Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
539 results about "Wavelength selectivity" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
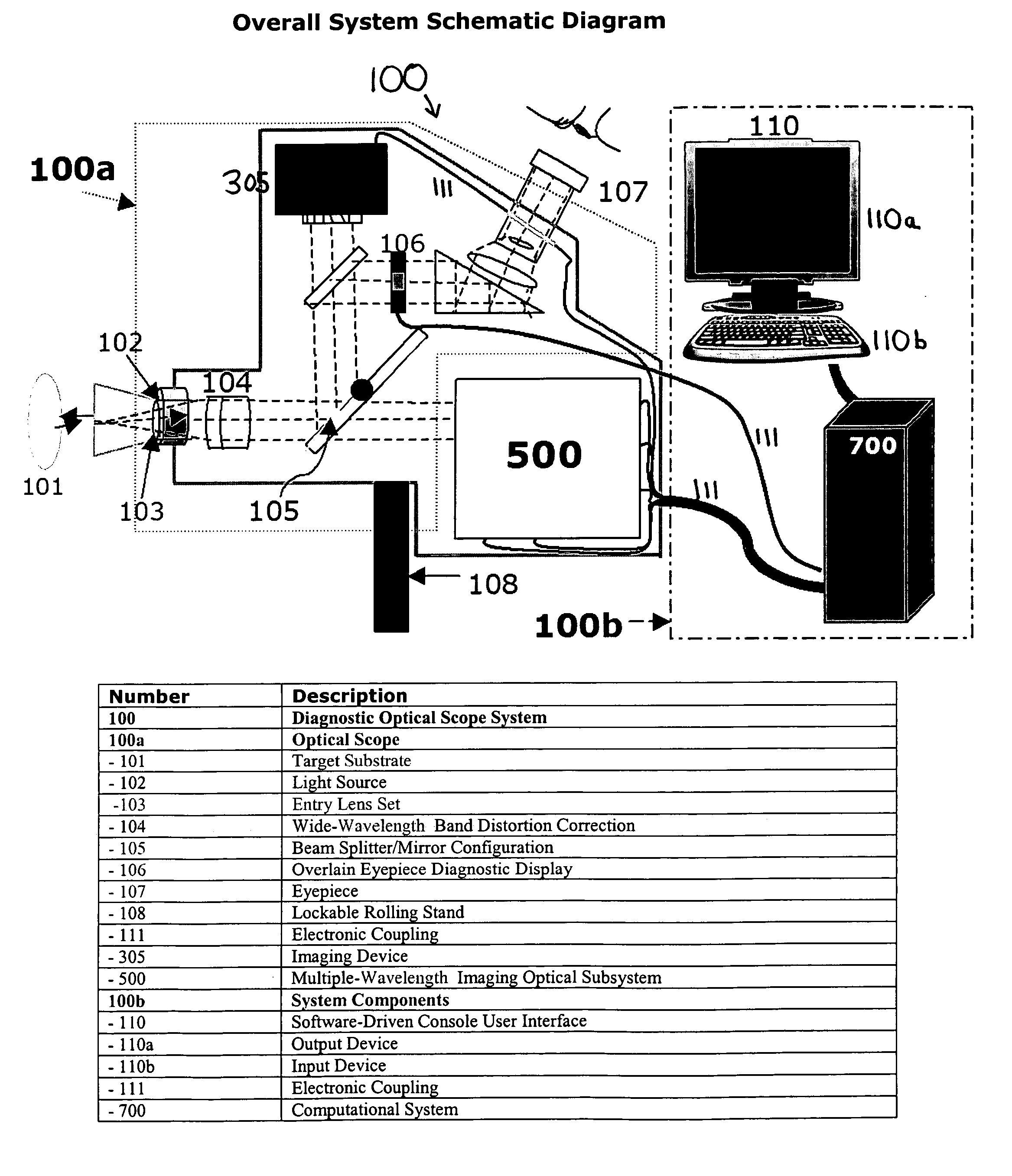
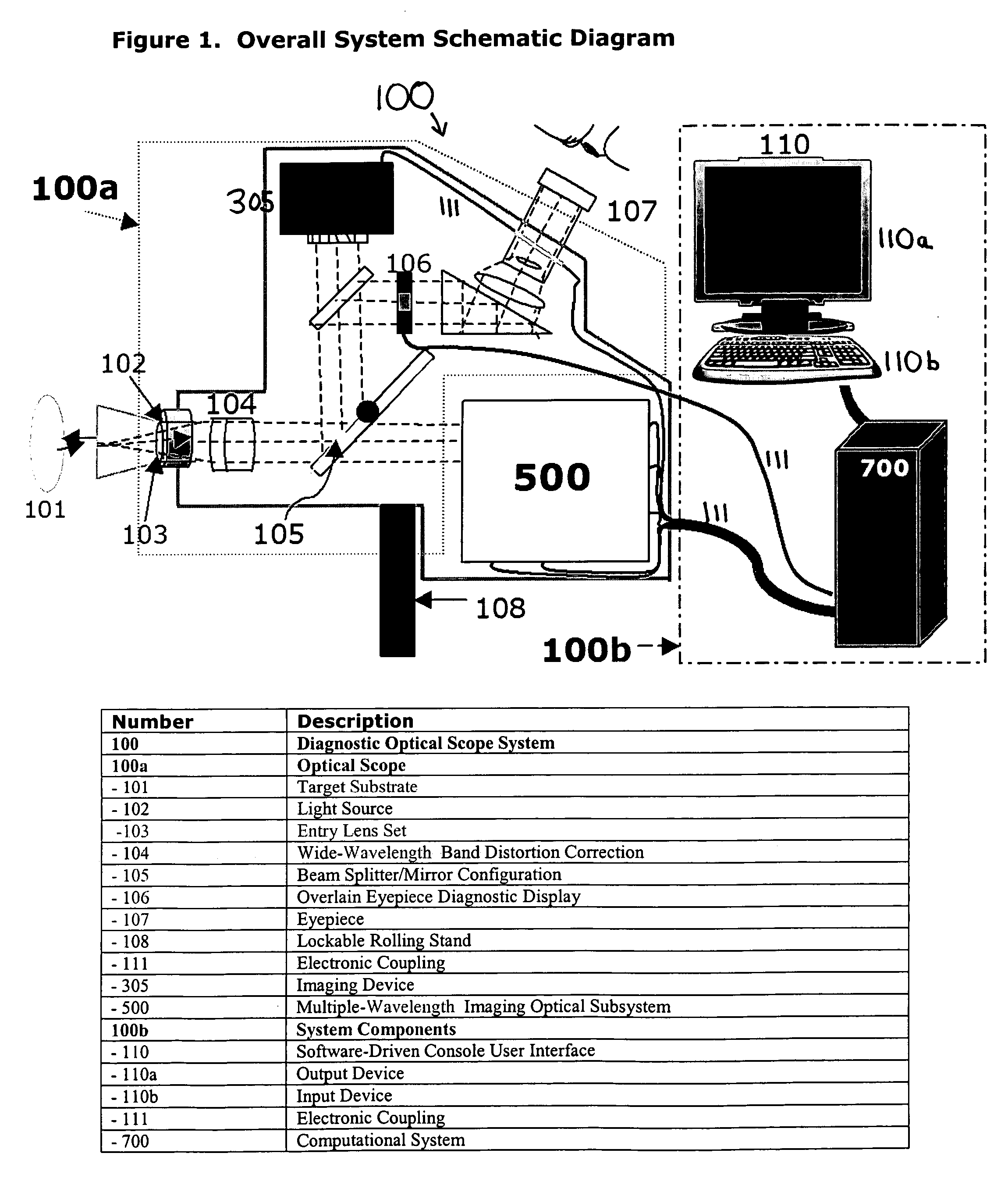
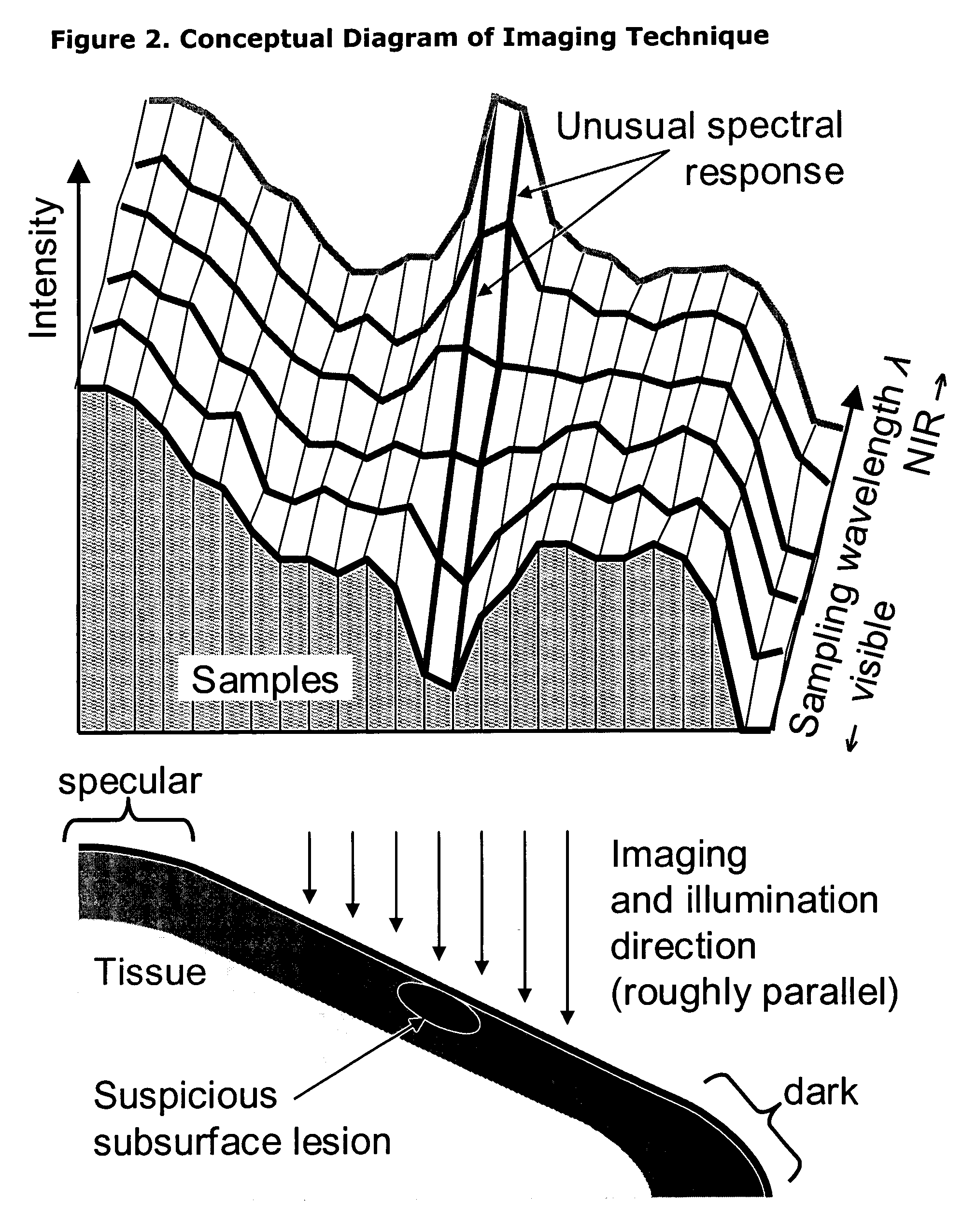
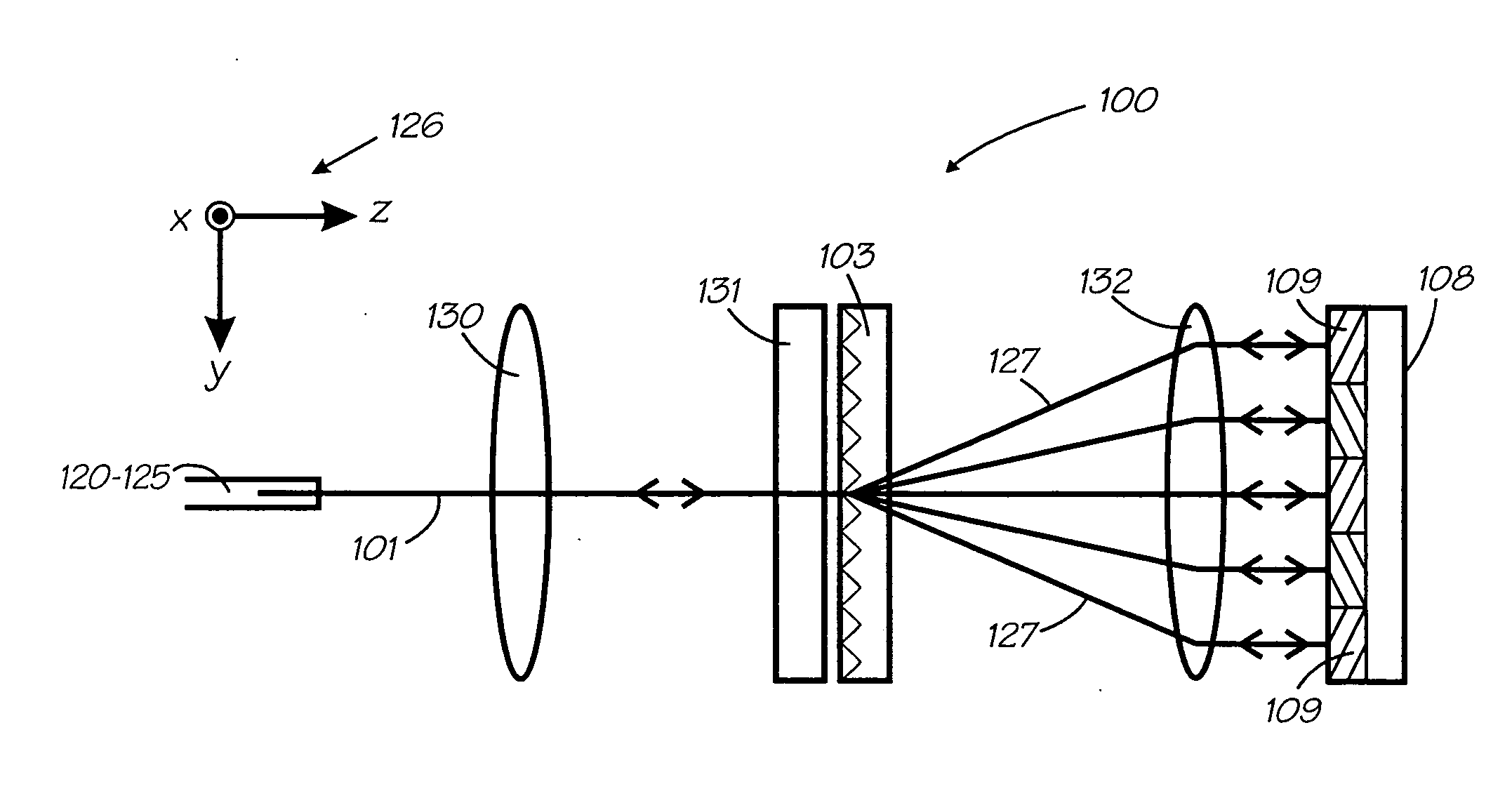
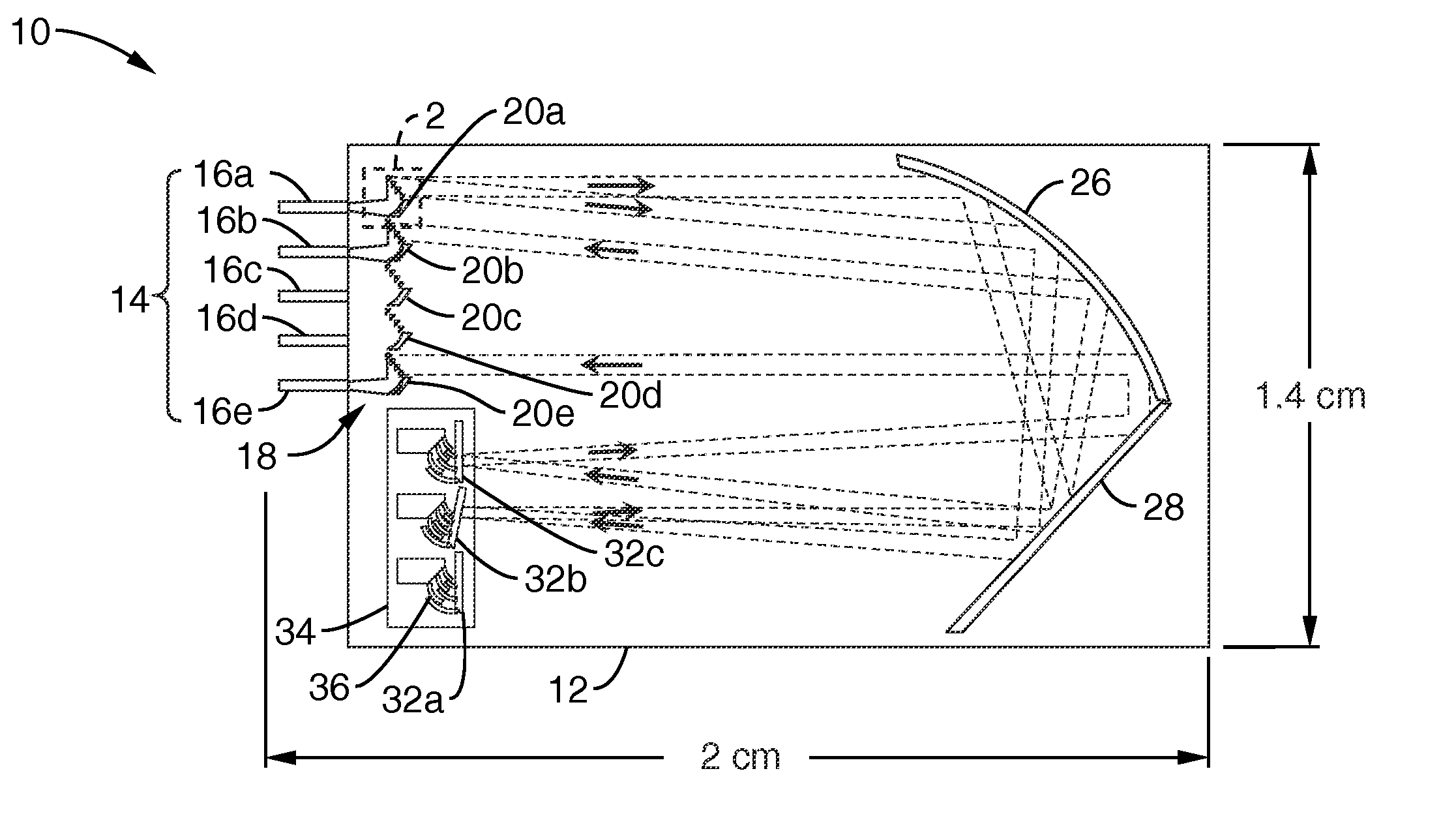
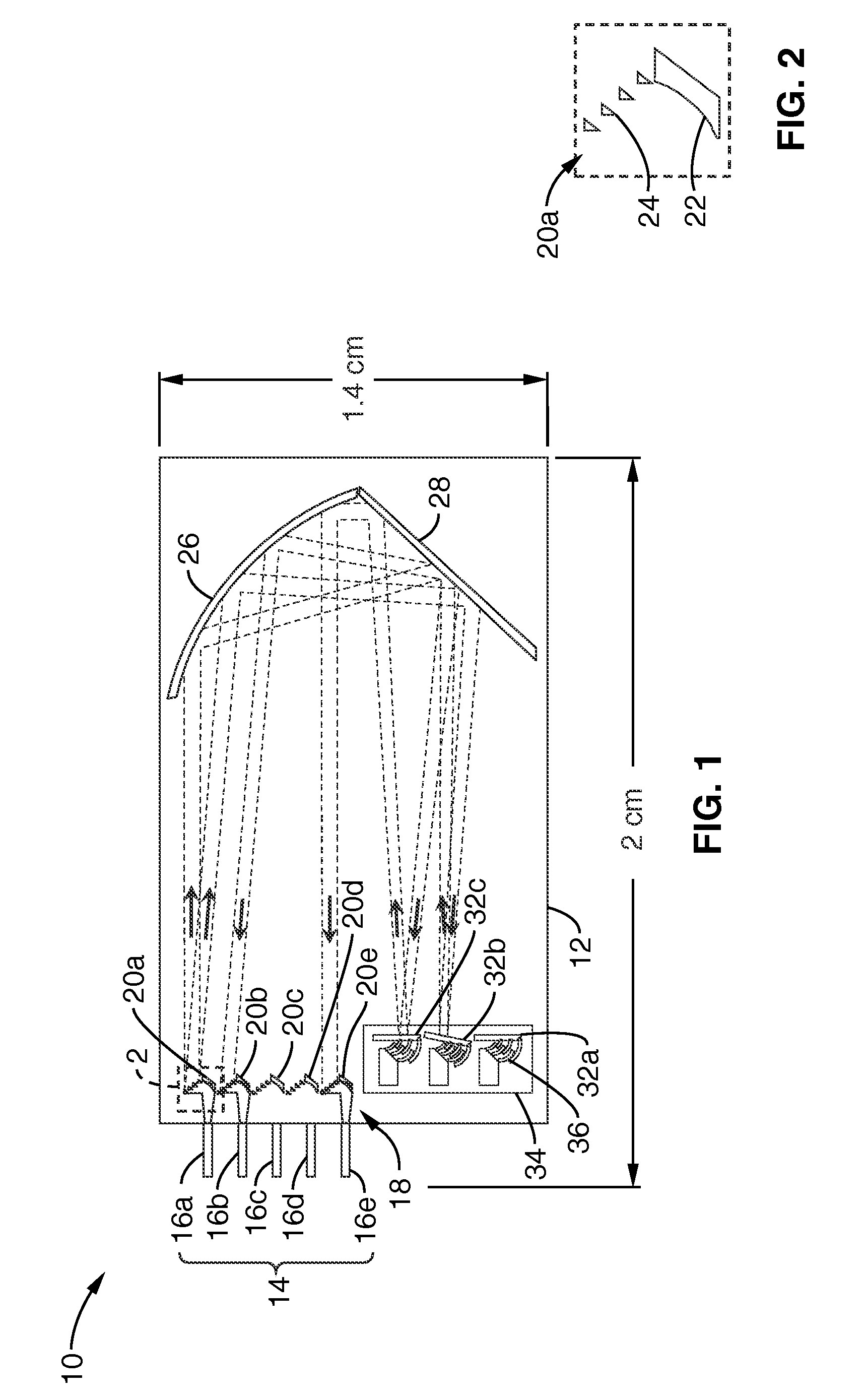
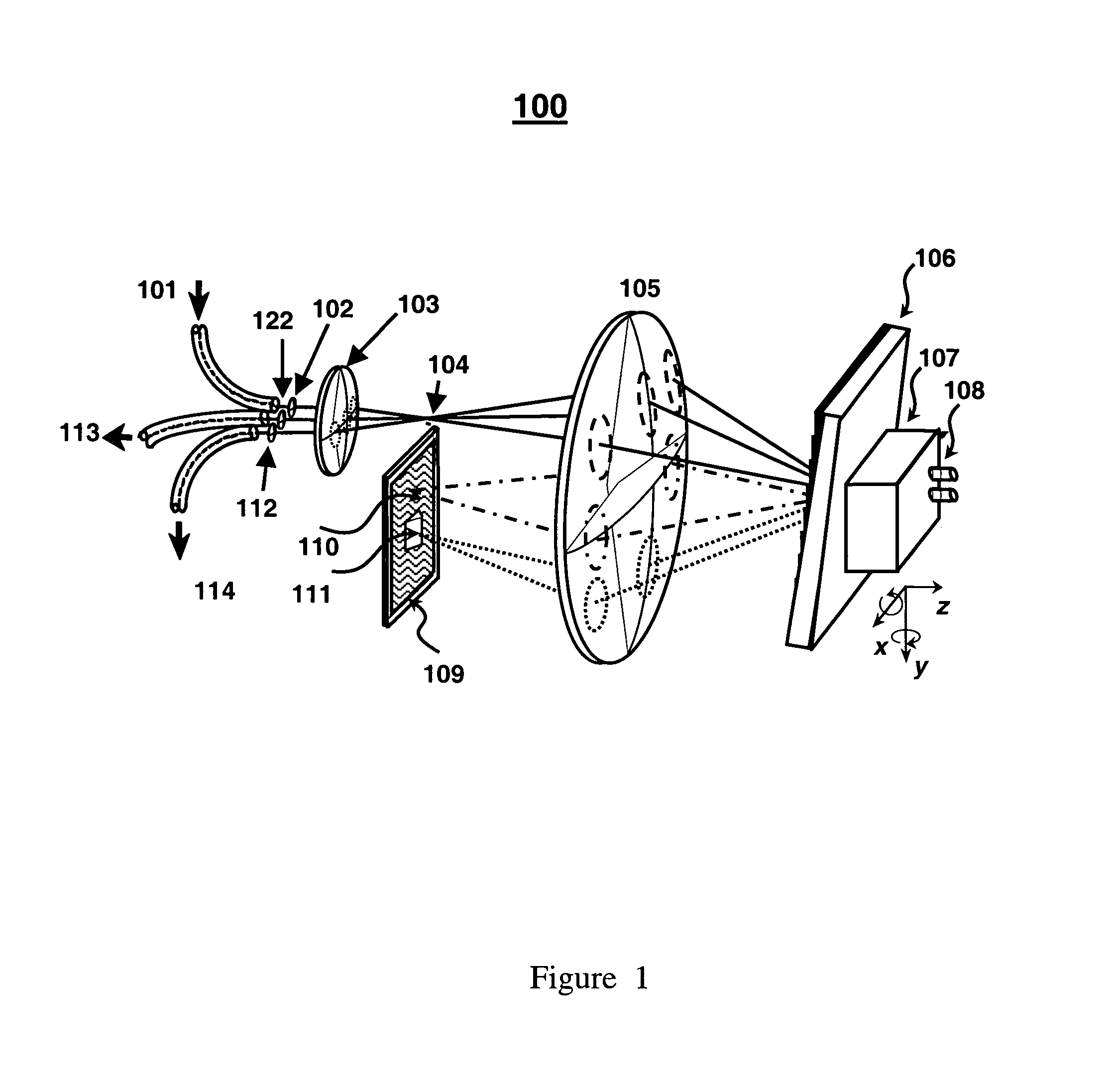
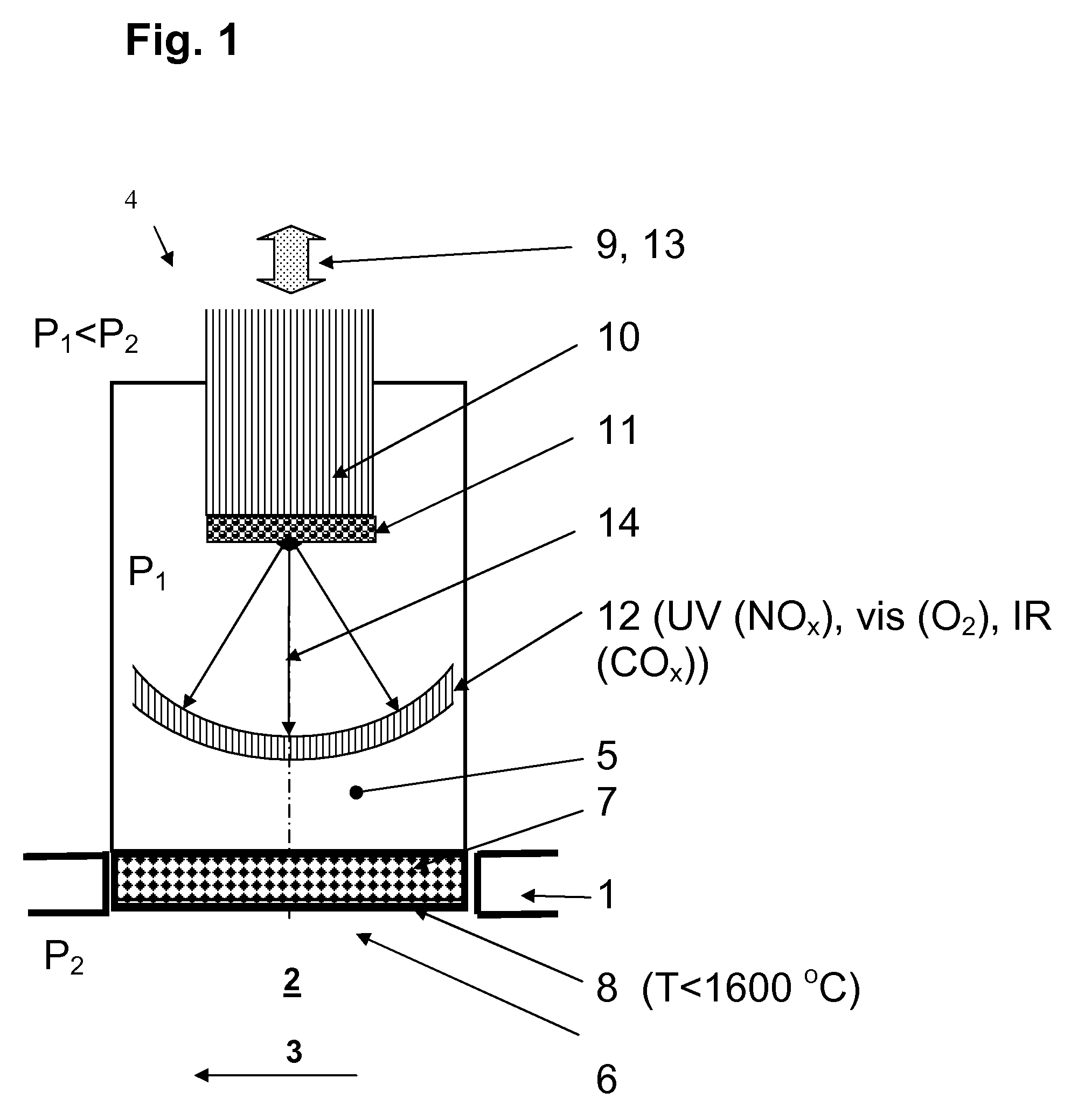
Apparatus, system and method for optically analyzing a substrate
InactiveUS20060184040A1Quality improvementDiagnostics using lightScattering properties measurementsLength waveLight filter
An apparatus for optically analyzing a substrate. The apparatus includes: (a) a light source for directing light onto the substrate; (b) optics for creating an optical path from light reflected from the substrate; and (c) a multiple wavelength imaging optical subsystem positioned in the optical path. The multiple wavelength imaging optical subsystem includes: (i) one or more filters which are capable of one or both of: (1) being alternatively or sequentially interposed in the optical path to extract one or more of wavelengths or wavelength bands of interest; or (2) having their wavelength selectivity adjusted to extract one or more wavelengths or wavelength bands of interest; and (ii) one or more imaging devices positioned to image the extracted wavelengths or wavelength bands of interest from the one or more filters; (d) an imaging device positioned in the optical path. Also a method is included, making use of the apparatus for analysis of a substrate.
