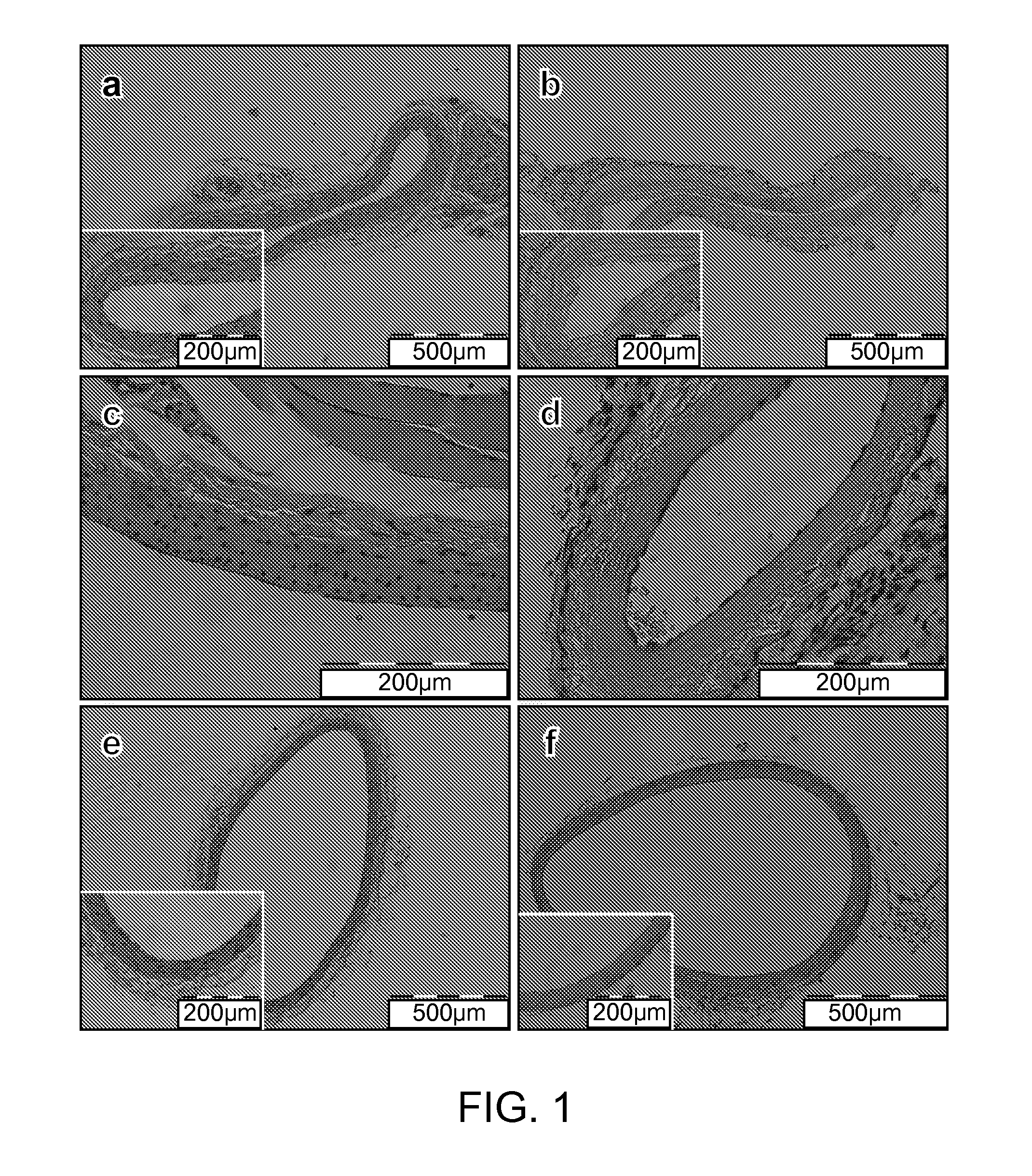
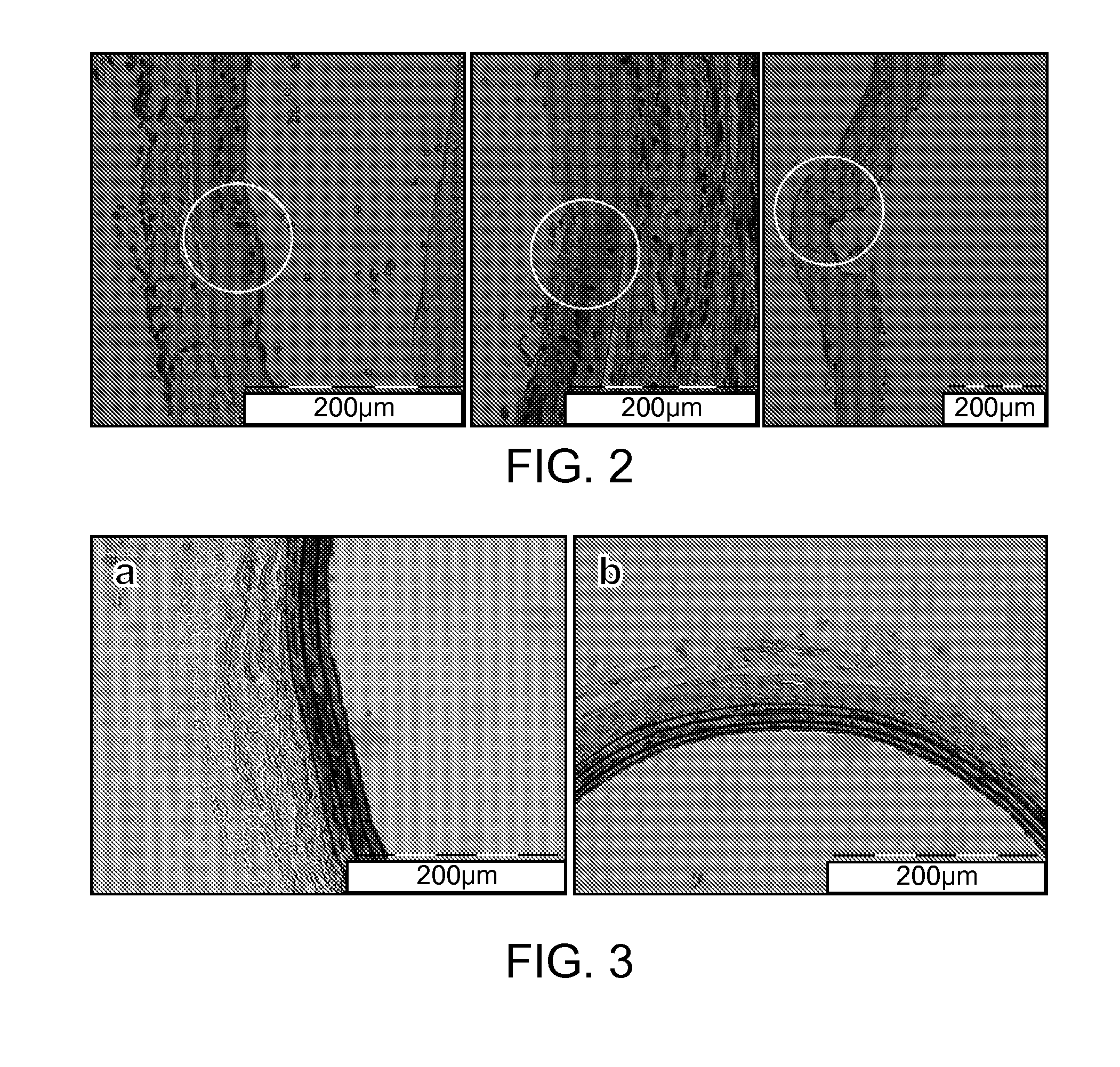
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
165 results about "Repair site" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
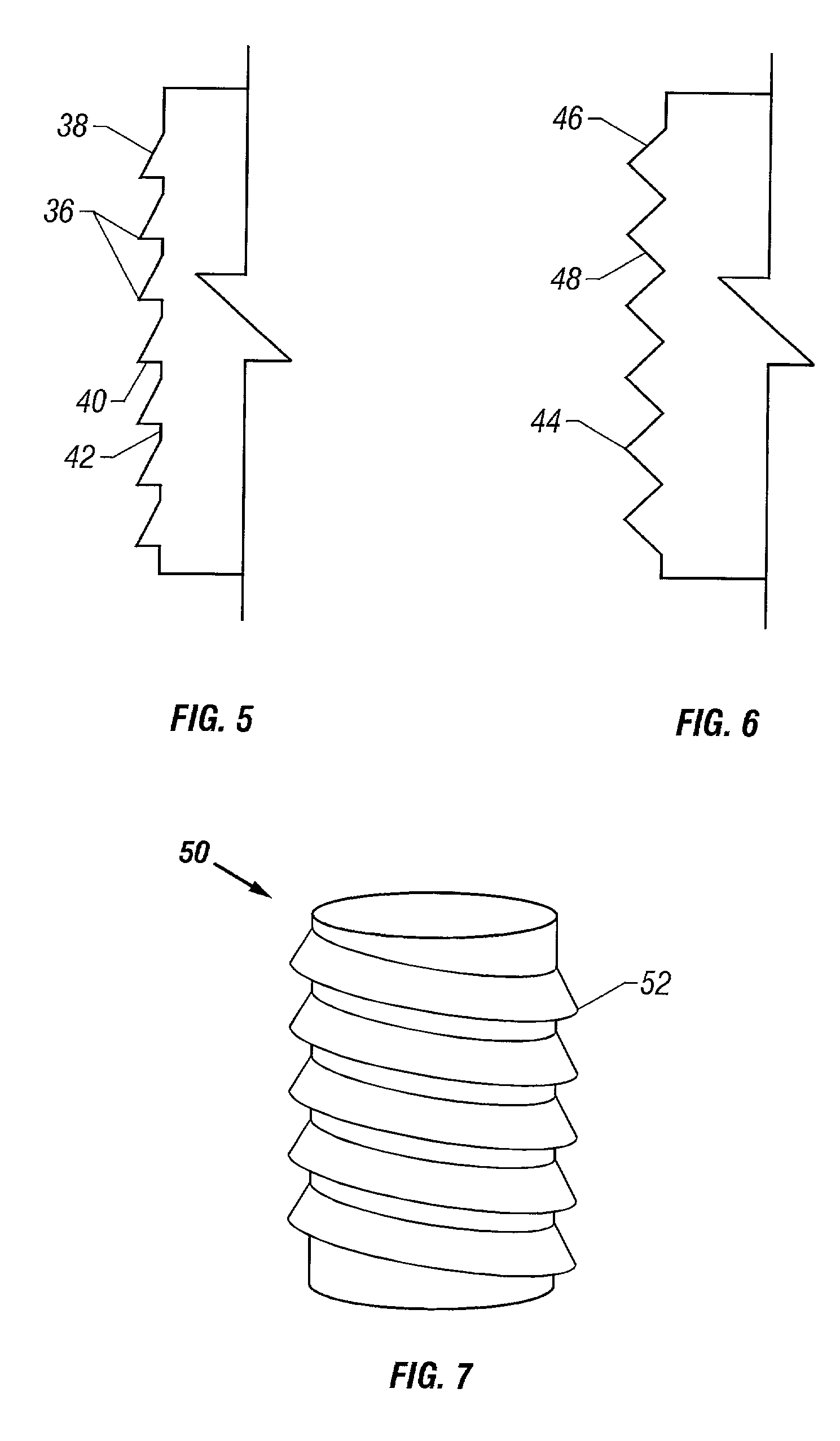
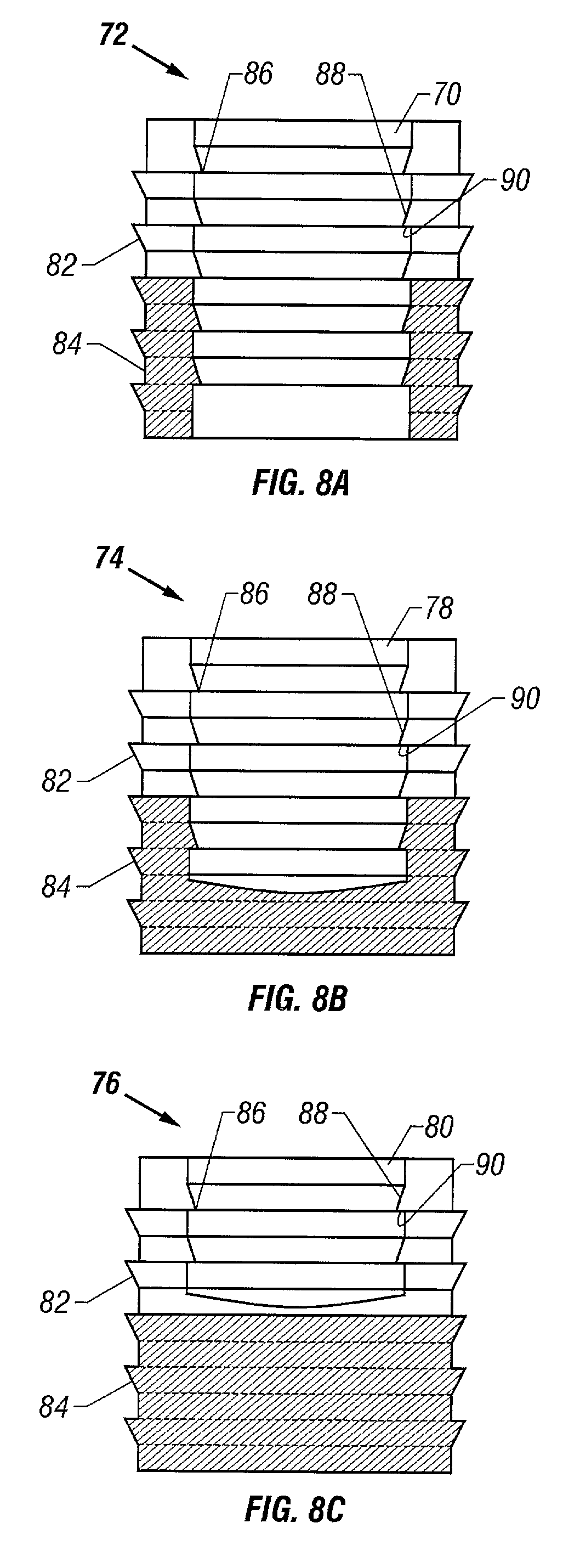
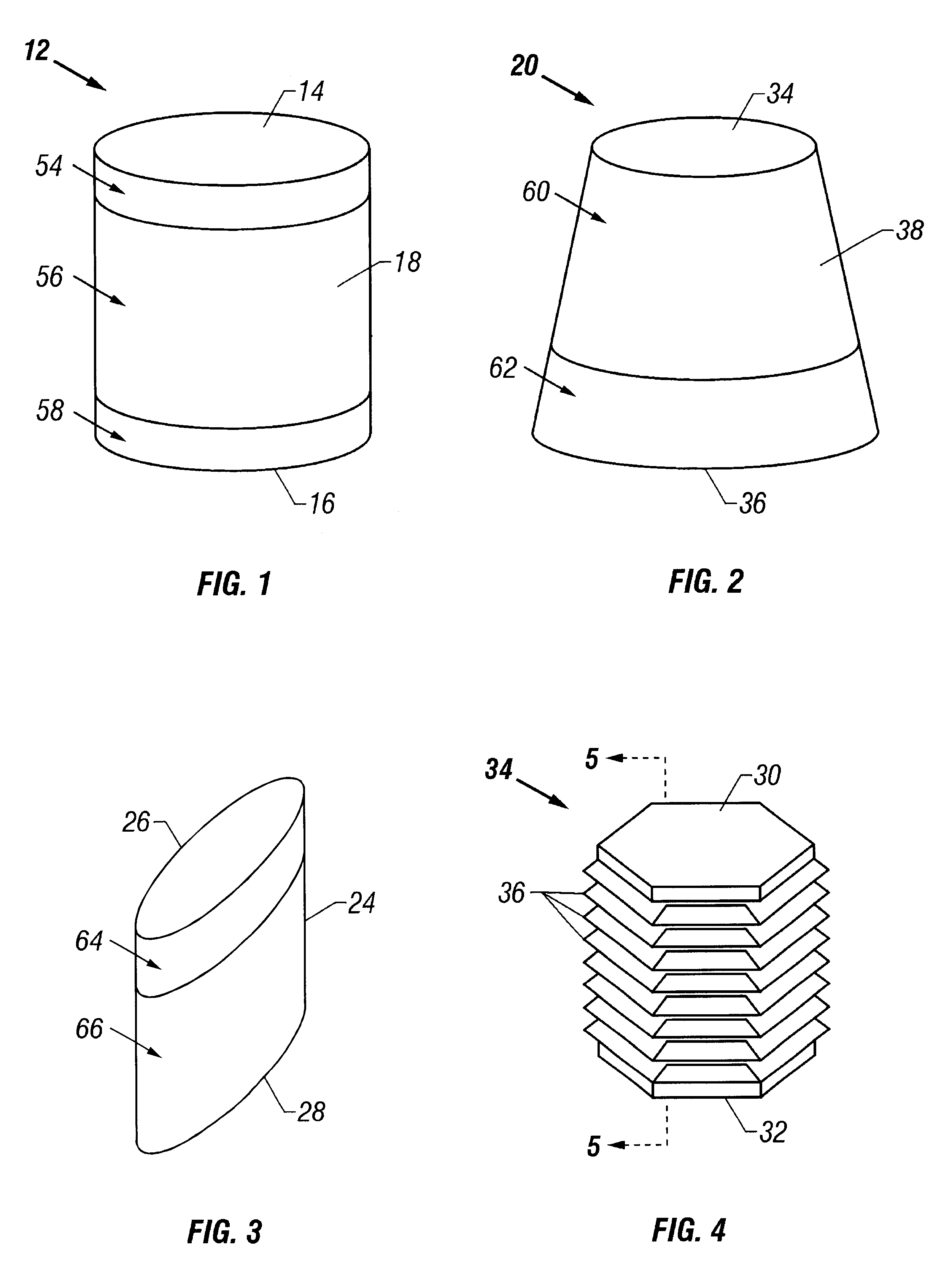
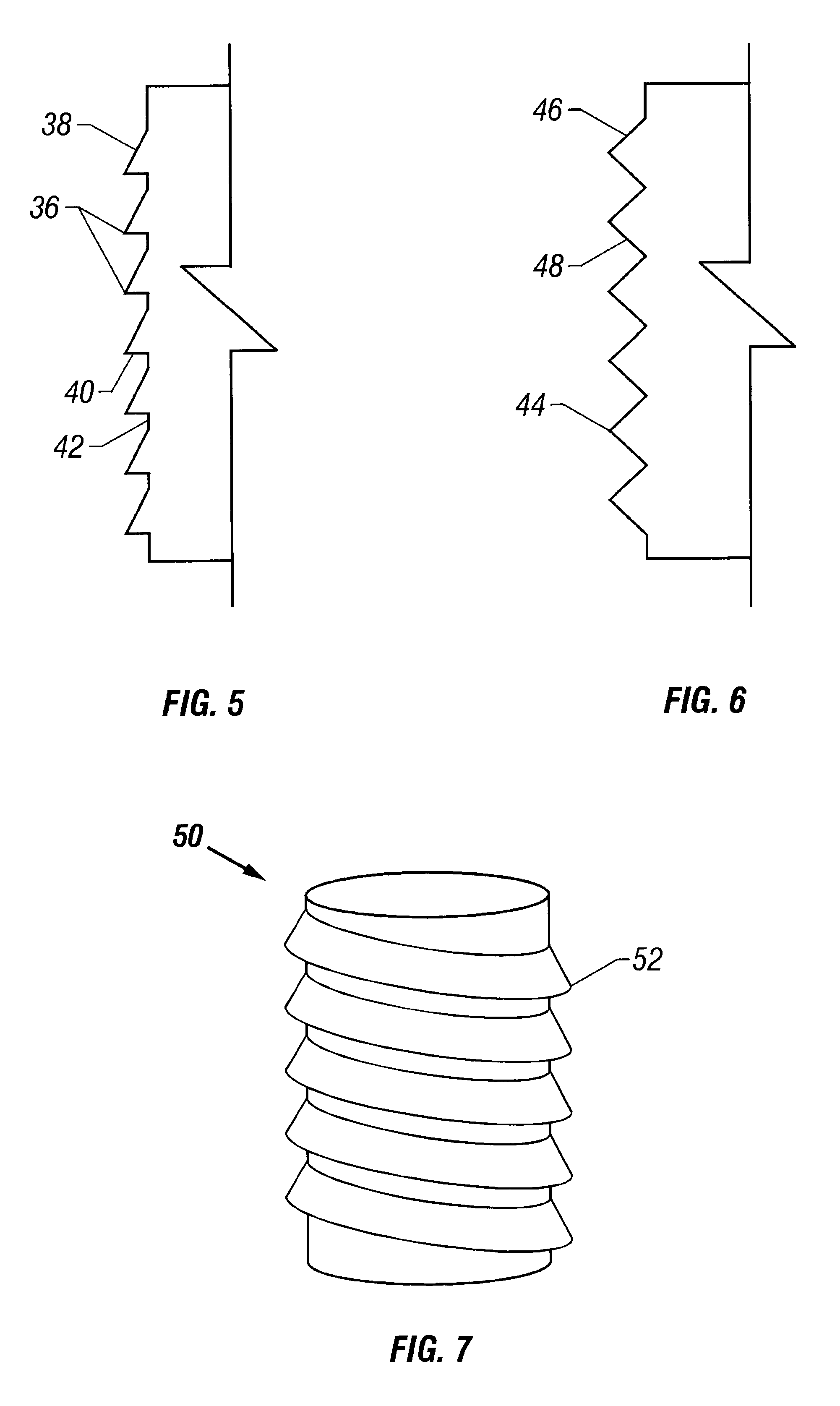
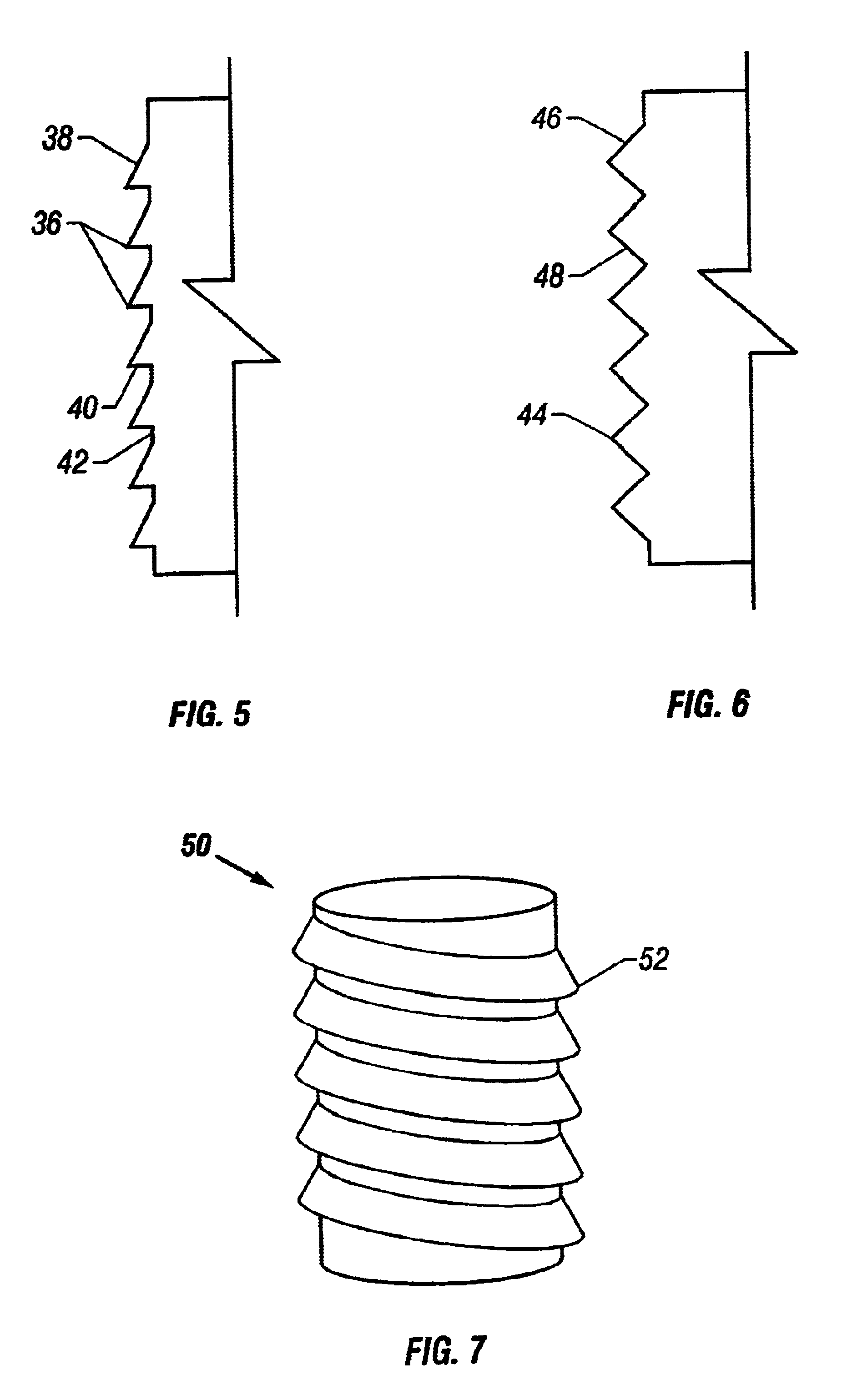
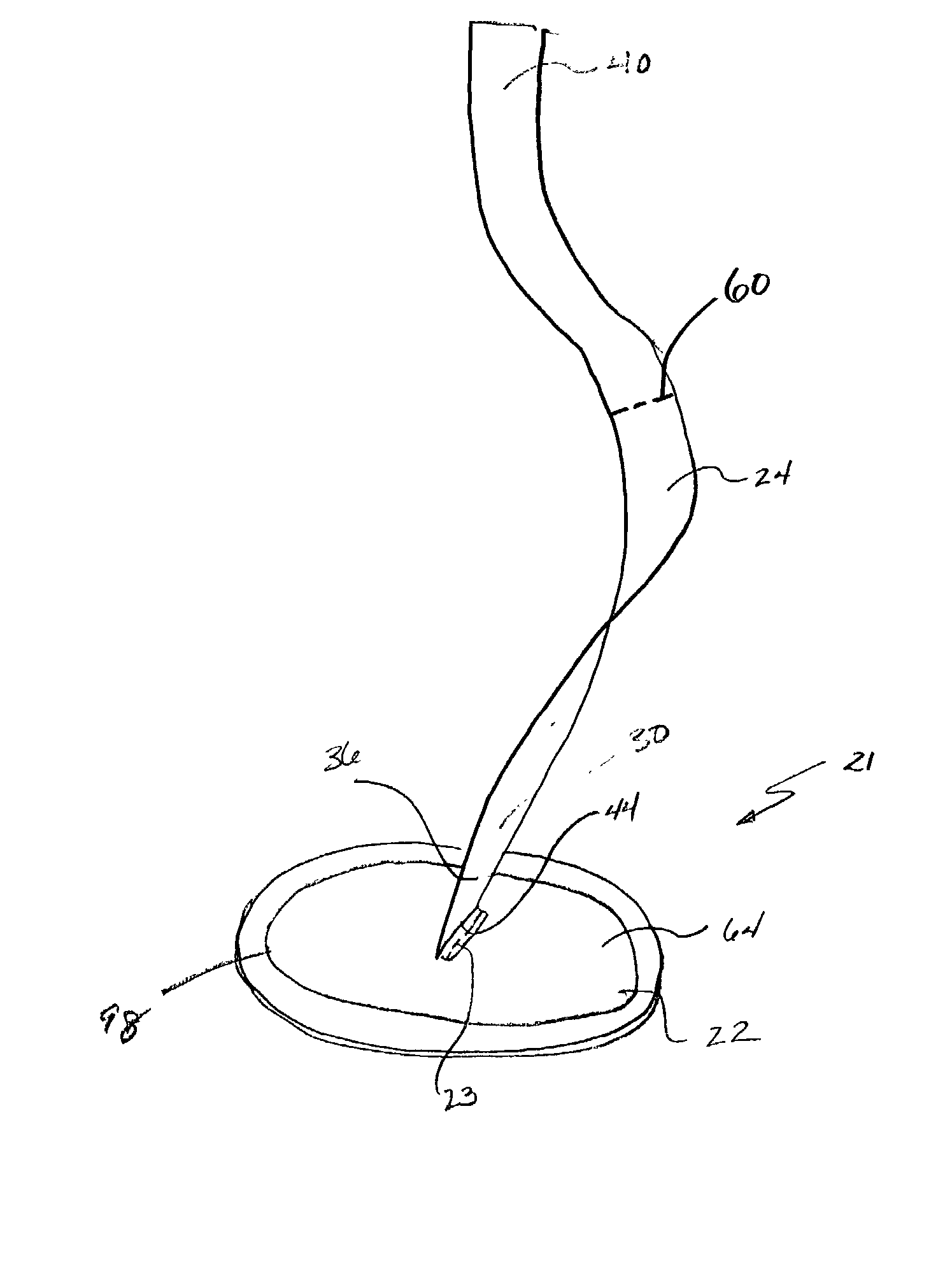
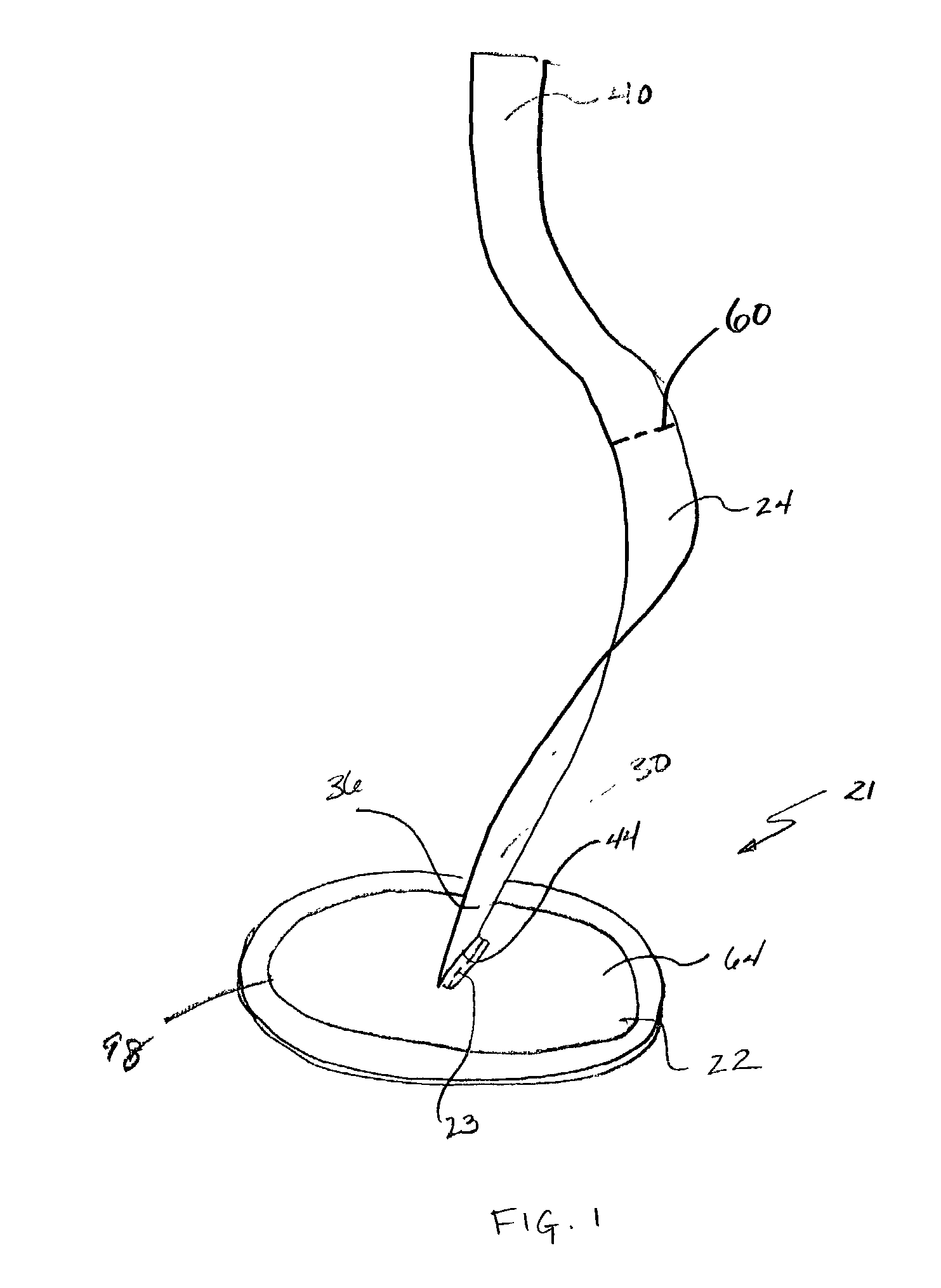
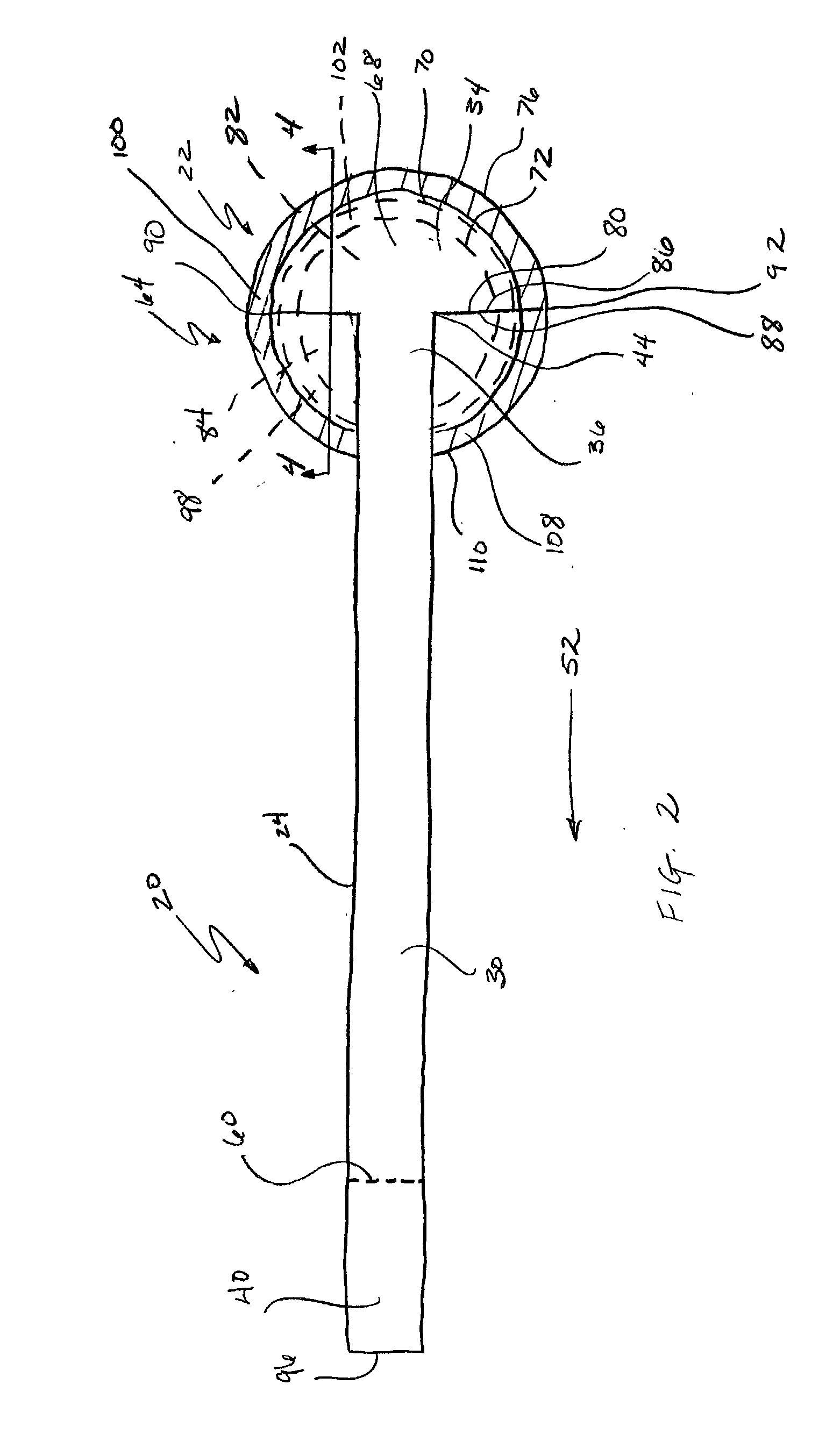
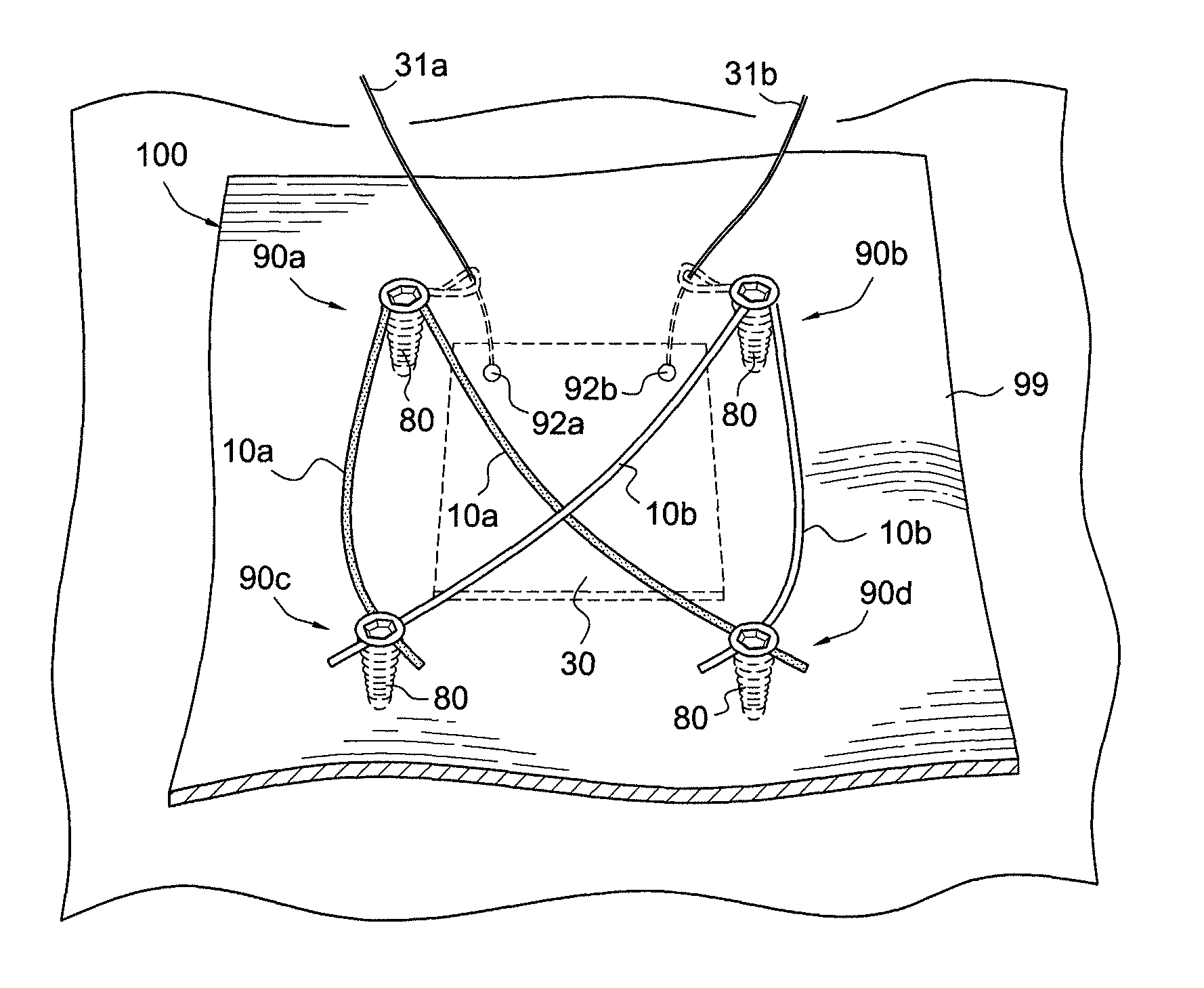
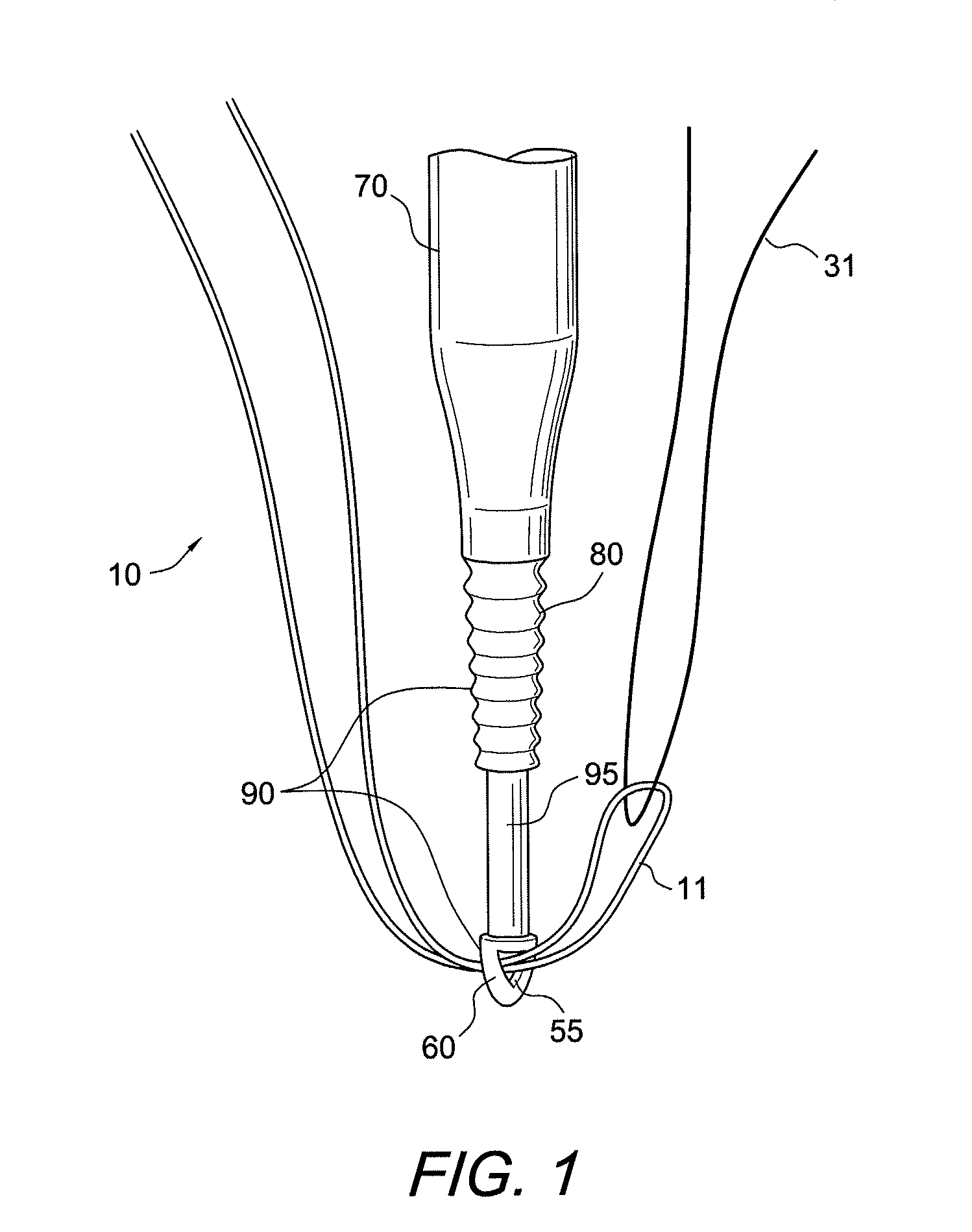
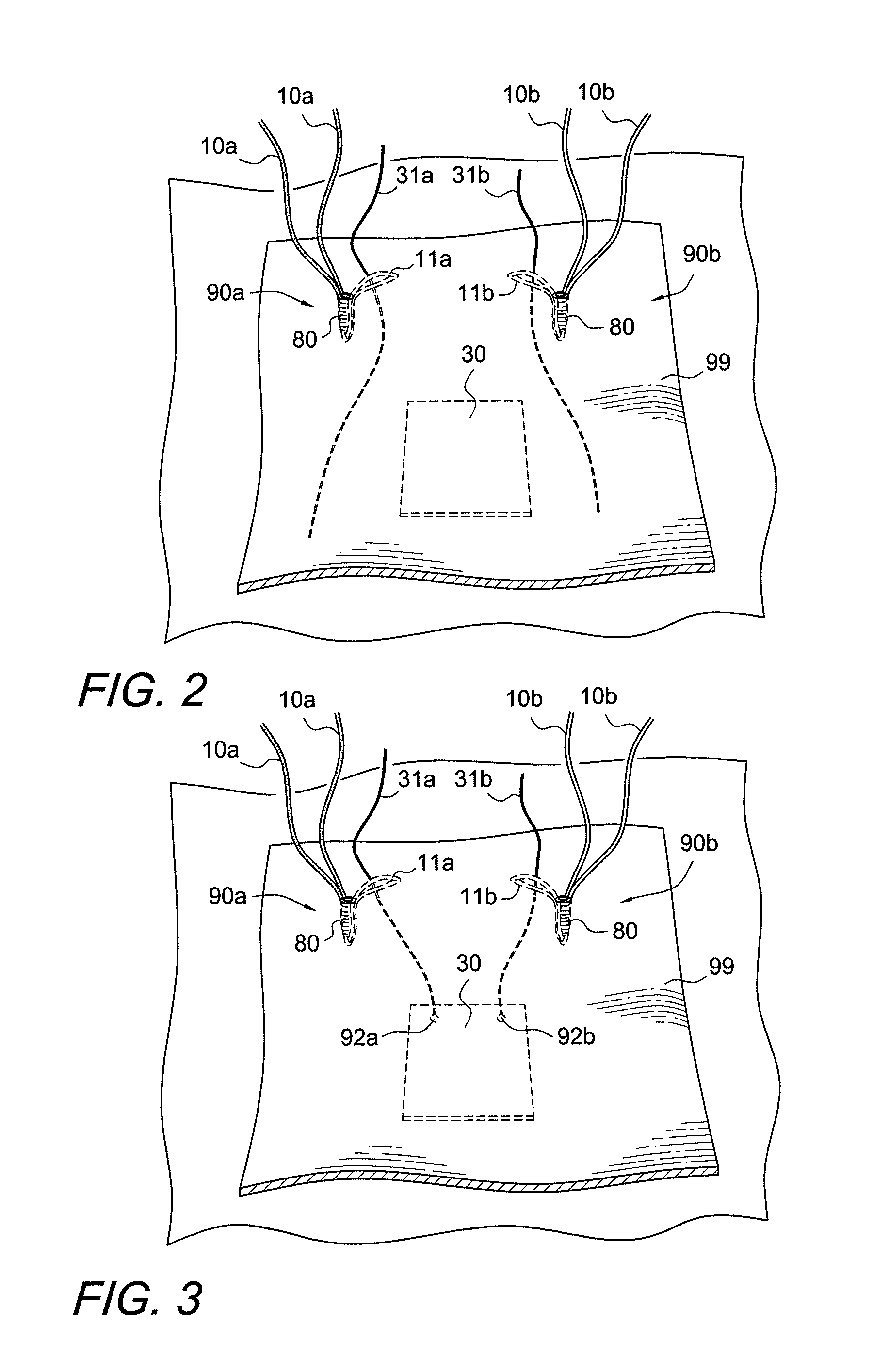
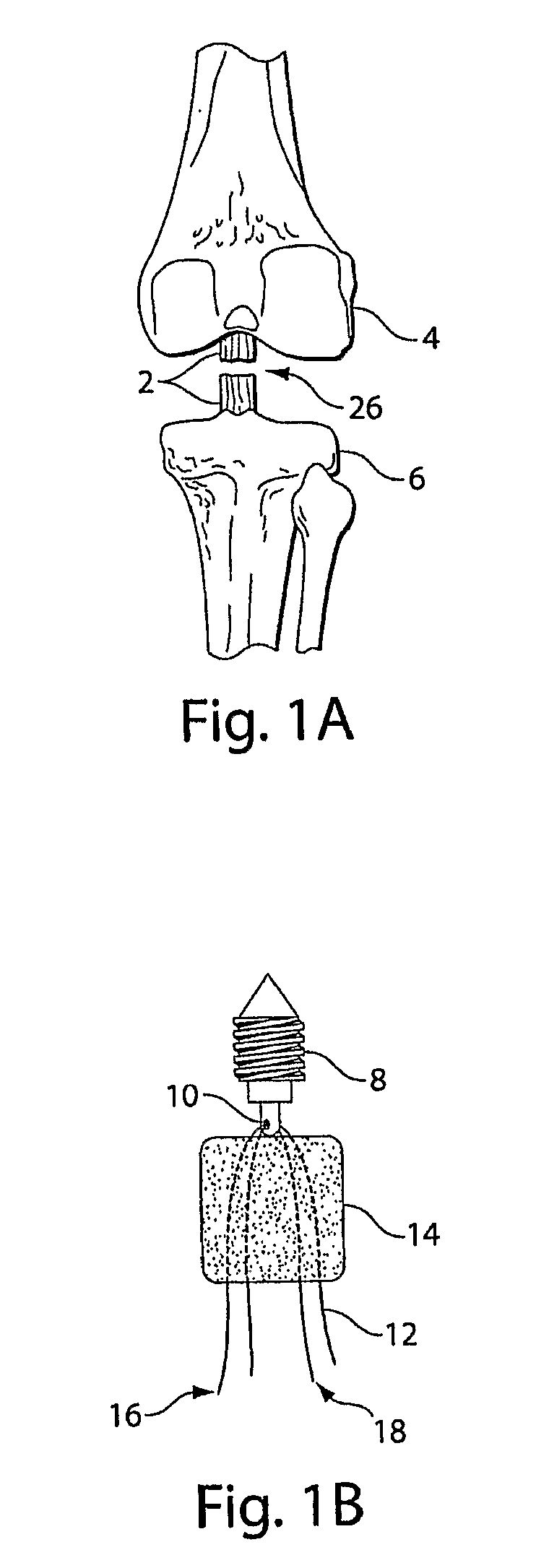
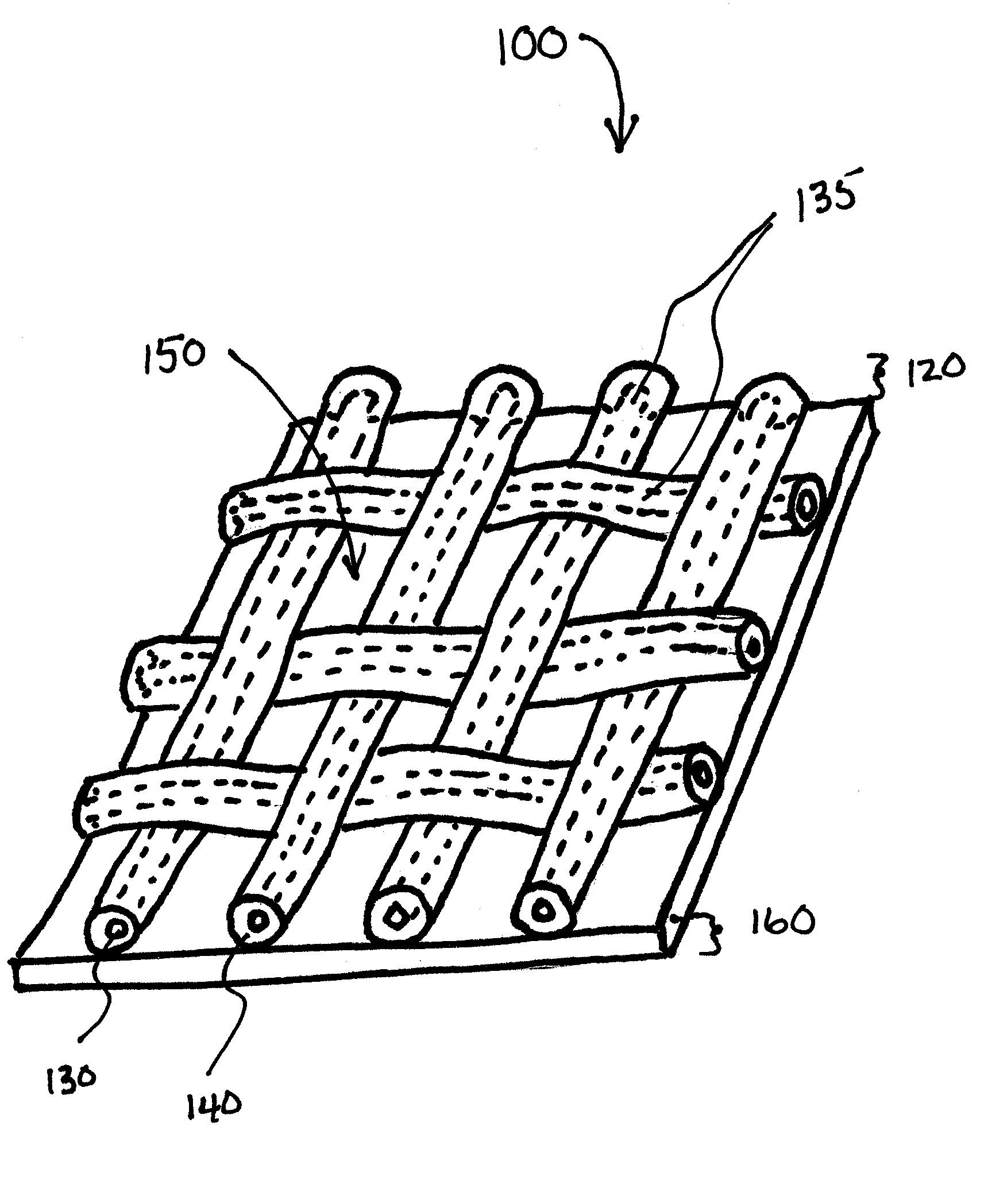
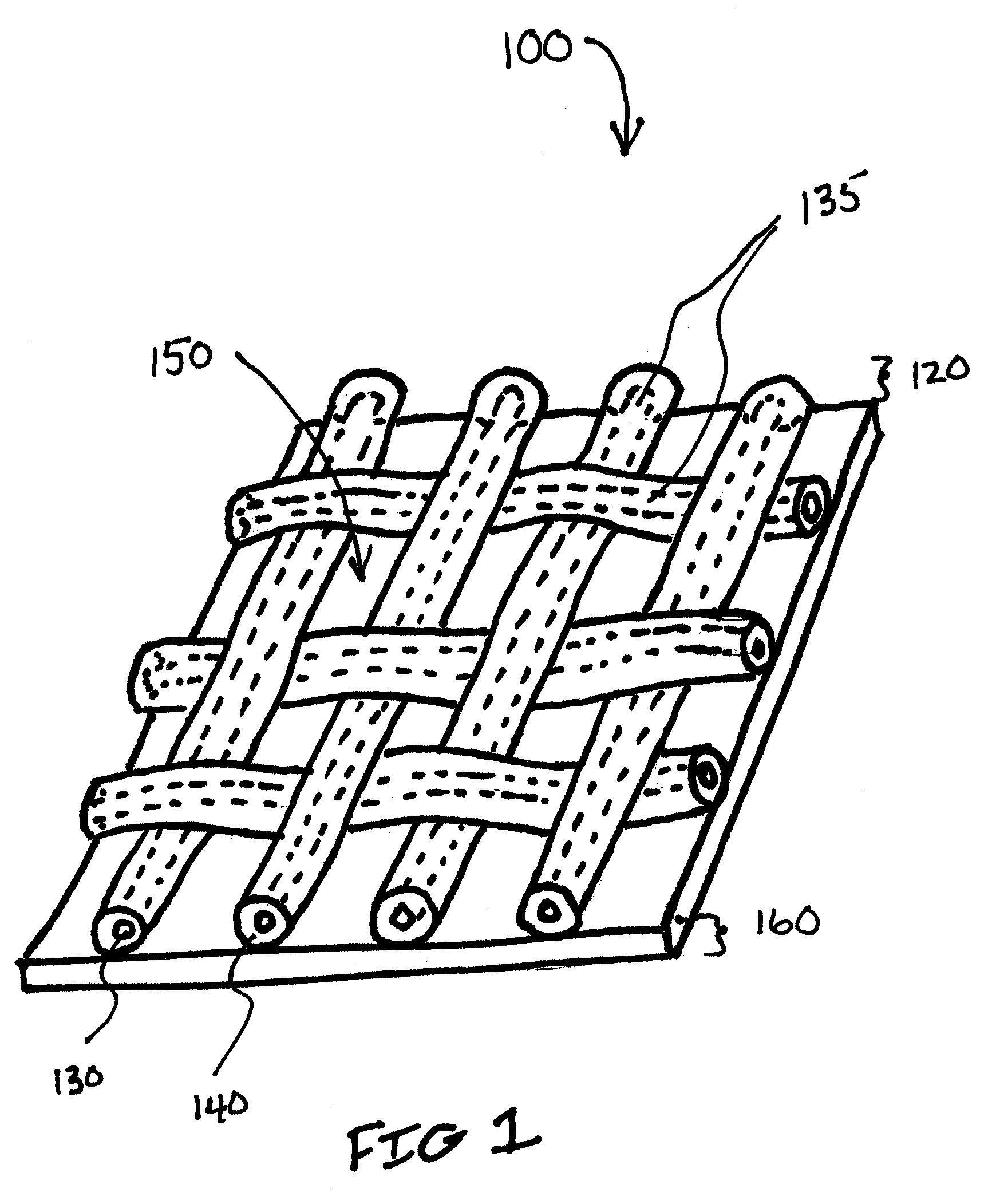
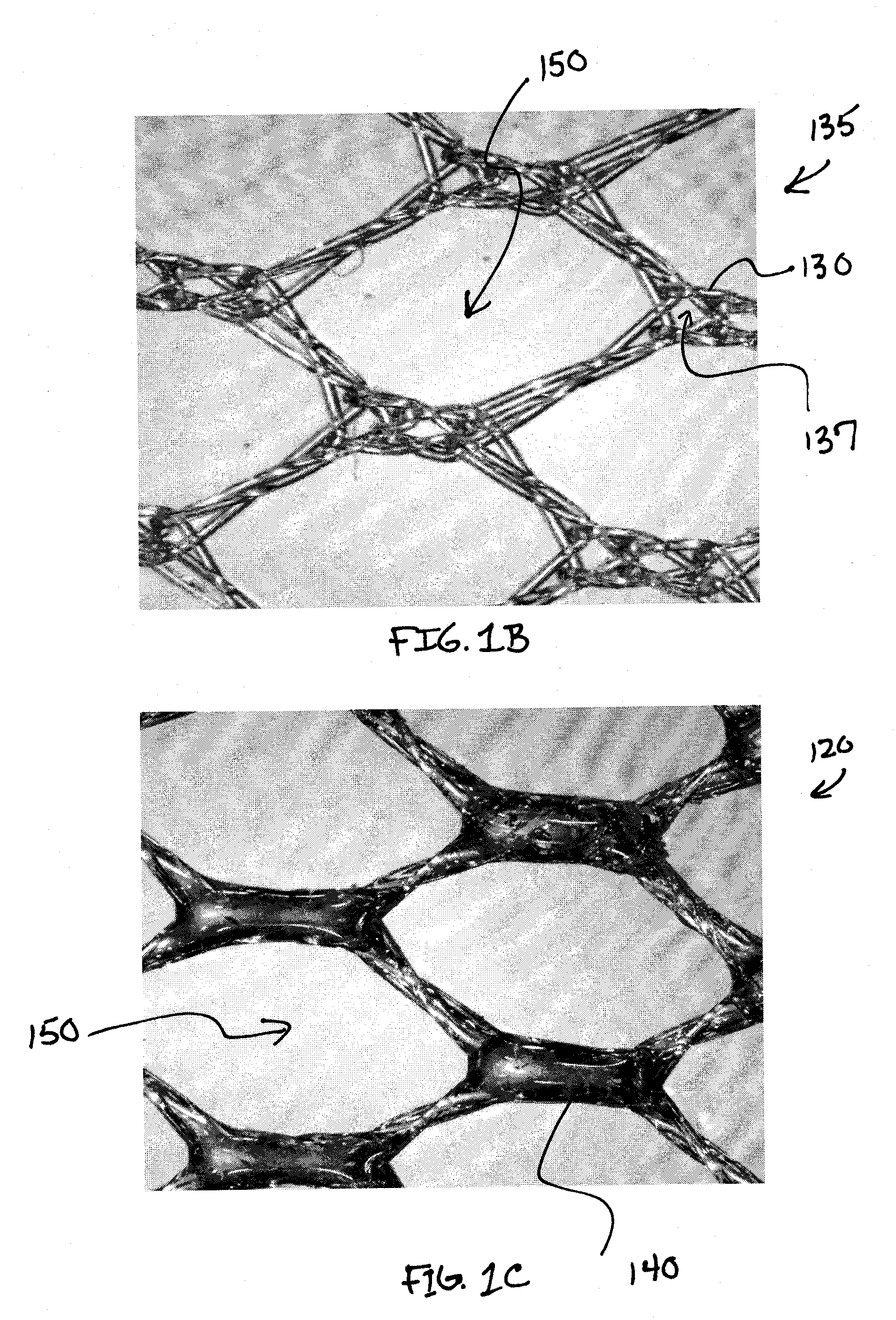
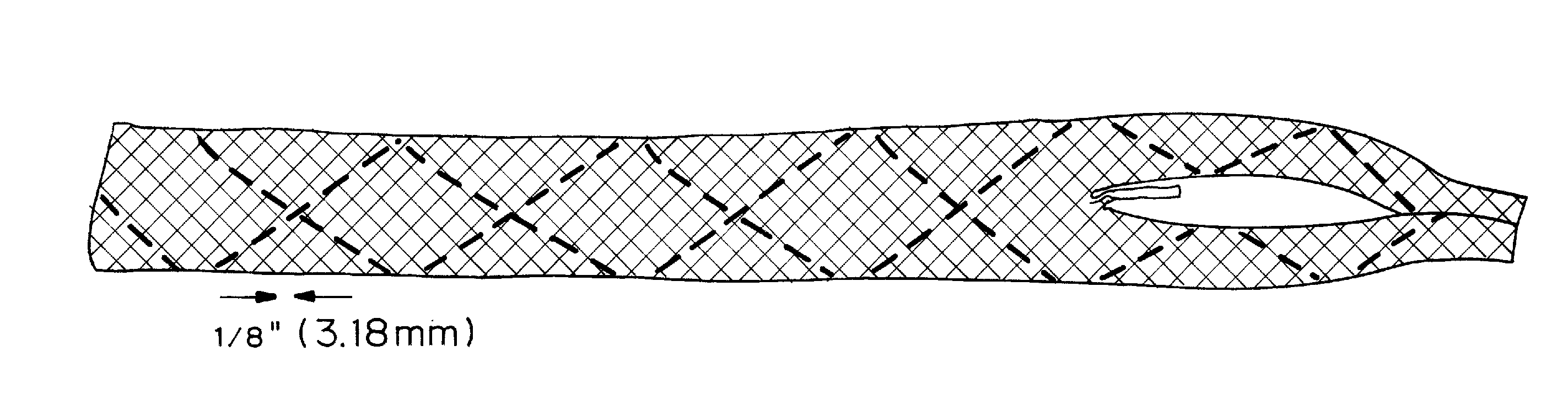
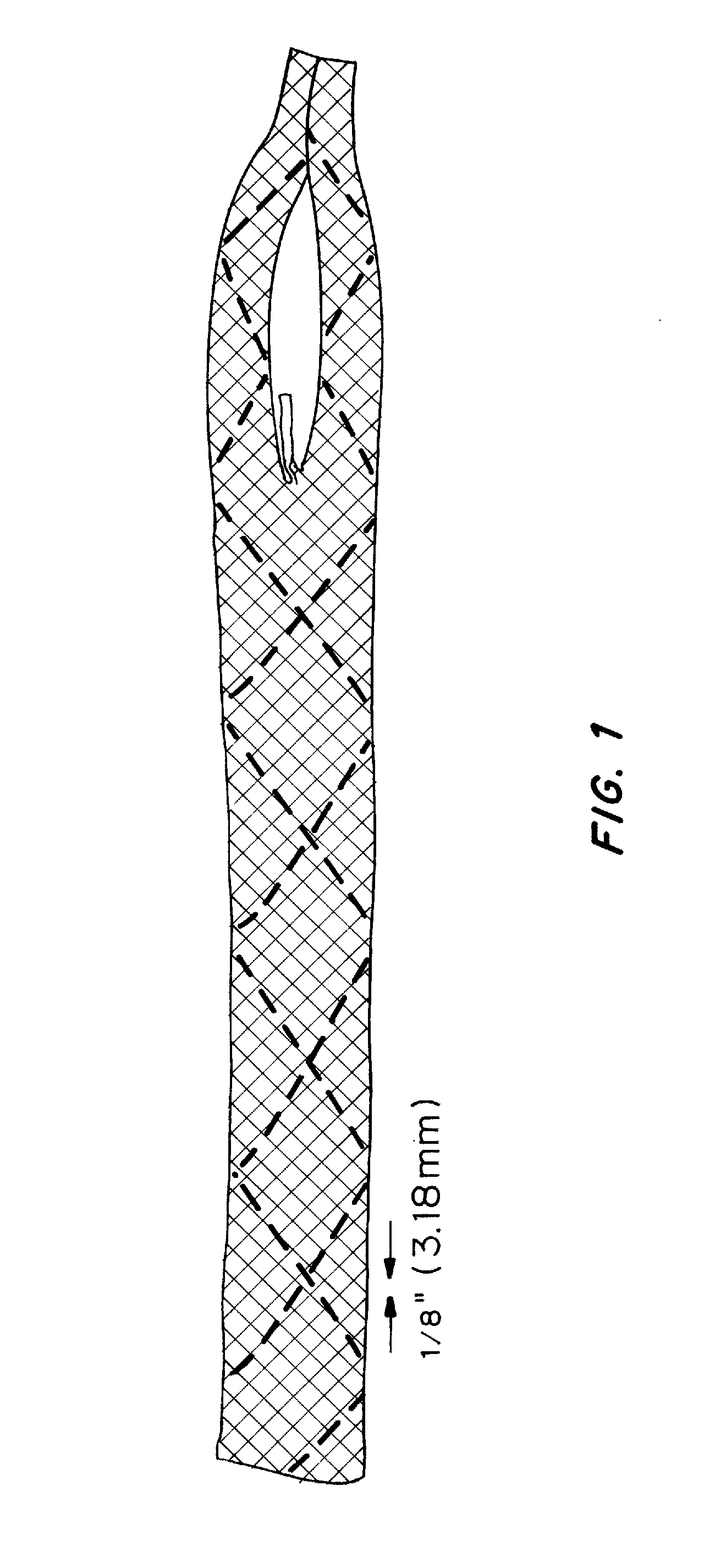
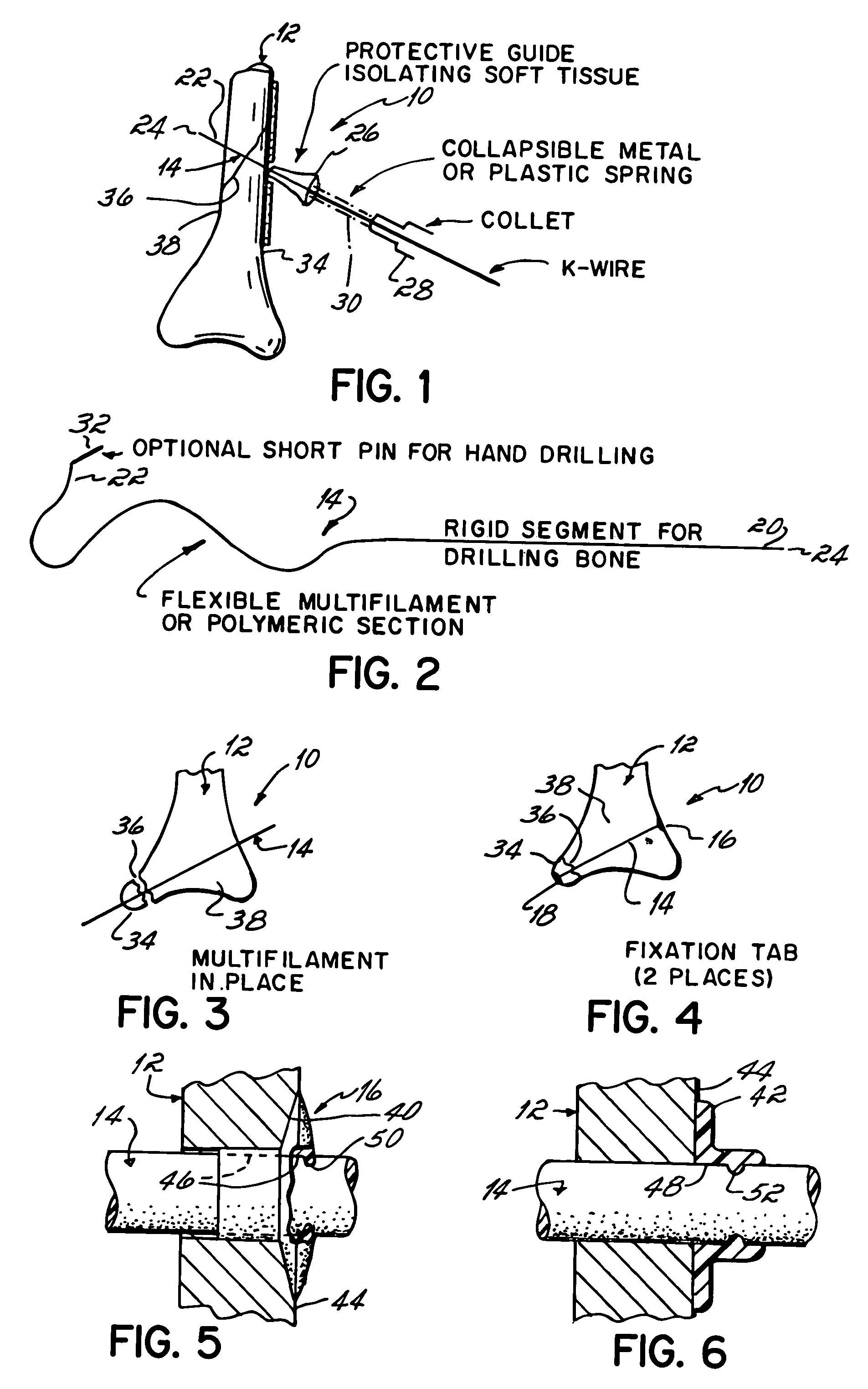
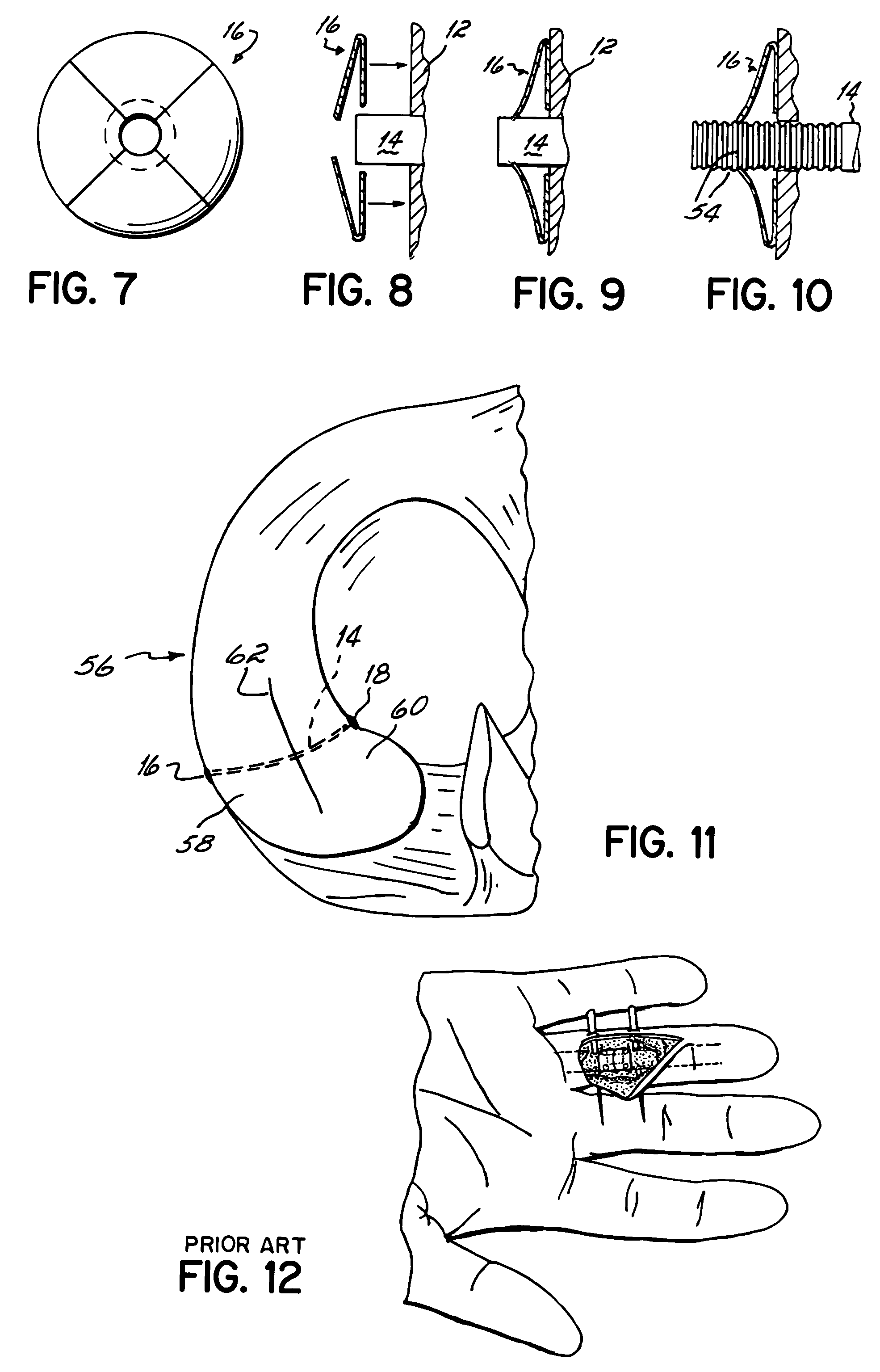
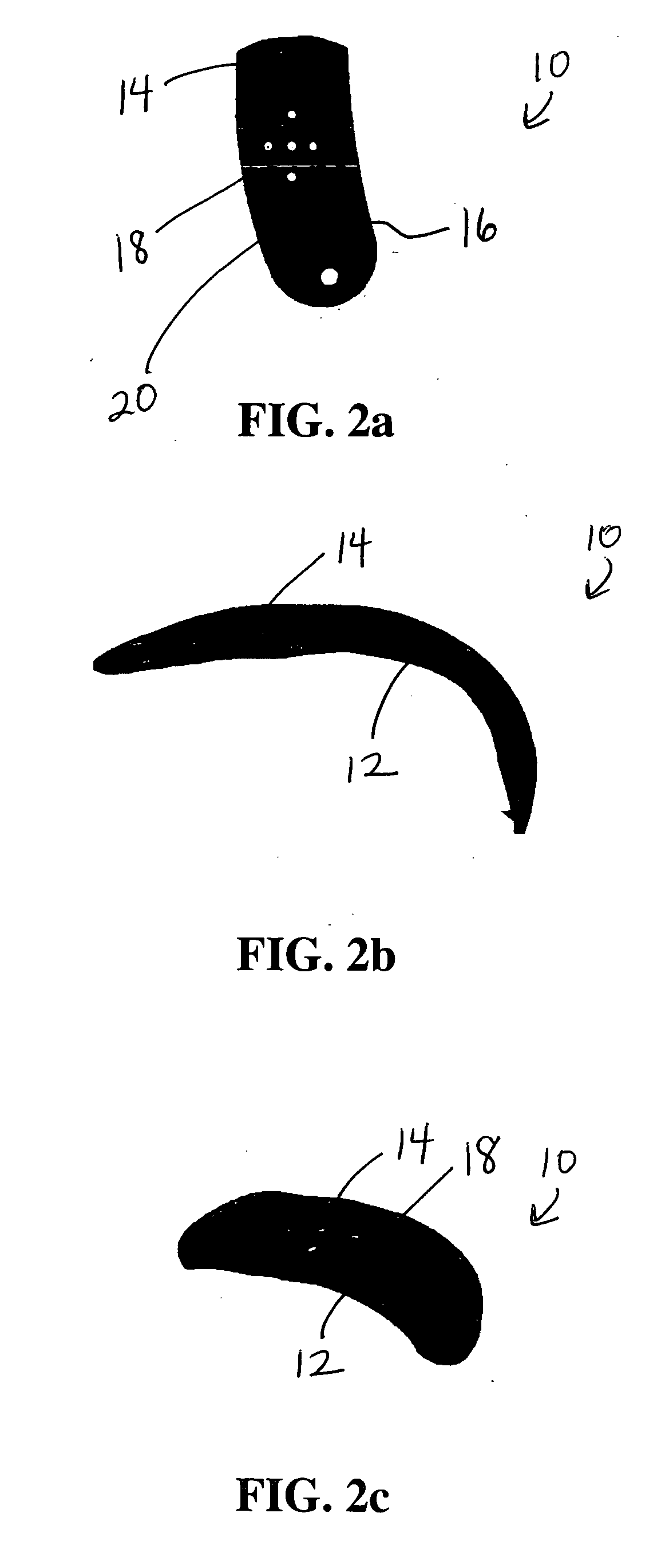
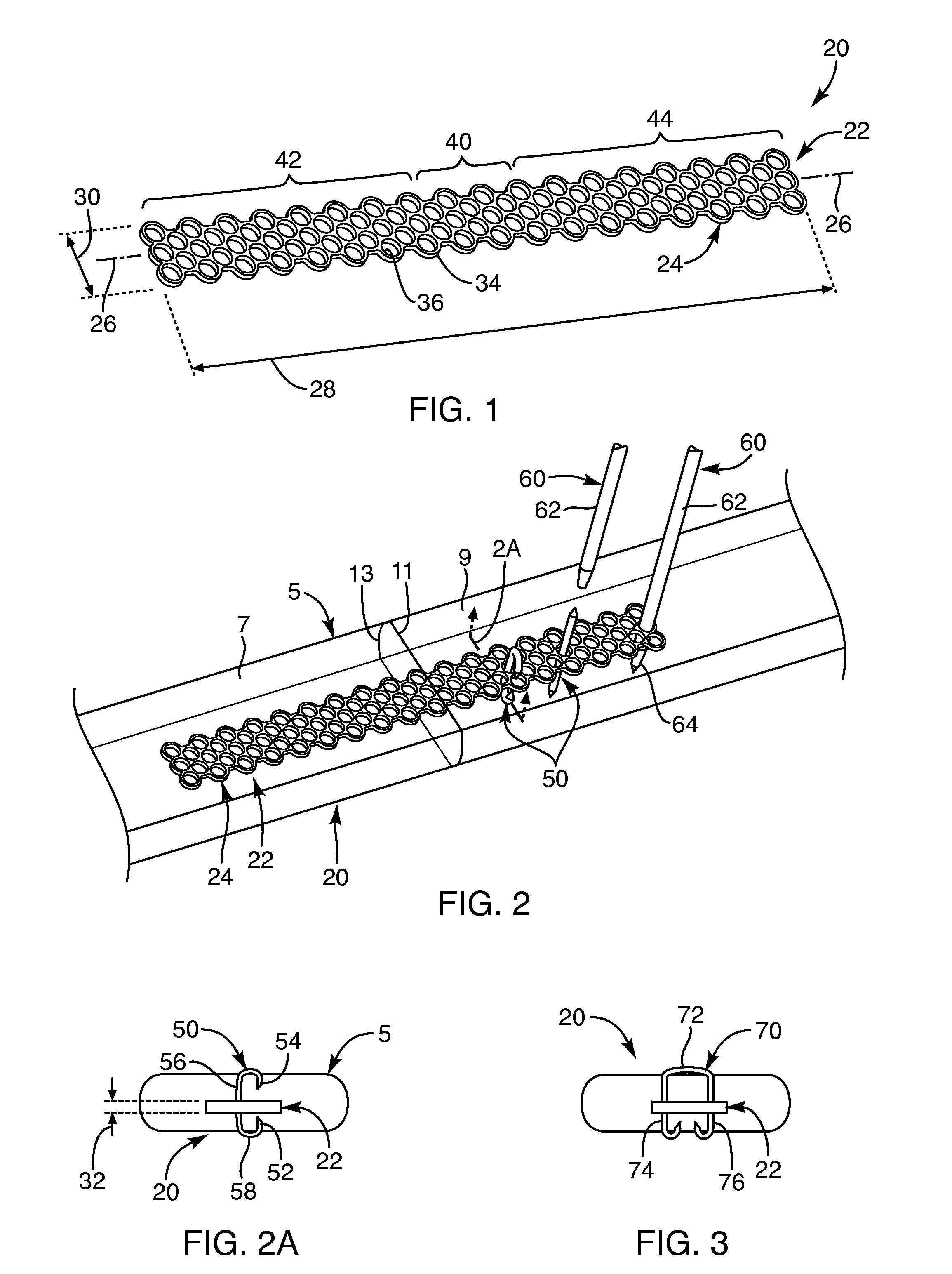
Soft tissue repair devices, systems, and methods
Owner:CONEXTIONS INC
Cartilage repair plug
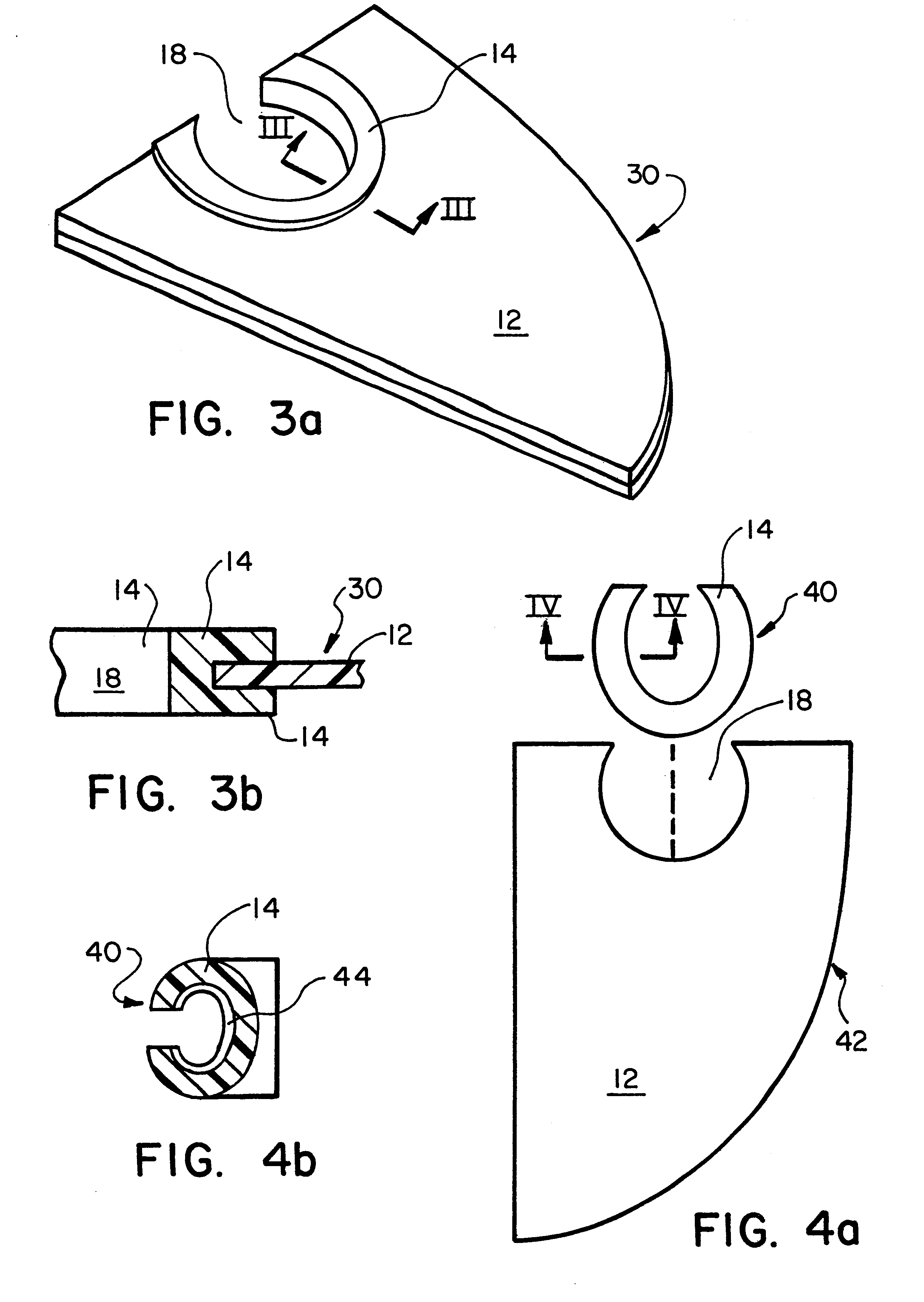
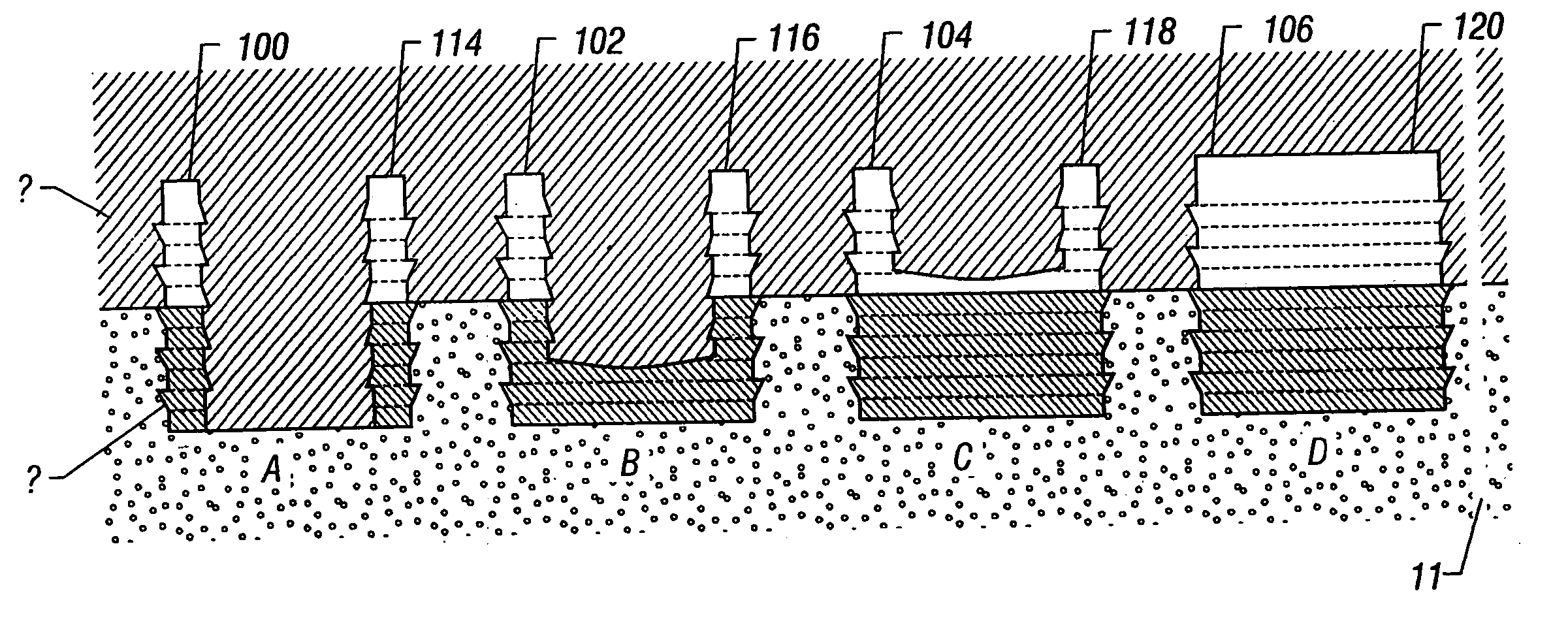
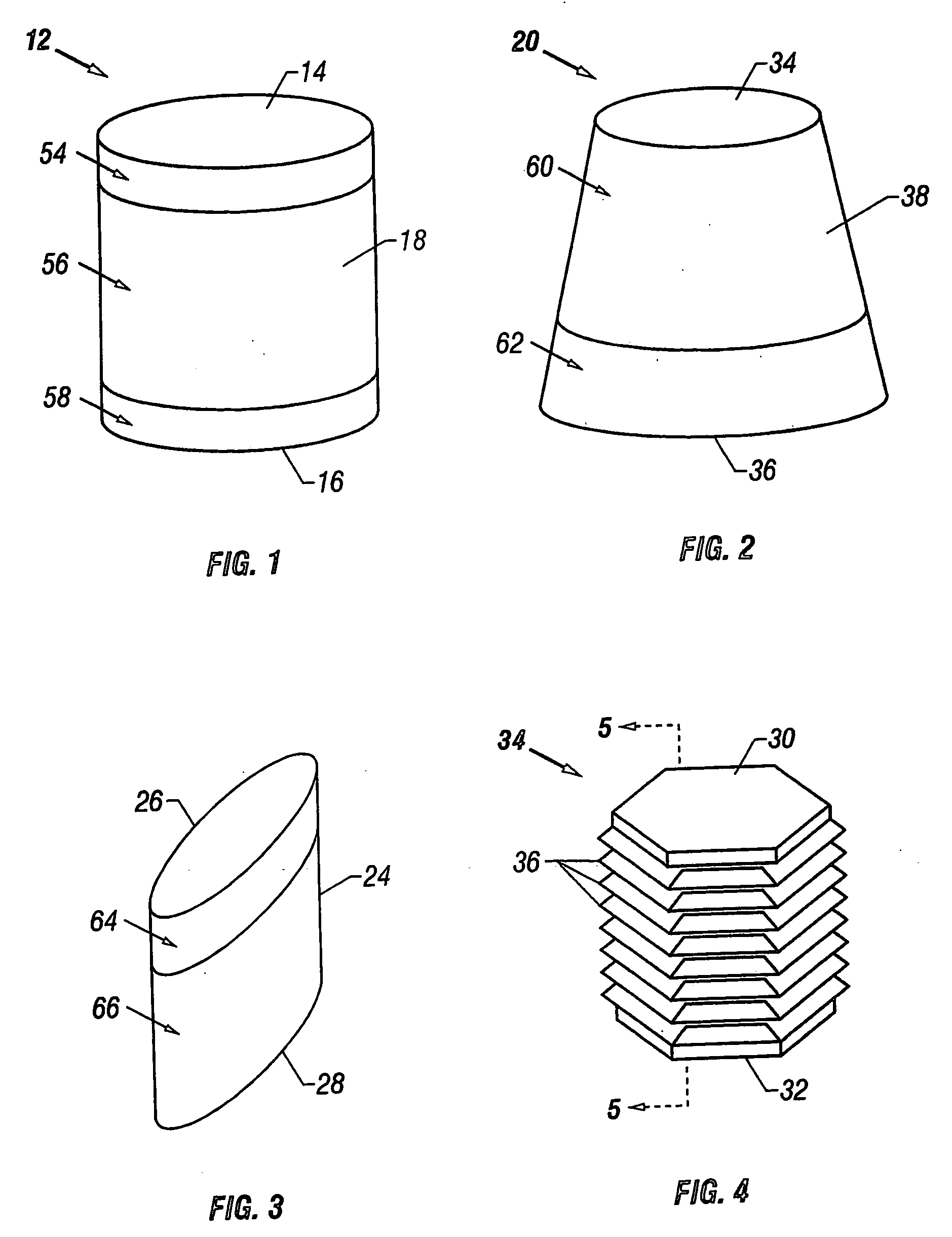
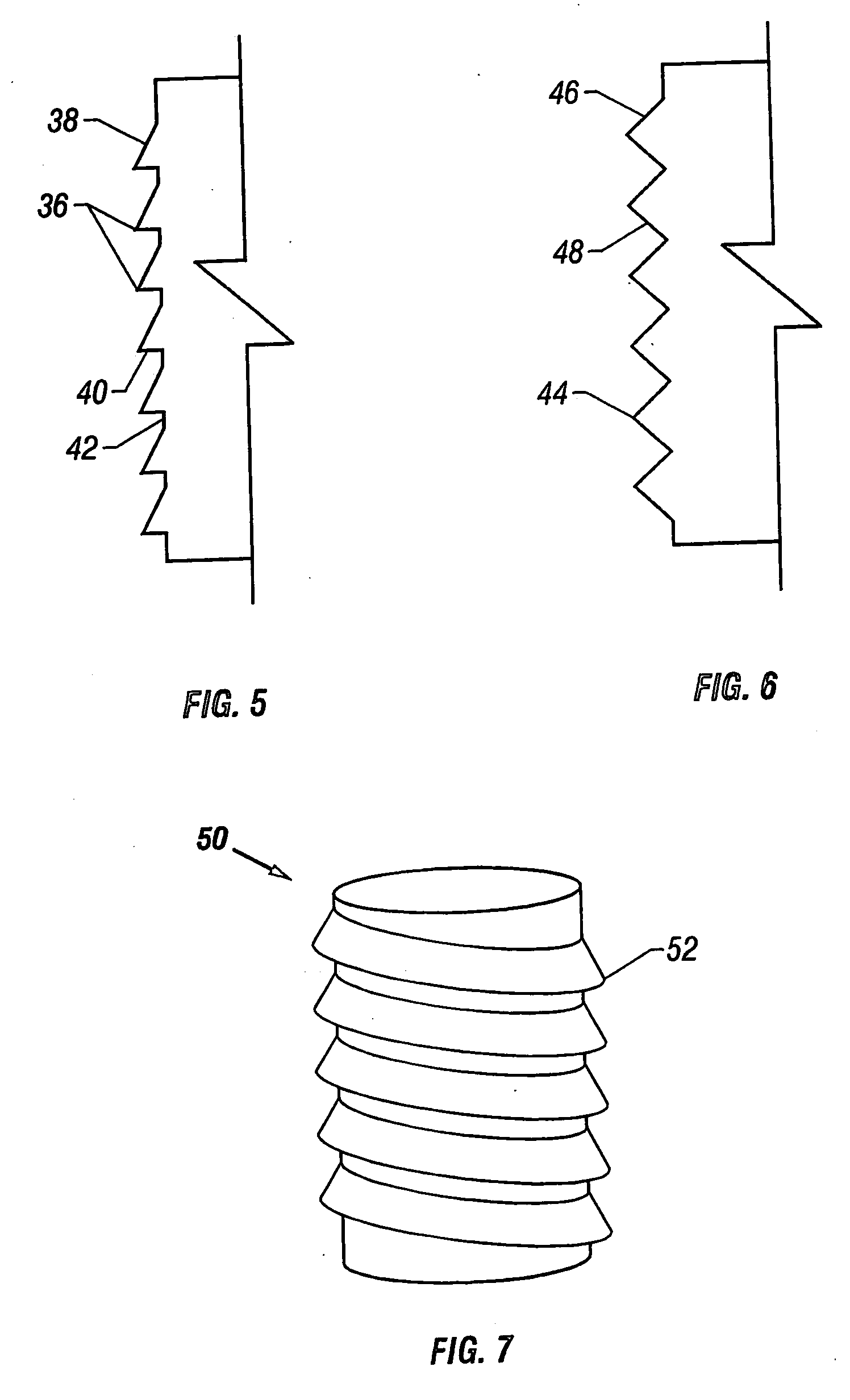
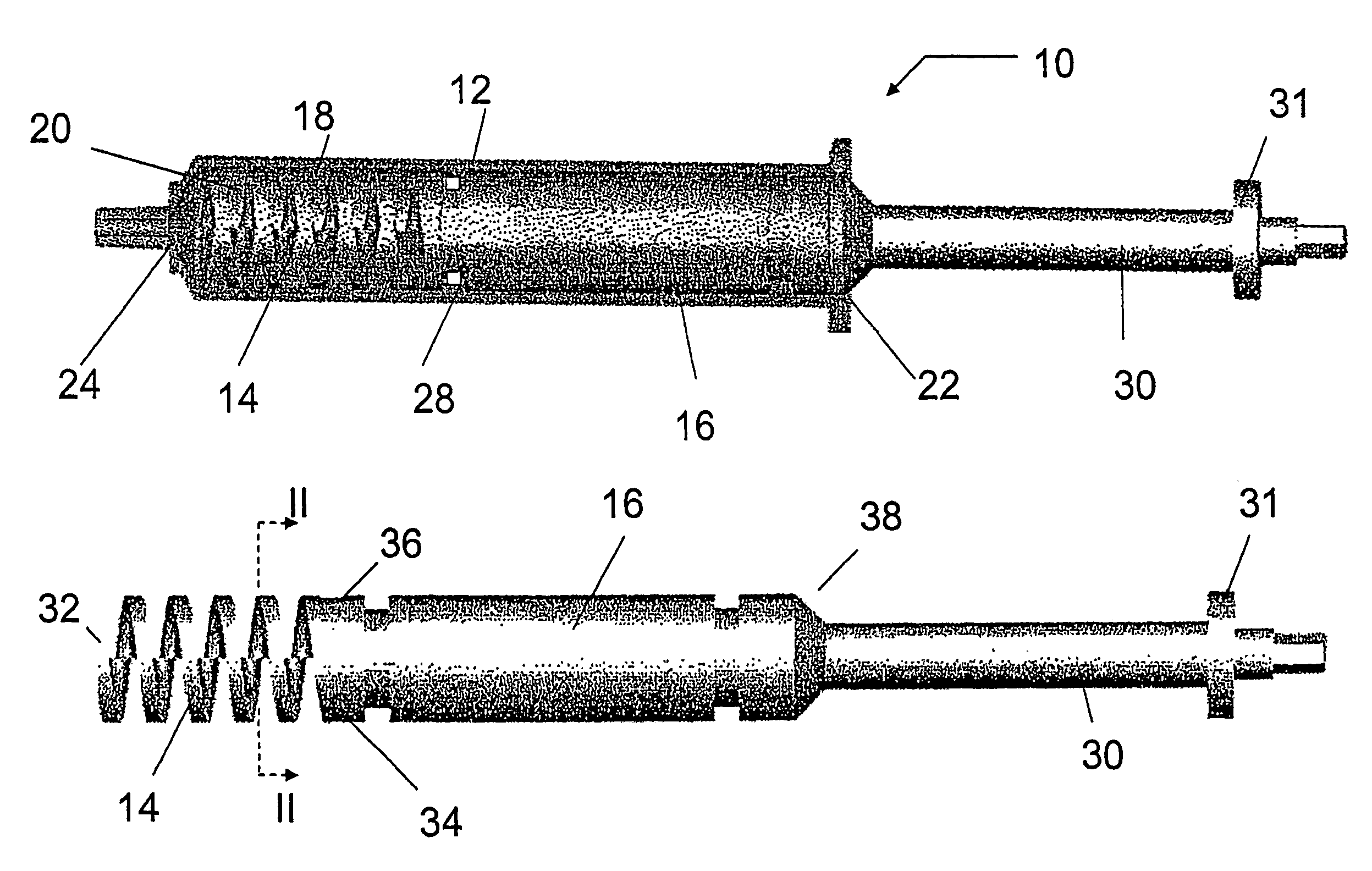
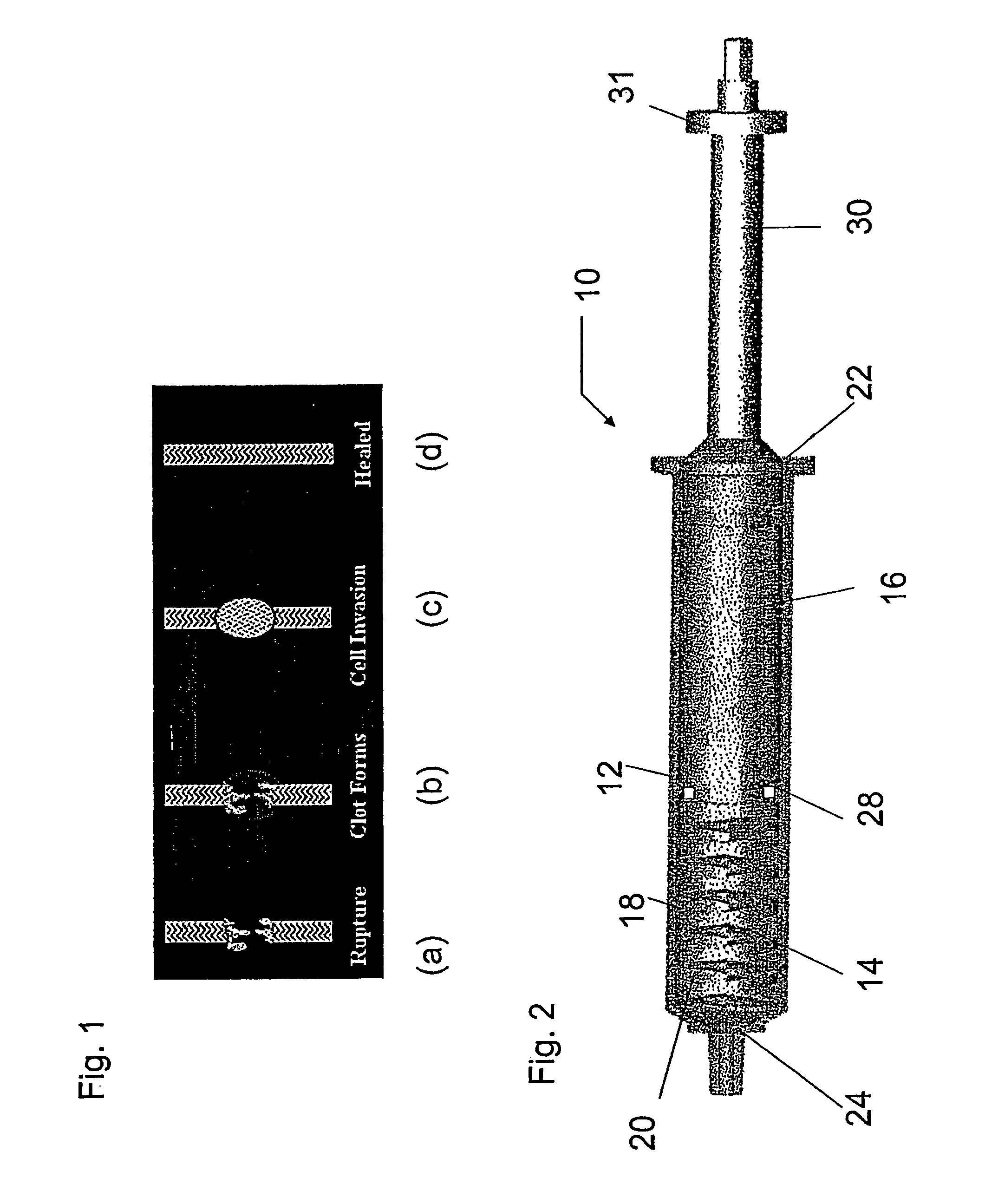
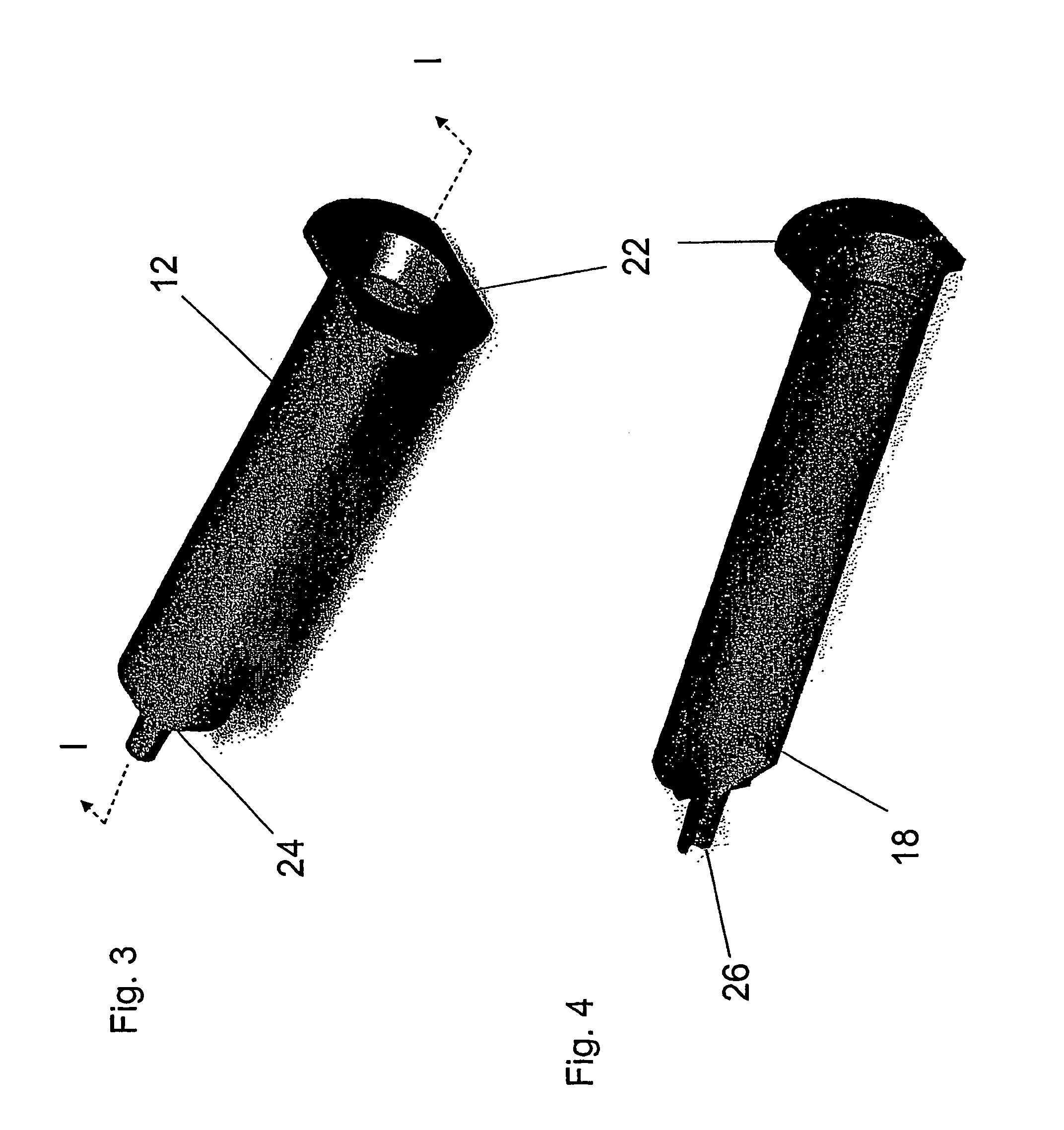
A cartilage plug, which is made from a biocompatible, artificial material, that is used to fill a void in natural cartilage that has been resected due to traumatic injury or chronic disease. Alternatively, the plug may be relied upon to anchor a flowable polymer to subchondral bone. The plug is prefabricatable in any size, shape, and contour and may be utilized either singly or in a plurality to fill any size void for any application. The plug may be formed of a laminated structure to match the physiological requirements of the repair site. A plurality of anchoring elements may share a single upper layer.
Owner:ABS
Cartilage repair plug
