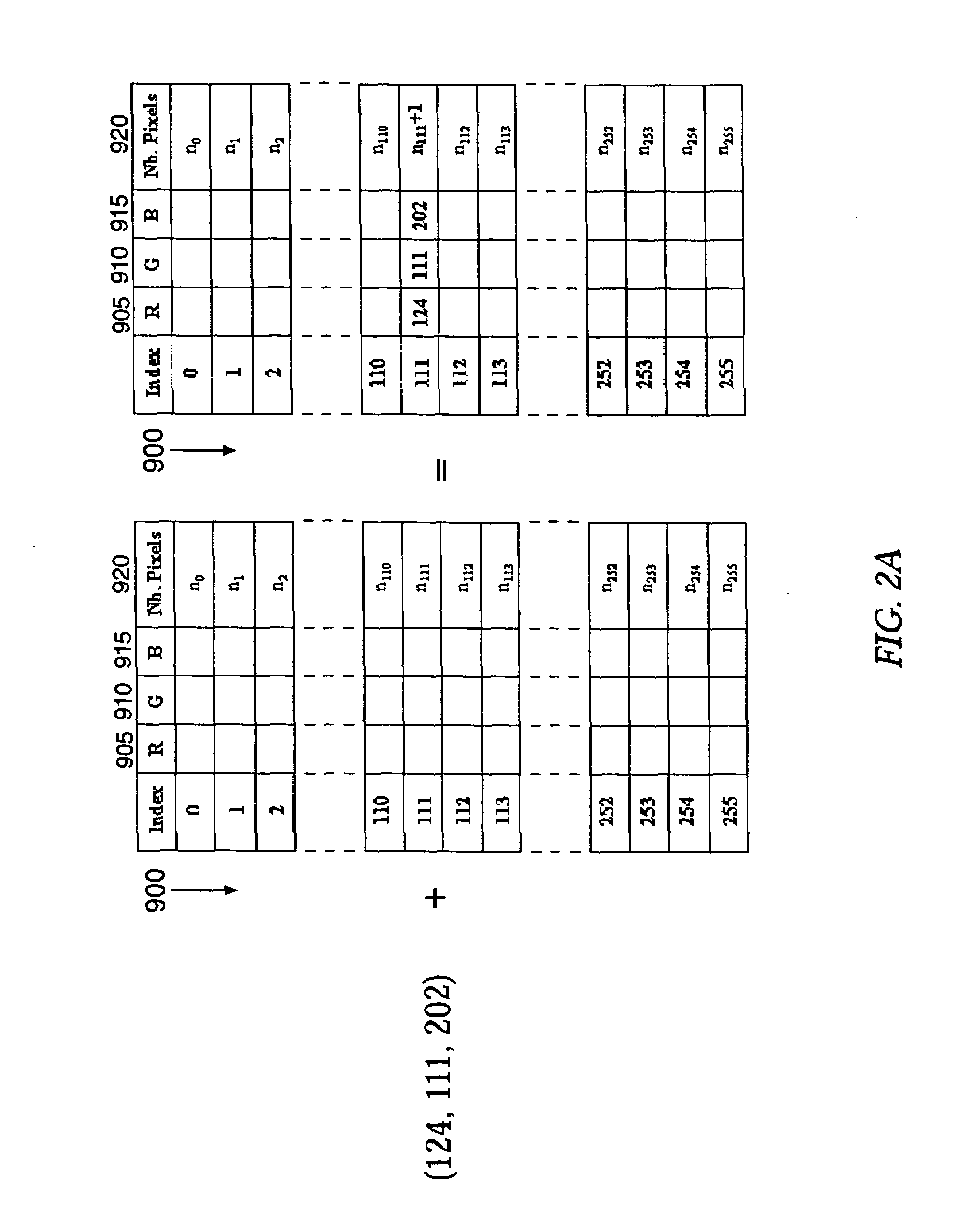
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
51 results about "Video microscopy" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Combined testing device and testing method of laser damage thresholds of film and optical element
ActiveCN101718712AReduce mistakesWide varietyScattering properties measurementsOptically investigating flaws/contaminationPhotovoltaic detectorsBeam splitter
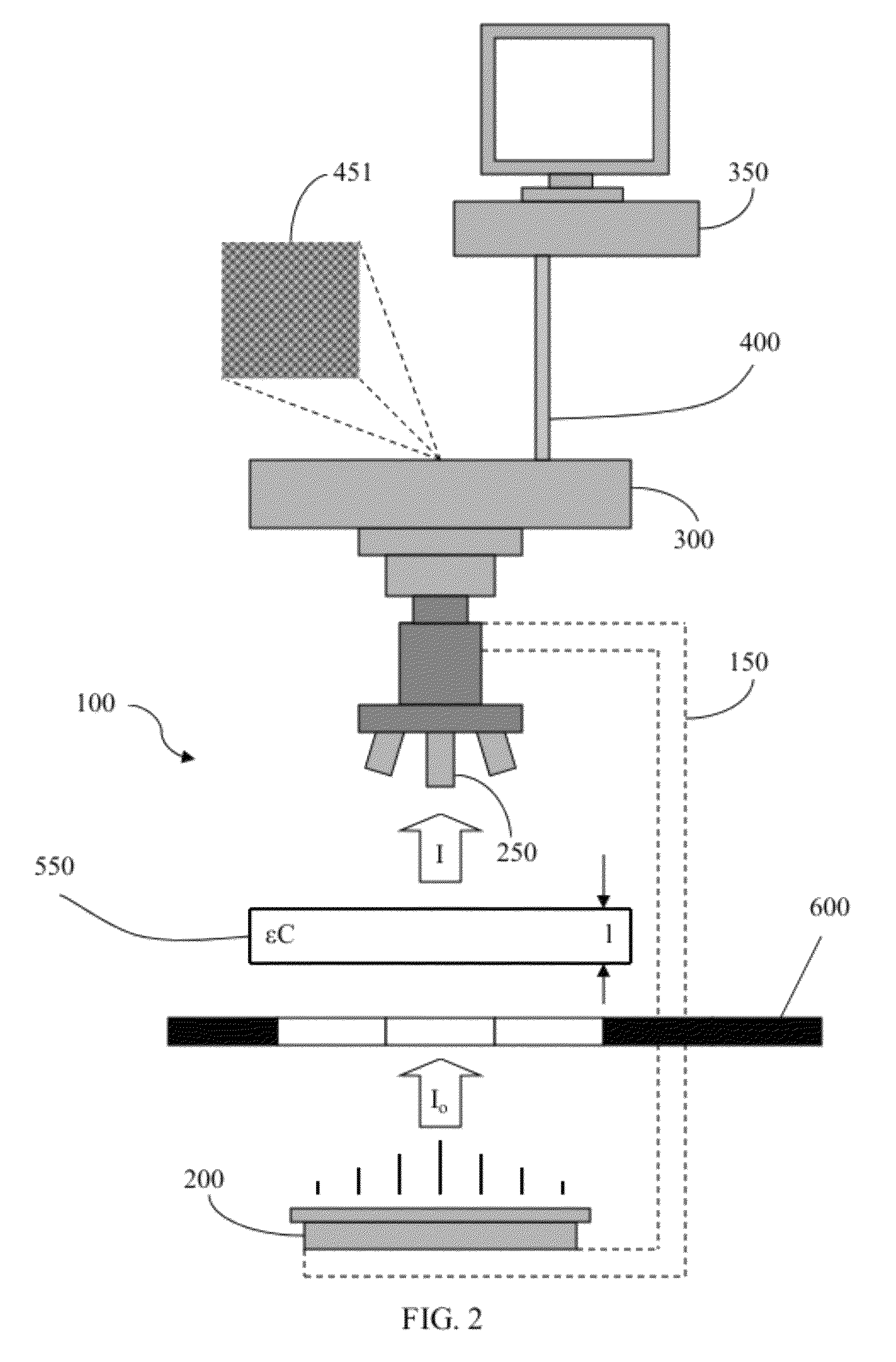
The invention relates to a combined testing device of the laser damage thresholds of a film and an optical element and a testing method utilizing the device. The traditional testing device and testing method have greater error and poor suitability for various film materials. The combined testing device of the laser damage thresholds of a film and an optical element comprises a testing assembly and a processing assembly, wherein the testing assembly comprises a Nd:YAG laser, a switch baffle, a first beam splitter, a focusing lens, a second beam splitter, a sample platform, a photodiode array, a convergent lens, an optoelectronic detector, a CCD camera, and the like; and the processing assembly comprises a computer. The testing method comprises the step of: conveying a testing result to judge whether various types of film samples are damaged or not by a CCD video microscopy judging method and a plasma flashing method according to a judgment criterion that one displayed damage is conformed The structure and the testing method of the invention has minimum testing error without error judgments and strong suitability and practicability.
Owner:XIAN TECHNOLOGICAL UNIV
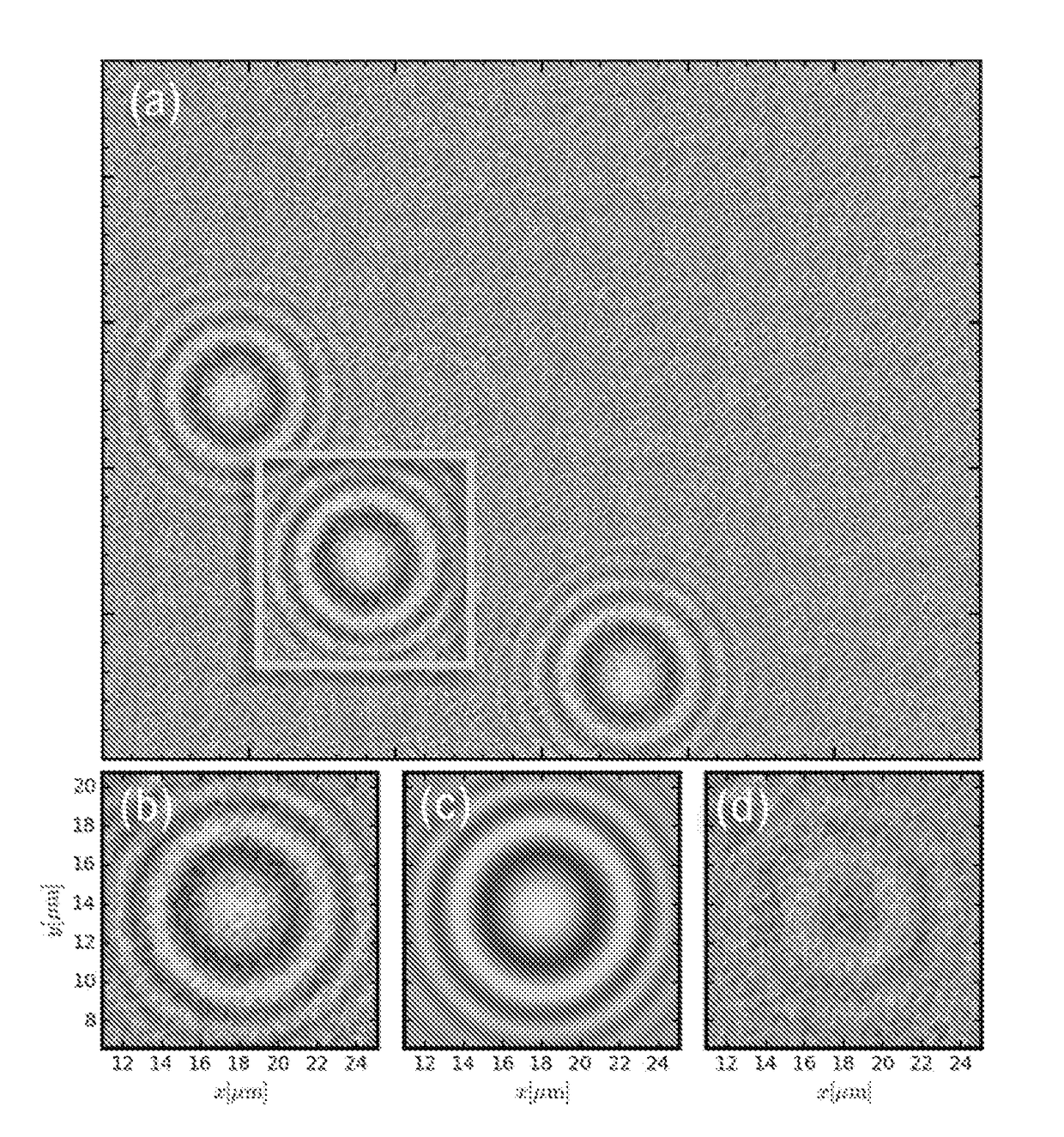
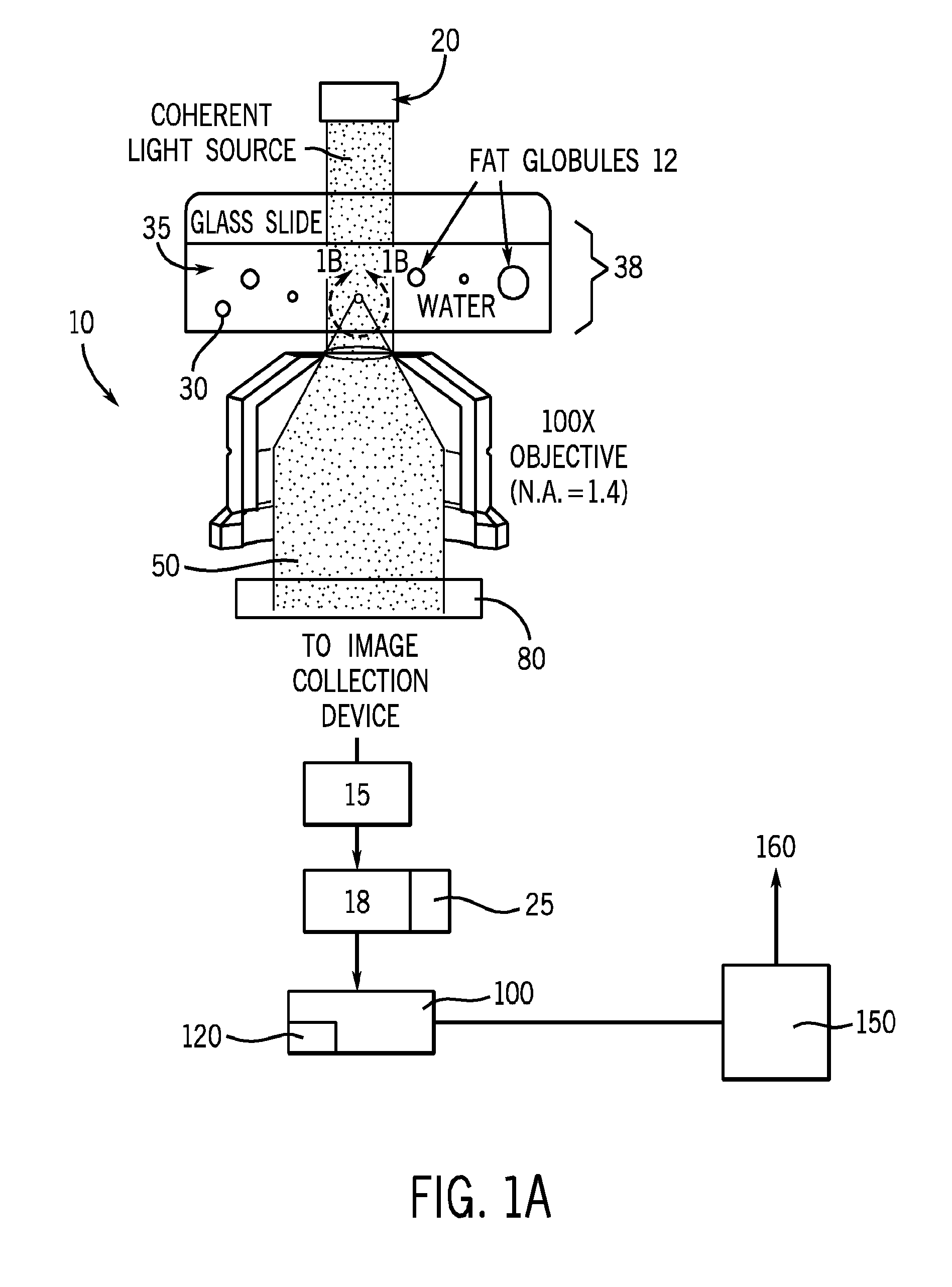
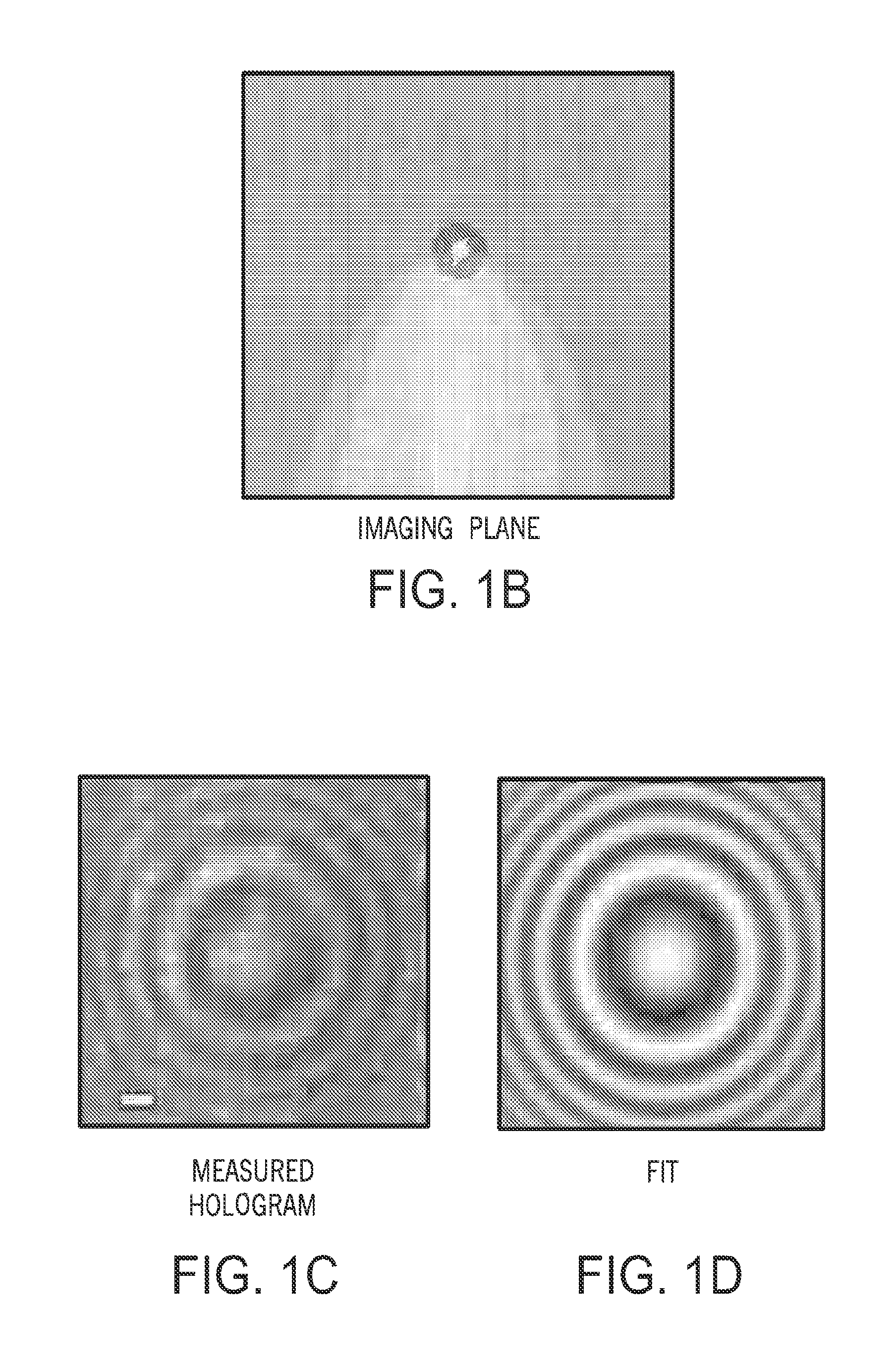
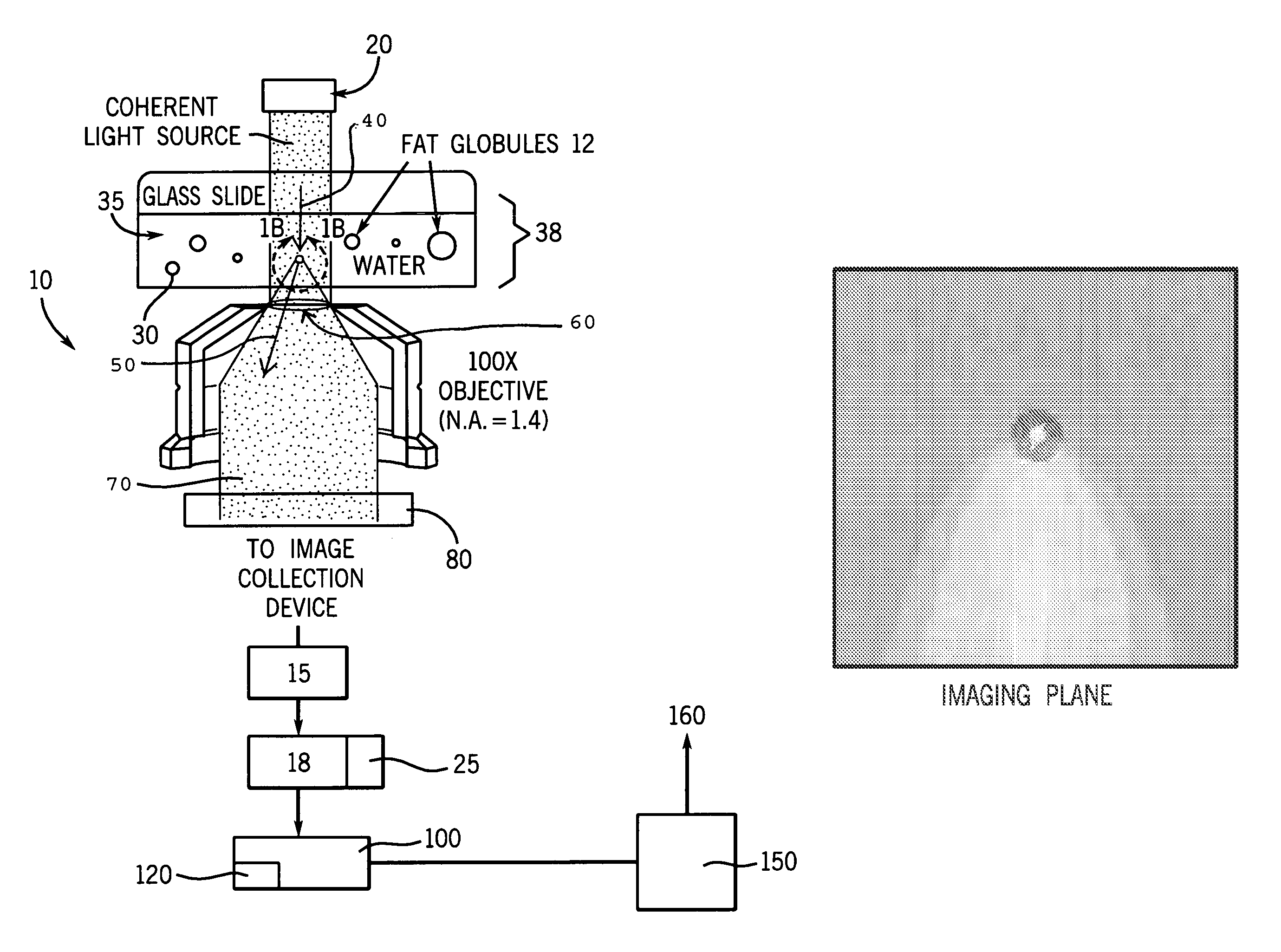
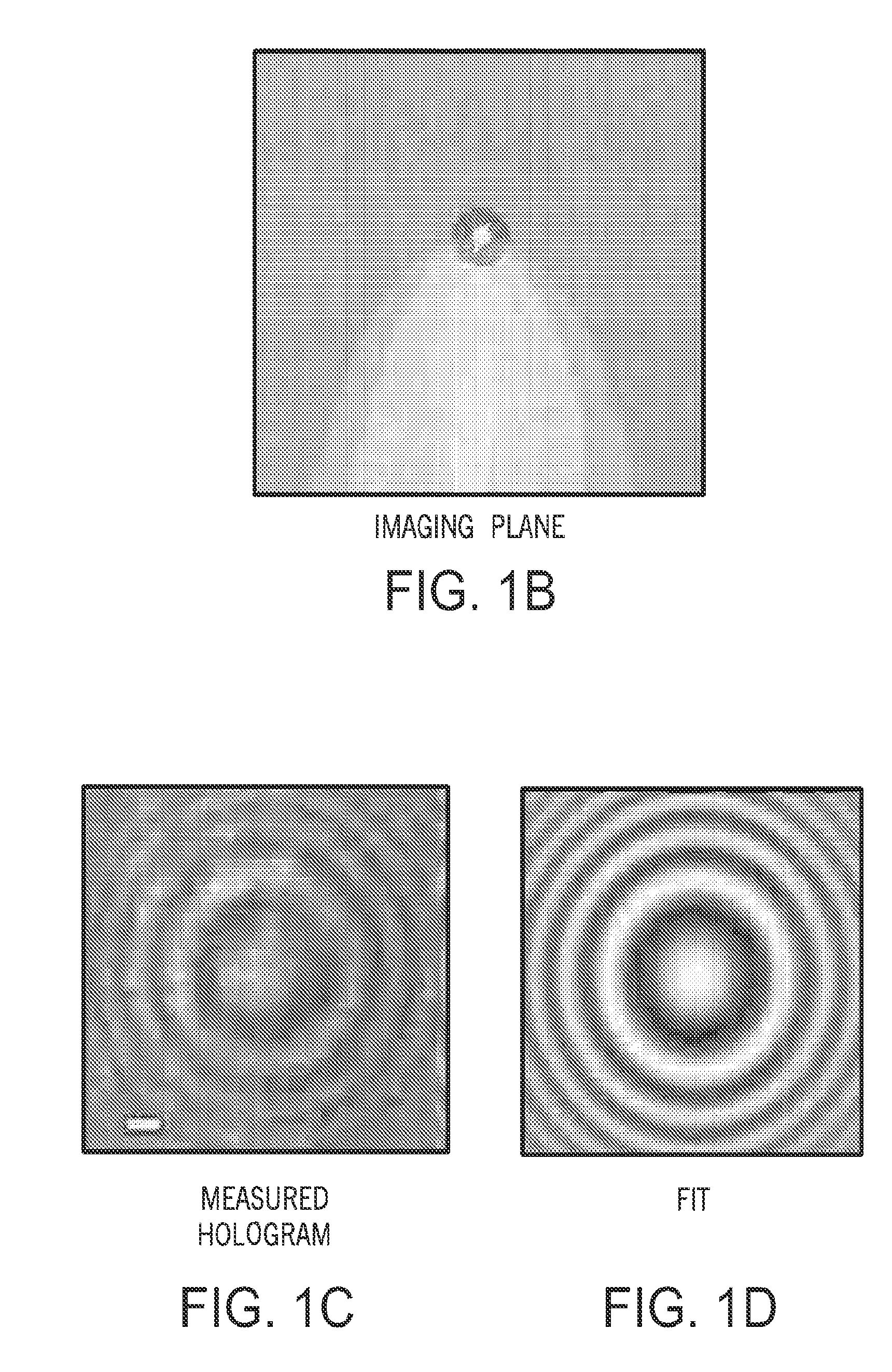
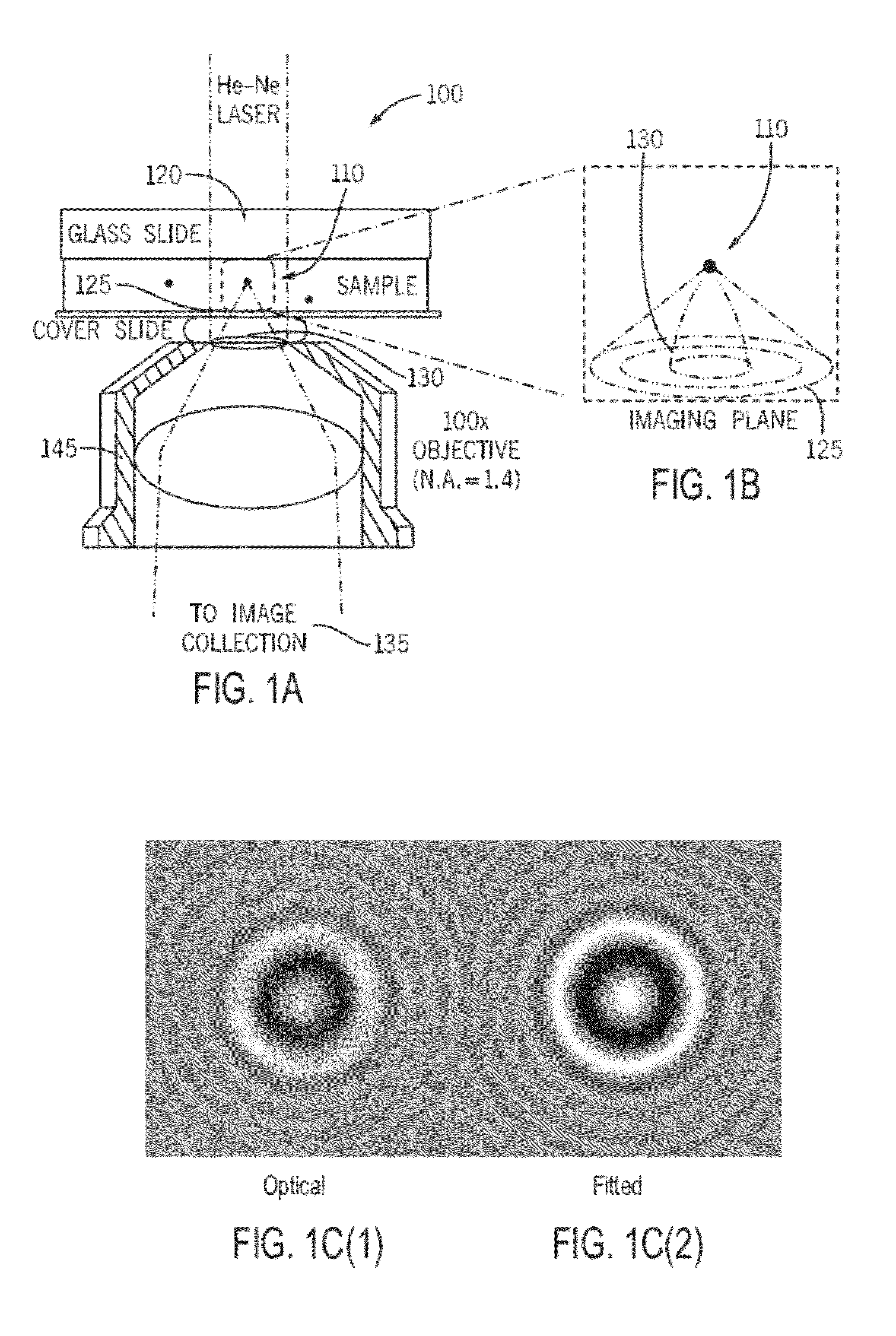
Tracking and characterizing particles with holographic video microscopy
ActiveUS20110043607A1Accurate representationTelevision system detailsNanoparticle analysisImage resolutionRefractive index
