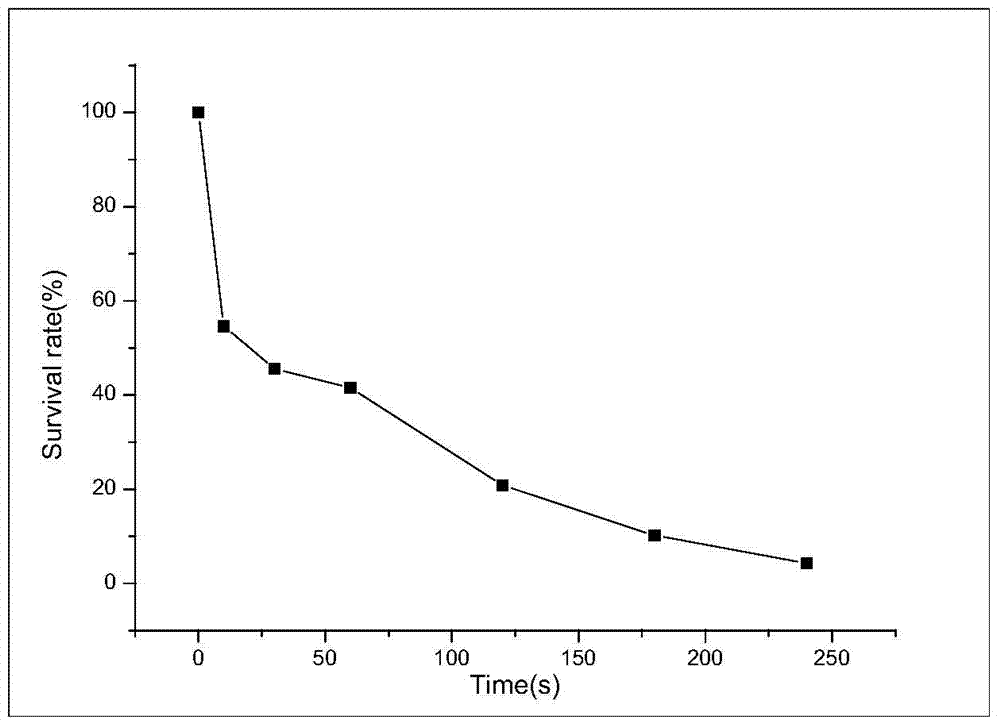
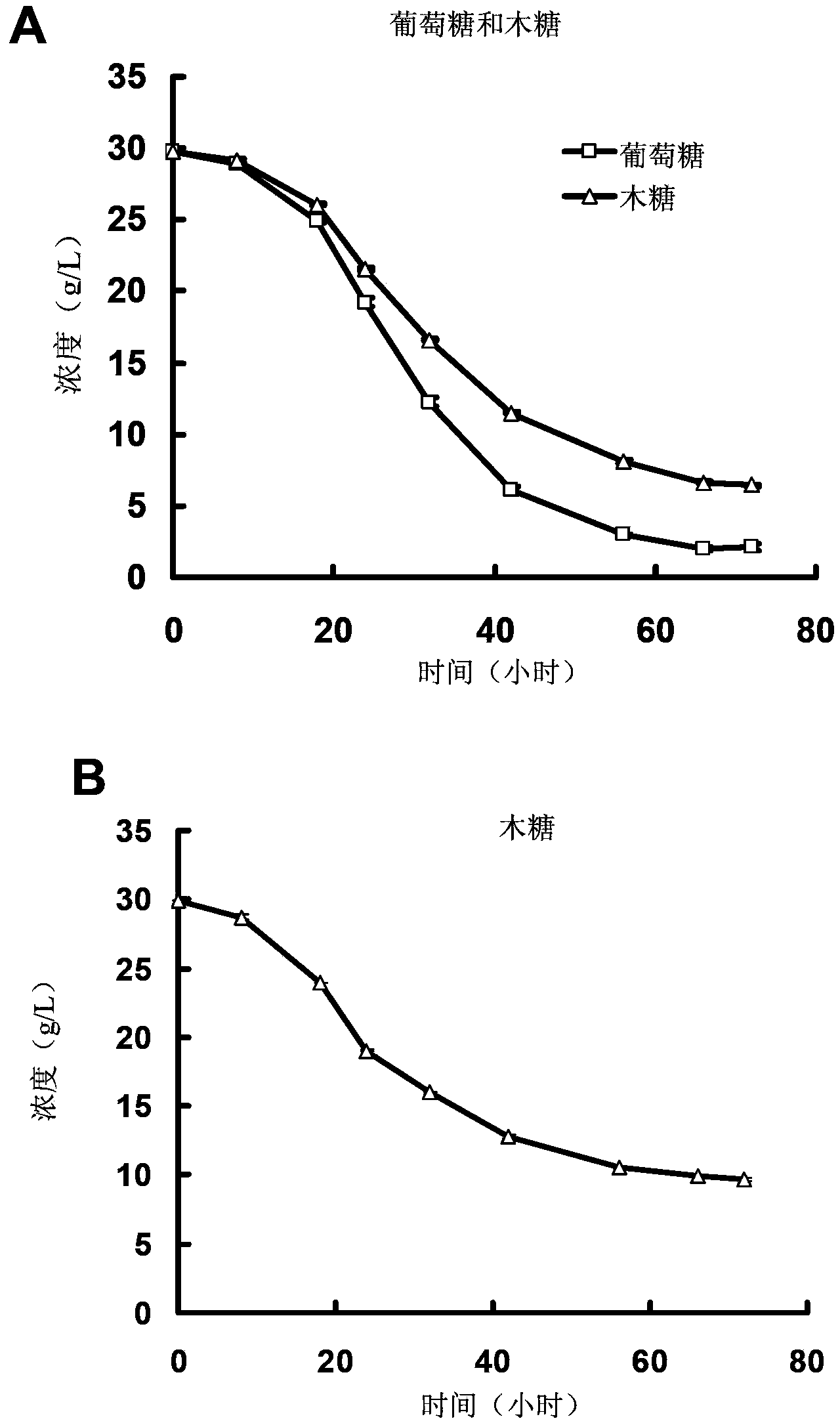
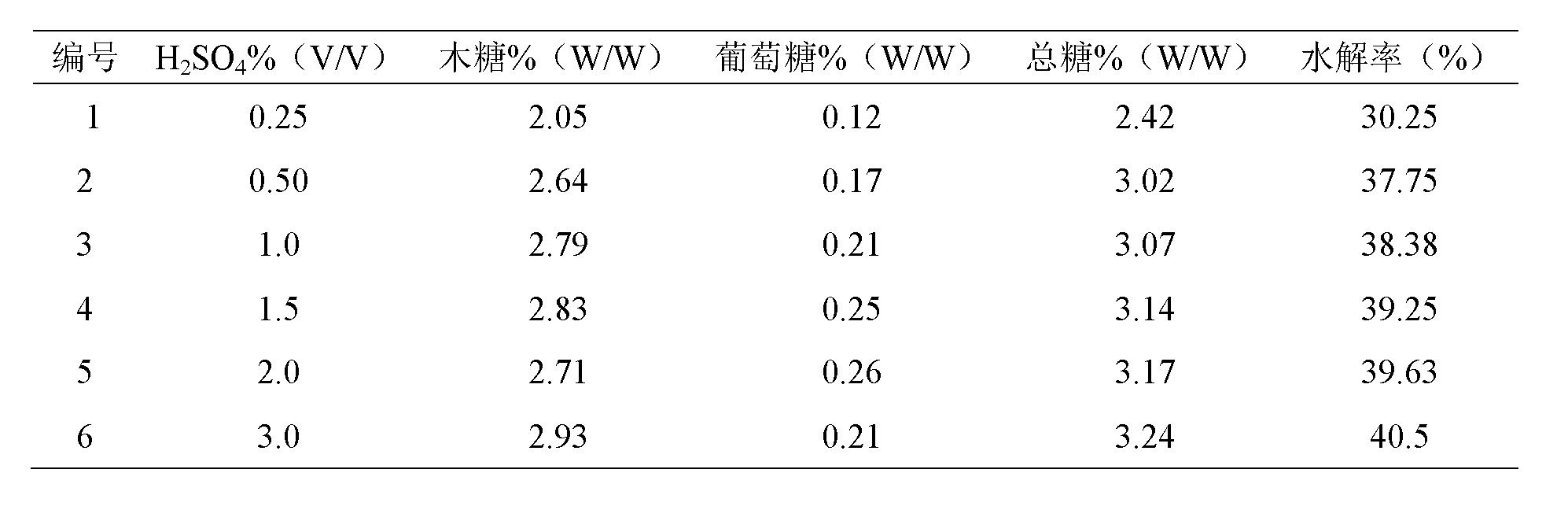
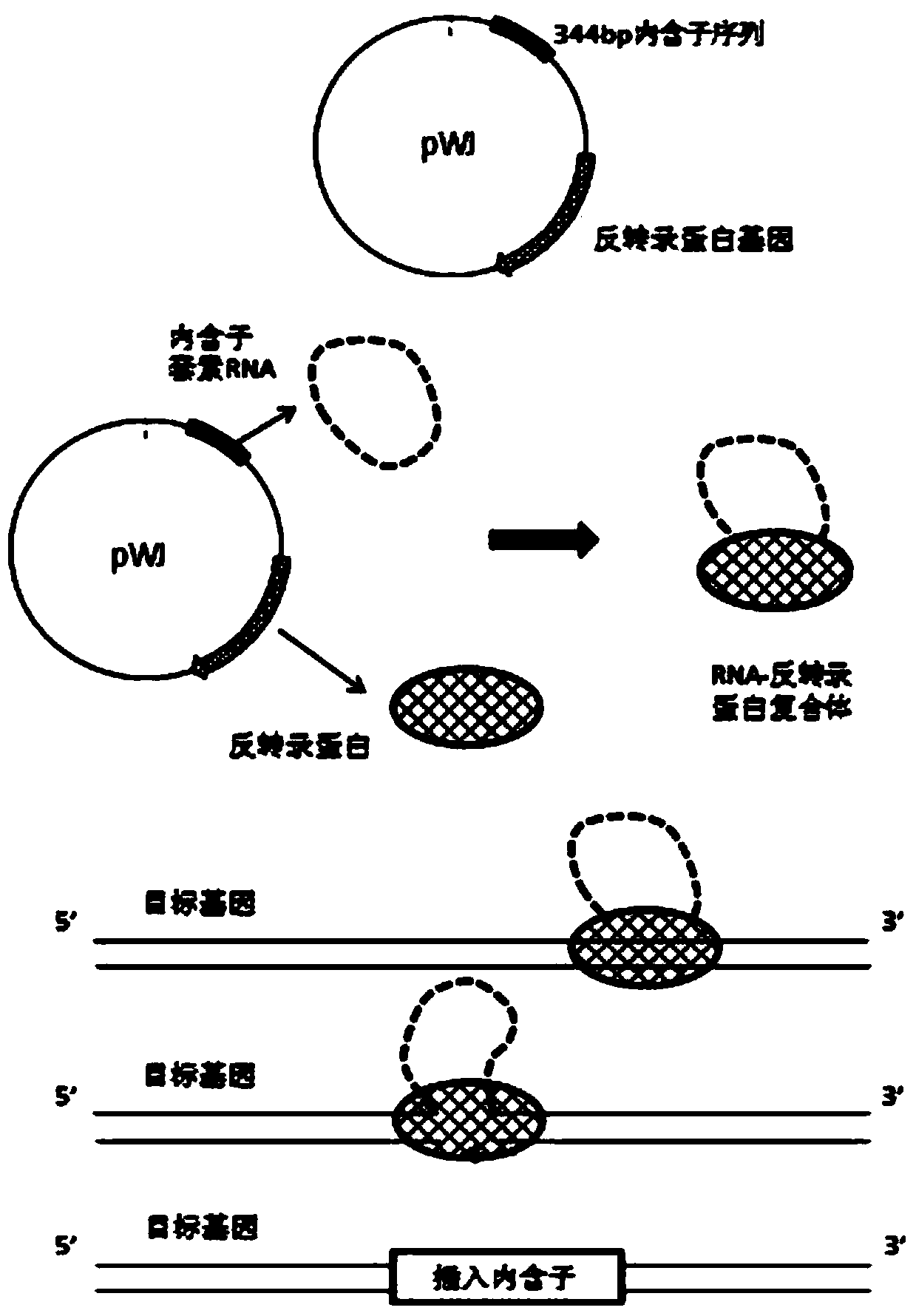
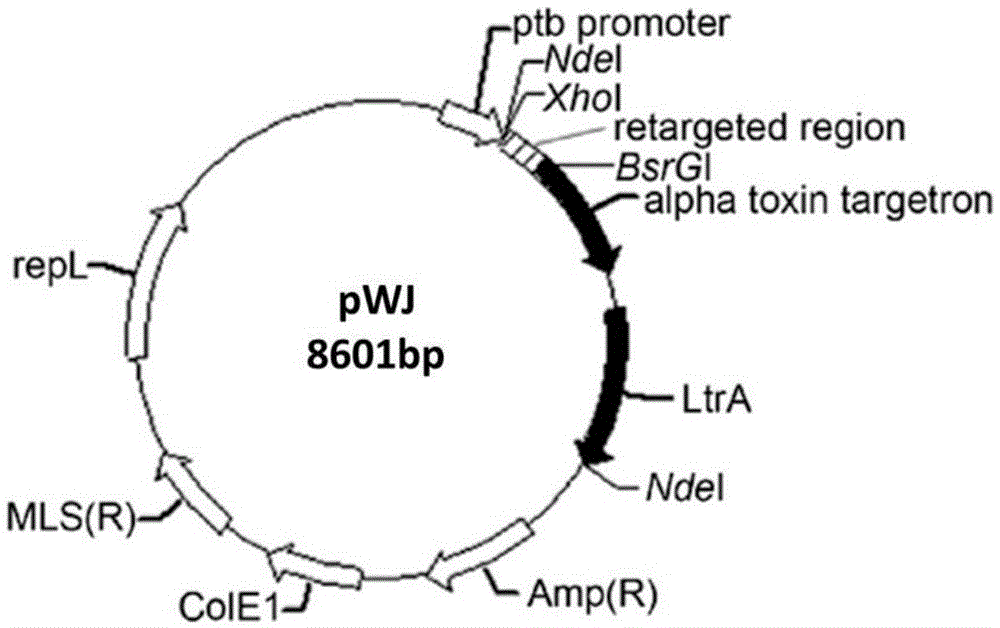
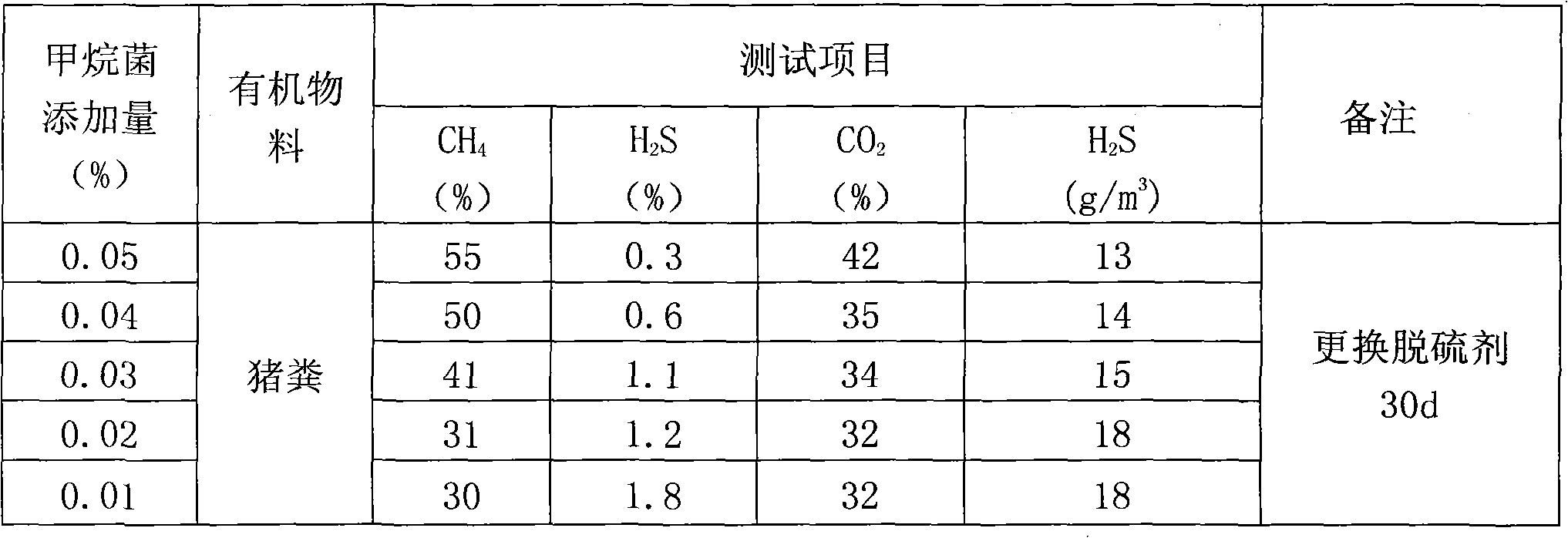
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
82 results about "Clostridium beijerinckii" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Clostridium beijerinckii is a gram positive, rod shaped, motile bacterium of the genus Clostridium. It has been isolated from feces and soil. Produces oval to subterminal spores. it is named after Martinus Beijerinck who is a Dutch bacteriologist.
