Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
141 results about "2d array" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
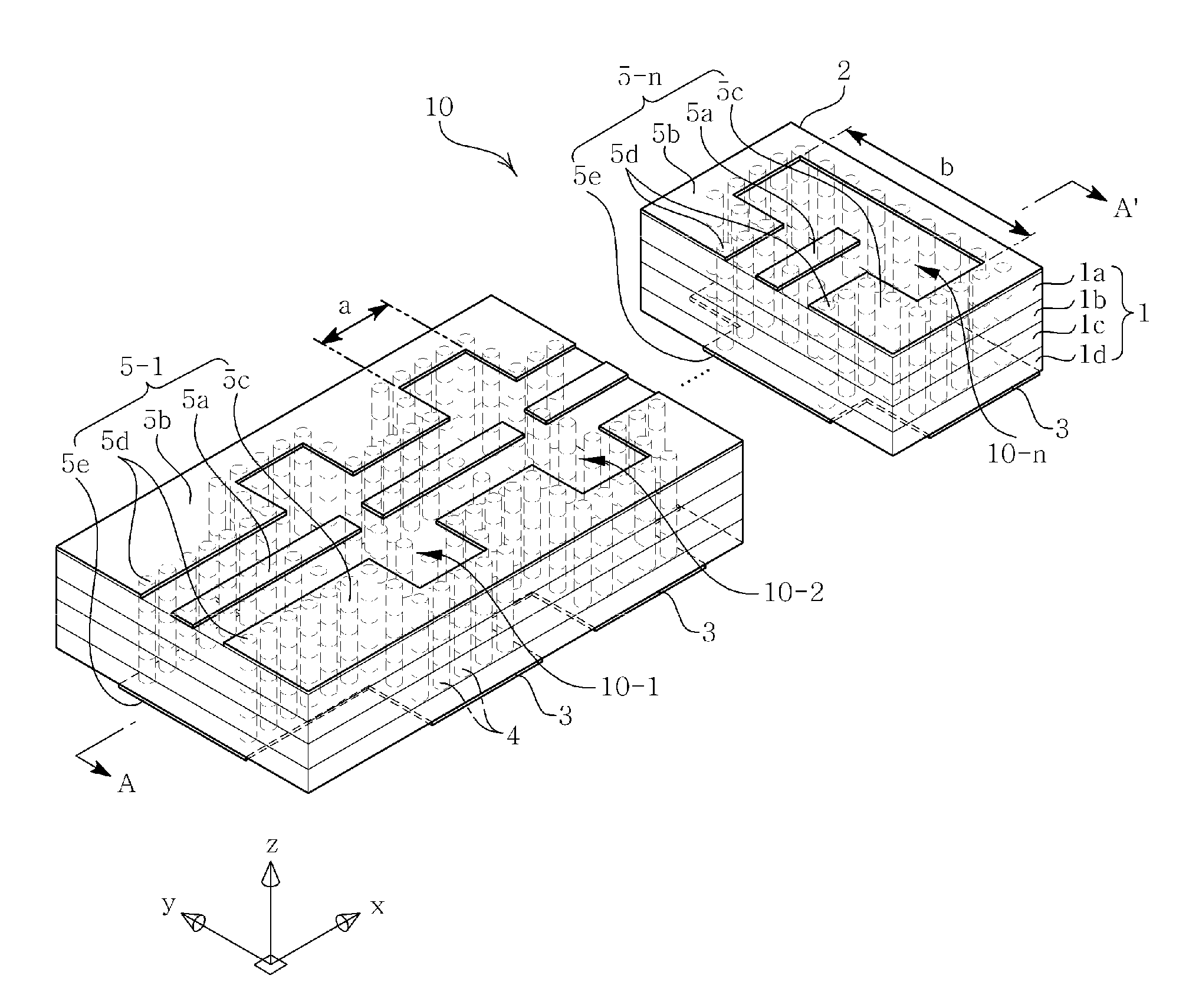
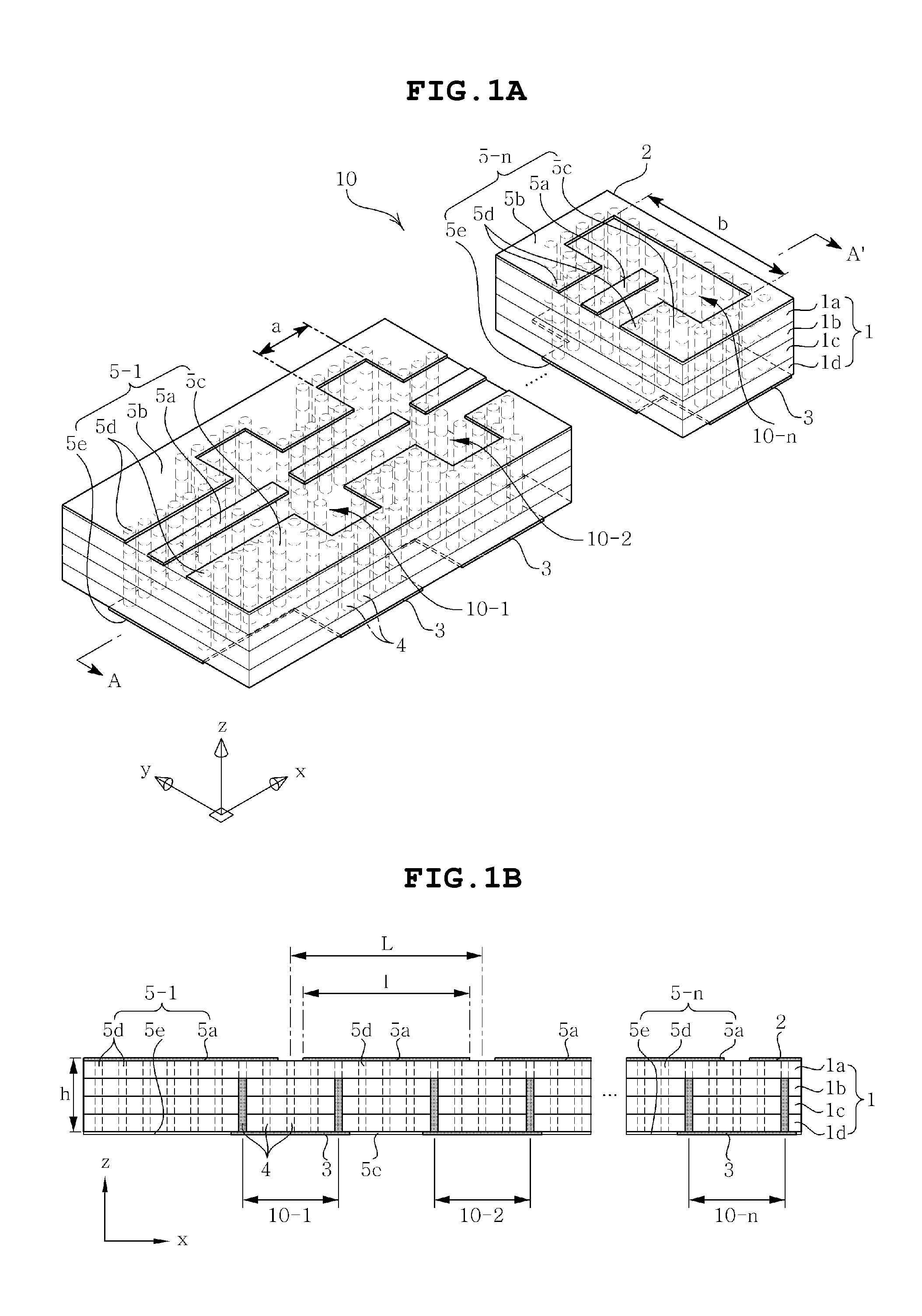
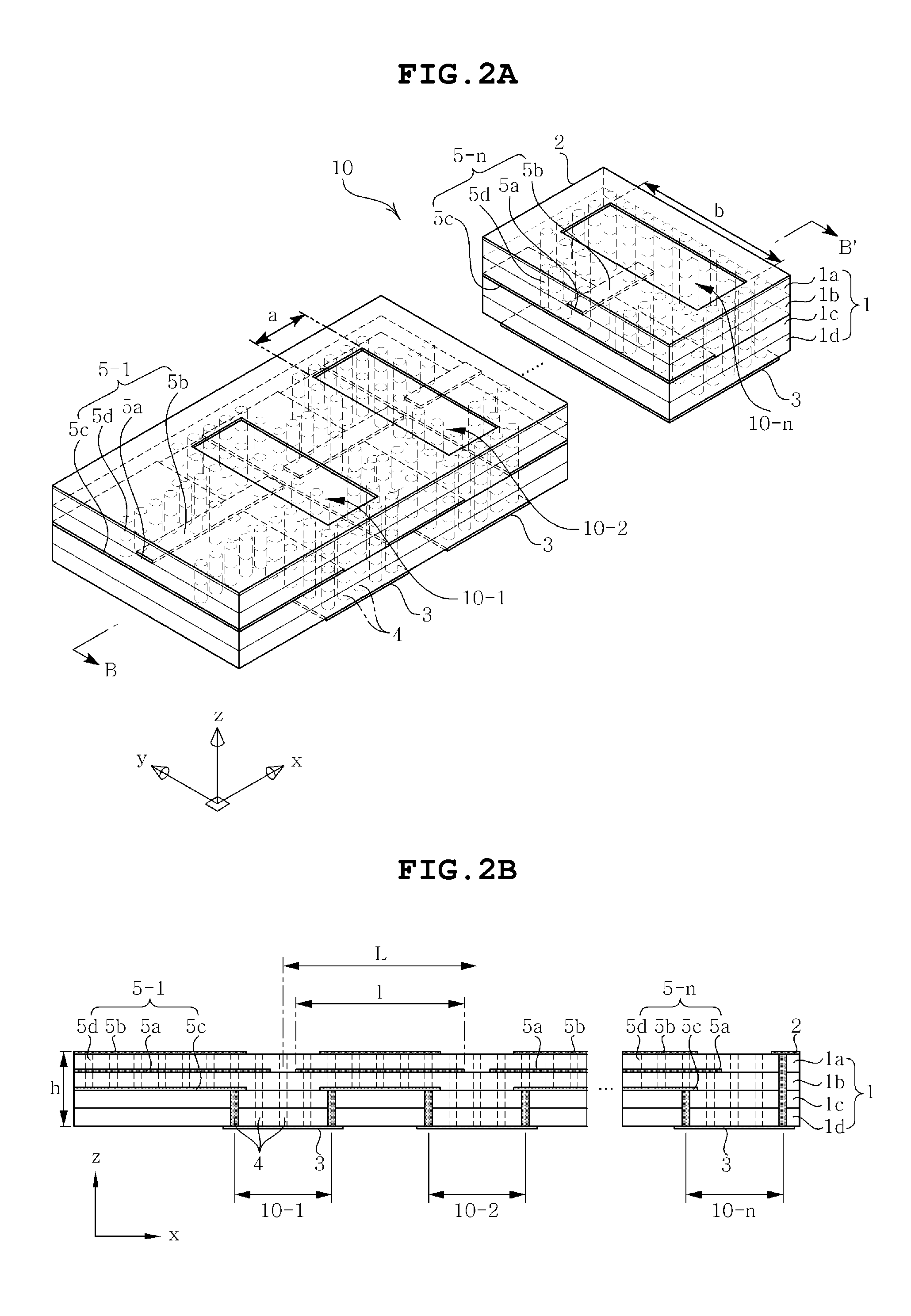
Dielectric resonator array antenna
InactiveUS20140043189A1Improve featuresIndividually energised antenna arraysElectrically short antennasTime delaysDielectric resonator antenna
Disclosed herein is a dielectric resonator array antenna including one or more series-feed type array elements installed to be arranged in parallel in a multilayer substrate, wherein first high frequency signals having the same or different phases or time delays are adjusted to be applied to the respective series-feed type array elements and respective radiated 1D array beams are individually used or combined to adjust beamforming of 2D array beams. Also, since the series-feed type array element is configured by connecting a plurality of dielectric resonator antennas in series, it can be easily and simply fed in series through coupling generated by the intervals between the feeding lines of the pertinent feeding unit of the plurality of dielectric resonator antennas connected in series. In addition, the broadband characteristics can be obtained by using the plurality of dielectric resonator antennas, whereby the overall antenna performance can be enhanced.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRO MECHANICS CO LTD +1
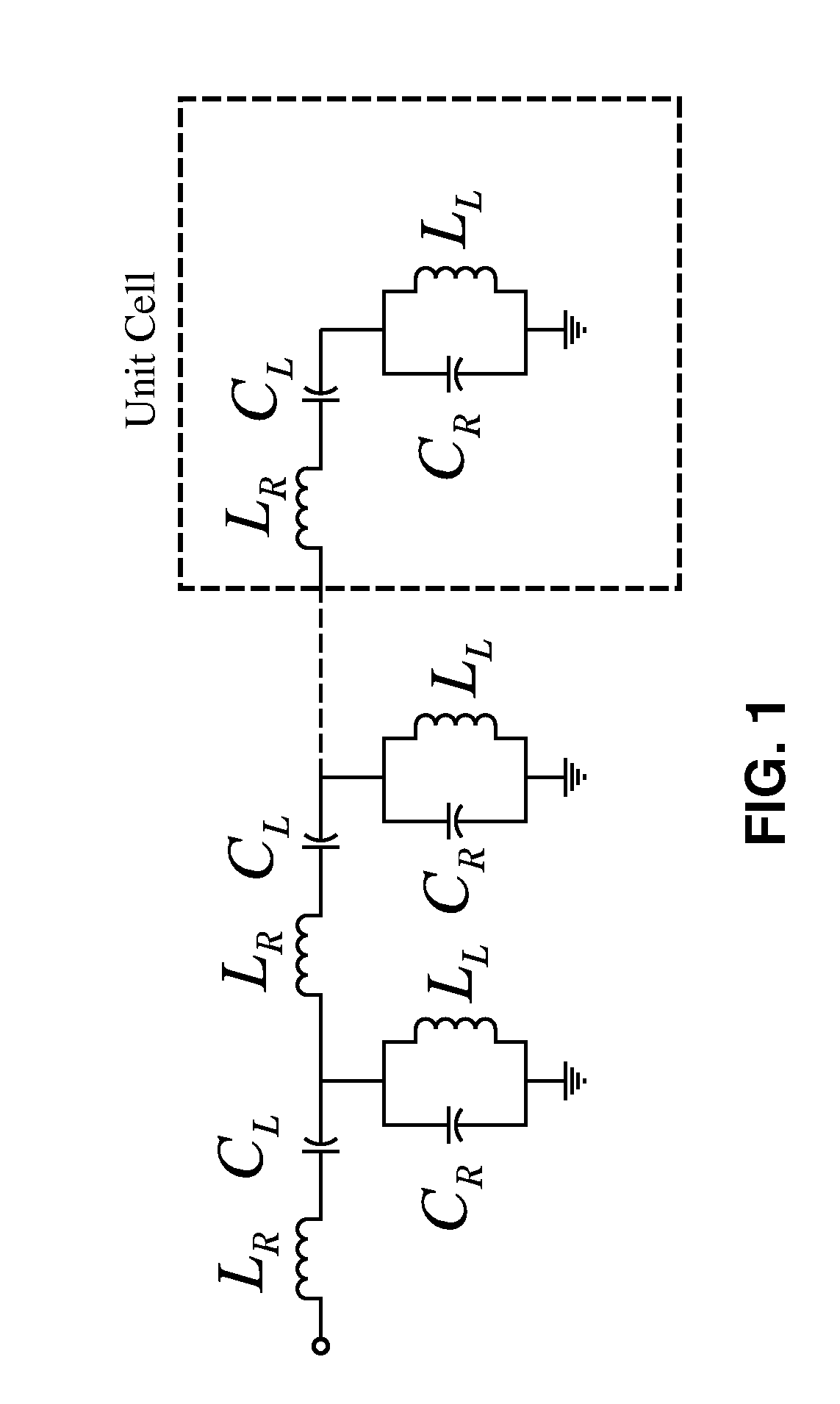
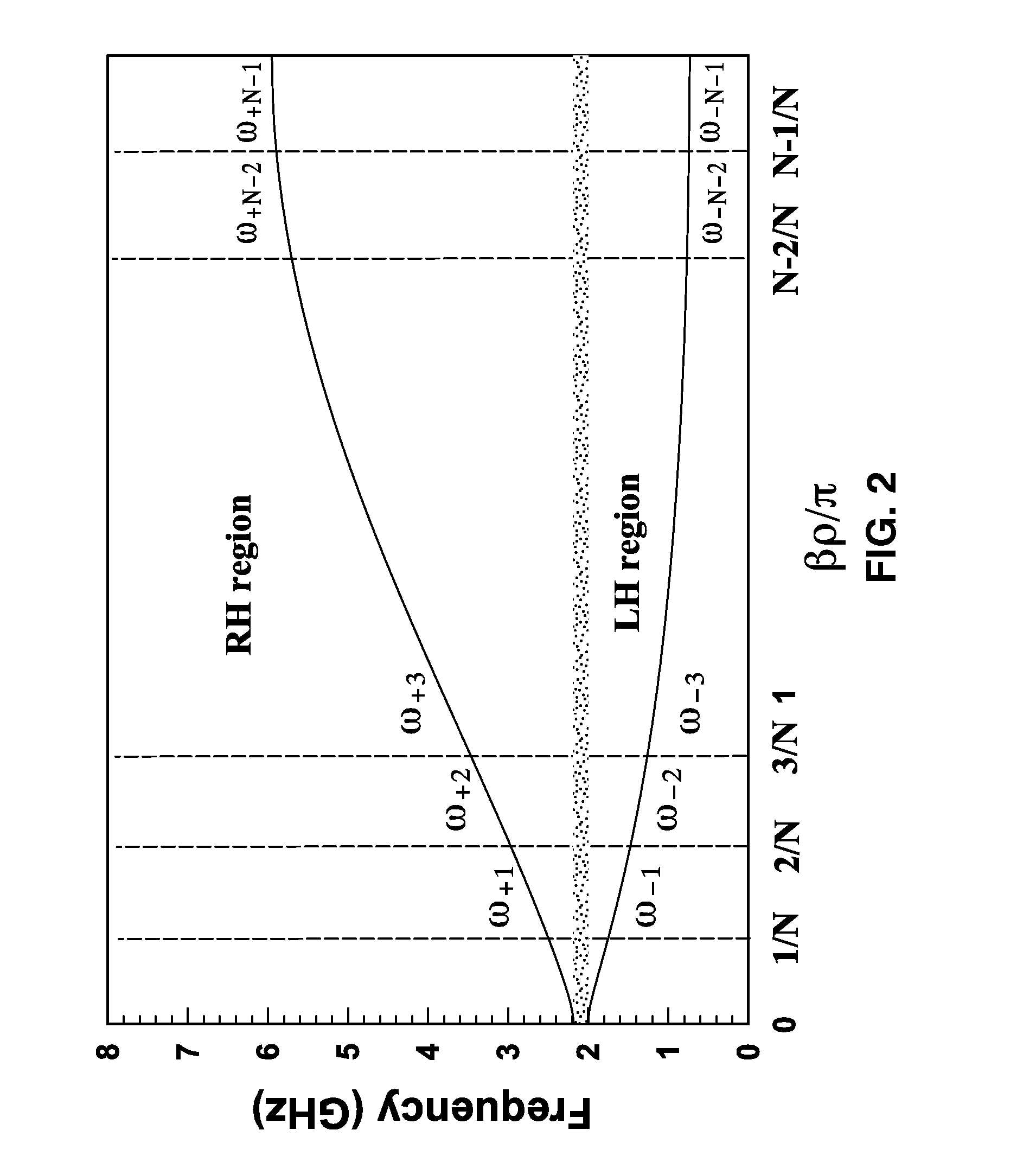
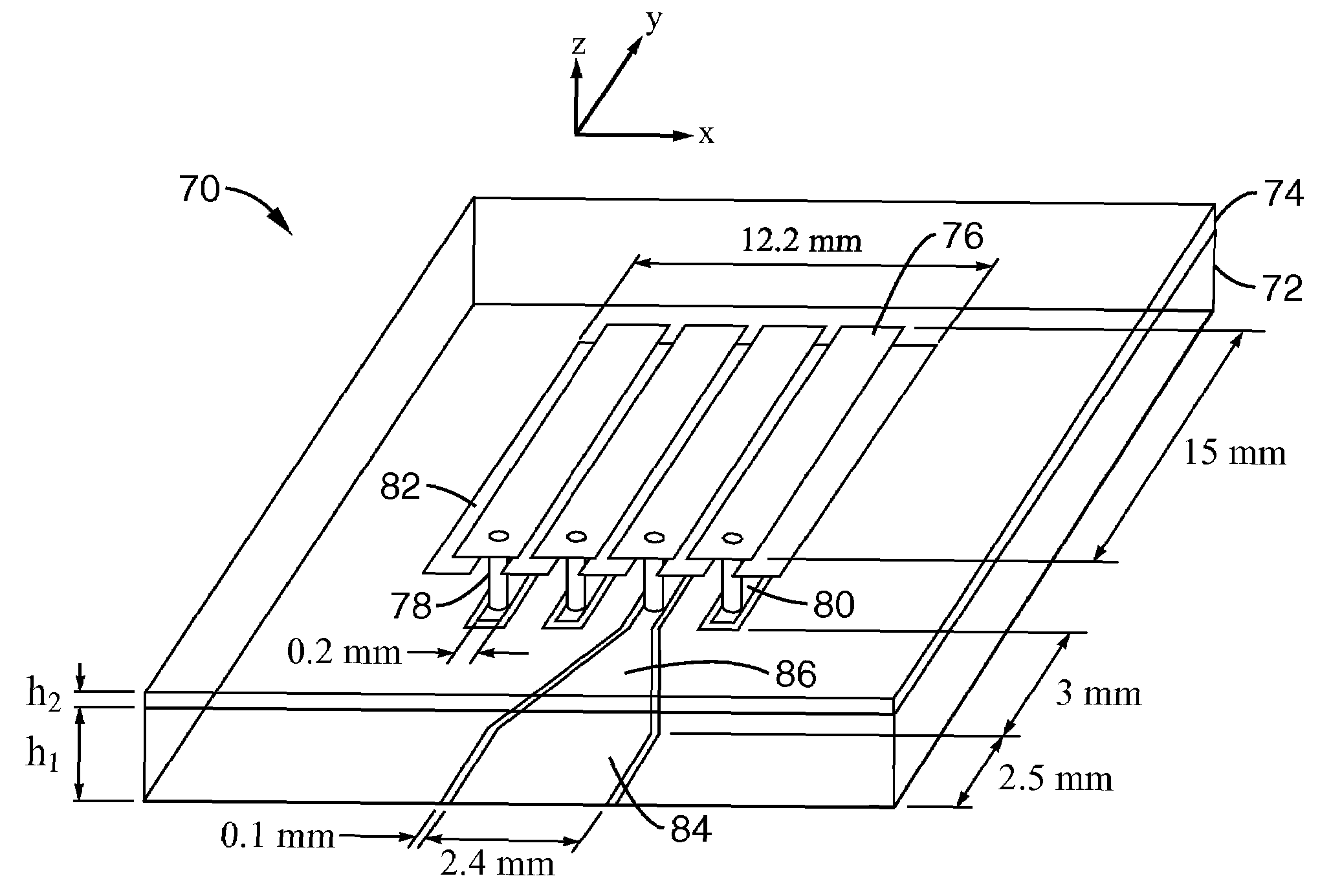
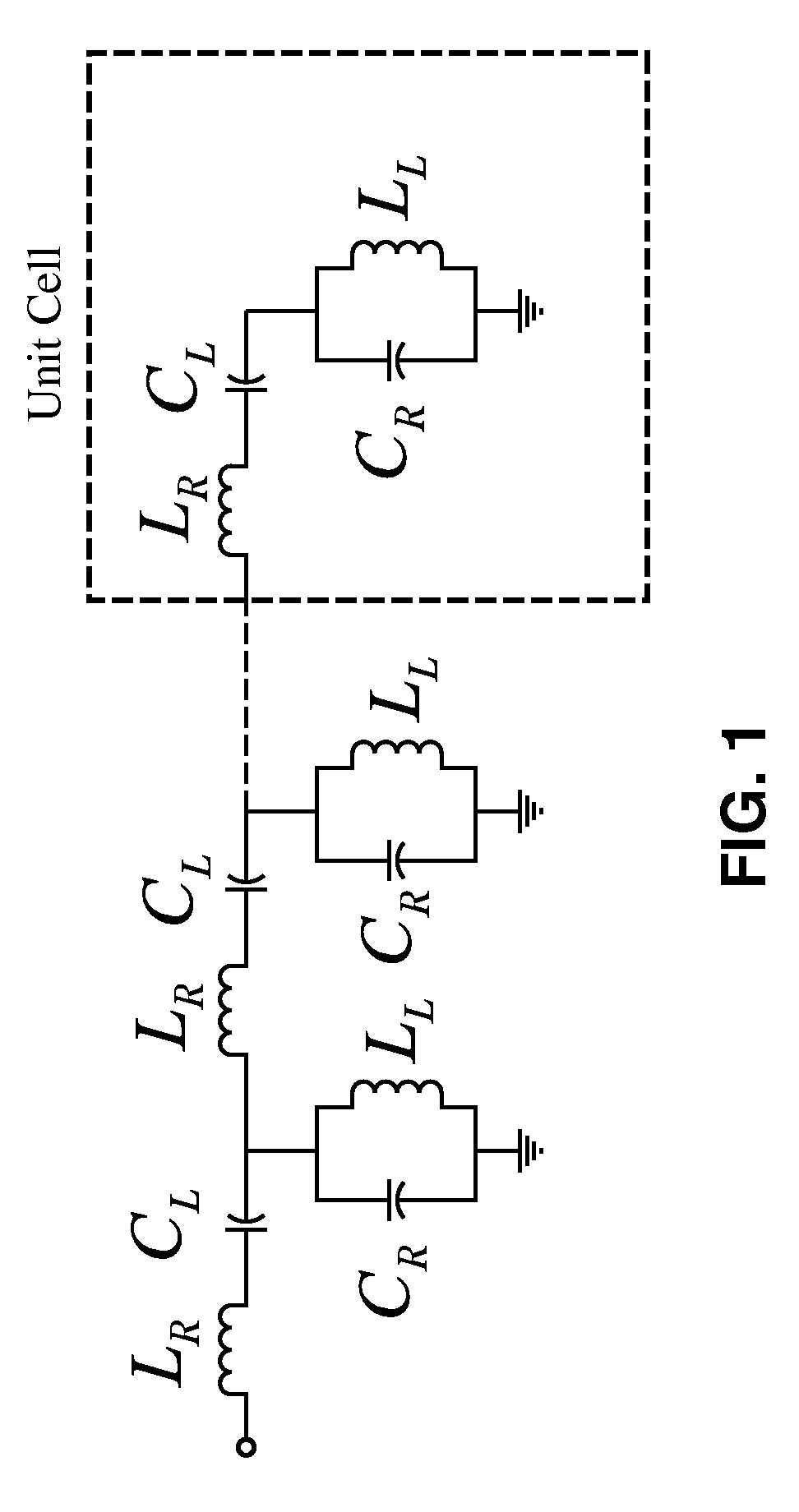
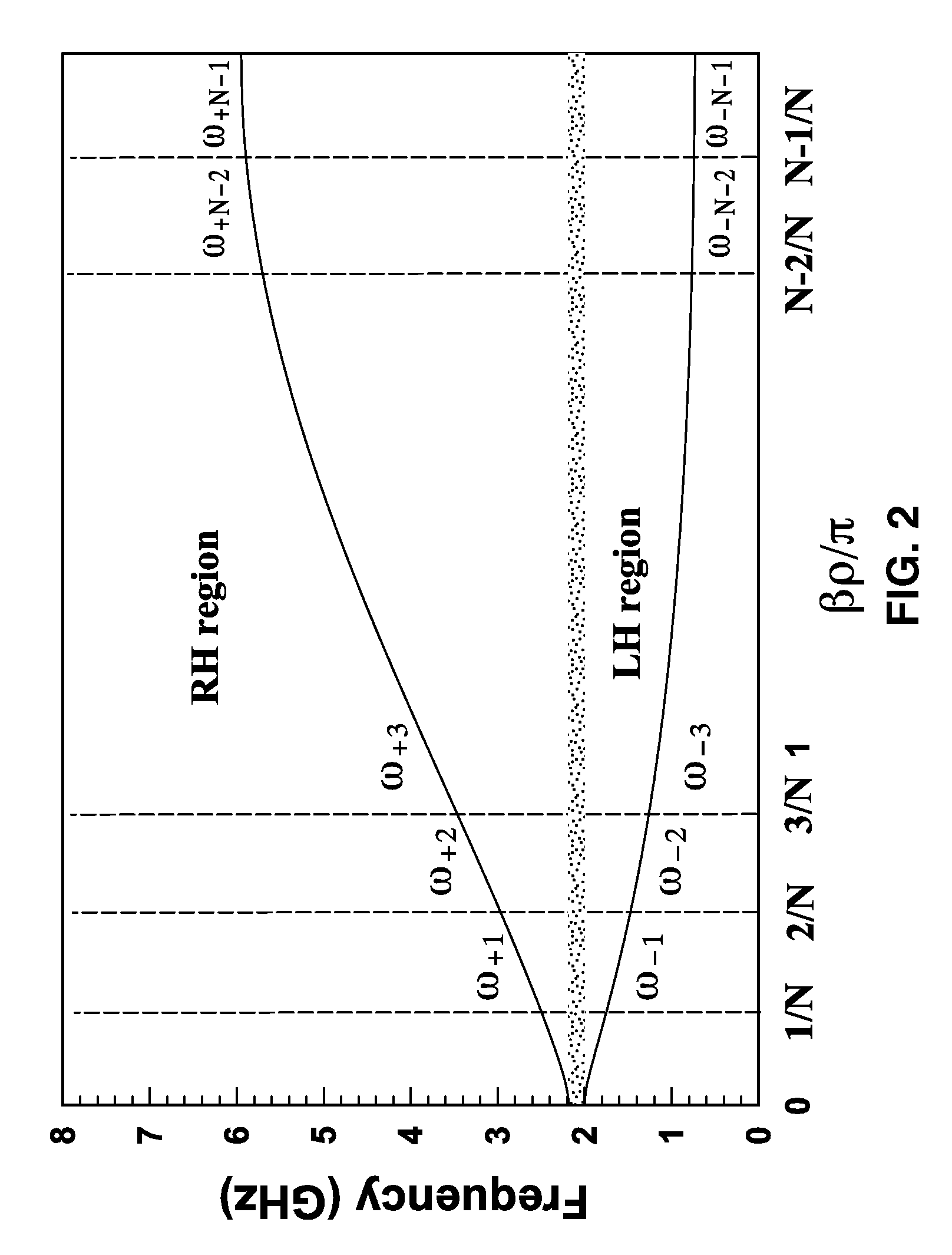
Composite right/left-handed transmission line based compact resonant antenna for RF module integration
ActiveUS20070176827A1Improve efficiencyAccurate manufacturing capabilitySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMetal-insulator-metalShunt capacitors
An apparatus based on composite right-handed or left-handed (CRLH) principles to provide a transmission line or antenna structure having a plurality of cells to which one or more feed ports are attached. The apparatus is based on an equivalent circuit Right-Hand (RH) series induction (LR) and shunt capacitor (CR), and Left-Hand (LH) series capacitor (CL) and induction (LL), in which effective permittivity (e) and permeability (m) of the structure are