Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
292 results about "Cladding mode" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
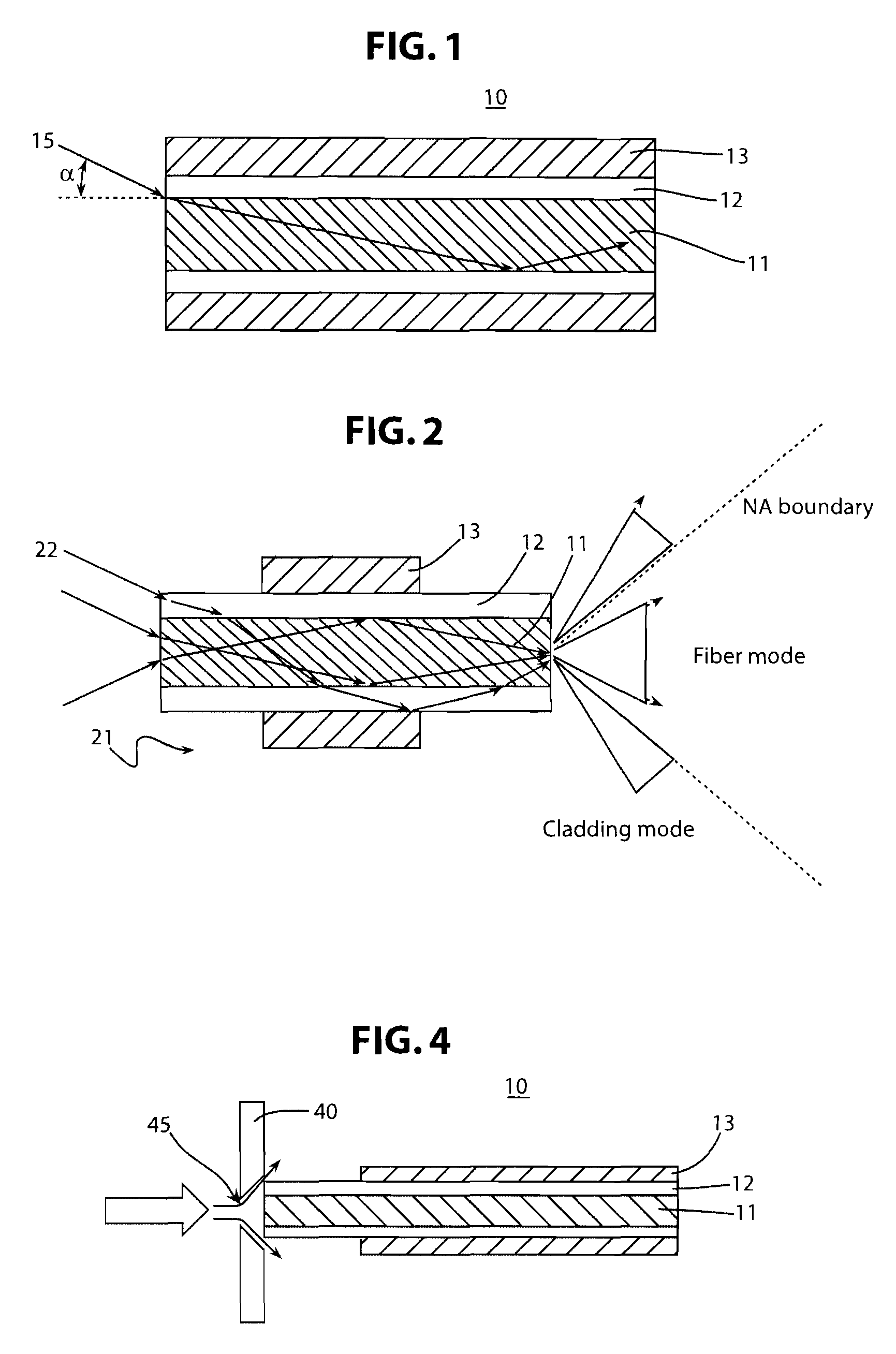
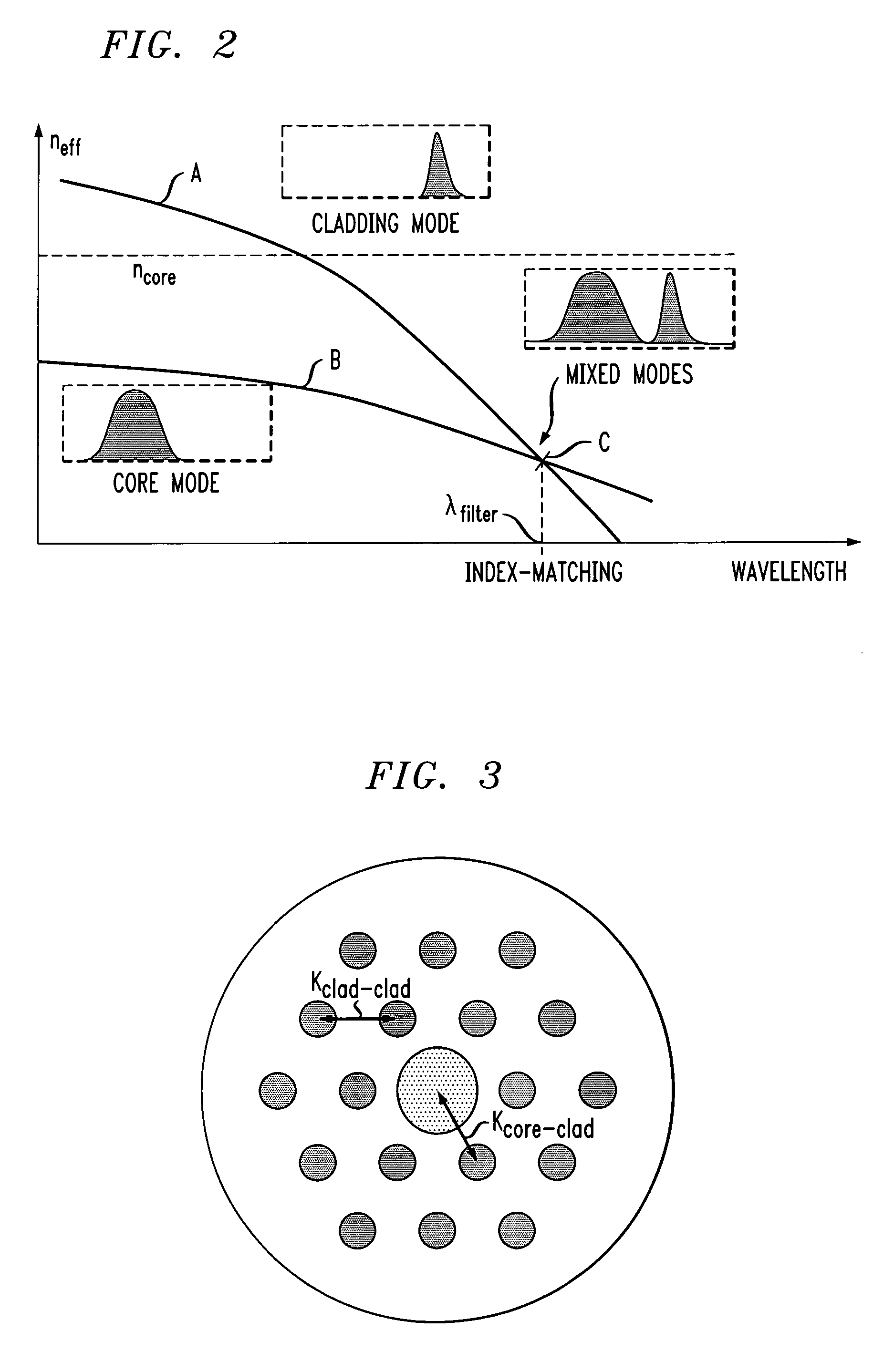
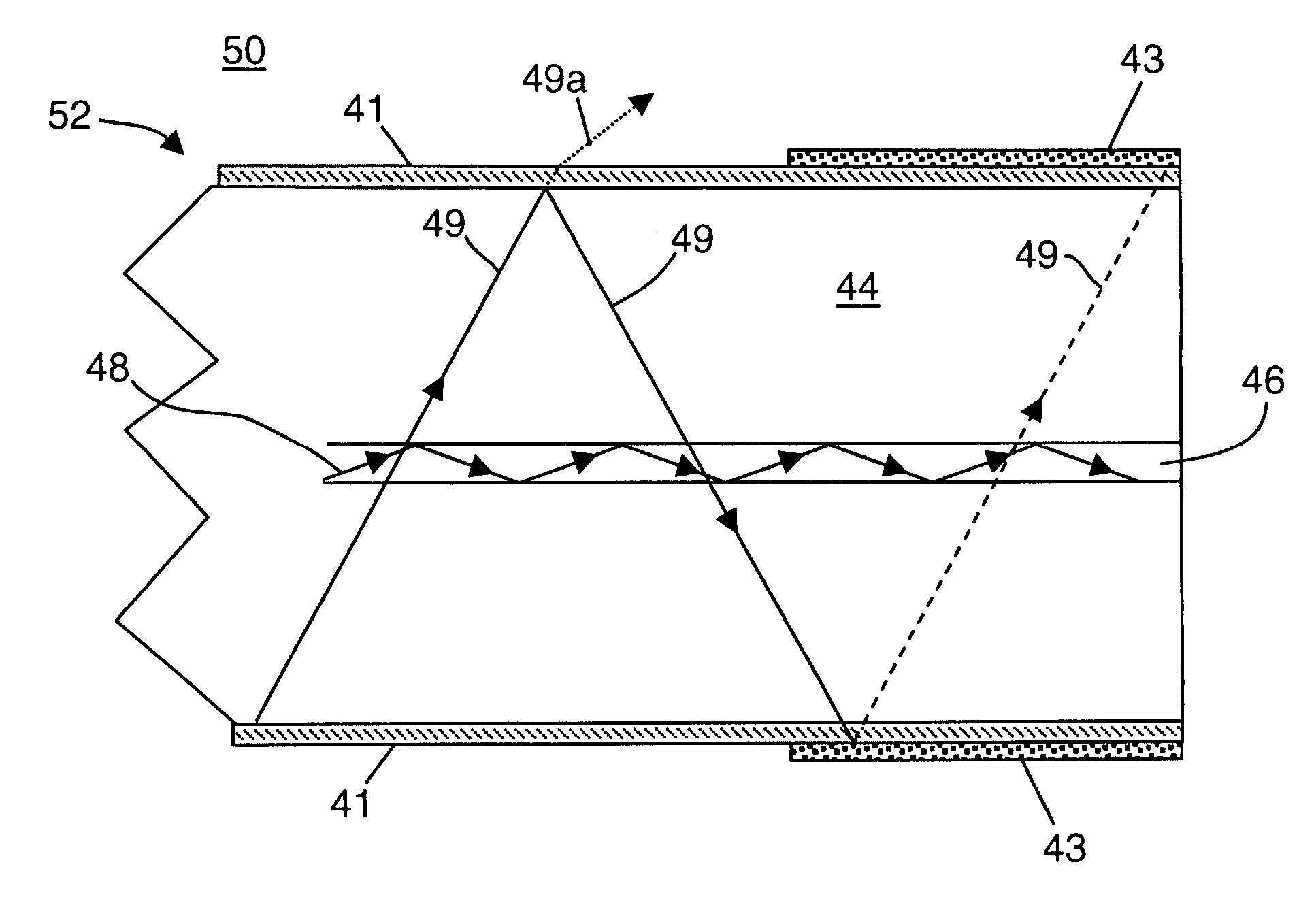
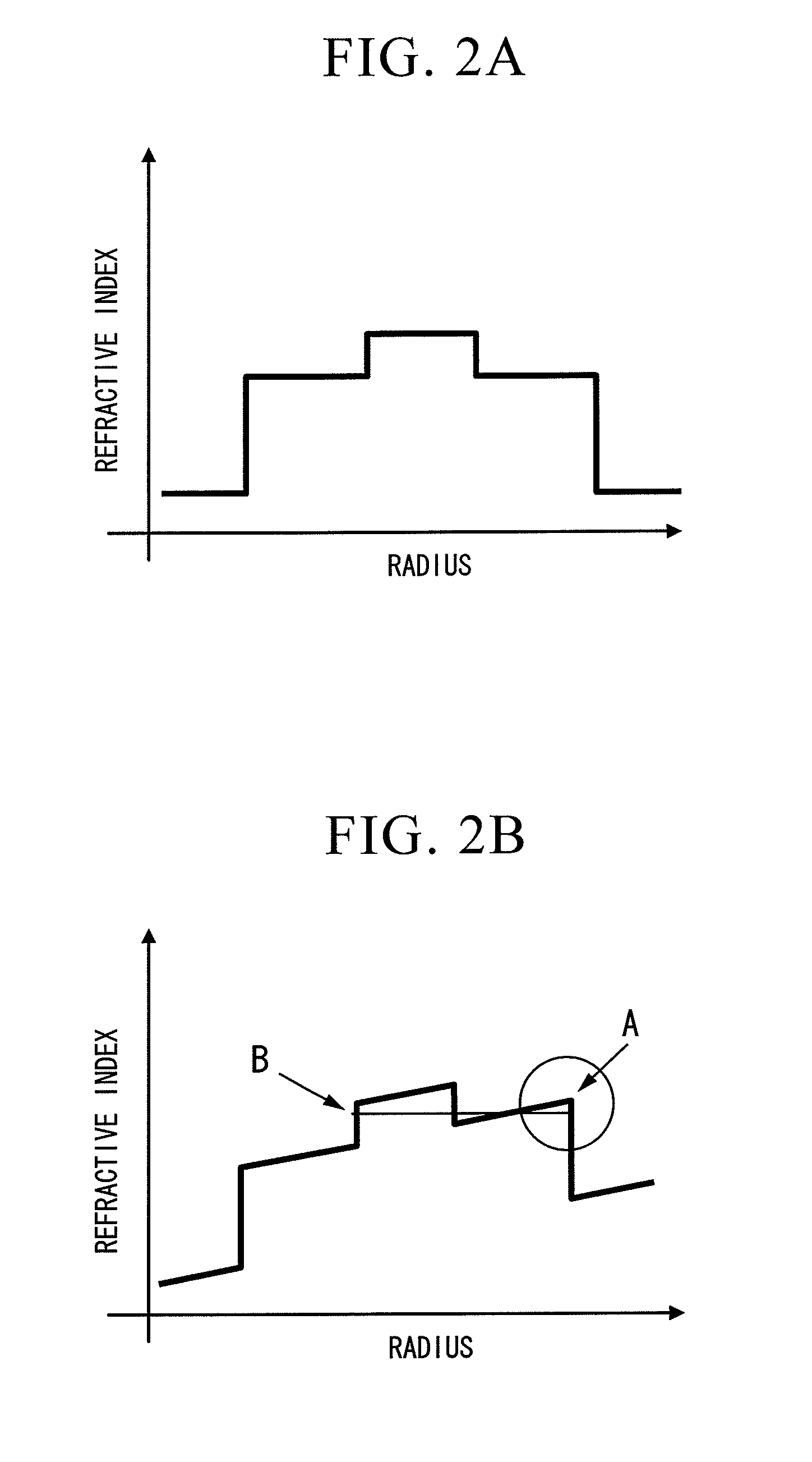
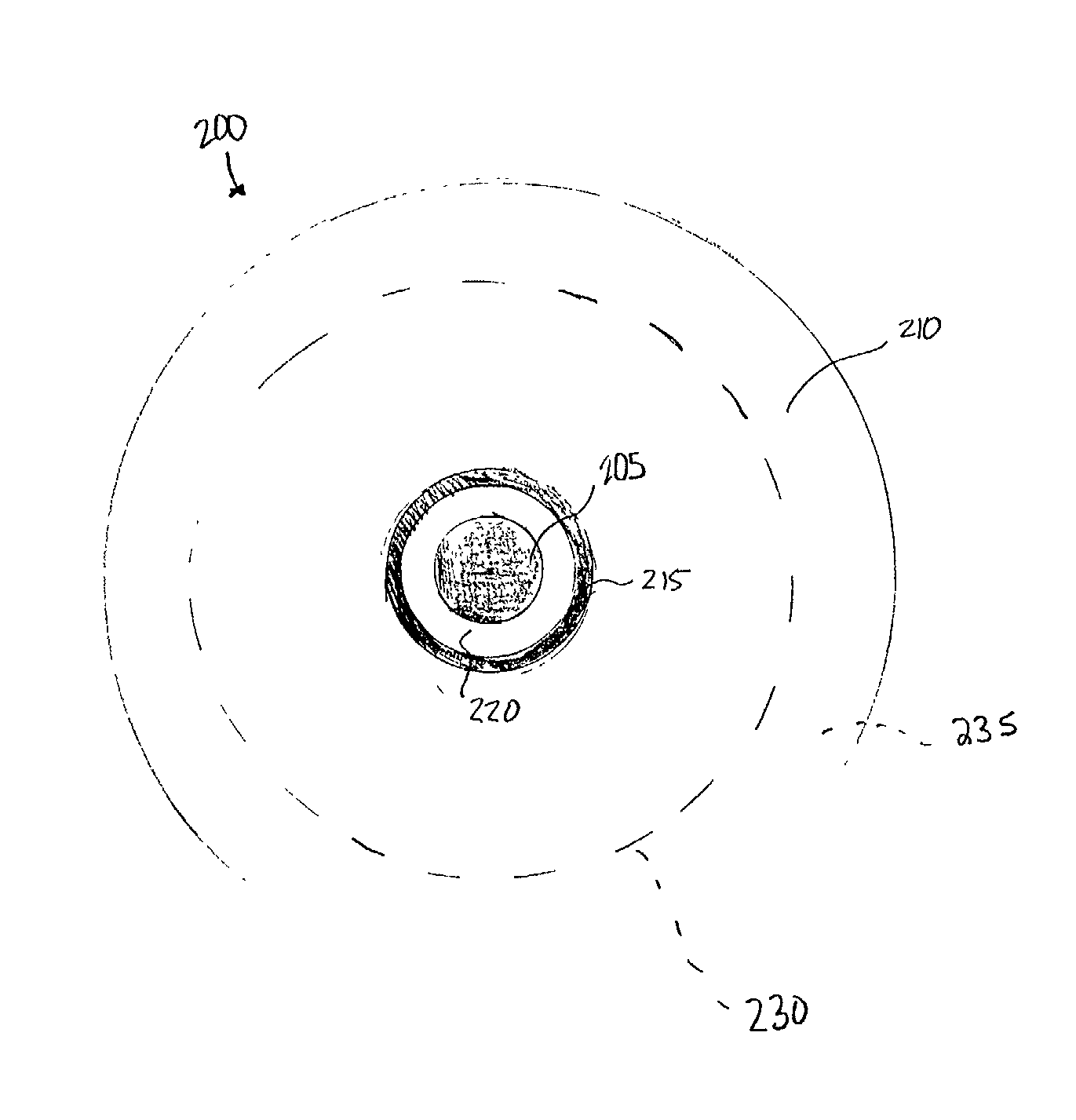
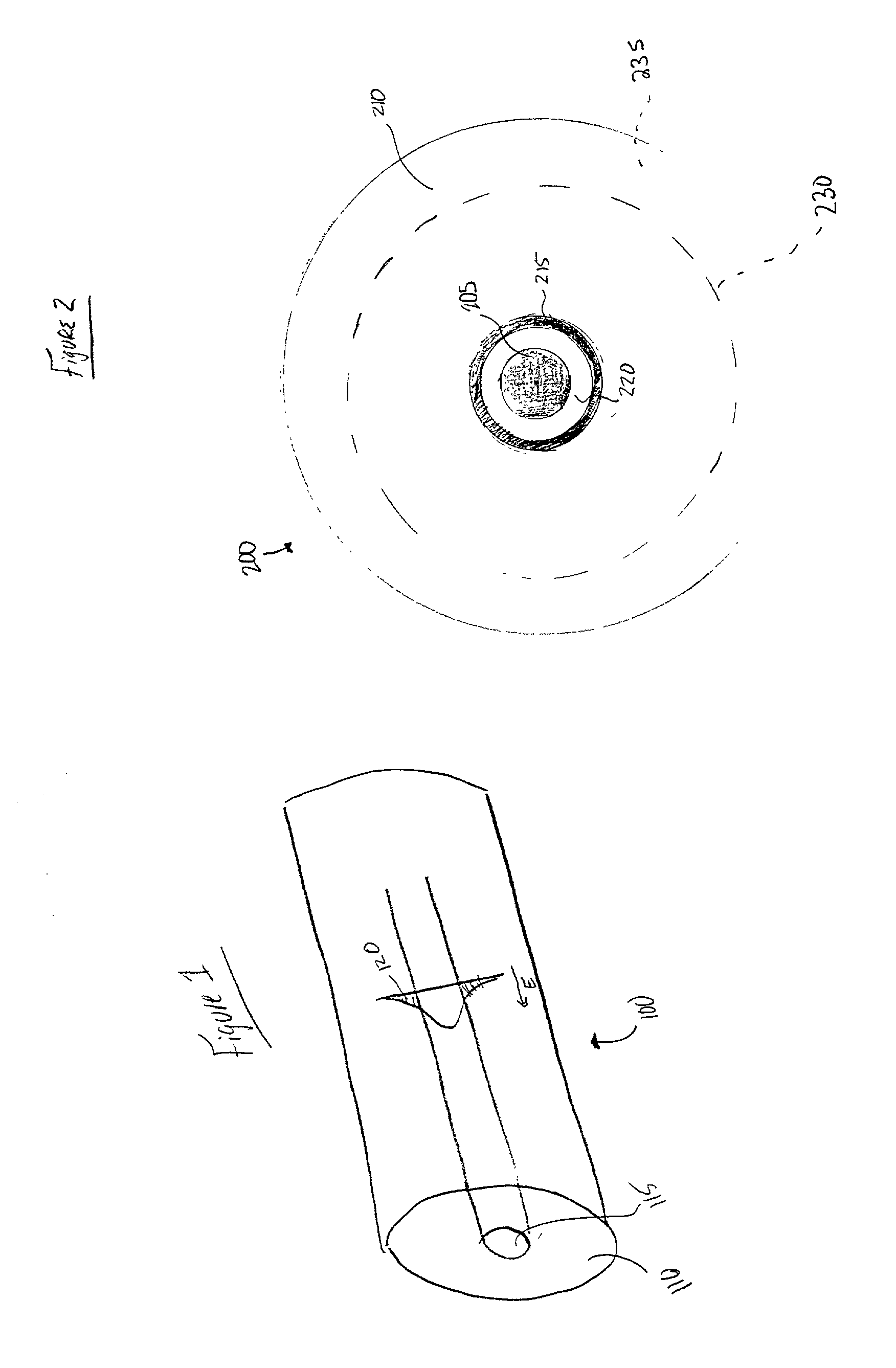
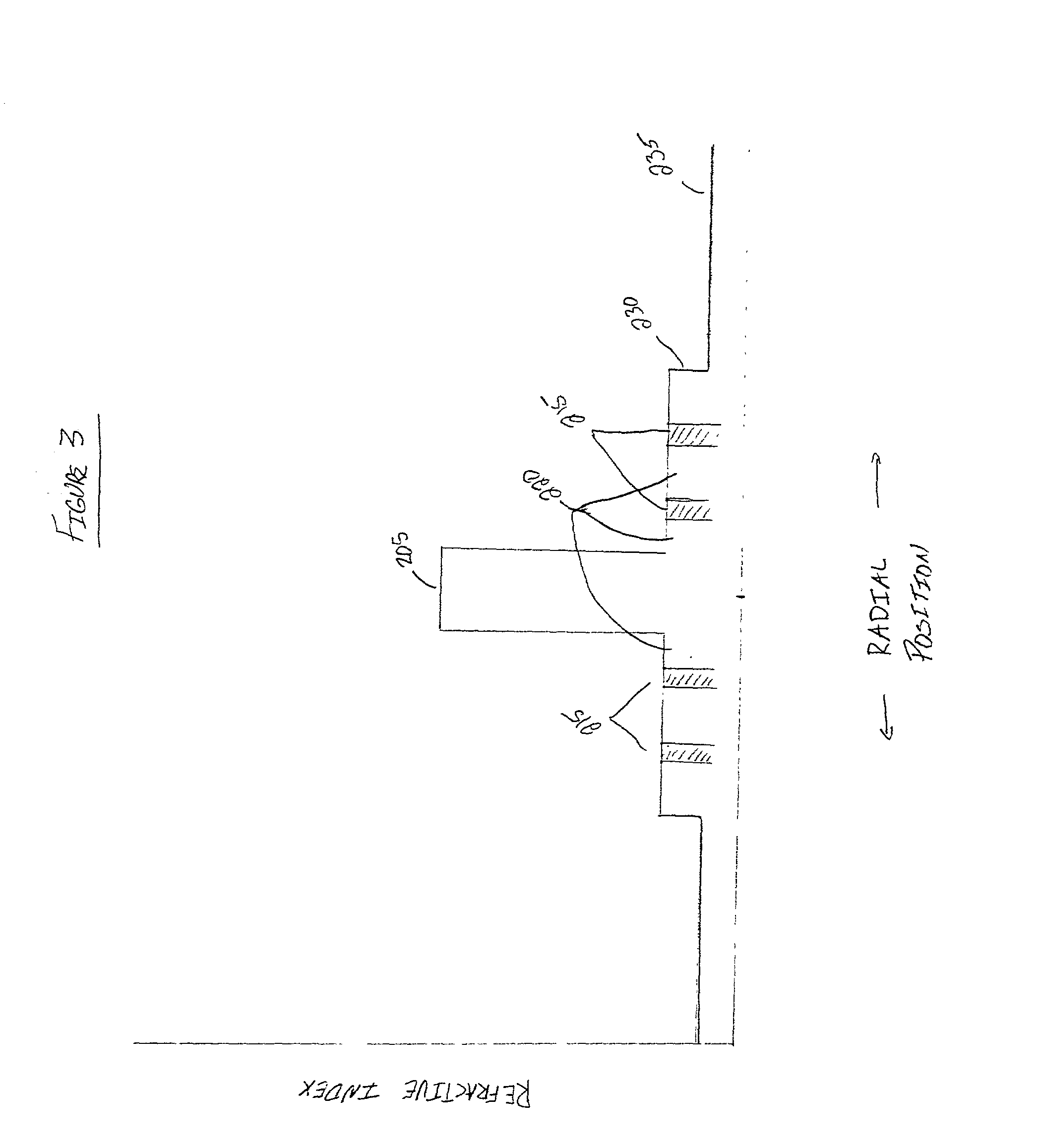
In fiber optics, a cladding mode is a mode that is confined to the cladding of an optical fiber by virtue of the fact that the cladding has a higher refractive index than the surrounding medium, which is either air or the primary polymer overcoat. These modes are generally undesired. Modern fibers have a primary polymer overcoat with a refractive index that is slightly higher than that of the cladding, so that light propagating in the cladding is rapidly attenuated and disappears after only a few centimeters of propagation. An exception to this is double-clad fiber, which is designed to support a mode in its inner cladding, as well as one in its core. This article incorporates public domain material from the General Services Administration document "Federal Standard 1037C".
