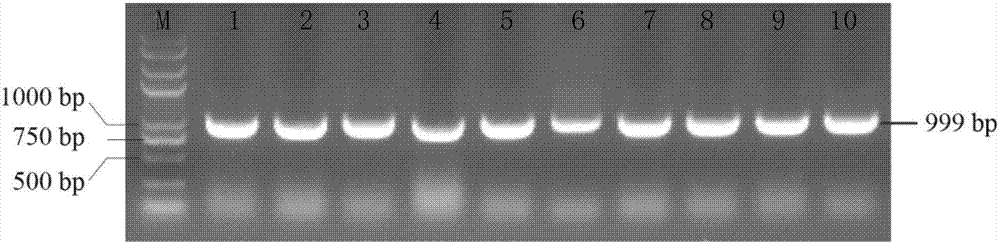
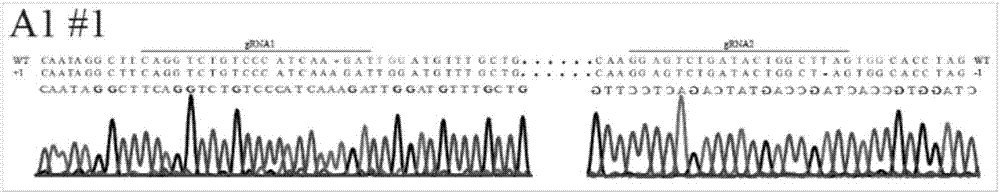
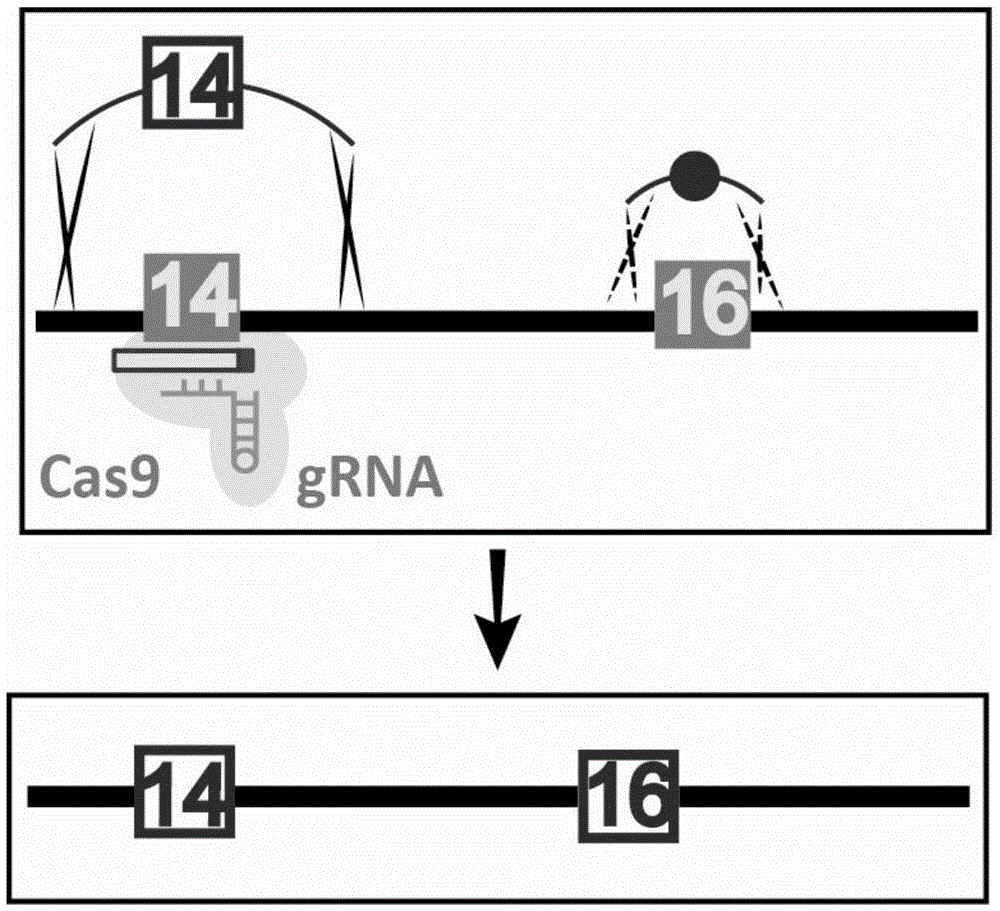
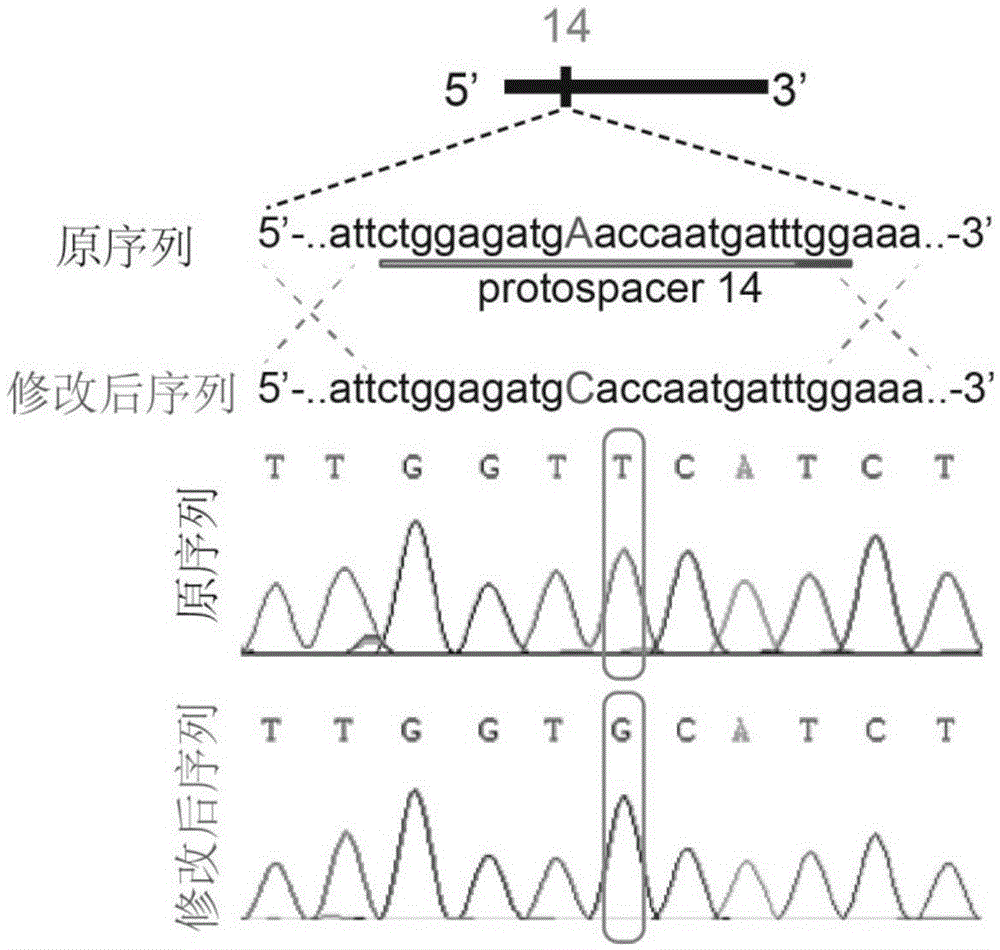
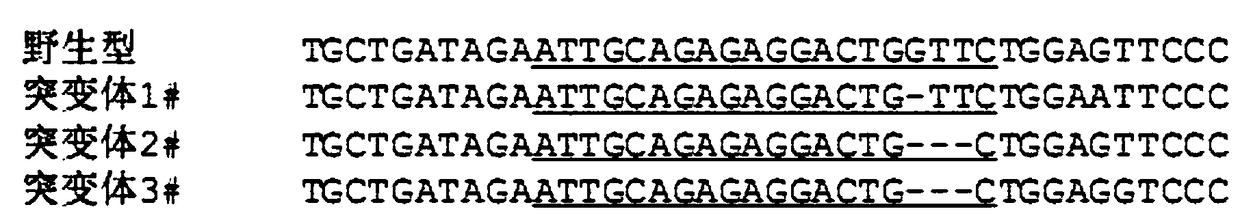Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1015 results about "Site-directed mutagenesis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Site-directed mutagenesis is a molecular biology method that is used to make specific and intentional changes to the DNA sequence of a gene and any gene products. Also called site-specific mutagenesis or oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis, it is used for investigating the structure and biological activity of DNA, RNA, and protein molecules, and for protein engineering.
Systems for in vivo site-directed mutagenesis using oligonucleotides
InactiveUS20040171154A1Large deletionImprove applicabilitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousSite-directed mutagenesis
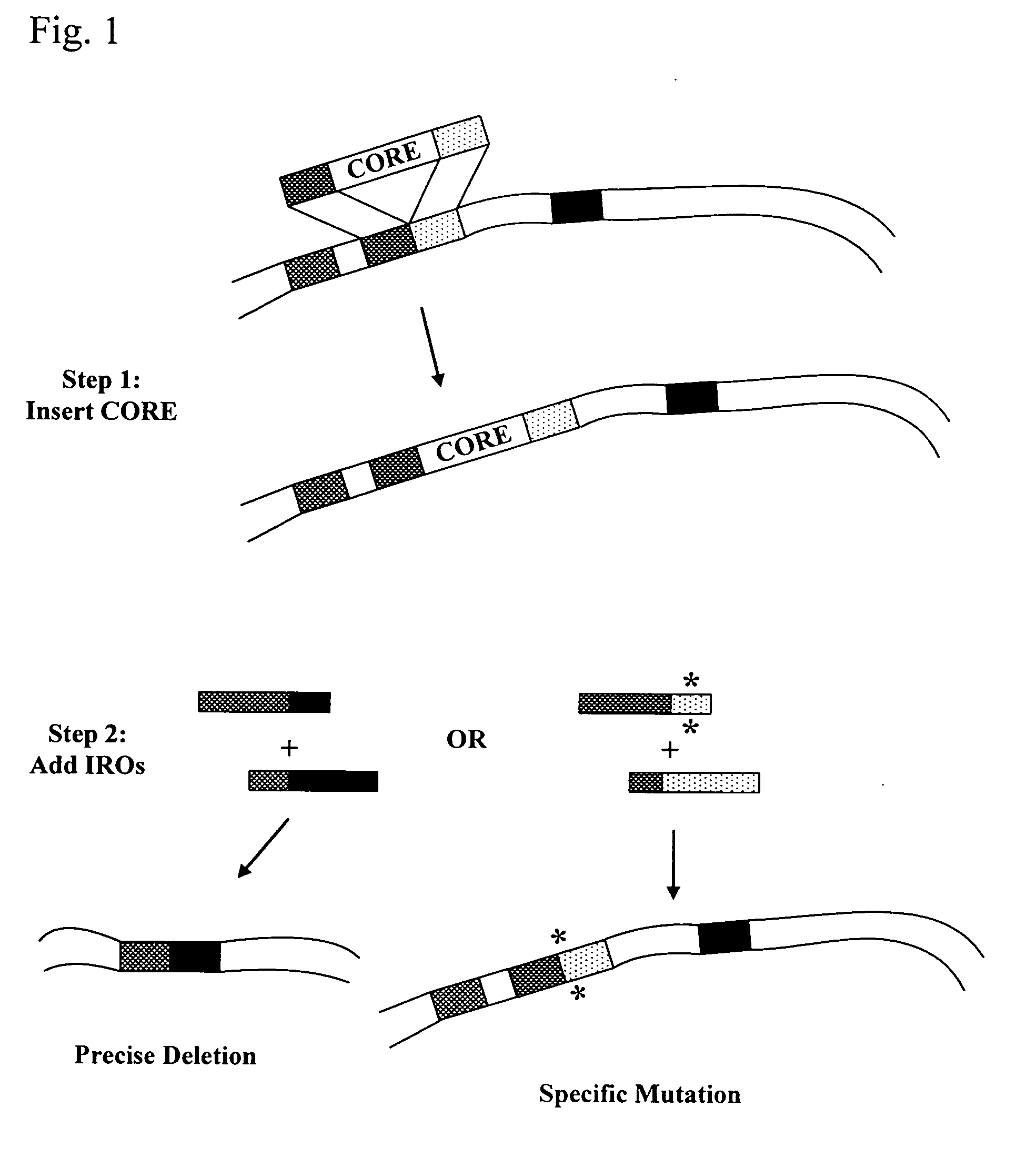
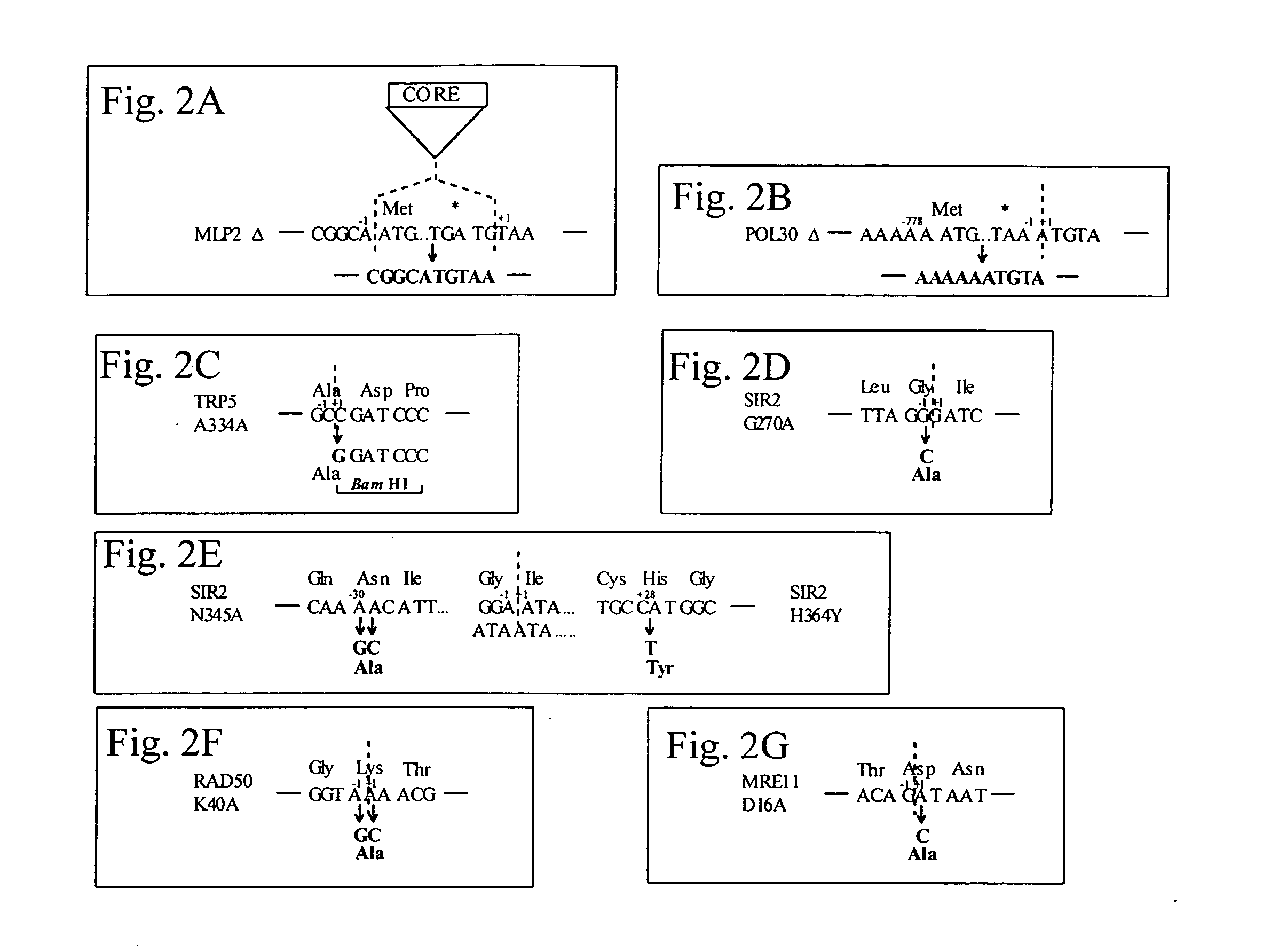
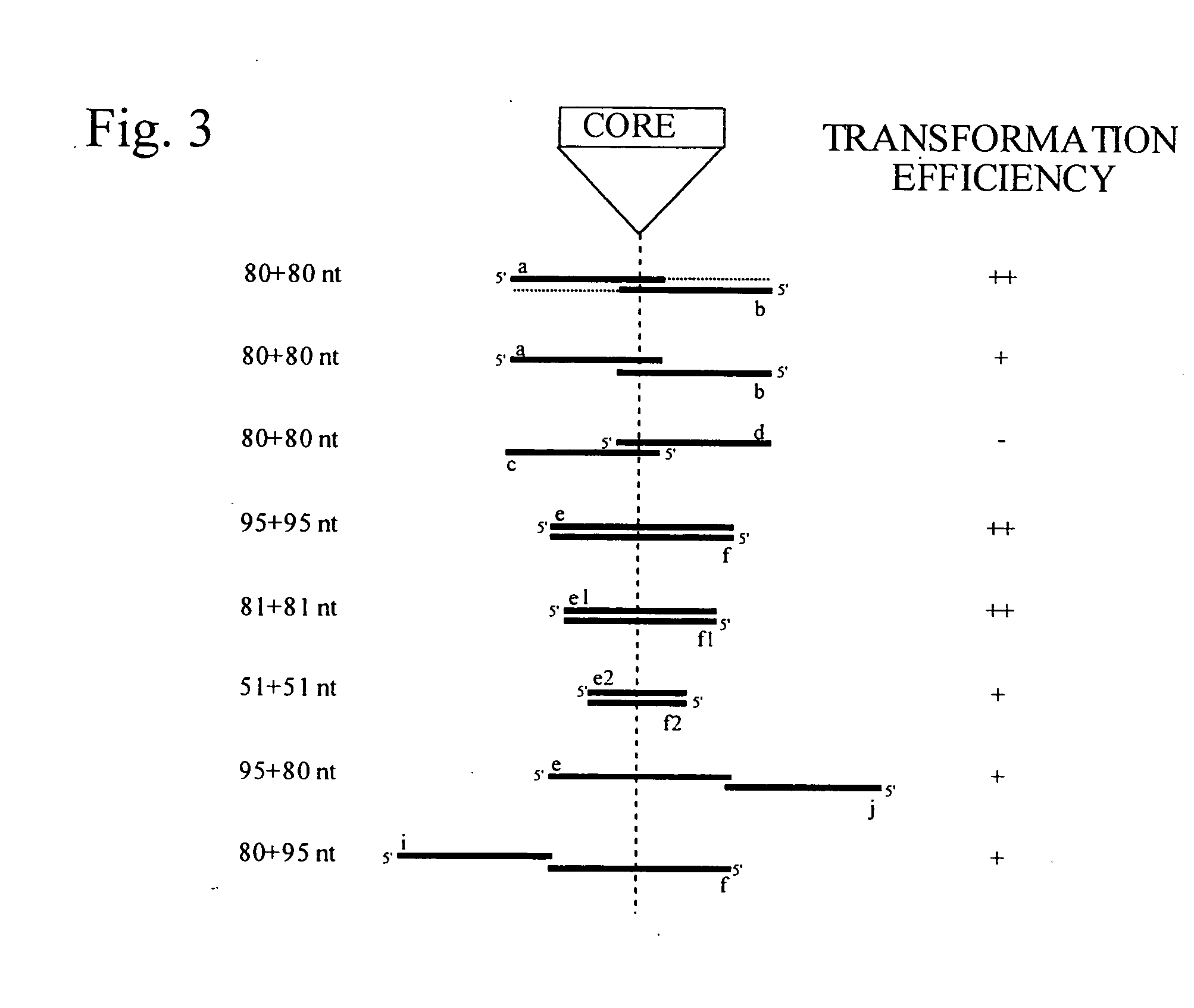
This disclosure provides several methods to generate nucleic acid mutations in vivo, for instance in such a way that no heterologous sequence is retained after the mutagenesis is complete. The methods employ integrative recombinant oligonucleotides (IROs). Specific examples of the described mutagenesis methods enable site-specific point mutations, deletions, and insertions. Also provided are methods that enable multiple rounds of mutation and random mutagenesis in a localized region. The described methods are applicable to any organism that has a homologous recombination system.
Owner:HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES DEPT OF THE GOVERNMENT OF THE US SEC THE
Cysteine variants of erythropoietin
The growth hormone supergene family comprises greater than 20 structurally related cytokines and growth factors. A general method is provided for creating site-specific, biologically active conjugates of these proteins. The method involves adding cysteine residues to non-essential regions of the proteins or substituting cysteine residues for non-essential amino acids in the proteins using site-directed mutagenesis and then covalently coupling a cysteine-reactive polymer or other type of cysteine-reactive moiety to the proteins via the added cysteine residue. Disclosed herein are preferred sites for adding cysteine residues or introducing cysteine substitutions into the proteins, and the proteins and protein derivatives produced thereby.
