Method for regulating and controlling synthesis of EPS (extracellular polymeric substance) of clostridium acetobutylicum
A technology of Clostridium acetobutylicum and extracellular polymers, applied in the field of genetic engineering, can solve problems such as unclear mechanisms and achieve high regulatory effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0029] Example 1: Construction method of Clostridium acetobutylicum CA_C2071 gene inactivation mutant.
[0030] 1. Design introns:
[0031] According to the CA_C2071 gene sequence (as shown in SEQ ID No: 1) of Clostridium acetobutylicum included in the NCBI database, a suitable insertion gene site (http: / / www.clostron.com) was designed with the help of software, and the insertion at Between 242-243 bases, an intron sequence is generated, and the sequence of the synthesized intron sequence S-242 is shown in SEQ ID NO:2.
[0032] 2. Construction of CA_C2071 insertion inactivation vector:
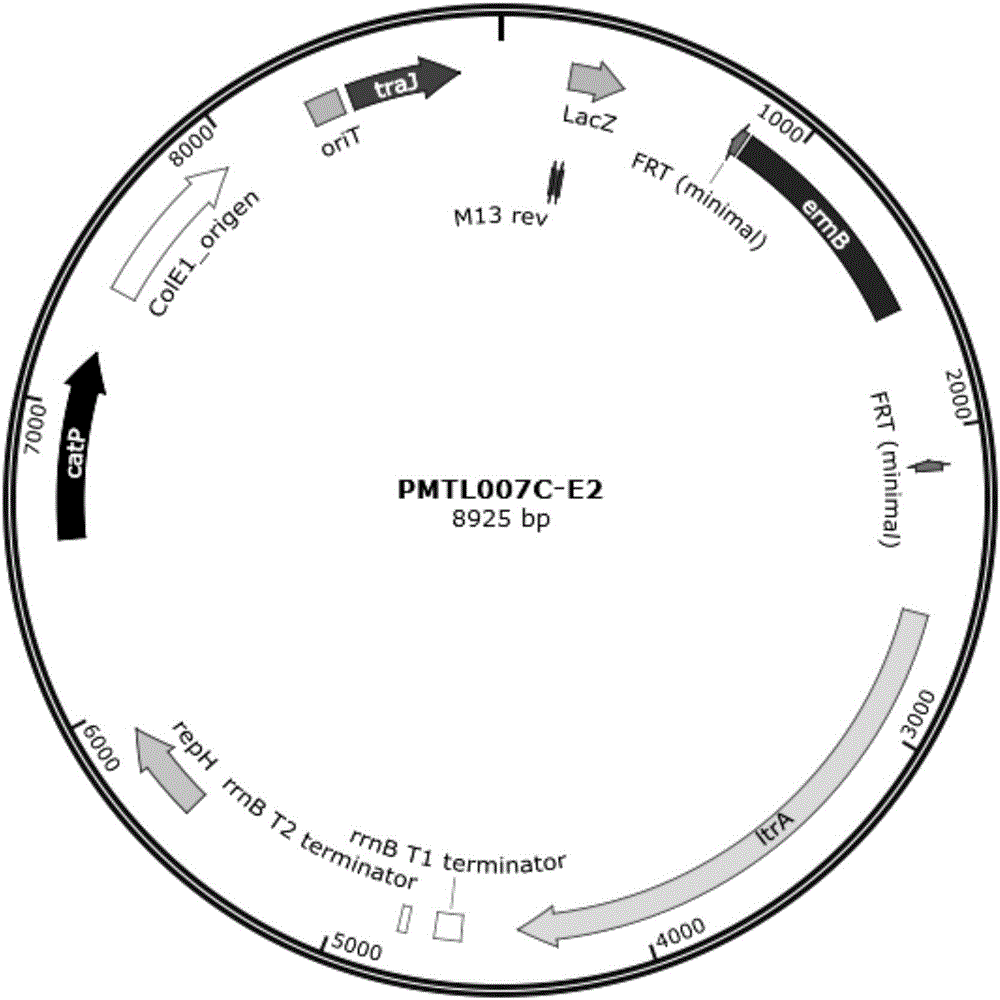
[0033] The vector PMTL007C-E2 was digested with XhoI and BsrGI, and its sequence is shown in SEQ ID NO:5. The digested product was purified by a purification kit (Takara), and connected to the intron sequence S-242 by one-step cloning (ClonExpress). Transform the recombinant plasmid connected by one-step cloning into Escherichia coli E.coli DH5a (our laboratory), spread it on LB plates cont...
Embodiment 2
[0040] Example 2: The process of immobilizing and fermenting the knockout bacteria and the starting bacteria in a 2L fermenter to synthesize extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).
[0041] Plate medium: yeast powder 3g / L, peptone 5g / L, glucose 10g / L, ammonium acetate 2g / L, sodium chloride 3g / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 3g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1g / L, phosphoric acid Dipotassium hydrogen 1g / L, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.1g / L, agar 15g / L, the rest is water.
[0042] Seed medium: yeast powder 3g / L, peptone 5g / L, glucose 10g / L, ammonium acetate 2g / L, sodium chloride 3g / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 3g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 1g / L, phosphoric acid Dipotassium hydrogen 1g / L, ferrous sulfate heptahydrate 0.1g / L, the rest is water.
[0043] Fermentation medium: glucose 60g / L, ammonium acetate 2.2g / L, potassium dihydrogen phosphate 0.5g / L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.5g / L, sodium chloride 0.01g / L, magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.2g / L , ferr...
Embodiment 3
[0047] Example 3: Observing the structure and thickness of the biofilm of the knockout bacteria and the original bacteria using a laser confocal microscope.
[0048] Proteobacteria biofilms were cultured using the slide biofilm culture method, stained with fluorescein isothiocyanate (FITC)-labeled concanavalin A (FITC-ConA) and pyridium iodide (PI) double immunofluorescent technique, and laser Confocal microscopy (CLSM) was used to observe the biofilm structure and the distribution of exopolysaccharides in it, and the biofilm was scanned layer by layer, and the thickness of the biofilm was calculated according to the Z-axis distance of the three-dimensional coordinate system.
[0049] The specific operation is as follows:
[0050] (1) Preparation of biofilm specimens
[0051] Put a 25mm×75mm glass slide in a 100mL Schott bottle, and put 50mL fermentation broth into it for anaerobic static culture. After culturing for 6, 24 and 72 hours, the slides were taken out, washed repe...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com