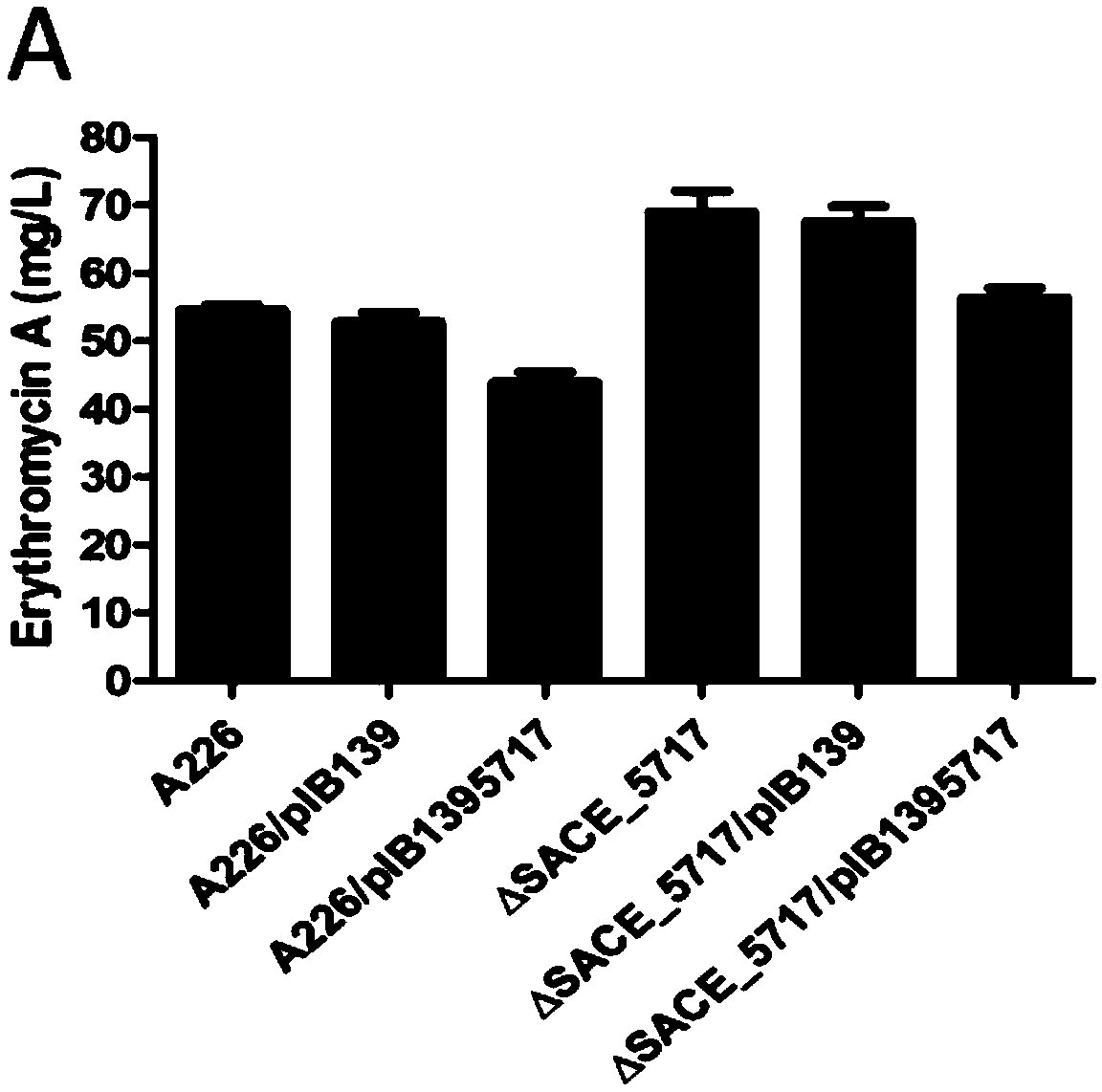Method for increasing output of erythrocin by SACE_5717 gene of saccharopolyspora erythraea
A technology of saccharopolyspora and erythromycin, which is applied in other directions of inserting foreign genetic material, genetic engineering, plant genetic improvement, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
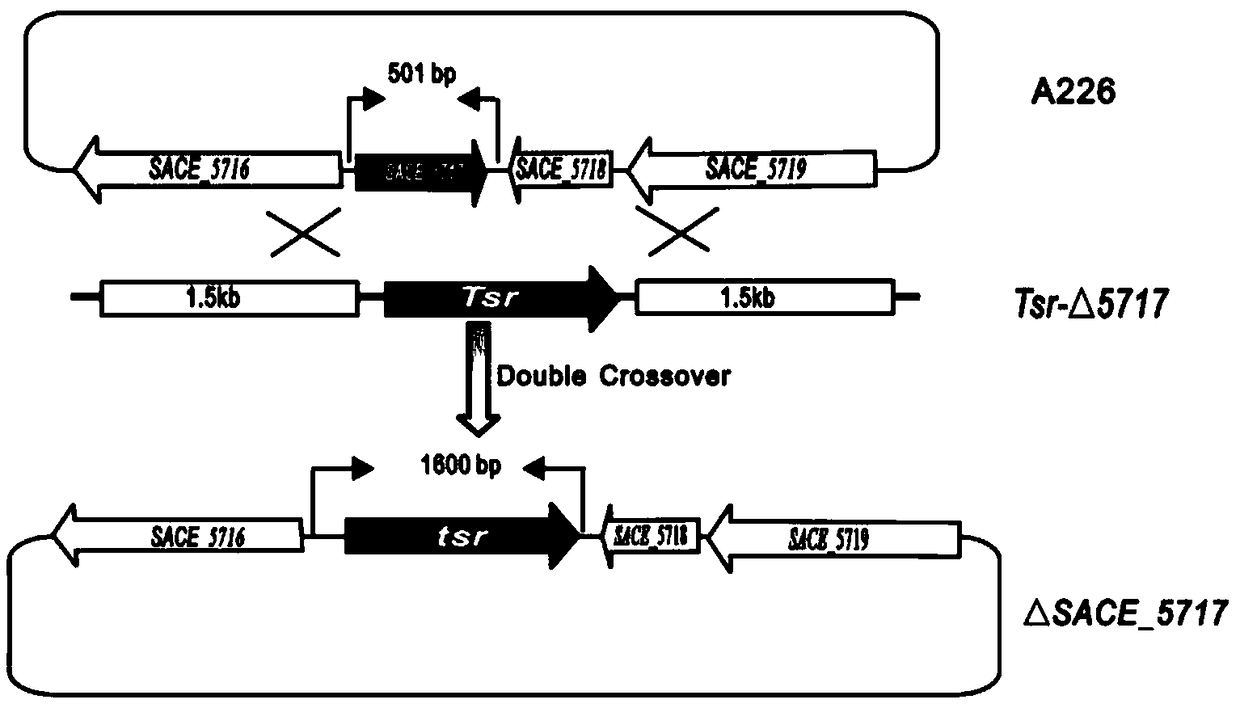
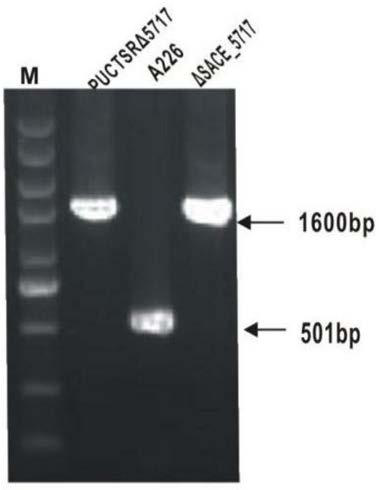
[0033] Construction of embodiment 1 SACE_5717 gene inactivation mutant:
[0034] The pUCTSR plasmid is a 1360bp thiostrepton resistance gene (tsr) inserted between the BamH I and Sma I restriction sites of pUC18. In order to knock out the SACE_5717 gene in Saccharopolyspora, use PUp1 / PUp2 and PD1 / PD2 as primers and the Saccharopolyspora genome as a template to amplify the homology arms of about 1.5 kb upstream and downstream of the SACE_5717 gene by PCR SU and SD DNA fragments.
[0035] The primers for PCR amplification of SU DNA fragments are PUp1, PUp2, the nucleotide sequence of PUp1 is shown in SEQ ID NO.3, and the nucleotide sequence of Pup2 is shown in SEQ ID NO.4; wherein, the " "AAGCTT" is the restriction site of HindIII, and "TCTAGA" in the sequence of Pup2 is the restriction site of Xbal.
[0036] The primers for PCR amplifying SD DNA fragments are PD1, PD2, the nucleotide sequence of PD1 is shown in SEQ ID NO.5, and the nucleotide sequence of PD2 is shown in SEQ ID ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] The construction of embodiment 2 SACE_5717 gene reversion bacterial strain:
