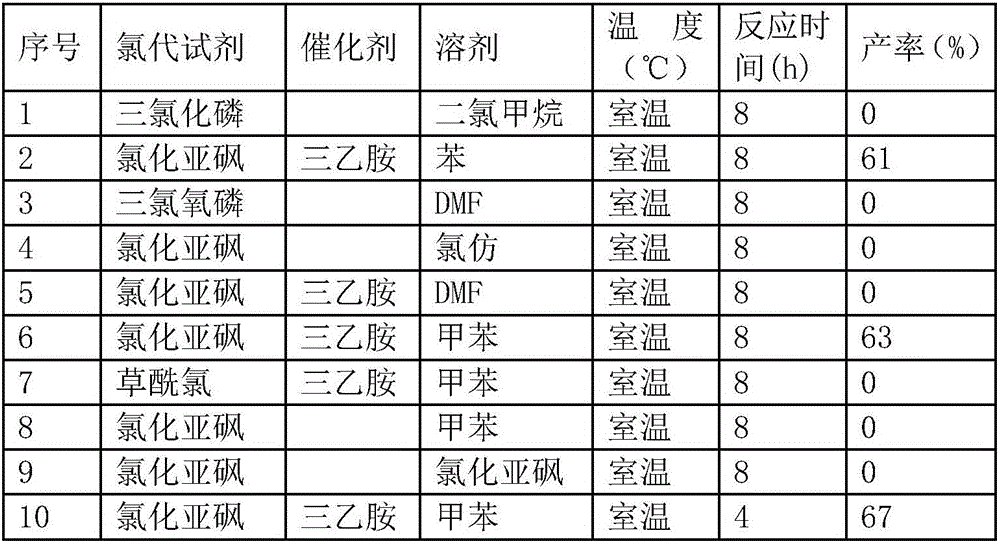
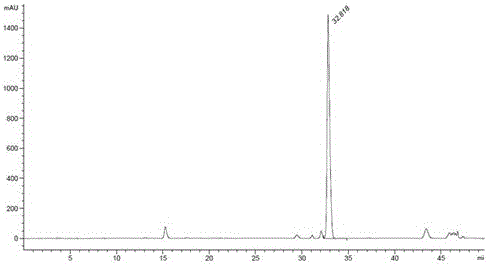
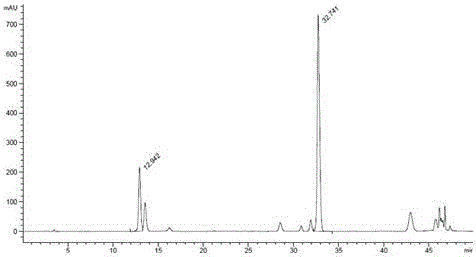
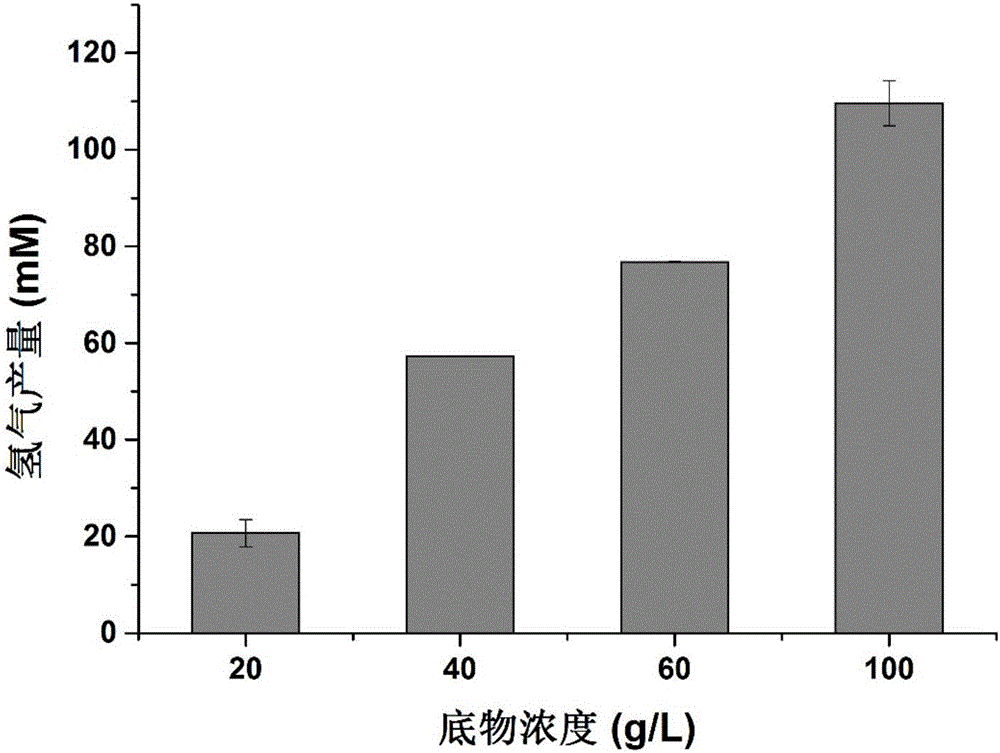
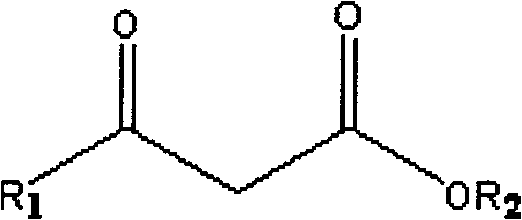
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
33results about How to "Improve substrate utilization" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Method for separating acetic acid in fermentation liquid for biohydrogen production by bipolar membrane electrodialysis technique
InactiveCN101525285AIncrease productionAvoid inhibitionSemi-permeable membranesCarboxylic compound separation/purificationBiohydrogenPollutant emissions
The invention relates to a method for separating acetic acid in fermentation liquid for biohydrogen production by bipolar membrane electrodialysis technique. The invention solves the problem that the prior method for separating acetic acid has complex technology, low current efficiency, large energy consumption and long operation time. The method comprises a first step of circularly pumping the pre-treated fermentation liquid for biohydrogen production into a separation chamber of a bipolar membrane electrodialyzer; a second step of circularly pumping pure water or acetic acid solution into an enriched chamber of the bipolar membrane electrodialyzer; and a third step of circularly pumping Na2SO4 electrolyte with the mass concentration of 5% into an anode chamber and a cathode chamber, and performing bipolar membrane electrodialysis so as to accomplish the separation of acetic acid in fermentation liquid for biohydrogen production. The operation time in the invention is decreased by more than 80%, the technology is simple, a separation system is of closed cycling, no pollutant is discharged, and the method is green and environment-friendly. The removal rate of acetic acid in the invention is more than 85%, the recovery rate of acetic acid is more than 85-95%, the current efficiency is up to 60-70%, and the energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
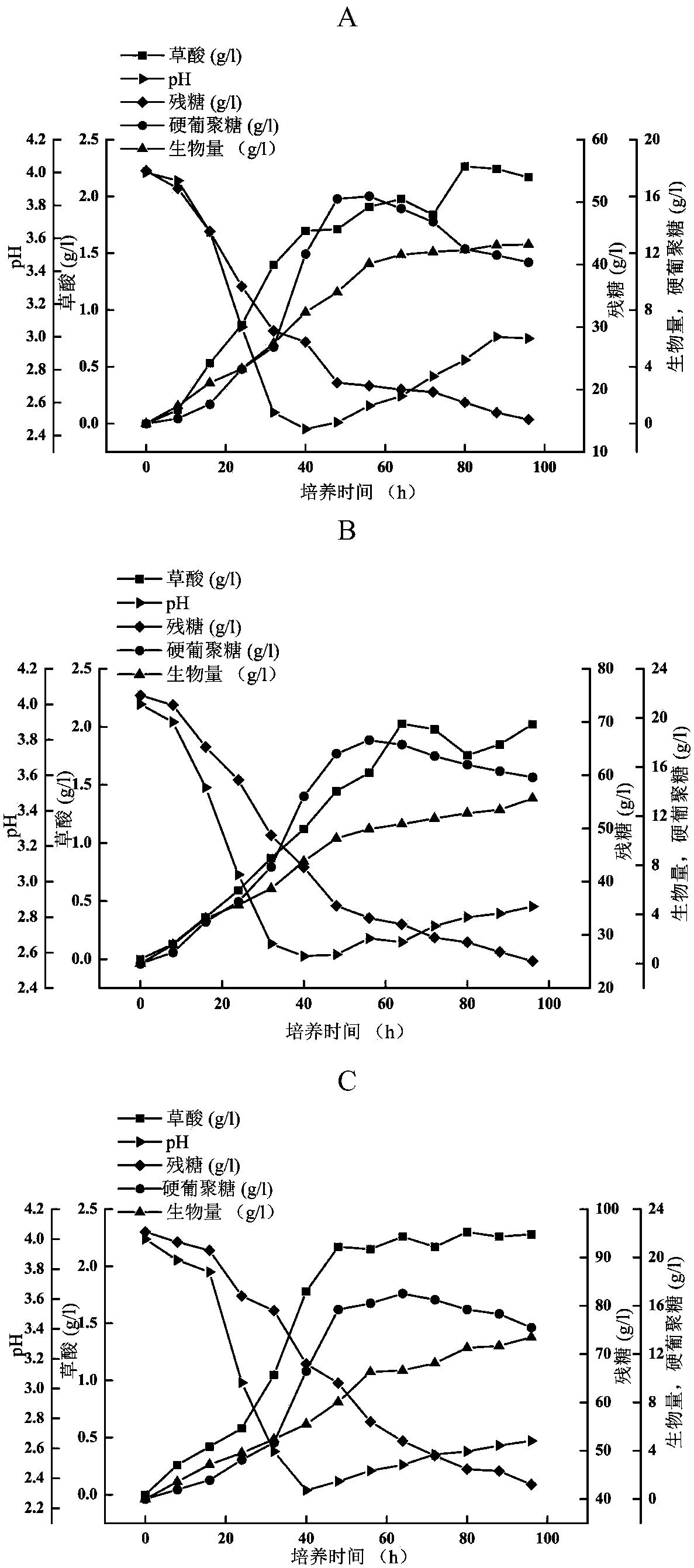
(Sclerotium rolfsii)WSH-G01 and method for producing scleroglucan by fermenting (Sclerotium rolfsii)WSH-G01
ActiveCN108441429AImprove substrate utilizationLow costFungiFood ingredient as thickening agentMicroorganismSaccharum
The invention discloses (Sclerotium rolfsii)WSH-G01 and a method for producing scleroglucan by fermenting the (Sclerotium rolfsii)WSH-G01, and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The method has the advantages that the strain CCTCC NO:M2017646 can be fermented for 56h at the glucose carbon source concentration of 75 g / L, and realize the output of the scleroglucan of about 20 g / L, indicating that the output effect is obviously better than the output effect of the existing international method that the output of scleroglucan reaches 26 g / L after culturing for 72h under the culture condition of 150 g / L saccharose; the utilization rate of a substrate is increased by 58%, and the cost is obviously reduced; the production technology is better than the existing glucan production technology, and the industrialized application prospect is important.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Process for preparing alcohol through utilizing xylose and glucose by microzyme
InactiveCN1629298AShorten the fermentation cycleImprove substrate utilizationBiofuelsFermentationYeastAlcohol
The invention provides a process for preparing alcohol through utilizing xylose and glucose by microzyme, in particular a process for preparing alcohol by using one of Pachysolen tannophilus 2.1662, Pachysolen tannophilus 32691, Candida shehatae ATCC 34887, xylose and glucose as substrate, the preparation comprises the steps of domestication, fluid culture, immobilization, enrichment culture. The invention can realize shortened production cycle and increased substrate output coefficient.
