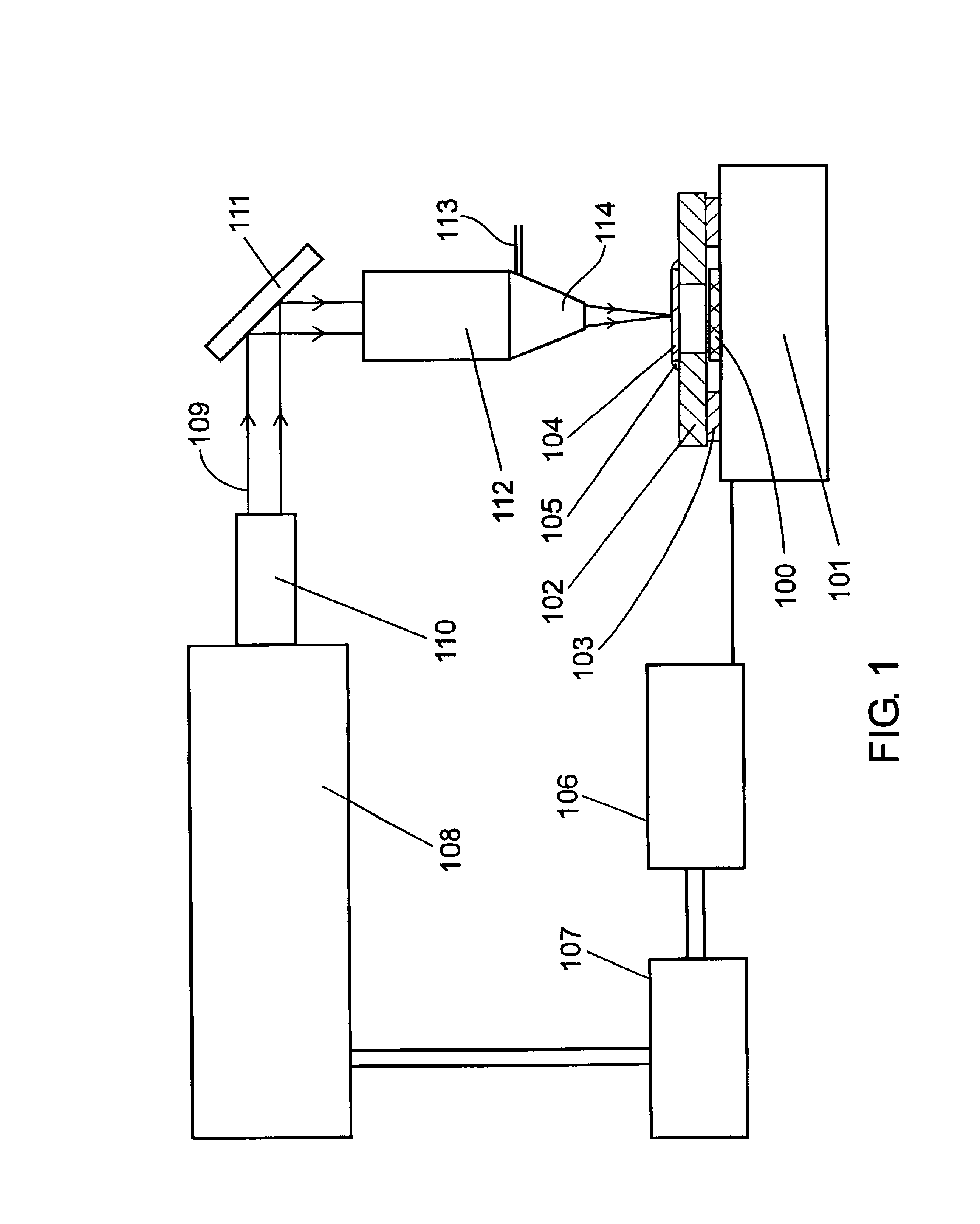
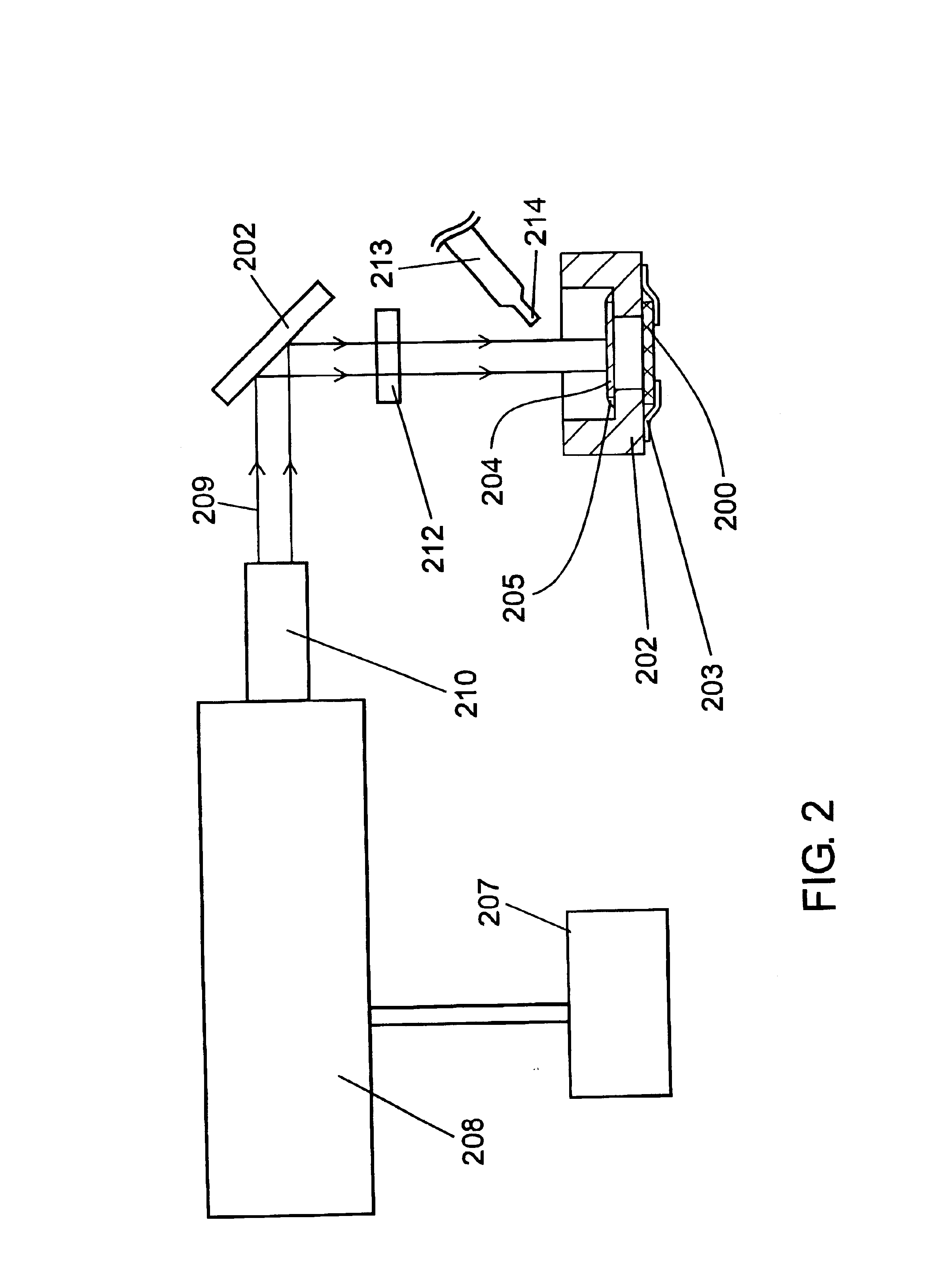
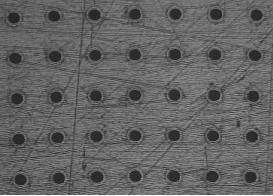
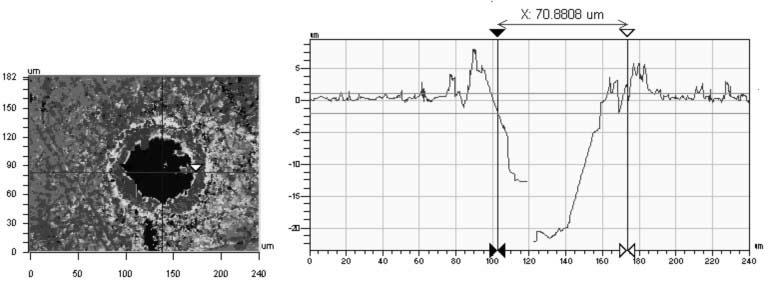
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
297 results about "Nd:YAG laser" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Nd:YAG (neodymium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet; Nd:Y₃Al₅O₁₂) is a crystal that is used as a lasing medium for solid-state lasers. The dopant, triply ionized neodymium, Nd(III), typically replaces a small fraction (1%) of the yttrium ions in the host crystal structure of the yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG), since the two ions are of similar size. It is the neodymium ion which provides the lasing activity in the crystal, in the same fashion as red chromium ion in ruby lasers.
Laser engraving methods and compositions, and articles having laser engraving thereon
ActiveUS20050095408A1Not easy to counterfeitDifficult to alterRadiation applicationsDecorative surface effectsThioester synthesisBarium sulphide
The invention provides a composition having laser engraving properties, comprising a host material and an effective amount of a laser enhancing additive. The laser enhancing additive comprises a first quantity of least one of copper potassium iodide (CuKI3) or Copper Iodide (CuI), and a second quantity at least one substance selected from the group consisting of zinc sulfide (ZnS), barium sulfide (BaS), alkyl sulfonate, and thioester. The composition can be engraved with grayscale images by an Nd:Yag laser and can be added to laminates or coatings. The composition can be used during the manufacture of many articles of manufacture, including identification documents.
Owner:L 1 SECURE CREDENTIALING
Method with functions of preheating and postheating for forming crack-free coating with high efficiency by three-light-beam laser-cladding technique
InactiveCN102383126ALow and adjustable dilution rateSmall heat affected zoneMetallic material coating processesLaser beam welding apparatusMelting tankHeat-affected zone
The invention discloses a method with functions of preheating and postheating for forming crack-free coating with high efficiency by a three-light-beam laser-cladding technique. The method comprises the following steps of: splitting a laser beam emitted by an Nd: YAG laser into two laser beams by using a laser beam splitter, namely a preheating laser beam for preheating the surface of a base material and a postheating laser beam for postheating the formed coating; then blowing alloy powder into a molten pool which is formed by focusing a laser beam emitted by a CO2 laser and acting the focused laser beam on the surface of the base material by using a powder nozzle, wherein after the CO2 laser beam moves away, a molten layer is cured and crystallized quickly to form the coating; and postheating the formed coating by adopting the postheating laser beam. The method has the advantages that: (1) the dilution rate of the coating is low and adjustable, and the coating is metallurgically combined with the base material, so the base material has a small thermal influence area and is deformation-free and crack-free; (2) residual inner stress in the coating can be eliminated effectively, a tissue can be improved, and the coating has high abrasion resistance, high corrosion resistance, high anti-cracking performance and high thermal shock resistance; and (3) relative to the processing efficiency in the conventional laser cladding technology, the processing efficiency in the method can be improved by 50 times to the maximum extent, so the processing cost is reduced greatly, and a large-scale industrialized application potential is realized.
Owner:NANCHANG HANGKONG UNIVERSITY
Lidar system for remote determination of calibrated, absolute aerosol backscatter coefficients
ActiveUS7656526B1Effort directedSafely and quickly and efficiently identifyRaman scatteringParticle size analysisBeam splitterAerosol backscatter
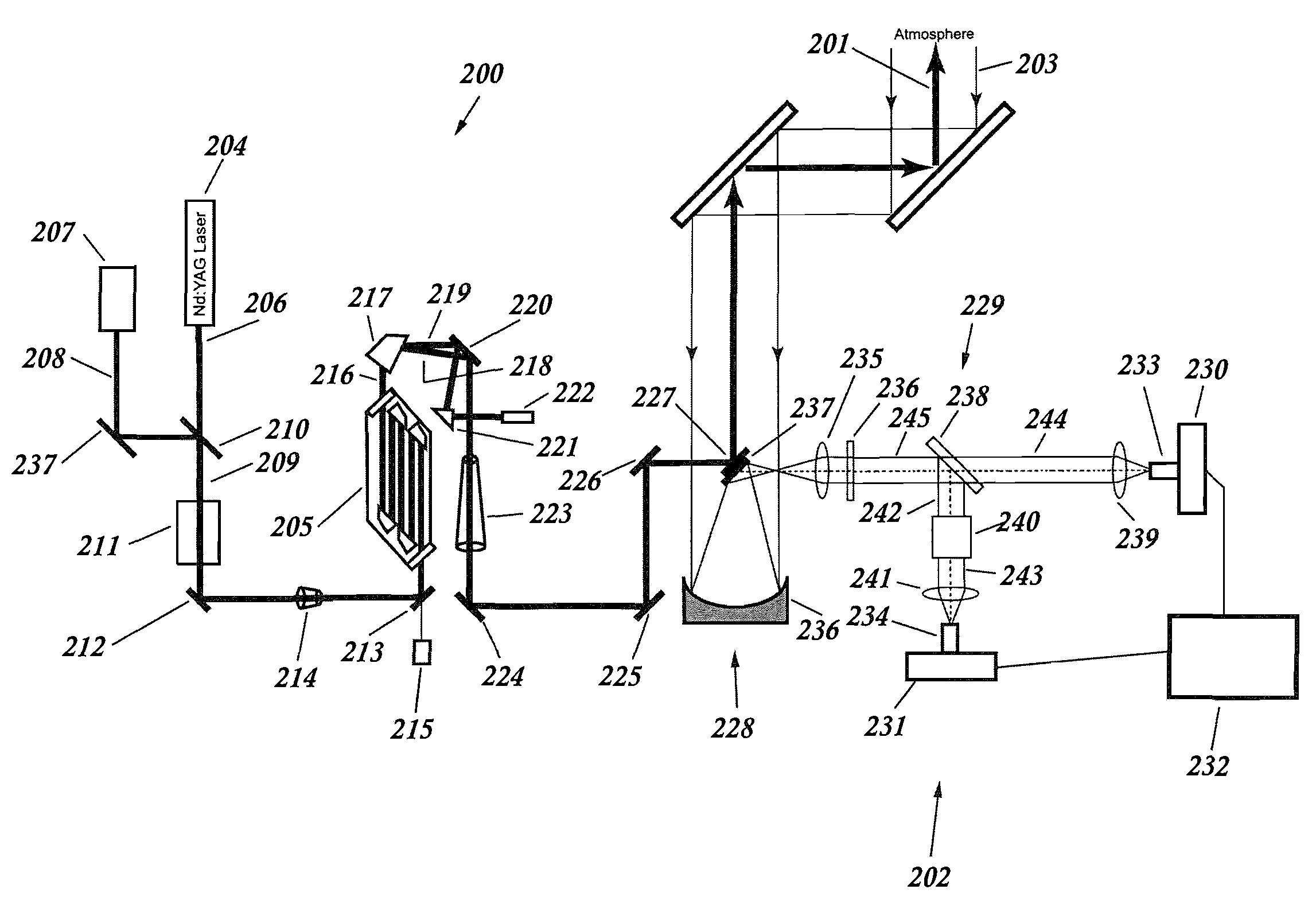
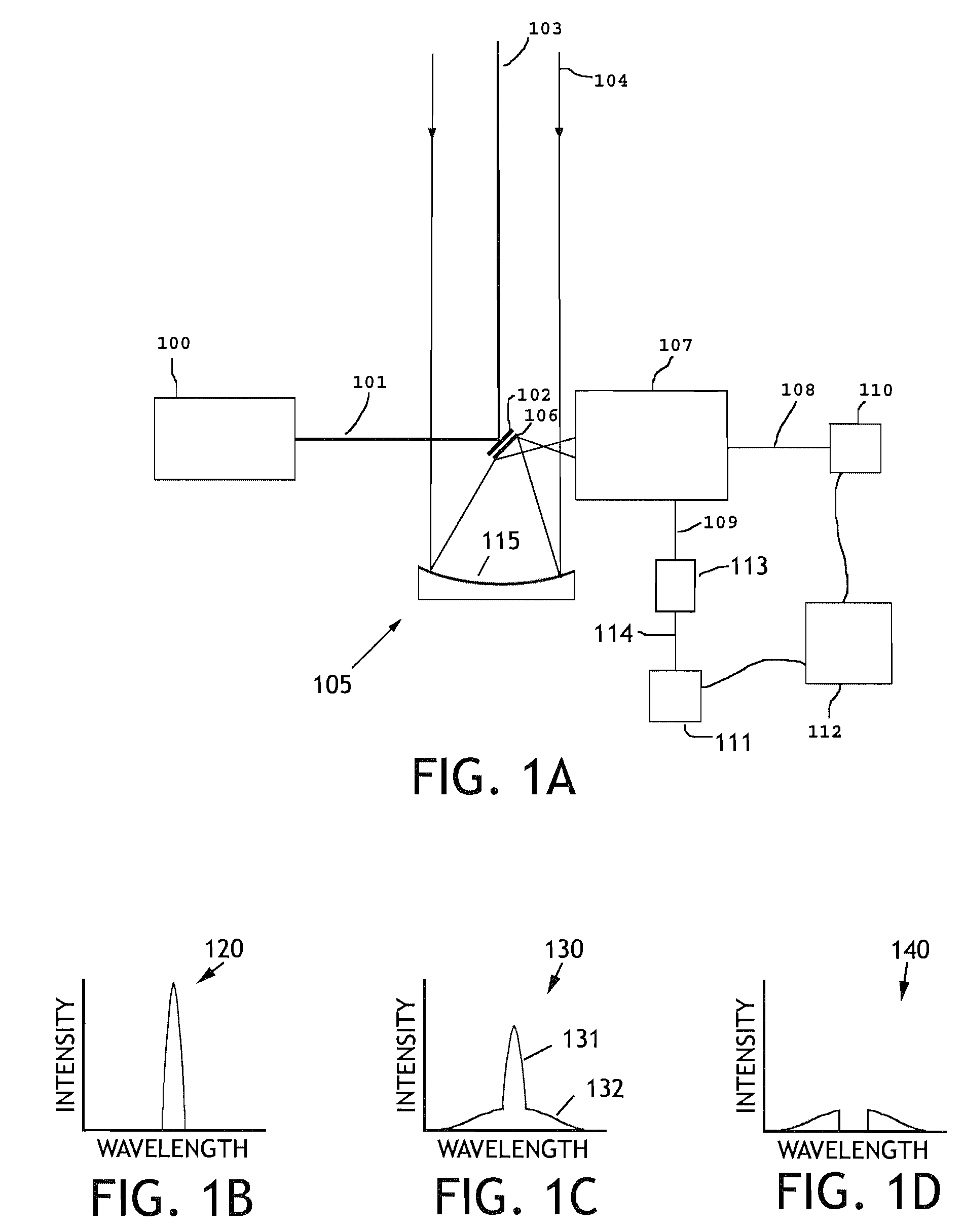
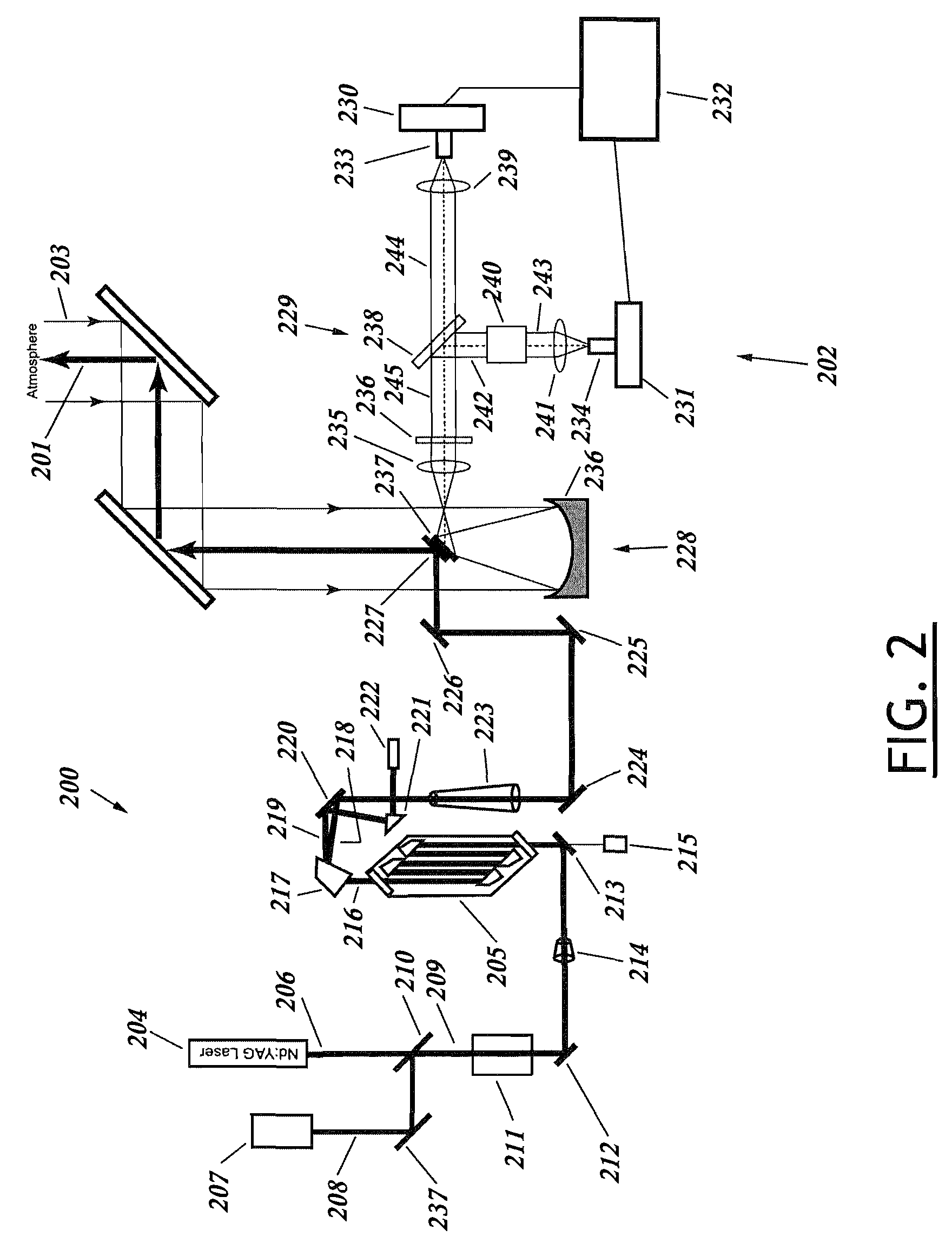
A lidar system capable of remotely identifying calibrated absolute aerosol backscatter coefficients of atmospheric aerosol particles by transmitting a beam of light and spectrally separating the intensity of Rayleigh and Mie backscattering is disclosed. The transmitter features high pulse energy to generate sufficient Rayleigh backscattering, enabling atmospheric scanning in a timely manner. The transmitter employs a seeded Nd:YAG laser and a seeded stimulated Raman scattering wavelength shifter to achieve narrow bandwidth, eye-safe laser pulses. The receiver employs a telescope, collimating lens, beam splitter, molecular absorption filter, focusing lenses, and avalanche photodiodes. Mie backscattering is blocked by the molecular absorption filter to provide a Rayleigh signal, which is used with knowledge of atmospheric density to calibrate the Mie signal. The system is intended for atmospheric research and aerosol monitoring applications where calibrated Mie scattering intensity is necessary to measure the optical depths of aerosol structures such as plumes, clouds, and layers.