In-line holography to create images of a specimen, such as one or more particles dispersed in a transparent medium. Analyzing these images with results from light scattering theory yields the particles' sizes with nanometer resolution, their refractive indexes to within one part in a thousand, and their three dimensional positions with nanometer resolution. This procedure can rapidly and directly characterize mechanical, optical and chemical properties of the specimen and its medium.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
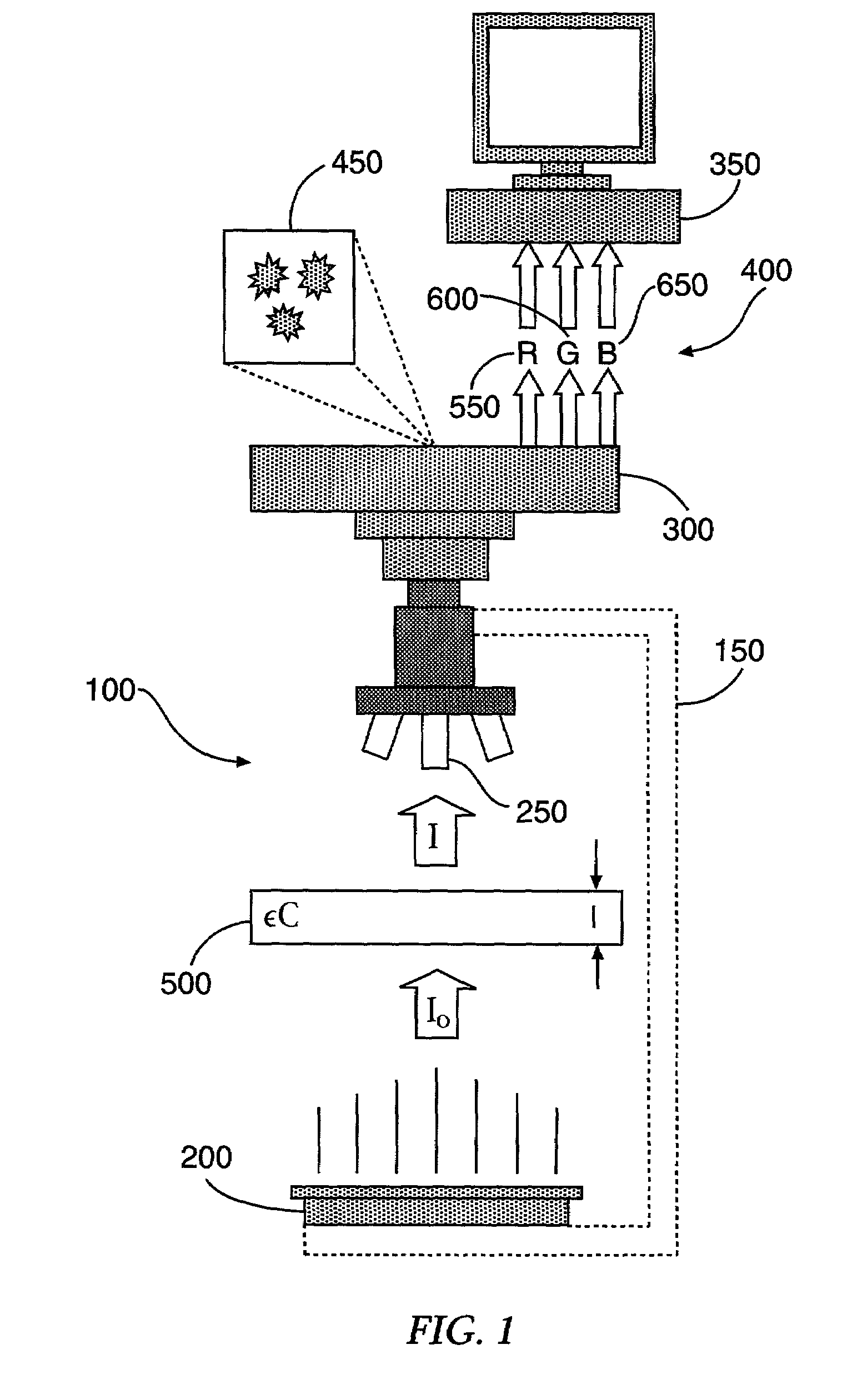
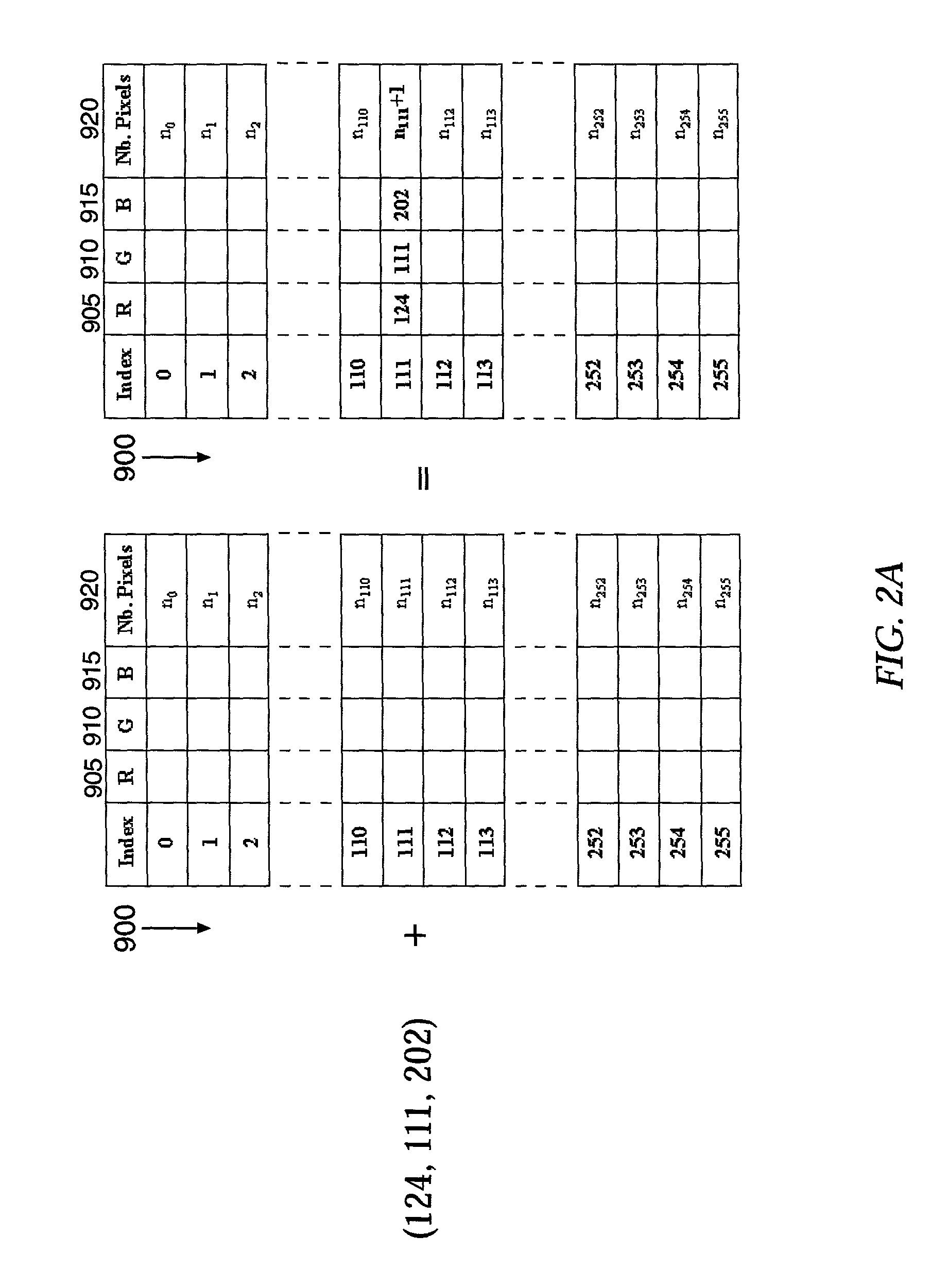
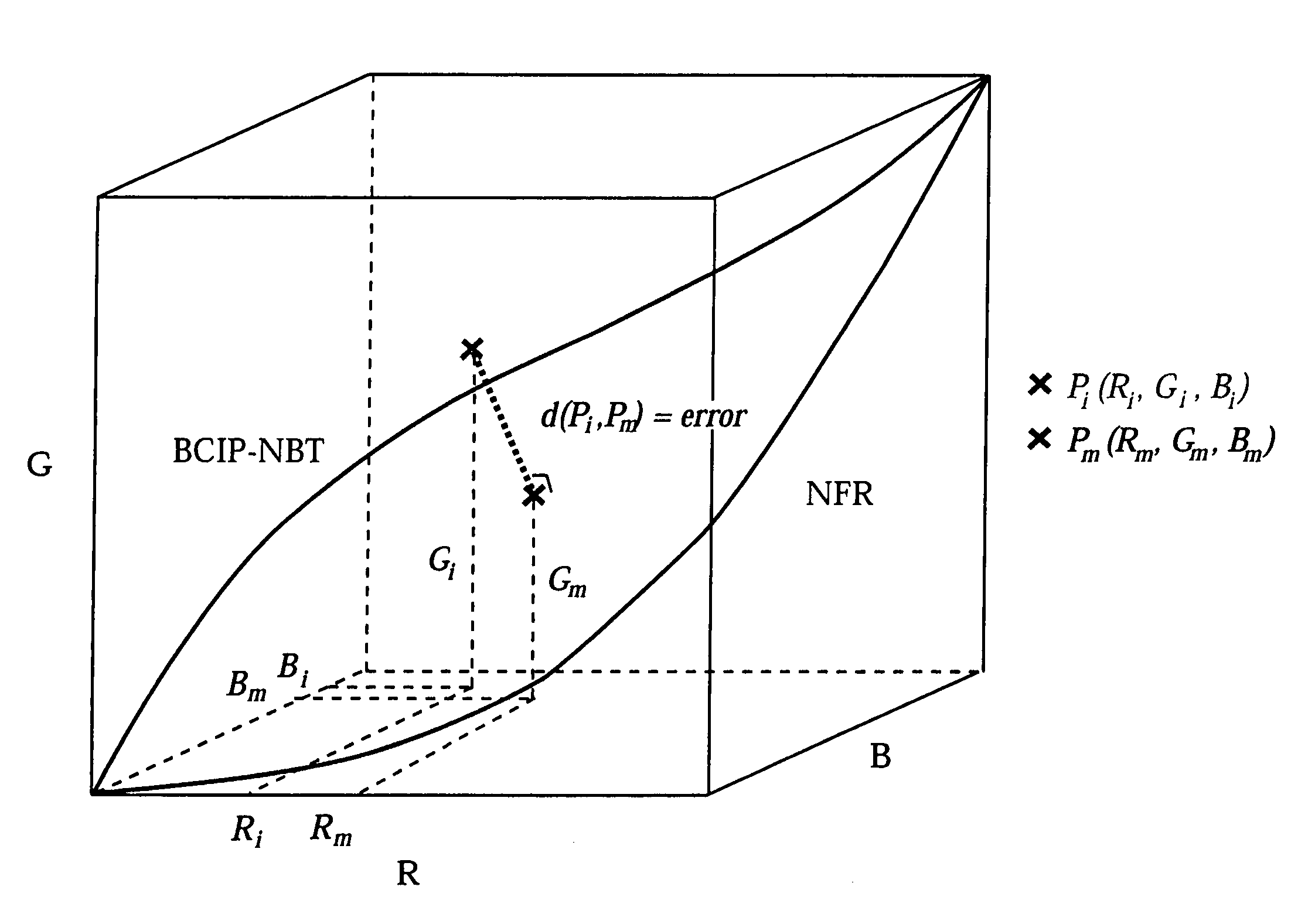
Method for quantitative video-microscopy and associated system and computer software program product
ActiveUS7133547B2Easy to determineEasy to watchImage enhancementImage analysisReference modelTransmittance
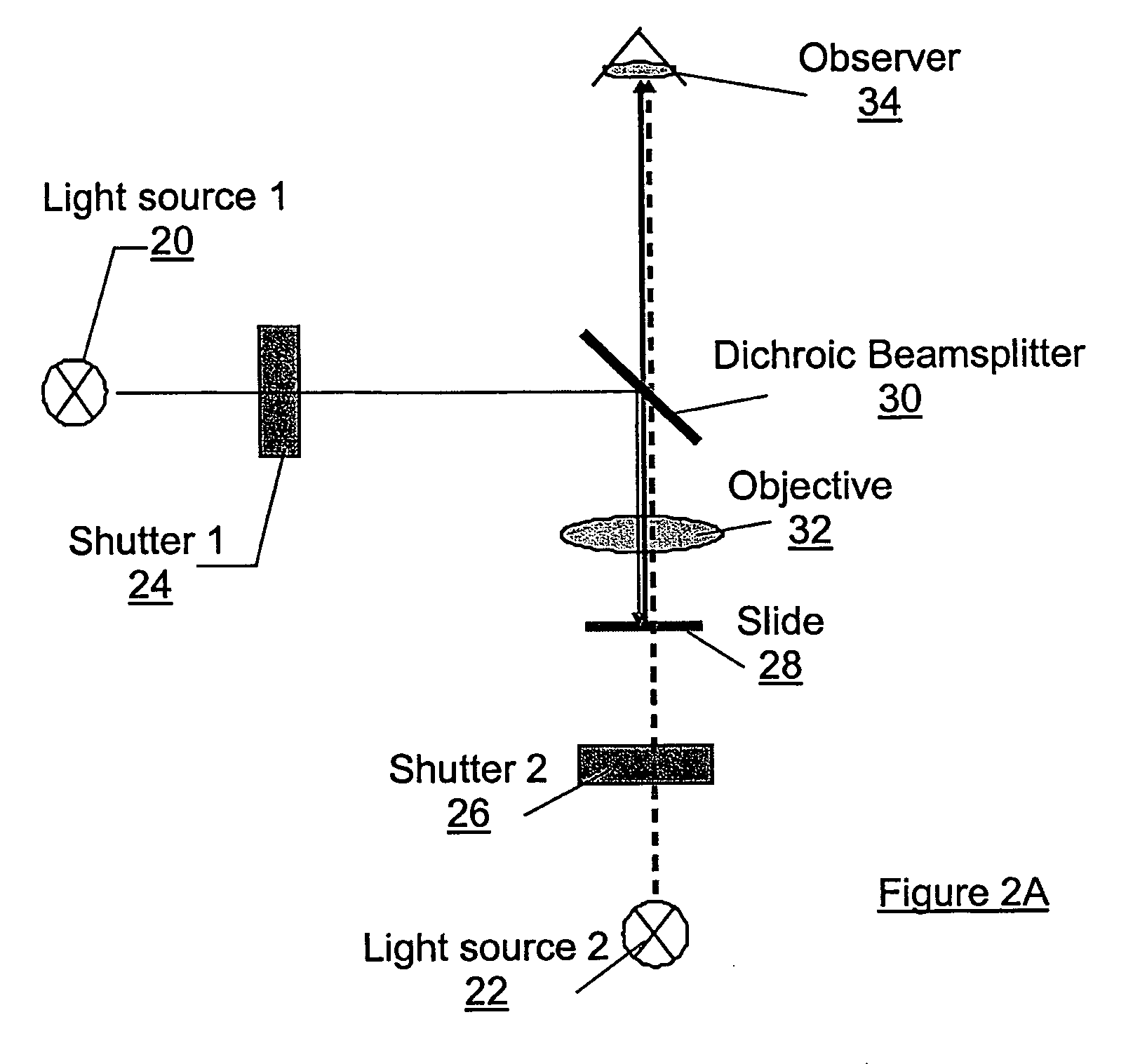
A method of determining an amount of at least one molecular species in a sample from an image of the sample captured by an image acquisition device is provided, each molecular species being indicated by a dye. A dye space representation of a plurality of dyes is formed by orthogonally adding the correspondence tables of the dyes, each correspondence table having a plurality of normalized RGB triplets and incrementally extending from 0% to 100% transmittance. The dye space representation has one dimension for each dye and provides a reference model for a combination of the plurality of dyes. Each pixel of an image of the sample stained with the combination of the plurality of dyes is compared to the reference model, each pixel having a color defined by an RGB triplet, so as to determine an optimal combination of normalized RGB triplets from the respective correspondence tables of the dyes producing the color of the respective pixel. An artificial image of the sample is then formed from the normalized RGB triplets for each dye as determined from the optimal combination. The artificial image thereby indicates a distribution of the respective dye over the sample image and facilitates determination of the amount of the corresponding molecular species. Associated methods, systems, and computer software program products are also provided.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
Method for quantitative video-microscopy and associated system and computer software program product
ActiveUS7065236B2Improve processing speedEasy to process in real timeImage enhancementImage analysisColor imageOptical density