Owner:CAPITAL NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Compositions and Methods Using Split Polymerases
The invention relates to compositions and methods utilizing split polymerase enzymes composed of at least two discrete polypeptides that stably associate to form a single polymerase. The invention further relates to nucleic acid constructs for expressing the split polymerases of the invention, and methods for using the split polymerases of the invention. The enzymes of the invention are useful in many applications calling for the detectable labeling of nucleic acids and are particularly useful in quantitative PCR (QPCR) and DNA sequencing applications.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Compositions and methods using split polymerases
ActiveUS9085762B2Improve substrate utilizationIncrease flexibilitySugar derivativesTransferasesPolymerase LBiology
The invention relates to compositions and methods utilizing split polymerase enzymes composed of at least two discrete polypeptides that stably associate to form a single polymerase. The invention further relates to nucleic acid constructs for expressing the split polymerases of the invention, and methods for using the split polymerases of the invention. The enzymes of the invention are useful in many applications calling for the detectable labeling of nucleic acids and are particularly useful in quantitative PCR (QPCR) and DNA sequencing applications.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Method for generating energy from hydrogen production bacteria and oily microalgae in stair-coupling mode
InactiveCN103555778AAccelerate the pace of industrializationImprove substrate utilizationMicroorganism based processesFermentationOrganic acidRenewable energy
The invention discloses a method for generating energy from hydrogen production bacteria and oily microalgae in a stair-coupling mode, and relates to the field of biological energy, and mainly aims at solving the problems that the conventional fermentation products in dark fermentation hydrogen production are hard to utilize, environment pollution is easy to cause, the substrate utilization rate is low and the energy production efficiency is low. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, taking the hydrogen production bacteria to culture, secondly, centrifuging an organic acid fermentation liquid, thirdly, inoculating the oily microalgae, and fourthly, extracting grease. According to the method, a dark fermentation hydrogen production technique is combined with a microalgae oil production technique, the problems that the fermentation products in the dark fermentation hydrogen production are hard to utilize and environment pollution is likely to happen are solved, and moreover renewable energy sources can be recycled, the substrate utilization rate is high, and the energy production efficiency is high. The method is mainly applied to the field of biological energy.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for enzymatic synthesis of theaflavin TF by virtue of tea polyphenol oxidase isoenzyme PPO1
InactiveCN104651426AImprove substrate utilizationSingle productFermentationSide productPolyphenol oxidase
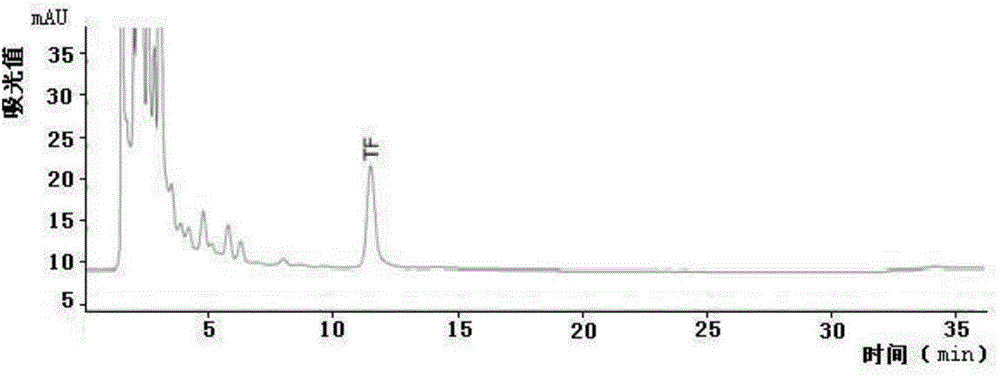
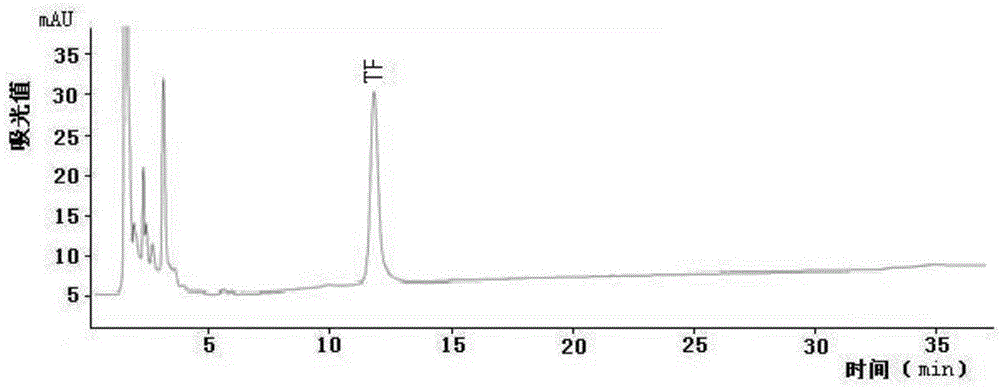
The invention discloses a method for enzymatic synthesis of theaflavin TF by virtue of tea polyphenol oxidase isoenzyme PPO1. The method is the optimization of a technique and a technology, which is capable of achieving the oriented enzymatic synthesis of a single theaflavin component TF through an enzymatic reaction with a shaking table as well as subsequent steps of extracting, centrifuging, concentrating, freeze-drying and the like by taking tea polyphenol oxidase isoenzyme PPO1 as an enzyme source, catechins EC and EGC components in tea polyphenol a major reaction substrates and a buffer solution at a certain pH value as a reaction system. The method overcomes shortcomings that multiple theaflavin components are generated simultaneously, a technology for separating and purifying the theaflavin components is complex, the preparation of a high-purity theaflavin component is quite difficult and the like in a conventional process which carries out the enzymatic synthesis of theaflavin by virtue of crude enzyme fluid of tea polyphenol oxidase; the method achieves a technological innovation that a single product is generated from enzymatic synthesis and a side product is avoided at reaction end, and the method avoids a technological bottleneck in subsequent separation and purification of the theaflavin component, so as to lay the theoretical and practical foundation for the green, safe and efficient large-scale industrial production and utilization of the theaflavin component.
Owner:HUNAN AGRICULTURAL UNIV
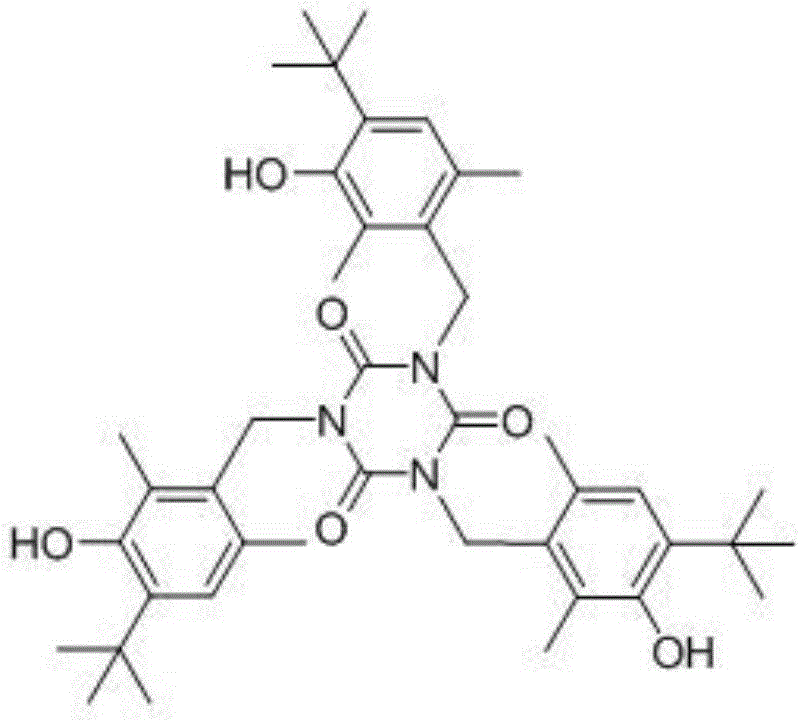
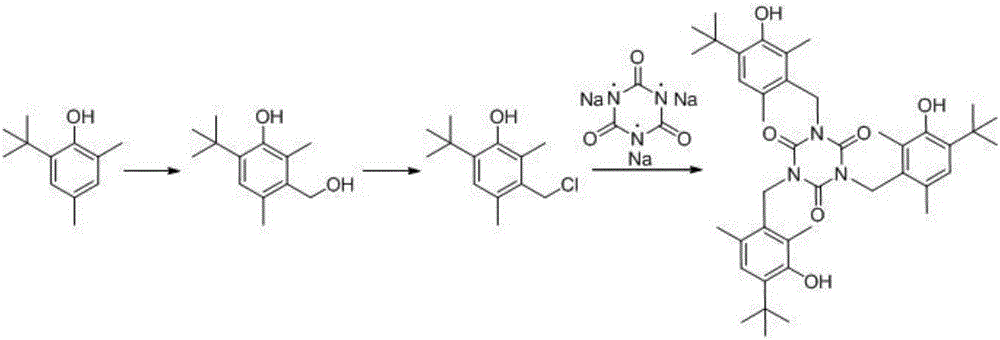
Synthesis method of antioxidant 1790
InactiveCN106699678AImprove substrate utilizationConducive to the protection of equipmentOrganic chemistrySolventChemistry
The invention discloses a synthesis method of an antioxidant 1790 and belongs to chemical field. By adoption of the synthesis method, the problems of serious pollution, low raw material utilization ratio and high cost in the existing method are solved. The synthesis method is implemented by three steps of: (1) preparation of 4-tert-butyl-3-hydroxyl-2,6-dimethyl benzyl alcohol, wherein 2,4-dimethyl-6-tert-butyl phenol, concentrated hydrochloric acid and paraformaldehyde are stirred at the temperature of 40 DEG C and return for 50 hours to obtain 4-tert-butyl-3-hydroxyl-2,6-dimethyl benzyl alcohol, and the product does not need to be purified; (2) preparation of 4-tert-butyl-3-hydroxyl-2,6-dimethyl benzyl chloride, wherein hydroxyl groups of the 4-tert-butyl-3-hydroxyl-2,6-dimethyl benzyl alcohol are chloro-substituted by thionyl chloride to obtain the 4-tert-butyl-3-hydroxyl-2,6-dimethyl benzyl chloride, the product can be obtained by crystallization of methyl benzene and methyl alcohol, and after removal of a solvent, the crystallized mother liquor can be continuously used as a raw material; and (3) preparation of a 1790 product. The synthesis method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the production cost is effectively reduced, the steps are simple and easy to operate, and the generated waste water is less, so that the industrial production is easy.
