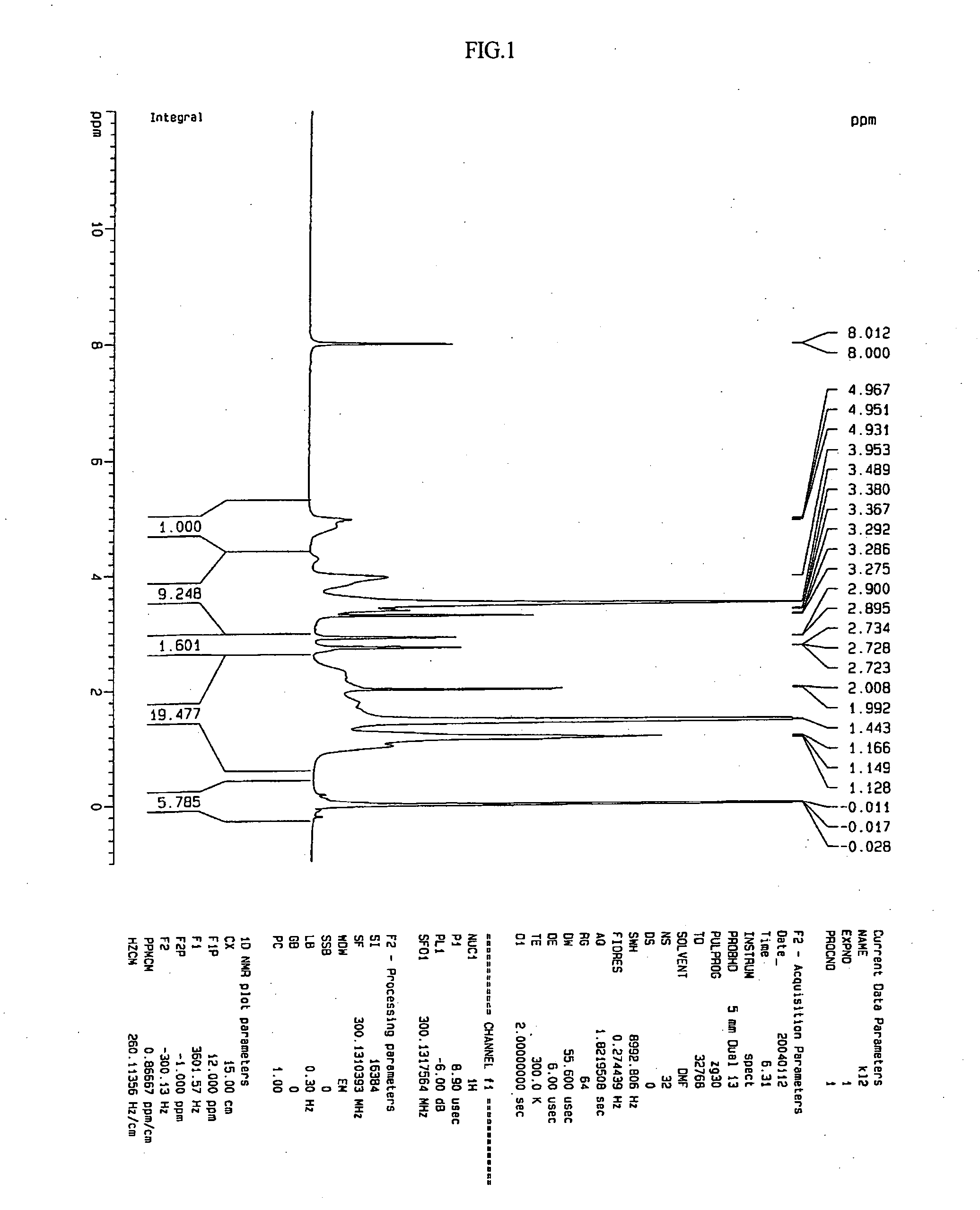
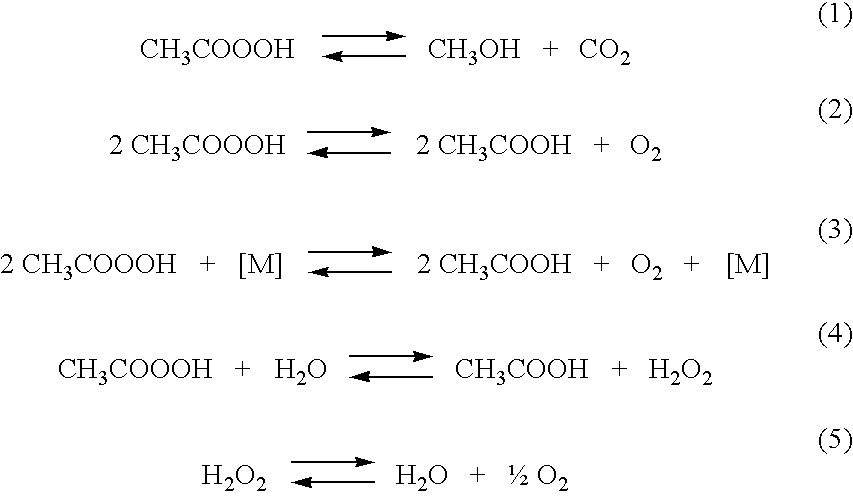Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
988 results about "Mole fraction" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In chemistry, the mole fraction or molar fraction (xᵢ) is defined as the amount of a constituent (expressed in moles), nᵢ divided by the total amount of all constituents in a mixture (also expressed in moles), nₜₒₜ: xᵢ=nᵢ/nₜₒₜ The sum of all the mole fractions is equal to 1: ∑ᵢ₌₁ᴺnᵢ=nₜₒₜ; ∑ᵢ₌₁ᴺxᵢ=1 The same concept expressed with a denominator of 100 is the mole percent or molar percentage or molar proportion (mol%).
High-melting polyolefin copolymer elastomers, catalysts and methods of synthesis
InactiveUS6169151B1Property is limitedOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsElastomerPolymer science
This invention relates to high melting polyolefin copolymers suitable as thermoplastic elastomers and catalysts and methods for their synthesis. These elastomeric olefin copolymers are characterized by a mole fraction of crystallizable component Xc from about 30 to about 99%; low glass transition temperatures, below -20° C., and typically below -50° C.; melting points above about 90° C.; high molecular weights; a molecular weight distribution MW / Mn< / =10; and a narrow composition distribution between chains of < / =15%. The novel copolymers of the invention range from reactor blends to multiblock copolymers that can be sequentially fractionated into fractions of differing crystallinities, which fractions nevertheless show compositions of comonomers which differ by less than 15% from the parent polymer (reactor product). The invention also relates to a process for producing such copolymers by utilizing an unbridged, substituted or unsubstituted cyclopentadienyl metallocene catalyst that is capable of interconverting between states with different copolymerization characteristics, which interconversion is controlled by selecting the substituents of the cyclopentadienyl ligands so that the rate of interconversion of the two states is within several orders of magnitude of the rate of formation of a single polymer chain. Where ri>rf the polymer can be characterized as multiblock; where ri<rf, the result is a polymer blend and where ri / rf is close to 1, the resulting polymer is a mixture of blend and multiblock. The metallocene catalysts of the invention are able to interconvert between more than two states, with embodiments of four states being shown in FIG. 2.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
Staged reactor process
In a process for the in situ blending of polymers comprising contacting ethylene and one or more comonomers in two or more fluidized bed reactors with a catalyst system comprising (i) a magnesium / titanium based precursor containing an electron donor and (ii) a hydrocarbyl aluminum cocatalyst, the improvement comprising (A) increasing or decreasing the melt flow ratio and / or molecular weight of the blend by, respectively, decreasing or increasing the mole ratio of a precursor activator compound to the electron donor or (B) increasing or decreasing the bulk density of the blend by, respectively, increasing or decreasing the mole ratio of a precursor activator compound to the electron donor, both (A) and (B) subject to defined provisos including partial pre-activation of the precursor.