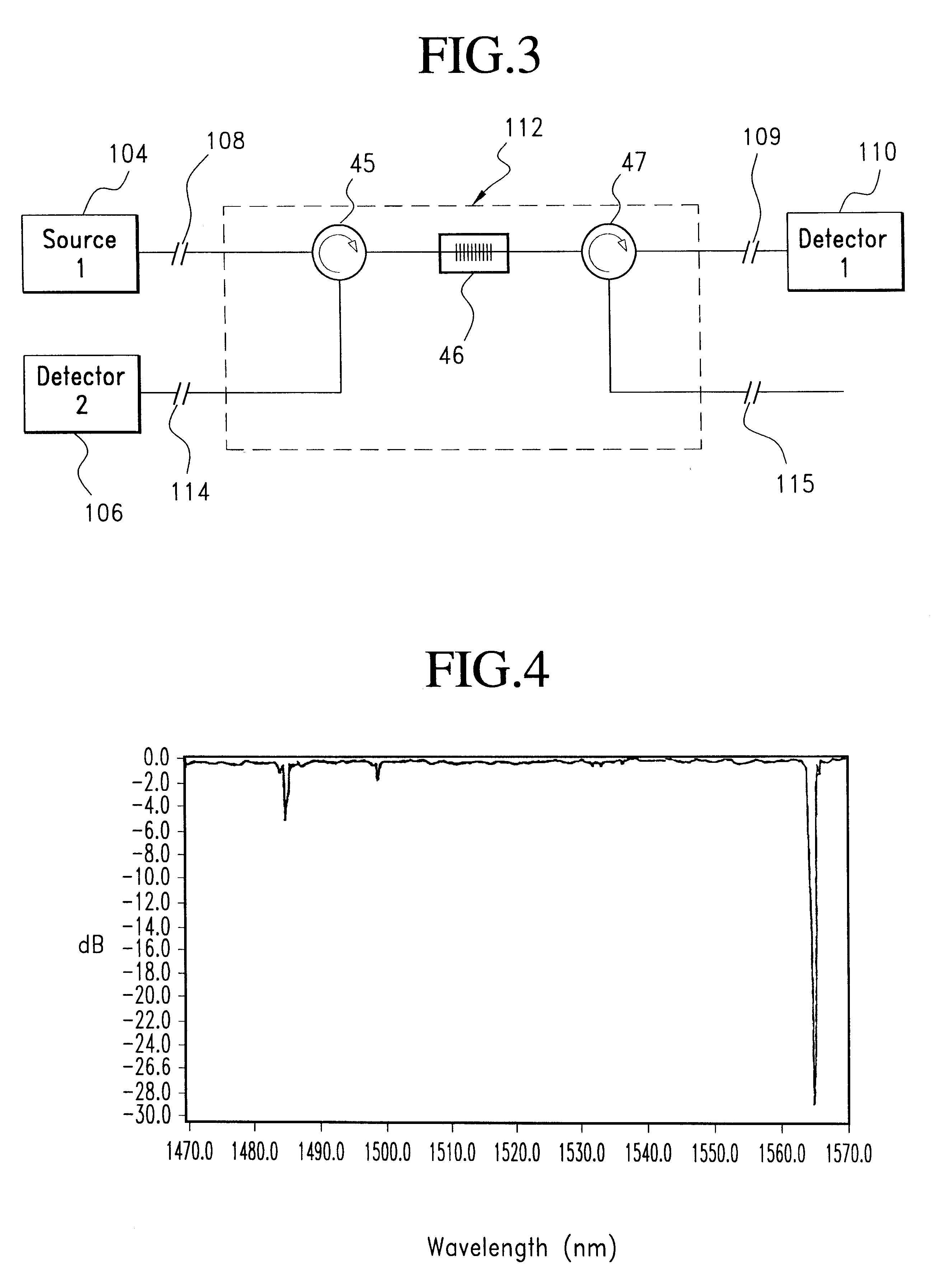
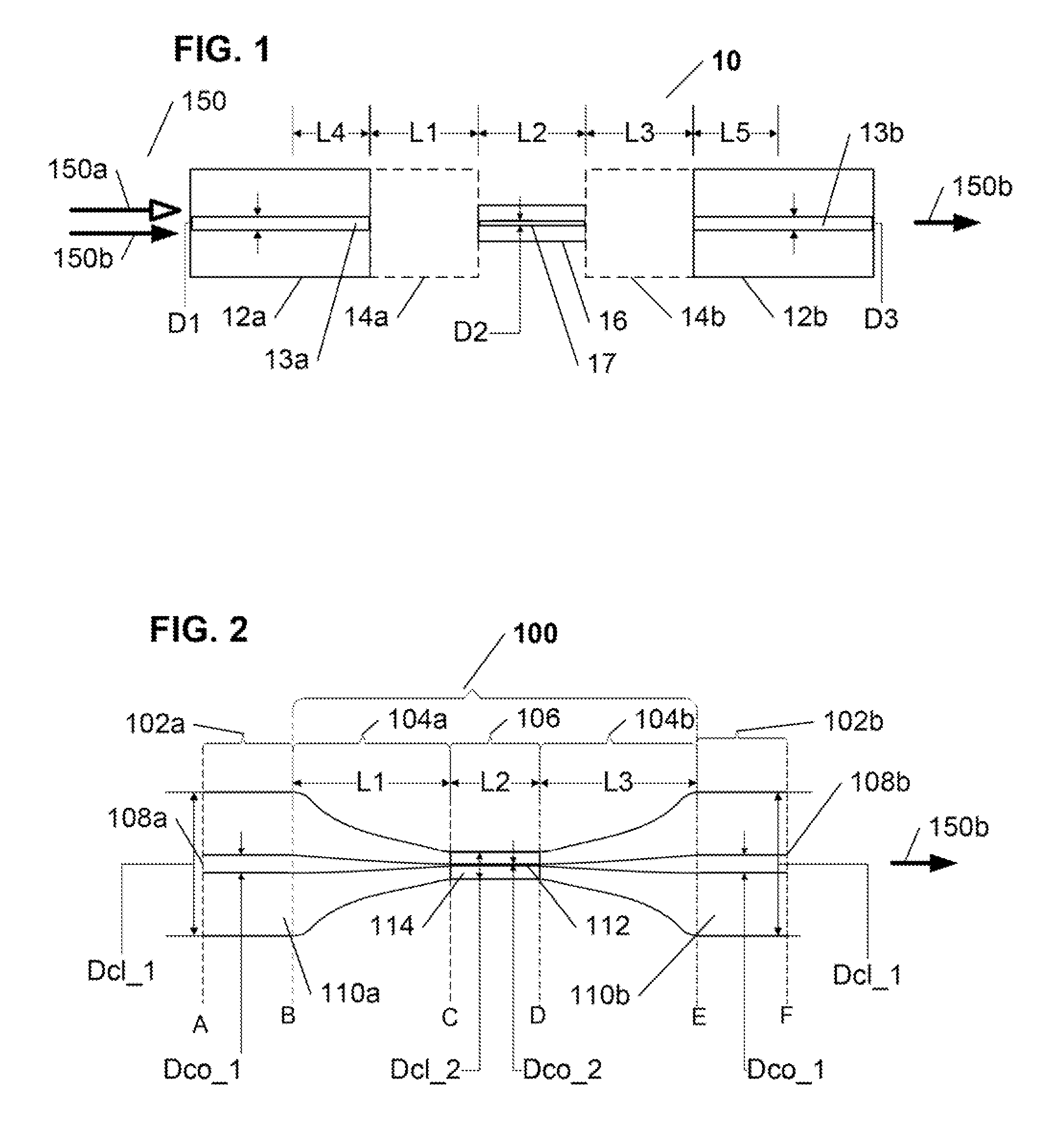
Apparatus and method for a high-gain double-clad amplifier
ActiveUS7526167B1Suppress instabilityEffectiveLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberLength wave
An optical apparatus design and method for suppressing cladding-mode gain in fiber- and other waveguide-amplification devices. In some embodiments, a signal-wavelength-absorbing core or region is included within the pump cladding or the pump waveguide, in order to absorb signal-wavelength radiation that occurs in the regions where only pump-wavelength radiation is wanted. This absorbing region prevents cladding-mode gain, thus preserving more pump-wavelength excitation for amplifying the desired signal radiation. In other embodiments, the refractive-index profile of the fiber or other waveguide is adjusted to reduce the numeric aperture and thus reduce the angle of light that will remain in the cladding. Since amplified spontaneous emission (ASE) occurs at all angles, a lower-NA fiber will leak a higher proportion of ASE (since a relatively lower portion of the ASE radiation is within the smaller angle that is retained within a low-NA fiber), while pump light, which was introduced into the fiber within the lower-NA angle will remain in the cladding.
Owner:LOCKHEED MARTIN CORP
Bragg grating and method of producing a Bragg grating using an ultrafast laser
A novel Bragg grating filter in optical waveguiding fiber with suppressed cladding mode coupling and method of producing same is disclosed. The novel grating structure is induced in both the core and the cladding of the optical fiber irrespective of the photosensitivity of the core or cladding to actinic radiation. Such core and cladding of the optical fiber need not be chemically doped to support the grating. The method incorporates an ultra short duration pulse laser source. Electromagnetic radiation provided from the laser propagates to a diffractive element positioned a specific distance to the target material such that the diffracted electromagnetic radiation forms a 2-beam interference pattern, the peaks of which are sufficiently intense to cause a change in index of refraction.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Wavelength-selective optical fiber components using cladding-mode assisted coupling
InactiveUS6850665B2High isolation between channelsIncrease light intensityWavelength-division multiplex systemsCoupling light guidesFiberGrating
A wavelength-selective optical device for coupling of light at predetermined wavelength from one optical fiber waveguide to another using at least two gratings and cladding-mode assisted coupling is disclosed. The transfer of light is performed using intermediate coupling to one or more cladding mode of the waveguides. In the case when the fibers have physically different cladding's, an arrangement for transfer of light from one cladding to another is required. The disclosed coupler has no back-reflection, small insertion loss, and very high channel isolation. The device can be used in wavelength-division multiplexing networks.