Owner:兰州精细化工有限责任公司 +1
Method for producing L-diaminocaproic acid through multistage continuous fermentation
InactiveCN106148444AShorten the lag periodImprove substrate utilizationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesContinuous fermentationBatch fermentation
The invention discloses a method for producing L- diaminocaproic acid through multistage continuous fermentation. The method includes: starting from escherichia coil to obtain an L-diaminocaproic product through fermentation above stage four; specifically stringing at least four fermentation tanks integrally, and controlling carbon source concentration and nitrogen source concentration in the fermentation tanks of different stages by regulating ventilatory capacity, initial sugar concentration of the primary fermentation tank, and addition rates, fermented-liquid outflowing rate and fermented liquid inflowing rate of carbon source filling containers and nitrogen source filling containers of the fermentation tanks; controlling the fermentation tanks of different stages to enable the specific growth rate of thallus of the fermentation tanks of the different stages to be 0.3-0.8h<1> to obtain the fermentation product. With the method, high thalli concentration in the fermentation system is maintained, lag phase of cells is shortened, substrate utilization is higher as compared with batch fermentation, target product quantity is high, yield is stable, operations of repeated tank washing, sterilizing, inoculating and the like are not needed, and production cost is lowered.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
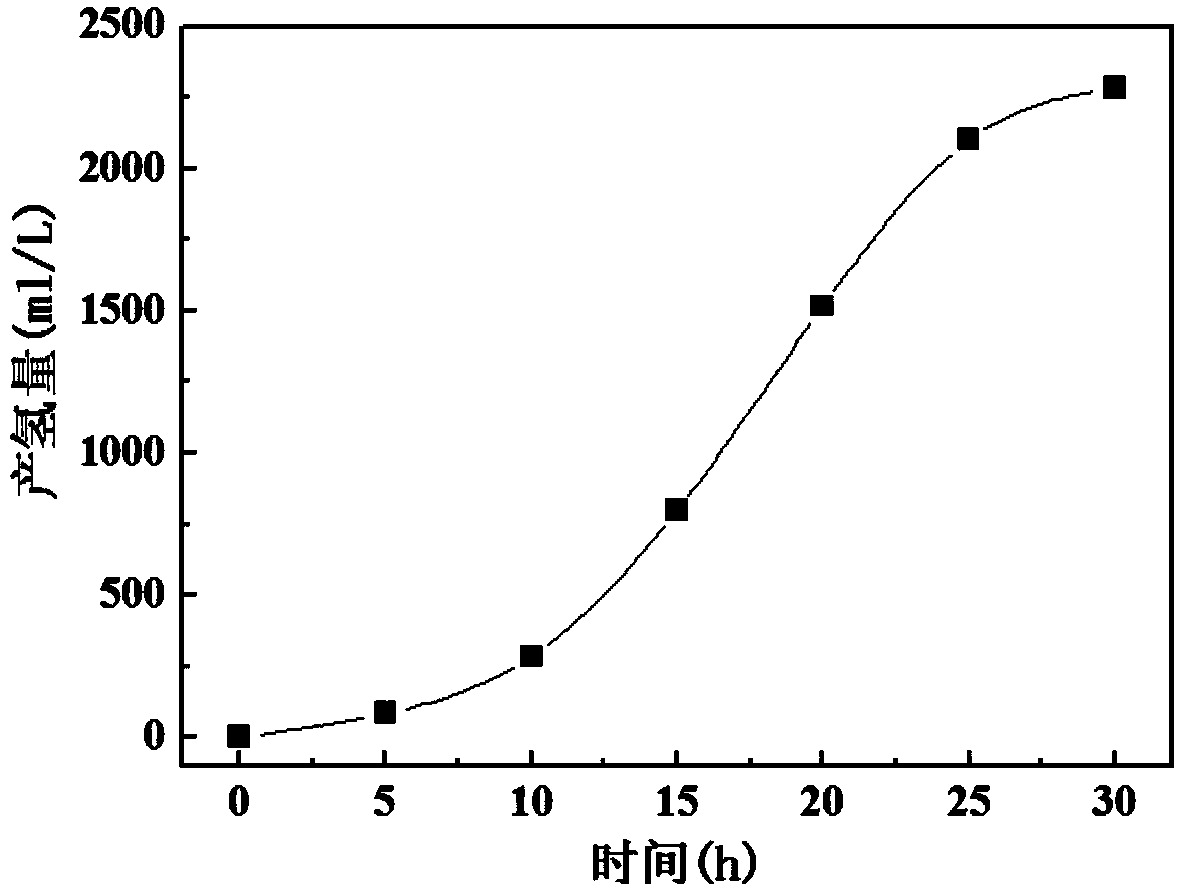
Method for generating hydrogen directly by non-detoxified acid pretreatment lignocellulose and application
InactiveCN107177634AImprove applicabilitySolve pollutionMicroorganism based processesFermentationCelluloseOrganic acid
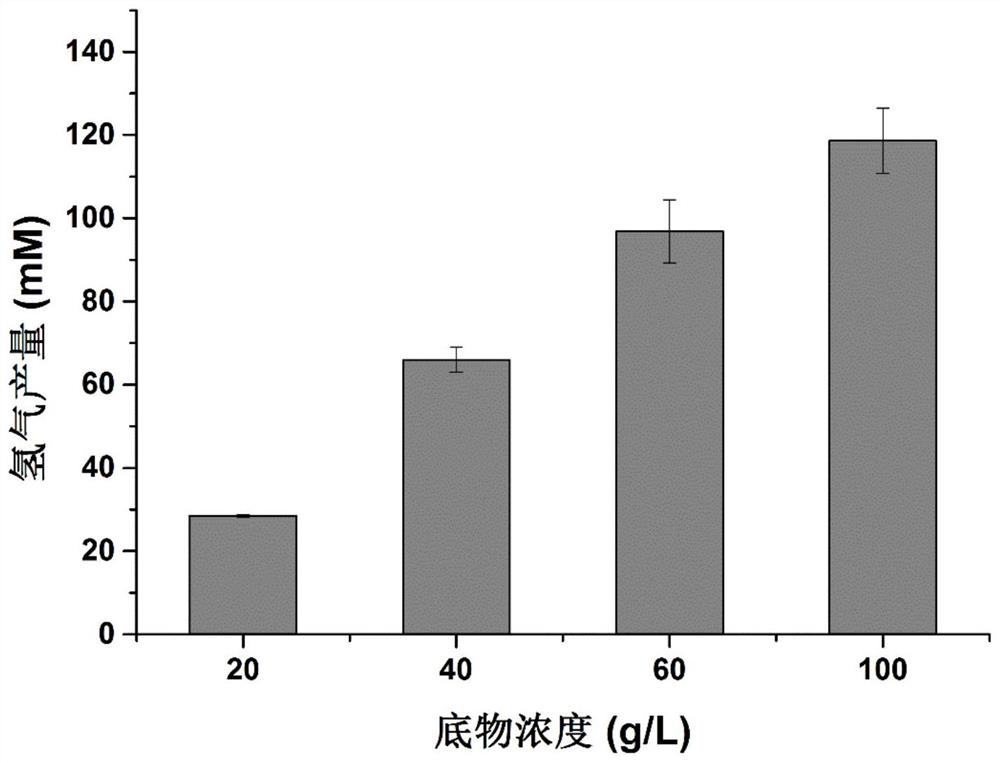
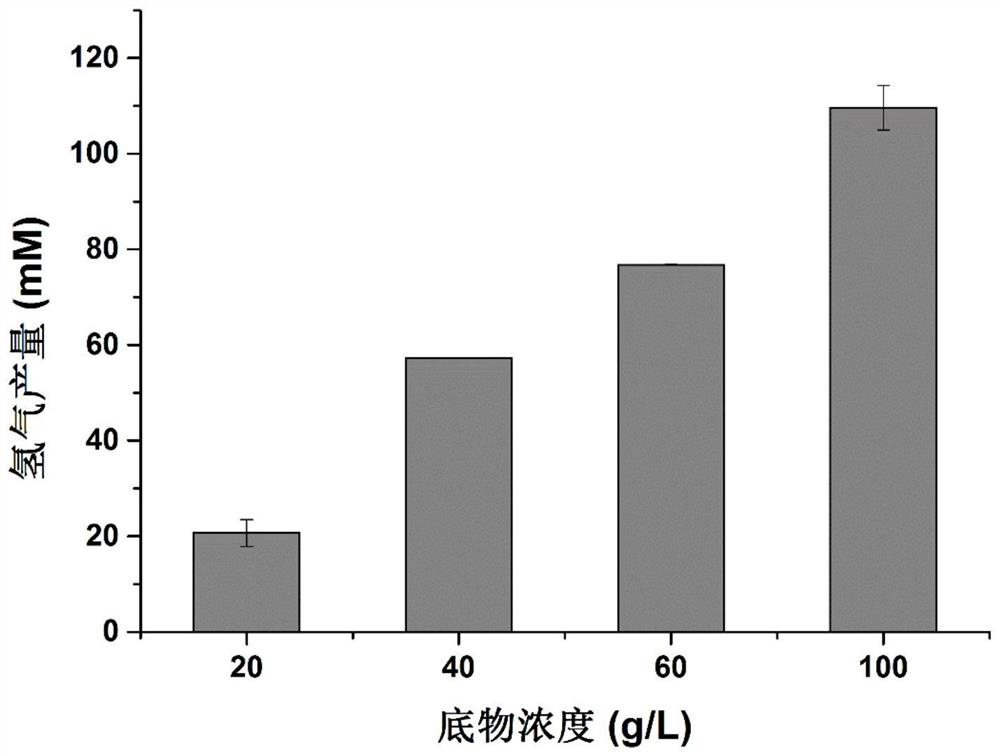
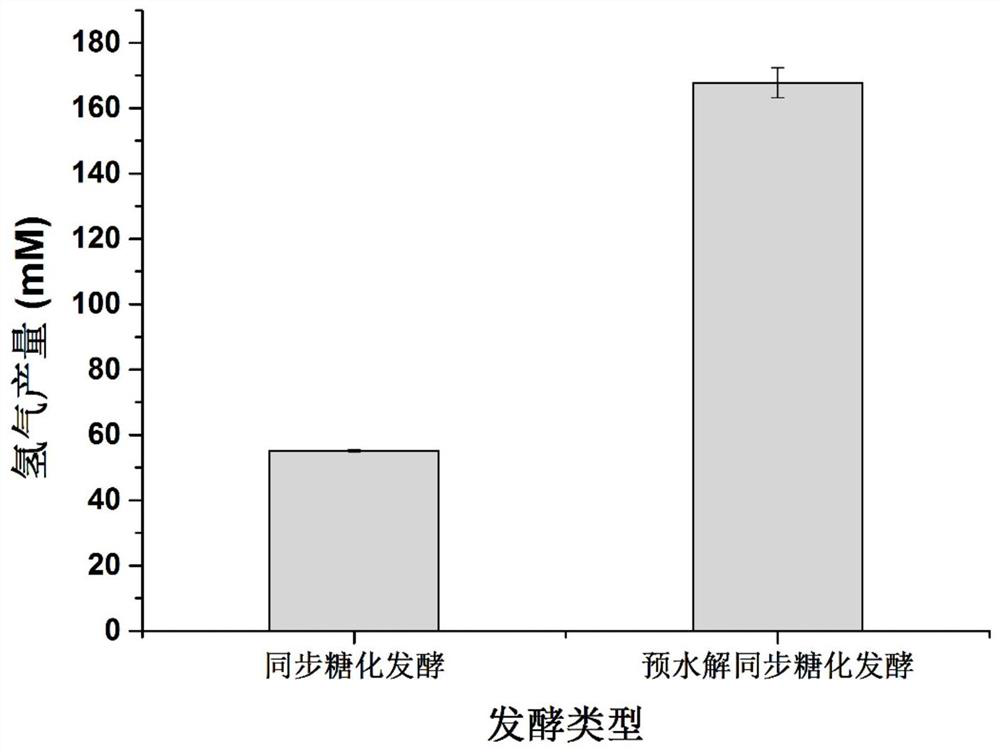