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
Cysteine variants of erythropoietin
The growth hormone supergene family comprises greater than 20 structurally related cytokines and growth factors. A general method is provided for creating site-specific, biologically active conjugates of these proteins. The method involves adding cysteine residues to non-essential regions of the proteins or substituting cysteine residues for non-essential amino acids in the proteins using site-directed mutagenesis and then covalently coupling a cysteine-reactive polymer or other type of cysteine-reactive moiety to the proteins via the added cysteine residue. Disclosed herein are preferred sites for adding cysteine residues or introducing cysteine substitutions into the proteins, and the proteins and protein derivatives produced thereby.
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
Immunogenic detoxified mutant E. coli LT-A-toxin
InactiveUS7115730B1Maximise adjuvanticityMaximise immunogenicityBacteriaSugar derivativesEscherichia coliAdjuvant
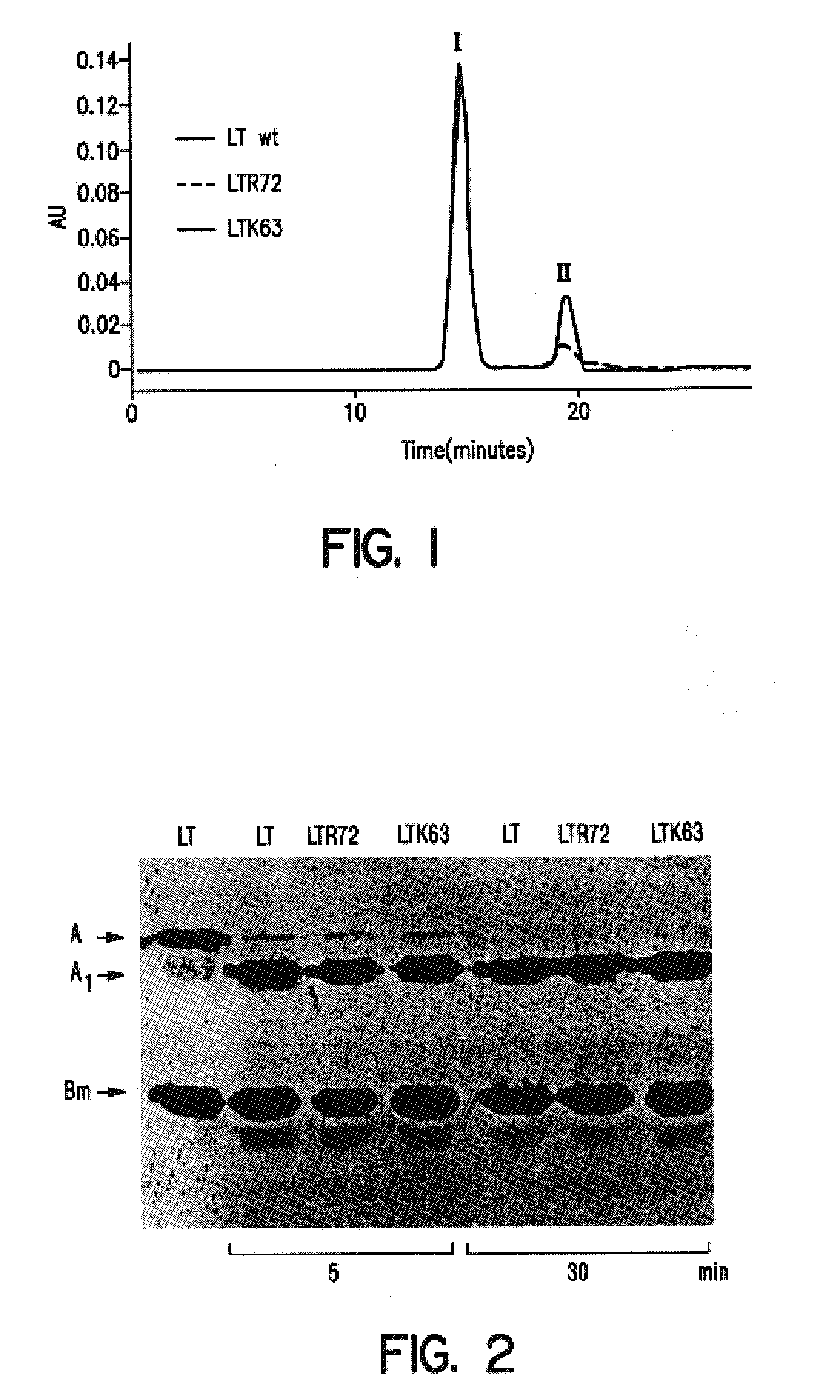
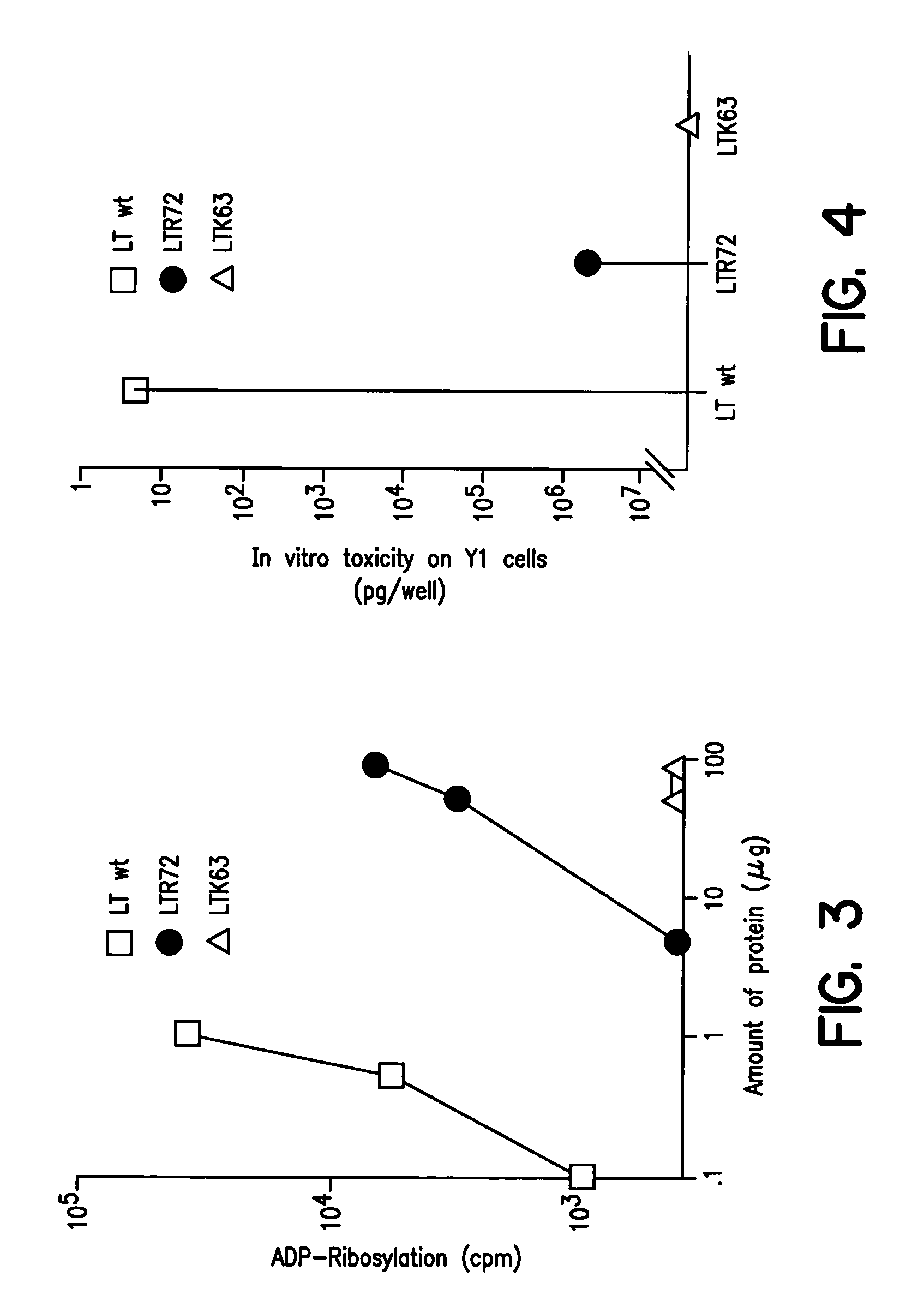
An immunogenic detoxified protein is provided which comprises the amino acid sequence of subunit A of an E. coli heat labile toxin (LT-A) or a fragment thereof in which at least amino acid Ala-72, numbered relative to SEQ ID NO:1, of the A subunits mutated, preferably by substitution with Arg. The toxoid is useful as vaccine against an enterotoxigenic strain of E. coli and is produced by recombinant DNA means by site-directed mutagenesis. It is also an effective adjuvant.
Owner:CHIRON CORP
Increasing the production of recombinant antibodies in mammalian cells by site-directed mutagenesis
InactiveUS20060019342A1Improve expression levelHigh purification yieldAnimal cellsSugar derivativesHeavy chainMammal
The present invention relates to a reliable, reproducible method for improving the producibility of an antibody. More specifically, this invention provides a method for modifying the heavy chain of an antibody to improve its producibility in eukaryotic cells. Additionally, the method of the invention may improve both antibody producibility and one or more antigen binding characteristics. The invention further provides modified antibodies which are better produced and which have either no change in their antigen binding characteristics or exhibit improved antigen binding characteristics.
