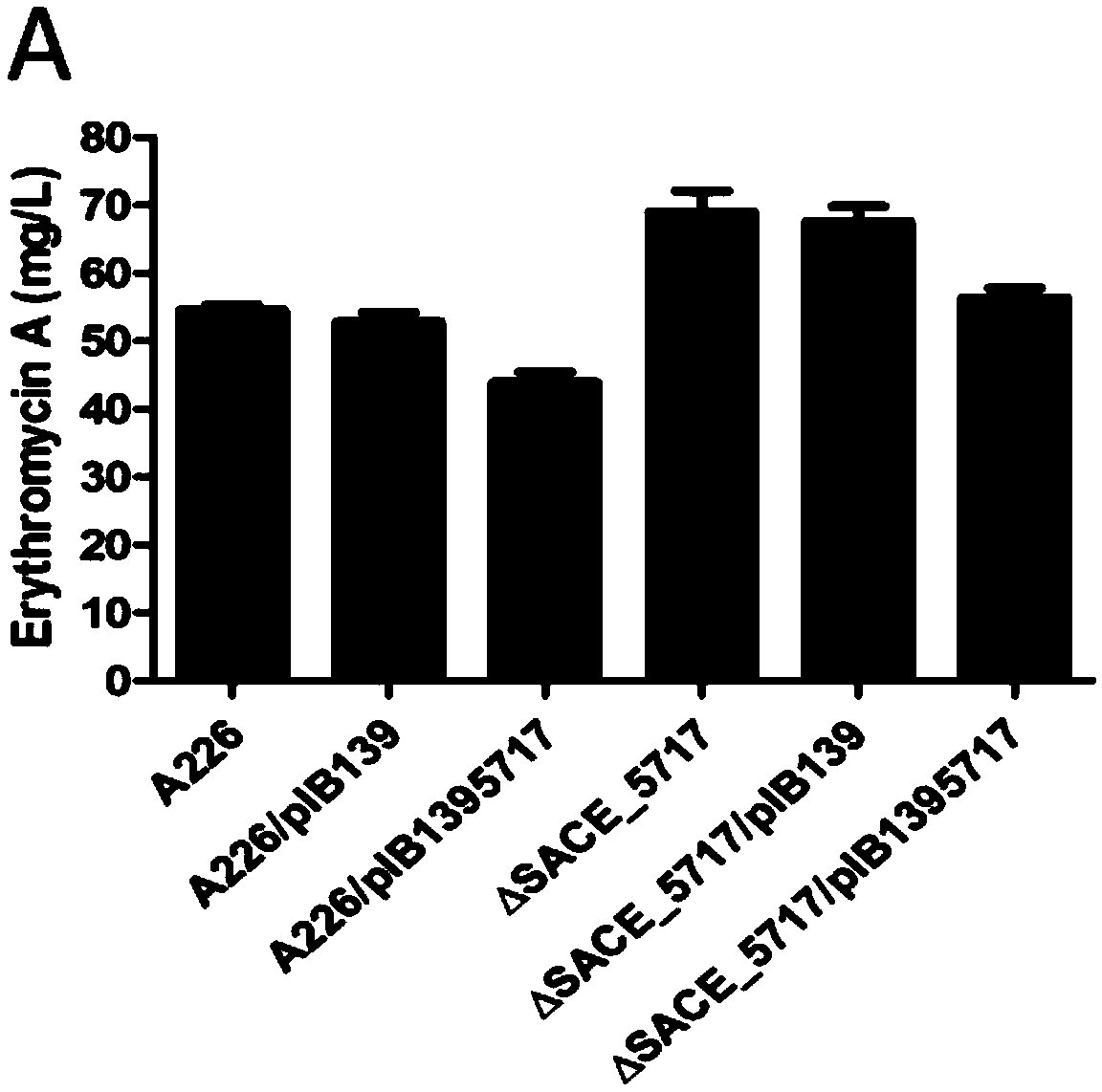Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
45 results about "Saccharopolyspora erythraea" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Saccharopolyspora erythraea, formerly known as Streptomyces erythraeus, is a species of actinomycete bacteria within the genus Saccharopolyspora. Saccharopolyspora erythraea produces the macrolide antibiotic erythromycin. Cytochrome P450 eryF (CYP107A1) originally from the bacterium is responsible for the biosynthesis of the antibiotic by C6-hydroxylation of the macrolide 6-deoxyerythronolide B.
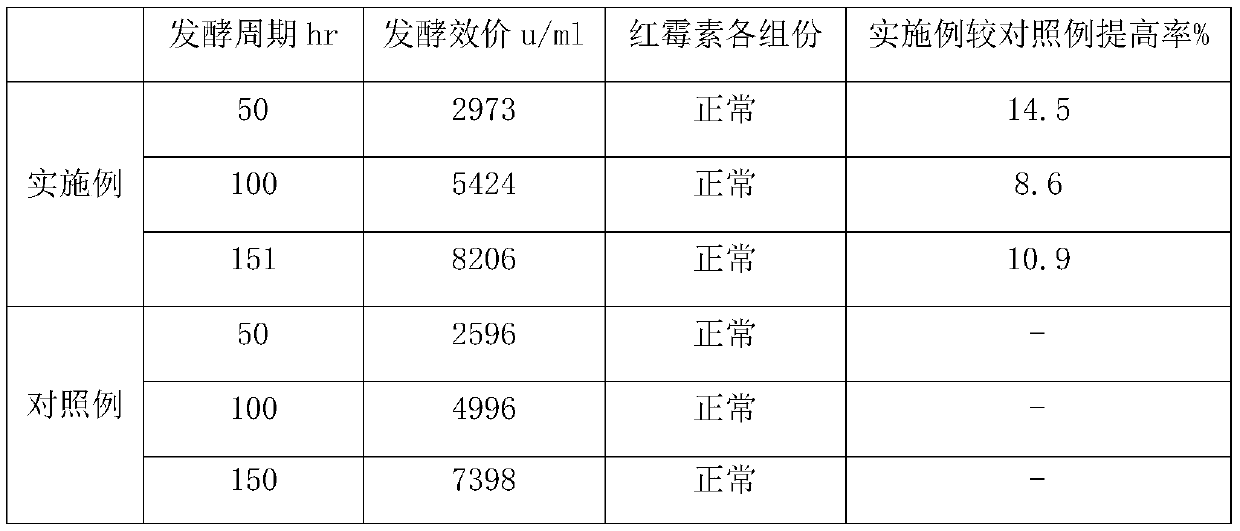
Method for producing erythrocin by virtue of fermentation
ActiveCN104419739ALow costThe fermentation process is simpleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCottonseed oil
The invention belongs to the field of biological fermentation and production and provides a method for producing erythrocin by virtue of fermentation. By taking saccharopolyspora erythraea as a starting germ, the method mainly comprises four steps of preparation of slant strains, preparation of shake-flask seed liquid, culture of seed liquid and process control of a fermentation tank. According to the method, soybean oil is replaced by refined cottonseed oil in a seed tank culture medium, a fermentation tank culture medium and the material supplementing process of a fermentation process, so that the fermentation cost is lowered; the fermentation valence and the content of erythrocin A are greatly increased based on an optimized fermentation process. The method is suitable for large-scale industrial production.
Owner:鲁南新时代生物技术有限公司
Method for increasing erythromycin yield by transforming saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_3980 gene
ActiveCN106520866AImprove fermentation yieldIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyTetR
The invention discloses a method for increasing the erythromycin yield by transforming the saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_3980 gene. In saccharopolyspora erythraea, the gene SACE_3980 is subjected to transcription regulation by genetic engineering and through TetR-deficient family to obtain an engineering strain with high erythromycin yield; and by adopting the obtained strain for fermentation production of erythromycin, the yield can be remarkably increased, and a new technical support is provided for increasing the erythromycin yield in industrial production.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
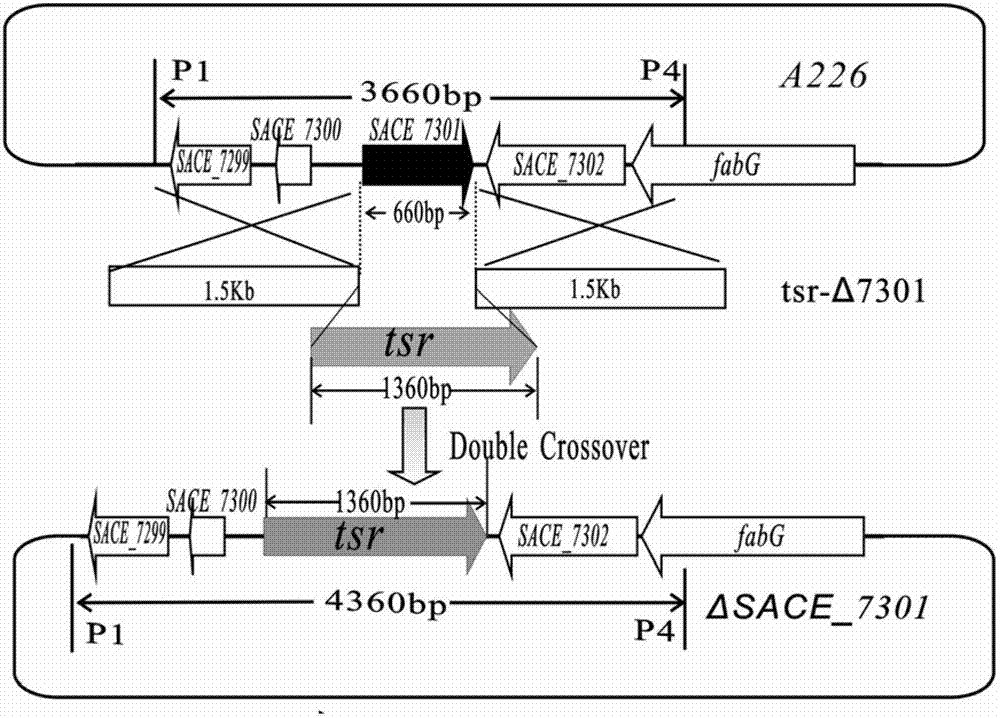
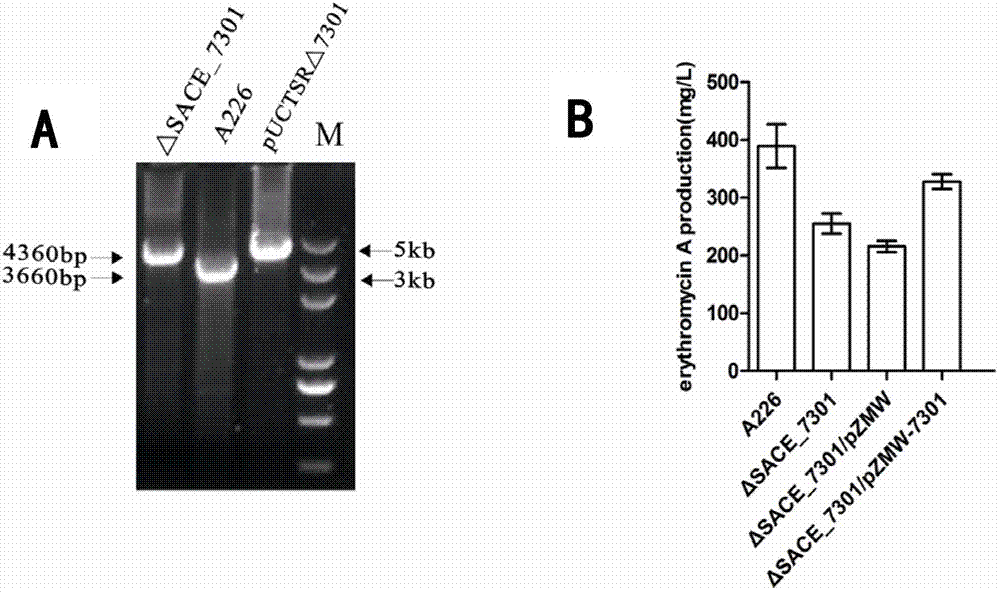
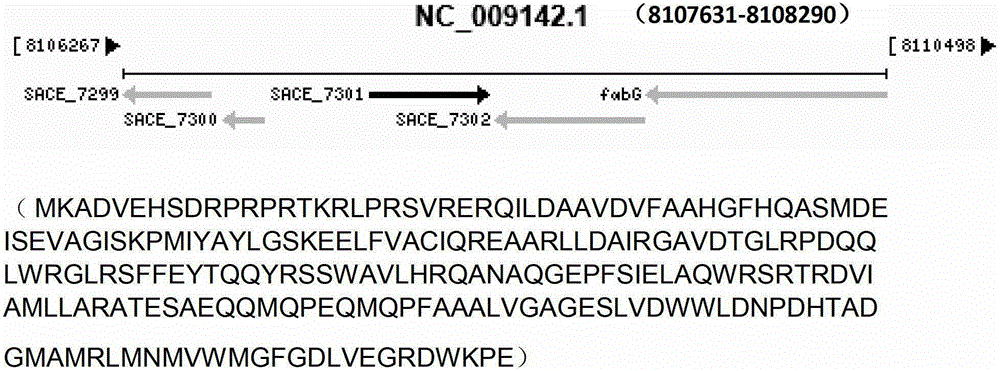
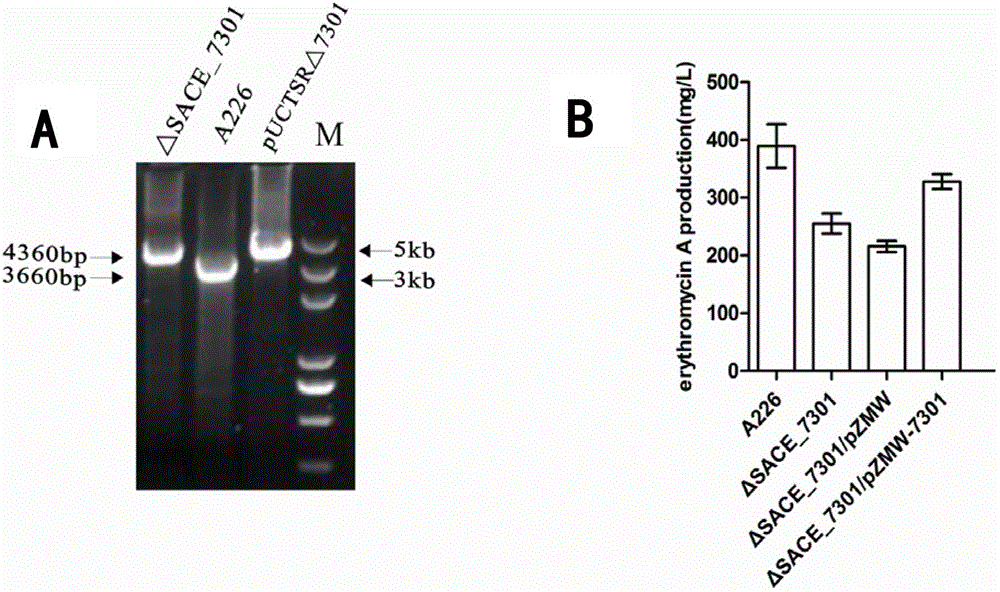
Method for improving erythromycin yield by saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_7301 gene pathway
ActiveCN103205451AImprove fermentation yieldReduce outputBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGene pathway
The invention discloses a method for improving erythromycin yield by a saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_7301 gene pathway. The method is characterized in that gene copy number of the saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_7301 or gene expression quantity of the SACE_7301 is increased by a gene engineering pathway so as to obtain high-yield engineering strains of saccharopolyspora erythraea erythromycin, and yield of the erythromycin can be improved by fermenting the strains obtained by the technology.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Saccharopolyspora erythraea and application thereof
ActiveCN102911874AGood genetic stabilityImprove the efficiency of producing erythromycinFungiMicroorganism based processesSaccharopolyspora erythraeaChemistry
