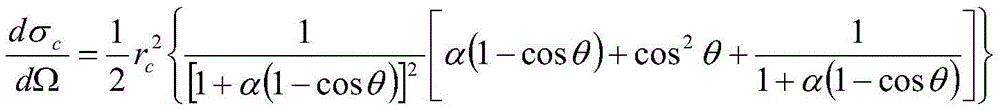Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
36 results about "Densitometry" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Densitometry is the quantitative measurement of optical density in light-sensitive materials, such as photographic paper or photographic film, due to exposure to light.
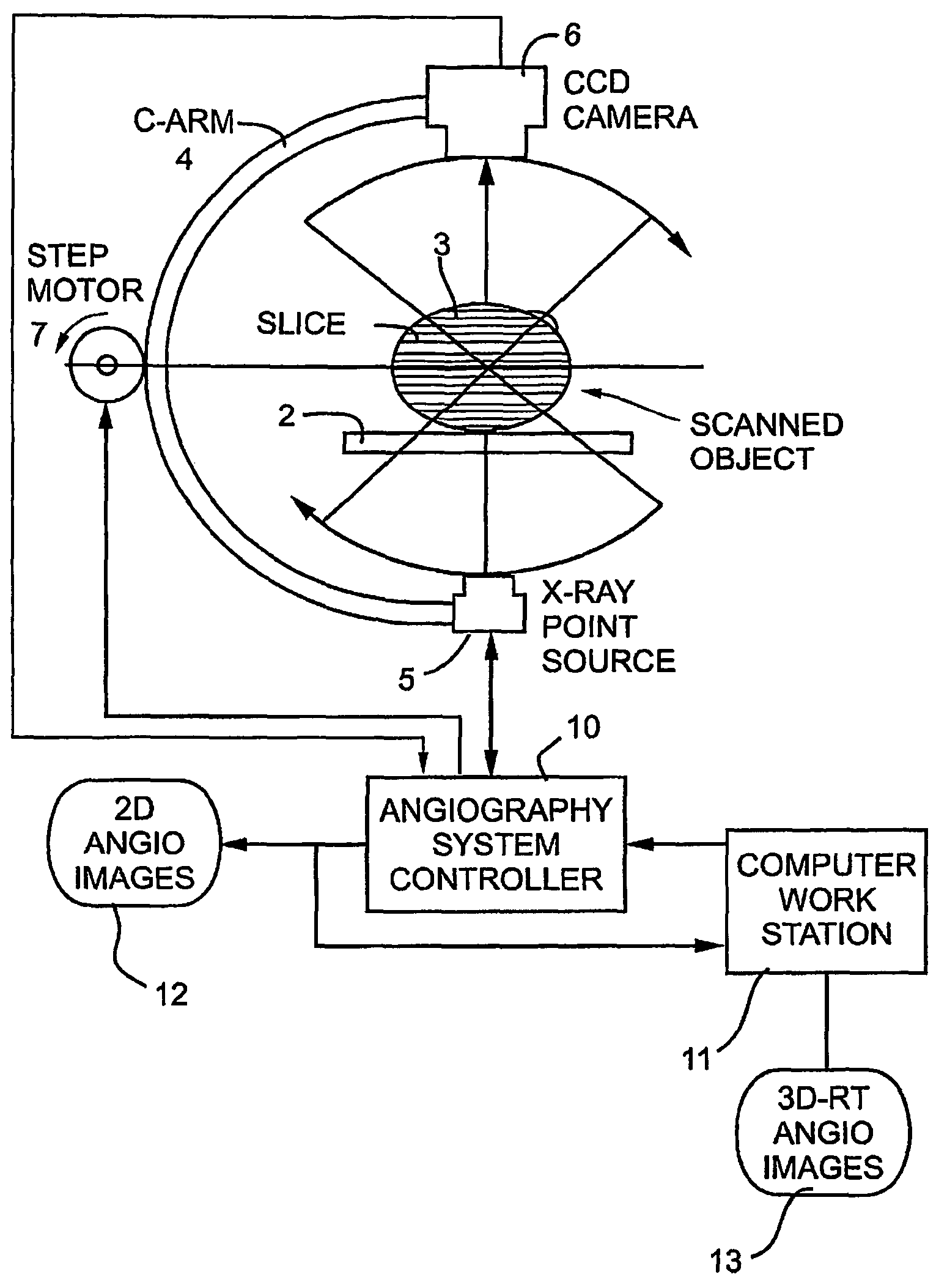
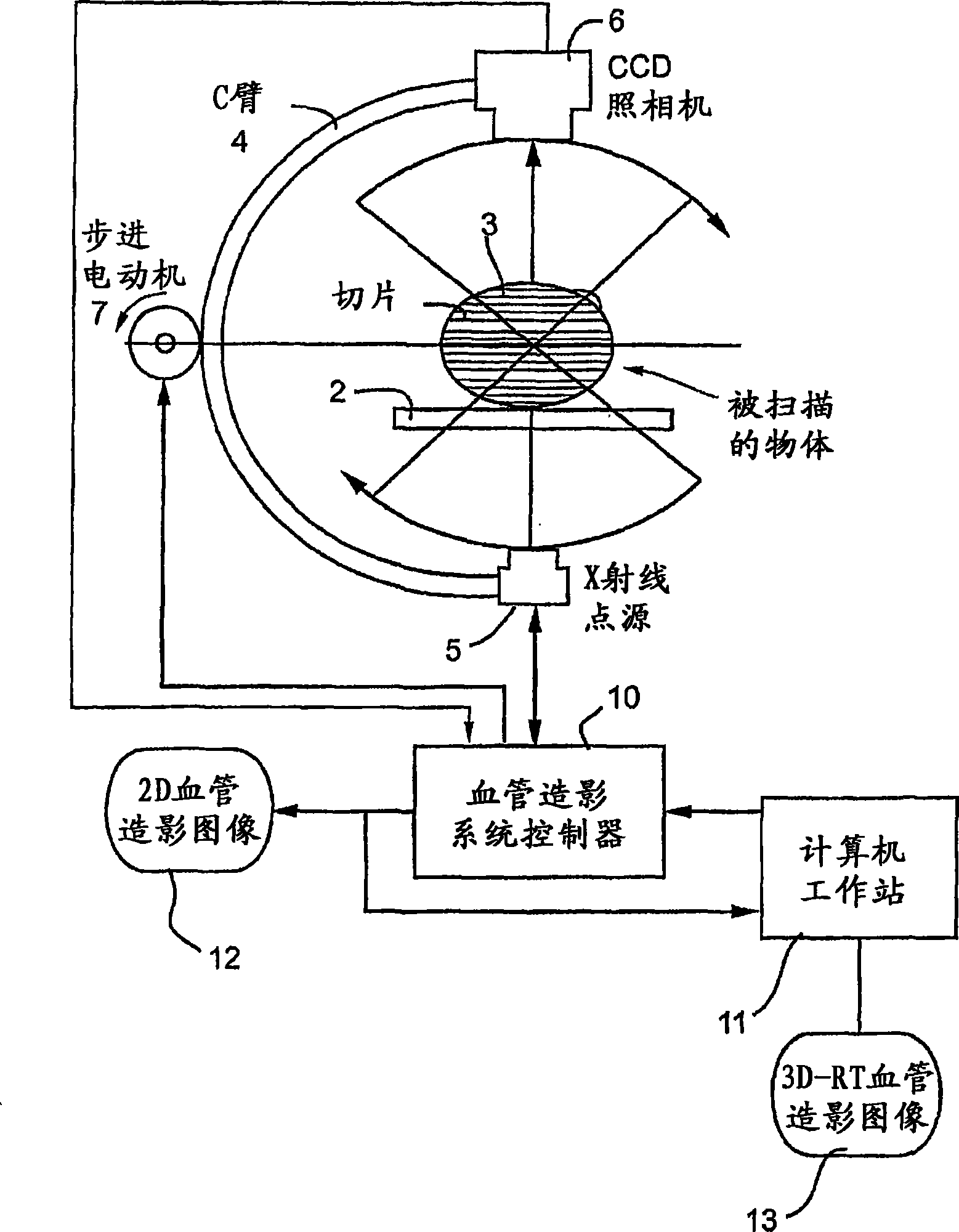
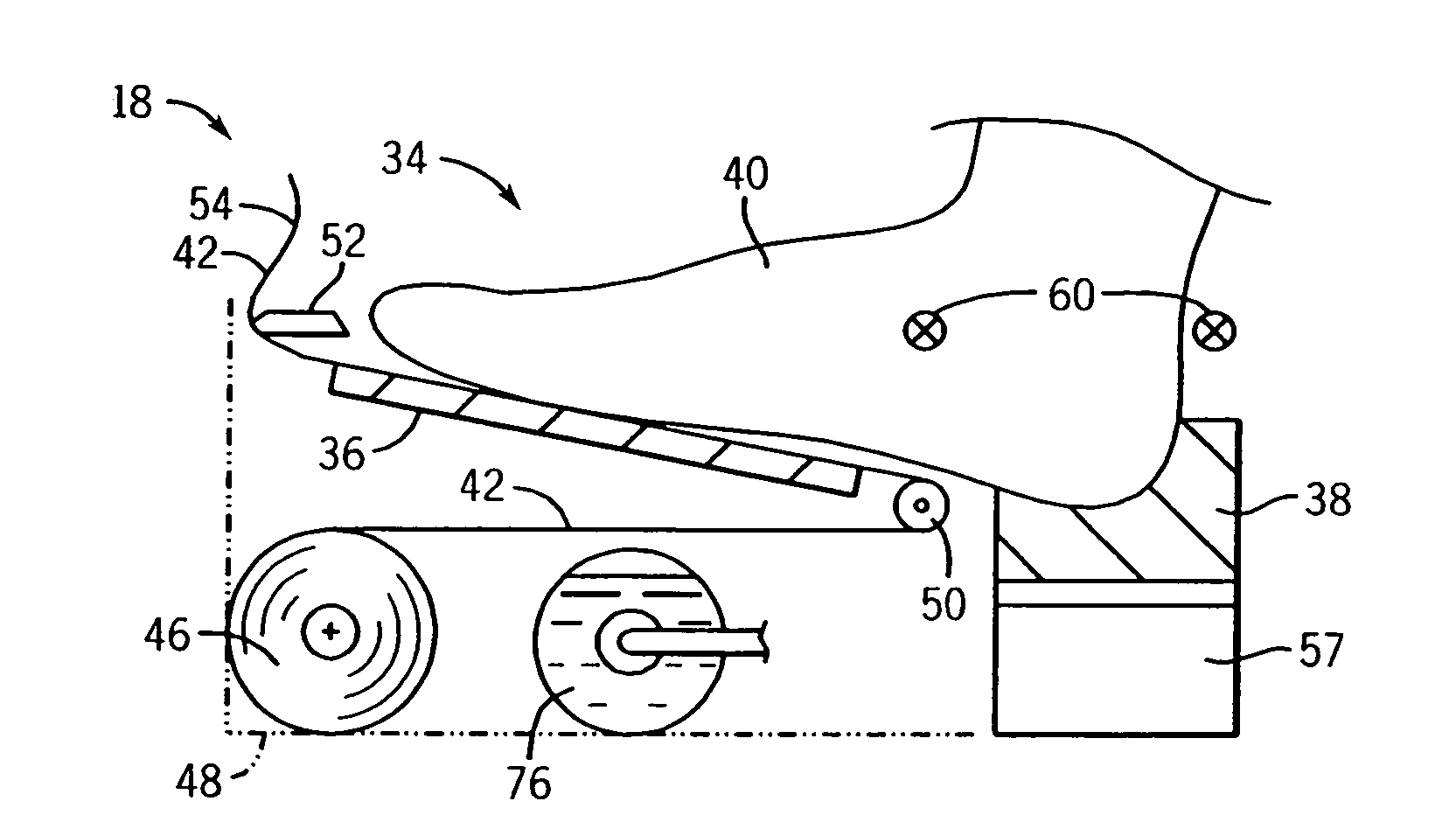
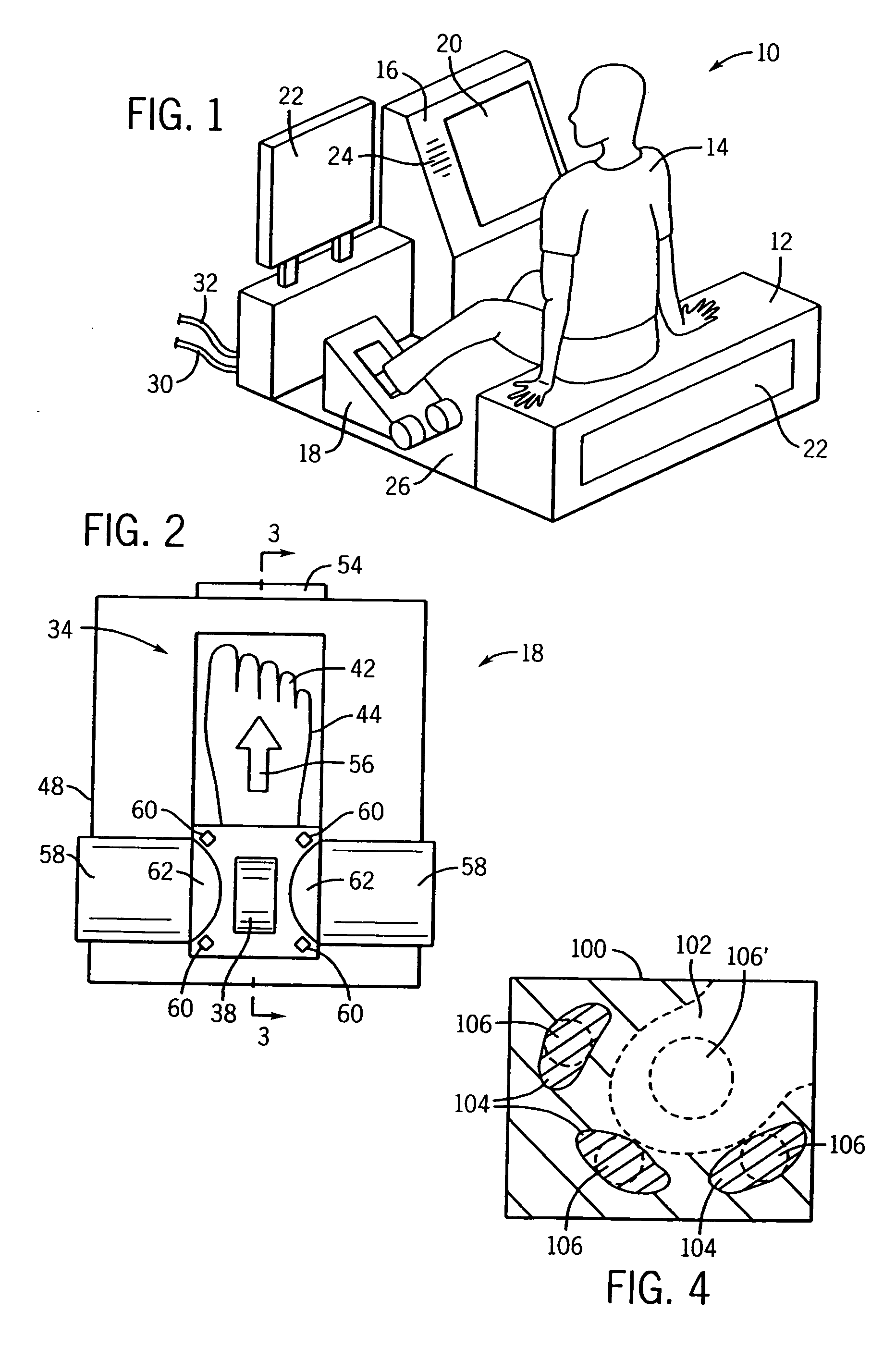
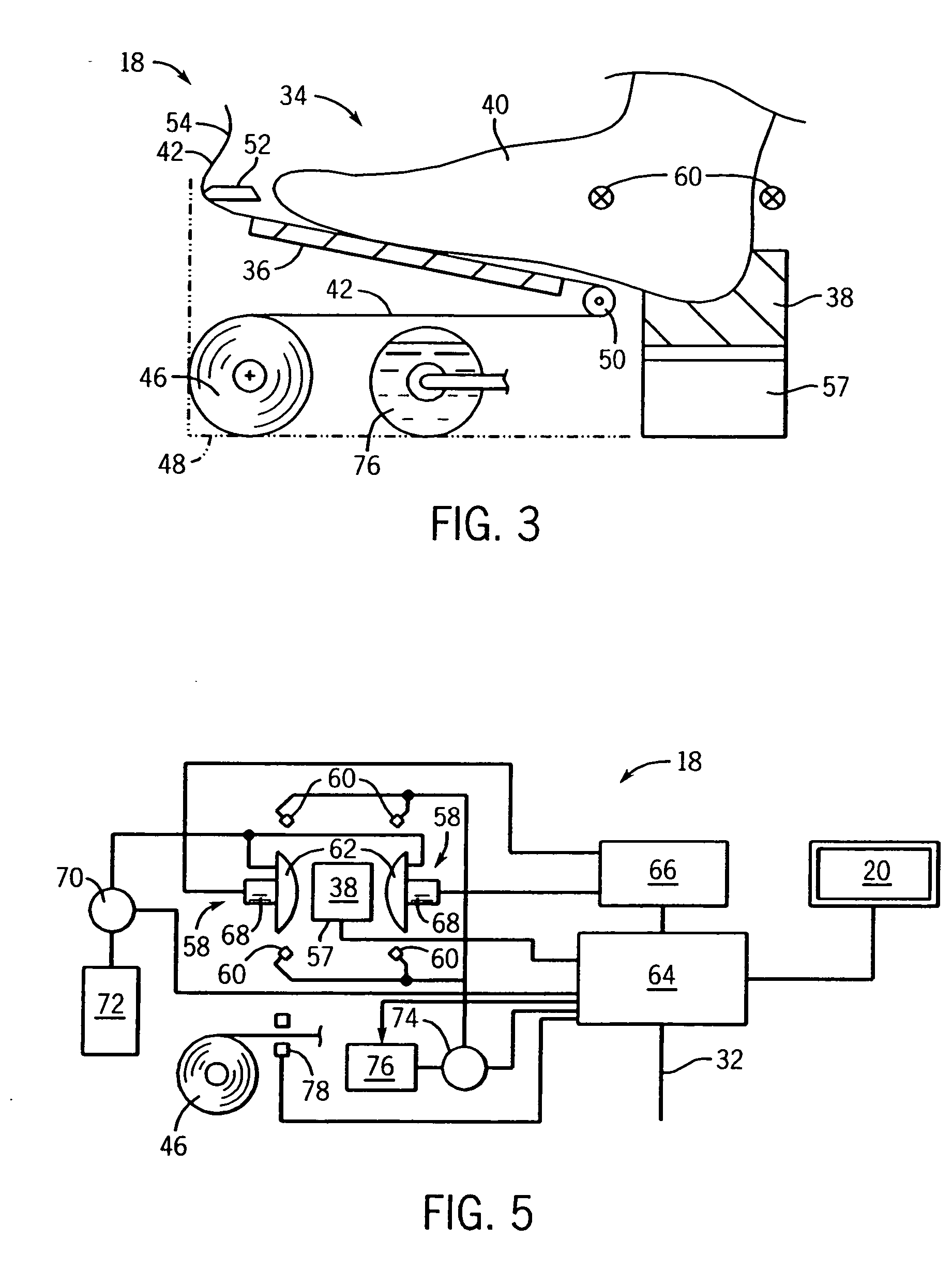
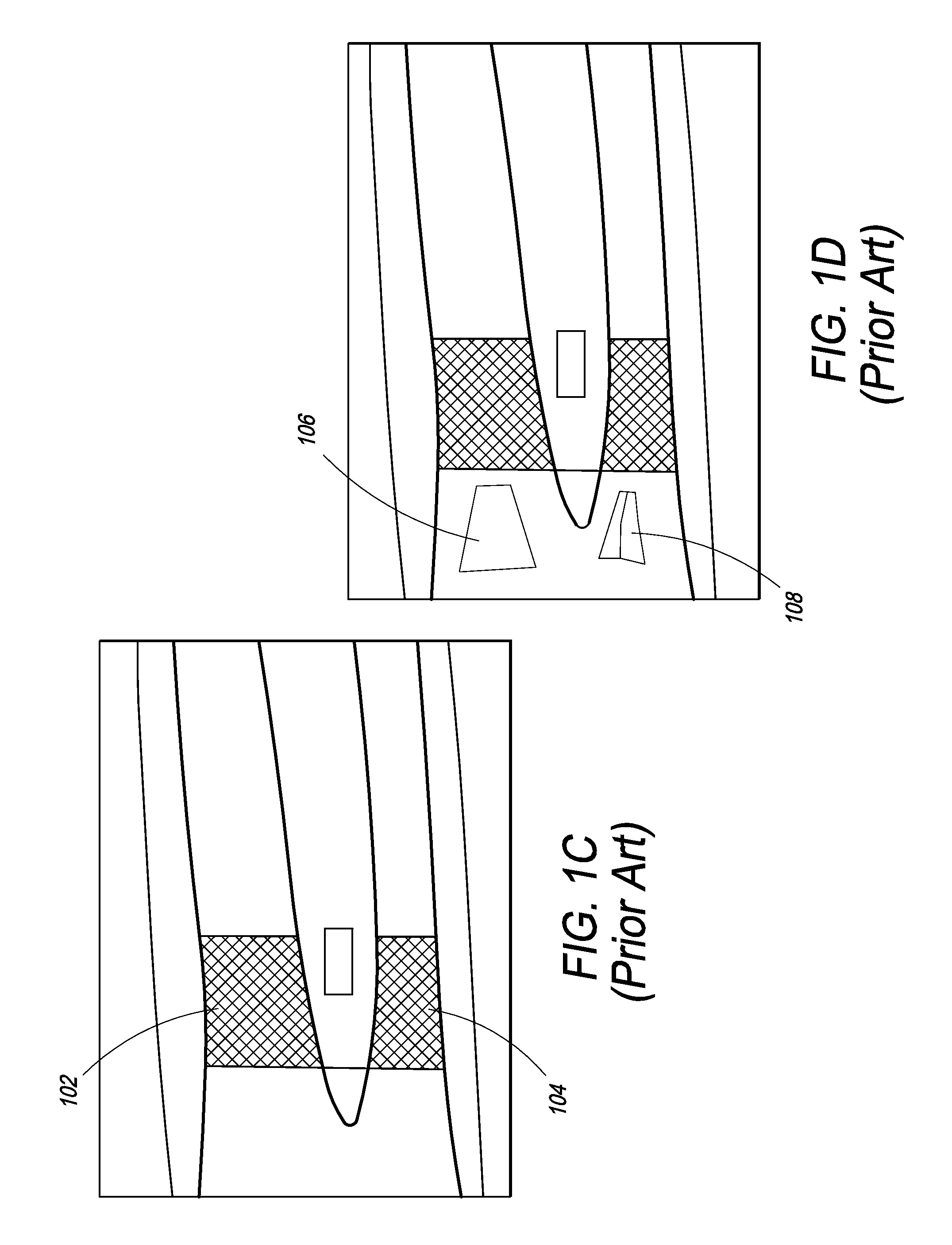
System and method for three-dimensional reconstruction of a tubular organ
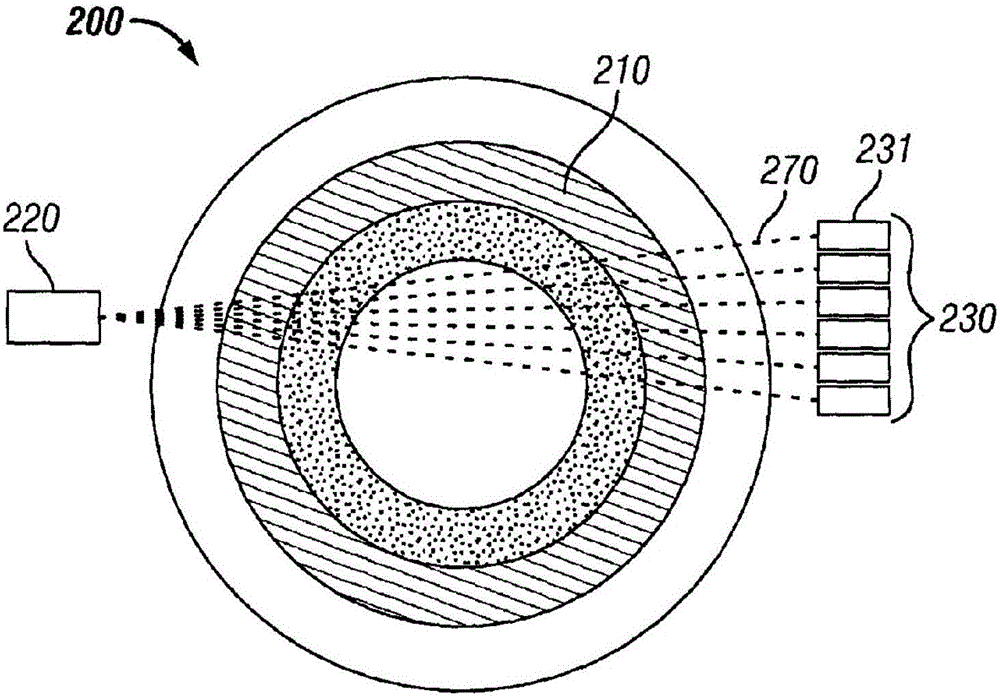
InactiveUS7742629B2Easy to useEliminate potential incorrect distortionImage analysisOptical rangefindersOptical densityDensitometry
Embodiments of the present invention include methods and systems for three-dimensional reconstruction of a tubular organ (for example, coronary artery) using a plurality of two-dimensional images. Some of the embodiments may include displaying a first image of a vascular network, receiving input for identifying on the first image a vessel of interest, tracing the edges of the vessel of interest including eliminating false edges of objects visually adjacent to the vessel of interest, determining substantially precise radius and densitometry values along the vessel, displaying at least a second image of the vascular network, receiving input for identifying on the second image the vessel of interest, tracing the edges of the vessel of interest in the second image, including eliminating false edges of objects visually adjacent to the vessel of interest, determining substantially precise radius and densitometry values along the vessel in the second image, determining a three dimensional reconstruction of the vessel of interest and determining fused area (cross-section) measurements along the vessel and computing and presenting quantitative measurements, including, but not limited to, true length, percent narrowing (diameter and area), and the like.
