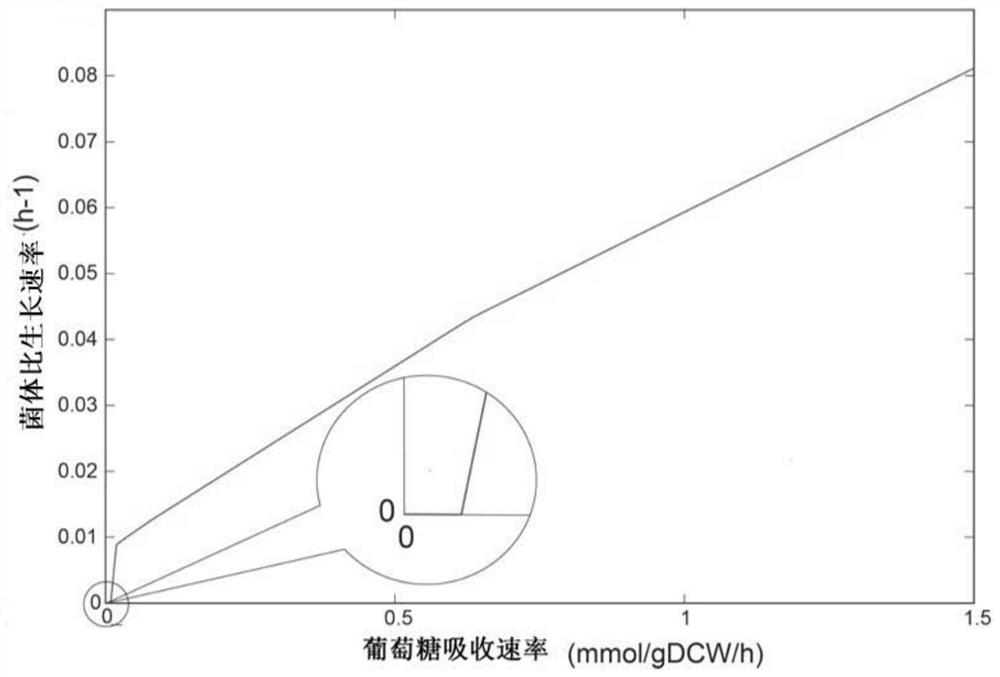
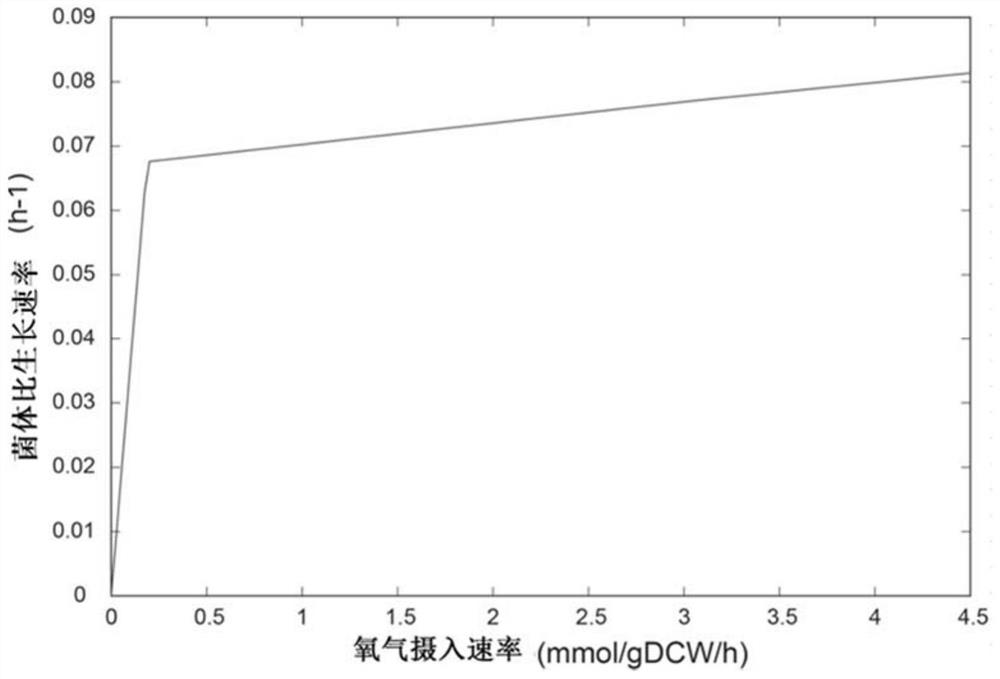
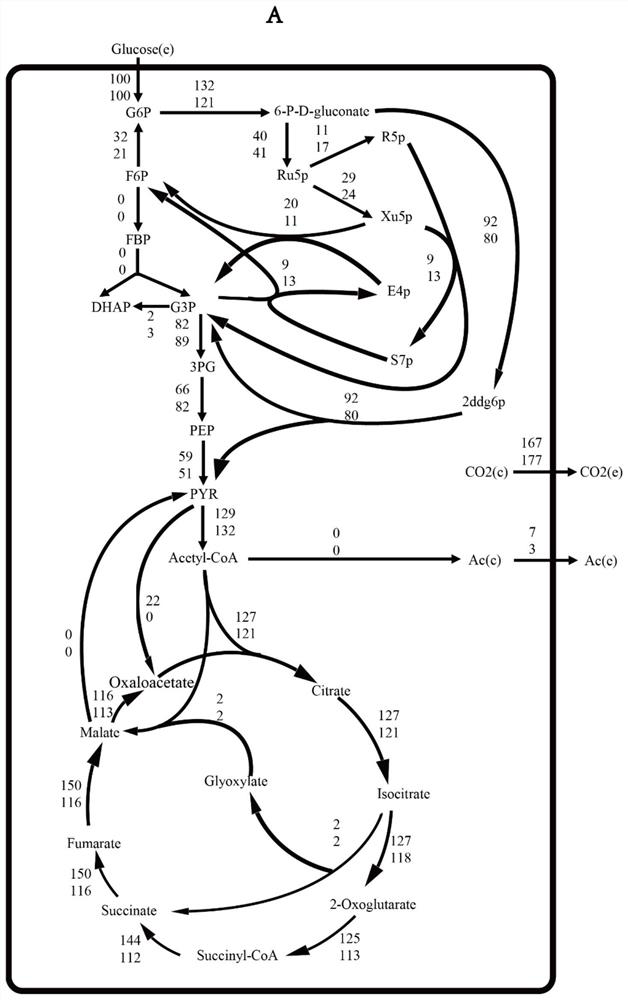
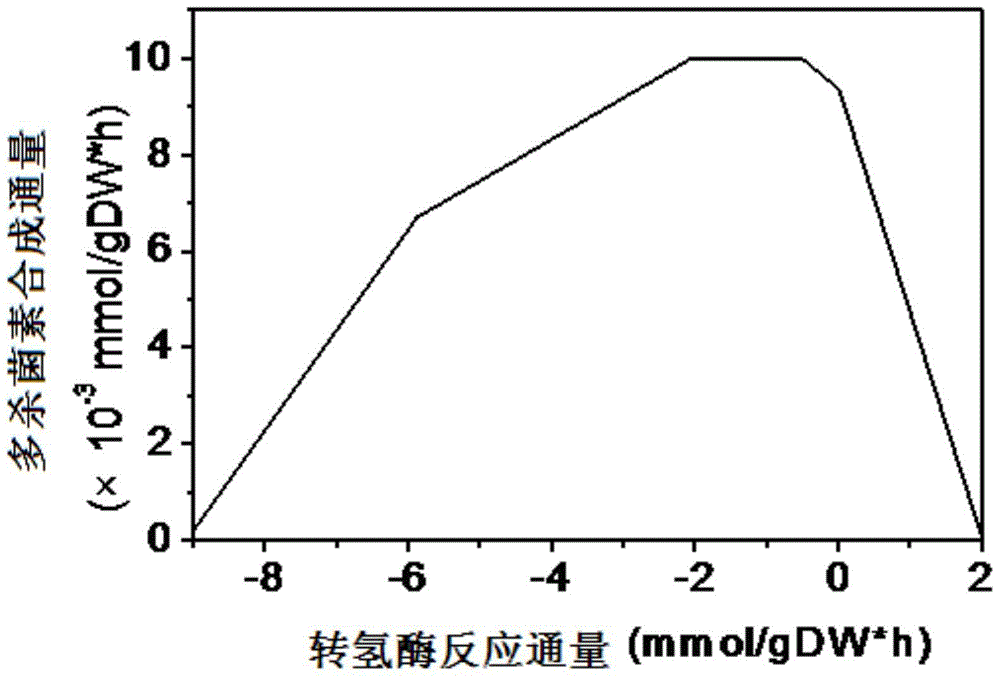
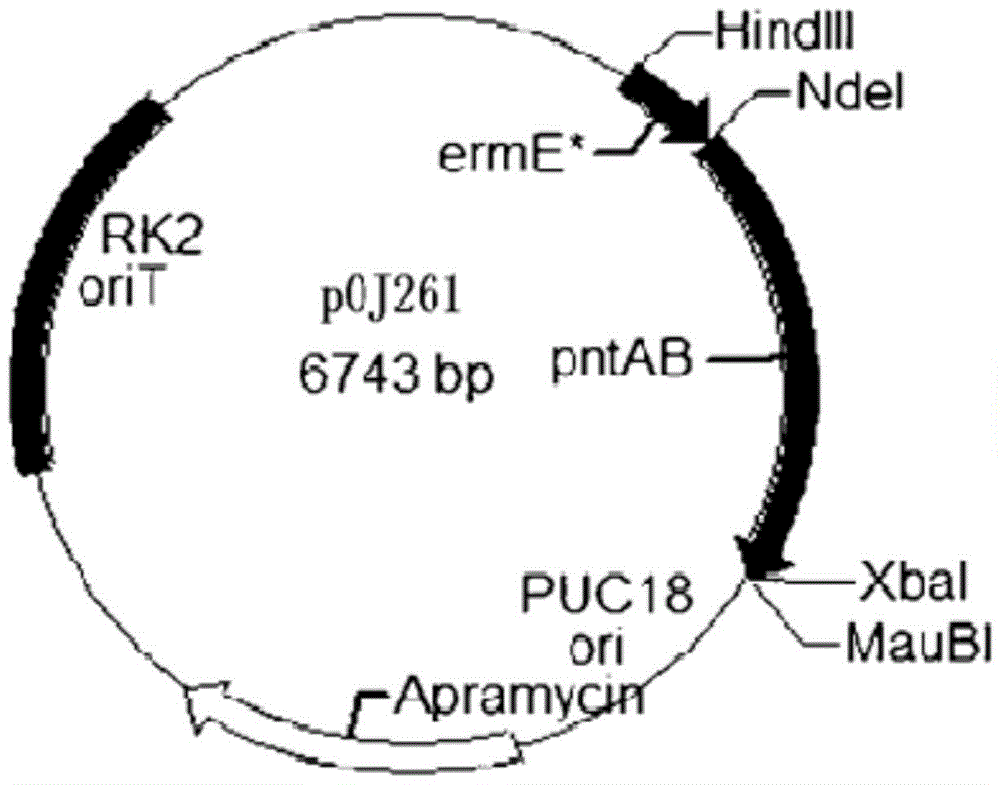
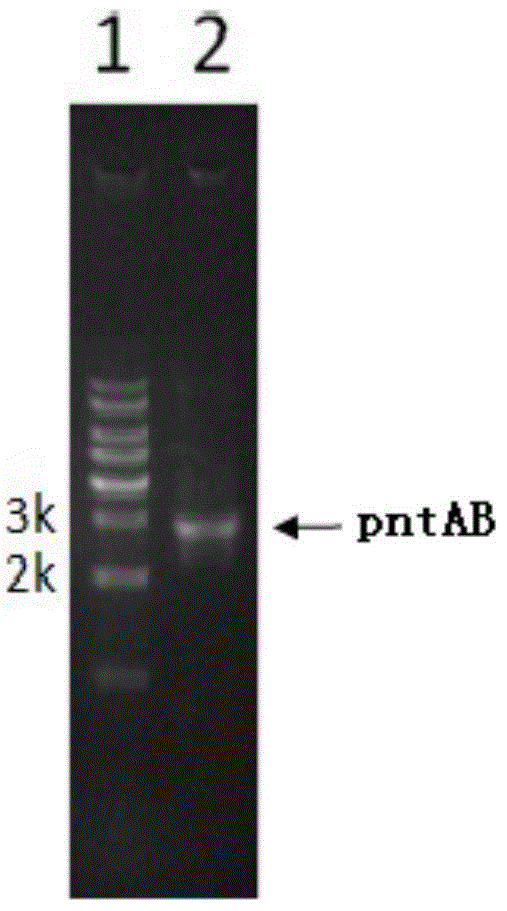
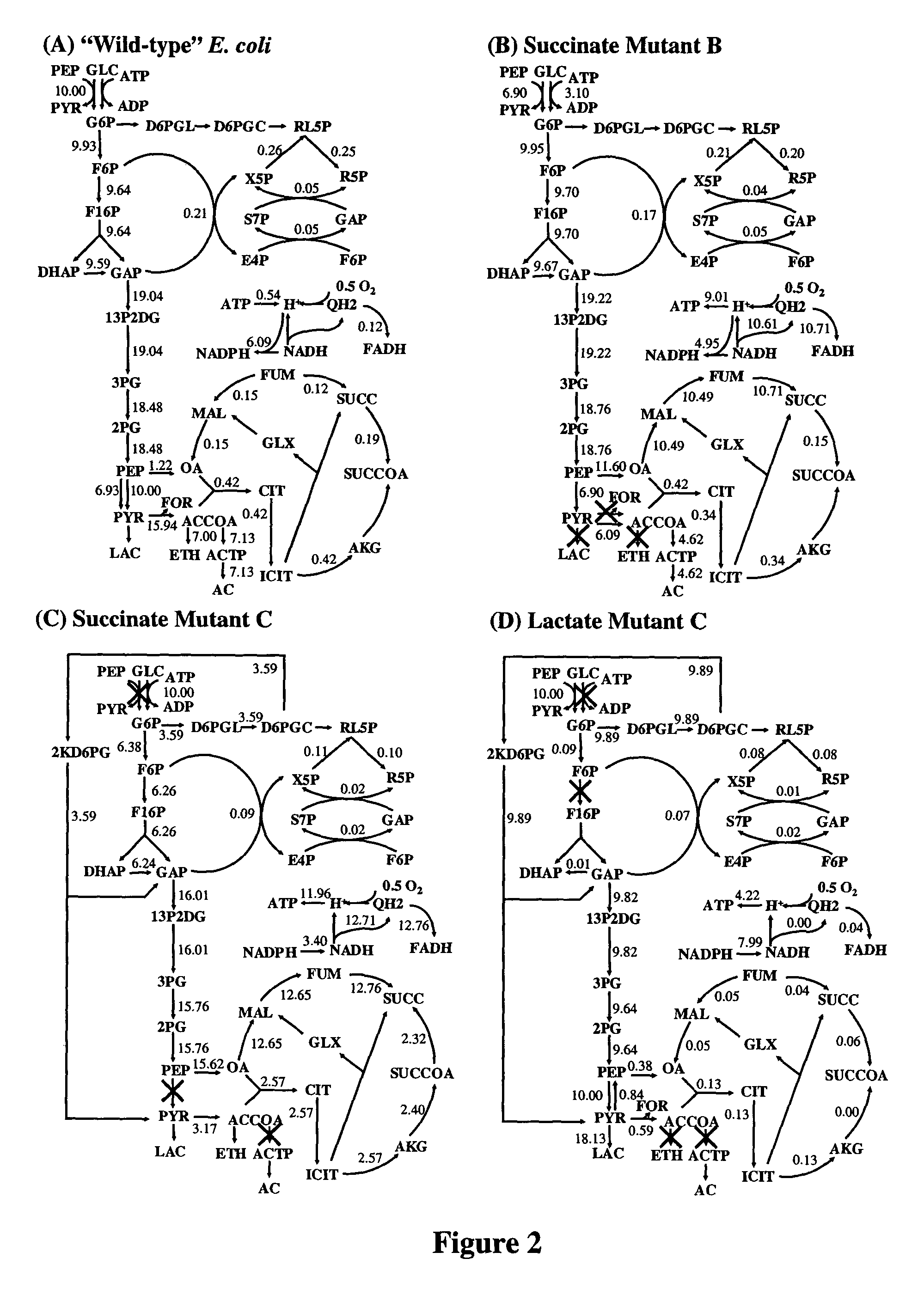
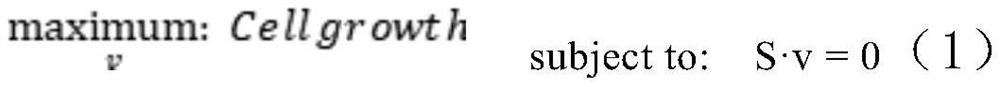Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
41 results about "Metabolic network model" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
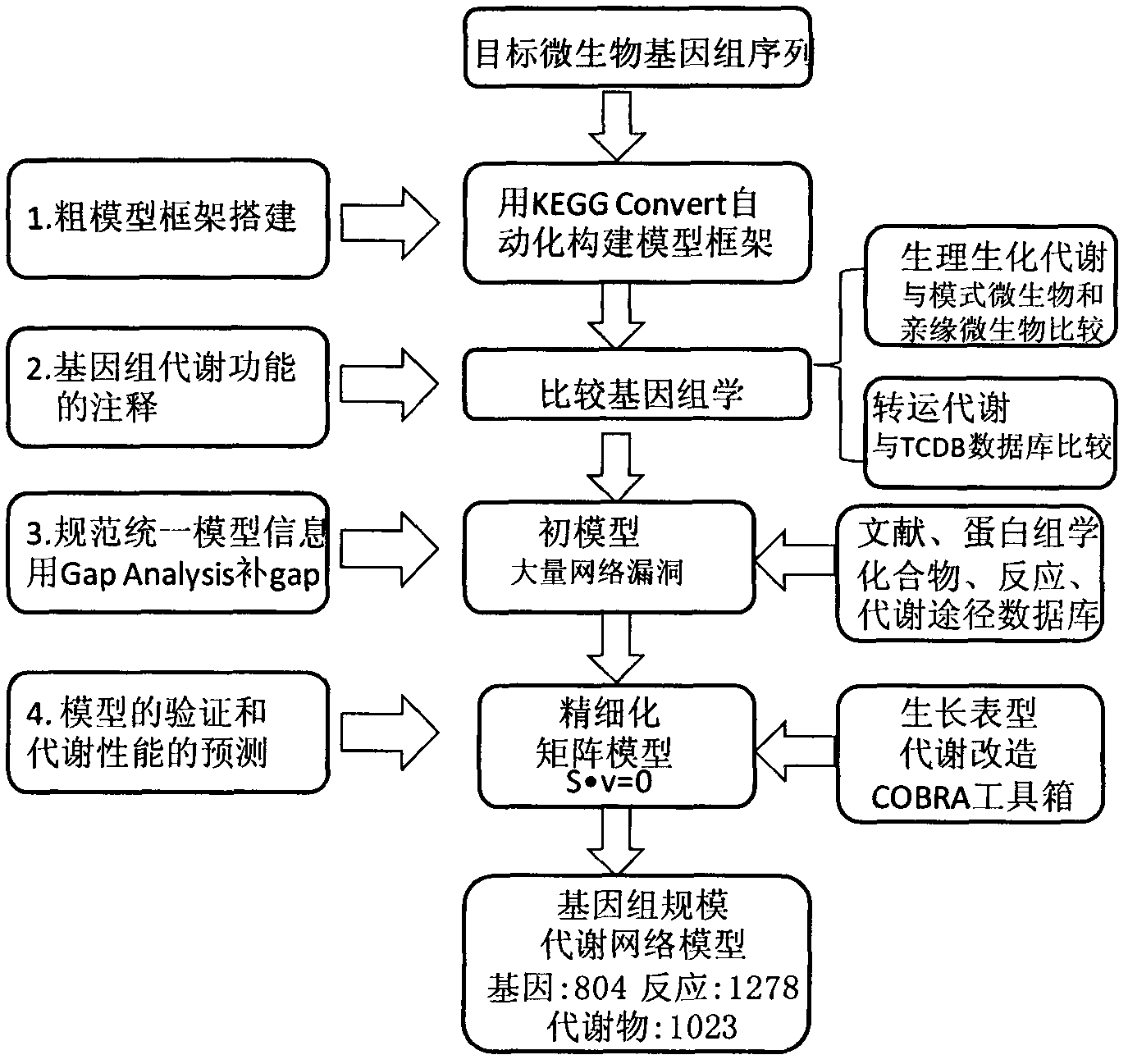
Aureobasidium pullulans genome scale metabolism network model and application thereof
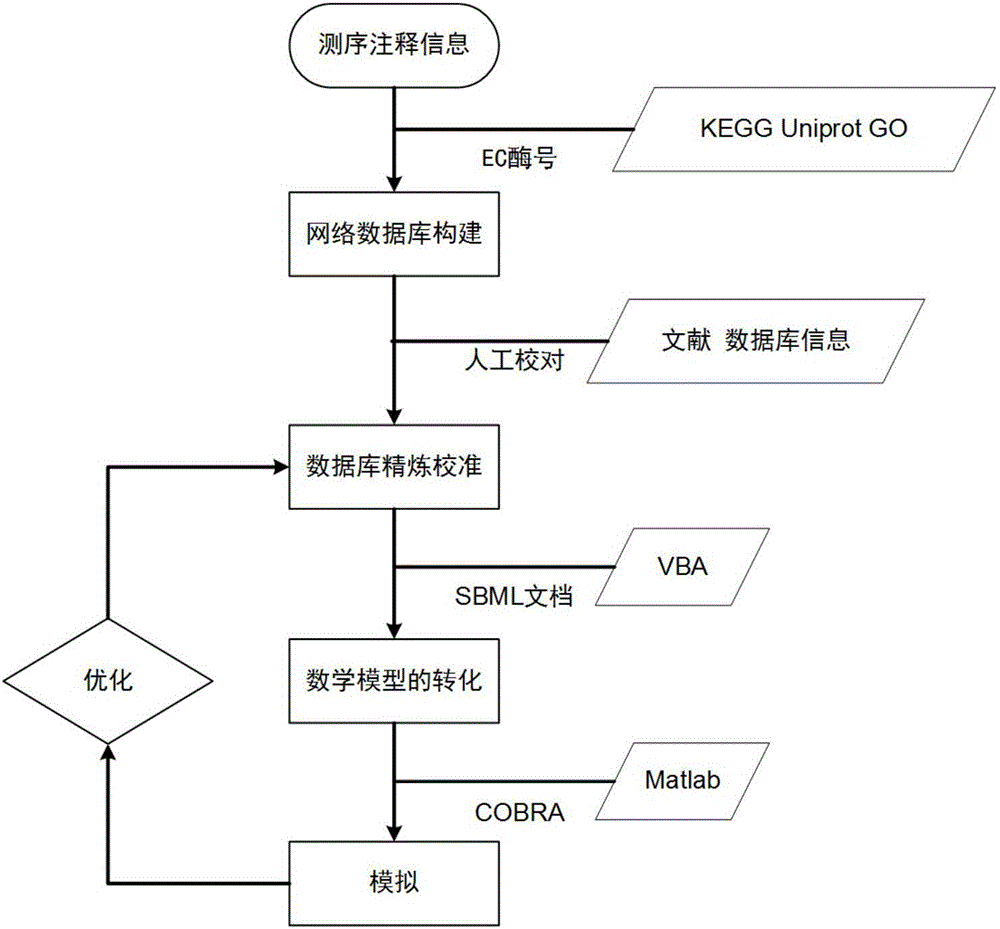
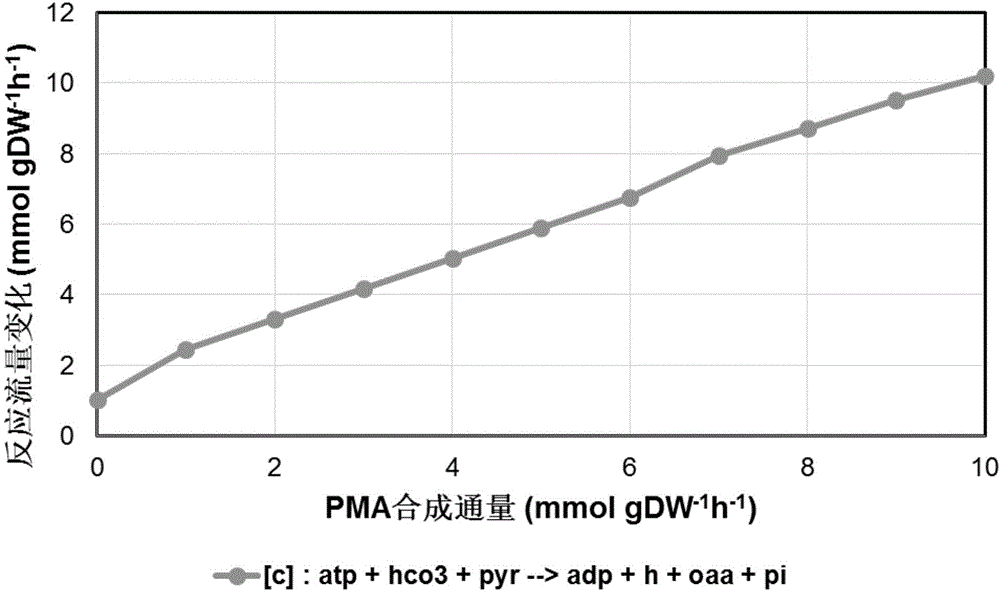
The invention discloses an aureobasidium pullulans genome scale metabolism network model and application thereof. Construction of the aureobasidium pullulans genome scale metabolism network model comprises four steps of building of a network database, refining and calibrating of the database, building of a mathematical model and validation and analysis of the model. According to the constructed aureobasidium pullulans genome scale metabolism network model, a gene target for potentially improving polymalic acid can be predicted, a guiding platform is provided for research and comprehensive analysis of aureobasidium pullulans, and the aureobasidium pullulans genome scale metabolism network model has great significance on transformation of the aureobasidium pullulans to obtain high-yield metabolic products of the polymalic acid and pullulan.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY +1
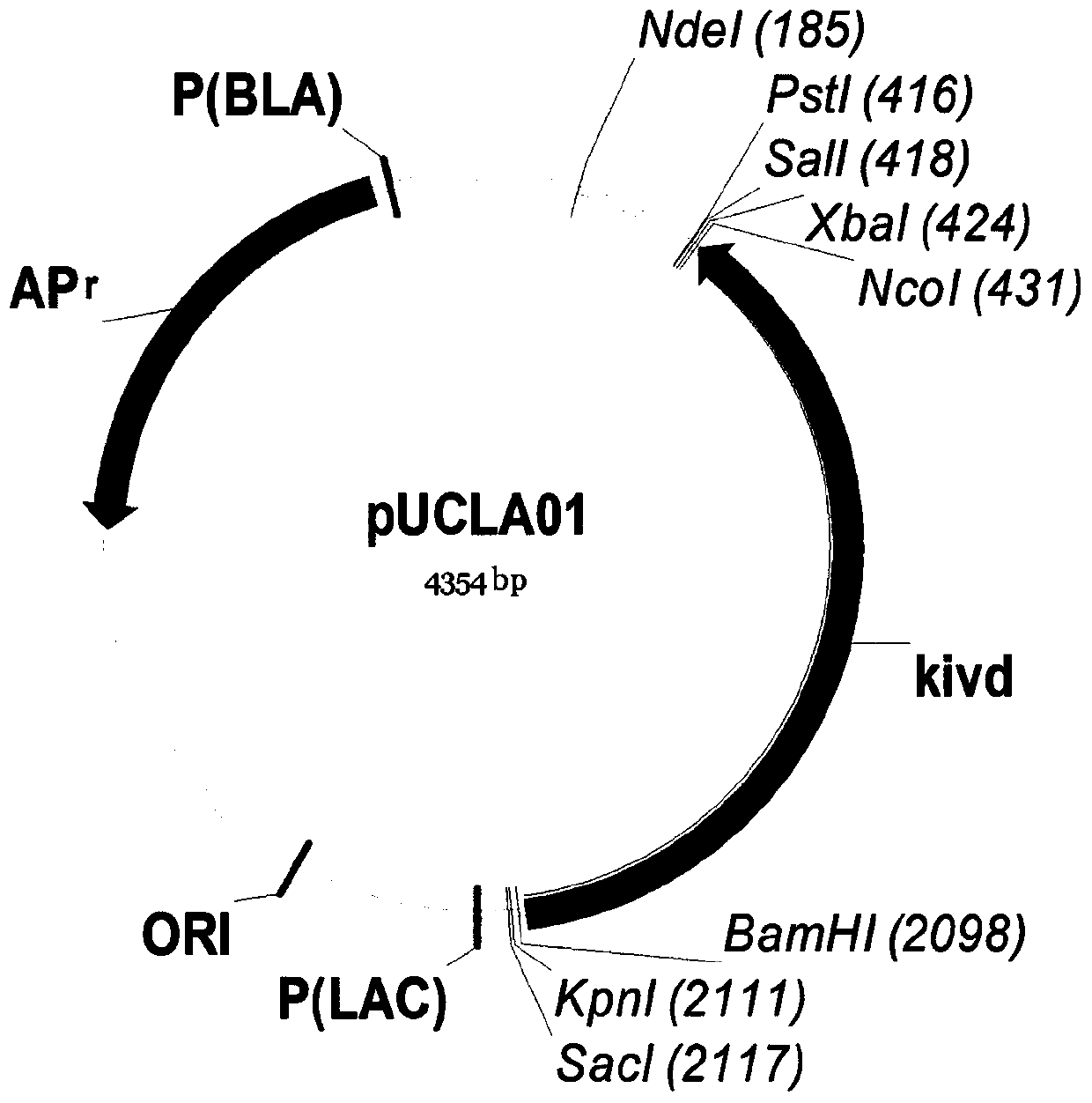
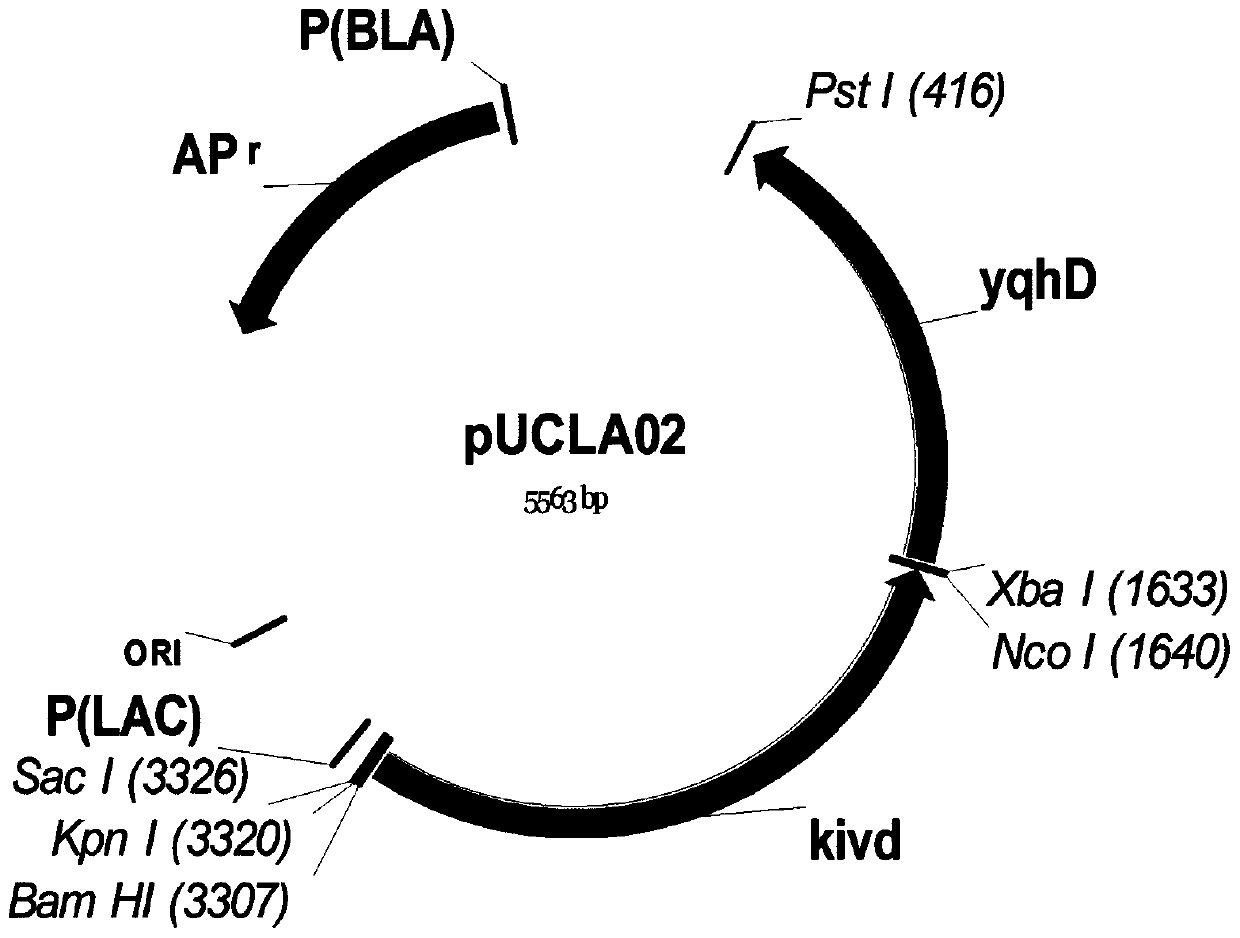
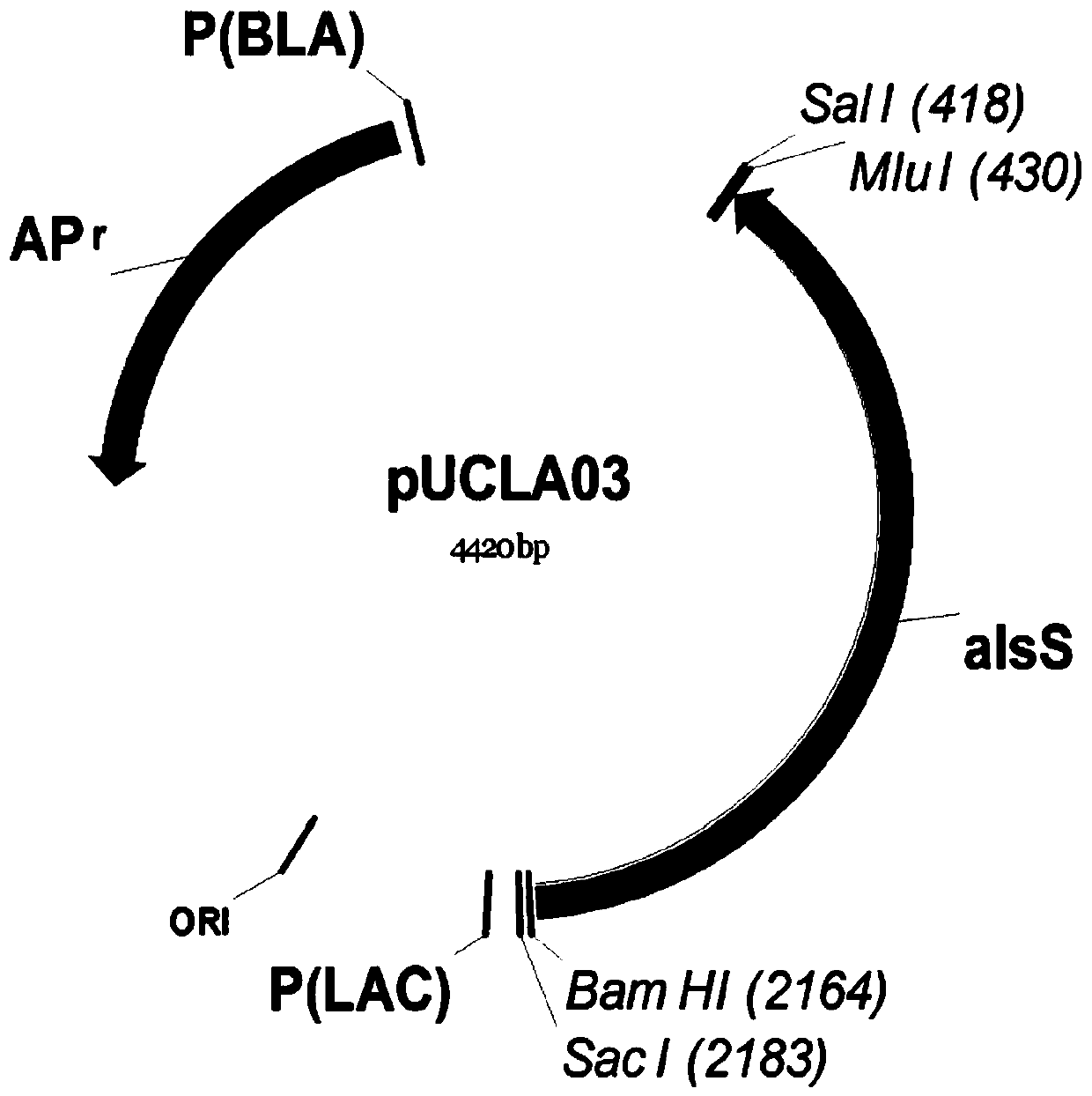
Isobutanol synthetic strain construction method implemented by guiding adjustment of intracellular reducing power based on genomic scale metabolic network model
InactiveCN104630250AIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationSynthetic biologyIsobutanol synthesis
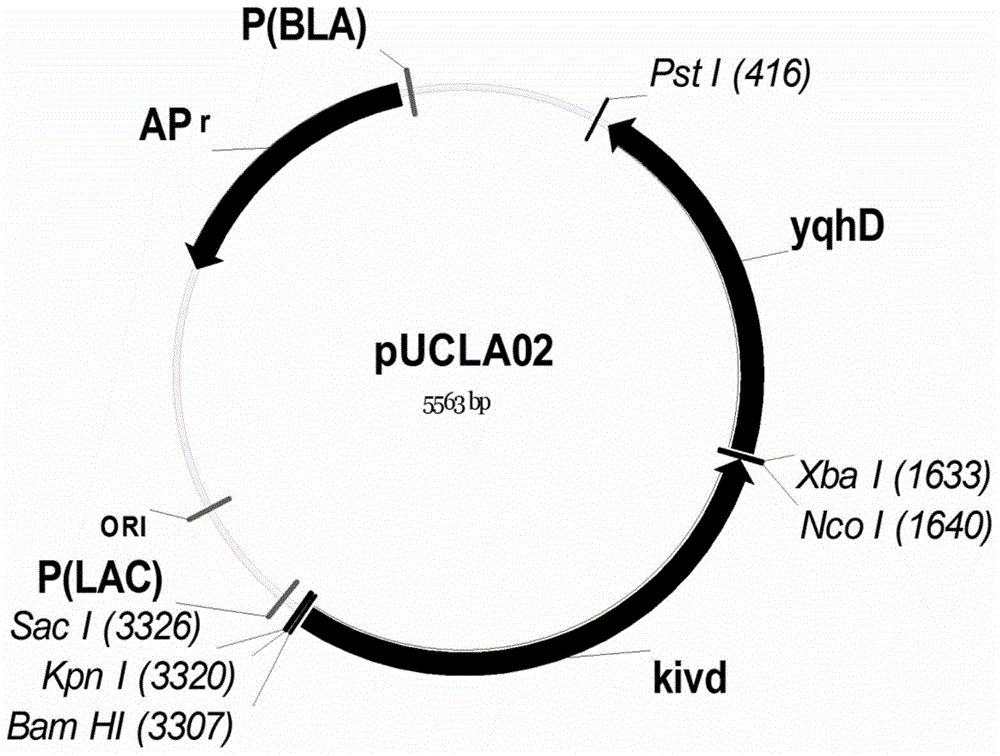
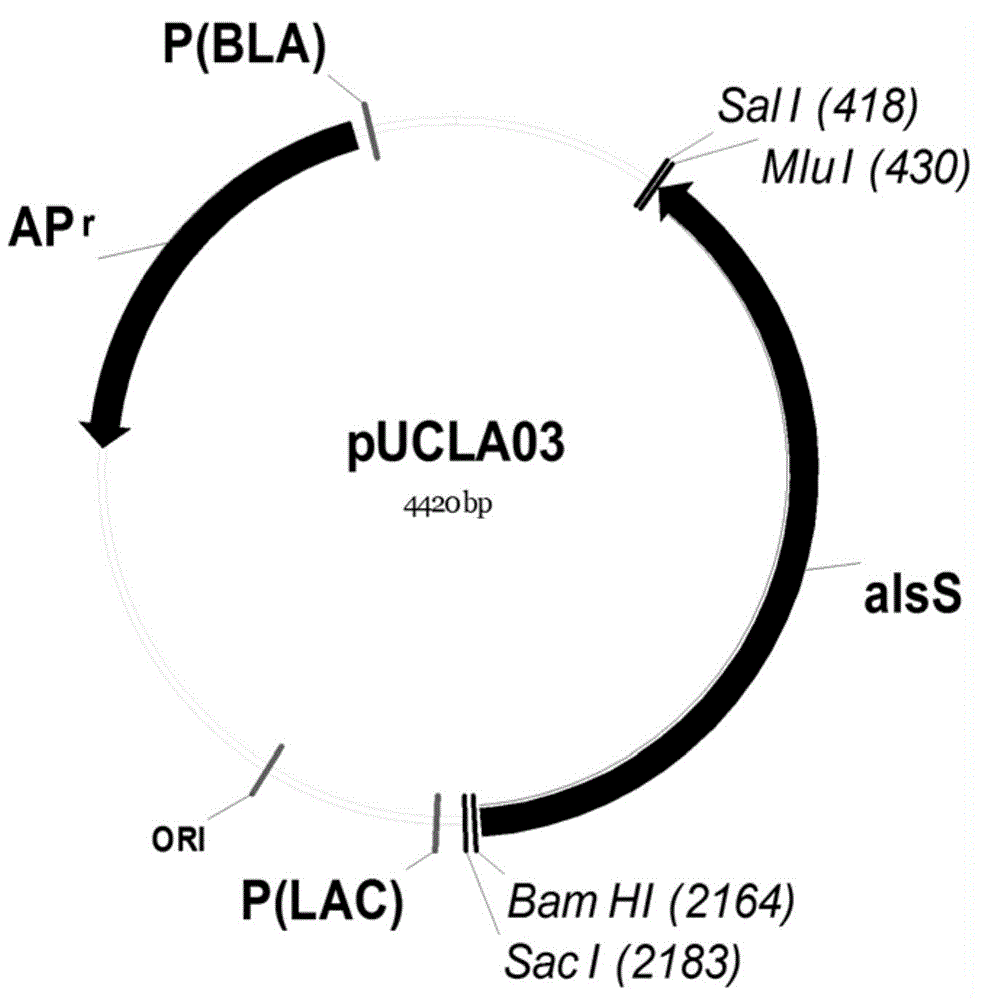
The invention provides an isobutanol synthetic strain construction method implemented by guiding the adjustment of intracellular reducing power based on a genomic scale metabolic network model. Based on the genomic scale metabolic network model, by adopting flow balance analysis and metabolic minimum adjustment analysis, the action law of different reconstruction modes of an intracellular reducing power metabolism to strain growth and isobutanol synthesis is simulated, and according to phenotypic coefficients, a conclusion that glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is a key target spot of the intracellular reducing power adjustment of an isobutanol synthetic strain is obtained. By using a synthetic biological artificially-regulated element, an NADP+ depended glycerin-3-phosphate dehydrogenase metabolic pathway is built and adjusted so as to match and balance the intracellular reducing power metabolism, thereby obtaining an efficient isobutanol synthetic strain. The intracellular NADPH / NADP ratio of the strain reaches 0.4-0.8, and when 20-50 g / L glucose as a substrate is adopted for carrying out batch fermentation, the yield of isobutanol can reach over 8 g / L in 36 h, which is increased by over 60%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
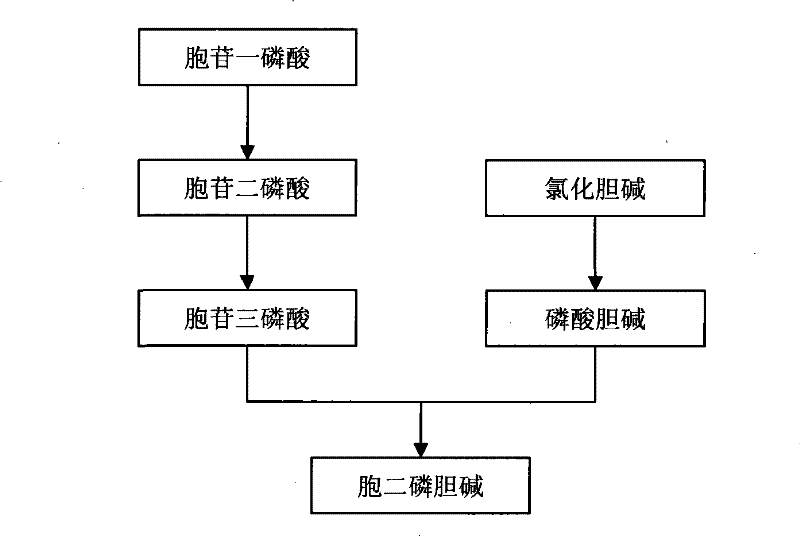
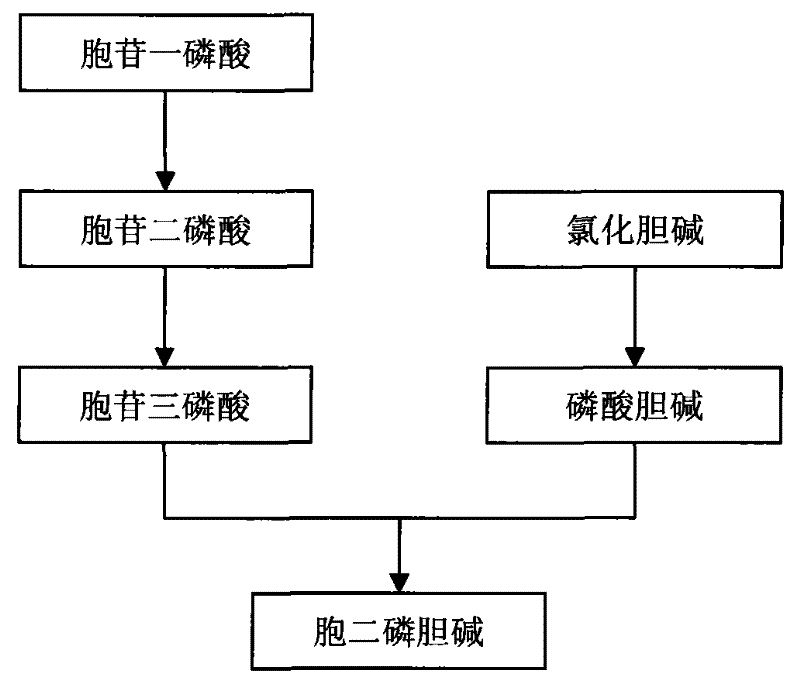
Method for preparing citicoline
InactiveCN101538598AIncrease profitAvoid investmentMicroorganism based processesFermentationPhosphate ionPhosphorylation
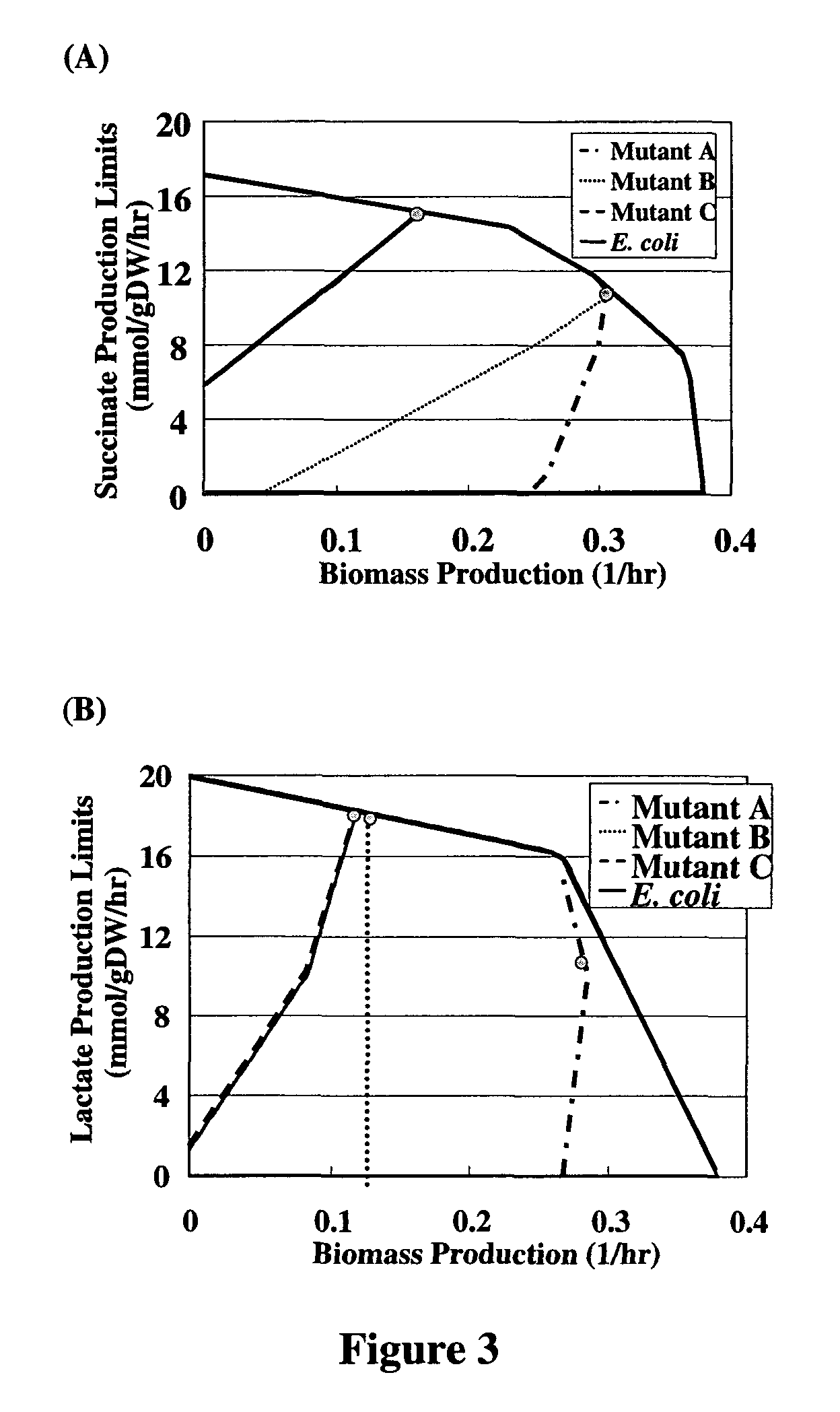
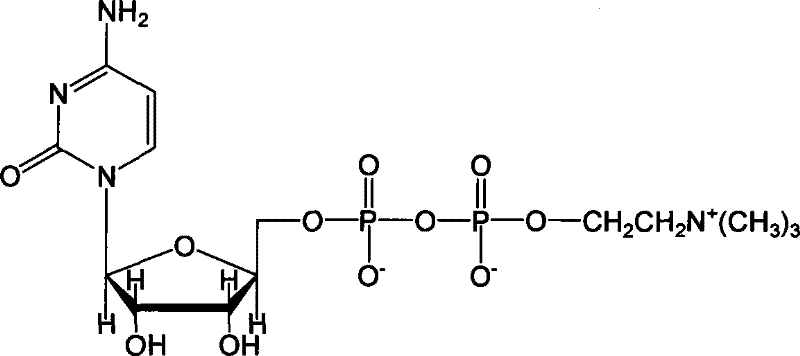
The invention discloses a method for preparing citicoline. The method comprises the following steps of taking choline chloride, phosphate ions and cytidine monophosphate or a precursor thereof as substrates, taking glucose, fructose, sucrose or maltose as an energy donor, adding a small-molecule chemical effect substance and utilizing the yeast-cell whole cells with permeability to catalyze and prepare the citicoline. By building a metabolic network model and metabolic flow analysis, adopting the small-molecule chemical effect substance to regulate and control metabolic flow so as to improve the efficiency of energy self-coupling and choline phosphorylation and utilizing the yeast cells with permeability to efficiently prepare the citicoline, the method has the advantages of greatly increasing product concentration and raising the utilization ratio of the substrates.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Isobutanol synthetic bacterium genome dimension metabolic network model and molecular modification method
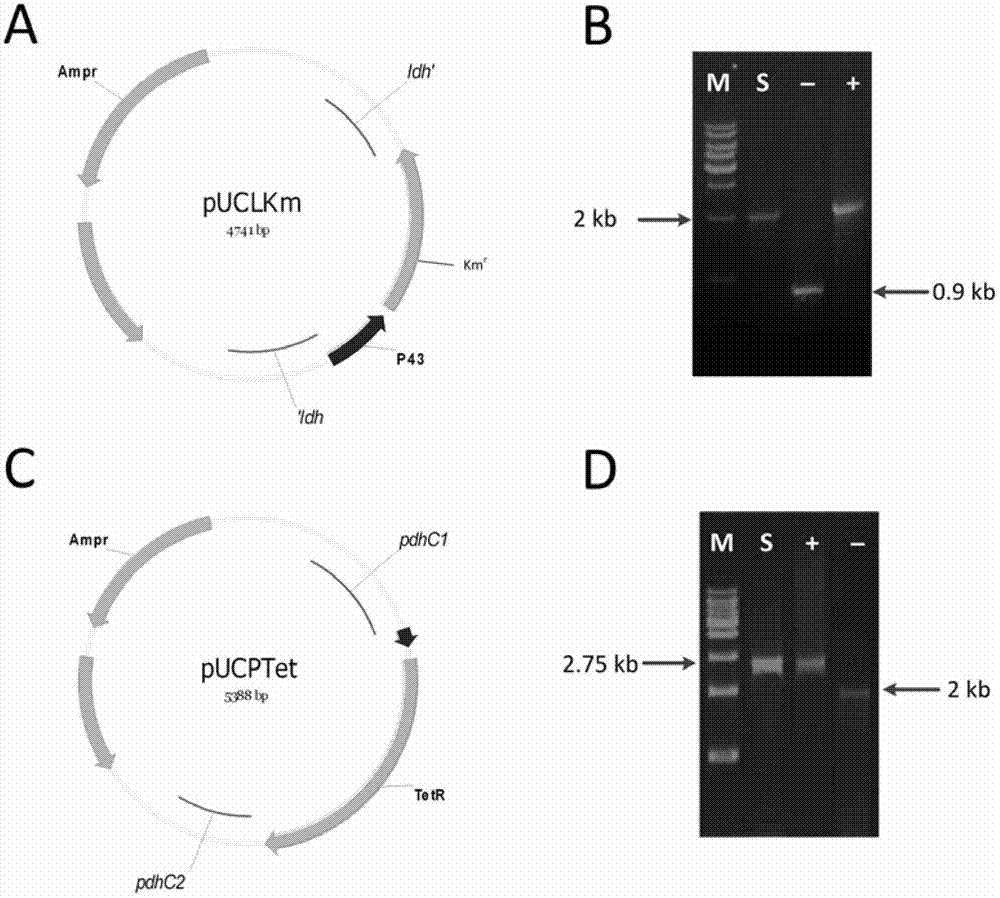
InactiveCN102768713ABacteriaMicroorganism based processesL-Lactate dehydrogenaseIsobutanol synthesis
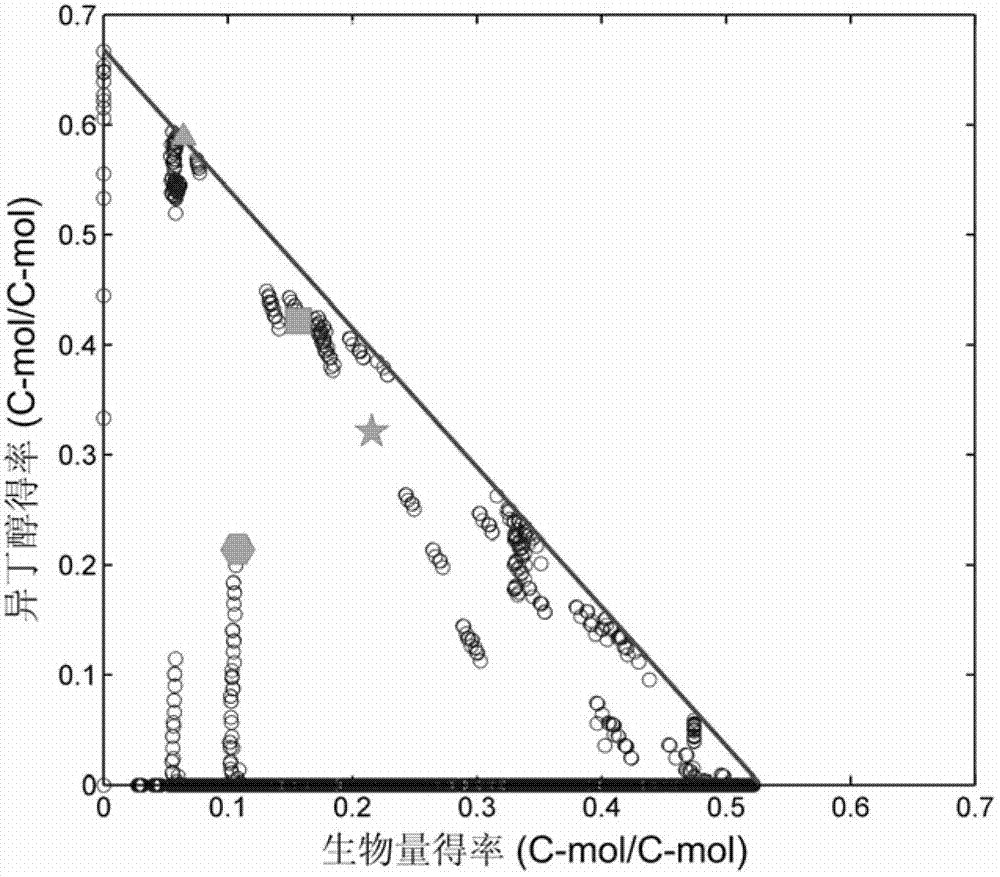
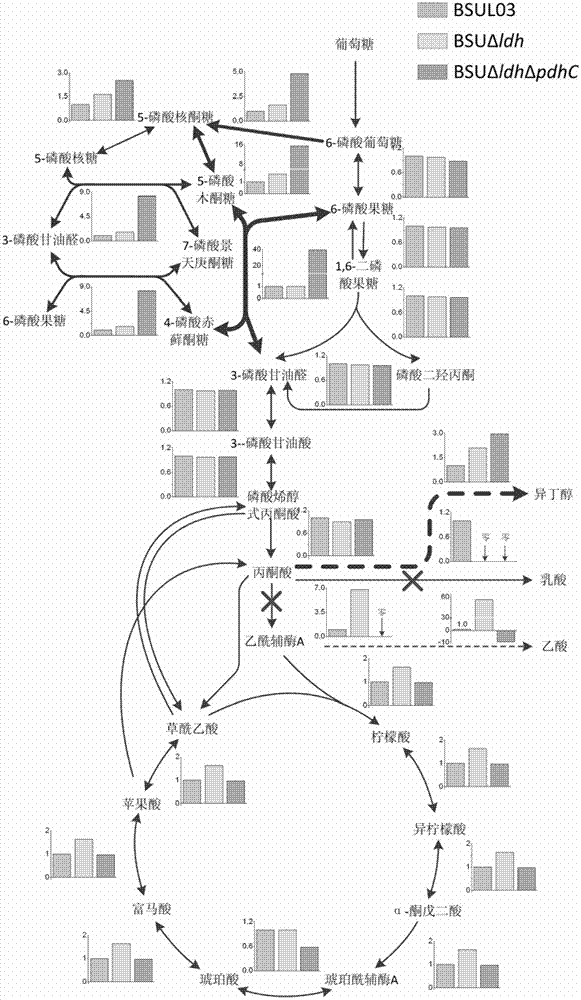
