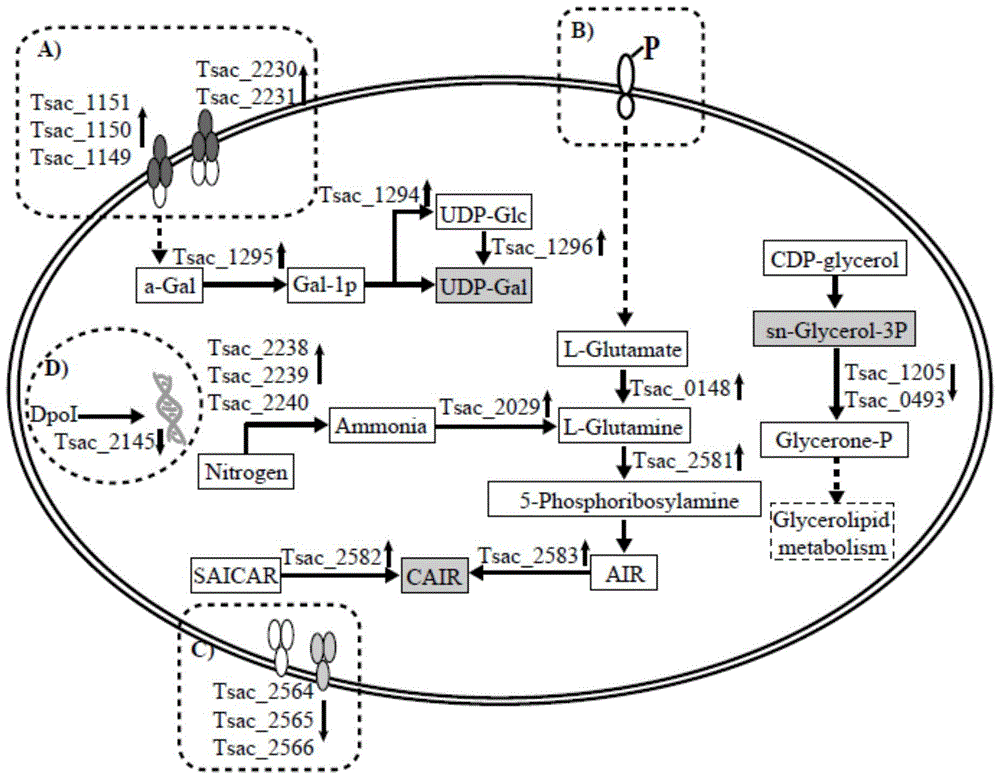
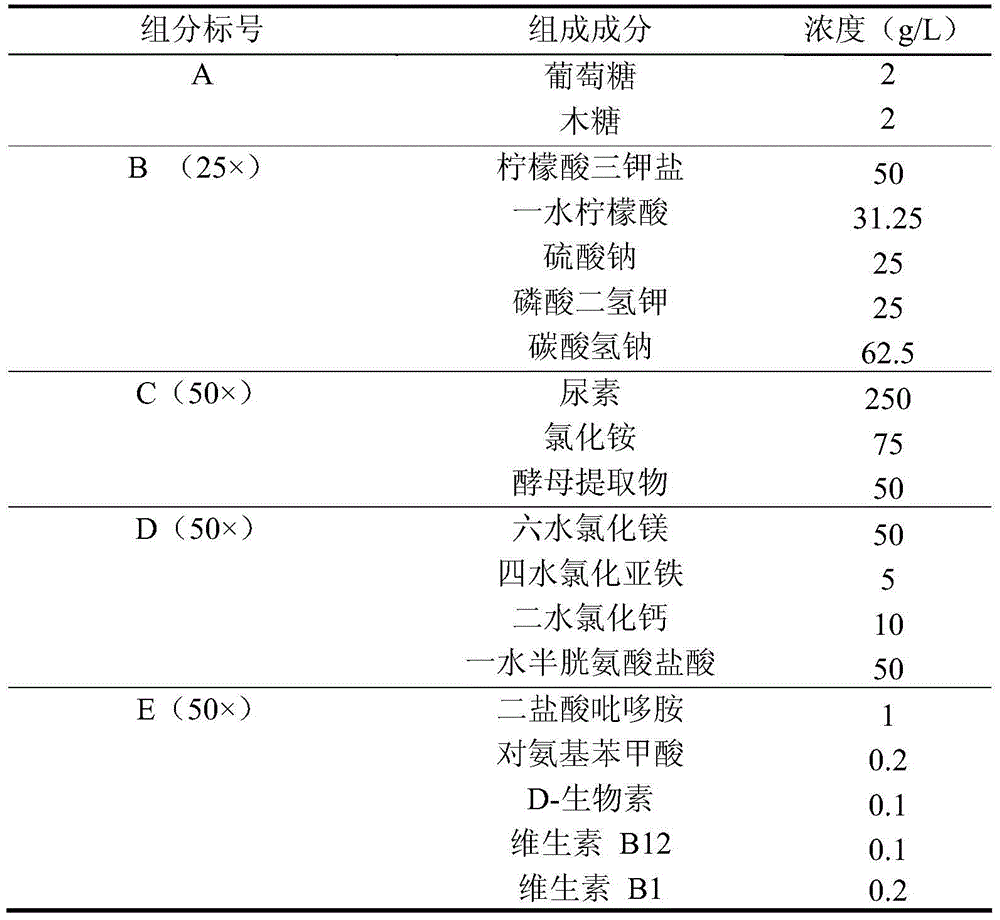
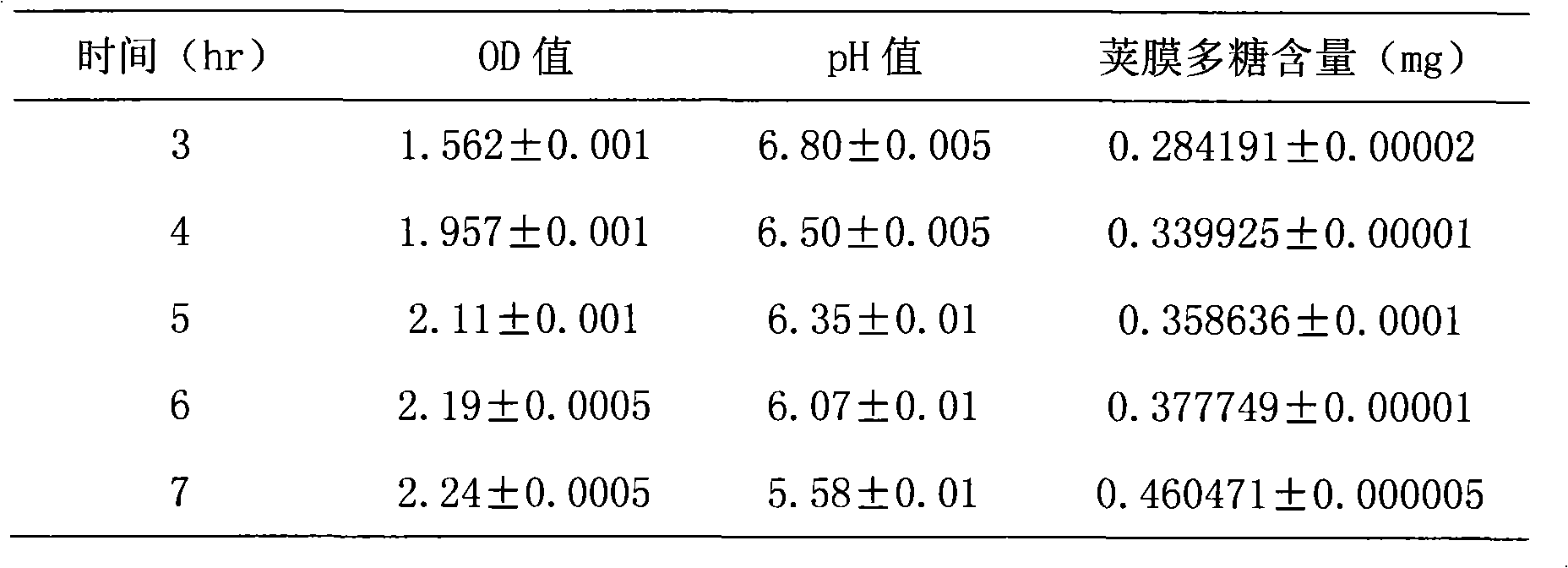
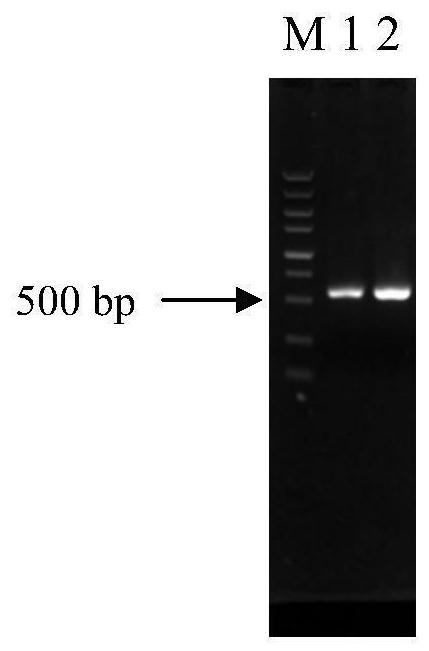
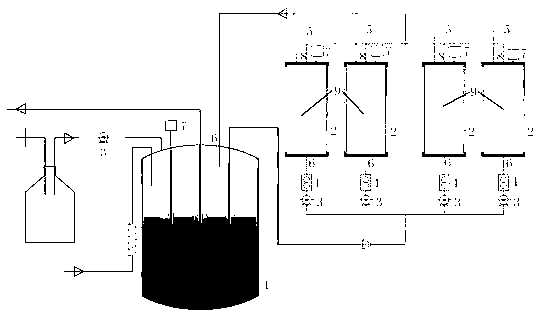
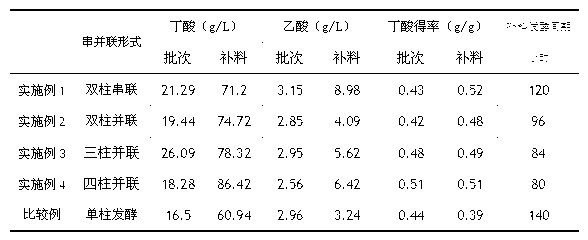
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
42results about How to "Shorten the lag period" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
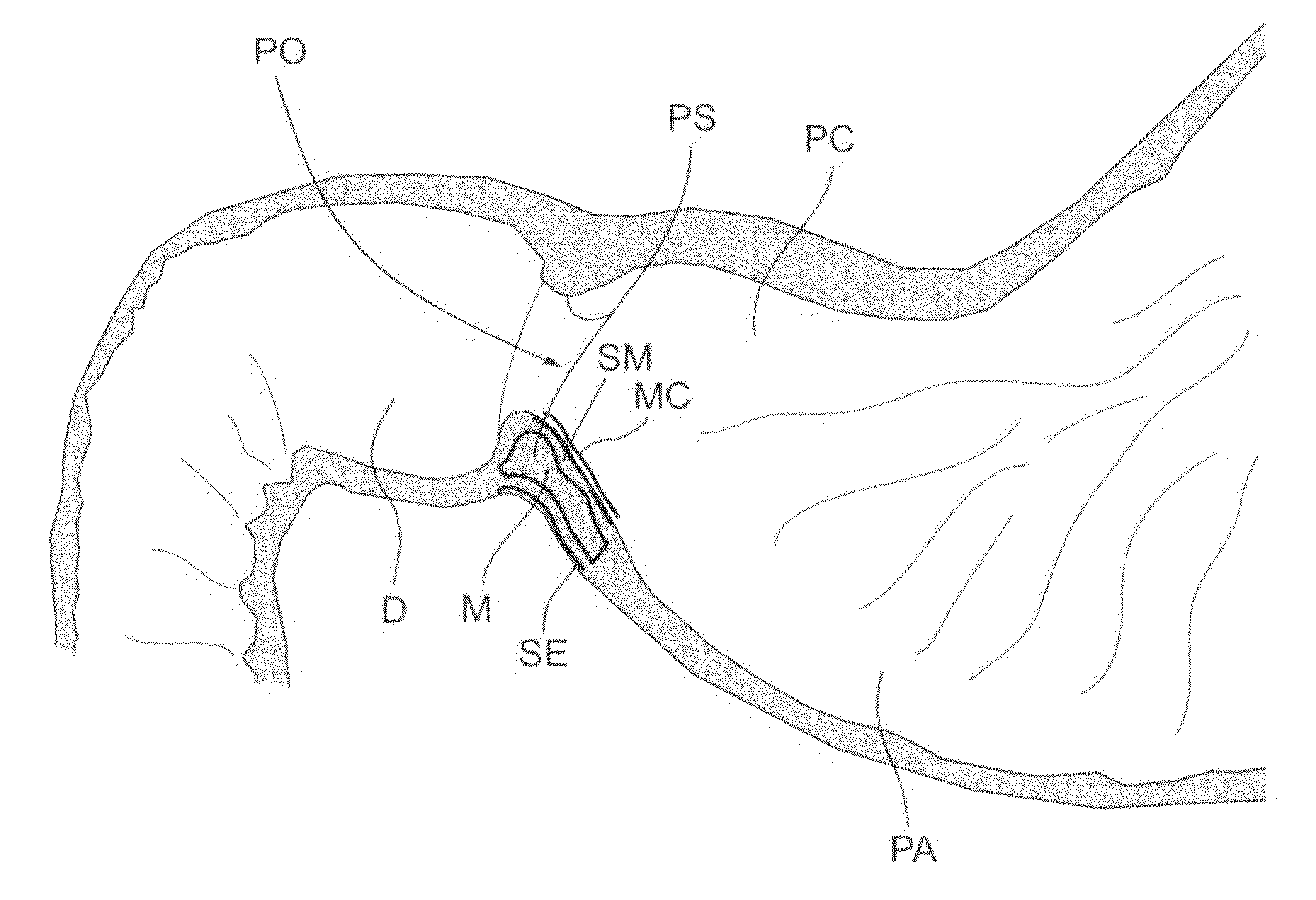
