Method for increasing yield of erythromycin by SACE_5754 gene pathway of Saccharopolyspora erythraea
A technology of Saccharopolyspora erythromycin and erythromycin, which is applied in the field of genetic engineering and can solve problems such as uneconomical, time-consuming erythromycin A, and unsuitability for wide application
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
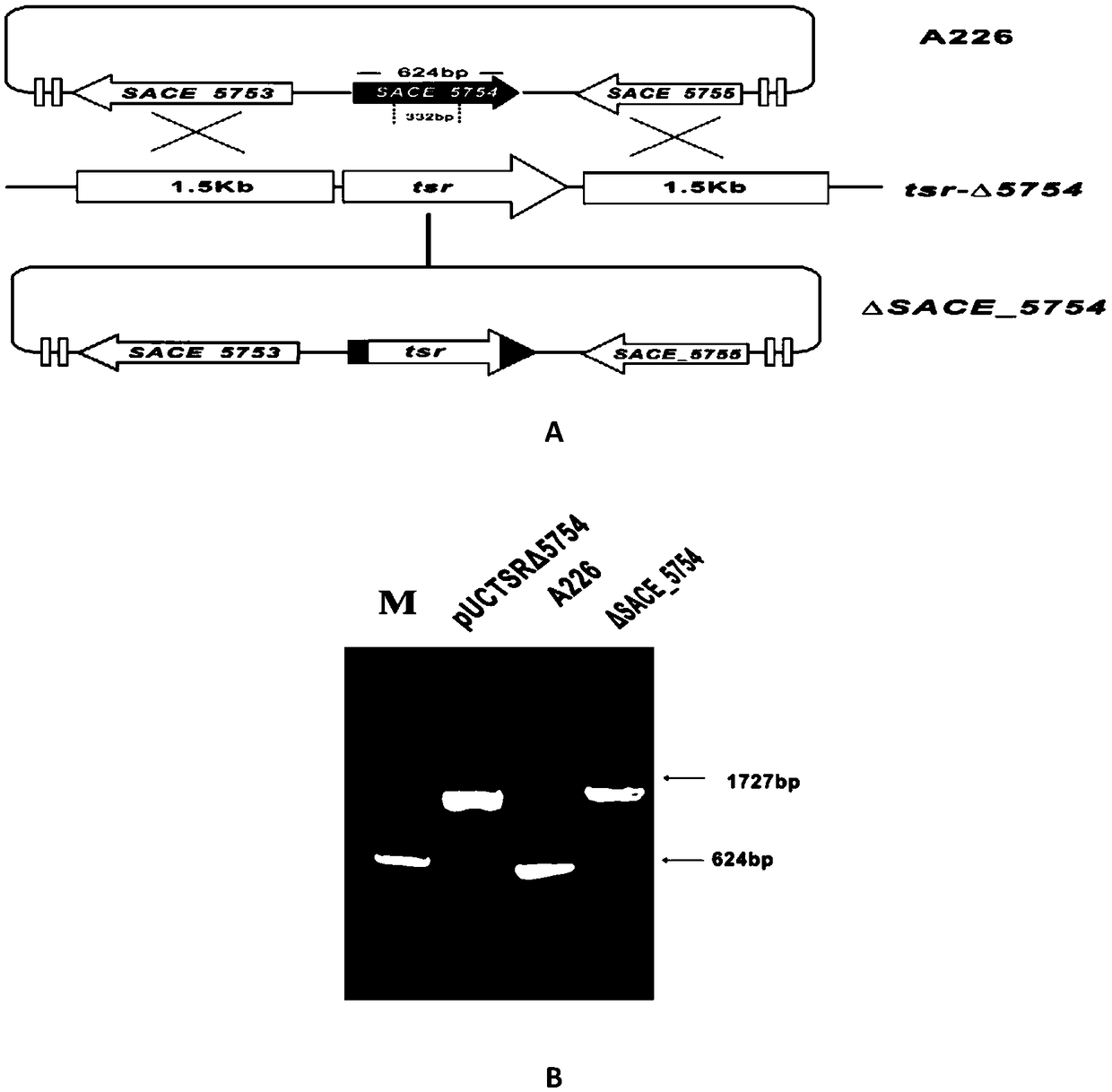
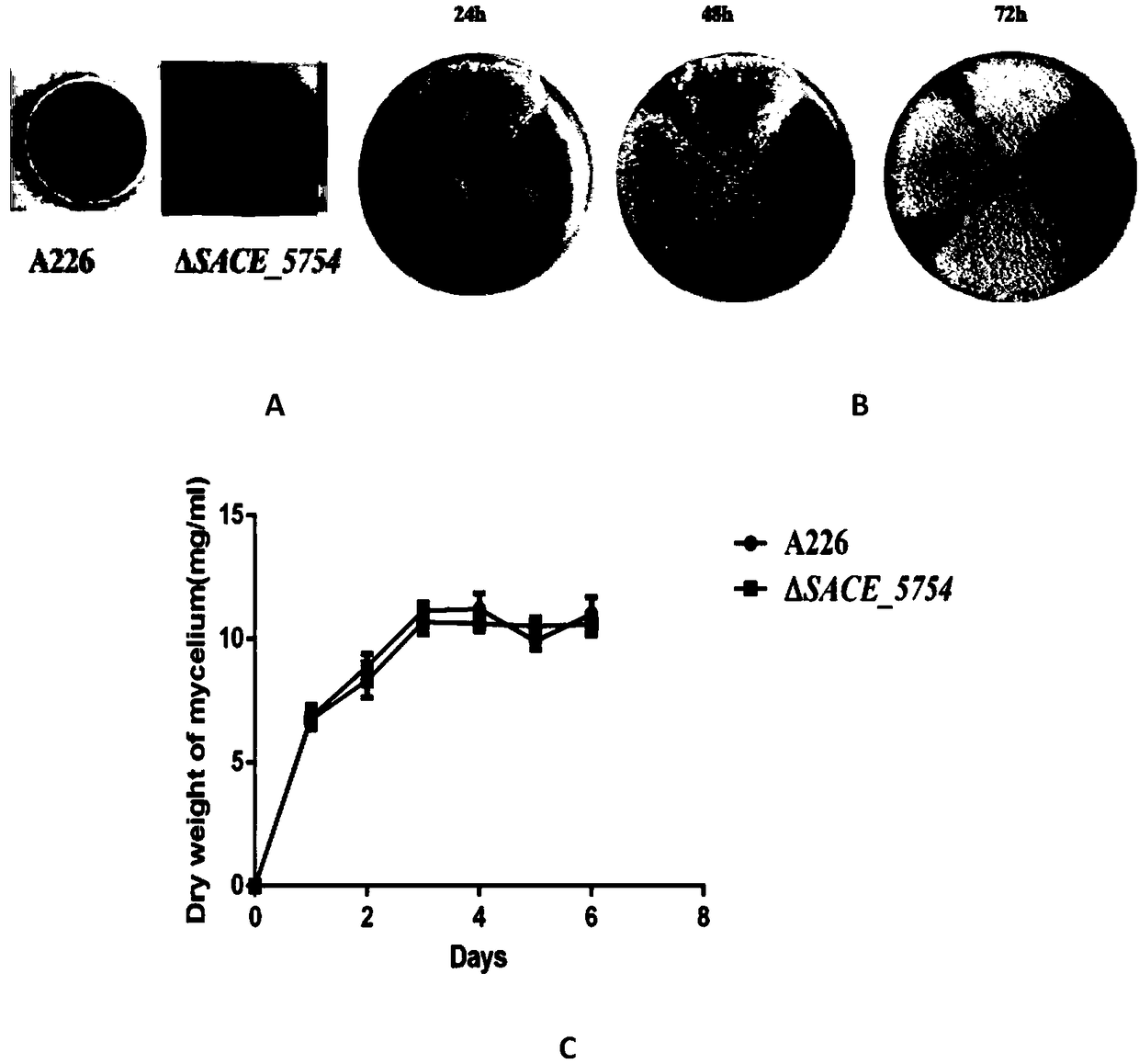
[0038] The bacterial strains and plasmids used in the examples are shown in Table 1. Escherichia coli were cultured in liquid LB medium at 37°C or on solid LB plates supplemented with 1.25% agar. The erythromycin-producing bacterium Erythropolyspora saccharopolyspora and its engineered strains were cultured in tryptone soybean broth (TSB) medium at 30°C or on R3M plates containing 2.2% agar.
[0039]
[0040]
[0041]
[0042] Bacteria and plasmids used in the present embodiment of table 1
[0043] In the examples, PEG3350, lysozyme, TES, casamino acids, thiostrepton, and apramycin were purchased from Sigma. TSB, yeast extract, and peptone were purchased from Oxoid. Glycine, agar powder, sodium chloride, and other biological reagents were purchased from reagent companies. The general operating techniques for Escherichia coli and Saccharopolyspora red mold follow standard operations. The synthesis of primers and DNA sequencing were completed by Sangon Bioengineering ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com