manipulated by the choice of CR, LR, CL, and LL. One embodiment describes mushroom antenna cells (1D or 2D array) in which vias extend up from a feed network on a ground plane through at least one dielectric region to each of a first plurality of conductive elements (plates or strips). Optionally, a second plurality of conductive elements are disposed between first and second dielectric layers to form metal-insulator-metal (MIM) capacitors to lower resonance frequency.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
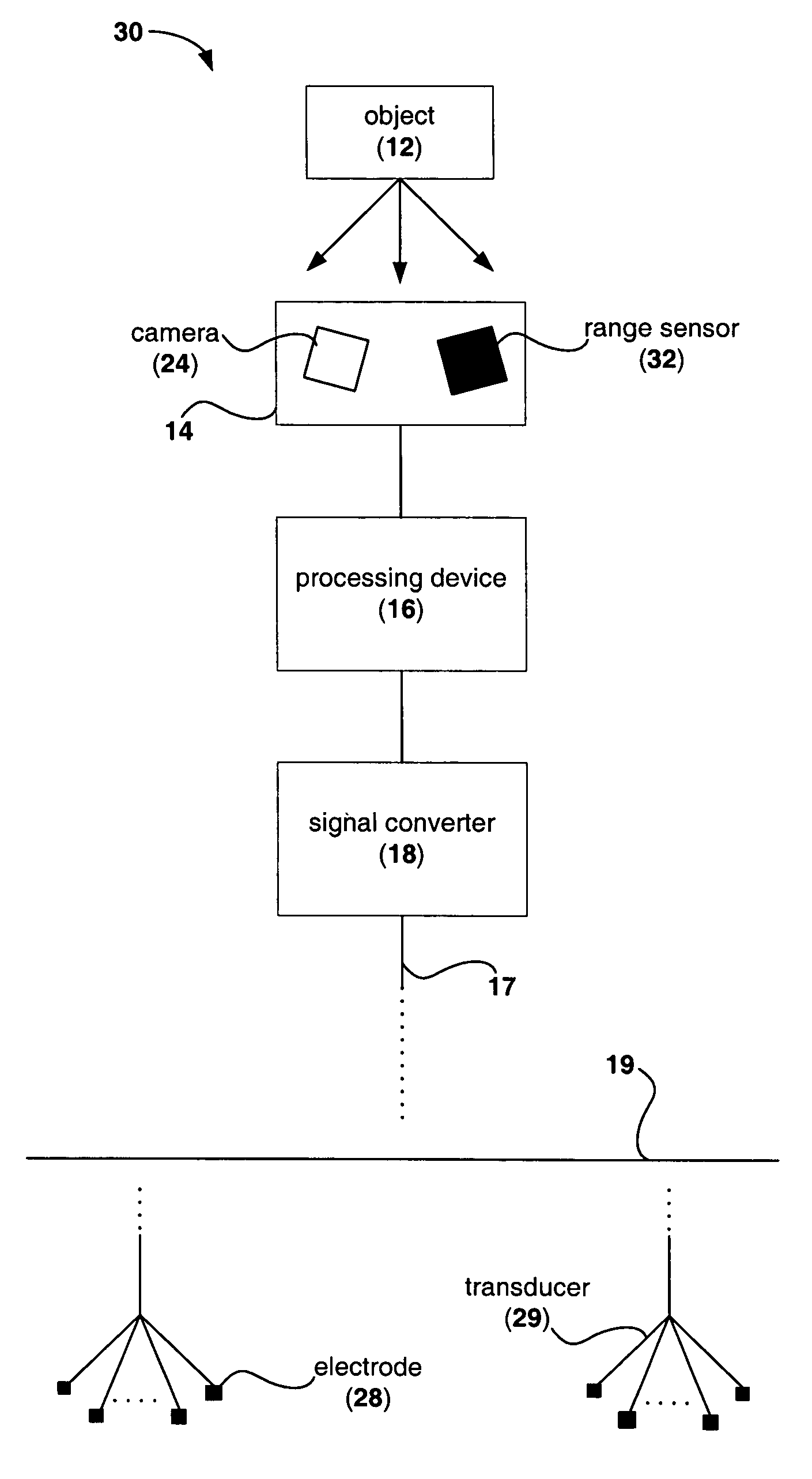
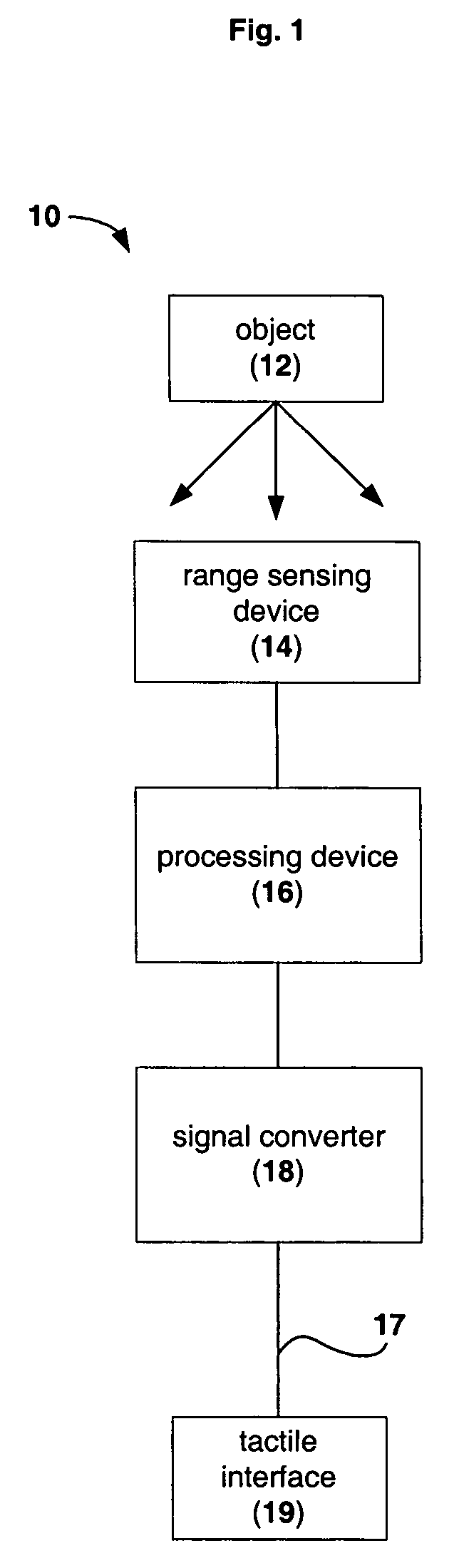
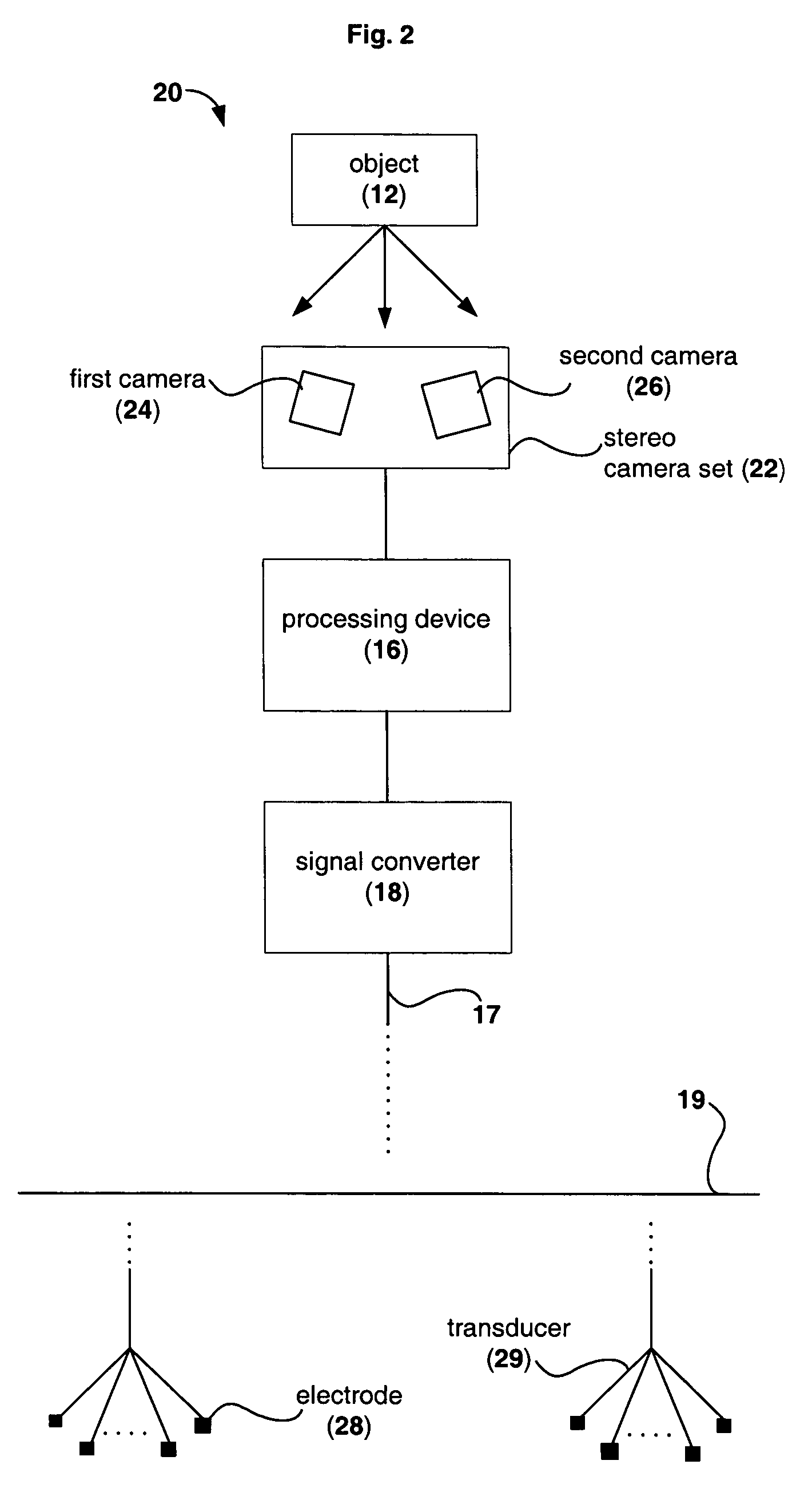
Device for providing perception of the physical environment
Owner:UNIV OF WOLLONGONG
Composite right/left-handed transmission line based compact resonant antenna for RF module integration
ActiveUS7446712B2Improve efficiencyAccurate manufacturing capabilitySimultaneous aerial operationsRadiating elements structural formsMetal-insulator-metalShunt capacitors
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Dual frequency band ultrasound transducer arrays
ActiveUS7727156B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSonificationArray aperture
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +4
High-efficiency light extraction structures and methods for solid-state lighting
InactiveUS20060237735A1Improve performanceImprove lighting effectsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesPhotonicsLight emitting device
A soft solder flowing into the recesses of a semiconductor thin film LED provides: (a) increased bonding strength and better mechanical durability, (b) improved heat dissipation, (c) enhanced light extraction when the LED film is bonded to a new carrier. Annealing localized islands of absorbing metal creates an ohmic contact. Those isolated islands are inter-connected by a layer of a highly reflective metal. This design enables a significant absorption reduction within the LED device and leads to a significant improvement of light extraction. Additionally, the light extraction efficiency of an isotropic light emitting device is improved via surface shaping of the device by a 2D-array of micro-lenses and photonic band gap structure. For manufacturability purpose the making of micron-size lenses of the surface of the chip may preferably be performed as a final step, preferably with optical lithography.