Owner:UNIV FOR ATMOSPHERIC RES
Repair process for aluminum nitride substrates
A method to repair Aluminum Nitride (AlN) substrates is disclosed wherein a frequency doubled Q-switched Nd:YAG laser is used to remove unwanted metallurgy. The substrate is place in a liquid filled work chamber which acts to prevent metallic species of AlN from forming. The repair site can be sealed with a novel polymer coating to prevent contamination or corrosion. Repairs can be made to buried or surface metallurgy.
Owner:IBM CORP
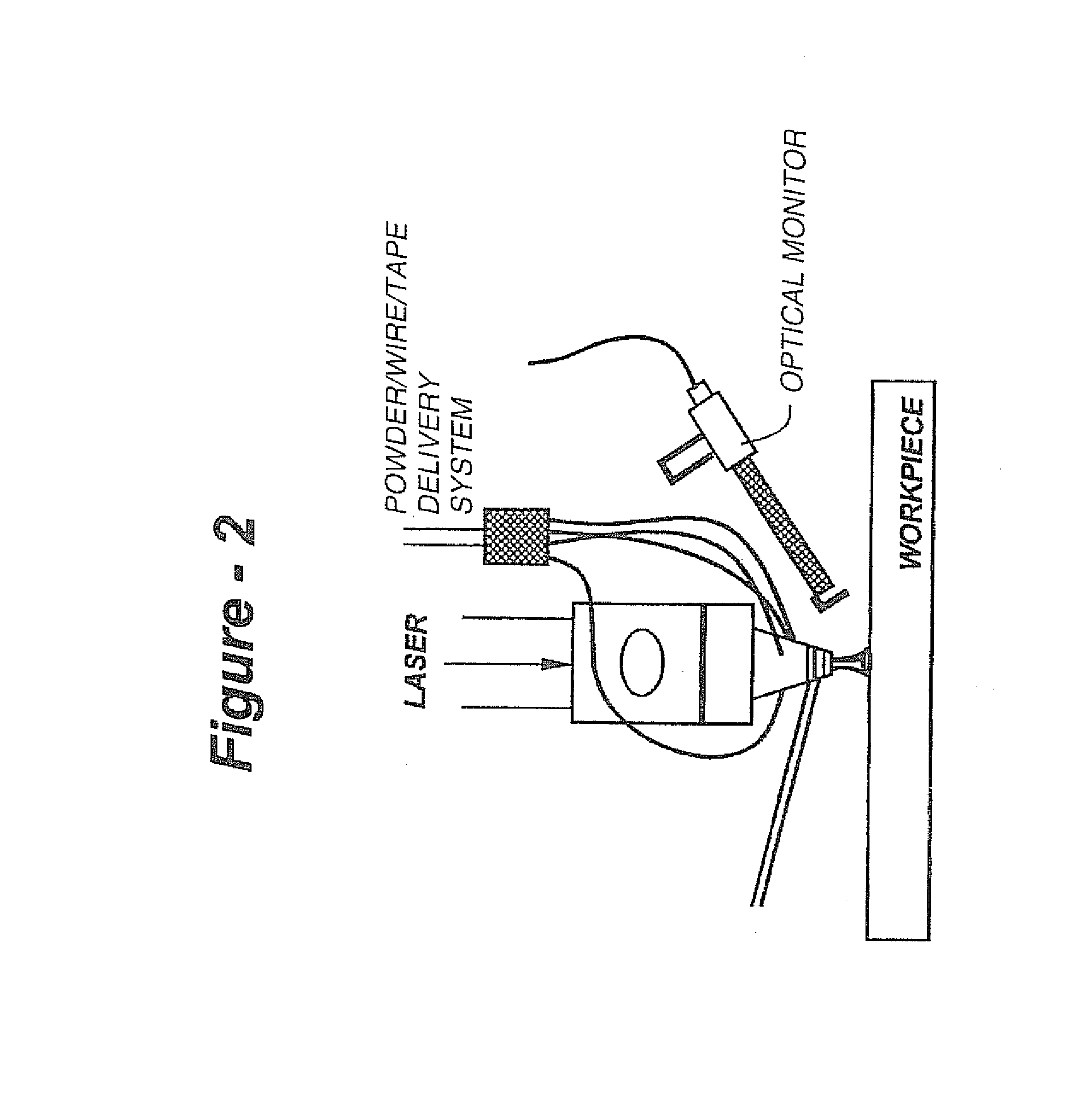
Direct metal deposition apparatus utilizing rapid-response diode laser source
InactiveUS7765022B2Rapid responseEnhanced dimensional controlAdditive manufacturing apparatusMolten spray coatingElectricityClosed loop
The present invention incorporates one or more diode lasers for the high-power CO2 or Nd-YAG lasers currently used in closed-loop DMD systems. Being semiconductor-based, such devices are almost instantaneously responsive to the electrical input. As such, a DMD system driven by a diode laser according to the invention provides a much faster response compared to other sources. The faster response time, in turn, provides for enhanced dimensional control and capability to produce intricate components with better dimensional accuracy.
Owner:DM3D TECH
Combined testing device and testing method of laser damage thresholds of film and optical element
ActiveCN101718712AReduce mistakesWide varietyScattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPhotovoltaic detectorsBeam splitter
The invention relates to a combined testing device of the laser damage thresholds of a film and an optical element and a testing method utilizing the device. The traditional testing device and testing method have greater error and poor suitability for various film materials. The combined testing device of the laser damage thresholds of a film and an optical element comprises a testing assembly and a processing assembly, wherein the testing assembly comprises a Nd:YAG laser, a switch baffle, a first beam splitter, a focusing lens, a second beam splitter, a sample platform, a photodiode array, a convergent lens, an optoelectronic detector, a CCD camera, and the like; and the processing assembly comprises a computer. The testing method comprises the step of: conveying a testing result to judge whether various types of film samples are damaged or not by a CCD video microscopy judging method and a plasma flashing method according to a judgment criterion that one displayed damage is conformed The structure and the testing method of the invention has minimum testing error without error judgments and strong suitability and practicability.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
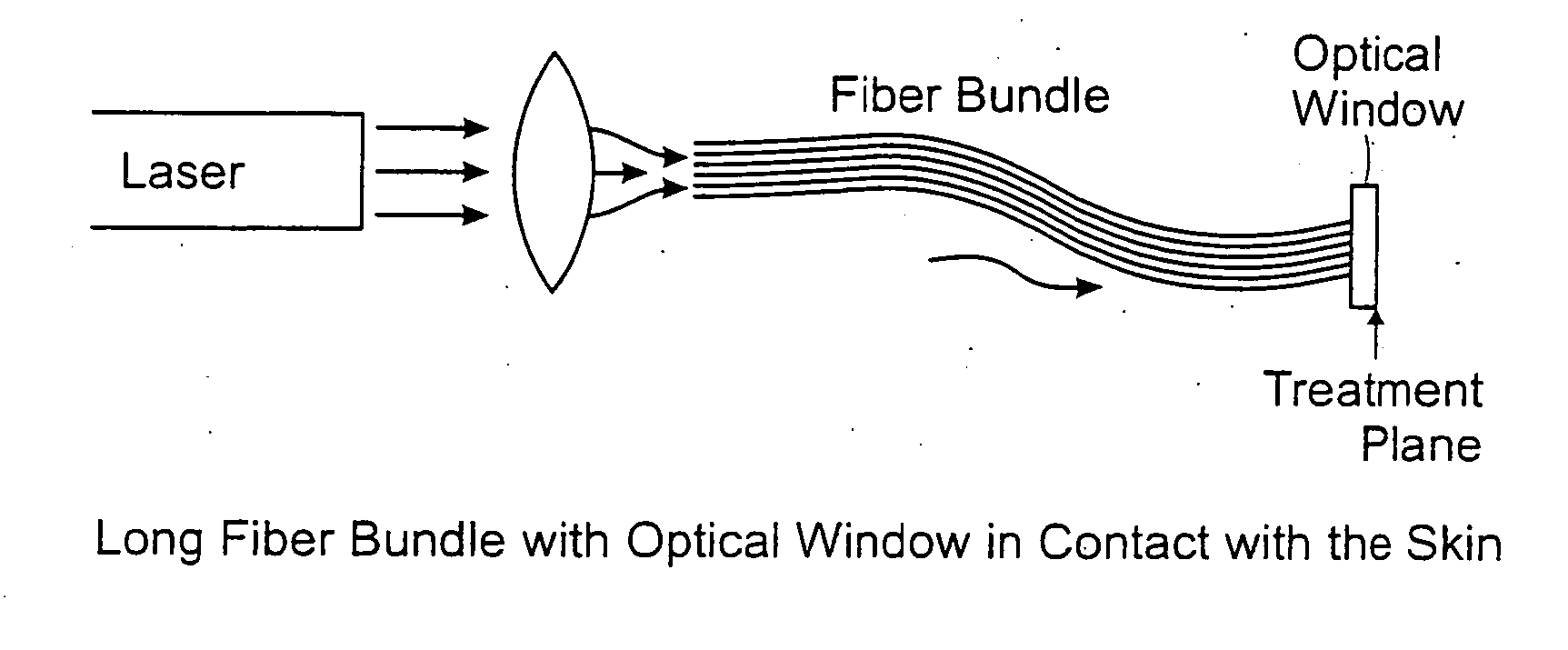
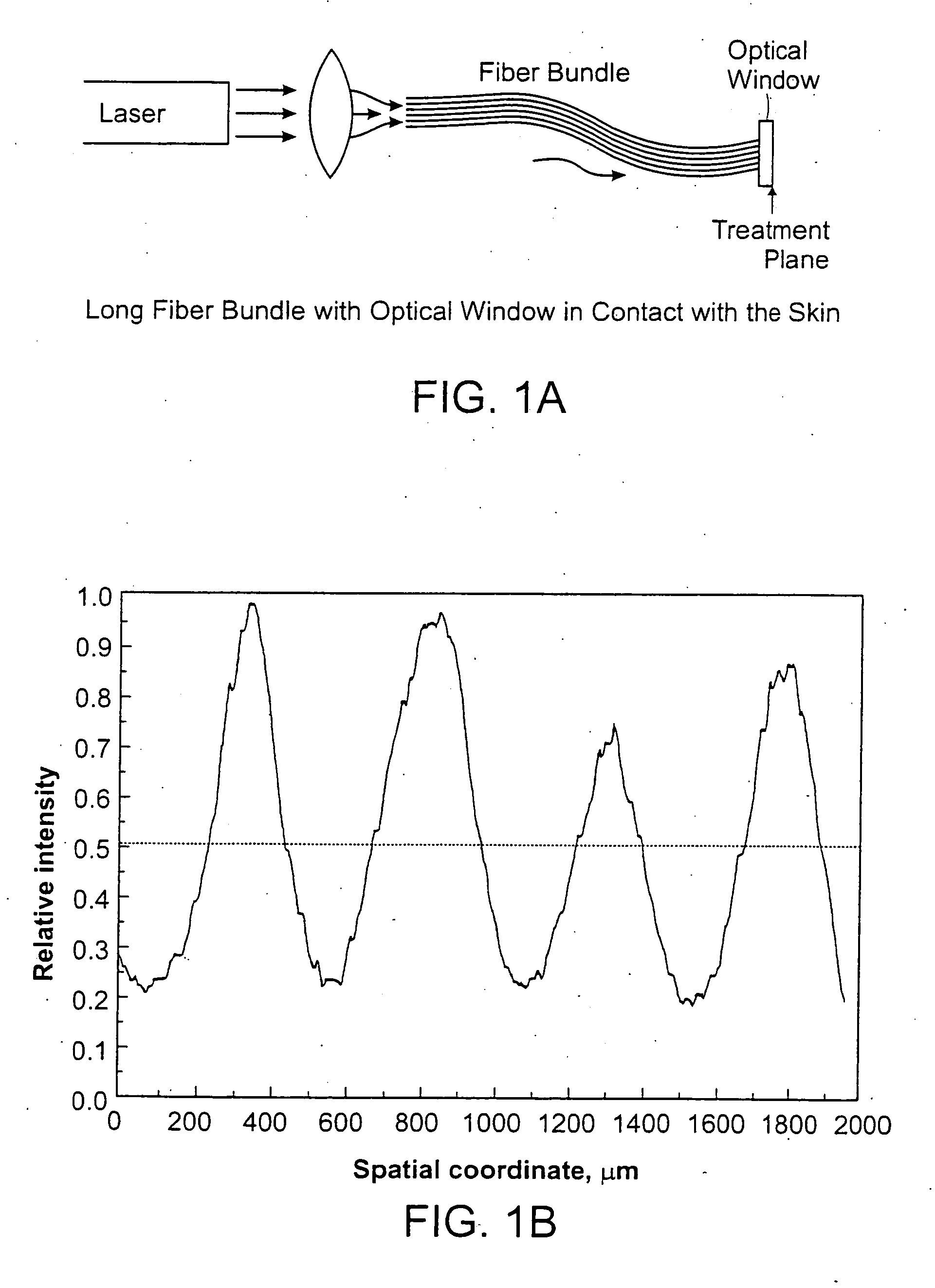