A method of determining an amount of at least one molecular specie comprising a sample is provided, each molecular specie being indicated by a dye. The amount of the molecular specie is determined from an image of the sample captured as image data by a color image acquisition device in a video-microscopy system. An optical density of the sample is first determined in each of a red, green, and blue channel at a particular pixel in the image. A corresponding optical density matrix is thereafter formed for that pixel. The optical density matrix is then multiplied by the inverse of a relative absorption coefficient matrix so as to form a resultant matrix for the pixel. The relative absorption coefficient matrix comprises a relative absorption coefficient for each dye, independently of the sample, in each of the red, green, and blue channels. The resultant matrix thus comprises the amount of each molecular specie, as indicated by the respective dye, for that pixel. Associated systems and computer software program products are also provided.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
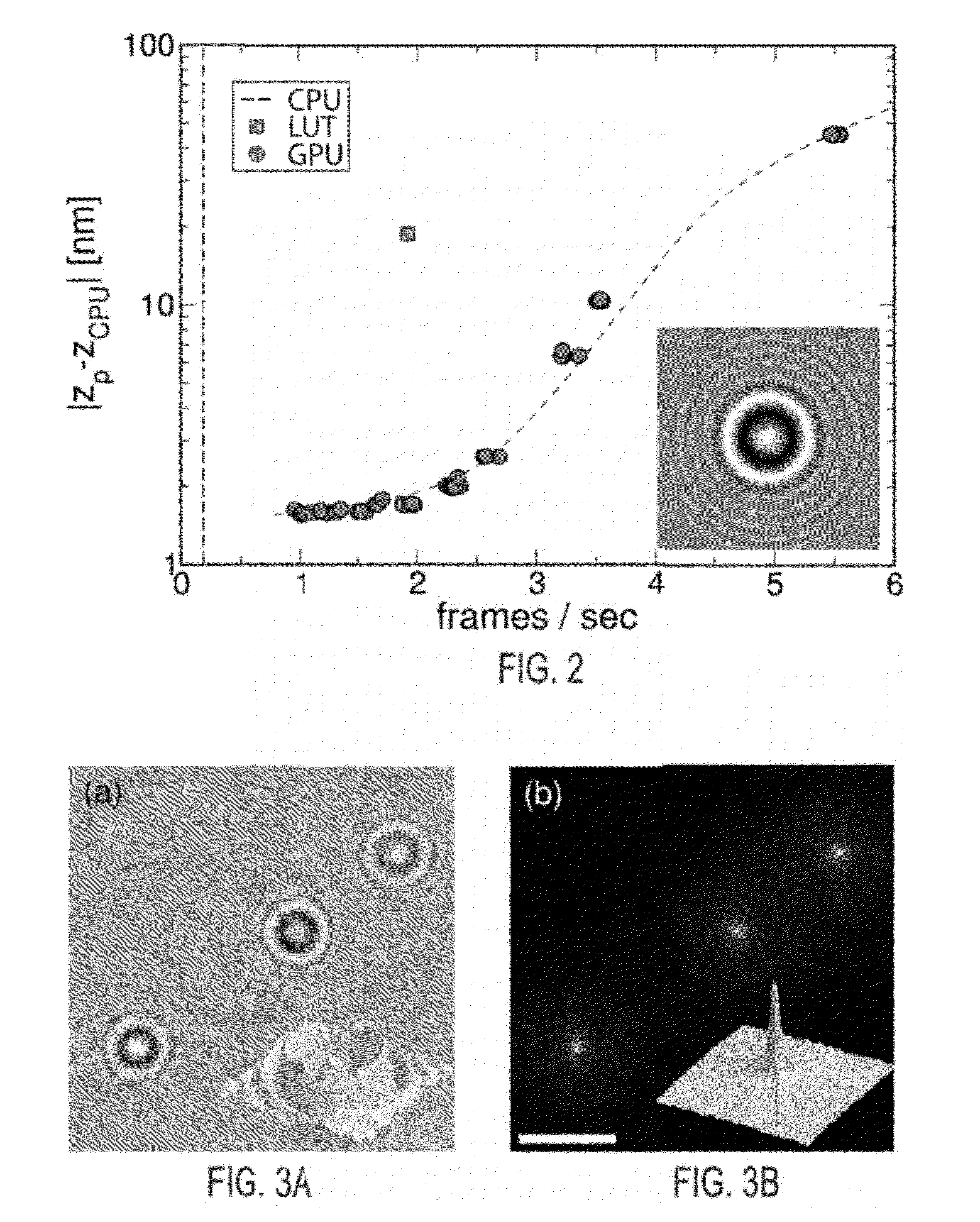
Automated real-time particle characterization and three-dimensional velocimetry with holographic video microscopy
ActiveUS20120135535A1Biological particle analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionParticle identificationRefractive index
An in-line holographic microscope can be used to analyze on a frame-by-frame basis a video stream to track individual colloidal particles' three-dimensional motions. The system and method can provide real time nanometer resolution, and simultaneously measure particle sizes and refractive indexes. Through a combination of applying a combination of Lorenz-Mie analysis with selected hardware and software methods, this analysis can be carried out in near real time. An efficient particle identification methodology automates initial position estimation with sufficient accuracy to enable unattended holographic tracking and characterization.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Methods of chromogen separation-based image analysis
Methods for chromogen separation-based image analysis are provided, with such methods being directed to quantitative video-microscopy techniques in cellular biology and pathology applications.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