Owner:MEDIMMUNE LLC
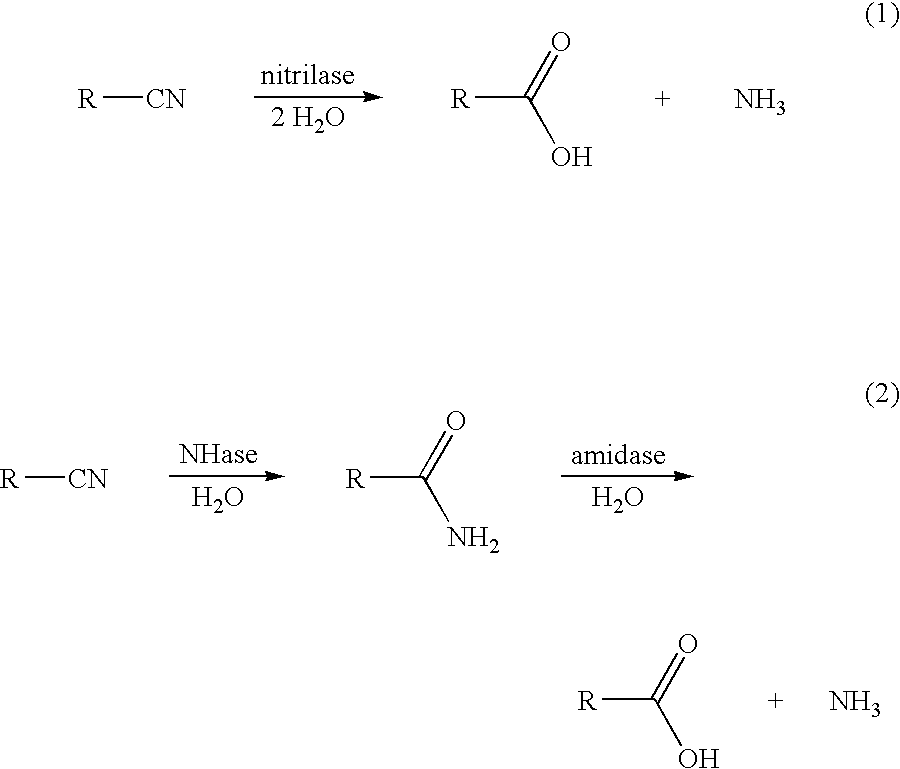
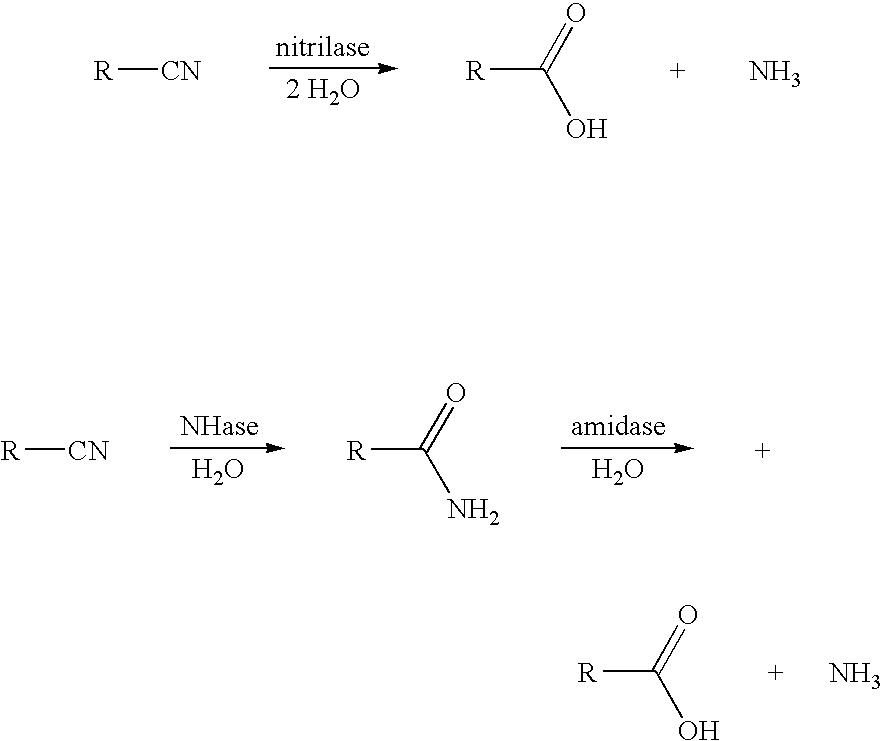
Production of 3-hydroxycarboxylic acid using nitrilase
This invention relates to nitrilase mutants having improved nitrilase activity for converting 3-hydroxynitriles to 3-hydroxycarboxylic acids. More specifically, the Acidovorax facilis 72W (ATCC 55746) nitrilase gene was mutated using error-prone PCR and site-directed mutagenesis to create nitrilase enzymes having improved nitrilase activity for converting 3-hydroxynitriles (e.g., 3-hydroxybutyronitrile or 3-hydroxyvaleronitrile) to the corresponding 3-hydroxycarboxylic acids. A process using these improved mutants to produce the 3-hydroxycarboxylic acids is also provided.
Owner:PURETECH SCI LLC
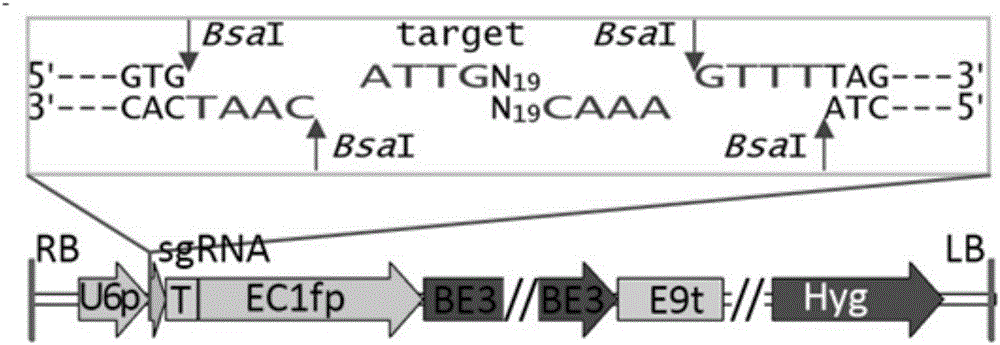
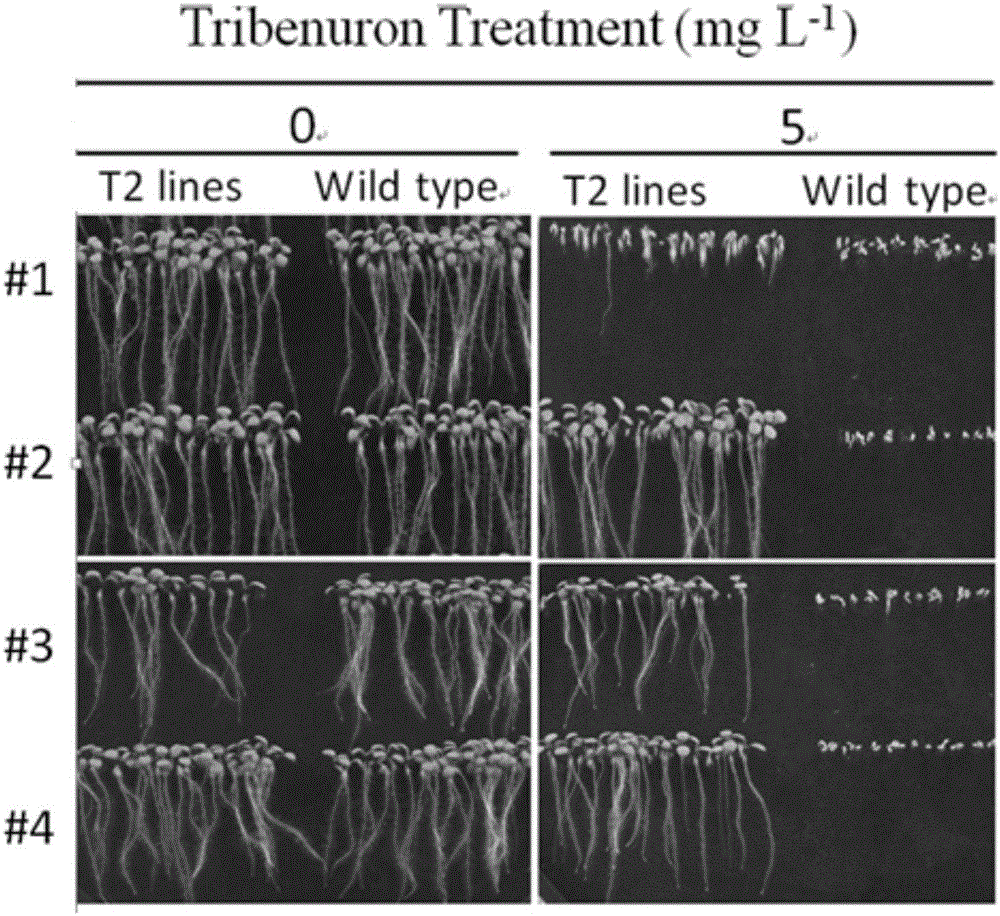
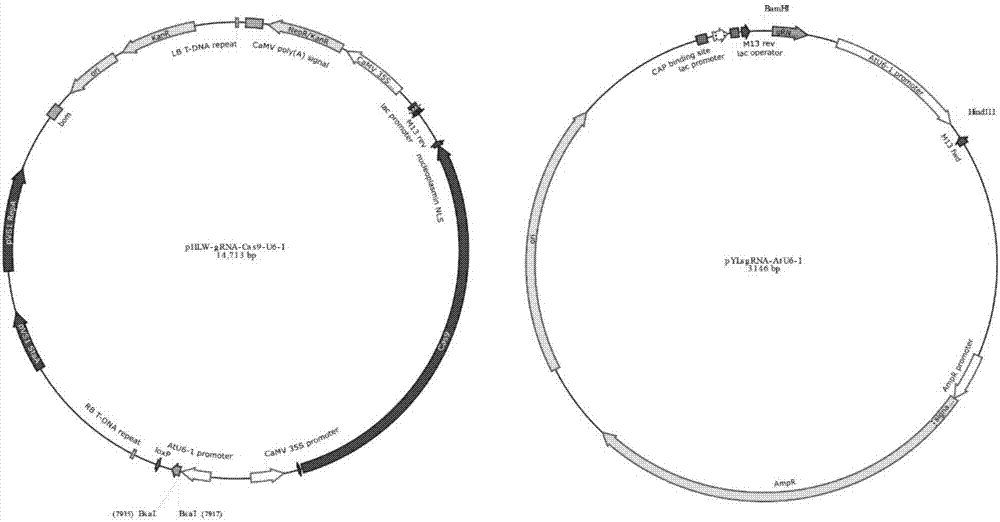
Gene site-directed mutation vector as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN106834341ANucleic acid vectorVector-based foreign material introductionCytosine deaminaseCytosine
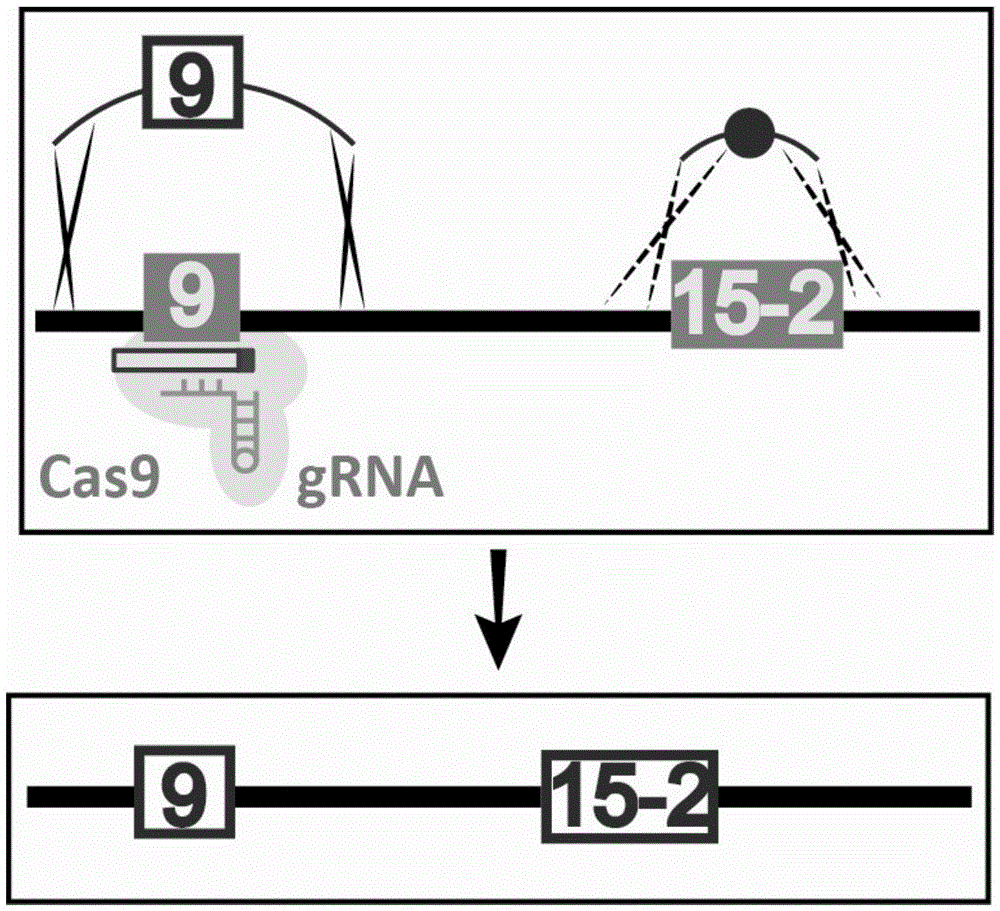
The invention belongs to the technical field of bioengineering and in particular relates to a gene site-directed mutation vector as well as a construction method and application thereof. The invention provides the gene site-directed mutation vector due to lots of optimizations, cytosine deaminase is guided to be close to cytosine through a CRISPR (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats) system, the cytosine is changed into uracil, then uracil is changed into thymine through self-repair in plant cells, and finally, site-specific mutagenesis from C to T is realized in plants so as to generate resistance to herbicides. In addition, point mutation can be produced in a non-sgRNA targeted area, and novel herbicide-resistant great agronomic traits are brought.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Compiling vector of kiwi fruit gene AcPDS based on CRISPR-Cas9 as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN107446924AEfficient site-directed mutagenesisBacteriaHydrolasesAgricultural scienceActinidia
The invention discloses a compiling vector of a kiwi fruit gene AcPDS based on CRISPR-Cas9 as well as a construction method and application thereof. The compiling vector of the kiwi fruit gene AcPDS based on CRISPR-Cas9 established can quickly and simply perform efficient site-specific mutagenesis on the kiwi fruit gene, so that the blank of a gene fixed point compiling technology in kiwi fruit is filled. Experimental results verify that by means of agrobacterium-mediated kiwi fruit genetic transformation, the compiling vector of the kiwi fruit gene AcPDS based on CRISPR-Cas9 performs site-specific mutagenesis on two target spots of the kiwi fruit gene AcPDS successfully, and meanwhile, an albefactedphenotype is induced.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Mutant-type lipases and applications thereof
The present invention provides mutant-type lipases which demonstrate superior lipolytic and esterific activities. The mutant-type lipases are characterized by an amino acid alteration at the residue immediately followed either the serine residue or the histidine residue or both residues of the Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad. The Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad is known to be the three residues, although occur far apart in the amino acid sequence of a lipase, that contribute to the hydrolytic activity in the active site of the lipase. The amino acid residue that follows the serine residue of the Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad is alanine. The amino acid residue that follows the histidine residue of the Ser-His-Asp catalytic triad is isoleucine. The wild-type lipase is preferably originated from Staphylococcus, particularly Staphylococcus epidermindis. The present invention also relates to a method for preparing the mutant-type lipases by site-directed mutagenesis using PCR and a method for utilizing the mutant-type lipase to catalyze synthesis of flavor esters to be used in food industry.
