Structural variation detection method
A technology for structural variation and detection methods, which can be used in the analysis of two-dimensional or three-dimensional molecular structures, genomics, instruments, etc., and can solve the problems of lack of annotations in calculation results, abnormal length of inserted fragments, and no annotation modules.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0097] Collected 15,000 samples from patients with solid tumors and hematological tumors, extracted DNA for paired-end second-generation capture library construction and sequencing, and extracted RNA from some samples for capture sequencing. For each sample library obtained by sequencing, for the DNA library, use the BWA alignment software to align with the human reference genome HG19; for the RNA library, use the BWA alignment software to align with the personalized transcriptome. The transcriptome is constructed as follows:
[0098] Select one transcript for each gene as the main transcript. The main transcript should be included in the COSMIC and ONCOKIB databases first. If it is not included, it must be the one recorded in the main transcript database in UCSC. If there is no one in the three databases To determine the main transcript, use the longest one as the main transcript.
[0099] The results obtained by comparison remove PCR duplication and error correction, and ge...
Embodiment 2
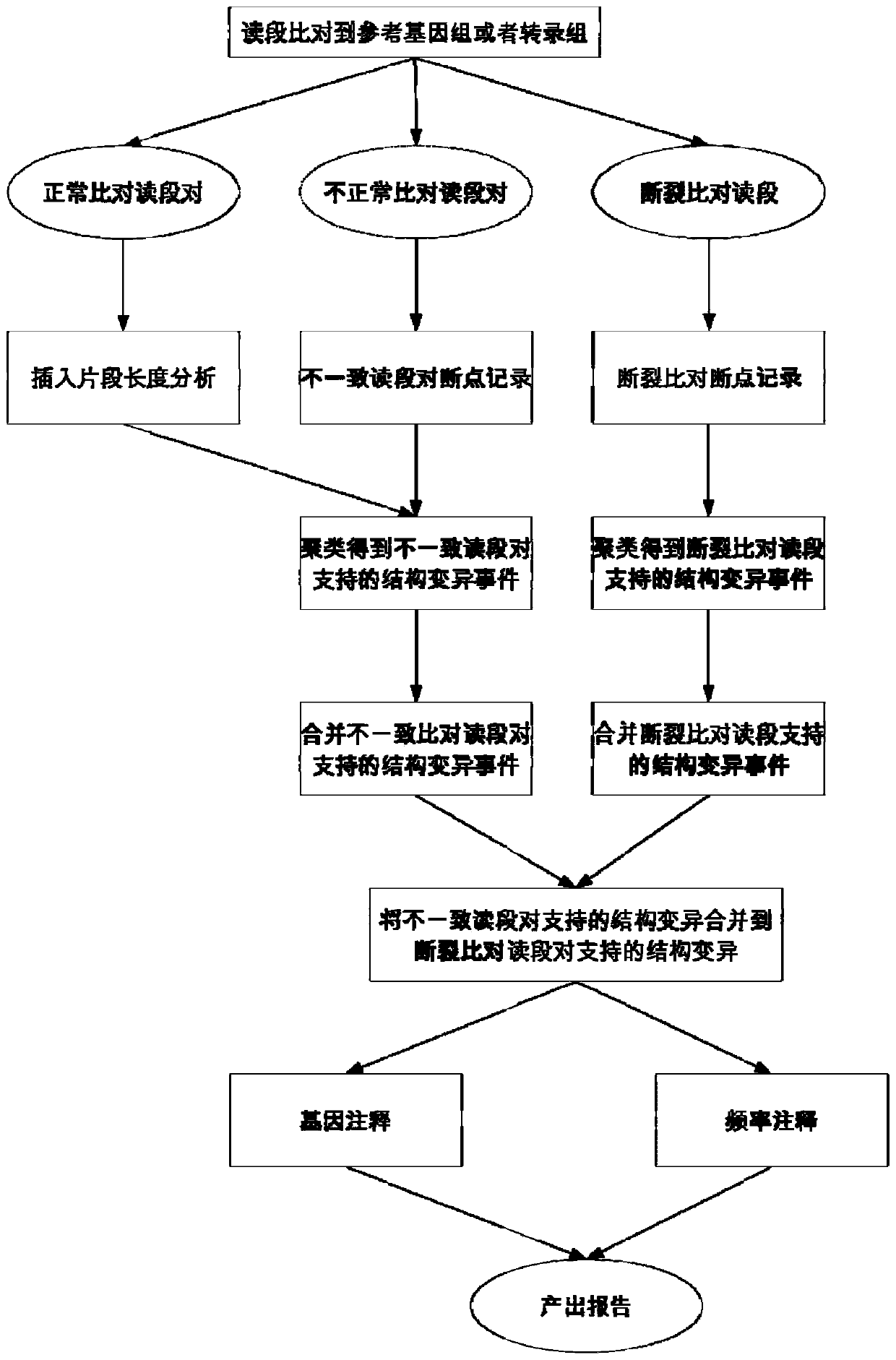
[0101] Traverse the alignment result file, take 1 million normal alignment reads (the extraction standard is that no break alignment occurs, and the read pair matches the normal reads, and does not support any structural variation) to count the length of the insert, and calculate the length of the insert The main parameters of the distribution, maximum, minimum, mean.
