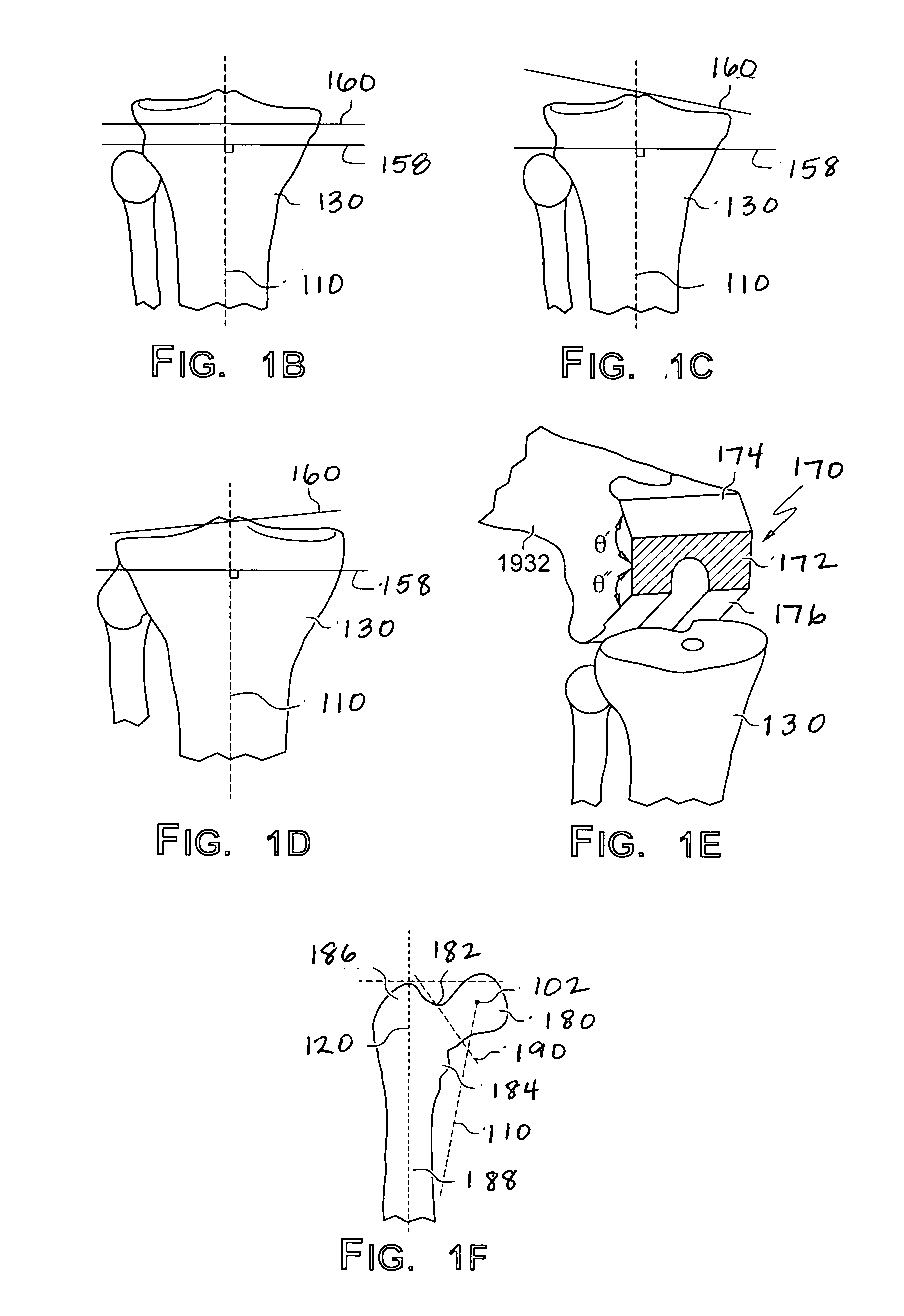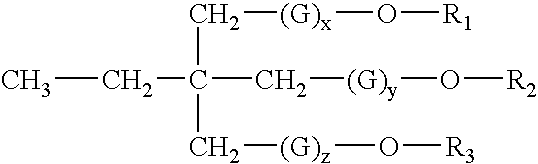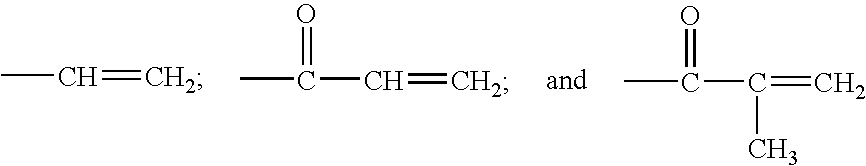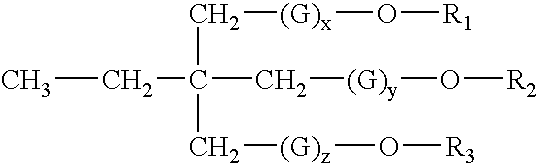Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
3495 results about "Repair material" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
But manufacturers have developed some excellent repair materials that include various polymers leading to higher bond strength and durability. Most repair materials today are polymer-modified concrete, meaning that the basic material is a portland cement and aggregate mixture with a polymer (typically latex) added.
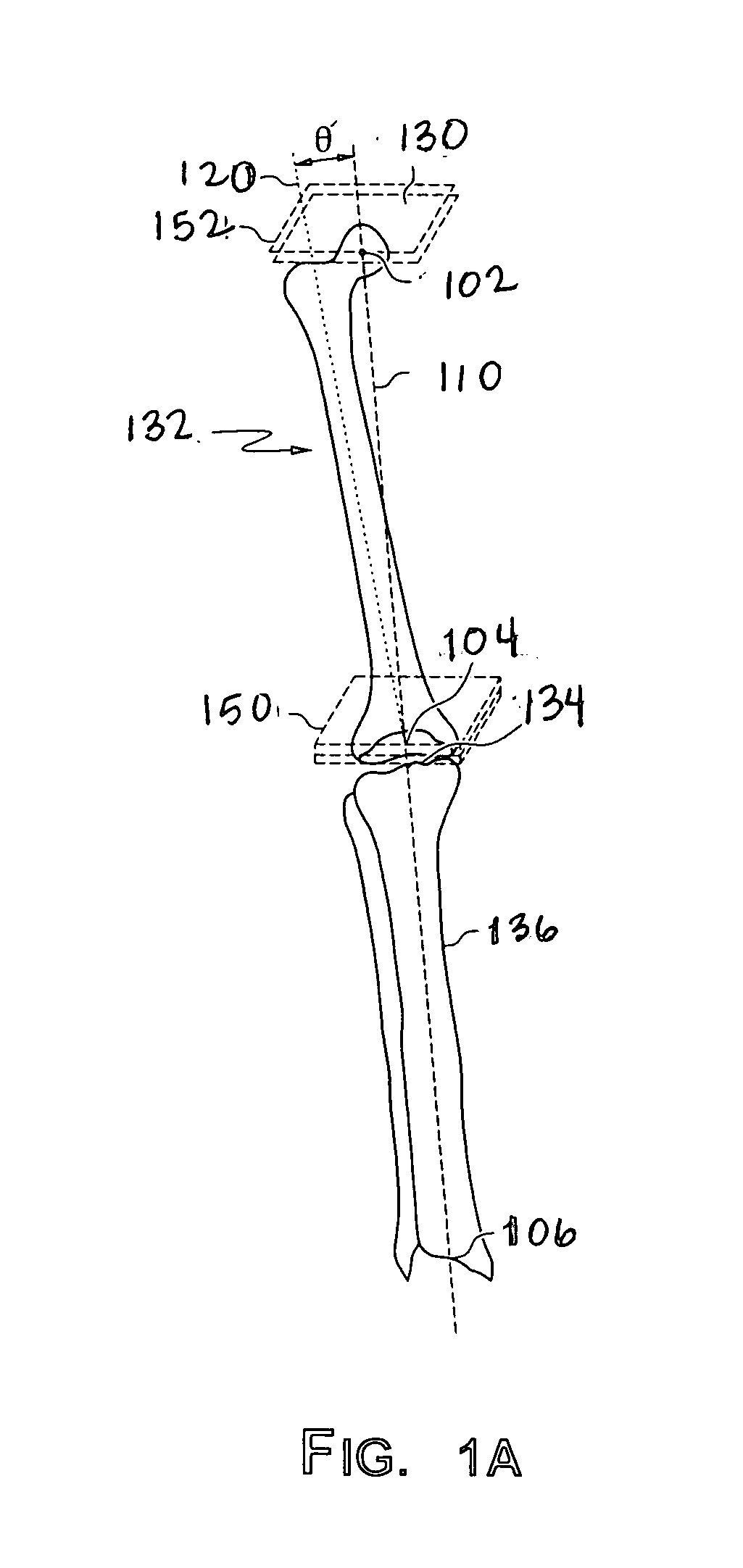
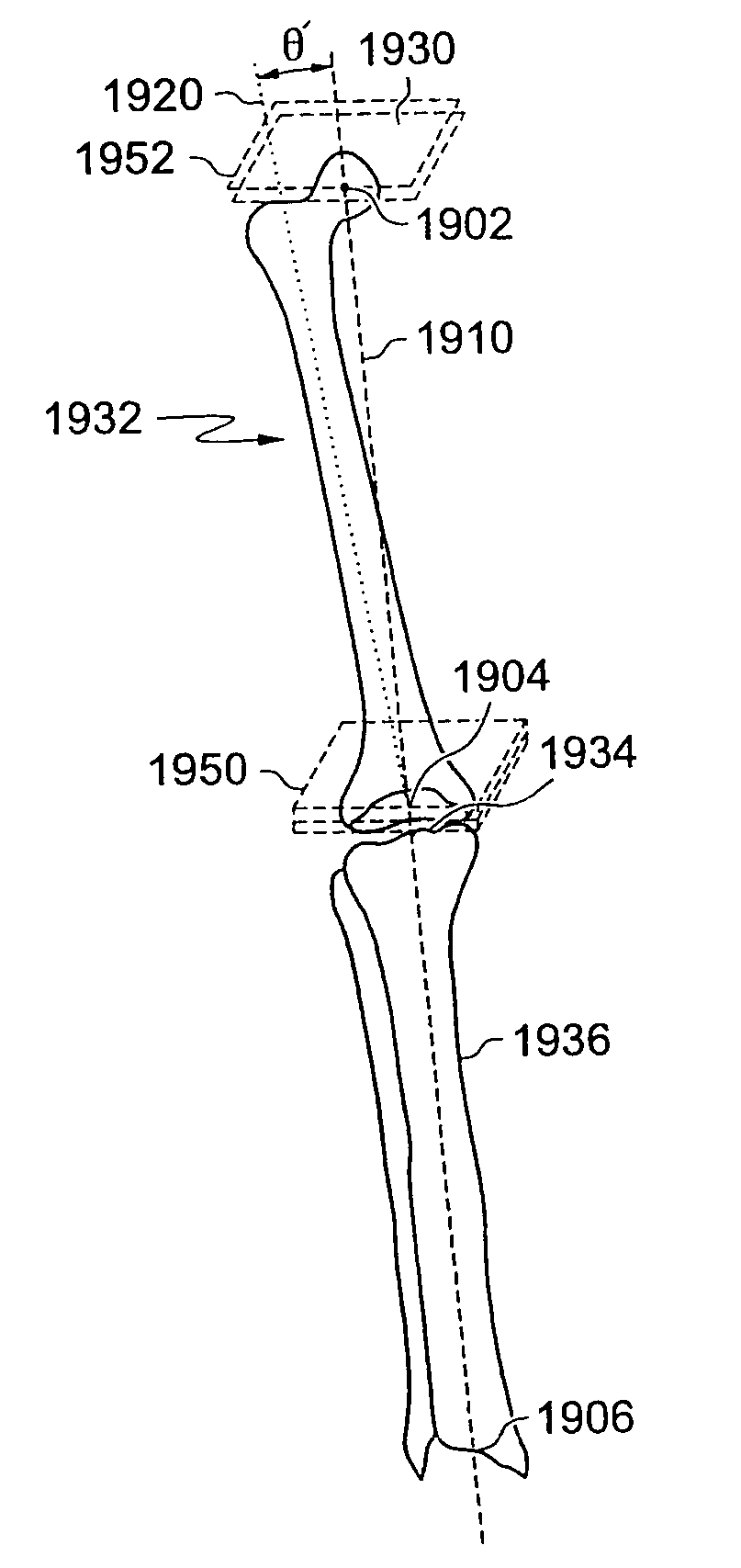
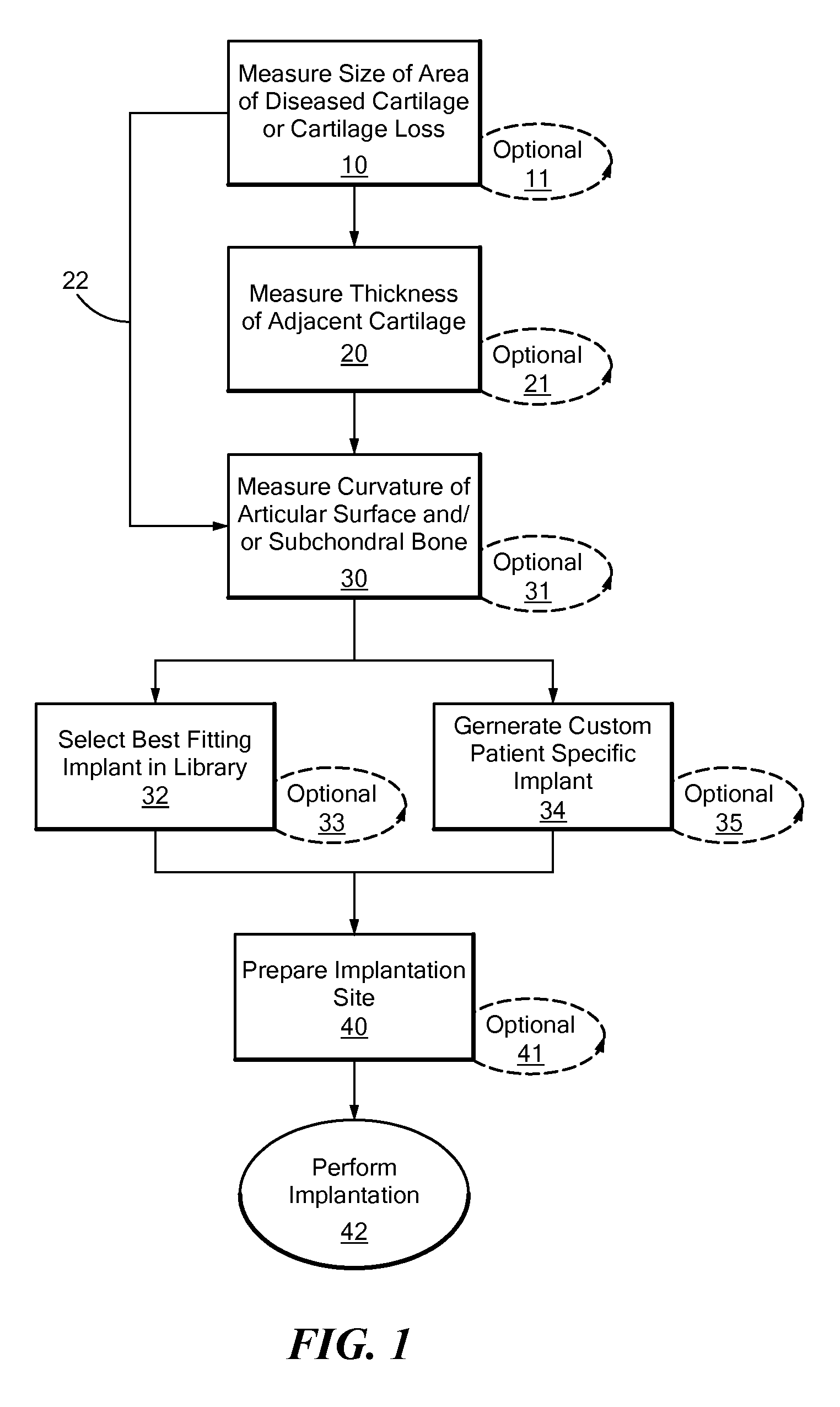
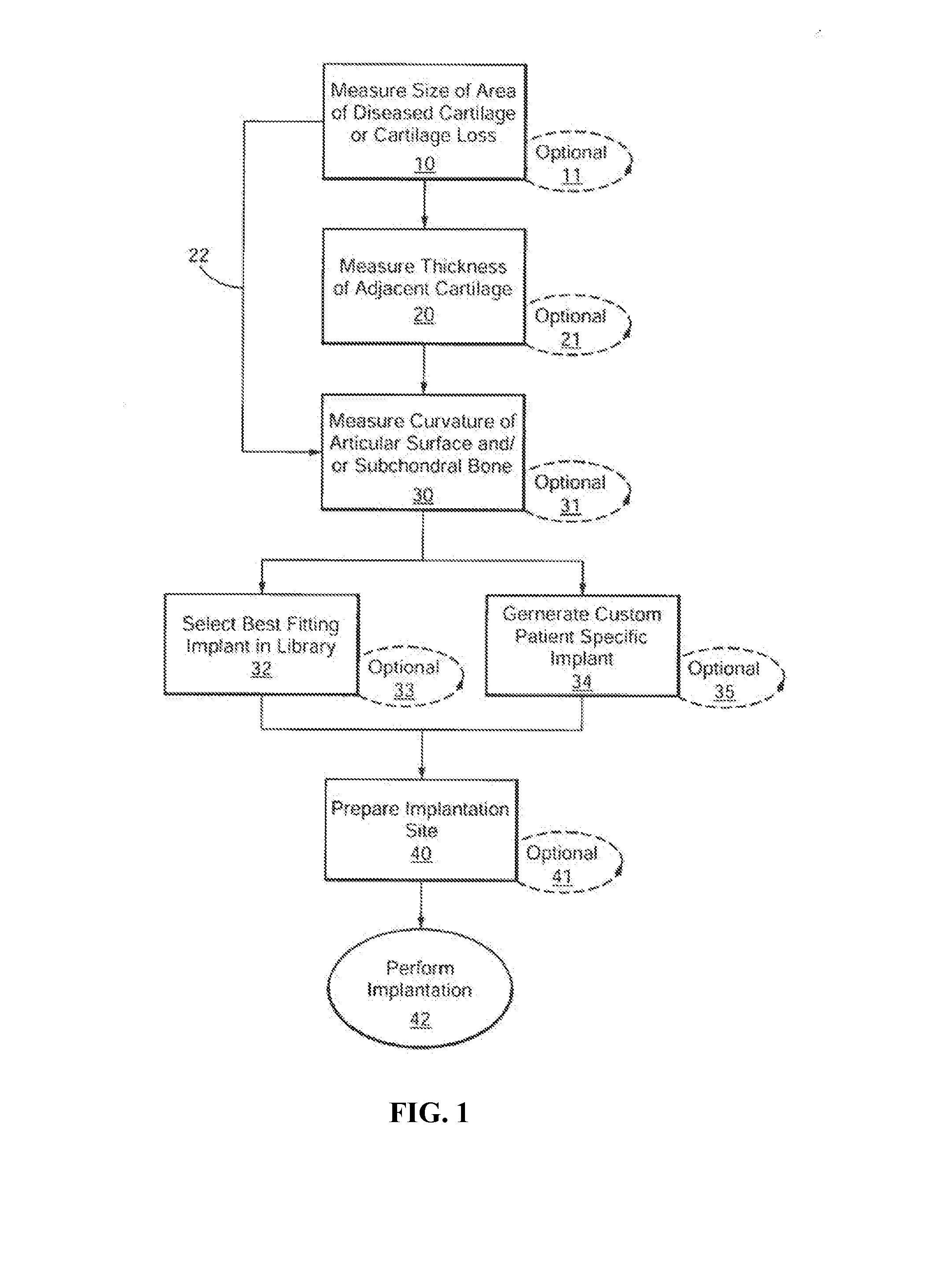
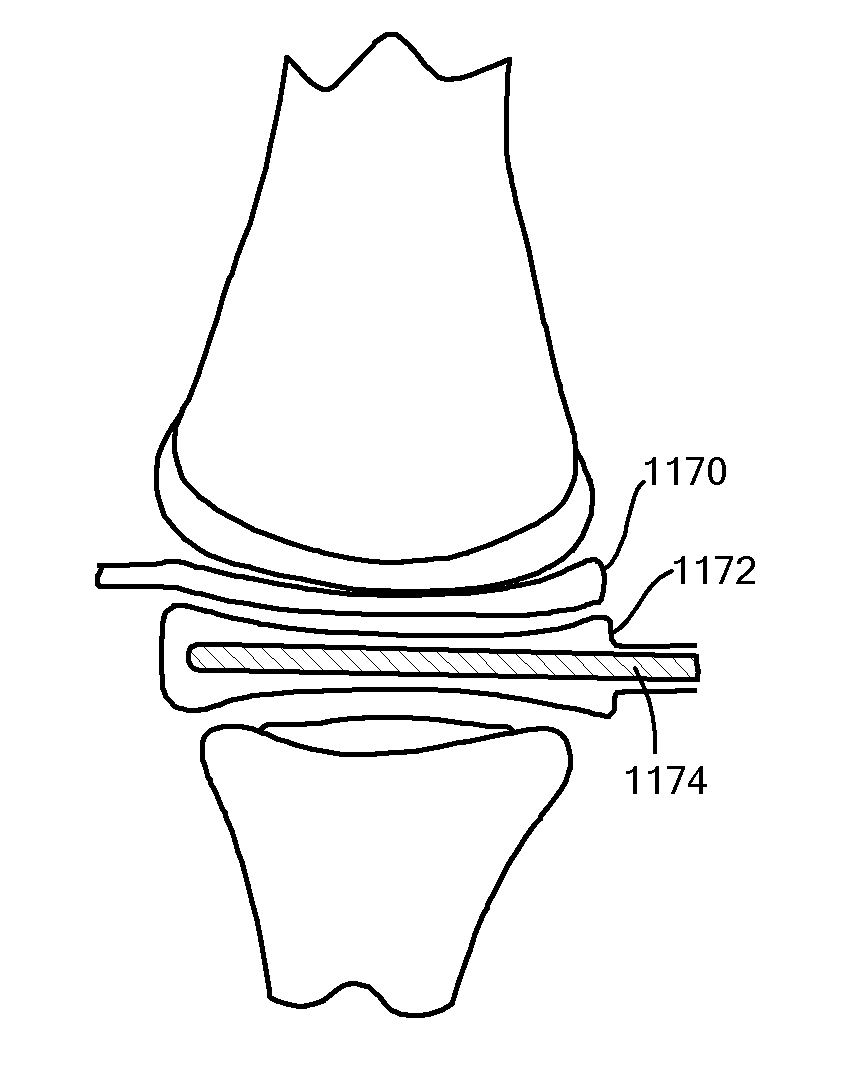
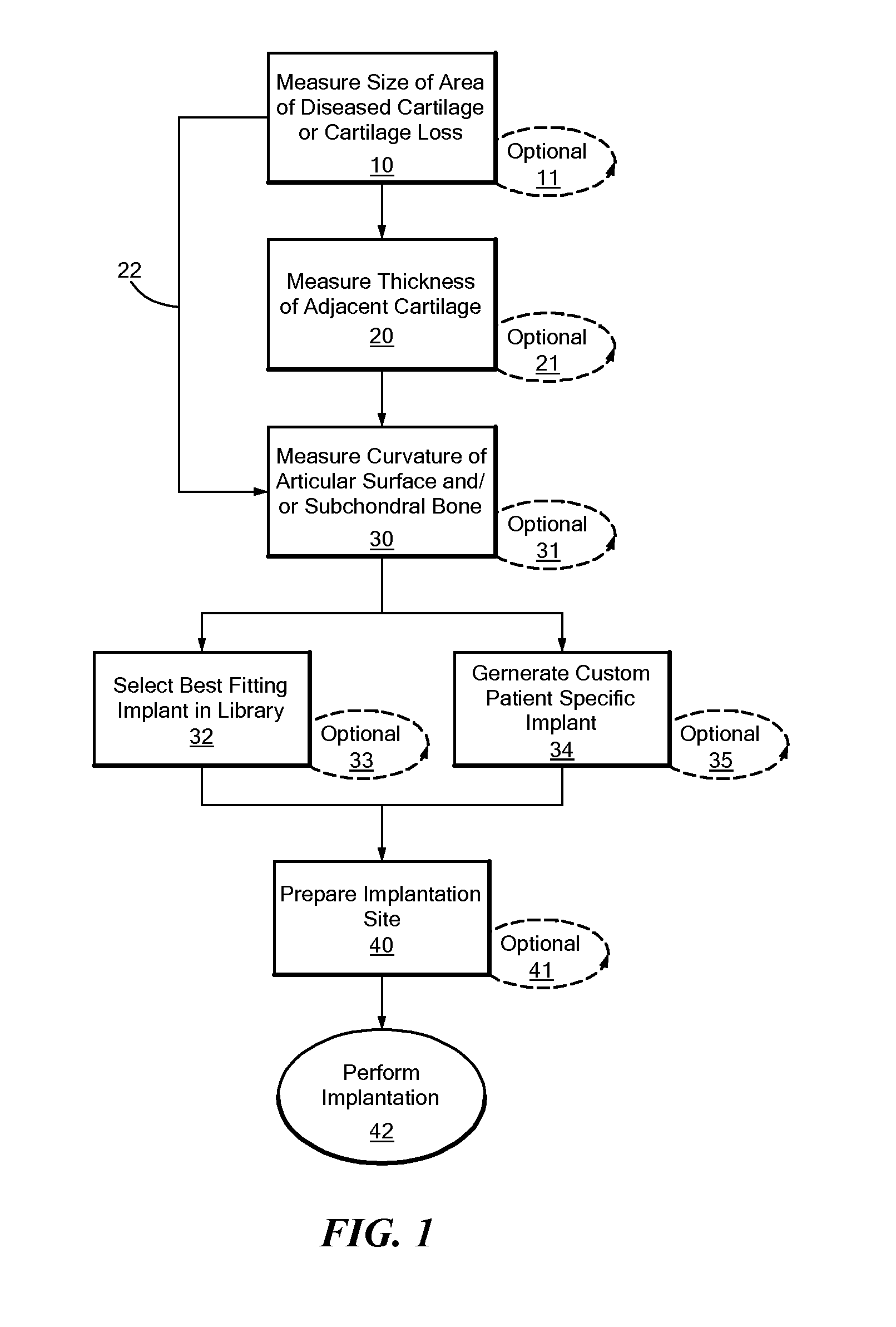
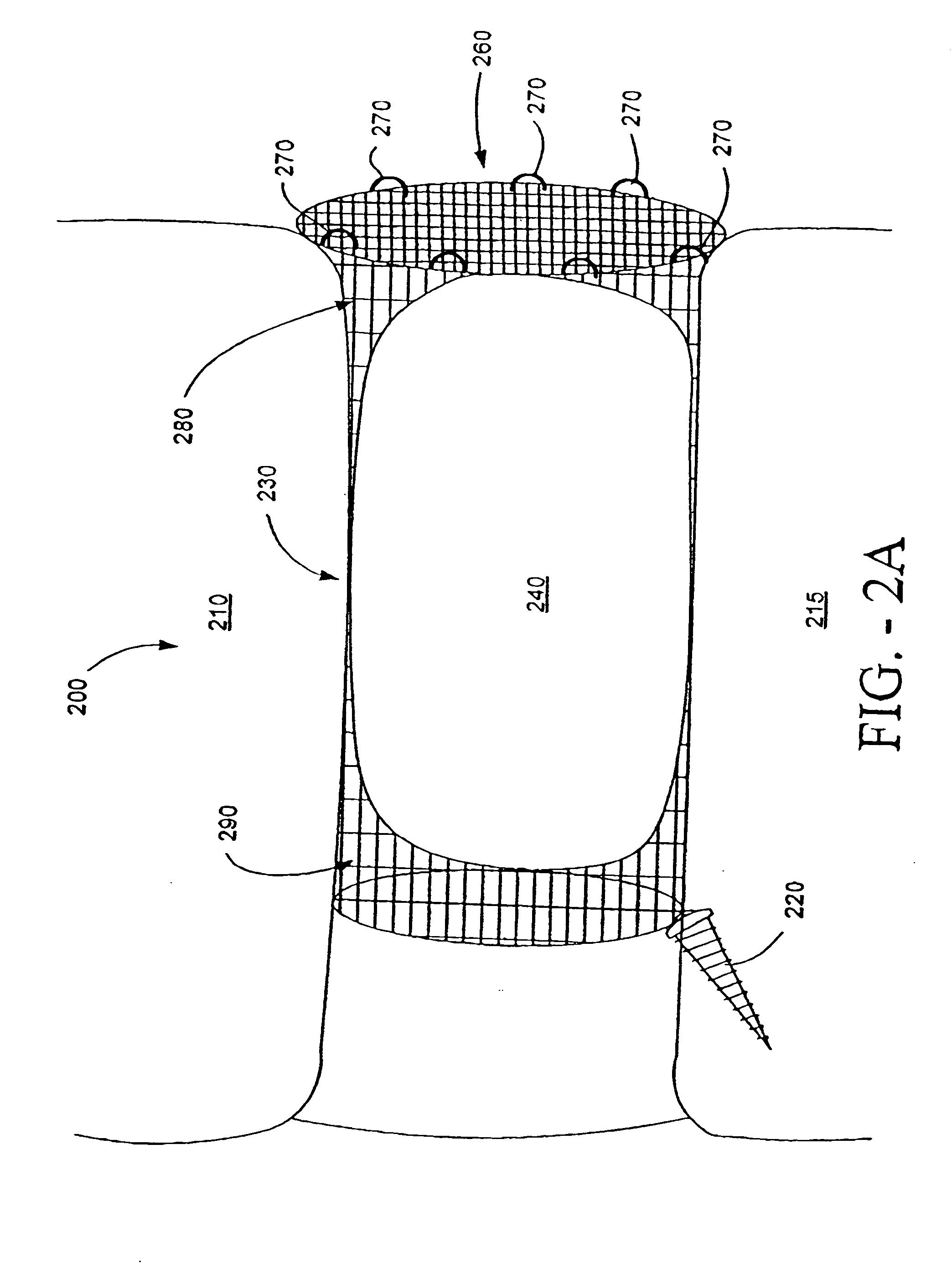
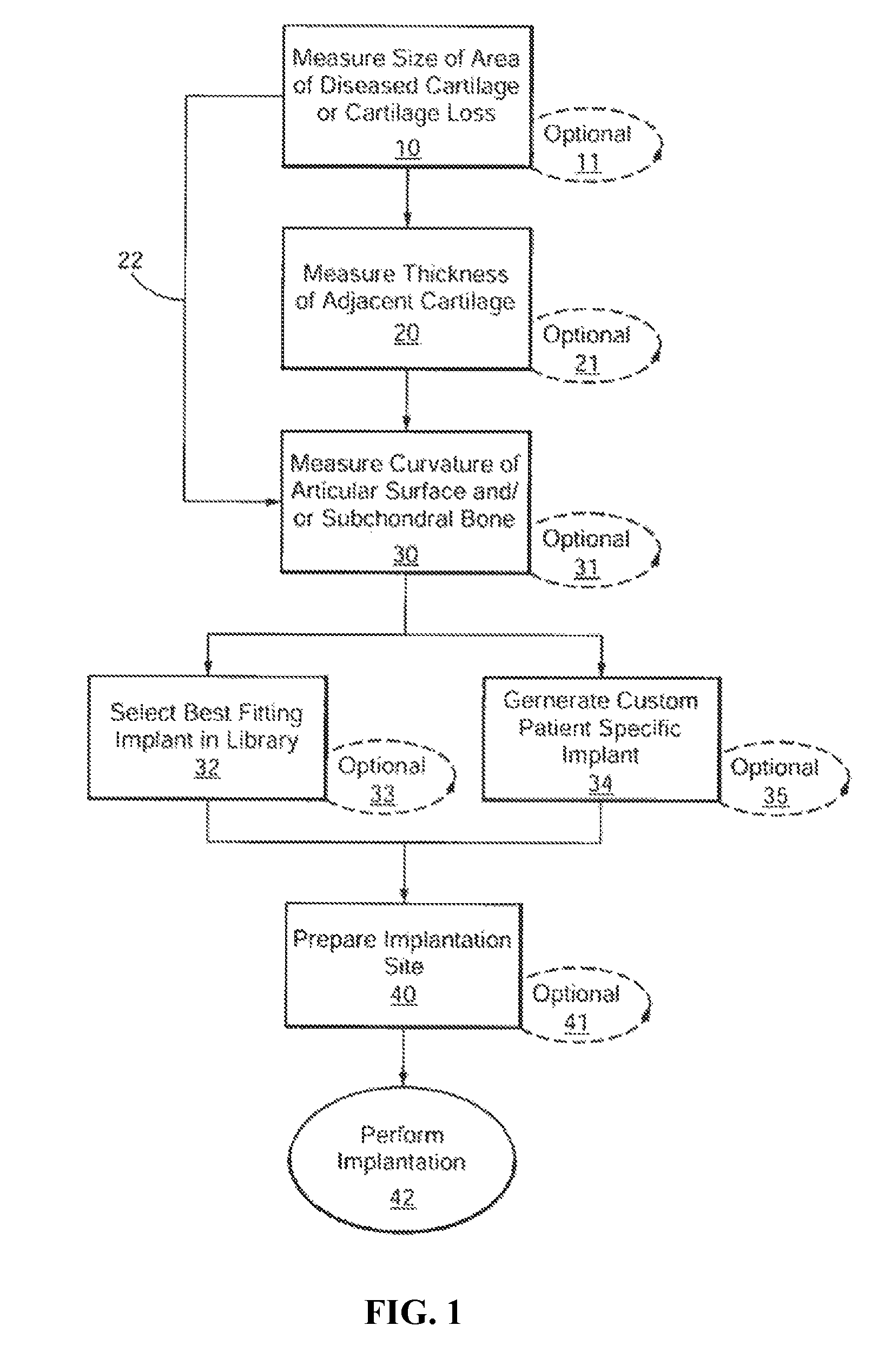
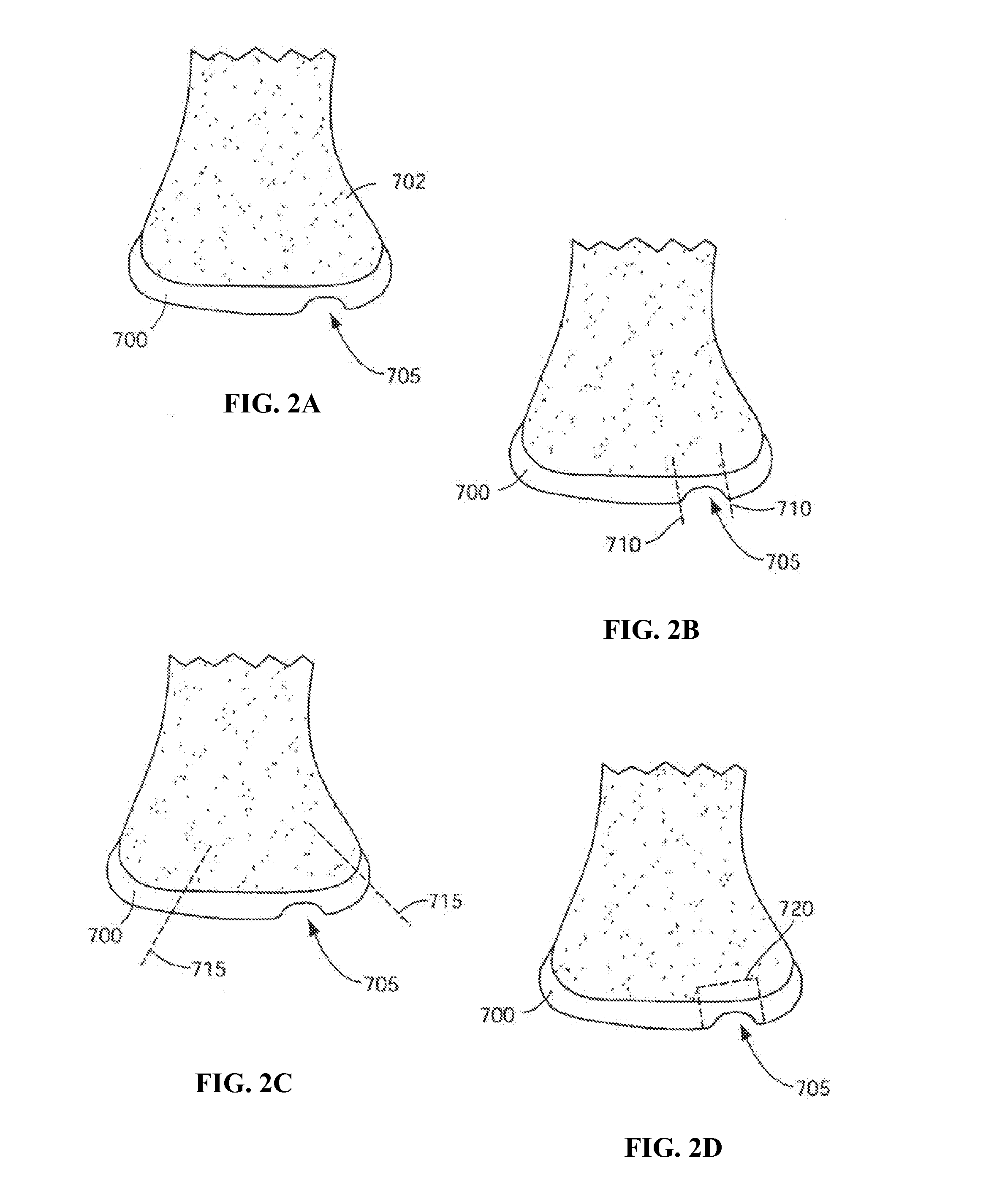
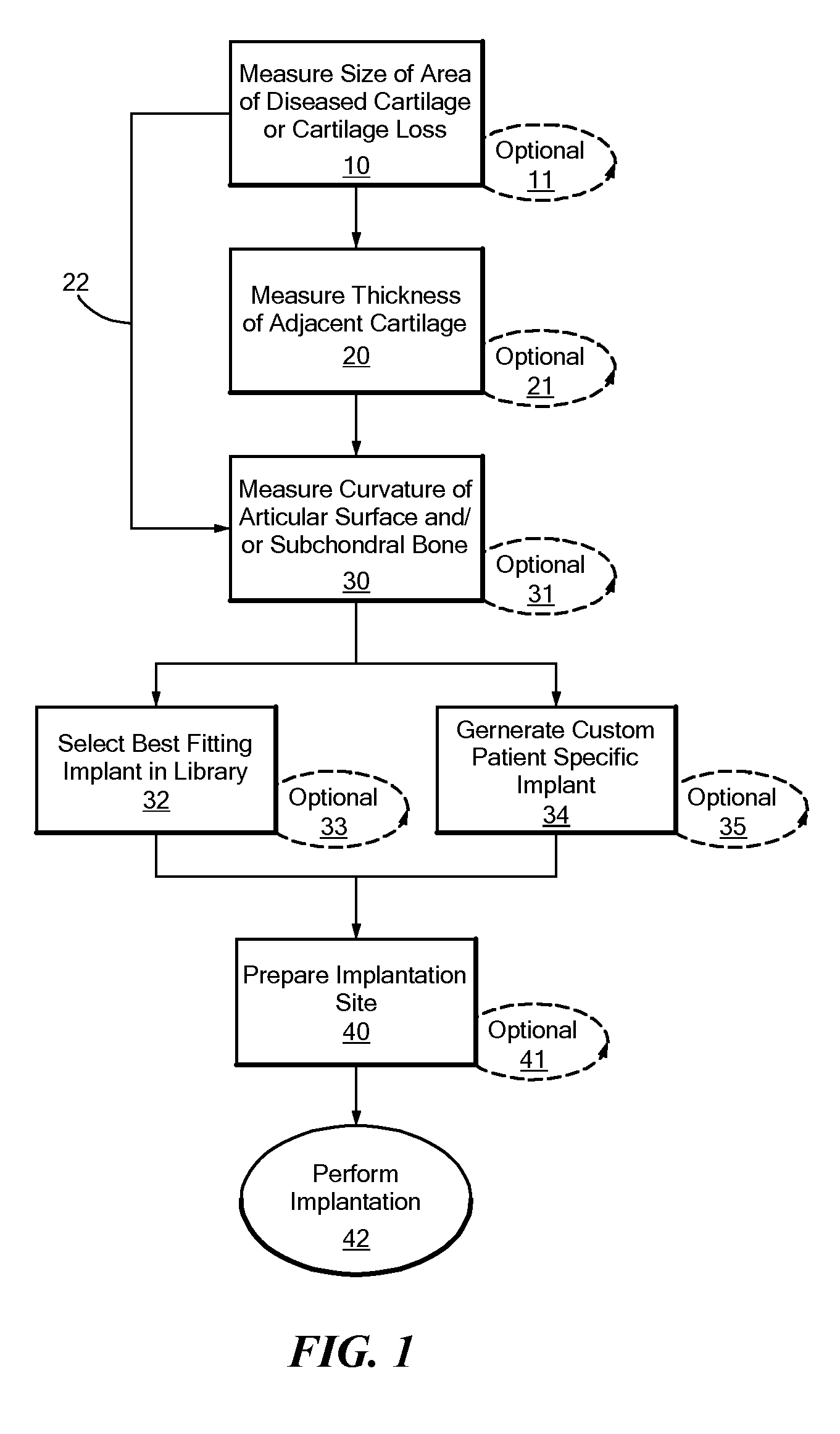
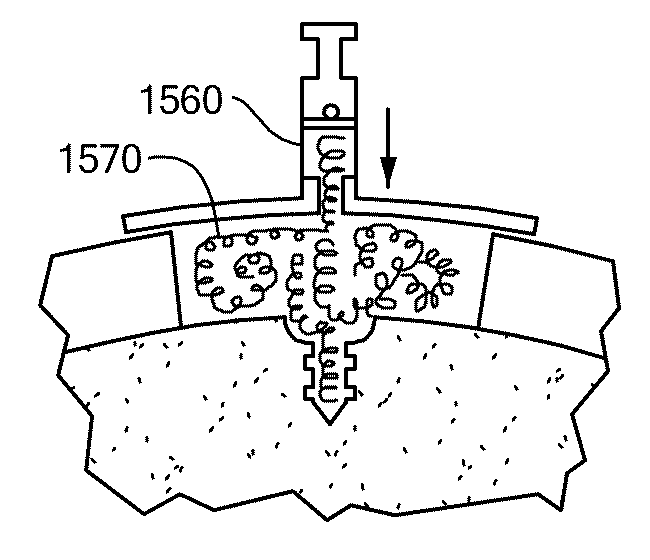
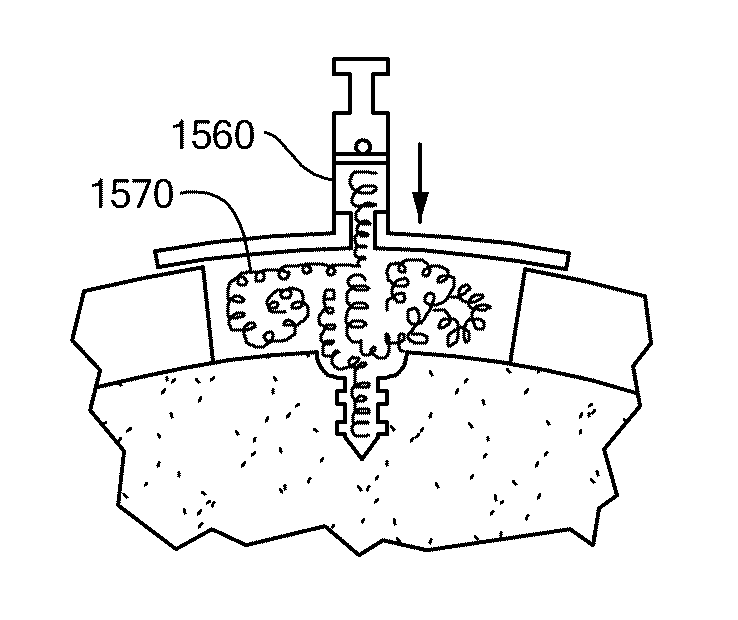