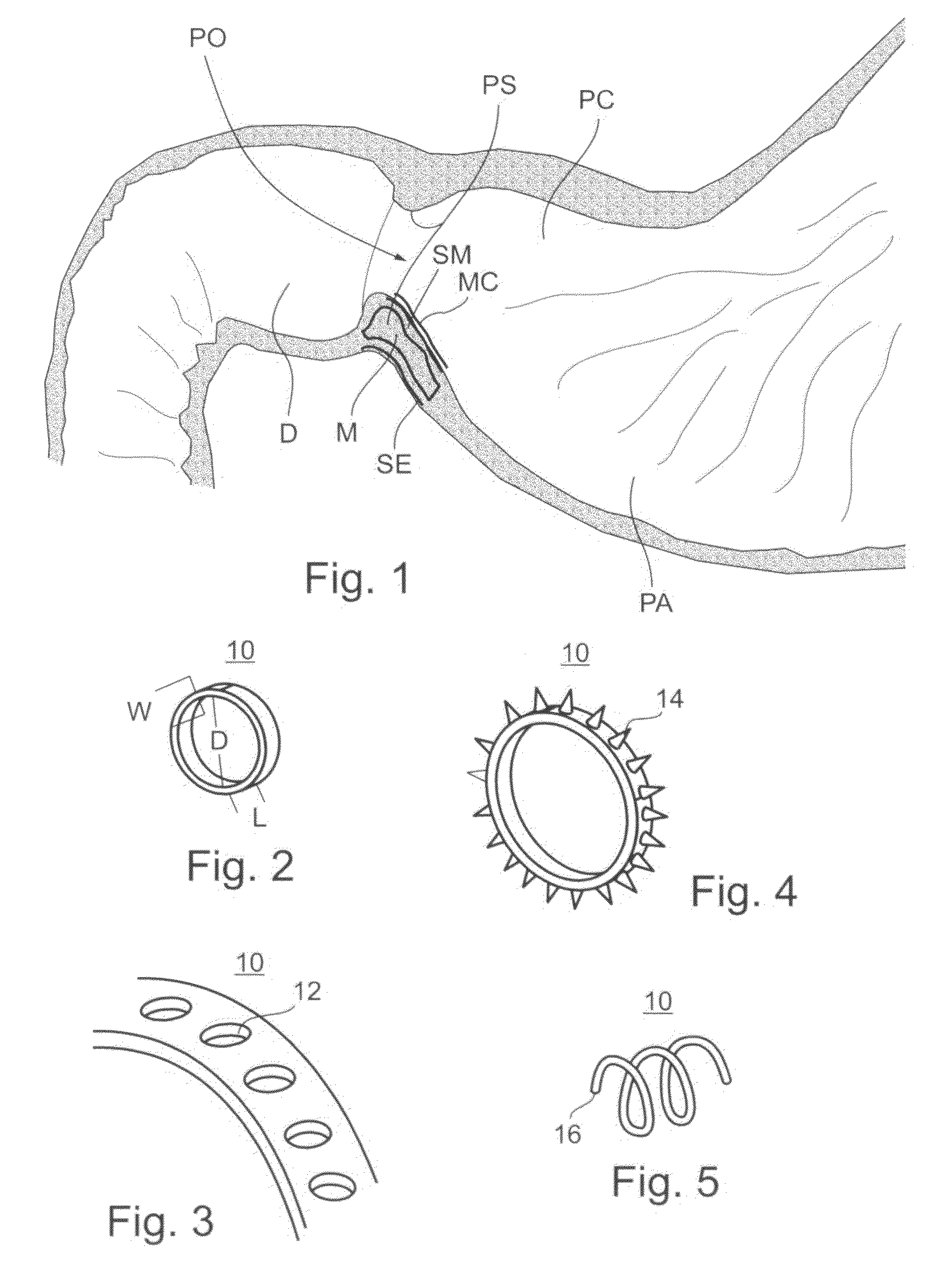
Pyloric Devices and Methods
InactiveUS20090118749A1Shorten the lag periodEffectively alter satietyObesity treatmentWound clampsGastrointestinal devicePyloric sphincter
A gastrointestinal device is provided. The device includes a band sized and configured for residing in or around a pyloric sphincter region of the subject. The band is functional in maintaining the pyloric sphincter at a fixed opening size.