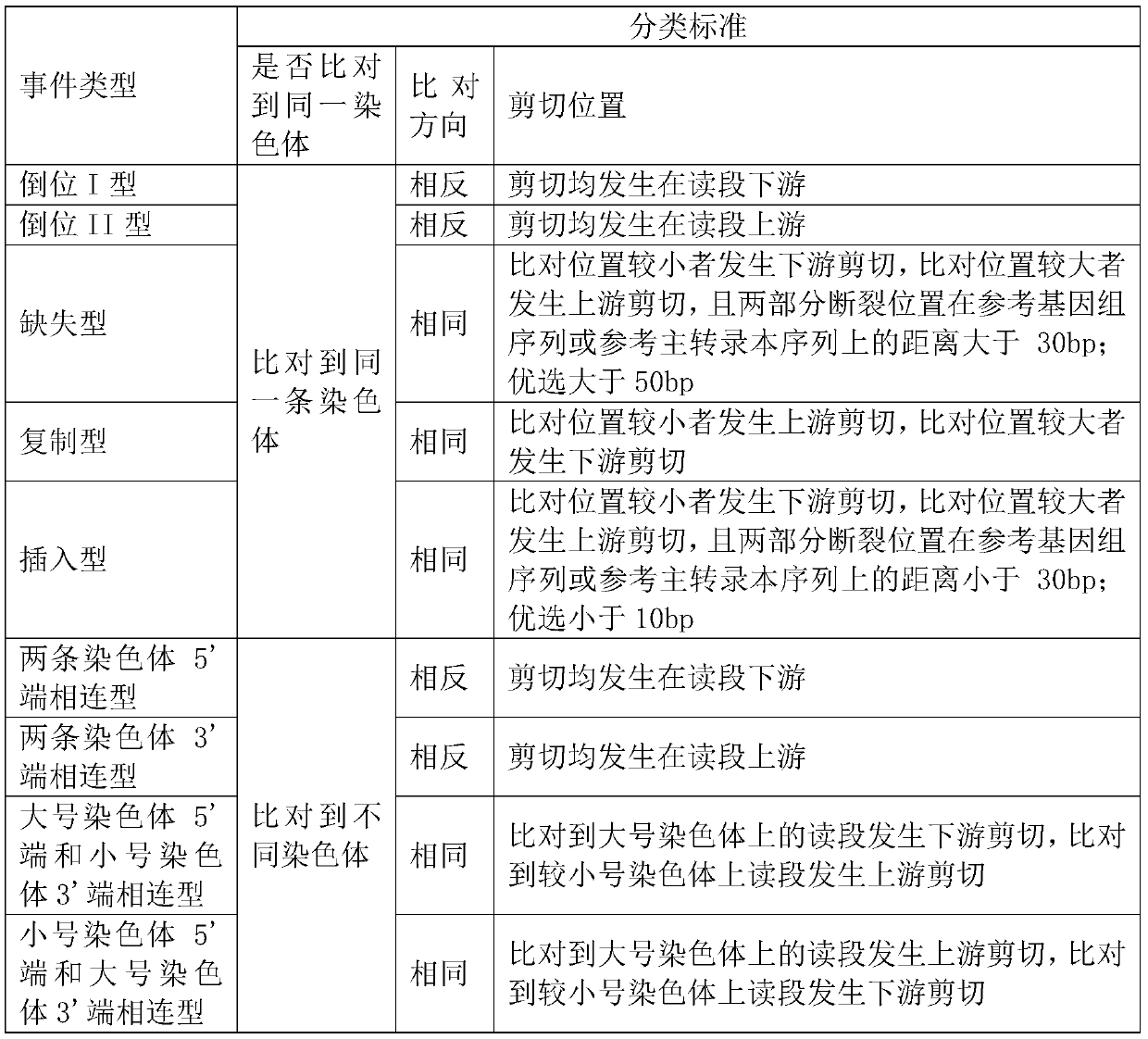
[0102] Traversing the alignment result file again, accessing all the reads, finding out all the reads with broken alignments and abnormally aligned reads, and respectively classifying the reads with broken alignments and the abnormally aligned reads according to the following characteristics Classification of read pairs: The read segments of the broken alignment are mainly classified according to the comparison of the two parts where the broken alignment occurs. The classification criteria include whether they are aligned to the same chromosome, whether they are aligned to different directions of the The cuttin...
Embodiment 3
[0122] The structural variation detection method of the present invention can simultaneously support the identification of RNA and DNA structural variation, but few methods in the prior art can support both identifications at the same time. For example, both DELLY and GeneFuse only support the identification of DNA structural variation, and TophatFusion only supports Supports RNA structural variation identification. In order to test the performance of the method of the present invention, it was compared with FusionMap, a commercial software capable of supporting both DNA and RNA structural variation identification.
[0123] 269 positive samples were extracted from the sequencing data in Example 1, and each sample had 1-2 fusions that had been verified by experiments. The method of DNA library sequencing analysis and FusionMap software were used to detect structural variation respectively. The results showed that the method in Example 2 can reach a detection rate of 100% (see...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com