Owner:ACAD SINIC
Site-directed mutation method for genomes of saccharomyces cerevisiae
InactiveCN105624187AEfficient mutationRapid implementation of mutationsFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismRepair site
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, in particular to a site-directed mutation method for genomes of saccharomyces cerevisiae. To-be-repaired single-base mutation sites on the genomes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be repaired by the aid of CRISPR / Cas9 technologies. Effects can be realized near the to-be-repaired sites by Cas9 proteins under the guidance actions of guide RNA (ribonucleic acid) if the mutation sites are positioned in PAM sequences (NGG) or front 11bp of the PAM sequences, and the genomes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be subjected to double-strand break at cut positions, so that donor DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) can be efficiently recombined. Compared with existing results, the site-directed mutation method has the advantages that the sites of the genomes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be efficiently and quickly mutated, and screening markers do not need to be integrated for the genomes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
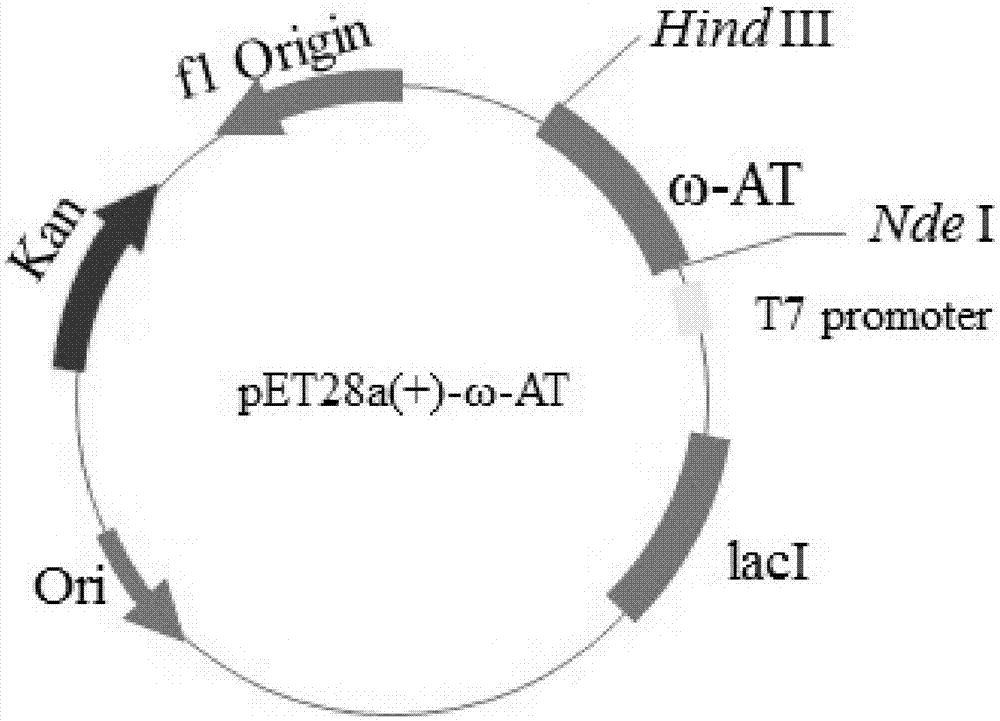
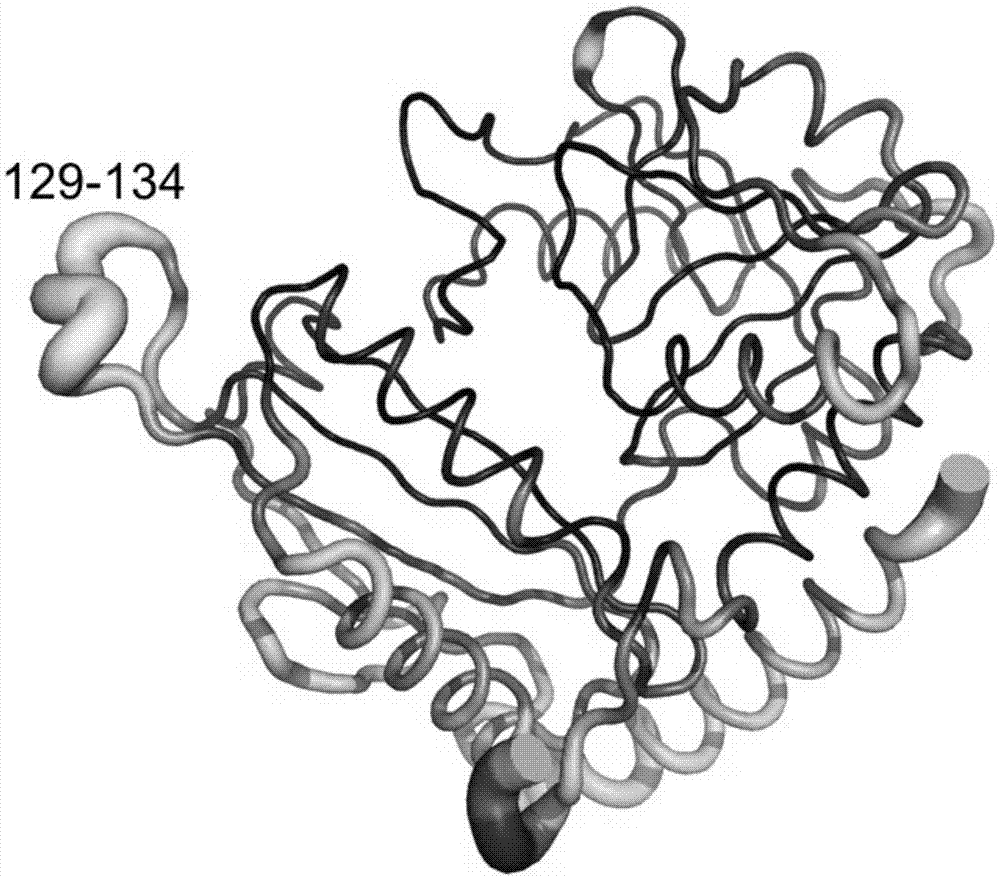
Omega-transaminase mutant and encoding gene and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN105441404AImprove thermal stabilityIncrease mutation successBacteriaTransferasesWild typeNucleotide sequencing
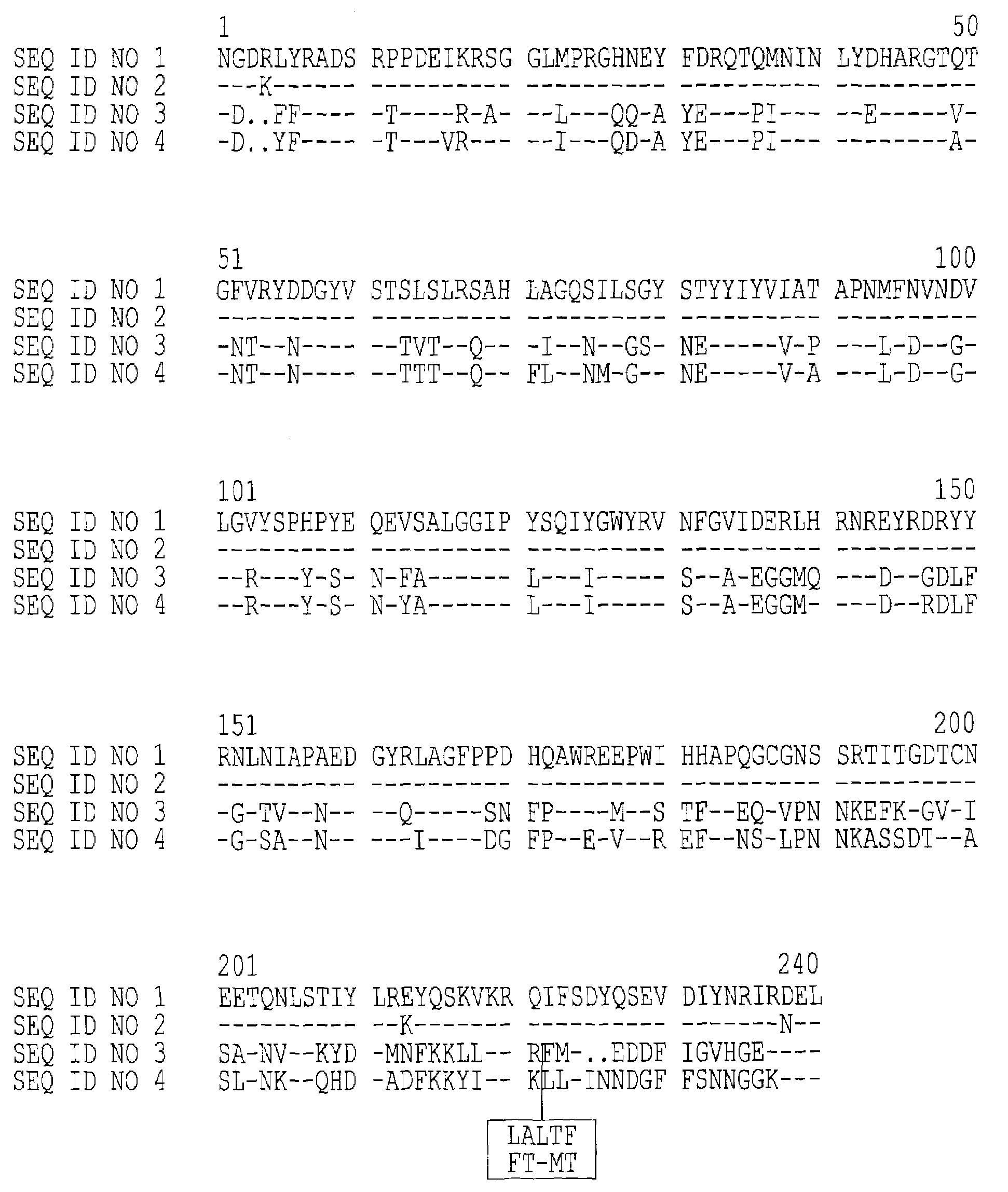
The invention discloses an omega-transaminase mutant and an encoding gene and preparation method thereof. The amino acid sequence of the omega-transaminase mutant is shown in SEQ ID NO.2 or SEQ ID NO.4 or SEQ ID NO.6 or SEQ ID NO.8 or SEQ ID NO.10. The nucleotide sequence of the omega-transaminase mutant is shown in SEQ ID NO.1 or SEQ ID NO.3 or SEQ ID NO.5 or SEQ ID NO.7 or SEQ ID NO.9. The invention further discloses an expression box, recombinant plasmid and converter containing the gene. Mutation site prediction is conducted on a wild omega-transaminase mutant through the combination of a temperature factor (B-factor) and the energy optimizing strategy, then site-specific mutagenesis is conducted, and the omega-transaminase mutant is prepared. The thermal stability of the selected mutant is higher than that of wild transaminase.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ORIENT GENE BIOTECH
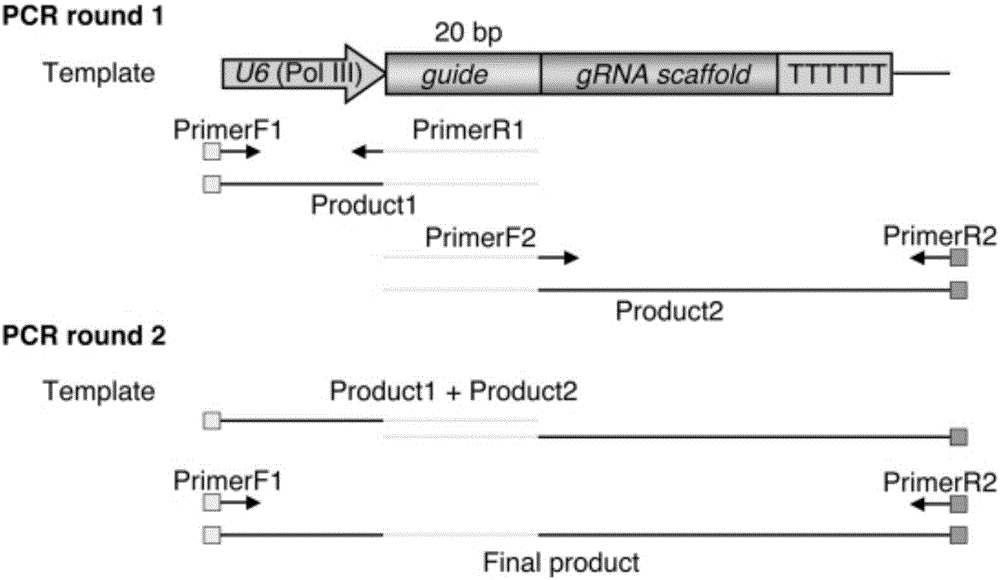
Method for site-directed mutation of rice CENH3 gene by using CRISPR-CAS9 technology
InactiveCN106755077AImplement site-directed mutagenesisShort experiment cyclePlant peptidesHorticulture methodsAgricultural scienceNucleotide
The invention provides a method for site-directed mutation of rice CENH3 gene by using a CRISPR-CAS9 technology. A CRISPR-CAS9-based sgRNA sequence is designed for the rice CENH3 gene, and a DNA fragment containing the sgRNA sequence is connected to a vector carrying the CRISPR / Cas to convert rice in order to realize the site-directed mutation of rice CENH3 gene, wherein the nucleotide sequence of the sgRNA action site is represented by SEQ ID NO:1. Rice endogenous gene CENH3 is edited through the CRISPR-CAS9 technology to obtain a CENH3 mutant, so a CENH3 mediated chromosome elimination mechanism is hopeful to be applied to the double haploid breeding process of rice.
Owner:HUAZHI RICE BIO TECH CO LTD
Safe and efficient CRISPR/Cas9 (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats/CRISPR associated protein 9) gene editing technology
InactiveCN108795902AImprove editing targetingImprove editing efficiencyHydrolasesDNA preparationA-DNASite-directed mutagenesis
The invention aims at the technical defects of off-target effects of an existing CRISPR / Cas9 (Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeats / CRISPR associated protein 9) gene editing technology to carry out site-directed mutation of an amino acid site on a site combined with a DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) sequence of Cas9 protein to obtain the Cas9 protein with low off-target efficiency,so as to realize a gene editing unction with higher targeting performance and higher efficiency. Meanwhile, the invention further provides a method for carrying out HEK293T cell gene editing by adopting a gene editing method.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHANGENE MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Cysteine variants of alpha interferon-2
The growth hormone supergene family comprises greater than 20 structurally related cytokines and growth factors. A general method is provided for creating site-specific, biologically active conjugates of these proteins. The method involves adding cysteine residues to non-essential regions of the proteins or substituting cysteine residues for non-essential amino acids in the proteins using site-directed mutagenesis and then covalently coupling a cysteine-reactive polymer or other type of cysteine-reactive moiety to the proteins via the added cysteine residue. Disclosed herein are preferred sites for adding cysteine residues or introducing cysteine substitutions into the proteins, and the proteins and protein derivatives produced thereby. Also disclosed are therapeutic methods for using the cysteine variants of the invention.