Owner:SVIP 2
Method for treating blue-green algae
InactiveCN105016488AImprove governance effectInhibition of breedingSustainable biological treatmentBiological water/sewage treatmentPre treatmentEnzyme
The invention provides a method for treating blue-green algae. The method includes the following steps of detecting a water body, placing padding and plants, mounting oxygenation devices, domesticating microorganisms, adjusting the water body, putting compound microorganisms, building an ecological system and strengthening treatment; wherein the water body to be treated is detected, pretreatment is conducted, a proper amount of water is taken to serve as habituated culture water for inhibiting external microbial communities for the algae, compound bacteria, enzymes and sugar are added to the habituated culture water, meanwhile, screening is conducted on the beneficial microorganisms three times to five times according to the existence condition of original indigenous and beneficial microorganisms of the water body, the screened beneficial microorganisms are extracted to be subjected to enlarge cultivation, the cultured composite microorganisms are put into the water body required to be treated, the composite microorganisms can destroy the blue-green algae structure, and accordingly, a proper growth breeding condition is provided for follow beneficial microorganisms and animals. According to the main mechanism of the method, the blue-green algae structure is mainly destroyed and utilized, and the method has the advantages of being advanced, reliable, safe, operable, low in investment and capable of generating the effect quickly and finally achieving the purpose that the water quality is purified.
Owner:黄吉森
Nano-iron-loaded biochar, preparation method of nano-iron-loaded biochar, and application of nano-iron-loaded biochar in dark fermentation hydrogen production process
InactiveCN107858379AEasy reunionAchieve releaseFerric oxidesCarbon preparation/purificationDark fermentationBiochar
The invention relates to nano-iron-loaded biochar, a preparation method of the nano-iron-loaded biochar, and an application of the nano-iron-loaded biochar in a dark fermentation hydrogen production process. Ferrite and soluble starch are taken as raw materials which are subjected to reaction under proper conditions and are dried and charred to obtain the nano-iron-loaded biochar, wherein the maincomponent of the nano-iron-loaded biochar is Fe2O3 / C, and the particle diameter range of the nano-iron-loaded biochar is 2-150nm. The biochar is of an amorphous structure, and Fe2O3 is of a mesoporous structure. By adding the iron-loaded biochar to an anaerobic fermentation system, a synergistic strengthening effect of iron and biochar in the dark fermentation hydrogen production process is realized, so that the hydrogen yield and the process stability are improved. Fe2O3 can not only release iron ions to enhance the activity of fermentative hydrogen producing bacterium hydrogenase but also increase the transfer rate of electrons; and furthermore, the biochar in nano-particles can enrich microorganisms, improve the concentration of hydrogen producing bacteria, buffer acid accumulation andrelieve ammonia inhibition.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Fermentation process for producing pravastatin by transforming compactin by using actinomadura yumaense
ActiveCN102757986AImprove conversion abilityRaise the level of fermentationMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismTrace element
The invention discloses a fermentation process for producing pravastatin by transforming compactin by using actinomadura yumaense. According to the fermentation process based on the conventional fermentation process, the transformation ability of the microbial substrate and the fermentation level of the pravastatin are improved by adding trace element solution into a fermentation culture medium and utilizing the effect of the trace elements completely; the transformation ability of the microbial transformation bacteria-actinomadura yumaense on the compactin and the fermentation level of the pravastatin are effectively improved by controlling the culture temperature of the actinomadura yumaense and the transformation temperature of the compactin by using actinomadura yumaense; and the fermentation level is far higher than that of the prior art. The fermentation process is simple and convenient to operate, low in cost and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:GUANGDONG BLUE TREASURE PHARMA
Method for improving 2-keto-L-gluconic acid fermentation efficiency
InactiveCN106434830AIncrease production intensityPromote growthMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyGluconic acid
The invention relates to a method for improving 2-keto-L-gluconic acid fermentation efficiency. The method is characterized in that in the process of mixed strains fermenting 2-keto-L-gluconic acid, the mixed strains comprise ketogulonigenium vulgare and bacillus megaterium, seed solution cultured to the middle and later periods of logarithmic growth is inoculated into fermentation tank optimum culture media to ferment and culture, sorbose is fed since fermentation time is 0h, and small material culture media are fed at the prior period of the logarithmic growth. According to the method, production intensity of the 2-keto-L-gluconic acid can be improved, efficiency is improved, production capacity is optimized, the content of the 2-keto-L-gluconic acid in fermentation solution can reach 115.6-150.3mg / ml, acid producing rate is 2.89-3.76g.(L.h)-1, and the conversion rate of glucose acid is 87.2-95.0%.
Owner:NINGXIA QIYUAN PHARMA
Biological reinforcing method of hydrogenogen compensating material cultivation and biological hydrogen production system
ActiveCN101402926AImprove hydrogen production performancePromote growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesHydrogenSludge
The invention discloses a fed culture method of hydrogen-producing bacteria and a biological enhancing method of a biological hydrogen producing system, which relates to a method for enhancing bacterial culture and the biological hydrogen producing system. The method solves the problems that the existing fermentation method has the defects of long startup time of a reactor, low hydrogen productivity and sludge loss during continuous operations of the biological hydrogen production. The method comprises the steps: A. hydrogen-producing bacteria are inoculated in nutrient solution in a fermentation tank for anaerobic fermentation; B. after the anaerobic fermentation, a part of fermentation solution is put into a biological hydrogen producing reacting device by a metering pump, and then fresh nutrient solution, which has the same volume as a part of fermentation solution put into the biological hydrogen producing reacting device, is added into the fermentation tank for ongoing anaerobic fermentation, thereby completing the fed culture of hydrogen-producing bacteria and the biological enhancement of the biological hydrogen producing system. The method shortens the startup time of the biological hydrogen producing reactor during the continuous operation to 15 days to 20 days, and increases the hydrogen productivity by 10 percent to 15 percent, thus avoiding the loss of active sludge.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Fermentation process for producing pravastatin by transforming compactin by using actinomadura yumaense
ActiveCN102757986BImprove conversion abilityRaise the level of fermentationMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismTrace element
The invention discloses a fermentation process for producing pravastatin by transforming compactin by using actinomadura yumaense. According to the fermentation process based on the conventional fermentation process, the transformation ability of the microbial substrate and the fermentation level of the pravastatin are improved by adding trace element solution into a fermentation culture medium and utilizing the effect of the trace elements completely; the transformation ability of the microbial transformation bacteria-actinomadura yumaense on the compactin and the fermentation level of the pravastatin are effectively improved by controlling the culture temperature of the actinomadura yumaense and the transformation temperature of the compactin by using actinomadura yumaense; and the fermentation level is far higher than that of the prior art. The fermentation process is simple and convenient to operate, low in cost and suitable for large-scale production.
Owner:GUANGDONG BLUE TREASURE PHARMA
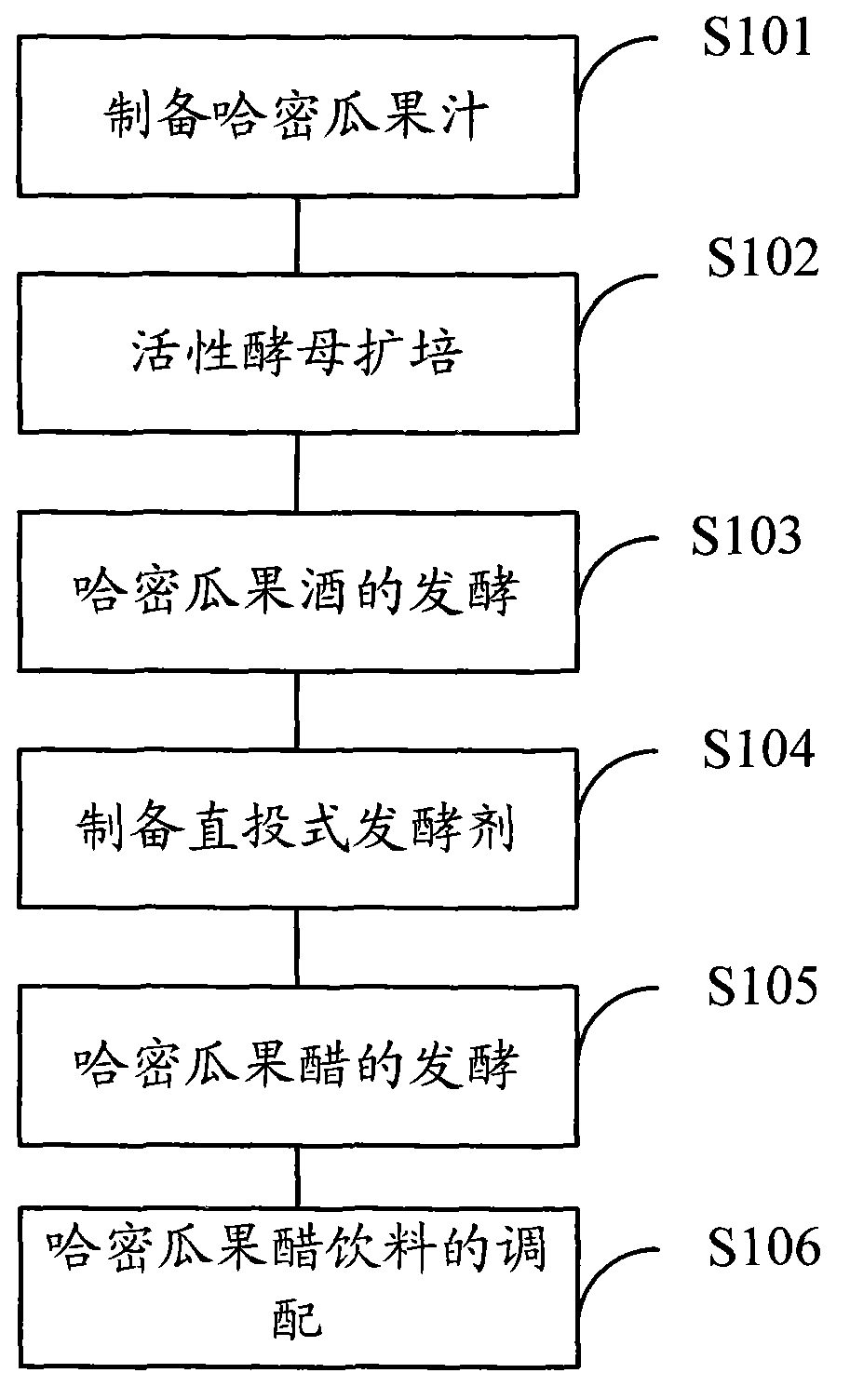
Method for preparing Hami melon vinegar beverage
InactiveCN102845800AIncrease profitShorten the lag periodVinegar preparationFood preparationAcetic acidSubmerged fermentation
The invention discloses a method for preparing a Hami melon vinegar beverage. The method comprises the steps of preparing Hami melon juice, expanding cultivation of active ferment, fermenting Hami melon wine, preparing a direct leavening agent, fermenting Hami melon vinegar and preparing the Hami melon vinegar beverage. The method combines a liquid submerged fermentation technology and a direct fermenting method and has the advantages of being quick in fermenting speed, short in fermenting period, high in raw material utilization ratio and acid producing efficiency and the like. The advantages of the liquid submerged fermentation technology are played to the most extent by controlling diameters including the leavening agent, fermentation liquor ingredients and the like. By adopting the direct leavening agent, the steps of earlier-stage activation, separation and purification, cultivation expanding and the like required by test tube acetic acid strains are omitted, a lag period of the acetic acid strains is shortened, and the overall fermenting process is shortened by more than 60 hours than that of the test tube strains. By controlling the process steps, functional ingredients of Hami melons are fully utilized, special flavor of the Hami melons is retained, and the beverage is gentle in sour, sweet, mellow, tasty and refreshing and enriches the fruit vinegar beverage market.