Owner:DICON FIBEROPTICS
Photonic Via Waveguide for Pixel Arrays
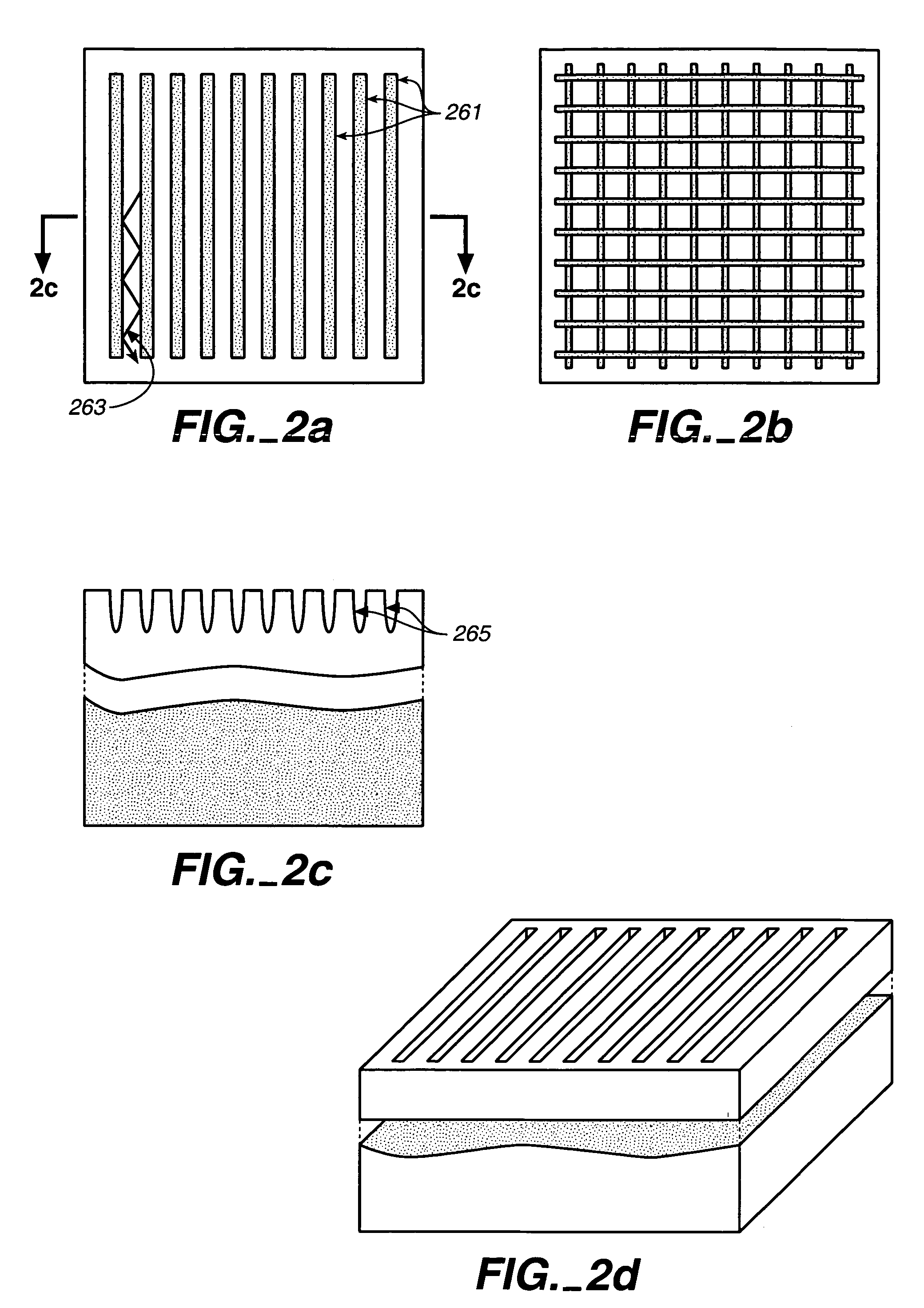
Photonic passive structure to couple and guide light between photonic active devices (101), such as photo-diodes, light emitting devices and light-valves, which may be arranged into 2D arrays, and the top of the metallization layer stack (110,111,112) interconnecting said devices, with said photonic passive structure comprising a hole (116) between the near surface of said photonic active Ndevices and the top of said metallization stack, said hole being filled with a dielectric (113) having embedded metal films (117) and in which the embedded metal thin films are connected to a planar perforated metal film (123,124) formed on top of the metallization stack.
Owner:QUANTUM SEMICON
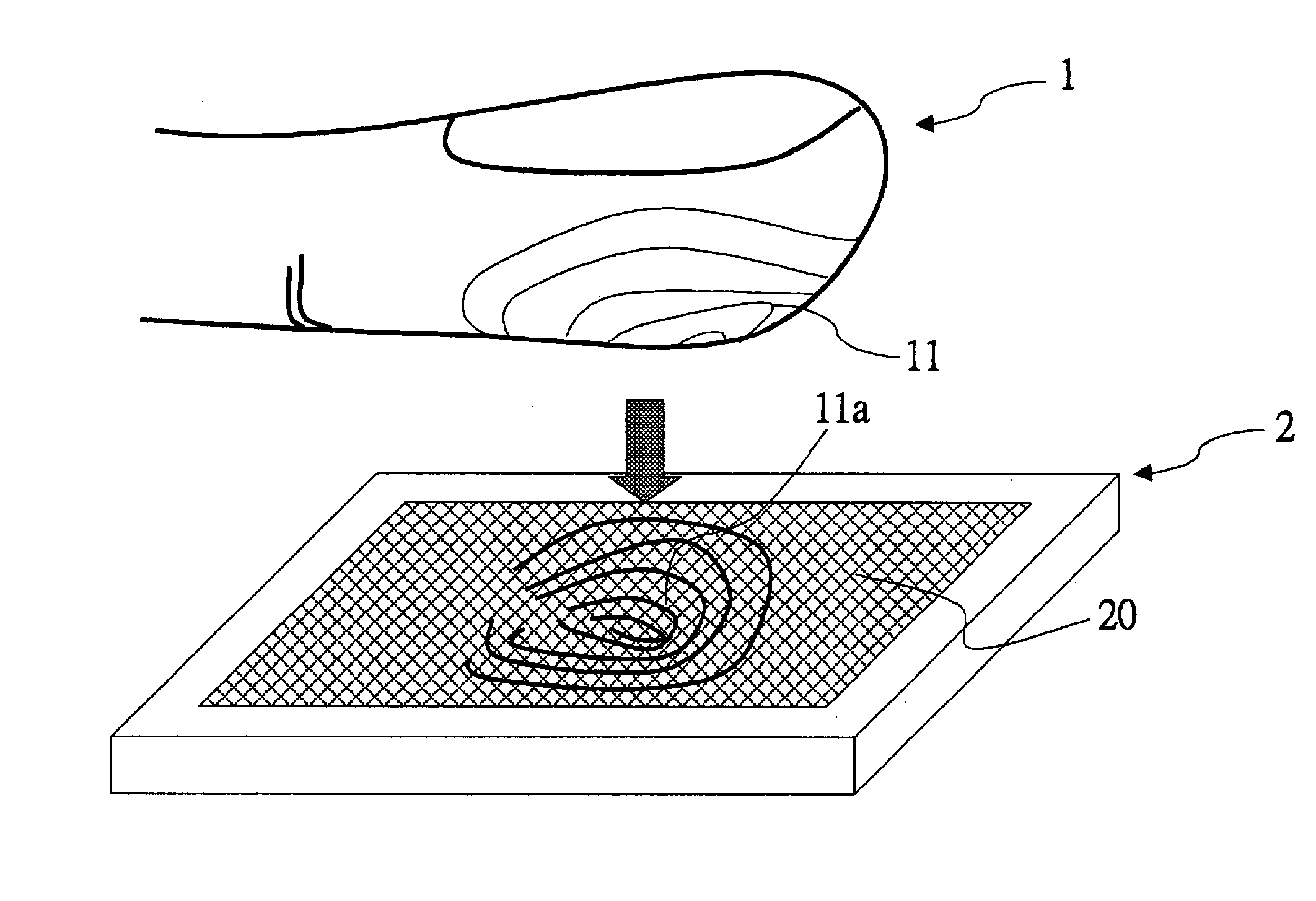
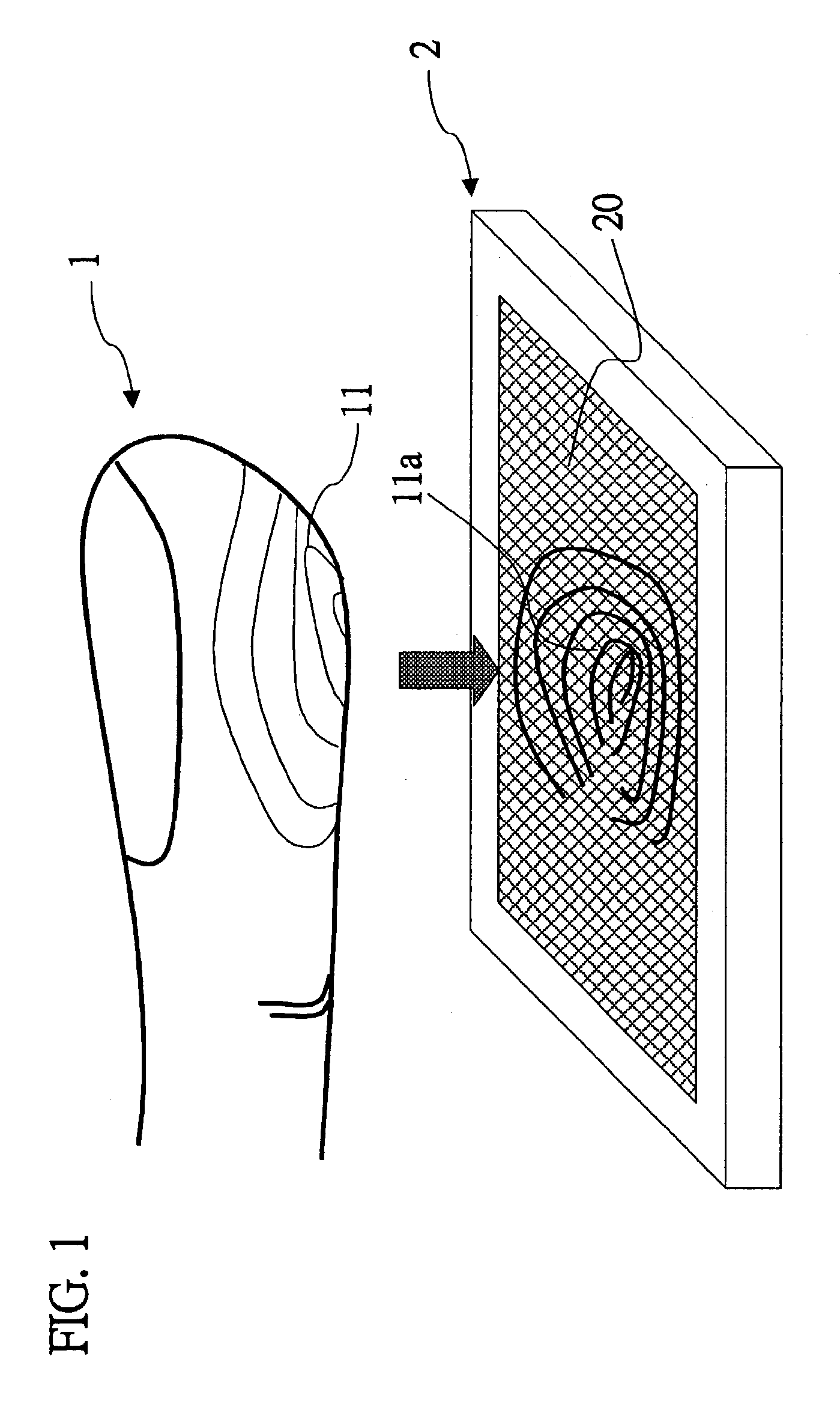
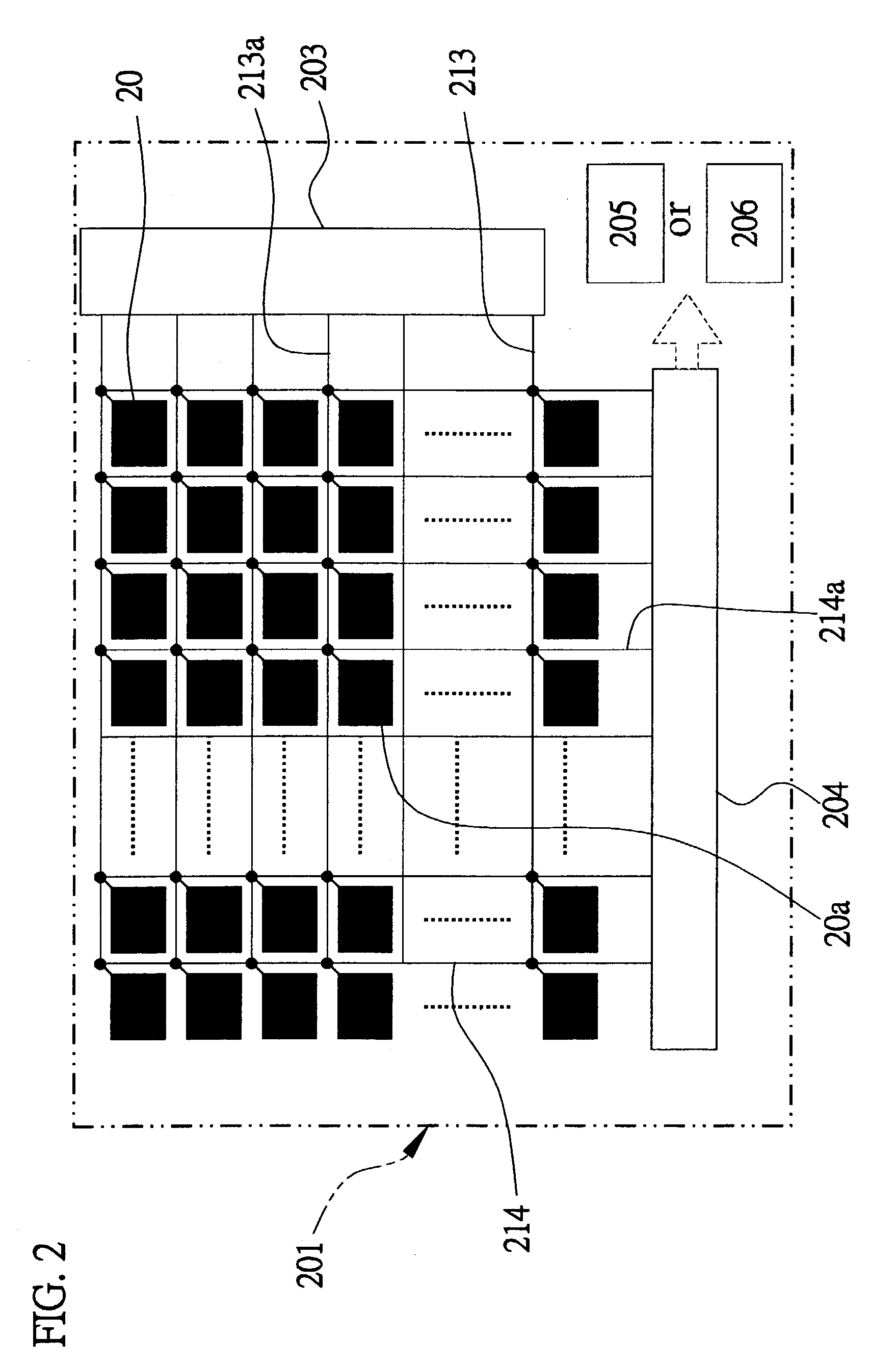
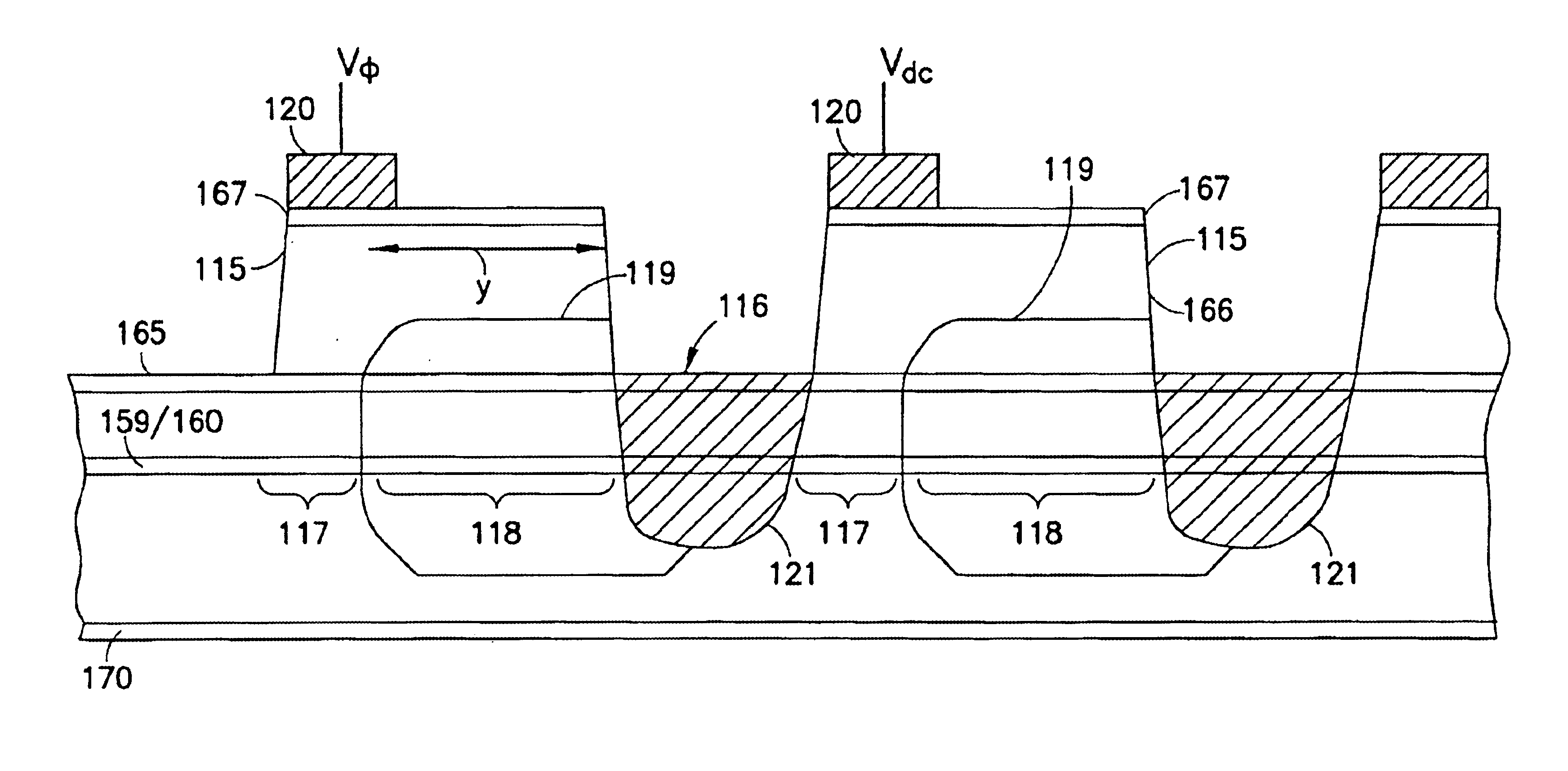
Capacitive fingerprint sensor
ActiveUS7099497B2Person identificationElectric/magnetic contours/curvatures measurementsCapacitance2d array
A capacitive fingerprint sensor includes a plurality of capacitive sensing members arranged in a 2D array. A charge-sharing principle is utilized to read signals in the capacitive sensing member. Each capacitive sensing member includes an insulating surface layer, a sense electrode, a reference electrode, a reference capacitor, and a signal reading circuit. The sense electrode is below the insulating surface layer. When a finger contacts the insulating surface layer, a sense capacitor is formed therebetween. The reference capacitor is connected between the reference and sense electrodes. The signal reading circuit is connected to the sense and reference electrodes, repeatedly provides control signals to charge the reference capacitor and then enable the reference and sense capacitor to share charges. Finally, the sense voltage of the sense electrode may be read.