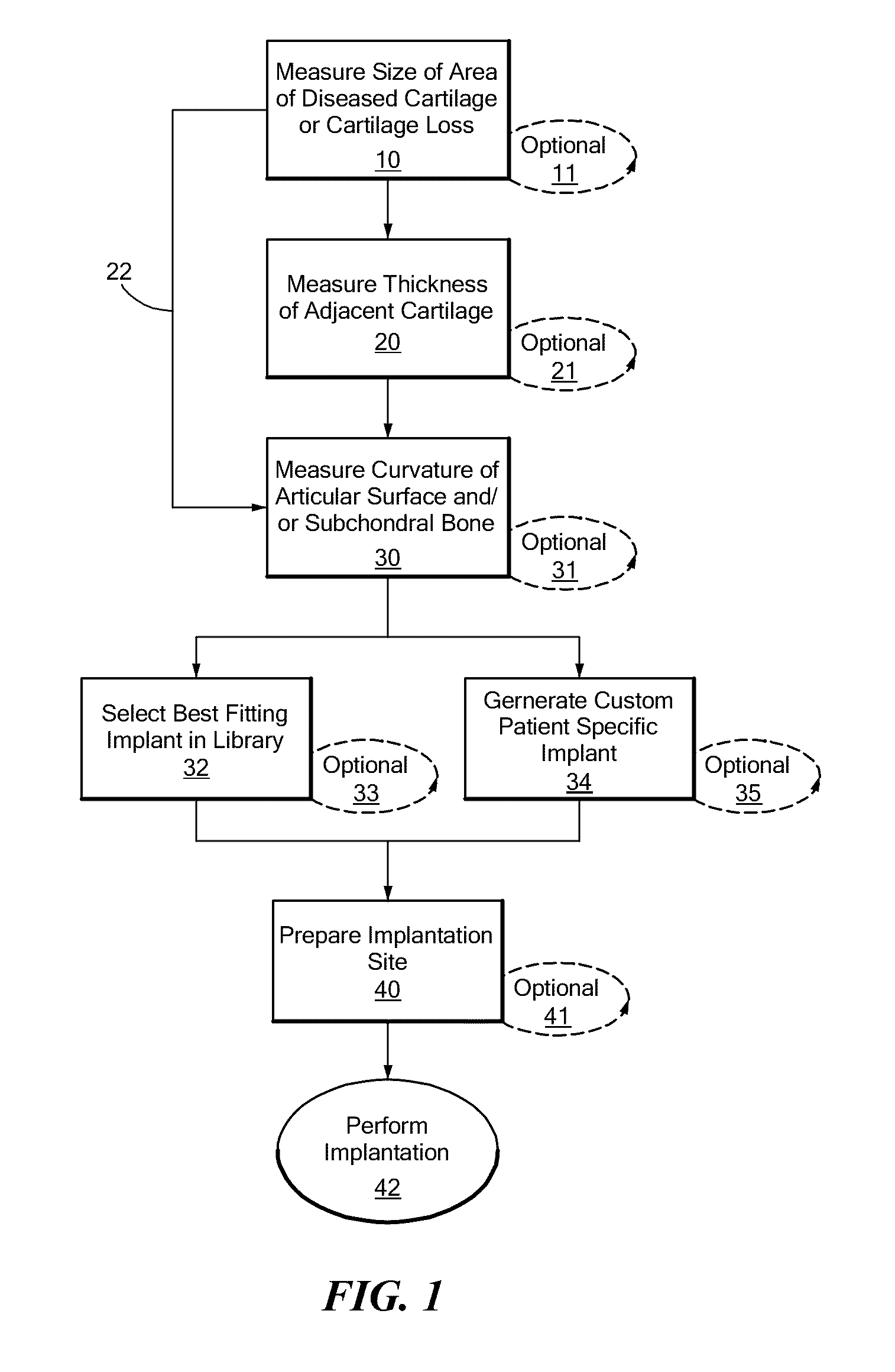
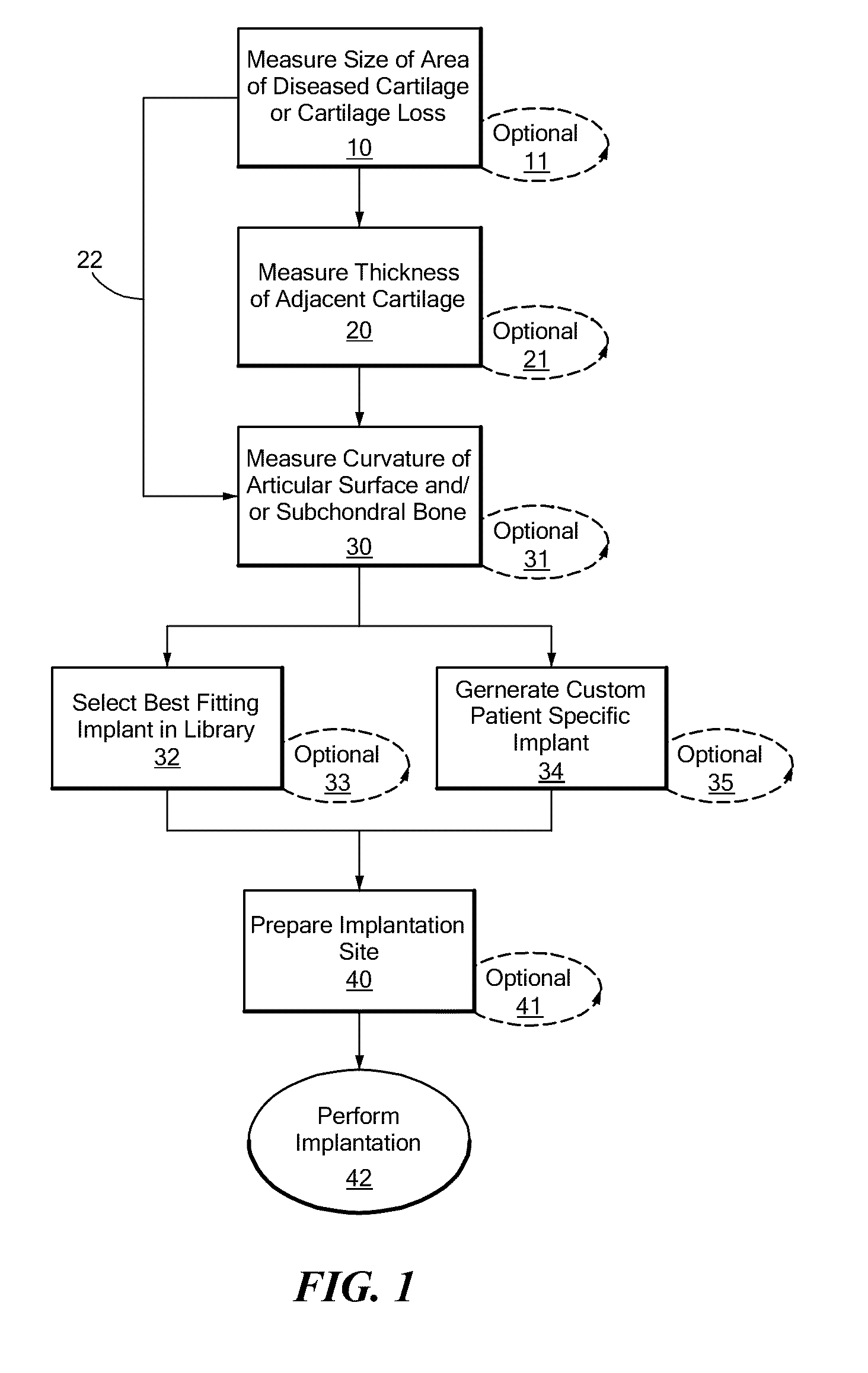
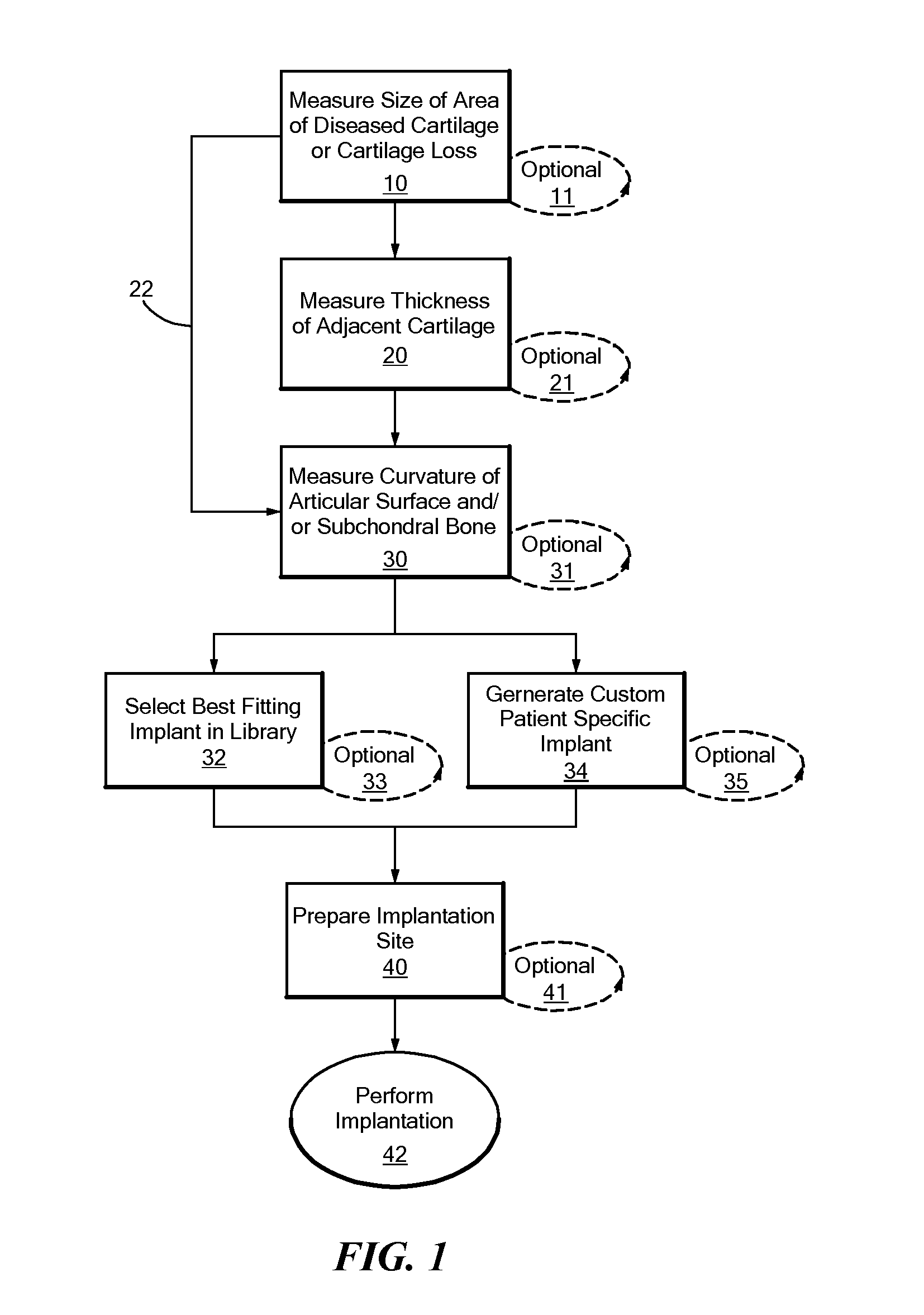
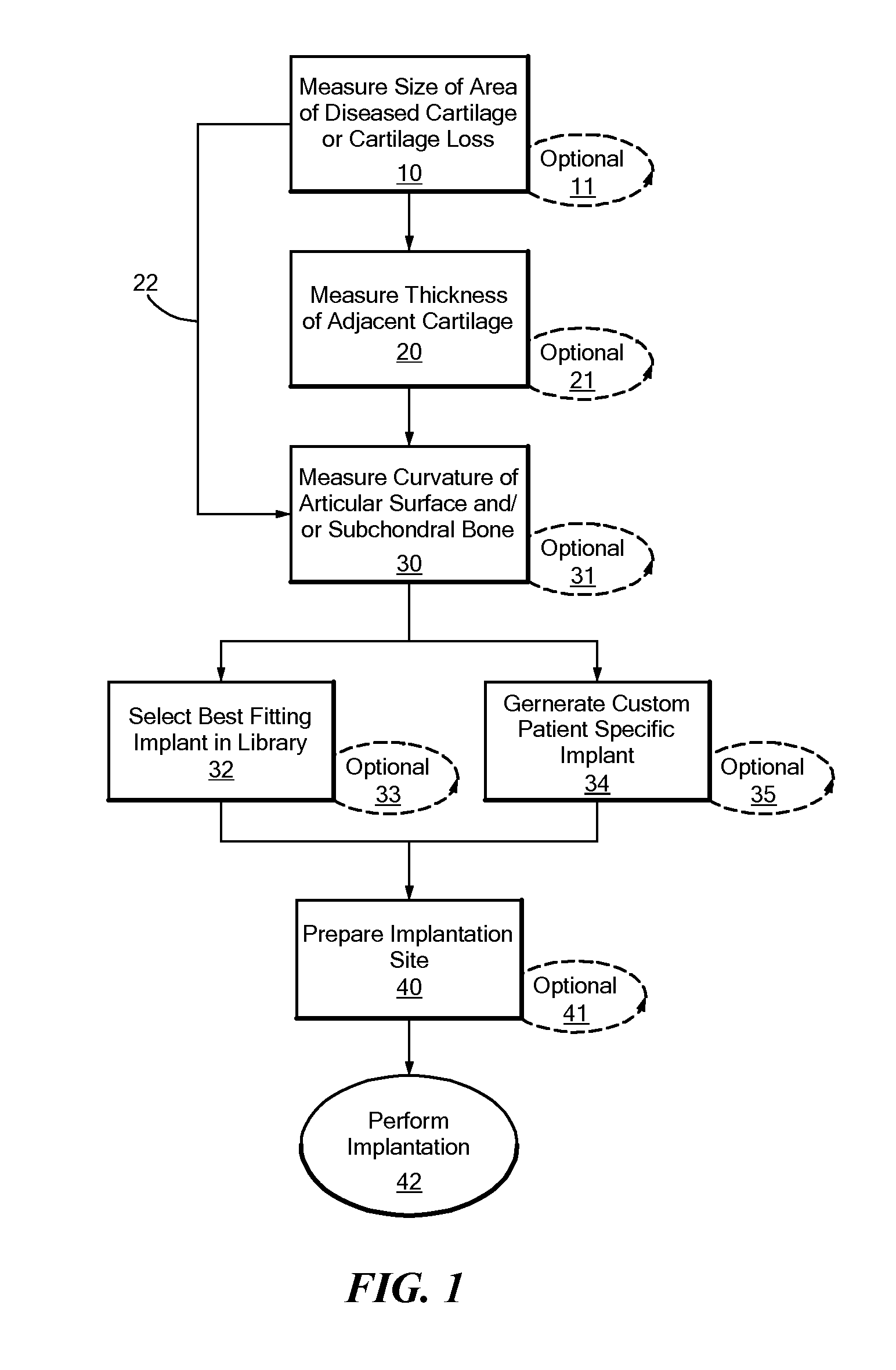
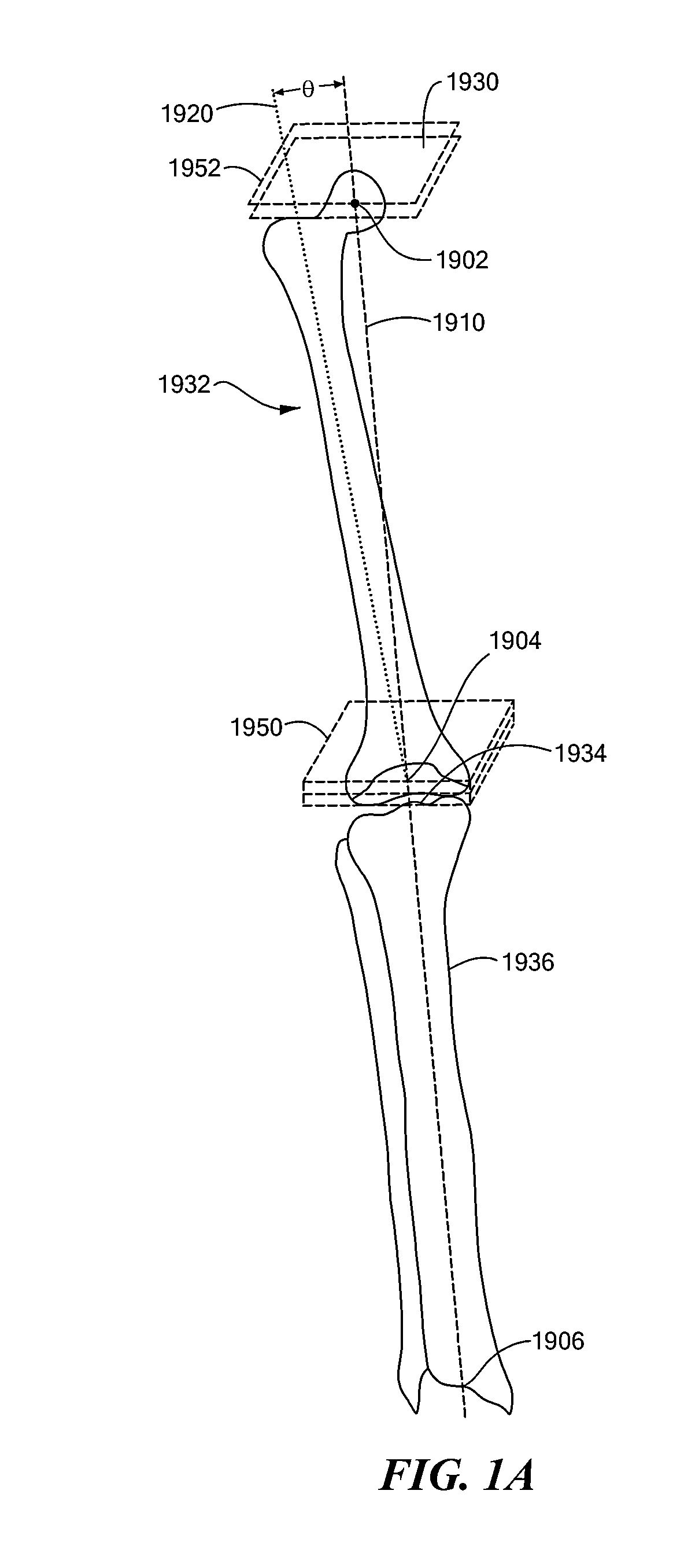
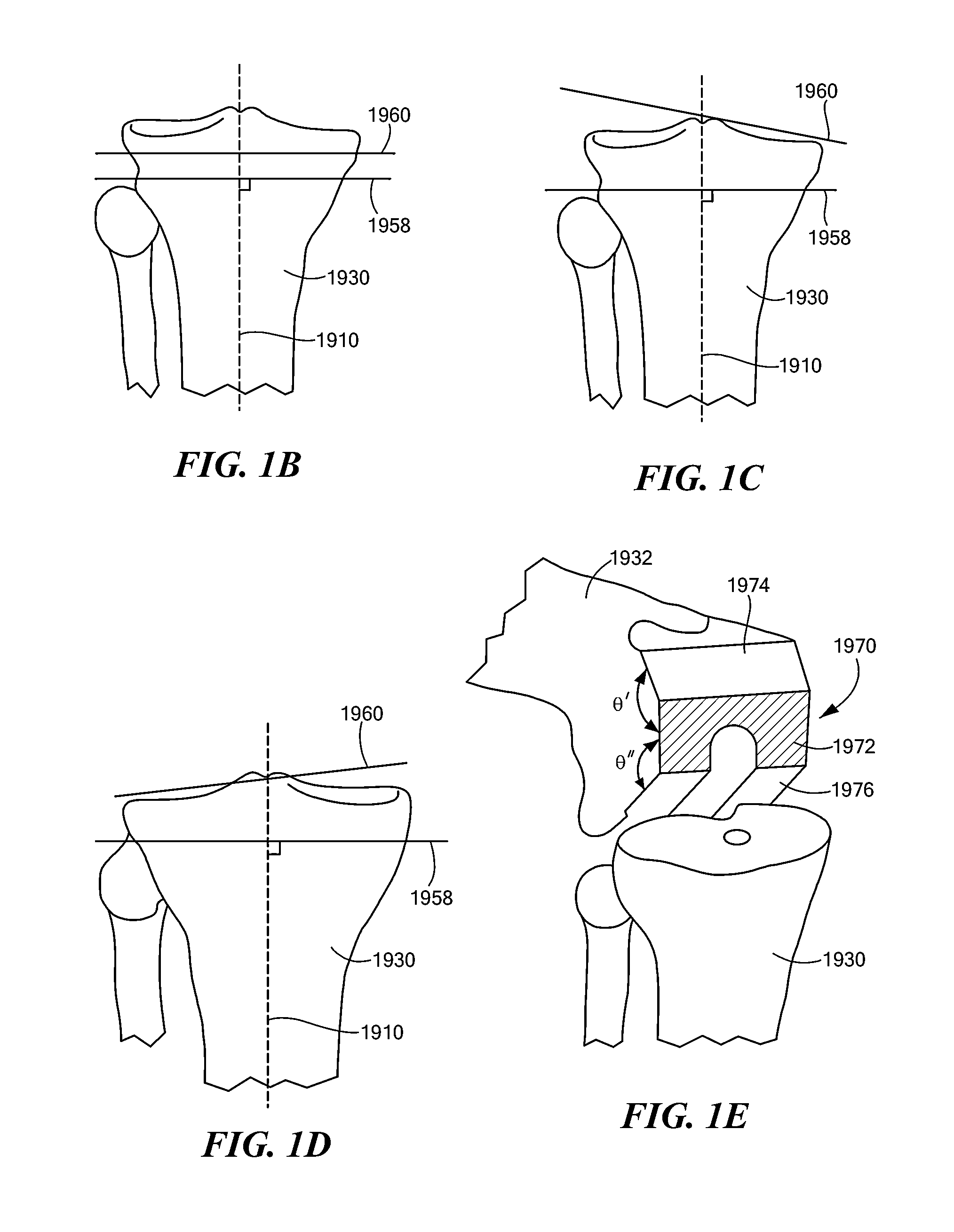
Patient Selectable Joint Arthroplasty Devices and Surgical Tools
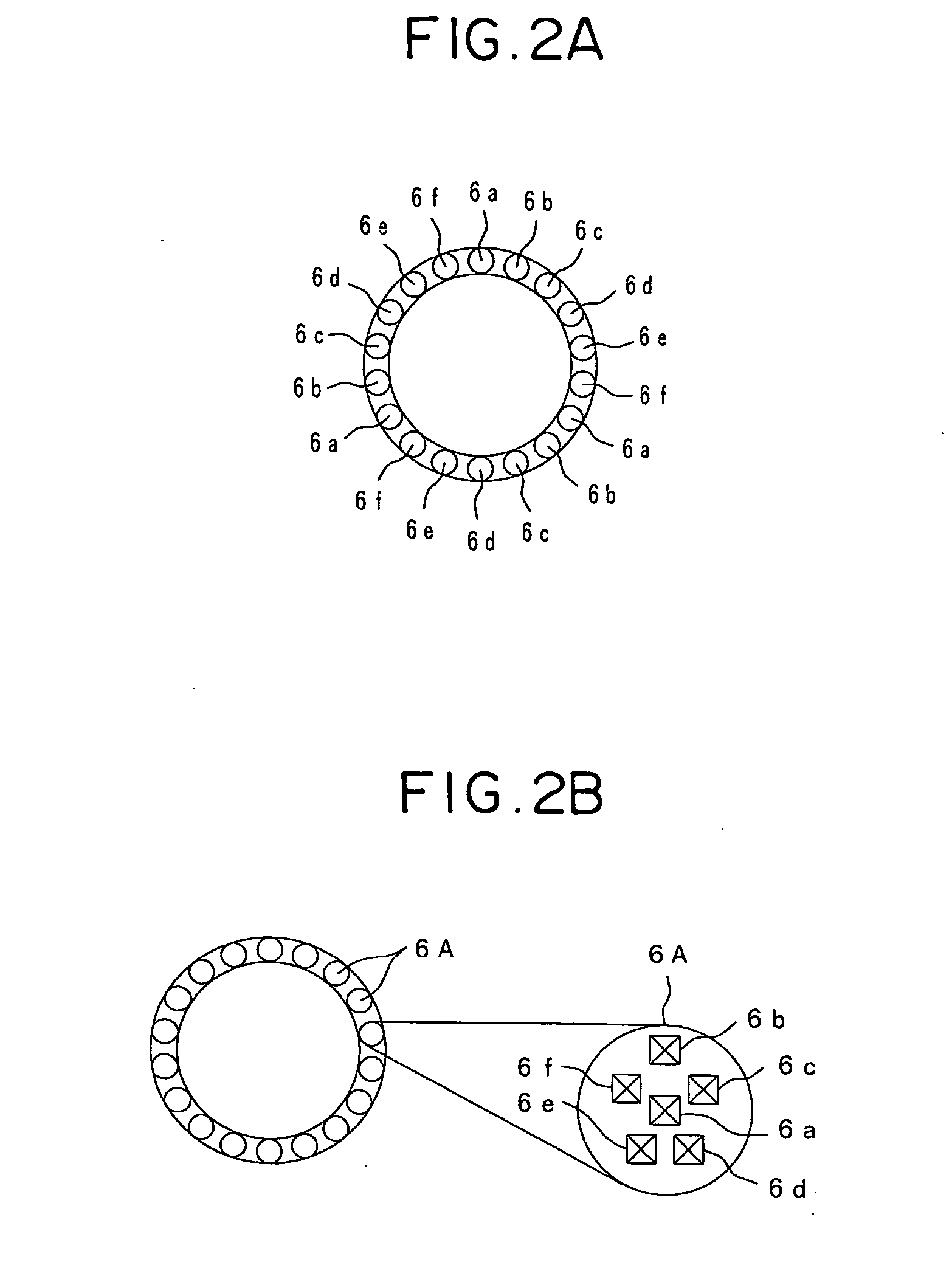
ActiveUS20070198022A1Accurate placementGeometric CADPerson identificationArticular surfacesArticular surface
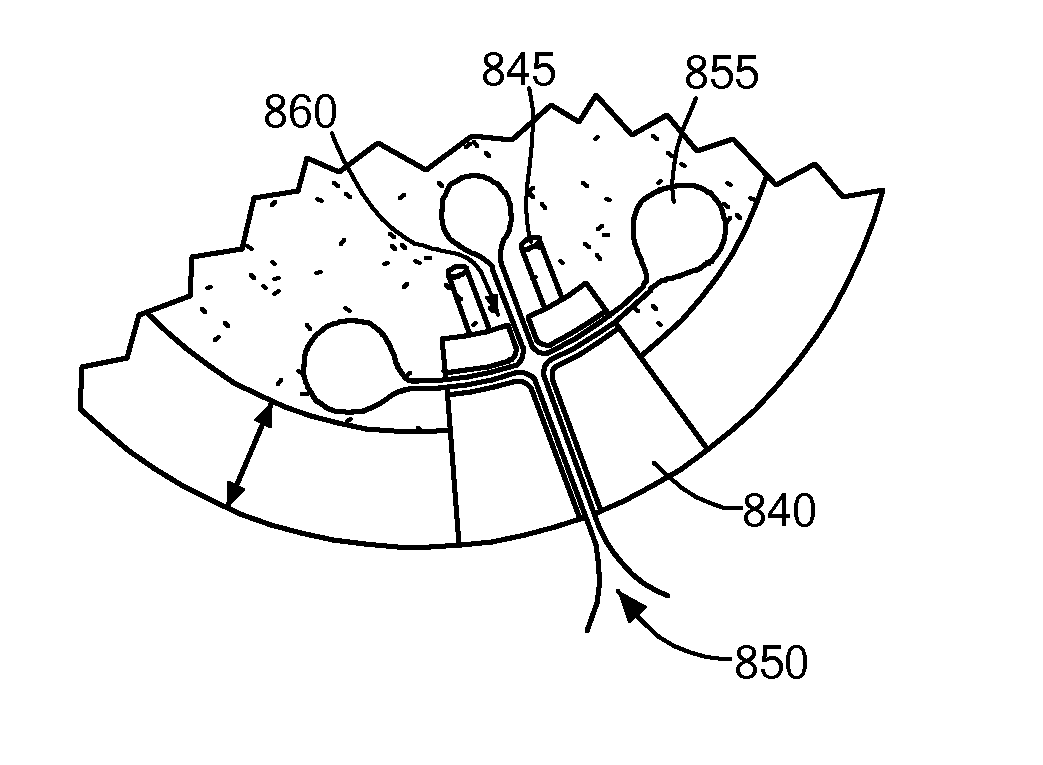
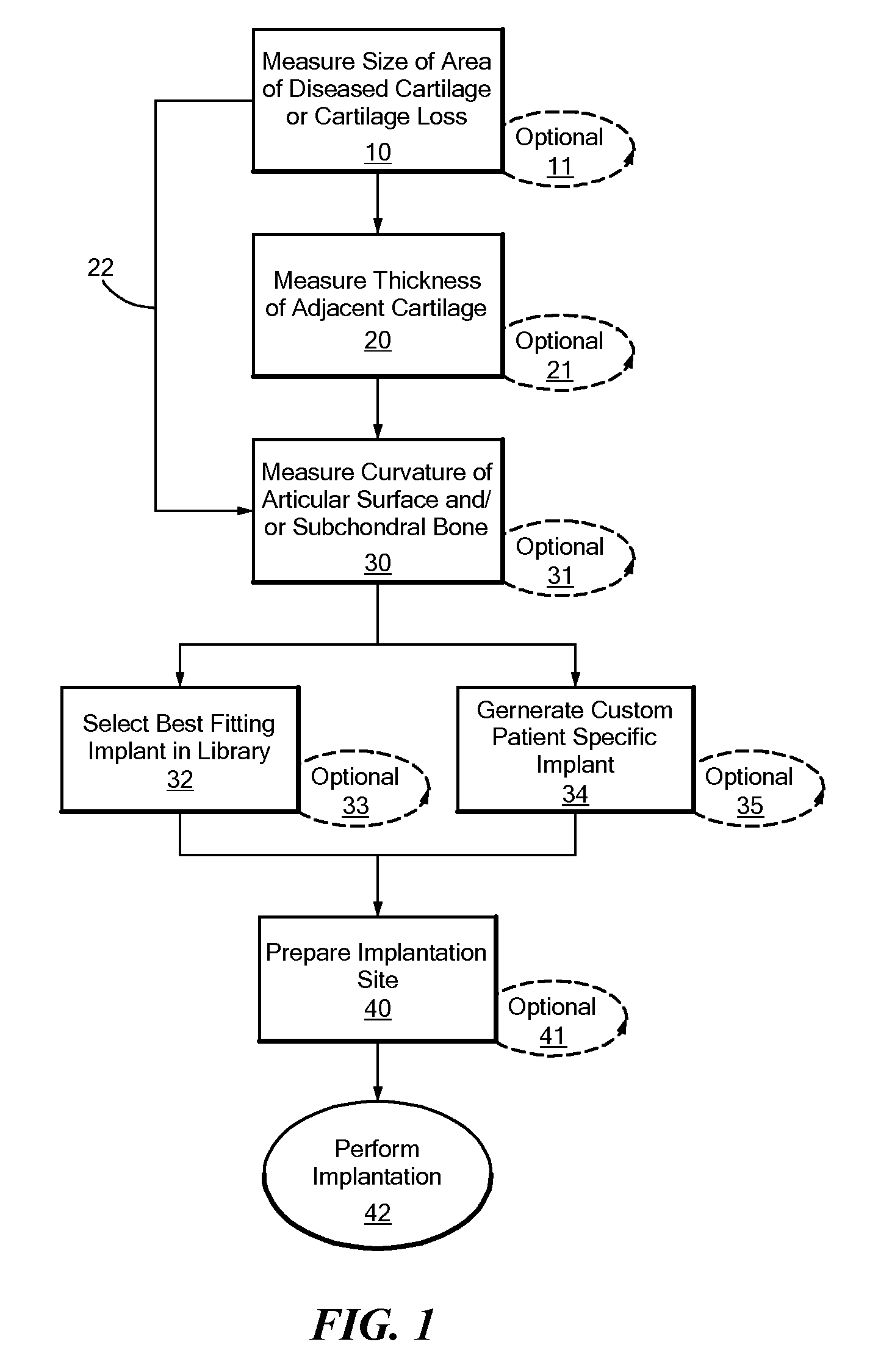
Disclosed herein are methods, compositions and tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Surgical tools facilitating increased accuracy, speed and simplicity in performing joint arthroplasty
Disclosed herein are tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Patient selectable joint arthroplasty devices and surgical tools facilitating increased accuracy, speed and simplicity in performing total and partial joint arthroplasty
Disclosed herein are methods, compositions and tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Surgical tools facilitating increased accuracy, speed and simplicity in performing joint arthroplasty