The invention relates to an isobutanol synthetic bacterium genome dimension metabolic network model and a molecular modification method. According to the method, the necessary path for the thallus growth and the isobutanol synthesis is calculated by a network module, the metabolic network model is subjected to the element mode analysis, the standard deviation coefficient of each gene is calculated, and the isobutanol biosynthesis yield of different genes is determined; the two key genes including an L-lactate dehydrogenase gene 1dh and a pyruvate dehydrogenase complex E2 subunit coding gene pdhC which are most important to the isobutanol biosynthesis are predicted according to a principle that the standard deviation coefficient is smaller than 0.35, the standard deviation coefficients of the two genes are respectively 2.5 to 3 and 1.5 to 2; and through the determination of the two genes, the isobutanol yield can be improved, and 0.5-0.6C-mol / C-mol glucose can be reached. The key genes which are most important to the isobutanol biosynthesis are obtained through utilizing the relative flux value and are used as modification target spots, the molecular modification of the isobutanol synthetic bacterium is guided, and the isobutanol yield is improved.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
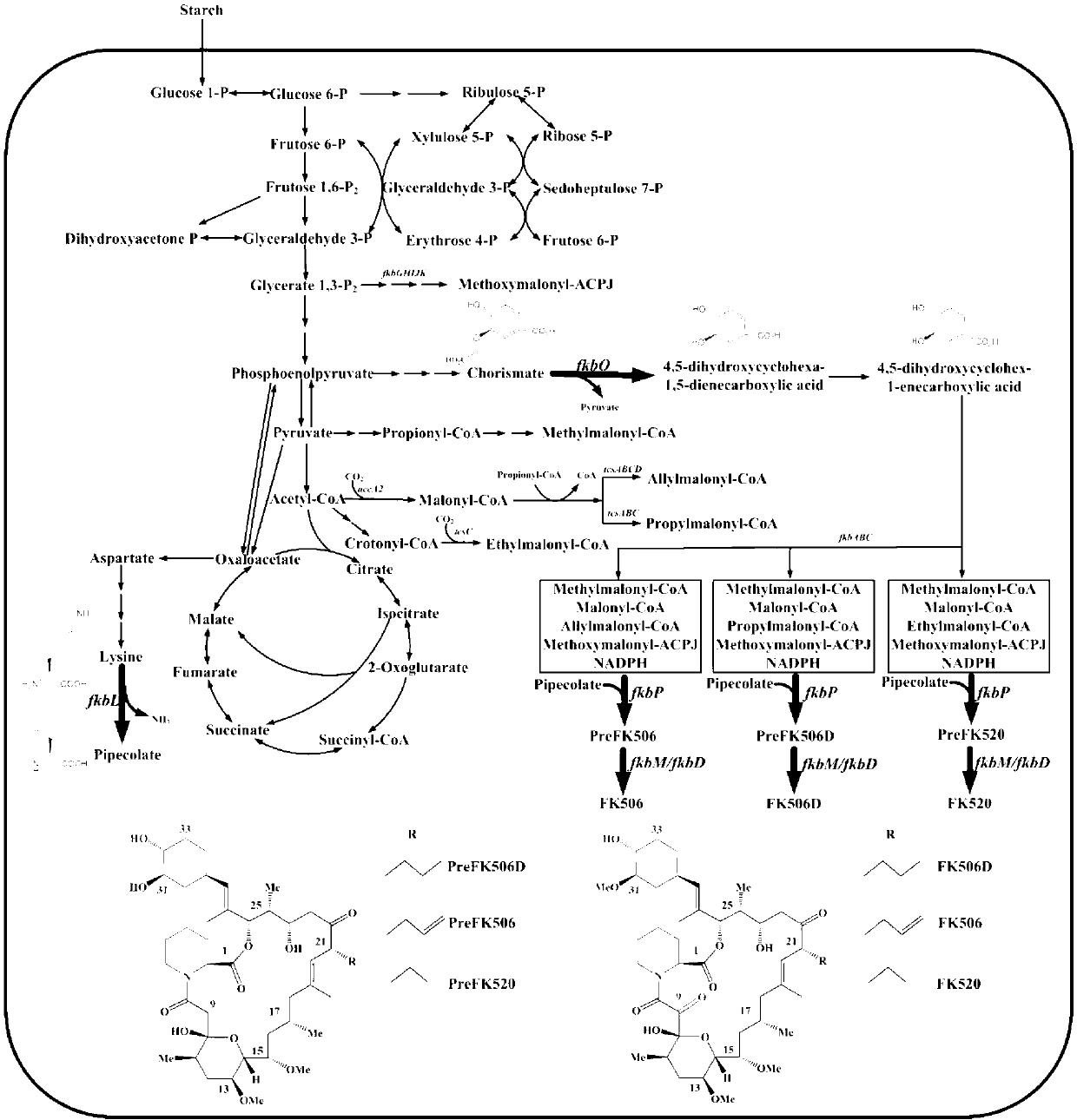
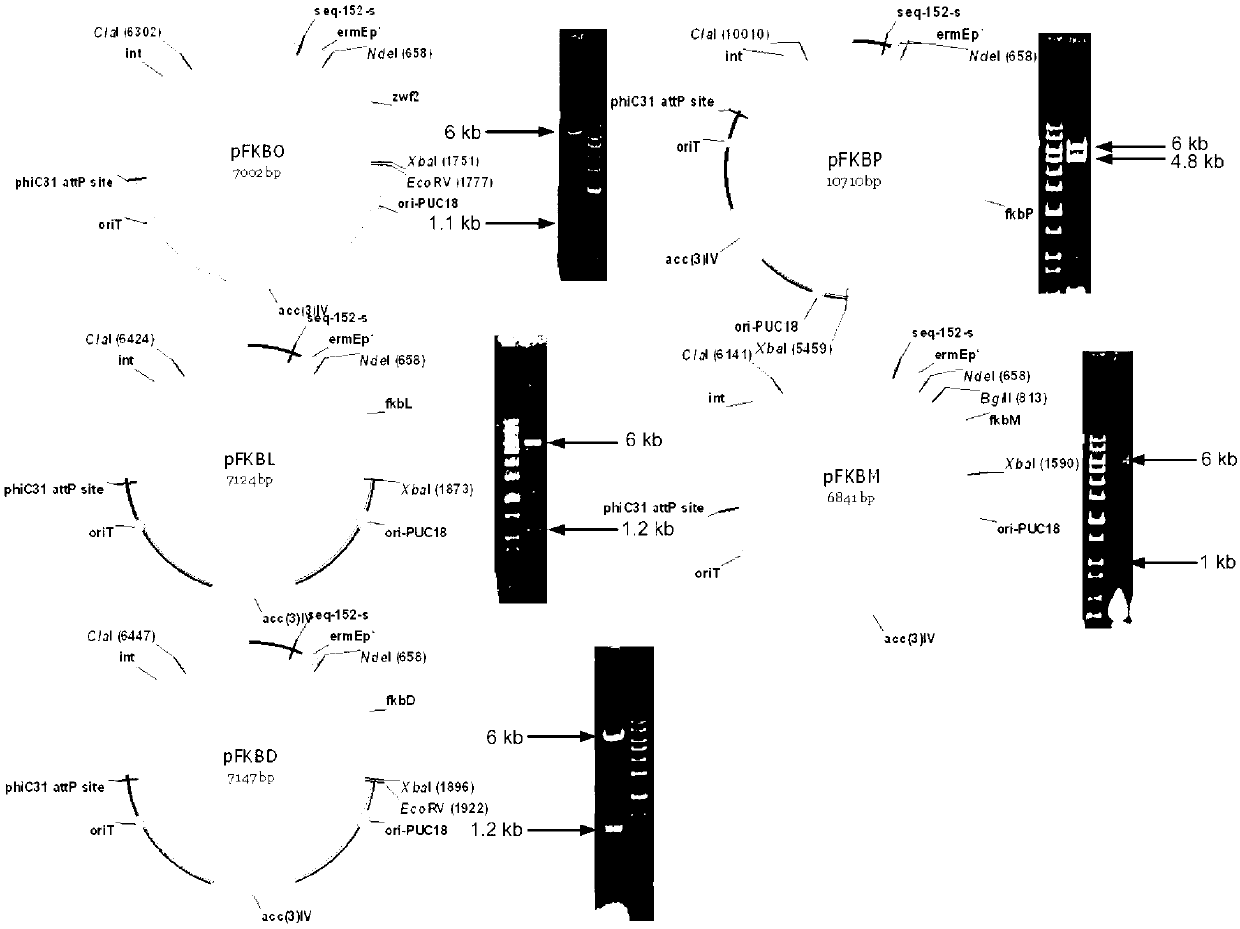
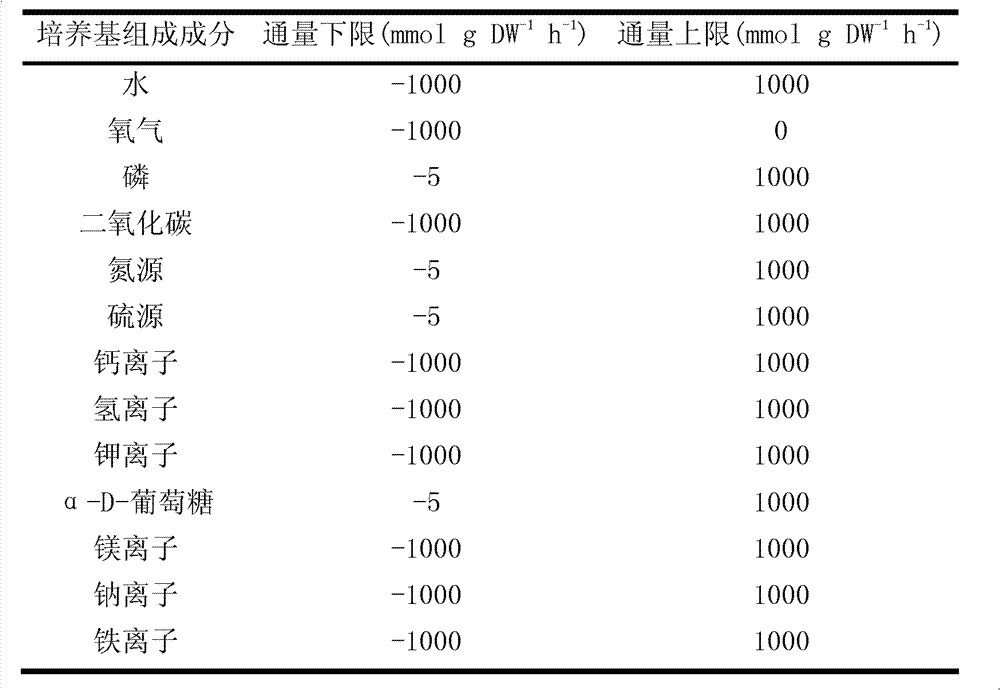
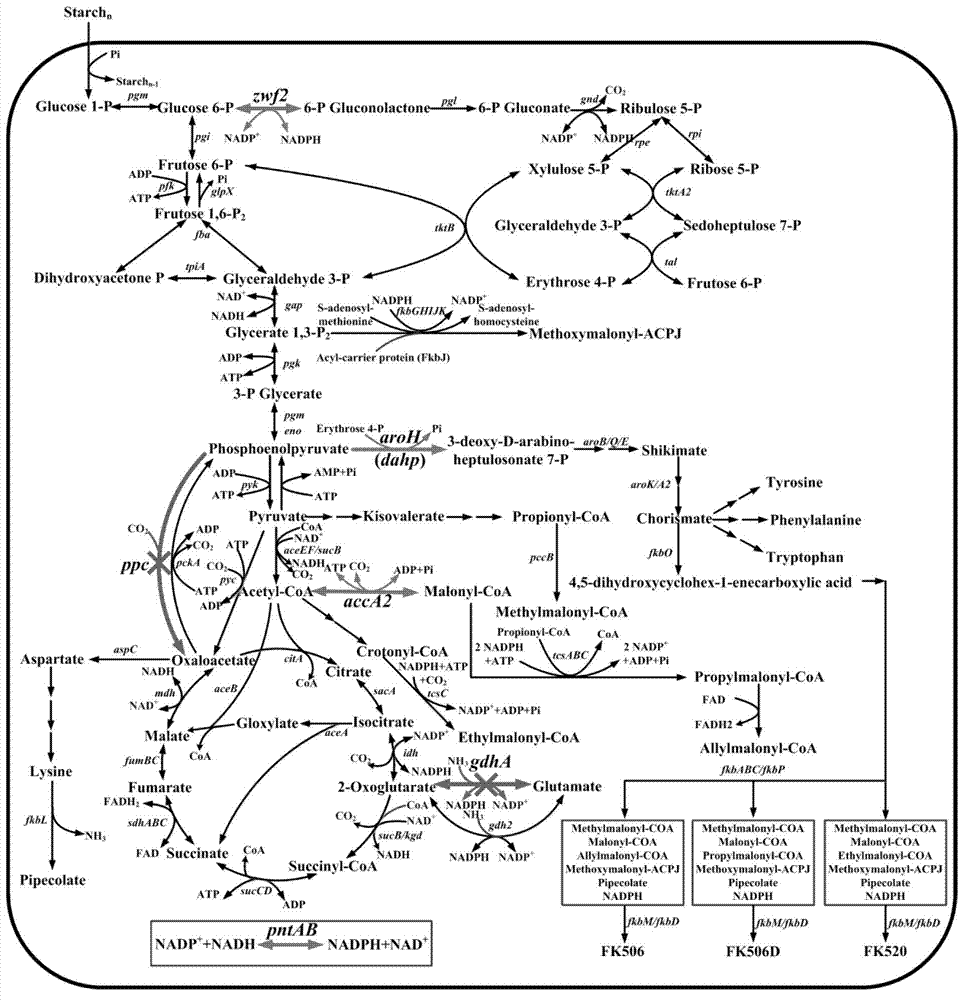
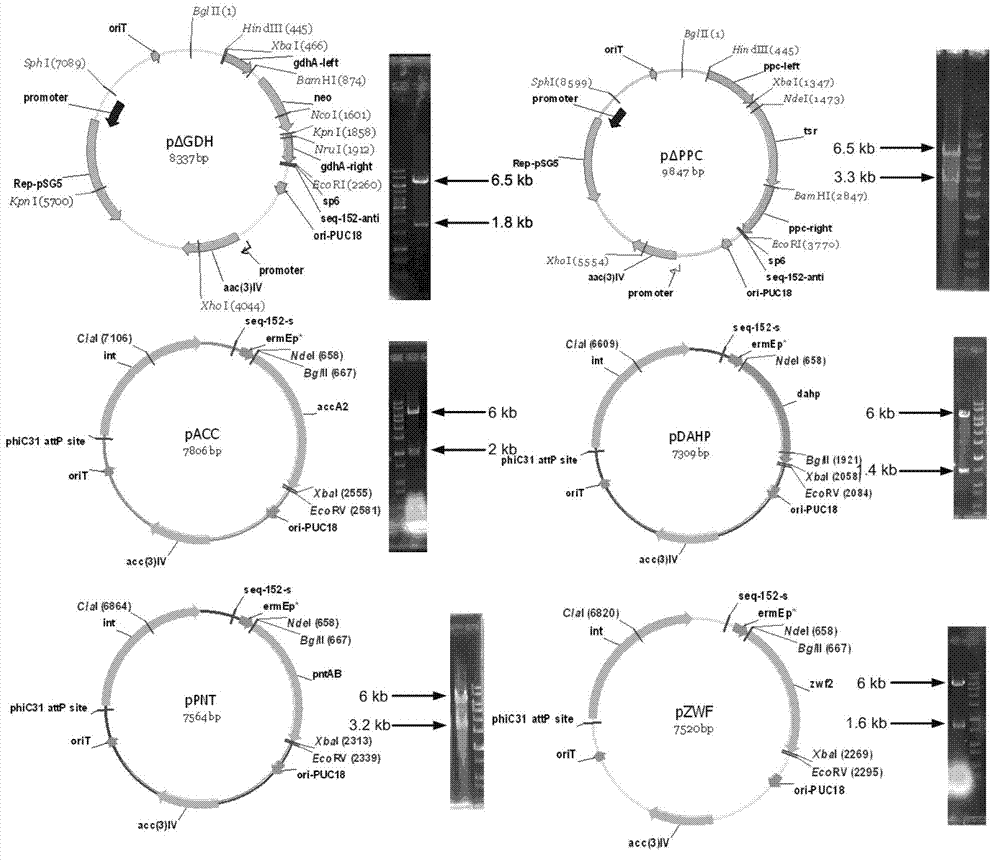
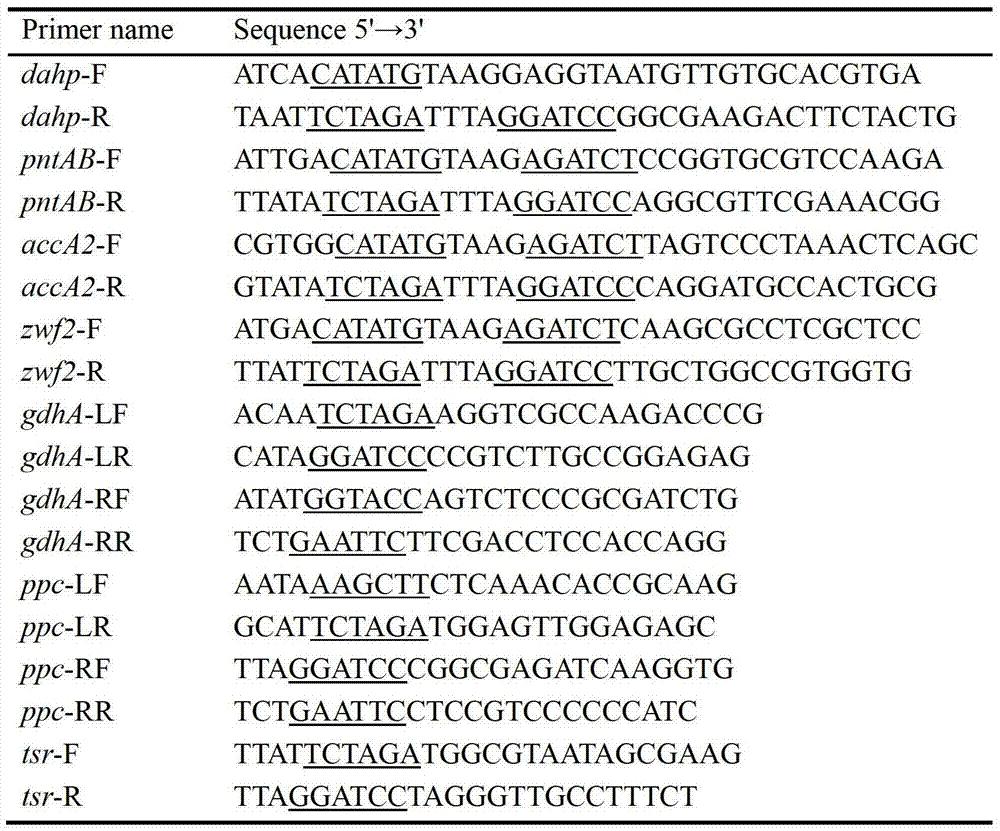
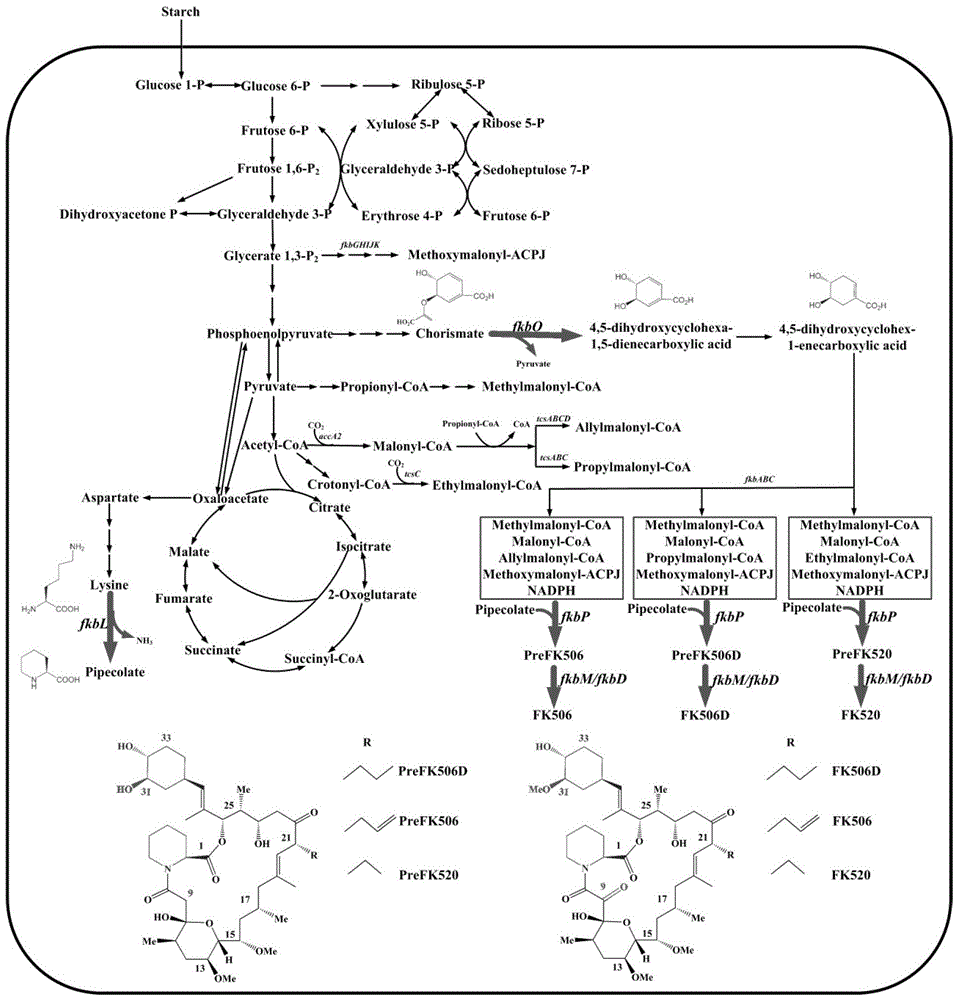
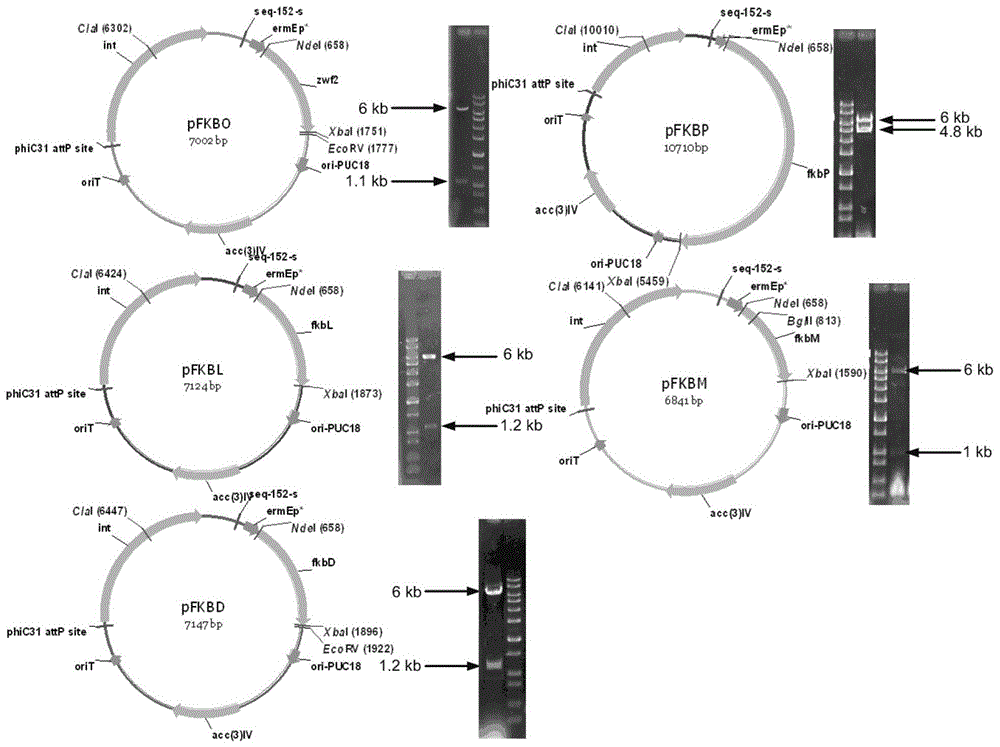
Secondary approach transformation method based on instruction of FK506 production bacterial strain wave chain streptomycete genome scale metabolic network model
InactiveCN103279689AIncrease production levelsImprove the experimental effectSpecial data processing applicationsMicroorganismGene cluster
The invention discloses a secondary approach transformation method based on an instruction of an FK506 production bacterial strain wave chain streptomycete genome scale metabolic network model. The model is based on annotation genes and physiology and biochemistry information. By comparing and analyzing the model with a streptomyces coelicolor genome, metabolic genes are found being highly conservative. Metabolic flux analysis is performed on a genome scale metabolic network, and therefore the model predicts a mutation bacterium secondary approach gene cluster transformation strategy for improving a production level. According to the secondary approach transformation method based on the instruction of the FK506 production bacterial strain wave chain streptomycete genome scale metabolic network model, the transformation method utilizes the genome scale metabolic network model to predict special structural genes in an FK506 bacterial strain secondary approach gene cluster, the production level of bacterial strains after transformation is improved by 20 percent to 90 percent, the special structural genes in the gene cluster are augmented to improve production capacity, and large application value is achieved in secondary approach rational transformation of microorganism immunosuppressor production bacterial strains. The high-efficiency and systematic method is provided for optimizing of the bacterial strains.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
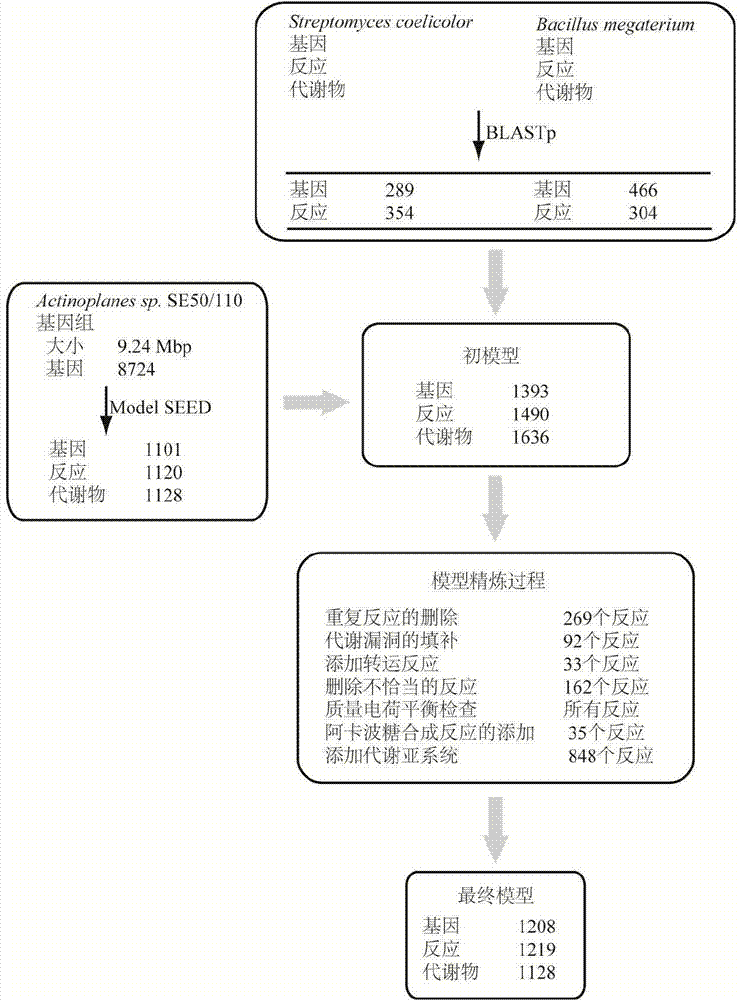
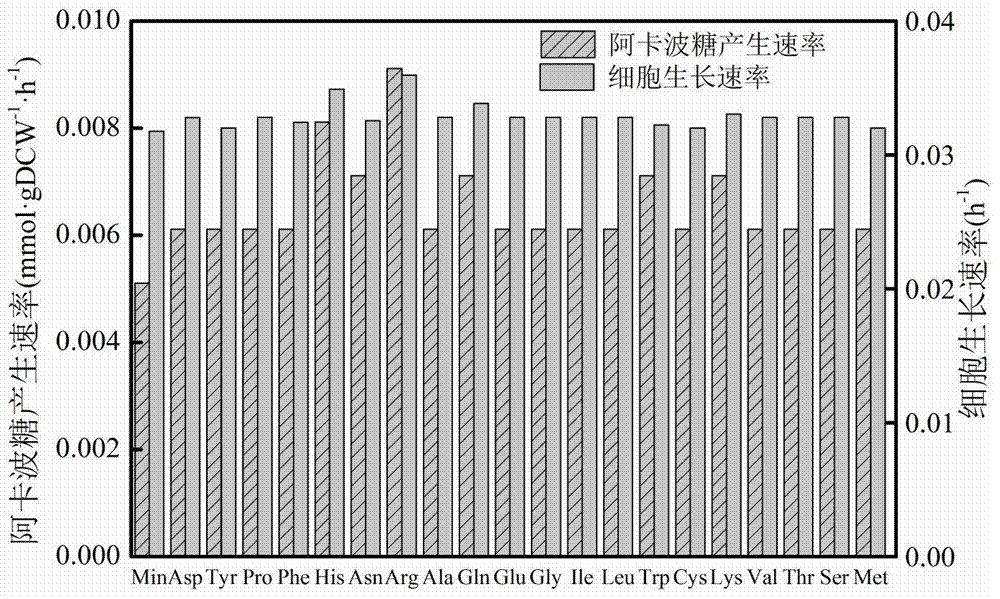
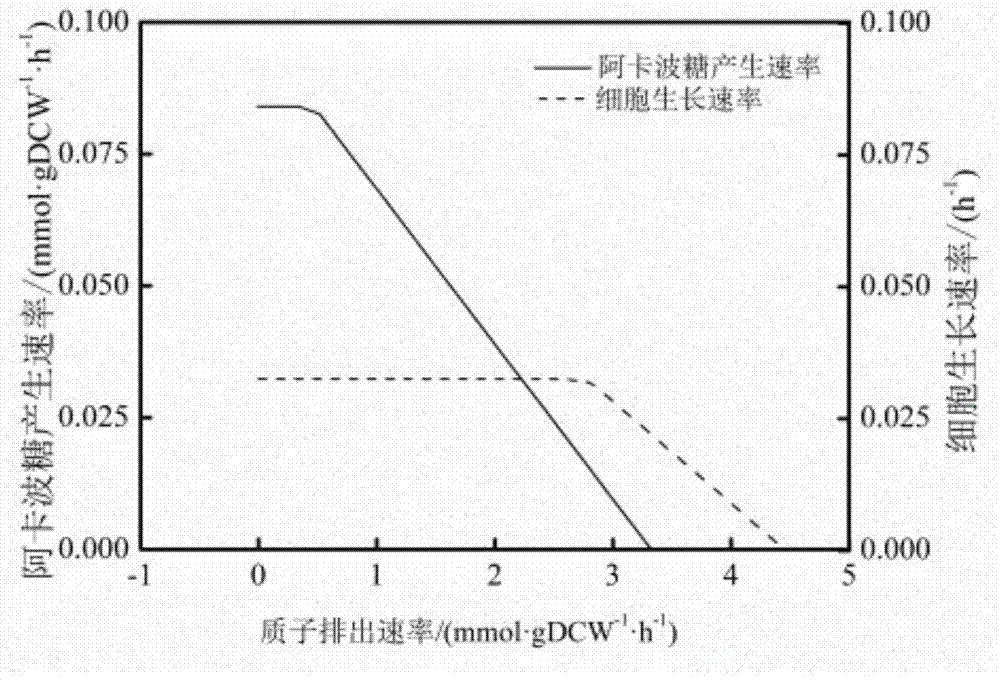
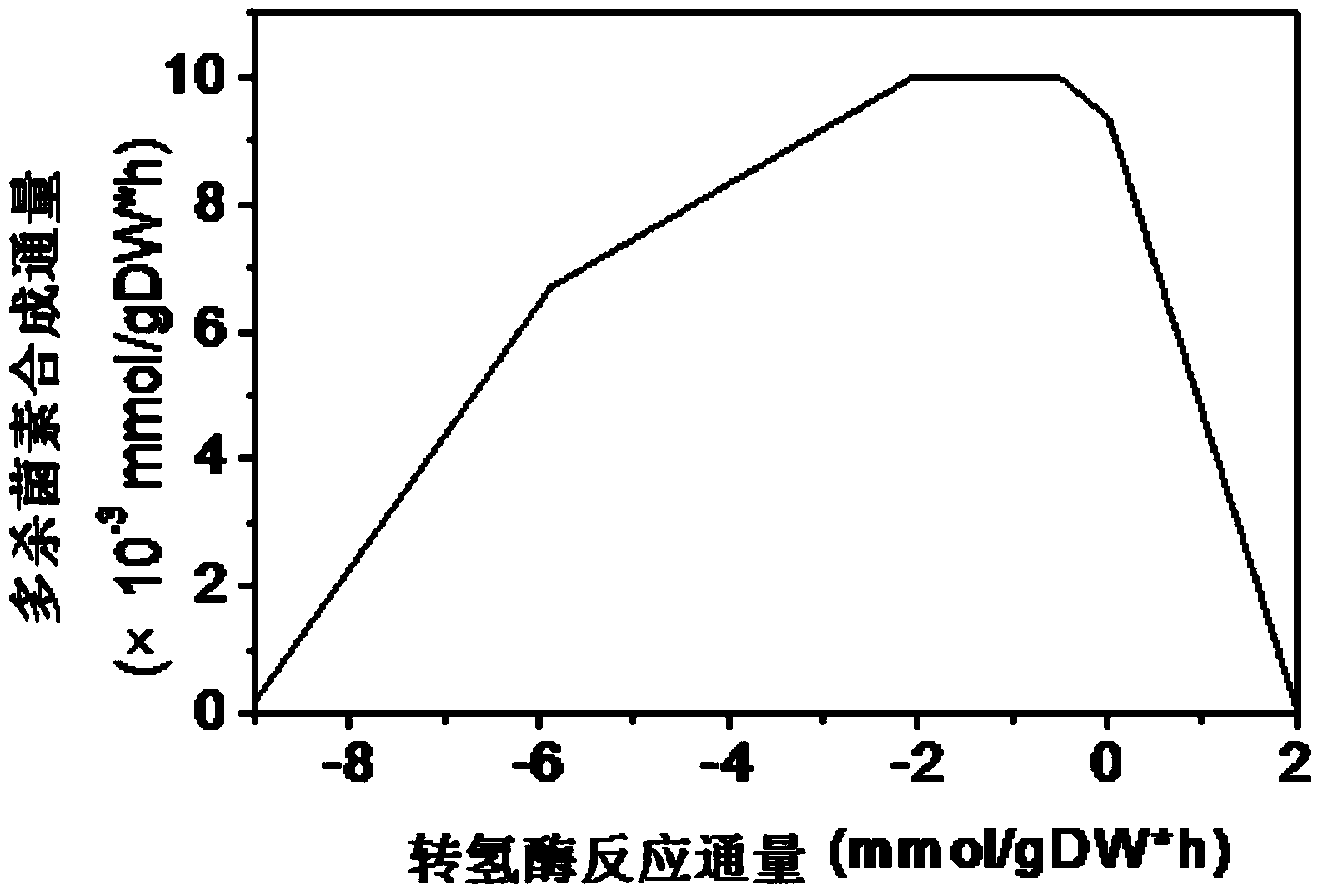
Method for establishing and analyzing scale metabolism network model of actinoplanetes genomes
InactiveCN104745661AImprove accuracyStrong reliabilityOrganic active ingredientsMetabolism disorderNetwork modelMetabolic network model
The invention discloses a method for establishing and analyzing a scale metabolism network model of actinoplanetes genomes, and belongs to the field of systems biology. Cell growth simulation, essential growth essential genes and reaction verification are carried on the scale metabolism network model of actinoplanetes genomes established based on the method on a system level, a strategy is provided for simulating and improving acarbose yield, and an important platform is provided for comprehensively understanding the metabolic characteristics of actinoplanetes and improving the acarbose fermentation level. The invention provides multiple methods for improving the acarbose yield, the acarbose yield can be increased by 53.5% by adding nicotinic acid, and the acarbose yield is respectively increased by 29.6%, 26.5%, 26.3%, 11.8% and 9.2% by adding glutamic acid, cysteine, lysine, glutamine and asparagines.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Saccharopolyspora spinosa genome scale metabolic network model and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN103729576AIncrease productionAchieving Pathway Molecular Modification MethodsSpecial data processing applicationsGene targetsBacterial strain
The invention discloses a saccharopolyspora spinosa genome scale metabolic network model and a construction method and application of the saccharopolyspora spinosa genome scale metabolic network model. The construction method includes the following steps that according to annotation information of saccharopolyspora spinosa genome sequences in KEGG and NCBI databases, a characteristic reaction for spinosad biosynthesis and a thallus sythesis reaction are added, a network reaction is manually refined, and then the saccharopolyspora spinosa genome scale metabolic network model is acquired. Through the saccharopolyspora spinosa genome scale metabolic network model, influences on improvement of the output of spinosad on a gene target spot can be predicted, the modification direction is finally determined, and the bacterial strain path molecule modification method is achieved. Experiments show that through genes predicted by the saccharopolyspora spinosa genome scale metabolic network model, genetically engineered bacteria obtained through modification can make the output of spinosad improved by 86.5% compared with wild bacterial strains. An instruction platform is provided for construction, research and analysis of the bacterial strains for efficiently producing and synthesizing spinosad.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for combined production of chiral hydroxy ester and uridine phosphinylideyne compounds
