Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1485results about "Beer fermentation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
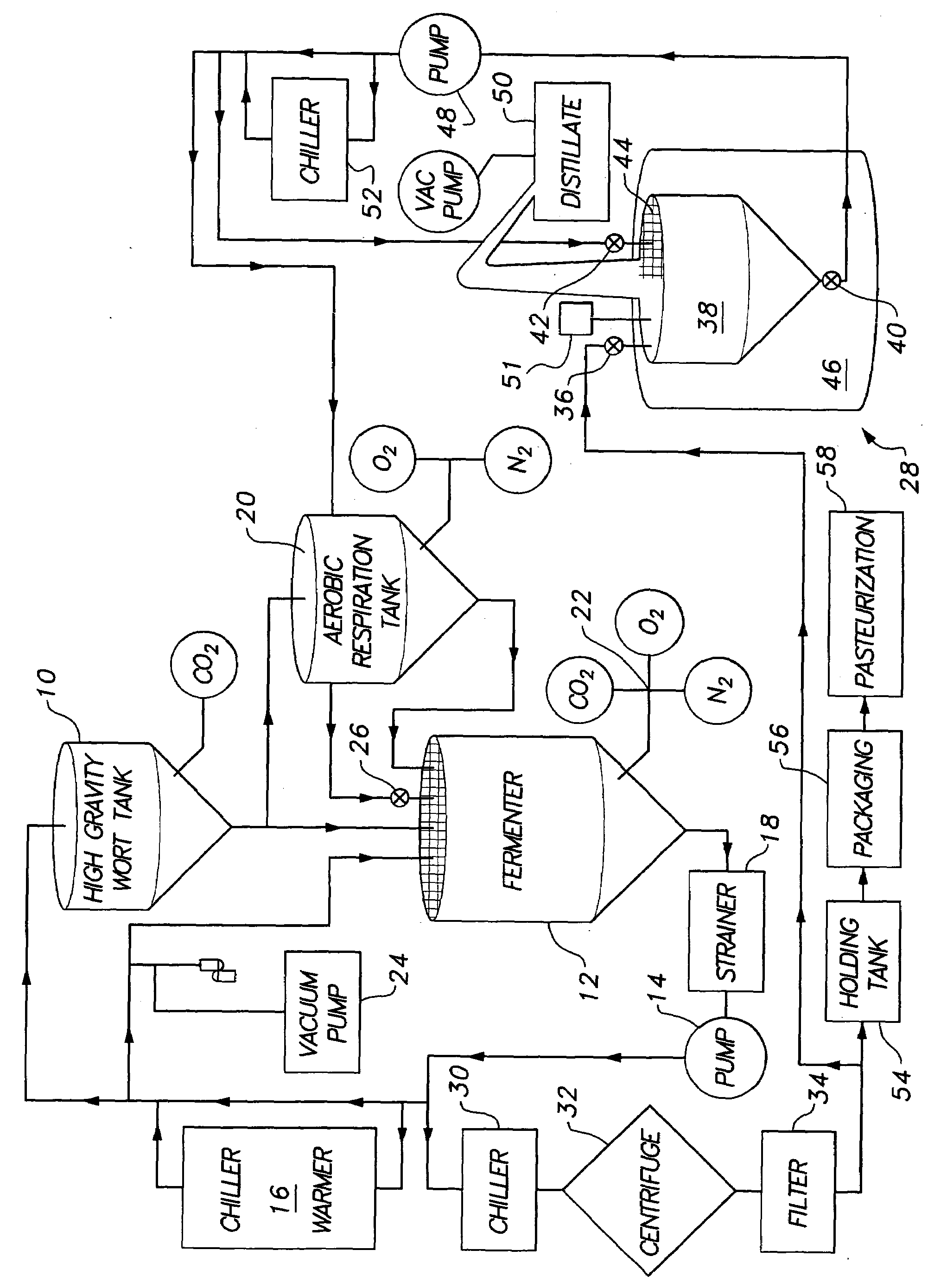
Ethanol distillation process
InactiveUS7572353B1Shorten the timeLess rapidlyFermented solutions distillation/rectificationOrganic compound preparationDistillationEvaporation
Owner:ICM
Silicone hydrogel lenses with water-rich surfaces
ActiveUS8480227B2Meet actual needsPretreated surfacesAlcoholic beverage preparationHigh water contentHigh oxygen
The invention is related to a hydrated silicone hydrogel contact lens having a layered structural configuration: a lower water content silicone hydrogel core (or bulk material) completely covered with a layer of a higher water content hydrogel totally or substantially free of silicone. A hydrated silicone hydrogel contact lens of the invention possesses high oxygen permeability for maintaining the corneal health and a soft, water-rich, lubricious surface for wearing comfort.
Owner:ALCON INC
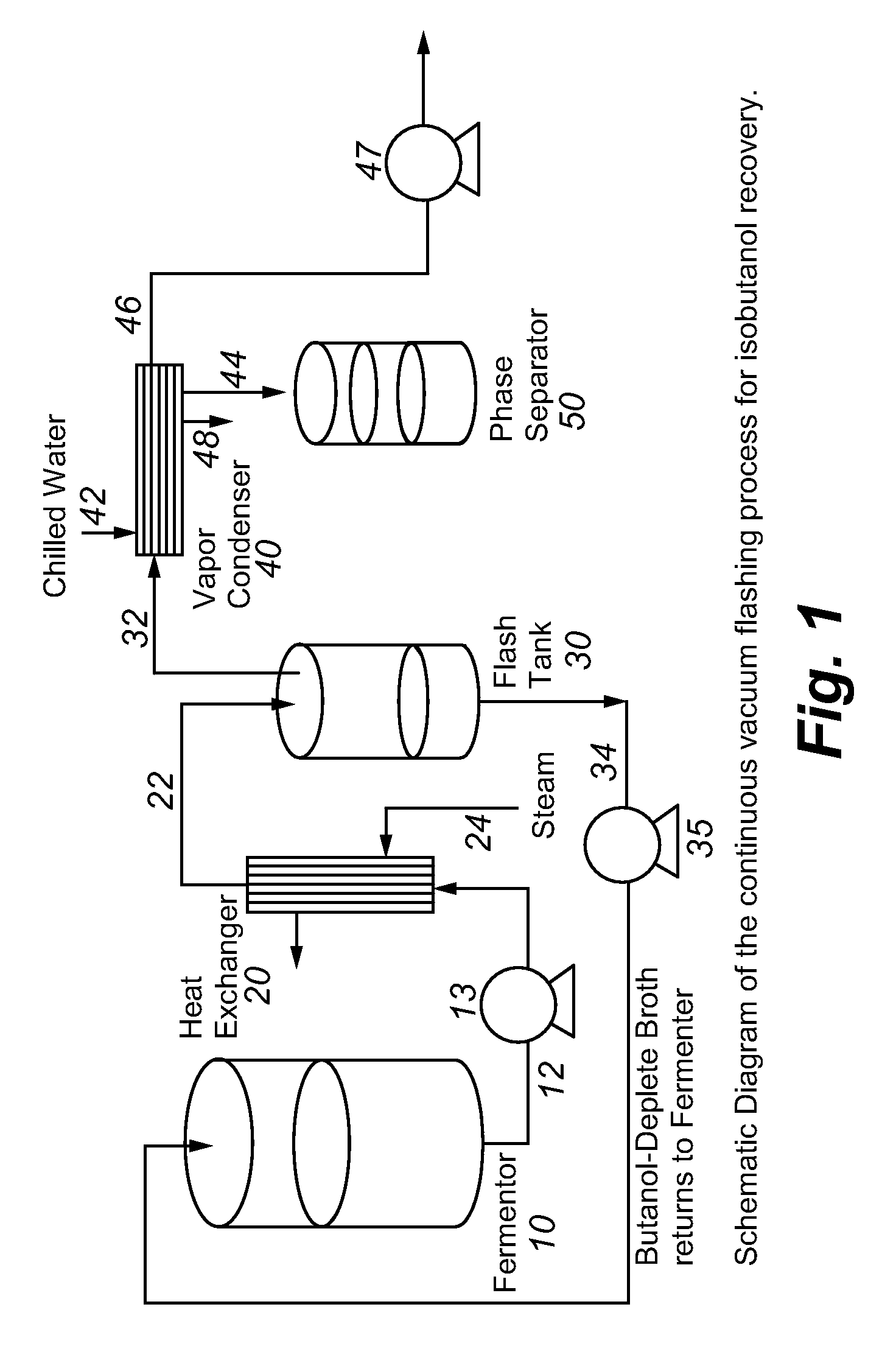
Recovery of higher alcohols from dilute aqueous solutions
ActiveUS20090171129A1High activityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsProduction rateAqueous solution
This invention is directed to methods for recovery of C3-C6 alcohols from dilute aqueous solutions, such as fermentation broths. Such methods provide improved volumetric productivity for the fermentation and allows recovery of the alcohol. Such methods also allow for reduced energy use in the production and drying of spent fermentation broth due to increased effective concentration of the alcohol product by the simultaneous fermentation and recovery process which increases the quantity of alcohol produced and recovered per quantity of fermentation broth dried. Thus, the invention allows for production and recovery of C3-C6 alcohols at low capital and reduced operating costs.
Owner:GEVO INC
Biopolymer structures and components
InactiveUS20050019545A1Keep shapeIncrease valueVehicle arrangementsAlcoholic beverage preparationBiopolymerEngineering
Structures can be formed from a composition, which can be referred to as a biopolymer, that includes fermentation solids and thermoactive material. Methods of making biopolymer products include for example extruding, injection molding, or compounding fermentation solid and thermoactive material. Structures formed from biopolymer can include lumber replacements, window components, door components, siding assemblies, and other structures.
Owner:POET RES INC
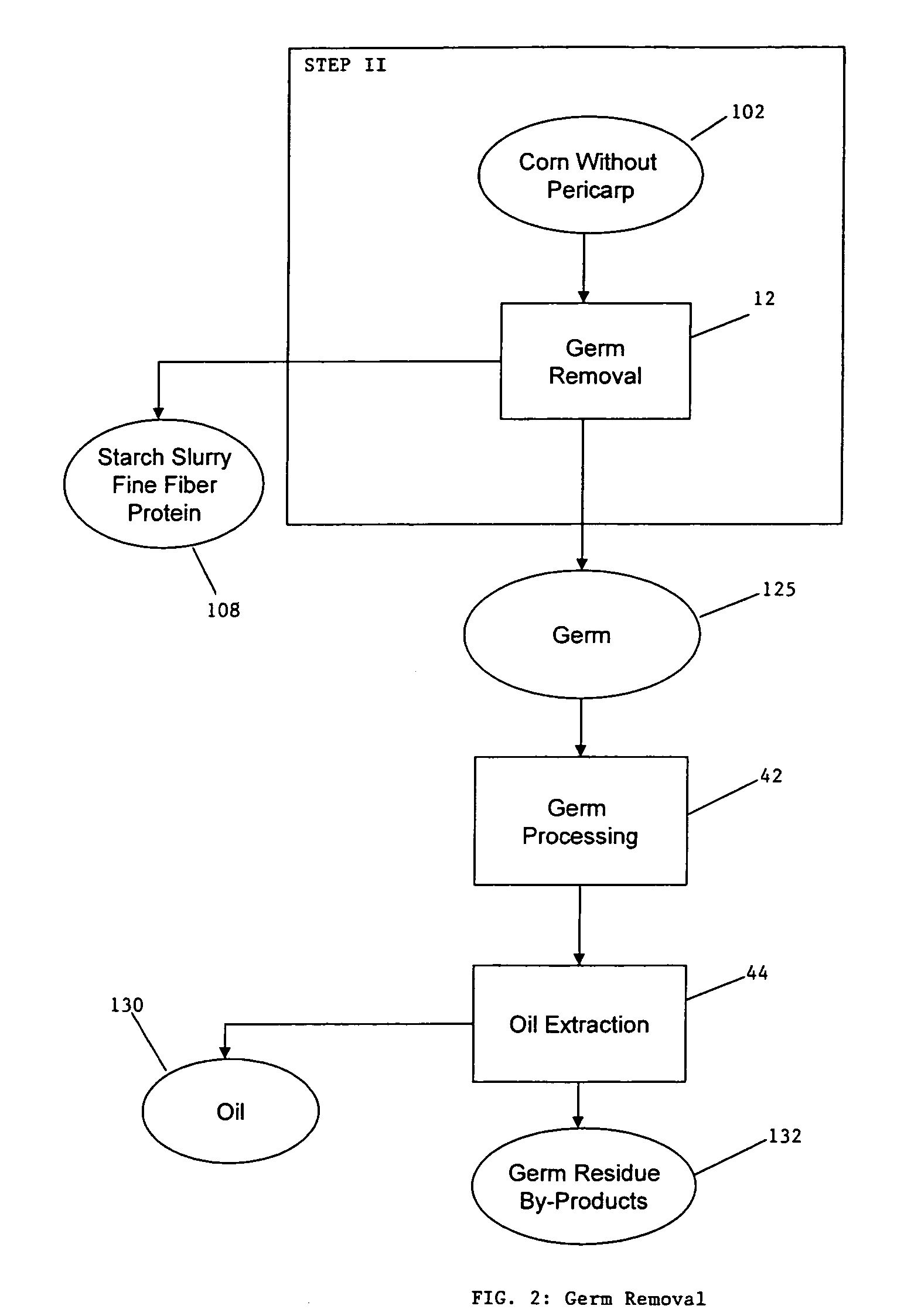
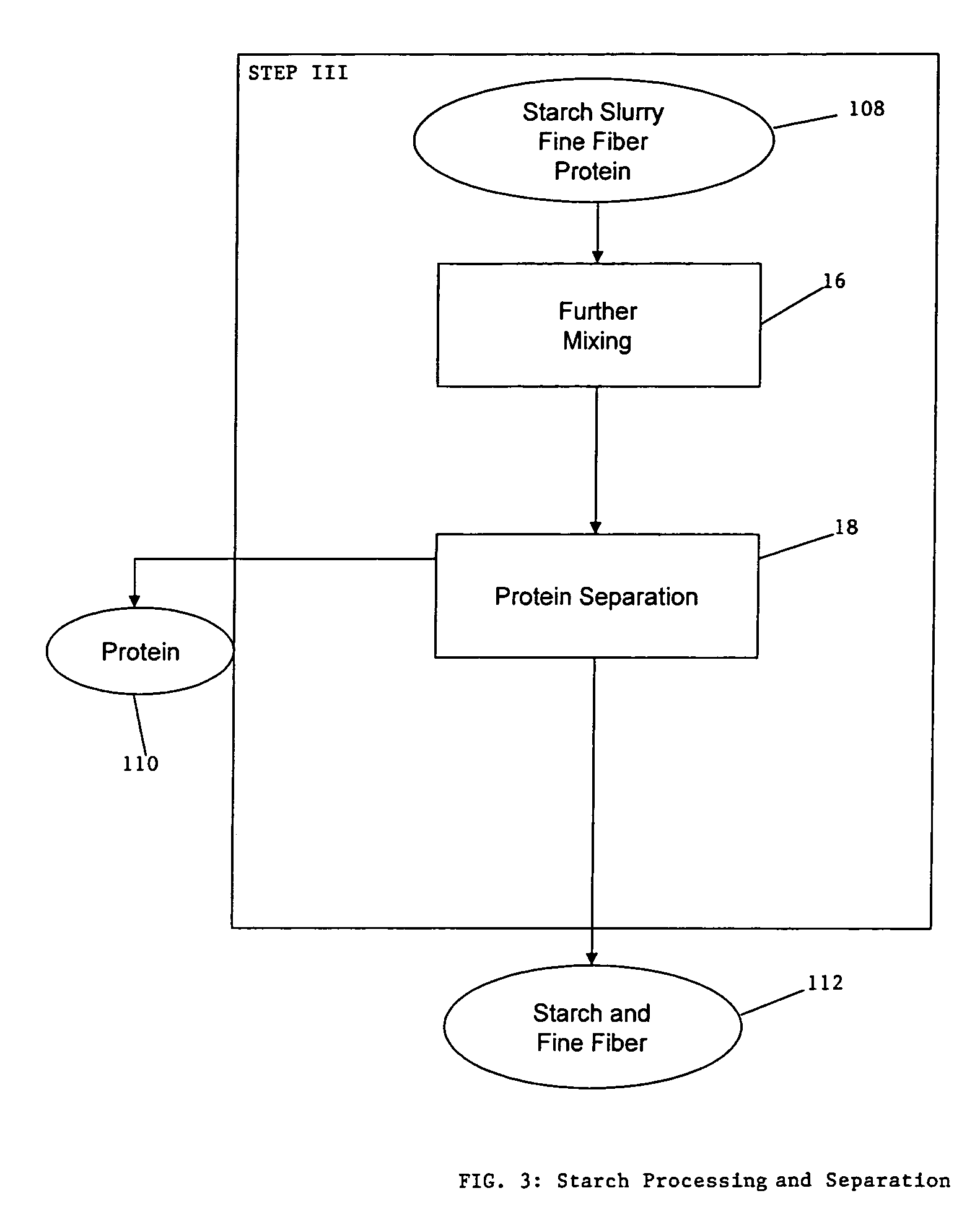
Process for the production of animal feed and ethanol and novel animal feed
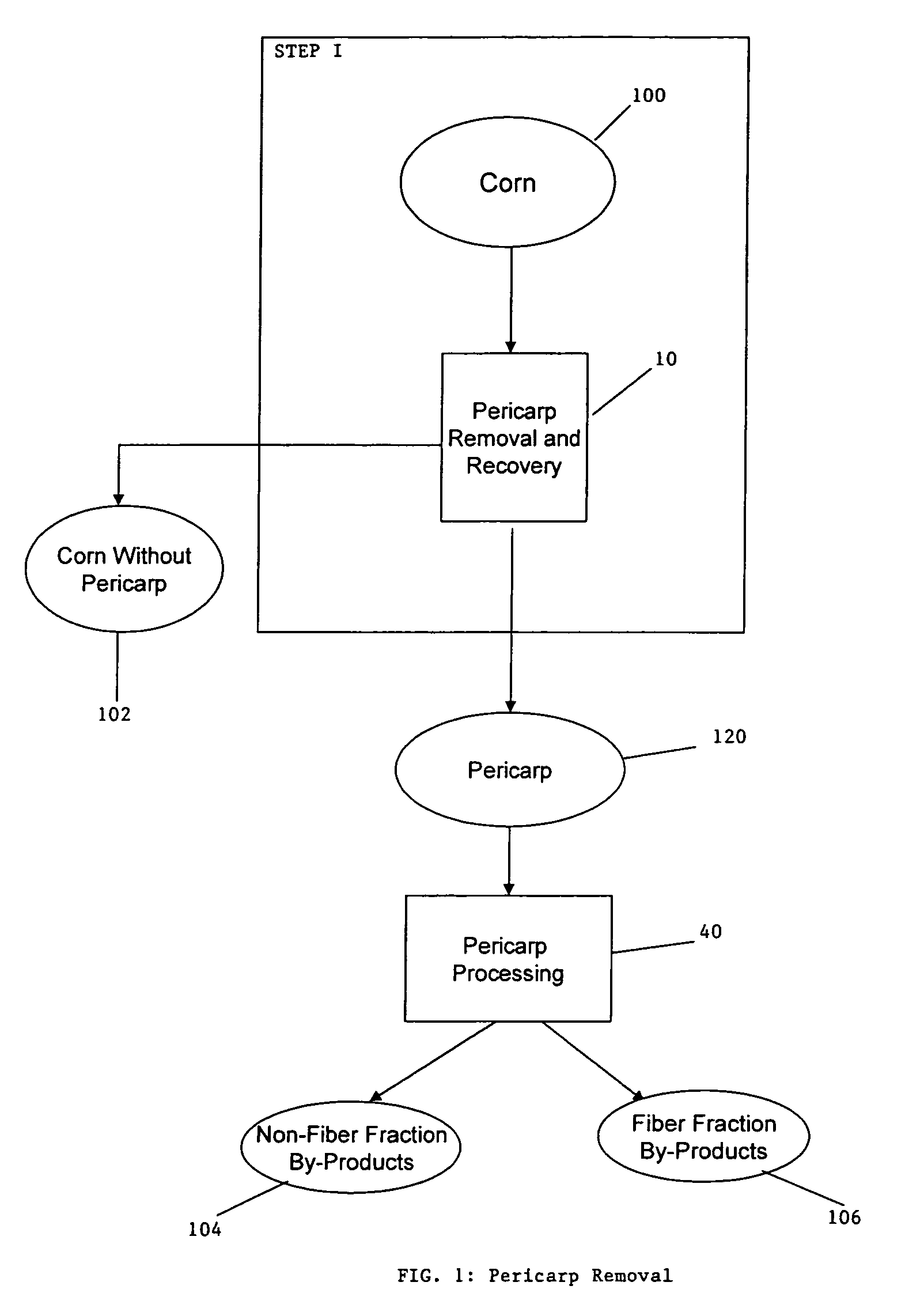
A method for the production of ethanol and a modified animal feed is provided. The method replaces the starch in known corn-based animal feed with biomass fiber treated to make it more digestible by animals. The process includes wherein the pericarp and germ are removed from the corn kernel and processed for by-products. The starch and protein are also removed and separated. The starch is then fermented and distilled to ethanol and stillage. The bioavailable modified animal feed comprises the pericarp and germ removed from corn kernels and optionally by-products of the pericarp and germ processing, and lignocellulosic materials. The modified animal feed may optionally include energy materials such as animal and vegetable fats, vegetable soapstocks, or glycerin, and combinations thereof.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Recovery of higher alcohols from dilute aqueous solutions