Special microorganism composite bacterial agent for directly decomposing and fermenting crops straws to generate marsh gas and application method thereof
InactiveCN101775359AGood degradation activityEasy to storeFungiBacteriaBacillus licheniformisVaccination
The invention discloses a special microorganism composite bacterial agent for directly decomposing and fermenting crops straws to generate marsh gas and application method thereof. The special microorganism composite bacterial agent is liquid or solid, and is formed by fermenting, culturing, combining and compositing one or a plurality of bacillus cereus, bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, bacillus megaterium, bacillus mucilaginosus, bacillus circulans, bacillus sphaerieus, clostridium sporogenes, clostridium acetobutylicum, clostridium barati, clostridium beijerinckii, clostridium thermocellum, trichoderma viride, trichodermareesei and aspergillus niger. Simultaneously, by taking the special microorganism composite bacterial agent as a vaccination bacterial agent, the invention provides an application method for decomposing the crops straws and accelerating the ferment to generate marsh gas; and the microorganism composite bacterial agent-treated crops straws have fast ferment speed, large marsh gas generation quantity, low treating cost and no secondary pollution, can be fermented to generate the marsh gas under the condition of no faeces of poultry, and have very wide application range.
Owner:刘相梅 +1
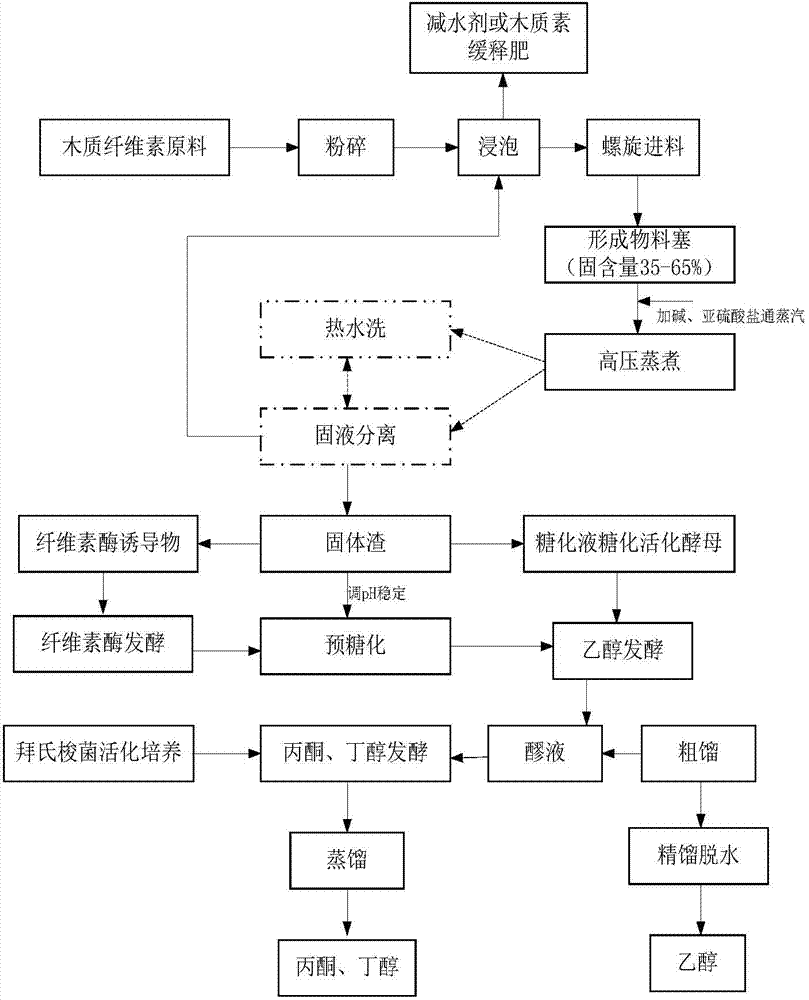
Method for comprehensive utilization of lignocellulosic biomasses
ActiveCN104774876AFully open the crystalline structureImprove accessibilityBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesAdditive ingredientFermentation
The invention discloses a method for the comprehensive utilization of lignocellulosic biomasses, which comprise the following steps: (1) crushing a raw lignocellulose material and adding water so as to form mixed liquid, adding alkaline for adjustment, adding sulfite, and cooking the obtained object so as to obtain a mixture; (2) carrying out solid-liquid separation on the mixture obtained in the step (1), washing and cooling an obtained solid, mixing liquid obtained by washing with liquid obtained by solid-liquid separation, cyclically applying the obtained mixture to the step (1), and when the dry matter content of the liquid reaches a certain value, drying the liquid so as to obtain sulfonated lignin; (3) adjusting the pH value of the solid washed in the step (2), adding cellulase liquid, and carrying out highly enriched material saccharification; (4) adding a yeast into saccharification liquid obtained in the steps (3) to ferment, and treating the fermented mixture so as to obtain anhydrous ethanol; and (5) feeding clostridium beijerinckii into the waste fermentation liquor obtained in the step (4) to ferment, and then distilling the obtained object so as to produce ethanol, acetone and butanol. According to the invention, the efficient utilization of main ingredients such as lignin, cellulose and hemicellulose in lignocellulose biomasses is realized.