The invention discloses a method for generating hydrogen directly by non-detoxified acid pretreatment lignocellulose and an application. The method includes the steps: inoculating thermophilic sucroclastic anaerobic bacillus seed solution into a fermentation culture medium; performing anaerobic fermentation to obtain the hydrogen. The fermentation culture medium is a culture medium taking the non-detoxified acid pretreatment lignocellulose as a carbon source. According to the method, two-stage fermentation is performed, or fermentation is performed after part of organic acid is additionally added. The yield of the hydrogen can reach 277.44mM (6.21L-H2 / L) by the aid of the two-stage fermentation method, the yield of the hydrogen can be improved by 63.9% by adding 10g / L acetic acid, and the biological hydrogen production efficiency of bagasse can be remarkably improved. The method is suitable for transformation of the bagasse through microorganisms.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Recombinant bacteria capable of synthesizing 3-hydracrylic acid by using glucan as well as construction method and application of recombinant bacteria
The invention provides recombinant bacteria capable of synthesizing 3-hydracrylic acid by using glucan as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant bacteria, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and fermentation engineering. Klebsiella pneumoniae is host bacteria for expressing a gene lgk capable of encoding levodextran kinase and a gene aldH capable of encoding aldehyde dehydrogenase. The construction method comprises the following steps: obtaining a recombinant carrier puC18-lgk-aldH, converting the recombinant carrier puC18-lgk-aldH into a competent cell of the host Klebsiella pneumoniae, and obtaining the recombinant bacteria. By use of the levodextran kinase gene lgk and the aldehyde dehydrogenase gene aldH which are optimized through a codon, in combination with the whole scheme, the substrate use rate is increased, and the yield is increased.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
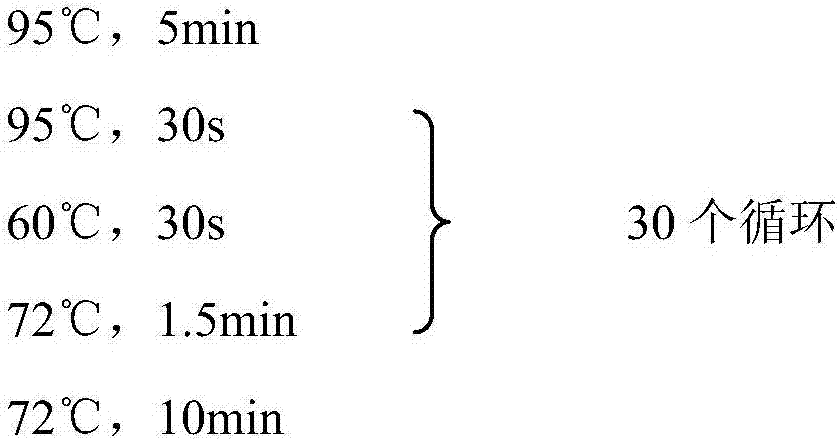
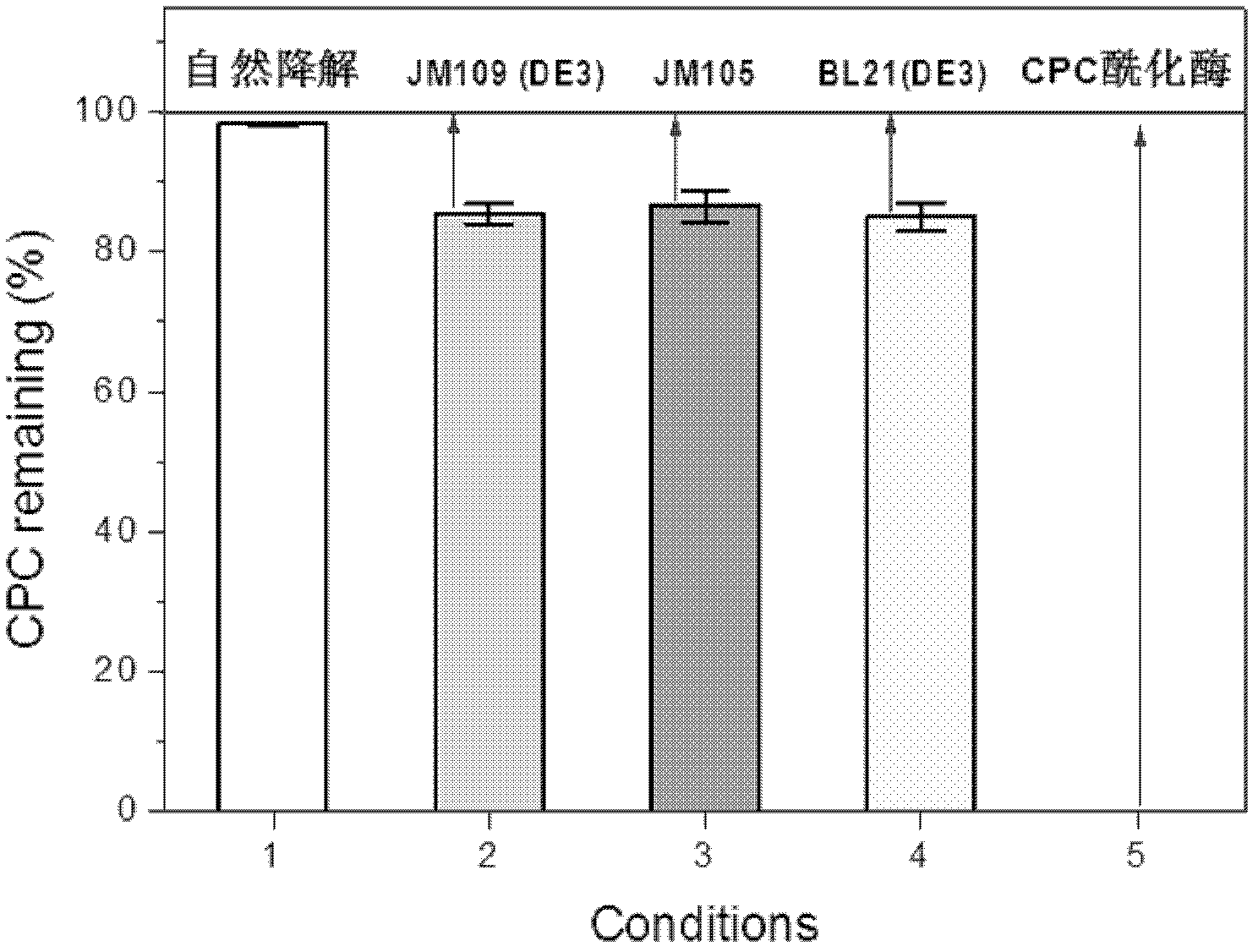
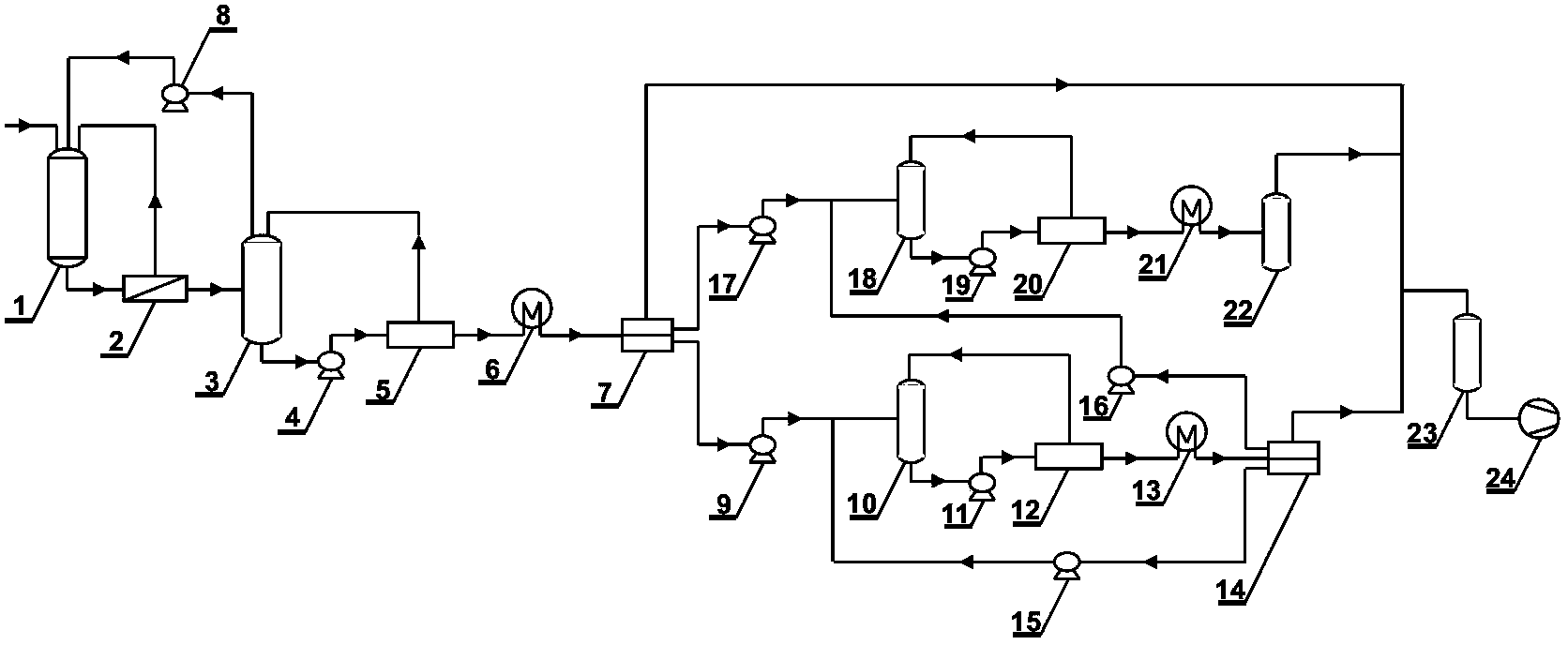
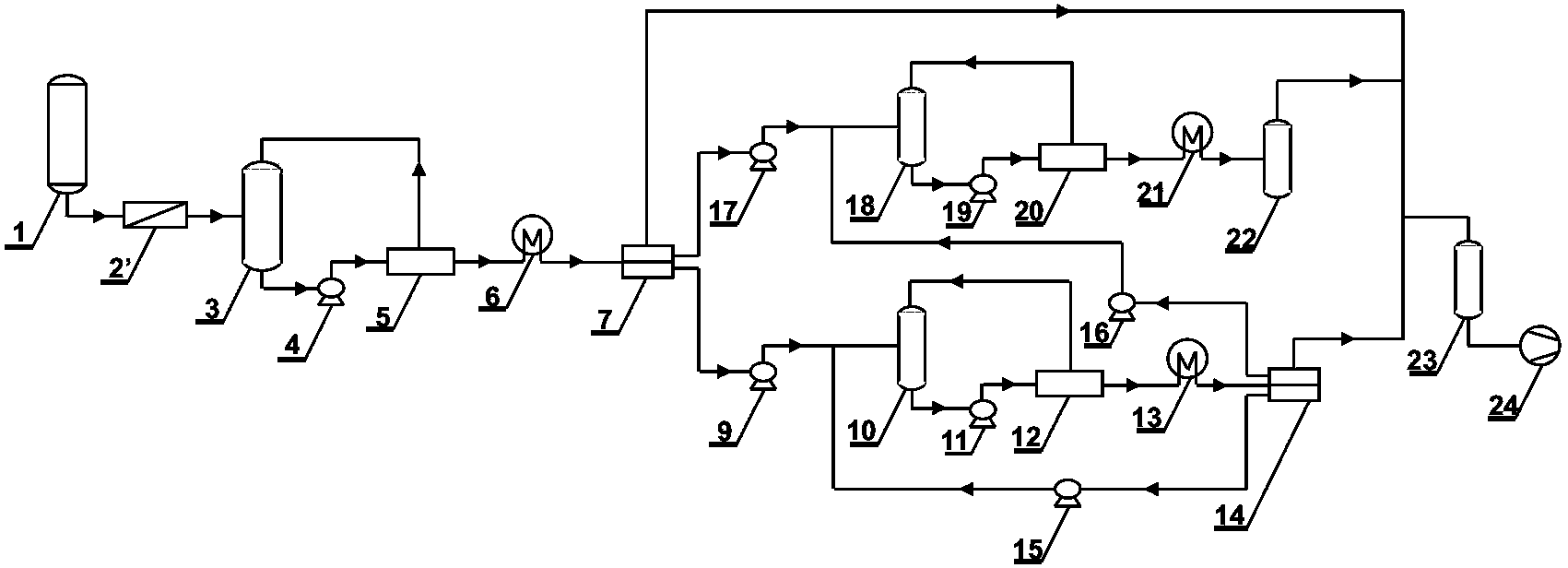
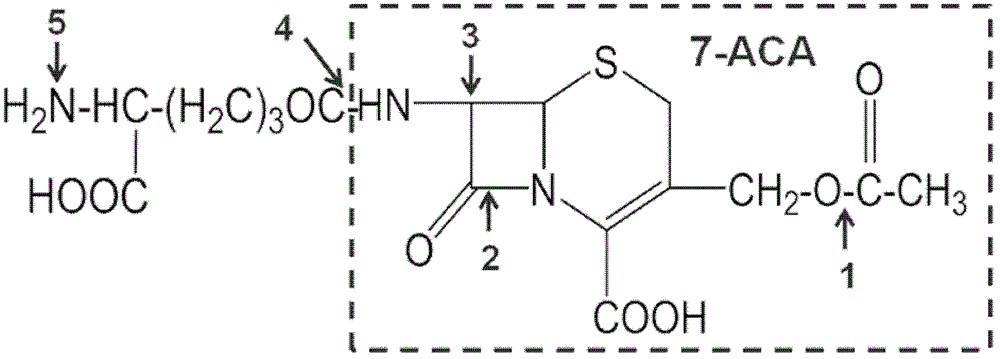
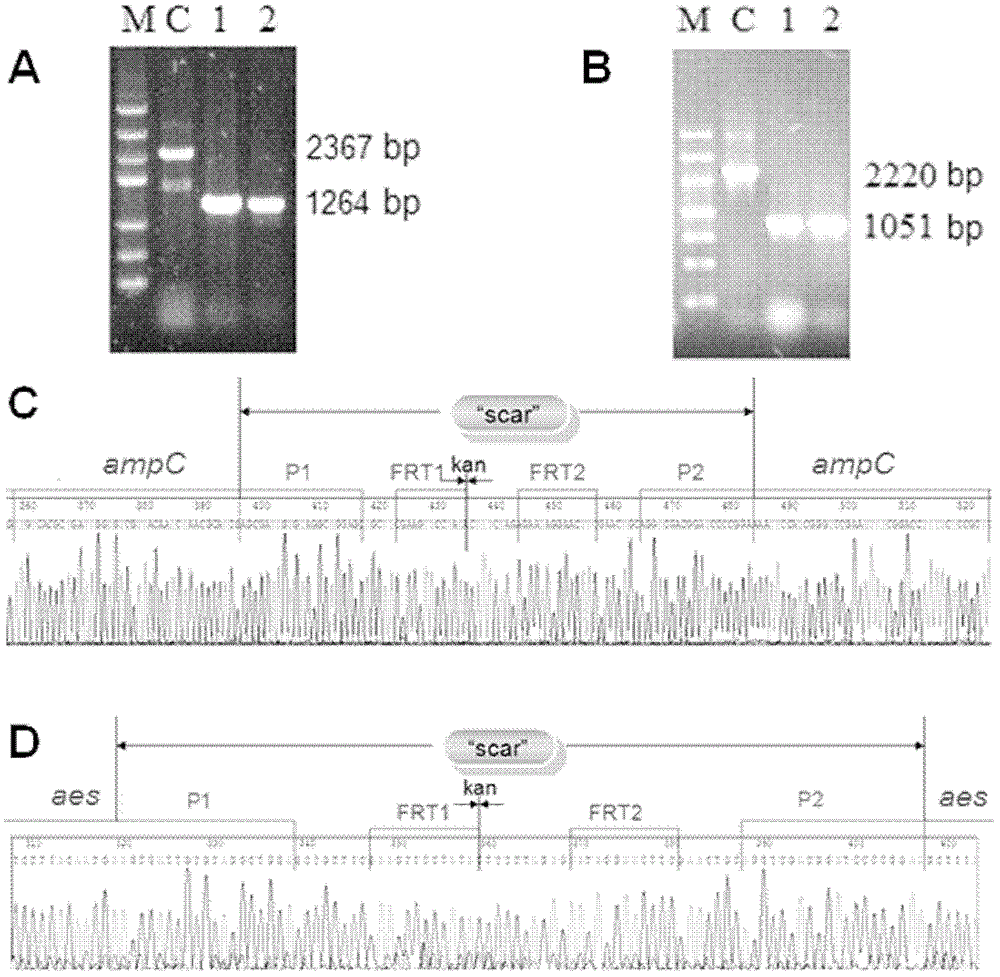
Method for reducing decomposition of cephalosporin C
ActiveCN102533920AImprove substrate utilizationLow raw material costMicroorganism based processesFermentationCephalosporin CDecomposition