Owner:MURATA MFG CO LTD +1
Fiber delivery system with enhanced passive fiber protection and active monitoring
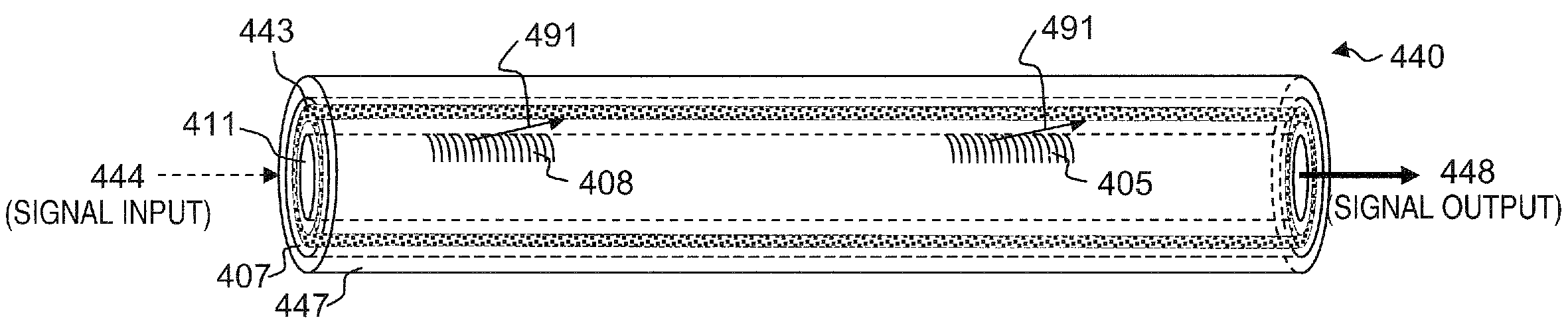
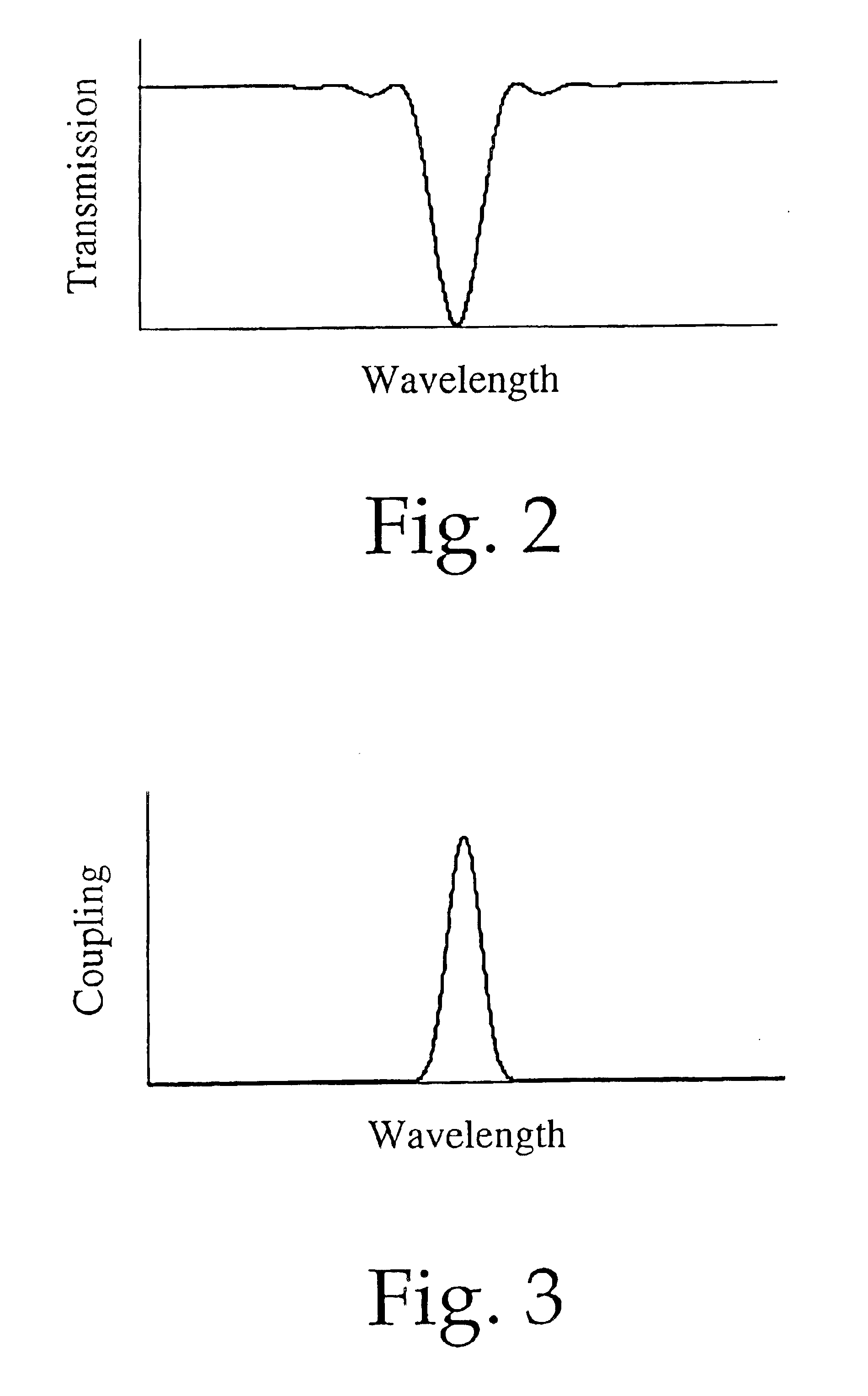
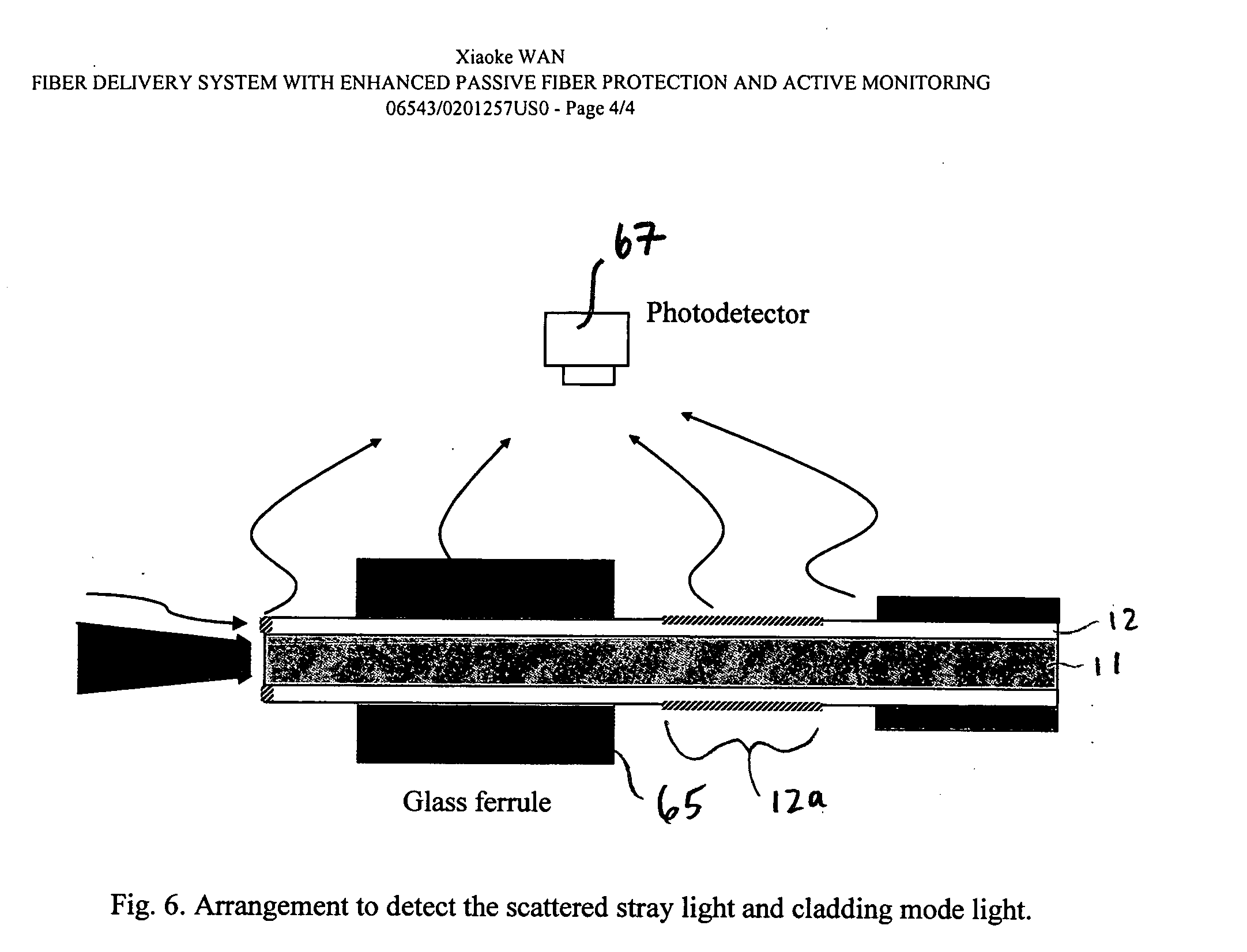
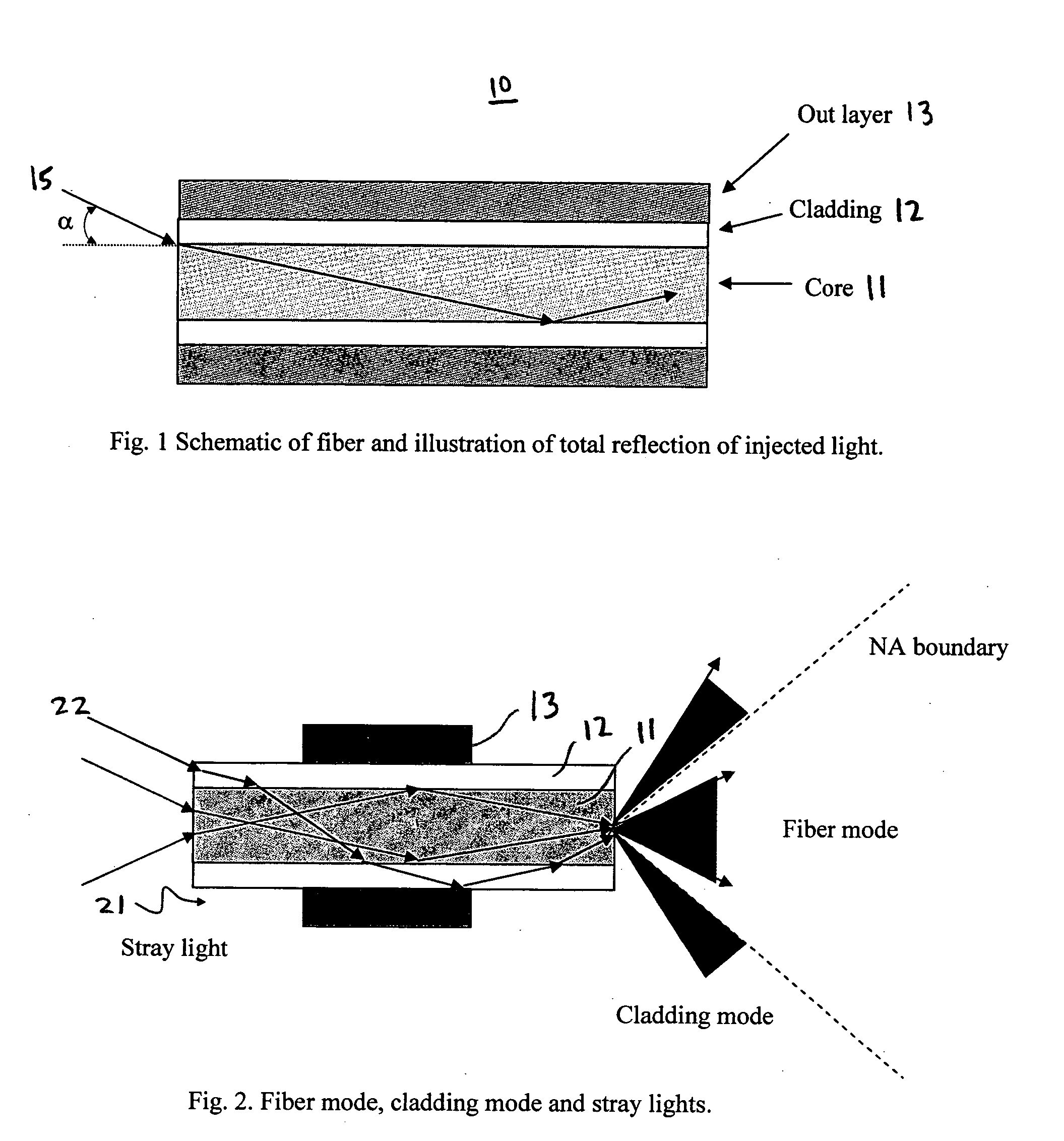
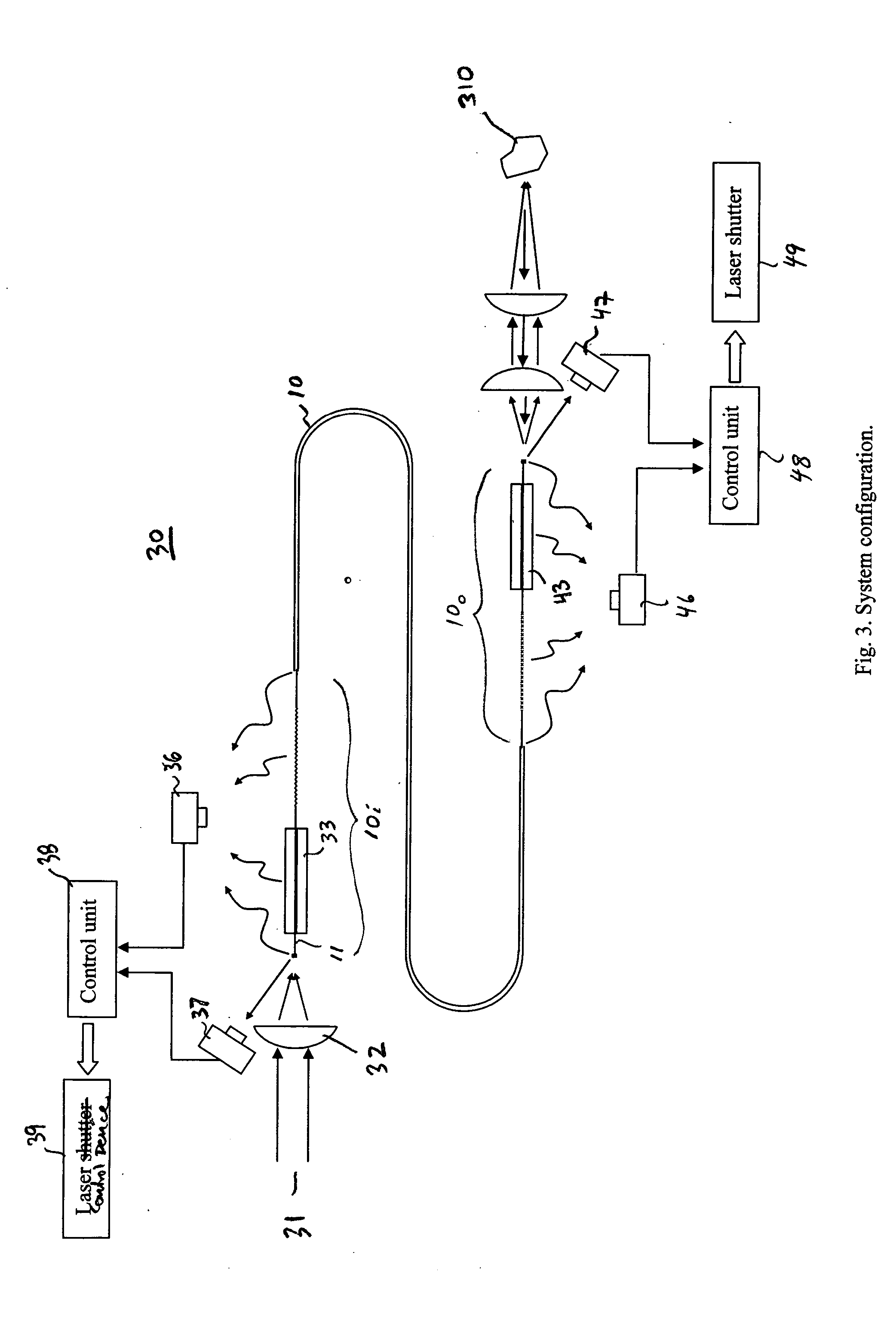
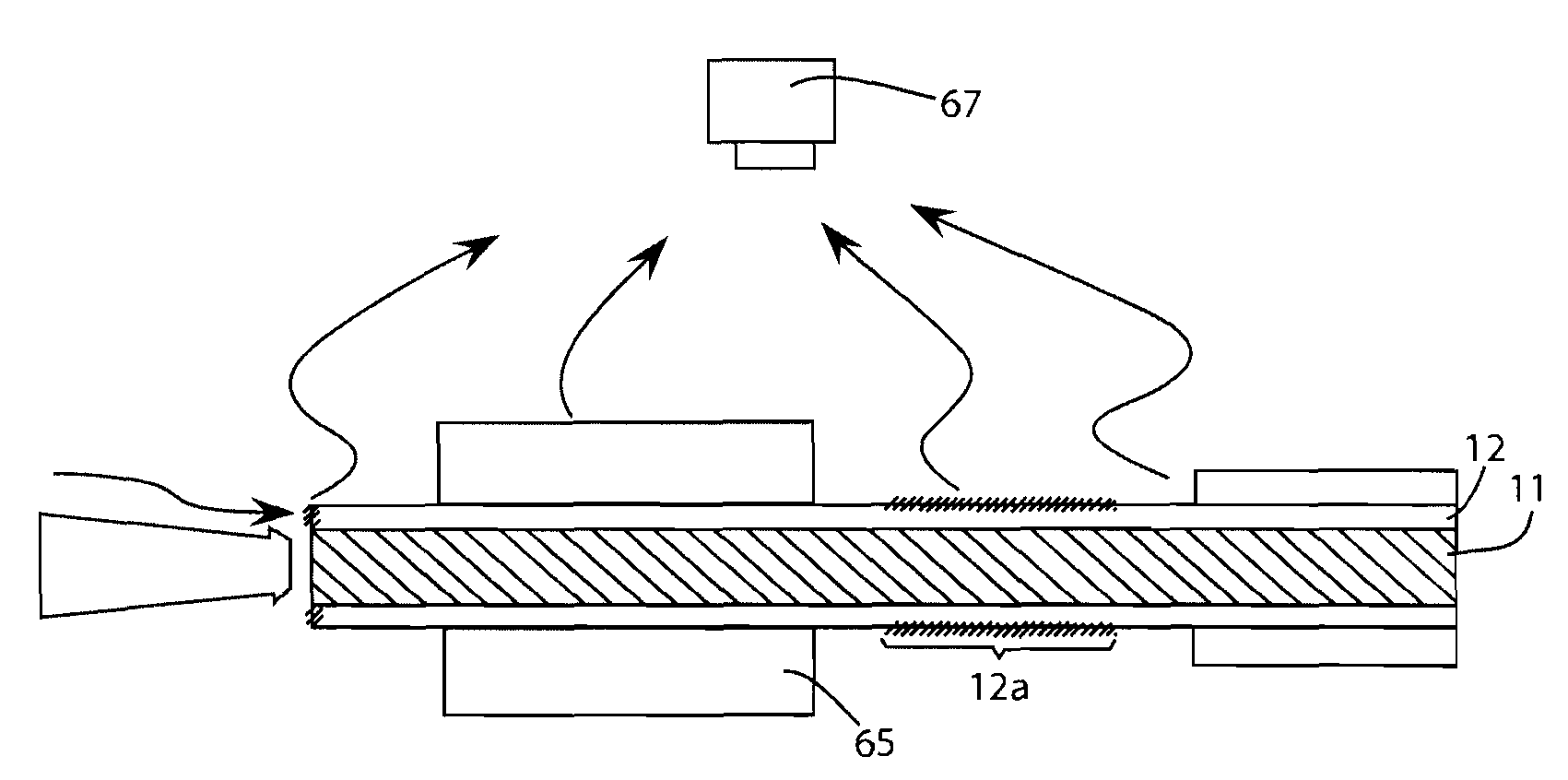
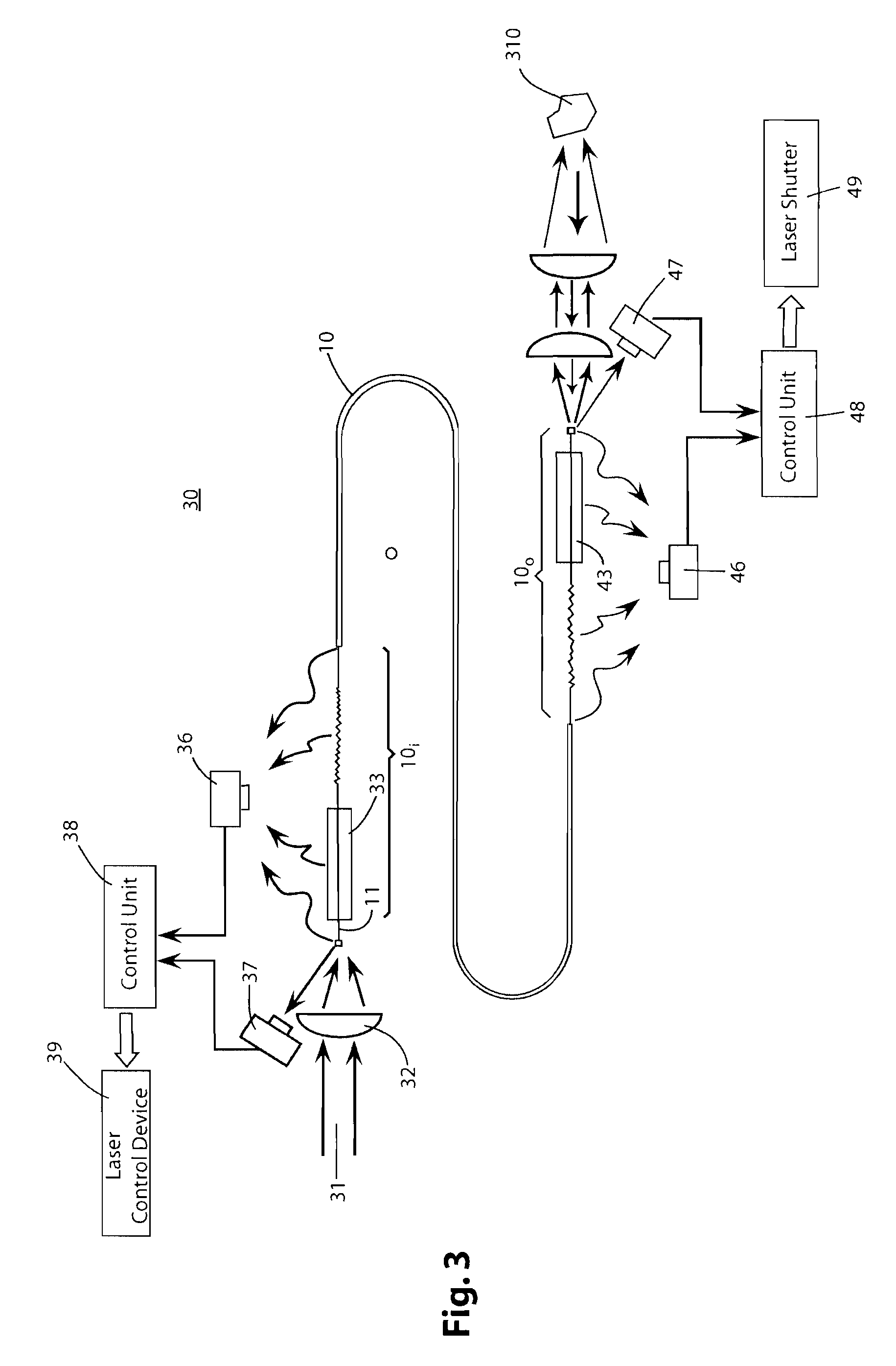
In an optical fiber system for delivering laser, a laser beam is focused onto an optical fiber at an injection port of the system. The end portions of the fiber have cladding treatments to attenuate stray light and cladding mode light, so as to enhance the protection of the outer layer joint points. Photodetector sensors monitor scattered stray light, cladding mode light, and / or transmitted cladding mode light. Sensor signals are provided to a control unit for analyzing the fiber coupling performance. If need be, the control unit can control a laser shutter or the like to minimize or prevent damage. In materials processing applications, the photodetector signals can be analyzed to determine the processing status of a work piece.
Owner:CONTINUUM ELECTRO OPTICS
Fiber delivery system with enhanced passive fiber protection and active monitoring
Owner:CONTINUUM ELECTRO OPTICS
Optical fiber filter for suppression of amplified spontaneous emission
ActiveUS7272287B2Enhanced spontaneous emissionCoupling light guidesMulticore optical fibreTotal internal reflectionRefractive index
An in-line, distributed optical fiber filter comprises a core region with a raised refractive index (with respect to the surrounding cladding material) so as to allow for total internal reflection (TIR) of the desired transmission wavelength(s). One or more raised index features are formed within the cladding region and are configured so as to result in mode mixing between the cladding mode and core mode at determined wavelength(s) to be removed by filtering. The parameters associated with determining the proper core specifications and cladding specifications can be separately determined to provide for enhanced performance in terms of both filtering unwanted signals and propagation of desired communication signals.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Cladding mode stripper
InactiveUS20140363125A1Improve efficiencyLower operating temperatureOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesFiberEngineering
An improved arrangement for stripping stray light energy that is propagating in the cladding layer of an optical fiber is provided. A cladding light stripper is provided that incorporates removal of at least a portion of the coating material and / or splicing the fiber to a fiber of differing diameter and / or having a bend of constant or decreasing or varying radius to efficiently remove cladding light while distributing heat dissipation in a controlled design across the device with respect to a specific direction of input (cladding) light.
