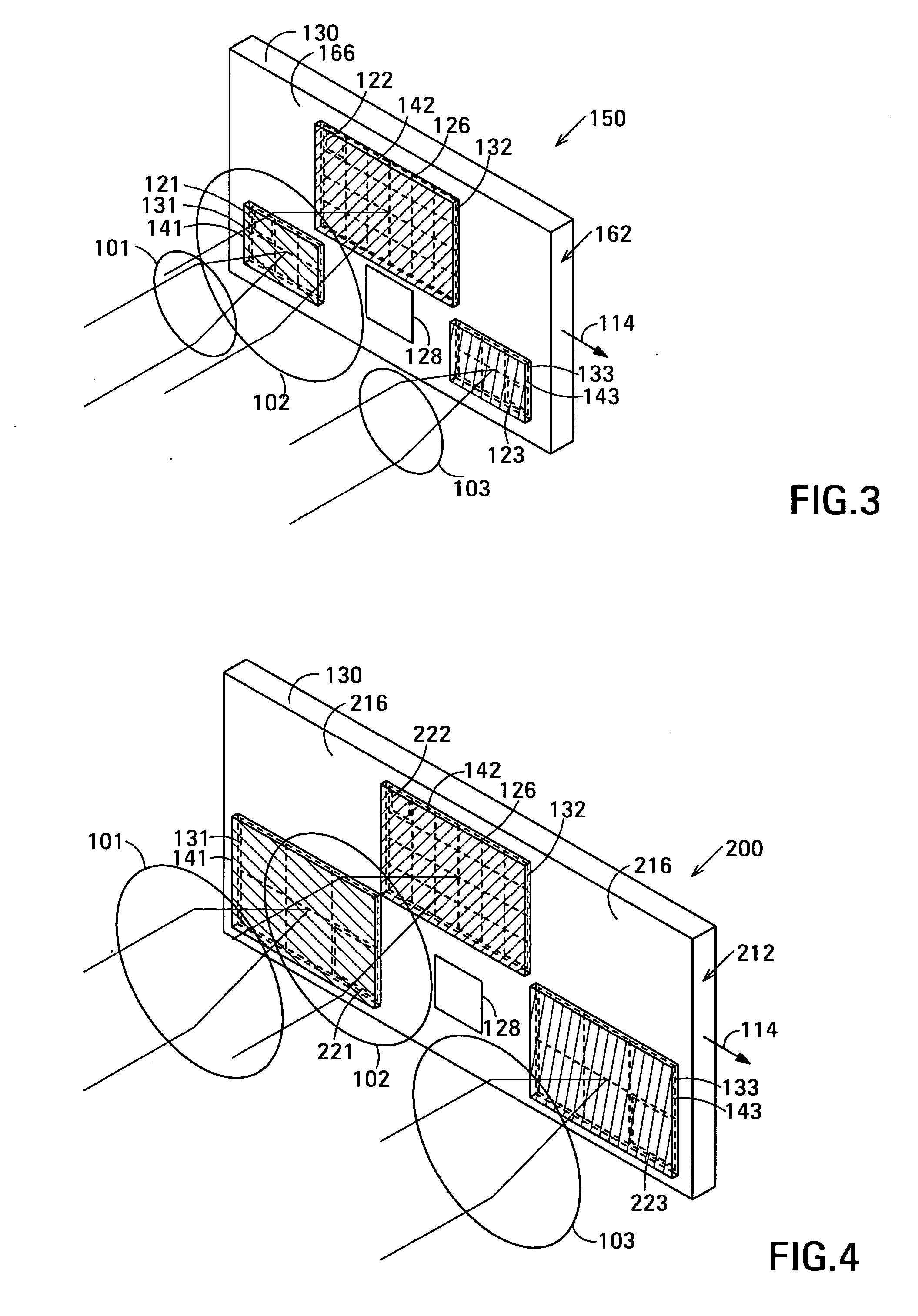
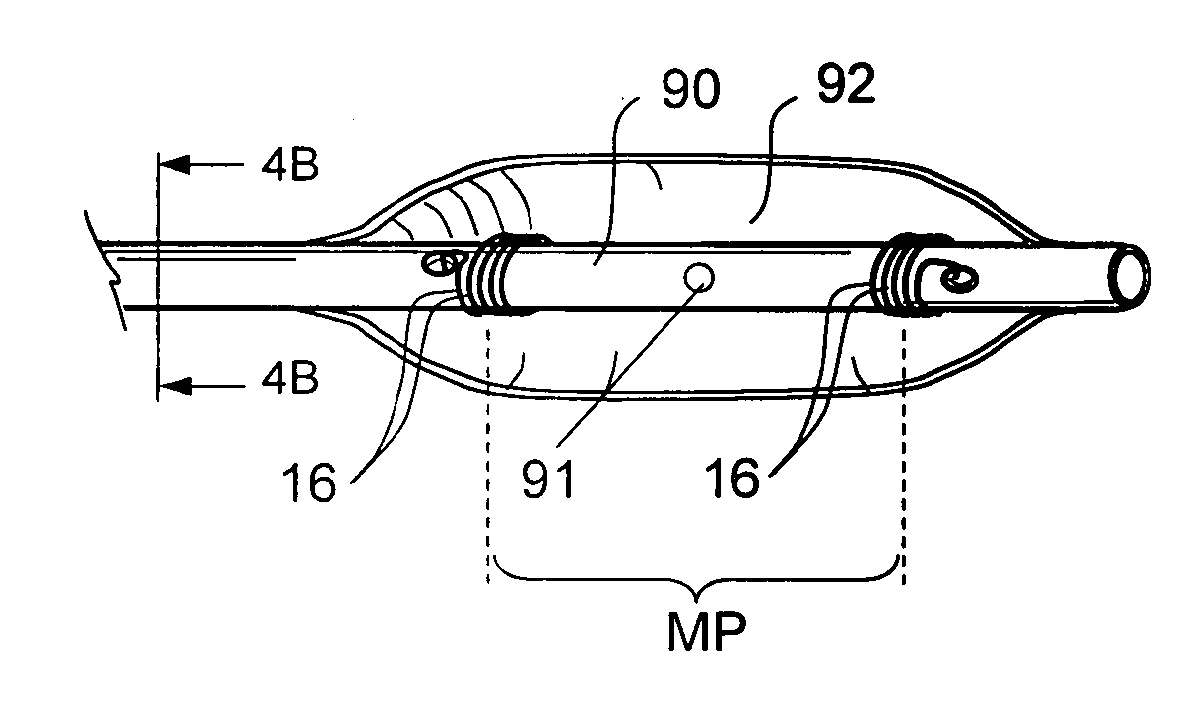
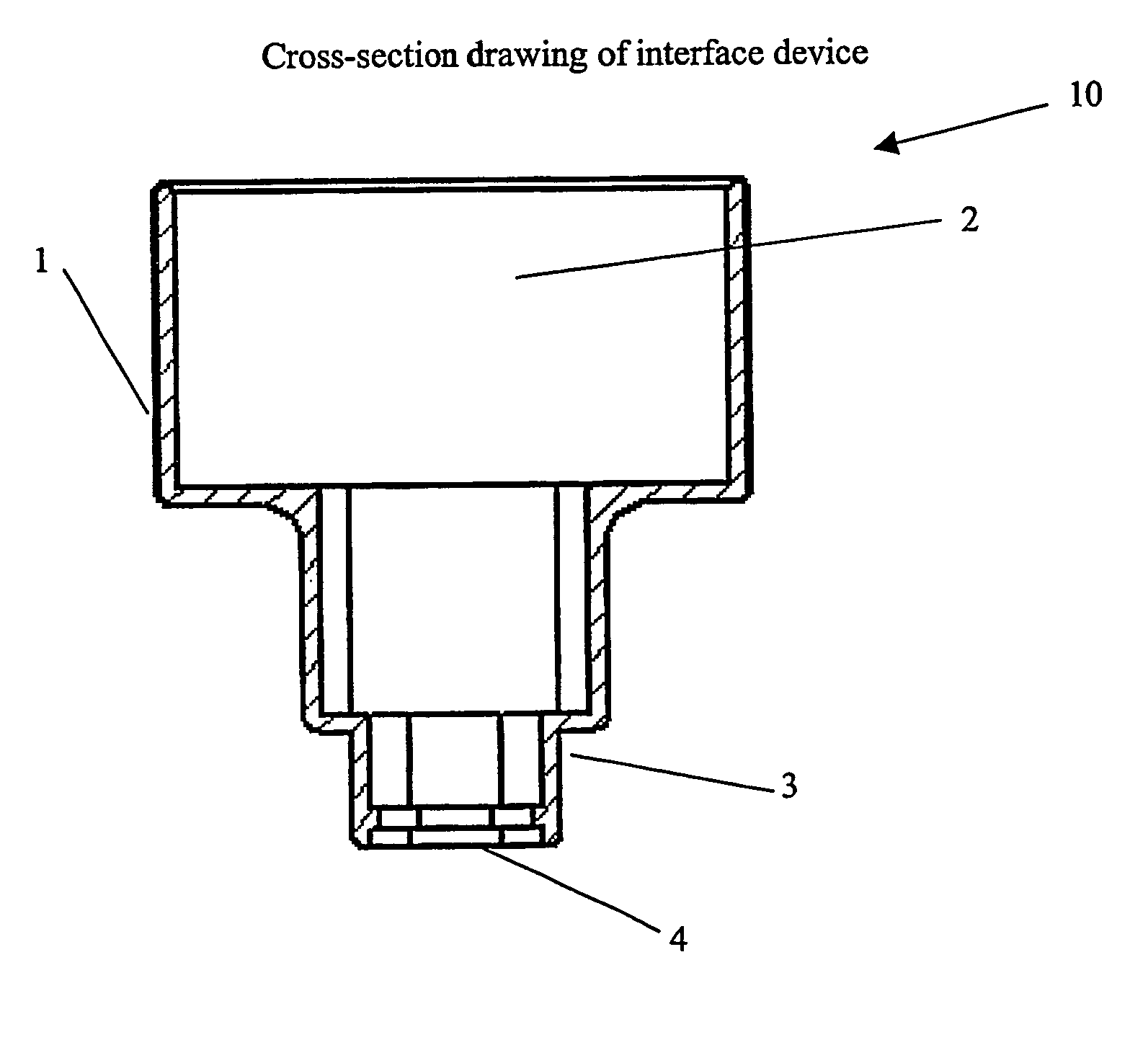
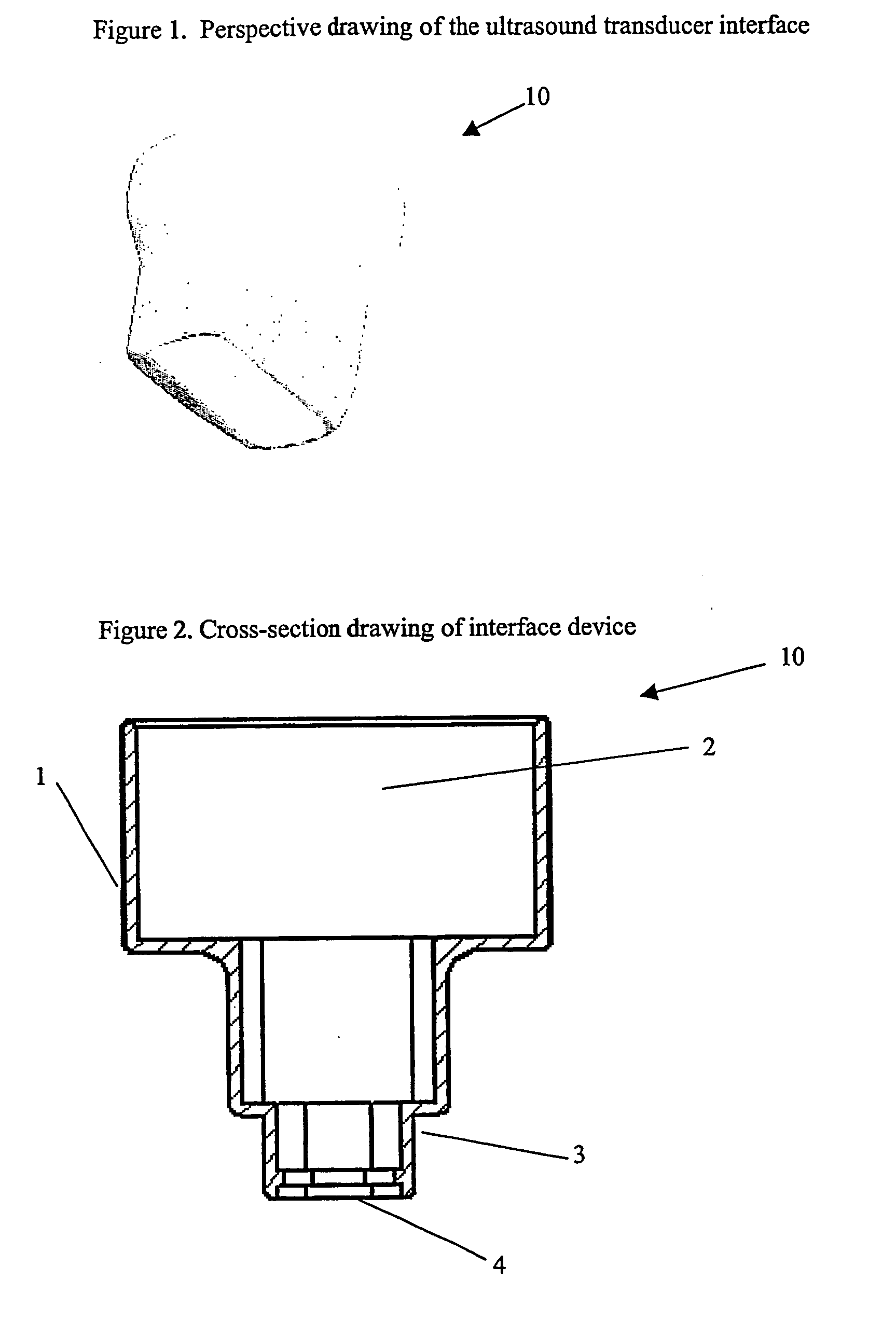
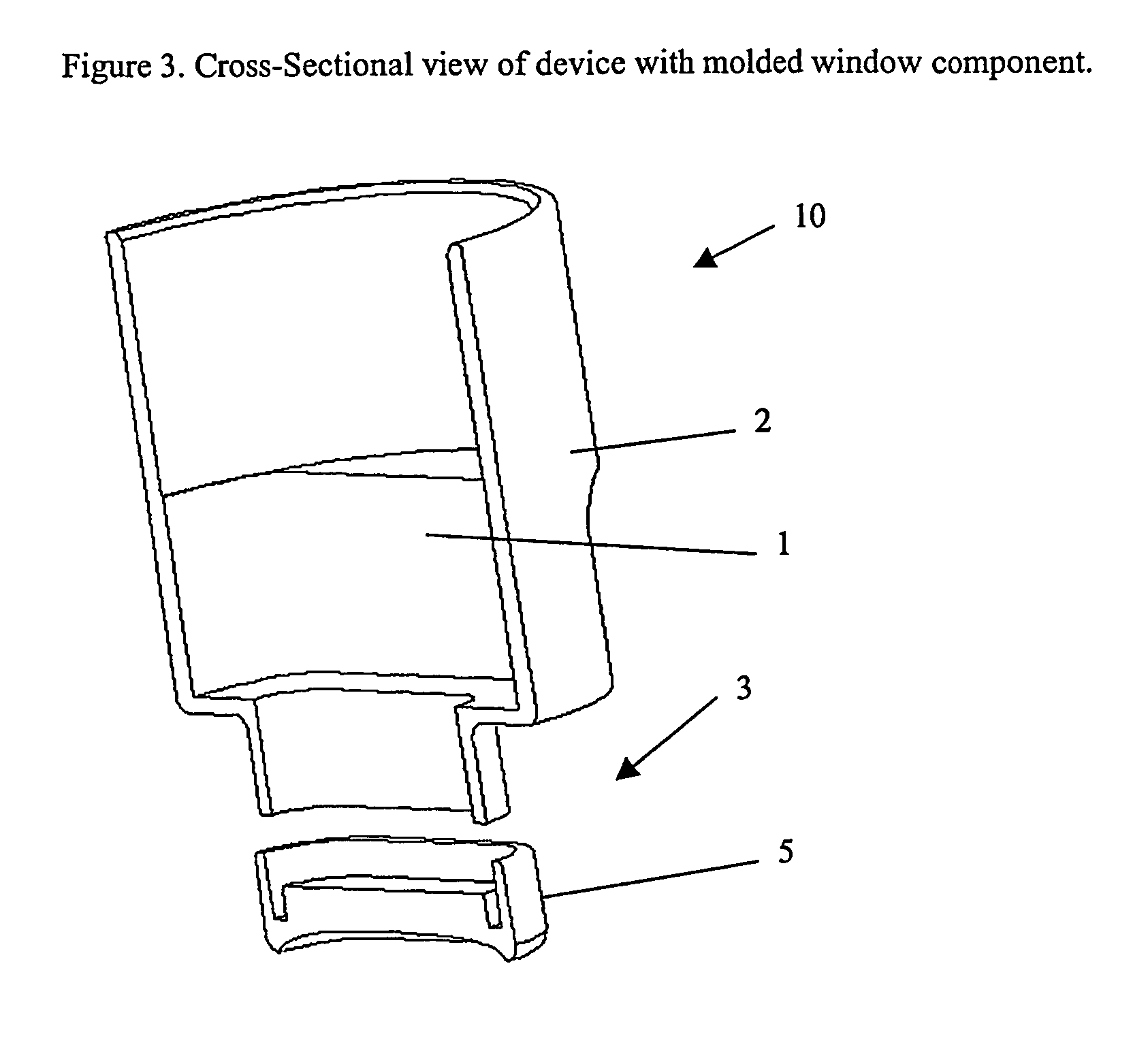
Ultrasound interfacing device for tissue imaging
A device (10) used with high frequency ultrasound provides a replaceable barrier between the ultrasound transducer and the tissues being imaged. The device (10) provides an acoustic pathway of minimal effect on the ultrasound signals, and furthermore provides for a safety barrier between a mechanical scanner and the tissues being imaged. The configuration of the device (10) allows it to function as a standoff for the ultrasound transducer to place the focus of the ultrasound beam at the desired depth of tissue for imaging. In addition, the device (10) may be sterilized and replaced as needed, providing sterile tissue contact surfaces. The device (10) has additional features, which are especially advantageous for diagnosis and surgery of the eye.
Owner:ISCI SURGICAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com