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and relates to a method for reducing decomposition of cephalosporin C (CPC). The method comprises the following steps: knocking out beta-lactamase genes and acetyl esterase genes of host bacteria by using a Red recombinant system; transforming cephalosporin C acylase genes into the host bacteria; expressing the cephalosporin C acylaseby using the host bacteria; preparing cephalosporin C acylase crude enzyme solution or immobilized cephalosporin C acylase crude enzyme; and adding the cephalosporin C acylase crude enzyme solution or immobilized cephalosporin C acylase crude enzyme into cephalosporin C substrate working liquid and catalyzing to generate 7-aminocephalosporin acid (ACA). CPC acylase is prepared by the method. In the process of catalyzing the CPC to generate 7-ACA by using the harvested crude enzyme, the utilization ratio of the CPC is increased to over 98 percent.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
Electronic paper display screen, display equipment and binding method
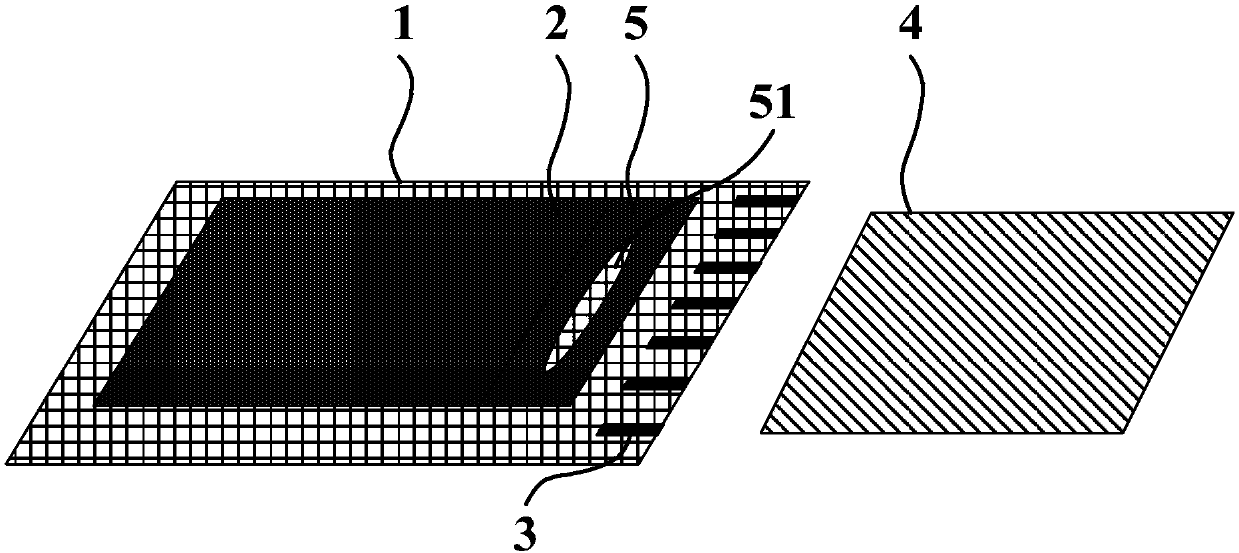
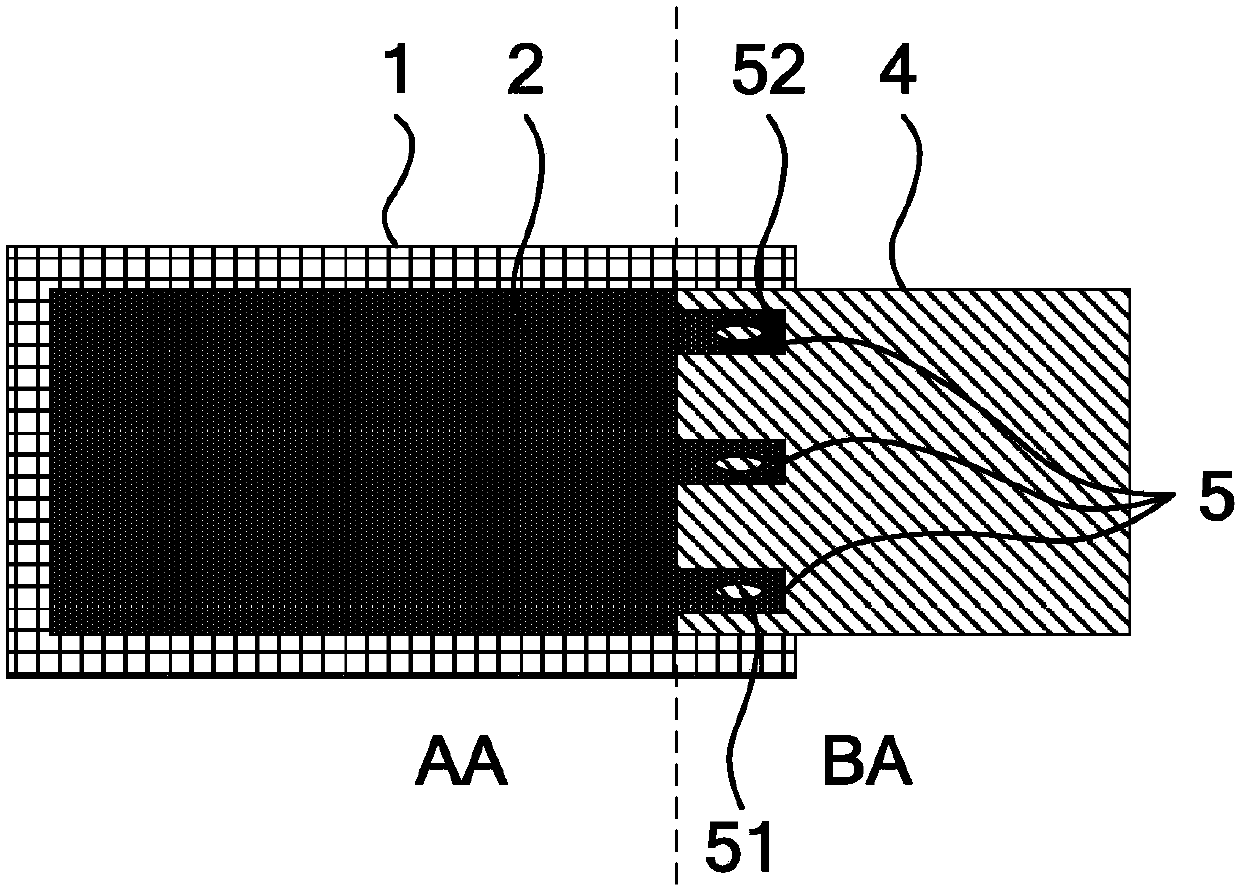
PendingCN107703693AImprove substrate utilizationImprove yield ratePrinted circuit manufactureNon-linear opticsChip on filmElectricity
The invention relates to the technical field of displaying, and discloses an electronic paper display screen, display equipment and a binding method. The technical purpose is to increase the substrateutilization rate of the electronic paper display screen, increase the yield of the electronic paper display screen and prolong the service life of the electronic paper display screen. The electronicpaper display screen comprises a substrate, electronic paper, a binding electrode, an electronic ink conduction structure and chip-on-film, wherein the substrate comprises a displaying area and a binding area, the electronic paper is arranged at one side of the displaying area of the substrate, and the electronic ink conduction structure which extends to the substrate binding area is arranged at the edge, close to one side of the binding area, of the electronic paper; the chip-on-film is electrically connected with the substrate through the binding electrode, and the end, close to the displaying area, of the chip-on-film is clamped between the substrate and the electronic ink conduction structure.