InactiveCN101724670AImprove conversion efficiencyLow costMicroorganism based processesFermentationYeastIncreased orotic acid
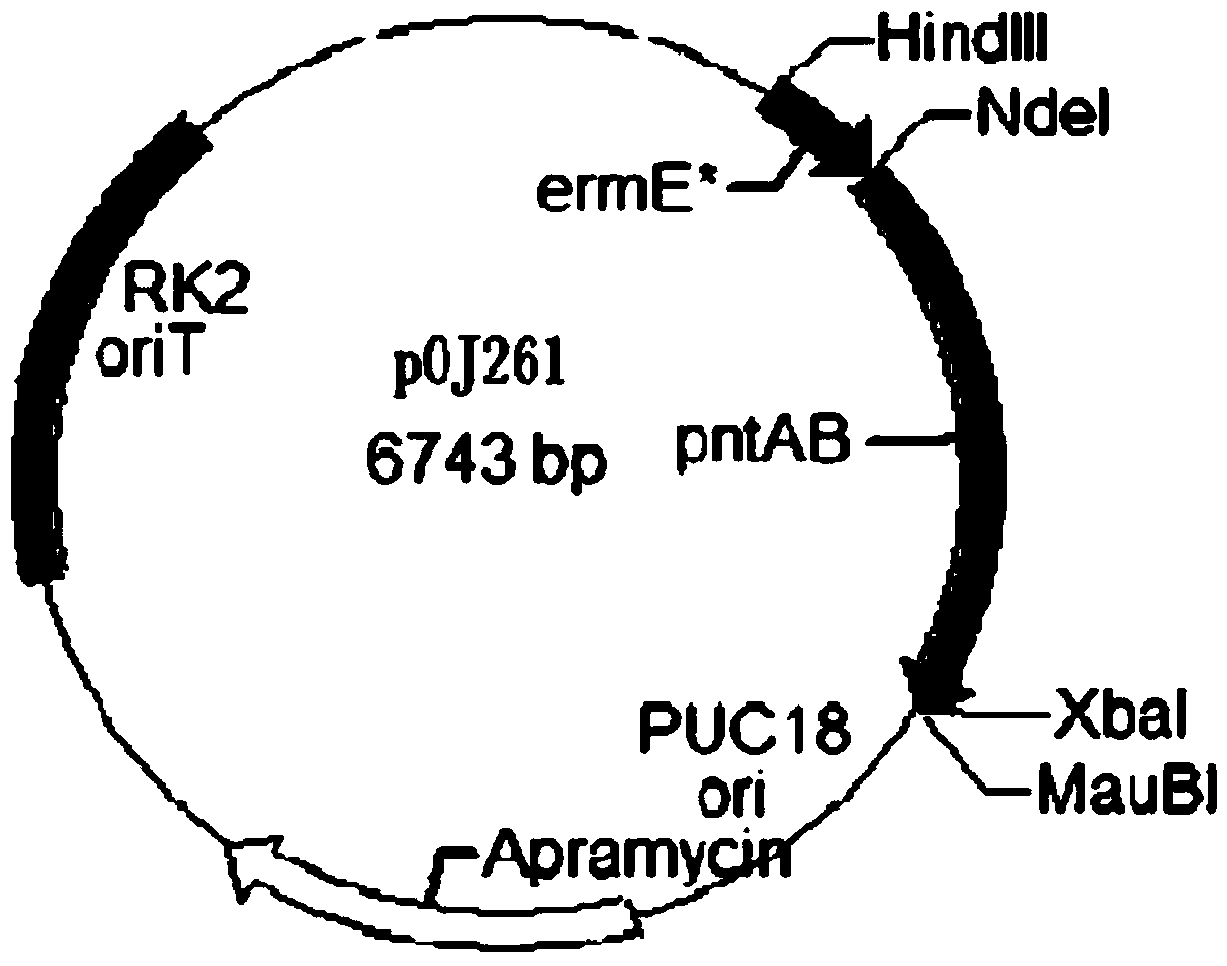
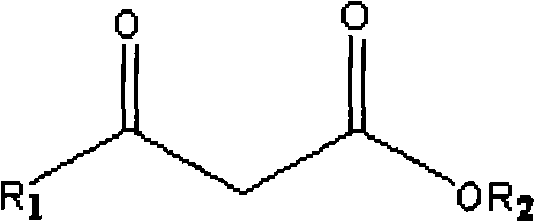
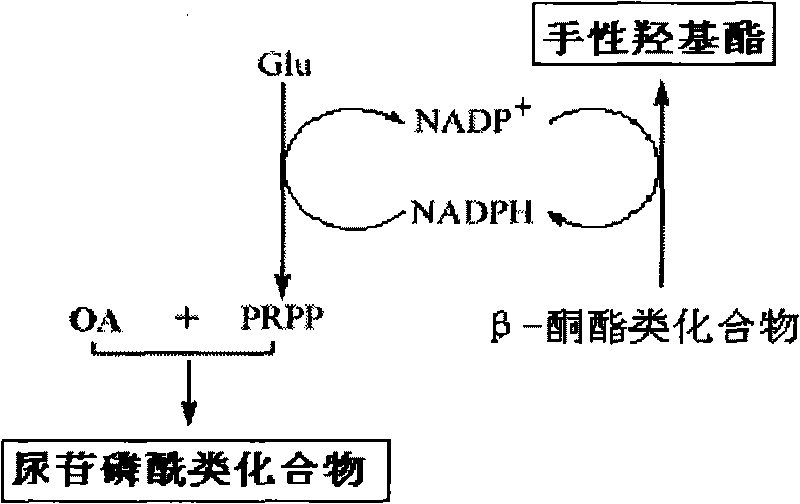
The invention discloses a method for combined production of chiral hydroxy ester and uridine phosphinylideyne compounds. In the method, orotic acid and beta-ketone ester compounds are used as substrates, glucose is used as an energy supplier, and yeast cells with permeability are used to prepare uridine phosphinylideyne compounds and chiral hydroxy ester at the same time. Based on the theory of full cell catalysis and metabolism engineering, the method uses the yeast cells with permeability to realize the combined production of the chiral hydroxy ester and the uridine phosphinylideyne compounds by establishing a metabolism network model and the metabolism flow rate analysis, so that the method has the advantages of improving yield, lowering production cost, shortening synthesis time and greatly improving the utilization ratio of the substrates.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Primary pathway transformation method under guidance of FK506 strain genome-scale metabolic network model
InactiveCN103276011AIncrease production levelsIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMetabolic network model
The invention discloses a primary pathway transformation method under the guidance of an FK506 strain genome-scale metabolic network model, which comprises the following steps of: adding the characteristic reaction and thallus synthesis reaction of FK506 biosynthesis according to the streptomyces tsukubaensis genome sequence, and performing manual refining on the network reaction to obtain an FK506 strain streptomyces tsukubaensis genome-scale metabolic network model; and analyzing the metabolic network model, and determining the primary pathway precursor key gene of FK506 biosynthesis through a flux equilibrium analysis and minimum metabolic regulation analysis method. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the strain production level after the transformation is improved by 80-100%. The method provides efficient guidance to the establishment, research and analysis of the primary pathway of the FK506 strain, and has great application prospects in the research process of FK506 strain transformation.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Pichia stipitis genome-scale metabolic network model construction and analysis method
The present invention describes an integrated genome-scale metabolic network model construction and analysis method with Pichia stipitis as an example, belonging to the system biology field. Based on the method, a constructed and obtained Pichia stipitis genome-scale metabolic network model is subjected to cell growth simulation of a system level and identification of a minimal gene and reaction set, and an important platform is provided for comprehensive understanding of metabolic characteristics and mechanism of the Pichia stipitis is provided.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
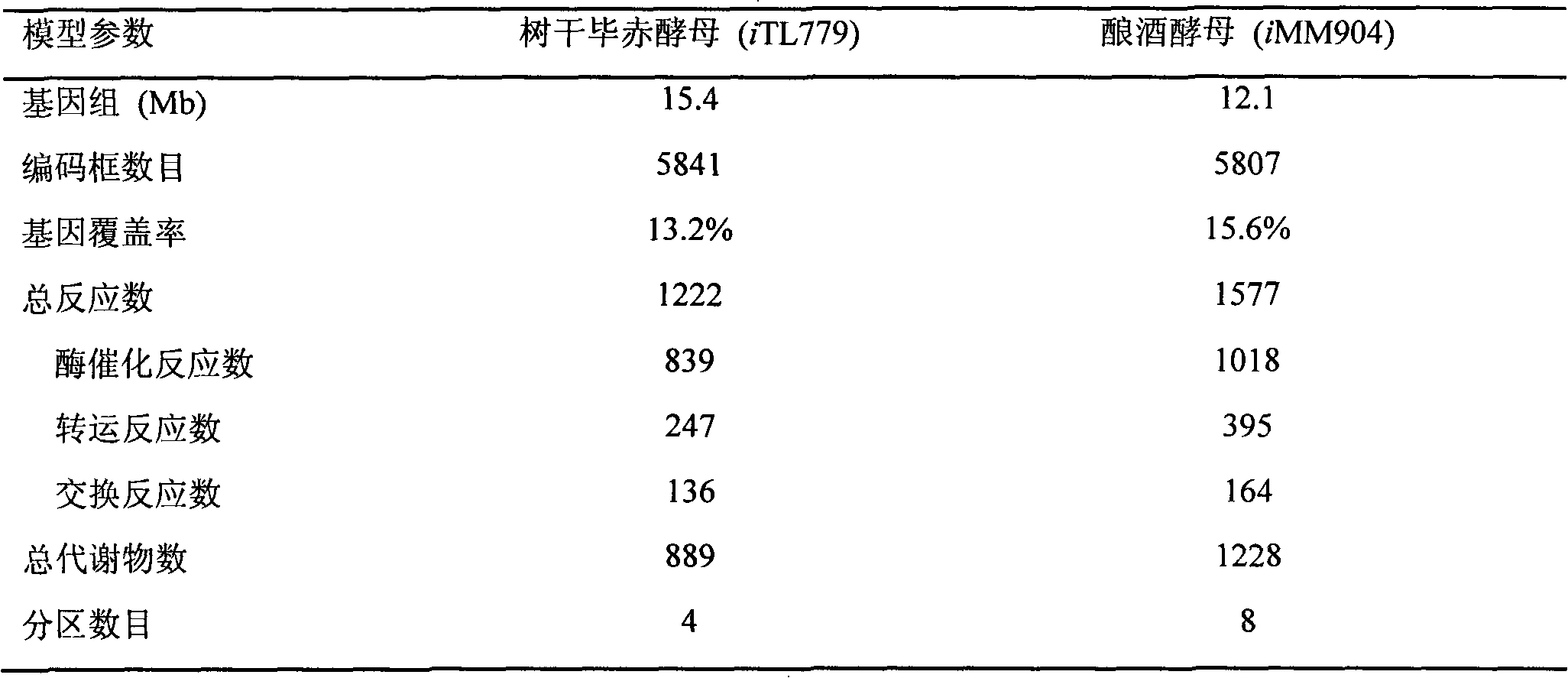
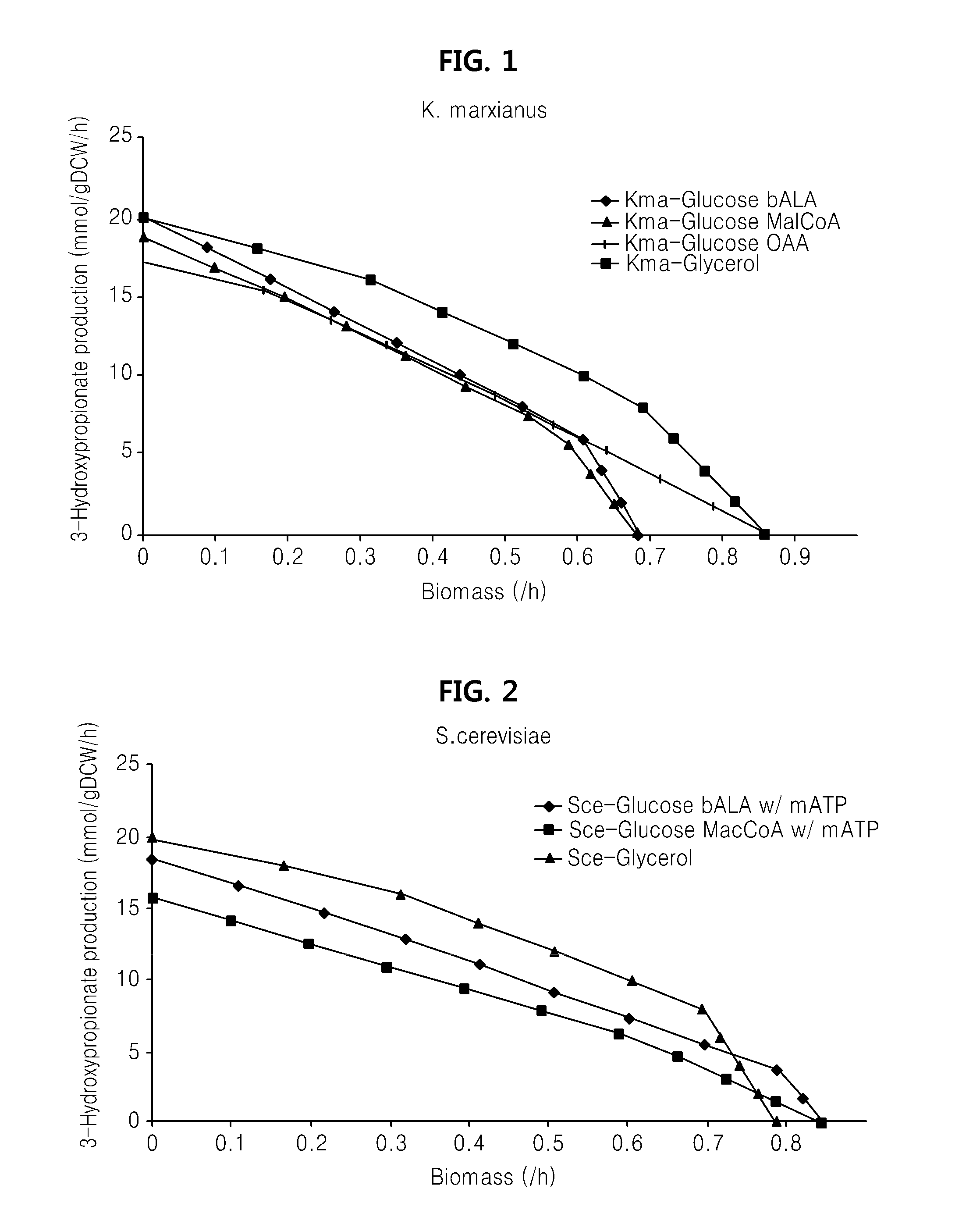
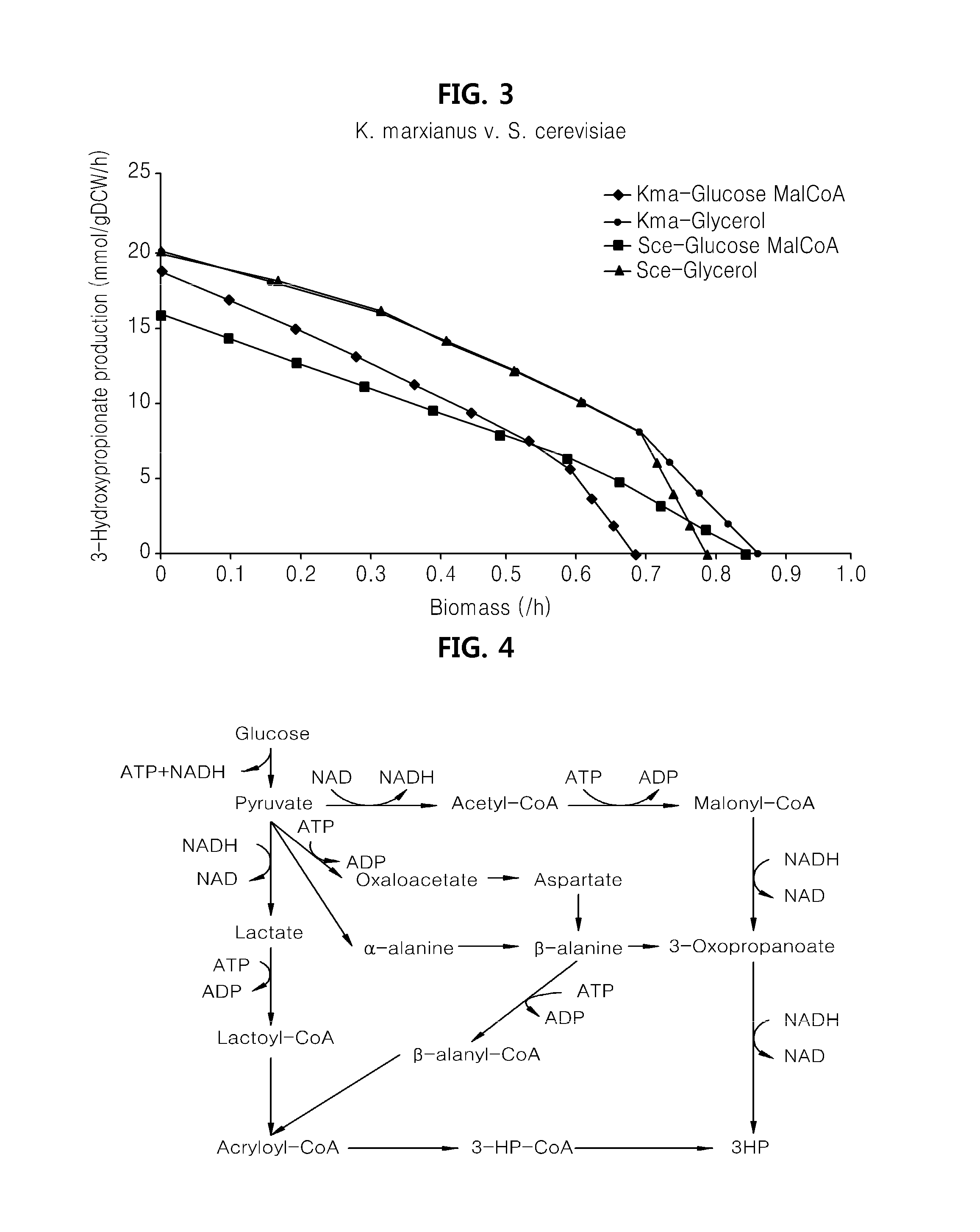
Genome-scale metabolic network model reconstruction of kluyveromyces marxianus and strategies for engineering non-native pathways for 3-hydroxypropionate production in kluyveromyces marxianus
InactiveUS20140093901A1Maximizing growth rateEfficient productionMicroorganismsMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnology3-Hydroxypropionic acid
Use of a metabolic network model for analyzing metabolic characteristics of microorganisms for producing a metabolic product, such as 3HP enabling estimation of productivity and cell growth speed of microorganisms, optimizing new metabolic pathway, and providing transformed microorganisms that may produce a specific metabolic product with high efficiency.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
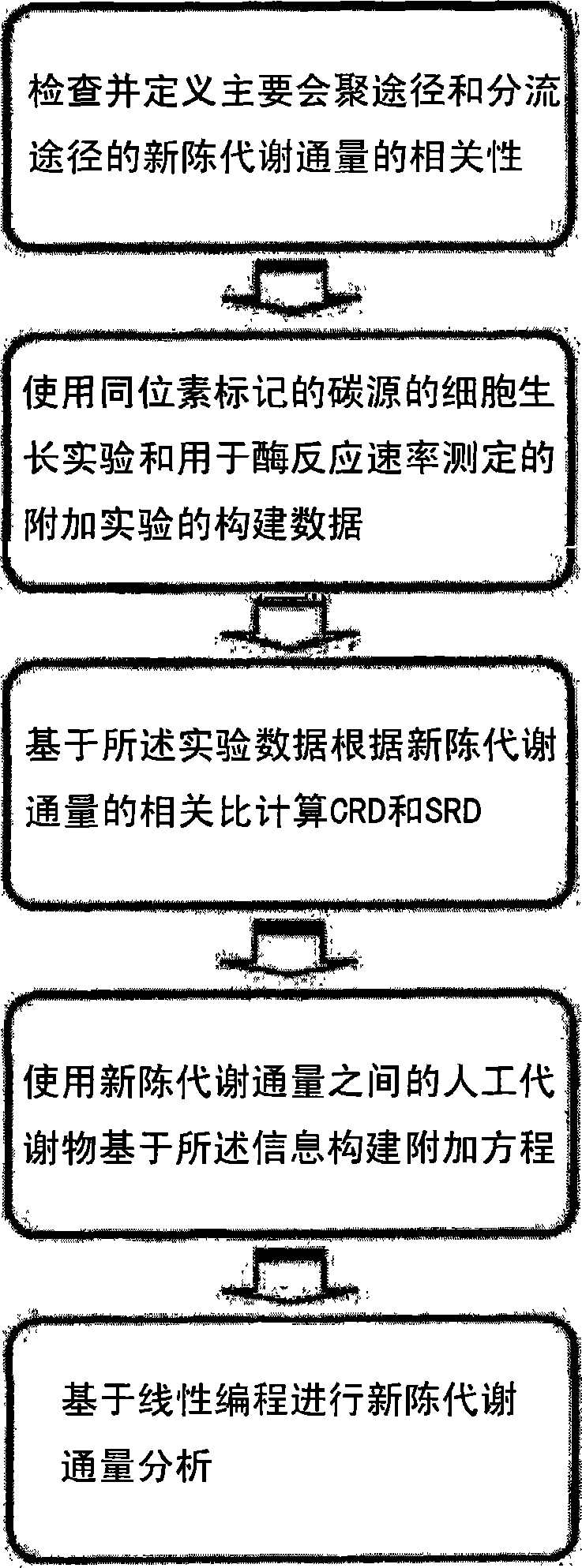
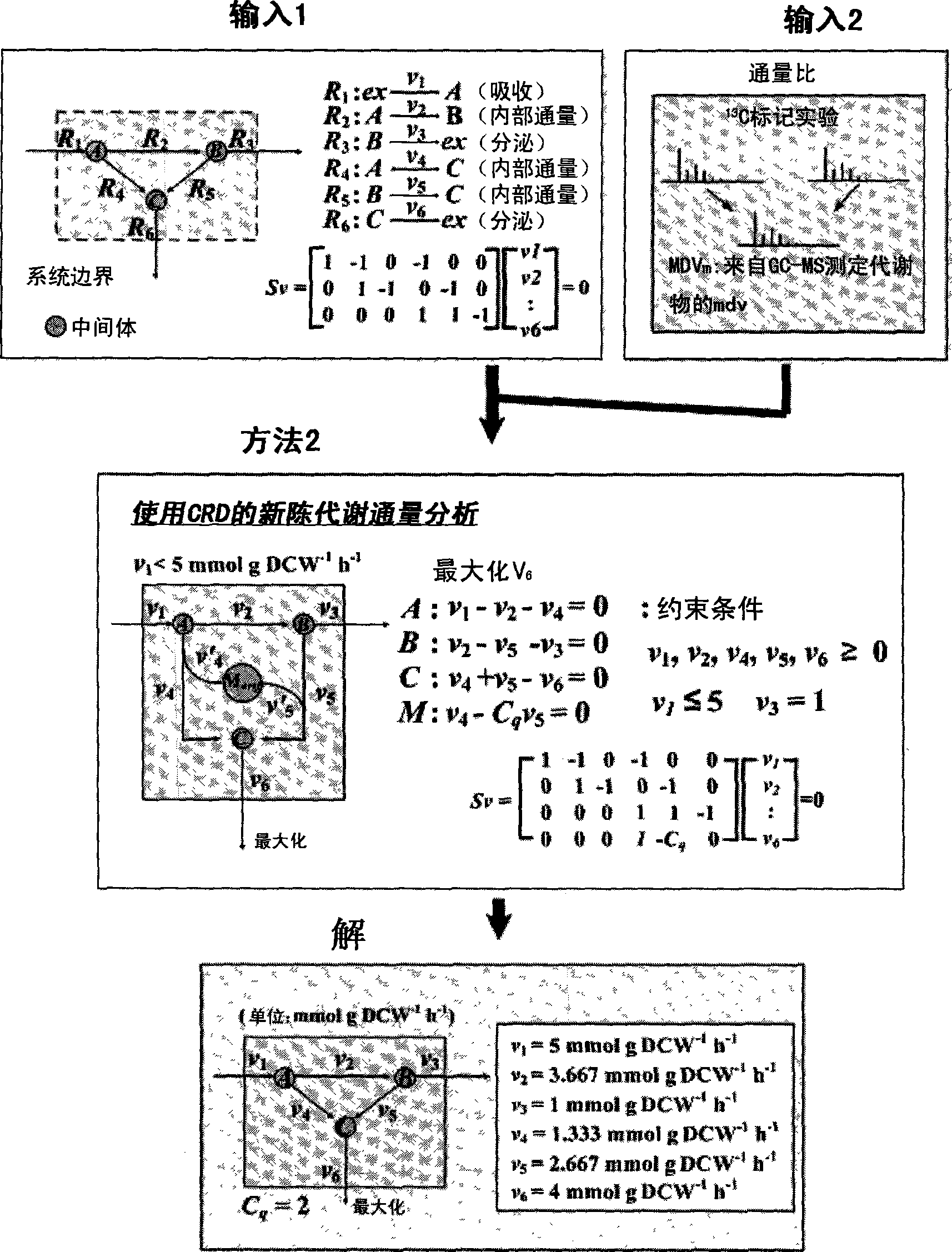
Method for analyzing metabolites flux using converging ratio determinant and split ratio determinant