ActiveUS8101808B2High activityBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsAqueous solutionAlcohol products
This invention is directed to methods for recovery of C3-C6 alcohols from dilute aqueous solutions, such as fermentation broths. Such methods provide improved volumetric productivity for the fermentation and allows recovery of the alcohol. Such methods also allow for reduced energy use in the production and drying of spent fermentation broth due to increased effective concentration of the alcohol product by the simultaneous fermentation and recovery process which increases the quantity of alcohol produced and recovered per quantity of fermentation broth dried. Thus, the invention allows for production and recovery of C3-C6 alcohols at low capital and reduced operating costs.
Owner:GEVO INC
Biopolymer and methods of making it
The present invention relates to a composition, which can be referred to as a biopolymer, including fermentation solid and thermoactive material. The present invention also includes methods of making the biopolymer, which can include compounding fermentation solid and thermoactive material. The present biopolymer can be formed into an article of manufacture.
Owner:POET RES INC
Use of hop polyphenols in beer
InactiveUS20070254063A1Great tasteReduce total powerBeer fermentationHops treatmentPolyphenolBrewing
The present invention relates to a new method for brewing beer comprising the addition of polyphenol-rich extracts prepared from hops at specific steps during or after the brewing process. The method enhances the mouthfeel, the reducing power and the stability of beer. Furthermore, beers comprising the polyphenol-rich extracts are provided.
Owner:CHEM & BIOCHEM ONDERZOEKSCENT CBOK
Method of making alcohol concentrate
ActiveUS20100047386A1Efficient extractionBeer fermentationWine preparationContinuous fermentationAlcohol
One embodiment of the present invention is method for making an alcohol concentrate using a nested batch fermentation process, wherein multiple rounds of wort fermentation, distillation and refortification, is described. The rounds are repeated until the desired concentration of fermented wort is obtained. Another embodiment of the present invention is a method for a continuous fermentation process, wherein portions of the fermentation are distilled and the remaining wort is returned to the active fermentation. This process is repeated until the desired concentration of the fermented wort is obtained. Yet another embodiment of the present invention is a method for extraction of hops compounds, wherein the distilled alcohol from the nested or continuous fermentation process is used.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE BEVERAGE TECH INC
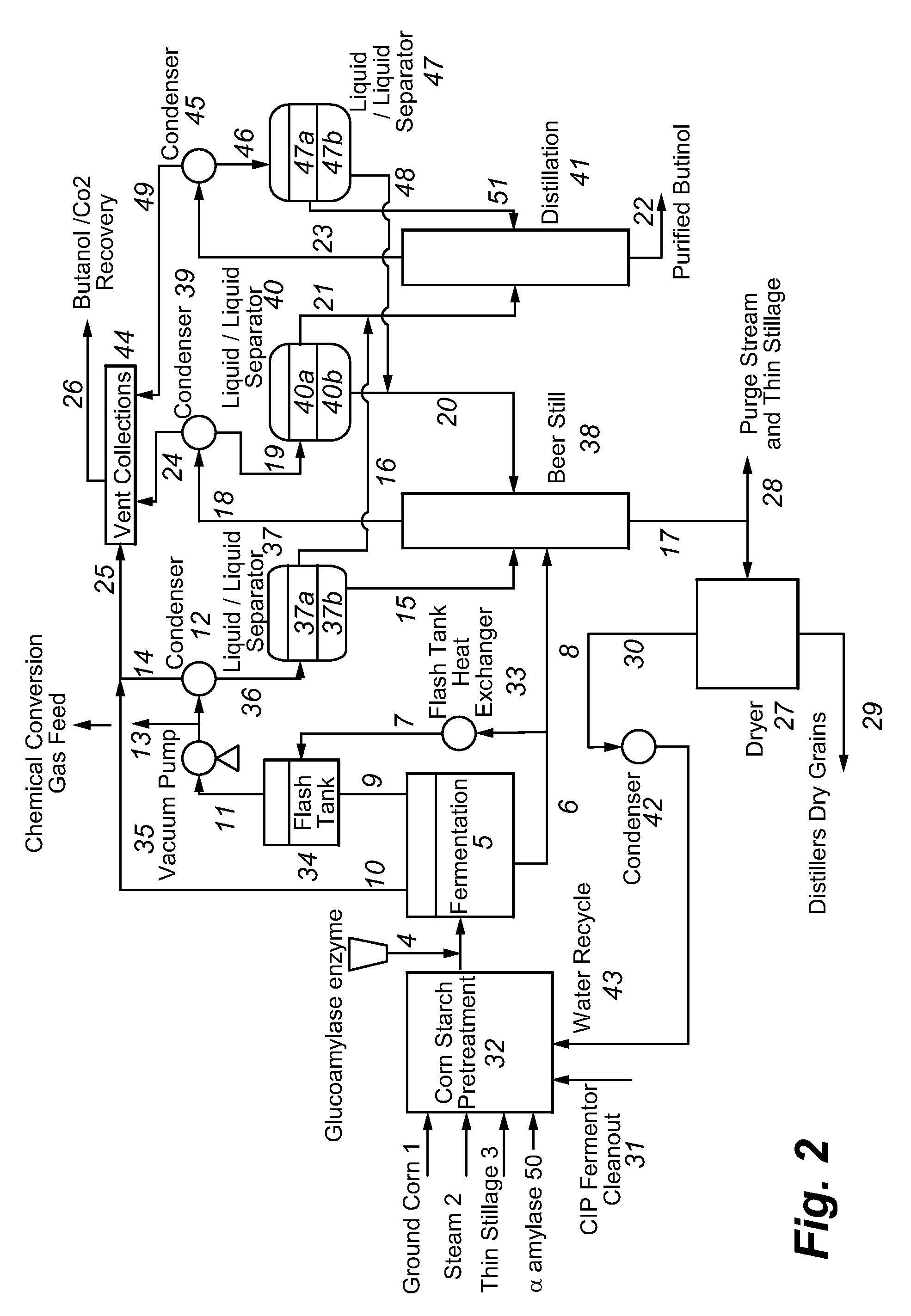
Systems and methods for alcohol recovery and concentration of stillage by-products
ActiveUS20110315541A1Efficient use ofHydrocarbon purification/separationHydroxy compound preparationAlcoholDistillation
Systems and methods for separating an alcohol, and in particular butanol, from a fermented feed and concentrating thin stillage into syrup includes operation of one or more alcohol recovery distillation columns using the heat supplied by steam generated from concentration of the thin stillage in a multi-train, multi-effect evaporation system.