A cartilage plug, which is made from a biocompatible, artificial material, that is used to fill a void in natural cartilage that has been resected due to traumatic injury or chronic disease. Alternatively, the plug may be relied upon to anchor a flowable polymer to subchondral bone. The plug is prefabricatable in any size, shape, and contour and may be utilized either singly or in a plurality to fill any size void for any application. The plug may be formed of a laminated structure to match the physiological requirements of the repair site. A plurality of anchoring elements may share a single upper layer.
Owner:ABS
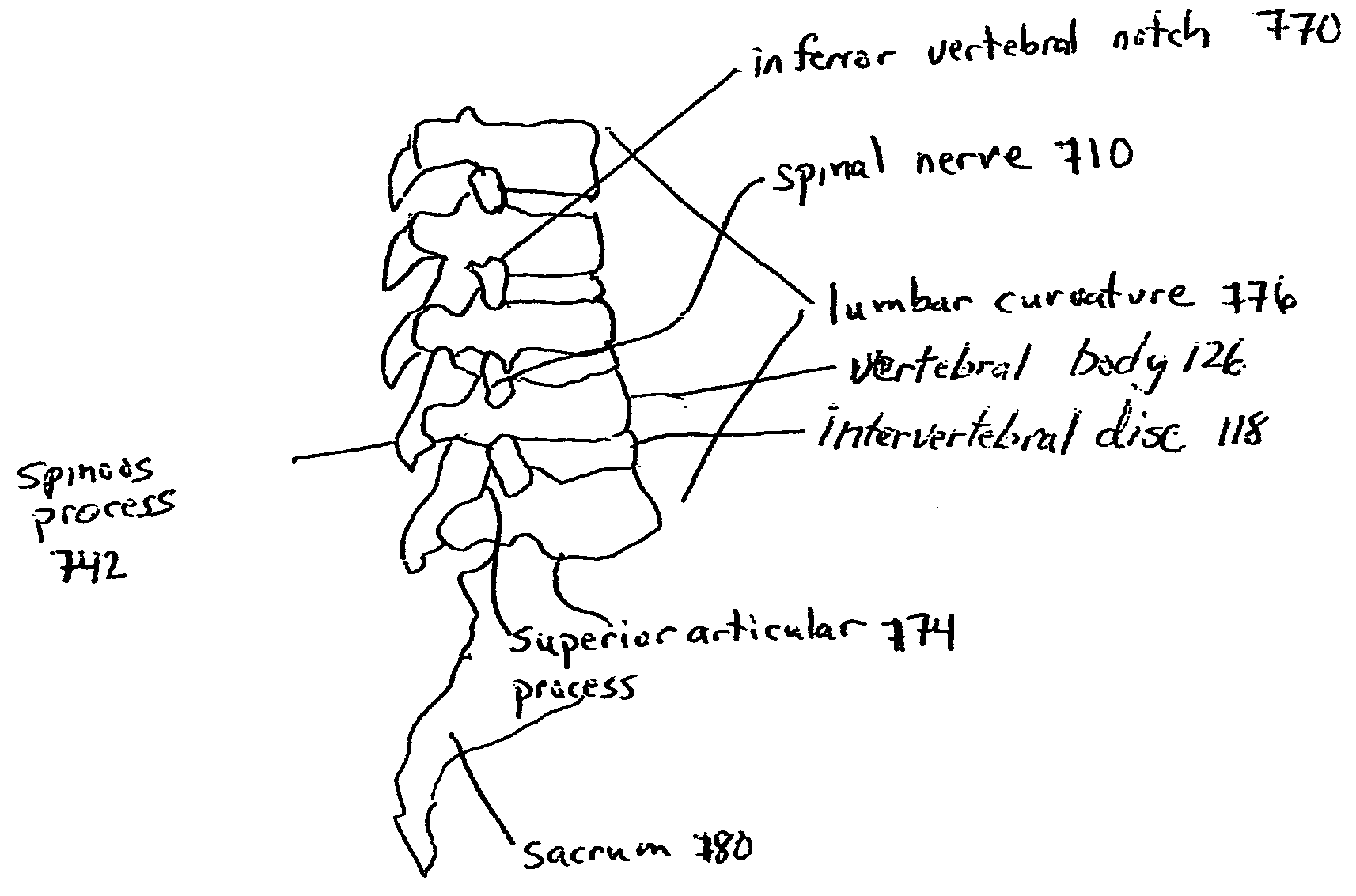
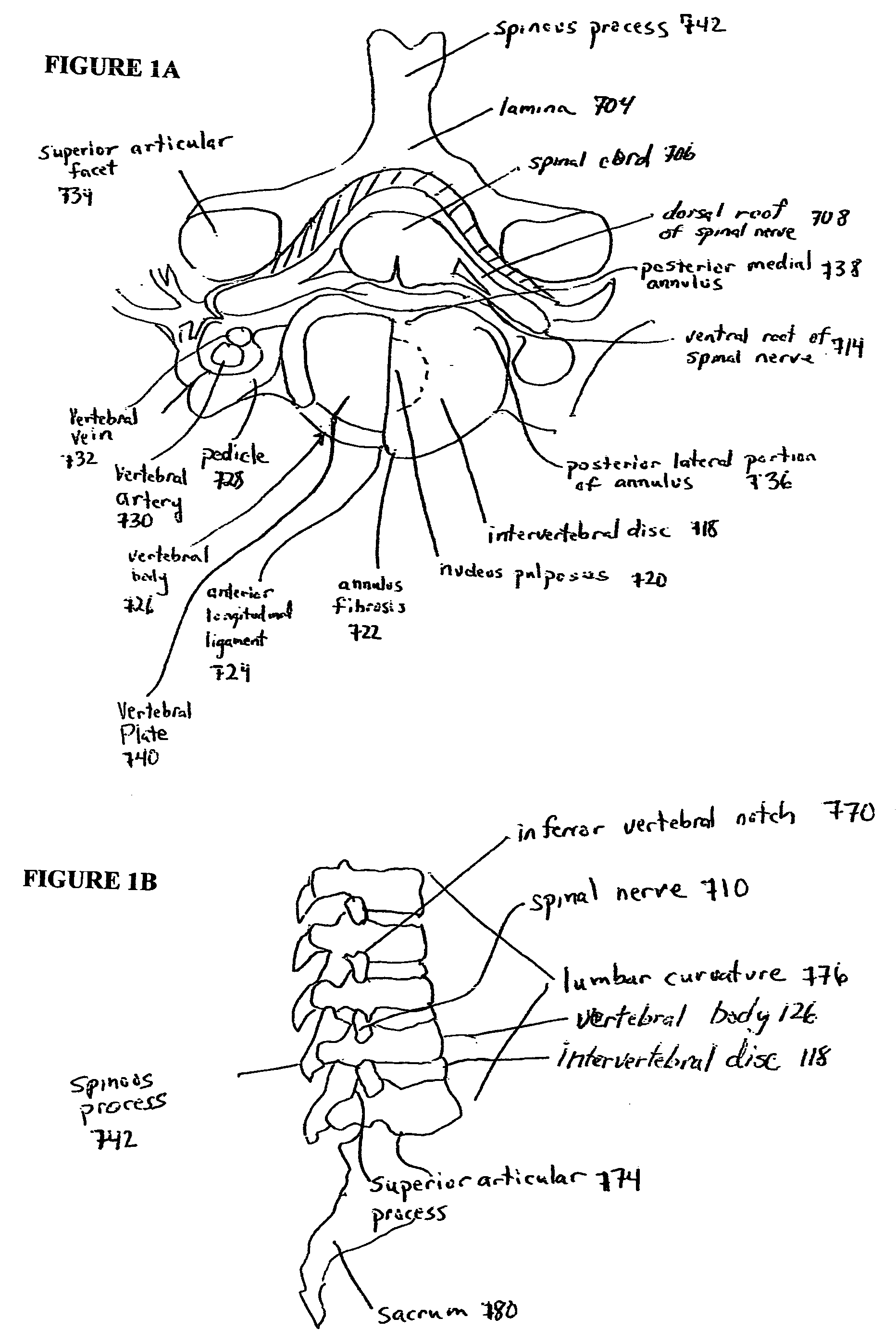
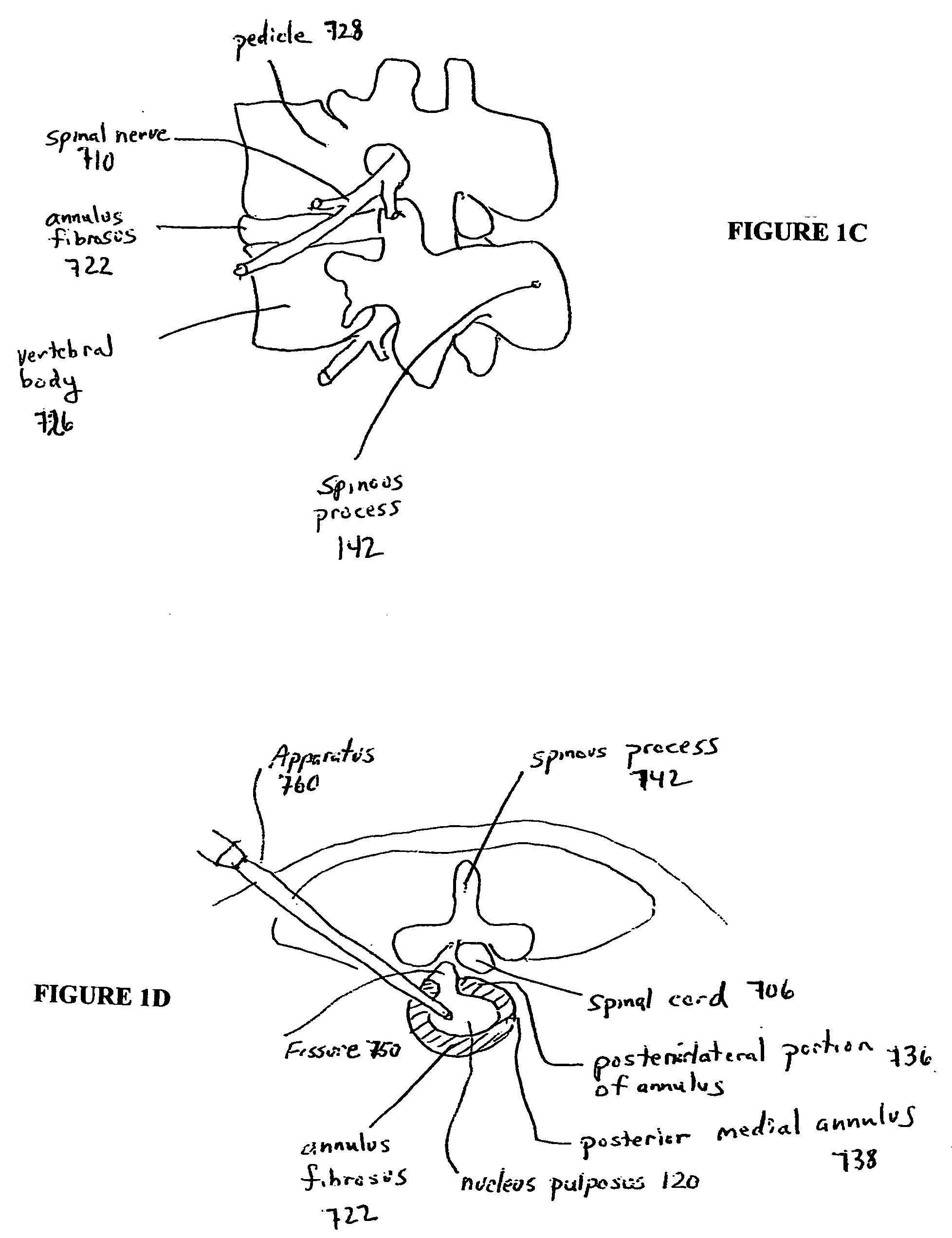
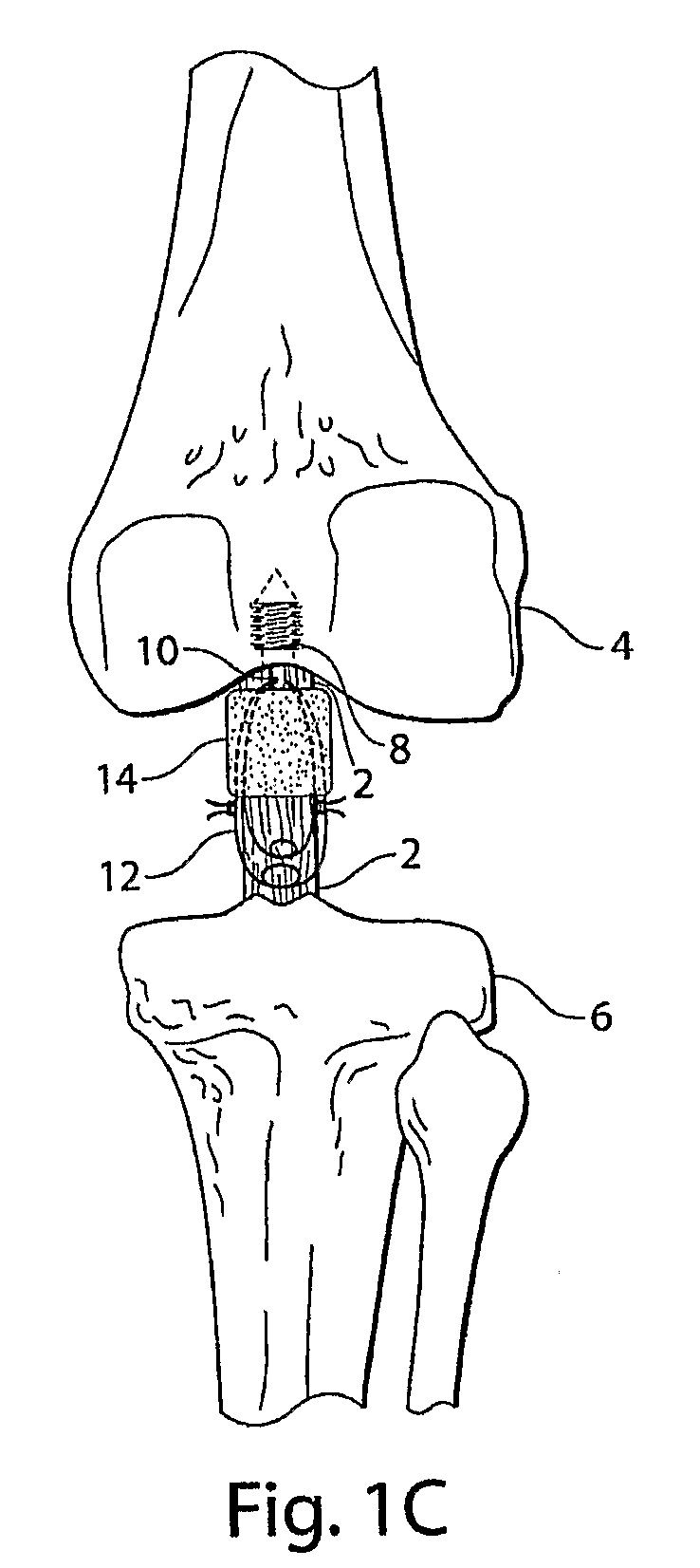
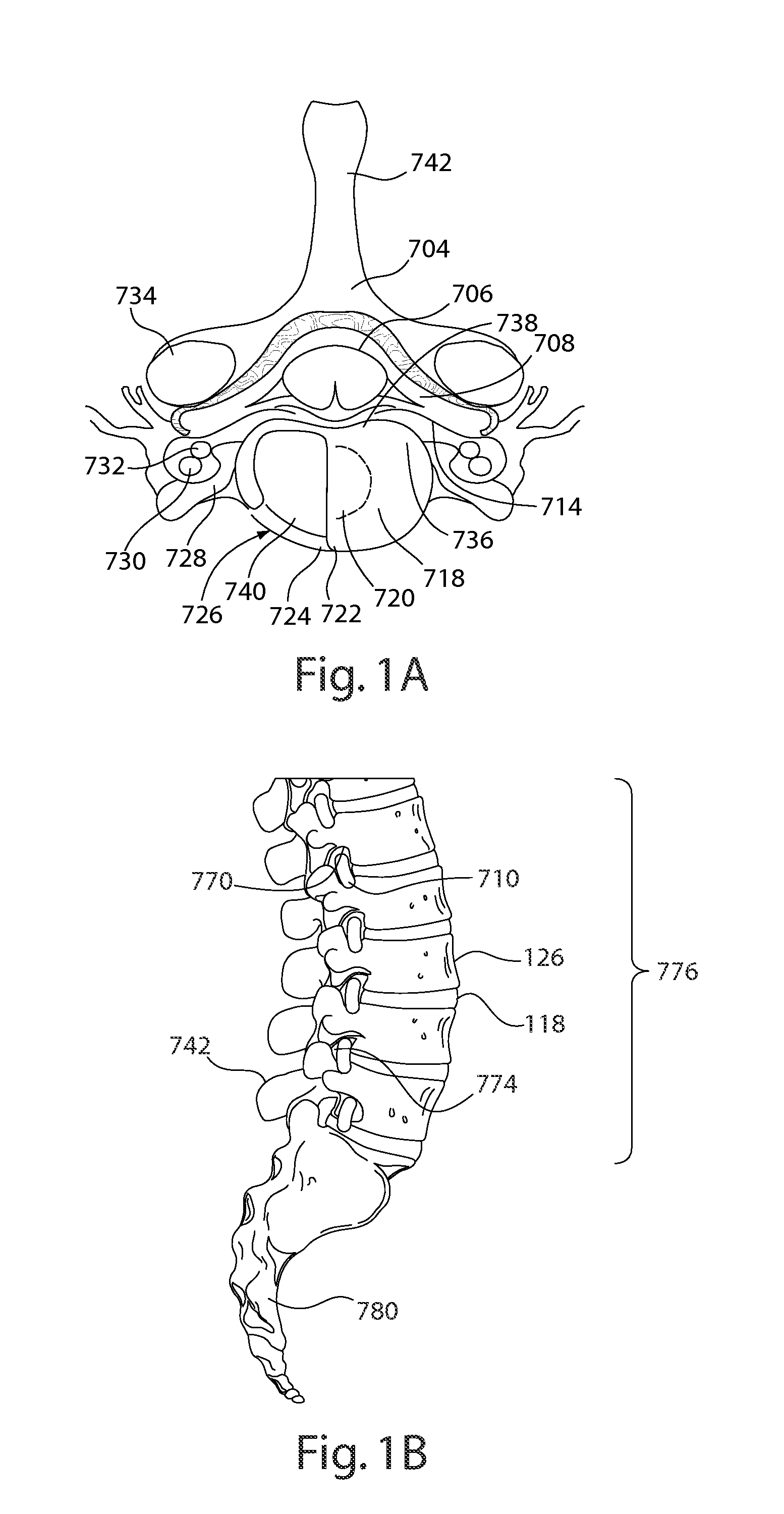
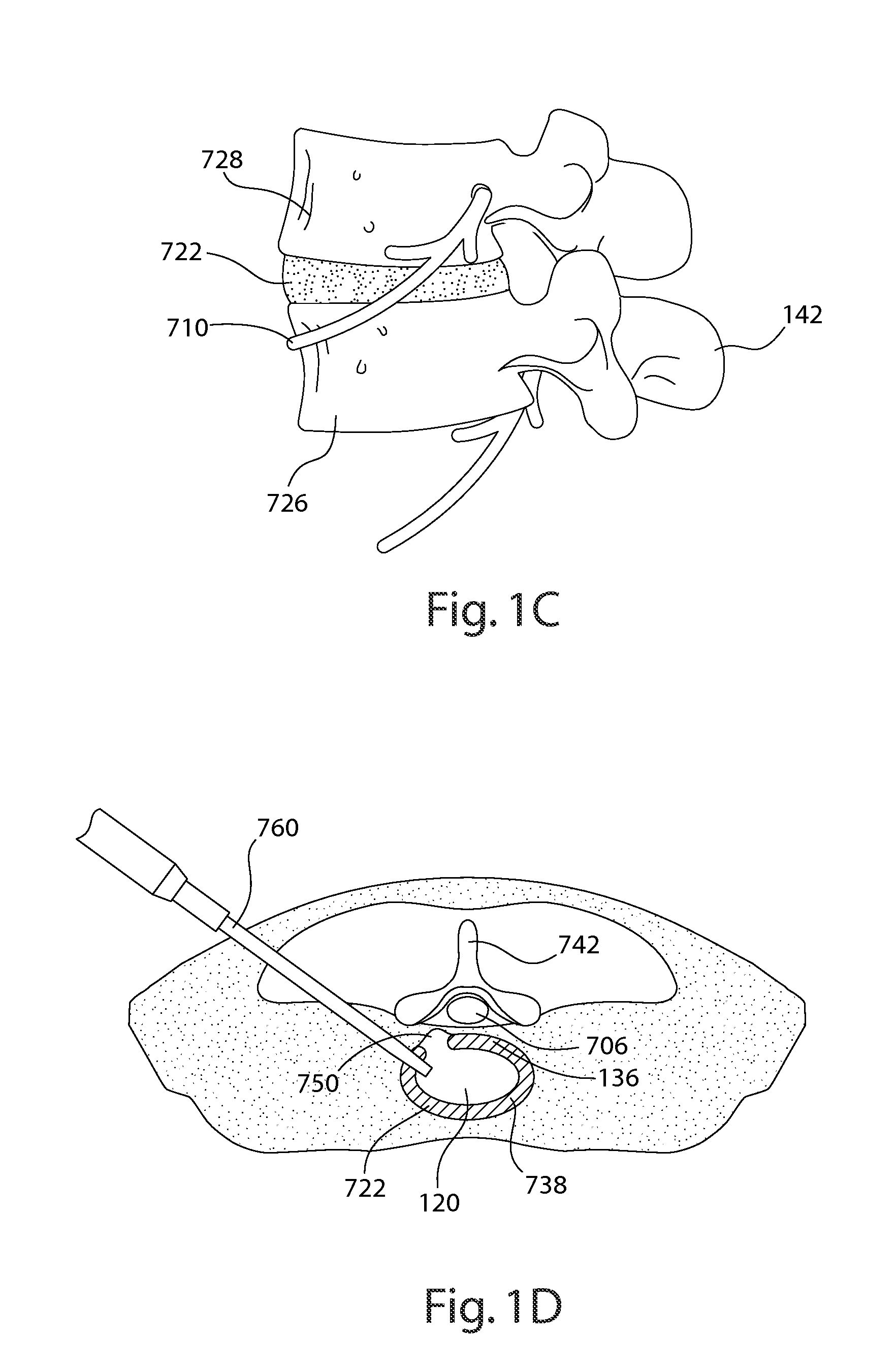
Devices and methods for spine repair
InactiveUS20050070913A1Strengthening intervertebral spaceEasy to operateSurgical furnitureBone implantRepair siteIntervertebral disk
Surgical methods of repairing defects and deficiencies in the spine are disclosed. The methods involve delivering a single part in-situ polymerizing fluid to (i) close a weakened segment or fissure in the annulus fibrosus, (ii) strengthen the annulus, (iii) replace or augment the disc nucleus, or (iv) localize a disc prosthesis. The methods may include placing a delivery conduit adjacent to the repair site and providing a liquid tissue adhesive to bond to and repair a disc defect or deficiency
Owner:PROMETHEAN SURGICAL DEVICES
Implantable prosthesis
InactiveUS6610006B1Reduce the possibilityReduce postoperative painDiagnosticsLigamentsRepair siteIntraabdominal pressure
An implantable prosthesis for repairing an anatomical defect, such as a soft tissue and muscle wall defect. The prosthesis is configured to reduce the likelihood that an applied force at the repair site, such as due to intraabdominal pressure or tissue shrinkage, can lead to detrimental effects associated with tension at the anchoring locations between the prosthesis and host tissue and / or contraction of the prosthesis. In this regard, the prosthesis may be configured to limit the amount of tension at the anchoring locations caused by the application of a force or pressure to the prosthesis and / or contraction of the prosthesis. Alternatively, the prosthesis may be configured to compensate for contraction of the prosthesis due to tissue shrinkage at the repair site. The prosthesis may be configured to both limit tension at the anchoring locations and compensate for tissue shrinkage. The prosthesis may facilitate a reduction in postoperative discomfort, a recurrence of the defect, or the creation of a new defect associated with tension and / or prosthetic contraction.