Owner:INNEROPTIC TECH
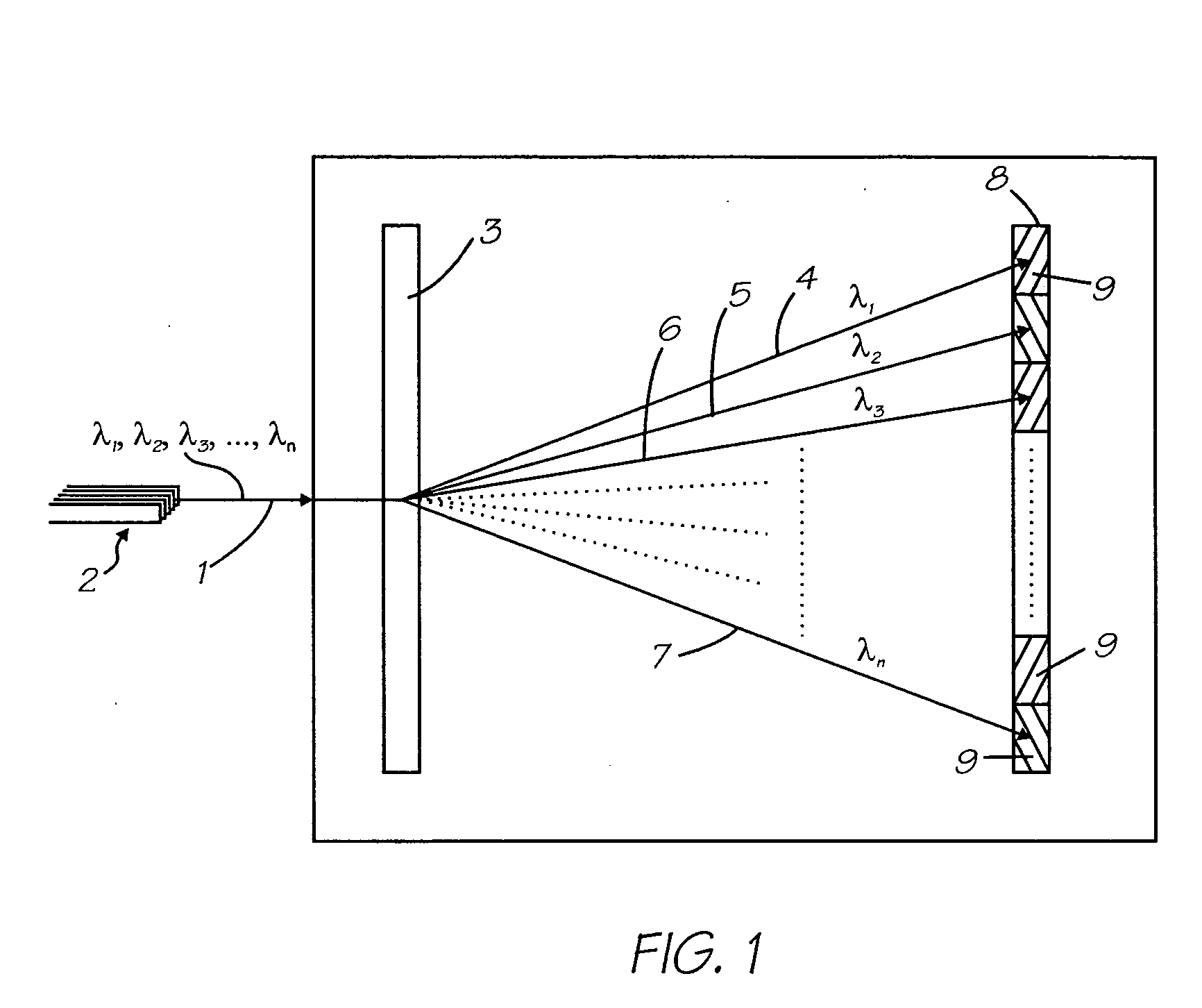
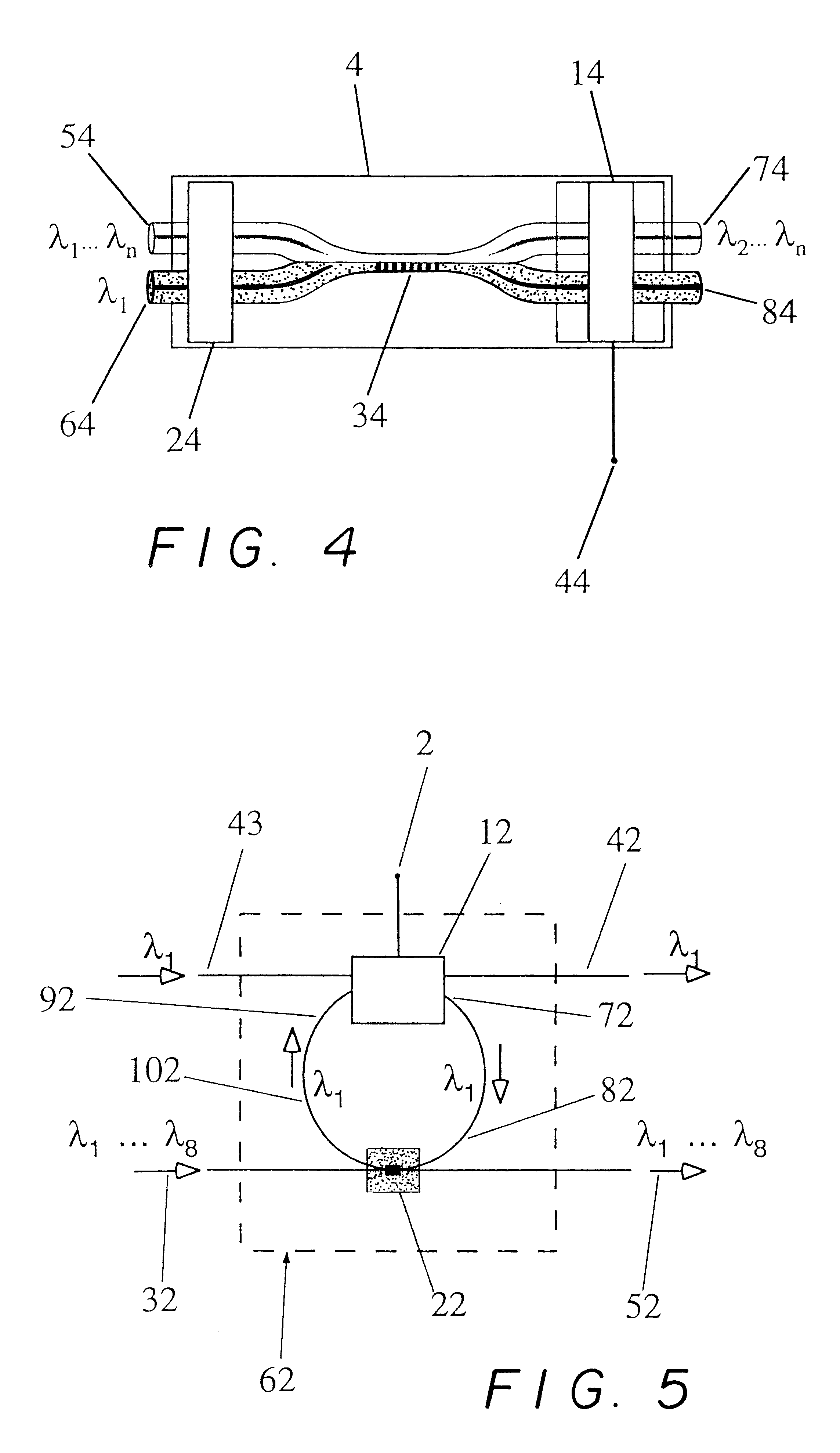
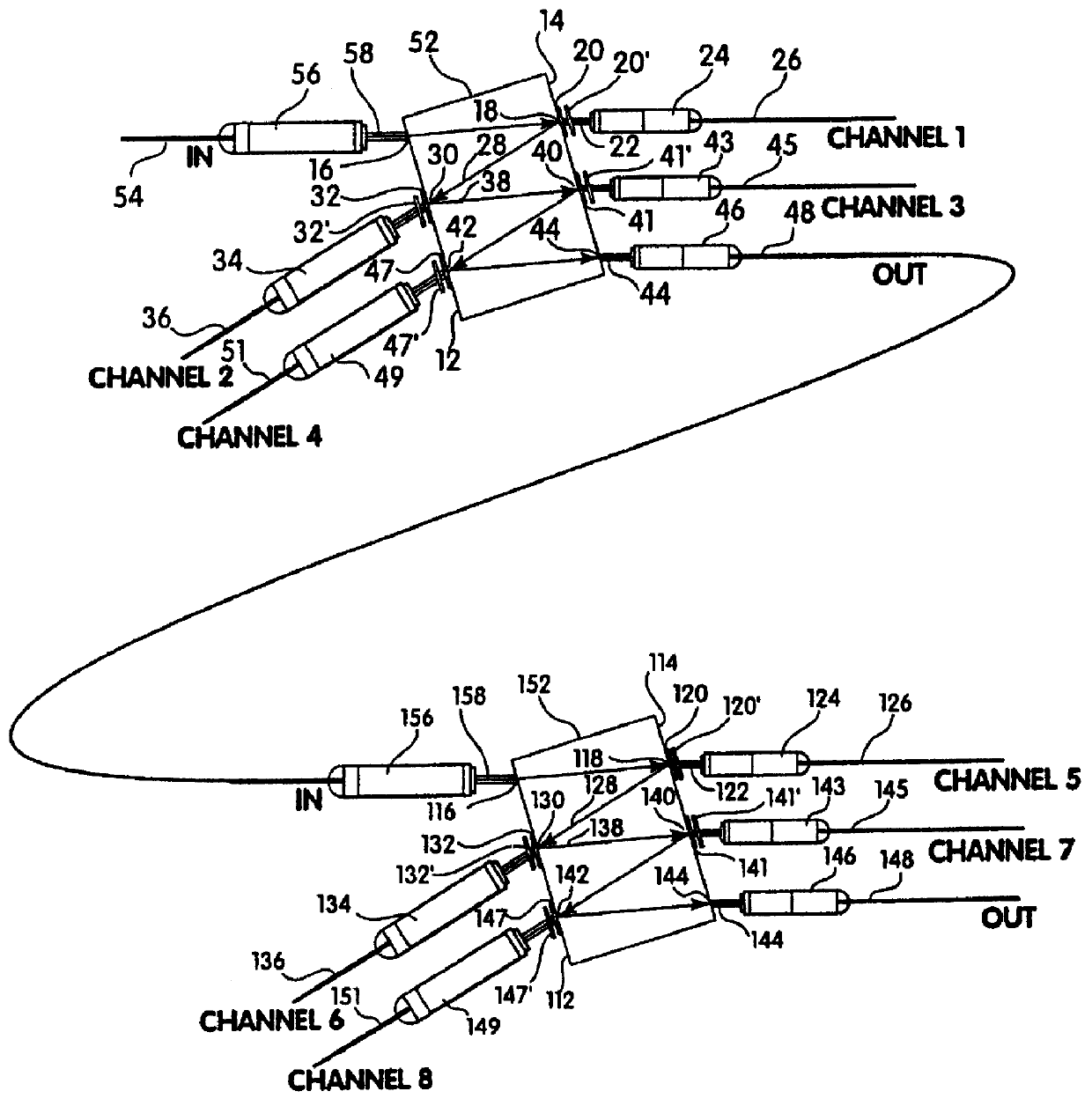
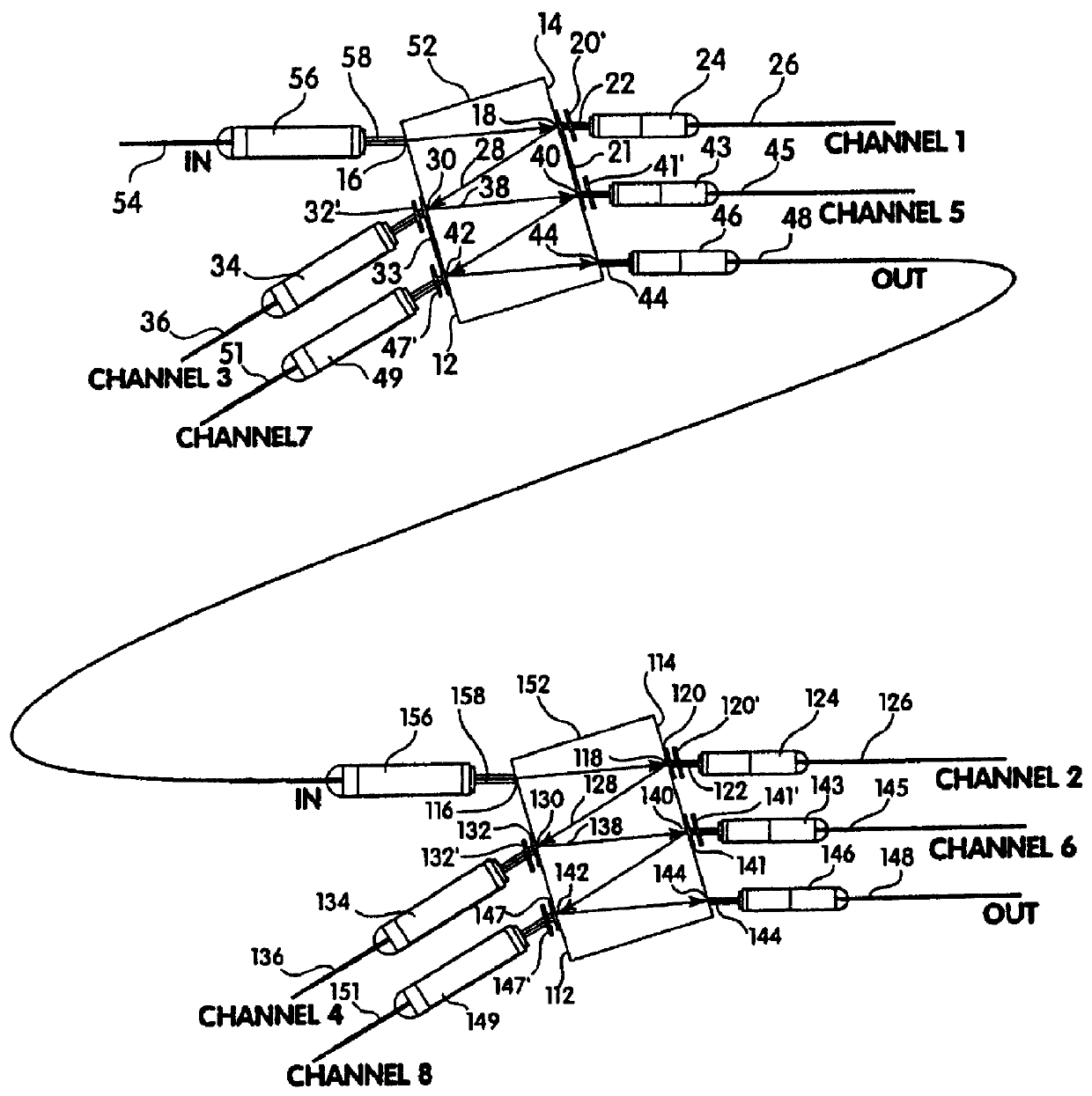
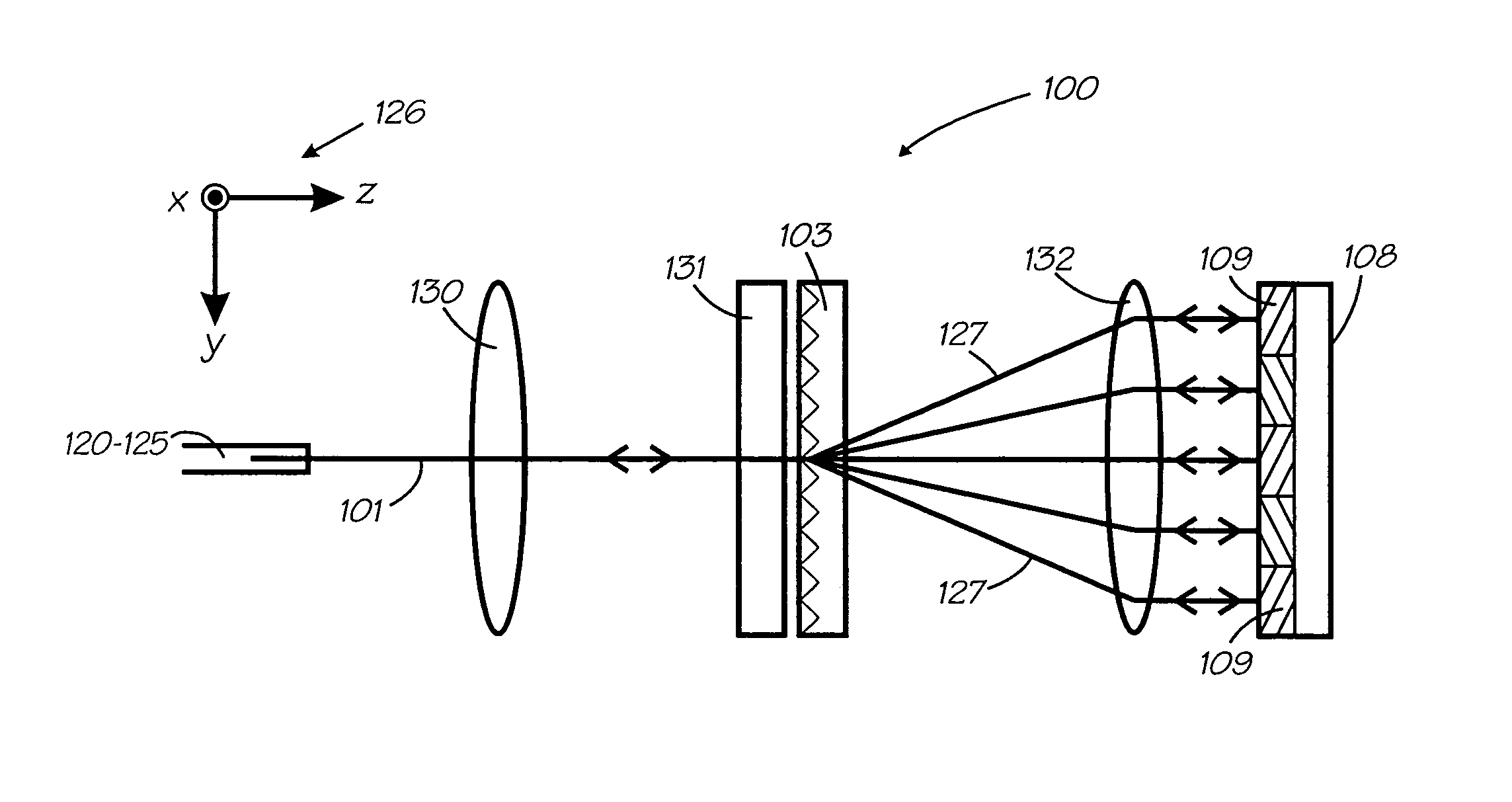
Wavelength selective reconfigurable optical cross-connect
ActiveUS20060067611A1Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesCross connectionLight beam
An optical coupling device including: at least a first input port for delivering an optical input signal beam that includes a plurality of wavelength channels; at least a first optical output port for receiving an optical output signal beam; a wavelength dispersion element for spatially separating the plurality of wavelength channels in the optical input signal beam to form a plurality of spatially separated wavelength channel beams; an optical coupling device for independently modifying the phase of each of the spatially separated wavelength channel beams such that, for at least one wavelength channel beam, a selected fraction of the light is coupled to the first output port and a fraction of the light is coupled away from the first output port.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Sub-wavelength grating integrated VCSEL
InactiveUS20070153860A1Good optical performanceEasy to manufactureLaser detailsLaser optical resonator constructionVertical-cavity surface-emitting laserGrating
A vertical cavity surface emitting laser (VCSEL) is described using a sub-wavelength grating (SWG) structure that has a very broad reflection spectrum and very high reflectivity. The grating comprises segments of high and low refractive index materials with an index differential between the high and low index materials. By way of example, a SWG reflective structure is disposed over a low index cavity region and above another reflective layer (either SWG or DBR). In one embodiment, the SWG structure is movable, such as according to MEMS techniques, in relation to the opposing reflector to provide wavelength selective tuning. The SWG-VCSEL design is scalable to form the optical cavities for a range of SWG-VCSELs at different wavelengths, and wavelength ranges.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Optoelectronic device incorporating an interference filter
InactiveUS20050117623A1Optical wave guidanceLaser optical resonator constructionOptical cavityResonance
A novel class of optoelectronic devices incorporate an interference filter. The filter includes at least two optical cavities. Each of the cavities localizes al least one optical mode. The optical modes localized at two cavities are at resonance only at one or at a few discrete selective wavelengths. At resonance, the optical eigenmodes contain one mode having a zero intensity at a node position between the two cavities, where this position shifts as a function of the wavelength. A non-transparent element, which is preferably an absorbing element, a scatterer, or a reflector, is placed between two cavities. At a discrete selective wavelength, when the node of the optical mode matches with the non-transparent element, the filter is transparent for light. At other wavelengths, the filter is not transparent for light. This allows for the construction of various optoelectronic devices showing a strongly wavelength-selective operation.