Owner:XIANGQUN SCI & TECH
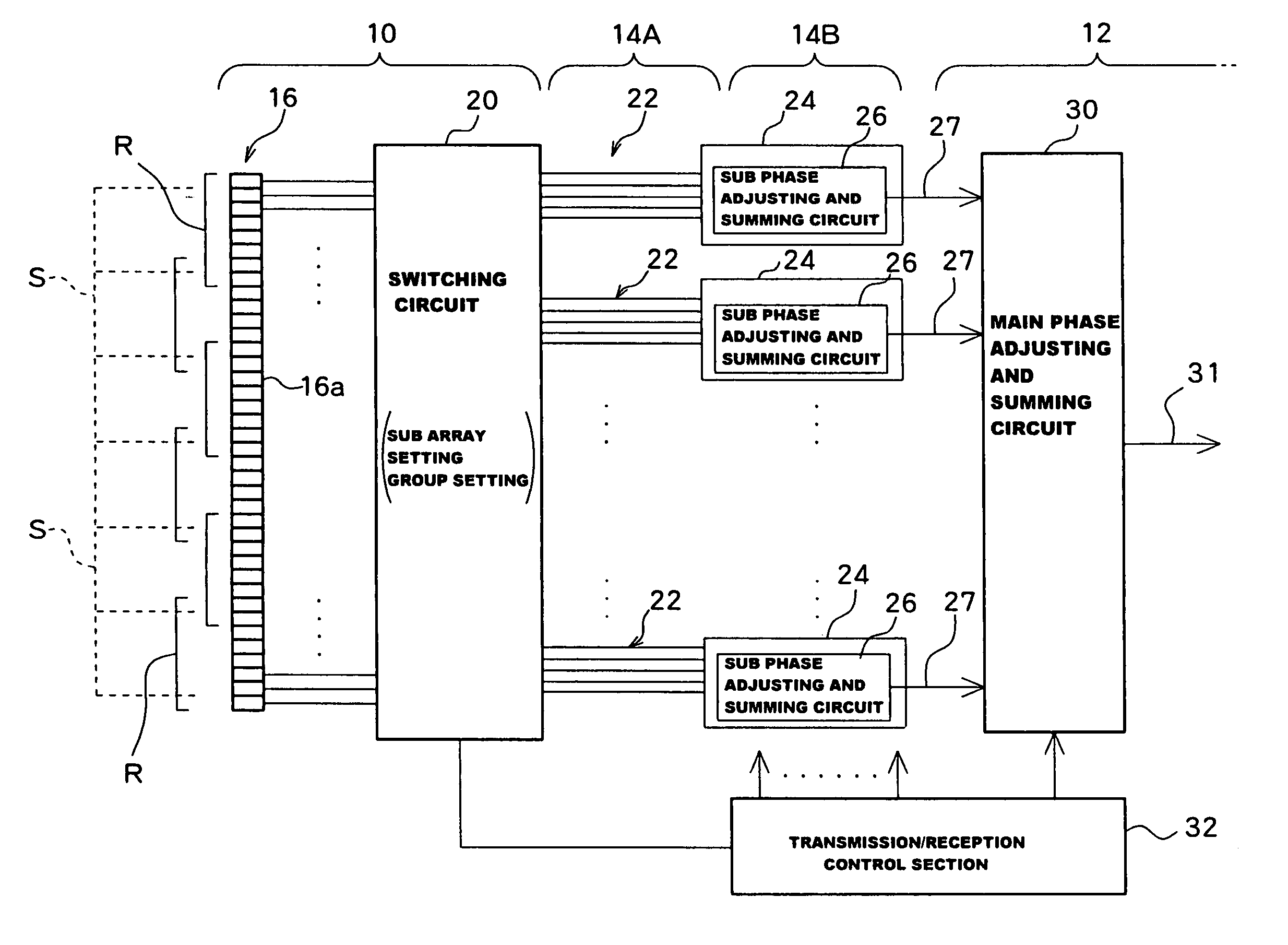
Apparatus and method for phased subarray imaging
InactiveUS7972271B2Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnostics3d imageImaging quality
An invention for coherent array image formation and restoration is taught. The invention is applicable for both 2D and 3D imaging using either 1D or 2D arrays, respectively. A transducer array is subdivided into subarrays, each subarray having a number of adjacent array elements. All elements of each subarray transmit and receive in parallel. The signals received from each subarray are delayed and summed to form scan lines, or beams. The low-beam-rate beams formed from each subarray are upsampled and interpolated prior to forming high-beam-rate images. Depending on the subarray geometry, a subarray-dependent restoration filter is also applied to the subarray beams. The restored beams from each subarray are combined to form the final high-beam-rate image. The invention significantly reduces the front-end hardware complexity compared to conventional methods such as full phased array imaging with comparable image quality.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
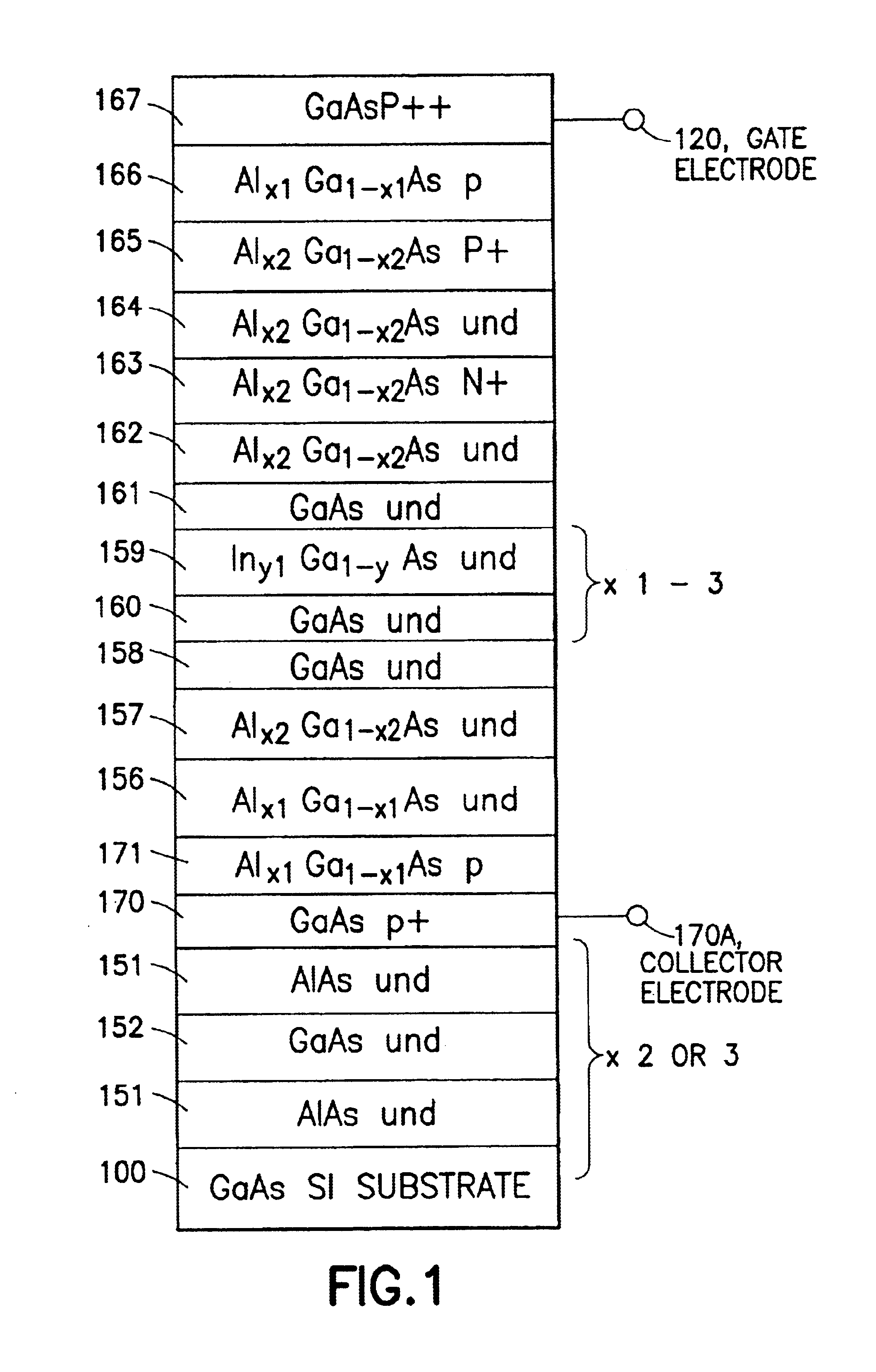
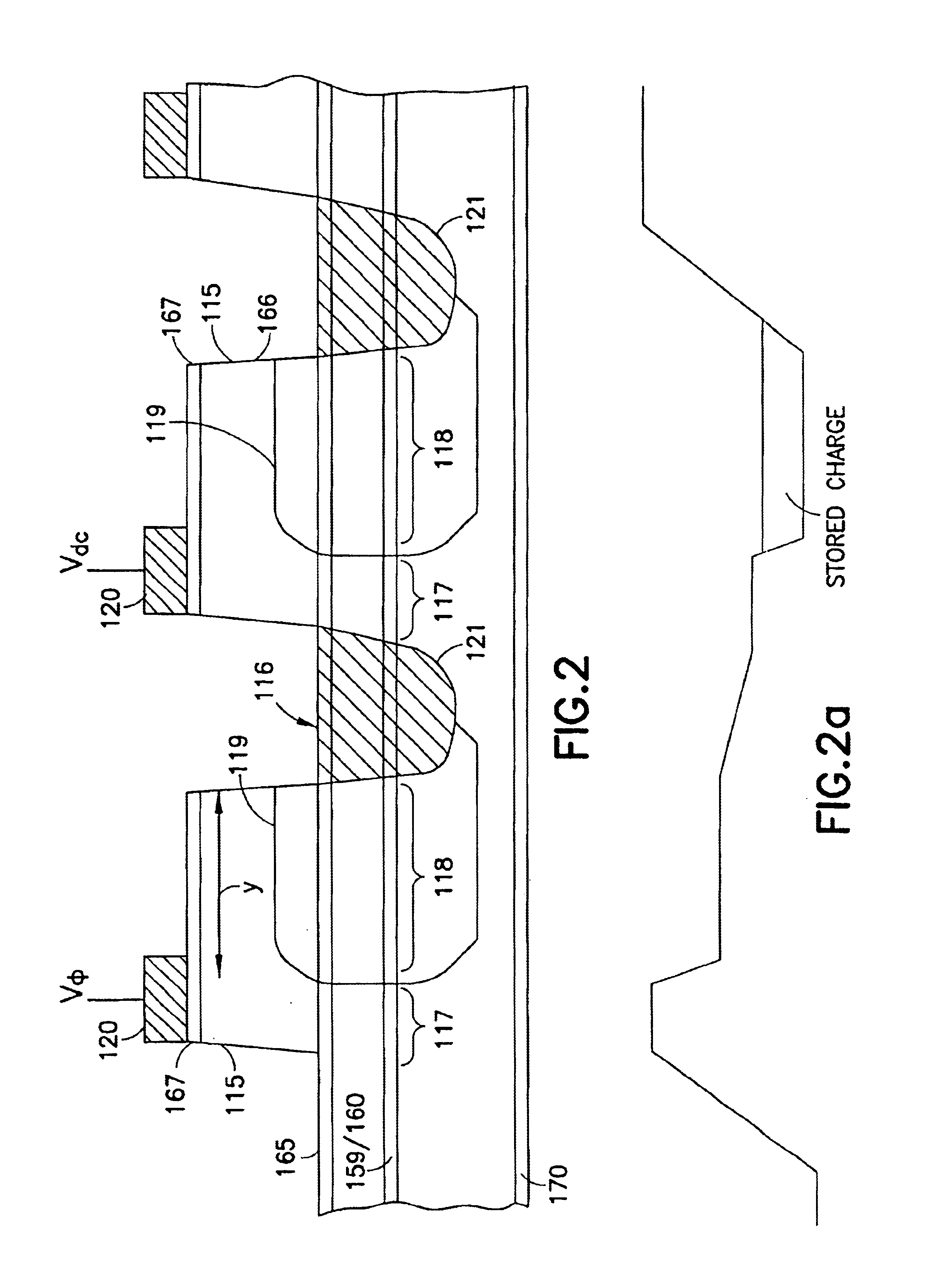
III-V charge coupled device suitable for visible, near and far infra-red detection
InactiveUS6870207B2Optimized drift velocityLower resistanceSolid-state devicesNanoopticsFar infraredElectron
A photon detector is obtained by using the intersubband absorption mechanism in a modulation doped quantum well(s). The modulation doping creates a very high electric field in the well which enables absorption of input TE polarized light and also conducts the carriers emitted from the well into the modulation doped layer from where they may recombine with carriers from the gate contact. Carriers are resupplied to the well by the generation of electrons across the energy gap of the quantum well material. The absorption is enhanced by the use of a resonant cavity in which the quantum well(s) are placed. The absorption and emission from the well creates a deficiency of charge in the quantum well proportional to the intensity of the input photon signal. The quantity of charge in the quantum well of each detector is converted to an output voltage by transferring the charge to the gate of an output amplifier. The detectors are arranged in the form of a 2D array with an output amplifier associated with the entire array or a row of the array as in the known charge coupled devices, or a separate amplifier could be dedicated to each pixel as in the known architecture of the active pixel device. This detector has the unique advantage of near room temperature operation because the dark current is limited to the generation across the semiconductor bandgap and not the emission over the quantum well barrier. The detector also has the advantage that the readout circuitry is implemented monolithically by the HFETs formed in the GaAs substrate simultaneously, with the detecting elements.