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
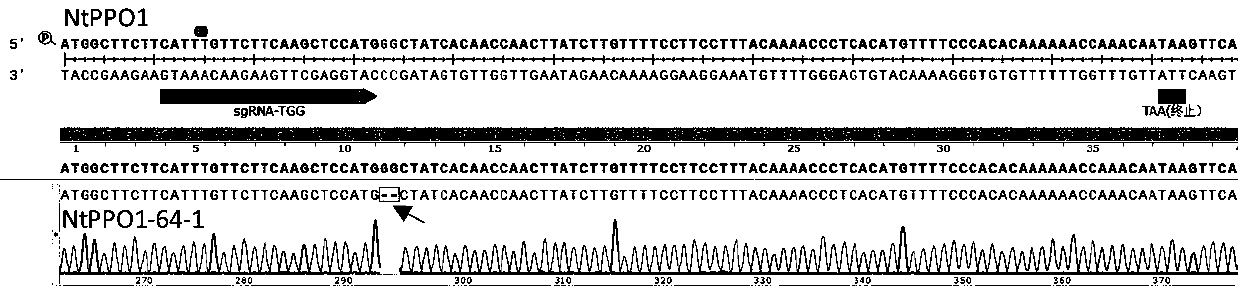
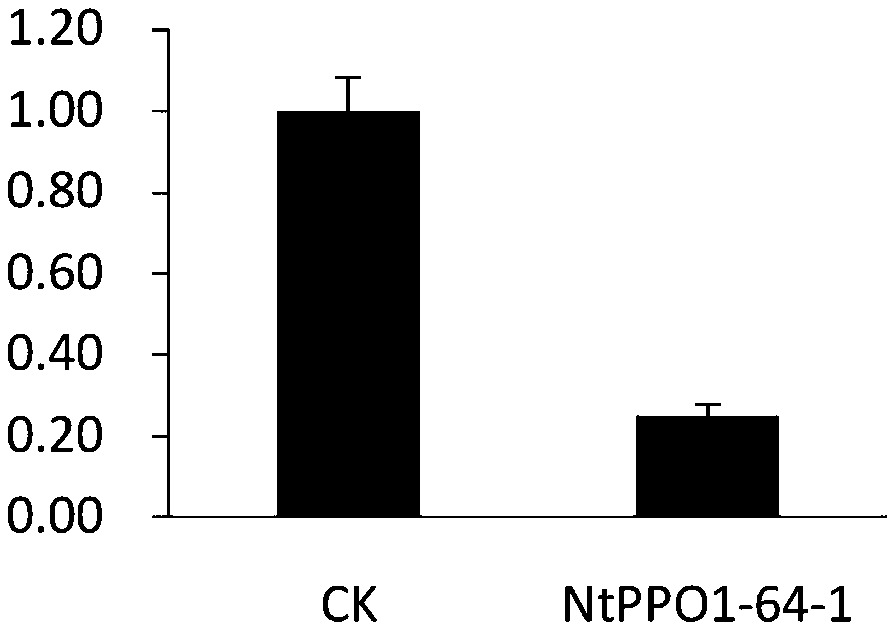
Tobacco polyphenol oxidase gene NtPPO1 and site-directed mutagenesis method and application thereof
InactiveCN107653256AReduce expressionReduce PPO enzyme activityHydrolasesOxidoreductasesNicotiana tabacumPolyphenol oxidase
The invention discloses a tobacco polyphenol oxidase gene NtPPO1 and a site-directed mutagenesis method and application thereof. The nucleotide sequence of the tobacco polyphenol oxidase gene NtPPO1 is shown in SEQ ID:No.1, the coded amino acid sequence is shown in SEQ ID:No.2. The invention further discloses a clone method of the tobacco polyphenol oxidase gene NtPPO1. The clone method comprisesthe specific steps that firstly, cDNAs of tobacco leaves are synthesized; secondly, PCR amplification of the NtPPO1 gene is conducted; thirdly, a CRISPR / Cas9 carrier of the NtPPO1 gene is constructed;fourthly, sequencing detection of the NtPPO1 gene mutation is conducted. The NtPPO1 gene has a wide application prospect in preventing tobacco browning. The tobacco polyphenol oxidase gene and the encoded protein thereof provide the gene and technology support for crops especially for anti-browning breeding of tobaccos.
Owner:YUNNAN ACAD OF TOBACCO AGRI SCI
Method for site-directed mutation of maize gene by means of CRISPR/Cas9 system
ActiveCN107022562AGood characterSite-directed mutagenesisPeptidesNucleic acid vectorDNA fragmentationA-DNA
The invention provides a method for site-directed mutation of a maize gene by means of a CRISPR / Cas9 system. An sgRNA sequence based on CRISPR / Cas9 is designed aiming at a target gene in maize, a DNA fragment for encoding the sgRNA sequence is connected to a vector carrying CRISPR / Cas9, and then maize transformation is conducted, so that site-directed mutation of a specific gene in maize is realized. Further, the vector containing CRISPR / Cas9 is transferred to an acceptor material carrying the target gene by means of a genetic transformation method, so as to obtain a site-directed mutation regeneration plant of the target gene. By the adoption of the method, site-directed mutation of a maize genome can be achieved. The method has the advantages that the experimental period is short, and operation is easy. Different target genes can be transformed in a site-directed mode by means of CRISPR / Cas9 systems with different targeting directions, a novel method is provided for improved breeding of maize, and the method is of great practical significance for maize trait improvement.
Owner:先正达集团股份有限公司
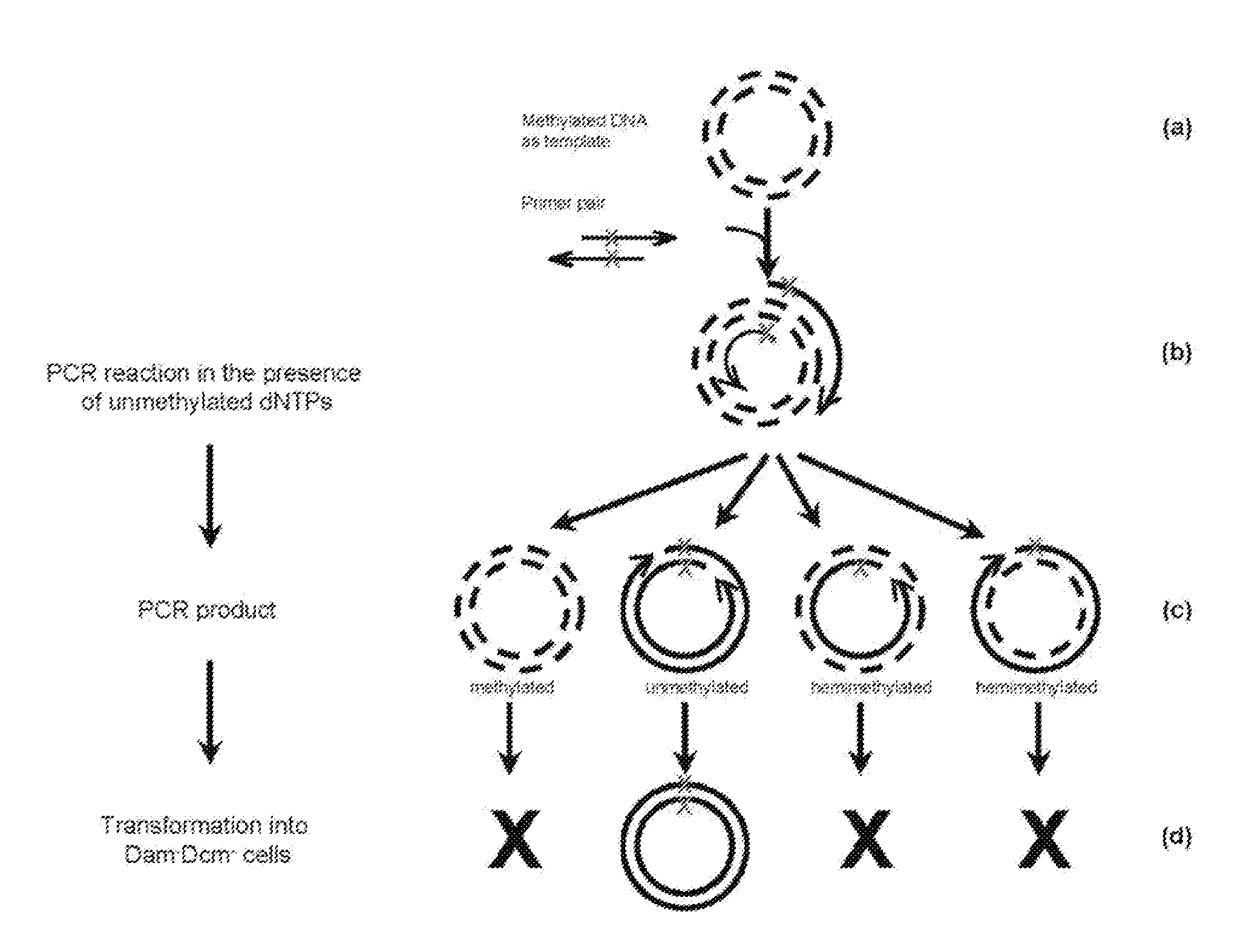
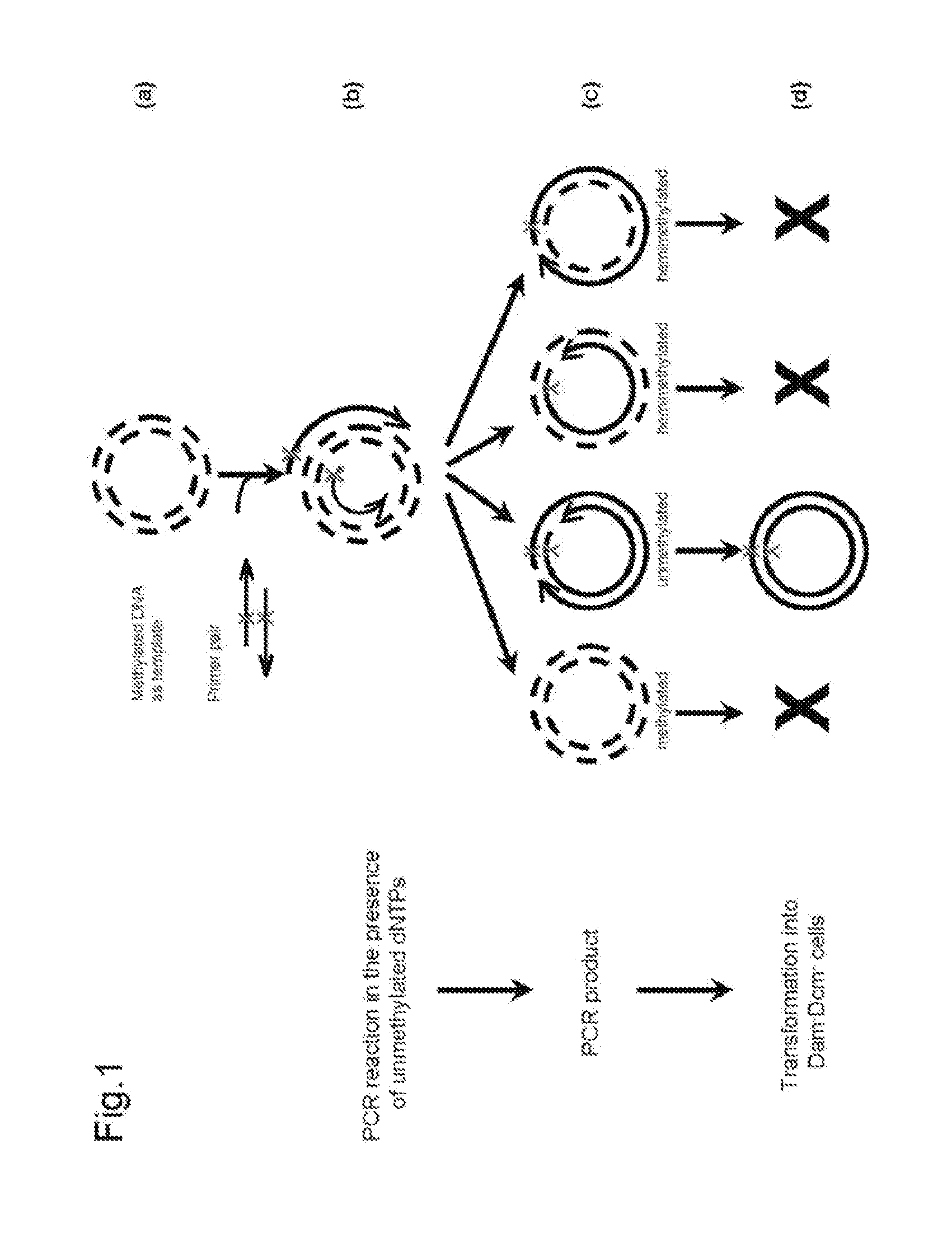
Site-directed mutagenesis in circular methylated DNA
InactiveUS20100267147A1Wide compatibilityEliminate effectiveBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliSite-directed mutagenesis
Site-specific mutation in methylated circular stranded DNA molecules is conferred by mutagenic primer pairs and methylase deficient Escherichia coli. The mutagenic primer pairs are complementary at 5′ end or 3′ end, or completely complementary to each other. Firstly, mutagenic primer pair is annealed to opposite strands of the methylated circular double-stranded parent DNA molecules. Then, polymerase chain reaction is performed by using unmethylated dNTPs to create unmethylated mutagenized double-stranded daughter DNA molecules. Finally, the reaction mixture of the methylated parent DNA molecules and unmethylated mutagenized daughter DNA molecules is transformed into a methylase deficient E. coli. The replication of methylated parent DNA is inhibited in methylase deficient host cell. In contrast, the unmethylated daughter DNA, which contains the desired mutation, are efficiently replicated in methylase deficient host cell and recovered thereafter. The invention also provides a kit for introducing site-specific mutations in accordance with the described method.
Owner:GM BIOSCI
Preparation for protein or peptide labeled by unnatural amino acid
PendingCN104099360AEfficient modification purposePurpose of avoiding degradationBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsGrowth hormonePolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to production and preparation for protein or peptide labeled by an unnatural amino acid. For example, the invention relates to human interferon alpha2b subjected to site directed mutagenesis and human interferon alpha2b subjected to site directed modification, and the interferon can be different species or different types. The invention also relates to a method for site directed mutagenesis and site directed modification of interferon. The method comprises using a gene codon expansion technology to introduce an unnatural amino acid to the interferon gene in a site directed way, and having the aid of an unnatural amino acid or a modification agent to realize site directed linkage between growth hormone, and, for example, polyethylene glycol. The invention further relates to application of interferon subjected to site directed mutagenesis or modification, such as application thereof as a stable long-acting interferon, and the like.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Production of 3-hydroxycarboxylic acid using nitrilase
This invention relates to nitrilase mutants having improved nitrilase activity for converting 3-hydroxynitriles to 3-hydroxycarboxylic acids. More specifically, the Acidovorax facilis 72W (ATCC 55746) nitrilase gene was mutated using error-prone PCR and site-directed mutagenesis to create nitrilase enzymes having improved nitrilase activity for converting 3-hydroxynitriles (e.g., 3-hydroxybutyronitrile or 3-hydroxyvaleronitrile) to the corresponding 3-hydroxycarboxylic acids. A process using these improved mutants to produce the 3-hydroxycarboxylic acids is also provided.