Owner:GEVO INC
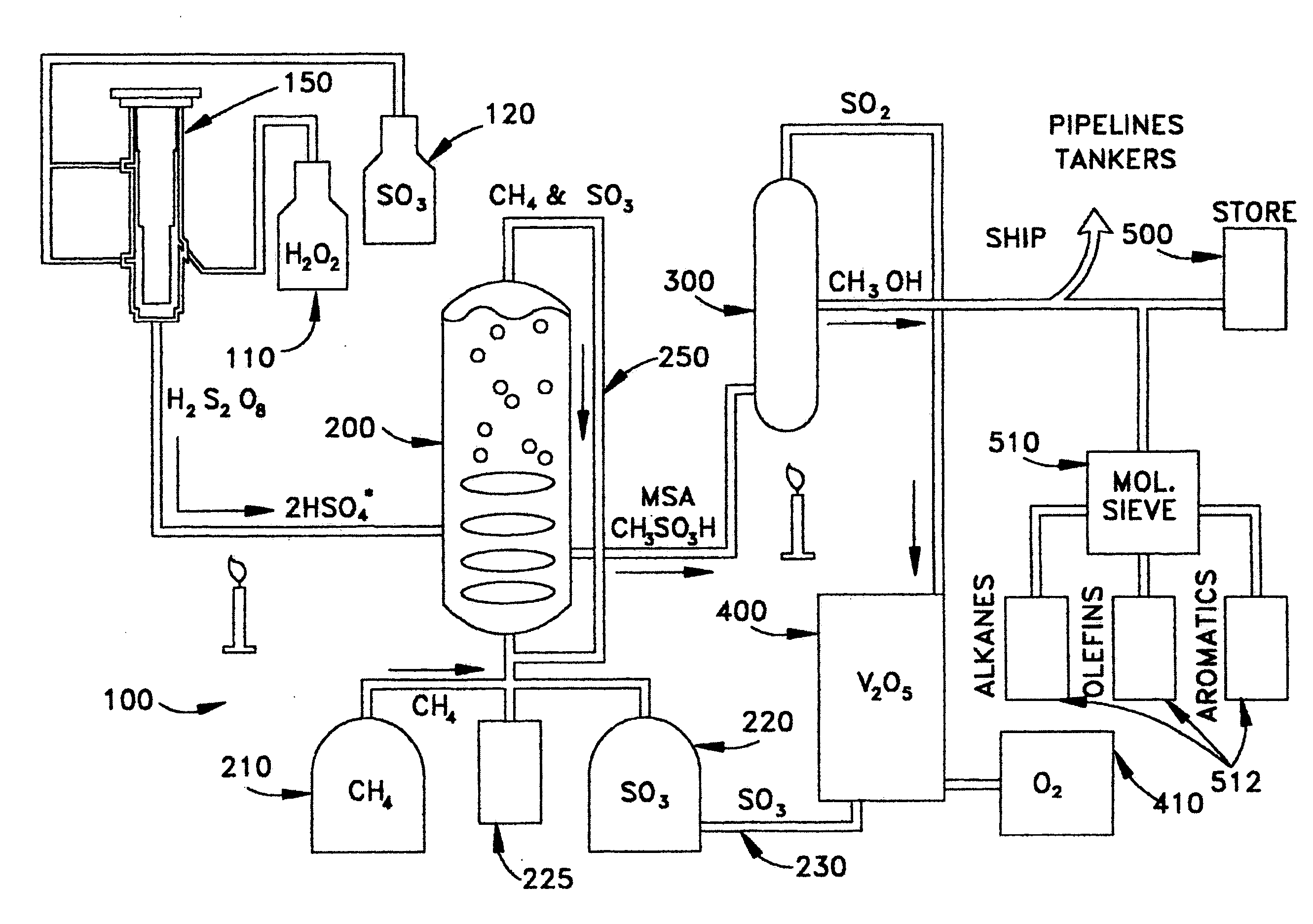
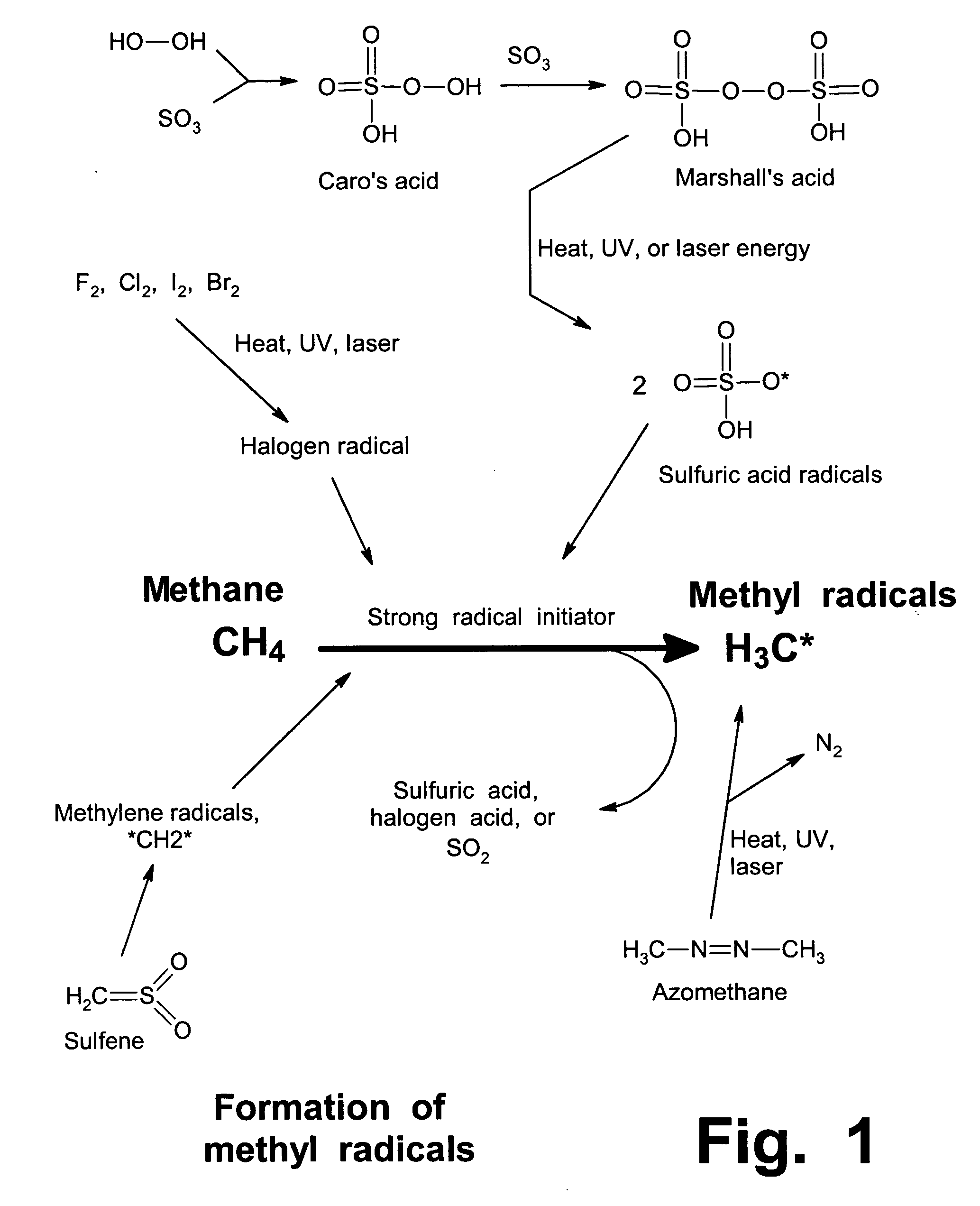
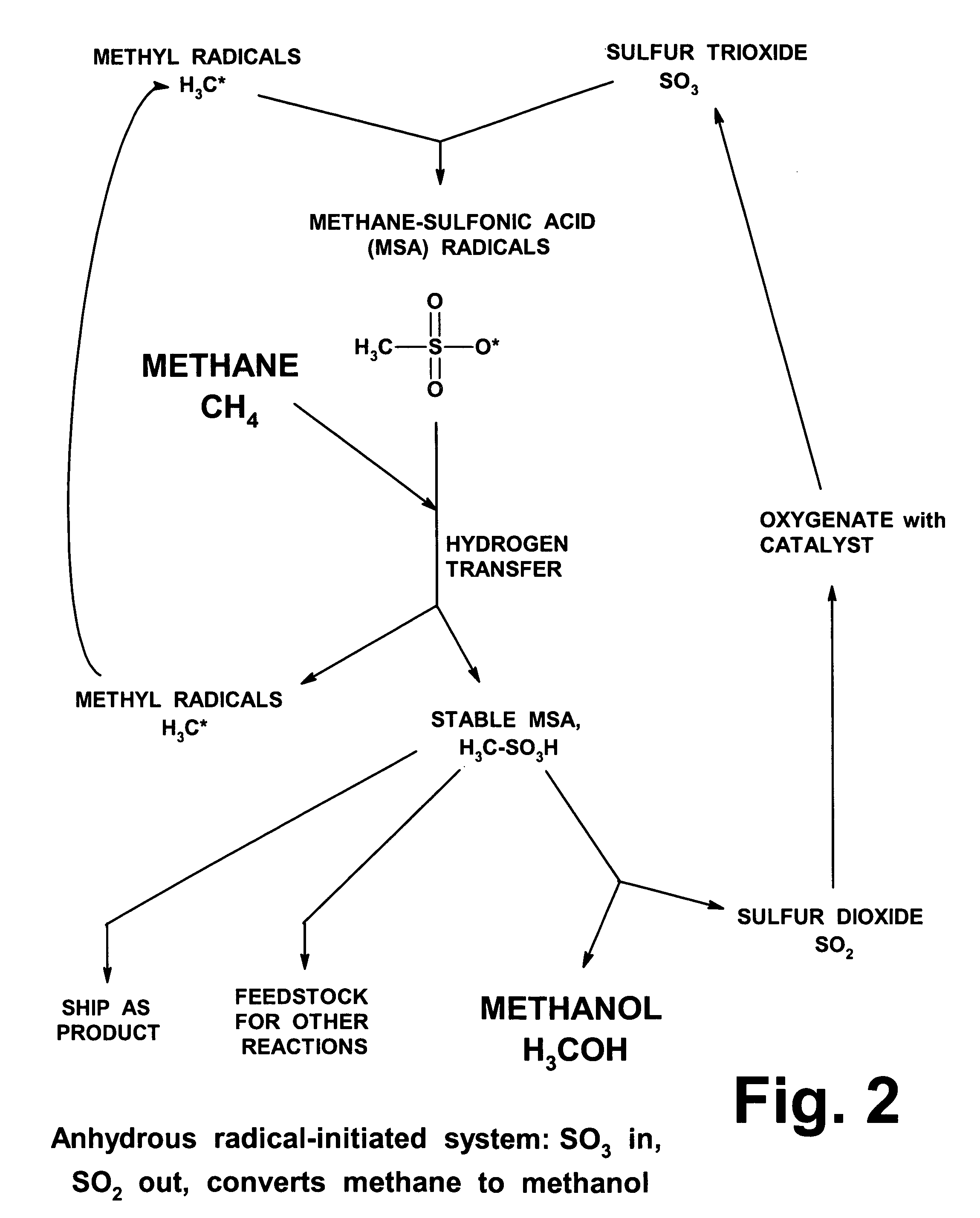
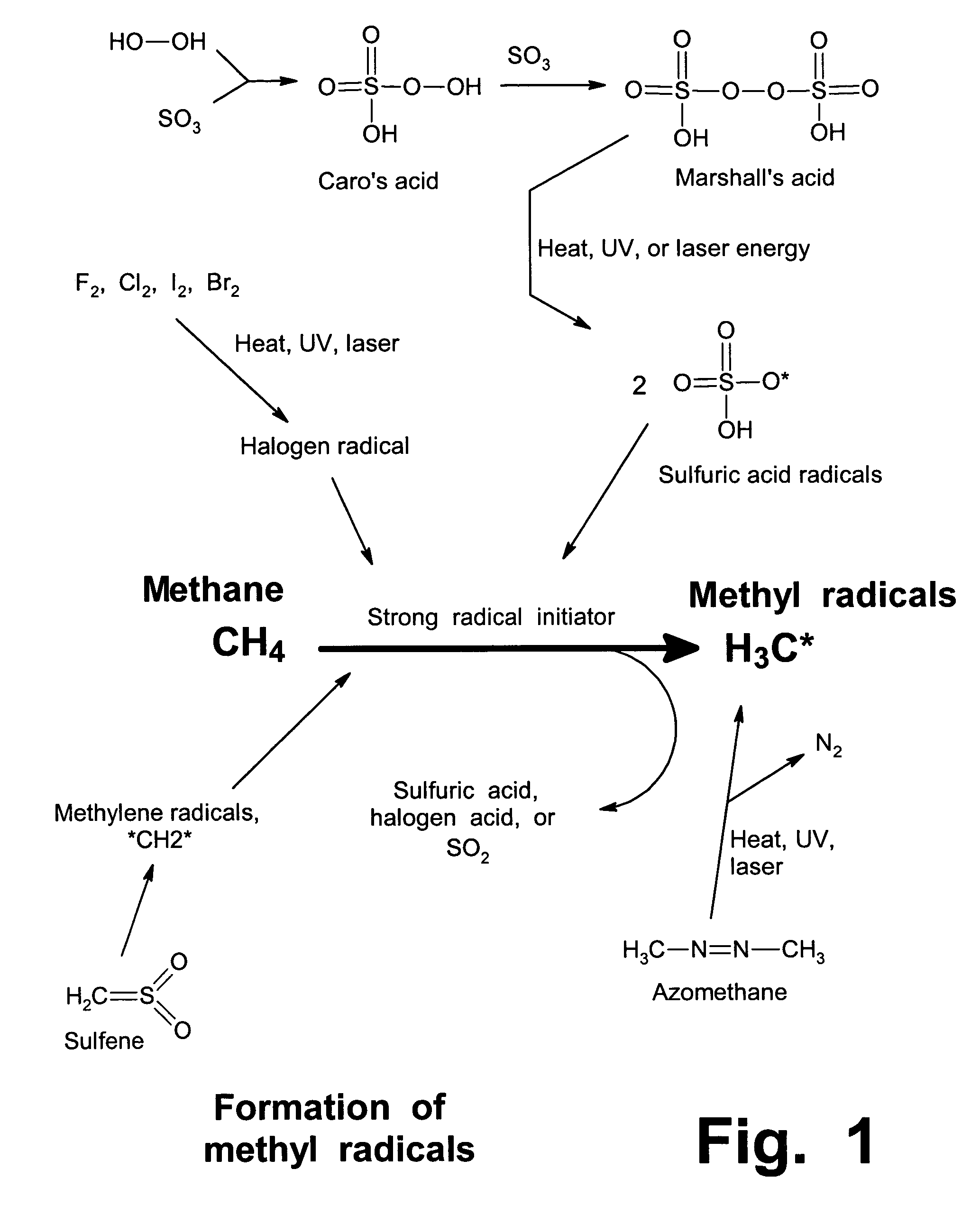
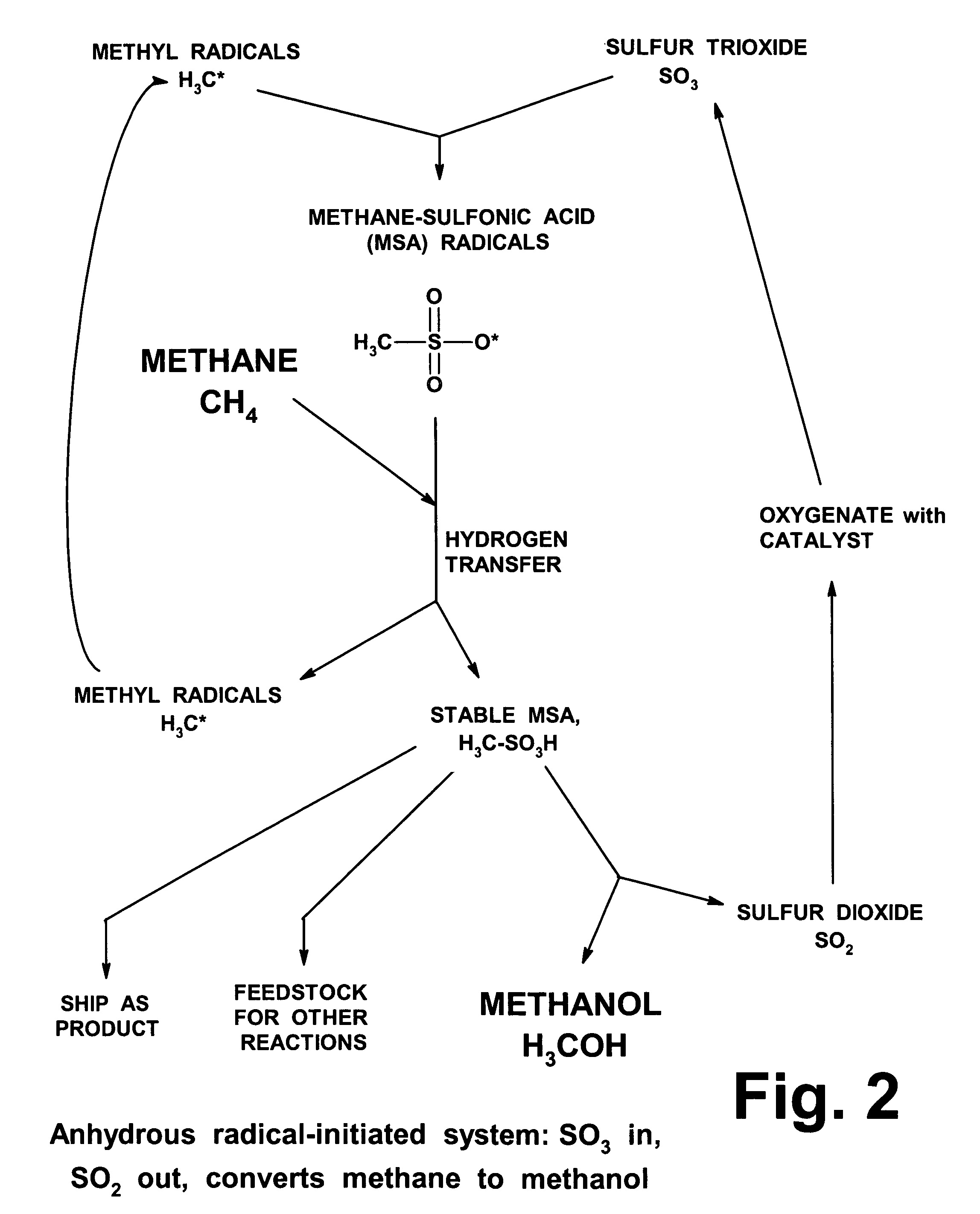
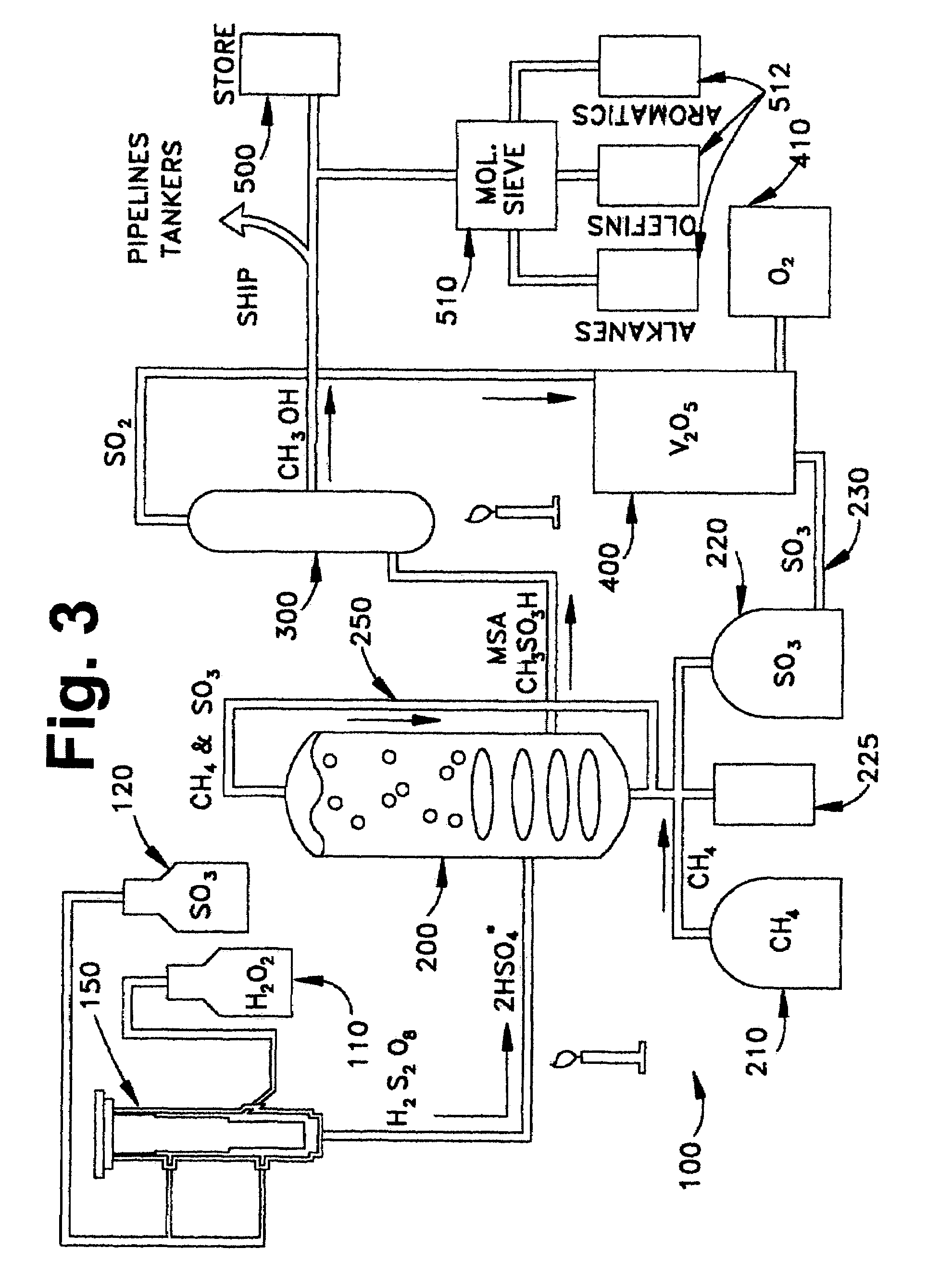
Anhydrous processing of methane into methane-sulfonic acid, methanol, and other compounds
ActiveUS20050070614A1Increases solubility and reaction rateEfficient removalHydrogenOrganic compound preparationLiquid fuelOxygen compound
Anhydrous processing to convert methane into oxygenates (such as methanol), liquid fuels, or olefins uses an initiator to create methyl radicals. These radicals combine with sulfur trioxide to form methyl-sulfonate radicals. These radicals attack fresh methane, forming stable methane-sulfonic acid (MSA) while creating new methyl radicals to sustain a chain reaction. This system avoids the use or creation of water, and liquid MSA is an amphoteric solvent that increasing the solubility and reactivity of methane and SO3. MSA from this process can be sold or used as a valuable chemical with no mercaptan or halogen impurities, or it can be heated and cracked to release methanol (a clean fuel, gasoline additive, and chemical feedstock) and sulfur dioxide (which can be oxidized to SO3 and recycled back into the reactor). MSA also can be converted into gasoline, olefins, or other valuable chemicals.