Owner:INNOLUME
Infrared vision with liquid crystal display device
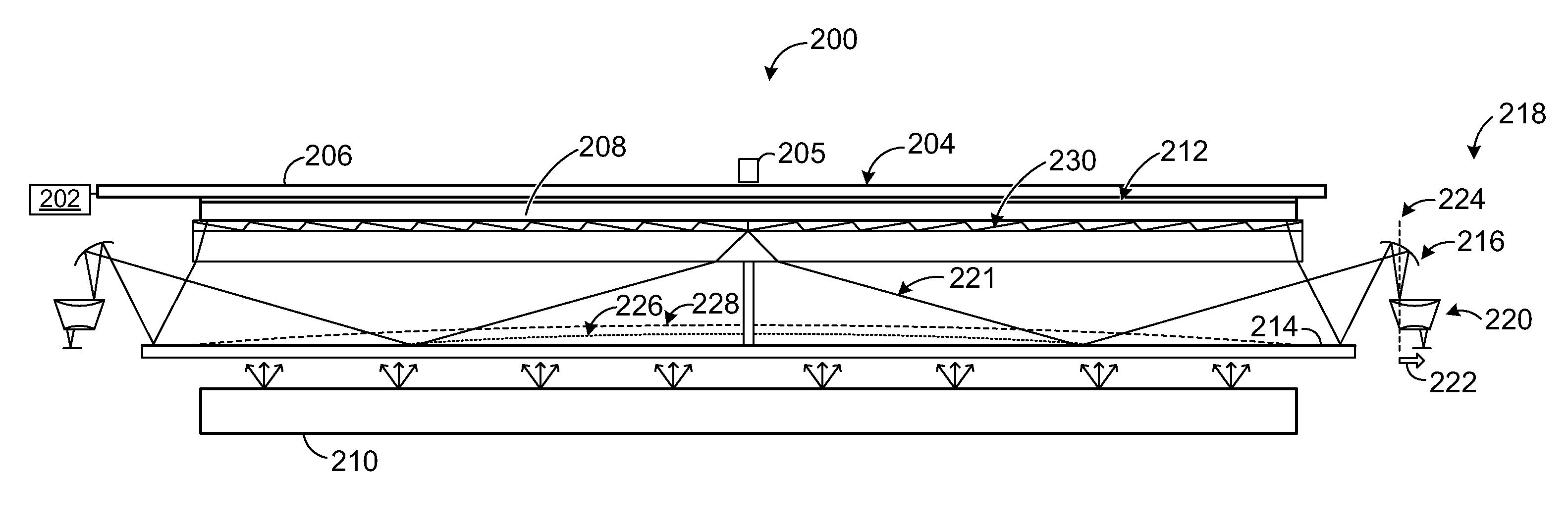
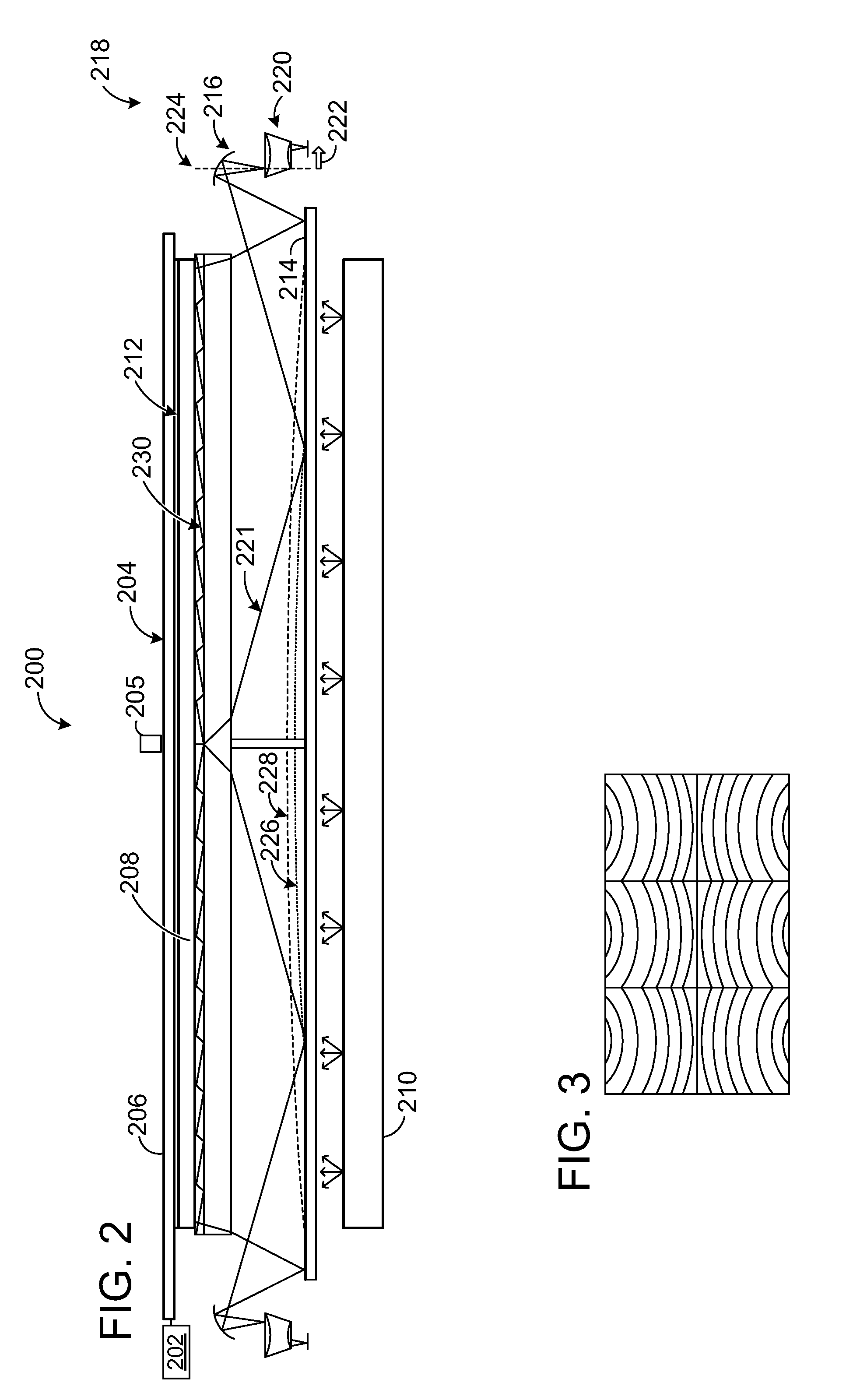
InactiveUS20110115747A1Well formedNon-linear opticsInput/output processes for data processingWavelength selectivitySmooth surface
Various embodiments related to infrared vision for a liquid crystal display (LCD) device are disclosed herein. For example, one disclosed embodiment provides a display system, comprising an LCD device and a display backlight configured to illuminate the LCD device by directing visible light toward an interior surface of the LCD device. The display system further comprises a wavelength-selective reflector disposed between the display backlight and the LCD device and having a smooth surface facing the interior surface of the LCD device, where the wavelength-selective reflector has a wavelength-selective coating configured to cause incident visible light from the display backlight to be transmitted through the wavelength-selective reflector to the LCD device, and cause incident infrared light reflected from an object on or near an exterior surface of the LCD device to be reflected off of the wavelength-selective reflector and directed to an infrared vision subsystem.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Scanned beam display
A display apparatus includes first and second IR or other light sources that produce light at respective first and second non-visible wavelengths. The light is modulated according to a desired image. The modulated light is then applied to a wavelength selective phosphor that converts each component of the light to a respective visible wavelength. In one embodiment, the image source is a scanned light beam display that scans an IR light beam onto a screen that carries the phosphor.
Owner:MICROVISION
Wavelength selective optical routers
InactiveUS6201909B1Wide wavelength band to be manipulatedLow insertion lossWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesBandpass filteringFiber
Using the wavelength selectivity and low loss characteristics of optical couplers, in which index of refraction gratings in a non-evanescent waveguide merged region reflect only a selected wavelength band, signal switching and control systems of novel characteristics are provided for multi-wavelength optical communication systems. In a router, for example, selected wavelengths or wavelength bands on an add / drop line can be added to or dropped from a main fiber, by cross switching between wavelength selective loops disposed sequentially in the lines. In a collector box, as another example, selected wavelength bundles can be routed from one fiber onto multiple fibers. In a bandpass filter a selected wavelength band is transmitted with low loss while those wavelengths outside the selected wavelength band are rejected with very high loss.
Owner:ARROYO OPTICS
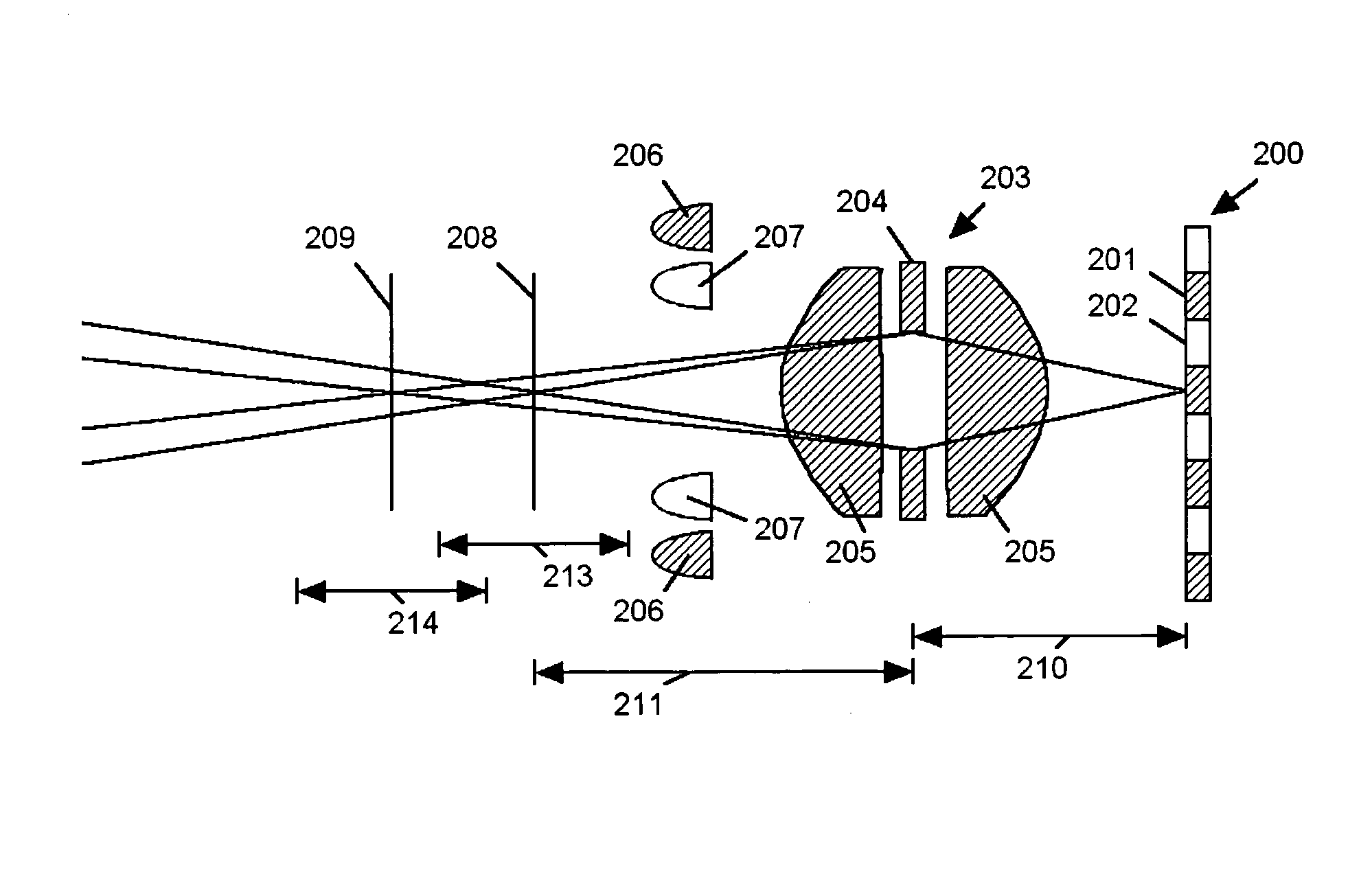
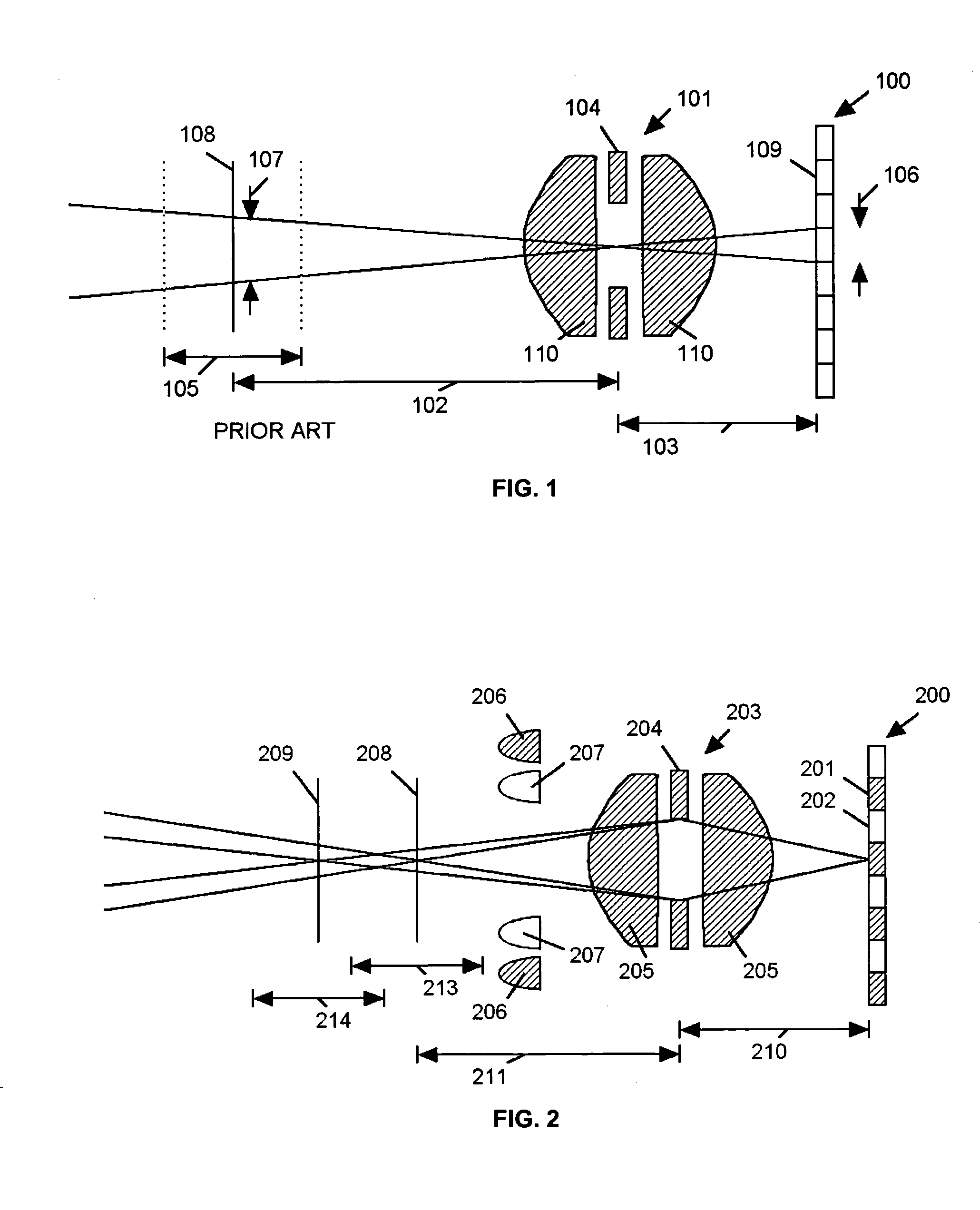
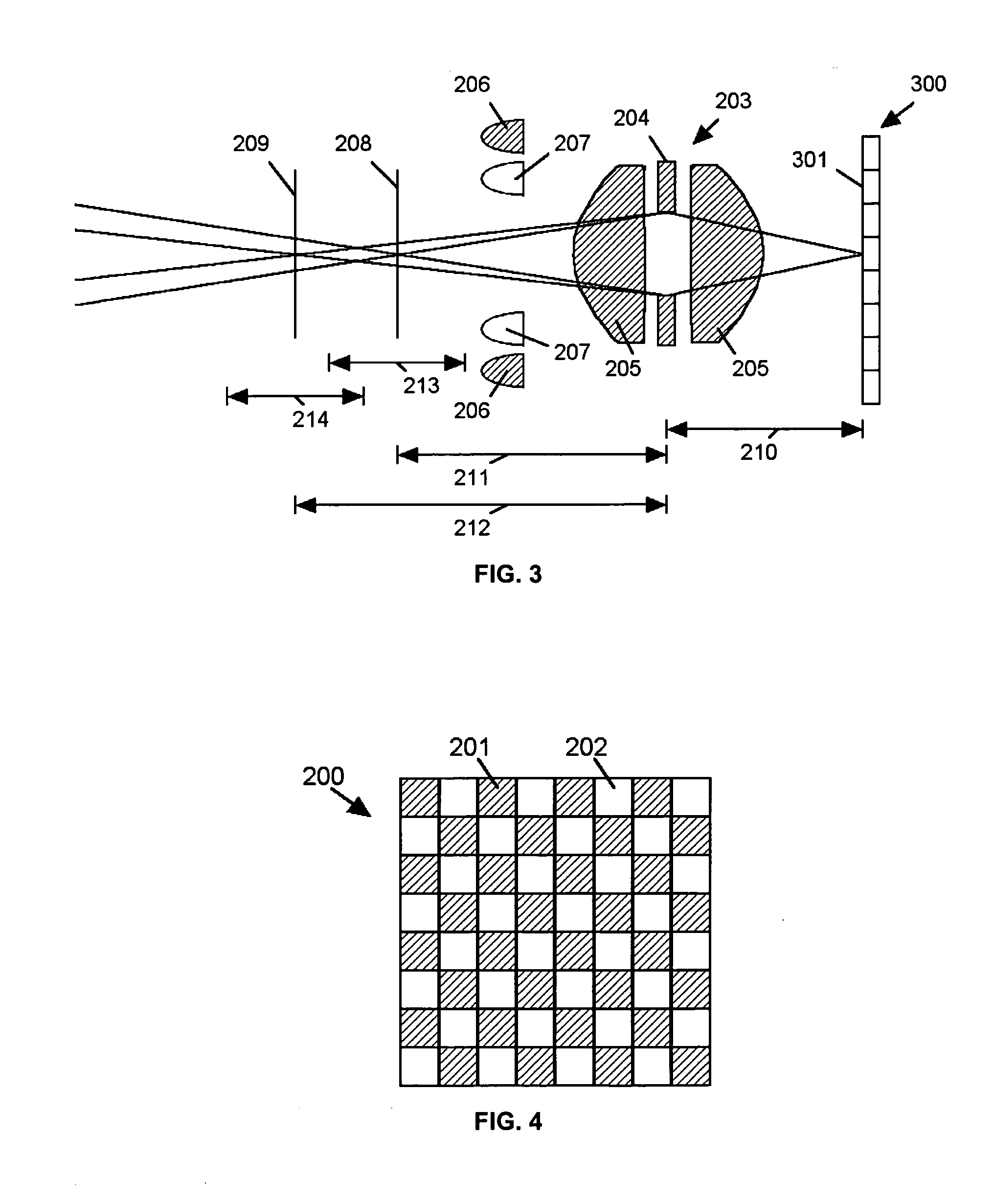
Extended depth of field imaging system using chromatic aberration
ActiveUS20060171041A1Lower optical magnificationHigh intensity illuminationVisual representatino by photographic printingSensing by electromagnetic radiationImage resolutionDepth of field
An imaging system (FIG. 3) is disclosed that has a wavelength dependent focal shift caused by longitudinal chromatic aberration in a lens assembly (203) that provides extended depth of field imaging due to focal shift (213,214) and increased resolution due to reduced lens system magnification. In use, multiple wavelengths of quasi-monochromatic illumination, from different wavelength LEDs (206,207) or the like, illuminate the target, either sequentially, or in parallel in conjunction with an imager (200) with wavelength selective (colored) filters. Images are captured with different wavelengths of illumination that have different focus positions (208,209), either sequentially or by processing the color planes of a color imager separately. Extended depth of field, plus high resolution are achieved. Additionally, information about the range to the target can be determined by analyzing the degree of focus of the various colored images.