Owner:PURETECH SCI LLC
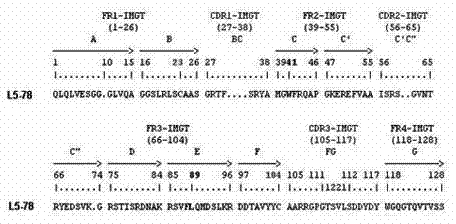
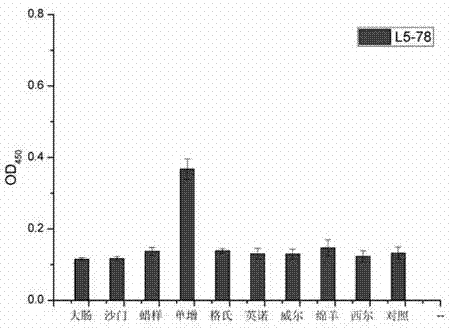
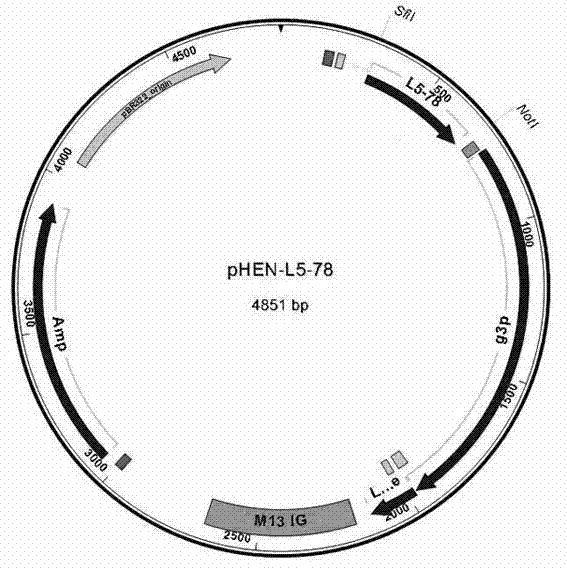
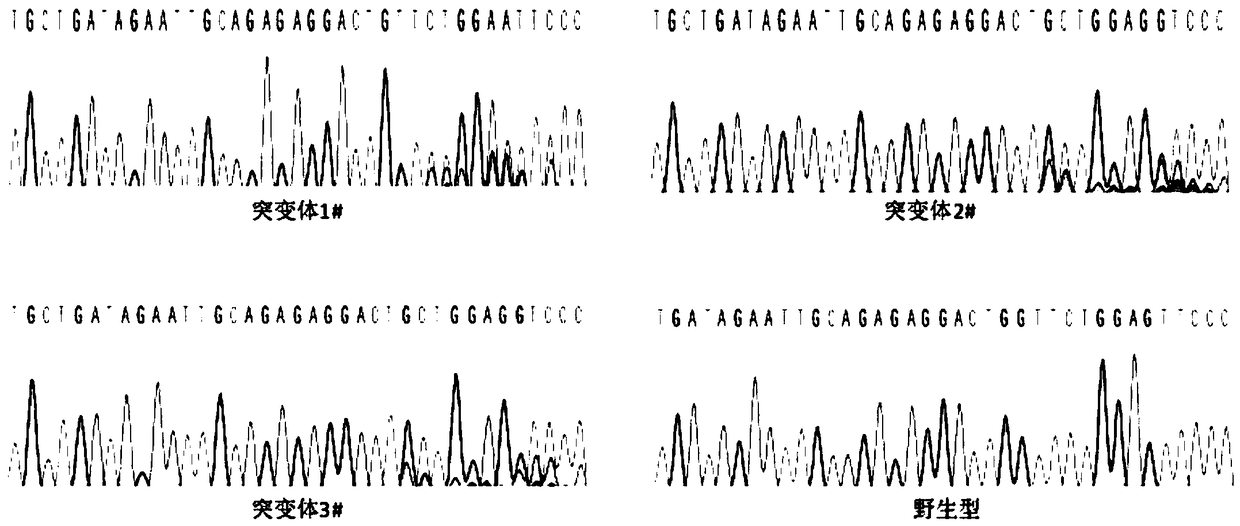
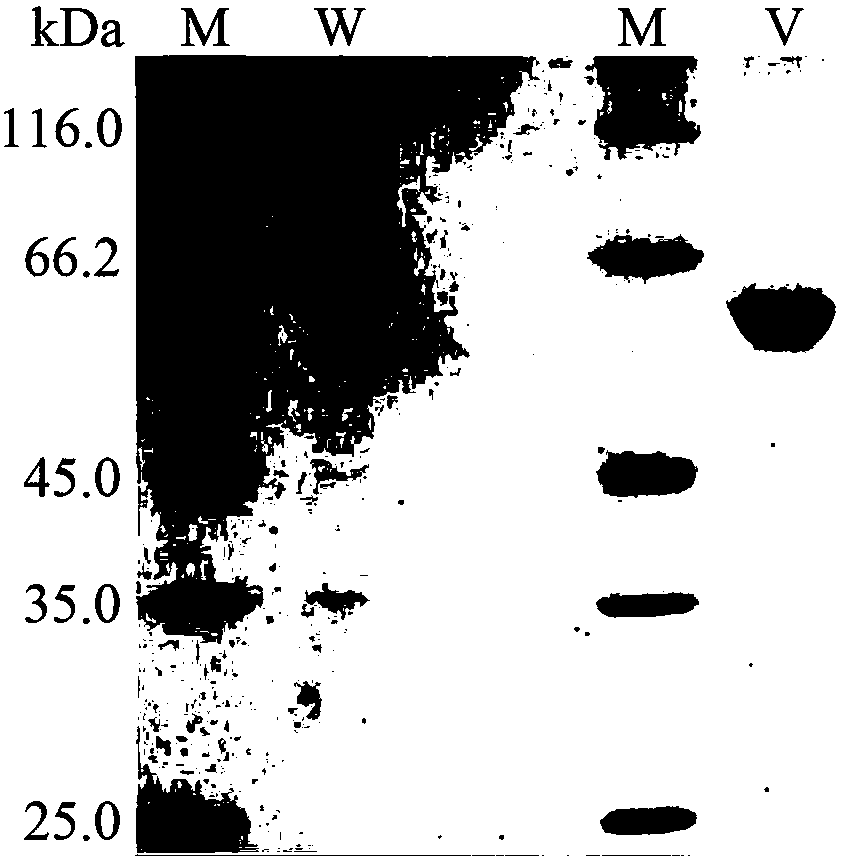
Single-domain heavy chain antibody L5-78 for Listeria monocytogenes
InactiveCN103497252AGood water solubilityImprove stabilityBacteriaImmunoglobulins against bacteriaAntigenADAMTS Proteins
The invention relates to a single-domain heavy chain antibody and polypeptide for Listeria monocytogenes. The antibody has the protein or polypeptide with the amino acid sequence disclosed as SEQ ID NO:1, and can be used in the fields of immune detection, antigen enrichment purification and the like. The amino acid sequence provided by the invention can be used as a precursor, can be modified by using a random or site-directed mutagenesis technique to obtain a mutant with better properties (affinity, specificity, stability and the like), and is used for developing proteins or polypeptides which are further used in medicine, industry and agriculture.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Construction method and application of eggplant CRISPR/Cas9 gene knock-out vector
InactiveCN108728486AEfficiently obtainedEasy accessHorticulture methodsPlant tissue cultureSite-directed mutagenesisMutation
The invention relates to a construction method and application of an eggplant CRISPR / Cas9 gene knock-out vector, and belongs to the field of a biological technology. The method comprises the followingsteps: designing a target site gRNA by taking genome DNA sequence of an eggplant WRKY26 gene as reference; constructing an expression box of the target site gRNA and Cas9 protein; inserting the expression box of the gRNA and the Cas9 protein into a binary expression vector; transferring recombinant plasmid into an agrobacterium EHA105 strain, mediating by EHA105 and transferring eggplant seed leaves to obtain a genetic transformation plant, and performing PCR and sequencing verification to determine a mutation strain. An eggplant SmWRKY26 gene serves as an example, and the eggplant gene is subjected to geodesic mutation rapidly, simply and efficiently.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Derivatives of growth hormone and related proteins, and methods of use thereof
Owner:BOLDER BIOTECH
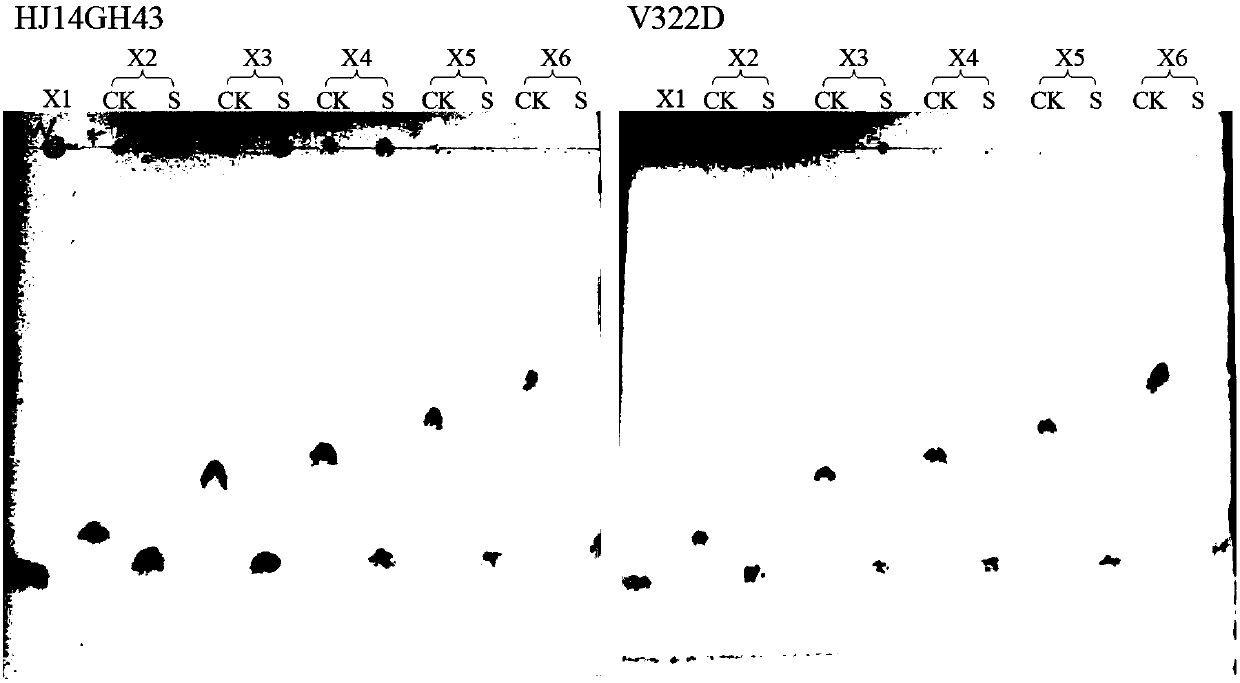
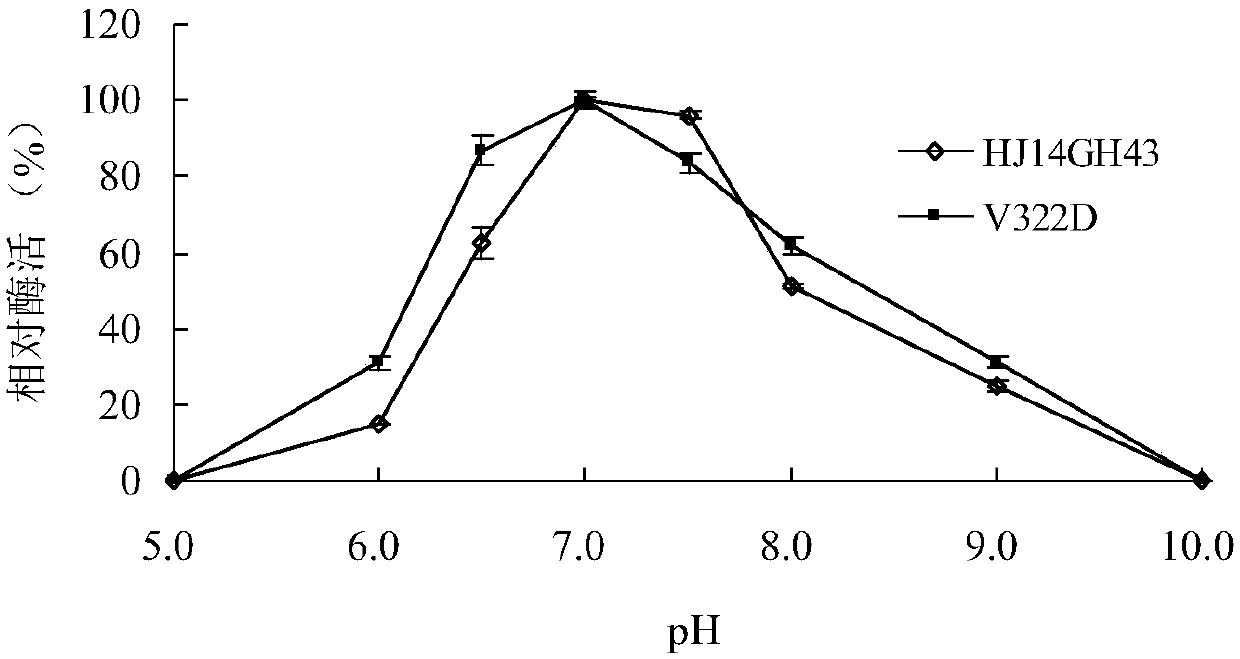
Low temperature xylosidase HJ14GH43 and salt-tolerant mutant thereof
The invention discloses low temperature xylosidase HJ14GH43 and a salt-tolerant mutant thereof. The amino acid sequence of the xylosidase is as shown in SEQ ID No.1, and the nucleotide sequence of a xylosidase gene hJ14GH43 for coding xylosidase HJ14GH43 is as shown in SEQ ID No.2; the amino acid sequence of the salt-tolerant mutant is as shown in SEQ ID No.3. The optimum pH of xylosidase HJ14GH43 is 7.0, and the optimum temperature is 25 DEG C. According to the low temperature xylosidase HJ14GH43 and the salt-tolerant mutant thereof, site-directed mutation is conducted on the basis of xylosidase HJ14GH43, valine at the 322 locus is mutated to be aspartic acid, the mutant V322D is obtained, and the activity and stability of the mutant V322D in NaCl are both improved. The HJ14GH43 and the salt-tolerant mutant thereof can be applied to food industries and aquatic feed.
