Optimized fermentation method of saccharopolyspora erythraea with sucC gene knocked out
A red Saccharopolyspora, gene knockout technology, applied in the field of fermentation engineering, can solve the problems of high cost, low yield, low effective components, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0046] Embodiment 1, the preparation of E3-△sucC genetically engineered bacteria
[0047] The industrial strain S. erythraea E3 strain (obtained from Shanghai Guojia Biochemical Engineering Technology Research Center Co., Ltd.) was used as the starting strain to prepare a genetically engineered strain for knocking out the succinyl-CoA synthetase gene (SucC).
[0048] The SucC gene was knocked out by insertional inactivation, and primers were designed during the insertional inactivation process to amplify a fragment of 1021 bp in length from 196 bp to 1216 bp behind the start codon of the SucC gene.
[0049] The primer sequences are as follows:
[0050] Upstream primers:
[0051] CCCAAGCTTGGGATGAGGCCAAGACGAA (SEQ ID NO: 1);
[0052] Downstream primers:
[0053] GAAGATCTTCGCCCTGGACGATGACCTTG (SEQ ID NO: 2).
[0054] The genome of the S. erythraea E3 strain was used as a template, and the above primers were used to amplify to obtain the target fragment, which was 1021 bp in l...
Embodiment 2
[0056] Embodiment 2, basic culture
[0057] 1. Plate seed culture
[0058] Prepare the flat seed medium according to the required amount, adjust the pH to 7.0 before sterilization, and then autoclave it together with the flat bamboo stick wrapped in kraft paper at 121°C for 30 minutes, and then place it on the ultra-clean workbench. The sterilized media is aliquoted into plates. Before inverting the plate, the temperature of the plate culture dish did not exceed 60°C, and the antibiotics Apra (concentration of 50 μg / ml) and thiostreptomycin (concentration of 100 μg / ml) were added.