Owner:VEOLIA NORTH AMERICA REGENERATION SERVICES LLC
Agglomerated zeolitic adsorbents, method for obtaining same uses thereof
InactiveUS6884918B1Amino compound purification/separationOrganic compound preparationSorbentSimulated moving bed
The present invention relates to agglomerated zeolitic adsorbents based on zeolite X with an Si / Al ratio such that 1.15<Si / Al≦1.5, at least 90% of the exchangeable cationic sites of the zeolite X of which are occupied either by barium ions alone or by barium ions and potassium ions whose Dubinin volume is greater than or equal to 0.240 cm3 / g.They are obtained by agglomerating zeolite powder with a binder, followed by the zeolitization of the binder, the exchange of the ions of the zeolite by barium ions (and potassium ions) and the activation of the adsorbents thus exchanged.These adsorbents are particularly suited to the adsorption of the para-xylene present in C8 aromatic hydrocarbon fractions in the liquid phase in processes of simulated moving bed type but also to the separation of sugars, polyhydric alcohols, cresols or substituted toluene isomers.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
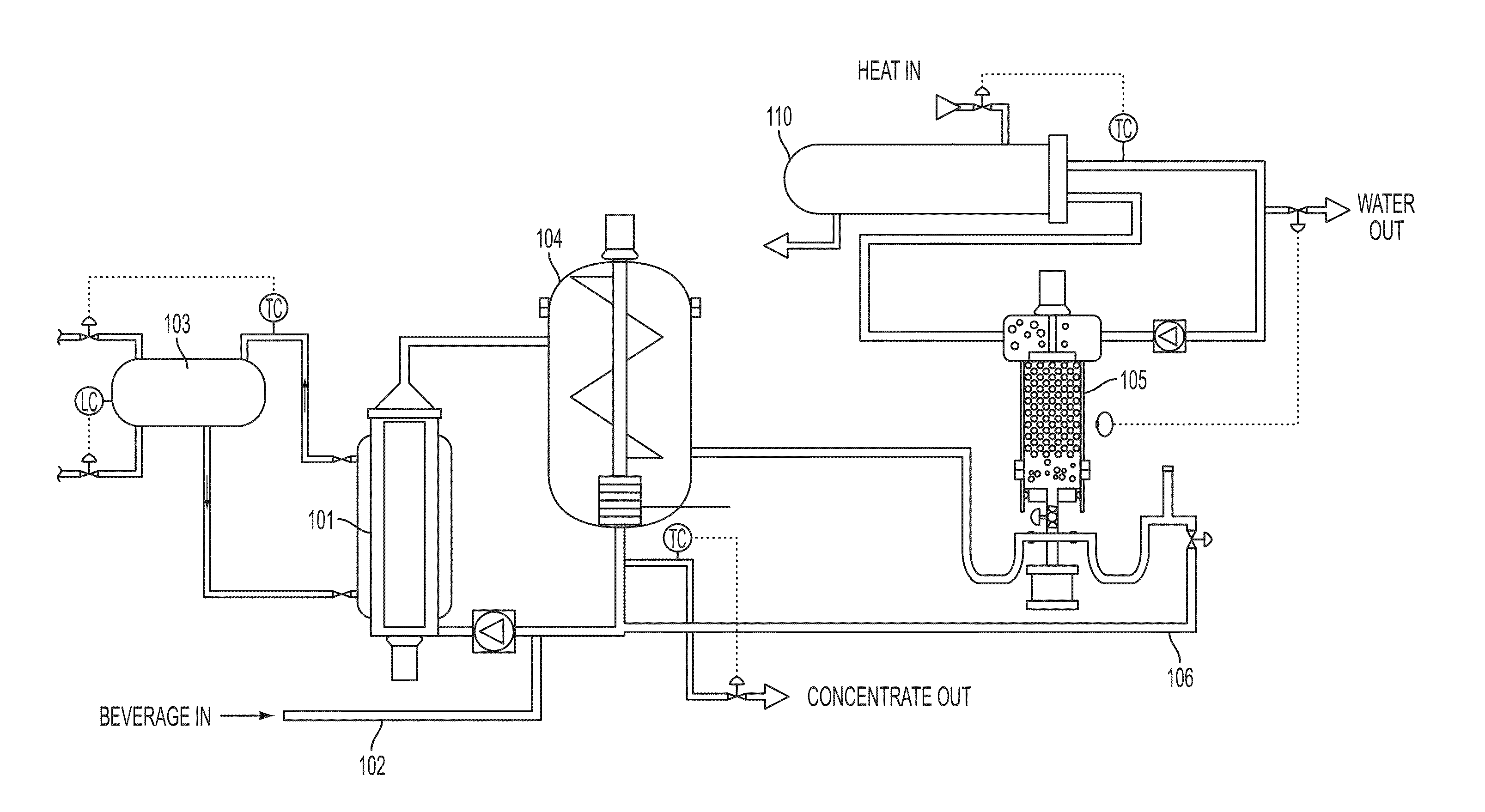
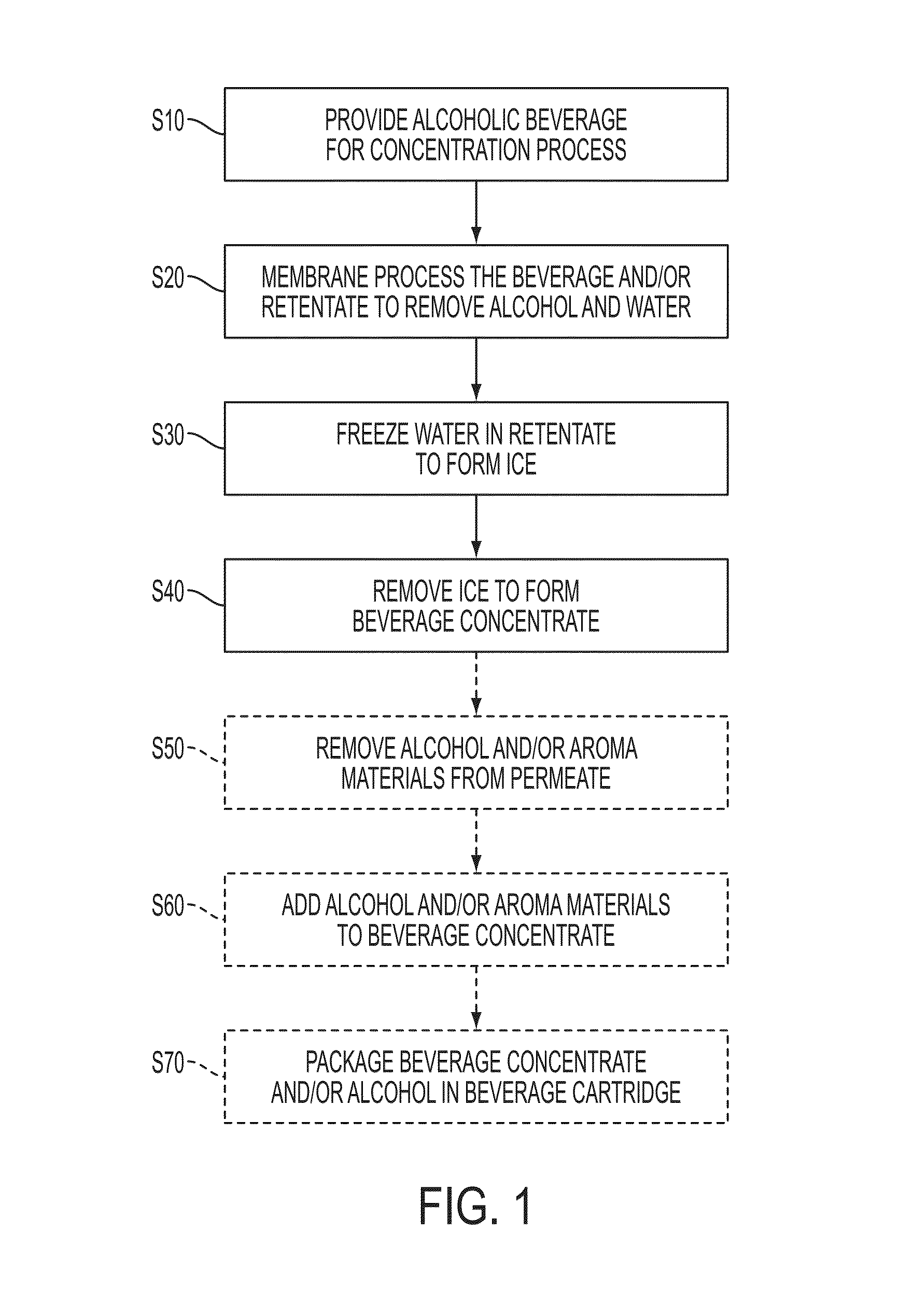
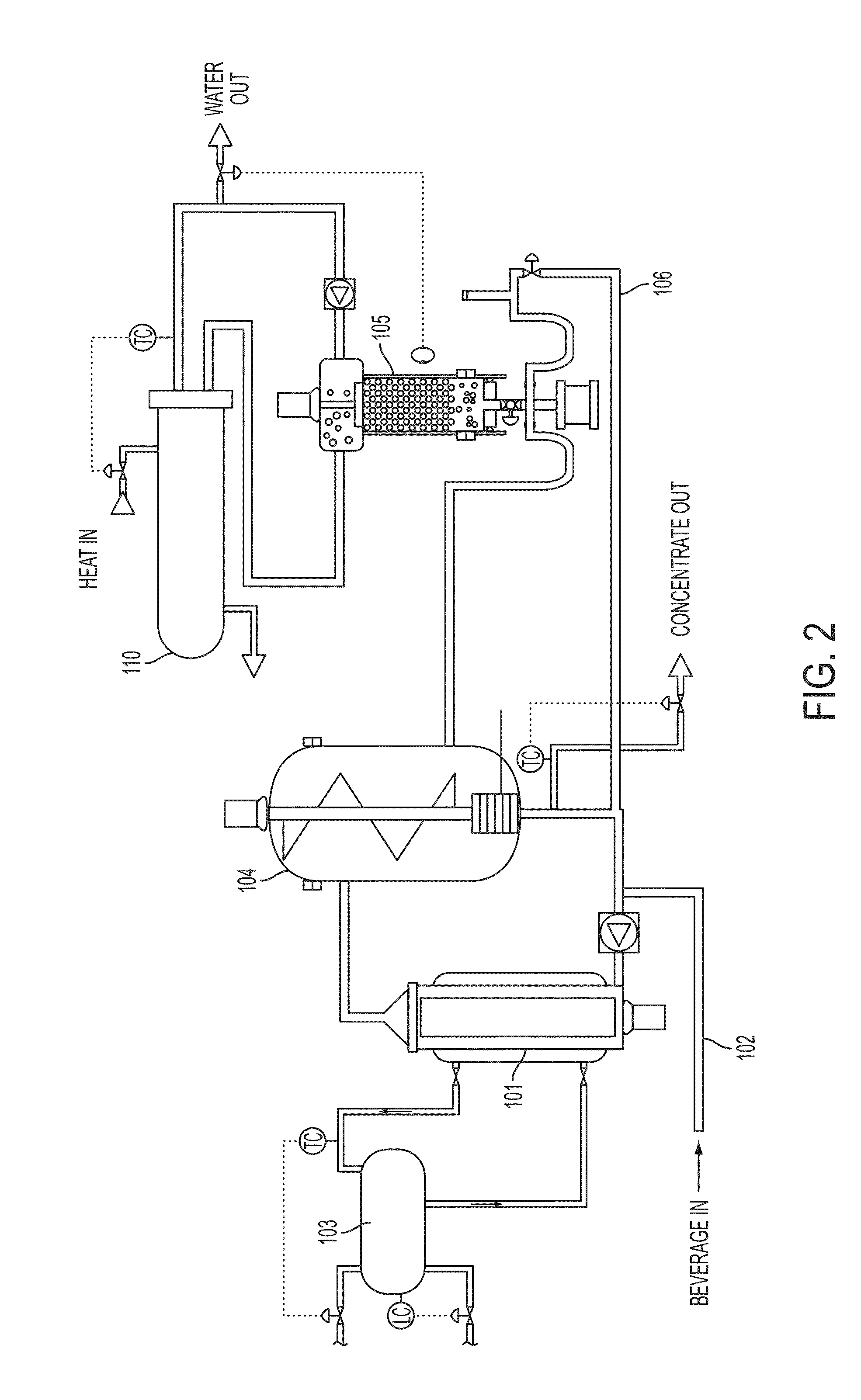
Alcoholic beverage concentrate process
ActiveUS20160230133A1Increase turbidityHigh alcohol contentBeer fermentationAlcoholic beverage preparationAlcohol contentWater content
Methods and systems for forming a concentrate from an alcoholic beverage, such as a beverage made by fermentation processes. A membrane process may be used to reduce water and alcohol content, followed by freeze concentration to further reduce water content.
