Method and apparatus for registration, verification, and referencing of internal organs
a technology of internal organs and methods, applied in the field of methods and apparatus for registration, verification, and referencing of internal organs, can solve the problems of reducing accuracy, electromagnetic tracking devices are subject to interference from ferromagnetic materials and conductors, and optical tracking devices suffer from line-of-site constraints
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
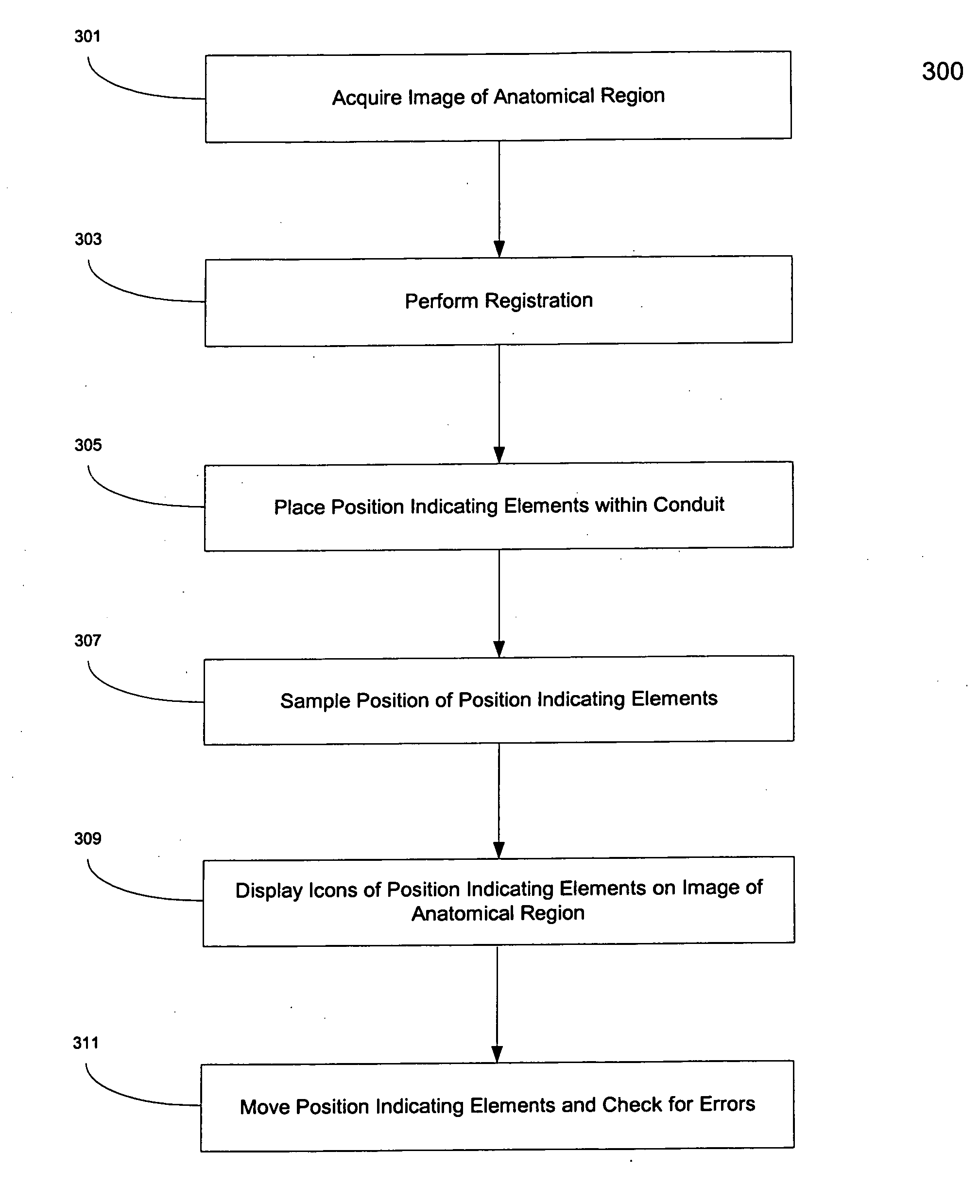
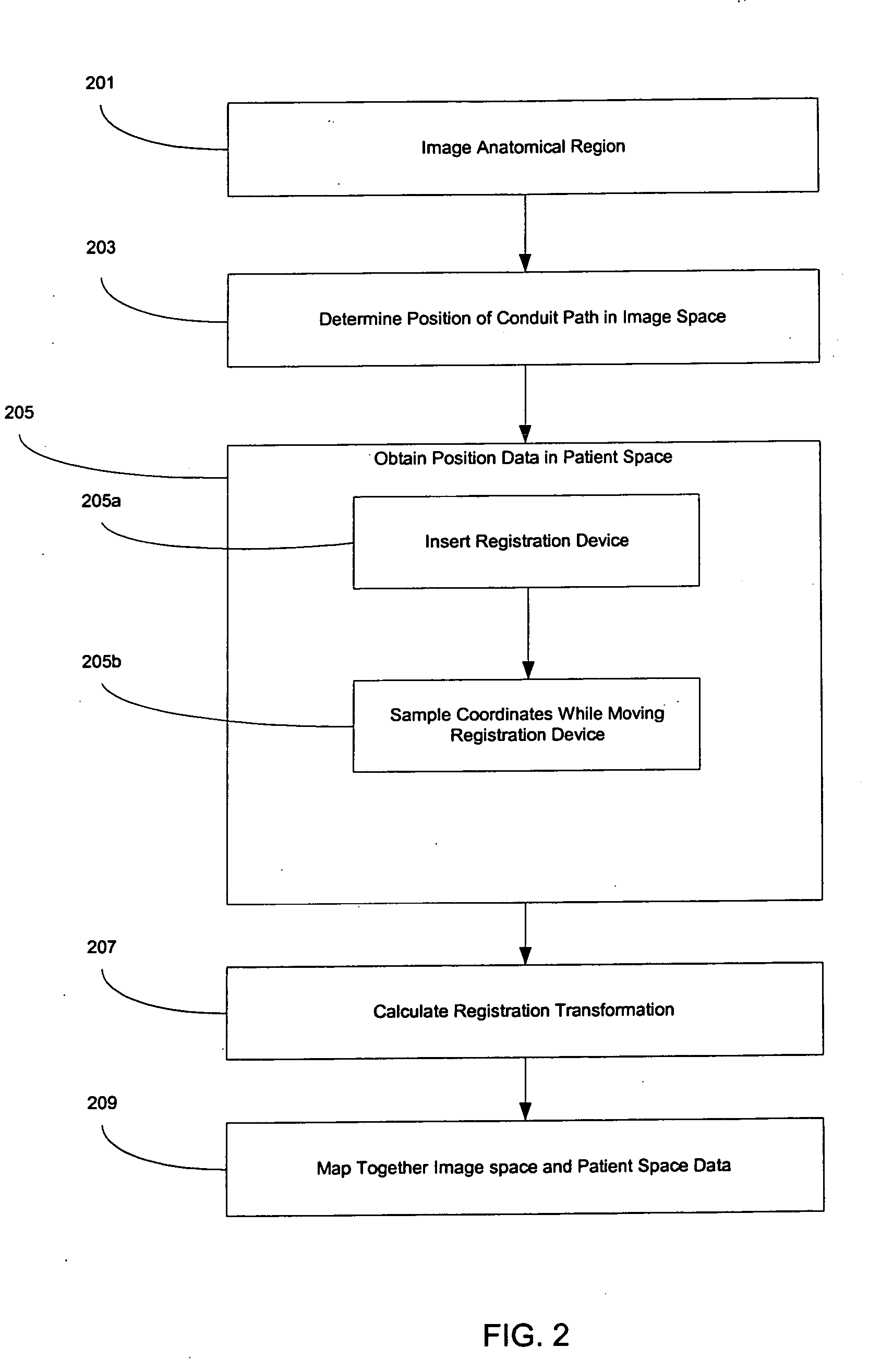
[0081] The invention provides systems and methods for registration of an anatomical region of a patient, verification of the registration of the anatomical region, and dynamic referencing of the anatomical region, wherein the anatomical region may include soft tissue and / or deformable bodies.