Owner:SHANDONG LONGLIVE BIO TECH CO LTD
Clostridium beijerinckii with high stress resistance and application thereof
InactiveCN102174433AStrong toleranceImprove sugar conversion rateBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFiberSolvent
The invention relates to Clostridium beijerinckii with high stress resistance which can directly utilize a virus-carrying wood fiber acid-hydrolyzed sugar solution for fermentation to produce butanol and an application thereof. The Clostridium beijerinckii disclosed by the invention has the category name of Clostridium beijerinckii IB4 and the collection number CCTCC No. is M2010310. Ion beam mutation is adopted, a resazurin flat plate containing inhibitors such as phenols and a shake flask are used for fermenting and screening, the obtained mutant strain uses a virus-carrying corncob acid-hydrolyzed sugar solution as a carbon source, the total solvent yield and butanol yield in a 2L fermentation tank are up to 10.3g / L and 7.1g / L respectively which are 4.3 times and 4.4 times of those obtained by adopting the starting strain cultivated under the same conditions, the sugar conversion rate is 0.35; and the Clostridium beijerinckii has the advantages of high stress resistance, high solvent yield, high sugar conversion rate and good repeatability, thereby being a good strain which is suitable for utilizing the wood fiber raw material to produce butanol.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Clostridium beijerinckii strain and applications thereof
The invention discloses a clostridium beijerinckii strain CM 20 with high yield of butanol, wherein the classification name of the clostridium beijerinckii strain CM 20 is Clostridium beijerinckii, and the clostridium beijerinckii strain CM 20 is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on June 17, 2014, and has the preservation number CGMCC No.9354. The clostridium beijerinckii strain CM 20 provided by the invention can be used for producing butanol with high yield through fermentation by utilizing lignocellulose enzymatic hydrolysate detoxified by calcium hydroxide, the total solvent yield can achieve 19g / l, the sugar utilization ratio is high, the yield of butanol is high, and the problems that the capacity of the strain and the raw materials are insufficient when the traditional biological fermentation method is adopted for producing butanol are solved.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Clostridium beijerinckii strain and screening method and use thereof
InactiveCN102533612ALow costBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementPrimary screeningMicrobiology
The invention discloses high-butanol-yield clostridium beijerinckii, which is obtained by sampling, enriching, primary screening, separating and secondary screening. The strain is identified as clostridium beijerinckii which belongs to the class of clostridium beijerinckii gxas.28. The collection number of the strain is CCTCCM2011454. According to the invention, butanol is produced by using molasses as a raw material and by fermentation of clostridium beijerinckii. The butanol yield is 9.42 to 13.11g / L, and the ratio of the butanol to total solvent reaches 70 to 85 percent.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Recombinant clostridium and construction method and use thereof
InactiveCN101423813AIncrease productionIncrease supplyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGramButanone
The invention discloses a recombinant clostridium, a method for constructing the same and application thereof. The method for constructing the recombinant clostridium is to introduce a gene for encoding formic dehydrogenase into a clostridium to construct a recombinant bacterium. The clostridium is an acetone butanol clostridium or a clostridium beijerinckii. The invention also discloses a method for producing butanol, which is to ferment and culture the recombinant bacterium constructed by the method for constructing the recombinant clostridium to produce the butanol. The yield of butanone produced through fermenting the recombinant acetone butanol clostridium constructed by the invention can reach as high as 14.1 grams per liter.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Clostridium beijerinckii and application thereof
The invention discloses clostridium beijerinckii XH0906 producing butanol and application thereof. The classification term of the clostridium beijerinckii XH0906 is clostridium beijerinckii which is preserved in CGMCC on 4th, May, 2014 and has the preservation number of CGMCCNo.9124. The strain can growth in a non-strict anaerobic environment and ferment to produce butanol. No sodium hydrosulfite needs to be added to remove oxygen into a fermenting culture medium. In the fermenting process, N2 needs not to be introduced to maintain the anaerobic environment, so that the phenomenon that thalli do not grow as a result of halfway oxygen removal is avoided, and the energy consumption is reduced; moreover, the clostridium beijerinckii XH0906 has the characteristics of high output of butanol, few acetone and ethanol byproducts and the like, the pressure of follow-up butanol recovery is alleviated, and the separating energy consumption is reduced.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Composite microbial agent for treating domestic garbage and method for treating domestic garbage by using composite microbial agent
InactiveCN106978370AIncrease functional diversityImprove applicabilityFungiBacteriaPseudomonas putidaMicrobial agent
The invention relates to a composite microbial agent for treating domestic garbage and a method for treating the domestic garbage by using the composite microbial agent. The composite microbial agent for treating the domestic garbage is prepared from the following components: brevendimonas diminuta, pseudomonas stutzeri, pseudomonas maltophilia, pseudomonas fluorescens, pseudomonas putida, candida utilis, candida lipolytica, schizosaccharomyces pombe, schizosaccharomyces octosporus, bacillus megatherium, bacillus subtilis, bacillus cereus, alcaligenes faecalis, clostridium beijerinckii, achromobacter denitrificans, nocardia coralline, and the like, wherein the parts by weight of the brevendimonas diminuta are 1-5, the parts by weight of the pseudomonas stutzeri are 1-5, the parts by weight of the pseudomonas maltophilia are 1-5, the parts by weight of the pseudomonas fluorescens are 1-5, the parts by weight of the pseudomonas putida are 1-5, the parts by weight of the candida utilis are 1-5, and the parts by weight of the candida lipolytica are 1-5.
Owner:哈尔滨明慧生物技术开发有限公司
Novel strain for producing butanol and method for producing butanol
ActiveCN103571772AStrong toleranceIncrease productionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesResazurinSugar
The invention discloses a novel clostridium beijerinckii strain for producing butanol. The strain has a classification name of clostridium beijerinckii IT66 (Clostridium beijerinckii IT66) and has a collection number of CCTCCM NO:2011404. The invention also discloses application of the clostridium beijerinckii in fermentation production of the butanol. The clostridium beijerinckii IB4 is subjected to continuous culture and plasma induced mutation by adopting a chemostat, and a strain which tolerates an inhibitor and is high in reducing power is screened through a resazurin flat plate and is high in acidolysis byproduct resistance, high in butanol ratio and high in solvent yield. When a non-detoxified corncob acidolysis sugar solution is a carbon source, the total solvent yield and butanol yield in a 5L fermentation tank respectively reach 11.3g / L and 9.1g / L and are respectively improved by 2.3 times and 2.4 times compared with those of an original strain cultured under the same conditions, the butanol ratio is 80 percent, the sugar conversion rate is 0.32, and the strain has significant social meaning and economic value.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Bacterial strain for producing alcohol fuels by synchronously utilizing glucose and xylose and application of bacterial strain
ActiveCN104673712A"Secondary Growth Phenomenon AvoidanceStable fermentationBacteriaBiofuelsCelluloseAlcohol fuel
The invention discloses a bacterial strain for producing alcohol fuels by synchronously utilizing glucose and xylose and application of the bacterial strain. The bacterial strain is clostridium beijerinckii SE-2 with a culture preservation number of CCTCC No.M2014384. The bacterial strain capable of synchronously utilizing glucose and xylose is obtained by synchronously utilizing glucose and xylose in a natural environment to produce butyl alcohol and screening an alcohol microorganism, is a Gram-positive gemma-bearing bacterium, and the glucose and xylose in corncob hydrolysate can be synchronously utilized to produce the butyl alcohol and alcohol. A secondary growth phenomenon in a fermentation process can be eliminated by synchronously utilizing glucose and xylose in lignocelluloses hydrolysate, the fermentation period is shortened, the substrate utilization efficiency in the production process and the production strength of equipment are improved, and the economical efficiency of the industry of producing the butyl alcohol and the alcohol by the lignocelluloses are improved.