Owner:CHANGSHA UNIVERSITY OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY
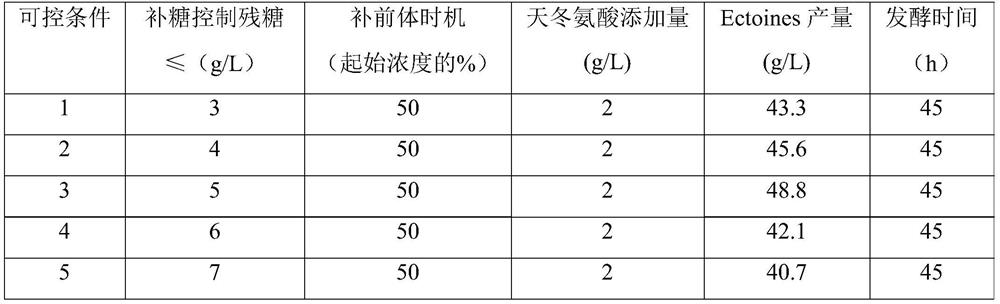
Culture medium and fermentation method capable of improving yield of corynebacterium glutamicum ectoines
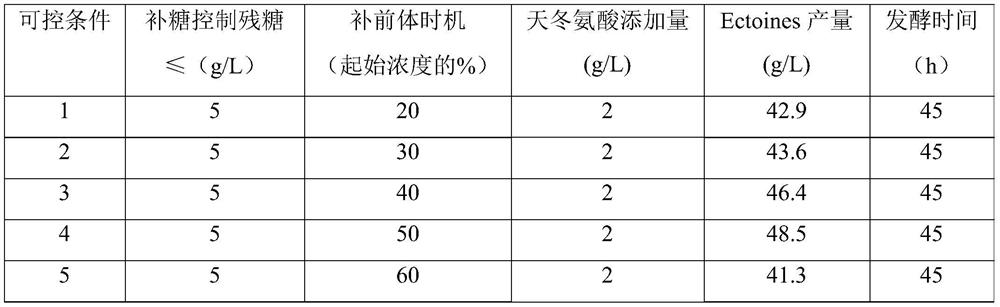
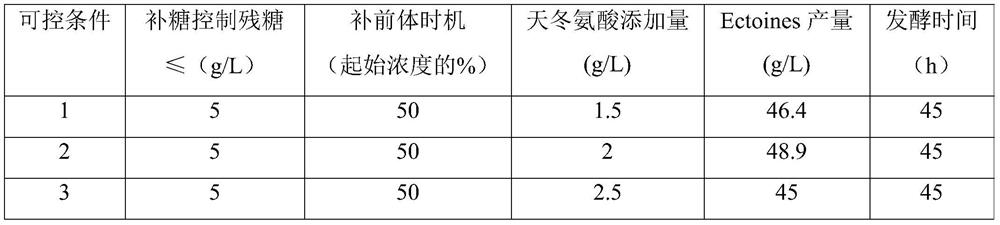
ActiveCN111893146AIncrease plasmid copy numberShorten the lag periodBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyAsparagus cochinchinensis
The invention discloses a culture medium and fermentation method capable of improving yield of corynebacterium glutamicum ectoines, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The invention provides aformula of a fermentation culture medium. The fermentation culture medium is rich in a carbon source, a nitrogen source, inorganic salt and compound trace elements, which are required for growth of corynebacterium glutamicum CG-ECT3; a strain is enabled to rapidly grow, reproduce and be cultured for 13 hours; OD600 can reach over 40; a plasmid copy number is increased; and time of a lag period and time of a logarithmic phase are shortened. Meanwhile, according to the invention, by controlling residual sugar and a precusor substance L-asparaginic acid in fermentation liquor to be replenished in the fermenting process, the acid-producing ability of the recombinant corynebacterium glutamicum CG-ECT3 is improved, a fermentation period is shortened, and after fermentation is carried out for 45h, yield of the ectoines can reach over 48g / L.
Owner:无锡晶扬生物科技有限公司
Method for producing L-diaminocaproic acid through multistage continuous fermentation
InactiveCN106148444AShorten the lag periodImprove substrate utilizationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesContinuous fermentationBatch fermentation
The invention discloses a method for producing L- diaminocaproic acid through multistage continuous fermentation. The method includes: starting from escherichia coil to obtain an L-diaminocaproic product through fermentation above stage four; specifically stringing at least four fermentation tanks integrally, and controlling carbon source concentration and nitrogen source concentration in the fermentation tanks of different stages by regulating ventilatory capacity, initial sugar concentration of the primary fermentation tank, and addition rates, fermented-liquid outflowing rate and fermented liquid inflowing rate of carbon source filling containers and nitrogen source filling containers of the fermentation tanks; controlling the fermentation tanks of different stages to enable the specific growth rate of thallus of the fermentation tanks of the different stages to be 0.3-0.8h<1> to obtain the fermentation product. With the method, high thalli concentration in the fermentation system is maintained, lag phase of cells is shortened, substrate utilization is higher as compared with batch fermentation, target product quantity is high, yield is stable, operations of repeated tank washing, sterilizing, inoculating and the like are not needed, and production cost is lowered.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Additive for synergetically promoting multiplication and colonization of intestinal probiotics and use method of additive
PendingCN106858066AShorten the lag periodMild responseAnimal feeding stuffAccessory food factorsNutrientOrganic acid
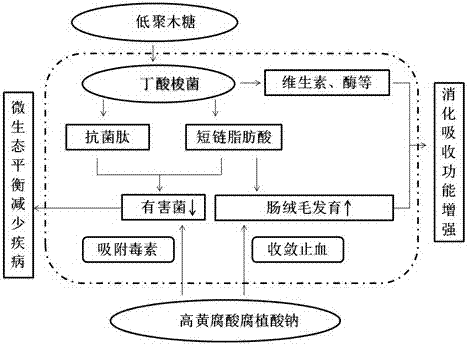
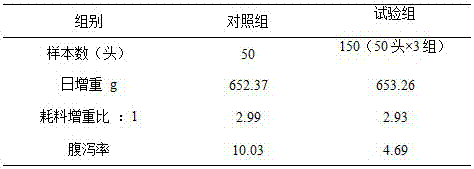
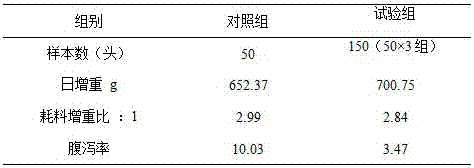
The invention relates to an additive for synergetically promoting multiplication and colonization of intestinal probiotics and a use method of the additive. The additive contains xylooligosaccharide, clostridium butyricum and high fulvic acid sodium humate, wherein the xylooligosaccharide is capable of supplying nutrients to the clostridium butyricum and promoting the multiplication of the multiplication in intestinal tracts; the clostridium butyricum is capable of secreting vitamins, growth factors and the like so as to promote the multiplication of the probiotics and simultaneously secreting organic acid, antibacterial peptide and the like so as to inhibit the growth of harmful bacteria; and the high fulvic acid sodium humate is capable of repairing the injury of intestinal mucosa, increasing the level of an probiotics adhesin receptor on the surface of intestinal mucosa and promoting the colonization of the probiotics in the intestinal tracts. By virtue of process coupling and function synergy of the xylooligosaccharide, the clostridium butyricum and high fulvic acid sodium humate, the intestinal microecological balance of beasts and birds is finally realized, the shielding and absorbing functions of the intestinal tracts are enhanced, the diarrhea rate is decreased, the feed utilization rate is increased, and furthermore, the dependence on antibiotics in a cultivation process is reduced.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH +3
Folium mori protein hydrolysate, preparation method thereof and enzyme beverage prepared from folium mori protein hydrolysate
PendingCN111449182AShorten the lag periodExtended log phaseFood ingredient functionsBiotechnologyPectinase
The invention relates to a folium mori protein hydrolysate, a preparation method thereof and an enzyme beverage prepared from the folium mori protein hydrolysate. The preparation method of the foliummori protein hydrolysate comprises the following steps of preparing folium mori into folium mori slurry, and adding biological enzymes into the folium mori slurry for enzymolysis, wherein the biological enzymes comprise cellulase, pectinase and neutral protease. When the folium mori protein hydrolysate is used for microbial fermentation, the lag phase of fermentation microorganisms can be shortened, the logarithmic phase of the fermentation microorganisms can also be prolonged, and fermentation products with relatively high active ingredient content can be obtained under the condition of shortfermentation time.