Owner:YUNNAN NORMAL UNIV
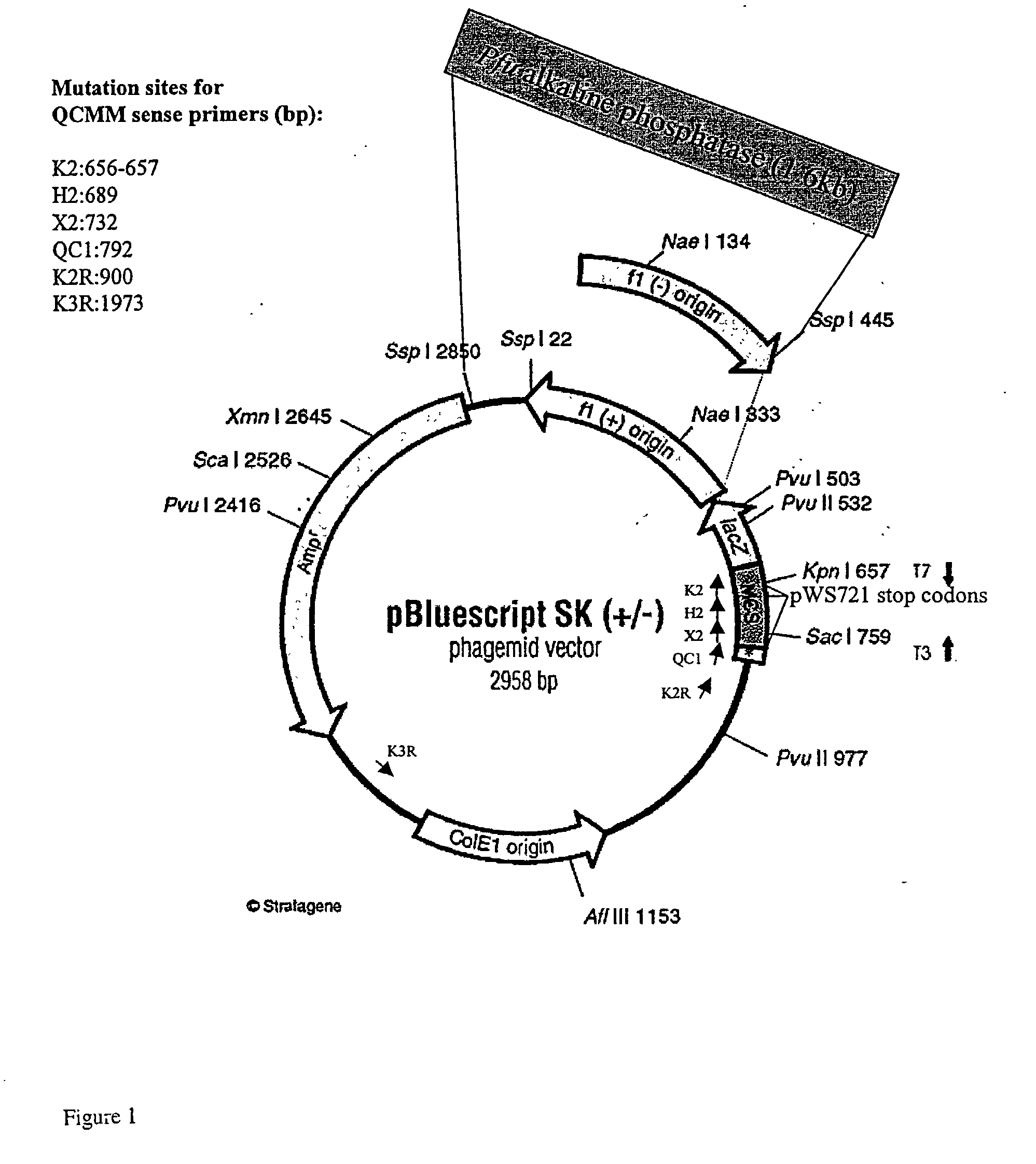
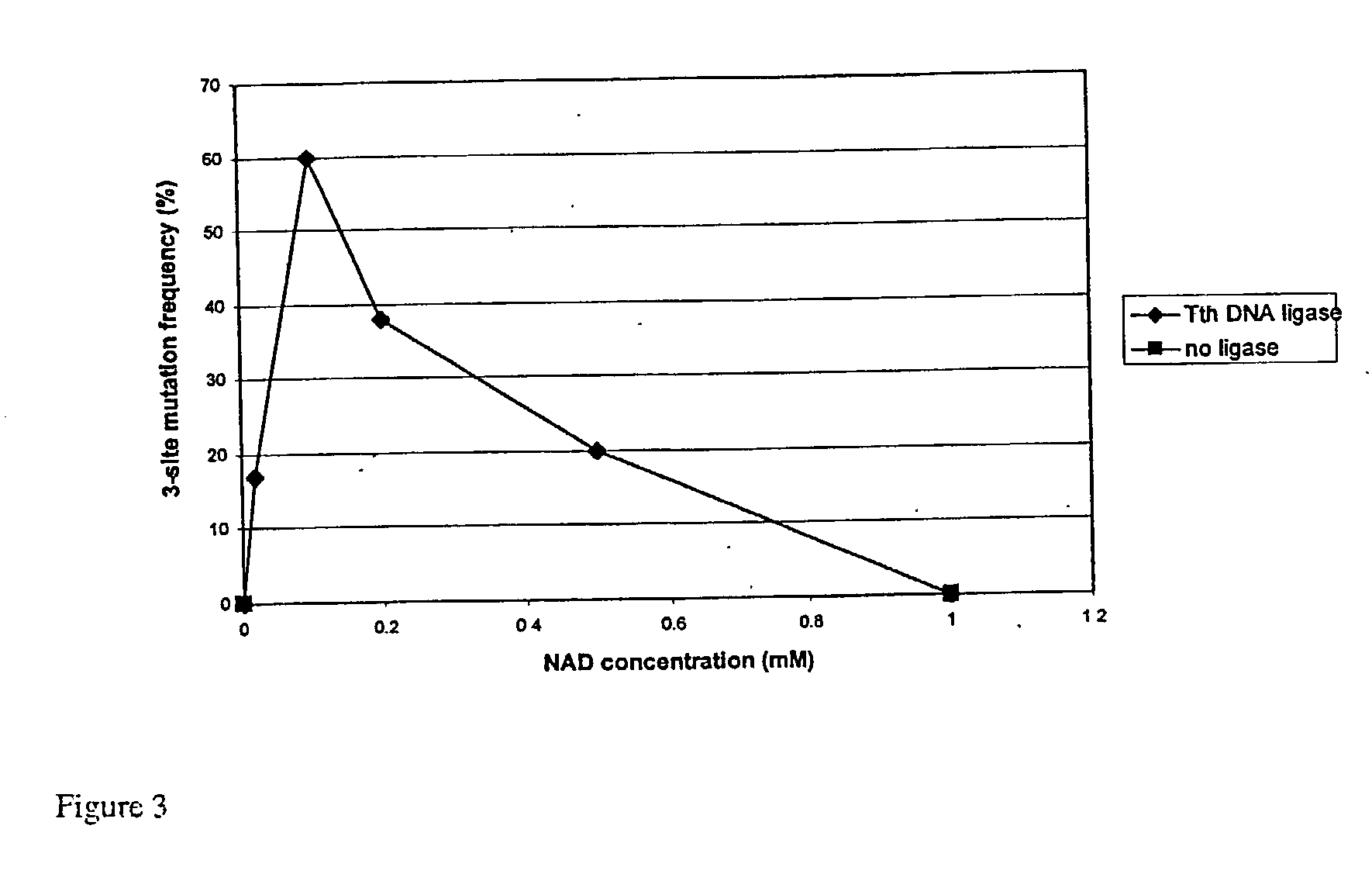
Multi-site mutagenesis
ActiveUS20060051748A1Optimized cycling conditionSimple methodSugar derivativesHydrolasesMulti siteMutation frequency
The present invention provides compositions and improved methods for multi-site directed mutagenesis and DNA shuffling. The present compositions and methods provide increased mutation frequency and increased number of transformants which allow one to sequence only a few clones in order to identify the correct mutants and to obtain the desired mutant by screening large number of transformants in a short time. Moreover, the inclusion of FEN-1, PEF and optimized buffer and cycling conditions provided in the present invention should also facilitate random mutagenized library construction and the mutagenesis of large or difficult templates.
Owner:AGILENT TECH INC
Site-specific mutagenesis high temperature resistant phytase gene TP and expression vector and application thereof
ActiveCN102943083AImprove stabilityHigh expressionHydrolasesAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyPichia pastoris
The invention provides site-specific mutagenesis high temperature resistant phytase gene TP and an expression vector and application thereof. Amino acid in a specific area in a phytase amino acid sequence is mutated into praline and arginine so as to enable the phytase to have a special stable protein structure. Simultaneously, a gene sequence is optimized to synthesize a phytase gene according to pichia pastoris codon preference and GC content, recombinant plasmids are built and transferred to pichia pastoris, and positive converters are obtained through screening to conduct induction expression to obtain the high temperature resistant phytase. Experiments prove that the phytase obtained through expression of the pichia pastoris can resist high temperature plasmids with the temperature higher than 85 DEG C, and survival rate reaches 85%. Popularization and application of the high temperature resistant phytase have substantial economical benefit and social benefit on development of feed animal husbandry of our country, and simultaneously great ecological benefit can be obtained.
Owner:TIANJIN CHIATAI FEED TECH
Modified barley α-glucosidase
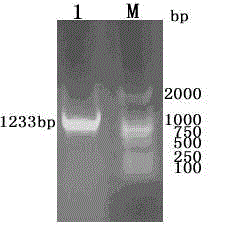
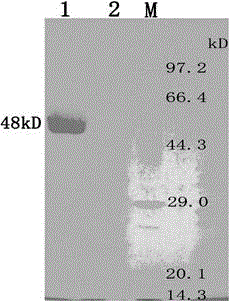
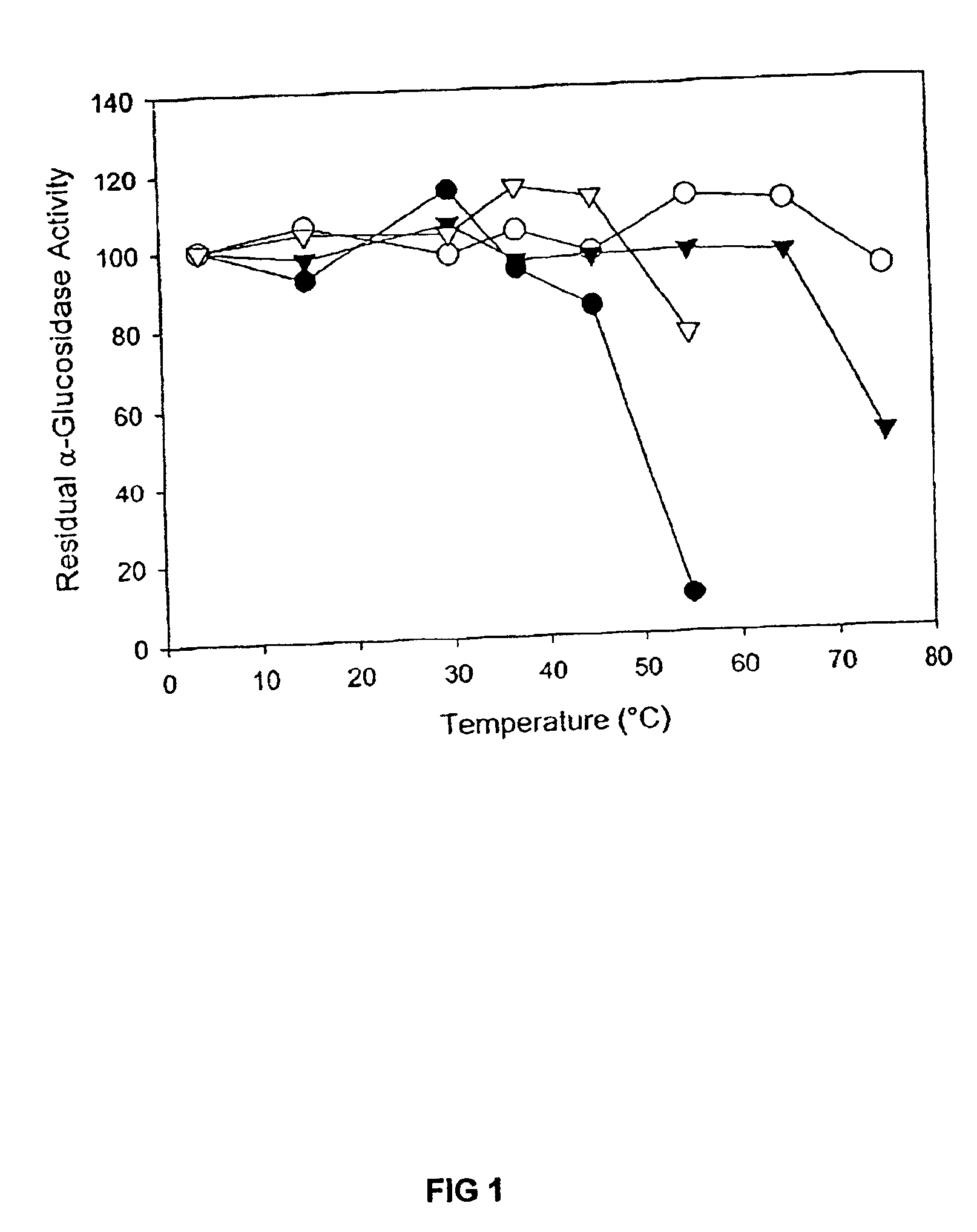
Barley α-glucosidase is an important enzyme in the conversion of barley starch to fermentable sugars during the industrial production of ethanol, as in brewing and fuel ethanol production. The enzyme is, however, relatively thermolabile, a disadvantage for an enzyme useful in industrial processes which are preferably conducted at elevated temperatures. Site directed mutagenesis has been conducted to make mutant forms of barley α-glucosidase which have improved thermostability. The sites for this site-directed mutagenesis were selected by sequence comparisons with the sequences of other α-glucosidase proteins which are more thermostable. The recombinant mutant enzymes thus produced have been demonstrated to improve the thermostability of the enzyme.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
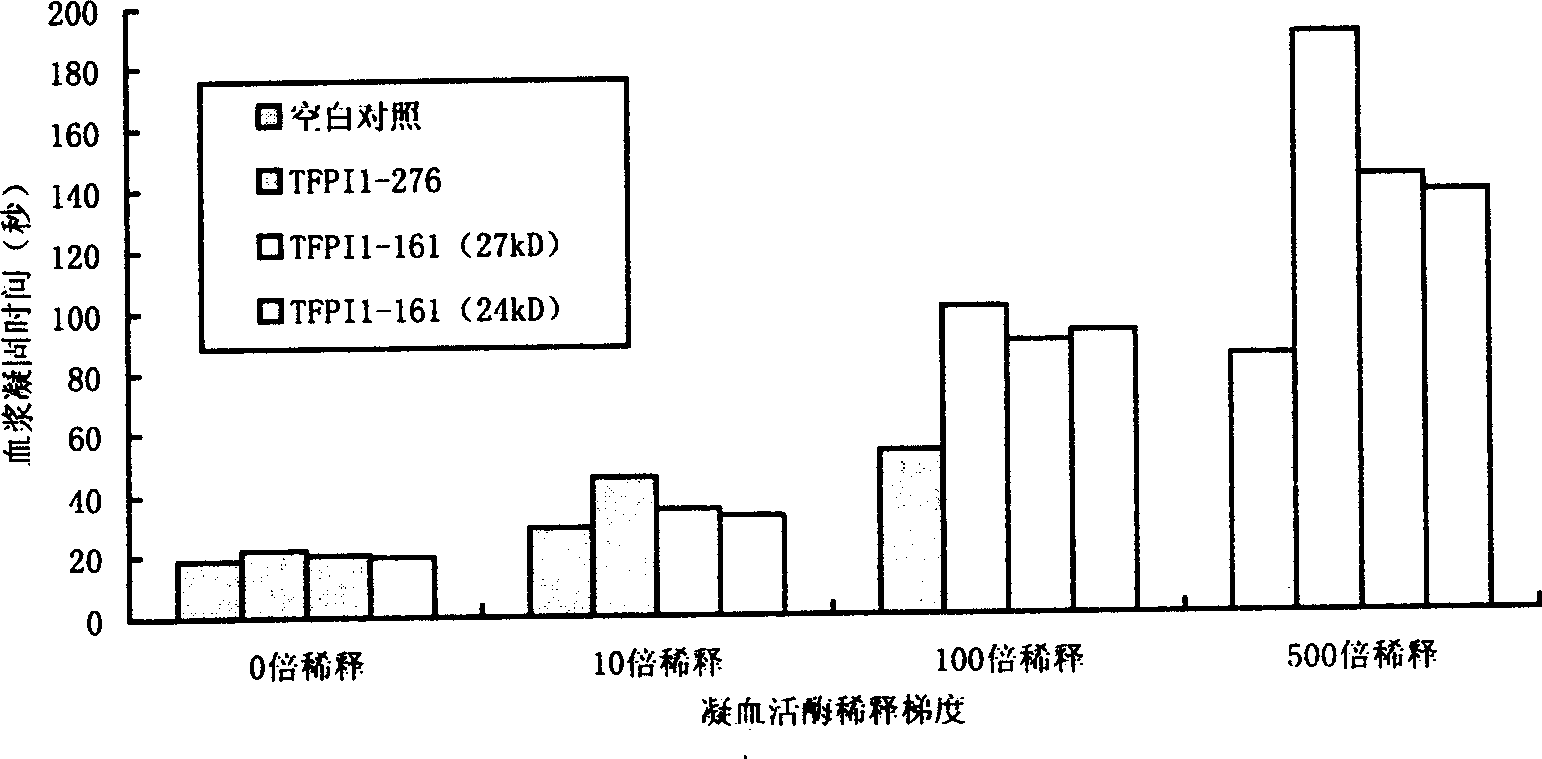
Long-acting reconbinant tissue factor channel inhibitor and preparing method thereof
InactiveCN1528894AExtended half-lifeHighly effective anticoagulantFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyInclusion bodies
The invention belongs to biology technology field, which concretely refers to controlled release tissue factor path inhibitor (LTFPI) and the manufacturing method, and the application. The invention analyzes and experiments the biology information science and structure molecular biology science of tissue factor path inhibitor (TFPI) and its acceptor low density lipoprotein acceptor correspondent protein (LRP), it ascertains the part where the TFPI carboxy end combines with LRP and is eliminated. It designs TFPI carboxy end mutant, which is recombined with primary nucleus or eukarya expressing carrier after constructing LTFPI gene through PCR location, it converts bacillus coli or bici yeast, sifts the high expression project fungus. The primary project fungus are yeasted and expanded, crushed, then they are centrifugated and collects the inclusion body, purifies the LTFPI through molecular sift and ion interchanging two-step method; the eukarya project fungus are carried on with two-step purifying directly. The half-life are prolonged, it has good pour-depressant function.