Owner:PRIMA ELECTRO NORTH AMERICA
Method for preparing ceramic particle enhanced metal matrix composite coating in laser cladding mode through asynchronous powder feeding method
ActiveCN105002492AImprove performanceSimple processMetallic material coating processesDecompositionLaser scanning
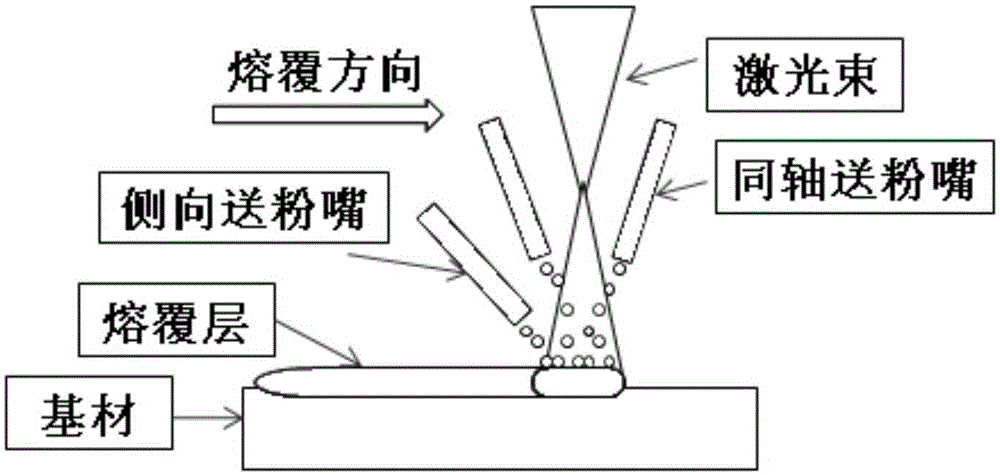
The invention provides a method for preparing a ceramic particle enhanced metal matrix composite coating in a laser cladding mode through an asynchronous powder feeding method. A lateral powder feeding nozzle is fixed to one coaxial powder feeding nozzle and assembled into an asynchronous powder feeding nozzle; the lateral powder feeding nozzle is used for feeding ceramic particle enhancing phases into the portion between the middle portion and the tail portion of the side, opposite to the laser scanning direction, of a molten pool; the coaxial powder feeding nozzles are used for feeding alloy powder or metal ceramic composite powder to the center of the molten pool; a laser device is used for conducting laser cladding, and then the ceramic particle enhanced metal matrix composite coating is obtained. According to the method, the coaxial powder feeding method and the lateral powder feeding method are combined, the ceramic particle enhancing phases are fed into the low-temperature region at the rear portion of the molten pool, so that the phenomena of nonuniformity of melting decomposition, clustering and distribution of the ceramic particle enhancing phases are reduced, and the ceramic particle enhancing phases are evenly distributed in the whole coating by keeping the original appearance to the maximum extent; accordingly, the ceramic particle enhancing phases are effectively retained and evenly distributed, and the performance of the composite coating can be substantially improved.
Owner:西安合方长激光智能科技有限公司
System and method of operating low coupling efficiency optical source by dissipating cladding modes
InactiveUS6865316B1Reduce thermal effectsDissipate optical powerCoupling light guidesOptical powerCladding mode
An embodiment is directed to a system for dissipating cladding modes of an optical fiber. In the system, a high power light source couples optical power into the optical fiber at a fiber coupling point thereby producing the cladding modes; material is indexed-matched to the optical fiber and is optically contacted to the optical fiber near the fiber coupling point; and a substrate layer is operable to provide a thermal sink for heat generated from dissipation of cladding modes of the optical fiber.
Owner:NLIGHT INC
Apparatus for combining optical radiation
ActiveUS20170017036A1Reducing and eliminating damageEliminate leaksLaser detailsCoupling light guidesOptical radiationPolymer coatings
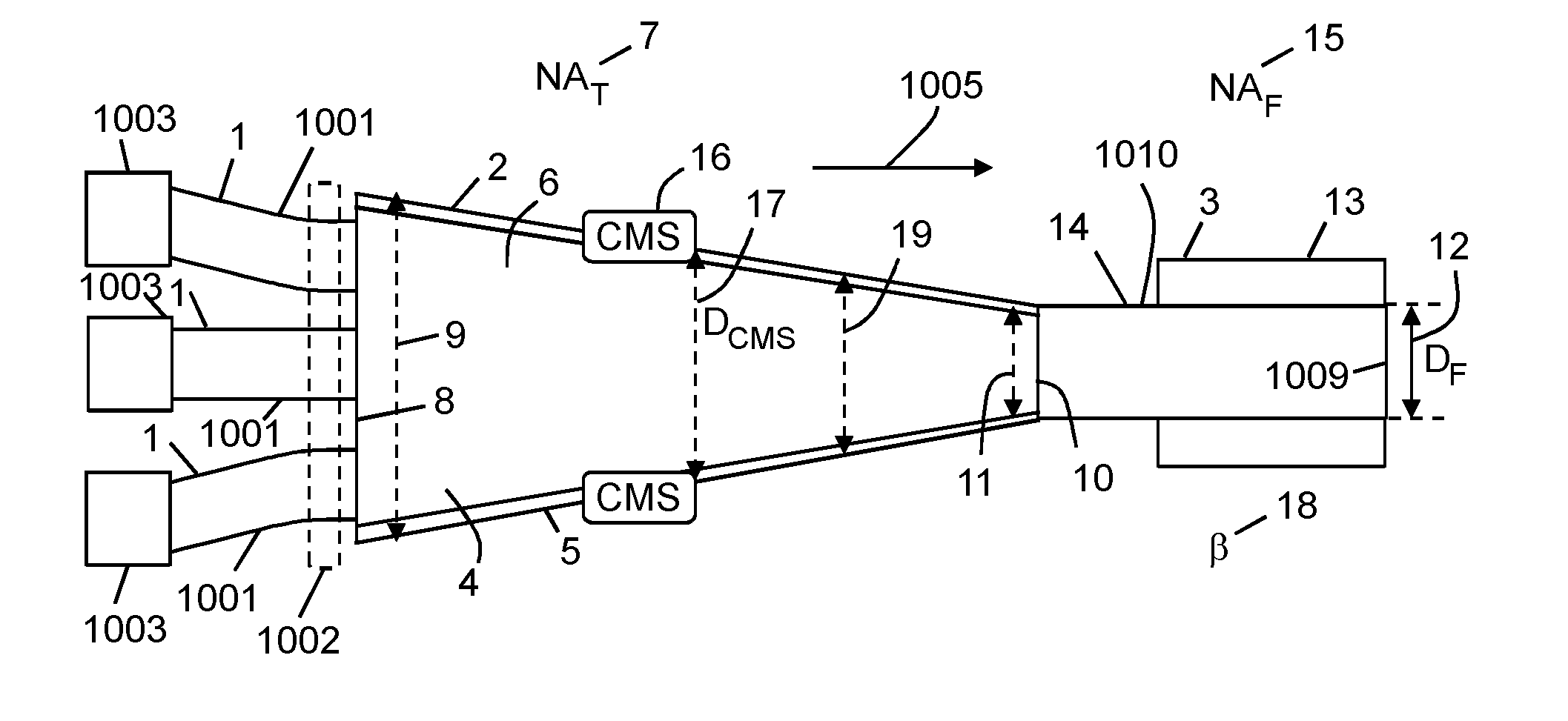
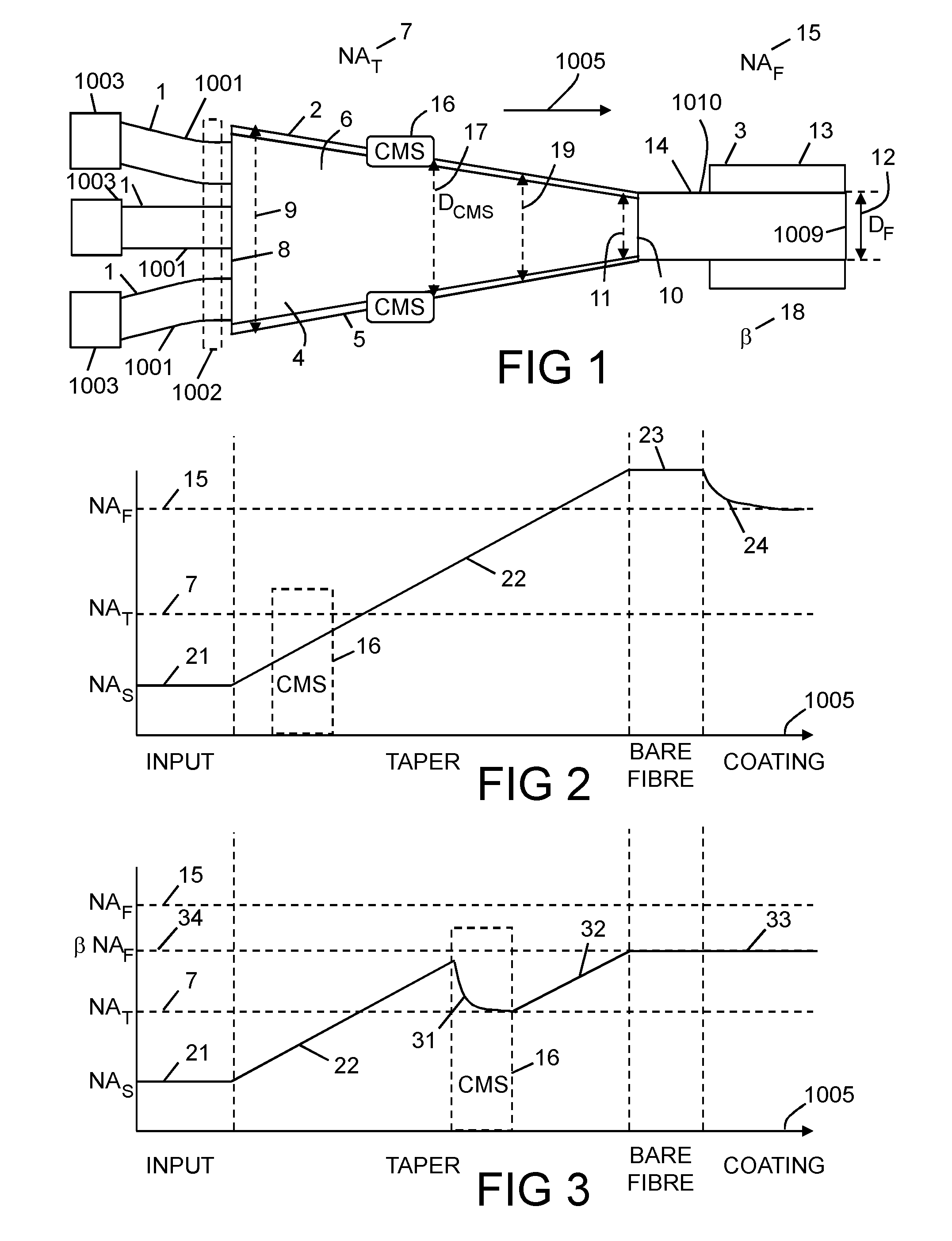
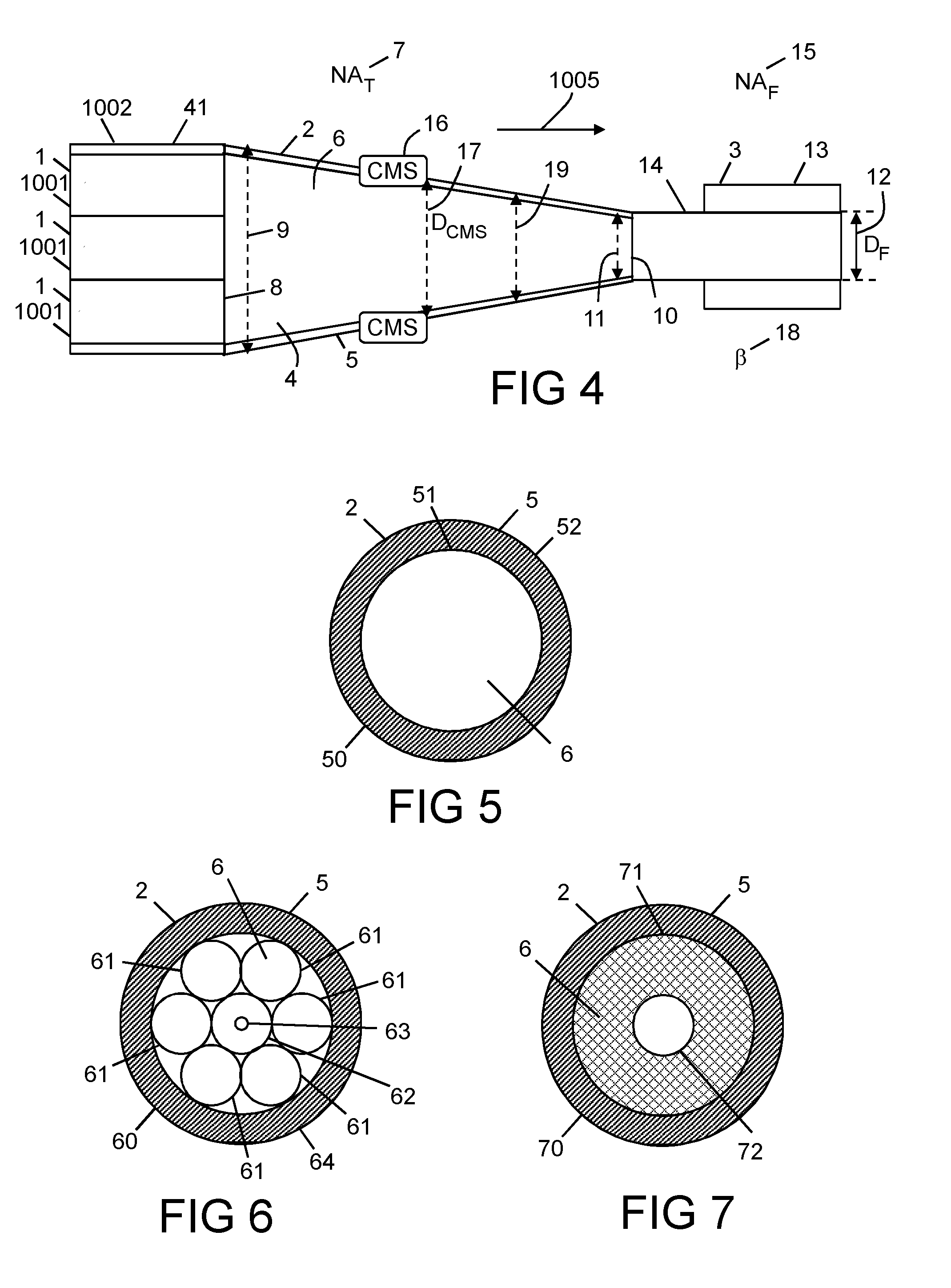
An apparatus for combining optical radiation, wherein the apparatus comprises a bundle of input optical fibres formed of glass, a taper, and an output optical fibre, wherein the taper is fused to the output optical fibre; and the apparatus comprises at least one cladding mode stripper to strip out higher order modes that would otherwise degrade a polymer coating on at least one of the input optical fibres and the output optical fibre.
Owner:SPI LASERS UK
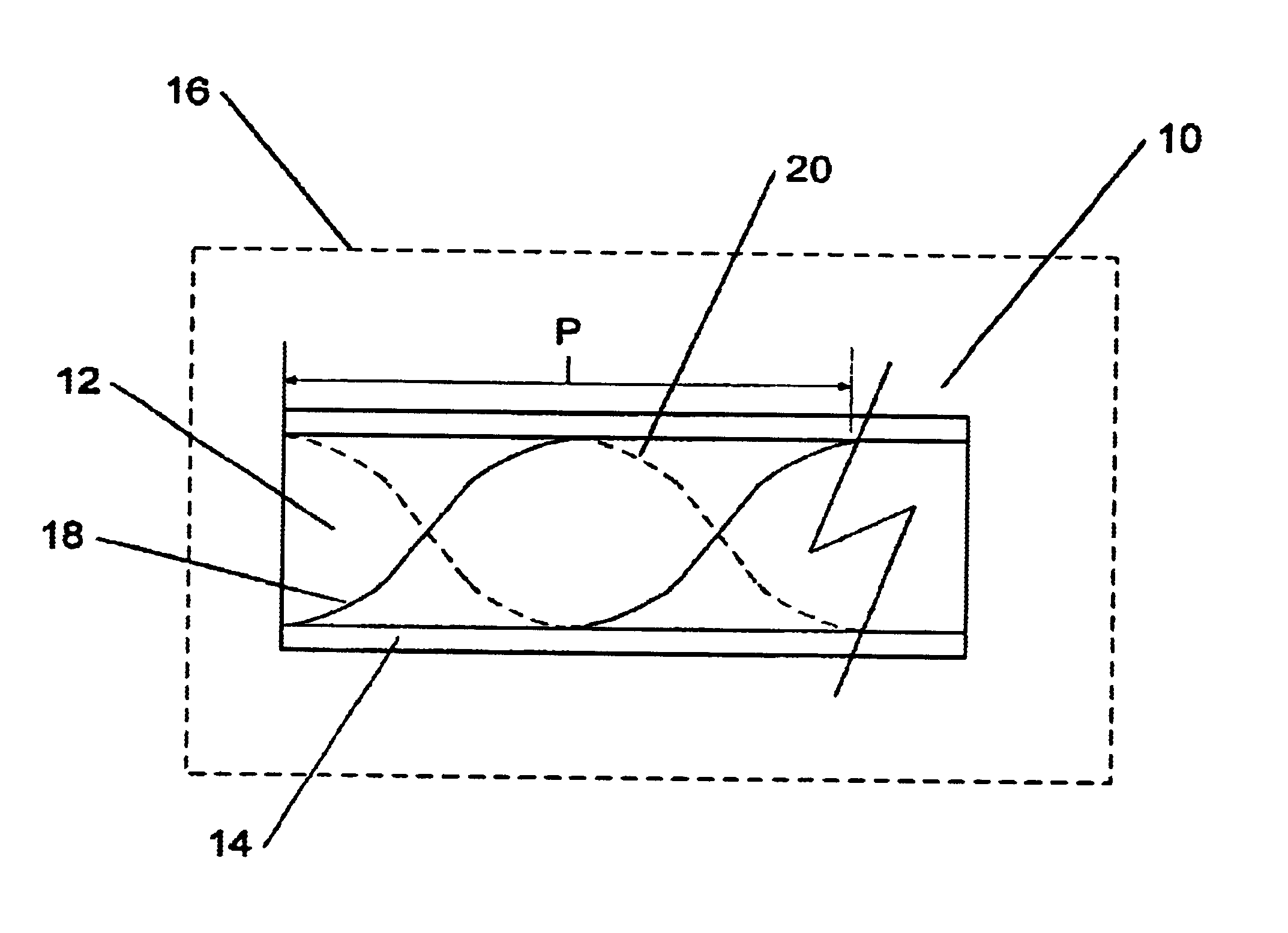
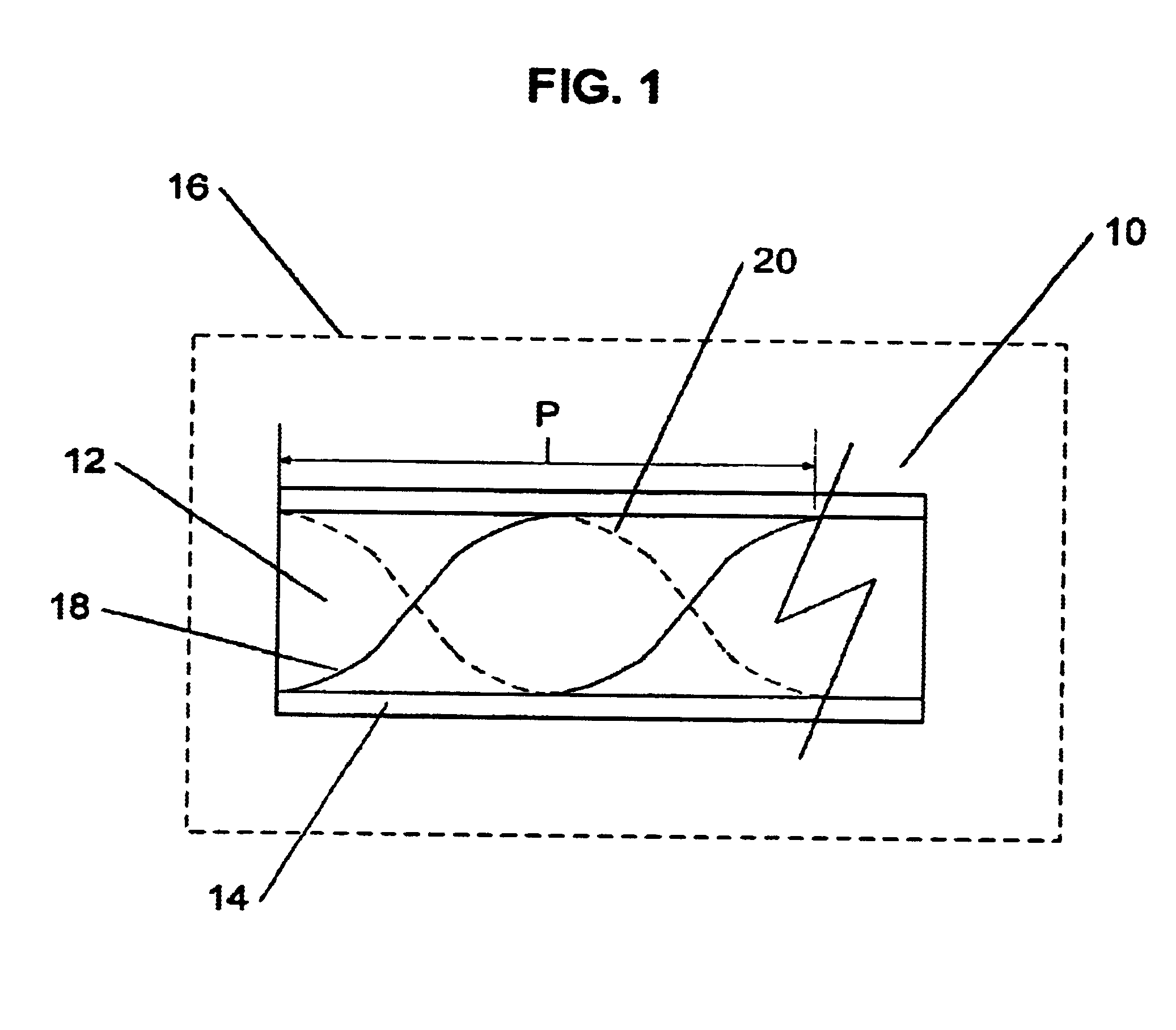
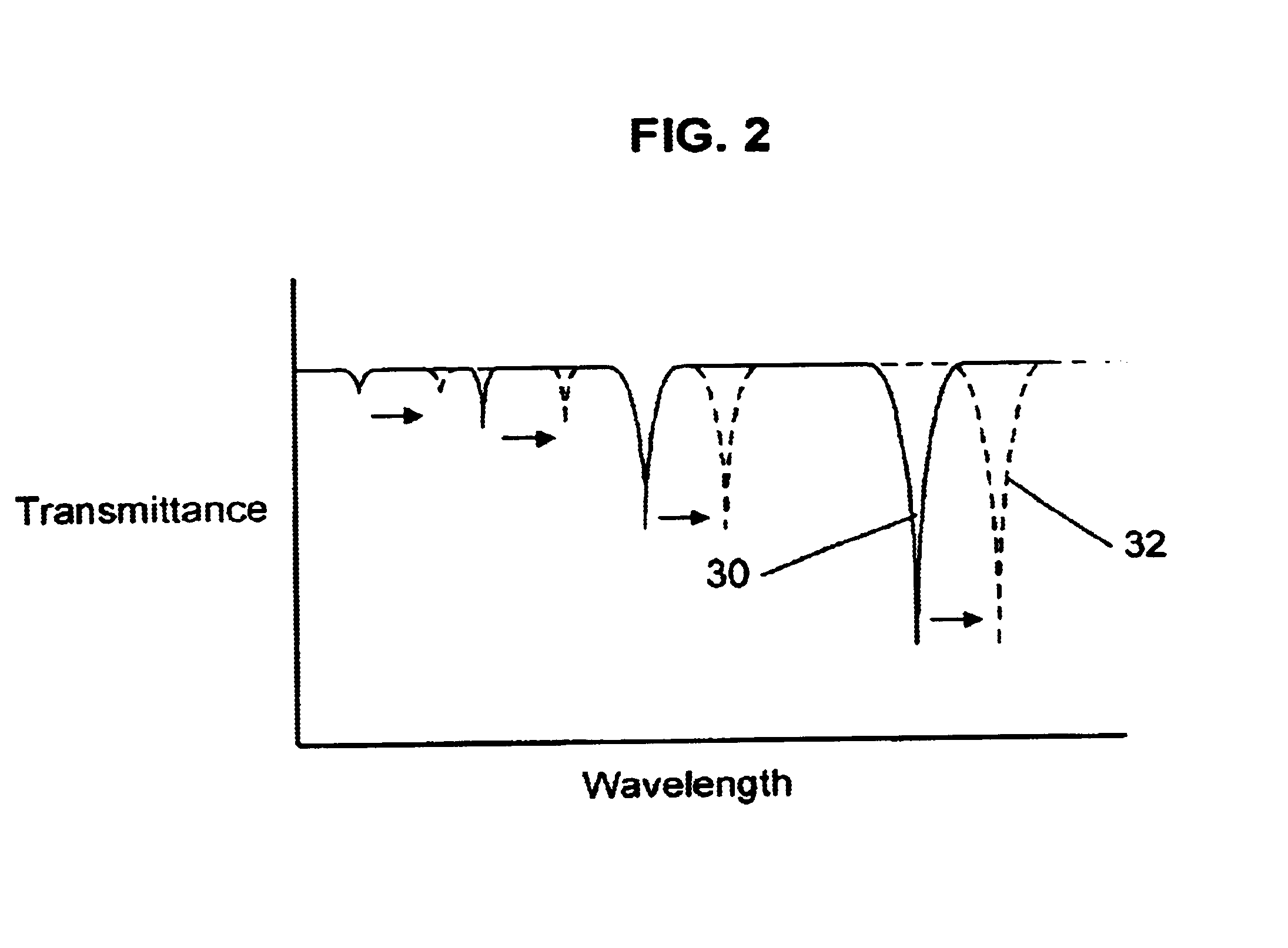
Long period chiral fiber grating apparatus
InactiveUS6925230B2Easy to useForce measurement by measuring optical property variationThermometers using physical/chemical changesGratingFrequency spectrum
A long period chiral fiber grating (“LPCFG”) that has a number of advantageous properties that can be readily utilized in a number of different applications is provided. The inventive LPCFG is a fiber grating having a pitch that exceeds the wavelength of light propagating therethrough. The LPCFG includes a number of dips in its transmission spectrum, but does not reflect any portion of the signal passing therethrough. The LPCFG is sensitive to changes in the refractive index of its external environment (or in the refractive index of a coating covering the LPCFG cladding). In response to changes in the external refractive index, the transmission dips shift proportionally to changes in the index, thus enabling the use of LPCFG as a fiber sensor element. In addition, the LPCFG is polarization sensitive—one circular polarized wave of one handedness is coupled to the cladding mode stronger than the wave of the other polarization handedness. This enables the LPCFG to be readily utilized in polarizers and for shaping the polarization spectra of signals passing therethrough (in one embodiment configured as multiple LPCFG elements having different pitches). The polarization sensitivity of the inventive LPCFG can also be used for verifying system integrity in chiral fiber sensor systems. In other embodiments of the present invention, the novel LPCFG can be used for modulating amplitude of the light signal propagating therethrough, or as a resonant active structure for add / drop filters.