Owner:PAIEON INC
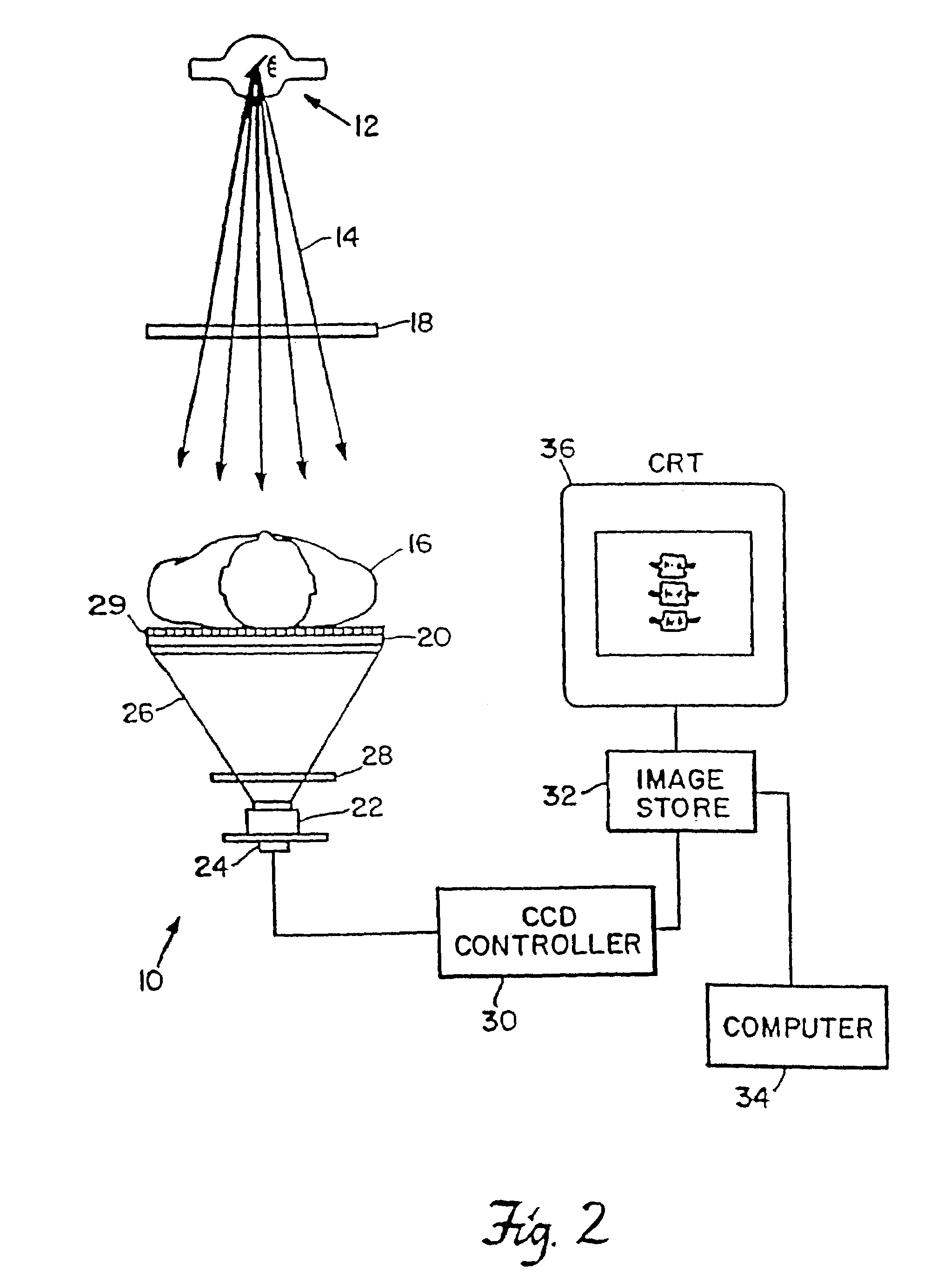
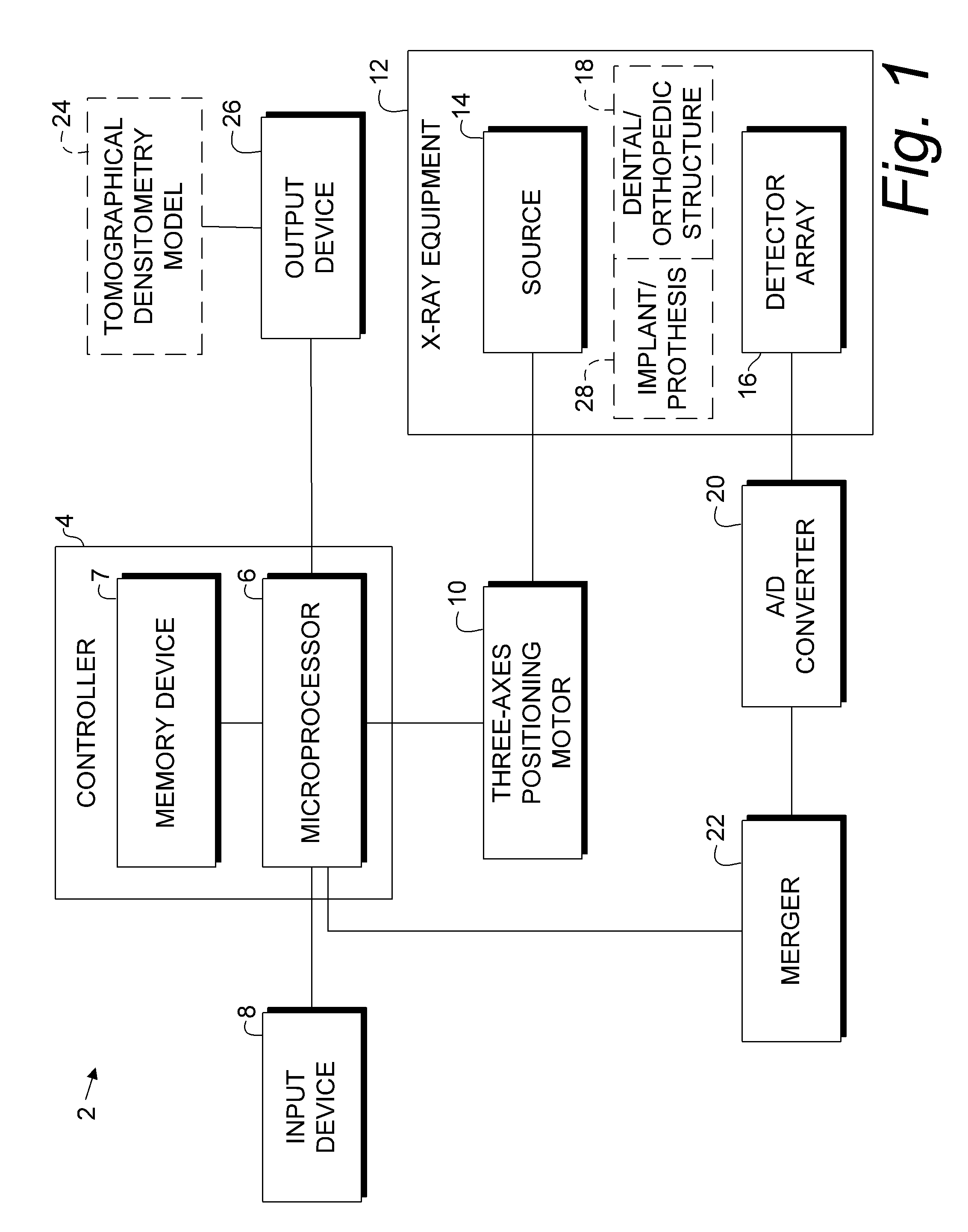
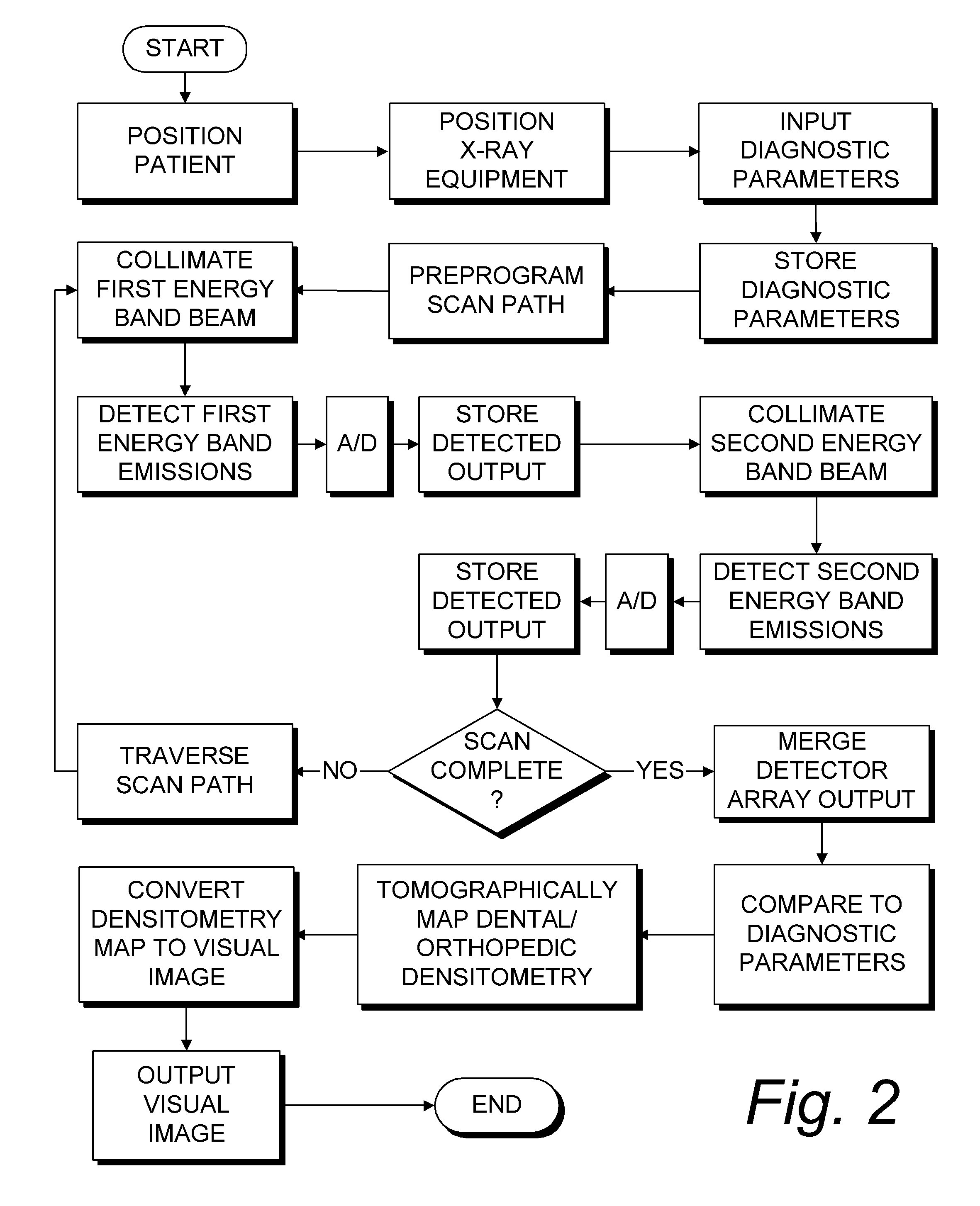
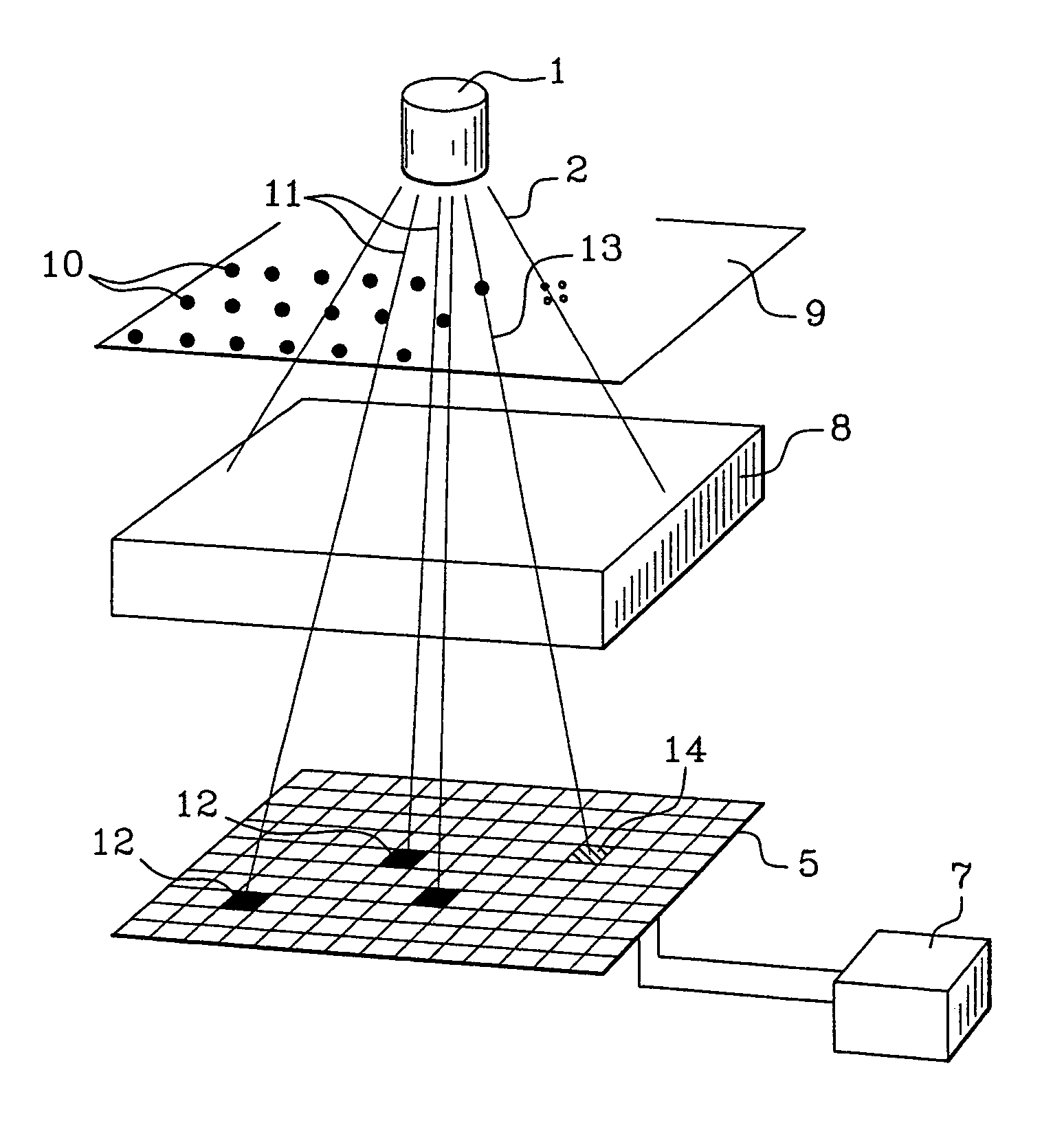
System for quantitative radiographic imaging
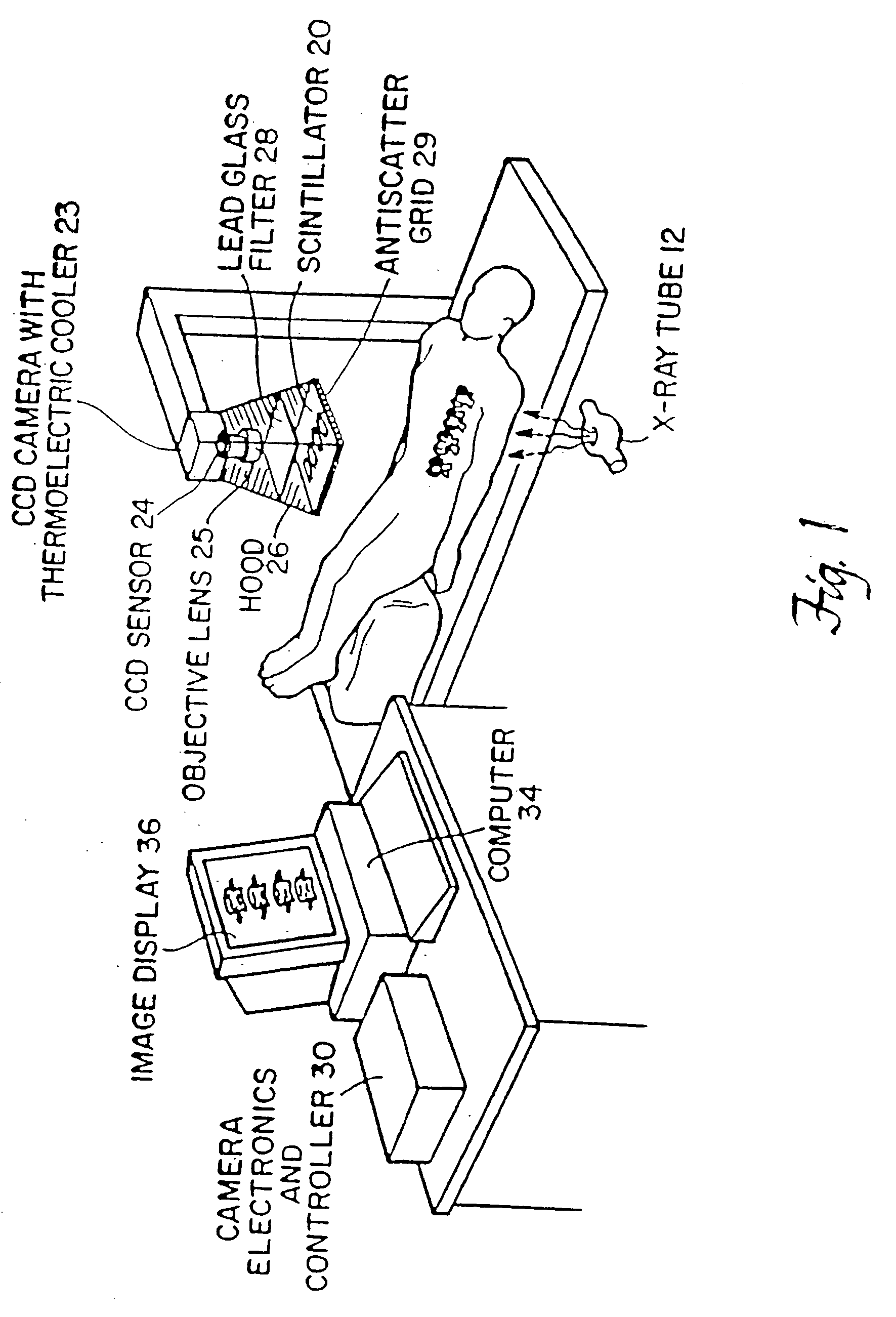
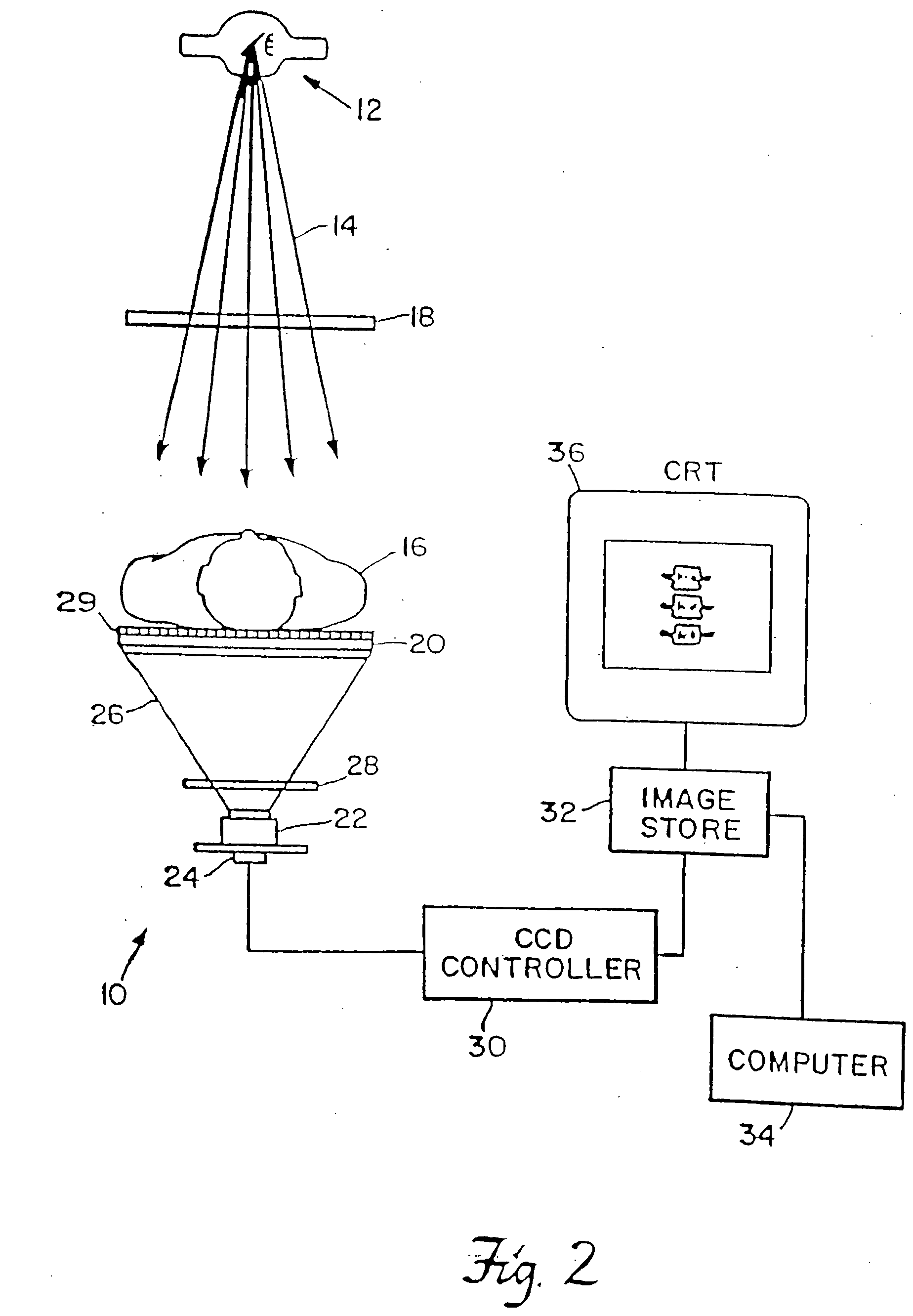
InactiveUS7330531B1Reduce and eliminate scattered radiationSuitable for applicationTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationX-rayDual energy
A system for spectroscopic imaging of bodily tissue in which a scintillation screen and a charged coupled device (CCD) are used to accurately image selected tissue. Applications include the imaging of radionuclide distributions within the human body or the use of a dual energy source to provide a dual photon bone densitometry apparatus that uses stationary or scanning acquisition techniques. An x-ray source generates x-rays which pass through a region of a subject's body, forming an x-ray image which reaches the scintillation screen. The scintillation screen reradiates a spatial intensity pattern corresponding to the image, the pattern being detected by a CCD sensor. The image is digitized by the sensor and processed by a controller before being stored as an electronic image. A dual energy x-ray source that delivers two different energy levels provides quantitative information regarding the object being imaged using dual photon absorptiometry techniques. Dual scintillation screens can be used to simultaneously generate images of low-energy and high-energy x-ray patterns. Each image is directed onto an associated respective CCD or amorphous silicon detector to generate individual electronic representations of the separate images.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS MEDICAL CENT
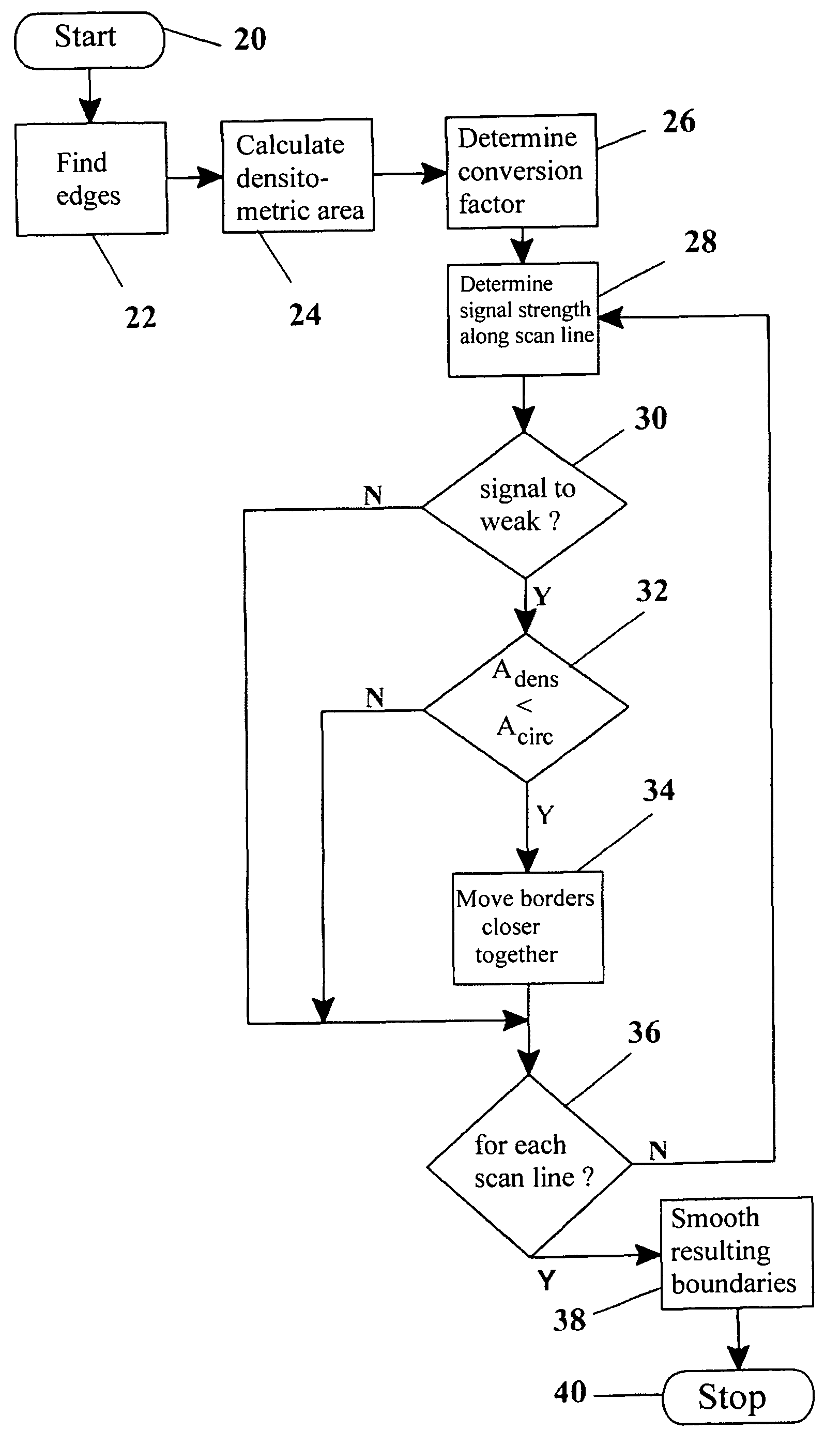
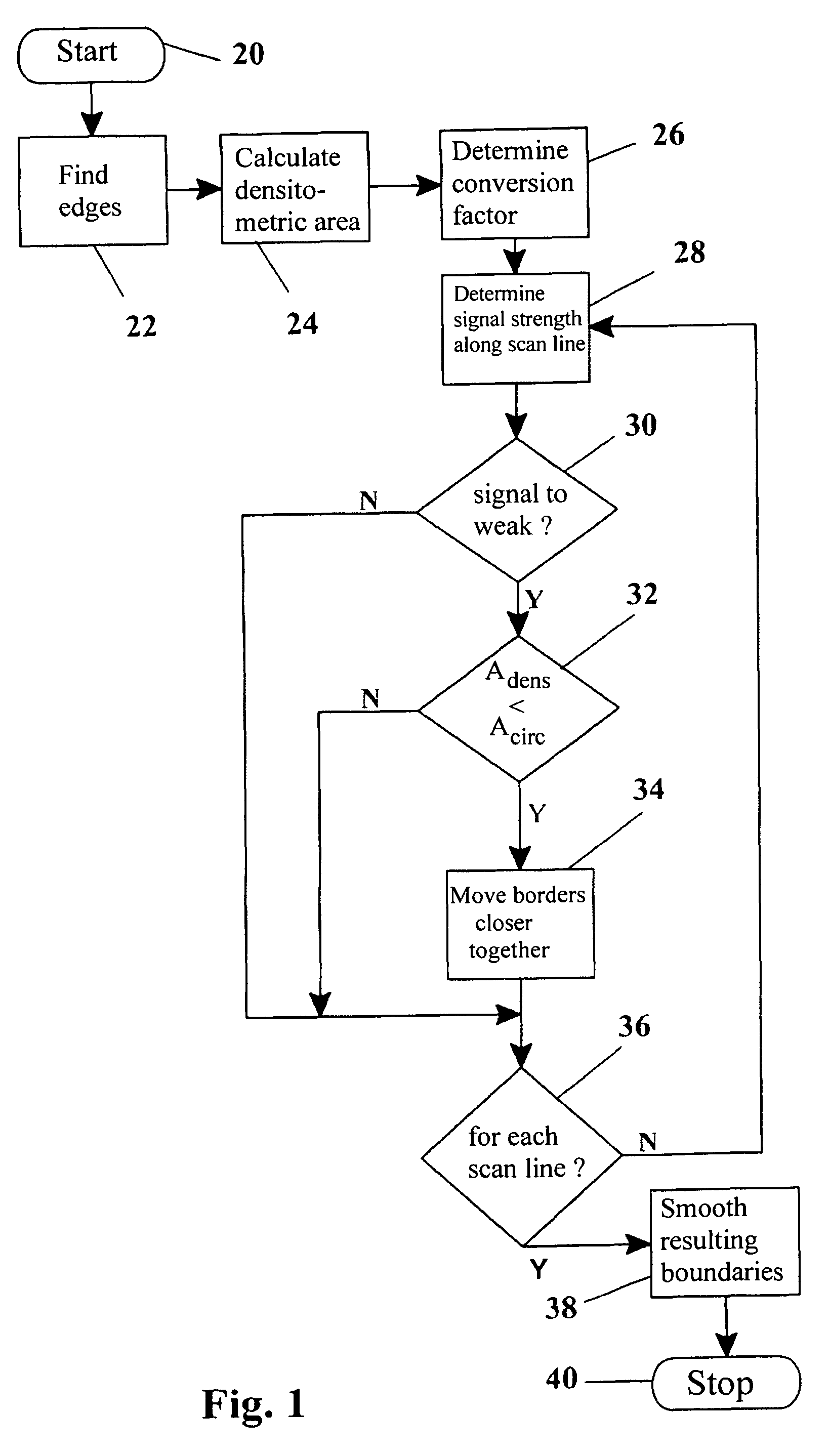
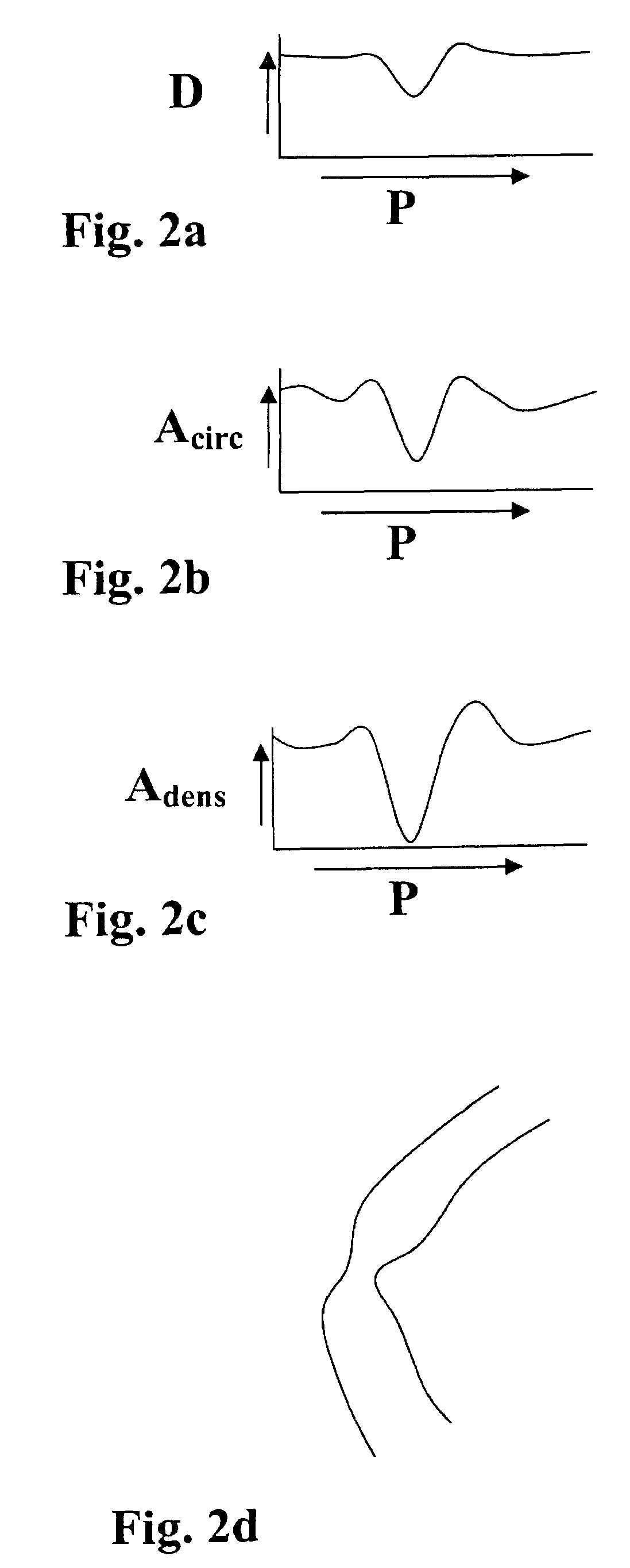
Method, apparatus and computer program for contour detection of vessels using x-ray densitometry
ActiveUS7970187B2Simple processRobust resultImage enhancementImage analysisRadiologyDifferential absorption
A method has been described for deriving contour data in X-Ray images for vessels with differential absorption through applying a contour-finding algorithm on a shadow image and finding the vessel borders through segmentation based on image intensities. In particular, the method uses the following steps: finding a densitometric area of an above mentioned vessel, and displacing one or both of the borders inward until the densitometric measurement result between the borders after such displacing will start to change significantly. Furthermore, a specific procedure is introduced to automatically determine the conversion factor to equate the densitometrically based diameter to the contour based diameter of the vessel and to discriminate bifurcating or parallel vessels.