Owner:ENERGY RES INST OF SHANDONG ACAD OF SCI
Clostridium beijerinckii for hydrogen generation via fermentation as well as fermentation method and application of clostridium beijerinckii
ActiveCN104164395ALow costImprove competitivenessBacteriaMicroorganism based processesWater bathsBiofuel
The invention discloses clostridium beijerinckii for hydrogen generation via fermentation as well as a fermentation method and an application of the clostridium beijerinckii. The clostridium beijerinckii is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) of the China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms (CCCCM), and has the preservation number of CGMCC No.9411. The culture method of the clostridium beijerinckii comprises the following steps: firstly, carrying out anaerobic culture on a freeze-stored liquid of the clostridium beijerinckii so as to obtain a cultured bacterial culture solution; centrifuging the bacterial culture solution and then resuspending thalli so as to obtain a resuspended bacterial solution taken as an inoculant source; inoculating the inoculant source into a hydrogen generation culture solution and carrying out photophobic culture on a constant-temperature shaking water bath for generating hydrogen until the hydrogen generation is finished. The clostridium beijerinckii can be fermented to generate hydrogen by utilizing a carbon source and a nitrogen source which are common in natural world and are difficultly utilized by the majority of microorganisms, and ethyl alcohol, butyl alcohol and other biofuels are generated while the hydrogen generation is carried out via the fermentation. The clostridium beijerinckii disclosed by the invention is the first novel multifunctional clostridium beijerinckii strain in the current report, and can be applied to the hydrogen generation of biomass via fermentation, the production of biofuels such as ethyl alcohol and butyl alcohol. Thus, the clostridium beijerinckii disclosed by the invention has a wide application prospect.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Method for increasing consumption rate of clostridium beijerinckii xylose
The invention discloses a method for increasing the consumption rate of clostridium beijerinckii xylose. Through knocking out transcriptional regulation factor xy1R of the clostridium beijerinckii xylose and clostridium araR and / or increasing the activity of a xylose transport protein, the clostridium can consume higher-concentration xylose and / or arabinose in a culture medium, so that higher-concentration products such as butanol, acetone and ethanol can be produced.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
Method for producing butanol by mixed fermentation of bagasse and molasses serving as raw materials
InactiveCN102703523AIncrease productionImprove conversion rateMicroorganism based processesFermentationMicroorganismHydrolysate
The invention discloses a method for producing butanol by mixed fermentation of bagasse and molasses serving as raw materials. The method comprises the following steps of: hydrolyzing the crushed bagasse by using dilute acid, directly mixing the obtained hydrolysate and the molasses to form the fermentation raw materials, and fermenting the fermentation raw materials by using Clostridium beijerinckii gxas. 28CCTCC M201454 to produce the butanol. The yield of the butanol can reach 11.07 g / L. By adopting the method, the sugar making byproduct of sugarcane can be effectively used for producing the butanol through fermentation, the process is simple, the raw material cost for producing the butanol by microbial fermentation is reduced, and the method has social significance and application value.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Clostridium beijerinckii with high stress resistance and application thereof
InactiveCN103911334AEfficiently improve stress resistanceImprove stress resistanceBacteriaBiofuelsBiotechnologyVanillic acid
The invention discloses clostridium beijerinckii with high stress resistance and an application of the clostridium beijerinckii. A gene Cbei_3304 of the clostridium beijerinckii strain with high stress resistance cannot be expressed normally, and a normal Cbei_3304 protein function is deleted, so that the clostridium beijerinckii has high stress resistance to toxic substances such as ferulic acid and vanillic acid, also has high stress resistance to toxic substances in virus-carrying wood fiber acidolysis sugar liquor, and can be used for producing butyl alcohol through fermentation very well. The invention provides a simple and efficient method for improving stress resistance of the clostridium beijerinckii. The clostridium beijerinckii which has high stress resistance to the toxic substances in the virus-carrying wood fiber acidolysis sugar liquor and can be used for efficiently producing butyl alcohol can be obtained by only enabling the clostridium beijerinckii to delete the normal Cbei_3304 protein function, so as to be helpful in promoting the efficient utilization of wood fiber resources.
Owner:GUANGDONG PROVINCIAL BIOENGINEERING INST (GUANGZHOU SUGARCANE IND RES INST)
Clostridium beijerinckii with high electricity yield and application thereof
InactiveCN103898031AIncrease production capacityEasy to useBacteriaFinal product manufactureMethyl ViologenPollution
The invention discloses clostridium beijerinckii with high electricity yield. The number of the strain is M13. Clostridium beijerinckii is collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on September 14, 2013, with collection number of CCTCC NO:M2013424. The invention also discloses an application of clostridium beijerinckii with high electricity yield to electricity generation. When 0.15g / L of methyl viologen serves as an electronic mediator, the maximum output voltage of clostridium beijerinckii in 1g / L of glucose seed solution is as high as 230mV, and the maximum output power density is 79.2mW / m<2>. Clostridium beijerinckii has the advantages that a process is simple, is convenient to operate, is pollution-free and is low in cost; utilization of fuel of clostridium beijerinckii is popularized more widely; the electron recovery rate is relatively high; the energy crisis is relieved; clostridium beijerinckii is an excellent strain suitable for microbial fuel cell study and application.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
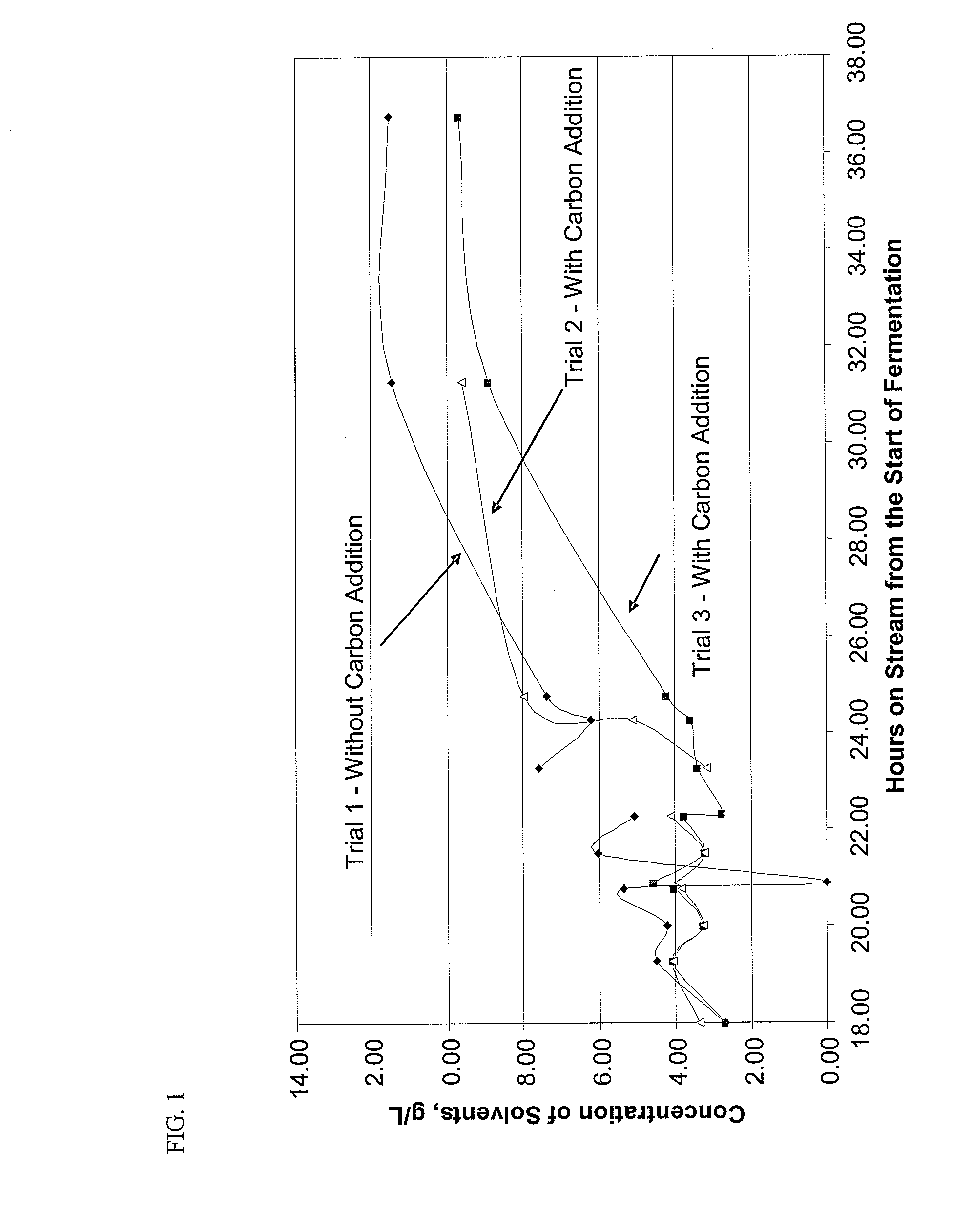
Process for solvent production utilizing liquid phase adsorption
Methods and systems are provided for the separation of solvents, including, but not limited to, butanol, from a fermentative solventogenesis reaction medium that utilizes Clostridium beijerinckii NCIMB 8052 or derivatives thereof, including, but not limited to, Clostridium beijerinckii BA101, ATCC No. PTA-1550, by contacting the reaction medium directly with an adsorbent that selectively adsorbs the solvent; separating the adsorbent / solvent adsorbate from the reaction medium; and desorbing the solvent adsorbate from the adsorbent.