The invention provides a new Saccharopolyspora erythraea (Saccharopolyspora erythraea) strain BJX001 with a preservation number of CGMCC No.4767. The invention further provides application to obtain erythrocin through the Saccharopolyspora erythraea. The experimental results show that a fermentation method of the strain, provided by the invention, has strong capacity of producing a component A of the erythrocin, a chemical titer for producing the erythrocin is up to 10000 mmg / mL of fermentation liquid, and after the strain is continuously inherited for five generations, the capacity of producing the effective component A of the erythrocin is kept at the original level, so that the heredity stability is good, the efficiency of production of the erythrocin is improved, and the method is simple and low in cost, and is suitable for popularization and application in production of the erythrocin.
Owner:北京燕化佰佳信作物科技有限公司
Method for constructing saccharopolyspora erythraea expression plasmid (pBlueV) containing vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene (vgb)
InactiveCN102234660AIncrease intakeImprove utilizationFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionPrimary metabolismProtein
The invention provides a method for cloning a saccharopolyspora erythraea expression plasmid (pBlueV) containing a vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene (vgb), belonging to the technical field of gene engineering. In the method, based on the fact that VHb (hemoglobin) can be combined with oxygen to form an oxygenated state, the VHb intervenes the oxygen related metabolic pathway of cells, thereby changing the original biological metabolism mode of the cells under oxygen-limited conditions, promoting the cell growth and protein synthesis under oxygen-deficient conditions, directly or indirectly affecting the action principles of primary metabolism and secondary metabolism of aerobes, firstly constructing an Escherichia coli expression plasmid pQEV, expressing the VHb with biological activity, and further constructing the saccharopolyspora erythraea expression plasmid (pBlueV). In order to realize high-density culture of cells and high-yield fermentation of metabolic products under oxygen-limited conditions, the invention provides an important pathway for homologous recombination of vgb gene elements and saccharopolyspora erythraea chromosome genomes.
Owner:邢安辉 +2
Method for recombining Saccharopolyspora erythraea strain containing exogenetic vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene (vgb)
InactiveCN102234654AUltimate titer increaseUltimate cost-effectivenessFungiMicrobiological testing/measurementBinding stateFermentation
The invention belongs to the technical field of gene engineering, and provides a method for recombining a Saccharopolyspora erythraea strain containing exogenetic vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene (vgb). In the method, vitreoscilla hemoglobin (VHb) expressed by the vitreoscilla hemoglobin gene (vgb) can be combined with oxygen to form an oxygen-binding state, and intervenes several key steps or branch pints in cell metabolic paths related with oxygen in the mode, so that the cell growth speed is improved, the cell respiration intensity is improved and the critical oxygen concentration of cells is reduced. In large dissolved oxygen change, a constant respiratory rate is kept, and the cell culture density and exogenetic gene expression are improved under low oxygen condition. The method solves the problem that in a large-scale bioreactor, because thalli are positioned in a viscous, enclosed and complicated environment with rich nutrients, oxygen required by massive mycelia in an exponential phase is limited, and the yield of erythrocin is reduced. The method has important application value for the antibiotic fermentation industry and high density cell culture, which have high oxygen consumption and take dissolved oxygen as a limiting factor.