The present invention relates to a method for analyzing metabolic flux using CRD and SRD. Specifically, the method comprising: selecting a specific target organism, constructing the metabolic network model of the selected organism, identifying the correlations between specific metabolic fluxes in the metabolic network model, defining the correlation ratios as CRD and SRD, determining the correlation ratios of the metabolic fluxes through the experiment for measuring metabolic flux ratios, modifying a stoichiometric matrix with the determined CRD, SRD and correlation ratios, and applying the modified stoichiometric matrix of the metabolic network model for linear programming. According to the inventice method, the correlation between influent / effluent metabolic fluxes with respect to specific metabolites in target organisms (including E. coli), the genome-scale metabolic network model of which was constructed, can be determined as relative ratio using useful information obtained from various experiments, including a growth experiment using a radioactive isotope-labeled carbon source and an assay for measuring enzymatic reaction. Thus, limit values from various experiments can be effectively applied, so that internal metabolic flux can be quantified and analyzed in a more accurate and rapid manner.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
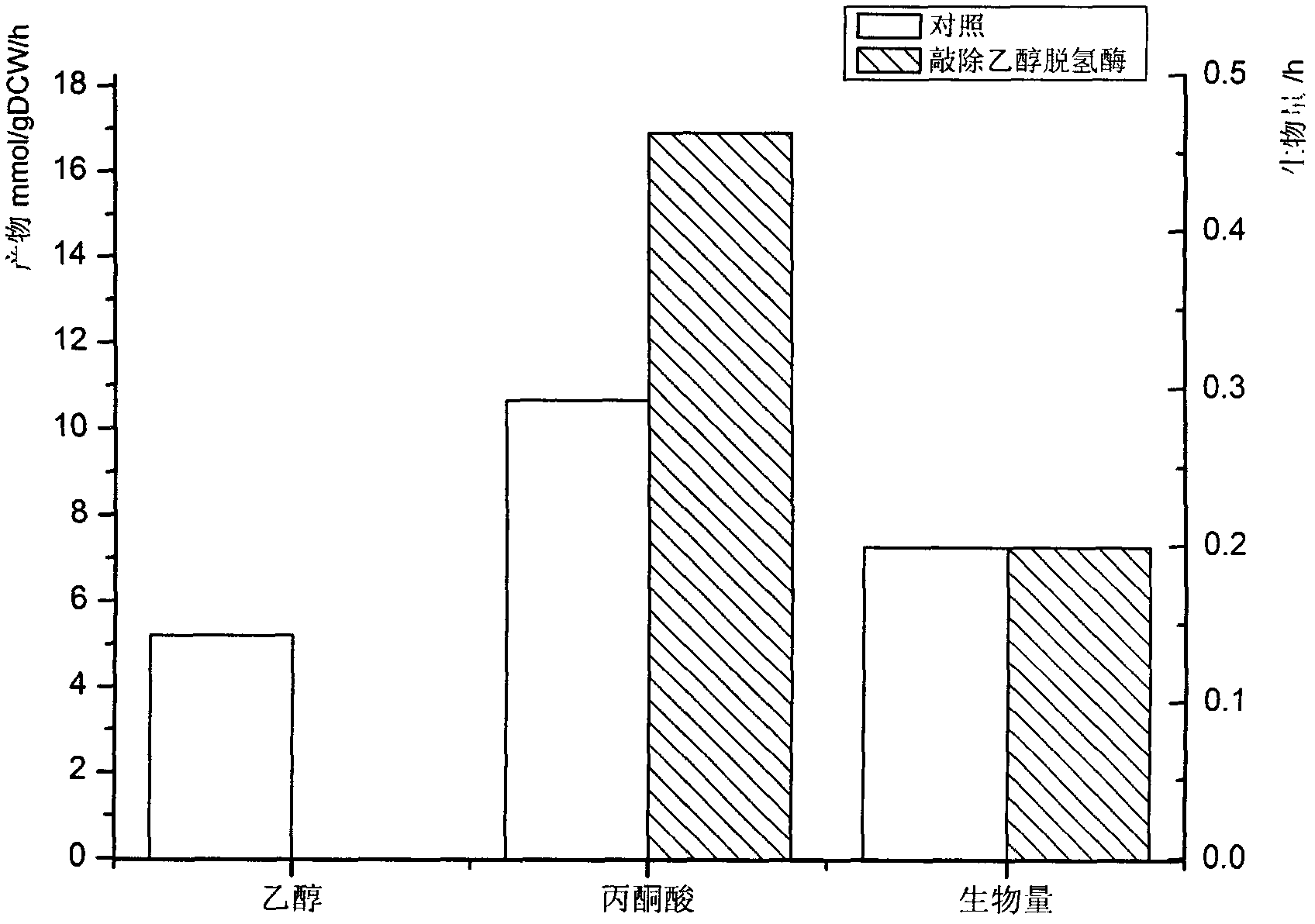
Construction and application technology of Torulopsis glabrata genome metabolism model
InactiveCN102622533AIncrease productionSpecial data processing applicationsTorulopsis glabrataEthanol dehydrogenase
The invention discloses a construction method and an application technology of a Torulopsis glabrata genome-scale metabolism network model, belonging to the field of systems biology. The construction method of the model is an all-round semi-automatic construction method of combining comparative genomics annotation and bacteria-specific information of Torulopsis glabrata protein homology based on an automatic model. The invention provides a method for characterizing auxotroph characteristics in a Torulopsis glabrata metabolism network by adding necessary nutrient substances, lacked in bacteria, to a biomass equation. Alcohol dehydrogenase is knocked out by using single genes in the Torulopsis glabrata metabolism network model, and flow equilibrium analysis is applied, so that the output of pyruvic acid is increased. The construction method and the application technology of the Torulopsis glabrata genome-scale metabolism network model provide a high-efficient platform for fully understanding and reforming physiological and biochemical metabolisms of the Torulopsis glabrata.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
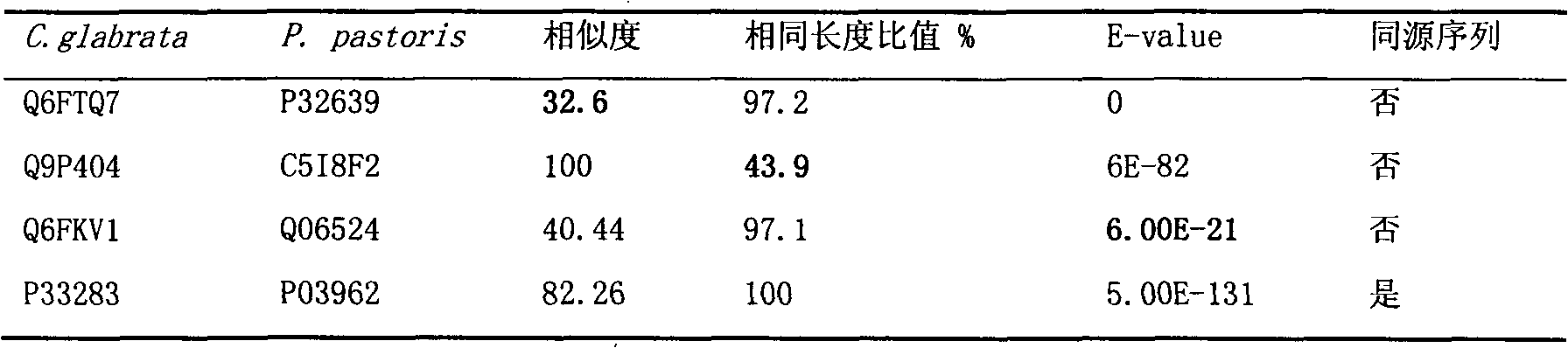
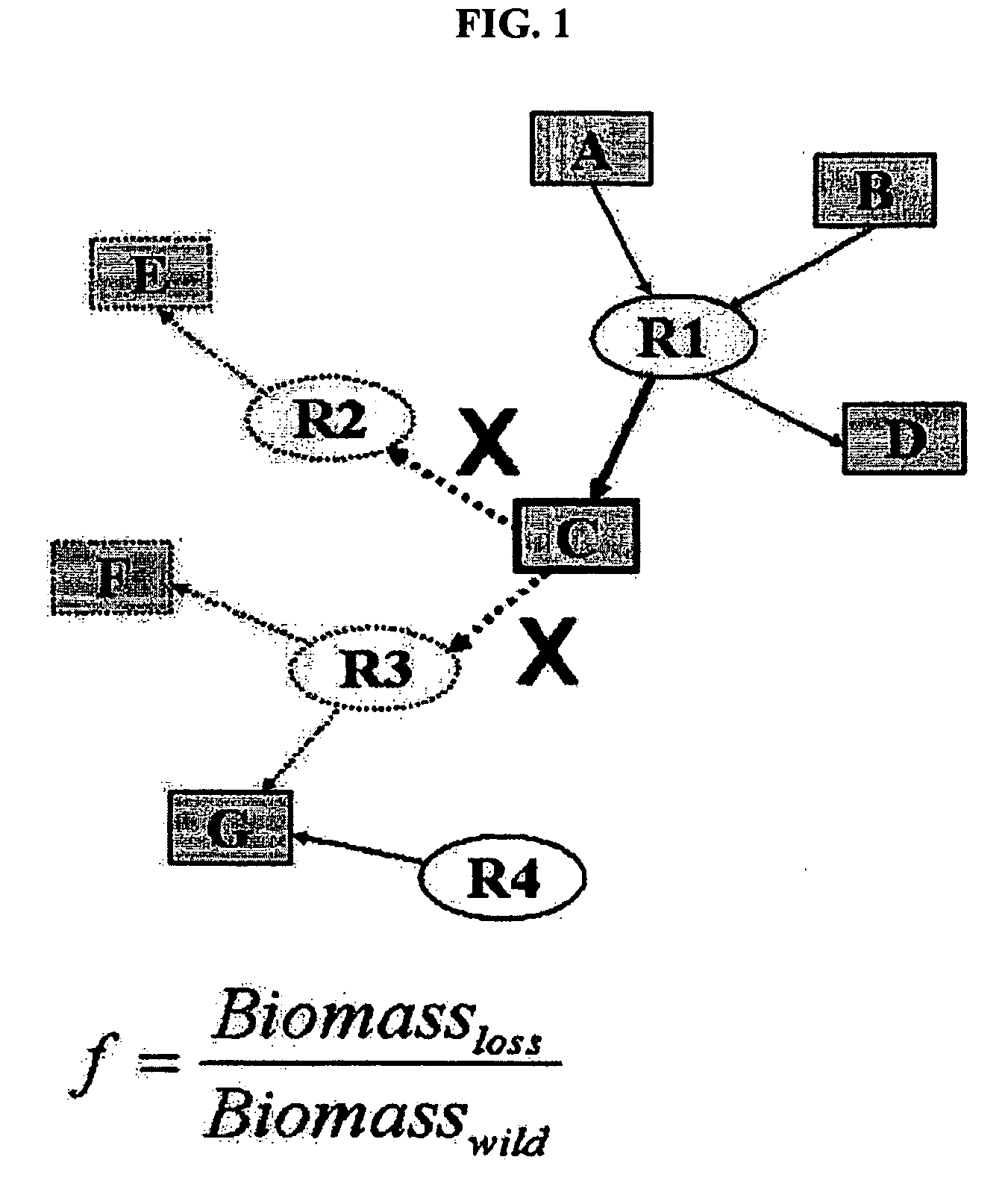
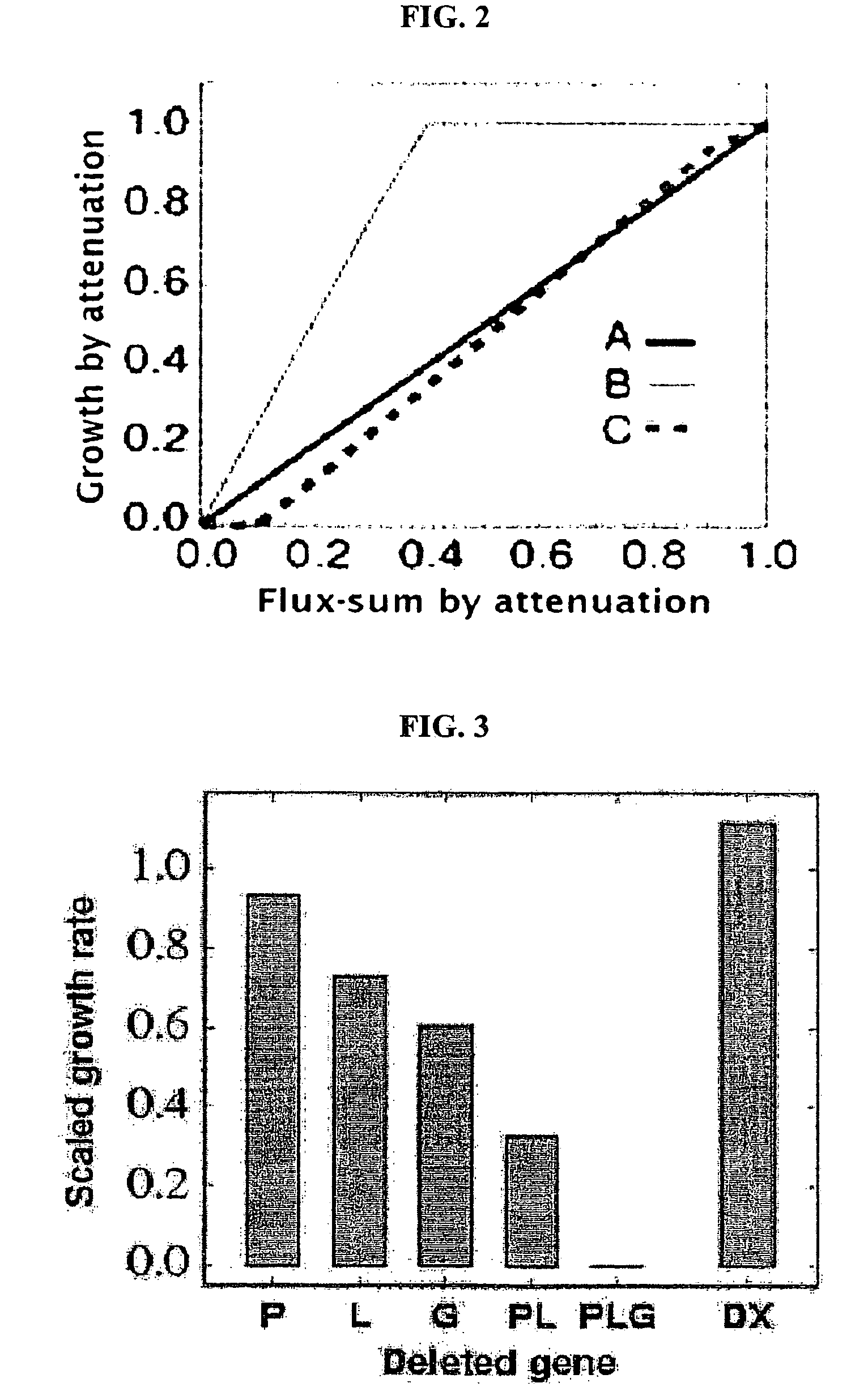
Method for screening essential metabolites in growth of microorganisms
ActiveUS20100143911A1Growth inhibitionDecreased cell growthBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyPathogenic microorganism
The present invention disclosed is a method for screening metabolites essential for the growth of microorganism using metabolic flux analysis. More specifically, the present invention relates to the method for screening metabolites essential for the growth of microorganism, by selecting a target microorganism, constructing a metabolic network model of the selected microorganism, inactivating the consumption reaction of each of metabolites in the constructed metabolic network model, analyzing the metabolic flux of the metabolites to select metabolites essential for the growth of the microorganism, and confirming the selected metabolites using the utilization of each of the metabolites, defined as flux sum (Φ). According to the present invention, metabolites essential for the growth of microorganism, and genes involved in the essential metabolites, can be screened in a convenient manner, and drug-target genes against pathogenic microorganisms can be predicted by deleting genes associated with the metabolites screened according to the method.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
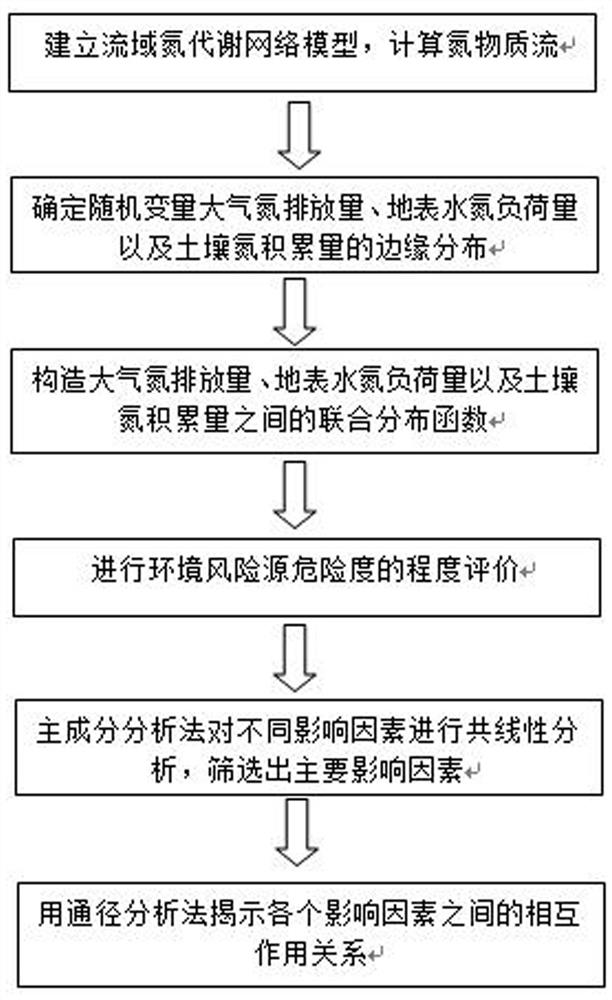
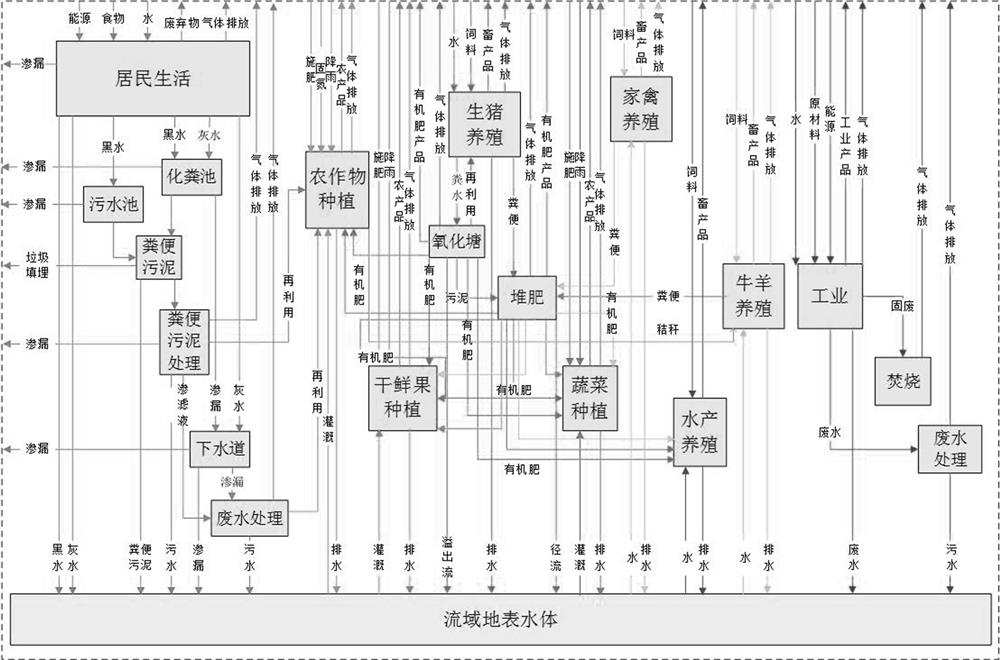
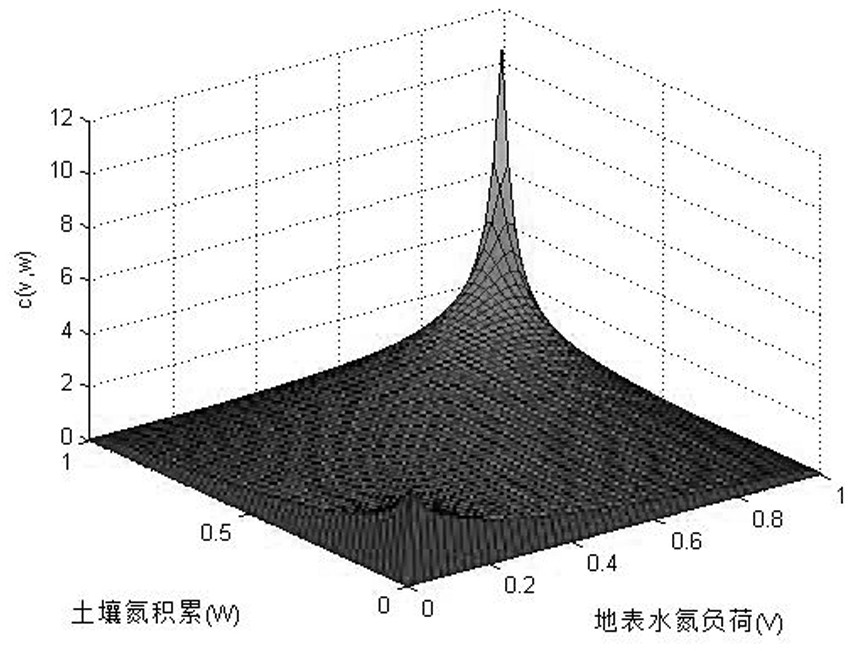
Copula function-based basin nitrogen metabolism environment risk evaluation method
The invention discloses a Copula function-based basin nitrogen metabolism environment risk evaluation method, which comprises the steps of establishing a basin nitrogen metabolism network model, and calculating a nitrogen substance flow; fitting an edge distribution function of the atmospheric nitrogen discharge amount, the surface water nitrogen load amount and the soil nitrogen accumulation amount; constructing a ternary joint distribution function of the atmospheric nitrogen discharge amount, the surface water nitrogen load amount and the soil nitrogen accumulation amount; calculating a multivariate joint distribution function value according to the ternary joint distribution function, and performing environmental risk evaluation; identifying key influence factors of the nitrogen metabolism environment risk by utilizing a principal component analysis method; and obtaining the interaction relationship among the influence factors of the nitrogen metabolism environment risk by using adrift diameter analysis method. According to the method, evaluation and grading of the nitrogen metabolism environment risk in the drainage basin are achieved according to multivariate joint distribution function values; key influence factors of the nitrogen metabolism environment risk are identified, the interaction relationship among the influence factors is explored, and a forming mechanism ofa basin nitrogen metabolism environment risk source is disclosed.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