Owner:PSC SCANNING INC
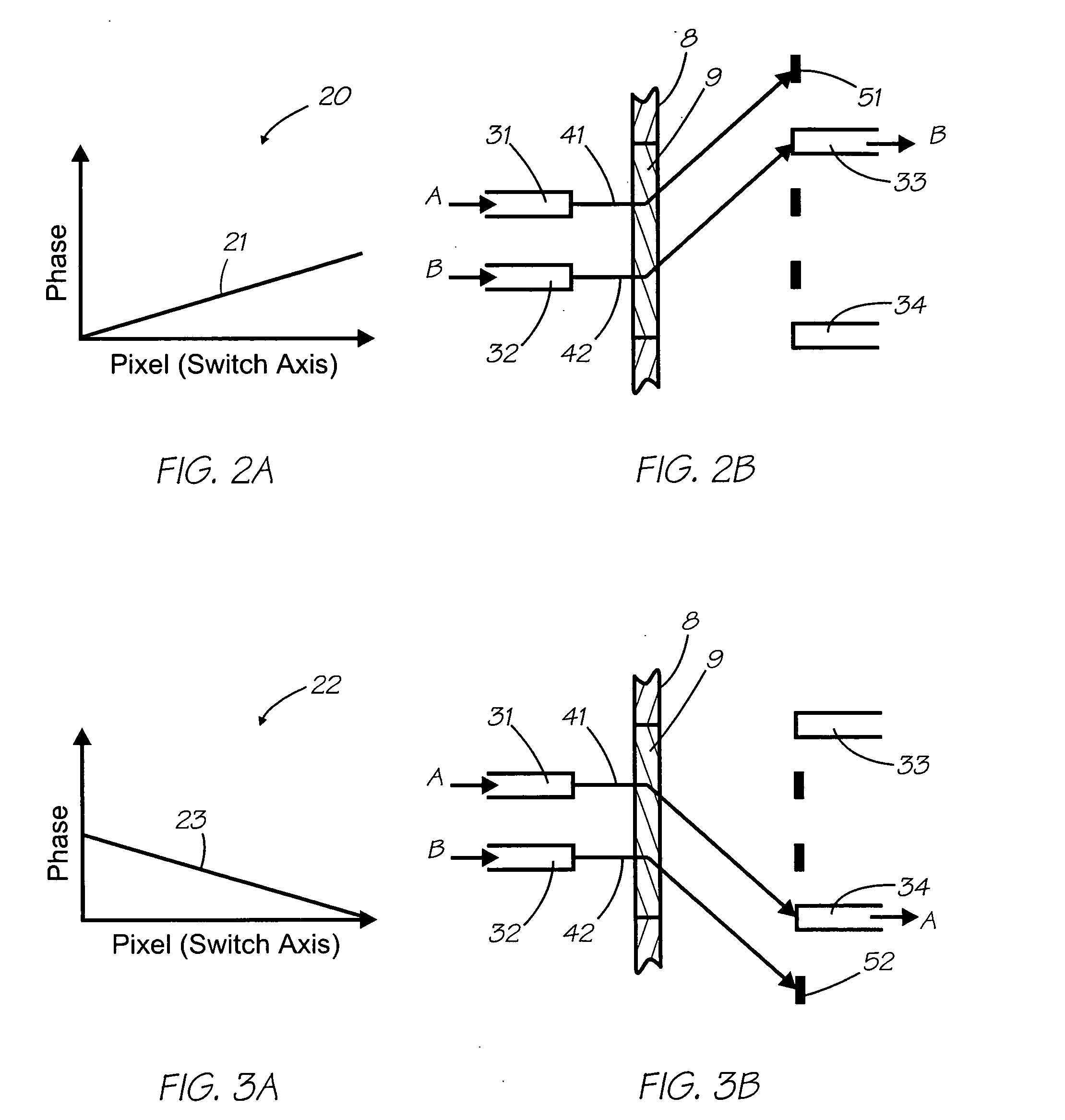
Monolithic mems-based wavelength-selective switches and cross connects
InactiveUS20070160321A1Minimizing insertion lossEliminate needCoupling light guidesCross connectionComb drive
Wavelength-selective 1×N switches (WSSs) and N×N cross-connects (WSXCs) are described which are fabricated as monolithic or hybrid devices. In a preferred embodiment, the optic ports, dispersion elements, and collimating elements are formed on a single monolithic substrate. A micromirror and actuator are either fabricated within the substrate or a separate micromirror is utilized forming a hybrid WSS or WSXC. The optical elements can be formed in an opaque substrate layer (e.g., silicon, SOI, and so forth) or in an optically transparent layer of a PLC material (e.g., silica-on-silicon). Embodiments describe the use of linear and rotary comb drives for actuating front surface mirrors, or solid-immersion micromirrors (SIMs). The switching devices reduce system footprint while reducing or eliminating the need for alignment of the optical elements.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Optical interconnection circuit among wavelength multiplexing chips, electro-optical device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20040264867A1Easy to makeThe transmission is compactRing-type electromagnetic networksLaser detailsMultiplexingLength wave
To provide an optical interconnection circuit among wavelength multiplexing chips, capable of increasing signal transmission speed and of being easily made minute thereby being simply and easily fabricated, an electro-optical device, and an electronic apparatus, an optical interconnection circuit among wavelength multiplexing chips, which is disposed on a substrate, includes micro-tile shaped elements having a light emitting function or a light receiving function with wavelength selectivity.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Switchable optical components
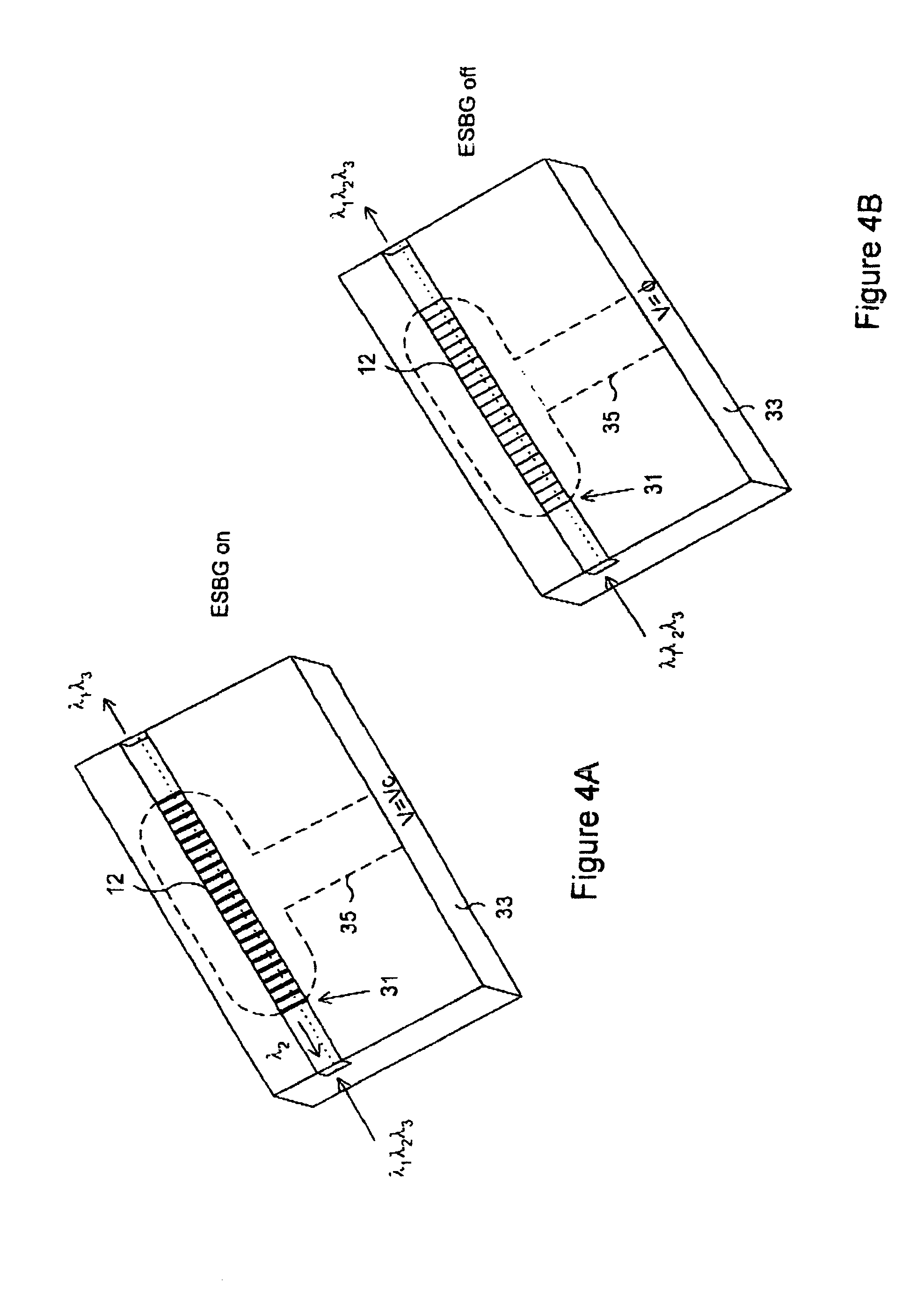
This invention relates to a number of components, devices and networks involving integrated optics and / or half coupler technology, all of which involve the use of electronically switchable Bragg grating devices and device geometries realized using holographic polymer / dispersed liquid crystal materials. Most of the components and devices are particularly adapted for use in wavelength division multiplexing (WDM) systems and in particular for use in switchable add / drop filtering (SADF) and wavelength selective crossconnect. Attenuators, outcouplers and a variety of other devices are also provided.
Owner:DOMASH LAWRENCE H +1
Graphene transistor based on metamaterial structure, optical sensor based on metamaterial structure, and application of graphene transistor
ActiveCN103117316APromote absorptionAdjustableRadiation pyrometrySpectrum investigationMicro nanoUltra-wideband
Disclosed are a graphene transistor based on a metamaterial structure, an optical sensor based on a metamaterial structure, and application of the graphene transistor. The graphene transistor sequentially comprises a liner, a grid metal layer, a grid medium layer, a grapheme layer and a source and drain metal layer from bottom to top. At least local area of the source and drain metal layer is provided with a periodicity micro-nano structure. The periodicity micro-nano structure, the grid metal layer and the grid medium layer match to form the metamaterial structure with the feature of complete absorption. By changing refractive index, thickness and the like of the periodicity micro-nano structure and the grid medium layer material, optical absorption frequency range of the metamaterial structure can be adjusted. Due to the feature of perfect wavelength selectivity absorption, higher flexibility and narrow-band response of the metamaterial structure, the graphene transistor can work under visible light to infrared even longer wave bands by selecting different metamaterial structures. By integrating optical sensor working in different wave bands, image sensors, spectrum detecting analyzing device and the like which can work in ultra-wide bands can be formed.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF NANO TECH & NANO BIONICS CHINESE ACEDEMY OF SCI
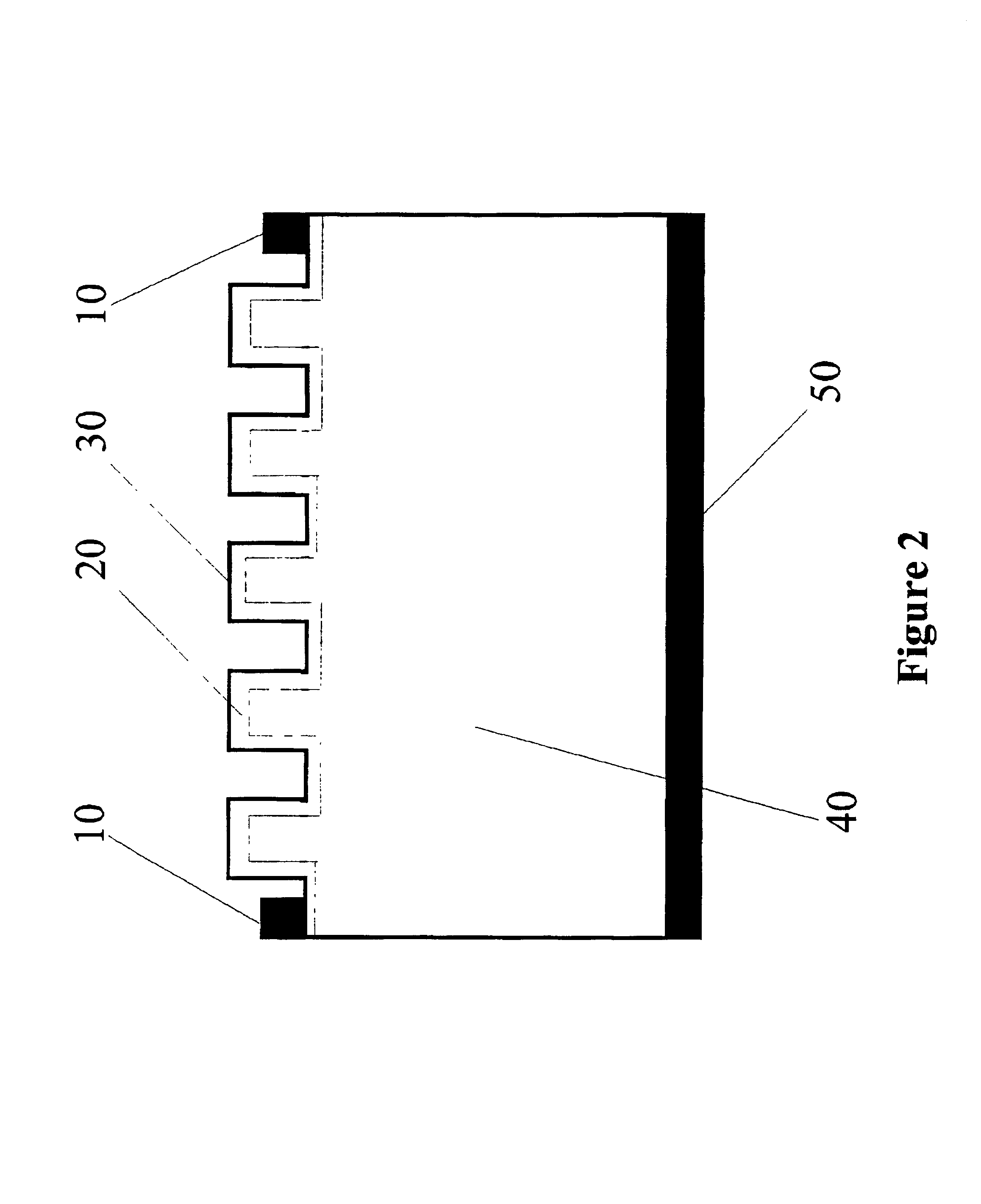
Wavelength-selective photonics device
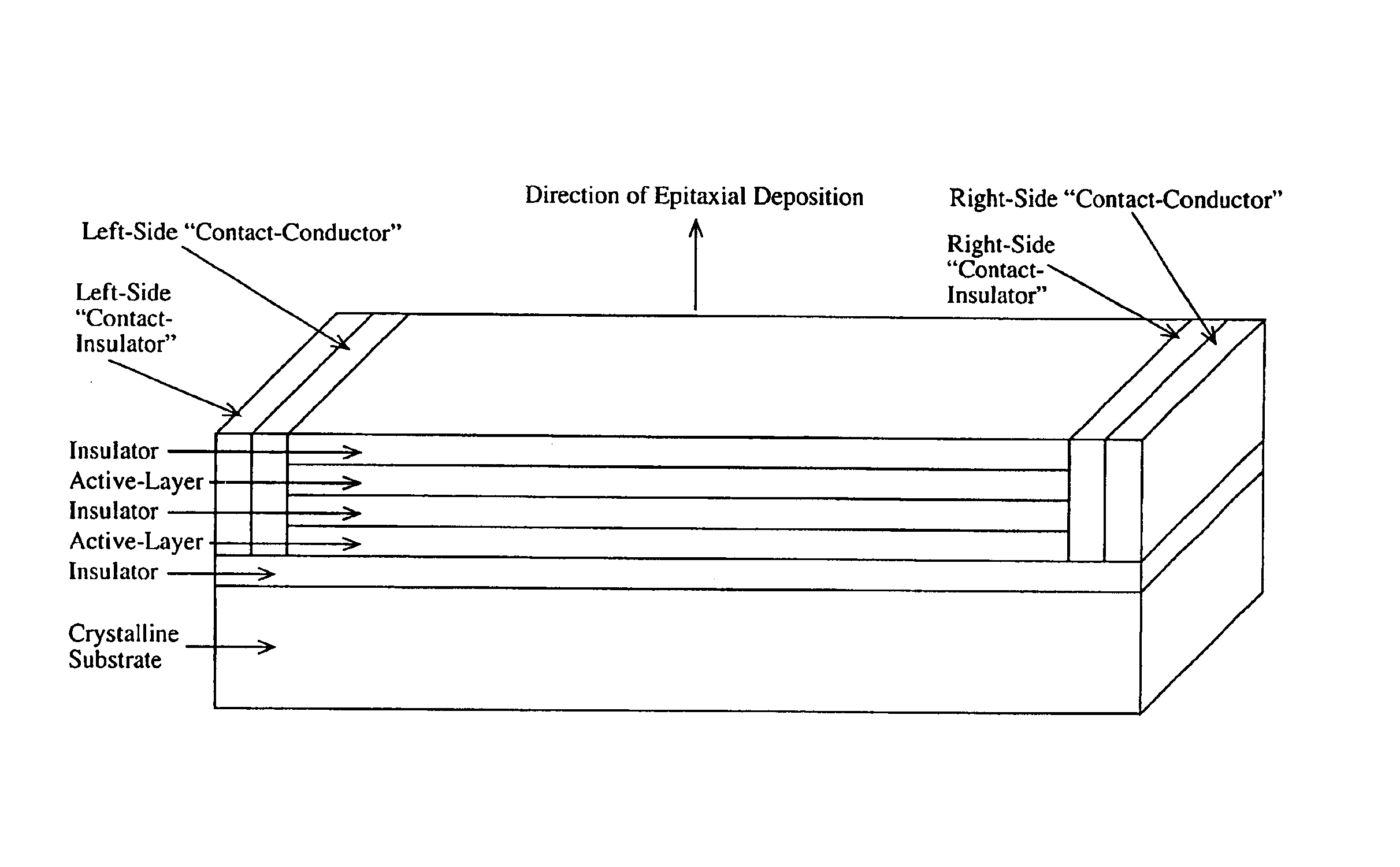
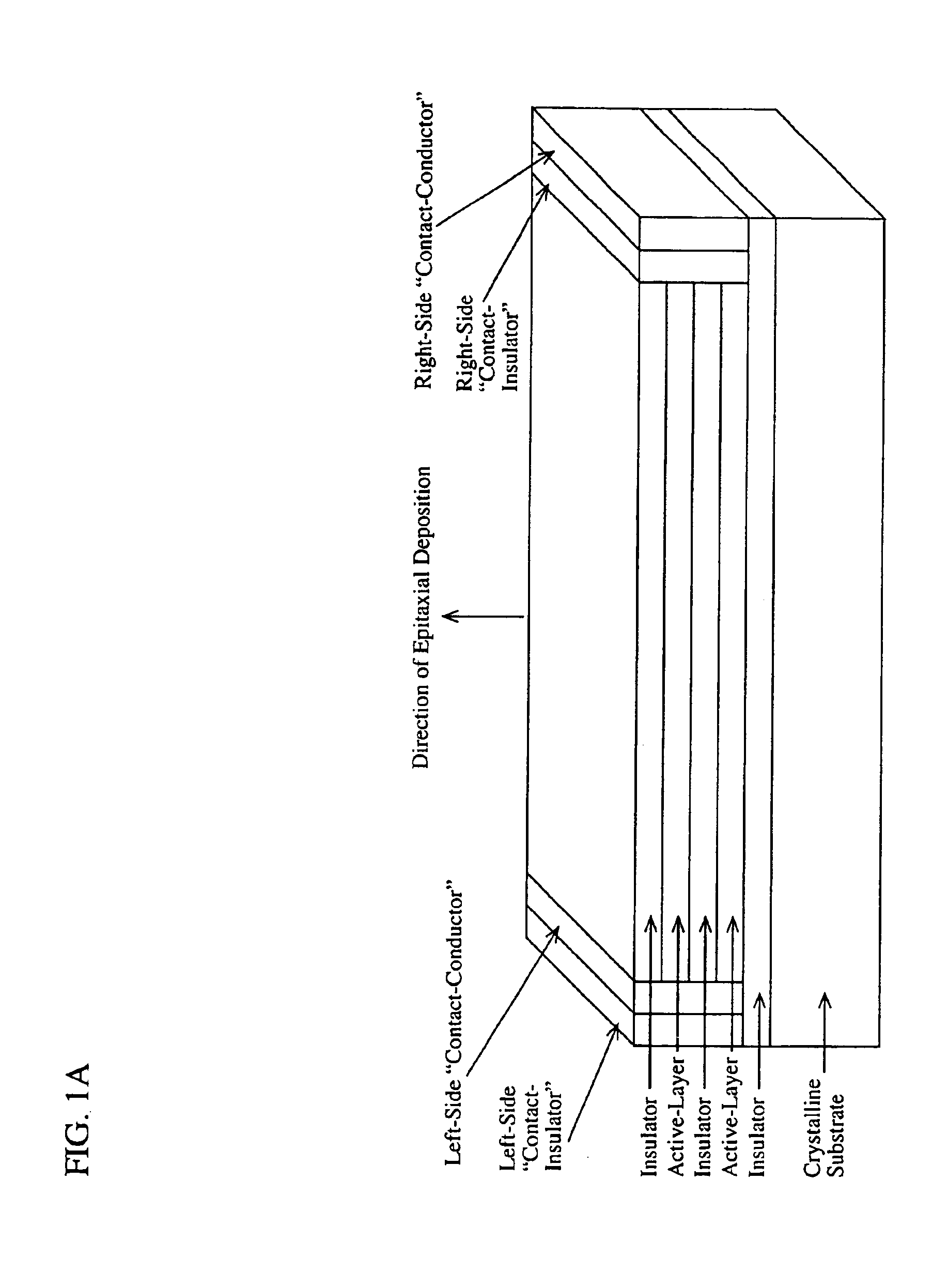
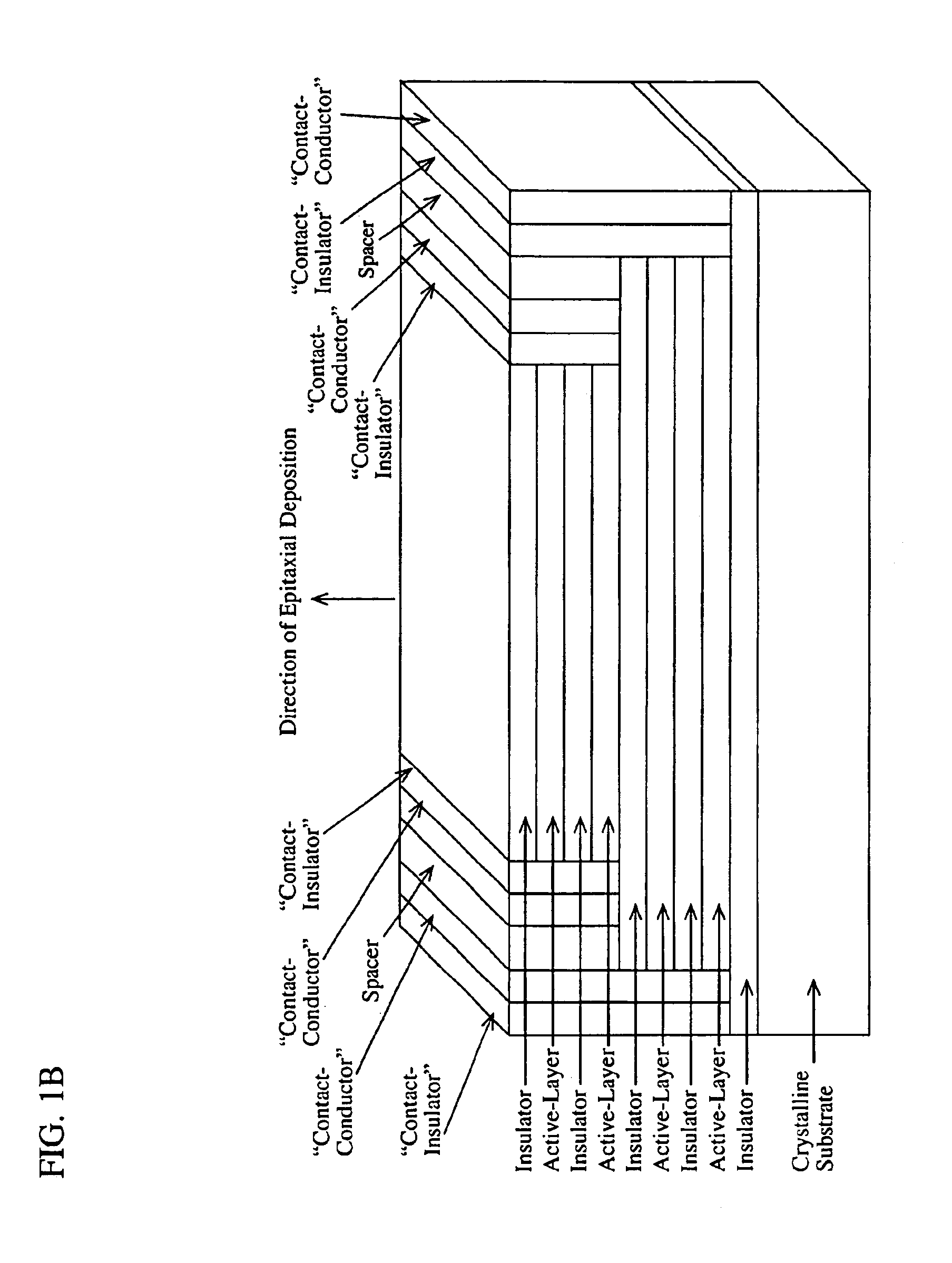
InactiveUS6891869B2Wide rangeOvercome limitationsSolid-state devicesNanoopticsPhoton emissionPhotonics
A device comprising a number of different wavelength-selective active-layers arranged in a vertical stack, having band-alignment and work-function engineered lateral contacts to said active-layers, consisting of a contact-insulator and a conductor-insulator. Photons of different energies are selectively absorbed in or emitted by the active-layers. Contact means are arranged separately on the lateral sides of each layer or set of layers having the same parameters for extracting charge carriers generated in the photon-absorbing layers and / or injecting charge carriers into the photon-emitting layers. The device can be used for various applications: wavelength-selective multi-spectral solid-state displays, image-sensors, light-valves, light-emitters, etc. It can also be used for multiple-band gap solar-cells. The architecture of the device can be adapted to produce coherent light.