Owner:CHIRAL PHOTONICS
Overlapping integral type prefabricated assembly structure for comprehensive pipe gallery and construction method thereof
ActiveCN106013228ALarge working spaceActive connectionArtificial islandsUnderwater structuresEngineeringAssembly structure
The invention discloses an overlapping integral type prefabricated assembly structure for a comprehensive pipe gallery and a construction method thereof. The overlapping integral type prefabricated assembly structure comprises envelop enclosures, a pipe gallery prefabricated assembly structure body, a bottom plate cushion course and a completely outer-cladding waterproof layer, wherein the envelop enclosures are located in a foundation pit; the pipe gallery prefabricated assembly structure body is arranged between the envelop enclosures; the bottom plate cushion course is arranged under the pipe gallery prefabricated assembly structure body; and the completely outer-cladding waterproof layer is arranged on the outer side surface of the pipe gallery prefabricated assembly structure body in a cladding mode. The upper portion of the pipe gallery prefabricated assembly structure body is filled with backfill earth, and the completely outer-cladding waterproof layer is arranged on the outer side surface of an outer side cast-in-situ part of the pipe gallery prefabricated assembly structure body in a cladding mode. The construction method of the overlapping integral type prefabricated assembly structure comprises the steps of prefabricated component machining, foundation pit excavation, bottom plate pouring, side wall construction, mid-partition construction, top plate construction, earth backfilling and the like. According to the overlapping integral type prefabricated assembly structure for the comprehensive pipe gallery and the construction method thereof, the prominent