Method for improving yield of erythromycin through saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_Lrp gene
A technology of Saccharopolyspora erythromycetes and erythromycin, which is applied in the direction of bacteria, bacterial peptides, viruses/phages, etc., and can solve the problem of less research on regulatory genes of Saccharopolyspora erythromycetes
Inactive Publication Date: 2016-11-23
ANHUI UNIVERSITY
View PDF1 Cites 4 Cited by
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
In 2007, Oliynyk et al. reported the genome sequence of Saccharopolyspora NRRL23338, but there are few studies on the regulatory genes of Saccharopolyspora. So far, only the regulatory genes of bldD (SACE_2077), SACE_7040, SACE_0012 and SACE_5599 have been reported.
Method used
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
View moreImage
Smart Image Click on the blue labels to locate them in the text.
Smart ImageViewing Examples
Examples
Experimental program
Comparison scheme
Effect test
Embodiment 1
[0028] 1 Materials and methods:
[0029] 1.1 Strains, plasmids and growth conditions
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
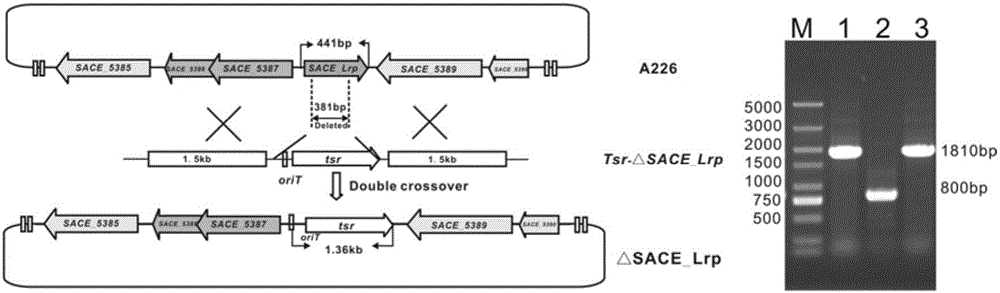
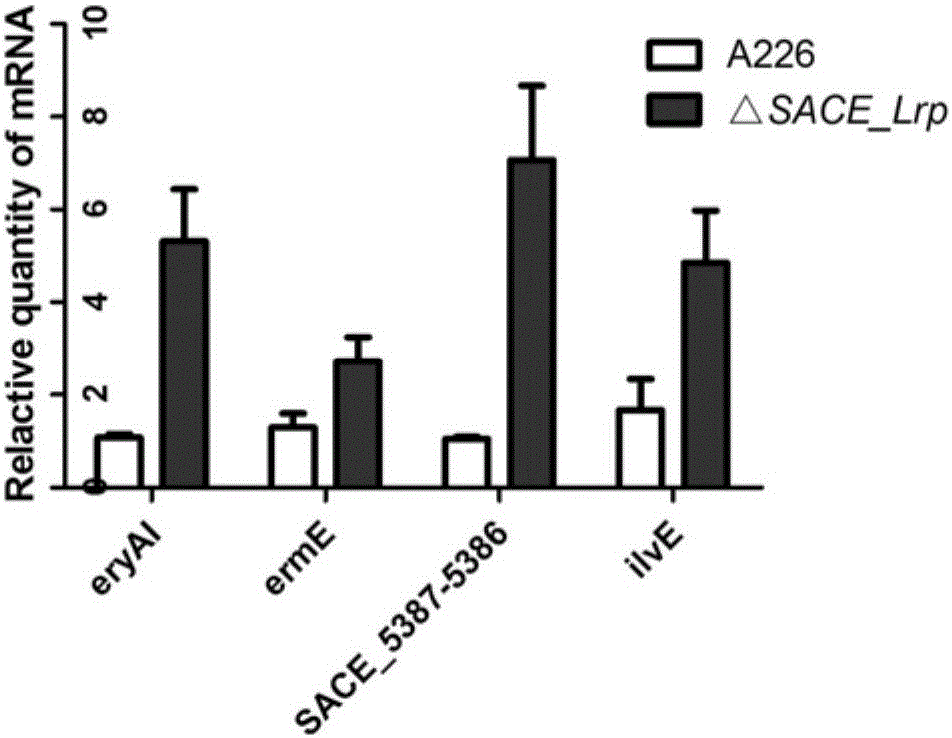
The invention discloses a method for improving the yield of erythromycin through a saccharopolyspora erythraea SACE_Lrp gene. The SACE_Lrp gene is inactivated in saccharopolyspora erythraea through a genetic engineering way, and a saccharopolyspora erythraea erythromycin high-yield engineering strain is obtained through excessively expressing a target gene SACE_5387-5386; the erythromycin is produced through fermenting the obtained strain, and the strain obtained by the technology is fermented, so that the yield of the erythromycin can be improved.
Description
technical field [0001] The present invention mainly relates to a method for increasing the yield of erythromycin by fermentation, in particular to a method for increasing the yield of erythromycin by inactivating the SACE_Lrp gene and / or overexpressing the SACE_Lrp target gene in Saccharopolyspora erythromycetes. Background technique [0002] Secondary metabolites of actinomycetes have a wide range of uses, such as antibiotics, anticancer agents, immunomodulators, insect repellents, and insect control agents. Among the 23,000 biologically active secondary metabolites discovered so far, more than 10,000 are produced by actinomycetes. However, the original production of these secondary metabolites is very low, and screening is required to obtain high-yielding strains for industrial production. In the past, industrial production strains were mainly obtained by random physical or chemical mutagenesis. The traditional random mutagenesis technique is not only time-consuming, but...
Claims
the structure of the environmentally friendly knitted fabric provided by the present invention; figure 2 Flow chart of the yarn wrapping machine for environmentally friendly knitted fabrics and storage devices; image 3 Is the parameter map of the yarn covering machine
Login to View More Application Information
Patent Timeline
 Login to View More
Login to View More Patent Type & Authority Applications(China)
IPC IPC(8): C12N15/74C12N1/21C12P19/62C12R1/01
CPCC07K14/195C12N15/74C12N2800/101C12P19/62
Inventor 张部昌刘静任敏吴杭
Owner ANHUI UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com