Owner:邢安辉 +2
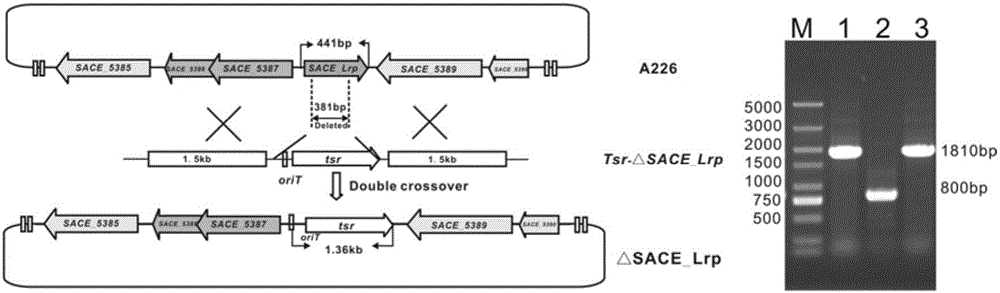
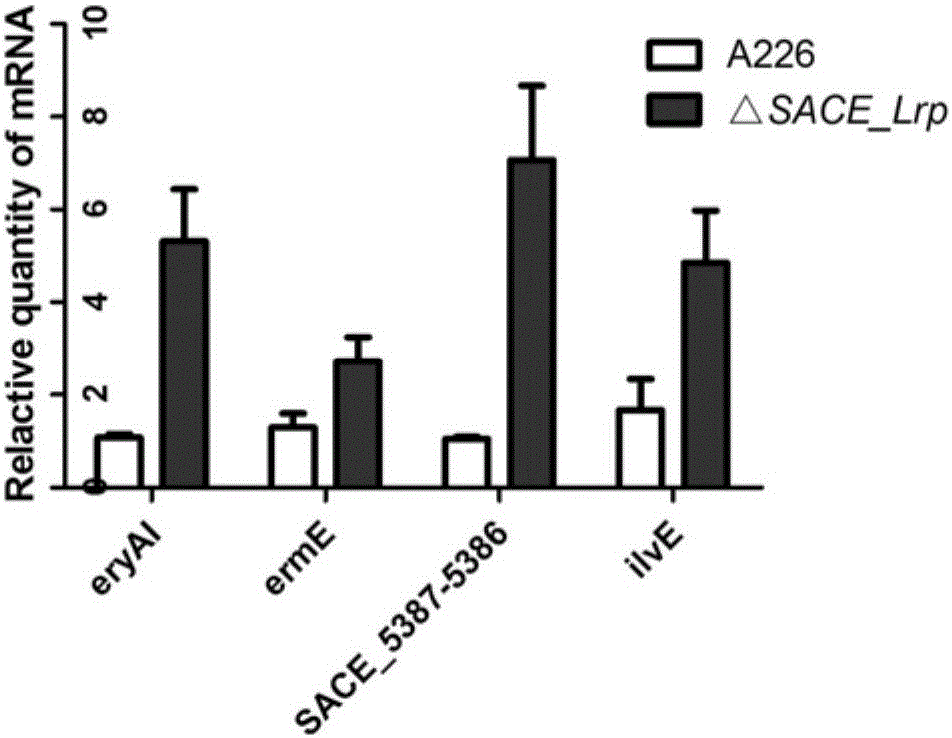
Method for improving yield of erythromycin through saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_Lrp gene
InactiveCN106148378AImprove fermentation yieldIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyGenetic engineering
The invention discloses a method for improving the yield of erythromycin through a saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_Lrp gene. The SACE_Lrp gene is inactivated in saccharopolyspora erythraea through a genetic engineering way, and a saccharopolyspora erythraea erythromycin high-yield engineering strain is obtained through excessively expressing a target gene SACE_5387-5386; the erythromycin is produced through fermenting the obtained strain, and the strain obtained by the technology is fermented, so that the yield of the erythromycin can be improved.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
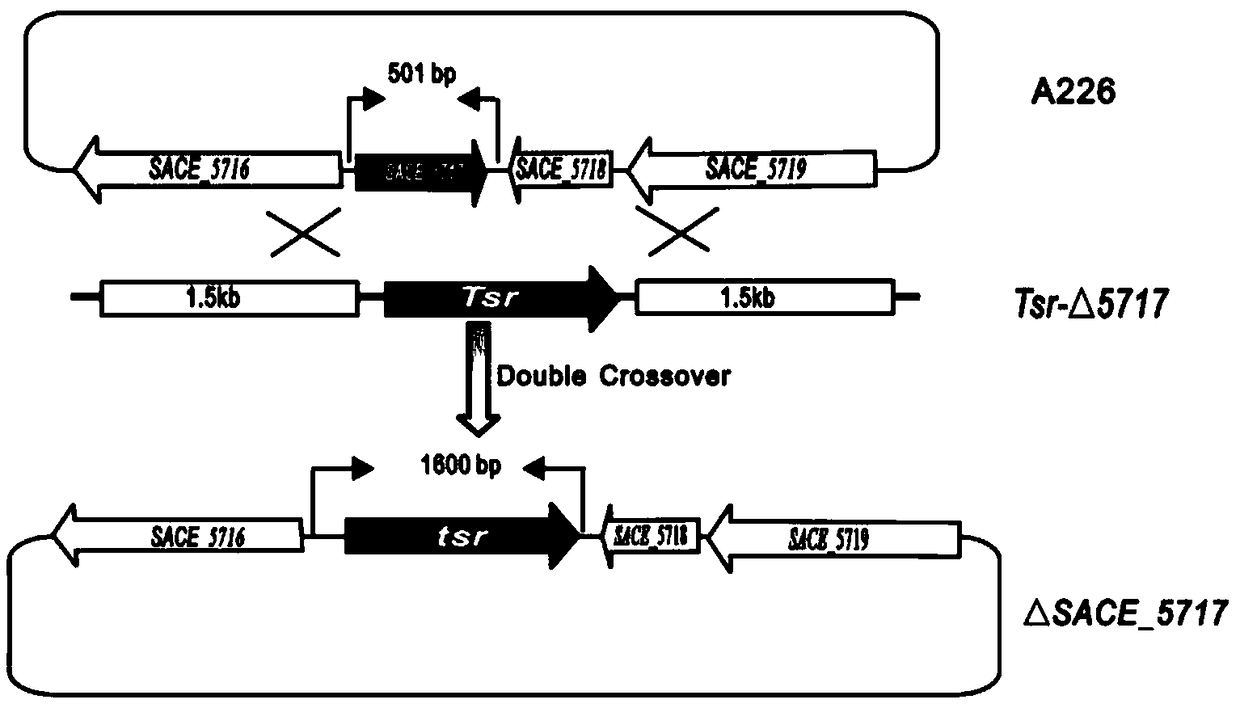
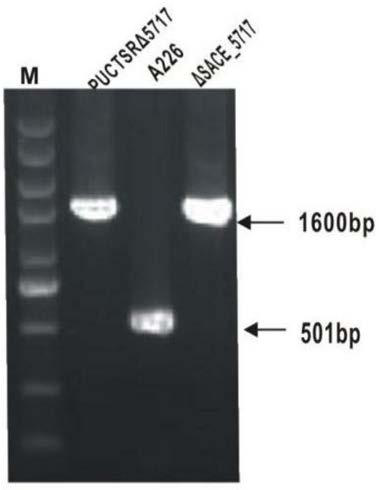
Method for increasing output of erythrocin by SACE_5717 gene of saccharopolyspora erythraea
ActiveCN109321618AImprove fermentation yieldIncrease productionStable introduction of DNABacteria peptidesBiotechnologyNucleotide
The invention provides a method for increasing output of erythrocin by an SACE_5717 gene of saccharopolyspora erythraea. The method comprises the following steps of deactivating the SACE_5717 gene inthe saccharopolyspora erythraea by a gene engineering path, so as to obtain a saccharopolyspora erythraea strain with high output of erythrocin; applying the saccharopolyspora erythraea engineering strain with high output of erythrocin, and fermenting, so as to produce the erythrocin, wherein a nucleotide sequence of the SACE_5717 gene is shown in SEQ ID NO.1; an amino acid sequence coded by the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO.2. The method has the advantages that the SACE_5717 gene in the saccharopolyspora erythraea is deactivated by the engine engineering path, so as to obtain thestrain with high output of erythrocin; the obtained strain with high output of erythrocin is used for fermenting to produce the erythrocin, so that the output of the erythrocin is increased, and the new technical support is provided for the increasing of output of the erythrocin in industrial production.
Owner:ANHUI AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY +1
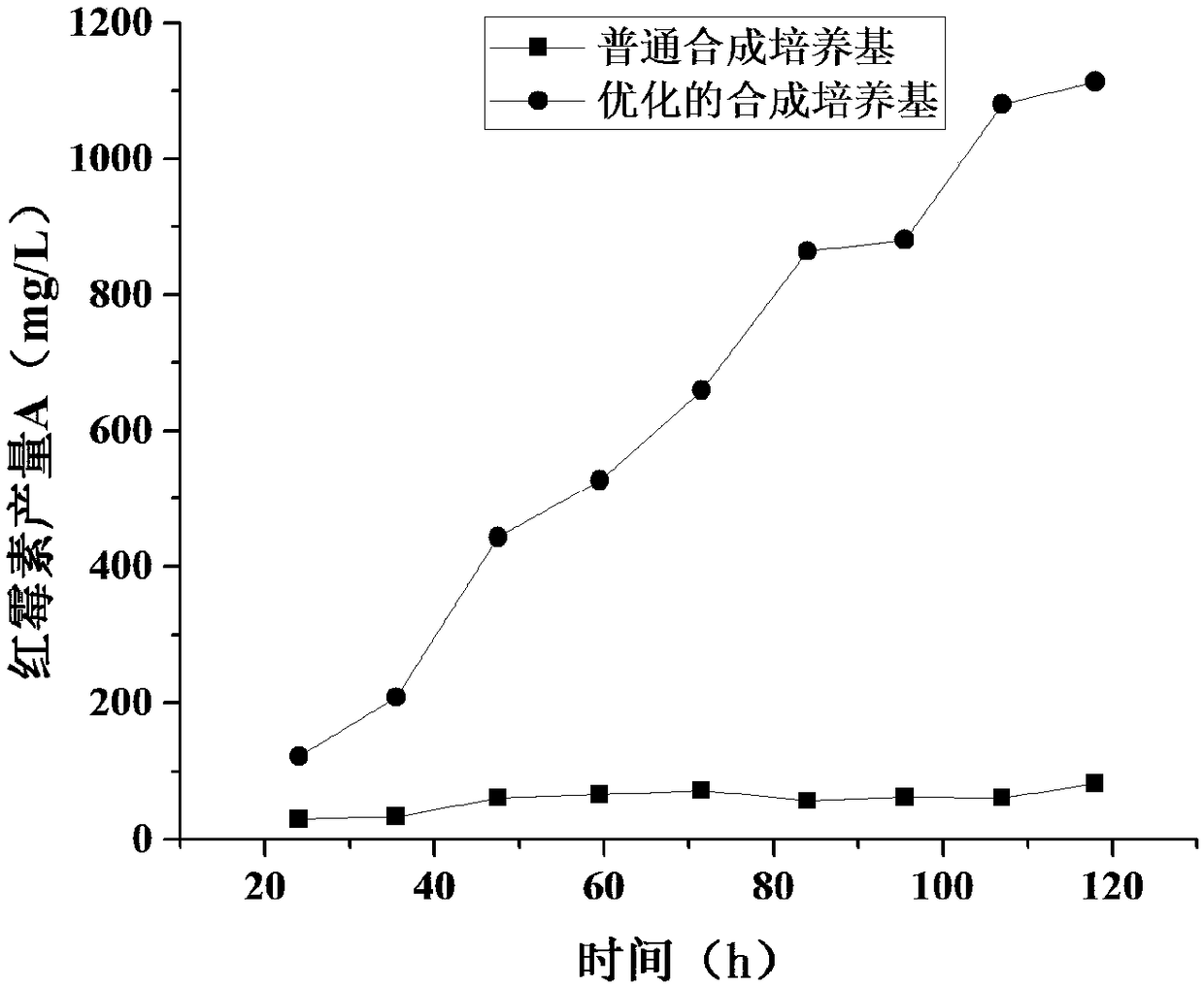
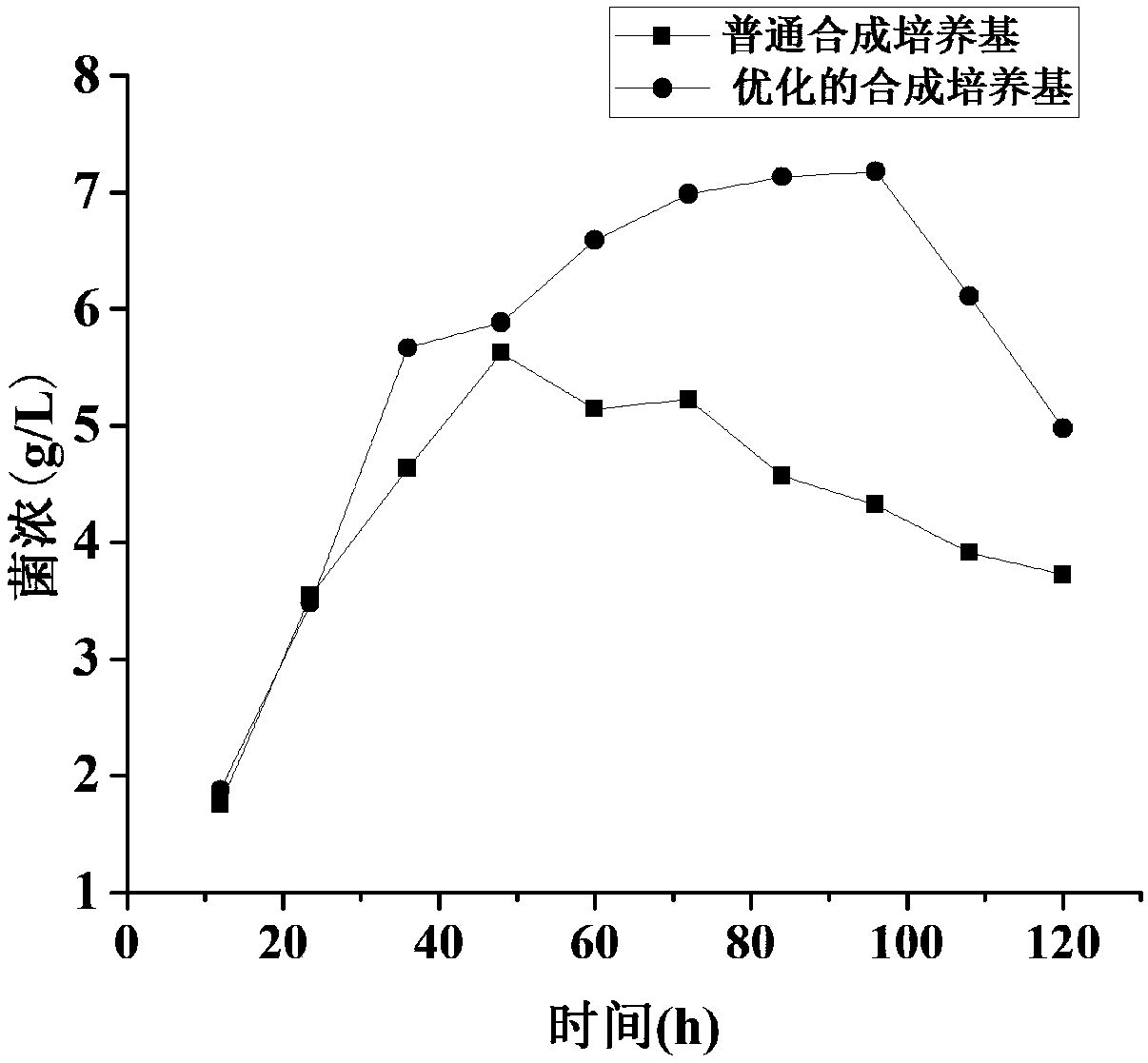
Synthetic medium for erythromycin fermentation
The invention belongs to the field of biological fermentation engineering, and relates to a synthetic medium for erythromycin fermentation. The synthetic medium comprises glucose, alanine, arginine, aspartic acid, cysteine, leucine, isoleucine, serine, threonine, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate, dihydrogen phosphate potassium, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, trisodium citrate, cobalt chloride hexahydrate, sodium tetraborate, ferric chloride, copper chloride, ammonium molybdate and calcium carbonate. The synthetic medium medium for the erythromycin fermentation is suitable for the growth of erythromycin producing bacteria such as saccharopolyspora erythraea, and can very obviously improve the yield of erythromycin.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Fermentation medium for improving erythromycin yield and method using the same
ActiveCN106337072AGood genetic stabilityIncrease productionMicroorganism based processesFermentationAmylaseMicroorganism