Owner:QUANTUM SEMICON
Spectroscopic imaging device employing imaging quality spectral filters
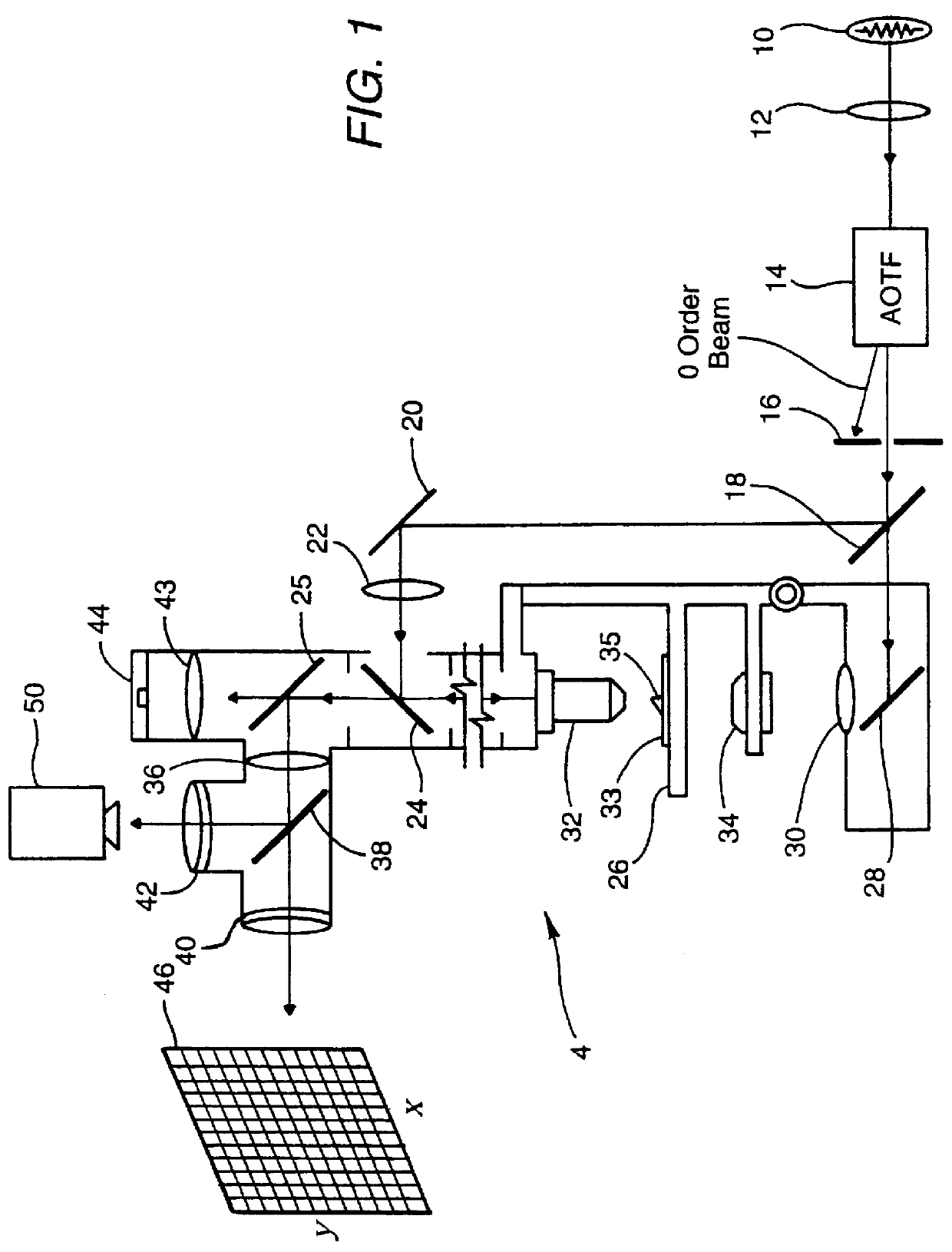
InactiveUSRE36529E1Retaining image fidelityQuick buildRadiation pyrometryInterferometric spectrometryLow speedImaging quality
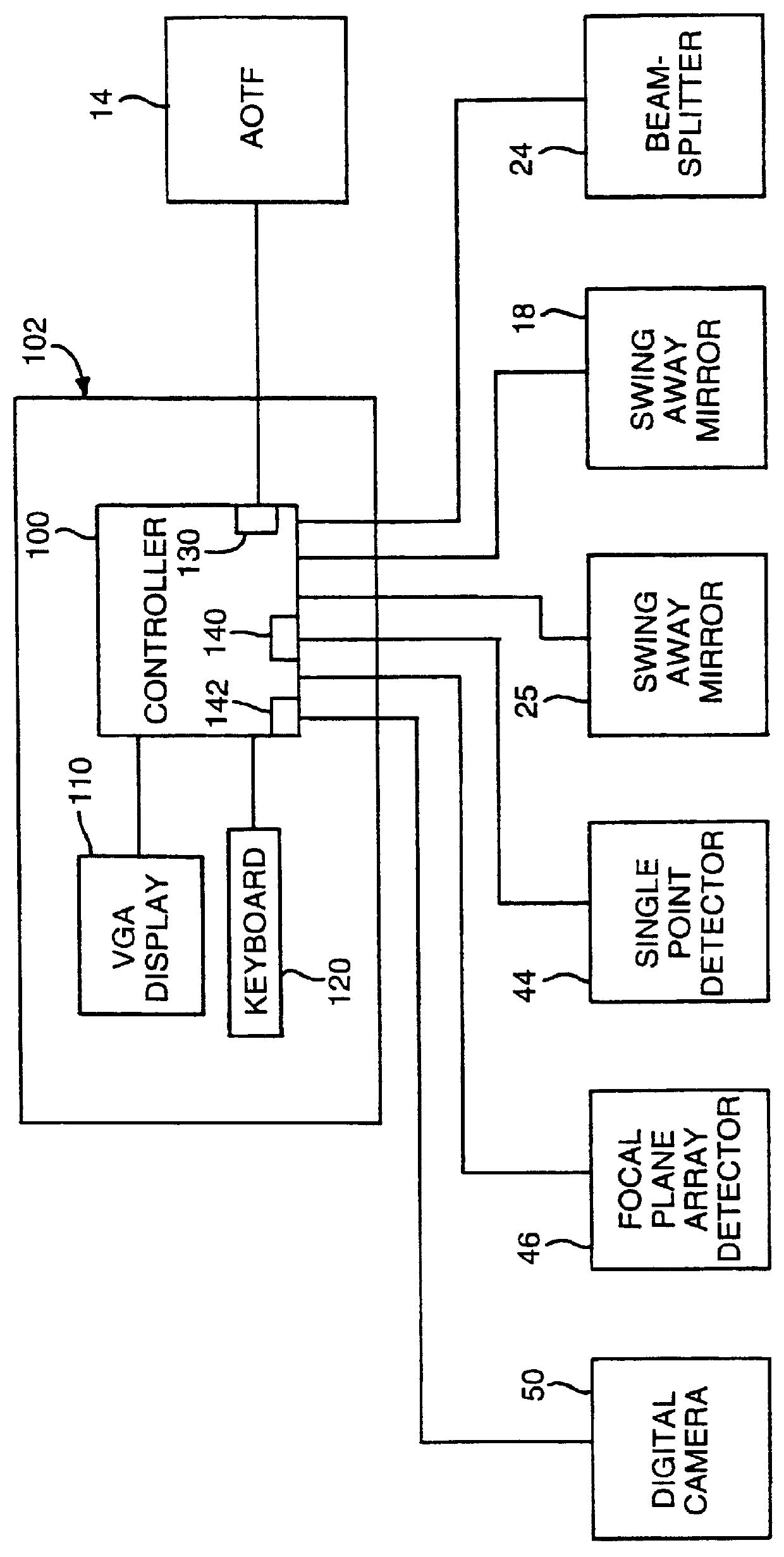
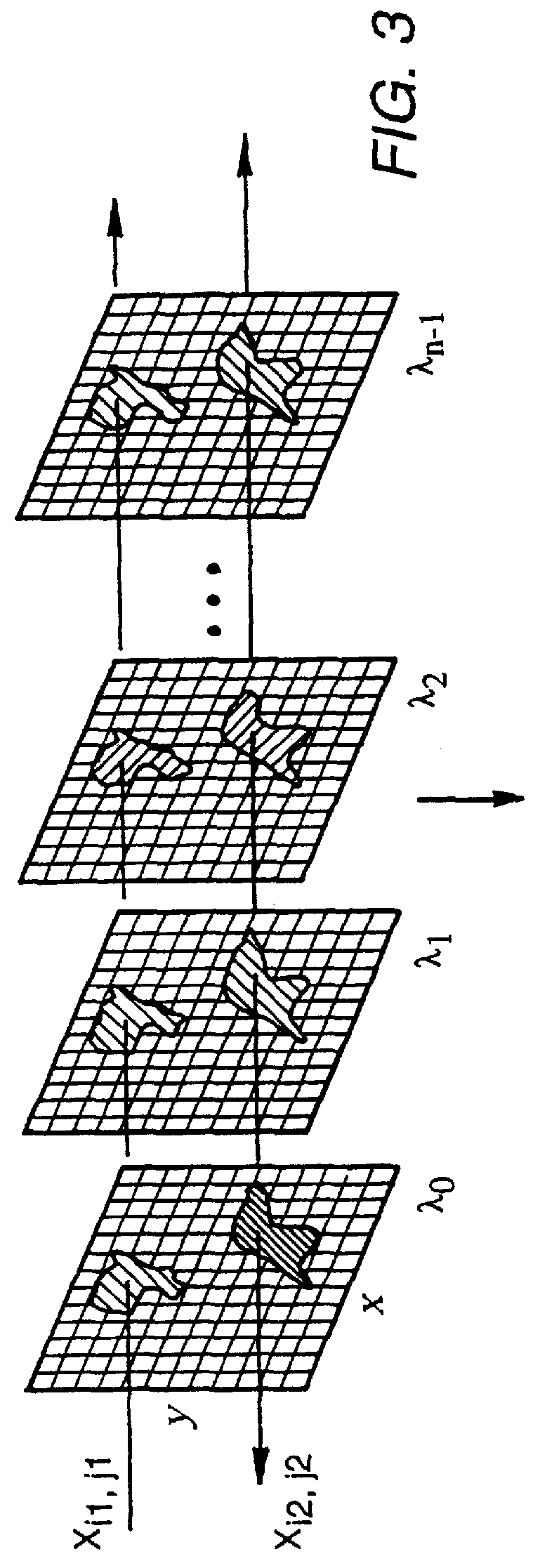
Techniques for providing spectroscopic imaging integrates an acousto-optic tunable filter (AOTF), or an interferometer, and a focal plane array detector. In operation, wavelength selectivity is provided by the AOTF or the interferometer. A focal plane array detector is used as the imaging detector in both cases. Operation within the ultraviolet, visible, near-infrared (NIR) spectral regions, and into the infrared spectral region, is achieved. The techniques can be used in absorption spectroscopy and emission spectroscopy. Spectroscopic images with a spectral resolution of a few nanometers and a spatial resolution of about a micron, are collected rapidly using the AOTF. Higher spectral resolution images are recorded at lower speeds using the interferometer. The AOTF technique uses entirely solid-state components and requires no moving parts. Alternatively, the interferometer technique employs either a step-scan interferometer or a continuously modulated interferometer.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
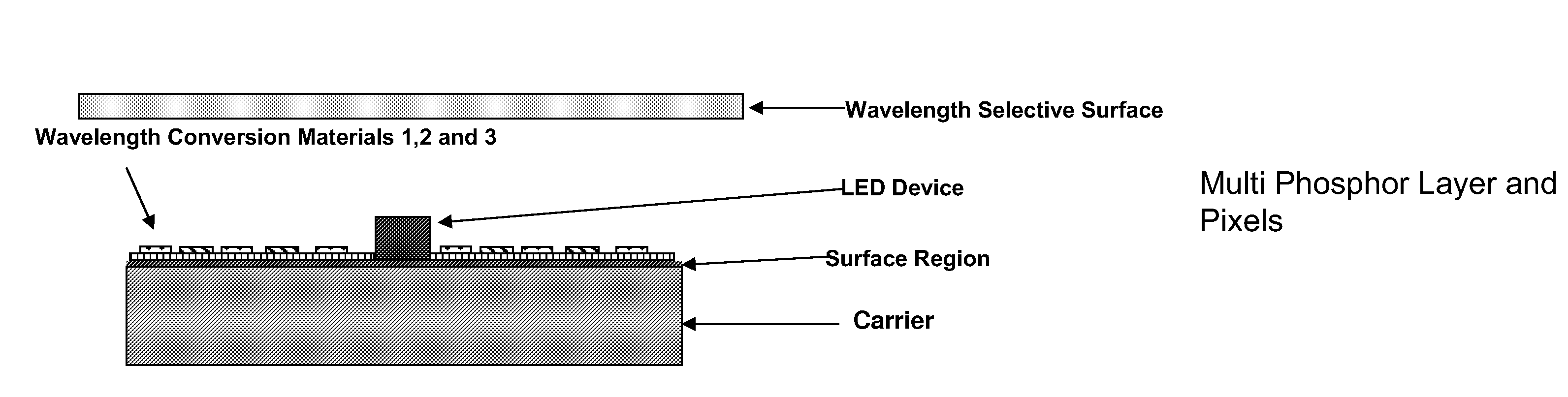
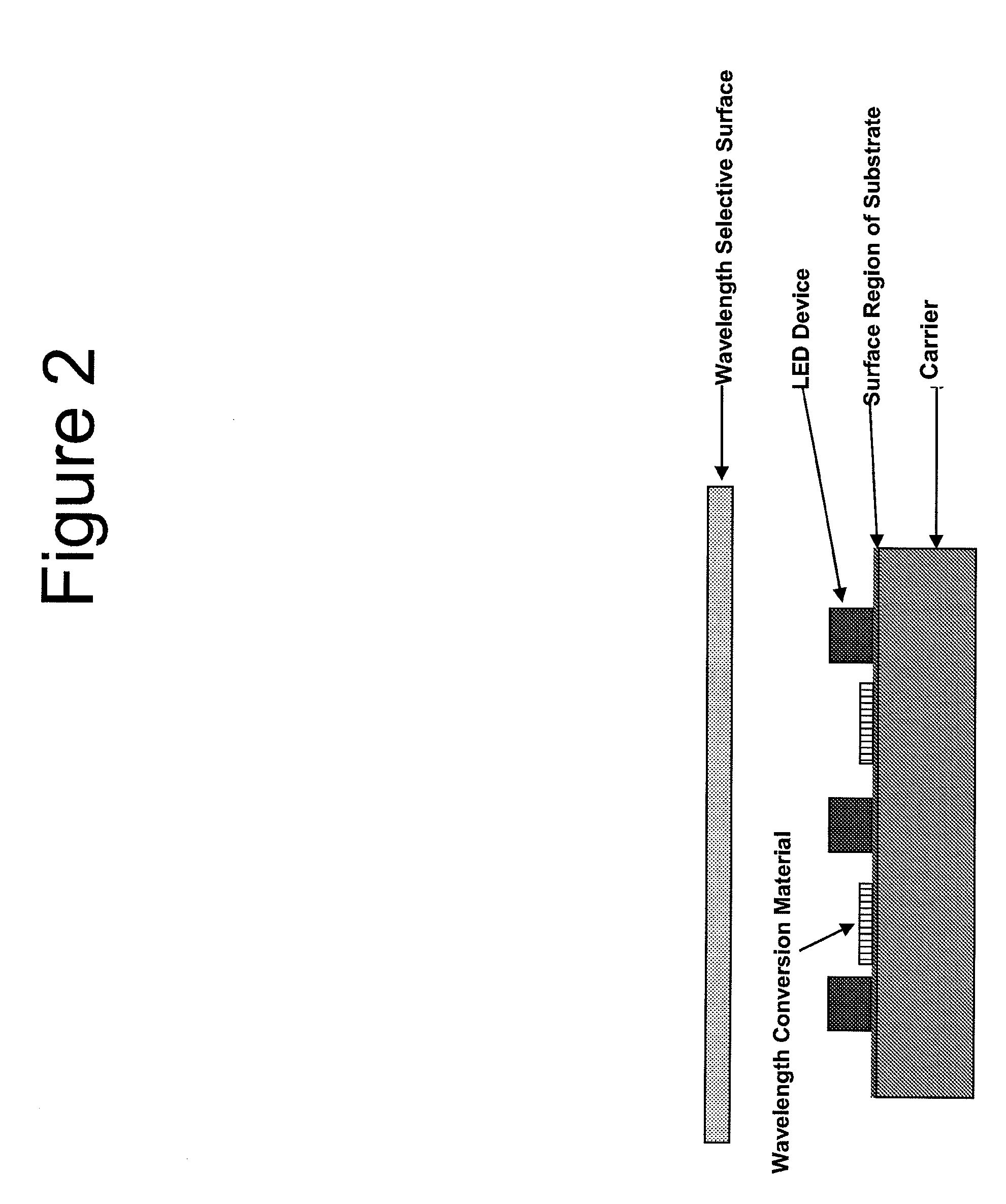
Reflection Mode Package for Optical Devices Using Gallium and Nitrogen Containing Materials
InactiveUS20110215348A1Easy to implementConvenient lightingPoint-like light sourceSolid-state devicesNitrogenLength wave
An optical device includes an LED formed on a substrate and a wavelength conversion material, which may be stacked or pixilated, within vicinity of the LED. A wavelength selective surface blocks direct emission of the LED device and transmits selected wavelengths of emission caused by an interaction with the wavelength conversion material.
Owner:SORAA
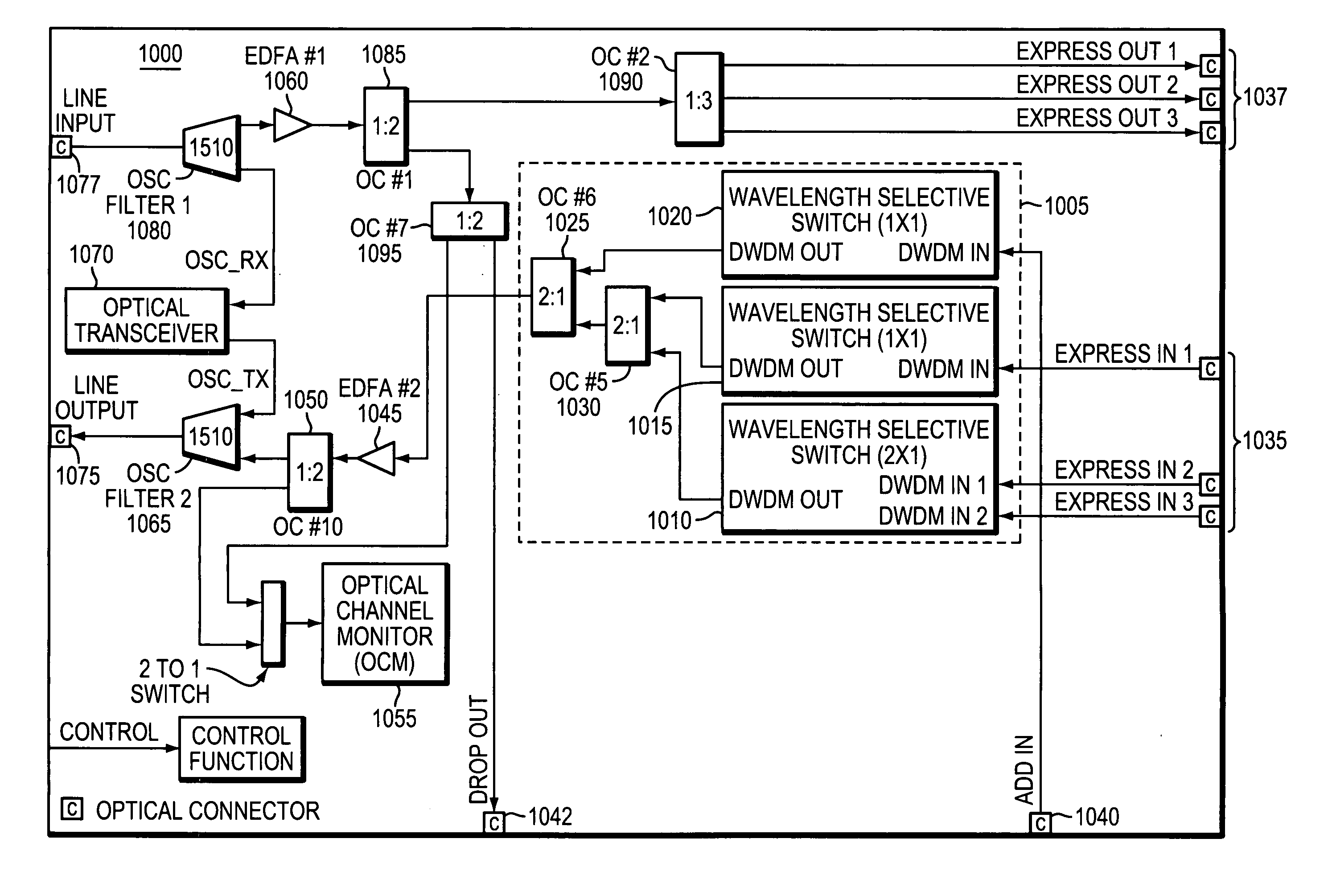
Methods and apparatus for reconfigurable add drop multiplexers
ActiveUS20090226168A1Less insertion lossMultiplex system selection arrangementsWavelength-division multiplex systemsWavelength selective switchingOptical coupler
Optical networks are increasingly employing optical network nodes having multiple interfaces to allow a node to direct optical signals received at any interface to any other interface connected to the node. Constructing a larger wavelength selective switching (WSS) module used in such a node can be complex and expensive. A method an apparatus for constructing a large WSS using parallelism is provided. In example embodiments, a larger WSS may include multiple parallel non-cascaded smaller WSSs and an optical coupler configured to optically couple the multiple parallel, non-cascaded smaller WSSs. This technique may be used to construct both N×1 and 1×N WSSs. Because the technique employs multiple parallel, non-cascaded WSSs, all inputs of a larger N×1 WSS and all outputs of a larger 1×N WSS are available receive or transmit external signals rather than being rather than being unavailable due to, for example, cascading smaller WSS devices together.