Owner:CR BARD INC
Implantable prosthesis
ActiveUS7101381B2Avoid it happening againHelp positioningLigamentsMusclesCongenital inguinal herniaRepair site
An implantable prosthesis for repairing an anatomical defect, such as a tissue or muscle wall hernia, including an umbilical hernia, and for preventing the occurrence of a hernia at a small opening or weakness in a tissue or muscle wall, such as at a puncture tract opening remaining after completion of a laparoscopic procedure. The prosthesis includes a patch and / or plug having a body portion that is larger than a portion of the opening or weakness so that placement of the body portion against the defect will cover or extend across that portion of the opening or weakness. At least one tether, such as a strap, extends from the patch or plug and may be manipulated by a surgeon to position the patch or plug relative to the repair site and / or to secure the patch or plug relative to the opening or weakness in the tissue or muscle wall. The tether may be configured to extend through the defect and outside a patient's body to allow a surgeon to position and / or manipulate the patch from a location outside the body. An indicator may be provided on the tether as an aid for a surgeon in determining when the patch or plug has been inserted a sufficient distance within the patient. A support member may be arranged in or on the patch or plug to help deploy the patch or plug at the surgical site and / or help inhibit collapse or buckling of the patch or plug. The patch or plug may be configured with a pocket or cavity to facilitate the deployment and / or positioning of the patch or plug over the opening or weakness.
Owner:DAVOL
Cartilage repair plug
InactiveUS6632246B1Facilitate cell ingrowthMechanically fixedBone implantDiagnosticsCartilage repairSurgical department