Method for quantitative video-microscopy and associated system and computer software program product
InactiveUS7602954B2Easy to determineEasy to watchImage enhancementImage analysisReference modelTransmittance
A method of determining an amount of at least one molecular species in a sample from an image of the sample captured by an image acquisition device is provided, each molecular species being indicated by a dye. A dye space representation of a plurality of dyes is formed by orthogonally adding the correspondence tables of the dyes, each correspondence table having a plurality of normalized RGB triplets and incrementally extending from 0% to 100% transmittance. The dye space representation has one dimension for each dye and provides a reference model for a combination of the plurality of dyes. Each pixel of an image of the sample stained with the combination of the plurality of dyes is compared to the reference model, each pixel having a color defined by an RGB triplet, so as to determine an optimal combination of normalized RGB triplets from the respective correspondence tables of the dyes producing the color of the respective pixel. An artificial image of the sample is then formed from the normalized RGB triplets for each dye as determined from the optimal combination. The artificial image thereby indicates a distribution of the respective dye over the sample image and facilitates determination of the amount of the corresponding molecular species. Associated methods, systems, and computer software program products are also provided.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
Method for preparing quantitative video-microscopy and associated system
ActiveUS20120262563A1Quality improvementReduce subjectivityImage enhancementImage analysisLength waveImage system
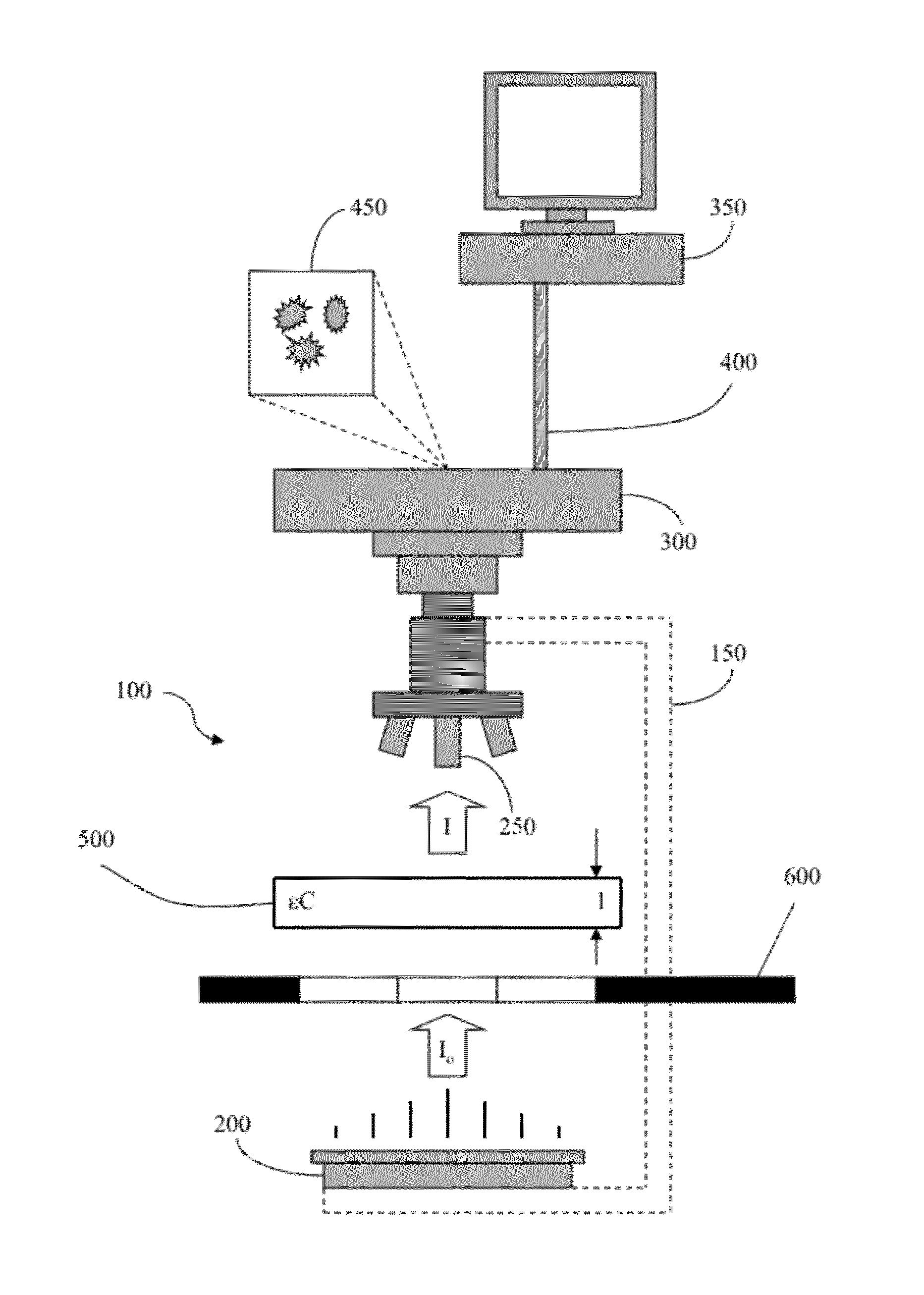
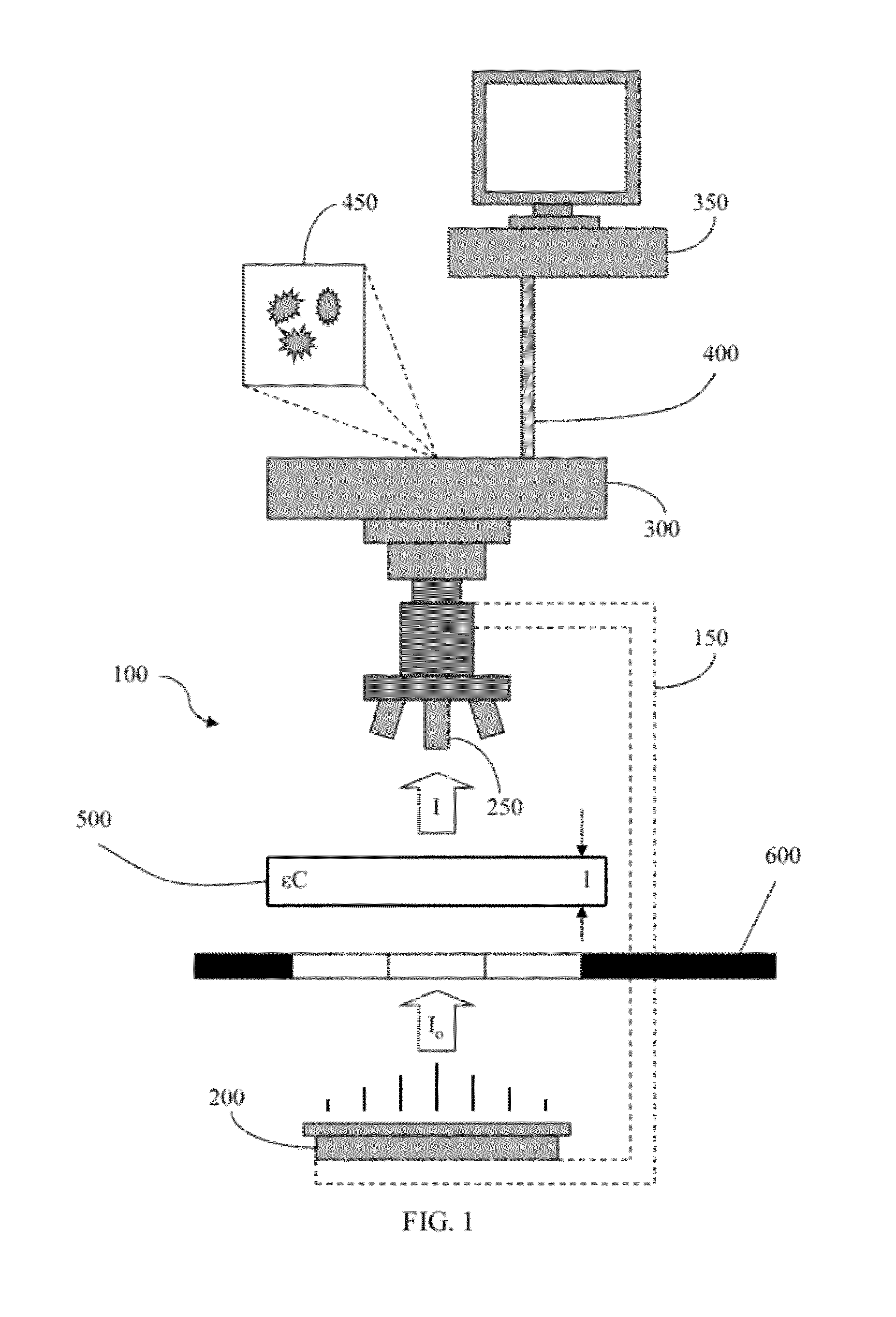
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to a method for calibrating an imaging system for analyzing a plurality of molecular species in a sample. According to one embodiment, the method comprises acquiring a plurality of images of the sample with an image acquisition device at a plurality of different wavelengths, comparing a region of interest associated with at least one of the images acquired at