Method for extracting intracellular coenzymes A and organic acids from saccharopolyspora erythraea
A technology of saccharopolyspora rubrum and organic acid, which is applied in the field of bioengineering and can solve the problems of intracellular metabolite analysis and research without saccharopolyspora rubrum, cell wall thickness, small cell diameter, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
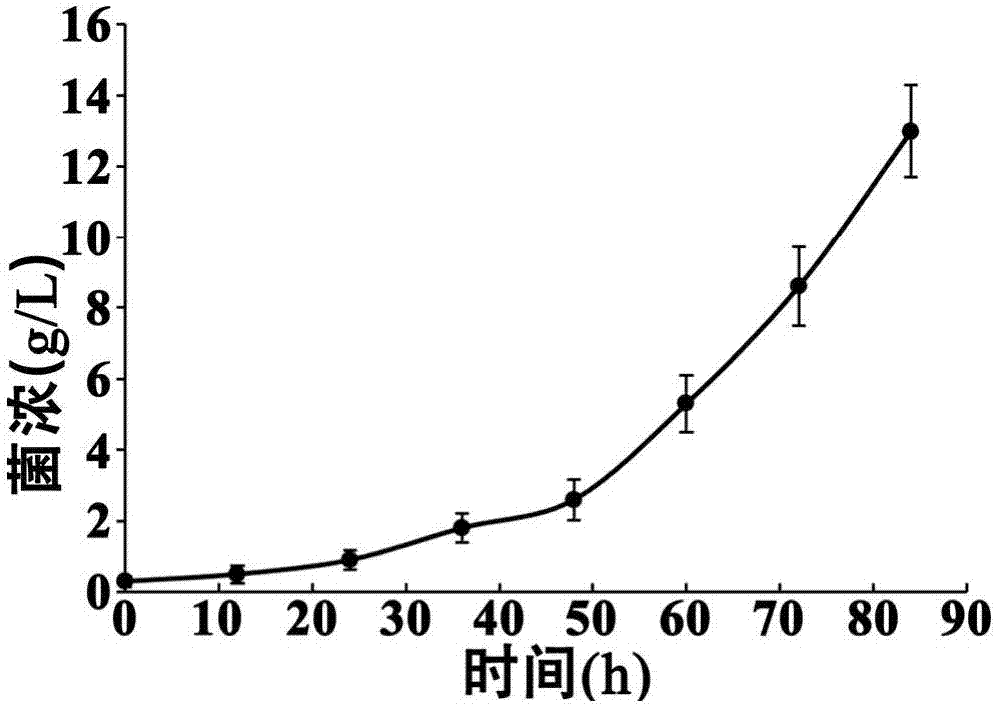
[0083] Embodiment 1, bacterial cell culture
[0084] 1. Strains and cultivation
[0085] (1) Strains
[0086] Saccharopolyspora erythraea E3 strain. Preservation method: Store the strain in 50% glycerol at -20°C.
[0087] (2) culture medium
[0088] Incline medium:
[0089]
[0090] Shake flask medium (g / L)
[0091]
[0092]
[0093] (3) Culture conditions
[0094] Incline culture
[0095] Use test tubes for slant culture. Spread the spores in the glycerol tube evenly on the slant medium with a bamboo stick, and culture at 34°C for 10 days.
[0096] shake flask culture
[0097] Take 20ml of sterile water and pour it into an inclined test tube, scrape off the spores on the inclined surface with a bamboo stick, pour the suspension into a 250ml shaker flask containing 5 small glass beads, and shake vigorously for 1min. Take 1ml of the spore suspension and add it to a 500ml shake flask containing 50ml shake flask culture medium. Put the shaker flask into a shak...
Embodiment 2
[0102] Embodiment 2, thalline inactivation and intracellular metabolite extraction
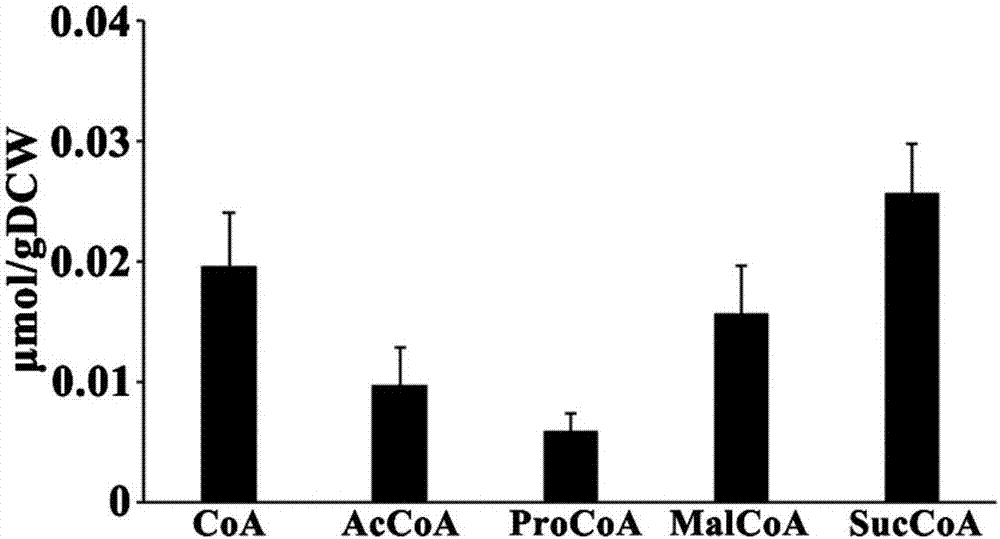
[0103] Coenzyme A substances and organic acids were obtained from Saccharopolyspora rubrum intracellularly by inactivation of bacteria and extraction of intracellular extracts.
[0104] 1. Inactivation method
[0105] The present inventors have found in research that when extracting organic acids from Saccharopolyspora rubrum, since the organic acid exists both inside and outside the cells of Saccharopolyspora rubrum, the cells must be cleaned after inactivation to remove the extracellular Effect of organic acids on determination of intracellular organic acid concentrations. Coenzyme A substances only exist in the cell, not outside the cell, and it is not necessary to remove the medium during the extraction process. Therefore, in the liquid nitrogen inactivation process, different methods of operation were adopted for the extraction of coenzyme A substances and organic acids.
[0106] Liqui...
Embodiment 3
[0130] Embodiment 3, intracellular metabolite extraction method comparison
[0131] After comparison, the inventor has focused on the following inactivation methods: liquid nitrogen inactivation and cold methanol inactivation; meanwhile, has focused on the following extraction methods: boiling ethanol method, liquid nitrogen freeze-thaw method and liquid nitrogen grinding method , to compare the advantages and disadvantages of these methods for the extraction effect of Saccharopolyspora rubrum intracellular extract.
[0132] 1. Analysis for the extraction and determination of intracellular coenzymes
[0133] The present inventors aimed at the four combinations of liquid nitrogen inactivation + liquid nitrogen freeze-thaw, liquid nitrogen inactivation + liquid nitrogen grinding, cold methanol inactivation + liquid nitrogen grinding, liquid nitrogen inactivation + boiling ethanol extraction, and the coenzyme A substances The performance of different extraction methods was compa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com