Methods and systems for laser treatment using non-uniform output beam
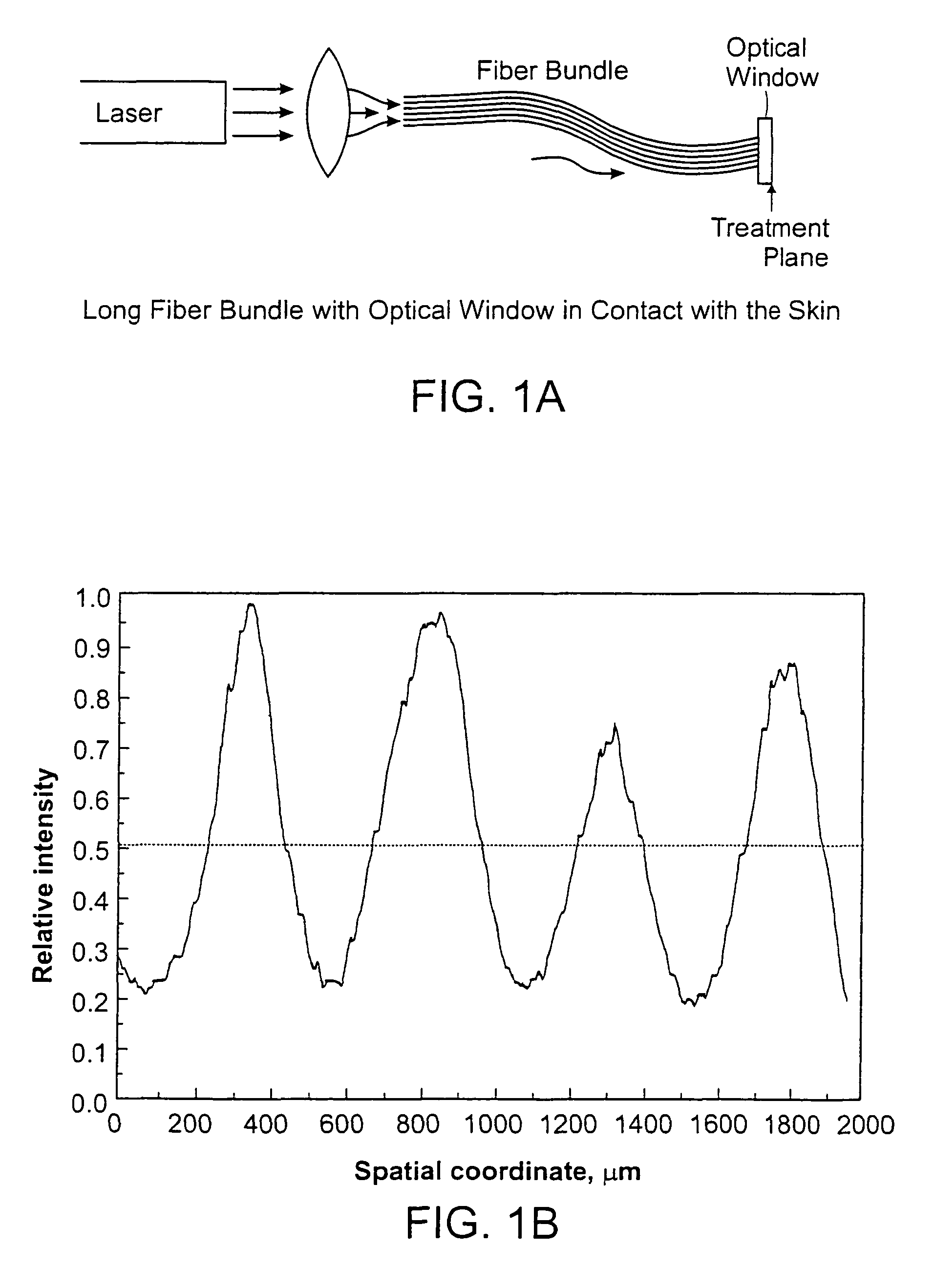
ActiveUS20060247609A1Increase the areaPromote absorptionDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsCollagen shrinkageNd:YAG laser
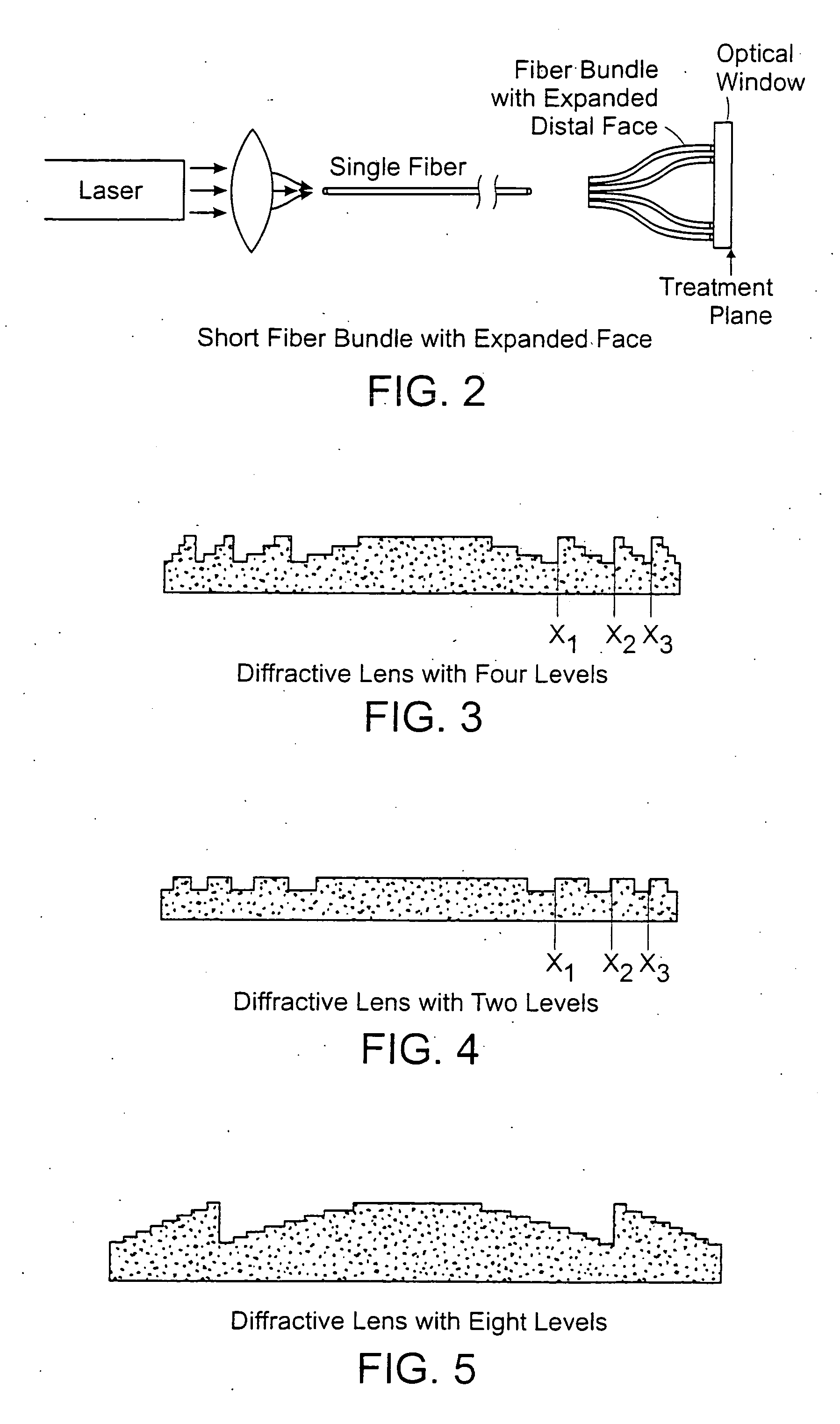
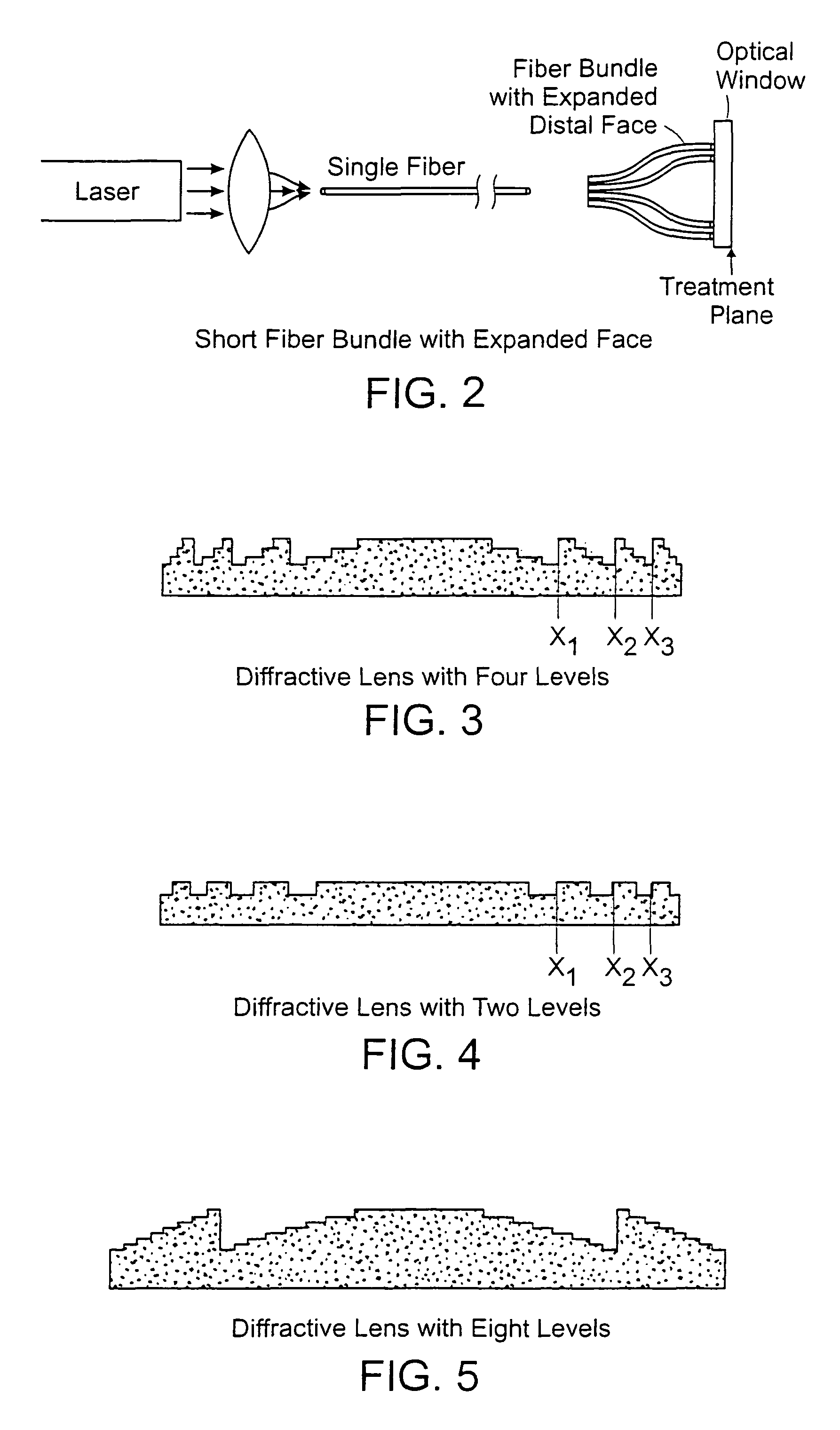
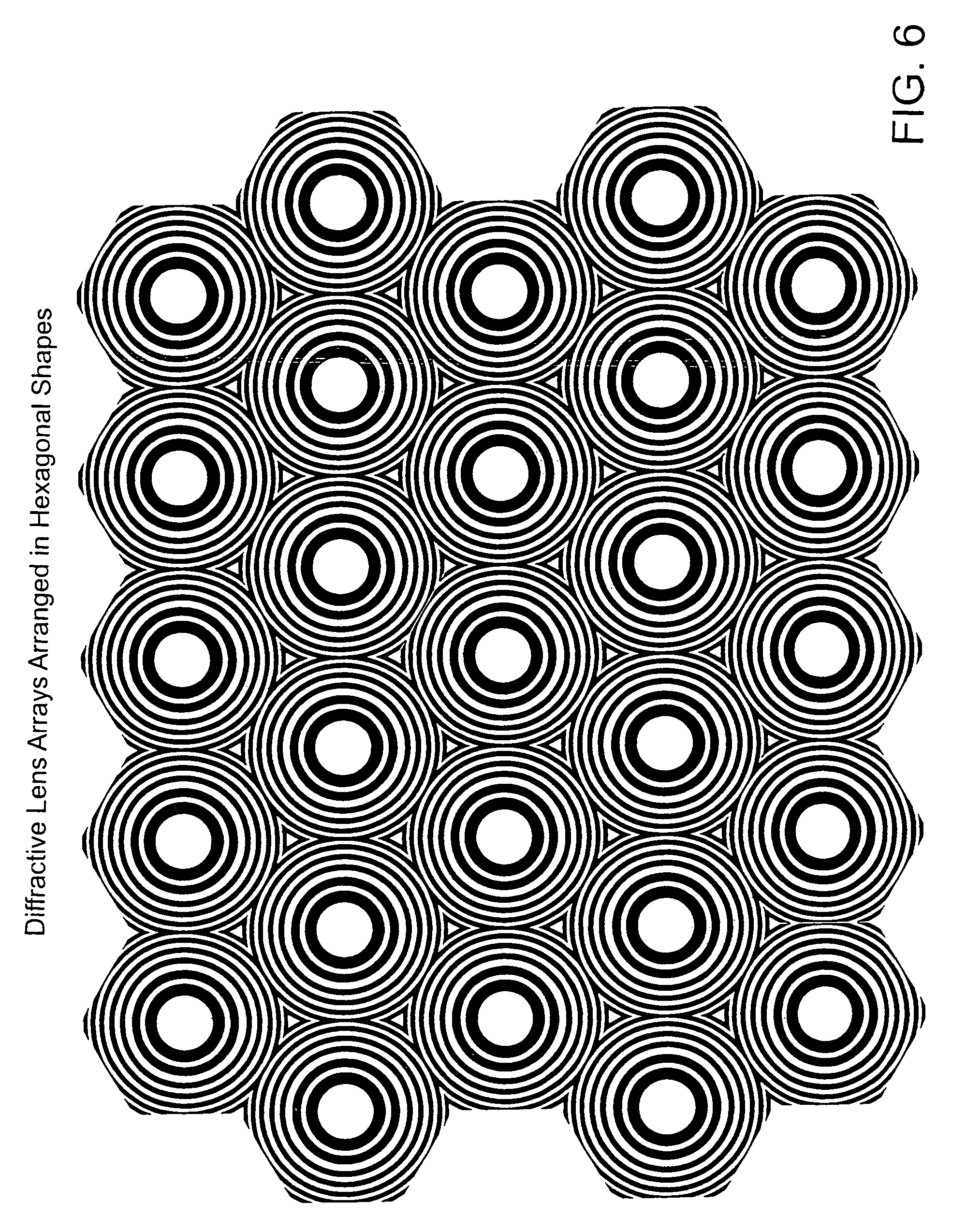
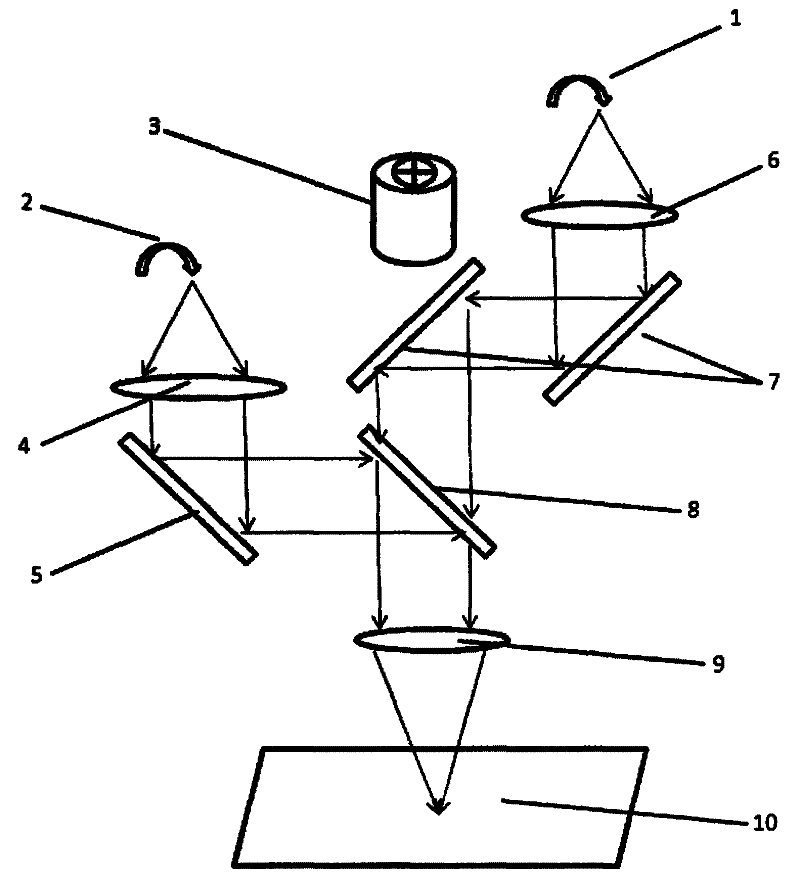
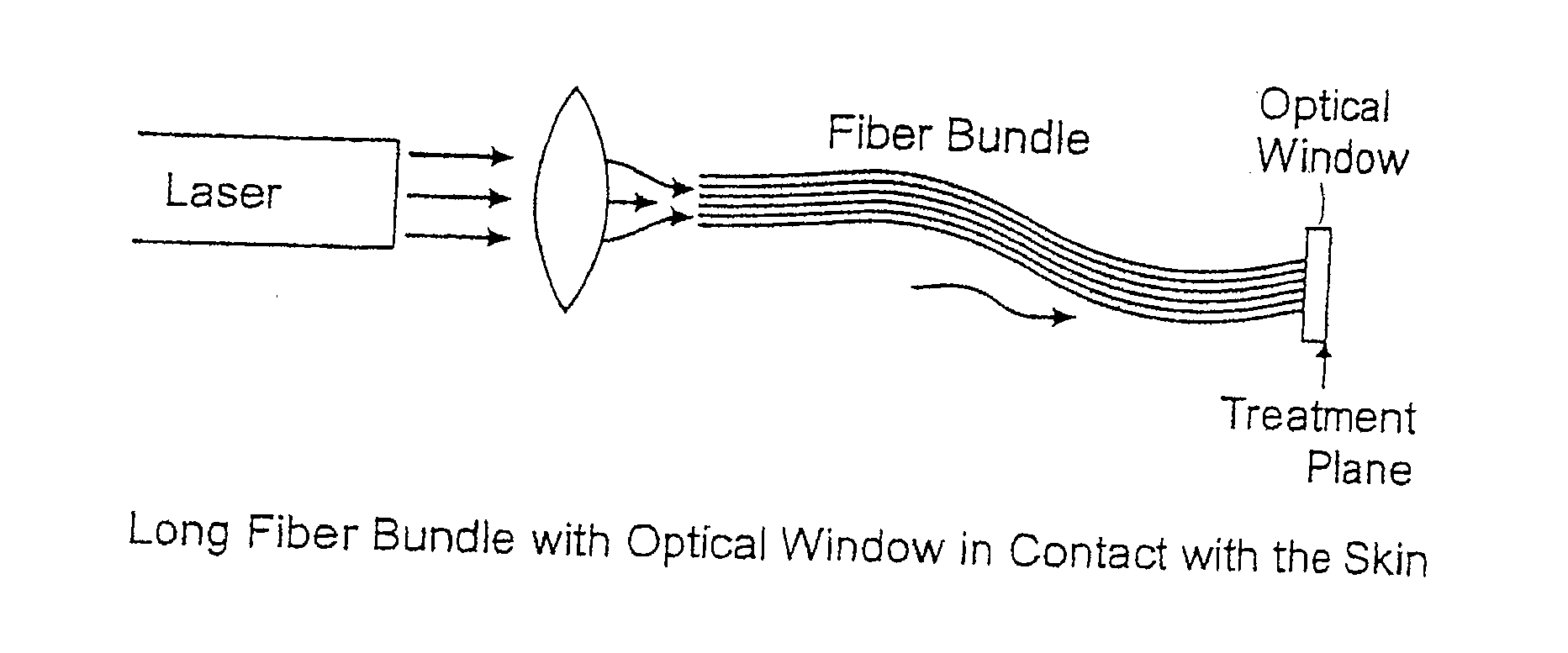
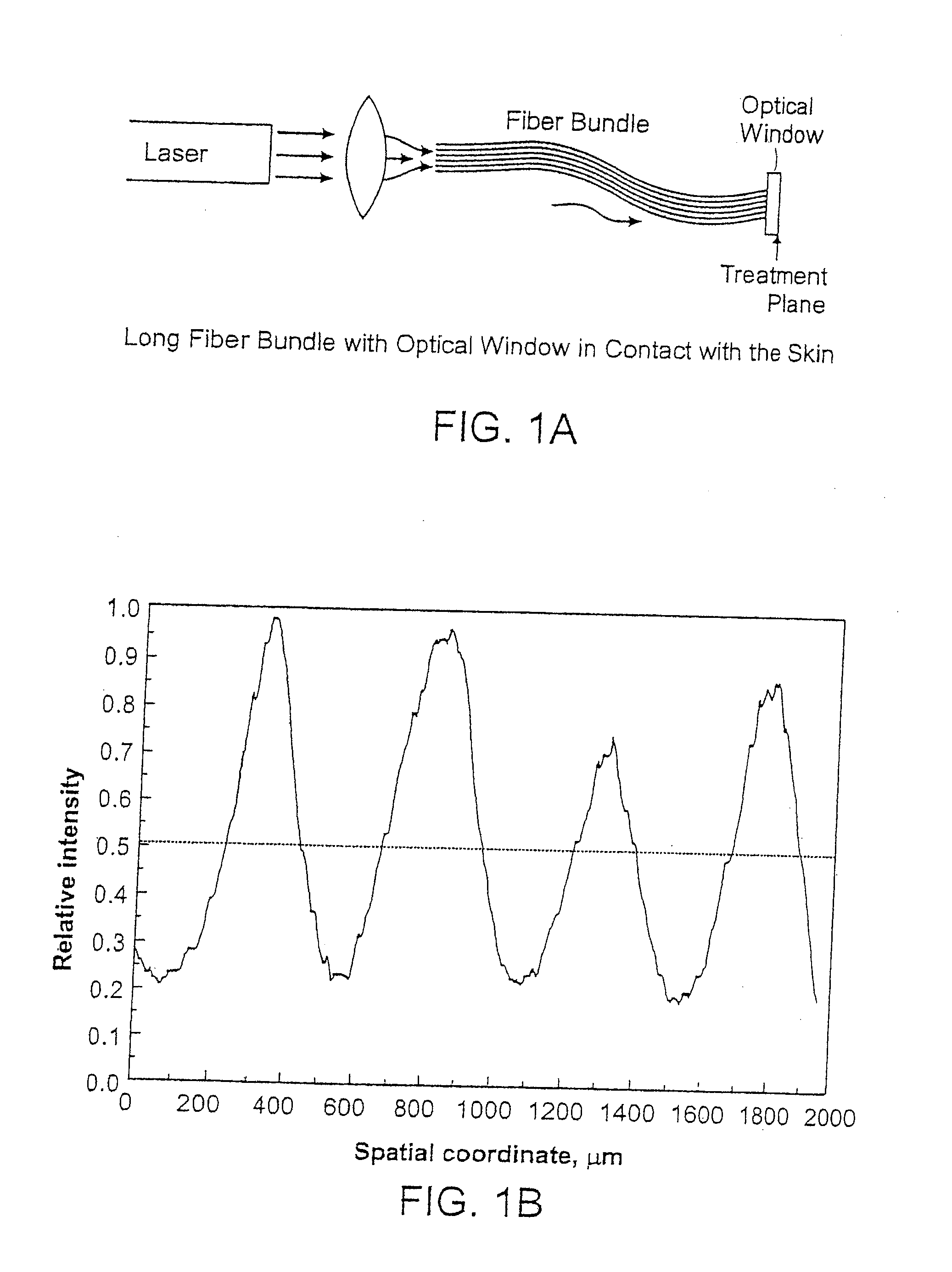
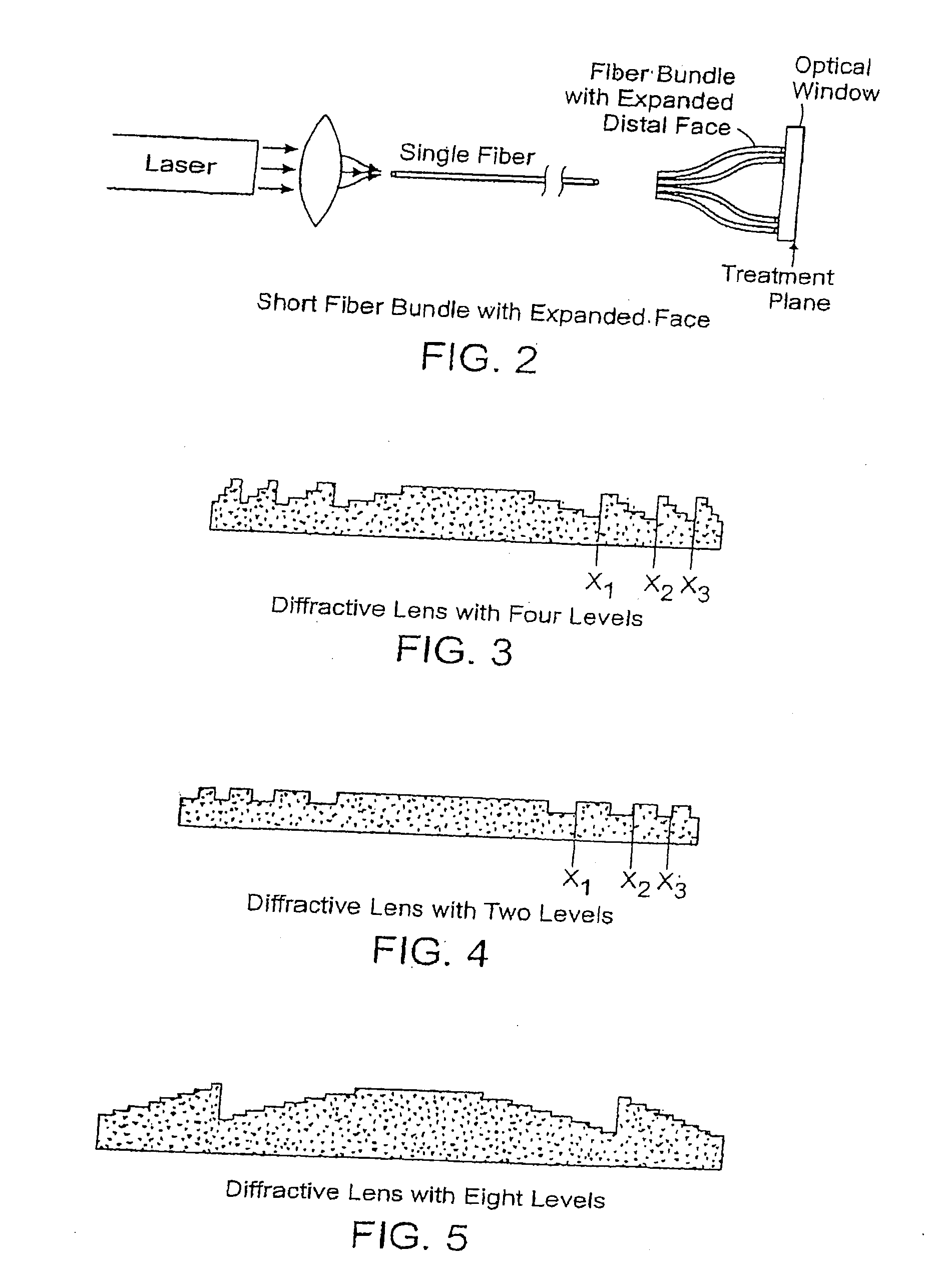
Methods and apparatus for treatment, such as skin rejuvenation treatment, using non-uniform laser radiation. A high-intensity portion of the laser radiation causes collagen destruction and shrinkage within select portions of the treatment area, while a lower-intensity portion of the radiation causes fibroblast stimulation leading to collagen production across other portions of the treatment area. An output beam from a laser source, such as an Nd:YAG laser, is coupled into an optical system that -modifies the beam to provide a large-diameter beam having a non-uniform energy profile, comprised of a plurality of high-intensity zones surrounded by lower-intensity zones within the treatment beam. The higher-intensity zones heat select portions of the target tissue to temperatures sufficient for a first treatment (e.g. collagen shrinkage), while the lower-intensity zones provide sufficient energy for a second treatment (e.g. stimulated collagen production). A large area of tissue, preferably 7-10 mm in diameter, can be treated simultaneously, while minimizing the risk of burning or other damage to the skin. In one embodiment, the invention uses a fiber bundle to provide a non-uniform energy output beam. In another embodiment, the invention uses a diffractive lens array to produce the non-uniform output beam. A cooling system can also be integrated with the laser treatment system.
Owner:CYNOSURE
Laser powder fusion repair of Z-notches with nickel based superalloy powder
A method is provided for repairing Z-notch wear surfaces on low pressure gas turbine engine turbine blades. The method is directed to turbine blades made of superalloy Inconel 713. Powdered Inconel 713 is welded to the Z-notch wear surface by directing an Nd:YAG laser beam upon the material. The laser beam is focused and traverses the wear surface in a stich-like pattern. The method allows Inconel 713 turbine blades to be repaired with the same material in a manner that does not generate cracking in the matrix material.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Methods and systems for laser treatment using non-uniform output beam
ActiveUS7856985B2Minimizing risk of burning and other damagePromotes collagen productionDiagnosticsSurgical instrument detailsCollagen shrinkageNd:YAG laser
Owner:CYNOSURE