Owner:SERICULTURE & AGRI FOOD RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Application of MAL33 gene deletion in improving tolerance of saccharomyces cerevisiae to lignocellulose hydrolysate inhibitor
The invention relates to application of MAL33 gene deletion in improving tolerance of saccharomyces cerevisiae to lignocellulose hydrolysate inhibitors, and belongs to the field of bioengineering. The invention provides an MAL33 gene deleted saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, and it is proved that compared with a control strain, the acetic acid tolerance of the deleted strain is greatly improved; the tolerance to other typical inhibitors and H2O2 in the lignocellulose hydrolysate is also improved; the delay phase in a glucose and xylose culture medium (YPDX) with 3.5 g / L acetic acid is shortened by 24 h, and the fermentation period of ethanol production by co-utilization of glucose and xylose is shortened by 20 h; the conditions of growth in a glucose and xylose culture medium (YPDX) containing a mixed inhibitor and ethanol production through co-fermentation of glucose and xylose are superior to those of a control strain; the invention provides an important method for improving the tolerance of the saccharomyces cerevisiae to the lignocellulose hydrolysate inhibitor, and provides a theoretical basis for overcoming the technical bottleneck in the production of second-generation fuel ethanol.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
A method for prolonging bread microorganism shelf life without chemical preservative
InactiveCN101156613AInhibition of bloomsExtended shelf lifePreservation by coolingMicroorganismChemical preservatives
The invention relates to a method dispensing with chemical antiseptic to prolong the shelf life of the bread microorganism, and the method belongs to the food fresh keeping and storing technology field. The utility model has the technique process that bread with quick zymotechnics is prepared firstly; then the bread is enclosed into a package, the two gases of the CO2 and the N2 are mixed, gas regulating packing is conducted, through vacuumizing, charging and hot sealing, the packing is finished, and then the packed bread in the normal temperature is stored or the bread is refrigerated. The invention adopts the physical method to overcome the limitation of the chemical antiseptic in antiseptic capability, can prolong the bacteria inhibiting time, preserve the edible quality of the bread for longer time, prevent the package from shrinking or collapsing in high CO2consistence, ensure the package to have handsome appearance and obvious effect for preventing the soft bread from deforming under pressure, facilitate the sale and the transportation of the bread, and charge the N2 simultaneously to delay the oxidation and rancidness, and restrain the growth of the aerobium.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
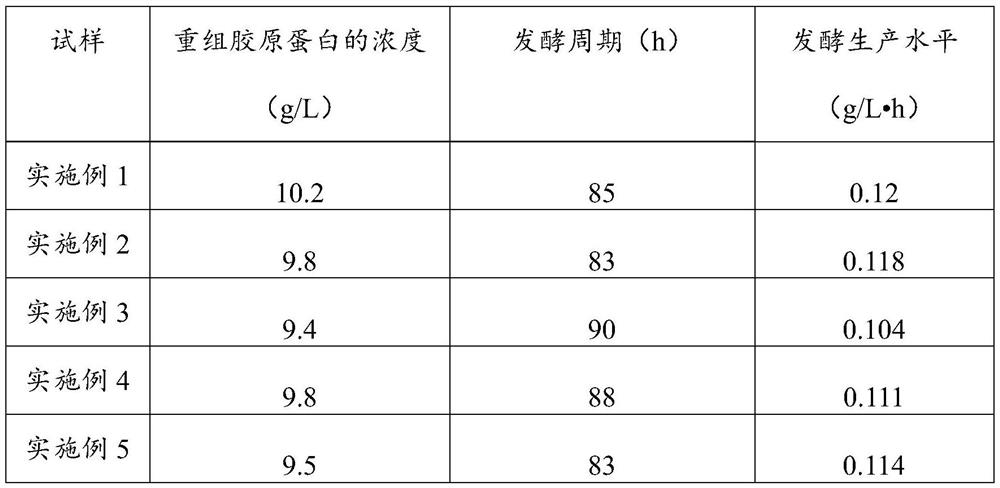
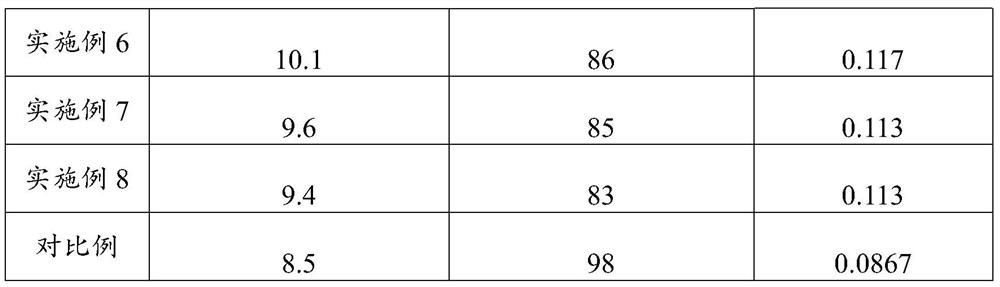
Fermentation technology for improving production level of recombinant collagen
PendingCN113789358AReduce the viscosity of the feed liquidReduce the concentration of salt ionsFungiConnective tissue peptidesPichia membranaefaciensMethanol
The invention provides a fermentation technology for improving the production level of recombinant collagen, and relates to the technical field of genetic recombination engineering bacterium fermentation. The fermentation technology for improving the production level of the recombinant collagen comprises the following steps of: S1, pichia pastoris engineering bacteria are inoculated into a seed tank to be cultured, glycerin and a supplemented medium are supplemented after dissolved oxygen is greatly increased, and when wet weight is increased to be larger than 100 g / L, the pichia pastoris engineering bacteria are transferred into a fermentation tank to start fermentation culture; S2, after the pichia pastoris engineering bacteria in the fermentation tank are cultured till the dissolved oxygen is greatly increased, a mixed carbon source material supplementation is carried out by using a carbon source culture medium and a supplemented medium, and the mixed carbon source material supplementation is stopped when the wet weight of the material is increased to be greater than 150g / L; and S3, after the carbon source is used up, methanol and the supplemented medium are added for carrying out induced expression until fermentation is finished. The fermentation technology disclosed by the invention can improve the expression quantity of the recombinant collagen and shorten a fermentation period, so that the fermentation production level of the recombinant collagen is improved, and the fermentation technology is suitable for stable industrial production.
Owner:西安德诺海思医疗科技有限公司
Production process of guanosine
The invention discloses a production process of guanosine. The production process comprises the following steps: activating strains, culturing seeds, fermenting and extracting guanosine. The production process is characterized in that the strain-activating step is performed as follows: unfreezing glycerol strains which are conserved at - 30+ / -3 DEG C to reach the room temperature, sucking 0.1+ / -0.02ml of the strains to be inoculated on an activation slope and standing and culturing at 34+ / -4 DEG C for 20-24 hours to obtain working seeds. The process has the characteristics of low investment and high guanosine yield, and is simple to operate.