Owner:EASTMAN RENEWABLE MATERIALS LLC
Method for producing isopropyl alcohol and butyl alcohol by fermenting lignocellulose serving as raw material
ActiveCN109486868AReduce loss rateOmit separabilityBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesLiquid glucoseFermentation
The invention relates to a method for producing isopropyl alcohol and butyl alcohol by fermenting lignocellulose serving as a raw material. The method includes the steps: firstly, performing steam blasting pretreatment on the lignocellulose raw materials at the pressure of 0.8-1.3MPa and the temperature of 120-160 DEG C; performing enzymolysis on the pretreated materials to obtain mixed hydrolysisliquid glucose of cellulose and hemi-cellulose; taking the mixed hydrolysis liquid glucose as a carbon source, and replenishing a carbon source, nutritive salt and vitamin to prepare a fermentation culture medium; inoculating seeds of Clostridium beijerinckii XH0906 into the fermentation culture medium, and producing the isopropyl alcohol and the butyl alcohol in a fermenting manner. According tothe method, steam blasting pretreatment on the lignocellulose raw materials is implemented, the isopropyl alcohol and the butyl alcohol are produced by fermentation of the Clostridium beijerinckii XH0906, and the method has the advantages of simple preparation process, high fermentation yield and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Thermoanaerobacter brockii alcohol dehydrogenase promoter for expression of heterologous proteins
The present invention discloses the isolation and use of a specific bacterial promoter region suitable for use in constructs for the high level production of heterologous proteins. This promoter is derived from the bacterial gene encoding for alcohol dehydrogenase, in particular the alcohol dehydrogenase genes isolated from the thermophilic bacterial strain T. brockii and the mesophilic bacterial strain Clostridium beijerinckii. It is now disclosed that using either the intact promoter region or certain specific fragments consisting of at least a 88 bp DNA sequence in the upstream untranslated region of the bacterial alcohol dehydrogenase gene, operatively linked to the nucleic acid sequences encoding a heterologous protein, and insertion into a DNA plasmid or any other suitable vector system, heterologous genes can be expressed in high levels in host cells. Heterologous proteins or peptides can be expressed constitutively at high levels. The proteins are obtained in their active folded form.
Owner:YEDA RES & DEV CO LTD +1
Composite microbial agent capable of reducing COD value of heavy-polluted wastewater
InactiveCN110240285APromote growthAdaptableBiological water/sewage treatmentRhodospirillum rubrumMicrobial agent
The invention provides a composite microbial agent capable of reducing a COD value of heavy-polluted wastewater. The composite microbial agent is characterized by comprising the following ingredients in parts by weight: 1-8.5 parts of Pseudomonas putida, 2-8 parts of Rhodococcus globerulus, 2-5 parts of Rhodospirillum rubrum, 5-10 parts of Clostridium beijerinckii, 1-5 parts of flocculating candida, 2-5 parts of Acinetobacter johnsonii, 5-12 parts of Acetobacter pasteurianus, 13-34.5 parts of hybrid bacillus and 22.5-48 parts of hybrid Lactobacilli. According to the composite microbial agent provided by the invention, the degradation efficacy and impact resistance to a degraded substrate are strengthened by using synergism of a variety of strain ingredient populations; and a degradation method is high in pertinency, high in response speed and simple in operation.
Owner:GUANGDONG RUIJIE ENVIRONMENTAL PROTECTION ENG CO LTD
High-tolerance clostridium beijerinckii and application thereof
The invention discloses high-tolerance clostridium beijerinckii M17 with the collection number of CCTCC NO:M2013425, and an application of the high-tolerance clostridium beijerinckii M17 in production of butanol. The strain is prepared through normal temperature plasma mutagenesis and screening, has high tolerance to toxic substances in a non-detoxified wood fiber acid hydrolysis sugar solution, and can be used for producing butanol very well through fermentation in a fermentation liquor of which the phenol concentration reaches up to 2.0g / L, wherein the total solvent yield of the strain reaches 10.9g / L, the butanol yield of the strain reaches 7.9g / L, and even if the phenol concentration reaches up to 2.4g / L, the strain disclosed by the invention also has a considerable butanol production capacity, thereby showing that the strain namely clostridium beijerinckii M17 not only has an efficient utilization rate for a bagasse acid hydrolysis sugar solution, but also has high tolerance on toxin inhibitors particularly phenolic compounds in the bagasse acid hydrolysis sugar solution; the clostridium beijerinckii M17 is the excellent strain suitable for producing butanol by fermenting the bagasse.