Owner:PIE MEDICAL IMAGING
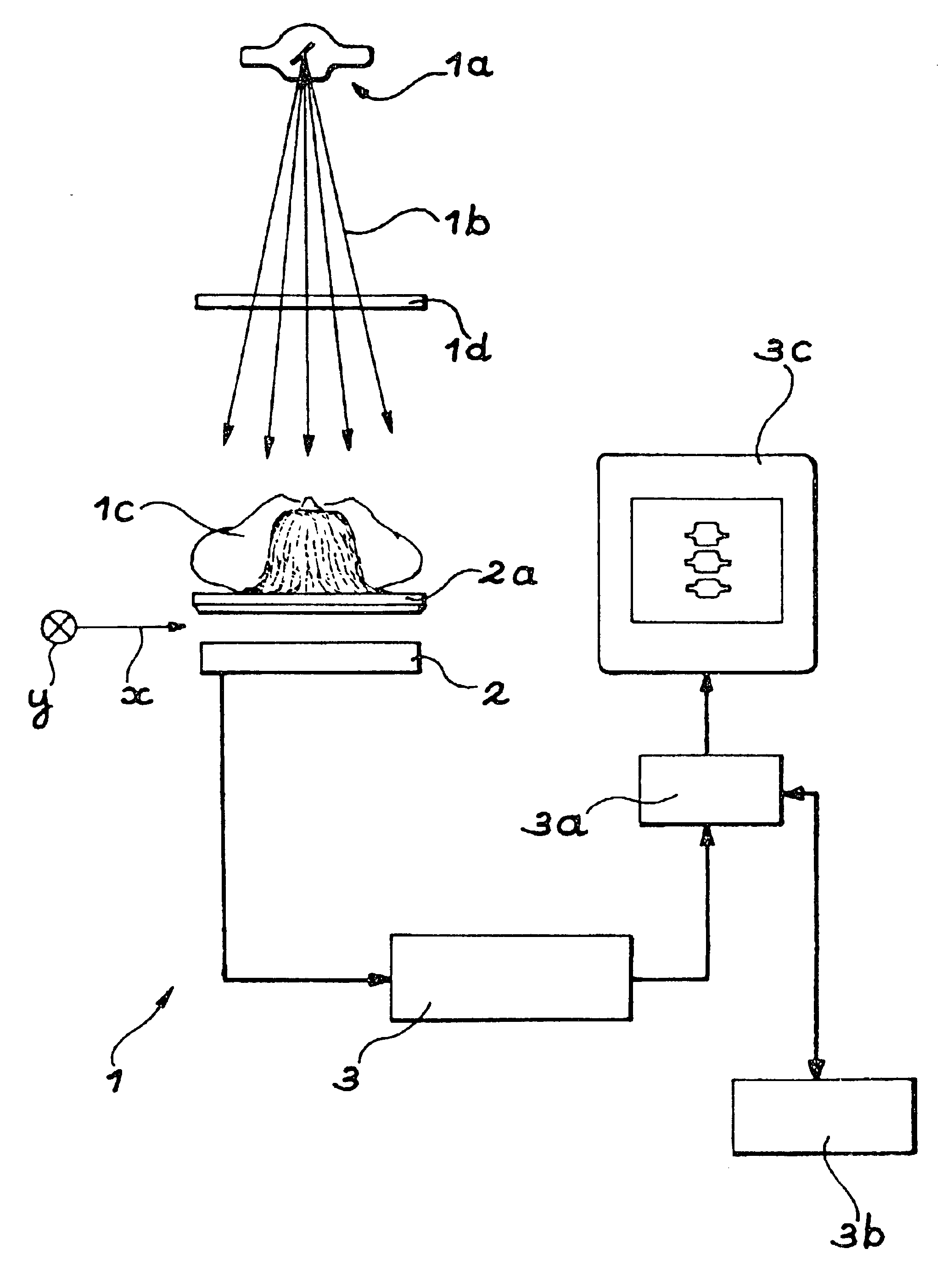
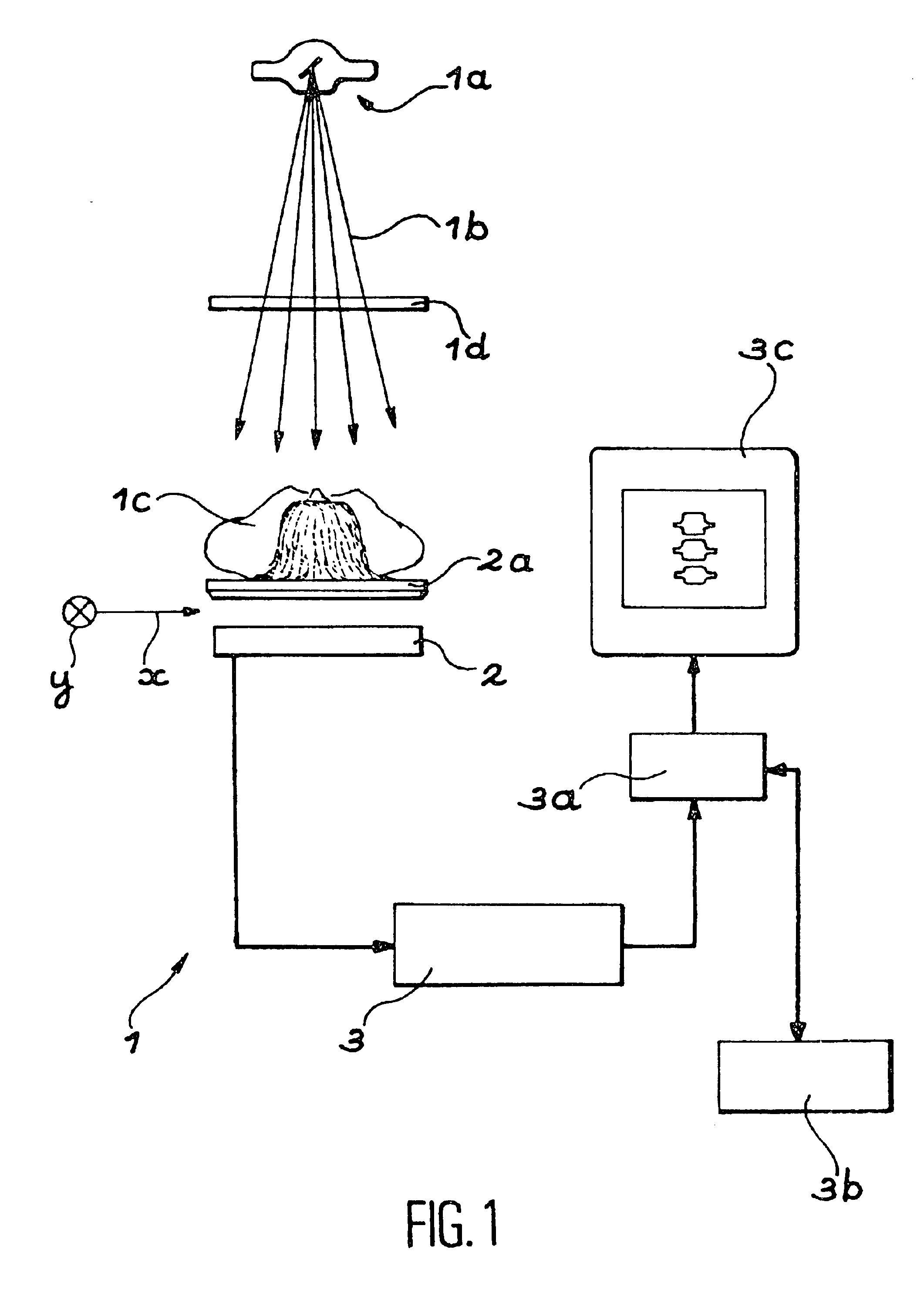
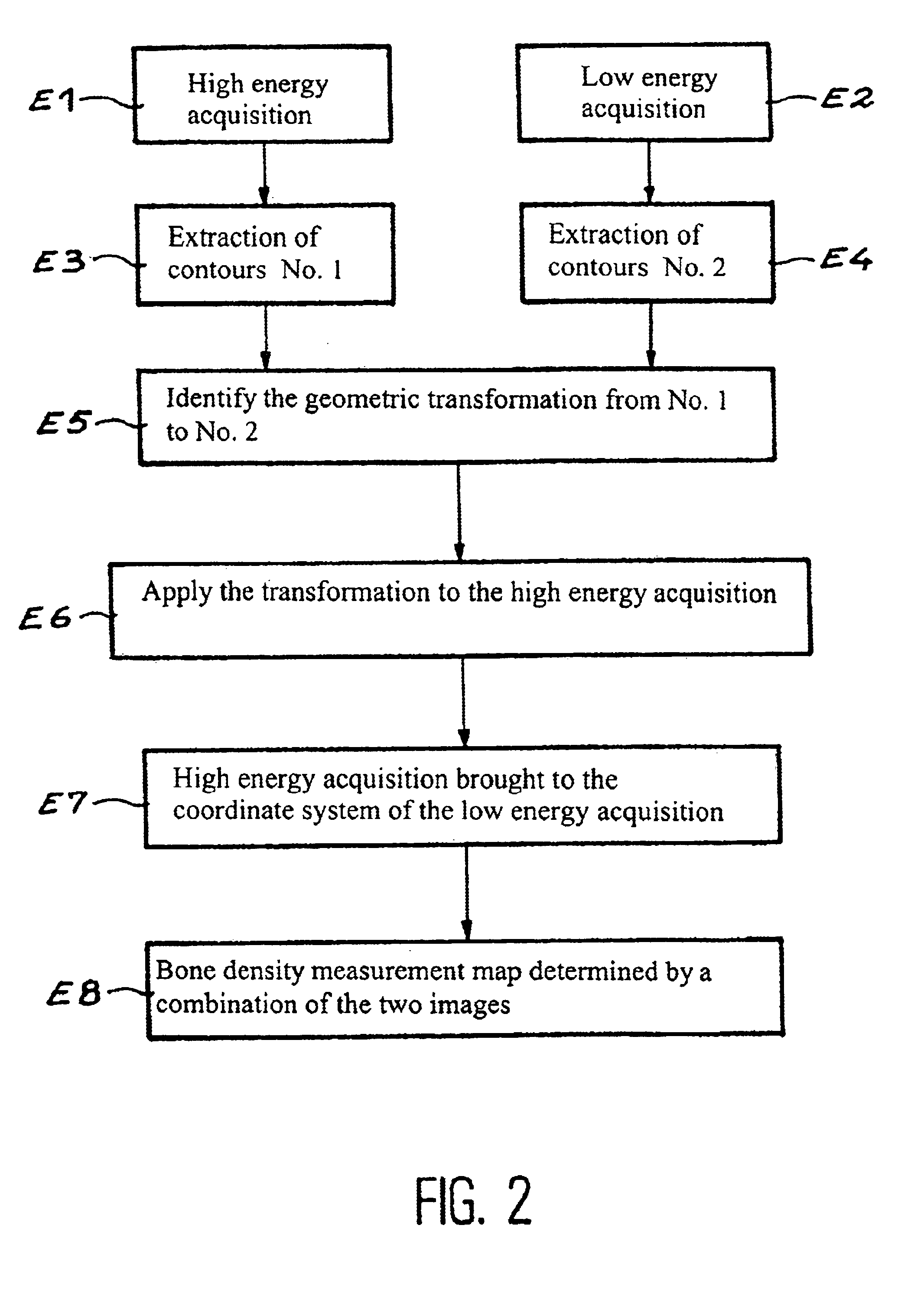
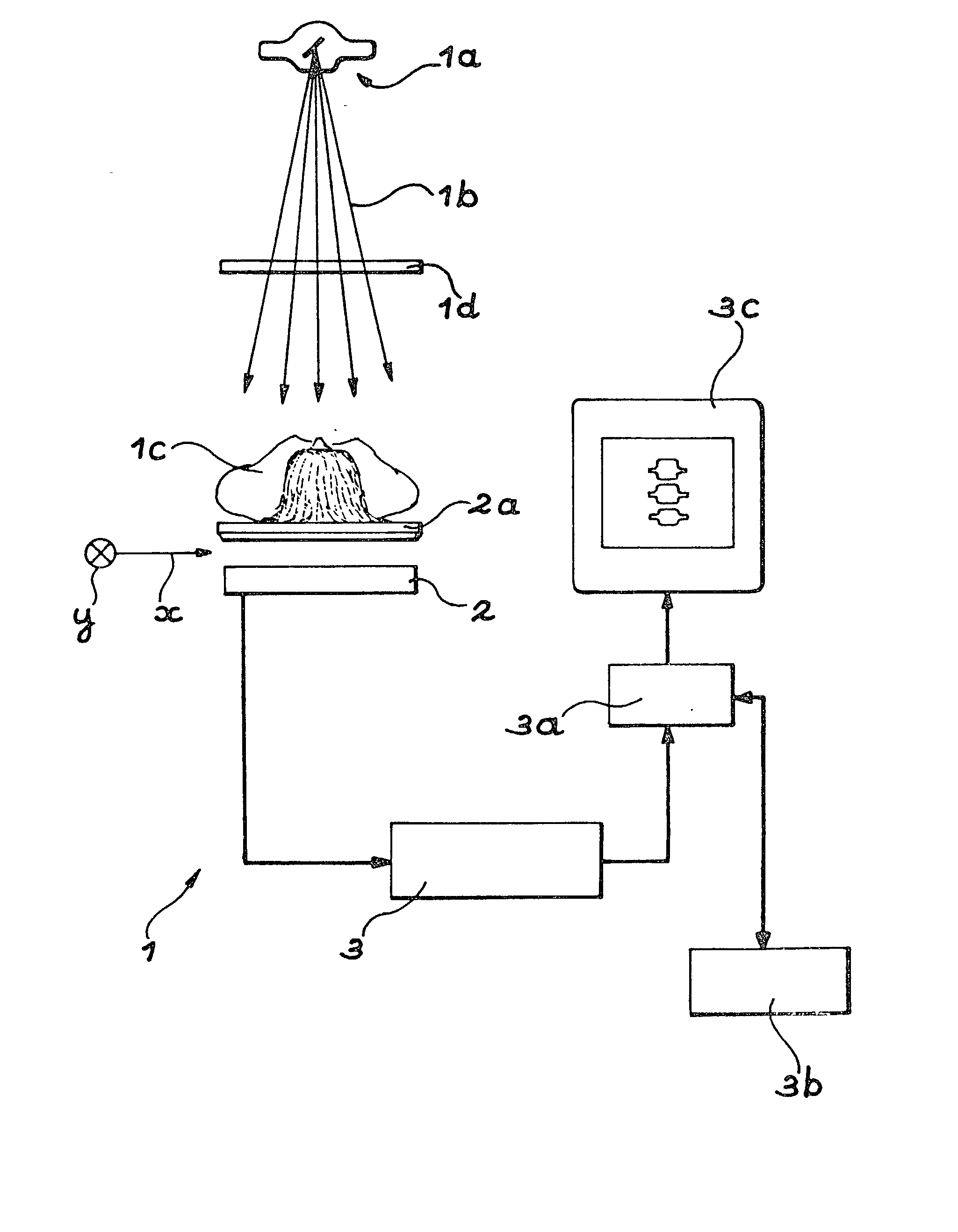
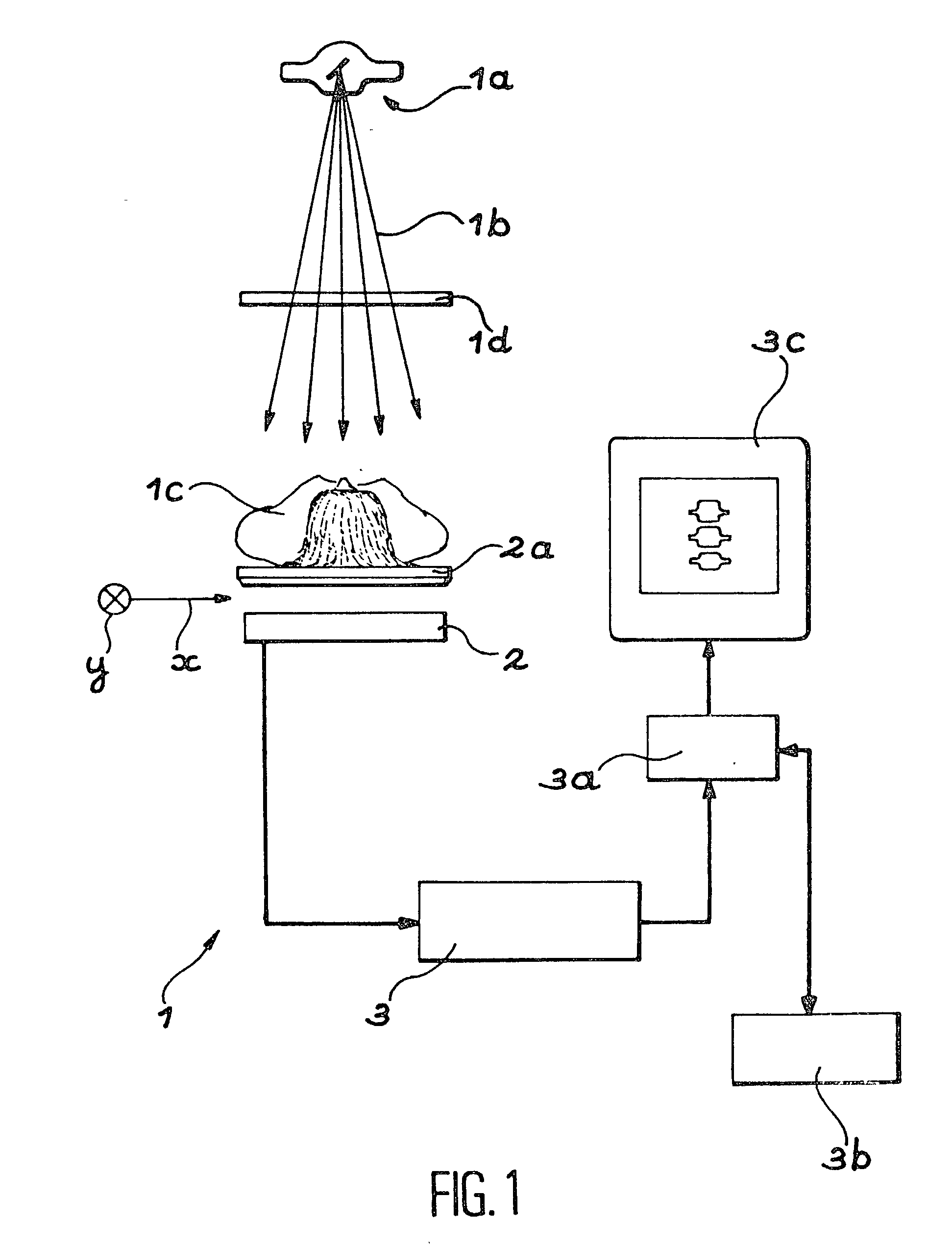
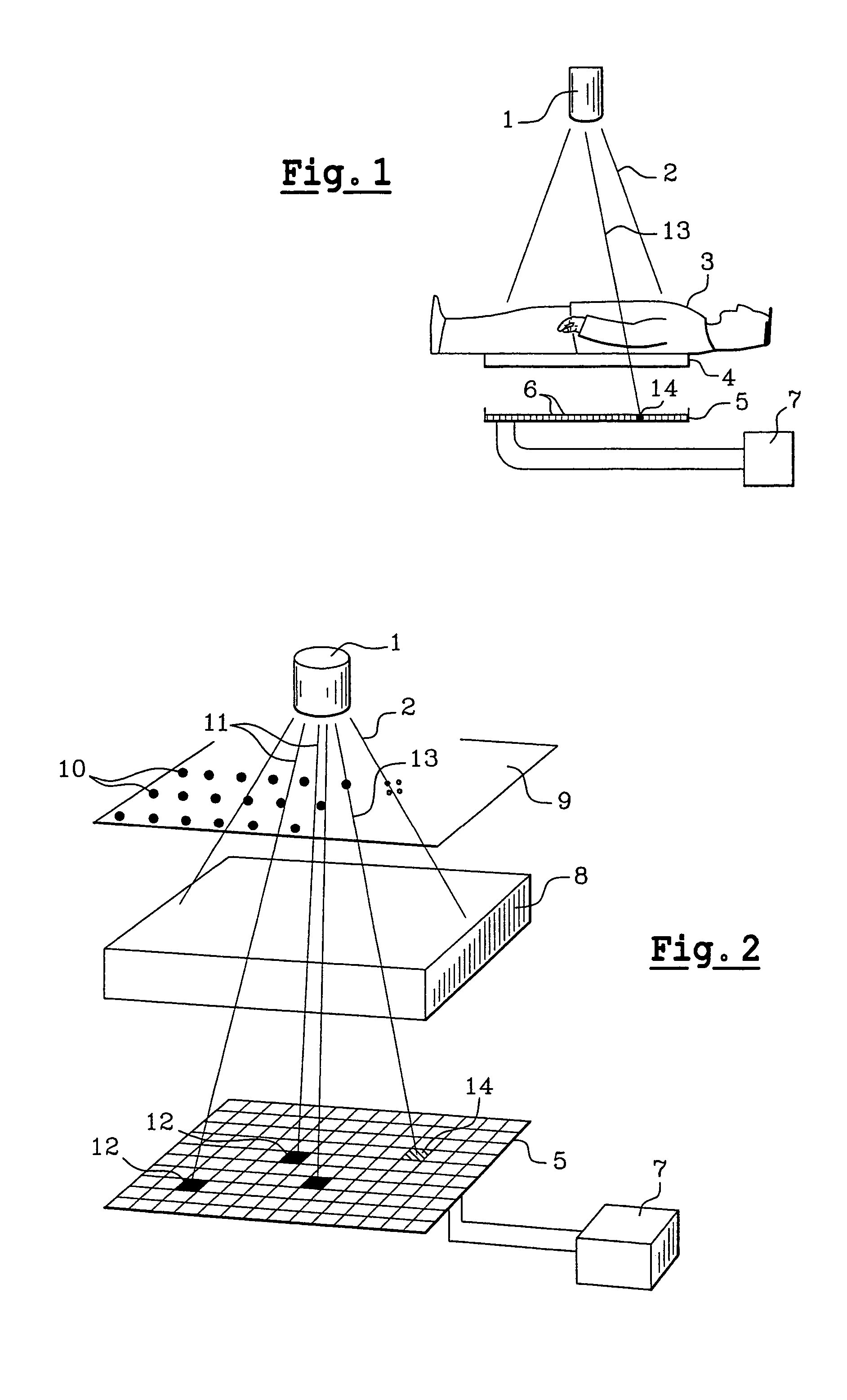
Method for using a bone densitometry system, with dual-energy x-radiation
InactiveUS6807249B2Help positioningOptimise centeringImage data processing detailsUsing wave/particle radiation meansBone densityHigh energy
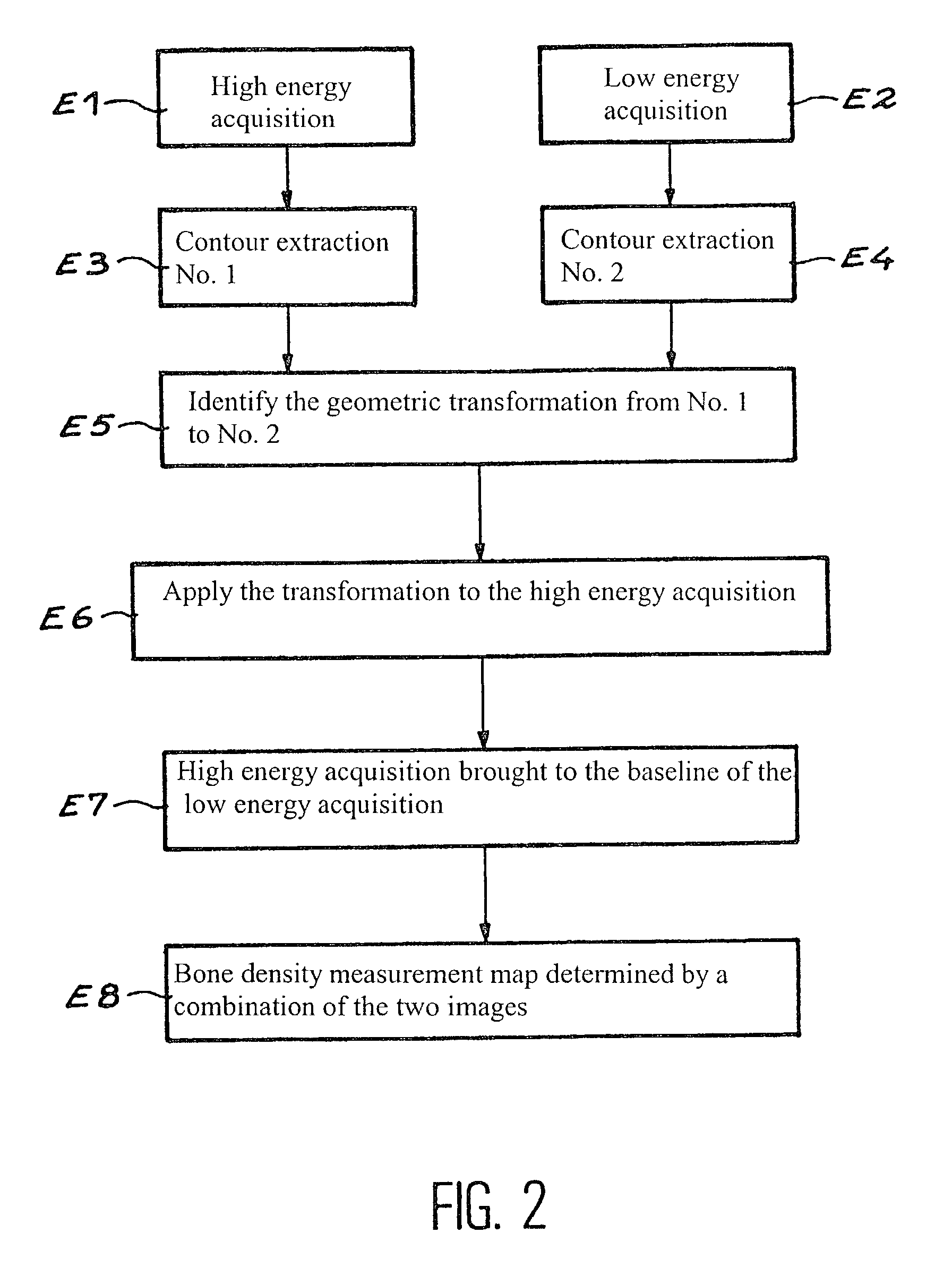
A process and osteodensitometry system using a dual-energy cone beam of X-rays is described. The system comprises an X-ray source capable of supplying a cone beam of X-rays with at least a first energy called the high energy and a second energy called the low energy, a two dimensional X-ray detector and electronic processor for processing images supplied by the detector. According to the process, a low energy image of a part of the anatomy of a patient, and a high energy image of the same part of the anatomy of a patient are acquired, and the images acquired at low energy and at high energy are matched before building up the map of bone densities of the part of the anatomy.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
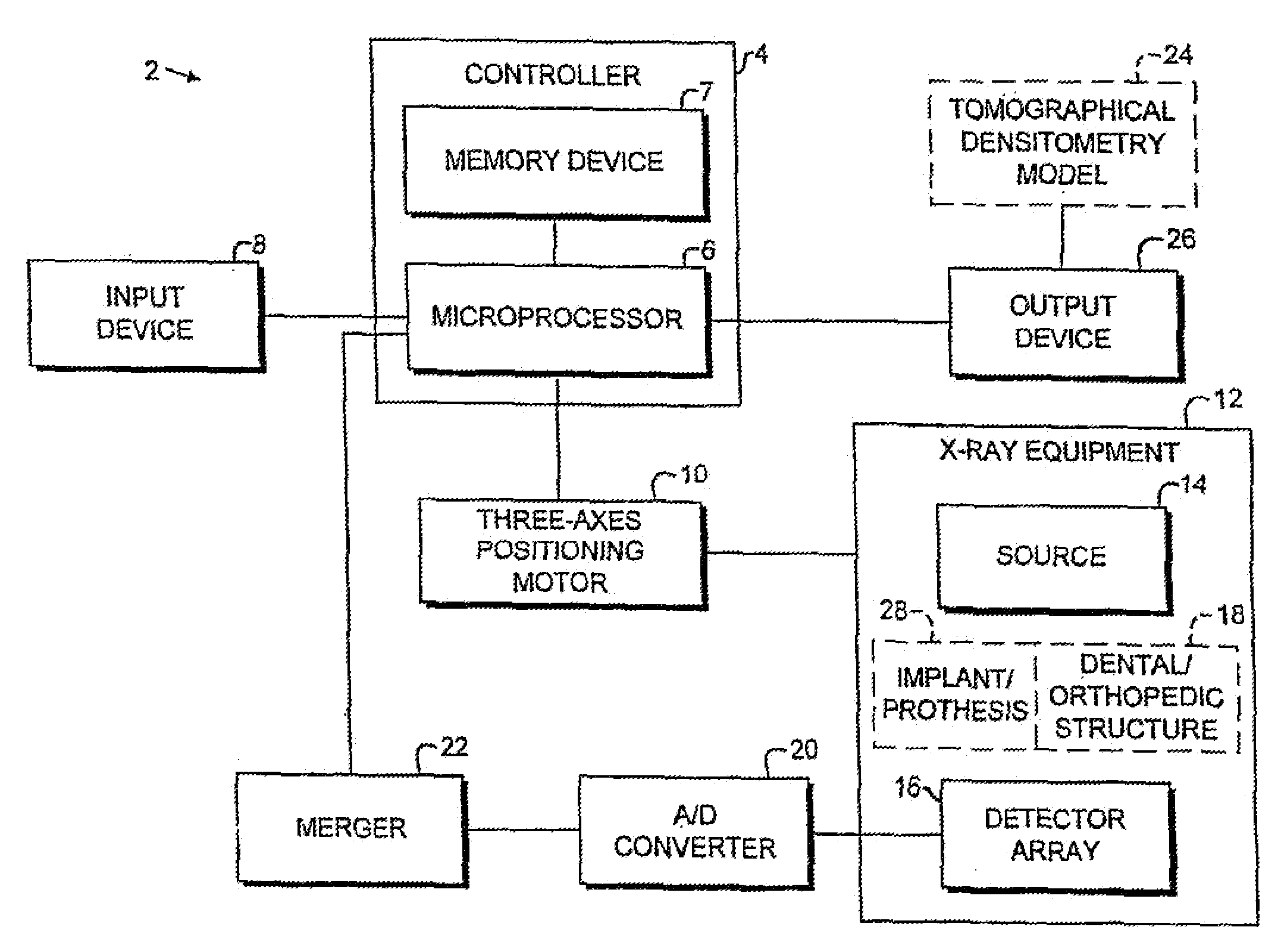
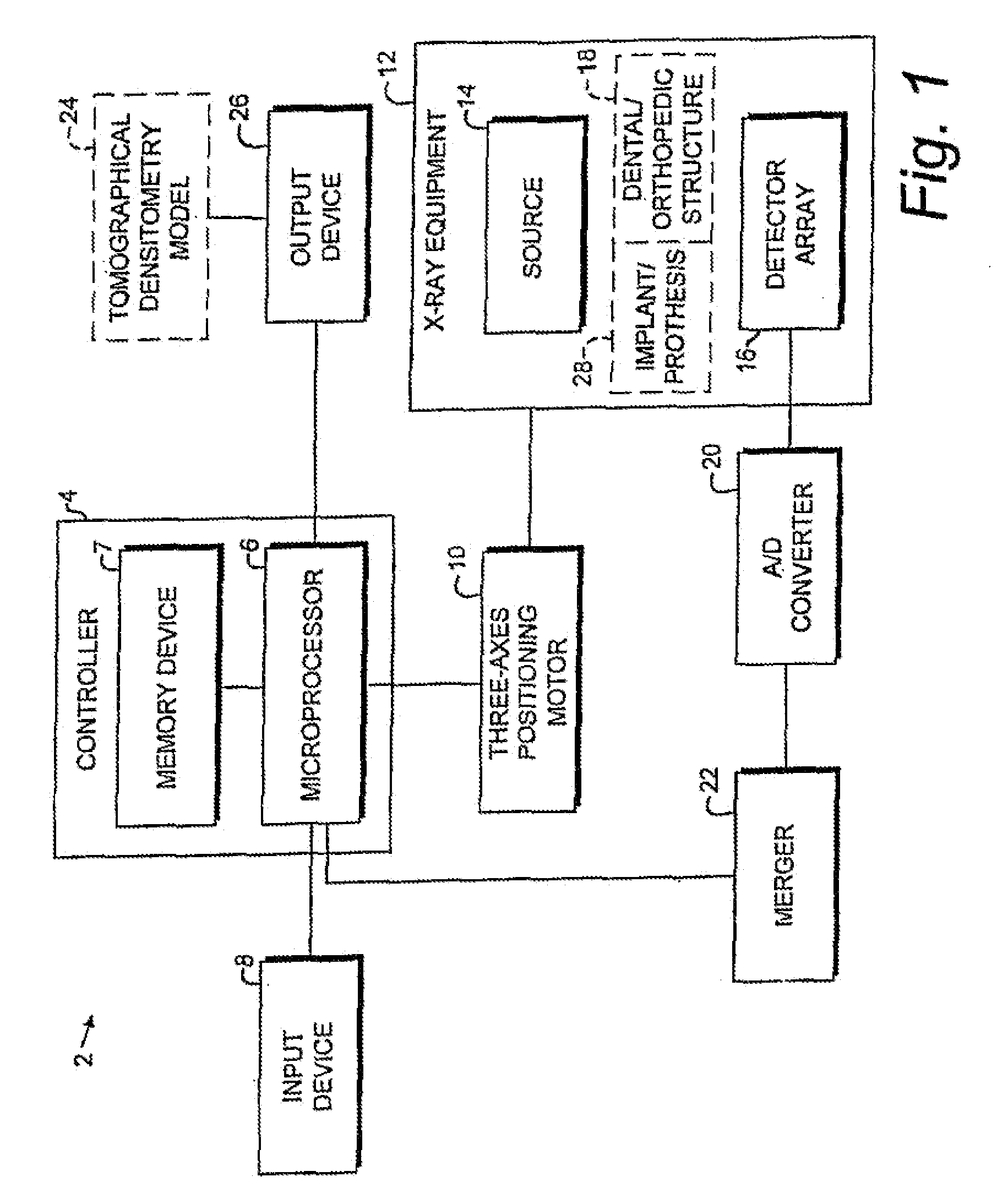
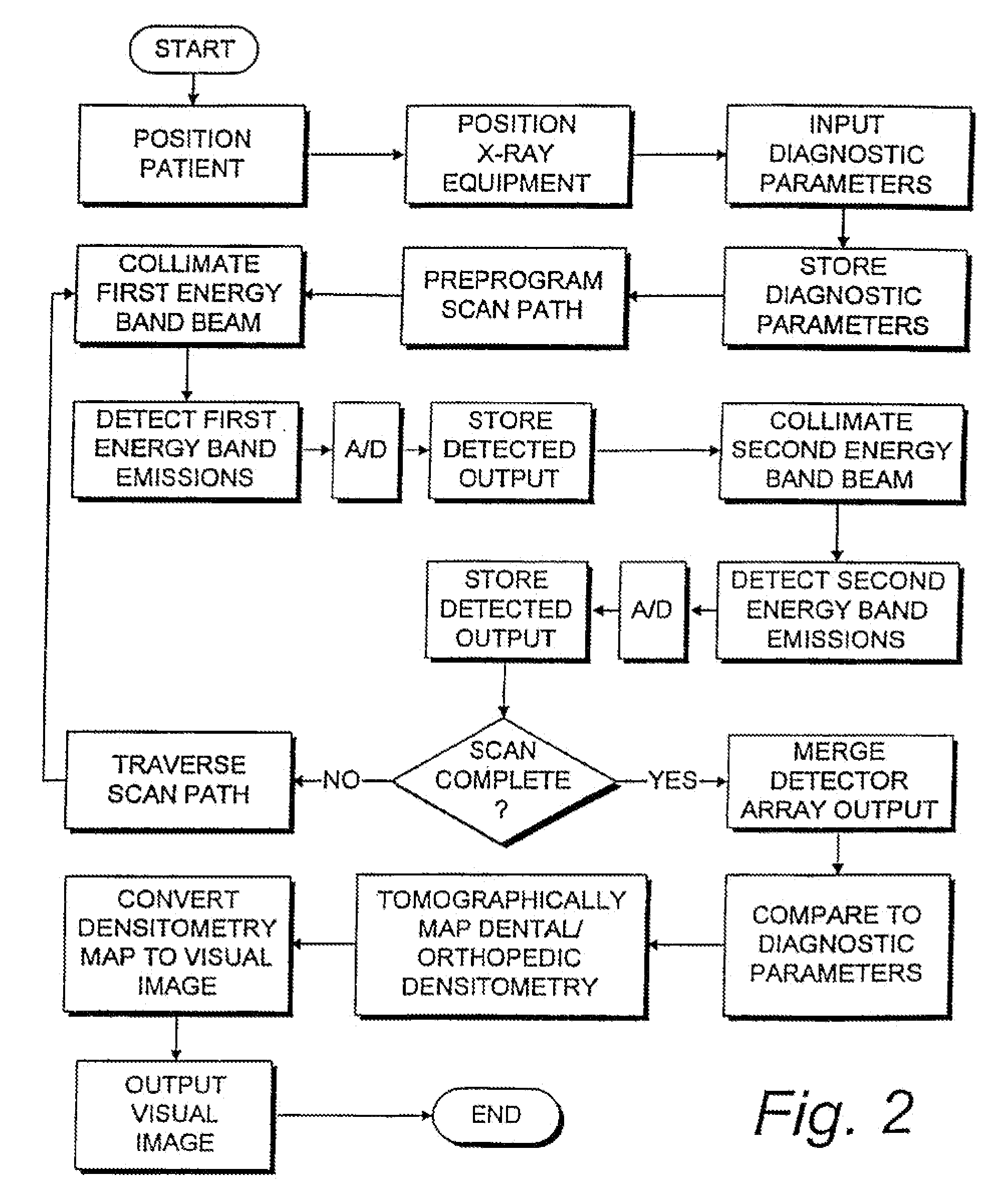
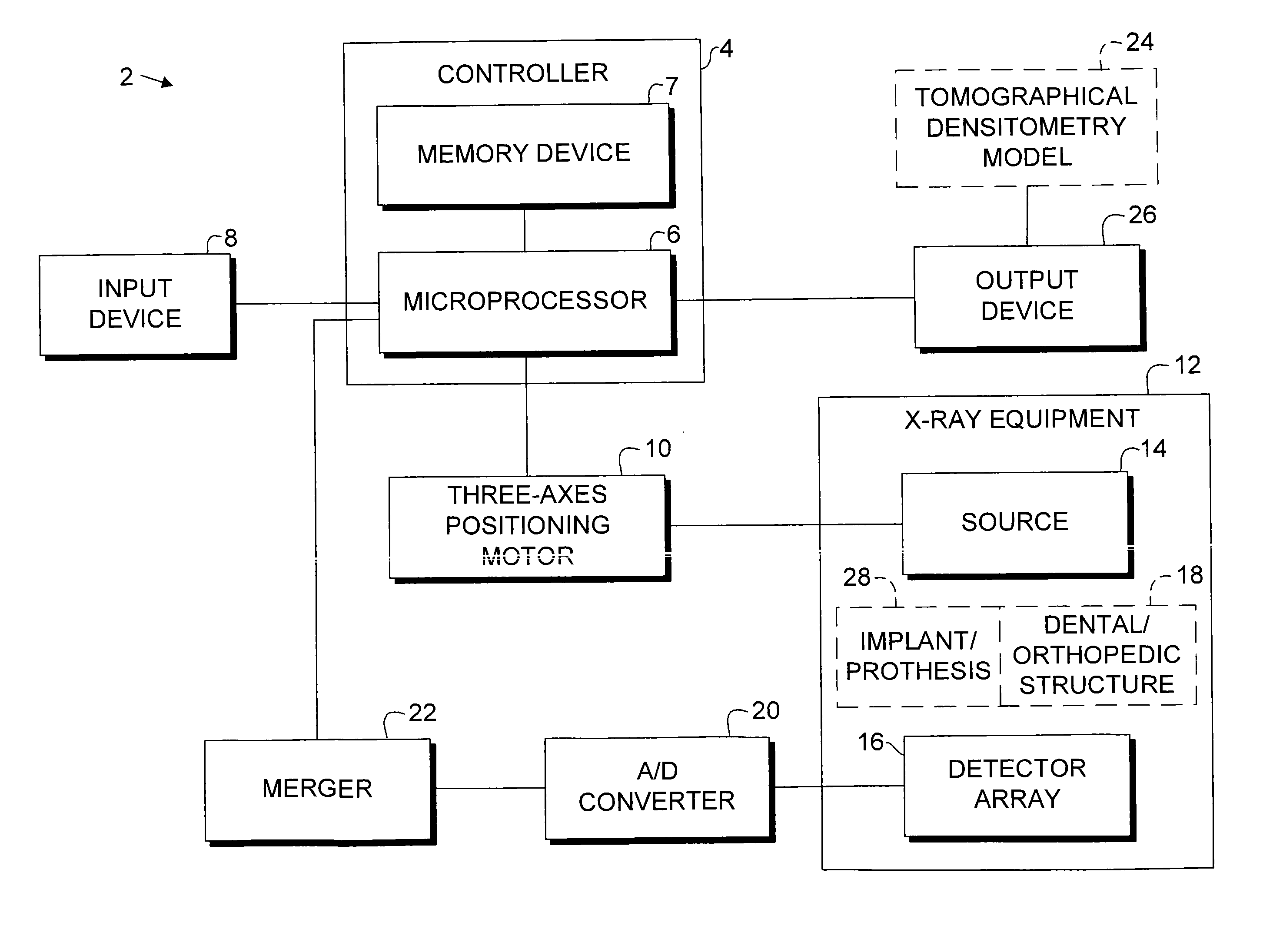
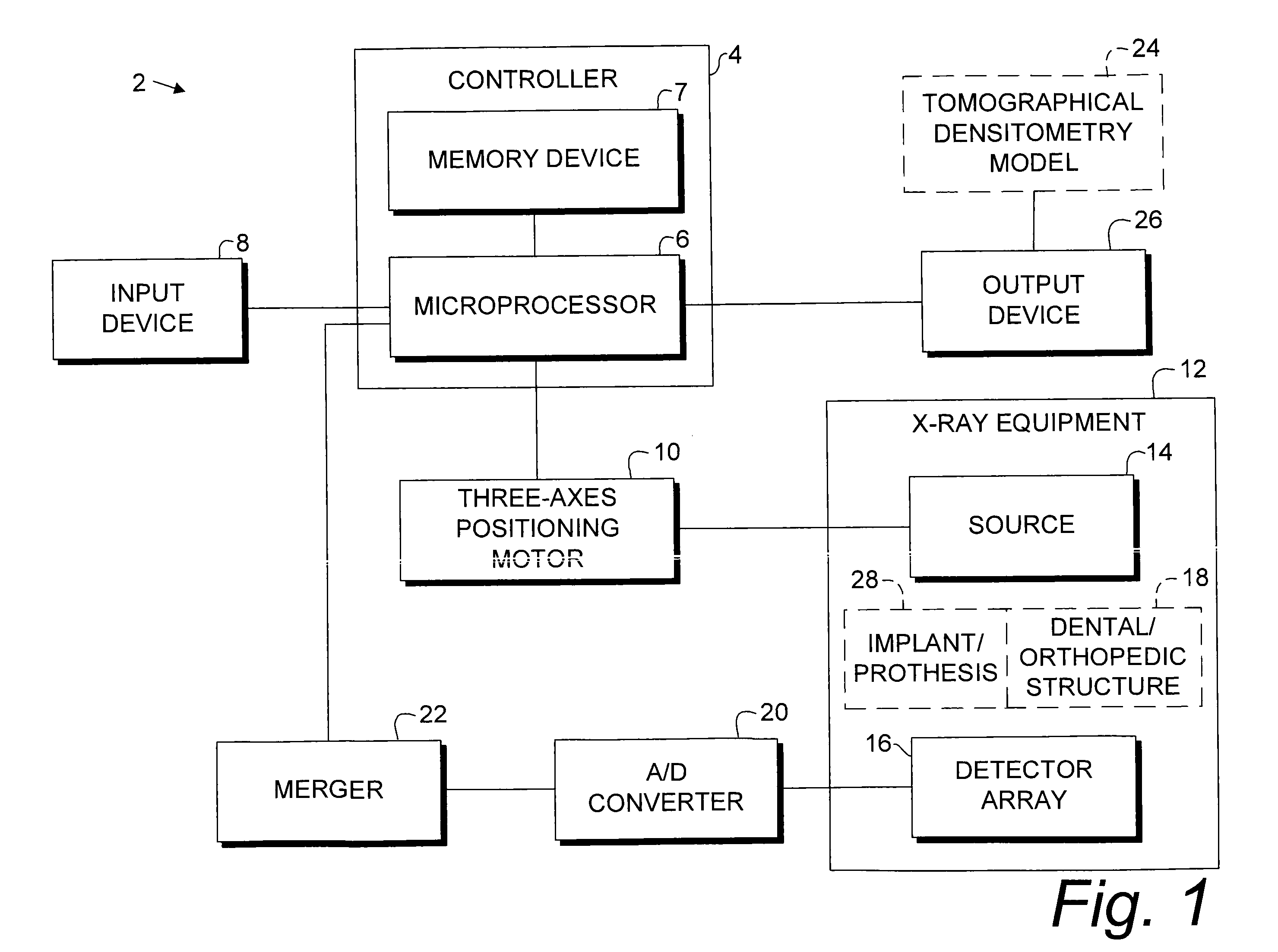
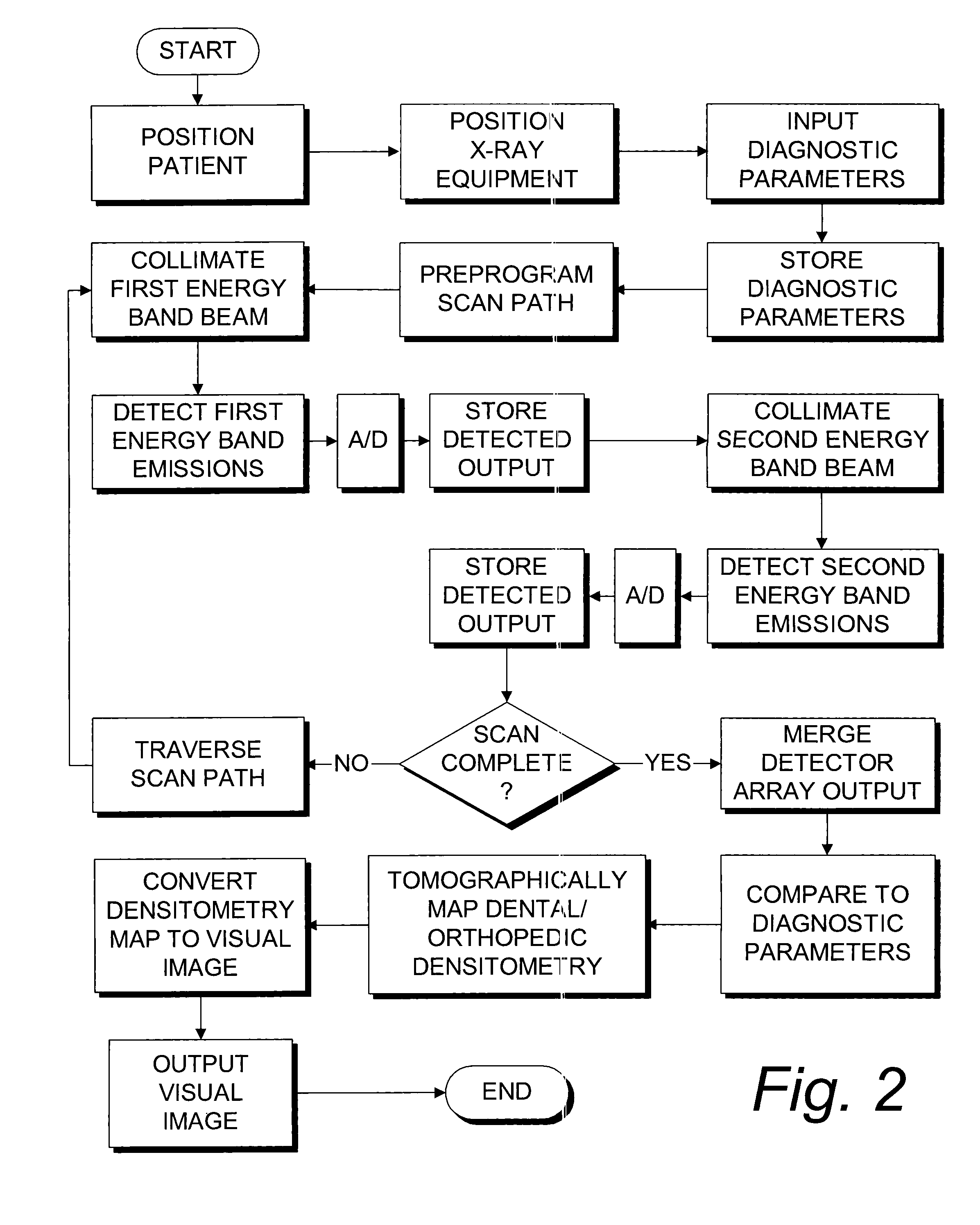
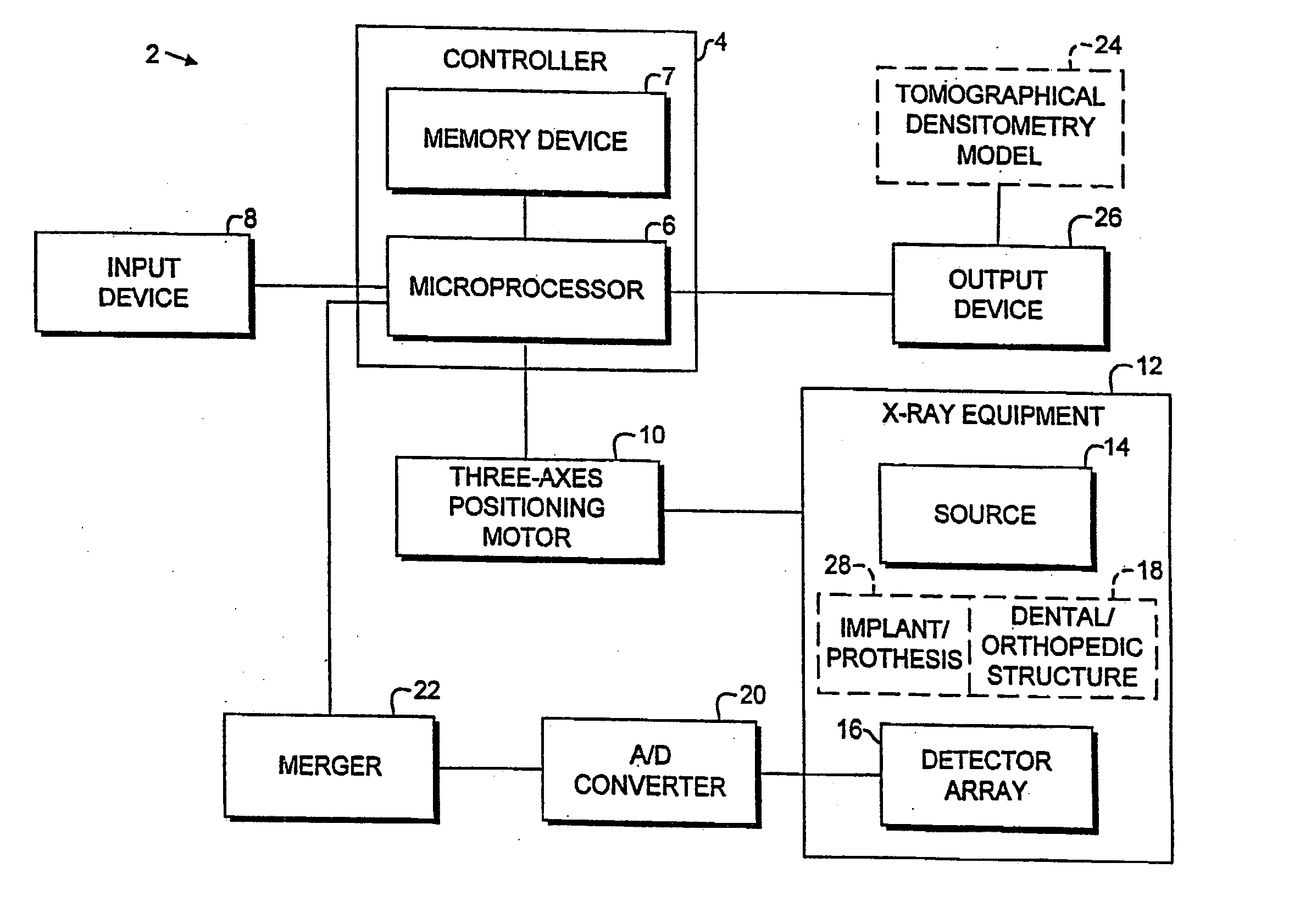
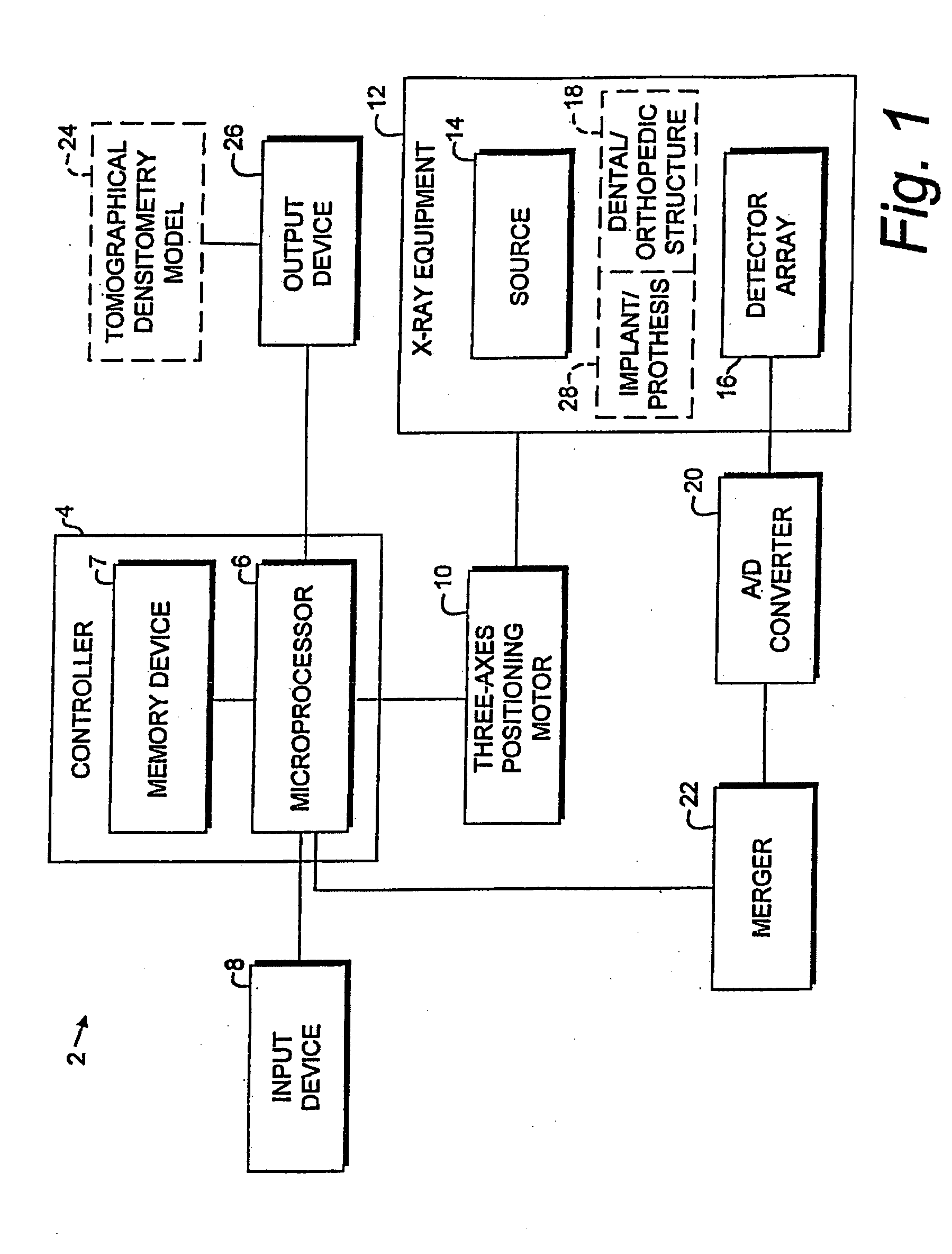
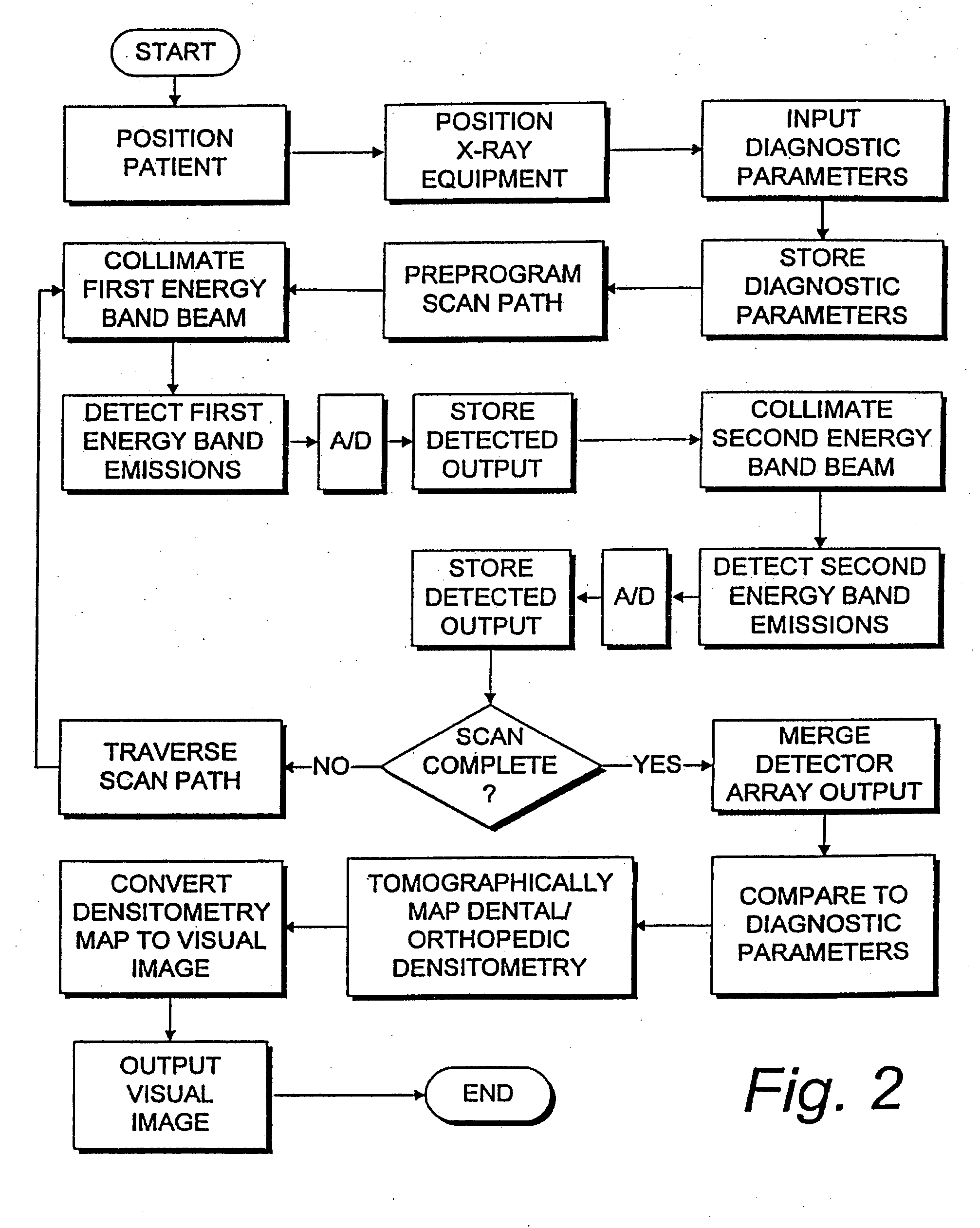
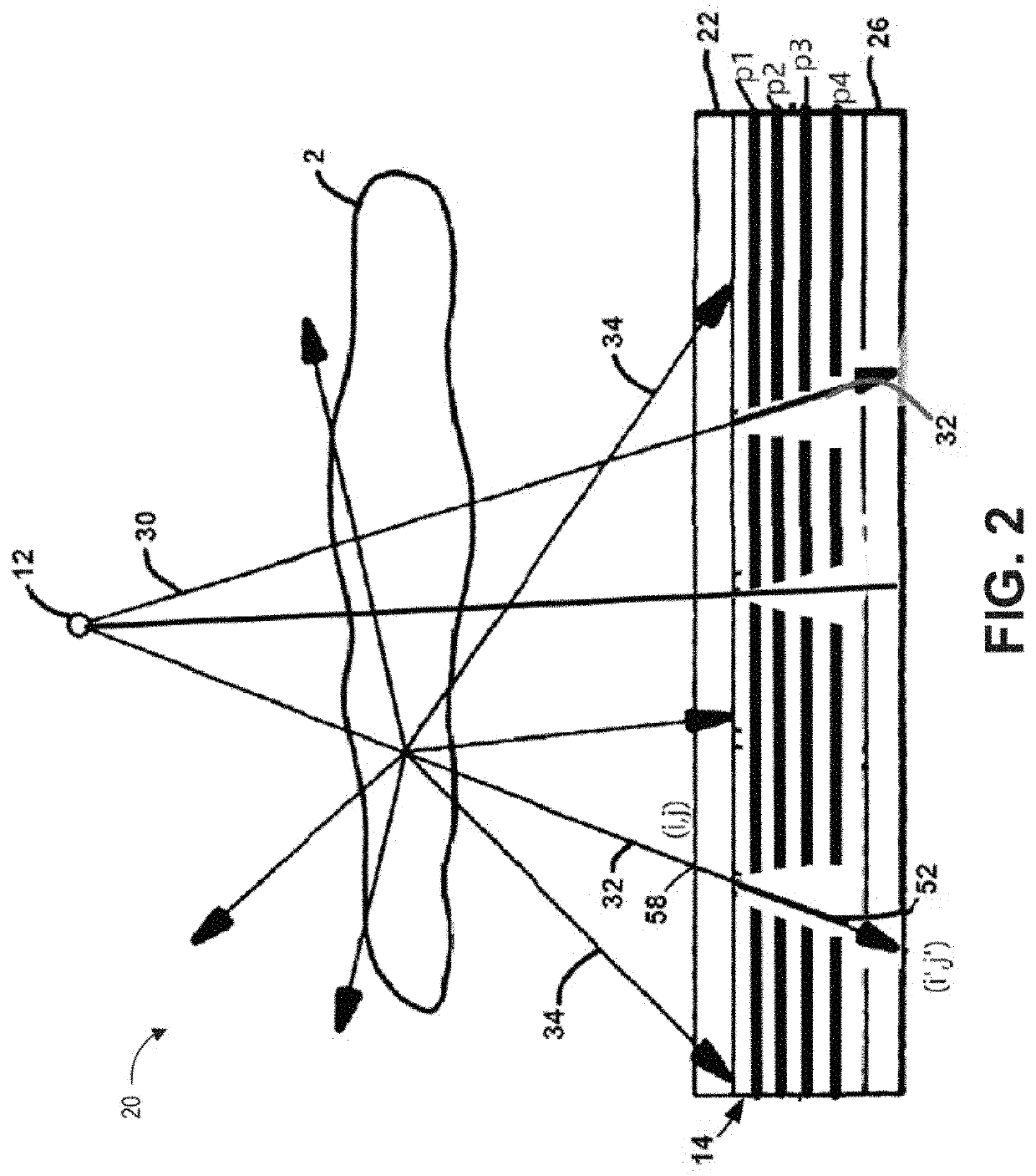
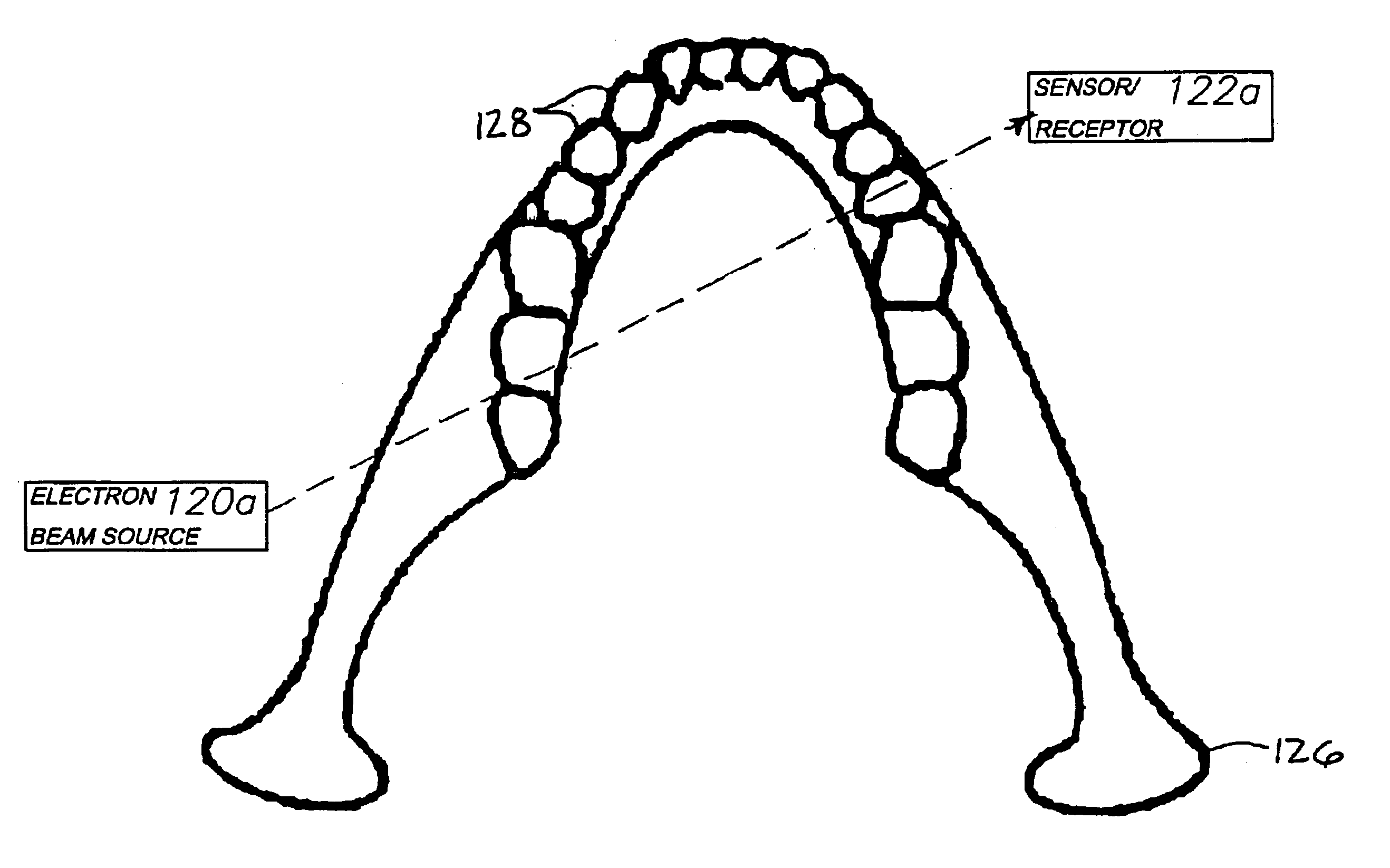
Digital modality modeling for medical and dental applications
InactiveUS20080051650A1X-ray/infra-red processesRadiation/particle handlingTomosynthesisDiagnostic Radiology Modality
A digital modality modeling system includes a computer with a digital memory adapted for storing patient densitometry information, an input and an output. An input subsystem includes a pair of source / receptor units mounted on a signal positioning subsystem, which is adapted for moving the source / receptor units through predetermined paths of movement, which can be circular or linear. The resulting tomographic data is synthesized to form any 3-D model or image, which is output