Owner:UNIV OF CONNECTICUT
Apparatus and method for phased subarray imaging
InactiveUS20050101867A1Reduction front-end electronic complexityLow beam rateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsImaging quality3d image
An invention for coherent array image formation and restoration is taught. The invention is applicable for both 2D and 3D imaging using either ID or 2D arrays, respectively. A transducer array is subdivided into subarrays, each subarray having a number of adjacent array elements. All elements of each subarray transmit and receive in parallel. The signals received from each subarray are delayed and summed to form scan lines, or beams. The low-beam-rate beams formed from each subarray are upsampled and interpolated prior to forming high-beam-rate images. Depending on the subarray geometry, a subarray-dependent restoration filter is also applied to the subarray beams. The restored beams from each subarray are combined to form the final high-beam-rate image. The invention significantly reduces the front-end hardware complexity compared to conventional methods such as full phased array imaging with comparable image quality.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
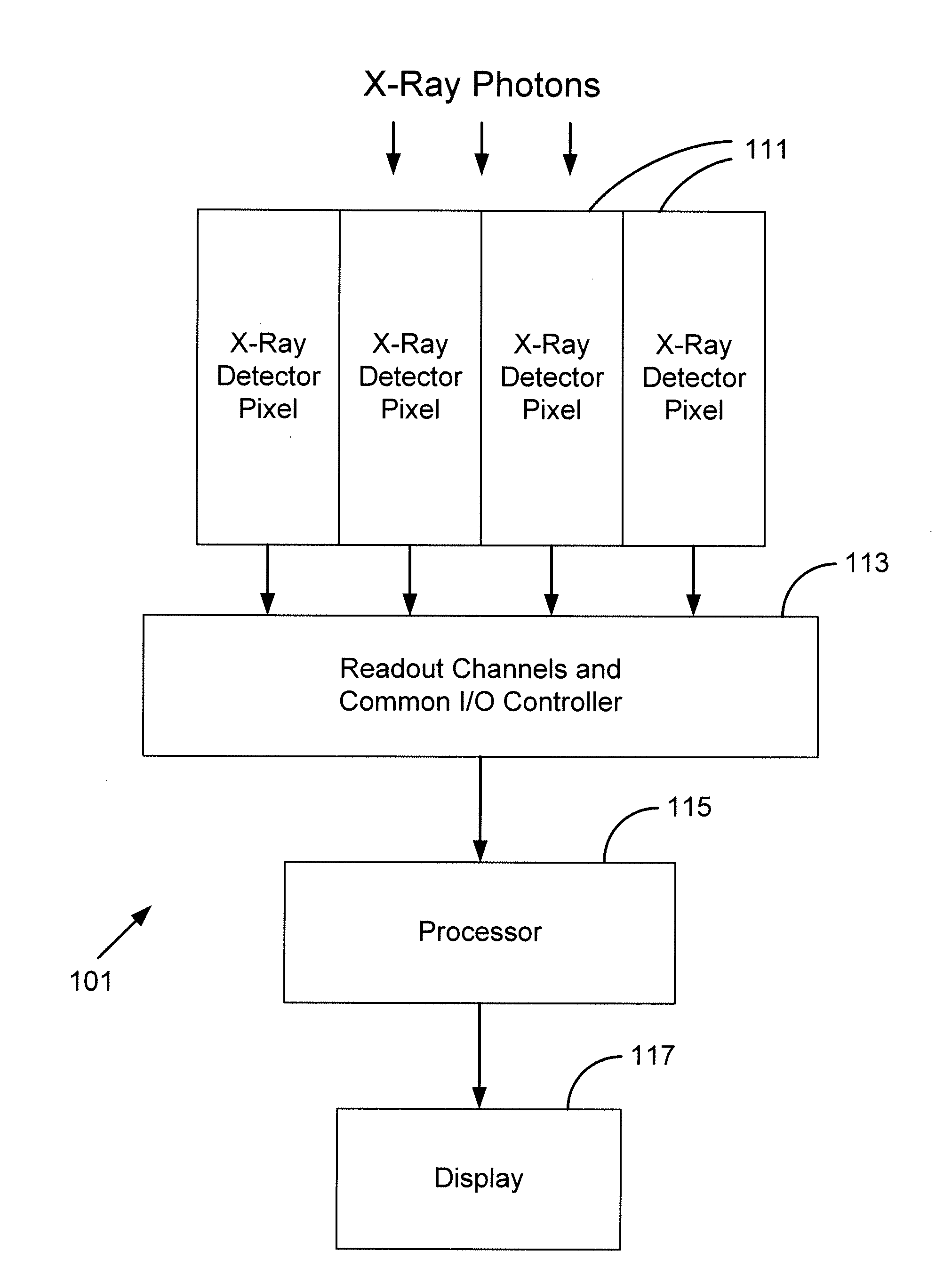
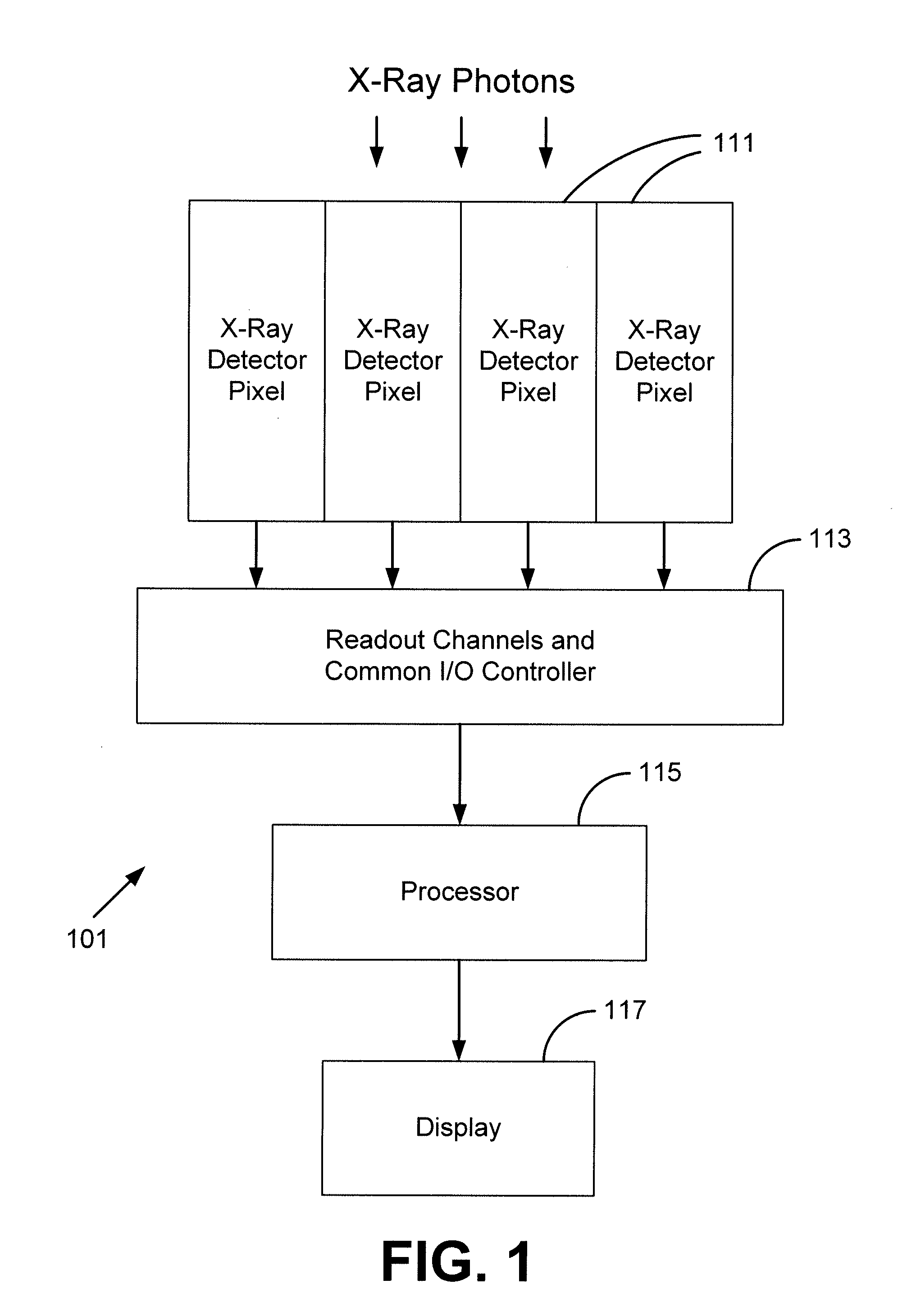
Silicon photomultiplier detector for computed tomography
InactiveUS20100316184A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingSoft x raySilicon photomultiplier
An x-ray detector module including a silicon photomultiplier and a computed tomography imaging system including the same is provided. The x-ray detector module includes optically coupled scintillation materials and silicon photomultiplier pixels. The x-ray detector pixels may have a constant axial profile with a polygonal cross section, which may be rectangular. A plurality of the x-ray detector pixels are generally arranged into 2D arrays. Each x-ray detector pixel may be connected to a dedicated electronic readout channel. In operation, the scintillation materials interact with incident x-ray photons to generate visible-light photons. The silicon photomultiplier pixels generate electrical signals in accordance with the number of visible-light photons generated by an incident x-ray photon. The electronic readout channels process the electrical signals to determine characteristics of the incident x-ray photons. Information of a plurality of x-ray photons are compiled to generate computed tomography images.
Owner:DXRAY
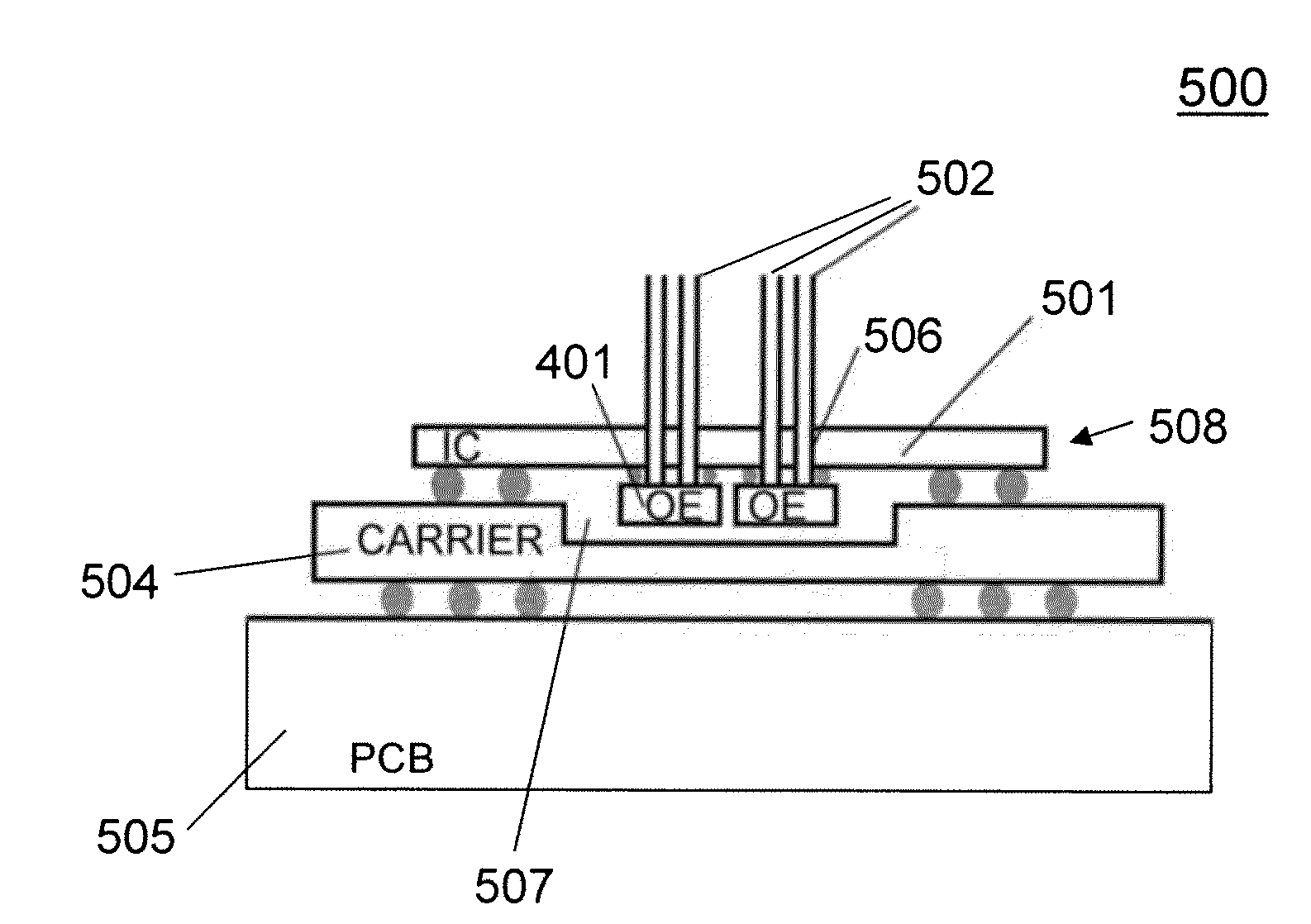
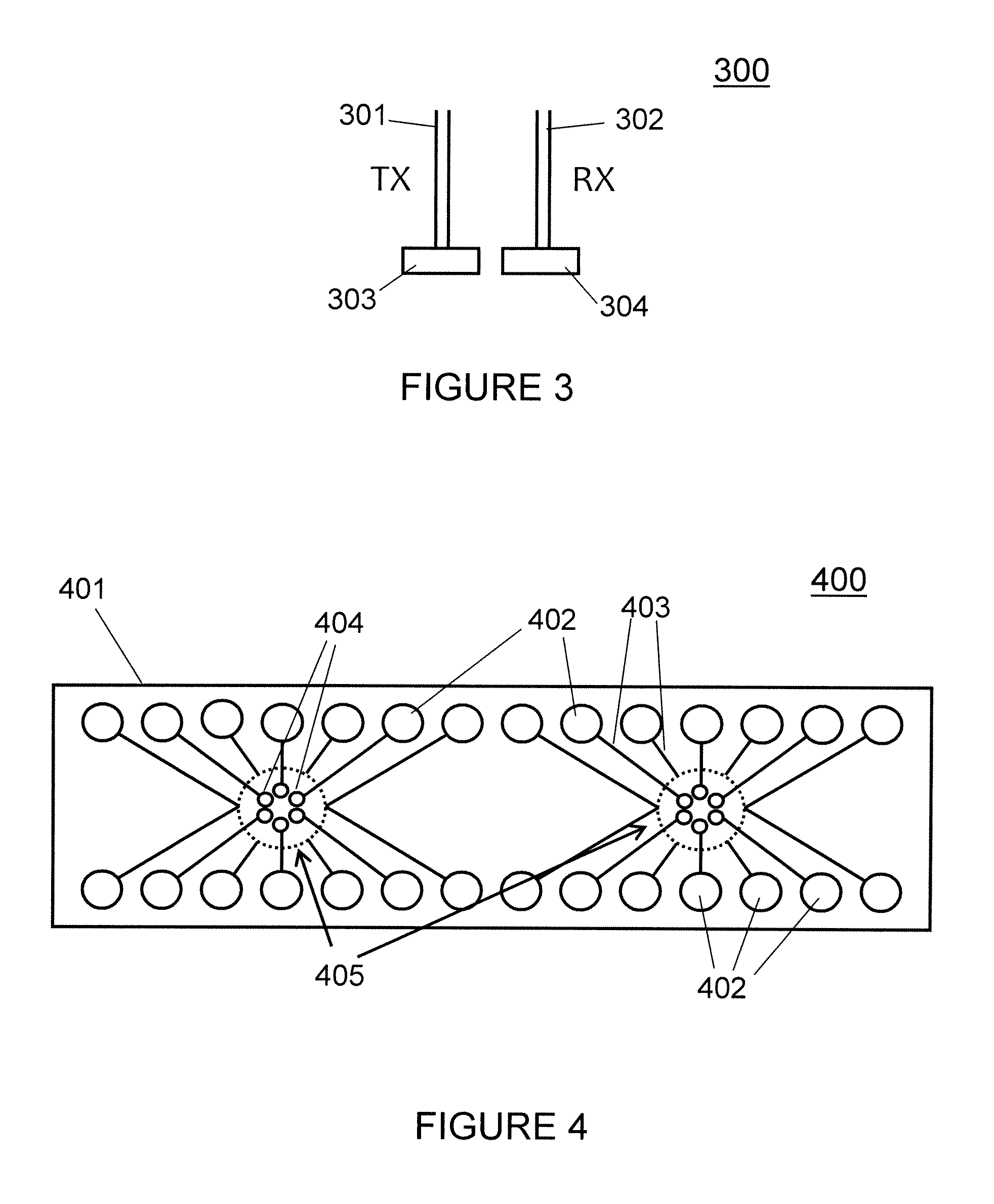
Packaged multicore fiber optical transceiver module
InactiveUS20120014639A1Enhanced couplingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCoupling light guidesTransceiver2d array
A method and structure for coupling to a plurality of multicore optical fiber strands. A first plurality of optoelectronic devices is provided on a surface of a substrate, the first optoelectronic devices being arranged in a 2D array pattern that corresponds to a 2D array pattern corresponding to different light cores of a first multicore optical fiber. A second plurality of optoelectronic devices is provided on the surface of the substrate, the second optoelectronic devices being arranged in a 2D array pattern that corresponds to a 2D array pattern corresponding to different light cores of a second multicore optical fiber. Each optoelectronic device on the substrate surface provides one of a receive function and a transmit function for interacting with a corresponding core of a multicore optical fiber strand.