A cartilage plug, which is made from a biocompatible, artificial material, that is used to fill a void in natural cartilage that has been resected due to traumatic injury or chronic disease is disclosed. Alternatively, the plug may be relied upon to anchor a flowable polymer to subchondral bone. The plug is prebricatable in any size, shape, and contour and may be utilized either singly or in a plurality to fill any size void for any application. The plug may be formed of a laminated structure to match the physiological requirements of the repair site. Additionally, ridges may be formed about the periphery of each plug to facilitate its anchoring to surrounding cartilage, bone and / or adjacent plugs. A procedure for resecting damaged or diseased cartilage and for implanting a replacement plug or plugs according to this invention, as well as a set of instruments for effecting the procedure, and a self-contained system for orthopedic surgeons, which includes a variety of differently sized and shaped plugs, as well as a set of instruments for the procedure are also disclosed.< / PTEXT>
Owner:ABS
Implantable prosthesis
ActiveUS20040087980A1Avoid it happening againHelp positioningLigamentsMusclesProcedure LocationWeakness
An implantable prosthesis for repairing an anatomical defect, such as a tissue or muscle wall hernia, including an umbilical hernia, and for preventing the occurrence of a hernia at a small opening or weakness in a tissue or muscle wall, such as at a puncture tract opening remaining after completion of a laparoscopic procedure. The prosthesis includes a patch and / or plug having a body portion that is larger than a portion of the opening or weakness so that placement of the body portion against the defect will cover or extend across that portion of the opening or weakness. At least one tether, such as a strap, extends from the patch or plug and may be manipulated by a surgeon to position the patch or plug relative to the repair site and / or to secure the patch or plug relative to the opening or weakness in the tissue or muscle wall. The tether may be configured to extend through the defect and outside a patient's body to allow a surgeon to position and / or manipulate the patch from a location outside the body. An indicator may be provided on the tether as an aid for a surgeon in determining when the patch or plug has been inserted a sufficient distance within the patient. A support member may be arranged in or on the patch or plug to help deploy the patch or plug at the surgical site and / or help inhibit collapse or buckling of the patch or plug. The patch or plug may be configured with a pocket or cavity to facilitate the deployment and / or positioning of the patch or plug over the opening or weakness.