for further analysis. A digital tomosynthesis method includes the steps of moving a pair of sensor / receptor units relative to a patient. The resulting signals output by the receptor are digitized and synthesized to form a 3-D image or model. Multiple depths of penetration and multiple widths can be captured from single acquisitions using digital tomosynthesis signal processing techniques.
Owner:OSSEO IMAGING
System and method for three-dimensional reconstruction of a tubular organ
Embodiments of the present invention include methods and systems for three-dimensional reconstruction of a tubular organ (for example, coronary artery) using a plurality of two-dimensional images. Some of the embodiments may include displaying a first image of a vascular network, receiving input for identifying on the first image a vessel of interest, tracing the edges of the vessel of interest including eliminating false edges of objects visually adjacent to the vessel of interest, determining substantially precise radius and densitometry values along the vessel, displaying at least a second image of the vascular network, receiving input for identifying on the second image the vessel of interest, tracing the edges of the vessel of interest in the second image, including eliminating false edges of objects visually adjacent to the vessel of interest, determining substantially precise radius and densitometry values along the vessel in the second image, determining a three dimensional reconstruction of the vessel of interest and determining fused area (cross-section) measurements along the vessel and computing and presenting quantitative measurements, including, but not limited to, true length, percent narrowing (diameter and area), and the like.
Owner:PAIEON INC
Method for using a bone densitometry system,with dual-energy x-radiation
InactiveUS20030026385A1Help positioningOptimise centeringImage data processing detailsUsing wave/particle radiation meansBone densityHigh energy
Process for use of an osteodensitometry system using dual-energy cone beam X-rays. The system (1) comprises an X-ray source (1a) capable of supplying a cone X-ray beam with at least a first energy called the high energy and a second energy called the low energy, a two dimensional X-ray detector (2) and electronic means (3a, 3b) for processing images supplied by this detector. According to this process, the low energy image of a part of the anatomy of a patient (1c) is acquired, and the high energy image of this part of the anatomy is acquired, and these images acquired at low energy and at high energy are matched before building up the map of bone densities of the part of the anatomy.