Owner:海菲尔(辽宁)生物科技有限公司
Mutation penicillin G acylase, recombinant expression plasmid and transformation engineering strains thereof
ActiveCN101177688AImprove synthesis abilityMaximum conversion rate increaseBacteriaHydrolasesHydrolysatePolymerase L
The invention relates to a gene, mutant plasmid and engineering bacteria which have improved synthesis performance to penicillin G acylase and are obtained by a gene site-directed mutagenesis method, and mutant enzyme can also be obtained with improved synthesis performance to penicillin G acylase by fermenting and purifying the engineering bacteria. Two enzymes Kpn I and Pst I are firstly used for cutting pUC18 by the invention, then T4 polymerase is adopted to make the ends blunt, and pZ01 is obtained through self-linkage; the enzyme of EcoR I is used for cutting pZ01, and then connected with pEES102 that is also cut by the enzyme of EcoR I, thereby obtaining the recombinant plasmid pY020; the pY020 is adopted as a template plasmid, and TaKaRa MuTanBEST Kit is utilized for conducting the site-directed mutagenesis to B.megaterium PGA, thereby obtaining the mutant plasmid with improved synthesis performance to the penicillin G acylase. The mutant plasmid is transformed to bacillus subtilis to obtain the required engineering bacteria. The engineering bacteria are amplified and fermented, and the mutant enzyme with improved maximum conversion rate of 7-ADCA and the ratio of synthetic product / hydrolysate can be obtained after the engineering bacteria are purified.
Owner:SHANXI WEIQIDA PHARMA IND
Method of developing corn dwarfing material via gene editing
PendingCN110128518AImportant breeding valuePlant peptidesFermentationGenome editingDNA fragmentation
The invention provides a method of developing a corn dwarfing material via gene editing. The method comprises designing, for target gene ZmGA20ox3 / ZmGA20ox5 of corn, a sgRNA based on CRISPR / Cas9, connecting a fragment having sgRNA-coding DNA to a Cas-carrying carrier, and converting the corn with the constructed carrier to achieve site-directed mutagenesis of the gene ZmGA20ox3 / ZmGA20ox5 so as toobtain a transgenic corn plant with corresponding gene function deficiency. The biological functionality of the corn gene ZmGA20ox3 / ZmGA20ox5 is disclosed herein for the first time; the corn gene ZmGA20ox3 / ZmGA20ox5 is edited through CRISPR / Cas9 technology; a mutant material with no transgenic gene insert fragment is acquired through further screening; the corn dwarfing material has important breeding value.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
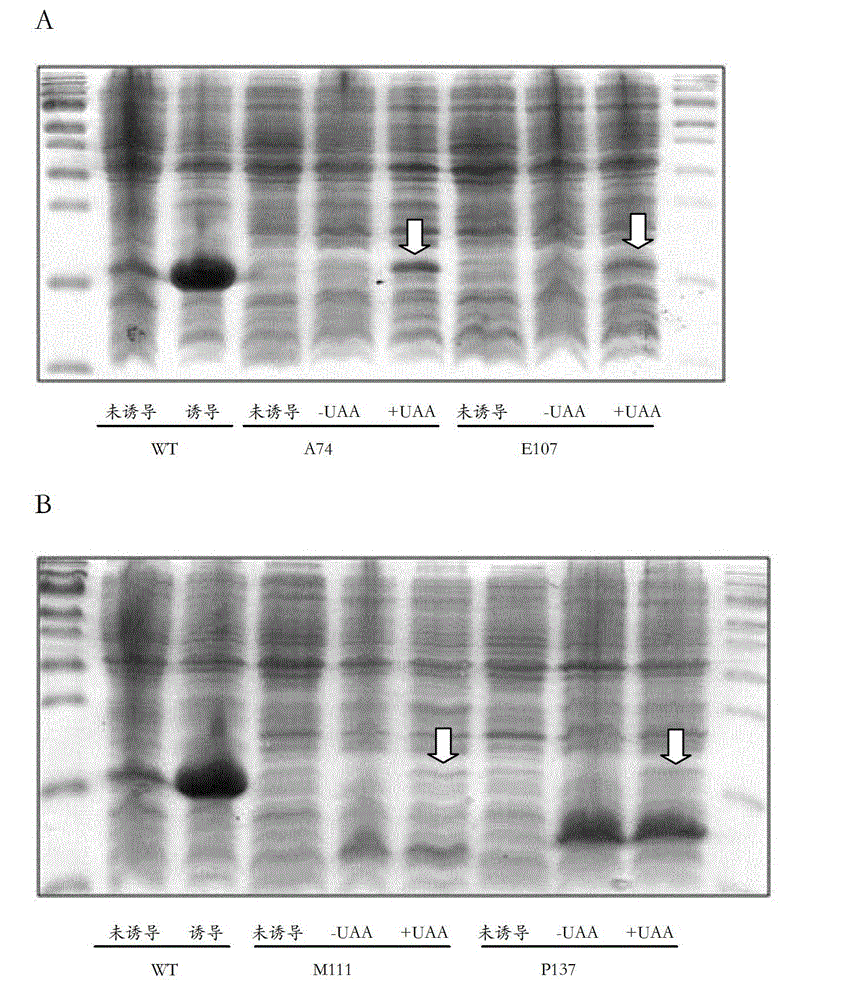
Viromembrane protein with site-specific mutagenesis and site-specific decoration, preparation method and applications of viromembrane protein
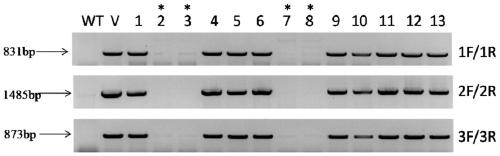
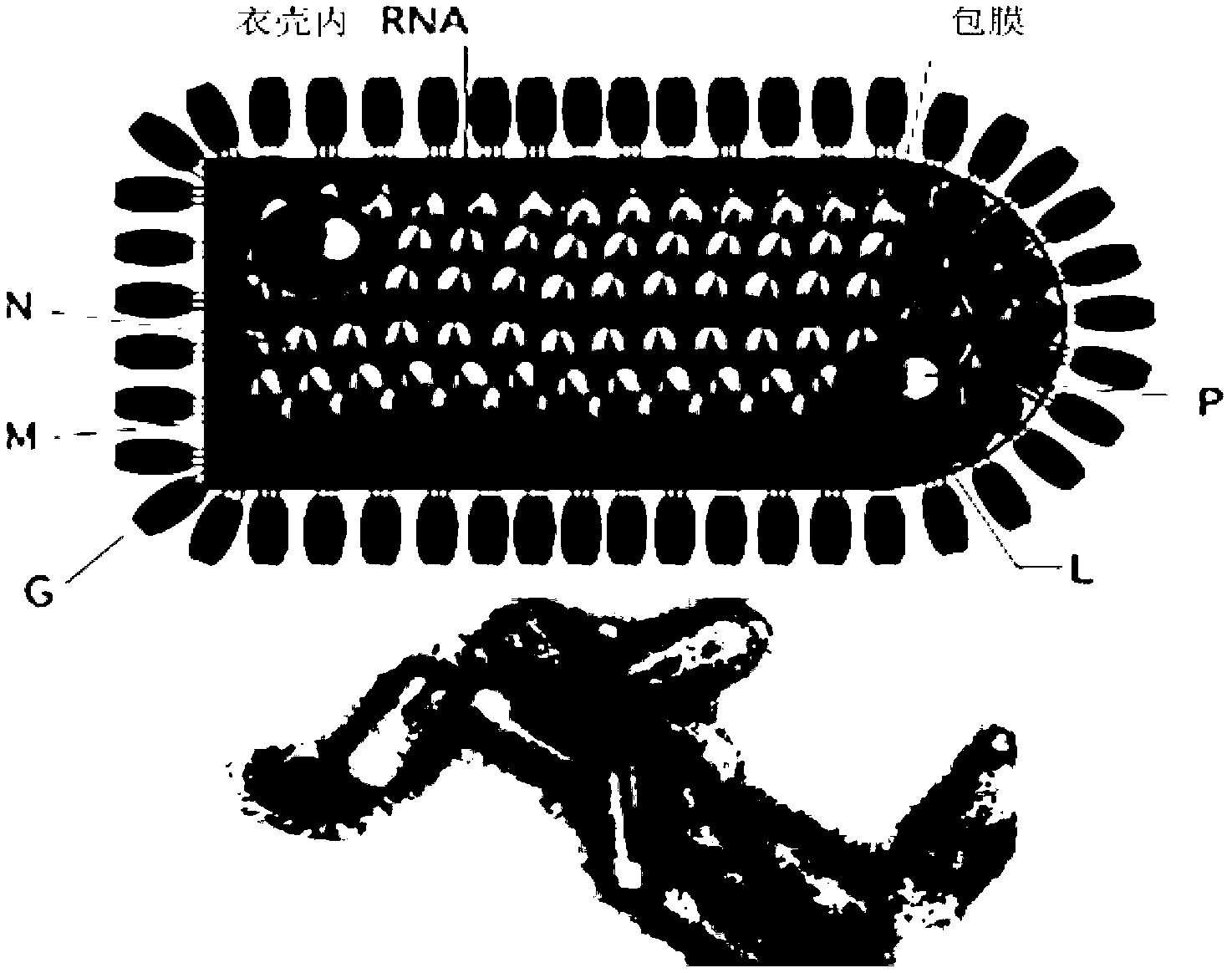
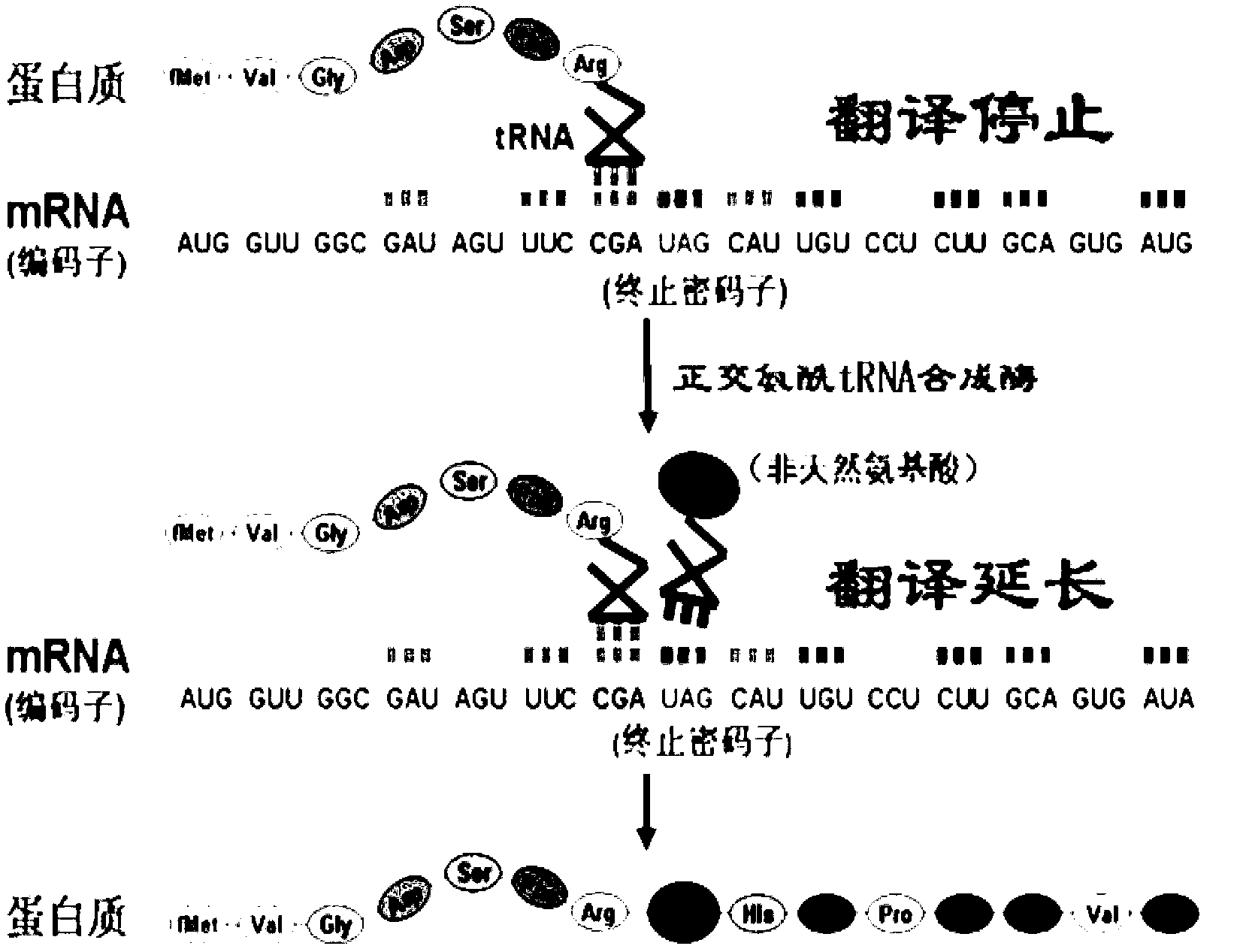
ActiveCN102838663AAvoid dissociationSsRNA viruses negative-senseBacteriaViral Membrane ProteinsUltraviolet lights
The invention discloses viromembrane protein with site-specific mutagenesis and site-specific decoration, a preparation method and applications of the viromembrane protein. Amber codon TAG is introduced to the specific site of envelope protein G (VSV G) gene of vesicular stomatitis virus, unnatural amino acid DiZPK with photo-crosslinking property is introduced to the specific site of VSV G by utilizing the orthorhombic aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase-tRNA through site-specific mutagenesis. In the interaction process of virus and host cells, the DiZPK photo-crosslinking reaction is triggered by 365nm ultraviolet light, the covalent bond is formed between the VSV G and interacting protein, the interaction dissociation can be avoided, and the powerful measure is provided for the research of the interaction of the virus and protein of the host cells.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com