Owner:IBM CORP
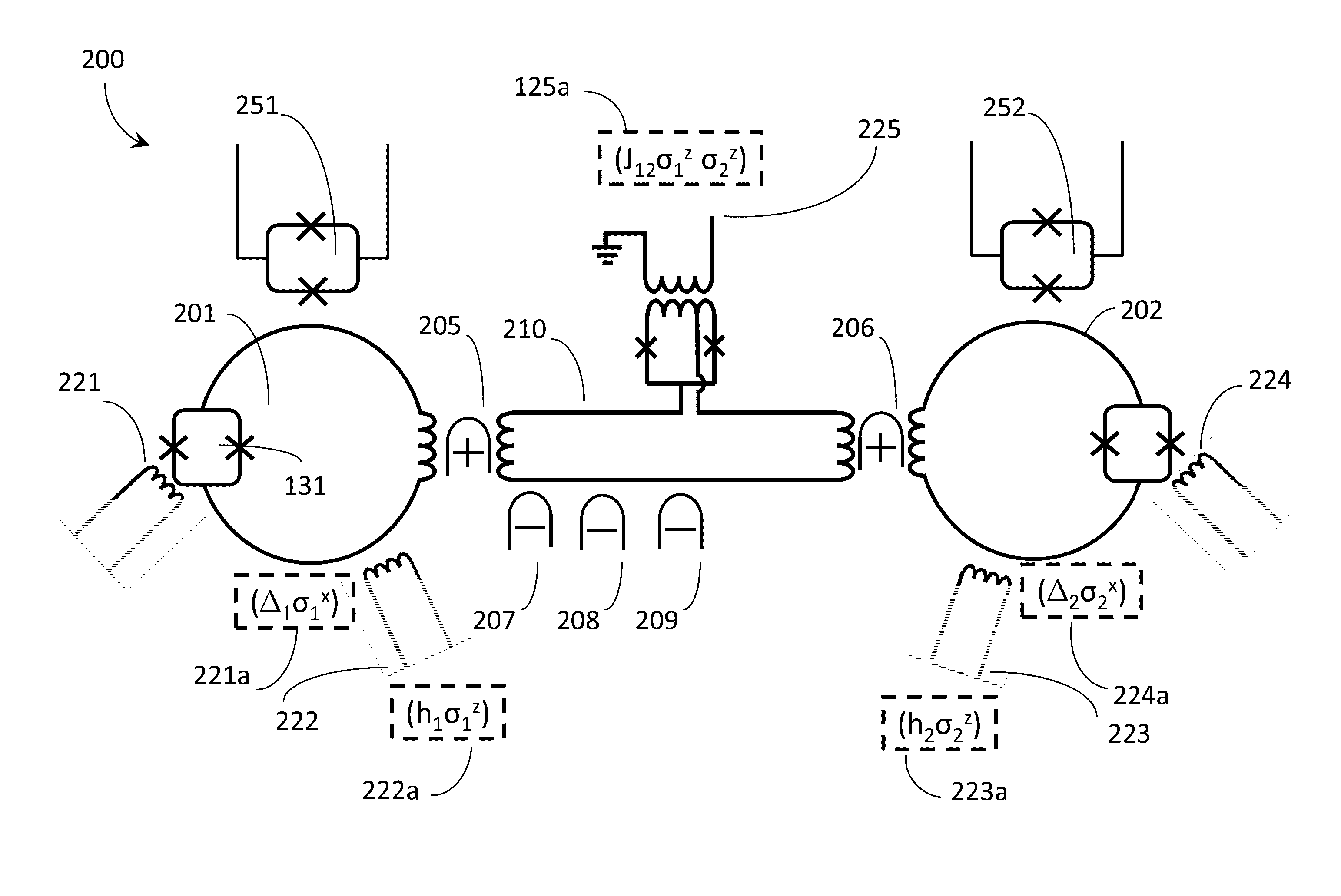
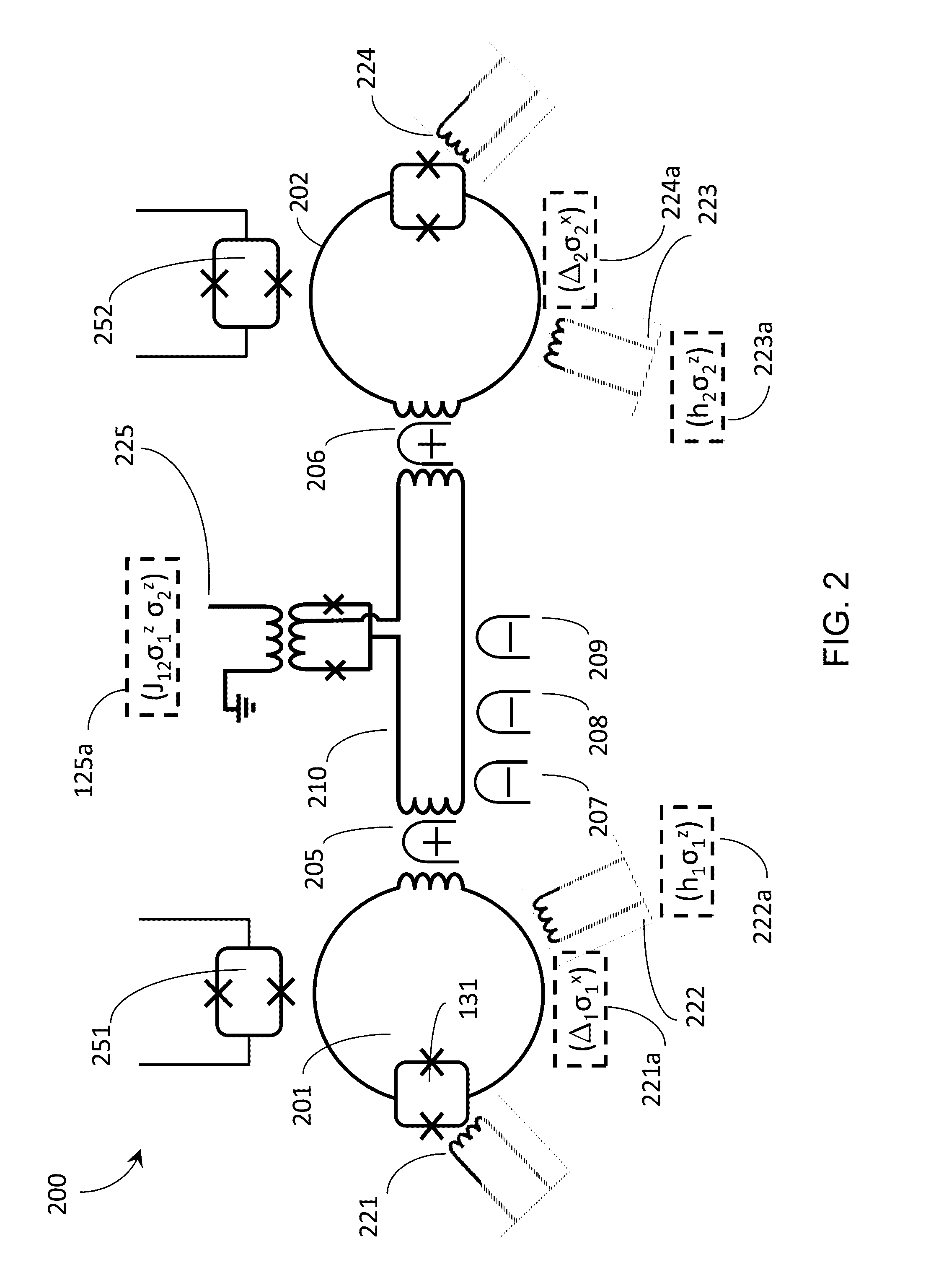
Quantum processor with instance programmable qubit connectivity
ActiveUS20160335558A1Process controlControl complexityQuantum computersDigital computer details2d arrayControl system
In a quantum processor some couplers couple a given qubit to a nearest neighbor qubit (e.g., vertically and horizontally in an ordered 2D array), other couplers couple to next-nearest neighbor qubits (e.g., diagonally in the ordered 2D array). Couplers may include half-couplers, to selectively provide communicative coupling between a given qubit and other qubits, which may or may not be nearest or even next-nearest-neighbors. Tunable couplers selective mediate communicative coupling. A control system may impose a connectivity on a quantum processor, different than an “as designed” or “as manufactured” physical connectivity. Imposition may be via a digital processor processing a working or updated working graph, to map or embed a problem graph. A set of exclude qubits may be created from a comparison of hardware and working graphs. An annealing schedule may adjust a respective normalized inductance of one or more qubits, for instance to exclude certain qubits.
Owner:D WAVE SYSTEMS INC
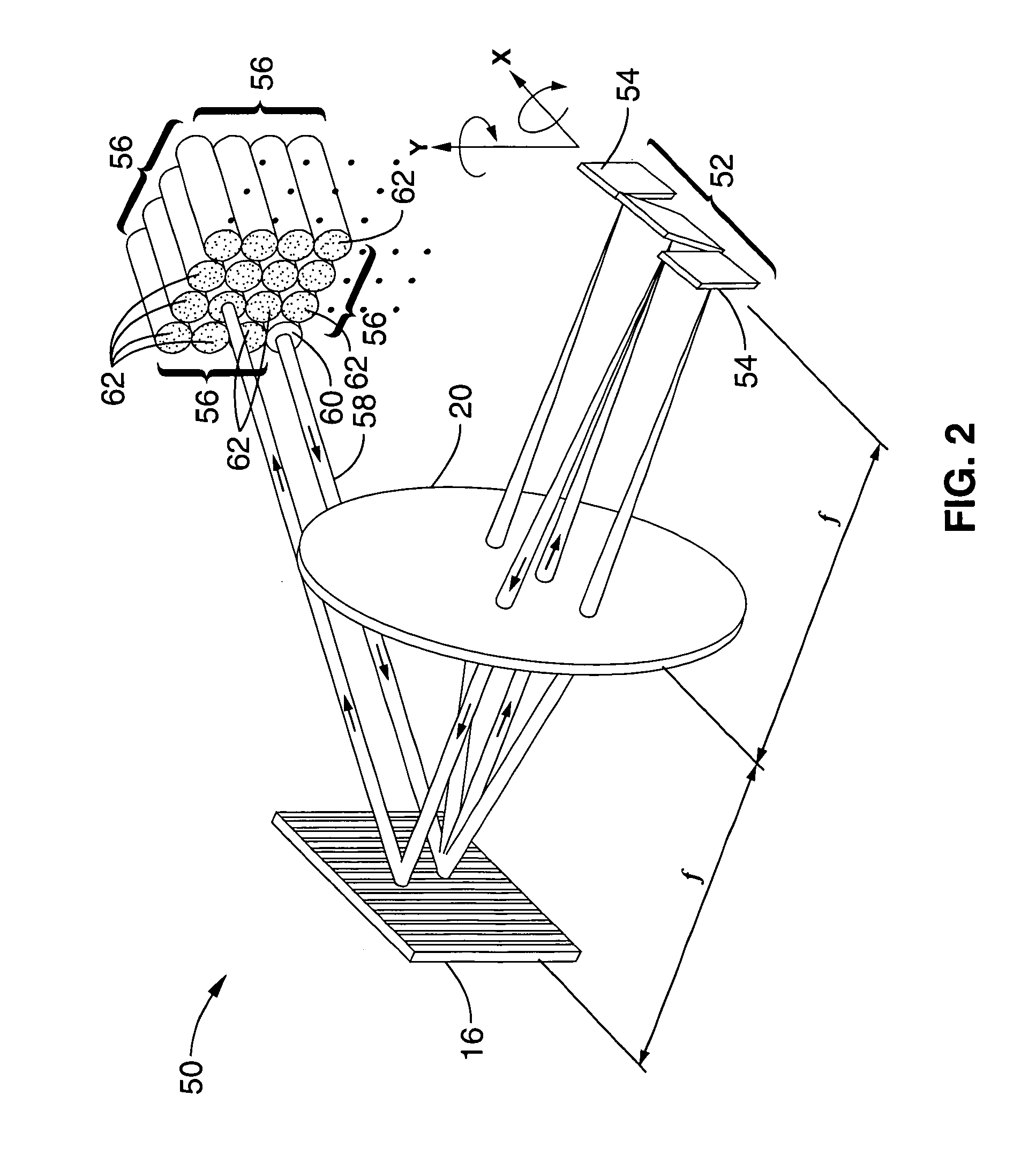
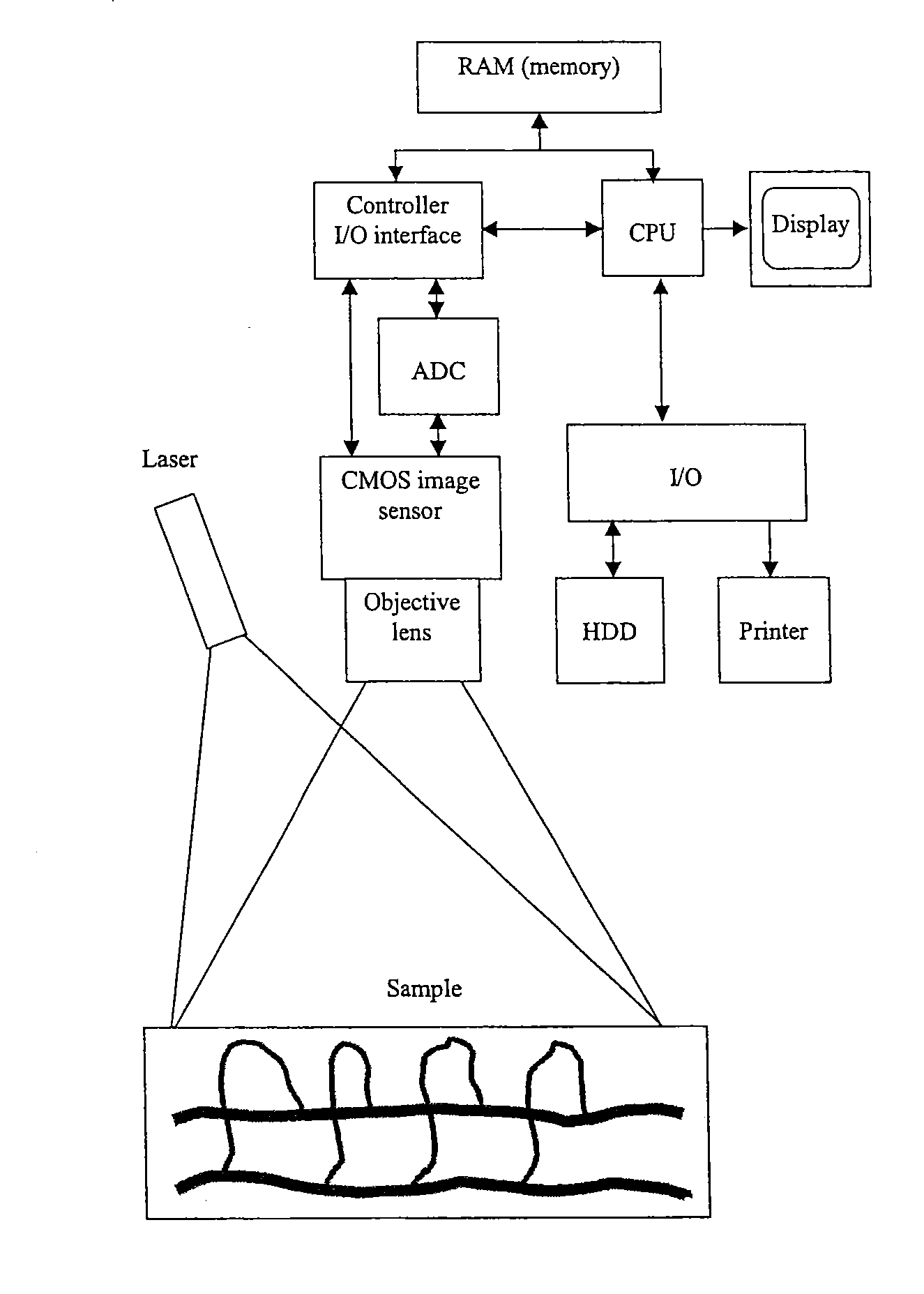
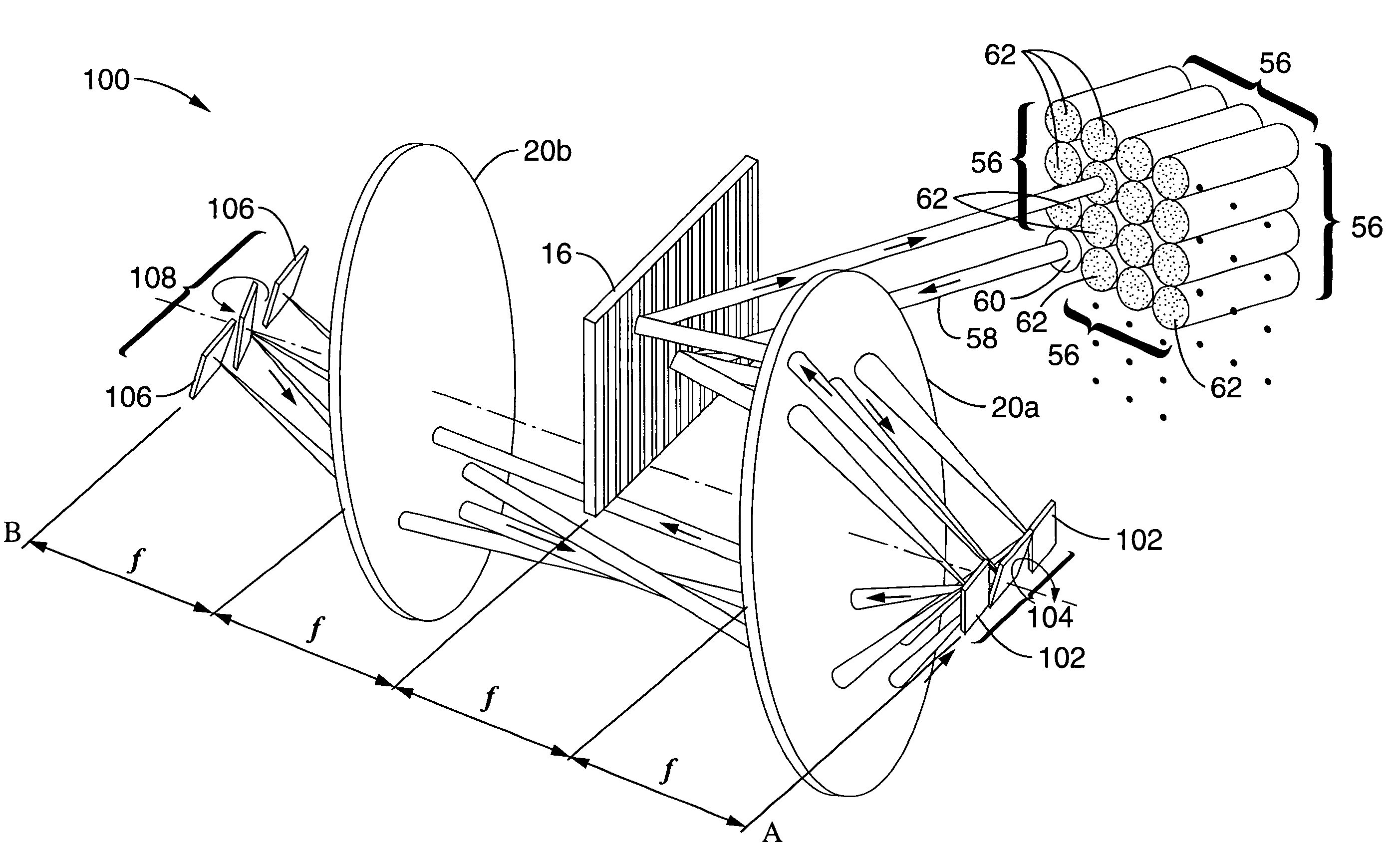
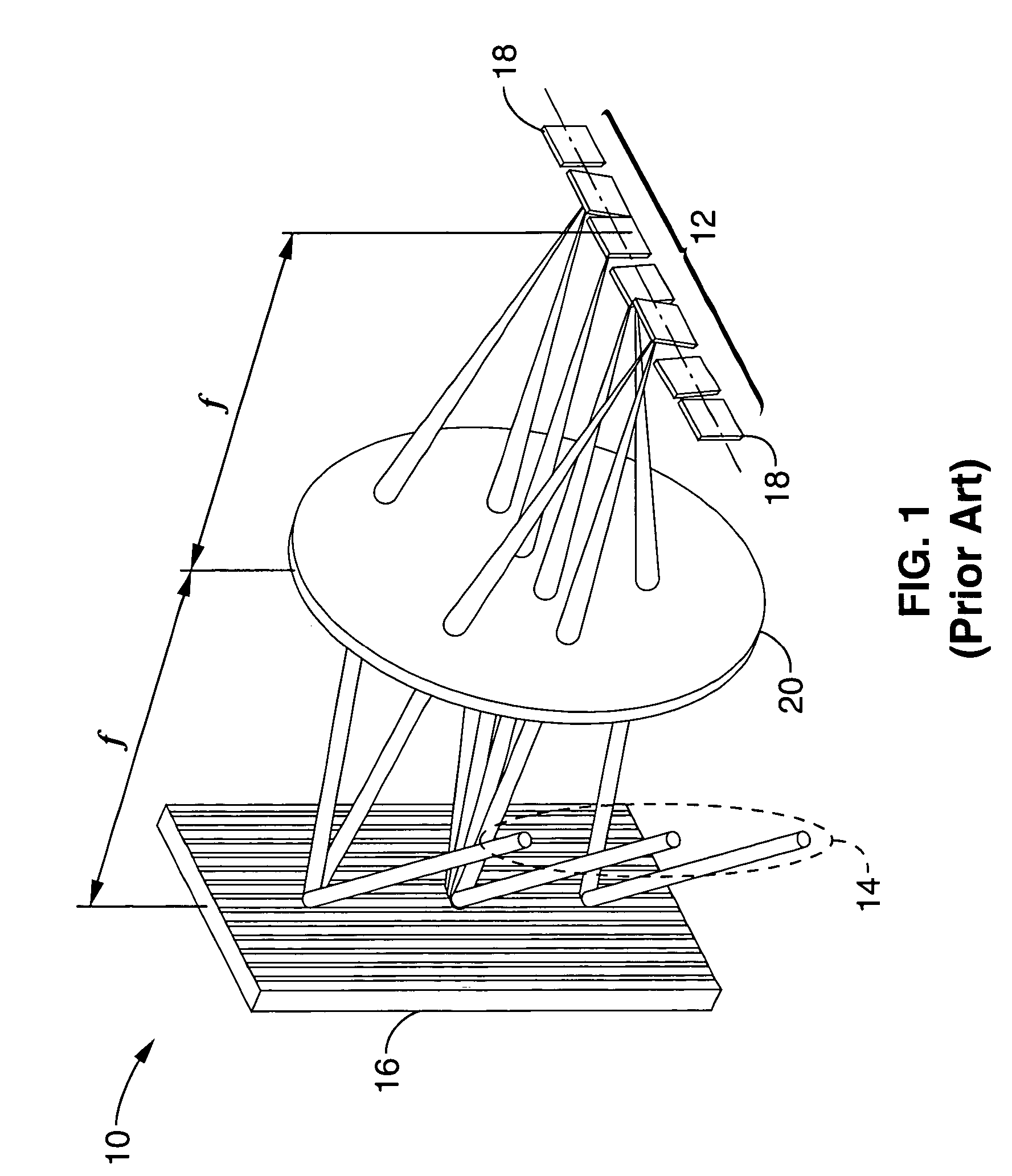
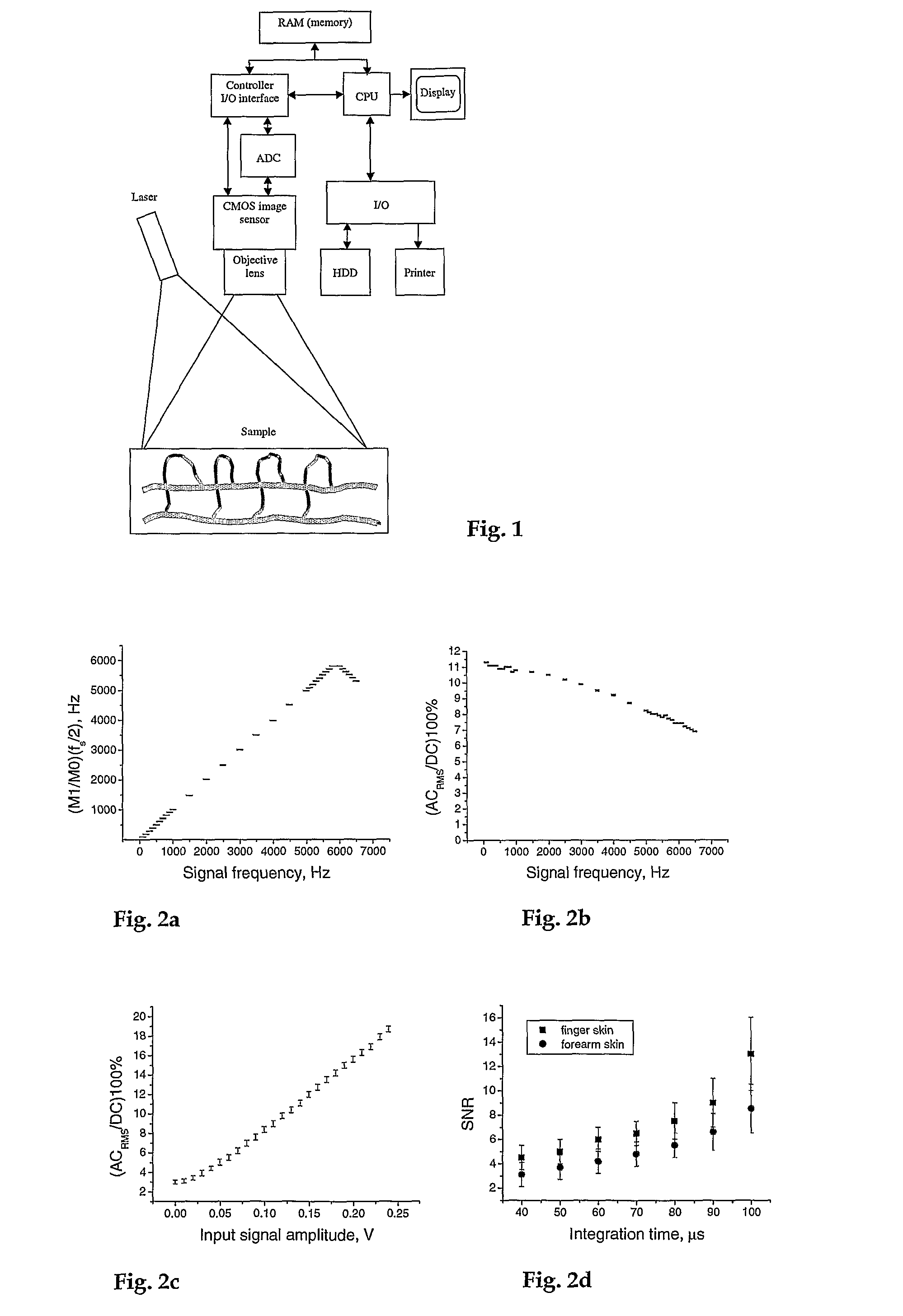
Instrument and Method for High-Speed Perfusion Imaging
A high-speed laser perfusion imaging instrument including a laser source, a detector, a signal-processing unit, data memory, and a screen to display results. A section of a sample surface is illuminated with laser light; reemitted light from the irradiated surface is collected by focusing optics on a 2D array of integrating photodetectors having elements that can be accessed individually or in a pre-defined selection of pixels at high speed. This 2D array measures intensity variations at each individual pixel. Average amplitude and mean frequency of the measured signal contain information about concentration and speed of moving blood cells. For real-time imaging, exposure time is used as a parameter to measure relative perfusion changes. These data are stored and processed with the signal-processing unit to deliver 2D flow maps of the illuminated sample section, and allow a simple overlay between a conventional image and processed flow maps.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Volumetric computed tomography (VCT)
InactiveUS20060002506A1Fast and reliableMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handling2d arrayX-ray
The present invention provides a volumetric computed tomography (VCT) system capable of producing data for reconstructing an entire three-dimensional (3D) image of a subject during a single rotation without suffering from cone beam artifacts. The VCT system comprises an array of source positions distributed along a line parallel to an axis of rotation, a plurality of collimators, and an array of x-ray detectors. In a preferred embodiment, a reversed imaging geometry is used. A 2D array of source positions provides x-rays emanating from each focal spot toward an array of detectors. The x-rays are restricted by a collimator array and measured by a detector array separately per each source position. The axial extent of the source array and the detector array are comparable to or larger than the axial extent of the portion of the object being imaged.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Ultrasound diagnosis apparatus
InactiveUS20040267126A1Quality improvementSurgeryHeart/pulse rate measurement devices2d arrayShape change
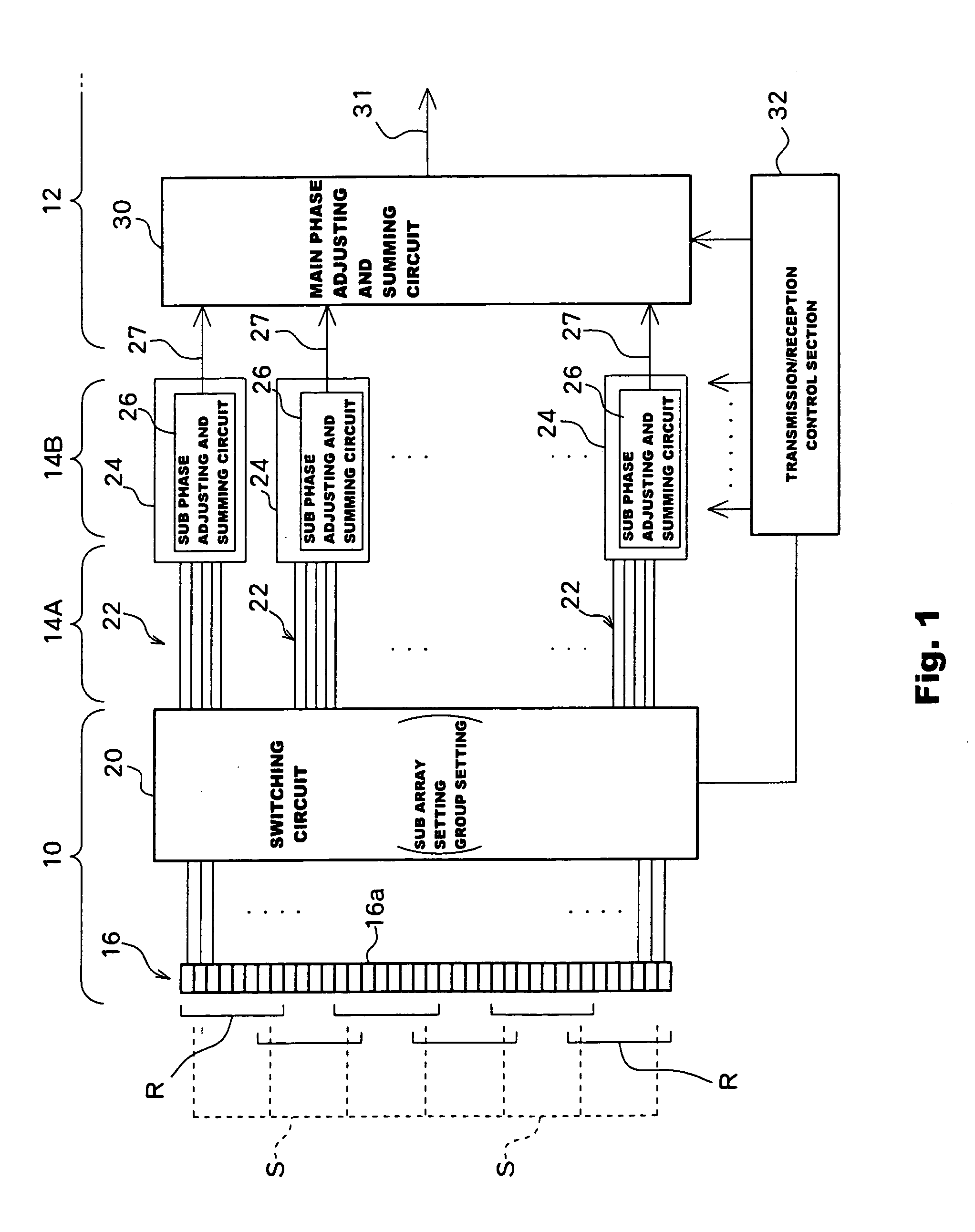
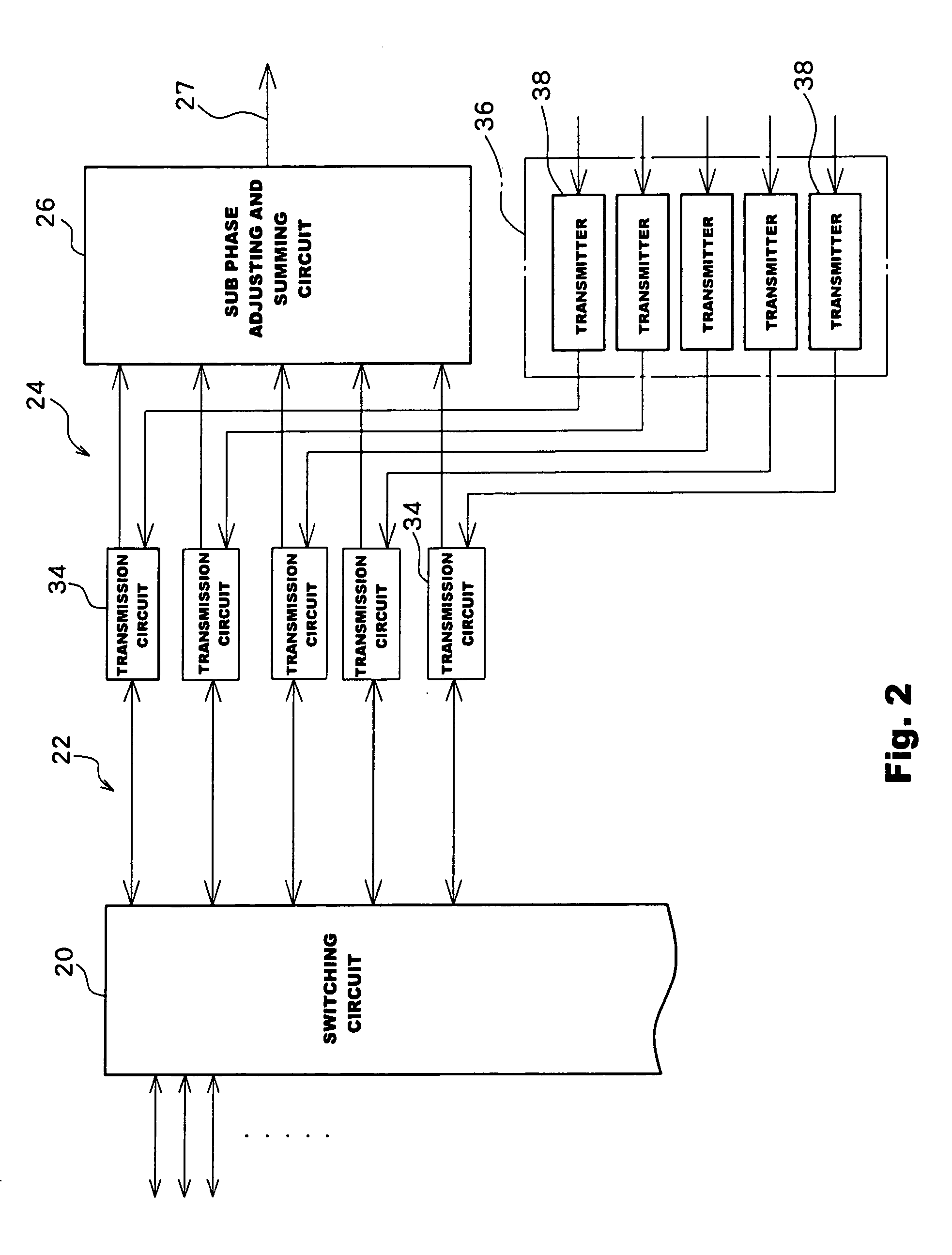
In an ultrasound diagnosis apparatus, a plurality of sub arrays are defined on a 2D array transducer. The sub array shape pattern of each sub array is adaptively changed in accordance with the beam scanning direction. Each sub array is composed of a plurality of groups, each of which is composed of a plurality of transducer elements. With the change of sub array shape pattern in accordance with a beam scanning direction, the group shape pattern of each group also changes. The sub array shape changes for each sub array, and a variable region is determined by the largest outer edge of the shape changed. The variable regions partially overlap with each other among a plurality of sub arrays. On a 2D array transducer, a plurality of sub arrays are always closely coupled with each other even when each sub array shape is changed.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
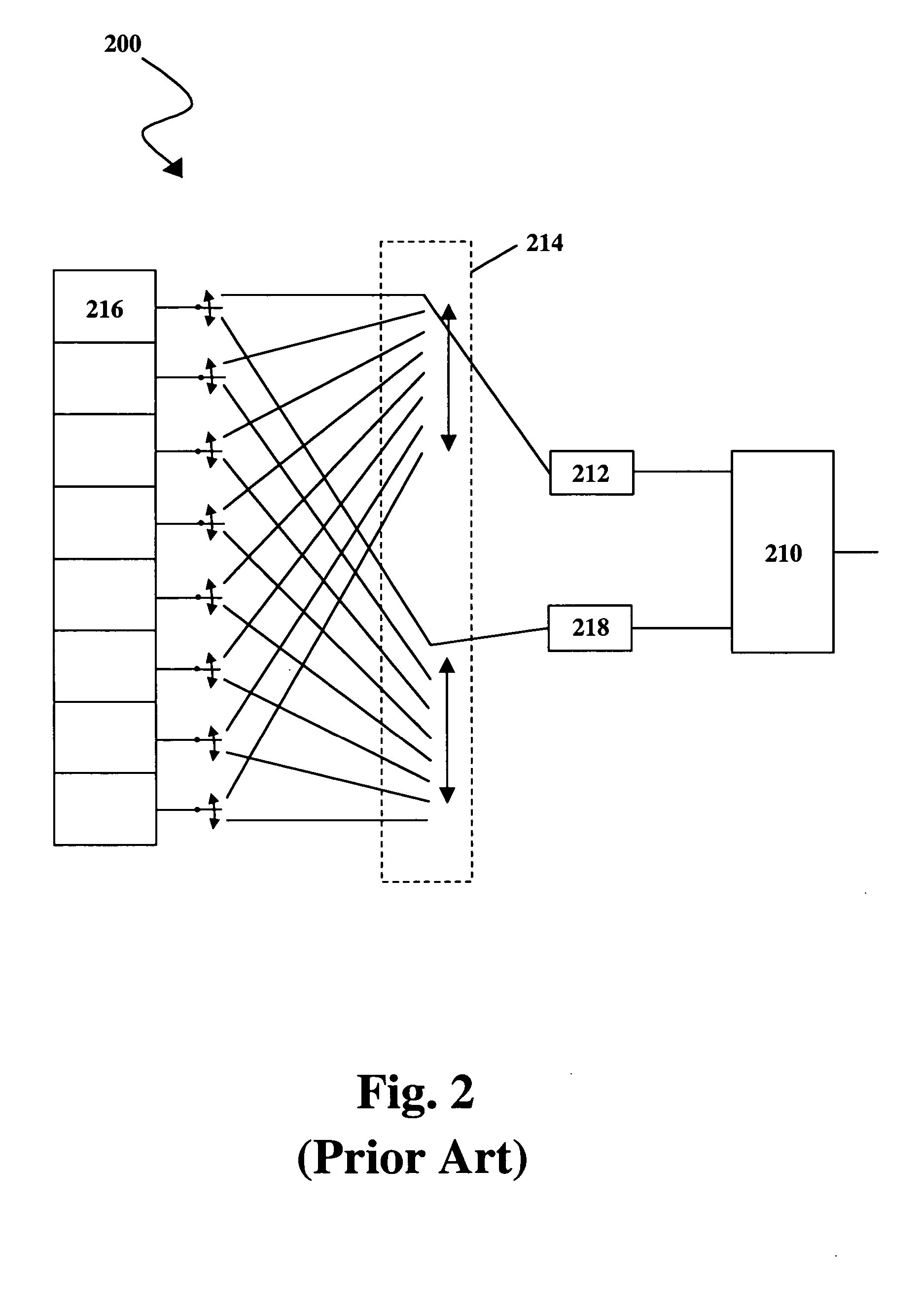
Wavelength-selective 1xN2 switches with two-dimensional input/output fiber arrays
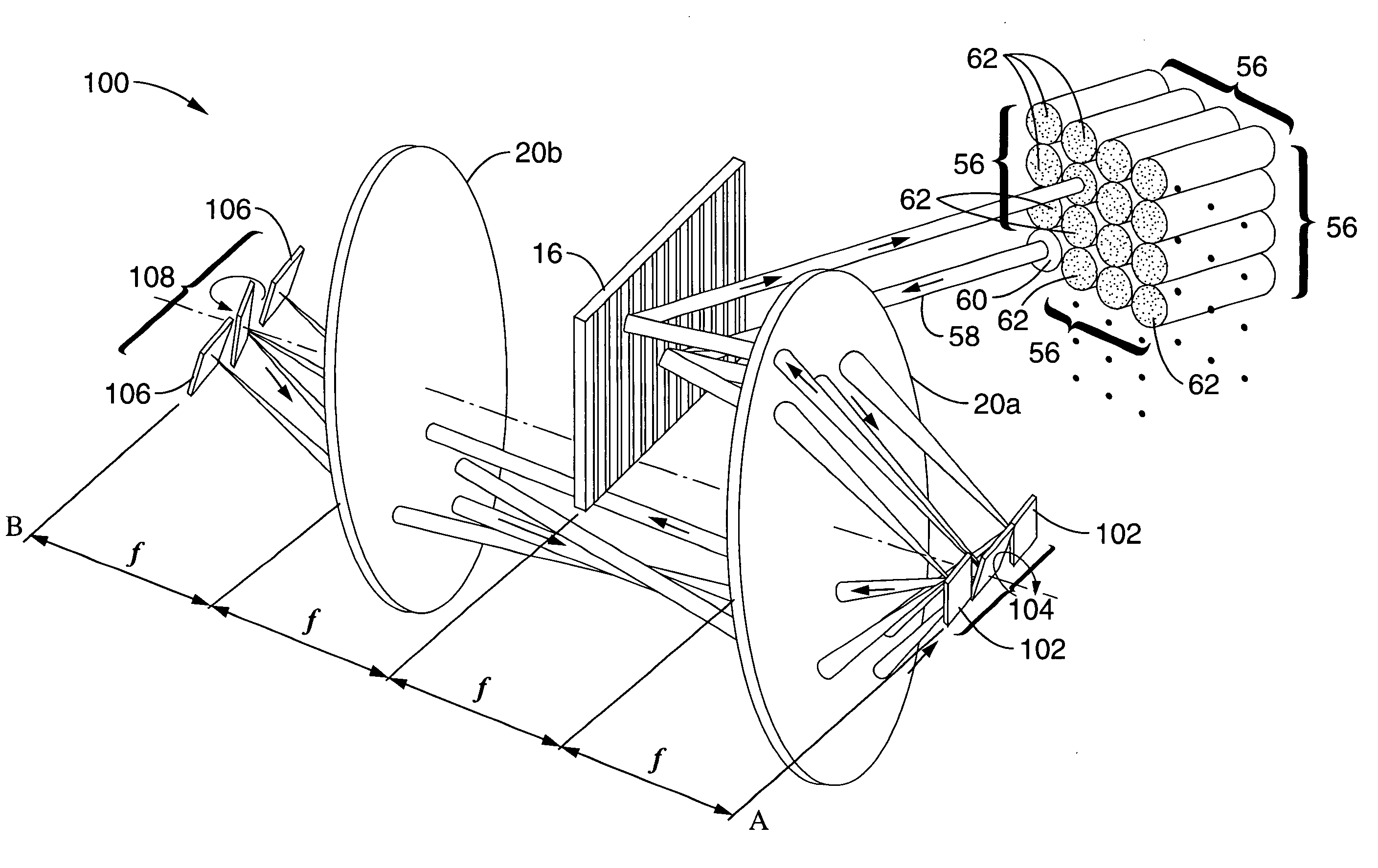
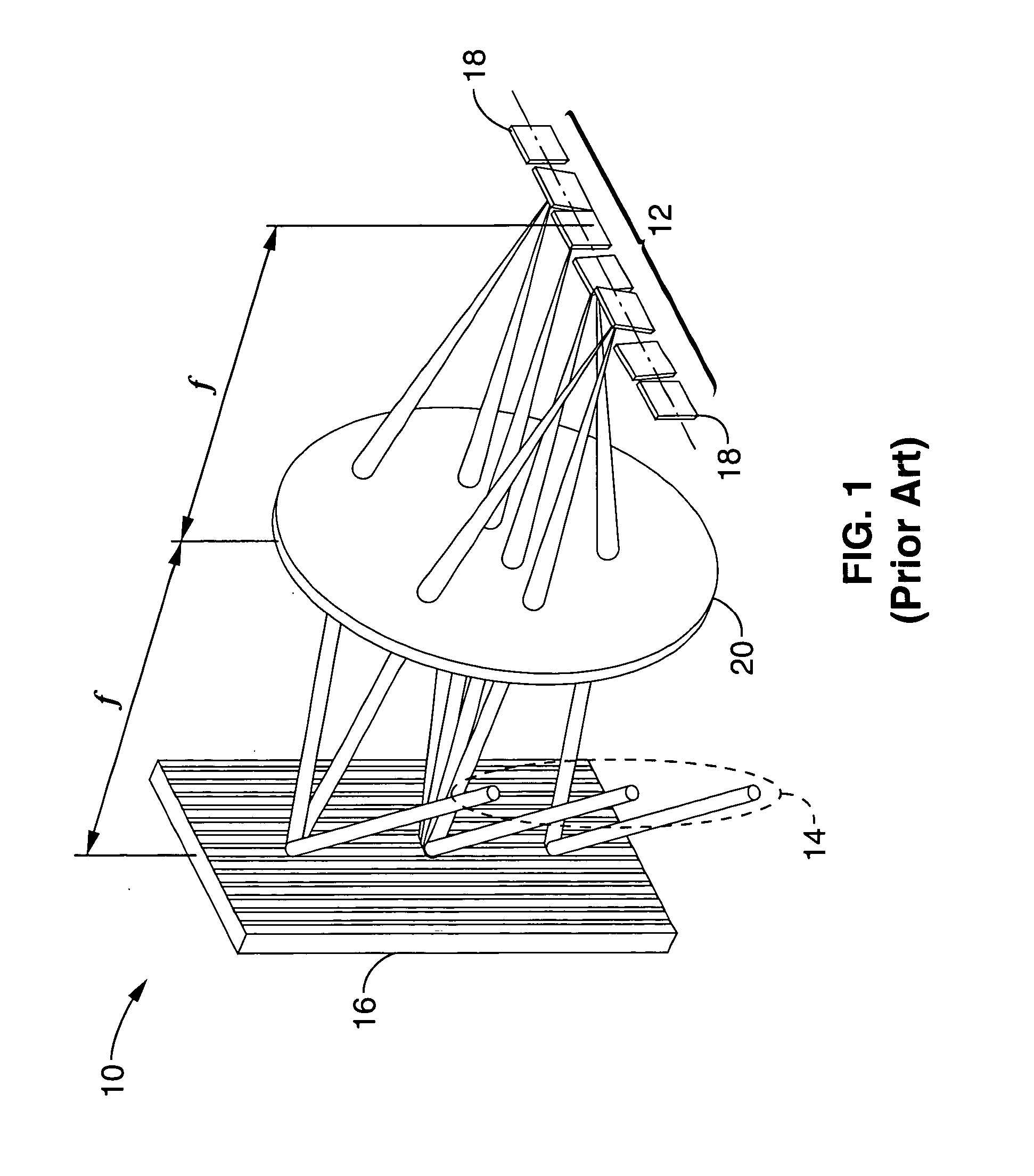
A 1×N2 wavelength selective switch (WSS) configuration in which switch elements are configured in a way that enables the input or output fibers to be arranged in a two-dimensional (2D) array. By employing 2D arrays of input / output channels, the channel count is increased from N to N2 for wavelength selective switches. In one embodiment, in which the components are arranged as a 2-f imaging system, a one-dimensional (1D) array of mirrors is configured such that each mirror has a dual scanning axis (i.e., each mirror can be scanned in X and Y directions). In another embodiment, in which the components are arranged as a 4-f imaging system, two 1D arrays of mirrors are configured with orthogonal scanning directions. In both embodiments, the number of ports is increased from N to N2.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Dual frequency band ultrasound transducer arrays
ActiveUS20070035204A1Eliminate the effects ofUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsPiezoelectric/electrostriction/magnetostriction machinesSonificationArray aperture