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Computer-assisted bone densitometer
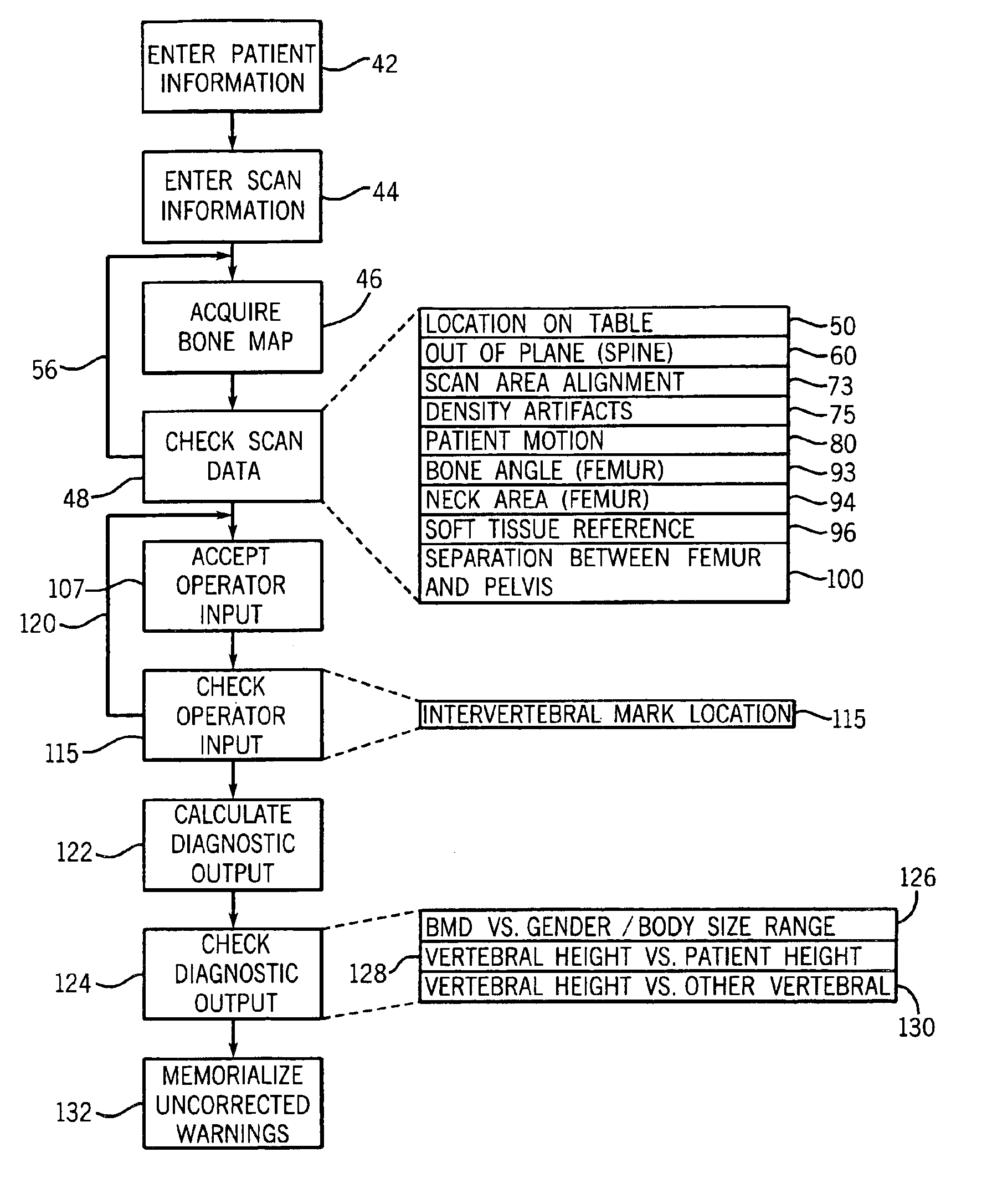
InactiveUS6892088B2Reduce errorsVolume/mass flow measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringComputer assistanceX ray densitometry
An x-ray densitometry system provides computer assistance to the operator in identifying possible sources of scanning or analysis error through computer review of the acquired data, operator input, and the ultimate diagnostic outputs.
Owner:GE MEDICAL SYST GLOBAL TECH CO LLC
Bone densitometry system for public use
InactiveUS20070016043A1Equipment costPatient positioningPatient positioning for diagnosticsDensitometryBiomedical engineering
An ultrasonic bone densitometer system is provided in a kiosk environment using computer driven patient instructions and simplified sanitizing procedures to allow unsupervised use by members of the public for screening purposes.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Biopsy method and gun set devices
InactiveUS20140228661A1Reduce transmissionCut evenlySurgical needlesDiagnostics using spectroscopyBiopsy methodsDensitometry
A novel set of biopsy-gun related tools are developed in order to make a better safer sampling and diagnosis, comprising a set of tools that takes the sample, releases a drug impregnated plug and additionally may inject drugs, measure pH and the molecular content of the penetrated tissues.A novel technology aiming to minimize the penetrated tissue damage, using a small diameter needle with capabilities for immediate spectroscopic analysis of the tissue, and followed by sampling and plugging of the tissue when needed.The invention describes a set of variable diameter thin tubes used to guide and insulate the penetrated organs, and a final operation of plugging the wounds with absorbable substances, impregnated with drugs.The supplementary low intensity radiation sources could increase the processes' accuracy and safety, offering the opportunity of gathering supplementary x-densitometry information.