one respective wavelength to a region of interest associated with at least one of the images acquired at a different wavelength, and aligning the plurality of images such that the region of interest associated with at least one of the images acquired at one respective wavelength corresponds to the region of interest associated with the at least one of the images acquired at a different wavelength.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
Methods of chromogen separation-based image analysis
Methods for chromogen separation-based image analysis are provided, with such methods being directed to quantitative video-microscopy techniques in cellular biology and pathology applications.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
Tracking and characterizing particles with holographic video microscopy
In-line holography to create images of a specimen, such as one or more particles dispersed in a transparent medium. Analyzing these images with results from light scattering theory yields the particles' sizes with nanometer resolution, their refractive indexes to within one part in a thousand, and their three dimensional positions with nanometer resolution. This procedure can rapidly and directly characterize mechanical, optical and chemical properties of the specimen and its medium.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
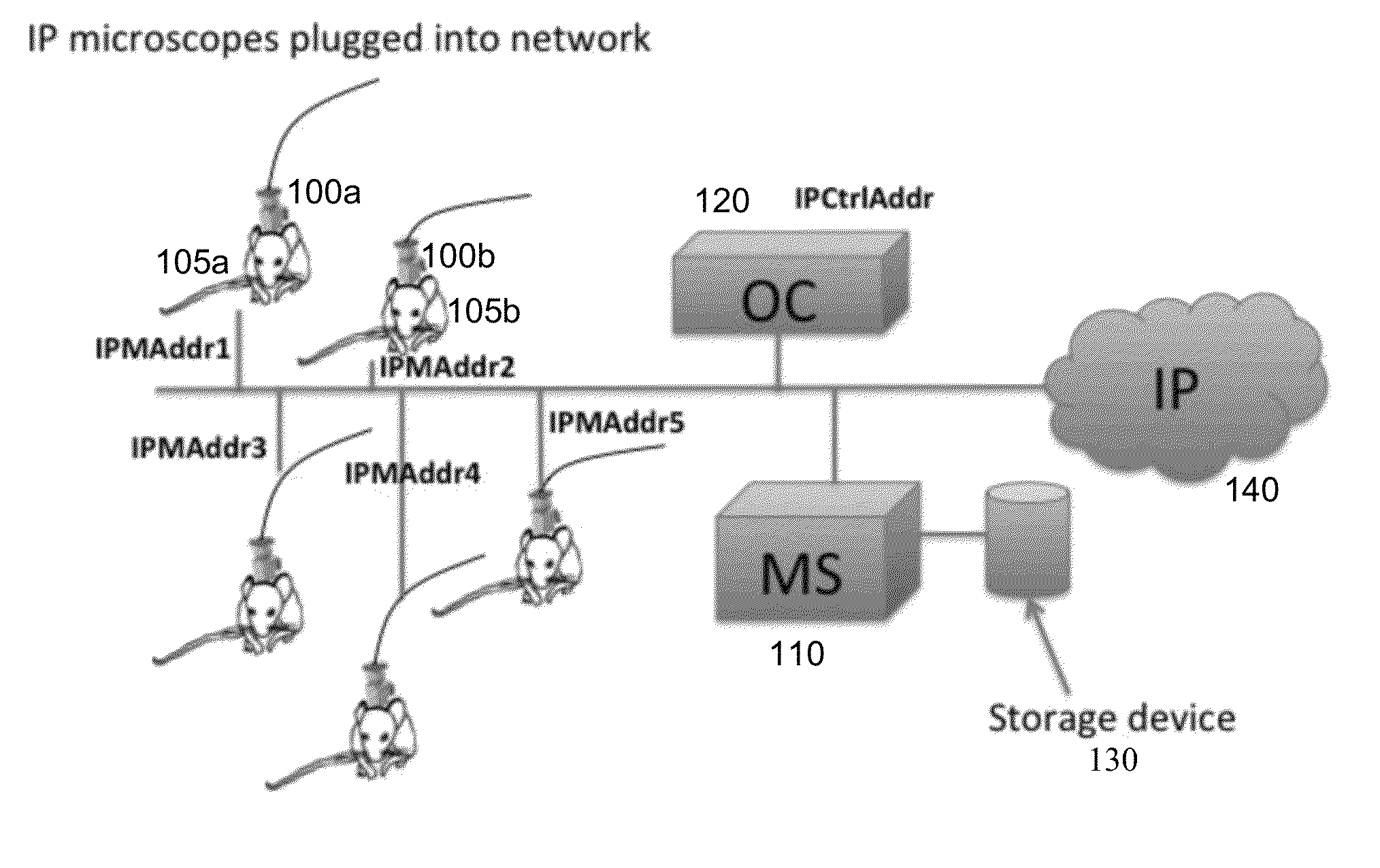
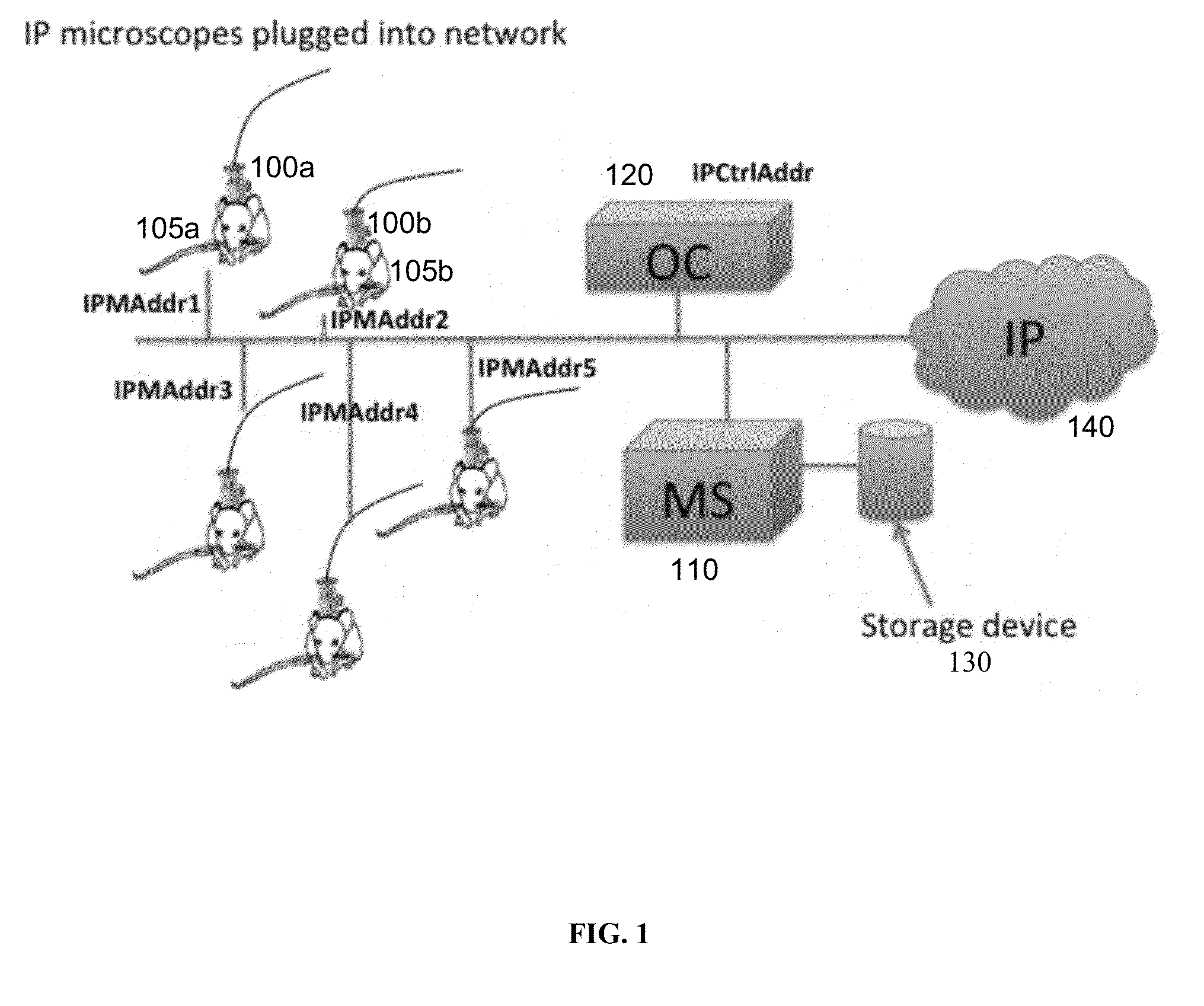
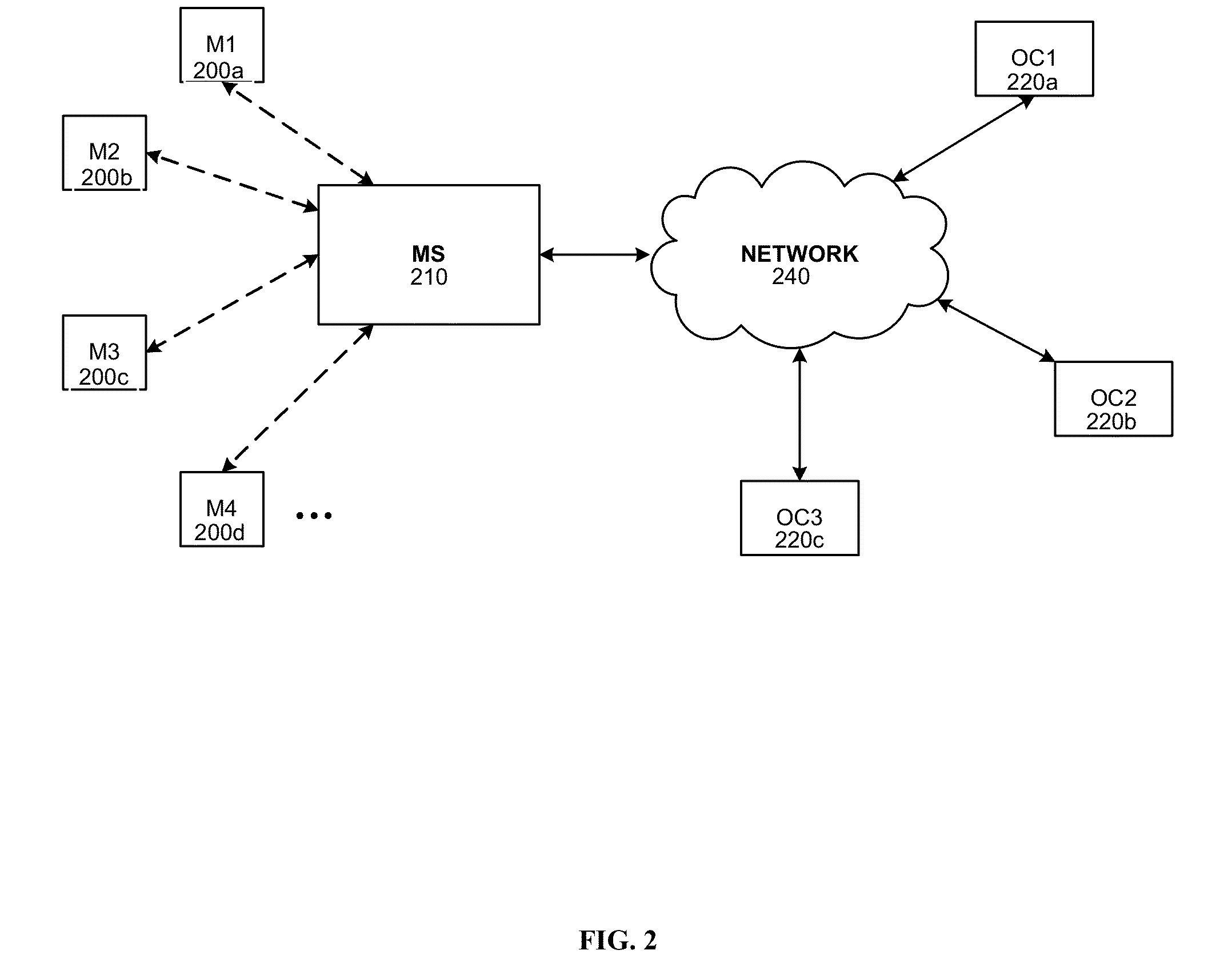
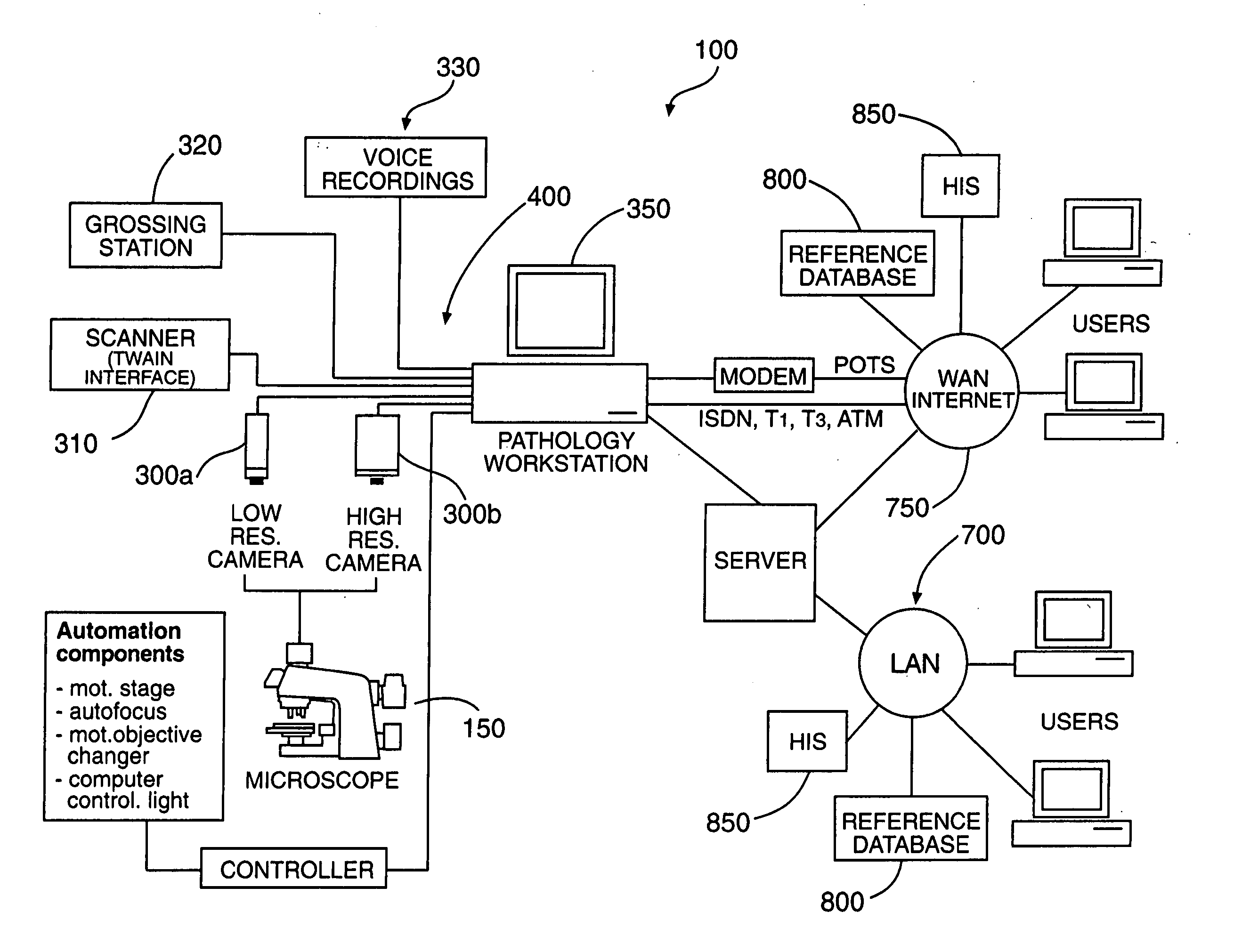
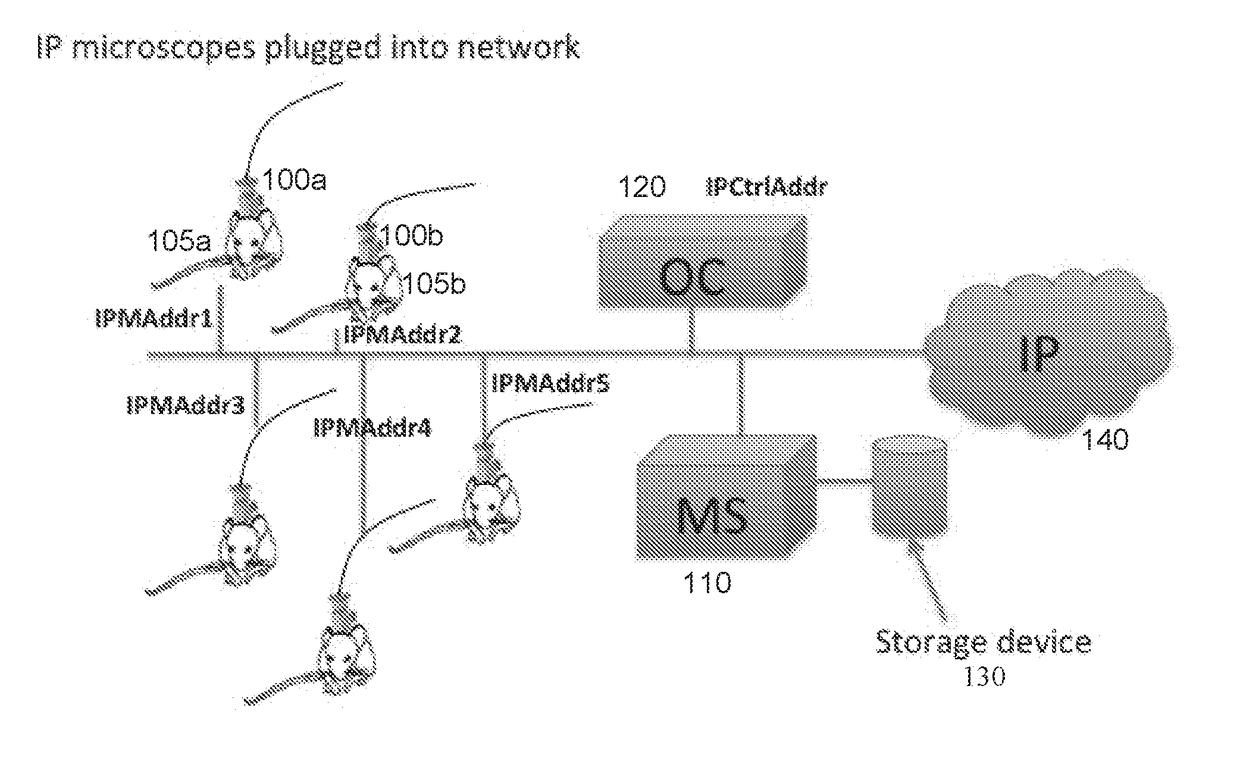
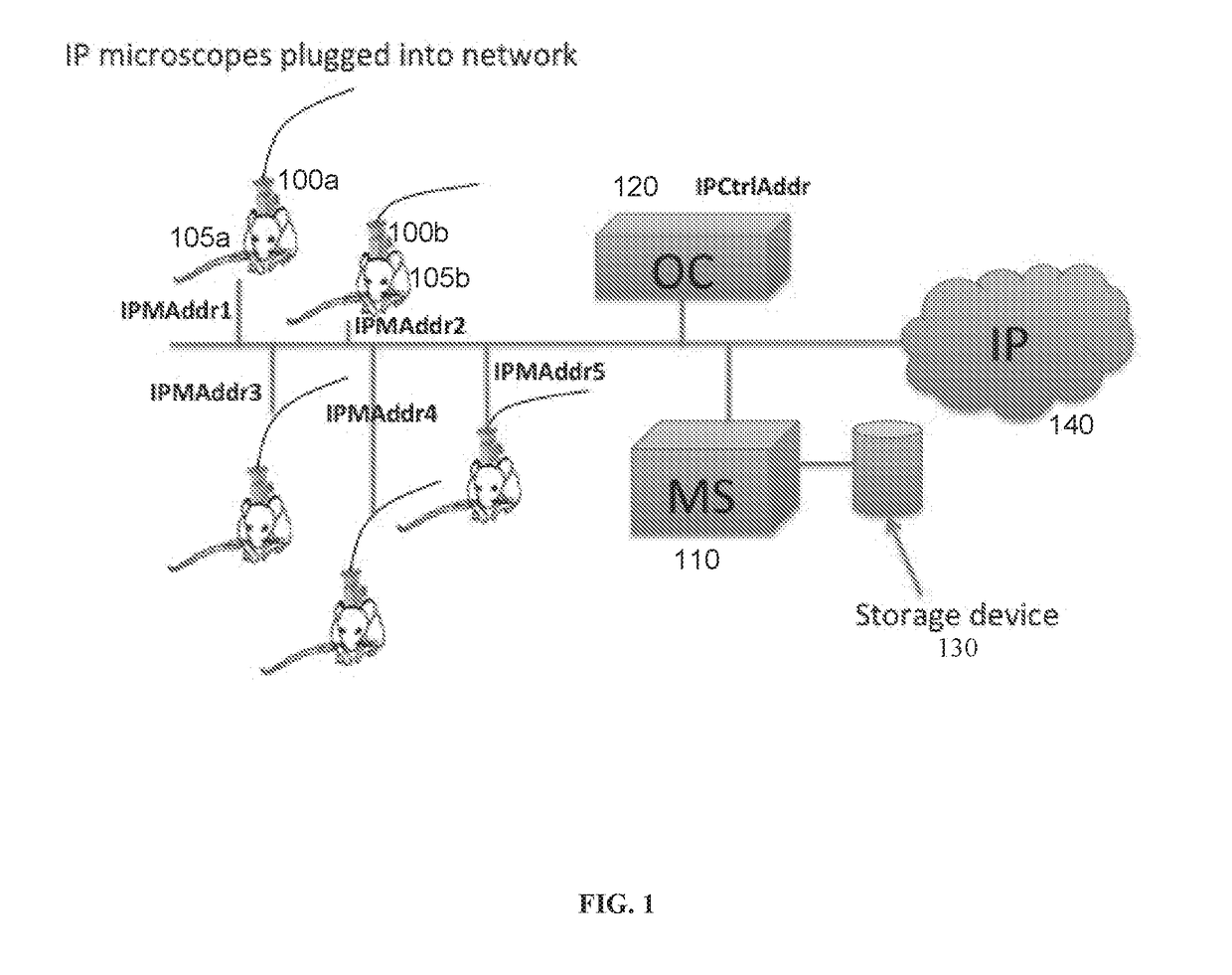
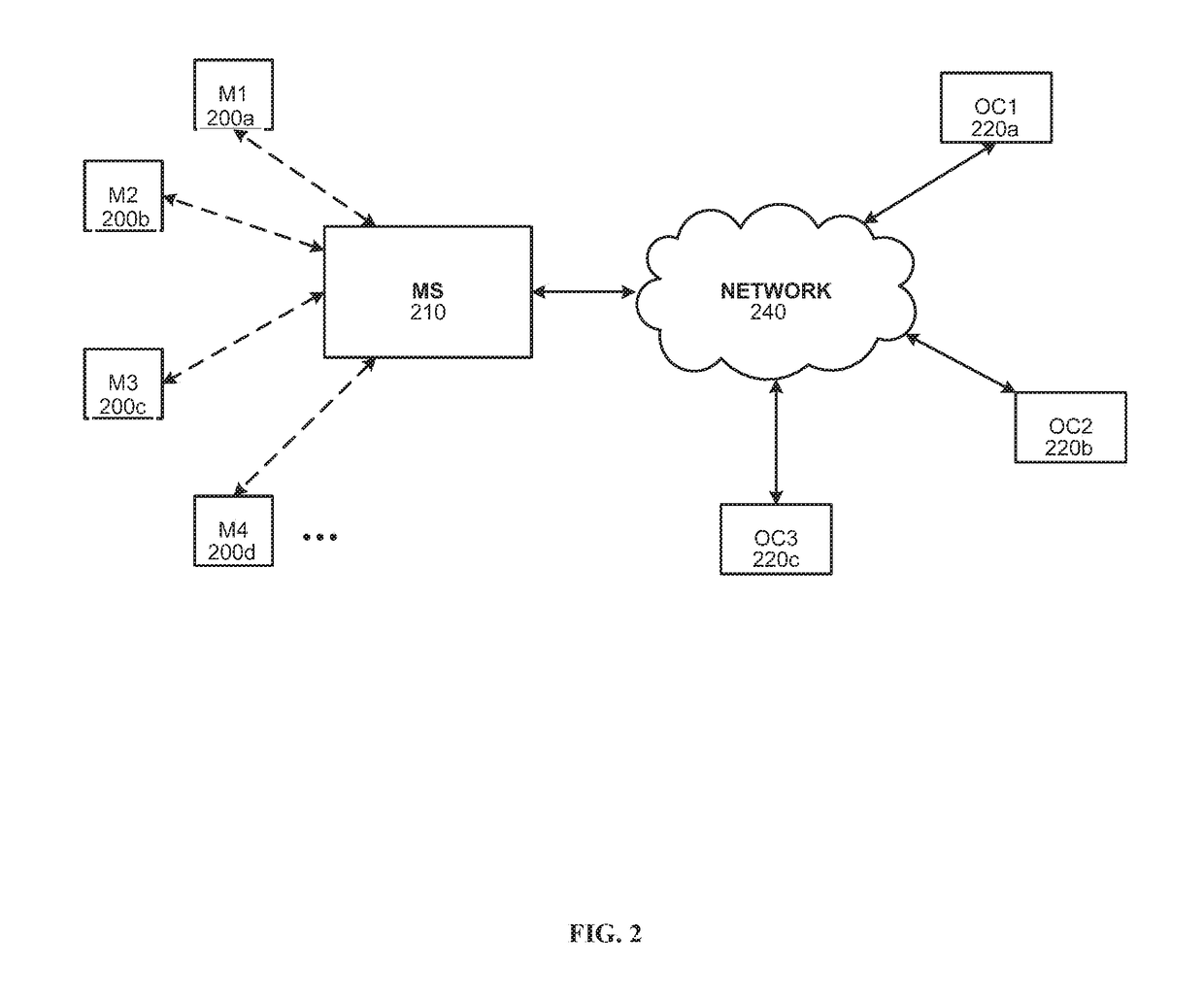
Systems and methods for distributed video microscopy
InactiveUS20140043462A1Improve throughputColor television detailsClosed circuit television systemsUser inputNetwork addressing
System and methods are provided for distributed microscopy. A plurality of microscopes may capture images and send them to a media server. The microscopes and the media server may be part of a local area network. The microscopes may each have a distinct network address. The media server may communicate with an operations console, which may be used to view images captured by the microscopes. The operations console may also accept user input which may be used to selectively control the microscopes.