Owner:GUANGDONG PROVINCIAL BIOENGINEERING INST (GUANGZHOU SUGARCANE IND RES INST)
Recombinant Clostridium beijerinckii for efficient sucrose fermentation and method for improving sucrose fermentation performance of Clostridium beijerinckii
ActiveCN108504616AImproving the Efficiency of Fermentative Production of ButanolImproves sucrose transport efficiencyBacteriaBiofuelsHeterologousSucrose
In the invention, the heterologous expression of sucrose transporter SUT1 and sucrase SUC2 in Clostridium beijerinckii is successfully realized by a genetic engineering method, and then sucrose is directly fermented by using a fermentation engineering method with sucrose as a sole carbon source to produce biobutanol. Compared with the fermentation of sucrose by the wild Clostridium beijerinckii strain, the method for fermenting sucrose by the recombinant Clostridium beijerinckii constructed by the invention has the advantages that the sucrose fermentation performance of Clostridium beijerinckii is improved and the butanol yield is significantly increased.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
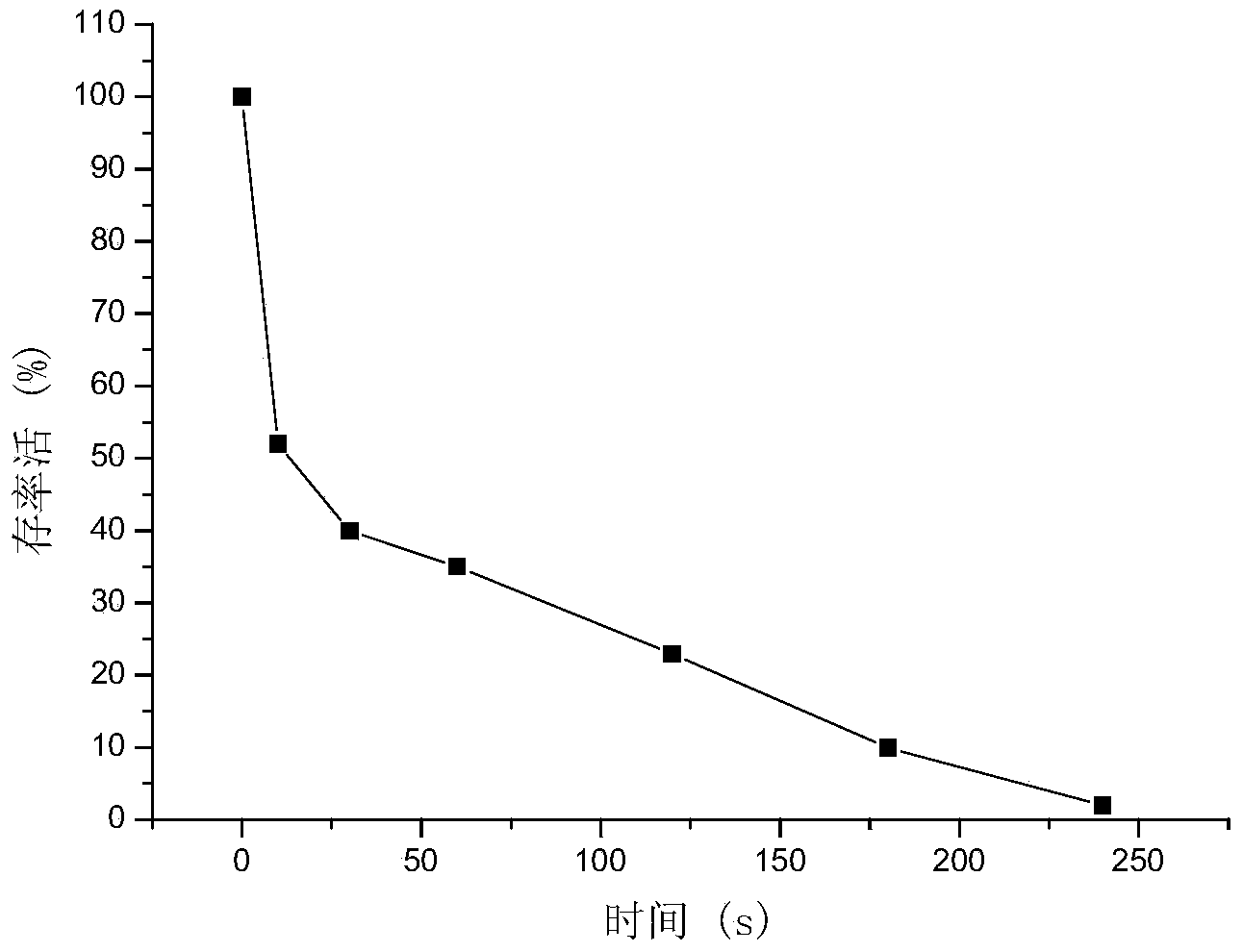
High ferulic acid stress resistance clostridium beijerinckii and application thereof
ActiveCN103667147AIncrease productionStrong stress resistanceBacteriaMicroorganism based processesFiberMutant strain
The invention discloses high ferulic acid stress resistance clostridium beijerinckii and an application thereof. The high ferulic acid stress resistance clostridium beijerinckii is classified and named Clostridium beijerinckii M11 with the collection number of CCTCC No:M2013423, and the collection date of the high ferulic acid stress resistance clostridium beijerinckii is December 14, 2013. A mutant strain obtained by adopting plasmas for mutating the clostridium beijerinckii and a ferulic acid containing resazurin flat plate and a shake flask for fermentation and screening can normally grow in a fermentation medium containing 0.8g / L of ferulic acid, the yield of butanol reaches 6.1g / L, and an original strain cultured under equal conditions hardly grows. Moreover, by using virus-carrying corncob acidolysis sugar liquid as a carbon source, the yield of butanol in a 2L fermentation tank reaches 6.4g / L, and the original strain cultured under equal conditions hardly grows. The high ferulic acid stress resistance clostridium beijerinckii has strong stress resistance, high butanol yield and good repeatability, and is an excellent strain suitable for the fermentation production of butanol by using wood fiber raw materials such as corncobs and the like.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Preparation and application method of special microorganism composite bacterial agent for directly decomposing and fermenting crop straws to generate marsh gas
InactiveCN109957527AIncrease productionInitial gas production time shortenedFungiBacteriaClostridium pasteurianumBacillus licheniformis
The invention discloses preparation and an application method of a special microorganism composite bacterial agent for directly decomposing and fermenting crop straws to generate marsh gas. The special microorganism composite bacterial agent is liquid or solid, and is formed by fermenting, culturing, combining and compositing of one or more of bacillus cereus, bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, bacillus megaterium, bacillus mucilaginosus, bacillus circulans, bacillus sphaericus, clostridium sporogenes, clostridium acetobutylicum, clostridium pasteurianum, clostridium beijerinckii, clostridium thermocellum, trichoderma viride, trichoderma pseudokoningii and aspergillus niger. Meanwhile, by taking the special microorganism composite bacterial agent as an inoculation bacterial agent,the invention provides the application method for decomposing the crop straws and accelerating the fermentation to generate marsh gas; the crop straws treated by the microorganism composite bacterialagent have fast fermentation speed, large marsh gas generation quantity, low treating cost and no secondary pollution, can be fermented to generate the marsh gas under the condition of no any faeces of poultry and livestock, and the application range is quite wide.
Owner:王旭宁
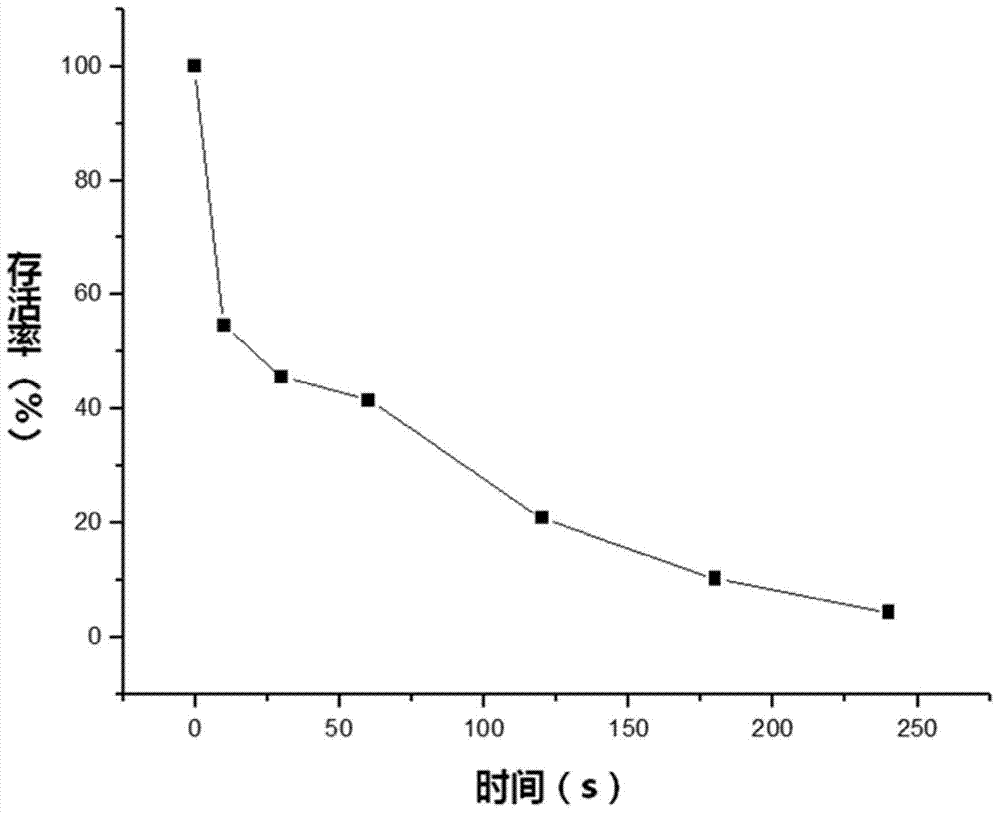
Method for improving stress resistance of clostridium beijerinckii to 4-hydroxycinnamic acid
ActiveCN105567603AImprove stress resistanceEfficiently improve stress resistanceBacteriaBiofuelsNucleotideSolvent
The invention discloses a method for improving stress resistance of clostridium beijerinckii to 4-hydroxycinnamic acid. The method comprises the steps that genes of a coenzyme Q oxidation-reduction enzyme subunit A with encoding relying on NADH in the clostridium beijerinckii are inactivated to be not normally expressed in the clostridium beijerinckii, and the nucleotide sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. The genes of the coenzyme Q oxidation-reduction enzyme subunit A with encoding relying on the NADH in the clostridium beijerinckii are inactivated through the type-two intron gene knockout technology. Results show that the recombination strain has the good passage stability; when the concentration of 4-hydroxycinnamic acid in the culture medium is 0.5 g / L, the original strain 8052 hardly produces a solvent, the built recombinant bacteria butanol yield reaches 3.4 g / L, and it shows that the stress resistance of the clostridium beijerinckii to the 4-hydroxycinnamic acid is improved through the method.