Owner:BOE TECH GRP CO LTD +1
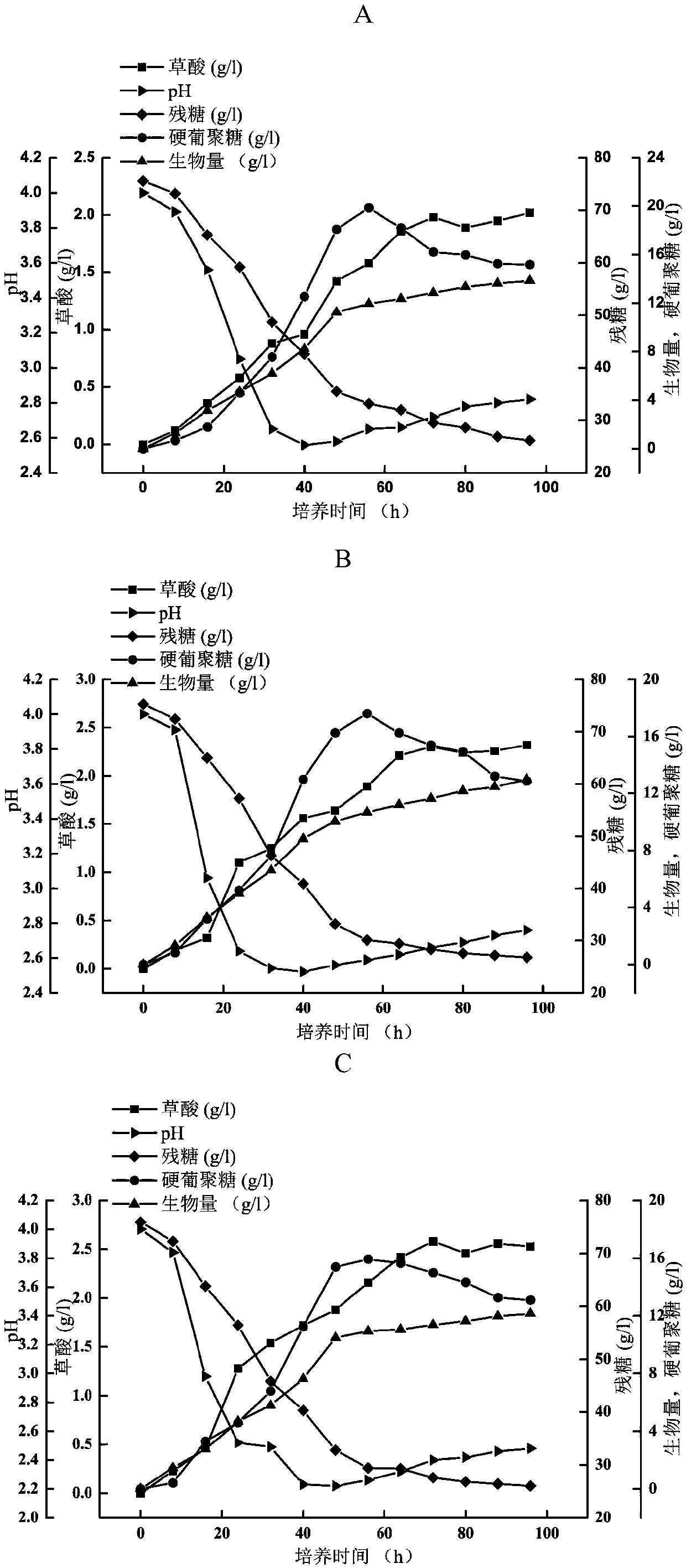
A kind of Sclerotinum and method for fermenting and producing scleroglucan
ActiveCN108441429BImprove substrate utilizationLow costFungiFood ingredient as thickening agentMicroorganismSucrose
The invention discloses a Sclerotinum and a method for fermenting and producing scleroglucan, belonging to the technical field of microbes. The strain CCTCC NO:M2017646 provided by the present invention can be fermented for 56 hours under the condition of glucose carbon source concentration of 75g / L to reach the effect of scleroglucan production of nearly 20g / L, which is obviously better than the current international scleroglucan production of 150g / L. Under the culture condition of L sucrose, the yield of 72h is 26g / L, the substrate utilization rate is increased by 58%, and the cost is significantly reduced. The method is superior to the existing dextran production process and has important industrial application prospects.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
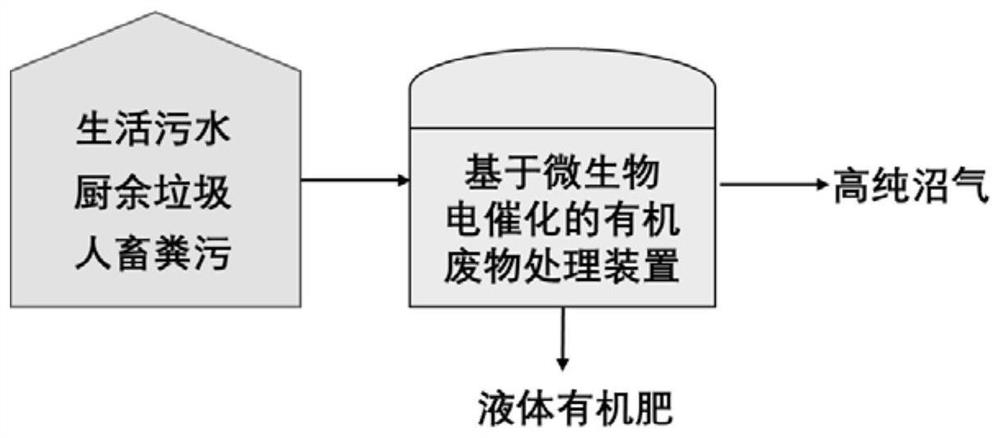
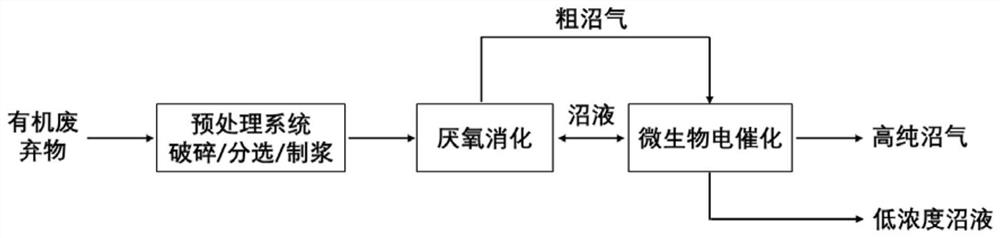
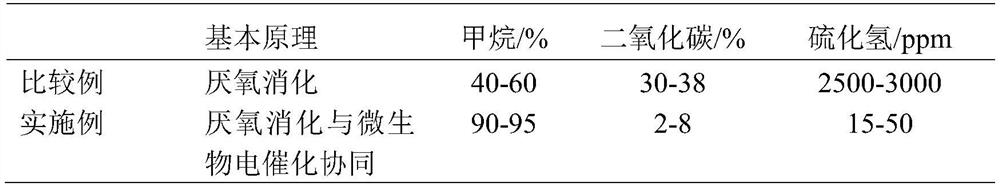
Microbial electro-catalysis-based small-sized organic waste treatment device and treatment method for villages and towns
ActiveCN112852599AOvercoming thermodynamic barriersImprove energy efficiencyBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBio-organic fraction processingMicroorganismElectron donor
The invention discloses a microbial electro-catalysis-based small-sized organic waste treatment device and treatment method for villages and towns; an anaerobic biogas digester is coupled with a microbial electro-catalysis system, and the small-sized movable organic waste treatment device suitable for villages and towns is constructed; and the electro-catalysis performance of electroactive microorganisms is utilized, the bottleneck problem that electron donors are insufficient in the anaerobic fermentation process is solved, deep treatment of organic waste is achieved on the anode, meanwhile, carbon dioxide in biogas is further converted into methane on a cathode, and biogas upgrading and purification are achieved. According to the method, the potential value of rural household biogas engineering can be fully excavated, the problem that the biogas engineering is idle is fundamentally solved, the pressure of rural energy requirements is relieved, the utilization way can be widened, the generated liquid organic fertilizer is used for farmland soil improvement, cooperative treatment of agricultural production and domestic waste can be achieved, and the purposes of heating and cleaning home furnishing, economical and efficient courtyard and harmless agricultural production are achieved.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Method for producing phycoerythrin and polyunsaturated fatty acid by using R. salina
ActiveCN106636264AFast growthIncrease biomassUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesLipid formationPhycoerythrin
The invention provides a method for producing phycoerythrin and polyunsaturated fatty acid by using R. salina. The method comprises the steps of culturing the R. salina by using a seed culture medium; inoculating an artificial seawater fermentation medium with the R. salina; culturing the R. salina by using light with different wave lengths and intensities. The method for producing the phycoerythrin and the polyunsaturated fatty acid by using the R. salina increases the substrate utilization rate, and improves the biomass as well as the fermentation level of total protein, the phycoerythrin, lipid and the polyunsaturated fatty acid, thus being very beneficial to promotion of industrial development of producing the phycoerythrin and the polyunsaturated fatty acid by fermenting the R. salina.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method of producing welan gum by tank-dividing method fermentation
InactiveCN103695498AImprove substrate utilizationReduce cumbersomeMicroorganism based processesFermentationCulture mediumsFermentation broth
The invention relates to a method of producing welan gum by utilization of alcaligenes fermentation and then by extraction with acetone. The method comprises S1. a step of preparing a strain preservation slant, wherein the alcaligenes ATCC31555 is inoculated onto a culture medium slant and cultured at a maintained temperature of 30 DEG C for 2-4 days and reserved for further use; S2. a step of picking a loop of the strain on the slant to a primary liquid seed culture medium by using an inoculating loop and culturing at 30 DEG C for 24 h to obtain primary liquid seeds; S3. a step of inoculating the primary liquid seeds to a secondary liquid seed culture medium according to an inoculation amount of 10%, and culturing at 28-38 DEG C for 12-24 h to obtain secondary liquid seeds; S3. a step of inoculating the secondary liquid seeds to a sterilized fermentation tank having a volume of 5 L and fermenting; S4. a step of discharging 1-3.5 L of fermentation liquid after fermentation is performed for 20-36 h, replenishing 1-3.5 L of a liquid fermentation culture medium, repeating for 2-3 times, and stopping the fermentation; and S5. a step of performing post-extraction of the fermentation liquid. The method shortens the fermentation period and increases the production efficiency and the yield.
Owner:天津科百生物科技研发有限公司
Production method of butyl alcohol by fermentation of biomass coupled with pervaporation separation
ActiveCN102757984BIncrease concentrationEnables in situ separation and removalMicroorganism based processesFermentationHigh concentrationOil phase
The invention relates to a production method of butyl alcohol by fermentation of biomass coupled with pervaporation separation. The production method comprises the following steps of: firstly, by utilizing the characteristic that an oil-water layering phenomenon of a penetration side liquid occurs after biomass fermentation liquor passes through an ethanol-permselective pervaporation membrane system, respectively carrying out high concentration of product butyl alcohol on water phase and oil phase at the penetration side by selecting the ethanol-permselective pervaporation membrane system and a water-permselective pervaporation membrane system to obtain high-concentration organic concentrate with few moisture content, wherein the concentration of the obtained organic concentrate can reach 99.5wt%, so that the separation efficiency is greatly improved and the energy consumption in the production process is reduced; and secondly, the production method couples the pervaporation technology with the biomass fermentation process so as to realize the timely separation and removal of butyl alcohol in the fermentation medium, reduce the inhibiting effect of butyl alcohol on microbial cell growth, improve the fermentation production rate and substrate utilization rate and greatly reduce the production cost.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
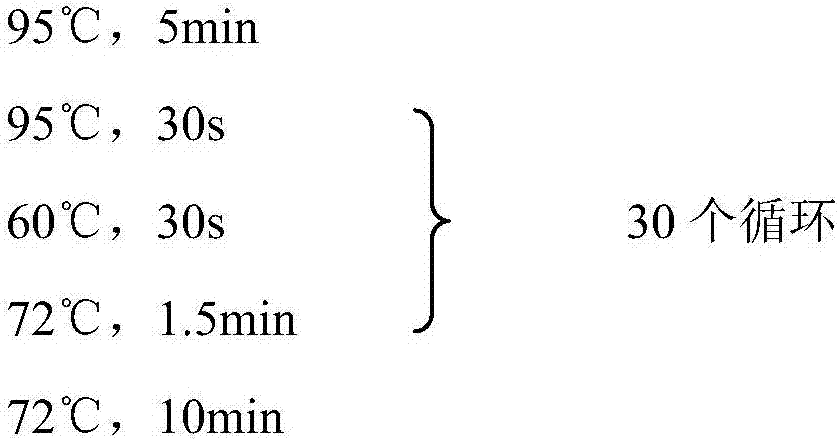
Method for reducing decomposition of cephalosporin C
ActiveCN102533920BLow costImprove substrate utilizationMicroorganism based processesFermentationDecompositionEsterase Gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and relates to a method for reducing decomposition of cephalosporin C (CPC). The method comprises the following steps: knocking out beta-lactamase genes and acetyl esterase genes of host bacteria by using a Red recombinant system; transforming cephalosporin C acylase genes into the host bacteria; expressing the cephalosporin C acylaseby using the host bacteria; preparing cephalosporin C acylase crude enzyme solution or immobilized cephalosporin C acylase crude enzyme; and adding the cephalosporin C acylase crude enzyme solution or immobilized cephalosporin C acylase crude enzyme into cephalosporin C substrate working liquid and catalyzing to generate 7-aminocephalosporin acid (ACA). CPC acylase is prepared by the method. In the process of catalyzing the CPC to generate 7-ACA by using the harvested crude enzyme, the utilization ratio of the CPC is increased to over 98 percent.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
A recombinant bacterium utilizing dextran to synthesize 3-hydroxypropionic acid and its construction method and application
The invention provides recombinant bacteria capable of synthesizing 3-hydracrylic acid by using glucan as well as a construction method and application of the recombinant bacteria, and belongs to the field of gene engineering and fermentation engineering. Klebsiella pneumoniae is host bacteria for expressing a gene lgk capable of encoding levodextran kinase and a gene aldH capable of encoding aldehyde dehydrogenase. The construction method comprises the following steps: obtaining a recombinant carrier puC18-lgk-aldH, converting the recombinant carrier puC18-lgk-aldH into a competent cell of the host Klebsiella pneumoniae, and obtaining the recombinant bacteria. By use of the levodextran kinase gene lgk and the aldehyde dehydrogenase gene aldH which are optimized through a codon, in combination with the whole scheme, the substrate use rate is increased, and the yield is increased.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI +1
A kind of method that uridine phosphoryl compound co-produces chiral hydroxyl ester
InactiveCN101724670BImprove regeneration efficiencyImprove substrate utilizationMicroorganism based processesFermentationCogenerationKetone
The invention discloses a method for co-producing chiral hydroxyl esters of uridine phosphoryl compounds. The method uses orotic acid and β-keto ester compounds as substrates, uses glucose as an energy donor, and utilizes permeable Simultaneous production of uridine phosphoryl compounds and chiral hydroxyl esters by yeast cells. The present invention utilizes the principles of whole-cell catalysis and metabolic engineering, establishes a metabolic network model and analyzes metabolic flow, and utilizes permeable yeast cells to co-produce uridine phosphoryl compounds and chiral hydroxyl esters, increasing the yield and reducing production costs , The synthesis time is shortened, and the utilization rate of the substrate is greatly improved.