Owner:UNION CARBIDE CHEM & PLASTICS TECH CORP
High-melting polyolefin copolymer elastomers, catalysts and methods of synthesis
InactiveUS6518378B2Property is limitedOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsCatalyst activation/preparationElastomerPolyolefin
This invention relates to high melting polyolefin copolymers suitable as thermoplastic elastomers and catalysts and methods for their synthesis. These elastomeric olefin copolymers are characterized by a mole fraction of crystallizable component Xc from about 30 to about 99%; low glass transition temperatures, below -20° C., and typically below -50° C.; melting points above about 90° C.; high molecular weights; a molecular weight distribution MW / Mn< / =10; and a narrow composition distribution between chains of < / =15%. The novel copolymers of the invention range from reactor blends to multiblock copolymers that can be sequentially fractionated into fractions of differing crystallinities, which fractions nevertheless show compositions of comonomers which differ by less than 15% from the parent polymer (reactor product). The invention also relates to a process for producing such copolymers by utilizing an unbridged, substituted or unsubstituted cyclopentadienyl metallocene catalyst that is capable of interconverting between states with different copolymerization characteristics, which interconversion is controlled by selecting the substituents of the cyclopentadienyl ligands so that the rate of interconversion of the two states is within several orders of magnitude of the rate of formation of a single polymer chain. Where ri>rf the polymer can be characterized as multiblock; where ri<rf, the result is a polymer blend and where ri / rf is close to 1, the resulting polymer is a mixture of blend and multiblock. The metallocene catalysts of the invention are able to interconvert between more than two states, with embodiments of four states being shown in FIG. 2.
Owner:BP AMOCO CORP +1
Liposomal products
InactiveUS6060080AHigh encapsulation efficiencyEasy to packLiposomal deliveryCholesterolWater soluble drug
A liposomal aqueous dispersion and method of making the liposomal aqueous dispersion is useful for encapsulation of drugs. The liposomal aqueous dispersion comprises: an aqueous suspension medium; multilamellar liposomes comprising an anionic phospholipid and cholesterol as essential components; neutral phospholipid in a mole ratio of 0 to 40% based on the total amount of said multilamellar liposomes; and a cation moiety-containing water-soluble drug, wherein the electrolyte concentration of said aqueous suspension medium is not more than 40 mM.
Owner:DAIICHI PHARMA CO LTD
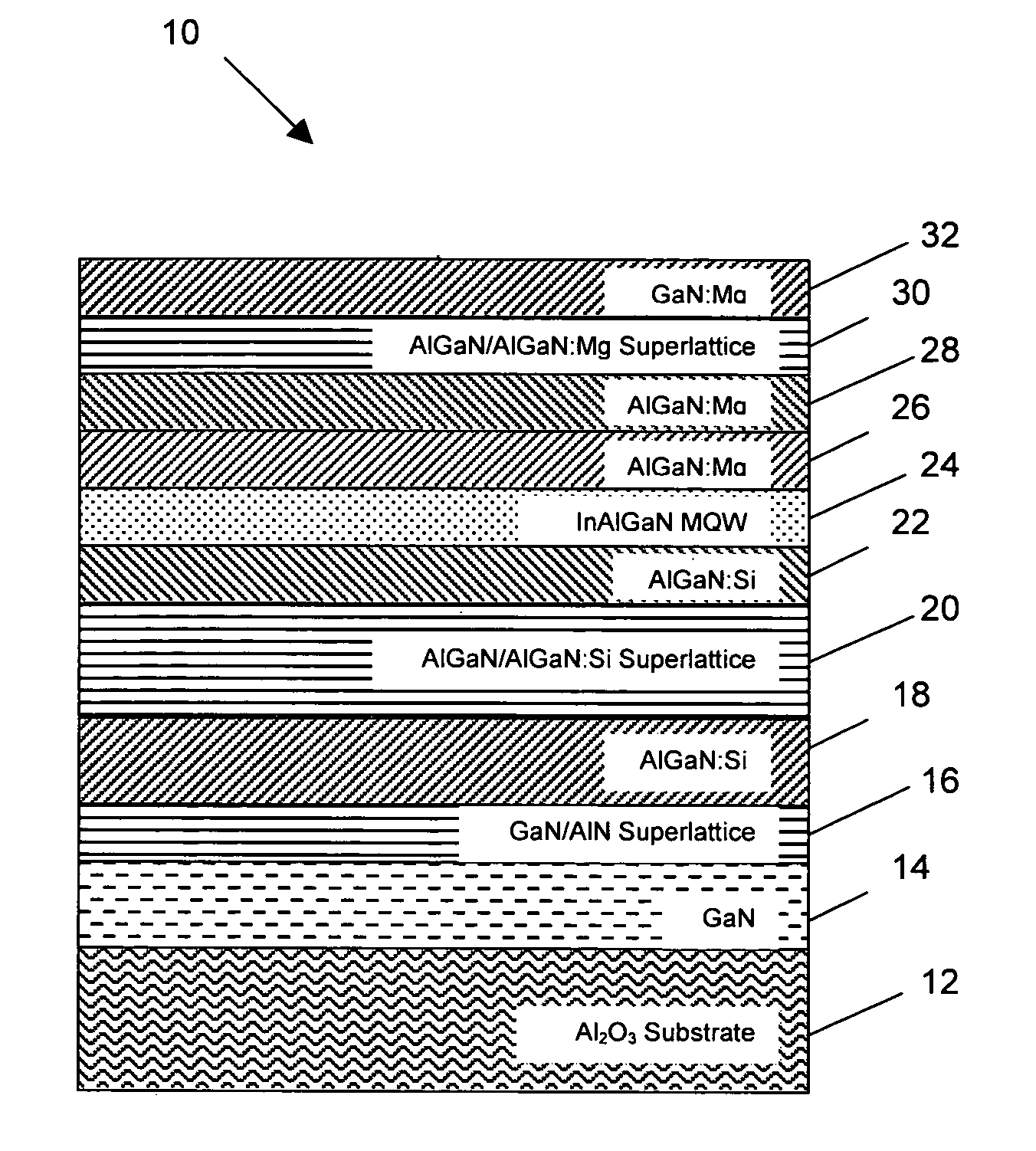
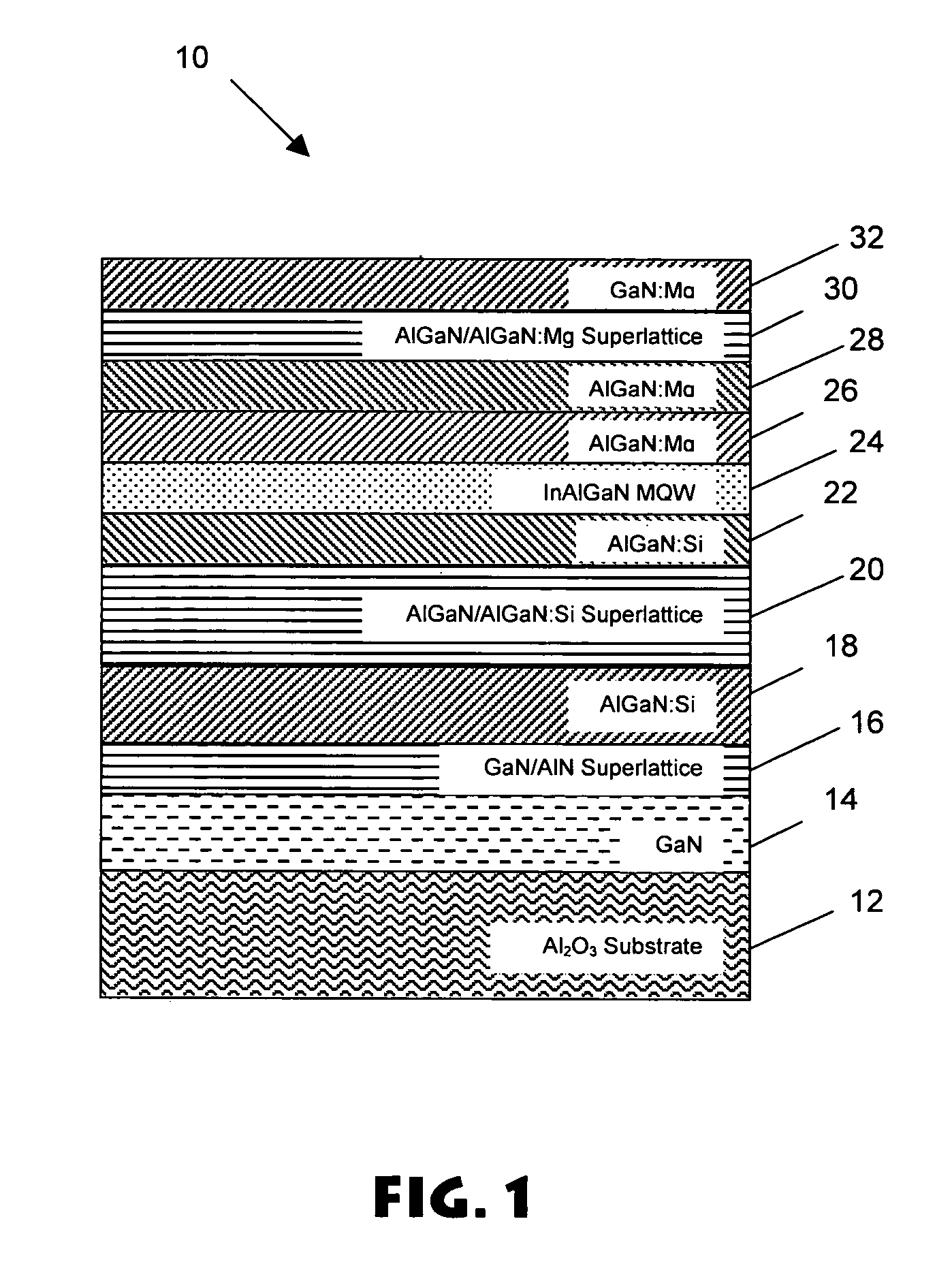
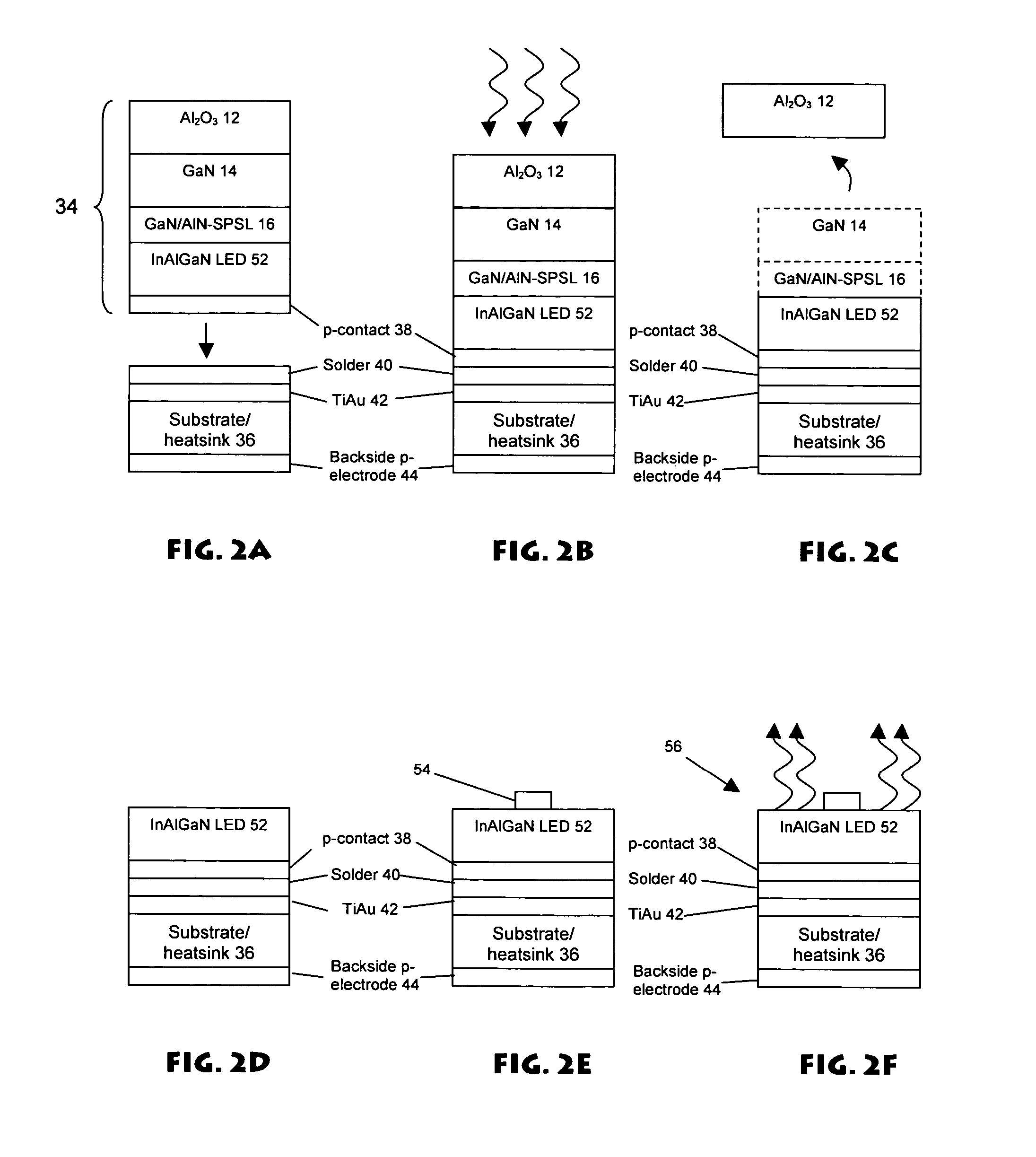
Superlattice strain relief layer for semiconductor devices