Owner:VARIABLE GAUGE CATHETER INC
Osseo classification system and method
An osseo classification and digital modality modeling system includes a computer with a digital memory adapted for storing patient densitometry information, an input and an output. An input subsystem includes a pair of source / receptor units mounted on a signal positioning subsystem, which is adapted for moving the source / receptor units through predetermined paths of movement, which can be circular or linear. The resulting tomographic data is synthesized to form any 3-D model or image, which is output for further analysis and classifying osseo structure and / or prosthetic osseointegration. An osseo classification and digital tomosynthesis method includes the steps of moving a pair of sensor / receptor units relative to a patient. The resulting signals output by the receptor are digitized and synthesized to form a 3-D image or model. Multiple depths of penetration and multiple widths can be captured from single acquisitions using digital tomosynthesis signal processing techniques. Osseo structure and / or prosthetic osseointegration is classified using the densitometry data.
Owner:OSSEO IMAGING
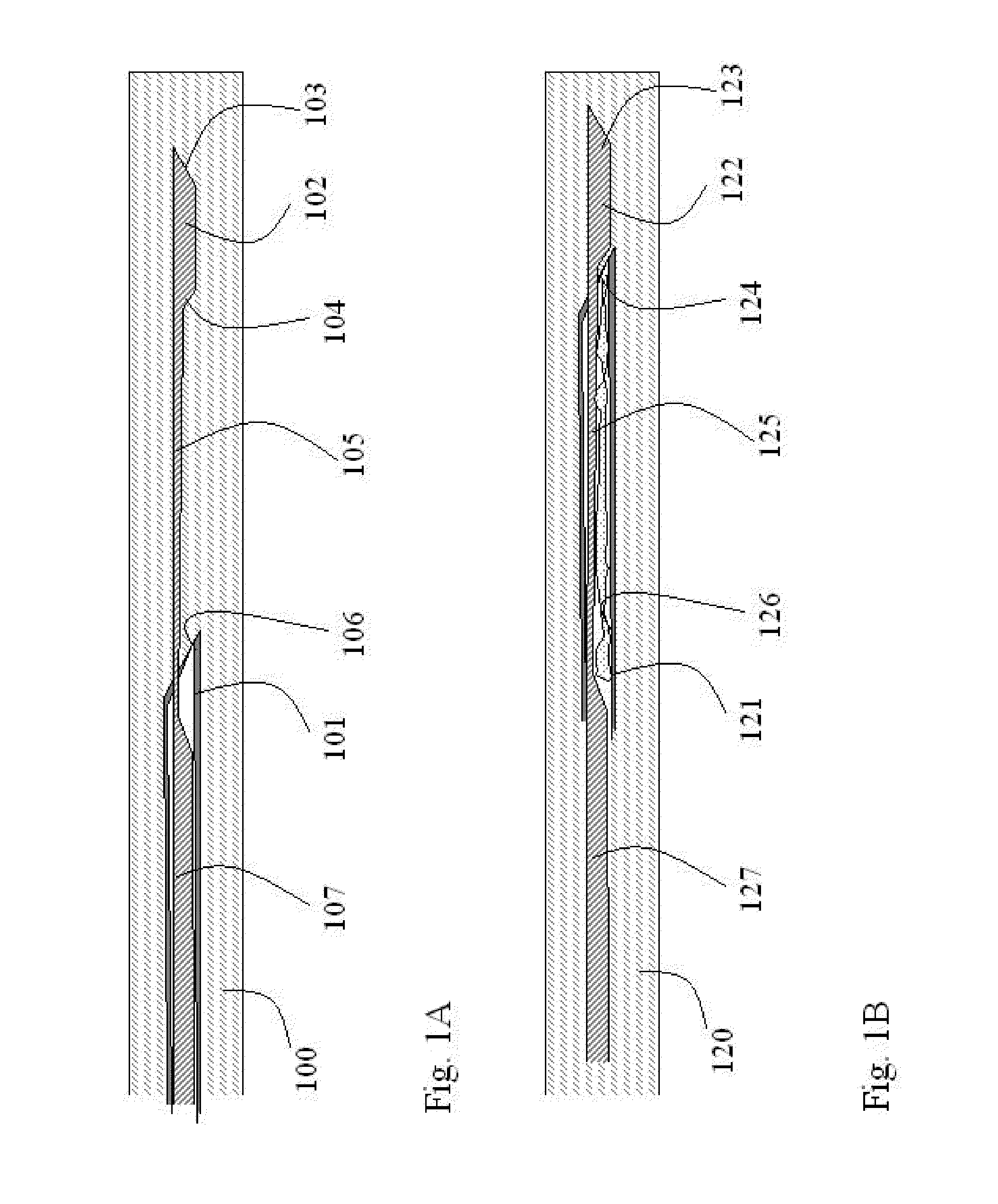
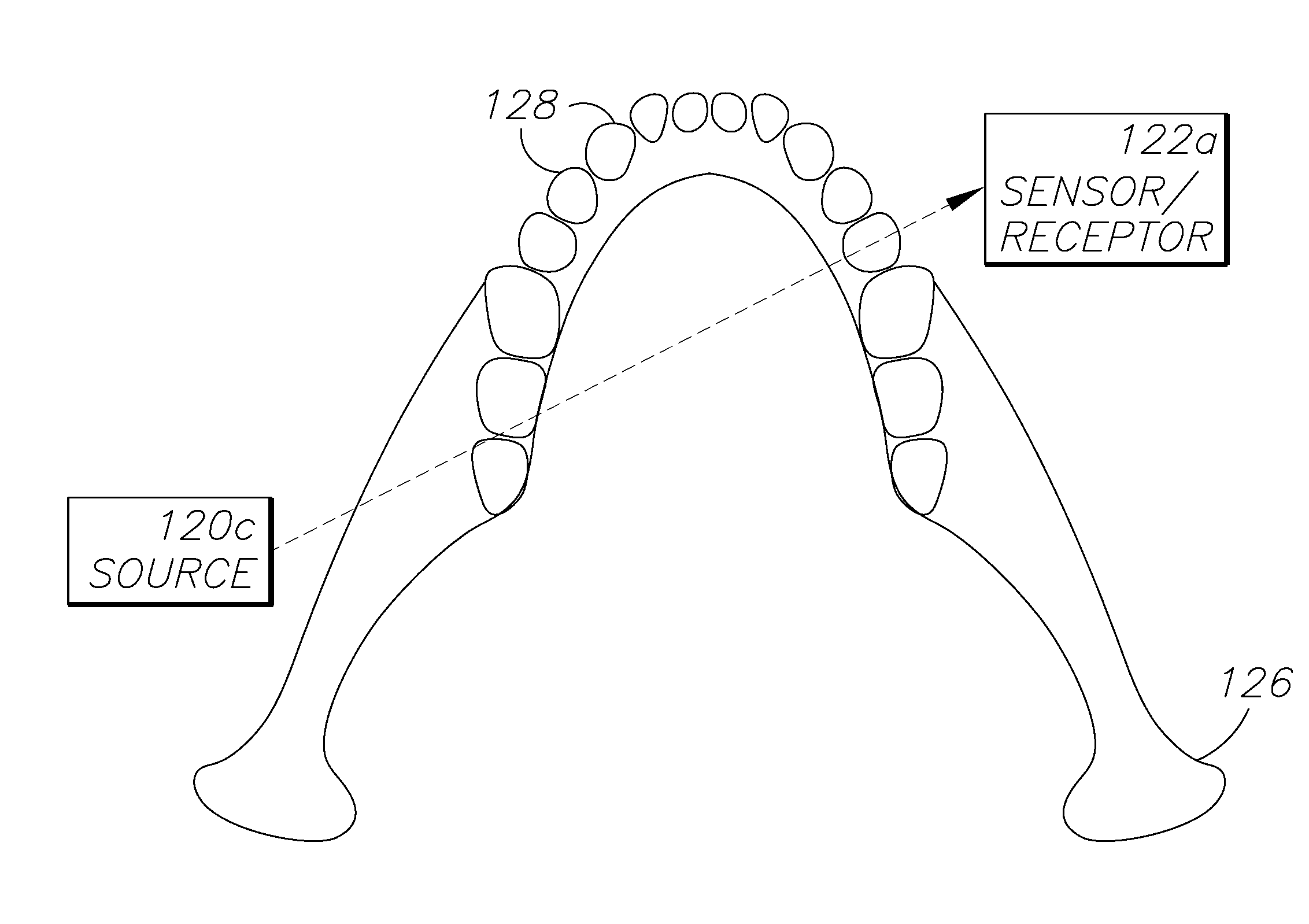
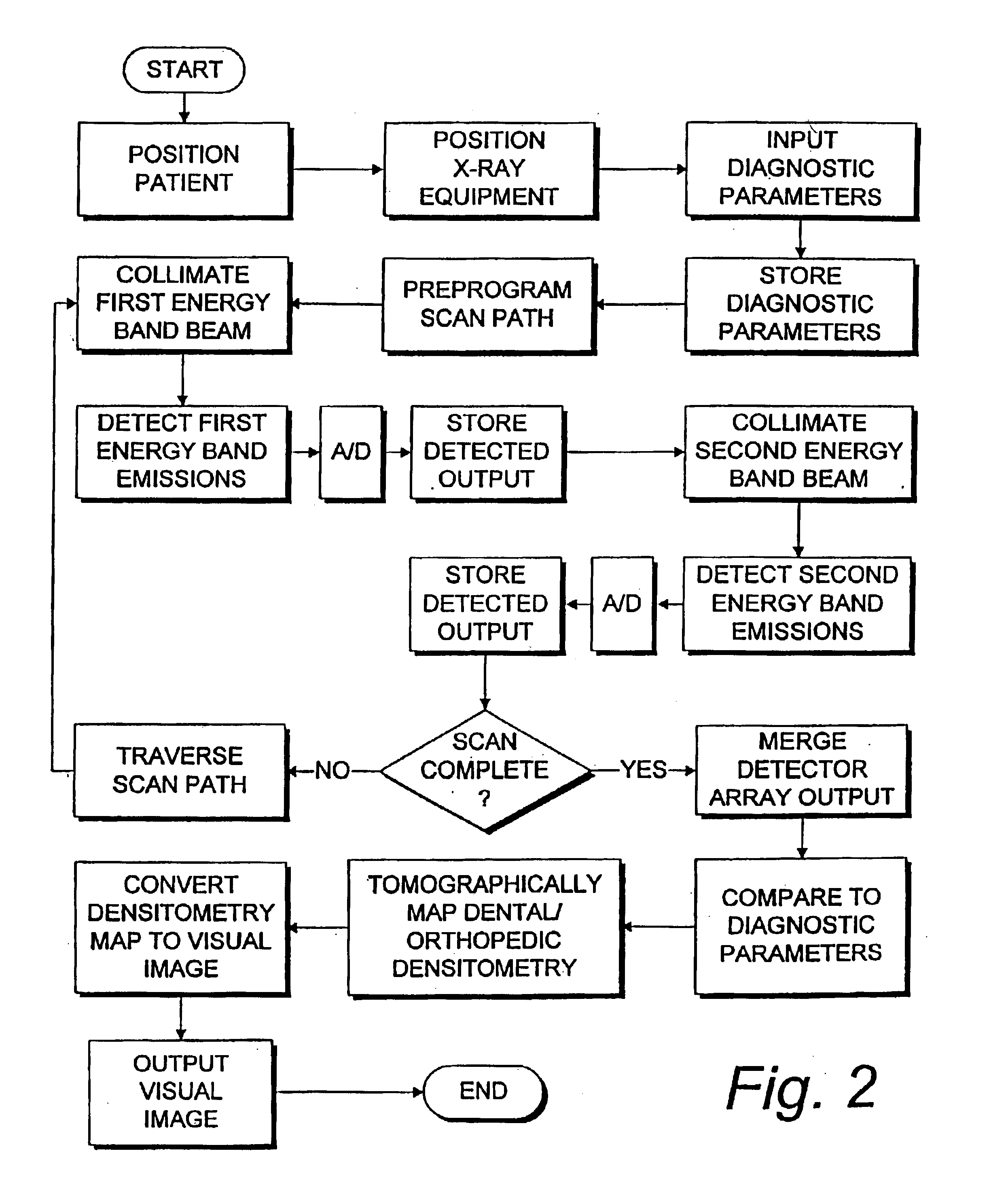
Dental and orthopedic densitometry modeling system and method
InactiveUS20060008050A1Reduce operating costsFacilitates the monitoring of decalcificationComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringDentistryDensitometry
A dental or orthopedic densitometry modeling system includes a computer with a digital memory adapted for storing patient densitometry information, an input and an output. A dental or orthopedic input device includes energy source and an energy sensor, both of which can be either external or intraoral to the patient. The sensor transfers densitometry signals to the computer, which creates, stores and compares digital densitometry models. A densitometry modeling method includes the steps of creating a densitometry database consisting of dental or orthopedic information and obtaining current dental or orthopedic densitometry information from a patient. The current information is compared to the database, which can include the patient's previous densitometry models, and an updated patient densitometry model is created.
Owner:OSSEO IMAGING
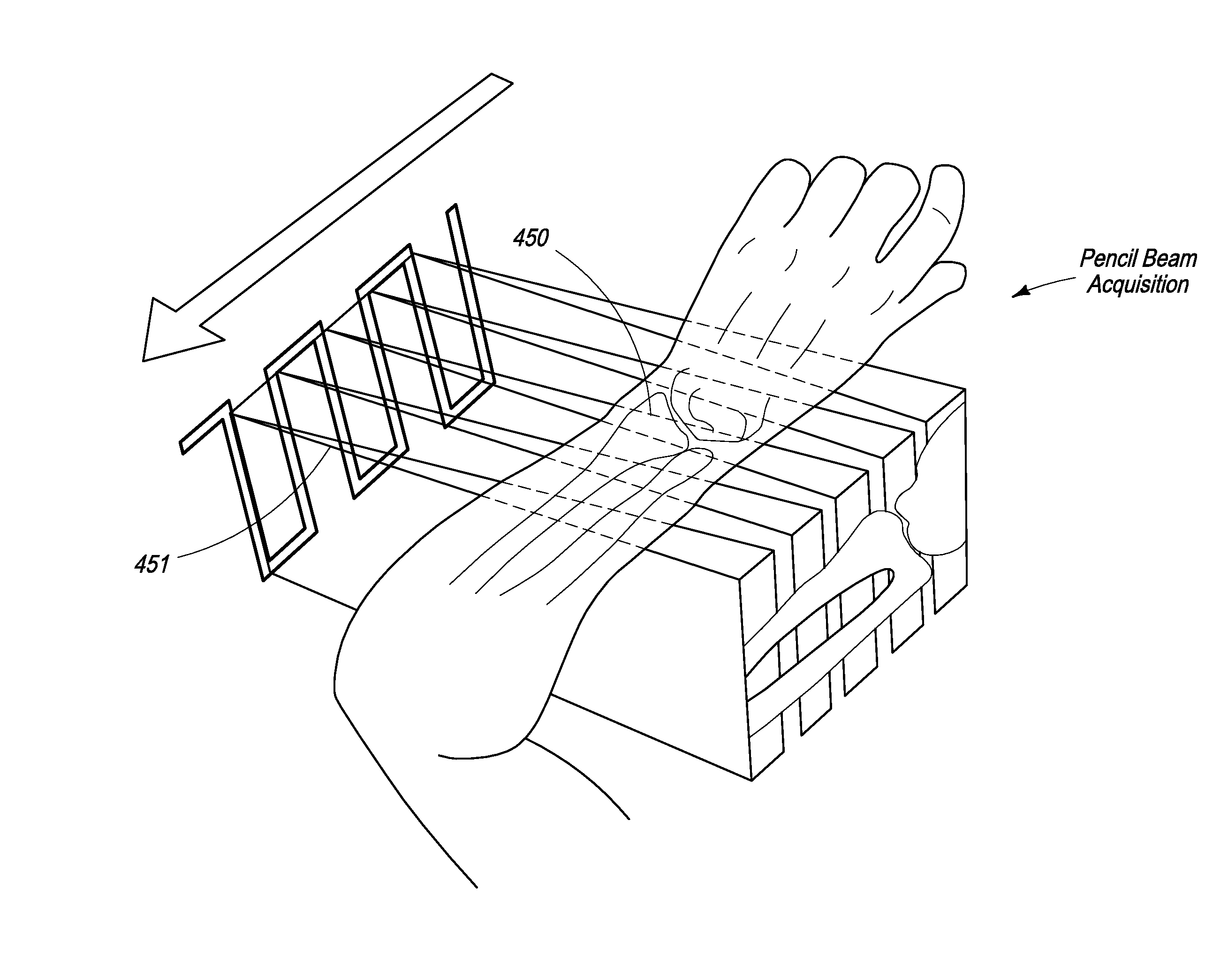
Apparatus for Bone Density Assessment and Monitoring
InactiveUS20100284515A1High energyUsing wave/particle radiation meansX-ray apparatusDysostosisBone density
The present invention relates to a dual energy X-ray apparatus and method for osteoporosis assessment and monitoring. The present invention takes a bone densitometry reading of a patient's wrist to assess osteoporosis and monitor bone loss condition by repeat measurements along with therapy. The bone densitometry system has an X-ray source, dual energy detectors, an arm-rest to place the patient's arm, a motion system to move the source-detector gantry along the patient's forearm, and a computer with a database to archive the wrist image, calculate the bone mineral density, maintain a history of patient information, and generate patient history reports.
Owner:OSTEOMETER MEDITECH
System for quantitative radiographic imaging
InactiveUS20080304620A1Reduce and eliminate radiationTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesX-rayDual energy
A system for spectroscopic imaging of bodily tissue in which a scintillation screen and a charged coupled device (CCD) are used to accurately image selected tissue. Applications include the imaging of radionuclide distributions within the human body or the use of a dual energy source to provide a dual photon bone densitometry apparatus that uses stationary or scanning acquisition techniques. An x-ray source generates x-rays which pass through a region of a subject's body, forming an x-ray image which reaches the scintillation screen. The scintillation screen reradiates a spatial intensity pattern corresponding to the image, the pattern being detected by a CCD sensor. The image is digitized by the sensor and processed by a controller before being stored as an electronic image. A dual energy x-ray source that delivers two different energy levels provides quantitative information regarding the object being imaged using dual photon absorptiometry techniques. Dual scintillation screens can be used to simultaneously generate images of low-energy and high-energy x-ray patterns. Each image is directed onto an associated respective CCD or amorphous silicon detector to generate individual electronic representations of the separate images.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Apparatus and methods for x-ray imaging
PendingUS20210244374A1Enhance the imageIncrease speedTomosynthesisTomographyTwo dimensional detector3d image
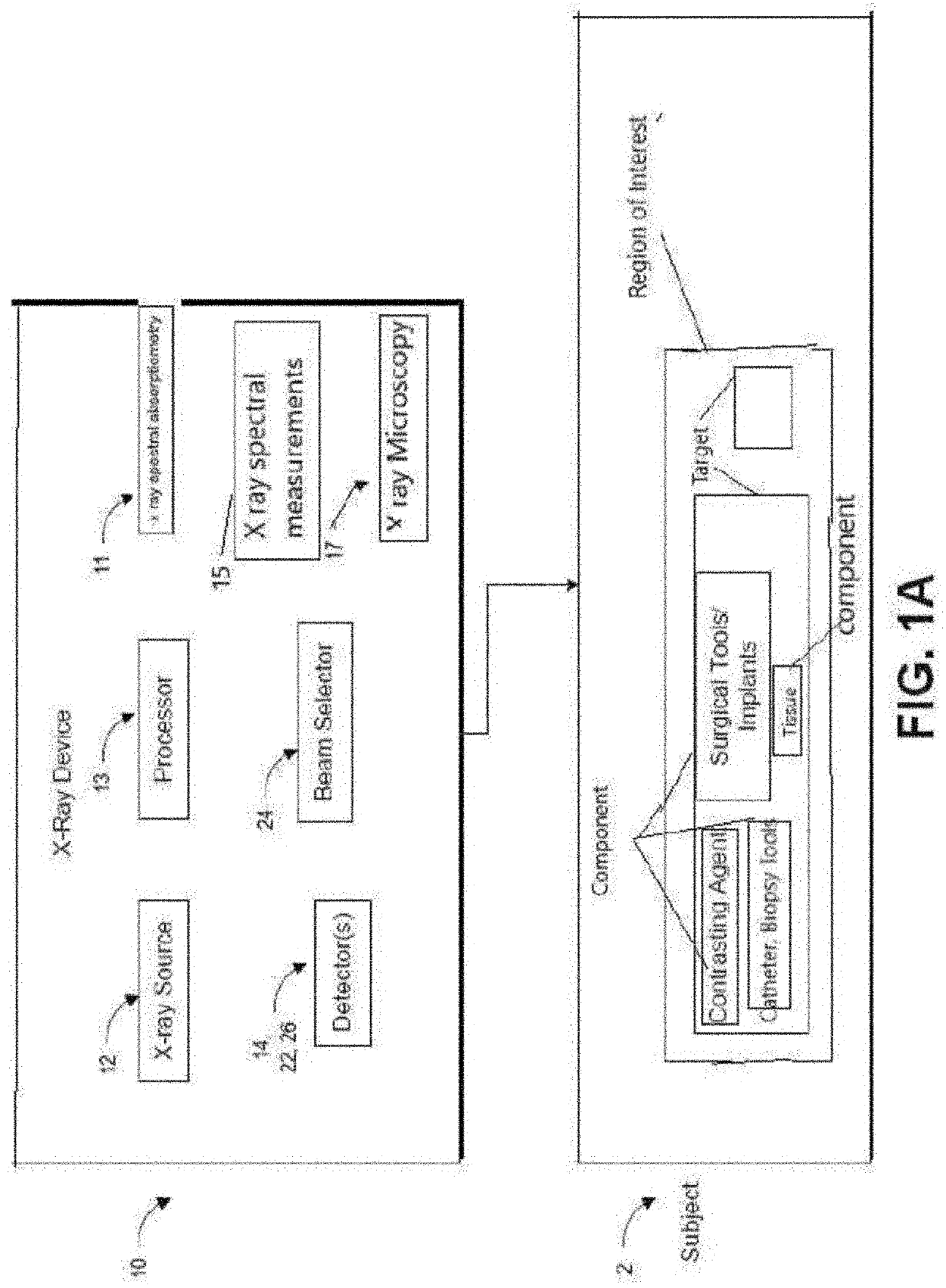
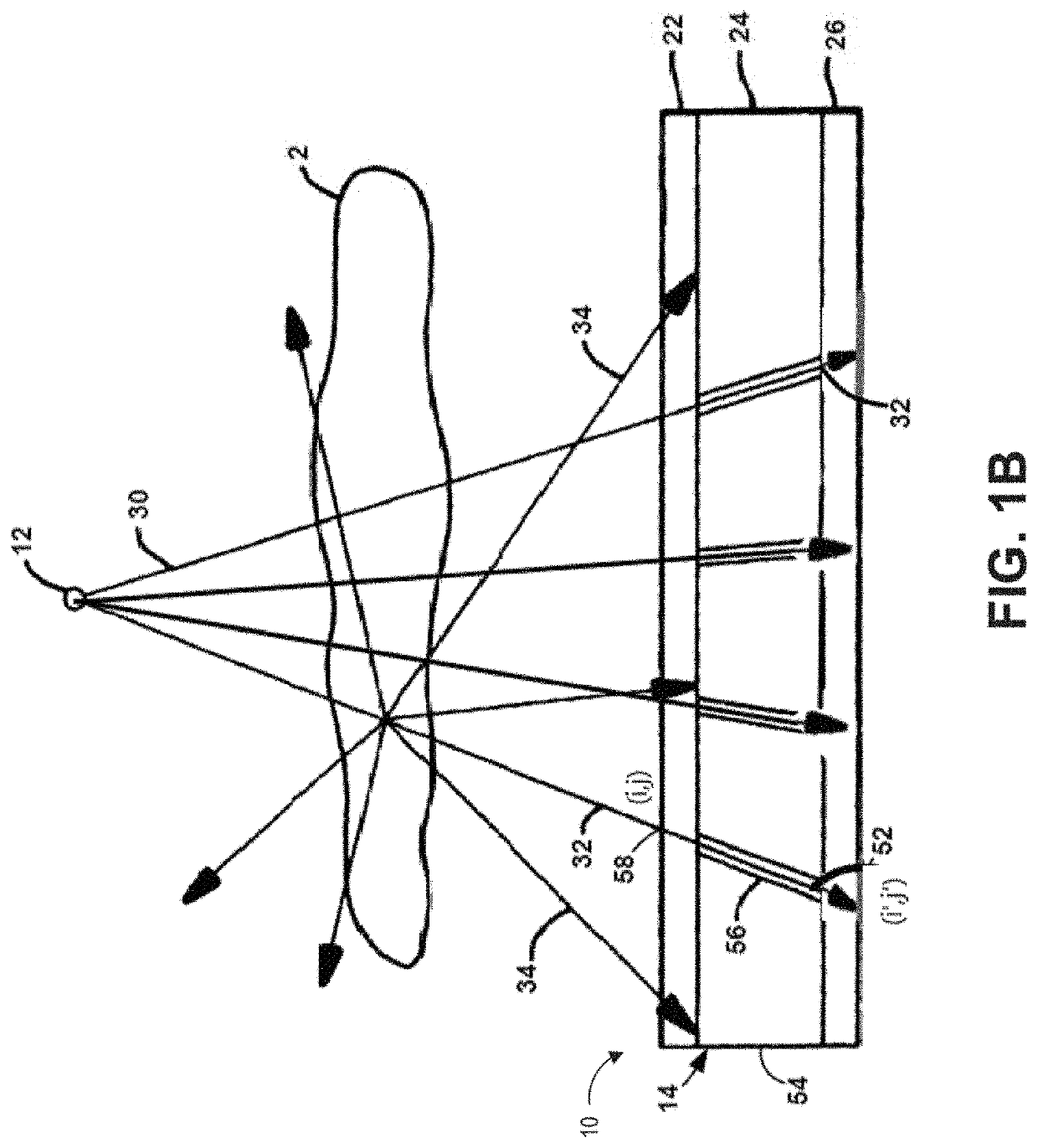
An x-ray apparatus and method can improve x-ray imaging in a variety of ways. For example, the improve x-ray apparatus can reduce scatter from x-ray images acquired by two-dimensional detectors. An improved 2D x-ray apparatus can provide 3D imaging for medical and / or industrial applications. An improved 2D x-ray apparatus and method can produce separate material imaging, and composition analysis for characterization and correlation of image, densitometry, and composition information of individual component or individual material within a single subject. Non-rotational 3D microscopy, combining 2D or 3D full field x-ray imaging and high resolution 2D or 3D x-ray microscopy or spectral absorptiometry and spectroscopy can achieve a higher resolution and wider field of view in x-ray imaging and quantitative analysis in 3D and real time. The x-ray apparatus can improve tracking and / or surgical guidance in time and / or space.