Owner:INSCOPIX
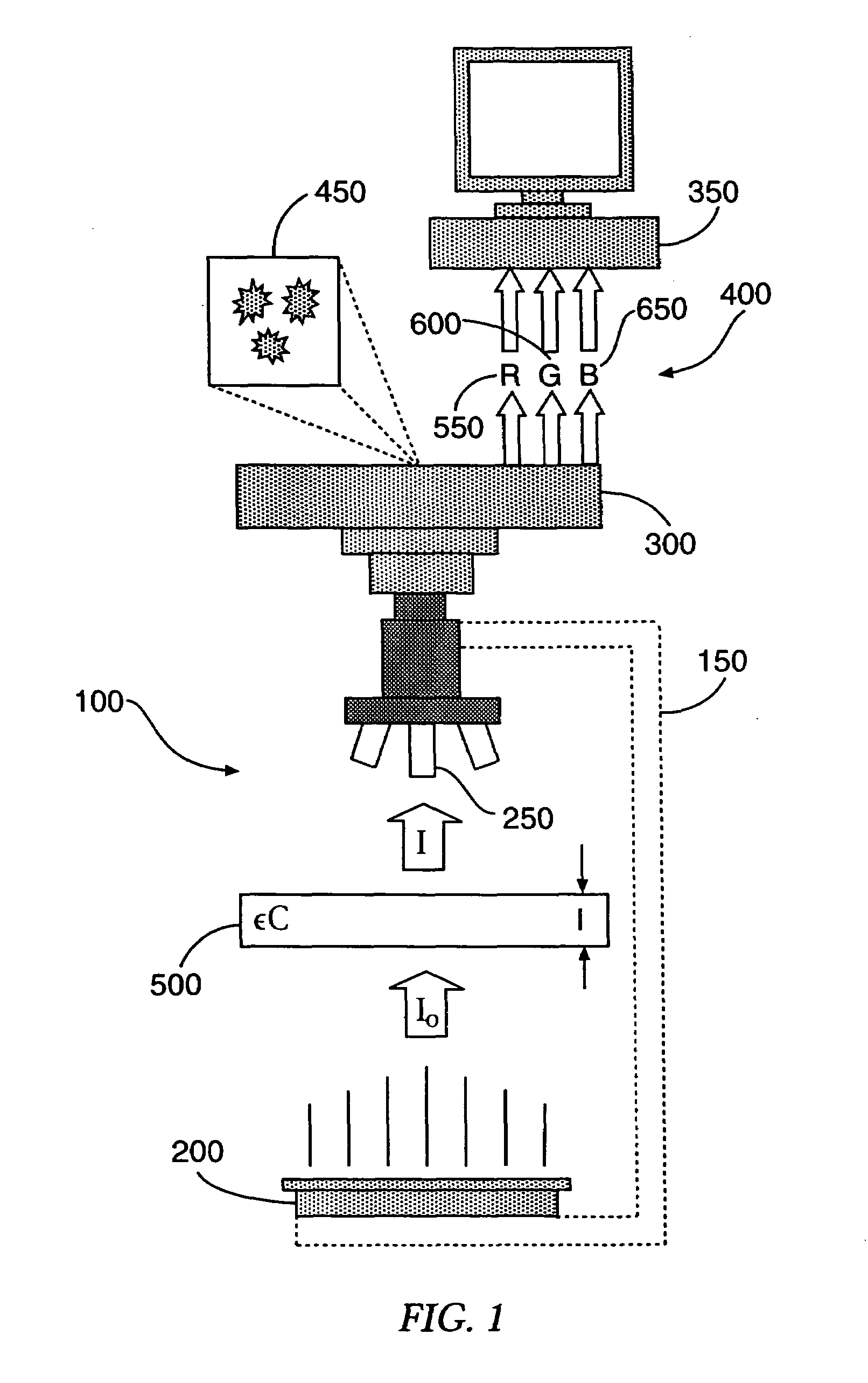
Video microscopy system and multi-view virtual slide viewer capable of simultaneously acquiring and displaying various digital views of an area of interest located on a microscopic slide
InactiveUS20090006969A1Cost efficientHigh resolutionCathode-ray tube indicatorsMicroscopesVirtual slideData file
A slide viewer capable of simultaneous display of more than one representation of an area of interest of a slide is provided. The slide viewer includes a database containing at least two data files representing different representations for a same area of interest on one or multiple correlated slides or at least two different digital presentations of the same representation. The representations are views of different illumination and / or of different contrast. Associated with the database are a processor and a display. The processor retrieves data files representing different representations of the same of area of interest and displays them on the display. A user is allowed to simultaneously view representations of the same area of interest, where the representations are of views different from each other by either illumination and / or contrast or by the digital information content presented, and / or by the information acquired from multiple correlated slides.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
High-speed leather identification method
ActiveCN102809537AThe sample preparation process is simpleSimple sample preparation methodMaterial analysis by optical meansMicroscopic imageMicroscopic scale
The invention relates to the technical field of leather identification, in particular to a high-speed leather identification method. The method comprises the following steps: lying a leather sample under an atmospheric condition, and standing; allowing the static leather sample to be subjected to surface sampling and / or cross section sampling so as to respectively obtain a leather surface sample and / or a leather cross section sample; placing the leather surface sample and / or leather cross section sample in an objective table of a super-field-depth three-dimensional video microscopy for imaging, and shooting the microscopic image; and identifying the leather according to the leather microscopic characteristics displayed by the microscopic image. The method provided by the invention has the advantages of fastness in sampling, simplicity and convenience in operation, chemical reagent prevention in fixing and dyeing, high identification speed, high efficiency, low cost and the like.
Owner:GUANGZHOU QUALITY SUPERVISION & TESTING INST
Method for optimization of quantitative video-microscopy and associated system
ActiveUS20120262564A1Effective detection and quantificationAccurate estimateImage enhancementImage analysisComputer visionMicroscope
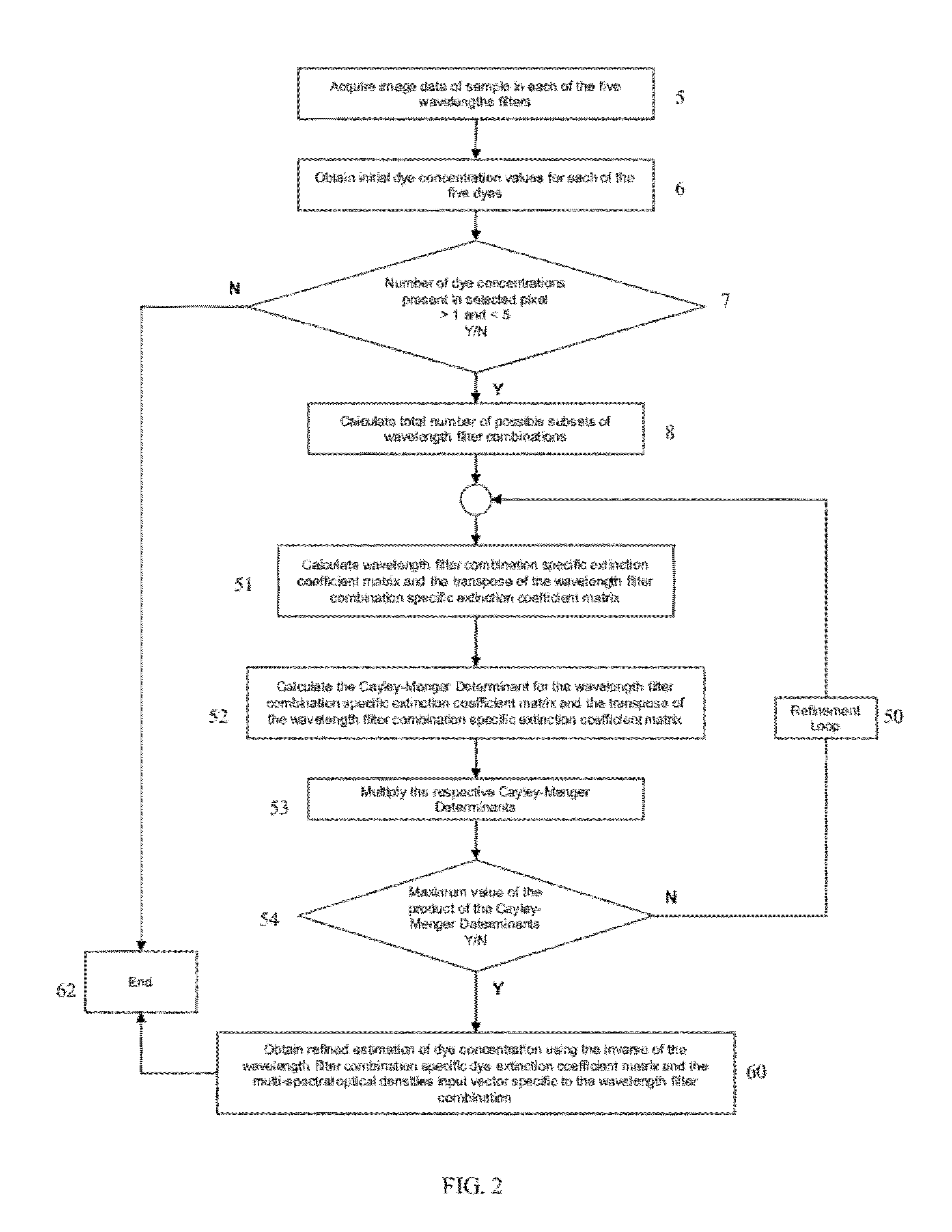
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to a method for determining an amount of a plurality of molecular species in a sample, each molecular specie being indicated by a dye. According to one embodiment, the amount of a plurality of molecular species is determined by acquiring a plurality of images of the sample, determining an amount of each molecular specie, as indicated by a respective dye, for each pixel at each corresponding pixel location in the plurality of images, and refining the amount of a plurality of molecular species at one or more pixel locations in the plurality of images. Associated systems and computer program products are also provided.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
Method for quantitative video-microscopy and associated system and computer software program product
ActiveUS20060204068A1Improve processing speedEasy to watchImage enhancementImage analysisReference modelTransmittance
A method of determining an amount of at least one molecular species in a sample from an image of the sample captured by an image acquisition device is provided, each molecular species being indicated by a dye. A dye space representation of a plurality of dyes is formed by orthogonally adding the correspondence tables of the dyes, each correspondence table having a plurality of normalized RGB triplets and incrementally extending from 0% to 100% transmittance. The dye space representation has one dimension for each dye and provides a reference model for a combination of the plurality of dyes. Each pixel of an image of the sample stained with the combination of the plurality of dyes is compared to the reference model, each pixel having a color defined by an RGB triplet, so as to determine an optimal combination of normalized RGB triplets from the respective correspondence tables of the dyes producing the color of the respective pixel. An artificial image of the sample is then formed from the normalized RGB triplets for each dye as determined from the optimal combination. The artificial image thereby indicates a distribution of the respective dye over the sample image and facilitates determination of the amount of the corresponding molecular species. Associated methods, systems, and computer software program products are also provided.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
Automated real-time particle characterization and three-dimensional velocimetry with holographic video microscopy
ActiveUS9316578B2Biological particle analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionParticle identificationRefractive index
An in-line holographic microscope can be used to analyze on a frame-by-frame basis a video stream to track individual colloidal particles' three-dimensional motions. The system and method can provide real time nanometer resolution, and simultaneously measure particle sizes and refractive indexes. Through a combination of applying a combination of Lorenz-Mie analysis with selected hardware and software methods, this analysis can be carried out in near real time. An efficient particle identification methodology automates initial position estimation with sufficient accuracy to enable unattended holographic tracking and characterization.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
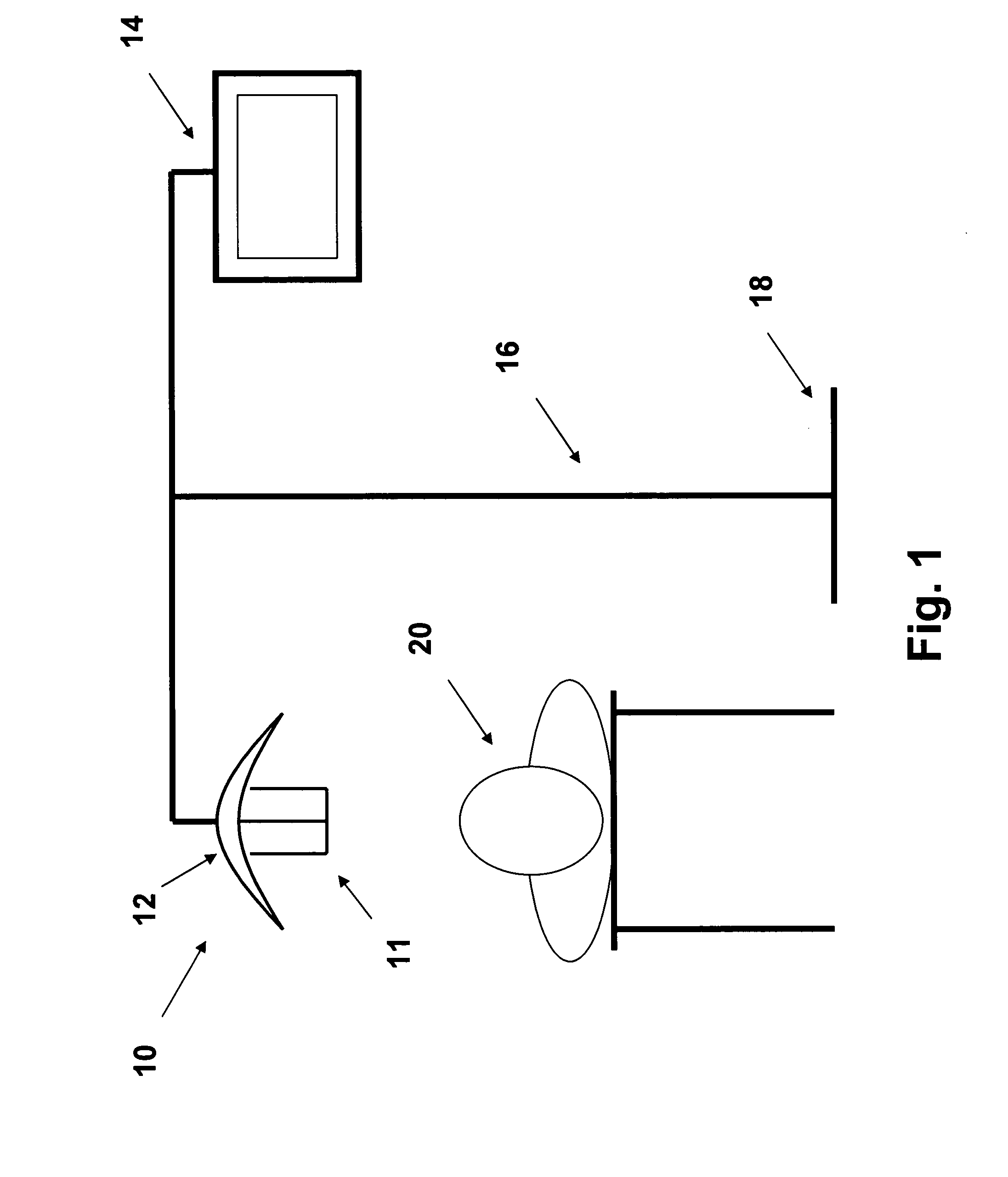
Stereo video microscope system
A stereo video microscope system (10), comprising: a stereo video microscope (11) having two output channels for providing stereo image data and including an internal lighting; a display unit (14) having two input channels for receiving and displaying stereo image data; and a control unit operably connected to the stereo video microscope (11) and the display unit (14) such that the control unit can control the operation of the stereo video microscope (11) and the display unit (14) and the flow of stereo image data between the two output channels of the stereo video microscope (11) and the two input channels of the display unit (14). In one embodiment the control unit is configured for performing an image rotation and / or exchanging the output channels such that the stereo image is always upright.