problems of force bearing of joints, water seepage of connection seams and the like in the underground engineering prefabrication process are solved; and the structural modes of bottom plate casting in situ, side wall single-layer overlapping, mid-partition double-layer overlapping, top plate overlapping, all-joint casting in situ and completely outer-side waterproof layer cladding are adopted, so that effective connection and the waterproof function of the joints are ensured.
Owner:CHINA STATE CONSTRUCTION ENGINEERING CORPORATION +1
Optical Fiber Gain Medium with Modal Discrimination of Amplification
InactiveUS20080025363A1Easy to controlEasy to adjustLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberRefractive index
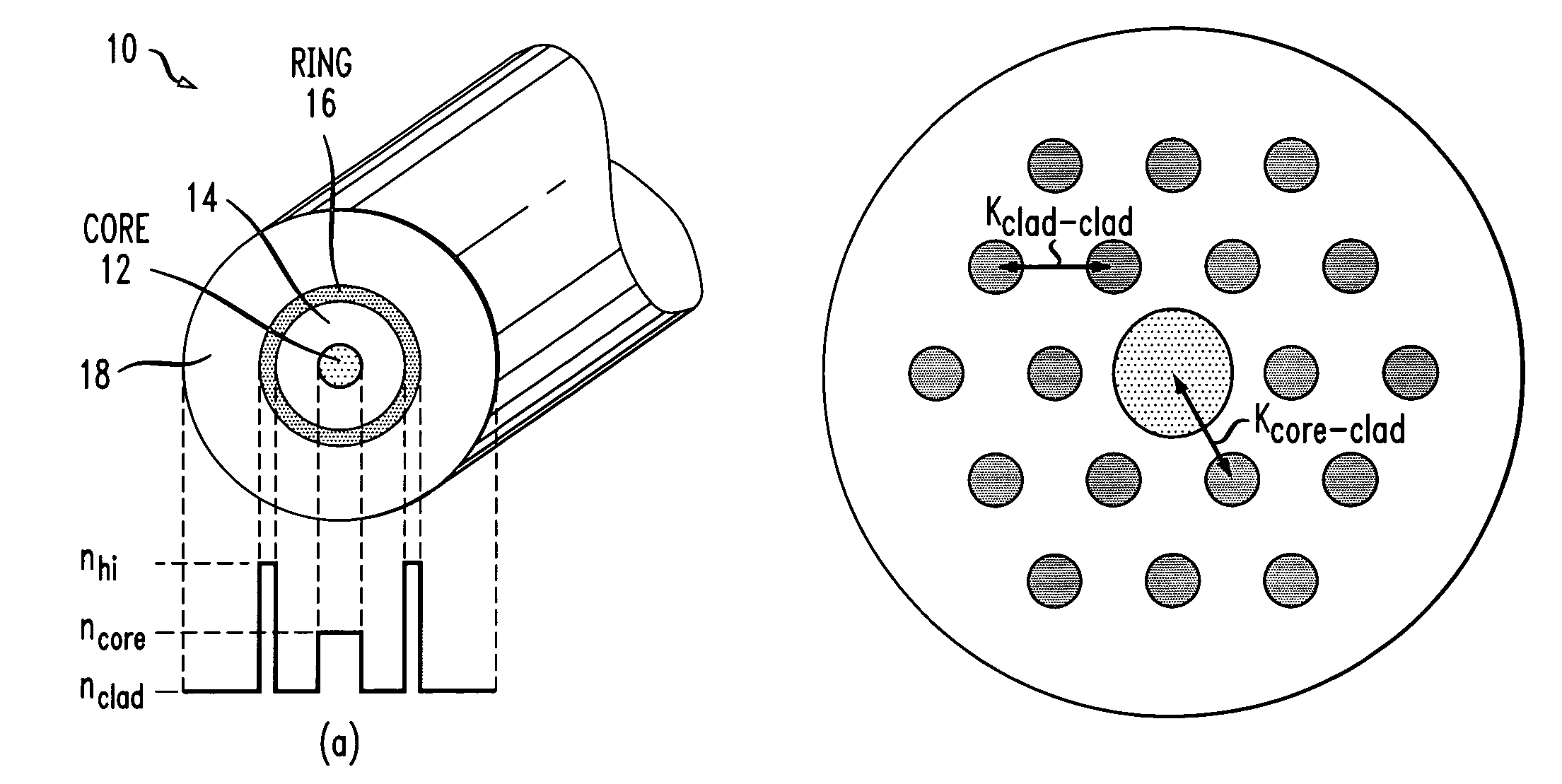
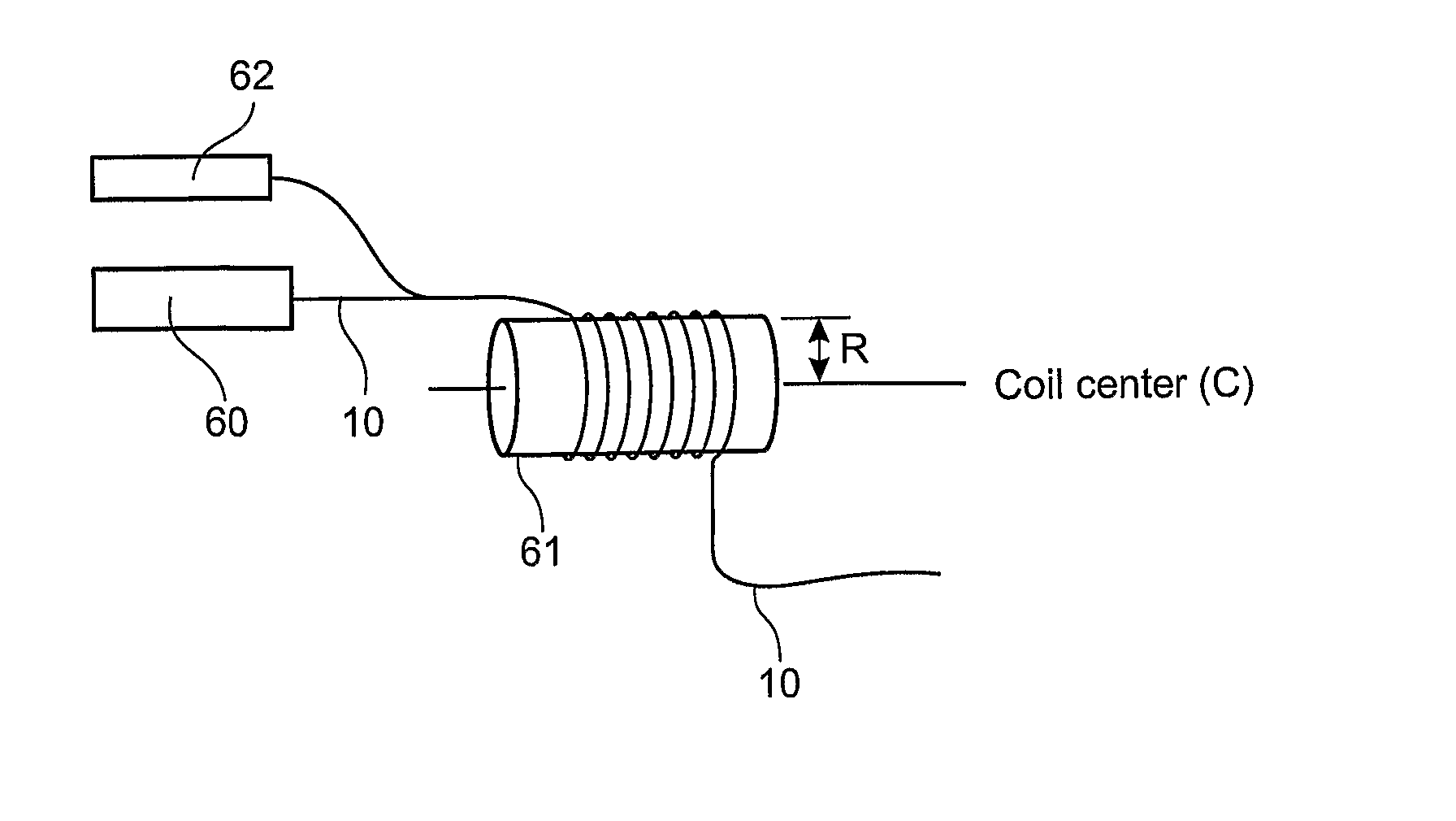
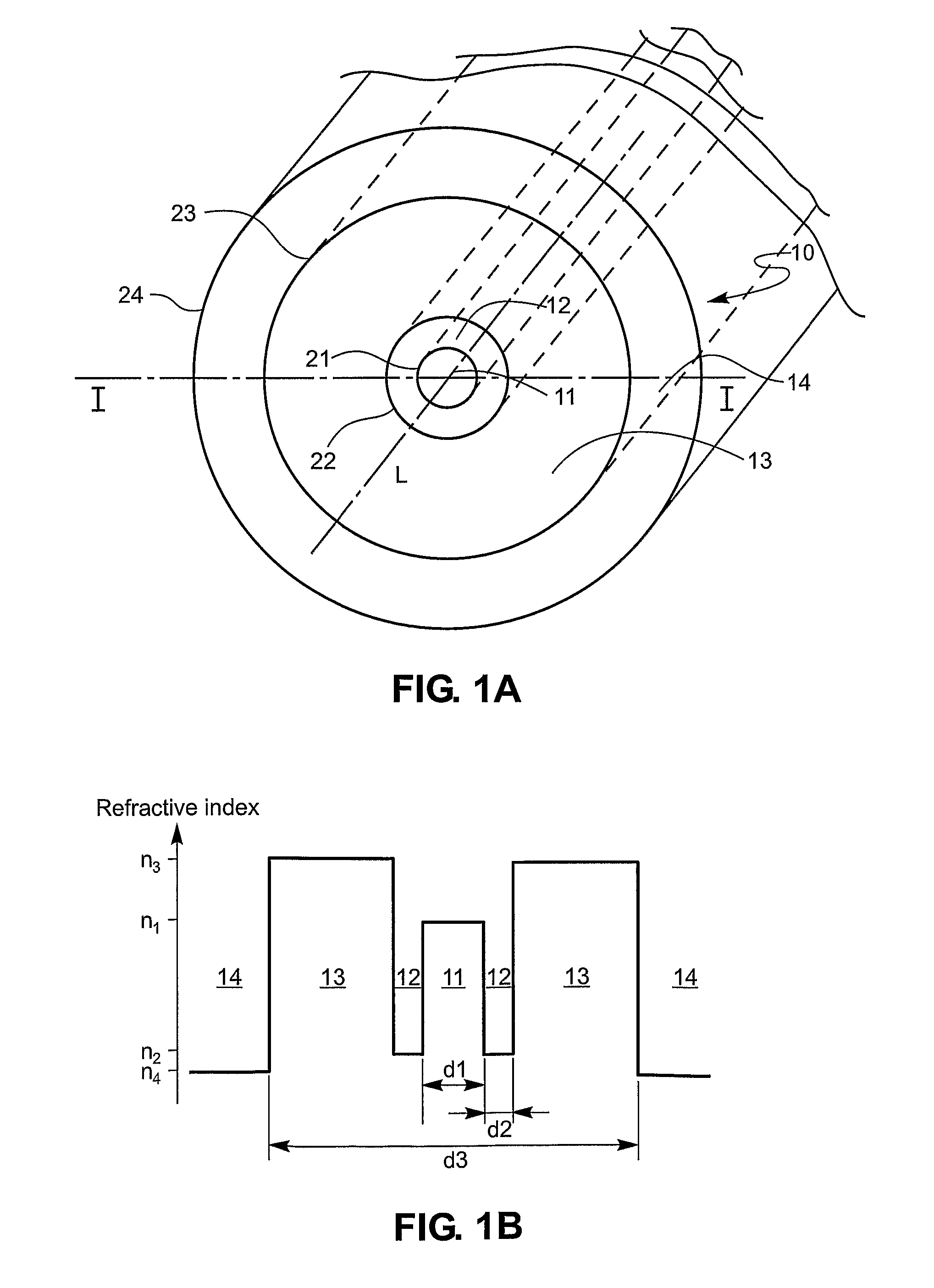
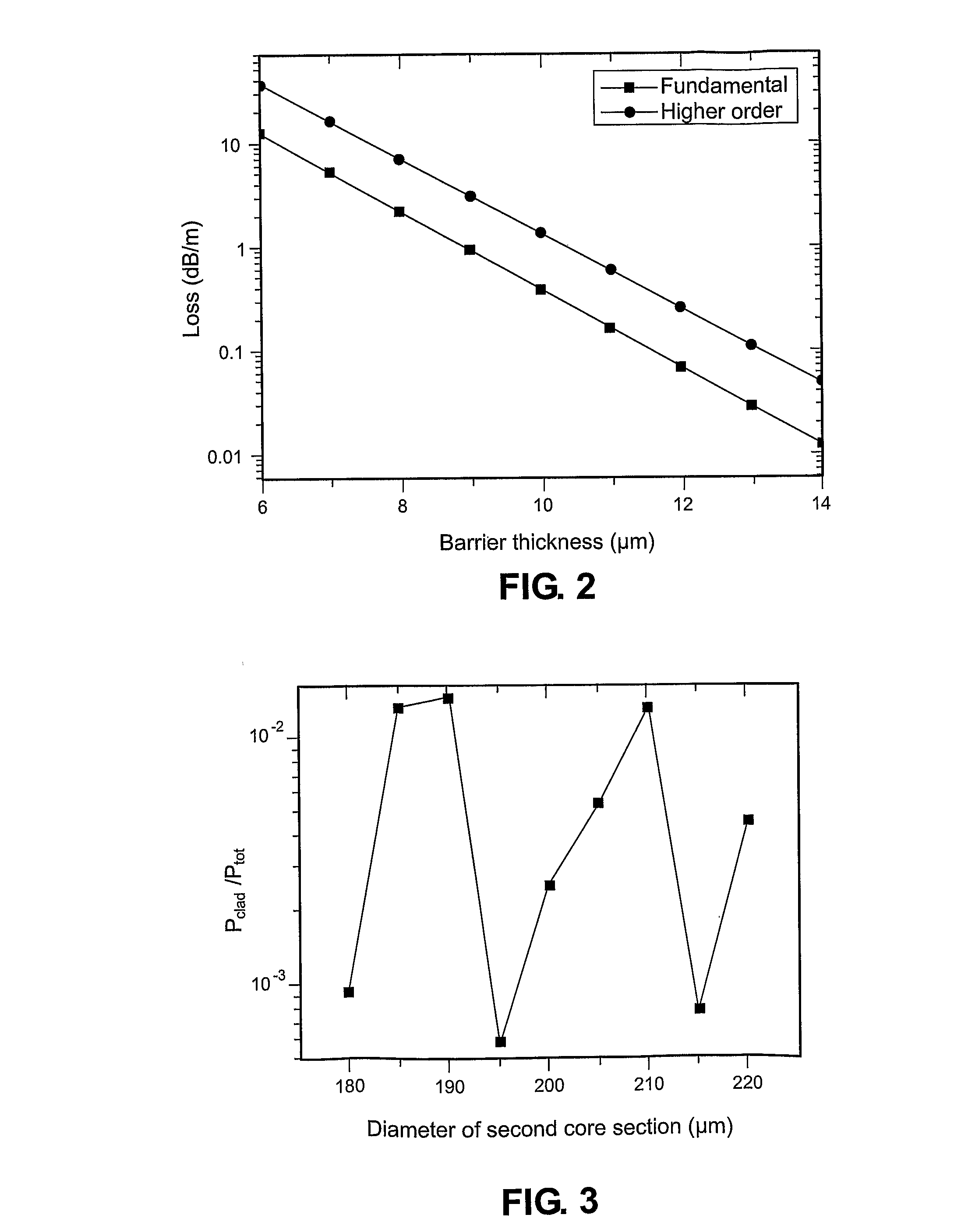
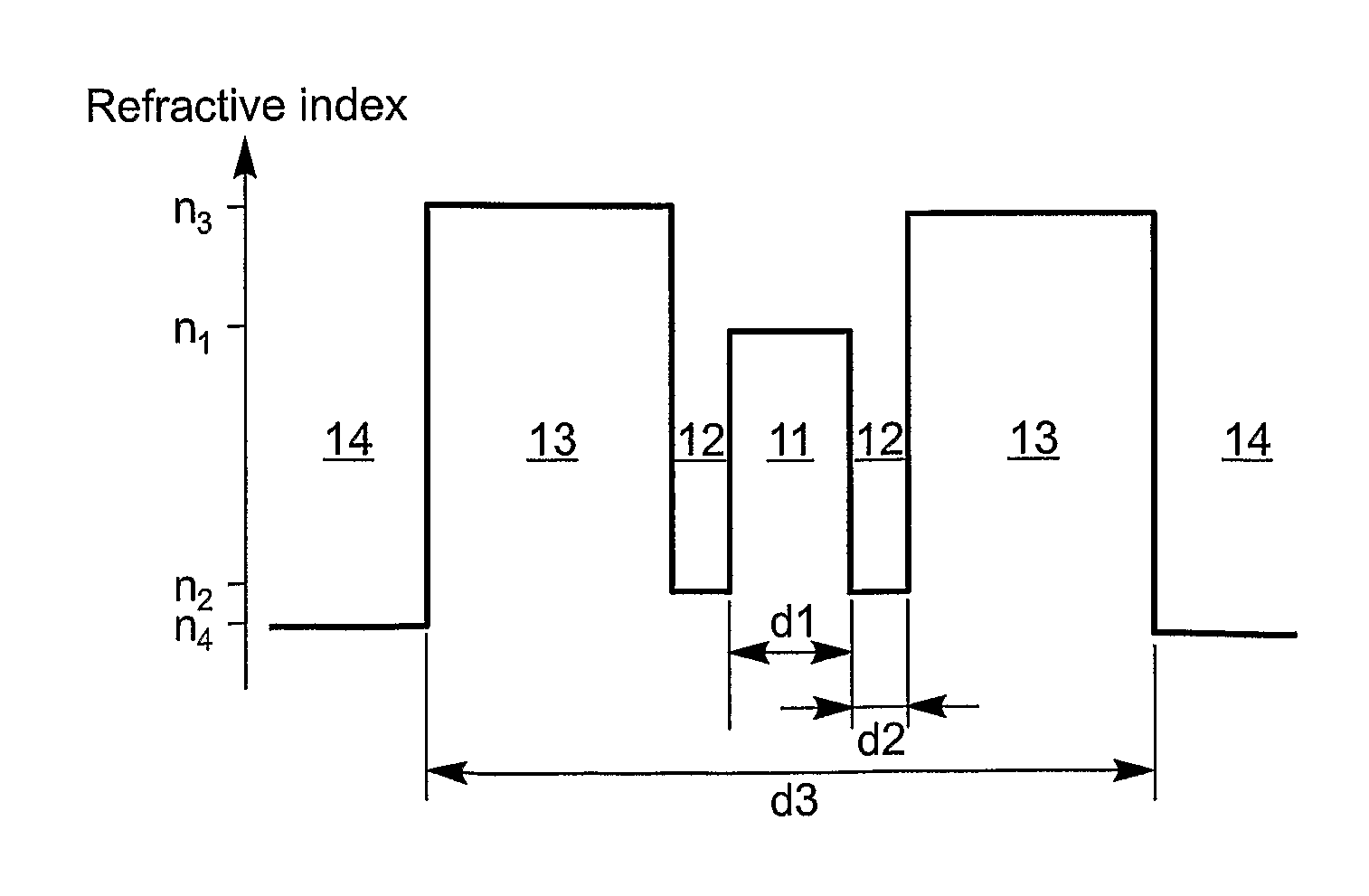
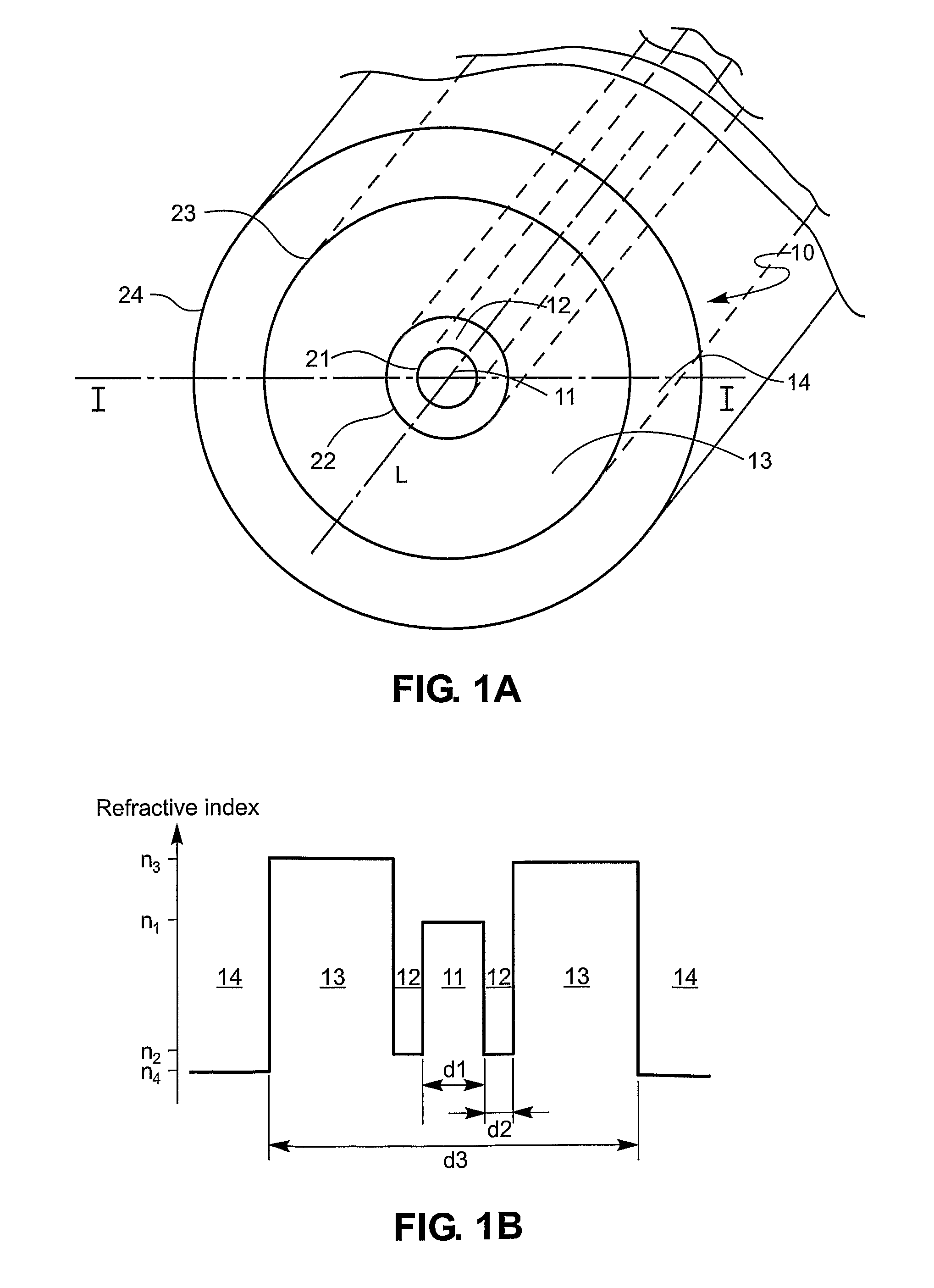
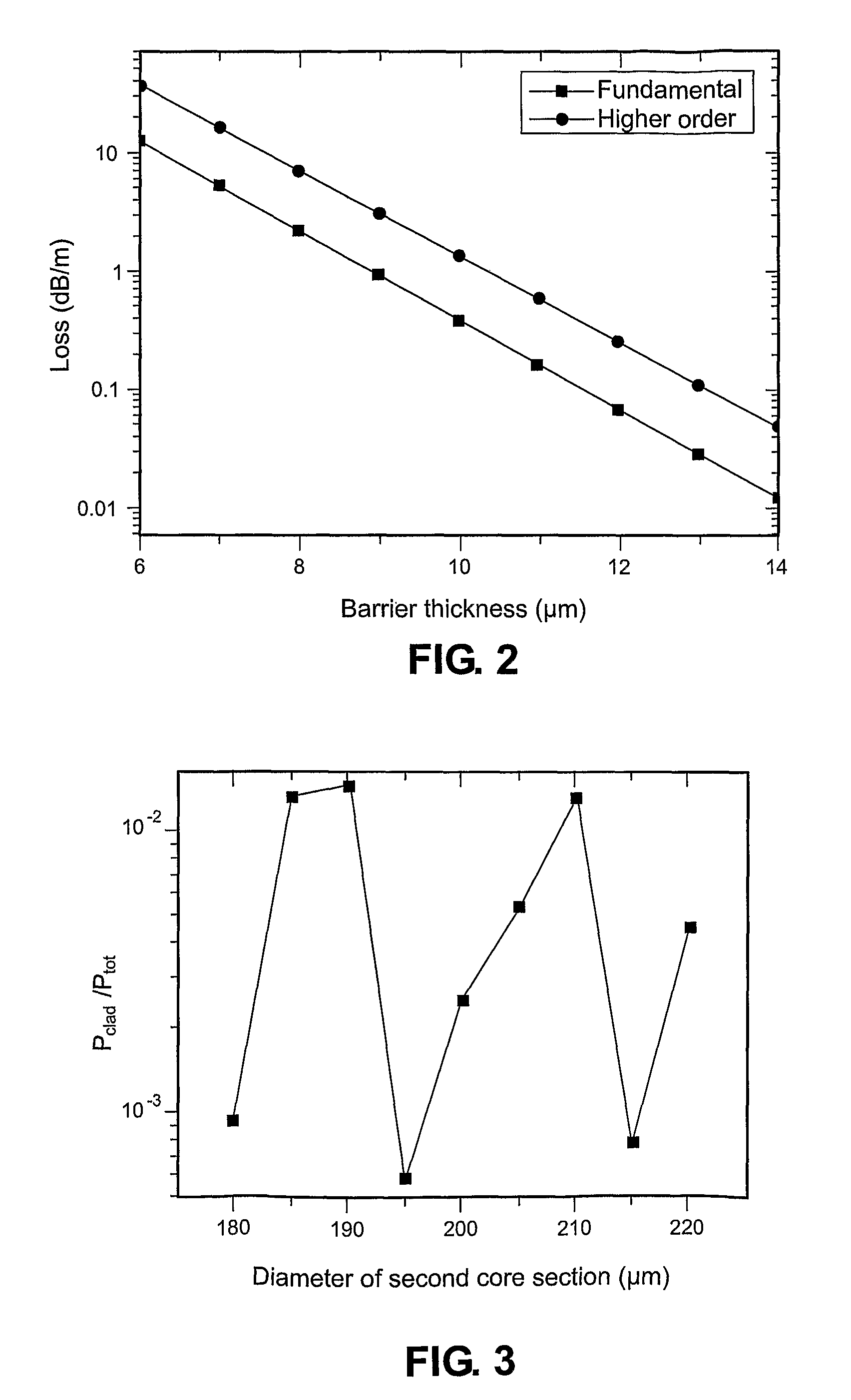
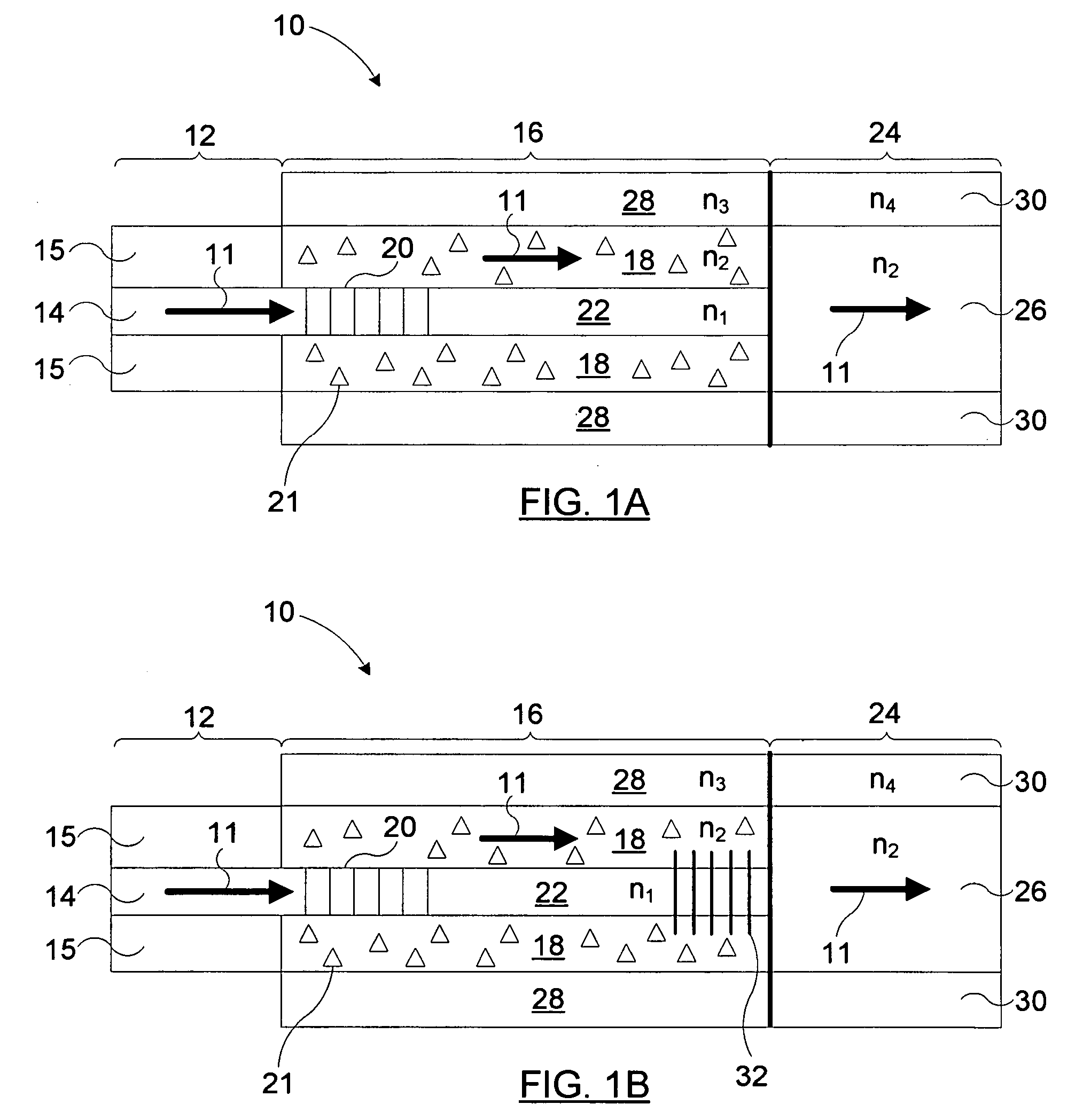
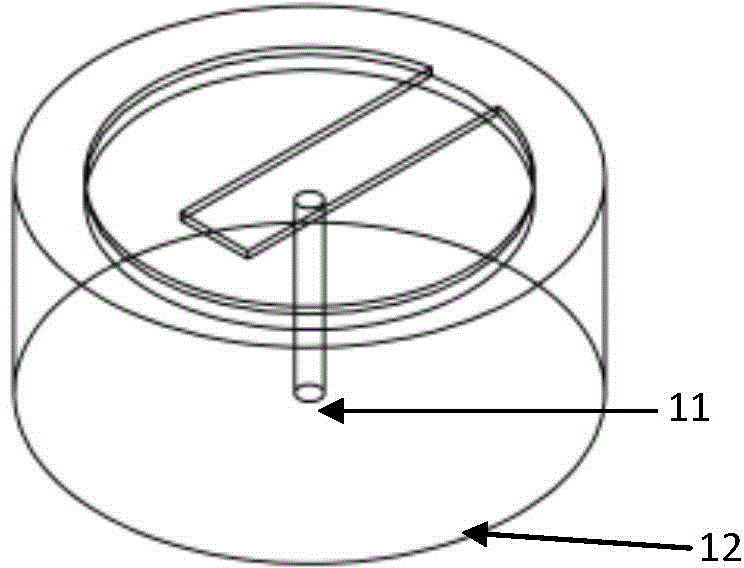
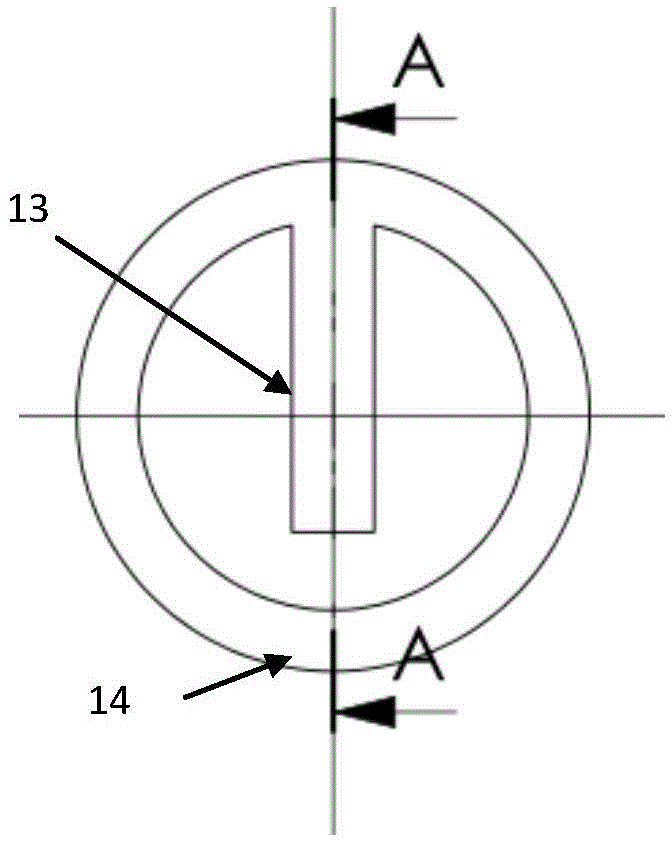
An active multimode optical fiber consisting of a first core section (11), a thin barrier layer (12) material having a thickness (d2) and a lower refractive index than that of the first core section by an index difference (Δn), a second core section (13) having a refrective index equal or higher than that of the first core section, and a cladding (14) having an index lower than that of the first core section. Said index difference and said thickness are selected so that a fundamental core mode couples less strongly with said cladding modes than higher order core modes. A scheme of changing the symmetry of the fiber for reduced sensitivity of the fundamental mode of the first core section to resonance effects.