Owner:DAVOL
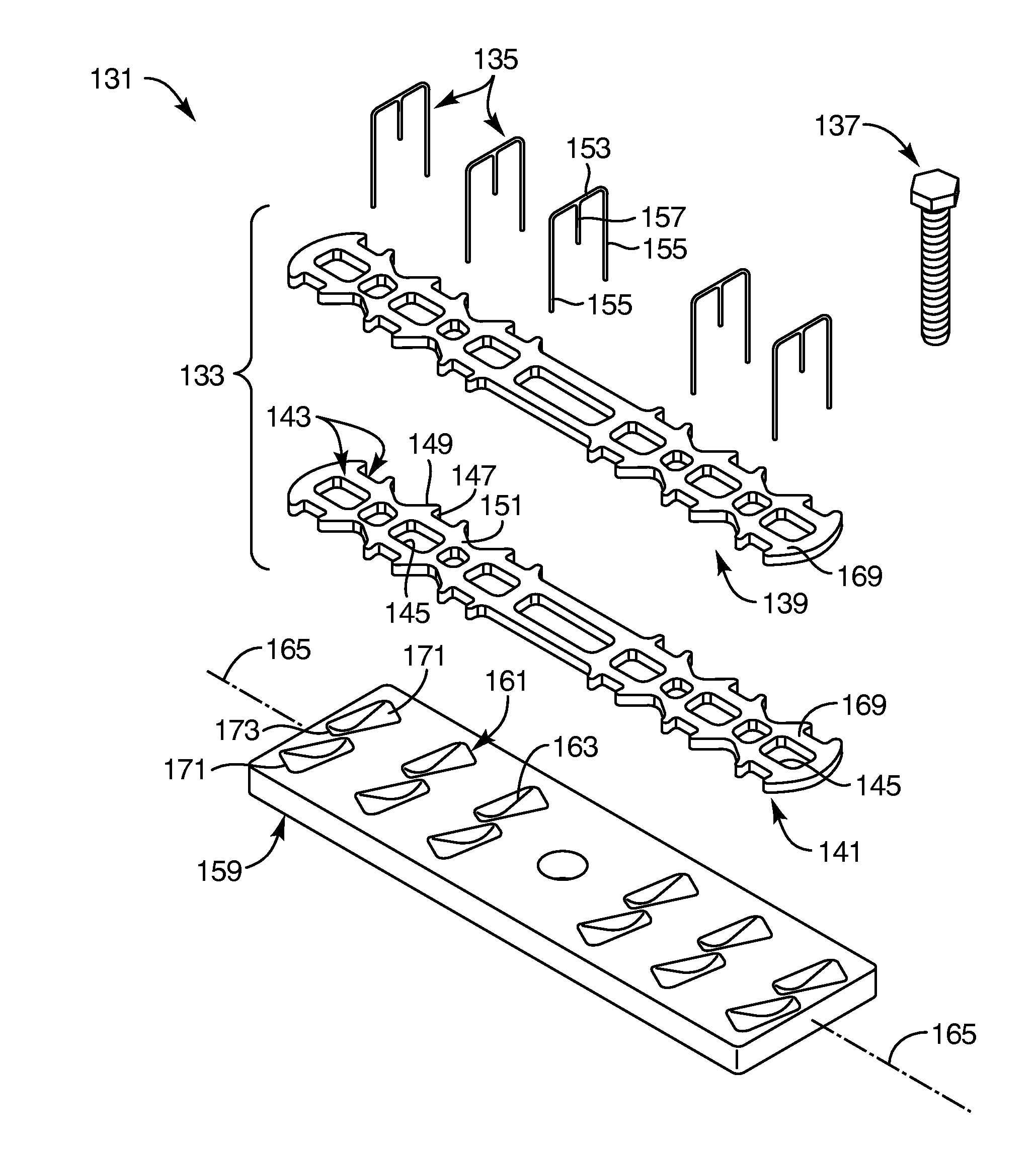
Method of forming knotless double row construct with graft or patch fixed under repair site
Systems and methods for soft tissue to bone repairs, without knot tying. The soft tissue repair includes the steps of (i) providing a medial row formed of a plurality of medial anchors, the medial anchors comprising suture or tape attached to each of the bodies of the medial anchors, the suture or tape forming a loop when the medial anchors are placed within tissue; (ii) passing traction sutures through each of the corresponding loop of the nearest medial anchor; (iii) passing through the tissue (rotator cuff) the free limbs of the suture or tape attached to each of the medial anchors, and one end of the traction suture (passed through the corresponding loop) at their respective points; (iv) bringing the other end of the traction suture (through a lateral cannula) underneath the tissue (the rotator cuff) and then securing the passed end of the traction suture to a graft or patch located underneath the tissue (rotator cuff); and (v) adjusting the position of the graft or patch by pulling end of the traction suture passed through the tissue (rotator cuff).
Owner:ARTHREX
Methods and procedures for ligament repair
InactiveUS20090306776A1Facilitate anterior cruciate ligament regenerationPromote healingSuture equipmentsPeptide/protein ingredientsRepair siteLigament structure
Methods and devices for the repair of a ruptured ligament using a scaffold device are provided. Aspects of the invention, may include a scaffold attached by a suture to an anchor. In aspects of the invention, the anchor may be secured to a bone near or at the repair site.
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Devices and methods for spine repair
InactiveUS7632294B2Avoid squeezingMinimally invasiveSurgical furnitureBone implantRepair siteProsthesis
Surgical methods of repairing defects and deficiencies in the spine are disclosed. The methods involve delivering a single part in-situ polymerizing fluid to (i) close a weakened segment or fissure in the annulus fibrosus, (ii) strengthen the annulus, (iii) replace or augment the disc nucleus, or (iv) localize a disc prosthesis. The methods may include placing a delivery conduit adjacent to the repair site and providing a liquid tissue adhesive to bond to and repair a disc defect or deficiency.