ActiveUS7547925B2High aluminum contentLow working voltageSolid-state devicesNanoopticsLength waveLight-emitting diode
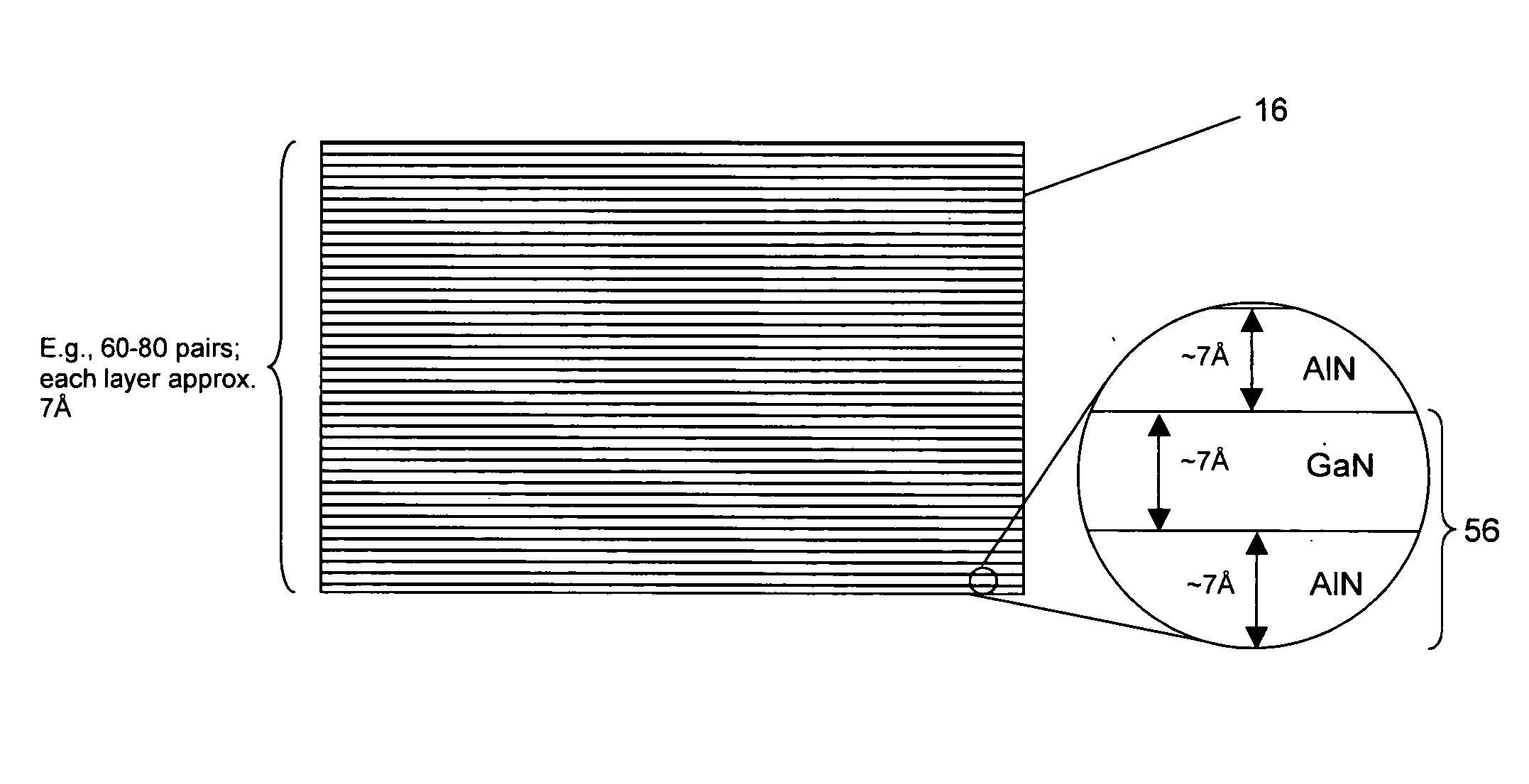
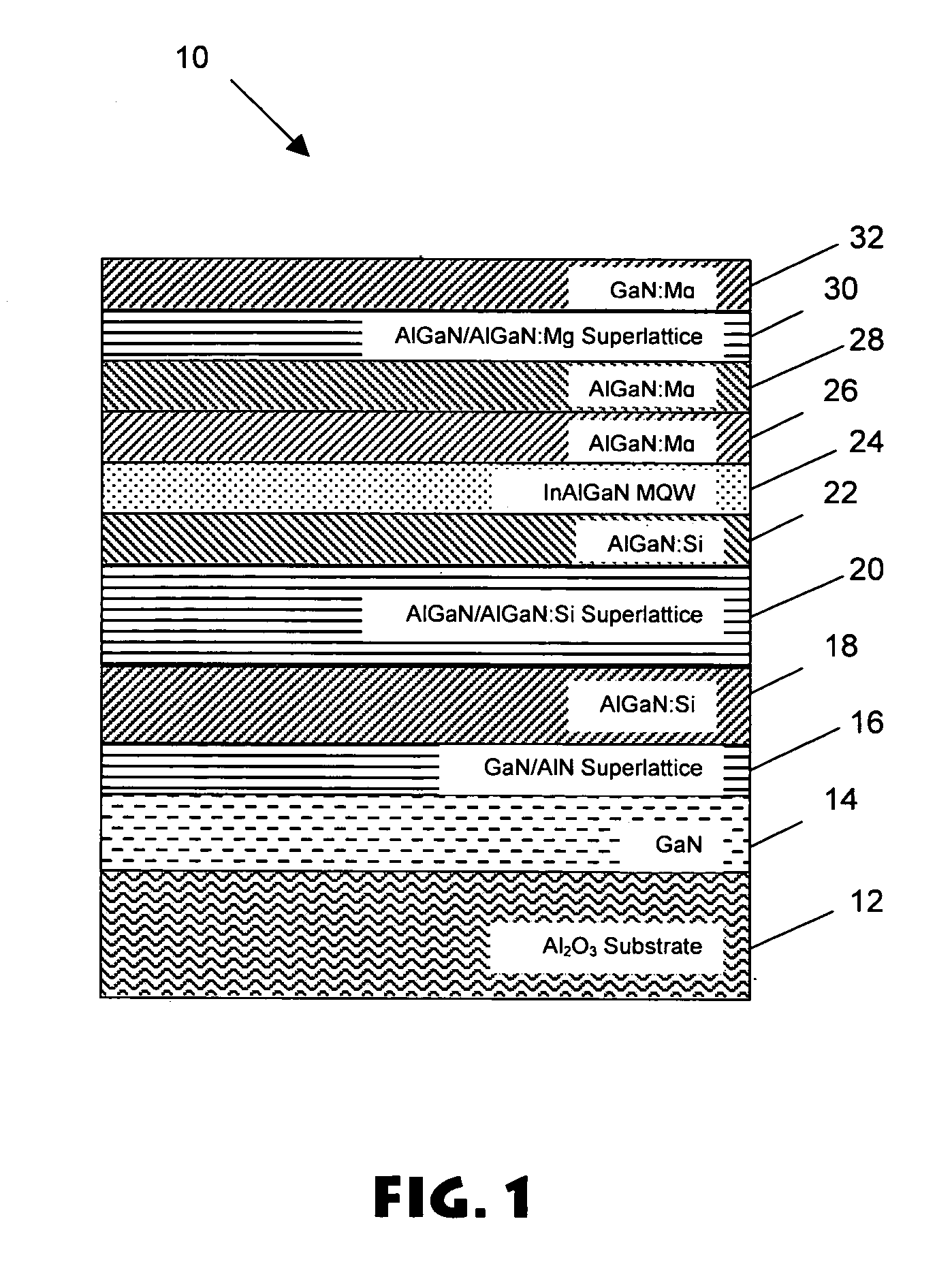
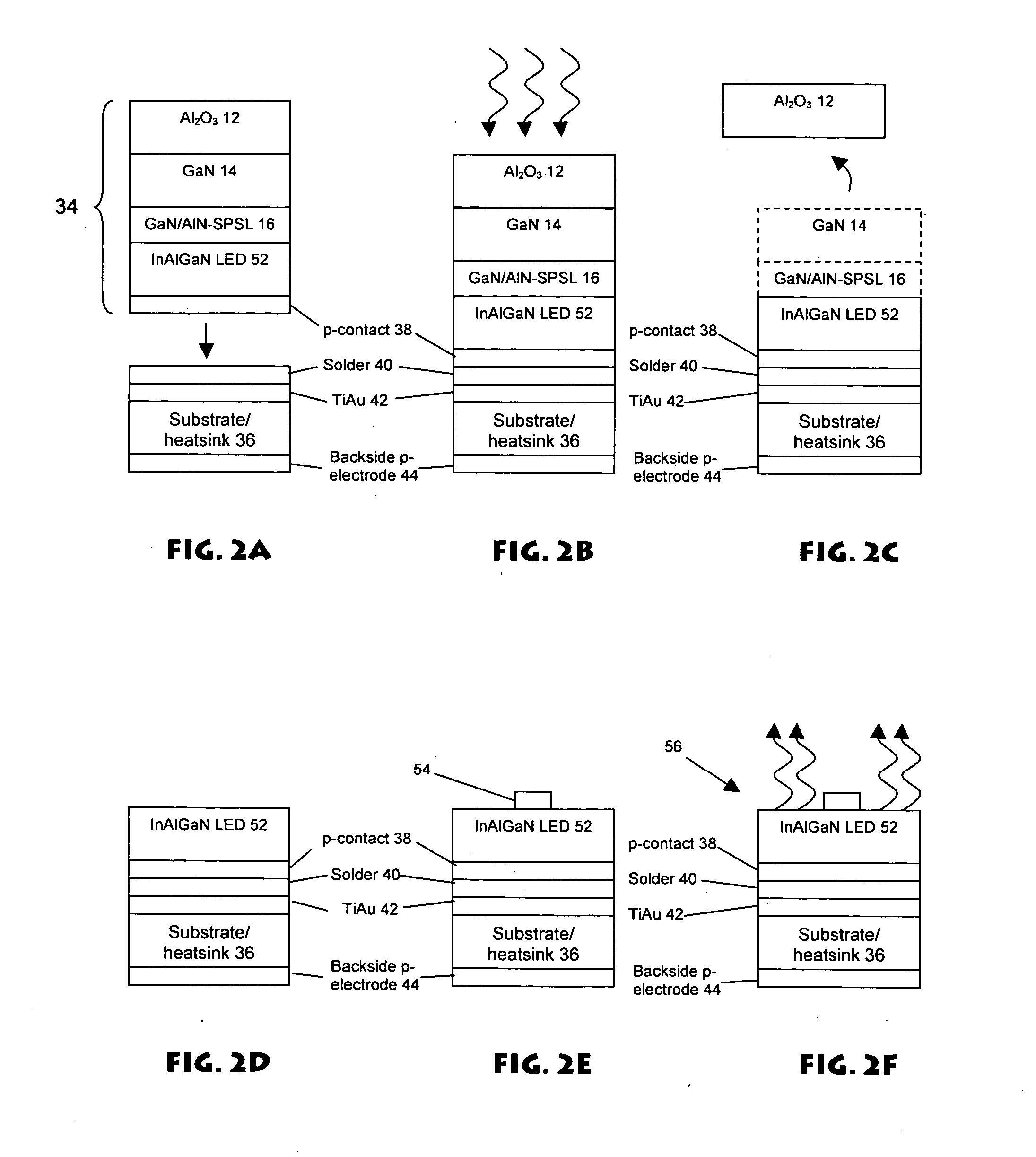
A GaN / AlN superlattice is formed over a GaN / sapphire template structure, serving in part as a strain relief layer for growth of subsequent layers (e.g., deep UV light emitting diodes). The GaN / AlN superlattice mitigates the strain between a GaN / sapphire template and a multiple quantum well heterostructure active region, allowing the use of high Al mole fraction in the active region, and therefore emission in the deep UV wavelengths.
Owner:XEROX CORP
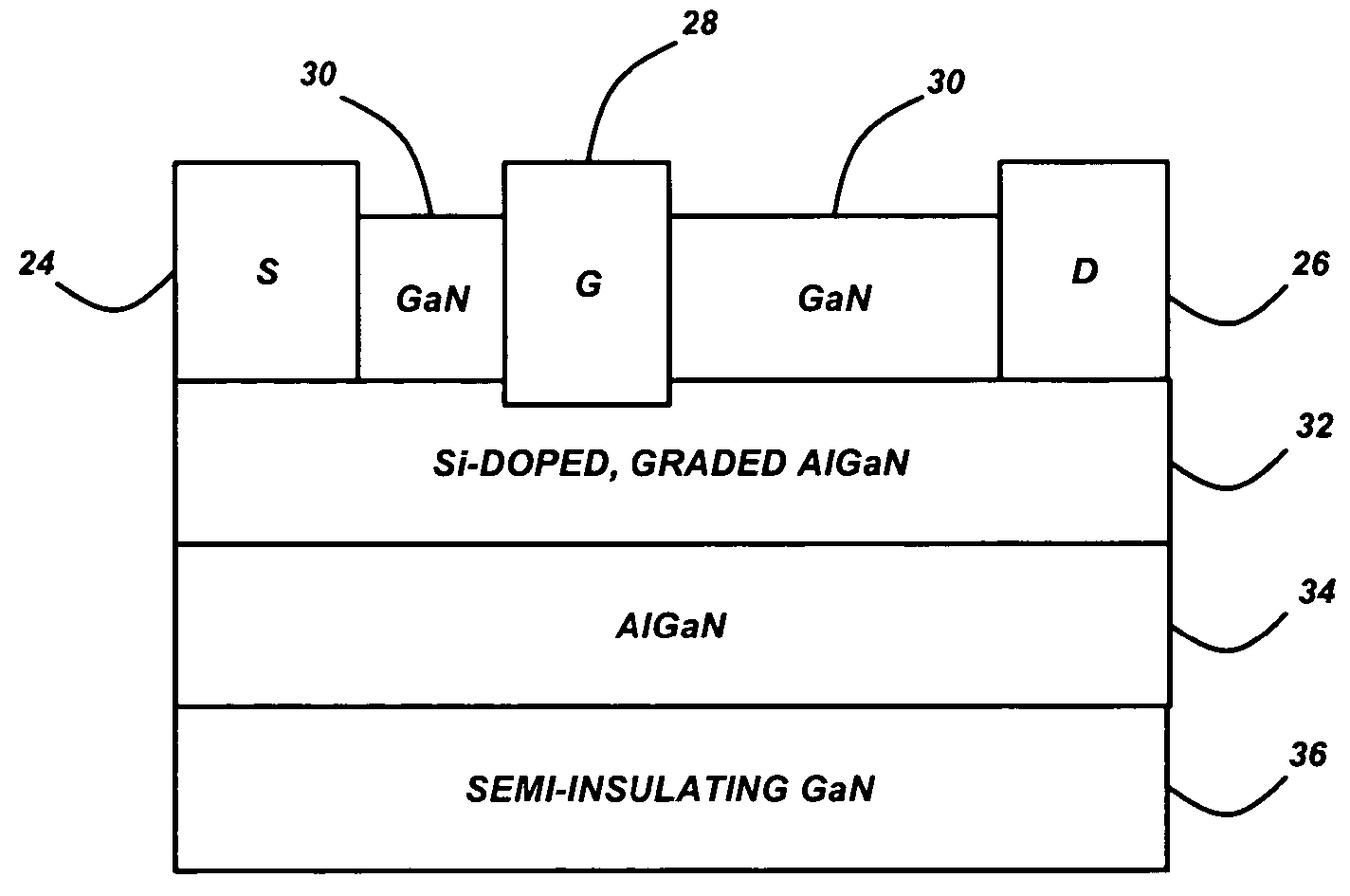
GaN/AIGaN/GaN dispersion-free high electron mobility transistors
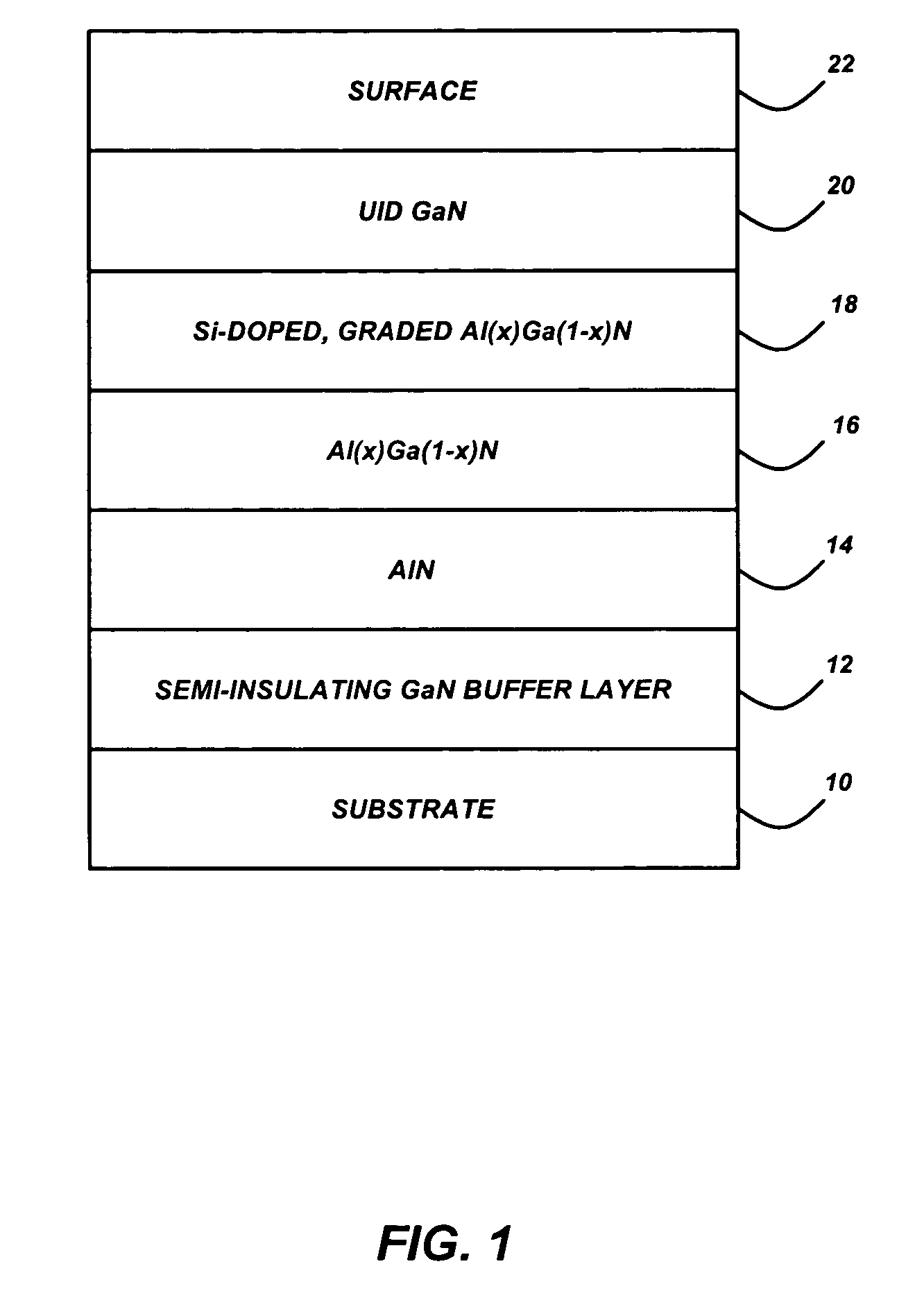
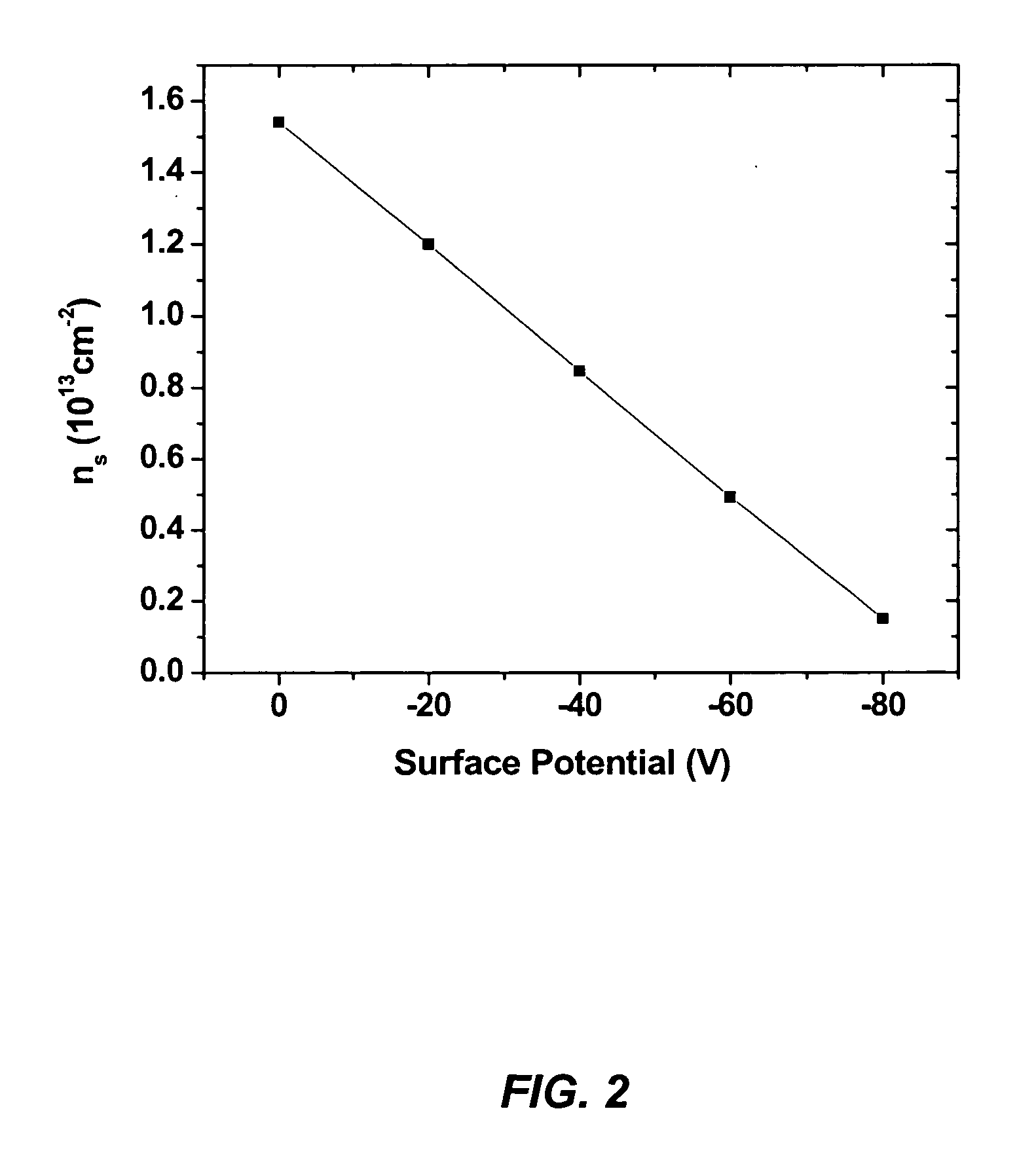
InactiveUS20050077541A1High electron mobilitySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh electronGallium nitride
A dispersion-free high electron mobility transistor (HEMT), comprised of a substrate; a semi-insulating buffer layer, comprised of gallium nitride (GaN) or aluminum gallium nitride (AlGaN), deposited on the substrate, an AlGaN barrier layer, with an aluminum (Al) mole fraction larger than that of the semi-insulating buffer layer, deposited on the semi-insulating buffer layer, an n-type doped graded AlGaN layer deposited on the AlGaN barrier layer, wherein an Al mole fraction is decreased from a bottom of the n-type doped graded AlGaN layer to a top of the n-type doped graded AlGaN layer, and a cap layer, comprised of GaN or AlGaN with an Al mole fraction smaller than that of the AlGaN barrier layer, deposited on the n-type doped graded AlGaN layer.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
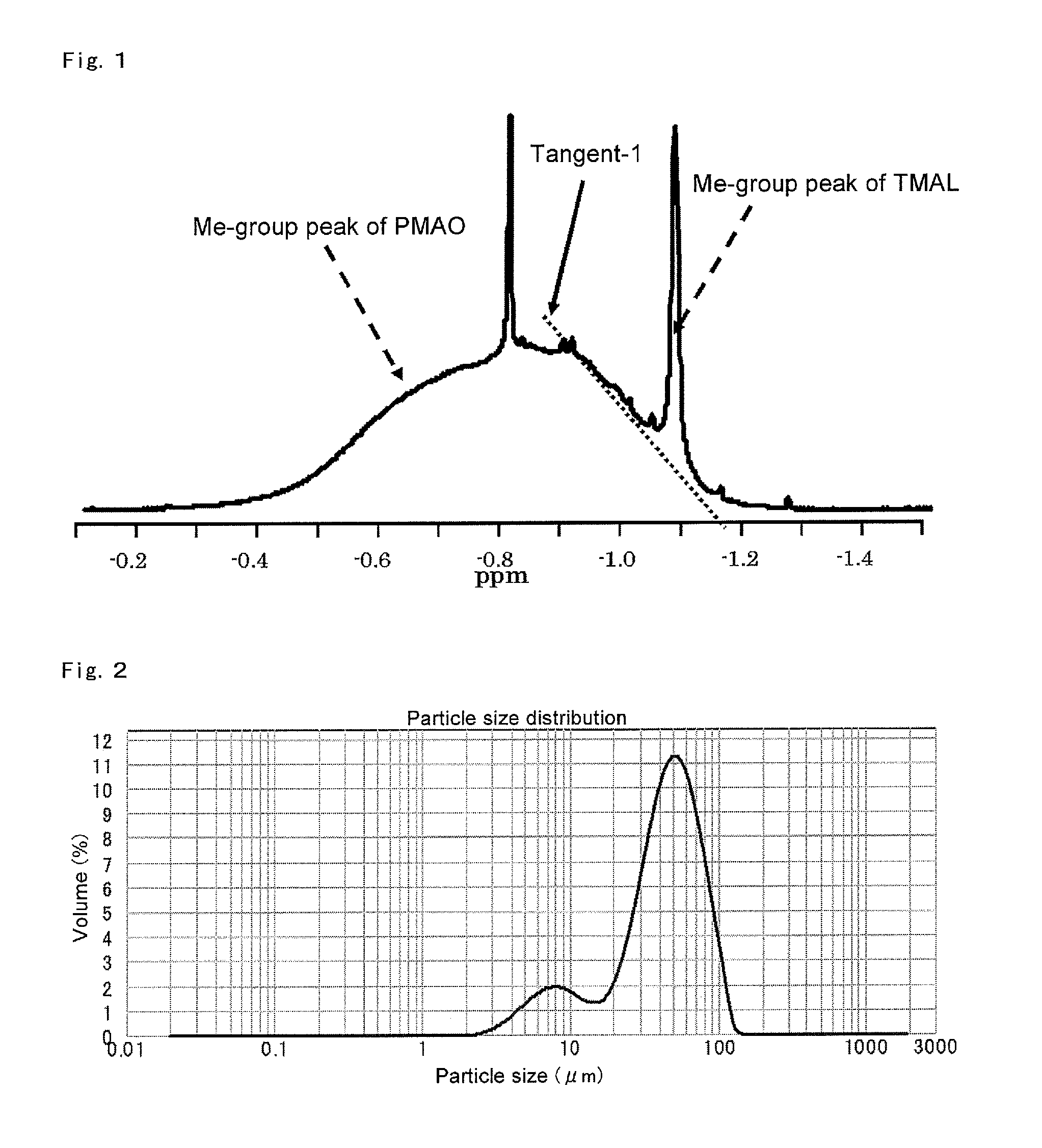
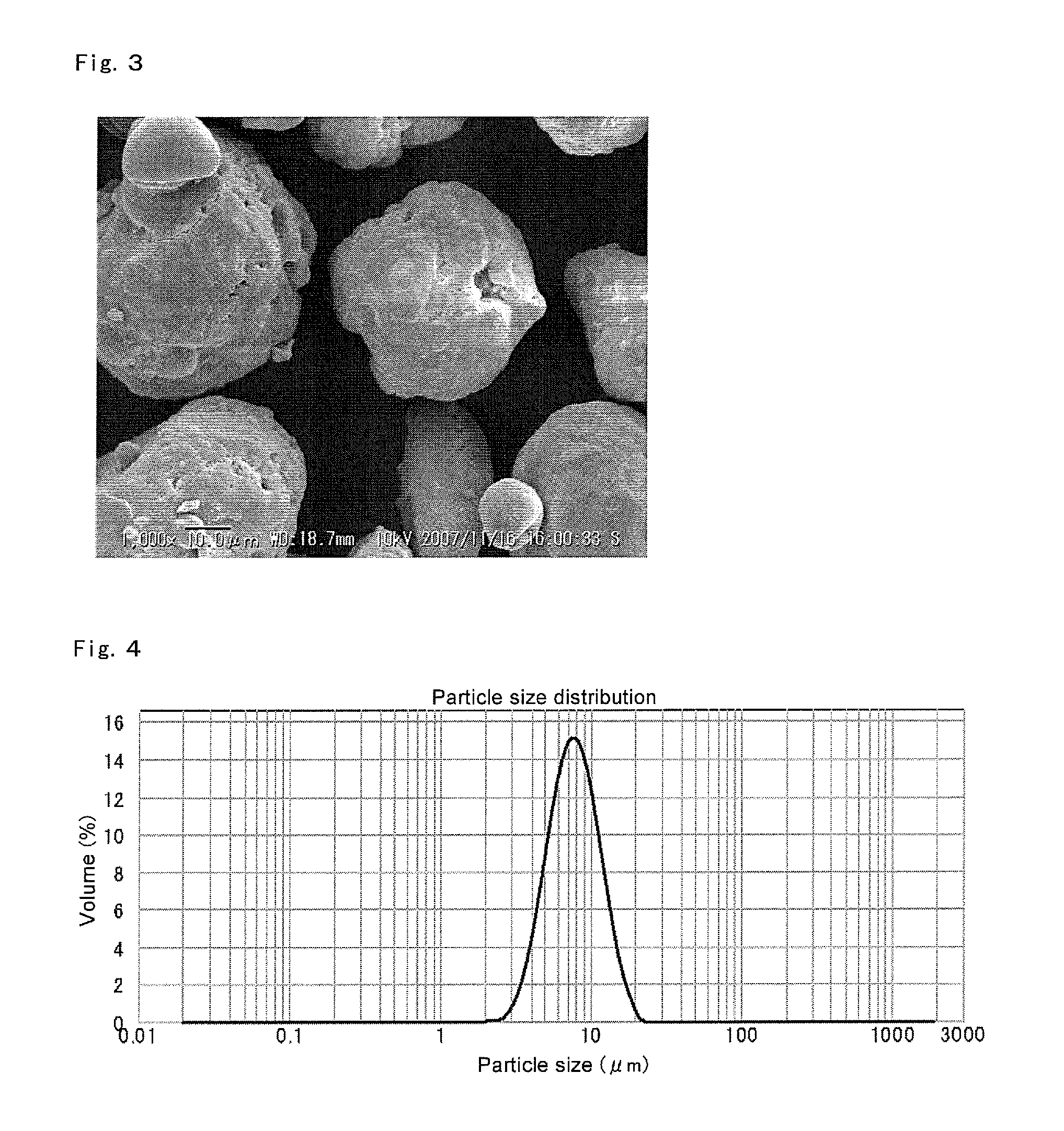
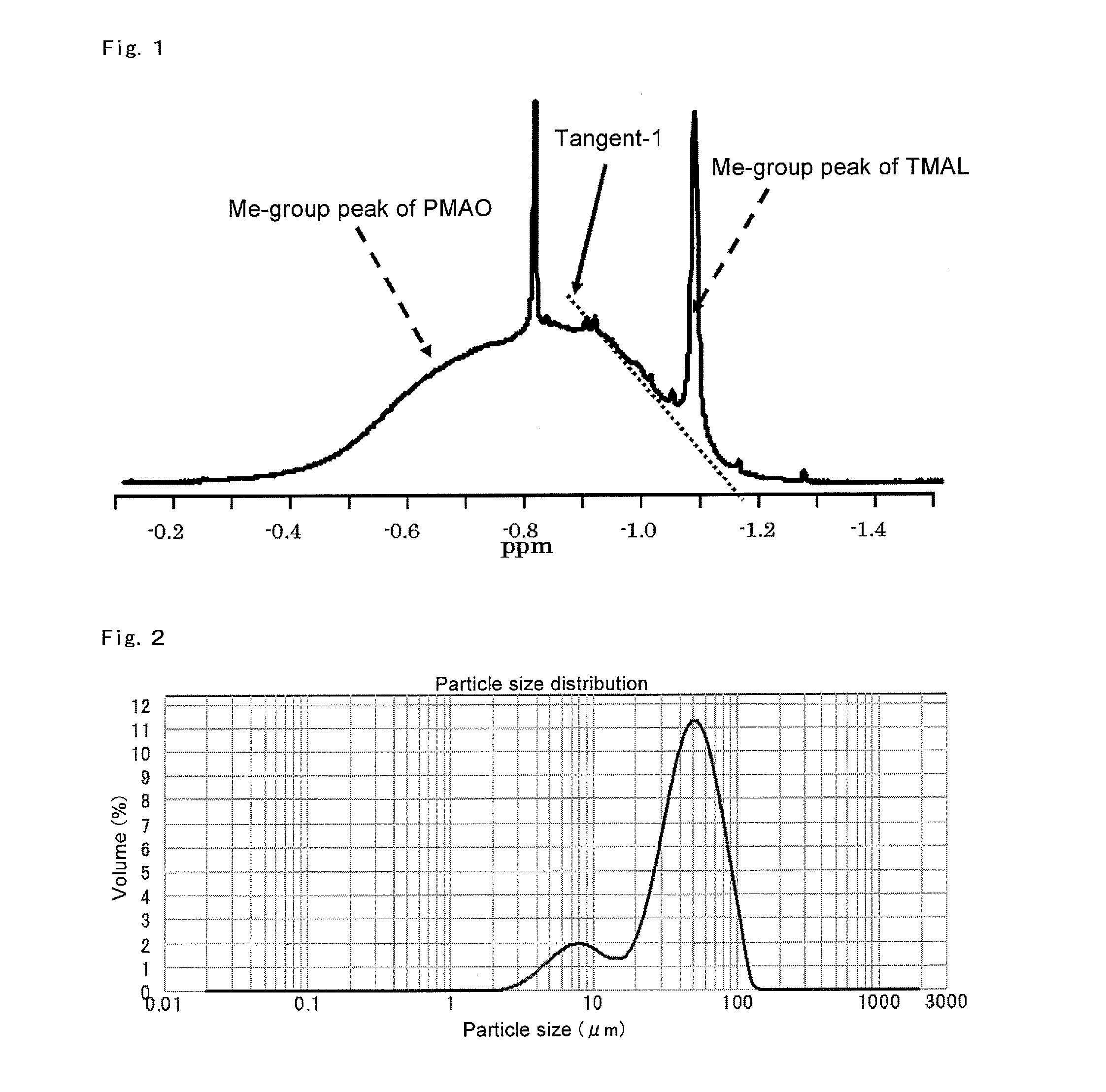
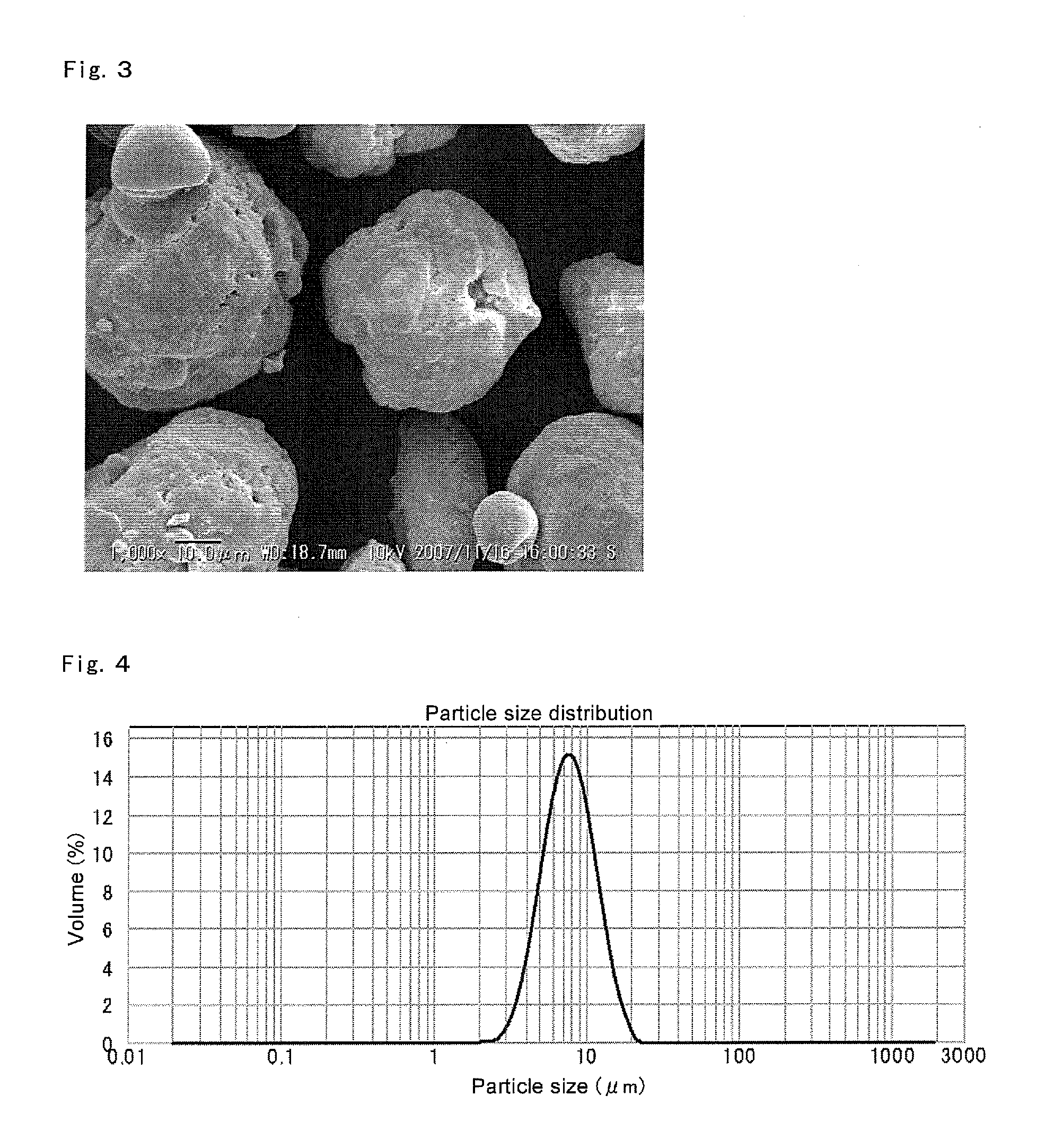
Method for manufacturing a small particle diameter product of solid polymethylaluminoxane composition
ActiveUS9340630B2Easy to optimizeHigh yieldGroup 3/13 element organic compoundsThin material handlingParticulatesDiameter product
A solid polymethylaluminoxane composition is provided having uniform particle diameter in the form of fine particles of less than 5 μm employed to polymerize olefins with high polymerization activity without silica. A method for manufacturing thereof, a polymerization catalyst, and a method for manufacturing a polyolefin are also provided. The solid polymethylaluminoxane composition: has an aluminum content within a range of 36 mass % to 43 mass %; has a mole fraction of methyl groups derived from trimethylaluminum moieties relative to the total number of mols of methyl groups of 12 mol % or less; and is particulate having a median diameter based on volume within a range of 0.1 μm to less than 5 μm. In a step of heating an aromatic hydrocarbon solution containing trimethylaluminum and the polymethylaluminoxane to cause solid polymethylaluminoxane composition to precipitate, prior to or during the heat treating step, a dry, inert gas is bubbled through.