[0040] In order to introduce the SACE_5717 gene in ΔSACE_5717, PCR amplification SACE_5717 gene primers were designed, namely P3 and P4; the nucleotide sequence of P3 is shown in SEQ ID NO.9, and the nucleotide sequence of P4 is shown in SEQ ID NO.10 where, "CATATG" in the P3 sequence is the NdeI restriction site, and "TCTAGA" in the P4 sequence is the XbaI restriction site.
[0041] The SACE_5717 gene was amplified from the Saccharopolyspora Rhododerma A226 genome, inserted between the Nde I and Xba I restriction sites of pIB139, and the expression plasmid pIB139-5717 was constructed, and then pIB139 was transformed into pIB139 by PEG-mediated protoplast transformation -5717 was imported into ΔSACE_5717. After preliminary screening with apramycin, the apramycin resistance gene (apr) was identified by PCR, and the obtained revertant strain was named ΔSACE_5717 / pIB139-5717.
Embodiment 3
[0042] Overexpression of SACE_5717 gene in embodiment 3 Saccharopolyspora erythromycetes A226:
[0043] pIB139-5717 was introduced into Saccharopolyspora Erythromycetes A226 by PEG-mediated protoplast transformation technology, and the apramycin resistance gene (apr) was used for PCR identification, and the obtained strain was named A226 / pIB139-5717.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com