Disclosed herein are tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Patient Selectable Joint Arthroplasty Devices and Surgical Tools
ActiveUS20090222014A1Improve and optimize positionAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgical navigation systemsSurgical operationArticular surfaces
Disclosed herein are tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Surgical Tools for Arthroplasty
InactiveUS20080281328A1Accurate placementAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgical navigation systemsArticular surfacesArticular surface
Disclosed herein are methods, compositions and tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Patient Selectable Joint Arthroplasty Devices and Surgical Tools Incorporating Anatomical Relief
ActiveUS20120041446A1Improve fitMore natural movementAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgical navigation systemsArticular surfacesArticular surface
Disclosed herein are methods, compositions and tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Surgical Tools Facilitating Increased Accuracy, Speed and Simplicity in Performing Joint Arthroplasty
InactiveUS20090307893A1Metal rolling stand detailsDiagnostic recording/measuringArticular surfacesArticular surface
Disclosed herein are tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Joint Arthroplasty Devices and Surgical Tools
InactiveUS20100160917A1Accurate placementImage analysisInternal osteosythesisArticular surfacesArticular surface
Disclosed herein are methods, compositions and tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
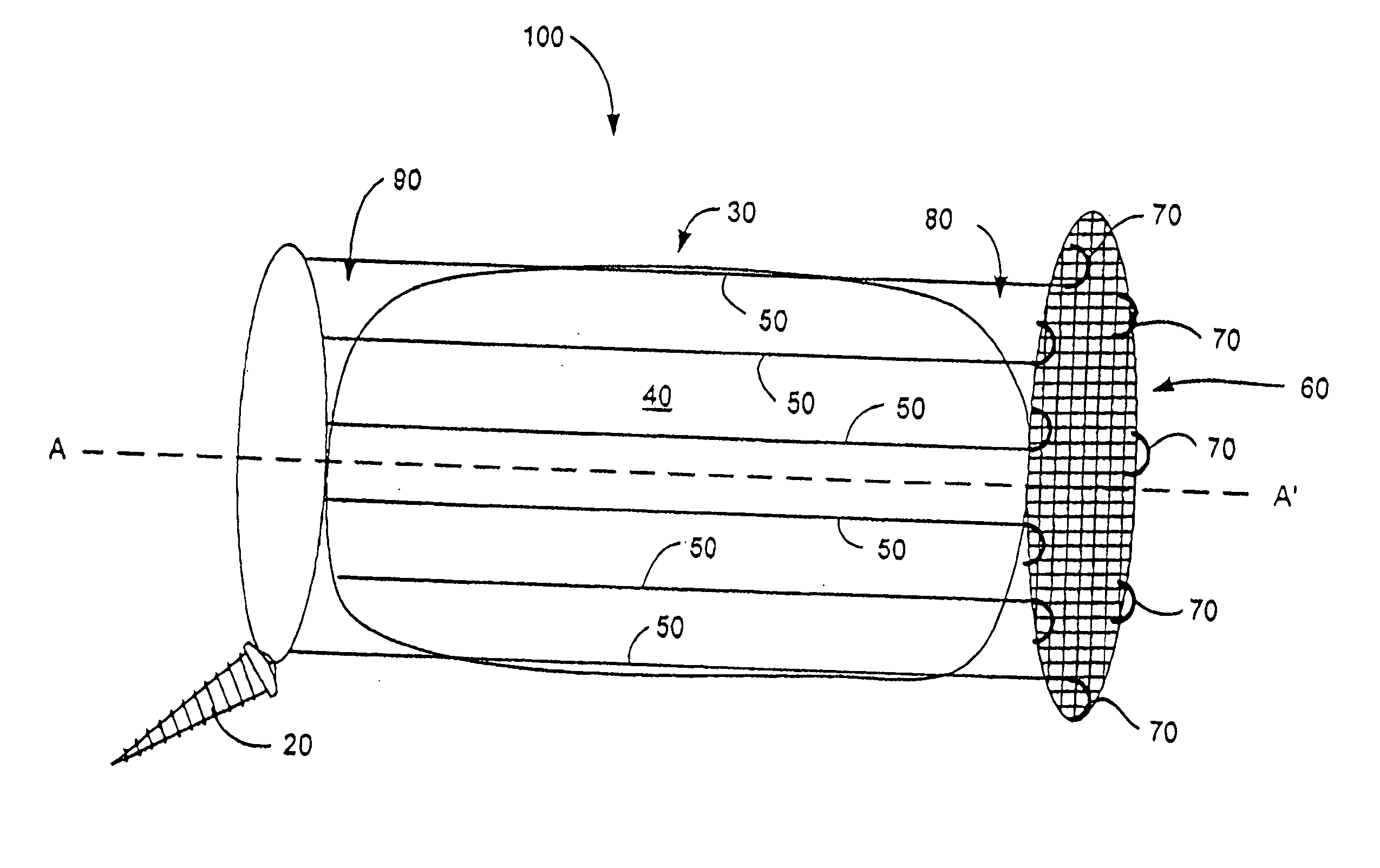
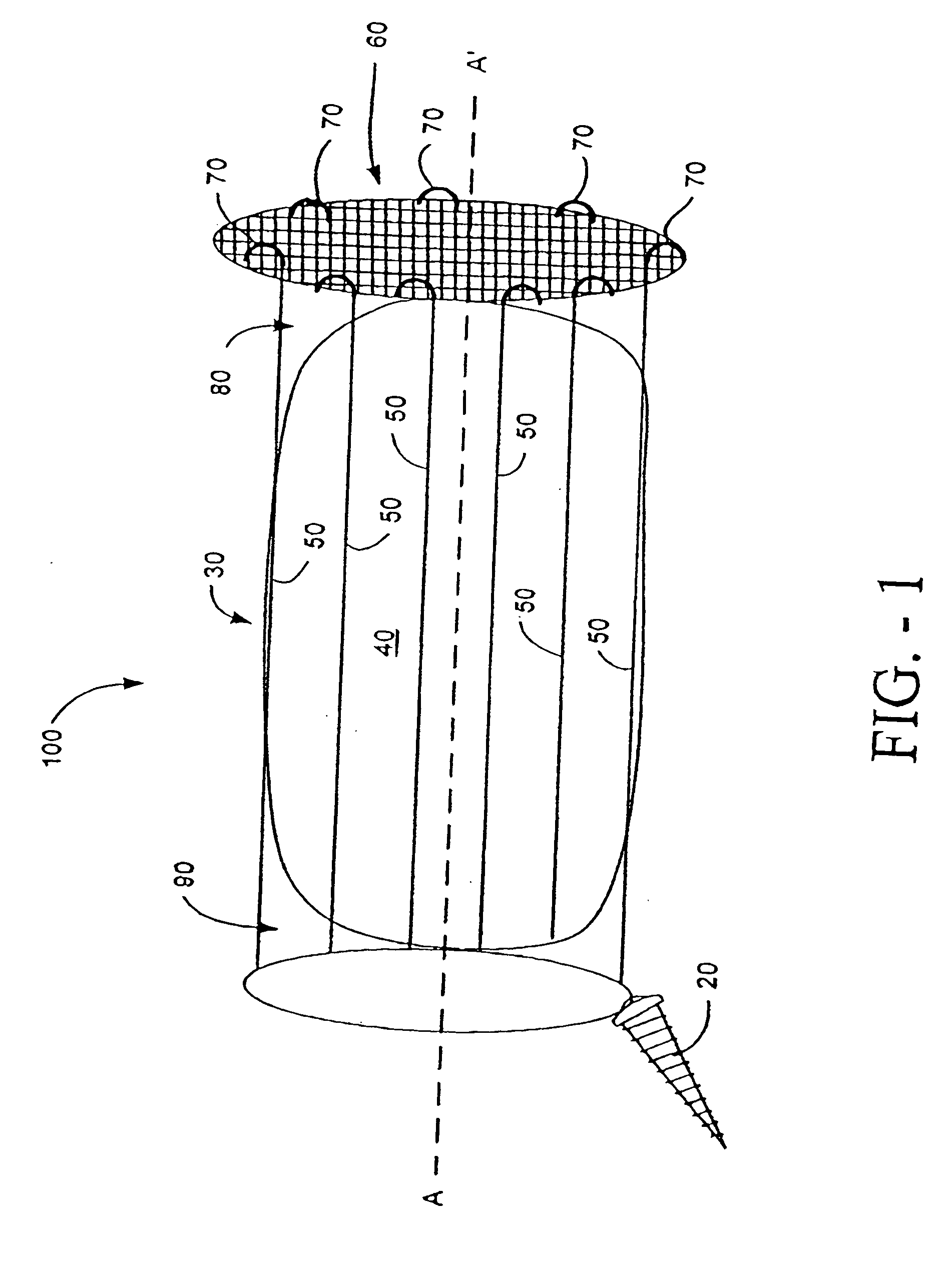
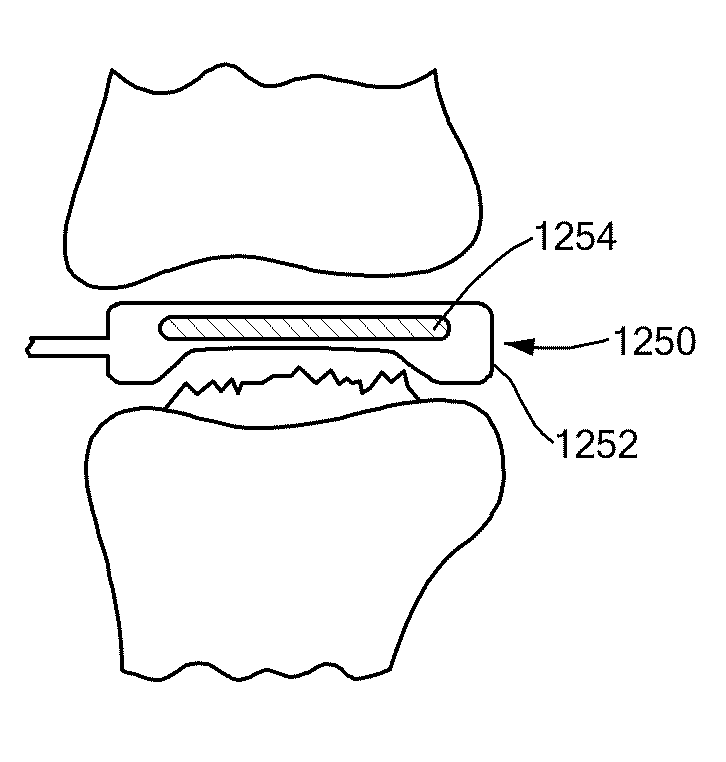
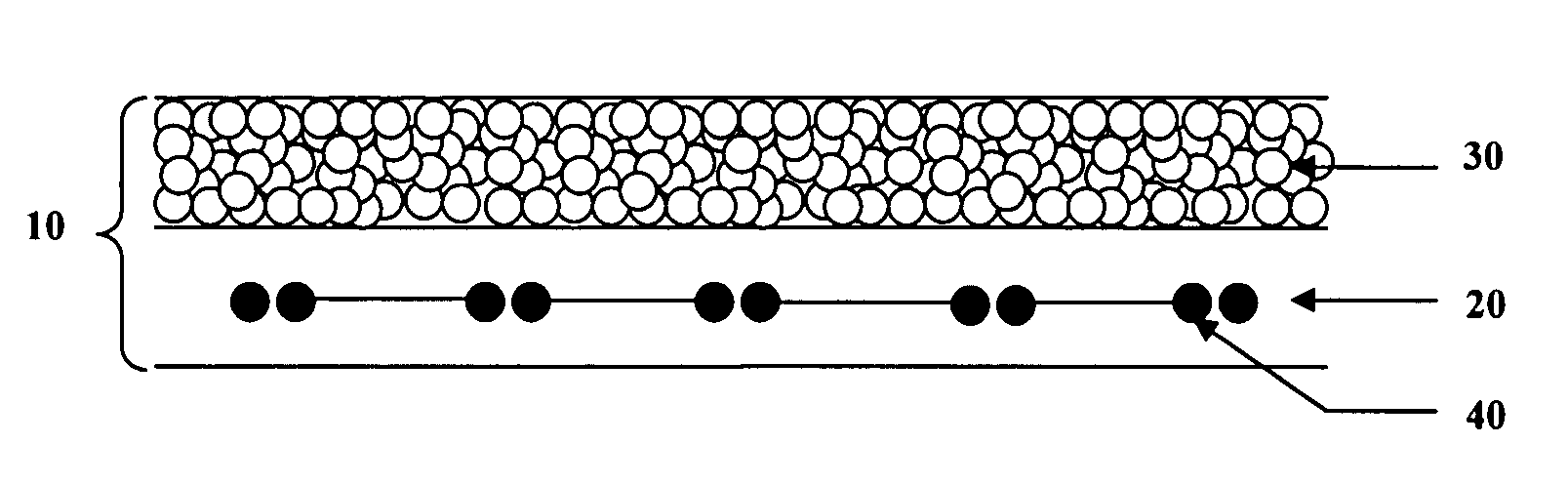
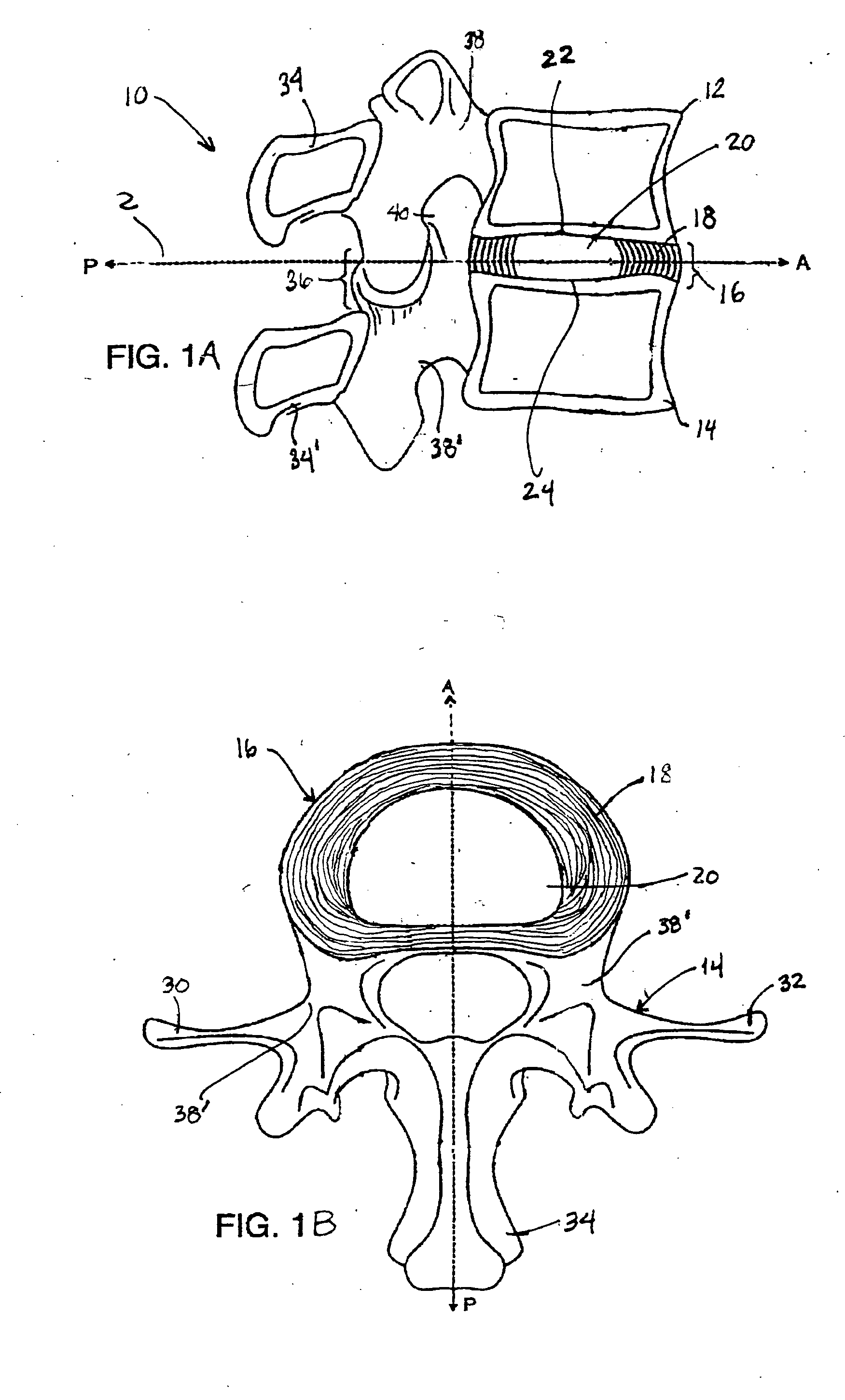
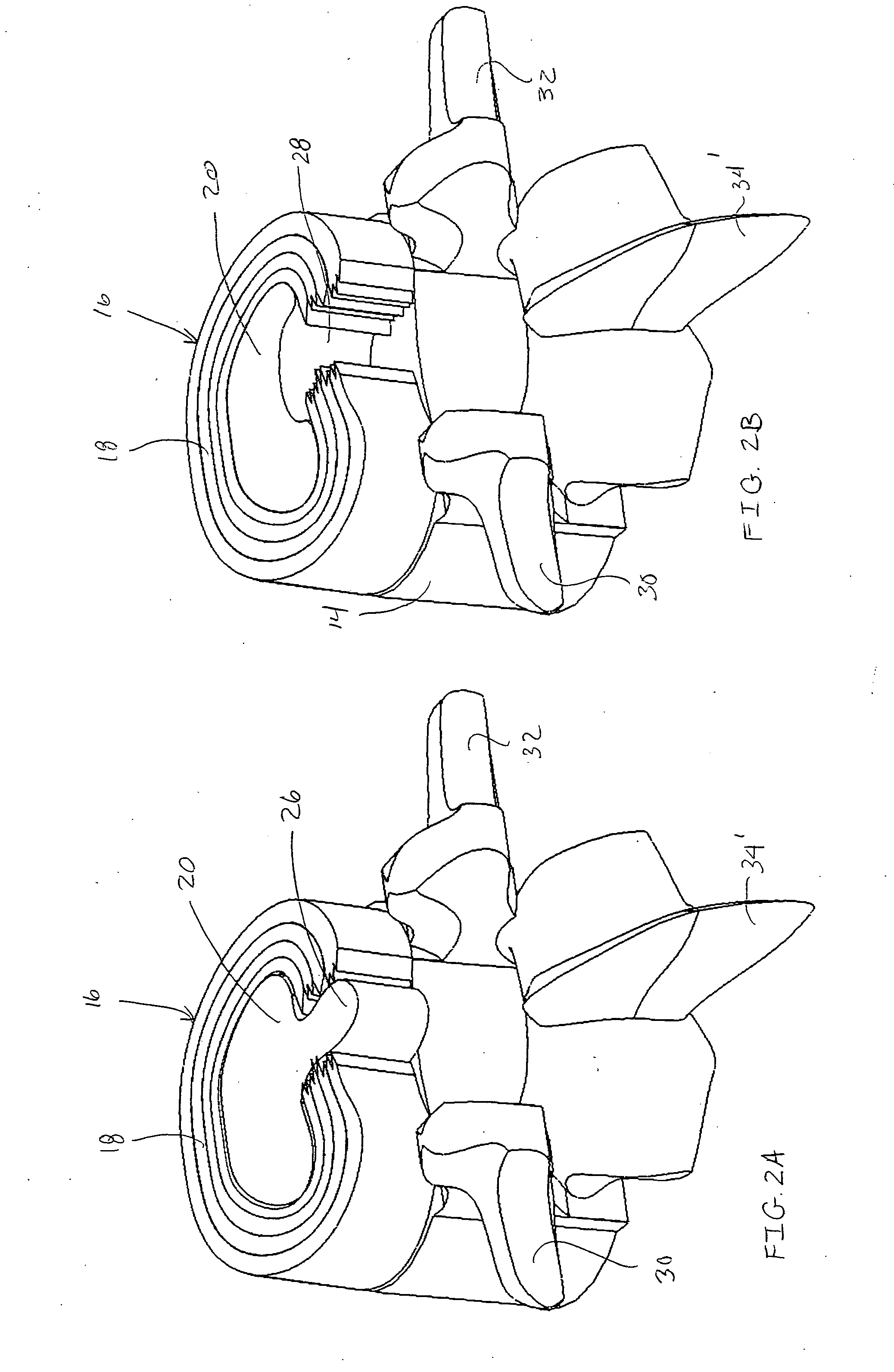
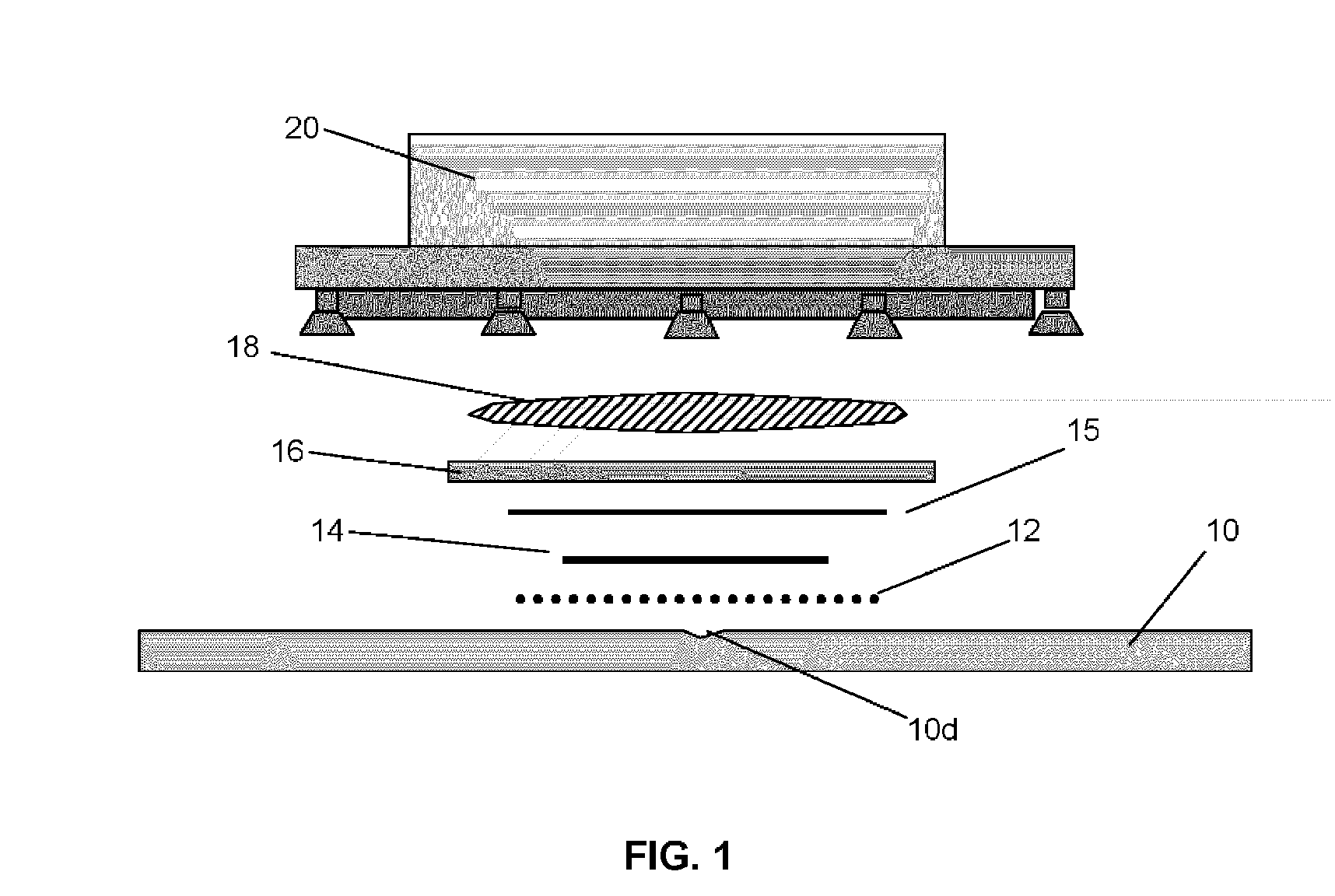
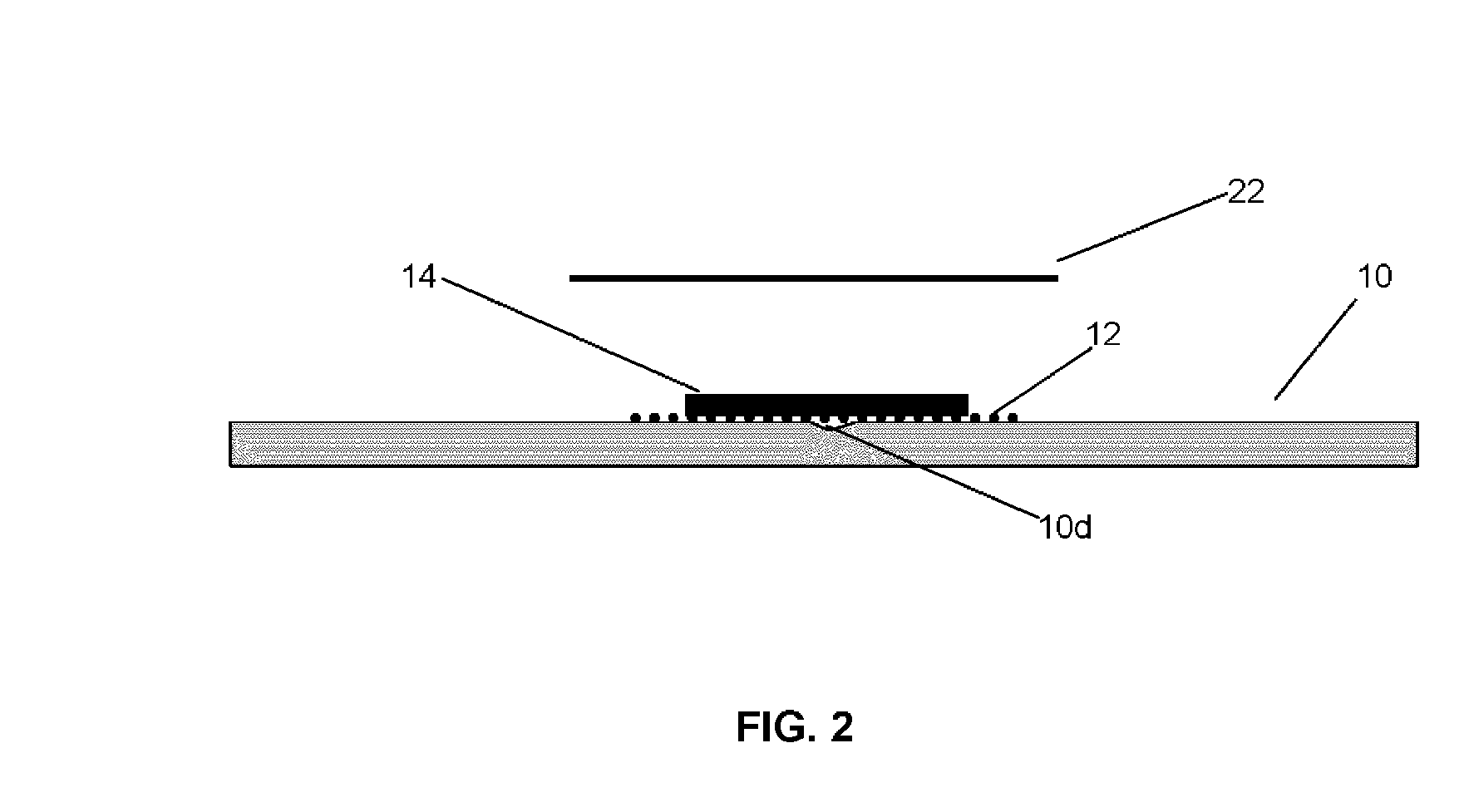
Disk repair structures for positioning disk repair material
The present invention is directed to a device that can be placed between two adjacent vertebrae, and that is used to repair an injury or defect in the anulus of the intervertebral disk. The implant is characterized