Owner:TOSOH FINECHEM CORP
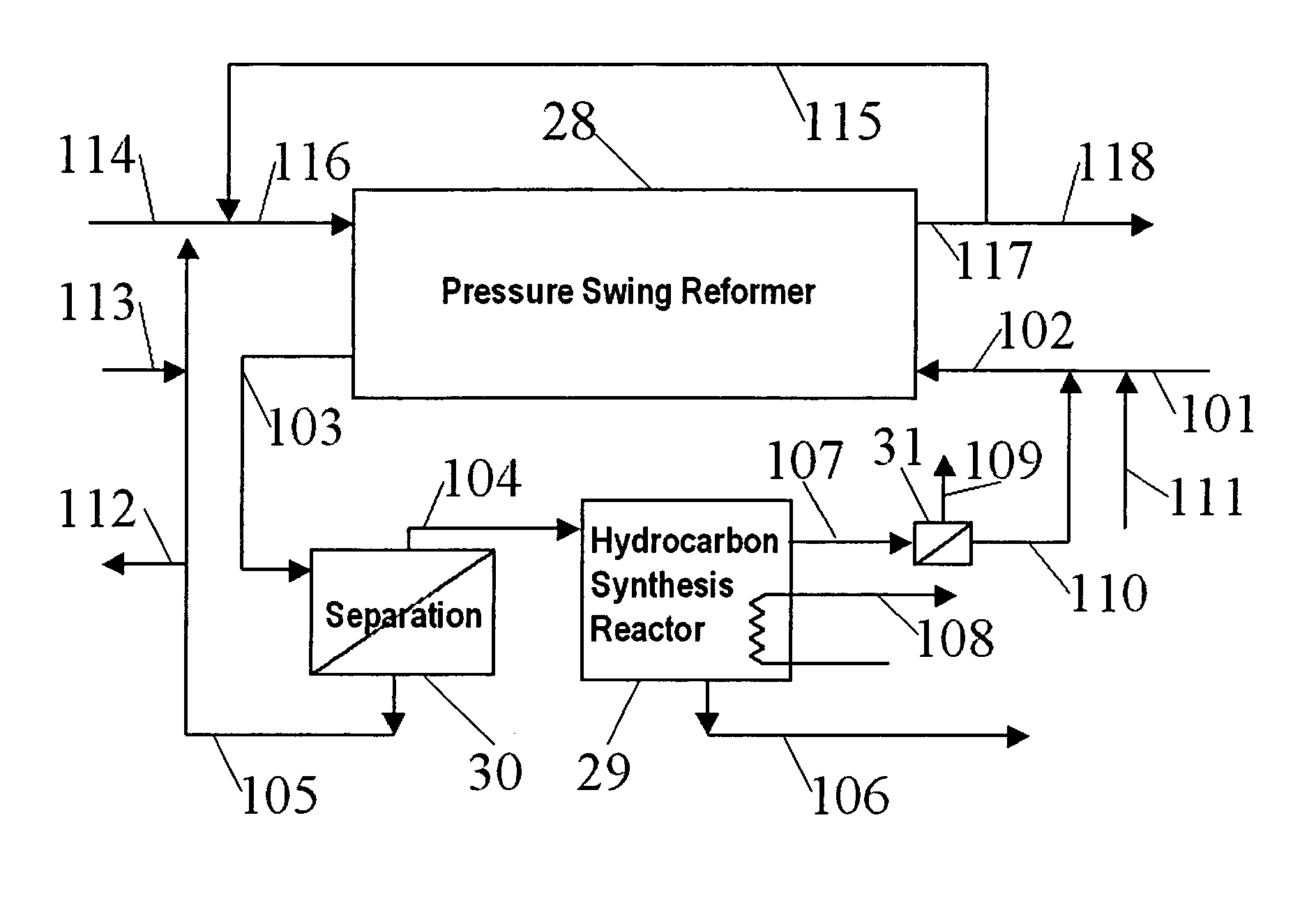
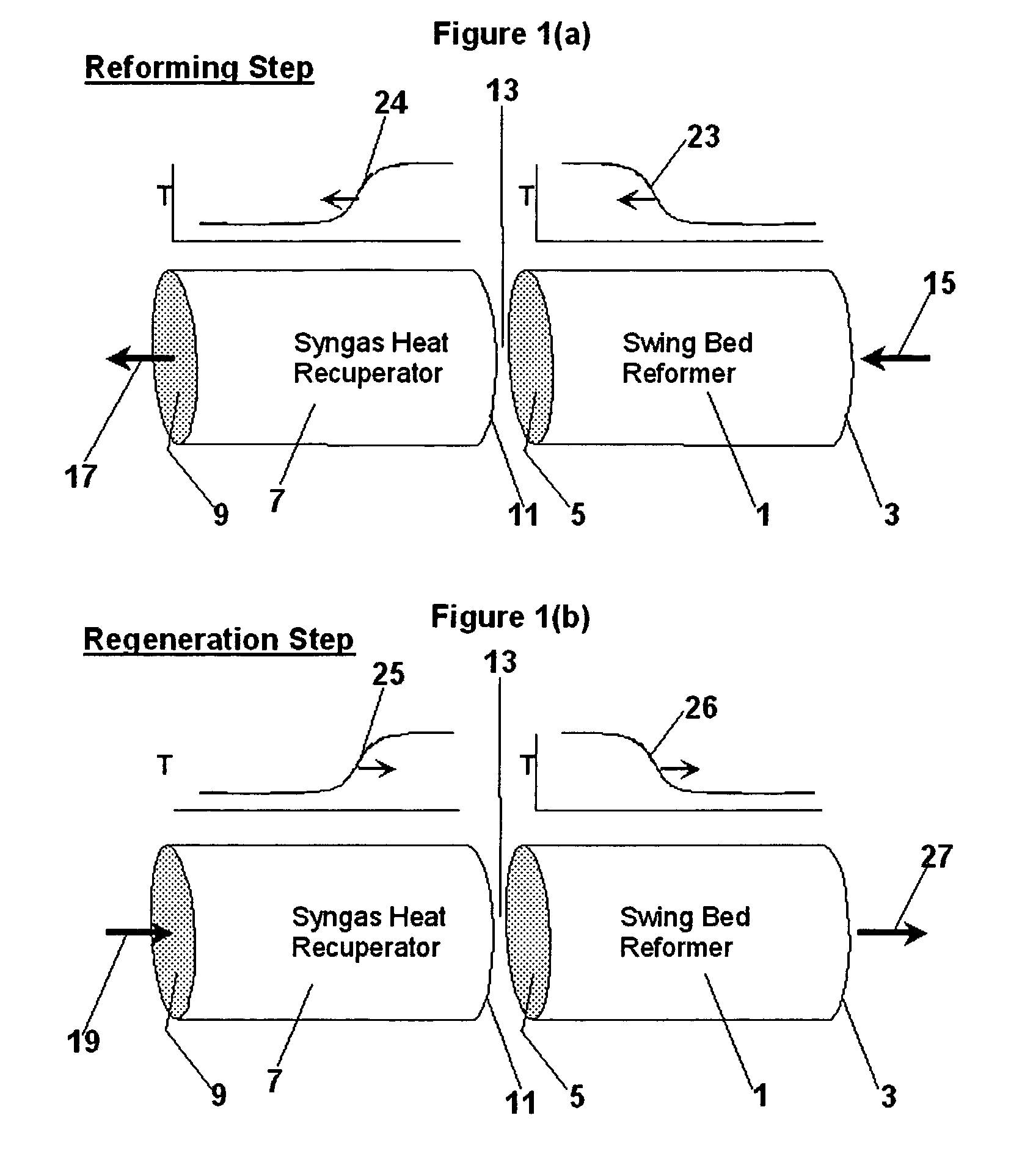
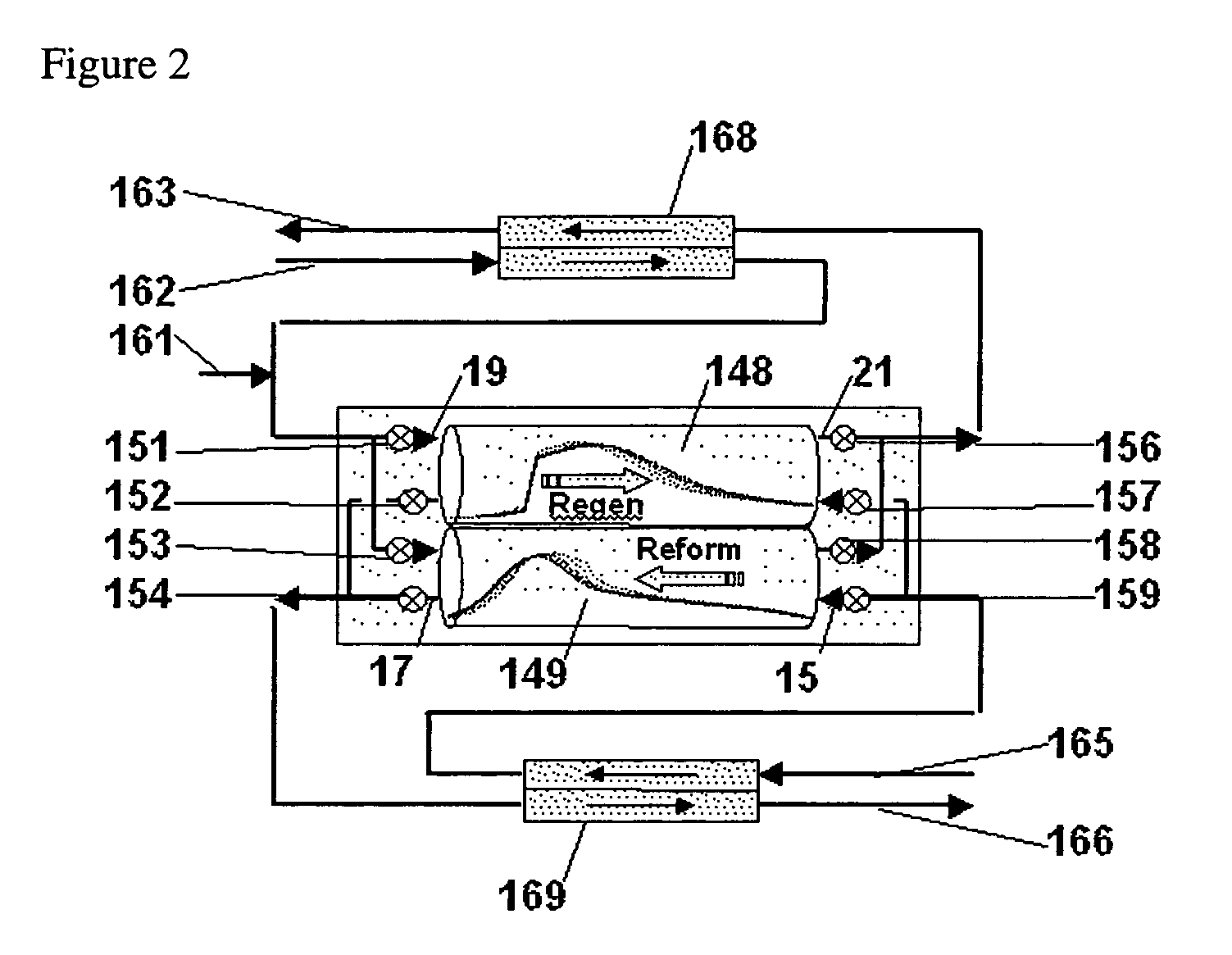
Hydrocarbon synthesis process using pressure swing reforming
ActiveUS7053128B2HydrogenOrganic compounds purification/separation/stabilisationLiquid productHydrogen
The invention provides a method for producing liquid hydrocarbons by first generating in a pressure swing reformer a synthesis gas stream having a mole ratio of H2:CO greater than 2:1. Then, a portion of the hydrogen is separated to produce a synthesis gas stream having a mole ratio of H2:CO of about 2:1 which steam is then introduced into a hydrocarbon synthesis reactor for conversion to liquid products.
Owner:EXXON RES & ENG CO
Solid support-polymethylaluminoxane complex, method for producing same, olefin polymerization catalyst, and method for producing polyolefin
ActiveUS8975209B2Conveniently obtainHigh polymerization activityOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsOrganic chemistry methodsPolyolefinOlefin polymerization
Disclosed is a solid support-polymethylaluminoxane complex exhibiting a higher polymerization activity than a conventional substance and being homogeneous. Also disclosed is a method for producing an olefin-based polymer having a favorable quality using the complex and a transition metal compound. The complex comprises a coating layer containing polymethylaluminoxane and trimethylaluminum on the surface of a solid support. The coating layer comprises a solid polymethylaluminoxane composition in which (i) the content of aluminum is in a range of 36 to 41 mass % and (ii) the molar fraction of methyl groups derived from a trimethylaluminum moiety to the total number of moles of methyl groups is 12 mol % or less. Also disclosed is an olefin polymerization catalyst comprising the complex and a transition metal compound represented by general formula (III): MR5R6R7R8 as catalyst components, and a method for producing a polyolefin comprising polymerizing an olefin using the catalyst.
Owner:TOSOH FINECHEM CORP
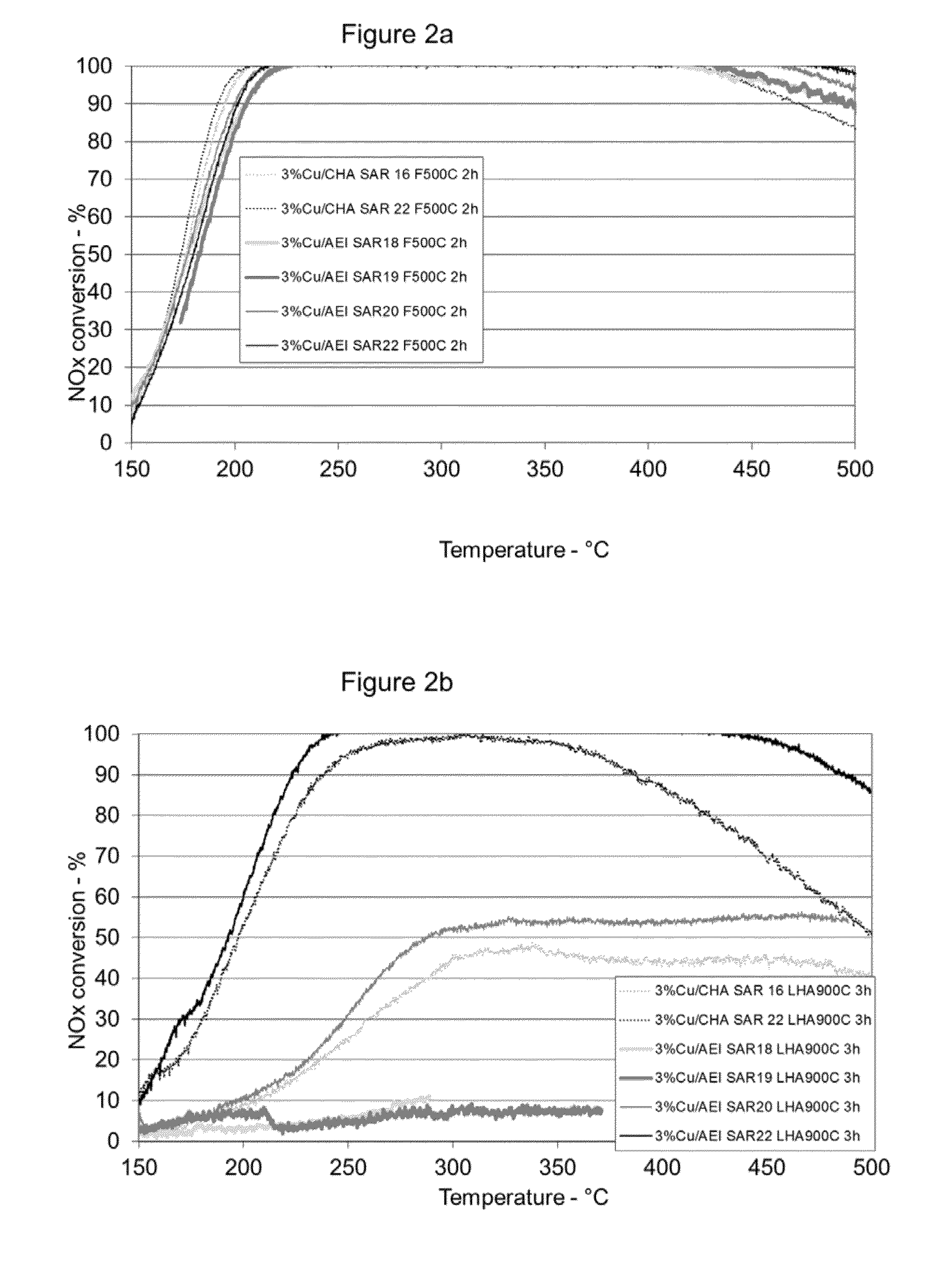
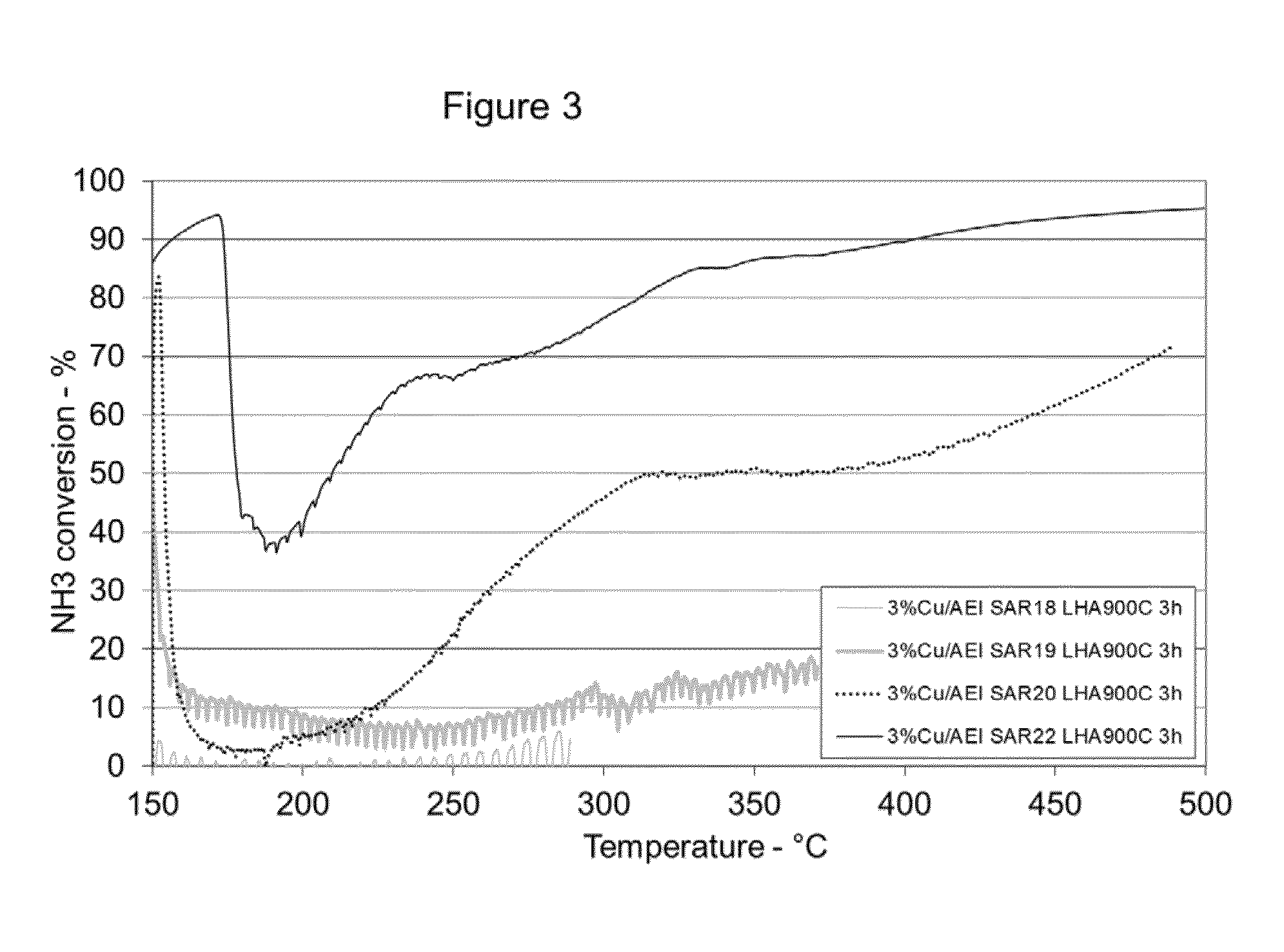
Catalyst for treating exhaust gas
ActiveUS20140271426A1Improve catalytic performanceCombination devicesNitrogen compoundsMolecular sieveSilicon dioxide
Provided is a catalyst composition having an aluminosilicate molecular sieve having an AEI structure and a mole ratio of silica-to-alumina of about 20 to about 30 loaded with about 1 to about 5 weight percent of a promoter metal, based on the total weight of the molecular sieve material. Also provided are method, articles, and systems utilizing the catalyst composition.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
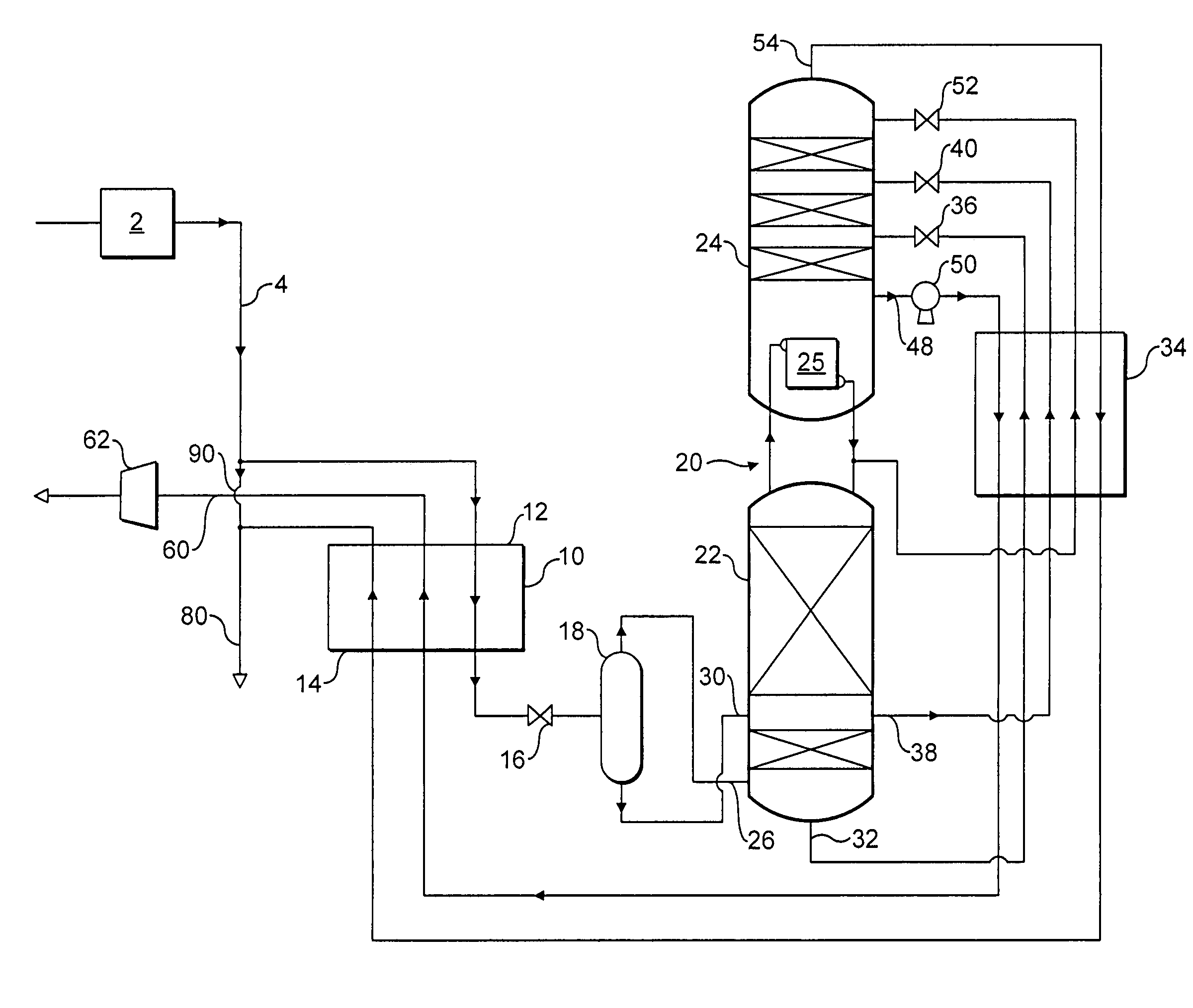
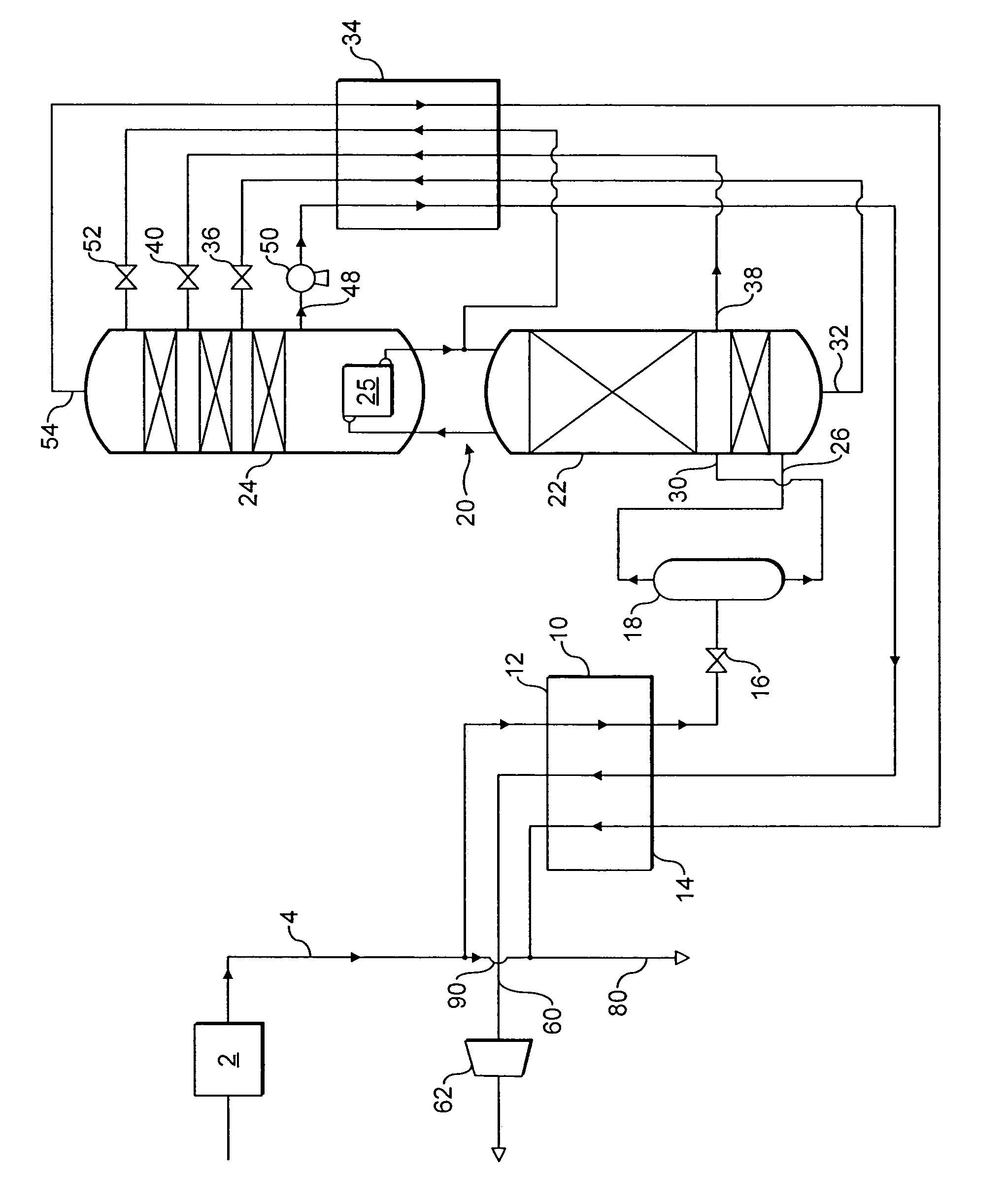
Nitrogen rejection method and apparatus
Nitrogen is rejected from a feed natural gas stream comprising methane and nitrogen so as to form a primary methane product. The mole fraction of nitrogen in the feed natural gas increases over a period of time. The feed natural gas stream is cooled in a main heat exchanger and is rectified in a double rectification column. A primary product methane stream and a secondary nitrogen-enriched product stream are withdrawn from the rectification column. The secondary nitrogen-enriched product stream has a mole fraction of methane at or above a chosen minimum value when the said mole fraction of nitrogen is at a minimum. When the said mole fraction of nitrogen rises to a value at which the mole fraction of methane in the secondary nitrogen-enriched product stream falls below the chosen minimum, a part of the feed gas is introduced through conduit into the secondary nitrogen-enriched product stream so as to restore its mole fraction of methane to the chosen minimum value or a value thereabove.