The invention relates to a fermentation medium for improving an erythromycin yield and a method using the same, belongs to the field of microbes and provides a Saccharopolyspora erythraea fermentation medium and a method for preparing erythromycin through the medium. Through use of a proper amount of amylase in the fermentation medium, optimization of components of a bacterial strain medium and a fermentation medium and control of other culture conditions, an erythromycin yield is improved. The fermentation medium has an erythromycin yield of 11200 micrograms per milliliter, has a simple formula, has a low cost and is suitable for industrial large-scale production.
Owner:牡丹江佰佳信生物科技有限公司
Method for increasing erythromycin fermentation titer
InactiveCN105296571AHigh oxygen demandChange viscosityMicroorganism based processesFermentationNitrogen sourceOxygen
The invention relates to a method for increasing erythromycin fermentation titer. The method is characterized in that during a process for fermentation production of erythromycin by taking Saccharopolyspora erythraea as an original strain, an ammonium sulfate solution is slowly added. According to the invention, the ammonium sulfate solution is fed after fermentation is carried out for 60 hours, due to massive breeding of mycelia at this period, large utilization of a nitrogen source of a base material is carried out, oxygen demand of a broth is large, broth viscosity is large, volume is increased, by slowly feeding the ammonium sulfate solution, broth viscosity is changed, dissolved oxygen is improved, synthesis of components of erythromycin can be adjusted, nitrogen source supplement can be simultaneously carried out, thalline vitality is increased, an erythromycin secretion period is prolonged, and an erythromycin fermentation level can be increased.
Owner:NINGXIA QIYUAN PHARMA
Method for conjugational transfer of saccharopolyspora erythraea industrial producing strain
ActiveCN106011128AImprove junctional transfer efficiencyConducive to directed genetic modificationHybrid cell preparationMicroorganism based processesWater bathsSpore
The invention discloses a method for conjugational transfer of a saccharopolyspora erythraea industrial producing strain. The method comprises the steps: selecting mature saccharopolyspora erythraea spores, pretreating, then putting in a TSB liquid culture medium containing Mg<2+>, germinating in static water bath, then cleaning, and carrying out suspension treatment to obtain receptor bacteria; and mixing donor bacteria and receptor bacteria spores, culturing in a coated 2CMY solid conjugational transfer plate culture medium, and growing to obtain a conjugational transfer factor. The method has the advantages of convenience in operation, and simple and easy implementation, and the conjugational transfer efficiency of saccharopolyspora erythraea can reach 2*10<-5>, the situation of difficult genetic manipulation of the saccharopolyspora erythraea industrial producing strain can be well overcome, and convenient conditions are provided for directional genetic modification and gene function research of the saccharopolysporaerythraea industrial strain.
Owner:HEC PHARM
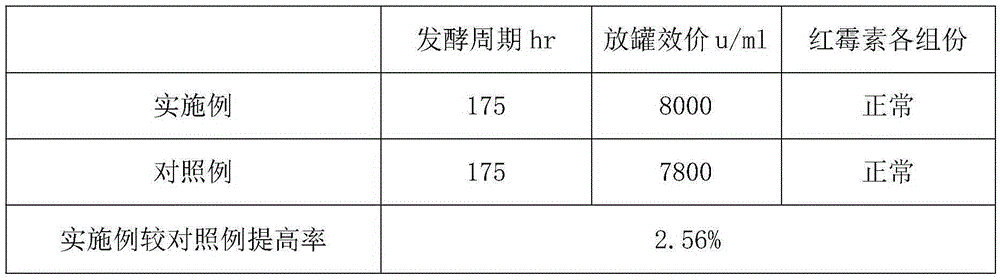
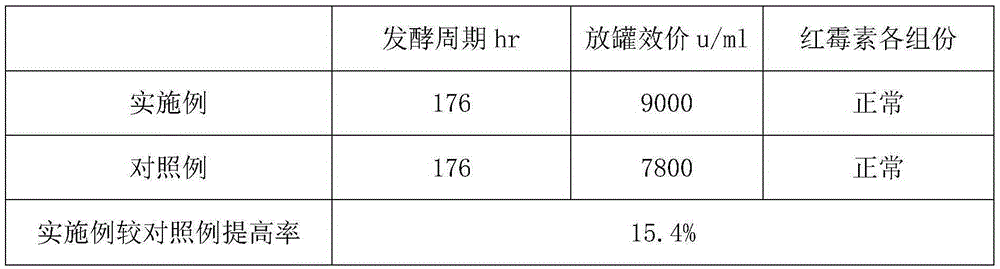
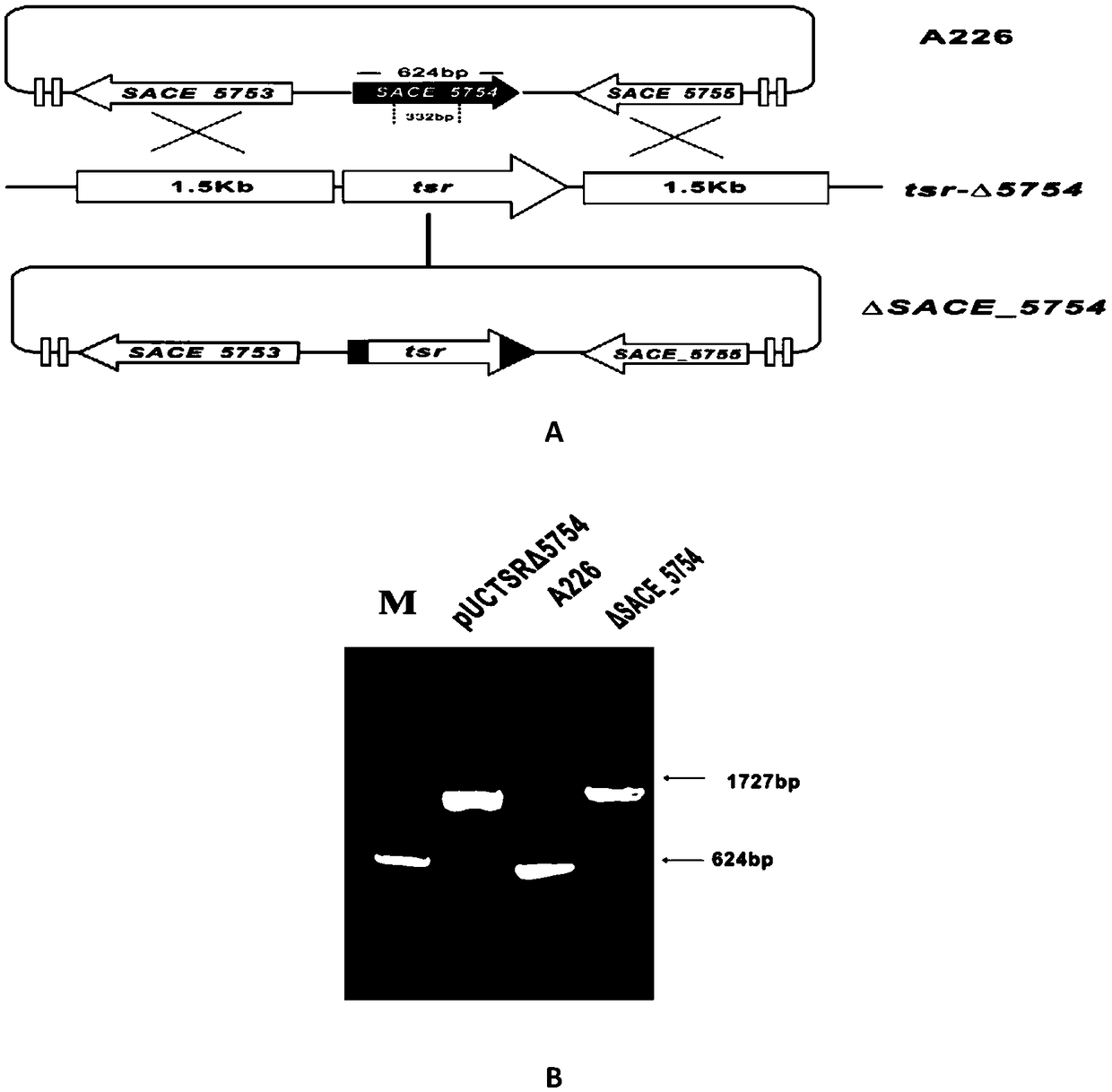
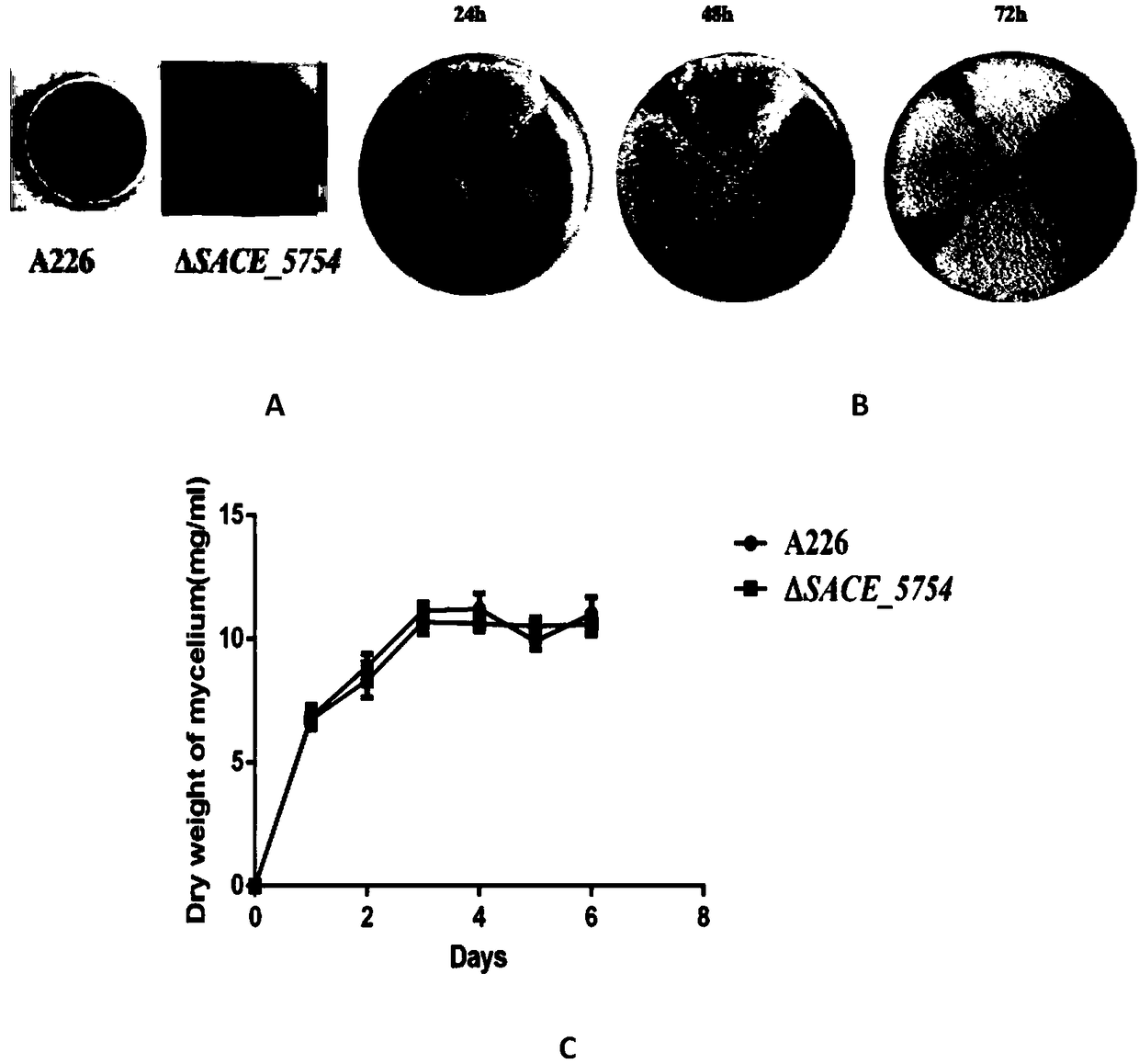
Method for increasing yield of erythromycin by SACE_5754 gene pathway of Saccharopolyspora erythraea