Laser engraving methods and compositions, and articles having laser engraving thereon
InactiveUS20050003297A1Not easy to counterfeitDifficult to alterRadiation applicationsLayered productsThioester synthesisBarium sulphide
The invention provides a composition having laser engraving properties, comprising a host material and an effective amount of a laser enhancing additive. The laser enhancing additive comprises a first quantity of least one of copper potassium iodide (CuKI3) or Copper Iodide (CuI), and a second quantity at least one substance selected from the group consisting of zinc sulfide (ZnS), barium sulfide (BaS), alkyl sulfonate, and thioester. The composition can be engraved with grayscale images by an Nd:Yag laser and can be added to laminates or coatings. The composition can be used during the manufacture of many articles of manufacture, including identification documents.
Owner:L 1 SECURE CREDENTIALING
Laser chemical fabrication of nanostructures
InactiveUS6864190B2Easy to operateBig and deep poreLayered productsSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNd:YAG laserNanostructure
Disclosed is a process for fabricating luminescent porous material, the process comprising pre-treating a substrate (e.g. crystalline silicon) with laser radiation (e.g from a Nd:YAG laser) in a predetermined pattern followed by exposing the irradiated substrate to a chemical stain etchant (e.g. HF:HNO3:H2O) to produce a luminescent nanoporous material. Luminescent porous material having a luminescence maximum greater than about 2100 meV may be produced by this method. Such nanoporous materials are useful in optoelectronic and other semiconductor devices.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Process method for welding aluminum and aluminum alloy material by laser
InactiveCN101850472ASmall sizeEasy to closeGrinding machinesWelding/soldering/cutting articlesOrganic solventHigh energy
The invention relates to laser welding and discloses a process method for welding aluminum and aluminum alloy material by laser. The process method comprises steps of: (1) selecting an Nd:YAG laser with high beam quality and high energy density; (2) adopting double-beam laser to weld aluminum and aluminum alloy material, wherein the distance between the two beams is 0.6-1.0 mm, and the energy ratio of the two beams is larger than 1:1; (3) surface treatment of a material to be welded: removing greasy dirt and dust with an organic solvent and removing an oxidation film by mechanical cleaning and / or chemical cleaning; and (4) utilizing the two-beam laser to weld the aluminum and the aluminum alloy material. A needle body, a sleeve and a lead of the invention are manufactured into a whole; therefore, the invention solves adaptability of the laser welding to assembly precision, enhances the stability of welding process and improves welding line quality.