Ultrasound probes that transmits / receives ultrasound pulses with frequencies both in a low frequency (LF) and a high frequency (HF) band, where the radiation surfaces of said HF and LF bands at least have a common region. Several solutions for transmission (and reception) of LF and HF pulses through the same radiation surface are given. The arrays and elements can be of a general type, for example linear phased or switched arrays, or annular arrays or elements with division in both azimuth and elevation direction, like a 1.5D, a 1.75D and a full 2D array. The LF and HF element division and array apertures can also be different.
Owner:ANGELSEN BJORN A J +4
Instrument and method for high-speed perfusion imaging
A high-speed laser perfusion imaging instrument including a laser source, a detector, a signal-processing unit, data memory, and a screen to display results. A section of a sample surface is illuminated with laser light; reemitted light from the irradiated surface is collected by focusing optics on a 2D array of integrating photodetectors having elements that can be accessed individually or in a pre-defined selection of pixels at high speed. This 2D array measures intensity variations at each individual pixel. Average amplitude and mean frequency of the measured signal contain information about concentration and speed of moving blood cells. For real-time imaging, exposure time is used as a parameter to measure relative perfusion changes. These data are stored and processed with the signal-processing unit to deliver 2D flow maps of the illuminated sample section, and allow a simple overlay between a conventional image and processed flow maps.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Wavelength-selective 1xN2 switches with two-dimensional input/output fiber arrays
A 1×N2 wavelength selective switch (WSS) configuration in which switch elements are configured in a way that enables the input or output fibers to be arranged in a two-dimensional (2D) array. By employing 2D arrays of input / output channels, the channel count is increased from N to N2 for wavelength selective switches. In one embodiment, in which the components are arranged as a 2-f imaging system, a one-dimensional (1D) array of mirrors is configured such that each mirror has a dual scanning axis (i.e., each mirror can be scanned in X and Y directions). In another embodiment, in which the components are arranged as a 4-f imaging system, two 1D arrays of mirrors are configured with orthogonal scanning directions. In both embodiments, the number of ports is increased from N to N2.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Instrument and method for high-speed perfusion imaging
A high-speed laser perfusion imaging instrument including a laser source, a detector, a signal-processing unit, data memory, and a screen to display results. A section of a sample surface is illuminated with laser light; reemitted light from the irradiated surface is collected by focusing optics on a 2D array of integrating photodetectors having elements that can be accessed individually or in a pre-defined selection of pixels at high speed. This 2D array measures intensity variations at each individual pixel. Average amplitude and mean frequency of the measured signal contain information about concentration and speed of moving blood cells. For real-time imaging, exposure time is used as a parameter to measure relative perfusion changes. These data are stored and processed with the signal-processing unit to deliver 2D flow maps of the illuminated sample section, and allow a simple overlay between a conventional image and processed flow maps.
Owner:ECOLE POLYTECHNIQUE FEDERALE DE LAUSANNE (EPFL)
Volumetric computed tomography (VCT)
InactiveUS7072436B2Fast and reliableMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handling2d arrayX-ray
The present invention provides a volumetric computed tomography (VCT) system capable of producing data for reconstructing an entire three-dimensional (3D) image of a subject during a single rotation without suffering from cone beam artifacts. The VCT system comprises an array of source positions distributed along a line parallel to an axis of rotation, a plurality of collimators, and an array of x-ray detectors. In a preferred embodiment, a reversed imaging geometry is used. A 2D array of source positions provides x-rays emanating from each focal spot toward an array of detectors. The x-rays are restricted by a collimator array and measured by a detector array separately per each source position. The axial extent of the source array and the detector array are comparable to or larger than the axial extent of the portion of the object being imaged.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Ultrasound diagnosis apparatus
InactiveUS7322936B2Improved profileSide lobes can be reducedUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSurgerySonification2d array
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Volumetric computed tomography (VCT)
InactiveUS7145981B2Fast and reliableMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handling2d arrayX-ray
The present invention provides a volumetric computed tomography (VCT) system capable of producing data for reconstructing an entire three-dimensional (3D) image of a subject during a single rotation without suffering from cone beam artifacts. The VCT system comprises an array of source positions distributed along a line parallel to an axis of rotation, a plurality of collimators, and an array of x-ray detectors. In a preferred embodiment, a reversed imaging geometry is used. A 2D array of source positions provides x-rays emanating from each focal spot toward an array of detectors. The x-rays are restricted by a collimator array and measured by a detector array separately per each source position. The axial extent of the source array and the detector array are comparable to or larger than the axial extent of the portion of the object being imaged.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Unipolar, intraband optoelectronic transducers with micro-cavity resonators