by having a flexible structure anchored to the vertebral bone, the flexible structure connected with a patch held in place over the injury or defect. The flexible structure has a hollow interior space which can sustain inside it a hydrogel cushion. The hydrogel cushion acts as a shock absorber for the spine, maintains height of the intervertebral disk space, and prevents further disk herniation due to the narrowing of the intervertebral disk space.
Owner:KYPHON
Joint Arthroplasty Devices and Surgical Tools
InactiveUS20100168754A1Accurate placementImage analysisInternal osteosythesisArticular surfacesArticular surface
Disclosed herein are methods, compositions and tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
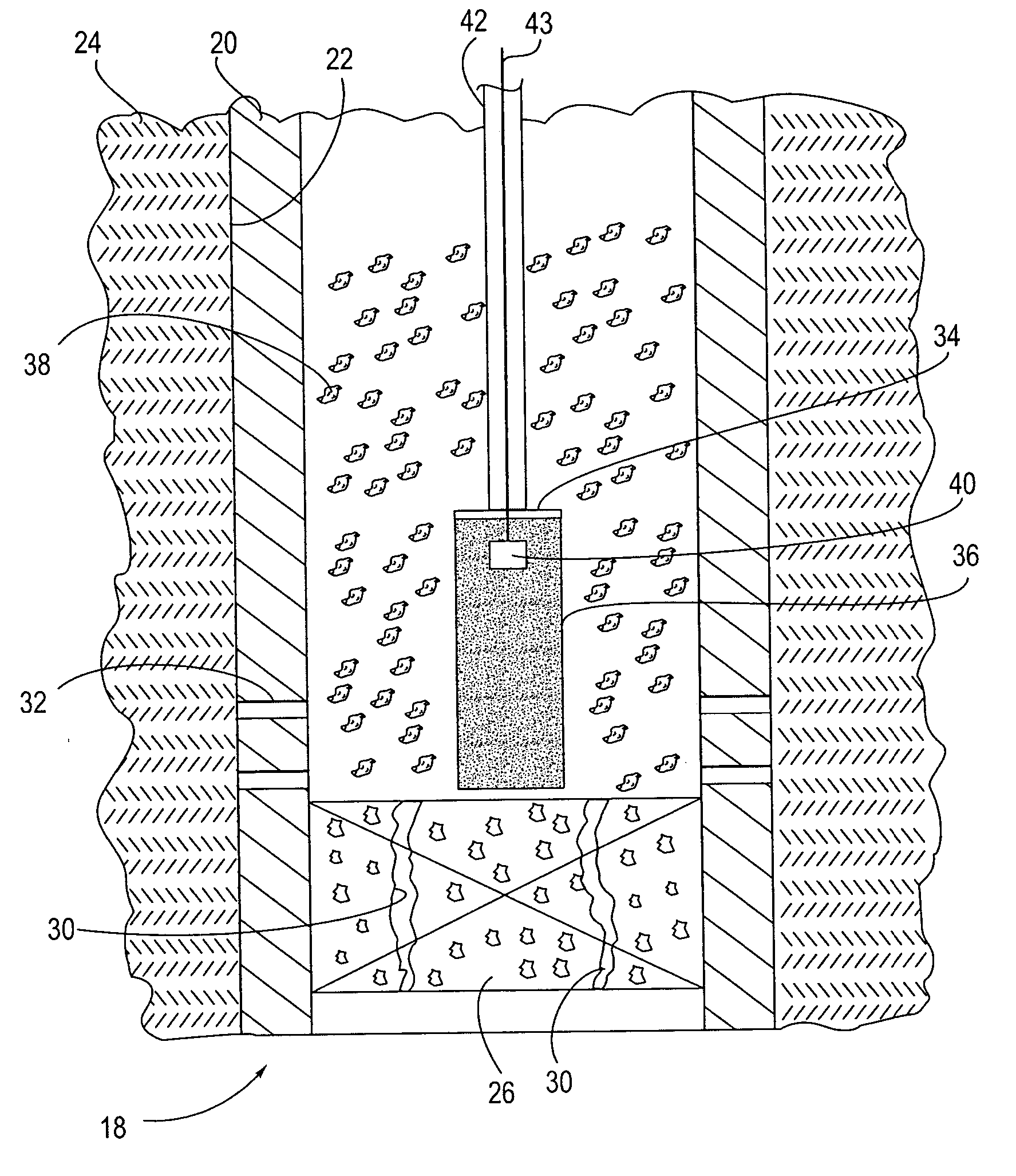
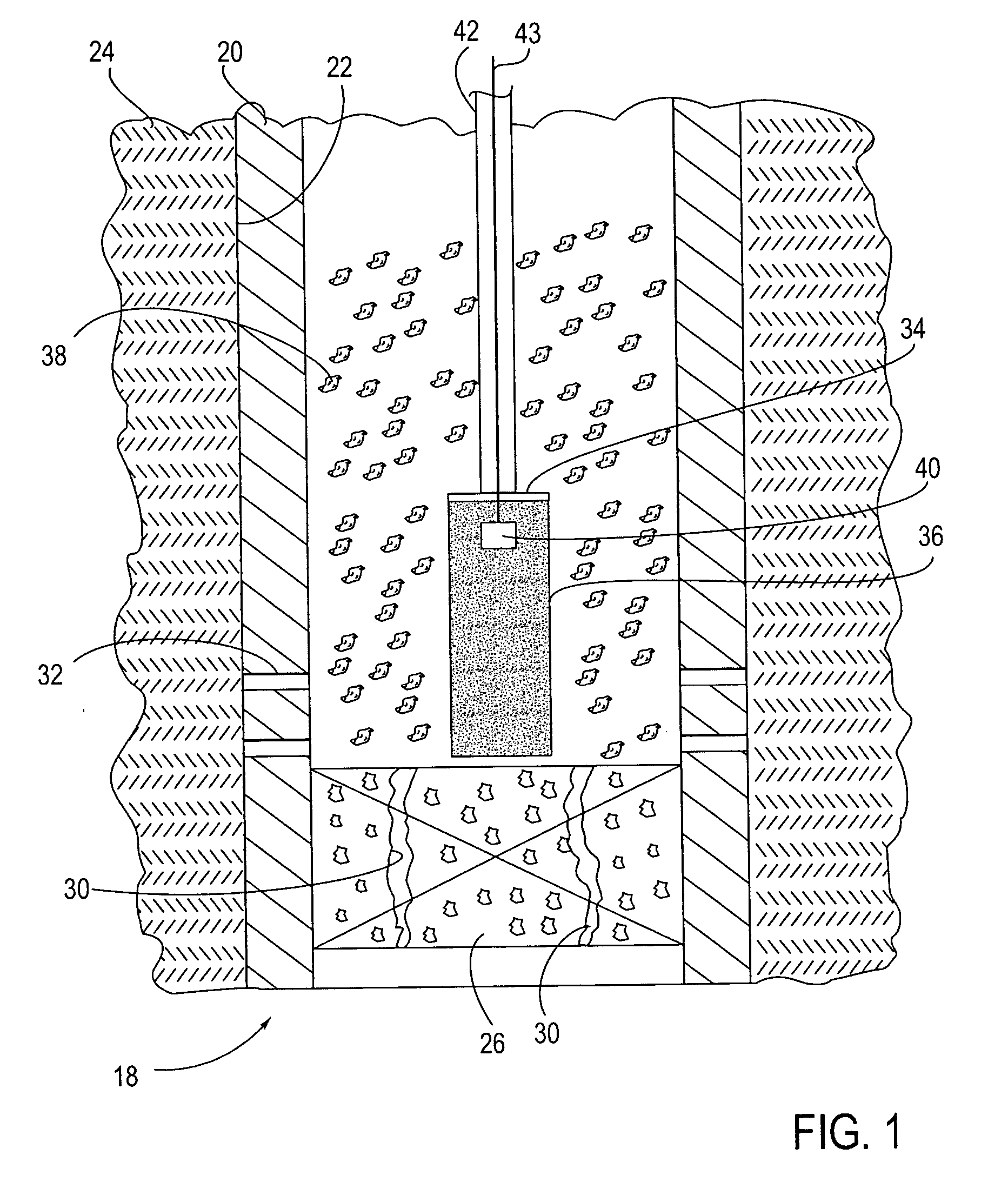
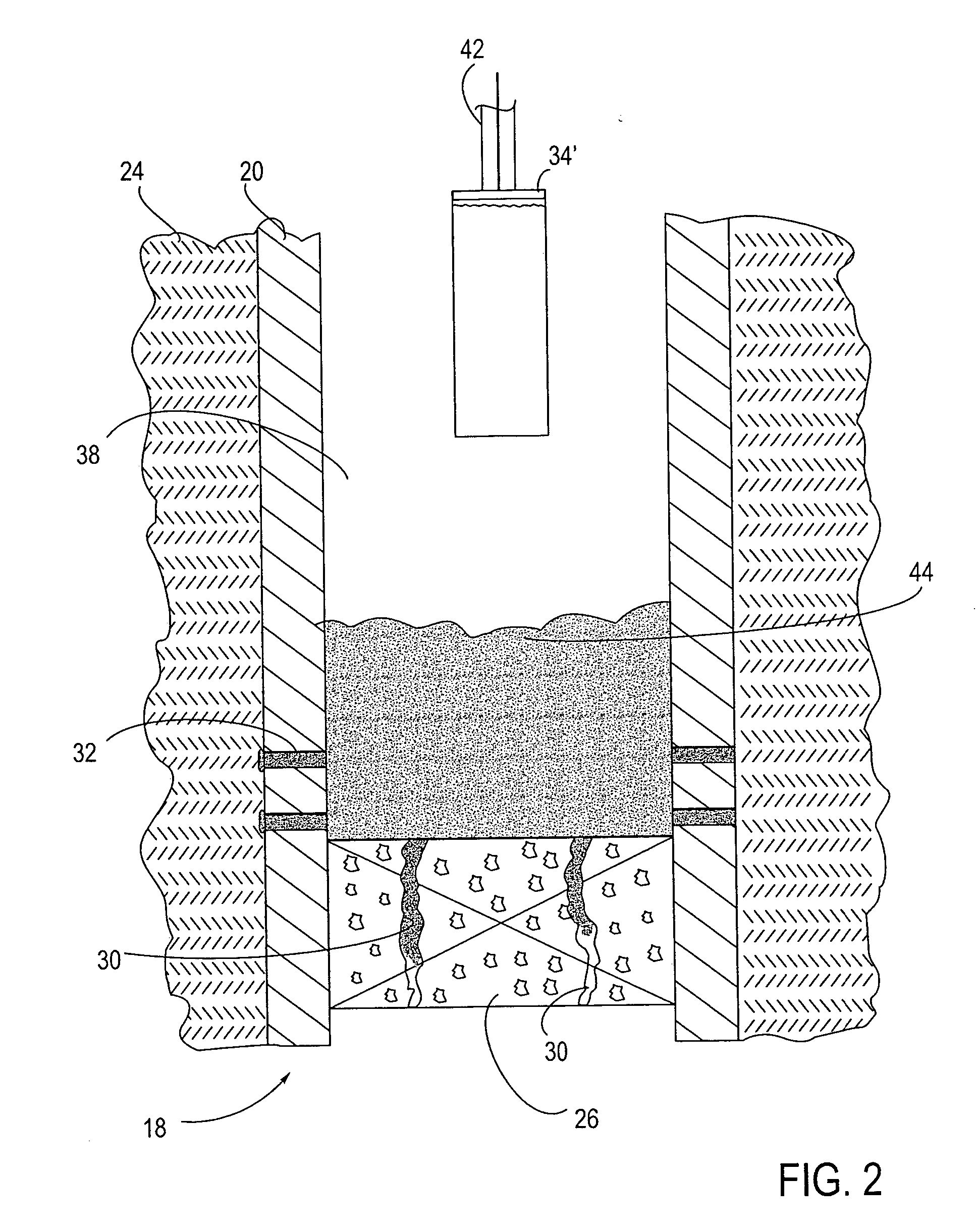
Method and apparatus for repair of wells utilizing meltable repair materials and exothermic reactants as heating agents
A method and apparatus are described for creating a fluid seal in a subterranean well structure having a fluid seal defect. The method comprises introducing a meltable repair material proximate a structure in a subterranean well which has a fluid seal defect or enhanced seal capacity is required or it is desired to temporarily or permanently hydraulically isolate a portion the well or strengthen the structural integrity of well tubulars or tubular hangers. Exothermic reactant materials are located proximate the meltable repair material. The exothermic reactant material is ignited or an exothermic reaction otherwise initiated which supplies heat to and melts the meltable repair material into a molten mass. The molten mass flows and solidifies across the structure and the fluid seal defect to effect a fluid seal in the subterranean well structure or the structural integrity is enhanced. Examples of preferred exothermic reactant materials include thermite, thermate, fusible chemical reactants such as ammonium chloride and sodium nitrate, and oxidizers and accompanying hydrocarbon based fuels. Examples of preferred meltable repair materials include solder or brazing materials and eutectic metals which expand upon cooling and solidifying from a molten state.