Owner:ROFIN SINAR LASER
Magnetic control tunable optical fiber comb filter
InactiveCN102141691AAchieve tuningBroaden the passband rangeCladded optical fibreOptical waveguide light guideGratingOptical fiber coupler
The invention relates to a magnetic control tunable optical fiber comb filter belonging to the technical fields of optical fiber sensing and optical fiber communication. The magnetic control tunable optical fiber comb filter comprises a broadband light source, an optical fiber coupler, an optical fiber environment, a magnetic field generating unit and a photoelectric detector, wherein the optical fiber environment comprises a left arm optical fiber, a right arm optical fiber and a PCFG (Photonic Crystal Fiber Grating). The magnetic control tunable optical fiber comb filter is characterized in that the PCFG cladding is provided with five large shaddock-form air holes of single-layer structures, and magnetofluid is filled into the large air holes through a capillary phenomenon and changes in the refraction index under the action of a variable magnetic field to change the effective refraction index of a PCFG cladding and cause the wavelength movement of a harmonic peak coupled between a PCFG base mode and a cladding mode so as to realize the tunability as the output characteristics of the filter. Because of different lengths of the left arm optical fiber and the right arm optical fiber in the optical fiber environment, two paths of light signals reflected by the PCFG have a light path difference and are subjected to interferences when returning to the optical fiber coupler so that a comb filter effect is generated in an output spectrum of the filter.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
Tapered fiber gratings and applications
Optical filter devices in accordance with the invention are based on tapered optical fibers having transversely distributed refractive index variations in a small diameter waist region where waves are propagated in combined cladding / air-guided modes. The grating has a periodicity selected for reflection of a selected center wavelength and the waist diameter and grating pattern split the wavelengths of the lossy cladding modes from the backreflected signals by more than 10 nm. Such wavelength selective optical fiber devices have a variety of applications. In one application, a tapered fiber grating with optical circulators is used to add or drop optical signals for communication via a common transmission path. In another application, the tapered fiber grating is used with grating assisted mode couplers and circulators to form an add / drop multiplexer. In another application, these components are used with optical switches to produce programmable add / drop filters and crossconnects.
Owner:ARROYO OPTICS
Method for improving precision of stepped components in laser spot-changing direct formation mode
ActiveCN104923784APlay a compensatory roleSolve the problem of inconsistent growth heightAdditive manufacturing apparatusIncreasing energy efficiencyLifting capacitySpray nozzle
The invention discloses a method for improving precision of stepped components in a laser spot-changing direct formation mode. The method includes the steps that a cladding test is performed firstly, the sectional width and height data of a single-track cladding layer under different technological parameters are obtained, orders of a sectional curve of the cladding layer under different aspect ratios are fitted out, and the function relationship between the orders of the sectional curve of the cladding layer under the different aspect ratios and the height and lifting capacity of the single-track cladding layer is built; then single step-shaped tracks corresponding to the same lifting capacity are built, the technological parameters of the laser spot-changing cladding single tracks are determined according to the single step-shaped tracks, and a highly-smooth cladding layer is formed in a cladding mode through laser spot-changing direct formation; after one cladding layer is completed, a spray nozzle is lifted by a layering height, new fusion tracks are formed in a cladding mode through the single step-shaped tracks, and operations circulate until manufacturing of a three-dimensional part is completed. By means of the method, the highly-smooth cladding layer is obtained, the phenomenon that the top of the cladding layer is not even and portions of small aspect ratios are prone to tension fracture is avoided, and the method improves formation precision and guarantees formation quality.
Owner:KUSN BAOJIN LASER TAILOR WELDED
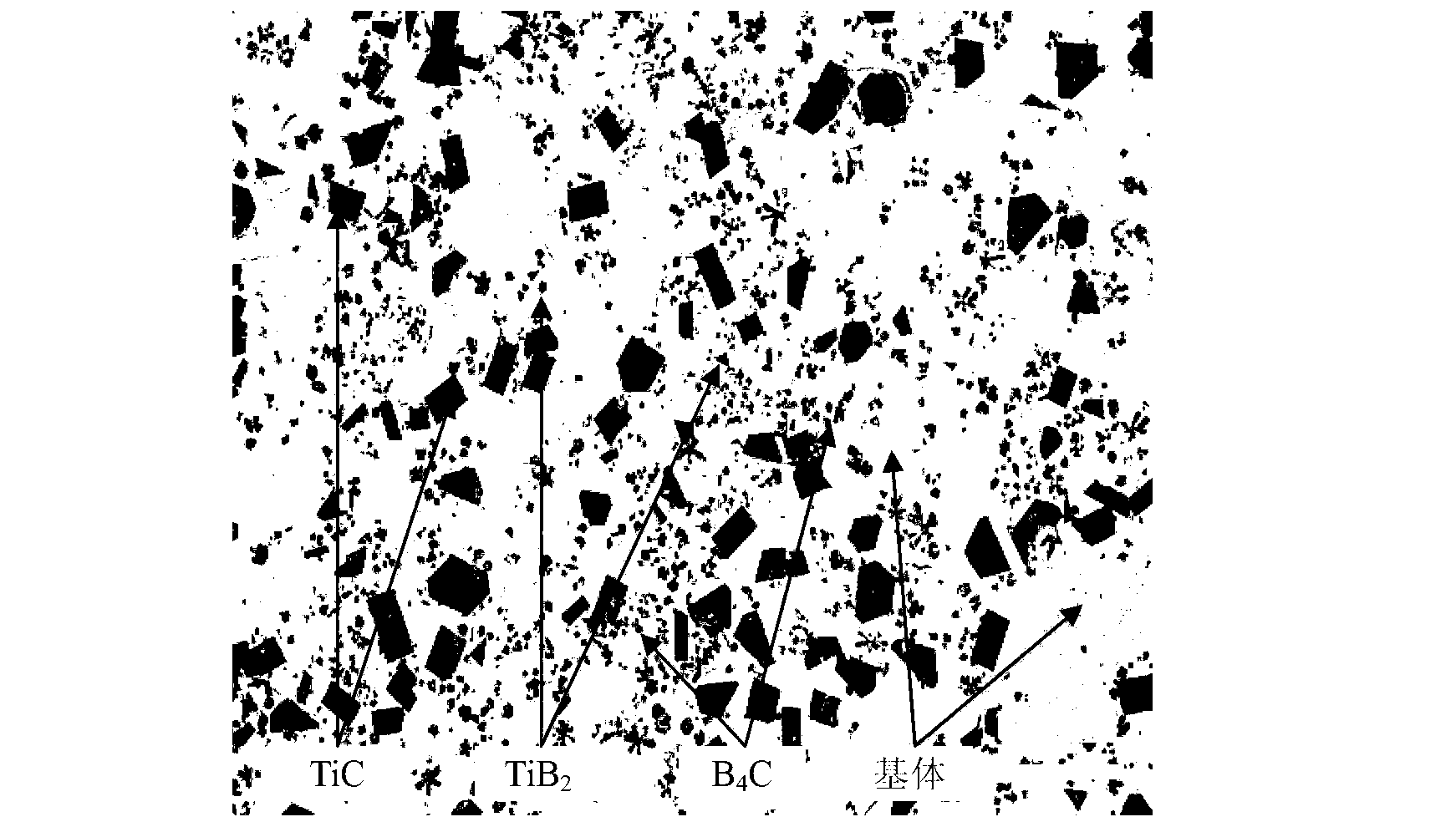
Laser cladding in-situ synthesis ceramic phase reinforced Fe-base cladding layer and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103290406ADense tissueHigh microhardness valueMetallic material coating processesAlloyPre treatment
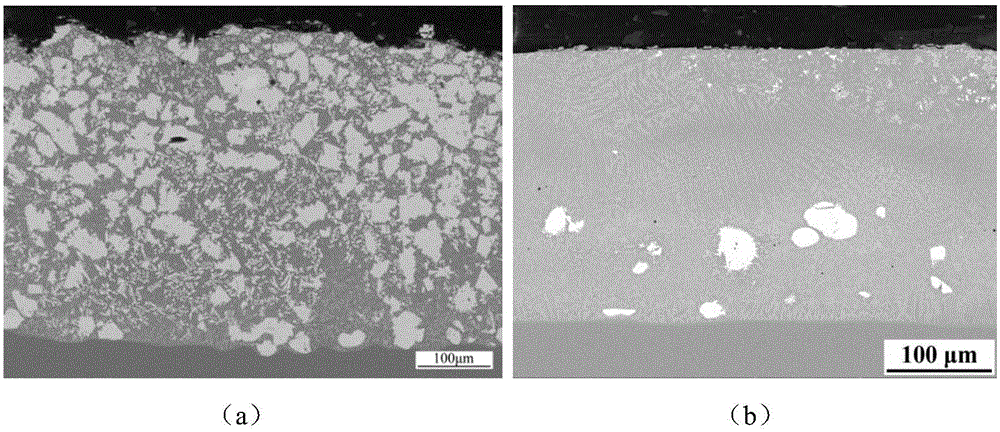
The invention relates to a laser cladding in-situ synthesis ceramic phase reinforced Fe-base cladding layer and a preparation method thereof, and belongs to the technical field of laser cladding. In-situ synthesis ceramic hard phases mainly comprise TiC, TiB2 and B4C. The coating is prepared according to the following steps of: firstly pretreating a base body; then proportioning alloy power in proportion by adopting a synchronous powder delivery laser cladding mode, and then sufficiently mixing and drying to use as a cladding material; regulating the process parameters of laser cladding in the presence of argon, wherein the cladding material carries out in-situ reaction under the irradiation of laser energy to generate a ceramic hard phase and shows good metallurgical bonding with the base body. The coating disclosed by the invention is compact in tissue without pores or cracks, achieves the large microhardness value more than 1000 HV and has very good application prospect in the field of laser surface modification.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Magnetic field sensor based on magnetic fluid and micro-nanofiber evanescent field
InactiveCN103278782AIncreased sensitivityEasy to operateMagnetic field measurement using magneto-optic devicesRefractive indexLaser light
The invention discloses a magnetic field sensor based on a magnetic fluid and a micro-nanofiber evanescent field. The magnetic field sensor comprises a laser light source, a single mode fiber, a magnetic fluid, a micro-nanofiber, a photoelectric detector and a mode coupling element formed on the basis of welding. The laser light source is connected with the micro-nanofiber immersed in the magnetic fluid through the single mode fiber, when light is transmitted along the micro-nanofiber, a large part of energy is transmitted in the form of the evanescent field, the micro-nanofiber enhances the interaction between an optical field and an external substance, the change of an external magnetic field changes the refractive index of the magnetic fluid in which the micro-nanofiber is immersed, i.e. the refractive index of the surrounding environment of the micro-nanofiber is changed, a part of light is continuously propagated through a fiber core, the other part of light is conducted on the interface of the micro-nanofiber and the magnetic fluid in the form of the evanescent field, and after entering the ordinary single mode fiber at the rear end, the other part of light is coupled into a cladding layer. After the two parts of light pass the mode coupling element which is formed on the basis of welding, the cladding layer mode is coupled to the fiber core, and is interfered with the residual fiber core mode, and the two parts of light finally enter the photoelectric detector. Magnetic field information can be modulated by detecting the strength of the light after interference.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
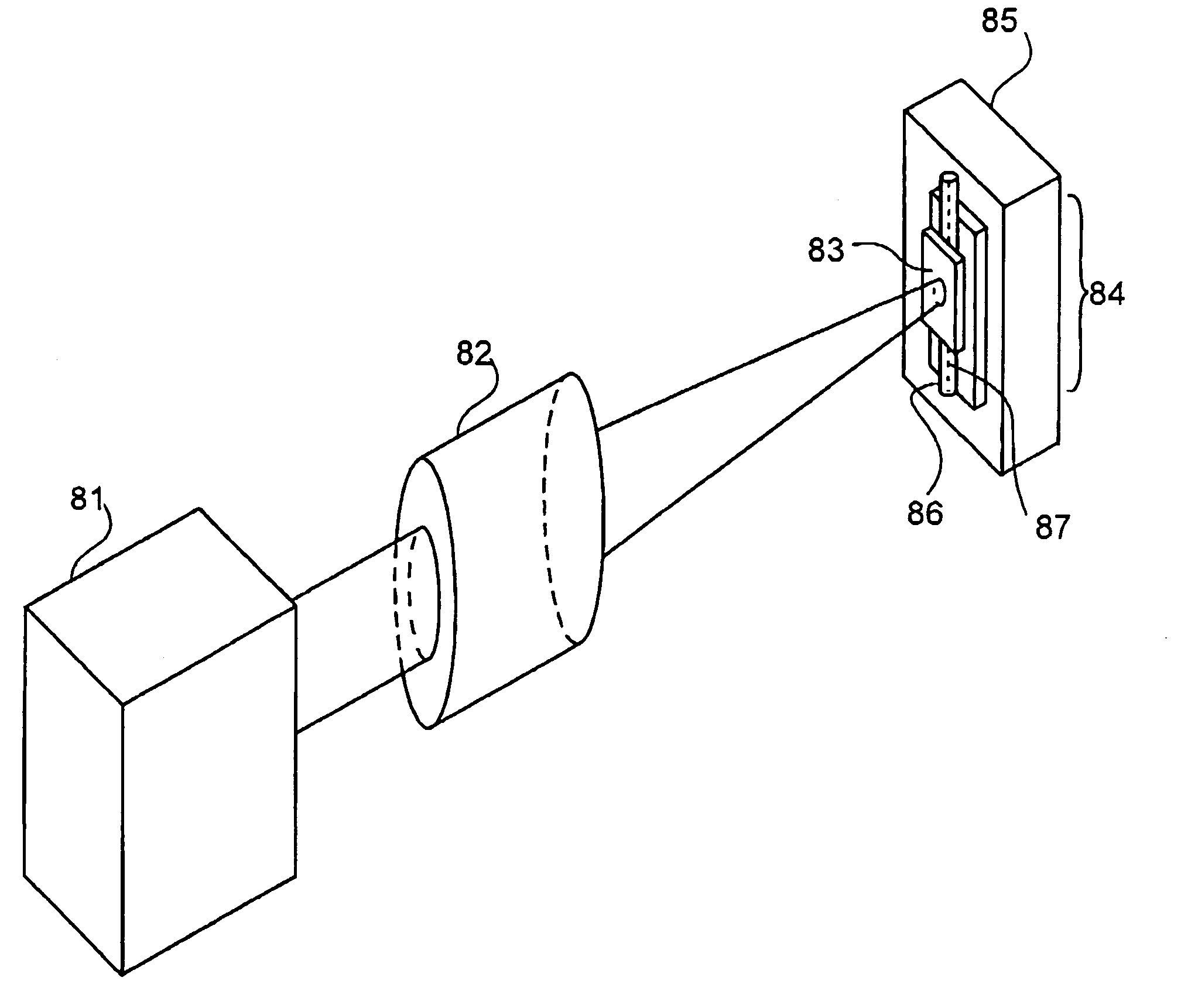
Polarization maintaining optical fiber polarizer
A novel in-fiber polarizer is provided that is implemented in an optical fiber structure based on a polarization maintaining (“PM”) optical fiber, and that is configured to impart a predetermined desired polarization to a light signal transmission of a predetermined at least one wavelength transmitted therethrough. The inventive polarizer comprises a PM optical fiber structure, with an entry end for receiving incident light and an exit end for outputting polarized light, having an optical fiber core, having at least one core mode and a core propagation constant, surrounded by a cladding, having at least one cladding mode and a cladding propagation constant, that further comprises a reduced core diameter region of a predetermined length between its entry and exit ends, wherein various predefined parameters of the modified PM optical fiber structure, including but not being limited to, the core and cladding propagation constants, the value of the reduced core diameter, and the length of the reduced core diameter region are selected and configured to produce a constructive interference for one light polarization of the input light signal, corresponding to the desired polarization, and to produce a destructive interference for a polarization orthogonal to the desired polarization, to thereby only output, at the polarizer exit end, the desired polarization component of the light signal transmission at the at least one wavelength. Additional embodiments of the inventive polarizer include multiple sequential polarizer structures with specially configured interconnects.
Owner:CHIRAL PHOTONICS
Optical fiber gain medium with modal discrimination of amplification
InactiveUS7760771B2Precise adjustment and controlHigh gainLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberRefractive index
An active multimode optical fiber consisting of a first core section (11), a thin barrier layer (12) material having a thickness (d2) and a lower refractive index than that of the first core section by an index difference (Δn), a second core section (13) having a refractive index equal or higher than that of the first core section, and a cladding (14) having an index lower than that of the first core section. Said index difference and said thickness are selected so that a fundamental core mode couples less strongly with said cladding modes than higher order core modes. A scheme of changing the symmetry of the fiber for reduced sensitivity of the fundamental mode of the first core section to resonance effects.
Owner:ROFIN SINAR LASER
High-power fiber amplifier
InactiveUS20090231682A1Laser detailsReflectometers using simulated back-scatterOptoelectronicsAmplifier
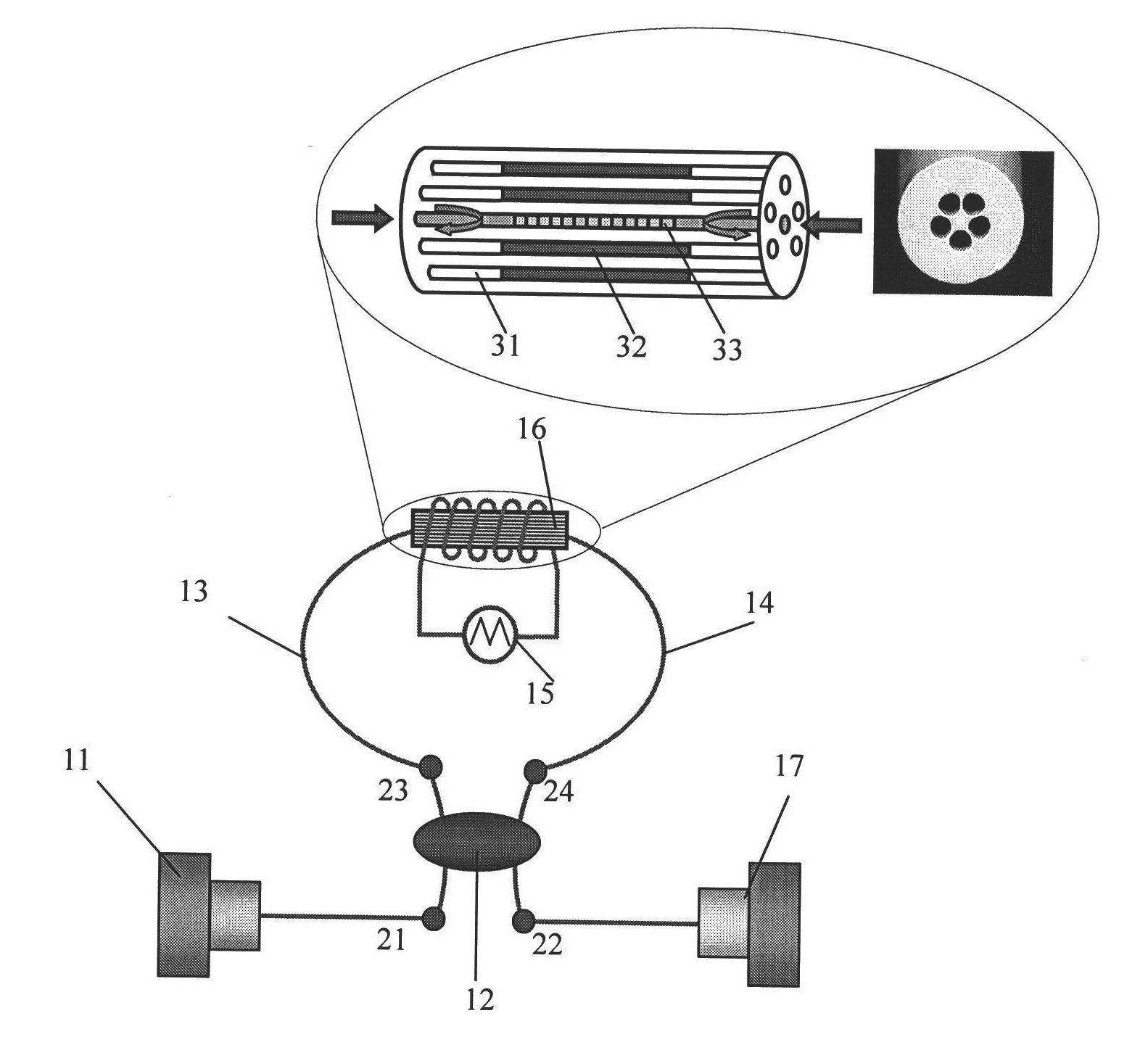
Fiber light amplifiers adapted for high power application are provided. In embodiments of the invention, the light signal to be amplified is coupled to a cladding mode of an active waveguide region which is cladding doped. The amplified light is coupled to an output fiber have waveguiding properties matching those of the active cladding of the active waveguide region. In other embodiments, two or more amplifying stages are provided coupled by a wavelength selective loss element which couples the Stokes wave co-propagating with the signal to be amplified out of the signal guiding mode prior to the onset of SRS.