ActiveCN109136253AIncrease productionReduce outputMicroorganism based processesFermentationBiotechnologyGene pathway
The invention discloses a method for increasing yield of erythromycin by a SACE_5754 gene pathway of Saccharopolyspora erythraea, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the method, SACE_5754 is deleted from the Saccharopolyspora erythraea by the genetic engineering pathway, target genes SACE_0388 and SACE_6149 of the Saccharopolyspora erythraea are overexpressed, ahigh-yield erythromycin engineering strain is obtained, and when the obtained strain is applied to fermented production of erythromycin, yield can be substantially increased, and therefore, a new technical support is provided for erythromycin yield increase in industrial production.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
3-deoxy-3-carbonyl-erycin lactone b and its engineeirng strain and application
The present invention relates to 3-deoxy-3-carbonyl-erycinlactone B, its engineering bacterial strain and application. The chemical structural formula of invented product is disclosed. The engineering bacteria of present invention is (Saccharopolyspora erythraea) MICGMCC No.0604. The invented compound is used in the preparation of antibiotics.
Owner:INST OF BIOENG ACAD OF MILITARY MEDICAL SCI OF THE CHINESE
Method for producing erythrocin at high yield
ActiveCN102586366ARaise the level of fermentationSimple methodMicroorganism based processesFermentationFermentation brothMicrobiological culture
The invention provides a method for producing erythrocin at high yield. In the method, Saccharopolyspora erythraea CGMCC (China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center) 4.197 is taken as a fermentation strain, dissolved oxygen is improved through water supplementation, and a fermentation level of the erythrocin is improved; and experiment proves that when water starts to be supplemented after fermentation is carried out for 30-100h and the water supplementation amount is 5-30% of the volume of fermentation liquid, the defects that oxygen supply is not enough duding the fermentation due to overhigh concentration of strains are improved, and the average fermentation level is improved from 600u / ml to 2000u / ml. The method for producing the erythrocin at high yield, provided by the invention is simple and feasible and has positive reference significance to other types of high- oxygen-consumption fermentation.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Engineering bacteria for producing erythromycin and application of the engineering bacteria
InactiveCN102604879AHigh potencyHigh copy numberAntibacterial agentsOrganic active ingredientsBiotechnologyEukaryotic plasmids
The invention discloses engineering bacteria for producing erythromycin and application of the engineering bacteria. The invention claims a recombinant strain obtained by introduction of a recombinant plasmid into Saccharopolyspora erythraea. The recombinant plasmid is obtained by insertion of ermE* promoter, eryBII protein encoding gene and eryF protein encoding gene into multiple cloning sites of an initial vector; the ermE* promoter can initiate expression of the eryBII protein encoding gene and the eryF protein encoding gene; and the ATCC access number of the Saccharopolyspora erythraea strain is 11635. The engineering bacteria provided by the invention can be directly fermented to obtain erythromycin with titer up to 8,000U / ml in fermentation broth, the production cost is low, and the strain is a production strain with high production and application values.