Owner:武汉楚天激光(集团)股份有限公司
Micro-embedded self-lubricating texture on surfaces of gear and cam and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102628544AImprove adaptabilityImprove lubrication and anti-wear performancePortable liftingBase-materialsLaser processingHexagonal boron nitride
The invention discloses a micro-embedded self-lubricating texture on the surfaces of a gear and a cam and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: performing micro texture processing on the surfaces of the gear and the cam by an Nd: YAG laser processing technology; and embedding a solid lubricant into the micro texture on the surfaces of the gear and the cam by a molding bonding technology of a self-lubricating composite material. The self-lubricating composite material comprises the following formula components in percentage by mass: 15 to 85 percent of polyimide (PI), 0 to 85 percent of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), 10 to 40 percent of MoS2, 0 to 15 percent of WS2, 0 to 16 percent of graphite fluoride, 5 to 15 percent of graphite, 0 to 12 percent of PbO, 0 to 6 percent of antimony trioxide, 0 to 10 percent of CaF2 or BaF2, 0 to 15 percent of hexagonal boron nitride, 0 to 15 percent of nano lubricant and 0 to 5 percent of additive. According to the micro-embedded self-lubricating texture, the self-lubricating texture is subjected to micro embedding on the surfaces of the gear and the cam to ensure that the solid lubricant on the friction surface is stably supplied and uniformly coated, so that the lubrication and anti-wear properties of friction pairs such as the gear and the cam under complicated and harsh operating conditions are improved.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Test device for turbulent flow gas-liquid blending flow field in transverse flow
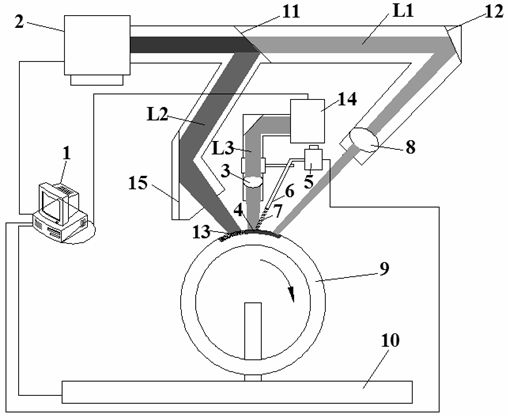
A device for testing a turbulent flow blending flow field in a crosscurrent comprises a blending test section communicated with a main airflow; an atomizing nozzle is arranged on the blending test section and communicated therewith; matt paint is uniformly applied onto the inner wall of the blending test section; a plurality of slits are formed on the lateral wall of the blending test section; a double pulse Nd:YAG laser is arranged on one side of the blending test section, and the slits are formed on the side; a CCD camera is arranged at the outlet of the blending test section; and the double pulse Nd:YAG laser and the CCD camera are connected with a computer through a PIV synchronous controller separately. The invention addresses the difficulties in filming the flow field of a rotating flow centrifugal nozzle in a limited passage during the process of atomizing blending in the cross flow, such as liquid accumulation on the inner wall, the influence of ambient light, the arrangement of the camera and frequent calibration due to the filming of different sections, and at last can obtain a clear blending particle picture, thereby obtaining the important information about the flow field, the velocity field, the distribution of vorticity and the like.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
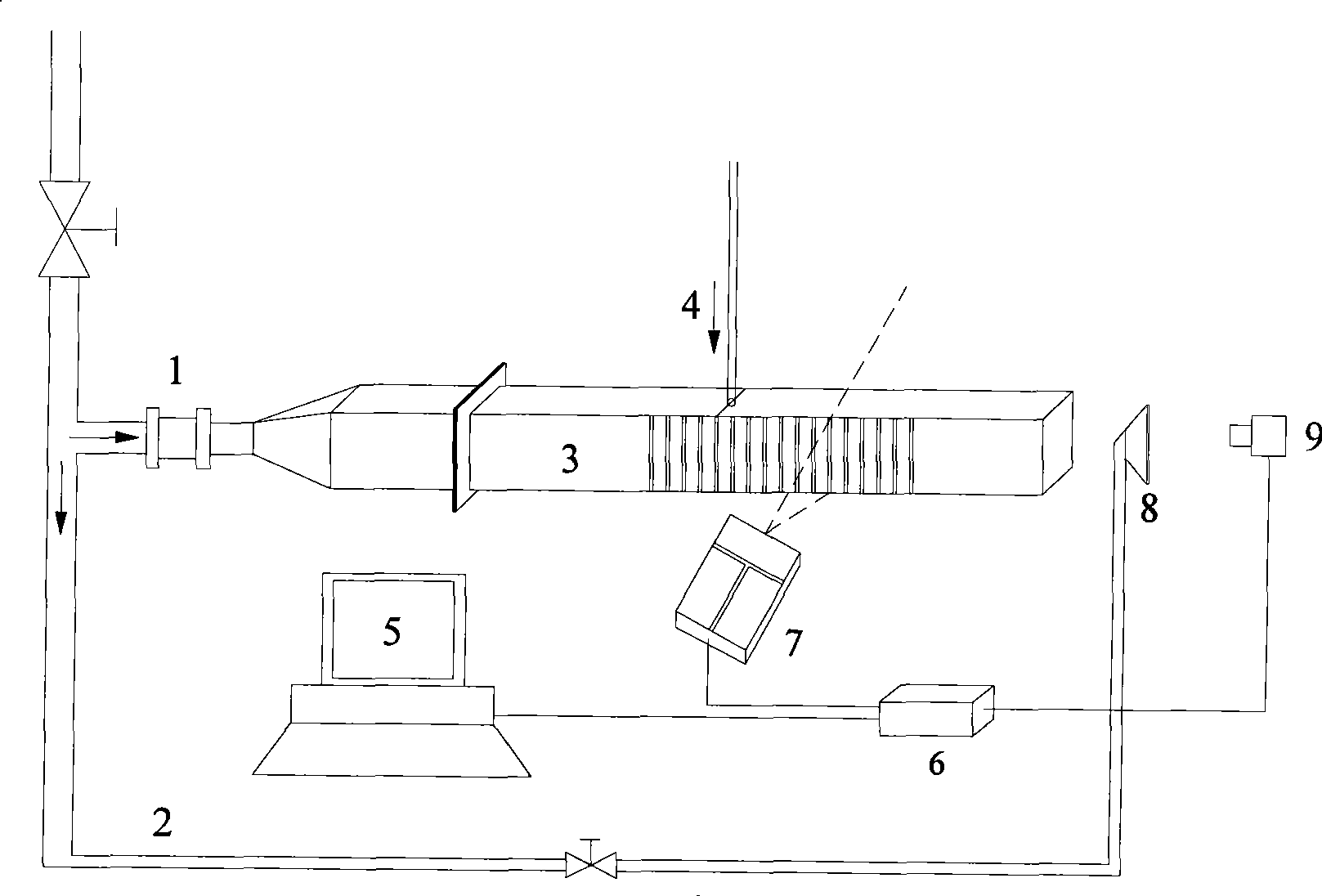
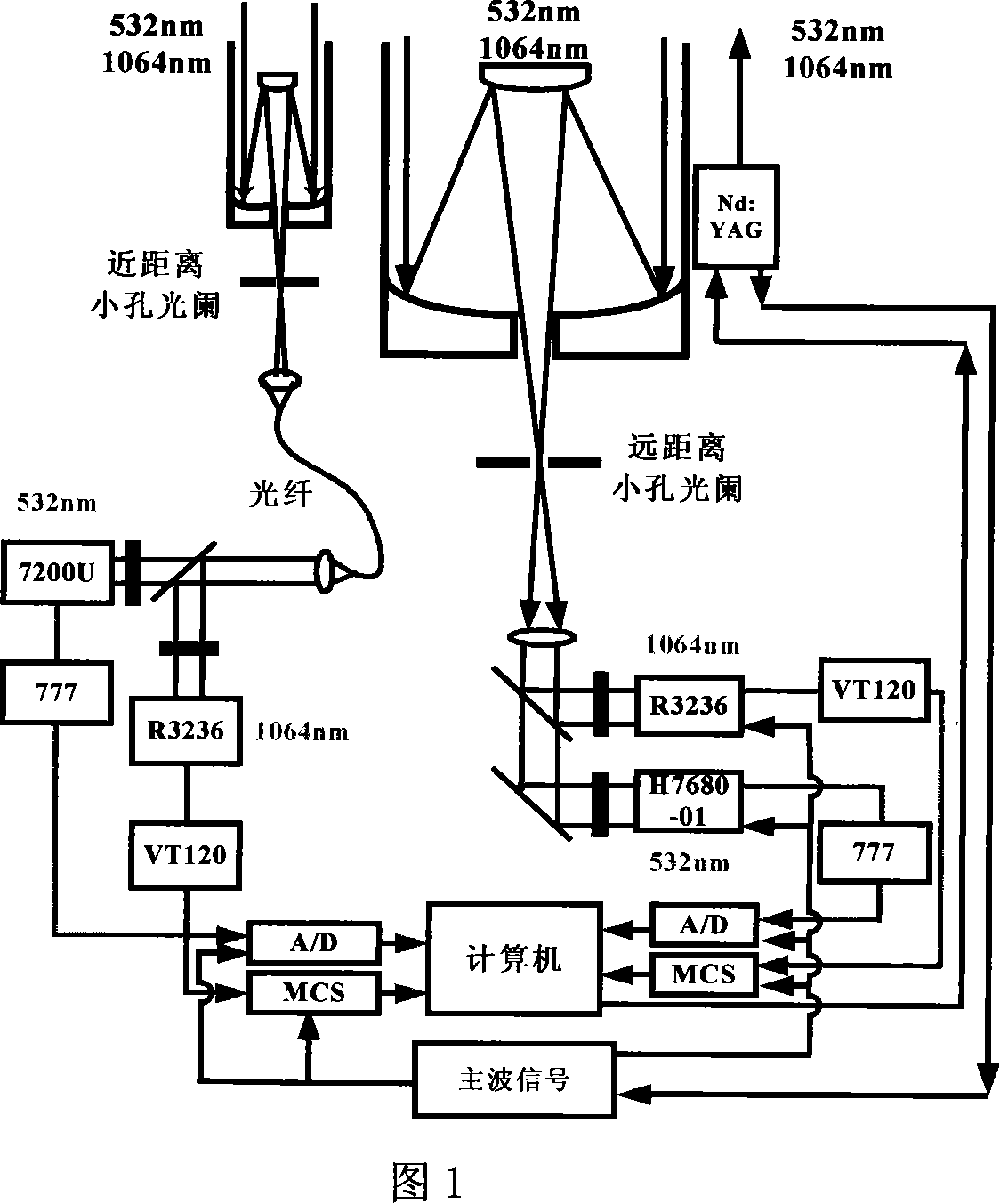
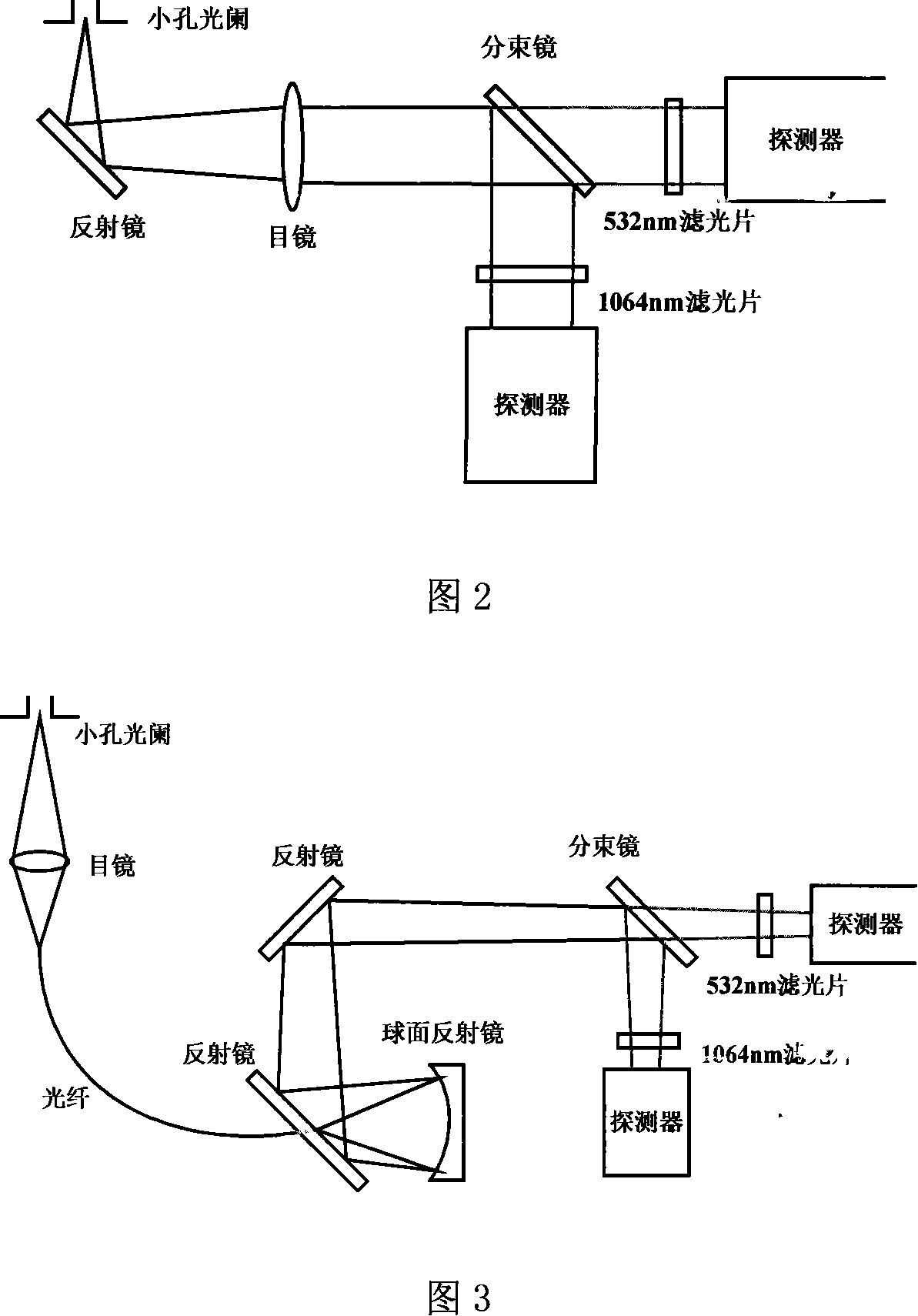
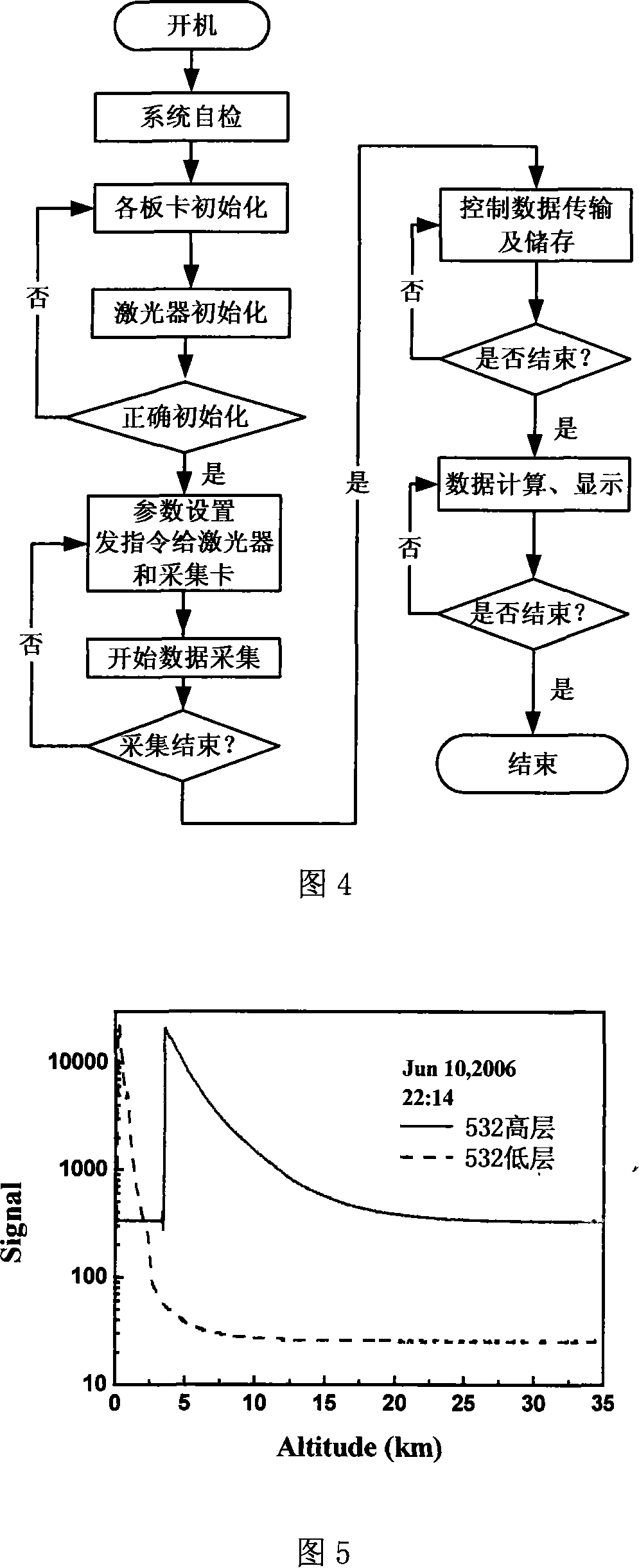
Dualwavelength dual-field Mie scattering laser radar structure and its detecting method
InactiveCN101071171AShorten the timeCorrected overlap factorElectromagnetic wave reradiationNd:YAG laserWavelength
This invention discloses dual field view dual-wavelength laser radar scattering meters structure and detection methods, including laser launch unit echo signal receiver modules, the follow-up optical modules, signal detection and acquisition module and control unit; The laser launch unit using Nd: YAG laser, launching 532 nm and 1064 nm wavelength of the laser pulse at the same time and received by the diameters of 400 mm and 200 mm telescope. Two receiving optical telescope module are follow-up optical module. Optical signal from the follow-up optical module are received by the detection and acquisition module and control unit. atmospheric aerosol extinction coefficient of the vertical profile and continuous distribution, and extinction coefficient level of continuous distribution, can be analyzed through the various atmospheric aerosol optical parameters.
Owner:ANHUI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Compact continuous wave tunable infrared lasers and method therefor
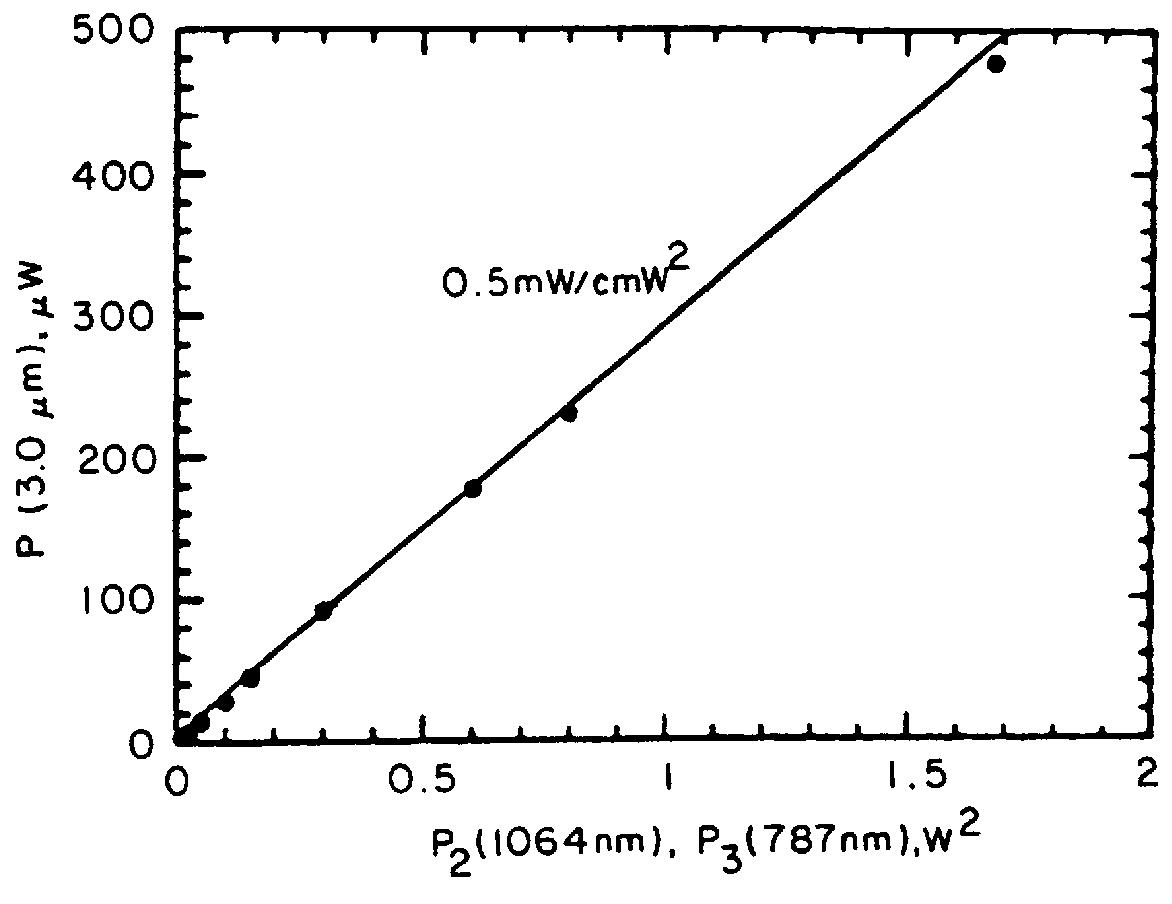
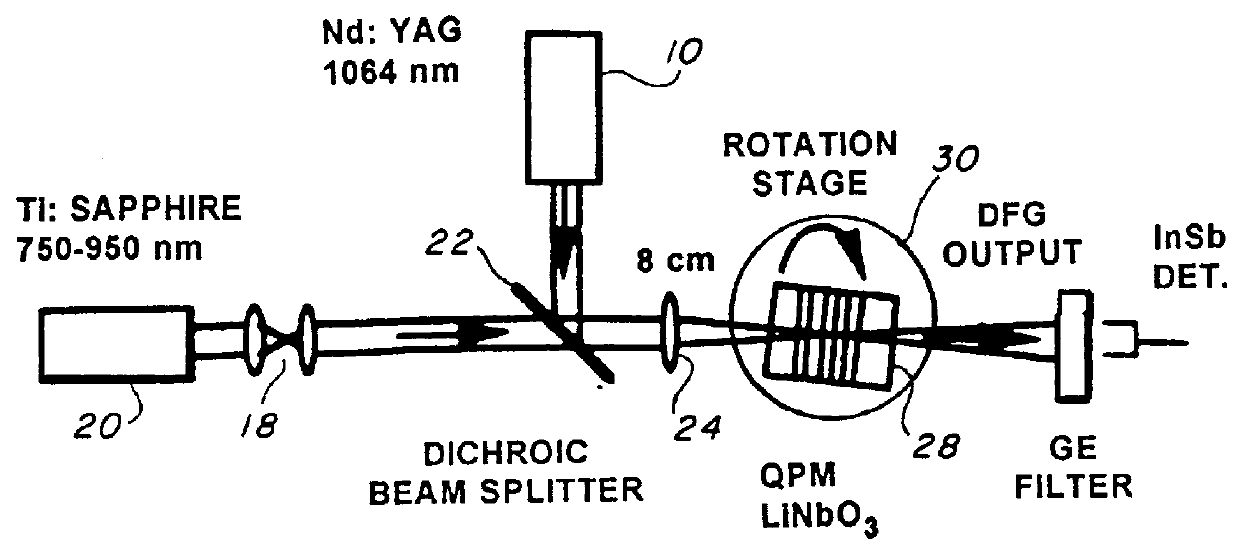
A bulk, quasi-periodic phase-matched difference-frequency (DFG) process in field-poled LiNbO.sub.3 bulk crystal permits continuous tunability of the output radiation in the 3.0-4.1 .mu.m wavelength range through grating rotation. DFG in QPM-LiNbO.sub.3 crystal, carried out using a Nd:YAG laser and a high power semiconductor laser at the quasi-phased matching (QPM) degeneracy point, results in an ultra wide 0.5 .mu.m acceptance bandwidth, permitting crystal rotation-free wavelength tuning of 4.0-4.5 .mu.m, with 0.2 mW output power at 4.5 .mu.m.