Owner:CHEVROU USA INC
Patient selectable joint arthroplasty devices and surgical tools incorporating anatomical relief
ActiveUS8623026B2Reduce the amount requiredImprove fitAdditive manufacturing apparatusSurgical navigation systemsArticular surfaceRepair material
Disclosed herein are methods, compositions and tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Patient Selectable Joint Arthroplasty Devices and Surgical Tools
InactiveUS20110213374A1Accurate placementGeometric CADAdditive manufacturing apparatusArticular surfacesSurgical operation
Owner:CONFORMIS
Patient Selectable Joint Arthroplasty Devices and Surgical Tools
InactiveUS20110213429A1Accurate placementGeometric CADAdditive manufacturing apparatusArticular surfacesArticular surface
Owner:CONFORMIS
Patient Selectable Joint Arthroplasty Devices and Surgical Tools
InactiveUS20110213428A1Accurate placementGeometric CADAdditive manufacturing apparatusArticular surfacesSurgical operation
Disclosed herein are methods, compositions and tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Patient Selectable Joint Arthroplasty Devices and Surgical Tools
InactiveUS20110213377A1Accurate placementGeometric CADAdditive manufacturing apparatusArticular surfacesArticular surface
Disclosed herein are methods, compositions and tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Patient Selectable Joint Arthroplasty Devices and Surgical Tools
InactiveUS20110213427A1Accurate placementGeometric CADAdditive manufacturing apparatusArticular surfacesSurgical operation
Disclosed herein are methods, compositions and tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Patient Selectable Joint Arthroplasty Devices and Surgical Tools
InactiveUS20110213430A1Accurate placementGeometric CADAdditive manufacturing apparatusArticular surfacesArticular surface
Disclosed herein are methods, compositions and tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Patient Selectable Joint Arthroplasty Devices and Surgical Tools
InactiveUS20110213431A1Accurate placementGeometric CADAdditive manufacturing apparatusArticular surfacesArticular surface
Disclosed herein are methods, compositions and tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Patient Selectable Joint Arthroplasty Devices and Surgical Tools
InactiveUS20110213368A1Accurate placementGeometric CADAdditive manufacturing apparatusArticular surfacesArticular surface
Disclosed herein are methods, compositions and tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
Patient Selectable Joint Arthroplasty Devices and Surgical Tools
InactiveUS20110213373A1Accurate placementGeometric CADAdditive manufacturing apparatusArticular surfacesArticular surface
Disclosed herein are methods, compositions and tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The articular surface repairs are customizable or highly selectable by patient and geared toward providing optimal fit and function. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
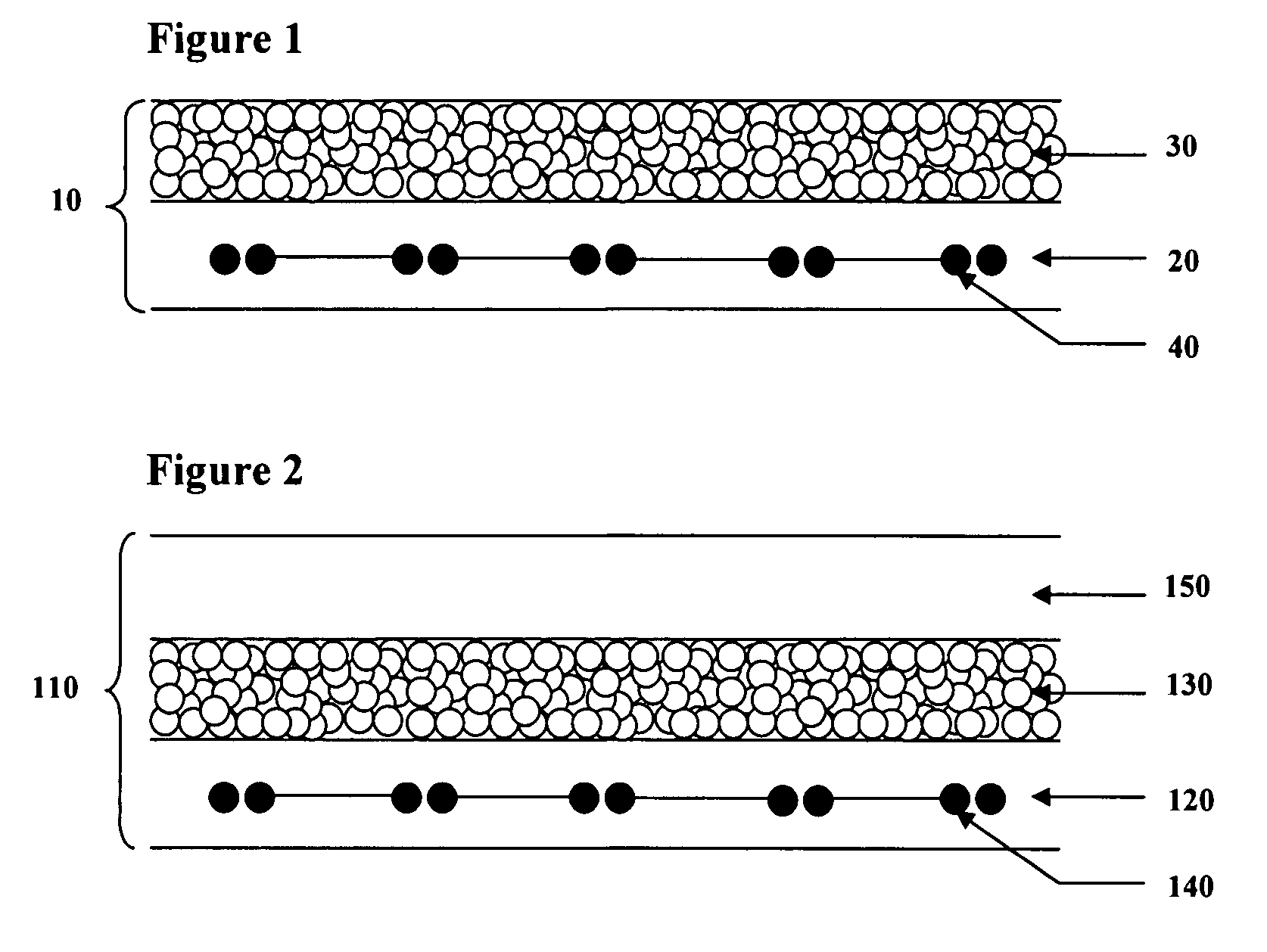
Method for treatment of defects in the intervertebral disc
InactiveUS20050069571A1Easy to processPromote regenerationBiocideJoint implantsIntervertebral discDefect repair
A minimally invasive spinal disc defect repair method is disclosed. The method relates to insertion of disc defect repair materials that are substantially two-dimensionally shaped and which allow for insertion and preferably self retention within the disc defect with plugging of the annulus fibrosis.
Owner:DEPUY ACROMED INC
Patient Selectable Joint Arthroplasty Devices and Surgical Tools
InactiveUS20130024000A1Additive manufacturing apparatusSurgical navigation systemsArticular surfacesArticular surface
Disclosed herein are tools for repairing articular surfaces repair materials and for repairing an articular surface. The surgical tools are designed to be customizable or highly selectable by patient to increase the speed, accuracy and simplicity of performing total or partial arthroplasty.
Owner:CONFORMIS
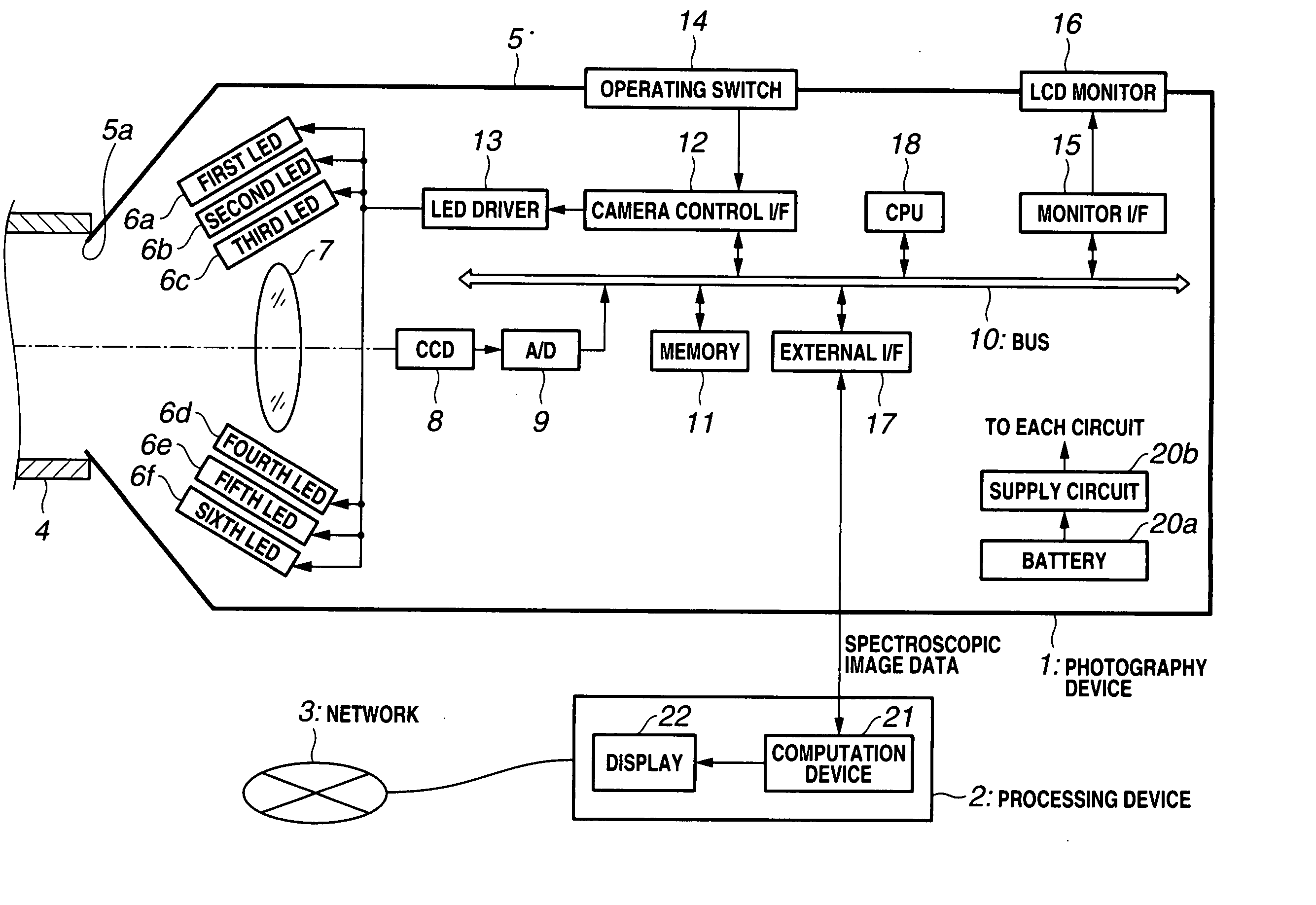
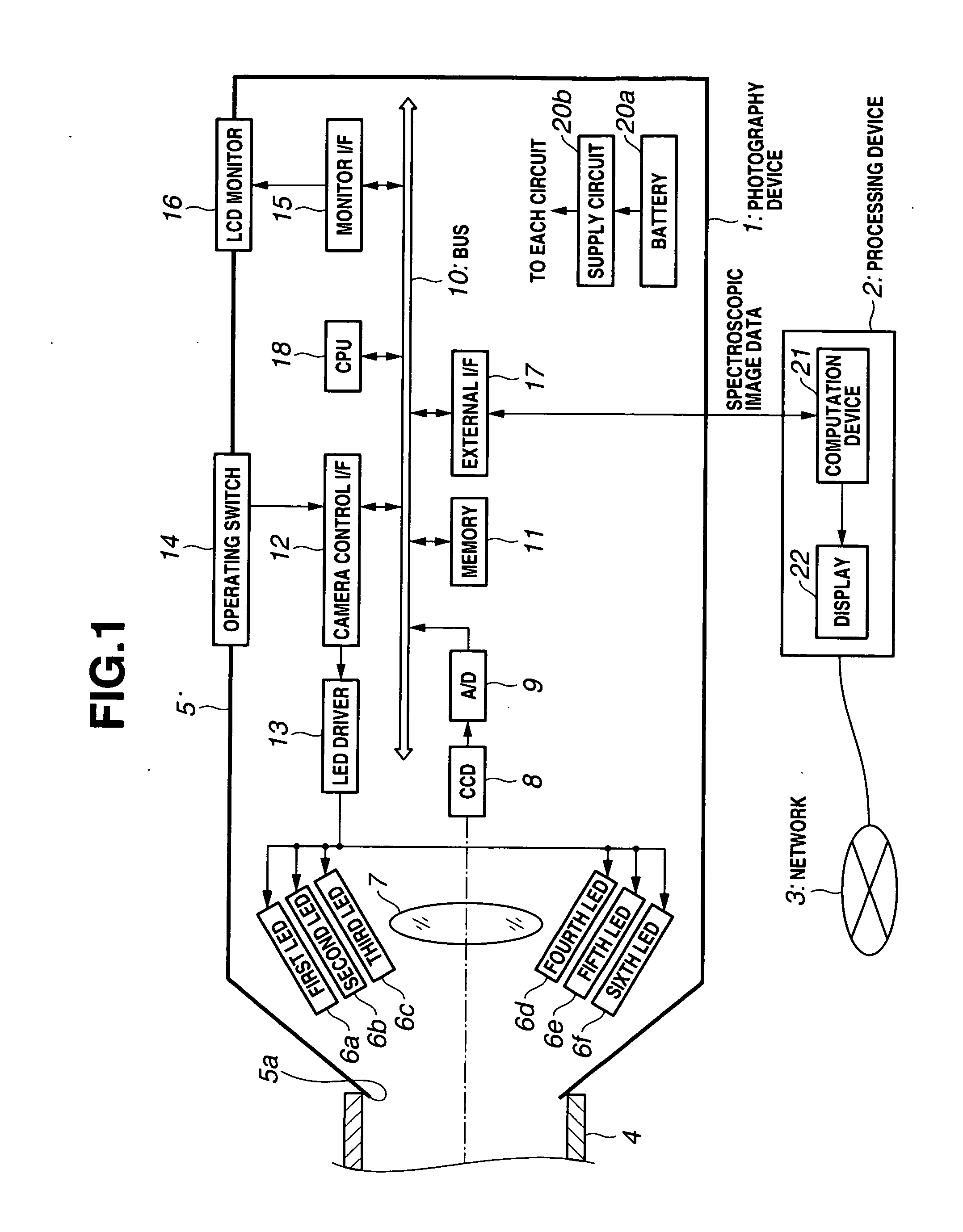
Image processing system and camera
The image processing system is applied to dentistry, for example, and performs photography of the teeth of a patient while causing a plurality of illumination light LEDs of different wavelengths to emit light by means of a photography device when producing a crown repair or denture of the patient, whereby image data are acquired. The image data are transmitted to a dental filing system constituting a processing device where color reproduction data are determined through computation. In addition, color reproduction data are transmitted to the dental technician's office via a public switched network. Therefore, a repair material compound ratio calculation database is searched and the compound data for a material that matches the hue of the patient's teeth are found, whereby a crown repair or denture or the like that very closely matches the color of the patient's teeth is produced.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Dural repair material
Multilayer structures including a porous layer and a non-porous layer having a reinforcement member are useful as dural repair materials.