Owner:NANJING TECH UNIV
A kind of production method of high optical purity α-arbutin and high adhesiveness dextran
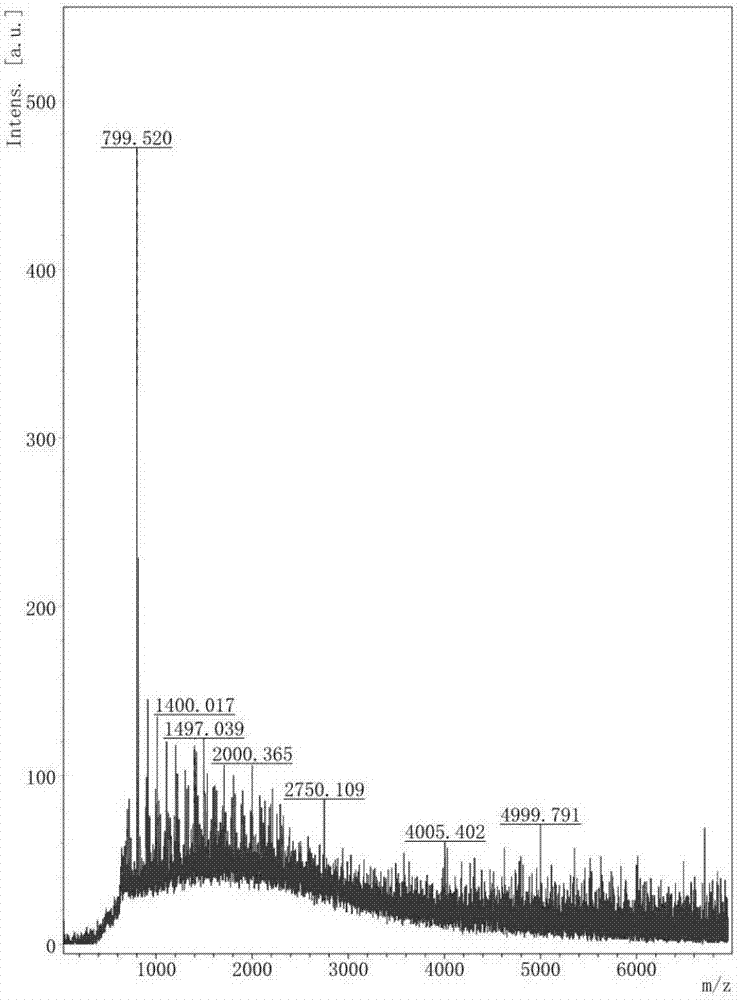
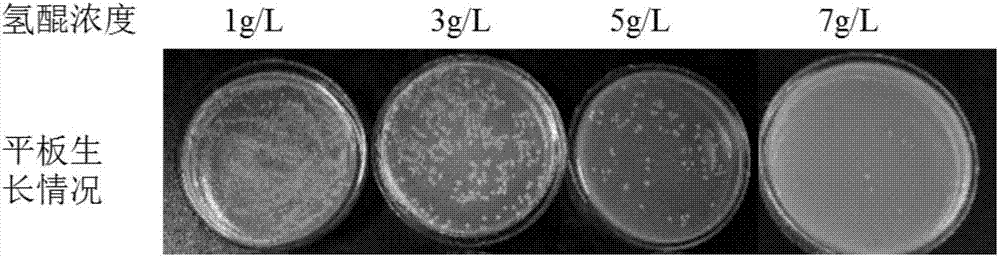
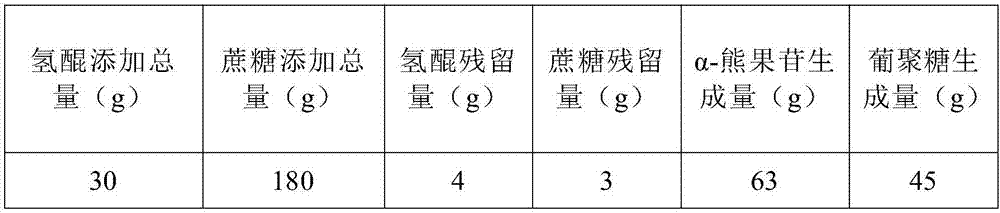
ActiveCN107099566BGood adhesionImprove performanceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyArbutin
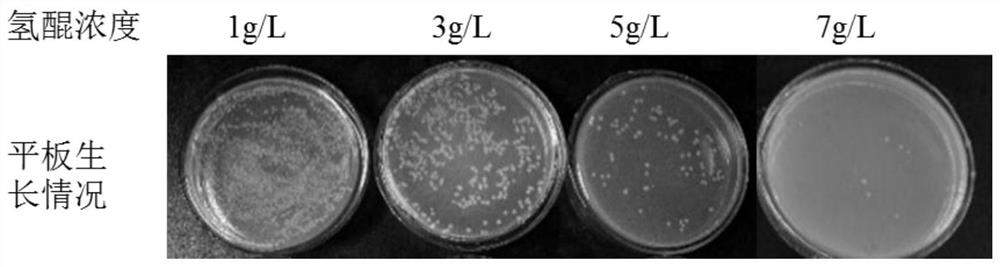
The invention discloses a co-production method for alpha-arbutin with high optical purity and glucan with high adhesion by using leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides. The method takes sucrose and hydroquinone as substrates to produce the alpha-arbutin and the glucan by fermenting in one step under the weak acid environment, and comprises the following steps: 1) first level seed culture: inoculating a leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides solution in a seed medium with 0.1 to 0.2% inoculation amount, and cultivating at 37 DEG C and 250rpm for 10 to 12 hours; 2) second level seed culture: transmitting a first level seed solution to the seed medium with 1 to 2% inoculation amount, and cultivating at 37 DEG C and 250rpm for 10 to 12 hours; 3) fermentation culture: inoculating a second level seed solution in a fermentation medium with 5 to 8% inoculation amount, adjusting pH in a fermentation process to be 6.0 to 6.8, blowing air in the whole fermentation process, controlling the air flow to be 0.1 to 0. 3vvm, and cultivating at 37 DEG C and 250 to 300rpm for 12 to 16 hours. According to the method, the alpha-arbutin with high optical purity and the glucan with high adhesion can be directly obtained by the fermentation of bacterial strain, and the method is high in substrate use rate, simple and quick in reaction, mild in condition, low in energy consumption, and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:CHANGMAO BIOCHEMICAL ENG CO LTD
A method and application of directly using non-detoxified acid to pretreat lignocellulose for hydrogen production
InactiveCN107177634BImprove applicabilitySolve pollutionMicroorganism based processesFermentationCelluloseAnaerobic bacteria
The invention discloses a method and application of hydrogen production by directly using non-detoxified acid to pretreat lignocellulose. The invention inoculates the thermophilic saccharolytic anaerobic bacillus seed liquid into the fermentation medium to carry out anaerobic fermentation to obtain hydrogen; wherein, the fermentation medium is a medium in which undetoxified acid pretreated lignocellulose is used as a carbon source. The invention carries out fermentation through two-stage fermentation or adding some organic acids. The present invention can reach 277.44mM (6.21L-H) through the output of two-stage fermentation hydrogen 2 / L); by adding 10g / L acetic acid, the production of hydrogen can be increased by 63.9%, which can significantly improve the biohydrogen production efficiency of bagasse. The method provided by the invention is suitable for transforming bagasse by microorganisms.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Chip packaging method
ActiveUS20220148887A1Simplify the packaging processSolve the real problemSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesElectrical connectionHigh transmission
A chip packaging method begins by fixing a chip to the top side of a substrate. The chip is then encapsulated in an encapsulant. After that, the encapsulant is drilled from its top side in order to have a through hole adjacent to the chip. Lastly, an area extending between the chip and the through hole and the hole wall of the through hole are plated with an electrically conductive metal to enable electrical connection between the chip and the substrate through the electrically conductive metal. The chip packaging method solves the problems of the conventional wire bonding method, simplifies the packaging process, and provides the packaged chips with high transmission efficiency.
Owner:LINGSEN PRECISION INDS
Production method for alpha-arbutin with high optical purity and glucan with high adhesion
ActiveCN107099566AGood adhesionImprove performanceMicroorganism based processesFermentationSucroseALPHA-ARBUTIN
The invention discloses a co-production method for alpha-arbutin with high optical purity and glucan with high adhesion by using leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides. The method takes sucrose and hydroquinone as substrates to produce the alpha-arbutin and the glucan by fermenting in one step under the weak acid environment, and comprises the following steps: 1) first level seed culture: inoculating a leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides solution in a seed medium with 0.1 to 0.2% inoculation amount, and cultivating at 37 DEG C and 250rpm for 10 to 12 hours; 2) second level seed culture: transmitting a first level seed solution to the seed medium with 1 to 2% inoculation amount, and cultivating at 37 DEG C and 250rpm for 10 to 12 hours; 3) fermentation culture: inoculating a second level seed solution in a fermentation medium with 5 to 8% inoculation amount, adjusting pH in a fermentation process to be 6.0 to 6.8, blowing air in the whole fermentation process, controlling the air flow to be 0.1 to 0. 3vvm, and cultivating at 37 DEG C and 250 to 300rpm for 12 to 16 hours. According to the method, the alpha-arbutin with high optical purity and the glucan with high adhesion can be directly obtained by the fermentation of bacterial strain, and the method is high in substrate use rate, simple and quick in reaction, mild in condition, low in energy consumption, and suitable for industrial production.