Owner:TELLABS OPERATIONS
Wavelength-selective optical fiber components using cladding-mode assisted coupling
InactiveUS6850665B2High isolation between channelsIncrease light intensityWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesFiberGrating
A wavelength-selective optical device for coupling of light at predetermined wavelength from one optical fiber waveguide to another using at least two gratings and cladding-mode assisted coupling is disclosed. The transfer of light is performed using intermediate coupling to one or more cladding mode of the waveguides. In the case when the fibers have physically different cladding's, an arrangement for transfer of light from one cladding to another is required. The disclosed coupler has no back-reflection, small insertion loss, and very high channel isolation. The device can be used in wavelength-division multiplexing networks.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD +1
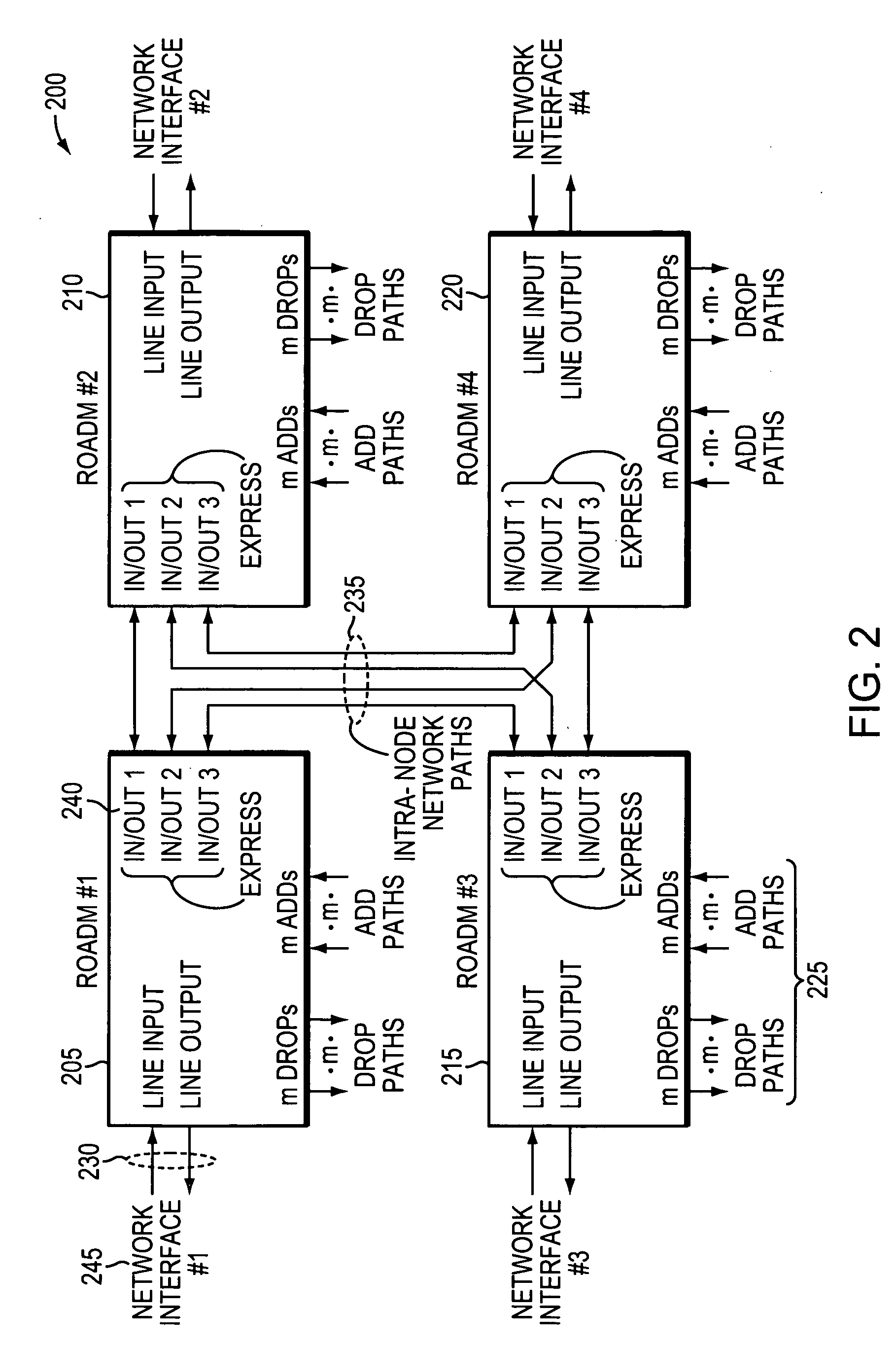
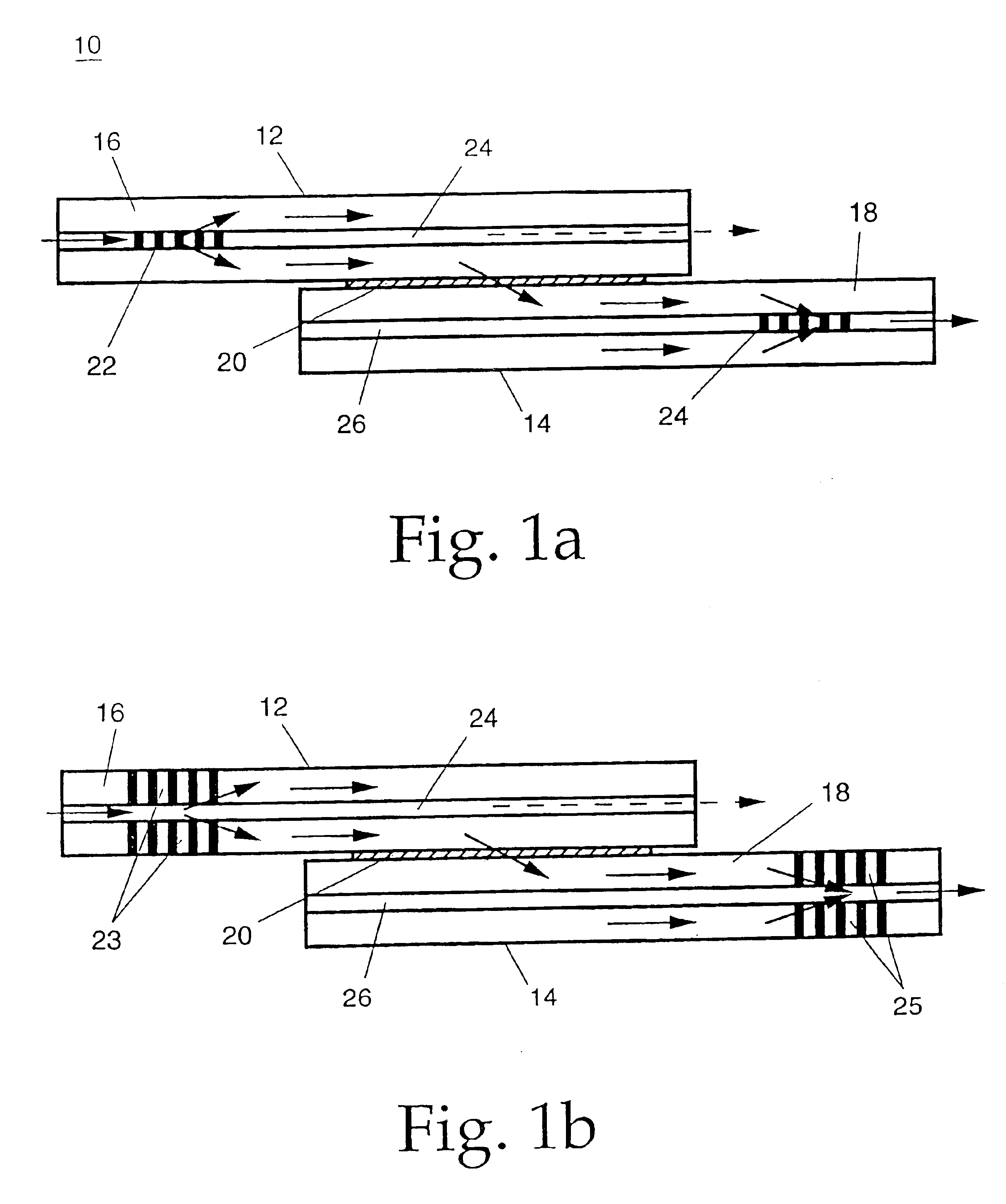
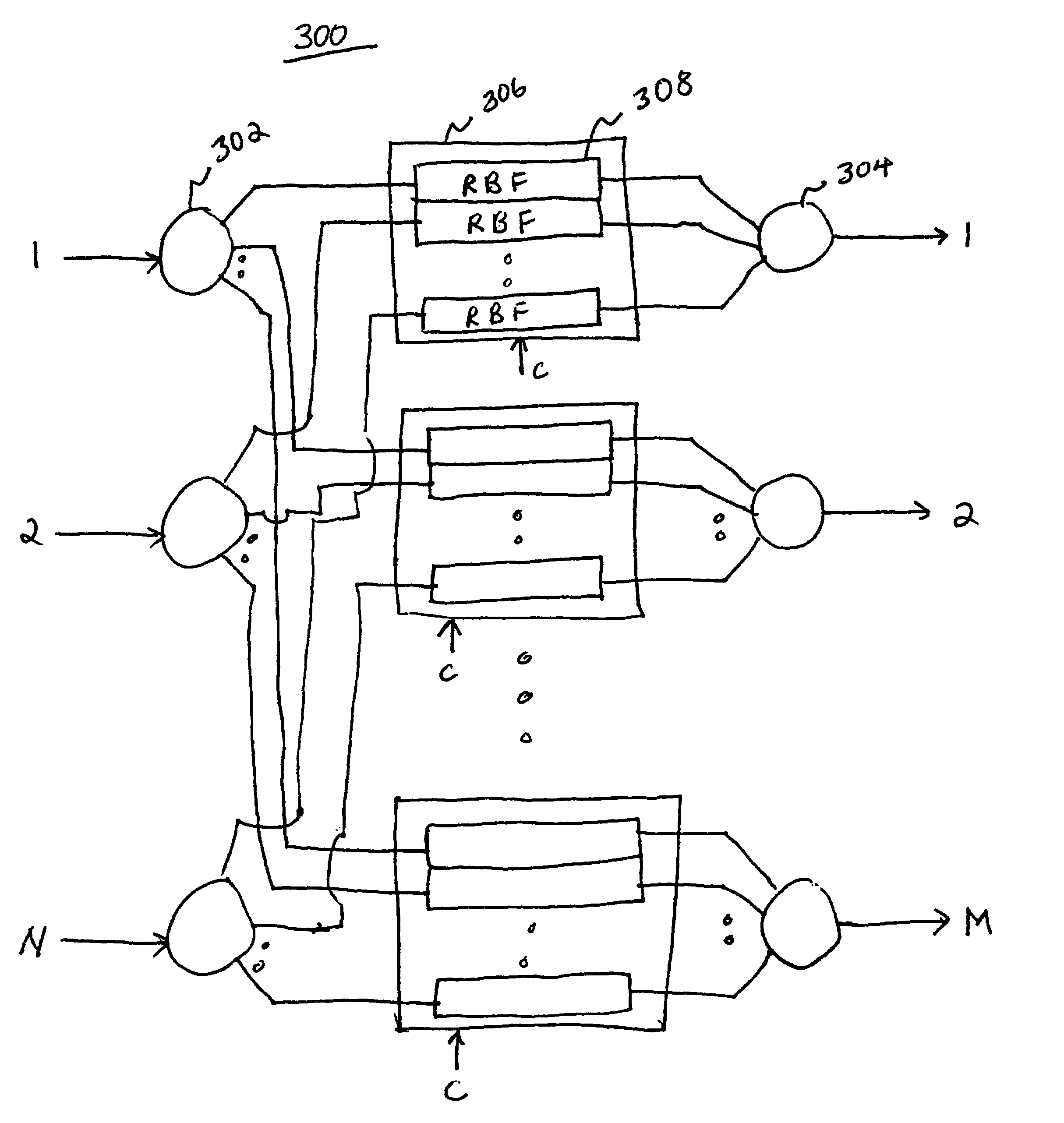
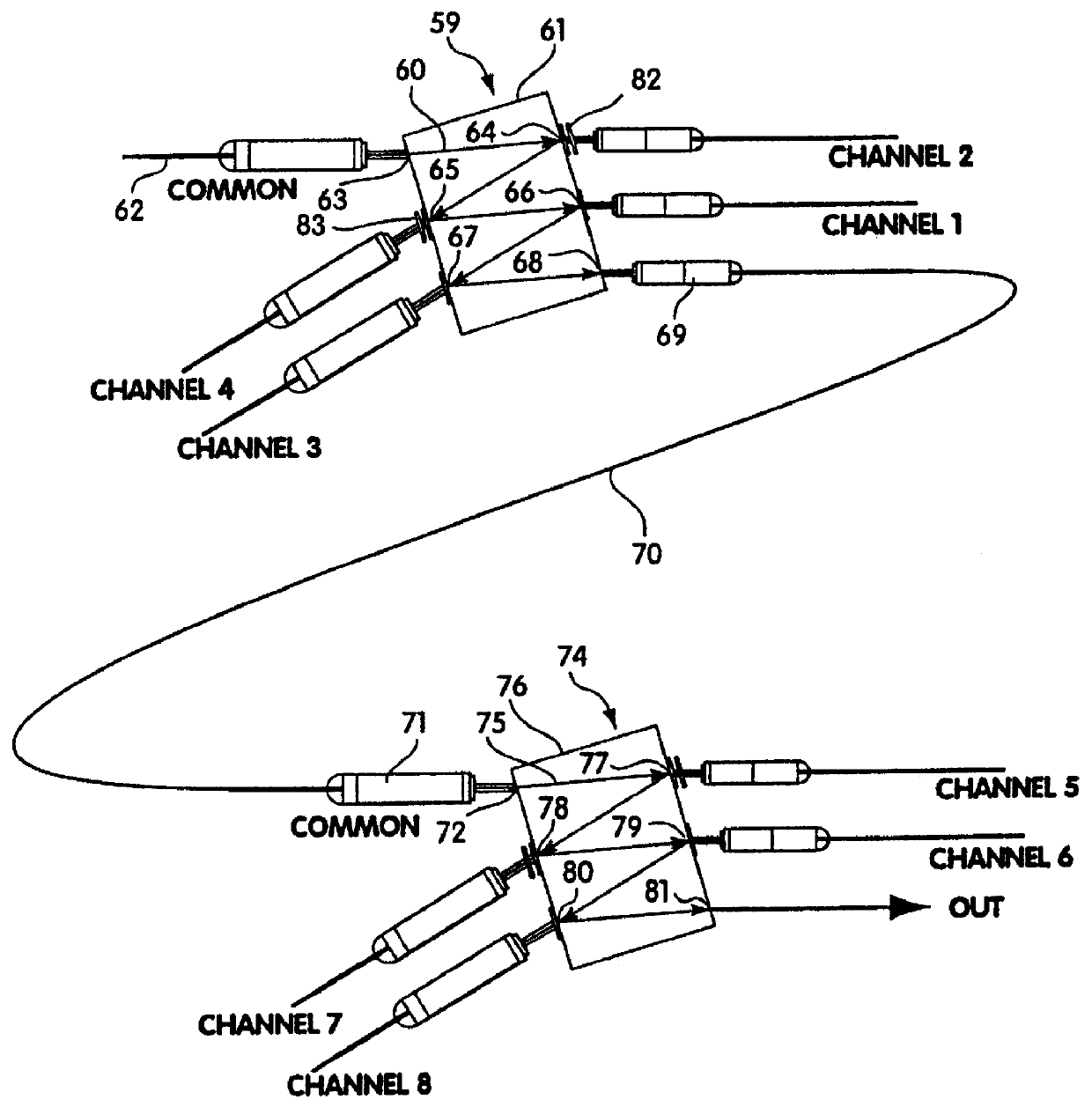
Flexible wavelength selective switch fabric with arbitrary add and drop capability
ActiveUS7231107B1Multiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesLength waveWavelength selectivity
A flexible wavelength switch fabric may be implemented with multiple groups of reconfigurable blocking filters or with multiple multi-in, single out wavelength selective switches. The behaviors of reconfigurable blocking filters are individually settable, such as channel blocking, channel spacing, transmission rate, and default blocking state. Add and drop taps may be added to provide arbitrary add / drop capability. Optical splitters / combiners used may be tunable so that insertion losses may be minimized for the overall network.
Owner:CIENA
Electro-optical switching fabric systems and methods
ActiveUS20130287397A1Multiplex system selection arrangementsCoupling light guidesEngineeringLength wave
An optical switch fabric, including: a first set of horizontal optical waveguides receiving a plurality of wavelengths; a plurality of wavelength-selective drop optical switches associated with the first set of horizontal optical waveguides, wherein the plurality of wavelength-selective drop optical switches are each configured to drop a selected wavelength from a horizontal optical waveguide of the first set of horizontal optical waveguides to an associated vertical optical waveguide of a plurality of vertical optical waveguides; and a plurality of controllable optical switches associated with the plurality of vertical optical waveguides, wherein the plurality of controllable optical switches are each configured to direct a selected wavelength from a vertical optical waveguide of the plurality of vertical optical waveguides to a horizontal optical waveguide of a second set of horizontal optical waveguides, and wherein the second set of horizontal optical waveguides output a plurality of wavelengths.