Owner:STAR LAKE BIOSCI CO INC ZHAOQING GUANGDONG
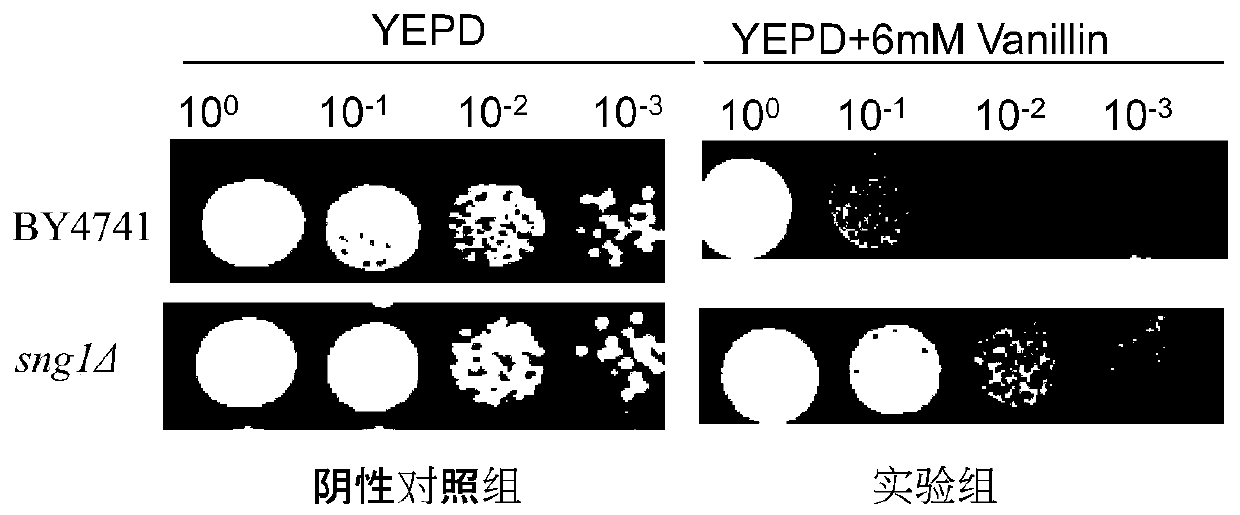
Application of gene SNG1 deletion in improving vanillic aldehyde resistance of saccharomyces cerevisiae
ActiveCN111549073AIncrease resistanceShorten the lag periodFungiStable introduction of DNACelluloseNucleotide
The invention discloses an application of saccharomyces cerevisiae SNG1 gene deletion in improving vanillic aldehyde resistance. The gene sequence of the related SNG1 gene deletion mutant is composedof -18 to +203 bp nucleotide fragments of a saccharomyces cerevisiae SNG1 gene, nucleotide fragments of loxp-KanMX4-loxp and +1446 to +1644 bp nucleotide fragments of the saccharomyces cerevisiae SNG1gene, and the nucleotide sequence of the mutant is as shown in SEQ ID No.1. Experiments prove that under no stress, the wild type is not different from the growth of the sng1 delta mutant disclosed by the invention; however, under the stress of vanillic aldehyde, the maximum specific growth rate of the sng1 delta mutant is 70% higher than that of a control strain, and the specific consumption rate of vanillic aldehyde is 52% higher than that of vanillic aldehyde. It is prompted that the mutant strain is suitable for vanillin / alcohol production or construction of a high-vanillin-tolerance saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for producing second-generation fuel ethanol or other high-value compounds by taking lignocellulose as a raw material.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
Method for reinforcing leaching of bornite through high-iron sphalerite
ActiveCN109022776AImprove leaching rateShorten the lag periodProcess efficiency improvementLeaching rateBornite
The invention provides a method for reinforcing leaching of bornite through high-iron sphalerite. The method includes the following steps that the high-iron sphalerite and the bornite are ground, andhigh-iron sphalerite powder and bornite powder are obtained; a 9K basic culture medium is subjected to high-temperature high-pressure steam sterilization, and the high-iron sphalerite powder and the bornite powder are intermittently sterilized; the sterilized high-iron sphalerite powder and the sterilized bornite powder are mixed, then the sterilized 9K basic culture medium is added, ore pulp is obtained, and then the pH value of the ore pulp is adjusted to 1.5-2.0; and the ore pulp is subjected to agitation leaching, and chemical conditions of a leaching solution are adjusted and controlled.The whole leaching period is shortened, meanwhile, the leaching rate and the leaching speed are greatly increased, and the method is clean and environmentally friendly, low in cost and suitable for large-scale application and popularization.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
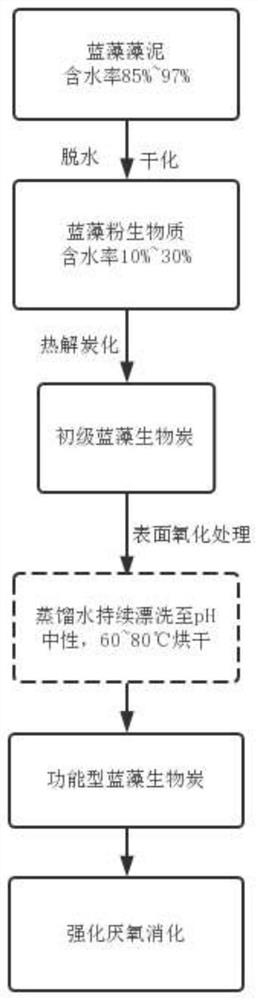
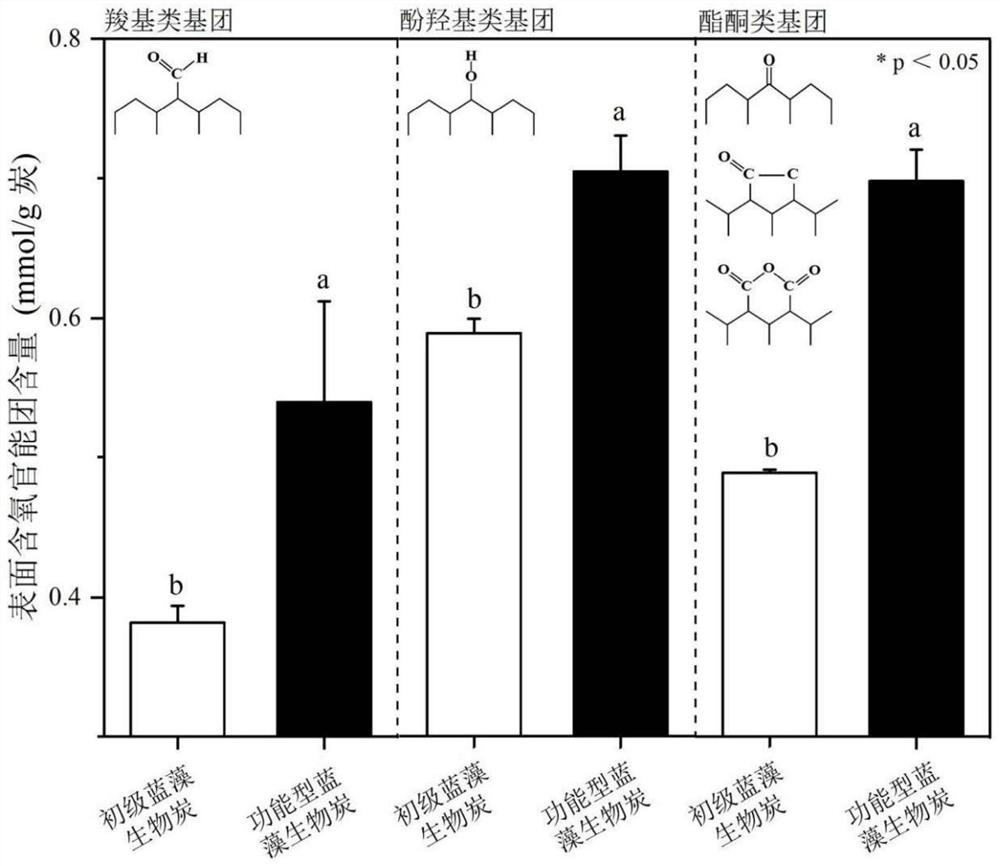
Method for preparing functional blue-green algae biochar and applying functional blue-green algae biochar to intensifying anaerobic digestion
ActiveCN114477691AImprove redox abilityIncrease productionWater treatment parameter controlWater contaminantsOxidation-Reduction ActivityMethane yield
The invention provides a method for preparing functional blue-green algae biochar and applying the functional blue-green algae biochar to intensified anaerobic digestion, and belongs to the technical field of solid waste resourceful treatment. The types and number of oxygen-containing functional groups on the surface of the blue-green algae biochar are directionally regulated and controlled by utilizing a hydrogen peroxide surface oxidation method, and the electron gaining and losing capability and the oxidation-reduction activity of the blue-green algae biochar material are remarkably improved. The preparation method of the functional blue-green algae charcoal based on surface oxygen-containing functional group directional regulation and control is established for the first time, and the functional blue-green algae charcoal is applied to an enhanced anaerobic digestion system, so that the methane production starting period can be shortened, the methane production rate is increased, and meanwhile, the methane yield is increased; and the overall efficiency of anaerobic digestion treatment of the organic wastes is further improved.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Liquor-fermentation production method of neutral protease
InactiveCN106987576AThoroughly sterilizedPromote absorptionHydrolasesMicroorganism based processesProcess optimizationNeutral protease
The invention provides a liquor-fermentation production method of neutral protease. The liquor-fermentation production method includes 1), culture activation, 2), seed cultivation, 3), liquor fermentation, and 4), extracting and refining of the neutral protease. The liquor-fermentation production method of the neutral protease has the advantages that through optimization of culture media and complete adoption of soluble culture media, the problems of large quantity of solid matters in existing culture media, high viscosity of the existing culture media, difficulty in after-treatment and high cost are solved; products with high enzyme activity are obtained through process optimization.
Owner:WUHAN SUNHY BIOLOGICAL
Escherichia coli YPC-SA-1 and application thereof
InactiveCN105586283AGrow fastShorten the lag periodBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses escherichia coli which rapidly adapts to an industrial raw material medium for production of succinic acid and an application thereof. The classification term of the escherichia coli is Escherichia coli YPC-SA-1, and its preservation number is CCTCC NO:M 2014178. The invention also discloses an application of the above escherichia coli to industrial raw material cultivation growth. Under the aerobic condition, the strain can rapidly adapt to industrial raw material growth environment and grows by the utilization of nutrient composition, and lag phase is 7-8 h, which is almost the same under the condition of analytical raw material culture. In comparison with an original strain, lag phase of the strain in the industrial synthetic medium is shortened by 12 h, and aerobic culture time is shortened by 15 h. The mutant strain YPC-SA-1 has laid a foundation for industrial efficient fermentation for production of succinic acid.