Owner:CHANGMAO BIOCHEMICAL ENG CO LTD
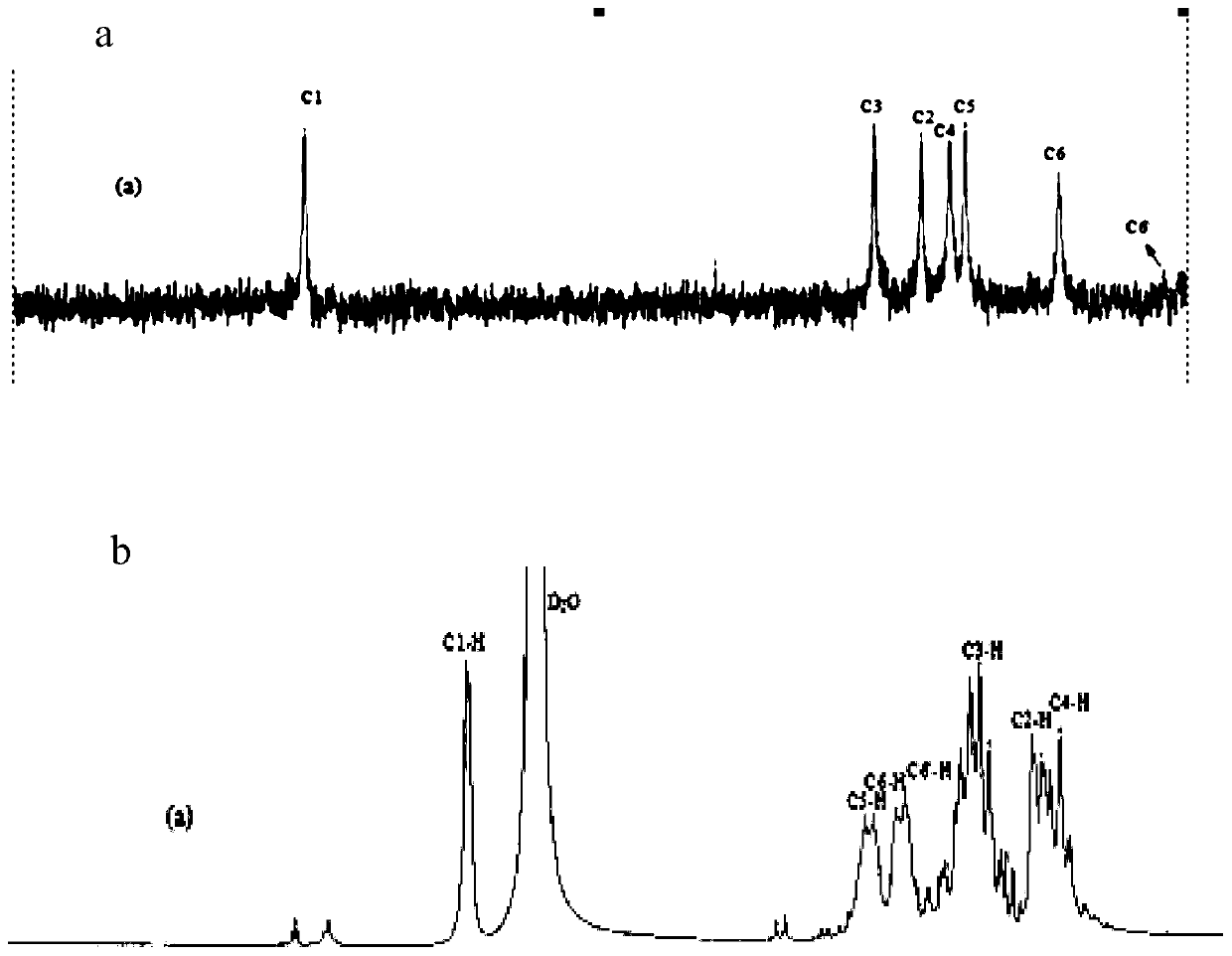
A kind of production method of high-viscosity micro-molecular weight dextran
ActiveCN106497999BImprove gelation performanceImprove performanceMicroorganism based processesFermentationDextranFermentation
The invention discloses a high-viscosity micro-molecular-weight dextran production method. The high-viscosity micro-molecular-weight dextran production method comprises the steps that leuconostoc mesenteroides is utilized and gluco disaccharide is used as a substrate, and fermentation production is performed in an alkaline range to obtain high-viscosity micro-molecular-weight dextran. The leuconostoc mesenteroides is leuconostoc mesenteroides G123, and a preservation number is CCTCC NO: M2014115. The dextran is at least one of maltose, cellobiose, trehalose, kojibiose or gentiobiose. The alkaline range is pH 7.0-8.0. The viscosity of the high-viscosity micro-molecular-weight dextran is not lower than 5800 cP, and the molecular weight ranges from 1000 Da to 2500 Da. The micro-molecular-weight dextran is high in viscosity, is excellent microbial metabolism glue and has wide application prospect. The production method is mild in reaction condition, low in energy consumption, high in yield and applicable to industrial large-scale production.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
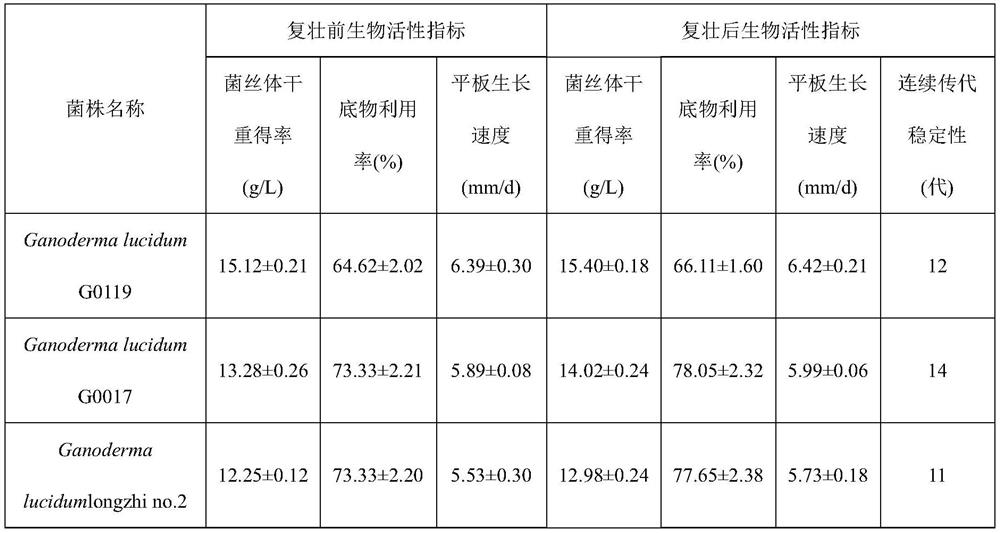
Rejuvenation method of special ganoderma lucidum strain for liquid fermentation
PendingCN112779207AIncrease body yieldHigh yieldFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMycelium
The invention discloses a rejuvenation method of a special ganoderma lucidum strain for liquid fermentation. The method comprises the following steps: (1) shake-flask culture and screening: transferring activated parent ganoderma lucidum mycelia into a shake-flask for culture, and screening out shake-flask fermentation liquor of which the biological activity index is equivalent to that of the parent for later use; (2) plate culture and screening: re-inoculating the fermentation liquor which is obtained by shake flask screening and has the same biological activity index as the parent into a plate for culture, and selecting out the plate with high growth speed for later use; and (3) shake-flask culture verification: transferring the ganoderma lucidum mycelia cultured on the standby flat plate into a shake flask for subculture verification, wherein the flat plate strain used for shake-flask fermentation liquor with the biological activity index equivalent to that of a parent and stable subculture is the rejuvenated ganoderma lucidum strain. By applying the rejuvenation method disclosed by the invention, the problems of strain degradation, weak strain activity and poor strain quality caused in the passage process of liquid culture of the ganoderma lucidum strain can be effectively solved, and a strain guarantee is provided for liquid large-scale sustainable fermentation production of the ganoderma lucidum strain.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Method for separating acetic acid in fermentation liquid for biohydrogen production by bipolar membrane electrodialysis technique
InactiveCN101525285BIncrease productionAvoid inhibitionSemi-permeable membranesCarboxylic compound separation/purificationBiohydrogenPollutant emissions
The present invention relates to a method for separating acetic acid in fermentation liquid for biohydrogen production by bipolar membrane electrodialysis technique. The invention solves the problem that the prior method for separating acetic acid has complex technology, low current efficiency, large energy consumption and long operation time. The method comprises a first step of circularly pumping the pre-treated fermentation liquid for biohydrogen production into a separation chamber of a bipolar membrane electrodialyzer; a second step of circularly pumping pure water or acetic acid solution into an enriched chamber of the bipolar membrane electrodialyzer; and a third step of circularly pumping Na2SO4 electrolyte with the mass concentration of 5% into an anode chamber and a cathode chamber, and performing bipolar membrane electrodialysis so as to accomplish the separation of acetic acid in fermentation liquid for biohydrogen production. The operation time in the invention is decreased by more than 80%, the technology is simple, a separation system is of closed cycling, no pollutant is discharged, and the method is green and environment-friendly. The removal rate of acetic acid in the invention is more than 85%, the recovery rate of acetic acid is more than 85-95%, the current efficiency is up to 60-70%, and the energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Method for producing methane by synergistic treatment of biogas slurry and biogas based on microbial electrocatalysis
ActiveCN112695058BImprove energy efficiencyImprove substrate utilizationMicroorganism based processesWaste based fuelVolatile fatty acidsElectrochemistry
A method for biogas slurry advanced treatment and biogas upgrading to prepare methane based on microbial electrocatalysis. The biogas slurry is used to start the microbial electrochemical system, and the volatile fatty acids and refractory organic compounds in the biogas slurry are degraded under the action of anode electroactive microorganisms. And cooperating with sulfur-oxidizing microorganisms to oxidize hydrogen sulfide in raw biogas to polysulfides, while polysulfides act as redox shuttles to transfer electrons and protons generated at the anode to the cathode, and reduce them in the crude biogas under the action of methanogenic microorganisms at the cathode The carbon dioxide is methane, which realizes the simultaneous completion of advanced treatment of high-concentration biogas slurry, desulfurization and decarbonization of biogas.
Owner:CHINESE RES ACAD OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCI
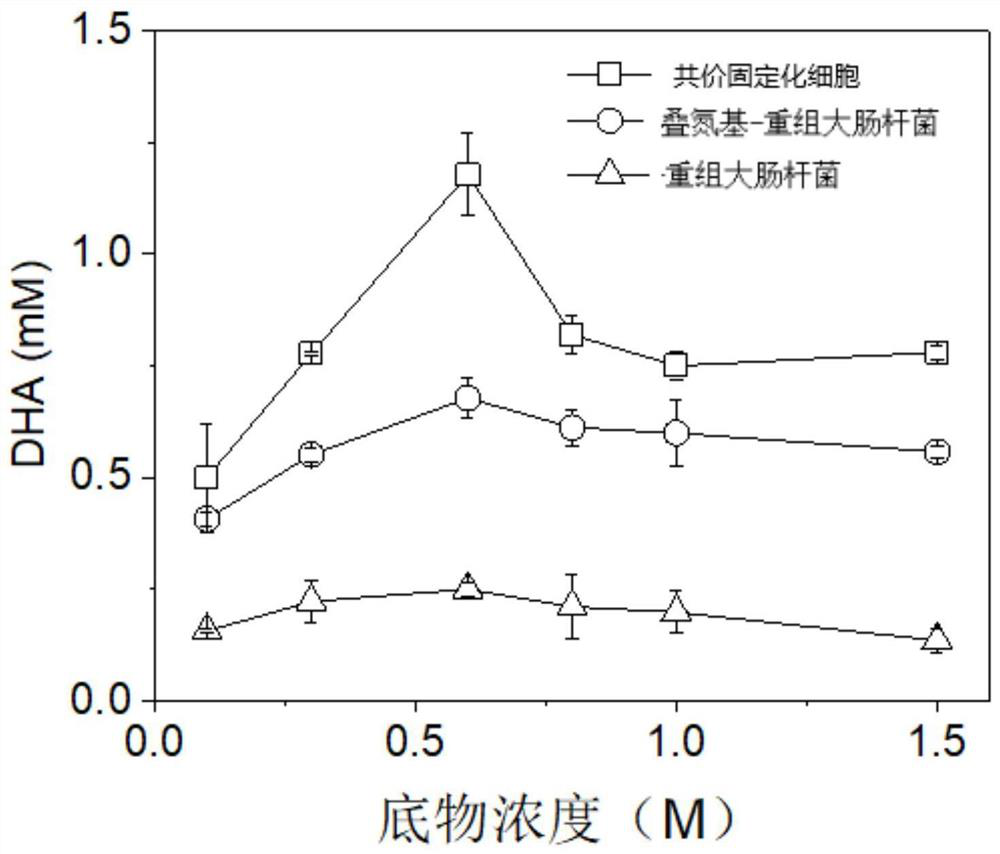
Covalent immobilized cell as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN113444717ACovalent immobilization achievedEfficient covalent immobilizationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention provides a covalent immobilized cell as well as a preparation method and application thereof, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. According to the method, firstly, a covalent immobilized cell is prepared, and the covalent immobilized cell is constructed by taking Fe3O4@SiO2-NH2-alkyne as a carrier and connecting with azido-modified recombinant escherichia coli; and then the covalent immobilized cell is applied to biotransformation of 1, 3-dihydroxyacetone, and the biotransformation process is mild in reaction condition, high in specificity, environmentally friendly and high in substrate utilization rate.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com