Owner:BEDFORD SYST LLC
Anhydrous processing of methane into methane-sulfonic acid, methanol, and other compounds
ActiveUS7282603B2Increases solubility and reaction rateEfficient removalHydrogenOrganic compound preparationSolubilityLiquid fuel
Anhydrous processing to convert methane into oxygenates (such as methanol), liquid fuels, or olefins uses an initiator to create methyl radicals. These radicals combine with sulfur trioxide to form methyl-sulfonate radicals. These radicals attack fresh methane, forming stable methane-sulfonic acid (MSA) while creating new methyl radicals to sustain a chain reaction. This system avoids the use or creation of water, and liquid MSA is an amphoteric solvent that increasing the solubility and reactivity of methane and SO3. MSA from this process can be sold or used as a valuable chemical with no mercaptan or halogen impurities, or it can be heated and cracked to release methanol (a clean fuel, gasoline additive, and chemical feedstock) and sulfur dioxide (which can be oxidized to SO3 and recycled back into the reactor). MSA also can be converted into gasoline, olefins, or other valuable chemicals.
Owner:VEOLIA NORTH AMERICA REGENERATION SERVICES LLC
Methanol synthesis
A process for synthesising methanol comprises the steps of: (i) reforming a hydrocarbon feedstock and separating water to generate a make-up gas comprising hydrogen and carbon oxides, the make-up gas mixture having a stoichiometric number, R, R=([H2]−[CO2]) / ([CO2]+[CO]) of less than 2.0, (ii) combining the make up gas with an unreacted synthesis gas to form a synthesis gas mixture, (iii) passing the synthesis gas through a bed of methanol synthesis catalyst to generate a product stream, (iv) cooling the product stream to recover a crude methanol stream from the unreacted synthesis gas, (v) removing a portion of the unreacted synthesis gas as a purge gas, and (vi) feeding the remaining unreacted synthesis gas to step (ii), wherein hydrogen is recovered from a portion of the purge gas and the make up gas, and the recovered hydrogen is included in the synthesis gas mixture.
Owner:JOHNSON MATTHEY PLC
Method of dewatering thin stillage processing streams
ActiveUS7497955B2Improve agglomerationAbility to withstandWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsSodium methacrylateSodium salt
A method dewatering thin stillage process streams generated in the processing of grain to ethanol comprising adding to the process streams an effective flocculating amount of an anionic copolymer comprising acrylic acid sodium salt, methacrylic acid sodium salt or 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid sodium salt to form a mixture of water and flocculated solids; and separating the water from the flocculated solids using a dewatering device.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Dehydrated polysaccharide gel containing microorganisms, a sugar and a polyol for producing fermented drinks
Improved fermentation activity of microorganisms in a polysaccharide gel such as an alginate gel is obtained after dehydration, staorage and rehydration by soaking the gel containing the microorganisms prior to dehydration in a sugar solution to provide in the gel an amount of sugar of at least 100 g / kg and less than 500 g / kg of gel, preferably less than 300 g / k of gel. The dehydration may be carried out in a fluidized bed or by lyophilization. The gel may be in the form of beads or fibers having a double layer structure formed by an internal layer or core of gel containing the microorganisms and an external lay er or envelope of gel essentially devoid of the microoraganisms. The sugar is preferably xylose, glucose, fructose, lactose or sucrose, and the sugar solution may contain a polyol such as sorbitol, inositol or glycerol to provide in the gel an amount of polyol of at least 30 g / kg of gel. The sugar solution may also contain a non-ionic surfactant such as sorbitan monostearate as a protecting substance to fur ther improve fermentation activity. The microorganisms in the gel are preferably yeast, and after rehydration the yeast containing gel is used in producing a fermented drink such as in secondary fermentaion of wine to produce sparkling wine or champagne.
Owner:MOET & CHANDON
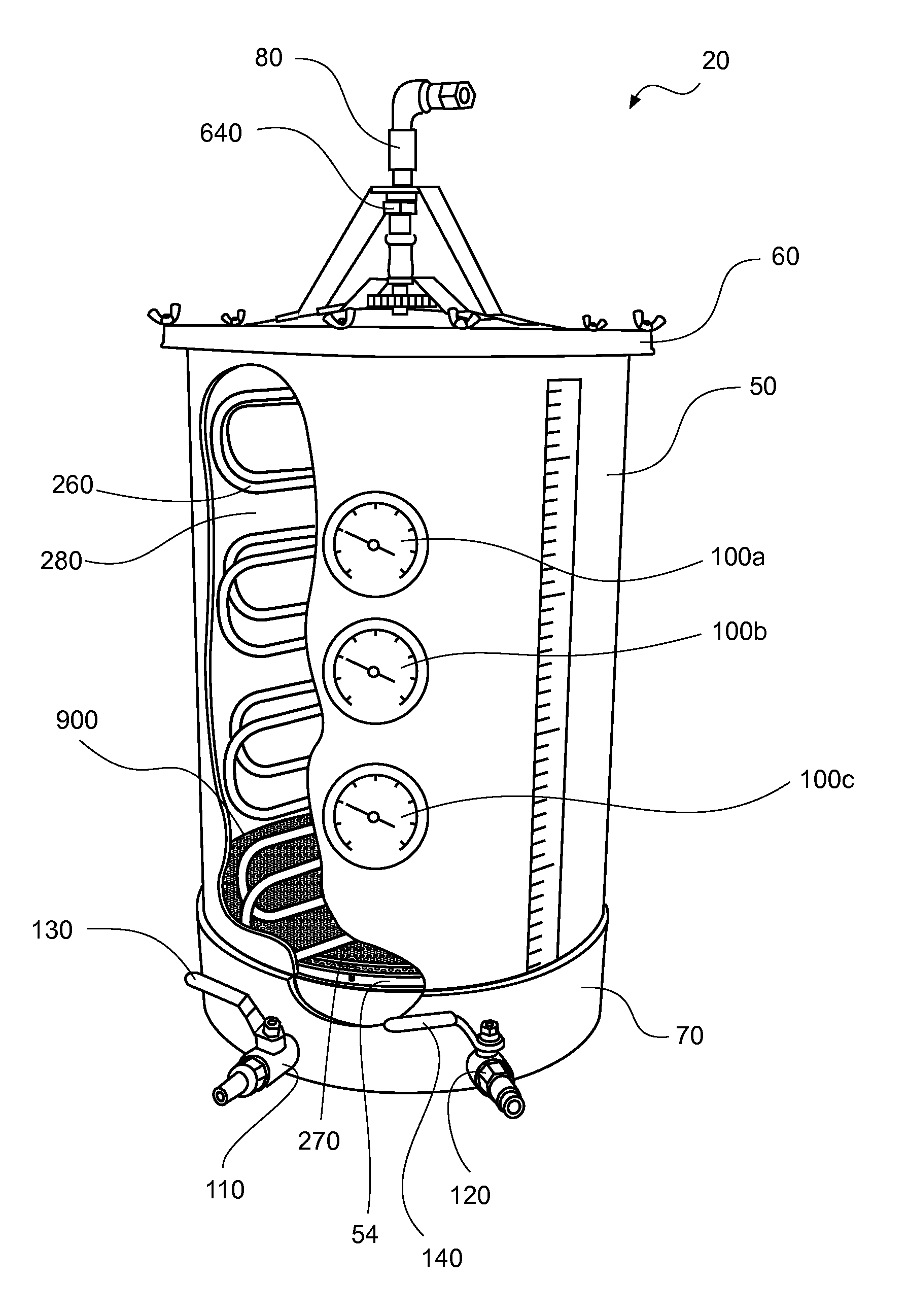
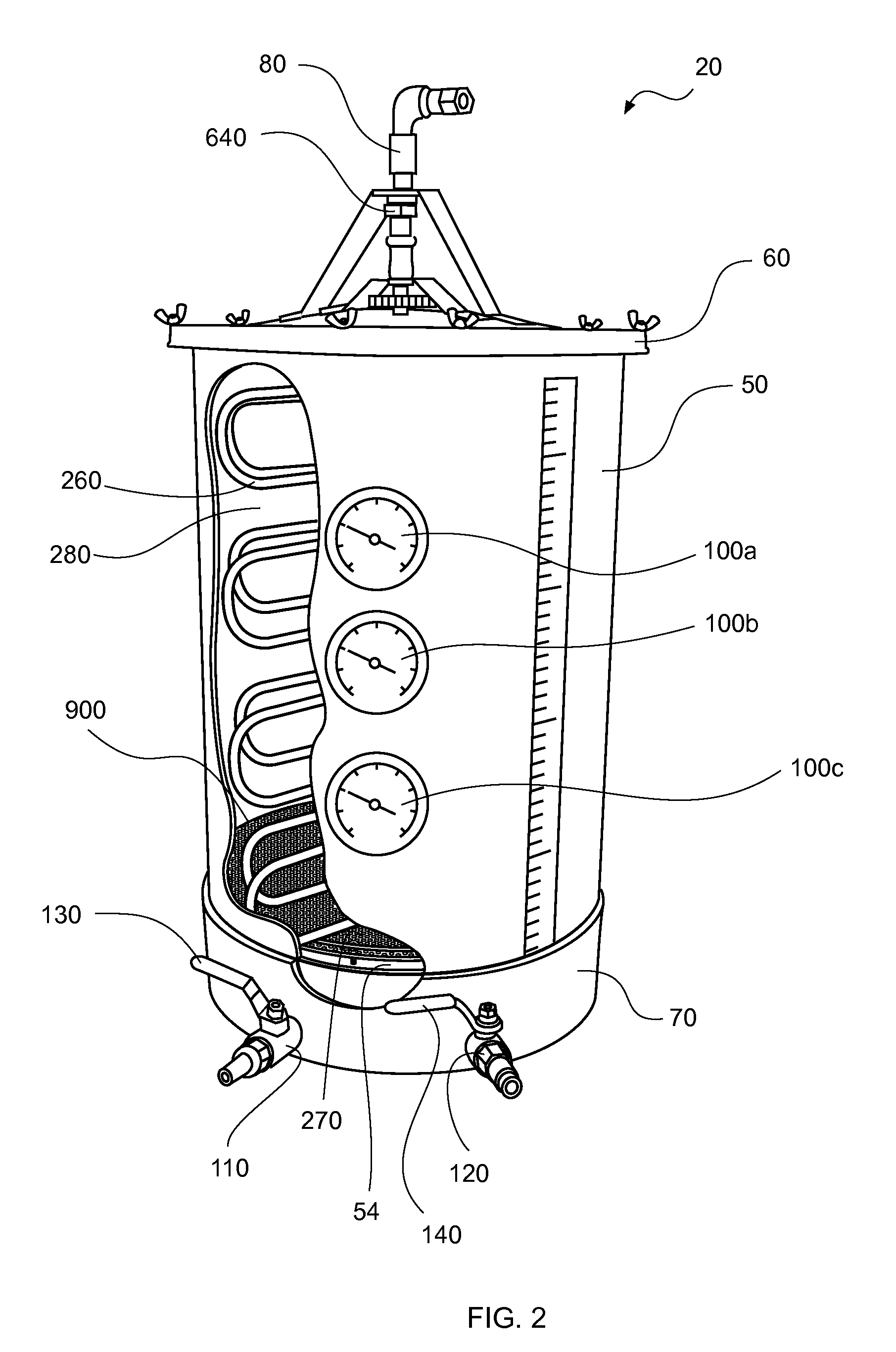
Heat exchanger for fermentation tank
InactiveUS20050077029A1Quality improvementReduce CooldownBeer fermentationWine preparationCoolant flowDouble wall
A device which is used to cool fermentation tanks and which can be used essentially in beer production, cooling and maturation, includes a vertical heat exchanger, which comprises single- or double-wall concentric cylinders and is positioned internally at the center of a tank. The length and capacity of the cylinders differ depending on the size and shape of the tank. A coolant flows through the cylinders in order to cool and to maintain a suitable temperature range. In addition, the double-wall cylinders which form the heat exchanger are interconnected by means of coolant flow and support tubes. Meanwhile, the exchanger is supported by the cone and the walls of the tank by means of tubes which are used for the passage of the coolant and the passage of signals. Moreover, the outer wall and the cone can be provided with a cooling jacket.
Owner:MORALES CERVANTES JOSE +1
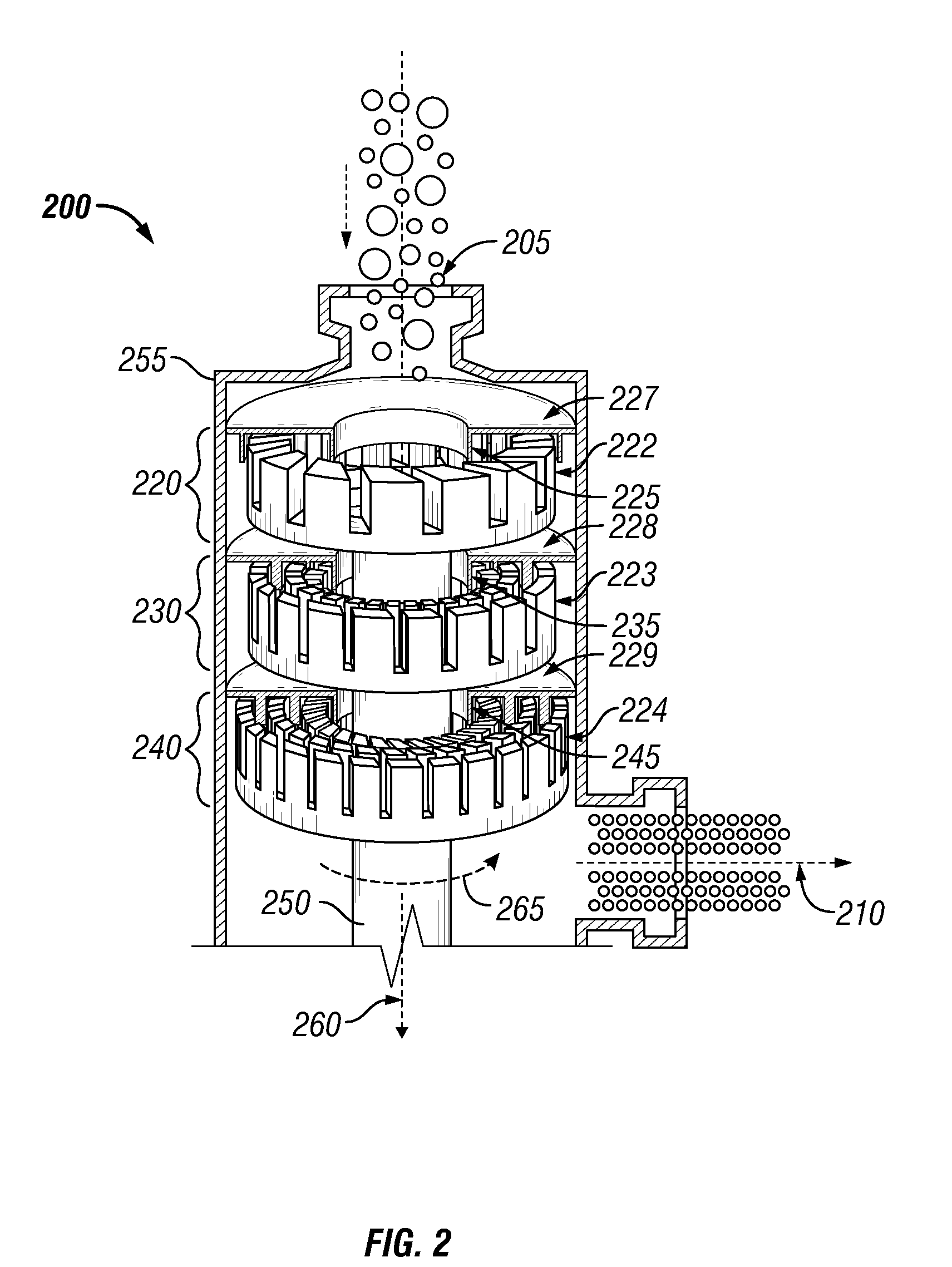
Mash/lauter tun and method of use thereof
ActiveUS20090285971A1Simplify the transfer processPromote sportsBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFiltrationVALVE PORT
A mash / lauter tun and method of converting grains to wort. The mash / lauter tun comprises a container with a double false bottom filter having two perforated plates disposed parallel with a space therebetween for receiving filtration media. The container further comprises thermometers extending to near the center of the tun and a rotating heat exchanger. In use, mash is loaded into the container and heated via the rotating heat exchanger by passing hot fluid through the rotating heat exchanger. The mash is then sparged by increasing pressure in the rotating heat exchanger above a threshold pressure via closure an outlet valve of the heat exchanger. The wort then passes through the double false bottom filter and is subsequently transferred to a brew kettle for boiling.