Owner:BURNS WILLIAM K +2
Thin flat glass for display purposes and method of cutting the thin flat glass into display sheets
InactiveUS20070158317A1Heating up fastCut more rapidlyGlass severing apparatusLaser beam welding apparatusFlat glassAdditive ingredient
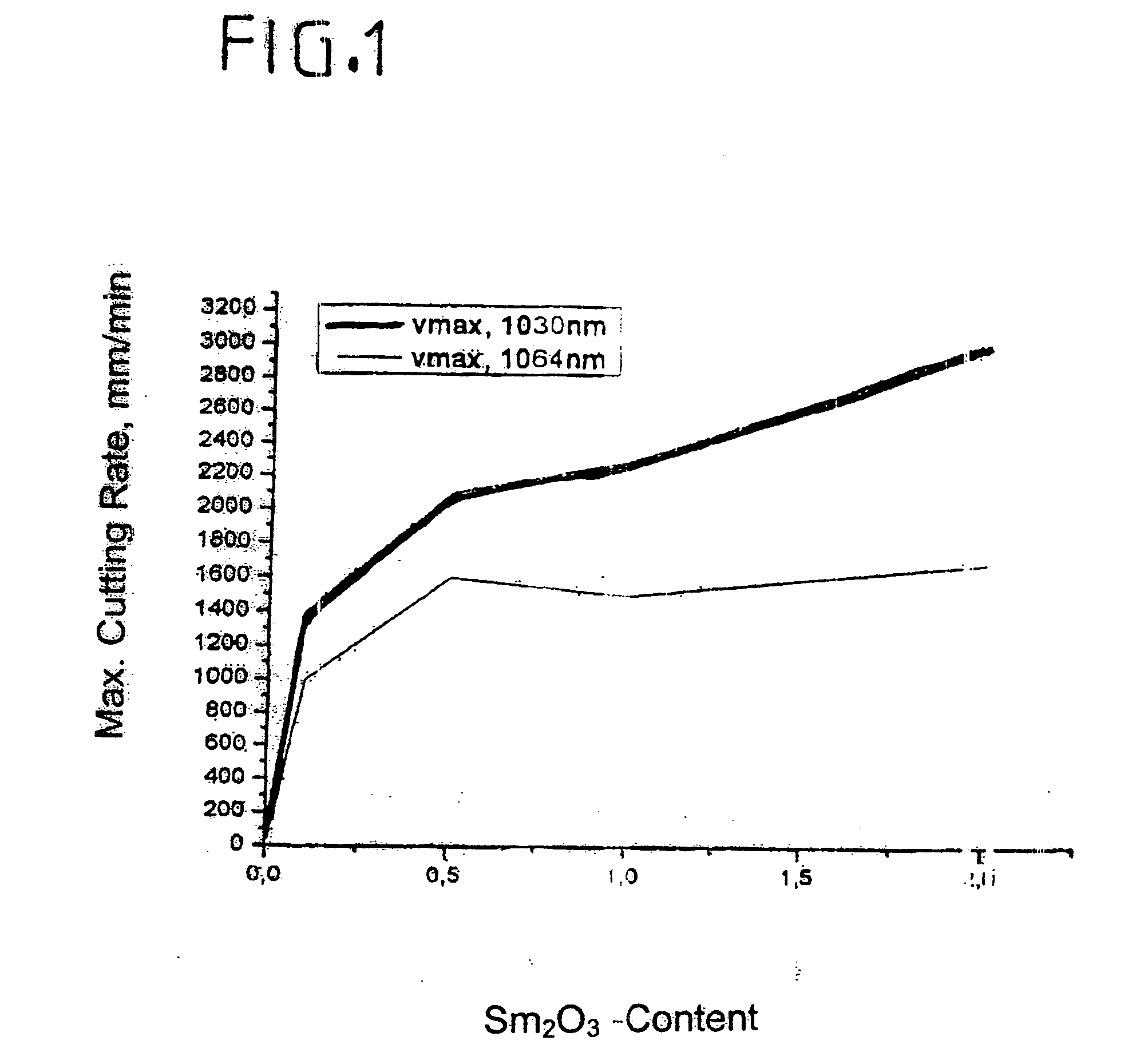
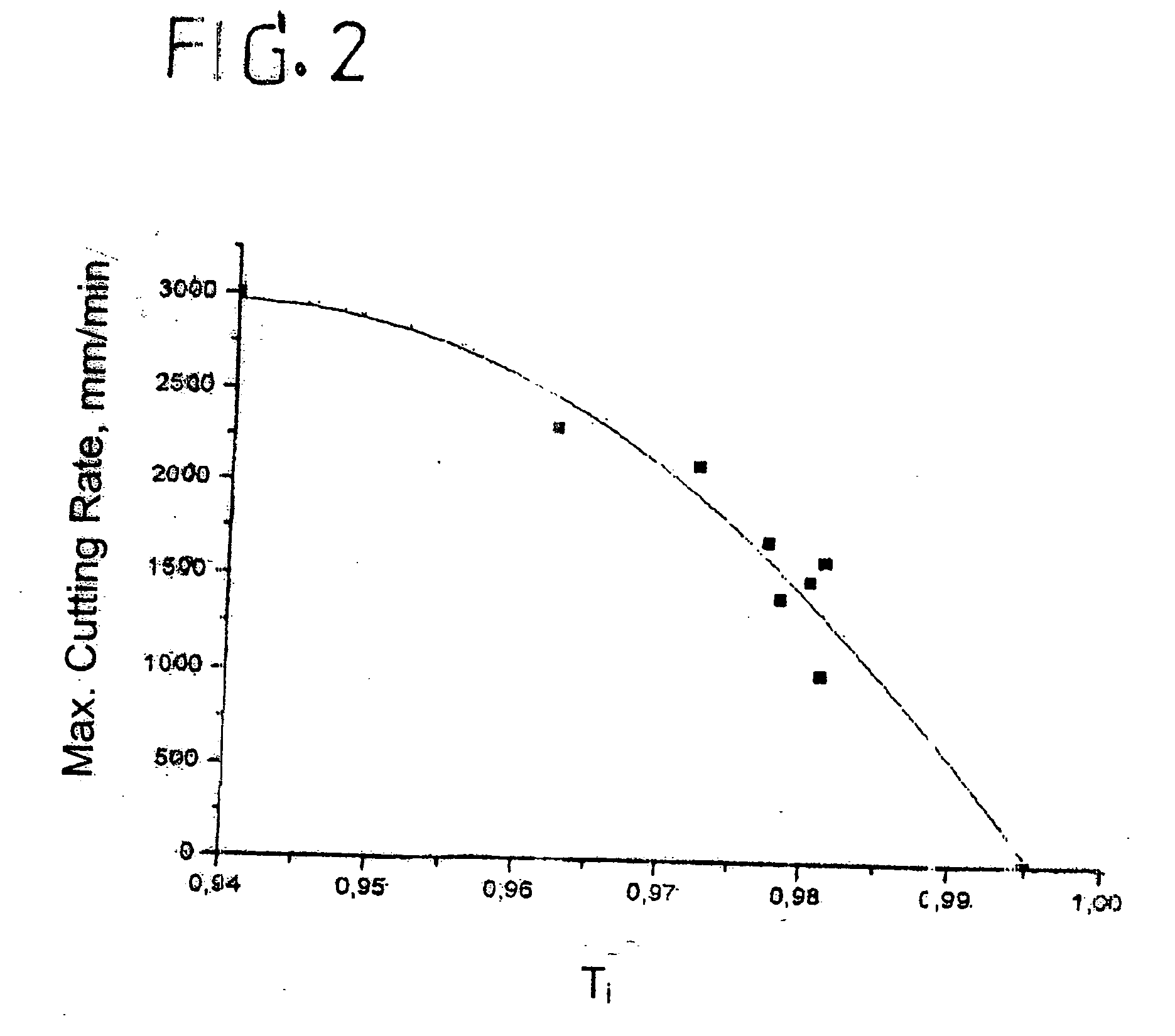
To improve the cutting properties, especially the cutting rate, of thin flat glass by means of a laser cutting beam from a Nd:YAG solid-state laser, the flat glass is provided during its manufacture with at least one additive ingredient that effectively absorbs radiation at a wavelength of 1.064 μm. Preferably the additive ingredient is preferably samarium oxide (Sm2O3). A method of cutting through a flat glass sheet whose composition contains at least one additive ingredient that absorbs a significant amount of radiation at a wavelength of 1.064 μm, which includes cutting the flat glass sheet with the focused radiation of a Nd:YAG laser, is also part of the present invention.
Owner:SCHOTT AG
Automated Non-Invasive Capsulectomy and Anterior Segment Surgical Apparatus and Method
InactiveUS20110245814A1Reduce required pulse energyImprove eyesightLaser surgeryDiagnosticsNd:YAG laserNon invasive
An economical computer-controlled non-invasive laser apparatus and method to perform anterior segment surgery in an eye are disclosed. The laser source may include a pumping laser, a Nd:YAG laser cavity gain media, a stimulated Raman converter crystal, intracavity beam diameter-reducing optics, and an intracavity Q-switching crystal. The laser pulses have a selected wavelength for anterior segment surgery. A laser pulse delivery and treatment control mechanism and method for the practicing surgeon are also provided. The laser pulses and delivery system may be used in anterior segment surgery for cataracts, where the laser pulses may be used to form the capsulotomy, to form the corneal incision or to disintegrate contents of the capsule before removal. The laser and delivery system may also the used to treat a capsule and lens for correcting or preventing presbyopia and to treat a cornea to correct visual deficiencies in an eye.
Owner:LUMEDICA +1
Method and apparatus for holographic recording of fast phenomena
InactiveUS6862121B2Television system detailsHolographic light sources/light beam propertiesShock waveMultiplexing
Holographic methods for recording fast movies whose speed is limited by the laser pulse duration if the recording material has sufficient sensitivity to reliably record a frame of the fast event with a single pulse. The method we describe uses the selectivity of multiplexed holograms to resolve frames that are recorded with adjacent pulses. Specially designed pulse generators are used to generate the signal and reference pulse trains. We experimentally demonstrate the system by making movies of laser induced shock waves with a temporal resolution of 5.9 ns, limited by the pulse width of the Q-switched Nd:YAG laser used in the experiments.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Dual-laser beam hybrid welding device and hybrid welding method
InactiveCN102500919AImprove absorption efficiencyCompact structureLaser beam welding apparatusNd:YAG laserErbium lasers
The invention provides a dual-laser beam hybrid welding device and a hybrid welding method. The dual-laser beam hybrid welding device comprises an ND: YAG (Neodymium-Doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet) laser beam light path, and a dual-laser beam light path which is provided with a semiconductor laser beam light path and is arranged on a vertical dual-laser beam lens cone body. The dual-laser beam light path is provided with an ND: YAG total reflection lens, a semiconductor total reflection and ND: YAG total transmission combined lens, and a semiconductor and ND: YAG total transmission gathering lens in sequence from top to bottom. According to the invention, the high-freedom degree welding machining can be realized; the structure of the dual-laser beam hybrid welding device is simple and small; the alignment position is more accurate; and the automation is easy to realize. The dual-laser beam hybrid welding device can be used for welding positions which cannot be welded in a conventional manner, and a high-reflection and high-thermal conductivity material which cannot be welded by single laser, so that the application field of laser welding is enlarged, particularly a working piece is pre-heated by using a continuous semiconductor laser. The absorption efficiency of a material of the working piece to ND: YAG laser is improved, the welding fusion depth is increased, the welding speed and the welding efficiency are improved, and the occurrence of air vents and cracks in the welding process of working pieces is avoided.
Owner:UNITED WINNERS LASER CO LTD
Laser welding heat treat process
A method for providing a pre-welding heat treatment to a workpiece surface is described wherein the method includes the steps of: generating through a laser generator a laser beam characterized by a power and focal point; positioning the laser generator such that the focal point of the laser beam is above the workpiece surface so as to generate a defocused laser beam; directing the defocused laser beam toward the workpiece surface so as to project a laser beam spot on the workpiece surface; scanning the laser beam spot over the workpiece surface thereby heating the workpiece surface so as to provide a pre-welding heat treatment; repositioning the laser generator such that the focal point of the laser beam is changed; and laser welding the workpiece with substantially the same power as in the generating step. The method is further adapted for use with a hand held Nd:YAG laser torch, and the workpiece may be a superalloy gas turbine engine component.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Methods And Systems For Laser Treatment Using Non-Uniform Output Beam
ActiveUS20100217248A1Minimizing risk of burning and other damagePromotes collagen productionSurgical instrument detailsRadiation therapyCollagen shrinkageLight beam
Disclosed herein are methods and systems for treatment, such as skin rejuvenation treatment, use non-uniform laser radiation. A high-intensity portion of the laser radiation causes collagen destruction and shrinkage within select portions of the treatment area, while a lower-intensity portion of the radiation causes fibroblast stimulation leading to collagen production across other portions of the treatment area. An output beam from a laser source, such as an Nd:YAG laser, is coupled into an optical system that modifies the beam to provide a large-diameter beam having a nonuniform energy profile, comprised of a plurality of high-intensity zones surrounded by lower-intensity zones within the treatment beam. The higher-intensity zones heat select portions of the target tissue to temperatures sufficient for a first treatment (e.g. collagen shrinkage), while the lower-intensity zones provide sufficient energy for a second treatment (e.g. stimulated collagen production).
Owner:CYNOSURE
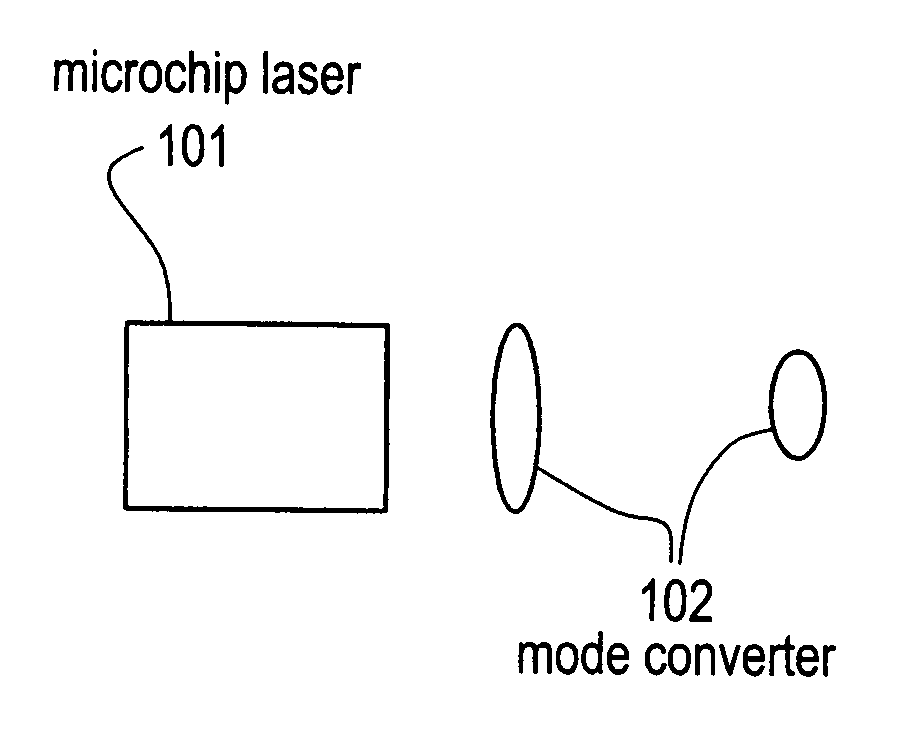
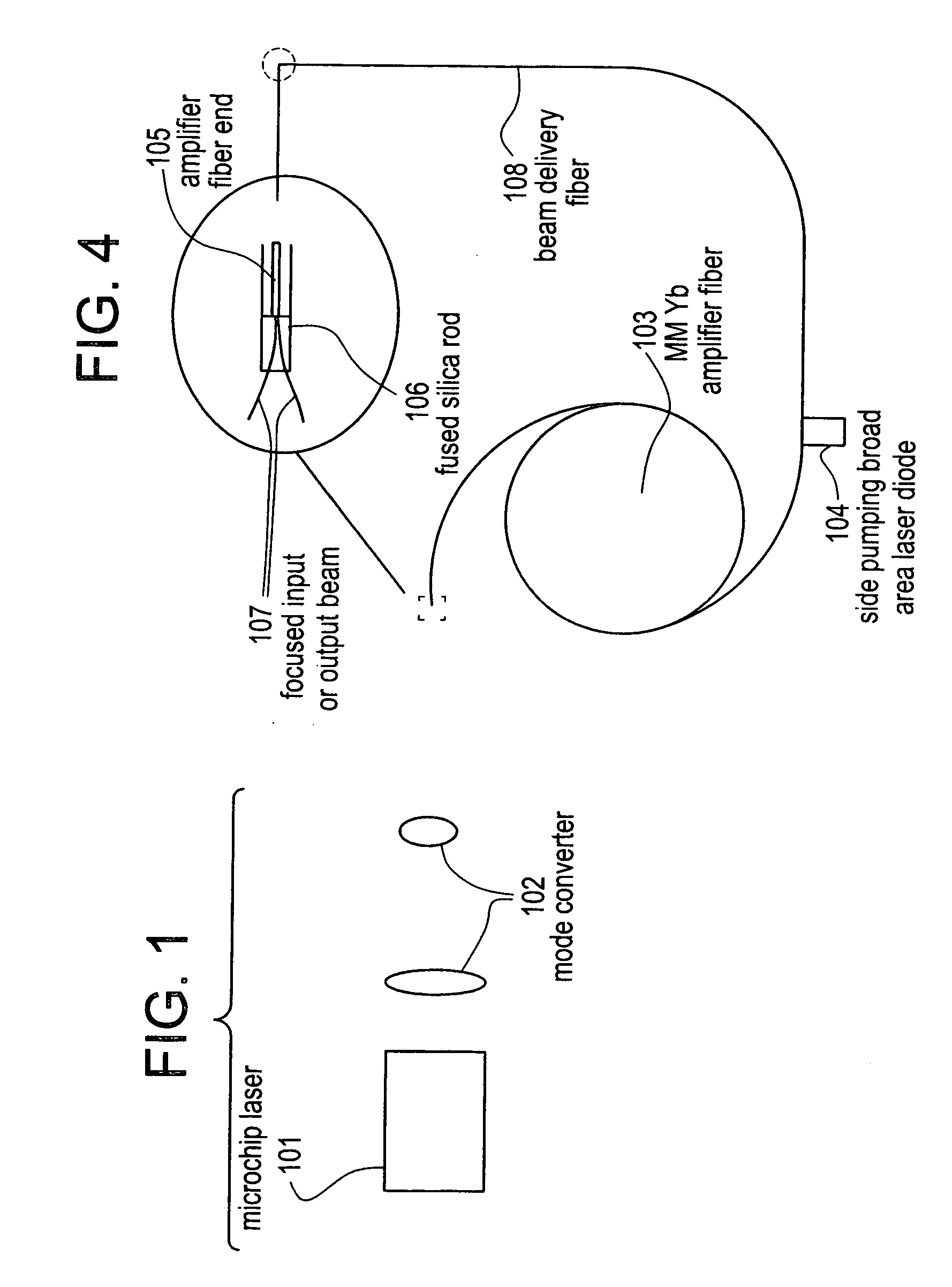
Microchip - Yb fiber hybrid optical amplifier for micro-machining and marking
InactiveUS20050243409A1Short pulse durationIncrease powerLaser using scattering effectsActive medium materialFiberLight beam
The invention describes techniques for the control of the spatial as well as spectral beam quality of multi-mode fiber amplification of high peak power pulses as well as using such a configuration to replace the present diode-pumped, Neodynium based sources. Perfect spatial beam-quality can be ensured by exciting the fundamental mode in the multi-mode fibers with appropriate mode-matching optics and techniques. The loss of spatial beam-quality in the multi-mode fibers along the fiber length can be minimized by using multi-mode fibers with large cladding diameters. Near diffraction-limited coherent multi-mode amplifiers can be conveniently cladding pumped, allowing for the generation of high average power. Moreover, the polarization state in the multi-mode fiber amplifiers can be preserved by implementing multi-mode fibers with stress producing regions or elliptical fiber cores These lasers find application as a general replacement of Nd: based lasers, especially Nd:YAG lasers. Particularly utility is disclosed for applications in the marking, micro-machining and drilling areas.