Owner:CIENA
Solar panel with optical films
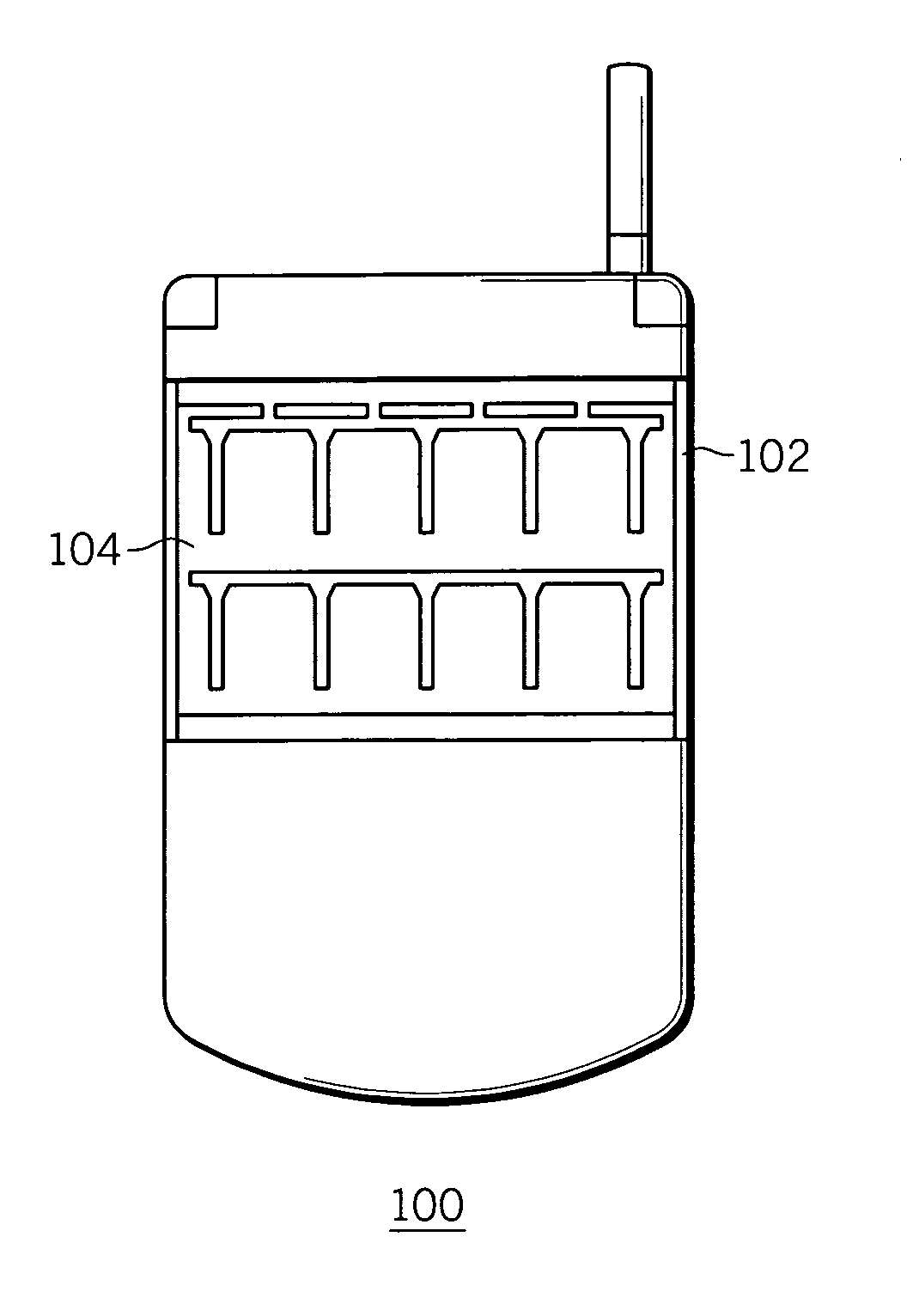
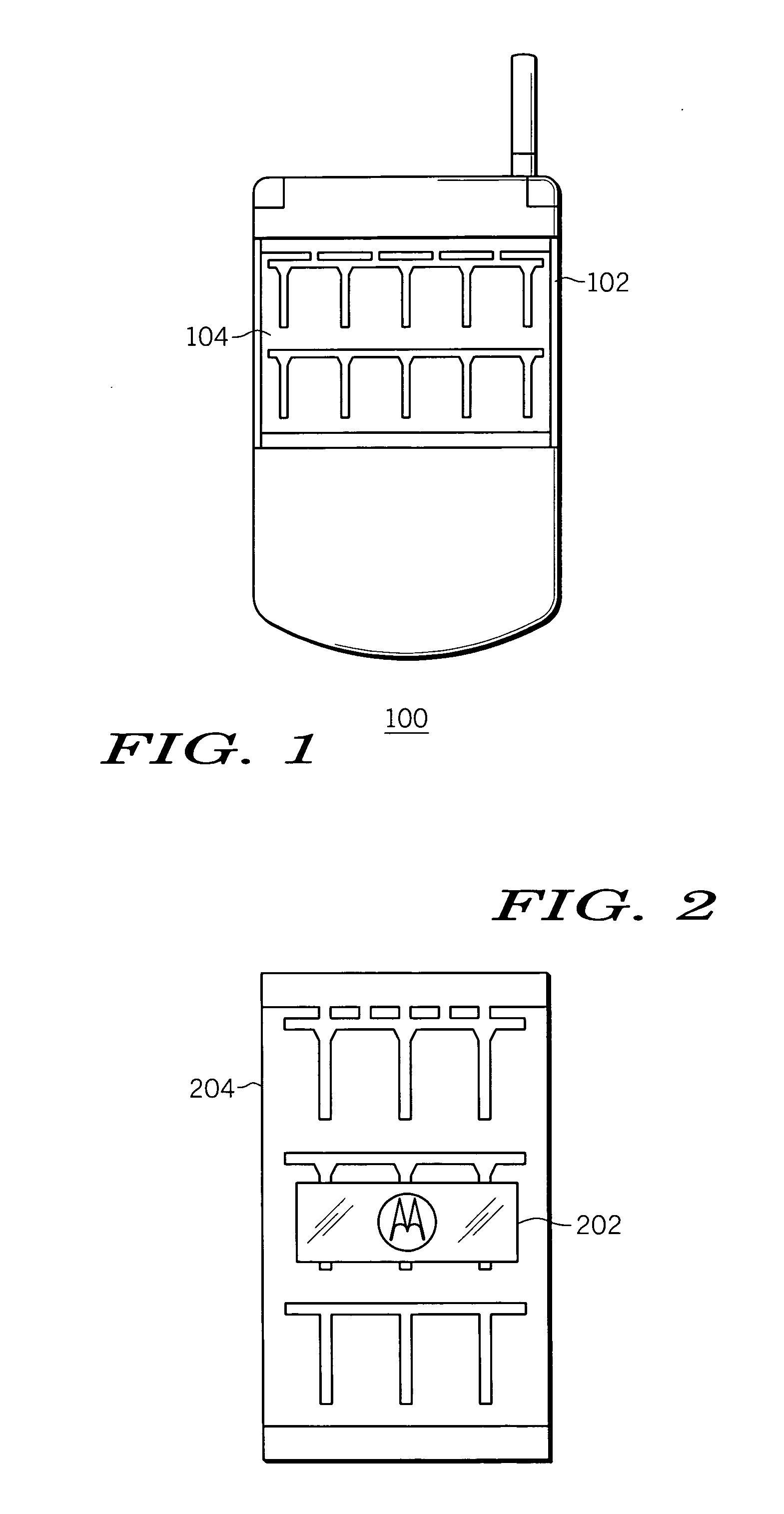
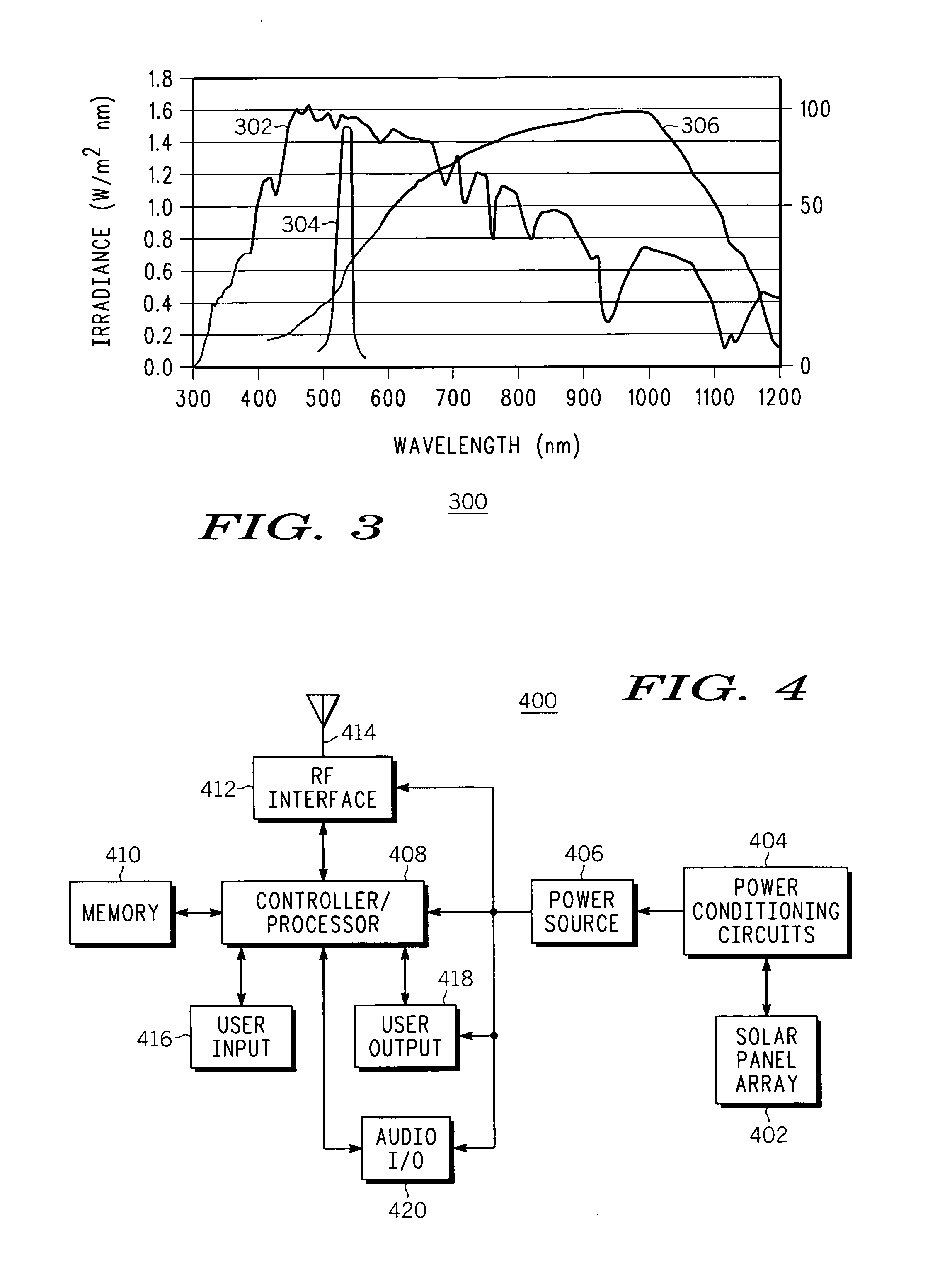
A solar panel mounting arrangement, and electronic device, and a wireless device, includes a solar panel (204); and a wavelength selectively reflective optical film (202) being disposed in front of the solar panel for the optical film to substantially reflect a pre-selected band (304) of solar irradiation frequencies (302) in the visible light range and incident on a front surface of the optical film (202) while allowing solar irradiation frequencies (302) outside of the pre-selected band (304) to substantially pass through the optical film (202) and irradiate the solar panel (204). The optical film (202) can include at least one of an iconic pattern, a company logo, and a photo, that is visible from the front of the optical film (202). The optical film (202) can include holographic film. The optical film can include a multi-layer film.
Owner:MOTOROLA INC
Optical fiber lasers
ActiveUS20140023098A1High intracavity powerEfficient frequency conversionLaser using scattering effectsOptical resonator shape and constructionResonant cavityRare earth
A fiber gain medium provided by a rare-earth doped fiber (10) is contained in a first resonant cavity by end reflectors (12, 18). The reflector (12) is wavelength selective to limit the frequency band of the first resonant cavity. The first resonant cavity also contains a second resonant enhancement cavity (16) with multiple transmission bands lying within the first resonant cavity's frequency band. Multiple standing wave modes of the first resonant cavity lie within both the frequency band of the first resonant cavity and the transmission bands of the second resonant cavity, and it is these standing wave modes that support laser action when the rare-earth doped fiber is suitably pumped by pump lasers (40).
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHAMPTON
Solar blind-UVC photochromic detector and method for calibration
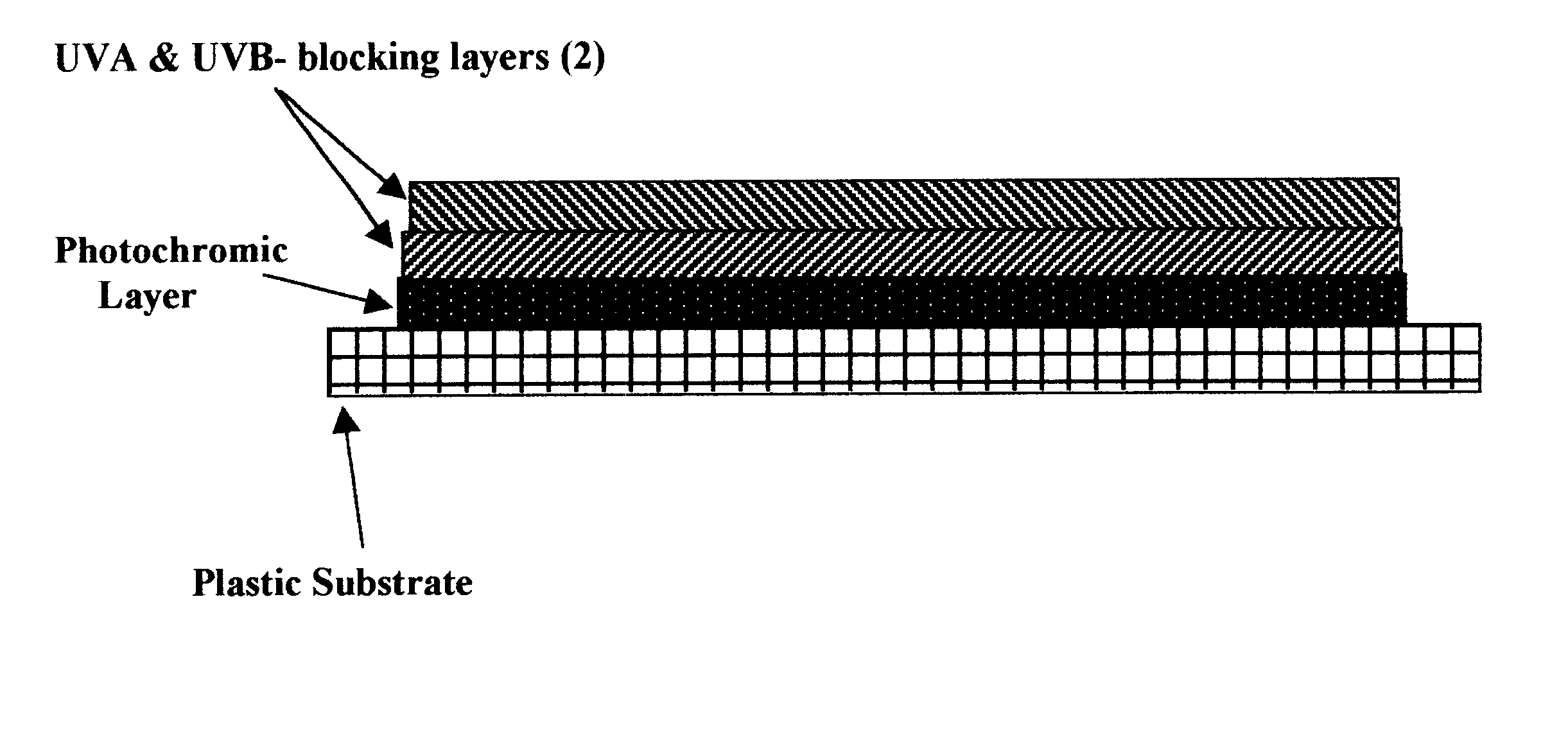
The present invention relates to an ultraviolet radiation detector in general and more specifically to a solar blind ultraviolet radiation detector; that is, a detector insensitive to the radiation of sunlight reaching the earth's surface but sensitive to UVC wavelengths in the spectrum, defined as the interval 200 nm-280 nm. The solar blind detector is base on the use of photochromic compounds in conjunction with ultraviolet wavelength-selective chemical blocks and their incorporation into optically clear polymer matrices. The photochromic compound is selected from the group comprising spiropyran molecules spirooxazine molecules and chromene derivatives. Applications for such device are as numerous as the sources of UVC radiation. An obvious use for such Solar Blind UVC detector is monitoring the output of UVC sources used in the decontamination of water and air (water treatment and air purification) and for sterilization of medical instruments.
Owner:GOUDJIL KAMAL
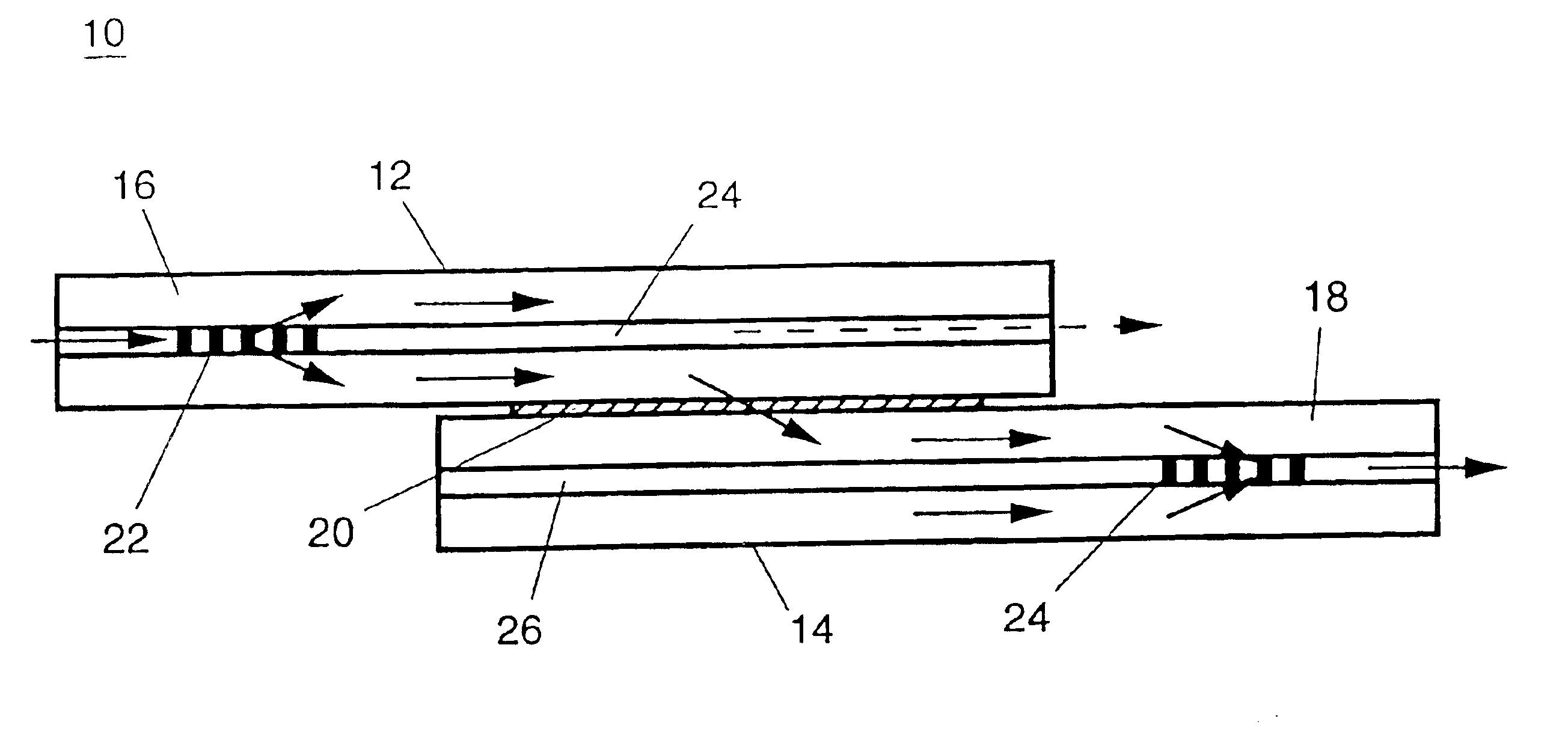
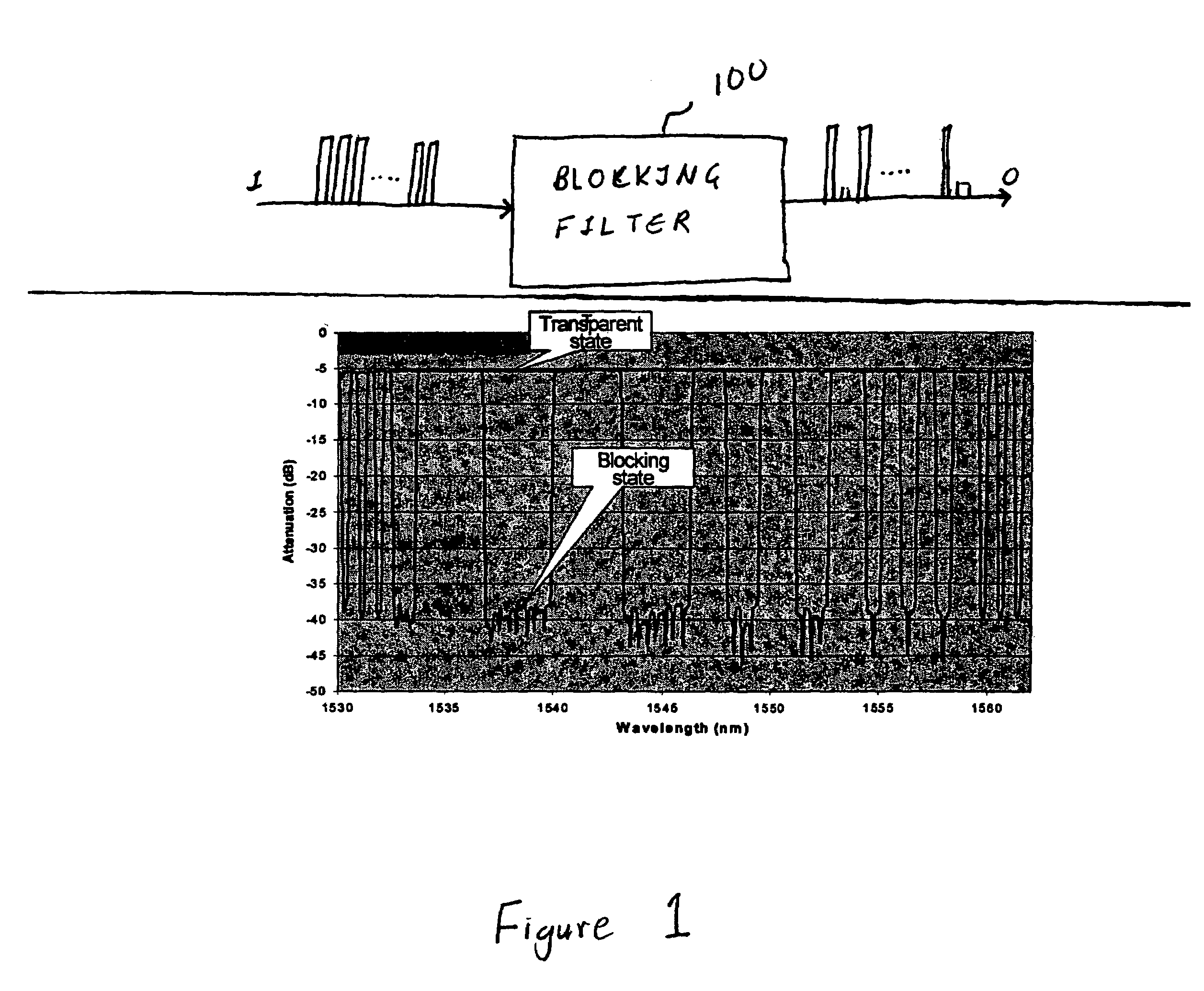
Cascading optical multiplexing device
InactiveUS6167171AReduce complexityLow costLaser detailsWavelength-division multiplex systemsFiberMultiplexing
An optical multiplexing device is provided comprising multiple wavelength division multiplexers cascaded together. A first one of the wavelength division multiplexers has a common port and multiple optical ports which are optically coupled to the common port. The common port may be optically coupled to a trunk line of a system employing wavelength division multiplexing, for example, a fiber-optic telecommunication system employing 4, 8, 16 or other number of multiplexed channels. The optical ports include multiple channel ports, each of which is transparent to a corresponding wavelength sub-range and reflective of other wavelengths. The second wavelength division multiplexer has a common port optically coupled to one of the optical ports of the first wavelength division multiplexer. The second wavelength division multiplexer also has multiple optical ports which are optically coupled to its common port and include multiple wavelength-selective channel ports. A waveguide, such as a fiber-optic line, can optically connect the common port of the second wavelength division multiplexer to an optical port of the first wavelength division multiplexer. The cascaded WDMs each may be optically coupled to the output of a passive coupler and a housing may be provided defining an enclosed space in which the optical multiplexing device is mounted. Optionally, additional WDMs may be cascaded with the first two WDMs in a parallel or branched formation, an in-line formation or some combination. Preferably, the channels are interleaved, such that they are removed from the multiplexed signal in certain non-sequential order. The optical multiplexing device also may employ compound interleaving wherein adjacent channels are multiplexed by different ones of the cascaded WDMs. The optical multiplexing devices can operate to add signals, remove signals or a combination of both.