Owner:BRODERICK WILLIAM
Saccharomyces cerevisiae and screening method and application thereof
ActiveCN101550400AShorten the fermentation cycleStrong low temperature fermentation abilityFungiBeer fermentationMicroorganismAlcohol
The invention relates to screening and application of saccharomyces cerevisiae suitable for the brewing of a series of kirschwasser, pertaining to the technical field of biological engineering. SC203 strain of the saccharomyces cerevisiae has been preserved in Center of General Microbiology of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms, with a registration number of CGMCC No. 2786. The strain is characterized by rapid growth, early fermentation, short fermentation cycle, strong tolerance against low temperature, acid, alcohol, sulfur dioxide and the like and is applicable to the brewing of such a series of kirschwasser as kirschwasser, ice kirschwasser, kirschwasser liqueur, kirschwasser ratafee and the like. In addition, the strain can also be used for the brewing of grape wine and other common ratafee and icewine.
Owner:山东九道生物科技有限公司
Barley for production of flavor-stable beverage
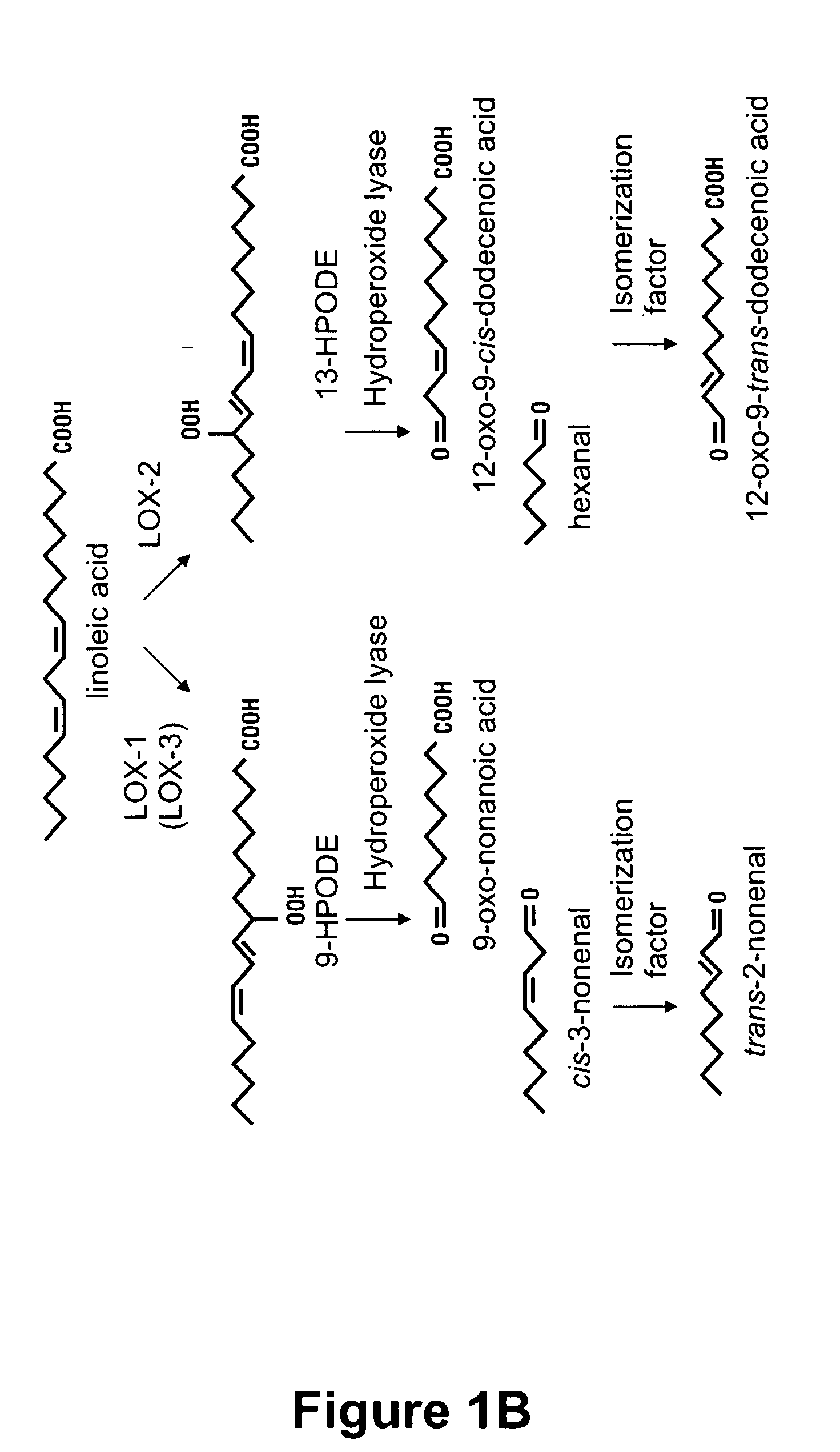
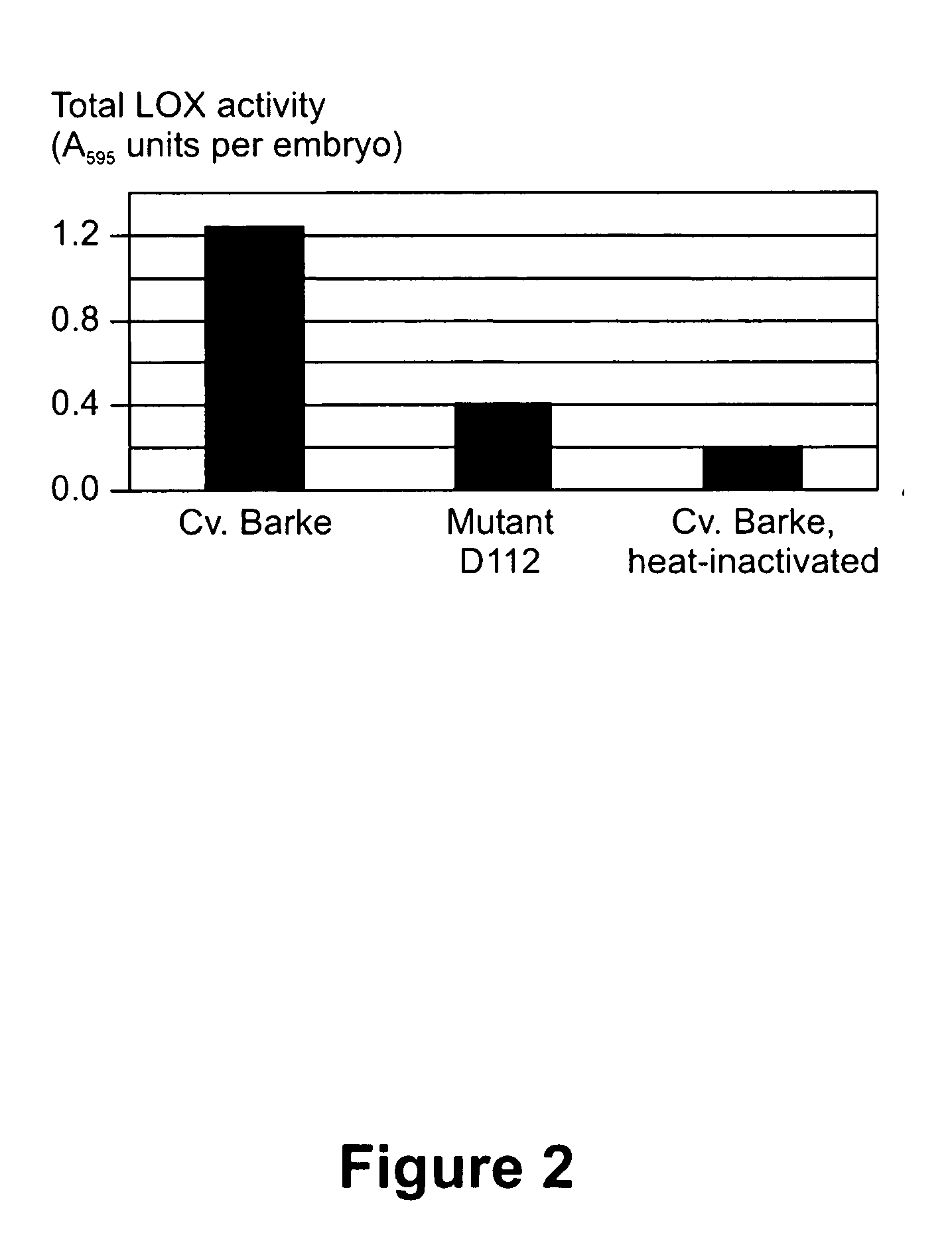
According to the invention, there is provided null-LOX-1 barley and plant products produced thereof, such as malt manufactured by using barley kernels defective in synthesis of the fatty acid-converting enzyme lipoxygenase-1. Said enzyme accounts for the principal activity related to conversion of linoleic acid into 9-hydroperoxy octadecadienoic acid, a lipoxygenase pathway metabolite, which—through further enzymatic or spontaneous reactions—may lead to the appearance of trans-2-nonenal. The invention enables brewers to produce a beer devoid of detectable trans-2-nonenal-specific off-flavors, even after prolonged storage of the beverage.
Owner:CARLSBERG BREWERIES AS
Production of consumable alcohols and components thereof
InactiveUS20050158798A1Quality improvementBeer fermentationMicrobiological testing/measurementAlcoholBiochemical engineering
The invention is directed to a process for producing consumable alcohols and components thereof, in particular for producing consumable alcohols and components thereof using high throughput rapid screening and production of combinatorial libraries of consumable alcohols and components. In particular, the consumable alcohol is wine, Scotch, cognac, ports, beer, gin, vodka, rum, sherry, champagne, tequila, and the like and components thereof. Most particularly, the consumable alcohol is wine, wine blends, and components thereof.
Owner:SHER JAIMES
Method of dewatering thin stillage processing streams
ActiveUS20070210007A1Improve agglomerationAbility to withstandWater treatment parameter controlWater treatment compoundsAcryditeSodium methacrylate
A method dewatering thin stillage process streams generated in the processing of grain to ethanol comprising adding to the process streams an effective flocculating amount of an anionic copolymer comprising acrylic acid sodium salt, methacrylic acid sodium salt or 2-acrylamido-2-methyl-1-propanesulfonic acid sodium salt to form a mixture of water and flocculated solids; and separating the water from the flocculated solids using a dewatering device.
Owner:ECOLAB USA INC
Method of stabilizing useful protein and useful protein compositions
InactiveUS6391296B1Improve biological activityActivity of protein can be maintainedPeptide/protein ingredientsWort preparationCrystallographyProtein composition
A method of stabilizing a useful protein by mixing a useful protein and an aqueous solution of a compound having the basic structure of arabic acid, and a stabilizied useful protein compositon containing a useful protein and a compound having the basic structure of arabic acid; gum arabic is preferred as a compound having the basic structure of arabic acid, and examples of a useful protein include cytokine and interferon; and a production method for canine interferon-gamma and stabilization thereof.
Owner:TORAY IND INC
Agglomerated zeolitic adsorbents, their process of preparation and their uses
InactiveUS20050170947A1Amino compound purification/separationMolecular sieve catalystsSorbentSimulated moving bed
The present invention relates to agglomerated zeolitic adsorbents containing zeolite X and an inert binder, the inert binder containing at least 80% by weight of clay which has undergone zeolitization by the action of an alkaline solution, the zeolite X having with an Si / Al ratio such that 1.15<Si / Al≦1.5, at least 90% of the exchangeable cationic sites of the zeolite X of which are occupied either by barium ions alone or by barium ions and potassium ions whose Dubinin volume is greater than or equal to 0.240 cm3 / g. They are obtained by agglomerating zeolite powder with a binder, followed by the zeolitization of the binder, the exchange of the ions of the zeolite by barium ions (and potassium ions) and the activation of the adsorbents thus exchanged. These adsorbents are particularly suited to the adsorption of the para-xylene present in C8 aromatic hydrocarbon fractions in the liquid phase in processes of simulated moving bed type but also to the separation of sugars, polyhydric alcohols, cresols or substituted toluene isomers.
Owner:ARKEMA FRANCE SA
High shear rotary fixed bed reactor
InactiveUS20100004419A1Low costReduce usageTransportation and packagingRotary stirring mixersFixed bedHomogeneous catalysis
A reactor comprising at least one contact surface made from, coated with, or impregnated by a catalyst, wherein the contact surface comprises a sintered metal or a ceramic, and wherein the reactor is configured to subject a reactant stream to shear. A system for carrying out a heterogeneously catalyzed reaction, the system comprising a reactor as described above and a pump configured for delivering reactants to the at least one reactor. A method for carrying out a heterogeneously-catalyzed reaction by introducing reactants into a reactor comprising at least one contact surface made from, coated with, or impregnated by a catalyst under conditions which promote production of a desired product, wherein the contact surface comprises a sintered metal or a ceramic, and forming a dispersion of reactants within the reactor, wherein the dispersion comprises droplets or gas bubbles of reactant with an average diameter of less than about 5 μm.