Owner:IMRA AMERICA
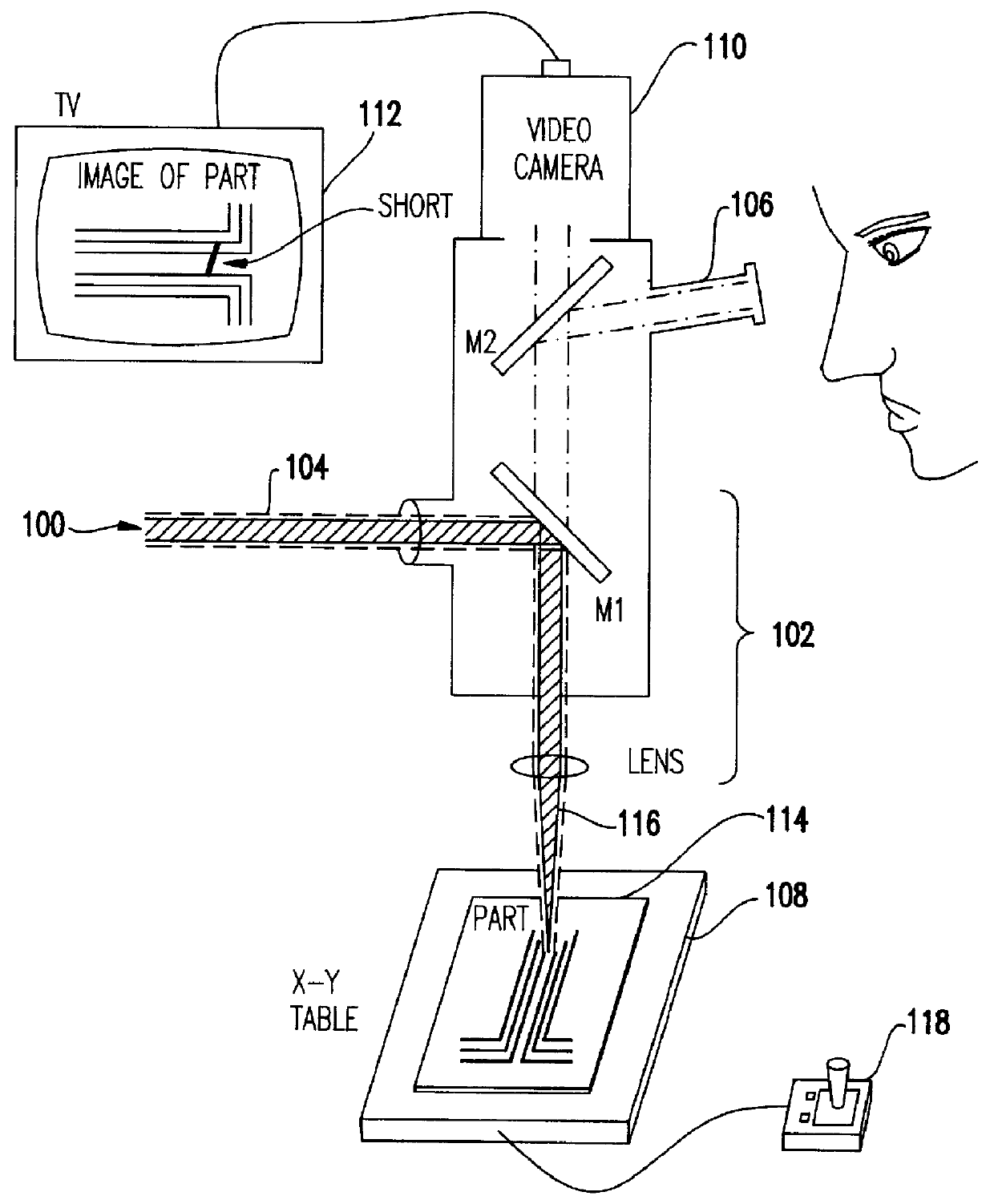
Laser repair process for printed wiring boards
InactiveUS6046429AIncrease productionLow costSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingPrinted circuits repair/correctingSurface layerOrganic layer
A method of repairing wiring shorts on a surface of an organic layer. The organic layer, which is preferably a SLC / ASM layer, may be a surface layer of a Printed Circuit (PC) board. The absorption spectrum of the organic layer is examined. Based on that absorption spectrum, a laser is selected with a wavelength such that the surface layer slightly absorbs, 1-10%, laser energy striking it. Thus, the laser removes metal on the surface, while slightly etching the surface layer and without effect on any metal buried in or beneath the surface layer. Preferably, the laser is an Nd:YAG laser having a wavelength in a range where the ASM layer absorption is between 2-5%, and the copper ablation rate is high.
Owner:IBM CORP
Sealing method for laser filler welding of hybrid integrated circuit package
ActiveCN103331520AImprove sealingMeet various requirements of packagingSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingLaser beam welding apparatusCrack freeShielding gas
The invention discloses a sealing method for laser filler welding of hybrid integrated circuit package. The sealing method comprises the following steps: 1, an aluminum alloy casing and an aluminum cover plate are rinsed by using acetone; 2, joints are assembled, a stepped groove is arranged in the aluminum alloy casing, the aluminum alloy cover plate is mounted on the aluminum alloy casing, the aluminum alloy casing and the aluminum alloy cover plate are butted by utilizing a tool, the butting mode is corner joint, and a joint gap is formed at the joints; 3, pre-filler is filled in the joint gap; 4, spot welding is carried out, a Nd:YAG (nipigin-doped: yttrium aluminum garnet) laser is adopted, the relative positions of the aluminum alloy casing, the aluminum alloy cover plate and the pre-filler are fixed, and the spot welding is proceeded in protective gas; 5, the overall welding is carried out, the Nd:YAG laser is adopted, a mouth-shaped welding form is adopted, and the welding process is proceeded in the protective gas. With the adoption of the sealing method, the welding reliability is good, the air-tight seal is good, and the welding seam is attractive and crack-free.
Owner:WUXI HUACE ELECTRONICS SYST
Laser annealing apparatus
InactiveUS7519252B2High-quality workingCompact operationCladded optical fibreSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingNd:YAG laserQ-switching
Owner:LASERFRONT TECH
Method for manufacturing structural circuit integrated part based on fused deposition modelling technology
ActiveCN106863770ARealize all-in-one layered printingReduce processAdditive manufacturing apparatus3D object support structuresCopper platingEngineering
The invention a method for manufacturing a structural circuit integrated part based on a fused deposition modelling technology. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: first, establishing a three-dimensional model, reserving a conductive channel position, realizing separated sprinting of a structural part single-layer substrate and a conductive channel outer edge by utilizing a double-spraying head fused deposition machine tool, scanning to activate the outer edge of the conductive channel by using third-harmonic generation Nd:YAG laser out of the machine tool, and circulating layer by layer in such manner to complete the modelling of the solid body of the part; finally, performing electroplating on the solid body in a copper plating solution so that the reserved conductive channel is filled with metal copper, and completing machining. According to the method, integrated printing of a complex three-dimensional circuit of the structural part can be realized; the process is simple; the assembling is avoided; the method has a good application prospect in the fields of aerospace and precise electronics and electrical appliances.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF AERONAUTICS & ASTRONAUTICS
1064nm semiconductor laser therapeutic instrument
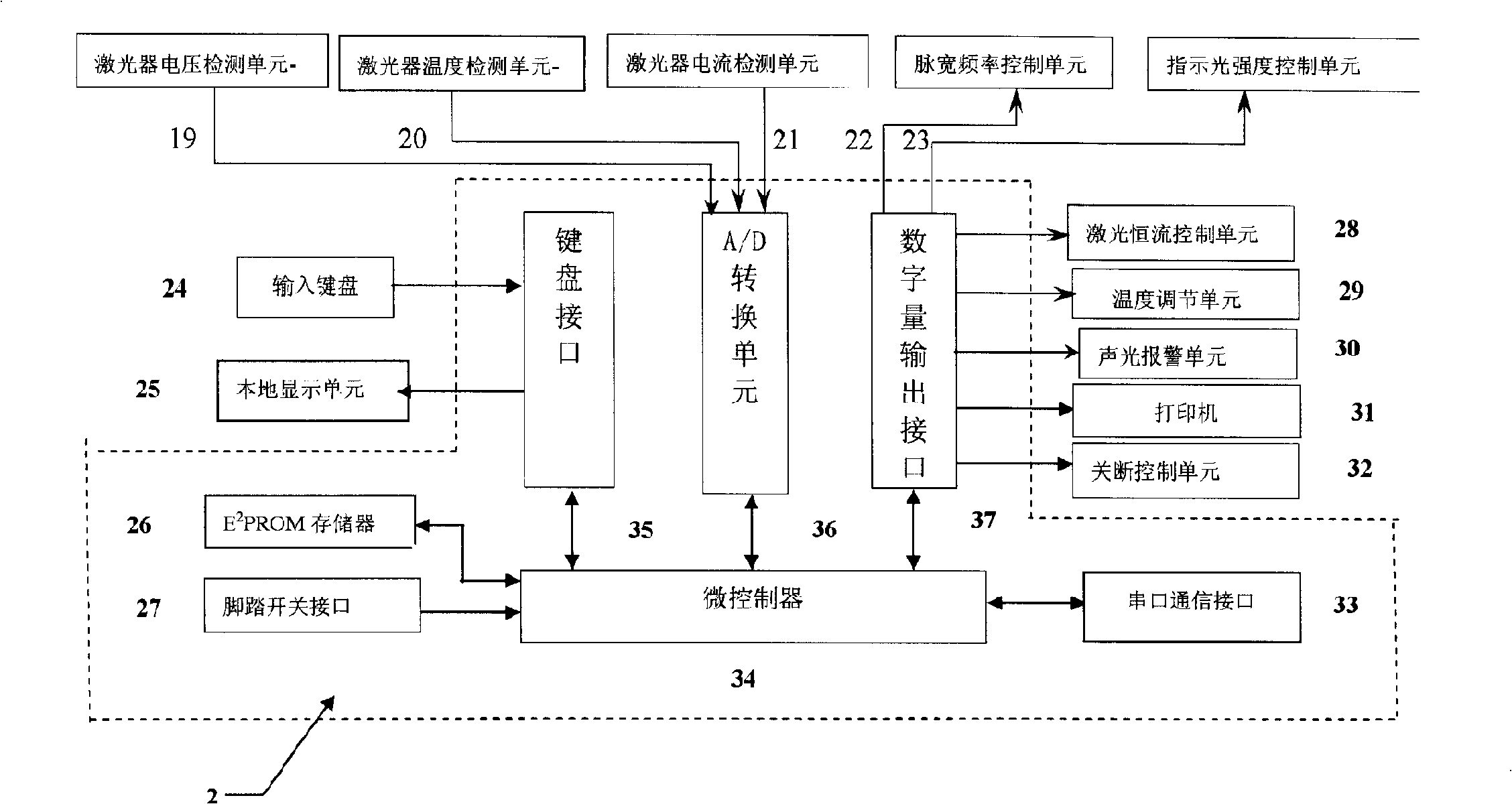
InactiveCN101264031AReduce volumeReduce weightSurgical instrument detailsRadiation therapyMicrocontrollerNd:YAG laser
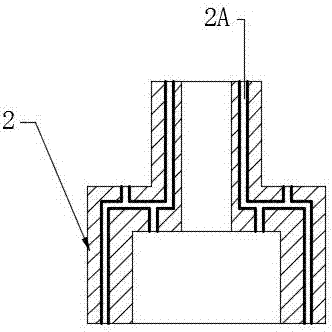
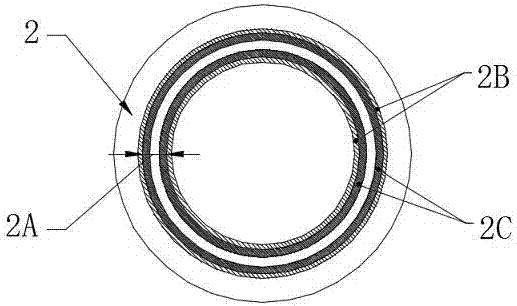
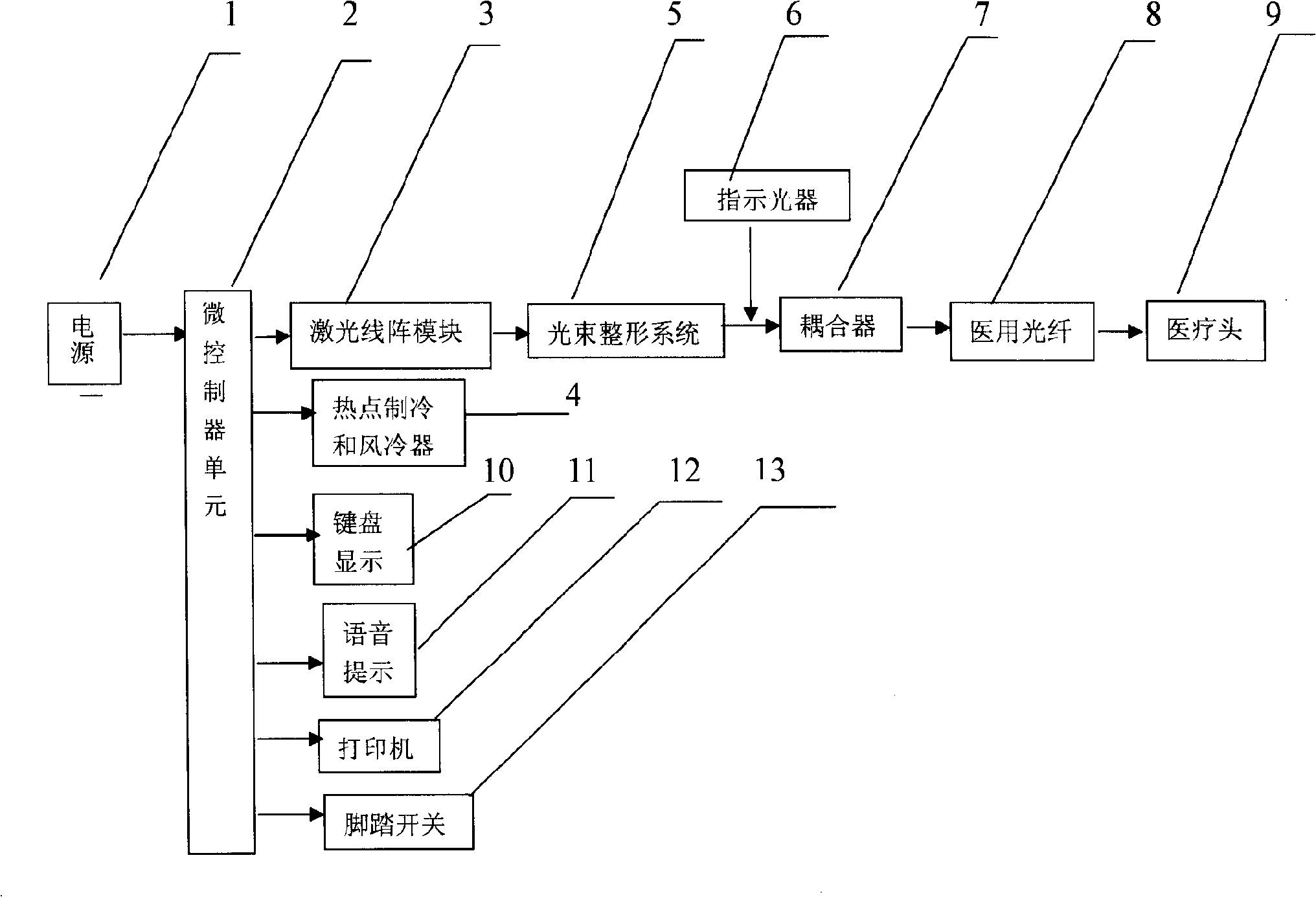
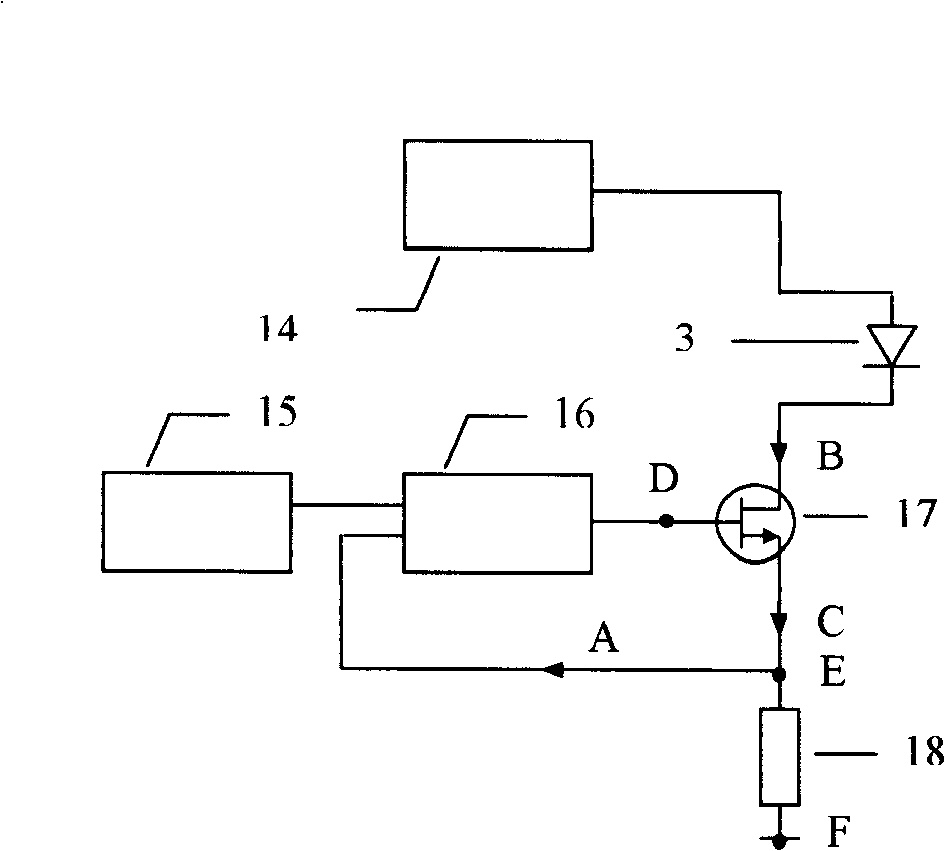
The invention relates to a high power semiconductor laser therapy instrument with 1064 nm wavelength comprising a power supply 1, a microcontroller unit 2, a 1064nm semiconductor laser linear-array mode 3, a thermoelectric and air-cooled refrigerator 4, a laser beam shaping system 5, a laser indicator 6, a coupler 7, a medical optical fiber 8, a medical head 9, keyboard 10, a voice warning-apparatus 11, a printer 12 and a foot switch13.As the whole solid laser crystal and the large power supply in the Nd:YAG laser are removed comparing with the prior 1064nm wavelength laser therapy instrument using Nd:YAG laser, the laser therapy instrument with 1064 nm wavelength has the advantages of compact size, light weight, high efficiency, simple structure, no water-cooling, simple operation and easy modularization. The semiconductor laser treatment instrument with 1064nm laser output is more concise, economical and practical.