Owner:SINOPEC YANGZI PETROCHEM +1
A kind of thermophilic anaerobic bacterium and the method for using it to produce ethanol
InactiveCN104263680BPromote accumulationShorten the lag periodBacteriaBiofuelsMicroorganismAnaerobic bacteria
The invention relates to the field of microbial strains, in particular to a thermophilic anaerobic bacillus and a method for producing ethanol by using it. The bacterial strain of the present invention is Thermoanaerobacterium aotearoense P8G3#4, which has been preserved in the General Microorganism Center of China Microbiological Culture Collection Management Committee, the preservation number is CGMCC NO.9000, and the preservation date is April 3, 2014 . The method of utilizing said bacterial strain to produce ethanol: first prepare the seed liquid of thermophilic anaerobic bacillus CGMCC9000, then transfer the thermophilic anaerobic bacillus CGMCC9000 seed liquid to the fermentation medium with 10-15% w / w inoculation amount, in Stirring culture under anaerobic conditions, and finally ethanol is separated from the fermentation broth. The strain has good genetic stability, stable yield traits, and the fermentation lag period is shortened to 1 / 4 of the original one, saving energy consumption.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Low-carbon carotenoid production method
InactiveCN105648020ARetention contentStable contentMicroorganism based processesFermentationFruit juiceRhodotorula
The invention discloses a low-carbon carotenoid production method. Trimmings of canned yellow peaches are taken as a main raw material and subjected to microwave color fixing, freezing, breaking and biological enzymolysis, juice with higher carotenoid content is obtained, a fermentation medium is obtained after component adjustment, Rhodotorula benthica with high carotenoid yield is inoculated to the fermentation medium for graded inoculation and temperature-shift fermentation, the Rhodotorula benthica is enabled to be proliferated to the greatest extent, fermentation broth is subjected to ultrahigh-pressure homogenization, vacuum centrifugation, demulsification and separation, an emulsion is obtained, and the finished product carotenoid is obtained after extraction, separation and purification of the emulsion, wherein the cell biomass of the fermentation broth is 38-52 g / L, and the yield of the carotenoid is 47-61 mg / L. The production method is simple, short in cycle, high in efficiency, energy-saving and environment-friendly, adopts low-temperature and bio-processing technologies in the whole process, reduces the production cost, eliminates hidden danger of environmental pollution, lays a firm foundation for sustainable development in the technical field of deep processing of the canned yellow peaches and has positive economic and social development significance.
Owner:邵素英
Culture medium of meningitis Neisseria
ActiveCN101597582BConducive to reproduction and growthPromote reproductive growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBacteroidesArginine
Owner:INST OF MEDICAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
Application of mal33 gene deletion in improving tolerance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to lignocellulose hydrolyzate inhibitors
The present invention relates to MAL3 3 The application of gene deletion in improving the tolerance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to lignocellulose hydrolyzate inhibitors belongs to the field of bioengineering. The present invention provides a strain MAL33 Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains with gene deletion have greatly improved tolerance to acetic acid; other typical inhibitors and H in lignocellulose hydrolyzate 2 o 2 The tolerance of the nutrient was also improved; the lag period in the 3.5 g / L acetic acid glucose-xylose medium (YPDX) was shortened by 24 h, and the fermentation cycle of ethanol production by co-utilization of glucose and xylose was shortened by 20 h; The growth and ethanol production of glucose and xylose co-fermentation in the glucose-xylose medium (YPDX) of inhibitors were better than those of the control strain; it provides a method for improving the tolerance of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to inhibitors in lignocellulose hydrolyzate , providing a theoretical basis for overcoming the technical bottleneck in the production of second-generation fuel ethanol.
Owner:QILU UNIV OF TECH
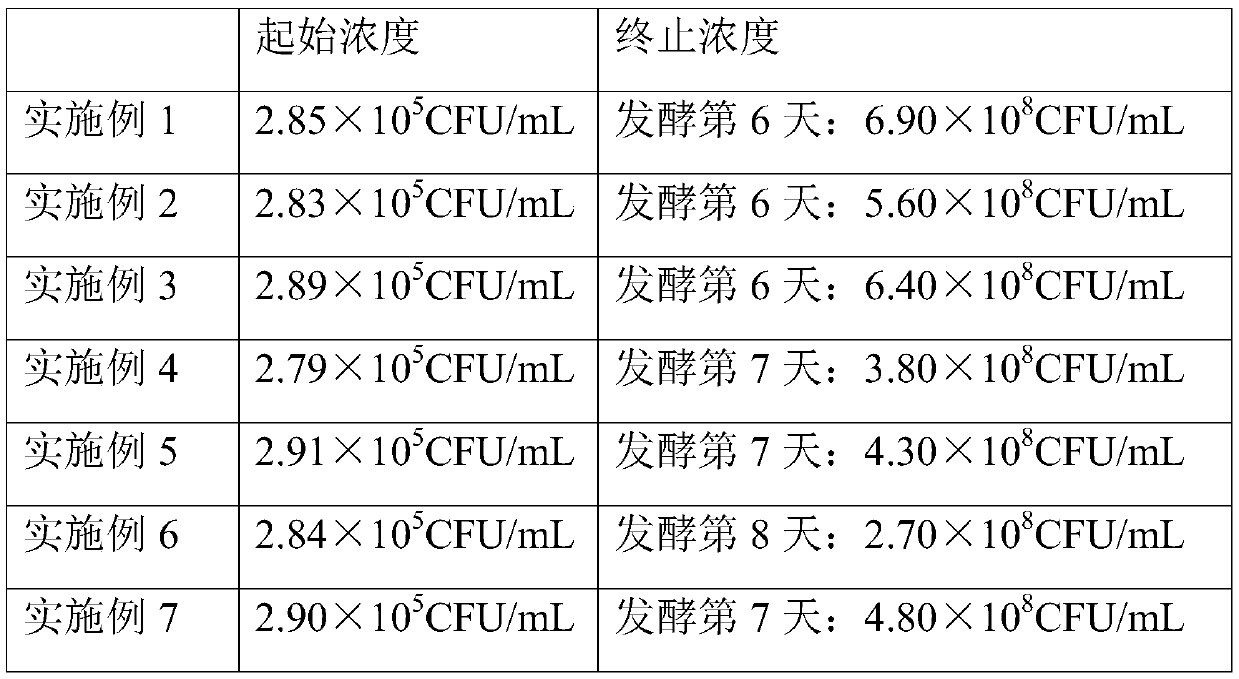
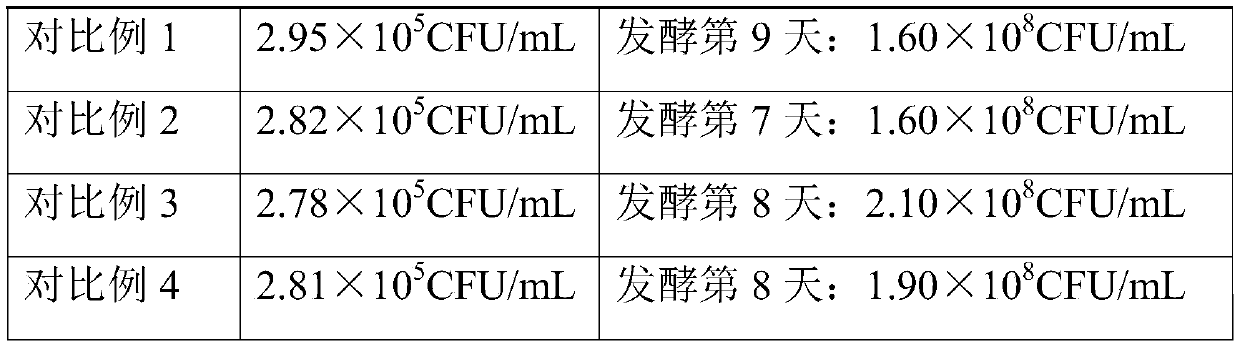
A method for shortening lagging period of lactic acid bacteria in fermented milk production
ActiveCN109463437BReduce dosageHigh densityMilk preparationBacteriaBiotechnologyLactic acid bacterium
Owner:上海昊岳生物科技有限公司
Method for efficiently producing carotenoid
InactiveCN106222227AImprove cold resistanceIncrease heat stressMicroorganism based processesFermentationTerra firmaMicrowave
The invention discloses a method for efficiently producing carotenoid. The method comprises the steps that juice with the high carotenoid content is obtained by taking canned yellow peach leftovers as main raw materials through microwave color fixing, frozen-breaking and biological enzymolysis, and after the ingredients are regulated, a fermentation medium is obtained; fractional inoculation and temperature-variable fermentation are conducted on oceanic red yeast inoculated with the high-yield carotenoid, so that the oceanic red yeast is maximumly proliferated; after fermentation liquid is subjected to ultrahigh pressure homogenizing, vacuum centrifuging and demulsifcation separating, emulsion is obtained, and after the emulsion is extracted, separated and purified, the finished carotenoid is obtained, wherein the cell biomass of the fermentation liquid is 38-52 g / L, and the yield of the carotenoid is 47-61 mg / L. The preparation method is simple, the cycle is short, the efficiency is high, energy is saved, environmental friendliness is achieved, a low-temperature bio-processing technique is adopted in the whole process, the production cost is reduced, hidden environmental pollution danger is eliminated, a firm foundation is laid for sustainable development of the field of yellow peach deep processing technologies, and the positive economic and social development significance is achieved.