Owner:SOFRADIM PROD SAS
Systems and methods for augmenting intervertebral discs
Systems, devices and methods are provided for augmenting intervertebral discs. The systems include implantable annulus repair and augmentation devices as well as implantable prosthetic materials for replacing a portion of or augmenting the annulus and / or the nucleus pulposus. The systems further include instruments for implanting the subject devices and materials in a minimally invasive manner. The methods are directed to the minimally invasive implantation of one or more of the subject annulus repair devices and the prosthetic materials concurrently.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
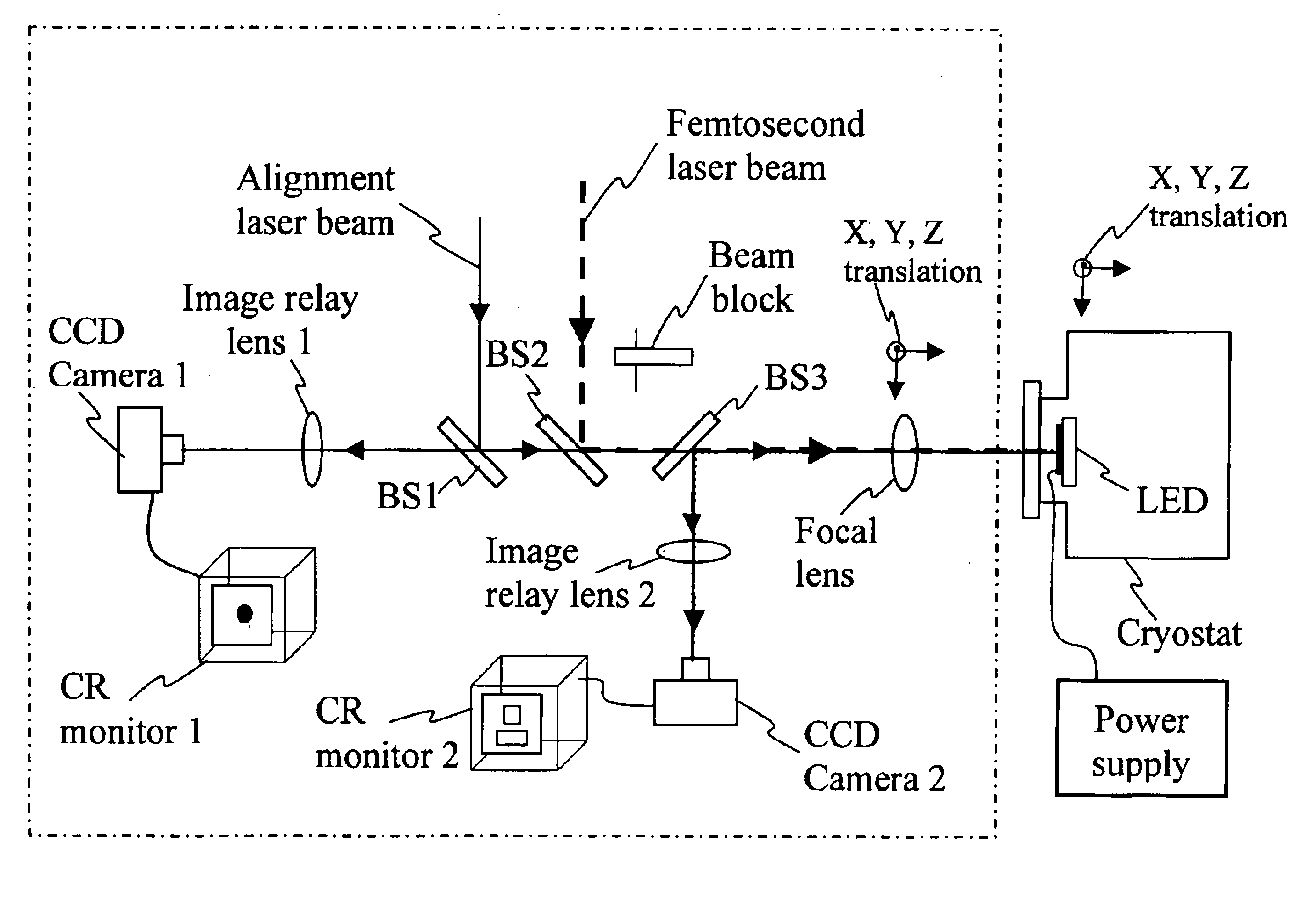
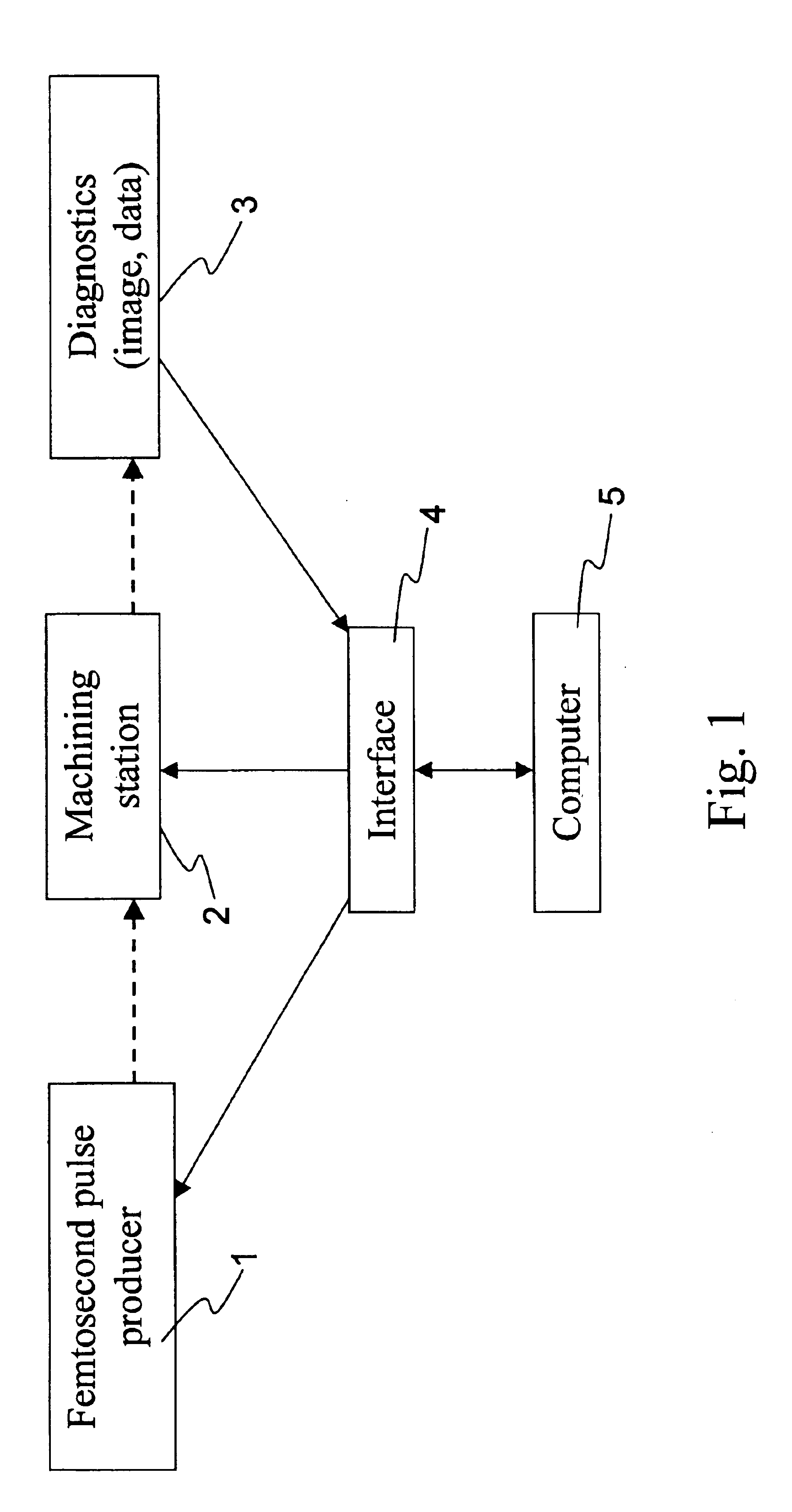
Method and apparatus for repair of defects in materials with short laser pulses
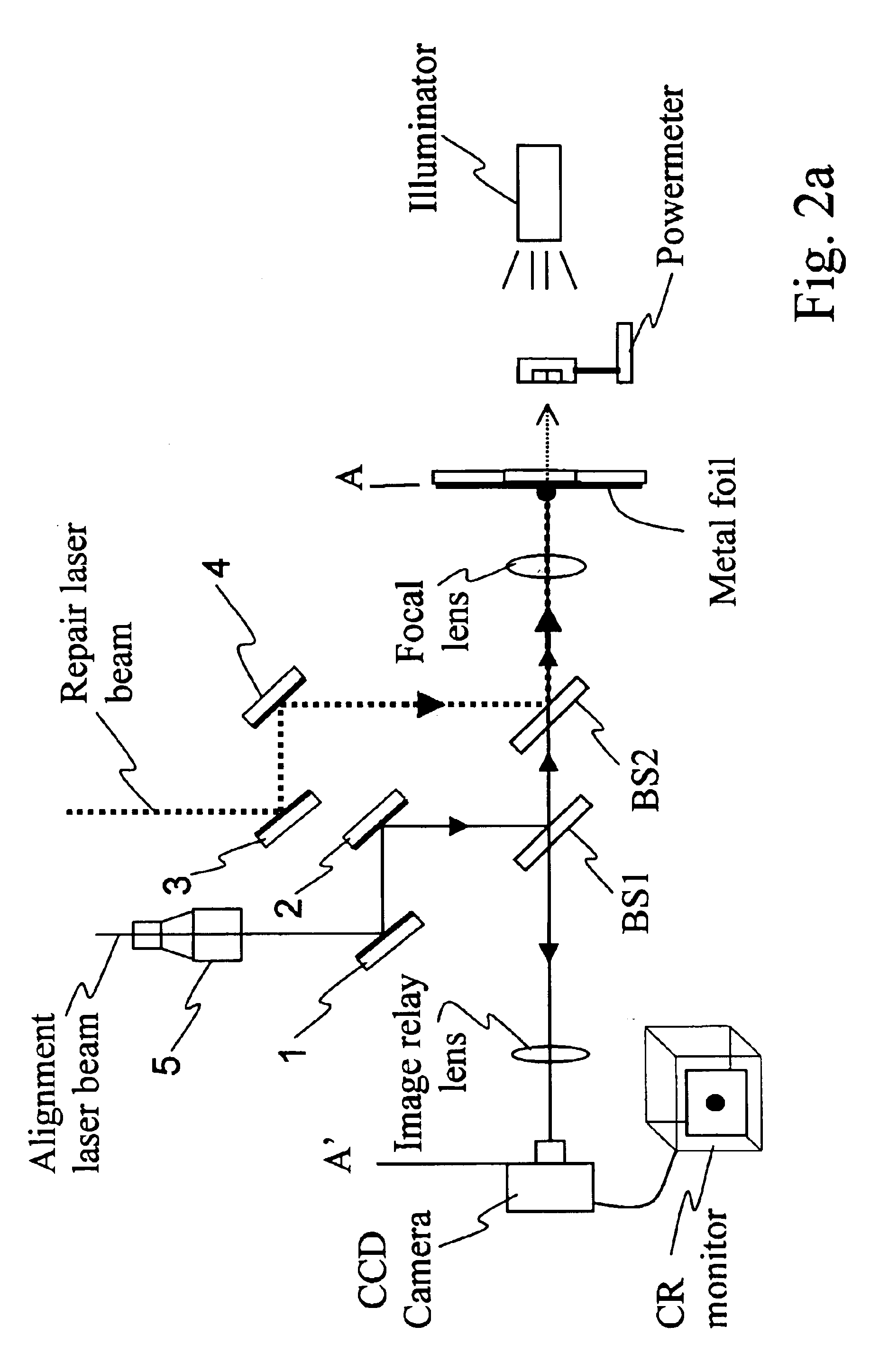
InactiveUS6878900B2Minimize damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOriginals for photomechanical treatmentRepair materialEngineering
A method of accurately and precisely providing desired functionality to an electronic or opto-electronic component is disclosed in which a Femtosecond laser pulse is used to ablate material from a surface of or from within a component. The component is in active operation during the ablation process in order to facilitate the ablation process. The process also involves detection and feedback to indicate when a repair is sufficiently complete. The detection is also performed while the component is powered allowing in-situ detection and ablation. Of course, forms of facilitation other than feedback such as monitoring are also applicable to the invention.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Dental restorative compositions
InactiveUS6837712B2Reduce Shrinkage ProblemsImprove mechanical propertiesCosmetic preparationsImpression capsFunctional monomerRepair material
A composition and a method of use as a dental restorative. A series of highly alkoxylated tri-functional monomers are used as a low viscosity monomer in a photo- or self-curable dental composition that resulted in low polymerization shrinkage. The mechanical strength of the restorative material was not compromised. The restorative composition may be used as a dental filling material, a cement, a liner / base, or an adhesive.
Owner:THE KERR
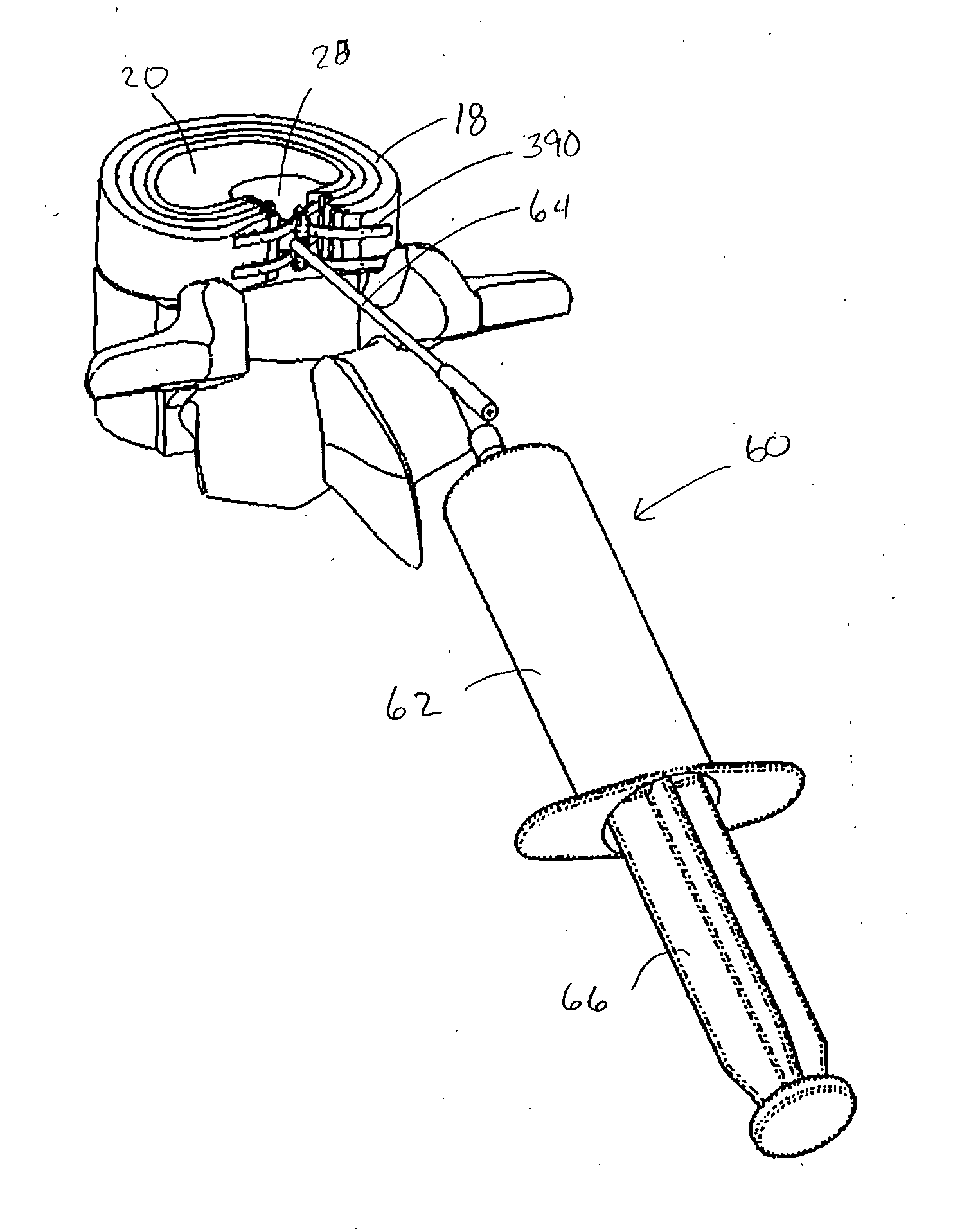
Fast line maintenance repair method and system for composite structures
InactiveUS20070095457A1Minimum skillQuick fixLighting and heating apparatusLayered productsAdhesiveRepair material
A fast line maintenance repair process for damaged composite structures includes the application of a pre-cured patch that uses a quick curing paste adhesive to bond the patch to the structure. The adhesive is cured at relatively low elevated temperatures provided by a chemical heat pack. The low temperature cure eliminates the need to dry out the part and permits the application of the repair in a hazardous environment. In a typical commercial airline application, airline maintenance personnel can install the repair at the flight gate. The repair is intended to restore the structure to a desired load capability in approximately one hour. The repair can be removed if need be with less overall damage than would occur upon removal of typical mechanically fastened repairs. All or some of the repair materials and tools can be provided in a portable kit.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com