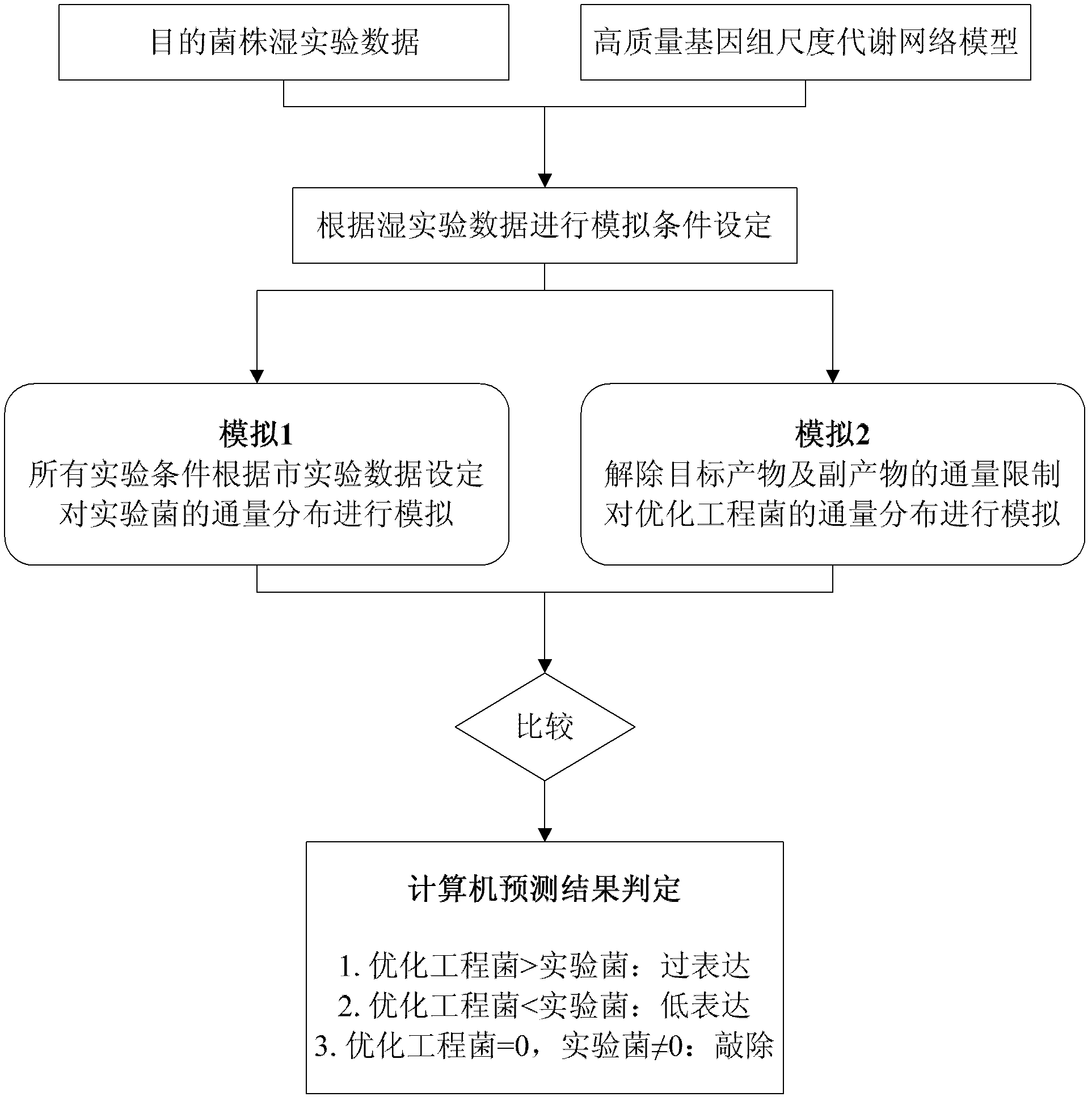
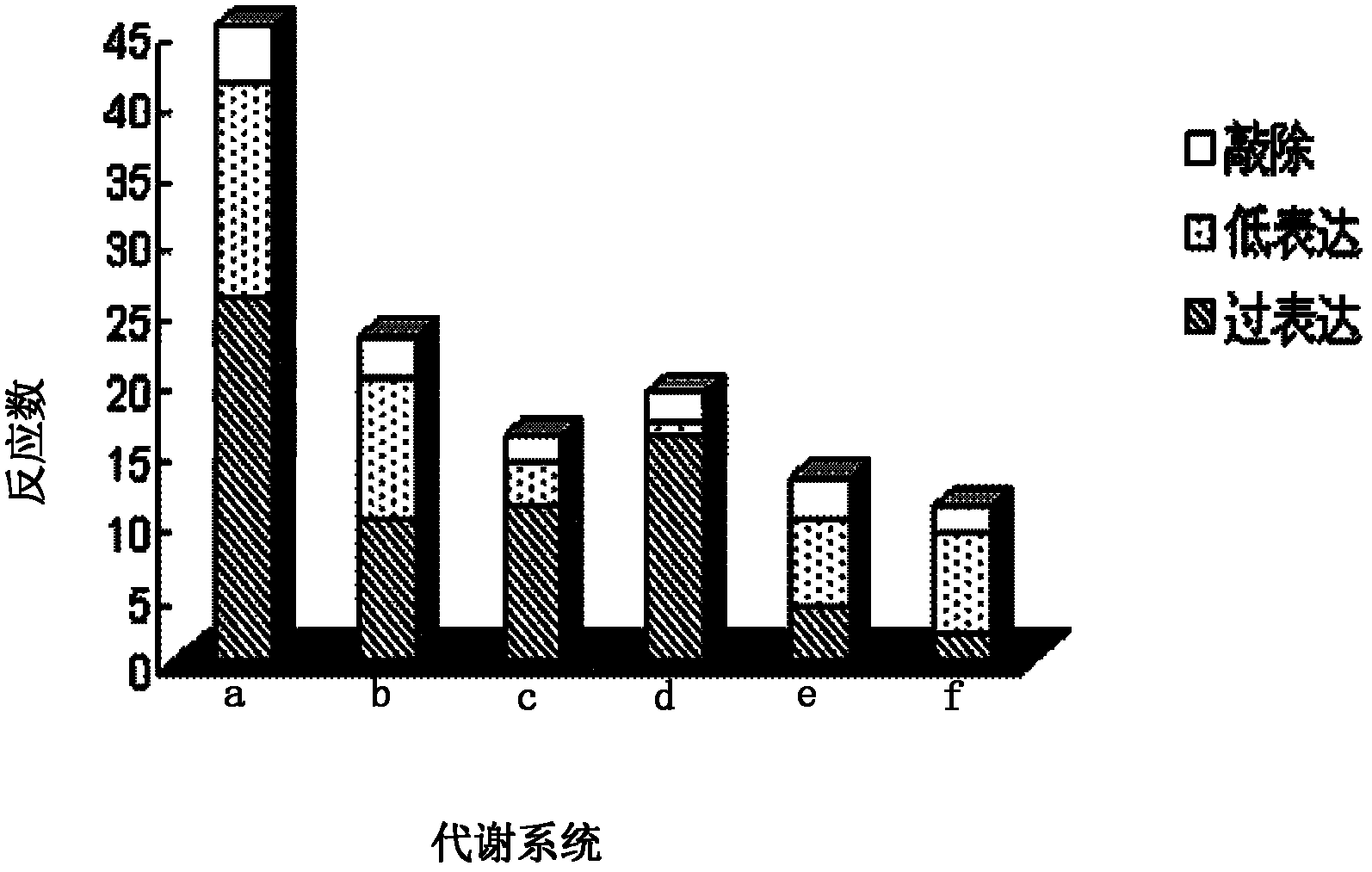
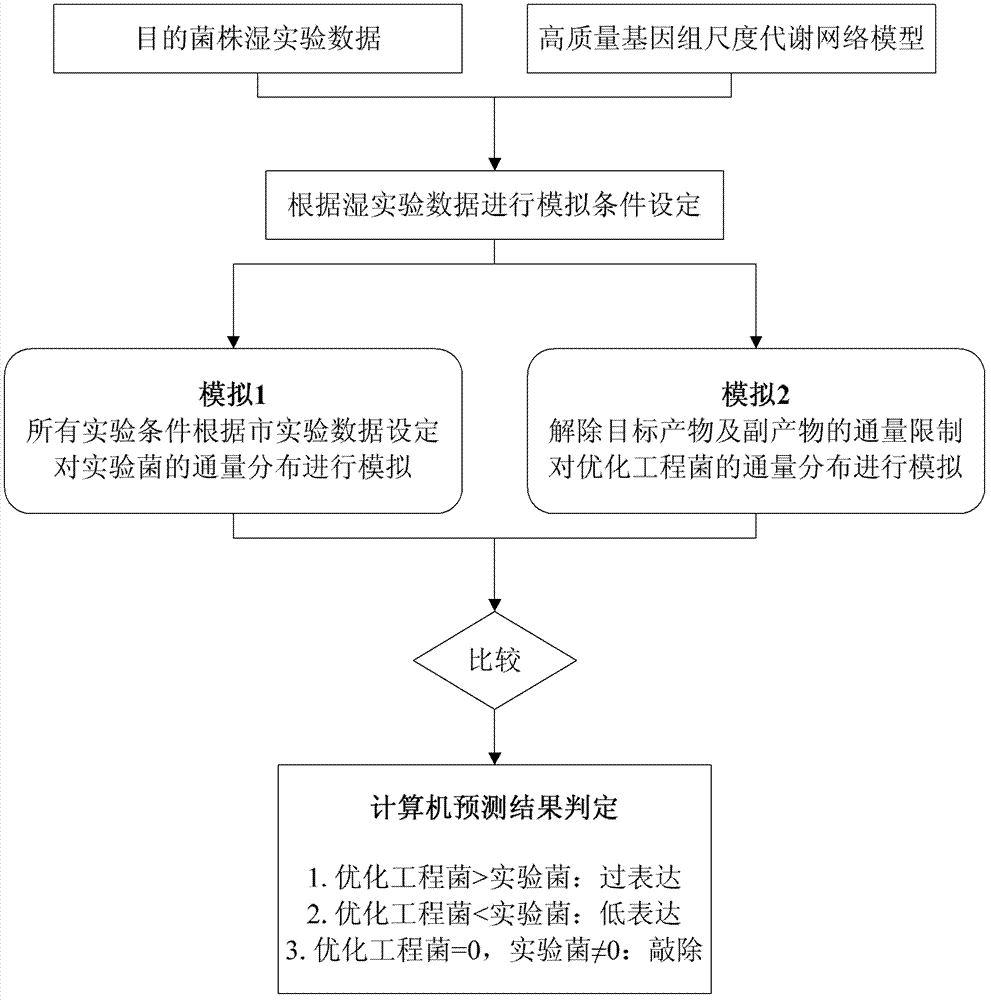
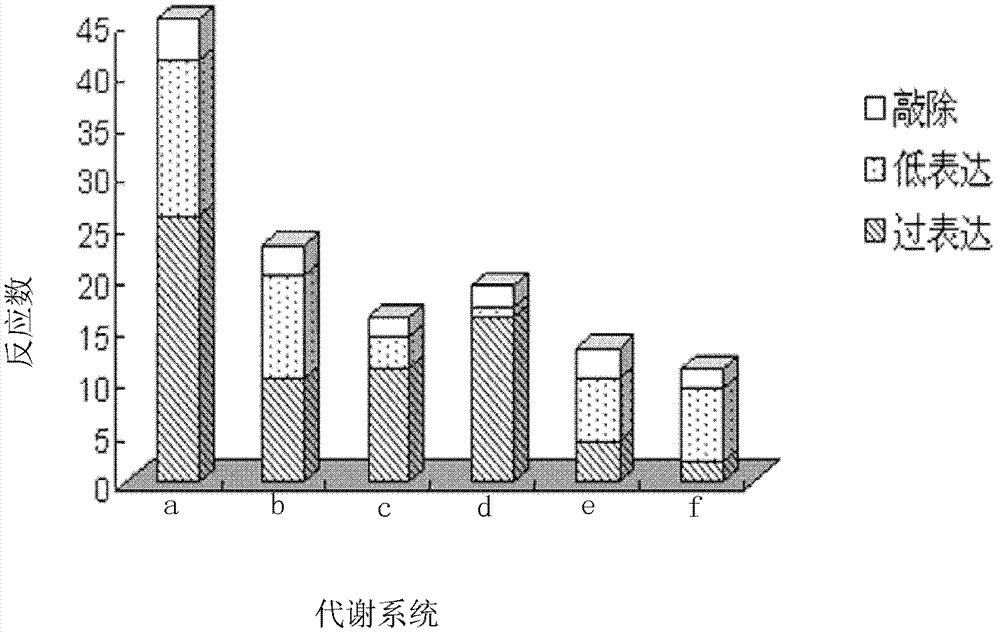
Genome scale metabolic network model-based metabolic engineering design prediction method
InactiveCN102629304ASolve the problems that are difficult to apply to the guidance of engineering bacteria experimentsIncrease product yieldSpecial data processing applicationsNetwork modelMetabolic network
The invention discloses a genome scale metabolic network model-based metabolic engineering design prediction method, which comprises the following steps of: acquiring target bacteria wet experimental data and a high-quality genome scale metabolic network model respectively; setting simulation conditions according to the wet experimental data; simulating the growth state of experimental bacteria to obtain metabolic flux distribution and simulating the growth state of optimized engineering bacteria to obtain metabolic flux distribution; comparing the two metabolic flux distributions to determine difference of reaction flux distribution between the two metabolic flux distributions; obtaining a corresponding gene prediction result according to the comparison result and gene-reaction correspondence of the genome scale metabolic network model, thereby determining metabolic engineering modification required for modifying the experimental bacteria into the optimized engineering bacteria to make a corresponding wet experimental strategy. The genome scale metabolic network model-based metabolic engineering design prediction method can be applied to any species with a genome scale metabolic network and simulating and predicting any product in a network model computing capacity range, and particularly has great guiding significance to metabolic engineering bacteria with unclear gene sequences.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
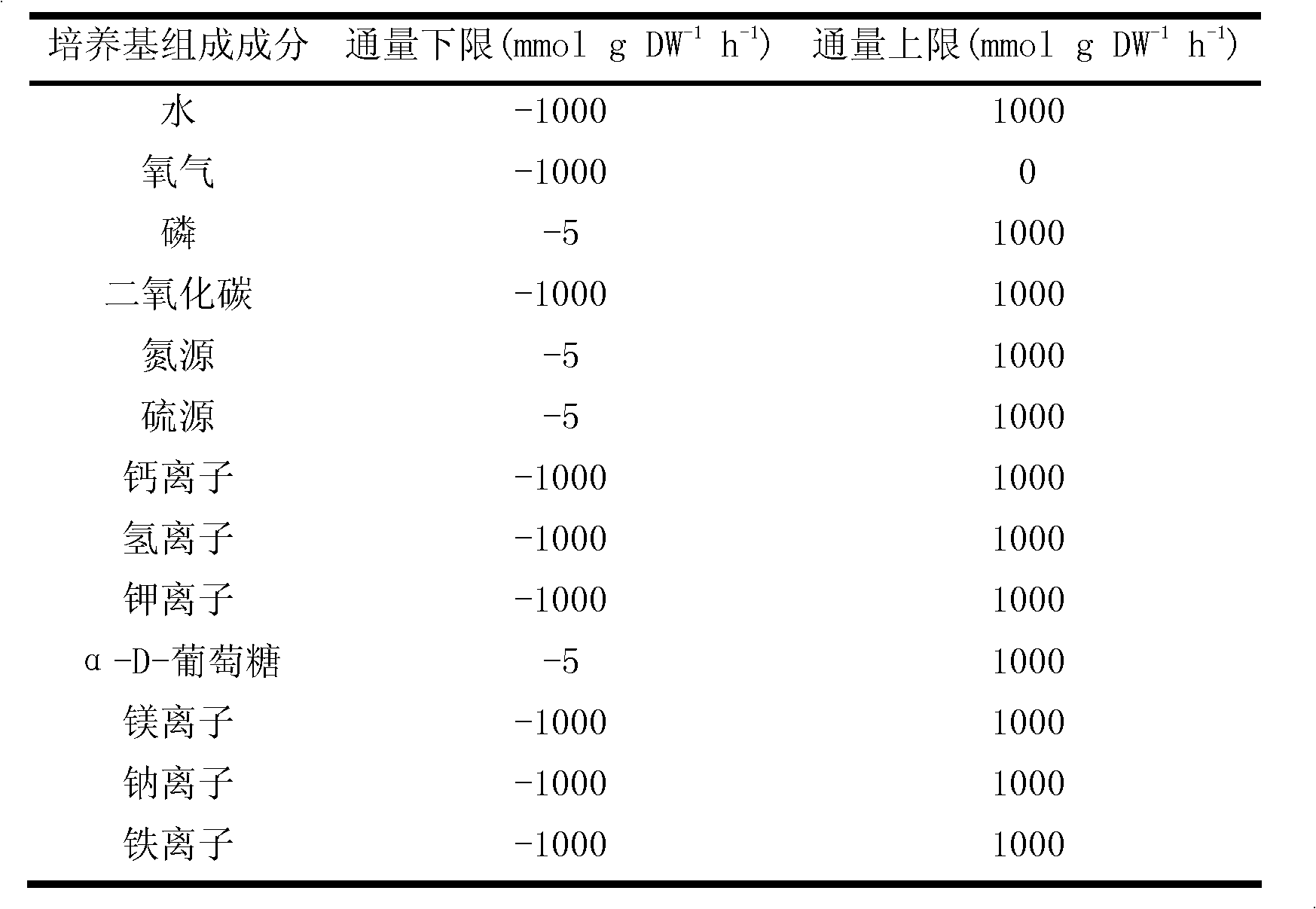
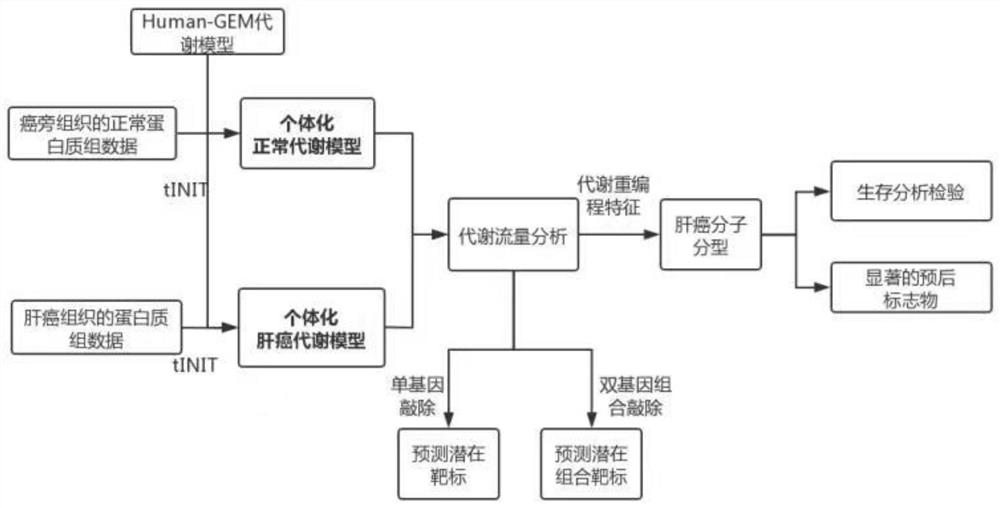
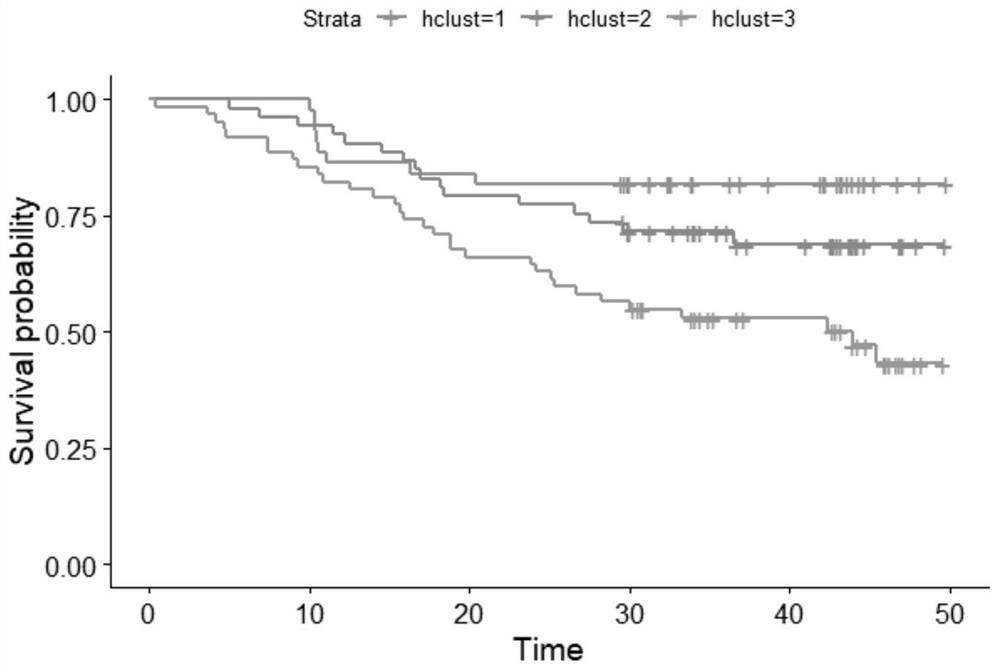
Tumor typing and potential target prediction method based on individualized metabolism model
PendingCN113362956ASignificantly different survival curvesImprove effectiveness responseMedical simulationMedical data miningPredictive methodsMolecular typing
The invention discloses a tumor typing and potential target prediction method based on an individualized metabolism model. The tumor typing and potential target prediction method comprises the following steps: step 1, constructing a tumor patient individualized metabolism network model; step 2, performing accurate molecular typing based on the metabolic characteristics of the individualized metabolic network model of the tumor patient in the step 1; and 3, predicting a gene which has important influence on the growth of tumor cells as a potential target based on the individualized metabolic network model of the tumor patient in the step 1. The method has the following advantages: 1, the survival curve difference corresponding to the molecular typing scheme established by the invention is more obvious; 2, the prognostic marker found based on the metabolic level can be detected through body fluid or blood, and is more convenient and easy to popularize. and 3, the predicted potential target is obtained based on quantitative simulation of tumor cell growth, patients of different types have personalized targets, and the drug effectiveness response can be improved.
Owner:王卓
Method for improving erythromycin yield by guiding n-propyl alcohol feeding through genome model
PendingCN113174418AComprehensive understanding of metabolic profilesImprove accuracyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPropanol
The invention discloses a method for improving erythromycin yield by guiding normal propyl alcohol feeding through a genome model, which comprises the following steps: in the fermentation process of saccharopolyspora erythraea genetically engineered bacteria, feeding ammonium sulfate and n-propyl alcohol 50-70 hours after the start of fermentation, wherein the n-propyl alcohol feeding rate is obtained by constructing a saccharopolyspora erythraea whole genome metabolic network model and analyzing the model. The whole genome metabolic network model of the saccharopolyspora erythraea genetically engineered bacteria is constructed to carry out systematic cell growth simulation, and a strategy is provided for increasing the yield of erythromycin. Under the guidance of a whole genome metabolic network model, the existing fermentation process of saccharopolyspora erythraea genetically engineered bacteria is optimized, and the yield of erythromycin is increased by regulating and controlling the supplementation rate of n-propanol.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
Genome-scale metabolic network model of Saccharopolyspora spinosa and its construction method and application
ActiveCN103729576BIncrease productionAchieving Pathway Molecular Modification MethodsSpecial data processing applicationsBacterial strainMetabolic network model