Owner:CORP DE LECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE DE MONTREAL
Method and apparatus for reduction of optical coupling between pump lasers and photodetectors in optical amplifiers
ActiveUS20060045452A1Reduce lightAvoid spreadingLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberPhotodetector
In a first aspect, the present invention comprises an optical filter comprising a fiber having a core and a cladding and a light-absorbing coating applied onto a portion of the fiber cladding, the coating attenuating loosely bound cladding modes. In another aspect, the invention comprises a fiber amplifier apparatus comprising fibers for delivering pump laser light and for monitoring signal light and at least one photodetector optically coupled to a monitoring fiber, wherein either an optical filter is disposed between a monitoring fiber and a photodetector or at least one of the fibers has a core and a cladding and a light-absorbing coating applied onto a portion of the fiber cladding. A method in accordance with the present invention includes providing an optical amplifier having fibers for delivering pump laser light and for monitoring signal light, and applying a light-absorbing coating onto a portion of one of said fibers.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
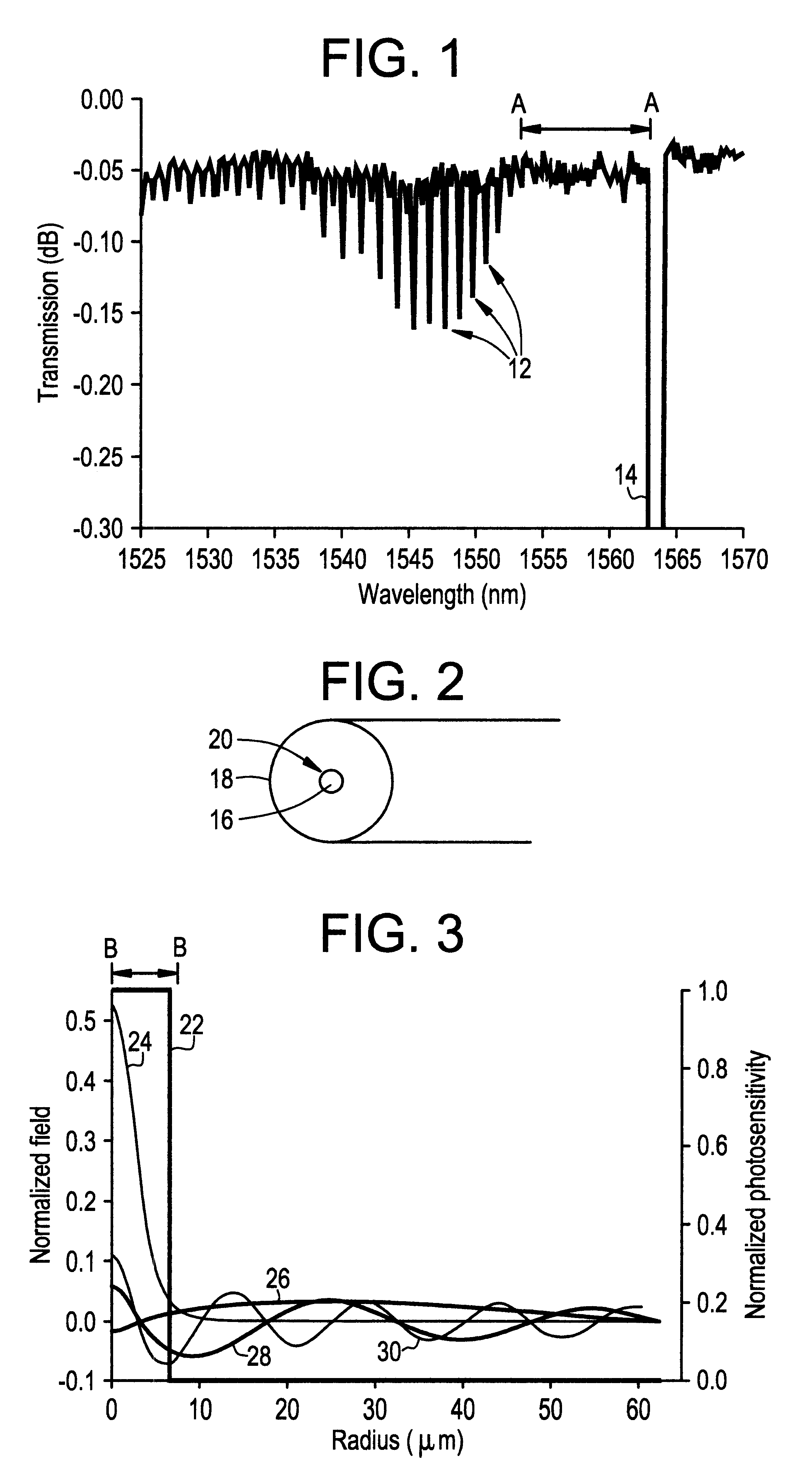
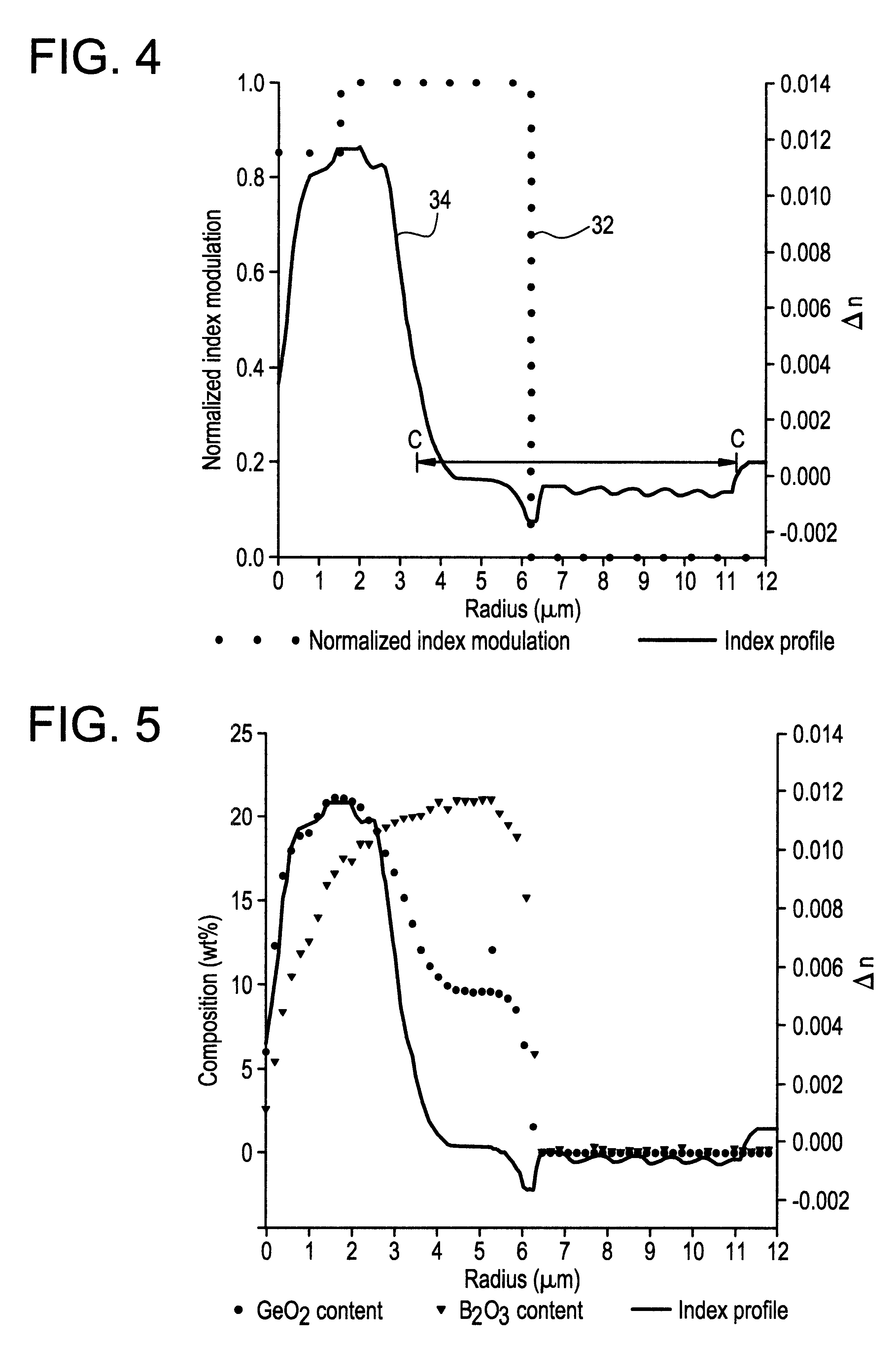
Fiber Bragg grating with cladding mode suppression
An optical waveguiding fiber has a photosensitive core and a cladding that includes a photosensitive inner cladding region adjacent the core and an outer cladding region. The inner cladding region and the outer cladding region have substantially equal indices of refraction. The photosensitivity of the inner cladding region is sufficient to cause a modulation of the index of refraction of the inner cladding when exposed to ultraviolet light. In another aspect of the invention, the optical fiber includes a grating in the core, which extends radially into the inner cladding region. The core and the inner cladding region of the optical fiber are doped with concentrations of Ge and B sufficient to impart photosensitivity to the inner cladding region, and to result in an index of refraction in the inner cladding region substantially equal to the index of refraction of the outer cladding region.
Owner:CORNING INC
Optical fiber cantilever beam microphone for photoacoustic spectrum detection and manufacturing method
InactiveCN104865192AImplement detectionReduce the volume of the absorption cellColor/spectral properties measurementsLaser etchingIntrinsic safety
The invention relates to an optical fiber cantilever beam microphone for photoacoustic spectrum detection and a manufacturing method of the microphone. The optical fiber cantilever beam microphone comprises a single-mode optical fiber, an optical fiber ceramic sleeve, a polymer cantilever beam and an annular polymer film for detecting a photoacoustic spectrum signal. The manufacturing method includes the steps: firstly, machining the annular polymer film to form the polymer cantilever beam in a pulse laser etching mode; secondly, fixing the formed polymer cantilever beam and the optical fiber ceramic sleeve in a laser melt cladding mode; finally, forming stable FP (Fabry Perot) cavities in the end faces of the polymer cantilever beam and the single-mode optical fiber. The optical fiber cantilever beam microphone has the advantages of high integration level, small size, sensitivity in detection, intrinsic safety and the like.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Optical fiber for single-mode operation
InactiveUS6839484B2Facilitate mode couplingReduce morbidityOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCouplingBasic mode
A single-mode fiber of increased core size consists of a “few-mode” fiber, of core size sufficient for guiding up to three high-order modes in addition to the fundamental mode, by interposing perturbations of such spacing along the fiber, as to selectively couple any such high-order modes to (unguided) cladding modes, thereby rejecting all but the fundamental mode. Unwanted coupling of the fundamental mode, leading to added fiber loss, is minimized by appropriate refractive index profile design.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
High-capacity multimode optical fiber systems
InactiveUS6839481B2Expedient and high-capacity operationCost advantageOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingCoupling light guidesFiberLength wave
Multimode optical fiber local area networks, both intrabuilding and interbuilding, are optimized to take advantage of the wide wavelength operating range offered by co-pending patent application Ser. No. 10 / 408,076 “Enhanced Multimode Fiber”—a fiber provided both with: longitudinally spaced perturbations for inducing mode coupling and thereby lessening mode dispersion; and with a radial discontinuity for discouraging conversion of bound-to-cladding-modes and thereby lessening added loss previously associated with induced mode coupling.
Owner:FURAKAWA ELECTRIC NORTH AMERICA INC
Method and apparatus for reduction of optical coupling between pump lasers and photodetectors in optical amplifiers
ActiveUS7430354B2Avoid spreadingPrevention of the entry of ambient pump laserLaser detailsOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingFiberPhotovoltaic detectors
In a first aspect, the present invention comprises an optical filter comprising a fiber having a core and a cladding and a light-absorbing coating applied onto a portion of the fiber cladding, the coating attenuating loosely bound cladding modes. In another aspect, the invention comprises a fiber amplifier apparatus comprising fibers for delivering pump laser light and for monitoring signal light and at least one photodetector optically coupled to a monitoring fiber, wherein either an optical filter is disposed between a monitoring fiber and a photodetector or at least one of the fibers has a core and a cladding and a light-absorbing coating applied onto a portion of the fiber cladding. A method in accordance with the present invention includes providing an optical amplifier having fibers for delivering pump laser light and for monitoring signal light, and applying a light-absorbing coating onto a portion of one of said fibers.
Owner:II VI DELAWARE INC
Multi-cladding optical fiber, optical fiber module, fiber laser, and fiber amplifier
InactiveUS20110305251A1Simple structureSubstantial single-mode propagationLaser using scattering effectsOptical fibre with graded refractive index core/claddingOptical ModuleRefractive index
Provided is a multi-cladding optical fiber which includes: a core with an average refractive index n1; and a cladding including an inner cladding with an average refractive index n2 formed on the periphery of the core, an intermediate cladding with an average refractive index n3 formed on the periphery of the inner cladding, and an outer cladding with an average refractive index n4 formed on the periphery of the intermediate cladding where n1>n2>n3>n4. Two or more axisymmetric modes exist in the core at a wavelength of the signal light; the two or more axisymmetric modes including a fundamental mode and at least a high-order mode. When the fiber is bent at a predetermined bending diameter, the high-order mode in the core disperses within the inner cladding due to coupling with an inner cladding mode, so that only the fundamental mode substantially propagates through the core.
Owner:THE FUJIKURA CABLE WORKS LTD +1
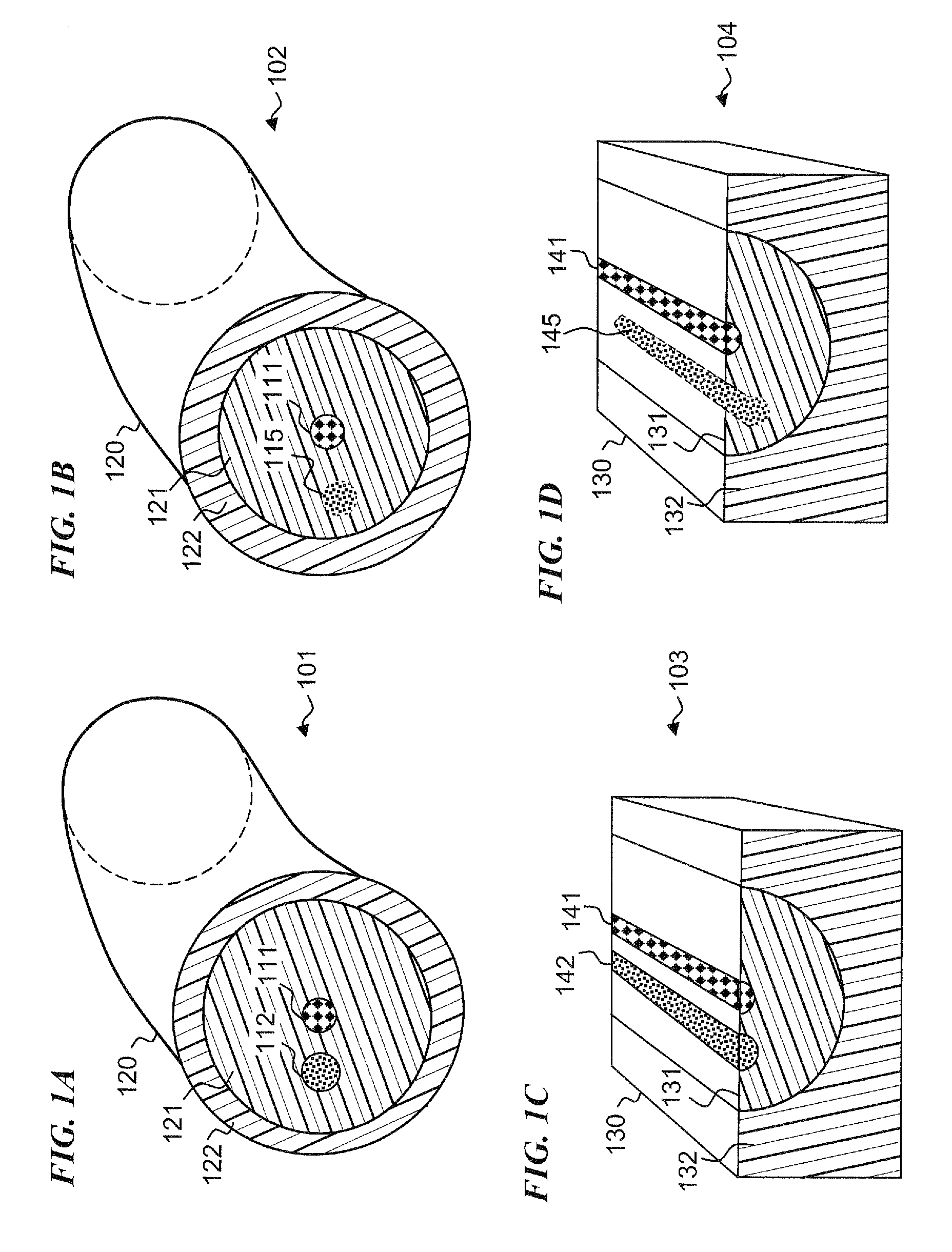
Optical fiber with reduced cladding-mode loss
InactiveUS20020126971A1Attenuating power propagatingReduce couplingOptical fibre with multilayer core/claddingCoupling light guidesCoupling lossFiber
The invention is directed toward an optical fiber that reduces the cladding mode coupling loss (CMCL) therein. The fiber includes a core, a cladding concentrically surrounding the core, and at least one lossy region concentrically surrounding the core. The lossy region is disposed within the cladding and is slightly displaced radially from the core.
Owner:VERRILLON
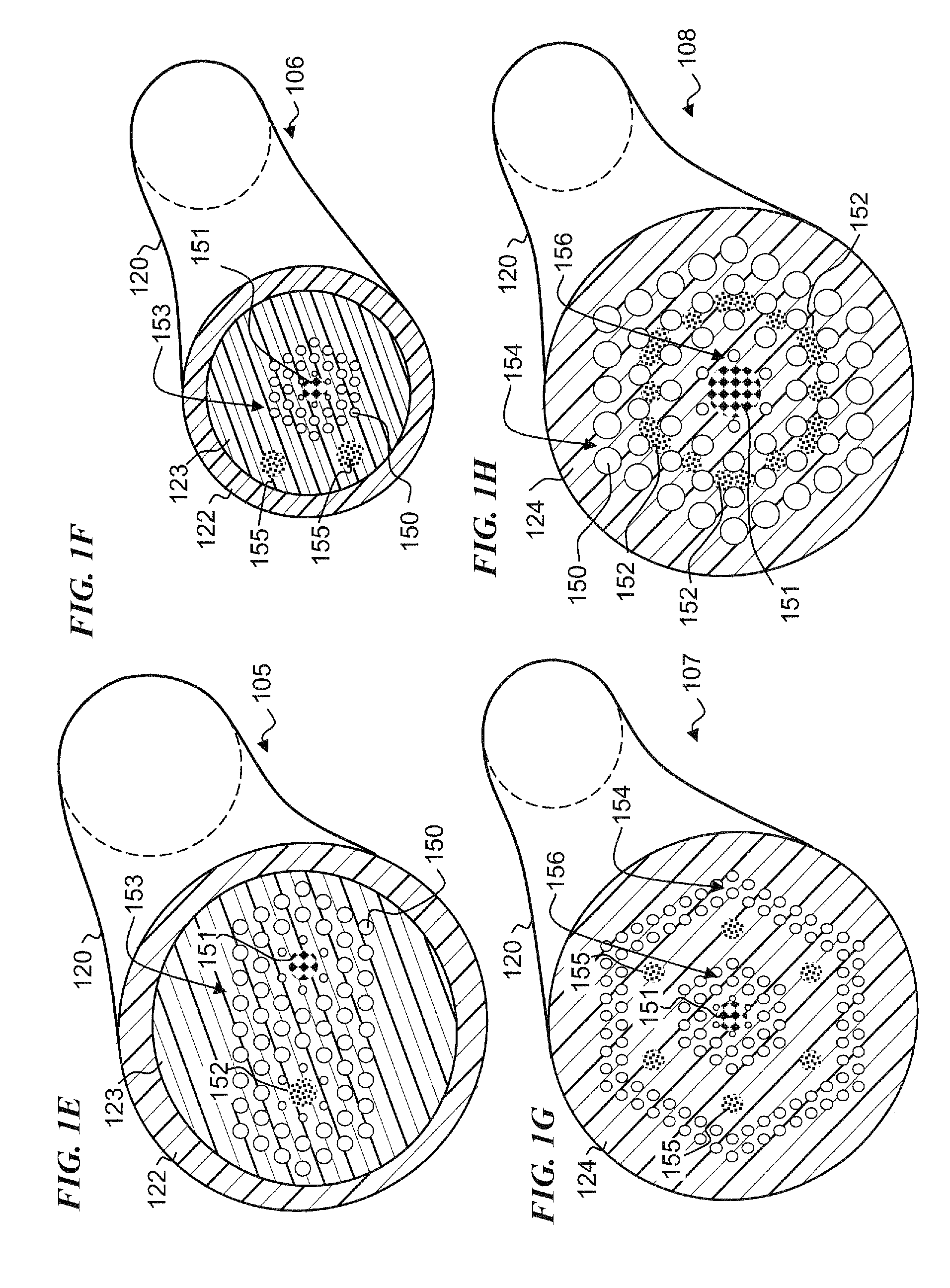
Double long period fiber grating (LPFG) temperature and humidity sensor
InactiveCN102620858ARealize simultaneous measurementImprove reliabilityPhase-affecting property measurementsThermometers using physical/chemical changesFiberGrating
Disclosed is a double LPFG temperature and humidity sensor. A temperature sensibilizing straight bar, a supporting straight bar and a metal casing are axially arranged between two sensing bodies, wherein a temperature sensitive LPFG is arranged on the temperature sensibilizing straight bar, a humidity sensitive LPFG is arranged in the metal casing, and tail fibers of the temperature sensitive LPFG and the humidity sensitive LPFG are welded together. When temperature and humidity in the external environment change, effective refractive indexes of a fundamental core mode and a cladding mode of the LPFG, grating period, resonant wavelength and refractive index change, then information of the temperature and the humidity of the environment can be obtained through detection of transmission wavelengths of the temperature sensitive LPFG and the humidity sensitive LPFG, and double parameters can be measured simultaneously. The double LPFG temperature and humidity sensor has the advantages of high measurement accuracy, simultaneous measurement of the temperature and the humidity, and the like; and can be used as the sensor which can measure the temperature and the humidity simultaneously.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com