Owner:THE BOC GRP PLC
Light emitting device
InactiveUS20050264161A1Effective lightingIncrease brightnessSustain/scan electrodesDischarge tube luminescnet screensDisplay deviceUltraviolet lights
A blue-emitting phosphor is optimized by controlling mole fractions typically of Mg and Si in Sr3-eMgbSi2cO8d:Eue or by further including an optimal amount of at least one additional component such as Ba or Ca. The resulting phosphor exhibits a higher brightness and a higher color purity upon excitation by ultraviolet light emitted as a result of discharge of xenon gas. The optimized phosphor is incorporated into light emitting devices such as lamps and PDPs, and further into display devices.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Superlattice strain relief layer for semiconductor devices
ActiveUS20070108456A1High aluminum contentEfficient productionSolid-state devicesNanoopticsLength waveLight-emitting diode
A GaN / AlN superlattice is formed over a GaN / sapphire template structure, serving in part as a strain relief layer for growth of subsequent layers (e.g., deep UV light emitting diodes). The GaN / AlN superlattice mitigates the strain between a GaN / sapphire template and a multiple quantum well heterostructure active region, allowing the use of high Al mole fraction in the active region, and therefore emission in the deep UV wavelengths.
Owner:XEROX CORP
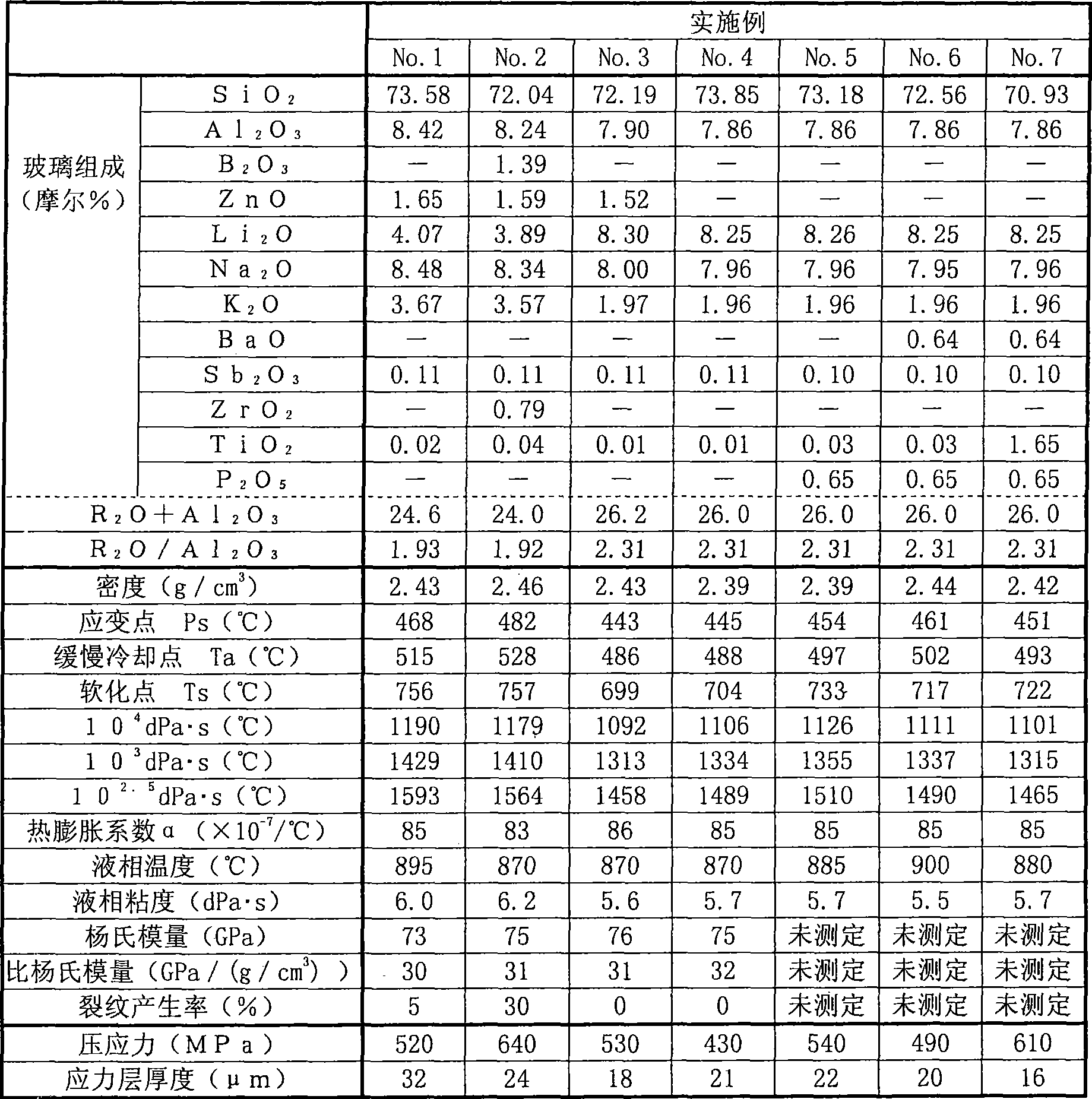
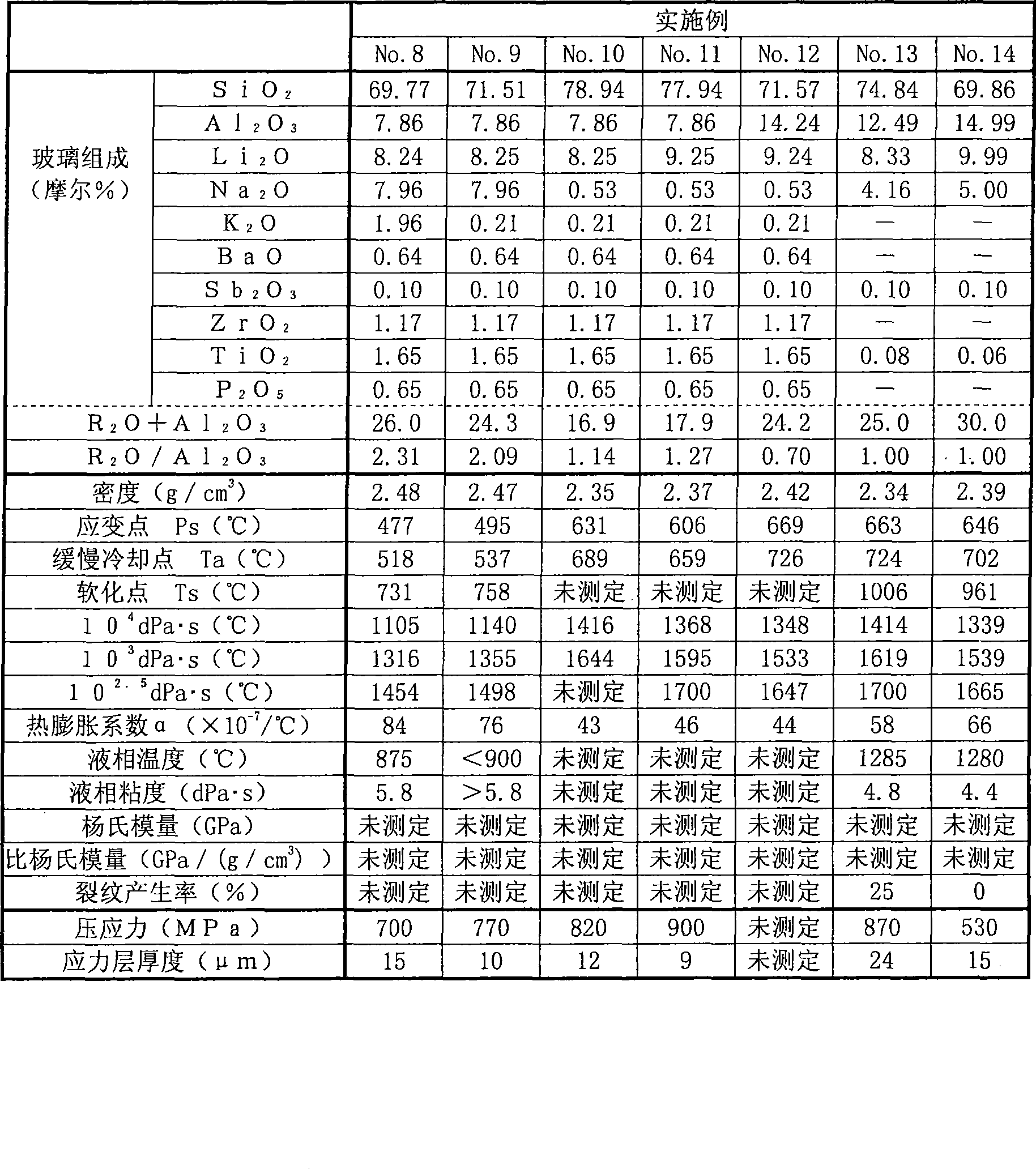
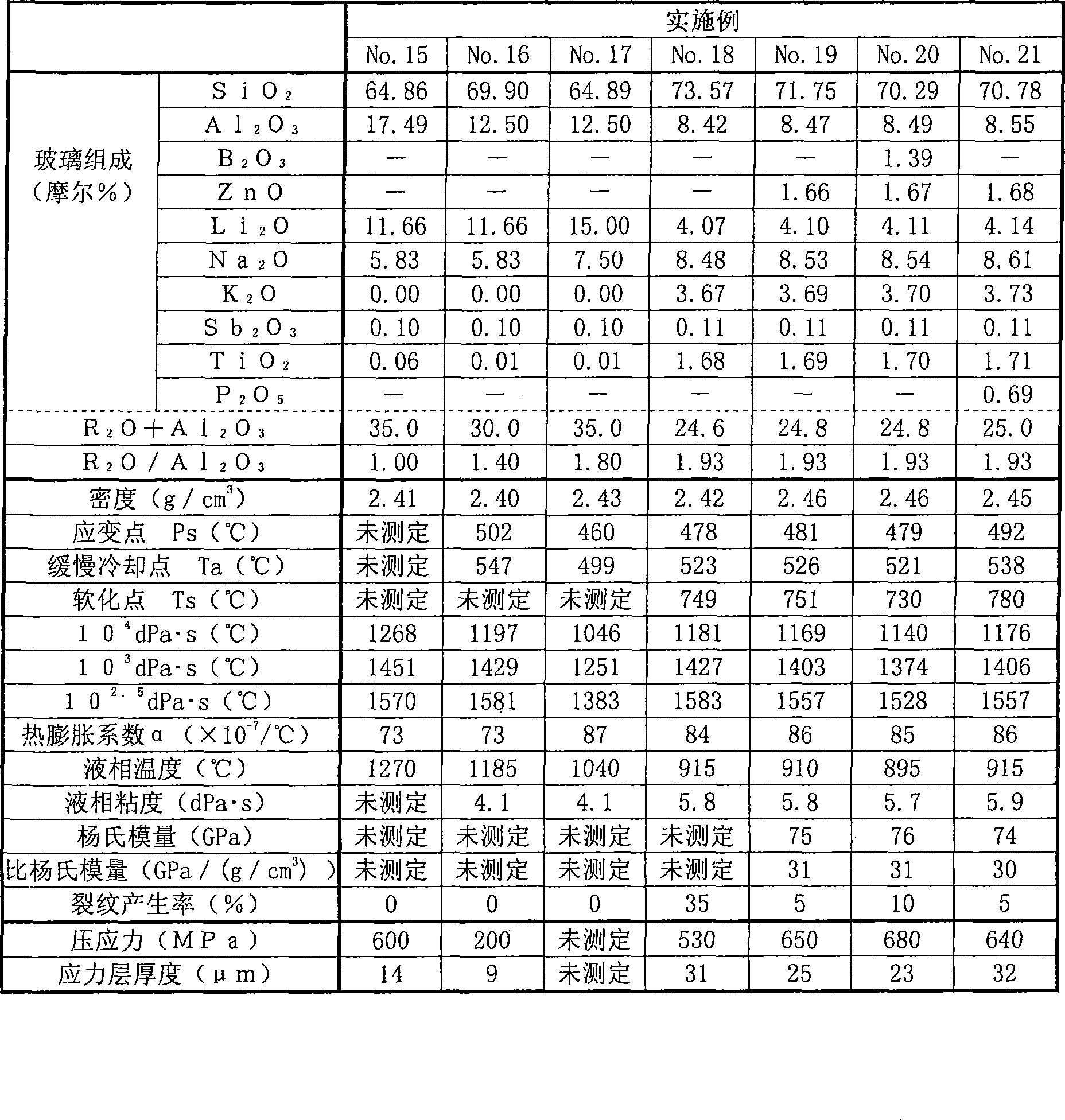
Reinforced glass substrate
The objective of the invention is to obtain a glass substrate satisfying ion exchange performance and devitrification resistance of a glass simultaneously and having higher mechanical strength compared to a conventional glass substrate. The tempered glass substrate which has a compression stress layer on a surface thereof, comprises a glass composition including, in terms of mole%, 50-85% of SiO2 , 5- 30% of Al2O3, 0-20% of Li2O, 0-20% of Na2O, 0-20% of K2O, 0.001-10% of TiO2, and 15-35% of Li2O+Na2O+K2O+Al2O3. The tempered glass substrate has a (Li2O+Na2O+K2O) / Al2O3 value of 0.7-3 in terms of mole fraction, and is substantially free of As2O3 and F.3 in terms of mole fraction, and is substantially free of As2O3 and F.
Owner:NIPPON ELECTRIC GLASS CO LTD
Compound metal oxide de-fluorine sorbent
ActiveCN1954906AImprove adsorption capacityWide pH rangeOther chemical processesWater/sewage treatment by sorptionSorbentRare earth
A complex metal oxide used as an adsorbent for removing fluorine from water is prepared from the transition metal chosen from Ti, V, Cr, Mn, Fe, Co, Ni, Cu and Zn, aluminum and RE metal chosen from Ce and La in the mole ratio of (0.5-1.5): (2-6): (0.5-1.5) through dissolving them in water to become aqueous solution, dropping alkali solution to make its pH=9.0-9.5, laying aside, centrifugal washing and separating by deionized water, drying, and grinding.
Owner:北京国中科创环境科技有限责任公司
Dilute Aqueous Peracid Solutions and Stabilization Method
A method for stabilizing a dilute peracetic acid solution containing less than about 5 wt % peracetic acid by controlling the concentration of hydrogen peroxide and the mole ratio of hydrogen peroxide to acetic acid and by introducing a stabilizer to provide sequestering activity. The method is particularly useful for the long-term stabilization of dilute peracetic acid solutions. Stabilized dilute peracetic acid solutions are also within the scope of this invention.
Owner:FMC CORP
Polyurethane foam material and its preparation method
The present invention relates to a novel polyurethane foam material and its production method. It is an aliphatic polycarbonate type polyurethane foam material synthesized by using carbon dioxide as initial raw material, in which the carbonate group content is betwene 15%-30%. Its production method adopts the aliphatic polycarbonate polyalcohol which is synthesized by using carbon dioxide and epoxy compound and whose number-average molecular weight is less than 10000, hydroxyl functionality is 2,3 or higher than that and the mole fraction of carbonate group in molecular is between 0.2-0.5; then makes the polyalcohol resin and diisocyanate and / or polycyanate produce reaction in the presence of catalyst, foaming agent, crosslinking or chain extender, foam stabilizing agent and other adjuvant to synthesize said invented product.