Owner:CORNING OCA CORPORATION
Wavelength selective reconfigurable optical cross-connect
ActiveUS7787720B2Wavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesCross connectionLight beam
An optical coupling device including: at least a first input port for delivering an optical input signal beam that includes a plurality of wavelength channels; at least a first optical output port for receiving an optical output signal beam; a wavelength dispersion element for spatially separating the plurality of wavelength channels in the optical input signal beam to form a plurality of spatially separated wavelength channel beams; an optical coupling device for independently modifying the phase of each of the spatially separated wavelength channel beams such that, for at least one wavelength channel beam, a selected fraction of the light is coupled to the first output port and a fraction of the light is coupled away from the first output port.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
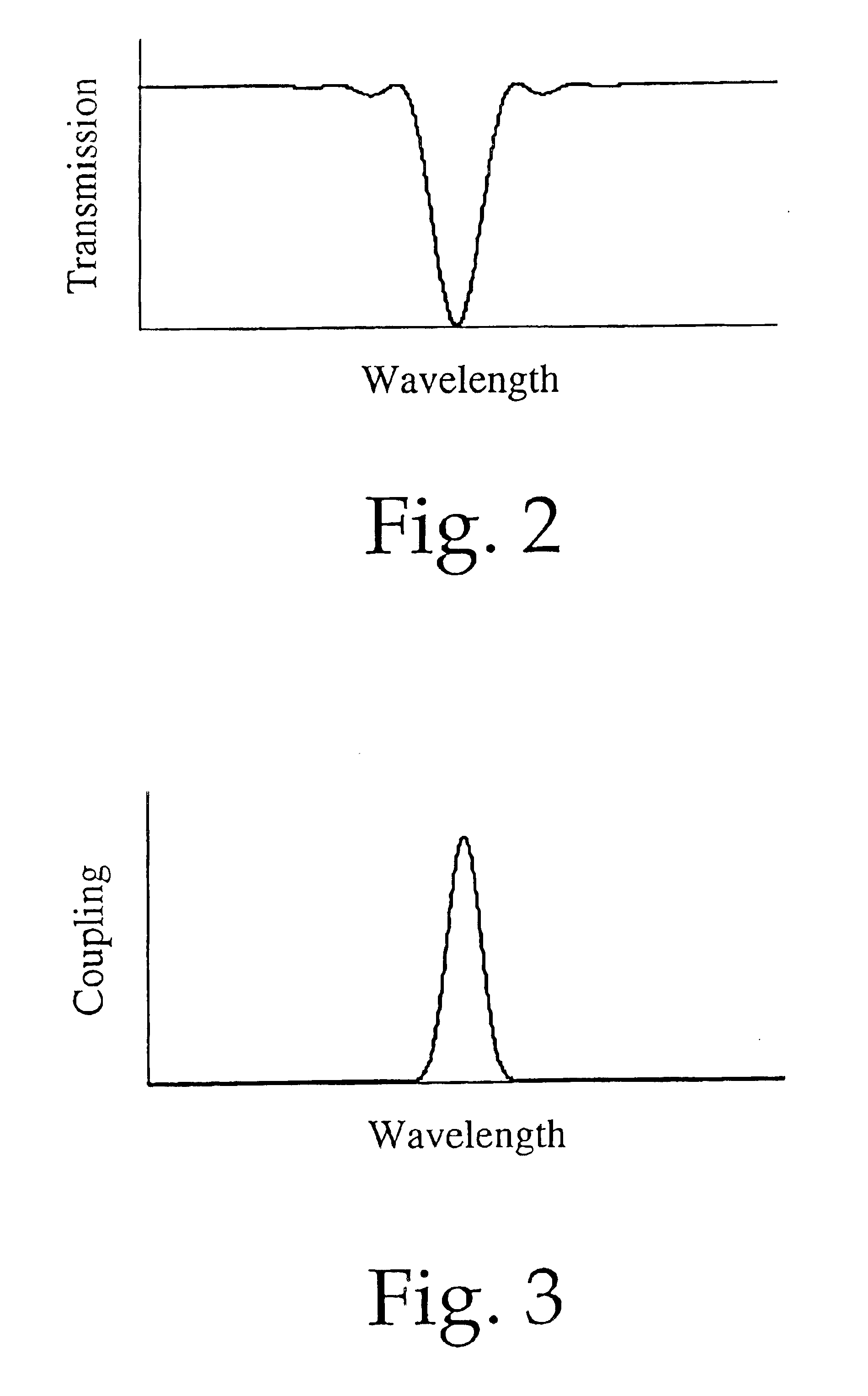
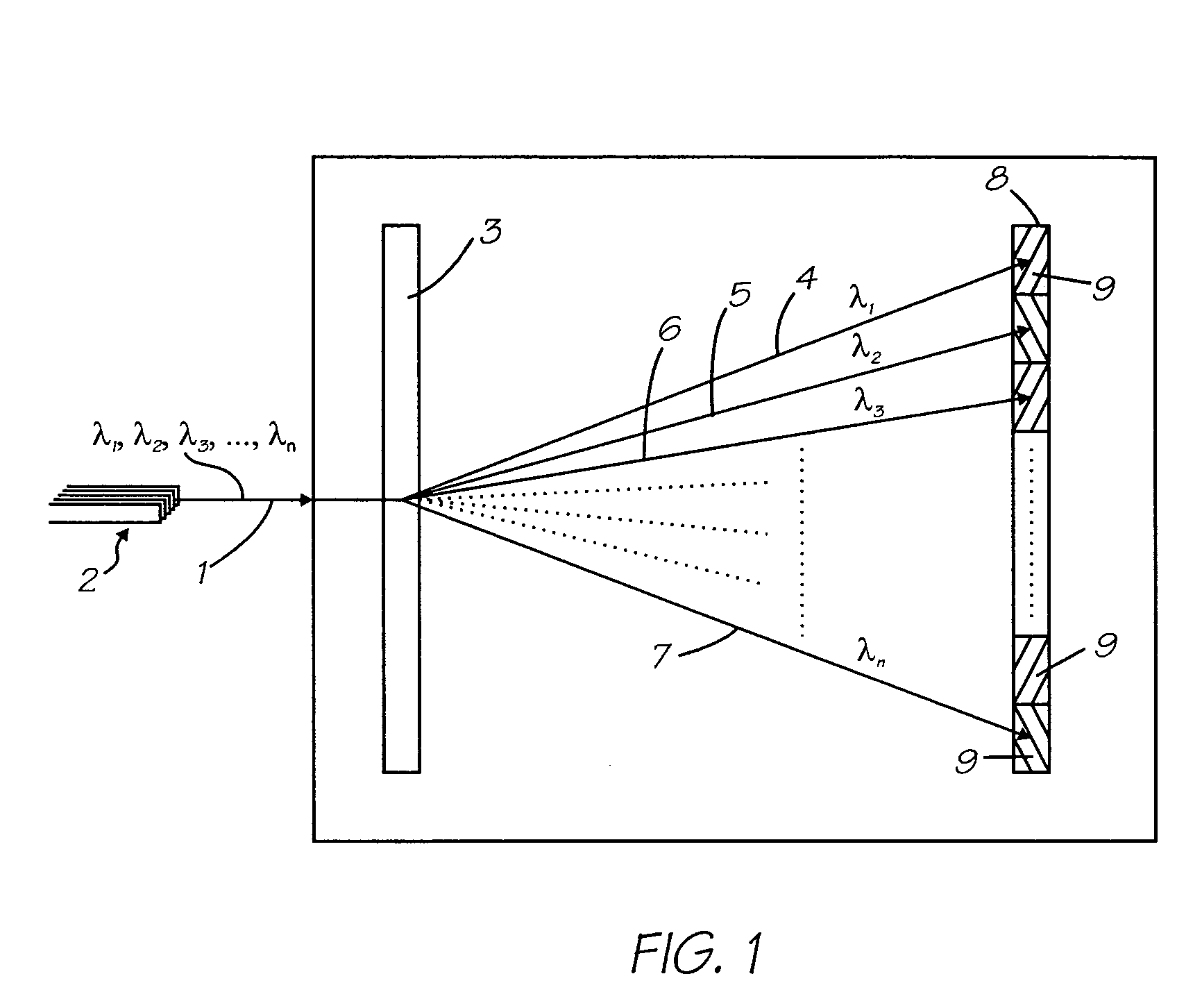
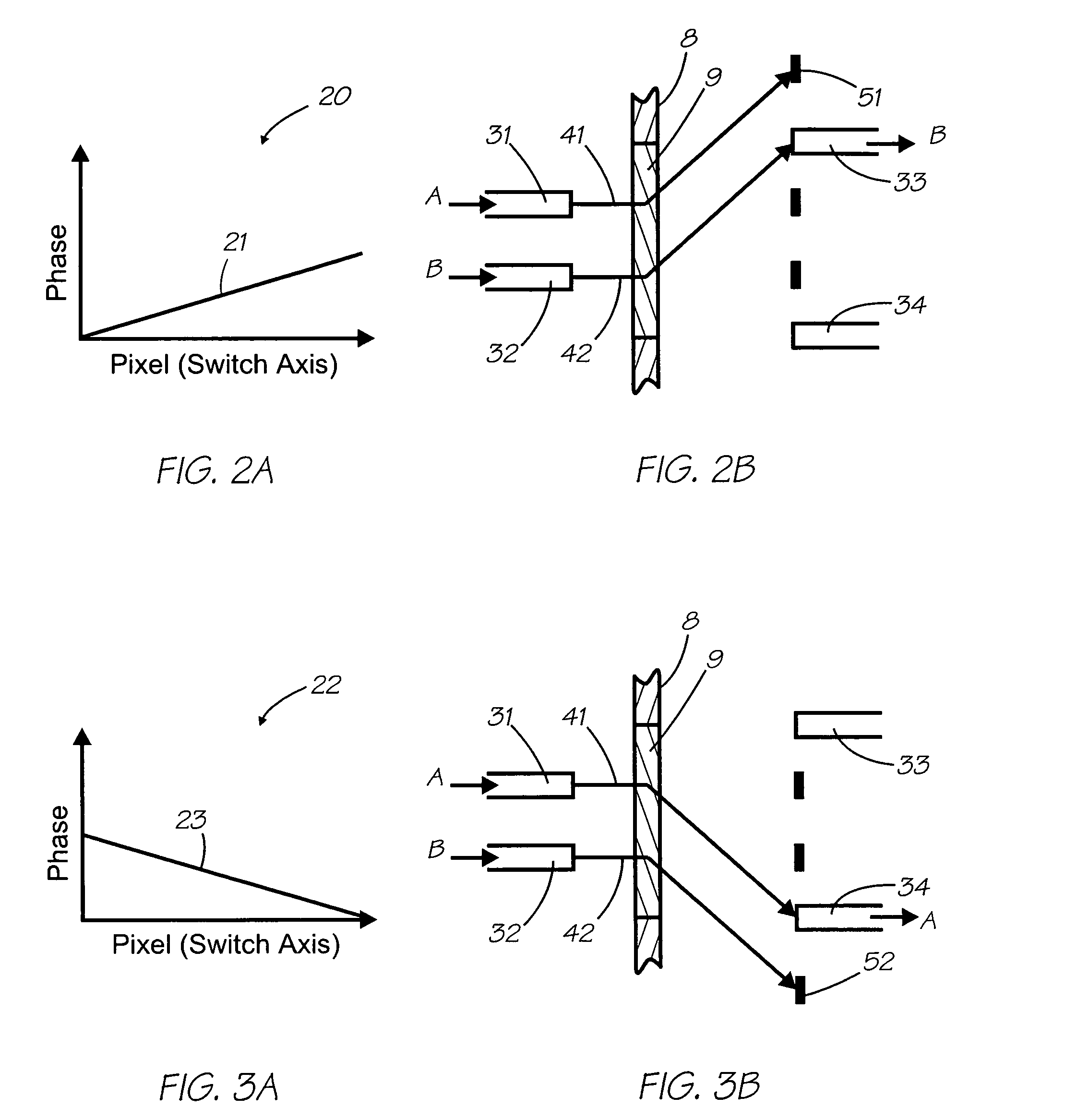
Spectral plane method and apparatus for wavelength-selective optical switching
We describe a variable bandwidth tunable optical spectral filtering device and associated method for selectively directing a portion of a wavelength multiplexed input signal, entering through one or more optical fibers, into one or more output signals provided to one or more optical fibers and / or electronic outputs. The optical filtering is accomplished using free-space diffractive wavelength de-multiplexing optics combined with a fixed (permanent) patterned structure located in the spectrally dispersed image plane. The structure can direct a selected spectral portion of the optical signal to one or more separate outputs, such as an optical fiber or power detector. A single active element in the optical path is used to spatially shift, or steer, the entire input spectrum at the dispersed spectral image plane, to control the portion of the input spectrum illuminating specific features on the permanent patterned structure. In one preferred embodiment, a device with a fixed selective area triangular shaped tilted reflective facet on a flat reflective surface is constructed such that the light reflected off the flat reflective surface and off the triangular reflective facet are selectively multiplexed back and directed to different output fiber ports. Inputs at different angles of incidence on the reflective structures may be deflected by the same structures to different output port fiber ports. A reconfigurable variable-bandwidth tunable optical add / drop multiplexing device is constructed using such a filtering device and an application of such an add / drop multiplexing in a optical transport network is demonstrated.
Owner:WILSON GORDON +1
Tunable plasmonic filter
A tunable plasmonic filter or an optical filtering method discloses plasmonic filter structure and a voltage or current source. An intensity or wavelength of light transmitted through the filter structure is modulated by the intensity of a voltage or current from the voltage or current source. The plasmonic filter structure is located between electrodes electrically connected to the voltage or current source. The plasmonic filter structure is configured such that the incident light is resonant with at least one plasmonic mode on the structure, and a predetermined wavelength will perturb the metallic plasmonic structure in surface plasmon on energy bands for the wavelength selective transmission of light.
Owner:NANOLAMBDA
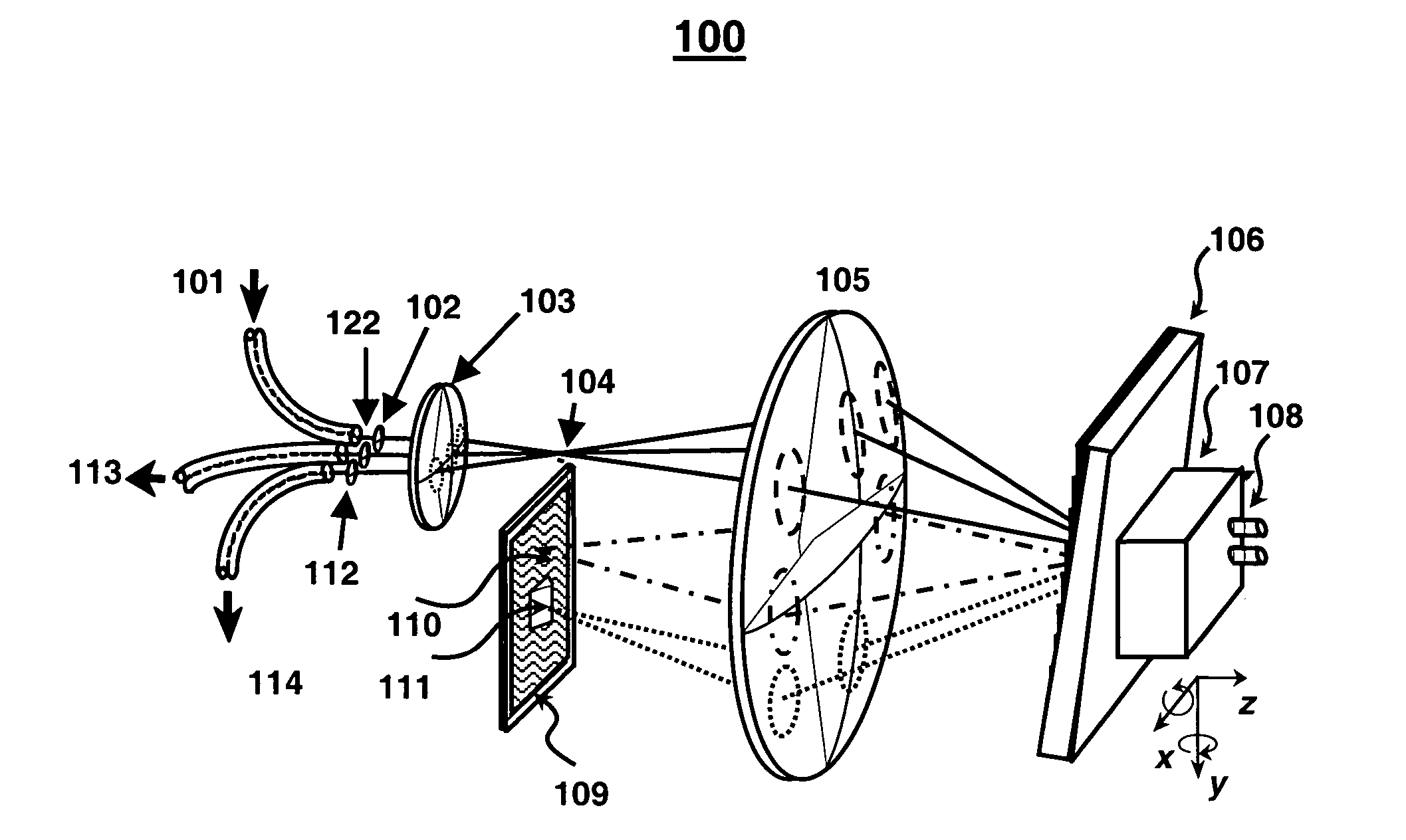
Wavelength-selective 1xN2 switches with two-dimensional input/output fiber arrays
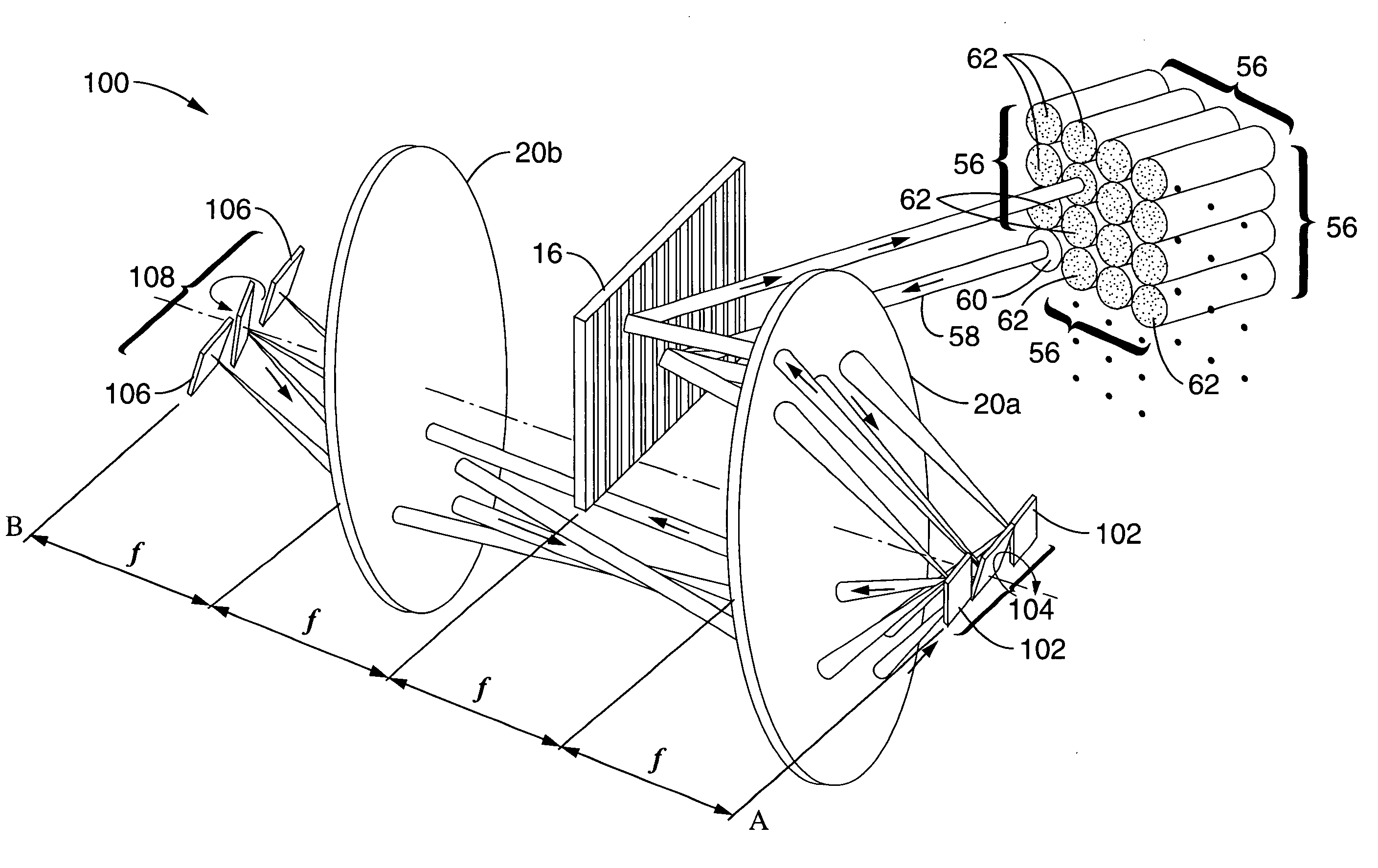
A 1×N2 wavelength selective switch (WSS) configuration in which switch elements are configured in a way that enables the input or output fibers to be arranged in a two-dimensional (2D) array. By employing 2D arrays of input / output channels, the channel count is increased from N to N2 for wavelength selective switches. In one embodiment, in which the components are arranged as a 2-f imaging system, a one-dimensional (1D) array of mirrors is configured such that each mirror has a dual scanning axis (i.e., each mirror can be scanned in X and Y directions). In another embodiment, in which the components are arranged as a 4-f imaging system, two 1D arrays of mirrors are configured with orthogonal scanning directions. In both embodiments, the number of ports is increased from N to N2.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Optical sheet member and display device
InactiveUS20160349573A1Extended Brightness RangeIncrease color rangeMechanical apparatusPolarising elementsSelective reflectionDisplay device
Provided are an optical sheet member including an optical conversion sheet containing a fluorescent material which absorbs at least a part of light in a wavelength range of 380 nm to 480 nm, converts the absorbed light into light in a wavelength range longer than that of the absorbed light, and re-emits the converted light, and a wavelength selective reflective polarizer functioning in the wavelength range of at least a part of the light in the wavelength range of 380 nm to 480 nm, in which both of front brightness and a color reproduction range are improved in a case of being incorporated into a display device using backlight which emits light having at least a blue wavelength range; and the display device.
Owner:FUJIFILM CORP
Optical sensor device for local analysis of a combustion process in a combustor of a thermal power plant
InactiveUS7650050B2Easy constructionInexpensive to fabricatePhotometryMaterial analysis by optical meansCombustorEngineering
Owner:ANSALDO ENERGIA IP UK LTD
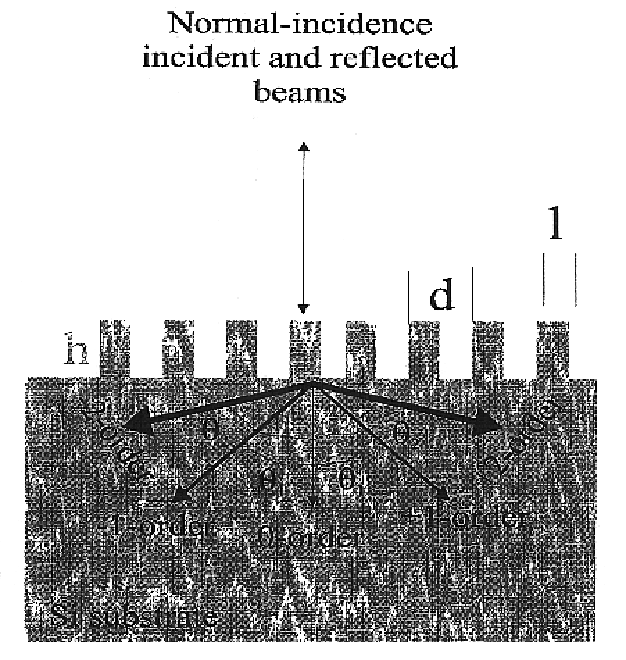
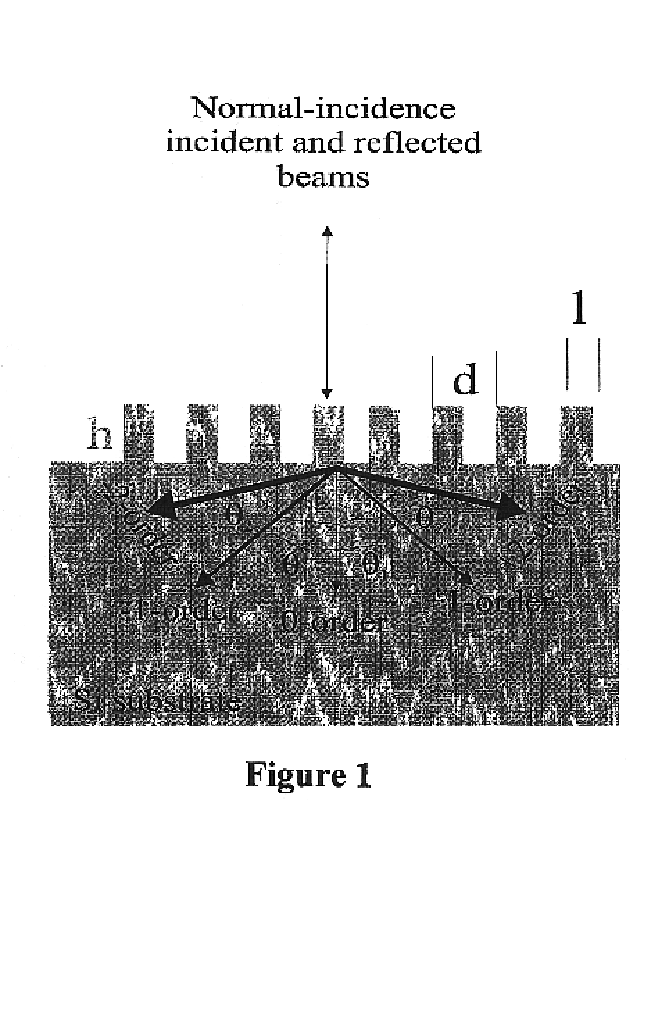
Enhanced light absorption of solar cells and photodetectors by diffraction
InactiveUS6858462B2Promote absorptionImprove performanceFinal product manufactureSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDiffraction orderGrating
Enhanced light absorption of solar cells and photodetectors by diffraction is described. Triangular, rectangular, and blazed subwavelength periodic structures are shown to improve performance of solar cells. Surface reflection can be tailored for either broadband, or narrow-band spectral absorption. Enhanced absorption is achieved by efficient optical coupling into obliquely propagating transmitted diffraction orders. Subwavelength one-dimensional structures are designed for polarization-dependent, wavelength-selective absorption in solar cells and photodetectors, while two-dimensional structures are designed for polarization-independent, wavelength-selective absorption therein. Suitable one and two-dimensional subwavelength periodic structures can also be designed for broadband spectral absorption in solar cells and photodetectors. If reactive ion etching (RIE) processes are used to form the grating, RIE-induced surface damage in subwavelength structures can be repaired by forming junctions using ion implantation methods. RIE-induced surface damage can also be removed by post RIE wet-chemical etching treatments.
Owner:SANDIA NAT LAB
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com