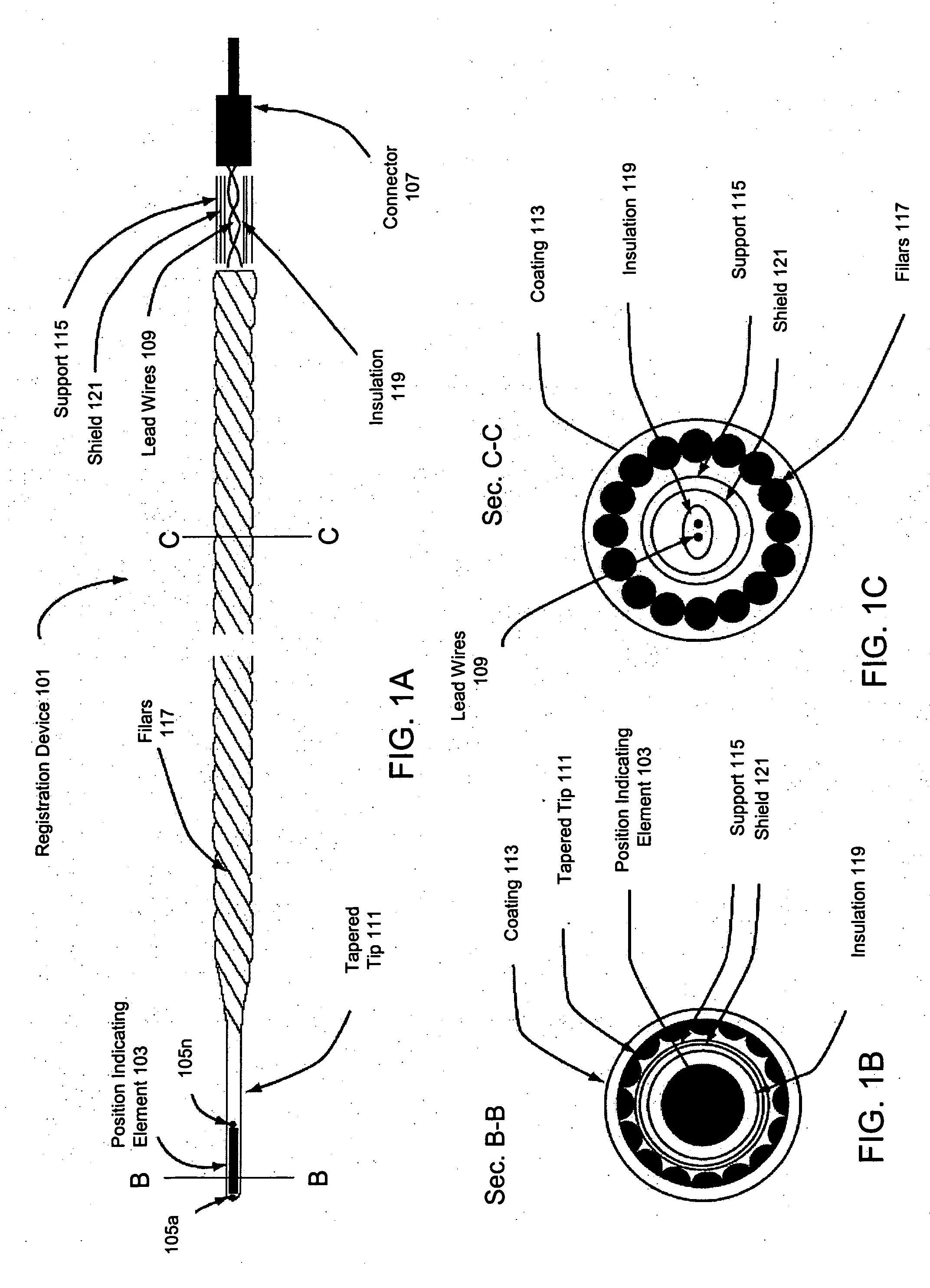
[0082] In one embodiment, the invention may use a conduit within an anatomical region of a patient to, inter alia, aid in providing image information and position information from within the anatomical region. This conduit may supply sufficient coordinate information regarding the anatomical region to be used for registration of the anatomical region. For example, a coronary artery surrounding the heart may provide sufficient topographical coordinate information regarding the heart to be used as a conduit for registration by a method of the invention.
[0083] In one embodiment, a conduit as used herein may include a naturally existing conduit within the anatomical region such as, for example, an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com