ActiveUS20050063438A1Broad impactLaser optical resonator constructionSemiconductor laser arrangementsNonlinear optics2d array
An optoelectronic transducer comprises a unipolar, intraband active region and a micro-cavity resonator. The resonator includes a 2D array of essentially equally spaced regions that exhibits resonant modes. Each of the spaced regions has a depth that extends through the active region and has an average refractive index that is different from that of the active region. The refractive index contrast, the spacing of the spaced regions, and the dimensions of the spaced regions are mutually adapted so that the array acts as a micro-cavity resonator and so that at least one frequency of the resonant modes of the array falls within the spectrum of an optoelectronic parameter of the active region (i.e., the gain spectrum where the transducer is a laser; the absorption spectrum where the transducer is a photodetector). In a first embodiment, the transducer is an ISB laser, whereas in a second embodiment it is a unipolar, intraband photodetector. In other embodiments, the laser is a surface-emitting ISB laser and the photodetector is a vertically-illuminated detector. In another embodiment, a nonlinear optical material is optically coupled to the micro-cavity resonator, which in one case allows an ISB laser to exhibit bistable operation.
Owner:ALCATEL-LUCENT USA INC +1
Rebinning methods and arrangements for use in compressing image-based rendering (IBR) data
InactiveUS20050031214A1Increase the compression ratioCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modification2d arrayJPEG
Rebinning methods and arrangements are provided that significantly improve the 3D wavelet compression performance of the image based rendering data, such as, e.g., concentric mosaic image data. Through what is essentially a selective cutting and pasting process the image data is divided into stripes that are then used to form a set of multi-perspective panoramas. The rebinning process greatly improves the performance of the cross shot filtering, and thus improves the transform and coding efficiency of 3D wavelet codecs. While the region of support after rebinning may cease to be rectangular in some cases, a padding scheme and an arbitrary shape wavelet coder can be implemented to encode the result data volume of the smart rebinning. With an arbitrary shape wavelet codec, the rebinning outperforms MPEG-2 by 3.7 dB, outperforms direct 3D wavelet coder by 4.3 dB, and outperforms a reference block coder (RBC) by 3.2 dB on certain tested concentric mosaic image scenes. Hence, the rebinning process nearly quadruples the compression ratio for selected scenes. Additional methods and arrangements are provided that include selectively dividing the image data into slits and rebinning the slits into a huge 2D array, which is then compressed using conventional still image codecs, such as, JPEG.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Multidimensional array rapid read-write method and apparatus on dynamic random access memory
InactiveCN1828773AIncreased column read and write speedSave storage spaceDigital storage2d arrayStatic random-access memory
The disclosed read-write method comprises: according to the capacity per line of DRAM and the read-write time ratio I / J of per row and column, determining the column value A=(CI / J)1 / 2 and row value B=(CJ / I)1 / 2 of sub-matrix divided by the 2D array; when writing 2D array on DRAM by row or column, writing the data labeled the AXB sub-matrix on one row of DRAM in turn; when reading the 2D array, selecting one by one the relative row by address conversion to read out all data in one row and turn to the next. Besides, there is an address generator in the control logic unit of DRAM. This invention saves time and space.
Owner:XIAOSHAN IND RES INST
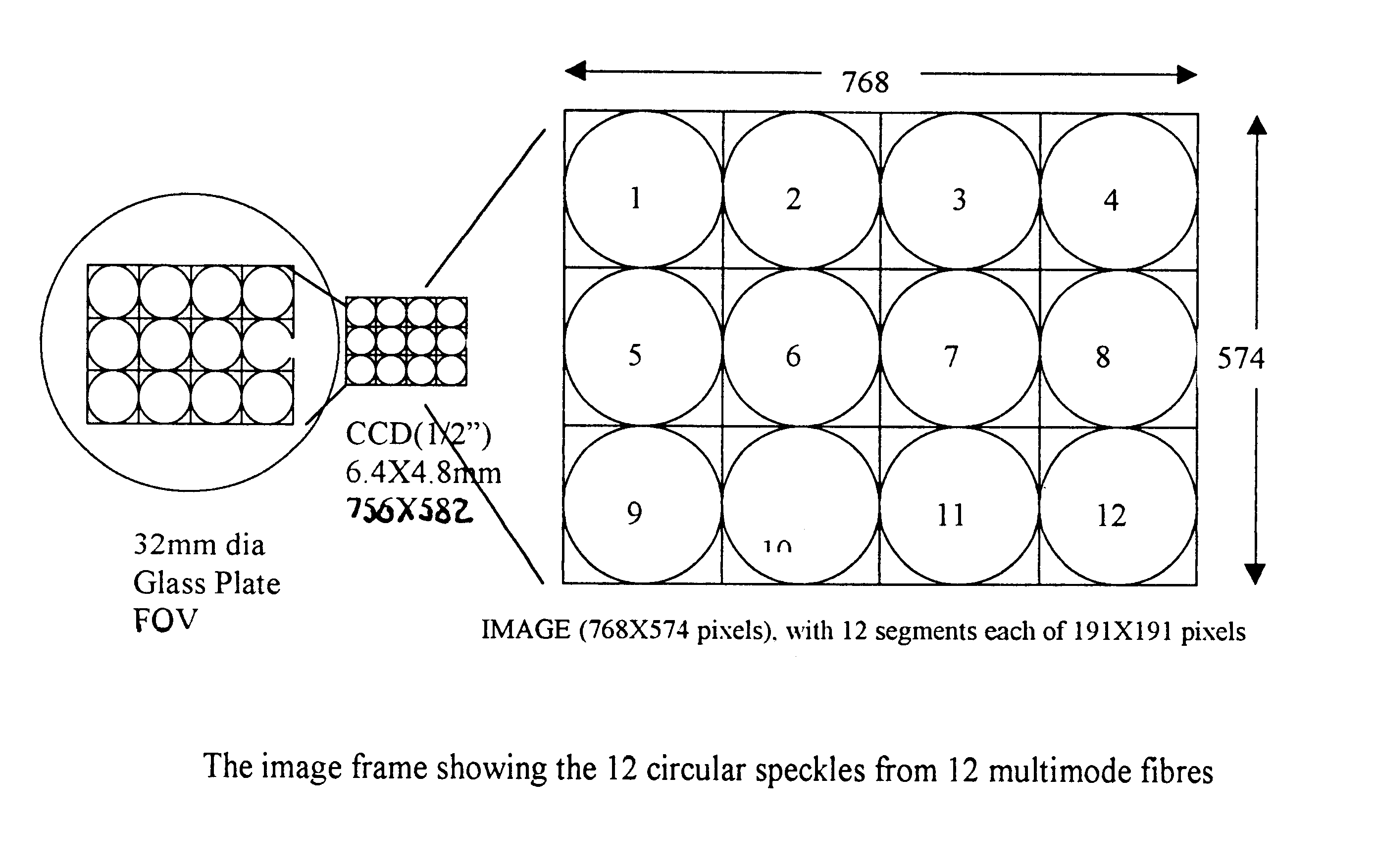
Multi-fiber optic 2D-array device for sensing and localizing environment perturbation using speckle image processing
InactiveUS6590194B2Increase the number ofSolid-state devicesForce measurement by measuring optical property variationFiber2d array
System for sensing perturbations in a distributed manner using an array of multimode fibers for localization (zone identification) of the perturbation, particularly, the present invention relates to a two dimensional array based speckle pattern sensing system having 4x3 (12) multimode fibers for sensing perturbation in multiple zones, said multimode fibers are imaged in parallel by a charge coupled device (CCD) camera and their speckle pattern analyzed by a conventional image processing hardware to determine the perturbations.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Apparatus and method for phased subarray imaging
ActiveUS20070208254A1Reduction front-end electronic complexityLow beam rateUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsInfrasonic diagnosticsImaging quality3d image
An invention for coherent array image formation and restoration is taught. The invention is applicable for both 2D and 3D imaging using either 1D or 2D arrays, respectively. A transducer array is subdivided into subarrays, each subarray having a number of adjacent array elements. All elements of each subarray transmit and receive in parallel. The signals received from each subarray are delayed and summed to form scan lines, or beams. The low-beam-rate beams formed from each subarray are upsampled and interpolated prior to forming high-beam-rate images. Depending on the subarray geometry, a subarray-dependent restoration filter is also applied to the subarray beams. The restored beams from each subarray are combined to form the final high-beam-rate image. The invention significantly reduces the front-end hardware complexity compared to conventional methods such as full phased array imaging with comparable image quality.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com