Owner:XENSELAB LLC
Method for measuring real density of double-density bottle powder
InactiveCN1664554AAccurate measurementHigh precisionSpecific gravity measurementBoiling pointDensitometry
The invention relates to a method of measuring the real density of the powder using double density bottles, which including the following steps: 1) weighing the quality of the density bottle A and B with the mass of ma and mb accurately, filling the bottle with agent fluid and weighing the quality m1, m2, checking the dielectric fluid density Rho0 corresponding to the temperature, compute the volume of the two bottle va, vb; 2) filling the bottle B with the powder to be measured, weighing the quality m3, and m[sample]=m3-mb; then filling the agent fluid to the surface of the powder 4.8-5.2mm, putting it to the vacuum chamber and pumping to the critical boiling point, keeping 28-32 minutes until the air bubble in the powder space output completely; 3) filling the agent fluid to bottle A,B at the same time, measuring the quality of bottle A m4, bottle B m5; 4) computing the sample's mass density according to the following formula: rho[sample]=m[sample] / v[sample]=(m3-mb)(m4-ma) / [(m4-ma)vb-(m5-m3)va].
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
Osseo classification system and method
Owner:OSSEO IMAGING
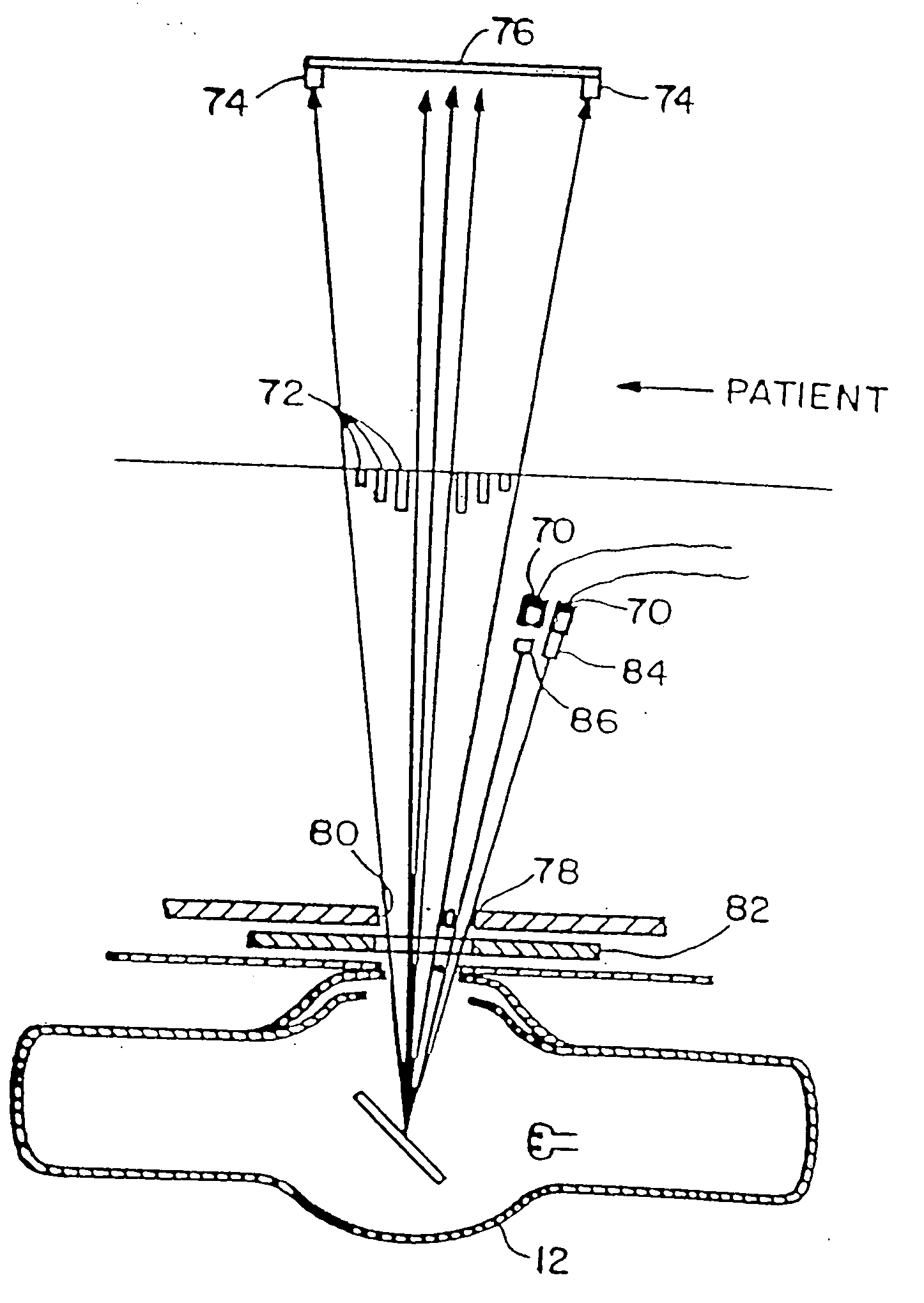
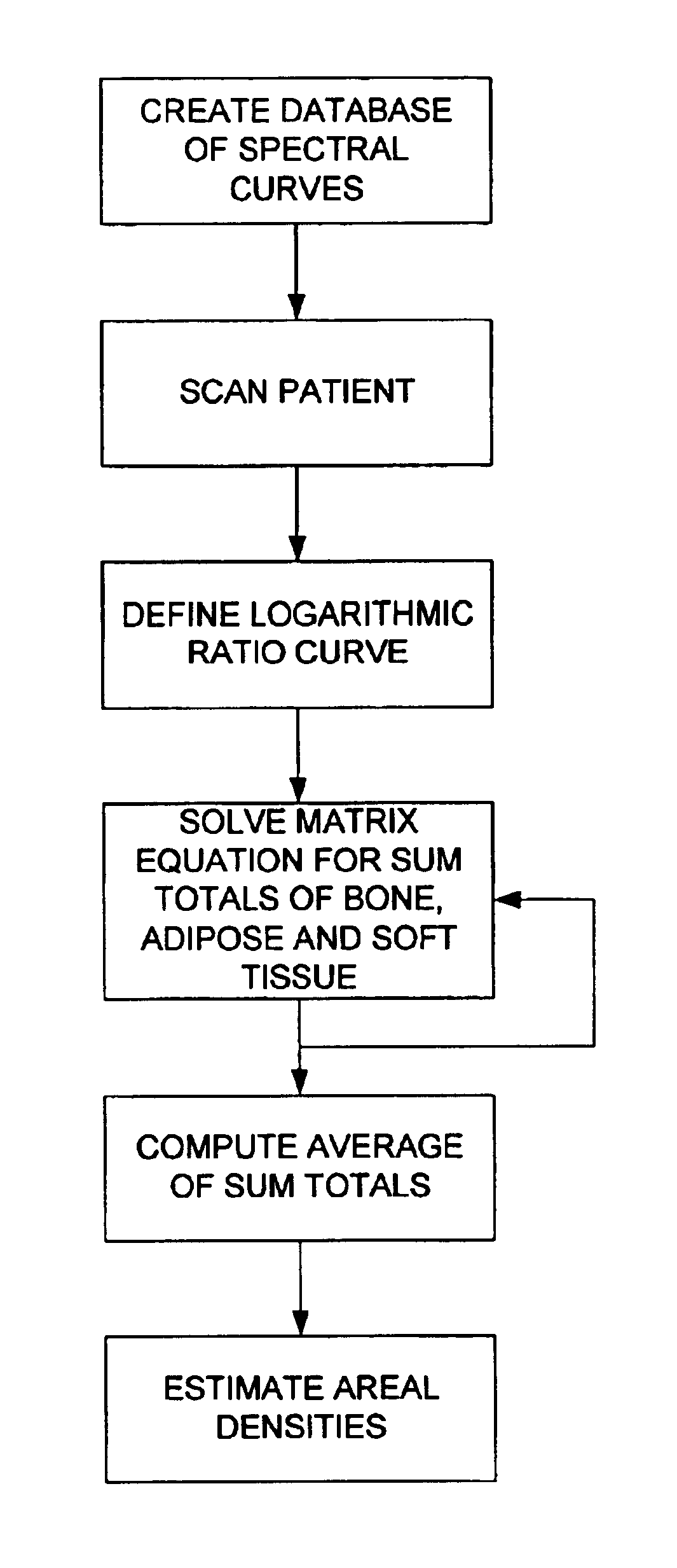
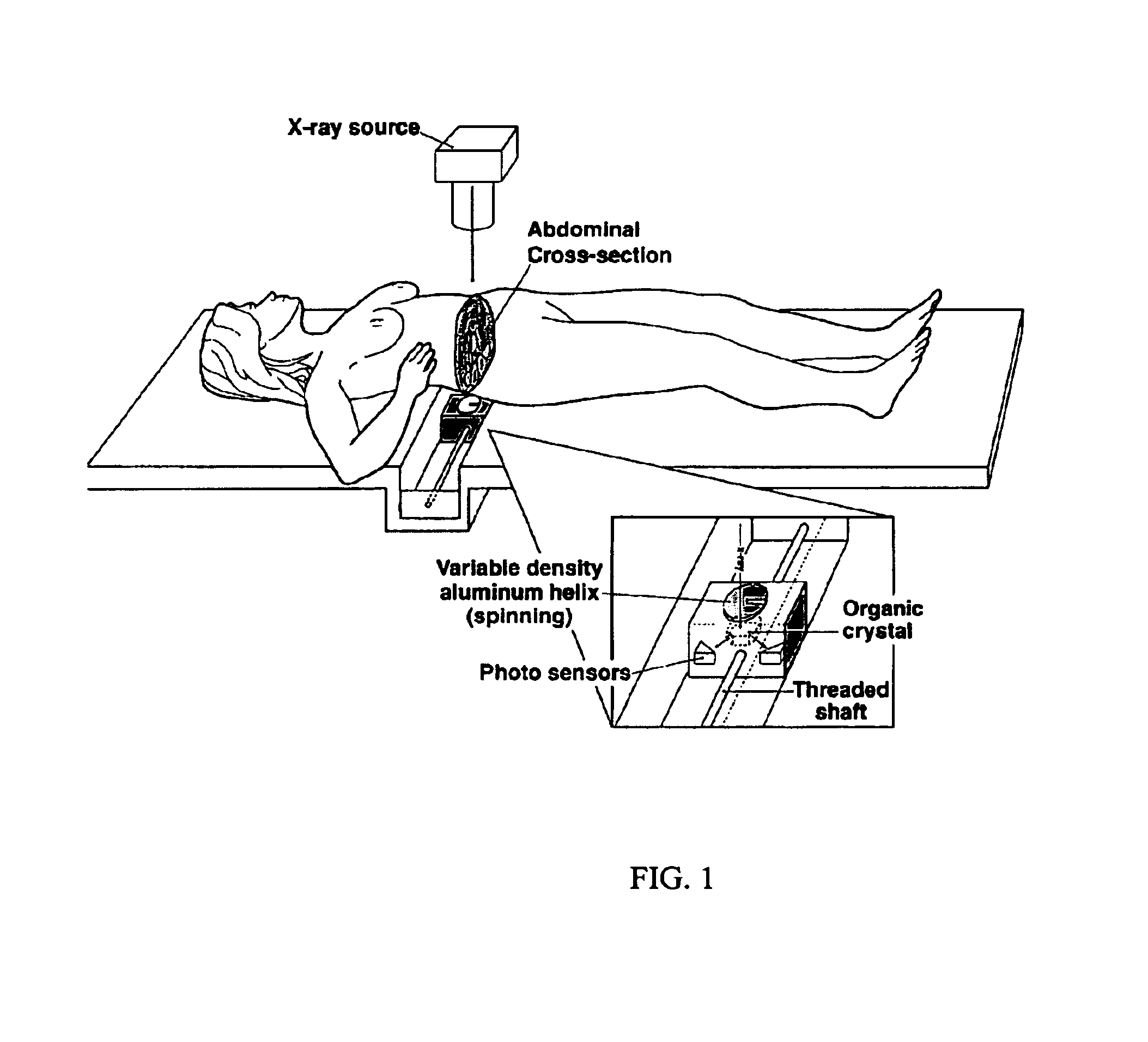
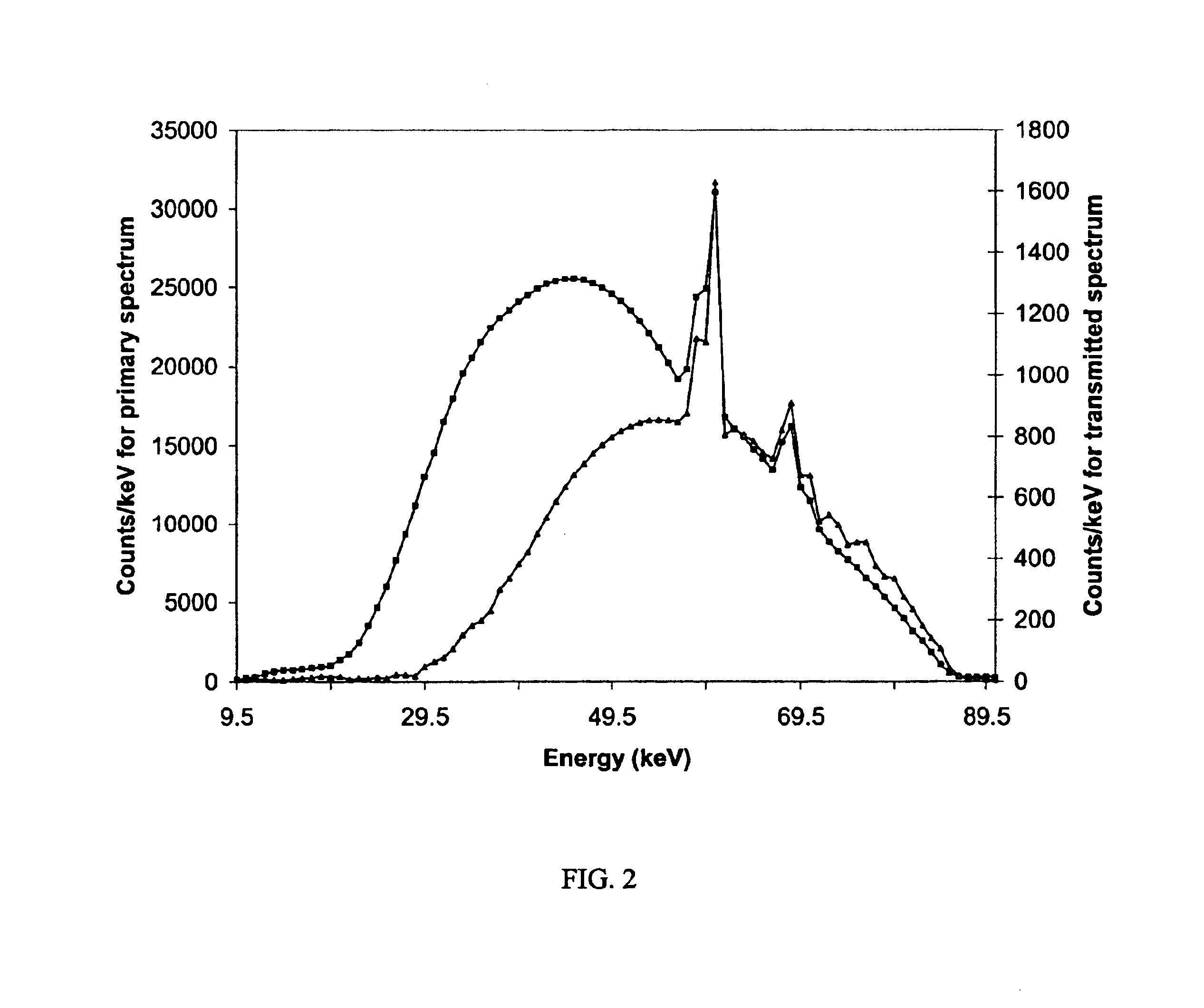
Three component x-ray bone densitometry
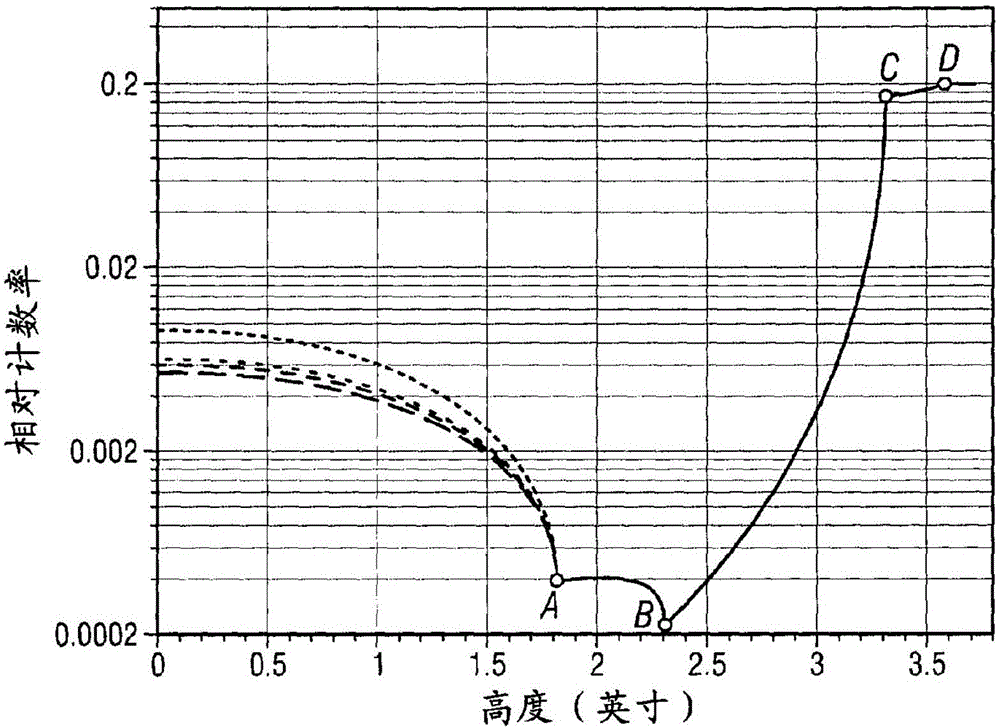
InactiveUS6909771B2Using wave/particle radiation meansMaterial analysis by transmitting radiationBone densityGrating
The in vivo three component areal density composition of a patient along a transmitted x-ray beam is derived by raster-scanning a collimated x-ray beam across a bony region of the patient, with each point scanned at different energies, and using matrix equations with a priori spectra information to solve for the relative areal density of soft tissue, fat and bone.
Owner:TEXAS SYST THE UNIV OF BOARD OF REGENTS
Method for estimating a scattered radiation, particularly to correct tomography or bone densitometry measurements
Owner:COMMISSARIAT A LENERGIE ATOMIQUE ET AUX ENERGIES ALTERNATIVES
Apparatus for bone density assessment and monitoring
InactiveUS8085898B2High energyParticle size analysisUsing wave/particle radiation meansBone densityX-ray
The present invention relates to a dual energy X-ray apparatus and method for osteoporosis assessment and monitoring. The present invention takes a bone densitometry reading of a patient's wrist to assess osteoporosis and monitor bone loss condition by repeat measurements along with therapy. The bone densitometry system has an X-ray source, dual energy detectors, an arm-rest to place the patient's arm, a motion system to move the source-detector gantry along the patient's forearm, and a computer with a database to archive the wrist image, calculate the bone mineral density, maintain a history of patient information, and generate patient history reports.
Owner:OSTEOMETER MEDITECH
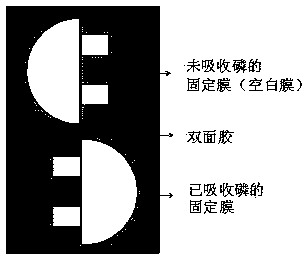
Diffusive gradients in thin films (DGT) method for determination of phosphorus content on the basis of computer-imaging densitometry (CID) technology
InactiveCN104048956AAvoid slicingPrevent extractionMaterial analysis by observing effect on chemical indicatorPhysical chemistryComputer image
A DGT (diffusive gradients in thin films) method for determination of phosphorus content on the basis of computer-imaging densitometry (CID) technology is as follows: a ZrO2 phosphorus fixation film is assembled into a DGT (diffusive gradients in thin films) device, the DGT device is put in a phosphorus medium for phosphorus absorption, then the film is put in hot water of 85 DEG C for heat treatment for 5 days to promote further fixation of phosphorus absorbed by the film, the ZrO2 phosphorus fixation film is put in a colorant for coloring, a scanner is used for scanning of the colored film, software is used for converting image color obtained by the scanning into gray scale, and according to an established phosphorus accumulation amount and surface gray scale calibration curve of the ZrO2 phosphorus fixation film, the obtained gray scale is converted into phosphorus accumulation amount; and the phosphorus content in the phosphorus medium can be calculated by use of Fick's first law of diffusion according to the phosphorus accumulation amount in the phosphorus fixation film surface. According to the method, the CID technology is used to avoid slicing, extracting and other operation, and the phosphorus accumulation amount in the phosphorus fixation film, the phosphorus content in the phosphorus medium, spatial distribution and other information and can be quickly and easily obtained.
Owner:NANJING INST OF GEOGRAPHY & LIMNOLOGY
Dental and orthopedic densitometry modeling system and method
InactiveUS6944262B2Reduce operating costsFacilitates the monitoring of decalcificationComputerised tomographsDiagnostic recording/measuringDigital storagePlastic surgery
A dental or orthopedic densitometry modeling system includes a computer with a digital memory adapted for storing patient densitometry information, an input and an output. A dental or orthopedic input device includes energy source and an energy sensor, both of which can be either external or intraoral to the patient. The sensor transfers densitometry signals to the computer, which creates, stores and compares digital densitometry models. A densitometry modeling method includes the steps of creating a densitometry database consisting of dental or orthopedic information and obtaining current dental or orthopedic densitometry information from a patient. The current information is compared to the database, which can include the patient's previous densitometry models, and an updated patient densitometry model is created.
Owner:OSSEO IMAGING
Method for measuring real density of double-density bottle powder
InactiveCN1320348CEasy to operateImprove work efficiencySpecific gravity measurementBoiling pointDensitometry
The invention relates to a method of measuring the real density of the powder using double density bottles, which including the following steps: 1) weighing the quality of the density bottle A and B with the mass of ma and mb accurately, filling the bottle with agent fluid and weighing the quality m1, m2, checking the dielectric fluid density Rho0 corresponding to the temperature, compute the volume of the two bottle va, vb; 2) filling the bottle B with the powder to be measured, weighing the quality m3, and m[sample]=m3-mb; then filling the agent fluid to the surface of the powder 4.8-5.2mm, putting it to the vacuum chamber and pumping to the critical boiling point, keeping 28-32 minutes until the air bubble in the powder space output completely; 3) filling the agent fluid to bottle A,B at the same time, measuring the quality of bottle A m4, bottle B m5; 4) computing the sample's mass density according to the following formula: rho[sample]=m[sample] / v[sample]=(m3-mb)(m4-ma) / [(m4-ma)vb-(m5-m3)va].