Owner:HRD CORP
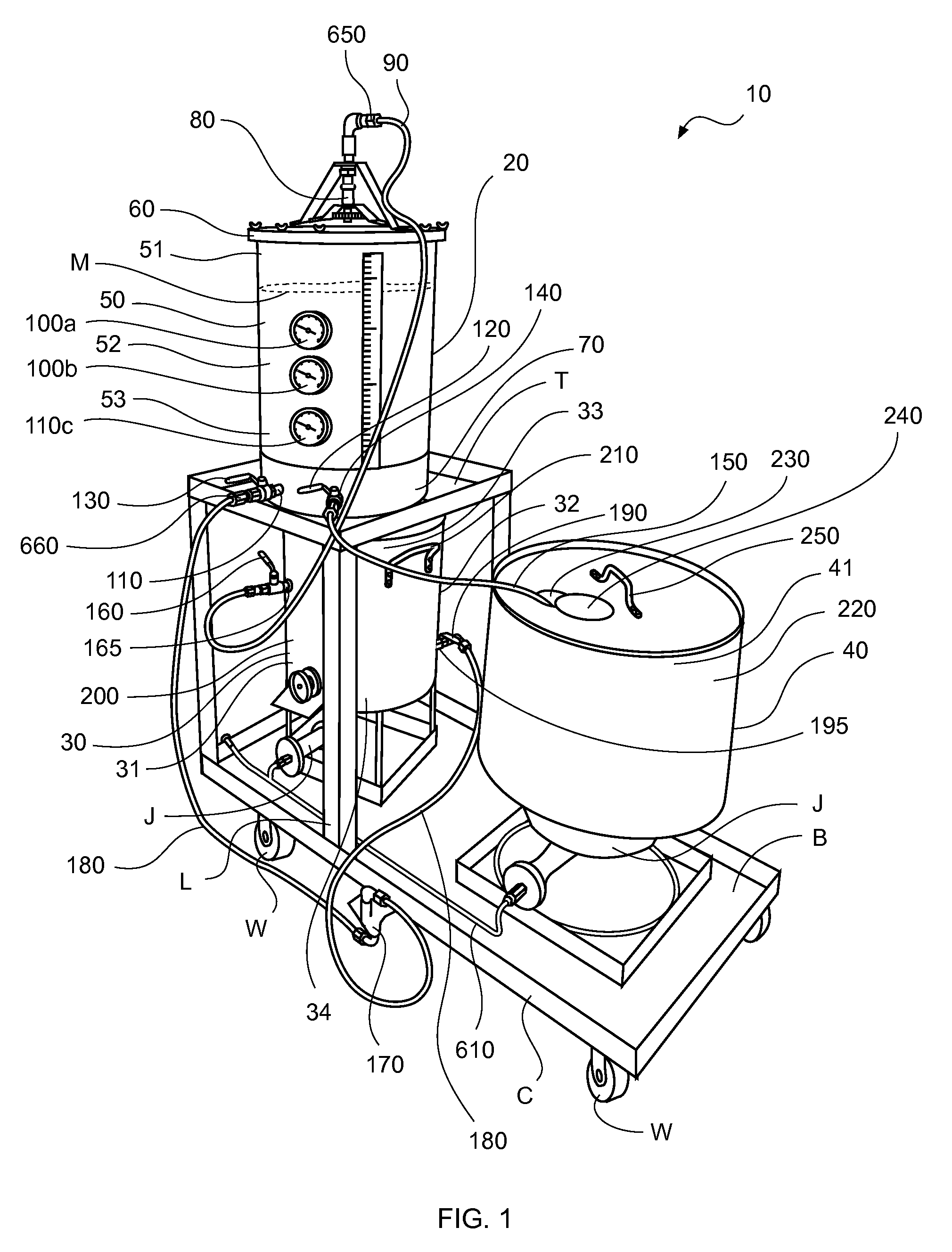
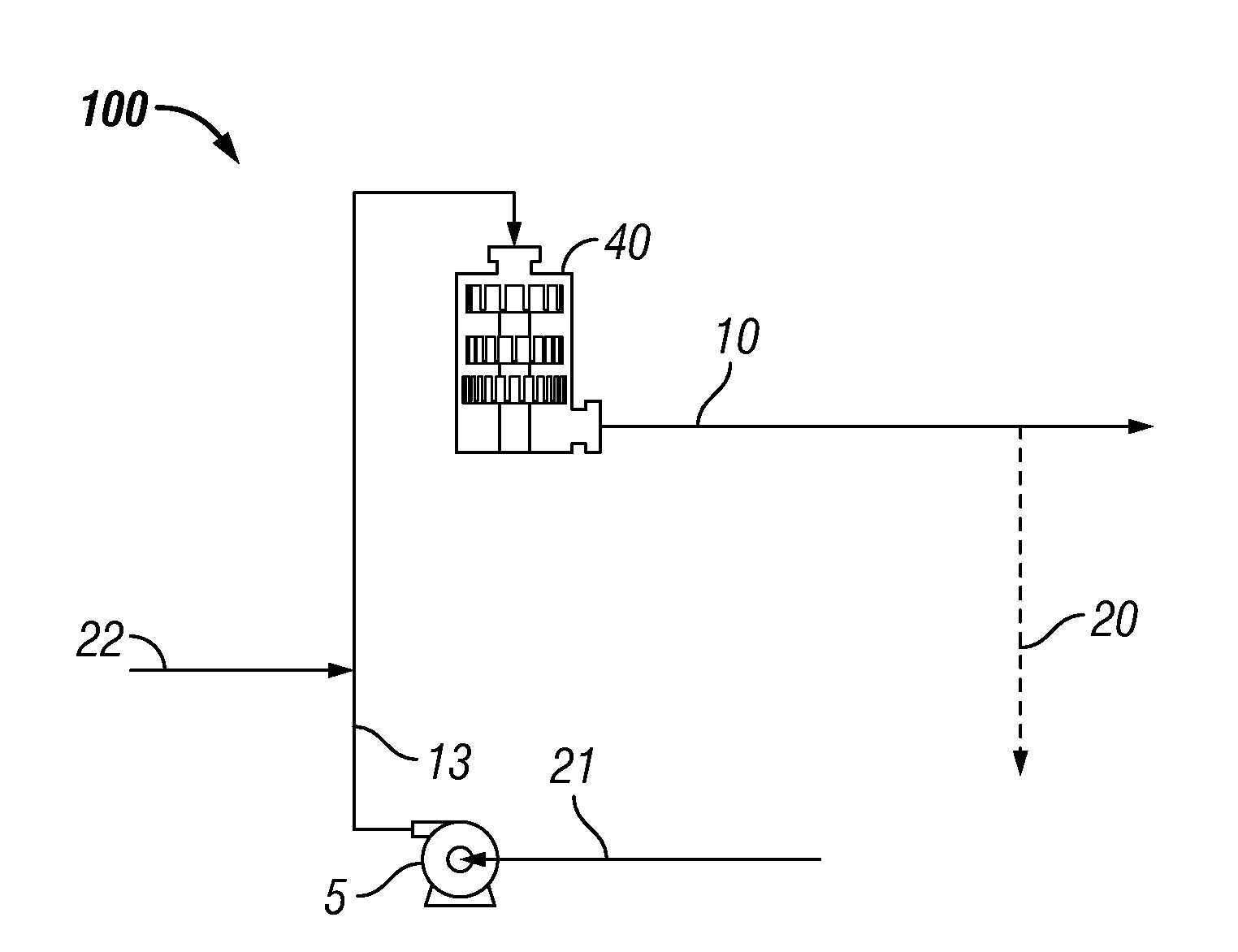
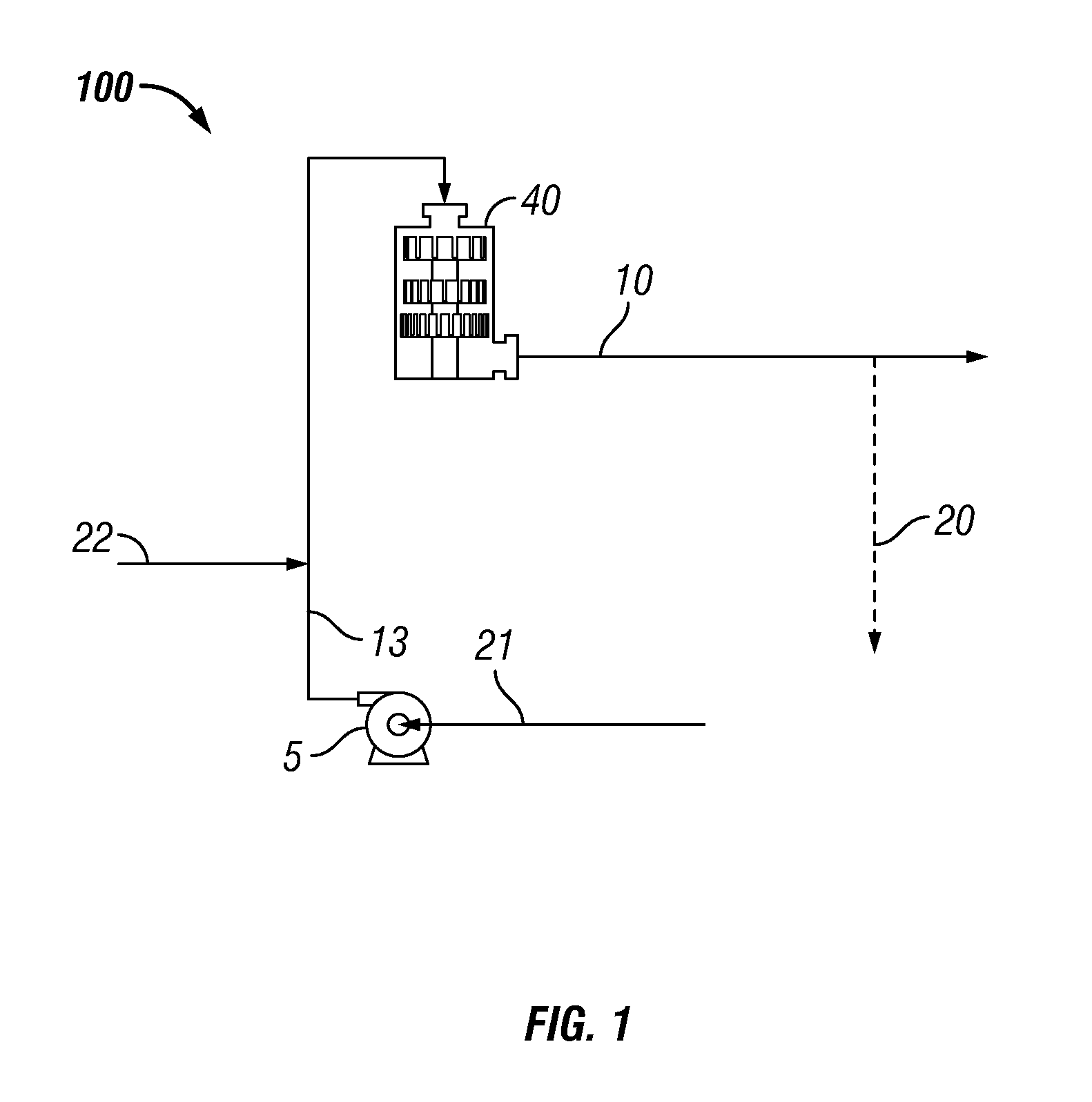
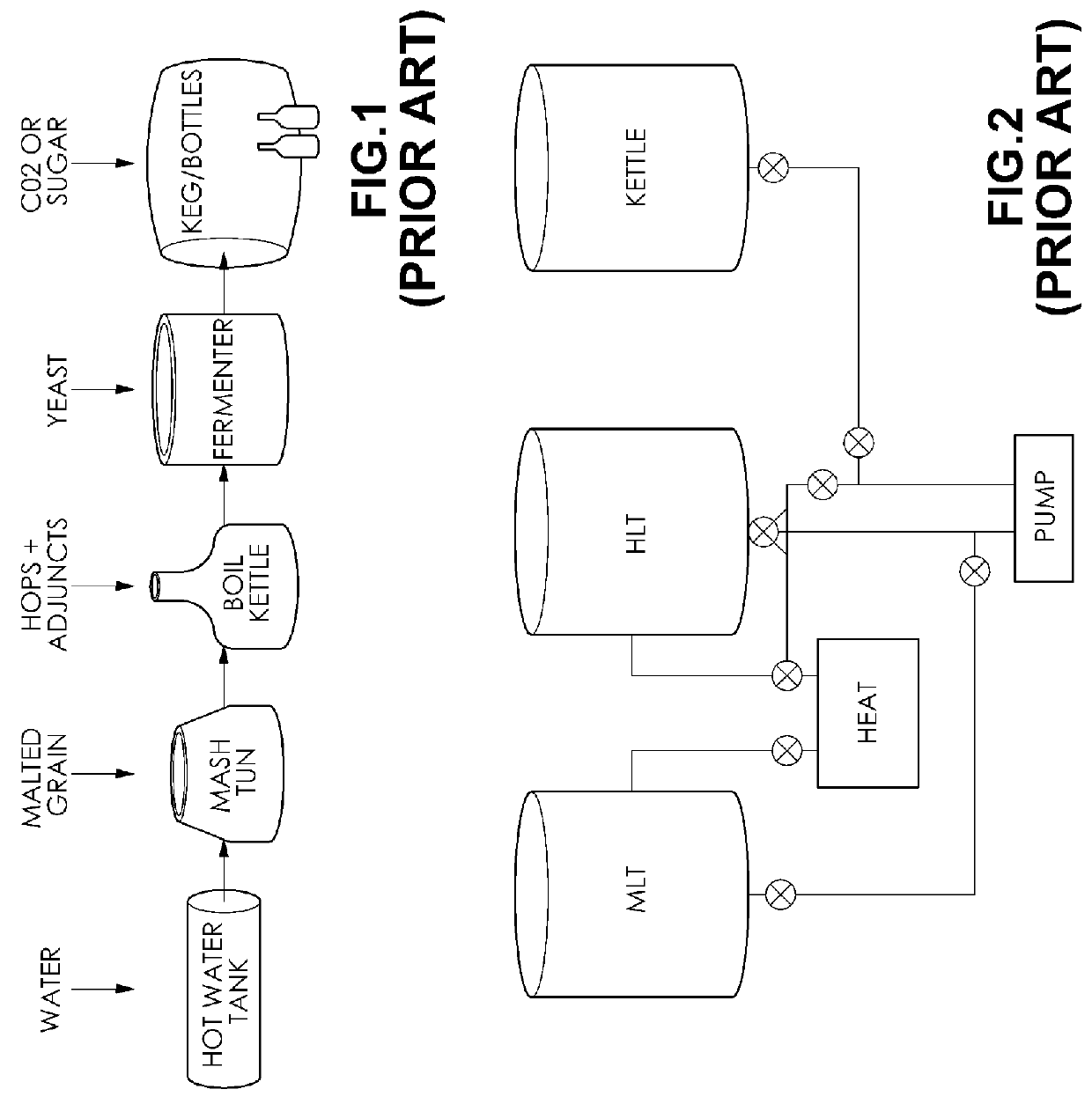
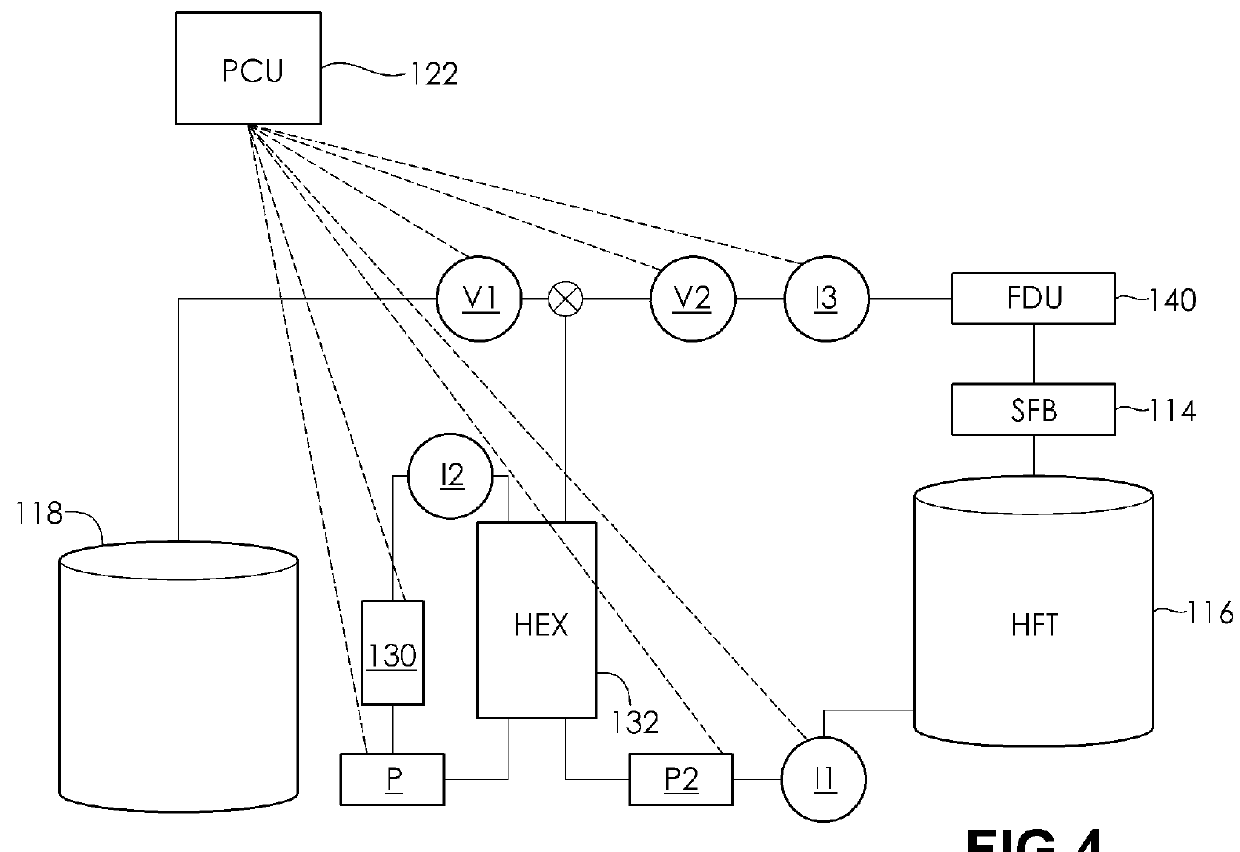
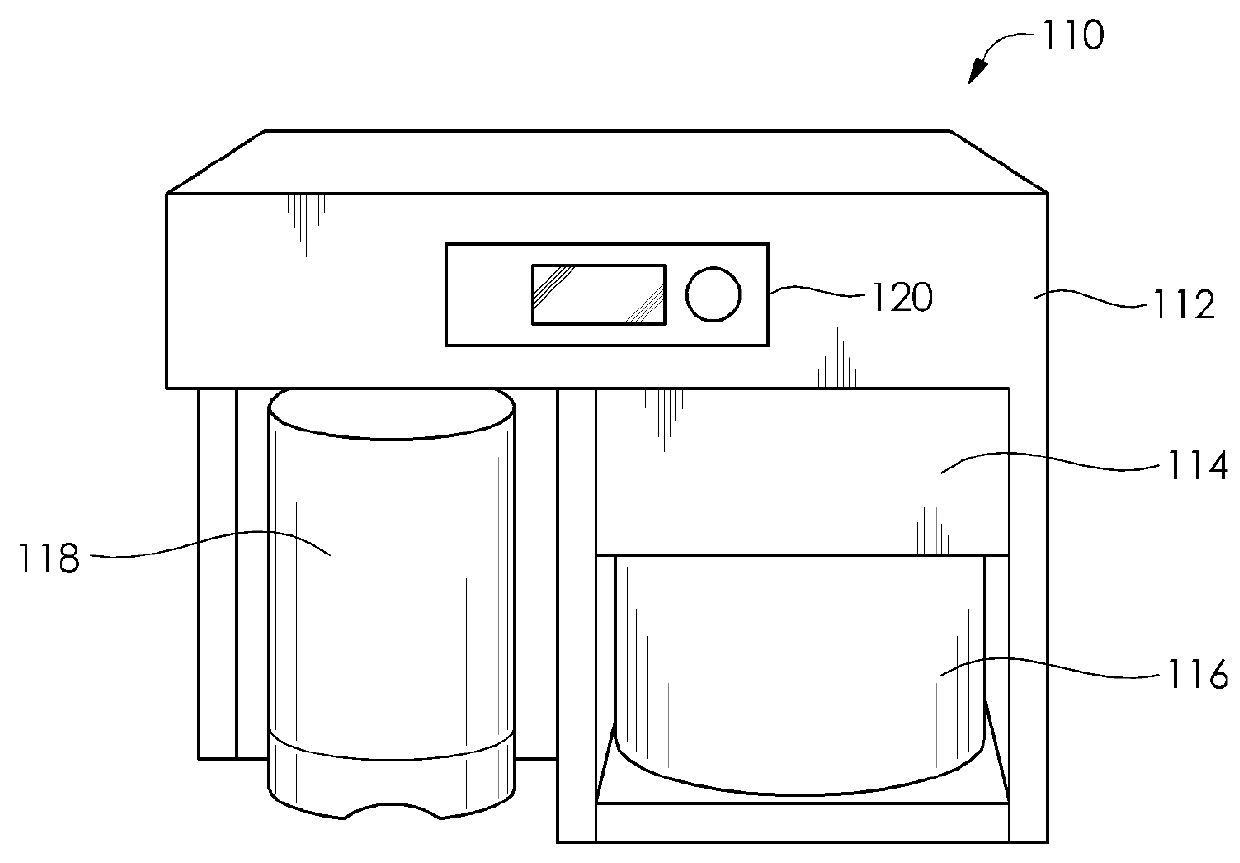
Simple, efficient automated all-grain beer brewing system
The present invention provides a method to create and a process for using a compact, automated, all-grain beer brewing appliance. The method may include a microprocessor-based Process Control System, a Heat EXchanger loop, a Fluid Distribution Manifold, a Step Filter Basket, a Hot Fluid Tank, pumps, valves, plumbing and brewing control instruments. The invention may also make use of a Filter-Keg in lieu of a Hot Fluid Tank allowing fermentation, conditioning and dispensing from a single replaceable vessel.
