Method for synthesizing secondary metabolites of saccharopolyspora erythraea by controlling gene dasR and application of gene dasR
A technology for Saccharopolyspora rubrum and secondary metabolites, which can be applied in the field of genetic engineering and can solve problems such as low efficiency, time-consuming and labor-intensive efficiency, and lack of genome sequence information.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
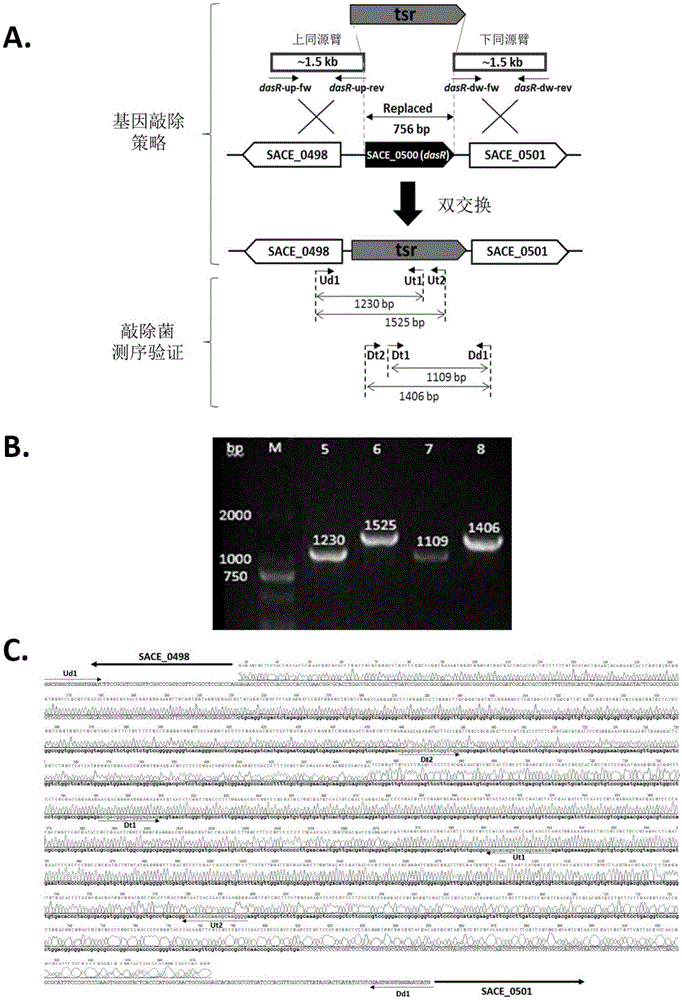
[0031] Construction of dasR Gene Knockout Engineering Bacteria Using Double Crossover Homologous Recombination Gene Knockout Technology
[0032] 1.1 Construction of dasR gene knockout plasmid
[0033] The pUC18-tsr plasmid is a 1.36 kb thiostrepton resistance gene (tsr) inserted between the BamHI and SmaI restriction sites of the pUC18 plasmid. In order to knock out the dasR gene in the Saccharopolyspora rubrum genome, dasR-up-fw / rev and dasR-dw-fw / rev were used as primers respectively, and the Saccharopolyspora rubrum genome was used as a template to amplify the dasR gene by PCR. Homology arm DNA fragments of about 1.5kb each in the upstream and downstream.
[0034] The primers used to amplify the DNA fragment of the upper homology arm are:
[0035] dasR-up-fw:5'-AACTGCAGGTCTCGGCCAGCTTCAGGG-3'
[0036] dasR-up-rev:5'-GCGGGATCCCGTTCCTCCCTACCACCGCAA-3'
[0037] The primers used to amplify the DNA fragment of the lower homology arm are:
[0038] dasR-dw-fw:5'-TATGGTACCTACAA...