Owner:MAIDAN BIOLOGICAL GROUP FUJIAN
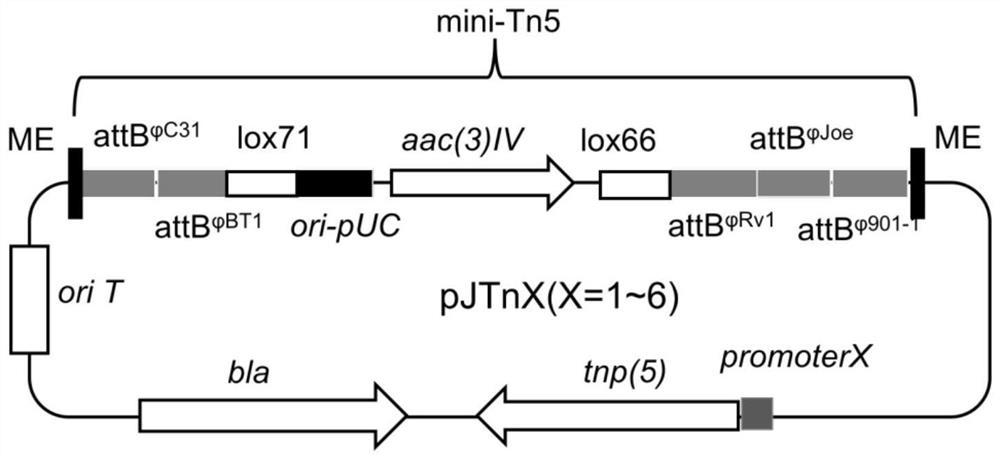
Transposon plasmids for saccharopolyspora spinosa and application of transposon plasmisd
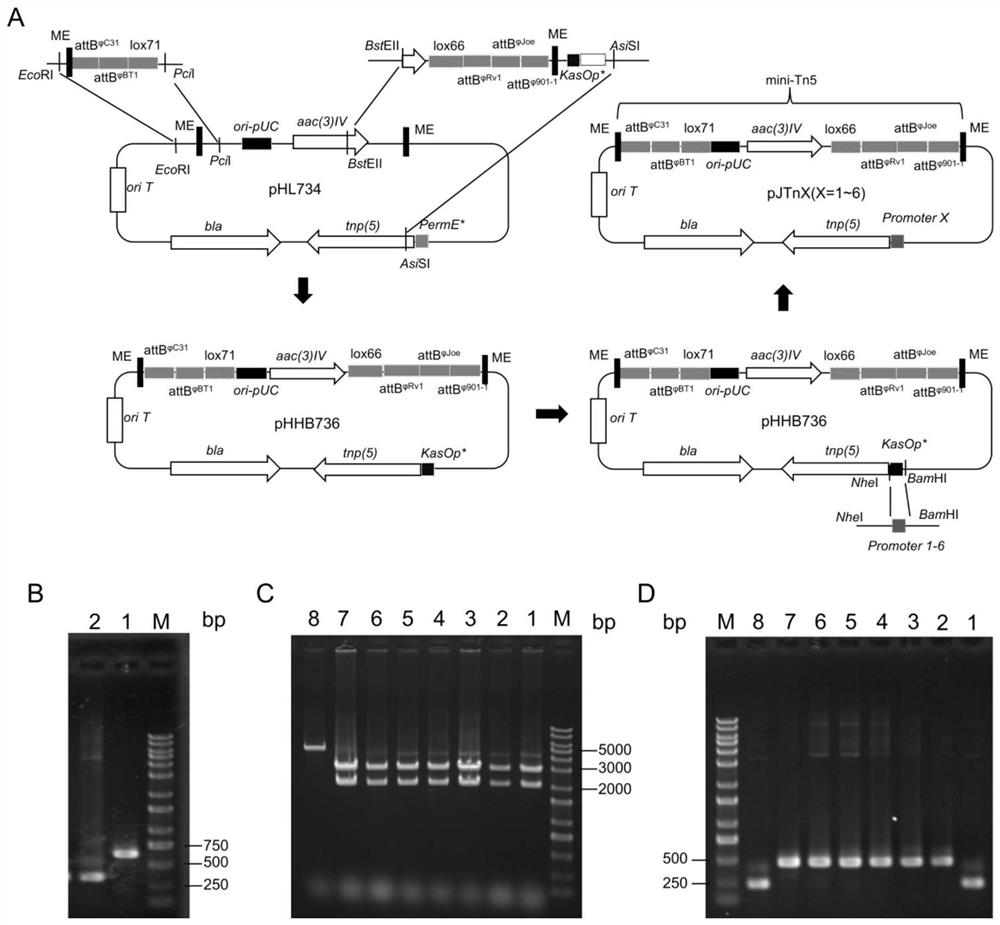
ActiveCN111909946AAchieve in vivo transposition mutagenesisAchieve saturation mutagenesisBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologySaccharopolyspora
The invention discloses transposon plasmids for saccharopolyspora spinosa and an application of the transposon plasmids. The transposon plasmids are Tn5 transposon plasmids pJTn1-pJTn6, the transposonplasmids can be subjected to efficient transposon in saccharopolyspora erythraea, pJTn1 and pJTn5 are successfully subjected to in-vivo transposon in saccharopolyspora spinosa, and 31 transposon mutants with different insertion sites are obtained. The yield of the saccharopolyspora spinosa in fermentation liquor is detected through transposon mutant fermentation, and it is found that transposon insertion has an obvious influence on the yield of saccharopolyspora spinosad. The transposon system has important significance in biosynthesis regulation and control of spinosad in the saccharopolyspora spinosa.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
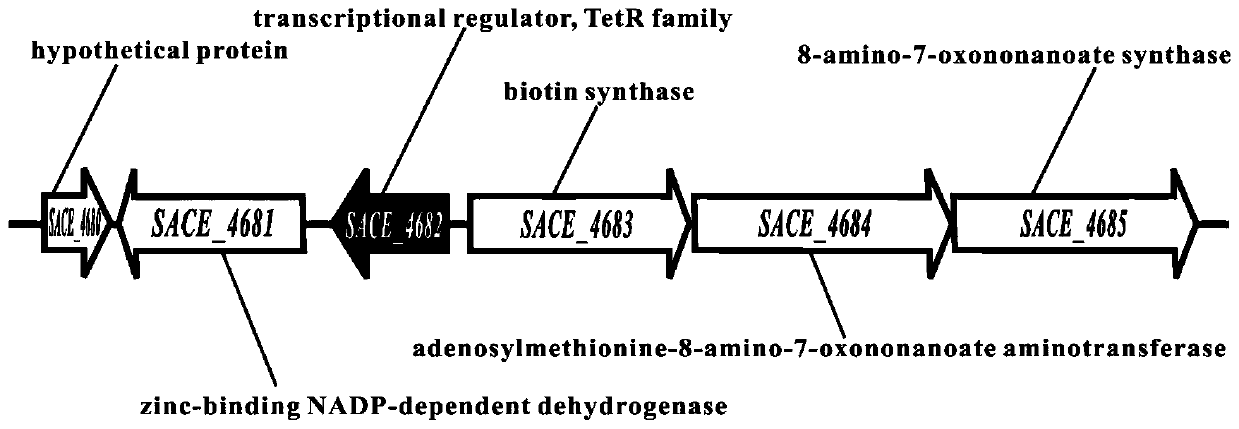
Method for improving yield of erythromycin by modifying saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_4682 gene
ActiveCN111139192AImprove fermentation yieldIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyRegulator gene
The invention discloses a method for improving the yield of erythromycin by modifying a saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_4682 gene. In the saccharopolyspora erythraea, a TetR family transcription regulation gene SACE_4682 is deleted by a genetic engineering method to obtain an erythromycin high-yield engineering strain, and the obtained strain is fermented to produce the erythromycin, so that a new technical support is provided for improving the yield of the erythromycin in industrial production.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
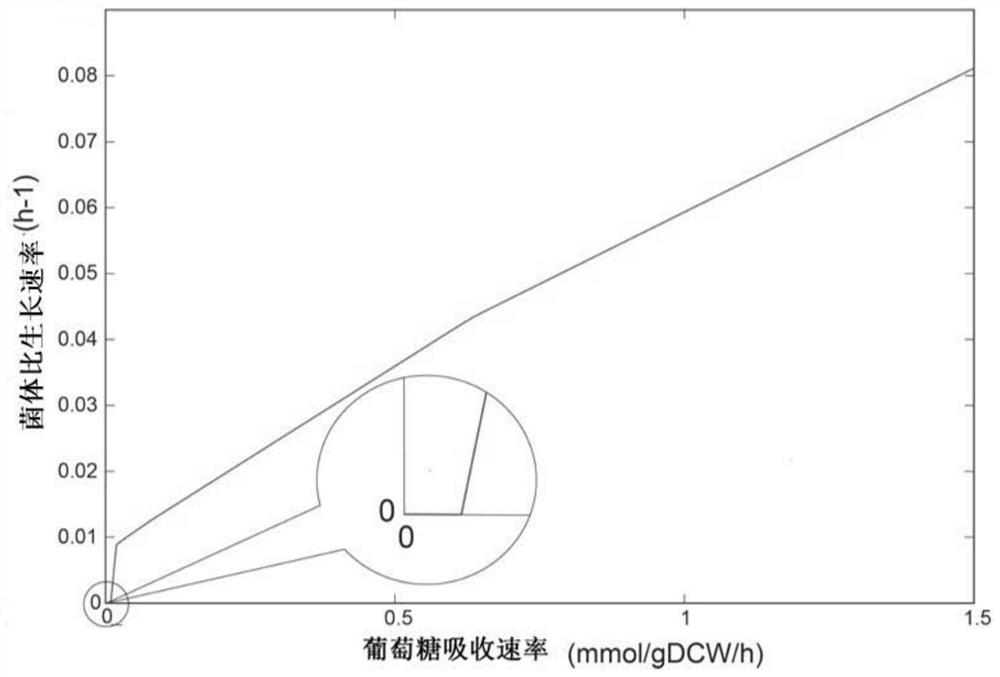
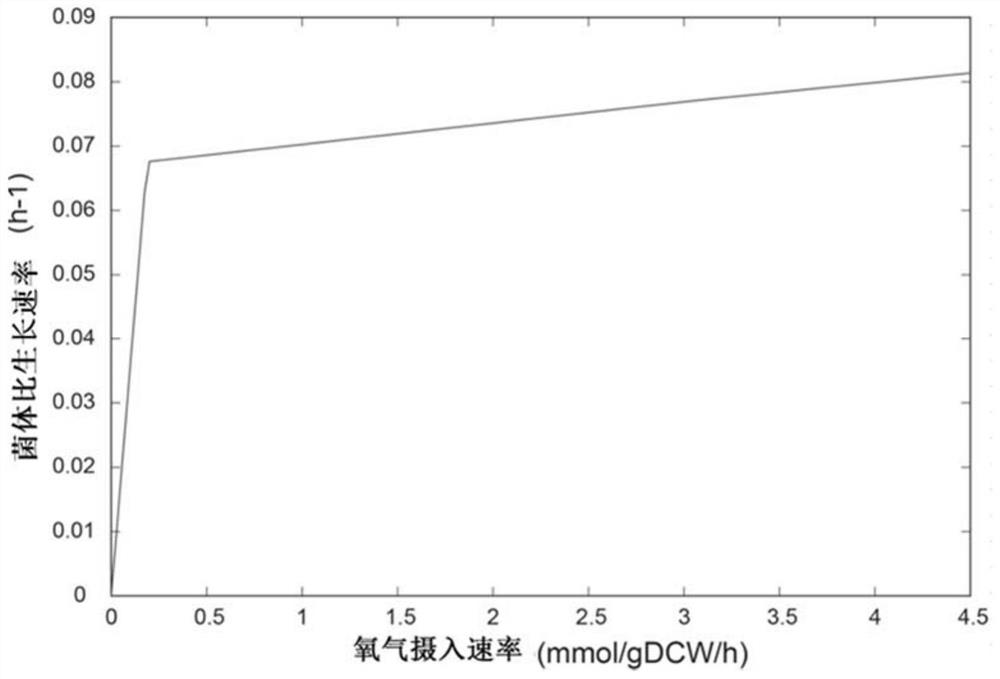
Method for improving erythromycin yield by guiding n-propyl alcohol feeding through genome model
PendingCN113174418AComprehensive understanding of metabolic profilesImprove accuracyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPropanol
The invention discloses a method for improving erythromycin yield by guiding normal propyl alcohol feeding through a genome model, which comprises the following steps: in the fermentation process of saccharopolyspora erythraea genetically engineered bacteria, feeding ammonium sulfate and n-propyl alcohol 50-70 hours after the start of fermentation, wherein the n-propyl alcohol feeding rate is obtained by constructing a saccharopolyspora erythraea whole genome metabolic network model and analyzing the model. The whole genome metabolic