Owner:GUANGDONG PROVINCIAL BIOENGINEERING INST (GUANGZHOU SUGARCANE IND RES INST)
Method for fermenting production of butanol
The invention relates to a method for fermenting production of butanol. The method comprises: (1) preparing a fermentation bacteria seed liquid, wherein the fermentation bacteria is Clostridium beijerinckii XH0906; and (2) preparing a fermentation culture medium, adding calcium carbonate into the fermentation culture medium, inoculating with the seed liquid prepared in the step (1), and carrying out fermenting culture to produce butanol. According to the present invention, the butanol is subjected to fermenting production under the facultative condition, and the method has characteristics of high butanol yield, less organic acid by-product and the like.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Method for improving ferulic acid stress resistance of clostridium beijerinckii
ActiveCN104894048AStrong stress resistanceImprove stress resistanceBacteriaFermentationNucleotideMicrobiology
The invention provides a method for improving the ferulic acid stress resistance of clostridium beijerinckii, and belongs to the technical field of gene engineering. According to the method, an FMN redoxin gene, coded in dependence on NADPH, in the clostridium beijerinckii is inactivated, so that the FMN redoxin gene cannot be normally expressed in the clostridium beijerinckii; the clostridium beijerinckii NCIMB 8052 is adopted; the FMN redoxin gene, coded in dependence on NADPH, in the clostridium beijerinckii is Cbei_4693 of which the nucleotide sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO: 1. The FMN redoxin gene, coded in dependence on NADPH, in the clostridium beijerinckii is inactivated according to the group II intron gene knockout technology. A recombinant strain obtained according to the method provided by the invention is relatively high in passage stability; when the concentration of ferulic acid in a culture medium is 0.5 g / L, the butanol yield of a starting strain 8052 is 0.7 g / L, and the butanol yield of the obtained recombinant strain reaches 5.6 g / L, that is, the ferulic acid stress resistance of the clostridium beijerinckii is improved according to the method.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Bactericide for generating methane and preparation technology thereof
InactiveCN101921707AQuick conversionWide range of temperature adaptationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesAgricultural scienceMass ratio
The invention relates to a microbial agent and a preparation technology thereof, belonging to the technical filed of agricultural production. In the preparation technology, Clostridium thermocellum, Clostridium beijerinckii, Methanocaldococcus jannaschii, Methanothermobacter wolfeii, Methanosarcina thermophila and Methanosarcina barkeri Schnellen are coordinated in mass ratio of 1-2:1-3:1:1:1:1-4, the total number of effective viable bacteria, the operation is carried out in an asepsis condition, and the product is kept is a dark place. To a house hold fermenting tank, a bactericide for generating methane is required to be added, the additive amount accounts for 0.1-0.2% of the feeding amount; to a semi-batch (semi-continuous) fermentation mode and a continuous fermentation mode, the additive amount accounts for 0.05-0.1% of the feeding amount. The bactericide for generating methane has wide adaptability to temperature, can generate methane continuously from 30 DEG C to 85 DEG C, and does not have strict requirements for organic matter materials. The technology can be used for household small-size methane tanks and large-scale industrial methane apparatuses to use.
Owner:刘秀丽
Clostridium tyrobutyricum for reducing content of n-butyl alcohol in Baijiu fermentation process
The invention discloses clostridium tyrobutyricum for reducing the content of n-butyl alcohol in a Baijiu fermentation process. According to the invention, strains are screened and separated from pitmud, the clostridium tyrobutyricum for reducing the content of the n-butyl alcohol is obtained through screening in a butanol culture medium, then influence of different addition proportions on synthesis of the n-butyl alcohol during co-culture is investigated in a five-grain culture medium system, and finally, a pit mud fermentation system is simulated to verify the reduction and control effect of the clostridium tyrobutyricum. In the simulated fermentation process of Baijiu, compared with a blank control only containing the pit mud, the clostridium tyrobutyricum is added, so that the generation amount of the n-butyl alcohol in the fermentation process can be reduced by 30.05%, and the content of a skeleton flavor substance namely ethyl caproate of strong aromatic Baijiu is increased by 25.77%; Compared with a high-butanol-yield fermentation system with clostridium beijerinckii 6Y-1, the system with the clostridium tyrobutyricum has the advantages that the generation amount of the n-butyl alcohol in the system can be reduced by 27.08%, and the content of the ethyl caproate is increased by 5.09%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Mutant strains of the genus clostridium beijerinckii
The present invention relates to mutant bacteria of the genus Clostridium beijerinckii, CNCM I-4985, CNCM I-4986, CNCM I-4987 and CNCM I-4988, deposited at the Institut Pasteur (CNCM, 25 rue du Docteur Roux, F-75724 PARIS Cedex 15, France) on 27 May 2015, and CNCM I-5027, CNCM I-5028 and CNCM I-5029 deposited at the Institut Pasteur (CNCM, 25 rue du Docteur Roux, F-75724 PARIS Cedex 15, France) on 26 Nov. 2015, which are useful in the fermentation of sugars for the production of isopropanol and butanol.
Owner:INST FR DU PETROLE +1
Cathodic electric fermentation method for preparing hydrogen and butanol by electron transfer mediator enhanced clostridium beijerinckii fermentation
ActiveCN112501213APreparation sustainablePromote growthBiofuelsMicroorganism based processesElectron transfer mediatorElectron flow
The invention discloses a cathodic electric fermentation method for preparing hydrogen and butanol by electron transfer mediator enhanced clostridium beijerinckii fermentation, and belongs to the technical field of clean energy production through microbial fermentation. The method solves the problems of low butanol output and yield, failure in transformation from an acid producing phase to a solvent producing phase and relatively high acetone proportion in a solvent in a butanol fermentation process for existing clostridium beijerinckii. According to the invention, the butanol is prepared by clostridium beijerinckii fermentation in a cathodic electric fermentation system; and by introducing electrodes and adding exogenous electron transfer mediator neutral red (NR), a fermentation environment can be controlled and optimized, original NAD+ / NADH balance of cells can be changed, shunting of different ways in microbial metabolism can be significantly optimized, more carbon and electrons ina microbial metabolism path are induced to flow to a butanol synthesis path, the output and yield of the biobutanol are improved, and more hydrogen is generated at the same time.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com