Embodiment 2
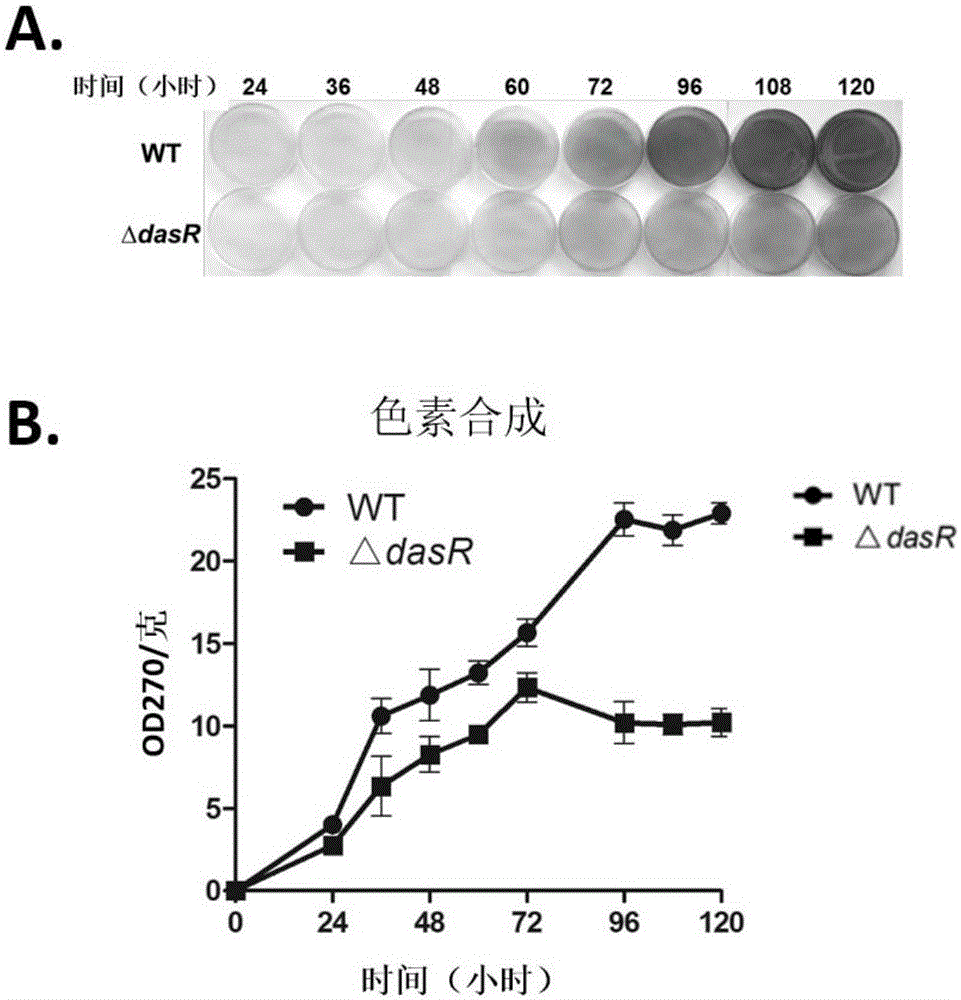
[0063] Determination of the Growth of DasR Gene Knockout Engineering Bacteria and the Production of Secondary Metabolites
[0064] 1.1 Determination of bacterial growth
[0065] Saccharopolyspora rubrum was activated in TSB, and R2YE plates were prepared and cellophane was laid on the surface, and wild-type strains and △dasR strains were inoculated respectively. Cultivate in a constant temperature incubator at 30°C, remove the cellophane and collect the bacteria at 24h, 36h, 48h, 60h, 72h, 96h, 108h and 120h respectively, and collect 3 plates of bacteria for each strain at each time point . Collect the thalli of 3 plates respectively in the 1.5ml centrifuge tube that has been weighed (referred to as the initial amount), and then dry it overnight (12h) in a 50°C oven to make it completely dry, and then weigh it (weighed). is the final amount), subtract the initial amount from the final amount to obtain the dry weight of the thalline (in milligrams).
[0066] The result is as...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com