The invention discloses a saccharopolyspora spinosa genome scale metabolic network model and a construction method and application of the saccharopolyspora spinosa genome scale metabolic network model. The construction method includes the following steps that according to annotation information of saccharopolyspora spinosa genome sequences in KEGG and NCBI databases, a characteristic reaction for spinosad biosynthesis and a thallus sythesis reaction are added, a network reaction is manually refined, and then the saccharopolyspora spinosa genome scale metabolic network model is acquired. Through the saccharopolyspora spinosa genome scale metabolic network model, influences on improvement of the output of spinosad on a gene target spot can be predicted, the modification direction is finally determined, and the bacterial strain path molecule modification method is achieved. Experiments show that through genes predicted by the saccharopolyspora spinosa genome scale metabolic network model, genetically engineered bacteria obtained through modification can make the output of spinosad improved by 86.5% compared with wild bacterial strains. An instruction platform is provided for construction, research and analysis of the bacterial strains for efficiently producing and synthesizing spinosad.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Genome scale metabolic network model-based metabolic engineering design prediction method
InactiveCN102629304BIncrease product yieldSpecial data processing applicationsPredictive methodsNetwork model
The invention discloses a genome scale metabolic network model-based metabolic engineering design prediction method, which comprises the following steps of: acquiring target bacteria wet experimental data and a high-quality genome scale metabolic network model respectively; setting simulation conditions according to the wet experimental data; simulating the growth state of experimental bacteria to obtain metabolic flux distribution and simulating the growth state of optimized engineering bacteria to obtain metabolic flux distribution; comparing the two metabolic flux distributions to determine difference of reaction flux distribution between the two metabolic flux distributions; obtaining a corresponding gene prediction result according to the comparison result and gene-reaction correspondence of the genome scale metabolic network model, thereby determining metabolic engineering modification required for modifying the experimental bacteria into the optimized engineering bacteria to make a corresponding wet experimental strategy. The genome scale metabolic network model-based metabolic engineering design prediction method can be applied to any species with a genome scale metabolic network and simulating and predicting any product in a network model computing capacity range, and particularly has great guiding significance to metabolic engineering bacteria with unclear gene sequences.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Primary pathway transformation method under guidance of FK506 strain genome-scale metabolic network model
InactiveCN103276011BIncrease production levelsIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMetabolic network model
The invention discloses a primary pathway transformation method under the guidance of an FK506 strain genome-scale metabolic network model, which comprises the following steps of: adding the characteristic reaction and thallus synthesis reaction of FK506 biosynthesis according to the streptomyces tsukubaensis genome sequence, and performing manual refining on the network reaction to obtain an FK506 strain streptomyces tsukubaensis genome-scale metabolic network model; and analyzing the metabolic network model, and determining the primary pathway precursor key gene of FK506 biosynthesis through a flux equilibrium analysis and minimum metabolic regulation analysis method. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the strain production level after the transformation is improved by 80-100%. The method provides efficient guidance to the establishment, research and analysis of the primary pathway of the FK506 strain, and has great application prospects in the research process of FK506 strain transformation.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Construction method of high-yield strain for transforming abinogen by using glucose
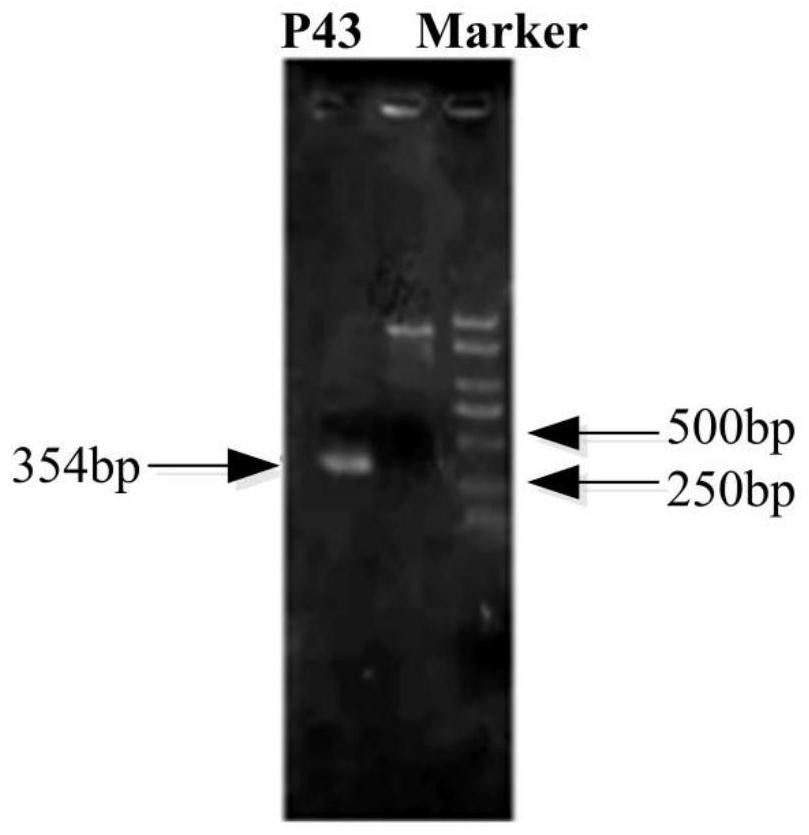
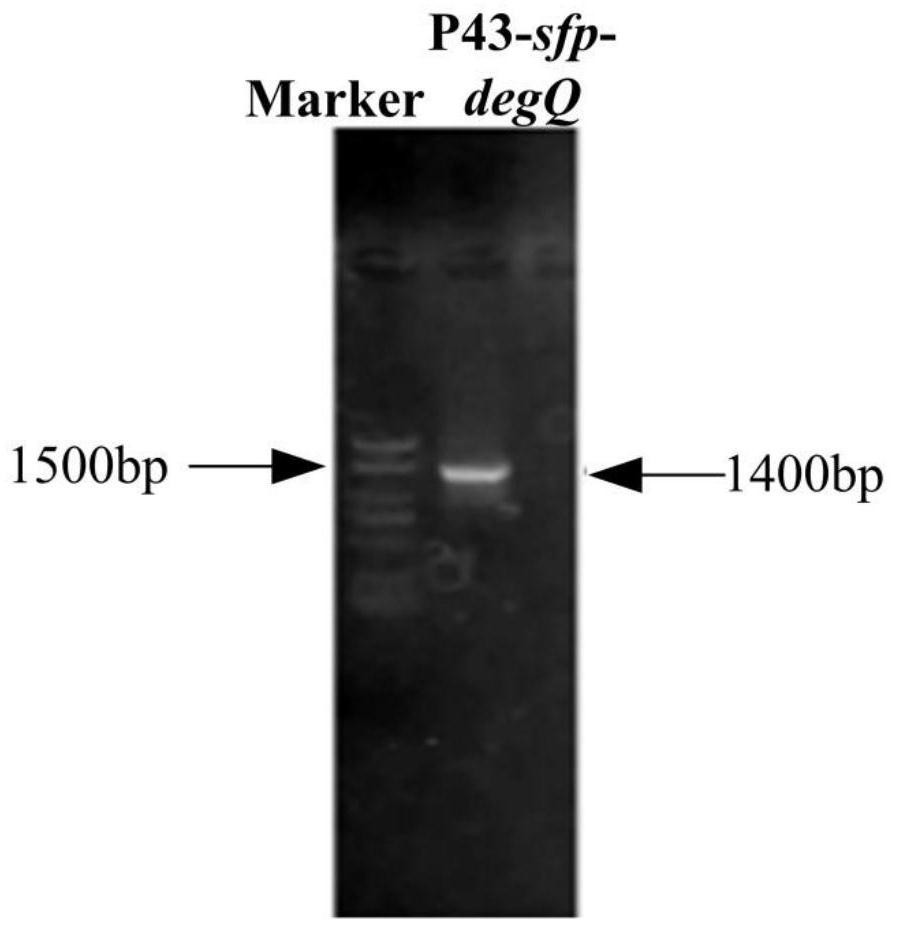
ActiveCN113265414AEasy to synthesizeIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesPeptidesBiotechnologyBacillus amyloliquefaciens
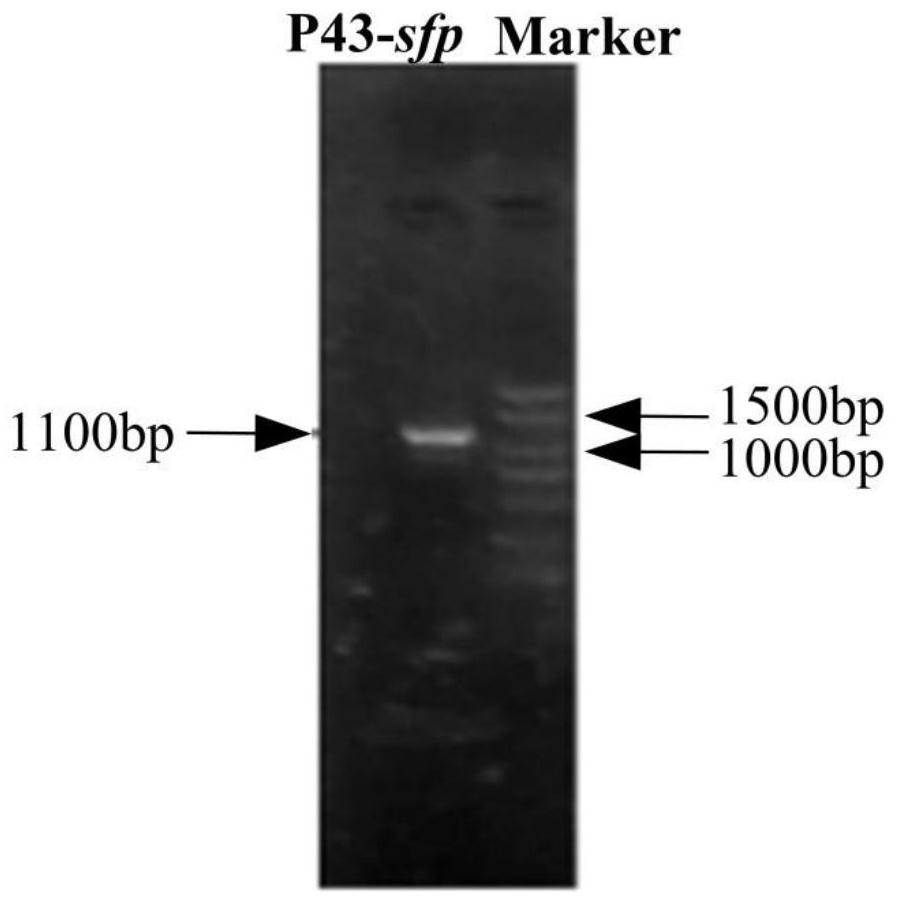
The invention provides a construction method of a high-yield strain for transforming abinogen by using glucose, which comprises the following steps: connecting a P43 promoter gene and a degQ gene from bacillus subtilis 168 and an sfp gene from bacillus amyloliquefaciens FZB42 in series to form a gene expression module pHP13-P43-sfp-degQ, and transferring the module into an original strain of the bacillus subtilis 168 to obtain a strain cell BSP000 for synthesizing abinogen. Three overexpression target genes accA, cypC and gapA are predicted by constructing a BSP000 strain genome scale metabolic network model, and the three genes are overexpressed in the BSP000 strain to obtain an engineering strain BSP003 with high yield of the abinogen, and the fermentation yield of the abinogen reaches 59.87 mg / L and is increased by 126% compared with that of an artificial strain BSP000. The method has a practical application value for realizing industrial production of the abundant essence.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