Owner:PROMETHEAN SURGICAL DEVICES
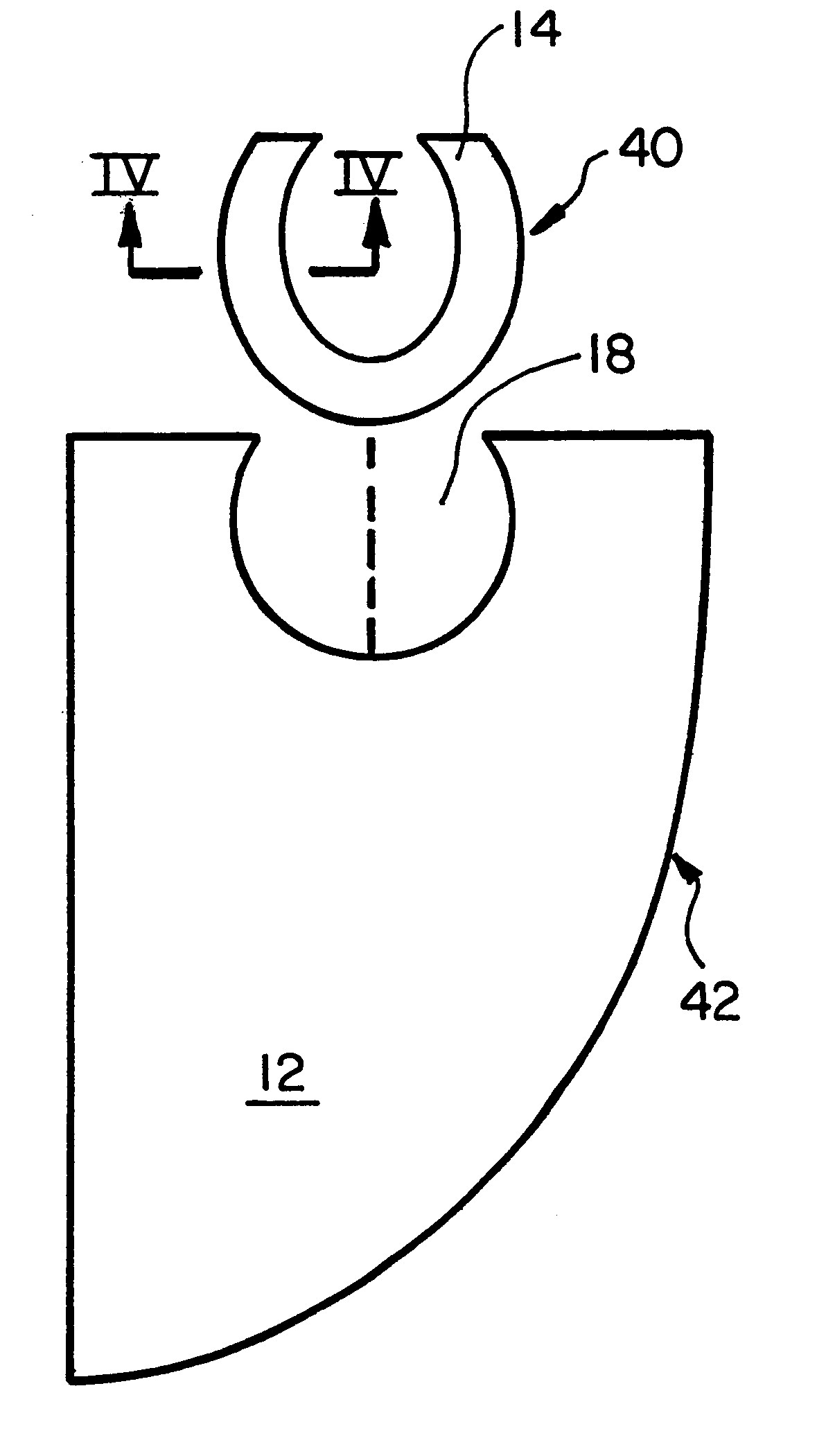
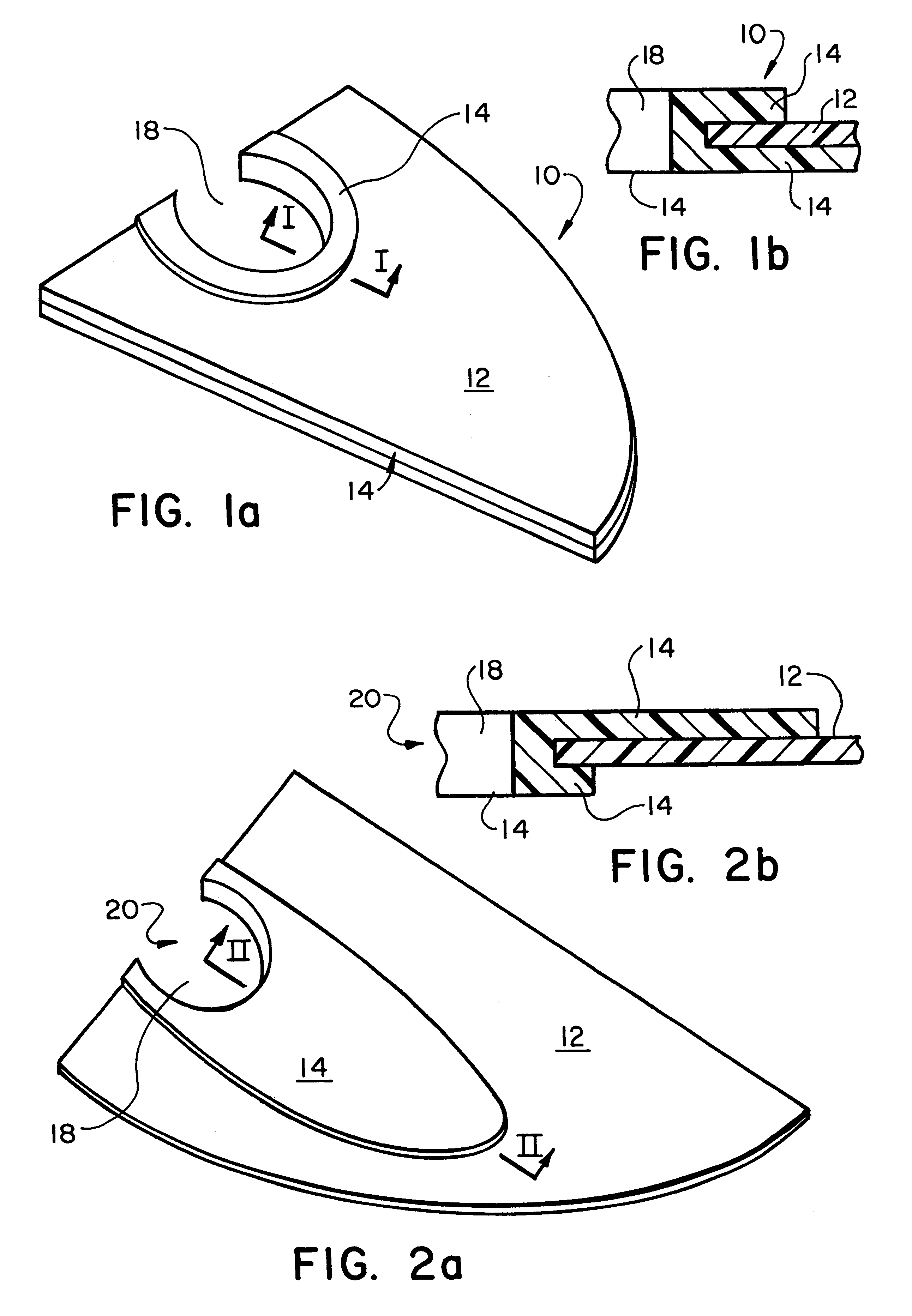
Devices, systems, and methods for repairing soft tissue and attaching soft tissue to bone
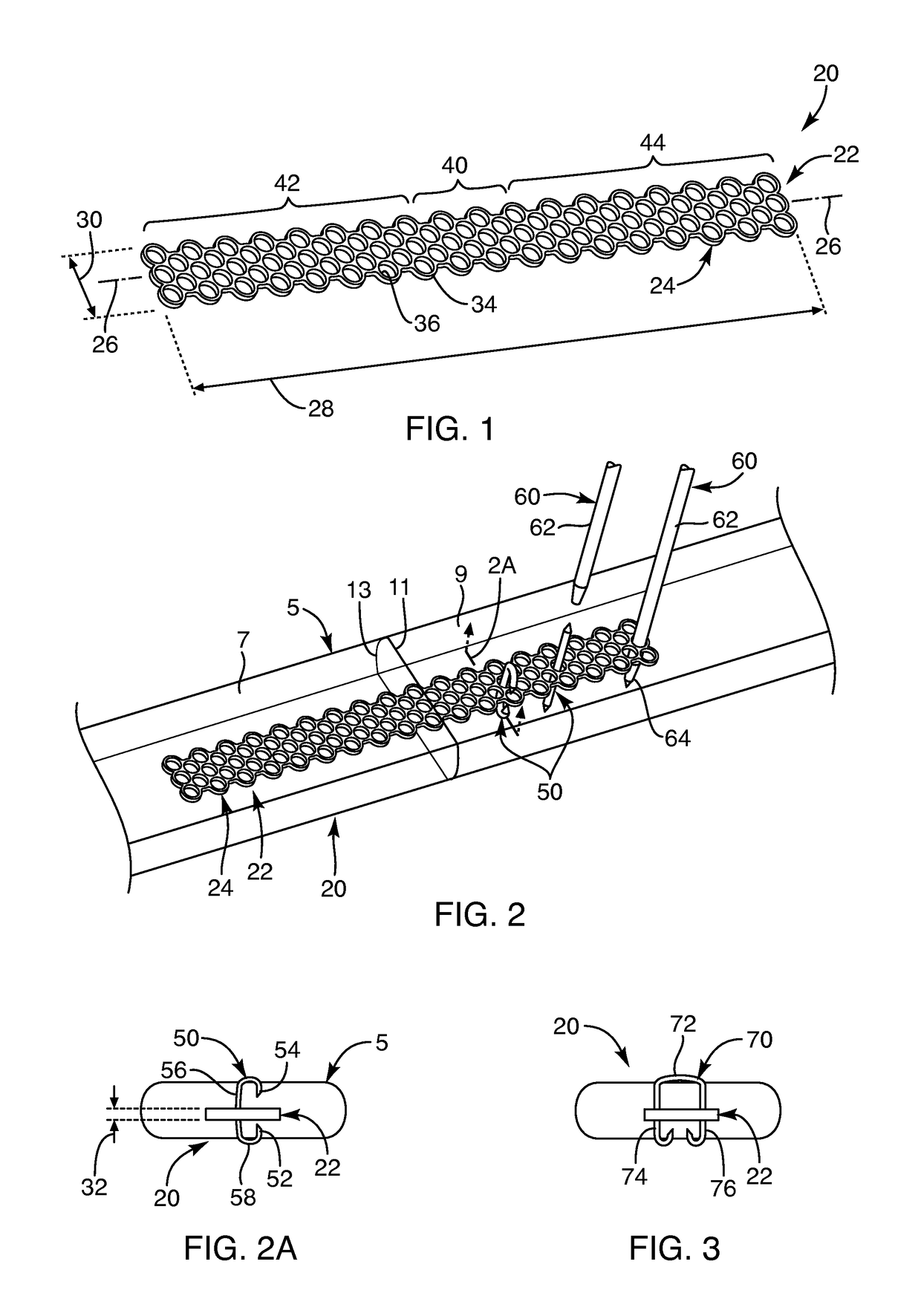
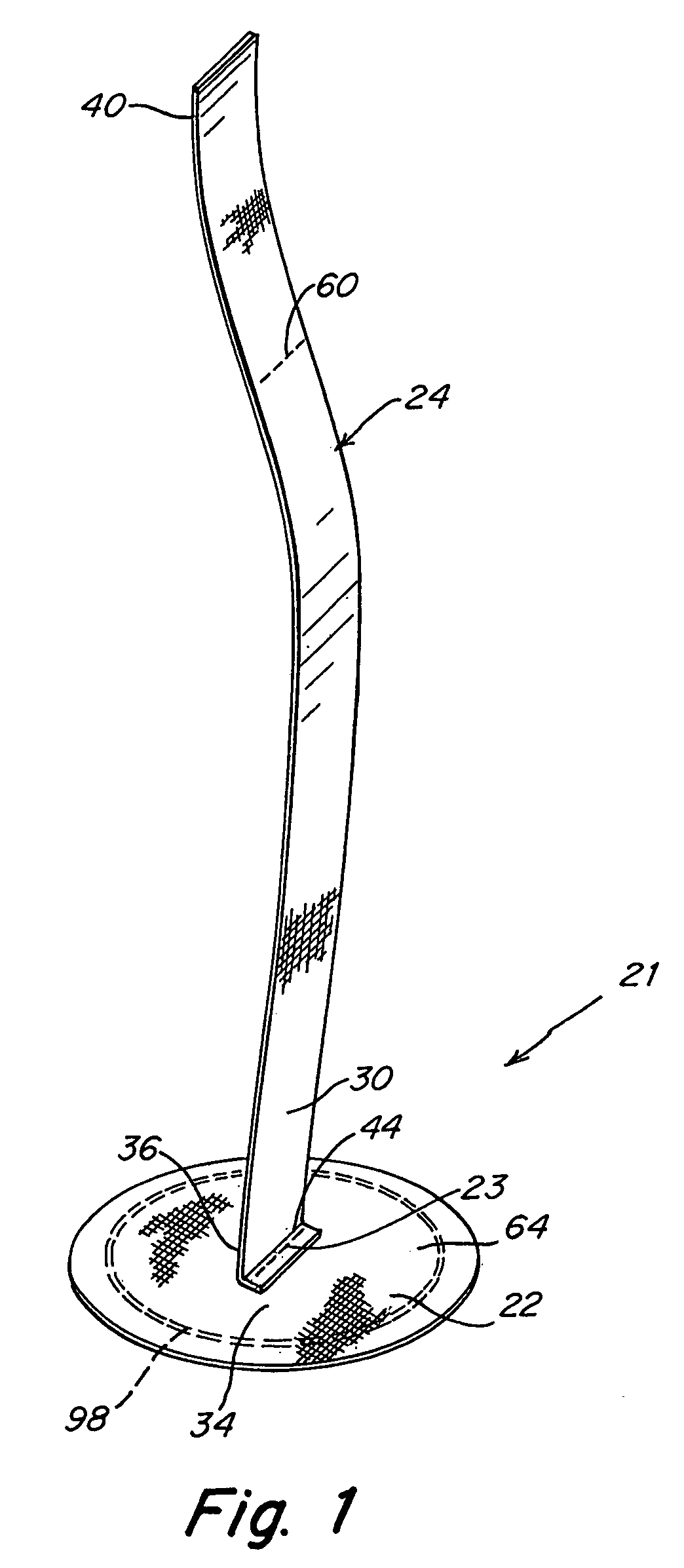
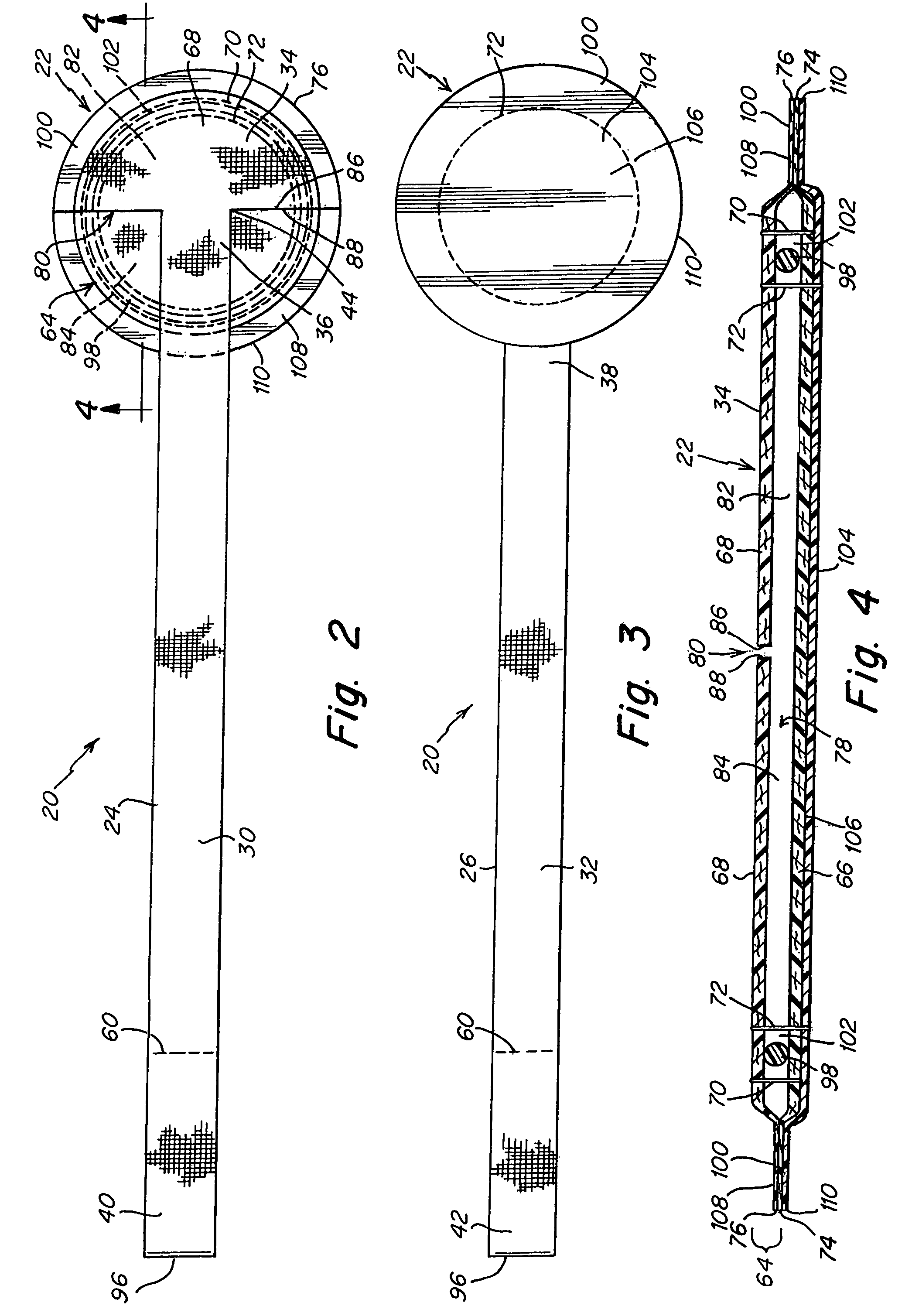
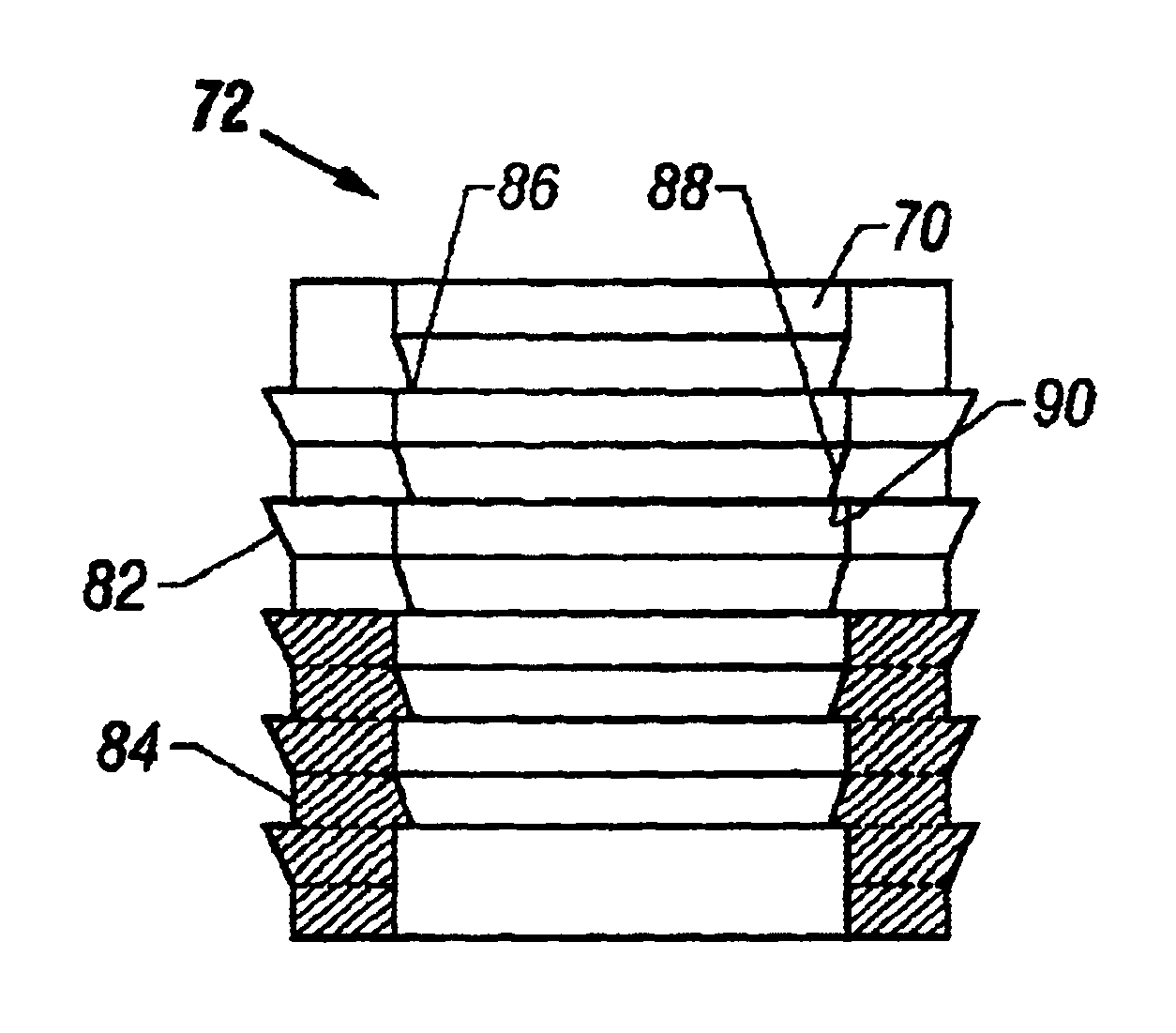
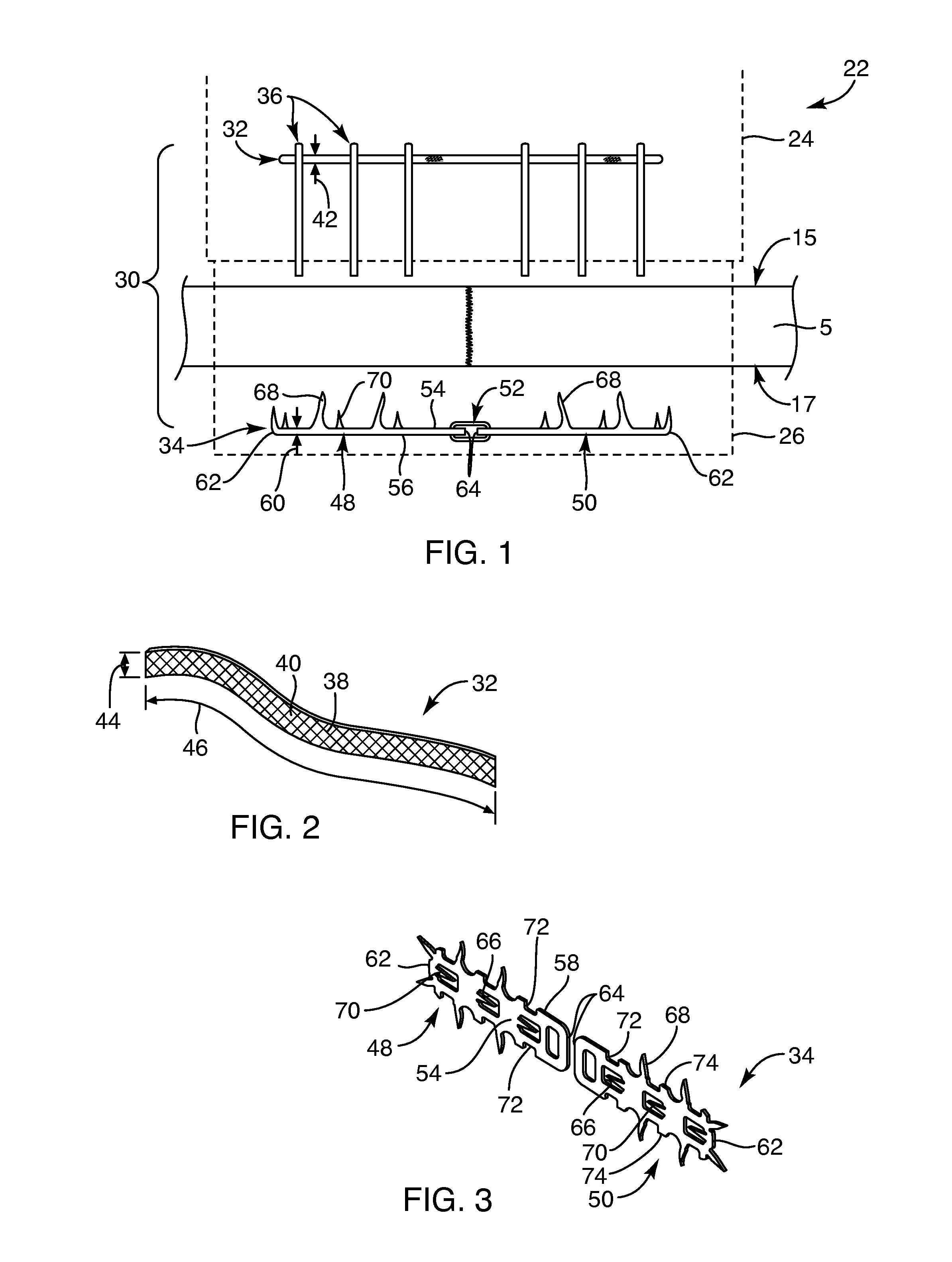
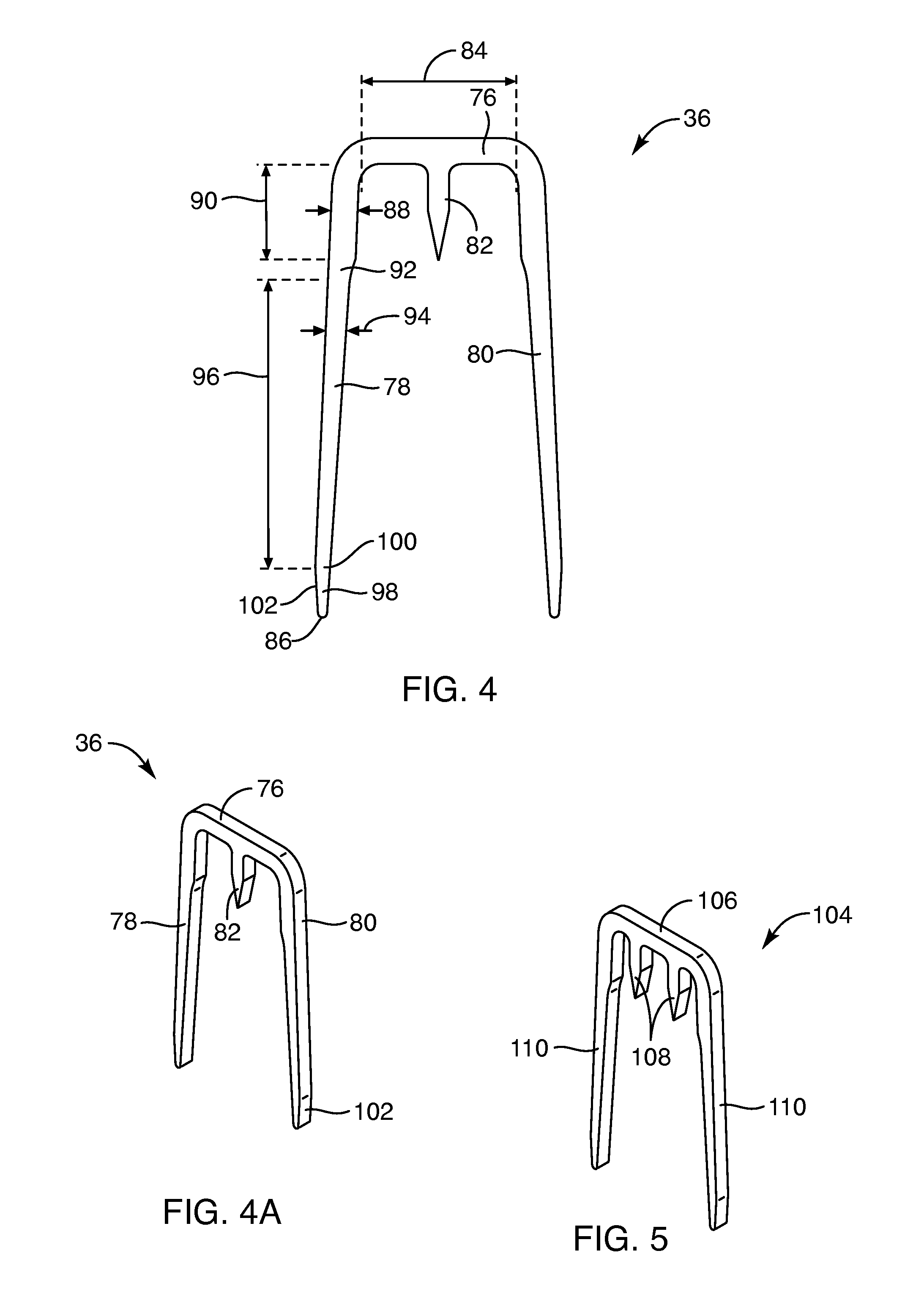
Devices, systems and / or methods for repairing soft tissue adjacent a repair site. In one embodiment, a repair device includes a plate member and an anchor. The plate member having a periphery, the plate member configured to be positioned along an outer surface of the soft tissue. The anchor includes a base and six legs extending from the base, the six legs extending from the base being moveable to a curled configuration such that the six legs wrap around separate portions of the periphery of the plate member with the soft tissue therebetween. In this manner, the repair device may be anchored to the soft tissue.
Owner:CONEXTIONS
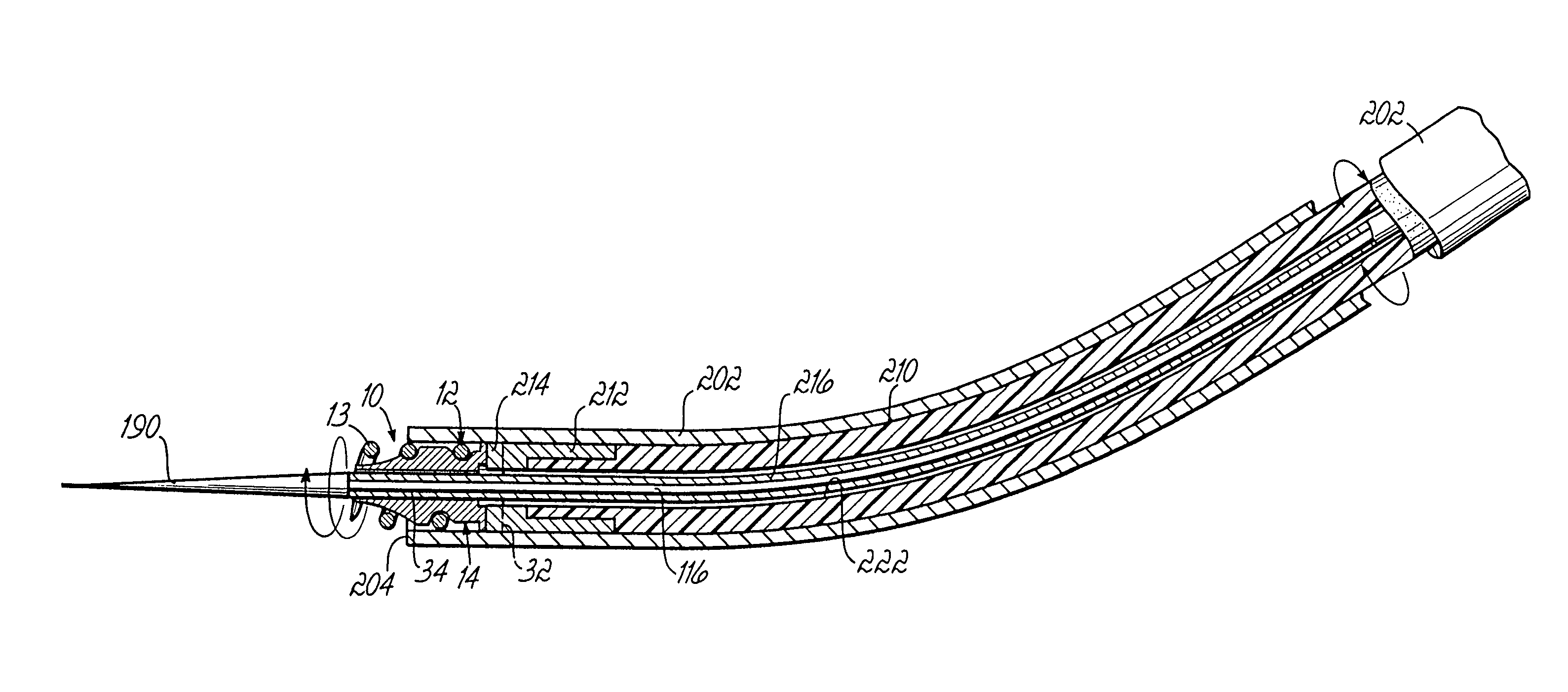
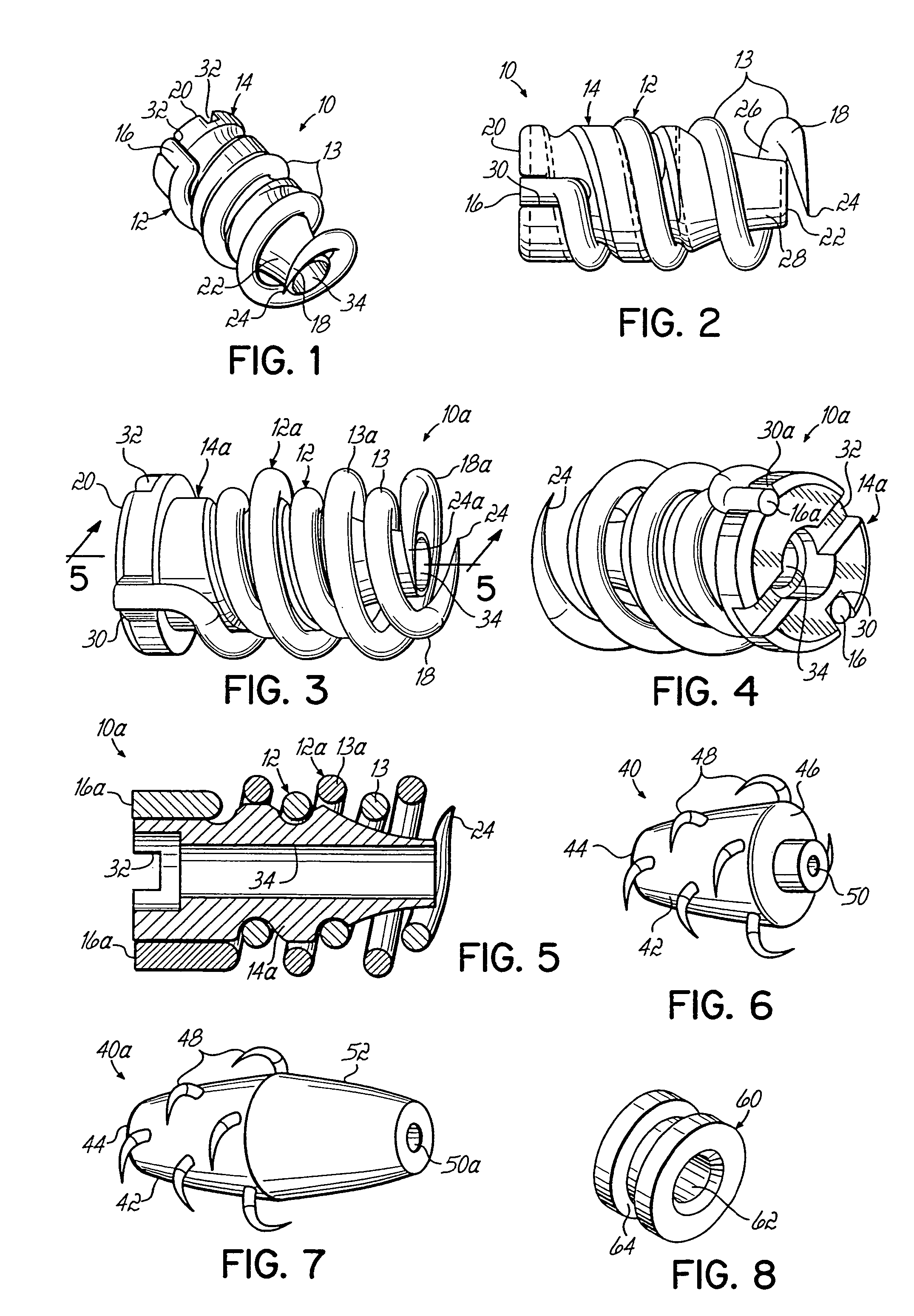
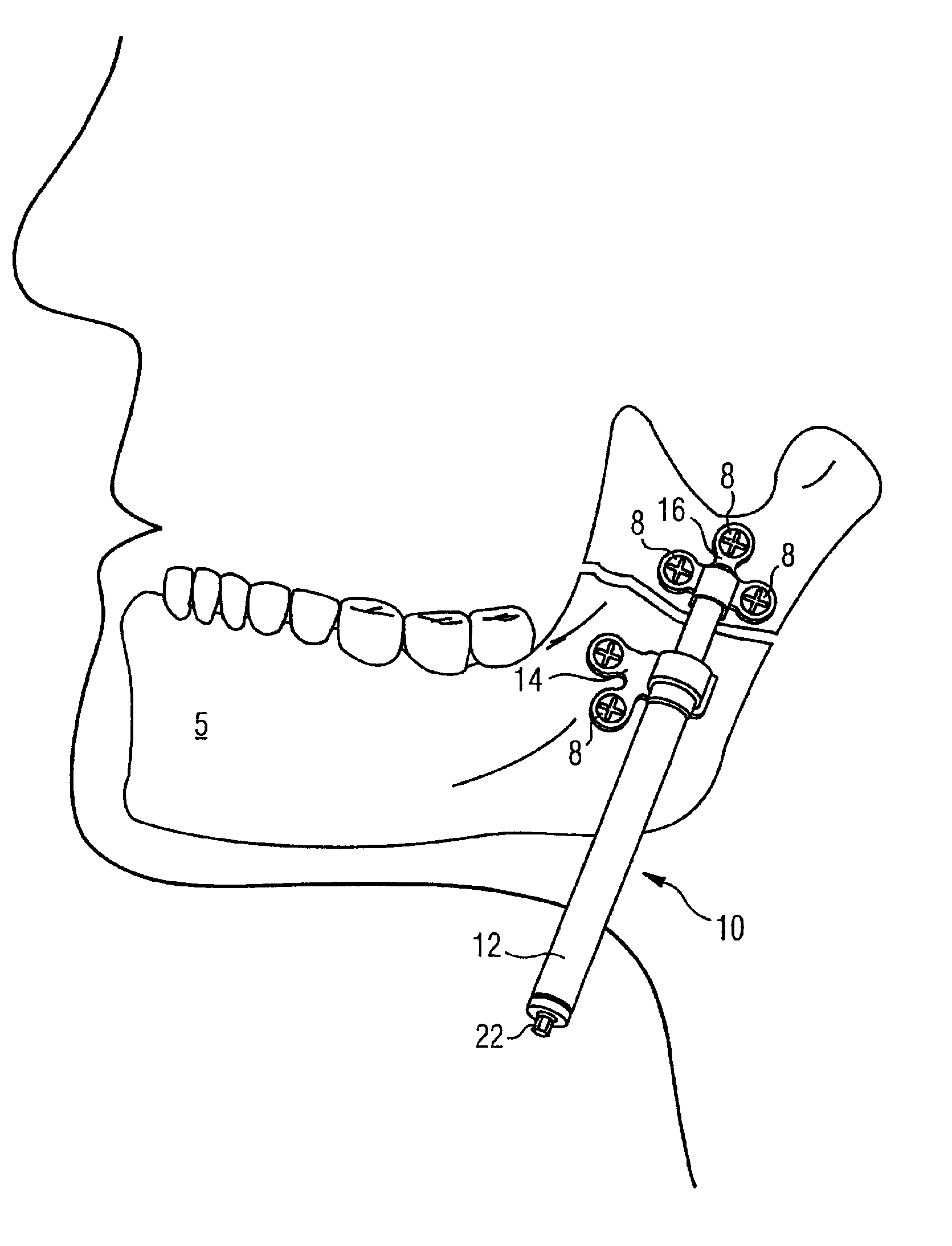
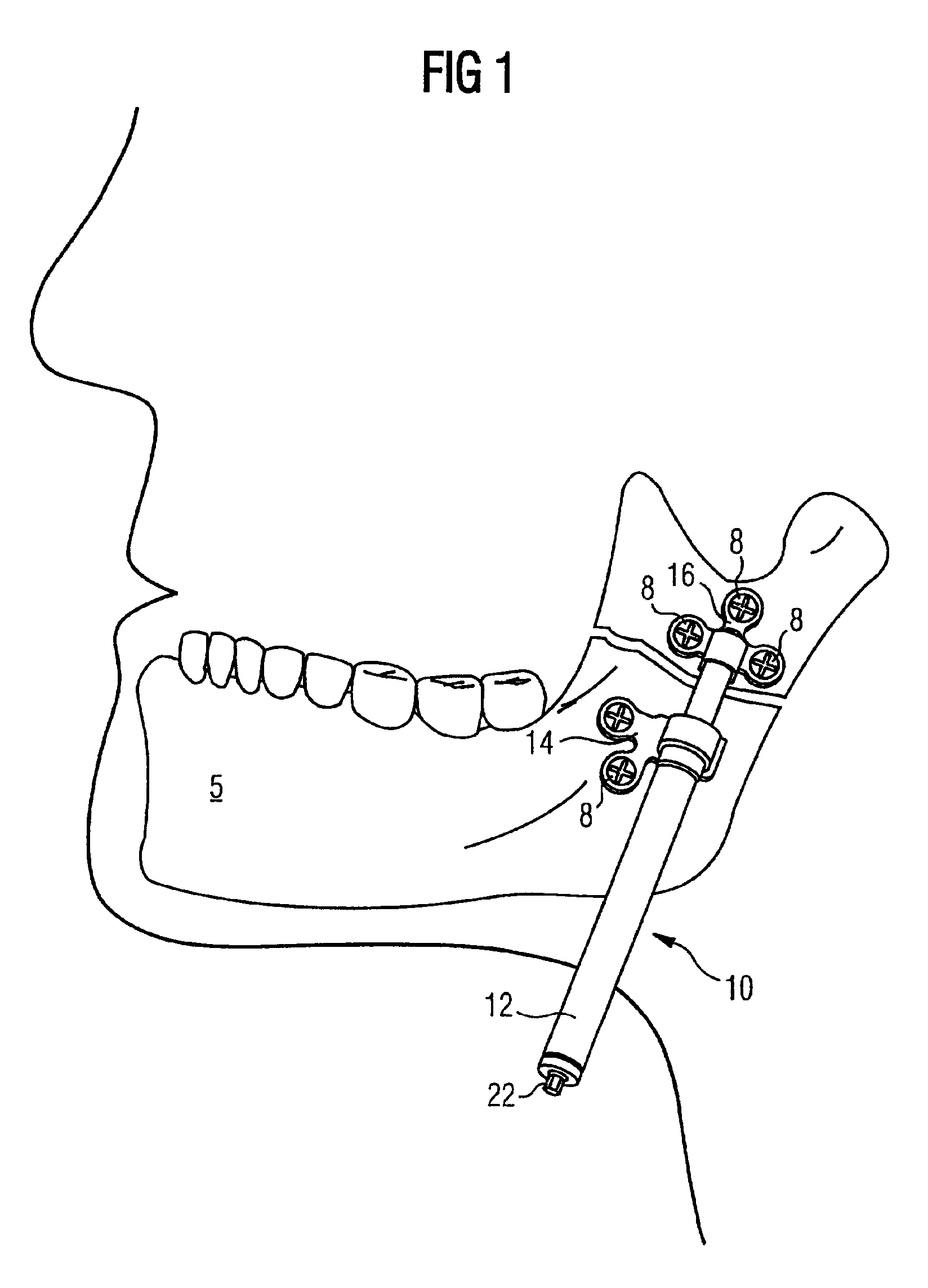
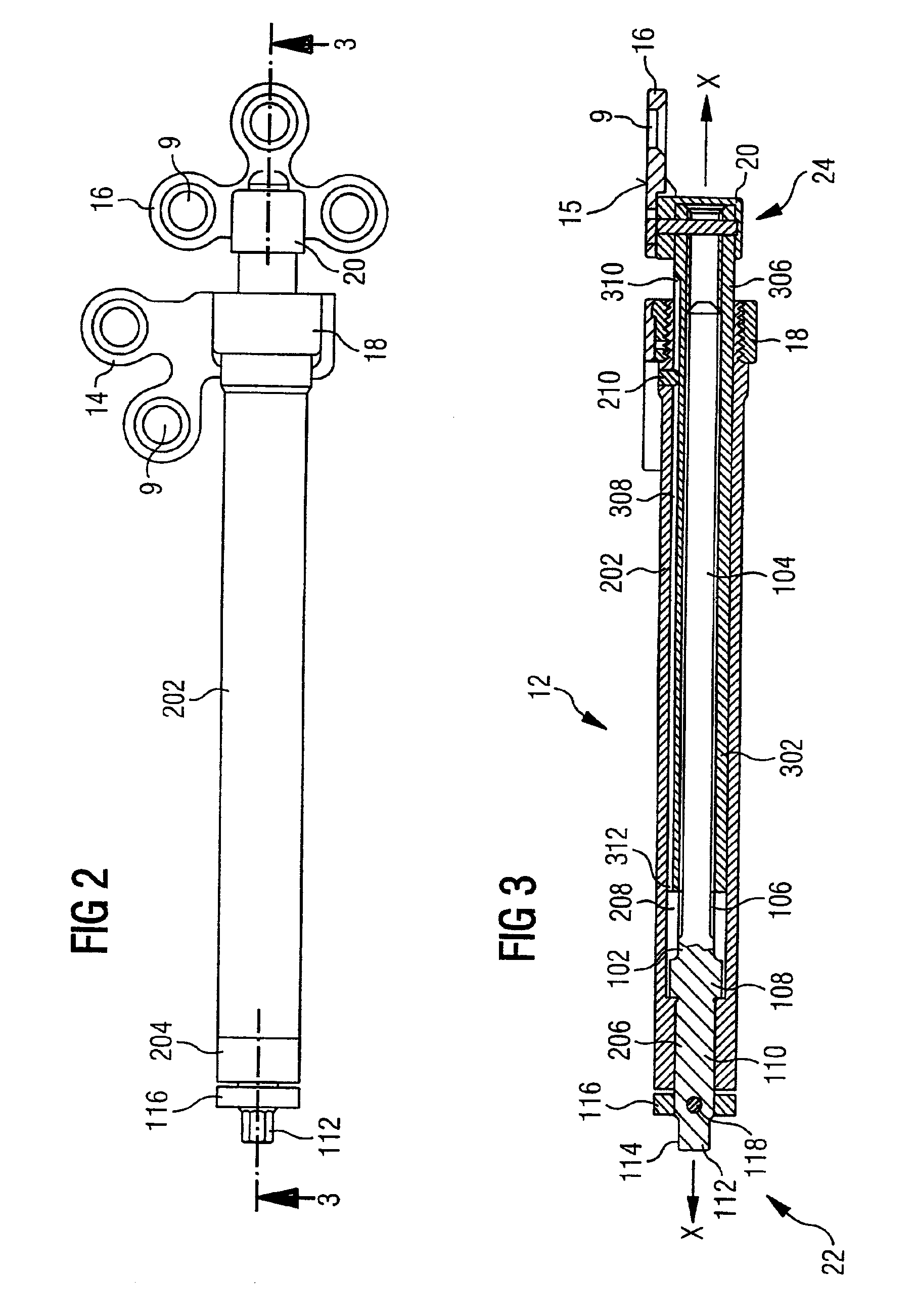
Apparatus and methods for tendon or ligament repair
Apparatus and methods for repairing damaged tendons or ligaments. Various repair apparatus include an elongate tensile member and a pair of anchor assemblies connected for movement along the tensile member on either side of a repair site, such as a tear or laceration. The anchor assemblies or structures may take many forms, and may include barbed, helical, and crimp-type anchors. In the preferred embodiments, at least one anchor structure is movable along the elongate tensile member to assist with adjusting a tendon segment to an appropriate repair position and the anchor structure or structures are then lockable onto the elongate tensile member to assist with affixing the tendon at the repair position. Tendon and / or ligament-to-bone repair apparatus and methods employ similar concepts.