Owner:JIANGSU ZHONGKE JINLONG CHEM
Thermal spray material and process for preparing same
ActiveUS20150096462A1Smooth thermal spray coatingFormed with easeMolten spray coatingRare earth metal compoundsRare-earth elementThermal spraying
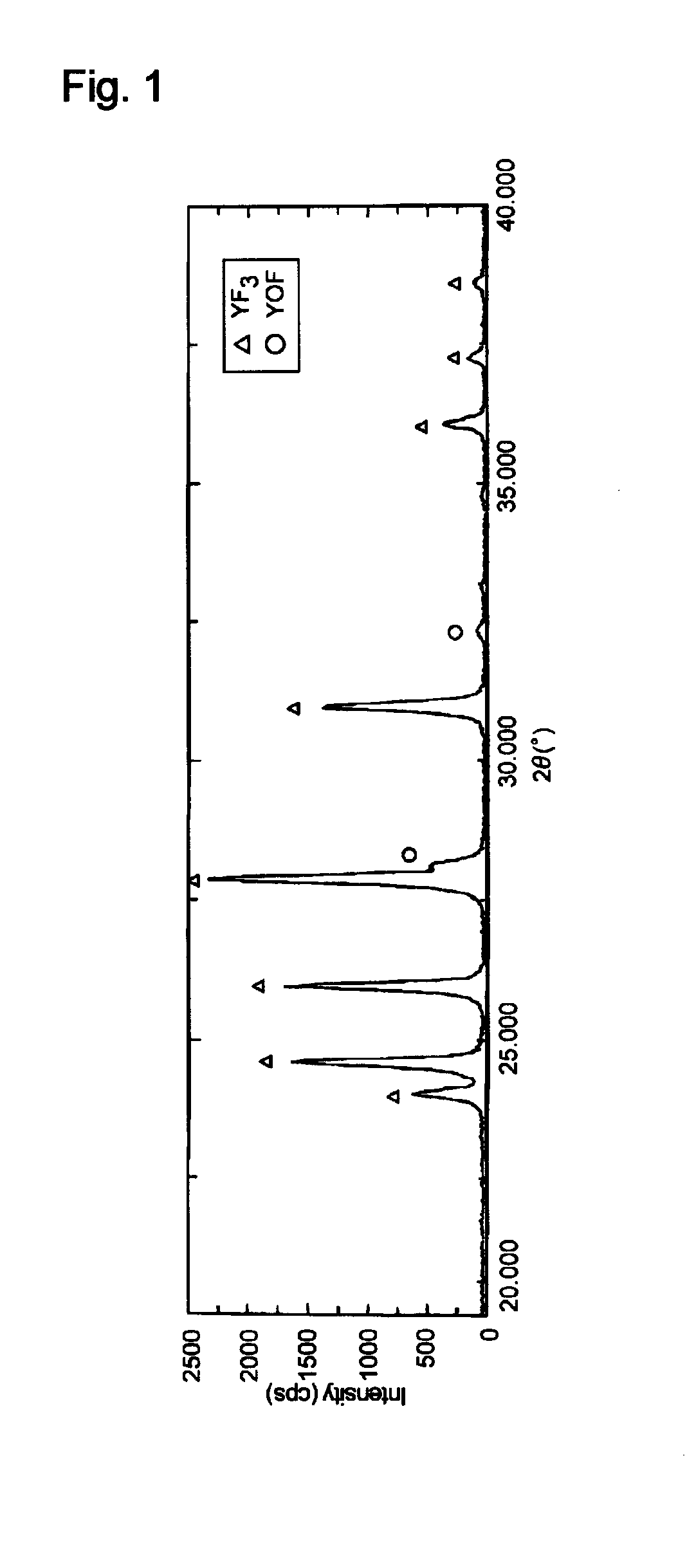
A thermal spray material includes granules of an oxyfluoride of yttrium (YOF). The granules may contain a fluoride of yttrium (YF3). The granules preferably have an oxygen content of 0.3 to 13.1 mass %. The granules preferably have a fracture strength of 0.3 MPa or more and less than 10 MPa. Part of yttrium (Y) of the granules may be displaced with at least one rare earth element (Ln) except yttrium, the molar fraction of Ln relative to the sum of Y and Ln being preferably 0.2 or less.
Owner:NIPPON YTTRIUM
Gas analyzer
ActiveUS20100110437A1Quick measurementShort intake tubeThermometer detailsSamplingFast measurementCoupling
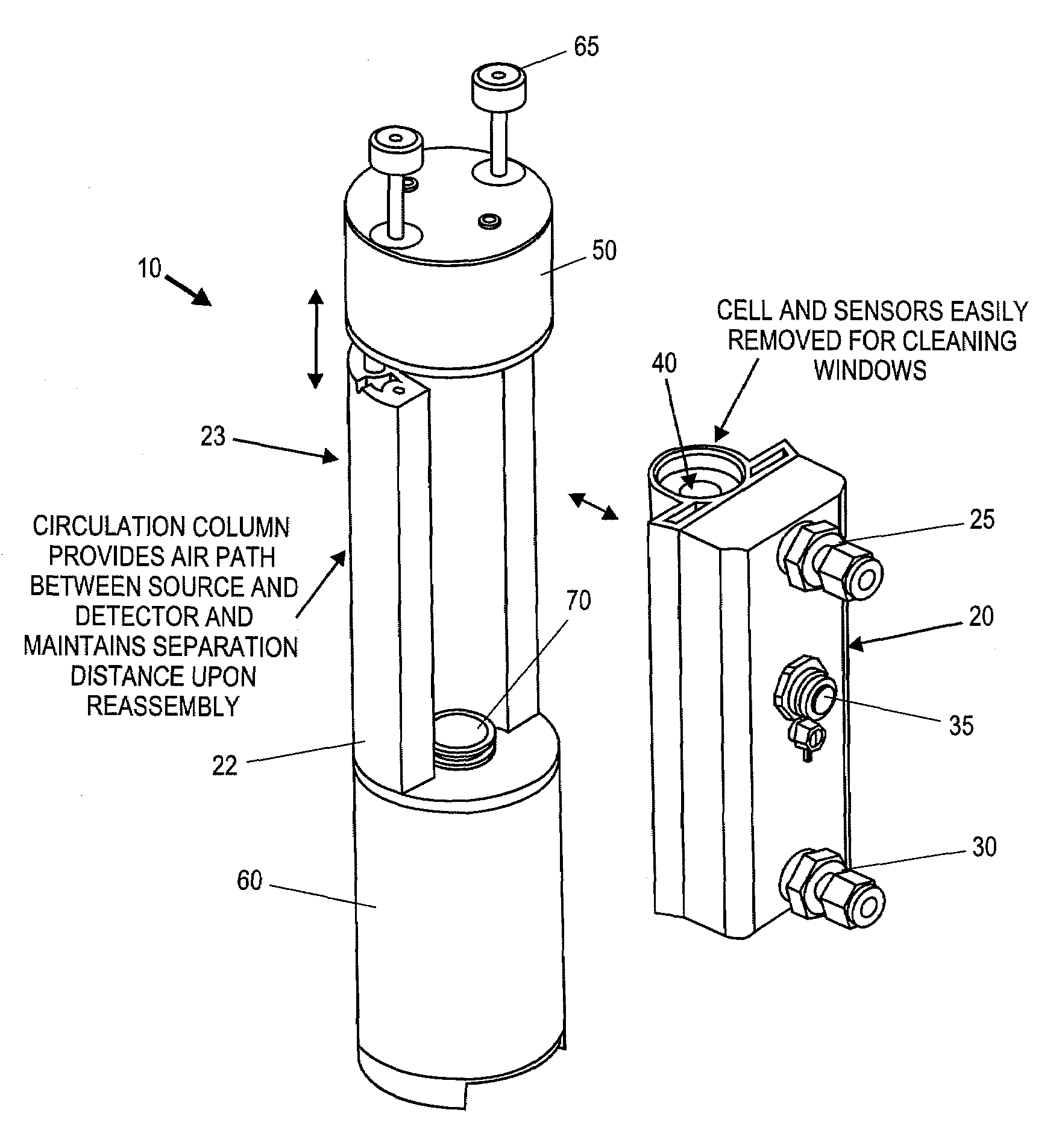
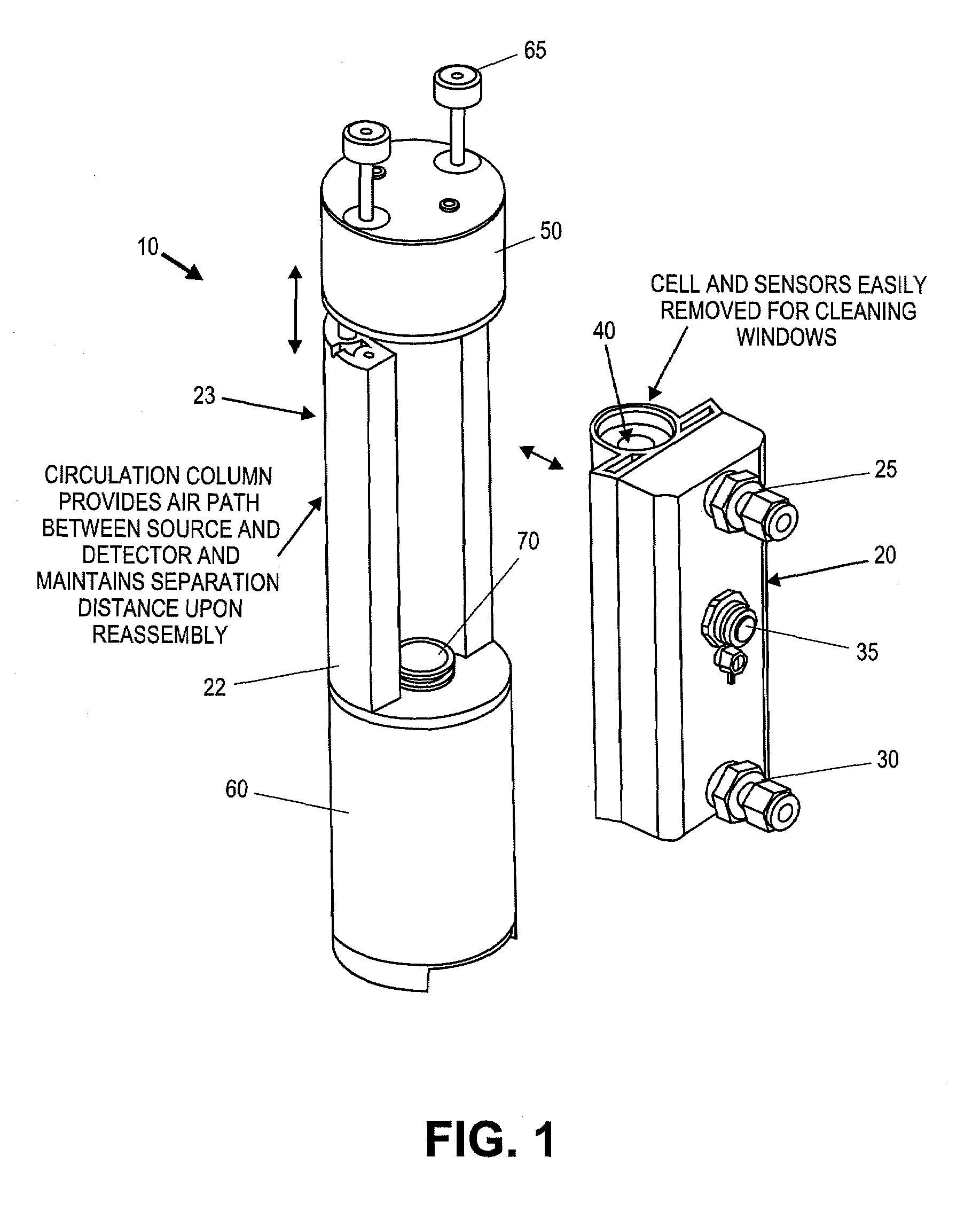
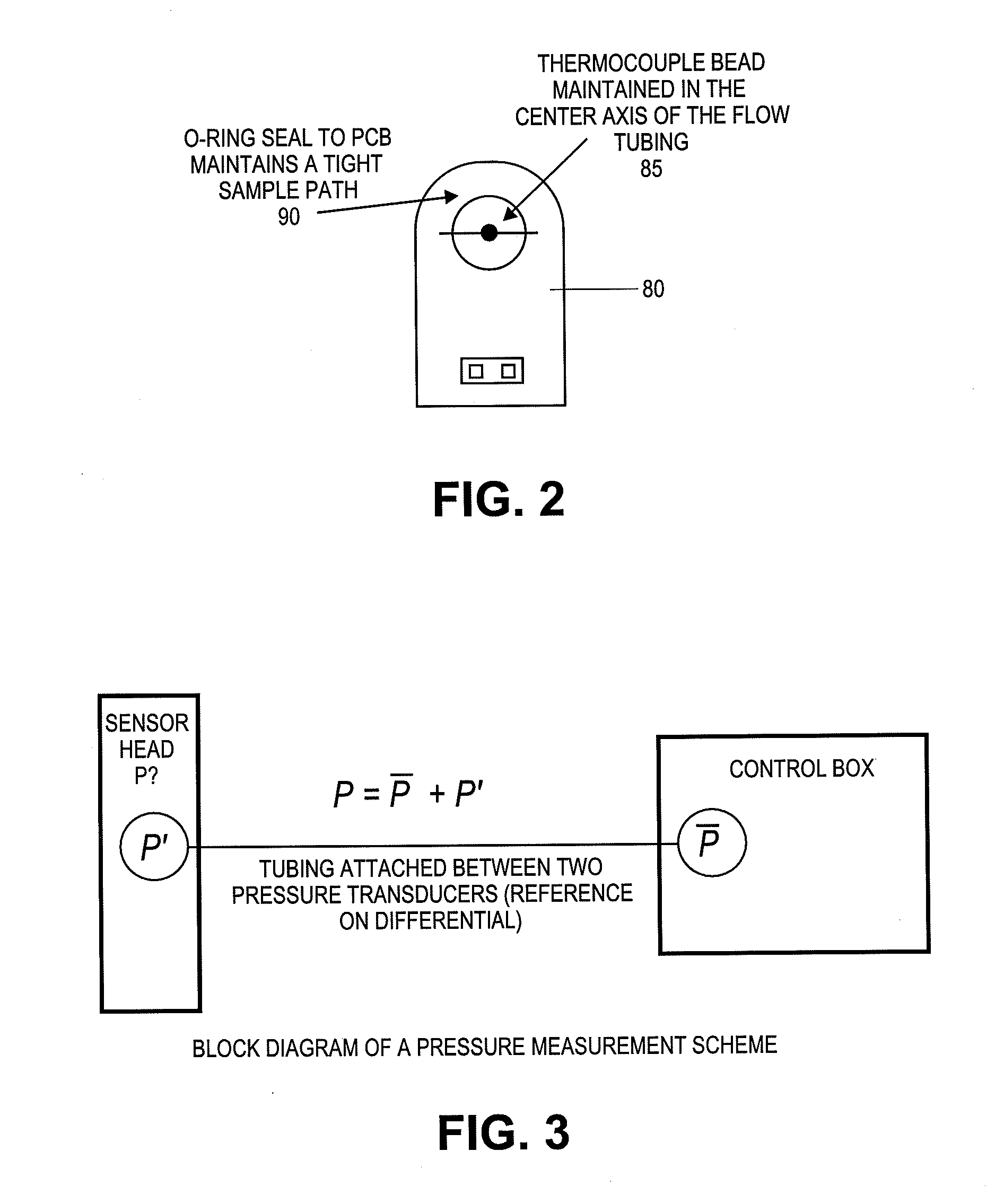
Gas analyzer systems and methods for measuring concentrations of gasses and in particular dry mole fraction of components of a gas. The systems and method allow for rapid measurement of the gas density and / or dry mole fraction of gases for a number of environmental monitoring applications, including high speed flux measurements. A novel coupling design allows for tool-free removal of a cell enclosing a flow path to enable in field cleaning of optical components.
Owner:LI COR
Ternary system sodium-bismuth titanate lead-free piezoelectric ceramics
InactiveCN101200370AExcellent piezoelectric propertiesPracticalDevice material selectionElectricityVolumetric Mass Density
The invention discloses a triple system (Na,Bi)TiO3-based lead-free piezoelectric ceramic material, the formula of the disclosed lead-free piezoelectric ceramic component is denoted with (1-x-y)(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3-x(Bi0.5K0.5)TiO3-yBi(Me)O3 and (1-x-y)(Bi0.5Na0.5)TiO3-x(Bi0.5K0.5)TiO-yBi(Me)O3+zM(a)O(b), in the formula x,y and z denote molar fractions, wherein x is bigger than or equal to 0 and smaller than or equal to 1.0, y is bigger than or equal to 0 and smaller than or equal to 0.2, z is bigger than or equal to 0 and smaller than or equal to 0.1, Me is trivalent metal element, M(a)O(b) is one or more oxides, wherein M is +1 to +6 valence and is an element that can be integrated with oxygen to form a solid oxide. The lead-free piezoelectric ceramic has high ceramic density and excellent performance, piezoelectric constant d33 can reach above 180pC per N, Kp can reach above 0.36. The lead-free piezoelectric ceramic adopts traditional electronic ceramic preparation process, and has low sintering temperature, simple and stable manufacture process and is suitable for industrialization production.