Owner:BEIJING KEHUITONG WISDOM SCI & TECH CO LTD
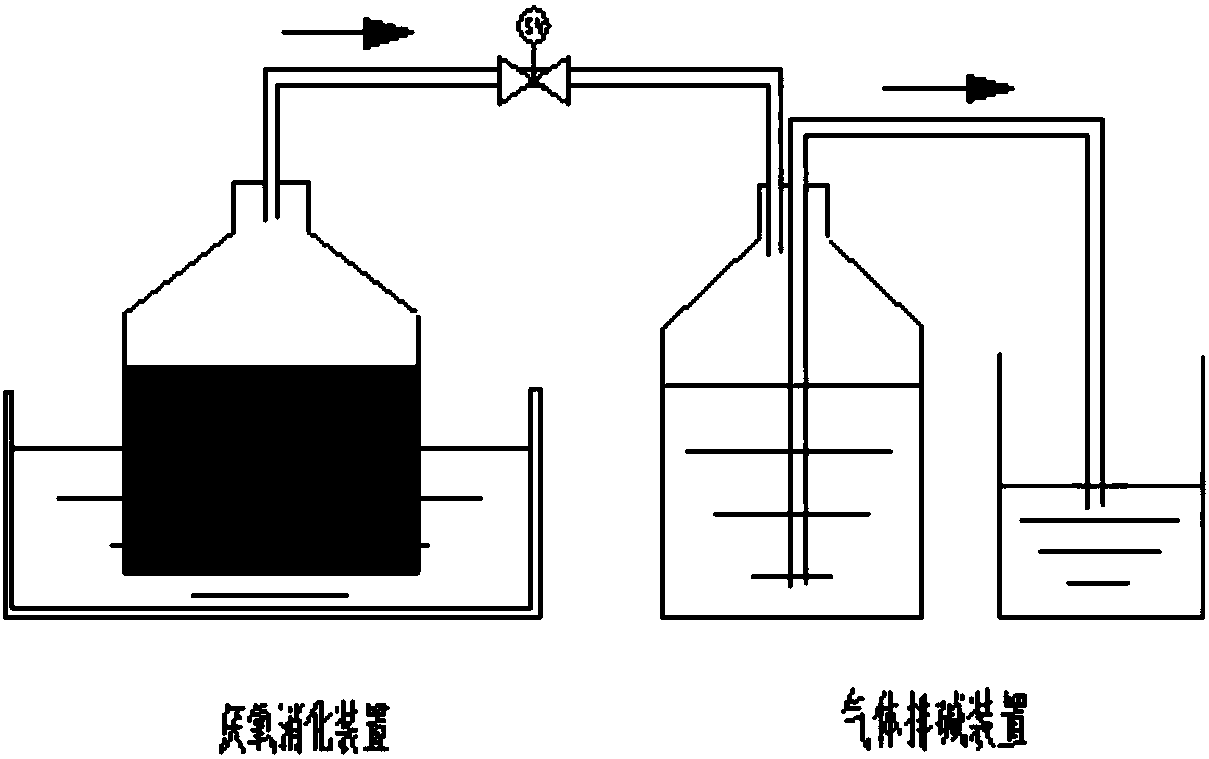
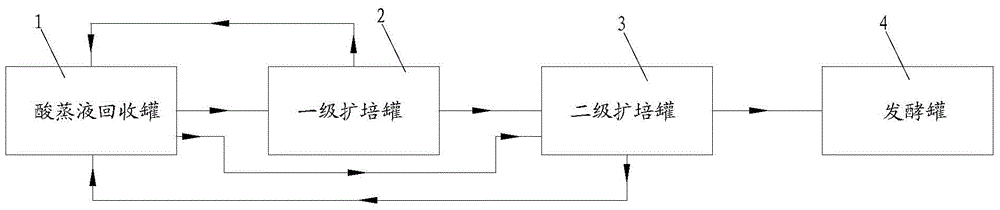
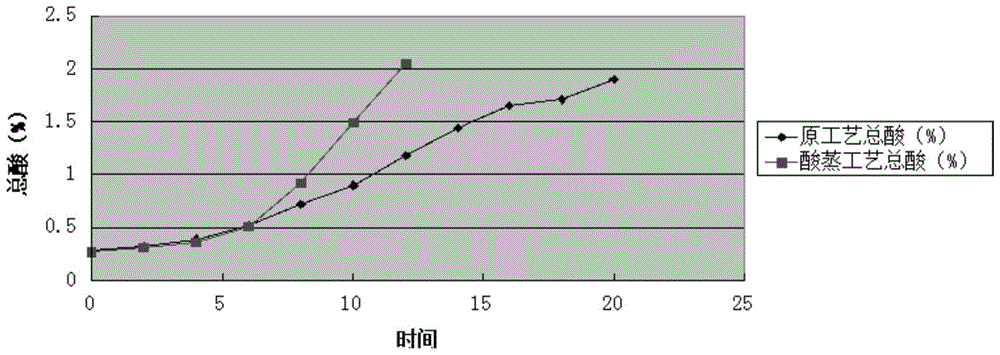
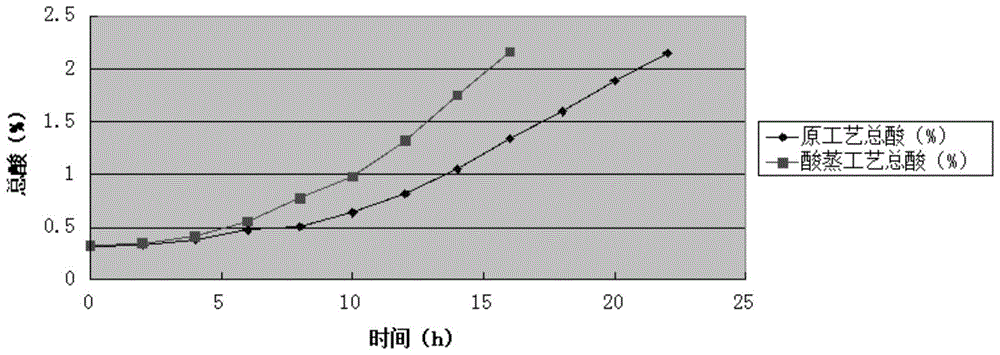
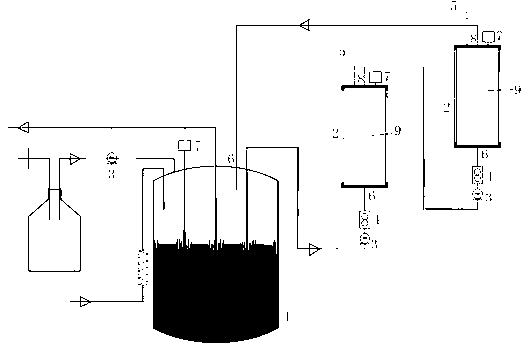
A process and system for acetic acid fermentation and expansion of acid steaming
The invention relates to an acetic fermentation expanding cultivation and acid steaming process and system. The process comprises the following steps that (1), pretreatment is conducted, wherein firstly, CIP alkaline wash and hot water wash are conducted in sequence on a first-level expanding cultivation tank, then wine vinegar is fed into the first-level expanding cultivation tank for acid steaming, the process conditions of the acid steaming are that the addition of wine vinegar is controlled to be one fifth of the volume of the tank and the total acid of the wine vinegar is not lower than 3%, the stirring speed of the first-level expanding cultivation tank is controlled to be greater than 730 rpm so as to ensure uniform distribution of steam in the tank, the wine vinegar is heated to be 90 DEG C and then lasts for 20 minutes, and the wine vinegar is discharged; (2), fruit wine is added in the pretreated first-level expanding cultivation tank, and then acetic acid bacteria seed fluid is added for first-level expanding cultivation. The wine vinegar is adopted for acid steaming on the expanding cultivation tank, the residual alkaline cleaning fluid is removed, the pH value in the expanding cultivation tank is reduced, the breeding environment of acetic acid bacteria is improved, the lag phase after seeds enter the new environment is shortened, and therefore the expanding cultivation period is shortened and the production cost is reduced.
Owner:广东天地壹号食品研究院有限公司
Type 2 streptococcus suis high-intensity fermentation medium and application
ActiveCN102533577BTo promote metabolismInhibit synthesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesStreptococcus constellatusChemistry
The invention belongs to the technical field of agriculture microbes, and particularly relates to a type 2 streptococcus suis high-intensity fermentation medium and application. The type 2 streptococcus suis high-intensity fermentation medium is characterized by comprising the following components in bulking value by percentage: 0.1 to 5.0 percent of tryptone, 0.1 to 5.0 percent of yeast powder, 0.01 to 2.0 percent of ammonium acetate, 0.01 to 2 percent of MgSO4.7H2O, 0.1 to 4.0 percent of K2HPO4.3H2O, 0.01 to 1 percent of KH2PO4, and 0.01 to 2.0 percent of glucose, and also comprising 1 to 15 volume percent of bovine serum; and before sterilization, the pH of the medium is adjusted to be 7.4 to 7.8. The streptococcus suis high-intensity fermentation medium contributes to the growth metabolism of the type 2 streptococcus suis, thallus is high in growth speed, the large bacterium amount can be obtained, and the viable count of the cultivated type 2 streptococcus suis can reach 8.5 billion. Raw materials of the medium are wide in source; and the medium is low in cost, and can effectively amplify the type 2 streptococcus suis, and meet the requirement that type 2 streptococcus suis vaccine is produced in large scale.
Owner:WUHAN KEQIAN BIOLOGY CO LTD +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com