network model of the saccharopolyspora erythraea genetically engineered bacteria is constructed to carry out systematic cell growth simulation, and a strategy is provided for increasing the yield of erythromycin. Under the guidance of a whole genome metabolic network model, the existing fermentation process of saccharopolyspora erythraea genetically engineered bacteria is optimized, and the yield of erythromycin is increased by regulating and controlling the supplementation rate of n-propanol.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH +1
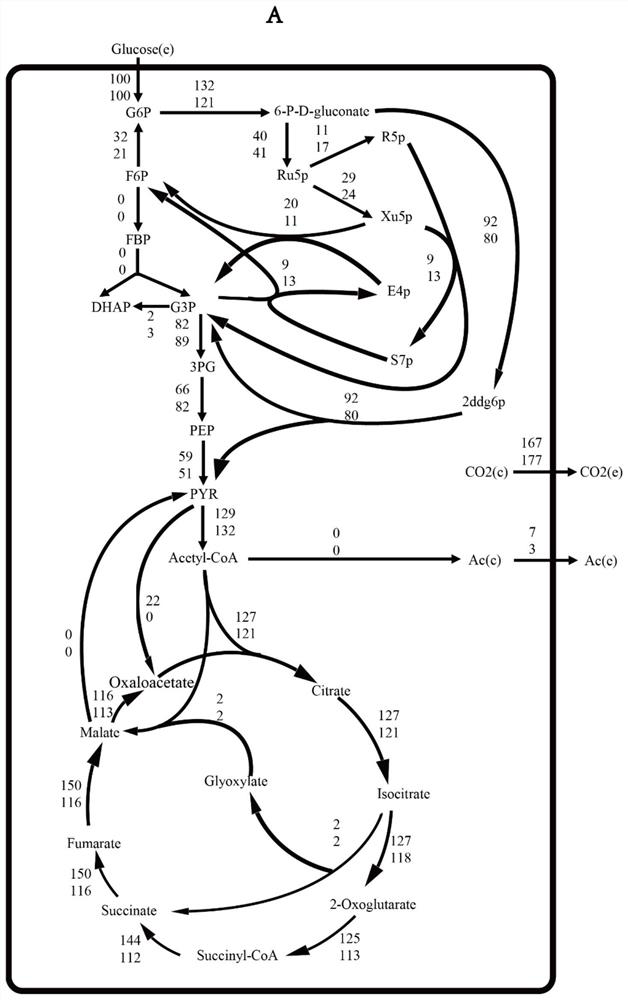
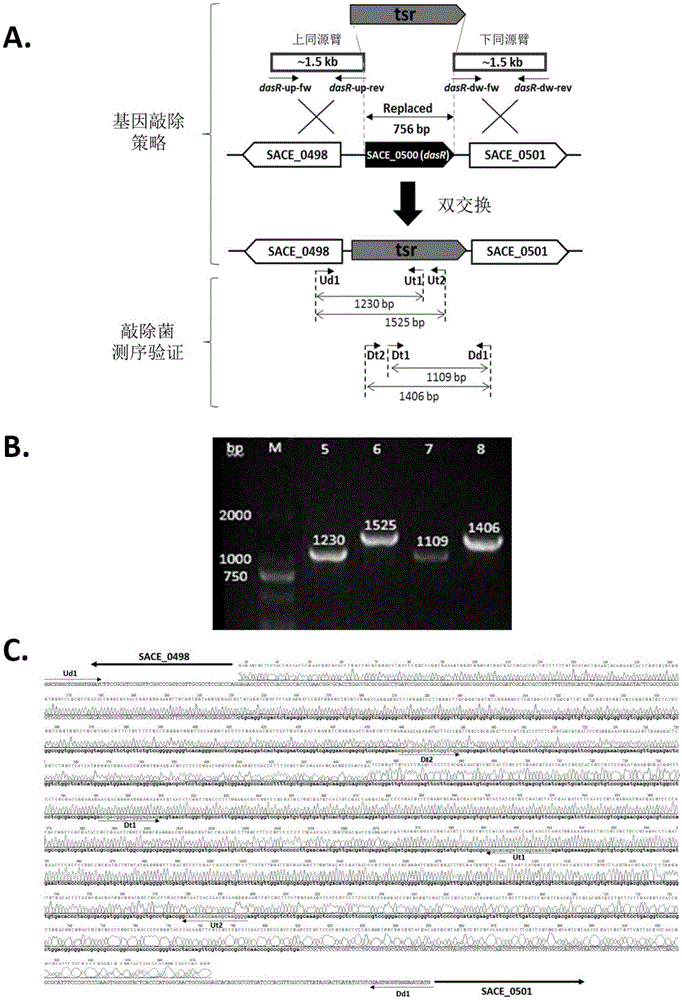
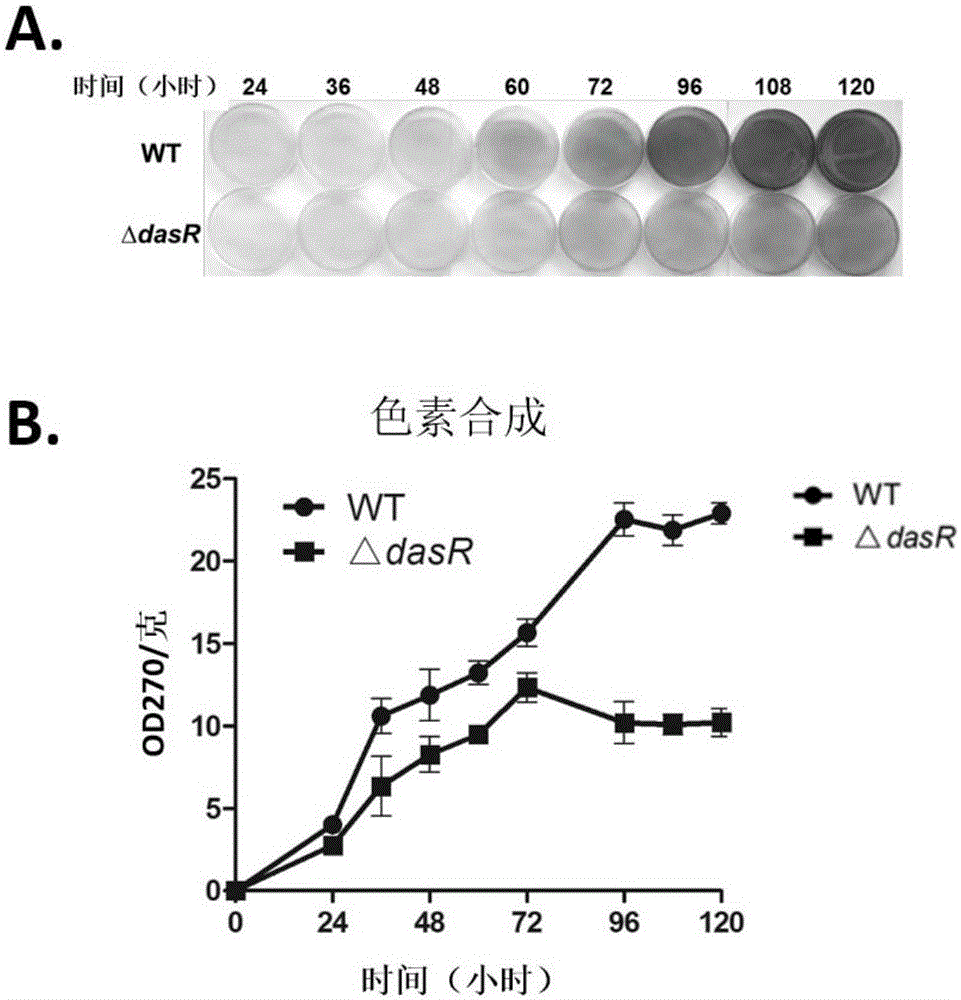
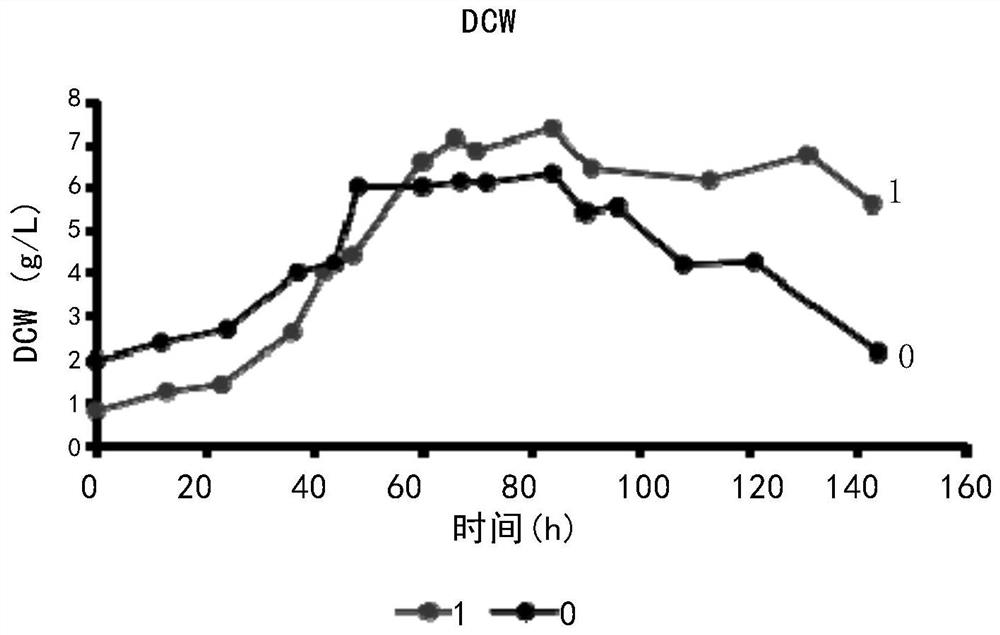
Method for synthesizing secondary metabolites of saccharopolyspora erythraea by controlling gene dasR and application of gene dasR
InactiveCN105039380AReduce generationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesSaccharopolyspora erythraeaWild type strain
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing secondary metabolites from an erythrocin-producing strain, namely saccharopolyspora erythraea under the influence of a dasR gene and an application of the dasR gene. The method comprises the following step: knocking out the dasR gene in a saccharopolyspora erythraea genome to obtain mutant engineering bacteria, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the dasR gene is a sequence in a sequence table. The invention also relates to a mutant strain obtained by knocking out of the dasR gene or an application of the mutant strain in influencing the yield of the secondary metabolites, wherein the secondary metabolites are erythrocin and reddish brown pigment specifically. Compared with a wild type strain in which the dasR gene is not knocked out, the engineering strain in which the dasR gene is knocked out has the characteristic that the amount of produced erythrocin and the pigment is reduced, which indicates that the gene is positively correlated to the production of the secondary metabolite.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Breeding method of erythromycin-producing strain mutagenesis by injecting plasma into spore bud
InactiveCN102851276AHigh positive mutation rateHigh mutation rateMutant preparationMicroorganism based processesSporeIon implantation
The invention relates to a breeding method of erythromycin-producing strain mutagenesis by injecting plasma into spore buds. The method is characterized in that cultivated saccharopolyspora erythraea spore buds are employed for plasma injection for mutagenesis. According to the invention, plasma is injected into the spore buds for mutagenesis of erythromycin-producing strain, so as to realize high mutagenesis rate, and quickly and effectively obtain erythromycin strain with high positive mutation rate; and the strain can be stabilized and purified for production to effectively improve production efficiency.