Owner:GUILIN UNIV OF ELECTRONIC TECH
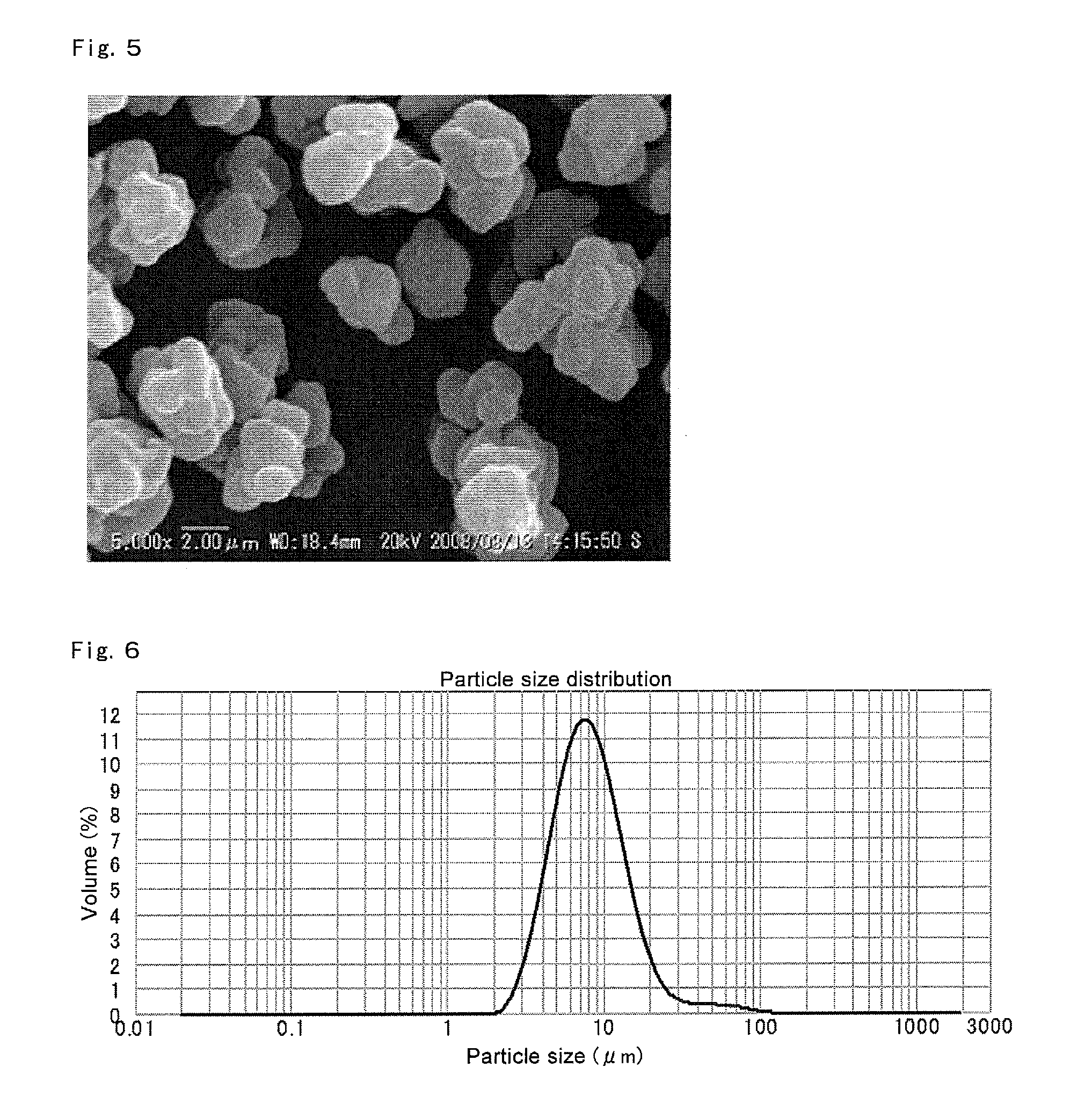
AEI/CHA eutectic molecular sieve containing triethylamine and synthetic method thereof
InactiveCN101450806AMolecular-sieve and base-exchange phosphatesMolecular-sieve silicoaluminophosphatesMolecular sieveChemical composition
The invention discloses an AEI / CHA eutectic molecule sieve containing triethylamine. An anhydrous chemical composition of the AEI / CHA eutectic molecule sieve is expressed as mR.(Six.Aly.Pz)O2, wherein x, y and z are molar fractions of Si, Al and P respectively; the x is between 0.001 and 0.98; the y is between 0.01 and 0.6; the z is between 0.01 and 0.6, x+y+z is equal to 1; the R is a template agent, and the m is a mole number of the R; and the value of the m is between 0.02 and 0.6. A preparation method for the AEI / CHA eutectic molecule sieve comprises the following steps: a) according to the mol ratio of oxides of various components, stirring and mixing evenly a silicon source, an aluminum resource, a phosphorus source, the template agent, and water are to obtain an initial gel mixture; and b) transferring the initial gel mixture into a stainless steel synthesis kettle to be sealed, then heating the kettle to a crystallization temperature of between 160 and 250 DEG C, and performing crystallization at constant temperature for 1 to 120 hours under the self-generated pressure, and separating a solid product, washing the solid product to be neutral, and drying the solid product to obtain the AEI / CHA eutectic molecule sieve. The molecule sieve can be used as a catalyst for an acid catalytic reaction after the template agent is removed through the baking.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for controlling an operating condition of a vehicle engine
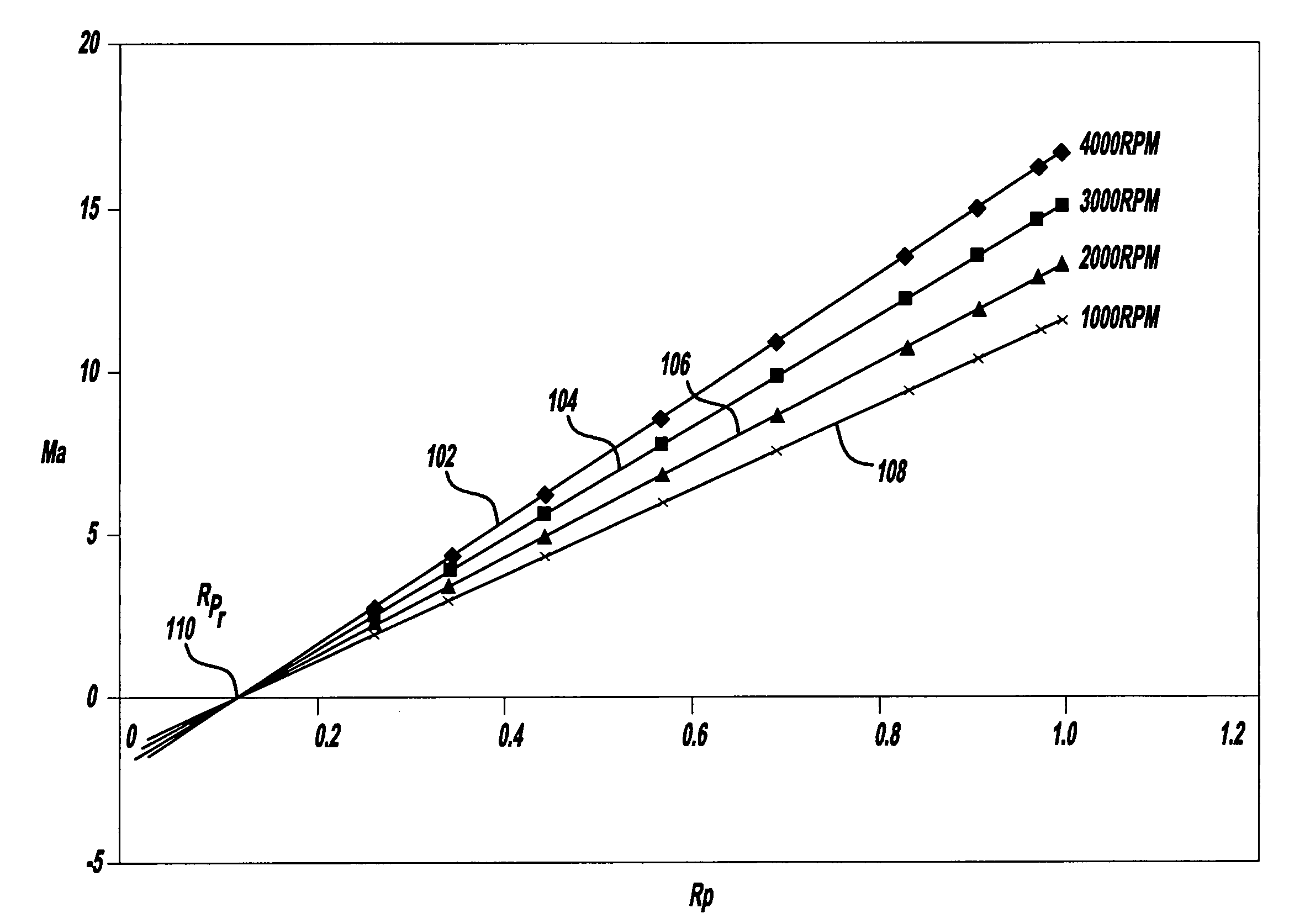
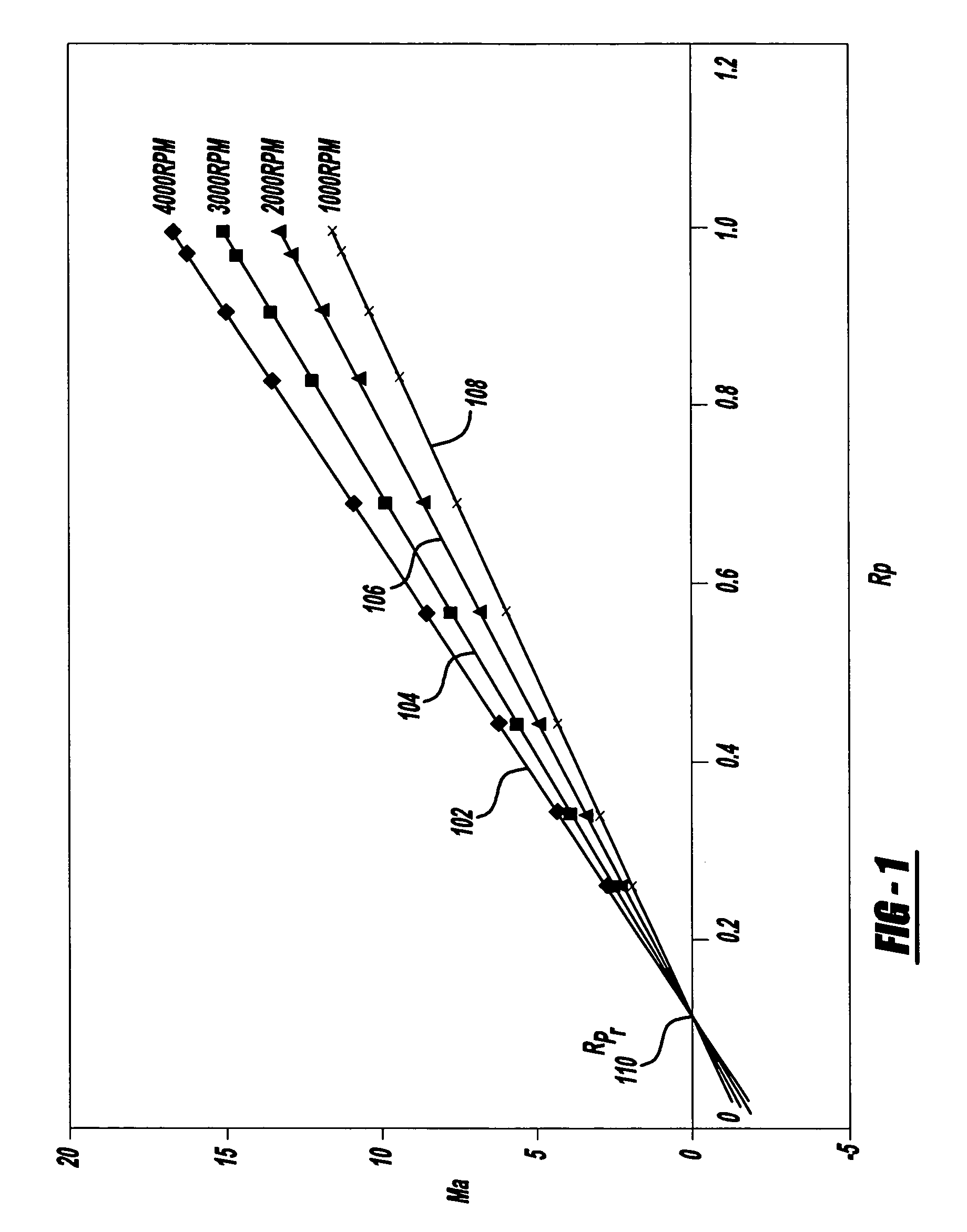
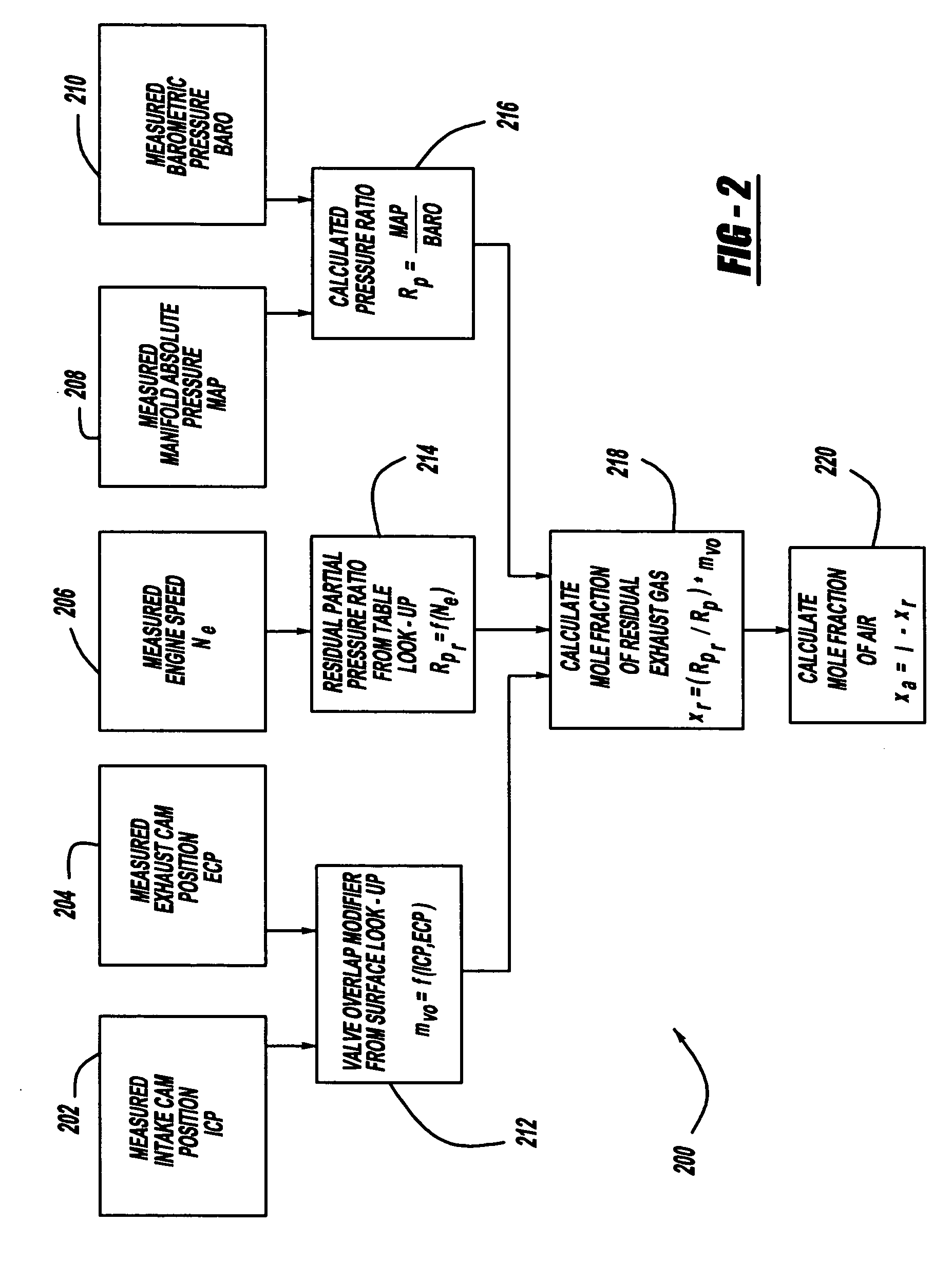
A residual ratio factor characterizing the amount of residual exhaust gas left in a selected cylinder at the end of a piston intake stroke is determined from tabular and surface models based on previously gathered dynamometer data from a test vehicle at various engine speeds. The residual ratio factor is then used to calculate the mole fractions of air and residual exhaust gas in the selected cylinder, which, in turn, are used to determine mass airflow at an engine intake port at the end of the intake stroke. The mass airflow can then be used to derive further models for determining an engine operating parameter, such as fuel / air ratio, required for achieving at preselected vehicle operating condition.
Owner:FCA US
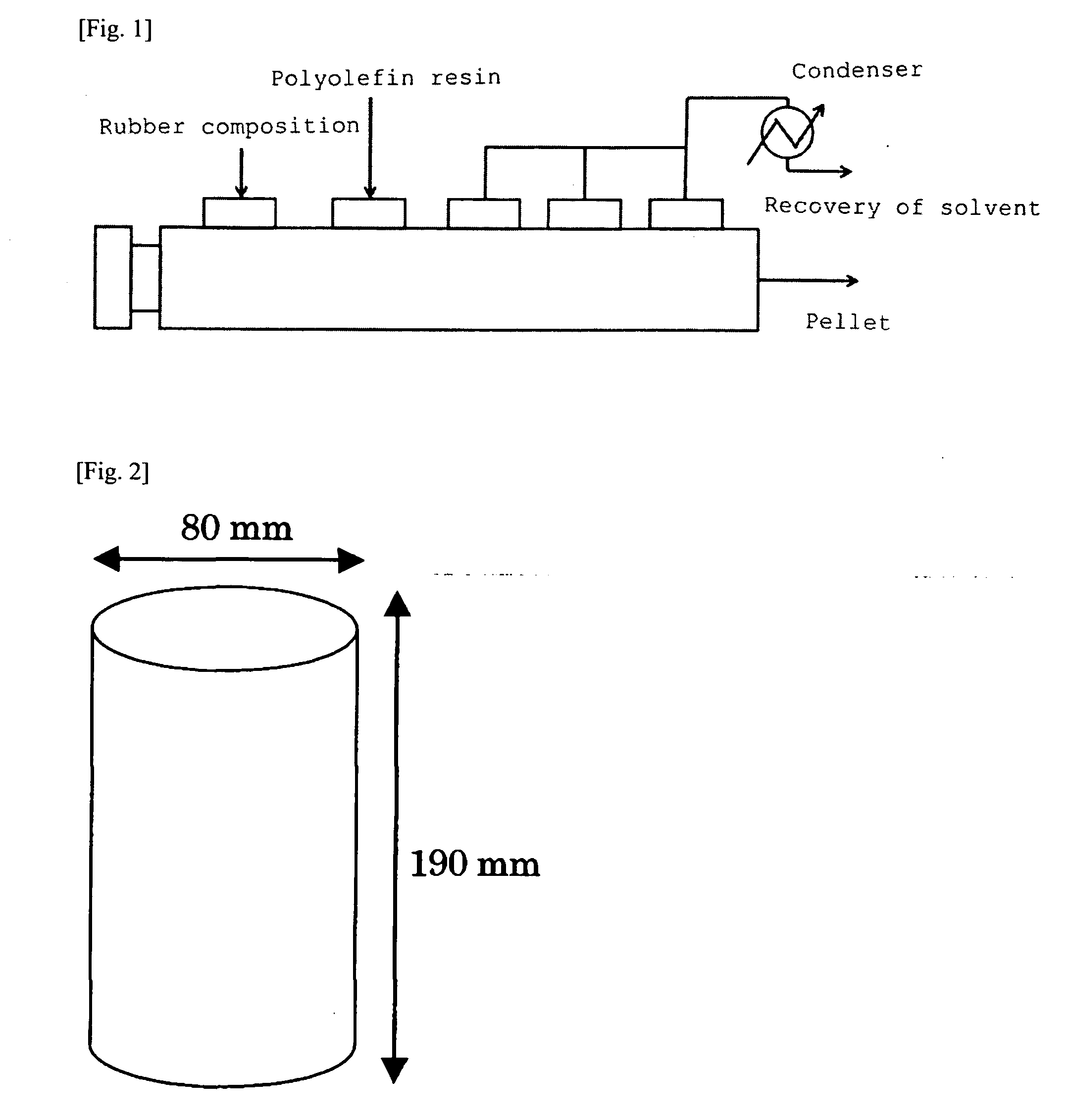
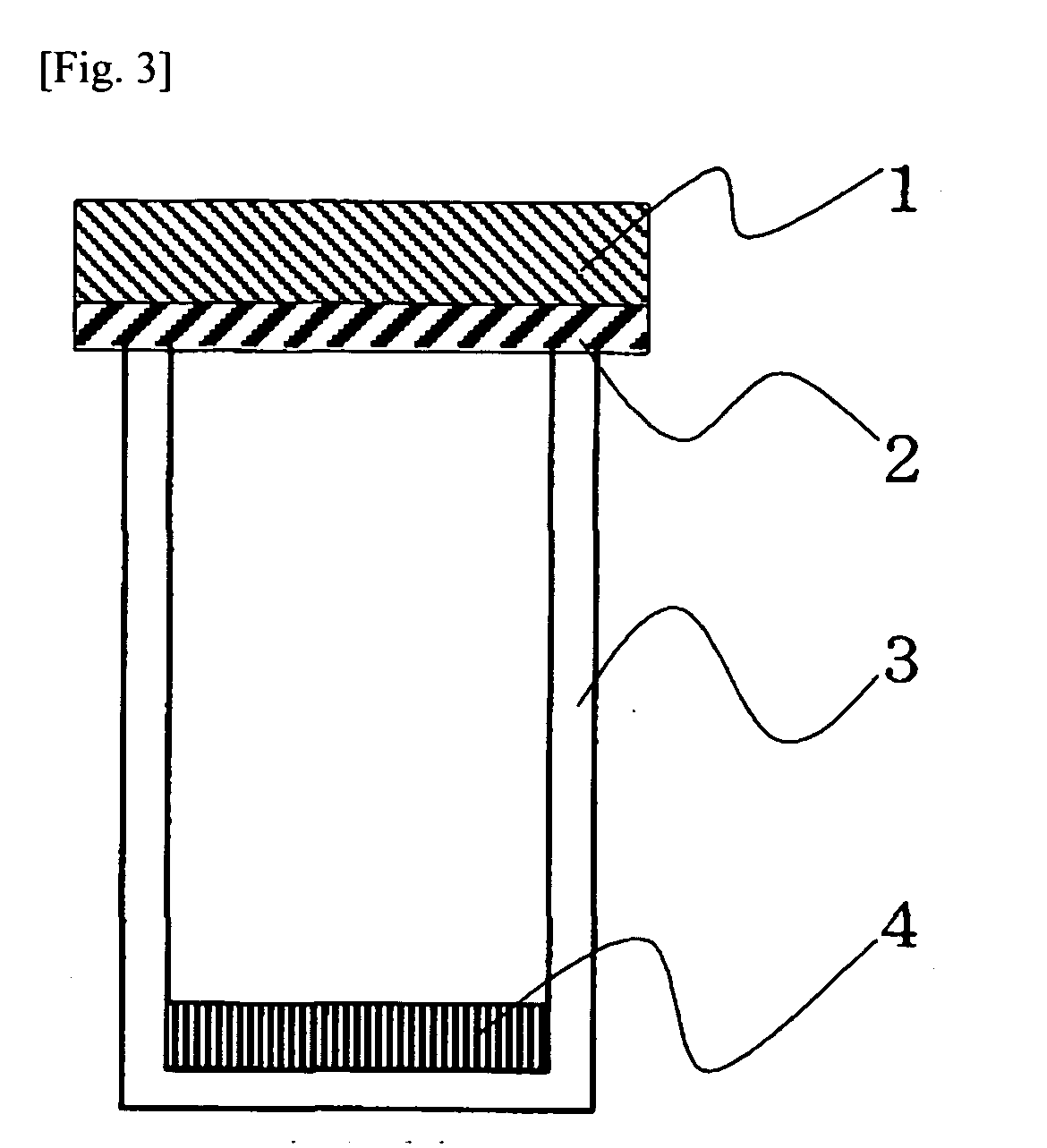
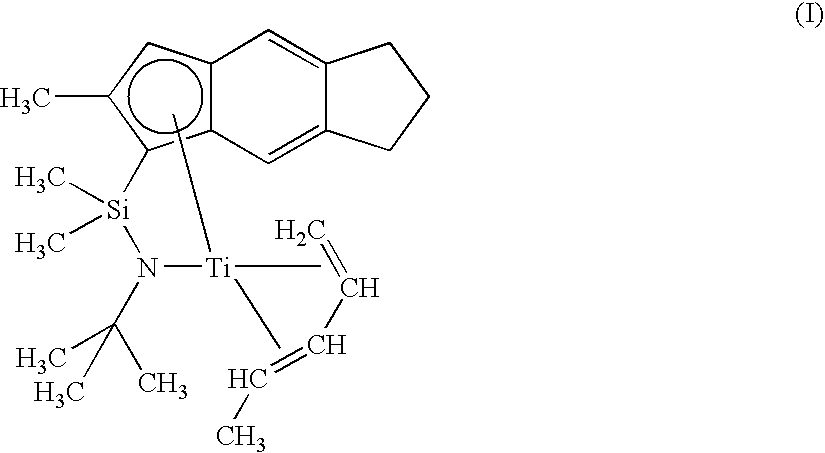
Rubber composition, crosslinked product and foam thereof, molded product therefrom, and use thereof
ActiveUS20090239014A1Excellent in rigidity and compression set and shape memory propertyImprove compatibilityClosuresOther chemical processesPolymer sciencePolyolefin
The present invention provides a molded product exhibiting excellent various properties by improving compatibility of an ethylene / α-olefin / non-conjugated polyene copolymer with a polyolefin resin and a rubber composition for forming the molded product. The present invention further provides a molded product which comprises a rubber composition, is inhibited from fogging and tackiness and is excellent in mechanical strength and heat aging resistance. The rubber composition of the invention comprises an ethylene / α-olefin / non-conjugated polyene copolymer (A), and a polyolefin resin (B) having Mn of not less than 10,000 and / or an ethylene / α-olefin copolymer (C) having Mn of 2500 to 5000, and satisfies the following requirements: (1) a maximum value and a minimum value of an ethylene distribution parameter P of the component (A) have a relationship of Pmax / Pmin≦1.4, and (2) the B value of the component (C) ([EX] / (2[E]×[X])) ([E] and [X] are molar fractions of ethylene and the α-olefin of 3 to 20 carbon atoms, respectively, and [EX] is a fraction of dyad sequence of ethylene / α-olefin of 3 to 20 carbon atoms) is not more than 1.05.