Owner:王峙皓
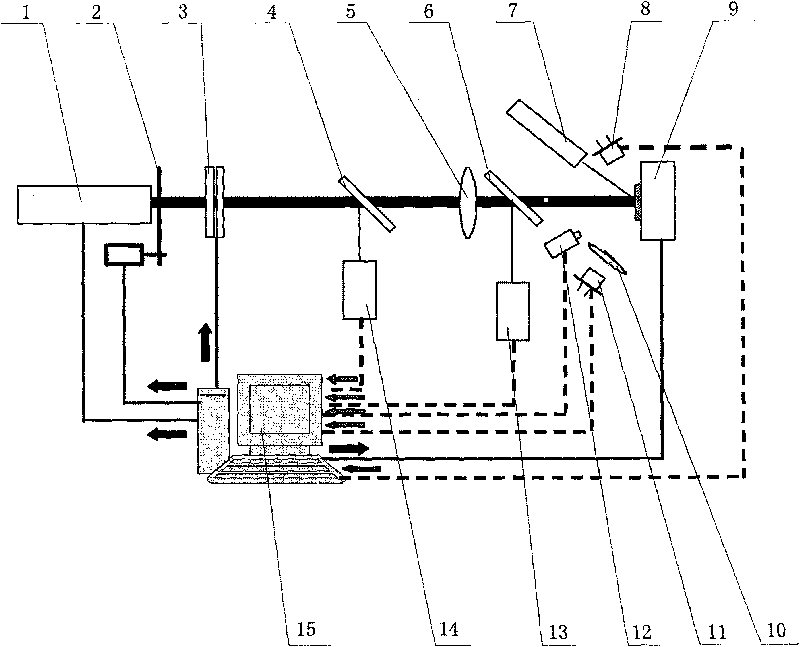
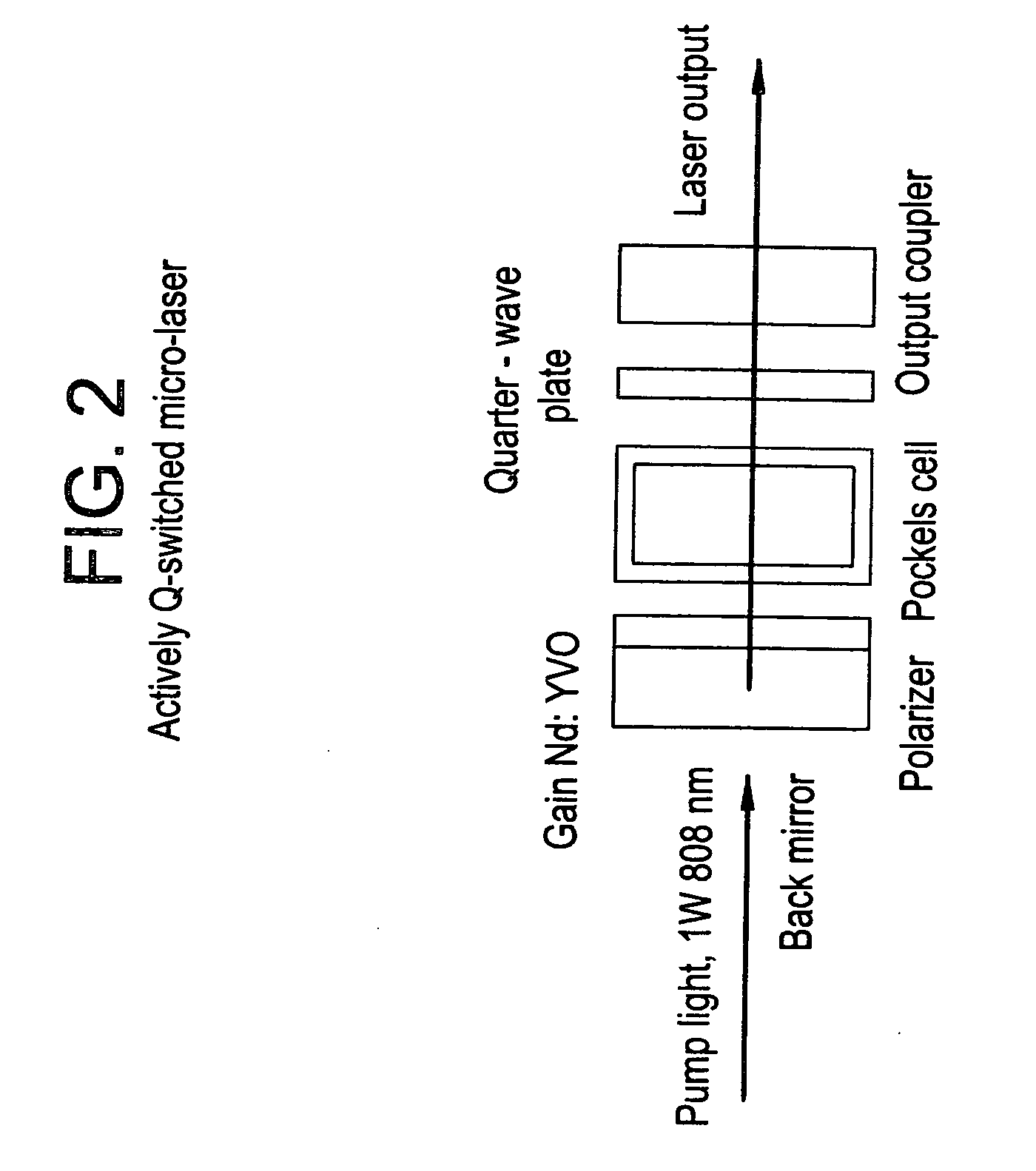
Double-electro-optic modulation QNdi:YAG laser
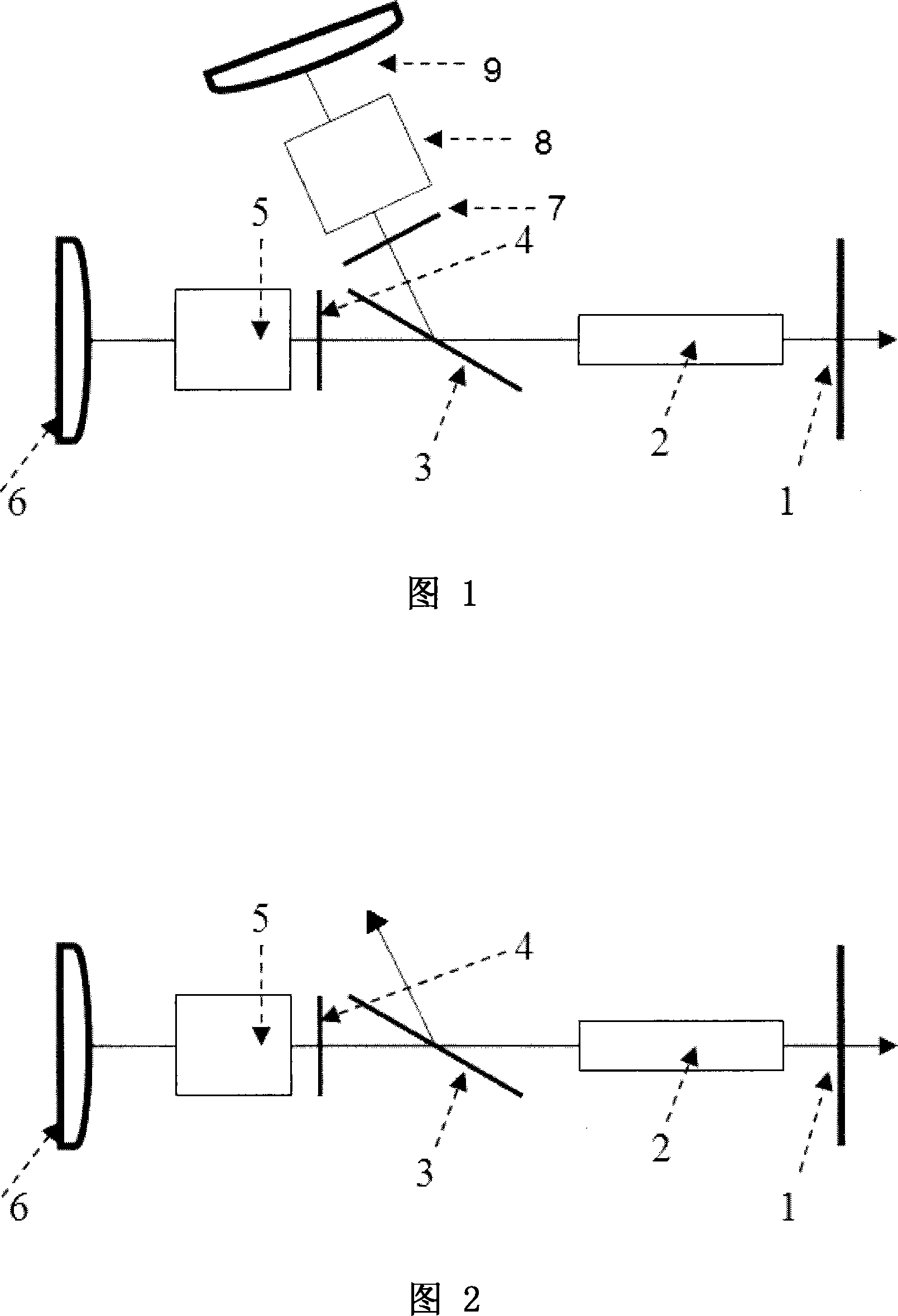
InactiveCN101022203ACompensation for thermal depolarization lossesEfficient outputOptical resonator shape and constructionCouplingPolarizer
A dual-photoelectric Q-switched Nd:YAG laser includes a main optical path on a main oscillation axes composed of an output coupling mirror, a Nd:YAG bar, a polariser, a first 1 / 4 wave plate, a first Q-switched crystal and a first back control mirror arranged orderly, in which, said polarizer is in Brewster angle with the opposite direction of emitted laser, which is charactered that a Q-switched branch is along the direction of depolarization lost of the polarizer and is composed of a second 1 / 4 wave plate, a second Q-switched crystal and a second back cavity mirror. This invention adds a Q-switched branch along the depolarization lost output optical path on the basis of the traditional Q-switched polarization cavity, so that, lost component is fed back to the cavity along the original path via the Q-switched switch to form effective laser output.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF OPTICS & FINE MECHANICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pulse infrared differential absorption laser radar system for detecting carbon dioxide concentration profile
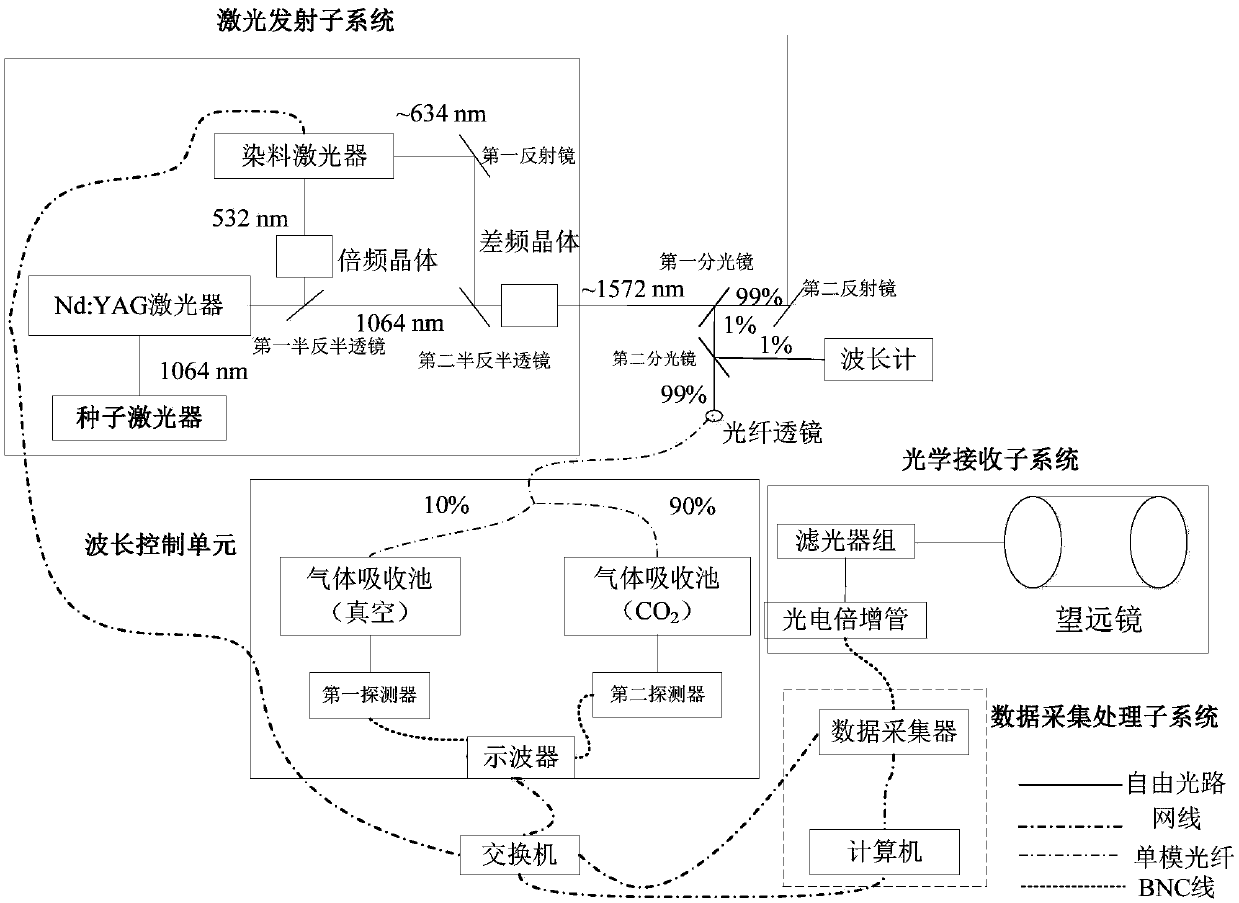
PendingCN109655843AHigh spatio-temporal resolutionHigh precisionElectromagnetic wave reradiationICT adaptationRadar systemsData acquisition
The invention provides a pulse infrared differential absorption laser radar system for detecting a carbon dioxide concentration profile, which comprises a laser emitting subsystem, an optical receiving subsystem and a data acquisition processing subsystem, wherein the laser emitting system comprises a seed laser, an Nd: YAG laser, a dye laser, a first reflecting mirror, a first half-reflecting half lens, a second half-reflecting half lens, a frequency doubling crystal, a difference frequency crystal, a first spectroscope and a wavelength control unit. The system can not only detect column concentration of atmospheric CO2, but also can obtain CO2 concentration profile distribution on a vertical path, particularly atmospheric CO2 concentration information near a boundary layer, and has important significance for carbon cycle research. The system has the advantages of low technical requirements, high stability, high detection precision and easy popularization, and is an important means for achieving atmospheric CO2 concentration profile measurement.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com