Owner:SWISS MEDICAL TECH
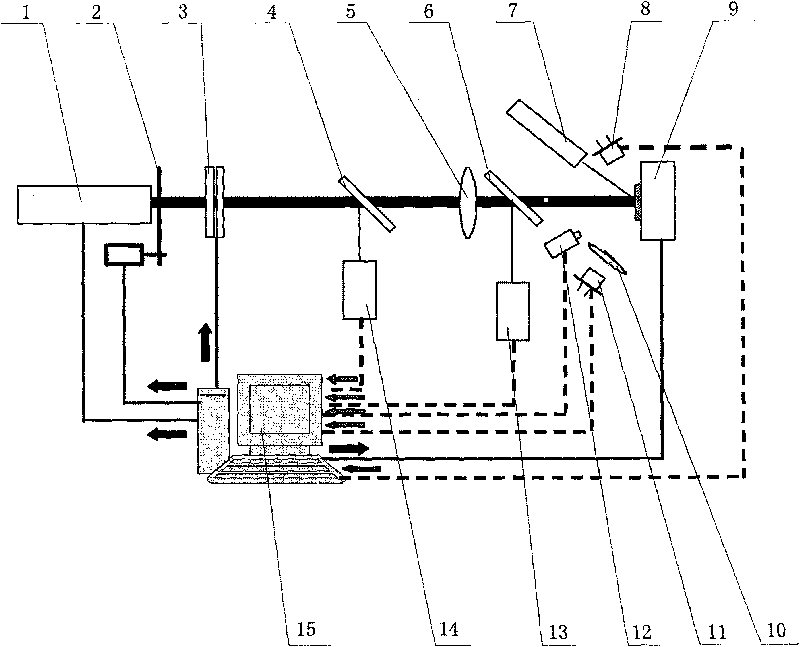
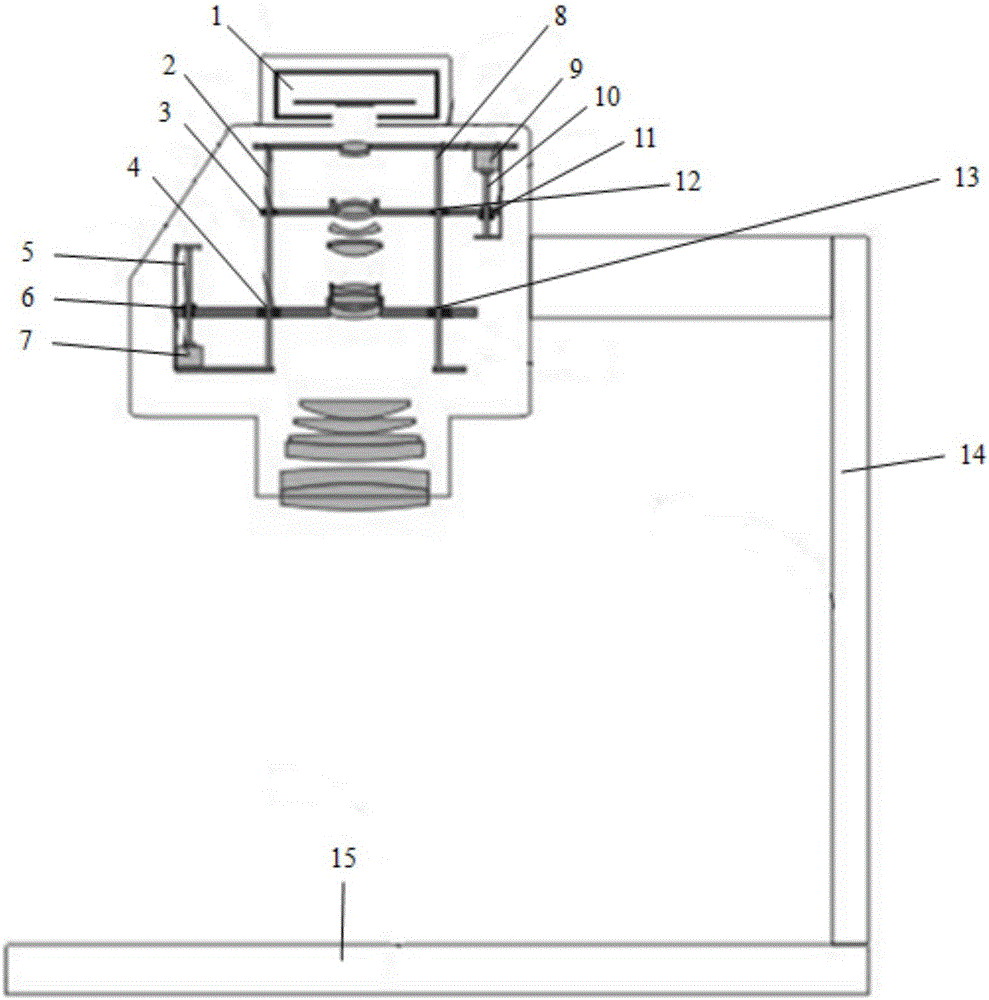
Video microscope with electric focusing and zooming and operation method thereof
The present invention relates to a video microscope with electric focusing and zooming and an operation method thereof. The video microscope comprises an image collection module (1), a support (14), a sample table (15), a focusing lens set (16), a continuous zooming lens set (17), an object lens eyeglass set (18), a focusing part and a continuous zooming part. The video microscope with electric focusing and zooming and the operation method thereof can control focusing and zooming through a motor so as to greatly optimize work efficiency, enhance operators' experience and have good application prospect.
Owner:奥影检测科技(上海)有限公司
Systems and methods for distributed video microscopy
ActiveUS20180220106A1Improve throughputClosed circuit television systemsMicroscopesMediaFLONetwork address
System and methods are provided for distributed microscopy. A plurality of microscopes may capture images and send them to a media server. The microscopes and the media server may be part of a local area network. The microscopes may each have a distinct network address. The media server may communicate with an operations console, which may be used to view images captured by the microscopes. The operations console may also accept user input which may be used to selectively control the microscopes.
Owner:INSCOPIX
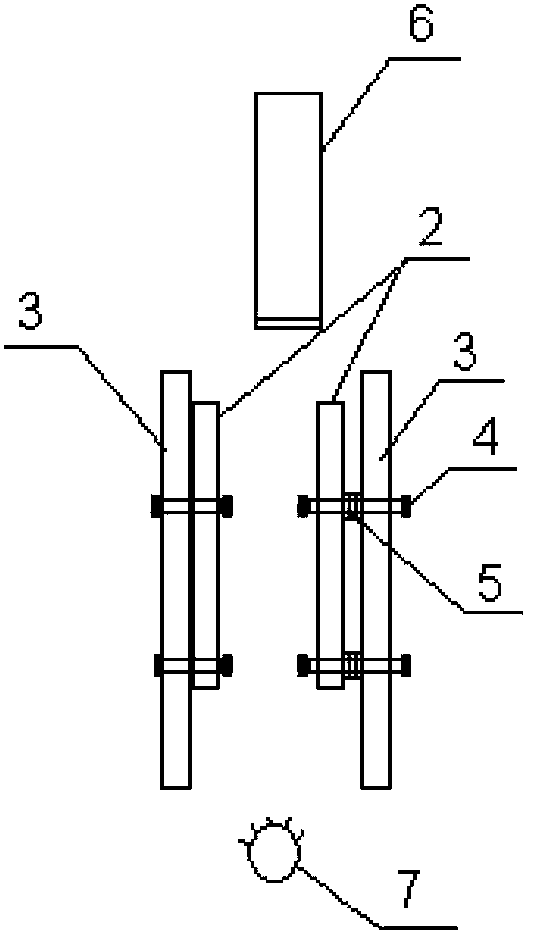
Accurate parallelism-adjusting device and adjusting method
ActiveCN103471526AChange distanceOptical rangefindersUsing optical meansComputer hardwareEngineering
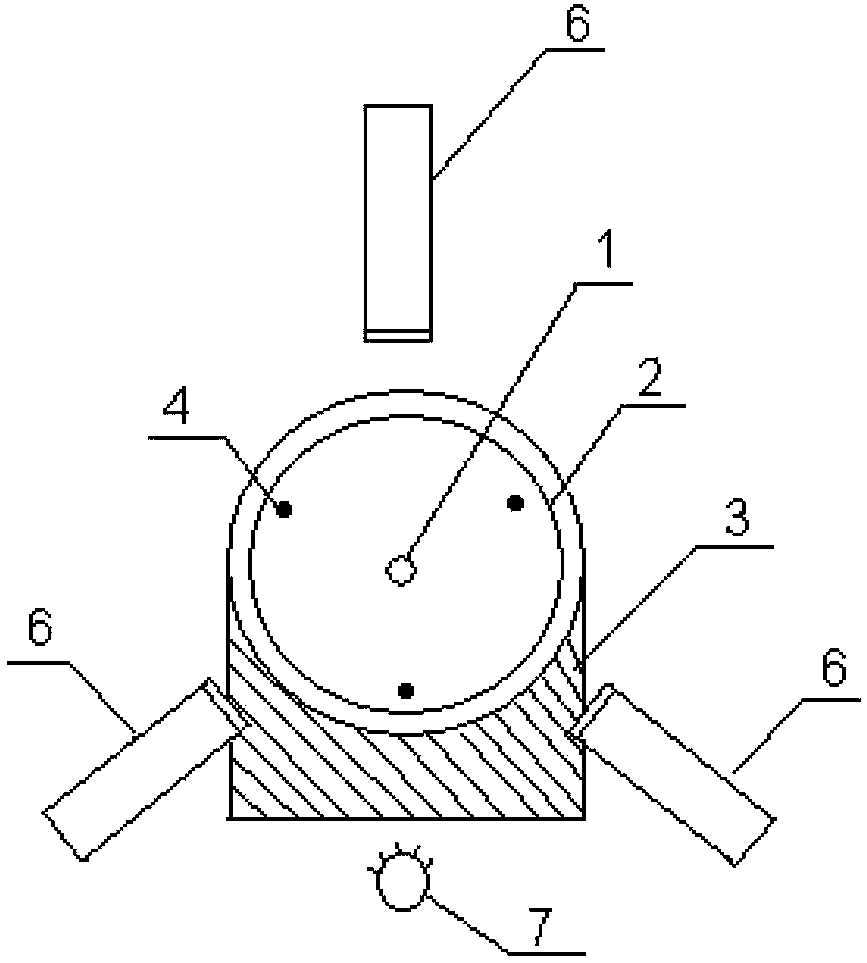
The invention relates to an accurate parallelism-adjusting device including carriers used for carrying two to-be-adjusted elements, two mobile supports used for supporting the carriers and three video microscopes. To-be-adjusted faces of the two to-be-adjusted elements are planes. A single-color light source is arranged right under the center of a distance between the two to-be-adjusted elements. The two mobile supports are arrayed in such a method that the to-be-adjusted surfaces are roughly parallel and opposite to each other. Each one of the carriers is connected with a corresponding mobile support through at least three adjustable fasteners which penetrate the carrier and the mobile support, wherein compression springs are sleeved on the fasteners and the two ends of each compression spring abut against the head end of a corresponding fastener and mobile support respectively. Objective lenses of the video microscopes are arranged at an outer edge of a gap between the two to-be-adjusted elements. The central axes of lens barrels of the three microscopes are in the same plane. The invention also provides an adjusting method for the parallelism-adjusting device. The parallelism-adjusting device is capable of ensuring real-time adjustability and detection of parallelism of the two to-be-adjusted elements.
Owner:CHINA INSTITUTE OF ATOMIC ENERGY
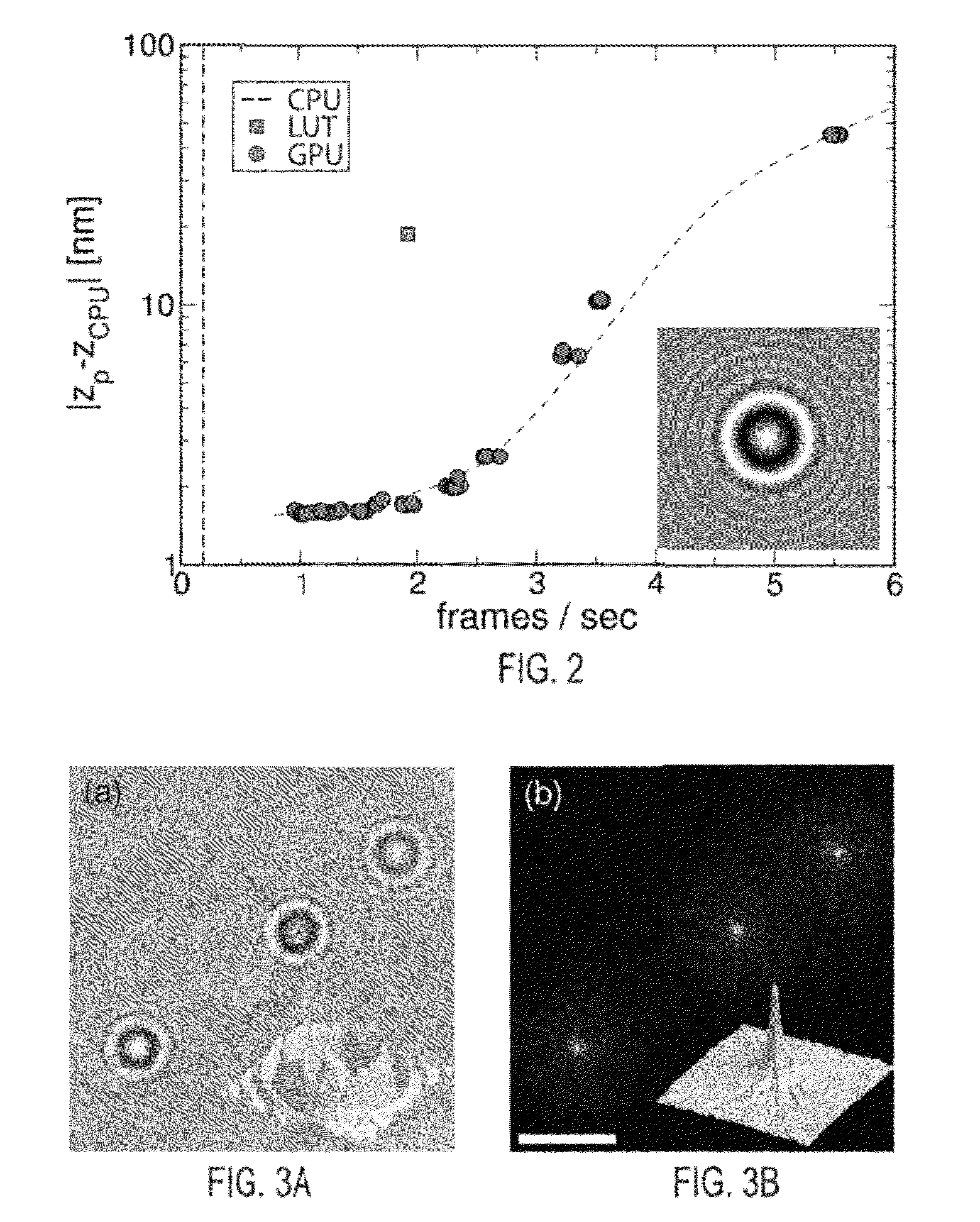
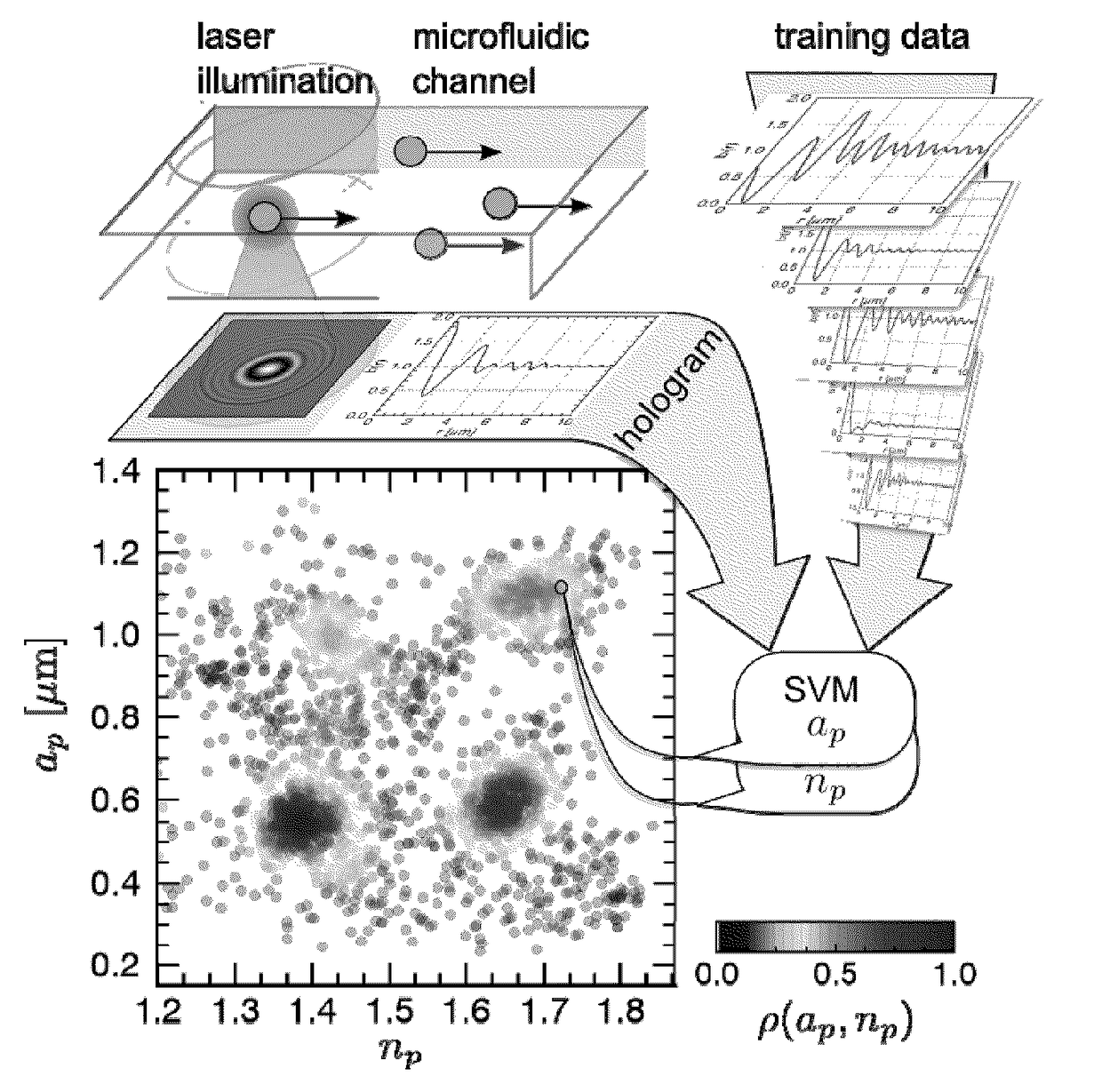
Machine-learning approach to holographic particle characterization
ActiveUS20170241891A1Computationally intensiveParticle size analysisIndividual particle analysisSupport vector machineData stream
Holograms of colloidal dispersions encode comprehensive information about individual particles' three-dimensional positions, sizes and optical properties. Extracting that information typically is computation-ally intensive, and thus slow. Machine-learning techniques based on support vector machines (SVMs) can analyze holographic video microscopy data in real time on low-power computers. The resulting stream of precise particle-resolved tracking and characterization data provides unparalleled insights into the composition and dynamics of colloidal dispersions and enables applications ranging from basic research to process control and quality assurance.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Method for healing copper thin film fatigue damages by plurality of times of laser impact
InactiveCN103320580AEasy to buildIncreased cumulative fatigue lifeFatigue damageConstant observations
The invention provides a method for healing copper thin film fatigue damages by a plurality of times of laser impact and relates to the technical field of machinery manufacturing and laser machining application. The method comprises the following steps: providing a fatigue damage prefabrication device and a laser impact healing device, wherein the fatigue damage prefabrication device comprises a micro-fatigue tester and a video microscope; the laser impact healing device comprises a pulse laser device, a light path adjusting device and a culture dish; carrying out fatigue damage prefabrication on a material and carrying out constant observation on the material; spraying a black coating which is not dissolved in water on the surface of a thin film material which is subjected to the fatigue damage prefabrication; fixing the material on a metal base body so that a laser beam is vertically emitted to the surface of the material; placing the metal base body for fixing the material into the culture dish filled with the water; taking the material from the metal base body down and placing the material into an acetone reagent for washing; cleanly washing the black coating coated on the material; repeating the process for 1-4 times. According to the method disclosed by the invention, crystal grains on the surface and the sub-surface of the material are continuously thinned, the working hardening degree is continuously improved and the accumulated fatigue life of the material is prolonged to the greatest extent.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
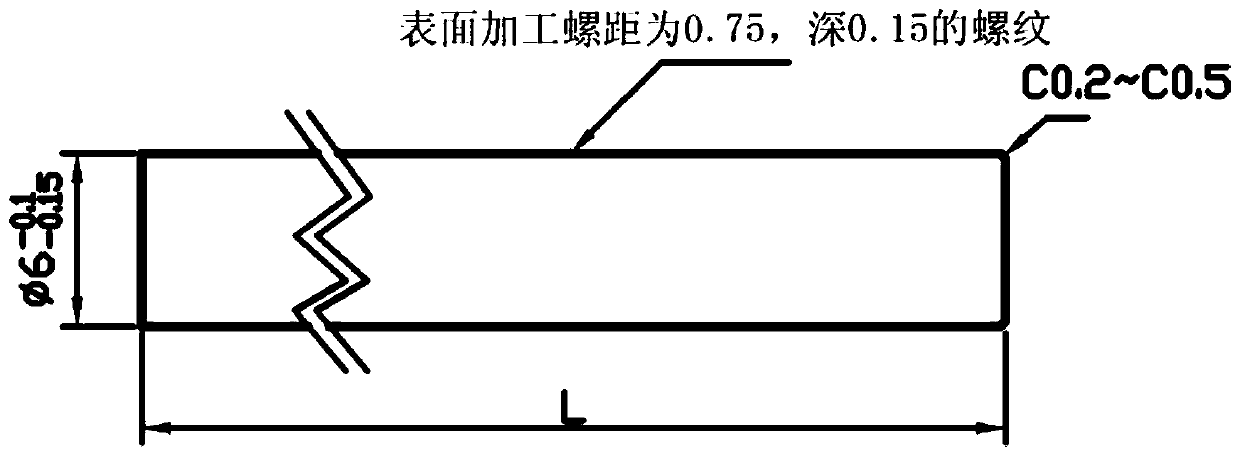
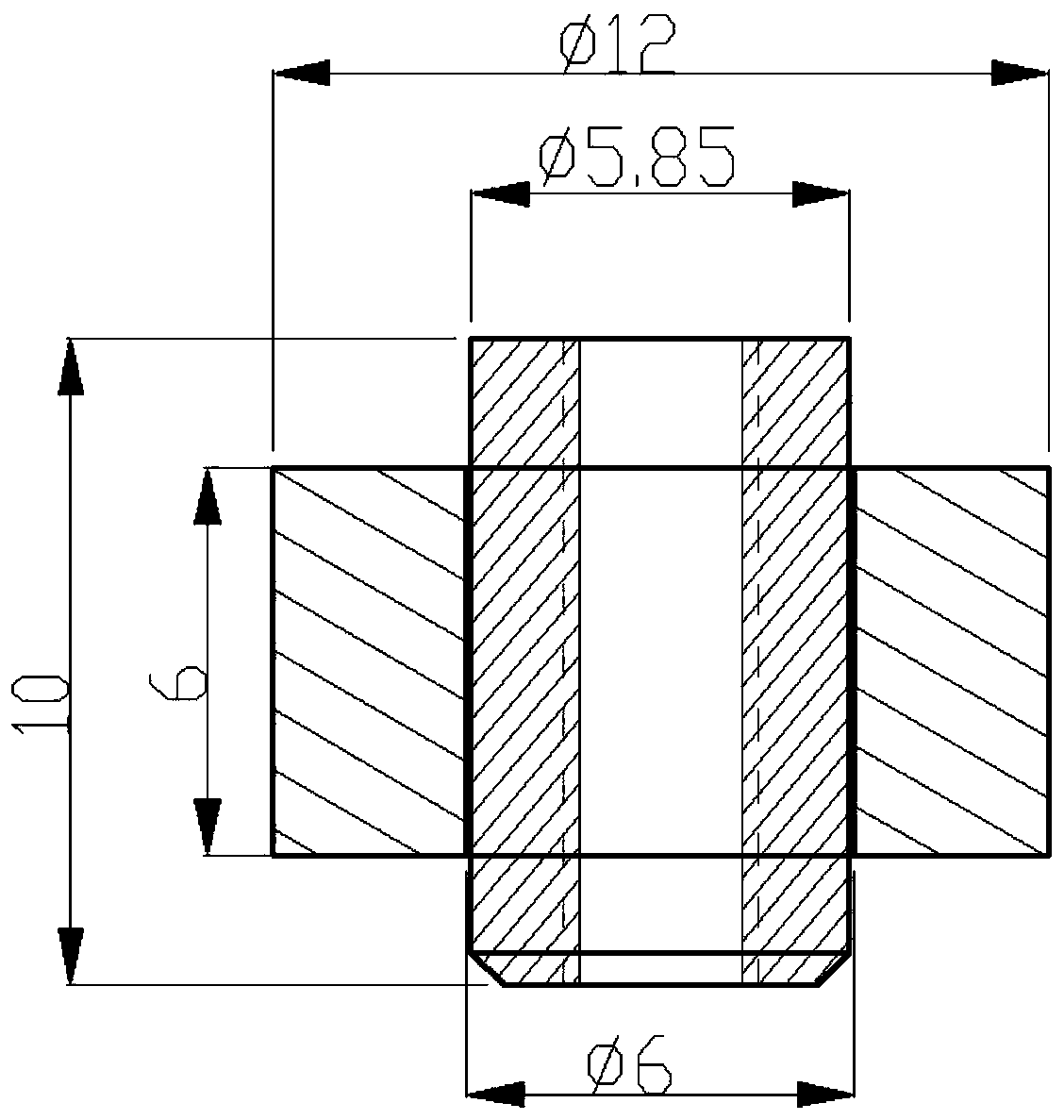
Preparation method of small-hole thread made of high-volume-fraction aluminum-based silicon carbide composite material
ActiveCN111037212AImprove machining accuracyQuality improvementSoldering apparatusCarbide siliconTitanium
The invention discloses a preparation method of a small-hole thread made of a high-volume-fraction aluminum-based silicon carbide composite material. The preparation method comprises the following steps of 1) machining a high-volume-fraction aluminum-based silicon carbide part until the margin of a single side is 2 mm; 2) machining a plug hole in the high-volume-fraction aluminum-based silicon carbide material; 3) machining a spiral line on the surface of a titanium column; 4) observing the inner surface of the hole; 5) pre-coating a bottom hole of the composite material with a brazing fillermetal; 6) cleaning the surface of a titanium alloy with alcohol, and coating the surface of the titanium column with the brazing filler metal; 7) brazing the titanium column and the high-volume-fraction aluminum-based silicon carbide; 8) performing stress-relief heat treatment after welding; 9) machining the end surface to the final size after brazing of the high-volume-fraction aluminum-based silicon carbide composite material and the titanium alloy column is completed; 10) detecting whether a weld joint area is qualified or not through a 50-time video microscope and X-rays on the appearanceof a weld joint after brazing of the high-volume-fraction aluminum-based silicon carbide composite material and the titanium alloy column is completed; and 11) machining a threaded hole bottom hole with the corresponding specification in the welded titanium column, and performing tapping.
Owner:BEIJING SATELLITE MFG FACTORY
Holographic detection and characterization of large impurity particles in precision slurries
Impurities within a sample are detected by use of holographic video microscopy. The sample flows through the microscope and holographic images are generated. The holographic image is analyzed to identify regions associated with large impurities in the sample. The contribution of the particles of the sample to the holographic images is determined and the impurities are characterized.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
Method for preparing quantitative video-microscopy and associated system