Owner:NINGXIA QIYUAN PHARMA
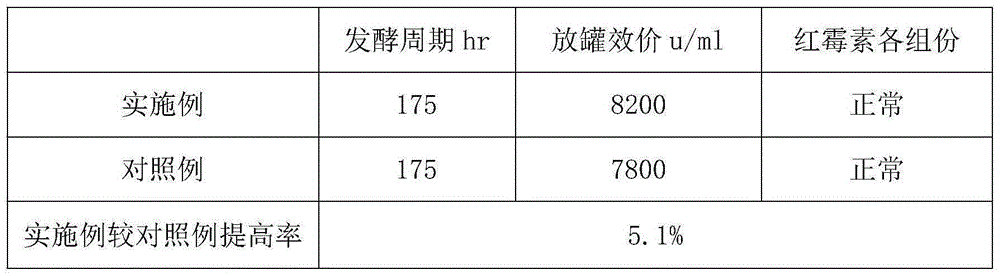
Optimized fermentation method of saccharopolyspora erythraea with sucC gene knocked out
PendingCN112553132ASolve the phenomenon of autolysisIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologySaccharopolyspora
The invention provides an optimized fermentation method of saccharopolyspora erythraea with an sucC gene knocked out. The inventor observes the phenomenon that the yield of erythrocin is influenced due to autolysis of engineering bacterium in the later period of the fermentation process, and further effectively reduces the autolysis of the saccharopolyspora erythraea with sucC gene knocked out byimproving the process of adjusting the pH value and adding ammonium sulfate in a specific time period; and besides, the proportion of erythromycin A of the genetically engineered bacterium in a totalerythromycin product is also greatly increased. Under the condition that a synthetic (type) culture medium is utilized, the yield and purity of the erythromycin A are high, and the method is suitablefor industrial application.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Novel method for fermentation production of erythrocin by utilizing saccharopolyspora erythraea
The invention relates to a novel method for fermentation production of erythrocin by utilizing saccharopolyspora erythraea. According to the method, glucose is taken as a carbon source, amino acid istaken as a nitrogen source, the saccharopolyspora erythraea is subjected to fermentation culture, at a proper fermentation stage, the carbon source and ammonium sulfate are replenished, and efficientproduction of the erythrocin is achieved. In addition, the method is environmentally friendly and low in culture cost.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Method for improving fermentation unit of erythromycin
PendingCN110747246APromote growth and reproductionIncrease synthesis rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMicrobiology
The invention relates to a method for improving a fermentation unit of erythromycin. The method is characterized in that in the process of taking saccharopolyspora erythraea as an original strain to produce the erythromycin by fermentation, nickel sulfate is added into a fermentation medium at the use amount of 0.03-0.06 g / L. According to the method, in the process of taking the saccharopolysporaerythraea as the original strain to produce the erythromycin by fermentation, an appropriate amount of the nickel sulfate is added into the fermentation medium of the erythromycin, the nickel sulfatecan participate in the processes of the growth and reproduction of bacterial cells and the synthesis of products, the nickel sulfate is used for stimulating the enzyme activity of the metabolic process, the growth and reproduction of bacteria are promoted, and more importantly, the synthesis rate of the products is promoted, so as to achieve the purposes of shortening the fermentation period, improving the fermentation technological level, and meanwhile reducing consumption.
Owner:NINGXIA QIYUAN PHARMA
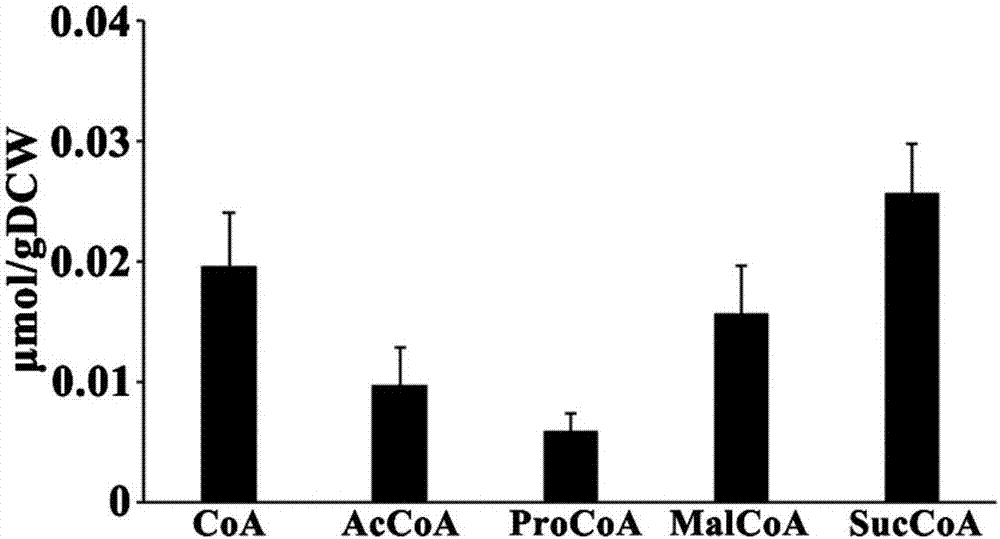
Method for extracting intracellular coenzymes A and organic acids from saccharopolyspora erythraea
The invention relates to a method for extracting intracellular coenzymes A and organic acids from saccharopolyspora erythraea. The inventor discloses a method suitable for extracting intracellular coenzyme A substances and organic acids from saccharopolyspora erythraea by comparison and analysis realized by using a method for extracting various intracellular metabolites, so that the basis can be provided for analyzing the metabolic characteristic in a synthesis process of erythrocin from the metabolic point of view.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
A kind of method for producing erythromycin by fermentation
ActiveCN104419739BLow priceSuitable for useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyCottonseed oil
Owner:鲁南新时代生物技术有限公司
Detection method and prevention method of phages specific to saccharopolyspora erythraea
InactiveCN112266977AEasy to observeEfficient detection methodMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisBiotechnologyMycelium
The invention relates to a detection method and a prevention method of phages specific to saccharopolyspora erythraea. The detection method comprises the following steps: mixing cultured saccharopolyspora erythraea mycelia into an upper culture medium of a double-layer plate culture medium, and then paving the cultured saccharopolyspora erythraea mycelia on a solidified lower culture medium of thedouble-layer plate culture medium; placing the culture medium in an environment needing to be detected for detection at regular time and fixed locations after being solidified, taking the culture medium back, carrying out constant-temperature culture for 28-34 hours at 35-37 DEG C and 40-45% RH, and observing and recording results. According to the method disclosed by the invention, the existenceof the phages can be intuitively observed, meanwhile the quantity and the sedimentation rate of the phages can be detected. The detection method of the invention is an effective, rapid, simple and convenient detection method for phages specific to saccharopolyspora erythraea. The detection method of the invention is suitable for detecting ambient air and also suitable for detection in a liquid environment. According to the invention, infection and outbreak of phages specific to saccharopolyspora erythraea can be effectively prevented.
Owner:NINGXIA QIYUAN PHARMA
Improving erythromycin production through the sace_7301 gene pathway of Saccharopolyspora erythromycetes
ActiveCN103205451BImprove fermentation yieldReduce outputBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyGene pathway
The invention discloses a method for improving erythromycin yield by a saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_7301 gene pathway. The method is characterized in that gene copy number of the saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_7301 or gene expression quantity of the SACE_7301 is increased by a gene engineering pathway so as to obtain high-yield engineering strains of saccharopolyspora erythraea erythromycin, and yield of the erythromycin can be improved by fermenting the strains obtained by the technology.
Owner:ANHUI UNIVERSITY
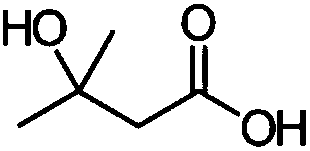
Method for preparing beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyric acid by enzymic method
ActiveCN108866017ACatalytic reaction conditions are mildPost-processing is simpleBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismCytochrome P450
A saccharopolyspora erythraea cytochrome P450 oxidase mutant with high enzyme activity is obtained by a directed evolution method. The mutant or an expressive microorganism of the mutant can efficiently catalyze beta-methylbutyric acid for performing hydroxylation reaction to generate the beta-hydroxy-beta-methylbutyric acid; the concentration of the beta-methylbutyric acid used as a substrate canreach 10g / L; after conversion for 24h, the conversion rate reaches 70 percent or higher; industrial application prospects are realized.
Owner:ZHEJIANG HUARUI BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com