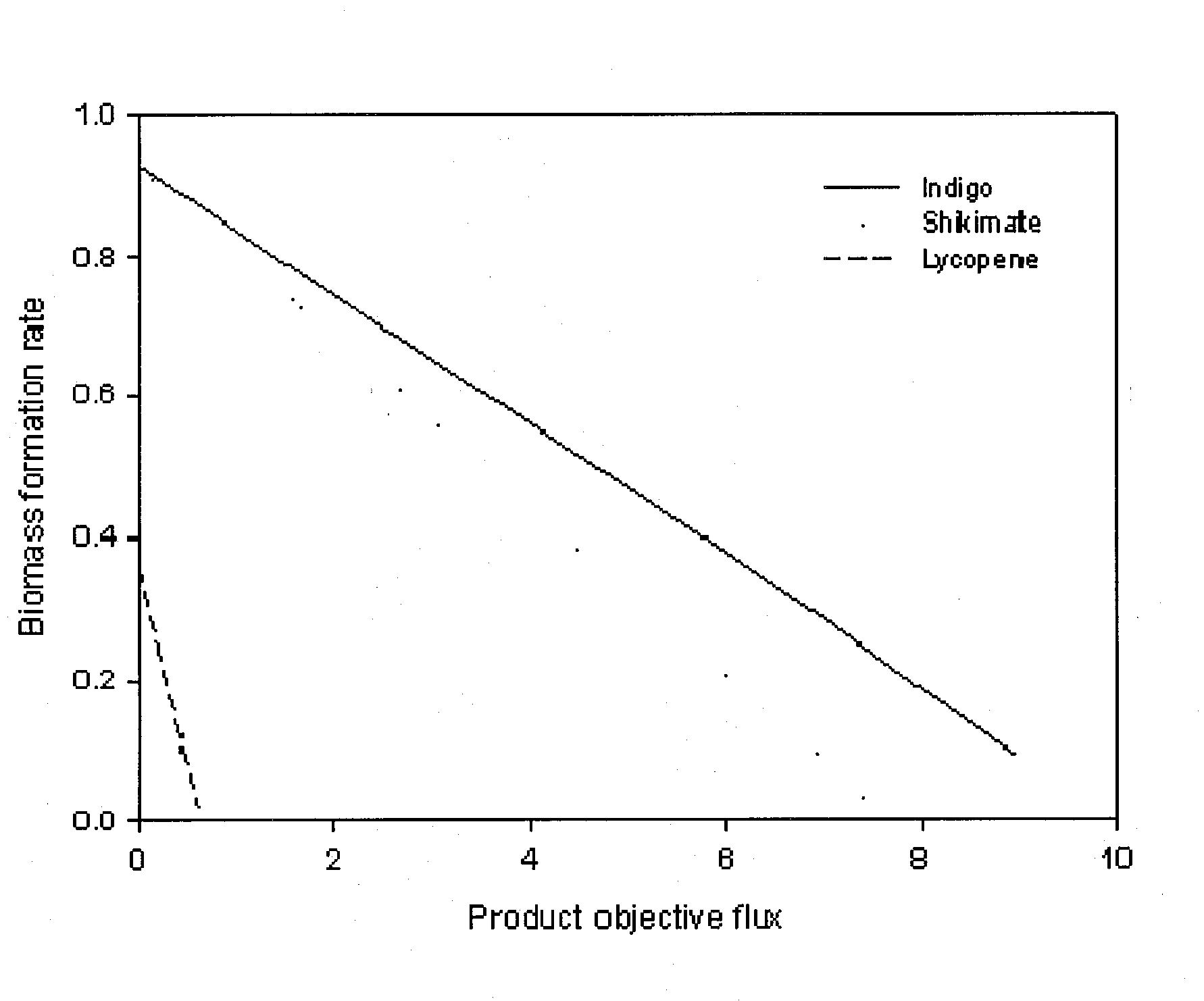
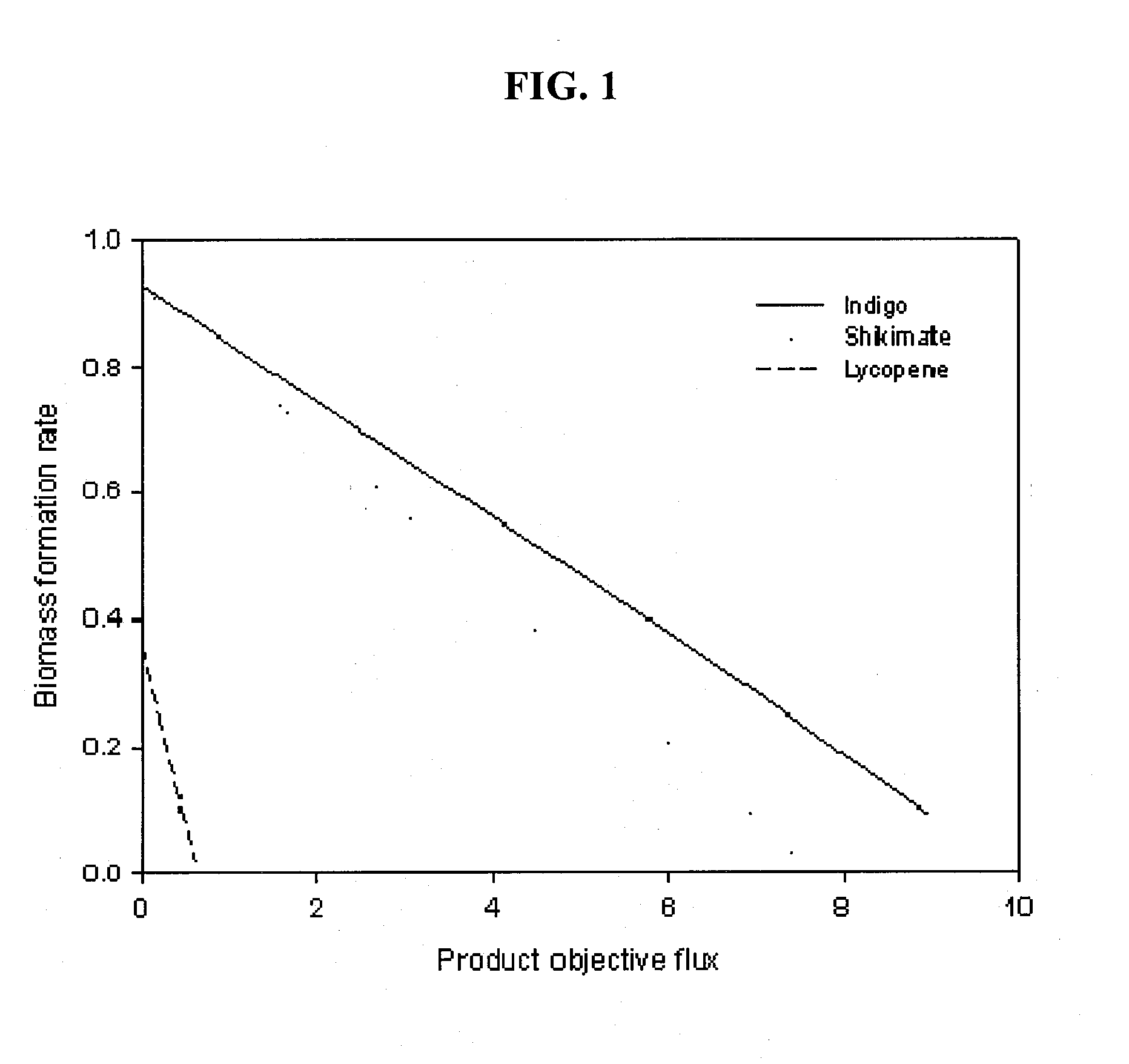
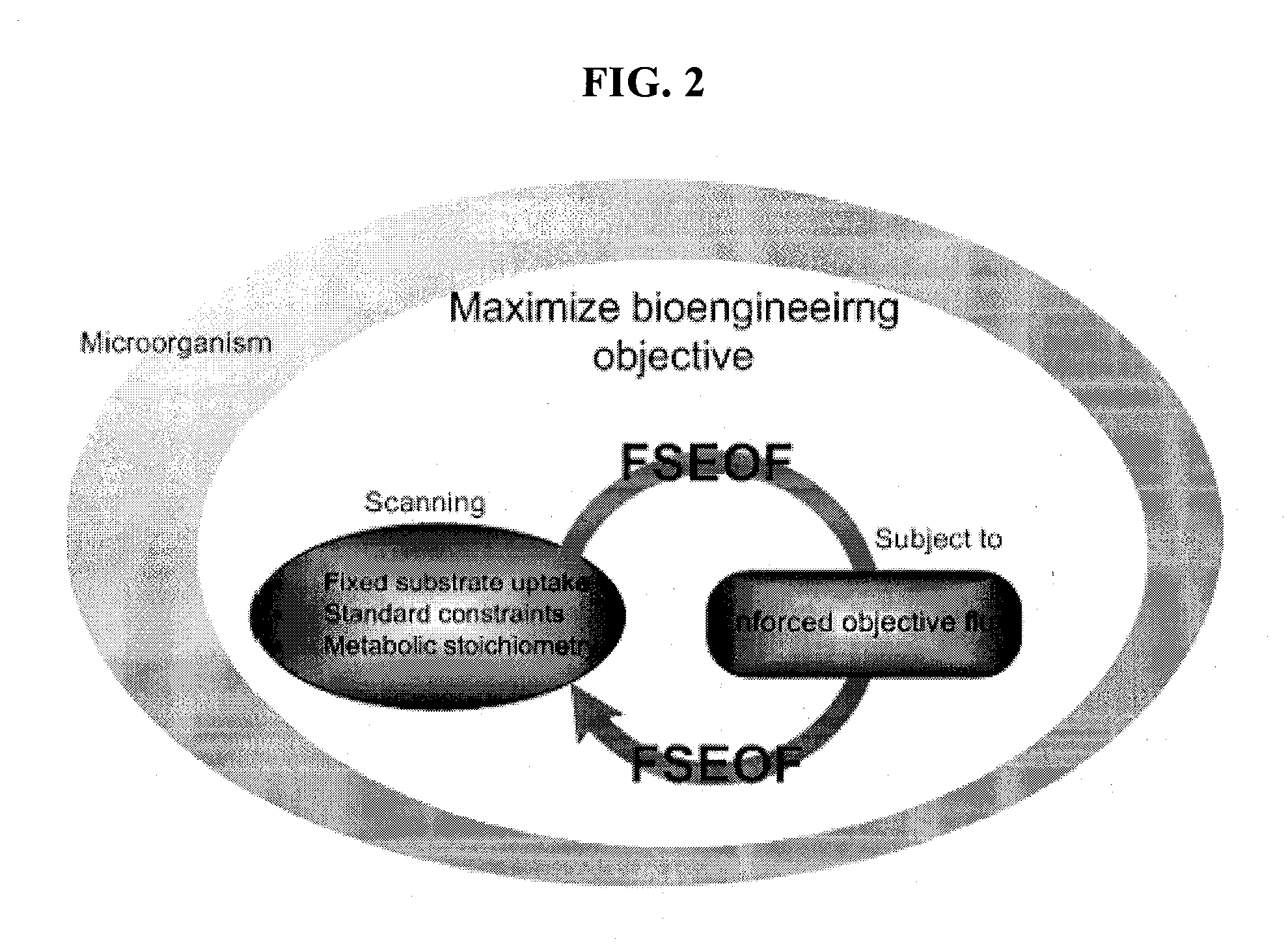
Method for Improving Organisms Using Flux Scanning Based on Enforced Objective Flux
ActiveUS20080220490A1Increase productionBacteriaDigital computer detailsBiotechnologyBiological body
The present invention relates to a method for improving useful substance-producing organisms using metabolic flux analysis, and more particularly to a method for improving a host organism producing a useful substance, the method comprising: calculating a maximum flux value corresponding to the theoretical maximum yield of the useful substance in the metabolic network model of the host organism for producing useful substance, and calculating the optimum value of metabolic flux associated with useful substance production in the metabolic network when the value of cell growth-associated metabolic flux is the maximum under the condition where fermentation data are applied or not applied; selecting metabolic fluxes whose absolute values increase from the range between the maximum value and the optimum value; screening genes associated with the selected metabolic fluxes; and introducing and / or amplifying the selected genes in the host organism. According to the invention, the production of the useful substance can be effectively improved by selecting metabolic fluxes to be amplified and genes involved in the metabolic fluxes from the range between the optimum value and maximum value of production-associated metabolic flux in the host organism for producing the useful substance, whose genome-level metabolic network model is constructed, and introducing and / or amplifying the selected genes in the organism.
Owner:KOREA ADVANCED INST OF SCI & TECH
Genome-scale metabolic network model of fk506-producing strain Streptomyces tsukuba to guide next-level pathway transformation
InactiveCN103279689BIncrease production levelsImprove the experimental effectSpecial data processing applicationsMicroorganismGene cluster
The invention discloses a secondary approach transformation method based on an instruction of an FK506 production bacterial strain wave chain streptomycete genome scale metabolic network model. The model is based on annotation genes and physiology and biochemistry information. By comparing and analyzing the model with a streptomyces coelicolor genome, metabolic genes are found being highly conservative. Metabolic flux analysis is performed on a genome scale metabolic network, and therefore the model predicts a mutation bacterium secondary approach gene cluster transformation strategy for improving a production level. According to the secondary approach transformation method based on the instruction of the FK506 production bacterial strain wave chain streptomycete genome scale metabolic network model, the transformation method utilizes the genome scale metabolic network model to predict special structural genes in an FK506 bacterial strain secondary approach gene cluster, the production level of bacterial strains after transformation is improved by 20 percent to 90 percent, the special structural genes in the gene cluster are augmented to improve production capacity, and large application value is achieved in secondary approach rational transformation of microorganism immunosuppressor production bacterial strains. The high-efficiency and systematic method is provided for optimizing of the bacterial strains.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Method for determining multiple optimization targets of microbial metabolism network model and application thereof
PendingCN113470732AImprove predictive plausibilityImprove reliabilityBiostatisticsArtificial lifeMetabolic network modelOptimization problem
The invention discloses a method for determining multiple optimization targets of a microbial metabolism network model and application of the method. According to the method, on the basis of a genome scale metabolic network model of microorganisms, a plurality of optimization targets are defined according to general rules of microorganism growth, constraint conditions are determined through flux equilibrium analysis, an optimization problem is constructed and solved, and a multi-target differential evolution method is adopted for a main body structure of the solving method. Firstly, an objective function is defined, and an initial population meeting constraint conditions is generated by using a general single-objective linear programming method according to a basic rule of biological growth; then, iteration is carried out according to the steps of the adjusted differential evolution algorithm, and a Pareto optimal solution set meeting an optimization target and constraint conditions can be obtained after iteration is completed; and finally, the Pareto optimal solution set is analyzed, and solving of the genome metabolism network model is completed. The method can be applied to prediction of key flux in central metabolism.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
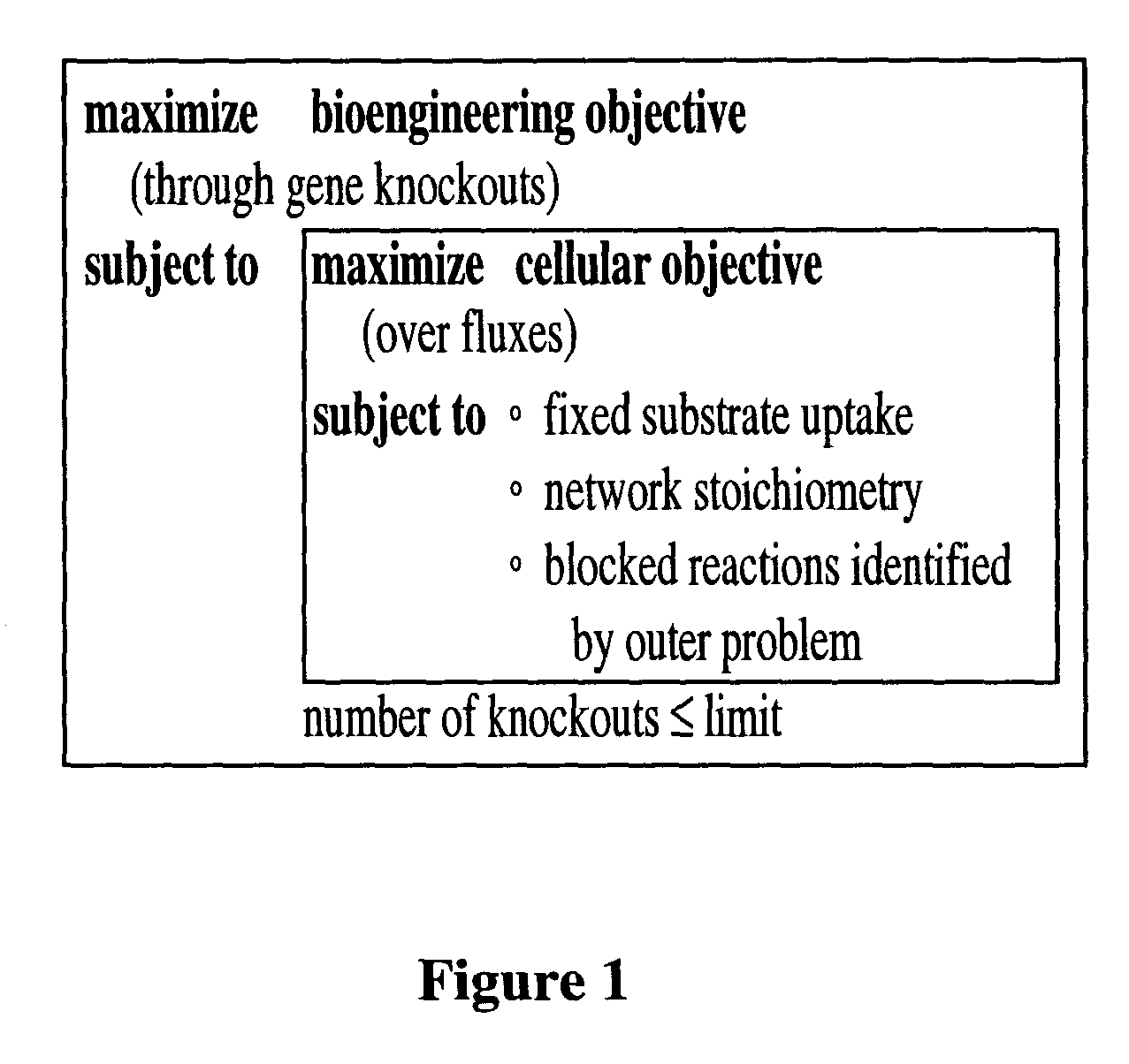
Method for determining gene knockouts
ActiveUS8027821B2Simple methodAnalogue computers for chemical processesRecombinant DNA-technologyBiological bodyMetabolic network