ActiveUS9275441B2Reducing subjectivity and inconsistencyHigh-quality dataImage enhancementImage analysisLength waveComputer science
Embodiments of the present invention are directed to a method for calibrating an imaging system for analyzing a plurality of molecular species in a sample. According to one embodiment, the method comprises acquiring a plurality of images of the sample with an image acquisition device at a plurality of different wavelengths, comparing a region of interest associated with at least one of the images acquired at one respective wavelength to a region of interest associated with at least one of the images acquired at a different wavelength, and aligning the plurality of images such that the region of interest associated with at least one of the images acquired at one respective wavelength corresponds to the region of interest associated with the at least one of the images acquired at a different wavelength.
Owner:TRIPATH IMAGING INC
Portable biomedical experiment box
InactiveCN103381375ASuit one's needsEasy to operateHeating or cooling apparatusAir-pressure/air-lock chambersMicroscopic observationBiomedical engineering
The invention discloses a portable biomedical experiment box. The portable biomedical experiment box comprises a large rectangular experiment box and a small rectangular microscope box. After a cover of the large rectangular experiment box is opened, the large rectangular experiment box is used as an experiment operation desk. A centrifuge, a chamber operation panel and a storage battery is arranged at a left side of the portable biomedical experiment box. A material storage cabinet is arranged at a right side of the portable biomedical experiment box. A small incubator arranged in the middle of the portable biomedical experiment box. A sterile operation cabinet can be assembled on the surface of the middle of the portable biomedical experiment box. A video microscope is stored in the small rectangular microscope box and the video microscope and a notebook computer can cooperate. The portable biomedical experiment box is a small comprehensive biomedical experiment chamber, can be used for common biomedical experiments, sterile operation, bacterial culture, microscope observation and parasite experiments, is convenient for operation and carrying, can satisfy a part of biomedical experiment requirements, and is suitable for being used in non-electrified areas such as fields and grasslands.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY FOR NATIONALITIES
Corrosion image binarization processing method
PendingCN109658389AAccurate processingReduce noiseImage enhancementImage analysisImaging processingMetallic materials
The invention belongs to the field of metal material corrosion, and particularly relates to a corrosion image binarization processing method. The method comprises the following steps: 1, treating a test piece; 2, observing and shooting a corrosion pit microscopic topography map of the test piece through a video microscope; Step 3, reading the corrosion pit microscopic topography map of the test piece, and preprocessing the corrosion pit microscopic topography map by adopting a binarization method to generate a basic corrosion topography grey-scale map; 4, reading the basic corrosion morphologygrey-scale map, and processing the basic corrosion morphology grey-scale map by adopting an improved Otsu algorithm to generate a binary image; Wherein the improved Otsu algorithm is an Otsu algorithm in which edge information and gray scale information of the basic corrosion morphology gray scale map are added. The improved Otsu algorithm is adopted to further carry out binarization processing on the image, so that the corrosion morphology in the corrosion image can be better restored, the image processing is more accurate, noise points are reduced, and many interference factors in the original corrosion morphology grey-scale map are eliminated.
Owner:SHENYANG AIRCRAFT DESIGN INST AVIATION IND CORP OF CHINA
Aero-engine turbine blade surface product layer analysis method
ActiveCN111487272AImprove integrityStop lossMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationUsing optical meansMetallurgyWire cutting
The invention belongs to the field of aero-engines, and particularly relates to an aero-engine turbine blade surface product layer analysis method. The method comprises the following steps: obtaininga cutting sample, making a part of the cutting sample into a metallographic sample, and carrying out morphology and component analysis on the cutting sample and the metallographic sample by using a scanning electron microscope; and carrying out phase analysis on the cutting sample and the metallographic sample by using an X-ray diffractometer, and measuring an average depth of a product layer of the metallographic sample by using a video microscope. Blades are cut through a diamond wire cutting machine, an influence on the product layer is small, and integrity of the product layer is improved;nickel plating protection is performed on the blade product layer so that losses of the product layer in a polishing and grinding process are greatly prevented, and the influence of an inlay on depthmeasurement of the product layer is also prevented; and instruments such as the scanning electron microscope, the X-ray diffractometer and the video microscope are combined to comprehensively analyzemorphology, a phase, components and a depth of the product layer so that efficiency is high, and guidance is good.
Owner:AECC SHENYANG ENGINE RES INST
Machine-learning approach to holographic particle characterization
Holograms of colloidal dispersions encode comprehensive information about individual particles' three-dimensional positions, sizes and optical properties. Extracting that information typically is computation-ally intensive, and thus slow. Machine-learning techniques based on support vector machines (SVMs) can analyze holographic video microscopy data in real time on low-power computers. The resulting stream of precise particle-resolved tracking and characterization data provides unparalleled insights into the composition and dynamics of colloidal dispersions and enables applications ranging from basic research to process control and quality assurance.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV
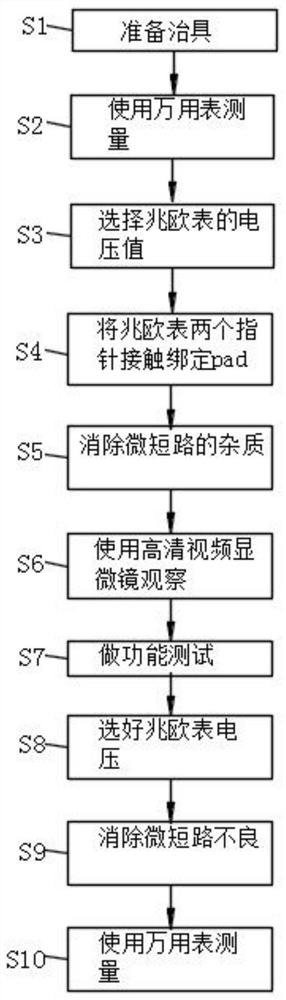
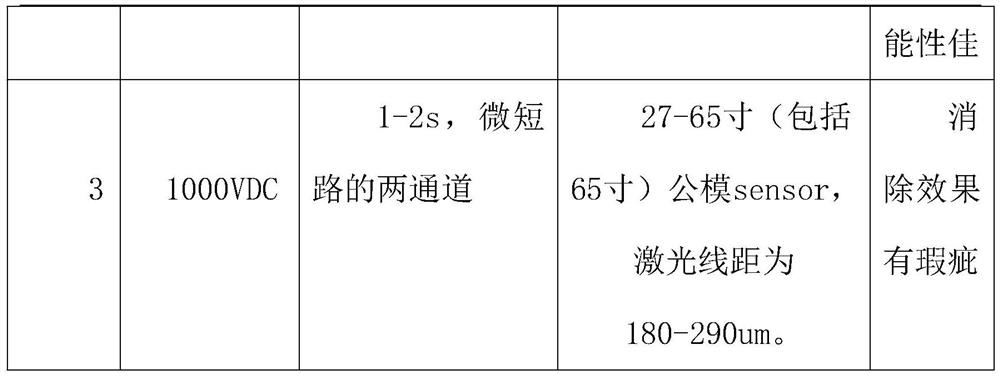
Process method for eliminating micro short circuit in production of functional sheet by using megohmmeter
ActiveCN111863628AImprove production straight-through rateEliminate micro-shortsSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingEngineeringMechanical engineering
The invention provides a process method for eliminating micro short circuit in the production of a functional sheet by using a megohmmeter. The invention relates to the technical field of functional piece micro-short circuit elimination. The method comprises the following steps: S1, preparing a jig, S2, measuring by using a universal meter, S3, selecting a voltage value of the megohmmeter, S4, contacting and binding two pointers of the megohmmeter with pad, S5, eliminating impurities of micro short circuit, S6, observing by using a high-definition video microscope, S7, performing a function test, S8, selecting the voltage of the megohmmeter, and S9, eliminating short circuit defects. In the present invention, the micro short circuit can influence touch accuracy and linearity, the program debugging is also an NG item; a functional sheet is a defective product when the micro short circuit occurs; if the micro short circuit cannot be repaired, the functional piece needs to be scrapped, the process can eliminate the micro short circuit, greatly improve the first pass yield of functional piece production and reduce the rejection rate, and compared with an old process, the impurities ofthe micro short circuit are ablated through the megohmmeter easily and quickly, the accuracy is high, and secondary badness, for example, a circuit is cut off when a short circuit position is cut offis not likely to be caused.
Owner:GUANGZHOU TOUCHKIT PHOTOELECTRIC TECH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com