Owner:PB FUNDING GRP LLC
Biopolymer structures and components including column and rail system
The present invention relates generally to structures formed from a biopolymer. The present invention more particularly relates to biopolymer structures and components formed from fermentation solids and thermoactive materials, including a column and rail system and the component parts of this system.
Owner:AGRI POLYMERIX LLC
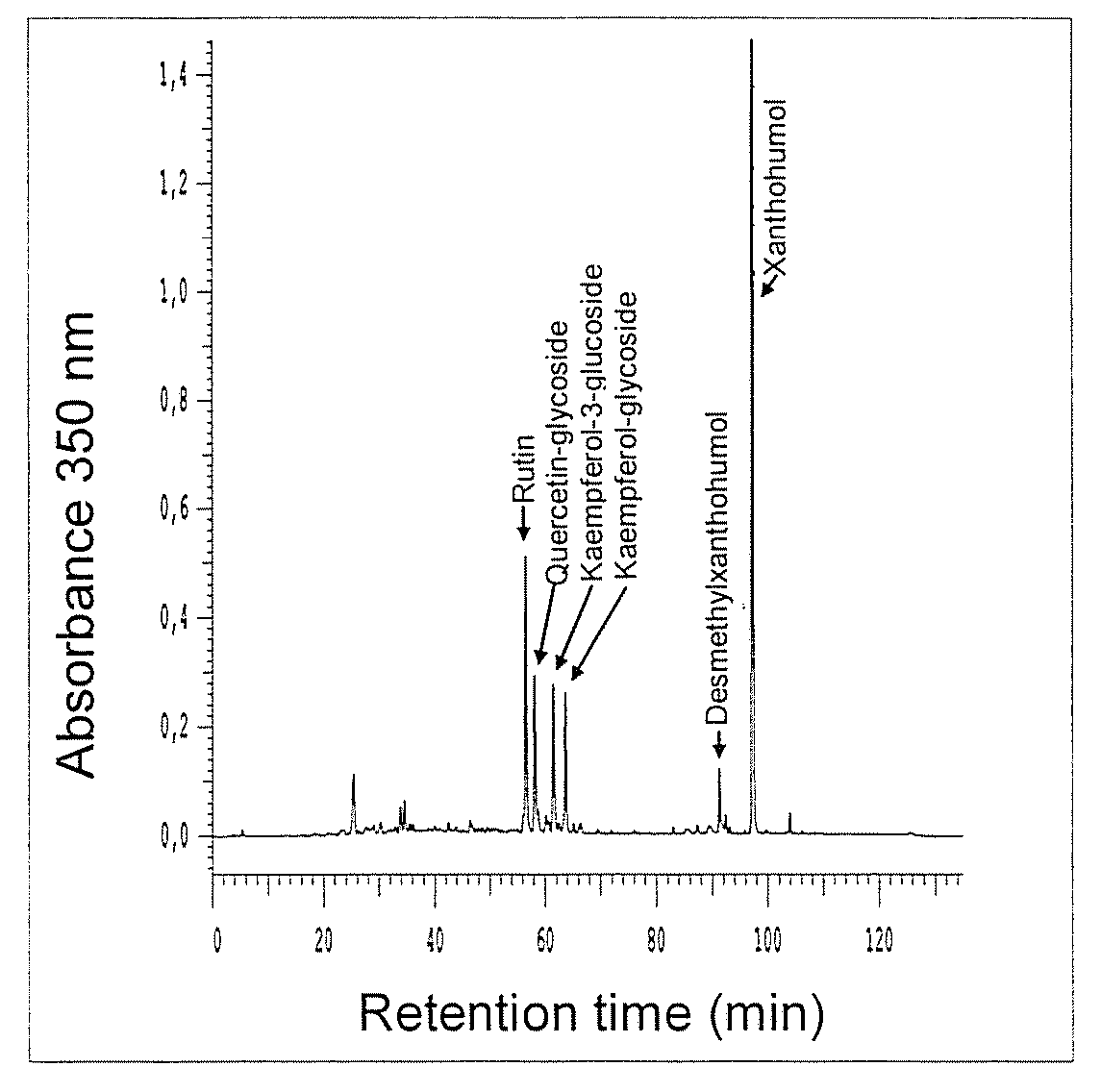
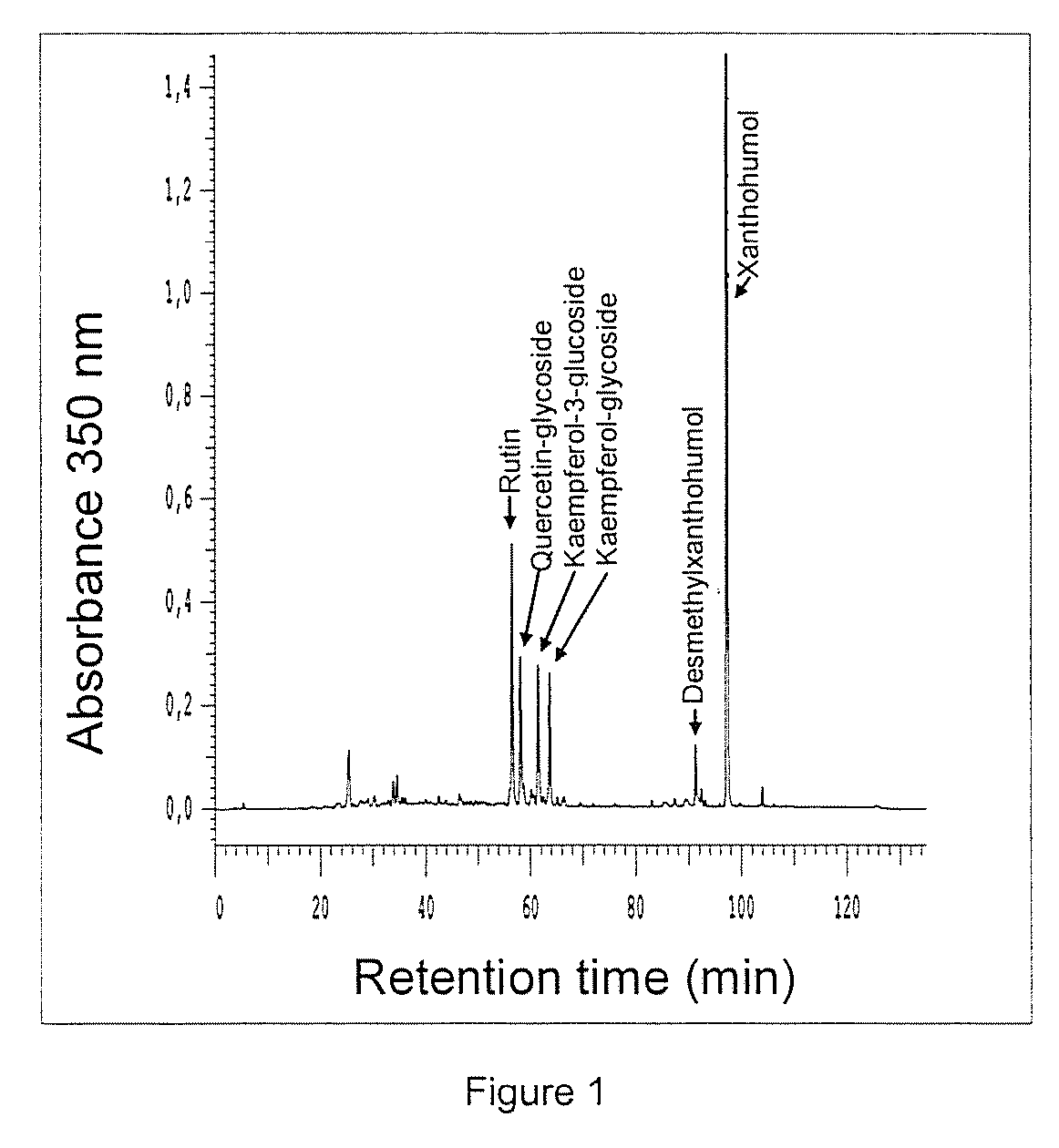
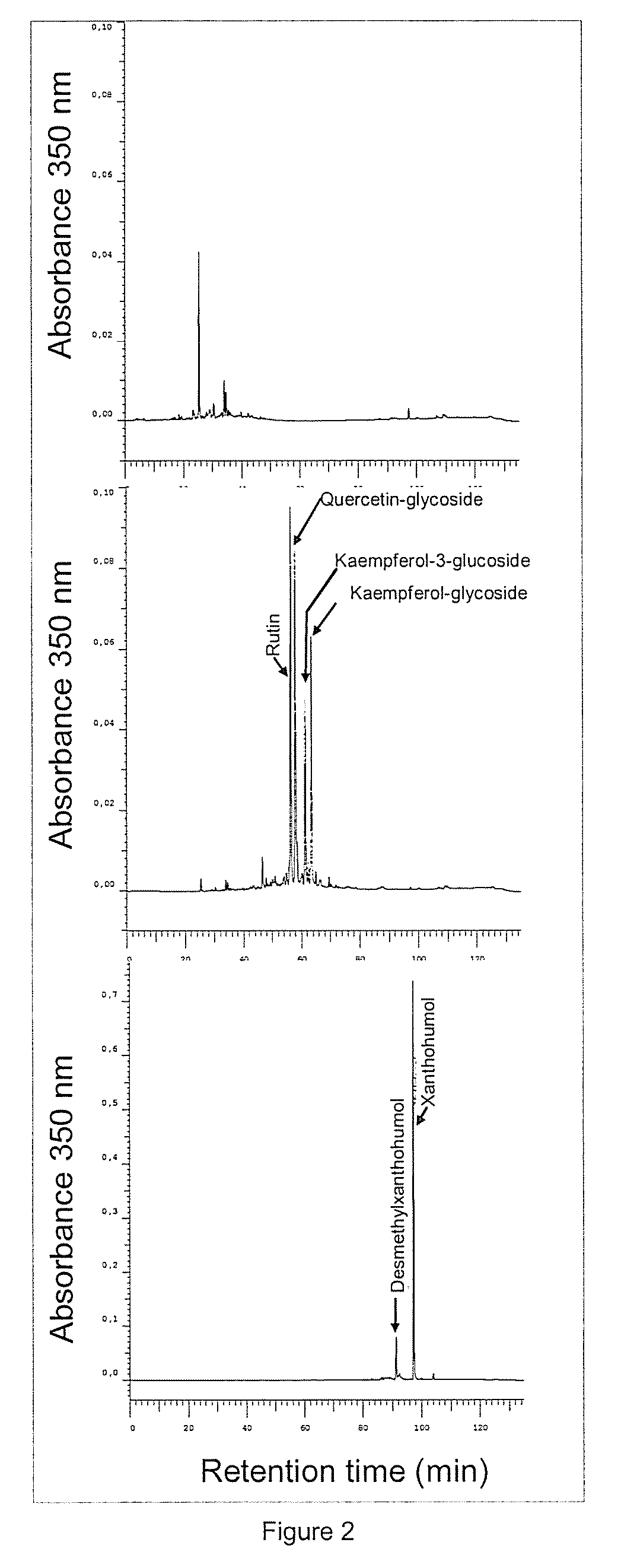
Natural Extract Containing Xanthohumol, and Method for the Production Thereof Products Produced Therefrom
The invention relates to a method for producing an extract containing xanthohumol (XN), which is obtained from toasted cereal products, cereal malt, coffee or cocoa. The XN-content in said extract is in the region of 10 mg / kg-2 g / kg xanthohumol. The use of XN-toasted extracts enables the XN-content of foodstuffs and pharmaceutical products to be increased in a natural manner.
Owner:ARCAINI ANTONIO
Packaged beverage
InactiveUS7014876B2Increase the amount of transferPromote absorptionFruit and vegetables preservationTea extractionAdditive ingredientHealth promotion
Provided is a packaged beverage comprising the following ingredients (A) and (B):(A) non-polymer catechins in an amount of from 0.092 to 0.5 g / 100 mL beverage,(B) an alcoholic precipitate in an amount of 0.015 g / 100 mL beverage or less in terms of the amount of magnesium, at a weight ratio (A) / (B) ranging from 30 / 1 to 50000 / 1. The packaged beverage of the present invention is the best suited beverage for health promotion, because drinking of it permits transfer of a large amount of catechins to the blood form the beverage and their absorption in the body is excellent.
Owner:KAO CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com