A method for determining candidates for gene deletions and additions using a model of a metabolic network associated with an organism, the model includes a plurality of metabolic reactions defining metabolite relationships, the method includes selecting a bioengineering objective for the organism, selecting at least one cellular objective, forming an optimization problem that couples the at least one cellular objective with the bioengineering objective, and solving the optimization problem to yield at least one candidate.
Owner:PENN STATE RES FOUND
A kind of method that uridine phosphoryl compound co-produces chiral hydroxyl ester
InactiveCN101724670BImprove regeneration efficiencyImprove substrate utilizationMicroorganism based processesFermentationCogenerationKetone
The invention discloses a method for co-producing chiral hydroxyl esters of uridine phosphoryl compounds. The method uses orotic acid and β-keto ester compounds as substrates, uses glucose as an energy donor, and utilizes permeable Simultaneous production of uridine phosphoryl compounds and chiral hydroxyl esters by yeast cells. The present invention utilizes the principles of whole-cell catalysis and metabolic engineering, establishes a metabolic network model and analyzes metabolic flow, and utilizes permeable yeast cells to co-produce uridine phosphoryl compounds and chiral hydroxyl esters, increasing the yield and reducing production costs , The synthesis time is shortened, and the utilization rate of the substrate is greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
A kind of preparation method of citicoline
InactiveCN101538598BIncrease profitAvoid investmentMicroorganism based processesFermentationPhosphate ionPhosphorylation
The invention discloses a preparation method of citicoline, which uses choline chloride, phosphate ion and cytidine monophosphate or its precursor as substrates, and uses glucose, fructose, sucrose or maltose as energy donors. Add small molecular chemical effect substances, and use permeable yeast cells to catalyze the preparation of citicoline. The present invention establishes a metabolic network model and analyzes metabolic fluxes, adopts small molecular chemical effect substances to regulate metabolic fluxes, thereby improving energy self-coupling and choline phosphorylation efficiency, and utilizes permeable yeast cells to efficiently prepare citicholine Alkali, the concentration of the product is greatly increased, and the utilization rate of the substrate is also improved.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
Automatic genomic metabolic network model modifying method
ActiveCN104699997AFix time saverEasy to fixSpecial data processing applicationsImaging processingNetwork model
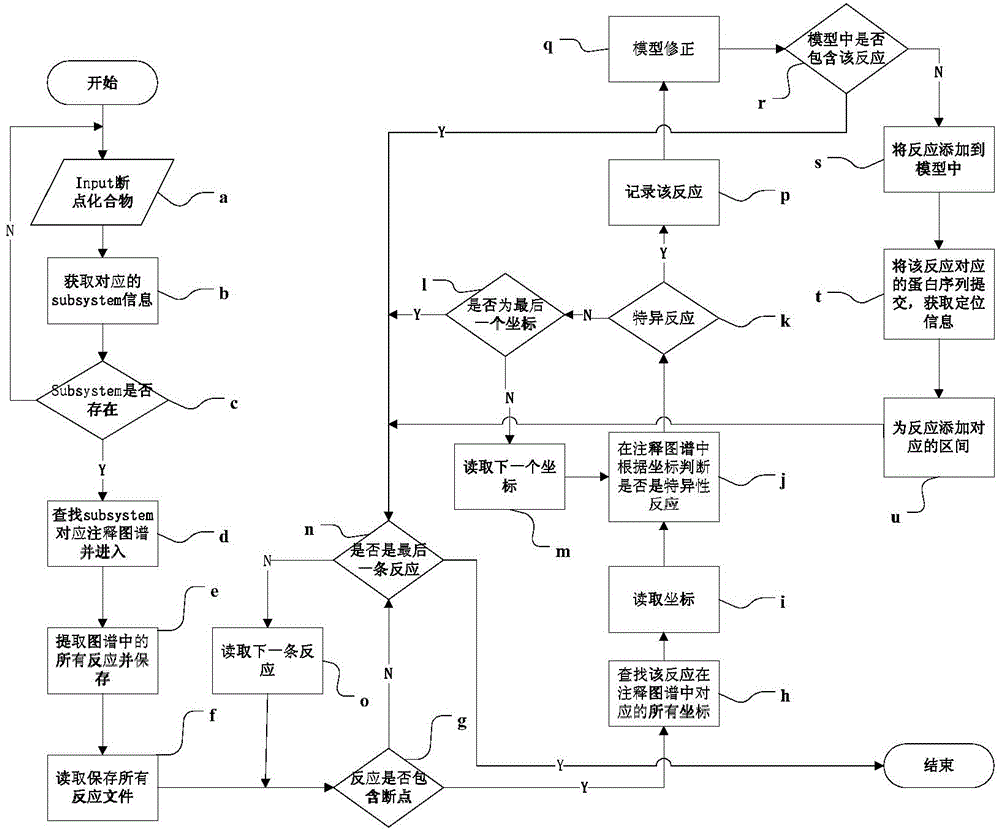
The invention discloses an automatic genomic metabolic network model modifying method. According to the automatic genomic metabolic network model modifying method, website script semanteme can be submitted and analyzed automatically by combining a hypertext transfer protocol with a Java control HttpClient and utilizing an image processing algorithm; a genomic metabolic network model is subjected to automatic breakpoint supplementing on the basis of online databases including a KEGG (Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes) database, a MetaCyc database, a MetRxn database and a plurality of protein region positioning and predicting websites; specific reactions high in reliability can be determined according to a protein region predicting result and a weight rating mechanism, and accordingly, an automatic modifying process of a rough metabolic network model is completed. The automatic genomic metabolic network model modifying method has the advantages of time saving and convenience, and an obtained modified model is more comprehensive and more accurate.
Owner:广州市康伦生物技术有限公司
A method for the construction of isobutanol-synthesizing strains guided by the regulation of intracellular reducing power based on a genome-scale metabolic network model
InactiveCN104630250BIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationSynthetic biologyIsobutanol synthesis
The invention provides an isobutanol synthetic strain construction method implemented by guiding the adjustment of intracellular reducing power based on a genomic scale metabolic network model. Based on the genomic scale metabolic network model, by adopting flow balance analysis and metabolic minimum adjustment analysis, the action law of different reconstruction modes of an intracellular reducing power metabolism to strain growth and isobutanol synthesis is simulated, and according to phenotypic coefficients, a conclusion that glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase is a key target spot of the intracellular reducing power adjustment of an isobutanol synthetic strain is obtained. By using a synthetic biological artificially-regulated element, an NADP+ depended glycerin-3-phosphate dehydrogenase metabolic pathway is built and adjusted so as to match and balance the intracellular reducing power metabolism, thereby obtaining an efficient isobutanol synthetic strain. The intracellular NADPH / NADP ratio of the strain reaches 0.4-0.8, and when 20-50 g / L glucose as a substrate is adopted for carrying out batch fermentation, the yield of isobutanol can reach over 8 g / L in 36 h, which is increased by over 60%.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com