Owner:MITSUI CHEM INC
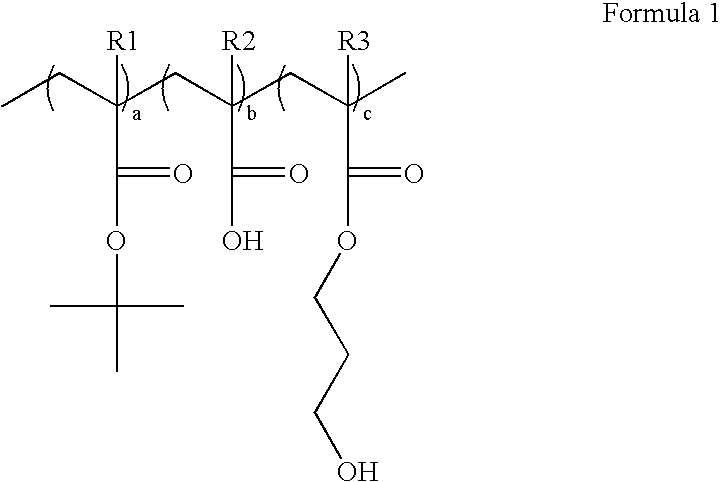
Top ARC polymers, method of preparation thereof and top ARC compositions comprising the same
ActiveUS20050239296A1Minimize scattered reflectionSuppresses dimensional changesPhotosensitive materialsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingAnti-reflective coatingHydrogen
Disclosed herein are a top anti-reflective coating polymer used in a photolithography process, a method for preparing the anti-reflective coating polymer, and an anti-reflective coating composition comprising the anti-reflective coating polymer. The disclosed top anti-reflective coating polymer is used in immersion lithography for the fabrication of a sub-50 nm semiconductor device. The top anti-reflective coating polymer is represented by Formula 1 below: wherein R1, R2 and R3 are independently hydrogen or a methyl group; and a, b and c represent the mole fraction of each monomer, and are in the range between 0.05 and 0.9. The top anti-reflective coating formed using the anti-reflective coating polymer is not soluble in water and can be applied to immersion lithography using water as a medium for a light source. Since the disclosed top anti-reflective coating can reduce the reflectance from an underlayer, the uniformity of CD is improved, thus enabling the formation of an ultrafine pattern.
Owner:SK HYNIX INC
Solid support-polymethylaluminoxane complex, method for producing same, olefin polymerization catalyst, and method for producing polyolefin
ActiveUS20130059990A1High yieldHigh polymerization activityOrganic chemistry methodsOrganic-compounds/hydrides/coordination-complexes catalystsPolyolefinOlefin polymerization
Disclosed is a solid support-polymethylaluminoxane complex exhibiting a higher polymerization activity than a conventional substance and being homogeneous. Also disclosed is a method for producing an olefin-based polymer having a favorable quality using the complex and a transition metal compound. The complex comprises a coating layer containing polymethylaluminoxane and trimethylaluminum on the surface of a solid support. The coating layer comprises a solid polymethylaluminoxane composition in which (i) the content of aluminum is in a range of 36 to 41 mass % and (ii) the molar fraction of methyl groups derived from a trimethylaluminum moiety to the total number of moles of methyl groups is 12 mol % or less. Also disclosed is an olefin polymerization catalyst comprising the complex and a transition metal compound represented by general formula (III): MR5R6R7R8 as catalyst components, and a method for producing a polyolefin comprising polymerizing an olefin using the catalyst.
Owner:TOSOH FINECHEM CORP
Rare earth alloy sintered compact and method of making the same
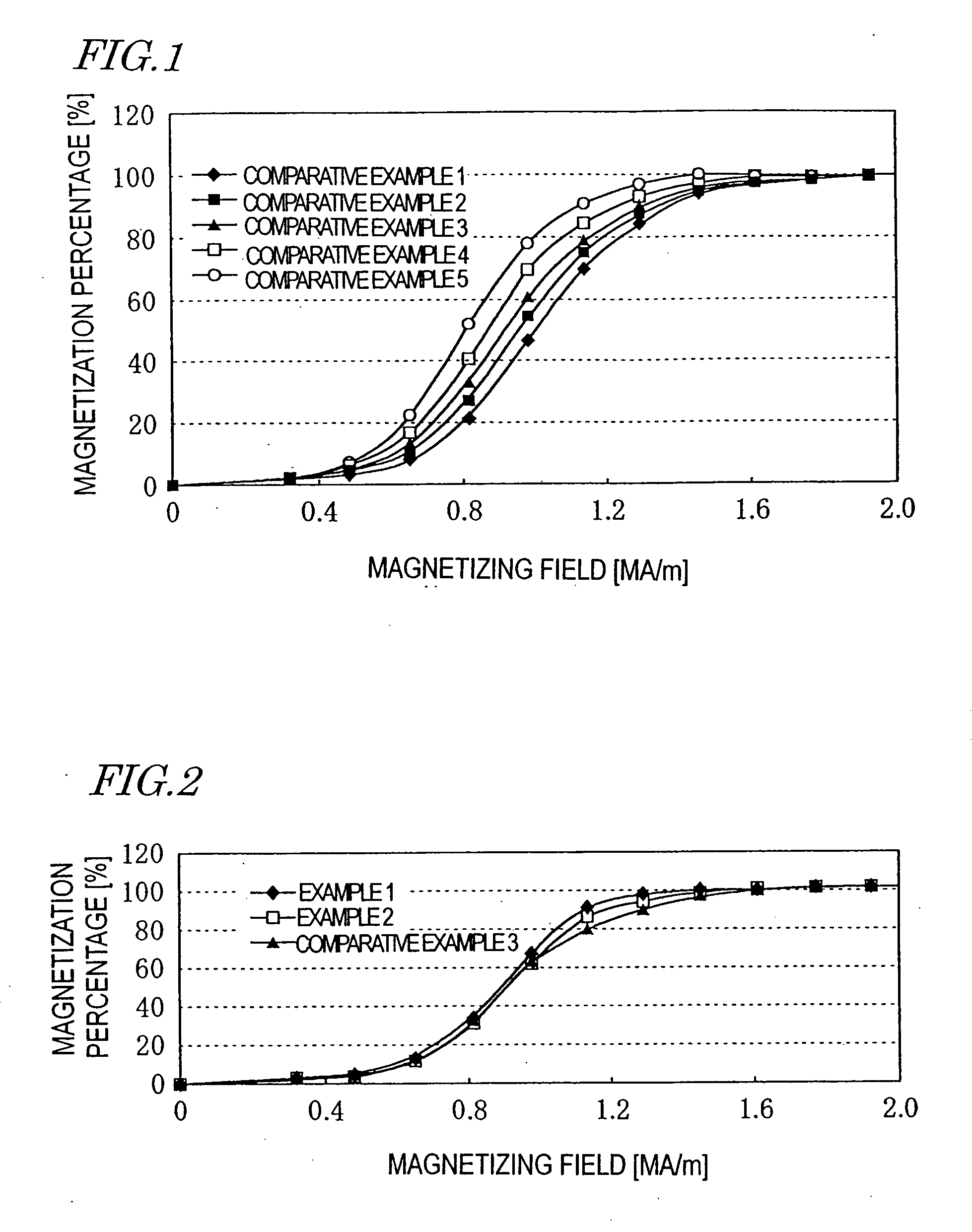
InactiveUS20050098238A1Fully magnetizedLower magnetizing fieldInductances/transformers/magnets manufactureMagnetic materialsRare-earth elementBoron
A rare earth alloy sintered compact includes a main phase represented by (LR1-xHRx)2T14A, where T is Fe with or without non-Fe transition metal element(s); A is boron with or without carbon; LR is a light rare earth element; HR is a heavy rare earth element; and 0<x<1. The sintered compact is produced by preparing multiple types of rare earth alloy materials including respective main phases having different HR mole fractions, mixing the alloy materials so that the sintered compact will include a main phase having an average composition represented by (LR1-xHRx)2T14A, thereby obtaining a mixed powder, and sintering the mixed powder. The alloy materials include first and second rare earth alloy materials represented by (LR1-uHRu)2T14A (where 0≦u<x) and (LR1-vHRv)2T14A (where x<v≦1) and including a rare earth element R(=LR+HR) at R1 and R2 (at %), respectively. ΔR=|R1−R2| is about 20% or less of (R1+R2) / 2.
Owner:HITACHI METALS LTD
Cationic polymerization initiation system and cationic polymerization method
The invention discloses a cationic polymerization initiation system and a cationic polymerization method. The cationic polymerization initiation system comprises at least one initiator, at least one Lewis acid and at least one additive. The initiator is a compound capable of providing protons or carbocations, wherein a mole ratio of the initiator to monomers is (5.0*10<-5> to 1.2*10<-2>): 1. The Lewis acid is a metal halide or an organic metal halide, wherein a mole ratio of the Lewis acid to the monomers is (5.0*10<-4> to 4.0*10<-1>): 1. The at least one additive is selected from sulfur-containing organic compounds, phosphorus-containing organic compounds and organic compounds containing sulfur and phosphorus, wherein a mole ratio of the at least one additive to the monomers is (1.0*10<-3> to 5.0*10<-2>): 1. The cationic polymerization initiation system has high activity, a low price and stable properties, is convenient for use, has high polymerization efficiency, and can greatly improve polymerization product molecular weight, wherein weight-average molecular weight of polymerization products obtained at a temperature of -60 DEG C is 1*10<6>.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Preparation method of polybutylene terephthalate/adipate butanediol copolyester
The invention relates to a preparation method of polybutylene terephthalate / adipate butanediol copolyester, which utilizes a titanium compound and an antimony compound as the composite catalyst, the mole ratio of terephthalic acid to adipate is 3:7-8:2, the ratio of the total mole of the terephthalic acid and the adipate to the mole of 1,4-butanediol is 1:1.0-1.8, esterification is carried out at normal pressure and the temperature of 150-220 DEG C, the pressure is reduced to high vacuum 10-150 Pa for the reaction, the final temperature for the reaction is 265-280 DEG C, and inert gas is utilized to recover the pressure to be normal to obtain the copolyester. The reaction time is shortened, the production amount of tetrahydrofuran is small, the intrinsic viscosity of copolyester chips is 0.90-1.32 dL / g, the hue b value of the product is between 0 and 8, the L value is between 68 and 85, and the product of the polybutylene terephthalate / adipate butanediol copolyester can be used in the fields of various soft package plastic products.
Owner:PETROCHINA CO LTD
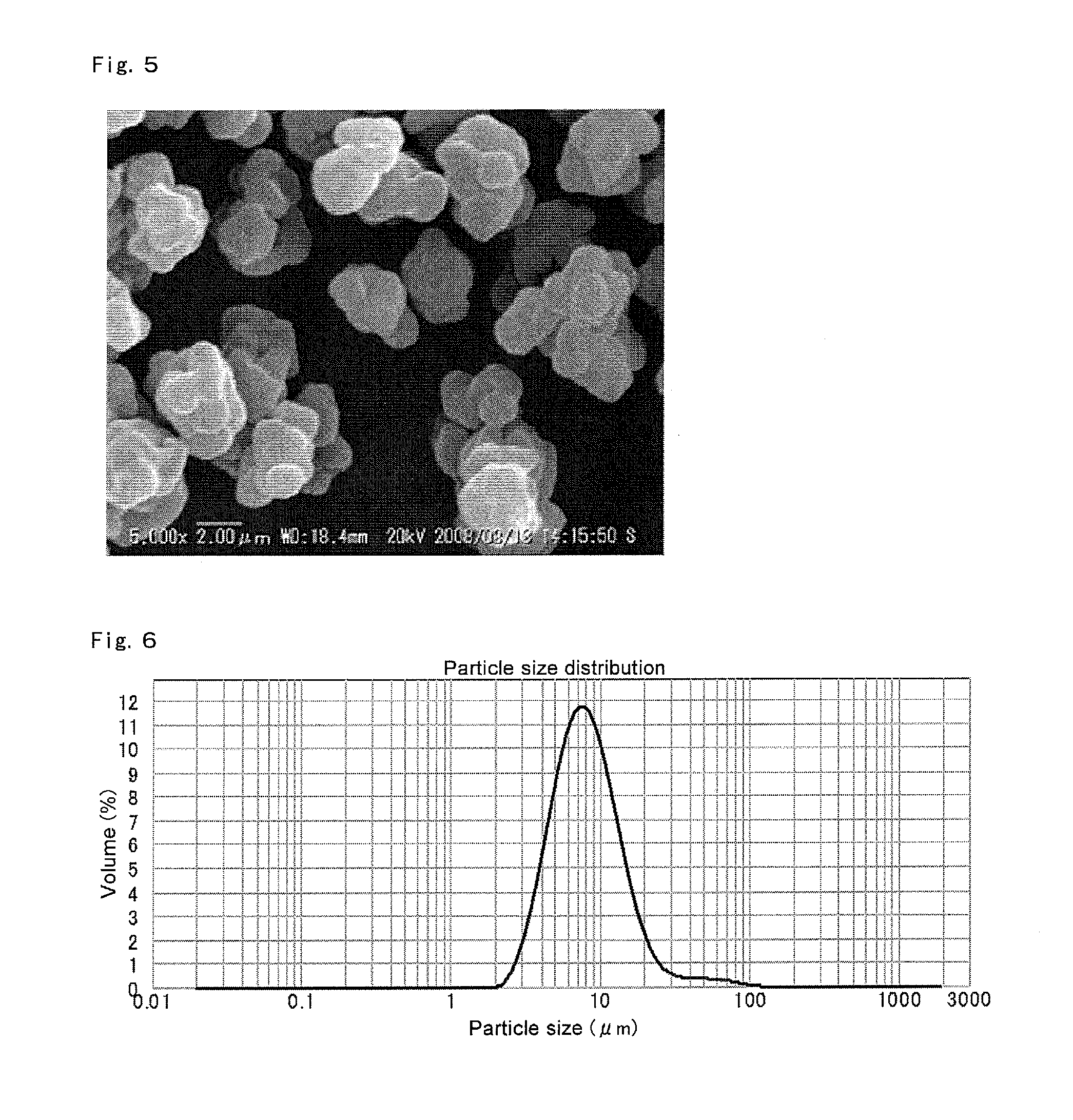
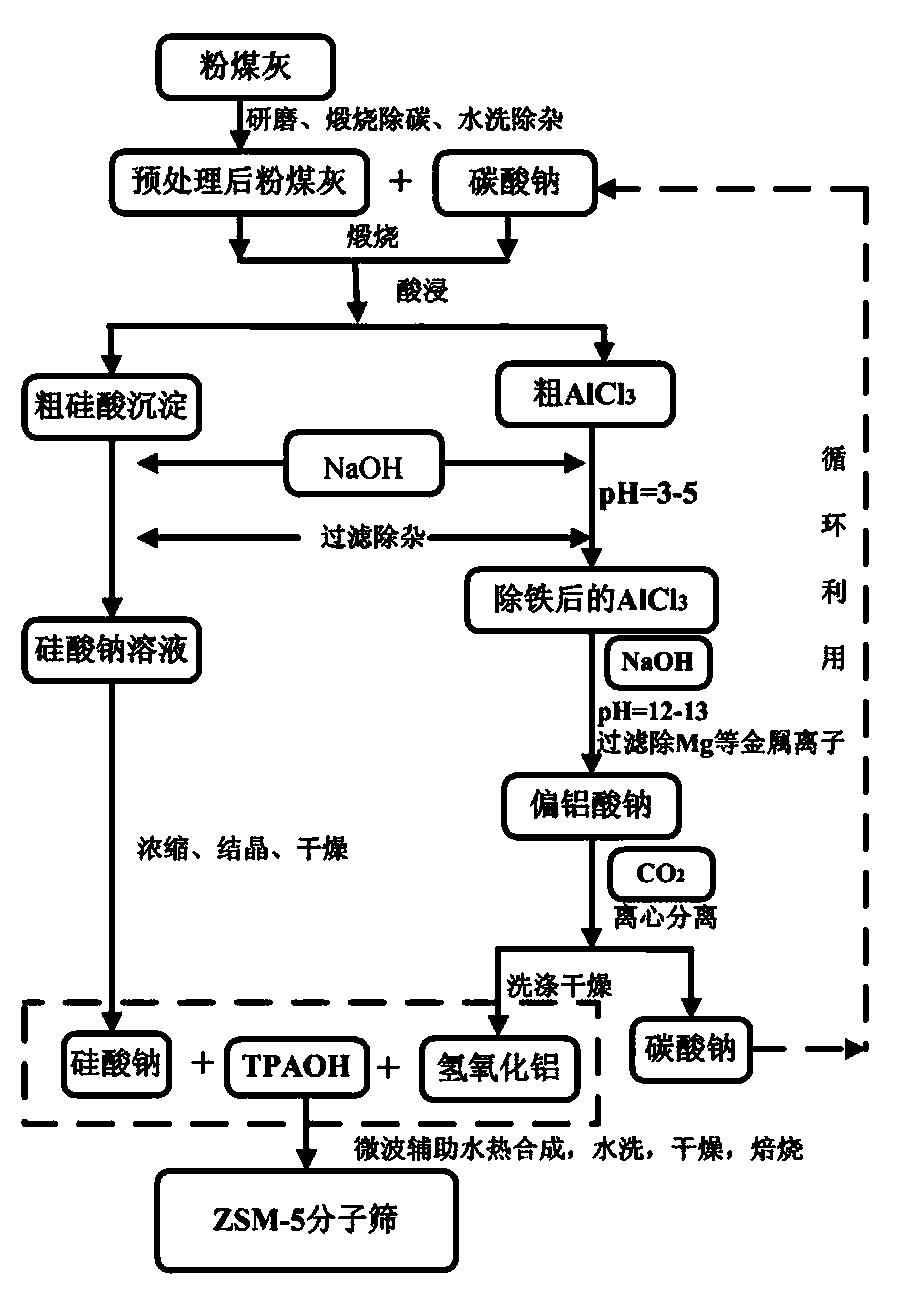
Method for preparing nano-scale ZSM-5 molecular sieve by using coal ash
InactiveCN103435064ARealize high-value utilizationExpand the range of raw materialsMaterial nanotechnologyPentasil aluminosilicate zeoliteMicrowaveAmmonium hydroxide
The invention relates to a method for preparing a nano-scale ZSM-5 molecular sieve by using coal ash. The method comprises the following steps: pre-treating coal ash; using the coal ash subjected to pretreatment to prepare aluminum hydroxide and sodium silicate; uniformly mixing the aluminum hydroxide and the sodium silicate which are obtained after the coal ash is processed with water and the template agent tetrapropyl-ammonium hydroxide, wherein molar fraction of the water, the tetrapropyl-ammonium hydroxide, the aluminum hydroxide and the sodium silicate are respectively 90-98 percent, 0.25-1.0 percent, 0.025-0.01 percent and 1-2 percent; performing microwave auxiliary synthesis for 24-72 hours at the temperature of 150-250 DEG C; taking out a product in a reaction kettle, washing for 2-5 times with water at the temperature of 60-80 DEG C, and drying at the temperature of 120 DEG C for 12-24 hours; after drying, roasting the product at the temperature of 600-800 DEG C for 4-8 hours to obtain a nano-scale ZSM-5 molecular sieve finished product, wherein the particle size of the ZSM-5 molecular sieve is 200-500 nm. According to the method, the synthesis cost of the ZSM-5 molecular sieve is reduced, the problem of environment pollution caused by coal ash is reduced, and high-value use of the coal ash is realized.
Owner:NORTHEAST GASOLINEEUM UNIV
Rod hydrotalcite-like compound and its prepn process
InactiveCN1974399ASimple processLow costCatalyst carriersOther chemical processesSodium stearateCrystal structure
The present invention discloses rod-shaped magnesia alumina hydrotalcite-like compound (HTlc) as one new shaped hydrotalcite-like compound. The rod-shaped magnesia alumina hydrotalcite-like compound has the crystal structure of hydrotalcite and chemical expression of [MII(1-x)MIIIx(OH)2]x+[An-x / n]x-mH2O, where, MII and MIII are bivalent and trivalent metal cation separately, An- is interlayer anion, x is the molar fraction of MIII in HTlc, m is the molar fraction of interlayer crystalline water. It is prepared through a traditional co-precipitation process under the induction of soft template or shape regulating agent sodium stearate. It has simple preparation process and low cost, and may be used as rubber and plastic additive, fire retardant, pesticide release controlling agent, etc.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com