[0059] After the plate is solidified, use an inoculation loop to dip the strains from the preserved glycerin tube, draw a line on the plate, and finally seal the plate with a parafilm, and place it in a constant temperature incubator at 35°C for one week until more obvious bacteria appear on the plate. Pale spores.
[0060] 2. Shake flask seed culture
[0061] Prepare 45ml of shake flask seed m...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Embodiment 3, culture process optimization
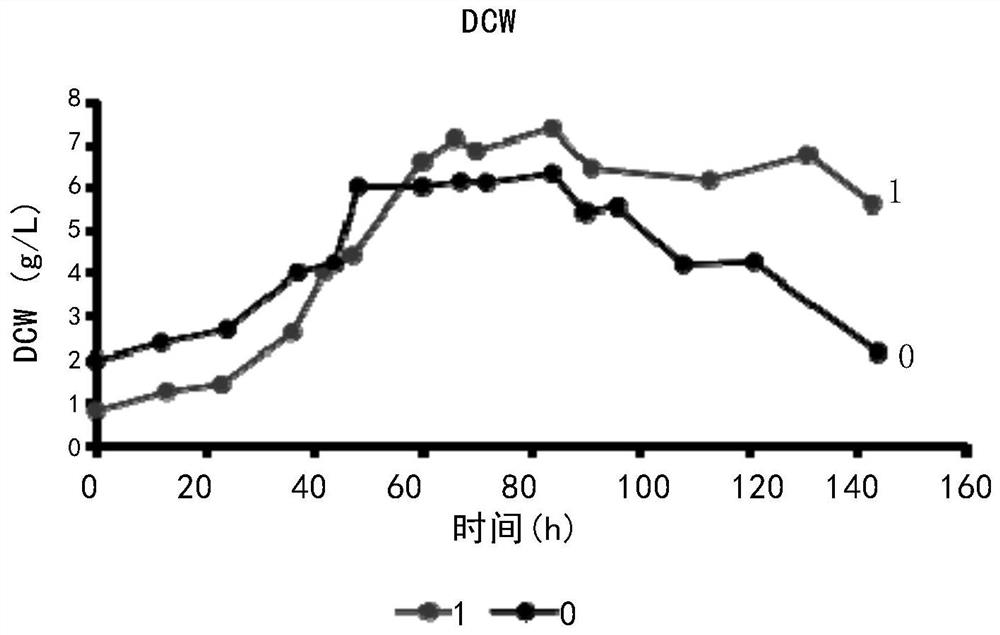
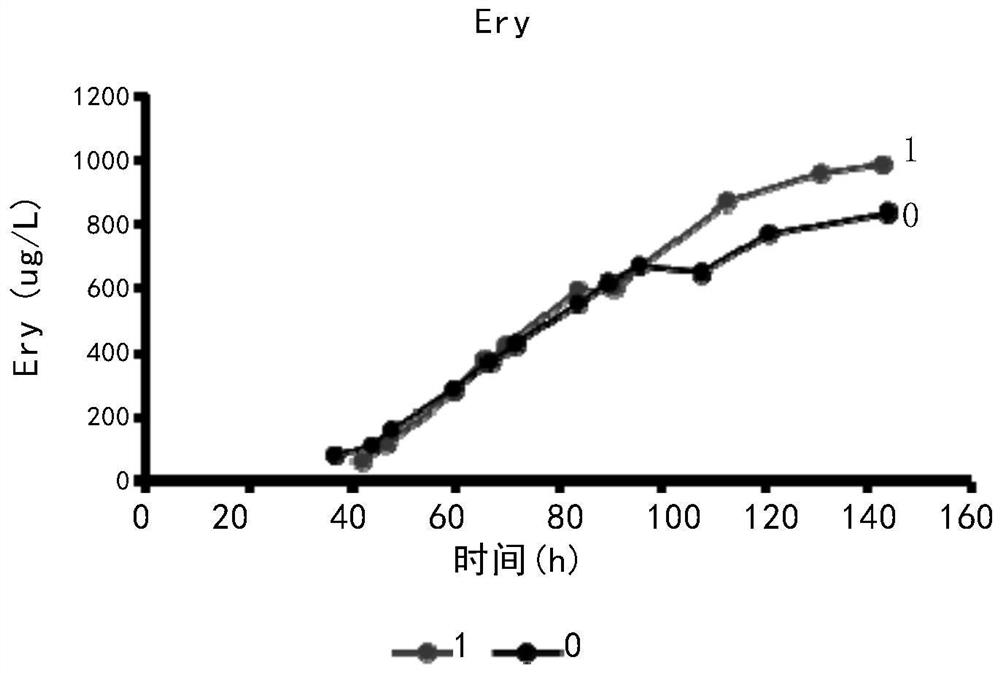
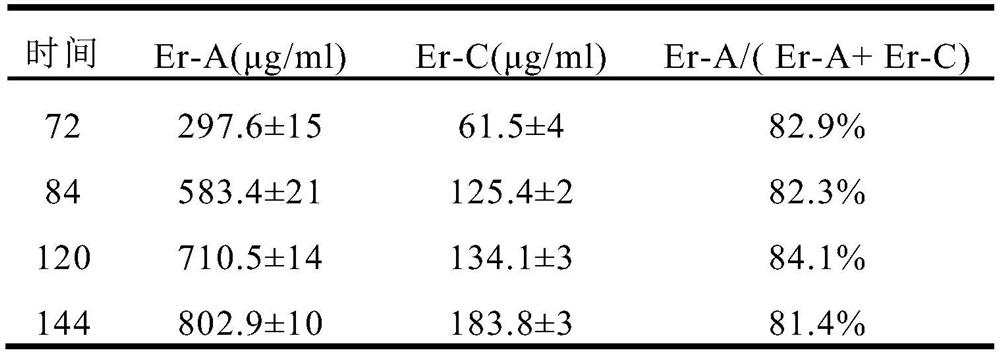
[0069] According to the growth of the E3-ΔsucC genetically engineered bacteria in Example 2 above, the inventors further optimized the cultivation process. After repeated adjustments to various culture conditions, it was found that the adjustment of the pH in the initial medium and the fermentation medium is relatively important. Although the starting strain S.erythraea E3 had a strong adaptability to pH, the E3-△sucC genetically engineered strain was not like this. Its acid production performance was different from that of the starting strain, making it necessary to adjust pH.
[0070] The fermentation process uses inexpensive synthetic media. The medium prepared according to the formula of the synthetic medium was fixed to 2370ml, the pH was adjusted to 7.0 before sterilization, and then poured into a 5L fermenter, and 1.5ml of antifoaming agent was added, and the fermenter was wrapped up and kept at 121°C Autoclave for 6...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com