Owner:TENDON TECH +1
Apparatus and Method for Limiting Surgical Adhesions
A composite prosthesis and method for limiting the incidence of postoperative adhesions. The composite includes a non-inflammatory or coated mesh and a barrier material which prevents exposure of tissue elsewhere in the body to tissue covered by the composite prosthesis. The barrier material is absorbable which allows tissue through-growth and localization of the composite prosthetic. In use, the composite prosthesis is positioned over the tissue defect and may be positioned with the barrier material oriented against the tissue defect or repair site.
Owner:PROMETHEAN SURGICAL DEVICES
Mechanically Competent Scaffold for Rotator Cuff and Tendon Augmentation
A device has been developed to augment the rotator cuff tendon tissue as it proceeds in healing. The device has two purposes: to provide initial stability to the rotator cuff repair site to allow early mobilization of the upper extremity of the patient, and to allow for reinforcement of rotator cuff tendon repairs to increase the likelihood of successful rotator cuff tendon repairs. The device consists of an inter-connected, open pore structure that enables even and random distribution and in-growth of tendon cells. The braided structure allows for distribution of mechanical forces over a larger area of tissue at the fixation point(s).
Owner:BIOREZ INC
Hernia prosthesis
A prosthesis and a method for repairing a tissue or muscle wall defect, such as an inguinal hernia, near a cord-like structure, such as the spermatic cord. The prosthesis comprises a layer of repair fabric having a cord opening therethrough that is adapted to receive the cord-like structure when the prosthesis is implanted at the repair site. The prosthesis also includes a cord protector that is attachable to the repair fabric at the opening to isolate the cord-like structure from the fabric in proximity to the opening. The repair fabric may be formed from a material which is susceptible to the formation of adhesions with sensitive tissue and organs. The cord protector may be formed from material which inhibits the formation of adhesions with sensitive tissue and organs. The cord protector may overlie a portion of at least one of the first and second surfaces of the repair fabric. The cord protector may extend substantially farther away from the opening edge on one of the first and second surfaces than on the other of the first and second surfaces. The cord protector may be configured as an insert that is separate from and attachable to the repair fabric. Alternatively, the cord protector may be integral with the repair fabric to form a composite prosthesis.
Owner:CR BARD INC +1
Repair process for aluminum nitride substrates
A method to repair Aluminum Nitride (AlN) substrates is disclosed wherein a frequency doubled Q-switched Nd:YAG laser is used to remove unwanted metallurgy. The substrate is place in a liquid filled work chamber which acts to prevent metallic species of AlN from forming. The repair site can be sealed with a novel polymer coating to prevent contamination or corrosion. Repairs can be made to buried or surface metallurgy.
Owner:IBM CORP
Apparatus and methods for securing tendons or ligaments to bone
InactiveUS7708759B2Eliminate increase of bulkWithout constricting the blood flow to the tendonSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisRepair siteEngineering
Owner:TENDON TECH
Native soft tissue matrix for therapeutic applications
InactiveUS20050288796A1Promote ex vivo regenerationEfficient and effectiveAnti-incontinence devicesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismTissue repairPerichondrium
A product for implantation within a soft tissue site of the human or animal body comprises a pulverized or morselized matrix of a substantially non-mineralized native soft tissue (NSTM) of the human or animal body, provided in a therapeutic amount to induce growth of native tissue or organs and healing at the tissue site. The NSTM is composed of at least one soft tissue selected from the group consisting of cartilage, meniscus, intervertebral disc, ligament, tendon, muscle, fascia, periosteum, pericardium, perichondrium, skin, nerve, blood vessels, and heart valves or from organs such as bladder, lung, kidney, liver, pancreas, thyroid, or thymus. Preferably, the NSTM is composed of a soft tissue of the same type of tissue native to the repair site. In another embodiment, the NSTM includes soft tissue of a different type than the tissue repair site.
Owner:AWAD HANI +2
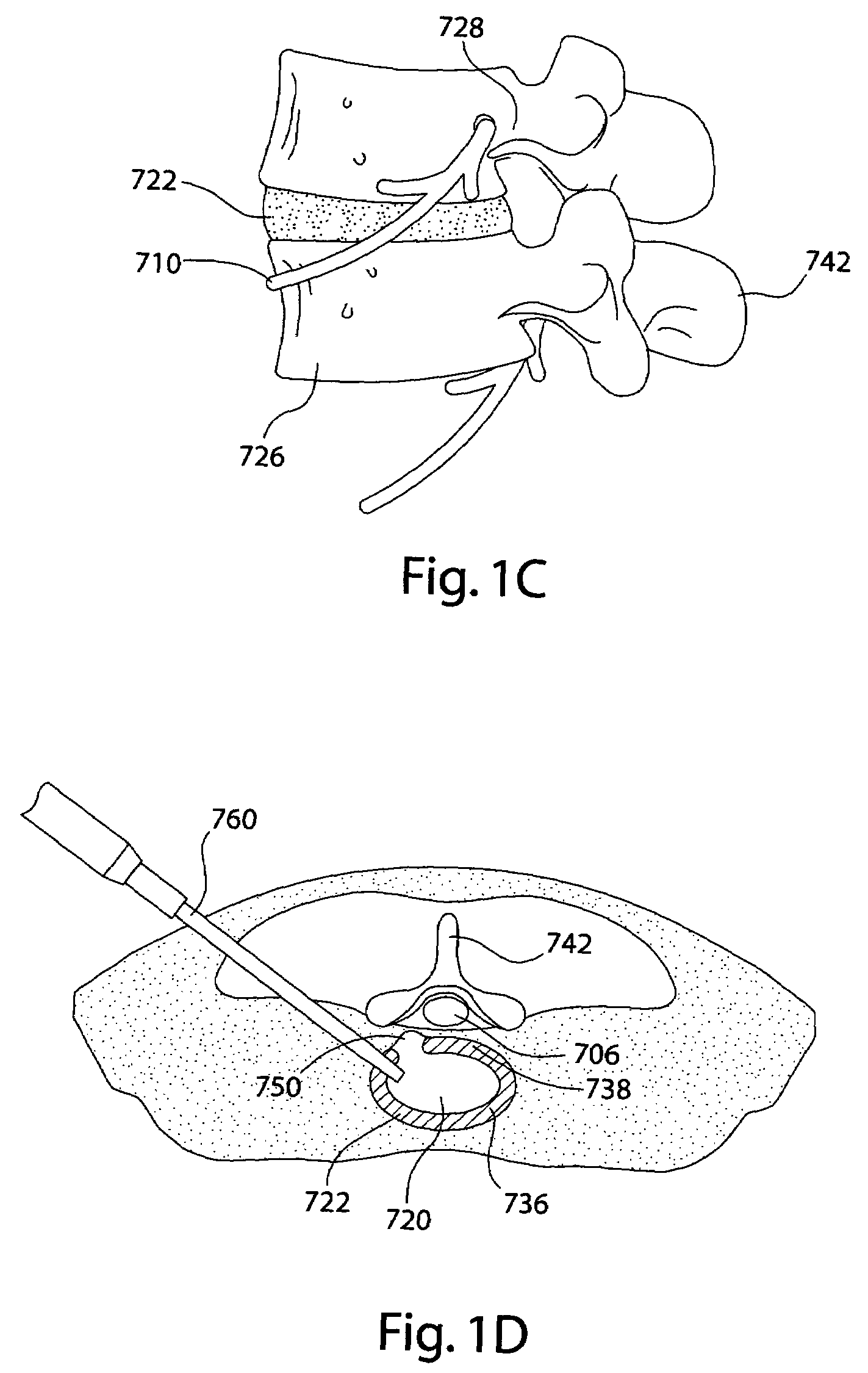
Method and system for joint repair
A method and system for repairing a defect area in a surface of a joint include providing a mold having a first surface and a second surface, positioning the mold within the joint such that at least part of the mold first surface overlies the defect area, and depositing a repair material under the mold first surface within the defect area to create a repaired site within the joint.
Owner:FELL BARRY M
Orthopedic system having detachable bone anchors
InactiveUS6884243B2Inhibition releaseEasy to disassembleInternal osteosythesisJoint implantsRepair siteMedicine
The present invention provides an improved orthopedic system in which the part of a device that attaches to the bone is detachable from the rest of the device. The system includes a proximal bone anchor, associated proximal fastener, a distal bone anchor, and associated distal fastener. The bone anchors are affixed to the bone on opposing sides of the bone repair site, which may be an osteotomy. The fasteners serve to releasably mechanically couple the orthopedic device, which may be a distractor, to the bone anchors. In a preferred embodiment, the bone anchors are made from a resorbable material.
Owner:SYNTHES USA
Cartilage repair plug
InactiveUS20040162622A1Easy inflowEasy to fixBone implantDiagnosticsCartilage repairSurgical department
A cartilage plug, which is made from a biocompatible, artificial material, that is used to fill a void in natural cartilage that has been resected due to traumatic injury or chronic disease is disclosed. Alternatively, the plug may be relied upon to anchor a flowable polymer to subchondral bone. The plug is prefabricatable in any size, shape, and contour and may be utilized either singly or in a plurality to fill any size void for any application. The plug may be formed of a laminated structure to match the physiological requirements of the repair site. Additionally, ridges may be formed about the periphery of each plug to facilitate its anchoring to surrounding cartilage, bone and / or adjacent plugs. A procedure for resecting damaged or diseased cartilage and for implanting a replacement plug or plugs according to this invention, as well as a set of instruments for effecting the procedure, and a self-contained system for orthopaedic surgeons, which includes a variety of differently sized and shaped plugs, as well as a set of instruments for the procedure are also disclosed.
Owner:ABS
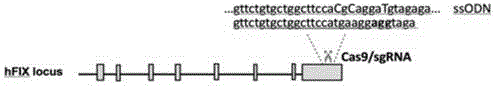
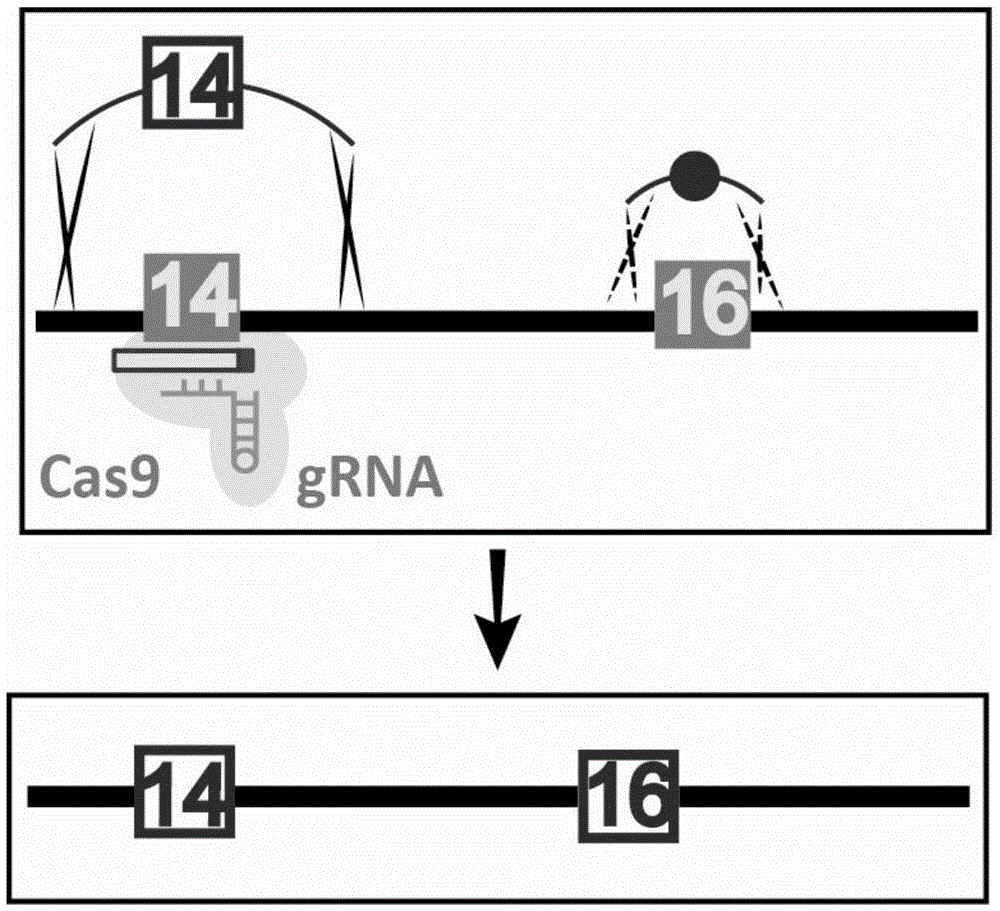
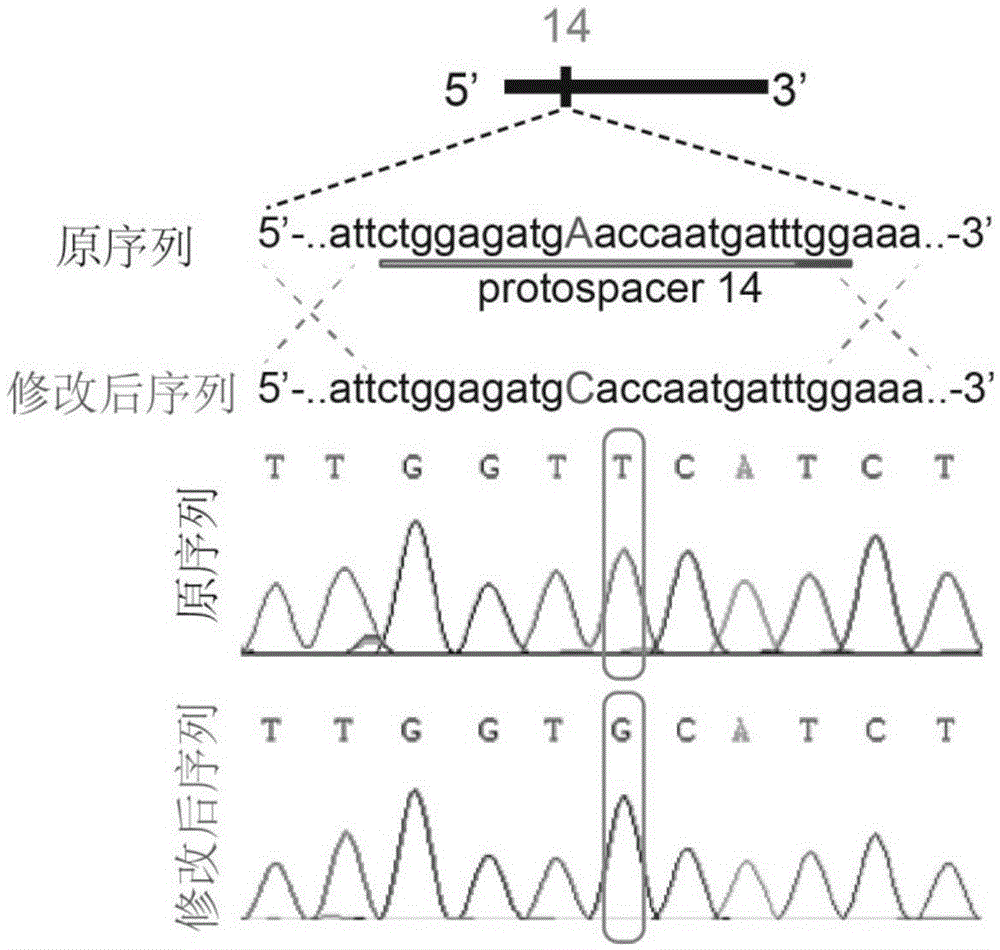
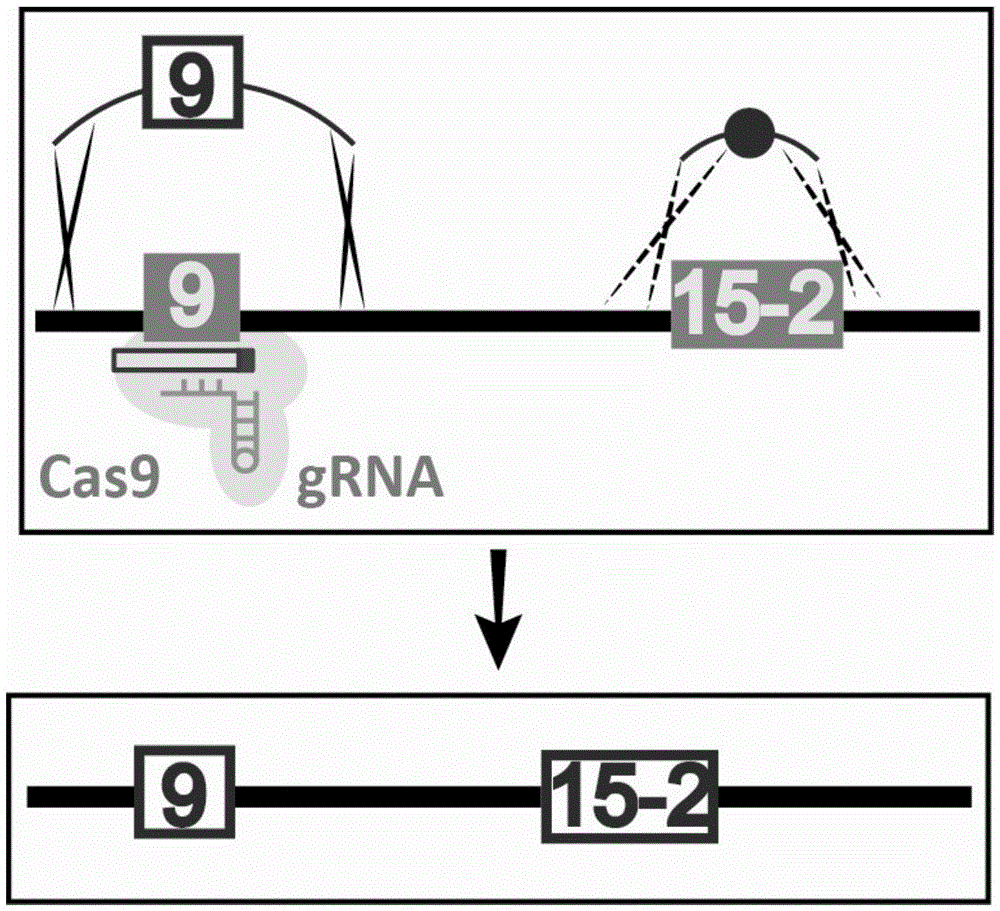
Site specific repairing carrier system and method of blood coagulation factor genetic mutation
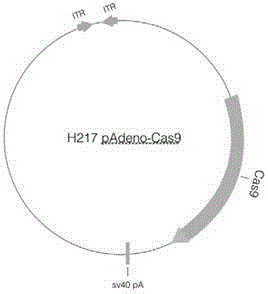
The invention discloses a method for carrying out in-situ repairing on blood coagulation factor F8 / F9. The method comprises the following steps: in a target genome sequence, selecting the mutation sites of blood coagulation factor as the gene sites for in-situ repairing; designing the binding sites of nuclease of sgRNA sequence of a CRISPR / Cas system; designing a homologous recombinant repairing donor sequence for in-situ repairing; delivering nuclease protein and / or sgRNA and the nucleotide sequence of the homologous recombinant repairing donor to the gene sites of in-situ repairing by a delivering carrier; generating damages to the genome DNA by the nuclease on the gene in-situ repairing sites; and inserting the homologous recombinant repairing donor sequence into the gene in-situ repairing sites so as to repair the gene or supplement the expression of gene. The in-situ repairing of mutation sites of blood coagulation factor can be applied to the clinic, and the method has the advantages of precise induction, safer and controllable process, and definite target.