Owner:CHINA UNIV OF GEOSCIENCES (WUHAN)
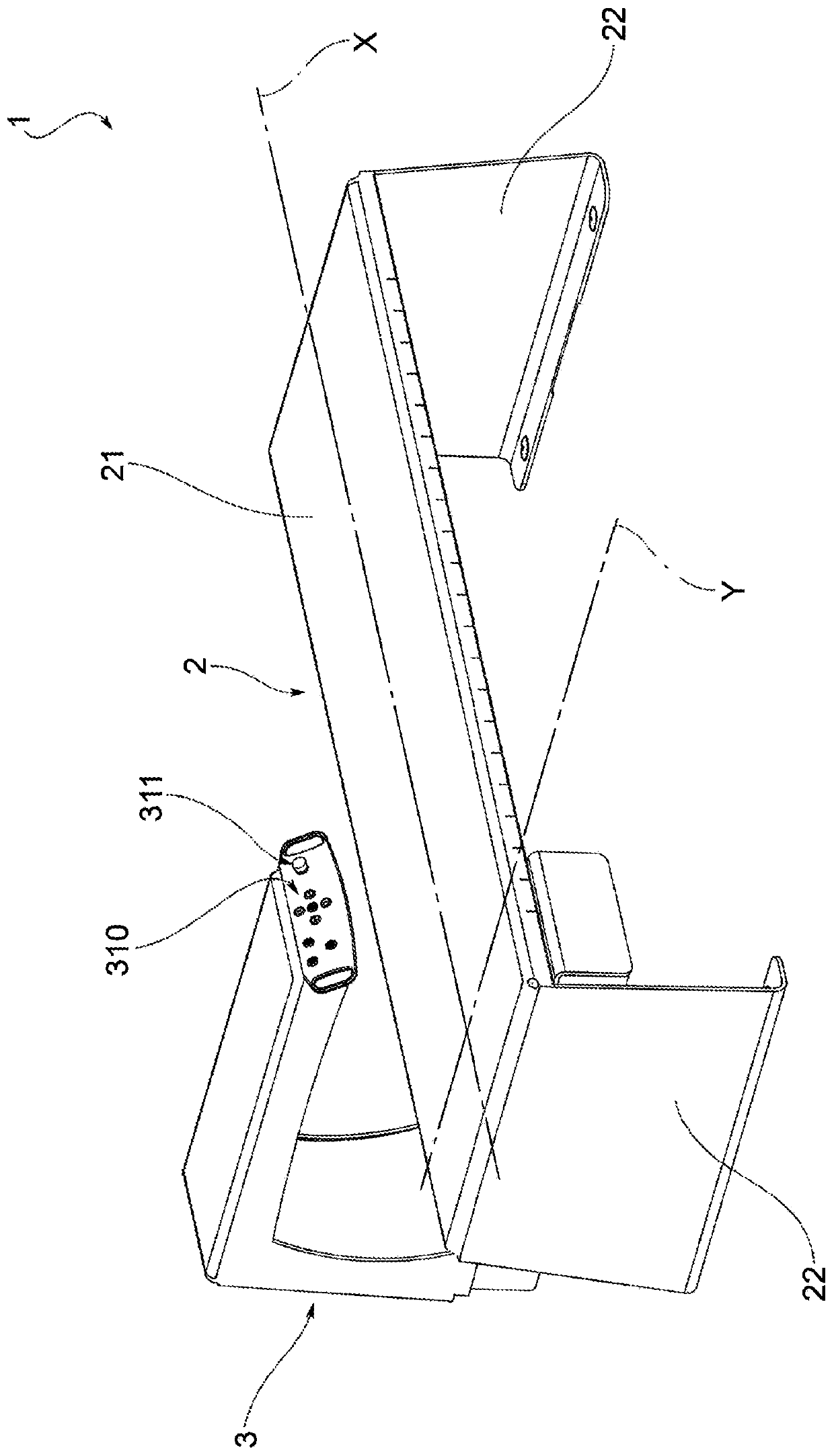
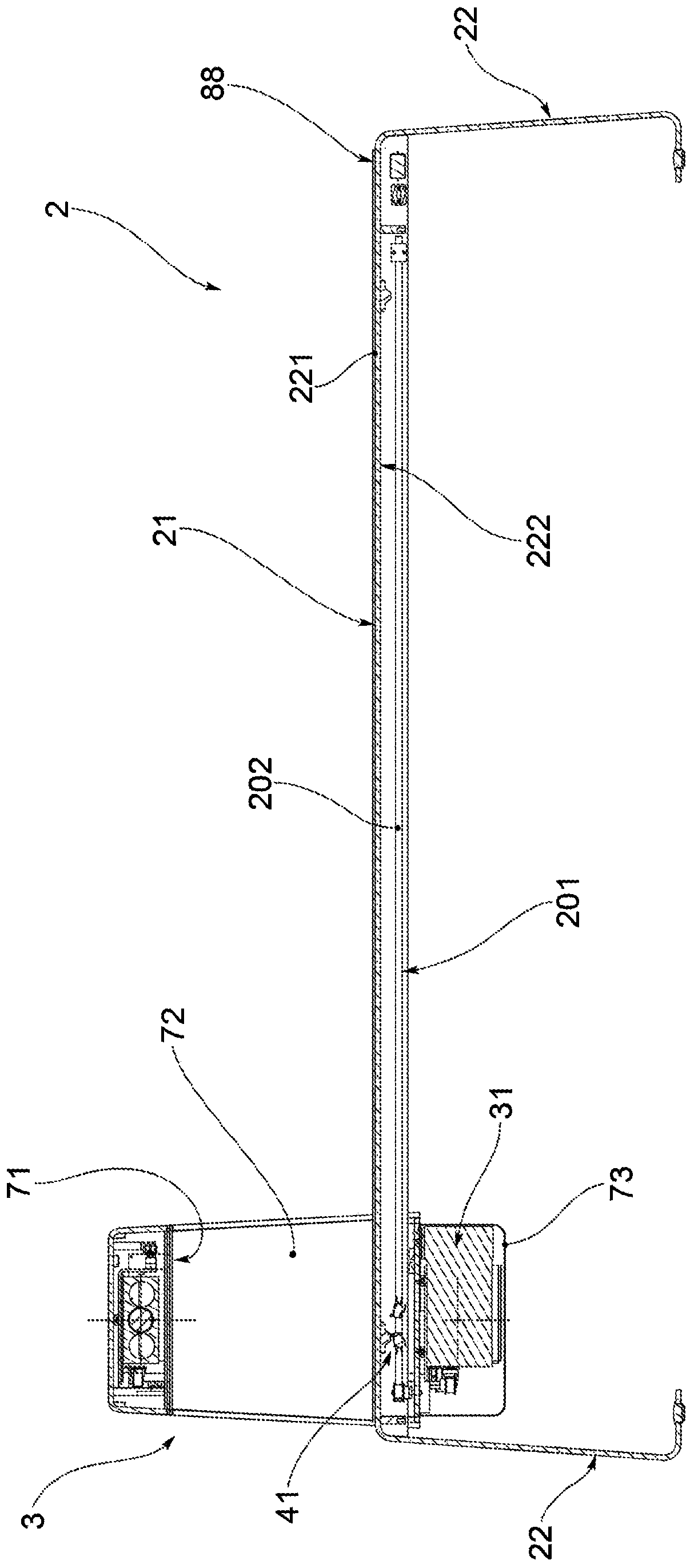
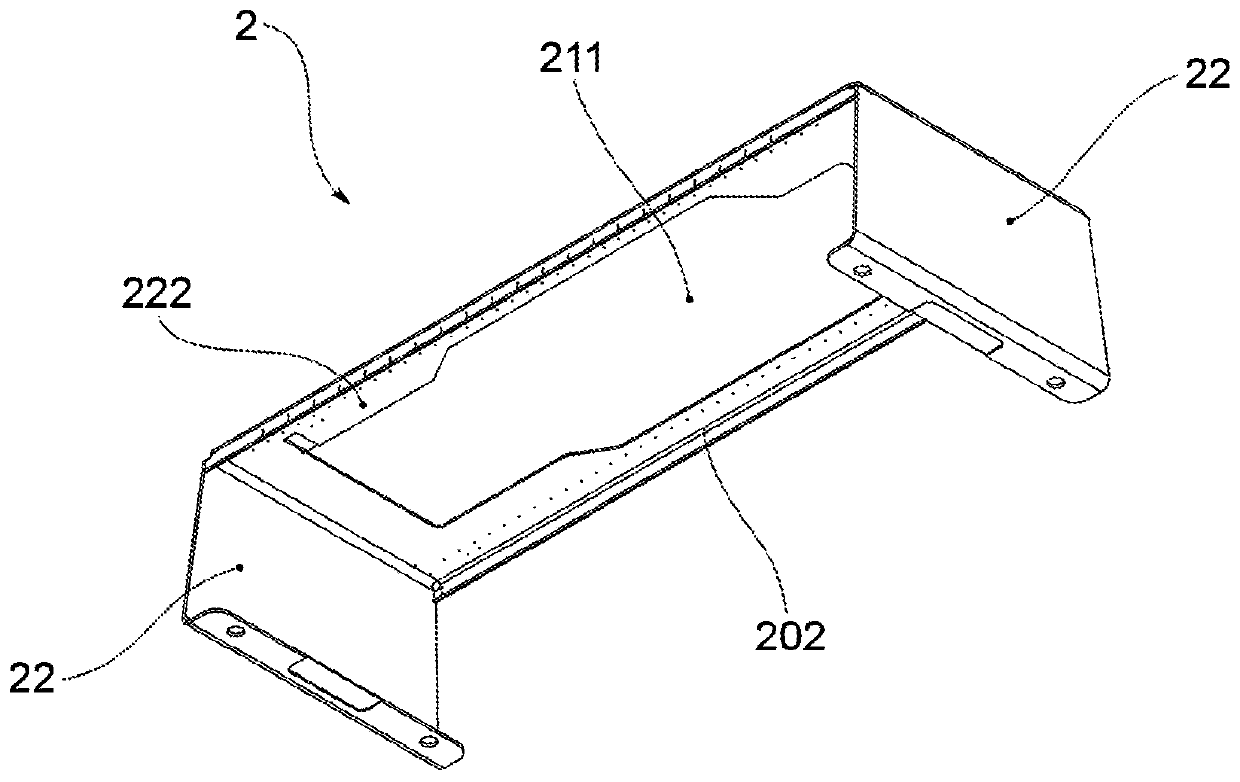
Apparatus for x-ray bone densitometry
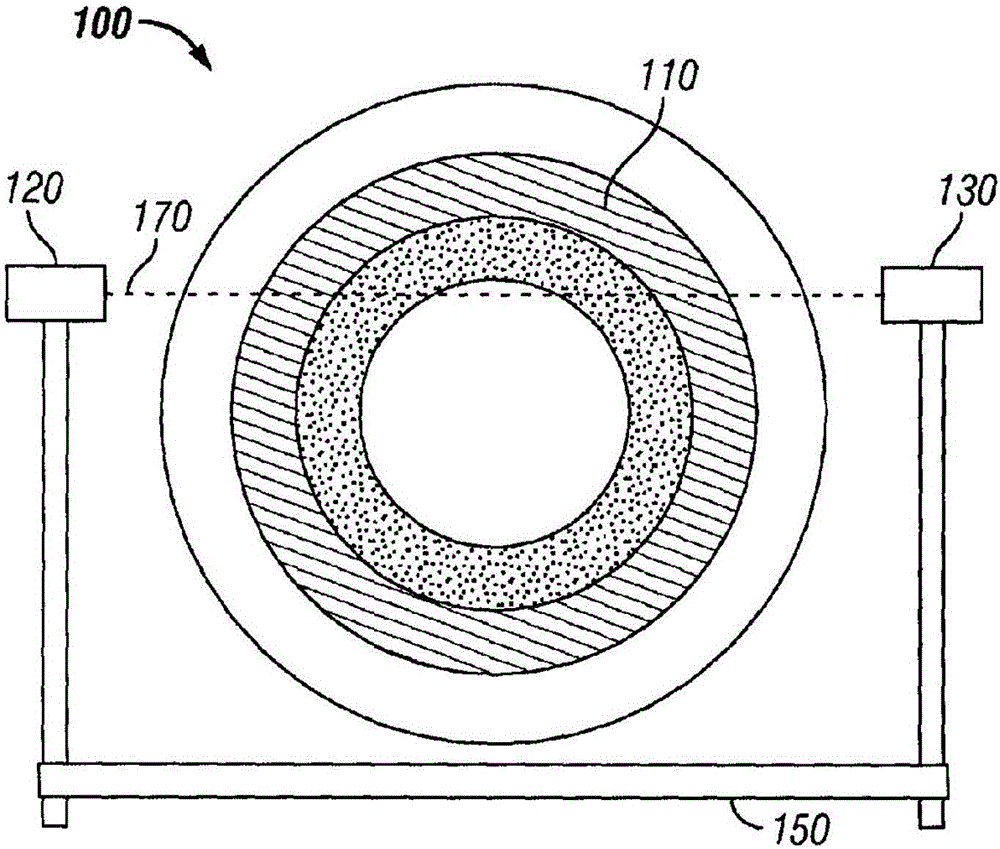
An apparatus for bone densitometry (1) comprises a patient-carrier frame (2) fitted with a support surface (21) for a patient and an arm (3) movable with respect to the frame (2) in a longitudinal direction (X) from the feet to the head of the patient. The arm is fitted with a generator-detector assembly comprising an X-ray generator (31) and an X-ray detector (32), mechanically aligned so that the collimated beam (F) of X-rays produced by the generator (31) centres the detector (32). In particular, the frame is a monocoque (2) and fully supports, at the support surface (21), the arm (3) in order to leave the space underneath the frame (2) free. Advantageously, moreover, in the case of apparatus with frame (2) made of aluminium, the frame itself also serves as a filter for X-rays.
Owner:EUROTEC MEDICAL SYST SRL
Construction method of a model for cynomolgus monkey osteoporosis caused by oophorectomy
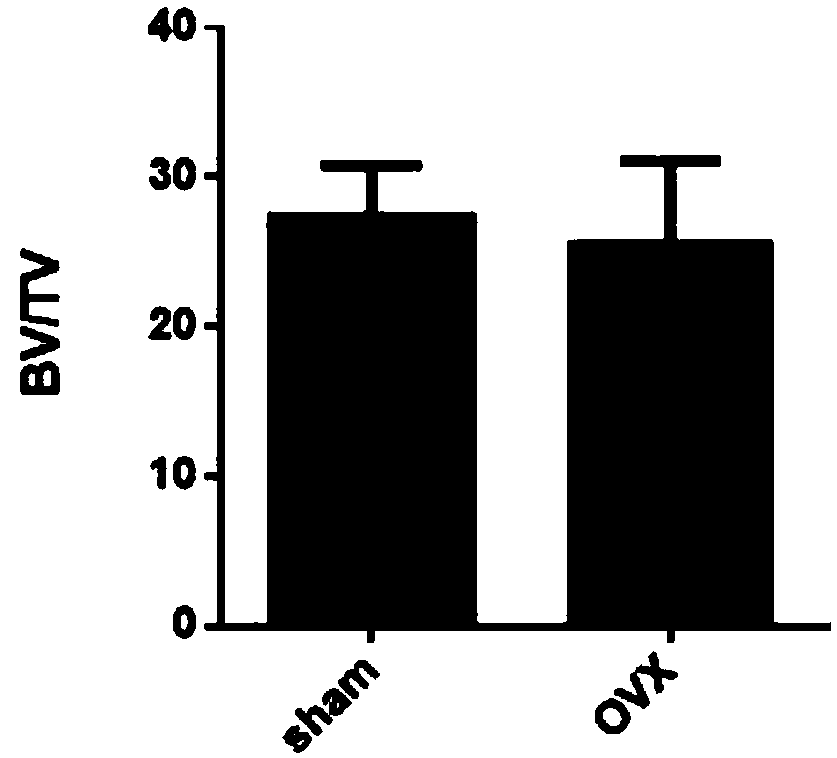
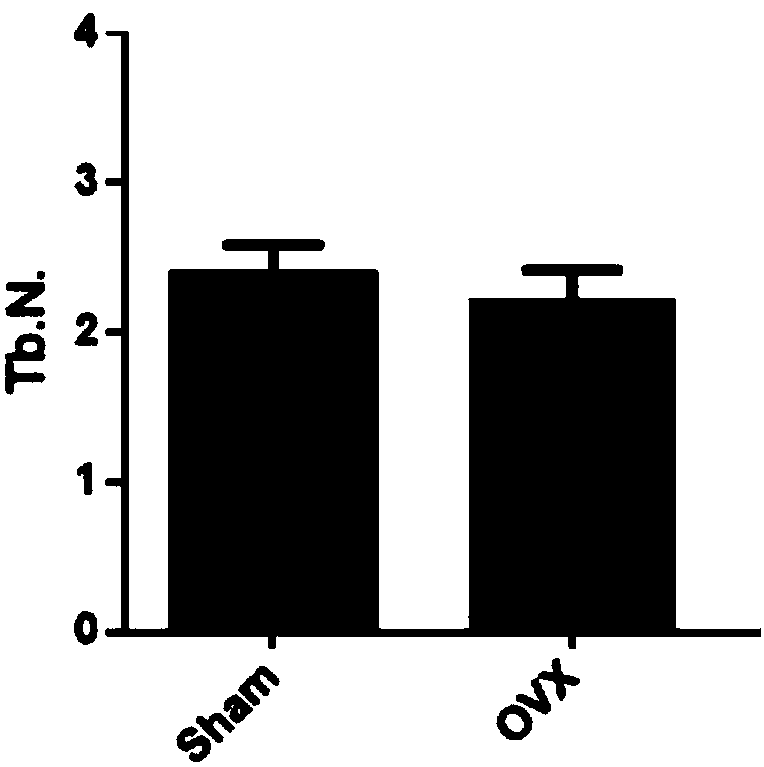
The invention relates to the technical field of biomedical research, and in particular relates to a construction method of a model for cynomolgus monkey osteoporosis caused by oophorectomy. The technical scheme is as follows: the cynomolgus monkey osteoporosis model is established through bilateral oophorectomy, then, through detection on serum bone conversion related indicators, lumbar vertebra bone densitometry, cancellous bone tissue morphologic and metrological testing and lumbar vertebra compression testing, the bone quality in each group is evaluated, the parameters show that due to theoophorectomy surgery, the bone absorption and bone formation parameters are increased, the bone mass and bone density are obviously reduced, and the mechanical strength is reduced. With the method, the model for cynomolgus monkey osteoporosis caused by oophorectomy can be effectively established, and reliable data for the treatment process is provided for further studying the osteoporosis of postmenopausal women medically.
Owner:澎立生物医药技术(上海)股份有限公司
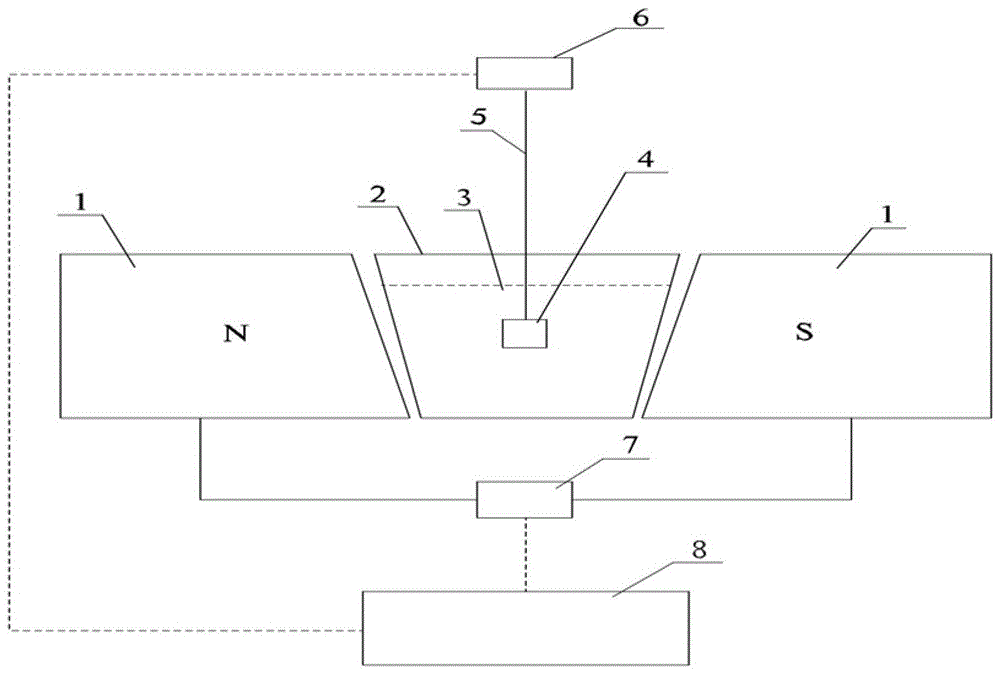
A device and method for measuring total volumetric density of rock samples
ActiveCN104142290BRapid determinationOptimizing the Porosity Measurement MethodPermeability/surface area analysisApparent densityPorosity
The invention provides a rock sample total volume variable density measuring device and method, belonging to the field of oil and gas geological exploration and development. The rock sample total volumetric density measuring device comprises a magnetic pole (1), a magnetic fluid tank (2) and a sample disk (4); the magnetic pole (1) includes an N pole and an S pole; the magnetic fluid tank (2) It is arranged between the N pole and the S pole of the magnetic pole (1); a magnetic fluid (3) is housed in the magnetic fluid tank (2), and the apparent density of the magnetic fluid (3) can be controlled and adjusted by the action of an external electromagnetic field; The sample disk (4) is arranged in the magnetic fluid tank (2), and is connected with a rock sample weighing instrument (6) arranged outside the magnetic fluid tank (2). The invention utilizes the variable density of the magnetic fluid to realize the rapid measurement of the total volume of the rock sample, optimizes the method for measuring the porosity of the rock sample, shortens the analysis period, and improves the work efficiency.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
A multifunctional X-ray bone densitometer
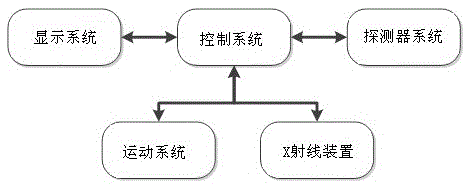
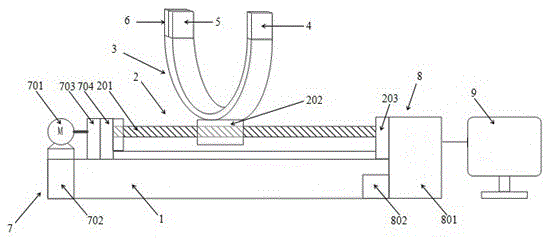
The invention discloses a multifunctional X-ray bone densitometer, which comprises a frame, a guide rail, a U-shaped arm, an X-ray generating device, an X-ray detector, an X-ray shielding device, a motion system, a control system and a display system; On the upper surface of the frame, the U-shaped arm is set on the guide rail, the motion system is set on one end of the frame and connected to the guide rail, the control system is set on the other end of the frame, and connected to the display system, and the display system is set independently or on the On the rack, the X-ray generating device is set at one end of the U-shaped arm, the X-ray detector is set at the other end of the U-shaped arm, which is at the same height as the X-ray generating device, and the X-ray shielding device is set at the U-shaped end. X-ray detector side of the arm. The multifunctional X-ray bone densitometer provided by the invention is easy to use, can realize limb fracture diagnosis, bone density measurement and osteoporosis prediction and diagnosis functions, and avoids the inconvenience caused by the use of large equipment.
Owner:SUZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Methods of detecting flow line deposits using gamma ray densitometry
InactiveCN106662436AMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUsing wave/particle radiation meansGamma rayDensitometry
Owner:SHELL INT RES MAATSCHAPPIJ BV
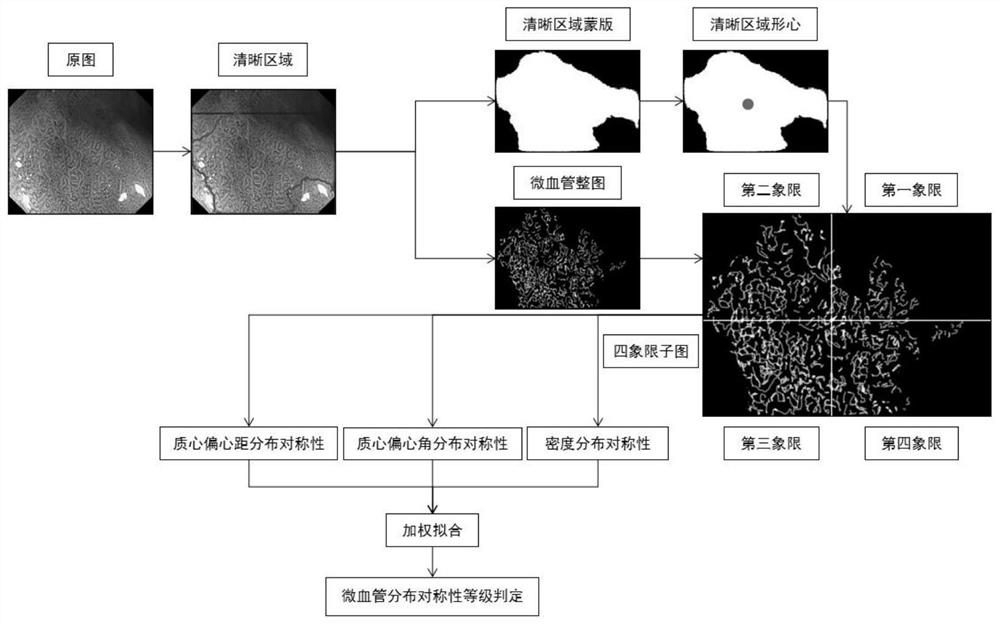
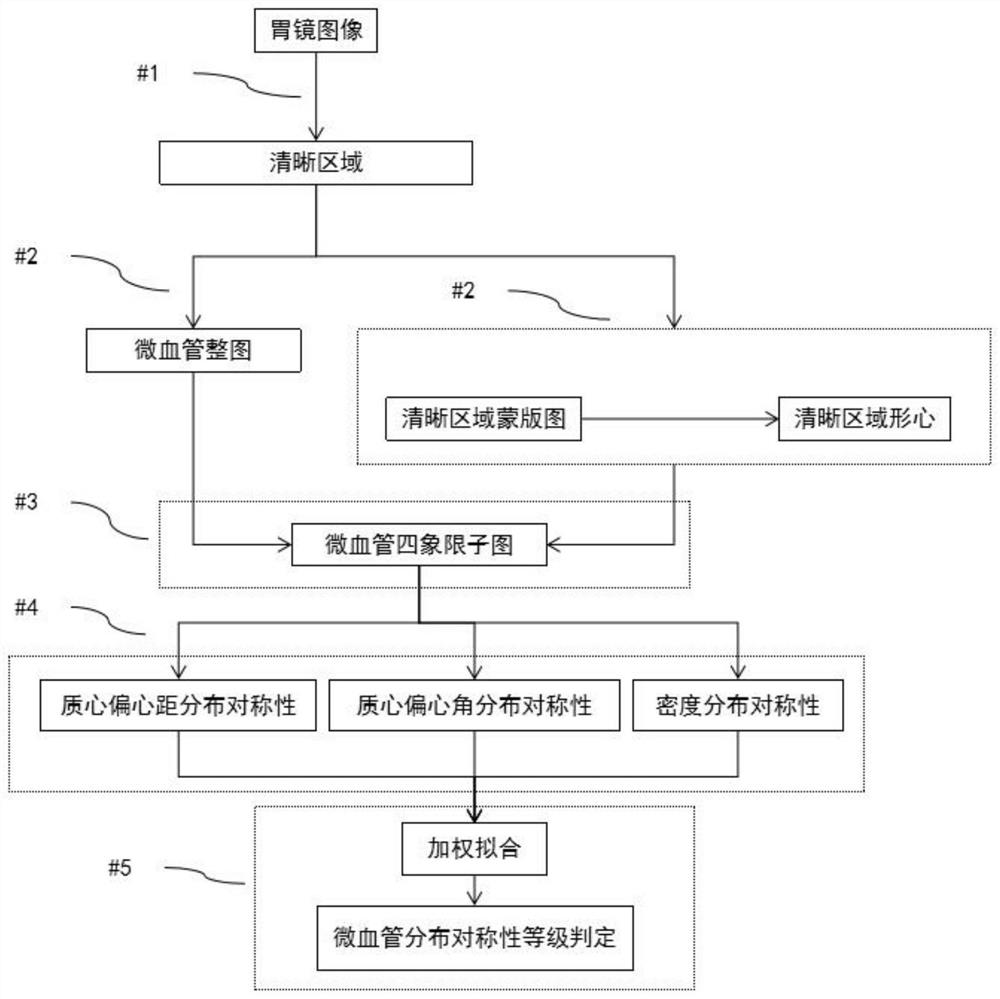
Quantification method of microvessel distribution symmetry in gastric mucosal staining and magnification imaging
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
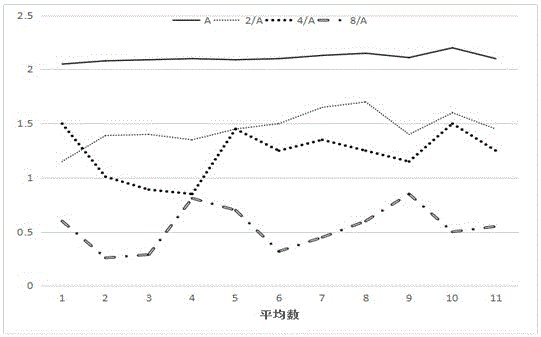
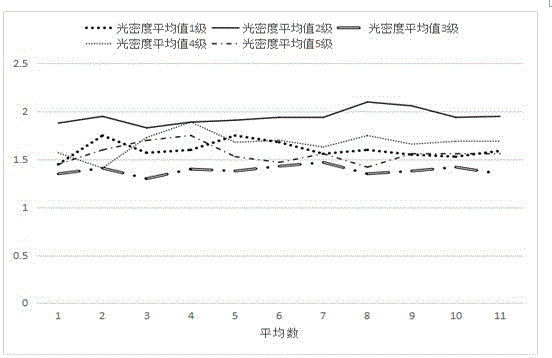
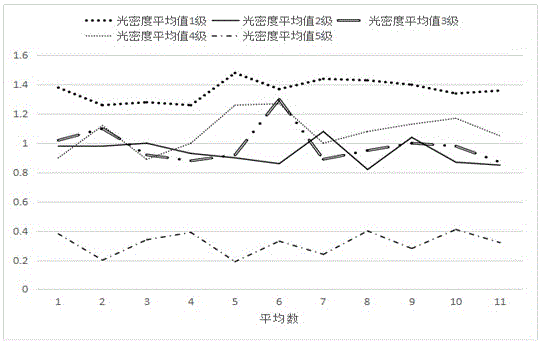
Cotton fiber maturity measuring method based on densitometry
InactiveCN105717073ASimple and fast operationHigh degree of automationTransmissivity measurementsCelluloseFiber
The invention relates to a method for measuring cotton fiber maturity based on an optical density method. The cotton fiber maturity is tested by using the optical density of the cotton fiber after iodine coloring. When the cotton fiber maturity is high, the more cellulose content, the higher the iodine blue reaction product concentration Higher, the greater the measured optical density, the concentration of liquid A is divided into four grades, namely A, A / 2, A / 4, A / 8, and the best A solution concentration of A / 4 tests the average optical density of cotton fibers, which can Clearly judge whether the cotton fiber is over-ripe, mature or immature. In the invention, under the action of swelling agent, the average optical density of the iodine blue reaction product between colored cotton fiber and iodine can indicate the maturity of cotton fiber. The invention has simple operation, high degree of automation, and is convenient for measurement on a general-purpose microscope.
Owner:INSPECTION & QUARANTINE TECH CENT OF GUANGDONG ENTRY EXIT INSPECTION & QUARANTINE BUREAU +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com