Owner:EAST CHINA NORMAL UNIV
Devices and methods for spine repair
InactiveUS20080221628A1Avoid squeezingMinimally invasiveSurgical furnitureDiagnosticsRepair siteProsthesis
Surgical methods of repairing defects and deficiencies in the spine are disclosed. The methods involve delivering a single part in-situ polymerizing fluid to (i) close a weakened segment or fissure in the annulus fibrosus, (ii) strengthen the annulus, (iii) replace or augment the disc nucleus, or (iv) localize a disc prosthesis. The methods may include placing a delivery conduit adjacent to the repair site and providing a liquid tissue adhesive to bond to and repair a disc defect or deficiency
Owner:PROMETHEAN SURGICAL DEVICES
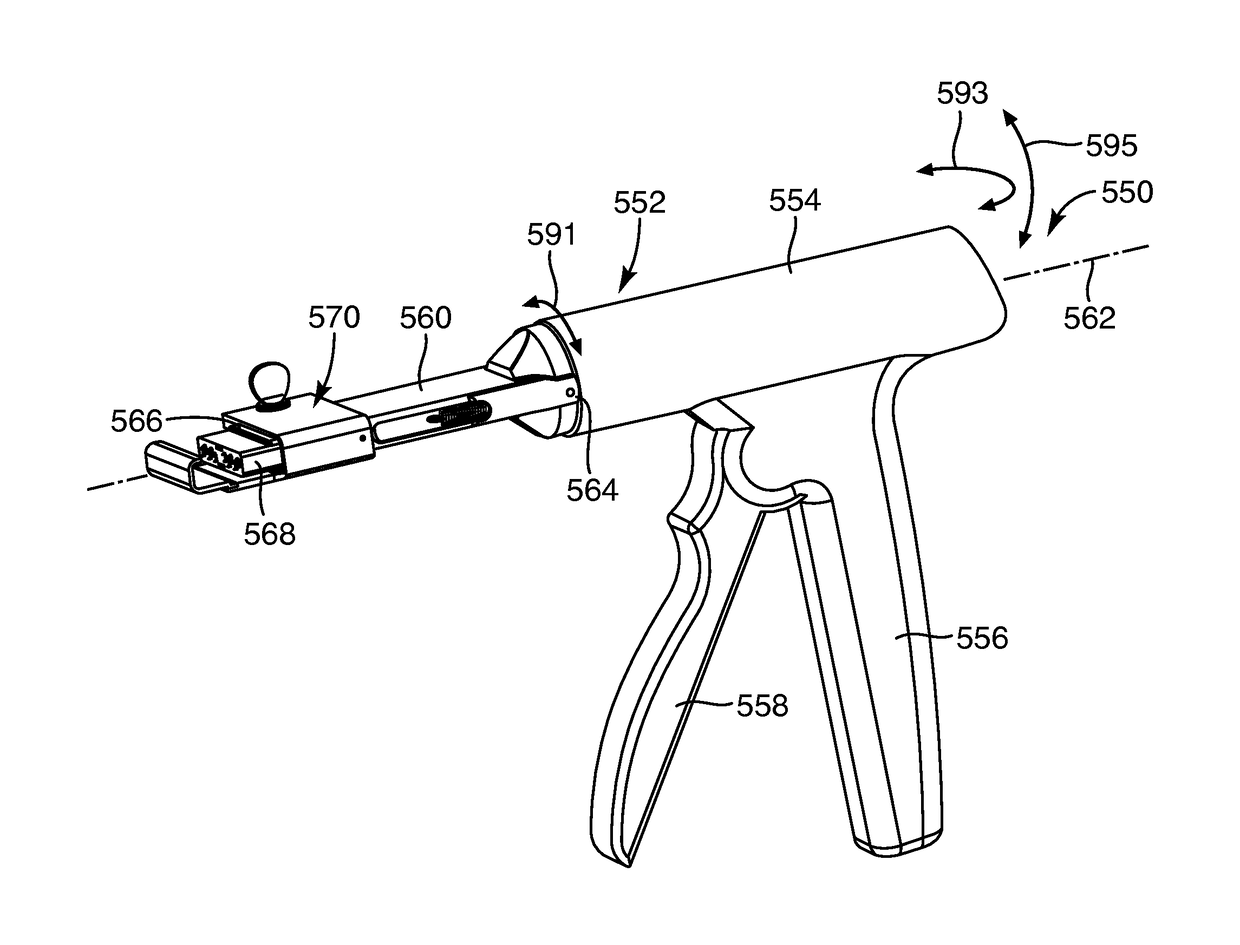
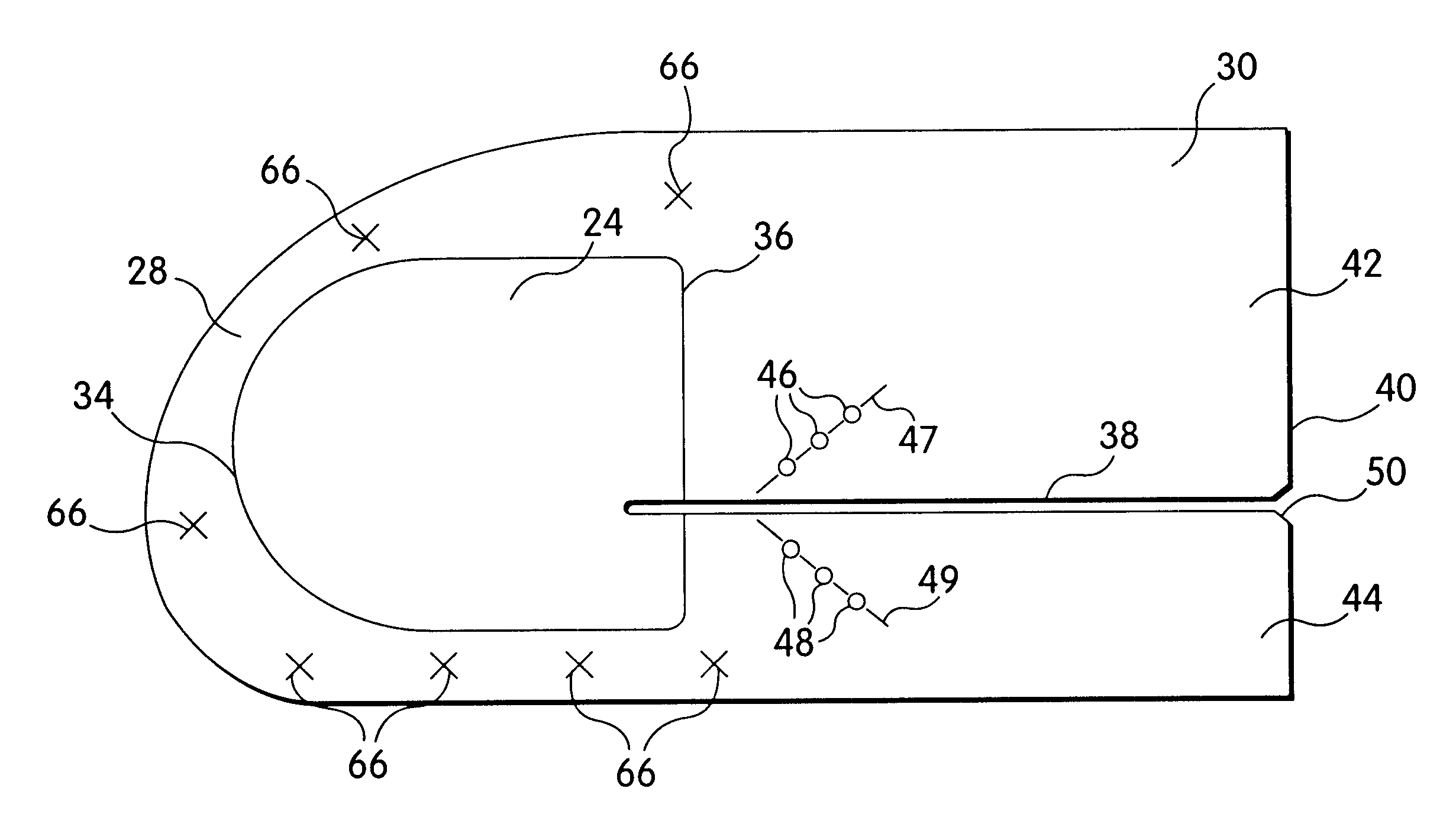
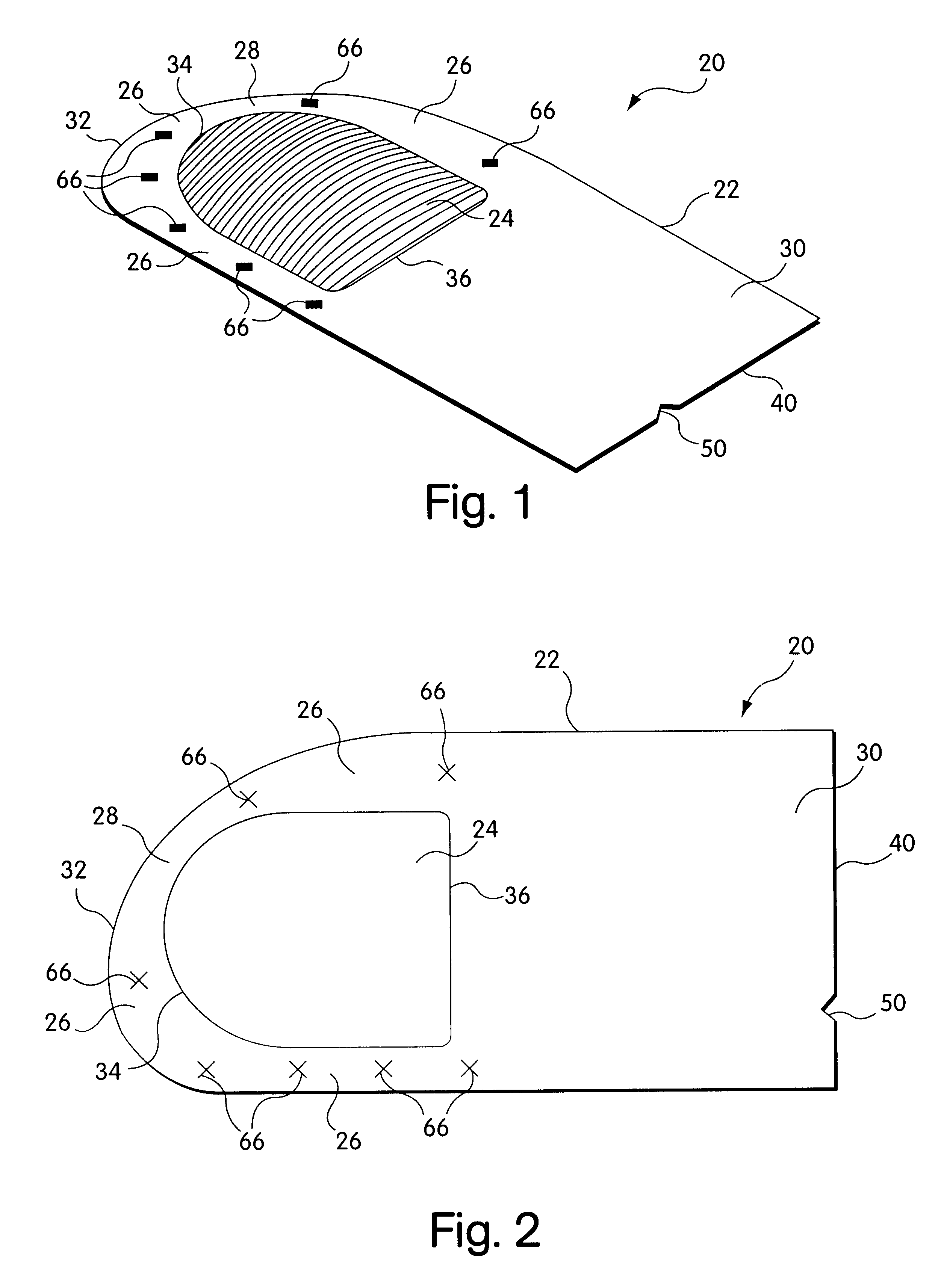
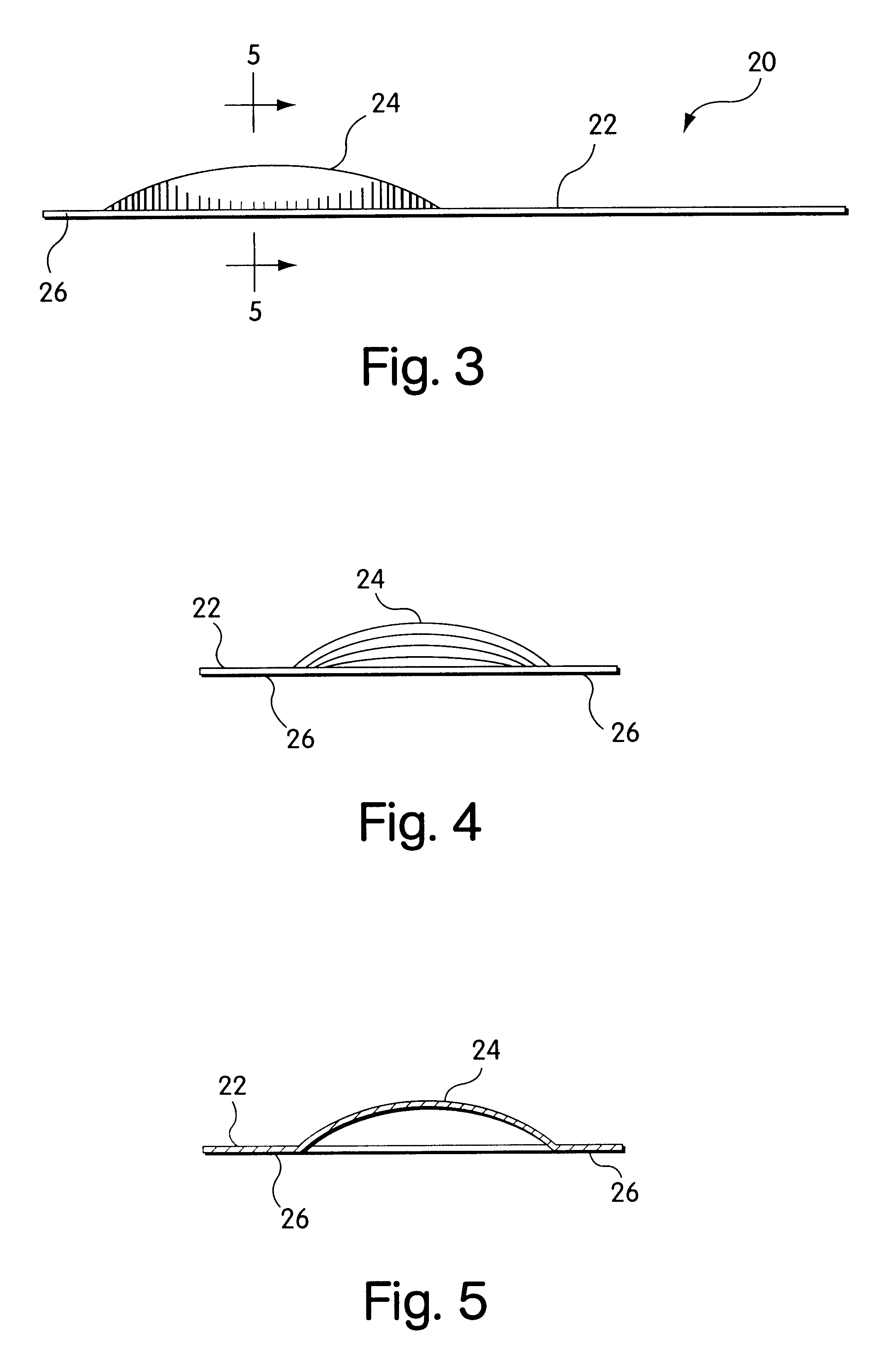
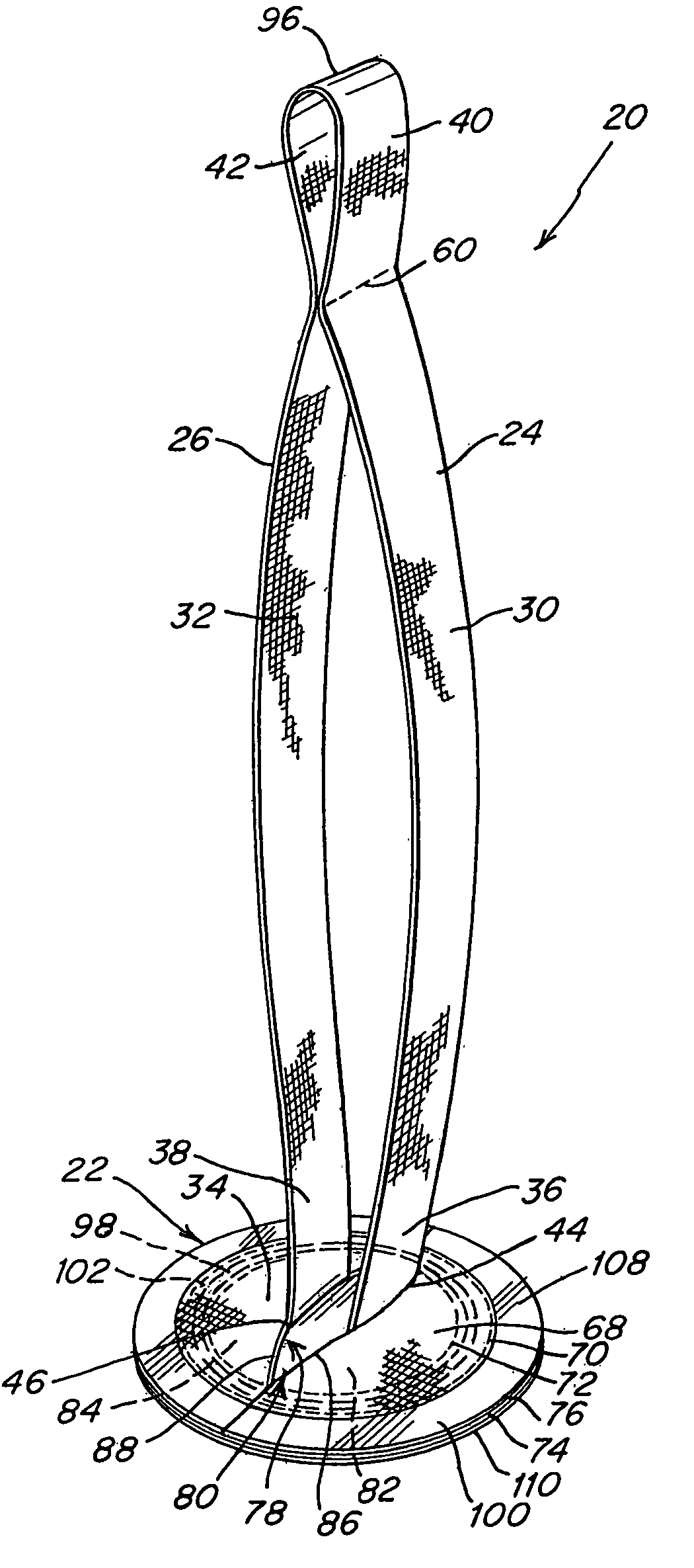
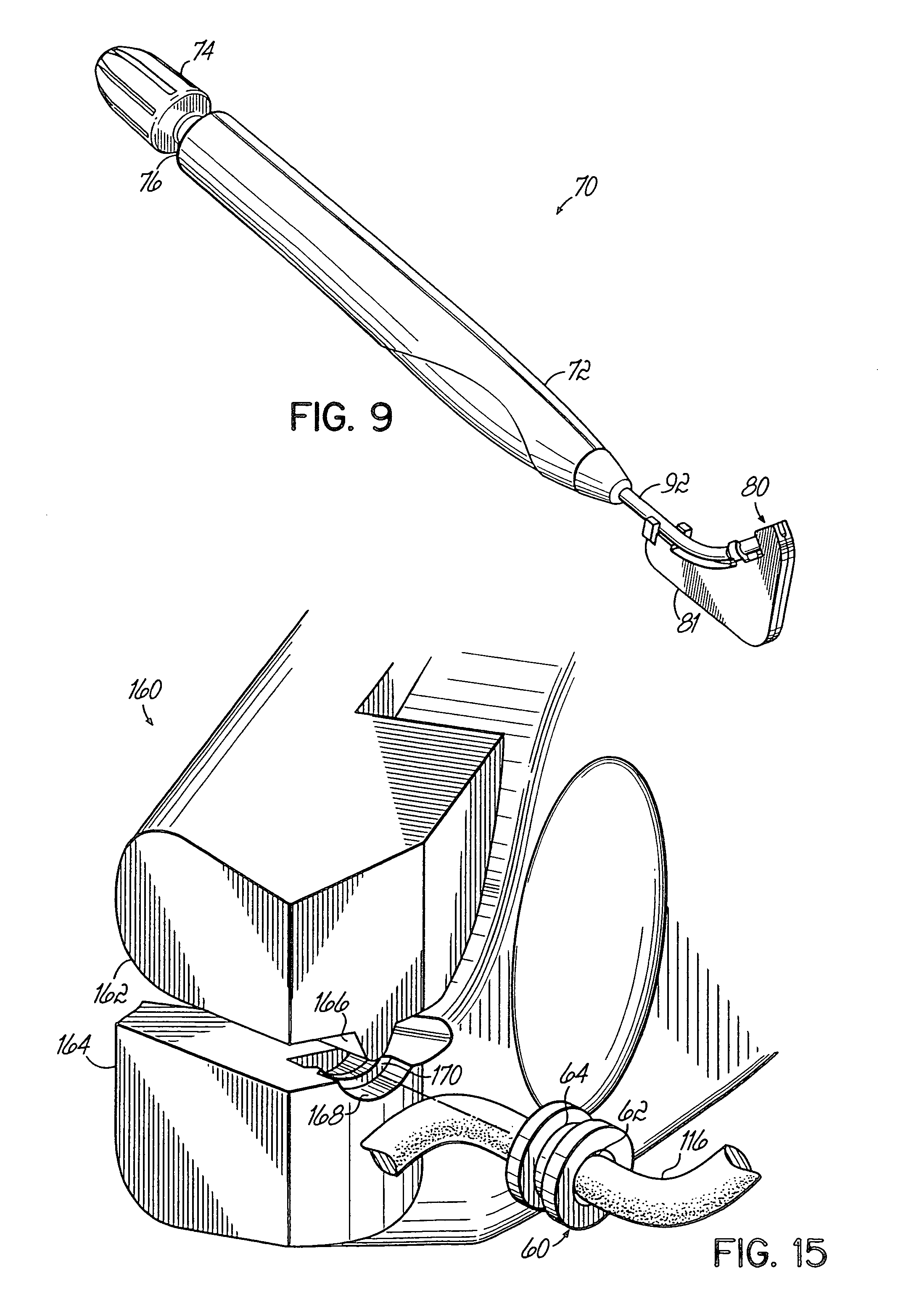
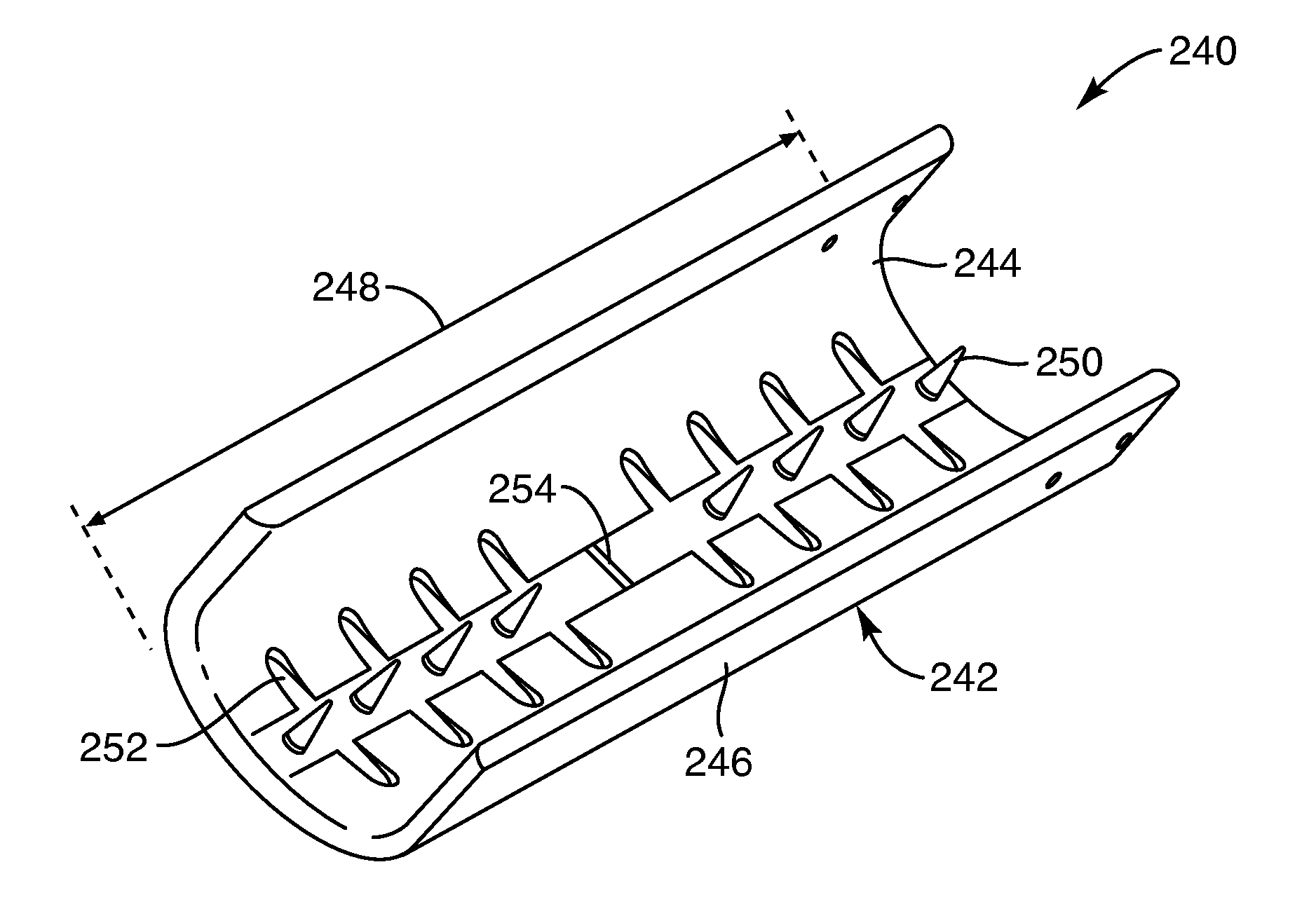
Soft tissue repair devices, systems, and methods
Devices, systems and / or methods for repairing a lacerated tendon or ligament adjacent a repair site. In one embodiment, a repair device includes an elongated flexible structure and multiple anchors, the multiple anchors pre-positioned with the elongated flexible structure. The repair device may be coupled to the tendon or ligament at the repair site with a delivery device. The repair device may be pre-positioned in a cartridge such that the cartridge is loaded into the delivery device. The lacerated tendon or ligament is positioned within a cradle portion of the delivery device such that the tendon is positioned between the cradle portion and the cartridge that holds the repair device. The delivery device may then be triggered to actuate and drive the repair device from the cartridge to couple to the lacerated tendon or ligament. In this manner, the repair device may be anchored to the lacerated tendon.
Owner:CONEXTIONS
Extracellular matrix material created using non-thermal irreversible electroporation
Extracellular matrix material is disclosed which is created by subjecting a target area to non-thermal irreversible electroporation (NTIRE) with a pulsed electrical field to kill cells in the absence of thermal damage. The dead cellular material may be removed and the remaining non-cellular matrix material may be implanted into a repair site to be treated medically or cosmetically.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Site-directed mutation method for genomes of saccharomyces cerevisiae
InactiveCN105624187AEfficient mutationRapid implementation of mutationsFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismRepair site
The invention relates to the field of microorganisms, in particular to a site-directed mutation method for genomes of saccharomyces cerevisiae. To-be-repaired single-base mutation sites on the genomes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be repaired by the aid of CRISPR / Cas9 technologies. Effects can be realized near the to-be-repaired sites by Cas9 proteins under the guidance actions of guide RNA (ribonucleic acid) if the mutation sites are positioned in PAM sequences (NGG) or front 11bp of the PAM sequences, and the genomes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be subjected to double-strand break at cut positions, so that donor DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) can be efficiently recombined. Compared with existing results, the site-directed mutation method has the advantages that the sites of the genomes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae can be efficiently and quickly mutated, and screening markers do not need to be integrated for the genomes of the saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
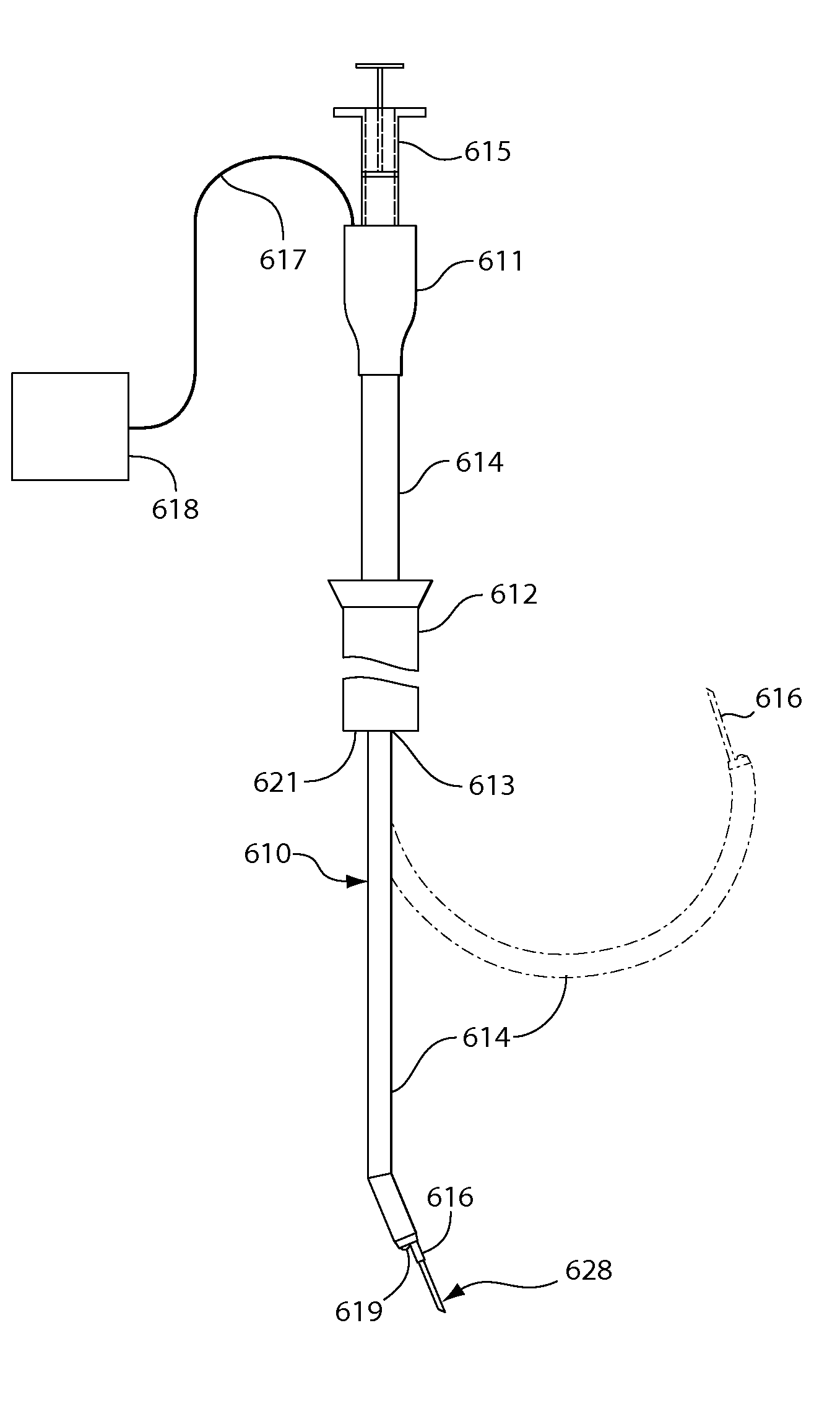
Device for mixing and delivering fluids for tissue repair
ActiveUS8308681B2Promote healingPromote repairAdditive manufacturing apparatusCannulasRepair siteTissue repair
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Extracellular matrix material created using non-thermal irreversible electroporation
ActiveUS8835166B2ElectrotherapyMammal material medical ingredientsRepair siteCell-Extracellular Matrix
Extracellular matrix material is disclosed which is created by subjecting a target area to non-thermal irreversible electroporation (NTIRE) with a pulsed electrical field to kill cells in the absence of thermal damage. The dead cellular material may be removed and the remaining non-cellular matrix material may be implanted into a repair site to be treated medically or cosmetically.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Implantable prosthesis
InactiveUS20030187516A1Reduce the possibilityReduce postoperative painDiagnosticsSurgeryRepair siteIntraabdominal pressure
Owner:AMID PARVIZ K +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com